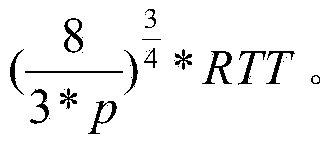Patents
Literature
92 results about "Retransmission timeout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
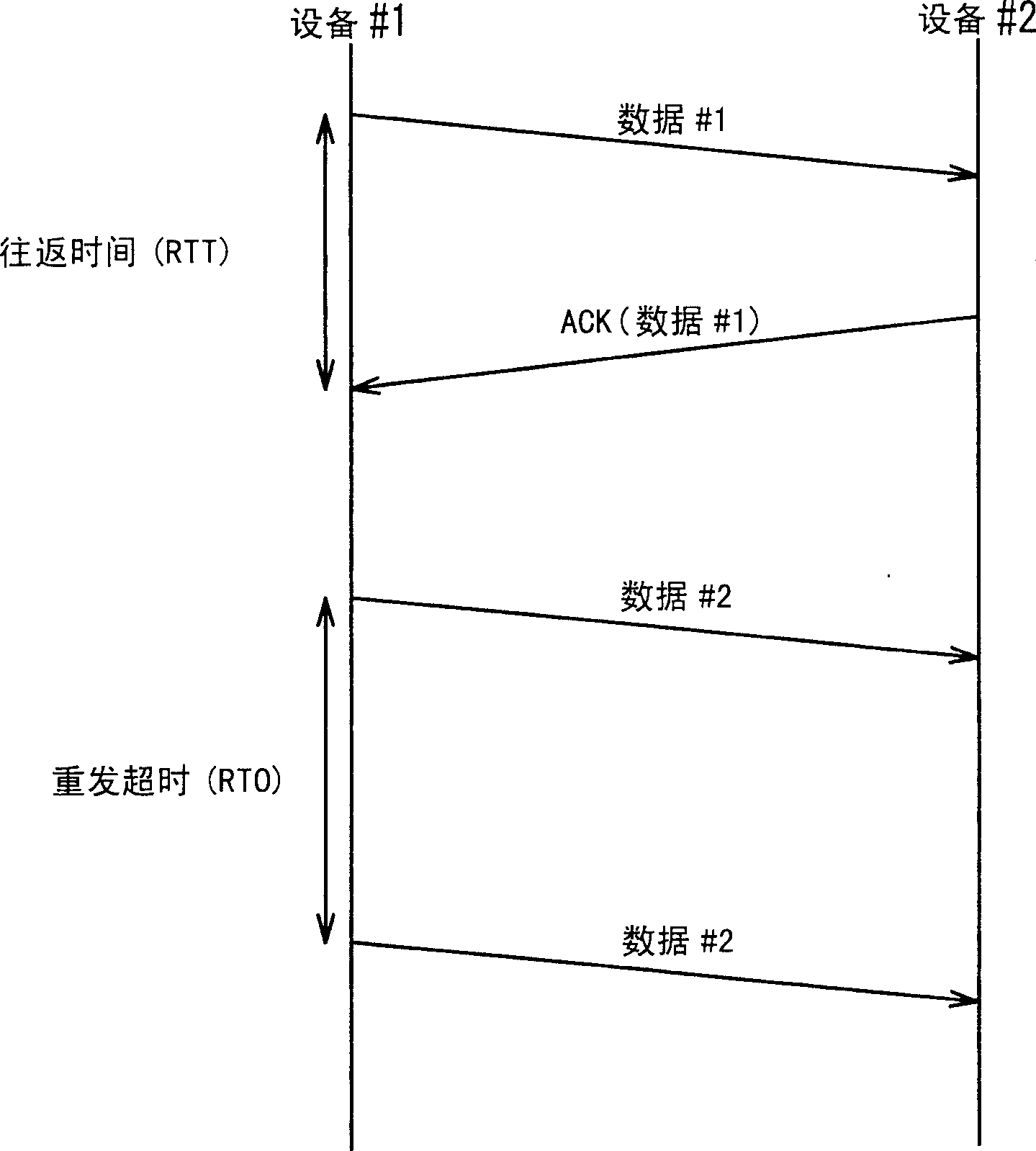
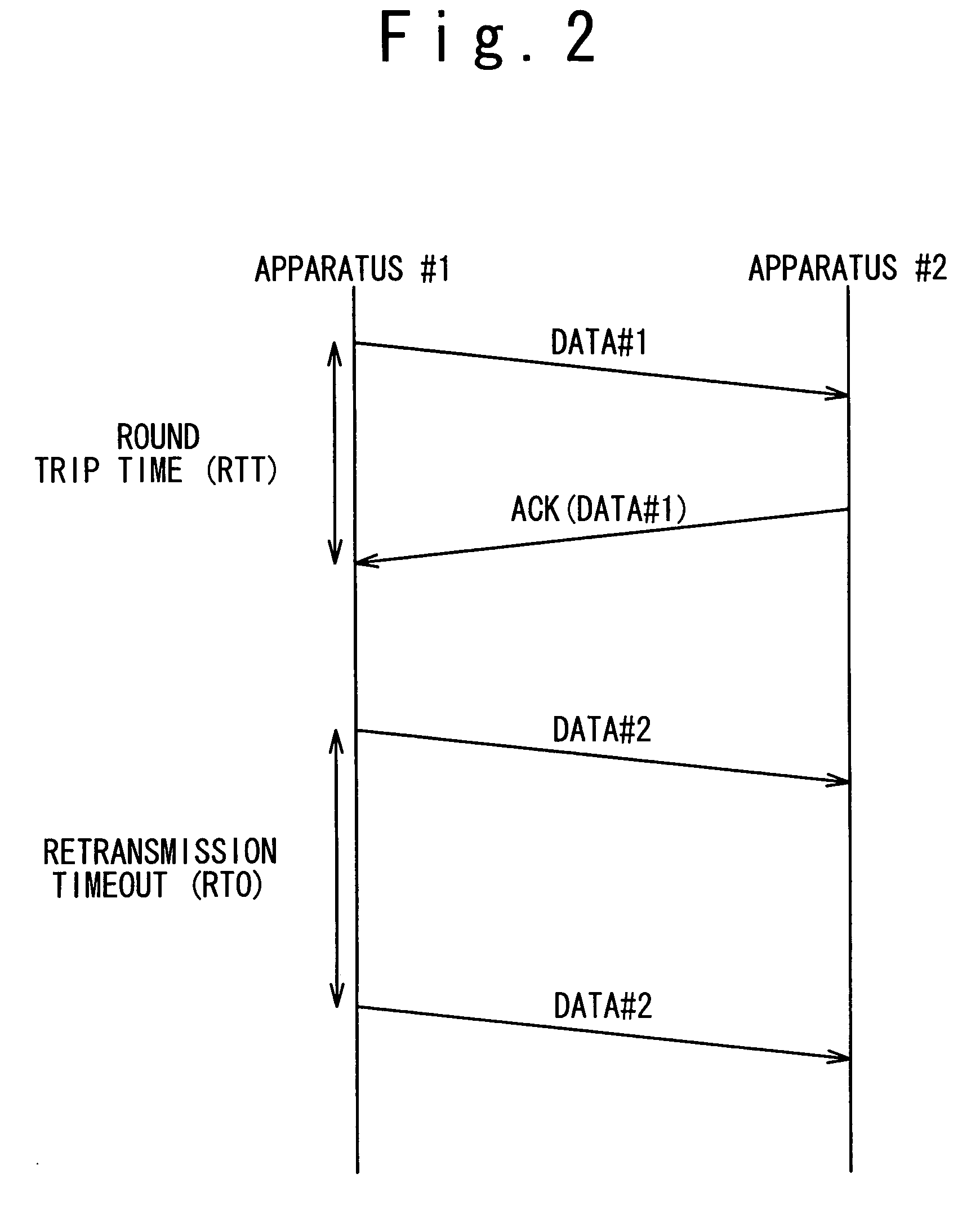
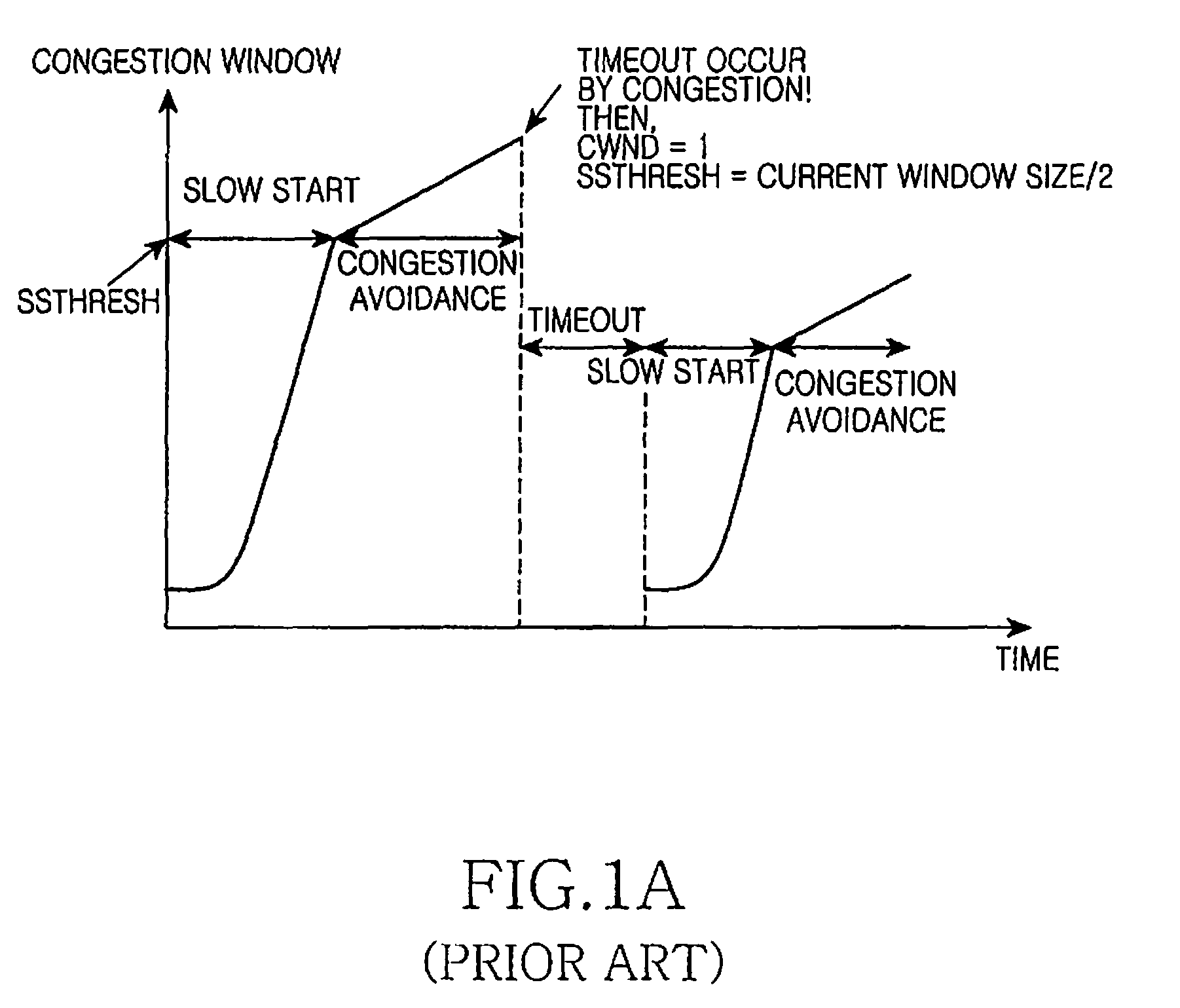
A retransmission timeout (RTO), on the other hand, is quite a different beast. An RTO occurs when the sender is missing too many acknowledgments and decides to take a time out and stop sending altogether. After some amount of time, usually at least one second, the sender cautiously starts sending again,...
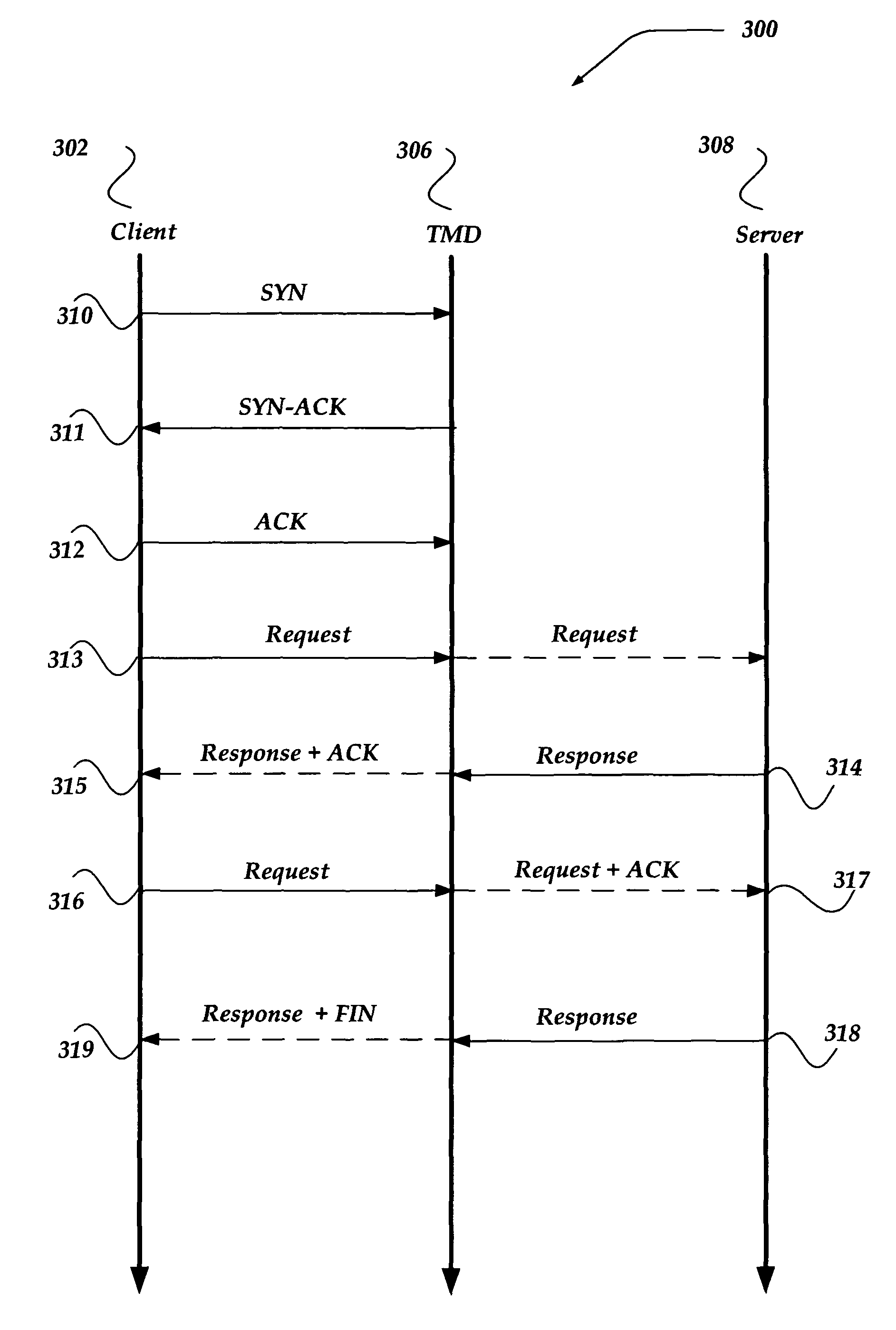
Coalescing acknowledgement responses to improve network communications
ActiveUS7826487B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork communicationClient-side
A system, apparatus, and method are directed to managing network communications by, in part, reducing a number of packets between a client and a server communicating through another device, such as a traffic management device (TMD). The invention reduces the number of packets communicated, in part, by coalescing acknowledgements (ACKs) and / or finish (FIN) flags into another packet. In one embodiment, if the client provides a substantially complete request for the server, an ACK to the request may be coalesced into a corresponding response from the server. When another request is to be provided to the server, within about half of the minimum retransmission timeout, an ACK to the prior response may be coalesced into a subsequent request to the server. Packet reduction may also be achieved by stretching a packet to insert additional data when the insertion maintains a packet size that is within a negotiated maximum segment size (MSS).
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
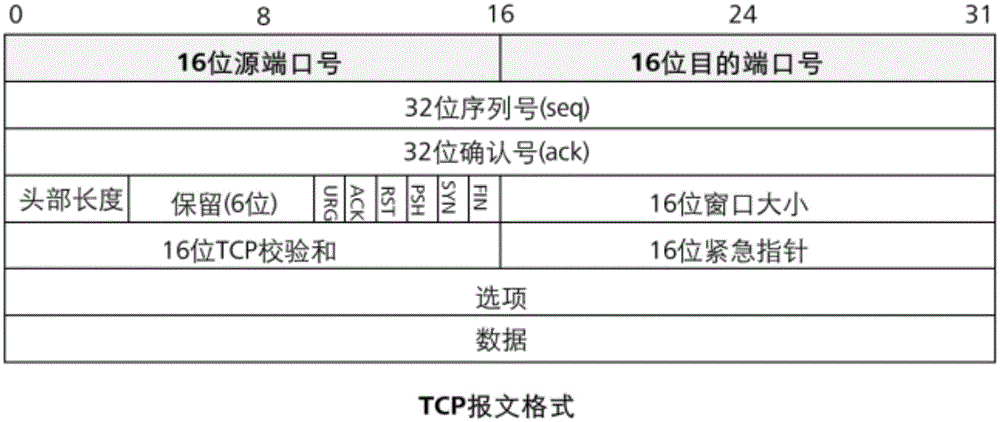
Method and apparatus for setting a TCP retransmission timer
A retransmission timer of a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) session is set based at least in part on the predicted mean round trip time differential of the TCP session. For example, in one embodiment, after receiving a non-duplicate acknowledgment, the predicted mean round trip time differential of the TCP session would be determined and used to further determine the predicted round trip time of the next transmitted data segment. In one embodiment, the predicted round trip time of the next transmitted data segment would be used to determine a retransmission timeout, the value of which would be inserted into a retransmission timer.
Owner:IST INT
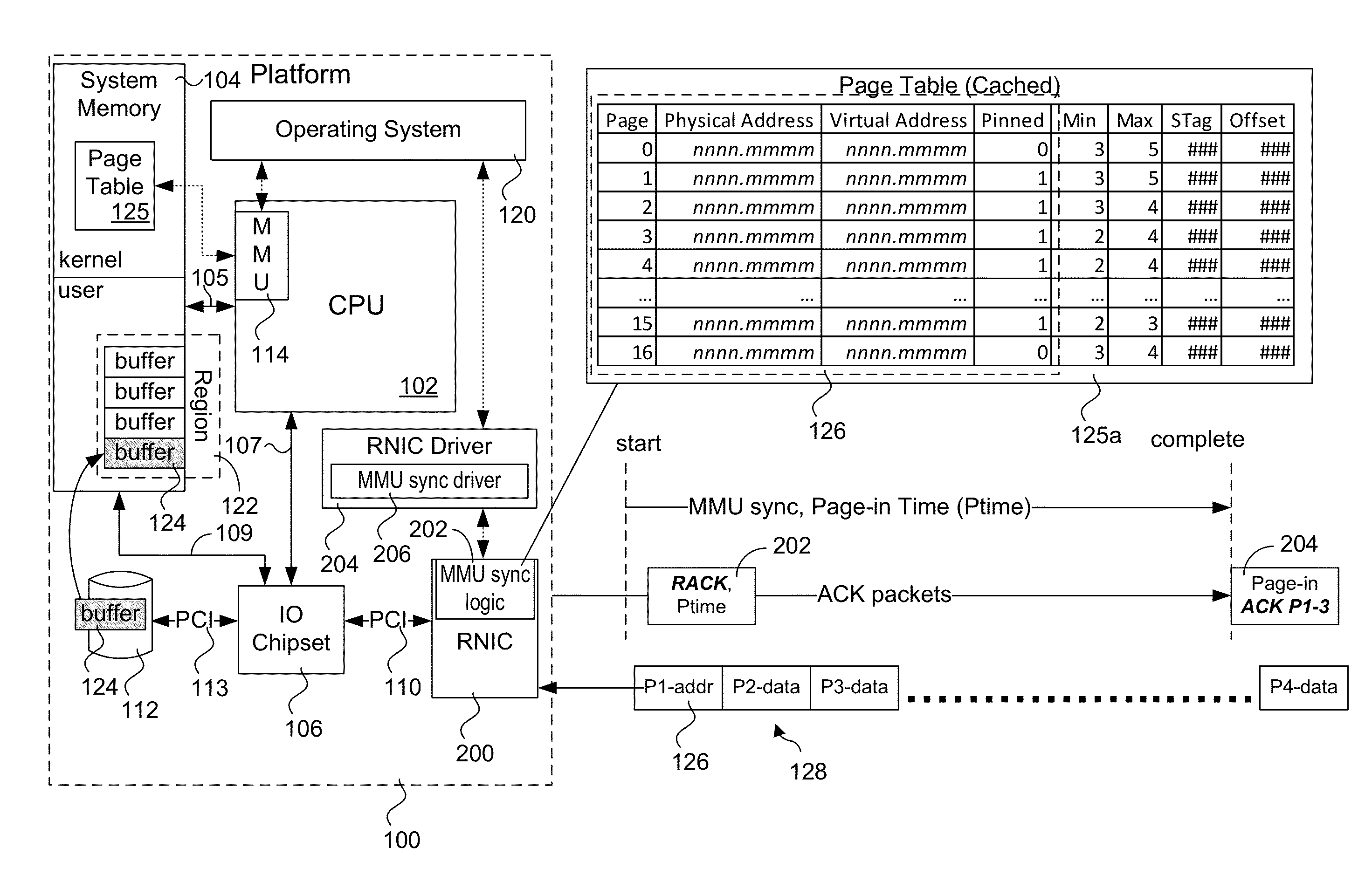
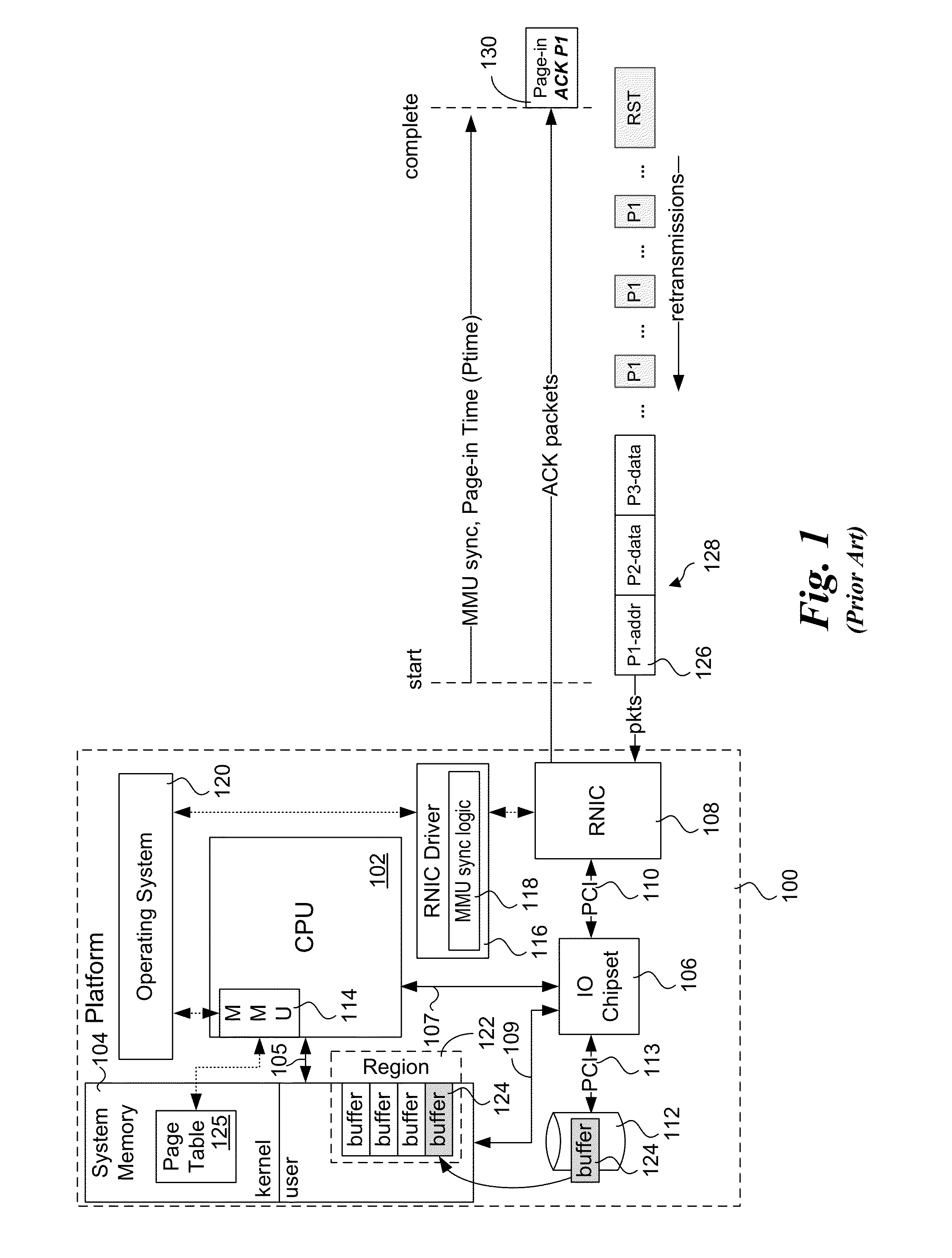
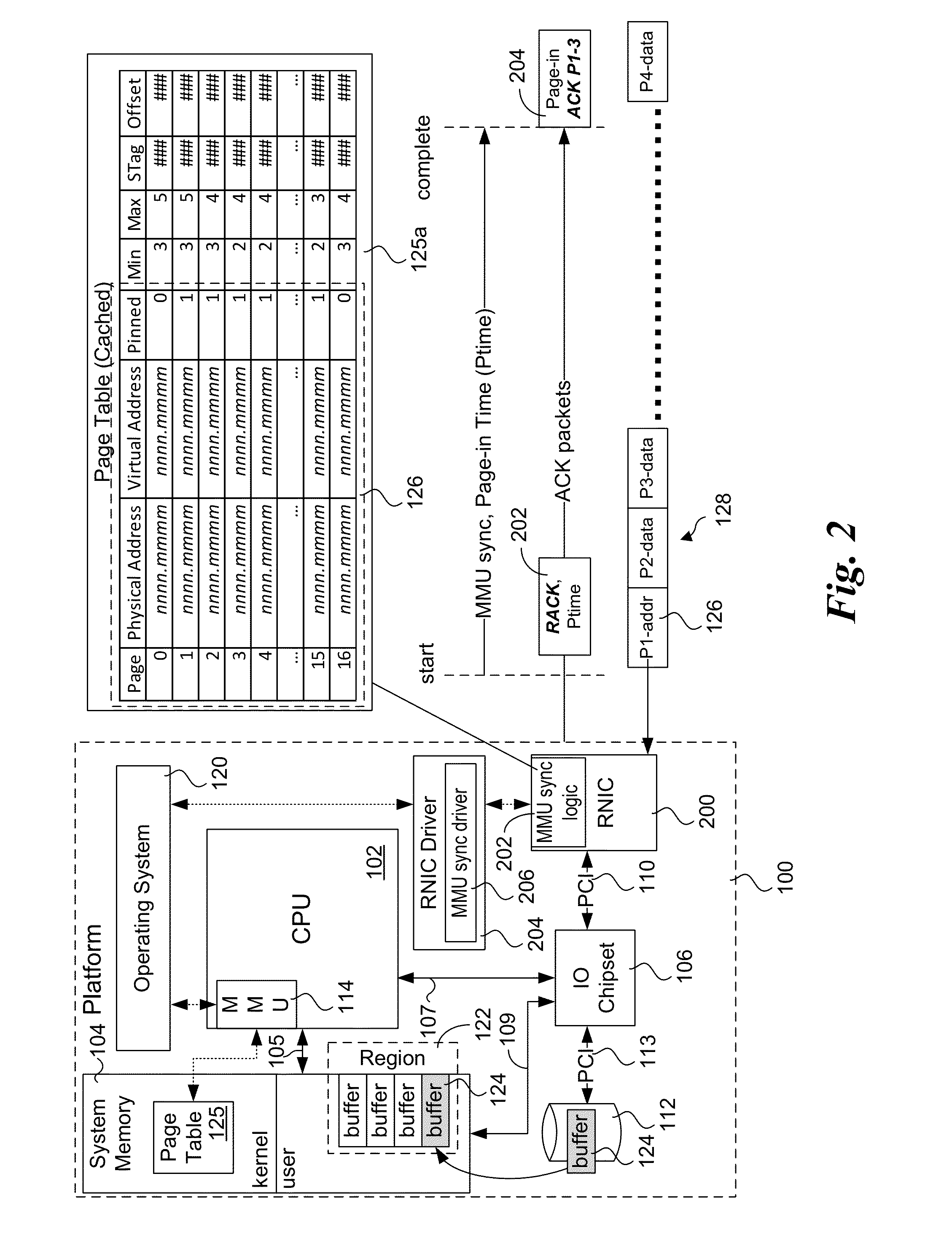
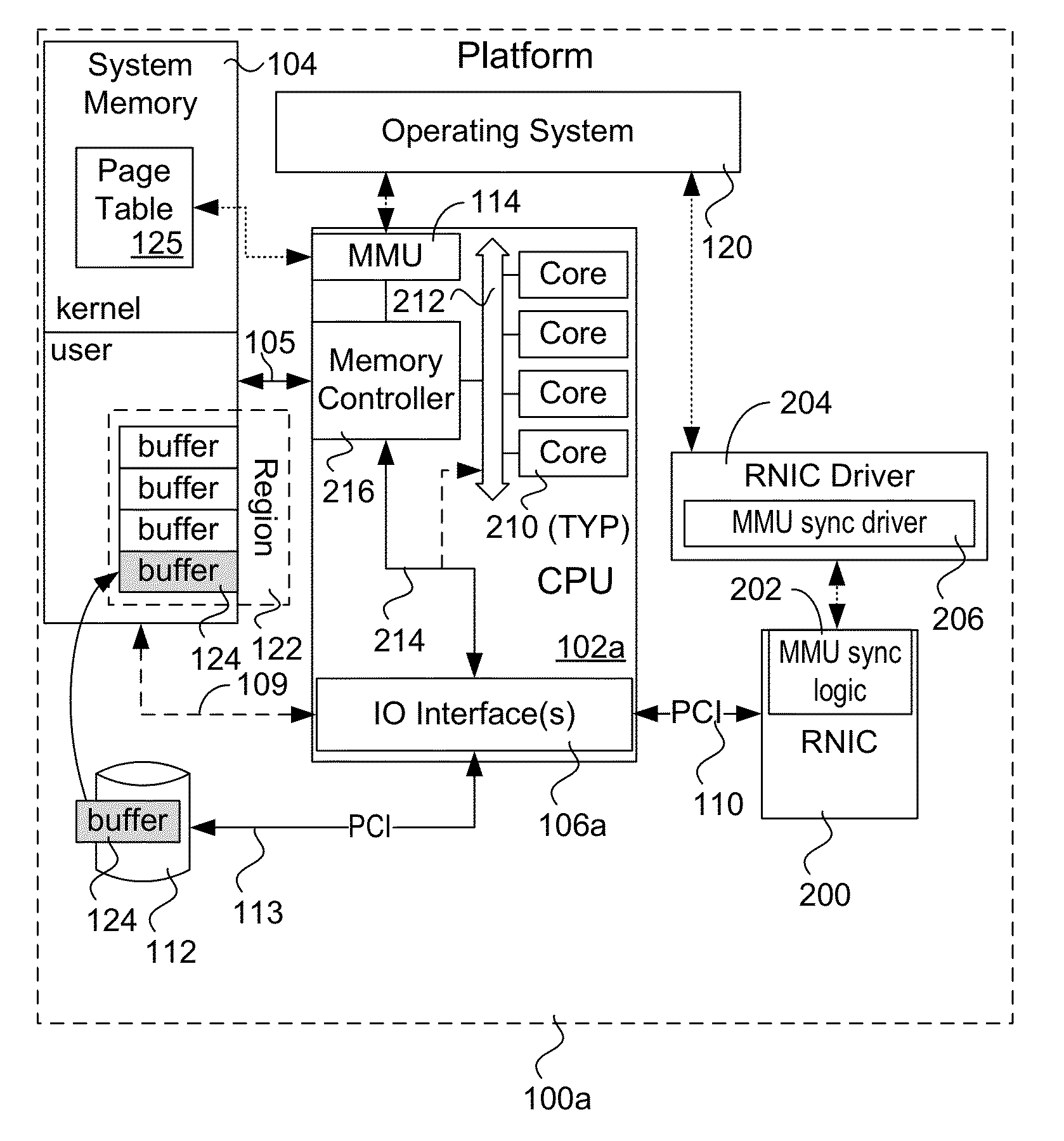
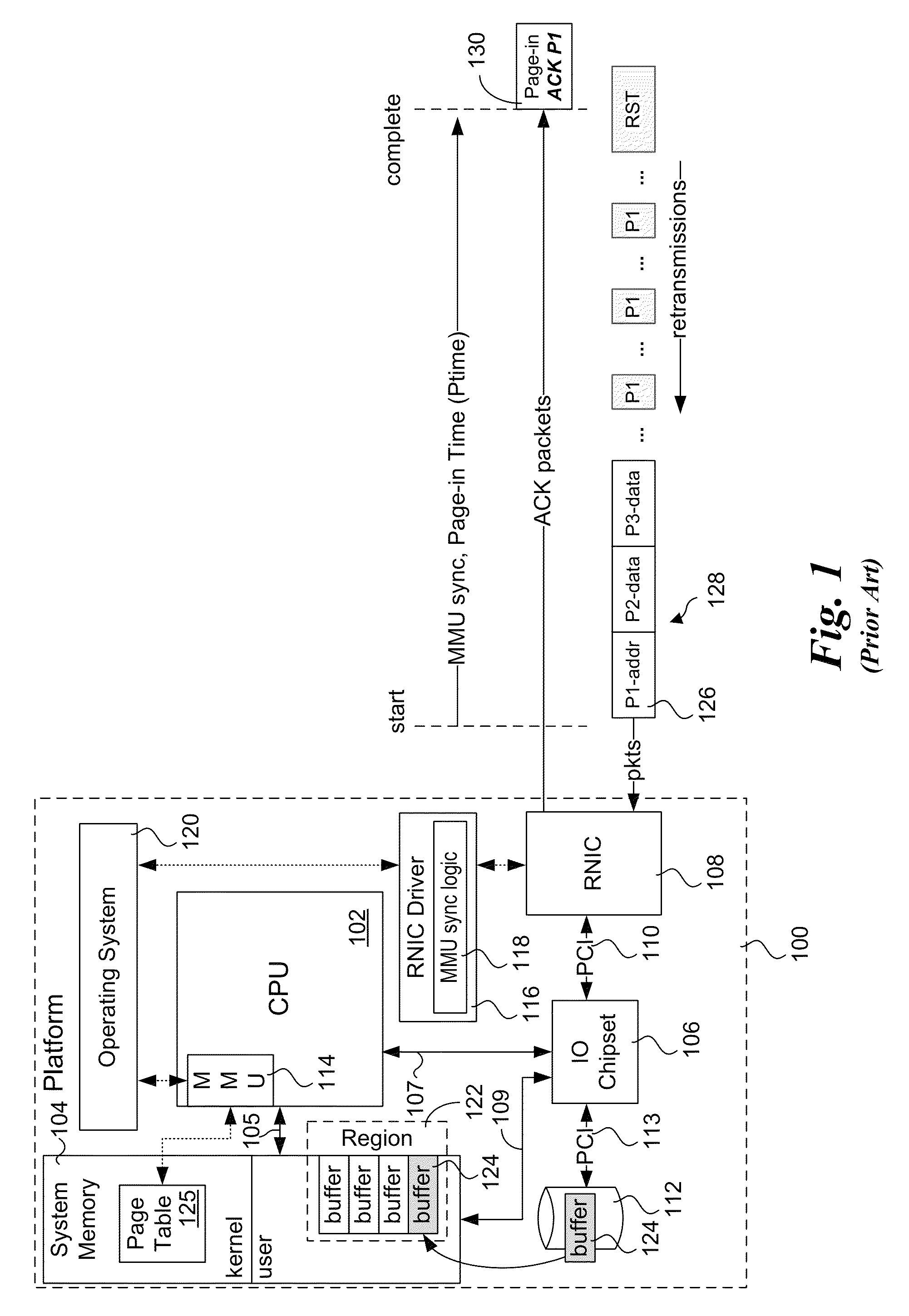
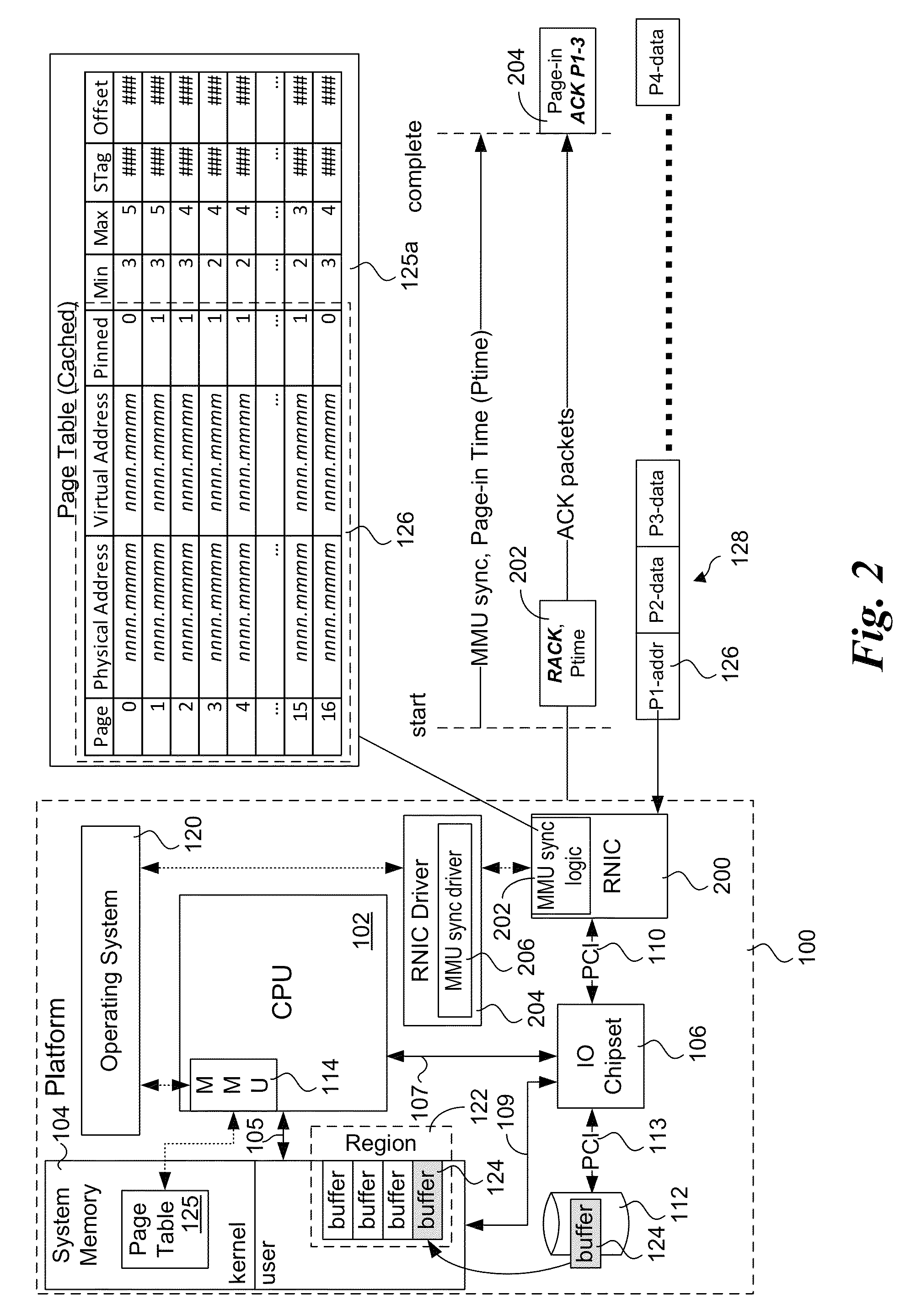
Explicit flow control for implicit memory registration
ActiveUS20140164545A1Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingImplicit memoryRetransmission timeout
Methods, apparatus and systems for facilitating explicit flow control for RDMA transfers using implicit memory registration. To setup an RDMA data transfer, a source RNIC sends a request to allocate a destination buffer at a destination RNIC using implicit memory registration. Under implicit memory registration, the page or pages to be registered are not explicitly identified by the source RNIC, and may correspond to pages that are paged out to virtual memory. As a result, registration of such pages result in page faults, leading to a page fault delay before registration and pinning of the pages is completed. In response to detection of a page fault, the destination RNIC returns an acknowledgment indicating that a page fault delay is occurring. In response to receiving the acknowledgment, the source RNIC temporarily stops sending packets, and does not retransmit packets for which ACKs are not received prior to retransmission timeout expiration.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method of reducing latency using adaptive retransmission timeouts
ActiveUS8468196B1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData adaptiveRetransmission timeout
In one aspect, a system and method are provided whereby latency in network communication protocols such as the TCP / IP suite of protocols is reduced by transmitting a new and second connection request from a sending device to a receiving device over a network based upon adaptively determined dynamic initial timeout values, where the dynamic initial timeout values are adaptively determined based upon data associated with one or more historical requests transmitted over the network by the sending device.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
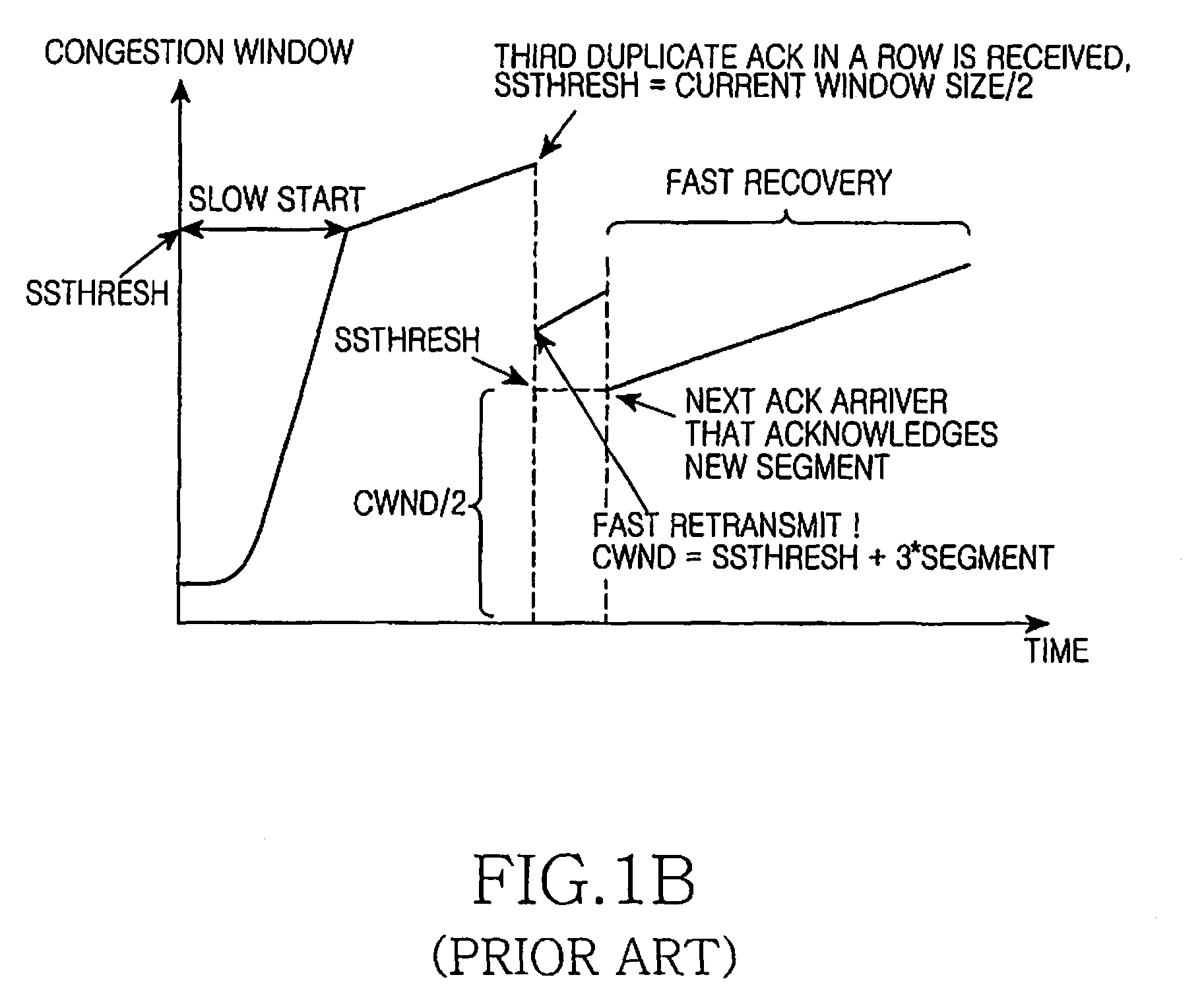
Method and System for a Fast Drop Recovery for a TCP Connection
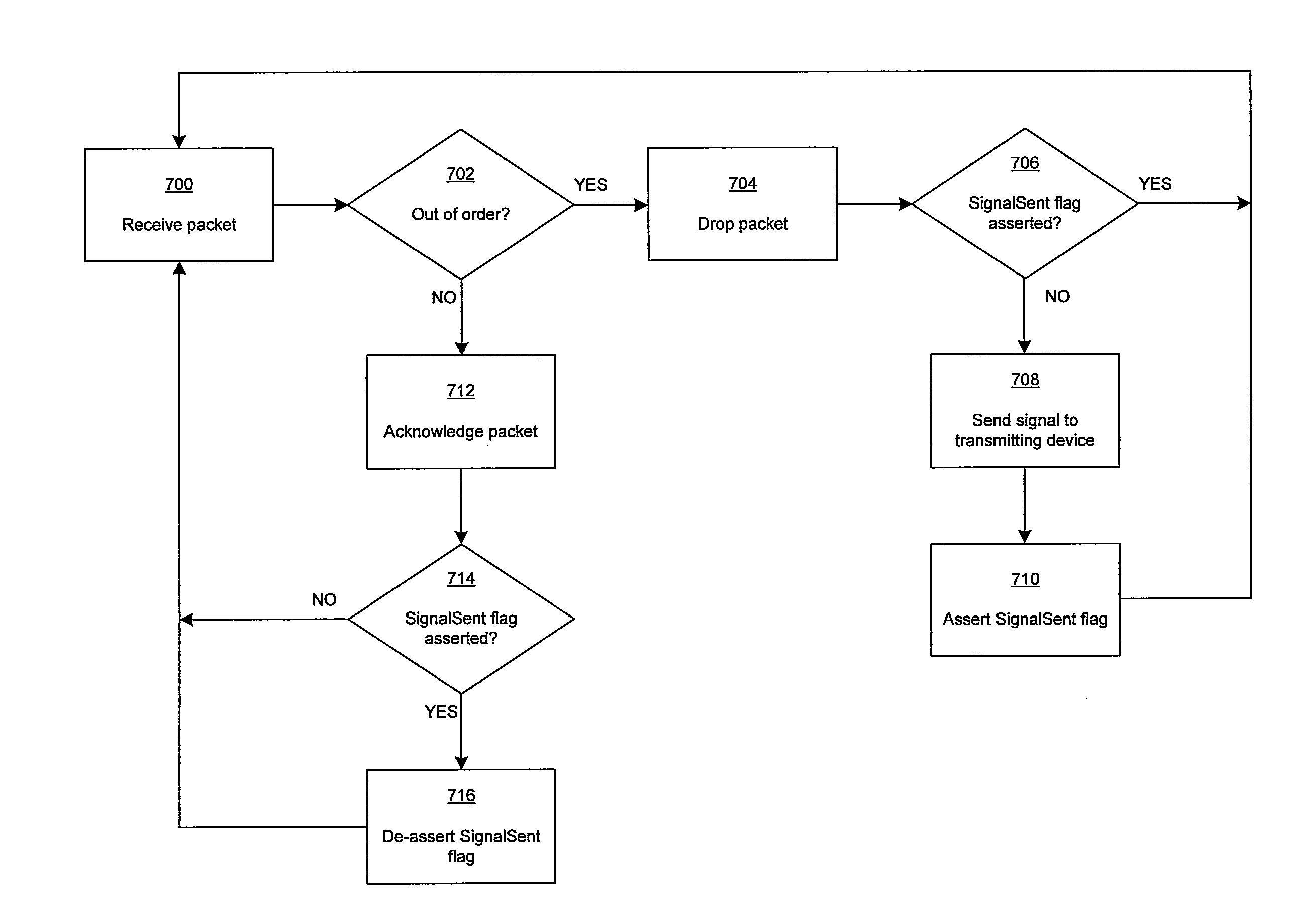
ActiveUS20090080332A1Reduce network congestionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetComputer science
Methods and systems for a fast drop recovery for a TCP connection are disclosed. Aspects of one method may include a receiving device on a network receiving an out-of-order data. The receiving device may then signal to a transmitting device on the network, which sent the out-of-order packet, to enter a congestion alleviation mode without waiting for a delay period. The network packet transfer may be via TCP protocol, for example. The delay period may comprise a retransmission time-out period if the receiving device does not save isles. If the receiving device does save one or more isles, the delay period may be a period associated with delayed ACK. The signal may comprise a TCP option and / or an available TCP flag. The signal may also comprise, for example, three duplicate ACKs. Other similar signals may be used for networks that use other protocols than TCP. Upon receiving out-of-order data, the receiving device may, for example, send the signal and then assert a signal-sent flag if it is not already asserted. When a new packet is received in order, the signal-sent flag may be de-asserted.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for optimizing a TCP session for a wireless network
InactiveUS20070223395A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCongestion windowPropagation delay
A plurality of network characteristics of a wireless network are determined and a plurality of TCP session parameters are updated. The network characteristics may be determined based at least in part on a comparison of the estimated bandwidth and estimated propagation delay of the wireless network and the typical bandwidths and propagation delays of one or more wireless networks. The TCP session parameters may be updated based at least in part on the network characteristics. The TCP session parameters may be used to limit the congestion window, retransmission timeout and slow start threshold.
Owner:IST INT
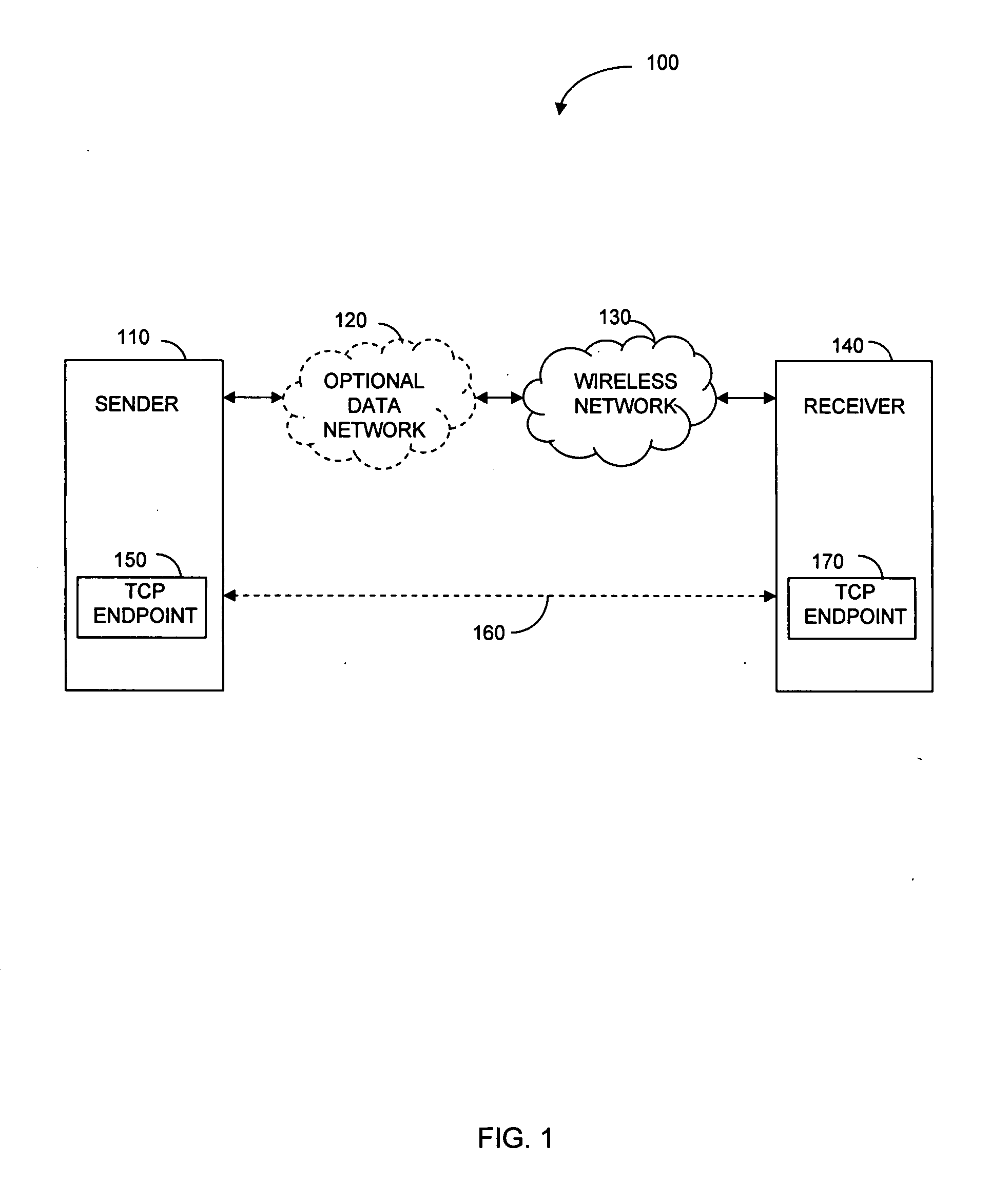
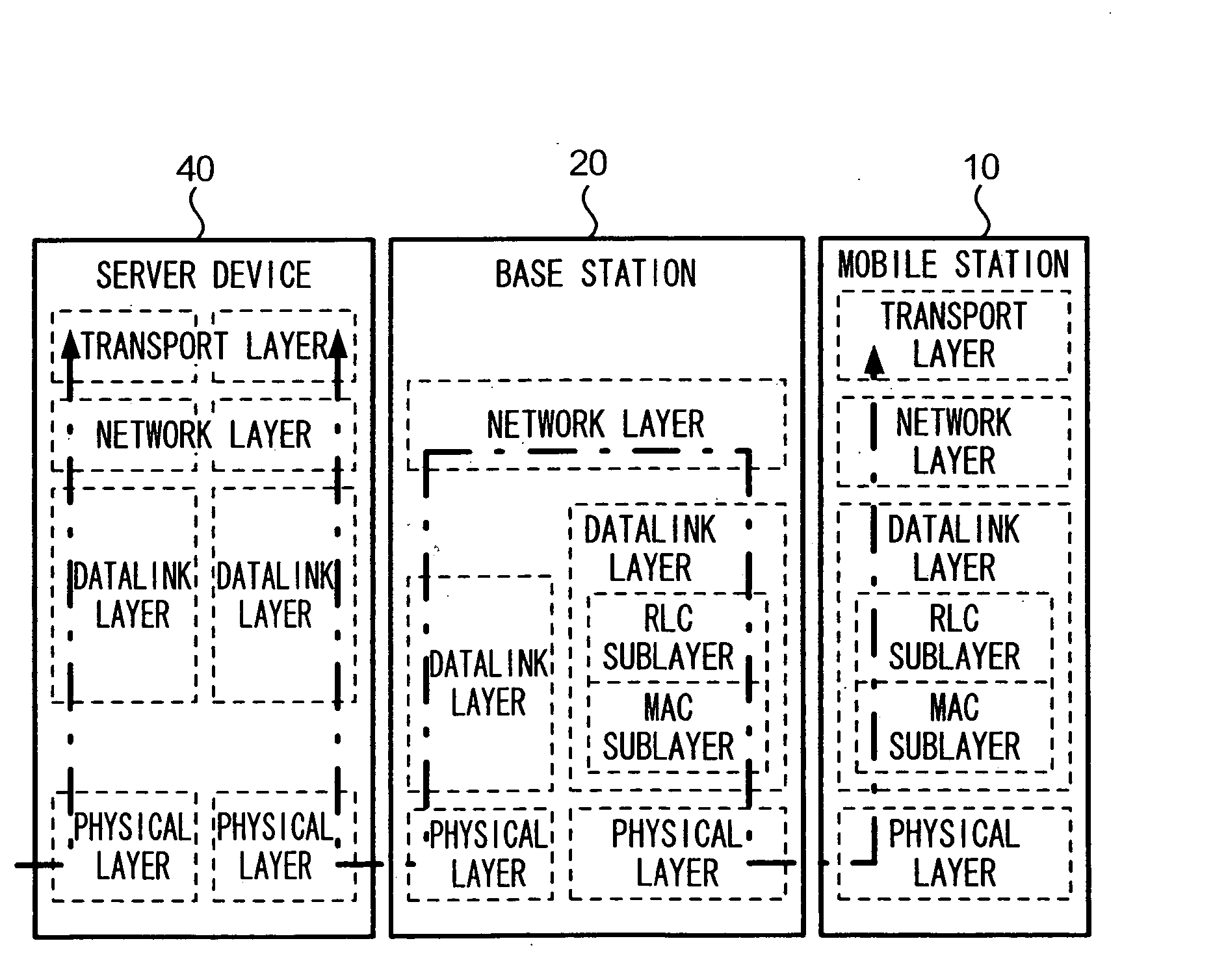
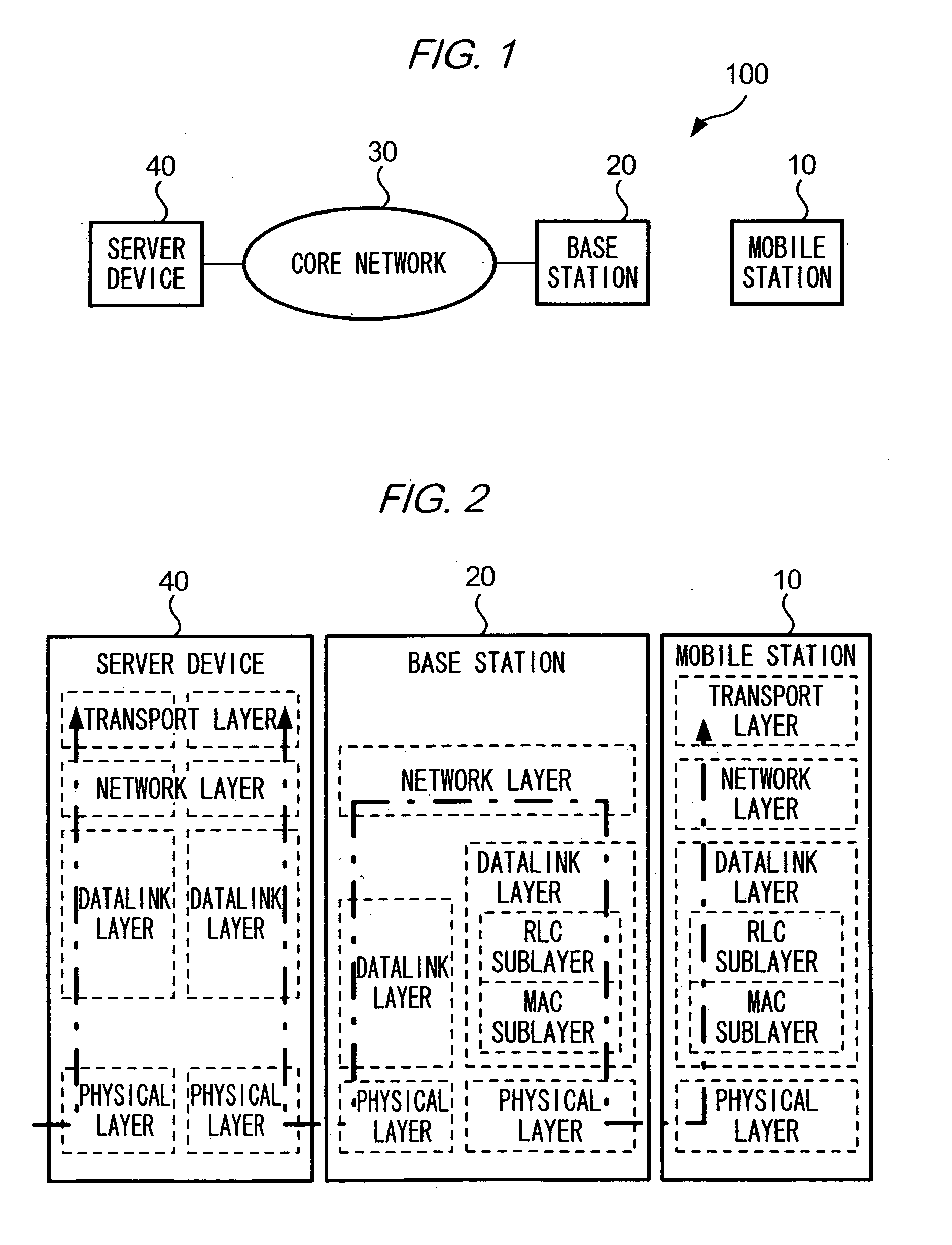
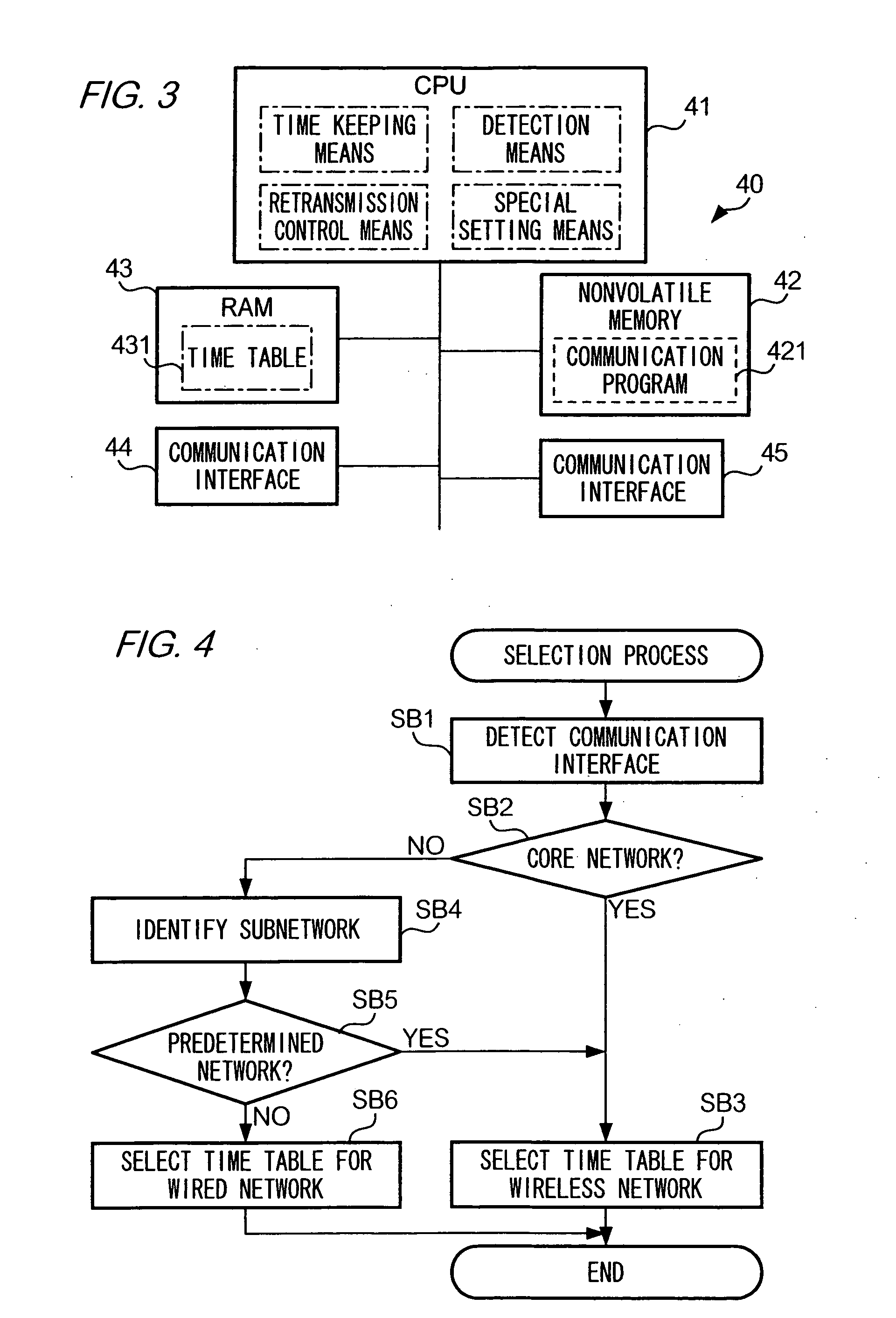
Transmitter device for controlling data transmission
InactiveUS20050190720A1Reduce generationReduce retransmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementData segmentTime segment
A CPU 41 of a server device 40 measures an elapsed time after transmitting a data segment, and suspends measuring time upon receiving an acknowledgement segment for the data segment. CPU 41 transmits a data segment whose elapsed time has reached a retransmission timeout value. CPU 41 sets, as a retransmission timeout value of a data block, a time value determined according to a monotonically increasing function of a number of transmissions of the data block, during a given time period after the second-time transmission of the data block, while CPU 41 sets a time value which is predetermined and is different from the time value determined by the monotonically increasing function during a period between the first-time transmission and immediately before the second-time transmission of the data block.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
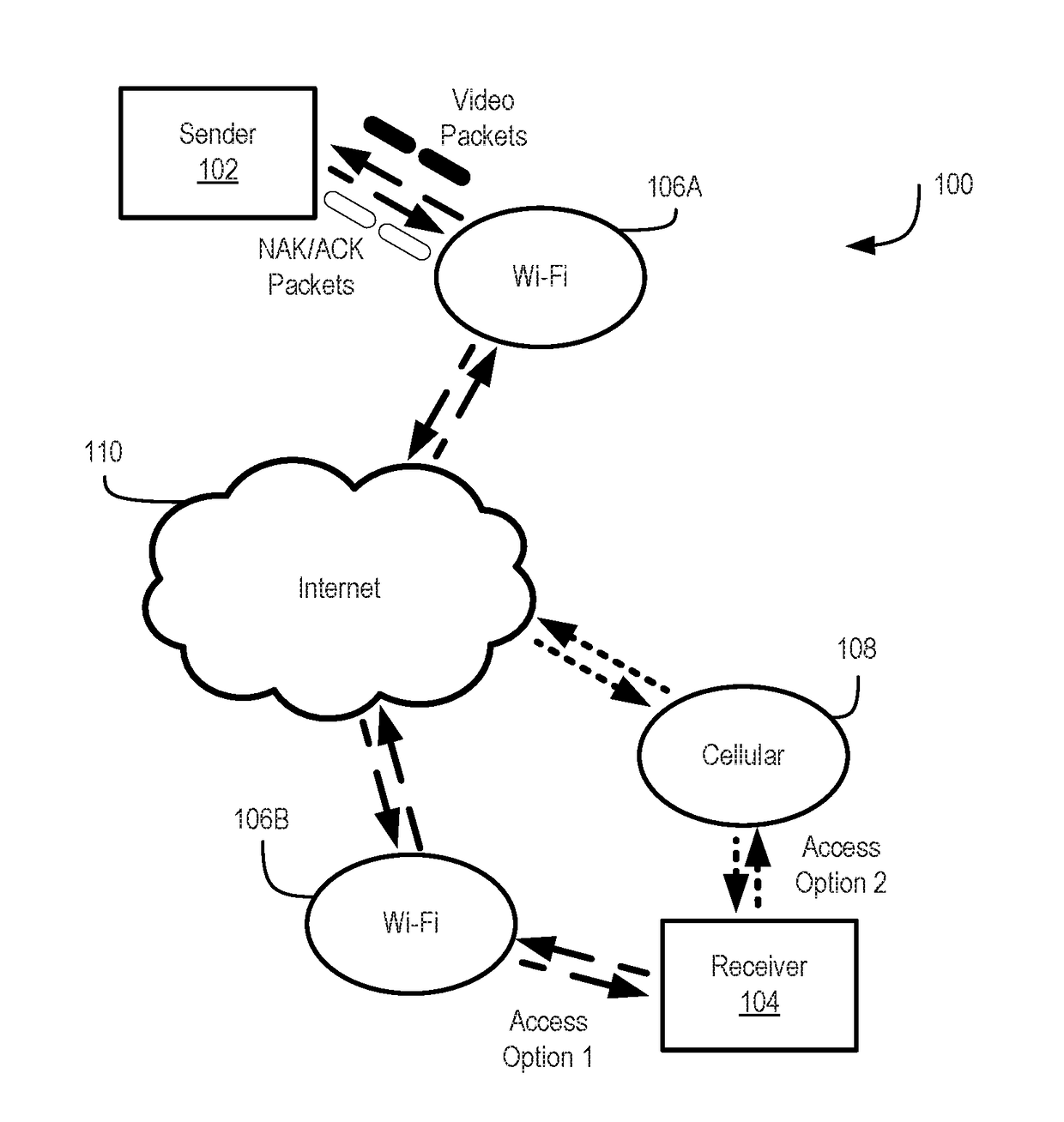
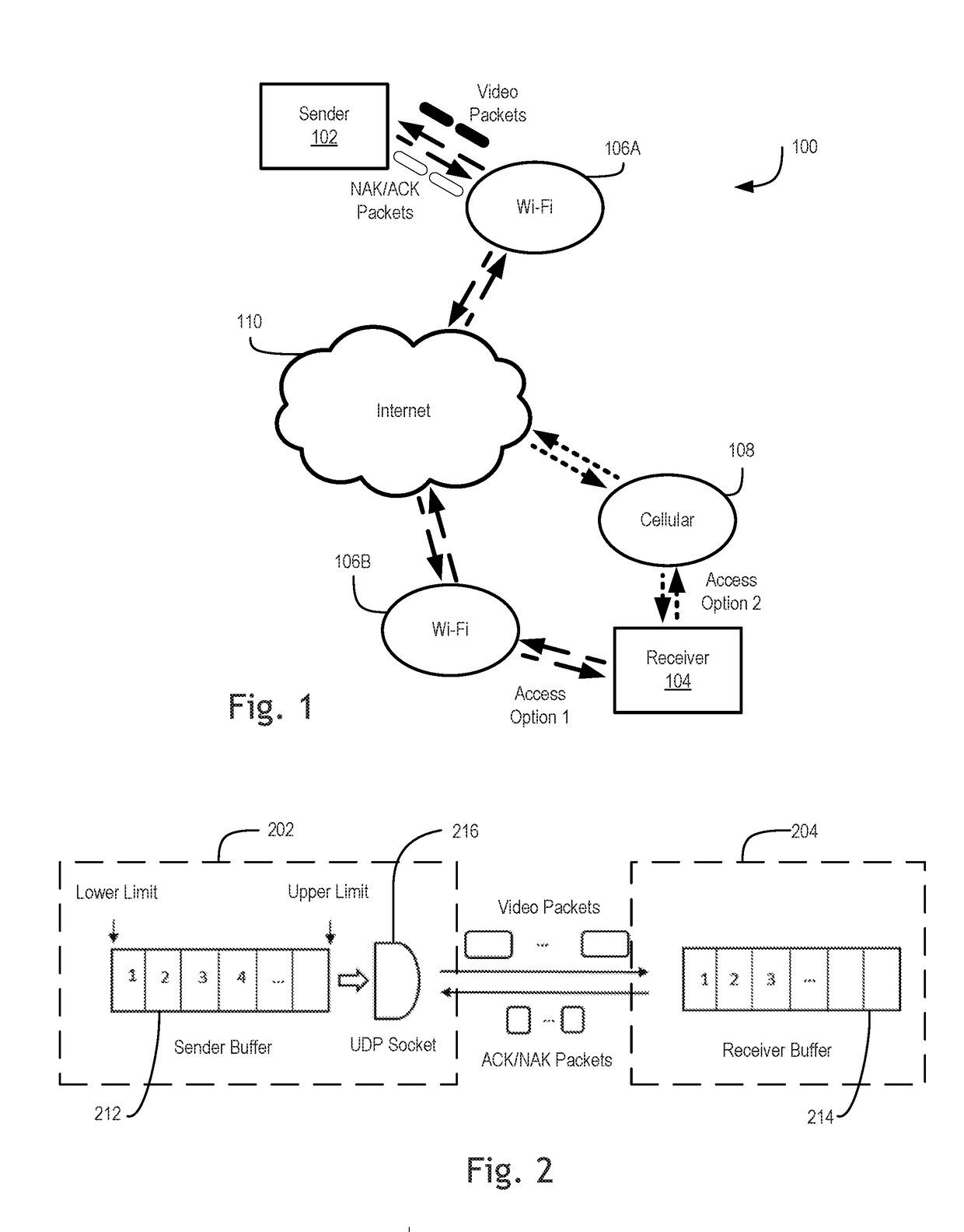
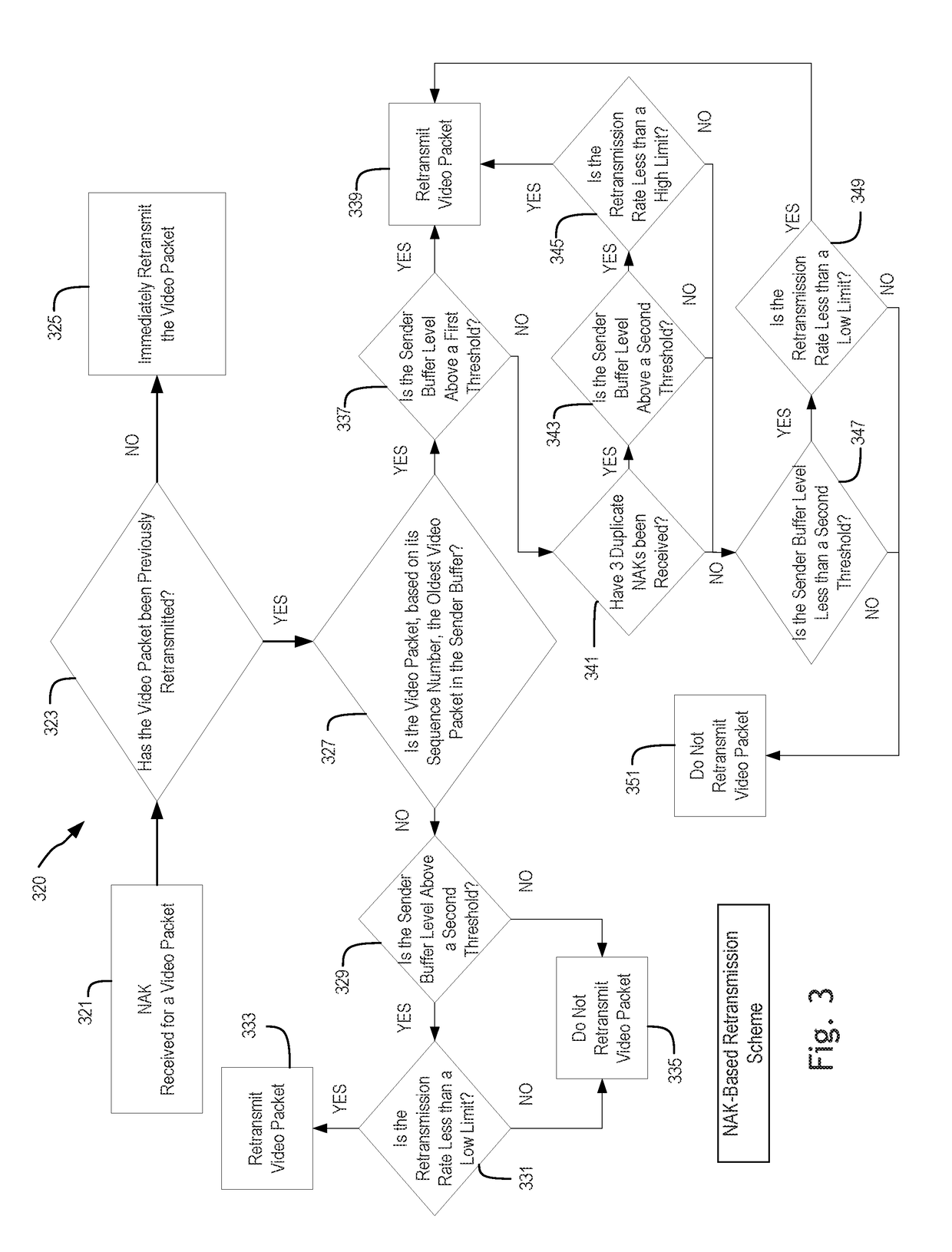
Buffer-aware transmission rate control for real-time video streaming system
ActiveUS20180332342A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSelective content distributionRetransmission timeoutTransmission rate
Systems and methods for buffer-aware transmission rate control for real-time video streaming are disclosed herein. An example method includes transmitting a first video packet at a transmission rate based on a buffer fill ratio of a buffer, where the transmission rate is adjusted in response to changes of the buffer fill ratio, selectively retransmitting a second video packet in response to a negative acknowledgement packet, where selectively retransmitting the second video packet is at least based on whether the second video packet has been previously retransmitted, a buffer level of the buffer, and a retransmission rate, and selectively retransmitting a third video packet in response to a non-receipt of an acknowledgement packet within a retransmission timeout, wherein selectively retransmitting the third video packet is at least based on whether the third video packet has been previously retransmitted, the buffer level of the buffer, and the retransmission rate.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Active path selection for SCTP
ActiveUS20030235151A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel parameterChannel network
A multi-channel network is disclosed in which channels can be designated as "active" or "inactive" and changes can be made from one channel to another based on a metric which is a function of various channel parameters such as throughput and stability. In one form, the metric is a linear combination of factors such as the mean of the round trip time sequence of previous packets (indicating throughput) and the sample variance of the sequence of retransmission timeout values computed for previous transmission attempts (indicating stability). Regardless of the specific form of the metric or the estimation procedures for the channel parameters, these factors are combined using user-specified weights which permit the user to emphasize the relative importance of individual factors, thereby characterizing the strategy whereby "active" or "inactive" paths are used.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
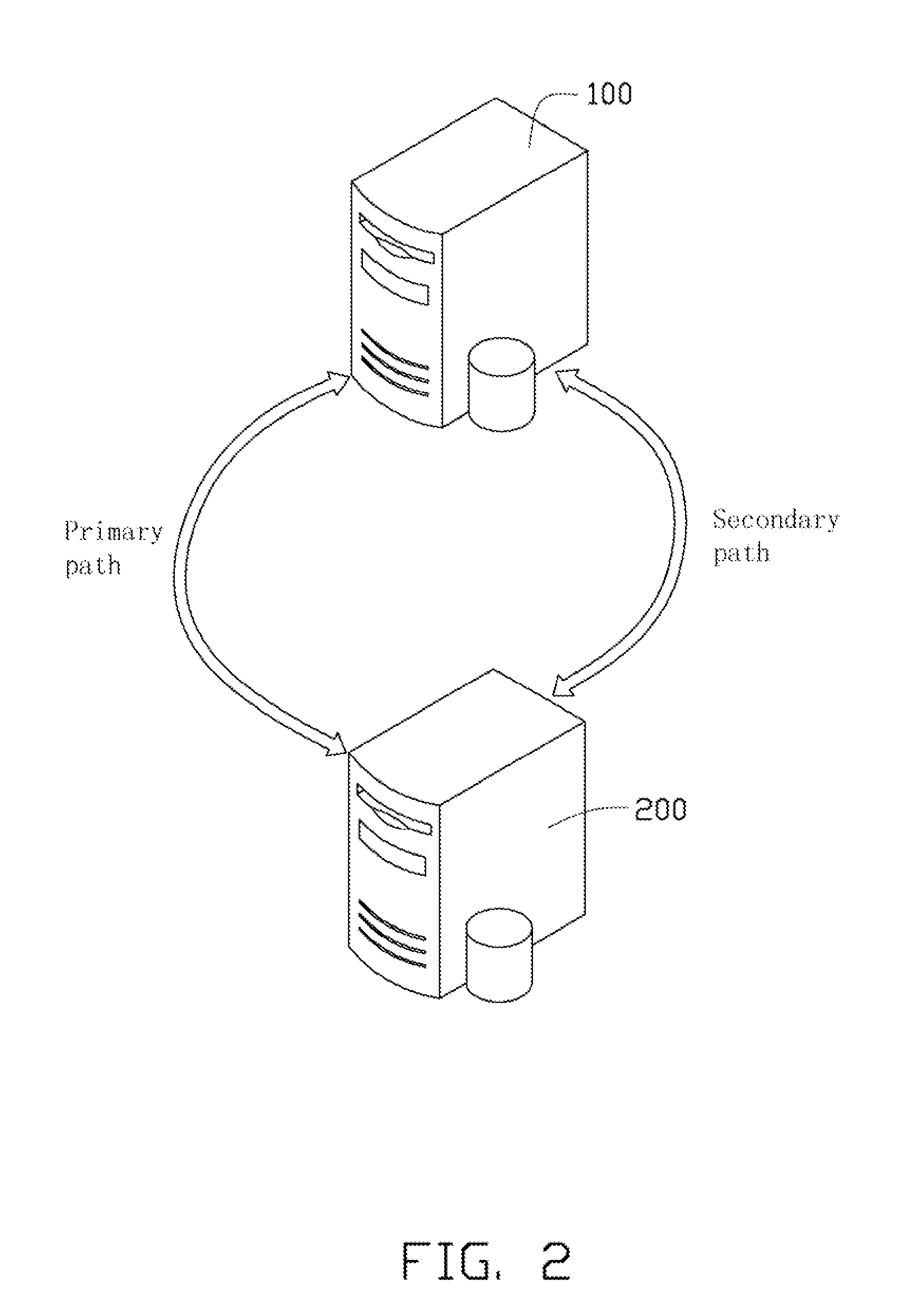
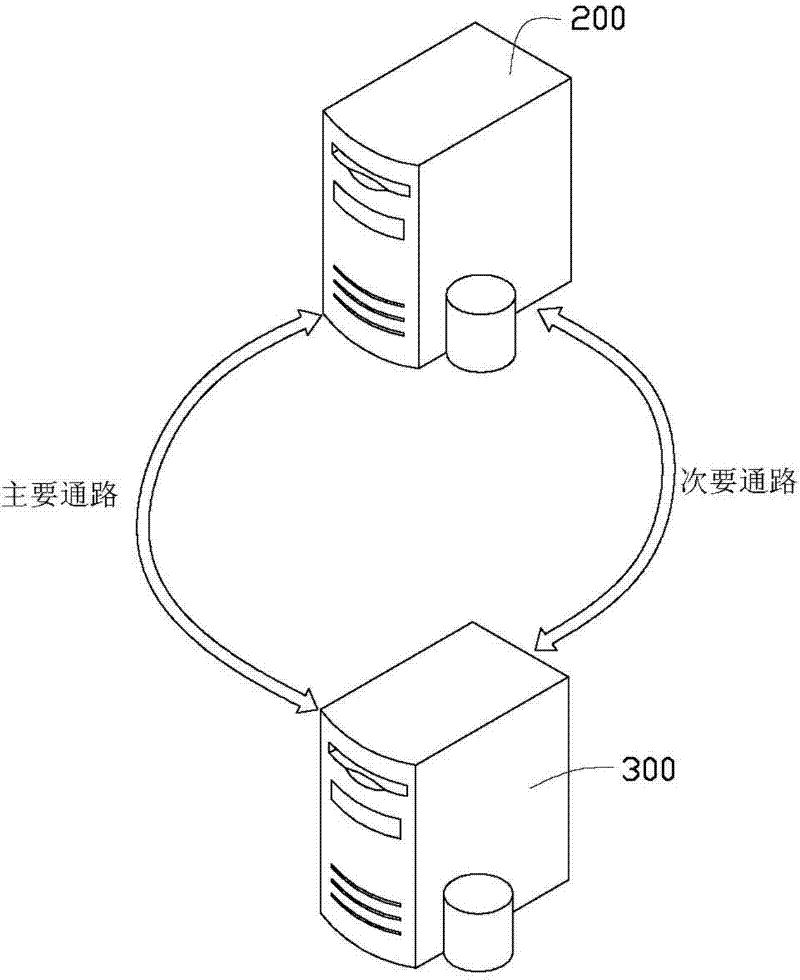
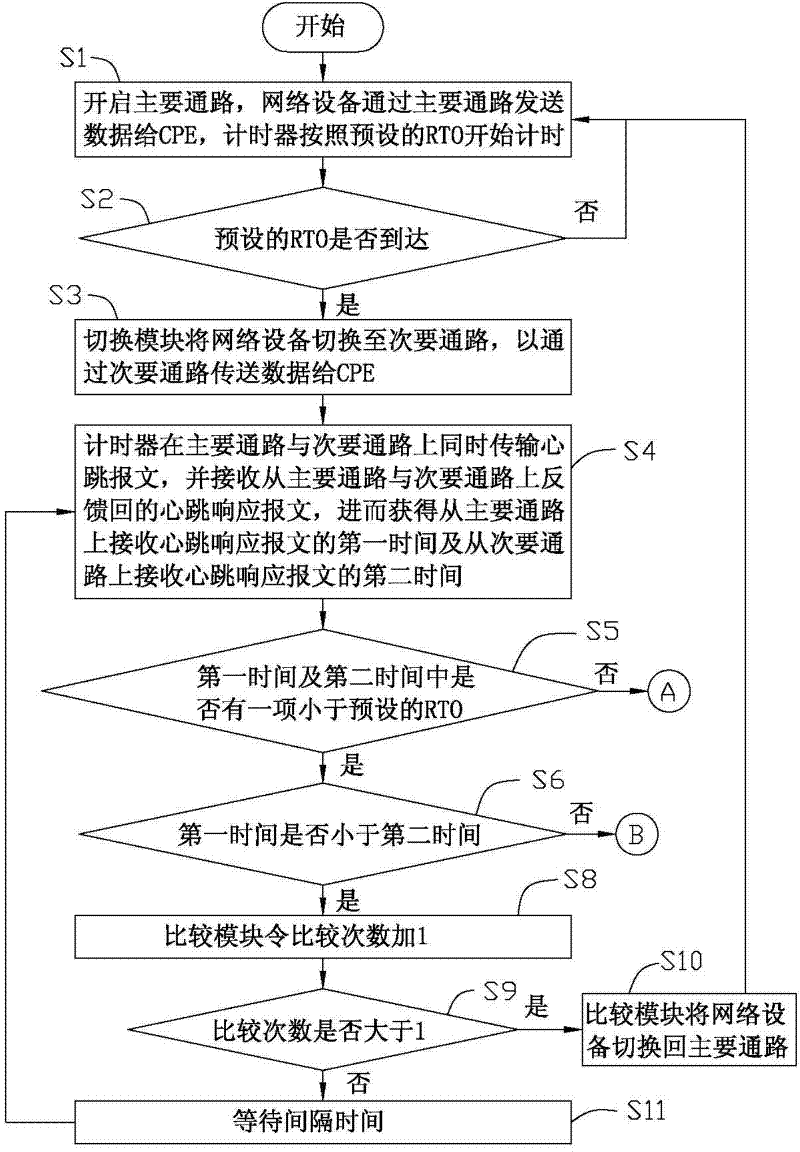
Network equipment and method for selecting communication path
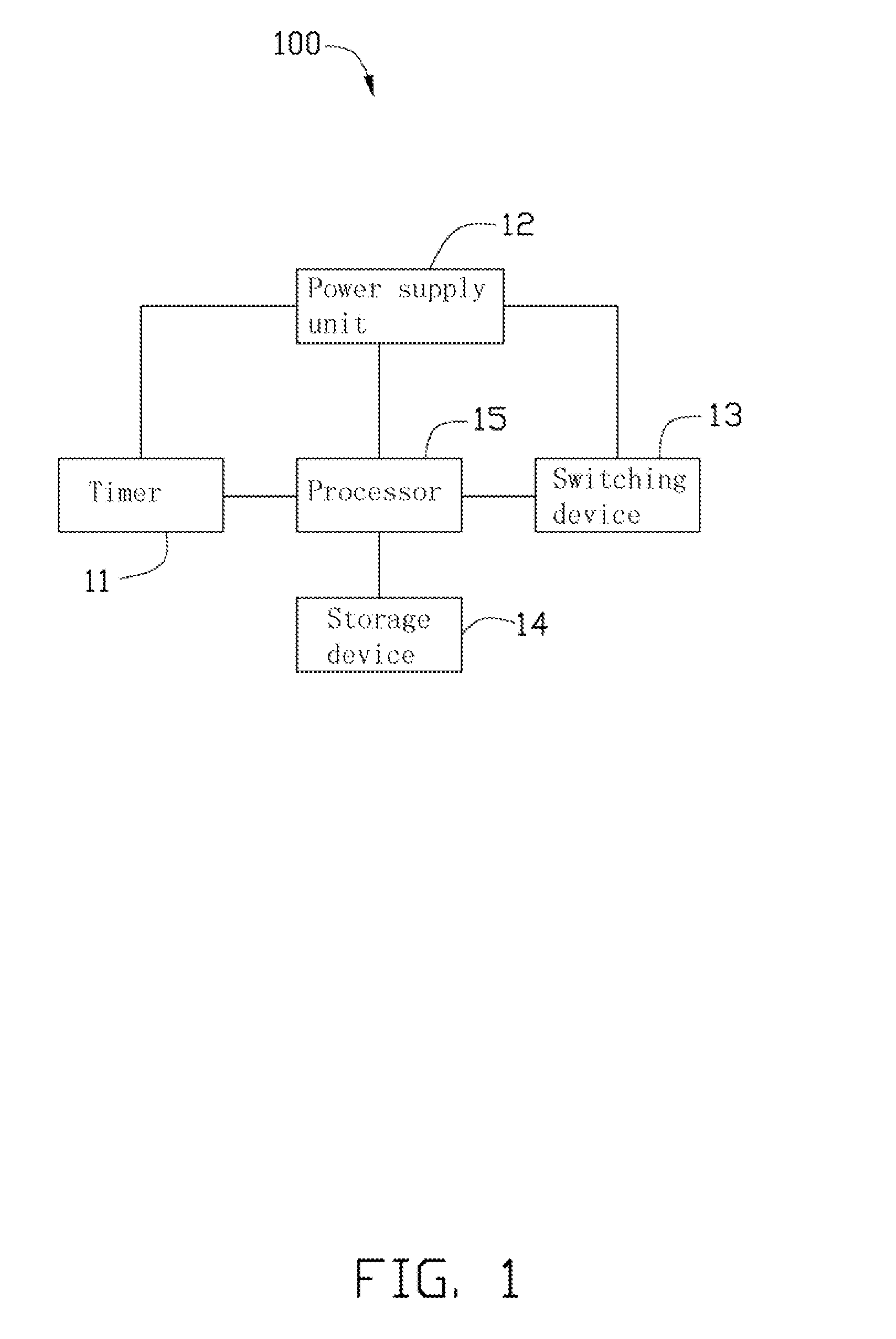
A network equipment is in communication with customer premises equipment (CPE) through a primary electrical path and a secondary electrical path, and includes a timer, a processor and a switching device. The timer provides heartbeat packets for the CPE via the primary electrical path and the secondary electrical path to obtain a first response time and a second response time corresponding to the primary and secondary electrical paths. The switching device is switched to the primary electrical path or the secondary path under the control of the processor. When the timer reaches a preset retransmission timeout, the processor controls the switching device to be switched to the secondary electrical path from the primary electrical path. When the second response time exceeds the first response time at least twice in succession, the processor enables the switching device to be selectively switched to the primary electrical path.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
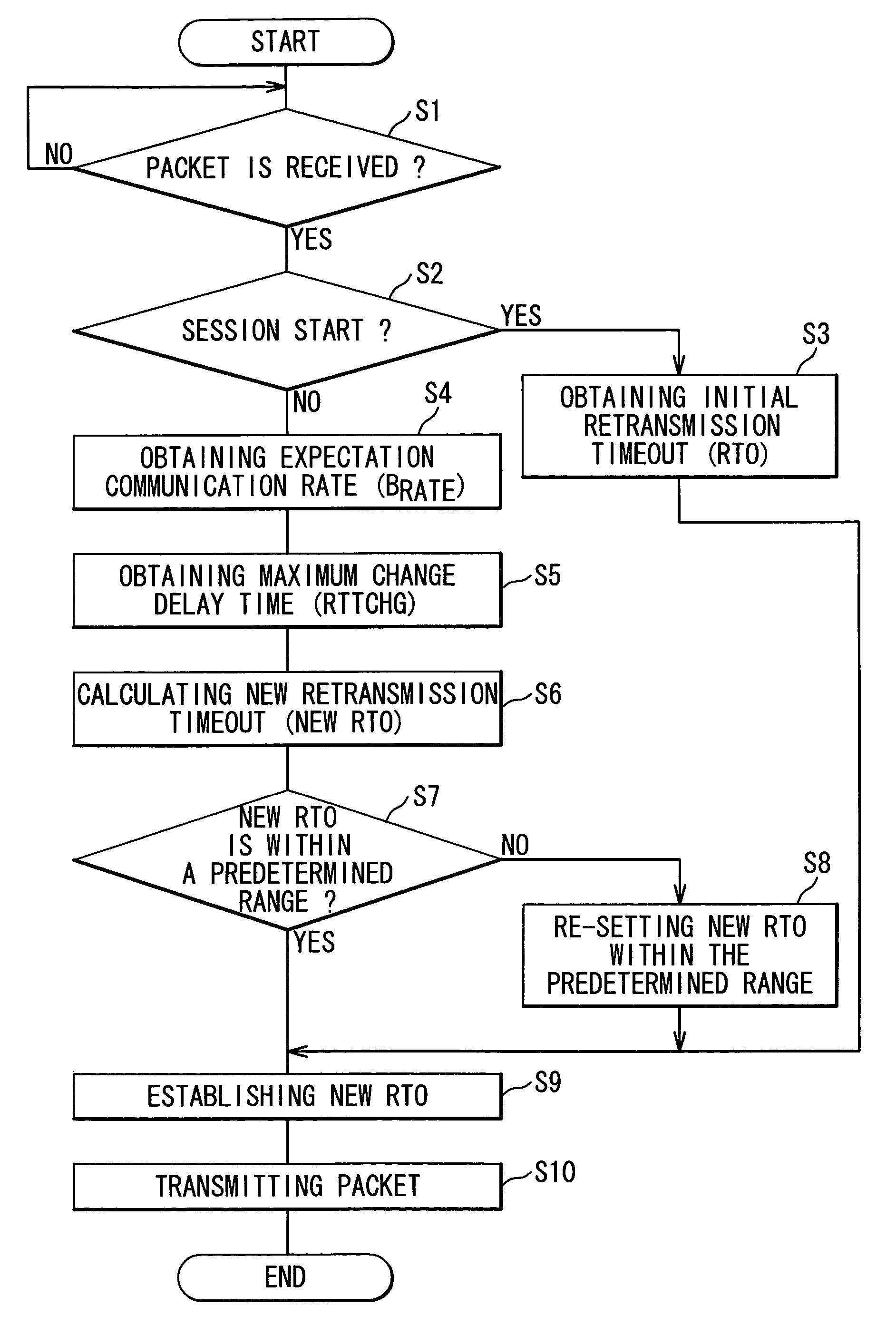
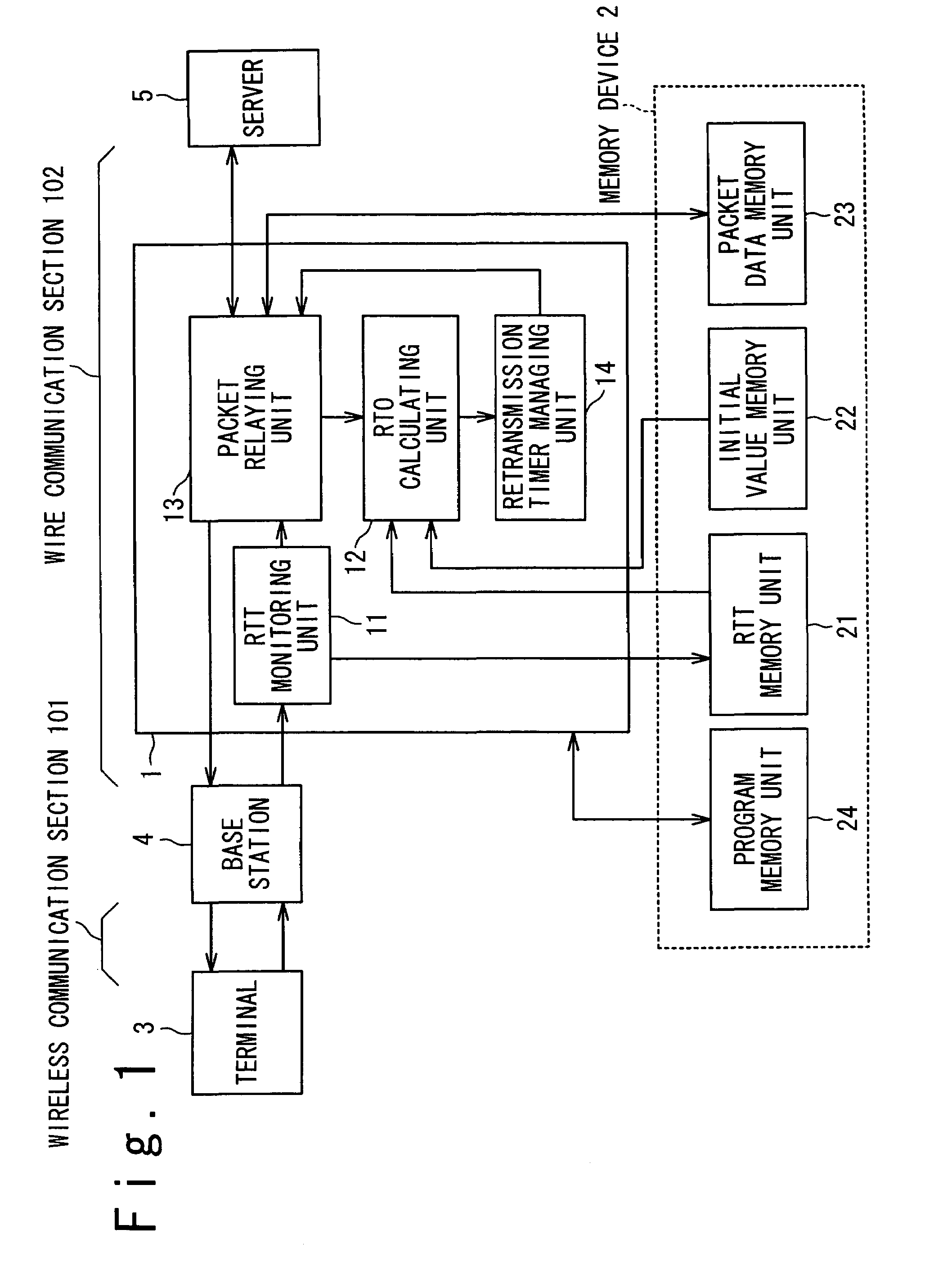
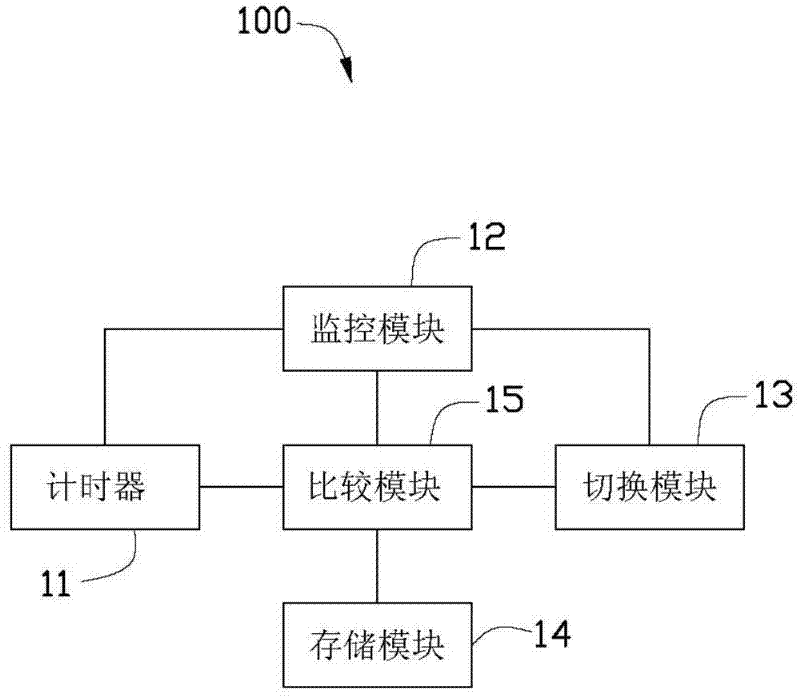
Wireless communication system and method which improves reliability and throughput of communication and retransmission timeout determining method
ActiveCN1551551AGood utilization rateShorten the timeError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemTrunking
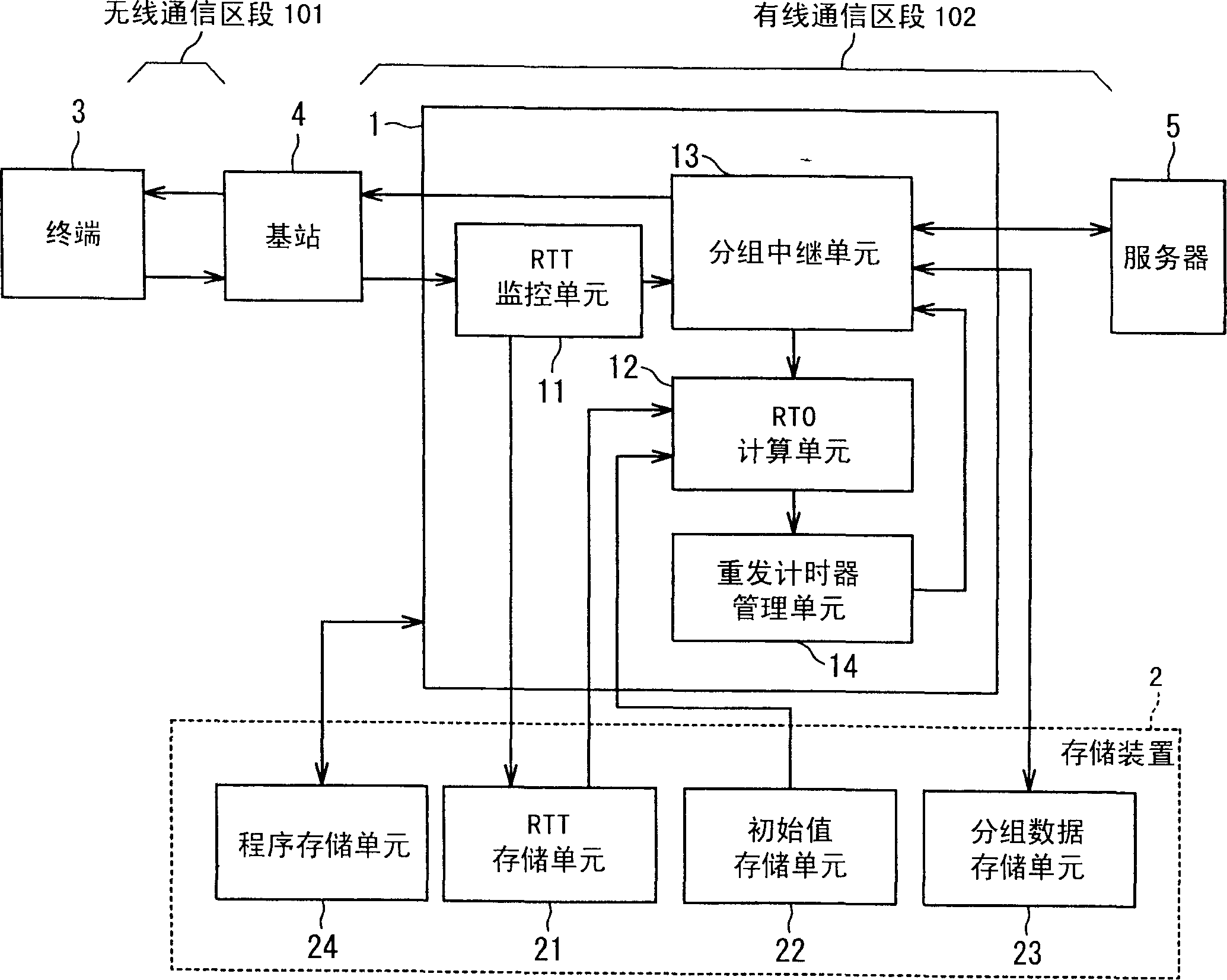
A wireless communication system includes a mobile terminal (3), a base station apparatus (4), a data relay apparatus (1) and a server apparatus (5). One of them includes a transmitting unit (13), a monitoring unit (11) and a determining unit (12). The transmitting unit (13) transmits a transmission data and receives an acknowledgement data (ACK) corresponding to the transmission data through a communication line (101+102). The monitoring unit (11) monitors the transmission data and the acknowledgement data (ACK). The determining unit (12) determines a retransmission timeout period (new RTO) based on a monitored result (Dsize, RTT) in a certain period. The transmitting unit (13) retransmits the transmission data when the acknowledgement data (ACK) is not received in the retransmission timeout period (RTO).
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
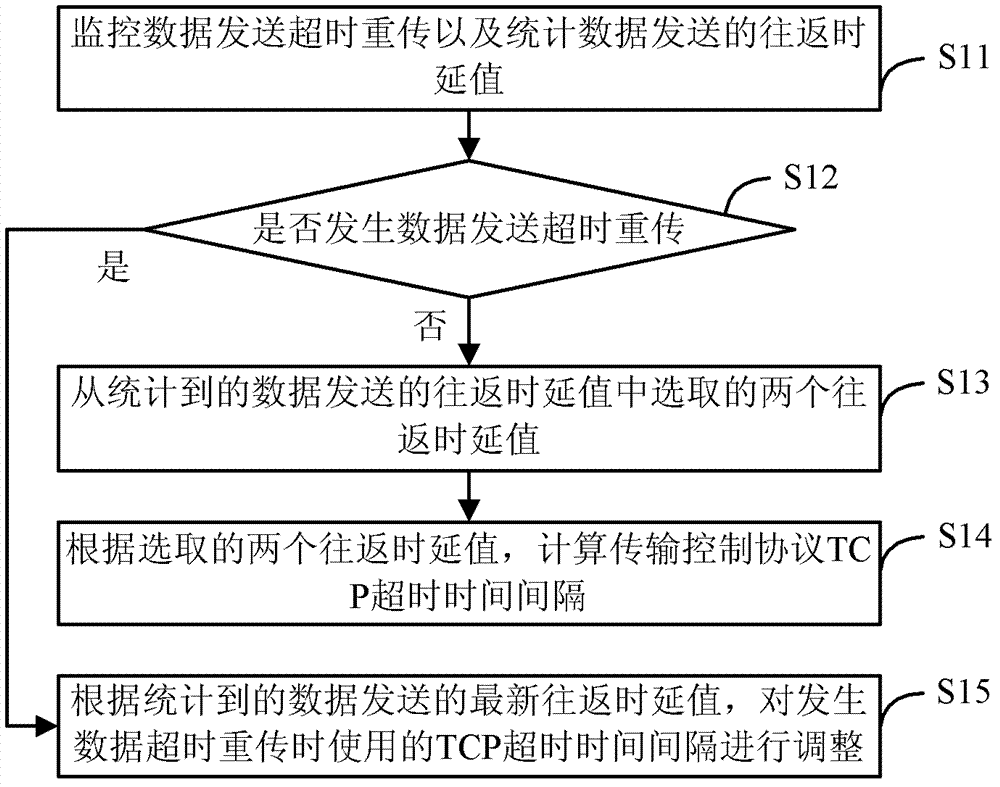
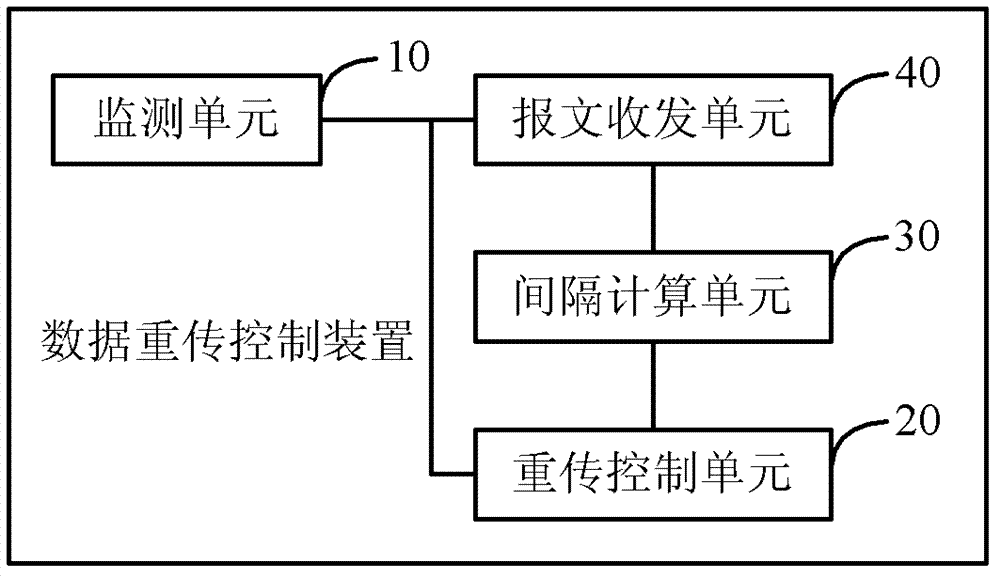
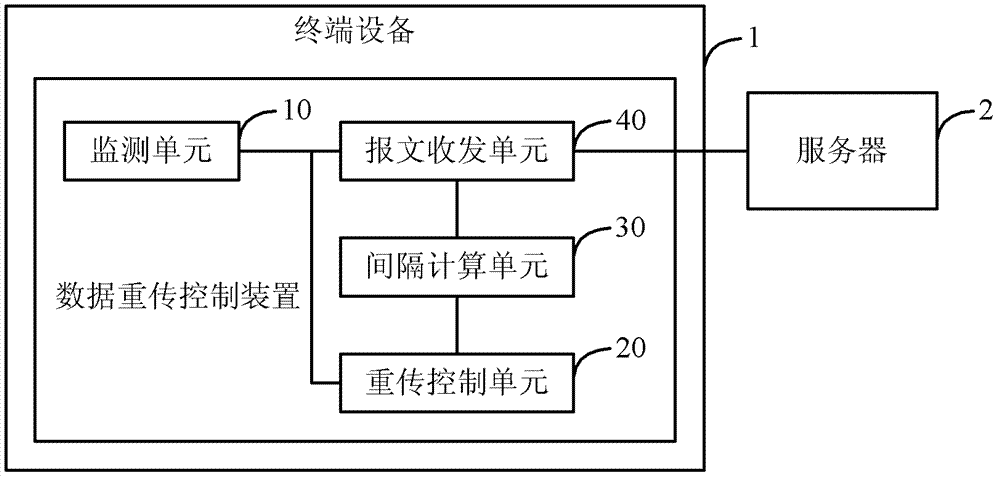
Data retransmission control method and device, and terminal equipment
ActiveCN103095434AFast transmissionAvoid excessive overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelTime delaysTerminal equipment
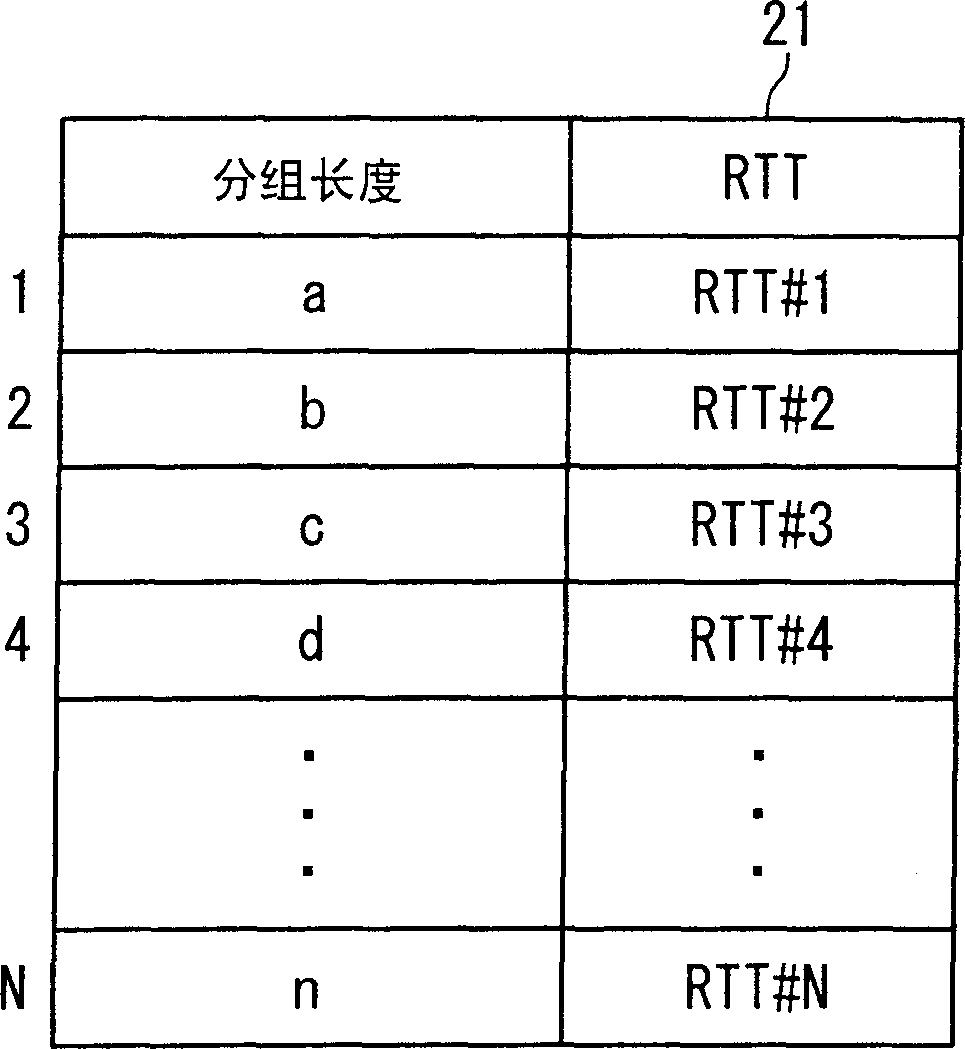
The invention discloses a data retransmission control method and a data retransmission control device, and terminal equipment. The method includes the steps: monitoring whether data sending retransmission timeout occurs; when the data sending retransmission timeout does not occur, calculating a transmission control protocol (TCP) time-out time interval according to two round-tripping time delay values which are selected from round-tripping values sent by data which are counted; after the data sending retransmission timeout occurs, a TCP time-out time interval which is used when the data sending retransmission timeout occurs is adjusted according to a newest round-tripping value sent by the counted data, and then obtaining the TCP time-out time interval which is after being adjusted. The method avoids that the time relay is too long or system overhead is too much.
Owner:山东汉鑫科技股份有限公司
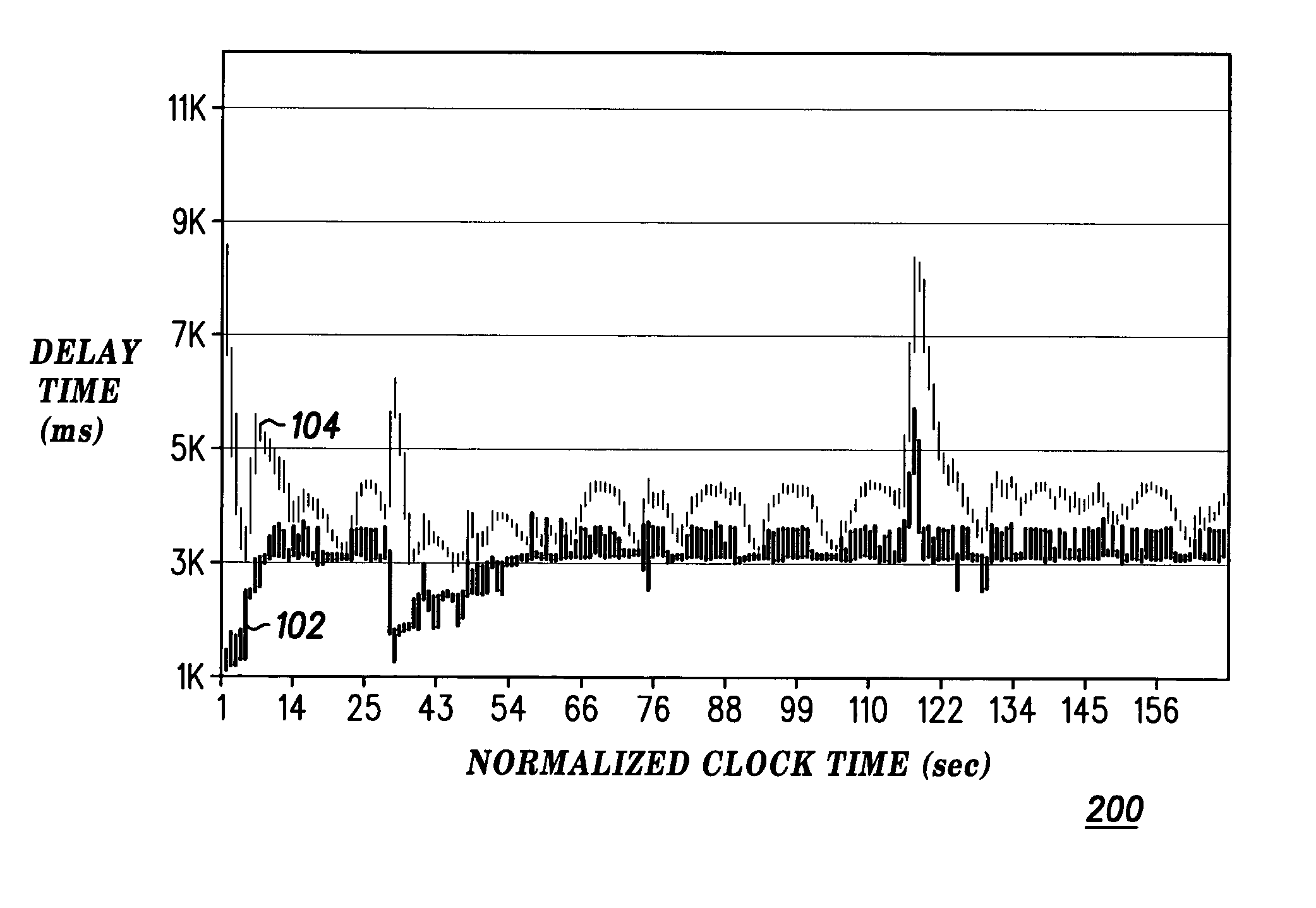
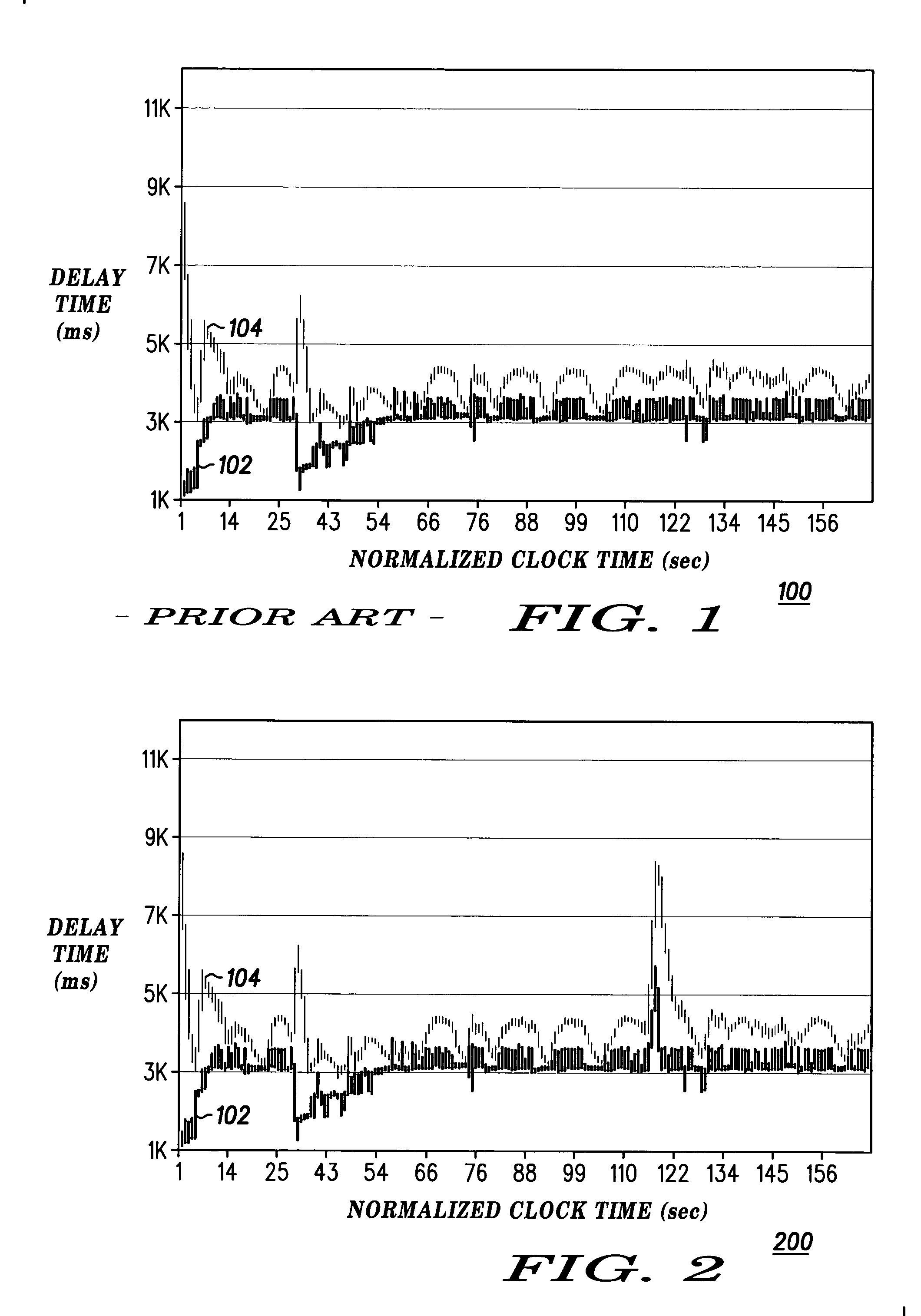
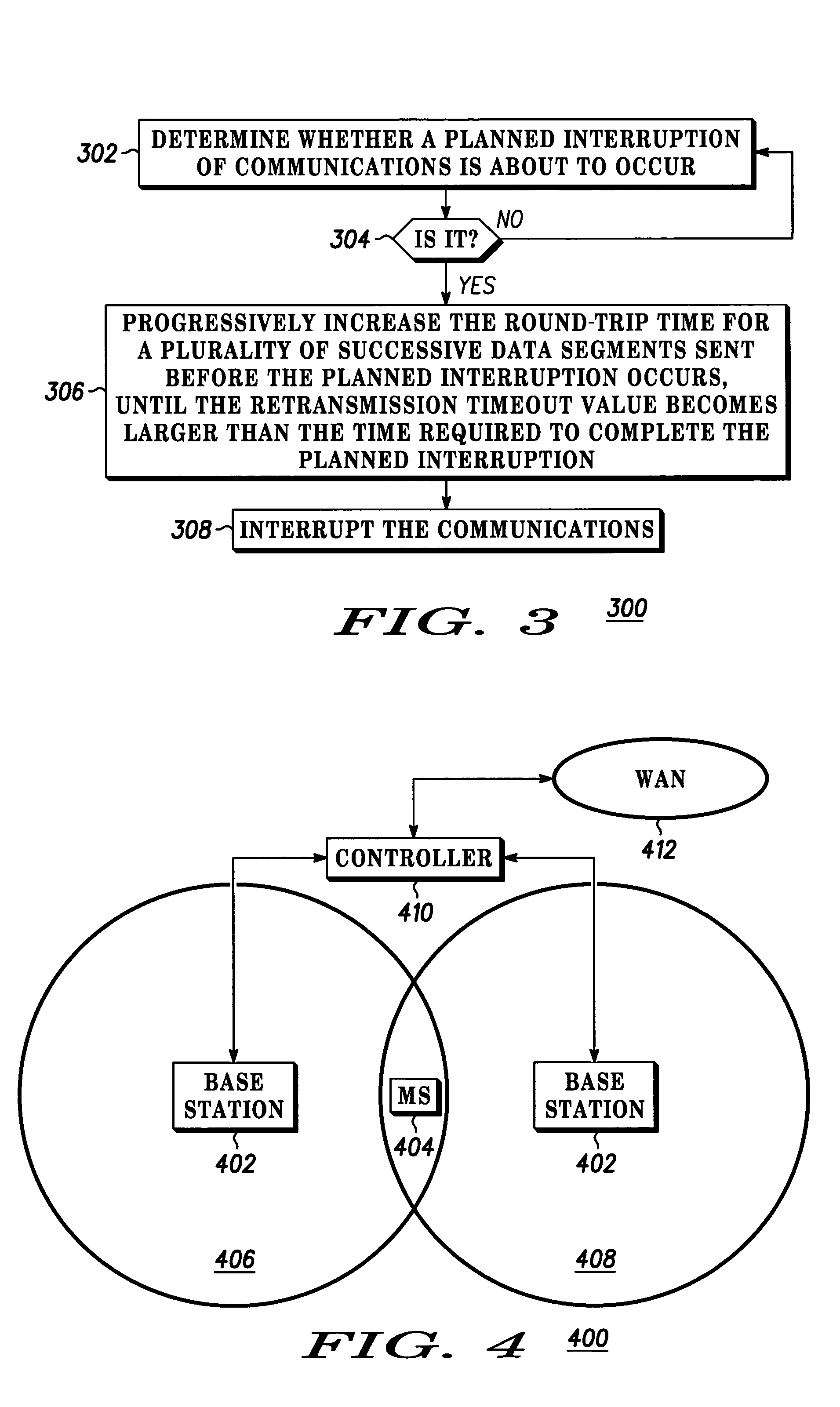
Method and apparatus for preventing a spurious retransmission after a planned interruption of communications
ActiveUS20050070246A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemData segment
In a wireless communication system (400), a mobile station (404) or a base station (402), or both working together, determine (302) whether a planned interruption in communications is about to occur; and, in response to determining that the planned interruption is about to occur, progressively increase (306) the round-trip time for a plurality of successive data segments sent before the planned interruption occurs, such that a retransmission timeout value calculated by a sender becomes larger than a time required to complete the planned interruption, thereby preventing a spurious retransmission.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
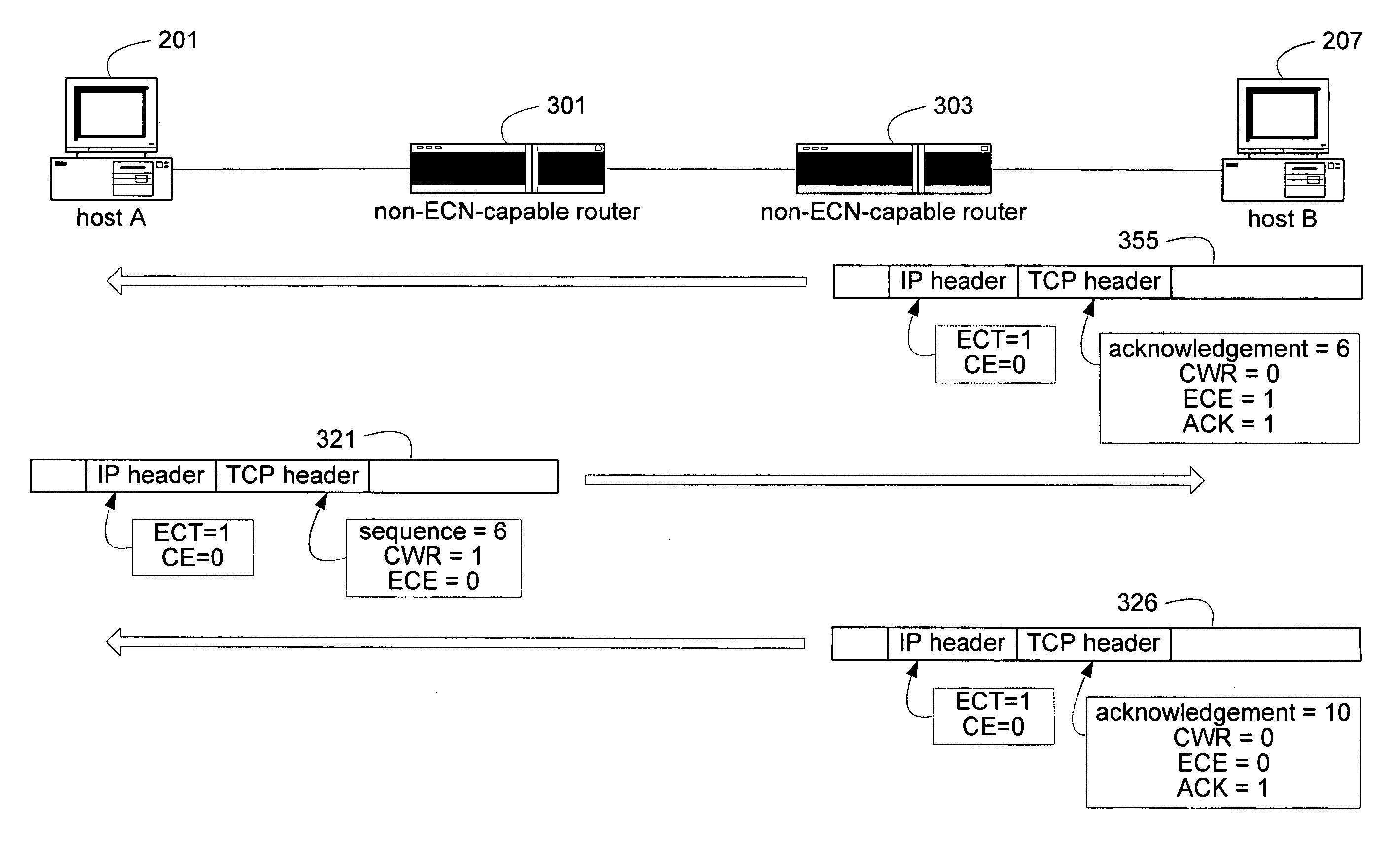
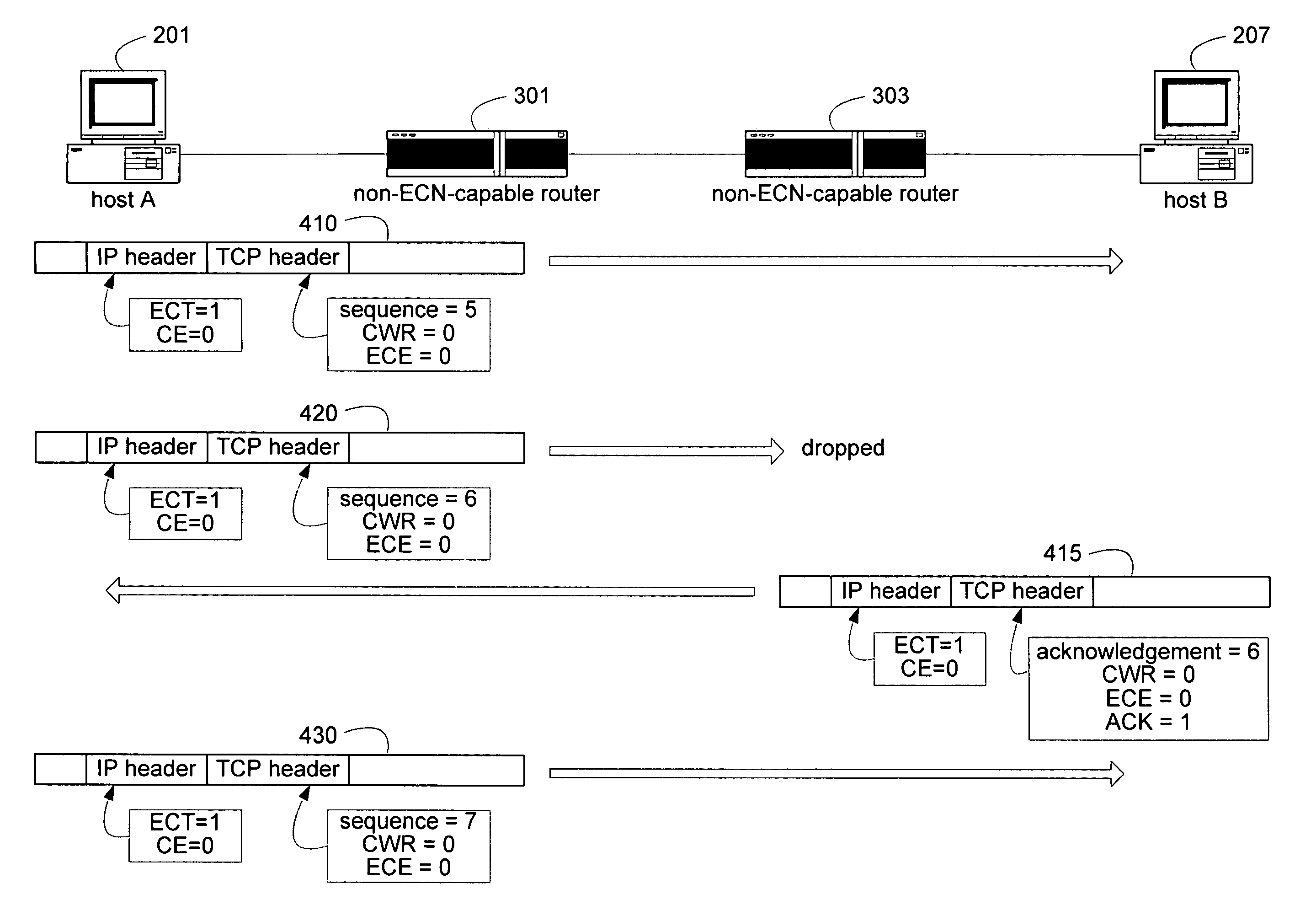
Unified congestion notification mechanism for reliable and unreliable protocols by augmenting ECN
A unified congestion notification mechanism can detect congestion at a recipient device either directly, such as via an explicit indicator, or indirectly, such as via dropped packets. Such congestion can then be indicated to the sending device either by leveraging an existing congestion notification mechanism, including by spoofing expected communications, or by creating a new congestion notification mechanism. Additionally, modifications to lossless protocols, such as TCP / IP can adapt them for use with streaming data while still implementing the unified congestion notification mechanism by eliminating retransmissions either as a result of the retransmission timeout or as a result of information conveyed as part of the acknowledgement packets.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Counterfeit TCP covert communication method based on SYN-ACK dual-server rebound pattern
InactiveCN103475706AMany optionsImprove concealmentError prevention/detection by using return channelIp addressCovert communication
The invention discloses a counterfeit TCP covert communication method based on an SYN-ACK dual-server rebound pattern. A covert information sending end is in communication with a covert information receiving end through a rebound server A or a rebound server B. A three-way handshake principle of connection is set up through a TCP, and covert information is embedded into a sequence number domain of the TCP and an acknowledgement number domain through a counterfeit source IP address and sent to a target end through rebound of the rebound server A. Meanwhile, the covert information feeds information back to the covert information sending end according to the modification operation of a sequence number and the modification operation of an acknowledge number and through the rebound server B, and the loss detection of the target end and the retransmission timeout of the target end are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
Wireless communication system which improves reliability and throughput of communication and retransmission timeout determining method used for the same
ActiveUS7417956B2Improve overall utilizationImprove throughputError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemDependability
A wireless communication system includes a mobile terminal, a base station apparatus, a data relay apparatus and a server apparatus. One of the mobile terminal, the base station apparatus, the data relay apparatus and the server apparatus includes a transmitting unit, a monitoring unit and a determining unit. The transmitting unit transmits a transmission data and receives an acknowledgement data corresponding to the transmission data through a communication line. The monitoring unit monitors the transmission data and the acknowledgement data. The determining unit determines a retransmission timeout period based on a monitored result by the monitoring unit in a certain period. The transmitting unit retransmits the transmission data when the acknowledgement data is not received in the retransmission timeout period.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Explicit flow control for implicit memory registration
ActiveUS9176911B2Digital computer detailsElectric digital data processingImplicit memoryComputer science
Methods, apparatus and systems for facilitating explicit flow control for RDMA transfers using implicit memory registration. To setup an RDMA data transfer, a source RNIC sends a request to allocate a destination buffer at a destination RNIC using implicit memory registration. Under implicit memory registration, the page or pages to be registered are not explicitly identified by the source RNIC, and may correspond to pages that are paged out to virtual memory. As a result, registration of such pages result in page faults, leading to a page fault delay before registration and pinning of the pages is completed. In response to detection of a page fault, the destination RNIC returns an acknowledgment indicating that a page fault delay is occurring. In response to receiving the acknowledgment, the source RNIC temporarily stops sending packets, and does not retransmit packets for which ACKs are not received prior to retransmission timeout expiration.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Adjusting to network latency changes
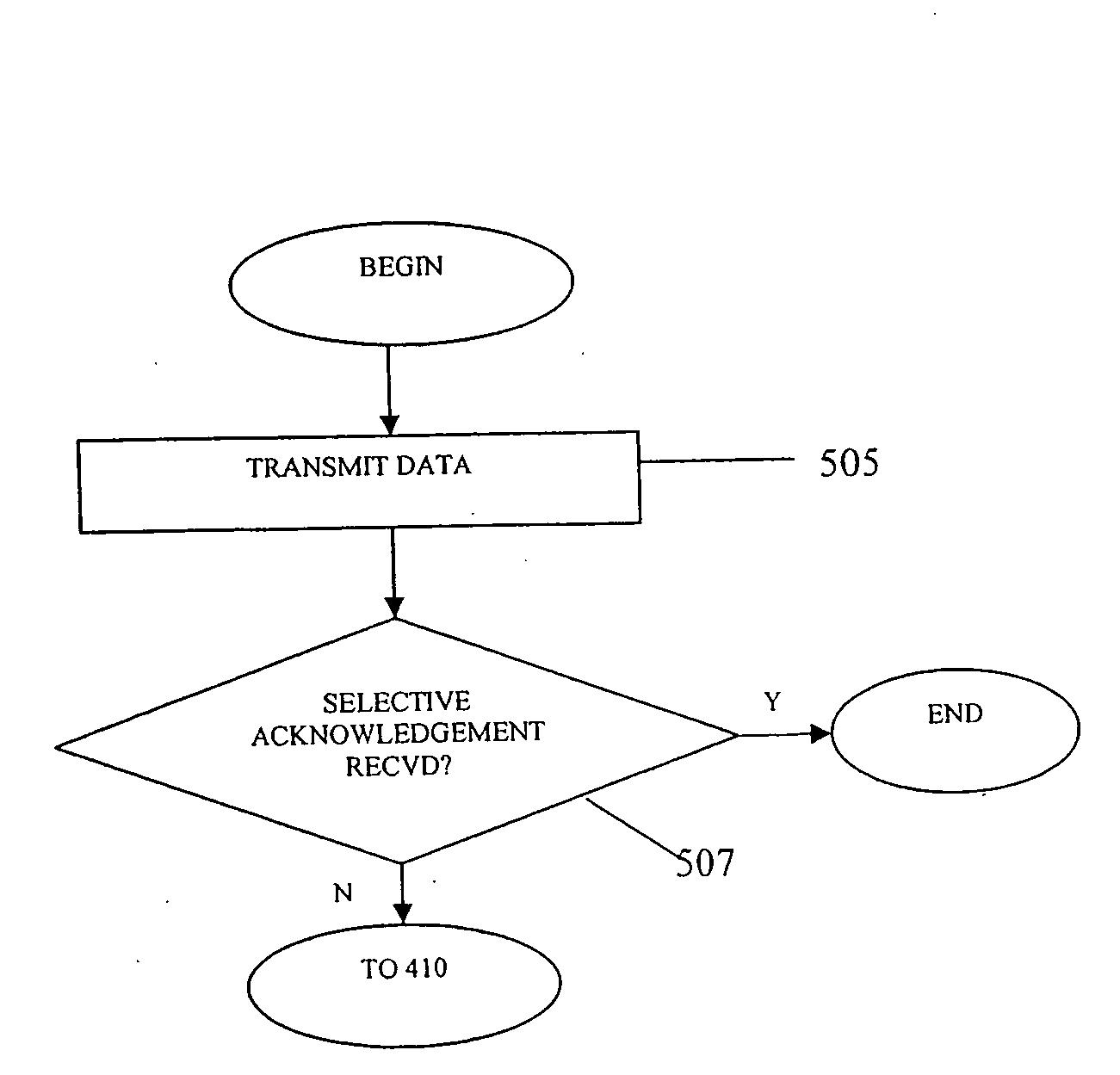
InactiveUS20080165684A1Promote recoveryError preventionTransmission systemsWaiting timeRetransmission timeout
Techniques are provided for adjusting to changes to the latency for a connection between two nodes on a network. In accordance with some embodiments, when a transmitting node encounters a retransmission timeout for a packet sent to a receiving node, the latency for the connection is newly measured and used to calculate a new retransmission timeout period for subsequent transmissions by the transmitting node. In some embodiments, the latency is not newly measured if the transmitting node receives a selective acknowledgement from the receiving node, since a selective acknowledgement may indicate that congestion on the network is only temporary.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for network transmission
InactiveUS20090245105A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient networkingError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityFuzzy rule
The method for the network transmission adjusts retransmission timeout timer (RTO) with the fuzzy rule to make the value of RTO change with network traffic. The method not only minimizes retransmission and lost packets, but also keeps utilization higher. The method is used to solve the congestion collapse problem in network transmission.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Method for setting the retransmission timeout period in a packet switched communication network
ActiveUS20060234644A1Improve performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsPacket switchedComputer science
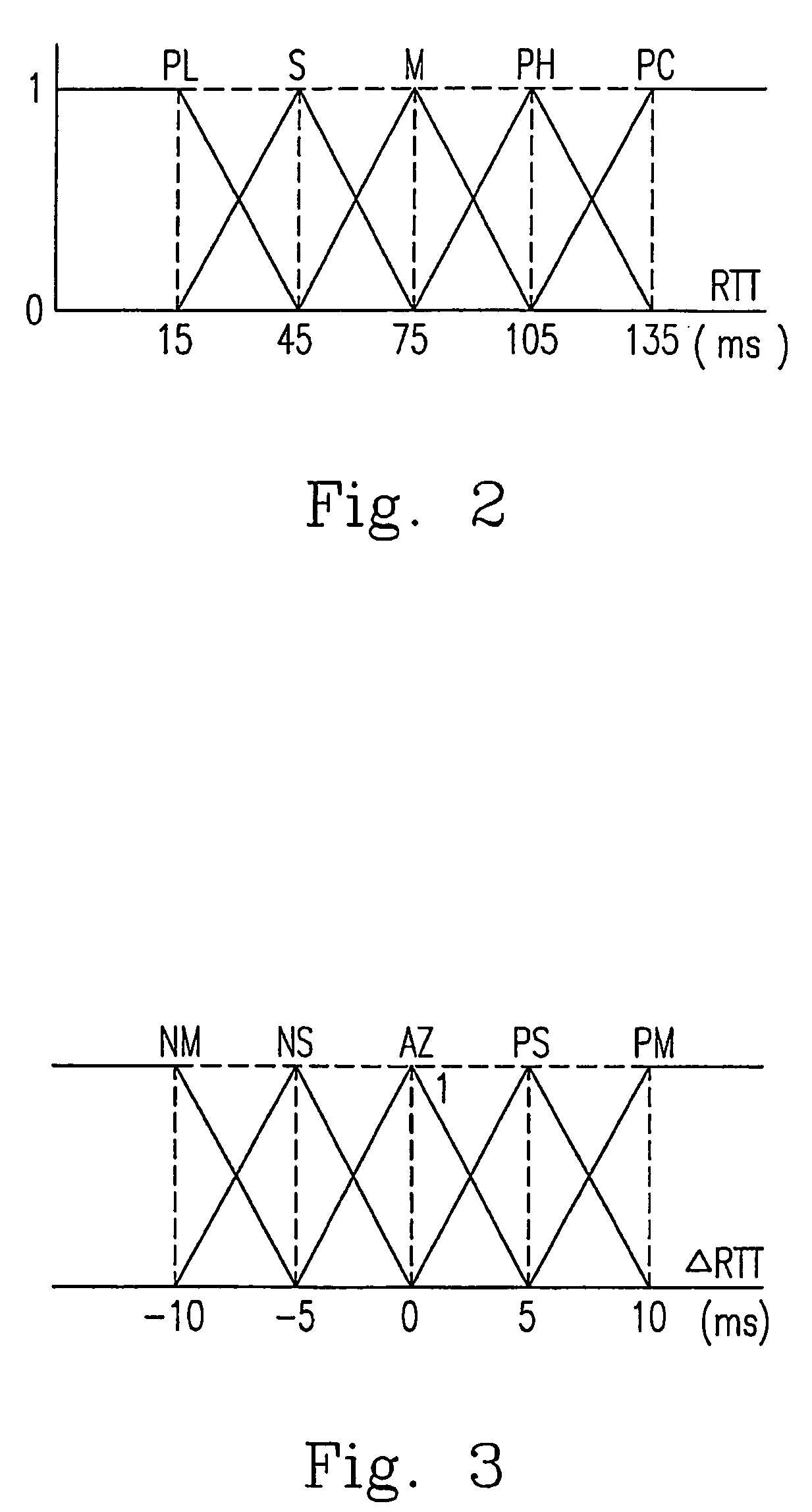
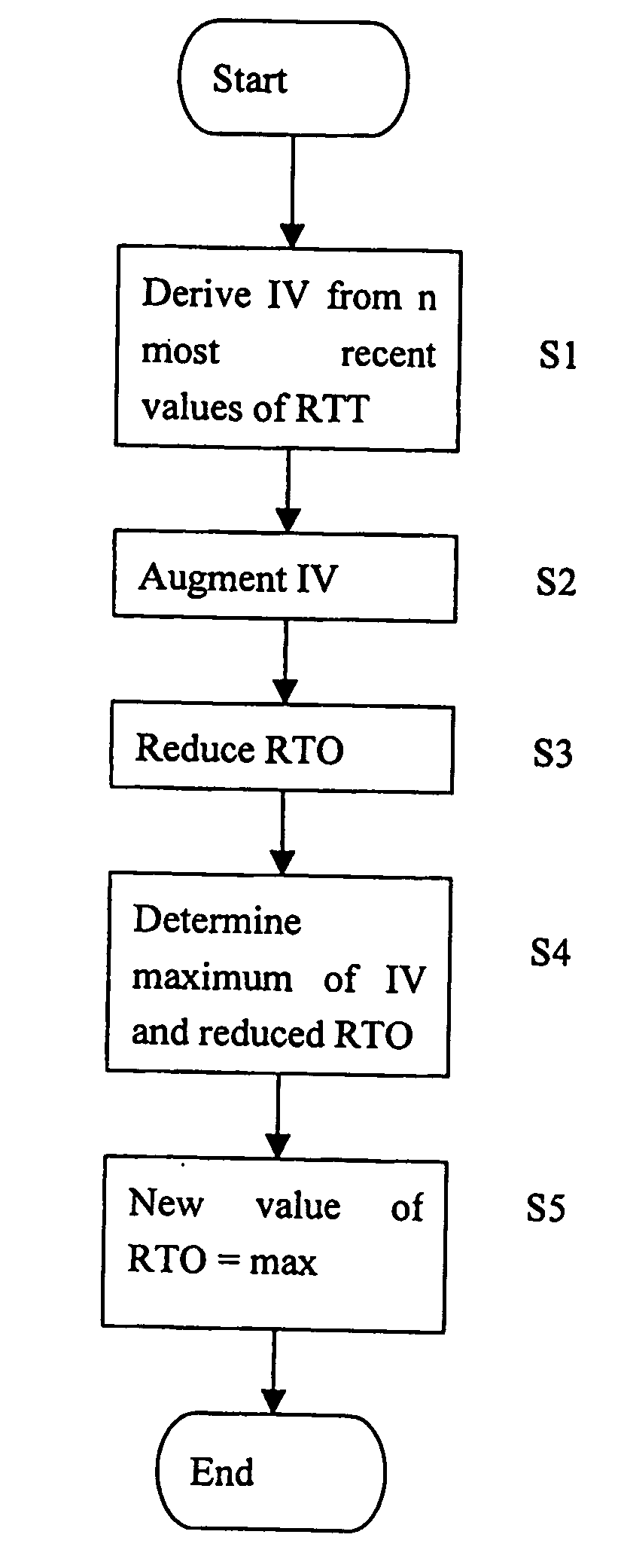
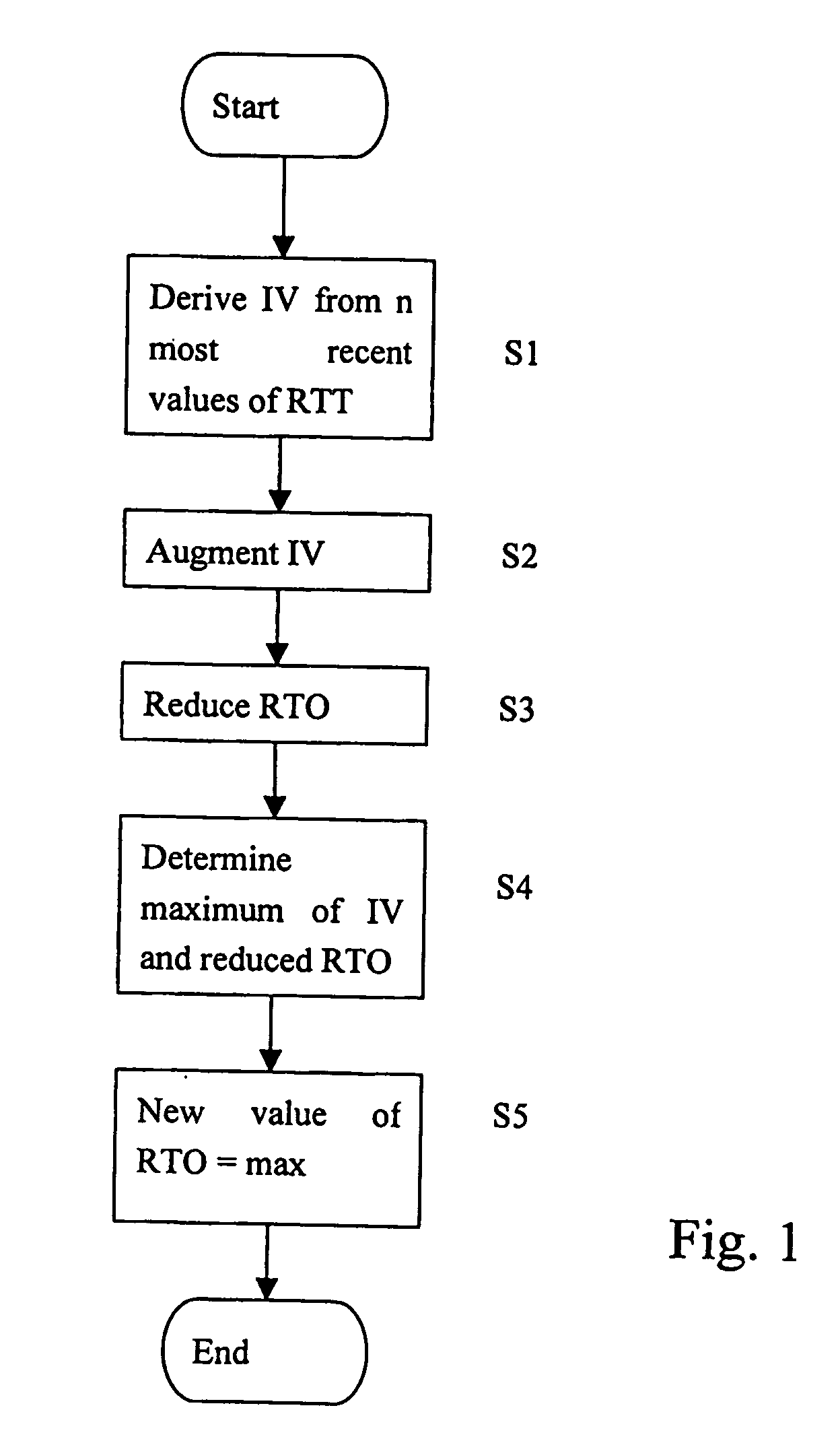
The present invention relates to a method for updating the value of a time-out period in a data unit sender. The updating comprises deriving an intermediate value from the n most recently measured values of a response time, augmenting the intermediate value, reducing the current value of the time-out period, determining the maximum from among at least the augmented intermediate value and the reduced current value of the time-out period, and setting a new value of the time-out period to set a maximum value.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Message transmission method and user equipment
ActiveCN106656431AReduce loss rateReduce the number of timeout retransmissionsError prevention/detection by using return channelError prevention/detection by transmission repeatPacket lossUser equipment
The invention discloses a message transmission method and user equipment. The method includes the following steps: a sending node transmits a plurality of messages to a receiving node, receives a plurality of confirmation messages from the receiving node, and after determining that a first message is lost based on the received plurality of confirmation messages, retransmits the first message; and if packet loss of the retransmitted message is detected, the sending node continuously retransmits the first message to the receiving node at least twice within a predetermined time interval. The scheme of the invention enables the retransmitted message to be timely detected and recovered after packet loss occurs, reduces the number of times of retransmission timeout, improves the transmission rate, at the same time, reduces the packet loss probability of the retransmitted message, and reduces the probability of retransmission timeout.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
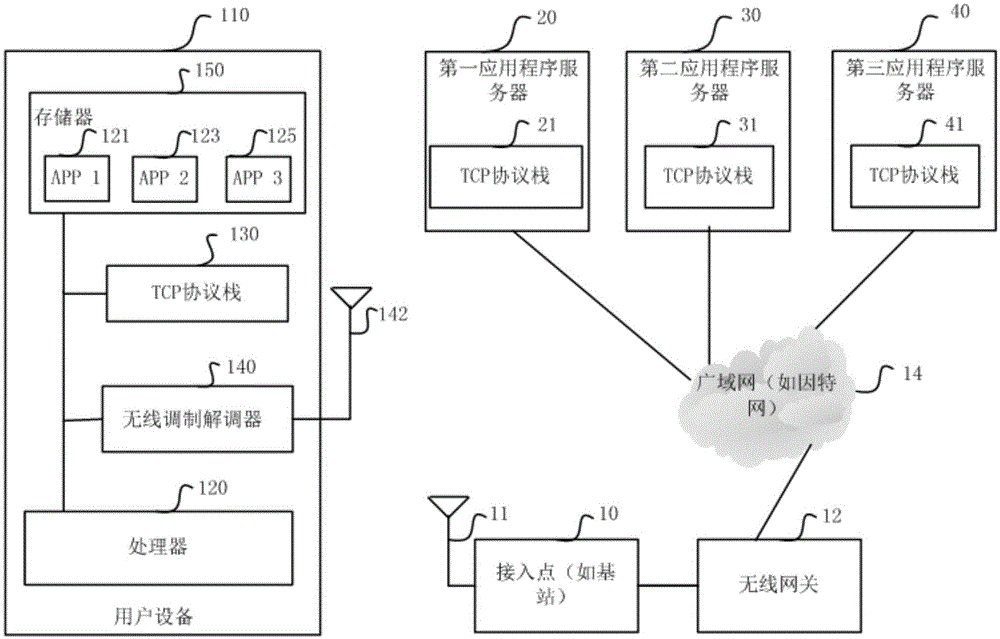
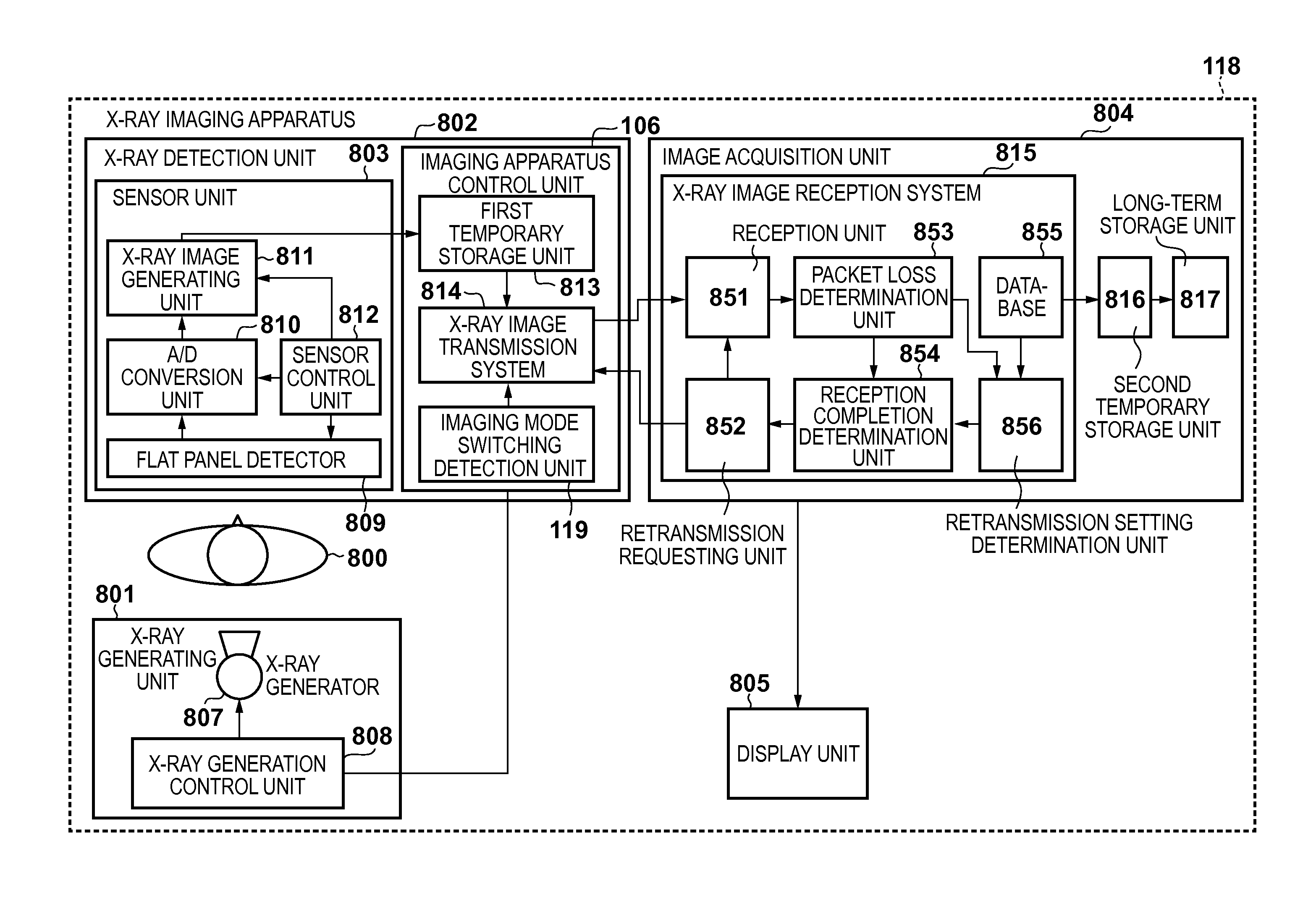
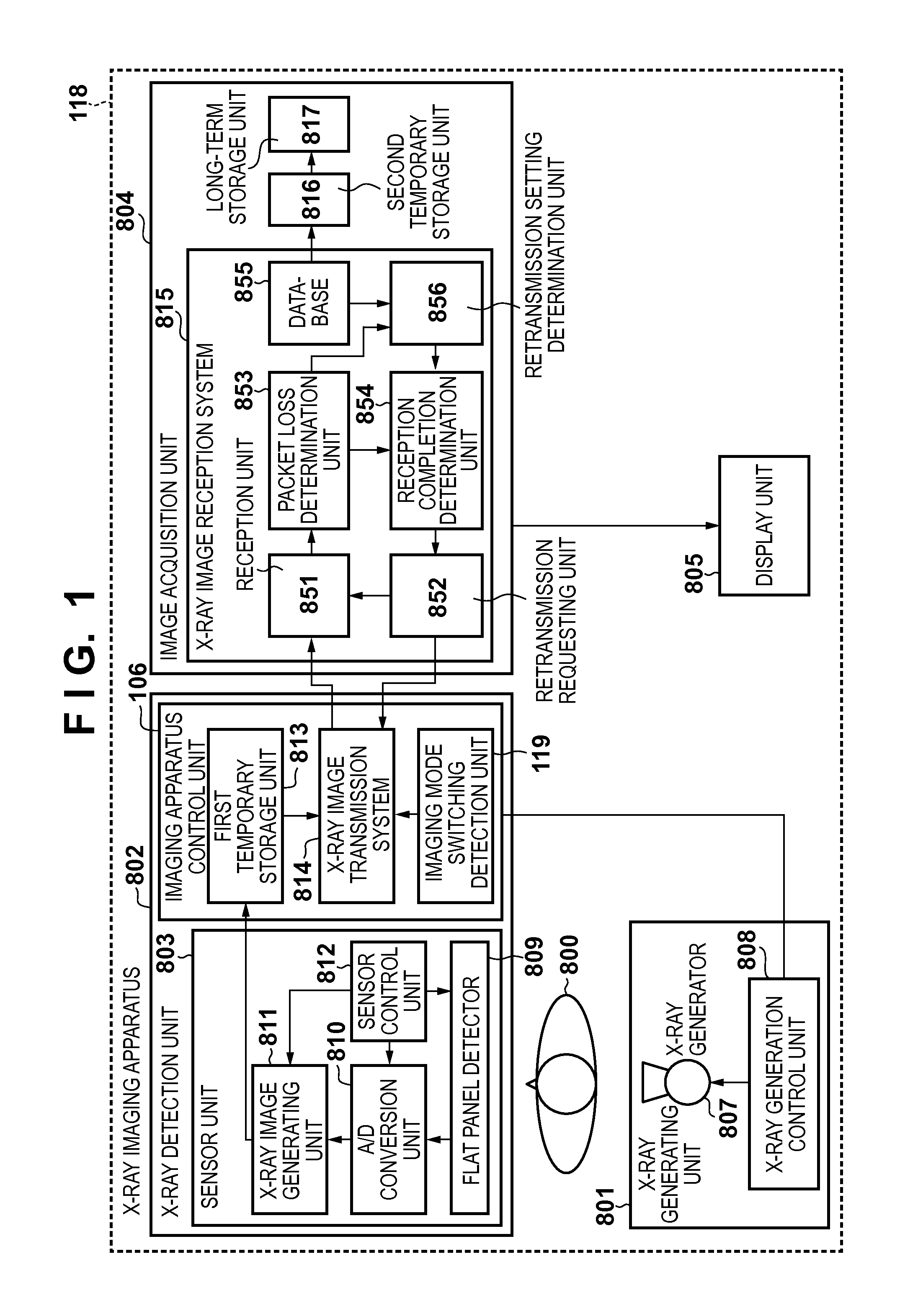
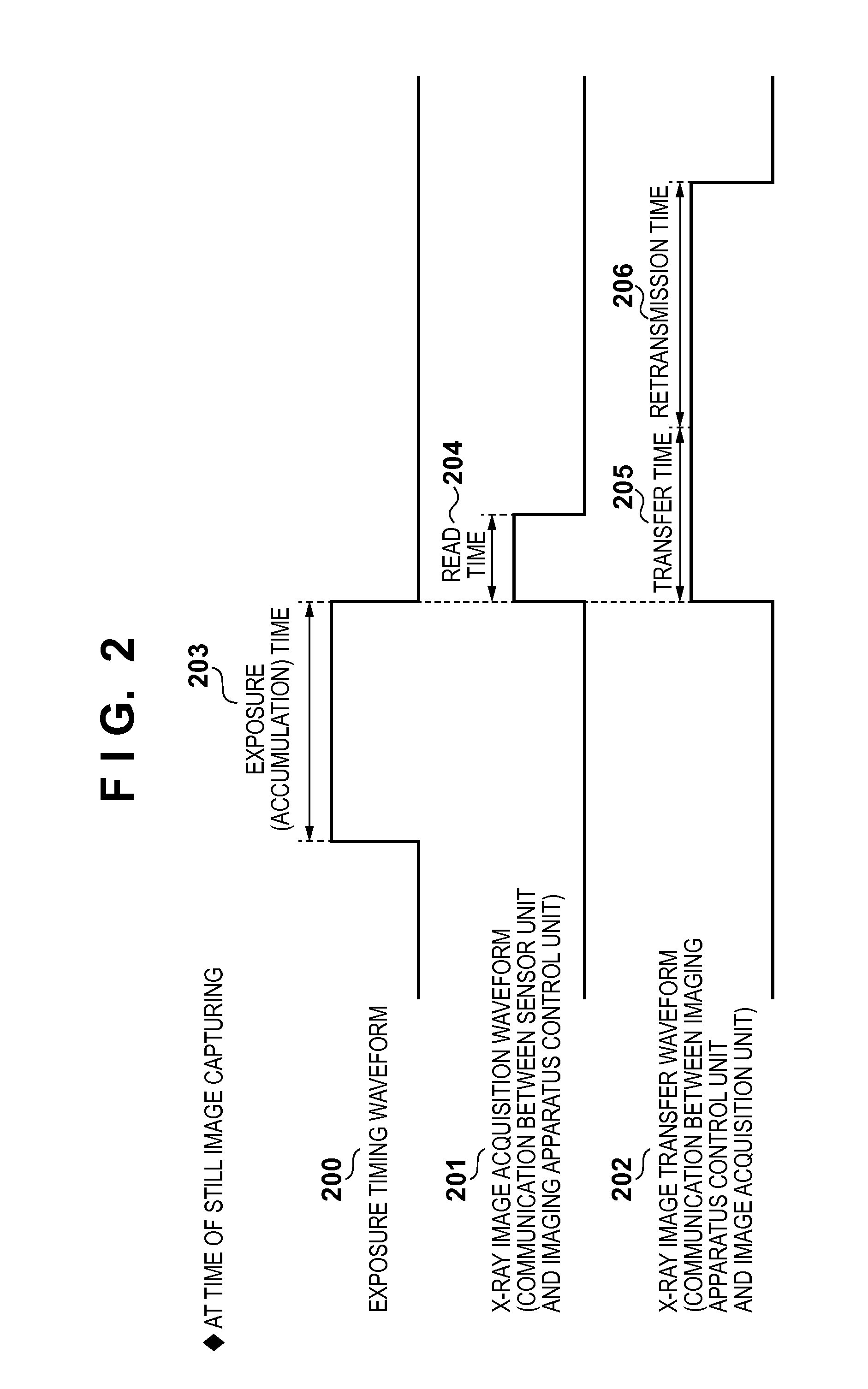
X-ray imaging apparatus, control device, radiation imaging apparatus, and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20130230141A1Reduce delaysTelevision system detailsReconstruction from projectionRadiation imagingX-ray
For image data being transferred last of a plurality of image data captured in a first imaging mode, a retransmission timeout time is set different from a retransmission timeout time for at least one image data different from image data, of the plurality of image data, which is transferred last.
Owner:CANON KK
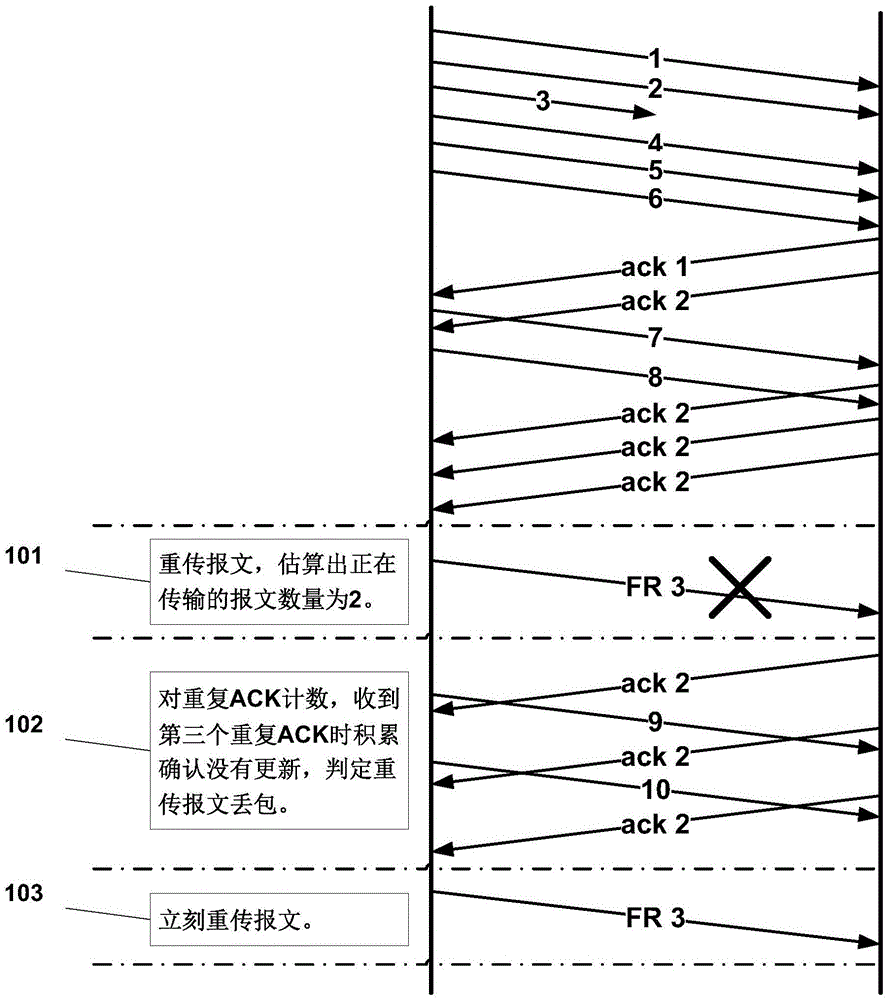
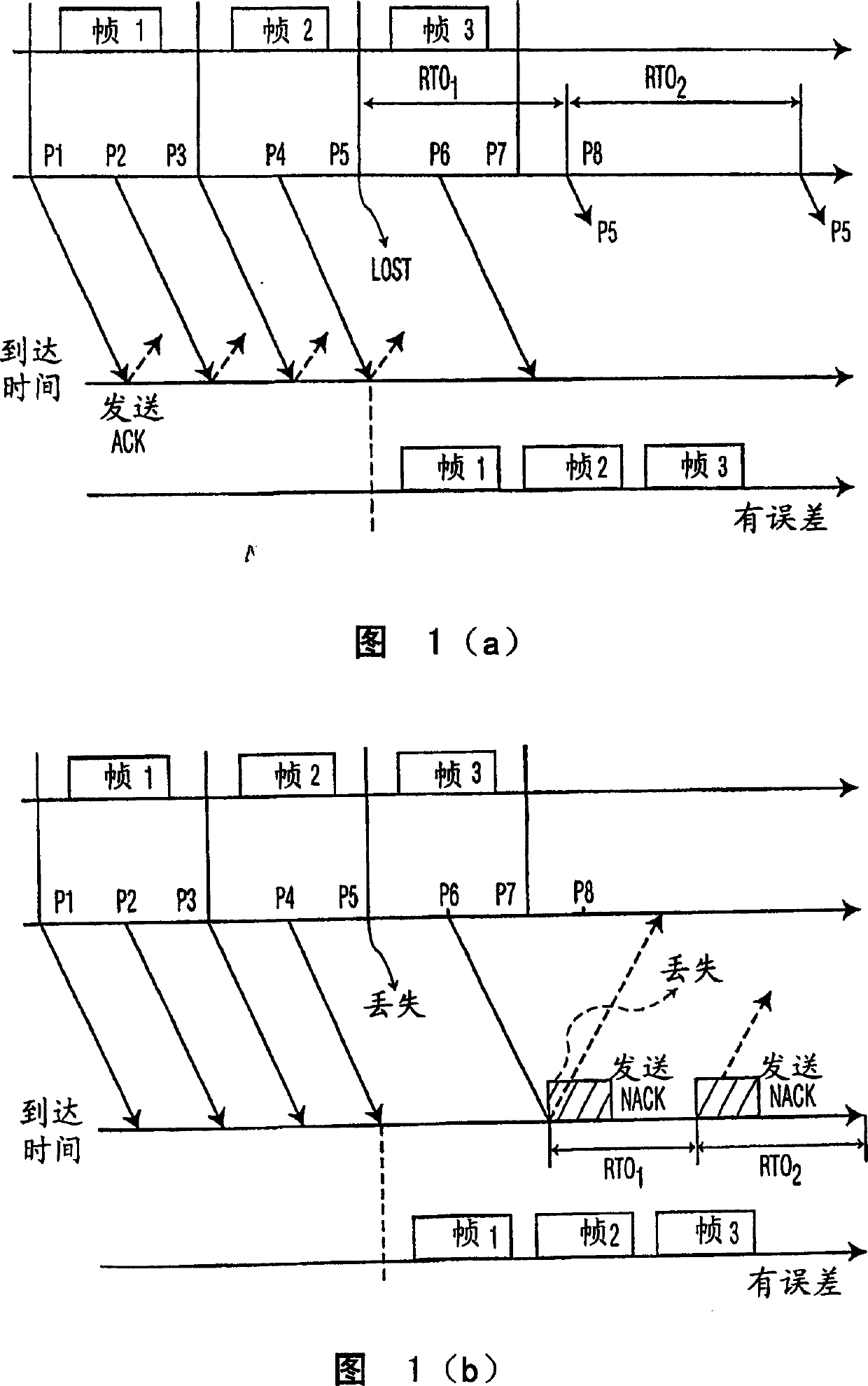
Method for efficient retransmission timeout estimation in NACK-based protocols
InactiveCN1430833AError prevention/detection by using return channelAdaptation strategy characterisationTTEthernetThe Internet
Disclosed is a system and method for estimating retransmission timeout (RTO) in a real-time streaming applications over the Internet between a server and a client. Accordingly, the present invention employs retransmission timeout (RTO) in NACK-based applications to support multiple retransmission attempts per lost packet, wherein the RTO is estimated by an actual around-trip delay (RTT) and a smooth inter-packet delay variance.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for sending ACK
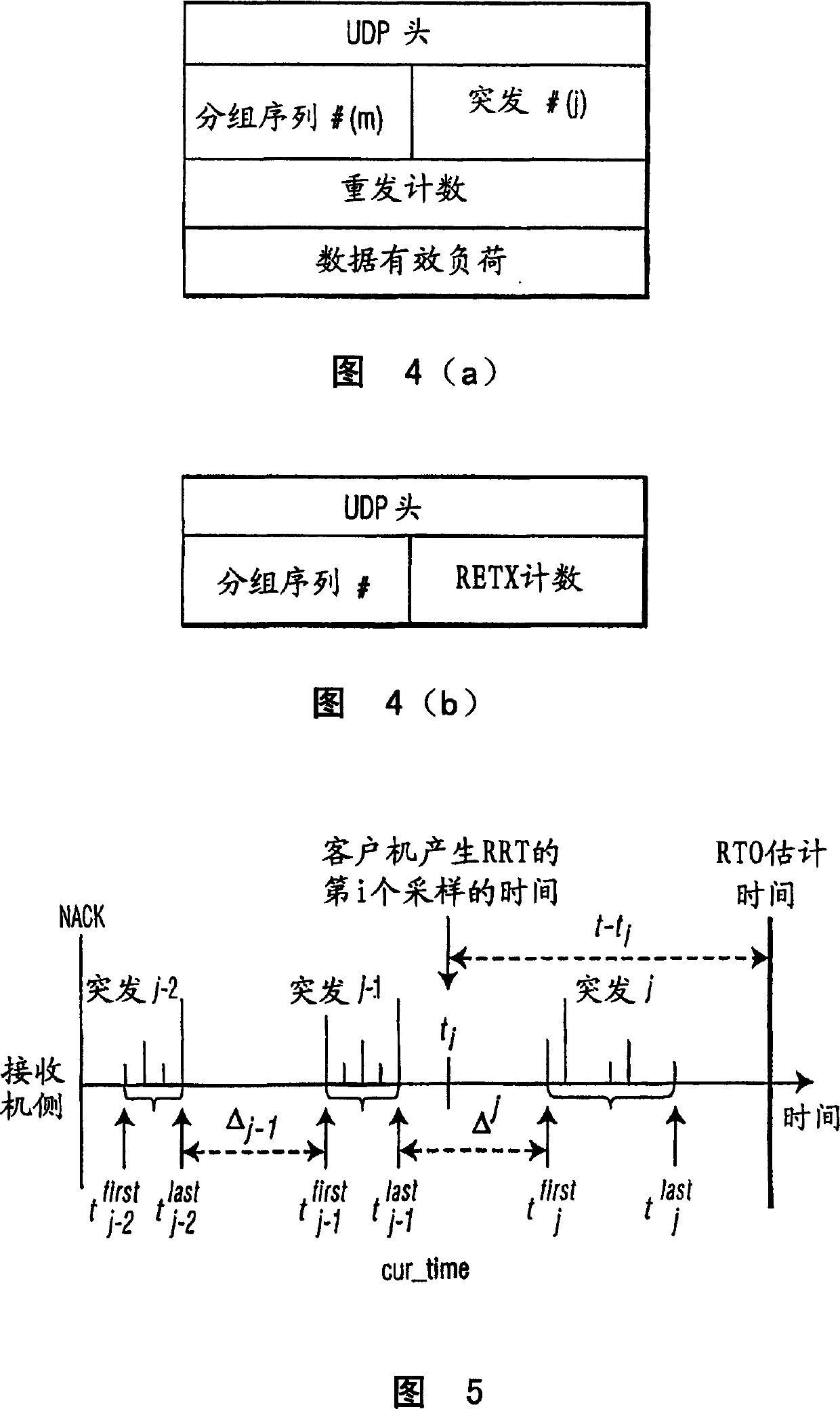
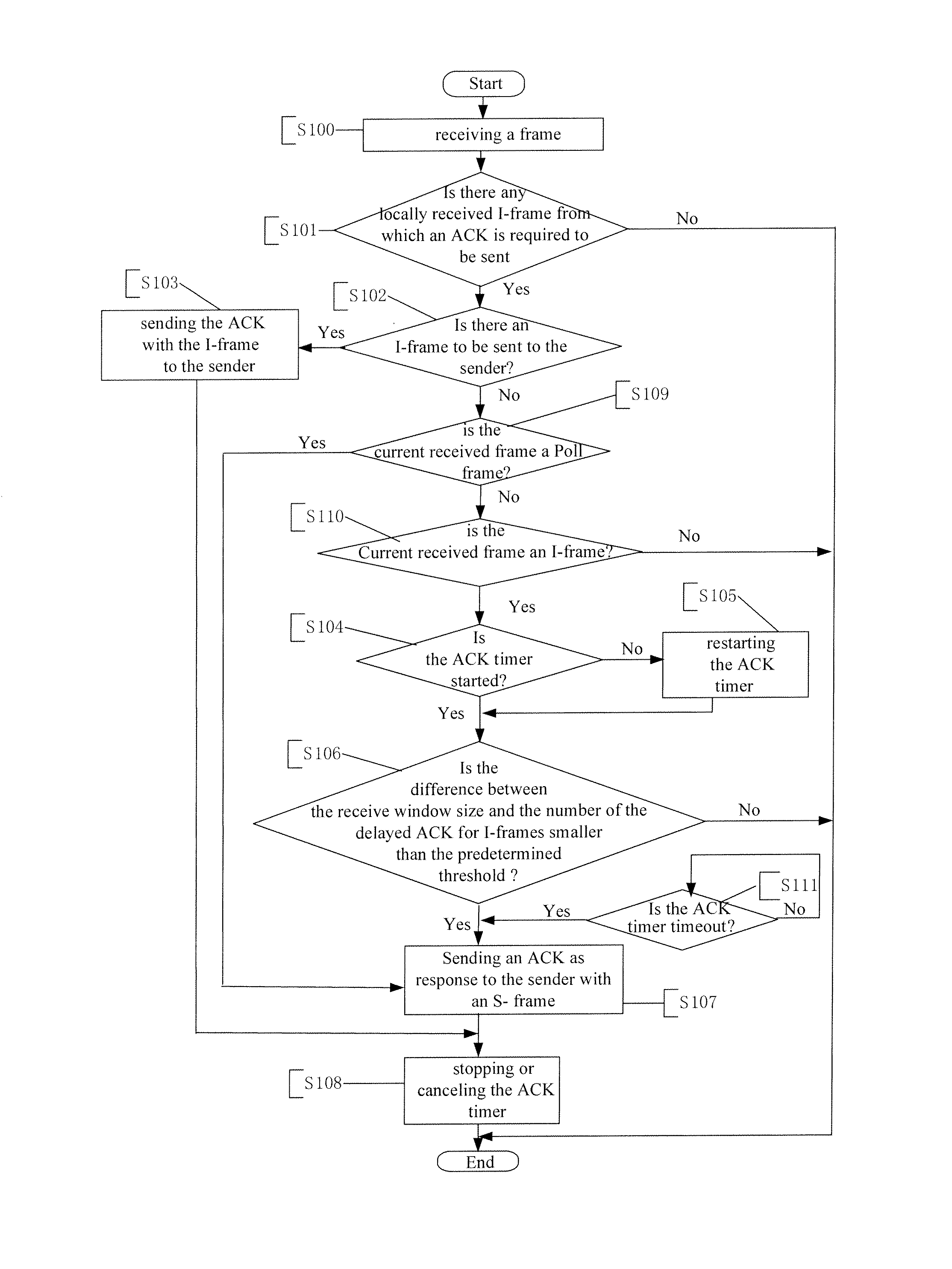
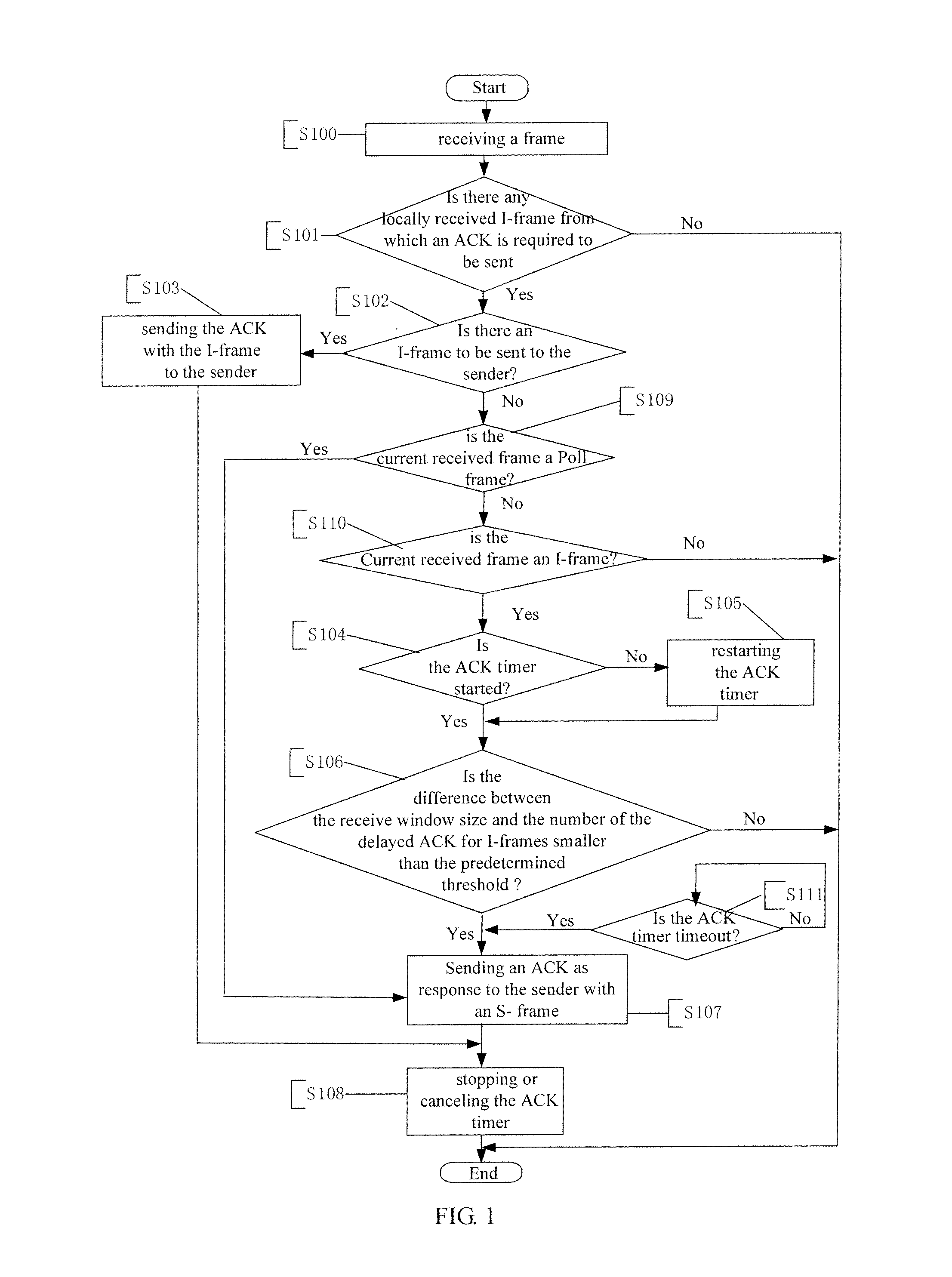
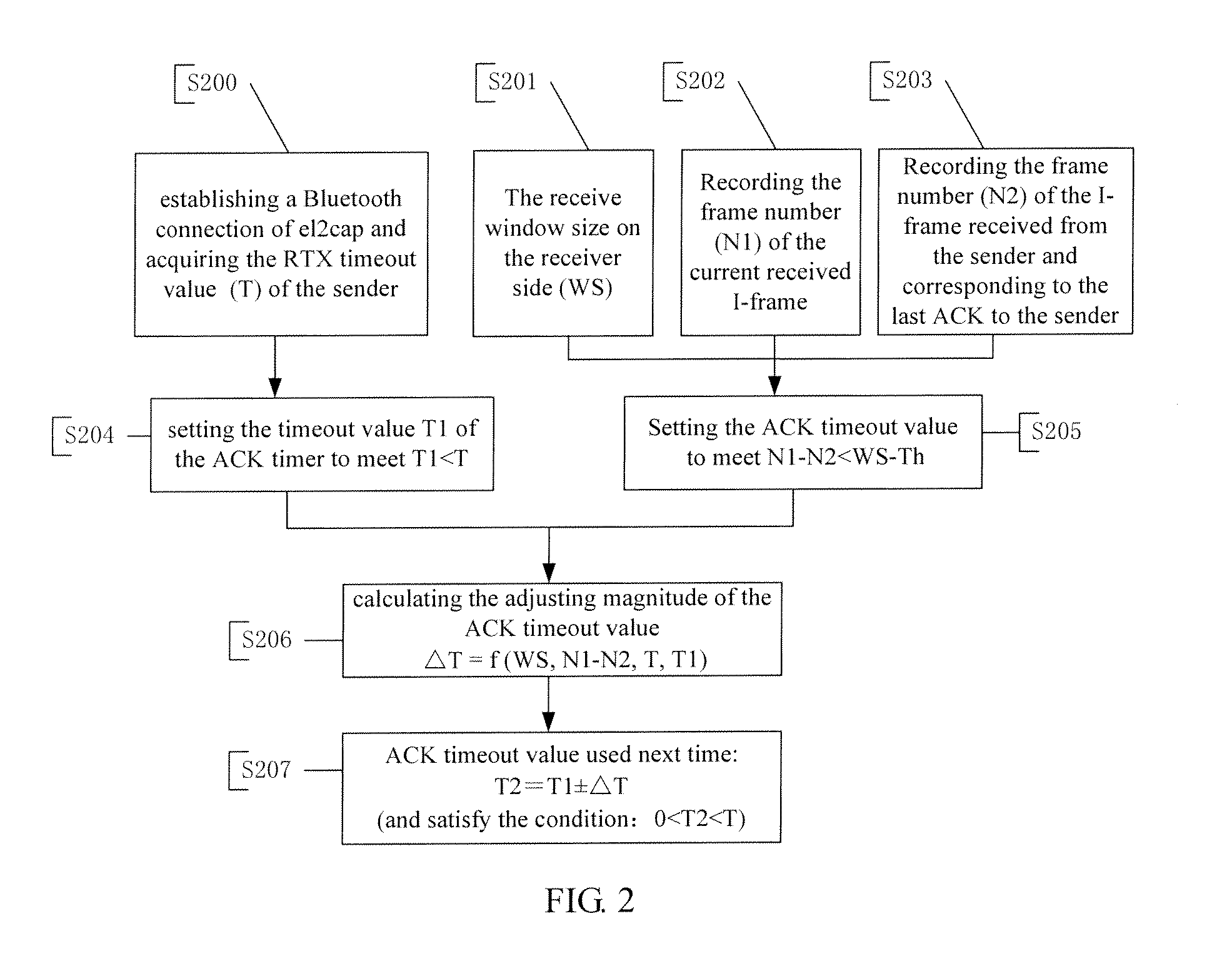
InactiveUS20110222447A1Improve bandwidth utilizationSolve the slow data transmission speedError preventionWireless network protocolsData transmissionTimer
A method for sending an ACK from the receiver to the sender is disclosed. The receiver starts an ACK timer with the ACK timeout value being smaller than the RTX timeout value. The ACK timer is stopped or cancelled when an ACK is sent from the receiver to the sender. When the number of the delayed ACK for I-frames is close to the receive widow size of the receiver or the ACK timer is timeout, the receiver sends an ACK to the sender actively. When the receiver receives a Poll frame from the sender due to RTX retransmission timeout, the receiver sends an ACK to the sender passively. The receiver adjusts the ACK timeout value used next time based on the following: timeout value of a current ACK timer, RTX timeout value of the sender, the receive widow size of the receiver and the number of I-frames for which ACKs have not been sent, in order to reduce the S-frames and stops of data transmission, thus improving the data transmission speed and the bandwidth utilization.
Owner:IVT TECH BEIJING
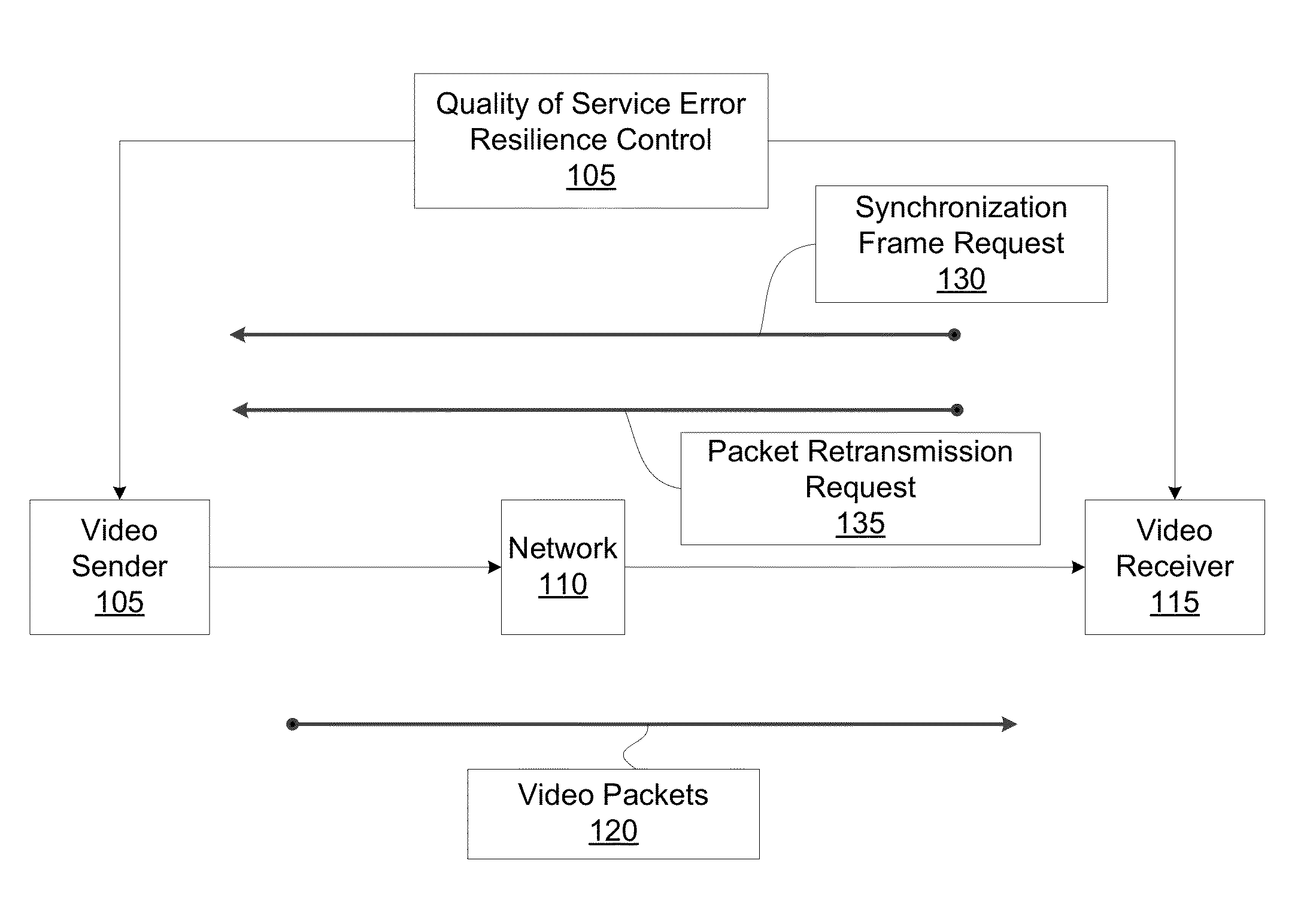
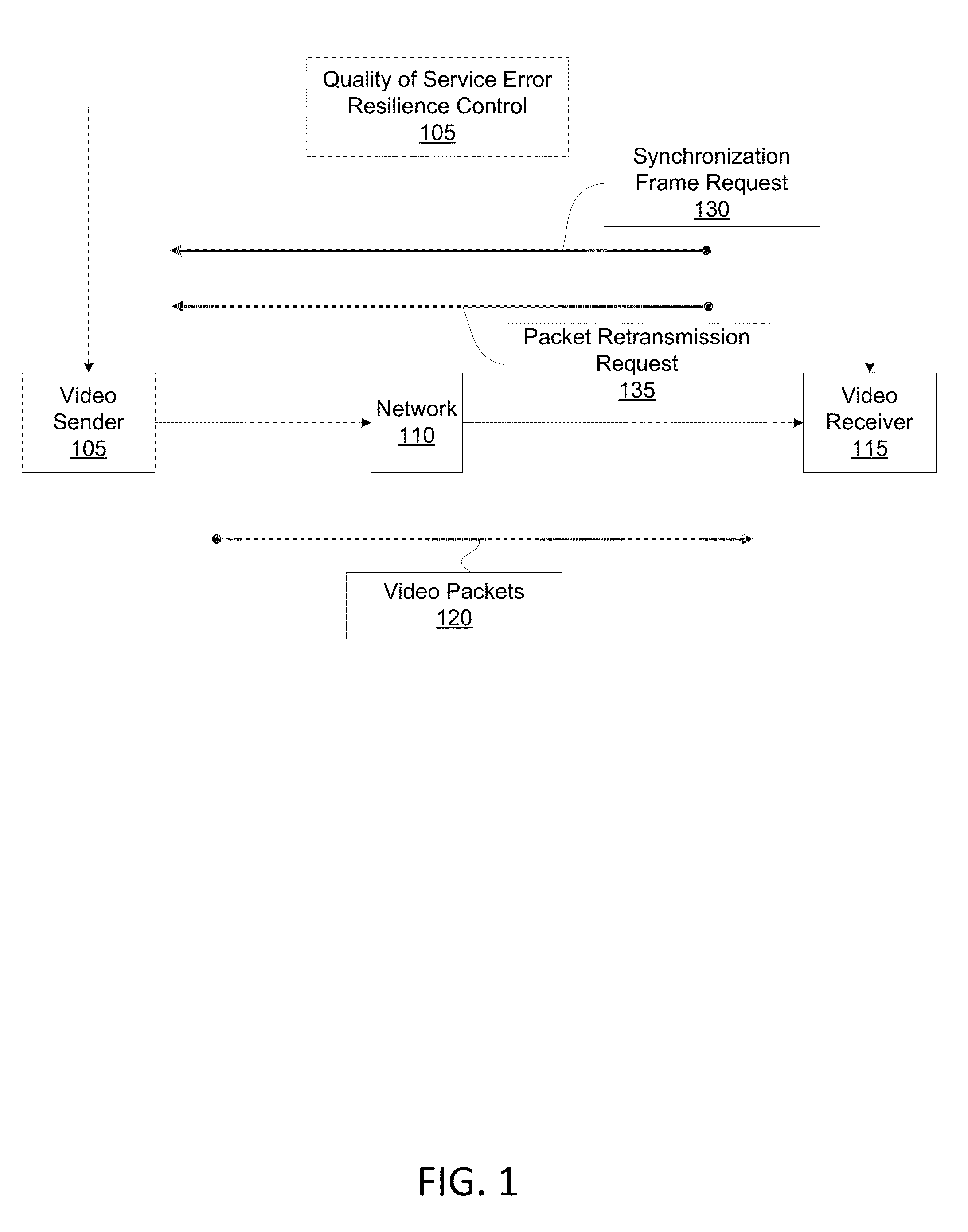
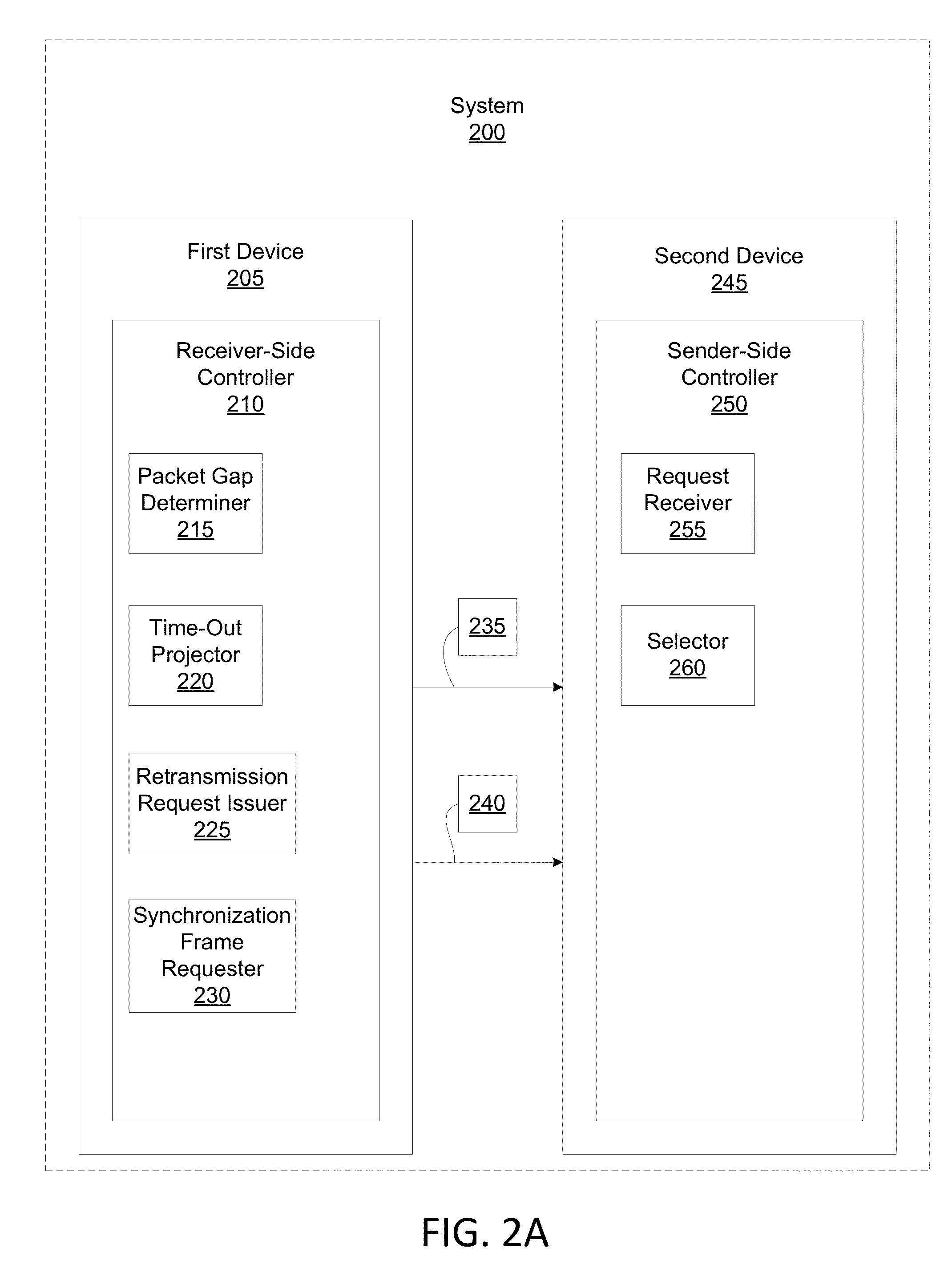
Joint retransmission and frame synchronization for error resilience control
ActiveUS20140192825A1Synchronisation error correctionTime-division multiplexData synchronizationPacket loss
A method for controlling error resilience in network communication is described. The method includes: determining, by a receiver-side controller, a packet gap representing a packet loss of a packet being communicated over a network; projecting, by the receiver-side controller, a retransmission time-out for at least one missing packet of the packet loss; issuing, by the receiver-side controller, a retransmission request for the at least one missing packet; if the packet gap is not filled within a first time period of the retransmission time-out, then issuing, by the receiver-side controller, at least one synchronization frame request; and selecting, by a sender-side controller, to respond to at least one of either of the retransmission request or the at least one synchronization frame request and neither of the retransmission request nor the at least one synchronization frame request.
Owner:TANGOME
Unified congestion notification mechanism for reliable and unreliable protocols by augmenting ECN
A unified congestion notification mechanism can detect congestion at a recipient device either directly, such as via an explicit indicator, or indirectly, such as via dropped packets. Such congestion can then be indicated to the sending device either by leveraging an existing congestion notification mechanism, including by spoofing expected communications, or by creating a new congestion notification mechanism. Additionally, modifications to lossless protocols, such as TCP / IP can adapt them for use with streaming data while still implementing the unified congestion notification mechanism by eliminating retransmissions either as a result of the retransmission timeout or as a result of information conveyed as part of the acknowledgement packets.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
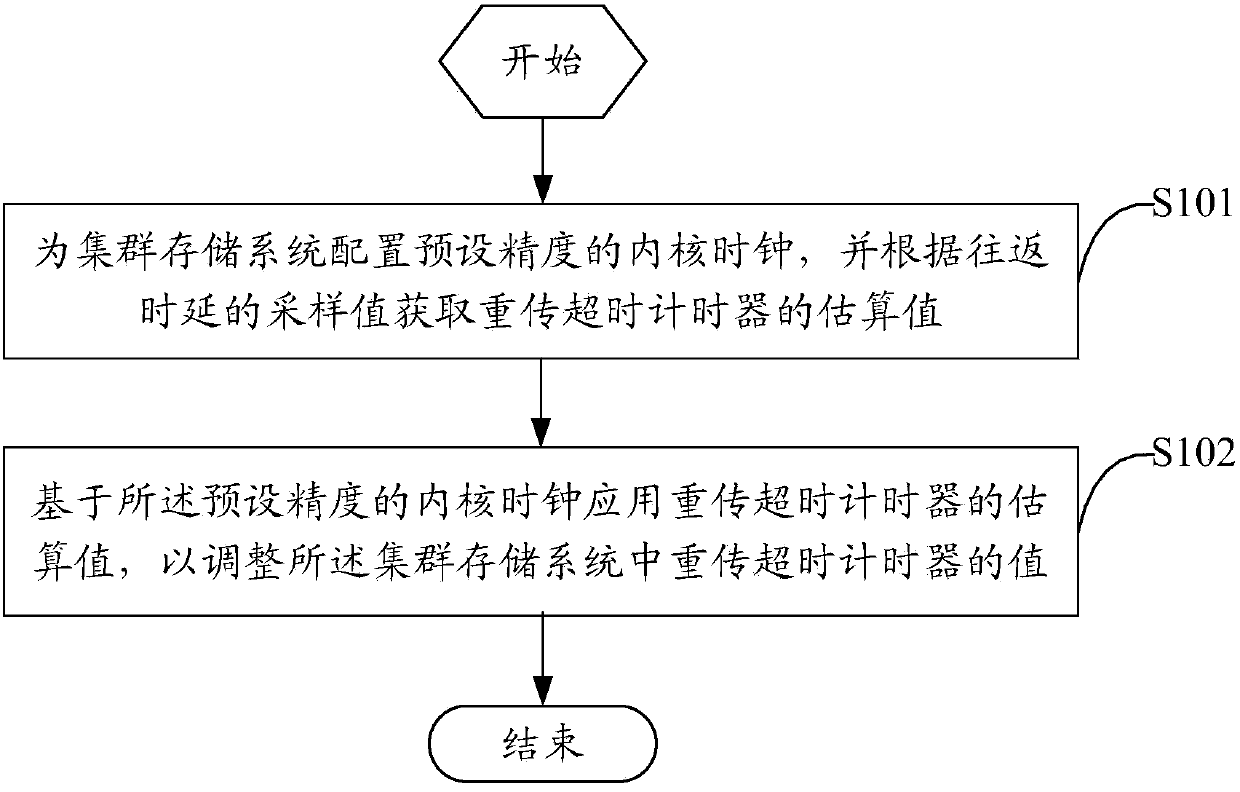
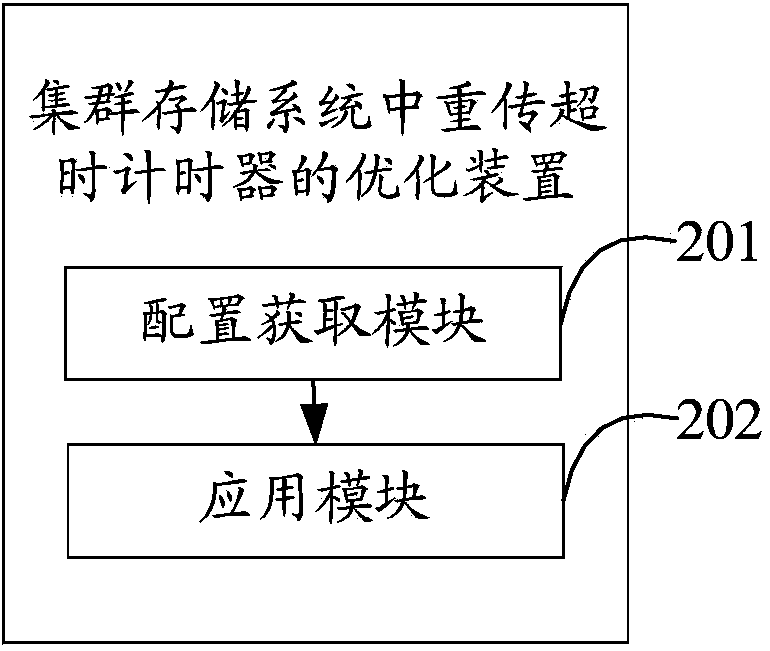
Method and device for optimizing retransmission timeout timer in cluster storage system
ActiveCN103401665ABalance Bandwidth Utilization ImpactError prevention/detection by using return channelEstimation methodsDelayed time
The invention discloses a method and a device for optimizing a retransmission timeout timer in a cluster storage system. The method comprises the steps of configuring a core clock with the preset precision for the cluster storage system, and acquiring an estimated value of the retransmission timeout timer according to a sampling value of the reciprocation delay time; and adjusting a value of the retransmission timeout timer in the cluster storage system on the basis of the core clock with the preset precision and applying the estimated value of the retransmission timeout timer. According to invention, the cluster storage system is configured with the core clock timer whose precision is at least at a microsecond level so as to set the precision of the retransmission timeout timer to be the microsecond level precision which is the same as that of the reciprocation delay time. Meanwhile, an appropriate estimation method is selected according to the sampling value of the reciprocation delay time and the clustering scale of the cluster storage system to acquire the estimated value of the retransmission timeout timer, thereby selecting an optimized estimated value of the timeout timer to balance influences imposed on the utilization rate of user bandwidth by forged retransmission and transmission timeout.
Owner:国家超级计算深圳中心(深圳云计算中心)
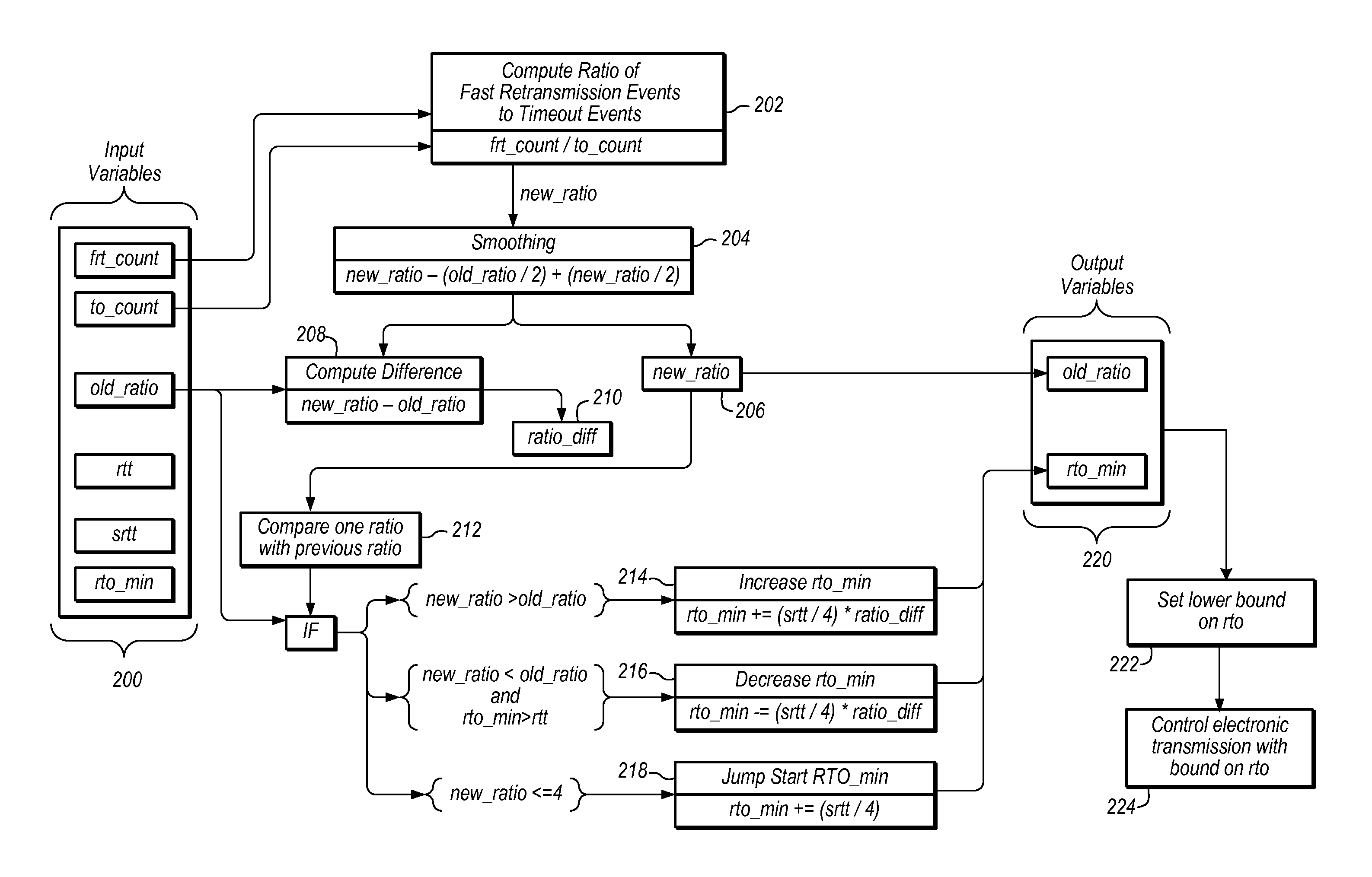
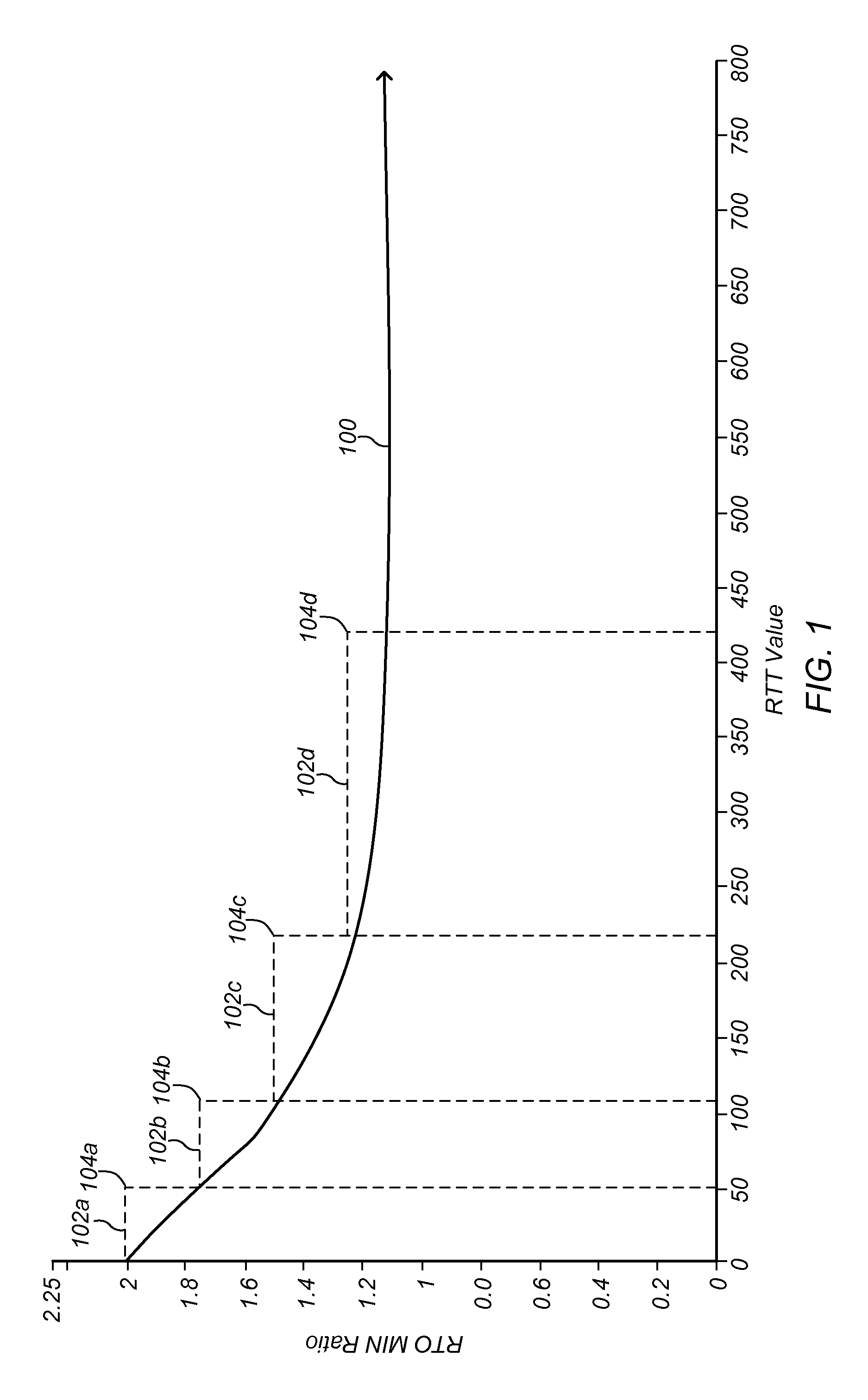
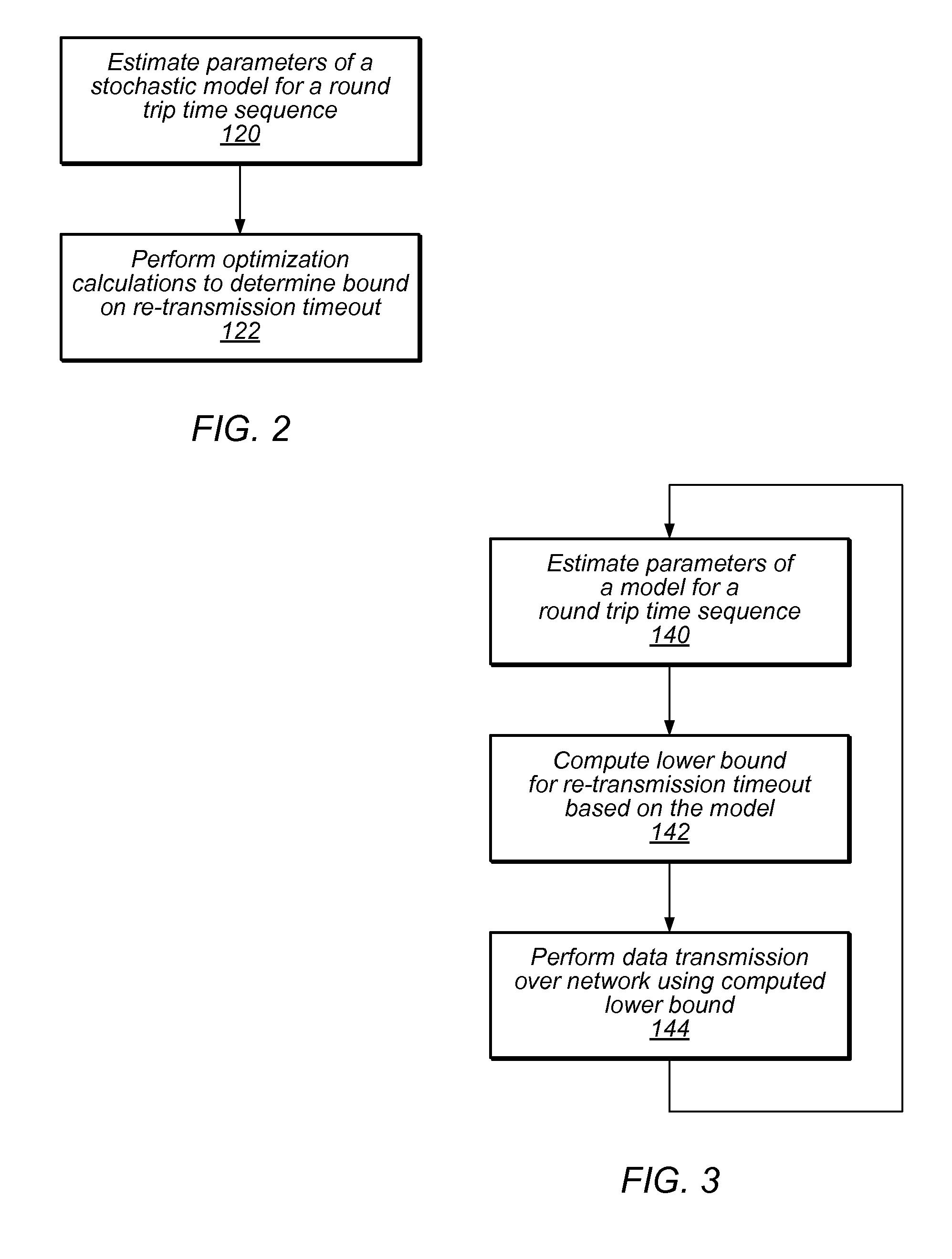
Optimization of retransmission timeout boundary
ActiveUS20150288586A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksElectronic transmissionRetransmission timeout
A method includes estimating a parametric model for a round-trip time sequence for an electronic transmission over a network. Optimization calculations may be performed to dynamically determine a bound (for example, a lower bound) on re-transmission timeout for an electronic transmission to be conducted over the network.
Owner:TEXAS STATE UNIVERSITY
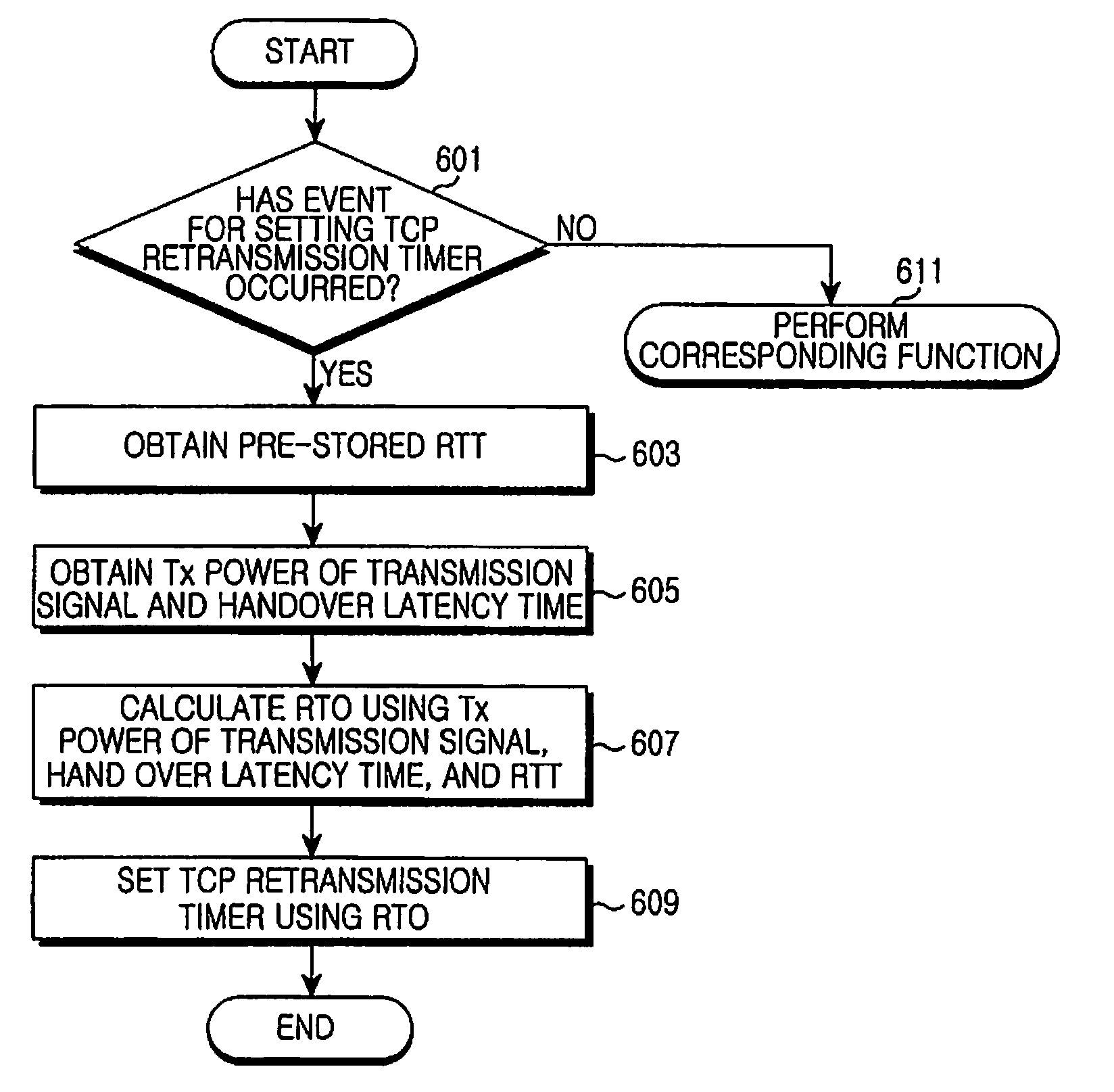
Apparatus and method for reducing latency in the transmission control protocol layer of a portable communication terminal
InactiveUS8155051B2Easy to usePreventing TCP latencyNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsTransmission latencyTime control
Improving a transmission latency of a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is provided. The apparatus includes a communicator transmitting a message for measuring power of a transmission signal to a radio access station (RAS) and receiving a response message corresponding to the message from the RAS; a TCP manager instructed by a controller to check and store a round trip time (RTT) required for receiving an acknowledgement (ACK) corresponding to data, which is transmitted from the portable terminal to the RAS; and the controller instructing the TCP manager to measure the RTT for measuring a retransmission timeout (RTO).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Network communication multi-channel selection method and system
InactiveCN102694713AIncrease transfer rateImprove transmission qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksTraffic capacityNetwork communication
The invention provides a network communication multi-channel selection method and a system. The network communication multi-channel selection method comprises the steps of turning on a primary path to transmit data through the primary path, and starting timing according to a preset retransmission timeout; judging whether the preset retransmission timeout arrives, and if the preset retransmission timeout arrives, switching to a secondary path to transmit data through the secondary path; simultaneously transmitting a heartbeat packet in the primary path and the secondary path through a stream control transmission protocol, receiving a heartbeat response packet fed back from the primary path and the secondary path, acquiring a first time when receiving the heartbeat response packet from the primary path and a second time when receiving the heartbeat response packet from the secondary path; and if the first time is less than the second time twice in succession, switching to the primary path.
Owner:ANHUI COMM IND SERVICE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com