Patents
Literature
59 results about "Maximum segment size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
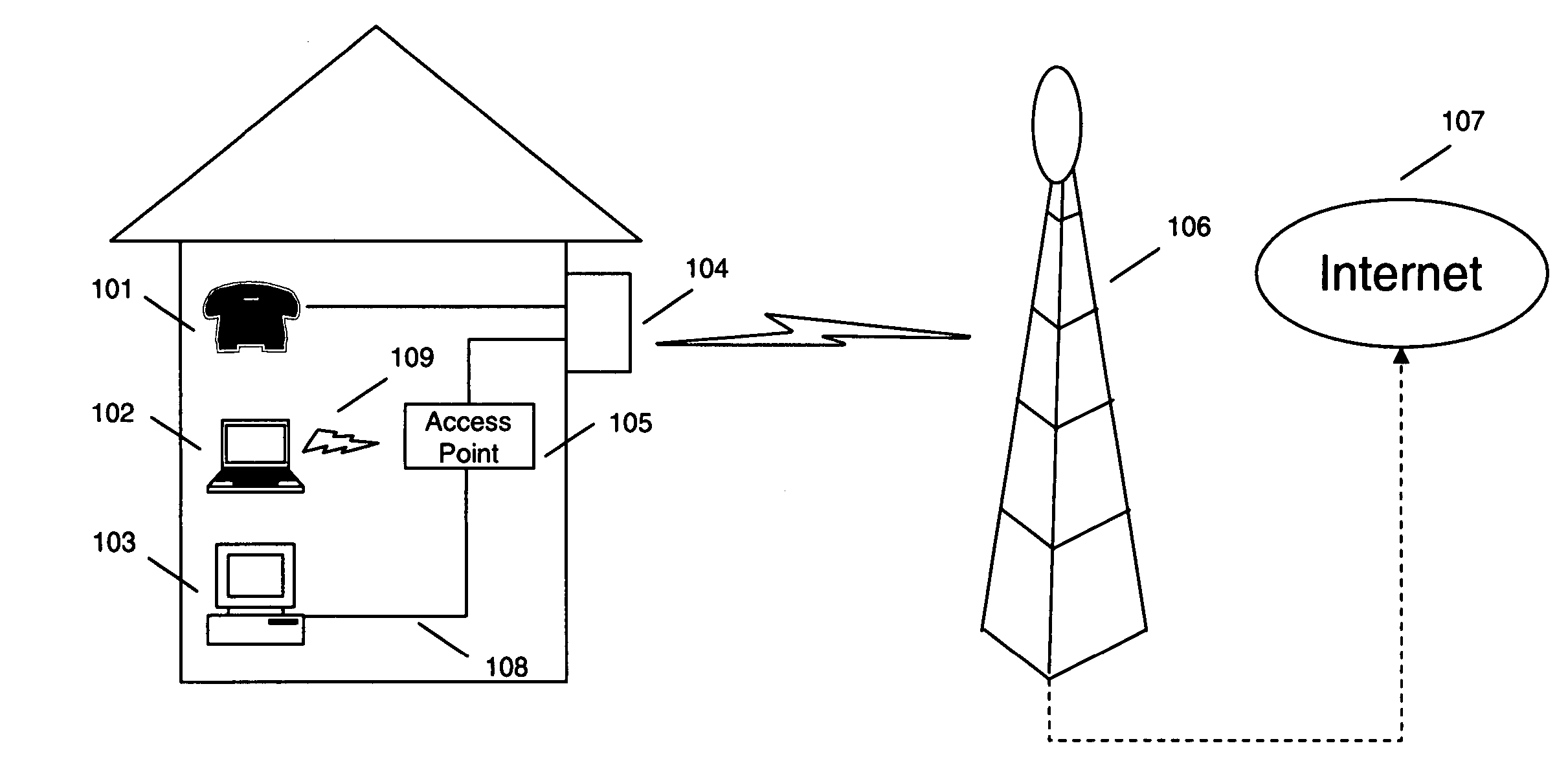
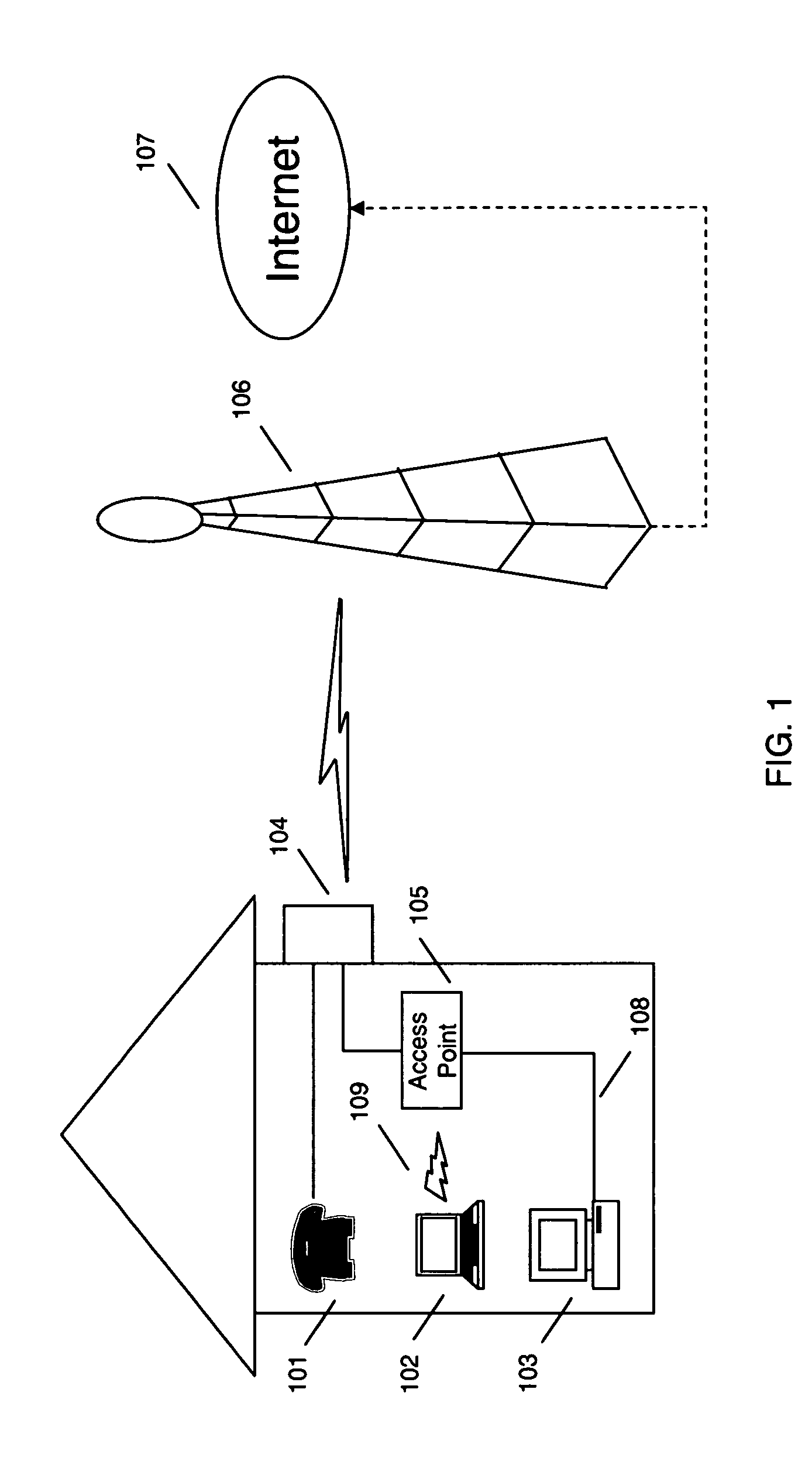
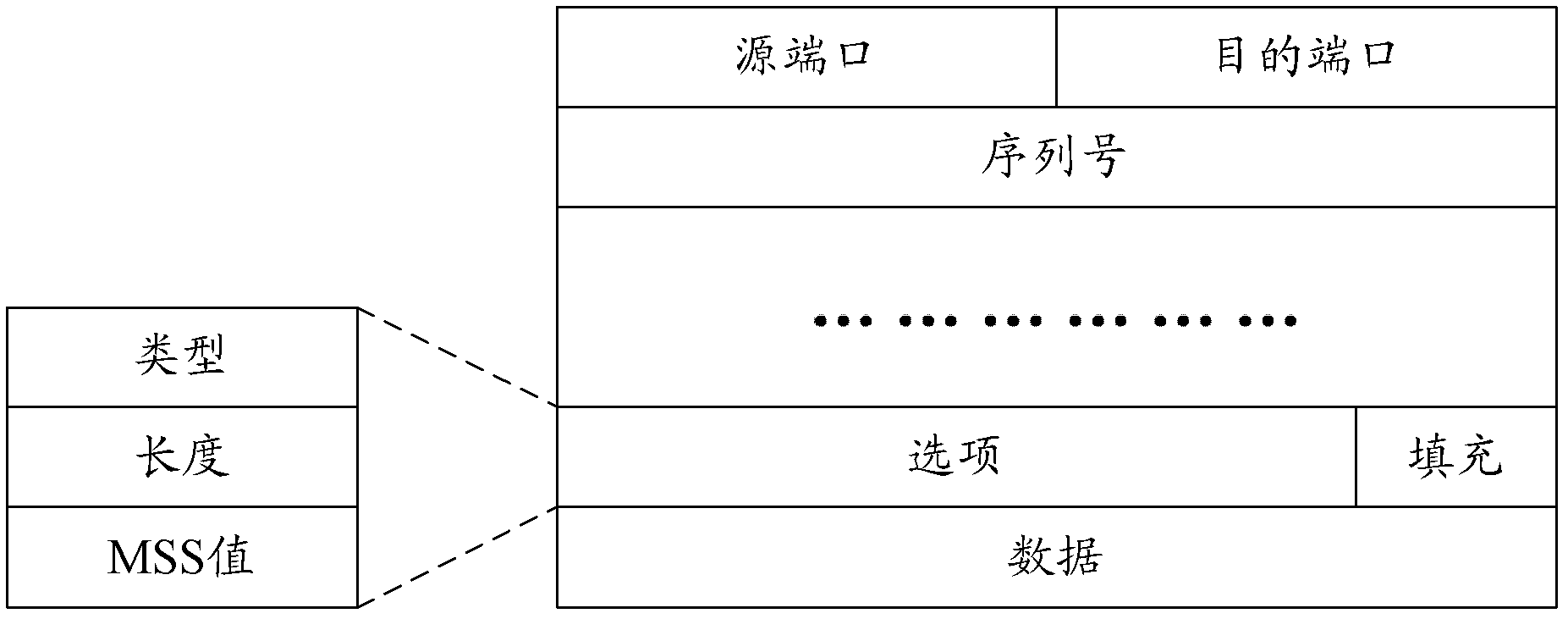
The maximum segment size (MSS) is a parameter of the options field of the TCP header that specifies the largest amount of data, specified in bytes, that a computer or communications device can receive in a single TCP segment. It does not count the TCP header or the IP header (unlike, for example, the MTU for IP datagrams). The IP datagram containing a TCP segment may be self-contained within a single packet, or it may be reconstructed from several fragmented pieces; either way, the MSS limit applies to the total amount of data contained in the final, reconstructed TCP segment.
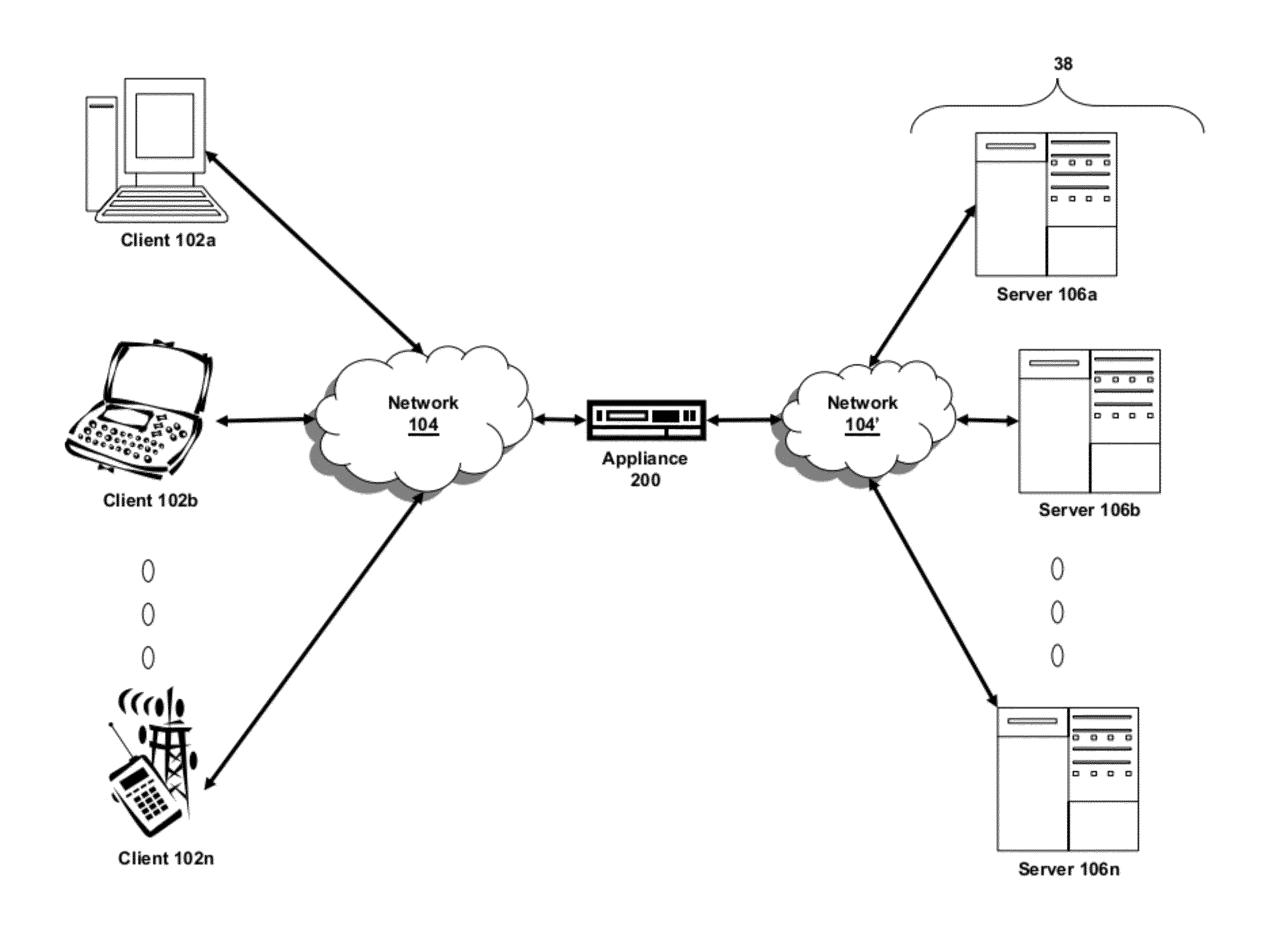
Mechanisms for avoiding problems associated with network address protocol translation
ActiveUS7006526B1Avoid problemsReduce morbidityError preventionTransmission systemsSize differenceSize increase
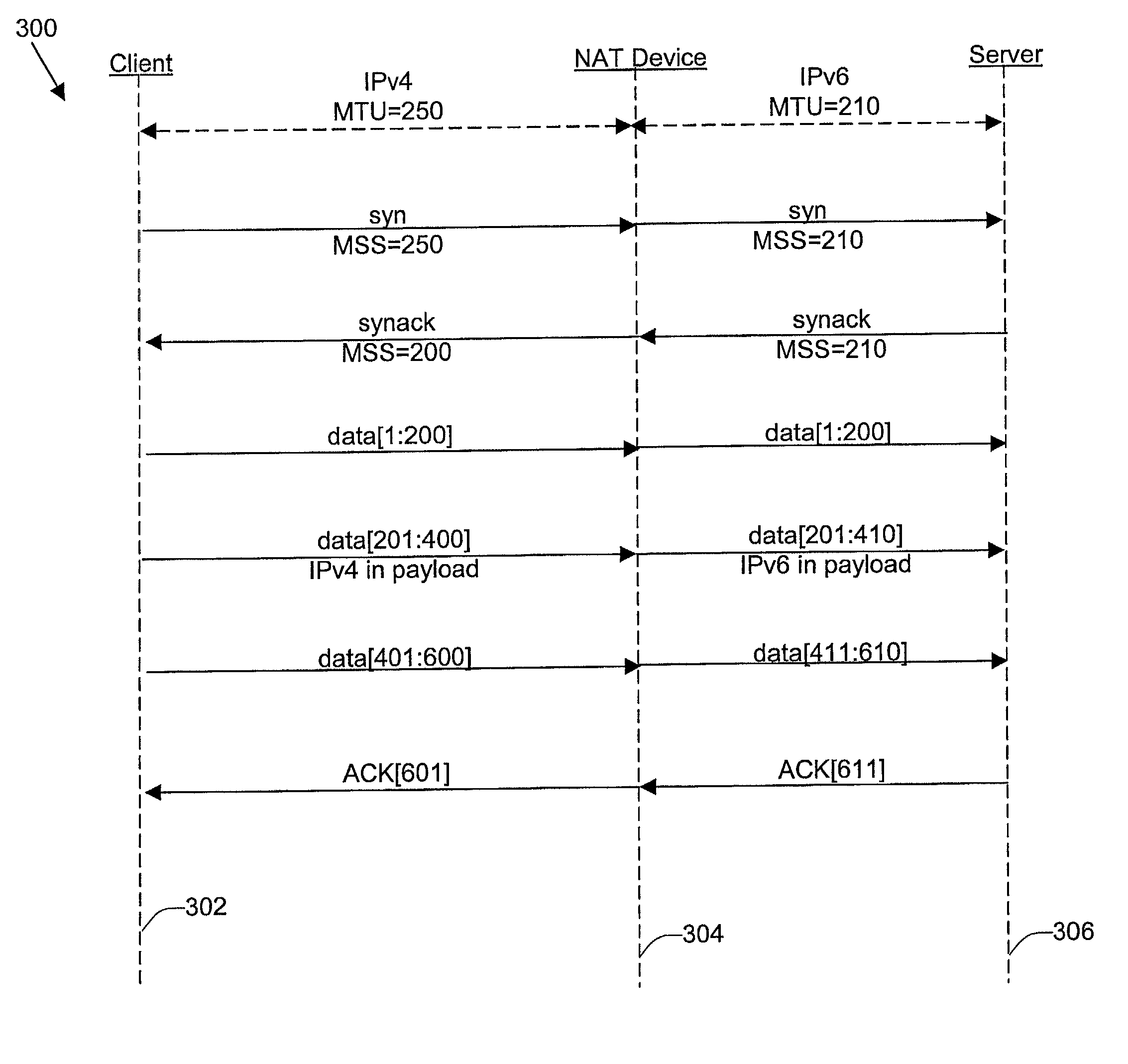
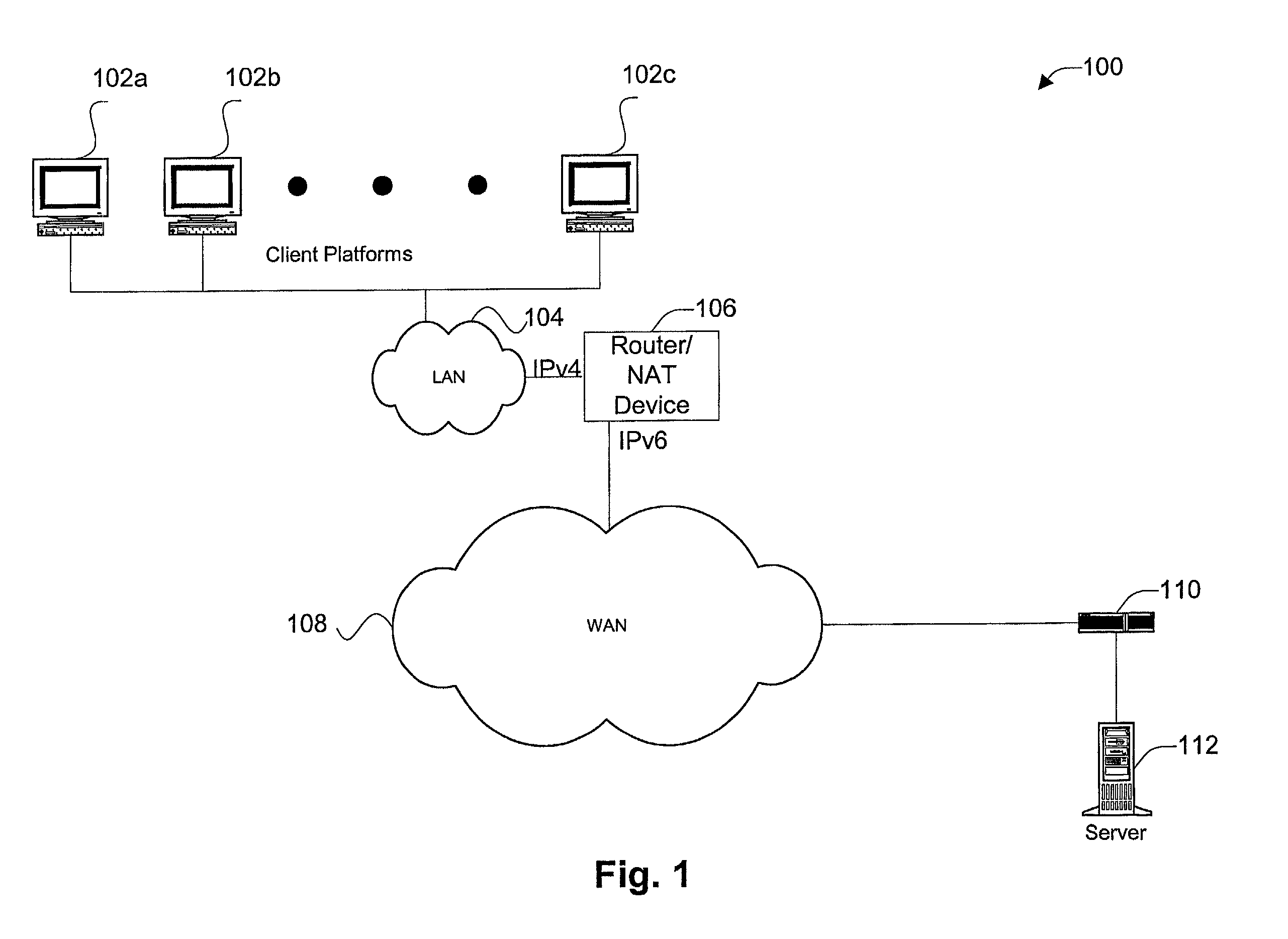
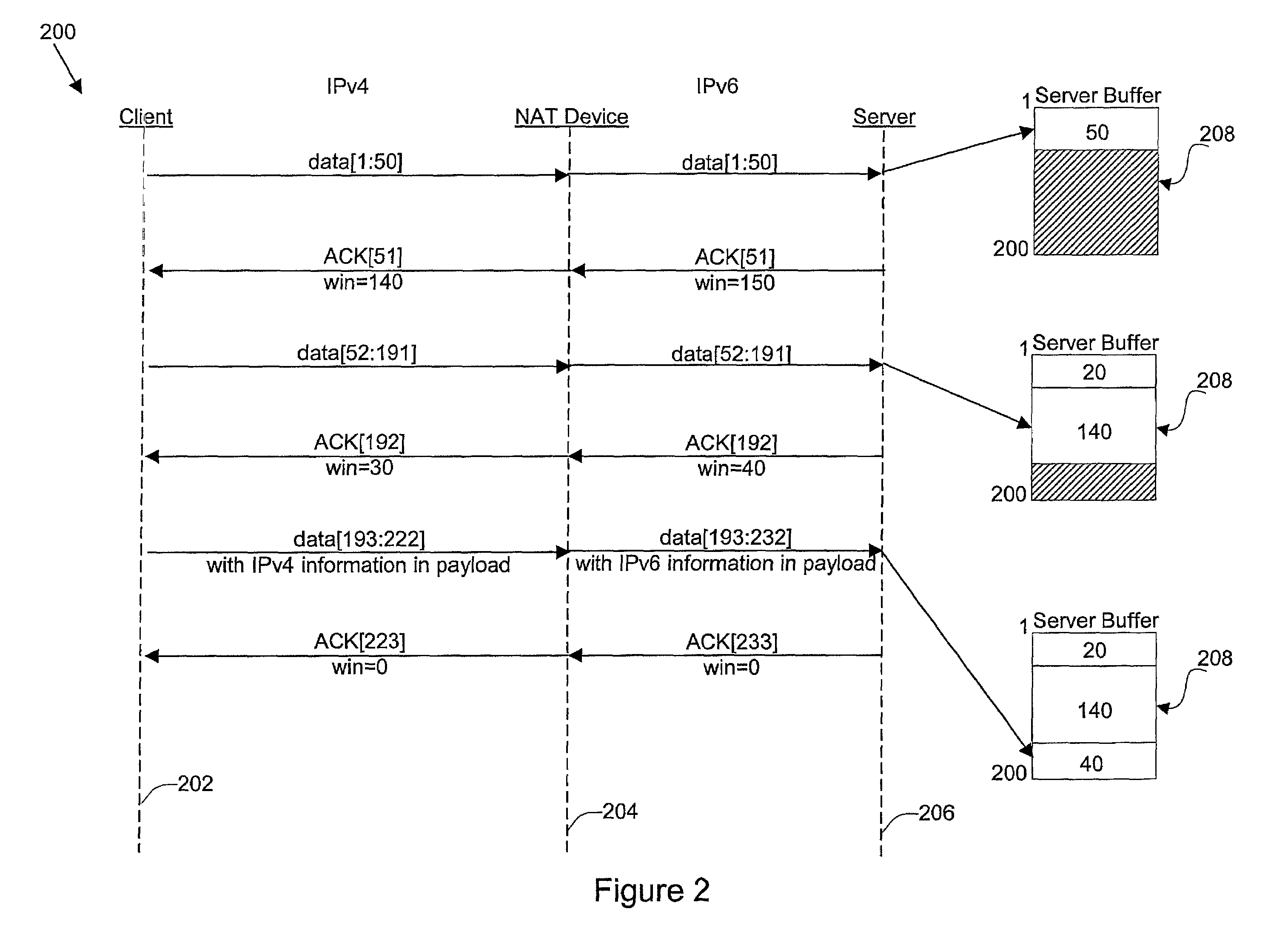
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for avoiding problems caused by converting between two different protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6. These problems may include, but are not limited to, fragmentation of packets, dropping of packets, and retransmission of packets. Avoiding these problems will reduce the incidence of transmission delays, bandwidth degradation, and additional processing in the packet's transmission path due to such problems. In general terms, the present invention provides mechanisms for modifying a protocol parameter, such as a TCP or UDP parameter, to avoid problems associated with protocol translation, such as fragmentation. In one implementation, the protocol parameter limits the size of a particular portion of the a packet transmitted by a sending computer node or device. For example, a packet size indicator is communicated to the sending computer node so that the sending computer node sends packets limited by the packet size indicator to thereby avoid associated with the size of such packets. In specific TCP embodiments, the size indicator specifies a window size and / or a maximum segment size. For example, if packets transmitted by a sending node to a receiving node are converted from IPv4 to IPv6 and the window size indicated to the sending node (e.g., by the receiving node) is 512 bytes, the window size is adjusted to 500 bytes before reaching the sending node. The adjustment amount may be based on an estimated size increase resulting from converting from IPv4 to IPv6. In this example, the window size is decreased by 12 bytes since a conversion from IPv4 to IPv6 where one 4 byte IPv4 address is changed to a 16 byte Ipv6 address has an associated size difference of 12 bytes. In a specific embodiment, actual changes in packet size may tracked and the adjusted size indicator may be dynamically based on such tracked changes. In other embodiments, the changes in packet size are predicted, and the adjusted size is preemptively changed as needed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
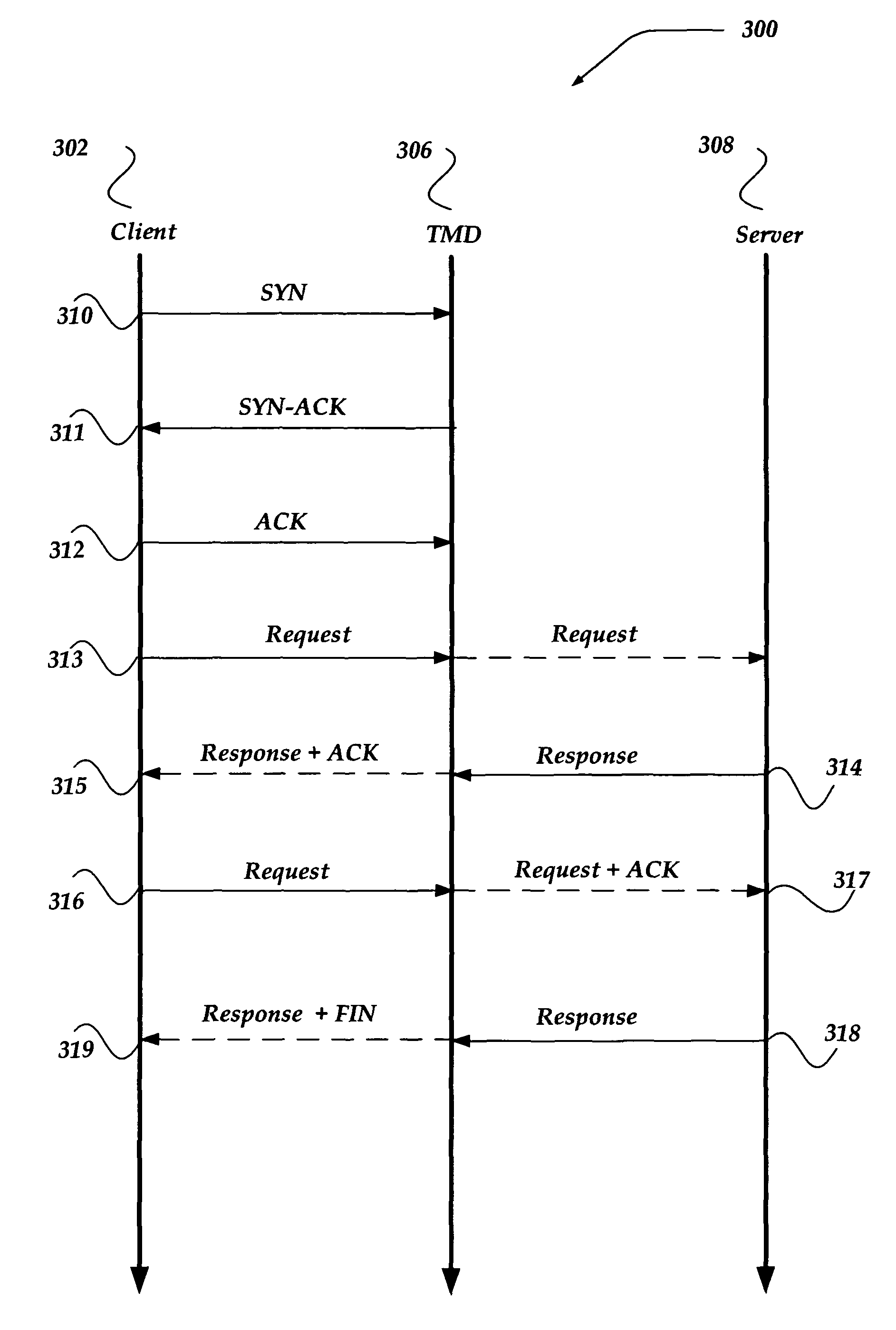
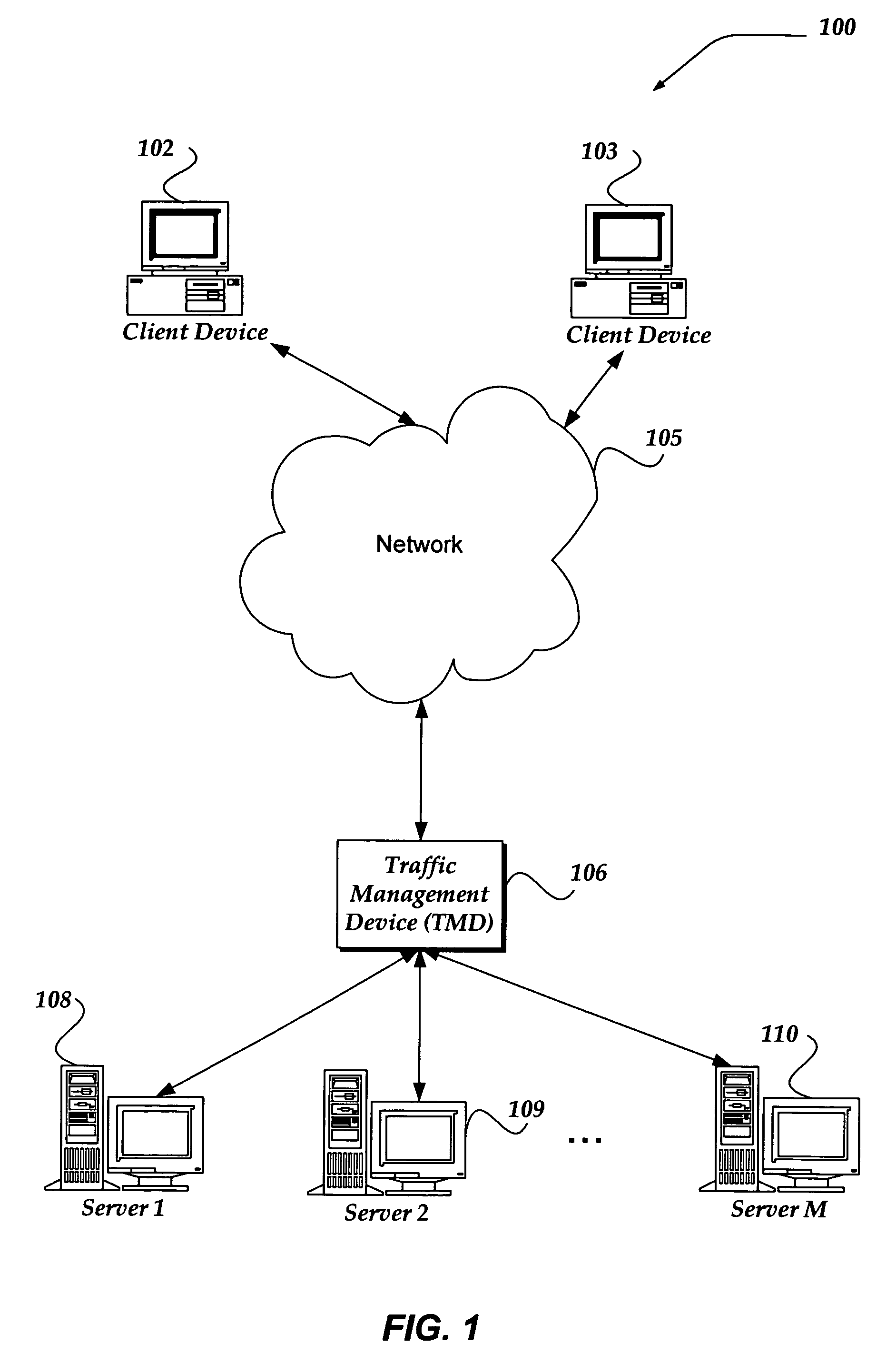
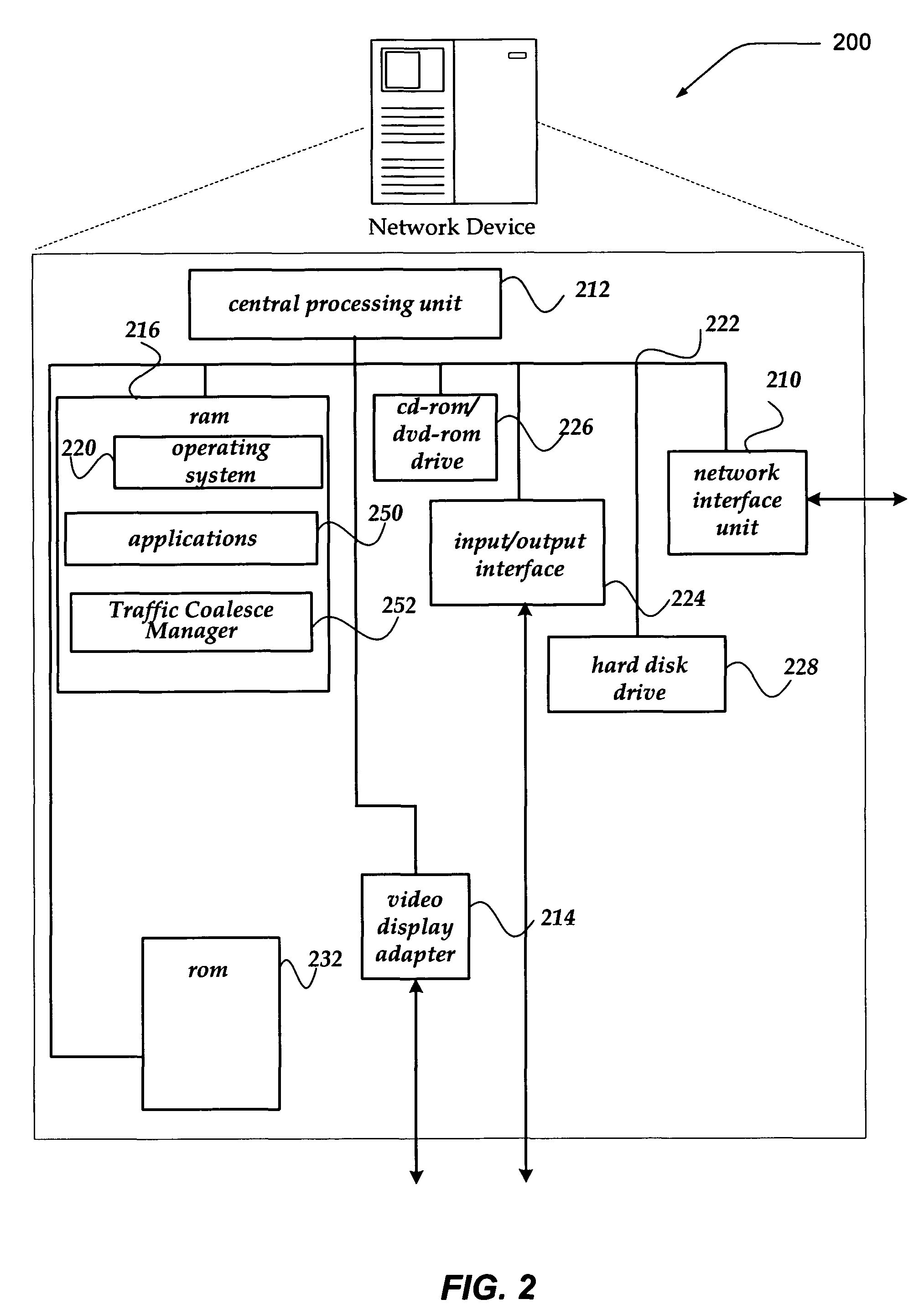
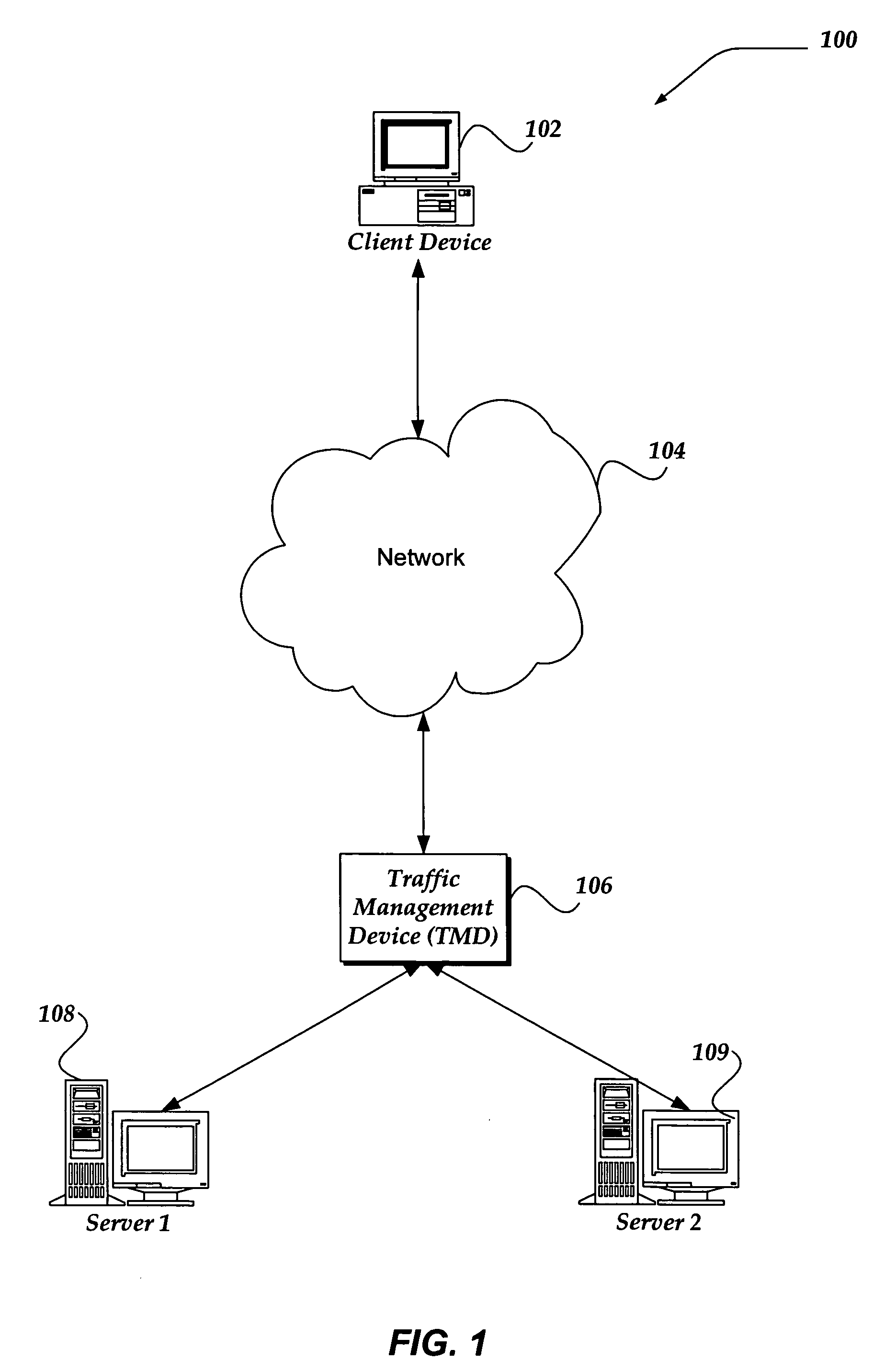
Coalescing acknowledgement responses to improve network communications
ActiveUS7826487B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork communicationClient-side
A system, apparatus, and method are directed to managing network communications by, in part, reducing a number of packets between a client and a server communicating through another device, such as a traffic management device (TMD). The invention reduces the number of packets communicated, in part, by coalescing acknowledgements (ACKs) and / or finish (FIN) flags into another packet. In one embodiment, if the client provides a substantially complete request for the server, an ACK to the request may be coalesced into a corresponding response from the server. When another request is to be provided to the server, within about half of the minimum retransmission timeout, an ACK to the prior response may be coalesced into a subsequent request to the server. Packet reduction may also be achieved by stretching a packet to insert additional data when the insertion maintains a packet size that is within a negotiated maximum segment size (MSS).
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
Packet size control technique
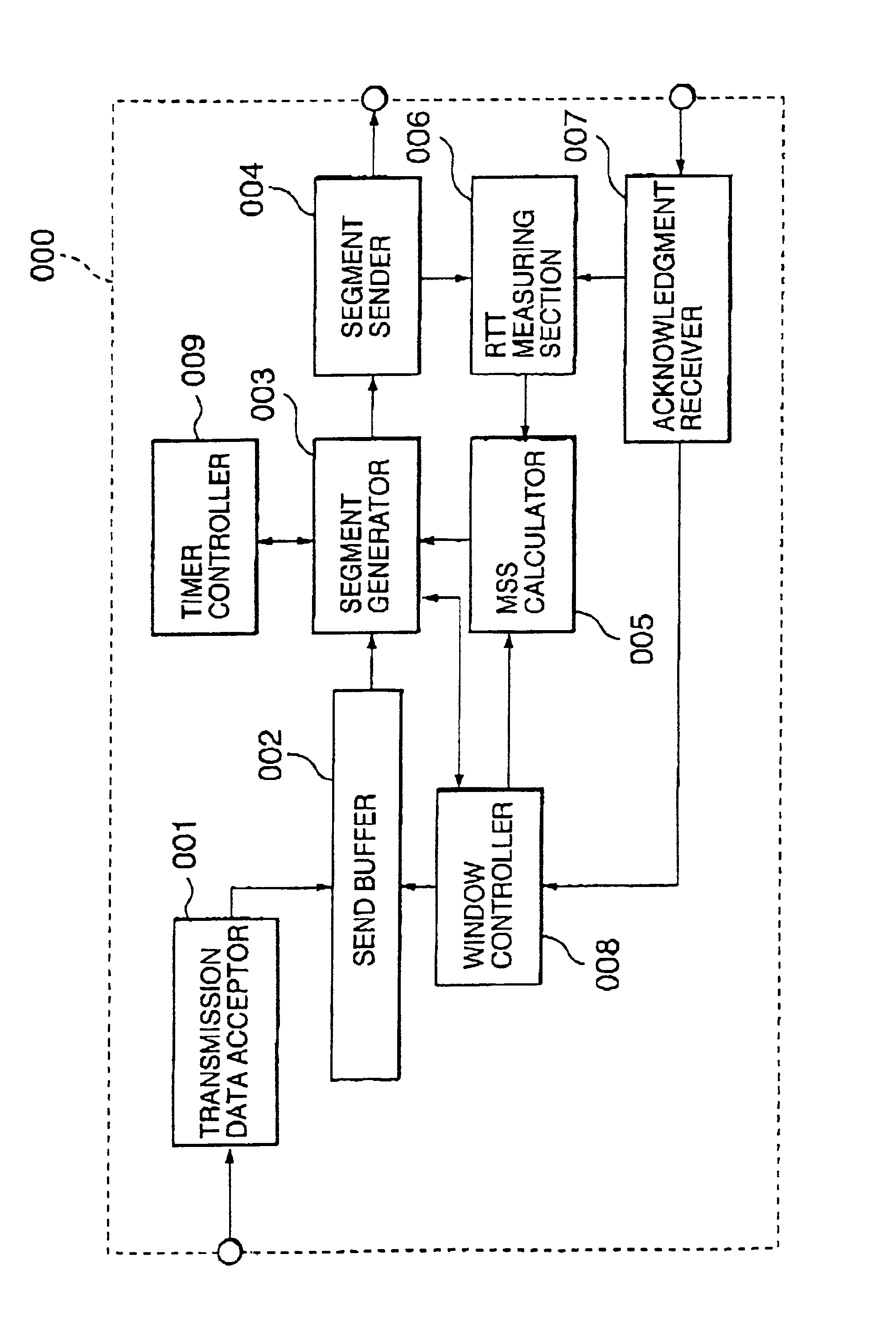
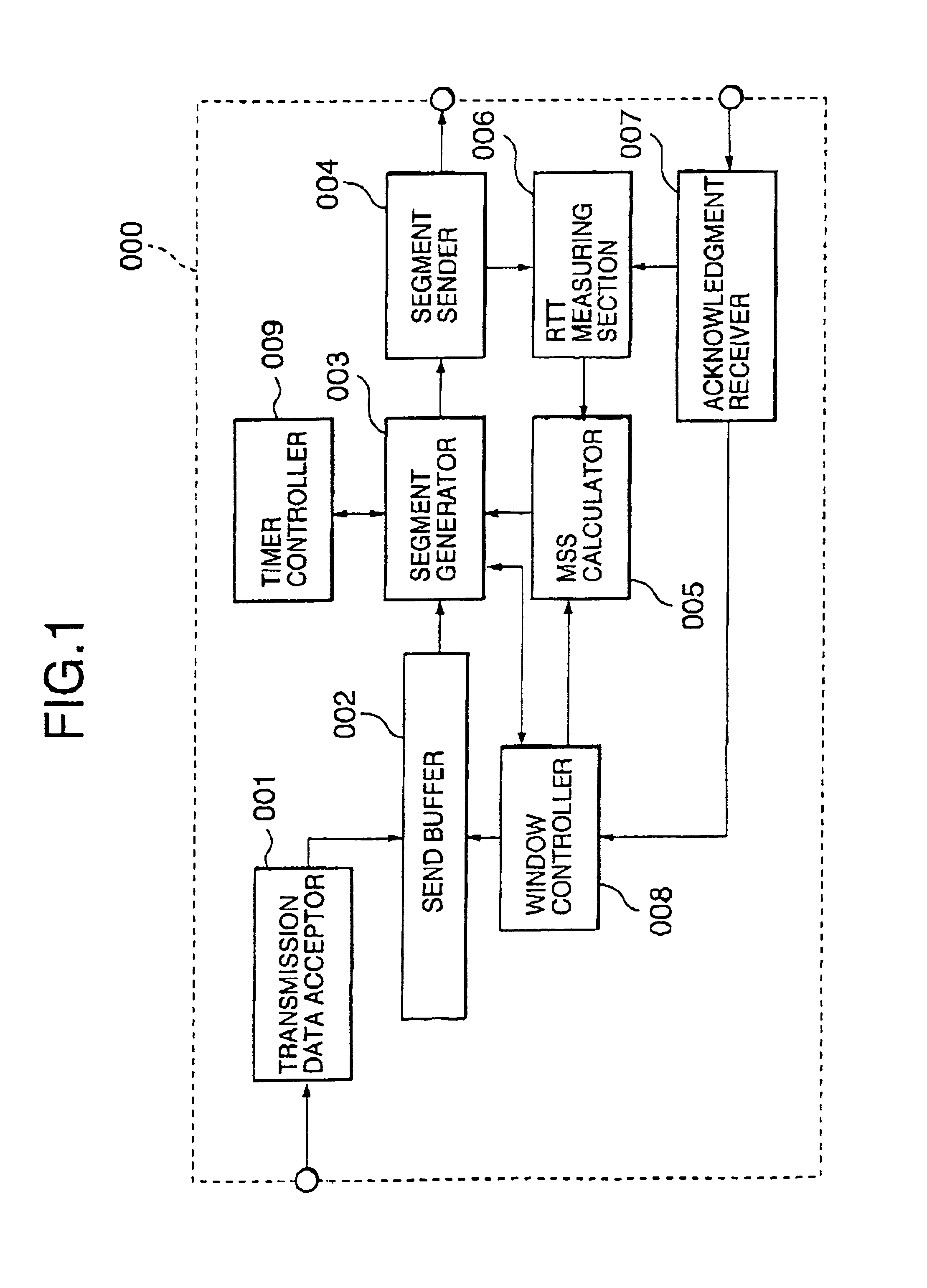
InactiveUS6934251B2Shorten the time periodImprove data transfer throughputTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowData link layer
A packet size control method allowing reduction in the period of time during which transmission is in a blocked state is disclosed. The size of a packet to be sent is determined depending on a measured round trip time (RTT), a current bandwidth of the data link layer, and a current congestion window size. First, a maximum segment size (MSS) is obtained based on the measured RTT and the current bandwidth of the data link layer using a table obtained by data transfer simulation. Thereafter, the obtained MSS is corrected using the current congestion window size. And the correct MSS is used to determine the final segment of data to be sent.
Owner:NEC CORP
Systems and methods for http-body DOS attack prevention with adaptive timeout
ActiveUS20140304798A1Facilitate mitigating adverse effectKeep for a long timeMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTransport layerClient-side
The present disclosure is directed generally to systems and methods for changing an application layer transaction timeout to prevent Denial of Service attacks. A device intermediary to a client and a server may receive, via a transport layer connection between the device and the client, a packet of an application layer transaction. The device may increment an attack counter for the transport layer connection by a first predetermined amount responsive to a size of the packet being less than a predetermined fraction of a maximum segment size for the transport layer connection. The device may increment the attack counter by a second predetermined amount responsive to an inter-packet-delay between the packet and a previous packet being more than a predetermined multiplier of a round trip time. The device may change a timeout for the application layer transaction responsive to comparing the attack counter to a predetermined threshold.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
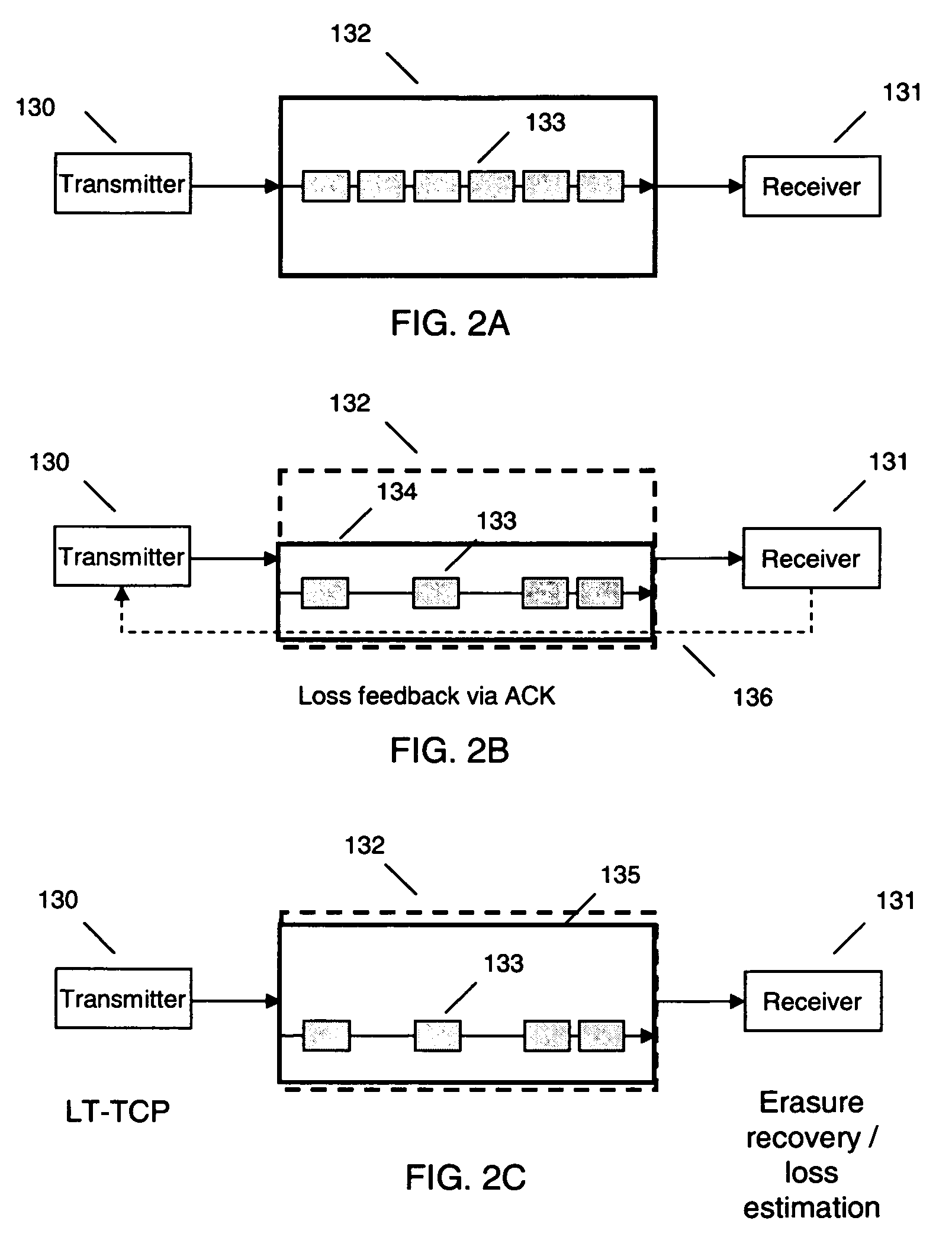
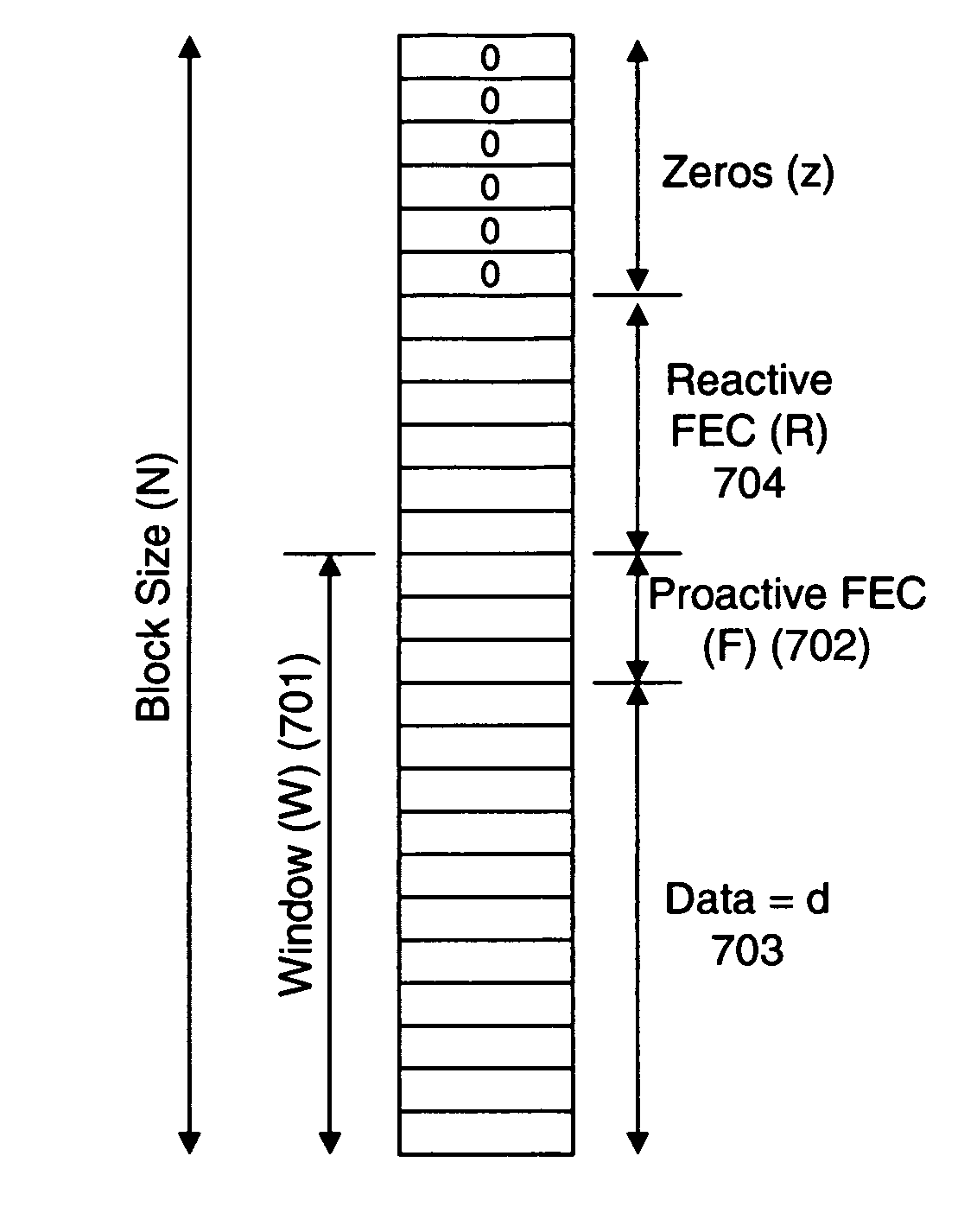
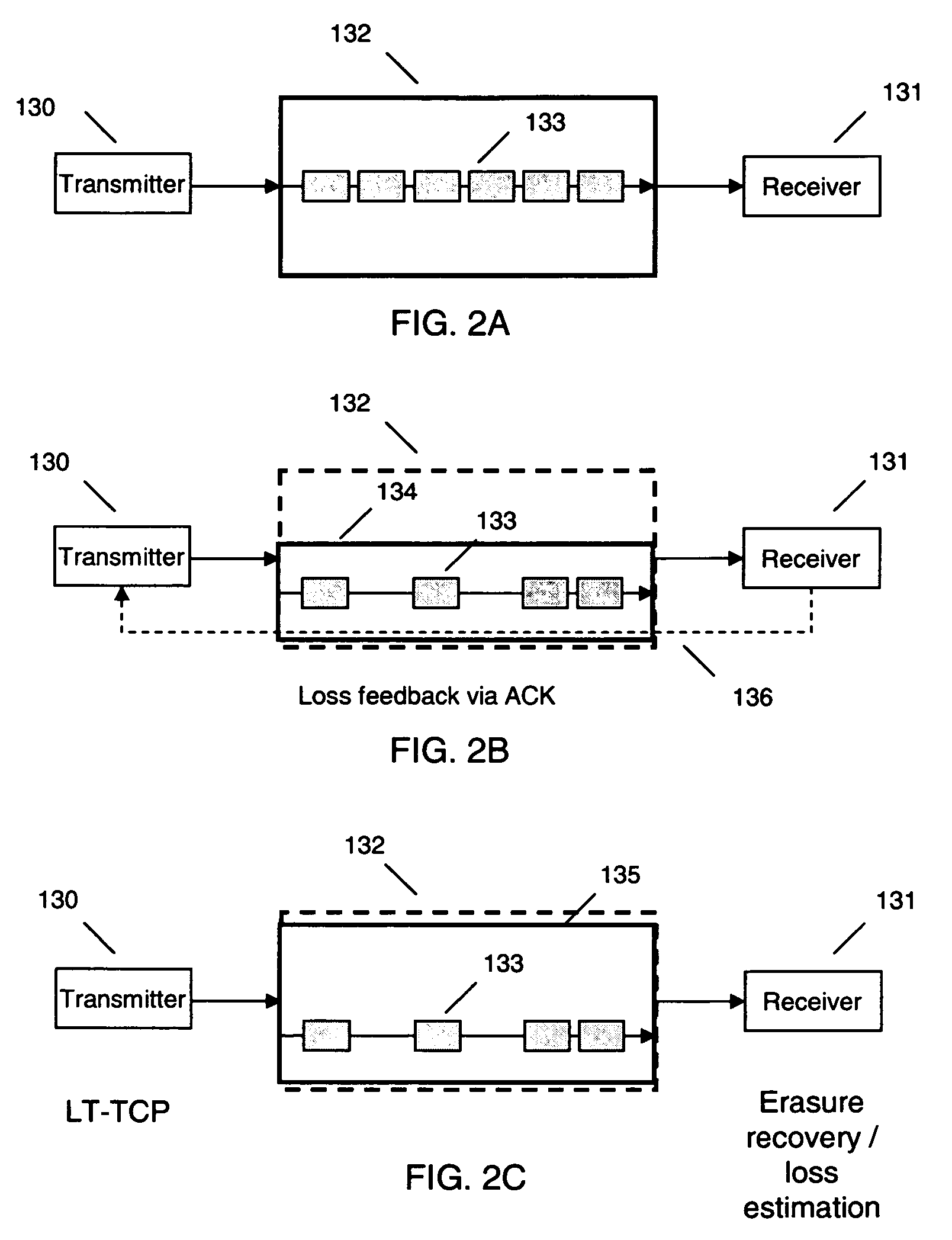
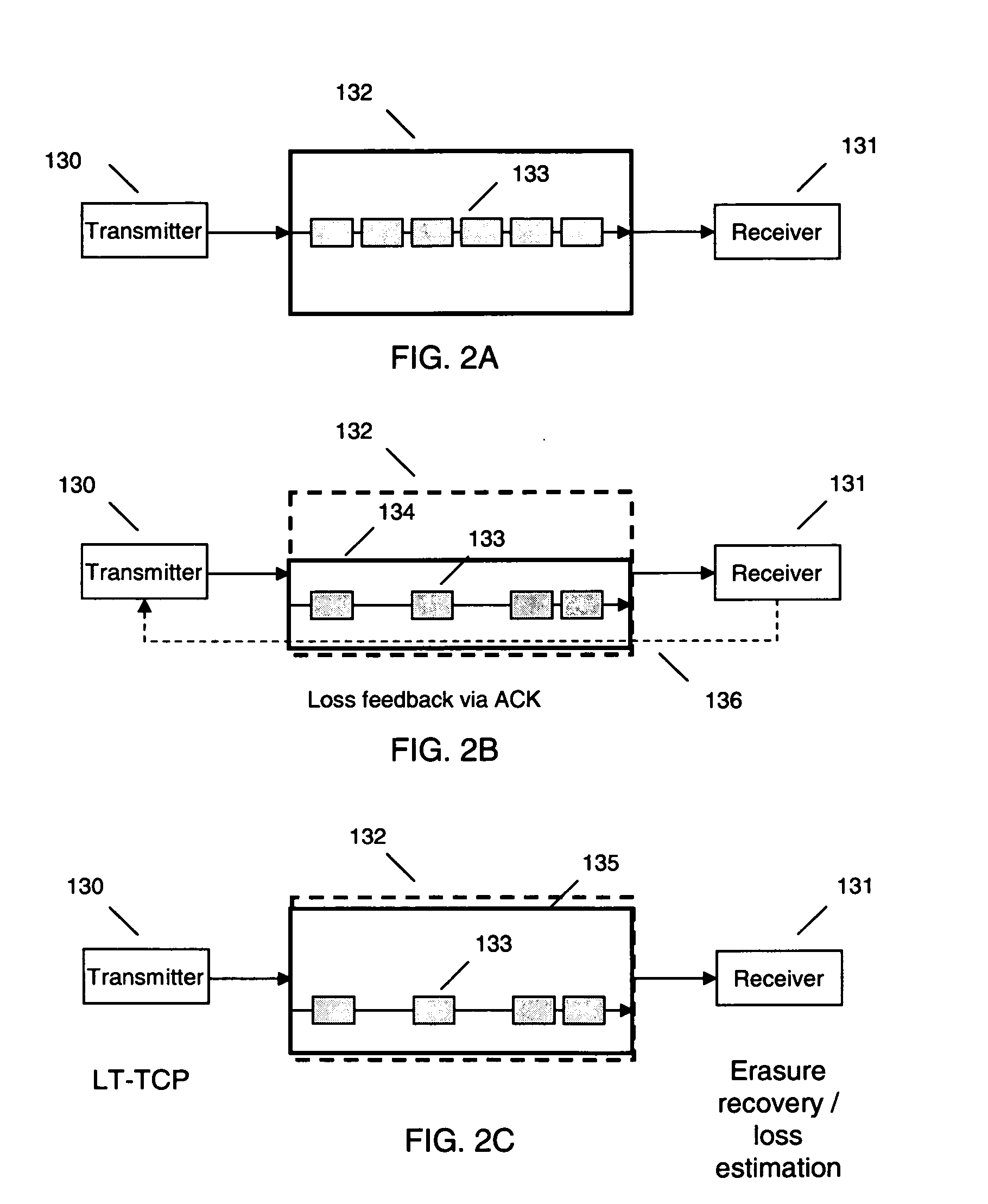
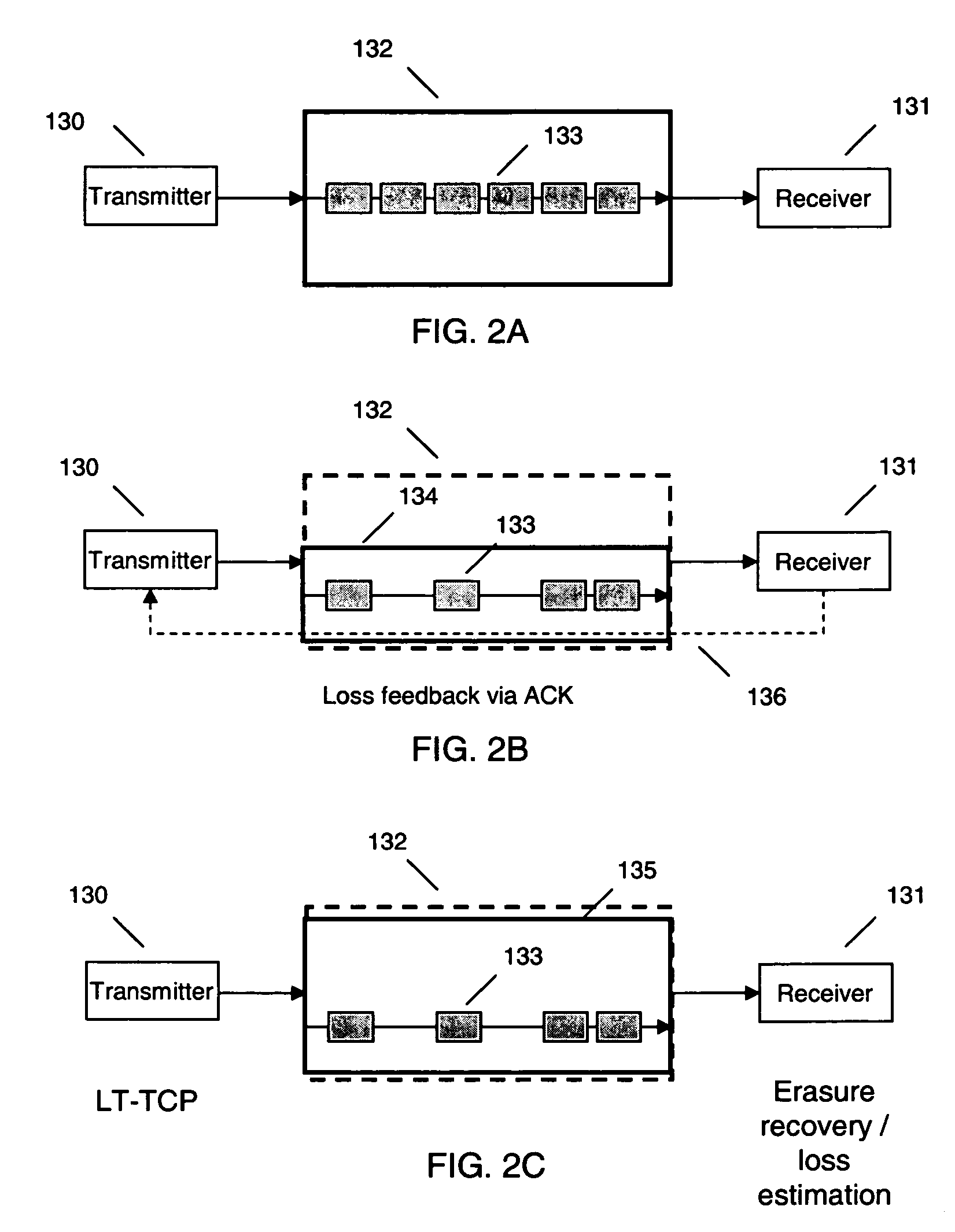
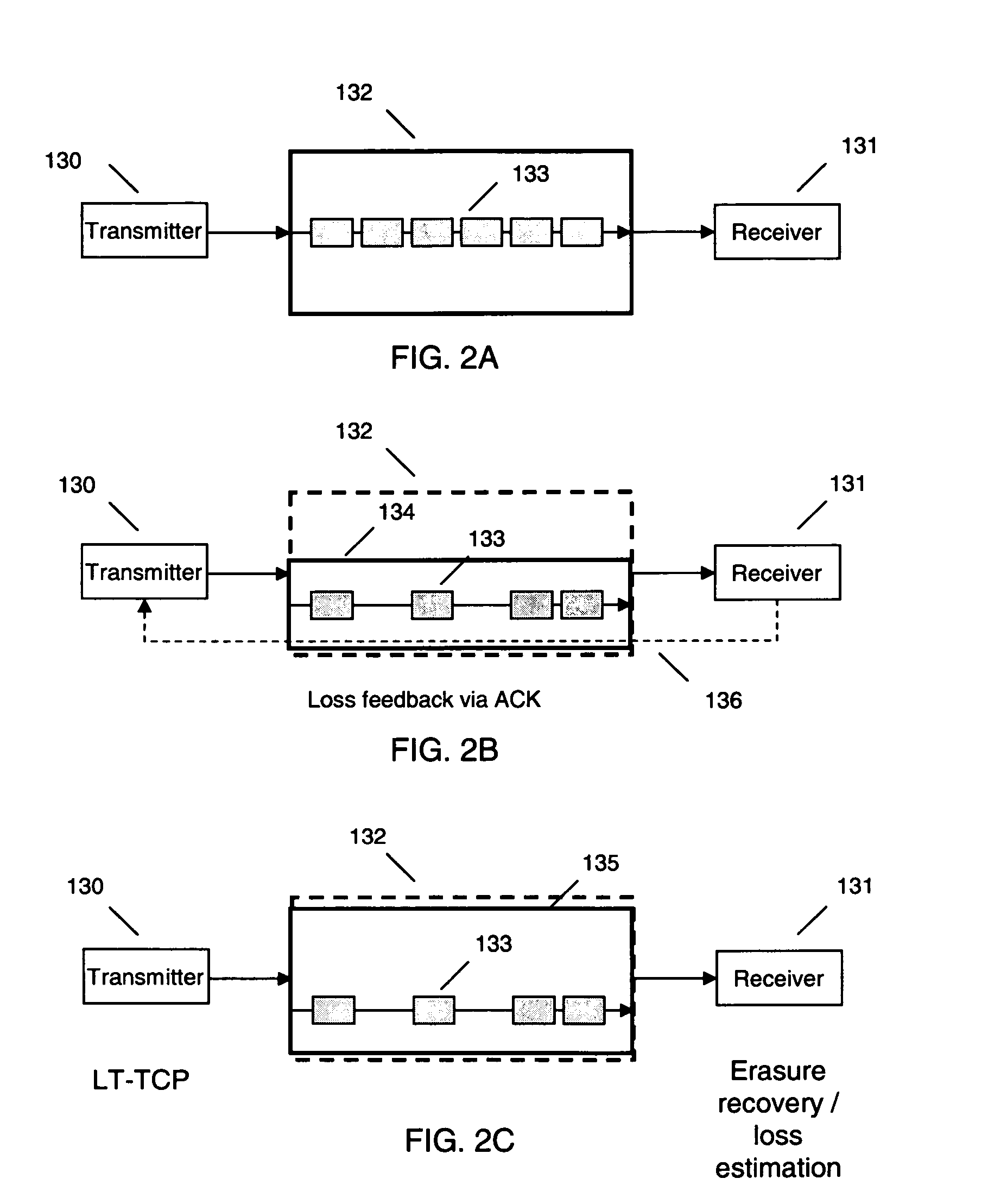
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
ActiveUS20060251011A1Reduction of congestion windowReduce window sizeTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission protocolCongestion window
Provided are apparatuses and methods for transmitting or receiving data packets in a data block in a communication network with a transport protocol. In one example, a loss tolerant TCP protocol is used in which a maximum segment size (MSS) may be adapted to a minimum granularity of a congestion window. Also, proactive forward error correction (FEC) packets may be added to a window of the data block. The number of proactive FEC packets may be determined, for example, based on an estimate erasure rate. In addition, reactive FEC packets may be added to the data block. Also, a receiver may receive data packets in a data block and process a selective acknowledgment (SACK) responsive to the data packets received.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
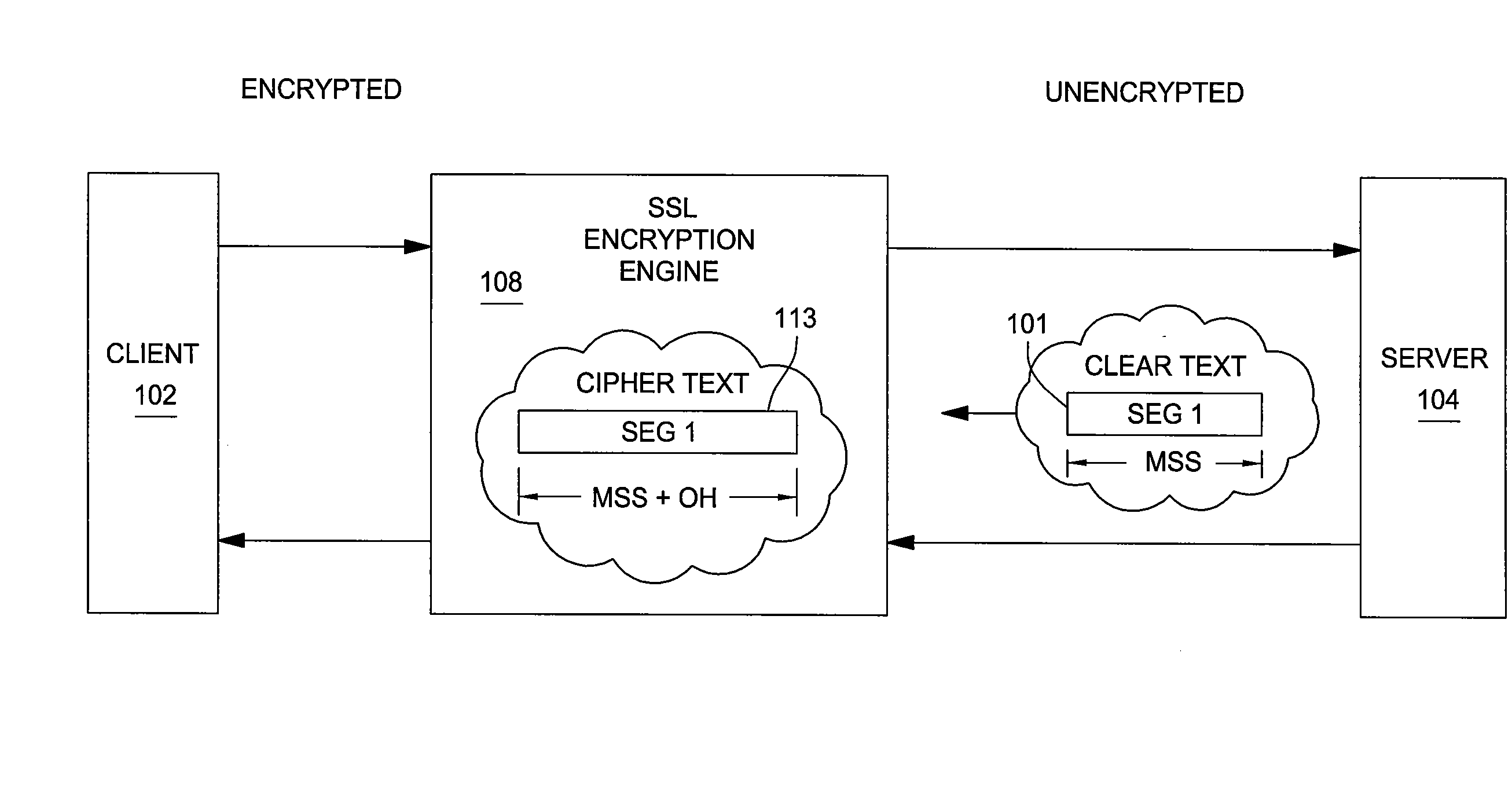
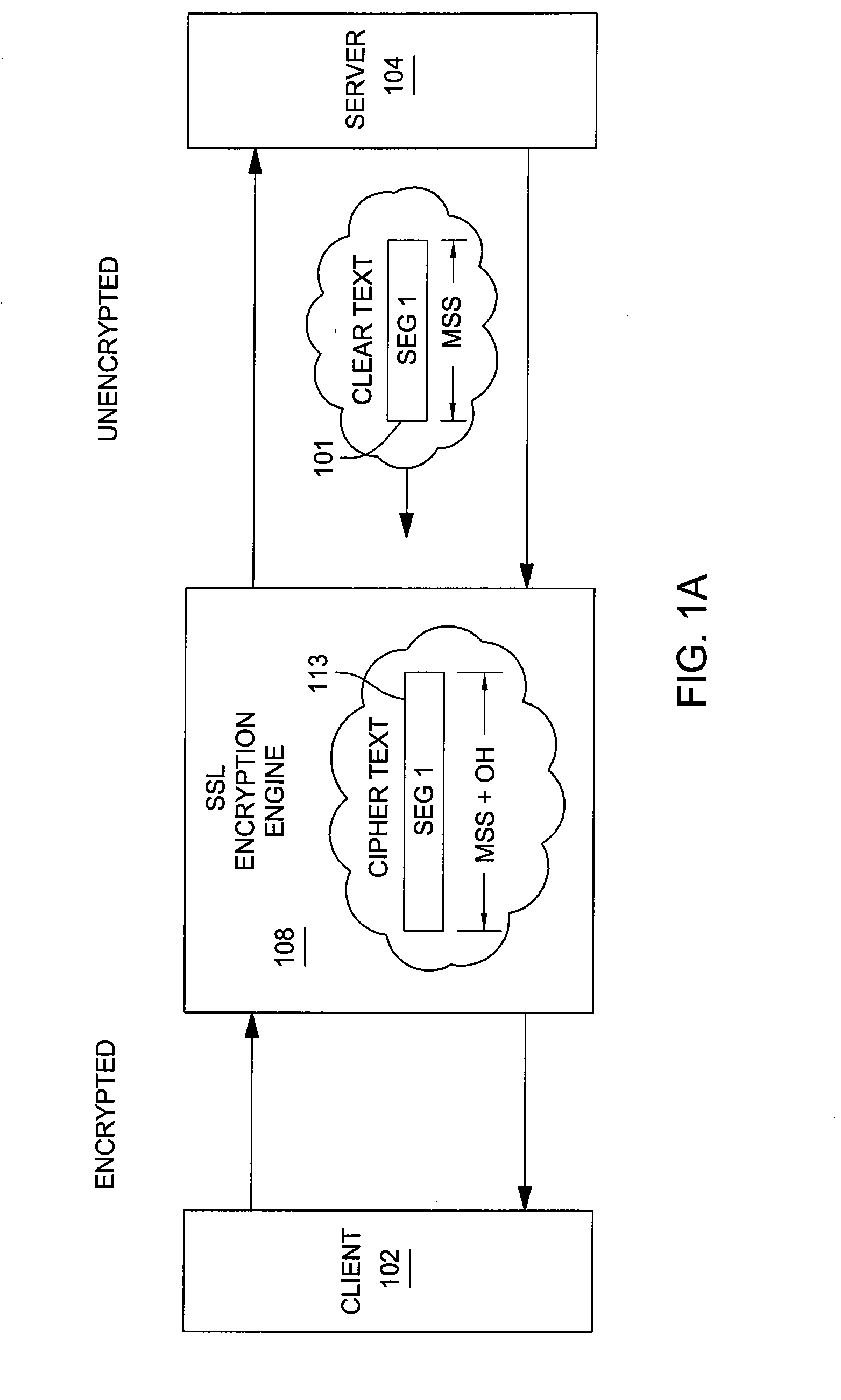
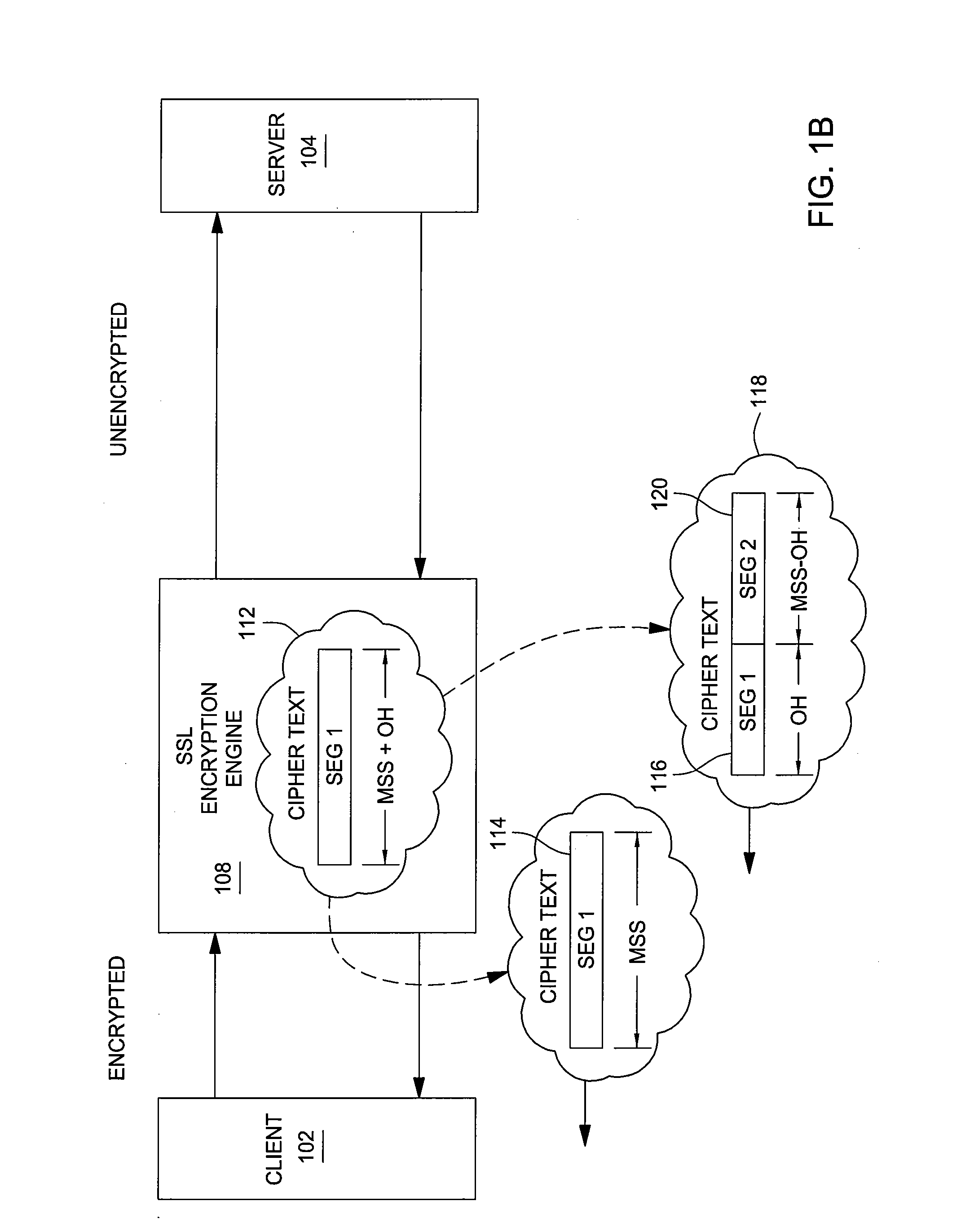
Method and apparatus to minimize latency by avoiding small TCP segments in a ssl offload environment
InactiveUS20070266233A1Establish connectionSecuring communicationComputer hardwareNetwork communication
Methods and apparatus for secure network communication in a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) by avoiding small Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) packets are provided. For some embodiments, these small packets may be avoided by adjusting a maximum segment size (MSS) used in transmissions between an encryption engine and a server to compensate for the amount of overhead added by the encryption process.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
ActiveUS7889654B2Reduce congestionReduce window sizeFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion windowTransmission protocol
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Systems and methods for synchronizing mss and pmtu in ncore and cluster systems
ActiveUS20140301395A1Improve academic performanceData switching by path configurationCluster systemsClient-side
Systems and methods of propagating maximum segment size and path maximum transmission unit of network paths between an intermediary device of a cluster with a plurality of destinations are described. A first core of a node including multiple cores and intermediary to a client and a plurality of servers may receive a response to a packet transmitted to a destination indicating that the packet has a size greater than a MTU of a network path between the node and a destination. The first core identifies the MTU of the network path and determines that the identified MTU is different than an MTU used by the first core. The first core replaces the MTU stored in an entry corresponding to the destination in a PMTU table maintained with the identified MTU. The first core transmits, to other cores of the node, the identified MTU to update each core's PMTU table.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
InactiveUS20060251010A1Reduction of congestion windowReduce window sizeNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowGranularity
Provided are apparatuses and methods for transmitting or receiving data packets in a data block in a communication network with a transport protocol. In one example, a loss tolerant TCP protocol is used in which a maximum segment size (MSS) may be adapted to a minimum granularity of a congestion window. Also, proactive forward error correction (FEC) packets may be added to a window of the data block. The number of proactive FEC packets may be determined, for example, based on an estimate erasure rate. In addition, reactive FEC packets may be added to the data block. Also, a receiver may receive data packets in a data block and process a selective acknowledgment (SACK) responsive to the data packets received.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
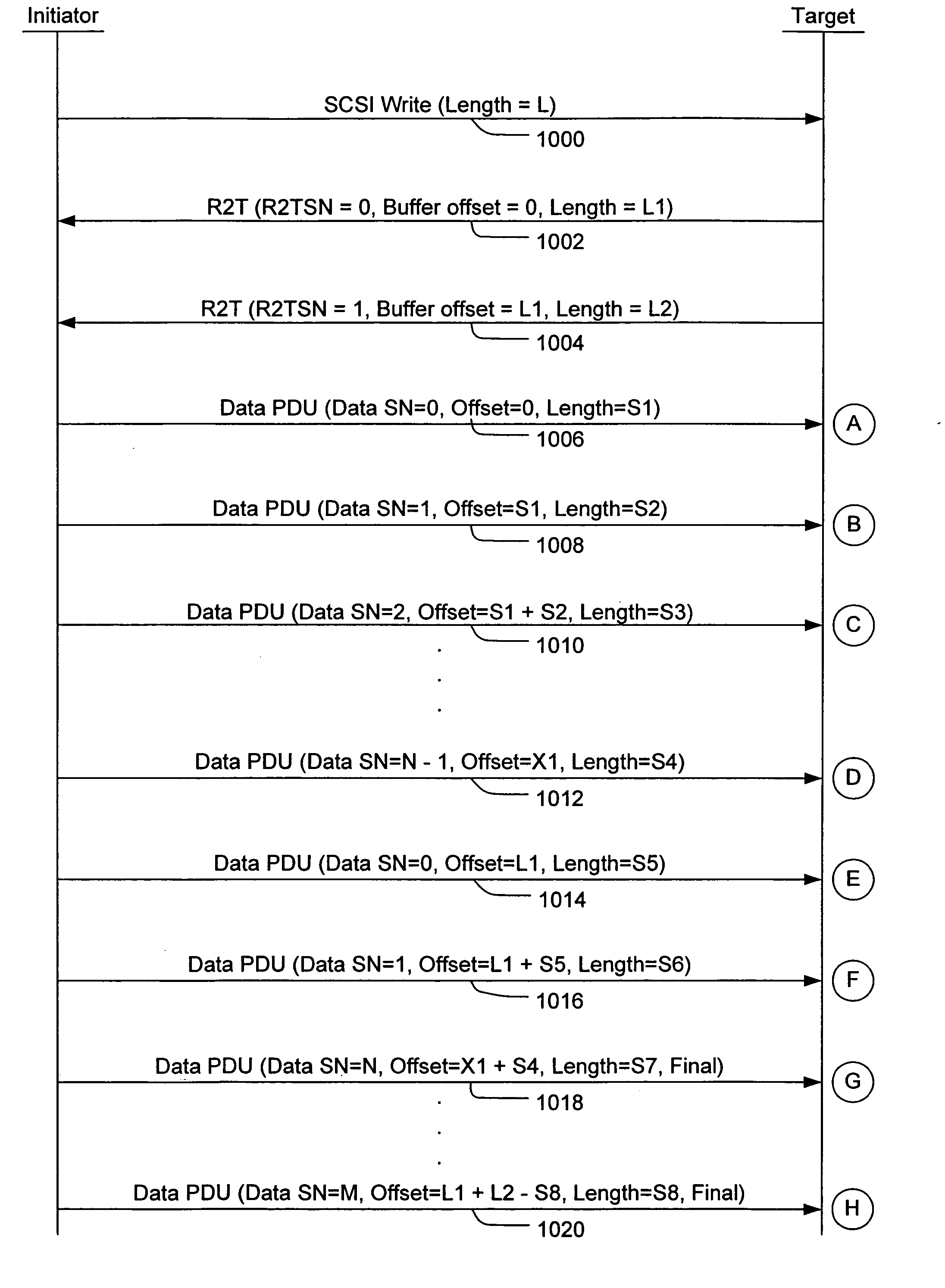
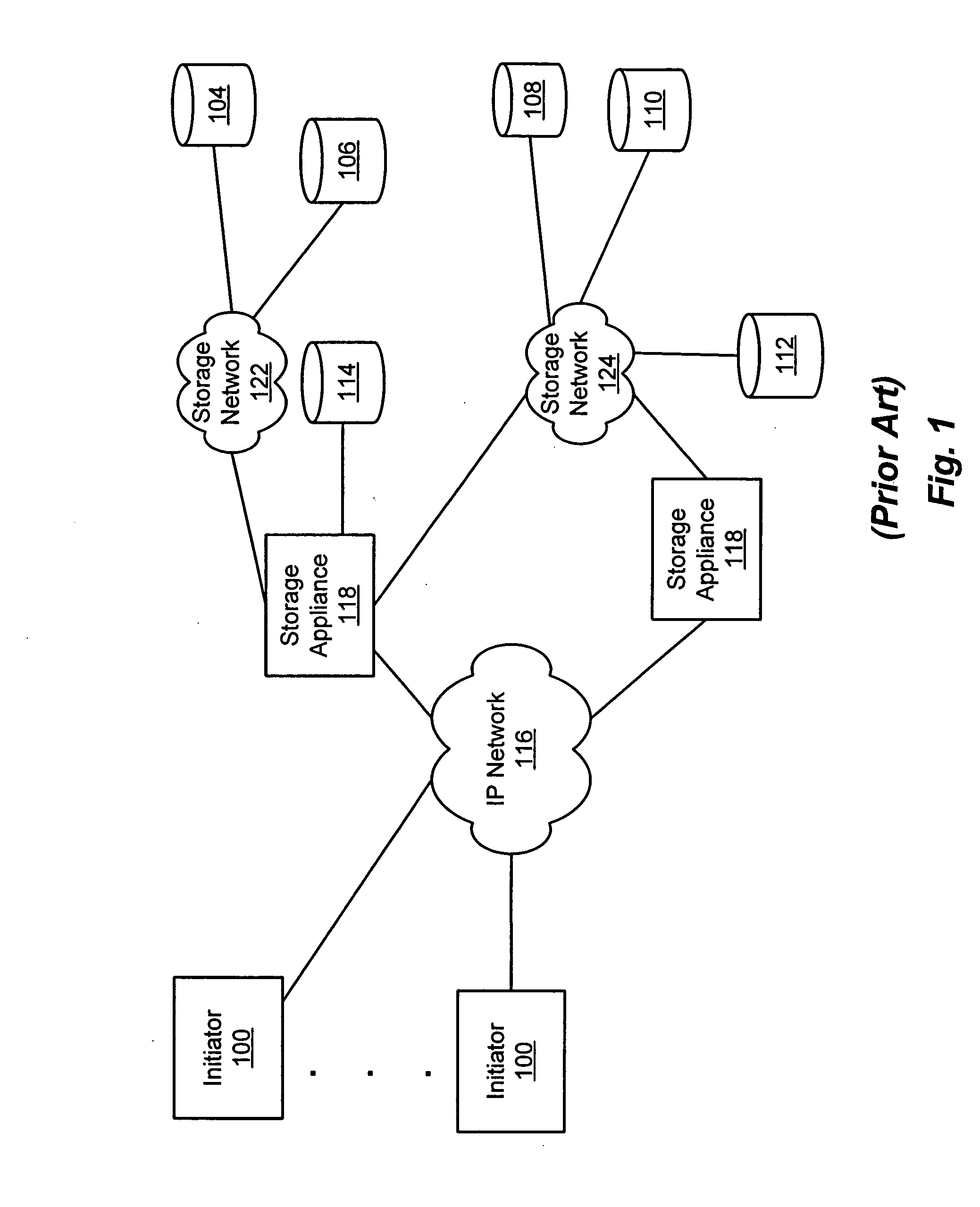
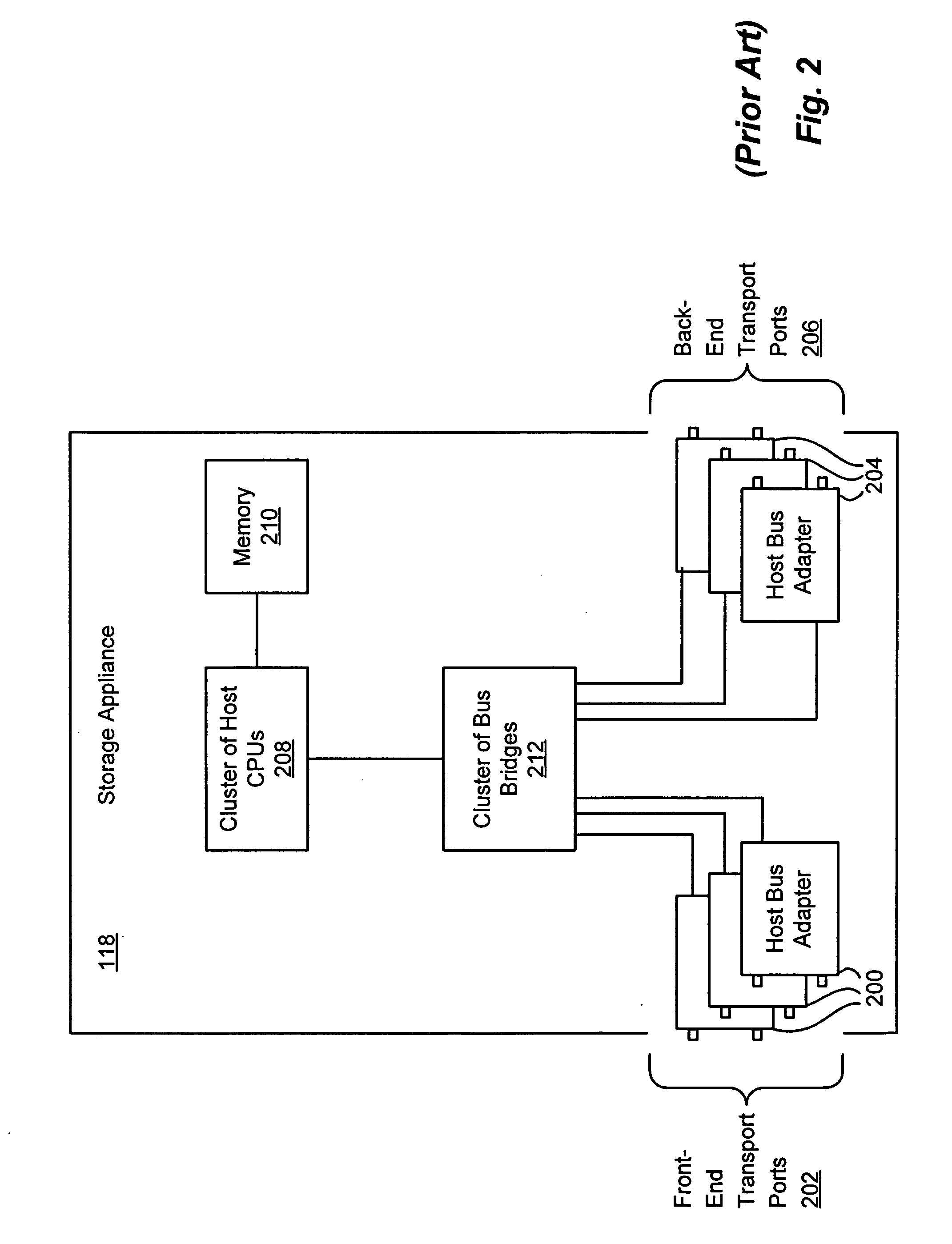
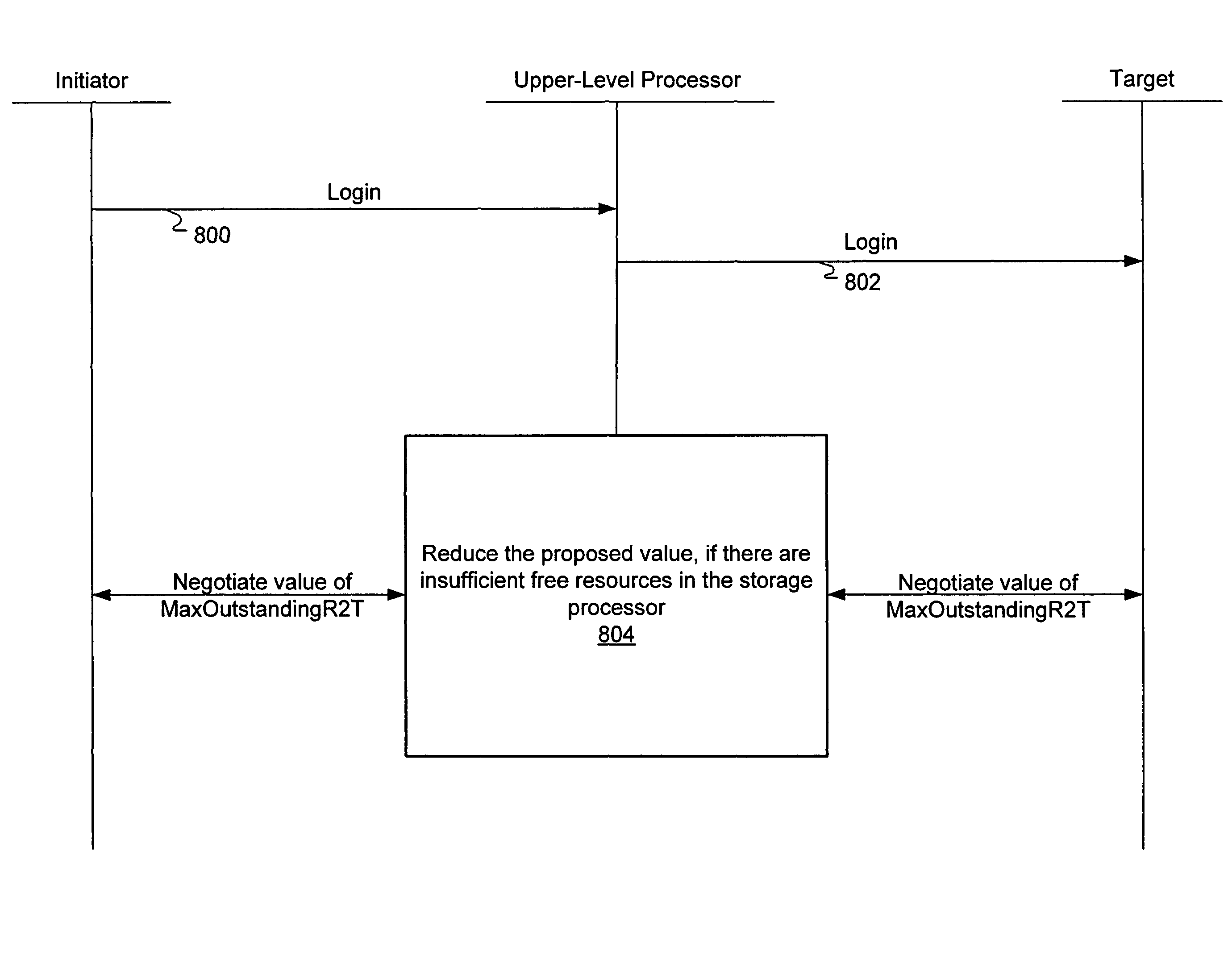
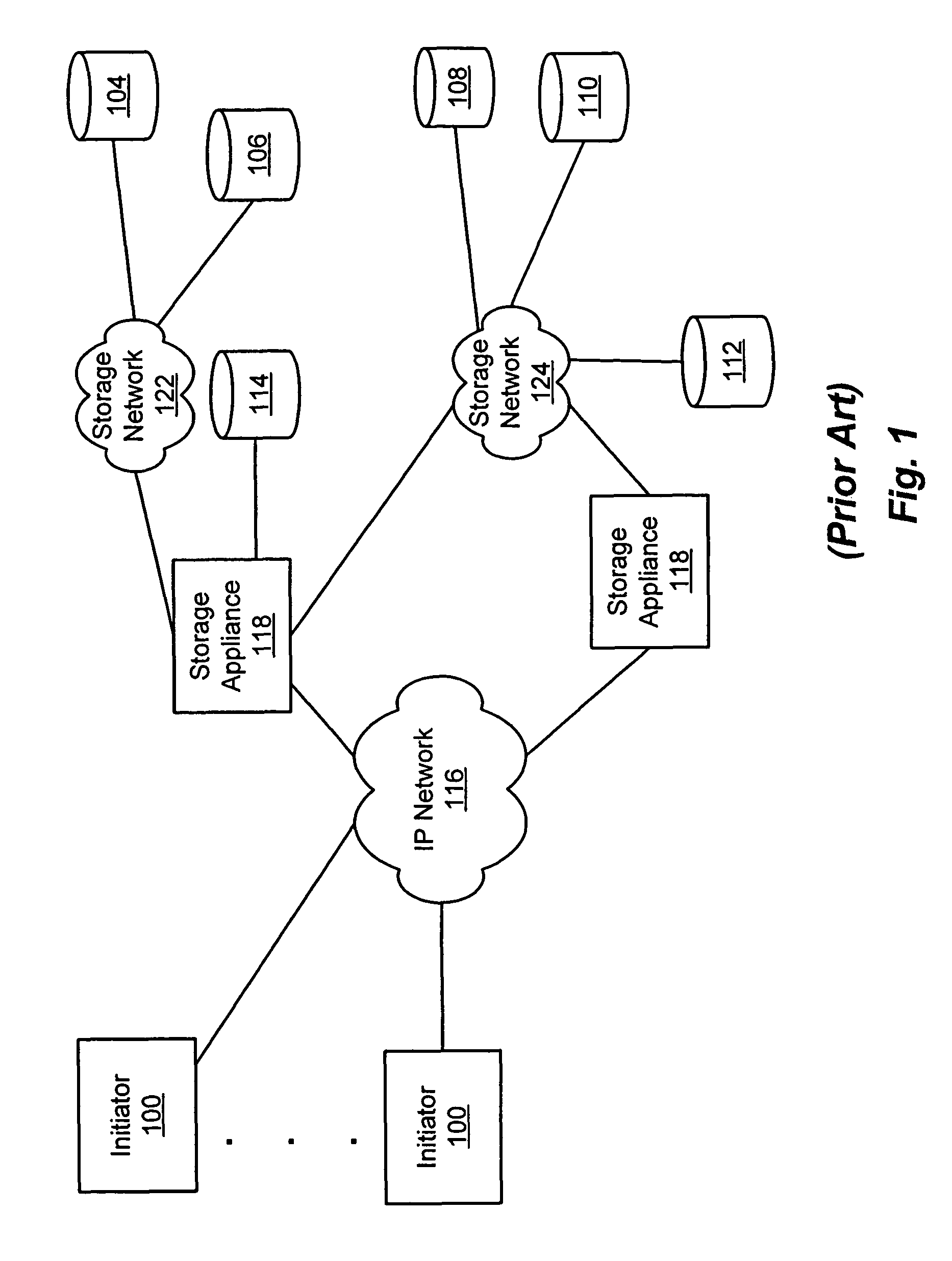
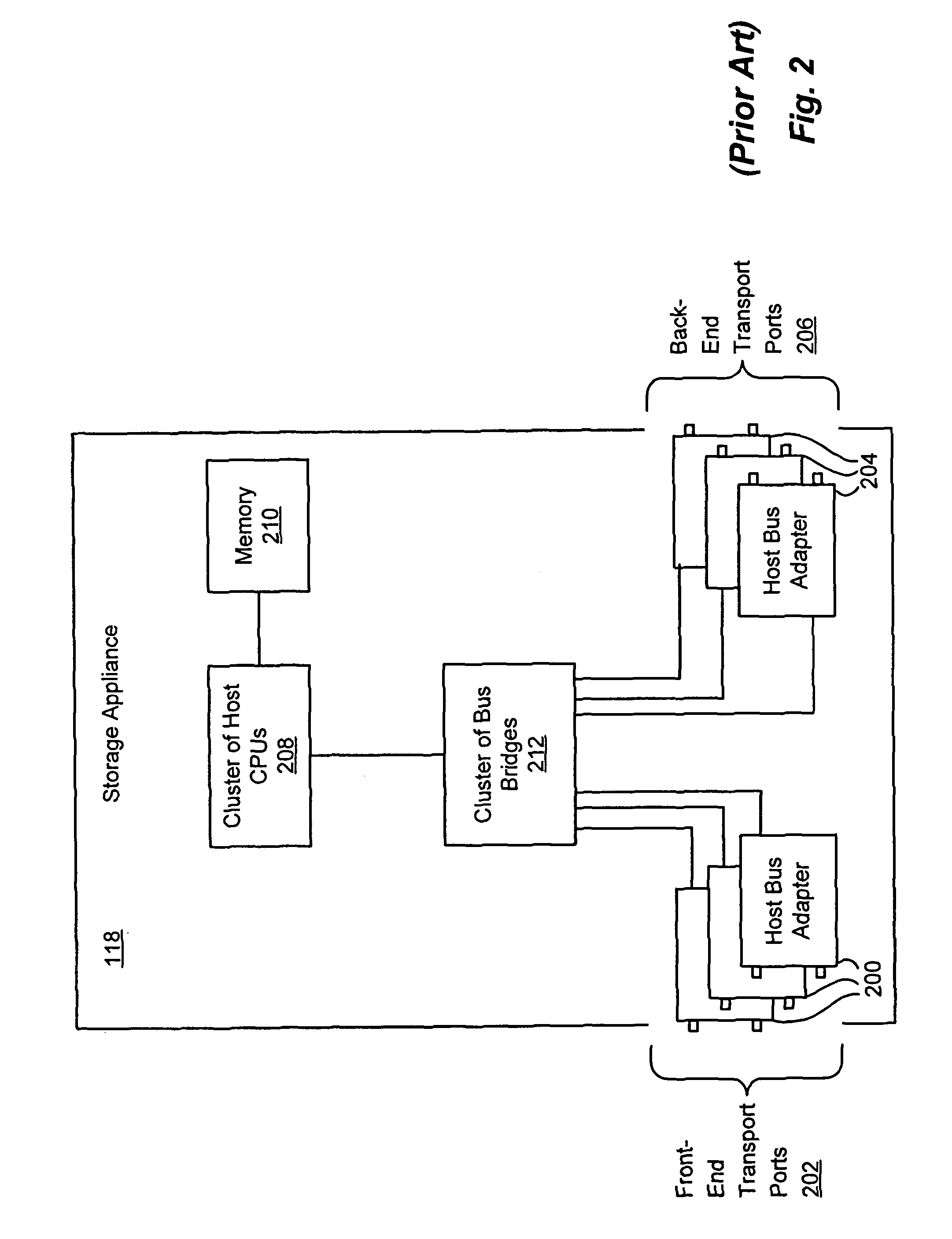
Storage processor for handling disparate requests to transmit in a storage appliance
InactiveUS20060248292A1Reduce memory requirementsShorten the timeMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingRAIDData segment
A storage processor is interposed between initiators and storage targets, such as storage appliances or storage devices in a storage network. The storage processor presents a target interface to the initiators and an initiator interface to the targets, and the storage processor transparently intercepts and processes commands, data and / or status information (such as iSCSI R2T and data PDUs) sent between the initiators and the targets. The storage processor presents a virtual device to the initiators and transparently implements the virtual device on the targets, such as a RAID-1. The storage processor negotiates acceptable operational parameters, such as maximum segment size, with the initiators and targets, such that the storage processor can pass data received from the initiators to the targets, without excessive data buffering. Consequently, when an initiator issues a write command, the storage processor is able to forward each segment of data received from the initiator to the appropriate target(s), without first buffering all segments of the write command.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
InactiveUS20060250949A1Reduction of congestion windowReduce window sizeError preventionTransmission systemsTransmission protocolCongestion window
Provided are apparatuses and methods for transmitting or receiving data packets in a data block in a communication network with a transport protocol. In one example, a loss tolerant TCP protocol is used in which a maximum segment size (MSS) may be adapted to a minimum granularity of a congestion window. Also, proactive forward error correction (FEC) packets may be added to a window of the data block. The number of proactive FEC packets may be determined, for example, based on an estimate erasure rate. In addition, reactive FEC packets may be added to the data block. Also, a receiver may receive data packets in a data block and process a selective acknowledgment (SACK) responsive to the data packets received.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
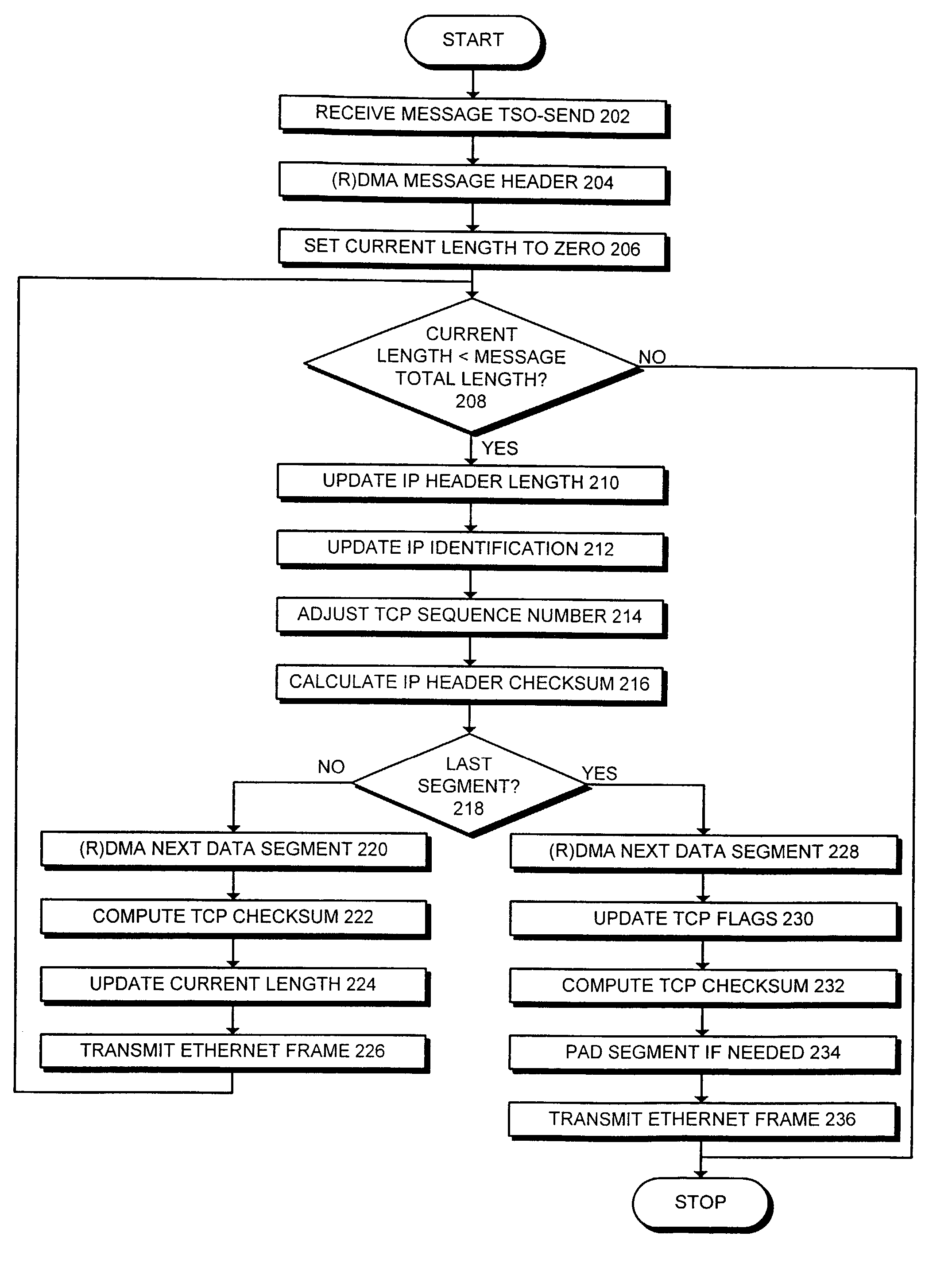
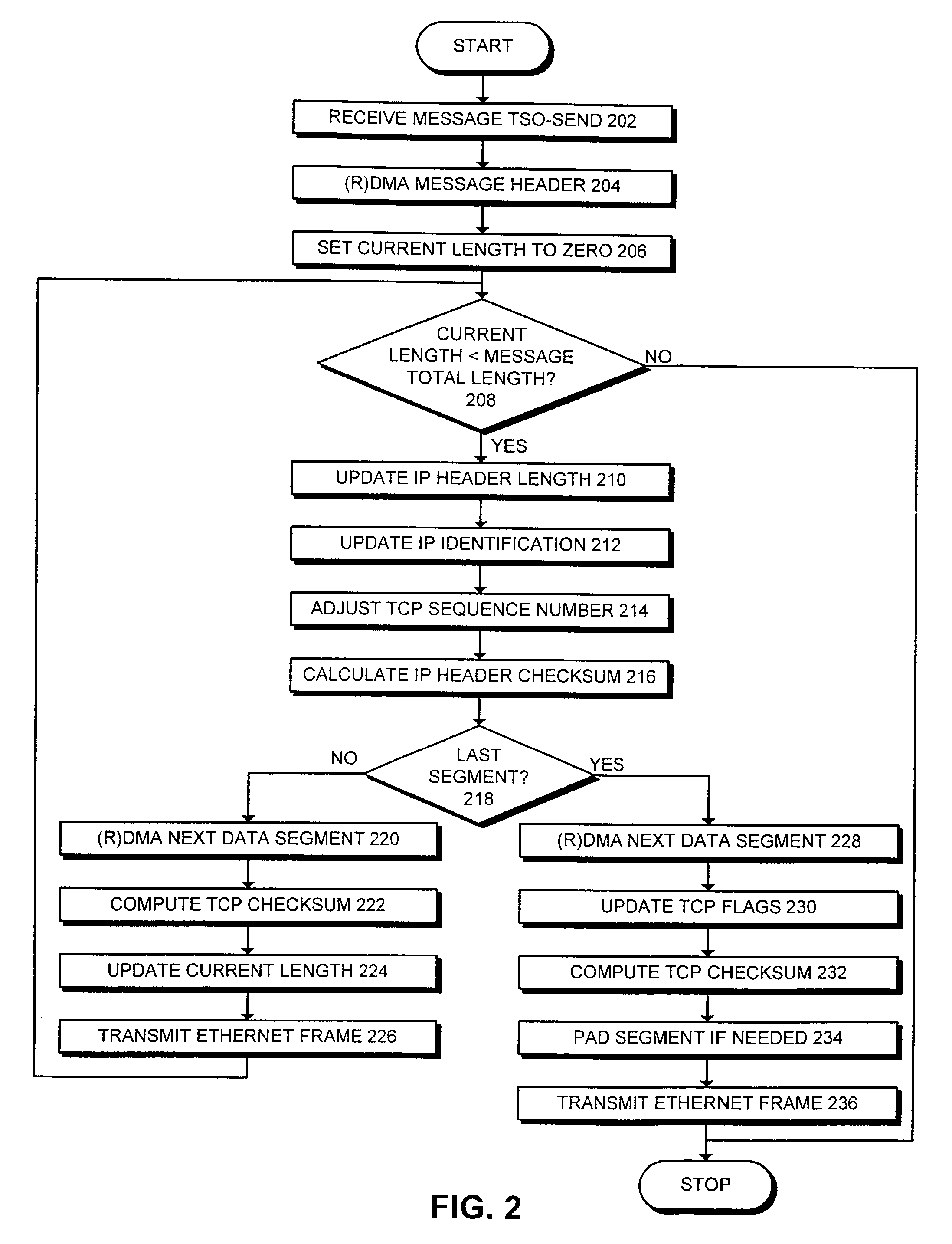
Method and apparatus for offloading message segmentation to a network interface card
ActiveUS7283522B2Easy to optimizeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationRemote direct memory accessMaximum segment size
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates offloading message segmentation from a central processing unit onto a network interface card. The system operates by first receiving a TSO-send message at the network interface card, wherein the TSO-send message contains information about the message to be sent. Next, the system uses a header address from the TSO-send message to access a message header from memory using remote direct memory access. The system then uses a payload address from the TSO-send message to access a payload from memory that contains message data using remote direct memory access. Finally, the network interface card segments the payload into a set of maximum segment size (mss) segments and transmits the set of mss segments on the network.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
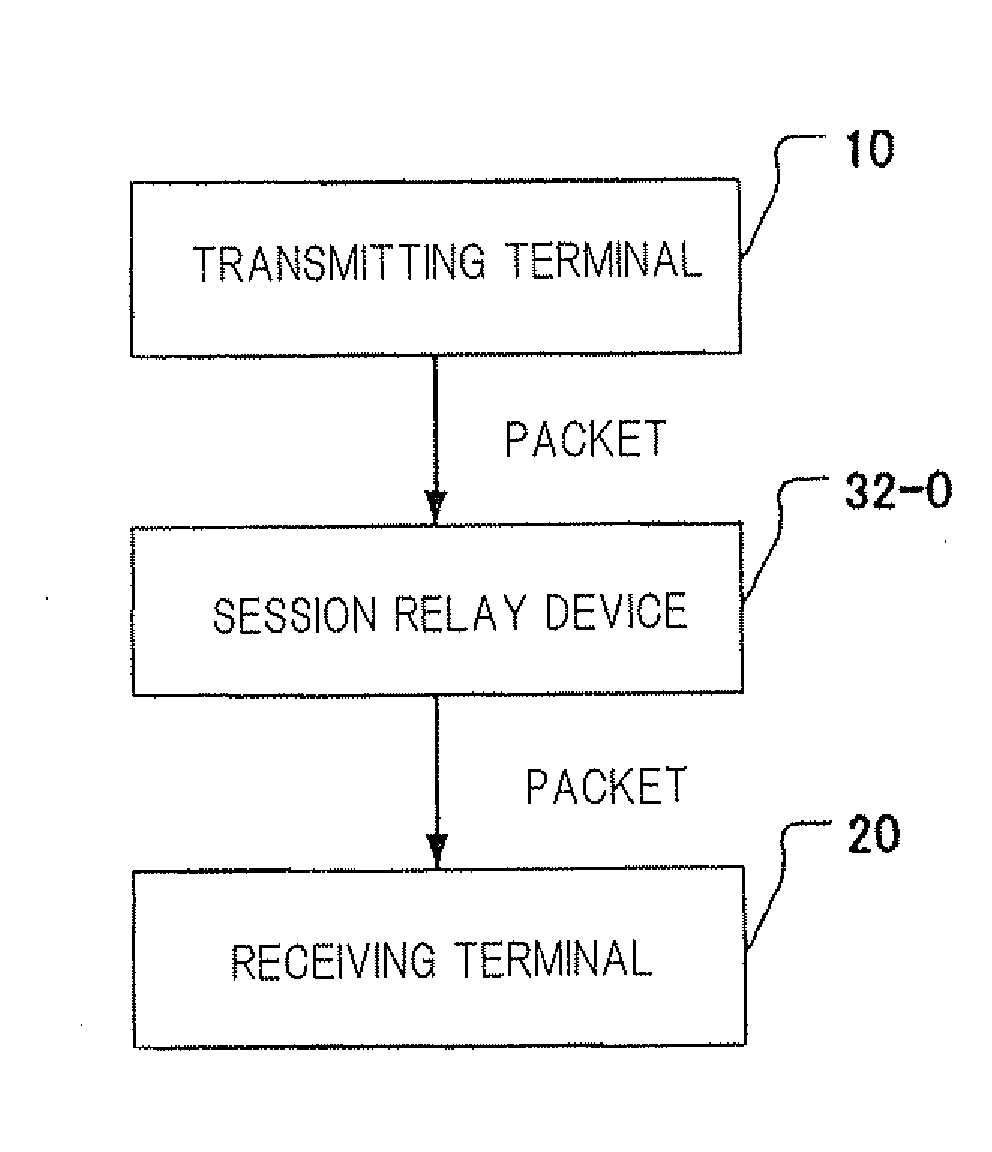
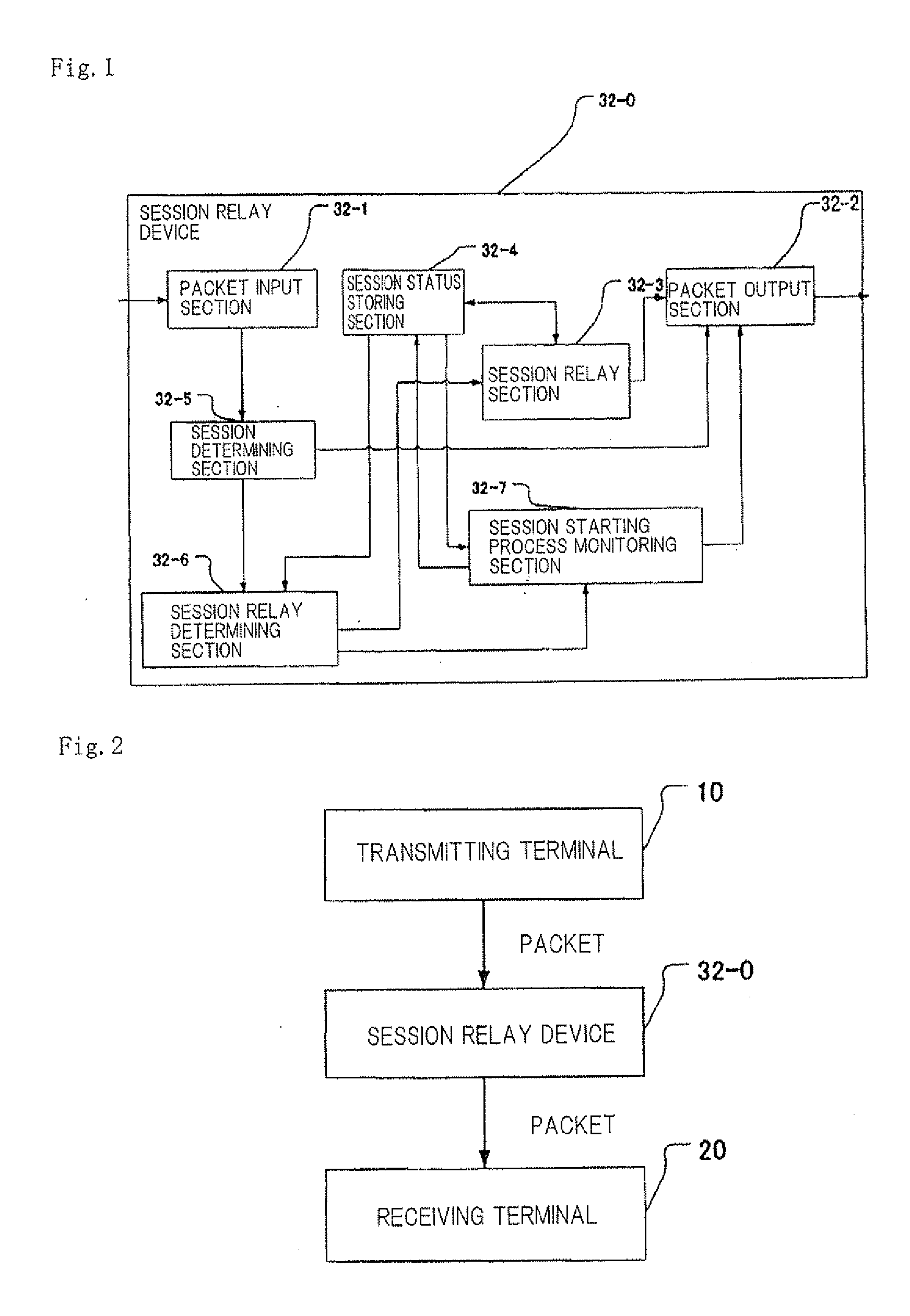
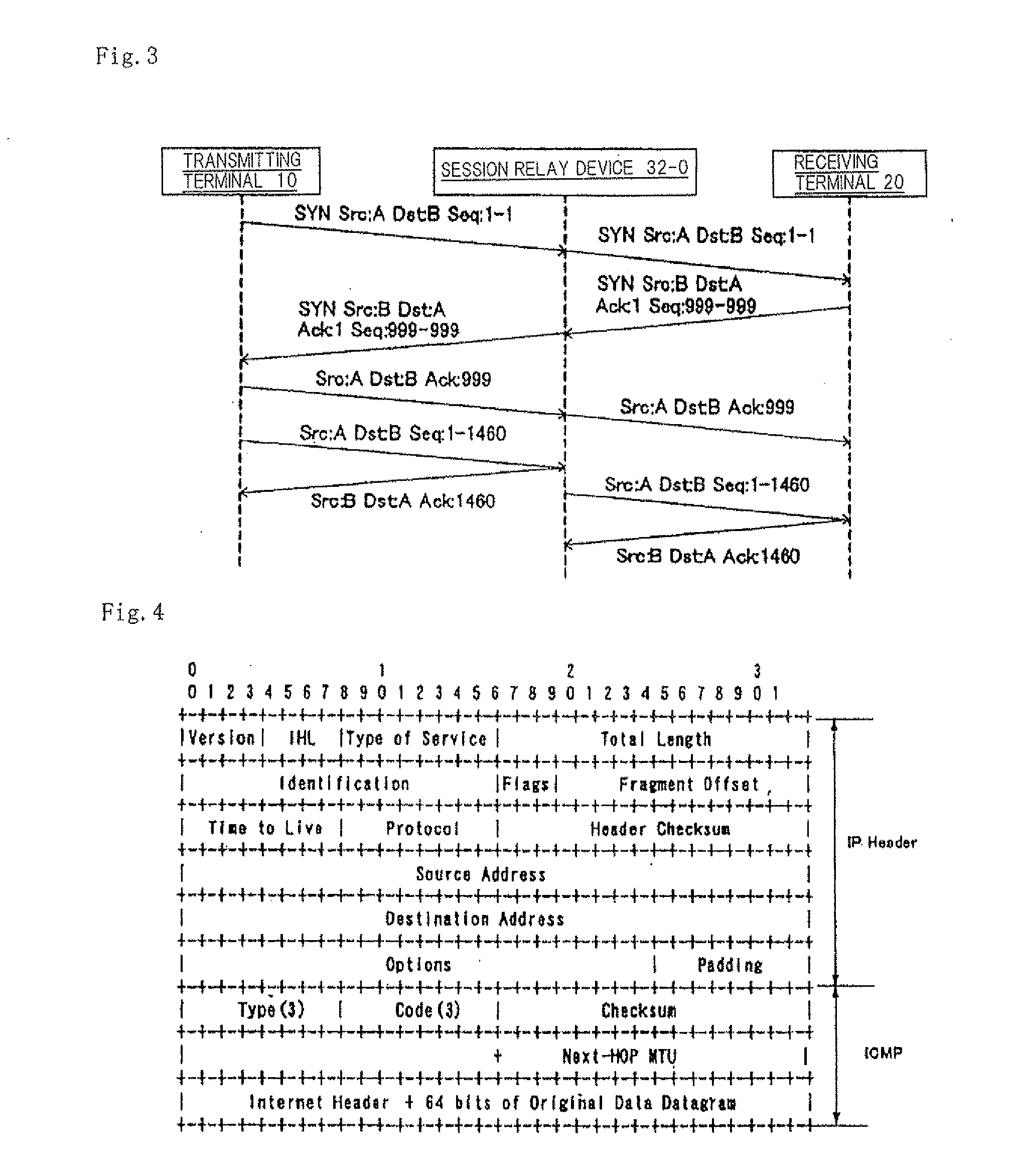
Session relay device and session relay method
ActiveUS20090268742A1Stable communicationMinimum processing costData switching by path configurationMaximum segment sizeOperating system
A session relay device which can reliably send a data packet resent from a source to a destination without the need for reconfiguring and dividing a segment is supplied. Session relay device 110, adapted to be disposed between terminals for transmitting and receiving data as packets to which sequence numbers representative of the order of segments to be transmitted are assigned, includes session relay section 110-3 that relays data transmitted as packets between a first session opened between session relay device 110 and a terminal on a transmission side and a second session opened between session relay device 110 and a terminal on a reception side. Session relay section 110-3 receives the retransmitted segment from a terminal on the transmission side, updates a maximum segment size of the second session with the segment size of the retransmitted segment, and transmits the retransmitted segment to a terminal on the reception side.
Owner:NEC CORP
Storage processor for handling disparate requests to transmit in a storage appliance
InactiveUS7870317B2Reduce memory requirementsShorten the timeMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingRAIDData segment
A storage processor is interposed between initiators and storage targets, such as storage appliances or storage devices in a storage network. The storage processor presents a target interface to the initiators and an initiator interface to the targets, and the storage processor transparently intercepts and processes commands, data and / or status information (such as iSCSI R2T and data PDUs) sent between the initiators and the targets. The storage processor presents a virtual device to the initiators and transparently implements the virtual device on the targets, such as a RAID-1. The storage processor negotiates acceptable operational parameters, such as maximum segment size, with the initiators and targets, such that the storage processor can pass data received from the initiators to the targets, without excessive data buffering. Consequently, when an initiator issues a write command, the storage processor is able to forward each segment of data received from the initiator to the appropriate target(s), without first buffering all segments of the write command.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
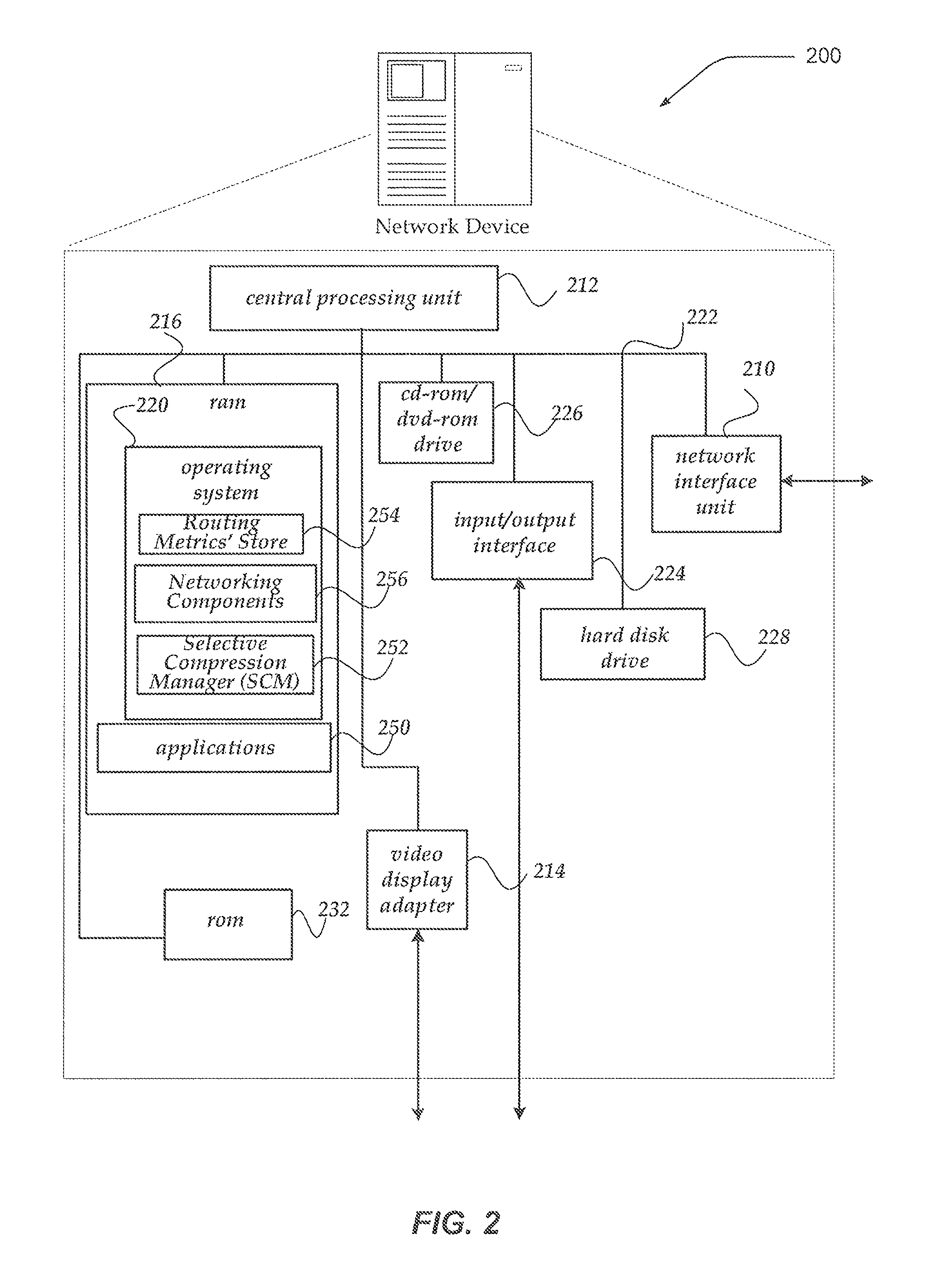
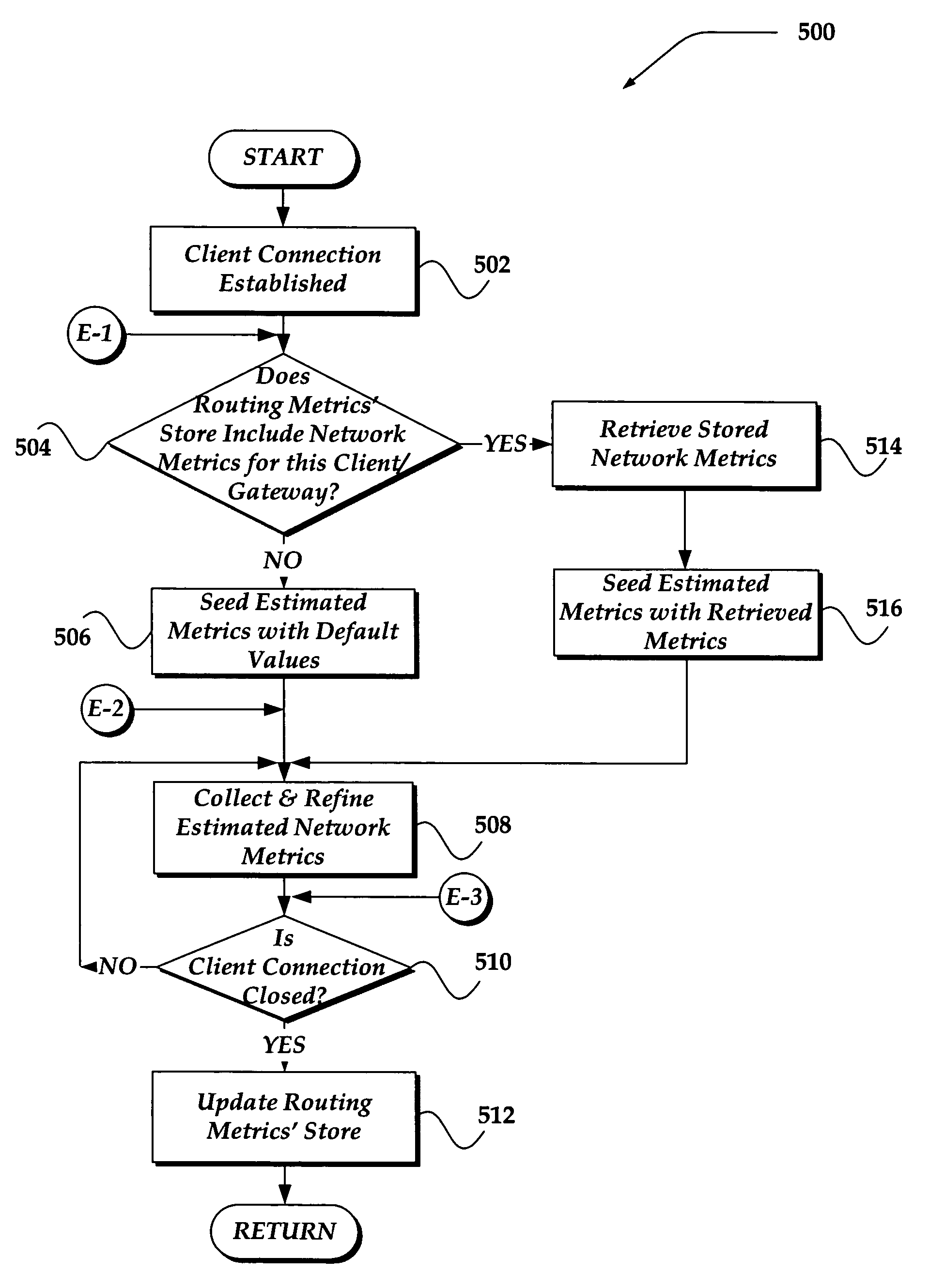
Selective compression for network connections
A system, apparatus, and method selectively provides content compression to a client based, in part, on whether the network connection from the client is determined to be a high latency, low-bandwidth connection. The present invention gathers one or more network metrics associated with the connection from the client. In one embodiment, the metrics include estimated TCP metrics, including smoothed round trip time, maximum segment size (MSS), and bandwidth delay product (BWDP). These estimated network metrics are employed to make an application layer decision of whether the client connection is a high latency, low-bandwidth connection. If it is, then content may be selectively compressed virtually on the fly for transfer over the network connection. In one embodiment, the selective compression uses a content encoding compression feature of the HTTP protocol standard.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
Systems and Methods for Learning MSS of Services
ActiveUS20120250530A1Avoid splittingSplitting packetError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsValue setClient-side
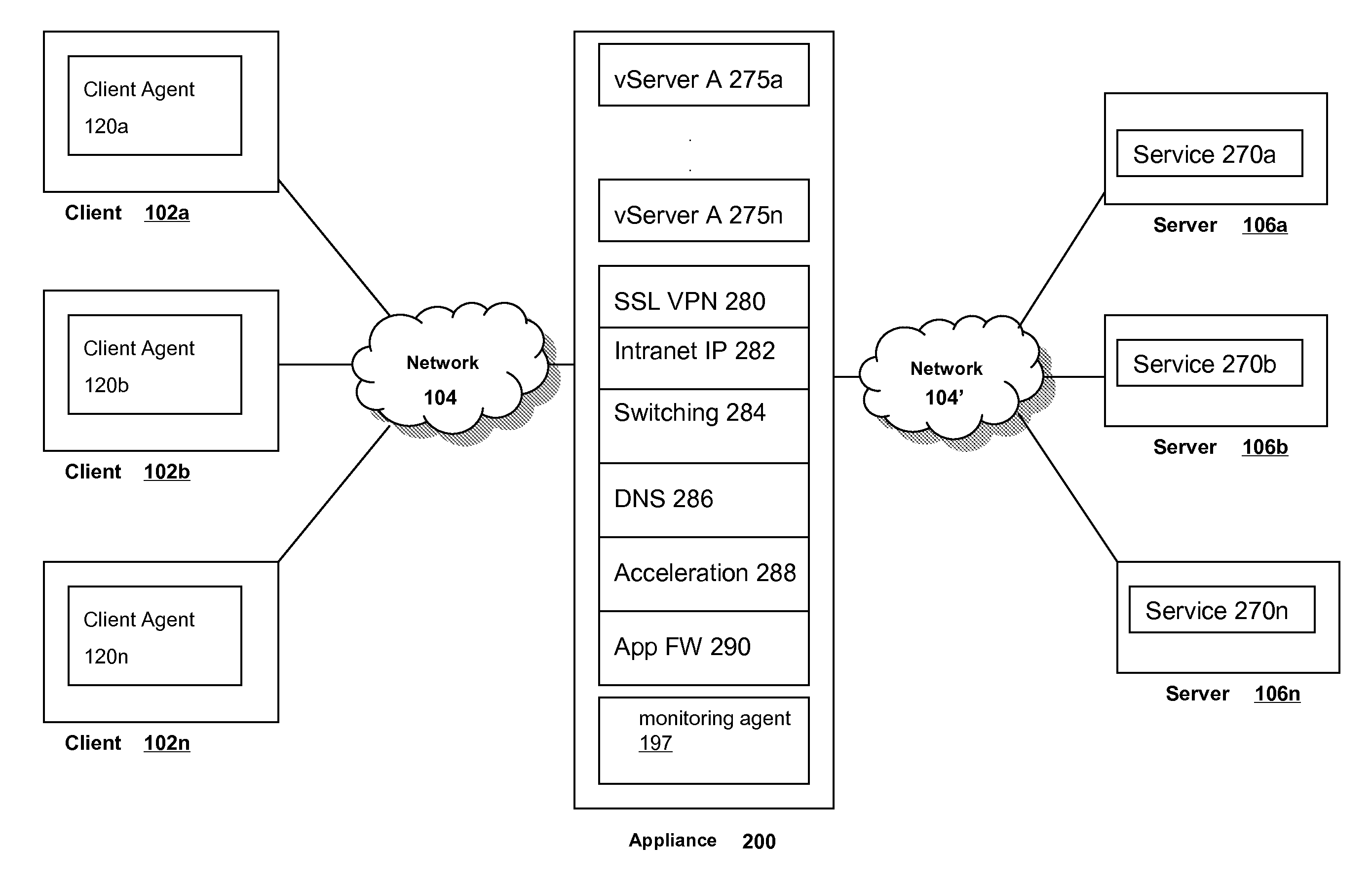
The virtual Server (vServer) of an intermediary device deployed between a plurality of clients and services supports parameters for setting maximum segment size (MSS) on a per vServer / service basis and for automatically learning the MSS among the back-end services. In case of vServer / service setting, all vServers will use the MSS value set through the parameter for the MSS value set in TCP SYN+ACK to clients. In the case of learning mode, the backend service MSS will be learnt through monitor probing. The vServer will monitor and learn the MSS that is being frequently used by the services. When the learning is active, the intermediary device may keep statistics of the MSS of backend services picked up during load balancing decisions and once an interval timer expires, the MSS value may be picked by a majority and set on the vServer. If there is no majority, then the highest MSS is picked up to be set on the vServer.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
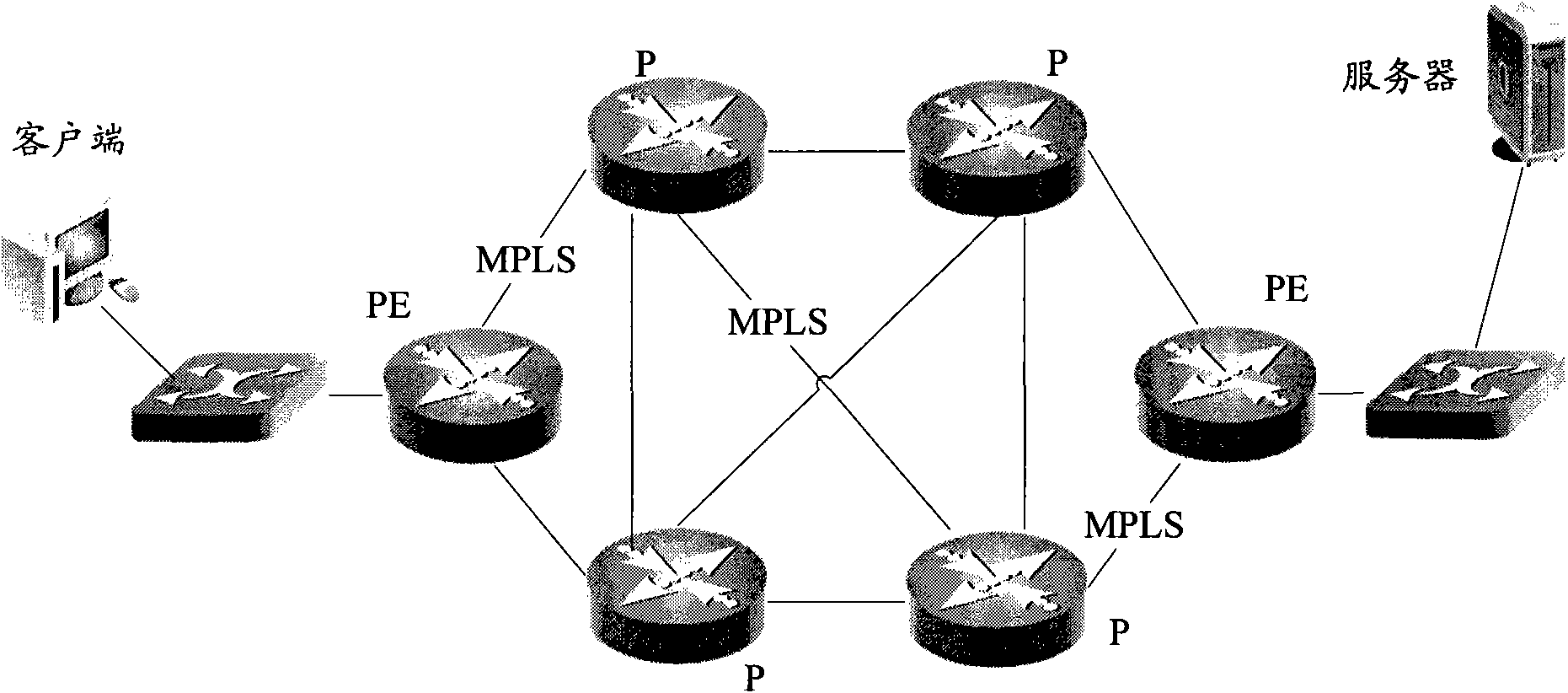
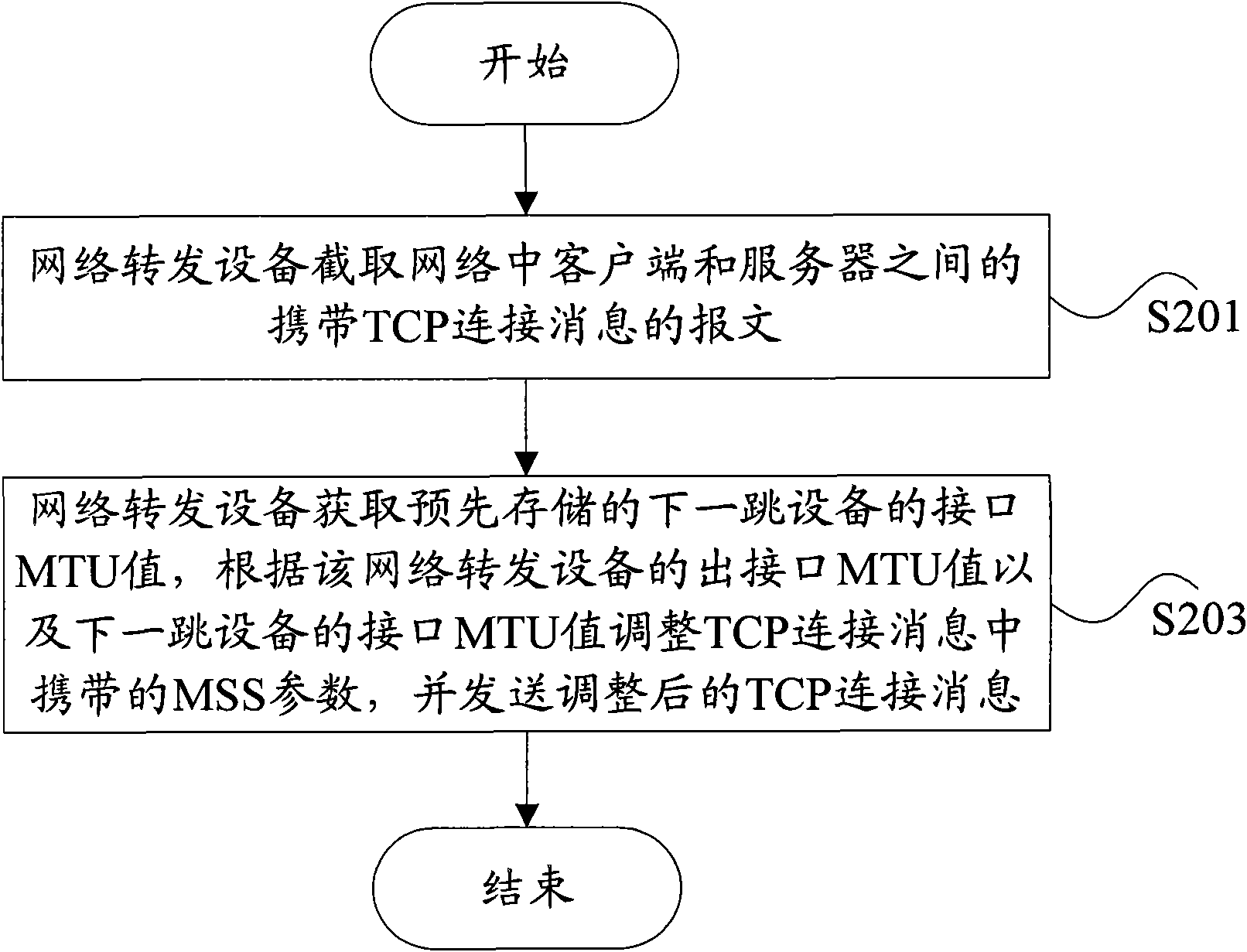
Negotiation method of maximum segmentation parameters and network forwarding equipment
InactiveCN101924689AIncrease success rateAvoid discardingData switching networksClient-sideMaximum segment size
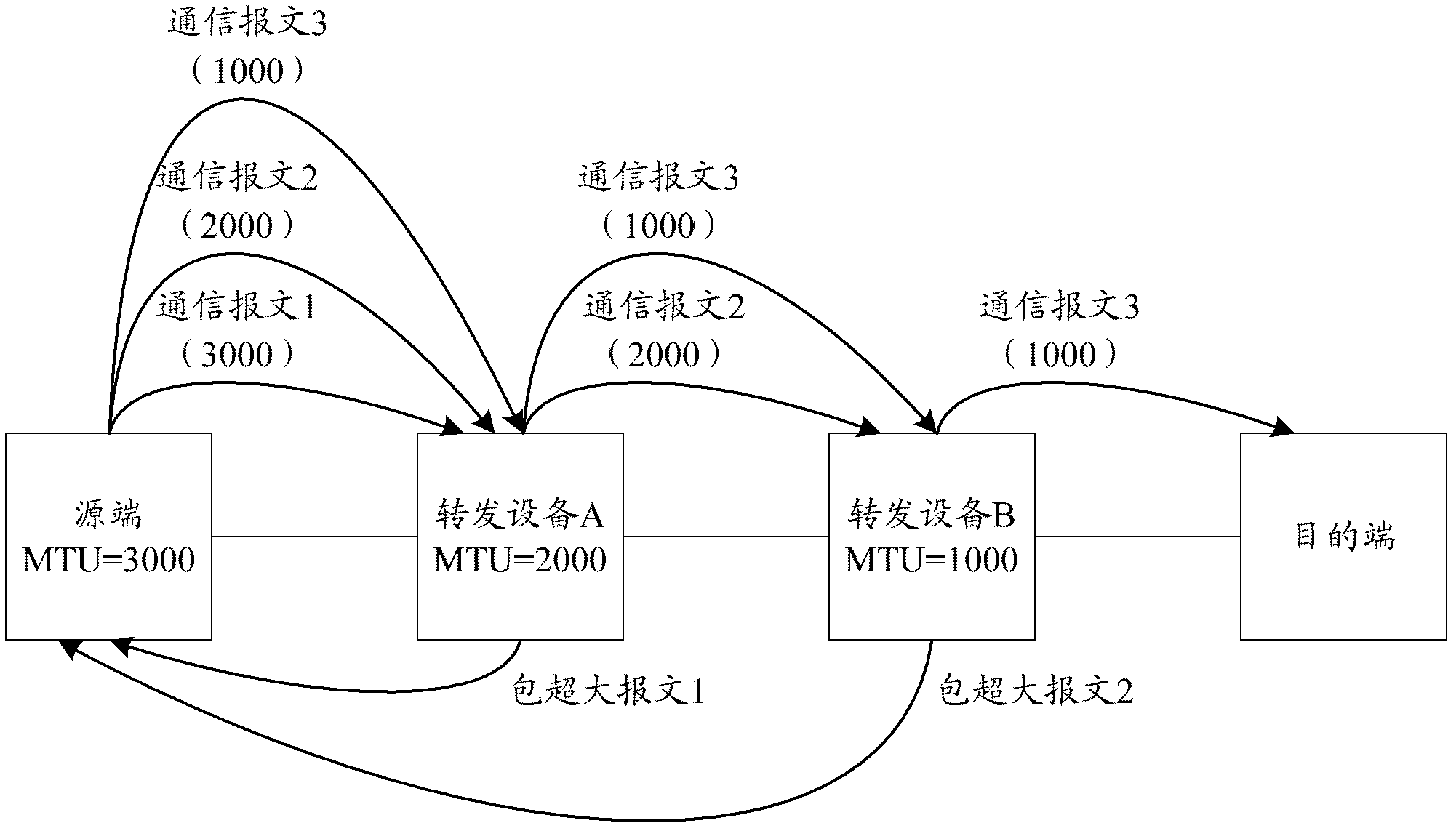
The invention discloses a negotiation method of maximum segmentation parameters and network forwarding equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: intercepting a message carrying a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection message between a client and a server in a network by the network forwarding equipment; acquiring a preliminarily stored interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value of next hop equipment by the network forwarding equipment; and adjusting an MSS (Maximum Segment Size) parameter carried in the TCP connection message according to the interface MTU value of the network forwarding equipment and the interface MTU value of the next hop equipment and sending the adjusted TCP connection message. The invention can avoid the occasion of data packet discarding since the messages are beyond the processing capacity of the equipment and improve the success ratio of message forwarding.
Owner:ZTE CORP
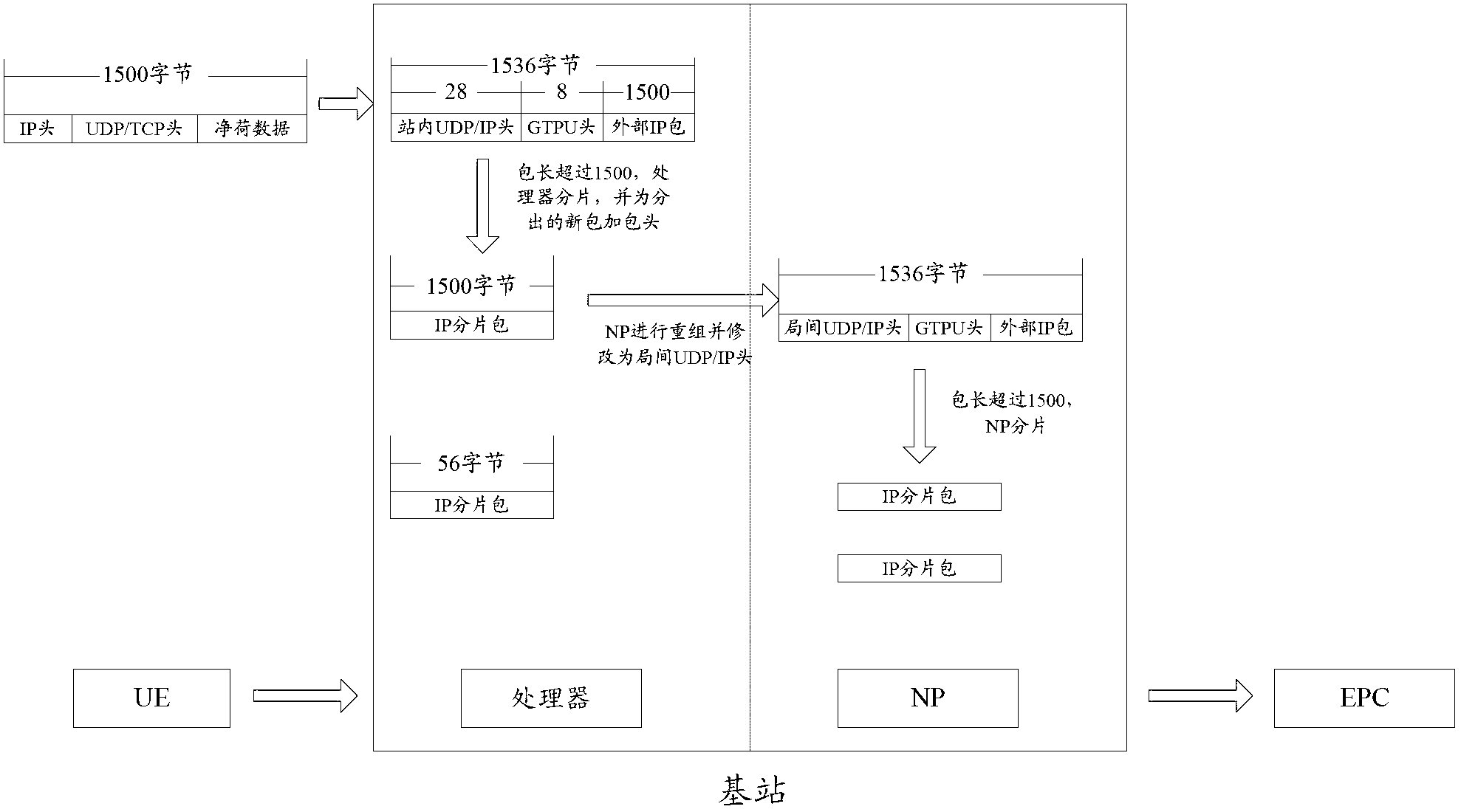
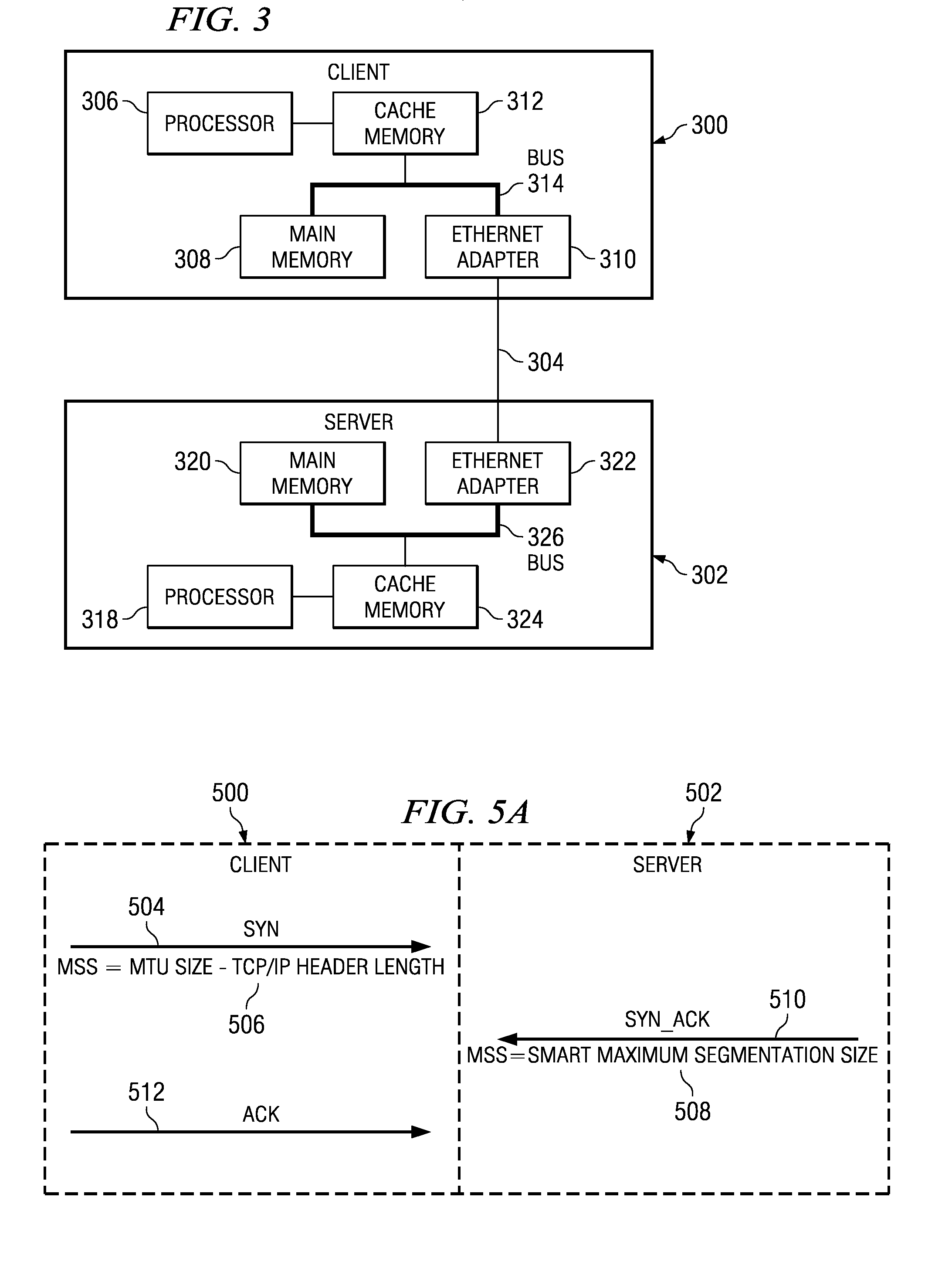
Method for improved network performance using smart maximum segment size
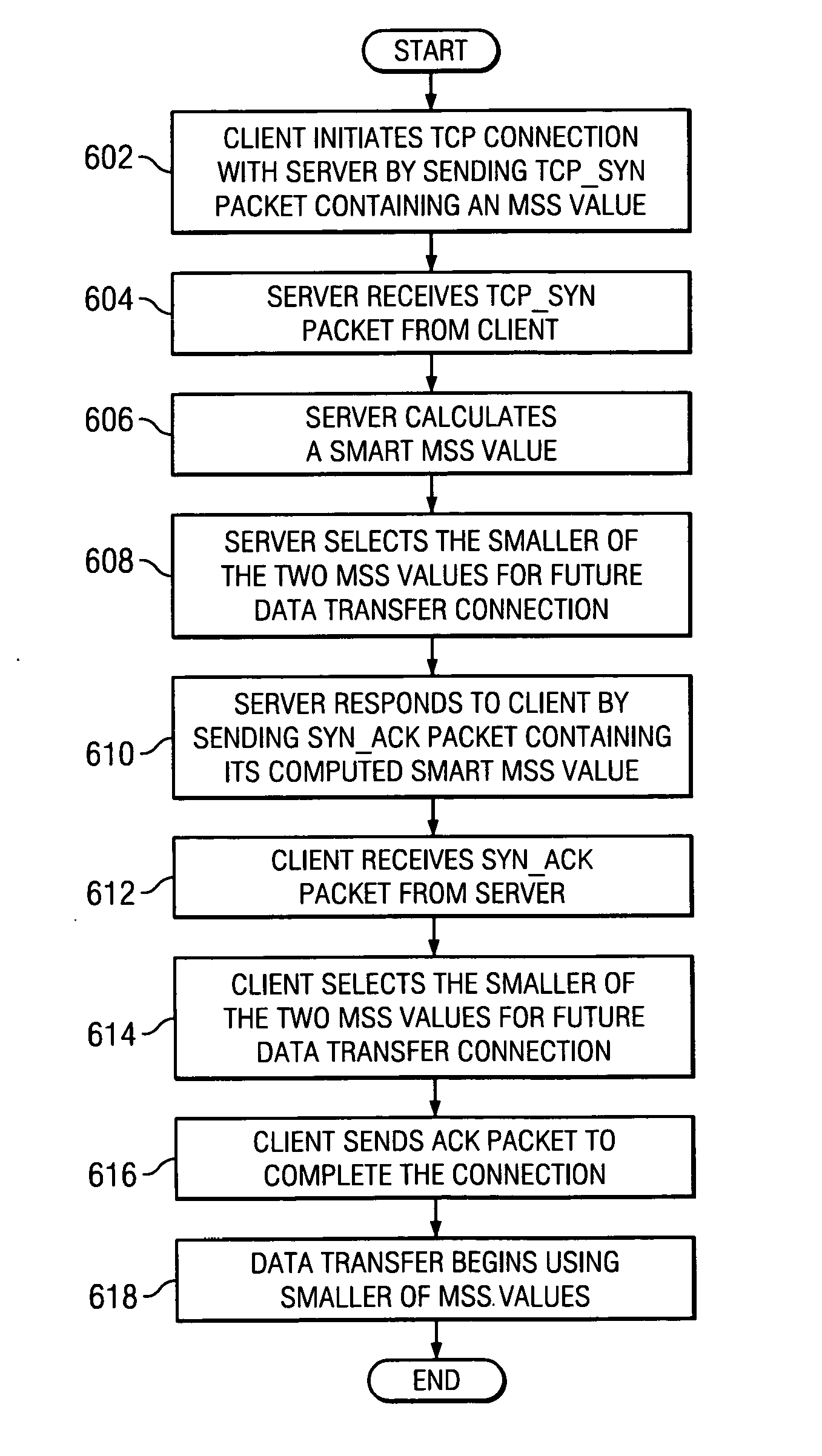
InactiveUS20070136481A1Improve network performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork connectionClient-side
A method, system, and computer program product for negotiating a smart maximum segment size of a network connection for a data transfer. A client request to initiate a network connection, which includes a first maximum segment size, is received at a server. The server calculates a second maximum segment size, wherein at least one of the first maximum segment size or the second maximum segment size is a cache line size aligned Ethernet frame size, or smart maximum segment size. The server determines the smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes and sends the second maximum segment size to the client. The client then selects the smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes, and sends an acknowledgement to the server to complete the connection. The smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes is used for the network connection and subsequent data transfer.
Owner:IBM CORP
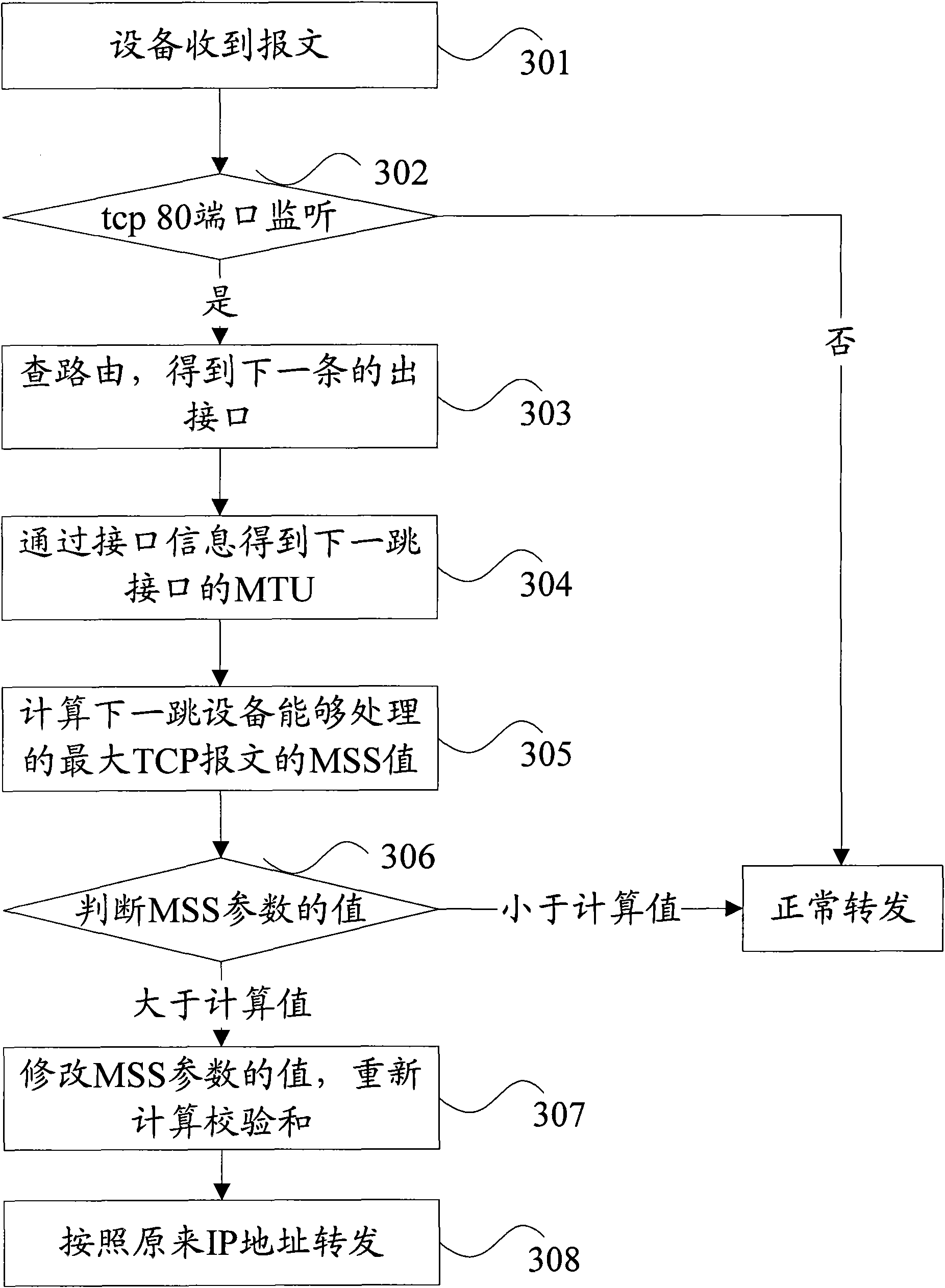
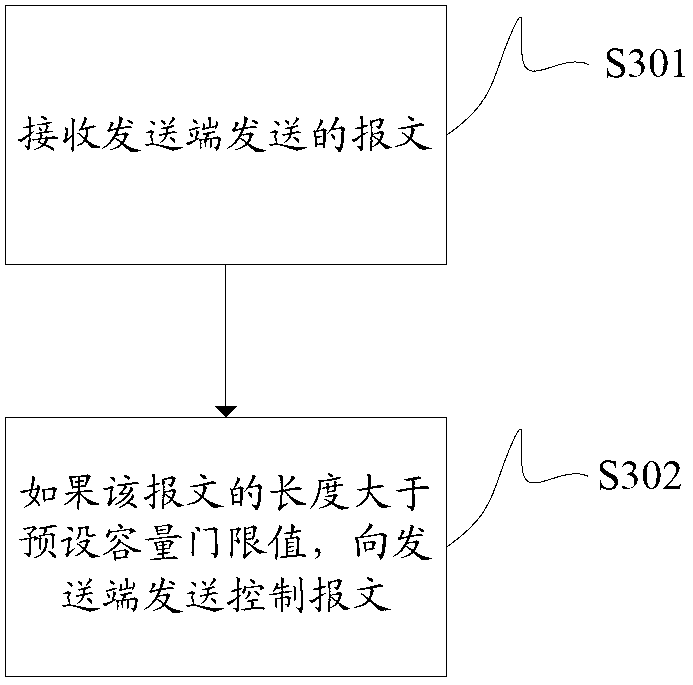
Method and device for determining maximum capacity of message
InactiveCN103079232AImprove efficiencyMeet needsNetwork traffic/resource managementMaximum segment sizeReal-time computing
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for determining the maximum capacity of a message, so as to prevent an NP (Network Processor) in a base station from performing fragmentation and reassembly on the message and increase the transmission efficiency of the base station. The method comprises the following steps that the message sent by a sending end is received; when the received message is determined as a transmission control protocol (TCP) message containing a maximum segment size (MSS) value, the MSS value of the message is compared with a preset capacity threshold; if the MSS value of the message is greater than the preset capacity threshold, the MSS value of the message is adjusted to the preset capacity threshold; and the TCP message carrying the adjusted MSS value is sent to a receiving end.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Loss tolerant transmission control protocol
InactiveUS7366132B2Reduce congestionReduce window sizeNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCongestion windowGranularity
Provided are apparatuses and methods for transmitting or receiving data packets in a data block in a communication network with a transport protocol. In one example, a loss tolerant TCP protocol is used in which a maximum segment size (MSS) may be adapted to a minimum granularity of a congestion window. Also, proactive forward error correction (FEC) packets may be added to a window of the data block. The number of proactive FEC packets may be determined, for example, based on an estimate erasure rate. In addition, reactive FEC packets may be added to the data block. Also, a receiver may receive data packets in a data block and process a selective acknowledgment (SACK) responsive to the data packets received.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Selective compression for network connections
A system, apparatus, and method selectively provides content compression to a client based, in part, on whether the network connection from the client is determined to be a high latency, low-bandwidth connection. The present invention gathers one or more network metrics associated with the connection from the client. In one embodiment, the metrics include estimated TCP metrics, including smoothed round trip time, maximum segment size (MSS), and bandwidth delay product (BWDP). These estimated network metrics are employed to make an application layer decision of whether the client connection is a high latency, low-bandwidth connection. If it is, then content may be selectively compressed virtually on the fly for transfer over the network connection. In one embodiment, the selective compression uses a content encoding compression feature of the HTTP protocol standard.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
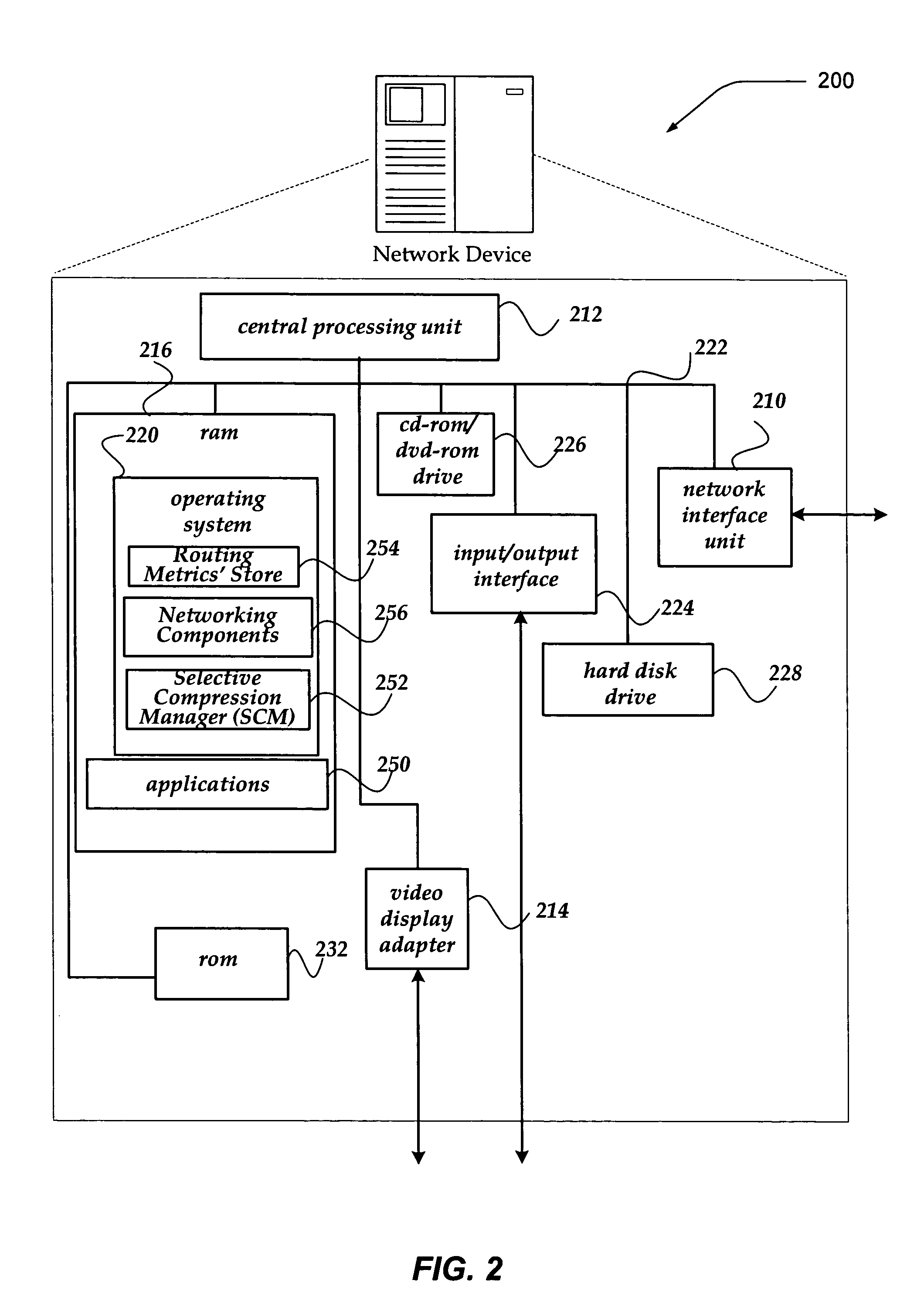
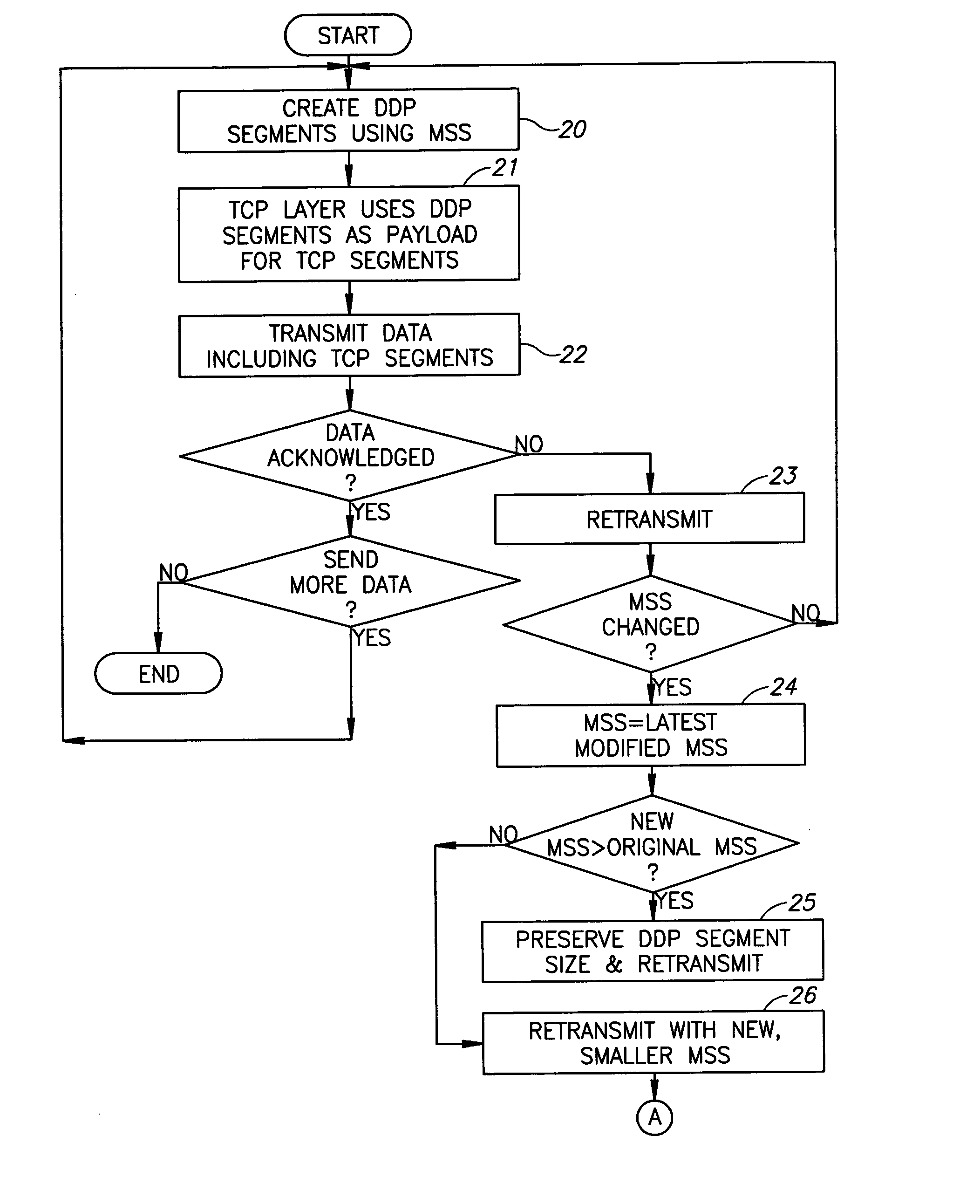
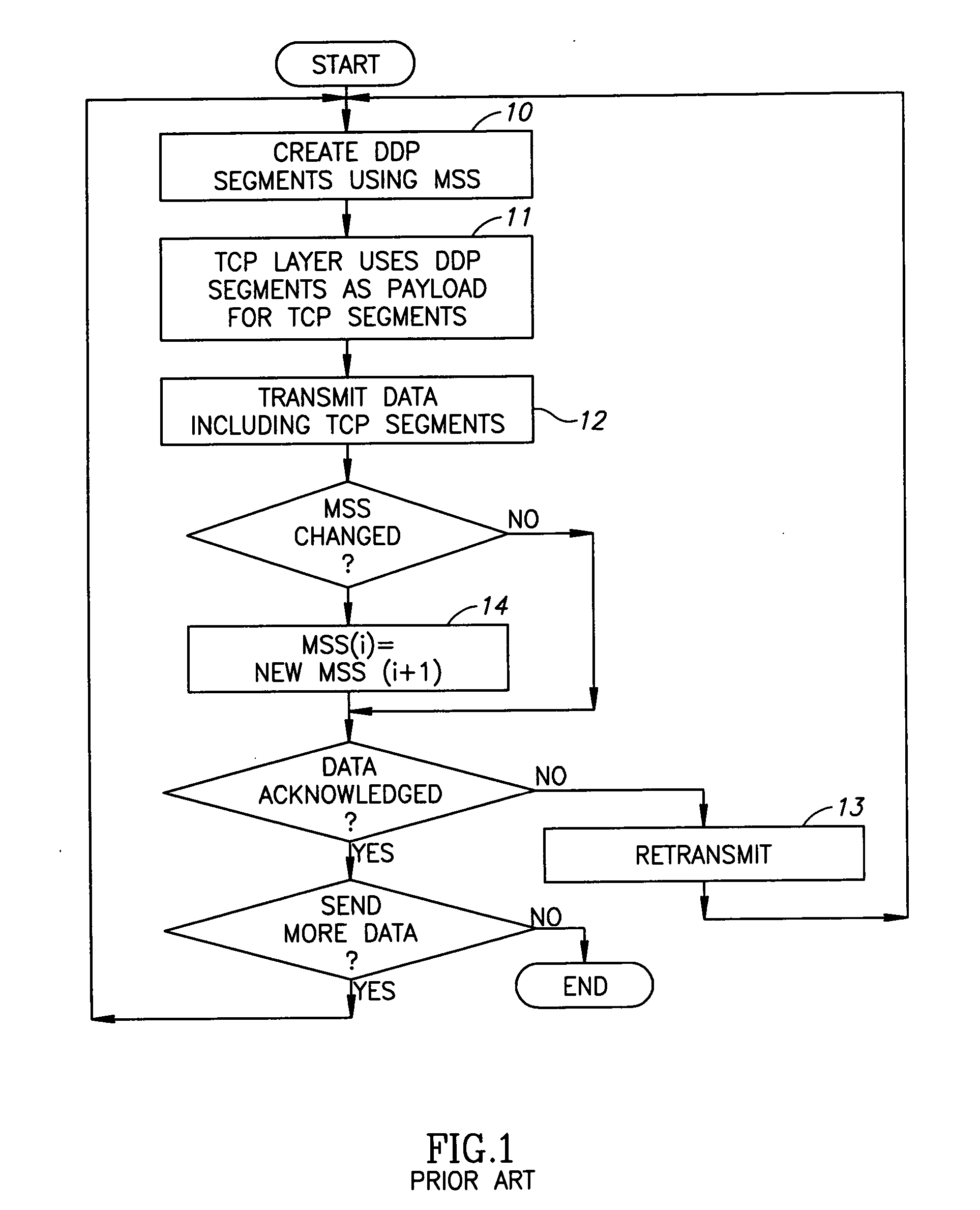
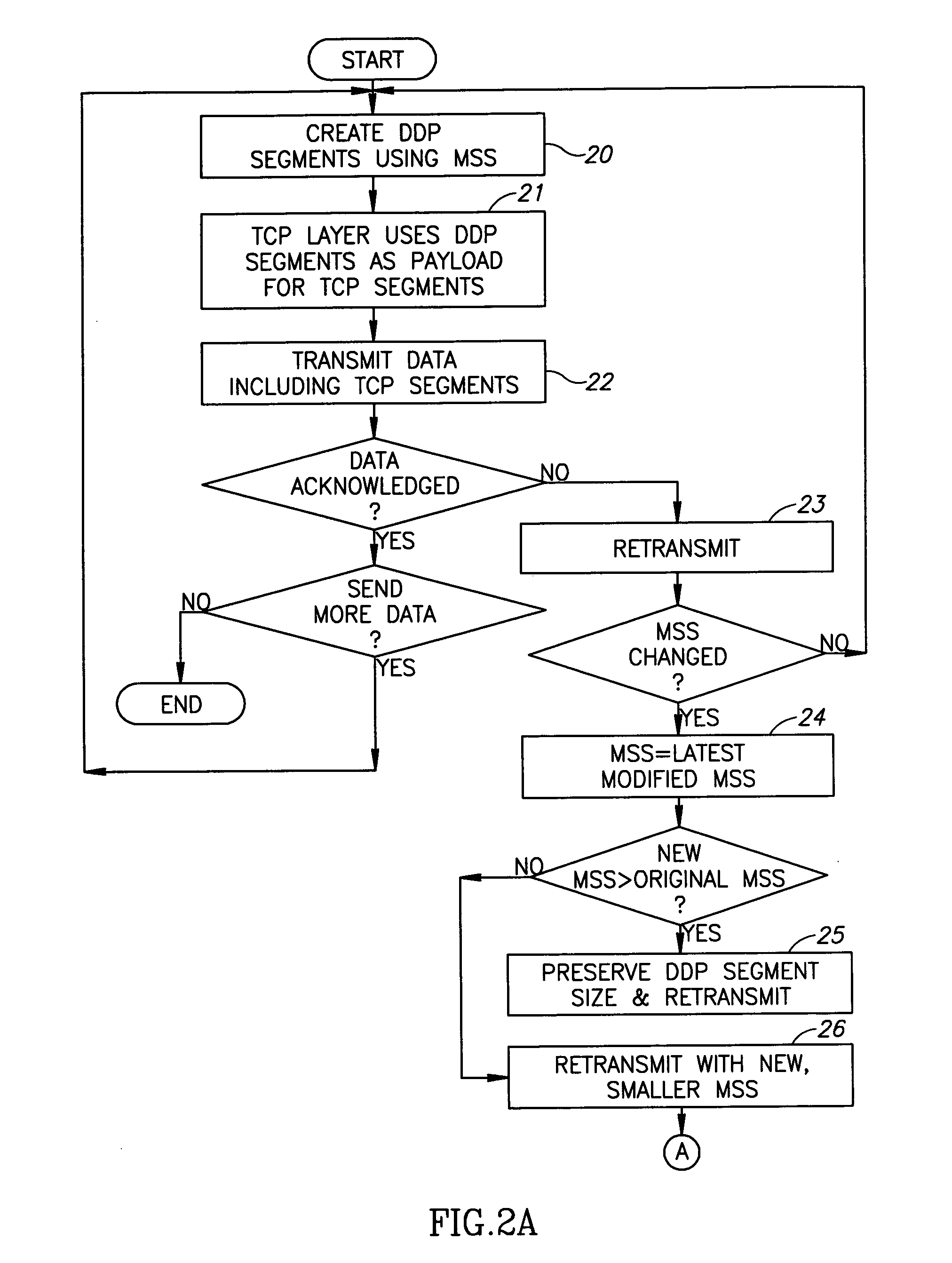
Recovery from MSS change
InactiveUS20050265352A1Data switching by path configurationTransport control protocolRemote direct memory access
A method for performing Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), the method including creating Direct Data Placement (DDP) segments of data using a Maximum Segment Size (MSS), called the original MSS, using the DDP segments as a payload for TCP (Transport Control Protocol) segments, TCP transmitting data including the TCP segments, and if the original MSS has changed to a new MSS, temporarily halting DDP segmentation until outstanding data has been acknowledged.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and device for path maximum transmission unit (PMTU) learning
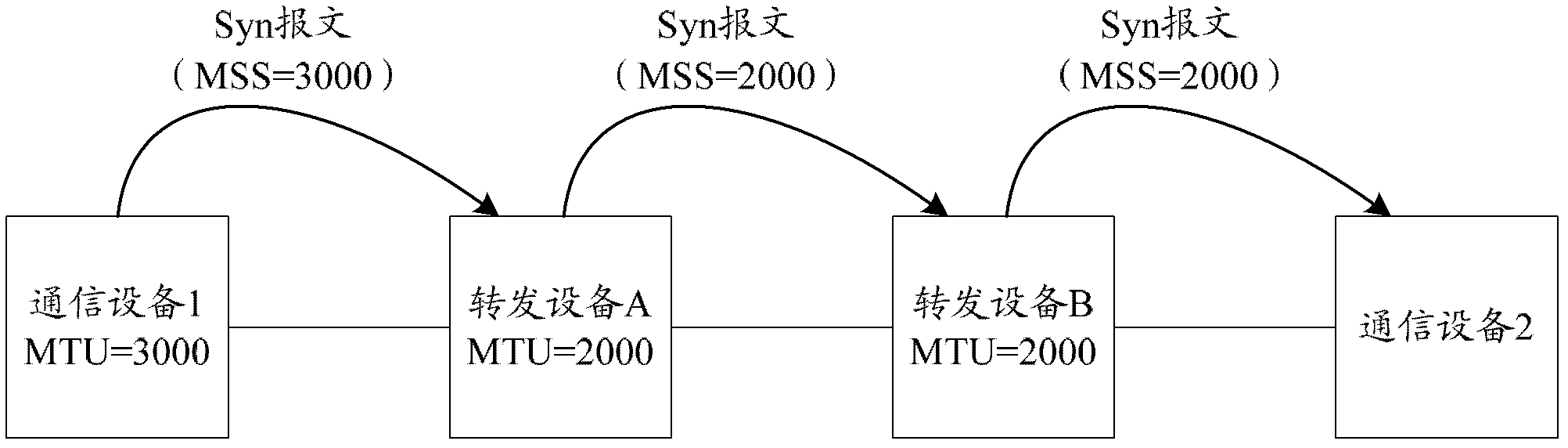
InactiveCN102594677AFast learningSave bandwidthData switching networksComputer networkMaximum segment size
The invention provides a method and a device for path maximum transmission unit (PMTU) learning. In a transmission control protocol (TCP) connection establishment process, forwarding equipment modifies a value of a maximum segment size (MSS) option in a Syn message, so that the value of the MSS option in the Syn message finally can be modified into the minimum of maximum transmission unit (MTU) values of all forwarding equipment in a transmission path; moreover, a final value of the MSS option in the Syn message is also carried by a Syn+Ack message and an Ack message, so that communication equipment can learn a PMTU by utilizing the value of the MSS option in the TCP connection establishment process, and is not required to learn the PMTU hop by hop in a communication process after the establishment of TCP connection; and therefore, PMTU learning speed can be increased, and a network bandwidth occupied by the PMTU learning can be saved. A change in the MTU value of the forwarding equipment also can be adapted by modifying a value of an MSS option in the Syn+Ack message by the forwarding equipment.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
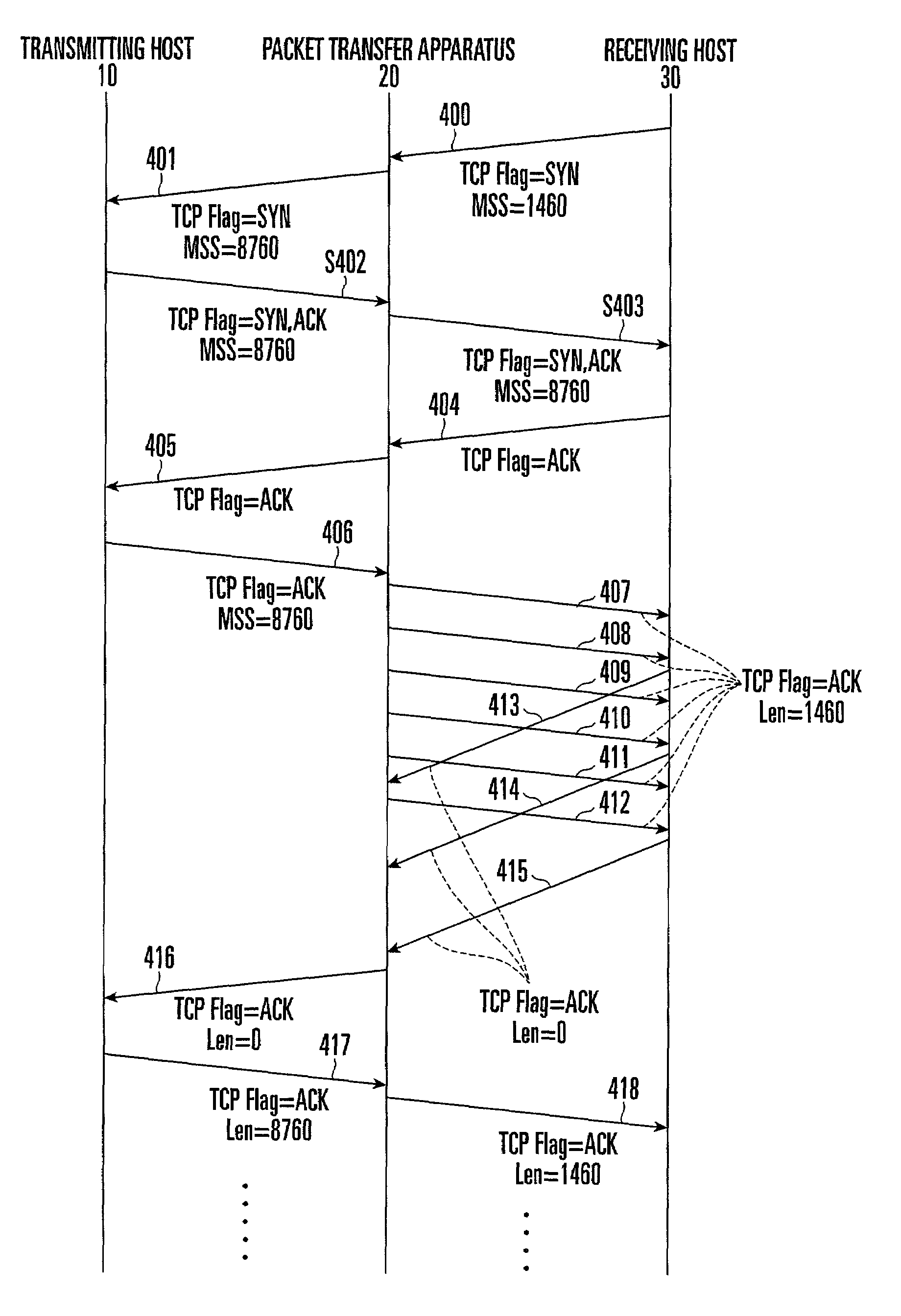
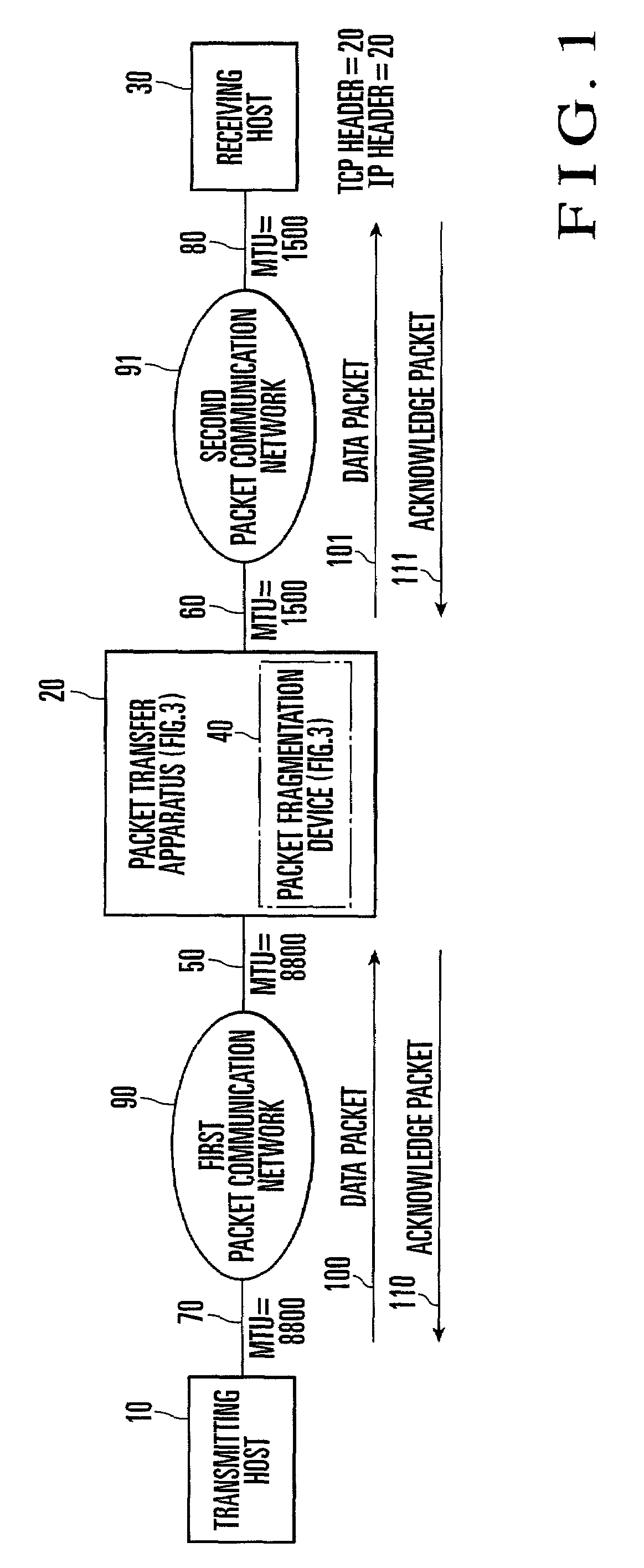
Packet transfer apparatus and method
ActiveUS7042907B2Increase packet transfer efficiency in transferring packetReduce transfer timeTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTransport layerComputer science
A packet transfer apparatus includes an MSS option rewrite unit and packet fragmentation unit. The MSS option rewrite unit determines a first maximum segment size used in a transport layer between a transmitting hosts and the packet transfer apparatus on the basis of path information between the transmitting hosts and the packet transfer apparatus, and notifies the transmitting hosts of the first maximum segment size. The MSS option rewrite unit determines a second maximum segment size used in a transport layer between a receiving hosts and the packet transfer apparatus on the basis of path information between the receiving hosts and the packet transfer apparatus, and notifies the receiving hosts of the second maximum segment size.
Owner:NEC CORP
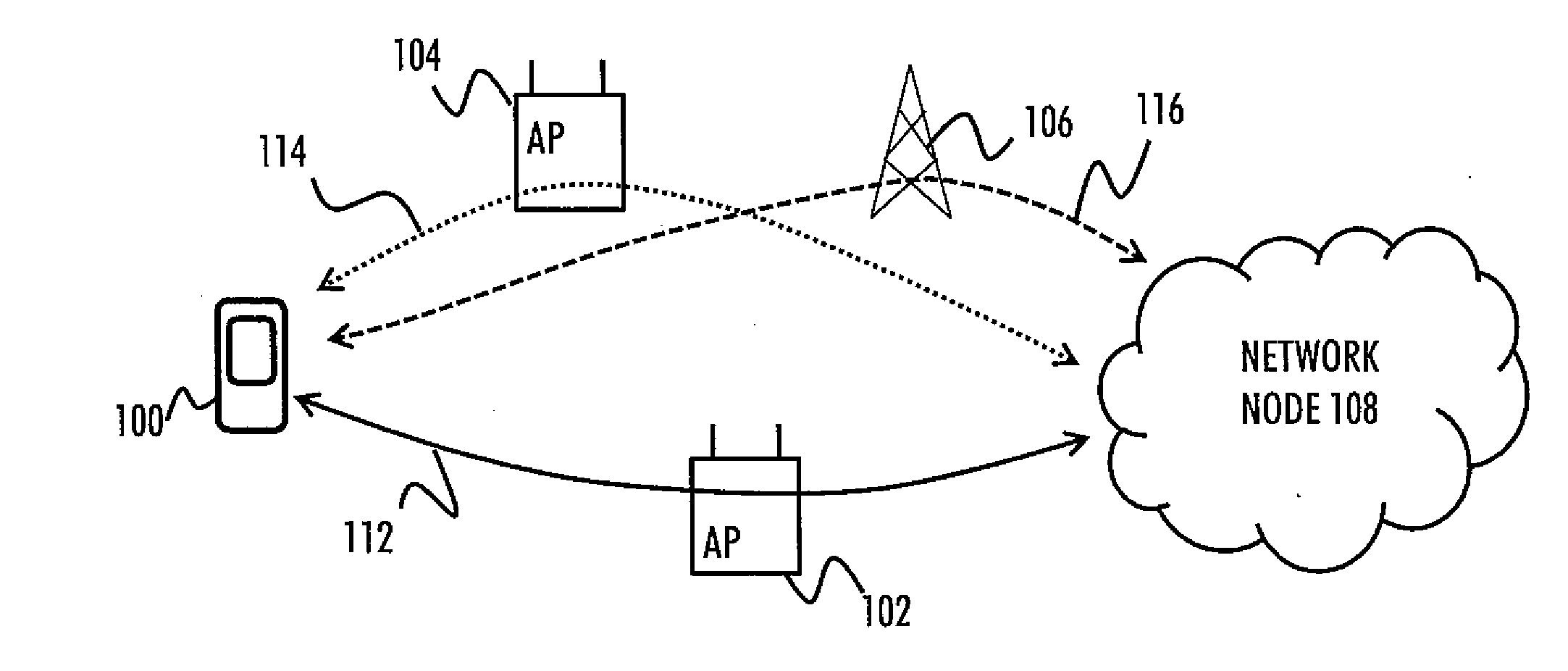
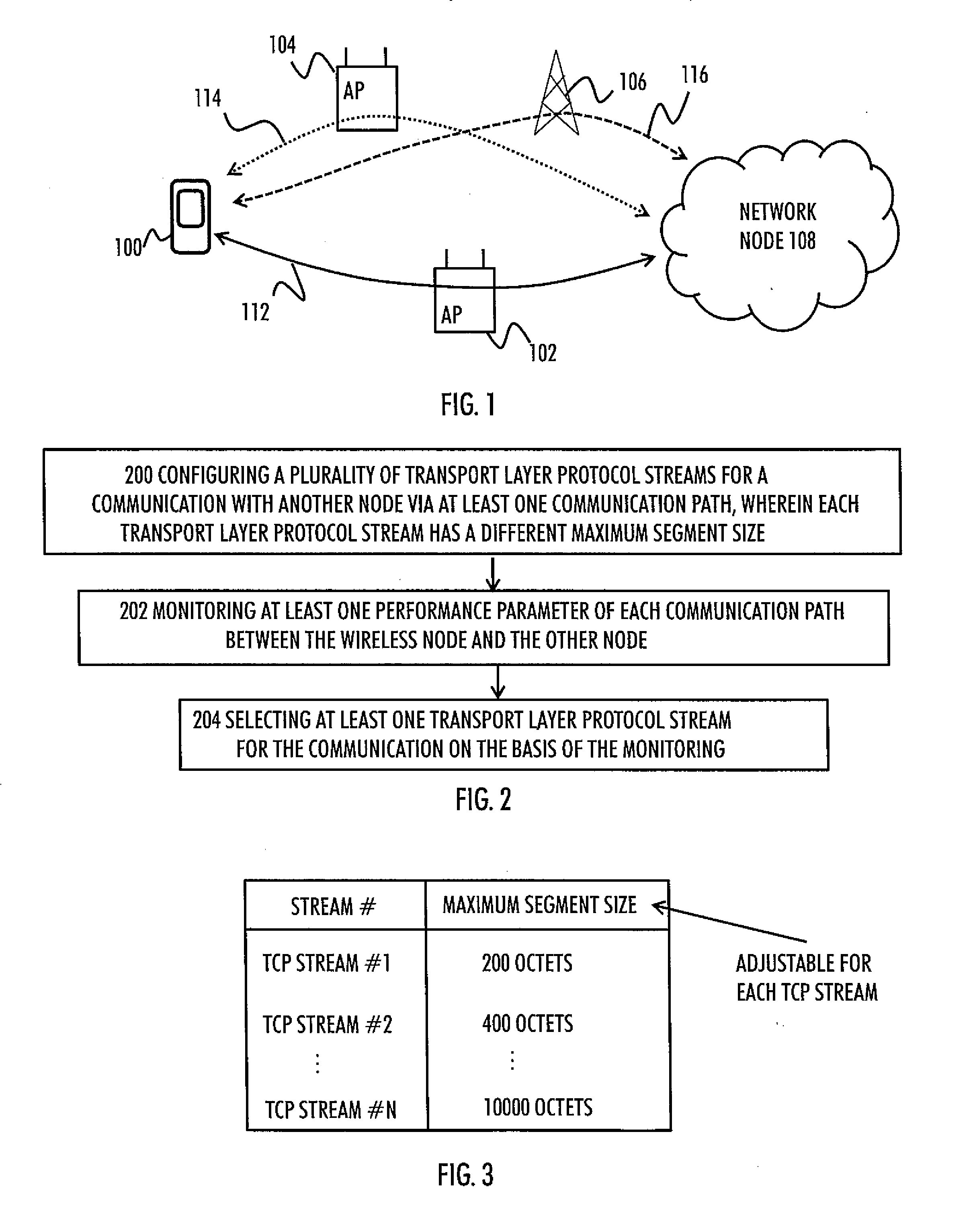
Communication Efficiency
InactiveUS20150106530A1Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsTransport layerMaximum segment size
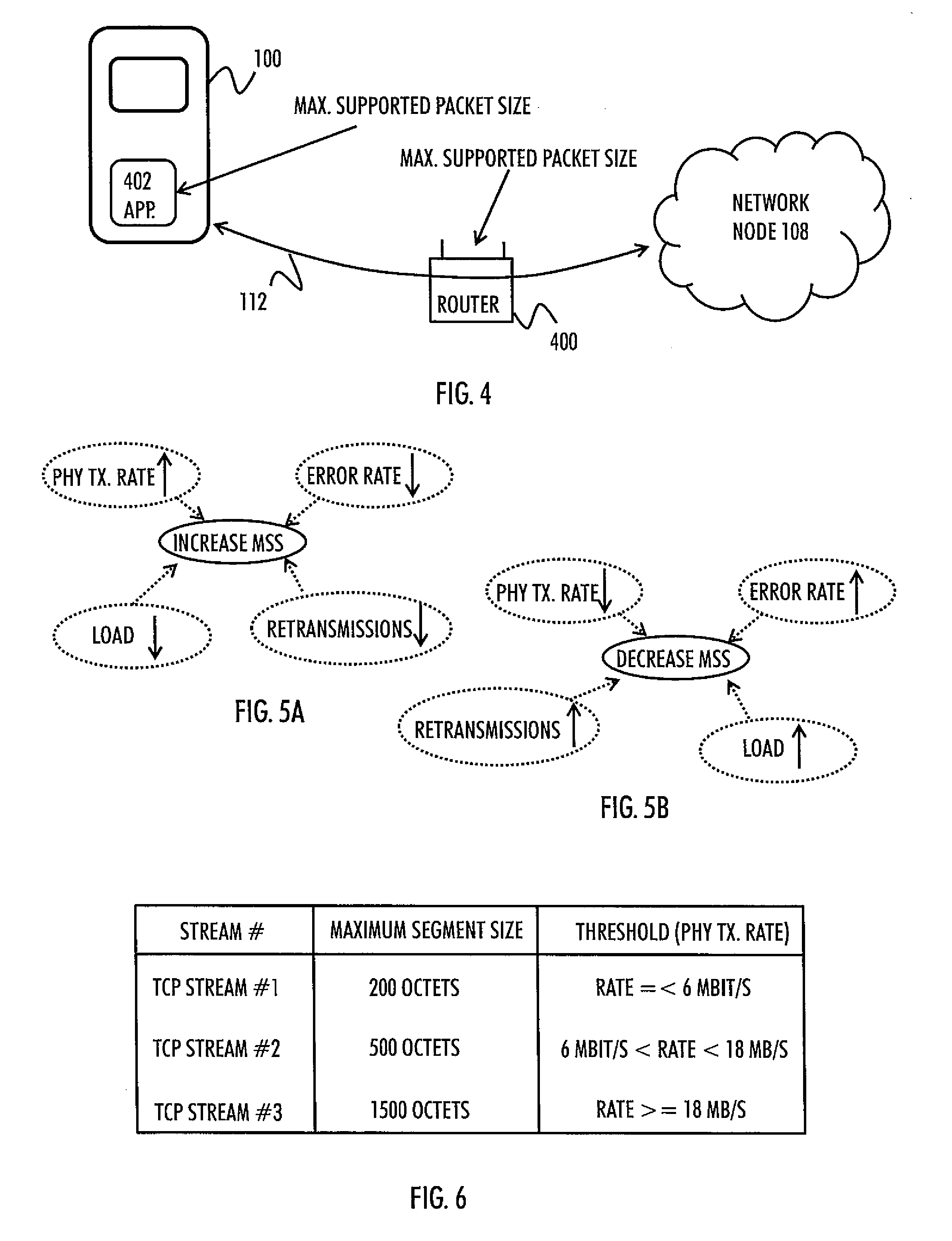
There is provided a solution in which a wireless node is caused to configure a plurality of transport layer protocol streams for a communication with another node via at least one communication path, wherein each transport layer protocol stream has a different maximum segment size; monitor at least one performance parameter of each communication path between the wireless node and the other node; and select at least one transport layer protocol stream for the communication on the basis of the monitoring.
Owner:RPX CORP
Synchronize (SYN) message transmitting method and device and network equipment
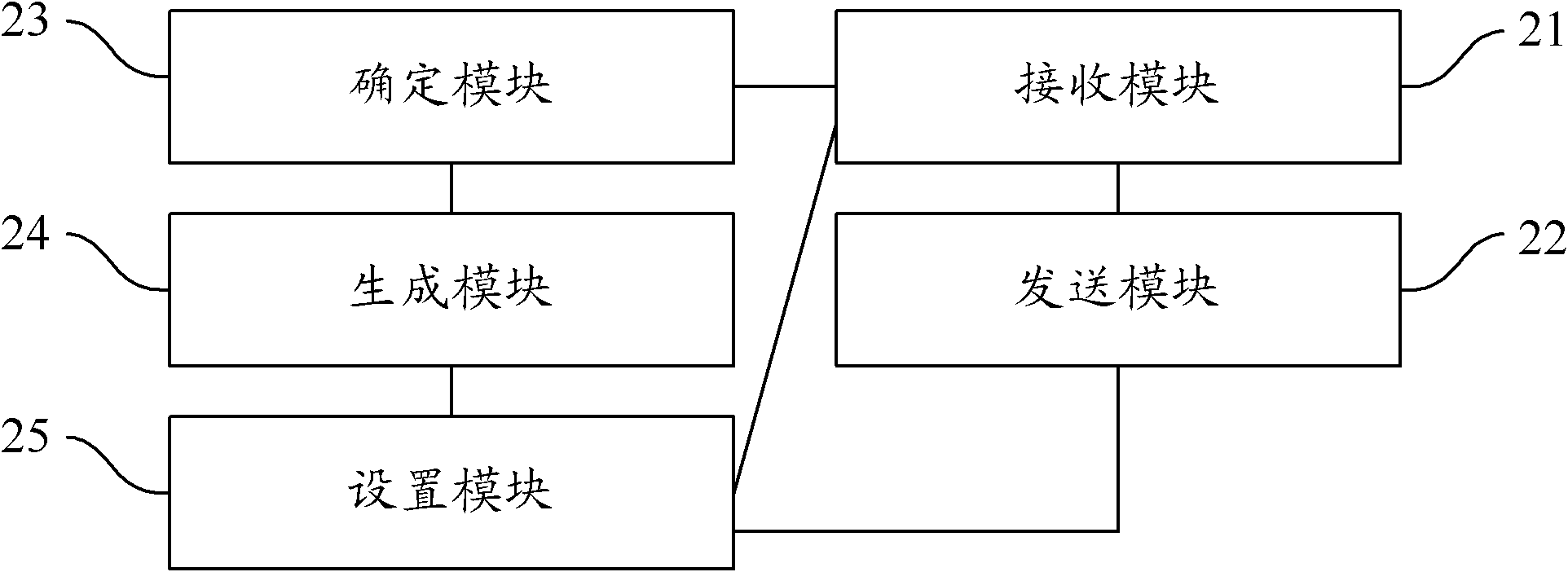
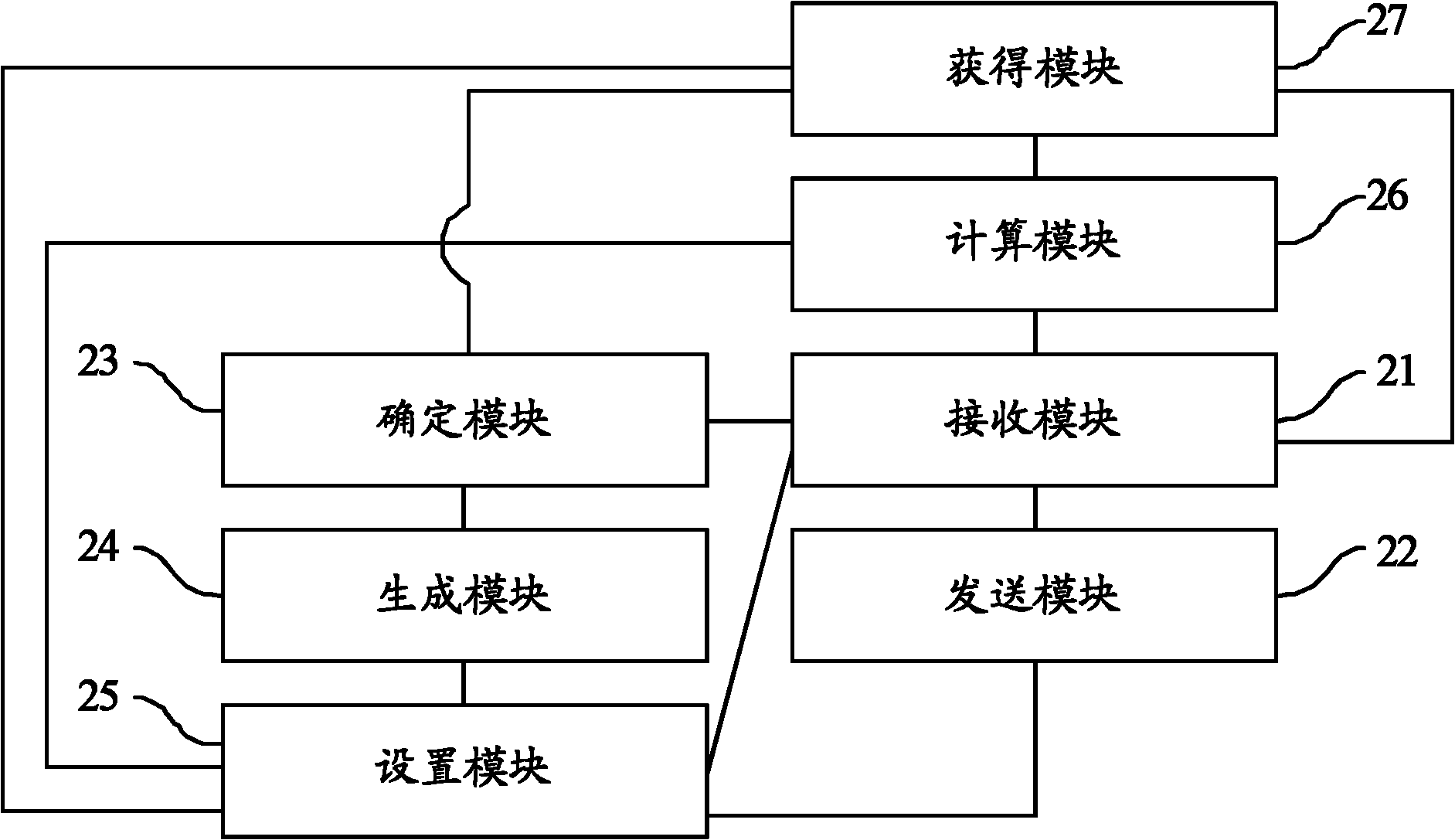
ActiveCN102427452ASolve the problem of discardingNetworks interconnectionSynchronising arrangementPrivate networkMaximum segment size
The invention provides a synchronize message transmitting method, a synchronize message transmitting device and network equipment. The synchronize message transmitting method comprises the following steps of: transmitting a synchronize confirmation message to a client after the synchronize message transmitting device receives a first synchronize message transmitted by the client; receiving a first confirmation message transmitted by the client aiming at the synchronize confirmation message; generating a second synchronize message if the first confirmation message is determined to be a legal message, and setting a value of a maximum segment size (MSS) option of the second synchronize message according to a confirmation number of the first confirmation message; and transmitting the second synchronize message with the set value to a server. Therefore, the MSS of the message transmitted by the server to the client is set to be a value of the MSS option of the second synchronize message through the server, and the problem that SYNCOOKIE cannot save the value of the MSS option of the SYN message, so that length of the message transmitted by the server to the client exceeds a maximum transmission unit (MTU) allowed by a virtual private network (VPN) channel so as to be discarded by a VPN gateway is solved.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Method for improved network performance using smart maximum segment size
InactiveUS20080244084A1Improve network performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork connectionClient-side
A method, system, and computer program product for negotiating a smart maximum segment size of a network connection for a data transfer. A client request to initiate a network connection, which includes a first maximum segment size, is received at a server. The server calculates a second maximum segment size, wherein at least one of the first maximum segment size or the second maximum segment size is a cache line size aligned Ethernet frame size, or smart maximum segment size. The server determines the smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes and sends the second maximum segment size to the client. The client then selects the smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes, and sends an acknowledgement to the server to complete the connection. The smaller of the first and second maximum segment sizes is used for the network connection and subsequent data transfer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
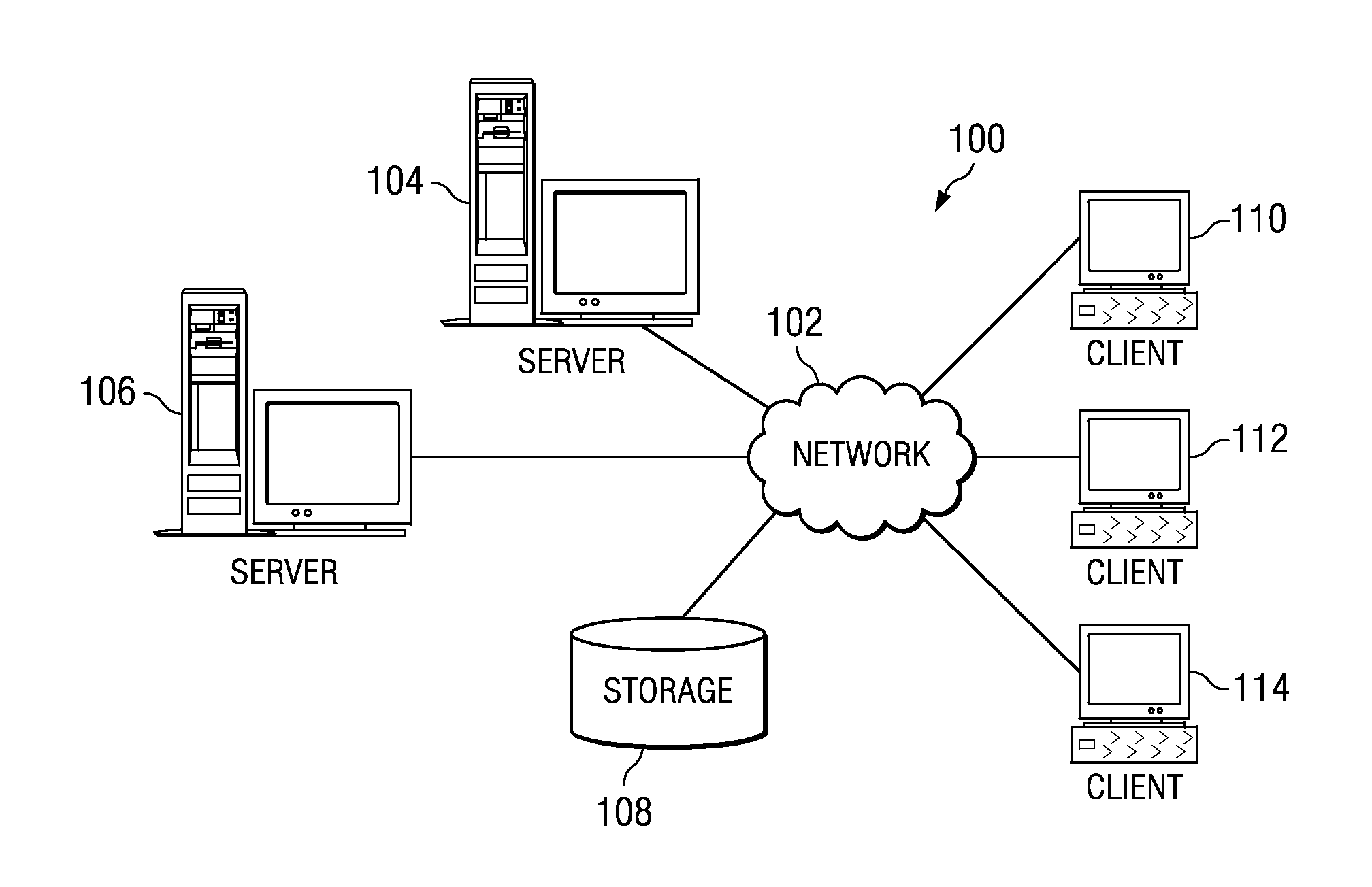
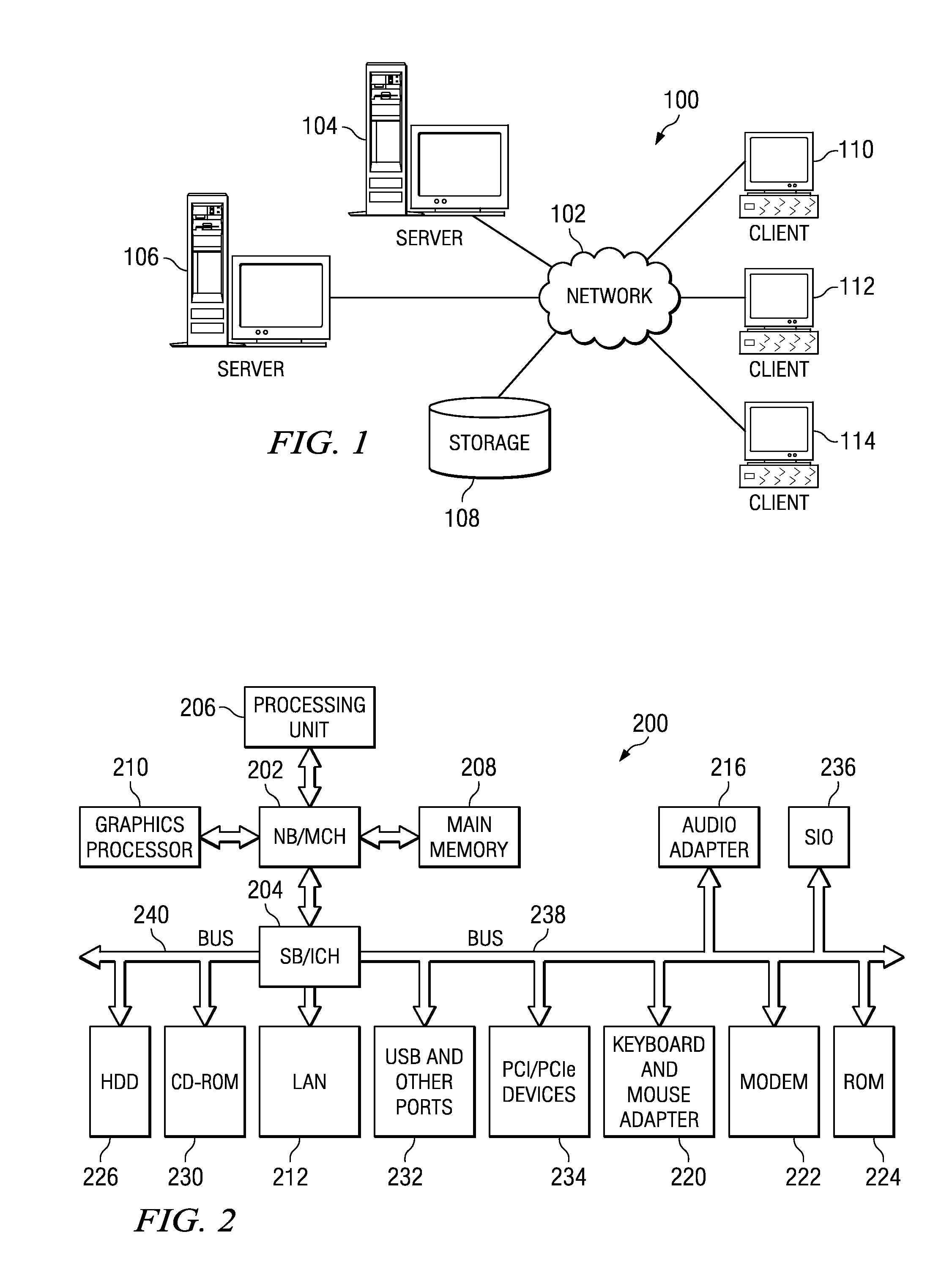
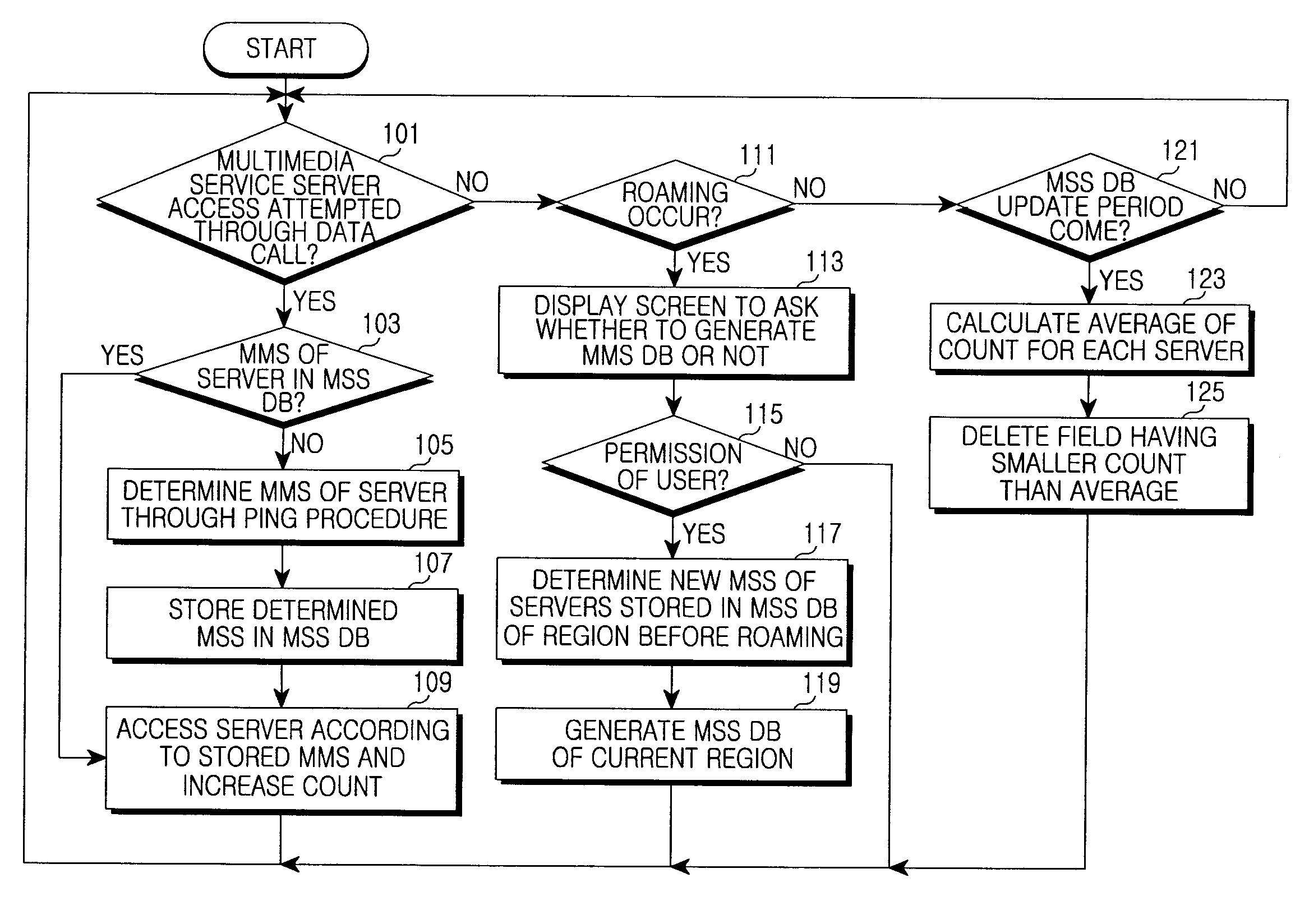
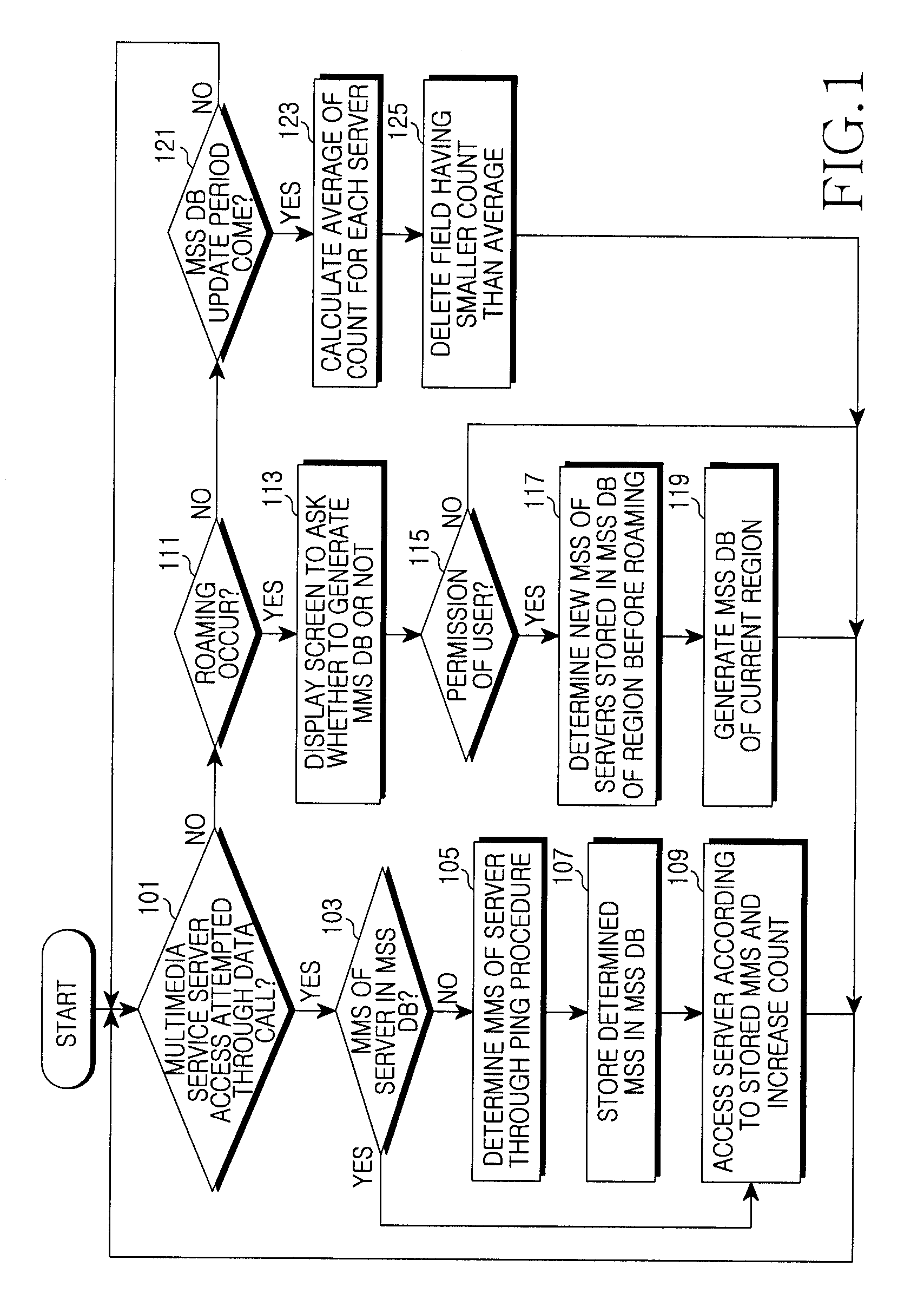
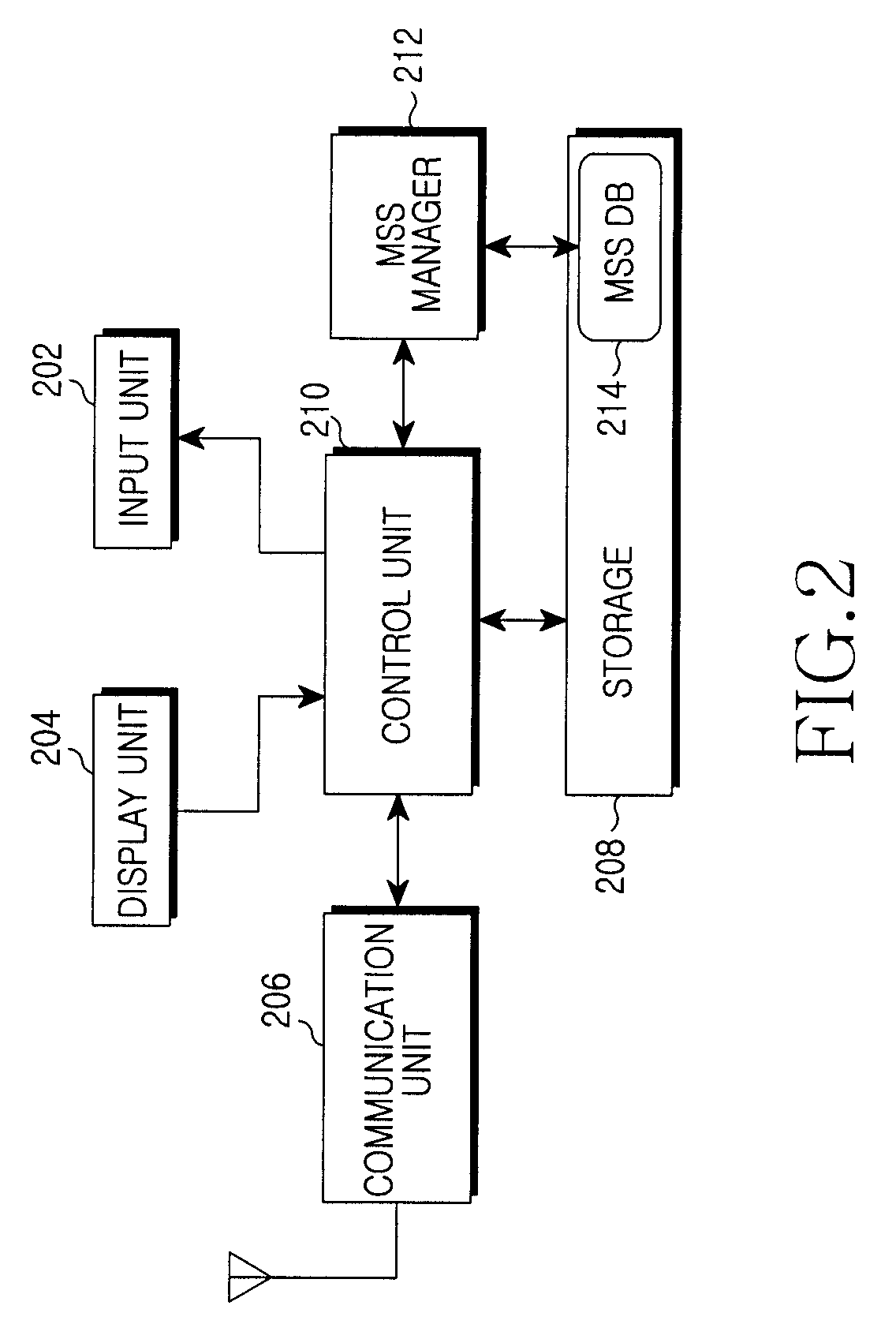
Apparatus and method of determining maximum segment size of data call in mobile communication system
InactiveUS20100290357A1Error preventionTransmission systemsMobile communication systemsMaximum segment size
An apparatus and method for determining a maximum segment size (MSS) in a mobile communication system. When the portable terminal accesses a multimedia service server through a data call, the method includes confirming whether or not a maximum segment size (MSS) of the server is stored; if the MSS is stored, the server is accessed using the MSS; and if the MSS is not stored, determining the MSS of the server through a ping procedure.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
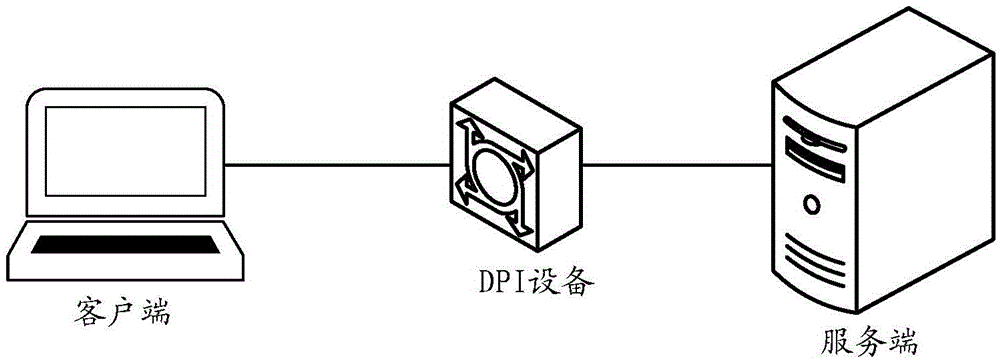
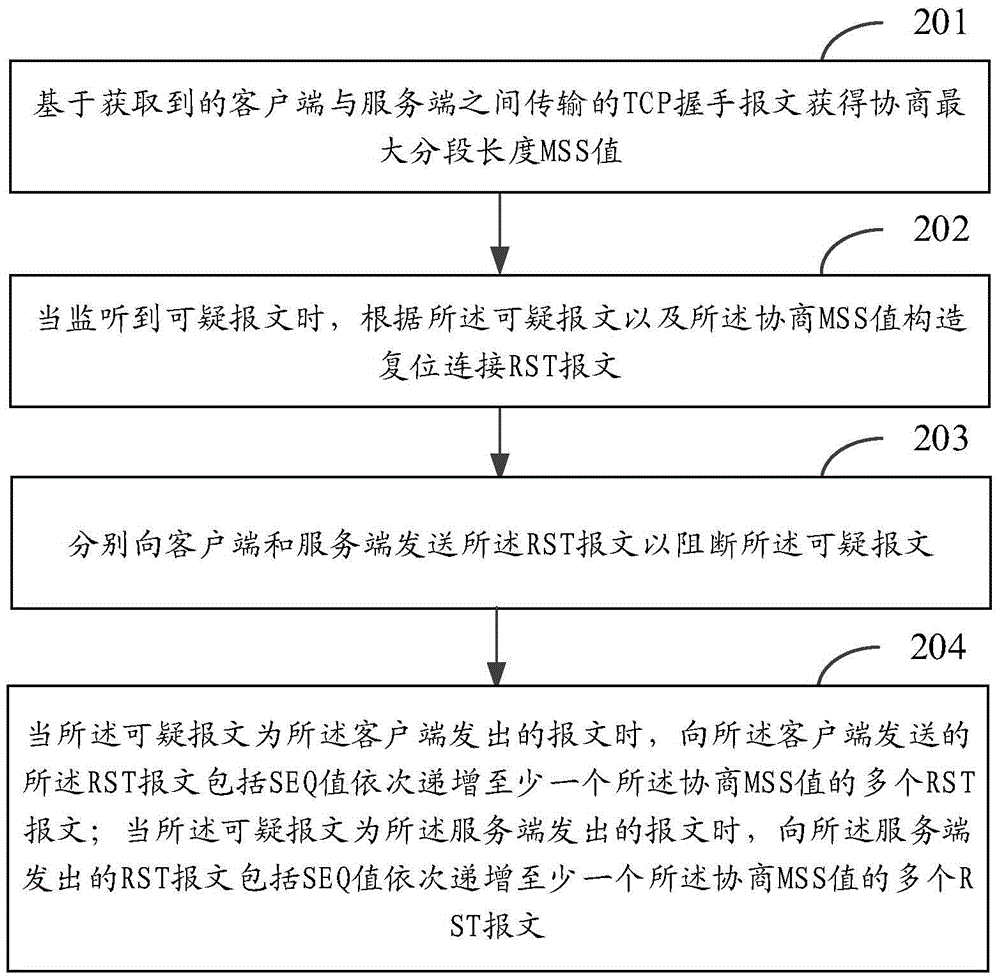
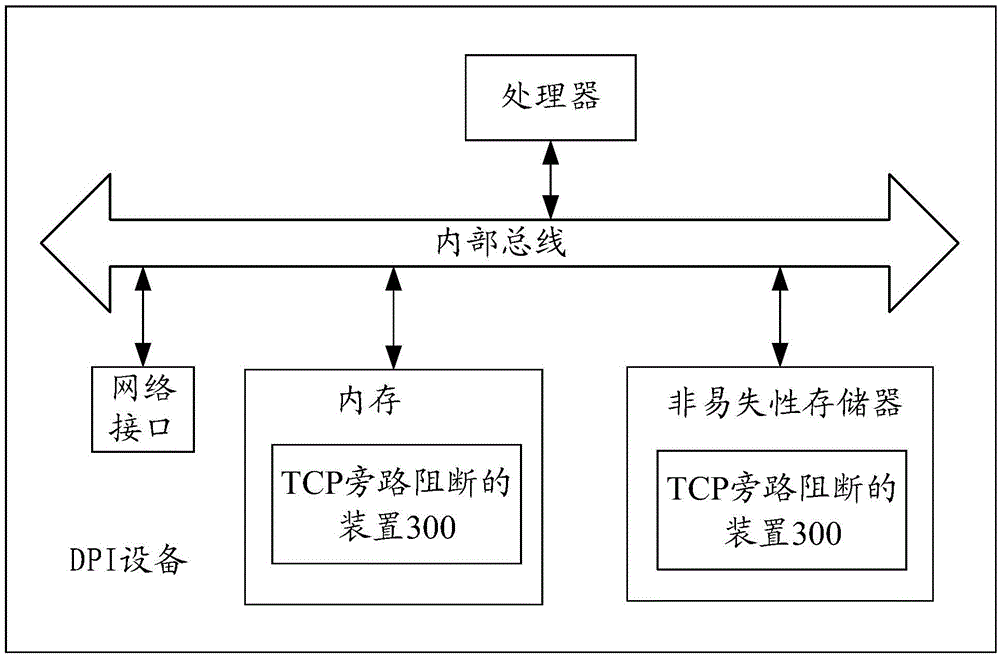
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) bypass blocking method and device
InactiveCN105939325ASolve the problem of low blocking success rateTransmissionComputer hardwareClient-side
The invention provides a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) bypass blocking method and device. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a negotiation maximum segment size MSS value based on an obtained TCP handshake message transmitted between a client and a server; constructing reset RST messages according to a suspicious message and the negotiation MSS value when the suspicious message is monitored; and sending the reset RST messages to the client and the server, thereby blocking the suspicious message, wherein when the suspicious message is the message sent by the client, the RST messages sent to the client comprise multiple RST messages of which SEQ values are successively increased by at least one negotiation MSS value, and when the suspicious message is the message sent by the server, the RST messages sent to the client comprise multiple RST messages of which SEQ values successively is increased by at least one negotiation MSS value. According to the method and the device, the multiple RST messages can be sent to the client and the server, and therefore, the problem that in the prior art, the blocking success rate is low can be solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DPTECH TECH
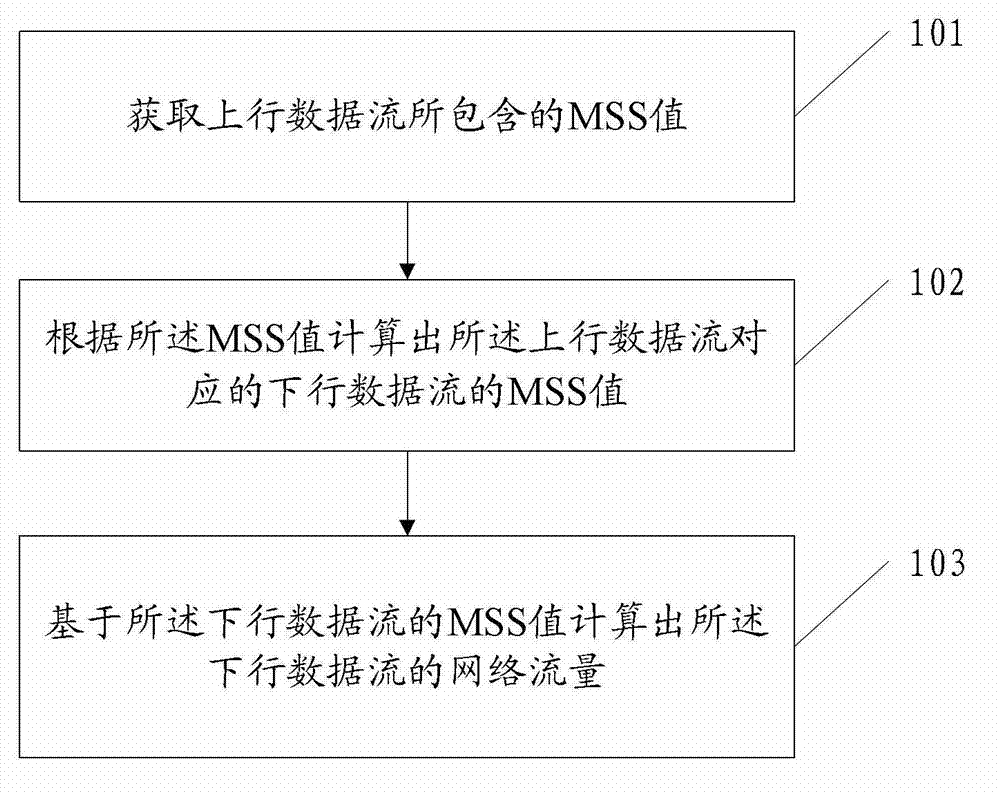
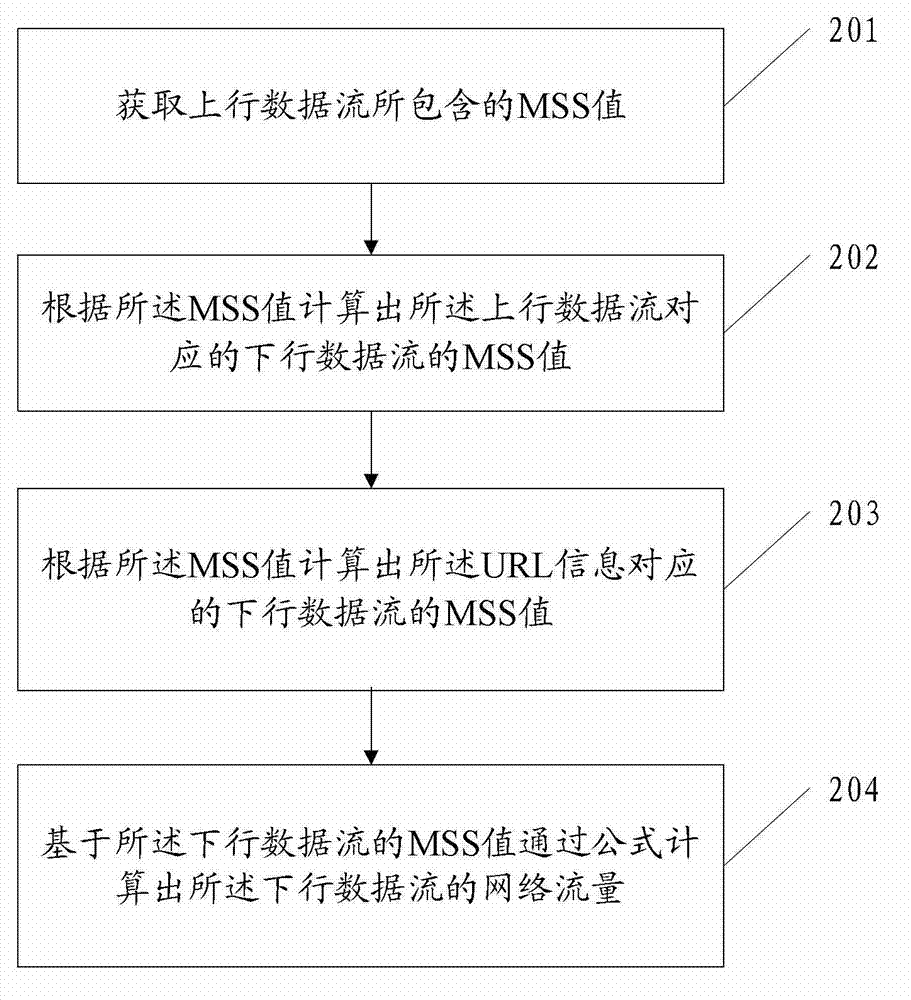
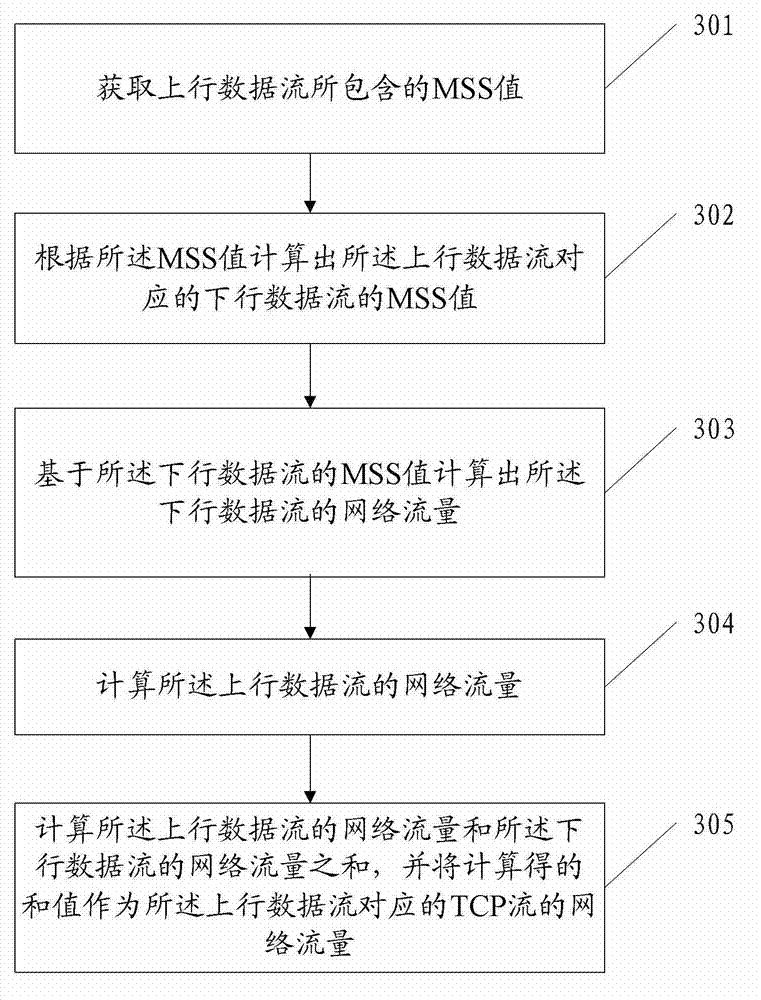
Flow statistical method and flow statistical equipment
The embodiment of the invention discloses a flow statistical method which comprises the following steps of: acquiring an MSS (Maximum Segment Size) value contained in uplink data stream; calculating an MSS value of downlink data stream corresponding to the uplink data stream according to the MSS value of the uplink data stream; and calculating the network flow of the downlink data stream according to the MSS value of the downlink data stream. The embodiment of the invention correspondingly provides flow statistical equipment. The method and the equipment provided by the embodiment of the invention can be used for realizing that flow analysis equipment used for analyzing uplink data stream under an asymmetric route scene can perform statistics on the network flow of the downlink data stream.
Owner:南通云尚找家纺电子商务有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com