Patents
Literature
1425 results about "IPv4" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
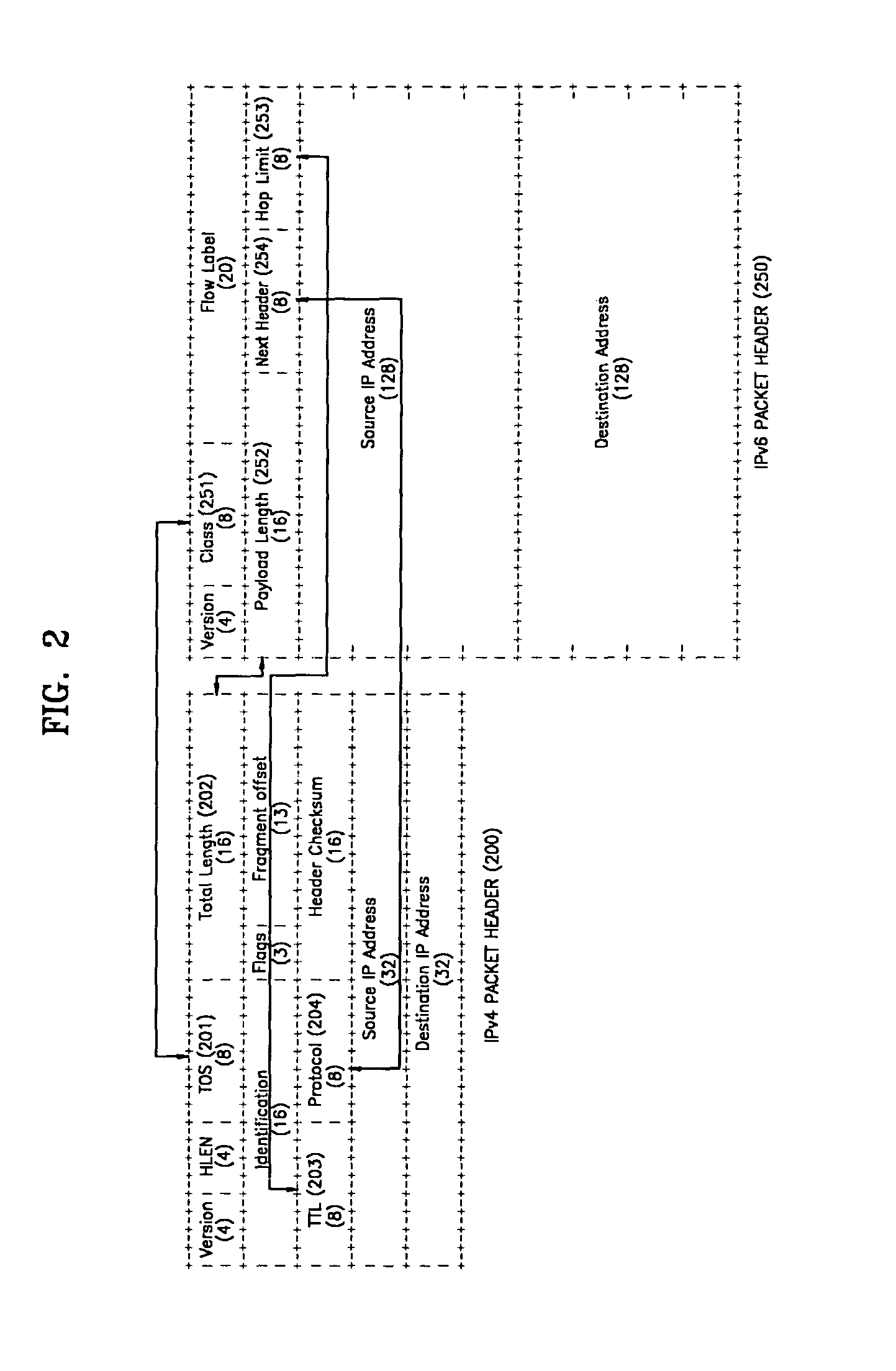
Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP). It is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the Internet and other packet-switched networks. IPv4 was the first version deployed for production in the ARPANET in 1983. It still routes most Internet traffic today, despite the ongoing deployment of a successor protocol, IPv6. IPv4 is described in IETF publication RFC 791 (September 1981), replacing an earlier definition (RFC 760, January 1980).
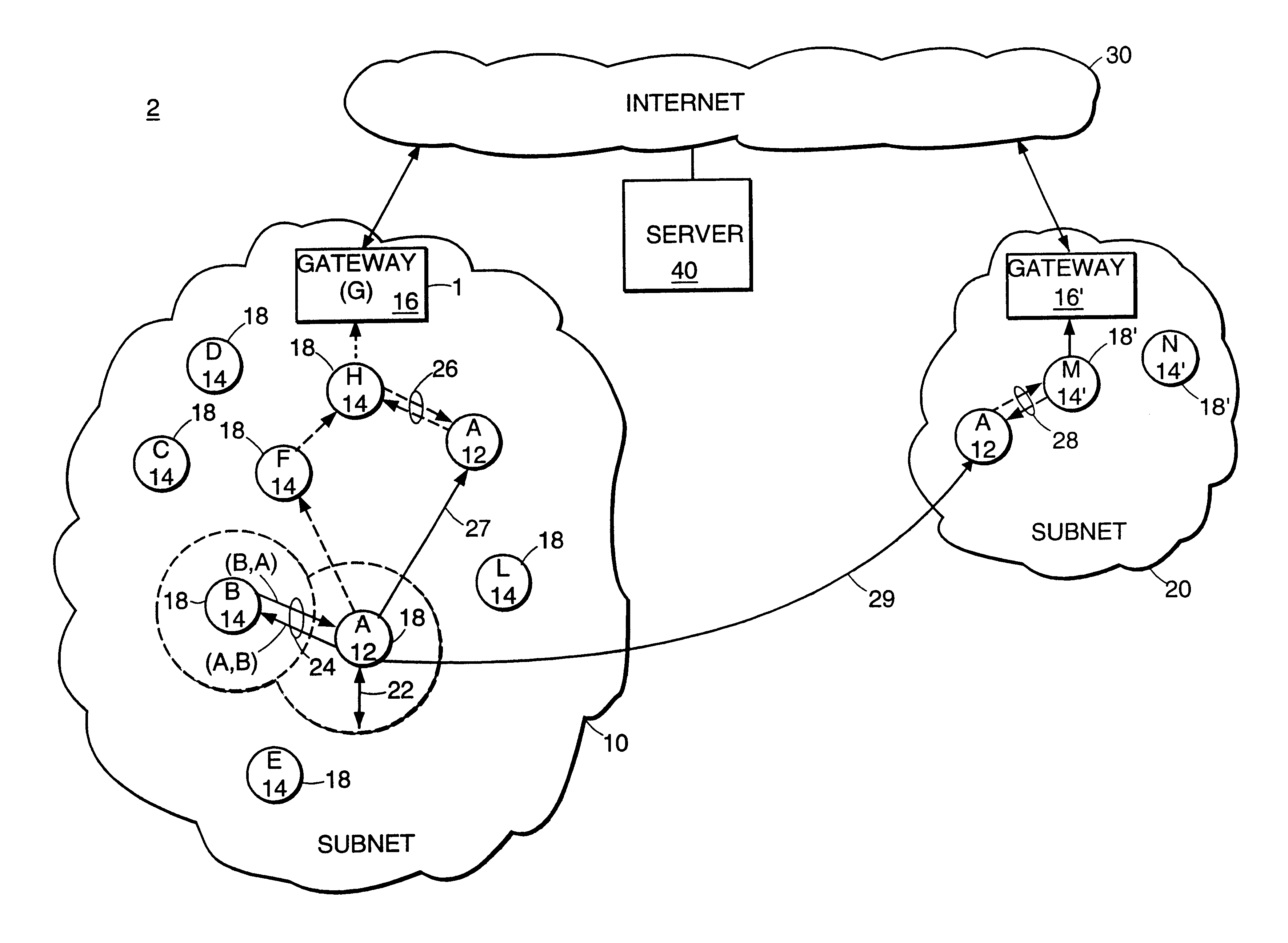
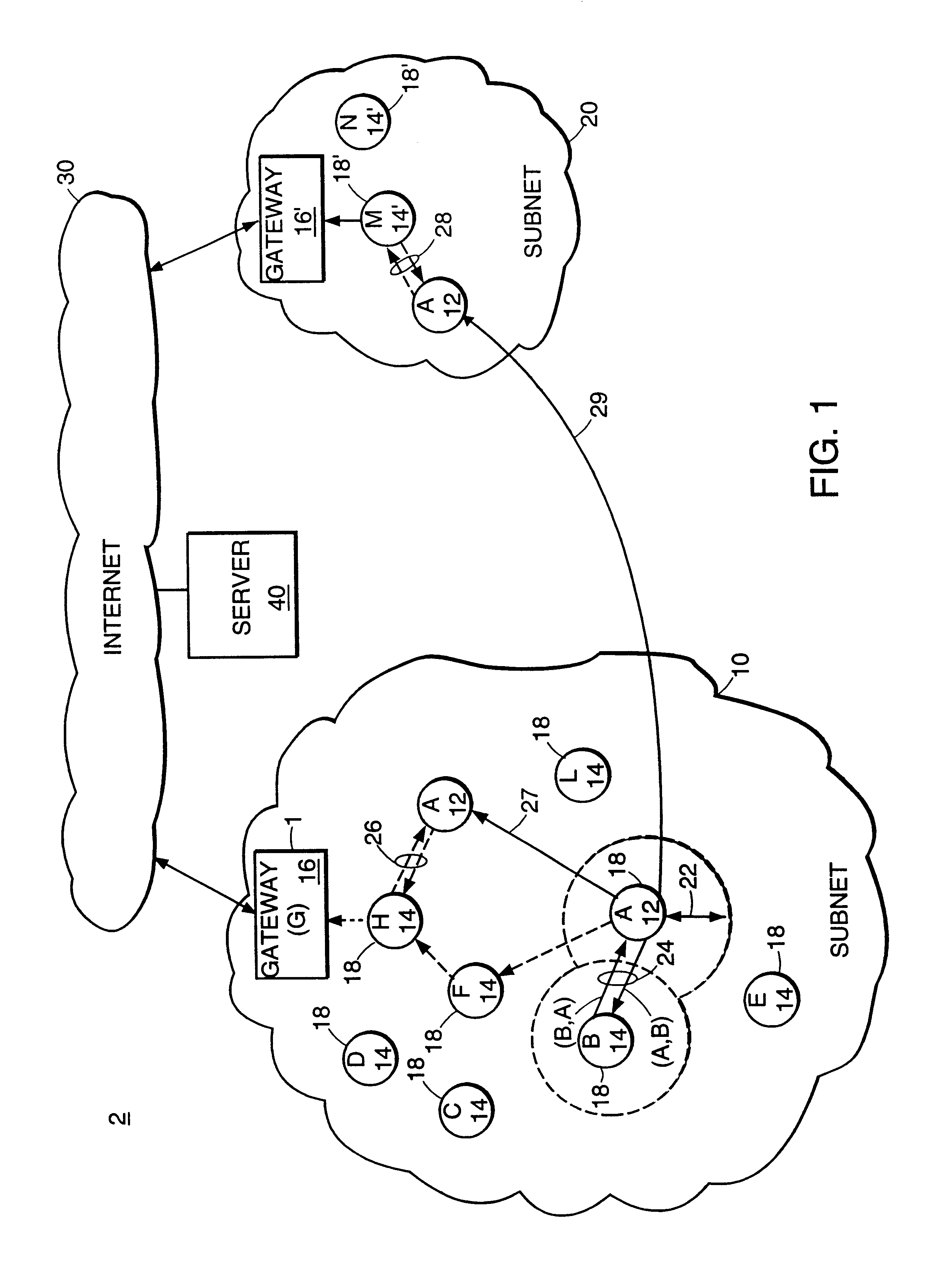
Mobile ad hoc extensions for the internet
InactiveUS6845091B2Easy to addImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTTEthernetNetwork measurement
Described is an internetworking system having various mobile ad hoc extensions to the Internet that are particularly suited to the dynamic environment of mobile ad hoc networks. The internetworking system includes any combination of a link-state routing protocol for disseminating topology and link-state information over a multi-hop network comprised of nodes, a neighbor discovery protocol that can detect the appearance and disappearance of new neighbor nodes, an address format that facilitates deployment of IPv6 nodes in a predominantly IPv4 network infrastructure, a queuing mechanism that can update information upon resuming interrupted communications between nodes, and dynamic network measurement techniques for adaptively using wireless bandwidth when establishing and maintaining connections between nodes and a server.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
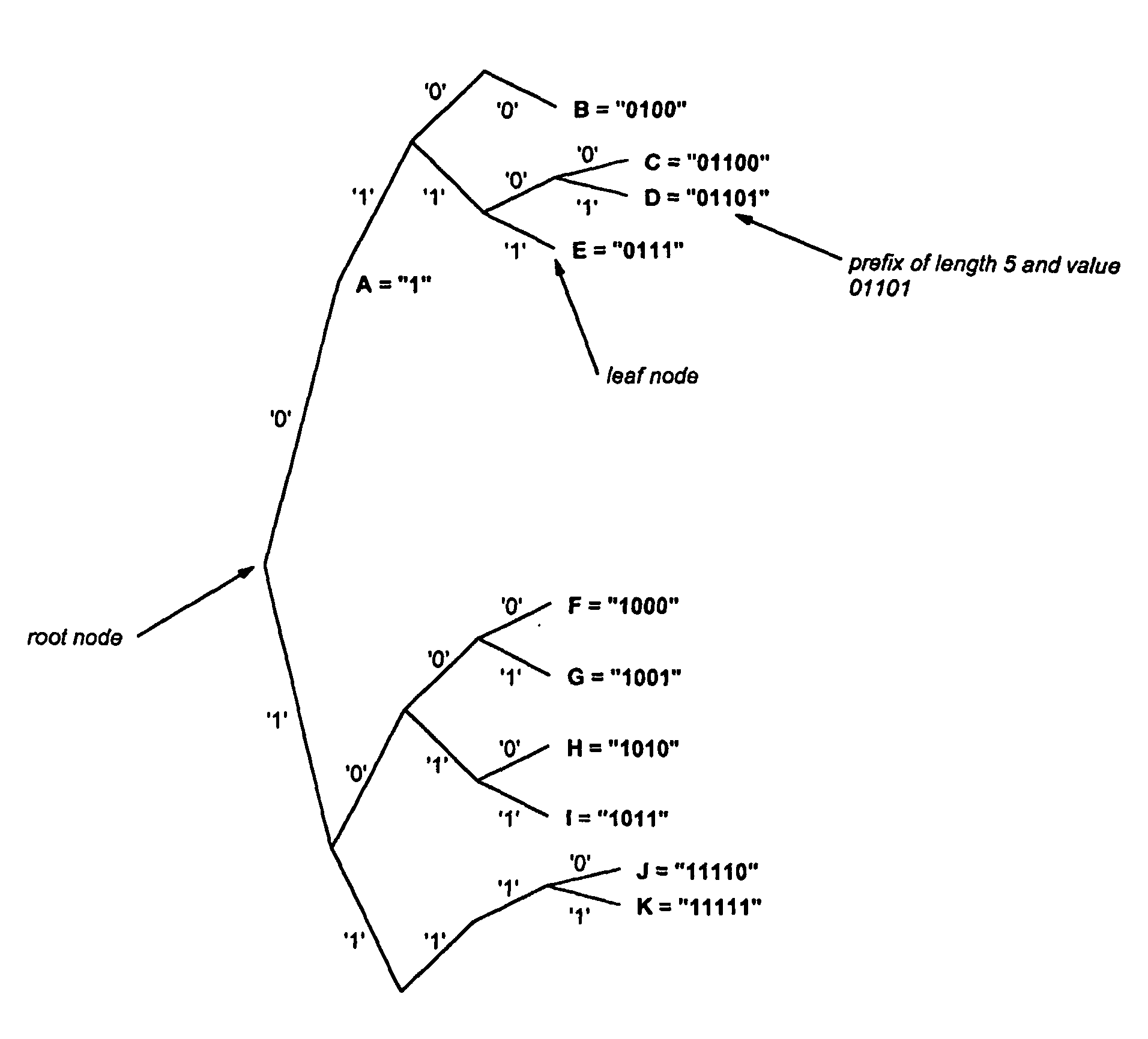
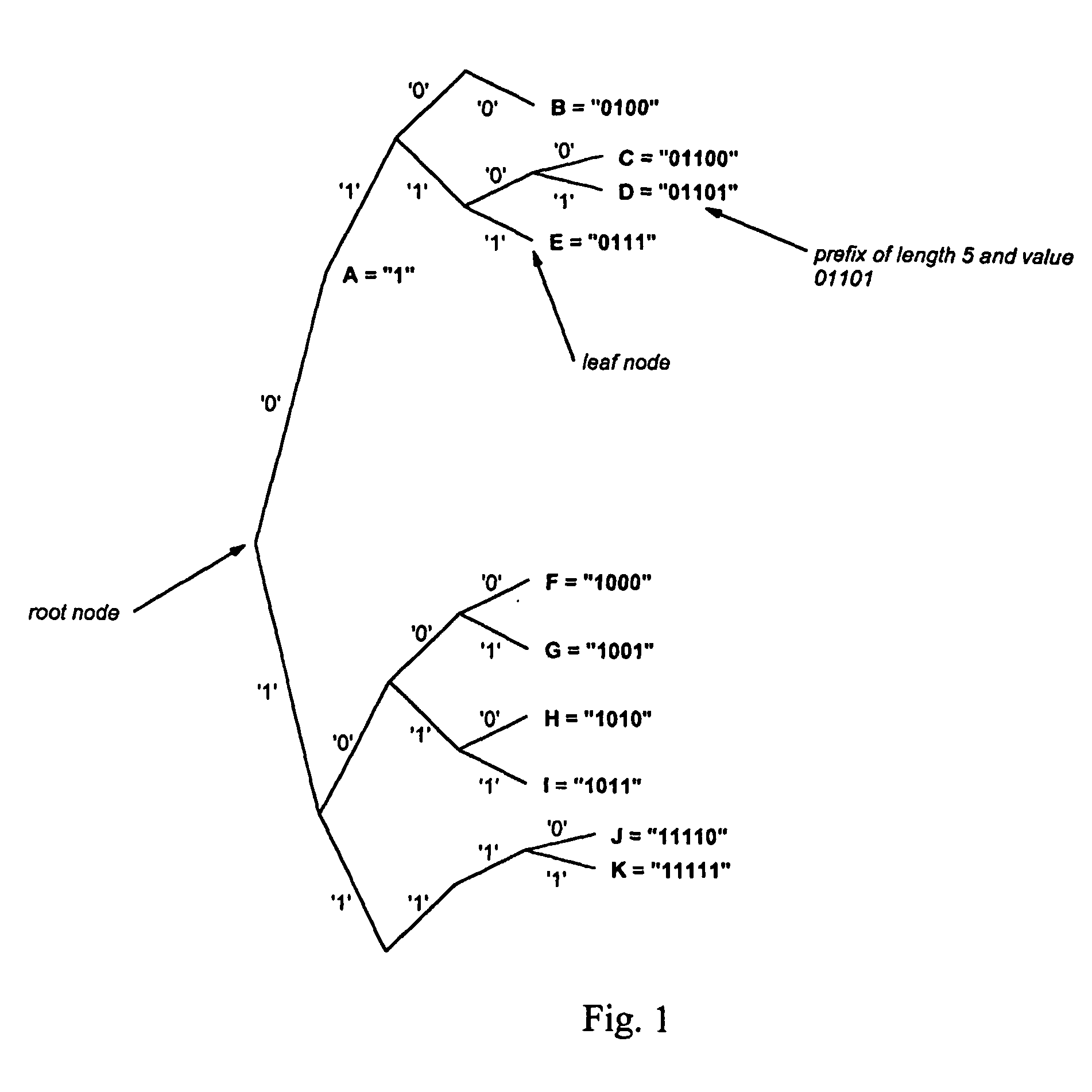
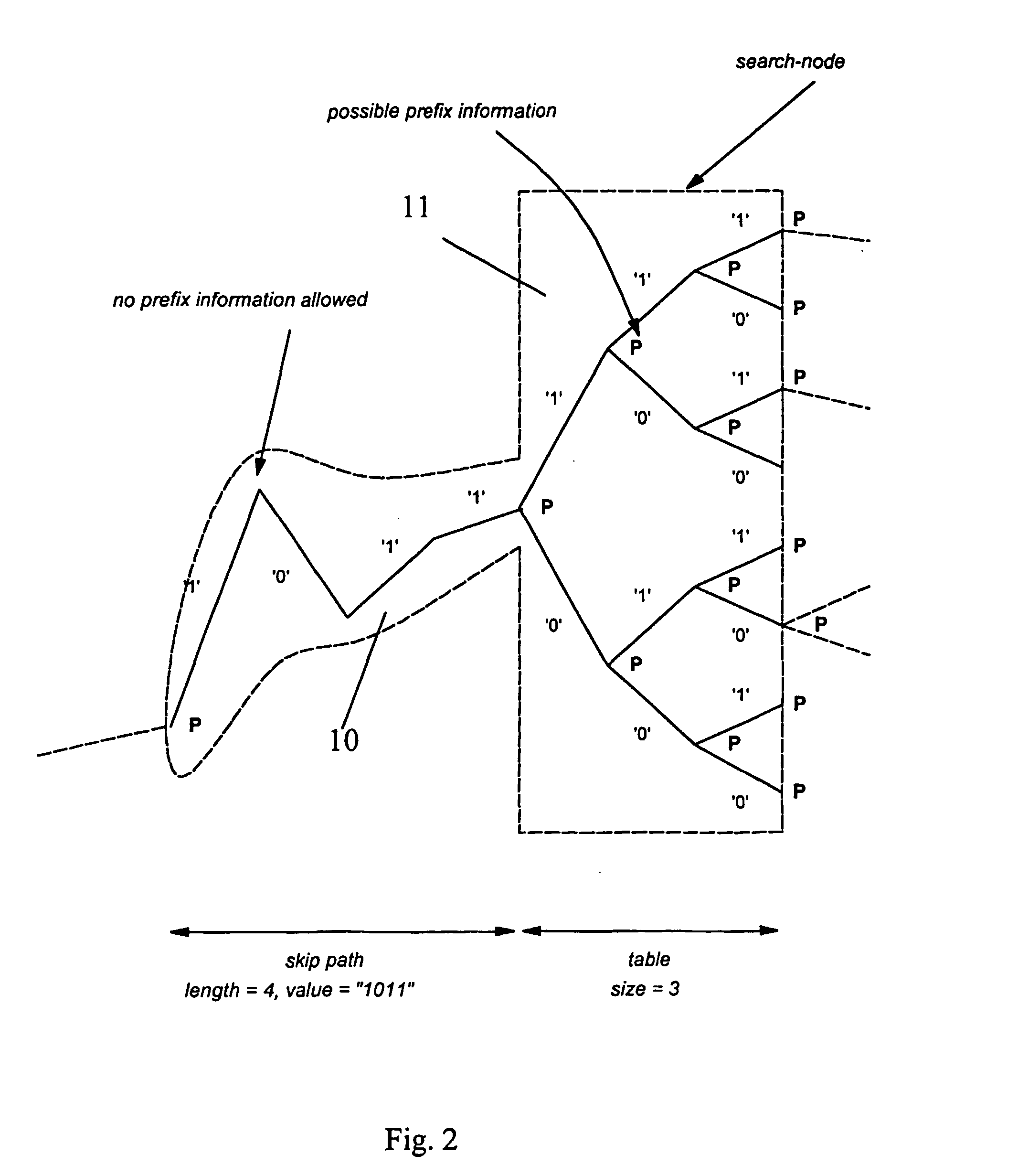
Efficient ipv4/ipv6 best matching prefix method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050171959A1Efficient searchData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMemory addressTheoretical computer science
The present invention provides a data-structure to store a search database and provides techniques to build this datastructure given a list of prefixes (P) and to search this database efficiently for a best matching prefix for an address D. The data-structure can be stored in standard memory (14), where values are stored associated with memory address locations. The data structure includes representations of addressable linked tables (FIG. 3b). The representations are related to a binary search trie (FIG. 1) and each linked table (T) has at least one entry. Entries in a table span more than one level of the binary search trie. The spanning feature relates to compression of a binary search trie into a finite number of levels (and hence tables). The finite number is less than the number of levels in the binary search trie. Hence the search algorithm is restricted to a finite, and predetermined number of search accesses to the tables to obtain a best-match result.
Owner:TRANSWITCH
Stateless Protocol Translation
Some aspects of the methods and systems presented relate to performing stateless address translation between IPv4 capable devices to IPv6 capable networks and devices. Stateless address translation may form a new IPv6 addresses by combining the IPv4 address of a device with an IPv6 prefix address assigned to the translator. The translation may also combine the IPv4 destination address and UDP port information with the new IPv6 address. Existing Domain Name Systems (DNSs) may be leveraged for resolving the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses across different networks.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Mechanisms for avoiding problems associated with network address protocol translation
ActiveUS7006526B1Avoid problemsReduce morbidityError preventionTransmission systemsSize differenceSize increase
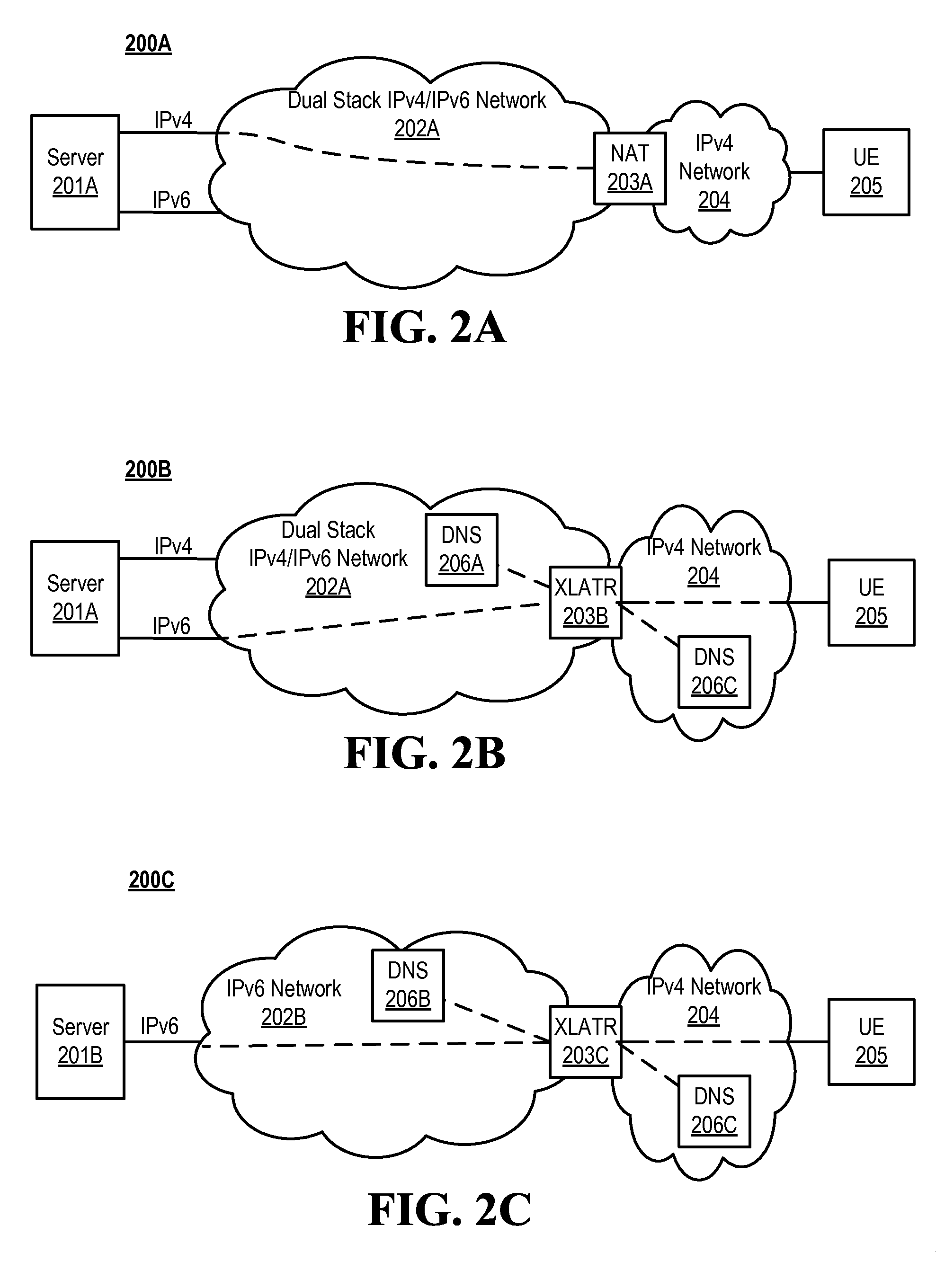
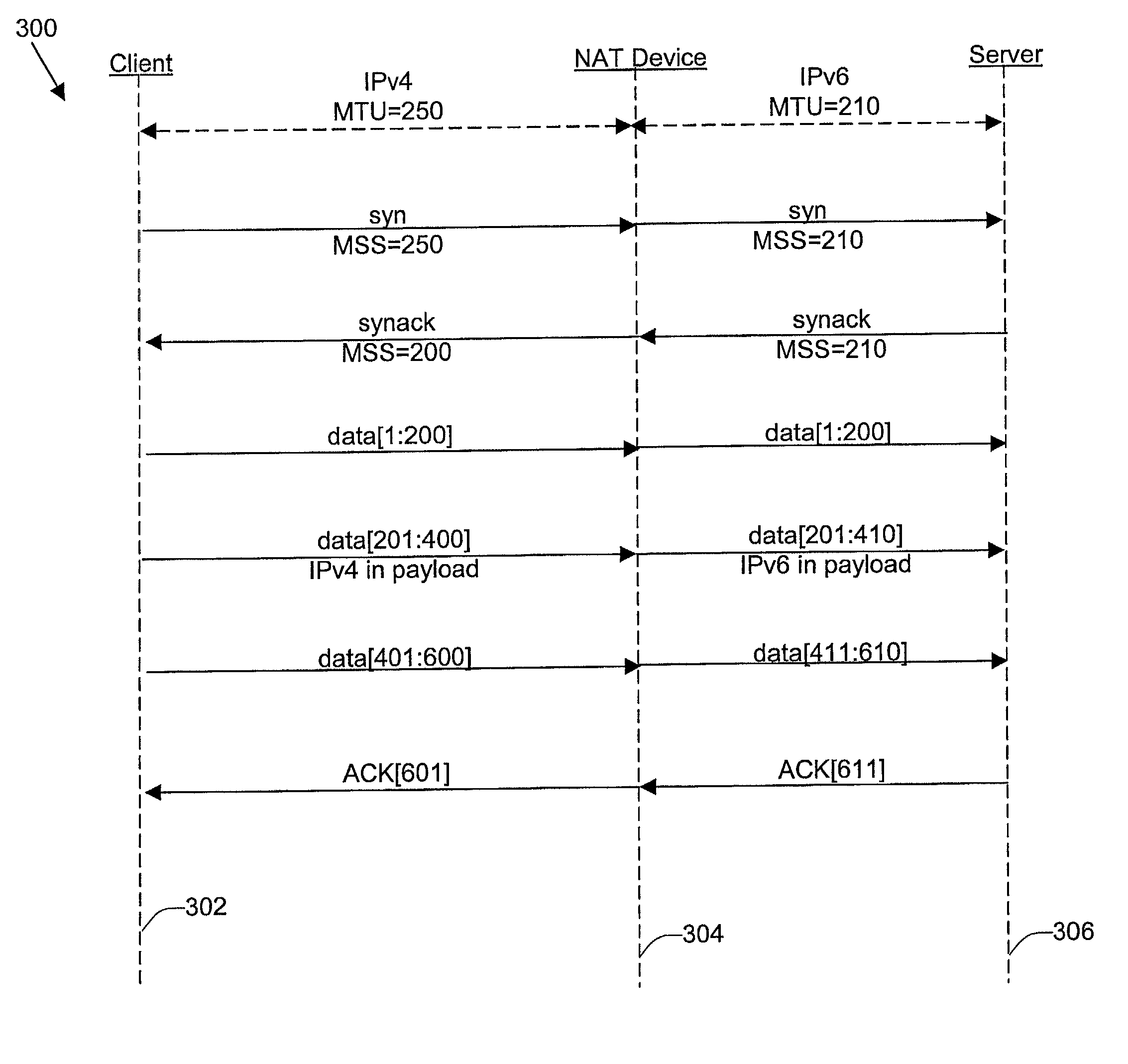
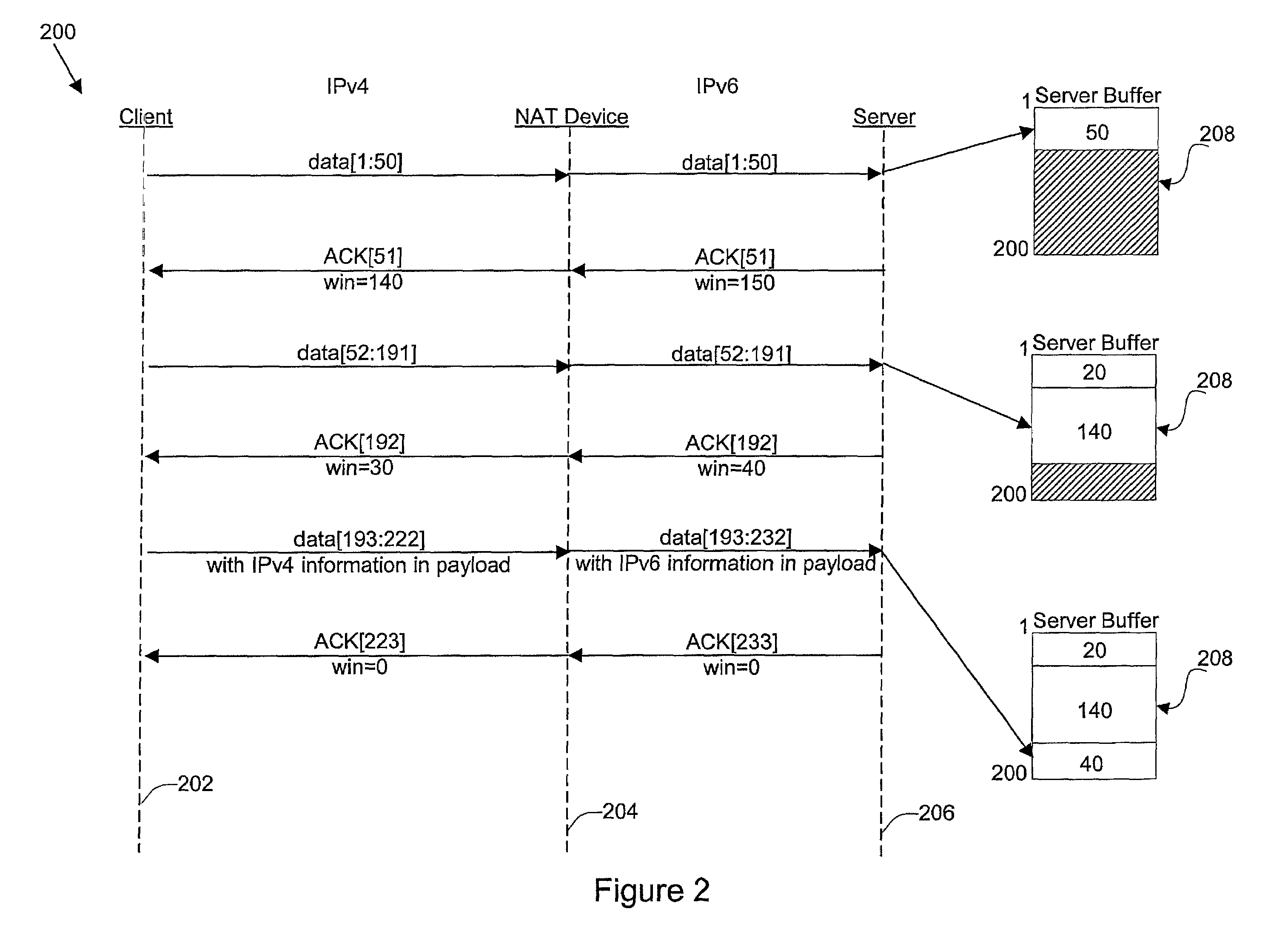
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for avoiding problems caused by converting between two different protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6. These problems may include, but are not limited to, fragmentation of packets, dropping of packets, and retransmission of packets. Avoiding these problems will reduce the incidence of transmission delays, bandwidth degradation, and additional processing in the packet's transmission path due to such problems. In general terms, the present invention provides mechanisms for modifying a protocol parameter, such as a TCP or UDP parameter, to avoid problems associated with protocol translation, such as fragmentation. In one implementation, the protocol parameter limits the size of a particular portion of the a packet transmitted by a sending computer node or device. For example, a packet size indicator is communicated to the sending computer node so that the sending computer node sends packets limited by the packet size indicator to thereby avoid associated with the size of such packets. In specific TCP embodiments, the size indicator specifies a window size and / or a maximum segment size. For example, if packets transmitted by a sending node to a receiving node are converted from IPv4 to IPv6 and the window size indicated to the sending node (e.g., by the receiving node) is 512 bytes, the window size is adjusted to 500 bytes before reaching the sending node. The adjustment amount may be based on an estimated size increase resulting from converting from IPv4 to IPv6. In this example, the window size is decreased by 12 bytes since a conversion from IPv4 to IPv6 where one 4 byte IPv4 address is changed to a 16 byte Ipv6 address has an associated size difference of 12 bytes. In a specific embodiment, actual changes in packet size may tracked and the adjusted size indicator may be dynamically based on such tracked changes. In other embodiments, the changes in packet size are predicted, and the adjusted size is preemptively changed as needed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Geo-spacial internet protocol addressing
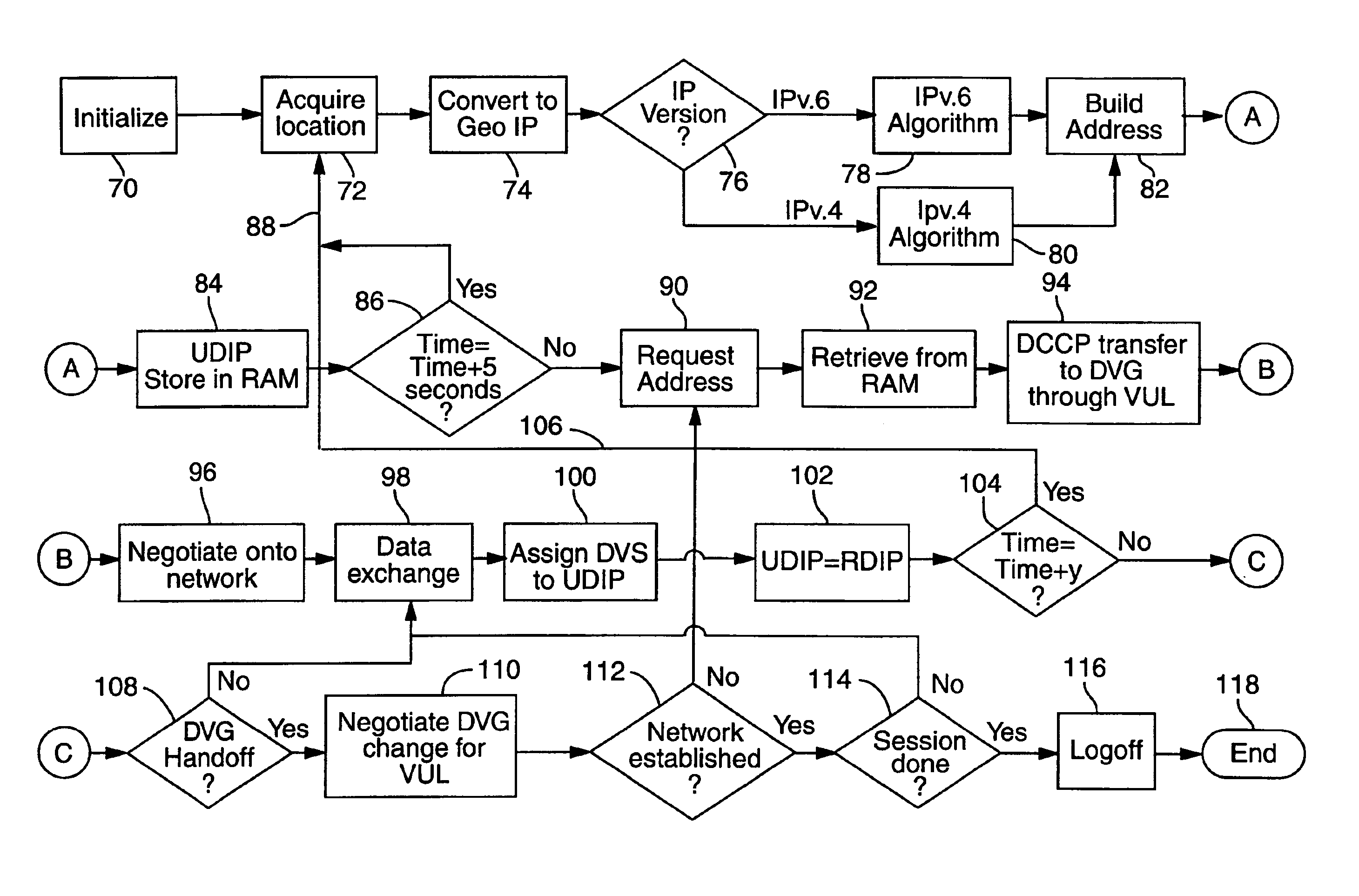
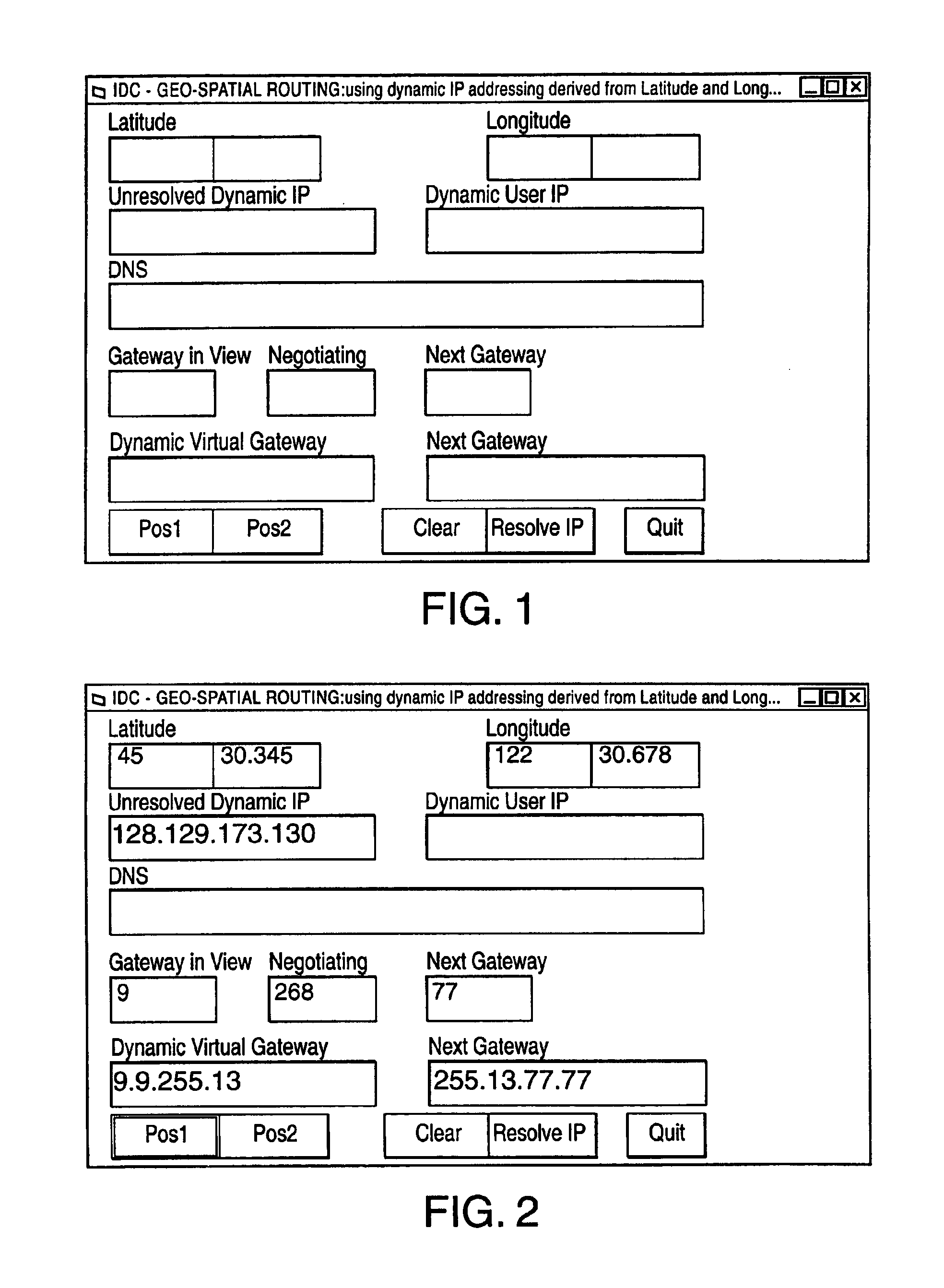
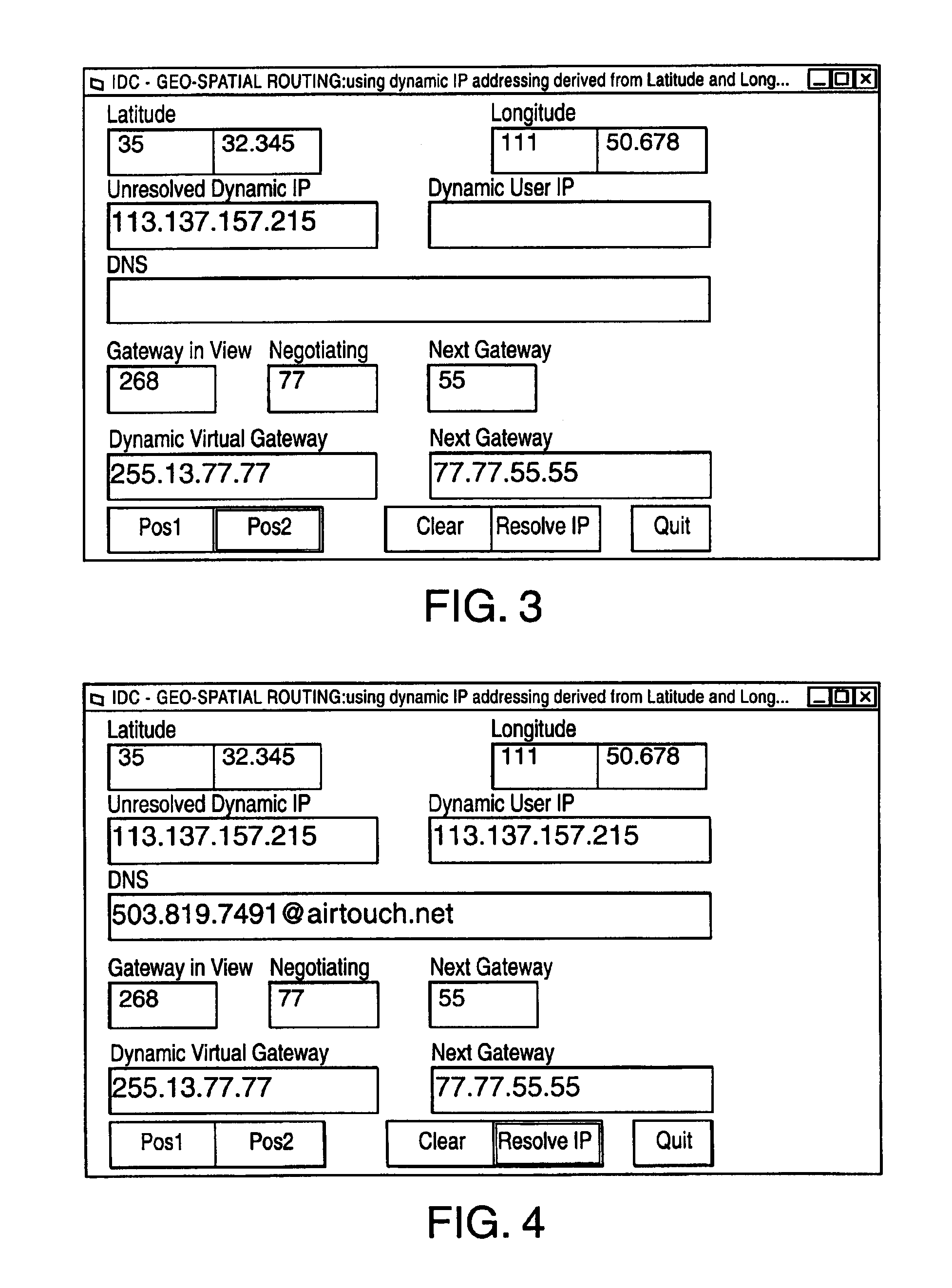
InactiveUS6920129B2Easy to useReadily availablePosition fixationTime-division multiplexLongitudeNetwork management
The invention provides for conversion of latitude and longitude to an addressing scheme that supports current TCP / IP (Ipv4) and future addressing (Ipv6 / Ipng) requirements. More specifically, it allows a decentralization of the unicast point to a device on the hosted network. Geographical Internet Protocol (geoIP) addressing will facilitate anycast routing schemes in which the nearest node has a statically assigned geoIP. Geo-routing and network management become a function of the geoIP address.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO +1
Systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system
The present application is directed towards systems and methods for providing link management in a multi-core system. In some embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing address resolution in IPv4 networks in a multi-core system. In other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing neighbor discovery in IPv6 networks in a multi-core system. In still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing network bridging in a multi-core system. In yet other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing link aggregation in a multi-core system. And in still other embodiments, the present application describes solutions for managing virtual routers in a multi-core system.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
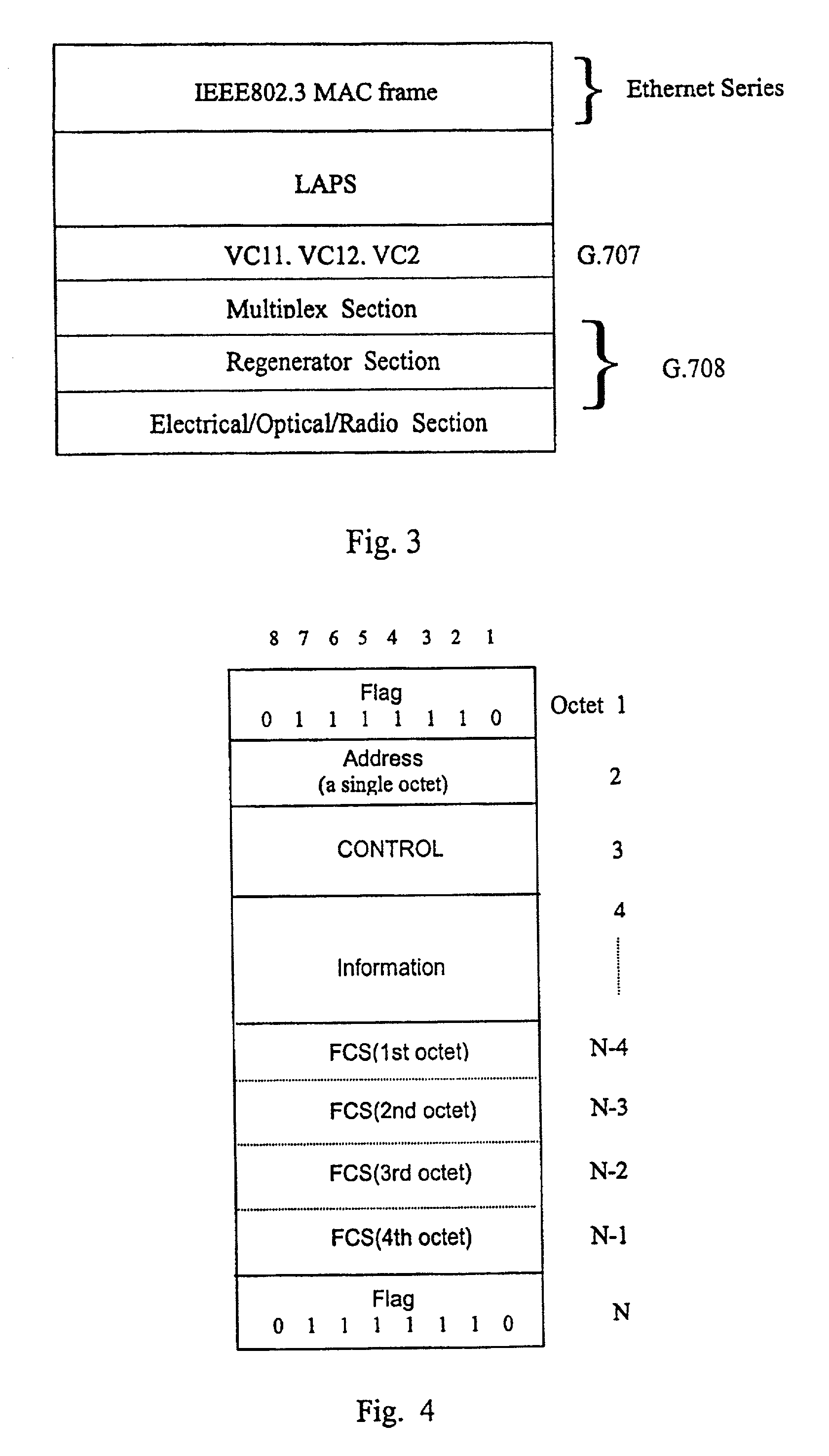
Interfacing apparatus and method for adapting Ethernet directly to physical channel
InactiveUS7031341B2Time-division multiplexTime-division multiplexing selectionLine cardFlag sequence
Owner:WUHAN RES INST OF POSTS & TELECOMM MII
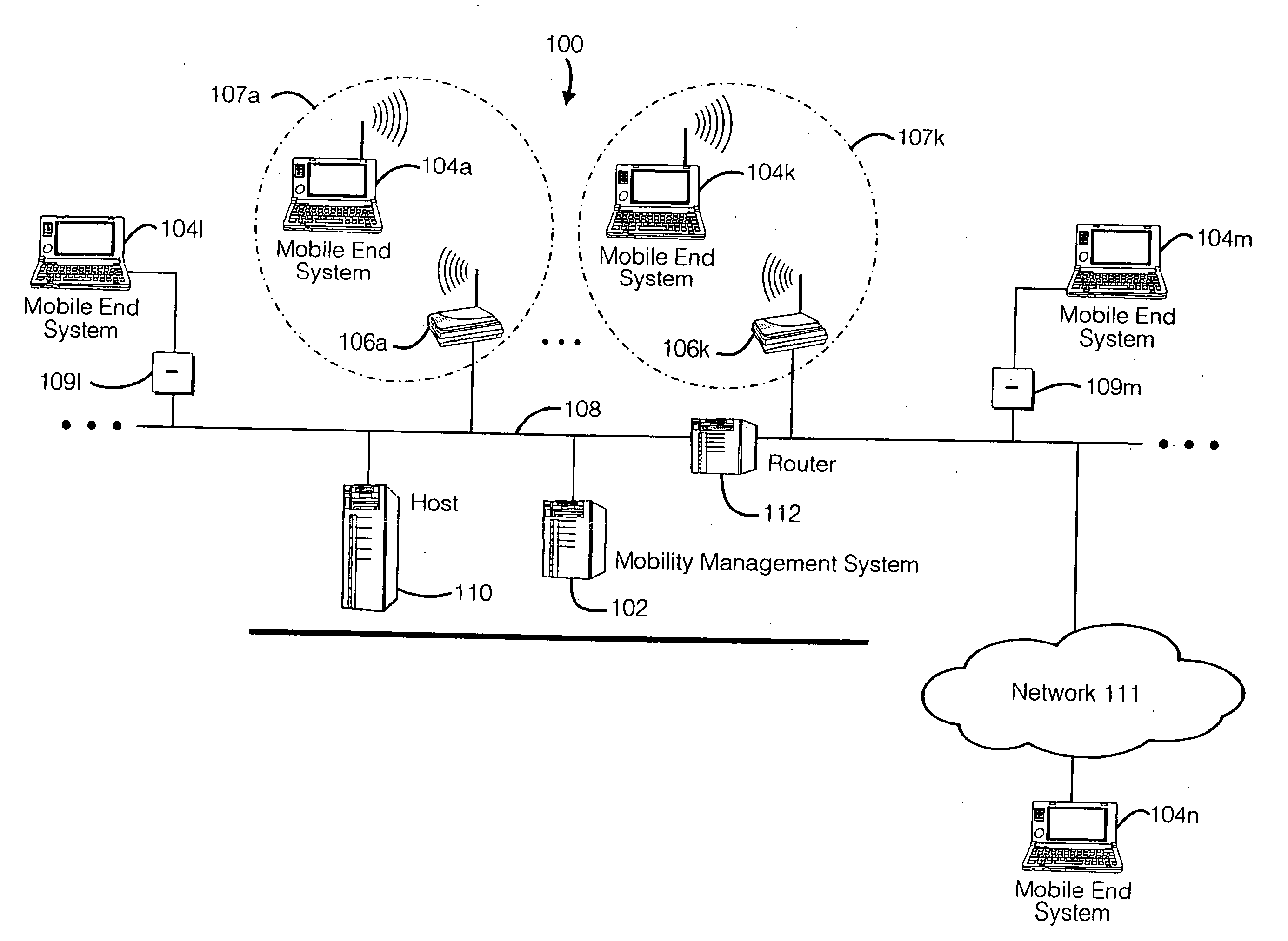
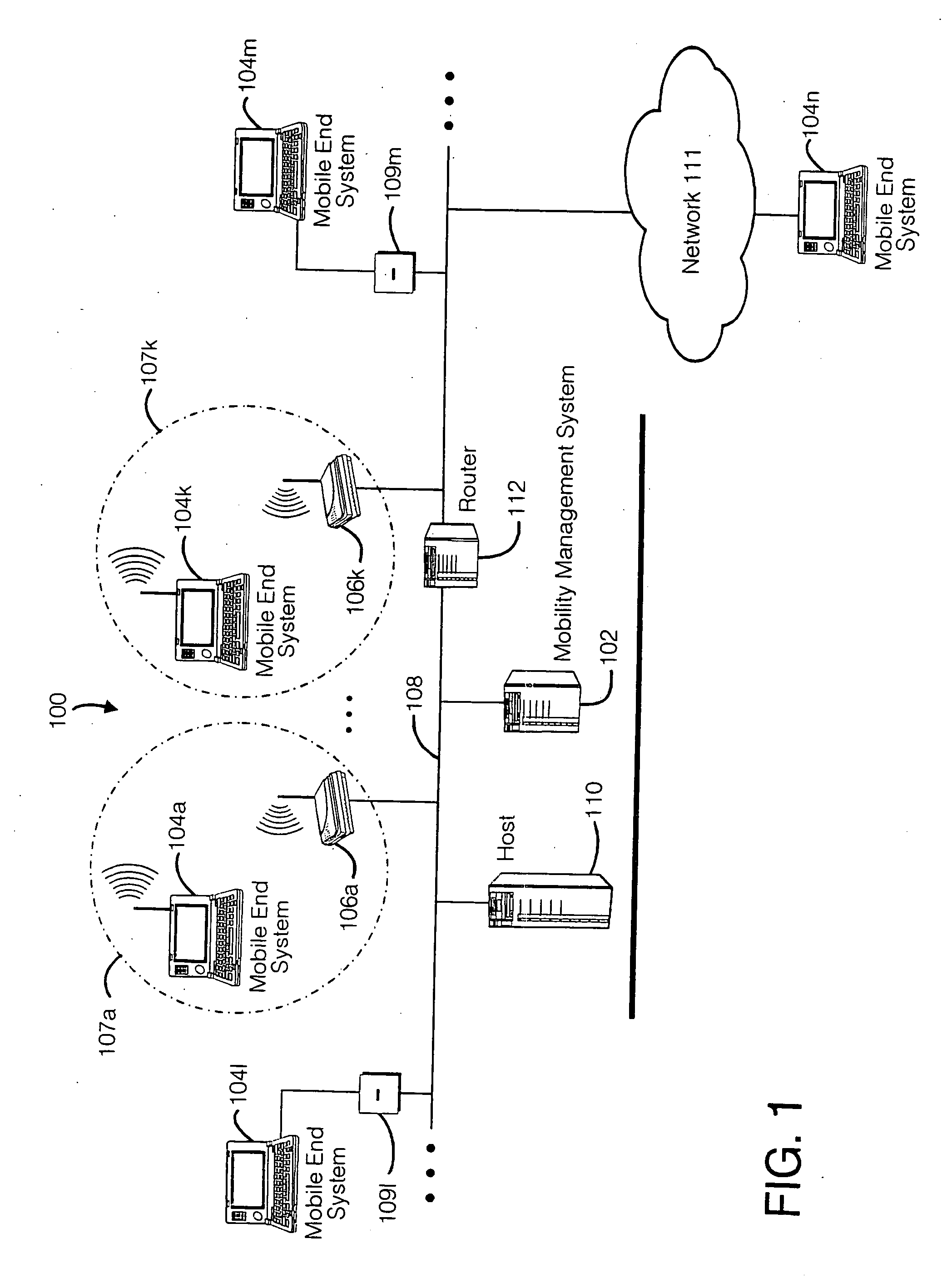
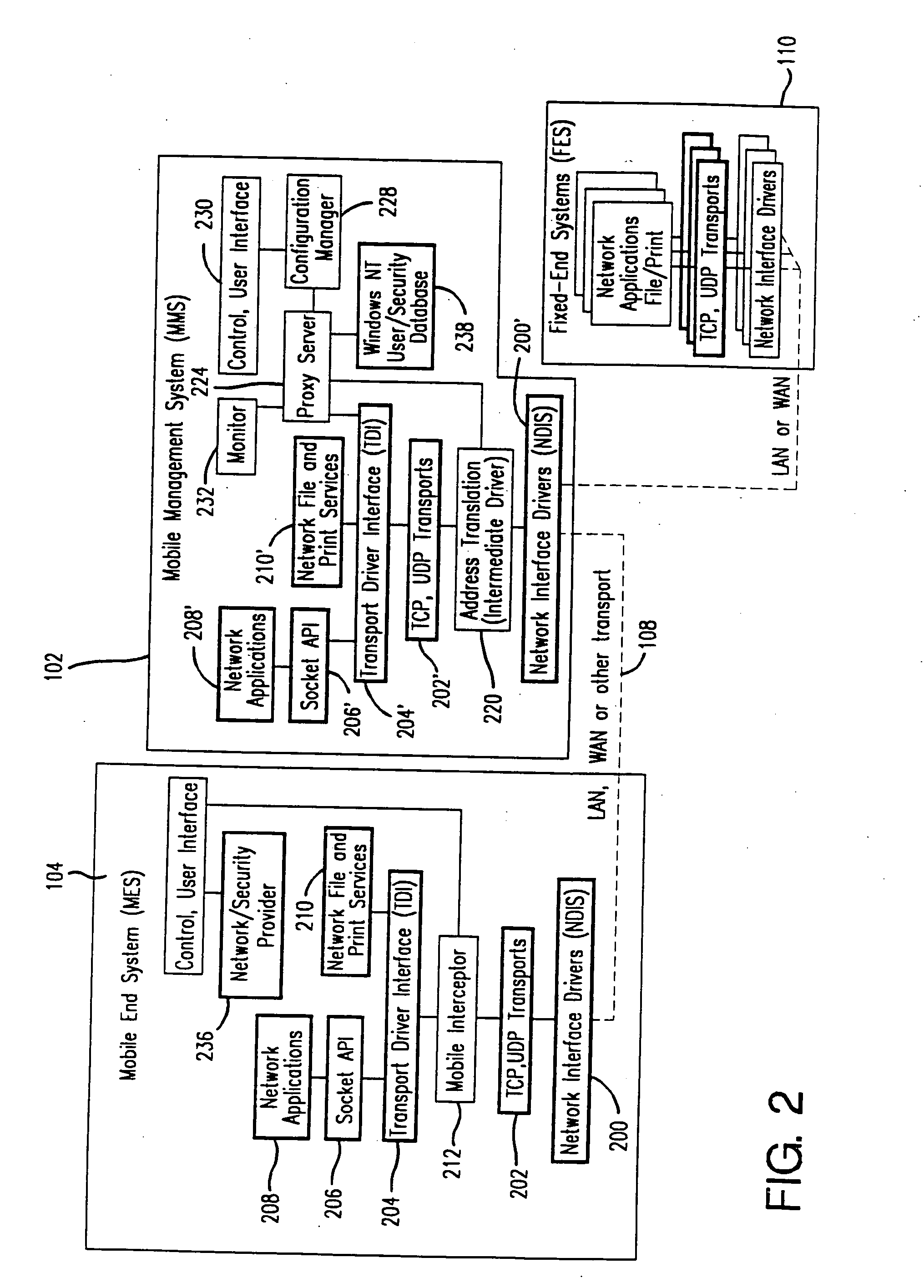
Mobile networking system and method
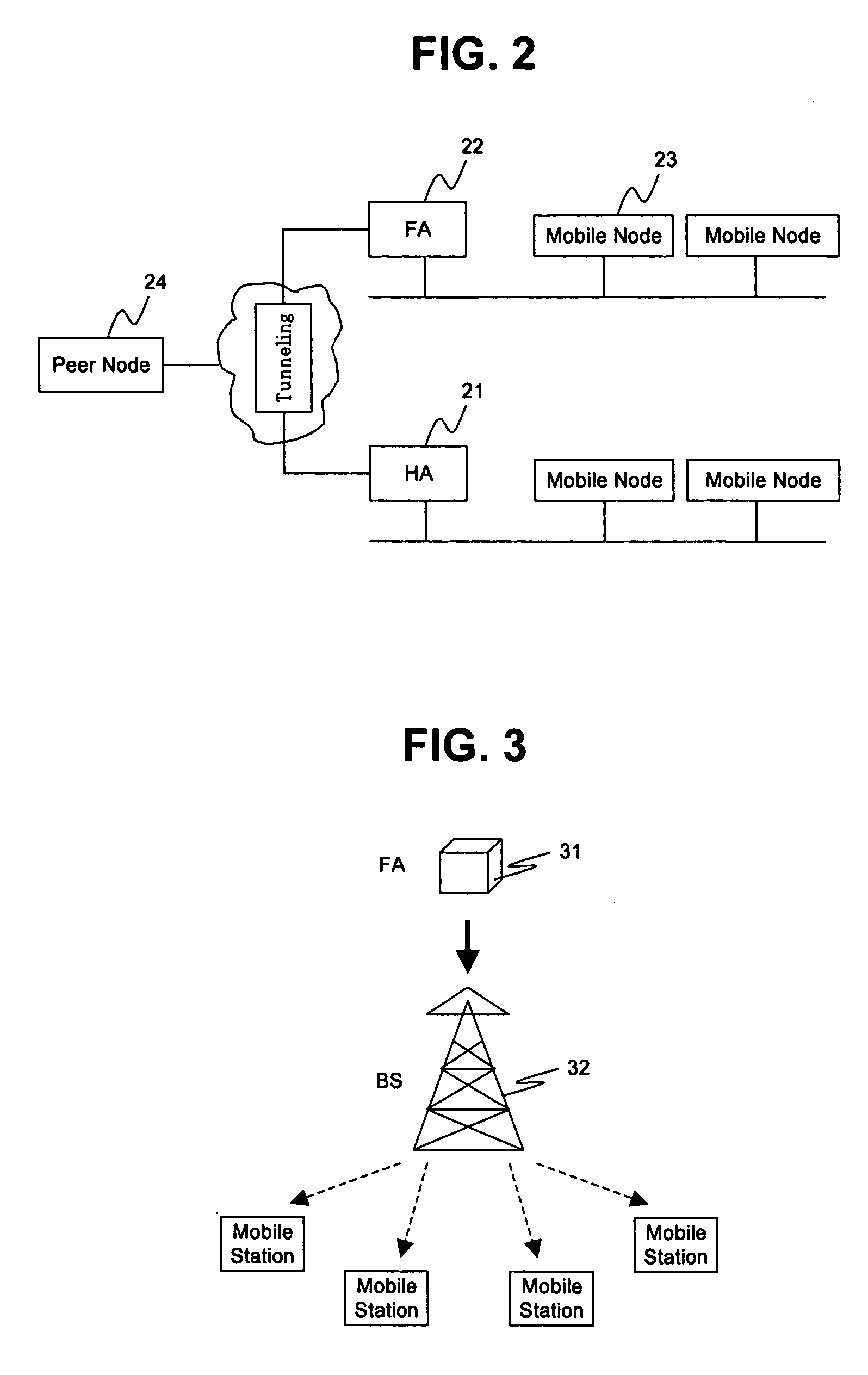
ActiveUS20060123079A1Take advantage ofEasy accessMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsMobile endNetwork address
A seamless solution transparently addresses the characteristics of nomadic systems, and enables existing network applications to run reliably in mobile environments. A Mobility Management Server coupled to the mobile network maintains the state of each of any number of Mobile End Systems and handles the complex session management required to maintain persistent connections to the network and to other peer processes. If a Mobile End System becomes unreachable, suspends, or changes network address (e.g., due to roaming from one network interconnect to another), the Mobility Management Server maintains the connection to the associated peer task—allowing the Mobile End System to maintain a continuous connection even though it may temporarily lose contact with its network medium. An interface-based listener uses network point of attachment information supplied by a network interface to determine roaming conditions and to efficiently reestablish connection upon roaming. The Mobility Management Server can distribute lists to Mobile End Systems specifying how to contact it over disjoint networks. Architectures are provided for bridging between IPv4 and IPv6 Internet Protocols.
Owner:MOBILE SONIC INC
Method and system capable of providing mobility support for IPv4/IPv6 inter-networking
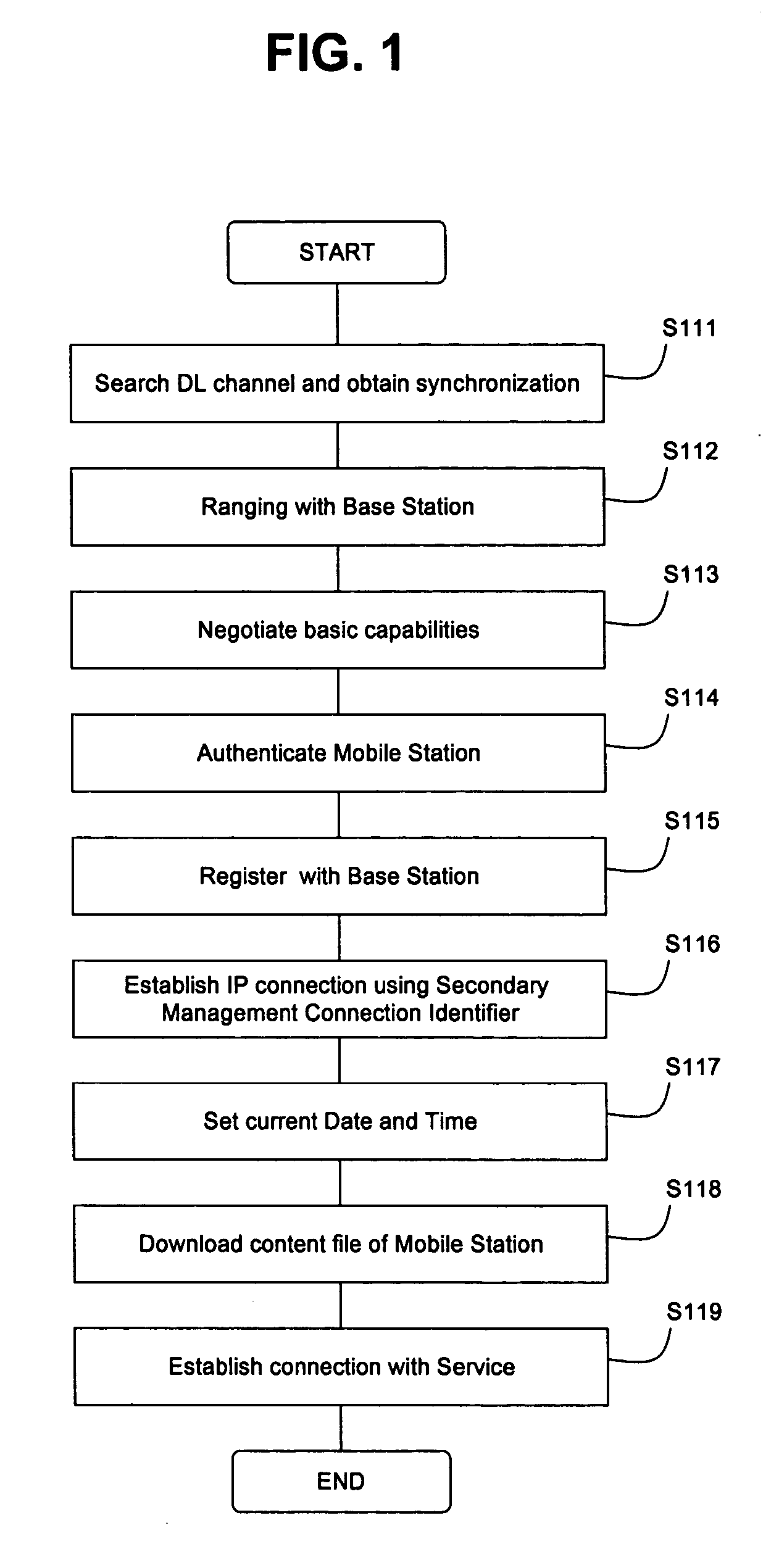
InactiveUS6862274B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork packetForeign agent
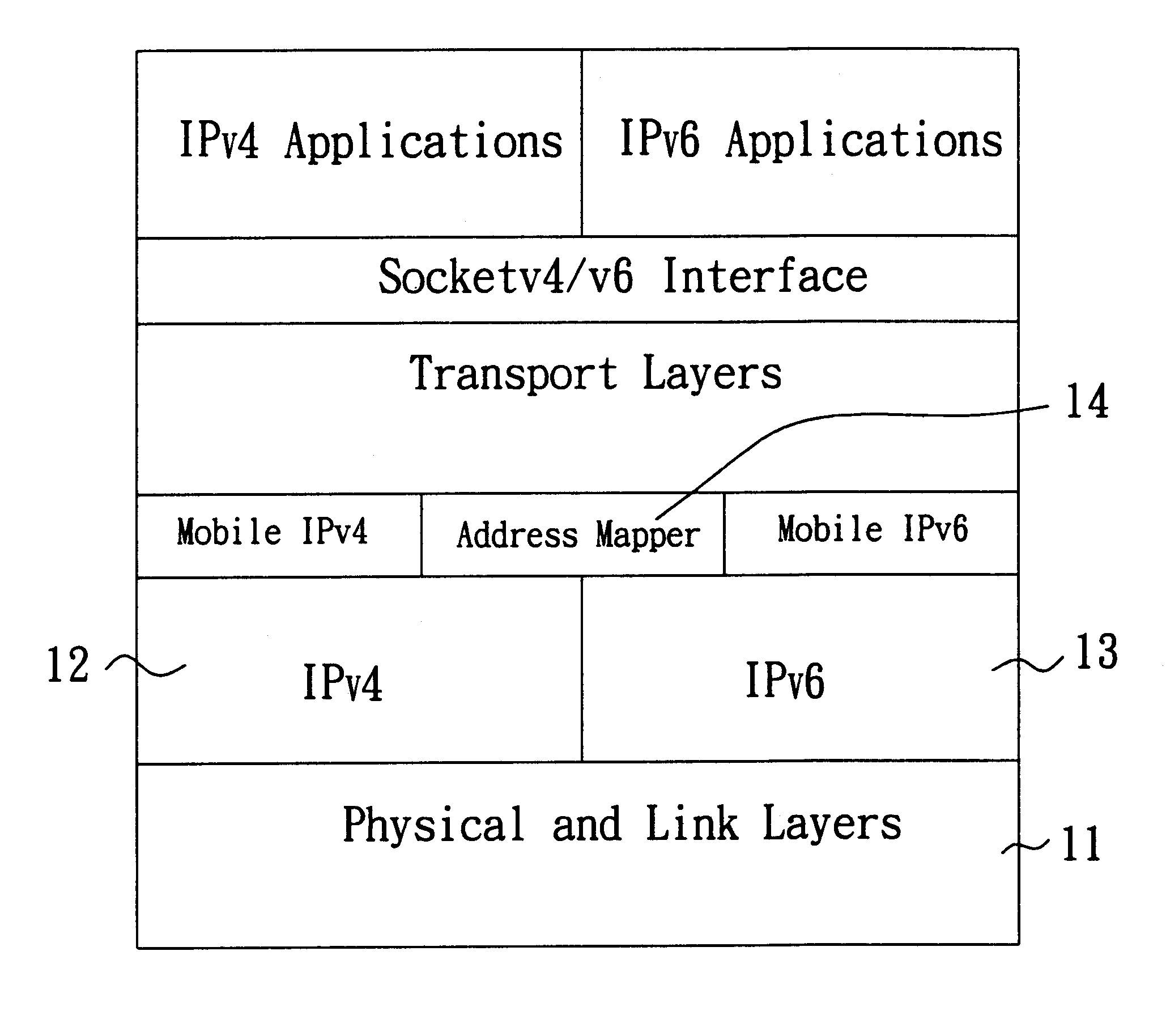
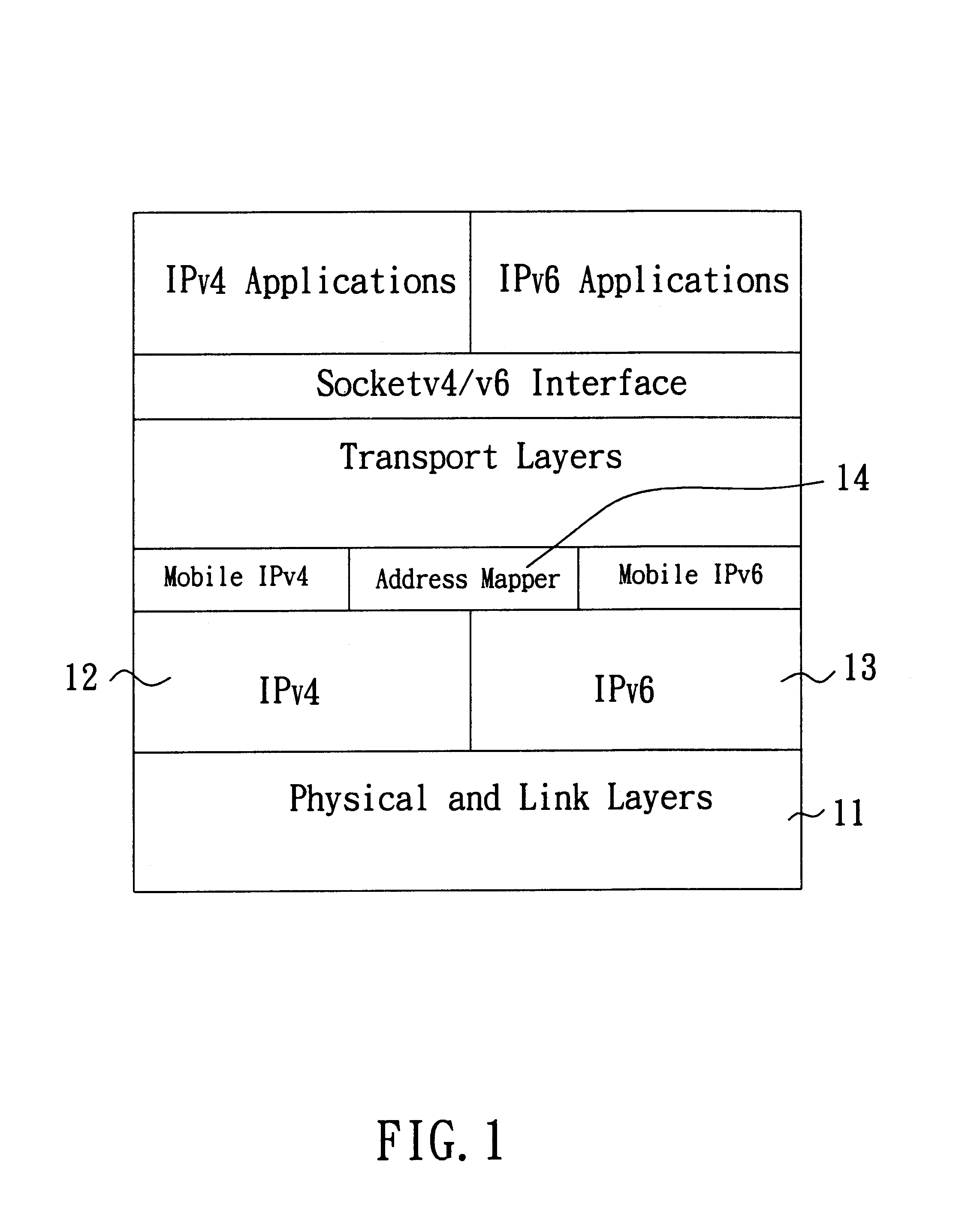
A method and system capable of providing mobility support for IPv4 / IPv6 inter-networking to a mobile node is disclosed. The mobile node in the system has an address mapper, an IPv4 protocol stack and an IPv6 protocol stack in the network layer. When moving from IPv4 to IPv6 networks, the mobile node registered an IPv4 address receives router advertisement packets from an IPv6 router, so as to obtain a IPv6 care-of-address, and resolve the IPv6 care-of-address by an IPv4 care-of-address. The address mapper issues an IPv4 message to register the IPv4 care-of-address. When moving from IPv6 to IPv4 networks, the mobile node registered an IPv6 address receives agent advertisement messages from a foreign agent, so as to obtain an IPv4 care-of-address, resolve the IPv4 care-of-address by an IPv6 care-of-address. The address mapper issues an IPv6 message to register and update binding information by the IPv6 care-of-address.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
IP addressing to support IPv4 and IPv6
InactiveUS20050265360A1Minimize power consumptionSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsIp addressBroadcasting
A broadcast dedicated connection identifier is used for broadcasting certain types of Internet Protocol (IP) control messages to allow proper IP address establishment for IPv4 and IPv6.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
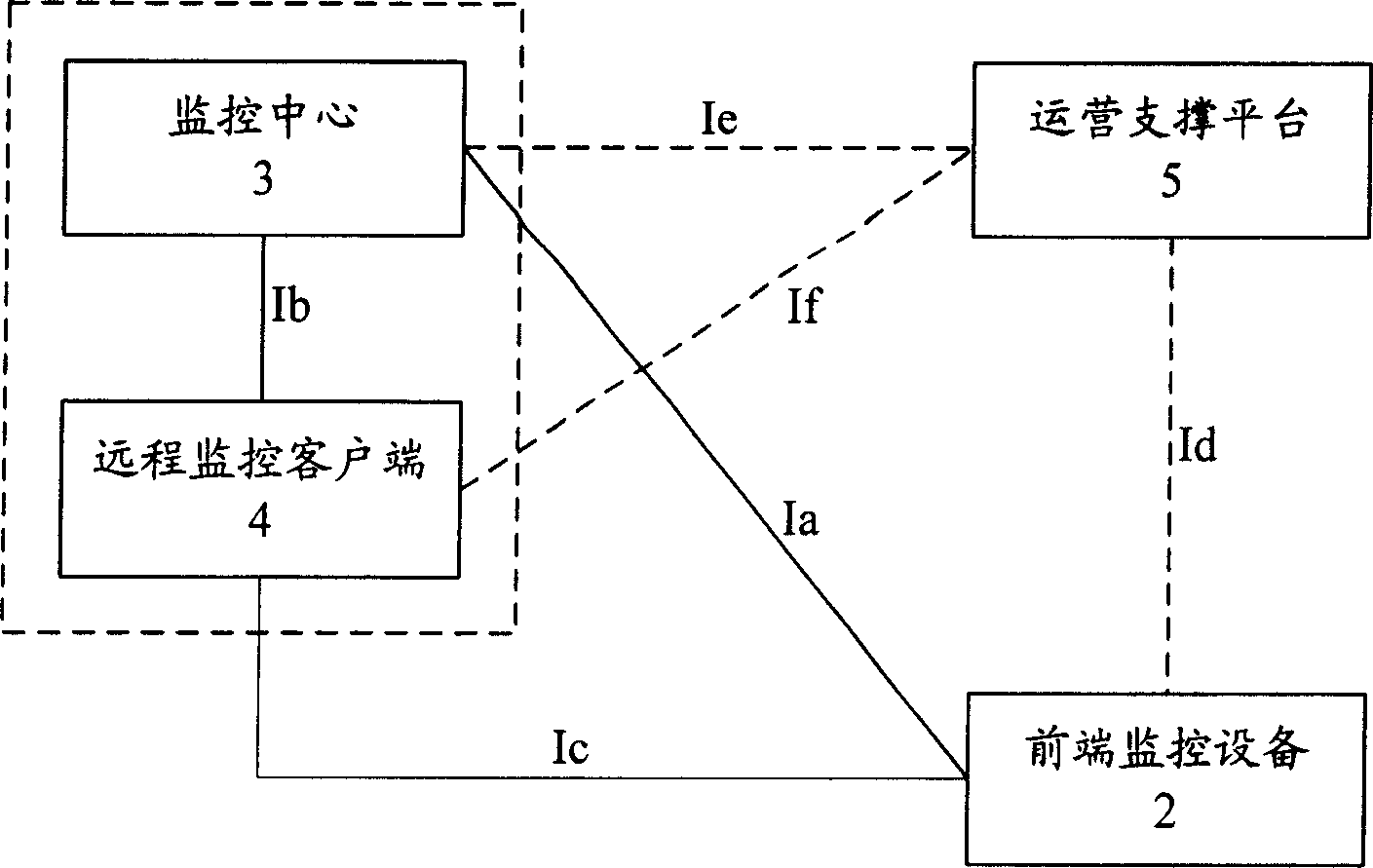
Remote vedio monitoring system based on next generation interconnection network and its implementing method
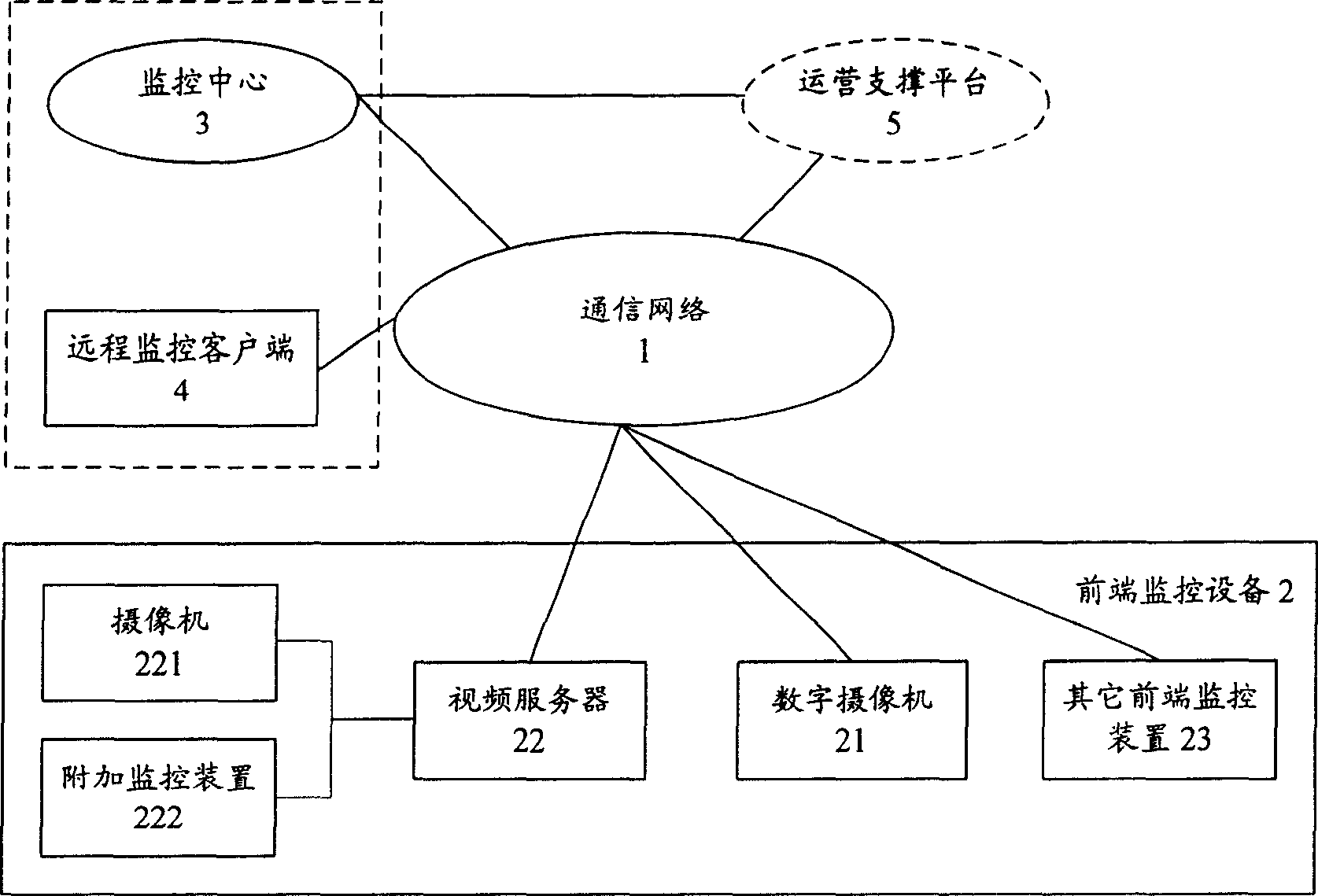
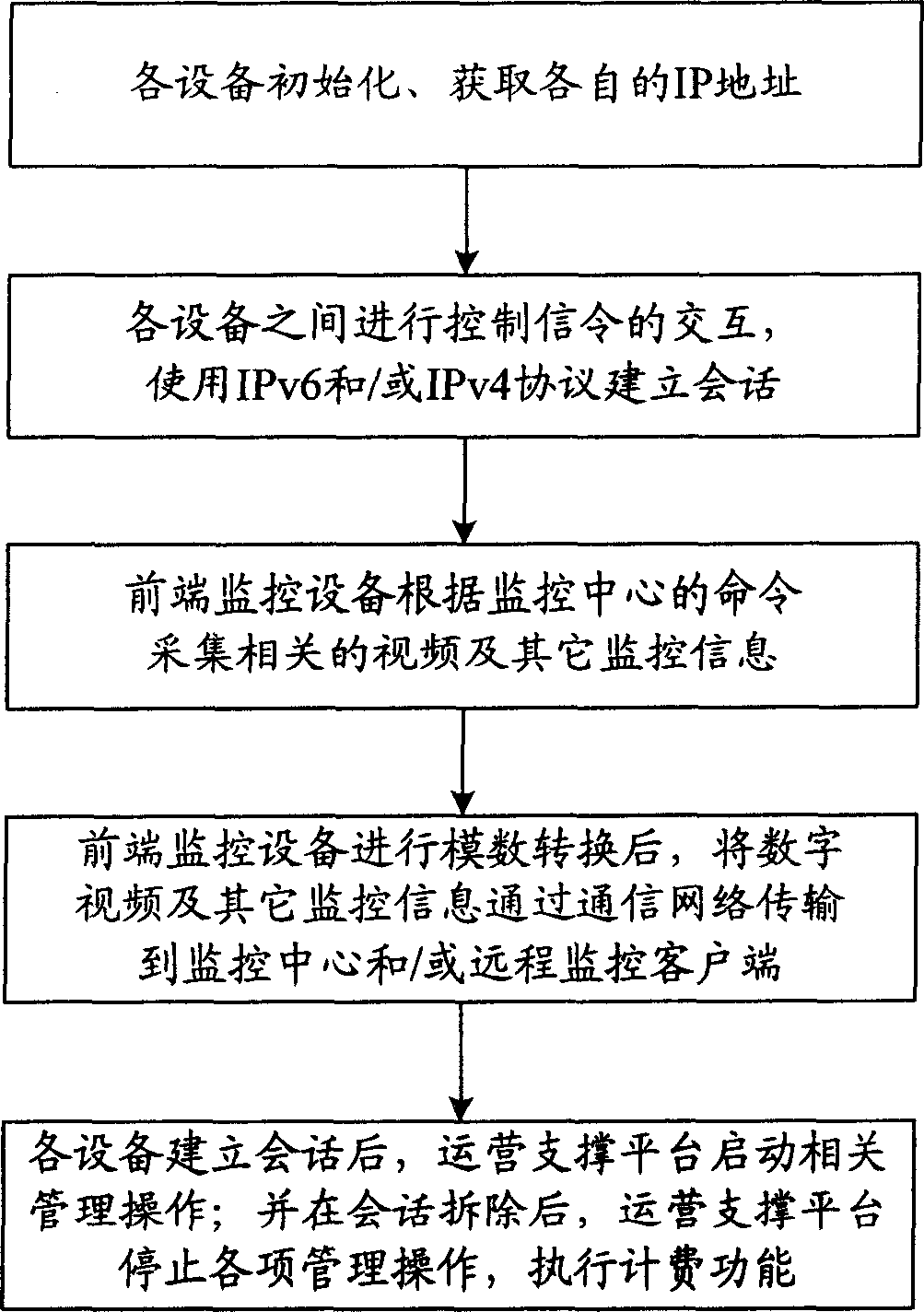
InactiveCN1913461ASimple structureComplete structureClosed circuit television systemsTransmission monitoringVideo monitoringDigital video
This invention relates to a remote video monitor system and a realization method based on the next generation, in which, said system is composed of a communication network, a front monitor device, a monitor center and a remote monitor customer end and a business supporting platform, provides business level remote video monitor service to the public by applying a multi-stage regional structure network topological and digital video compression coding technology, supporting two kinds of network protocols of IPv6 and IPv4 at the same time and using the IPv6 transmission data first, in which, coding addresses of the monitor nodes are ruled and unified and the monitor terminal is set with the only IP address in the world suitable for being accessed and applied at any time and any place.
Owner:BEIJING INTERNET INST
Communication using private IP addresses of local networks
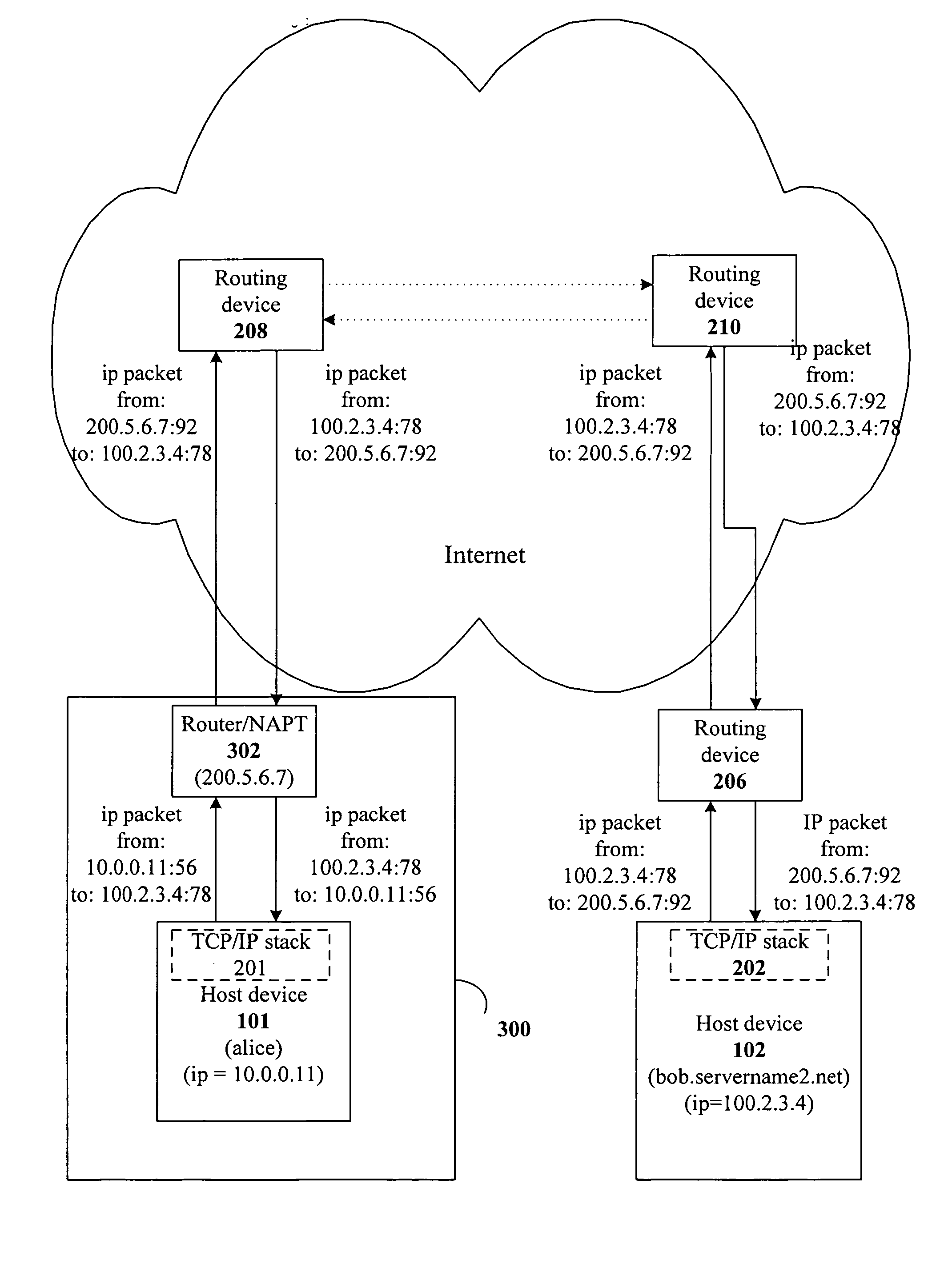
InactiveUS20070195800A1Improve abilitiesTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPrivate IPNAT traversal
A system, apparatus and method to use private IP addresses to designate host devices or nodes in different networks for communication purposes are described. Various embodiments of the invention address the problem of a shortage of public IP addresses under IPv4 architecture. In one embodiment of the invention, dynamic NAT penetration capabilities are provided which consequently expand the capability of running peer-to-peer applications on the Internet.
Owner:YANG ZHENG +2
Name-based routing system and method
Owner:128 TECH
Packet communication method and apparatus and a recording medium storing a packet communication program
InactiveUS6580717B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareInformation processing
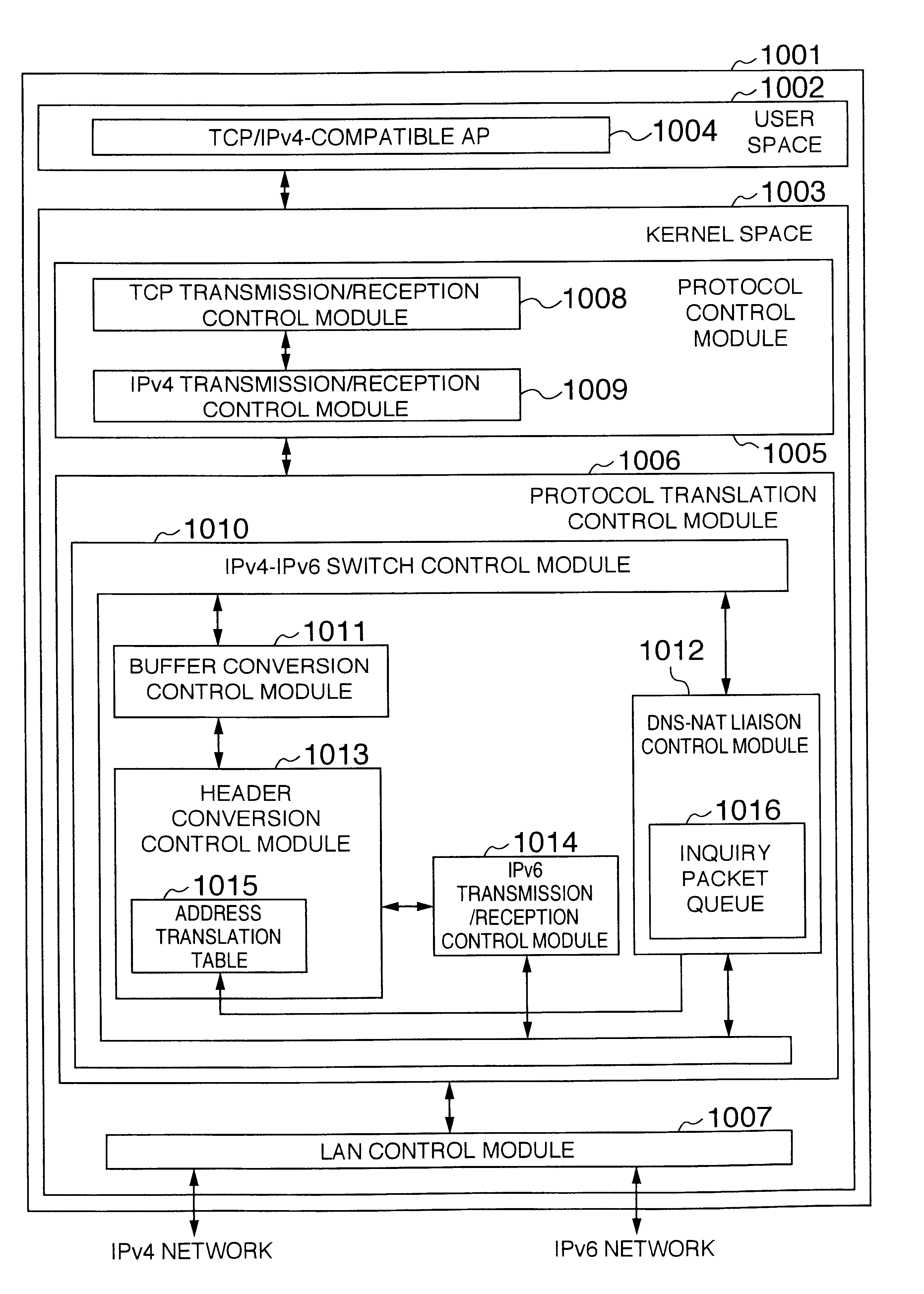
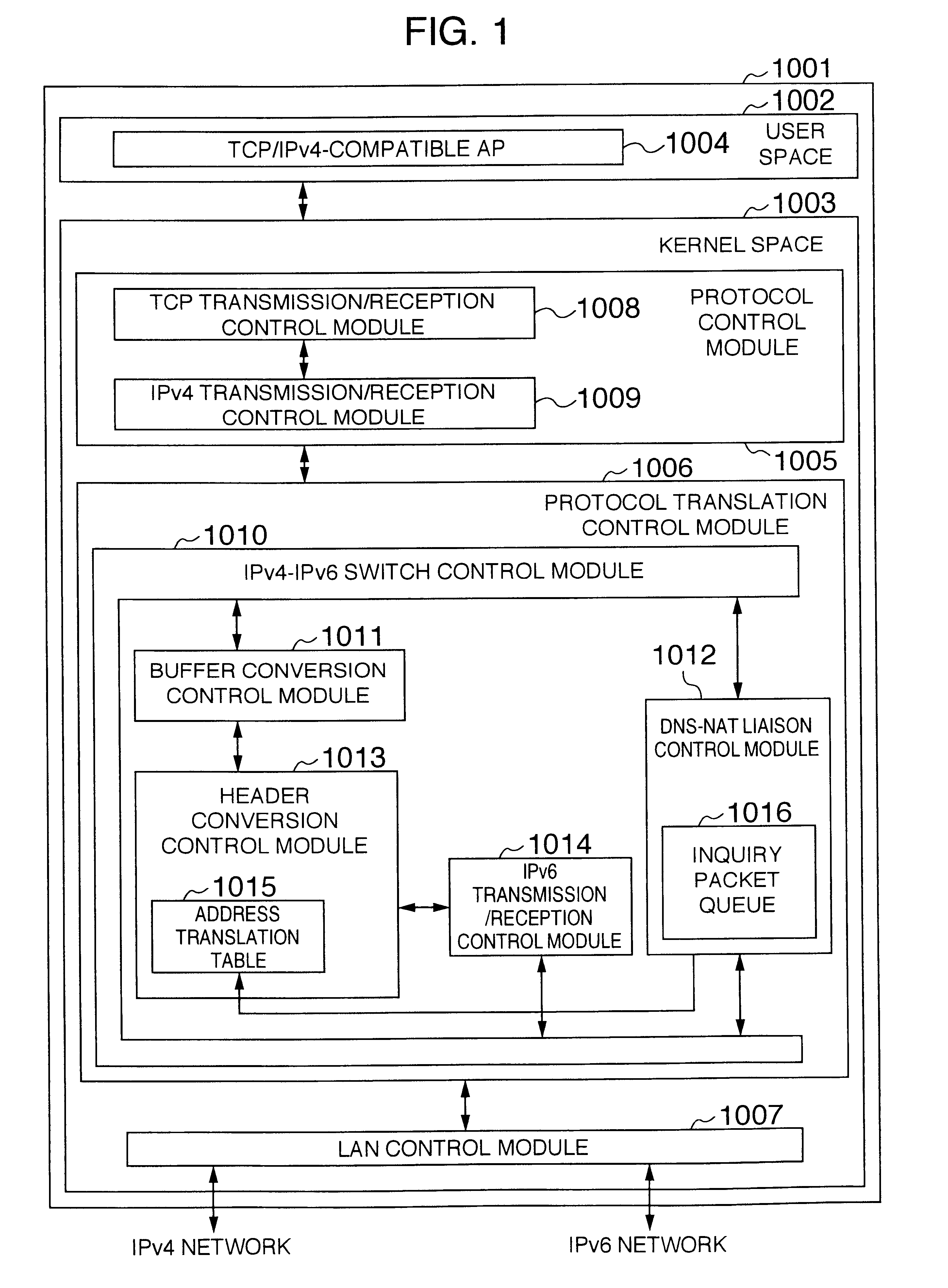
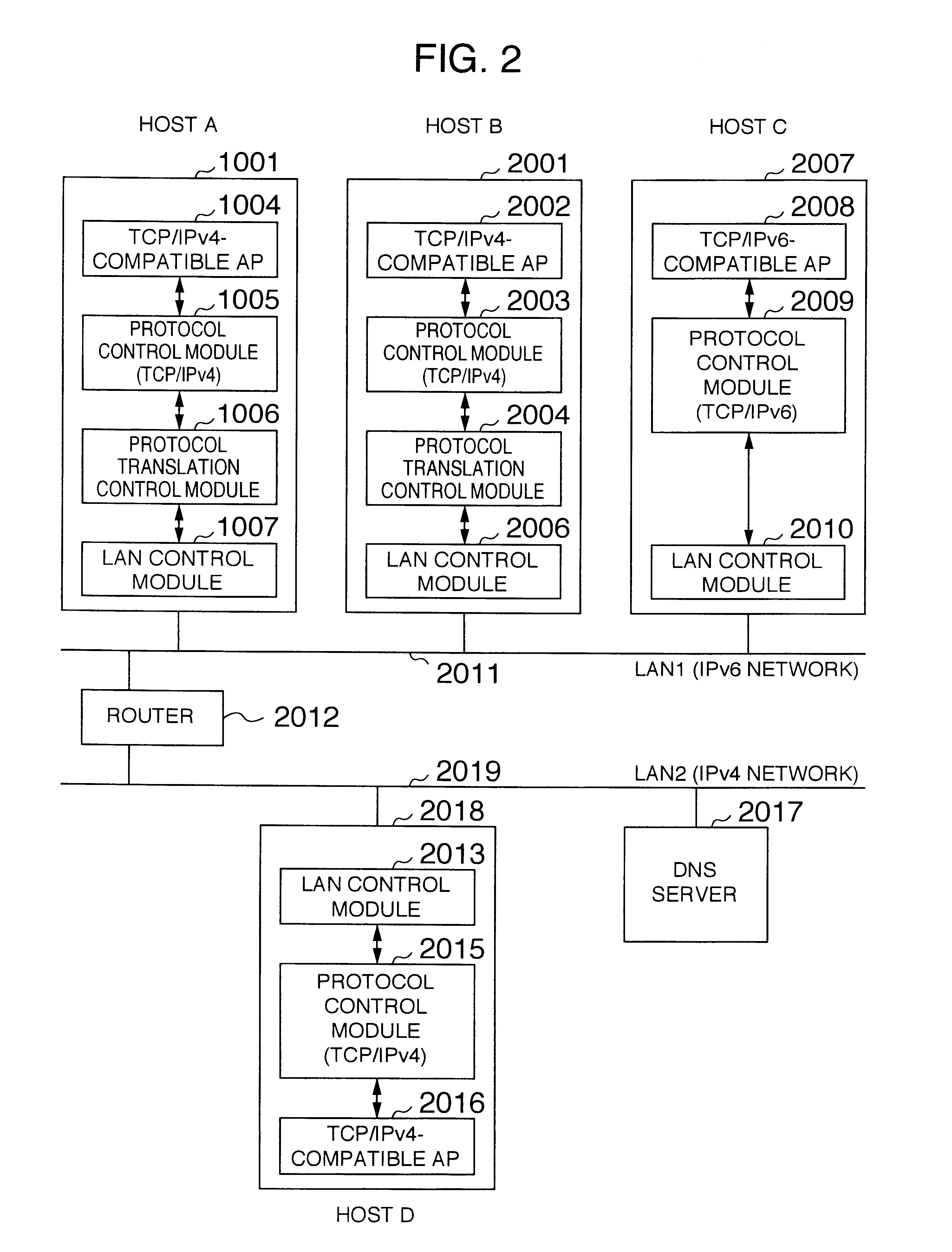
A packet communication method and a packet communication system capable of making an IPv4-compatible application operating on an information processing apparatus communicate with another information processing apparatus connected to an IPv6 network without using an address translation router. In the information processing apparatus connected to the IPv6 network incorporates, an IPv4-to-IPv6 protocol conversion control function is incorporated in a LAN driver. A protocol conversion control module receives an IPv4 packet from a protocol control module. When a send destination IPv4 address contained in a header of the packet is registered in an address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, an IPv6 address is generated to be sent onto a LAN. Unless the send destination IPv4 address contained in the packet header is registered in the address translation table incorporated in the protocol conversion control module, the IPv4 packet as received is intactly sent onto the LAN.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
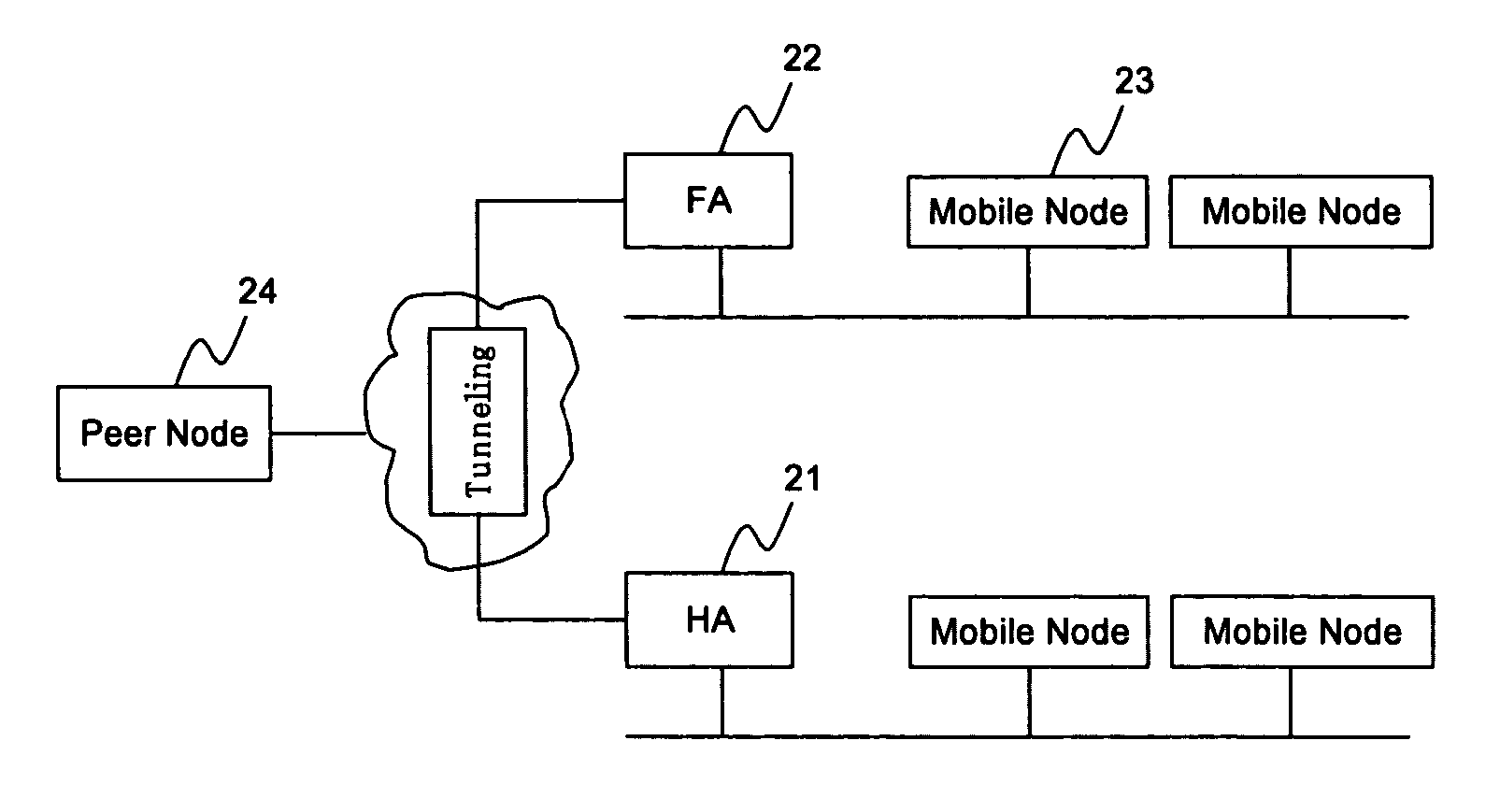
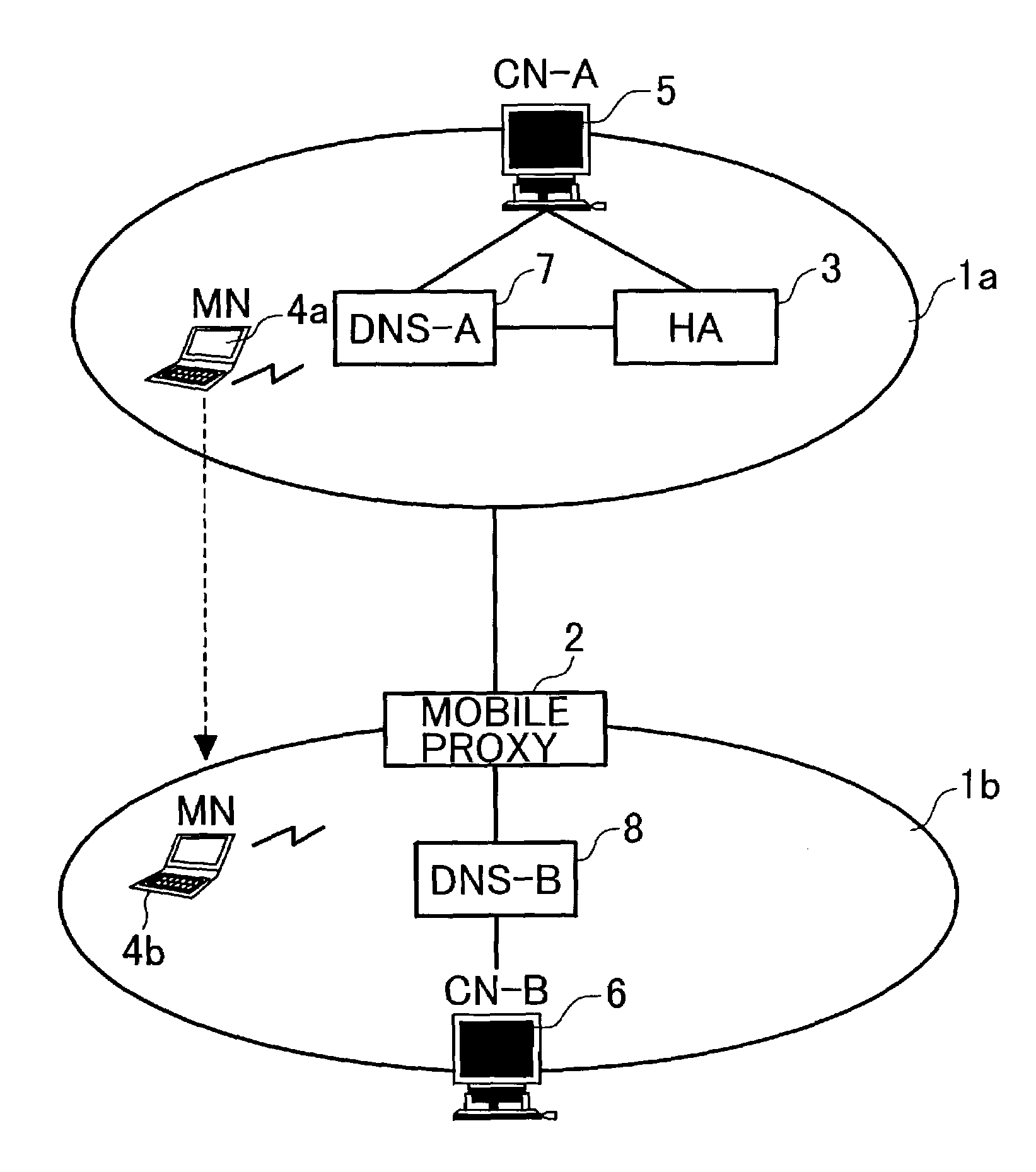
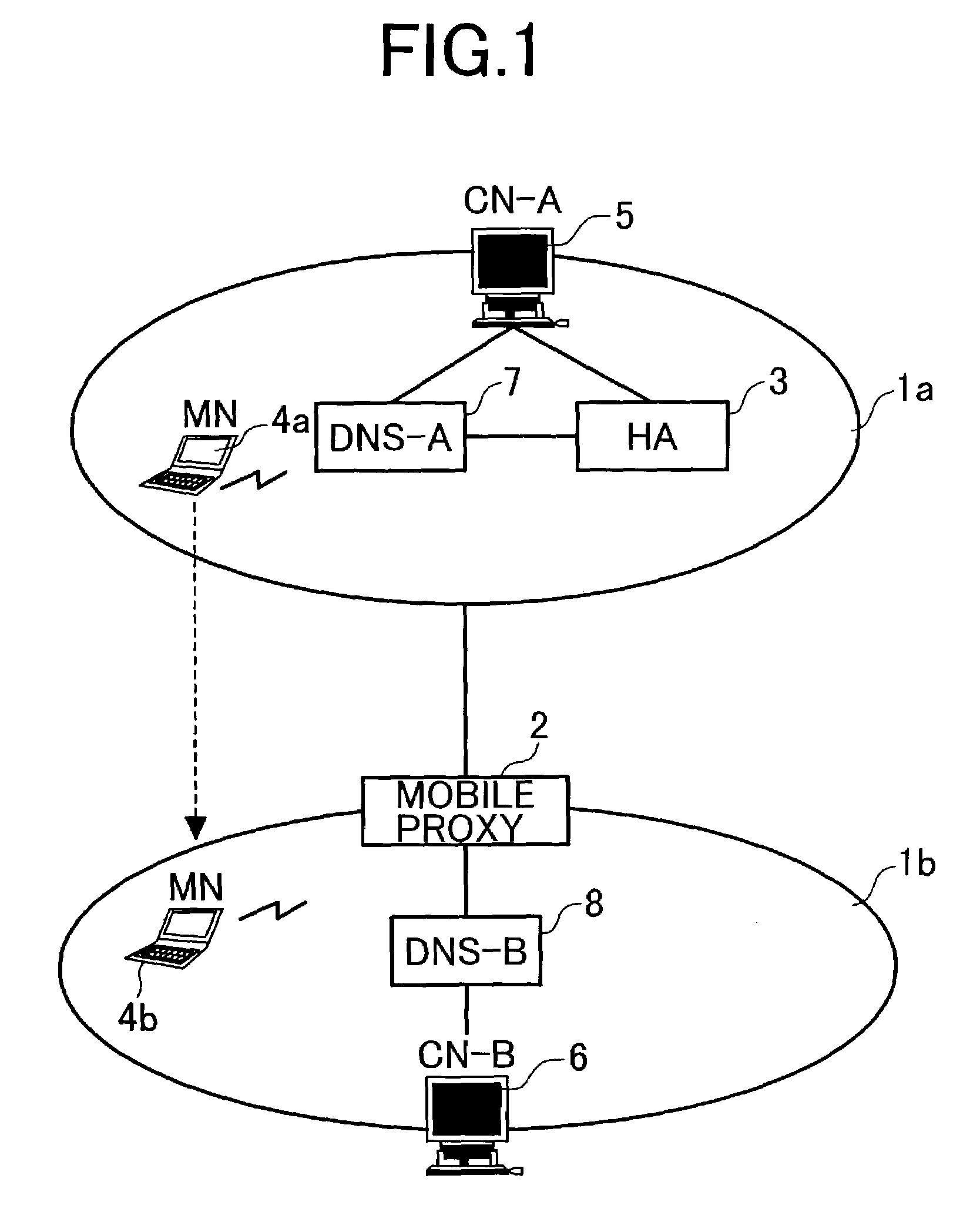
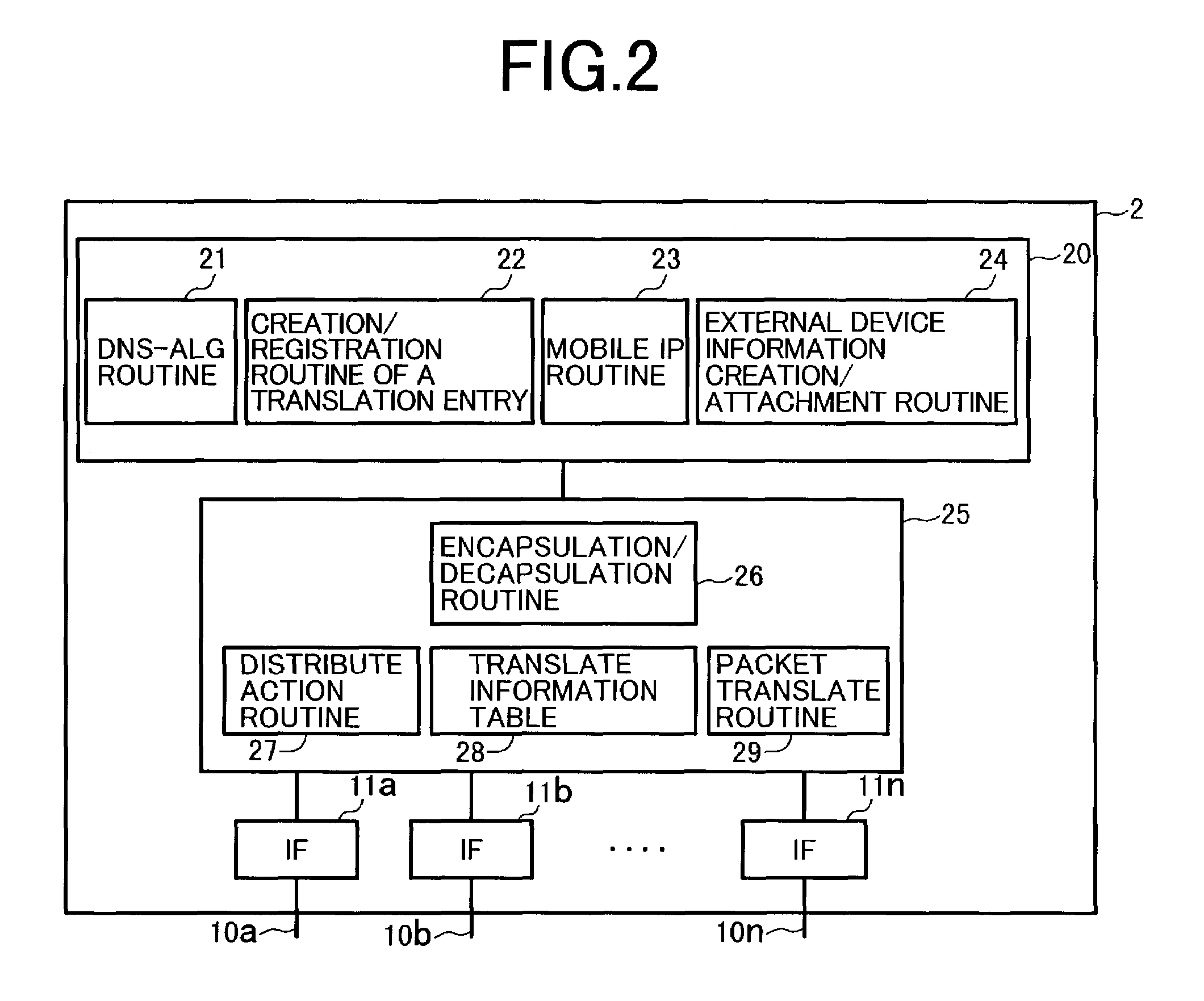
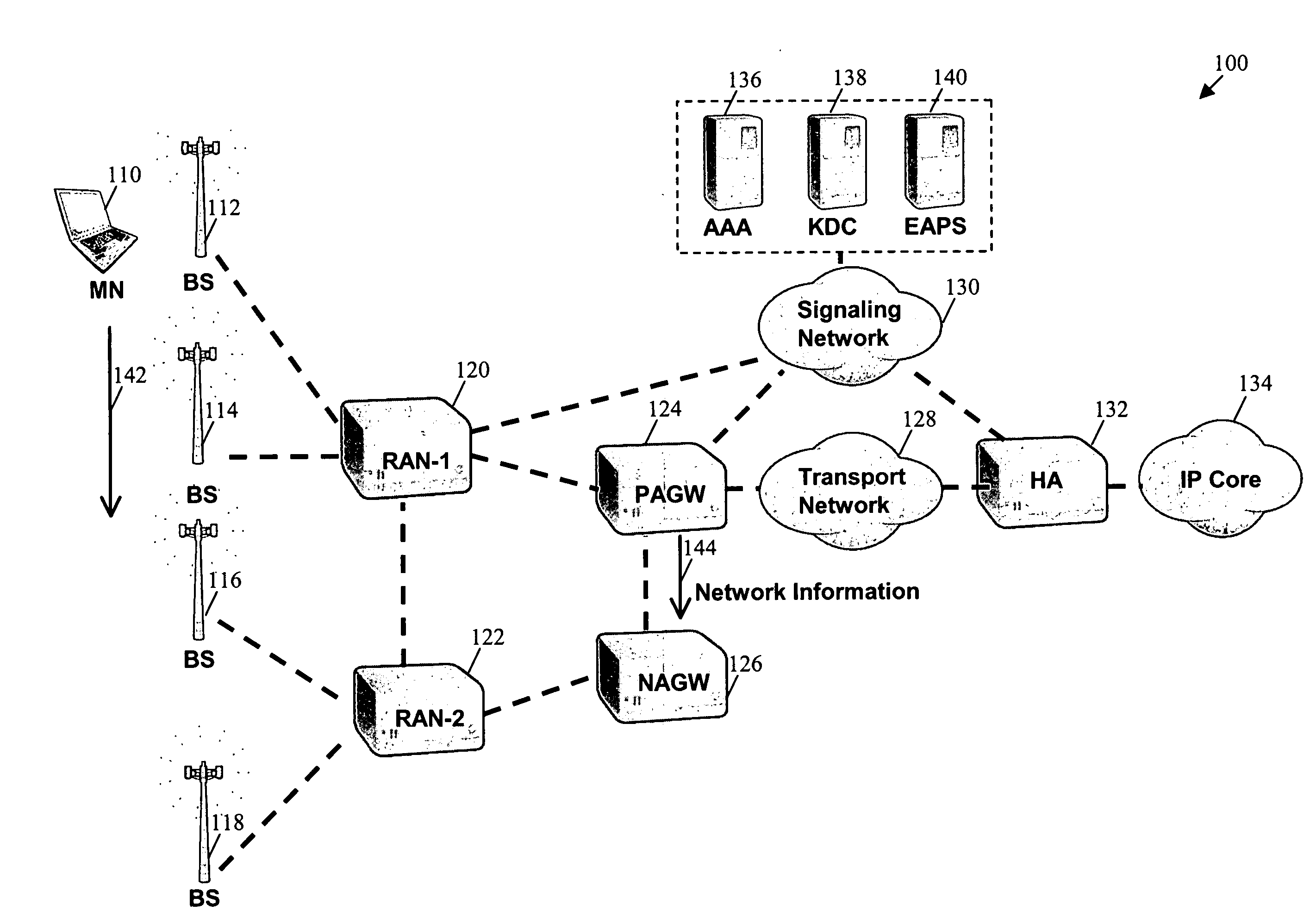
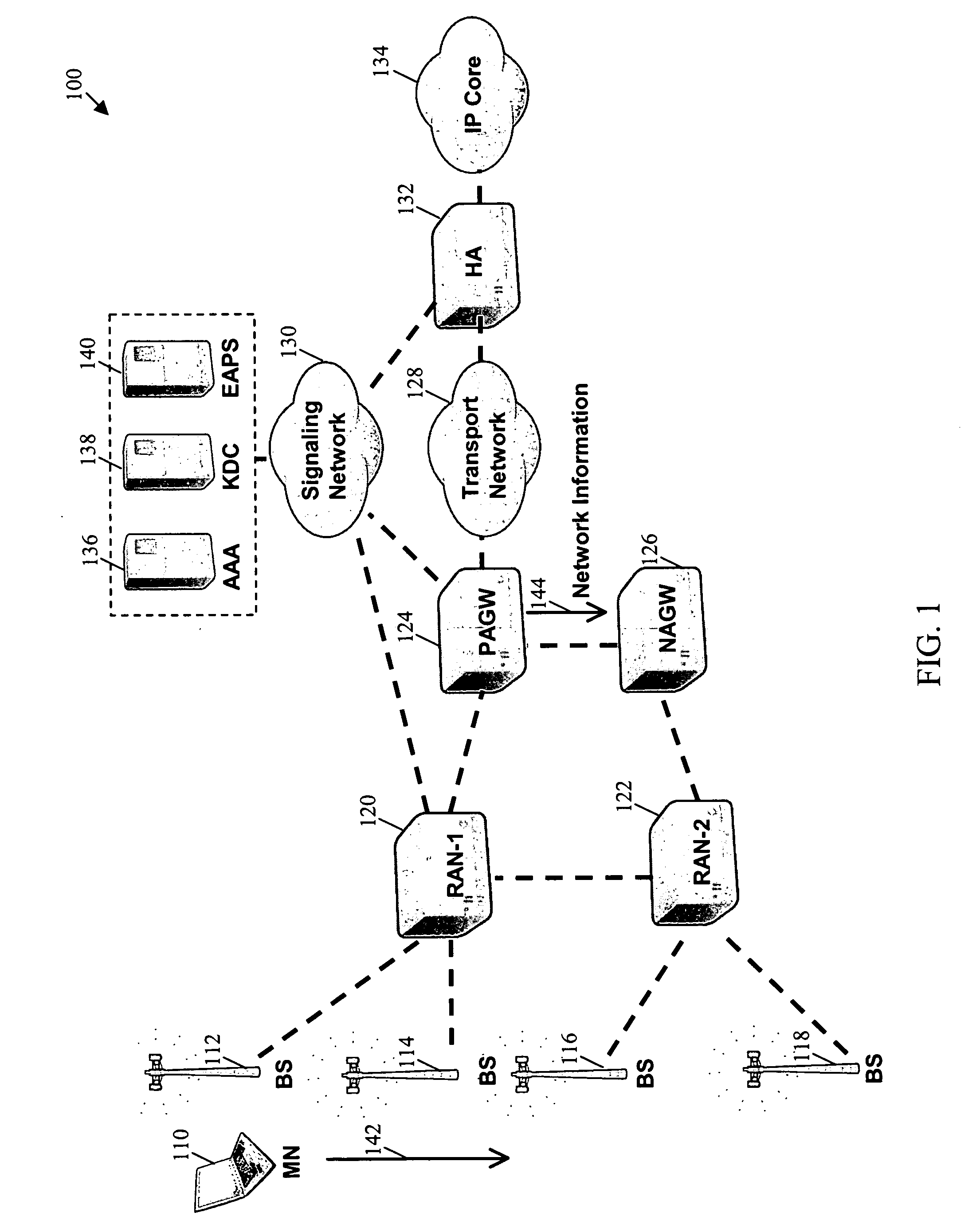
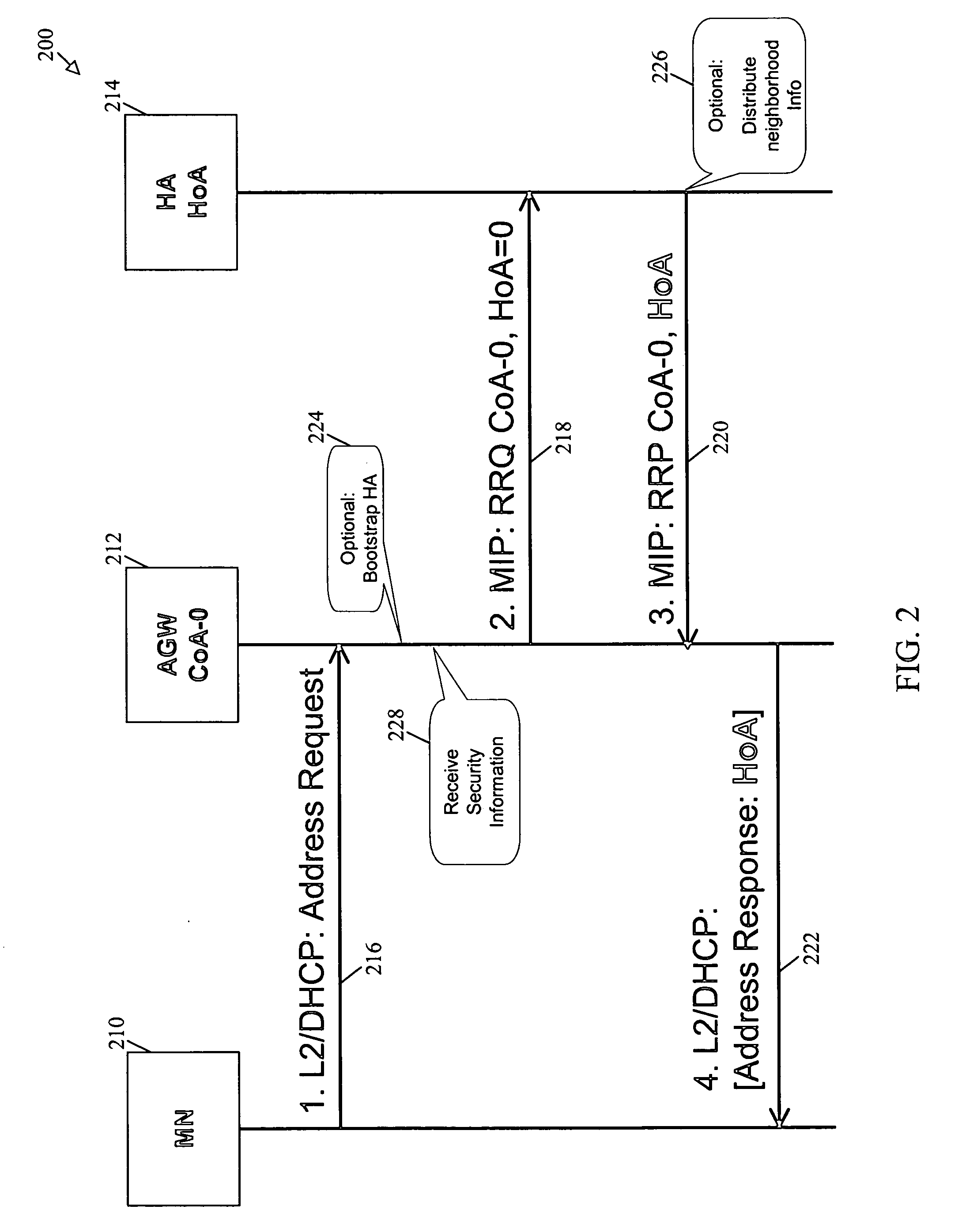
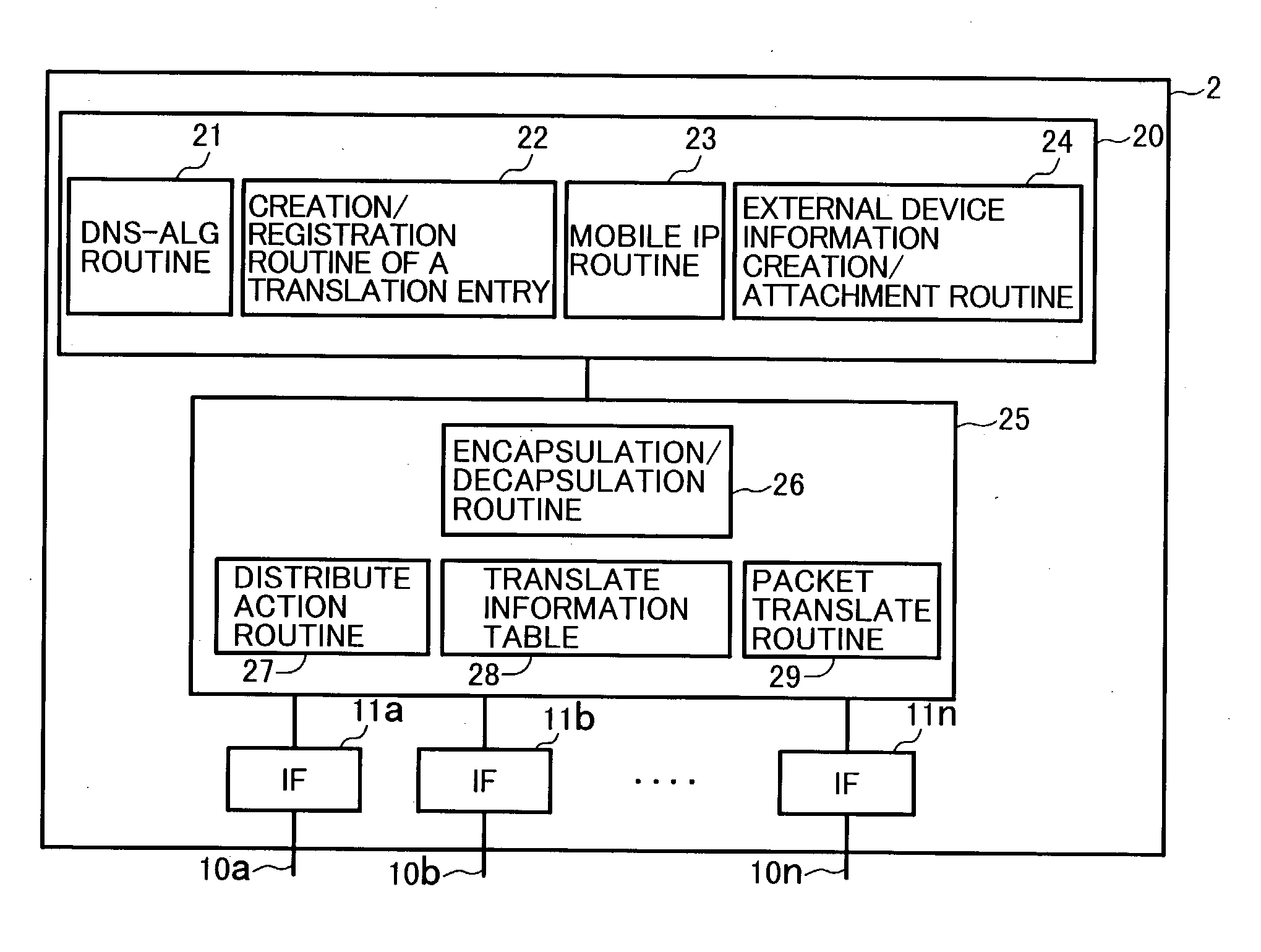
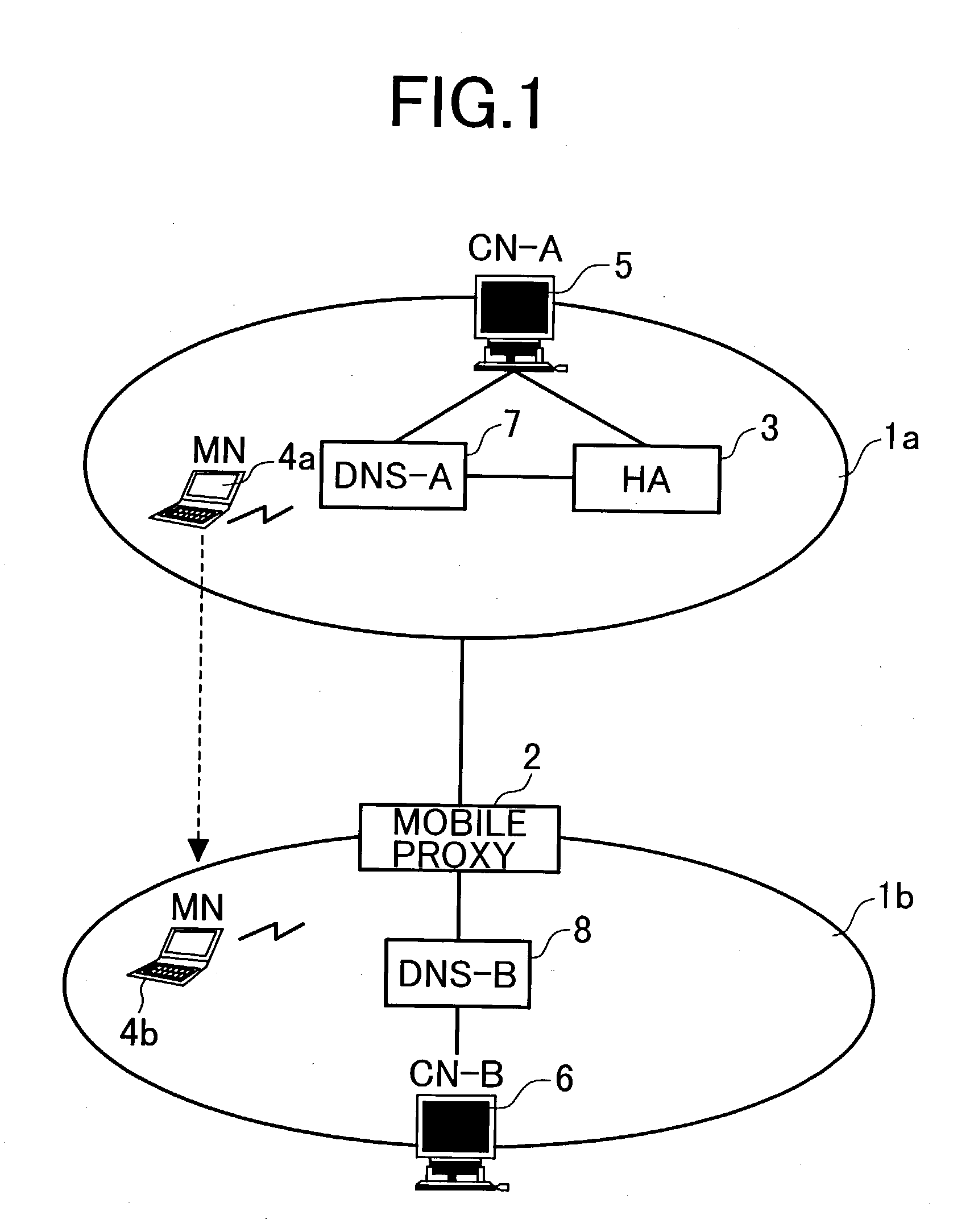
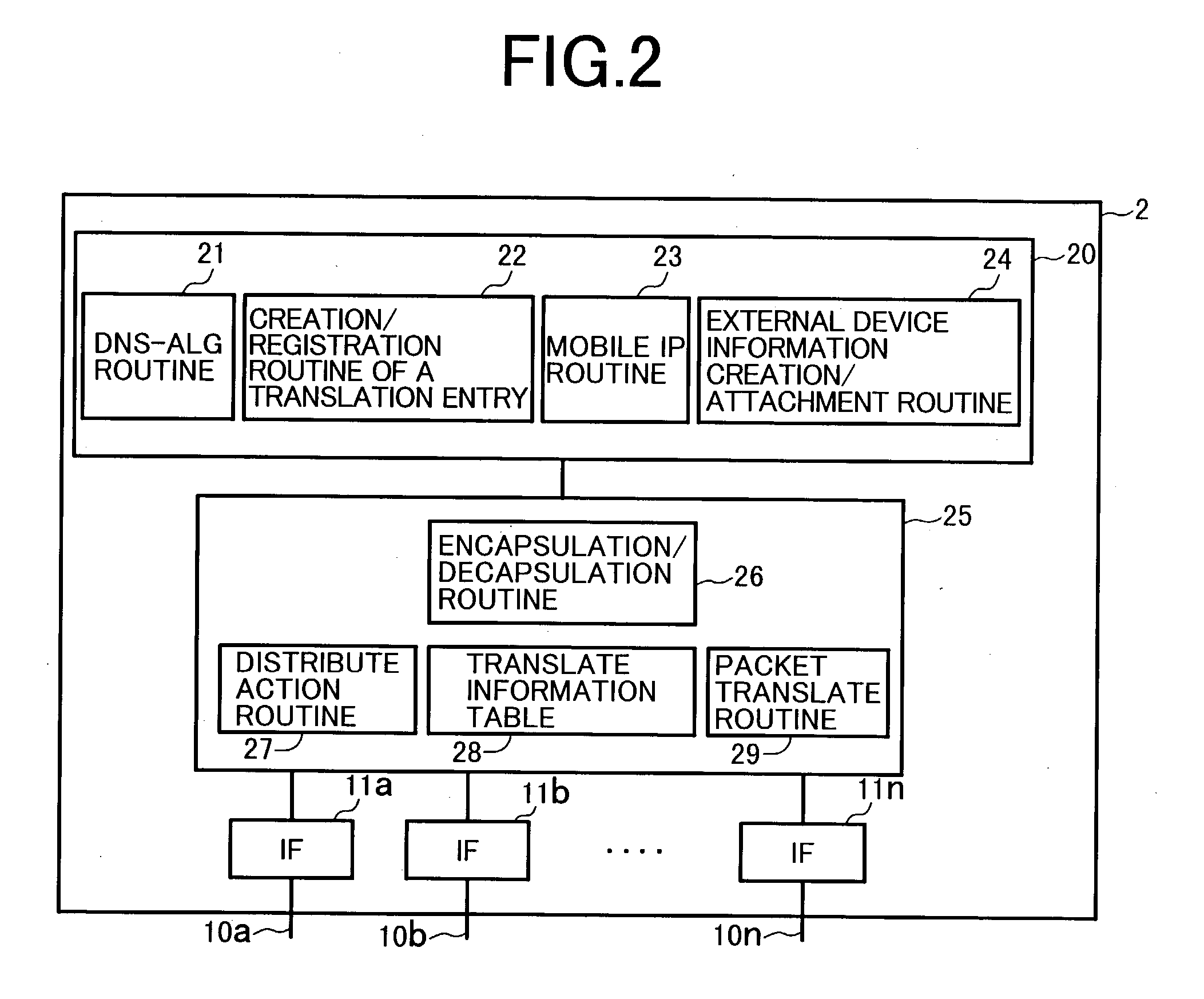
System using mobile proxy for intercepting mobile IP message and performing protocol translation to support multiple communication protocols between mobile networks
InactiveUS7162529B2Connection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork Communication ProtocolsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Since the Mobile IP is defined under the assumption that a mobile node roams between networks conforming to the same communications protocols, mobile communications between IPv4 and IPv6 are not possible. Further, a translation of the location registration messages also requires translating the format between different protocol layers. To solve this problem, a mobile proxy apparatus 2 is provided between a home network 1a and a foreign network 1b governed by different communications protocols. The mobile proxy apparatus 2 has a DNS-ALG function, a translator function and a Mobile IP function, and, by combining these functions, performs address translation and format translation on Mobile IP messages and user packets. The MN4 has Mobile IPv4 and Mobile IPv6 functions and executes communication suitable for the communications protocol governing the network to which it moves.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and device for realizing different IP data packet repeating using strategic flow
InactiveCN1612562AAvoid packet-by-packet lookupsDoes not affect interoperabilityTelephonic communicationData switching networksData streamInterconnection
Strategy stream mode adopted in the disclosed method and device is realized to support forwarding both IPv4 and IPv6 in same physical pipeline. Based on data stream types of different target IP, multielement attribute set of corresponding data packet is picked up, and strategy stream id is calculated. Forwarding entries of strategy stream is searched accurately based on the said id. If there is matched entry of strategy stream found, then modifying relevant content and forwarding operation are carried out according to the said entry. If there is no matched entry, then corresponding treatment is carried out for the data packet by control plane based on the attribute of the data packet. Synthesizing information in control plane and entry information related to applications generates a piece of forwarding entry for local strategy stream. The said generated forwarding entry is distributed to forwarding plane for latter data packet to use so as to avoid looking up packet of IPv4 or IPv6.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for mobility management on wireless networks
ActiveUS20070189255A1Reduce latencyReduce lost data packetUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsWireless mesh networkSecurity association
Systems and methods to manage network access (e.g., IPv4 and IPv6) and layer 3 mobility are provided. This can allow mobility management to be moved from a mobile node's stack to the access gateway, simplifying the stack and providing fast handoffs. The mobility management at an access gateway further allows a mobile node to keep its dynamically assigned IP address for the duration of a call session and through handoffs. The placement of access gateways in a domain of trust allows security information to be passed between access gateways in a handoff so that the security associations do not need to be re-authenticated with the mobile node. One or more of the above mobility management features can be used to provide a fast and seamless handoff for a mobile node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mobile proxy apparatus and mobile communication method
InactiveUS20030225900A1Connection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork Communication ProtocolsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Since the Mobile IP is defined under the assumption that a mobile node roams between networks conforming to the same communications protocols, mobile communications between IPv4 and IPv6 are not possible. Further, a translation of the location registration messages also requires translating the format between different protocol layers. To solve this problem, a mobile proxy apparatus 2 is provided between a home network 1a and a foreign network 1b governed by different communications protocols. The mobile proxy apparatus 2 has a DNS-ALG function, a translator function and a Mobile IP function, and, by combining these functions, performs address translation and format translation on Mobile IP messages and user packets. The MN4 has Mobile IPv4 and Mobile IPv6 functions and executes communication suitable for the communications protocol governing the network to which it moves.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
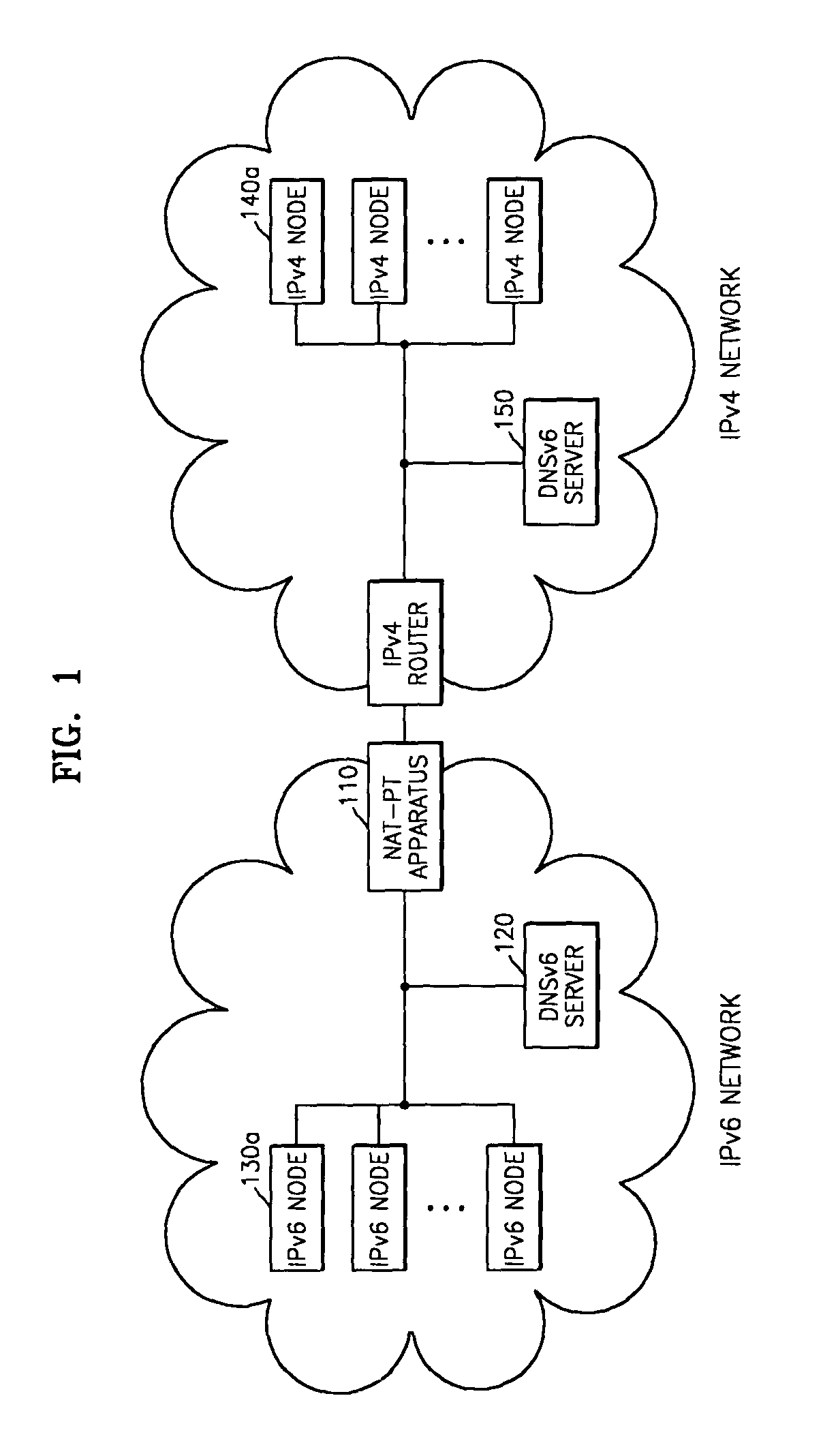
Method and apparatus for interconnecting IPv4 and IPv6 networks
A method and system for interconnecting an Internet protocol version 4 (IPv4) network and an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) network are provided. The system for interconnecting an IPv4 network and an IPv6 network includes IPv4 nodes, IPv6 nodes, and apparatuses for transmitting IP packets between the IPv4 nodes and the IPv6 nodes, wherein the apparatuses for transmitting IP packets share processing state information of the IP packets, using a predetermined message, to distribute their load of processing the IP packets. The IPv4-IPv6 interconnection method involves appropriately arranging NAT-PT apparatuses depending on the size of the networks such that packet processing speed and performance are improved over the use of a single NAT-PT apparatus.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for mixed mode of ipv6 and ipv4 DNS of global server load balancing
Systems and methods for providing one or more GSLB vServers to support both IPv4 and IPv6. The IPv6 support can be provided by permitting both A and AAAA domain name resolution. In other embodiments, the IPv6 support can be provided by modifying data structures to support IPv6 addresses.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
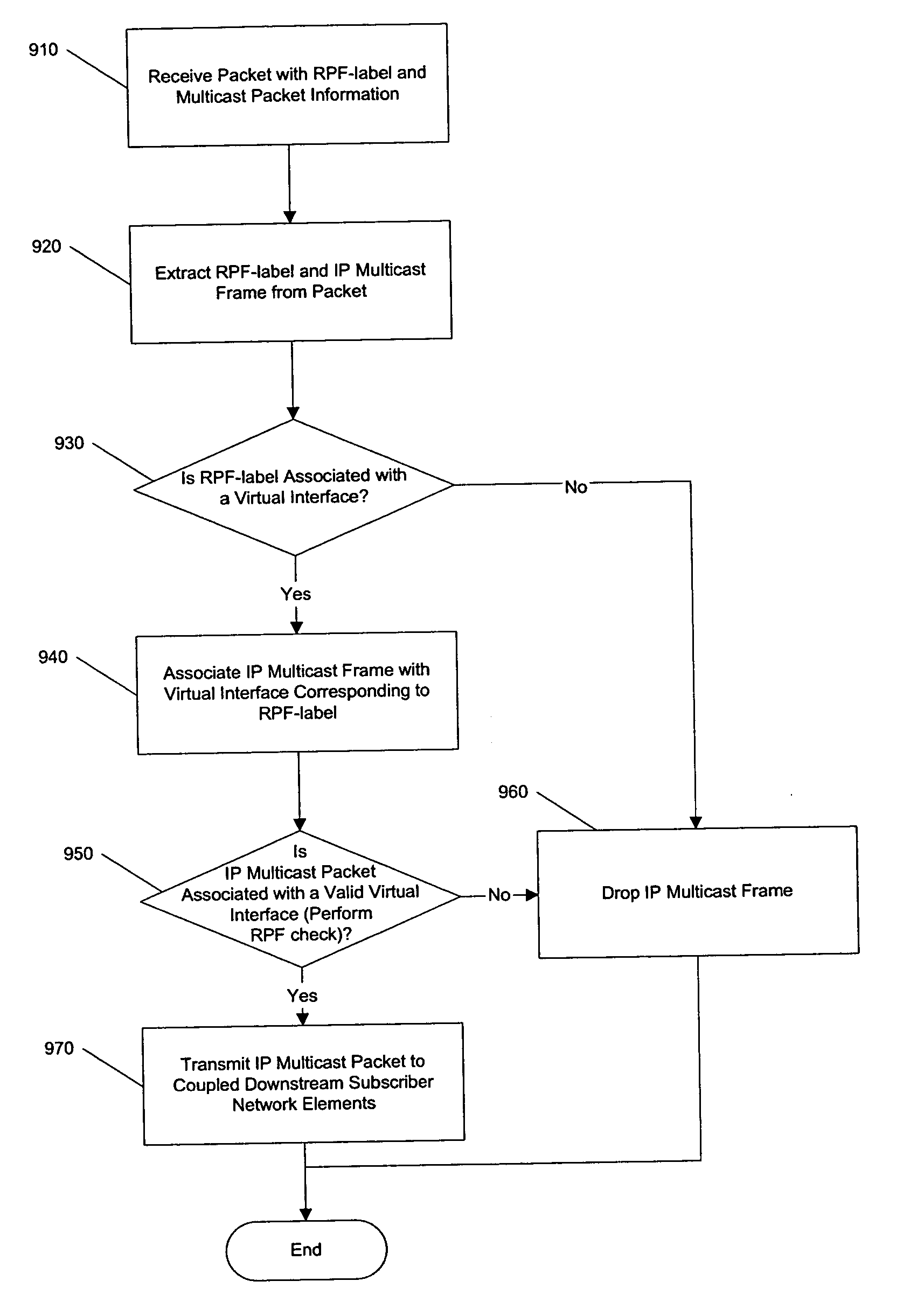
Transporting multicast over MPLS backbone using virtual interfaces to perform reverse-path forwarding checks
ActiveUS20060221975A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexReverse path forwardingData set
A mechanism is provided in which multicast reverse path forwarding can be performed at a provider network egress edge router wherein core routers of the provider network are not configured to support multicast protocols or point-to-multipoint LSPs. An embodiment of the present invention provides for the creation of virtual interfaces in the egress edge router element during configuration of a multicast connection in response to a subscriber request. A virtual interface will be associated with an upstream ingress edge router element and that ingress edge router element is provided a label associated with the virtual interface. Such a label can then be included in datastream packets transmitted through the provider network. The label can then be used by reverse path forward checking at the egress edge router element to ascertain whether the multicast datastream is being received by the correct upstream interface (e.g., the virtual interface associated with the ingress edge router element). In such a manner, core network router elements of the provider's network need not be configured to process multicast transmissions as such, nor need the core router elements be configured to use the same network protocols as those used by the customer networks (e.g., customer networks can use IPv6 while the core network routers can use IPv4).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
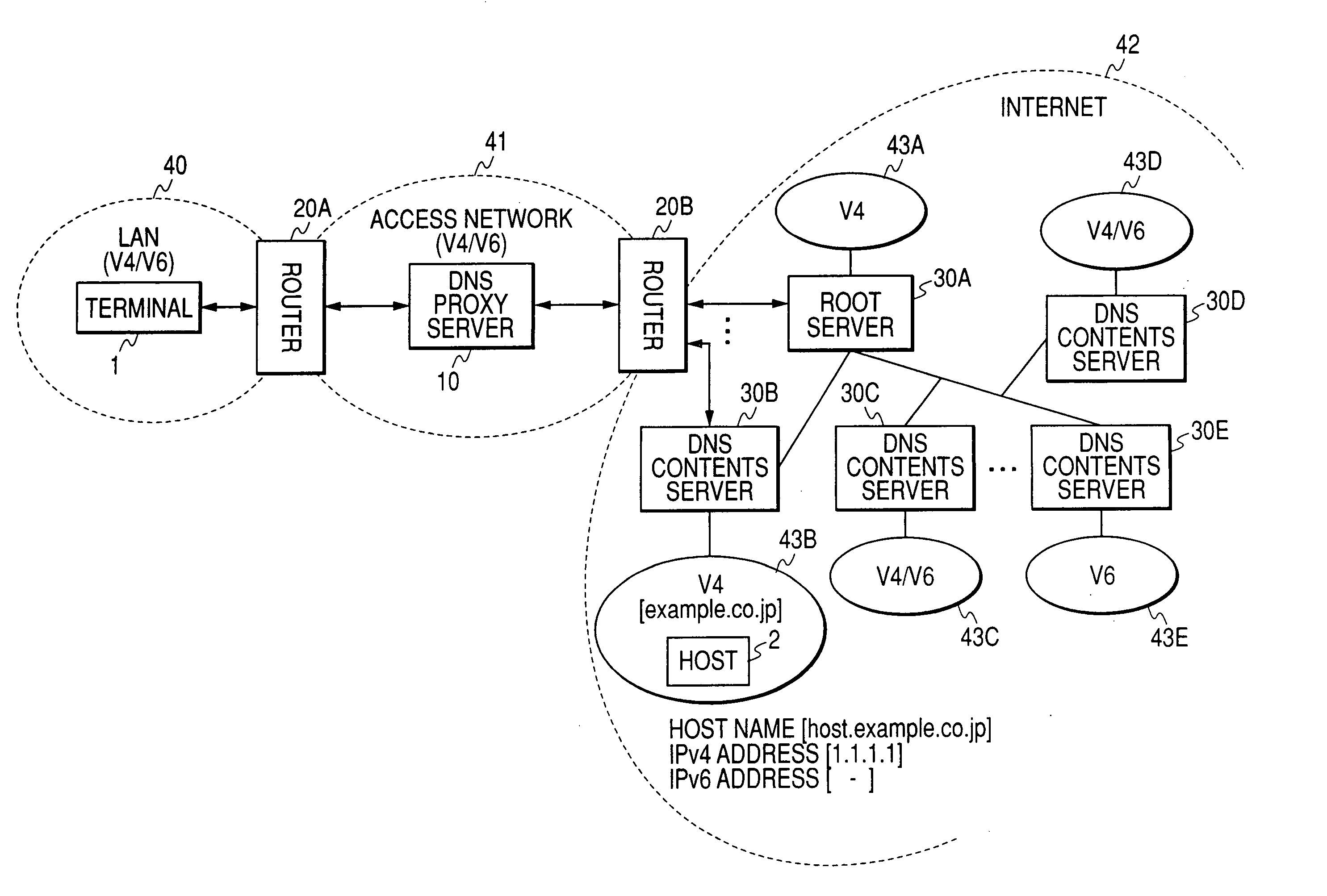
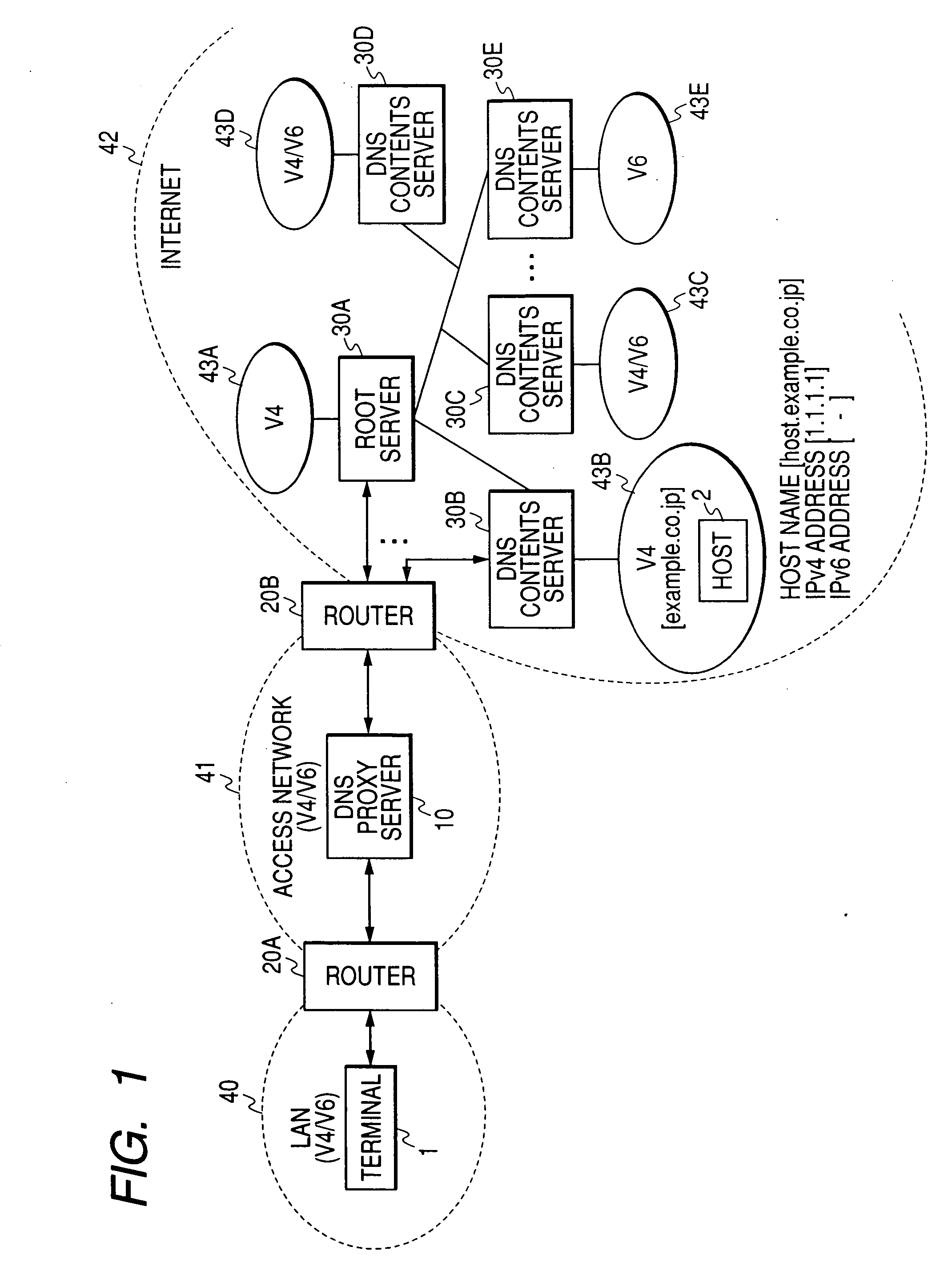
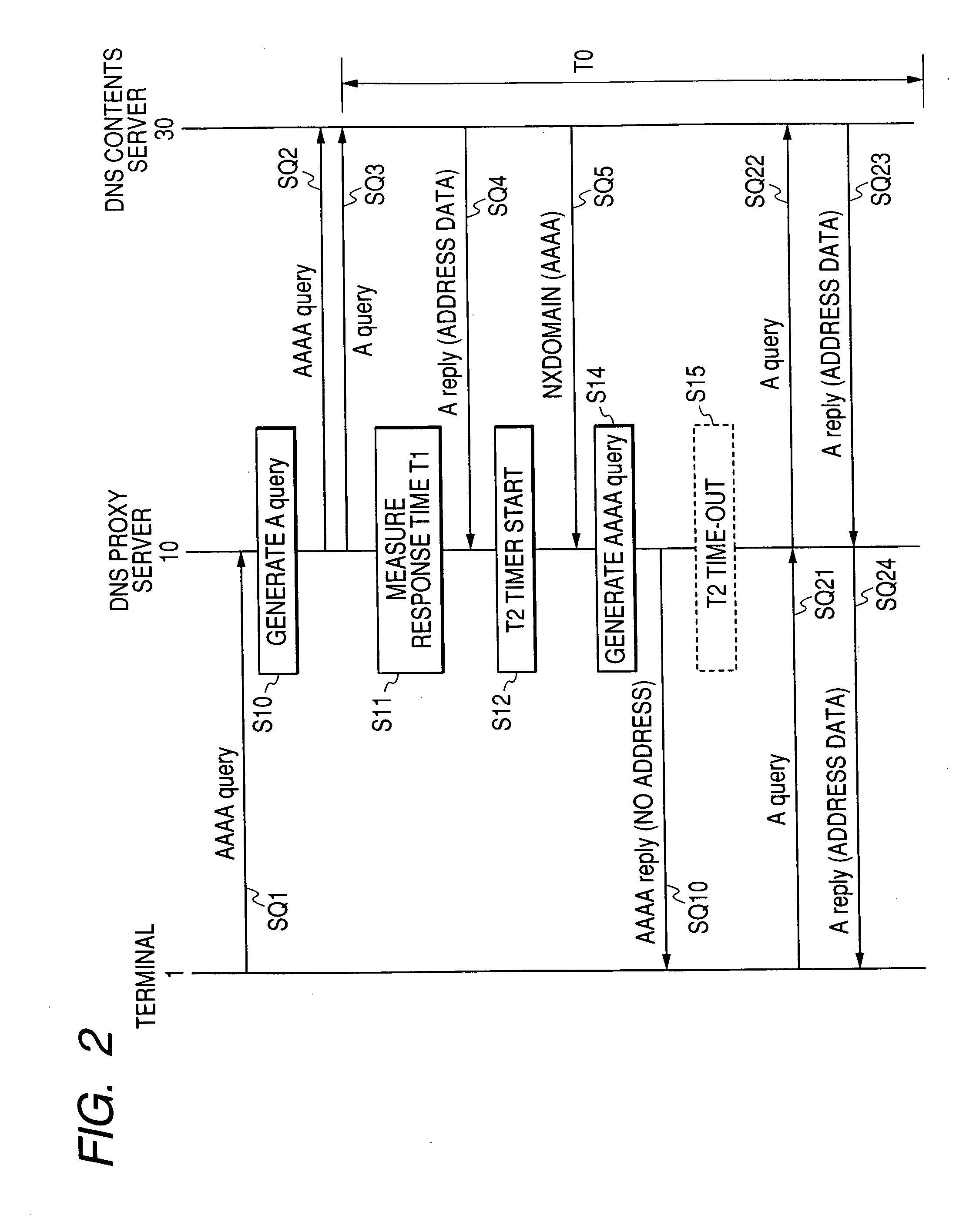
DNS server
InactiveUS20070124487A1Return quicklyShorten reply latency timeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDomain nameContent determination
Even if a mistaken reply to a host name resolution request of IPv6 is issued by a DNS contents server, a requesting terminal can still acquire an IPv4 address. When a host name resolution request of IPv6 (AAAA query) is received, a DNS proxy server generates a host name resolution request of IPv4 having an identical domain name, transmits this together with the AAAA query to the DNS contents server, and determines the DNS reply which should be returned to the terminal from the contents of the DNS reply of IPv6 (AAAA reply) and the DNS reply (A reply) of IPv4 received from the DNS contents server. Hence, even if a reply message showing a domain name error is received from the DNS contents server, if the A reply is correct, the DNS proxy server generates an AAAA reply showing that the desired address does not exist, and returns this to the terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Communication method, method for forwarding data message during the communication process and communication node thereof
ActiveUS20120176932A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsCode spaceIdentity recognition
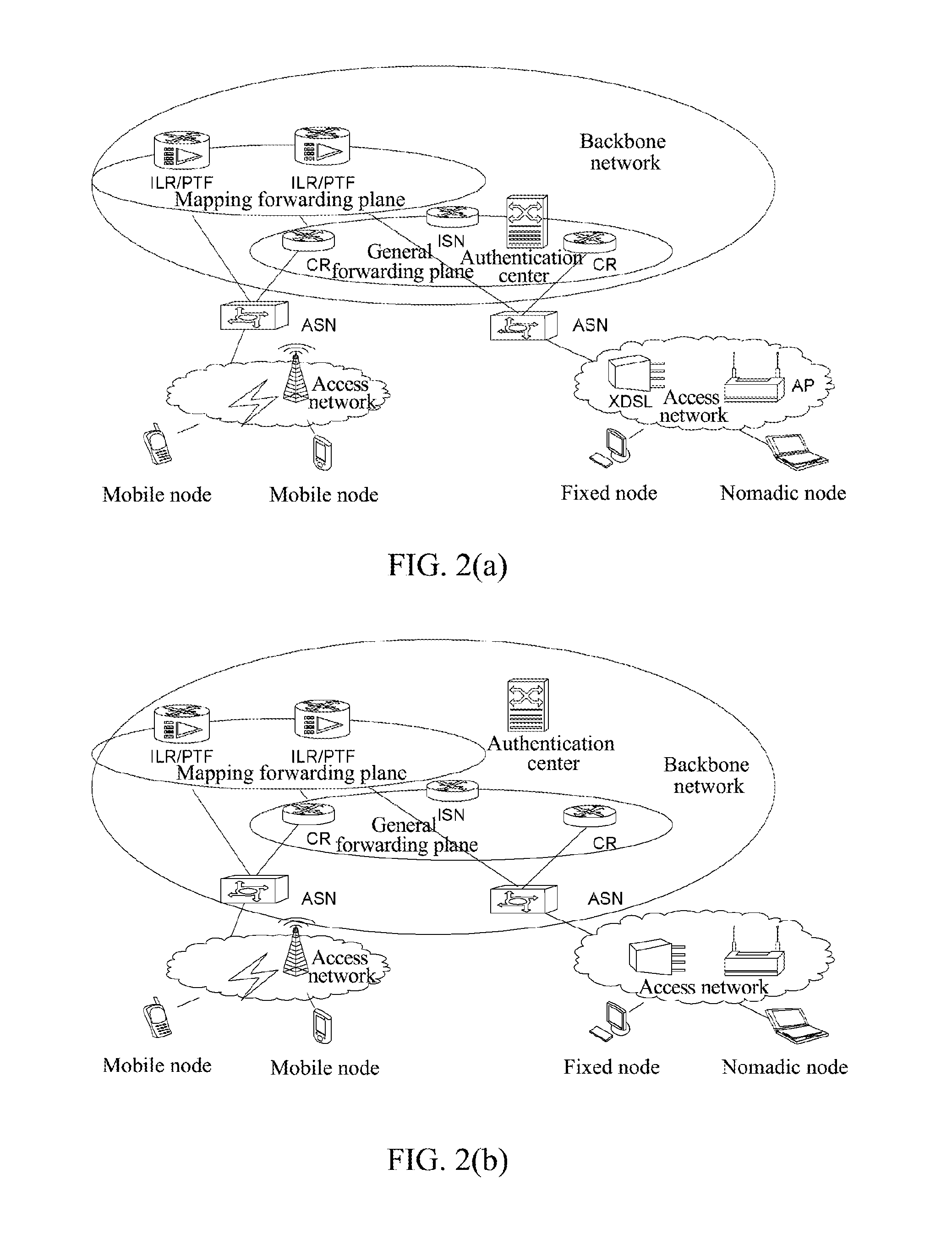
The present invention provides a communication method, and a method for forwarding a data message during the communication process and a communication node. Wherein, the configuration mode for identity recognition is clarified, and under the architecture based on access identifier and location separation in the network, a specific method for implementing identity recognition is provided, and the processing performed by each network element is regulated; the requirement for the number of the coding spaces is met, meanwhile the present invention realizes the intercommunication and interconnection with the legacy IP network, realizes the compatibility with the upper application programs of IPv4 / IPv6, and supports the various application programs of the IPv4 / IPv6 network to transplant smoothly to the architecture based on access identifier and location separation in the network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Architecture for Mobile IPv6 Applications over IPv4
InactiveUS20070050613A1Connection securityDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsClient-sideApplication software
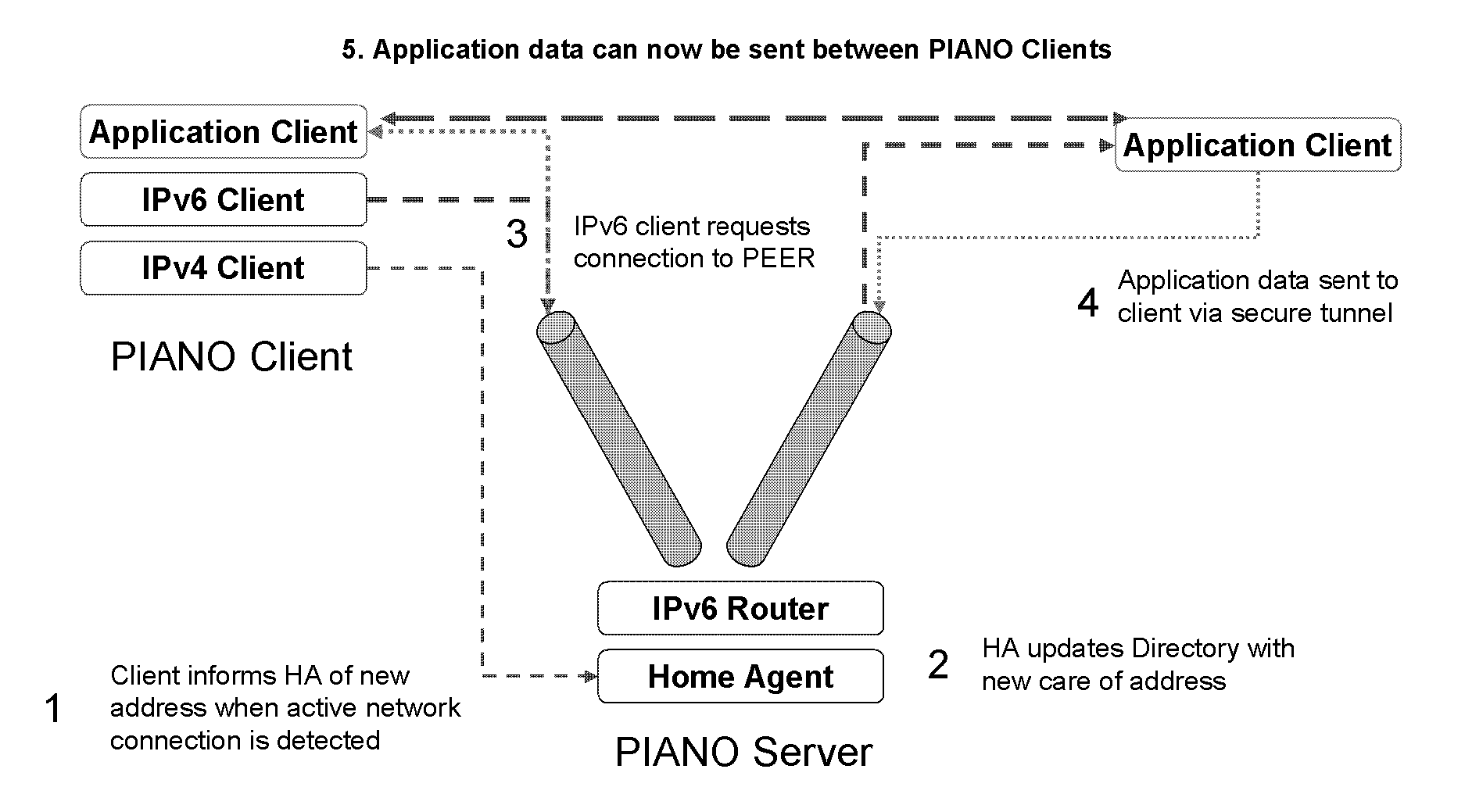
Mobile clients can execute IPv6 applications in an IPv4 environment without the need for any specialized IPv6 hardware or upgrades to the network infrastructure. The architecture provides a seamless, disruption-free connectivity experience for mobile clients. Mobile clients are automatically connected to other mobile clients irrespective of their network connectively, whether wireless, wire line, IPv4, IPv6, public or private. Mobile clients communicate with other mobile clients using a secure, end-to-end IPv6 tunnel. This creates a persistent VPN connection between two clients using software.
Owner:ISLAM JUNAID +2
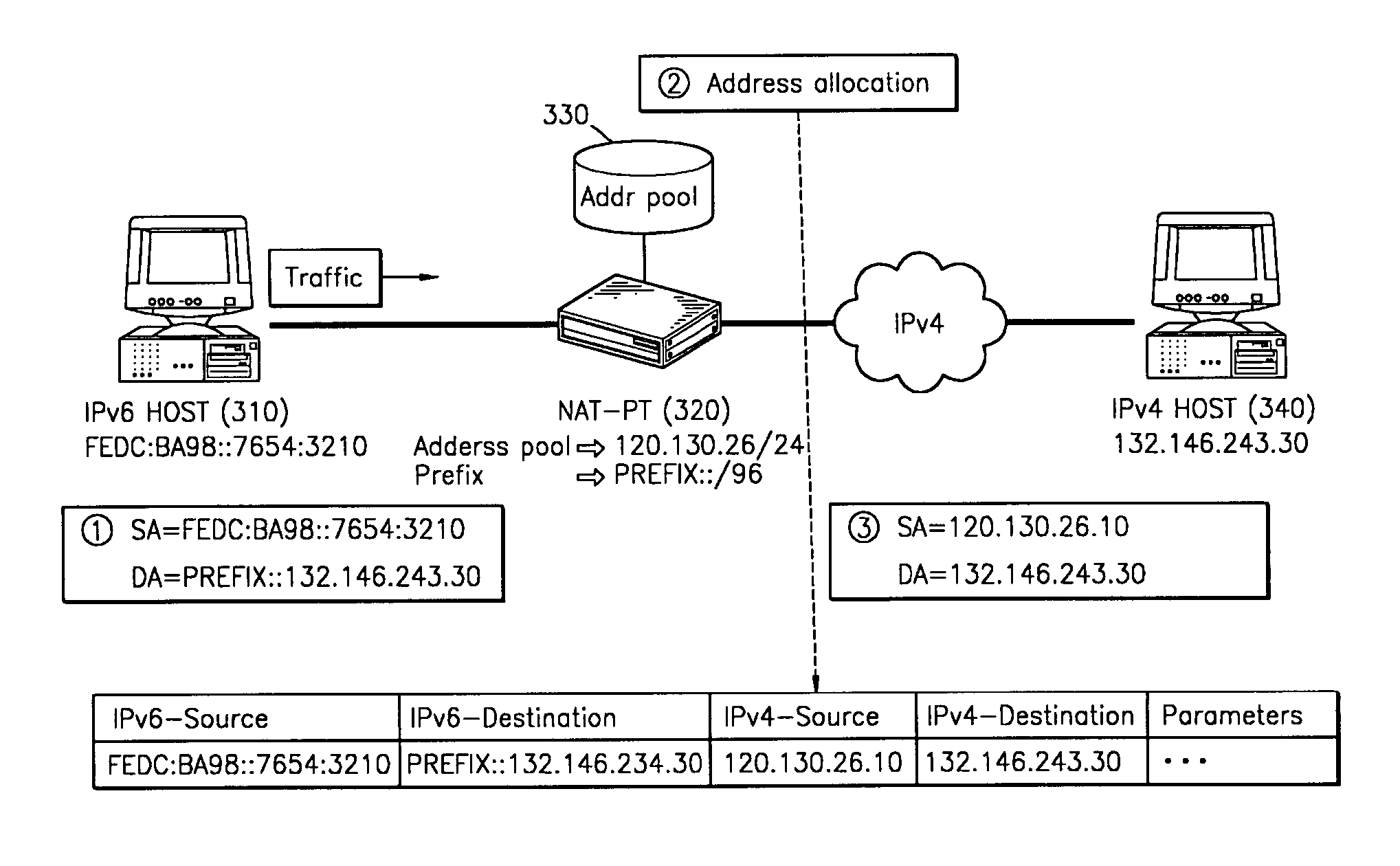
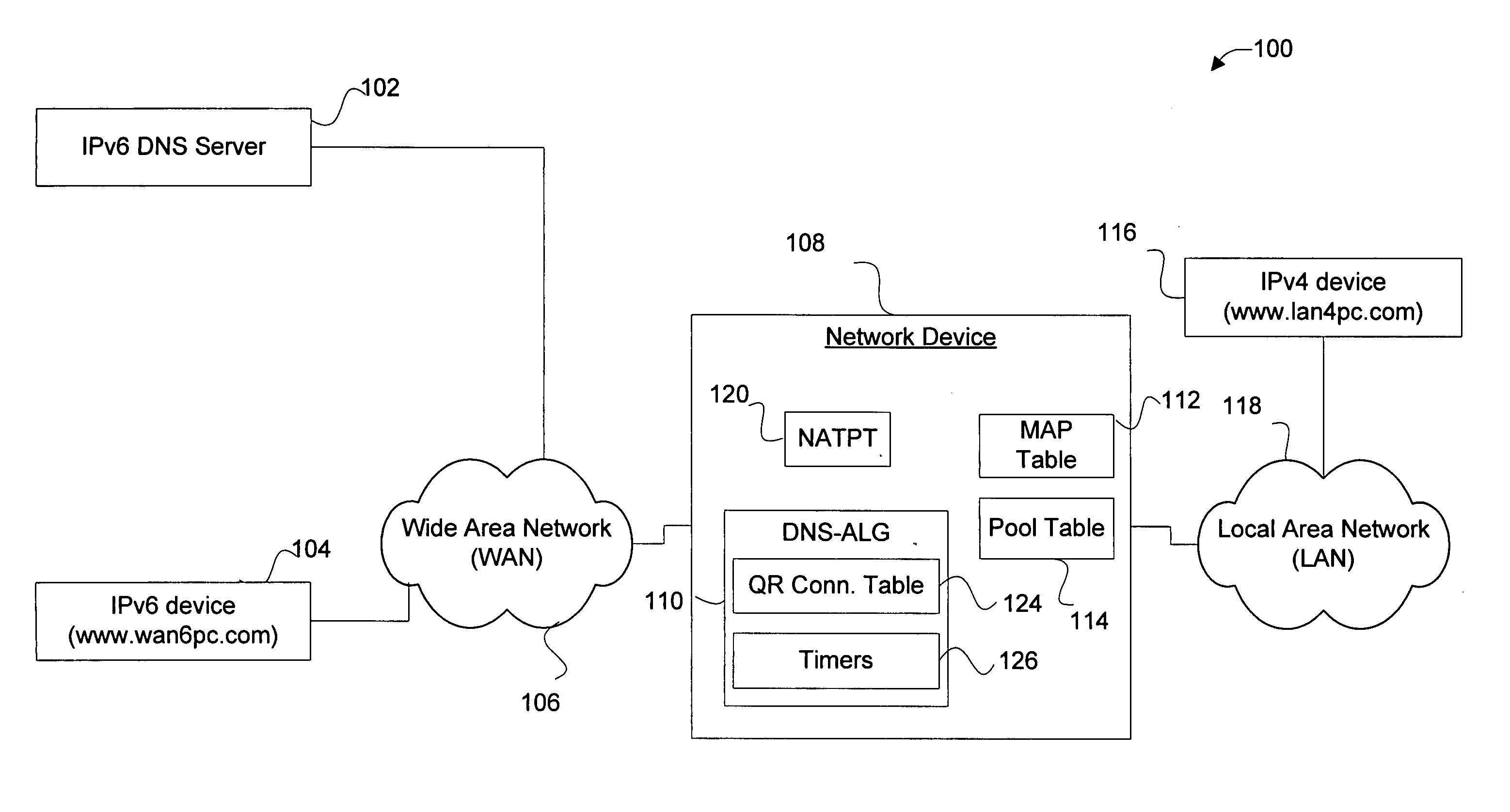
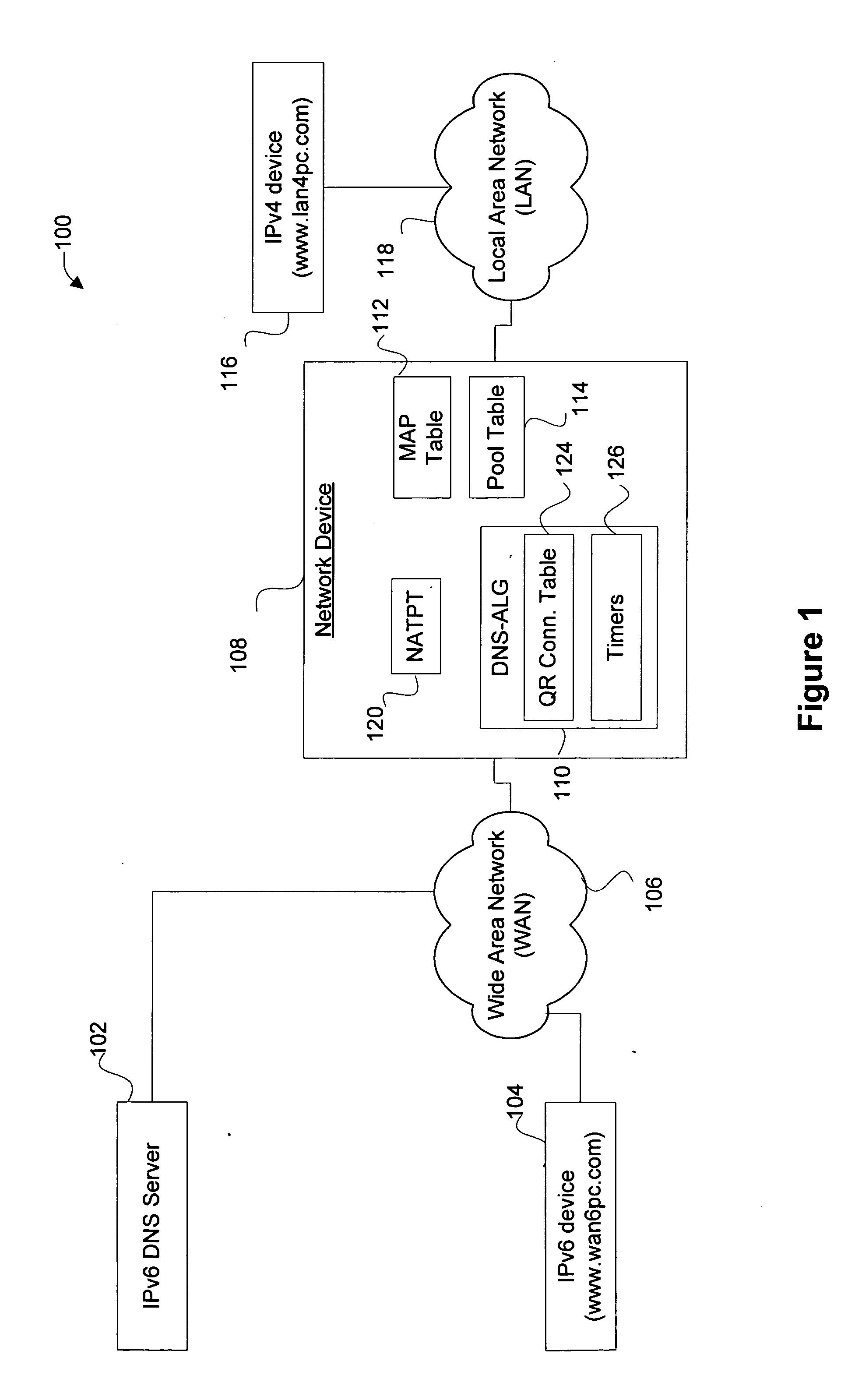
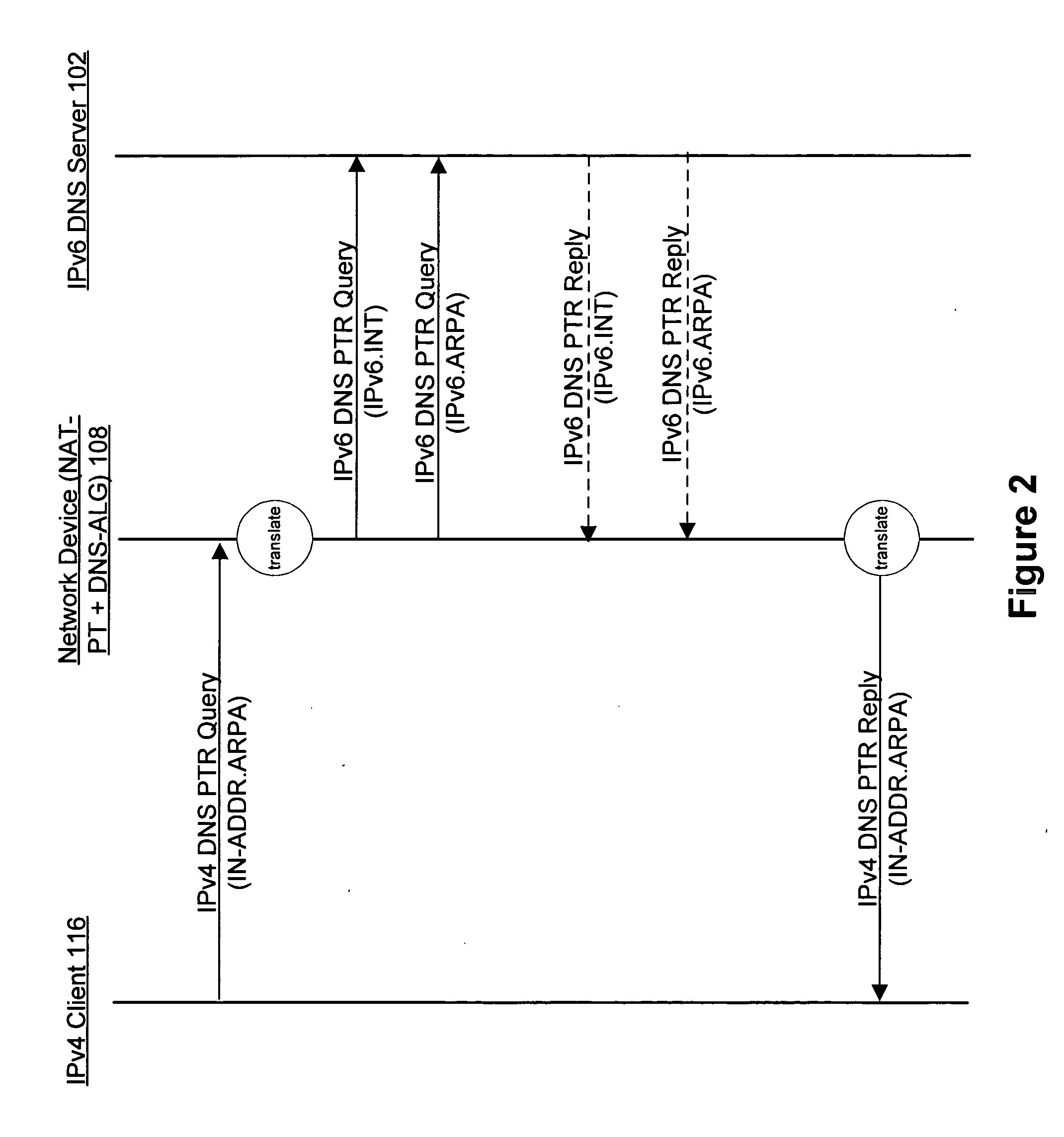
Method and apparatus for handling IPv4 DNS PTR queries across IPv4 and IPv6 networks
InactiveUS20050267978A1Efficient and reliable processingMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsDomain nameTheoretical computer science
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for efficiently and reliably handling DNS (domain name service) PTR (pointer) queries and replies across IPv4 and IPv6 networks. In general terms, an IPv4 DNS PTR query which is sent by an IPv4 device to an IPv6 DNS Server is intercepted or received, for example, by a network device configured with NAT-PT and DNS-ALG. The received IPv4 DNS PTR query is then translated into two different types of IPv6 DNS PTR queries: a query having an “IP6.INT” string and a query having an “IP6.ARPA” string. Both types of IPv6 queries are then sent to the IPv6 destination DNS Server. Whether the DNS sends an IP6.ARPA or an IP6.INT type reply or both types of replies back, a valid reply is identified (if present) and then translated before reaching the IPv4 device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
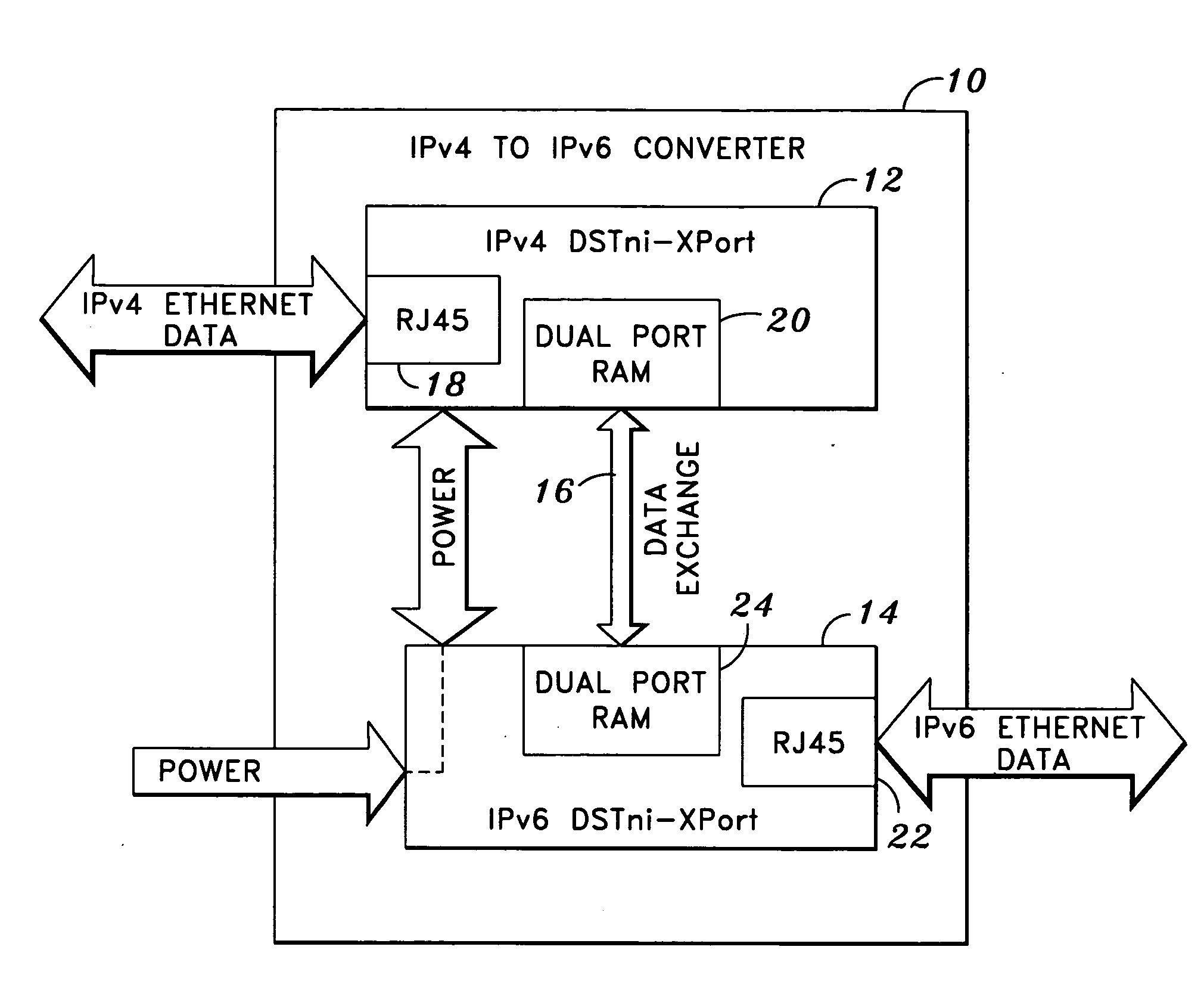
Communication protocol converter and method of protocol conversion
ActiveUS20050106941A1Minimized footprintElectric discharge tubesCoupling device detailsModularityEngineering
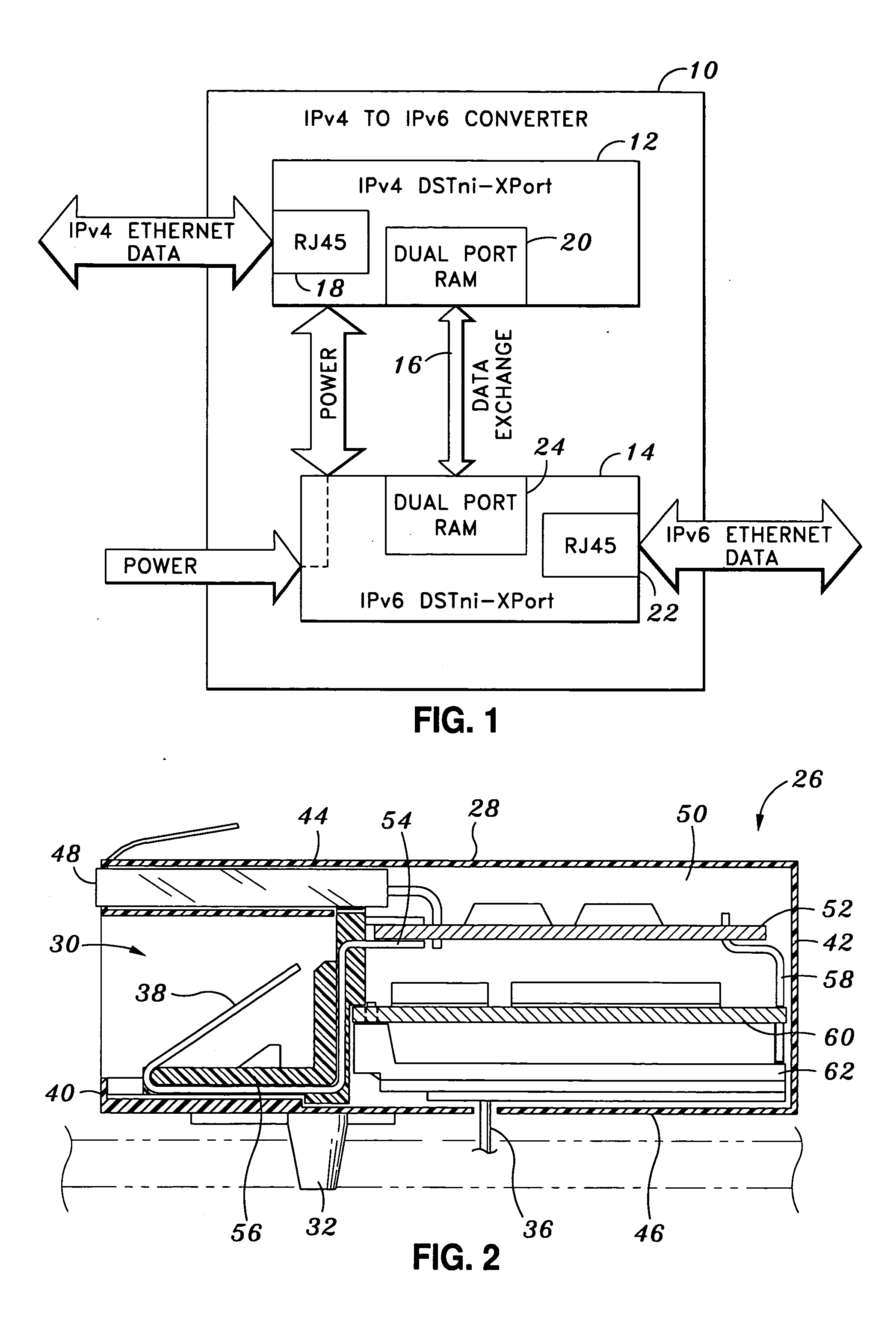
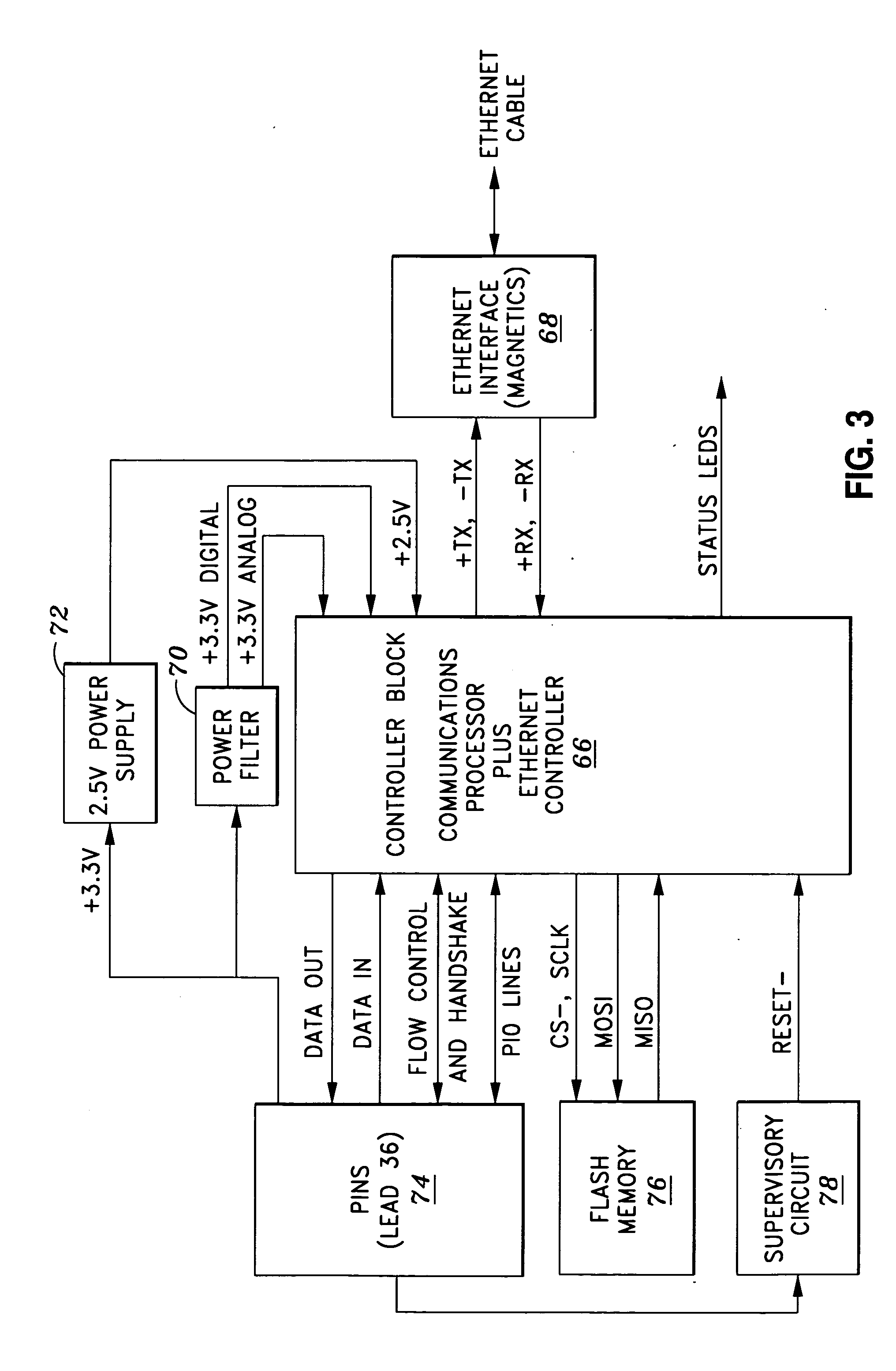
The present invention generally relates to a communication protocol converter to allow a legacy device utilizing IPv4 to operate across the network using IPv6. In a first embodiment of the invention, two modular Ethernet connectors are placed side-by-side. A first modular connector receives IPv4 Ethernet data which is converted to a raw data signal. The data is transmitted from the first modular connector to a second modular connector by a bidirectional data line. The second connector receives the raw data, and a raw data-to-Ethernet conversion is completed providing output at IPv6. The present invention utilizes the form factor structure of the Ethernet connectors, so that the entire electronic circuitry is contained within the connectors to complete the conversion. An alternate embodiment incorporates the connectors into a single housing and the conversion is completed internally by a microprocessor and embedded software. A method of IPv4 to IPv6 conversion is additionally disclosed.
Owner:LANTRONIX
Longest Prefix Match Scheme
ActiveUS20130031077A1Effectively reduces quantization lossComparison of digital valuesTransmissionExact matchIPv4
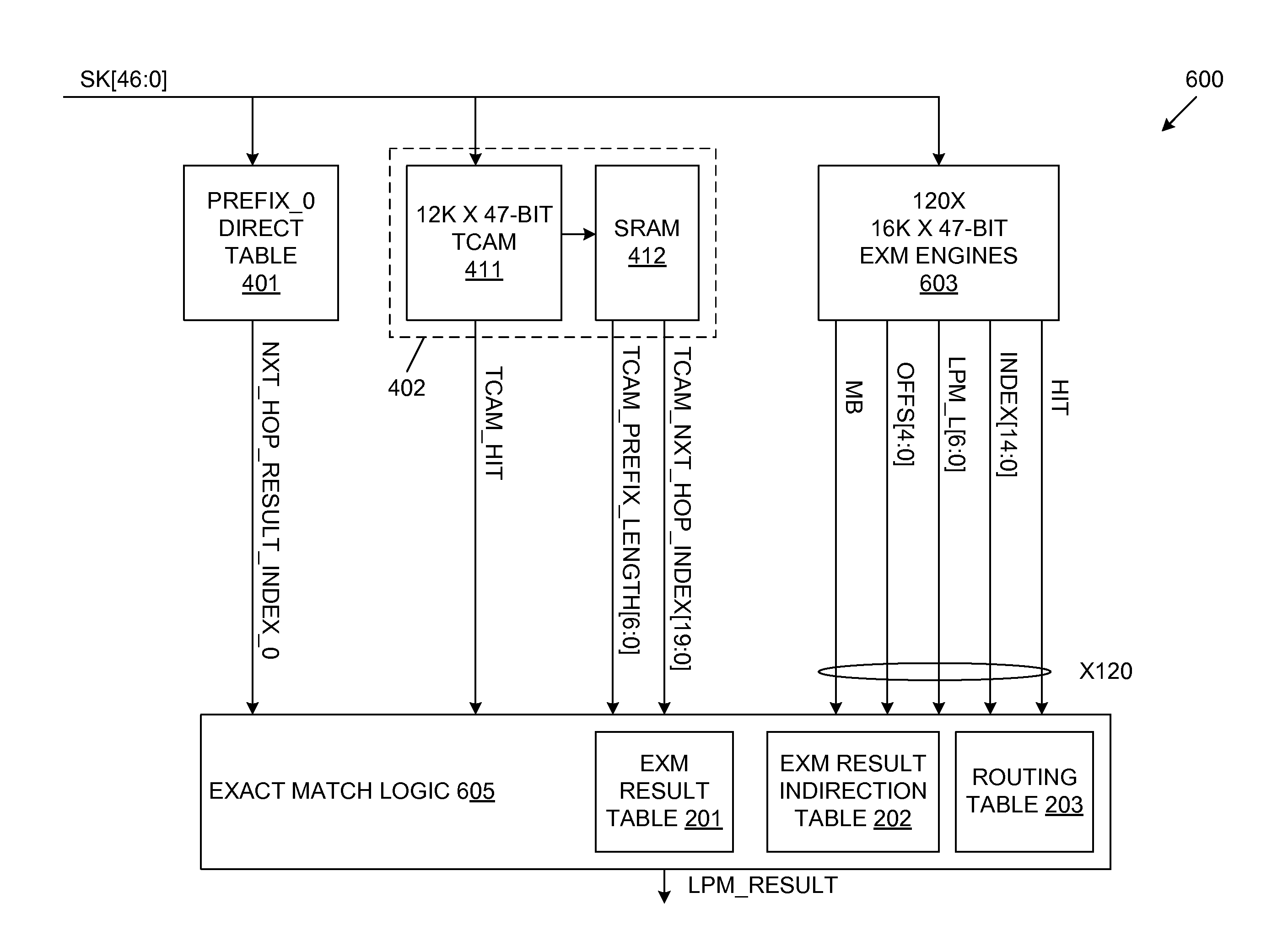
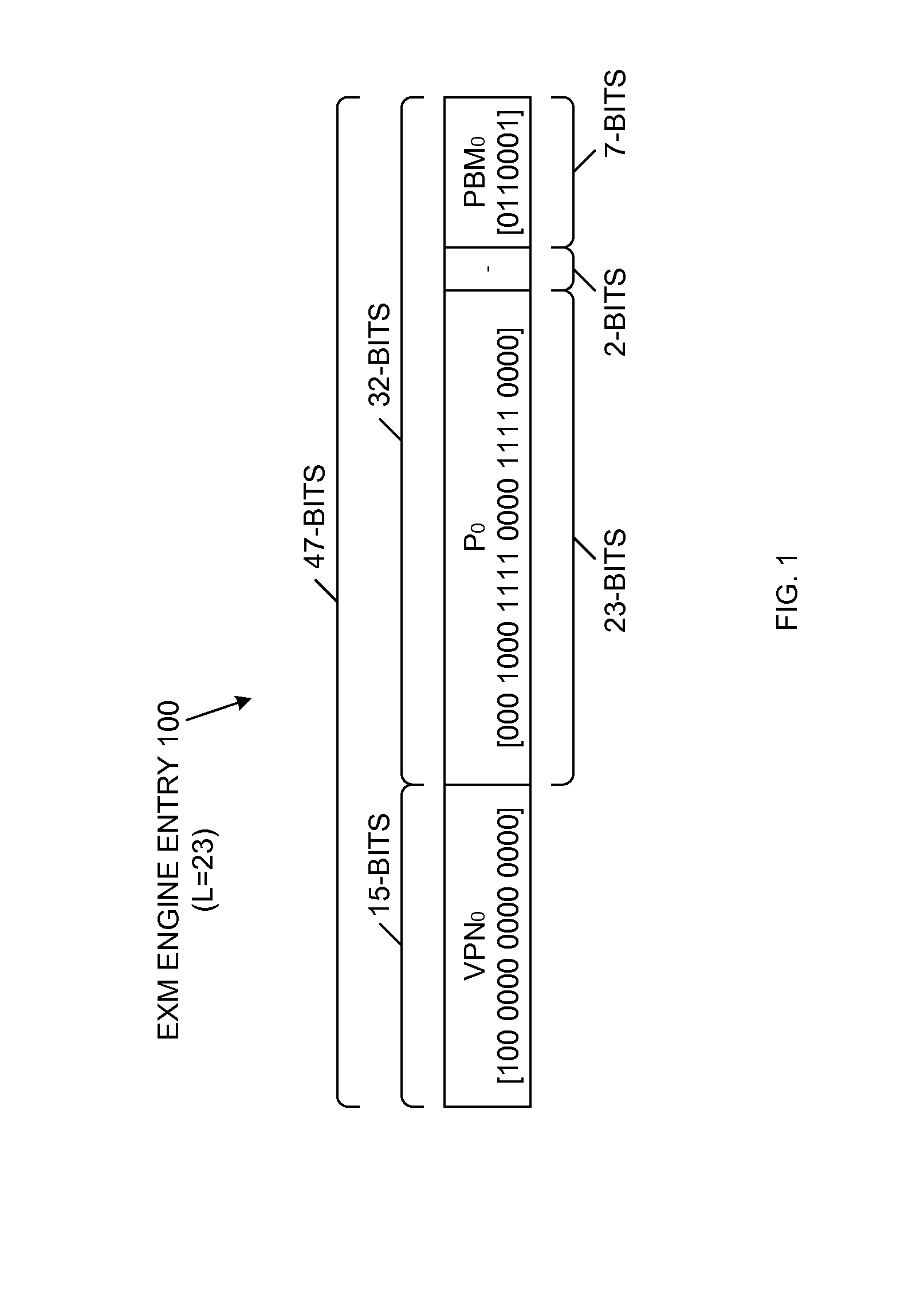
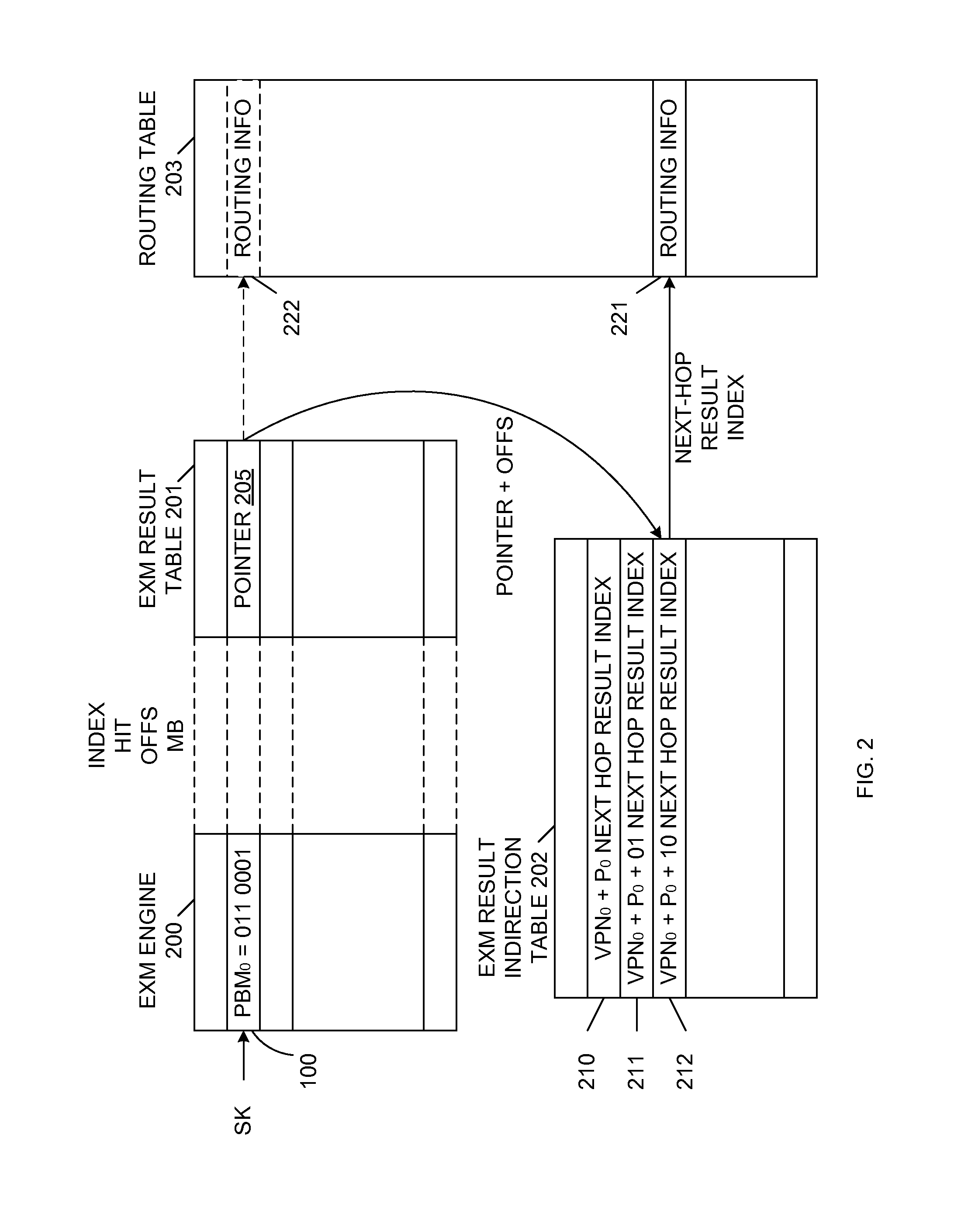
A LPM search engine includes a plurality of exact match (EXM) engines and a moderately sized TCAM. Each EXM engine uses a prefix bitmap scheme that allows the EXM engine to cover multiple consecutive prefix lengths. Thus, instead of covering one prefix length L per EXM engine, the prefix bitmap scheme enables each EXM engine to cover entries having prefix lengths of L, L+1, L+2 and L+3, for example. As a result, fewer EXM engines are potentially underutilized, which effectively reduces quantization loss. Each EXM engine provides a search result with a determined fixed latency when using the prefix bitmap scheme. The results of multiple EXM engines and the moderately sized TCAM are combined to provide a single search result, representative of the longest prefix match. In one embodiment, the LPM search engine supports 32-bit IPv4 (or 128-bit IPv6) search keys, each having associated 15-bit level 3 VPN identification values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Protocol conversion apparatus and method between IPv4 terminal and IPv6 terminal or between application programs using mapping table, and method of generating mapping table of protocol conversion apparatus
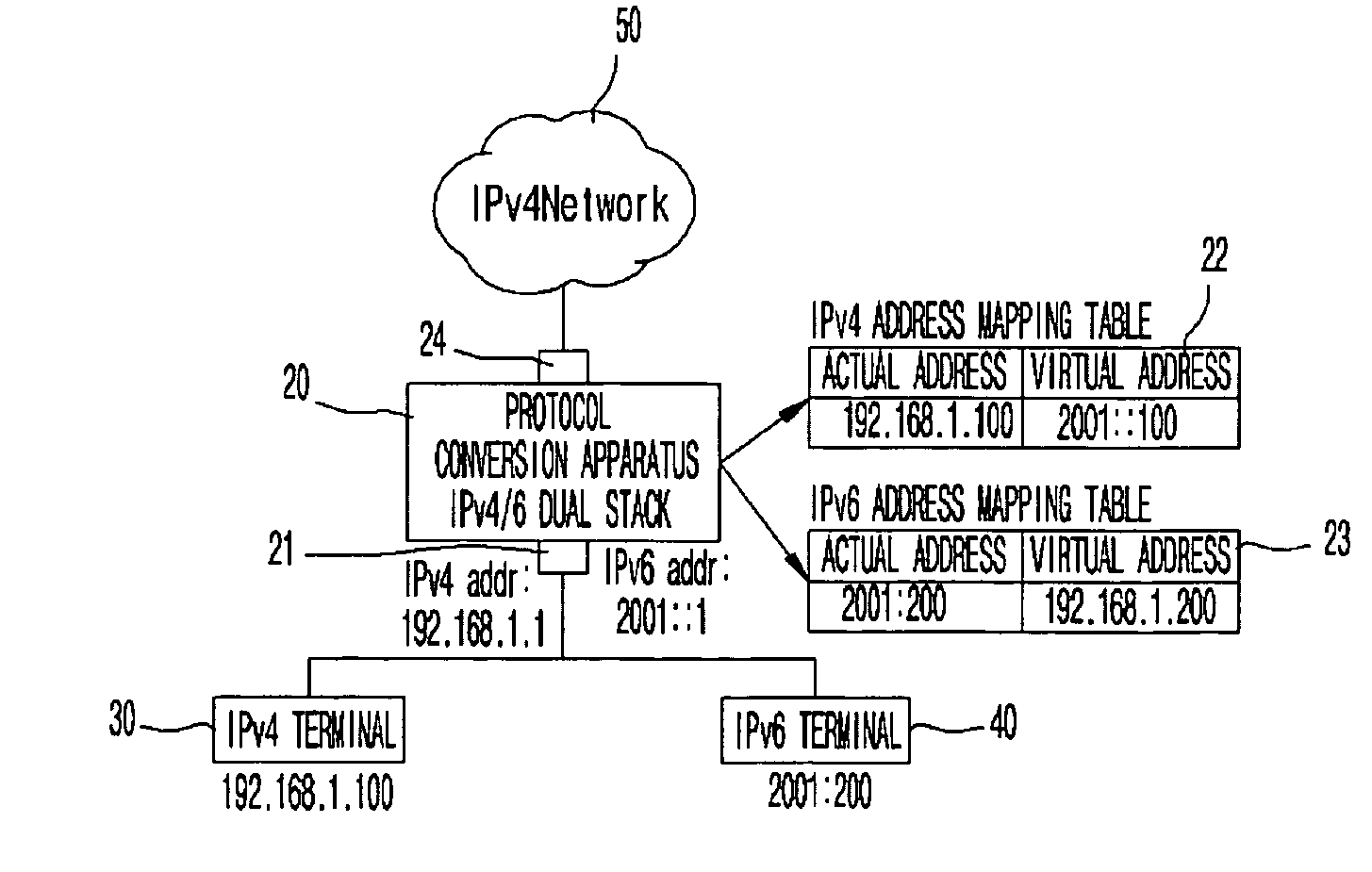
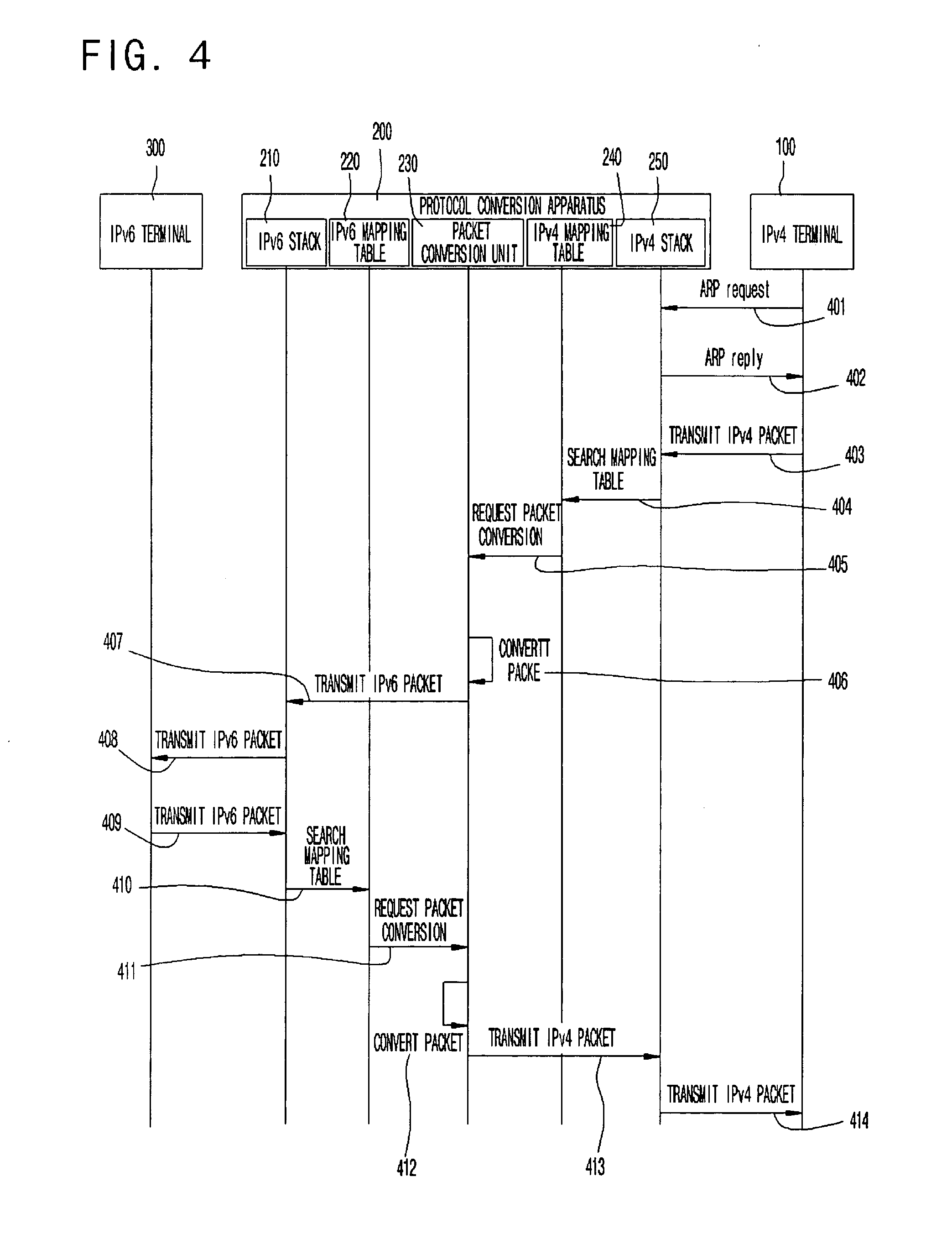
InactiveUS20080080519A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPhysical networkVirtual IP address
Provided is a protocol conversion apparatus and method supporting communication between terminals through a protocol conversion when IPv4 / IPv6 terminals coexist or a terminal supports an IPv4 / IPv6 dual stack in one physical network but an application service supports a specific protocol. A conventional SIIT protocol conversion technique can be used by receiving a communication request through an IPv4 and IPv6 dual stack for a communication request of an IPv4 terminal or an IPv6 terminal, and supporting a protocol conversion between the IPv4 / IPv6 terminal through a mapping table mapping respective actual IP address and virtual IP address of the IPv4 and IPv6, and performing communication between the IPv4 / IPv6 terminals. Therefore, it is possible to transparently communicate to each other in an IP protocol version. Moreover, a terminal communicates with another terminal in an external network through a conventional protocol or a protocol conversion technique without modification.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
IP network node and middleware for establishing connectivity to both the IPv4 and IPv6 networks
InactiveUS20050138166A1Multiple digital computer combinationsComputation using non-denominational number representationOperational systemProgram instruction
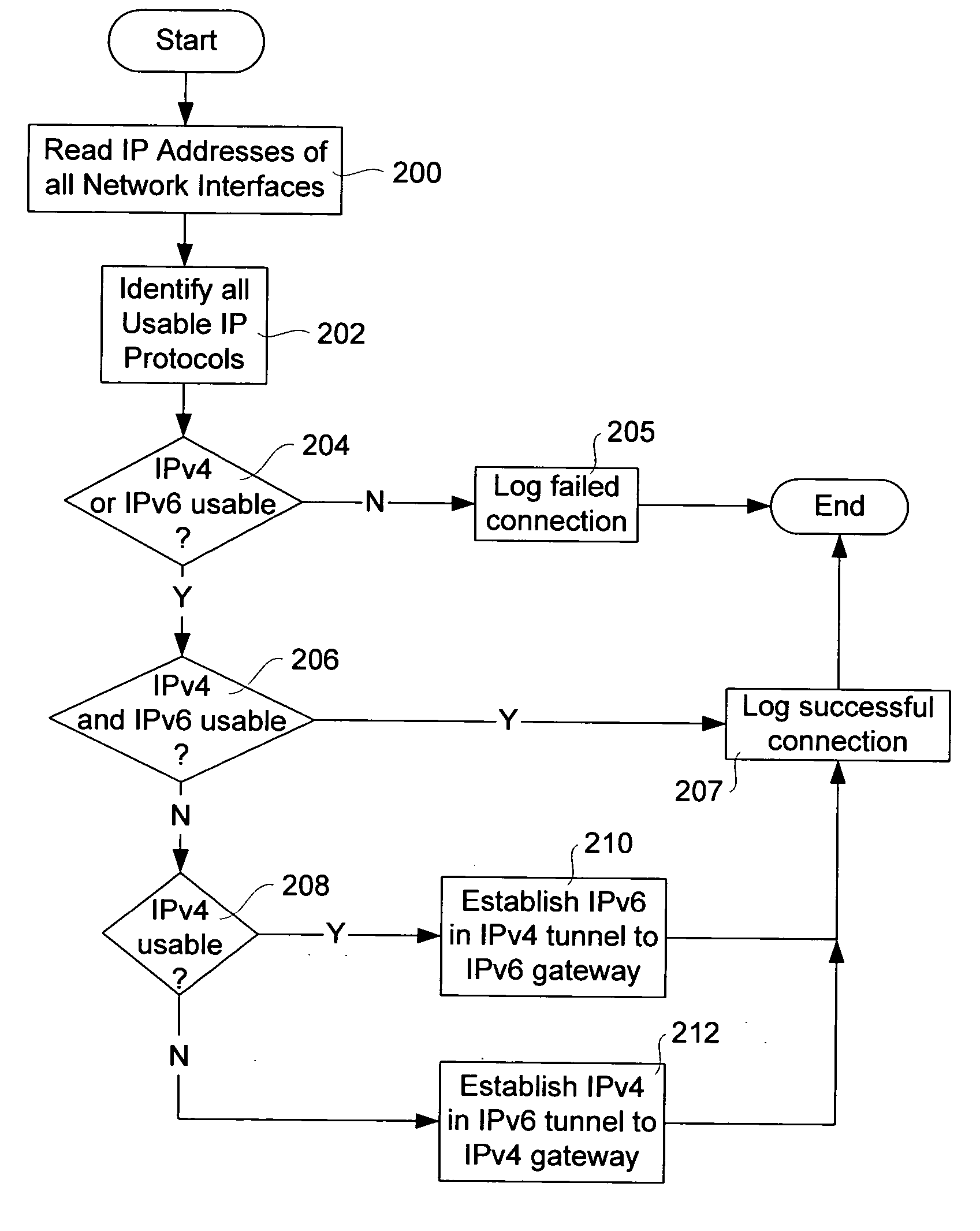
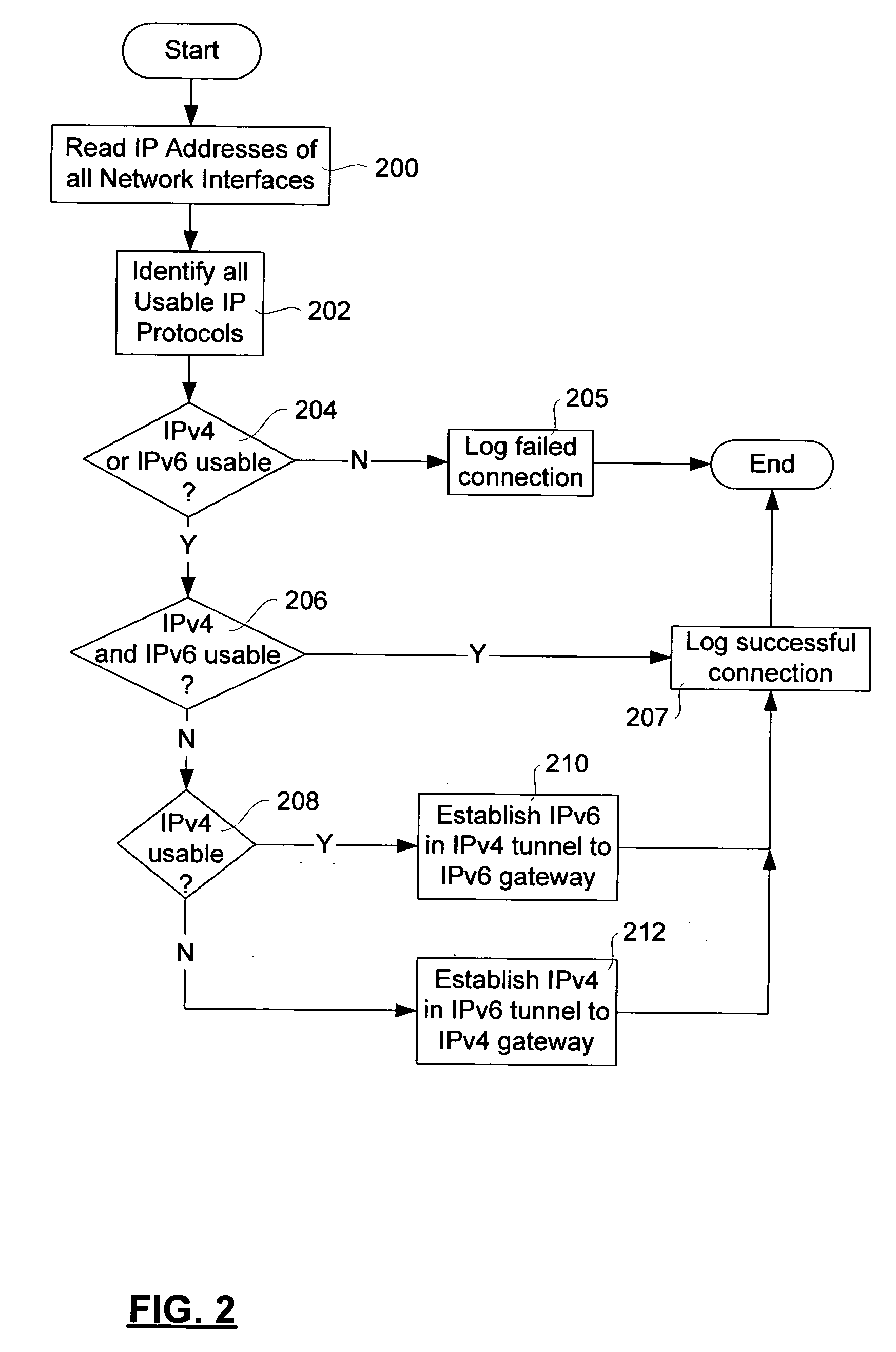
An Internet Protocol (IP) network node attempts to establish and maintain connectivity to both the Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) networks on initialization of one of the operating system and a program application. The IP node includes program instructions for determining IP addresses of all network interfaces associated with the node; program instructions for identifying all usable Internet protocols available on the node; program instructions for determining whether one of IPv4 and IPv6 are usable for communications with other IP nodes; and program instructions for establishing a tunnel through one of the IPv4 and IPv6 networks to a gateway for the other of IPv4 an IPv6 networks if the program instructions determine that either one of the IPv4 and IPv6 networks are not usable for communications with the other IP nodes.
Owner:HEXAGO
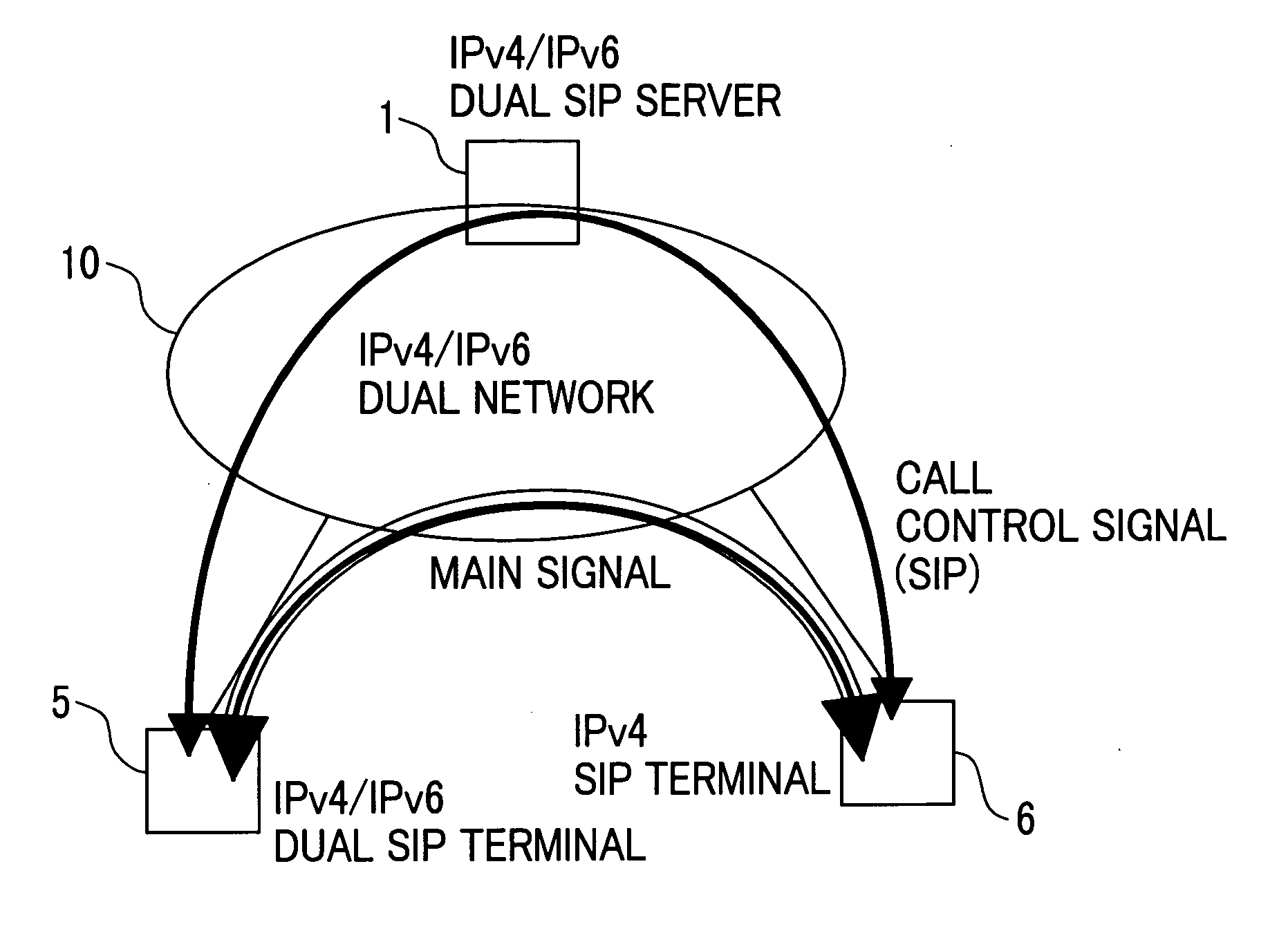
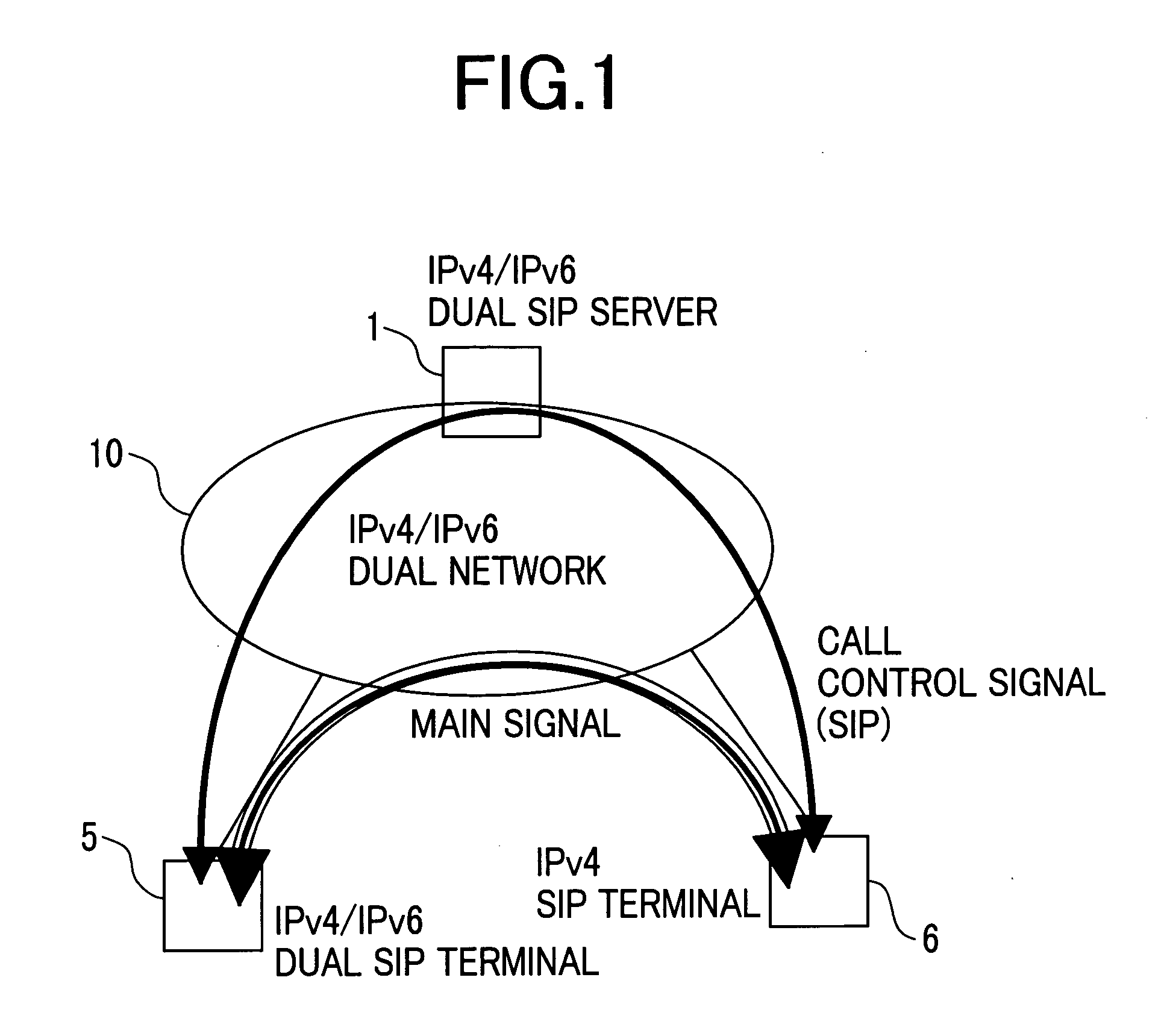
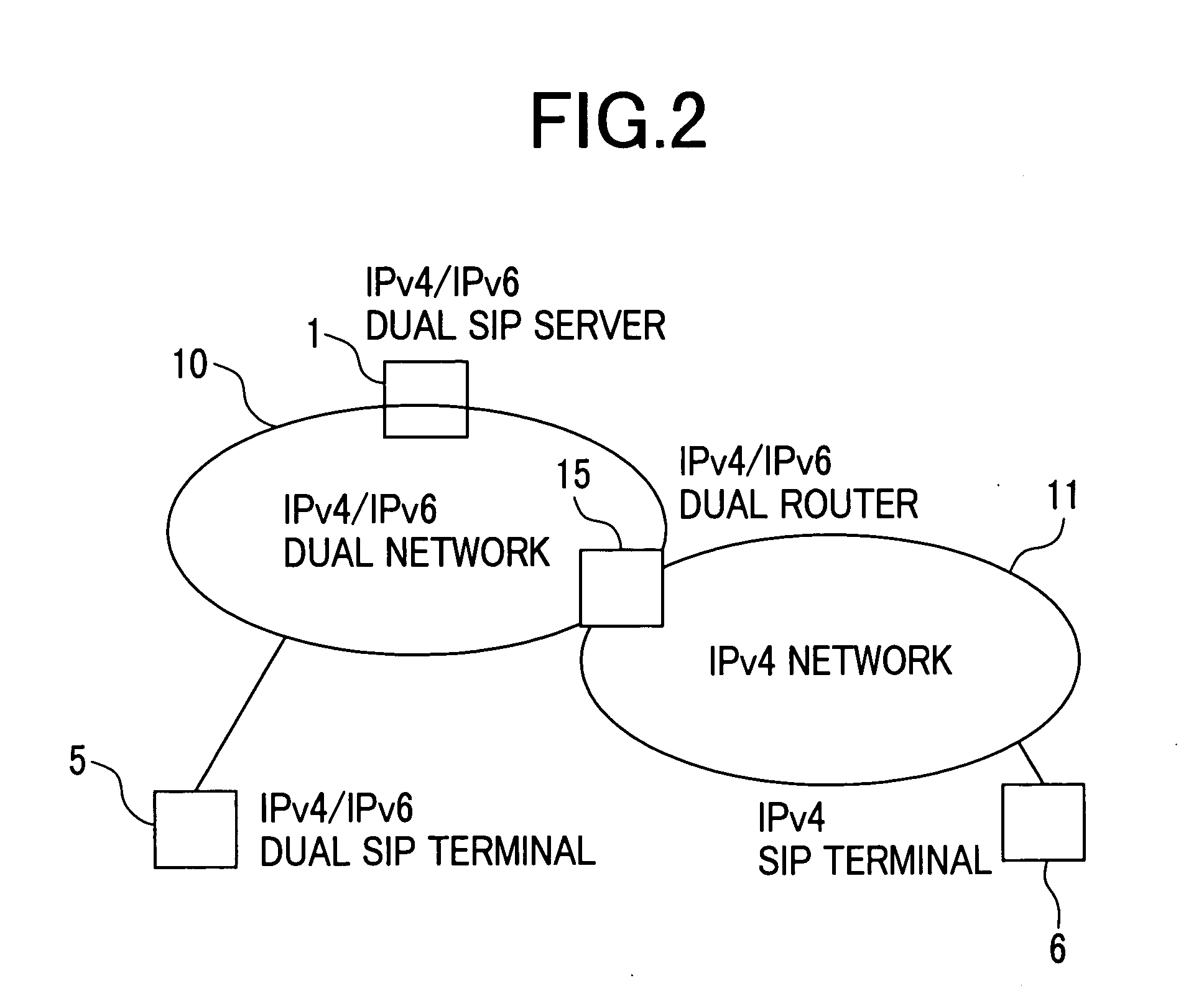
Session control system, communication terminal and servers
A SIP server having the function of accepting simultaneous IPv4 / IPv6 registrations from an IPv4 / IPv6 dual SIP terminal, recognizing a protocol communicable with a communication partner terminal, and notifying the IPv4 / IPv6 dual SIP terminals of the result of the recognition if necessary, thereby to allow VOIP communication between the IPv4 / IPv6 dual SIP terminal and an IPv4 terminal or an IPv6 terminal to be the communication partner.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com