Patents
Literature
117 results about "Ip router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The best way to find the IP address of your router is to use the command prompt. Open Run box and type “cmd” and hit enter. In the command prompt terminal, write the following command and execute. ipconfig. Your router IP address is listed in front of the “Default Gateway” text. This is the IP address of your router.
Mobile internet access
InactiveUS6804720B1Accounting/billing servicesMultiple digital computer combinationsCable Internet accessIp address
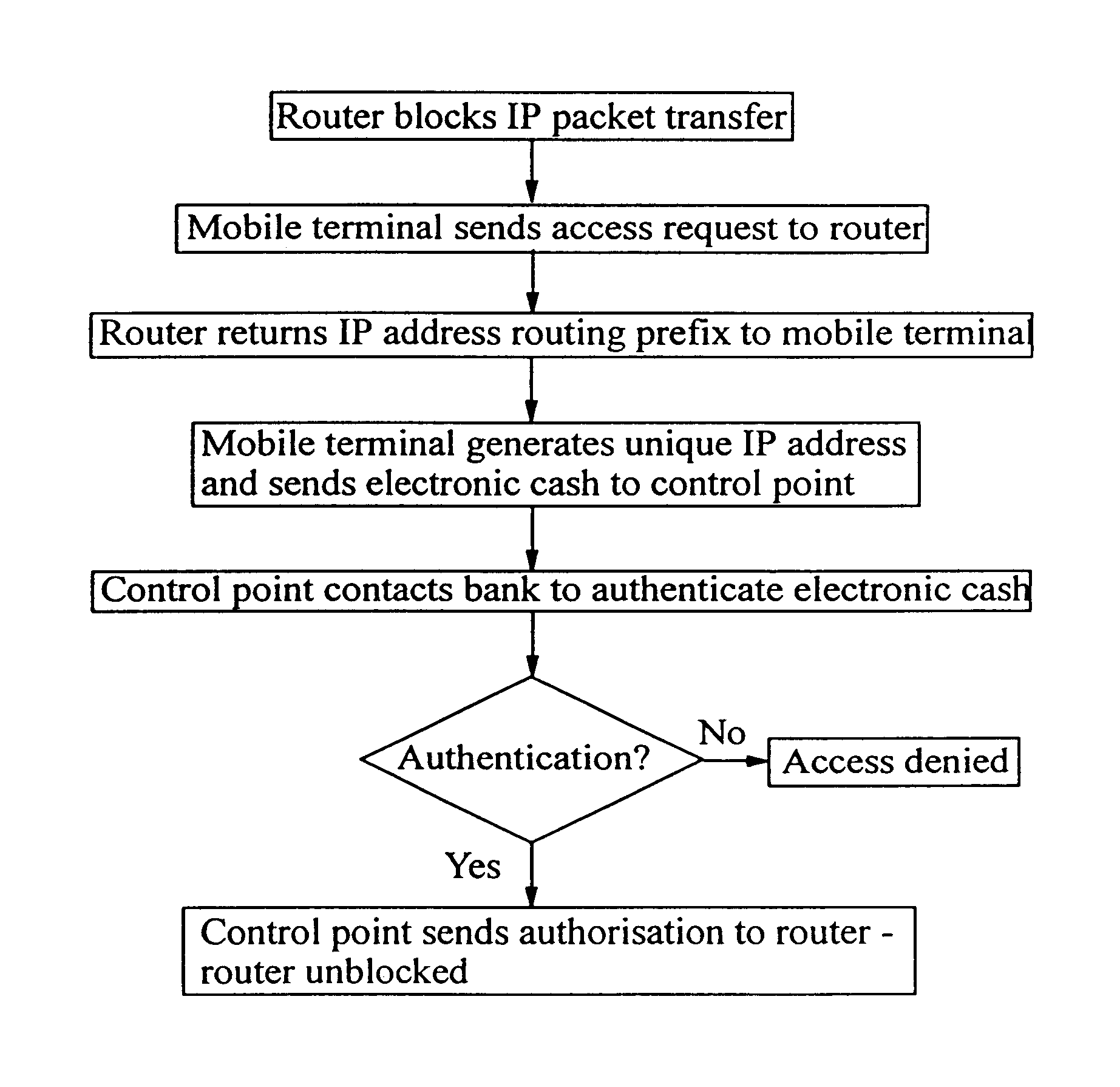
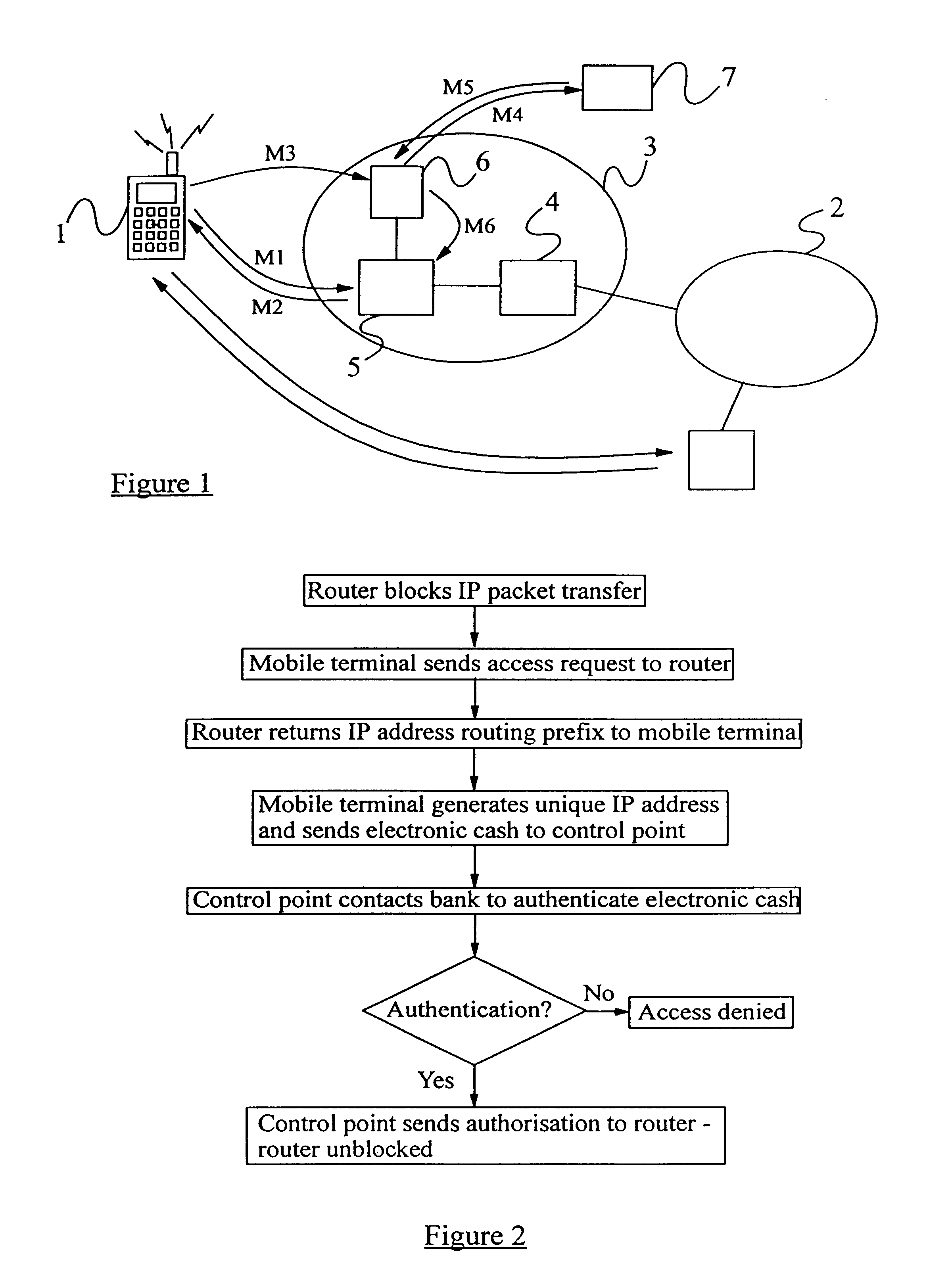
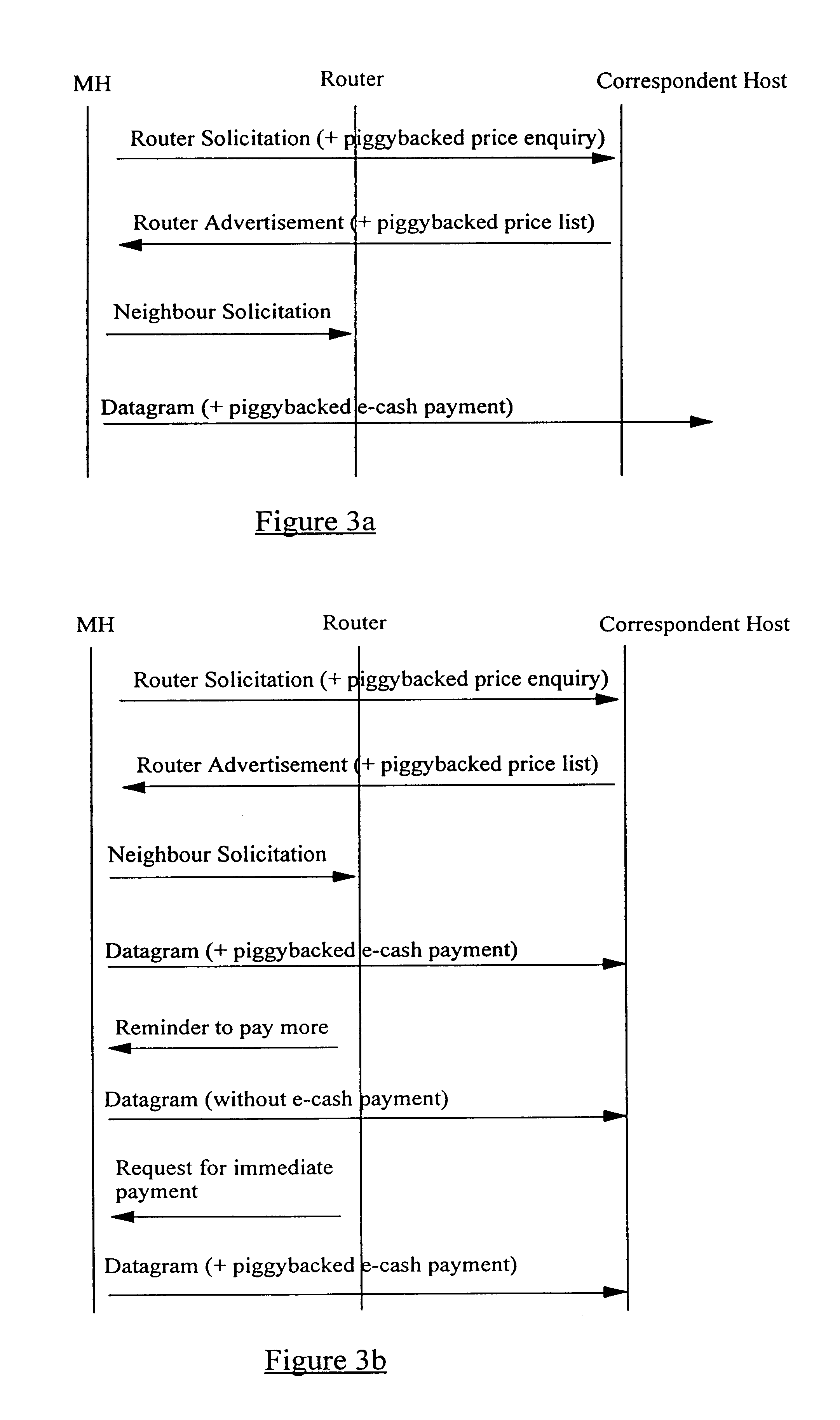
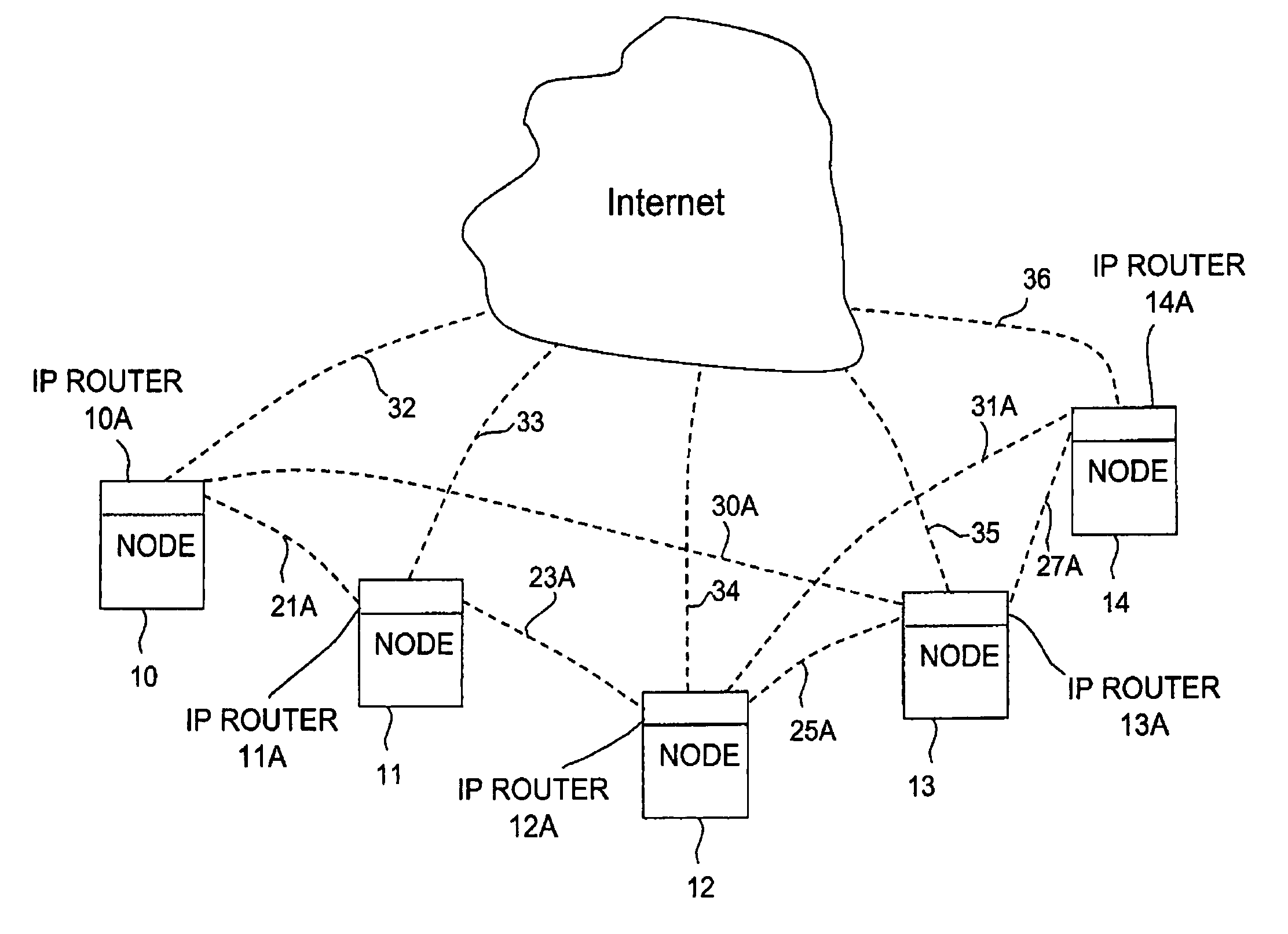
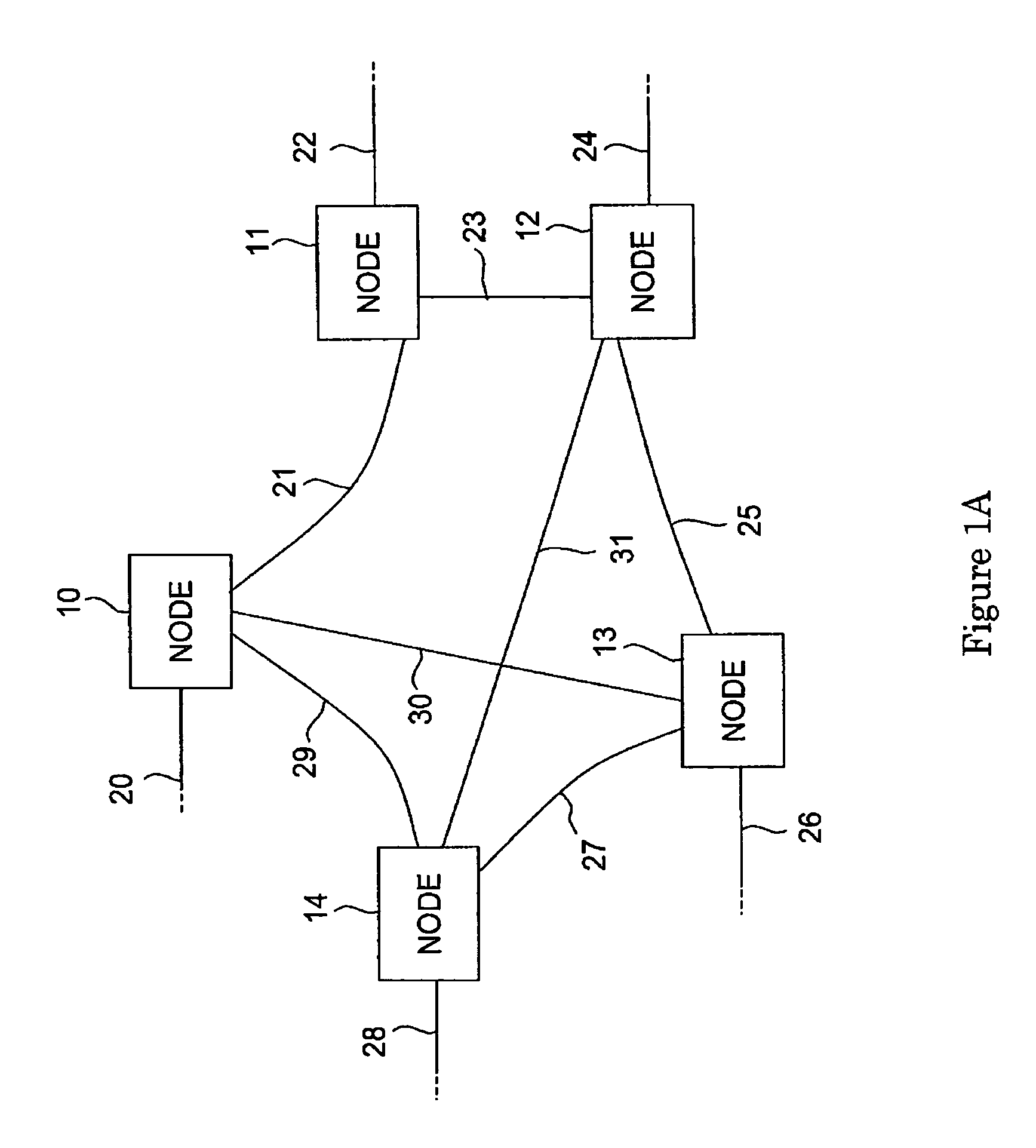
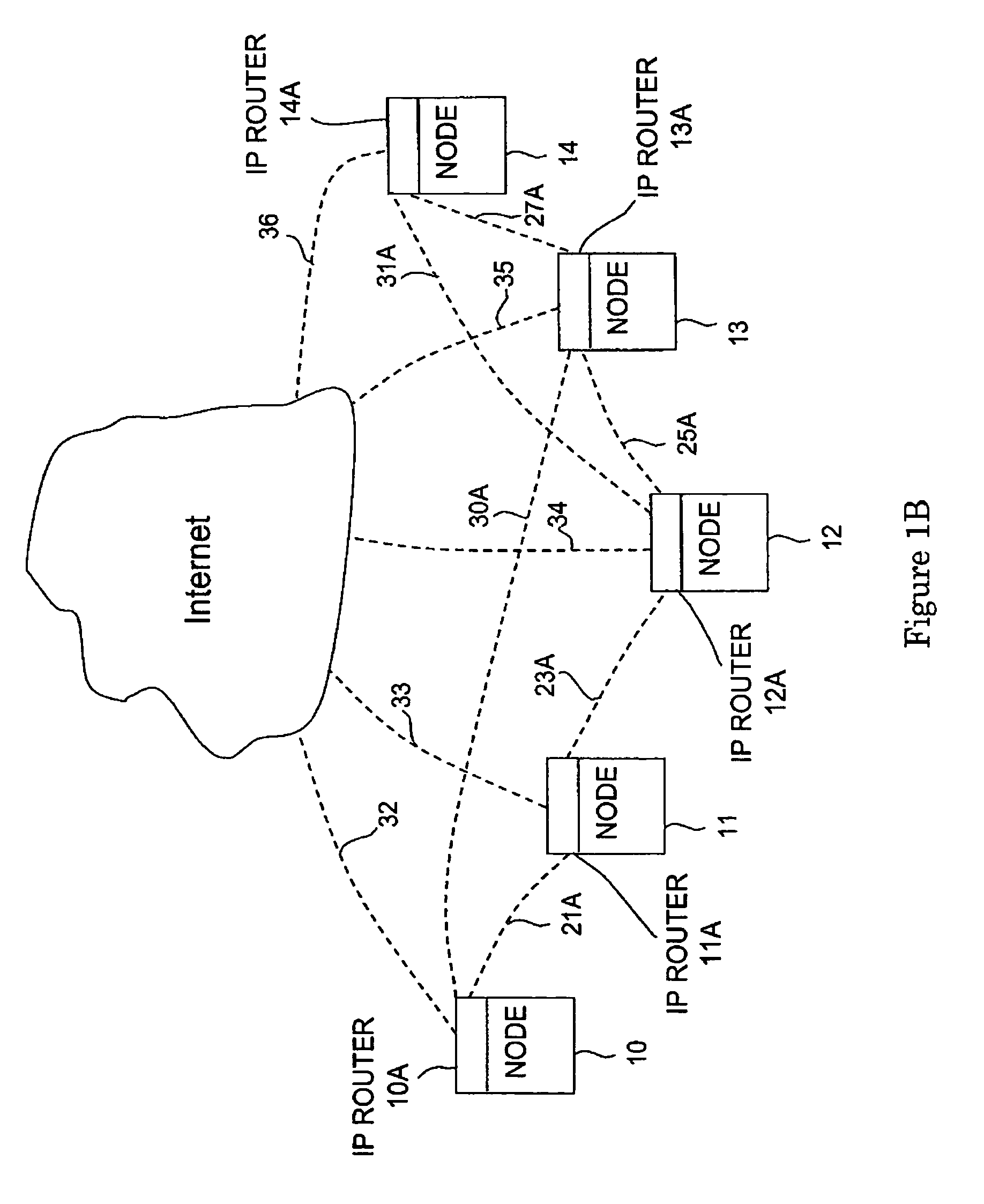
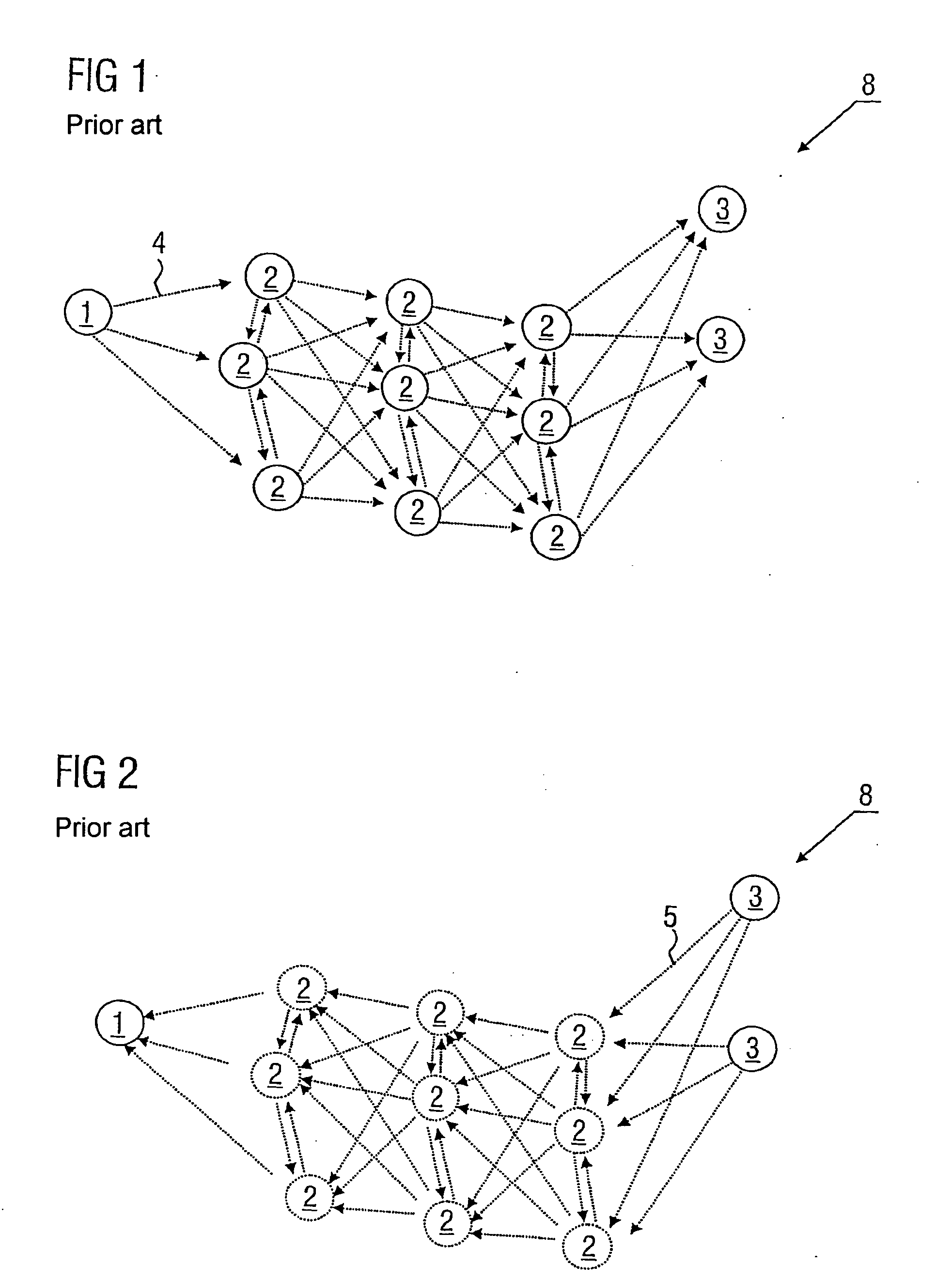
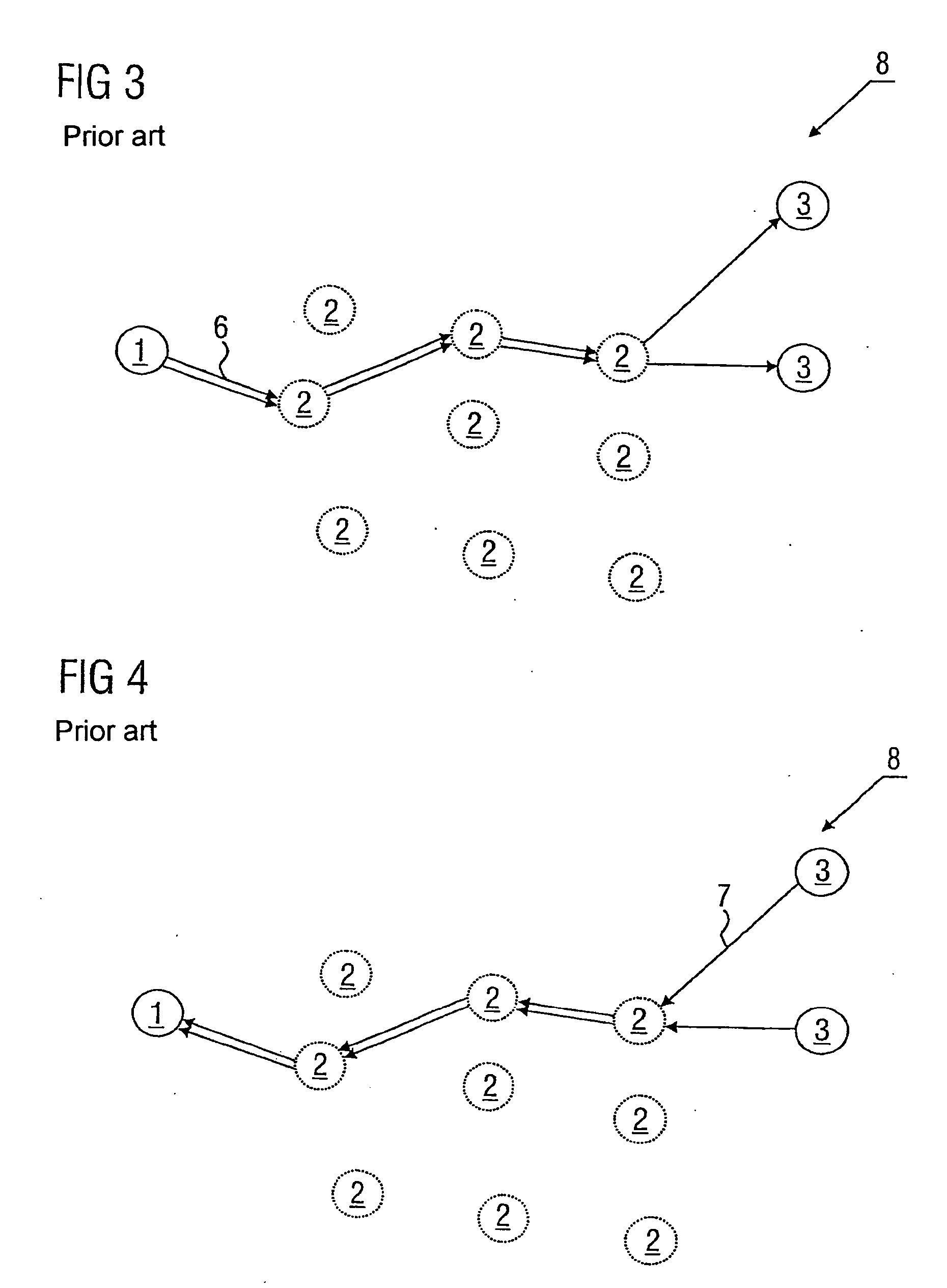
A method of authorizing an Internet Protocol (IP) enabled mobile host 1 to access the Internet 2 via an wireless LAN, GSM, UMTS access network 3 comprises initially sending an IP access request from the mobile host 1 to an IP router 5 within the access network 3. In response to receipt of said access request at the IP router 5, an IP address routing prefix is sent from the IP router 5 to the mobile host 1. Electronic cash is then forwarded from the mobile host 1 to a control point 6 within the access network 3. The control point 6 confirms the authenticity and / or sufficiency of the electronic cash and, providing that confirmation is made, sends an authorization message to the IP router 5. The IP router 5 blocks the transmission of IP packets between the mobile host 1 and the Internet 2 prior to receipt of the authorization message and permits the passage of IP packets only after an authorization message has been received.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
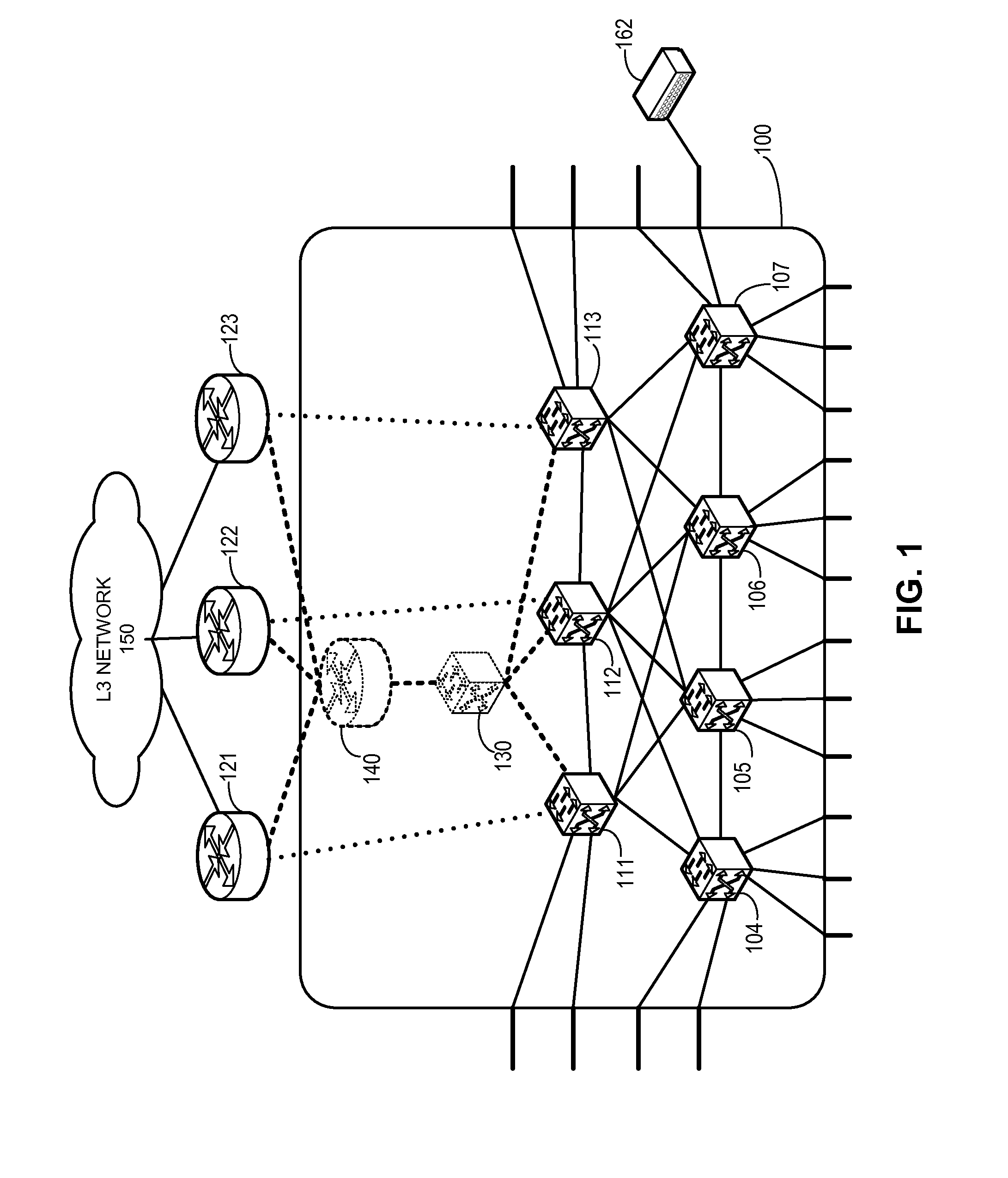
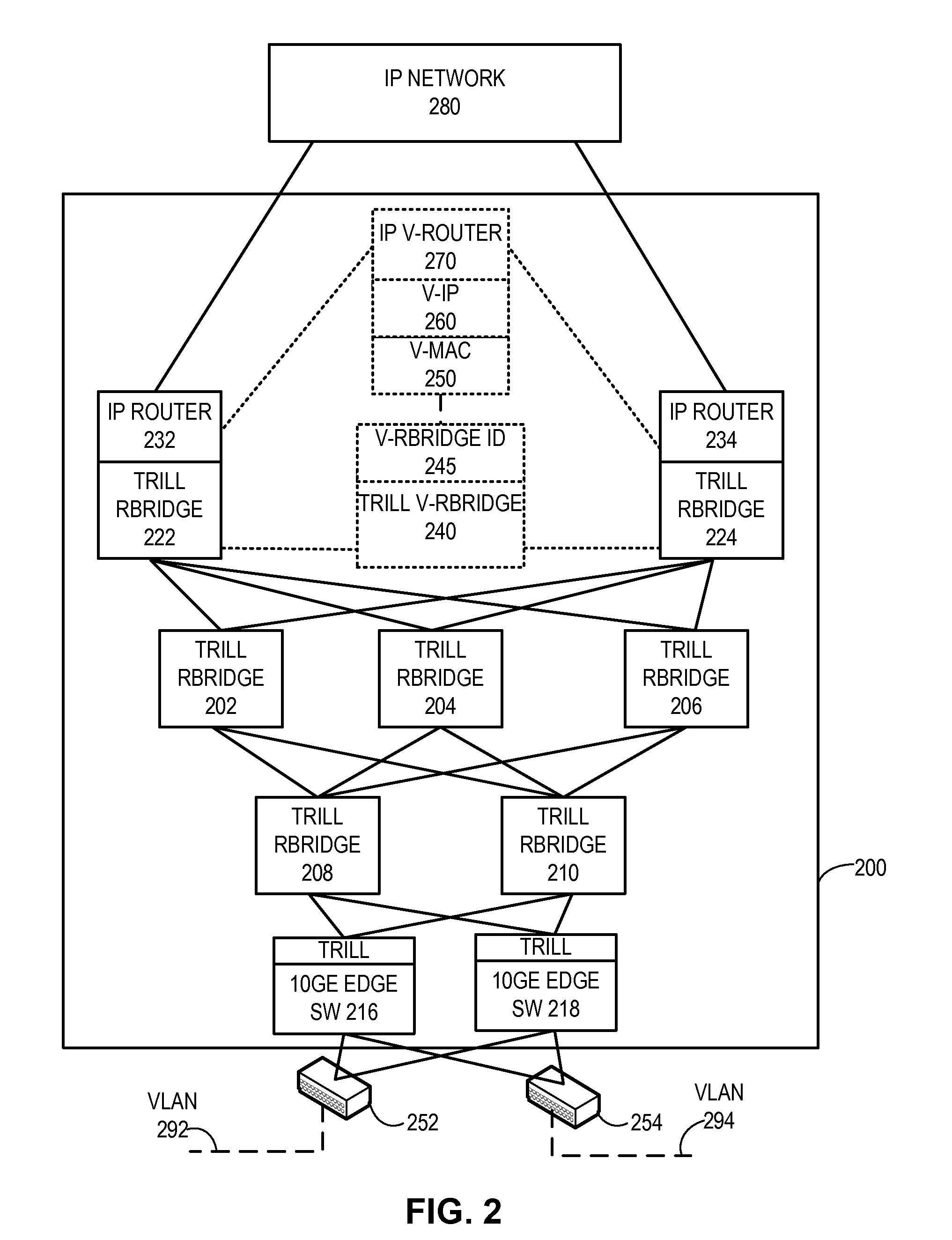
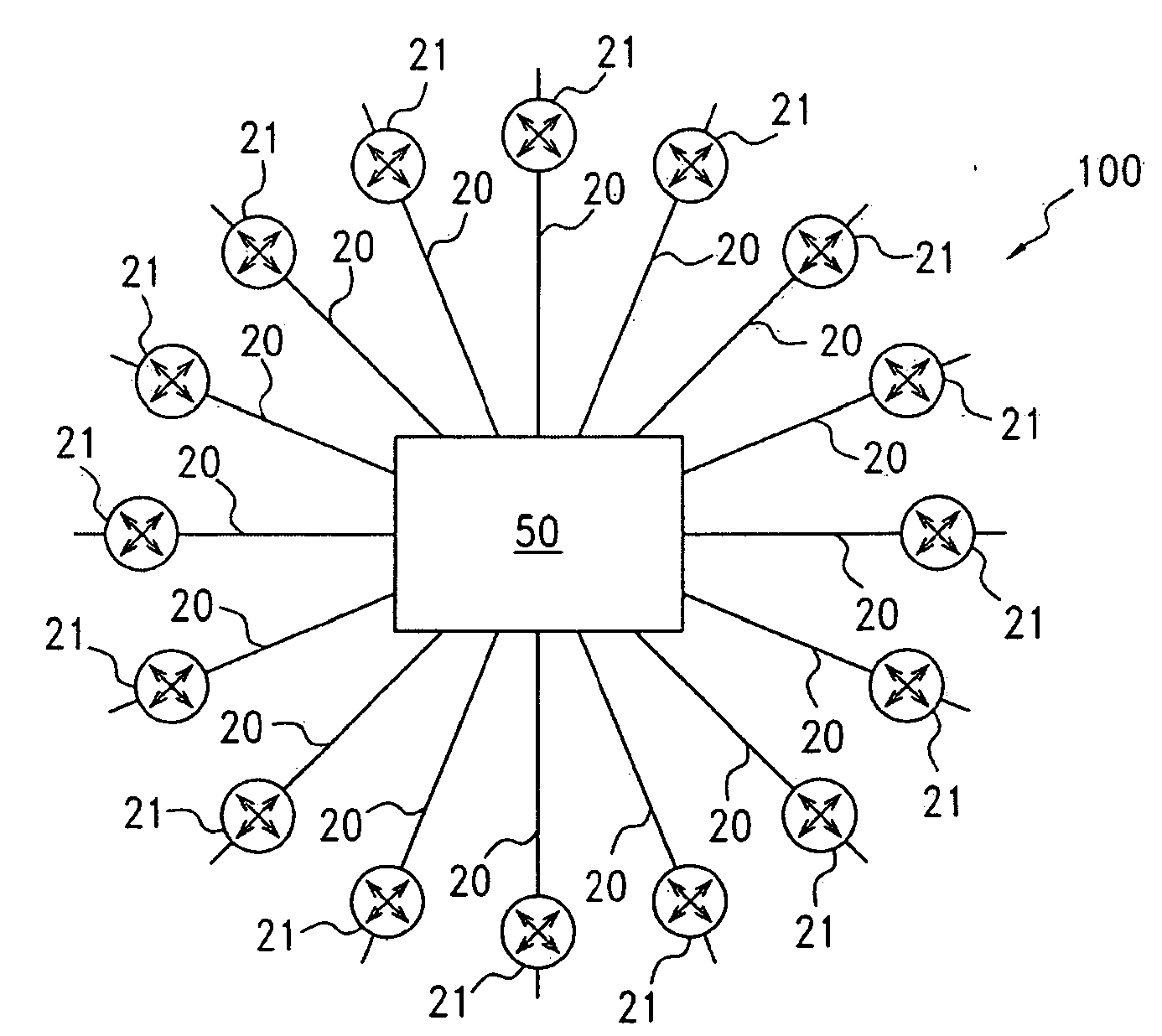
Trill based router redundancy
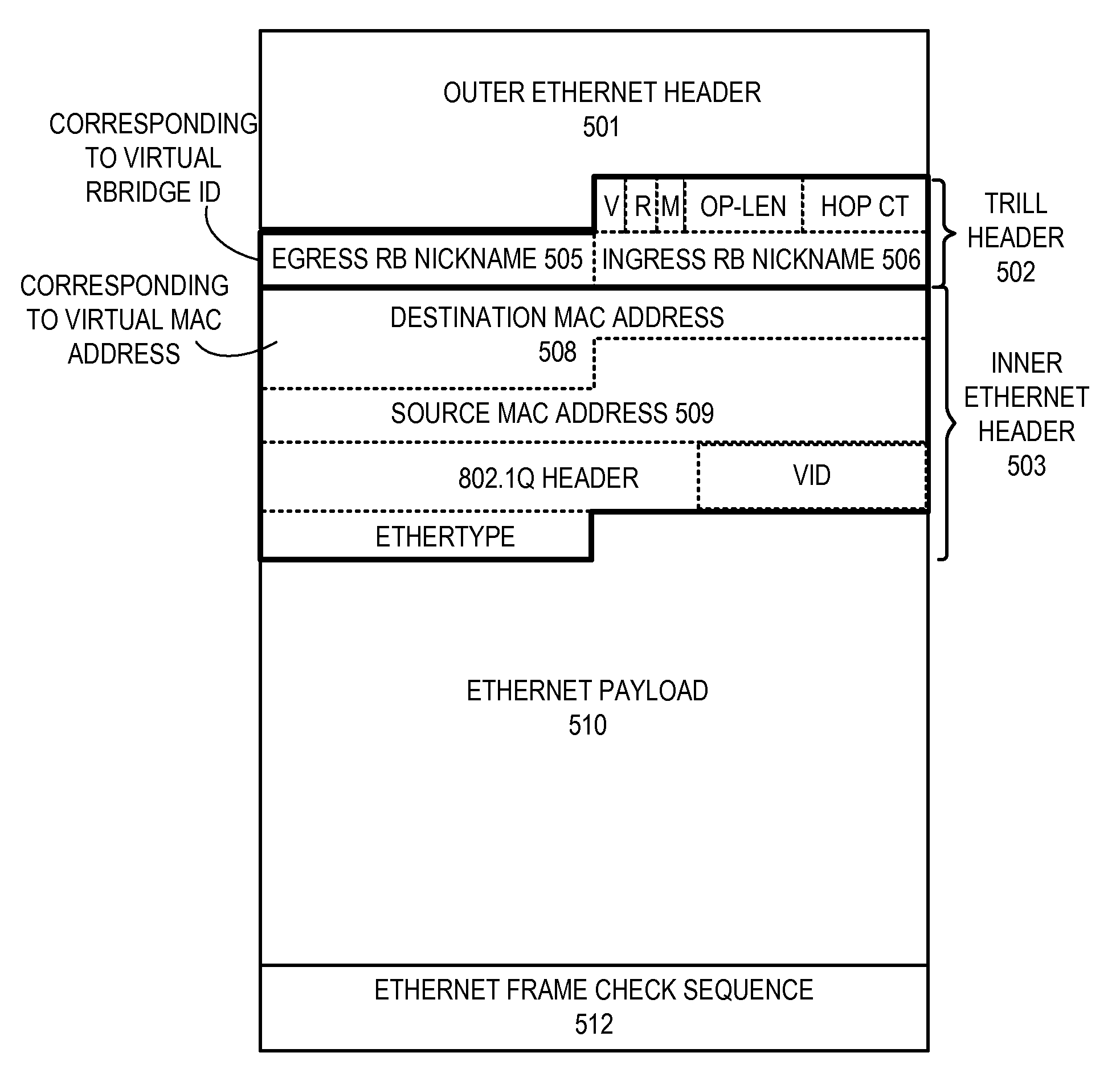
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switching system. The switching system includes a Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) header processor and an Internet Protocol (IP) header processor. The TRILL header processor is configured to identify a virtual routing bridge (RBridge) identifier in a packet, and the IP header processor is configured to identify a virtual IP address in the packet. The virtual IP address is assigned to a virtual IP router associated with the virtual RBridge identifier.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS20070280261A1Minimize delay jitterMeet bandwidth requirementsMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationCrossbar switchDifferentiated services
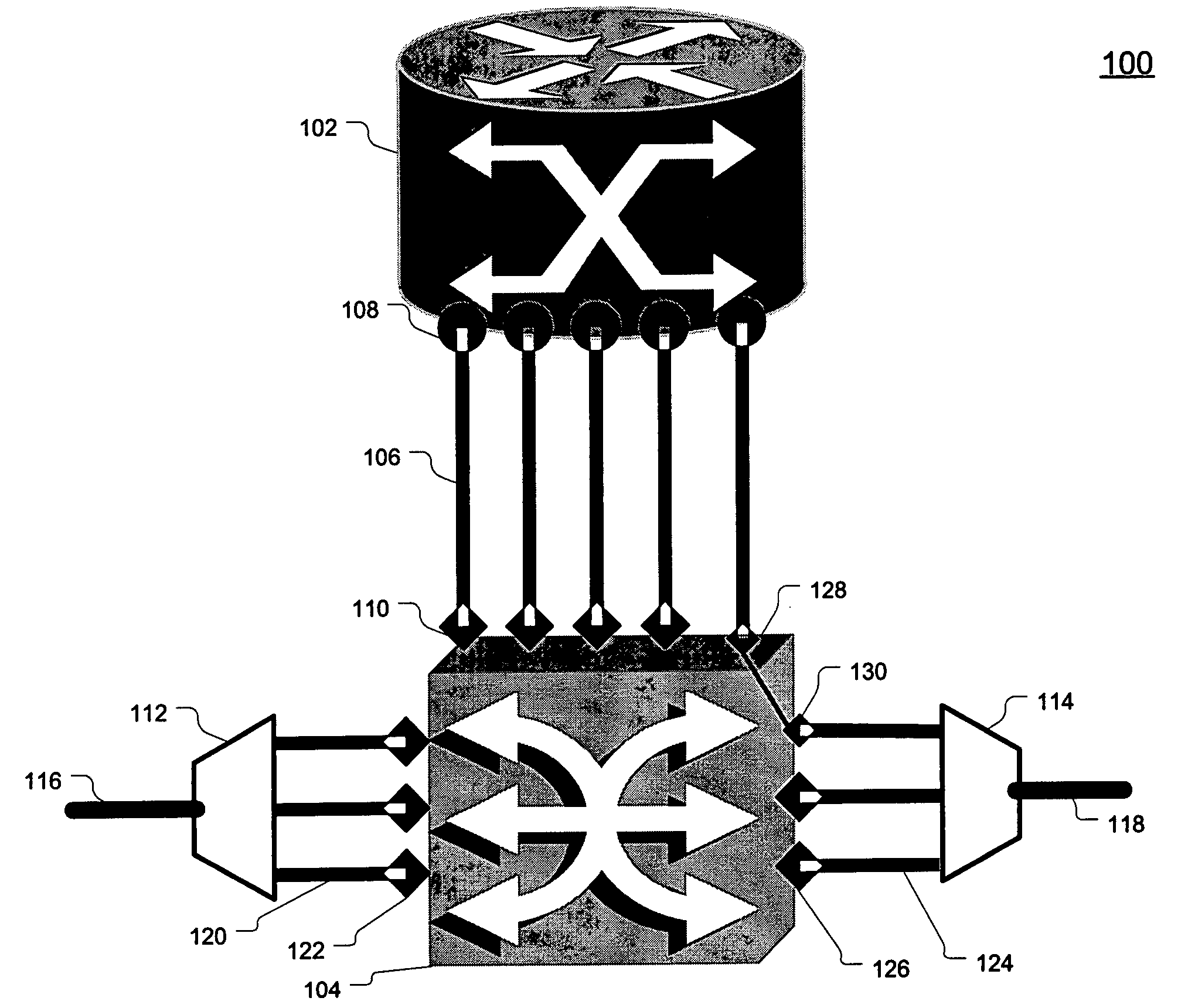
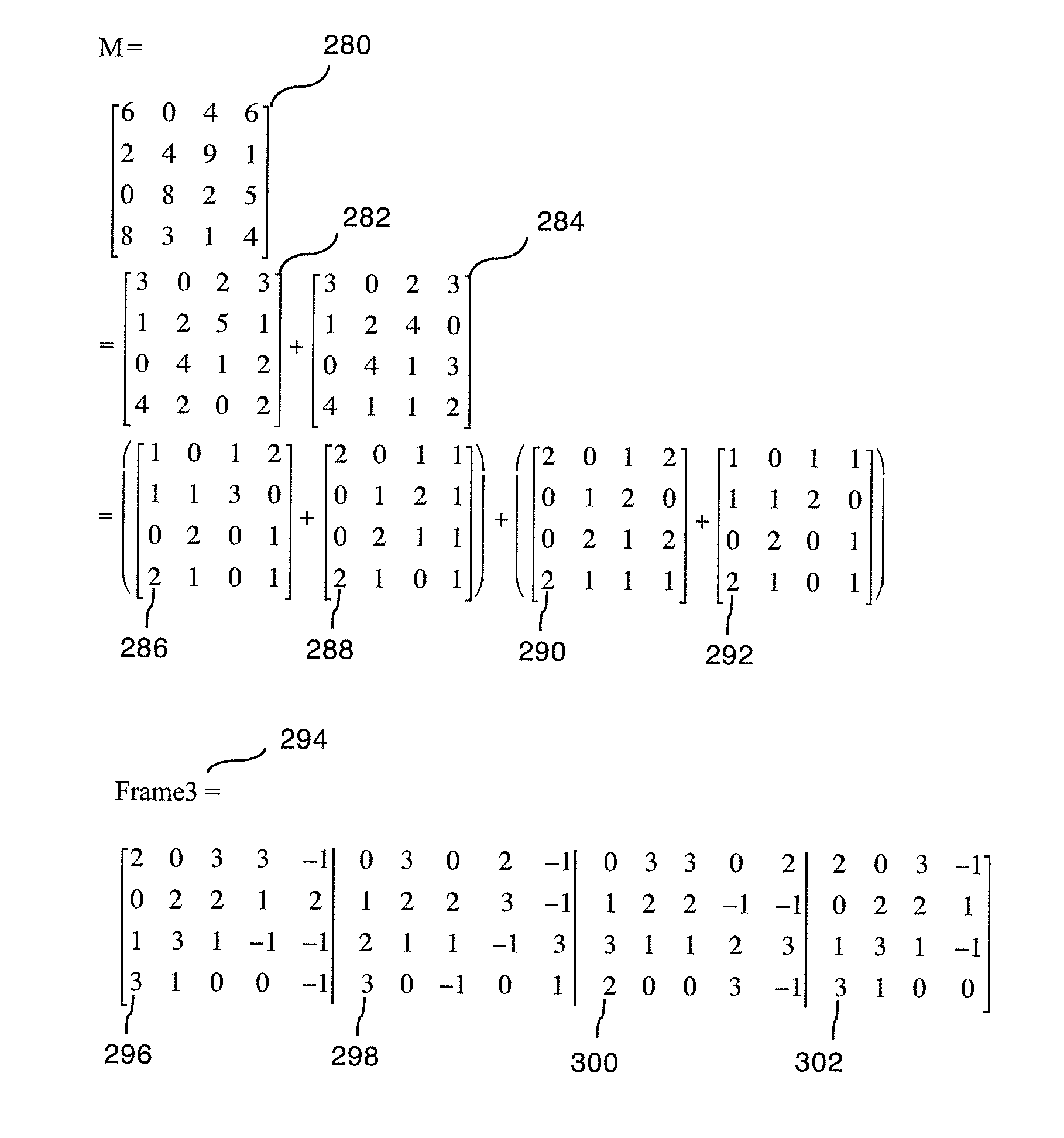
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(logN) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(NlogN) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
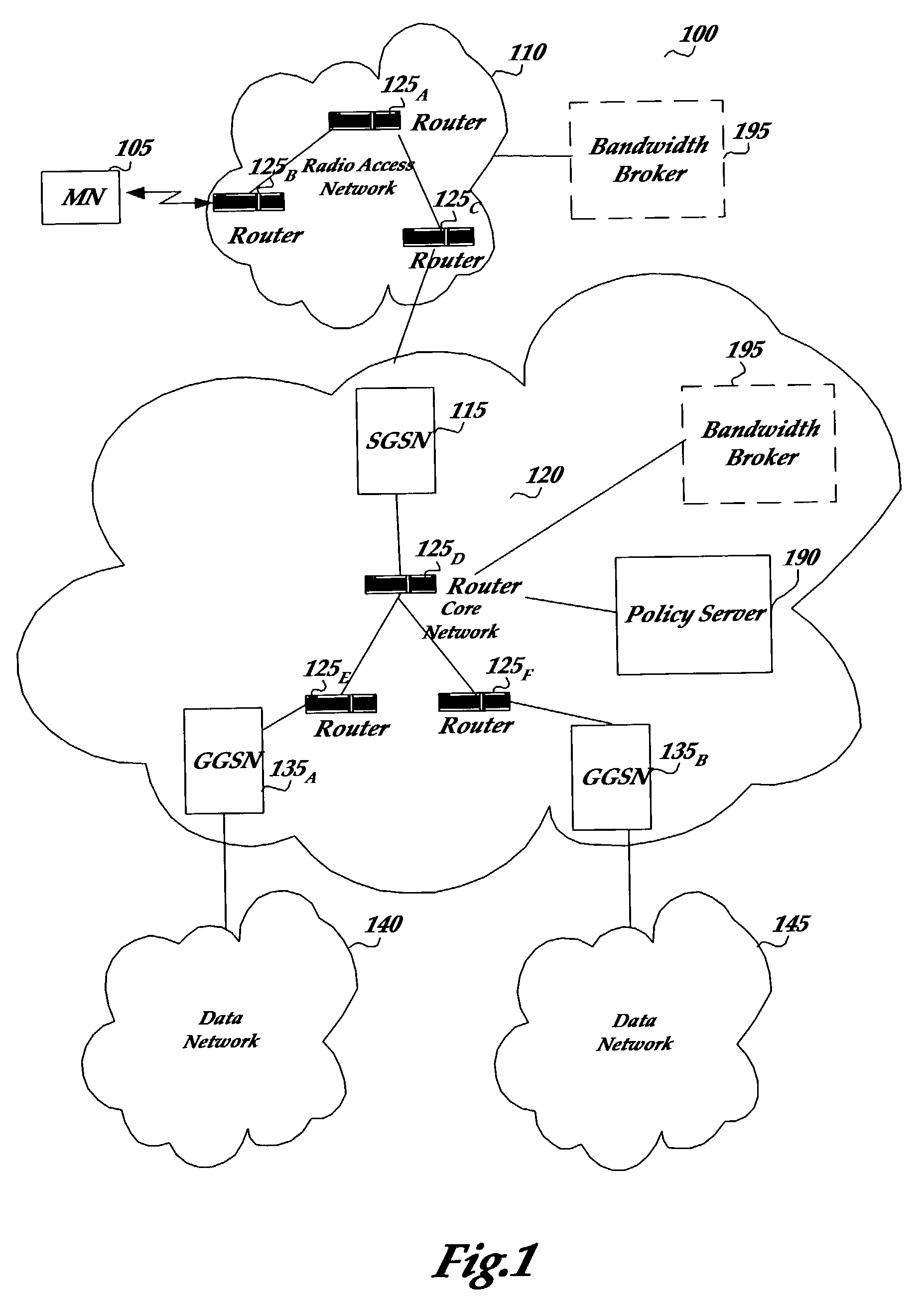
Managing internet protocol based resources in a packet-based access network
InactiveUS20060221933A1Well formedNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of serviceWireless router
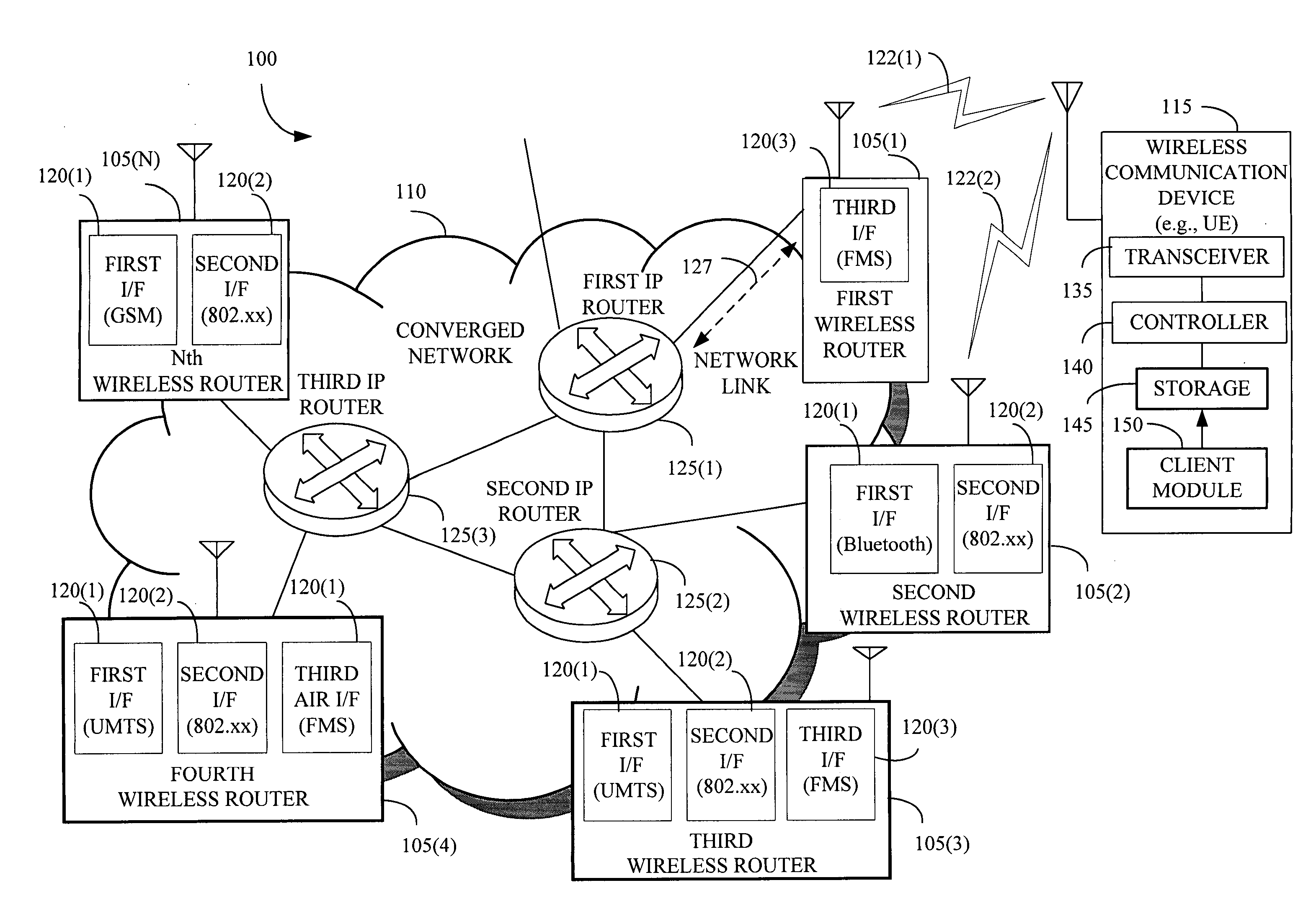
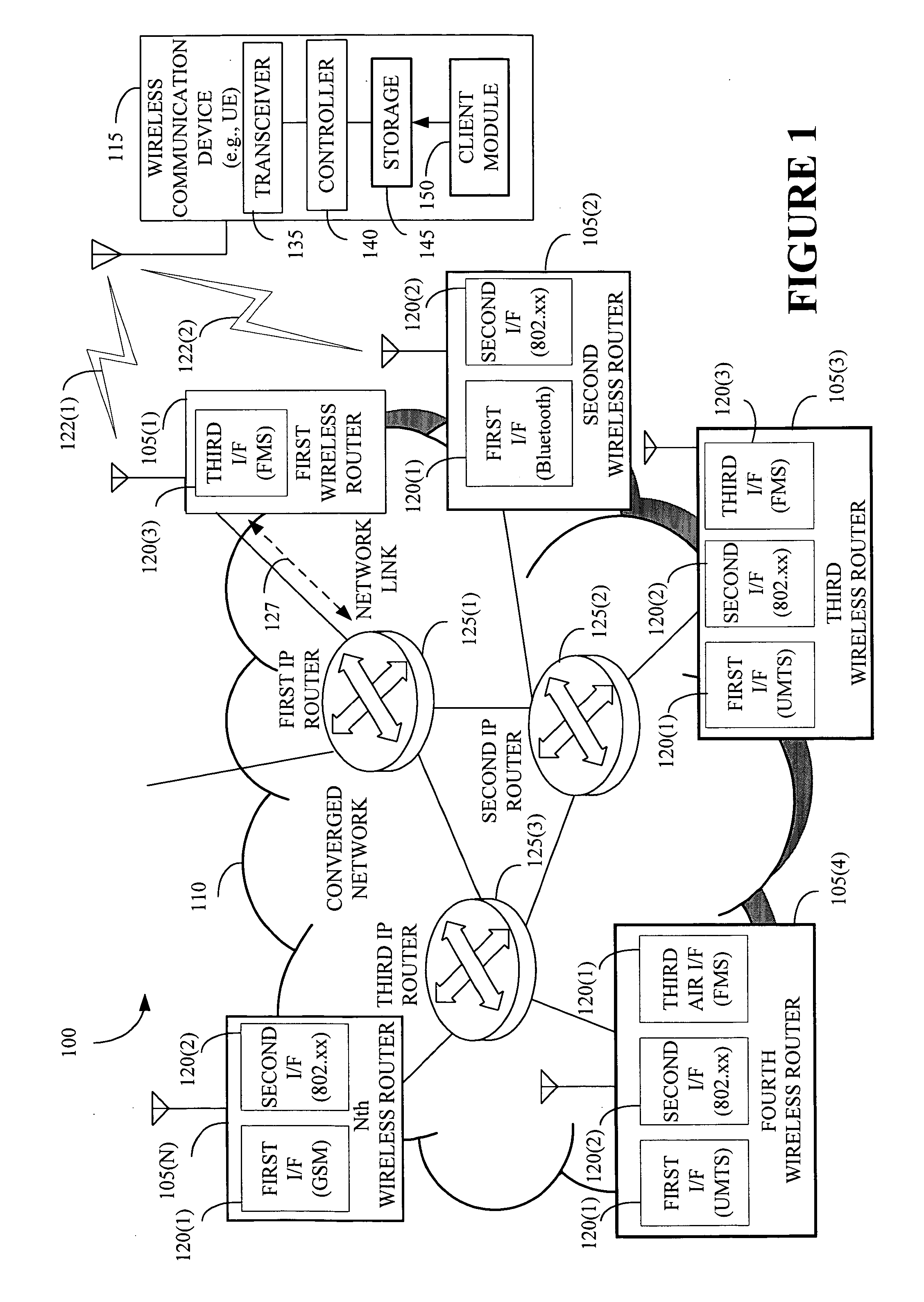
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for performing resource management of one or more Internet Protocol based resources to route a plurality of packets. To ensure a relatively high end-to-end service quality, the method and apparatus defines one or more user-service specific metrics being utilized by Internet Protocol (IP) mechanisms on a network layer to provide an IP-based resource management in a next generation network. A wireless router may provide wireless radio access using a resource management that captures one or more properties of at least one network link and at least one wireless link as metrics that may be used by IP mechanisms. Based on metric related distributed information, each router including a wireless router and an IP router may determine whether or not to forward a packet on an associated wireless link or a network link. By not differentiating between a wireless link and a network link, the wireless and IP routers may enable routing of the plurality of packets through a converged network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
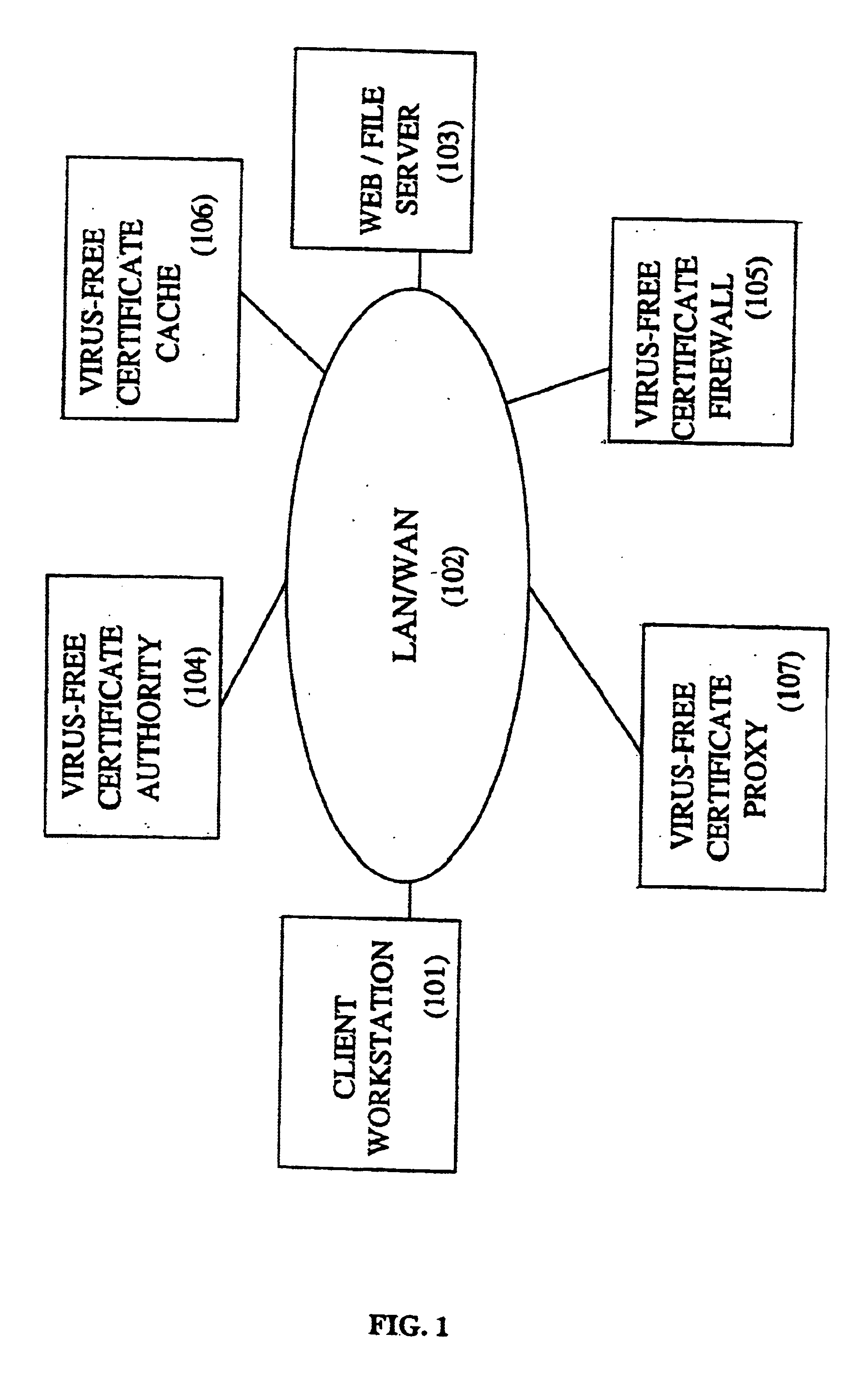
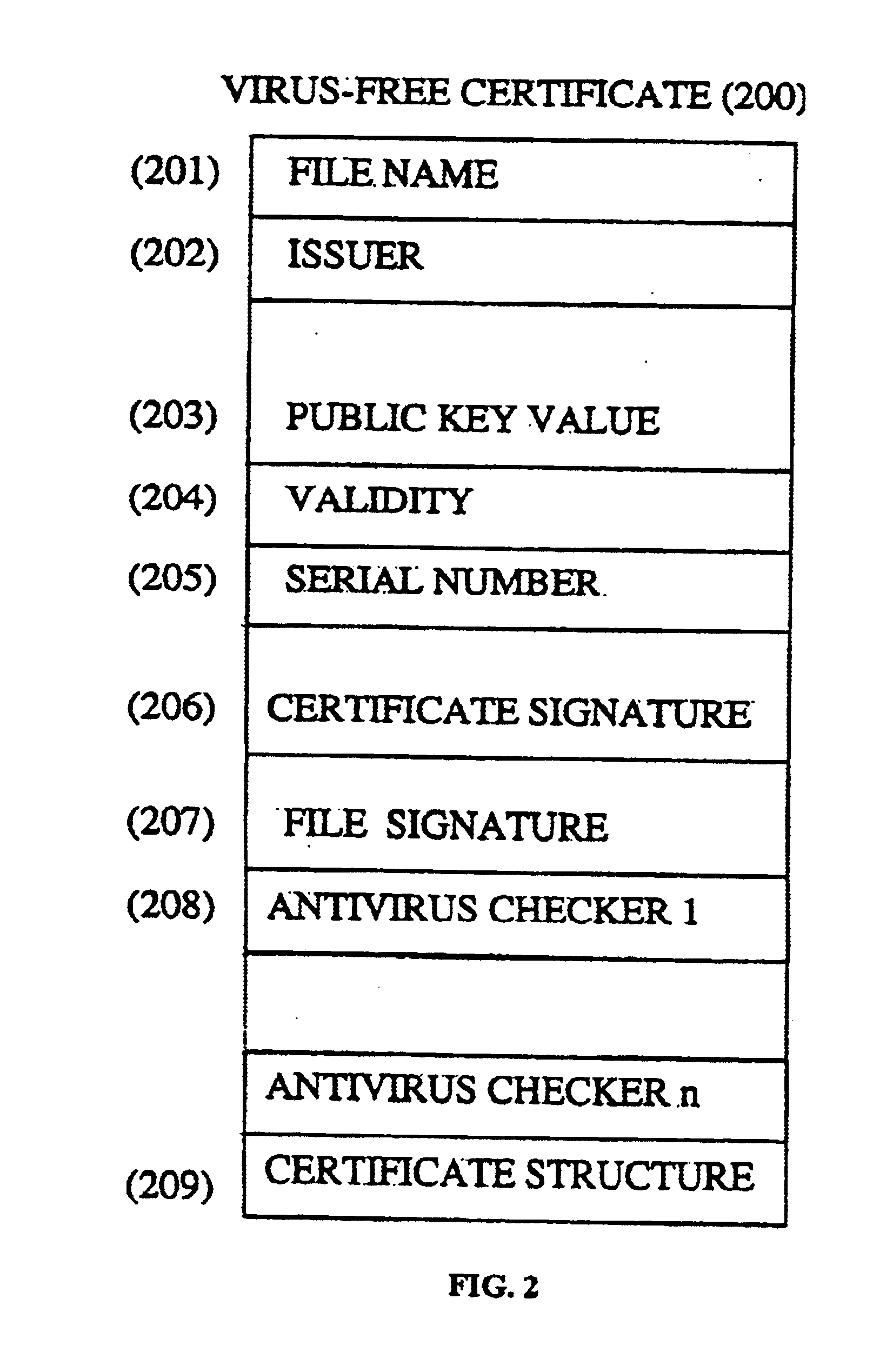
Method and system for caching virus-free file certificates
The present invention relates to computer viruses and more particularly to a method and system for caching anti-virus file certificates. Each anti-virus certificate associated with a file comprises a file signature. The file signature is generated by a virus-free certificate authority, which avoids the system, which receives the file to check this file for all existing viruses. The virus-free certificate authority validates the file against all known viruses, using one or several anti-virus checkers. In case of new viruses, only the virus-free certificate authority is changed and the only process performed by the system receiving the file is to verify the file against the file signature included in the virus-free certificate, and to filter the file according predetermined rules. The present invention drastically simplifies the computing resources for detecting viruses on network devices such as IP Routers and Firewalls.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC +1
Hybrid wireless access bridge and mobile access router system and method
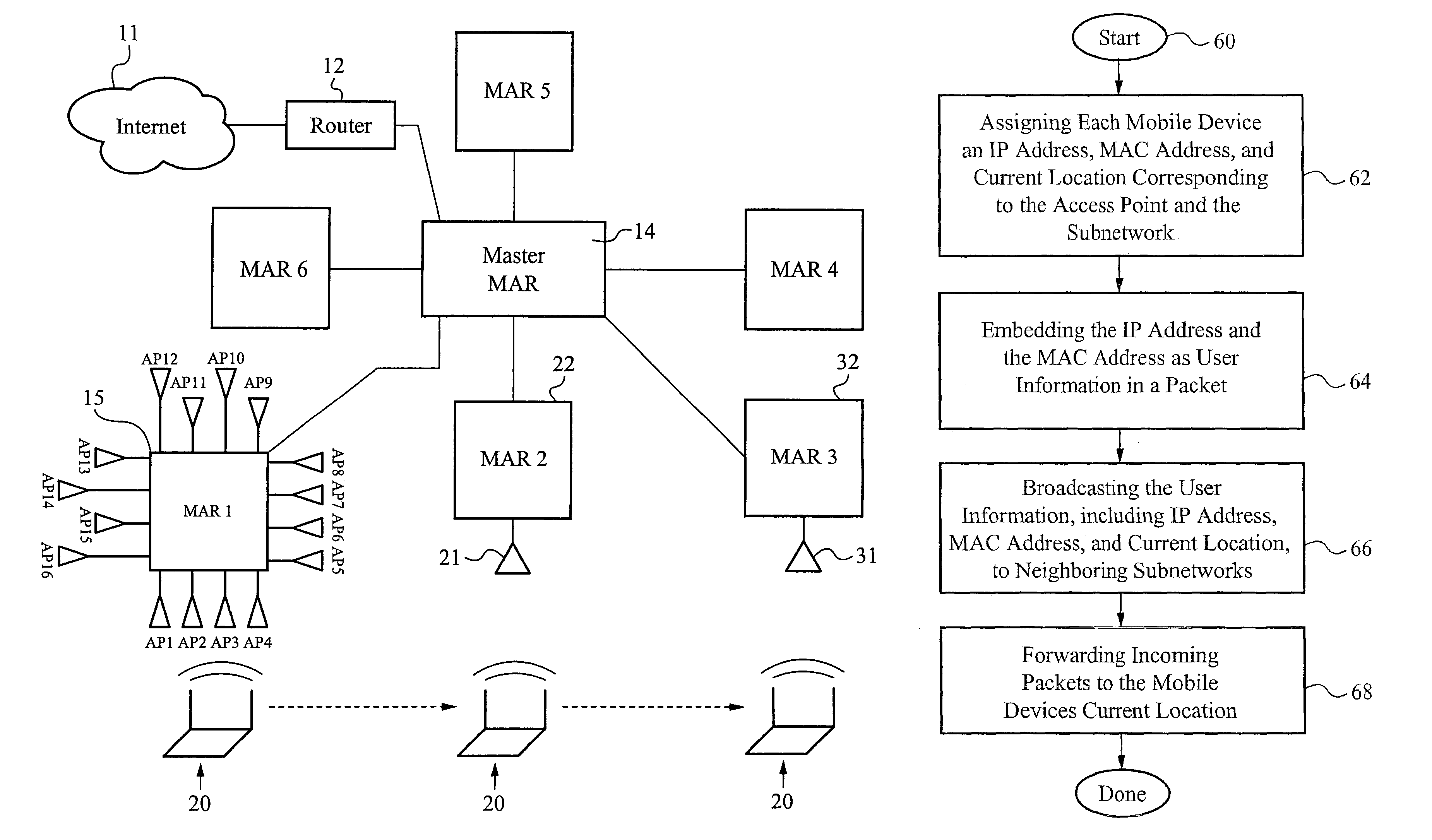
The present invention provides systems and methods that allow mobile devices, such as PDAs, mobile telephones, and laptops to roam seamlessly between subnets of a mobile wireless network and communicate through the network with local mobile devices and / or Internet sites without having to acquire a new or temporary Internet Protocol (IP) address. The network enables a wireline IP router to support wireless mobile devices. The network performs real-time soft-roaming to enable instantaneous connectivity of a visiting mobile device. Specifically, the network relies on the subnets to share IP addresses of the mobile devices.
Owner:AIR BROADBAND COMM
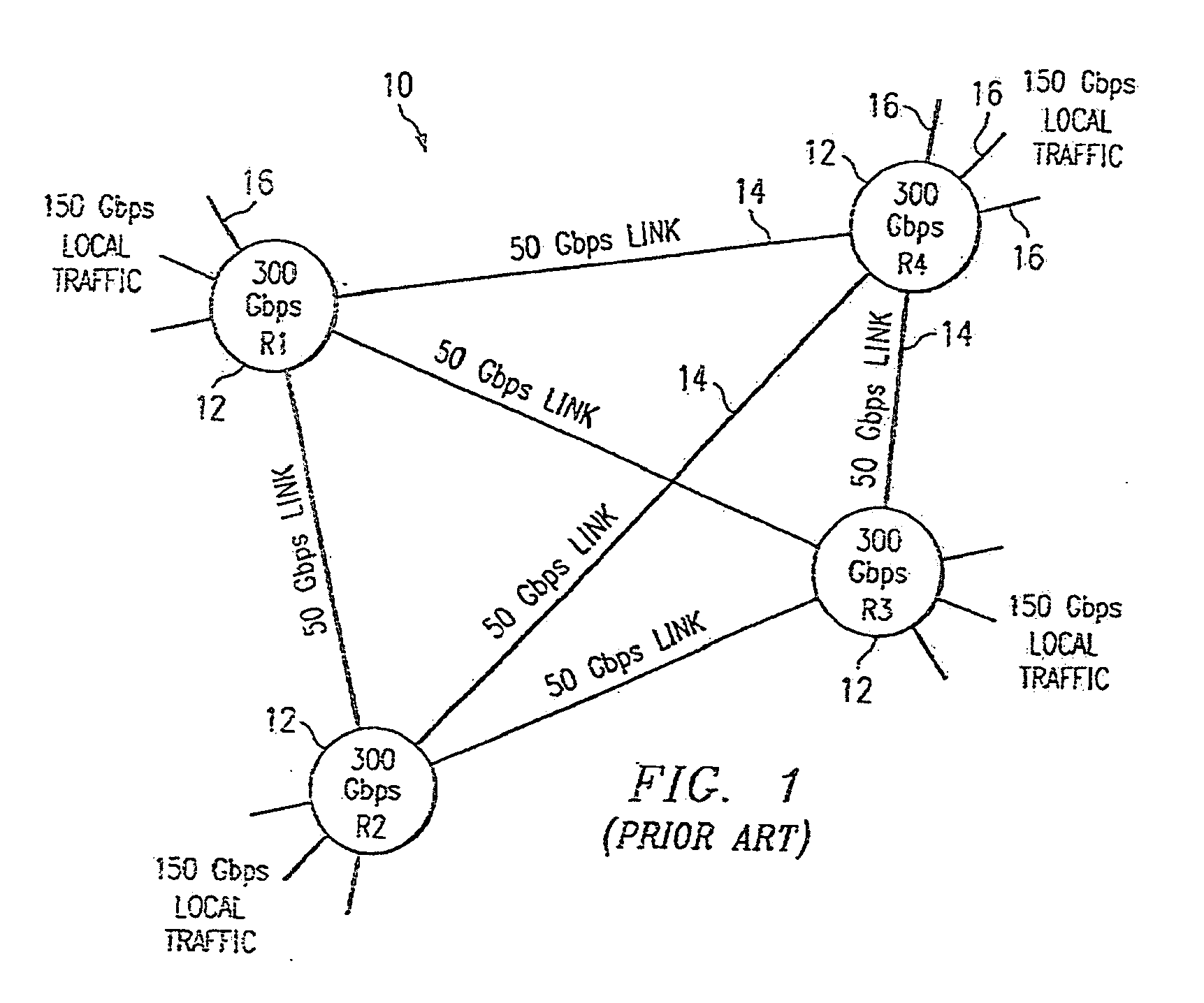
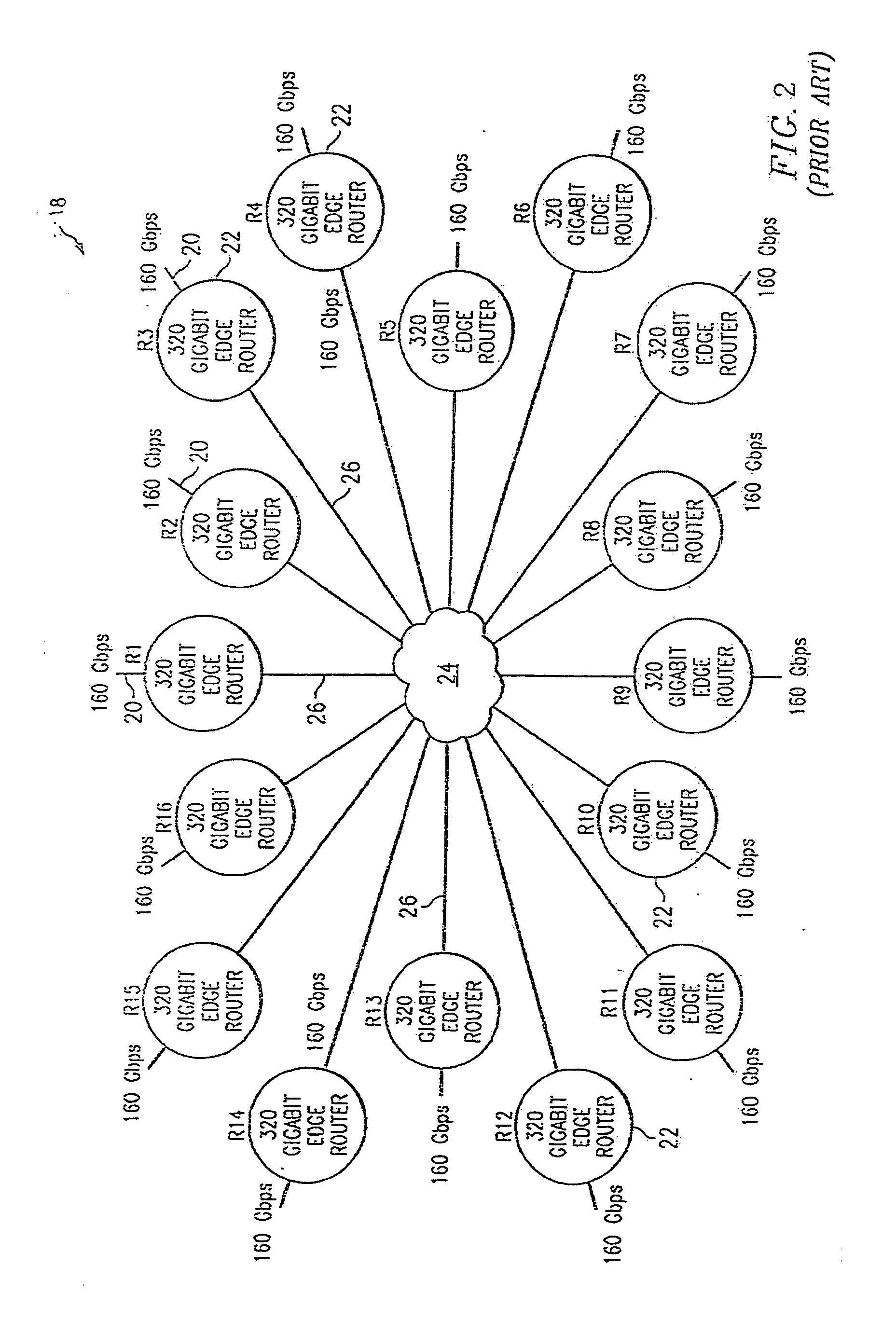
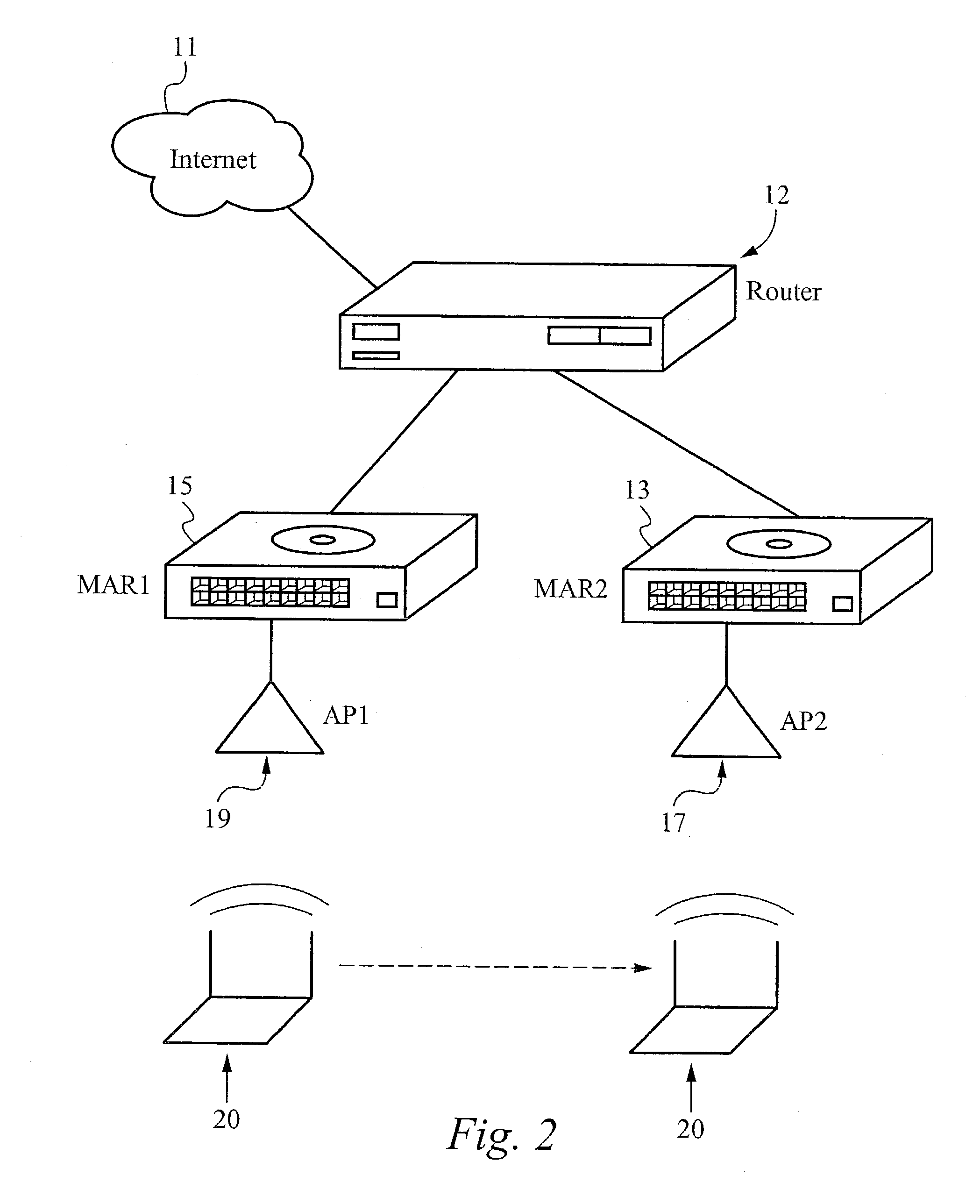
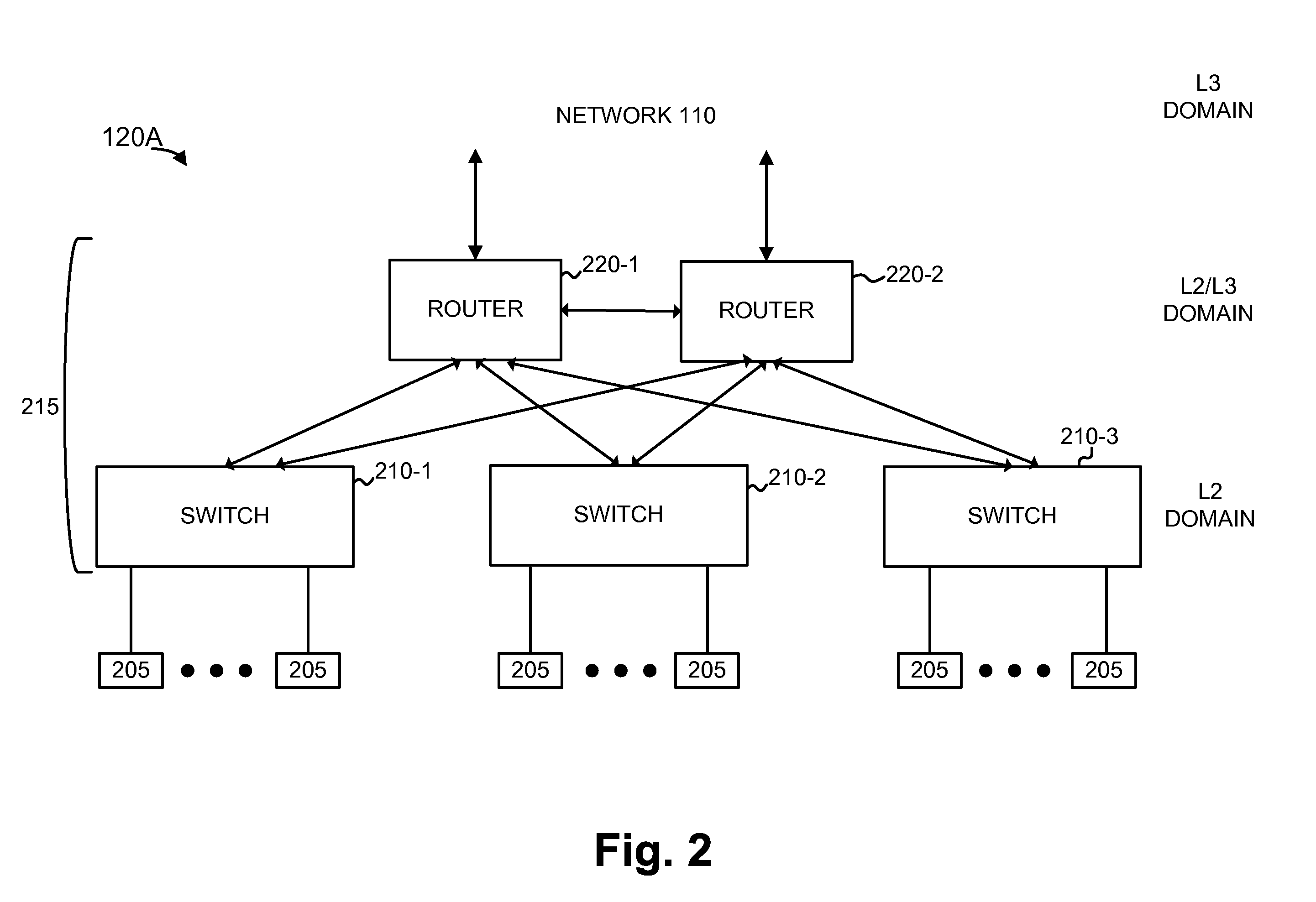
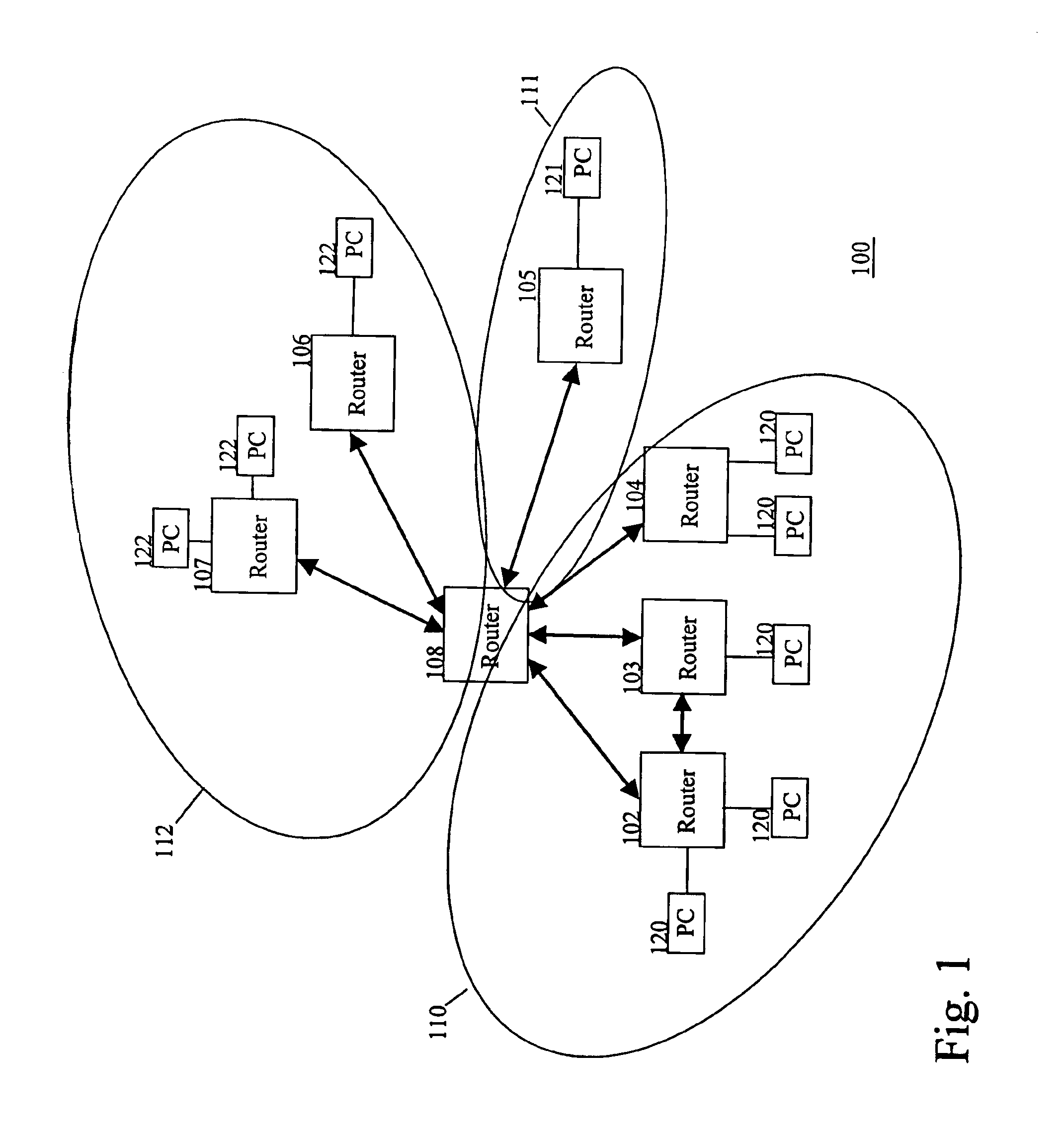
IP router, communication system and band setting method used therein and its program
ActiveUS20040172470A1Digital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityCommunications system
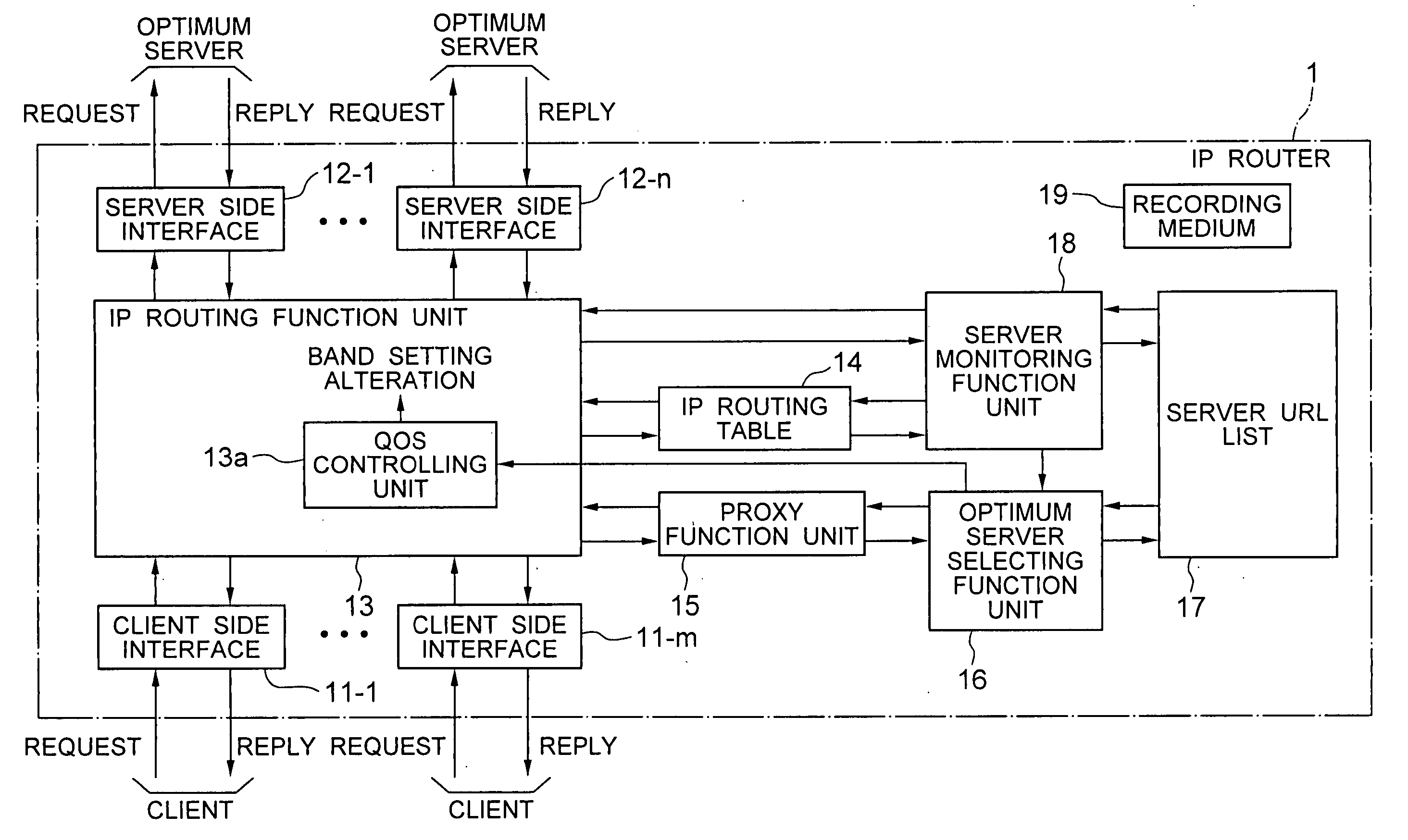
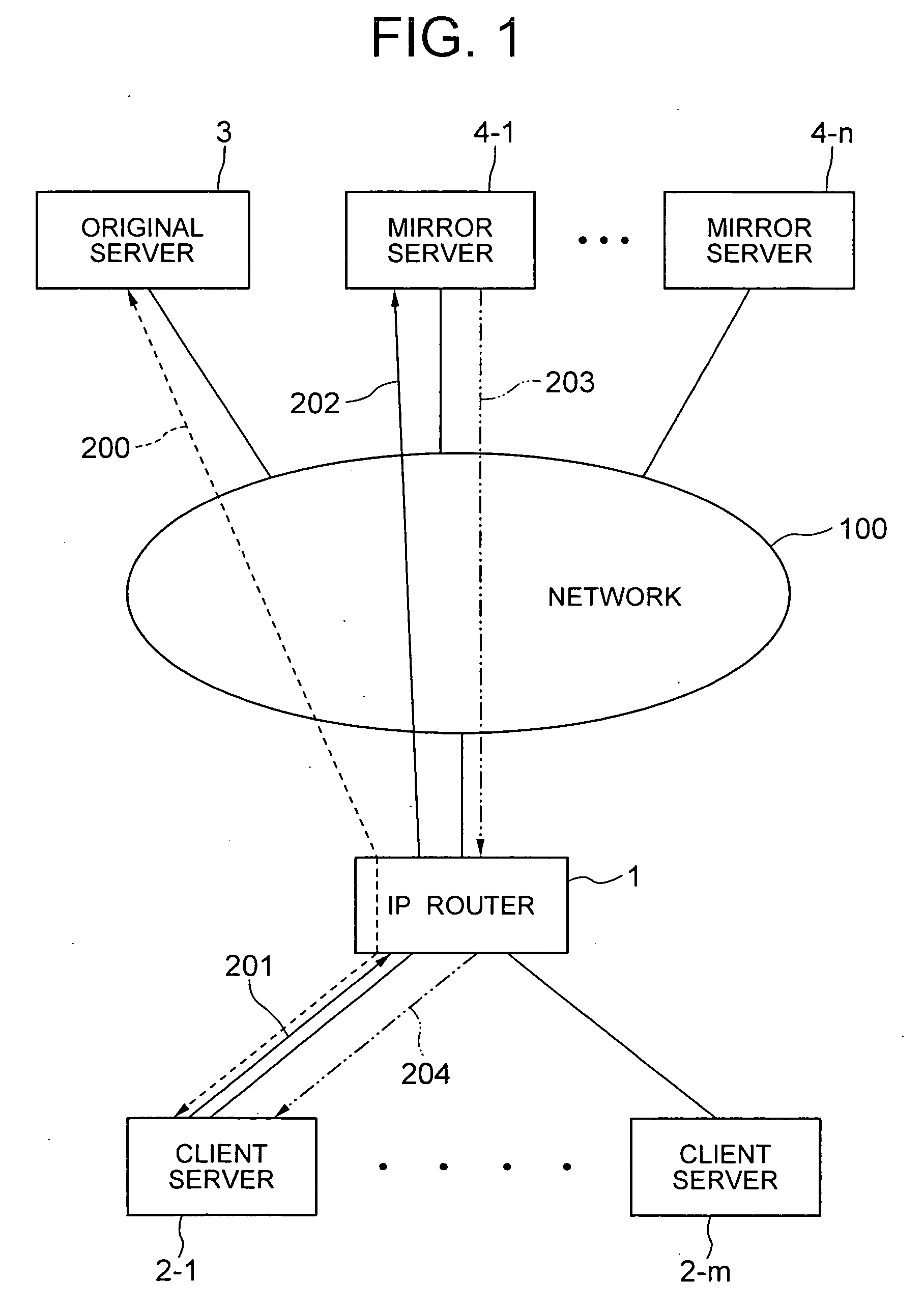
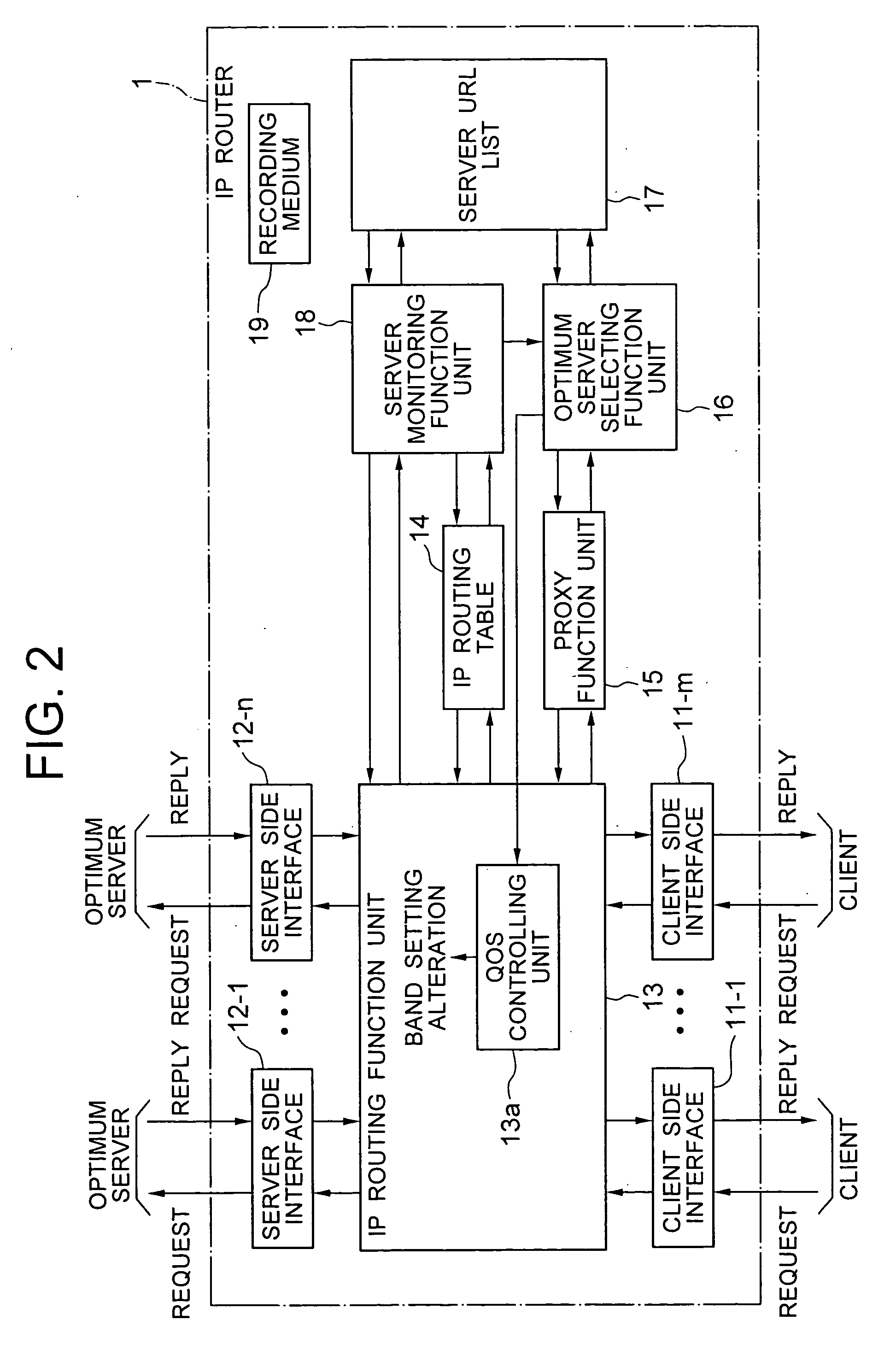
A server monitoring function unit recognizes a running / stopping state of each server, throughput and the like by performing a health check based on obtained positioning information of an original server and mirror servers, informs an optimum server selecting function unit of the information, and updates a server URL list based on the positioning information. When the server monitoring function unit detects a change in the network topology from a change in an IP routing table, the optimum server selecting function unit alters the selection criteria of the optimum server and informs a QoS controlling unit of a traffic change. The QoS controlling unit alters a band setting for each service class according to the traffic change informed.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
A method to realize fast reroute and router
InactiveCN101217457AFast convergenceMeet real-time business needsNetworks interconnectionPrivate networkIp router
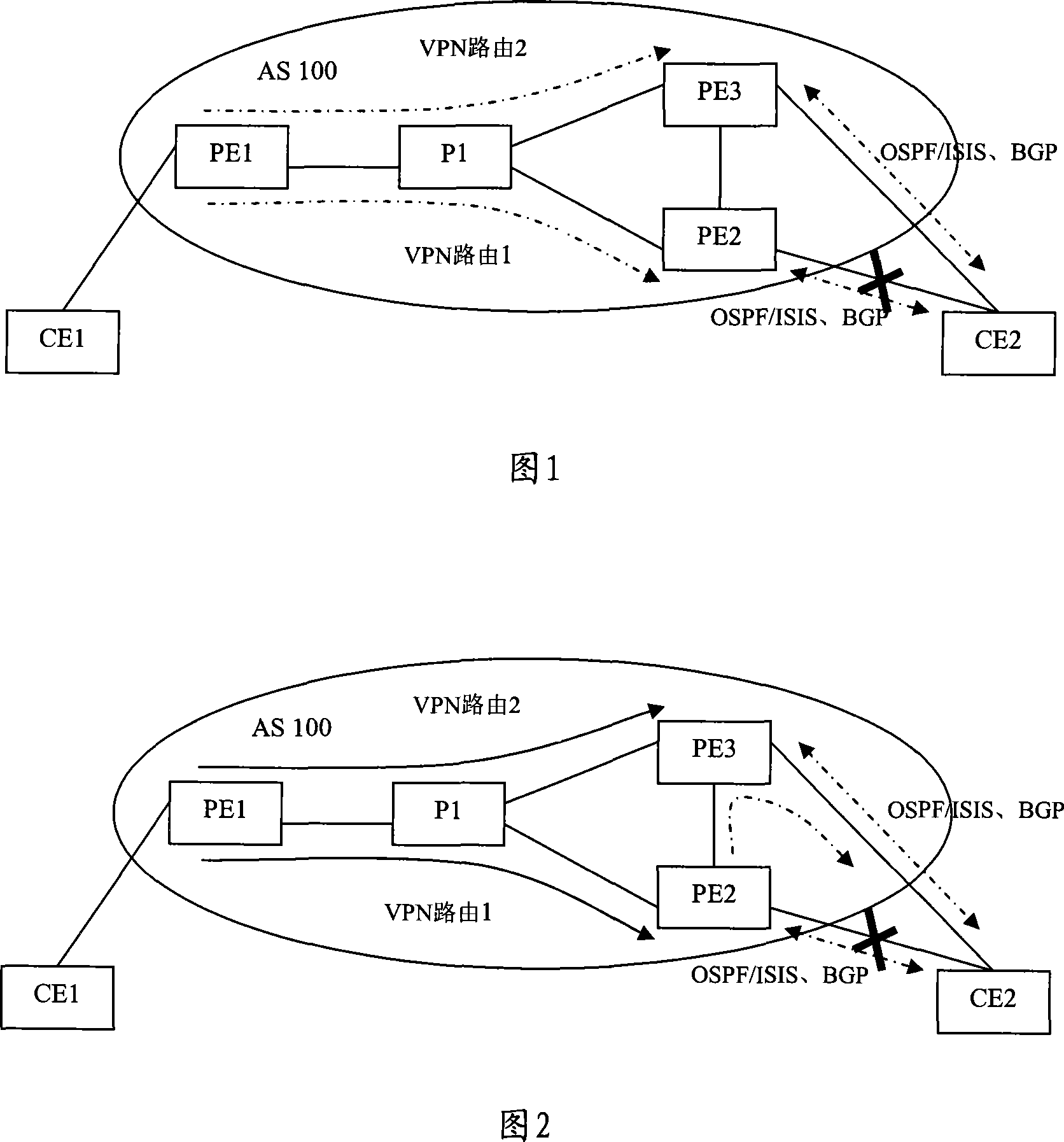
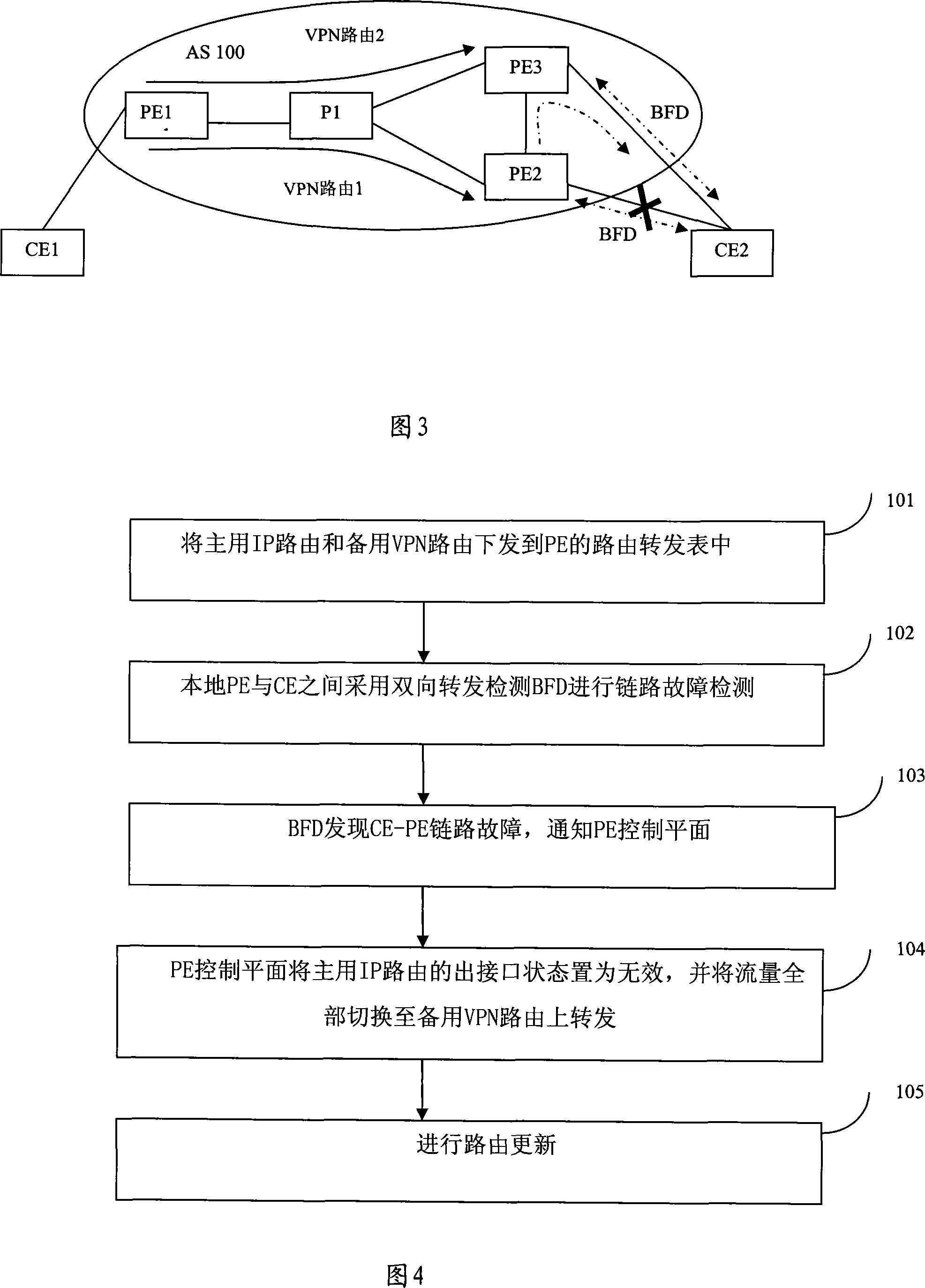
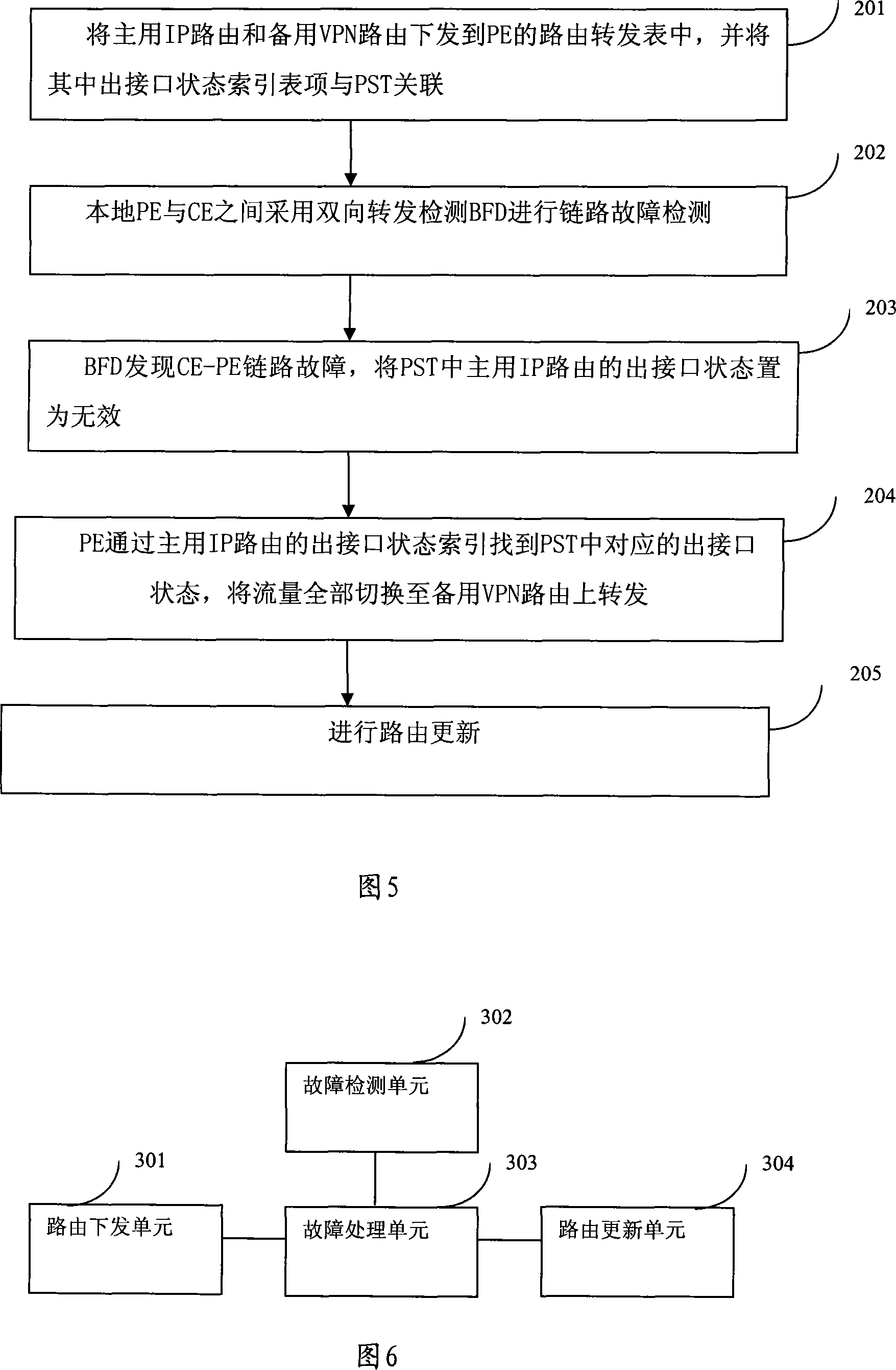
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a router for realizing fast reroute. The method of the invention example comprises that: the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router is down sent into the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE; the local PE and CE adopt bidirectional forwarding detection to check the link failure; when the link failure is detected, the flow are all switched to the spare VPN router to be forwarded. By adopting the method of the embodiment of the invention, the local PE-CE link failure can be rapidly detected and the main network IP router and the spare virtual private network VPN router can be down sent to the route forwarding table of network provider boundary routing equipment PE. The rapid detection of failure in the local PE-CE link is helpful to realize rapid convergence of VPN business and satisfies the real-time business requirement of the users.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
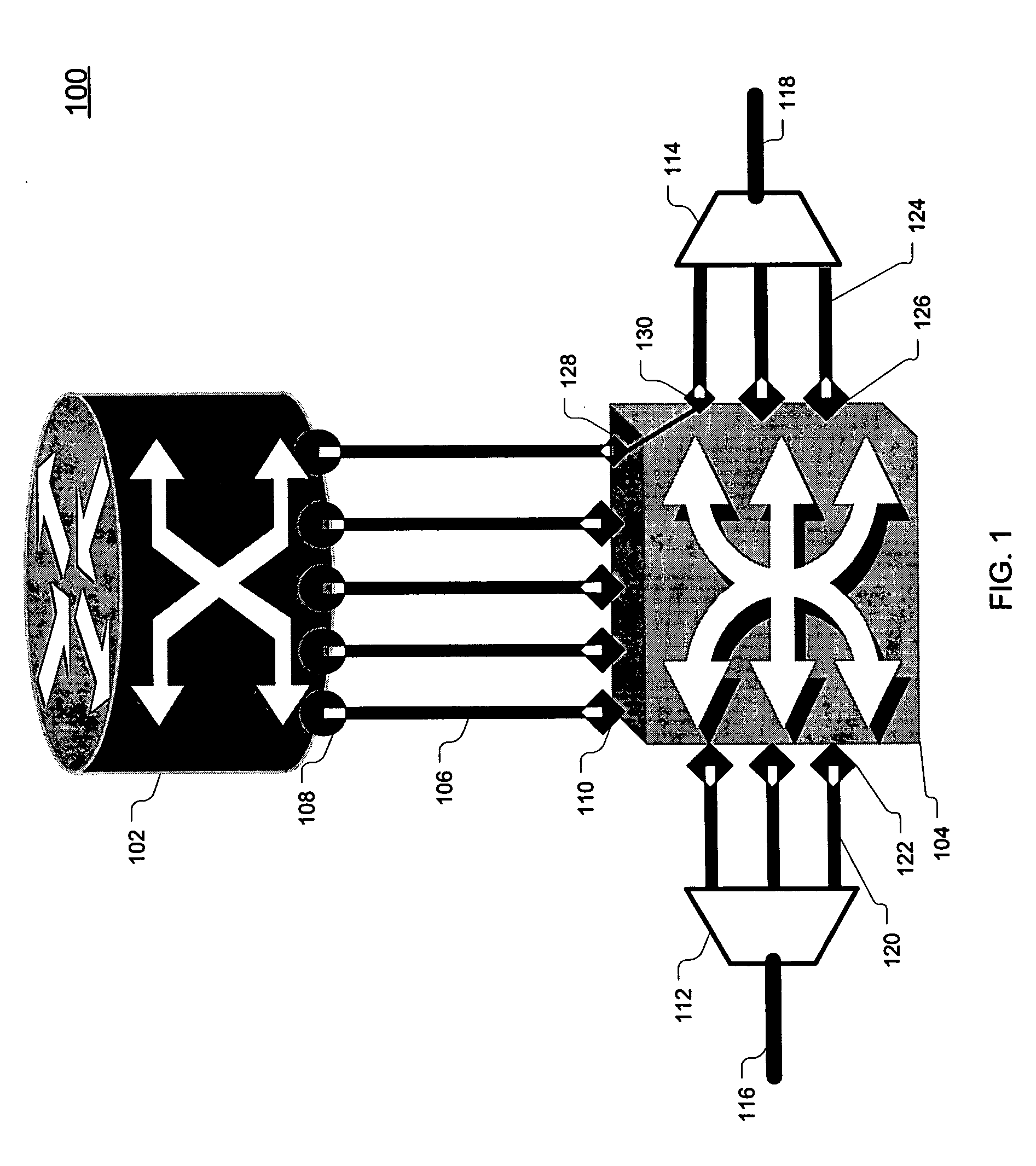
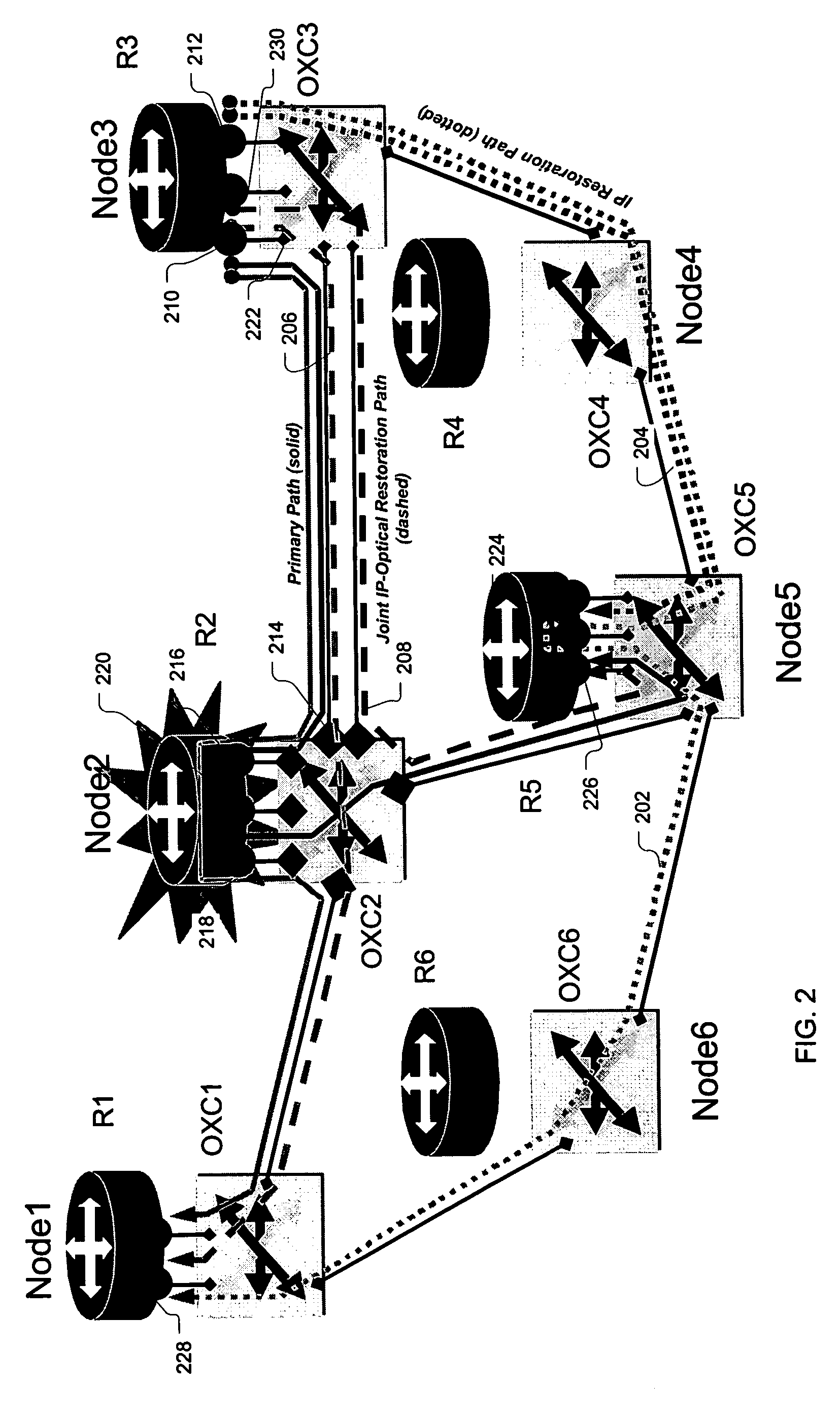
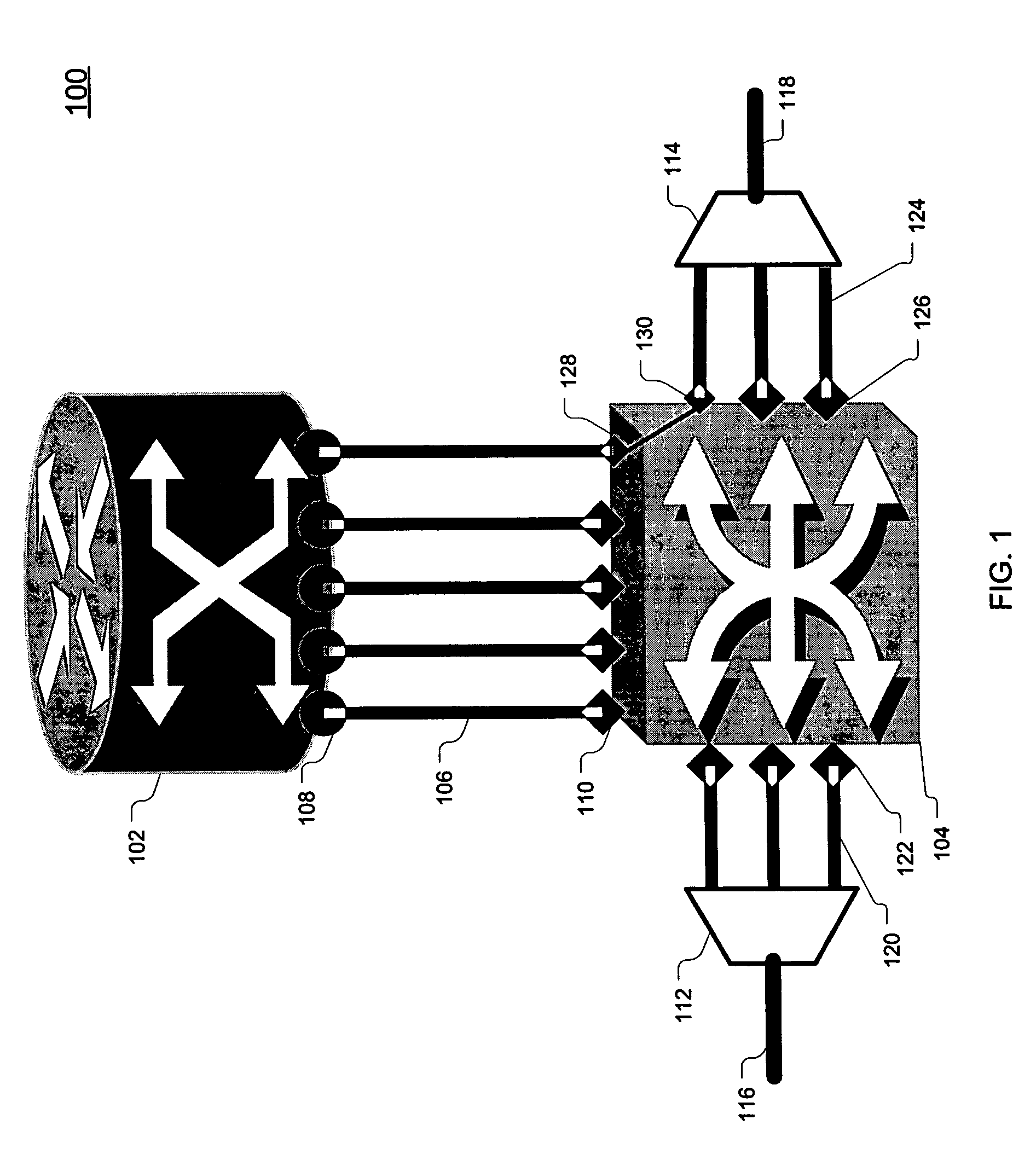
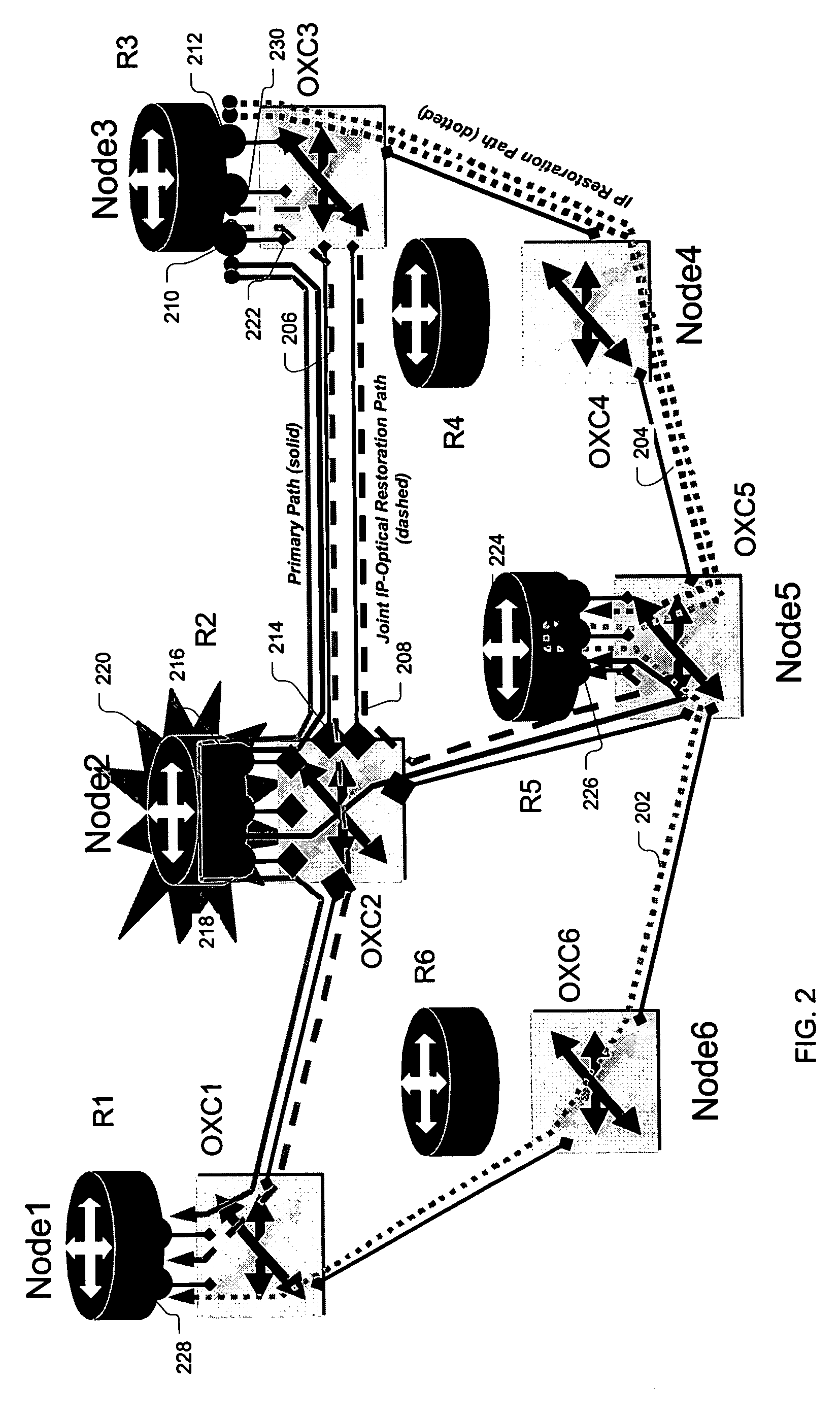
Joint-layer restoration in packet-over-optical networks
A joint “packet-optical” layer restoration mechanism protects against single, packet-layer router failures by managing network resources from both the packet layer and the optical transport layer in a synergistic manner. It reuses packet-layer router service-ports and / or transport-layer service wavelengths associated with optical switch-ports instead of reserving additional standby packet-layer router service-ports. It can reuse resources from primary paths that are unaffected by router failures and paths that exist for link-failure protection at the optical layer. Embodiments feature a modified node structure that includes both an IP router and a dynamically reconfigurable OXC, which dynamically establishes connectivity between IP-router ports and transport-layer optical fibers. The joint-layer router provides fine-granularity grooming at the IP layer and full-fledged wavelength networking via dynamic wavelength switching and / or wavelength translation at the optical layer. The latter can change the wavelength cross-connections on-demand to perform restoration or to modify the connectivity between IP routers in the network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Selection of multicast router interfaces in an l2 switch connecting end hosts and routers, which is running igmp and pim snooping
Multicast traffic received by a subnet that uses IGMP / PIM snooping may be efficiently processed so that only required multicast router interfaces are used. A router may, for example, receive a source-specific PIM join / prune message indicating that a multicast receiver of the multicast traffic is to join / leave a multicast group to receive / stop traffic from a multicast source; determine whether the router is a first hop router relative to a subnet of the multicast source; and forward, when the router is a first hop router relative to the subnet of the multicast source and is a non-designated router, the source-specific PIM join / prune message towards the subnet.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method for wavelength switch network restoration
A fiberoptic network with an optical supervisory channel in each of the optical fibers interconnecting the nodes of the network is described. Together with IP routers, the optical supervisory channels form a control network over which signaling and control signals are exchanged by which provisioning and restoration operations are performed at each node. To restore connections between the nodes upon a failure of the network, the control network helps to maintain at each node a synchronized database of network connections between the nodes, send messages to other nodes to initiate restoration operations by a node noticing the failure; and recalculate network connections around the failure by each node from a synchronized database at the node.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
Method and apparatus to schedule packets through a crossbar switch with delay guarantees
ActiveUS8089959B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationDifferentiated servicesCrossbar switch
A method for scheduling cell transmissions through a switch with rate and delay guarantees and with low jitter is proposed. The method applies to a classic input-buffered N×N crossbar switch without speedup. The time axis is divided into frames each containing F time-slots. An N×N traffic rate matrix specifies a quantized guaranteed traffic rate from each input port to each output port. The traffic rate matrix is transformed into a permutation with NF elements which is decomposed into F permutations of N elements using a recursive and fair decomposition method. Each permutation is used to configure the crossbar switch for one time-slot within a frame of size F time-slots, and all F permutations result in a Frame Schedule. In the frame schedule, the expected Inter-Departure Time (IDT) between cells in a flow equals the Ideal IDT and the delay jitter is bounded and small. For fixed frame size F, an individual flow can often be scheduled in O(log N) steps, while a complete reconfiguration requires O(N log N) steps when implemented in a serial processor. An RSVP or Differentiated Services-like algorithm can be used to reserve bandwidth and buffer space in an IP-router, an ATM switch or MPLS switch during a connection setup phase, and the proposed method can be used to schedule traffic in each router or switch. Best-effort traffic can be scheduled using any existing dynamic scheduling algorithm to fill the remaining unused switch capacity within each Frame. The scheduling algorithm also supports multicast traffic.
Owner:SZYMANSKI TED HENRYK
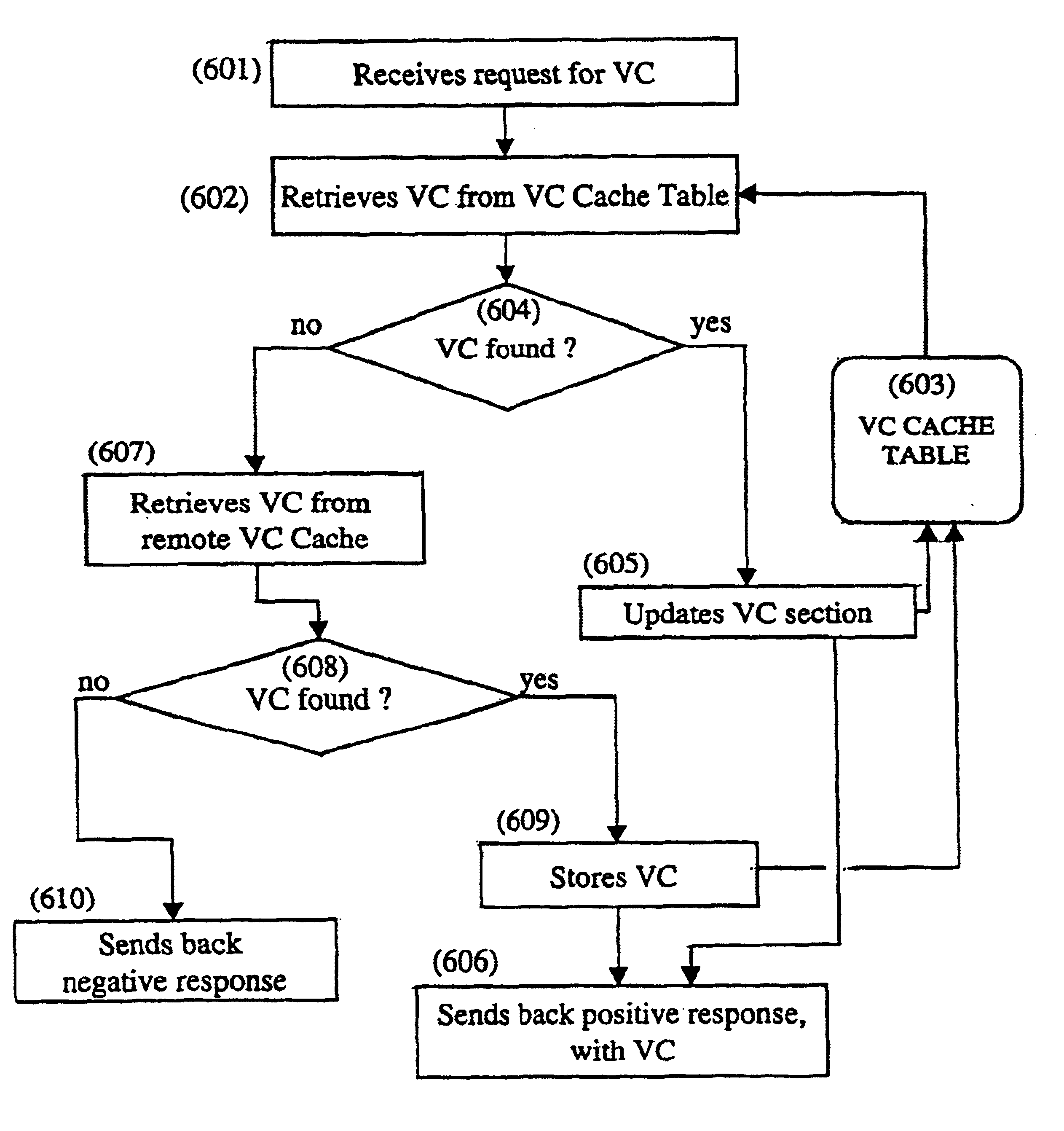
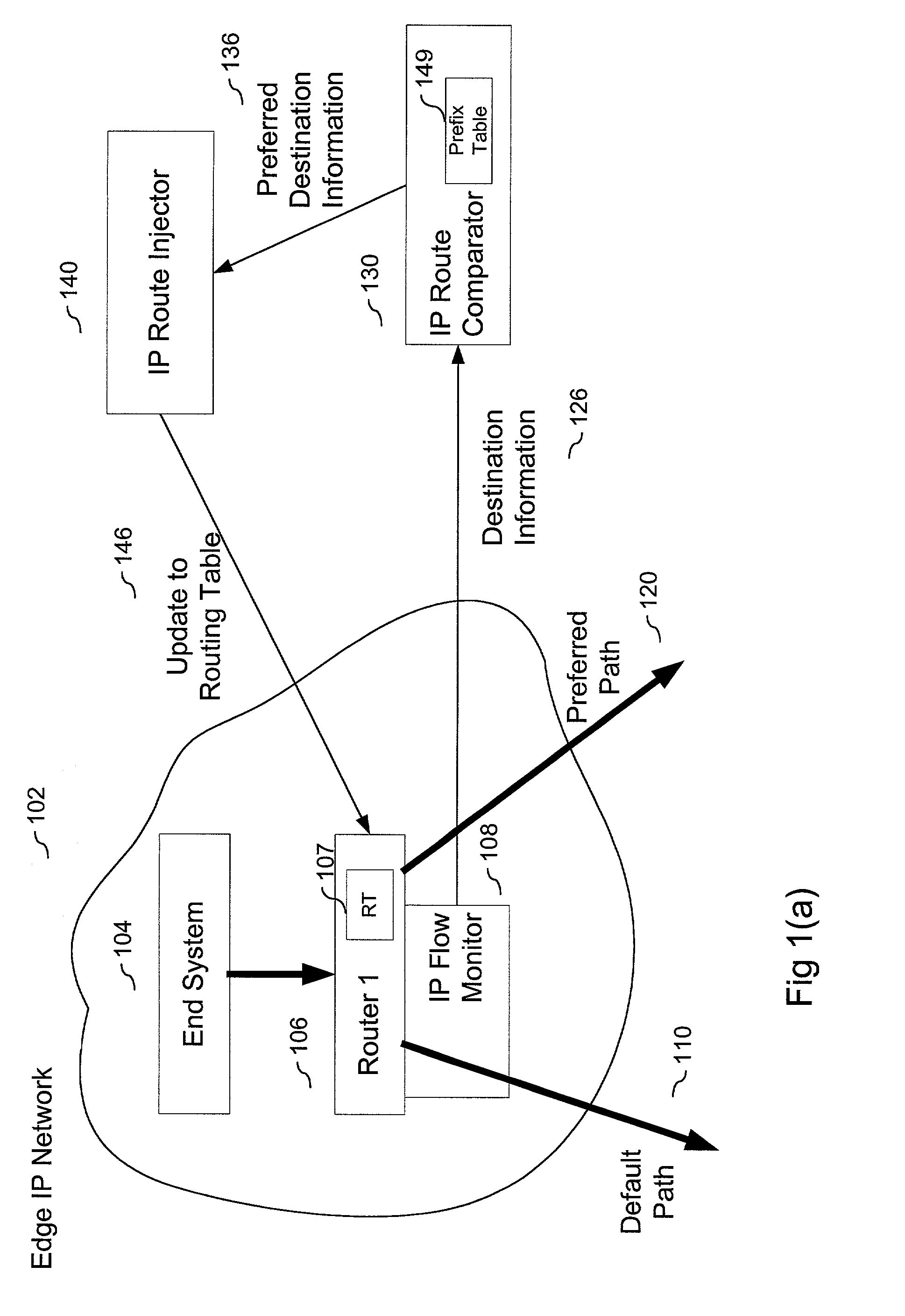
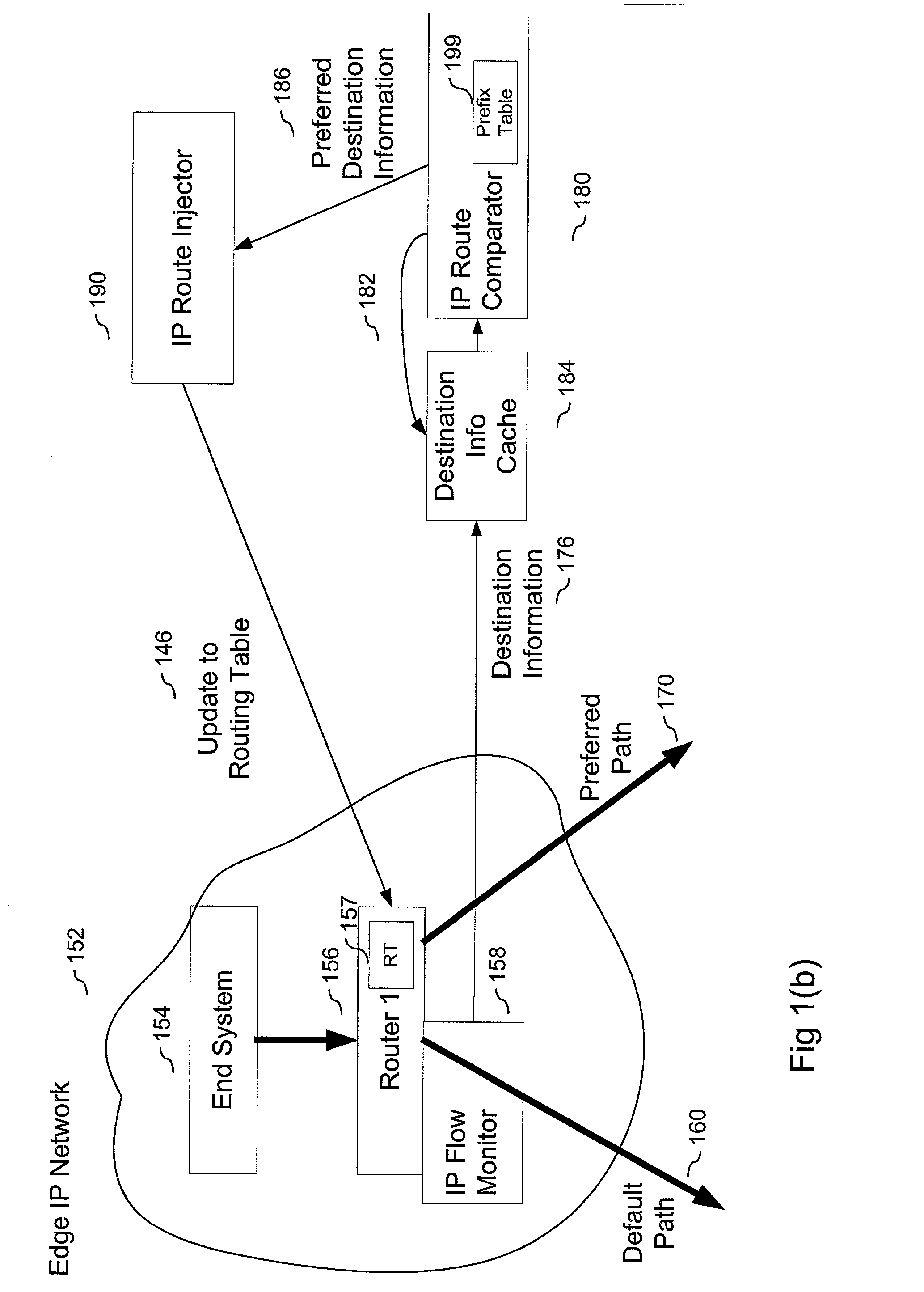
Method and system for route table minimization
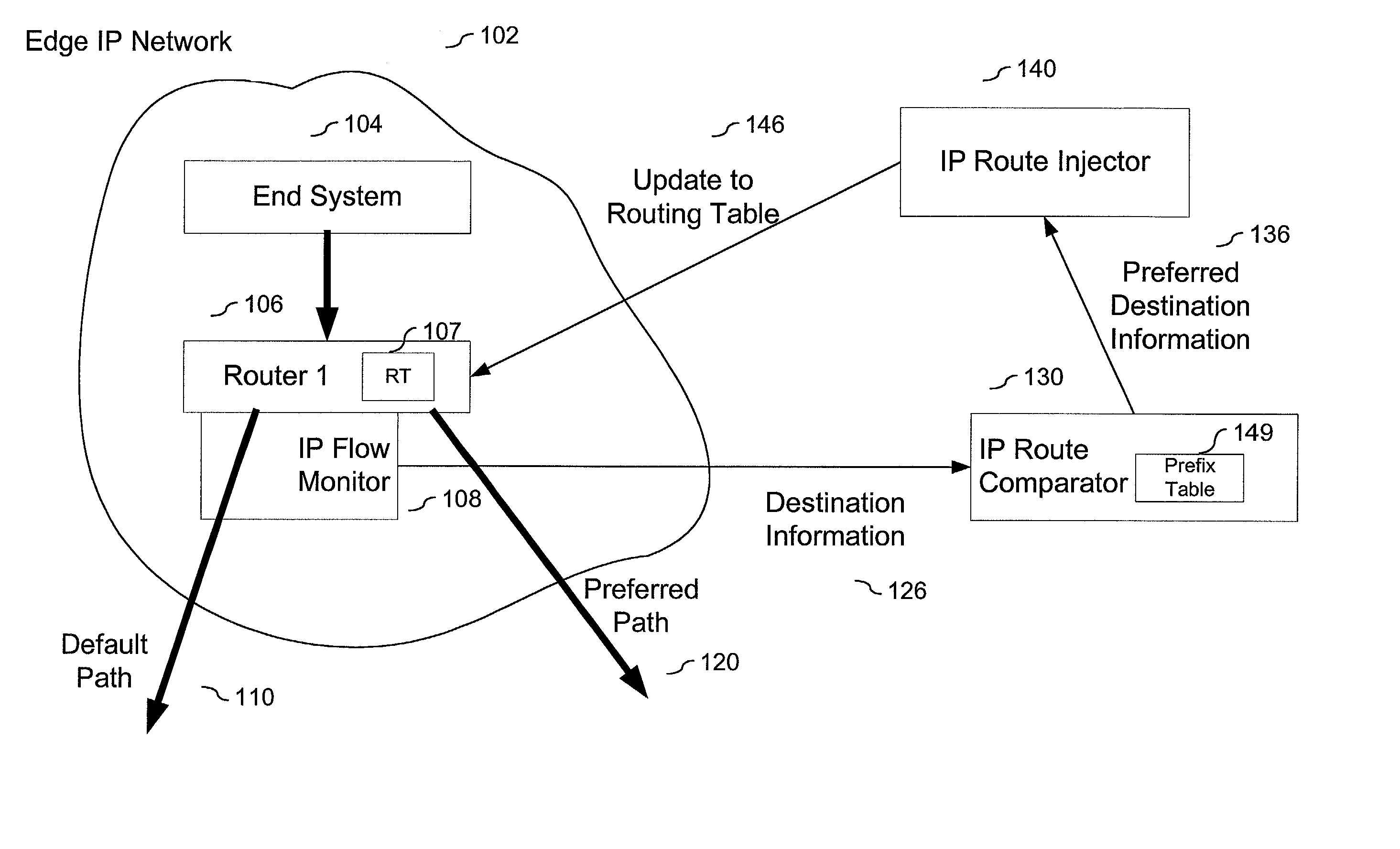
A method and system that includes an IP flow monitor in conjunction with an IP route comparator and an IP route injector to minimize the size of routing tables that need to be stored in a router of an IP network. The IP flow monitor monitors information, such as destination information that identifies and differentiates one IP flow from another. The monitored information is passed to the IP route comparator, which determines if it has stored preferred path information for the IP flow identified by the monitored information. If so, the preferred path information is passed to the IP route injector, which in turn passes it to the router in the edge network. The router updates it routing table in accordance with the new routing information. Other described embodiments include an embodiment having a cache and embodiments in which one or both of the IP route comparator and the IP route injector are local to the network (instead of being local). Still another embodiment includes a local IP route comparator that accesses preferred path information stored on a remote database.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC +2
Adaptive transport TCP/IP phone management
InactiveUS6847819B1Wireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetworking protocolIp router
A wireless communication device, comprising one or more intra-device modules, an internet protocol (IP) router for providing inter-device connectivity between a host and the intra-device modules, and one or more transport mechanisms, for coupling the IP router to the host. One or more intra-device modules are accessed via a standard internetwork protocol as if the intra-device modules were local servers.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
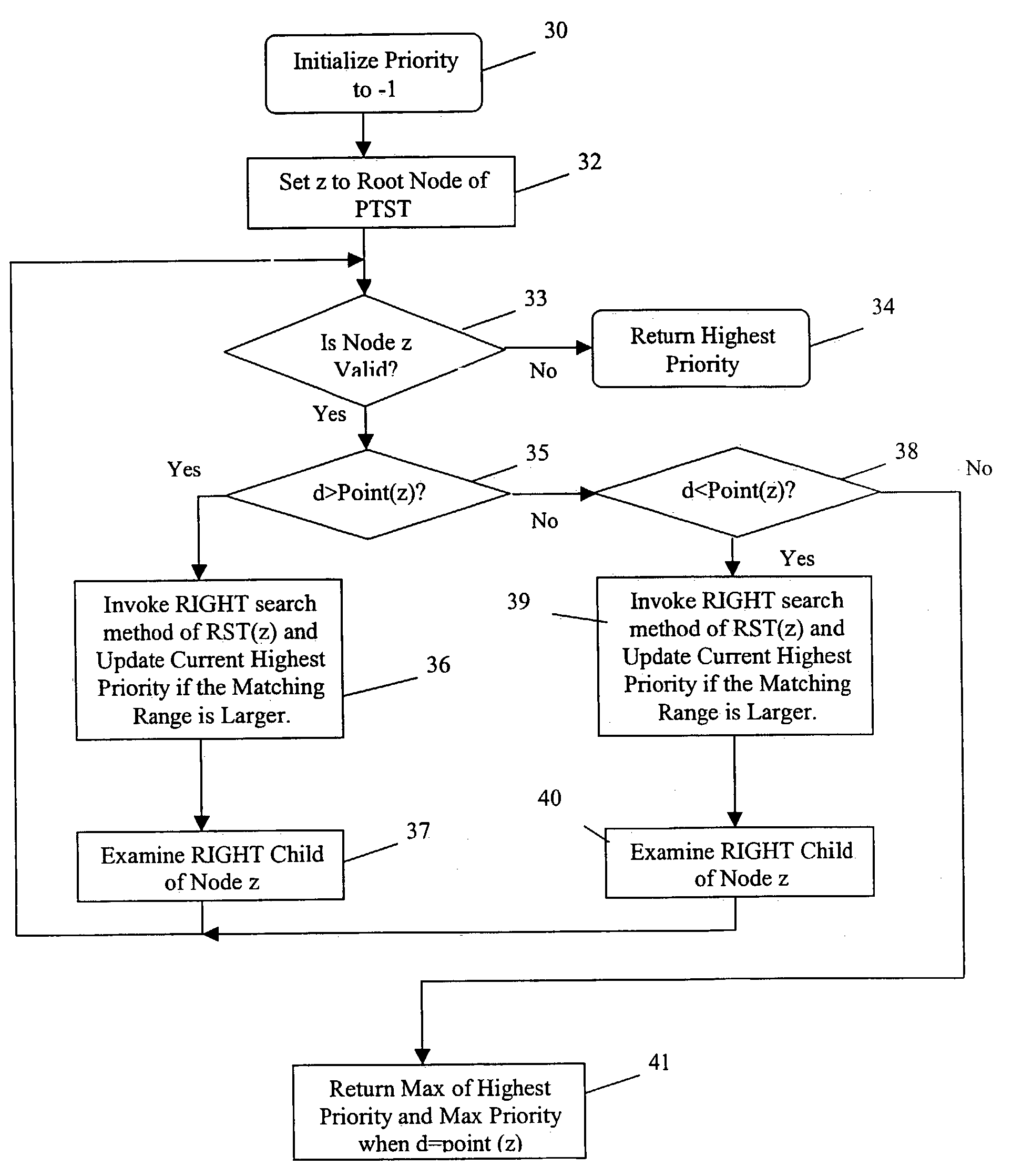
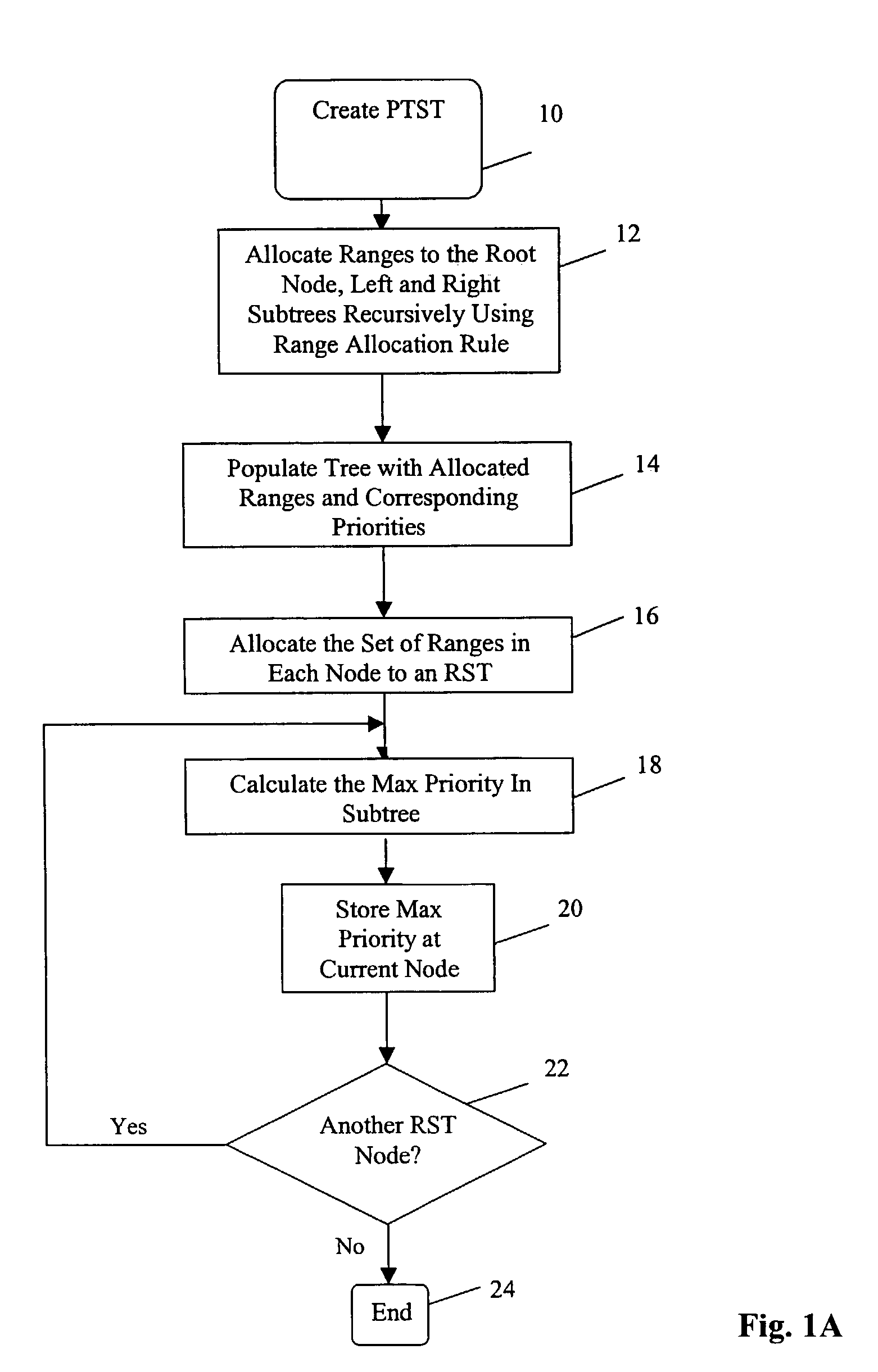
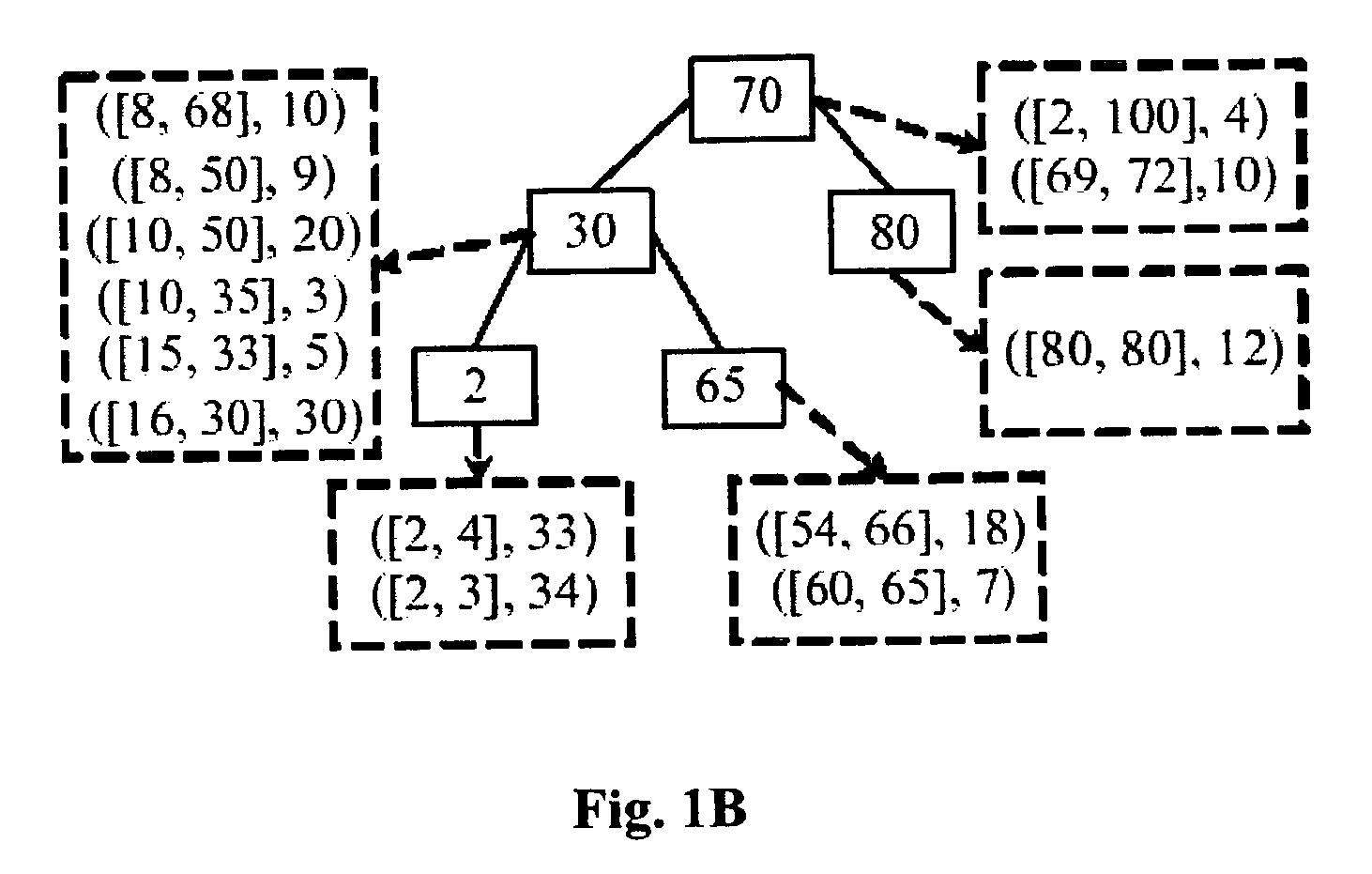
Dynamic IP router tables using highest-priority matching
InactiveUS7509300B2Shorten the timeEffective structureData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsIp routerThe Internet
An improved system and method is provided for packet routing in dynamic router tables. Specifically, the invention relates to a method and system for using tree data structures to select the highest priority rule that matches a destination address in dynamic Internet packet routing tables. In an embodiment, a data structure called BOB (binary tree on binary tree) for dynamic router tables in which the rule filters are nonintersecting ranges and in which ties are broken by selecting the highest-priority rule that matches a destination address is disclosed. Prefix filters are a special case of nonintersecting ranges and the commonly used longest-prefix tie breaker is a special case of the highest-priority tie breaker. When an n-rule router table is represented using BOB, the highest-priority rule that matches a destination address may be found in O(log2n) time; a new rule maybe inserted and an old one deleted in O(log n) time. For the case when all rule filters are prefixes, the data structure PBOB (prefix BOB) permits highest-priority matching as well as rule insertion and deletion in O(W) time, where W is the length of the longest prefix, each. When all rule filters are prefixes and longest-prefix matching is to be done, the data structures LMPBOB (longest matching-prefix BOB) permits longest-prefix matching in O(W) time; rule insertion and deletion each take O(log n) time. On practical rule tables, BOB and PBOB perform each of the three dynamic-table operations in O(log n) time and with O(log n) cache misses. The number of cache misses incurred by LMPBOB is also O(log n).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
IP encapsulation and routing over wireless radio networks
InactiveUS20110158160A1Reduce riskWireless commuication servicesTransmissionWireless mesh networkRadio networks
Various methods of operating a wireless mesh network are disclosed herein. According to various embodiments, an Internet Protocol (IP) router generates IP addresses for wireless sensor nodes that do not have native support for the IP protocol stack. The IP router then receives and translates an incoming IP request and routes the incoming IP request to the appropriate wireless sensor node. In some embodiments, an IP data packet can be encapsulated and routed using an IP router and an IP bridge device. In other embodiments, an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) session can be managed over a wireless mesh network.
Owner:ELSTER SOLUTIONS
Method for establishing a connection between a service requester (client) and a service provider (server) in a decentralized mobile wireless network
InactiveUS20070147313A1Easy to updateMinimizes problemConnection managementBroadcast service distributionRouting tableService provision
The invention relates to method for producing a link between a person requesting a service (Client) and a service provider (Server) 3 in a decentralized mobile radio network with a service / service provider search service (Service Discovery) wherein the person requesting the service (Client) sends a Service Discovery Request in the form of a multicast message to locally adjacent stations of the decentralized mobile radio network in order to localize an as yet unknown service provider (Server) who can provide the desired service, said stations being IP routers, and said stations forward the multicast message to neighboring stations thereof before finally forwarding it to the service provider (Server) who replies with a Service Discovery Reply. The message is characterized in that the routing information of the Service Discovery Request and the Service Discovery Reply are added to the routing tables of the stations in order to retrace the way back to the person requiring the service (Client).
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
Autoconfiguring IP routers
InactiveUS6912205B2Avoid disadvantagesTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIp routerNetwork layer
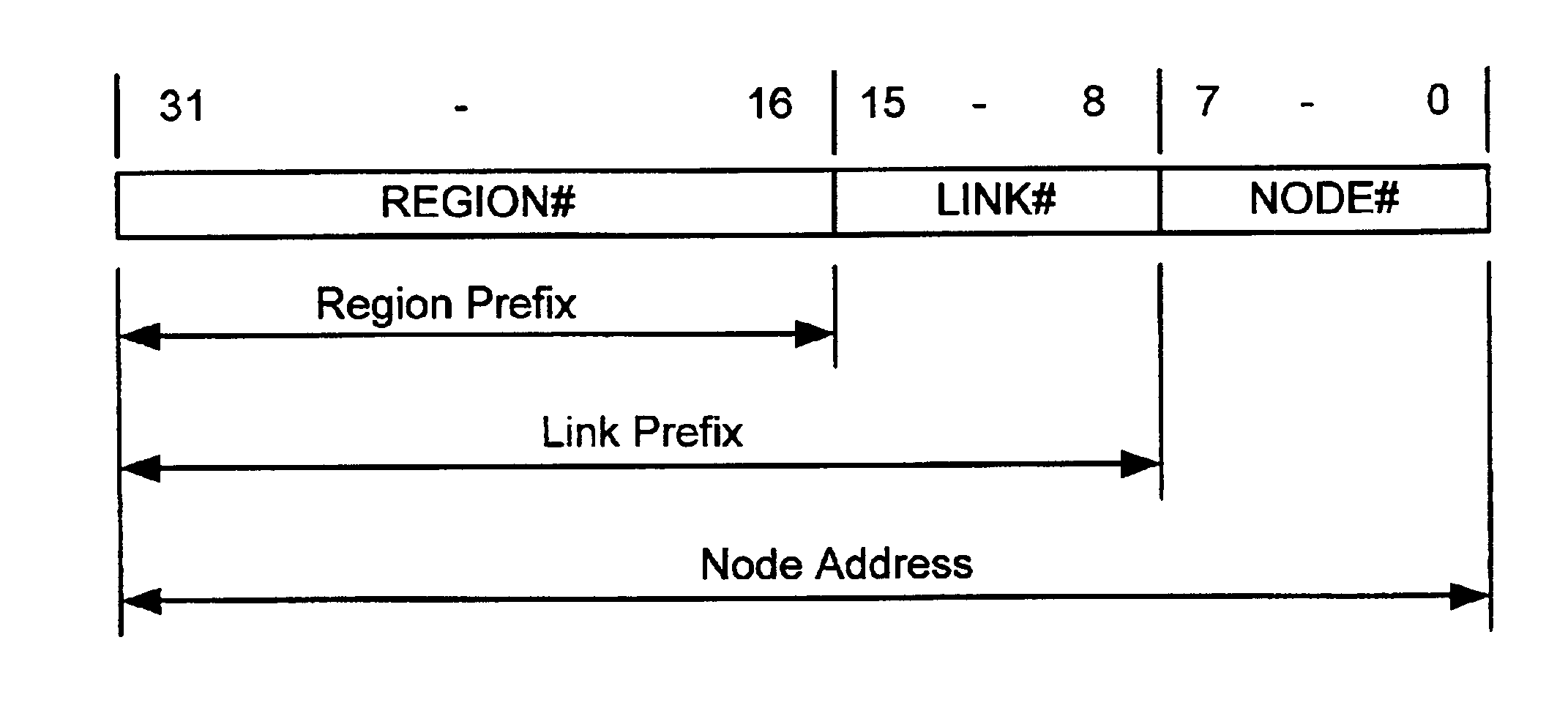
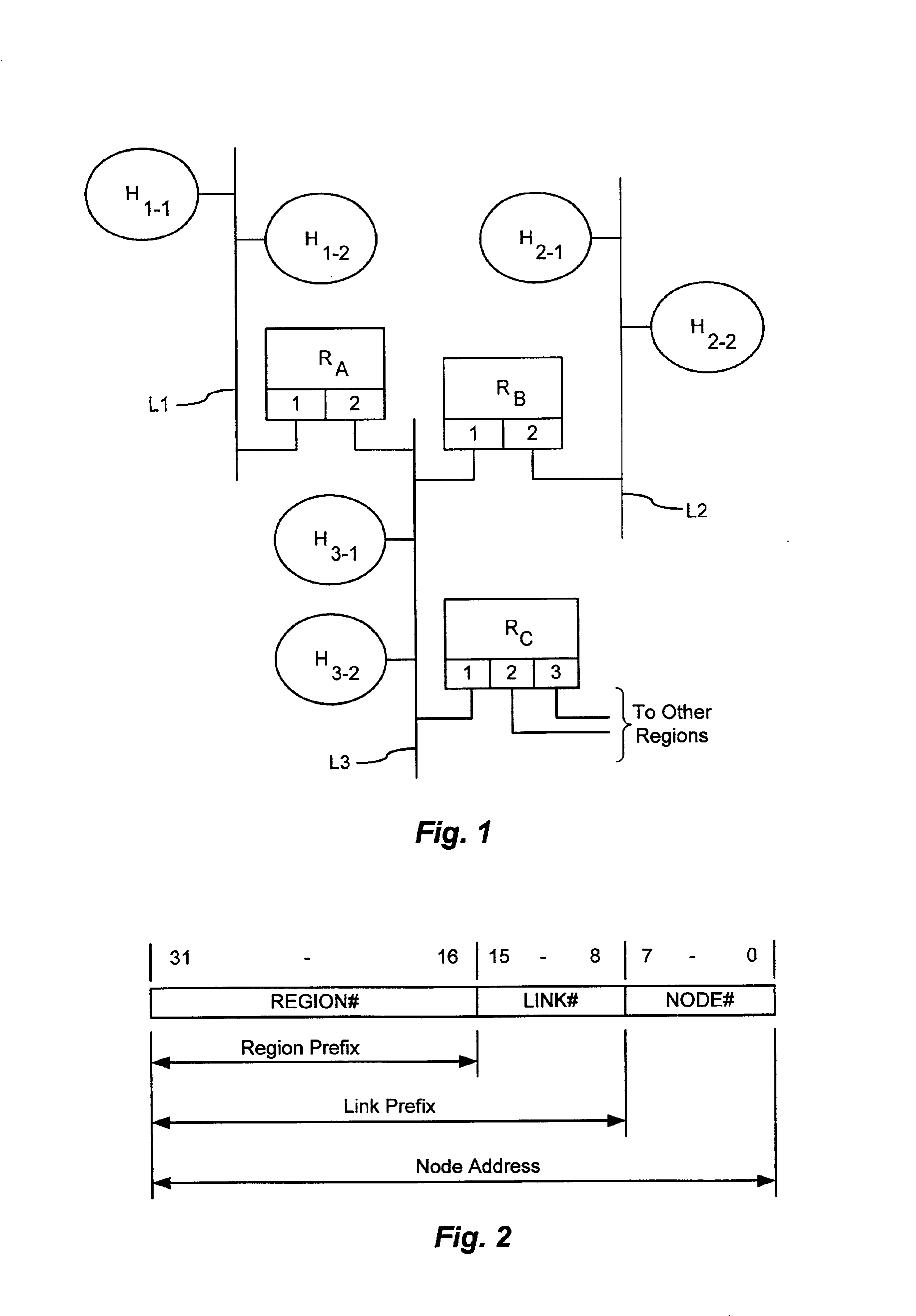
In automatically configuring network-layer addresses for network nodes in a network region, a specified router on each link generates link number request messages for the link. An address-assigning node assigns a region-wise unique link number to each link identified in a request message, and returns link number assignment messages containing the assigned link numbers. Each specified router assigns the link number from a received link number assignment message to a field of the network-layer addresses of the nodes on the associated link. According to a variation of the method, each specified router self-selects a link number and communicates with the other specified routers to avoid conflicts. Each specified router receives messages from the other specified routers containing numbers selected as region-wise unique link numbers for other links. Each specified router stores the received link numbers in association with the respective links in a local database. To configure a link number for the local link, a specified router selects a candidate region-wise unique link number not already associated with another link in the local database, generates a message containing the selected number, and propagates the message within the network region. Each specified router monitors the messages to detect when another specified router has selected the same link number. When this occurs, the specified router evaluates a conflict-resolution criterion to determine which router is entitled to keep a duplicate link number, and selects a new link number if necessary.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
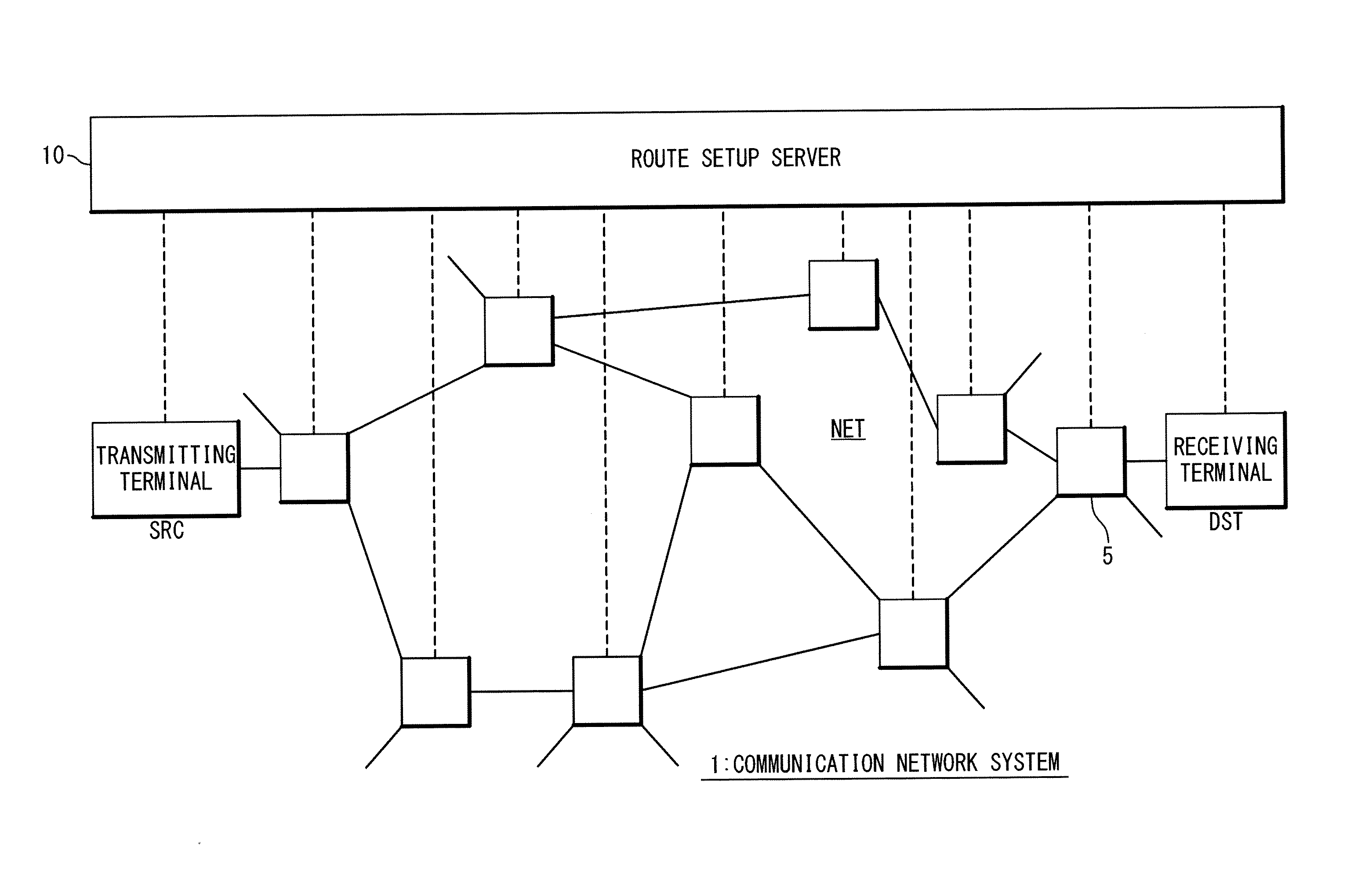
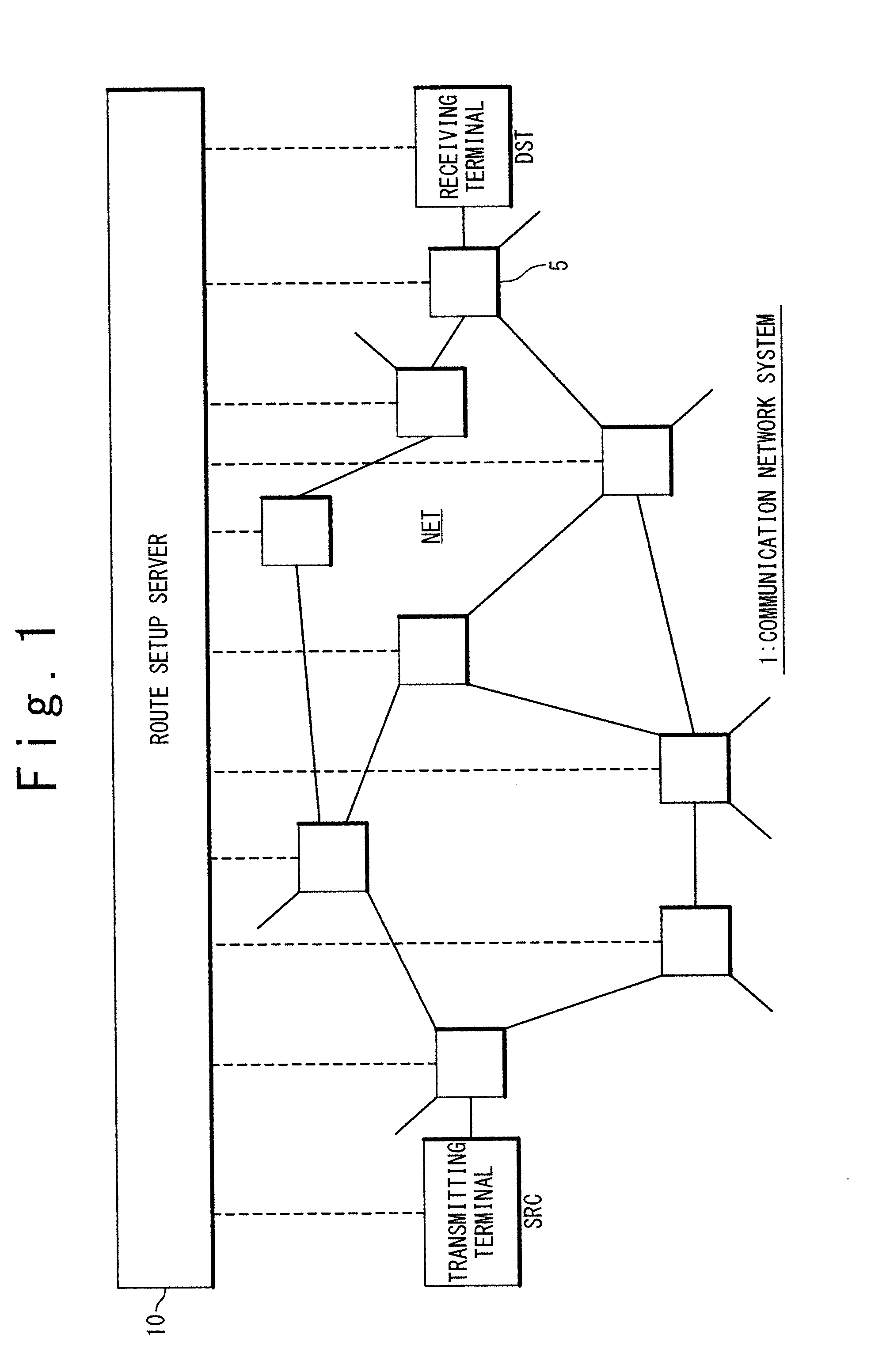
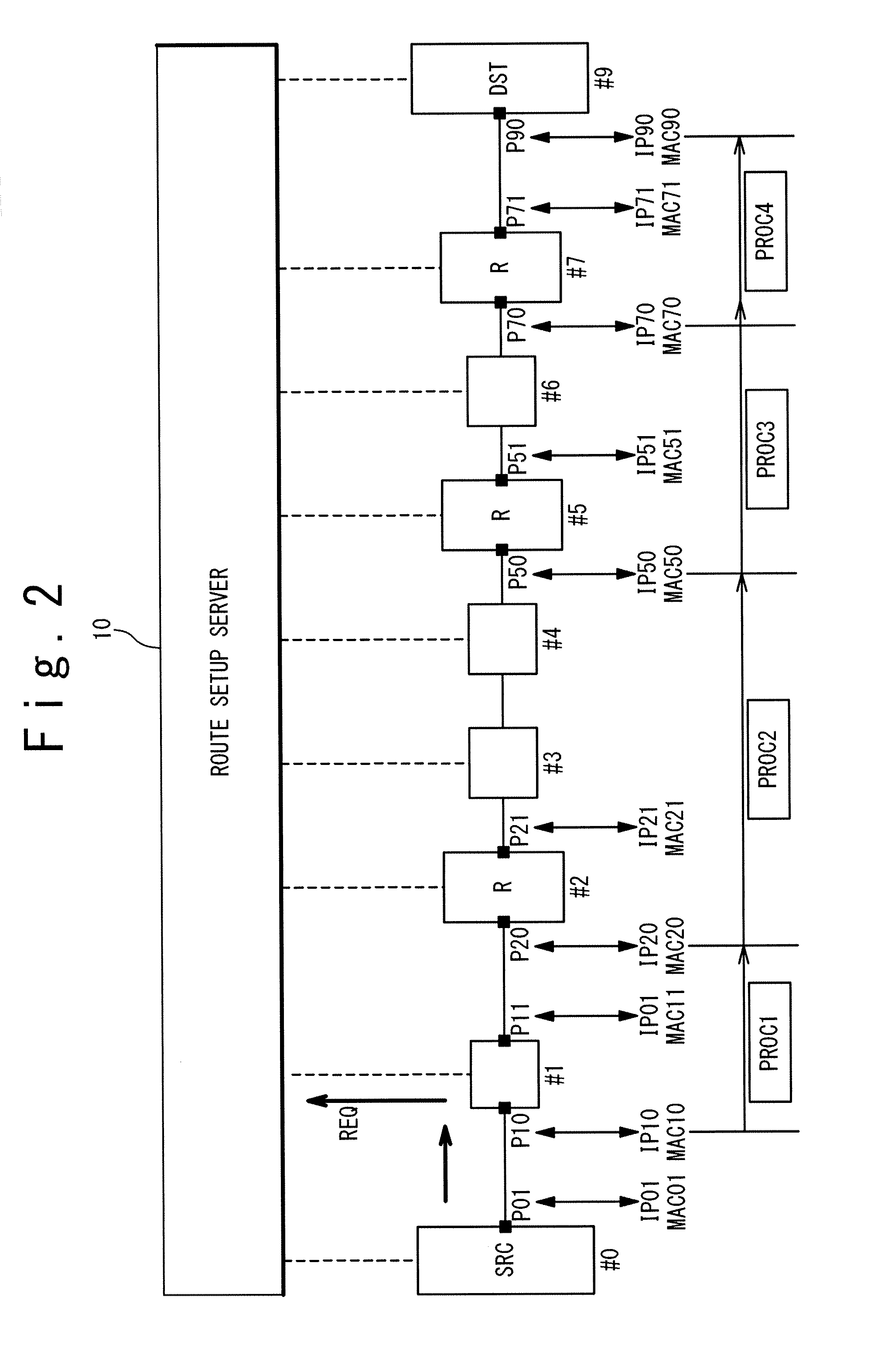
Route setup server, route setup method and route setup program
A route setup server has a storage unit, an IP routing unit and a flow management unit. A routing determination table indicating a router node assigned to an IP router among the plurality of nodes is stored in the storage unit. The IP routing unit has a software-based IP routing module having a same function as an IP router with respect to each router node. The flow management unit refers to the routing determination table to check whether or not a requestor node of a route setup request corresponds to any router node. The IP routing unit performs packet IP routing by using the software-based IP routing module associated with the corresponding router node to update a header of the packet. After that, the requestor node of the route setup request is updated to a destination node designated by a destination MAC address of the packet. Such the processing is repeated and thus the communication route is determined.
Owner:NEC CORP
General method for configuring WiFi device to make same to connect WiFi router
The invention discloses a general method for configuring a WiFi device to make the same to connect a WiFi router. The method includes the following steps that: step 1, a unidirectional physical data transmission channel is established between the WiFi device and the WiFi router; step 2, user configuration data are written and are adopted as multicast data packets, wherein the user configuration data include the SSID and password of the WiFi router; step 3, the WiFi router continuously sends the multicast packets through IP multicast; step 4, the WiFi device continuously scan all channels at intervals until a certain channel captures the multicast packets of a WiFi link layer, captures the multicast packets of the WiFi link layer, and filters the captured multicast data packets through a destination MAC address and multicast information so as to filter out illegal data packets, and obtains legitimate data packets, decrypts the data packets, performs analysis to obtain the SSID and password in the data, and is connected to the WiFi router; and step 5, if the WiFi device is successfully connected to the WiFi router, the WiFi device returns successful connection information to the WiFi device, otherwise, the method returns to the step 4, and scanning is further carried out.
Owner:SHENZHEN OGEMRAY TECH CO LTD
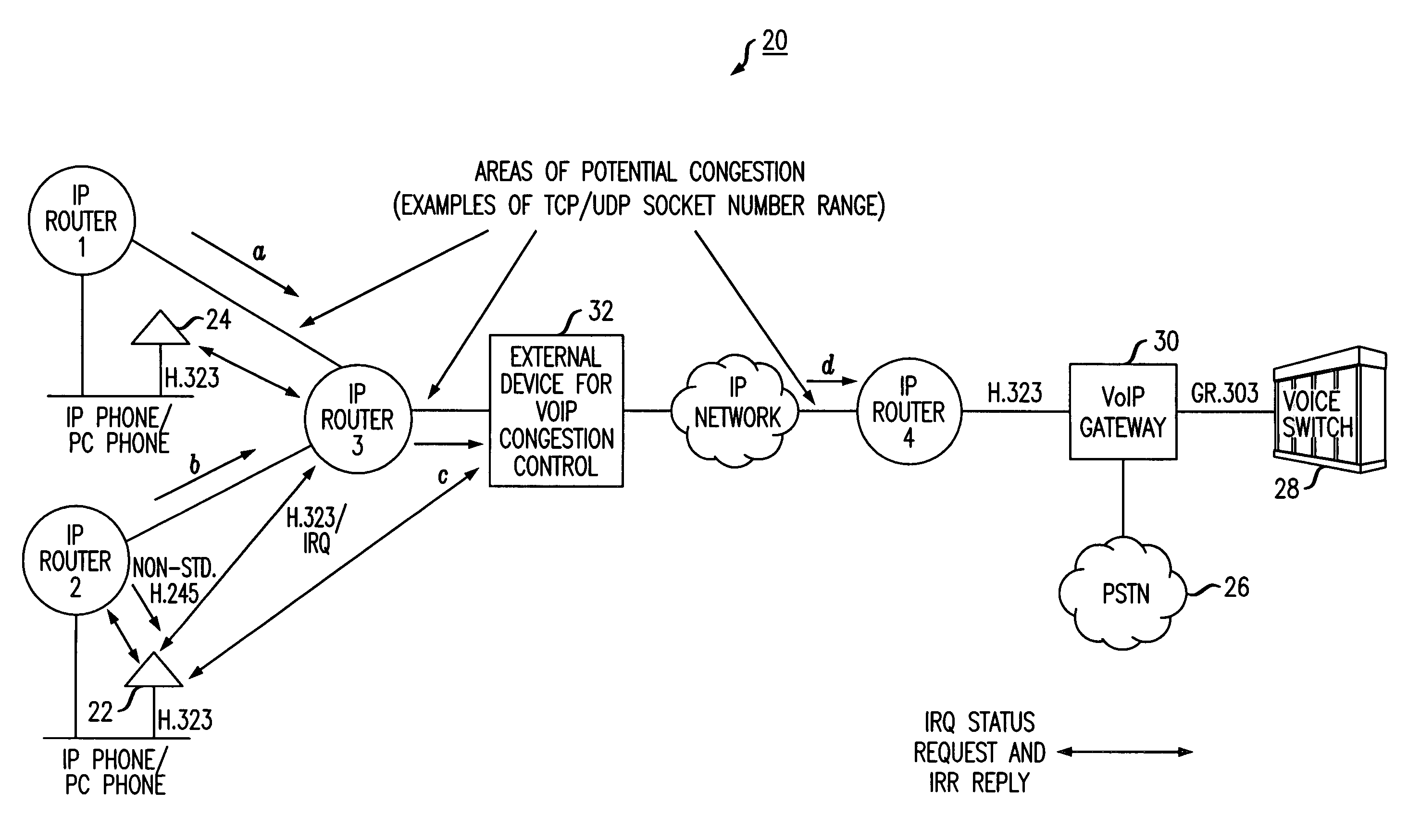
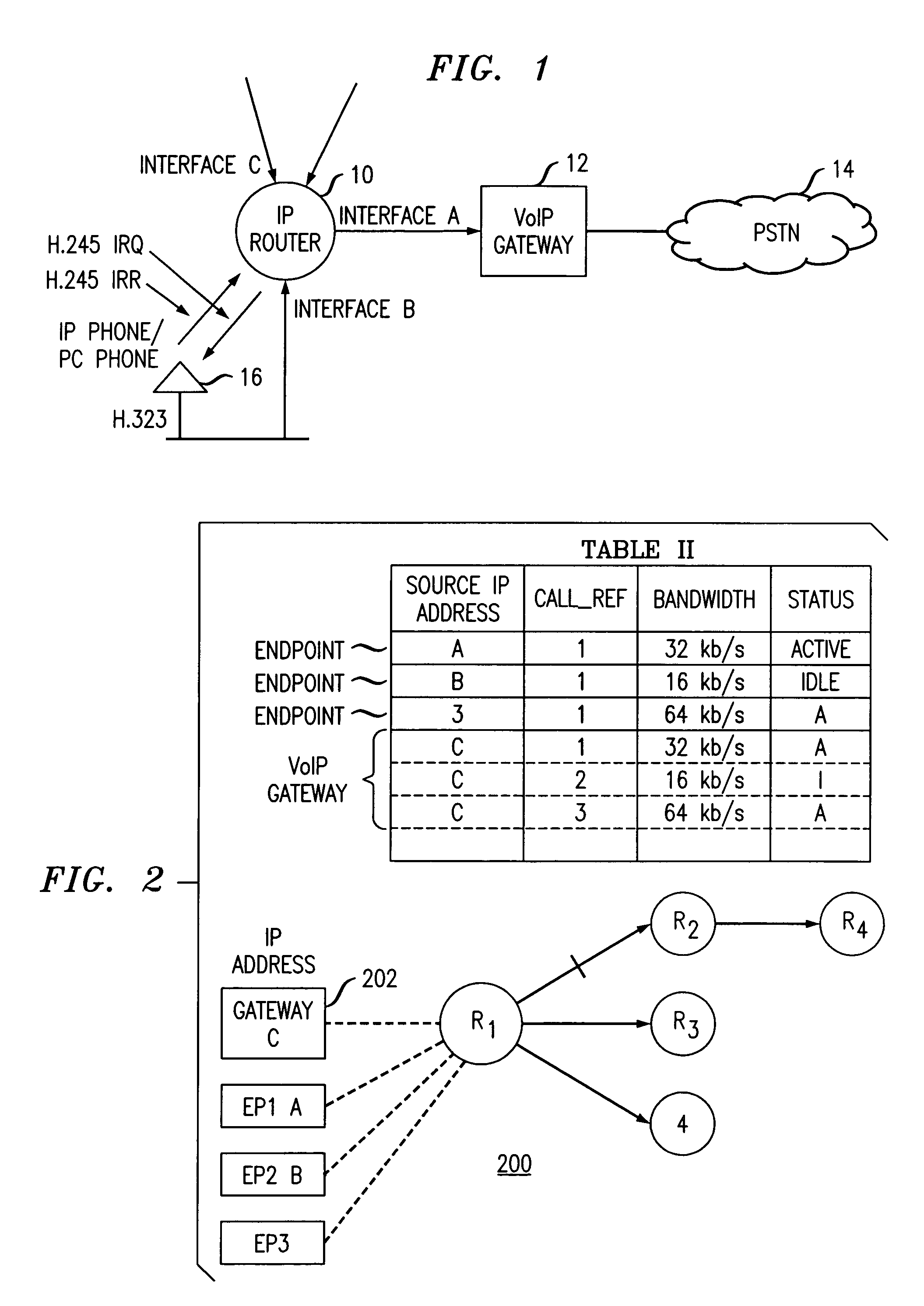
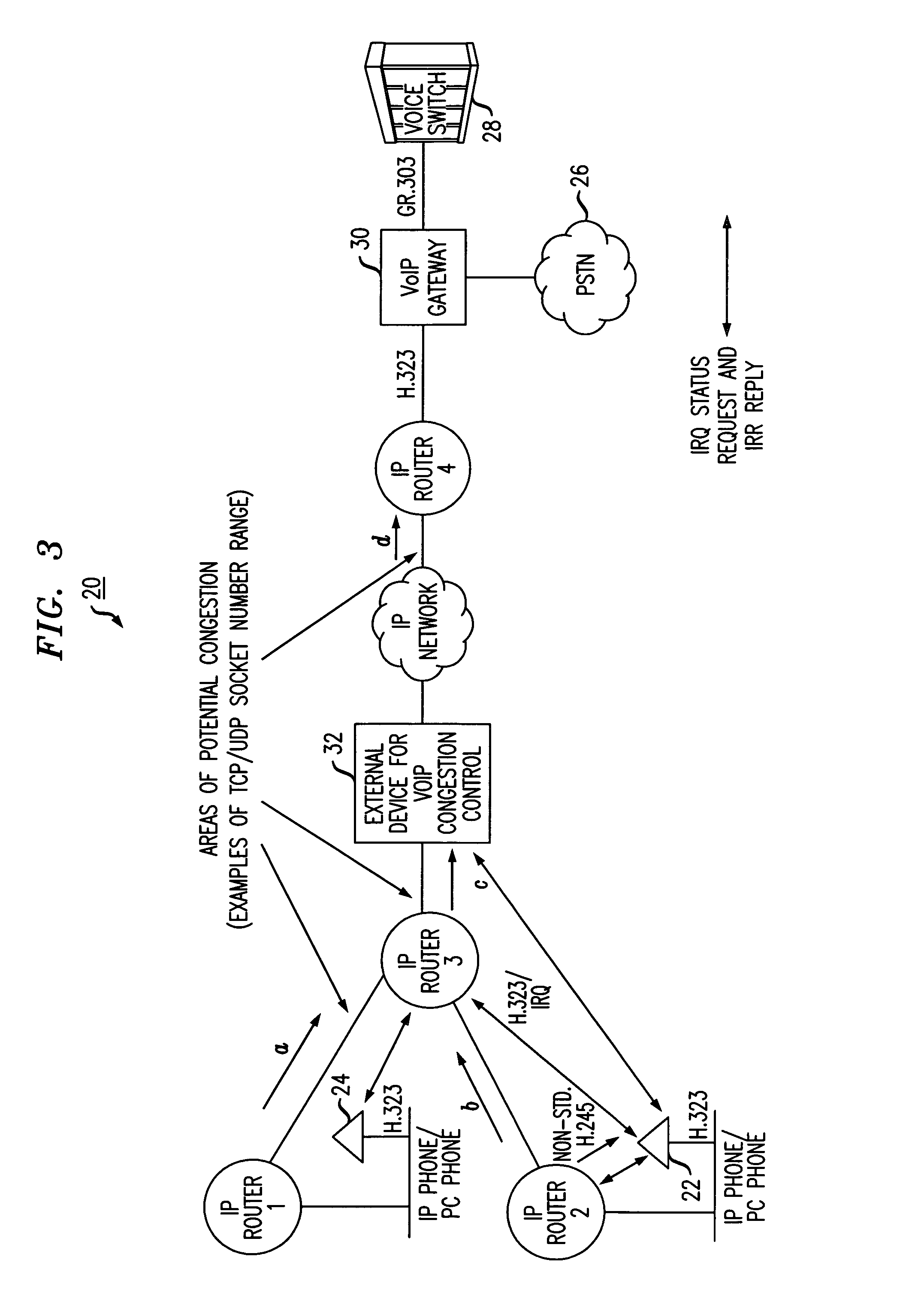
Method of providing quality of service (QOS) to voice applications in routed IP networks
InactiveUS7054327B2Simplify methodologyInterconnection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityConnection table
A simplified methodology for accomplishing traffic management in a packet based network is achieved by allowing allocation of bandwidth based on a count of the number of endpoint connections associated with a specific service for a corresponding network device. A network device (e.g., IP router) can be configured to count the number of TCP / IP and UDP / IP connections and bandwidth usage per interface. The counting can be done by identifying the IP Addresses, Type of Service (TOS), and TCP / UDP and / or UDP / IP socket number range in the IP Header of a packet and then querying a specific communication type. When reaching the maximum allowed connections or bandwidth for a specific service, the network device (e.g., IP router) stops forwarding any new calls by means of dropping packets of new calls and informing the given endpoints to disconnect the new calls. In one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a procedure for managing traffic flowing through individual routers of a packet network includes the steps of reserving a given amount of bandwidth on interfaces of the individual routers for specific types of communications traffic, periodically querying endpoint connections based on data from a corresponding router connection table, receiving responses from the periodic querying to determine a current connection status and bandwidth allocation of said endpoints and calculating current bandwidth allocation for a specific type communications service on an interface handled by the router. The router admits additional communications traffic for a specific type of communications service if bandwidth is available.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
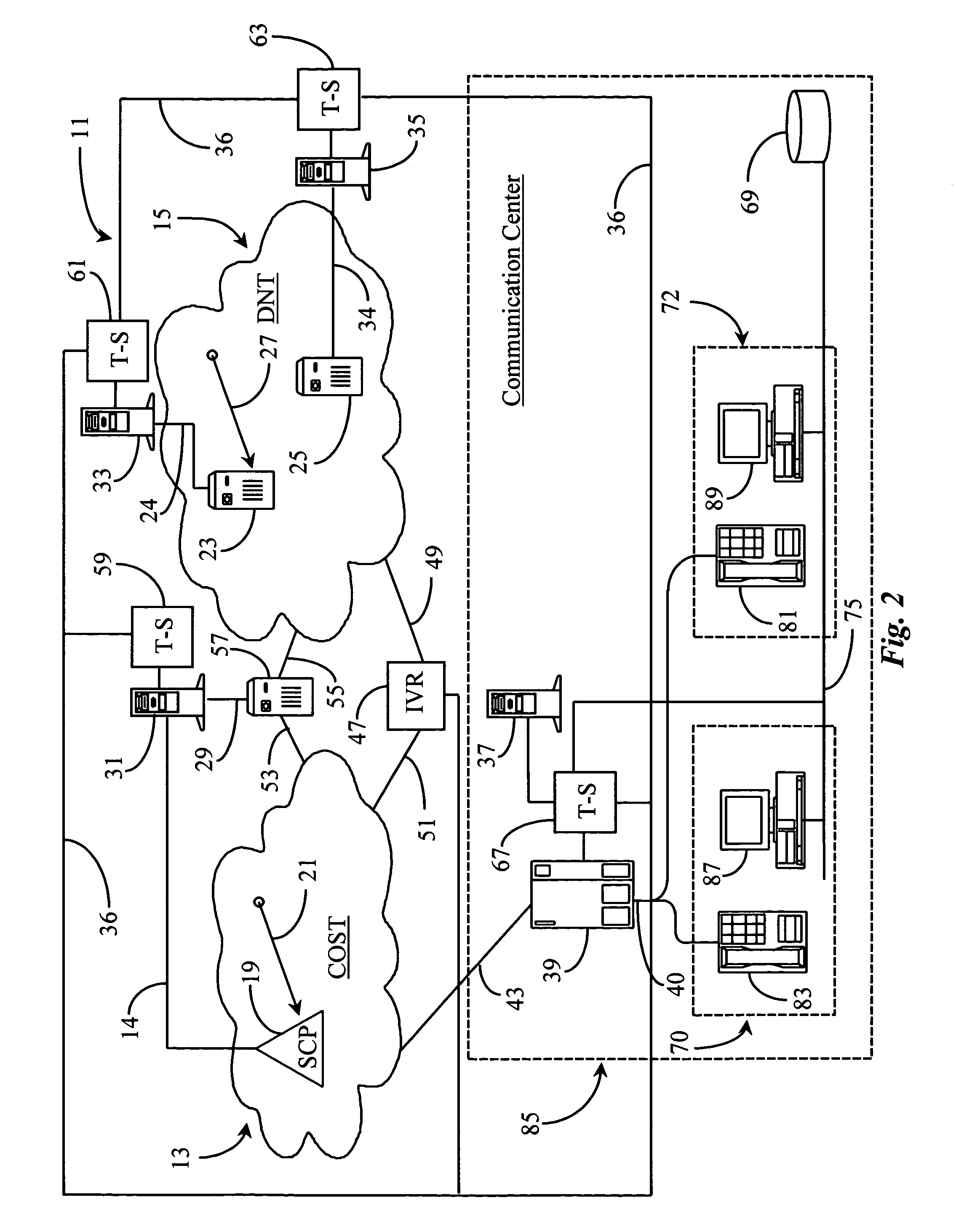
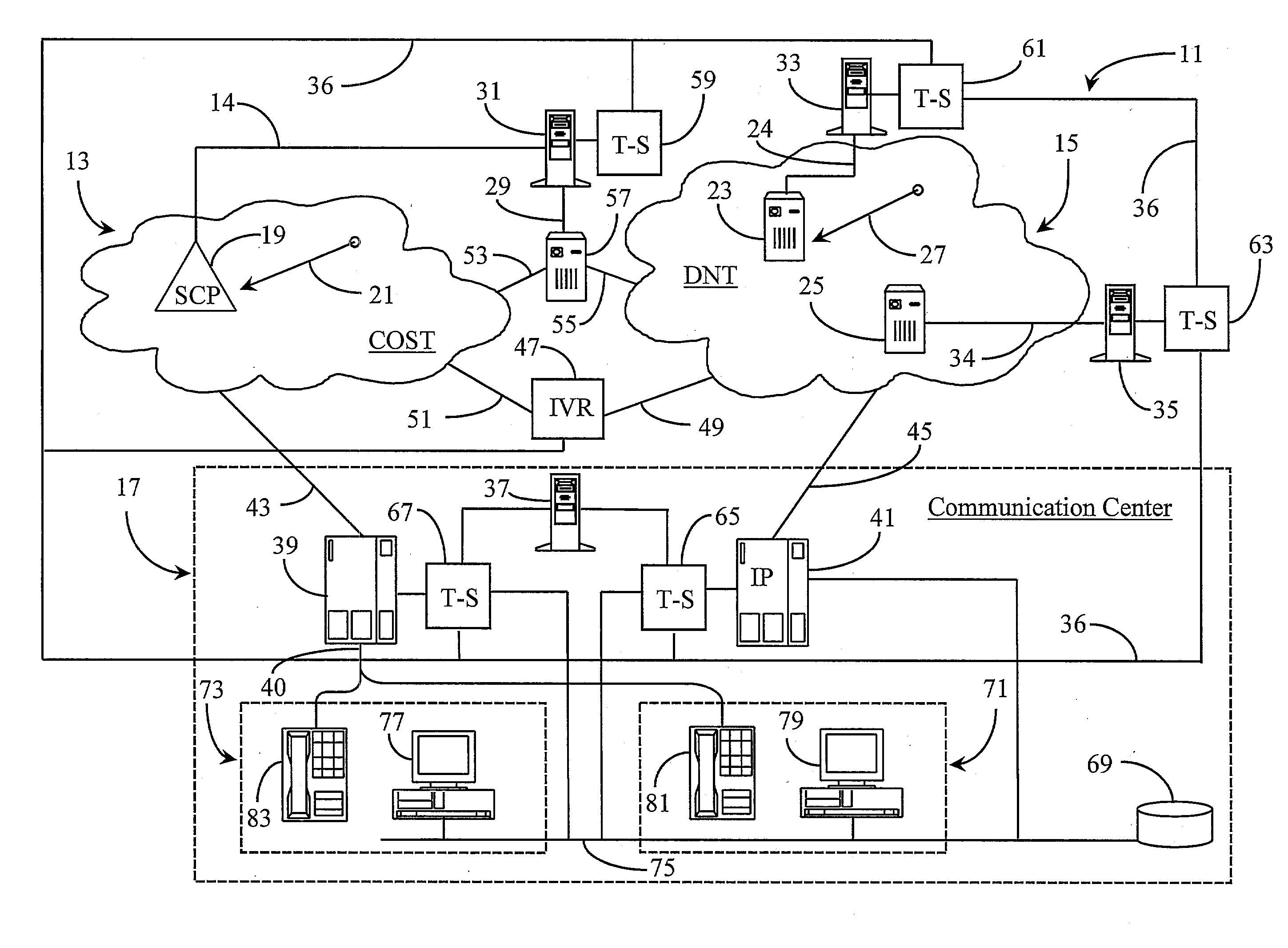
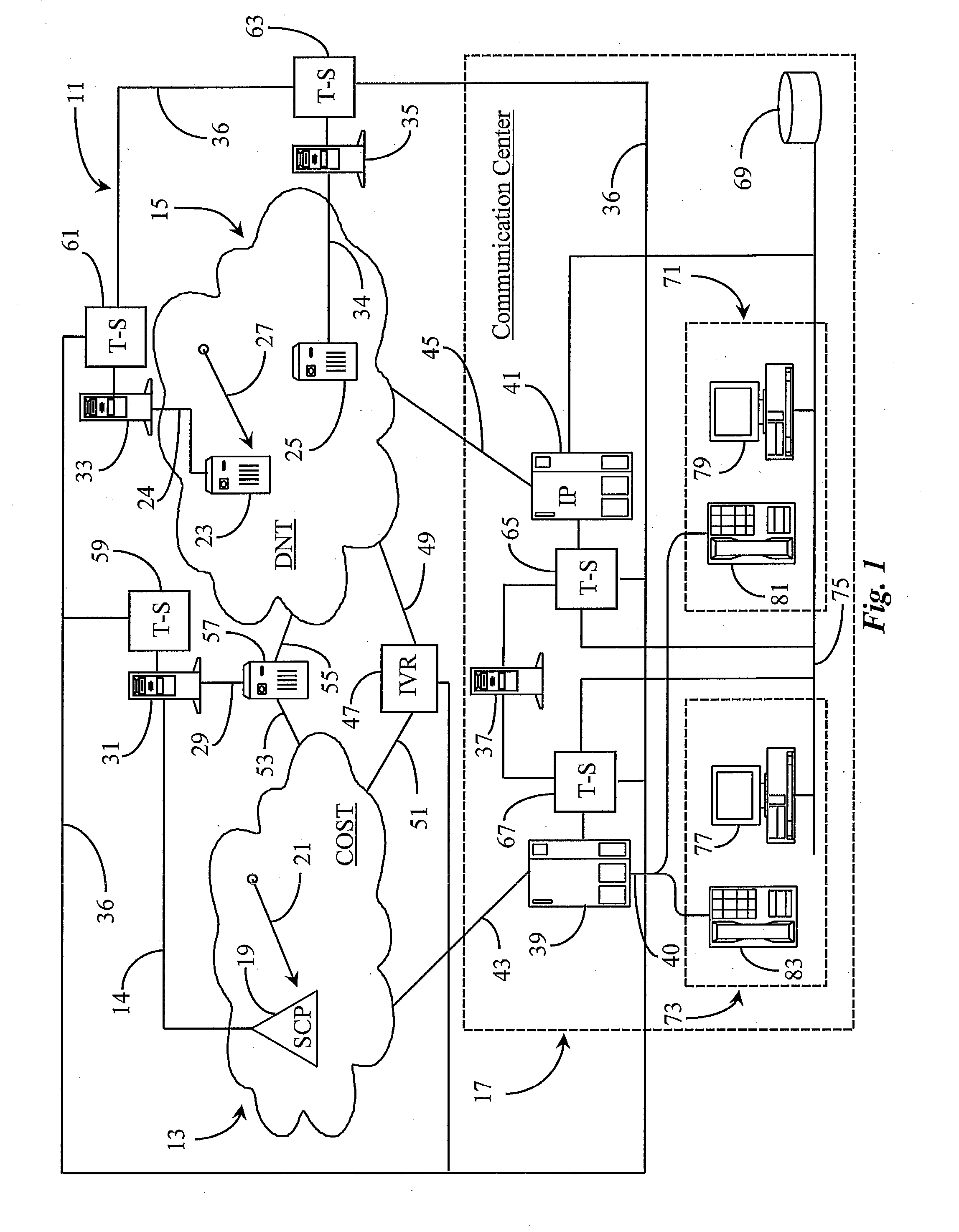
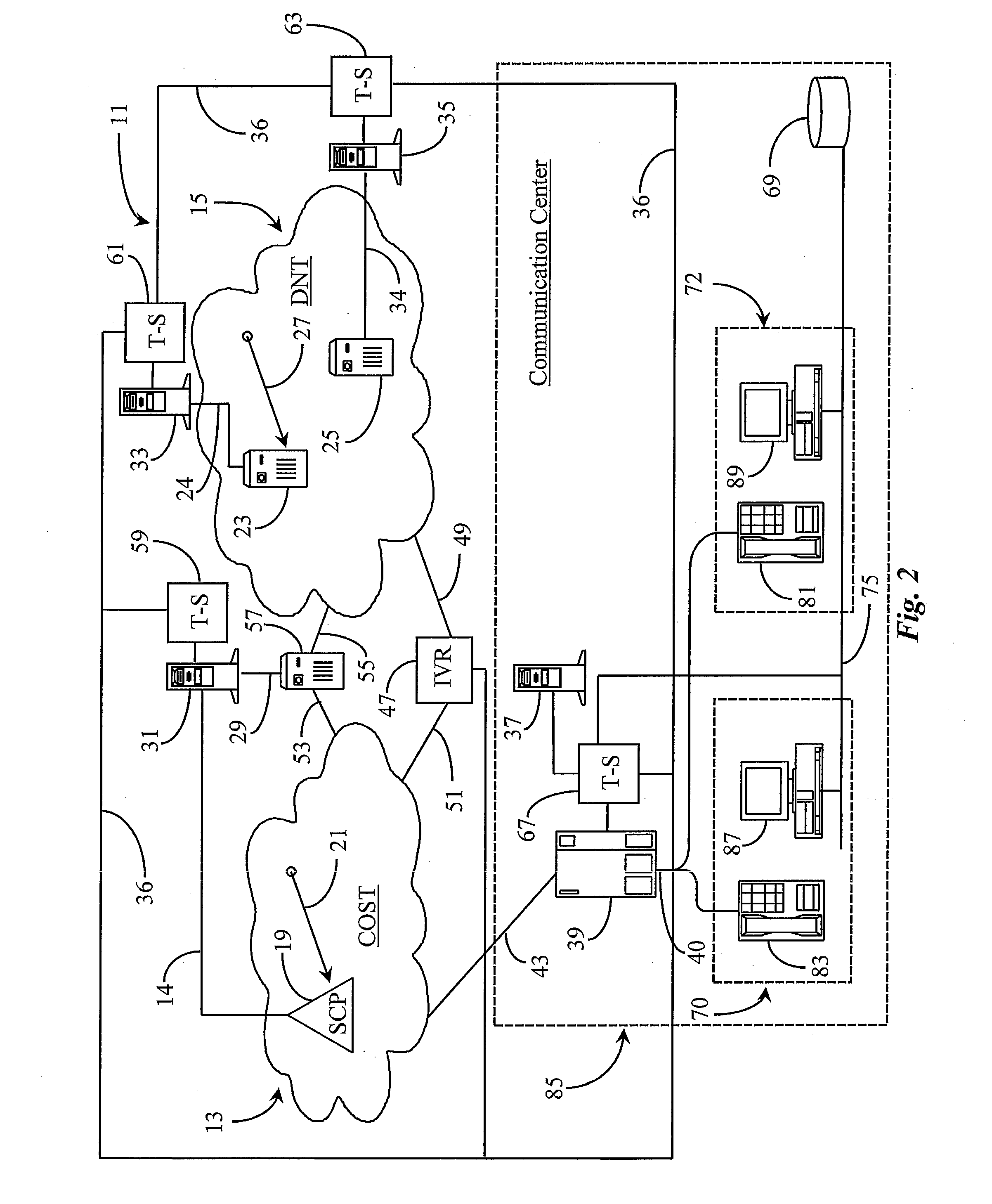
Telephony intelligence in a data packet network
A packet-data network is made intelligent in the sense of a connection-oriented, switched telephony (COST) network by enhancing one or more interconnected IP routers in the network with computer-telephony integration (CTI) processors executing CTI applications. No-charge-to-calling-party IP addresses are assigned and sponsored by various enterprises, who may also maintain call centers having at least one CTI-enhanced IP router connected to the network, and agent stations having IP telephones connected to the call-center-located IP router. With appropriate software and the CTI link to IP routers the performance of well-known conventional telephone systems may be provided in packet networks like the Internet.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMM LAB INC AS GRANTOR +3
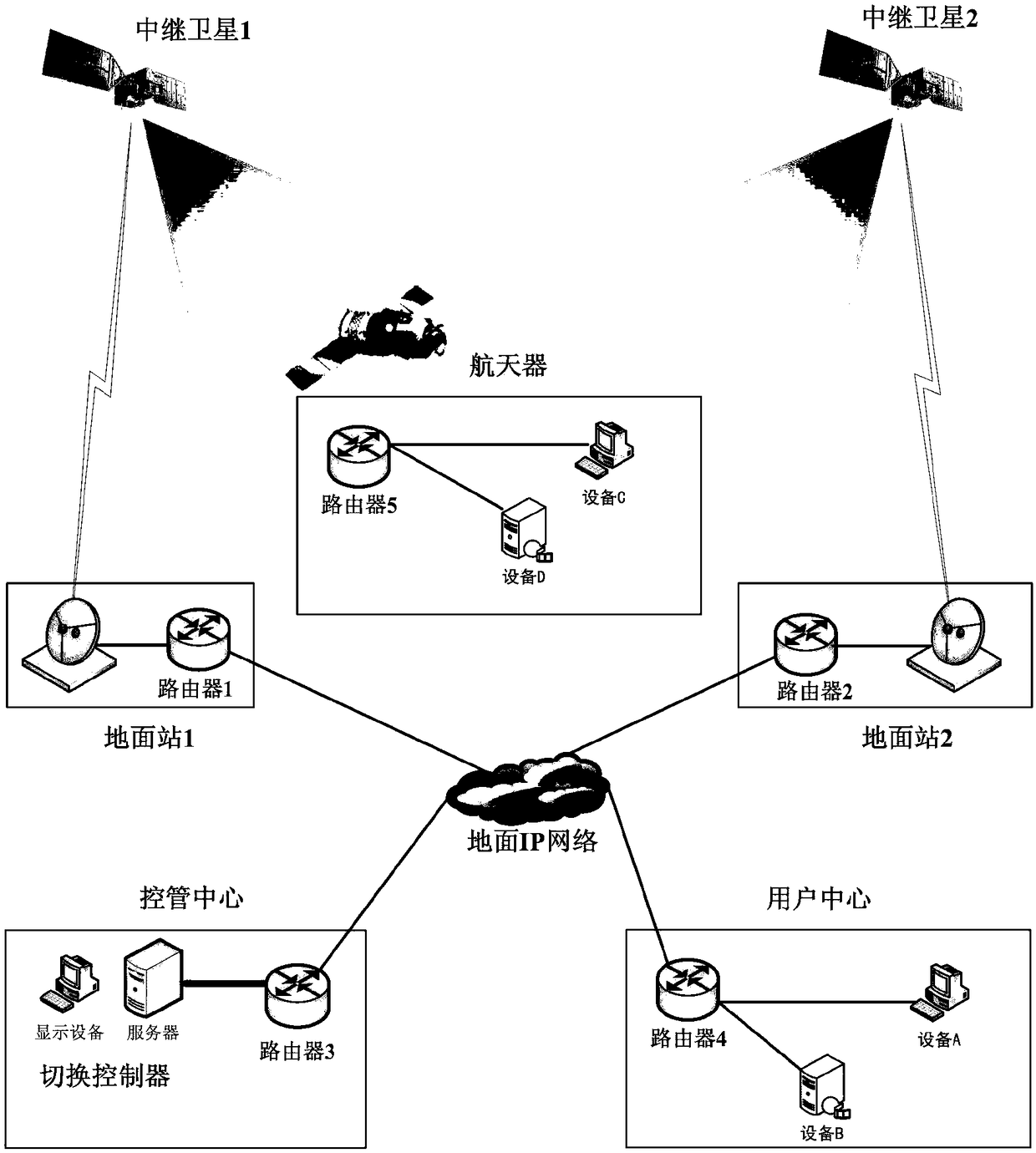
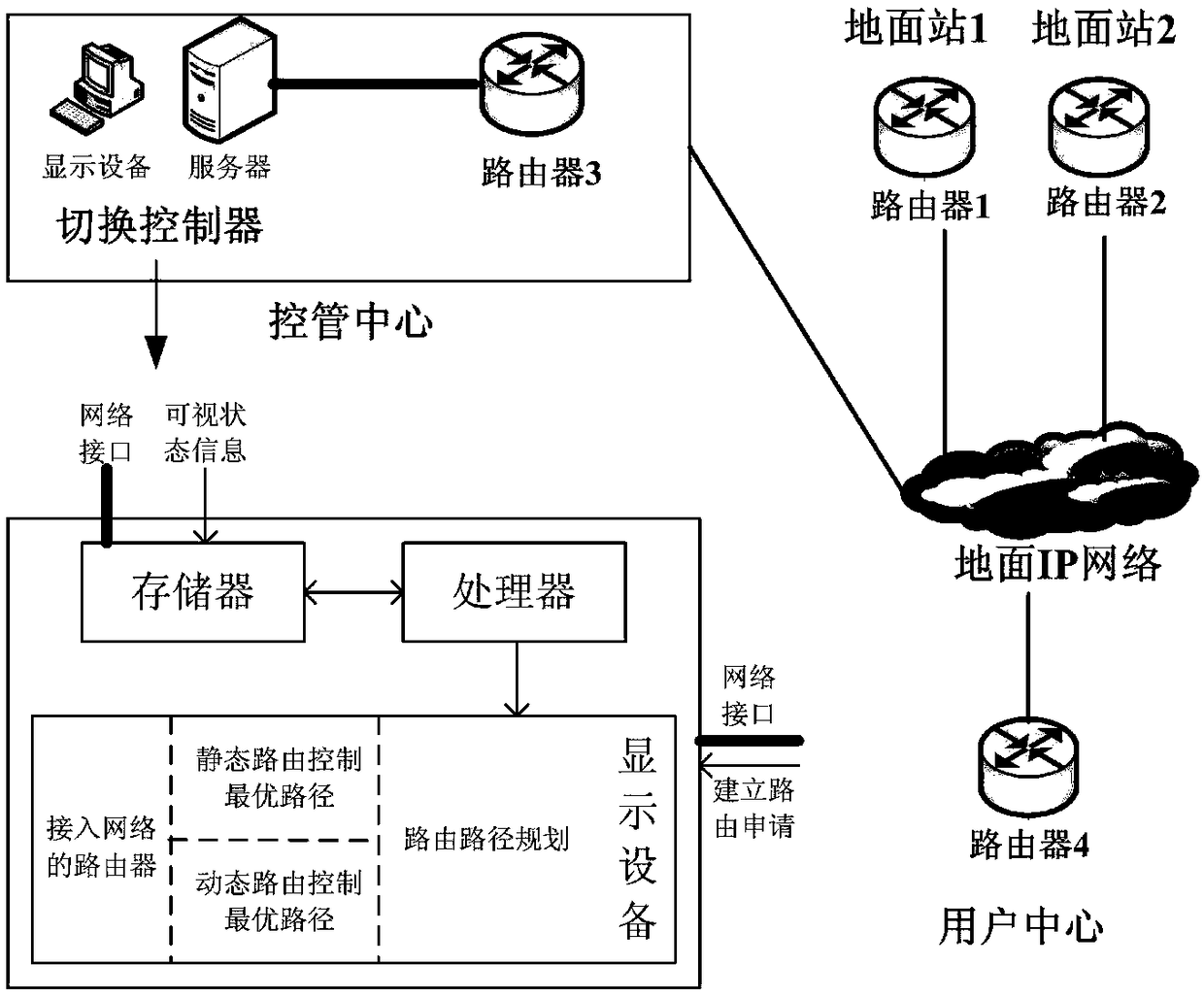
Mobile IP communication system and method for tracking and data relay satellite space-earth integration network
ActiveCN108832985AResolving automated switchingTroubleshoot dynamic routing fixesRadio transmissionData switching networksTelecommunications linkTracking and Data Relay Satellite System
The invention provides a mobile IP communication system and method for a tracking and data relay satellite space-earth integration network, which belong to the technical field of satellite communication. A handover controller uses an SNMP protocol to control an IP router; when a device in a user center needs to communicate with a device in a spacecraft, the handover controller selects an availabletracking and data relay satellite according to visual status information, and an optimal routing path is determined from a static routing table and a dynamic routing table; and thus, a forward communication link is built for data transmission. The provided static and dynamic routing control method is strongly adaptable to different tracking and data relay satellite network structures, the controlis simple, the realization is flexible, network devices in the tracking and data relay satellite system can be managed, and the problems of space-earth network link automatic switching and dynamic routing repair brought by movement of a fixed IP can be solved.
Owner:中国人民解放军32039部队
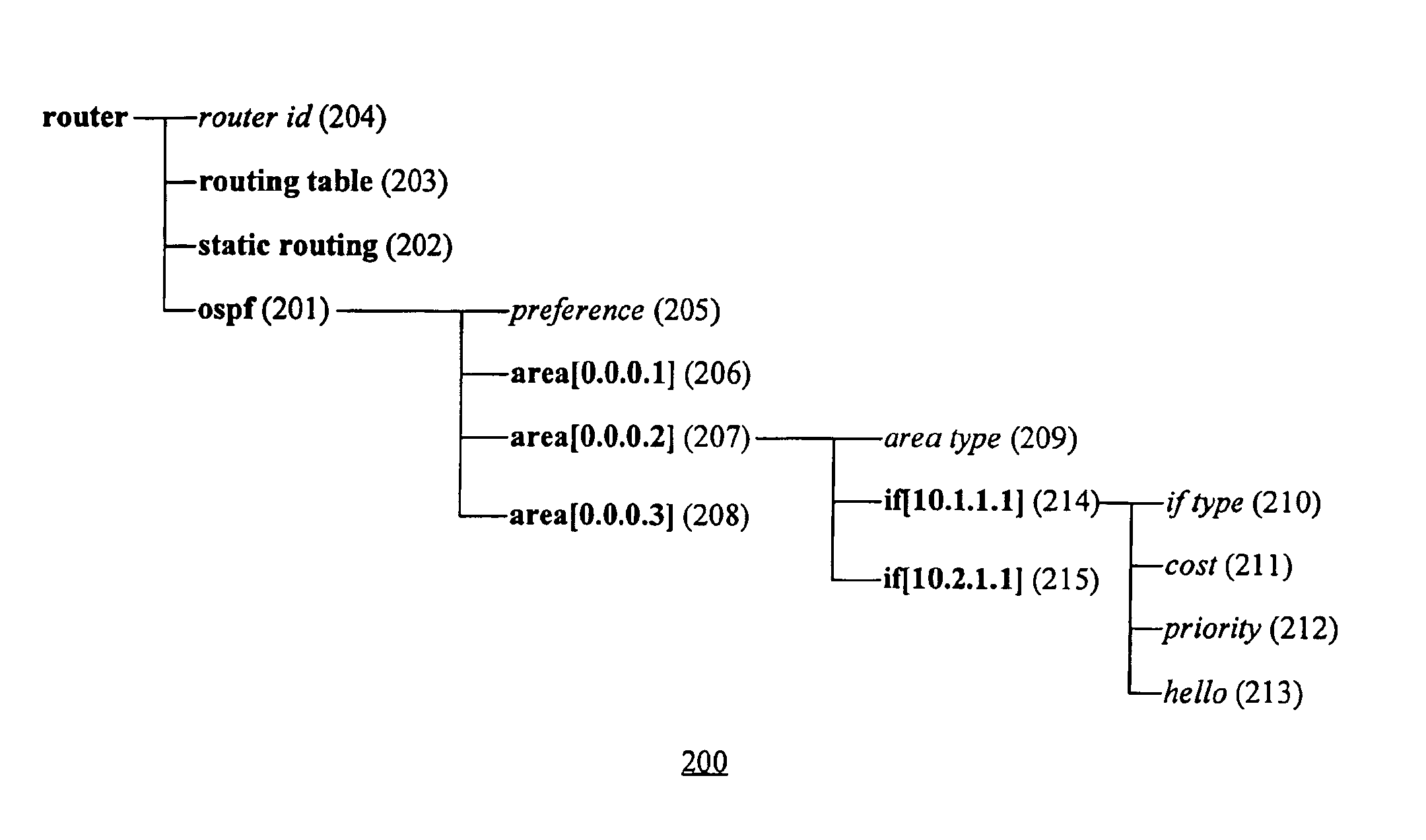
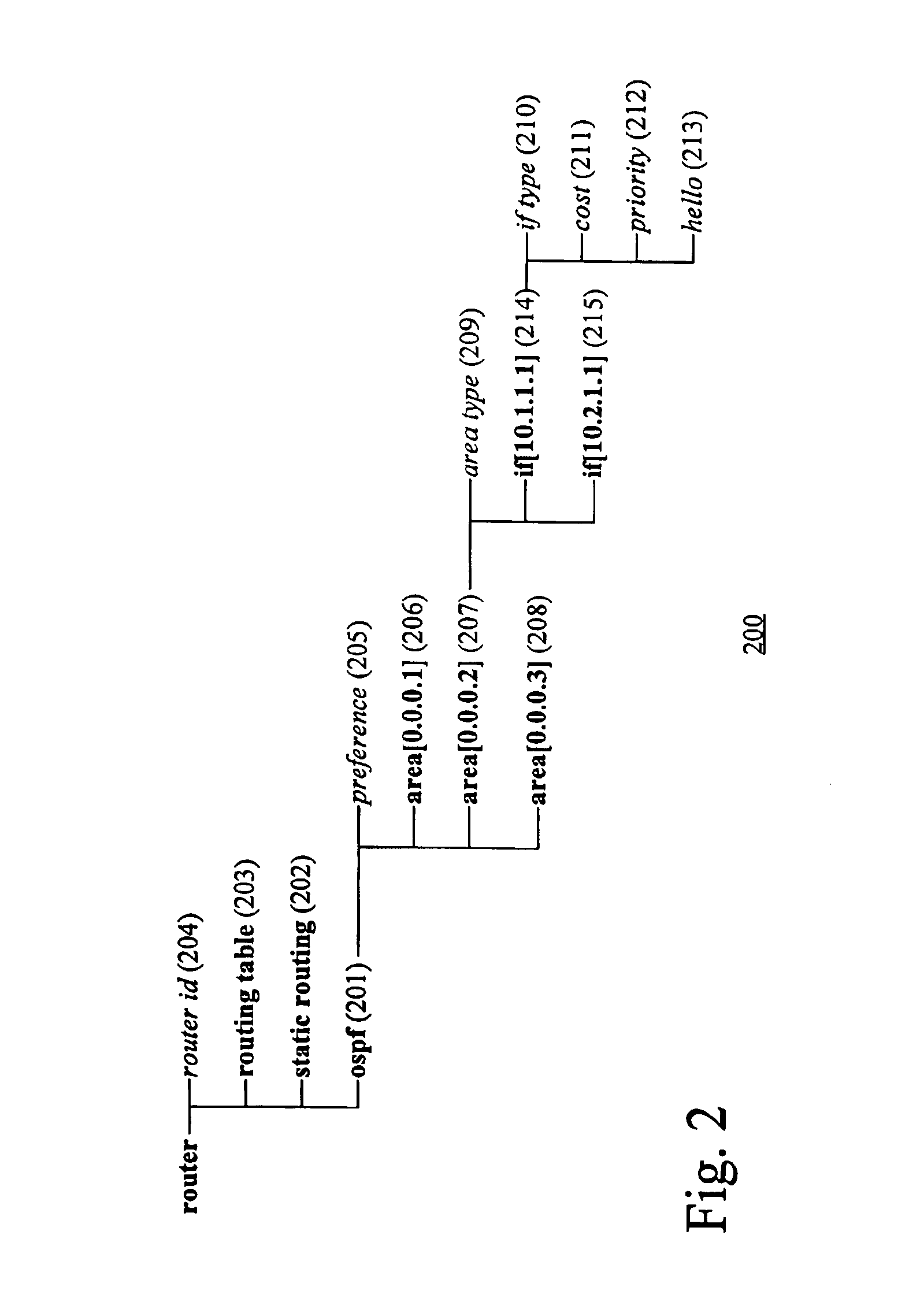
IP router with hierarchical user interface
InactiveUS6850976B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGraphical user interfaceIp router
A hierarchical interface component of a router transforms the flat feature presentation of traditional routers into a hierarchical feature presentation. The features are organized as functional components that include sub-components and attributes. Attributes store values relating to routing algorithms and components represent functionality relating to a routing algorithm and may contain additional components (sub-components) or attributes. The hierarchical interface allows a user to easily inspect, modify, and read the router attributes. Further, because the interdependencies of the attributes are clearly and visually displayed to the user, the user may more quickly understand the ramifications of changing a particular router attribute.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Telephony Intelligence in a Data Packet Network
InactiveUS20080049737A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsIntelligent networksIp routerIp address
A packet-data network is made intelligent in the sense of a connection-oriented, switched telephony (COST) network by enhancing one or more interconnected IP routers in the network with computer-telephony integration (CTI) processors executing CTI applications. No-charge-to-calling-party IP addresses are assigned and sponsored by various enterprises, who may also maintain call centers having at least one CTI-enhanced IP router connected to the network, and agent stations having IP telephones connected to the call-center-located IP router. With appropriate software and the CTI link to IP routers the performance of well-known conventional telephone systems may be provided in packet networks like the Internet.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMM LAB INC AS GRANTOR +3
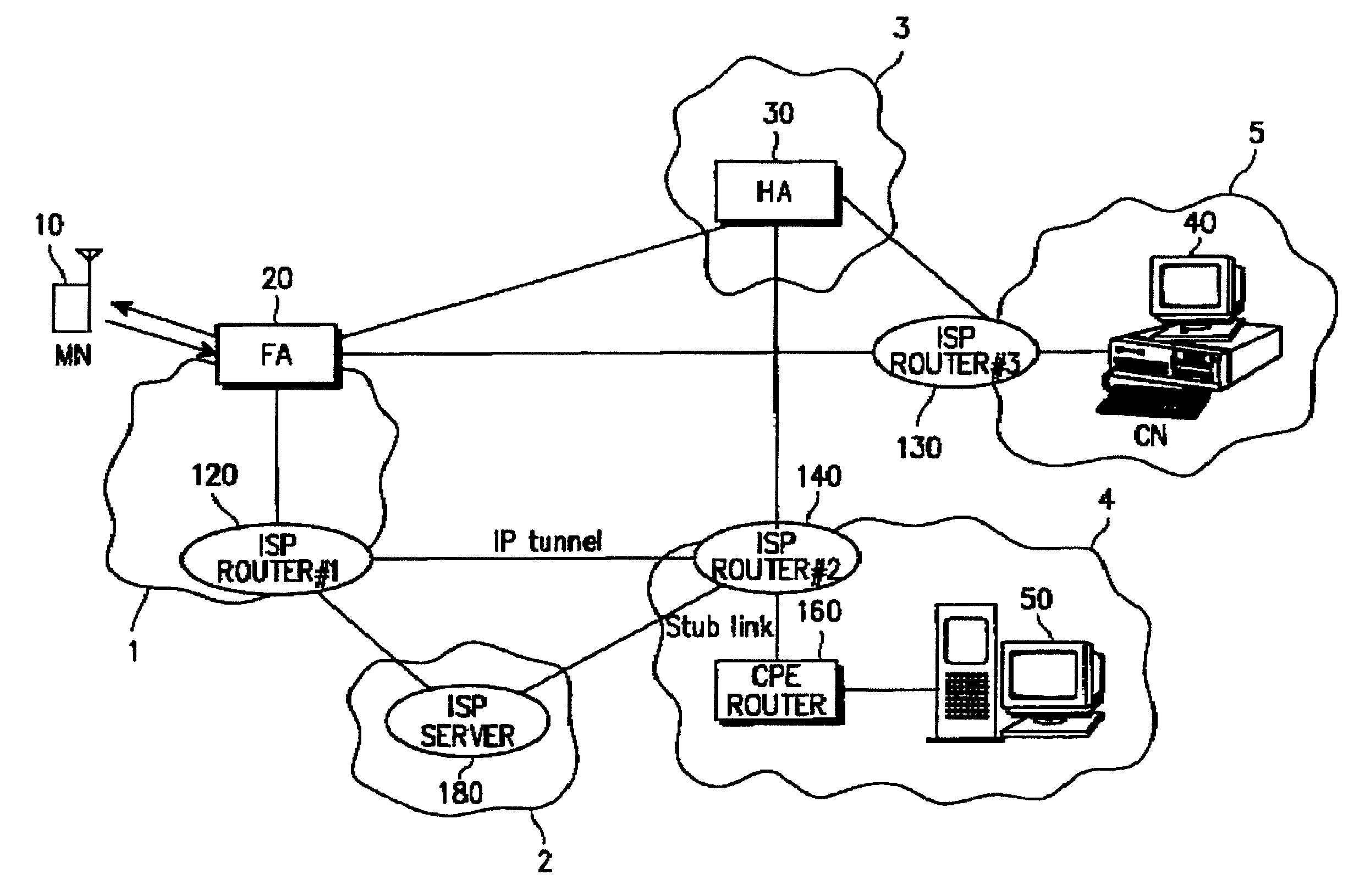
System and method for assigning a mobile IP to a mobile node
ActiveUS7512687B2Guaranteed to move normallyData stabilityMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsPrivate networkIp router
Disclosed is a system providing a VPN service by connecting a VPN (virtual Private Network) to a mobile communication network. A home agent (HA) stores location information of a mobile node (MN) and information on whether the MN is registered in the VPN. A foreign agent (FA) transmits a location registration request message to the HA by receiving location registration information of the MN, and transmits data to an ISP (Internet Service Provider) router in the same subnet upon receiving a VPN service request. A server provides the VPN service and a router network connects the VPN to the FA. The router network includes a server for searching an edge IP router in the network using an address of the FA. The HA prevents an MN from accepting a call request received from a specific node in an IP network while the MN is performing a VPN service.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for updating boundary gate protocol recursion router
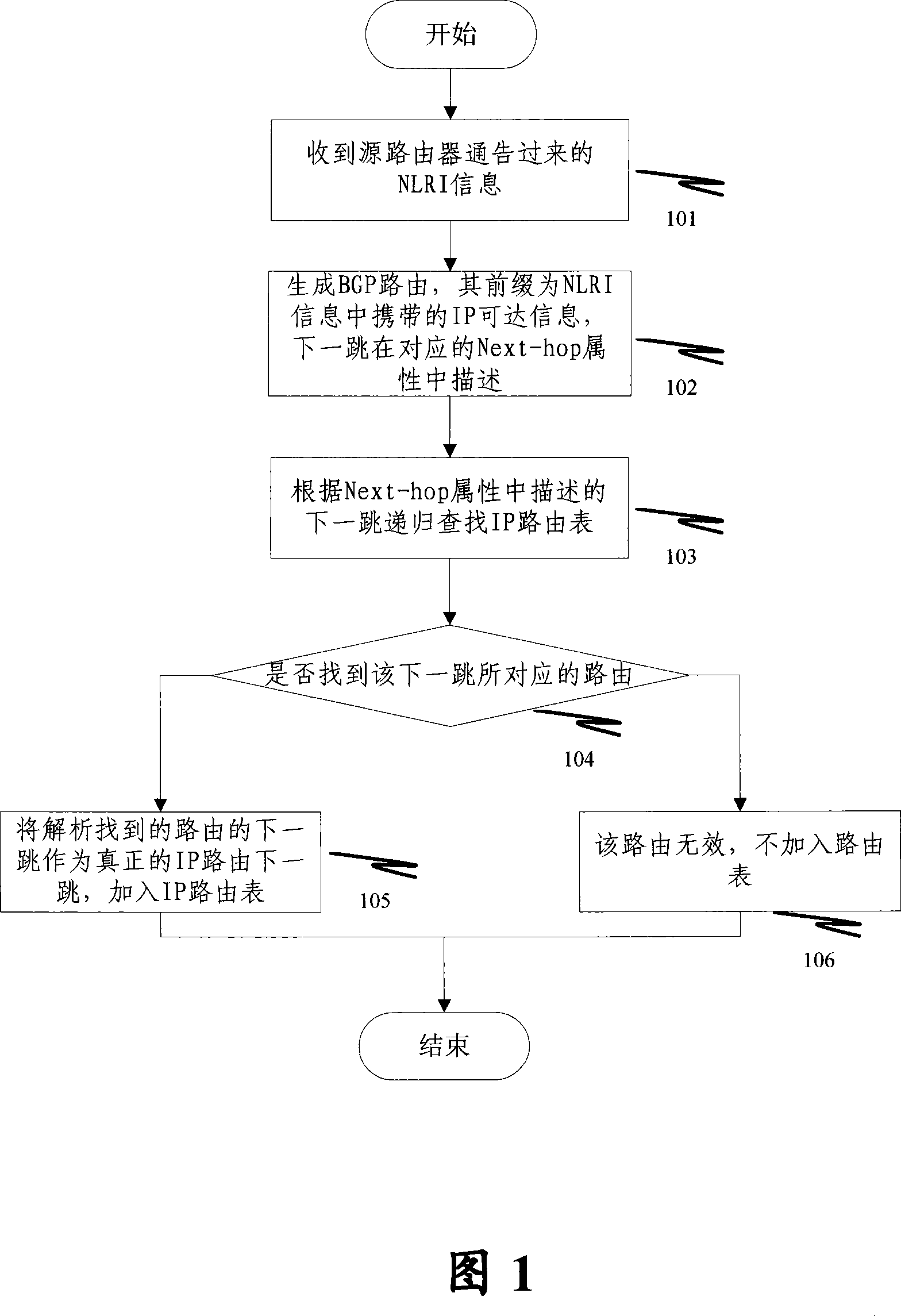
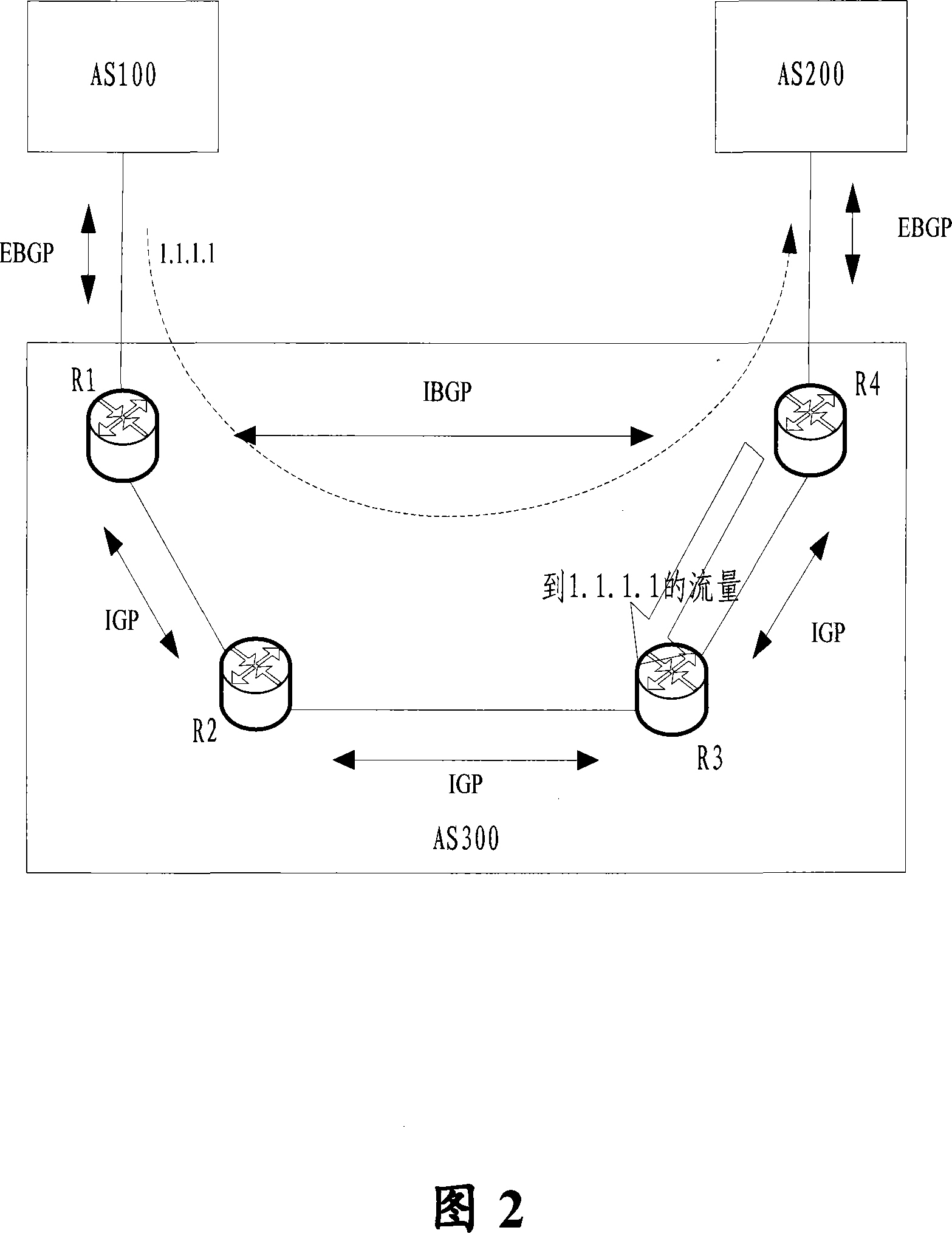
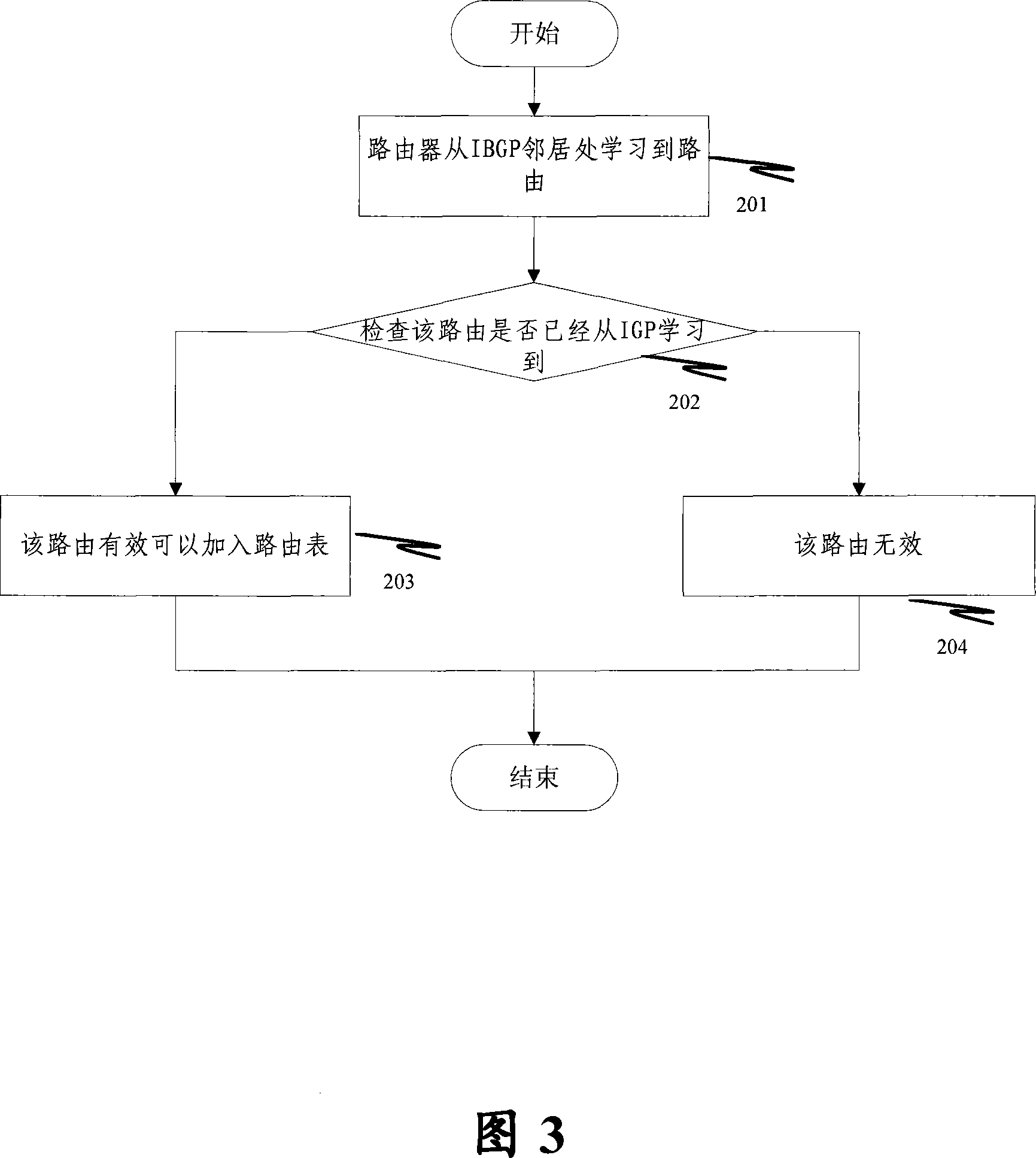
InactiveCN101076029AIncrease flexibilityResolve DropsNetwork connectionsBorder Gateway ProtocolRouting table
The method comprises: 1) the IP router for running BGP receives the route update message from I-BGP neighbor, and generates a BGP route; 2) according to said BGP route, looking up the route table to make the recursive resolution for the BGP next hopping, and detects if IGP has learnt the BGO route so as to decide if the route synchronization between IGP and BGP has been completed; 3) if yes, then comparing the IGP next hopping obtained through learning with the BGP next hopping after resolution in order to decide if they are consistent; if yes, then directly updating the IP route table, and the route is valid; if not, then according to the user's configuration requirement, making relevant route update.
Owner:刘莉敏
Joint-layer restoration in packet-over-optical networks
InactiveUS7346277B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsCross connectionTransport layer
A joint “packet-optical” layer restoration mechanism protects against single, packet-layer router failures by managing network resources from both the packet layer and the optical transport layer in a synergistic manner. It reuses packet-layer router service-ports and / or transport-layer service wavelengths associated with optical switch-ports instead of reserving additional standby packet-layer router service-ports. It can reuse resources from primary paths that are unaffected by router failures and paths that exist for link-failure protection at the optical layer. Embodiments feature a modified node structure that includes both an IP router and a dynamically reconfigurable OXC, which dynamically establishes connectivity between IP-router ports and transport-layer optical fibers. The joint-layer router provides fine-granularity grooming at the IP layer and full-fledged wavelength networking via dynamic wavelength switching and / or wavelength translation at the optical layer. The latter can change the wavelength cross-connections on-demand to perform restoration or to modify the connectivity between IP routers in the network.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
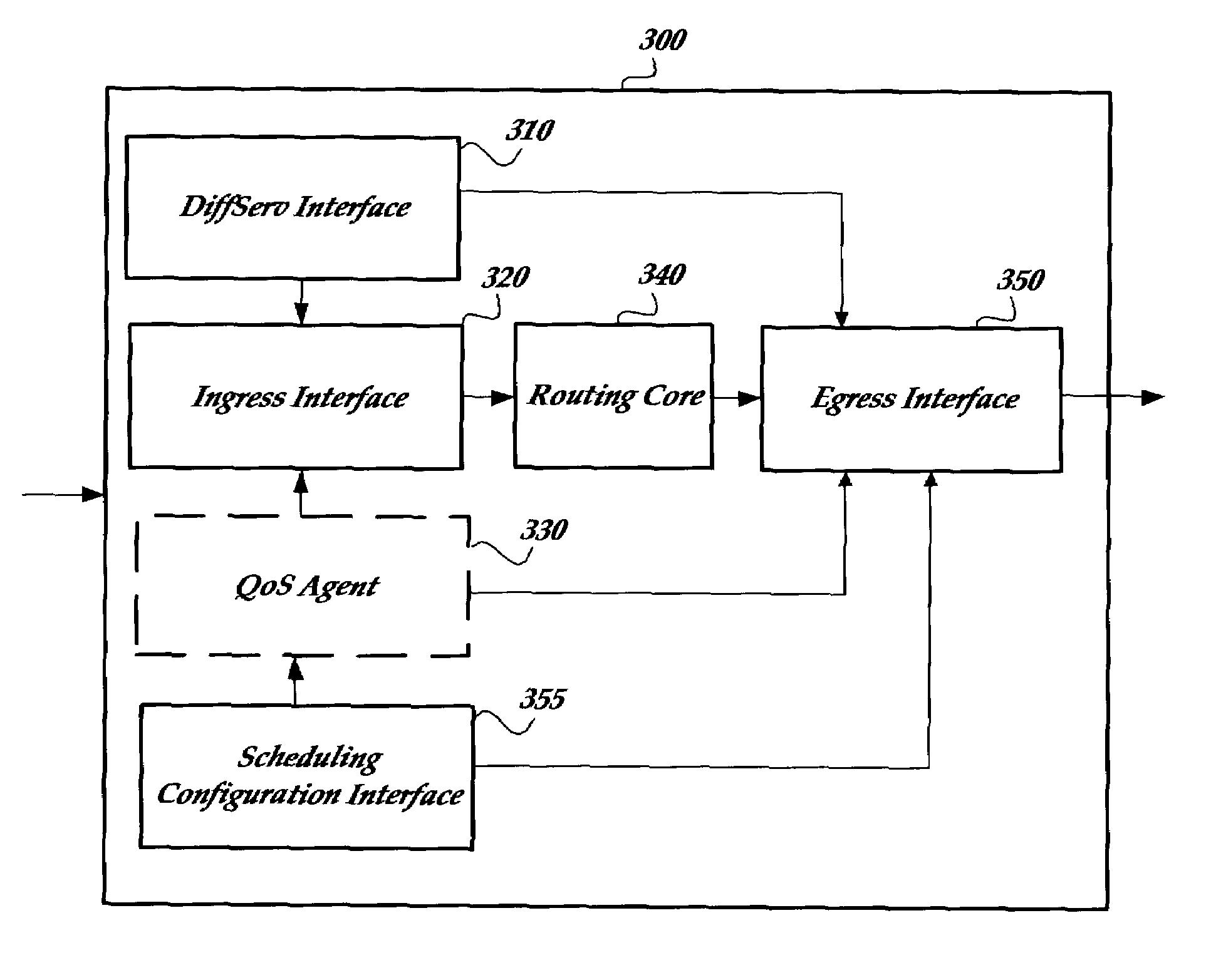
Programmable scheduling for IP routers
InactiveUS7023843B2Increases available QoS solution availableMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionDeficit round robinSingle stage
A scheduling system for IP routers is provided. A programmable scheduler for IP routers can support single stage and multistage scheduling. This allows flexible combinations of scheduling and widens dramatically the available QoS solutions to operators. With this kind of scheduling the router can be configured to support almost any known scheduling method or combination. Priority Queuing (PQ) and Deficit Round Robin (DRR) scheduling is scheduling is used according to one embodiment of the invention.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com