Patents
Literature
110results about How to "Reduce network congestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
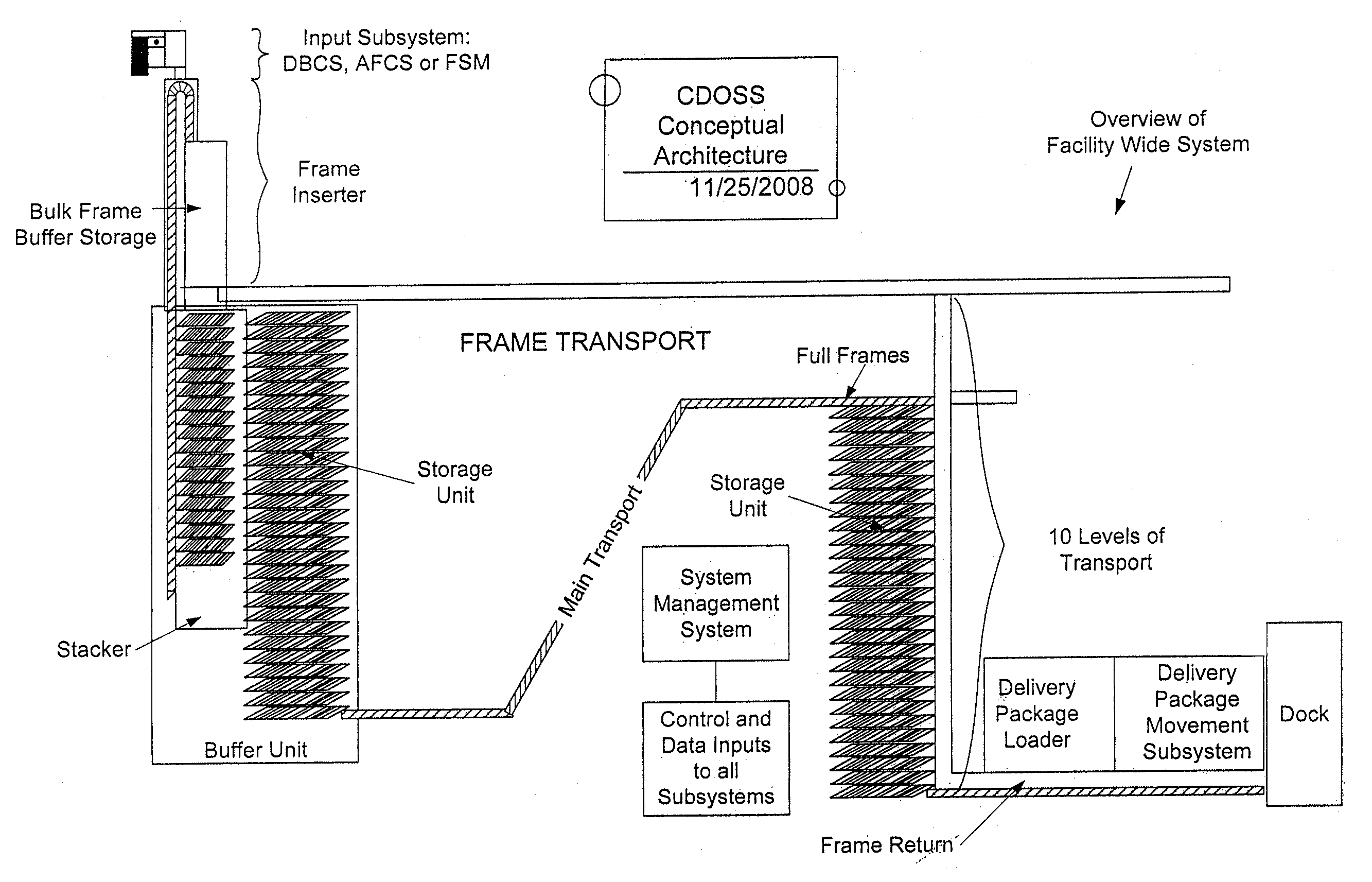
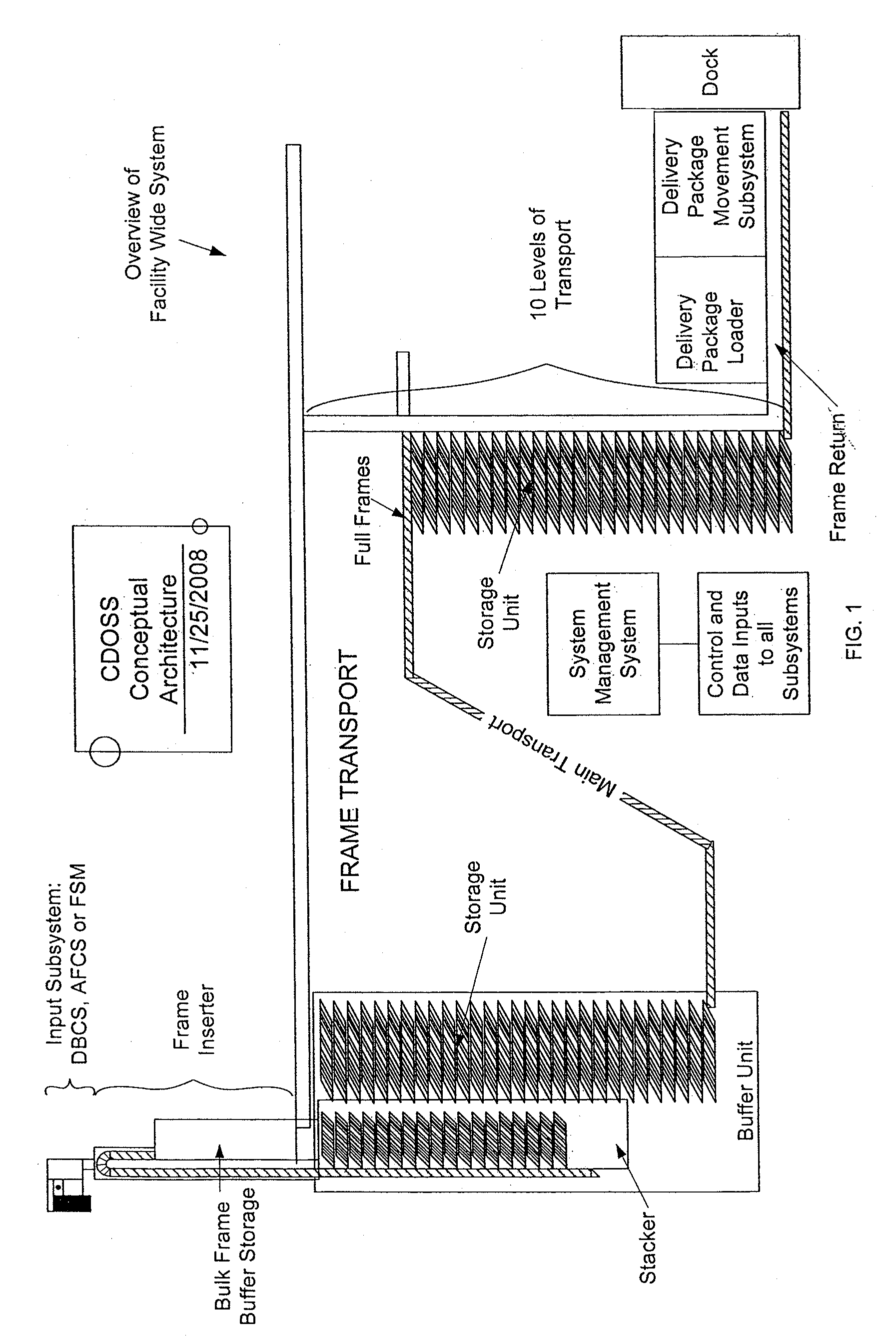
Facility Wide Mixed Mail Sorting and/or Sequencing System and Components and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110046775A1Reduce network congestionWidth minimizedConveyorsData processing applicationsEngineeringProduct processing
The invention generally relates to a facility wide sorting and / or sequencing system for improving product processing operations and, more particularly, to a facility wide system and related functionality for simultaneously sorting and sequencing mixed mail pieces such as, for example, flats and letter mail pieces. The flats and letter mail pieces are placed in frames so that all types of mail pieces can be sorted and / or sequenced simultaneously through merging and diverting a stream of filled trays into and out of different streams at a full or substantially full transport speed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
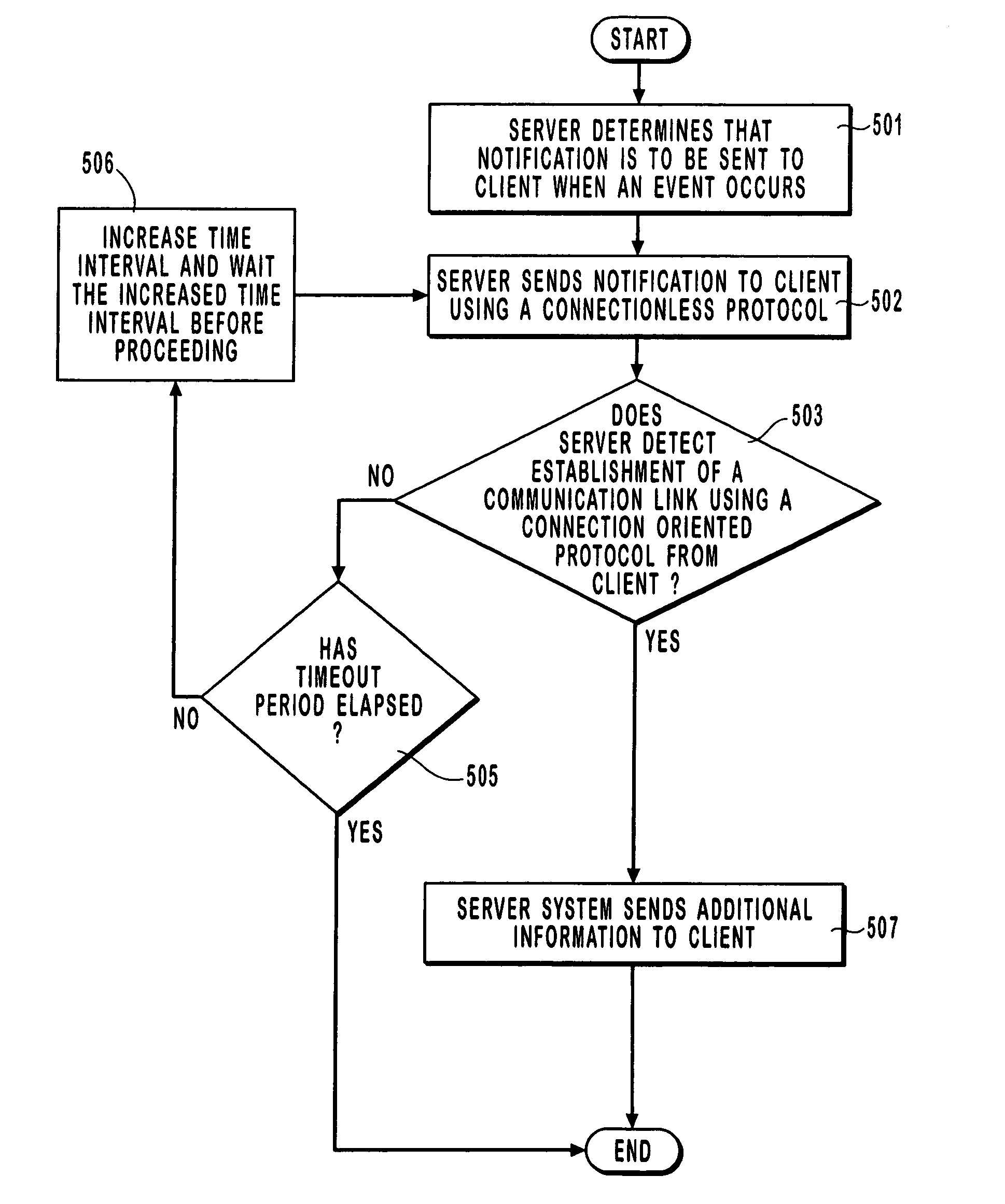
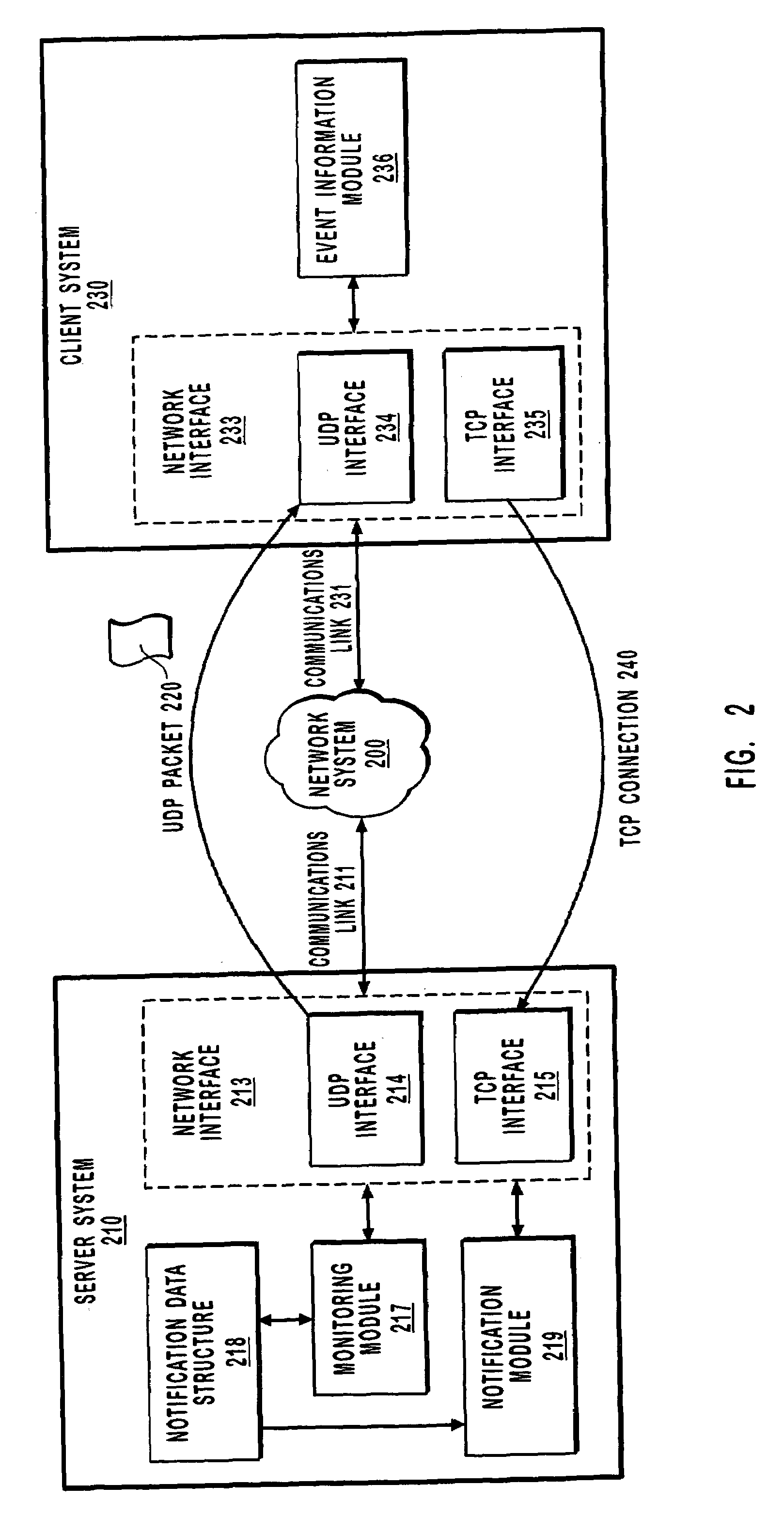
Efficiently sending event notifications over a computer network
InactiveUS6999992B1Reduce data volumeEliminate overheadMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication softwareClient-side
A method for efficiently sending notifications over a network. A client system requests to be notified when an event occurs. A server system receives the requests and monitors for the occurrence of the event. When the event occurs a single packet using a connectionless protocol (such as User Datagram Protocol) is sent to the client to notify the client of the occurrence of the event. Using a connectionless protocol to send notification reduces the overall amount of data on the network and thus reduces network congestion and the processing capacity of the server and client. When the client system receives notification an attempt to establish a connection using as connection-oriented protocol is executed. Additional data associated with the occurrence of the event is transferred over the connection. The server may repeatedly send notification using a connectionless protocol until a connection using a connection-oriented protocol is established. The server may send notification that notifies the client of the occurrence of multiple events simultaneously within a single packet. The server may also notify multiple applications of the occurrence of an event using a single notification.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
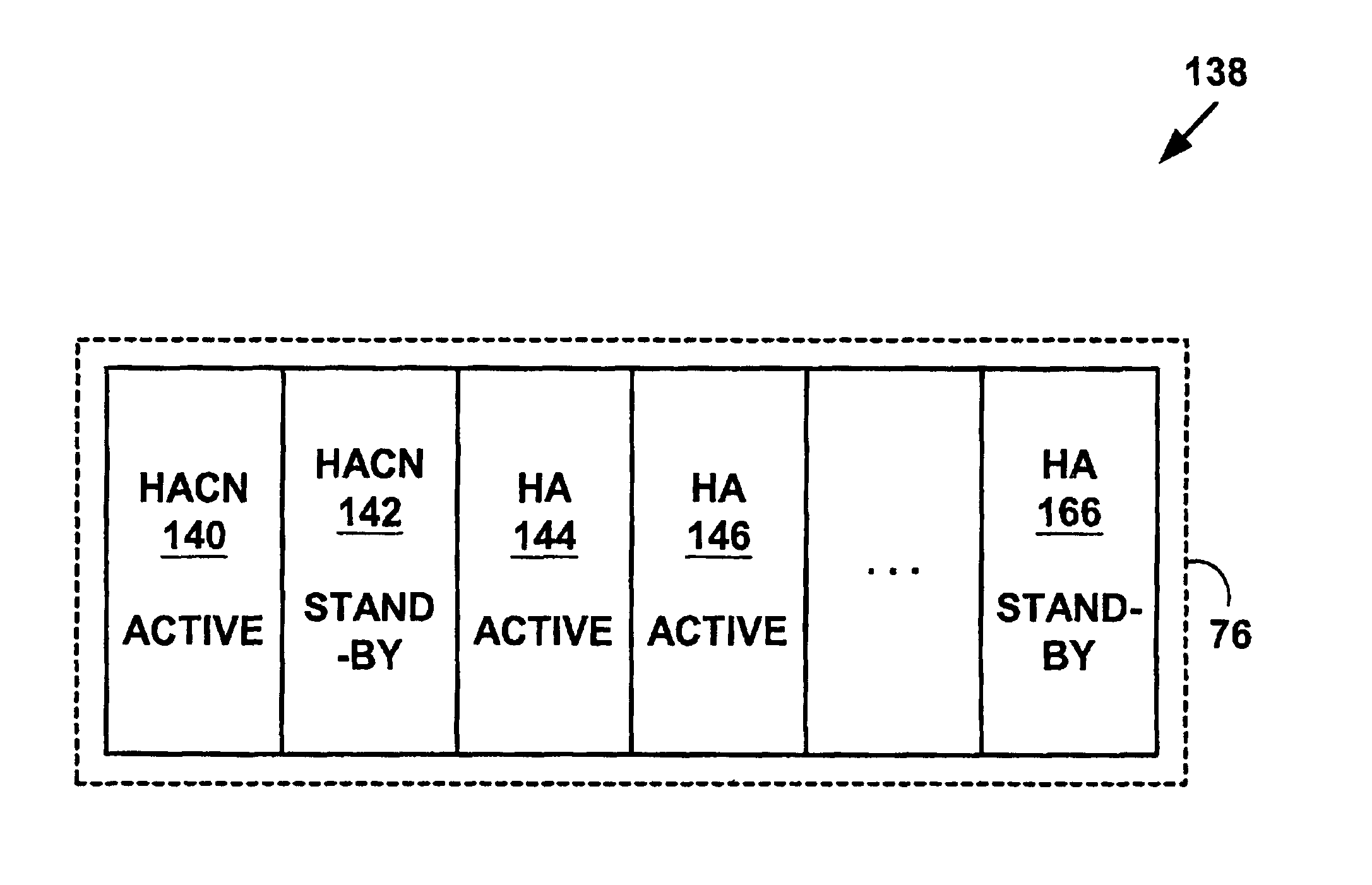
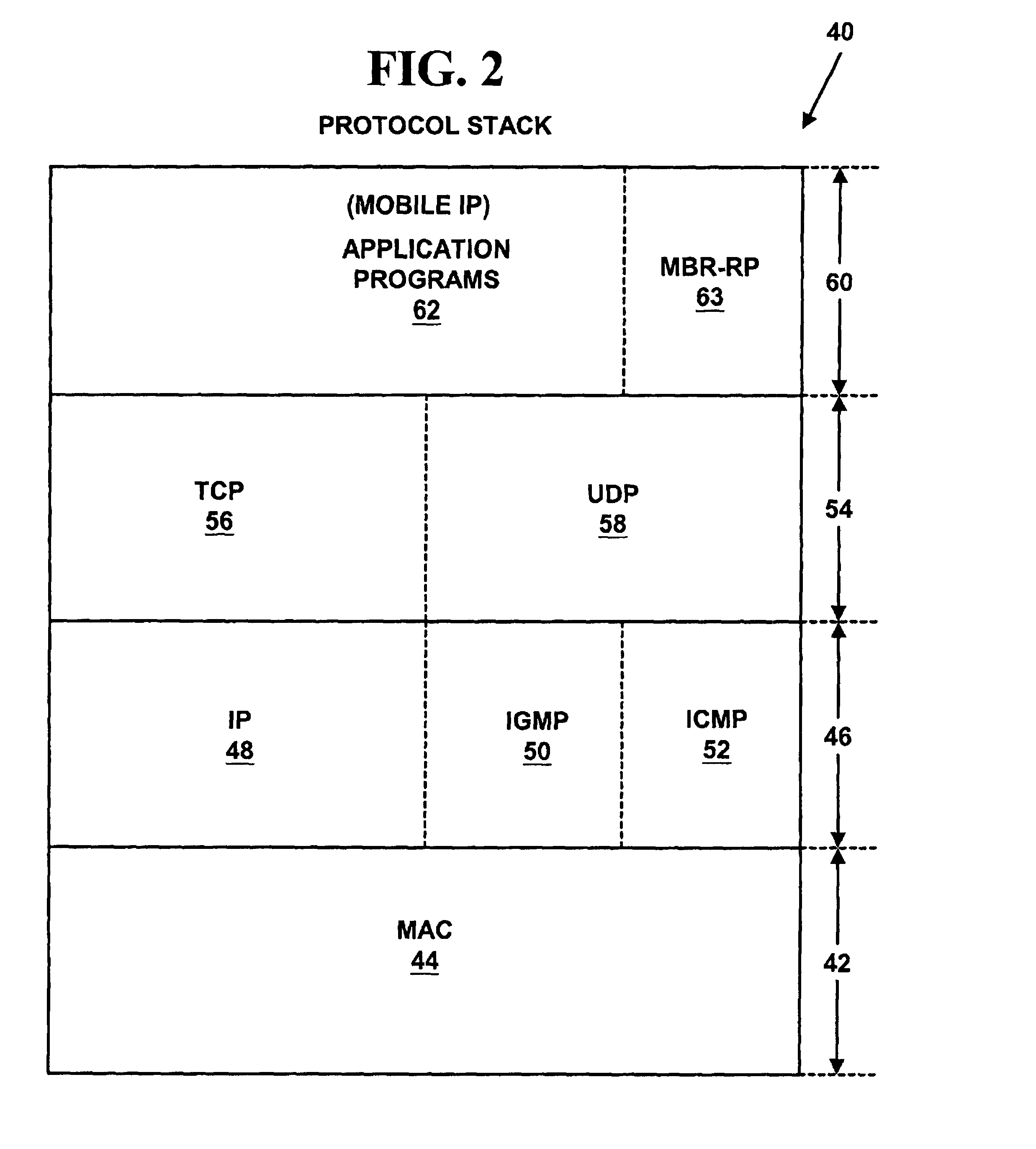
Method and system for mobile IP home agent redundancy by using home agent control nodes for managing multiple home agents
InactiveUS7080151B1Reduce failed callImprove user satisfactionMultiprogramming arrangementsCommmunication supplementary servicesComputer networkMulticast network
A method and system for Mobile Internet Protocol (IP) device redundancy. As mobile devices roam away from a home network and change a connective status, mobility binding records are sent to a multicast network address on the home network. The multicast network address multicasts the mobility binding records to other active Mobile IP home agent control nodes, standby home agent control nodes and standby home agents on the home network. The method and system allows standby home agent control nodes or standby home agents to be transparently switched for active home agent control nodes or active home agents that fail without downloading or uploading large numbers of mobility binding records after a failure. The method and system may also help reduce failed calls (e.g., data sessions including Voice over IP (VoIP), H.323, etc.), network congestion and improve user satisfaction in Mobile IP systems.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
Restoration in a telecommunication network
InactiveUS20060114818A1Easy to useReduce the possibilityError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkDynamic feature
A method is described for calculating a backup connection for restoring a nominal connection in a telecommunication network. The method performs the calculation of the backup connection taking into account updated values of parameters indicating at least one dynamic feature of a group of segments of the network. The dynamic parameters can be a measure of the performance of the segment, the degree of usage of the segment, the bandwidth overbooking of the segment or the bandwidth fragmentation or a combination of these measures.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
VOIP endpoint call admission
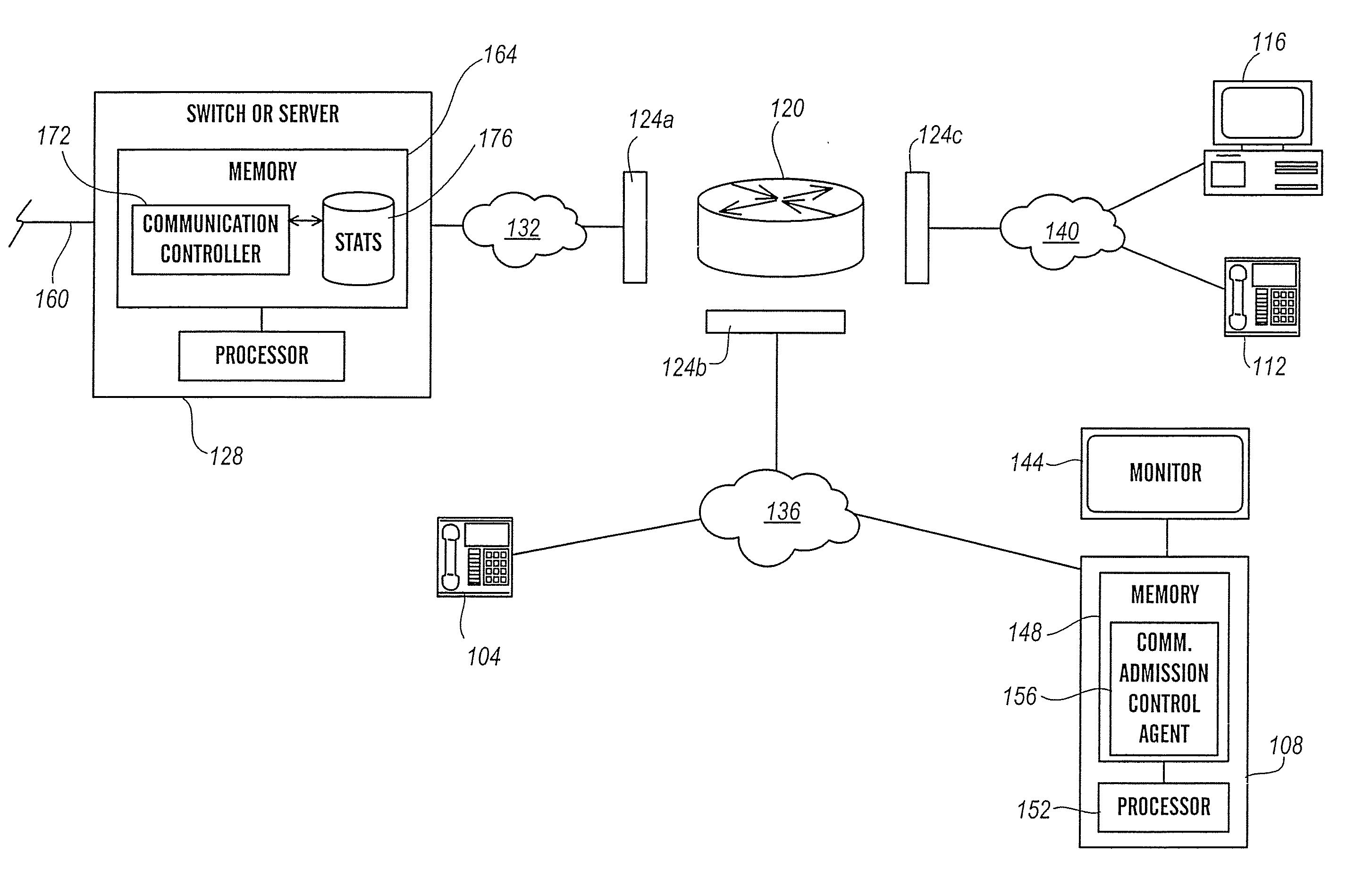
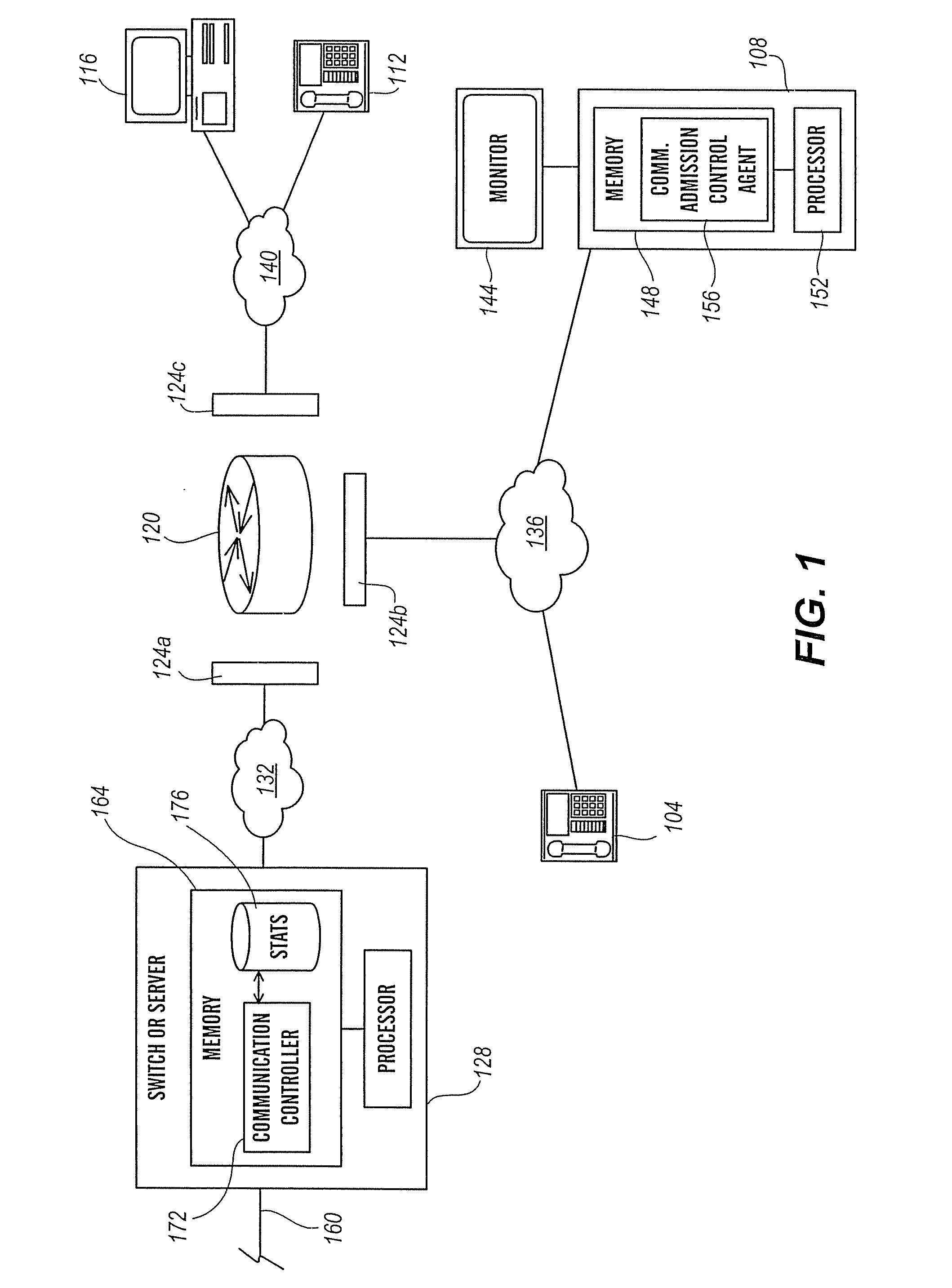
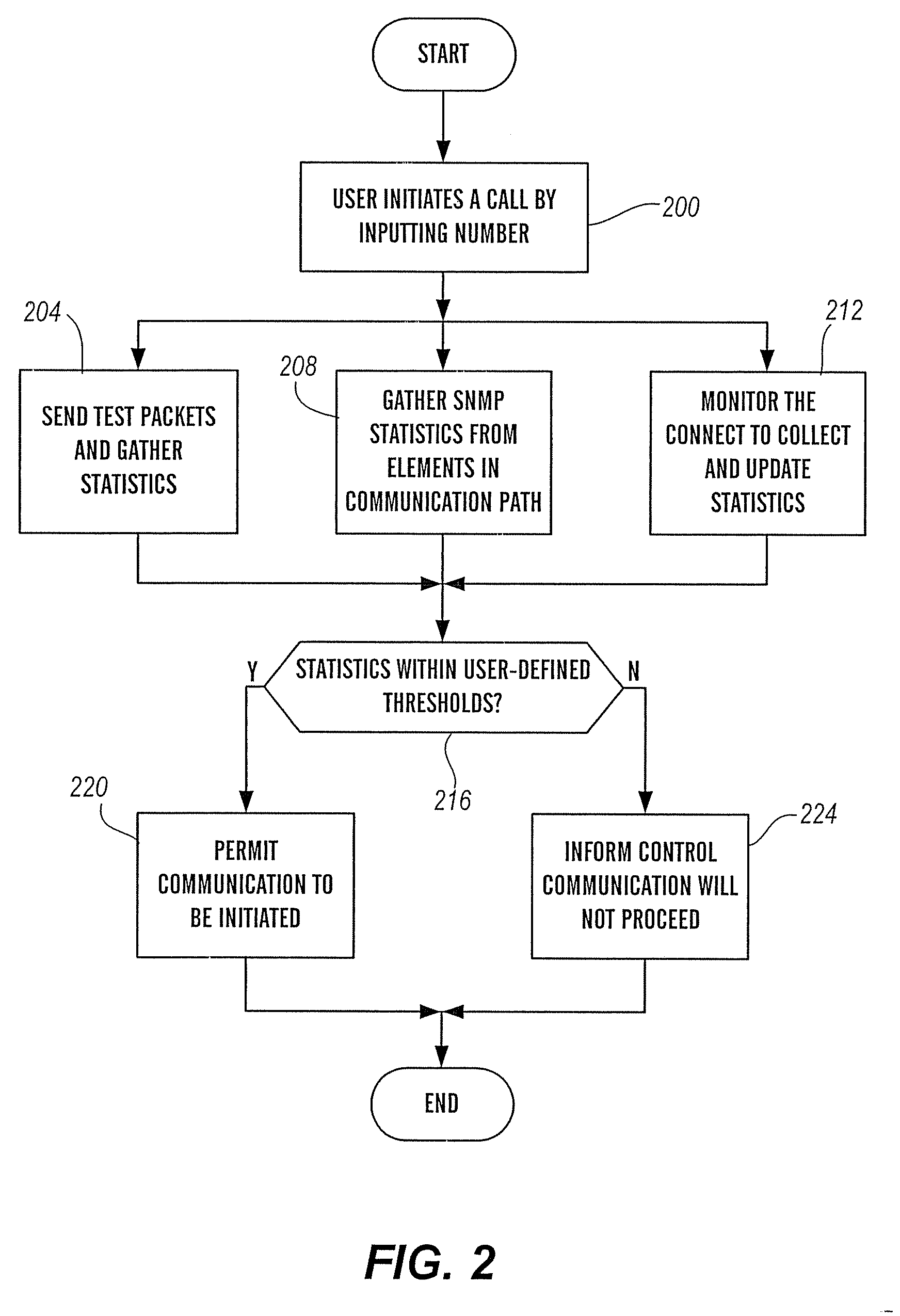
InactiveUS20070133403A1High likelihood of failureAvailable bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsRelevant information
The present invention is directed generally to an intelligent endpoint or communication device that can collect available bandwidth-related information metrics and / or perform call admission control functions. The present invention is further directed to an architecture comprising a switch or media server in communication with a plurality of subscriber communication devices in which the subscriber communication devices act as network nodes to collect available bandwidth-related information.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Methods And Systems For Providing Quality Of Service In Packet-Based Core Transport Networks
InactiveUS20080037552A1Effective carryFair sharingEnergy efficient ICTError preventionService-level agreementTraffic capacity
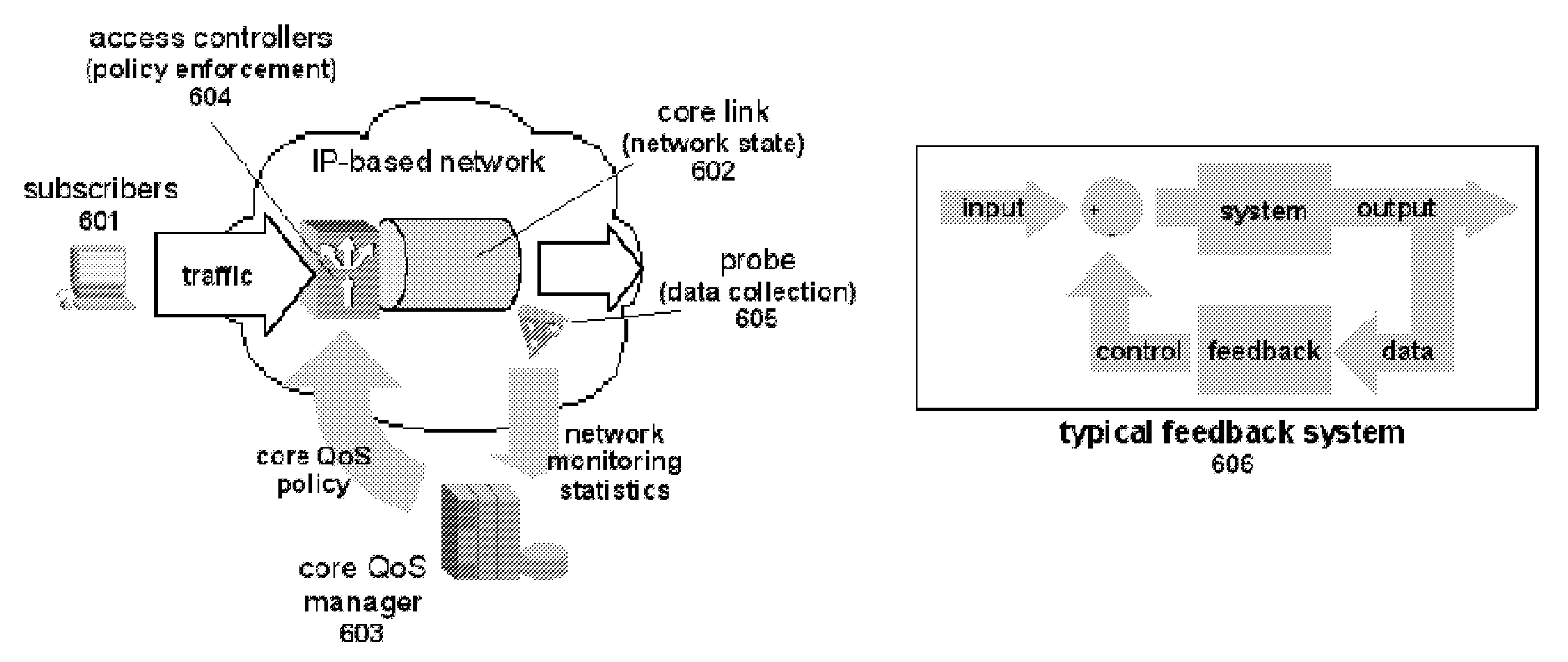
Methods and systems for providing necessary and sufficient quality-of-service (QoS), in a packet-based core transport network that utilizes dynamic setting of bandwidth management pipes or thresholds to obviate link congestion are disclosed. Congestion avoidance is a necessary and sufficient requirement in order to guarantee Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based core networks.A typical network is composed of a plurality of backbone links connecting edge nodes where backhaul links are aggregated. The backhaul links connect the backbone links to the remote sites serving the subscribers. In order to enforce bandwidth management policies, Access Controllers, which perform traffic shaping, are situated on each remote site.In the event of a violation of certain link threshold settings, dynamic adjustment of the bandwidth management policies on affected Access Controllers is enforced. Various algorithms in determining the correlation between the link nearing congestion and the source or destination of traffic streams are also discussed. This invention implements a feedback control loop wherein probes at various points in the network checks for congestion states to guide bandwidth management threshold decisions in order to maintain the condition of non-congestion throughout the network. Capacity planning and congestion avoidance mechanisms work hand-in-hand to fulfill Service Level Agreements (SLA).
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
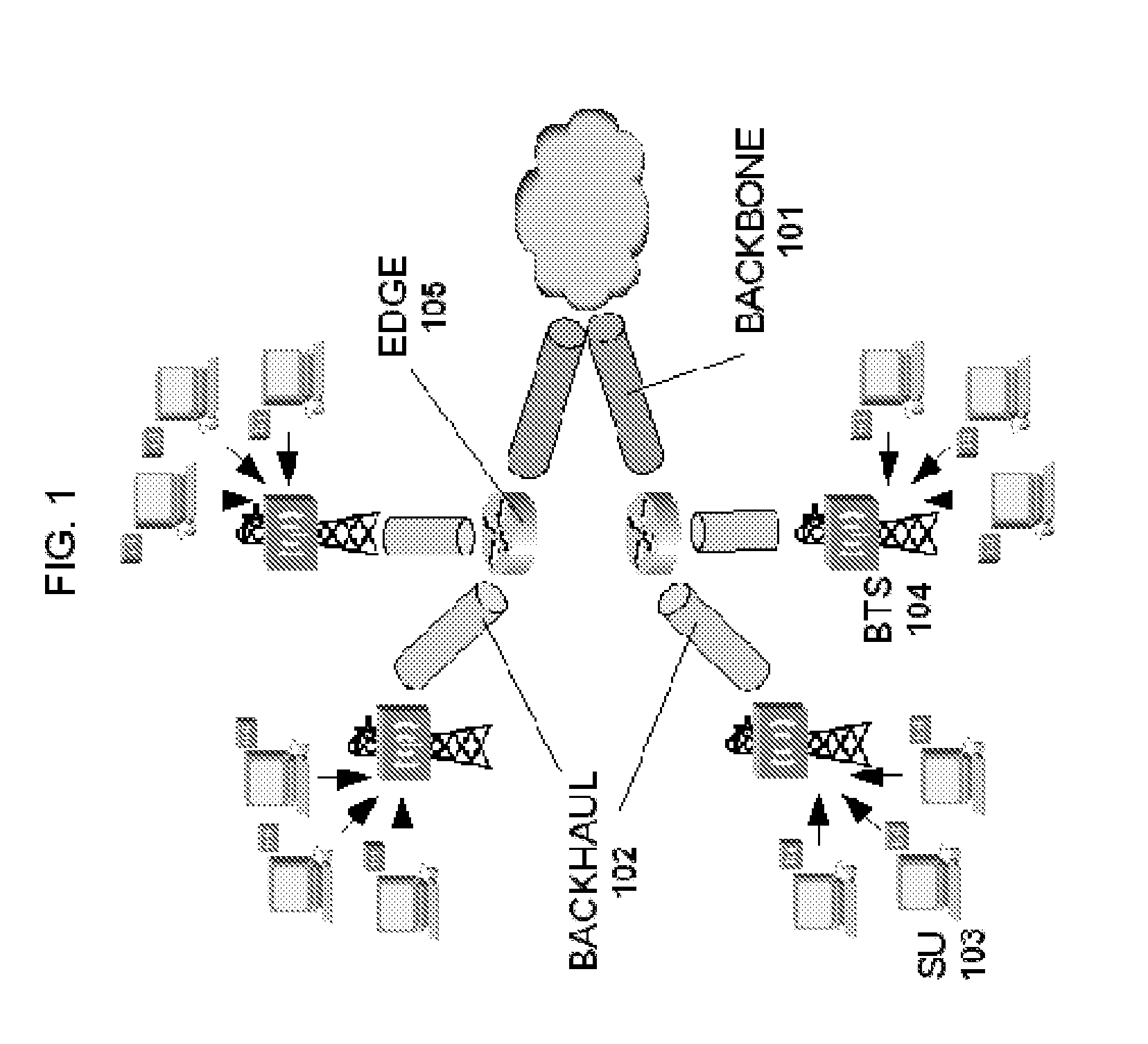
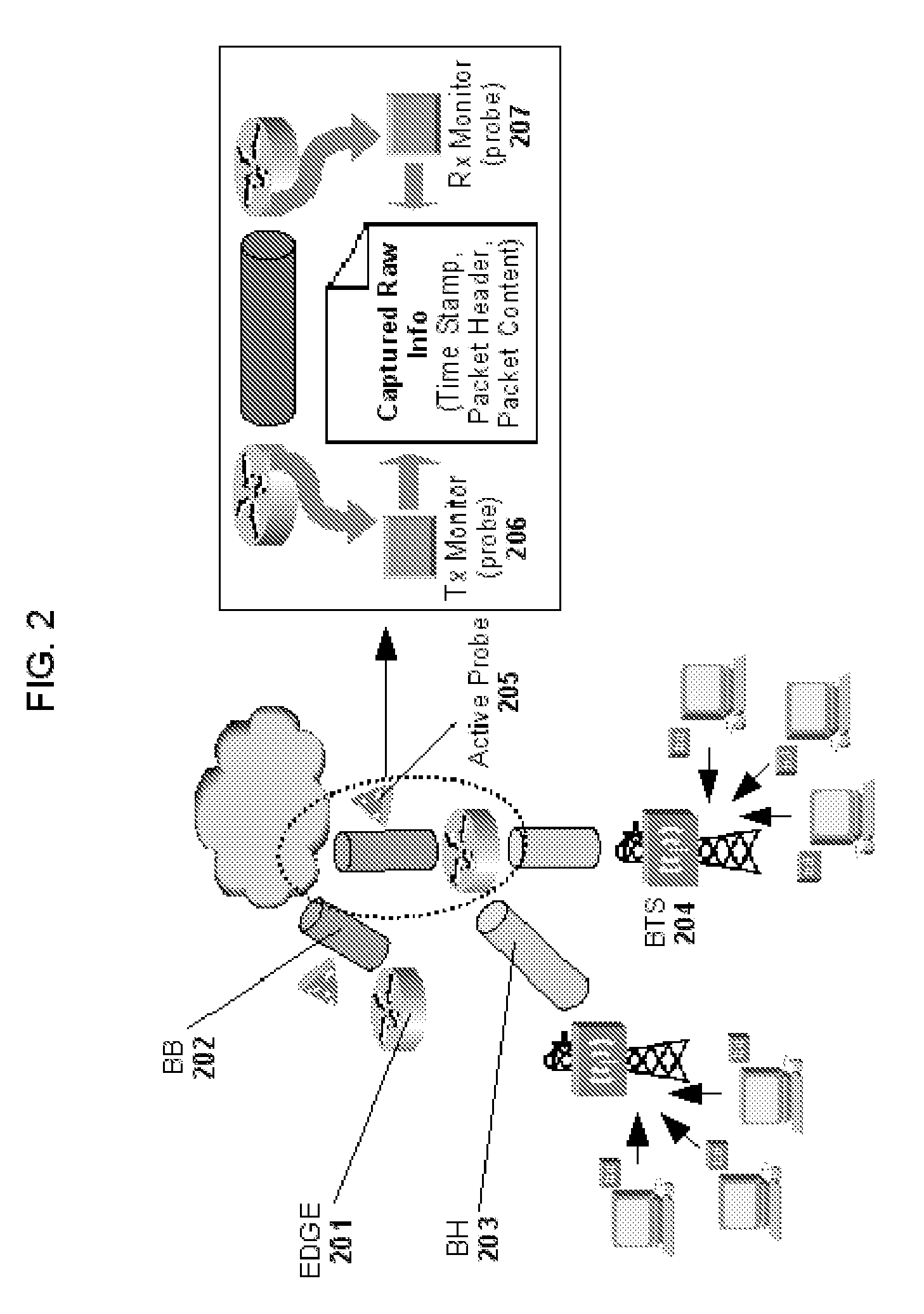
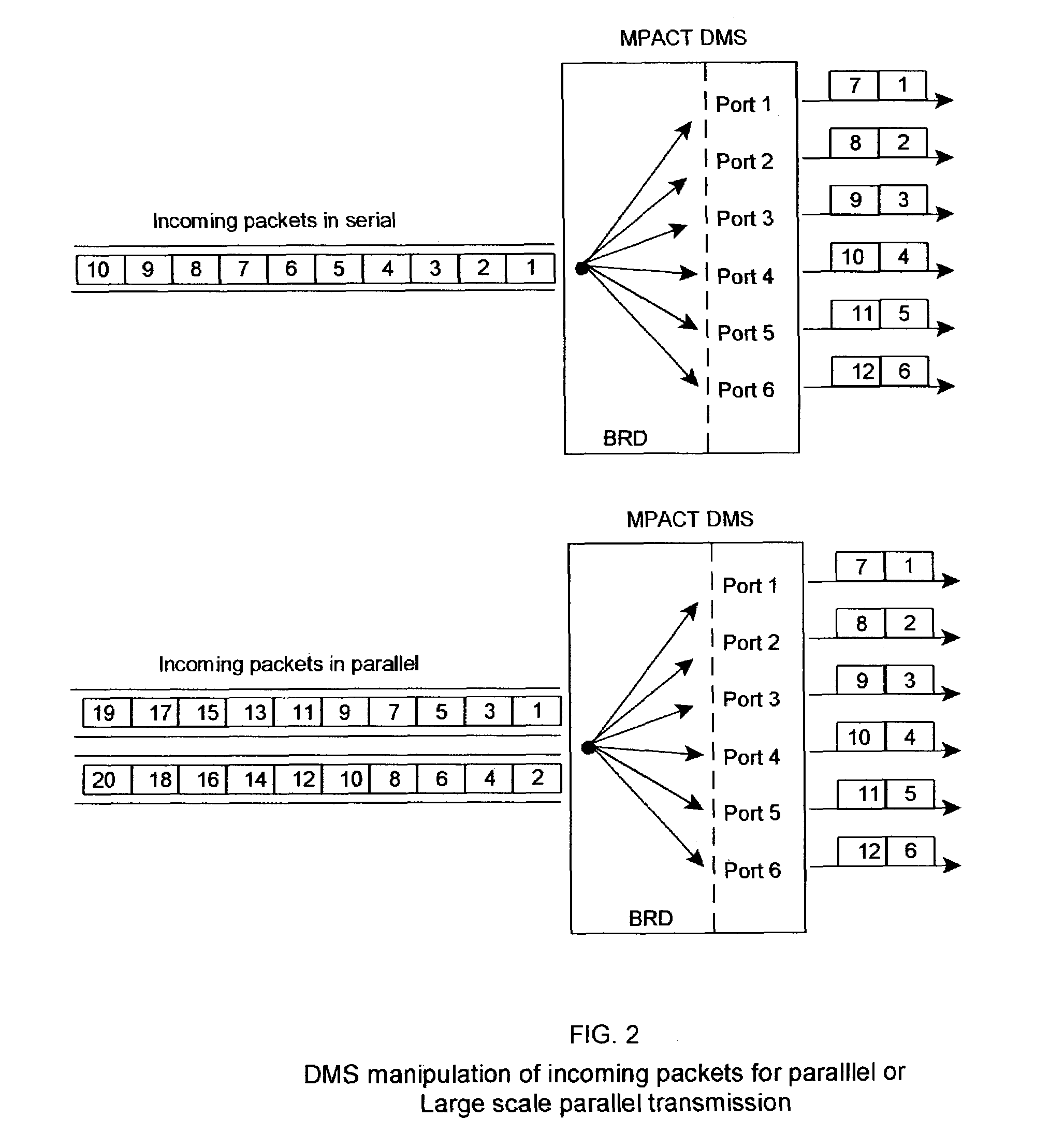
Massively parallel computer network-utilizing MPACT and multipoint parallel server (MPAS) technologies
InactiveUS7552192B2High bandwidthSmall sizeBroadband local area networksMultiple digital computer combinationsSerial transferOn demand
A Process and apparatus for high speed data transfer for communications networks, computers, computer networks and network interfaces, via software, and apparatus mimicking the human brain and nervous system, by utilization of highly distributed storage of data and massively parallel data transfer and reception over multiple channels / pathways resulting in greater bandwidth than that of serial transmissions. The primary purpose of which is to provide highspeed data transfer for data-on-demand networks such as Video-on-Demand. Therefore, the processes, architectures and topologies described herein may be interfaced with satellite systems, CATV systems, Virtual Networks, wireless services; utilized by Internet Service Providers, and any broadcaster / service provider capable of multiple channel / frequency broadcasts and reception via satellite, cable, terrestrial, or other mediums.
Owner:CARMICHAEL RONNIE GEROME
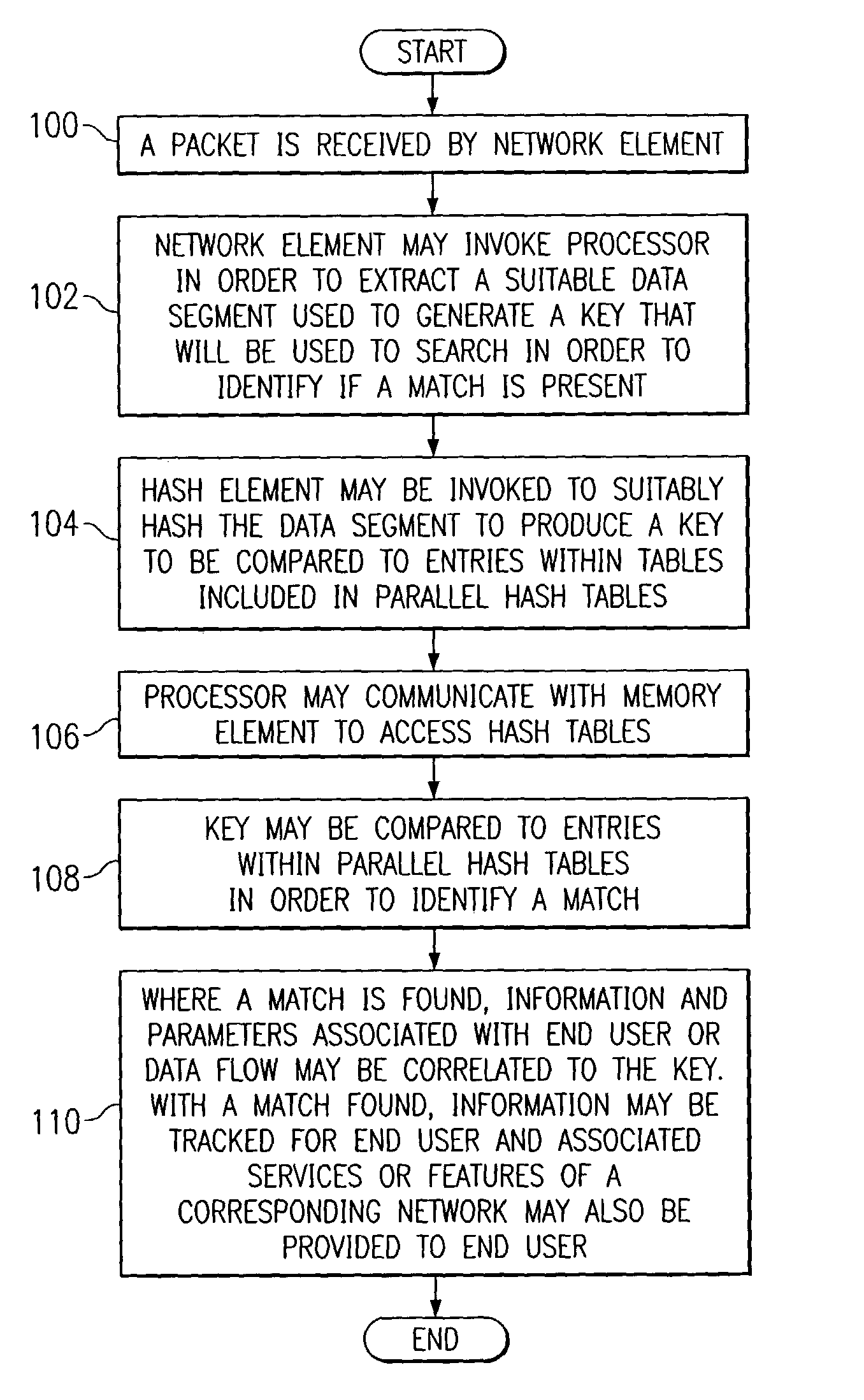
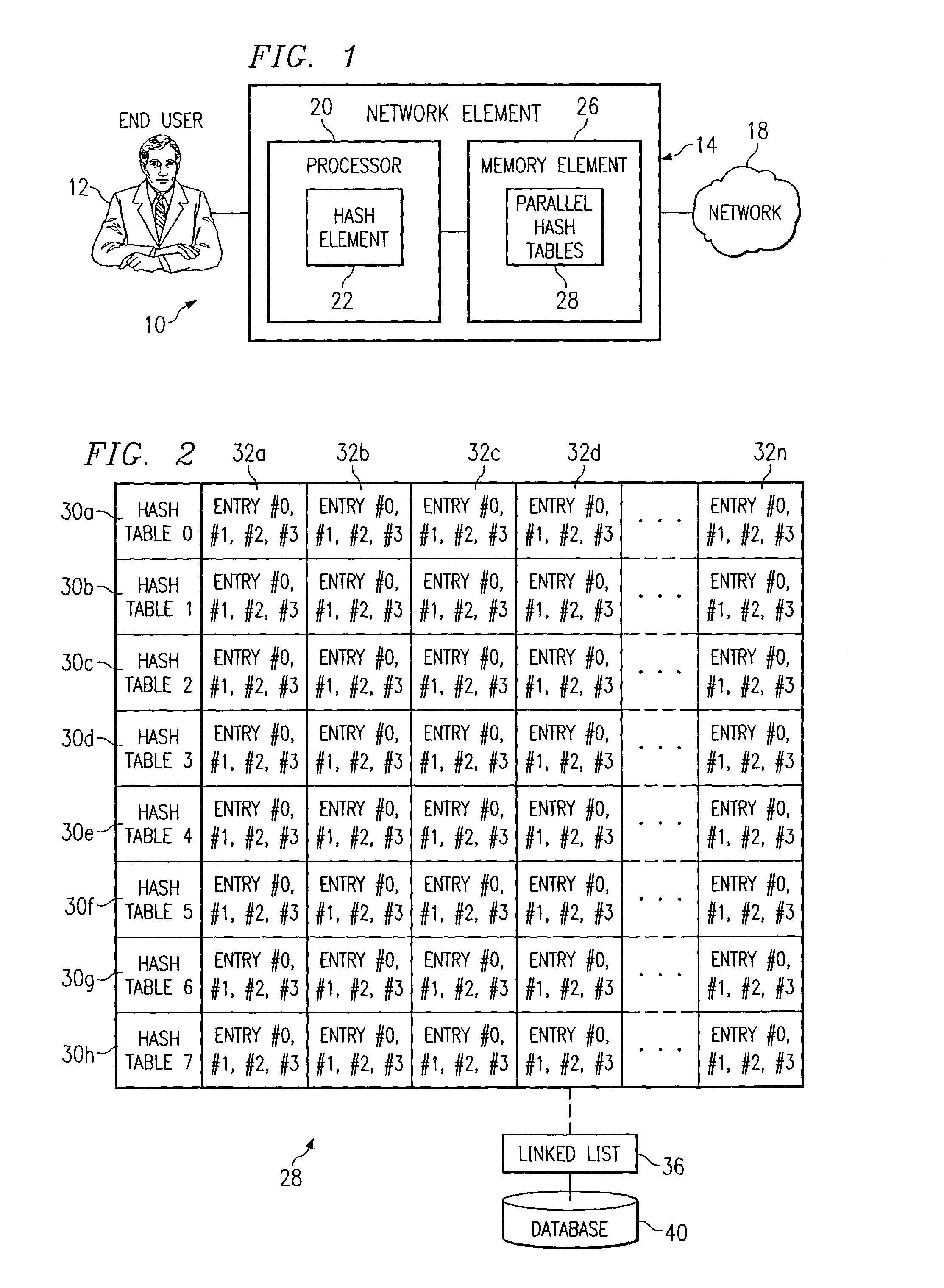
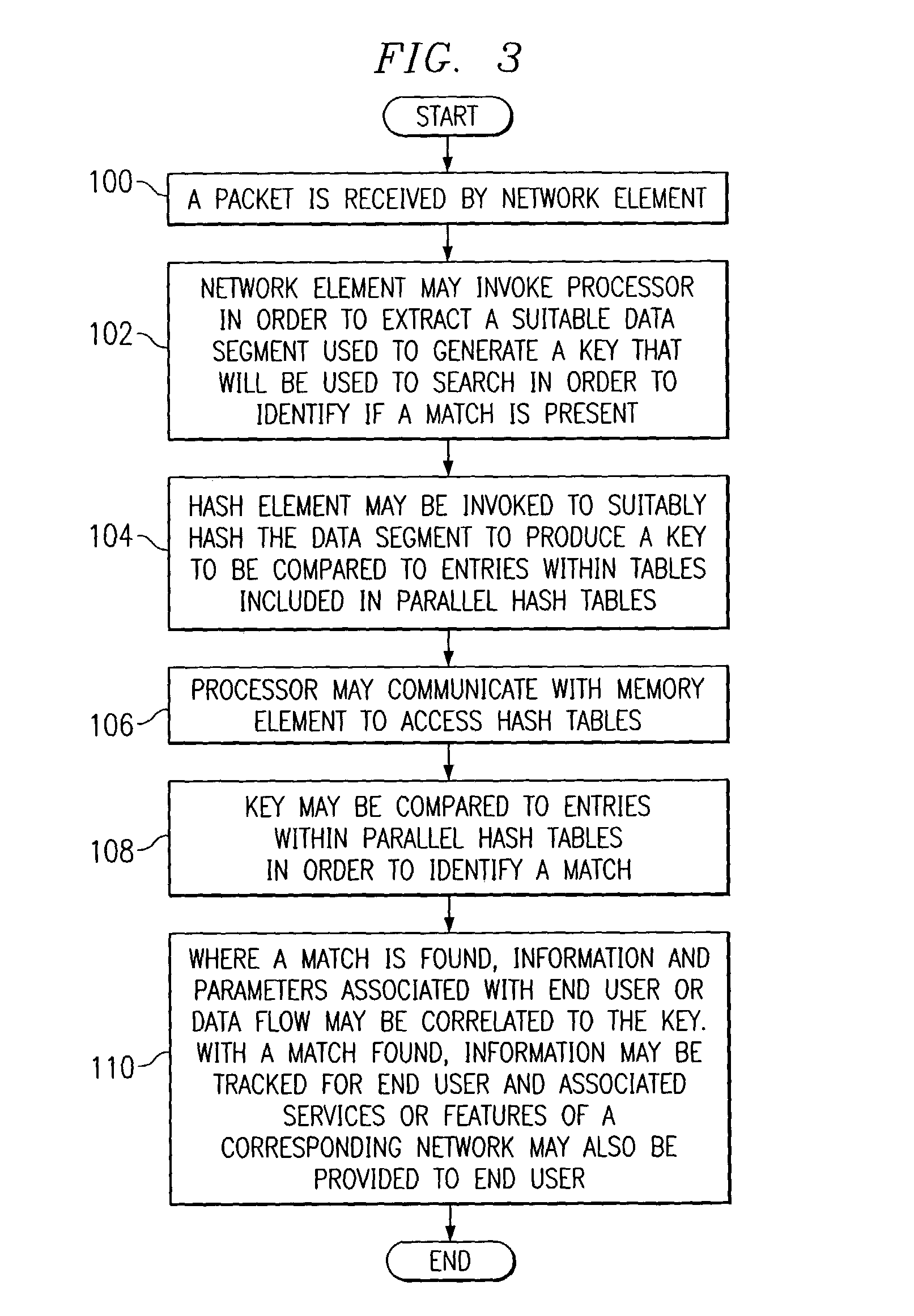
System and method for identifying data using parallel hashing
ActiveUS7069268B1Quick extractionQuick identificationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData streamTheoretical computer science
A method for identifying data is provided that includes receiving a data stream and performing a hashing operation on a portion of the data stream in order to identify a key that reflects an identity associated with the data stream. The method further includes storing a plurality of first and second hash table entries and comparing the key to the first and second hash table entries in order to evaluate if there is a match between the key and the first and second hash table entries.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for accelerating delivery of content in a computer network
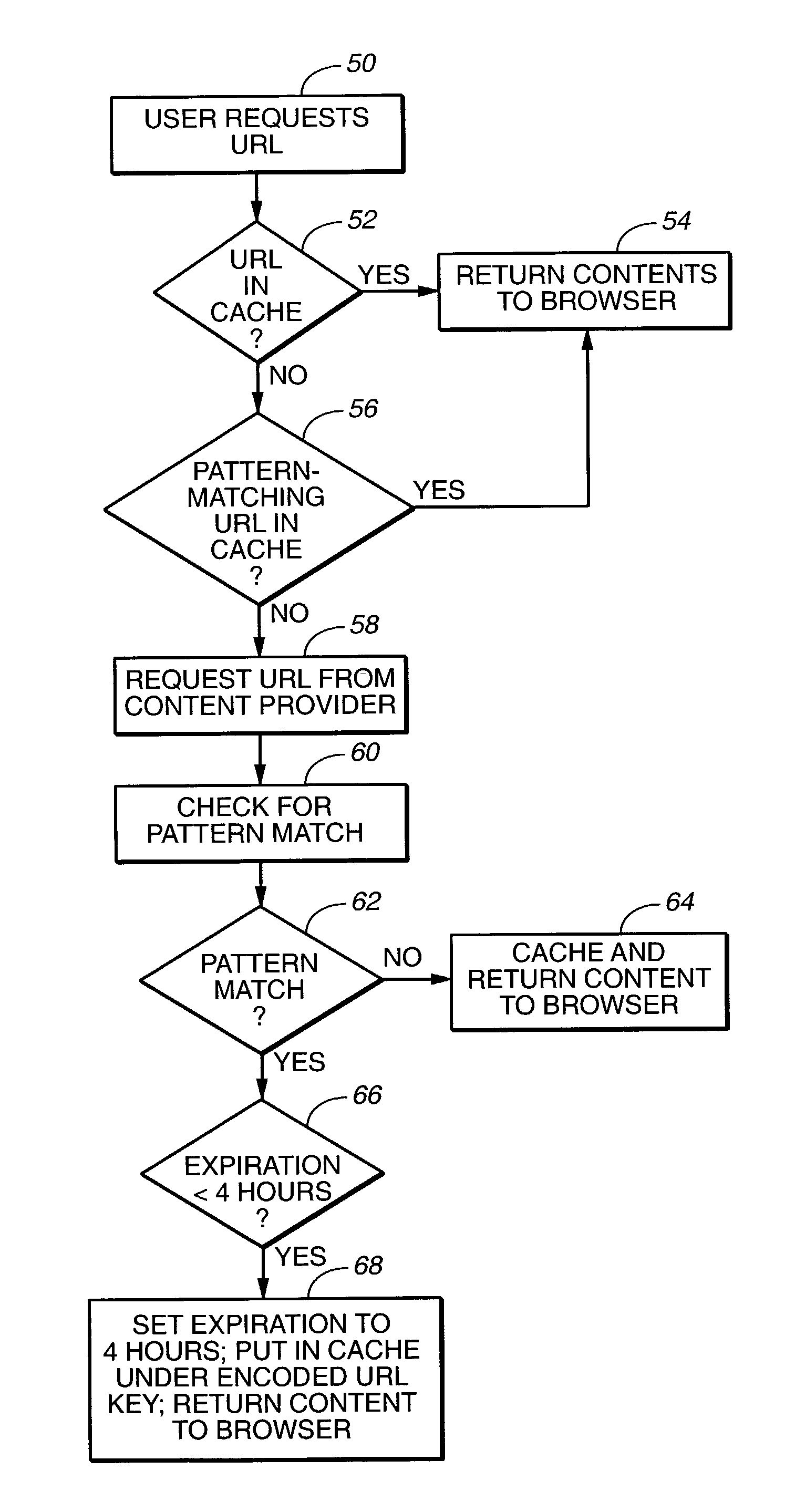
InactiveUS7054917B1Reduce network congestionReduce service latencyData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsThird partyClient-side
A method of reducing network congestion and service latency associated with downloading Web pages containing third party advertisements. In one embodiment, pattern recognition algorithms are employed to determine whether a request for a URL may be satisfied by the content associated with a URL which is contained in the client's cache; if there is a pattern match, the cached contents associated with the URL are delivered to the browser to satisfy the request. In another embodiment, images associated with HTML snippet ads are requested and cached by client software before they are requested by the browser downloading the Web page where the images will be displayed. In a third embodiment, latency is reduced by “time shifting,” wherein a cached ad is displayed while client software requests and caches the ad originally requested ad, which will be shown the next time the URL is requested. In other embodiments, this time-shifting technique may also be combined with the pattern-recognition technique and the approach to accelerating delivery of HTML snippet ads.
Owner:PROPEL SOFTWARE
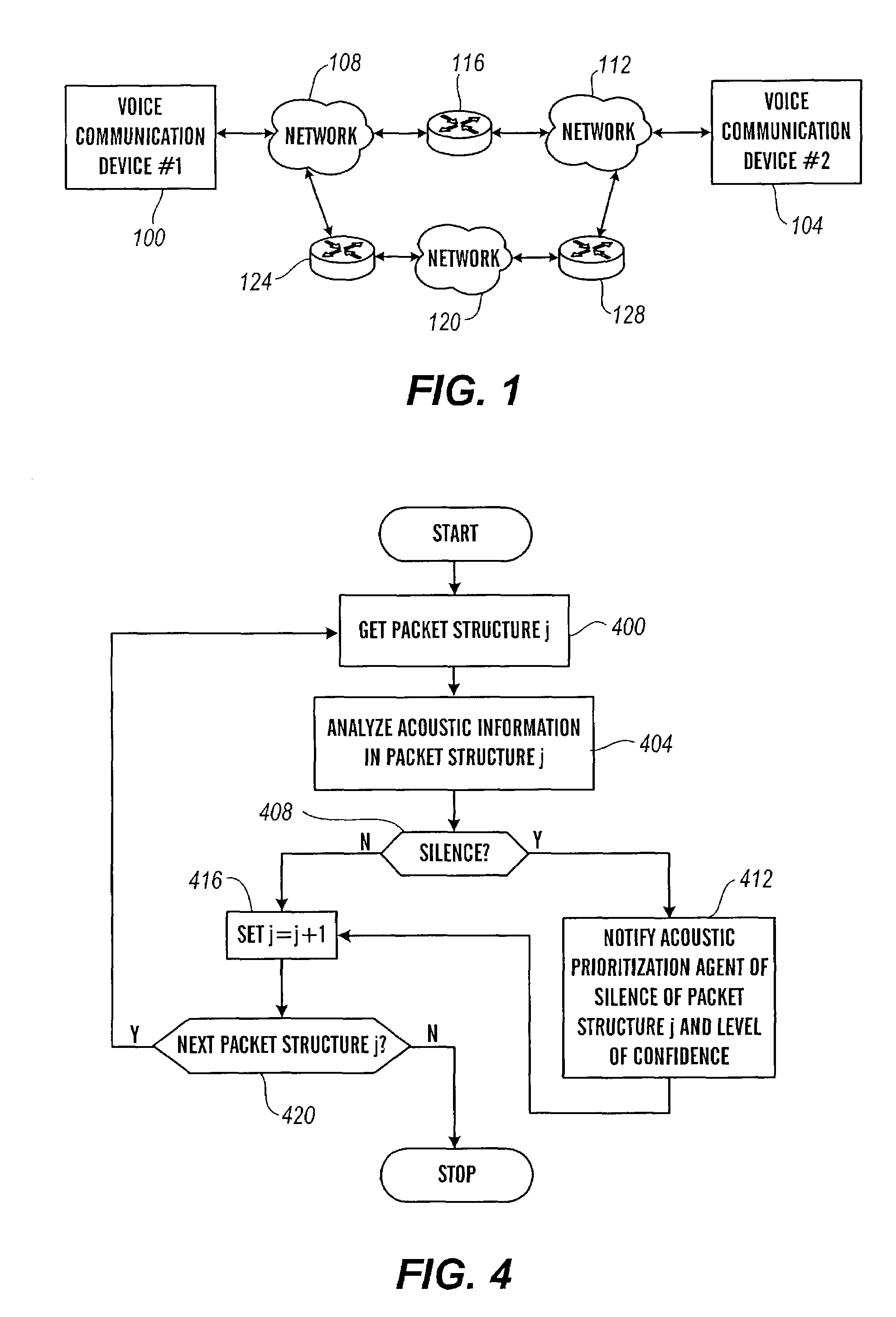
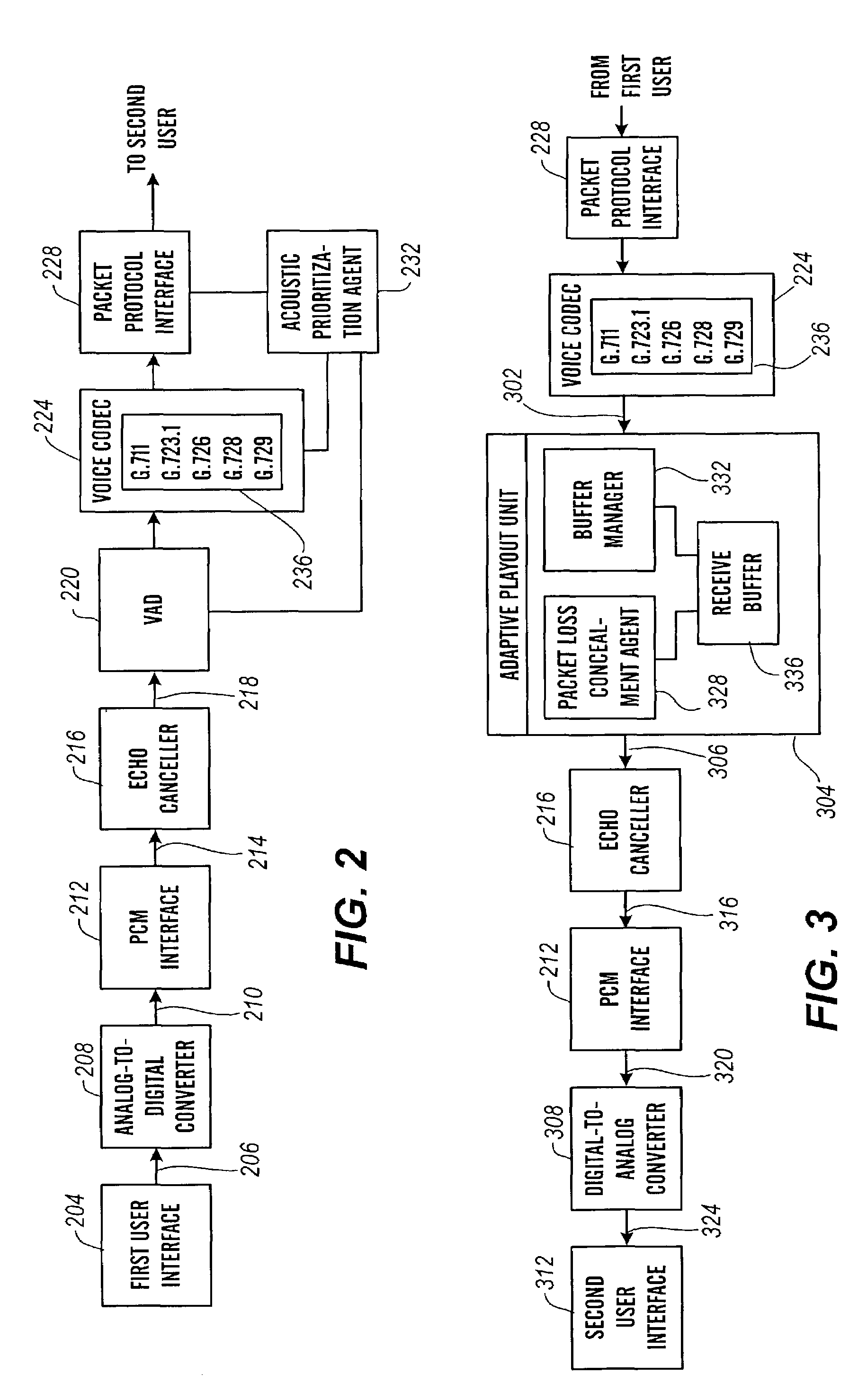
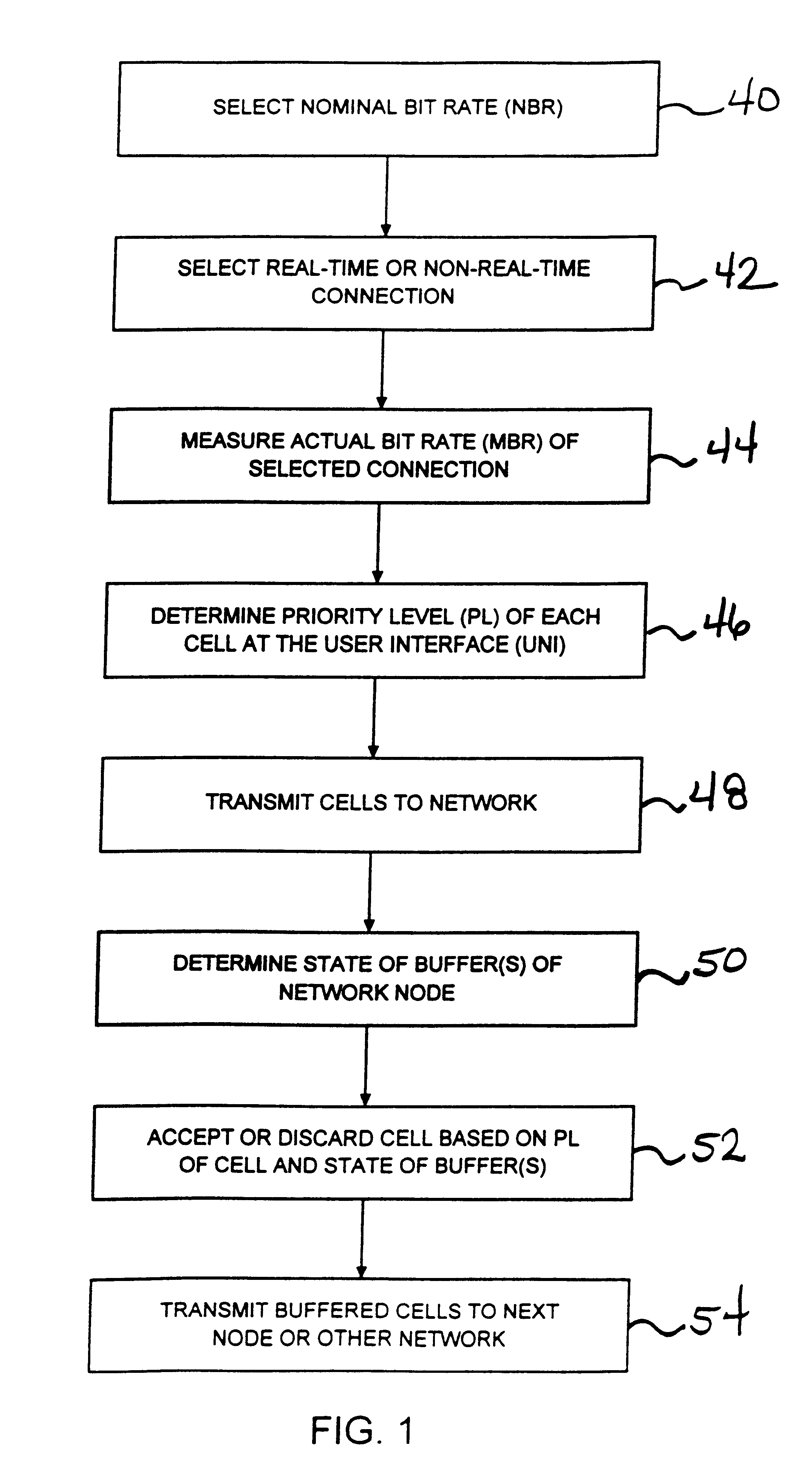
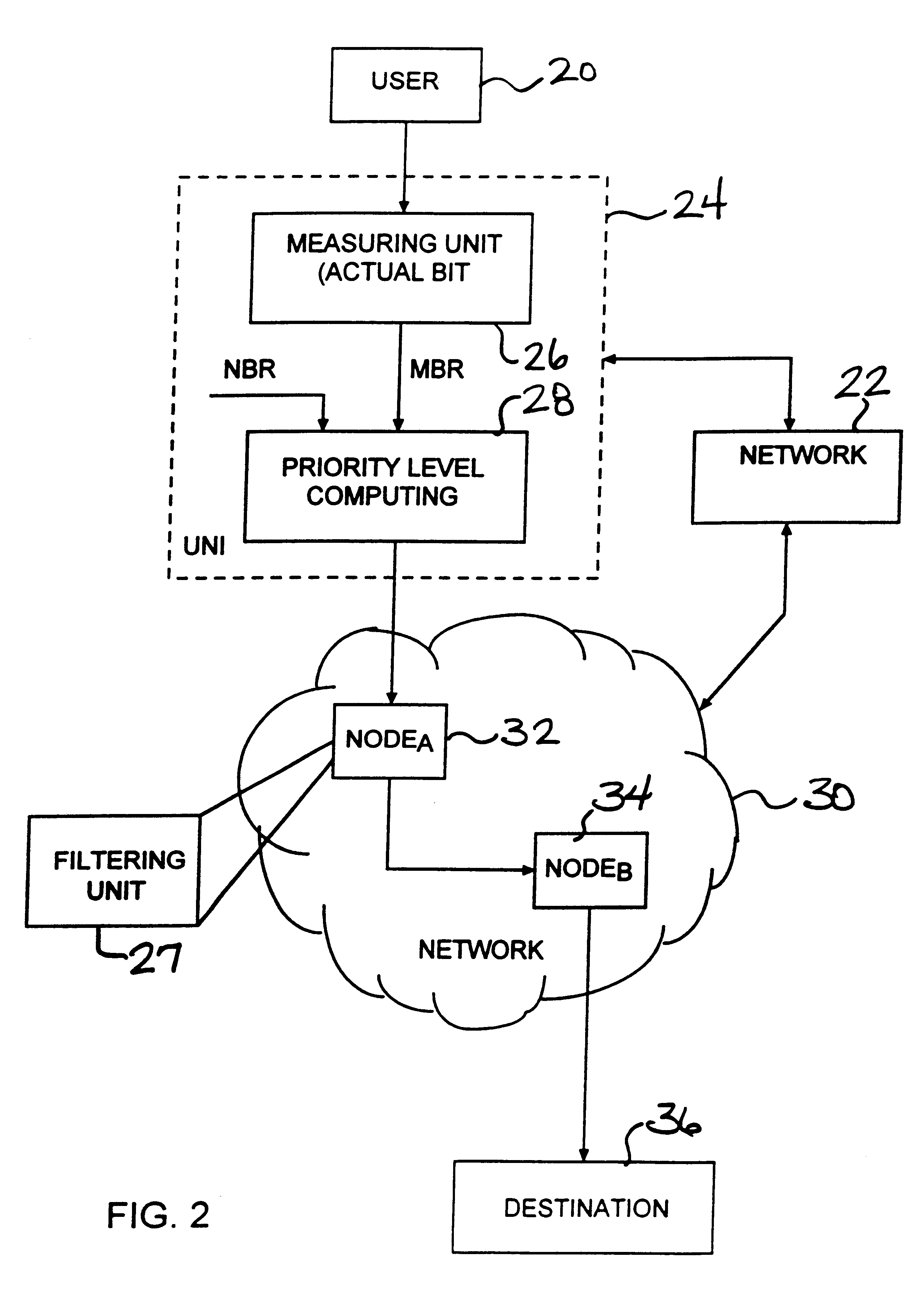
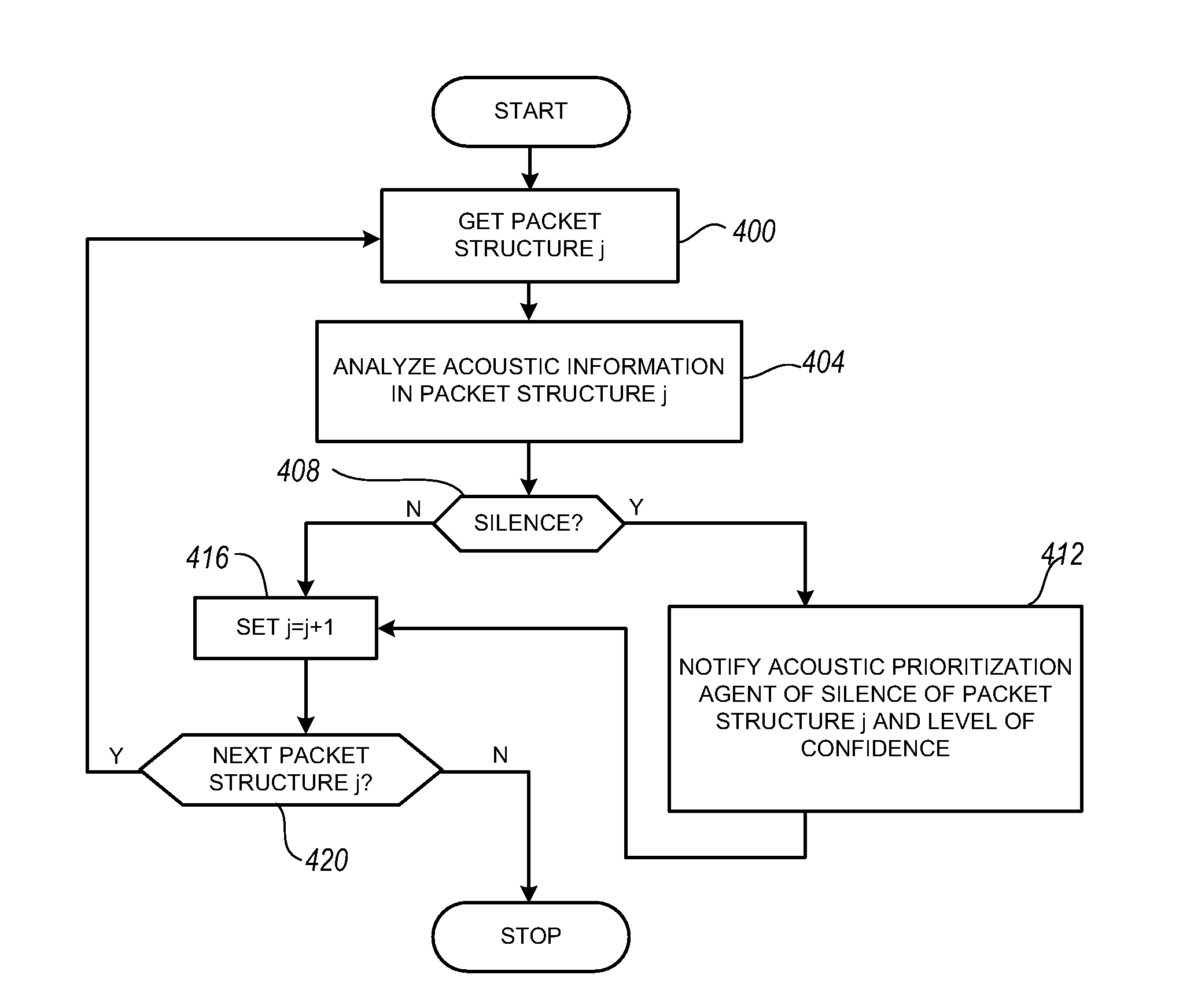
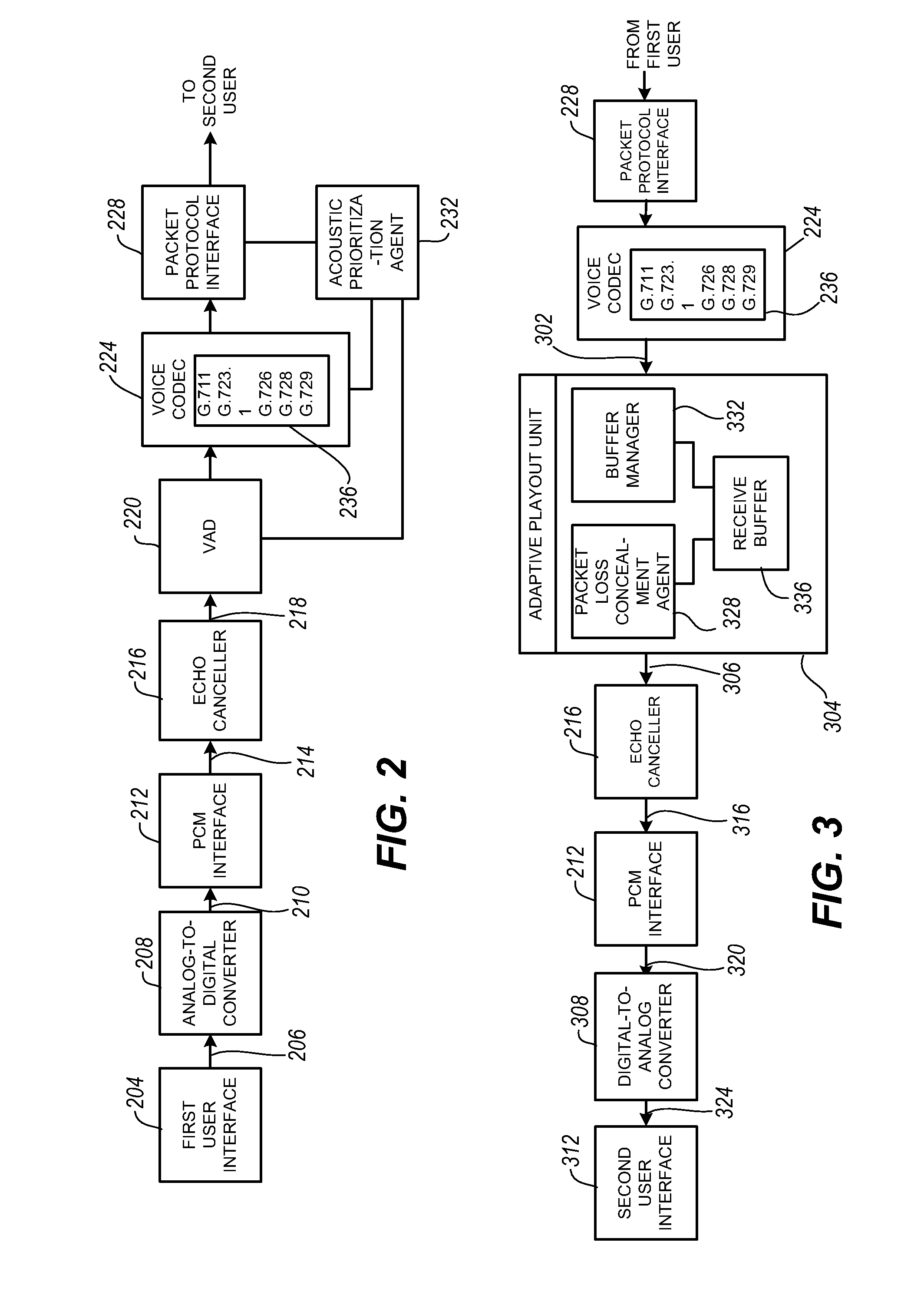
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
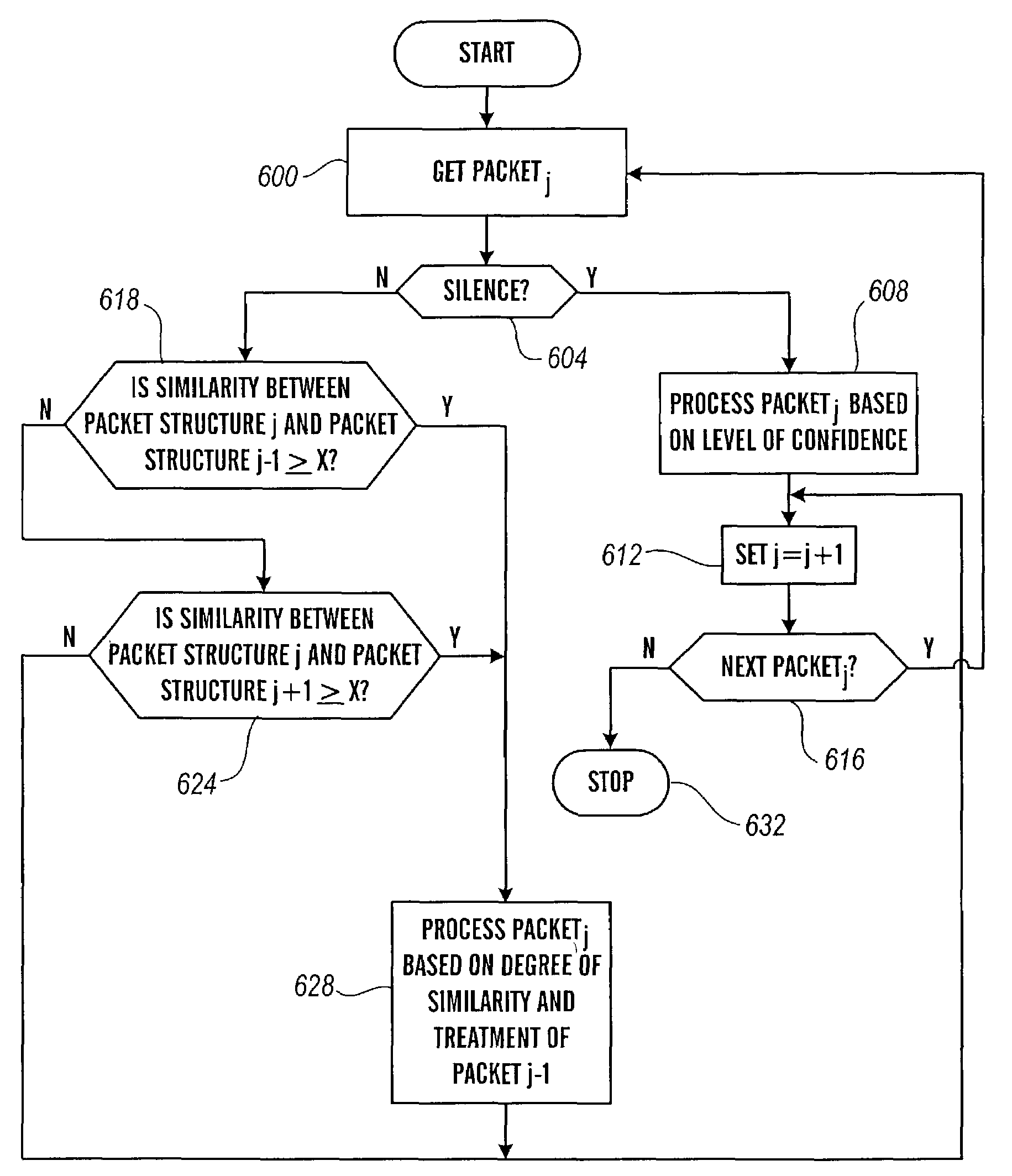
ActiveUS7359979B2Raise priorityReduce the possibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsSpeech recognitionVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
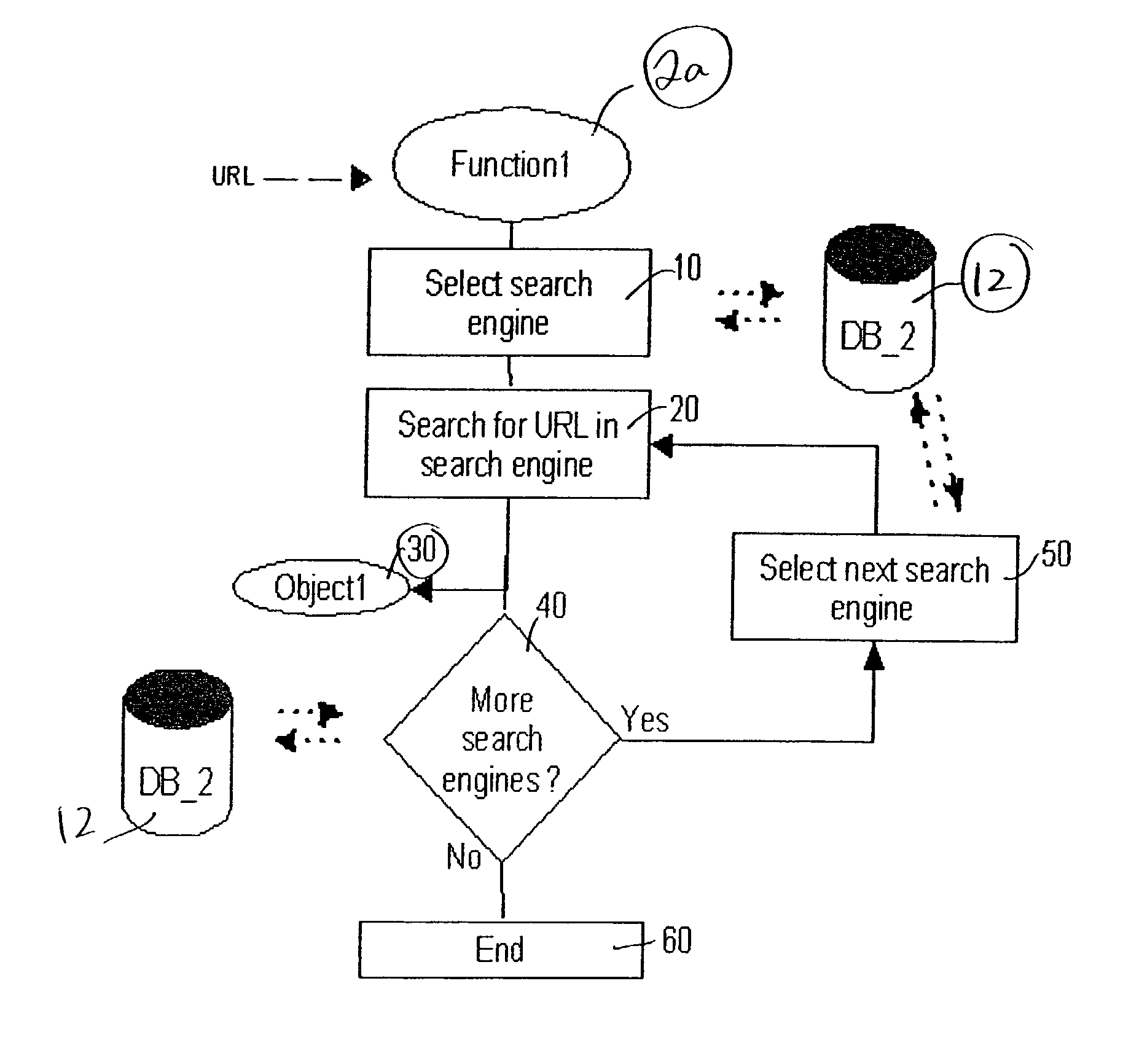
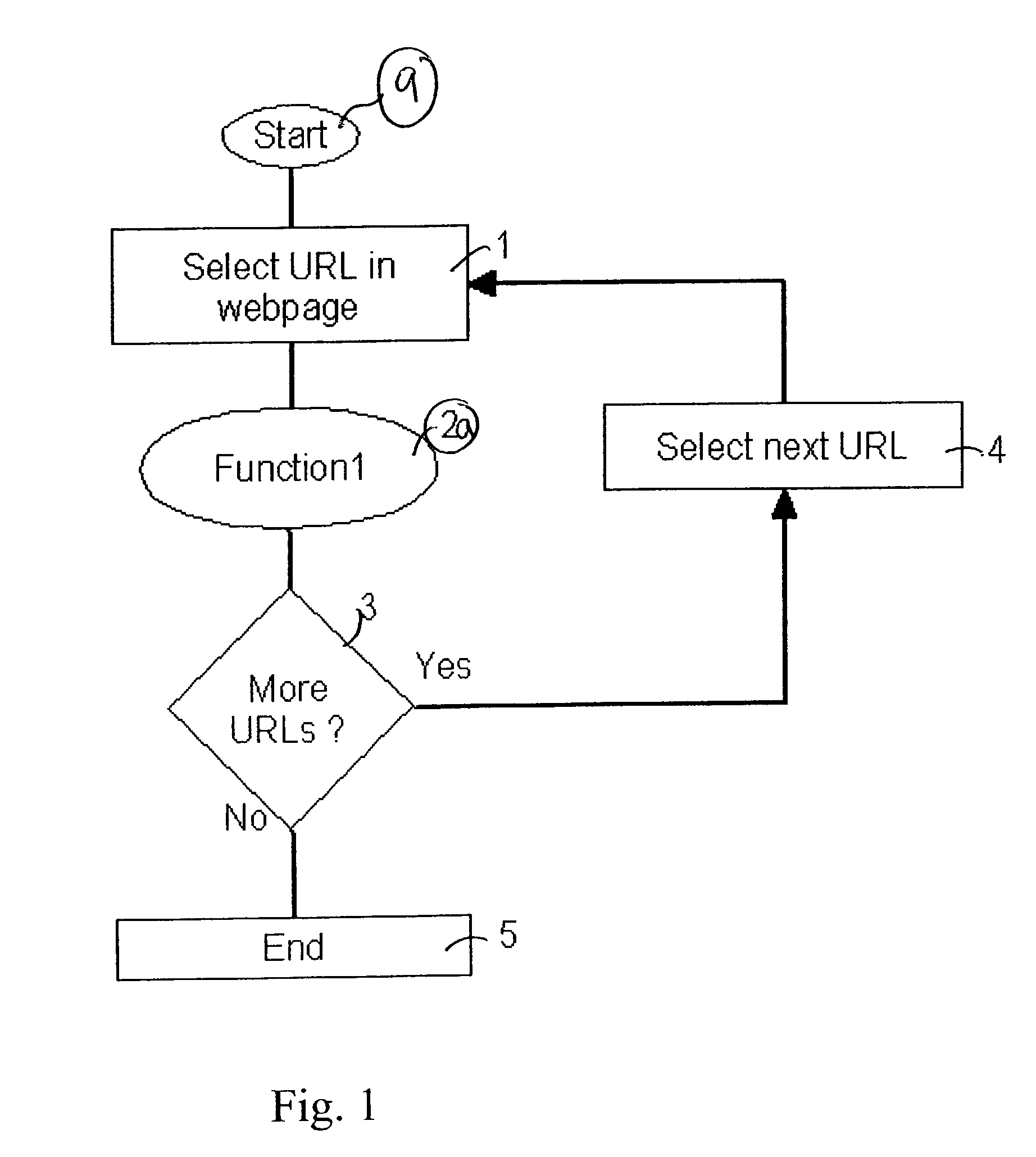
System and method for accessing content of a web page
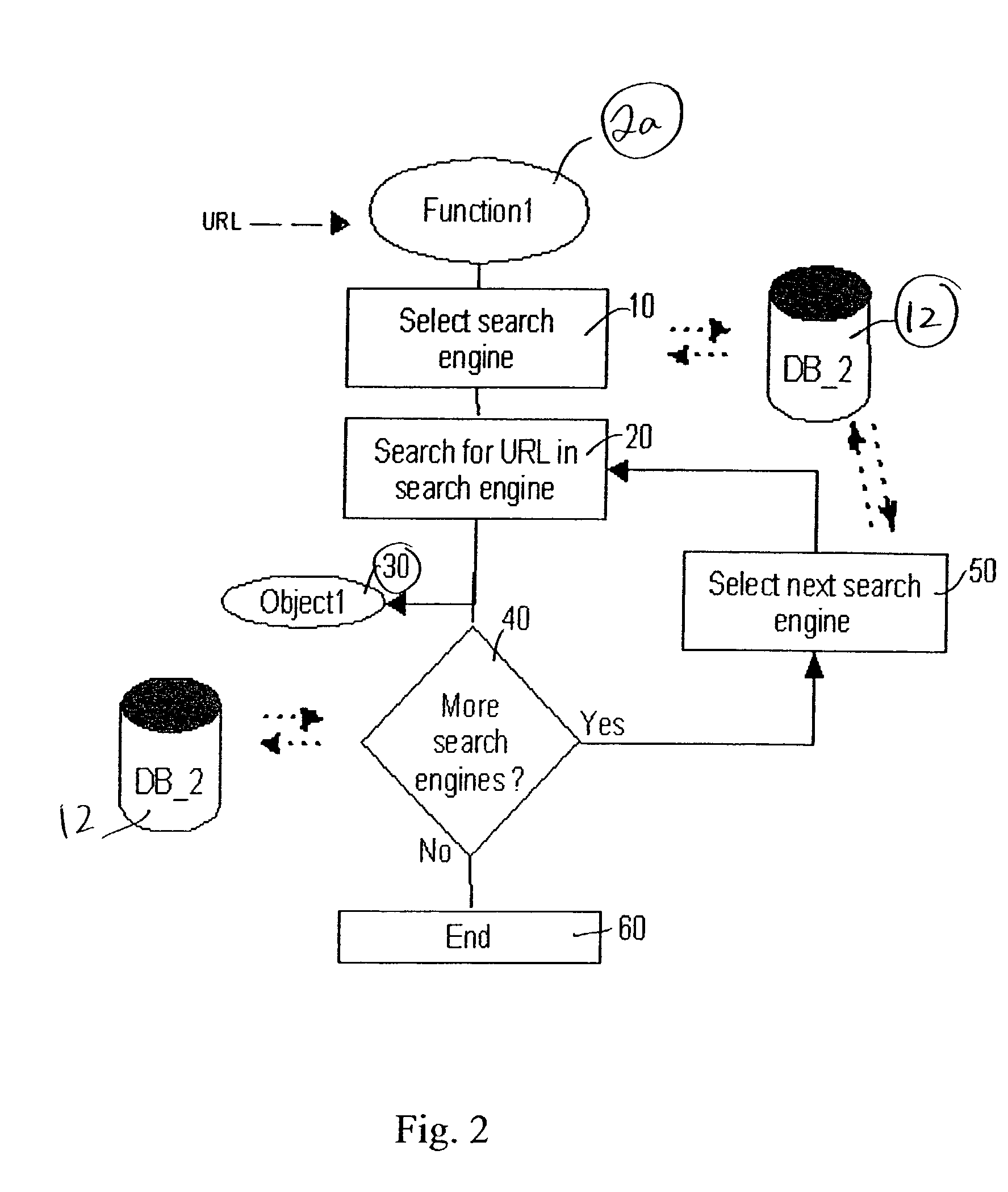
ActiveUS20040107296A1Reduce network congestionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalClient-sideWeb page
A process and system for visually displaying to a user at a client computer alternative web pages to a desired web page. The invention locates these alternative web pages in search engines by searching for alternative cached copies of web pages and / or mirror sites. A user may view a hotlink to a desired web page on an accessed web page and either be provided with a table of alternative web pages for manually selecting the alternative web page or the invention may automatically, dynamically select the best alternative web page to the originally selected web page.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
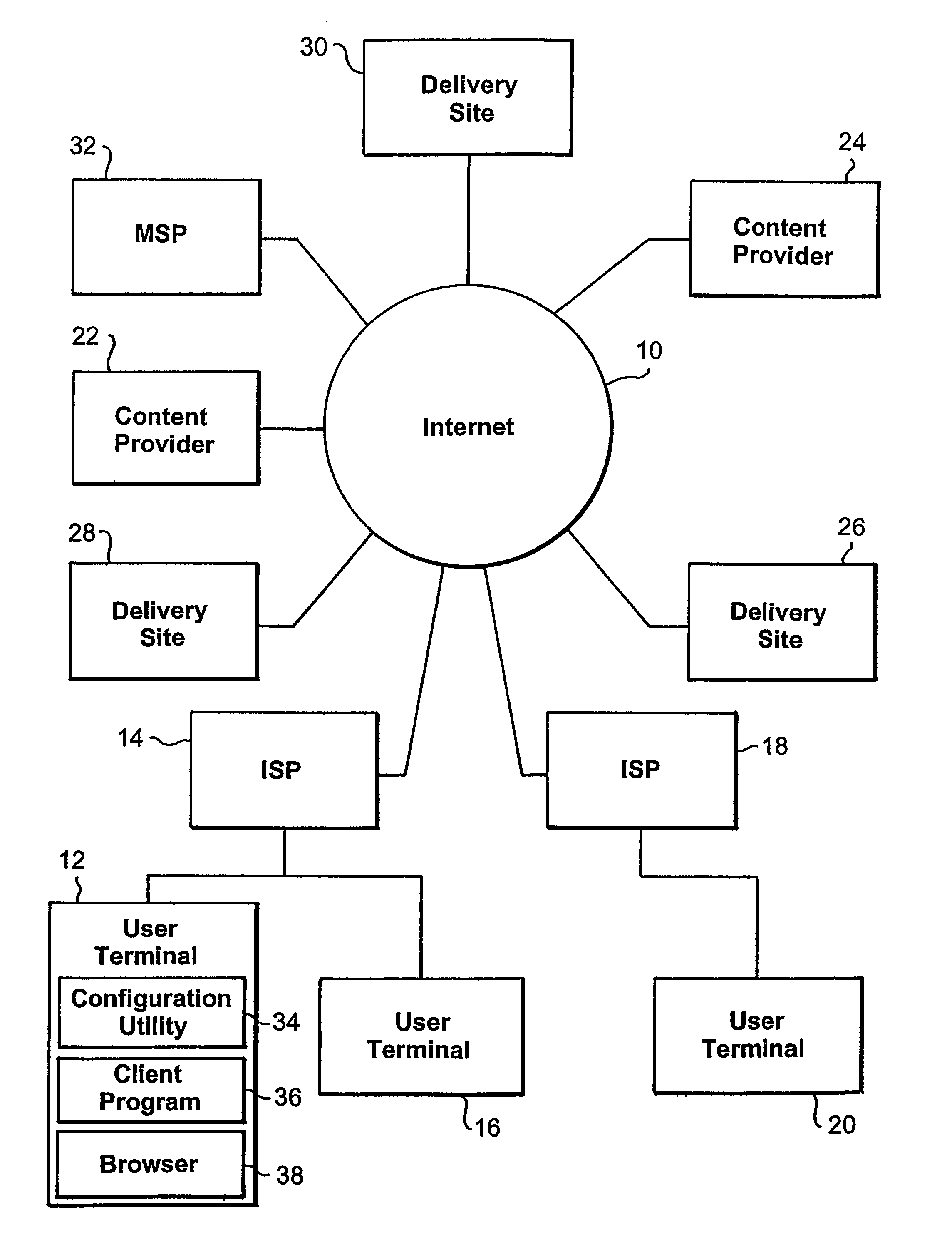
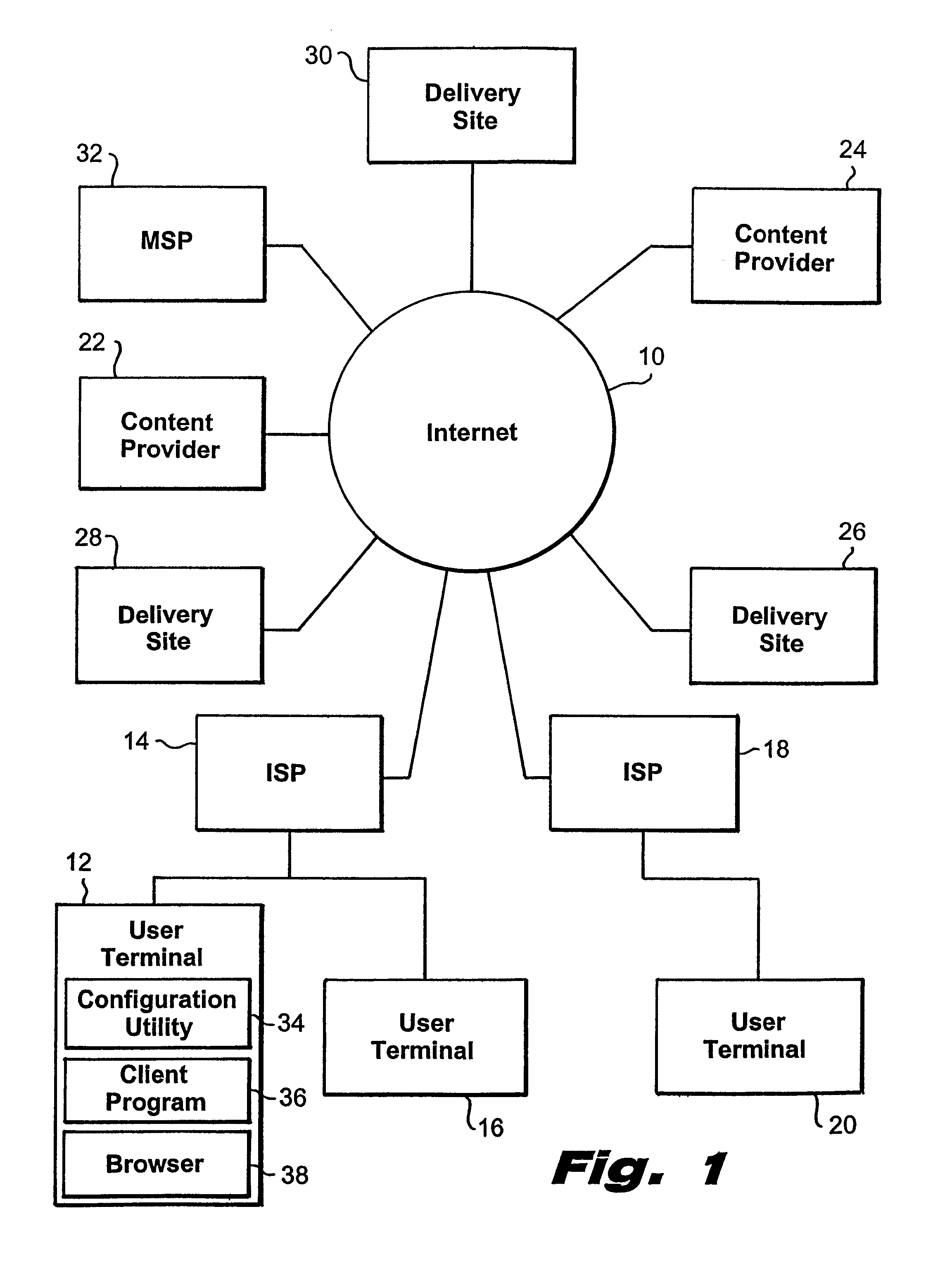
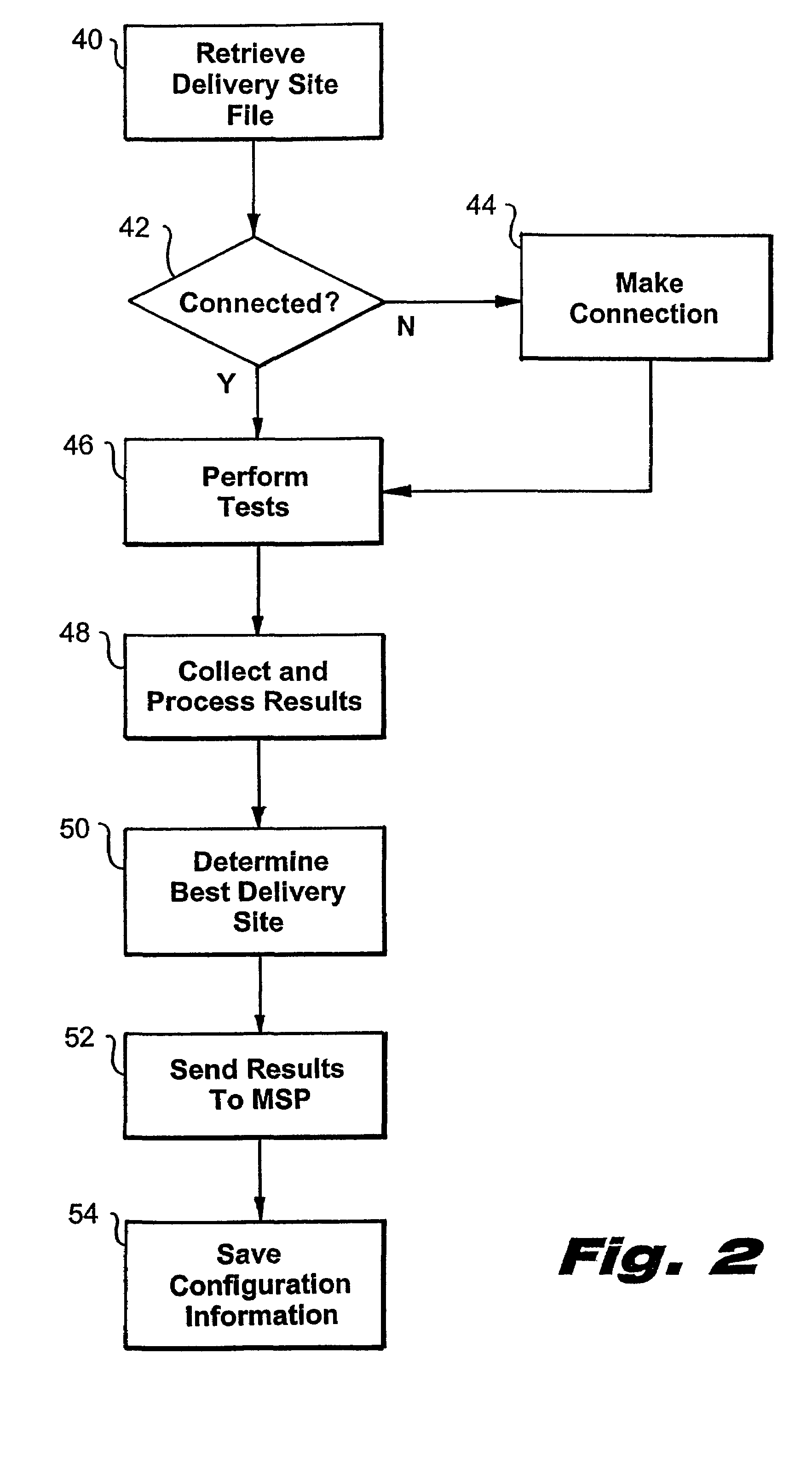
System and method for server-side optimization of data delivery on a distributed computer network
InactiveUS7366793B2Reduce in quantityImprove performanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsSystems managementDistributed computing
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
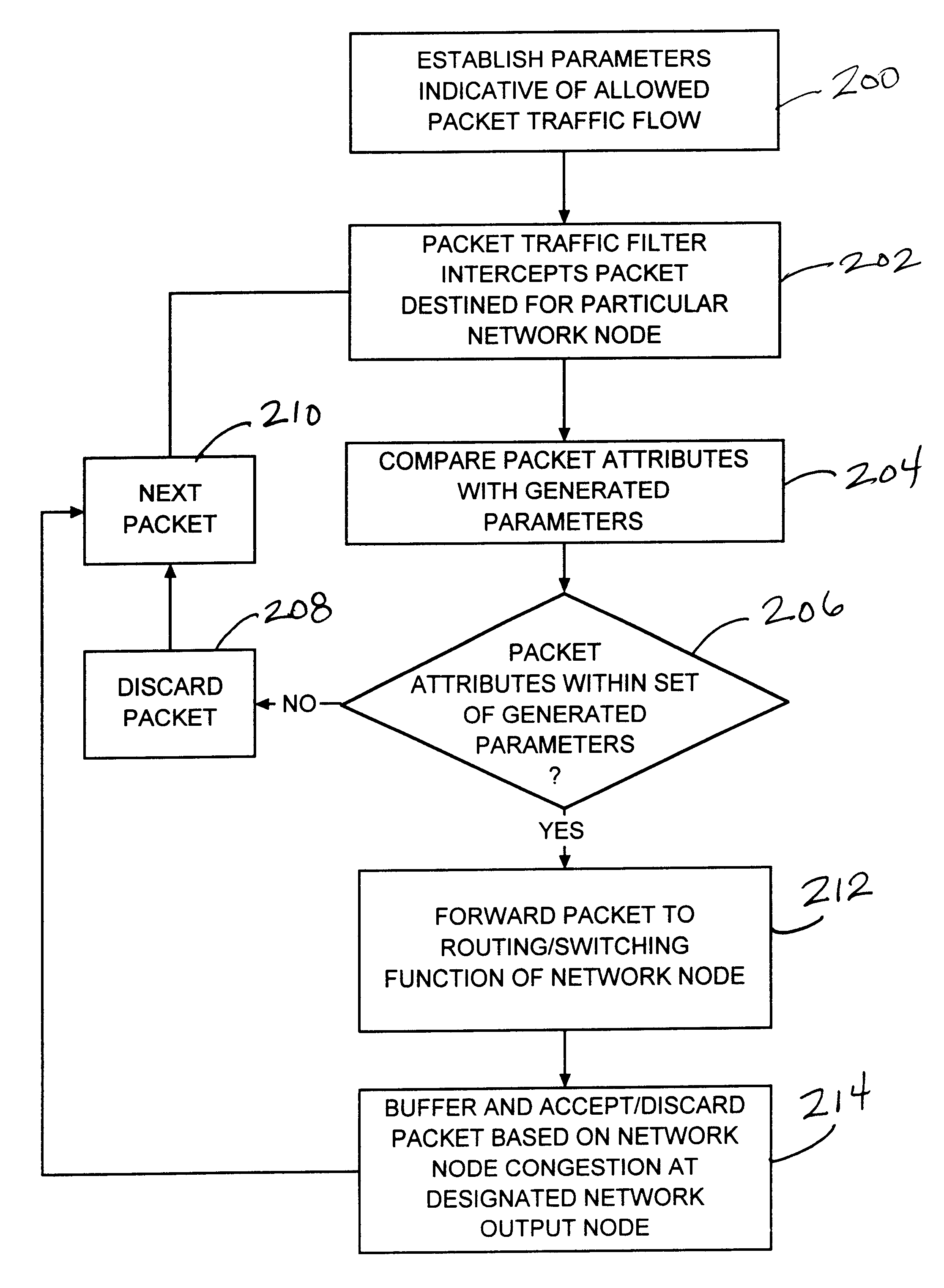
System and method for pre-filtering low priority packets at network nodes in a network service class utilizing a priority-based quality of service
InactiveUS6868061B1Lower the volumeReduce network congestionError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceNetwork packet
A system and method for reducing network node congestion by filtering out comparatively low priority packets prior to execution of other node functions, such as routing and switching, in packet-based network transmissions. The volume of packets is reduced by intercepting the information packets prior to their input to the network node. A portion of the intercepted packets are filtered out based on parameters corresponding to a probable packet acceptability at the network node. The remaining portion of the intercepted packets are forwarded to the network node for processing by the network packet functions.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
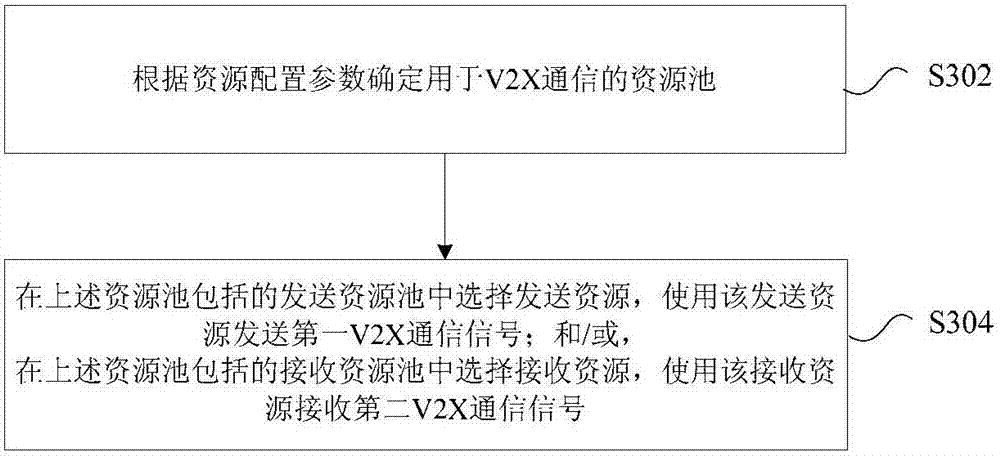
V2X communication method and apparatus in Internet of Vehicles
InactiveCN107040960AImprove power efficiencyReduce conflictPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementResource poolThe Internet
The invention provides a V2X communication method and apparatus in the Internet of Vehicles. The method comprises the following steps: determining a resource pool for V2X communication according to resource configuration parameters; selecting sending resources in the sending resources contained in the resource pool, and using the sending resources to send a first V2X communication signal; and / or, selecting receiving resources in the receiving resources contained in the resource pool, and using the receiving resources to receive a second V2X communication signal. By adoption of the V2X communication method and apparatus, the problems of low power consumption efficiency of end-to-end communication of the Internet of Vehicles, communication resource conflict and network congestion in the prior art are solved, and thus the effects of improving the power consumption efficiency of the end-to-end communication of the Internet of Vehicles, and relieving the communication resource conflict and the network congestion are realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
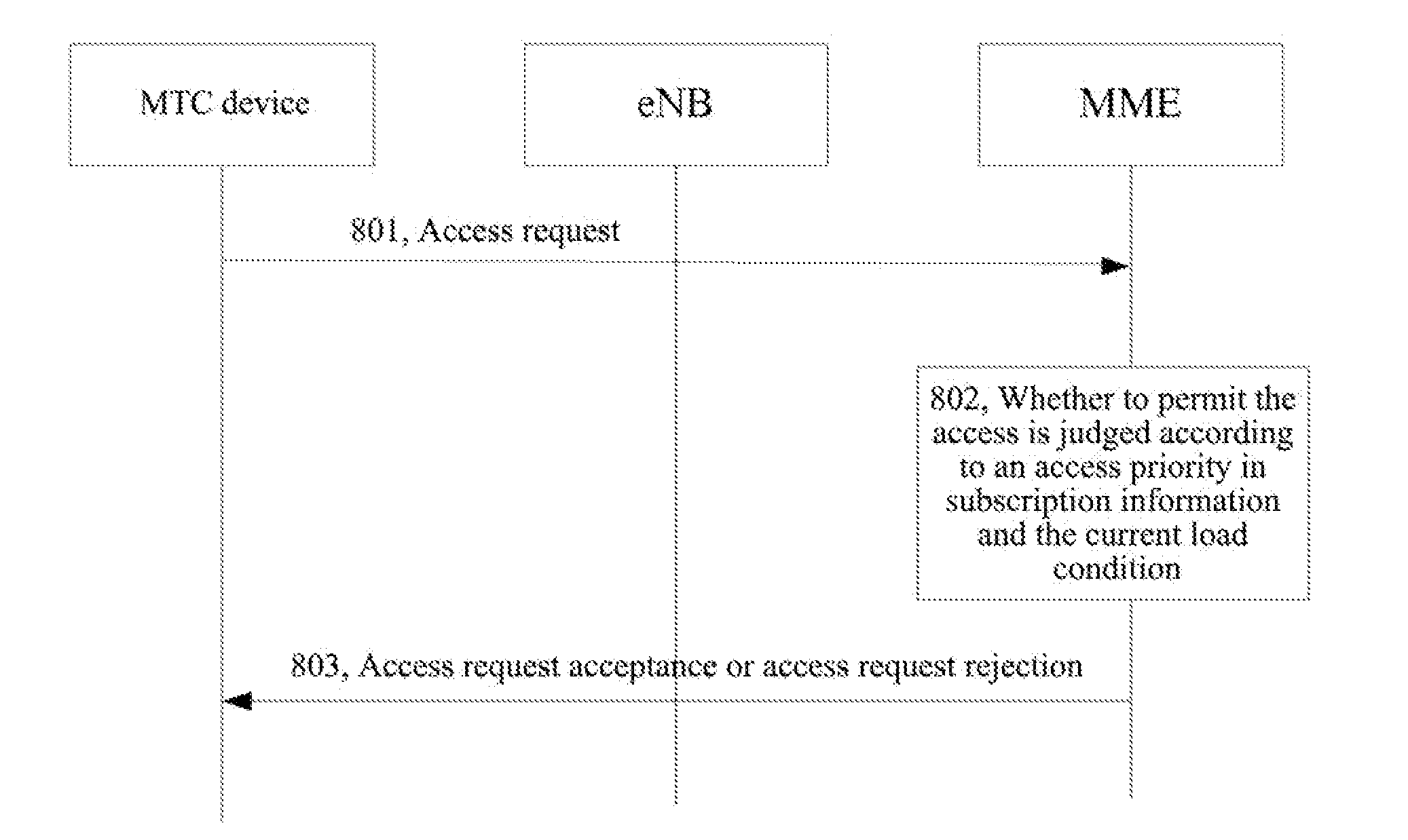
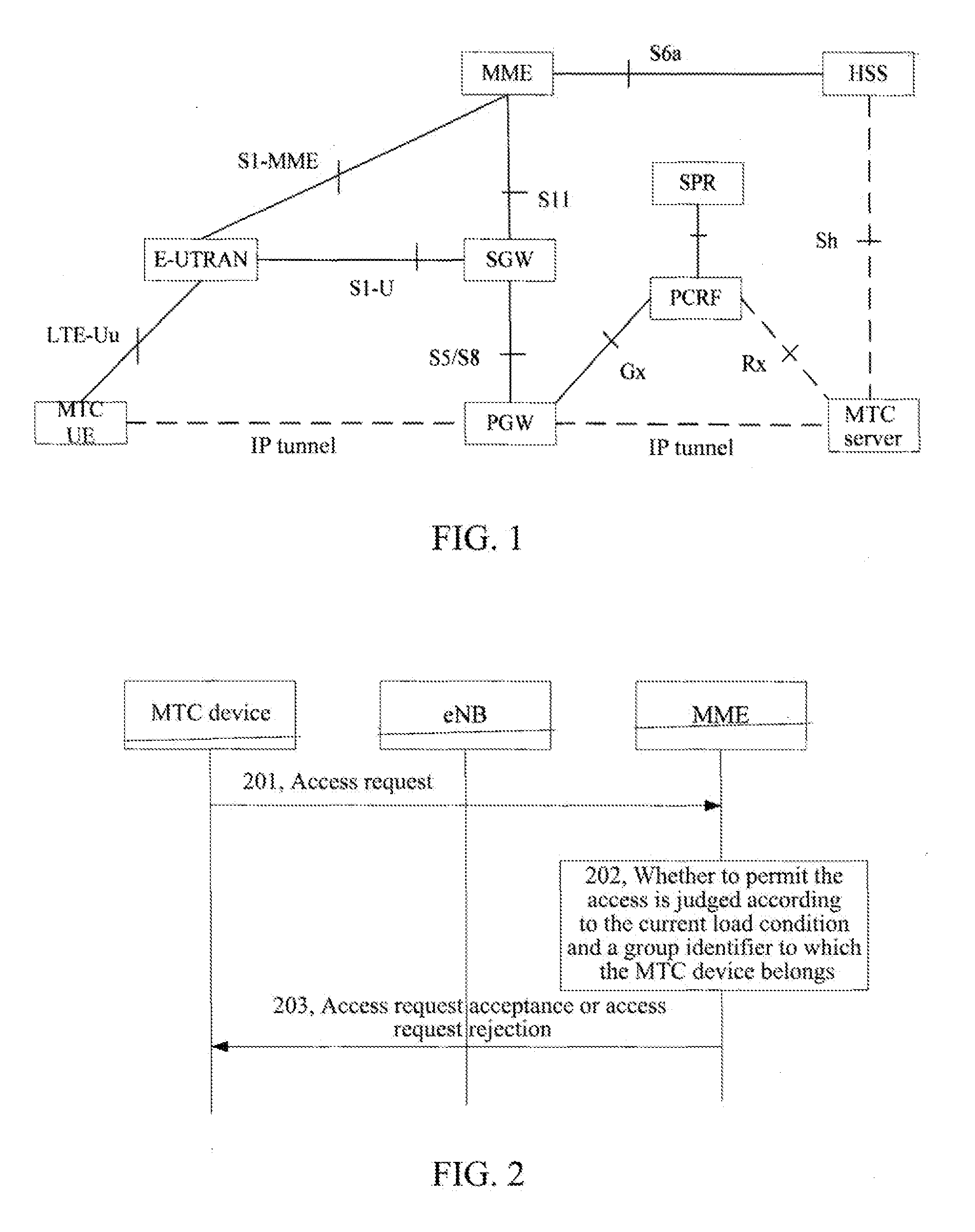
Method and System for Controlling Access of Machine Type Communications Devices
ActiveUS20130044596A1Reduce network congestionOptimize network resourcesError preventionTransmission systemsCommunication deviceAccess control
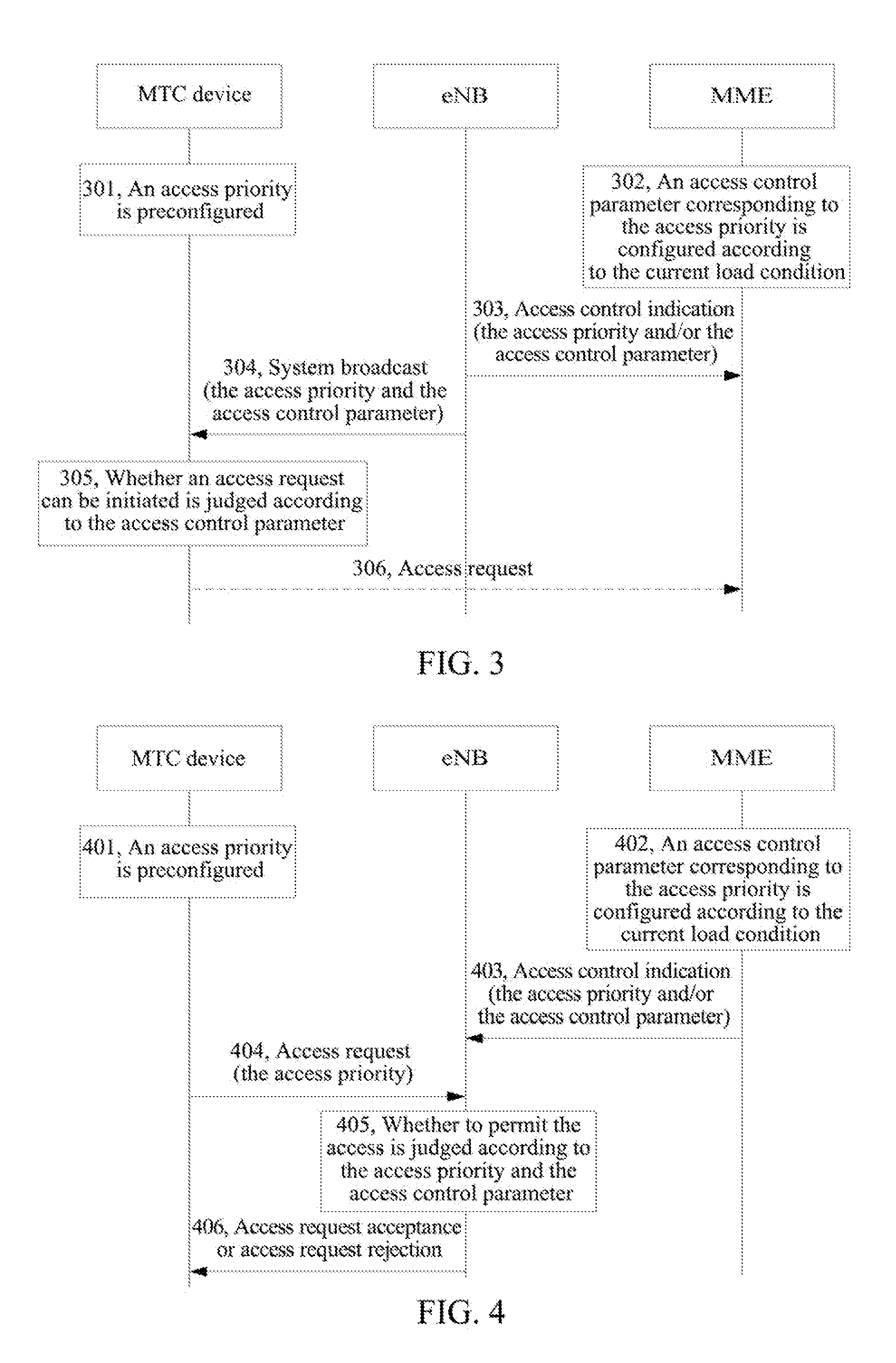
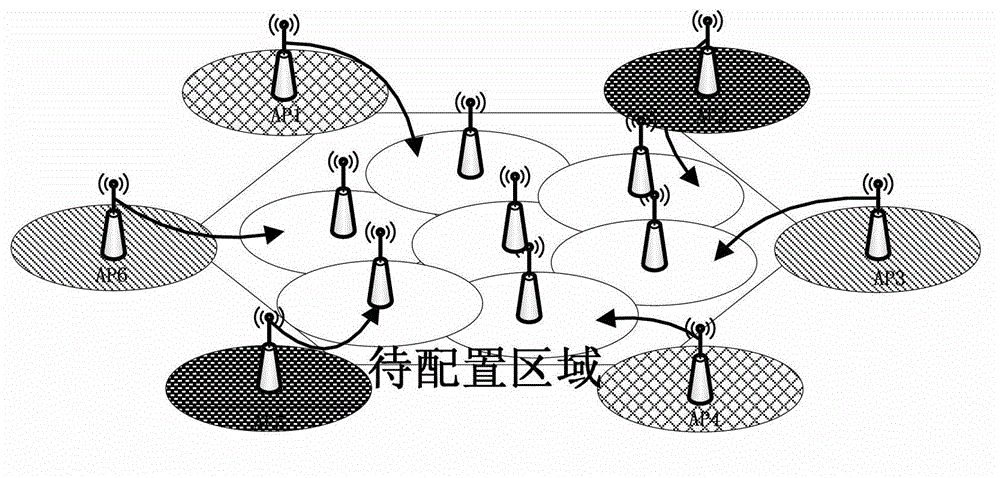
A method for controlling access of machine type communications device is provided by the present invention. The method includes: configuring an access priority to a machine type communications device; a network side configuring a corresponding access control parameter for an access priority needing an access control according to the current network load information, and sending the access priority needing the access control and the access control parameter to the machine type communications device; and according to an access priority of the machine type communications device and the received the access priority needing the access control and the access control parameter, the machine type communications device judging whether an access request can be initiated. A system for controlling access of the machine type communications device is also provided by the present invention.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Information channel and power combined self-configuration method for APs (Access Points) in wireless local area network
InactiveCN103338504AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce network congestionPower managementNetwork topologiesPower parameterBusiness efficiency
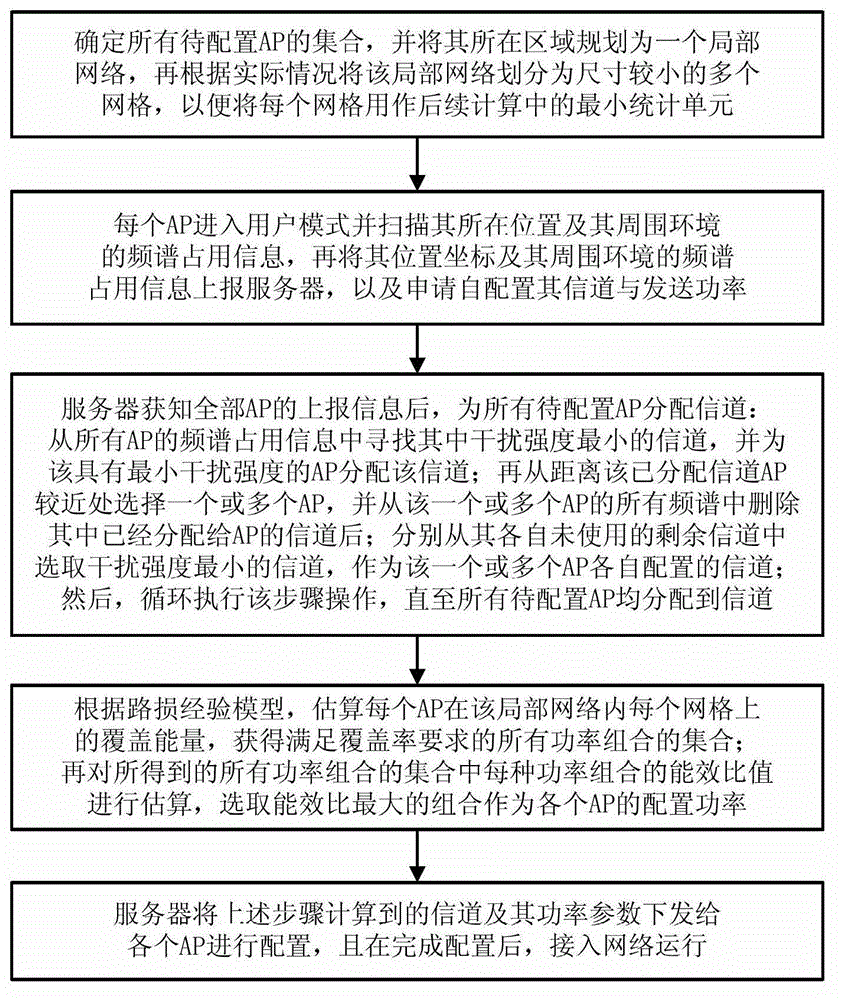
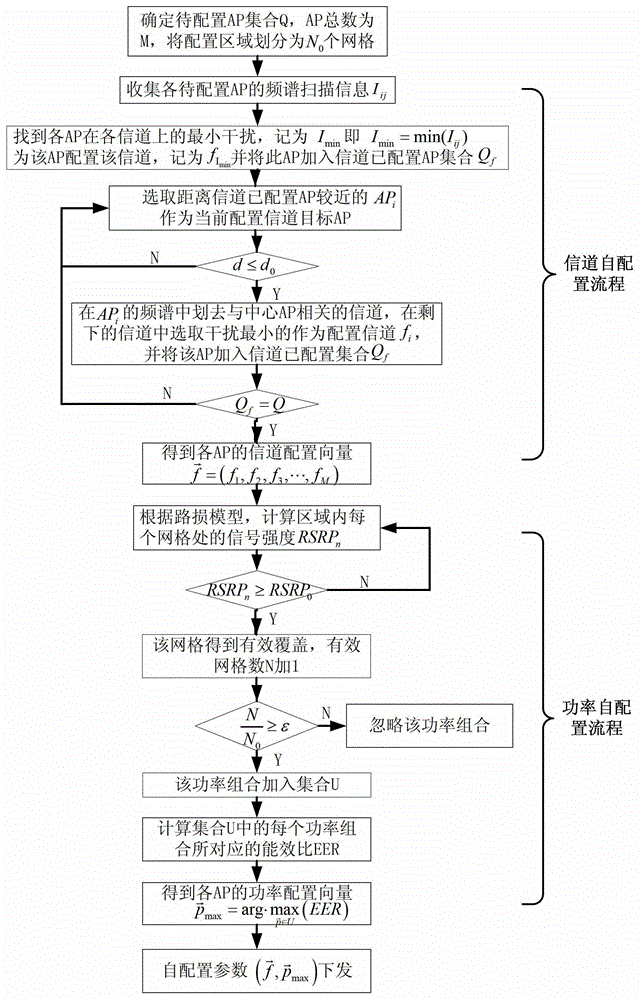
An information channel and power combined self-configuration method for APs (Access Points) in wireless local area network comprises the steps as follows: the area where the APs to be configured are located is selected as a local network, and the local network is divided into a plurality of grids according to practical conditions; each AP sends out a self-configuration request to a server and simultaneously reports the position coordinate of the AP and the scanned frequency spectrum use information of the ambient environment of the AP; the server analyzes the positions and the ambient environments of the APs according to the self-configuration requests of the APs, and allocates information channels and power parameters to the APs to be configured in combination with the use conditions of AP information channels in neighbor cells under the premises of meeting the coverage rate requirement and minimizing same frequency interference, that is, first the signal energy of each grid is estimated according to a path loss empirical model to learn the network coverage condition, and then the information channel and the power parameter eventually configured for each AP is obtained through calculation based on the principle that the energy efficiency ratio is highest, and are sent to the AP to be configured. The method provided by the invention is quick and effective, guarantees the region coverage requirement, avoids same frequency interference to the maximum extent and guarantees that the energy efficiency ratio of the network is highest.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
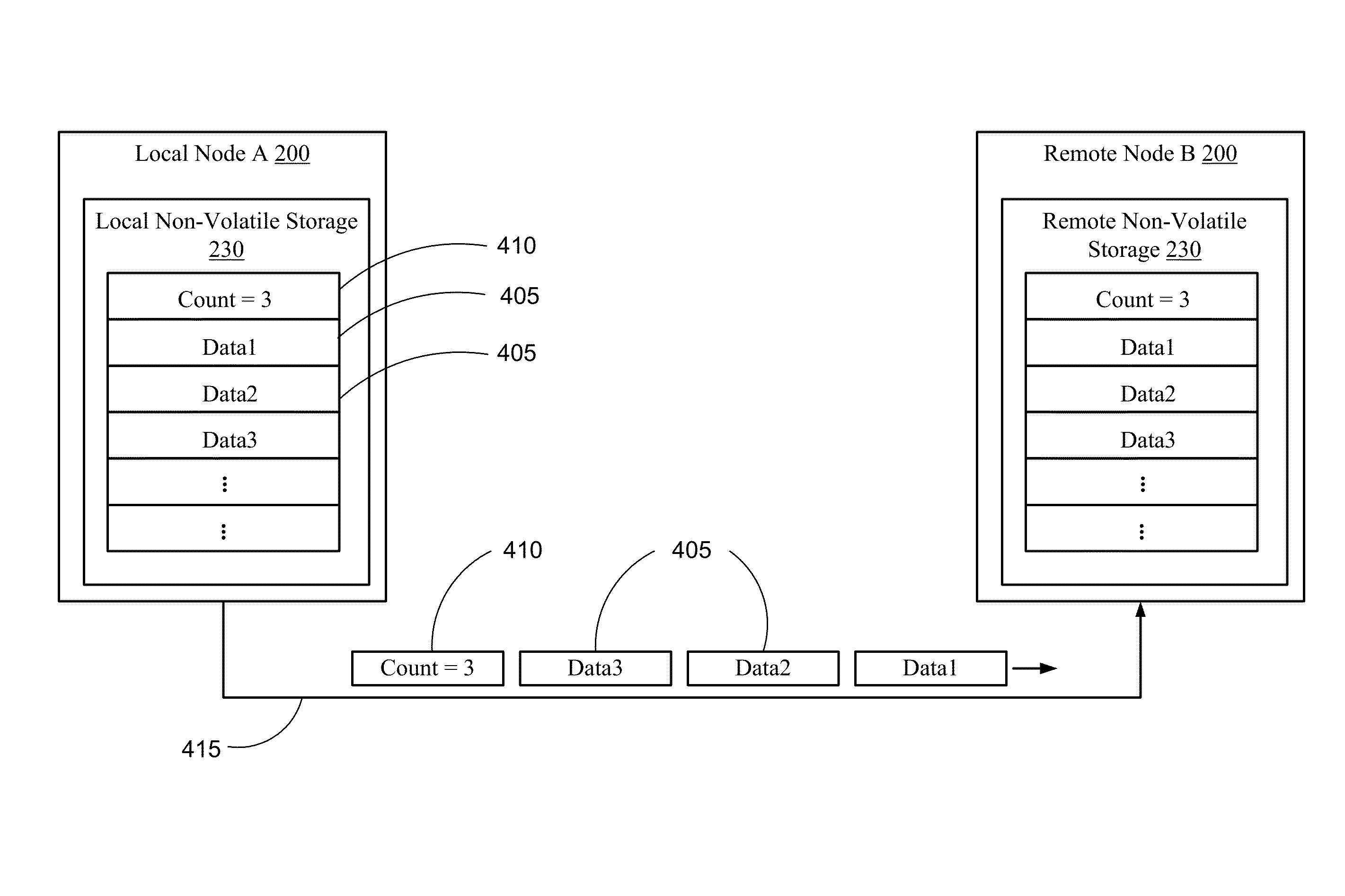
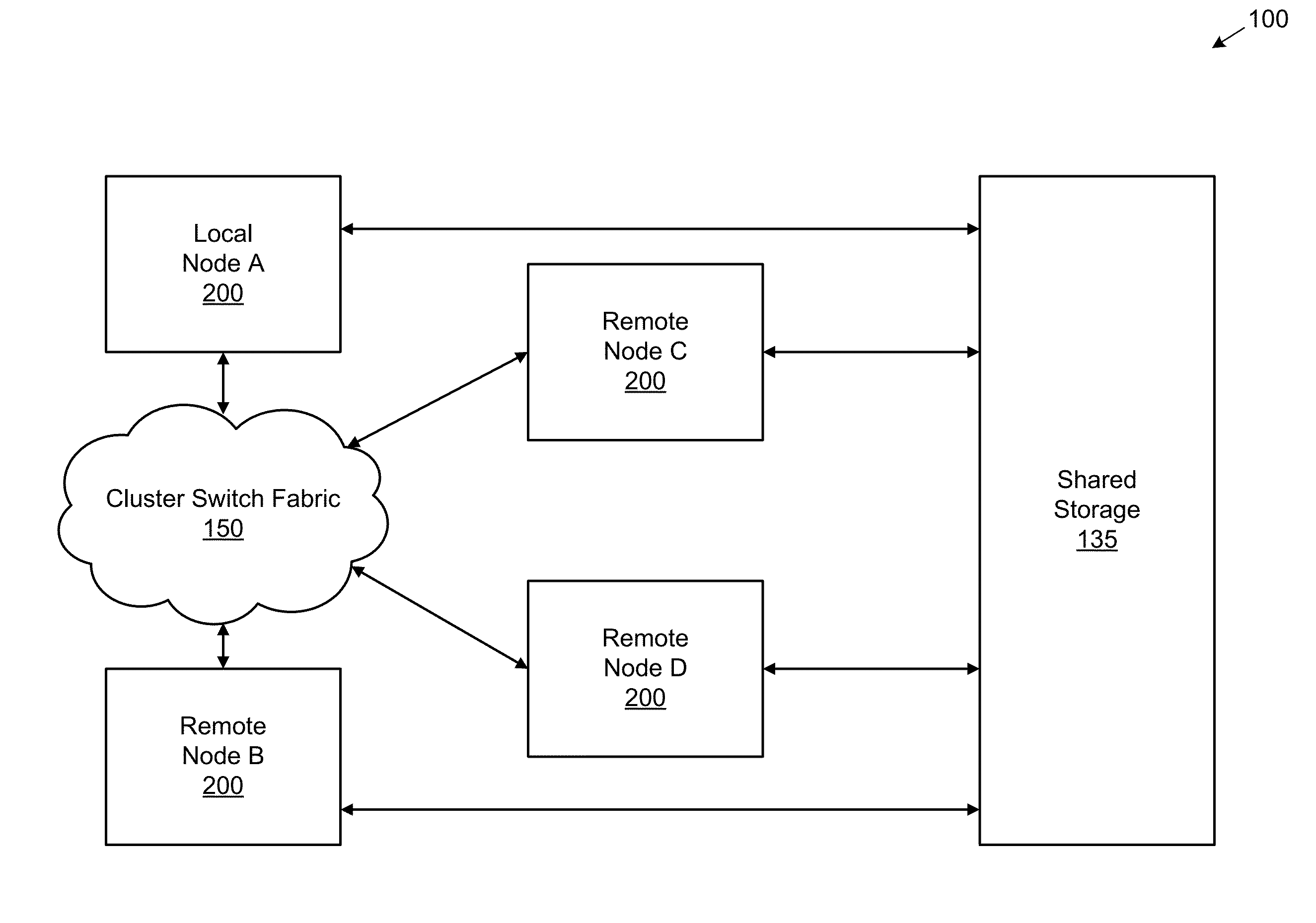
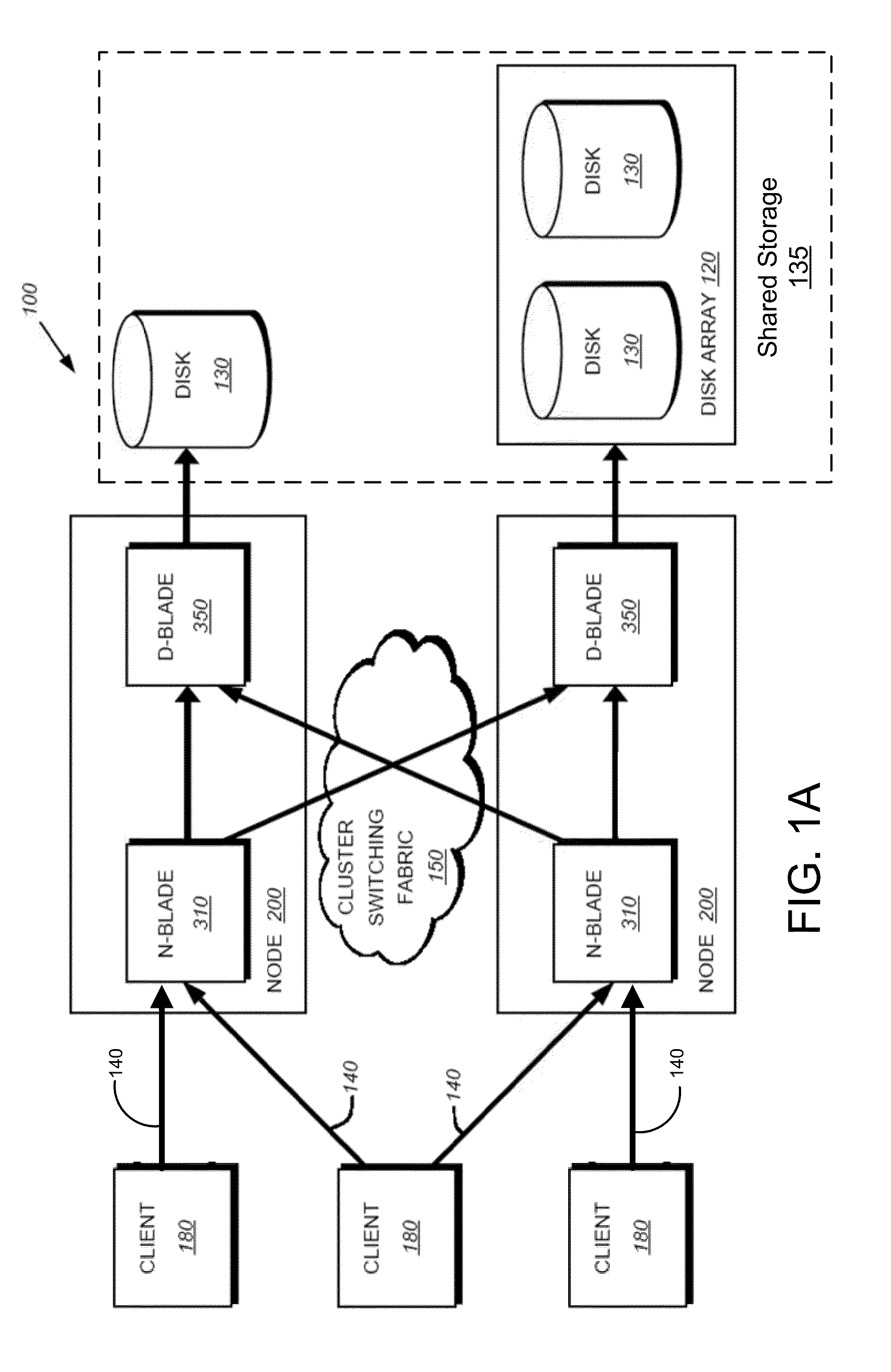
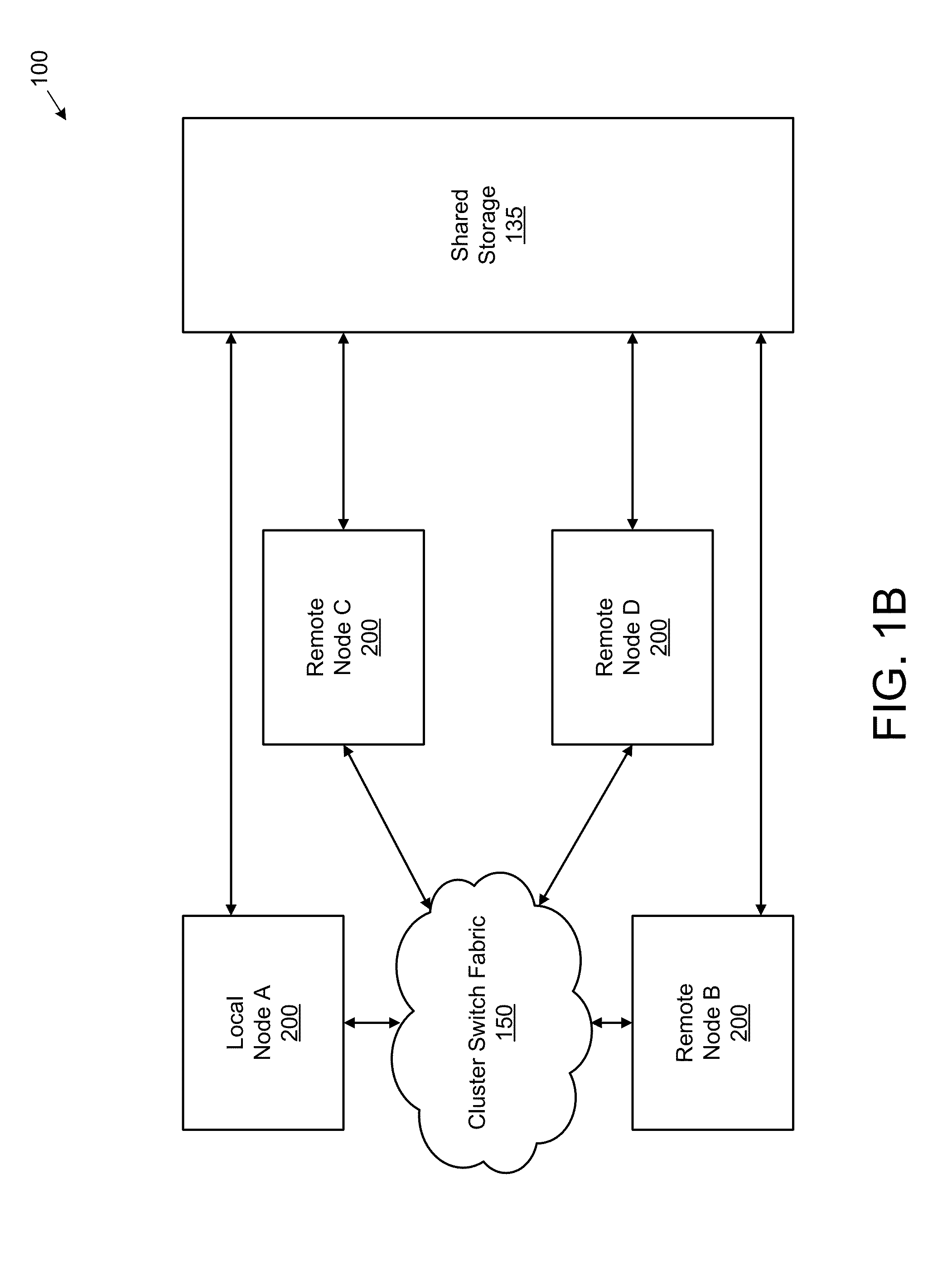
Coalescing metadata for mirroring to a remote node in a cluster storage system
ActiveUS8386433B1Network congestionReduce in quantityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setDatabase
Described herein are a system and method for remote mirroring / copying data and metadata sets from a local node to a remote node that reduces the number of metadata sets that are mirrored. In some embodiments, the local node may coalesce metadata sets into metadata chains, each metadata chain comprising a grouping of two or more metadata sets. In some instances, a “representative” metadata set of a metadata chain may be selected for sending to the remote node for storing, wherein the other metadata sets of the metadata chain are not sent to the remote node. In these embodiments, the selected metadata set may represent all the metadata sets in the chain and be the only metadata set in the chain that is transmitted and stored to the remote node. As such, the network congestion between the local and remote nodes may be reduced.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
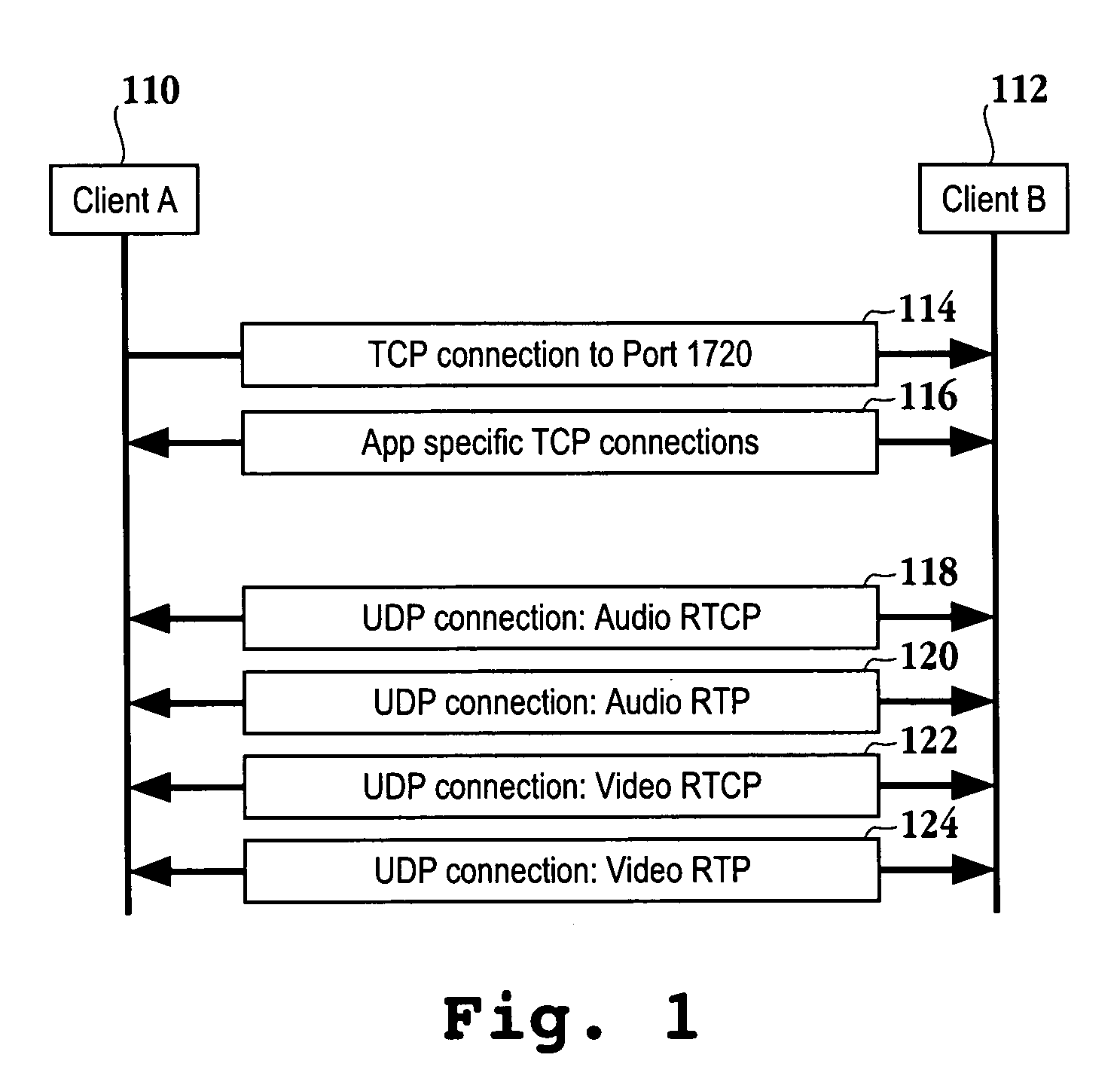
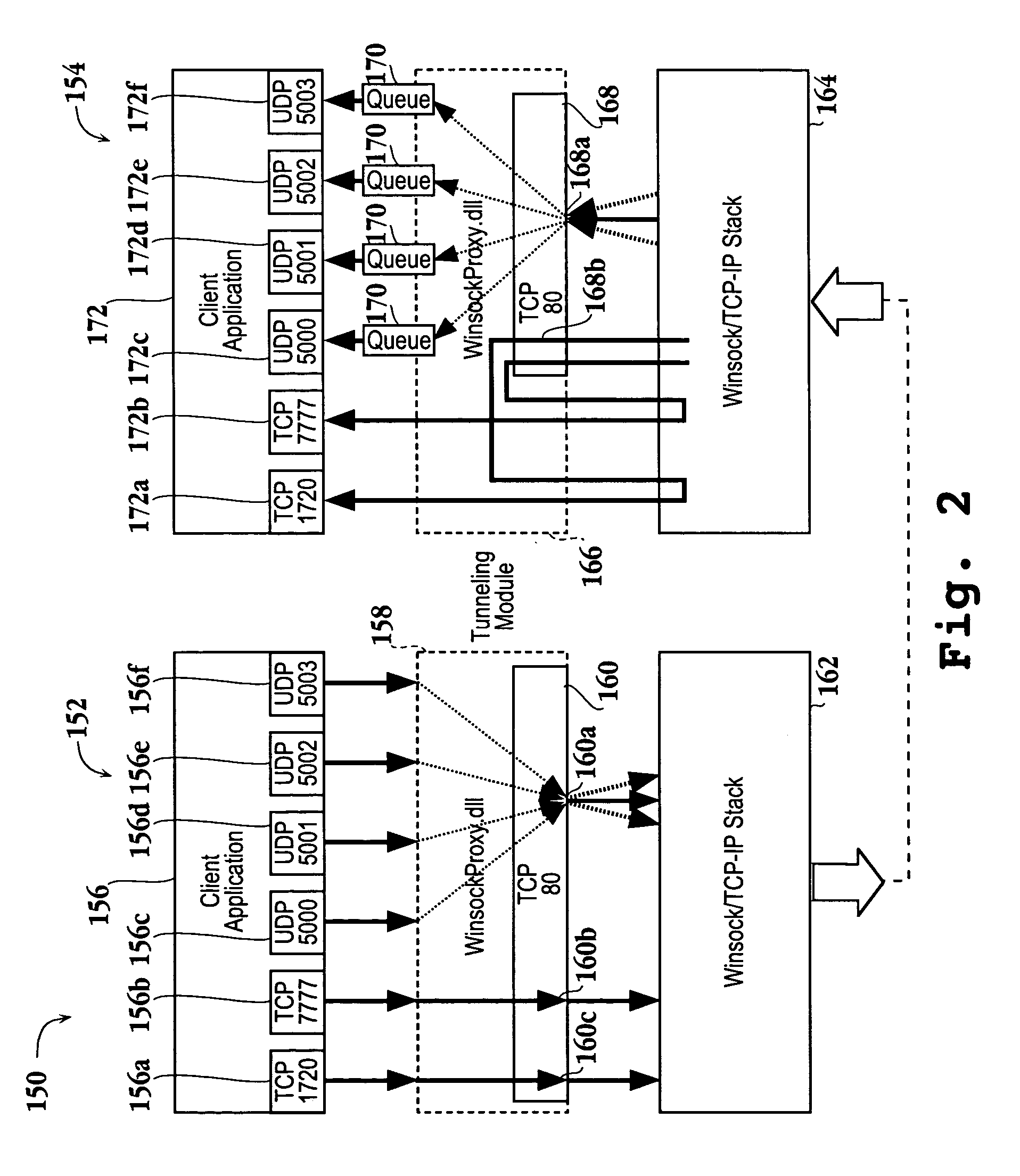
Apparatus and methods for tunneling a media streaming application through a firewall
InactiveUS20060235939A1Apparent advantageReduce network congestionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData connectionData port
When transmitting multimedia data associated with a multimedia application, a TCP / IP connection is established between a client application and a server application. UDP data is intercepted at an application level from one or more UDP data ports and channeled into one or more tunneling TCP data connections. TCP data is intercepted at the application level from one or more TCP data ports and re-directed to a tunneling TCP port. The channeled UDP data is received and dispatched to one or more local UDP data ports. Re-directed TCP data is received and then further re-directed to one or more local TCP data ports.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and method for server-side optimization of data delivery on a distributed computer network
InactiveUS20050063401A1Reduce in quantityImprove performanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsSystems managementDistributed computing
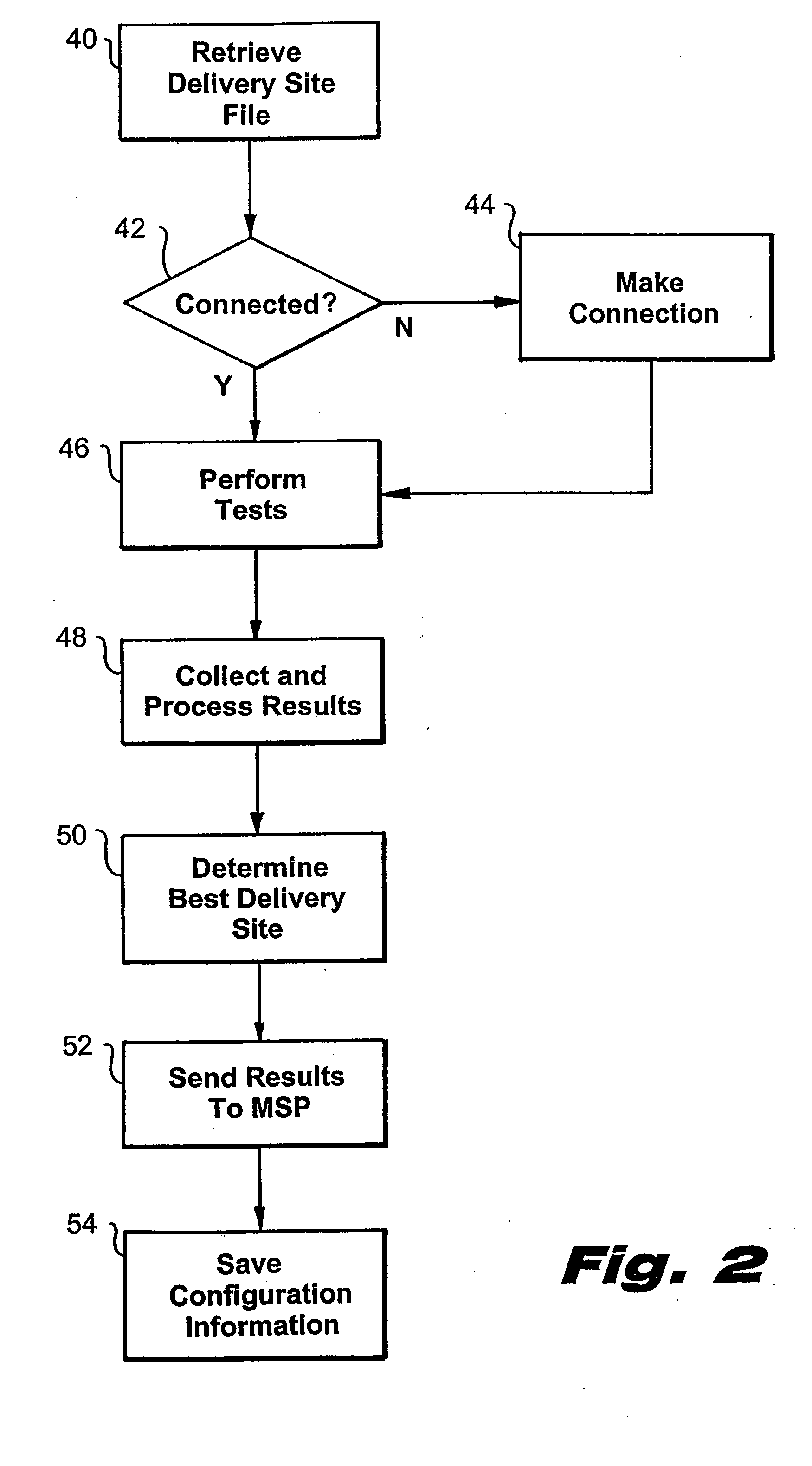
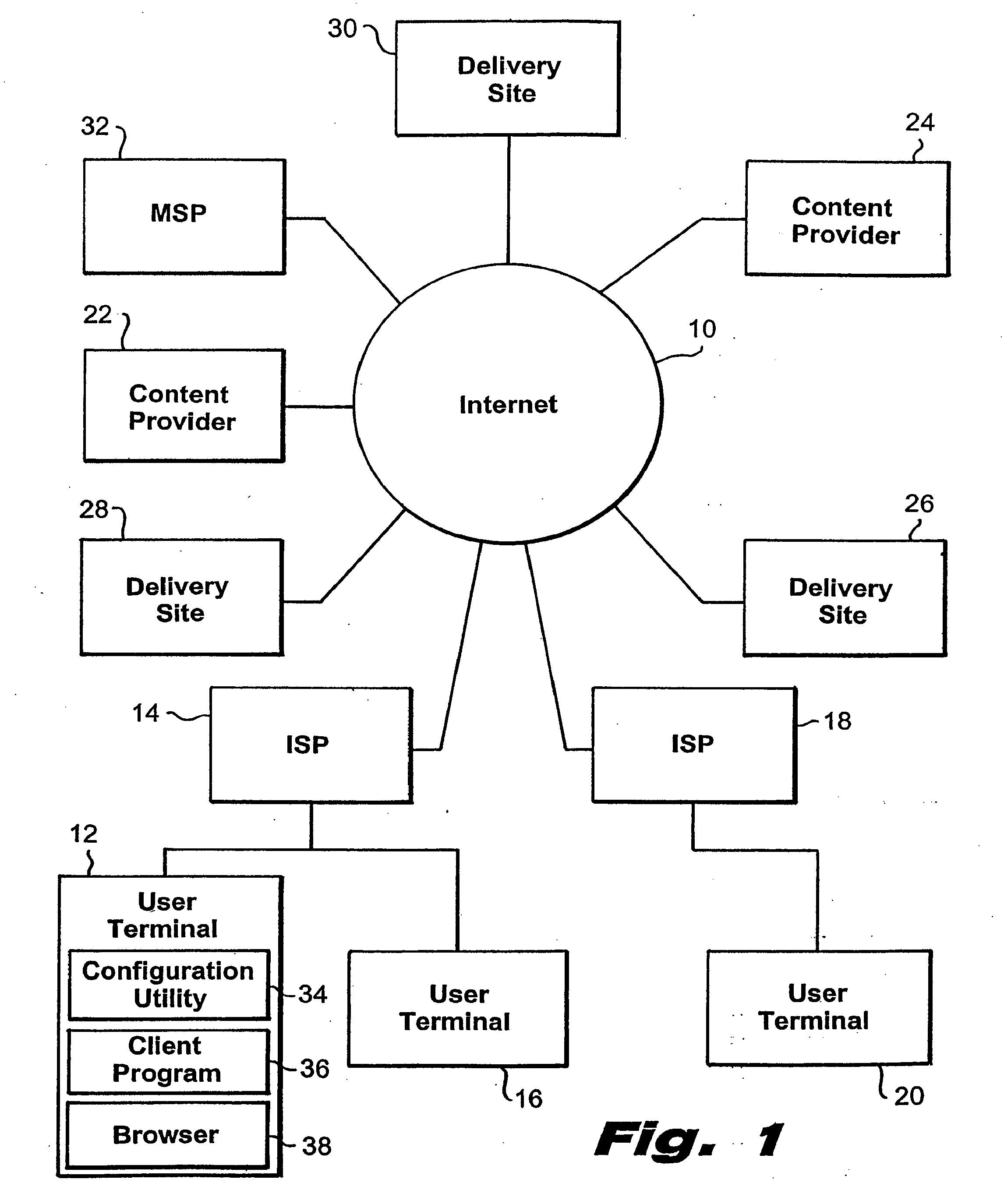
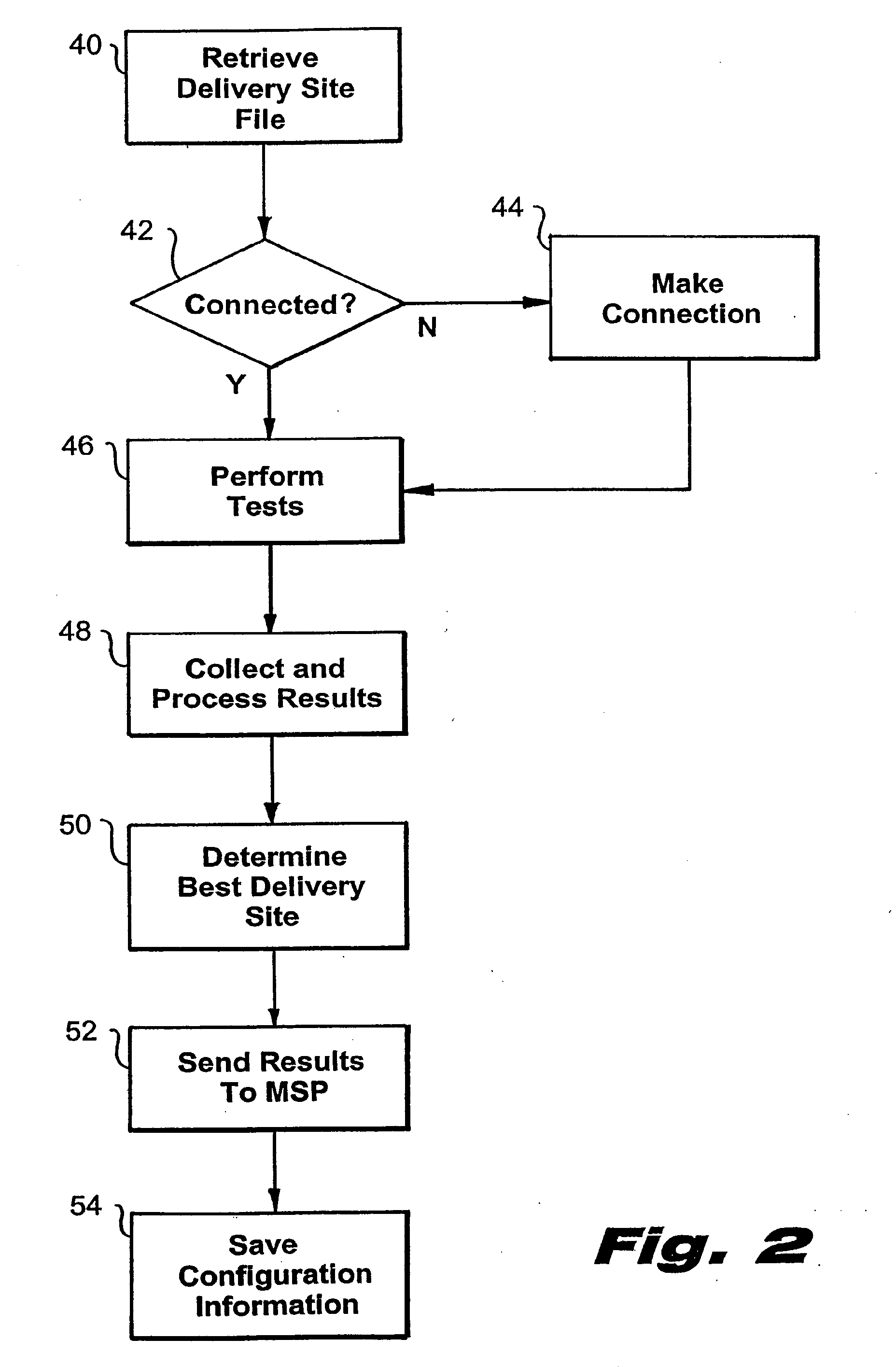
A system and method for the optimized storage and retrieval of video data at distributed sites calls for the deployment of “Smart Mirror” sites throughout a network, each of which maintains a copy of certain data managed by the system. User addresses are assigned to specific delivery sites based on an analysis of network performance with respect to each of the available delivery sites. Generalized network performance data is collected and stored to facilitate the selection of additional delivery sites and to ensure the preservation of improved performance in comparison to traditional networks.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Mechanism for autotuning mass data transfer from a sender to a receiver over parallel connections
InactiveUS20120054362A1Improve performanceIncrease or decrease the numberMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsData transmissionDistributed computing
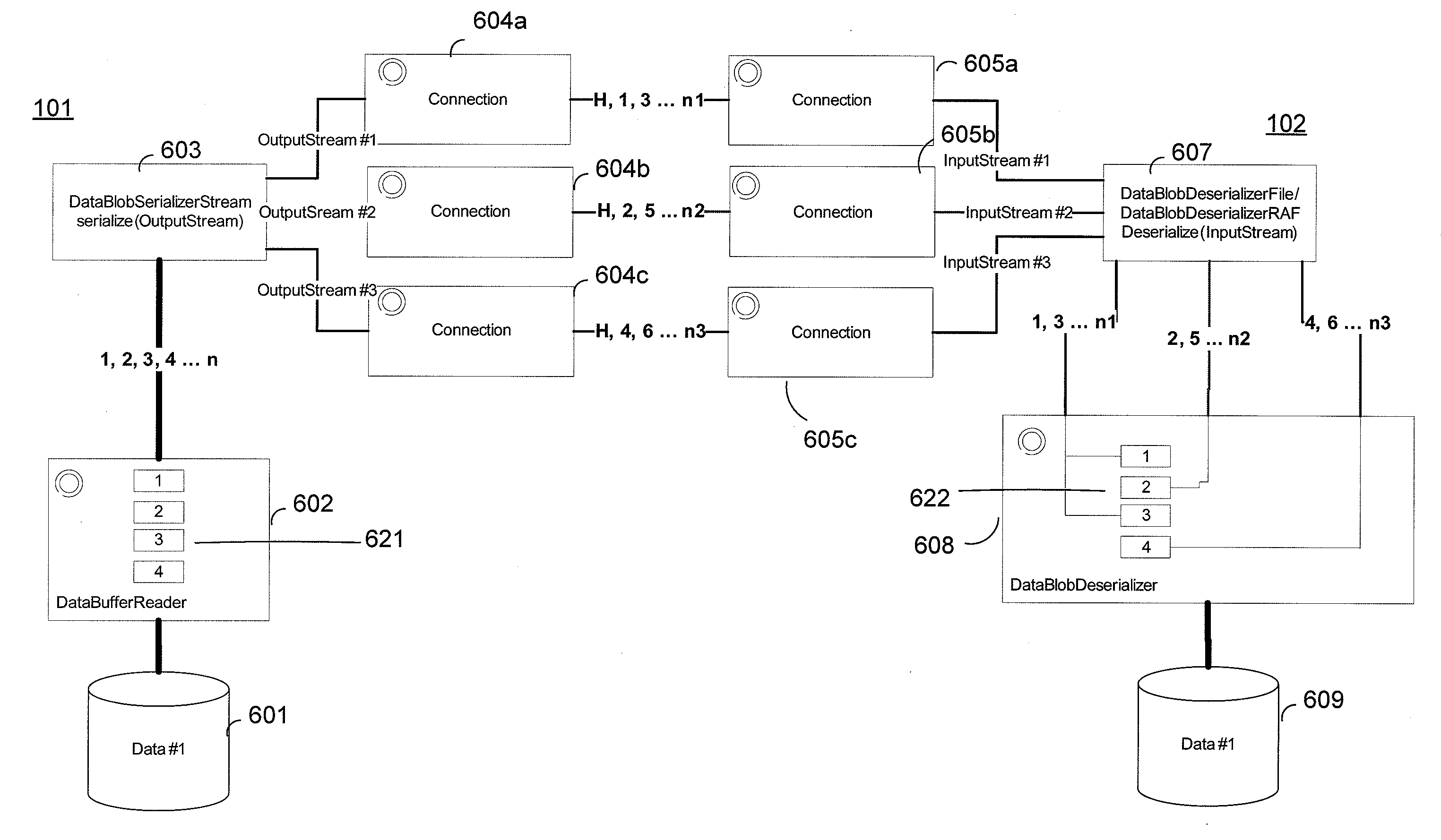
The present disclosure is directed to performing mass transfer of data over plural connections established between a sender and a recipient connected to the sender via a network. Data is sent from the sender to the recipient by divided sending of the data over the plural connections. The optimal number of connections between the sender and the recipient is autotuned by closing an existing connection when a detection is made that a bottleneck to mass transfer of data exists in an I / O storage system of the recipient, and by opening a new connection when the I / O storage system of the recipient is writing data faster than data is received from the network. The number of connections is further autotuned by opening a new connection when an I / O storage system of the sender is reading data faster than data is being sent out over the network, and by closing an existing connection when the I / O storage system of the sender is reading data slower than data is being sent out over the network and more than one sender is sending data to the recipient.
Owner:CANON KK
Communication system for improving data transmission efficiency of TCP in wireless network environment and a method thereof
InactiveUS20050232147A1Reduce network congestionAvoid congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiplexingCommunications system
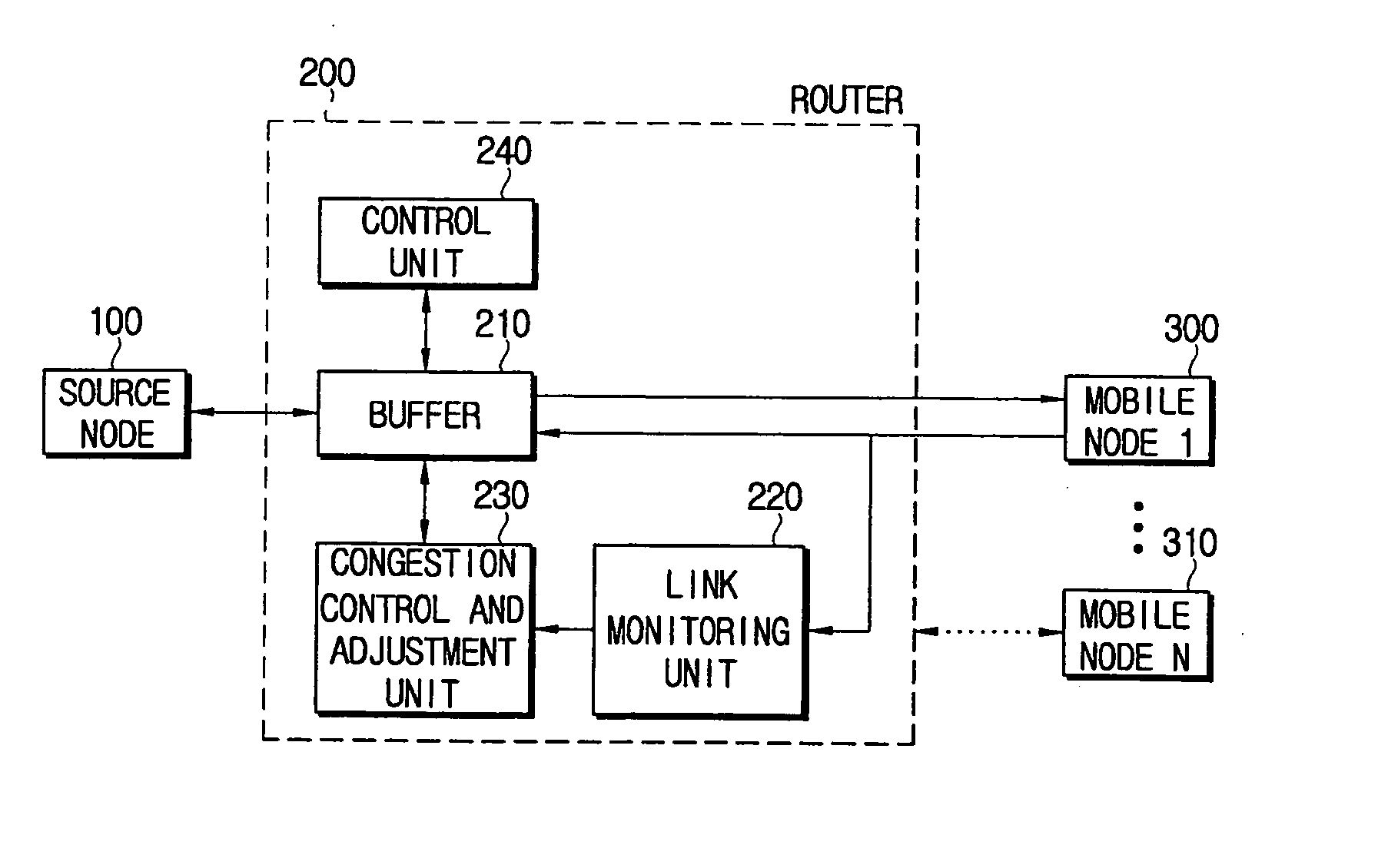
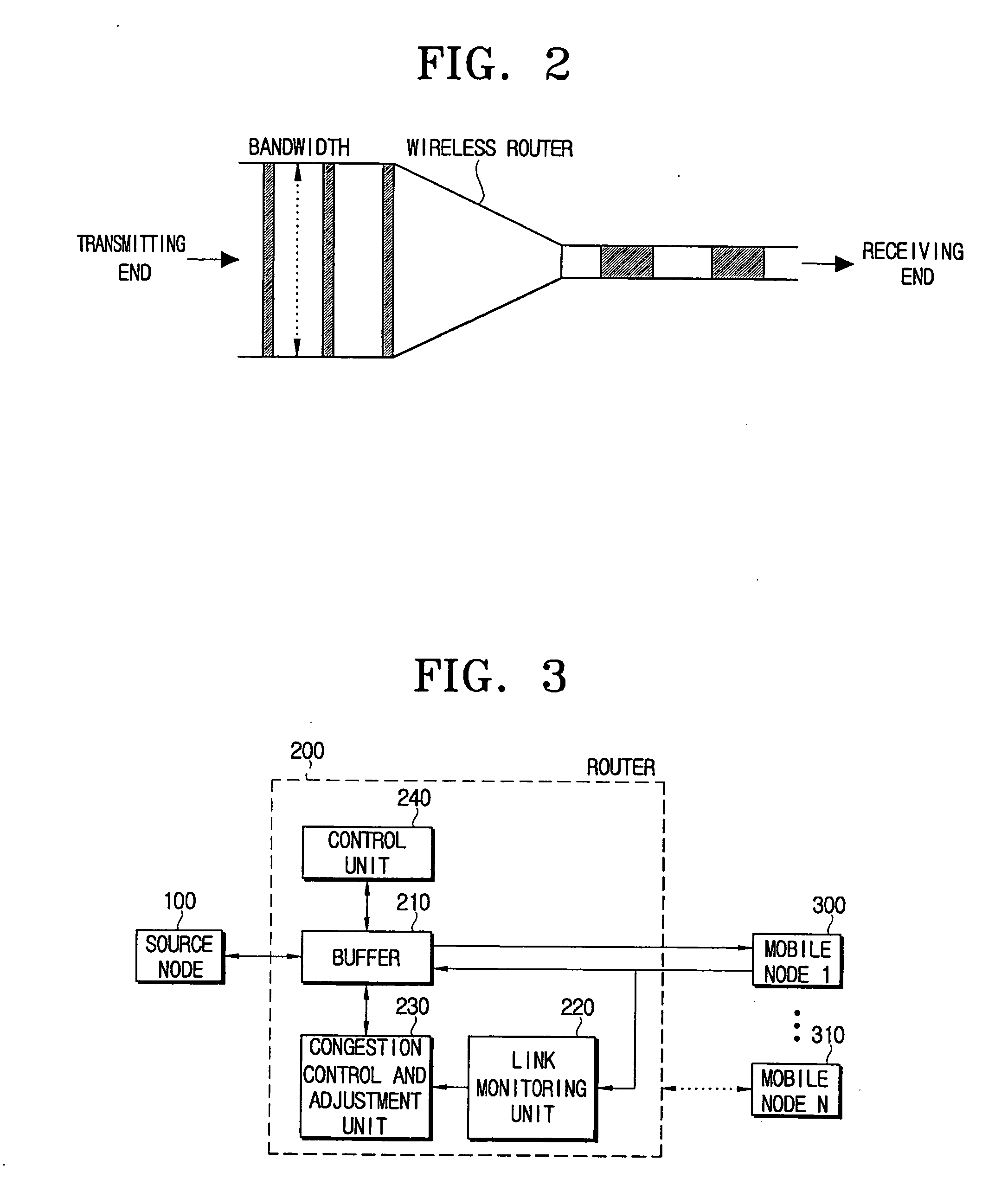
A communication system having a source node, at least one mobile node, and a router that transmits data packets transmitted from the source node to a corresponding one of the at least one mobile node and multiplexes response signals to the data packets received from the corresponding one of the at least one mobile node to transmit the multiplexed response signals to the source node. The communication system includes: a link monitoring unit which calculates a capacity of a wireless link between the router and the corresponding one of the at least one mobile node; and a congestion control and adjustment unit which adjusts window field values in the response signals according to the calculated capacity. The router transmits the response signals, the response signals including the adjusted window field values to the source node, and the source node sequentially transmits the data packets on the basis of the adjusted window field values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
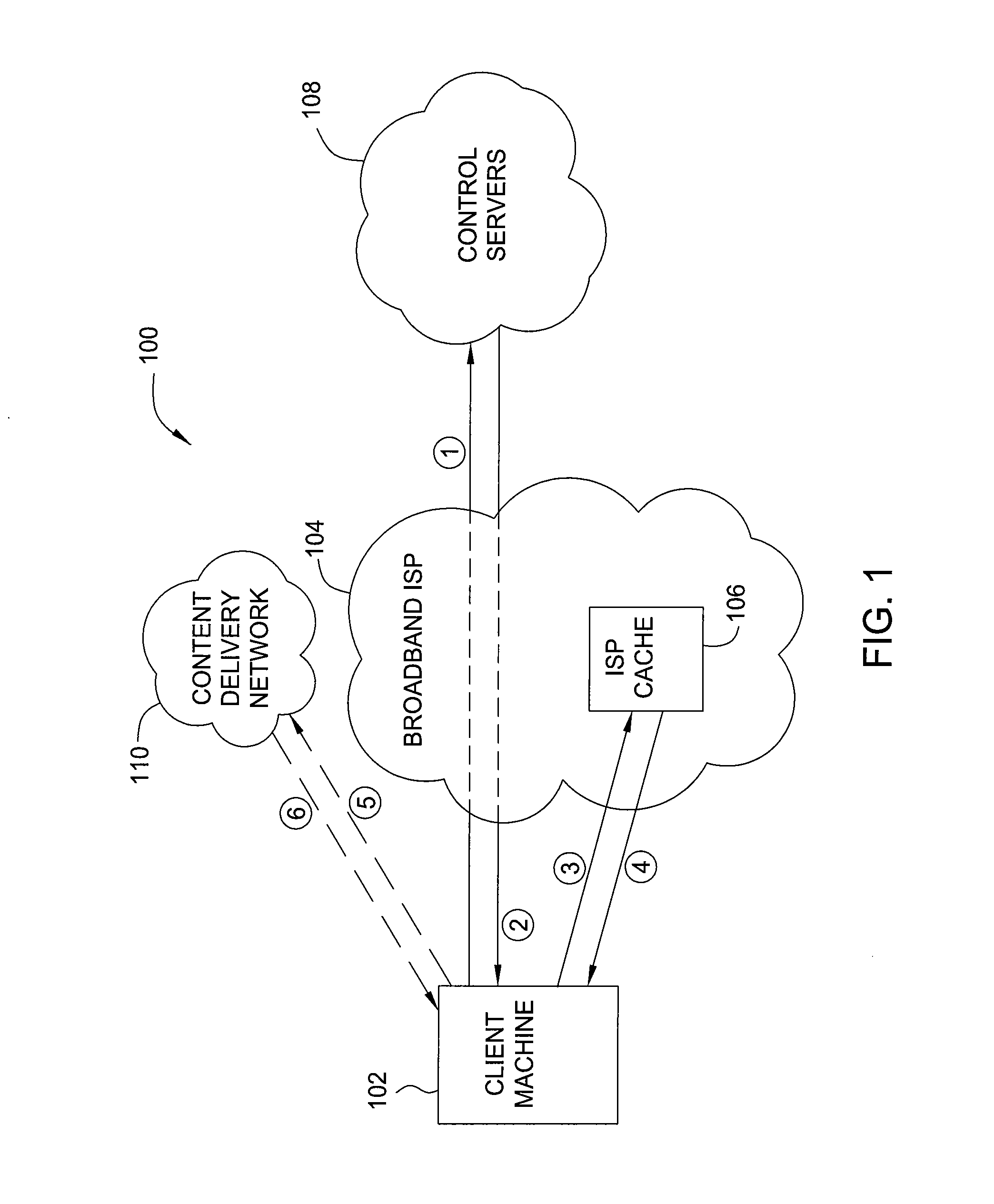
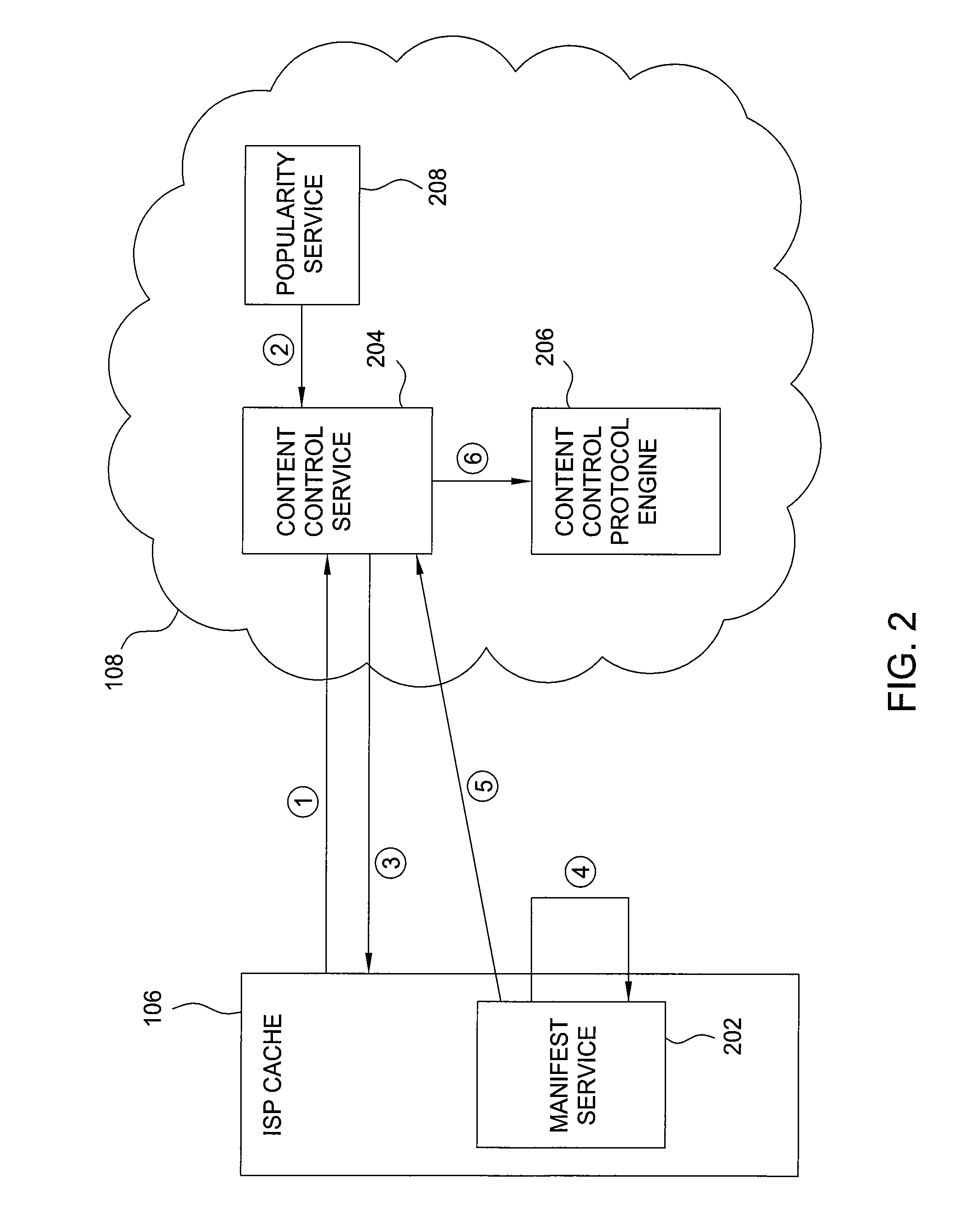
Managing content on an isp cache
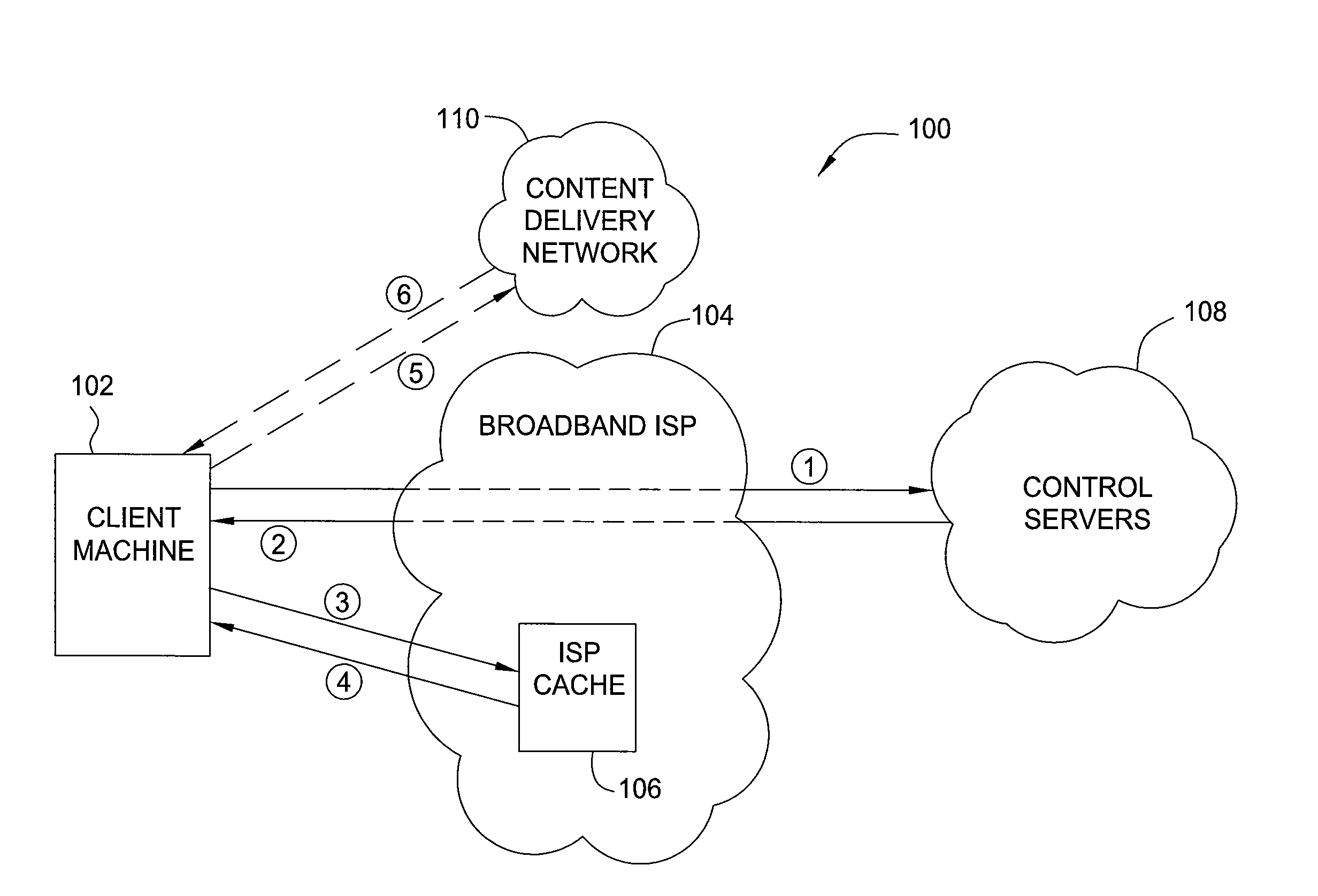
ActiveUS20140164547A1Reducing overall network traffic and congestionIncrease likelihoodDigital computer detailsWebsite content managementService provisionInternet service provider
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a method for updating content stored in a cache residing at an internet service provider (ISP) location that includes receiving popularity data associated with a first plurality of content assets, where the popularity data indicate the popularity of each content asset in the first plurality of content assets across a user base that spans multiple geographic regions, generating a manifest that includes a second plurality of content assets based on the popularity data and a geographic location associated with the cache, where each content asset included in the manifest is determined to be popular among users proximate to the geographic location or users with preferences similar to users proximate to the geographic location, and transmitting the manifest to the cache, where the cache is configured to update one or more content assets stored in the cache based on the manifest.
Owner:NETFLIX
Coalescing Metadata for Mirroring to a Remote Storage Node in a Cluster Storage System
ActiveUS20140214772A1Network congestionReduce in quantityError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsData setDatabase
Described herein are a system and method for remote mirroring / copying data and metadata sets from a local node to a remote node that reduces the number of metadata sets that are mirrored. In some embodiments, the local node may coalesce metadata sets into metadata chains, each metadata chain comprising a grouping of two or more metadata sets. In some instances, a “representative” metadata set of a metadata chain may be selected for sending to the remote node for storing, wherein the other metadata sets of the metadata chain are not sent to the remote node. In these embodiments, the selected metadata set may represent all the metadata sets in the chain and be the only metadata set in the chain that is transmitted and stored to the remote node. As such, the network congestion between the local and remote nodes may be reduced.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Packet prioritization and associated bandwidth and buffer management techniques for audio over IP
InactiveUS20080151921A1Raise priorityReduce the possibilityData switching by path configurationVoice communicationVoice activity
The present invention is directed to voice communication devices in which an audio stream is divided into a sequence of individual packets, each of which is routed via pathways that can vary depending on the availability of network resources. All embodiments of the invention rely on an acoustic prioritization agent that assigns a priority value to the packets. The priority value is based on factors such as whether the packet contains voice activity and the degree of acoustic similarity between this packet and adjacent packets in the sequence. A confidence level, associated with the priority value, may also be assigned. In one embodiment, network congestion is reduced by deliberately failing to transmit packets that are judged to be acoustically similar to adjacent packets; the expectation is that, under these circumstances, traditional packet loss concealment algorithms in the receiving device will construct an acceptably accurate replica of the missing packet. In another embodiment, the receiving device can reduce the number of packets stored in its jitter buffer, and therefore the latency of the speech signal, by selectively deleting one or more packets within sustained silences or non-varying speech events. In both embodiments, the ability of the system to drop appropriate packets may be enhanced by taking into account the confidence levels associated with the priority assessments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Dynamic IP router tables using highest-priority matching
InactiveUS7509300B2Shorten the timeEffective structureData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsIp routerThe Internet
An improved system and method is provided for packet routing in dynamic router tables. Specifically, the invention relates to a method and system for using tree data structures to select the highest priority rule that matches a destination address in dynamic Internet packet routing tables. In an embodiment, a data structure called BOB (binary tree on binary tree) for dynamic router tables in which the rule filters are nonintersecting ranges and in which ties are broken by selecting the highest-priority rule that matches a destination address is disclosed. Prefix filters are a special case of nonintersecting ranges and the commonly used longest-prefix tie breaker is a special case of the highest-priority tie breaker. When an n-rule router table is represented using BOB, the highest-priority rule that matches a destination address may be found in O(log2n) time; a new rule maybe inserted and an old one deleted in O(log n) time. For the case when all rule filters are prefixes, the data structure PBOB (prefix BOB) permits highest-priority matching as well as rule insertion and deletion in O(W) time, where W is the length of the longest prefix, each. When all rule filters are prefixes and longest-prefix matching is to be done, the data structures LMPBOB (longest matching-prefix BOB) permits longest-prefix matching in O(W) time; rule insertion and deletion each take O(log n) time. On practical rule tables, BOB and PBOB perform each of the three dynamic-table operations in O(log n) time and with O(log n) cache misses. The number of cache misses incurred by LMPBOB is also O(log n).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and switch for routing data packets in interconnection networks
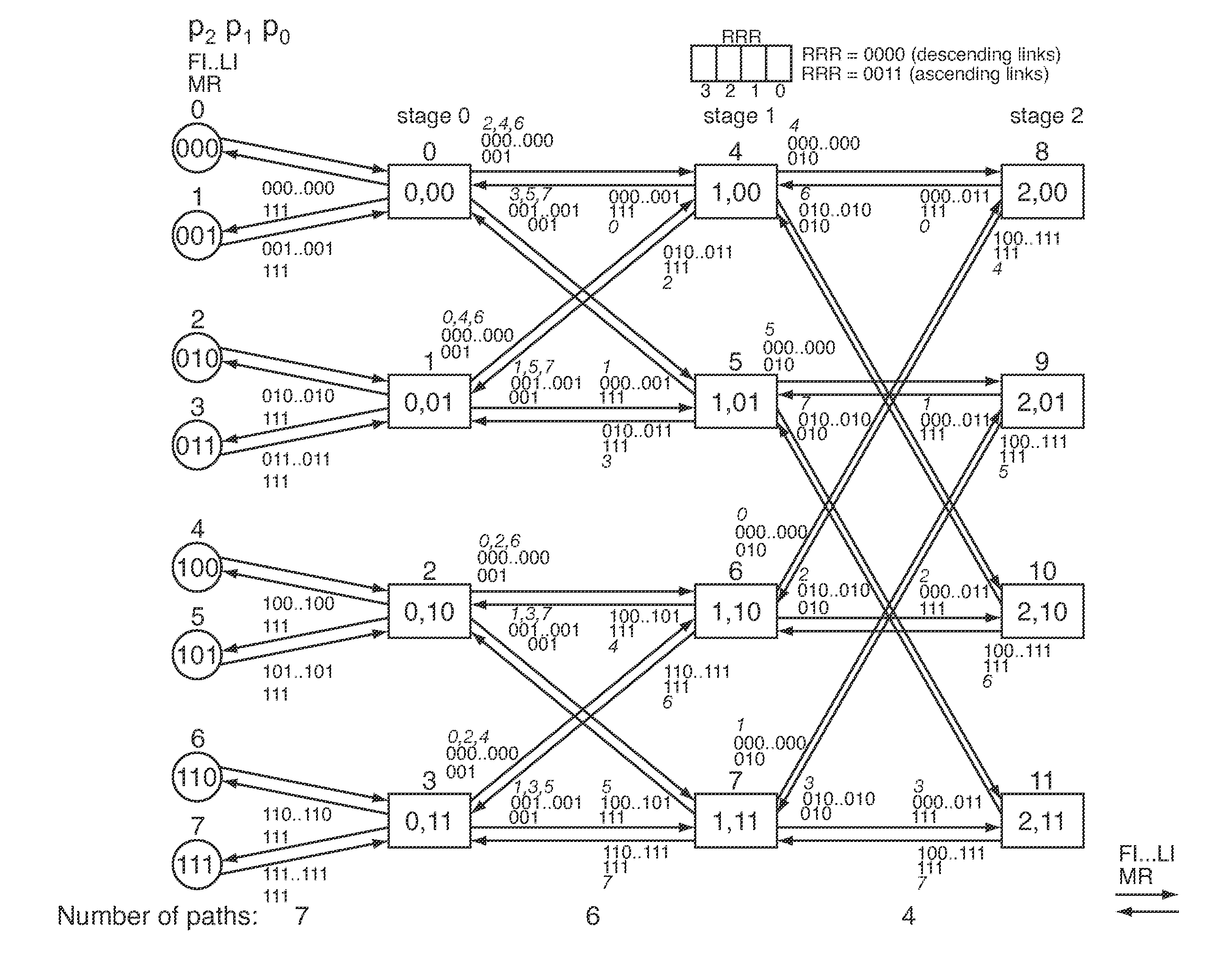
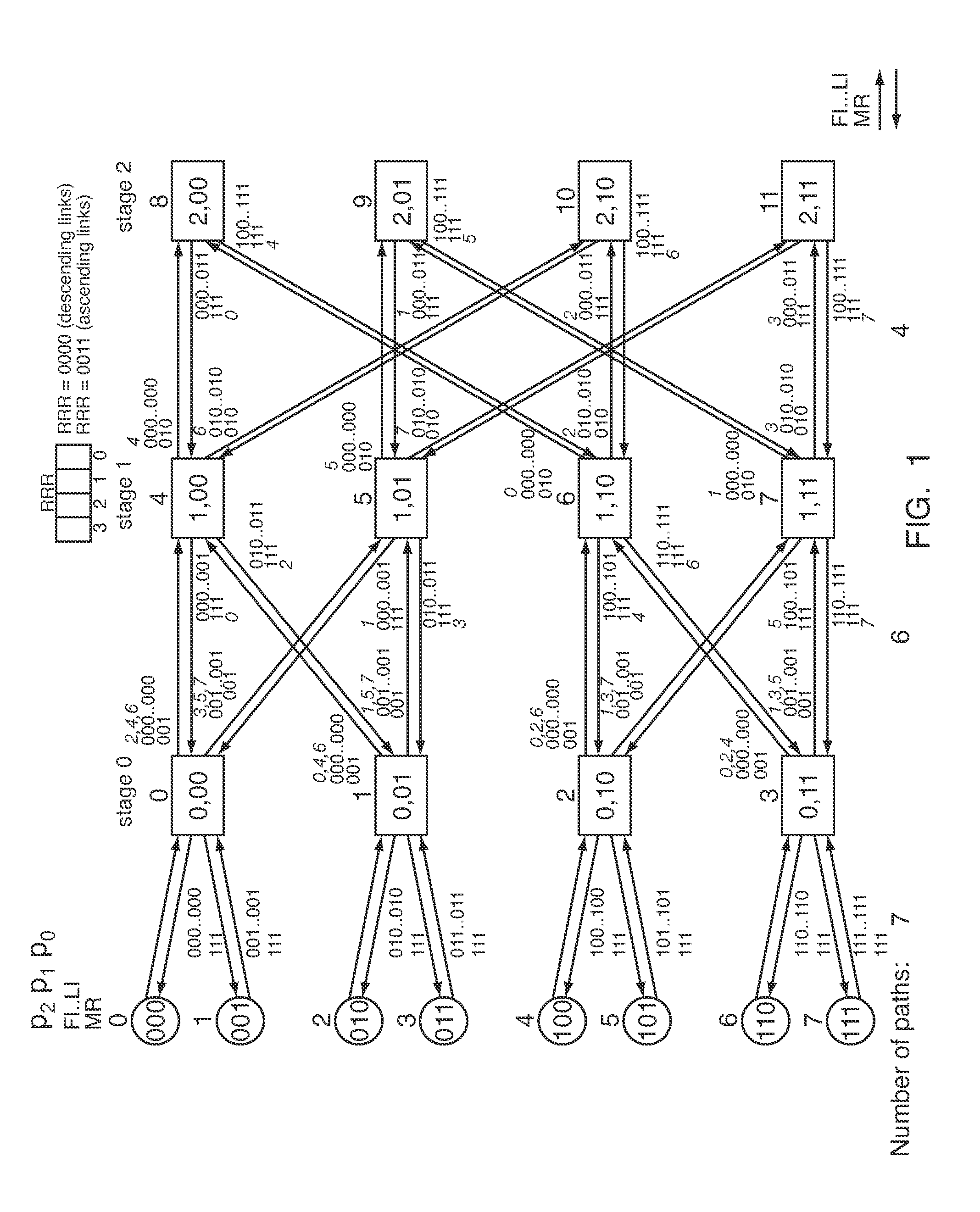
InactiveUS20090059913A1Easy to implementEfficient executionData switching by path configurationNetwork packetMultistage interconnection networks
The invention falls within the technology of multistage interconnection network such as fat-trees, comprising at least one switch located at a stage (s) and configured to send, through an output port from a number (k) of output ports forming an ordered list, at least a data packet containing a destination address identified by a n-tuple with a plurality (n) of components (pn−1, . . . , p1, p0), and sε{0 . . . (n−1)}. The invention has application for both source and distributed routing, as deterministic and as adaptive routing, selecting an output port to be the unique or the default option to forward the packets at the switch which is the output port that has a position in the ordered list of output ports corresponding to the component (ps) of the destination address at the position given by the stage (s) of the switch.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE VALENCIA
System and method for server-side optimization of data delivery on a distributed computer network
InactiveUS20080201488A1Reduce in quantityImprove performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionSystems managementDistributed computing
A system and method for the optimized storage and retrieval of video data at distributed sites calls for the deployment of “Smart Mirror” sites throughout a network, each of which maintains a copy of certain data managed by the system. User addresses are assigned to specific delivery sites based on an analysis of network performance with respect to each of the available delivery sites. Generalized network performance data is collected and stored to facilitate the selection of additional delivery sites and to ensure the preservation of improved performance in comparison to traditional networks.
Owner:KENNER BRIAN +2
Methods and apparatus for dynamic management and bandwidth allocation for content delivery
ActiveUS20140165121A1Reduce network congestionIncrease data rateBroadcast with distributionTwo-way working systemsCable networkBandwidth allocation
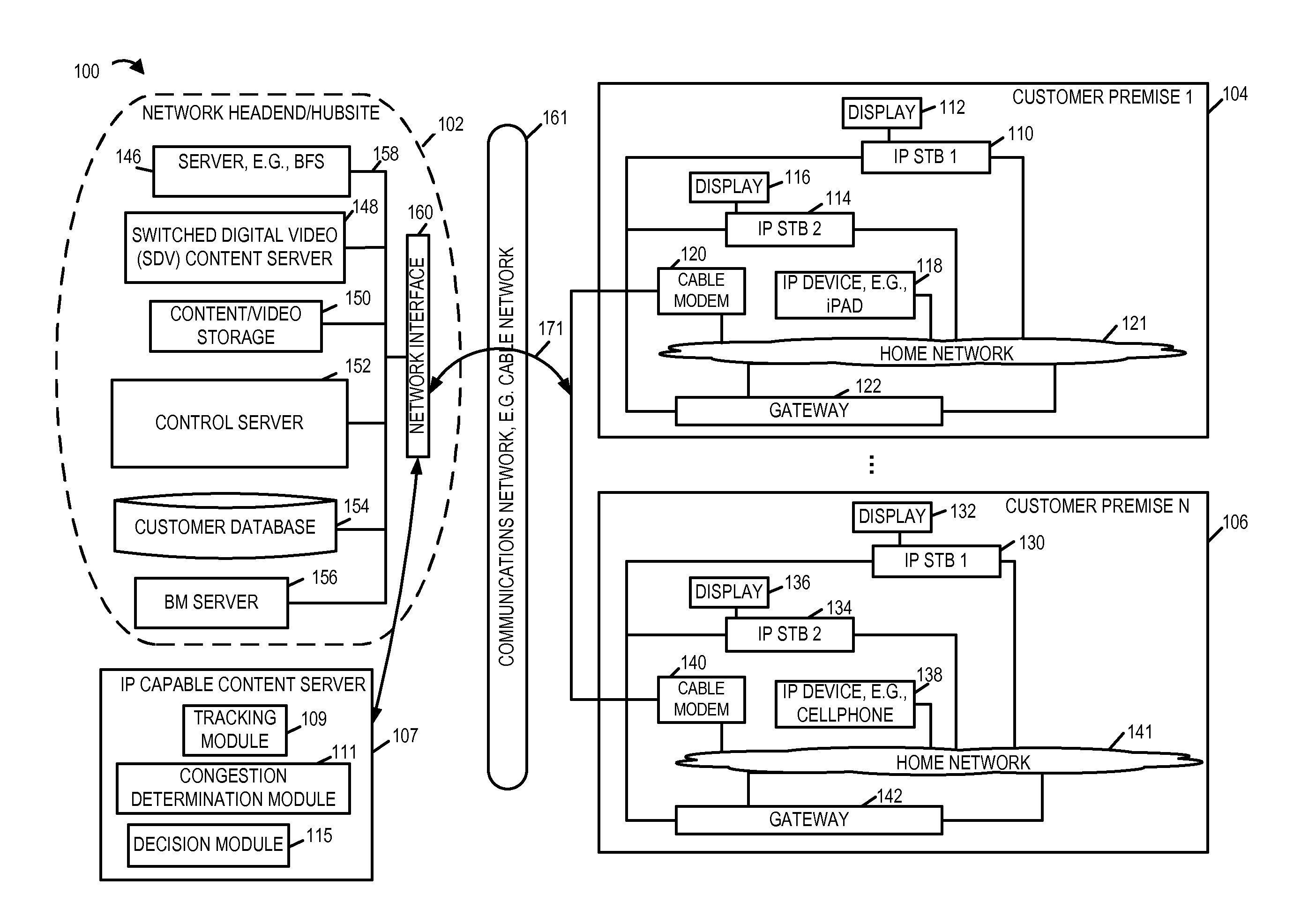
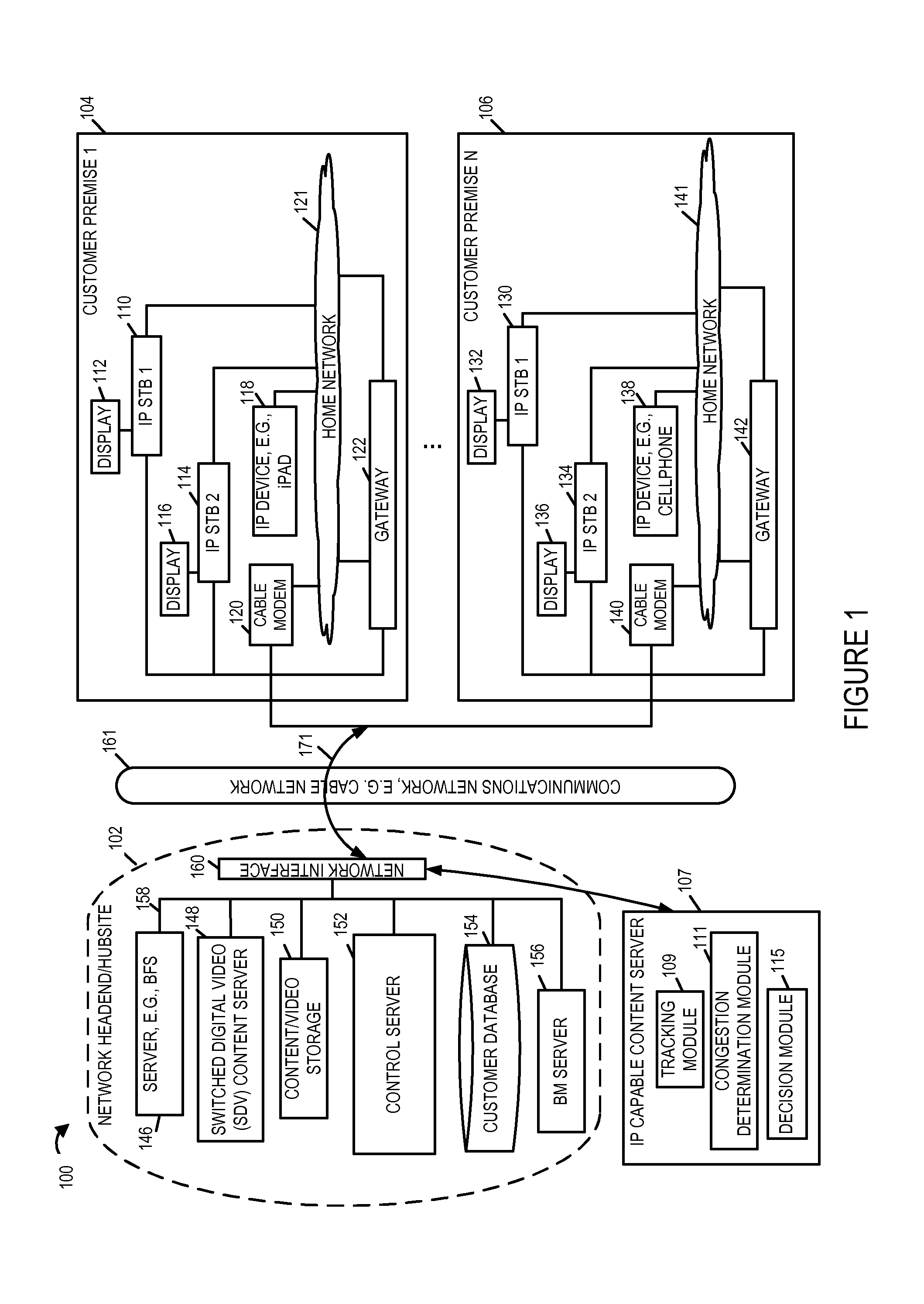
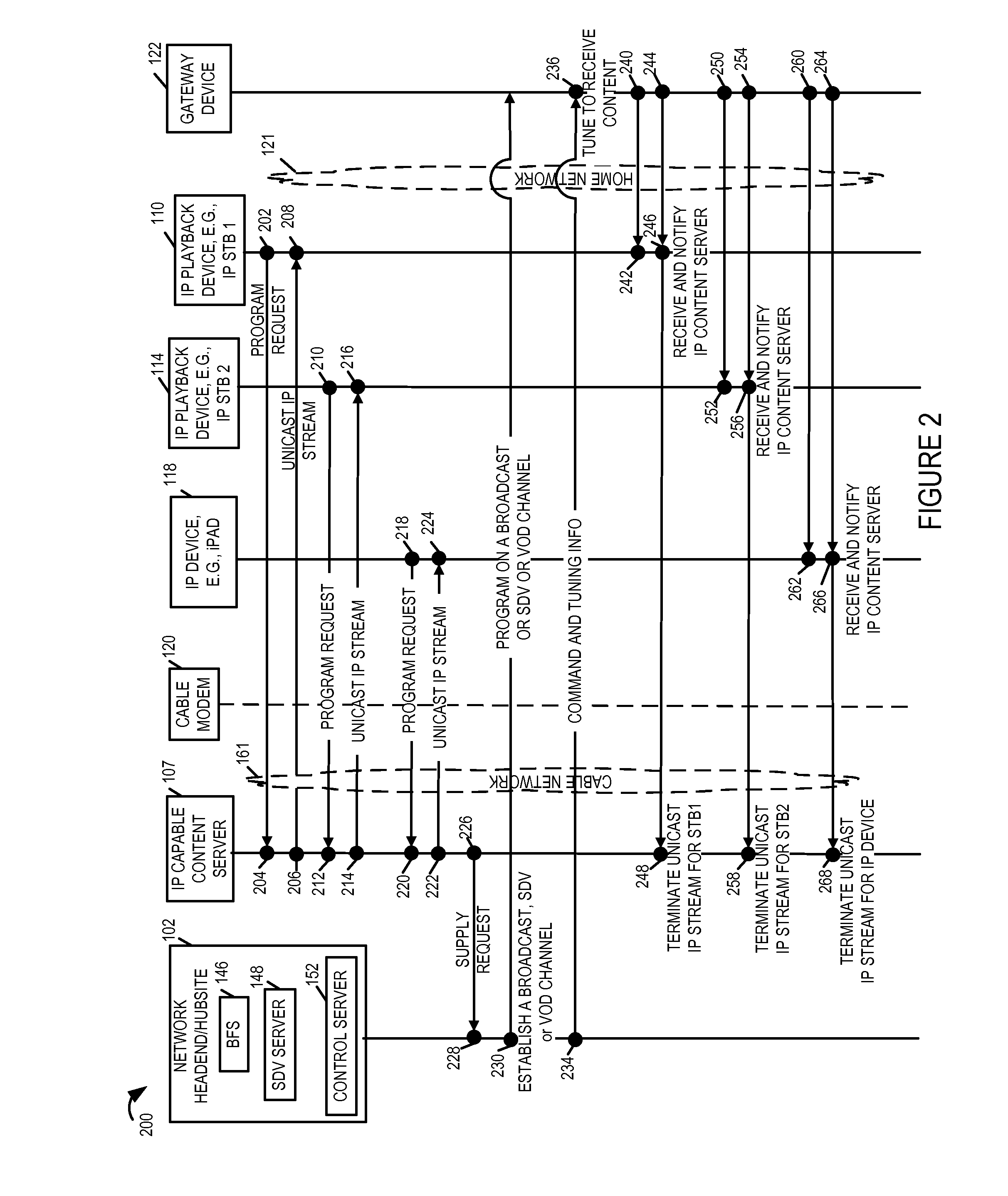
Methods and apparatus for content delivery and managing and conserving network bandwidth in a content delivery system are described. In accordance with one aspect of some embodiments, when the number content playback devices, e.g., IP set top boxes, iPADs, etc., in a region or service group receiving the same program content via individual unicast streams over a first network, e.g., cable network, exceeds a threshold number large, the IP capable playback devices are instructed to switch to receive the same programming content from a local device, e.g., a gateway device, via a home network. The local device receives the programming content via the cable network over a broadcast or SDV or VOD channel established by the cable service provider's headend / hubsite.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
Network congestion management systems and methods
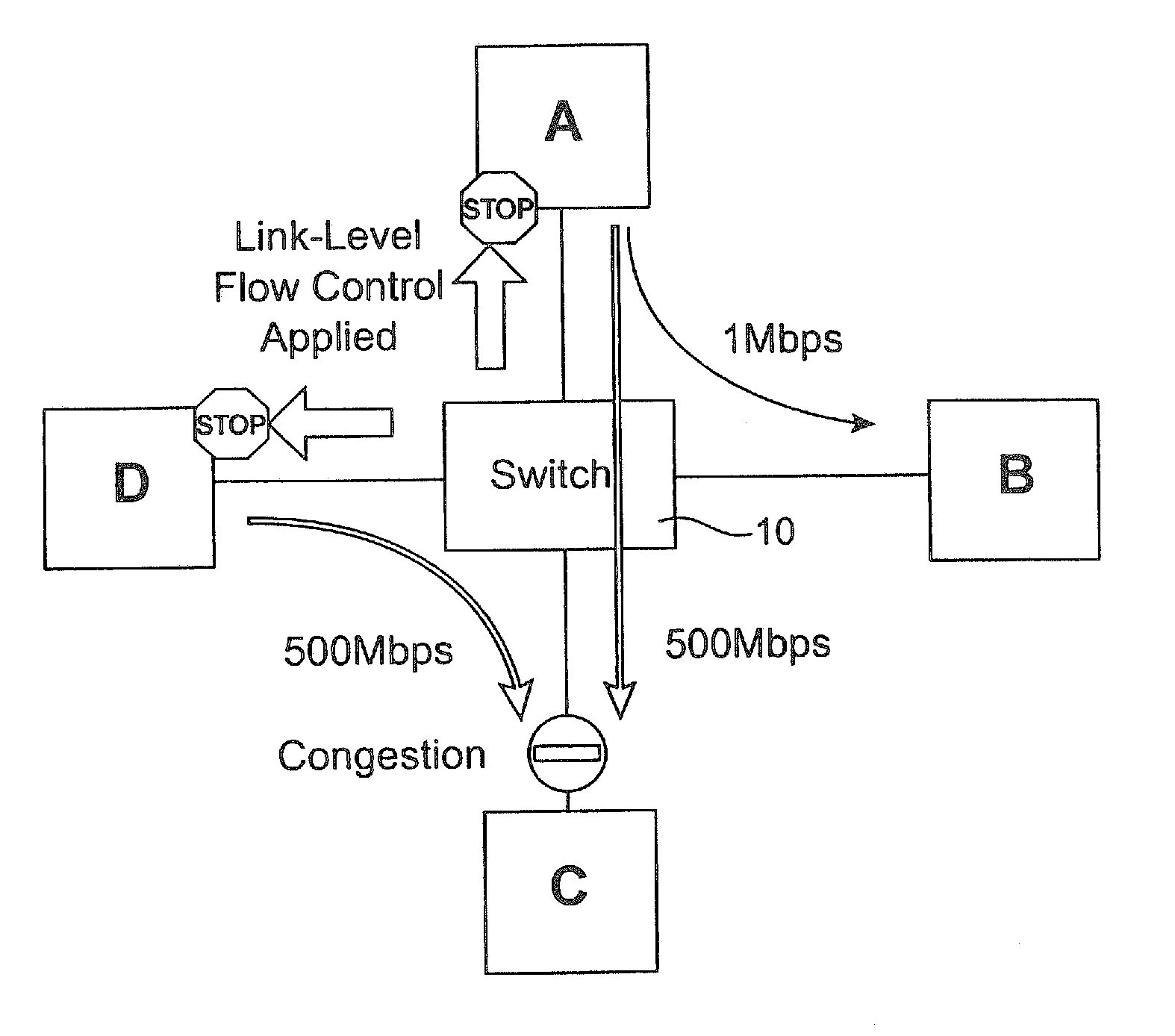
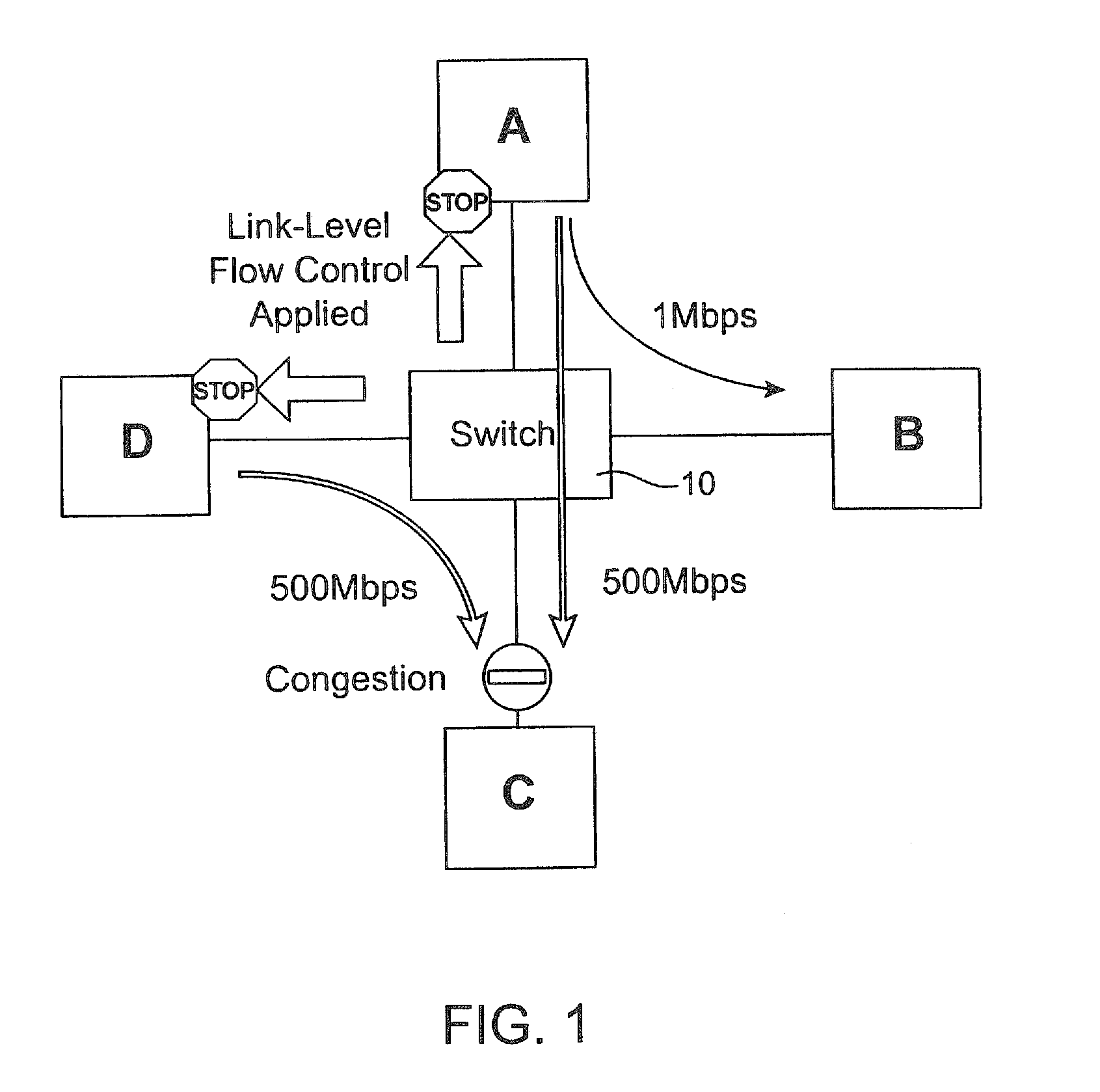
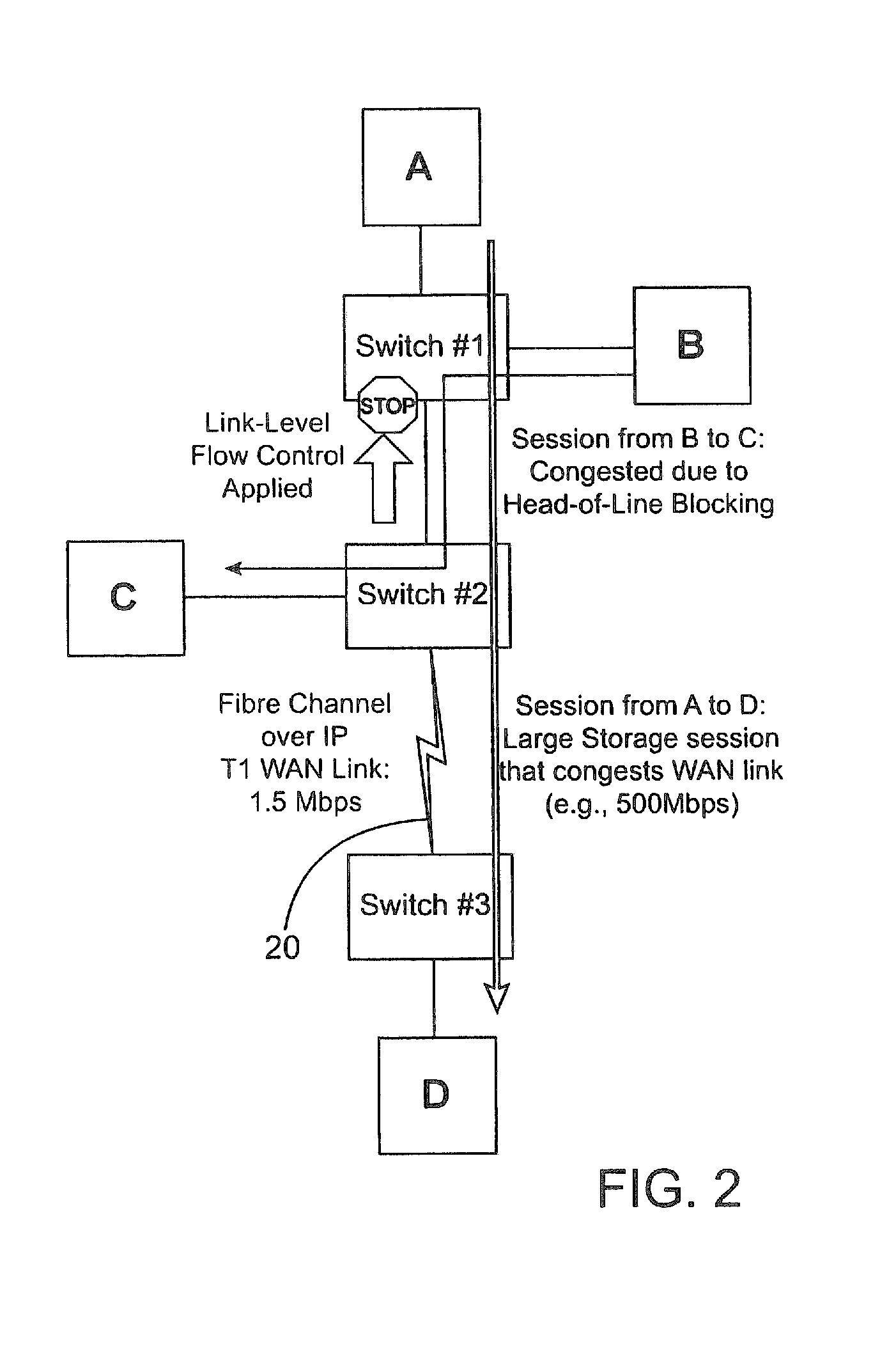
ActiveUS20100202294A1Minimize disruptionReduce network congestionEnergy efficient ICTError preventionSCSIStructure of Management Information
Systems, methods and software useful for overcoming network congestion problems including head-of-line blocking issues and other network congestion problems. In certain aspects, flow control mechanisms implemented in a switch device or other network device manage buffer and system level resources using a scheduler to control the amount of data requested from a local SAN fabric. Switches and other network devices configured according to the present invention monitor each individual SCSI task, and are configured to apply flow control measures to each active session when buffering resources become scarce, such as when buffering data for a slower-speed WAN link or TCP / IP based interconnects of any speed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
O(log n) dynamic router tables for prefixes and ranges
InactiveUS7523218B1Shorten the timeEffective structureDigital computer detailsTransmissionTheoretical computer scienceComputerized system
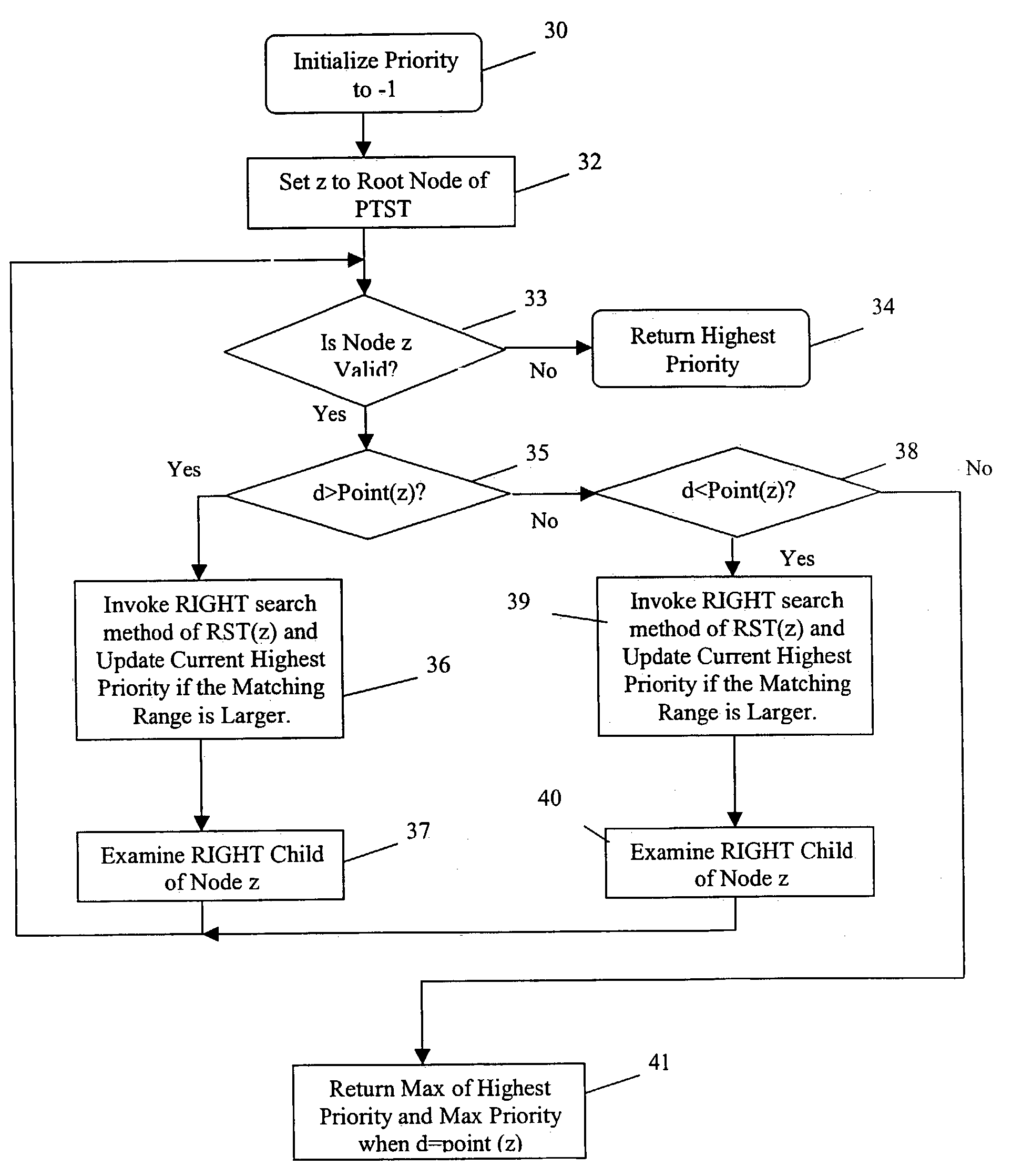
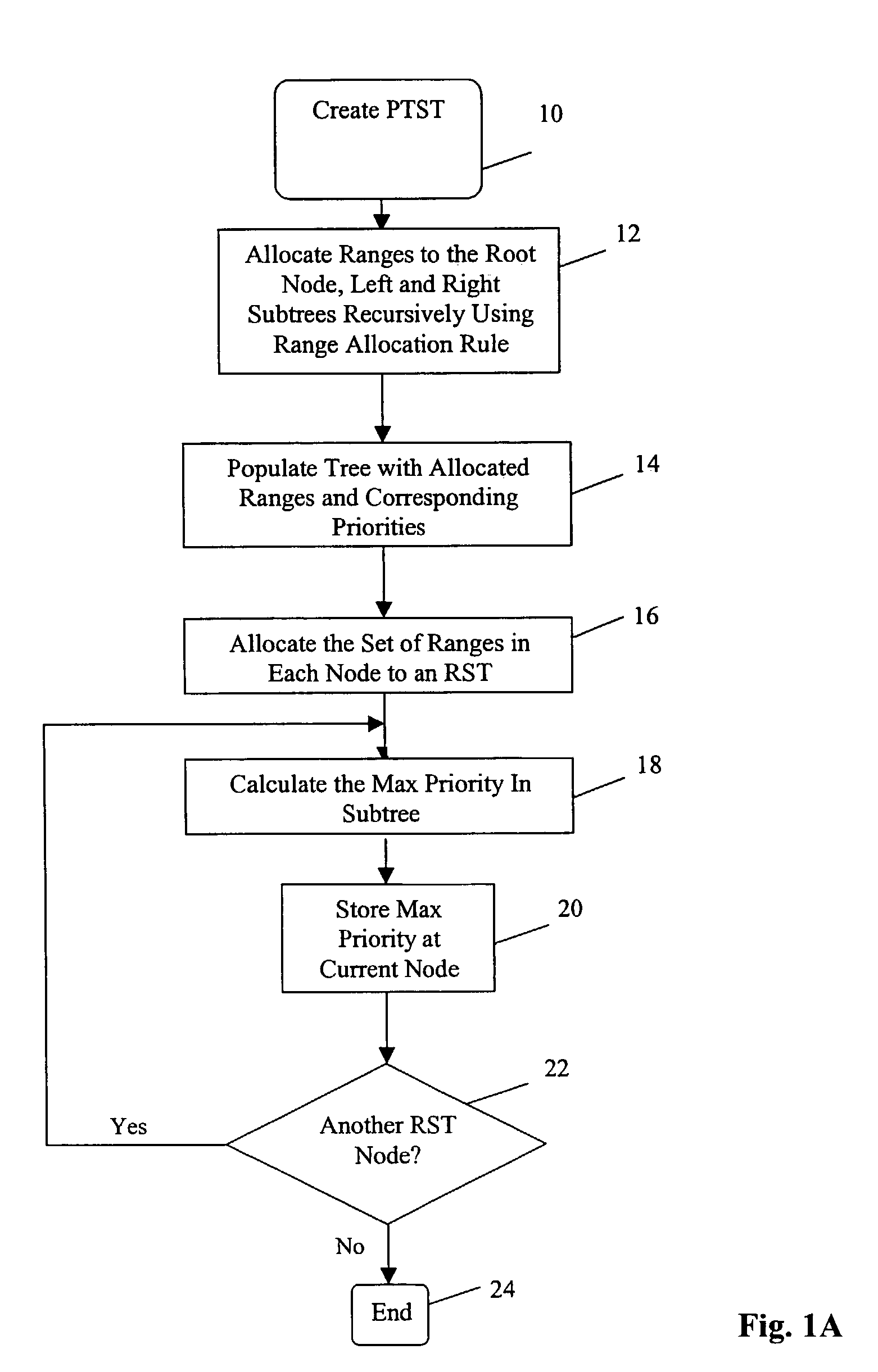
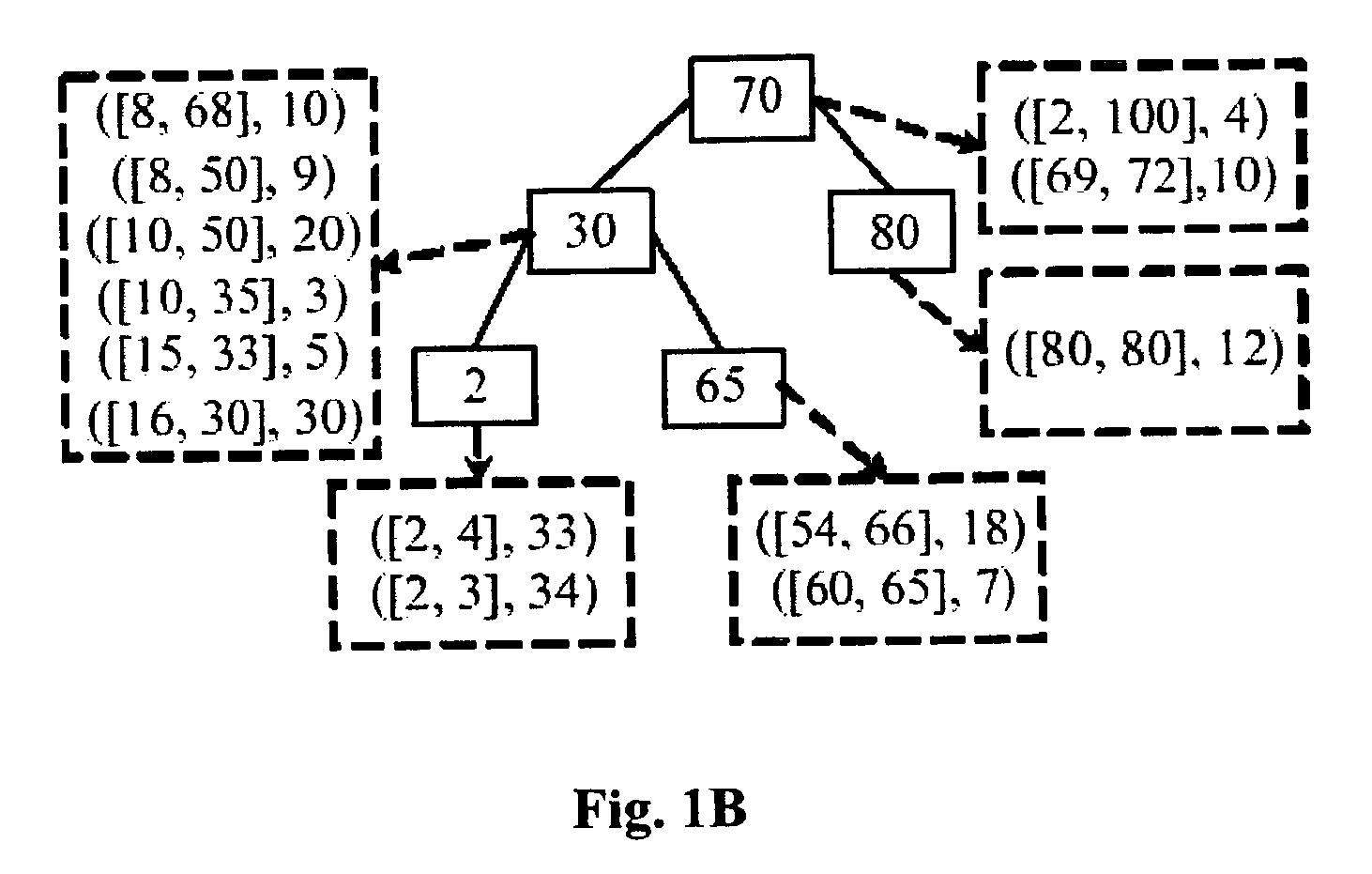
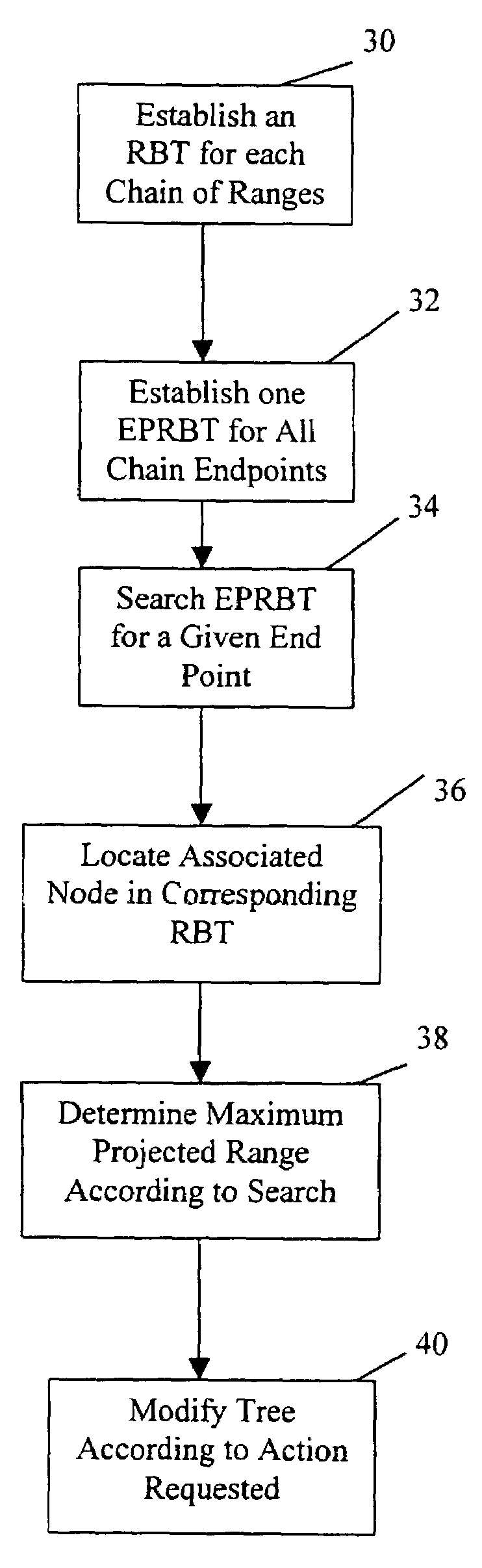
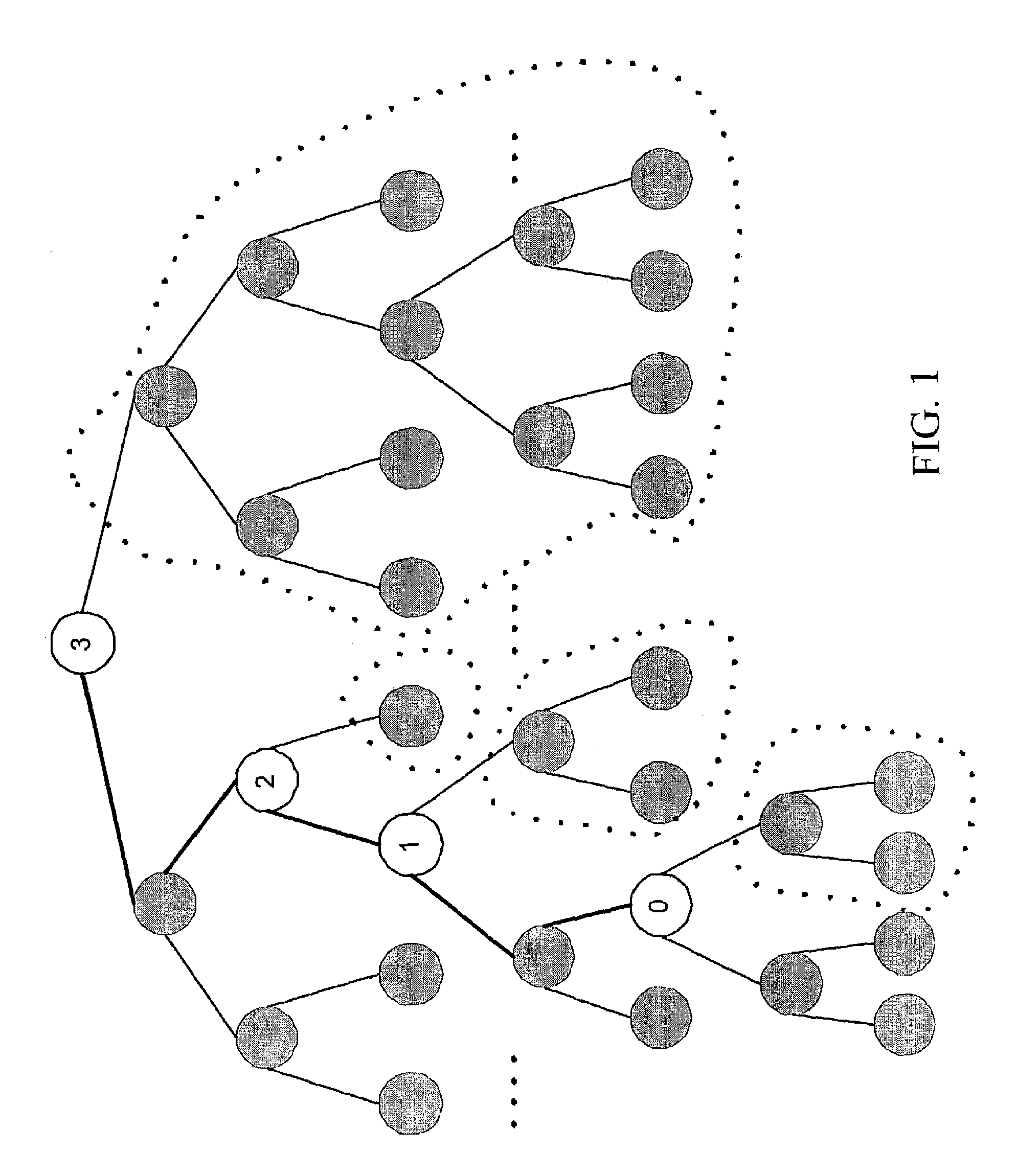
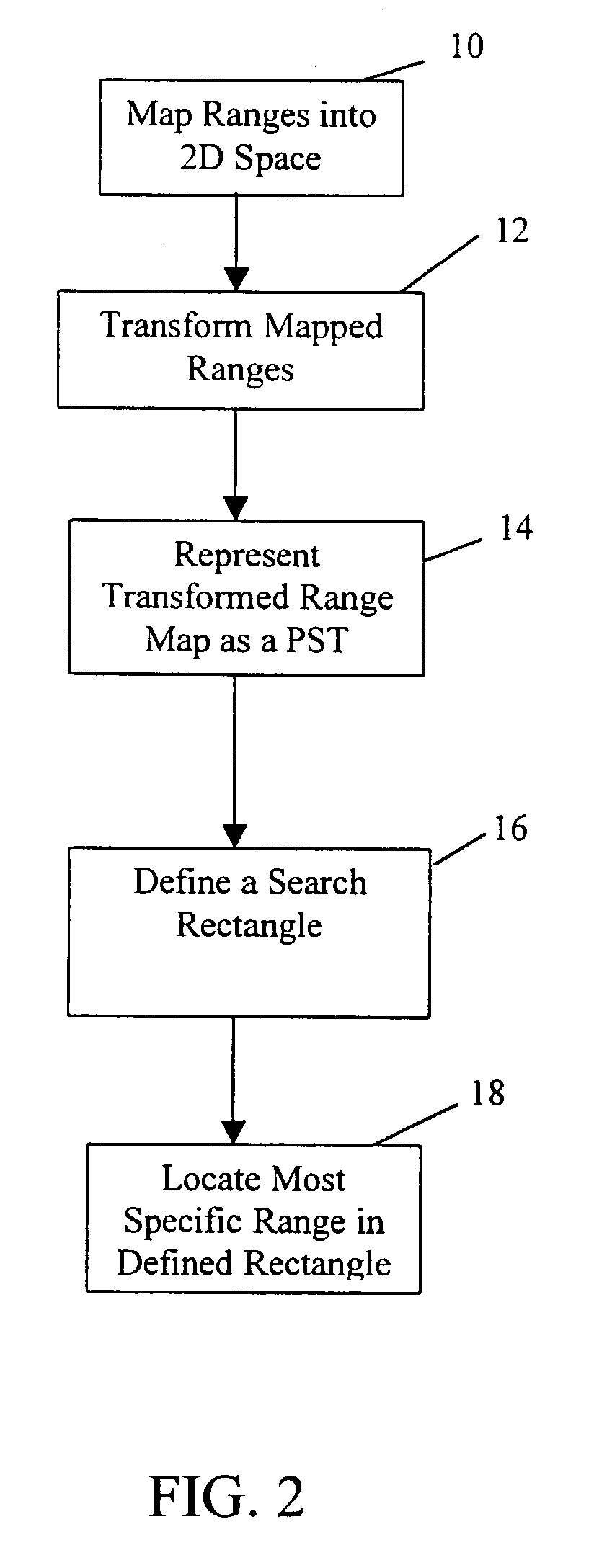
An improved system and method is provided for packet routing in dynamic router tables. Specifically, the invention provides a method, computer system, and computer readable media for using Priority Search Trees (PSTs) to match, insert, and delete rules in dynamic routing tables in O(log n) time. In a first embodiment, for a dynamic router table consisting of n pairs of tuples, each tuple comprising an address prefix and next-hop information, the invention provides a system and method, using a PST, for inserting a new tuple, deleting an existing tuple, and searching for the tuple with the longest matching prefix for destination address, wherein each operation is performed in O(log n) time. In a second embodiment, for a dynamic router table consisting of n pairs of tuples, each tuple comprising a range of destination addresses and next-hop information, the invention provides a system and method, using a PST and a set of red-black priority search tree (RBPST), for inserting a new tuple, deleting an existing tuple, and searching for the tuple with the most specific matching range, wherein each operation is performed in O(log n) time. The invention can be implemented in numerous ways to improve dynamic router table performance, including as a system, a device, a method, or a computer readable medium.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com