Patents
Literature
349 results about "Static routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Static routing is a form of routing that occurs when a router uses a manually-configured routing entry, rather than information from a dynamic routing traffic. In many cases, static routes are manually configured by a network administrator by adding in entries into a routing table, though this may not always be the case. Unlike dynamic routing, static routes are fixed and do not change if the network is changed or reconfigured. Static routing and dynamic routing are not mutually exclusive. Both dynamic routing and static routing are usually used on a router to maximise routing efficiency and to provide backups in the event that dynamic routing information fails to be exchanged. Static routing can also be used in stub networks, or to provide a gateway of last resort.
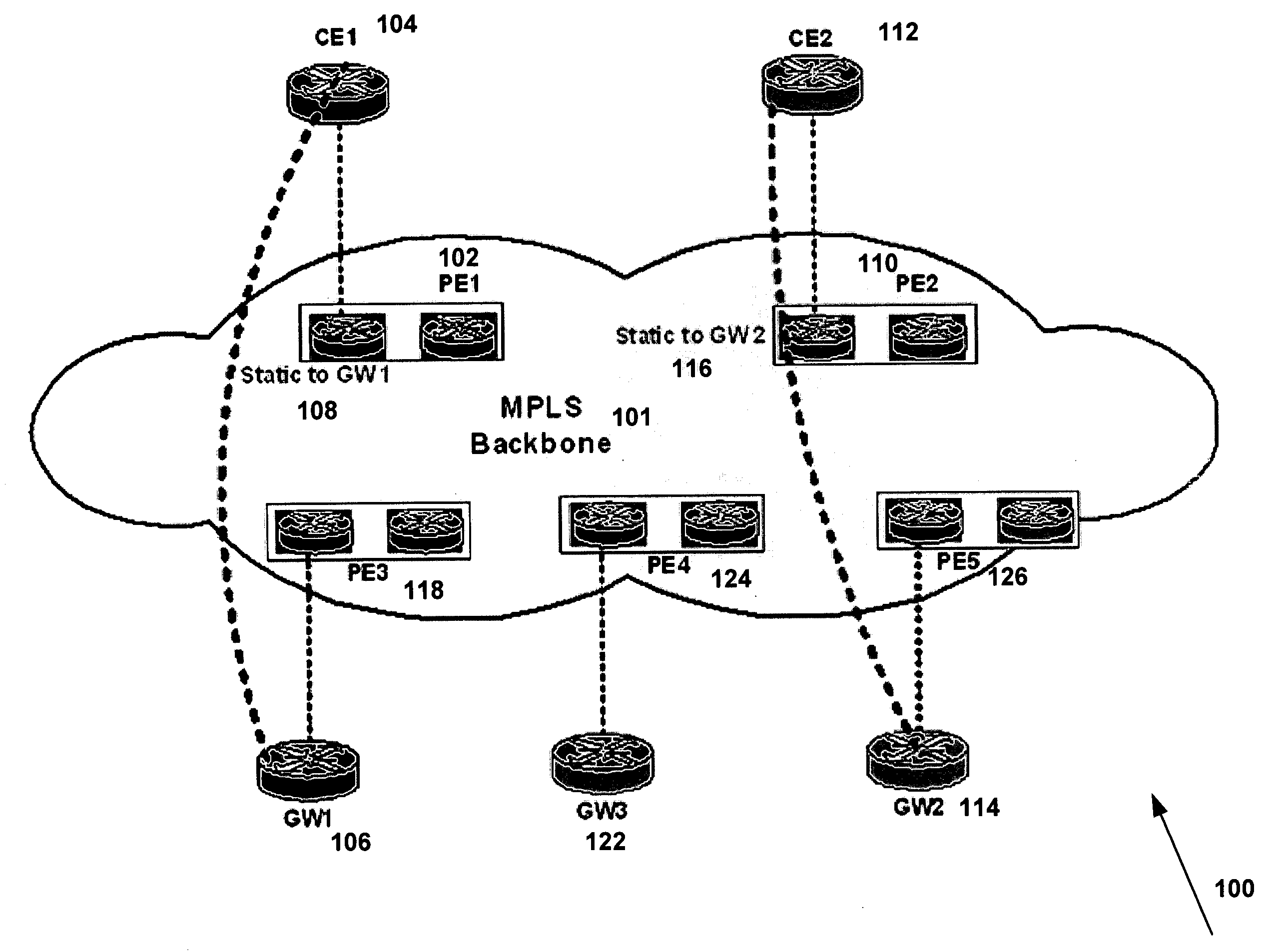
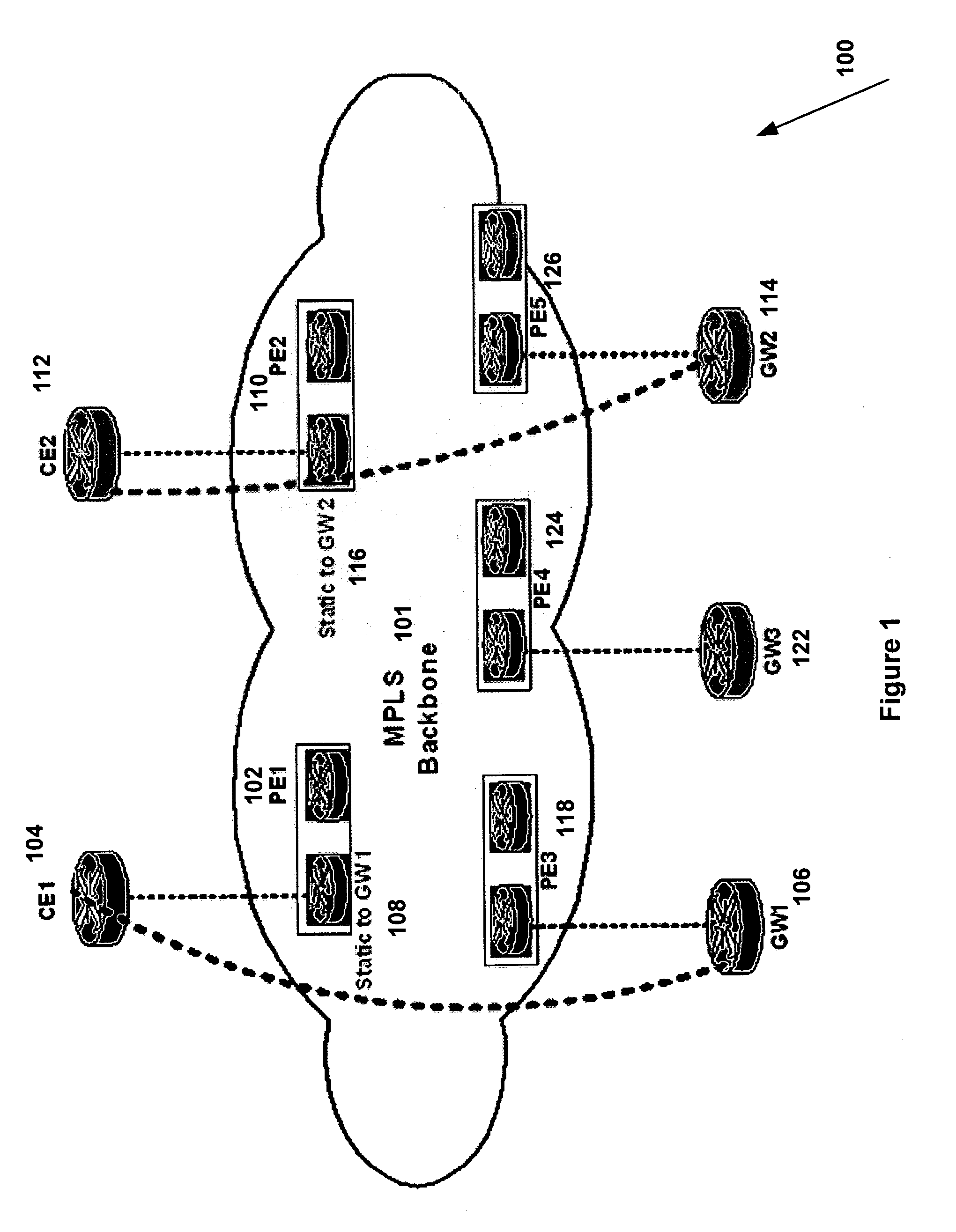
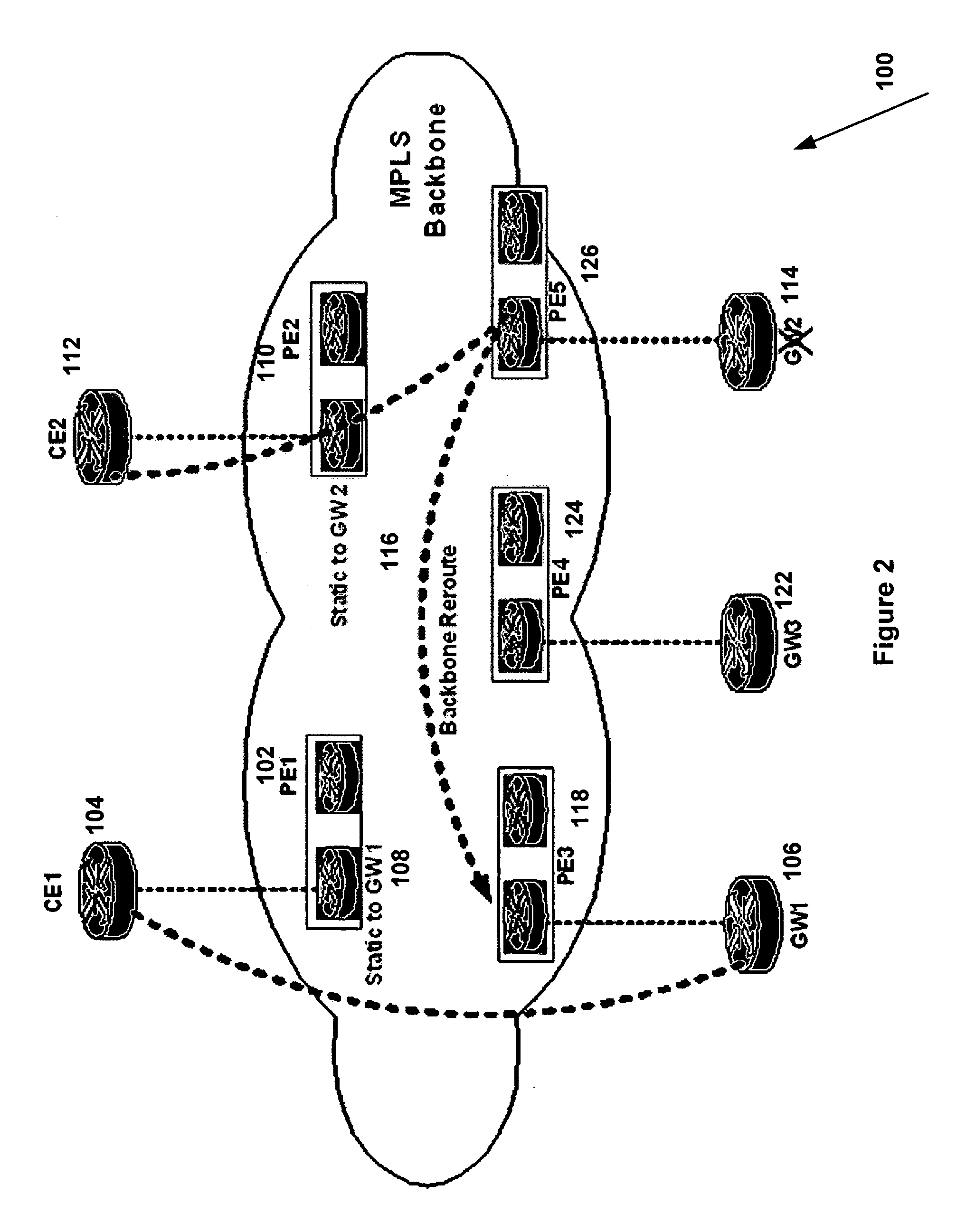
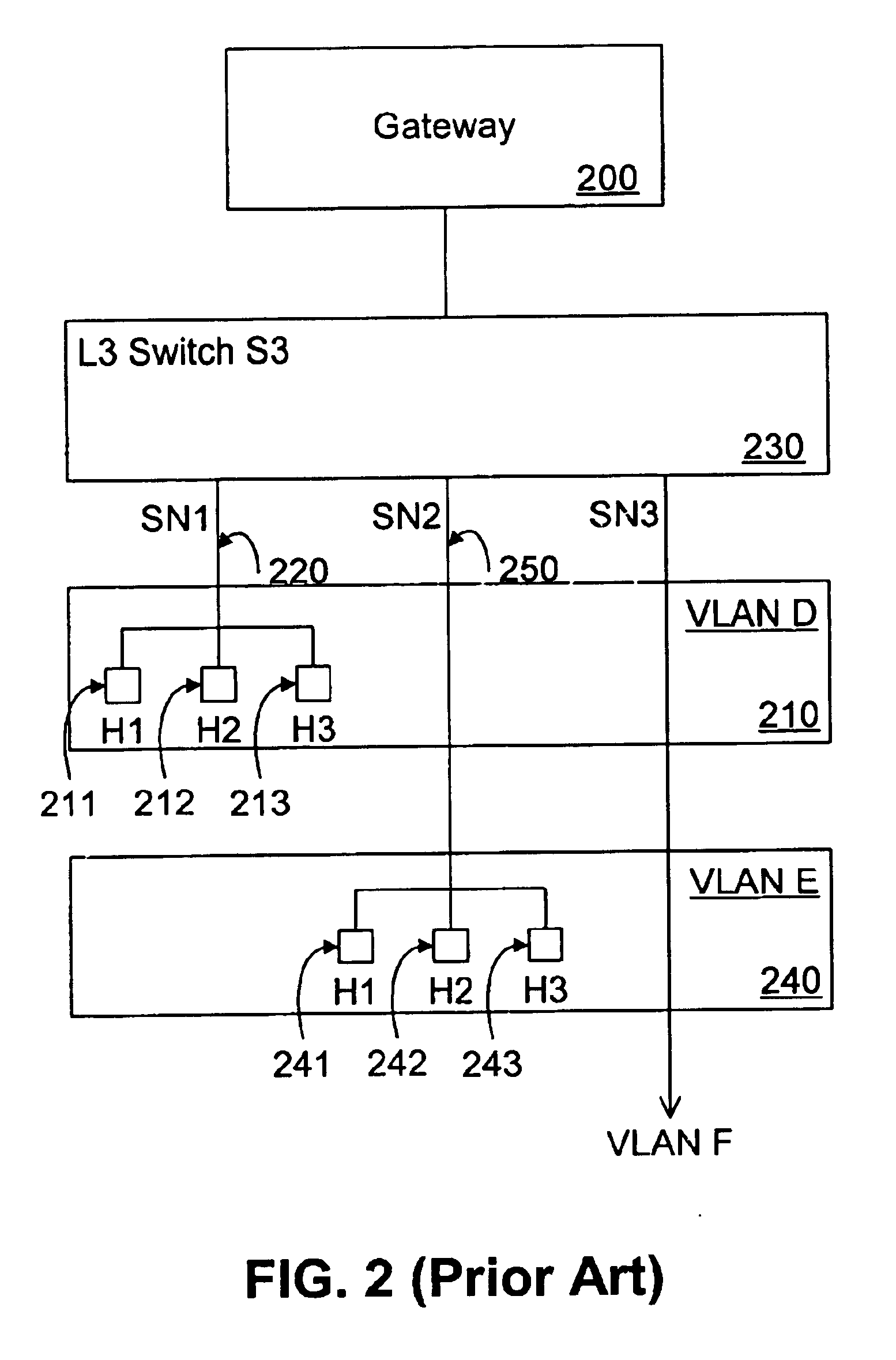
System and method for forwarding traffic data in an MPLS VPN
InactiveUS20080080517A1Data switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTelecommunications network
The present invention provides a system and method for forwarding traffic data in a MPLS VPN network within a telecommunications network. The method comprise a technique for gateway selection in the MPLS VPN by using a combination of recursive floating static routes in the PE routers and conditional route advertisements from the gateway CE routers. This method allows for choice of gateway on a per-PE per-VRF basis.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Cloud over IP session layer network
Cloud endpoints are secured using agents and a controller connected to the agents. A whitelist identifies components and processes of an authorized multi-tiered application for the cloud. An application profile for the application specifies valid computing flows between components of a tier and components of another tier, where components of the tier are executed at an endpoint and the other components of the other tier are executed at another endpoint. Endpoints are provisioned with static routing tables identifying at least one subnet destination. A request is received at a first endpoint to connect to a second endpoint. If the second endpoint falls within the at least one subnet destination, the controller performs one or more further security checks including checking the application profile flow, whitelist, and endpoint quarantine list. A network kernel table at an endpoint that includes the static routing table may be periodically checked to detect tampering.
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Method and system for VLAN aggregation
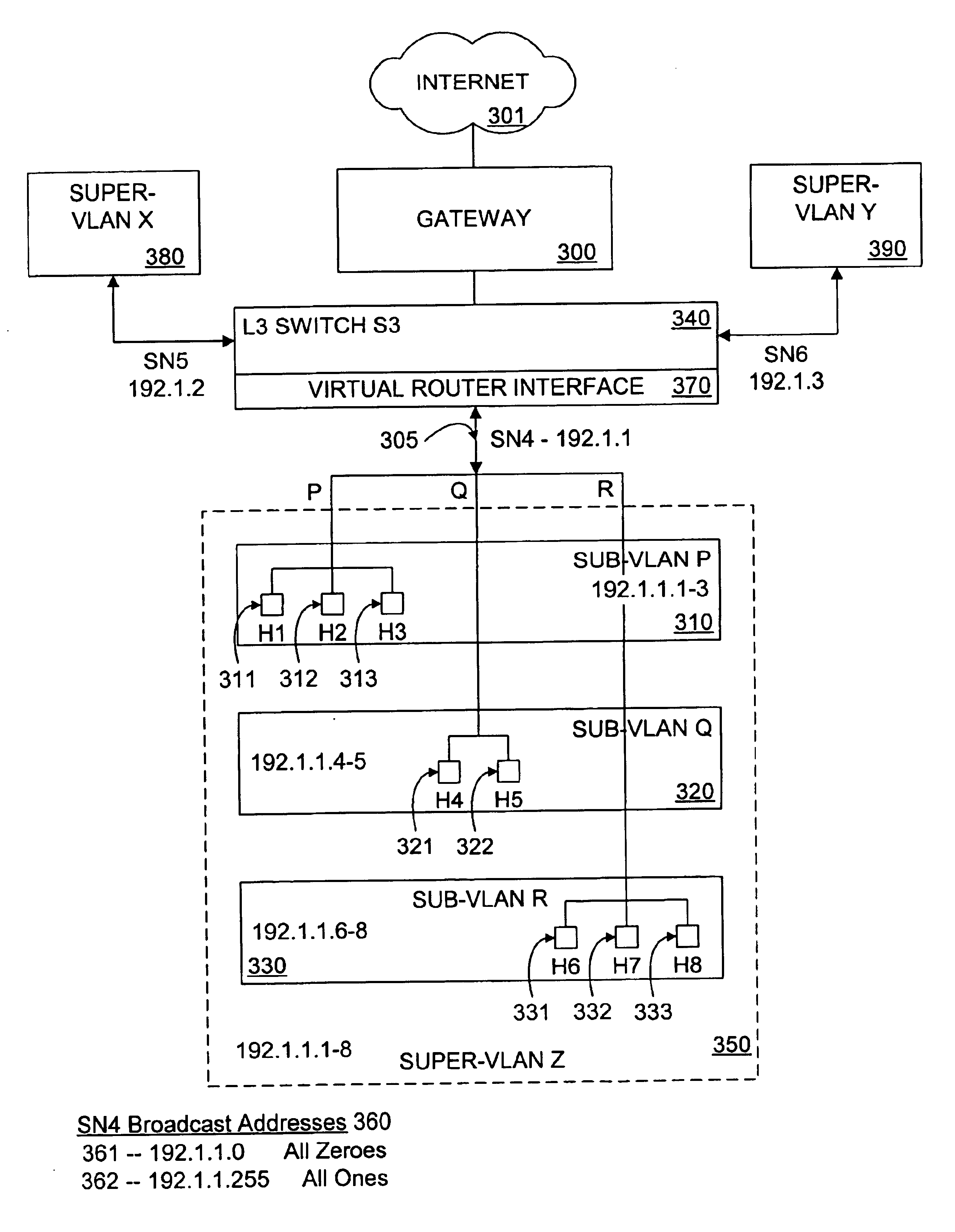
A method and system for an aggregated virtual local area network (VLAN) architecture in which several VLANs in a network share the same default router address and subnet mask, but remain isolated from one another's network traffic. Instead of the traditional method of assigning one subnet to a VLAN, each VLAN is assigned only a portion of a subnet's IP address space, and is further grouped into a super-VLAN uniquely associated with that subnet. Intra-VLAN traffic is forwarded only to host IP addresses assigned to that same VLAN according to a VLAN identifier carried in the data packet. Inter-VLAN traffic is processed by a virtual router interface which routes the data packet by applying the routing configuration for the subnet uniquely associated with the super-VLAN, according to a super-VLAN identifier carried in the data packet. The routing configuration used by the virtual router interface includes routing protocols, static routes, redundant router protocols and access-lists. Since each VLAN shares the same virtual router interlace, the traditional address overhead of a subnet is minimized, requiring only one default router and subnet mask, as well as only one pair of subnet broadcast addresses for all hosts on the subnet and the subnet itself. The aggregated VLAN architecture provides for the efficient use and management of a network's IP address space.
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
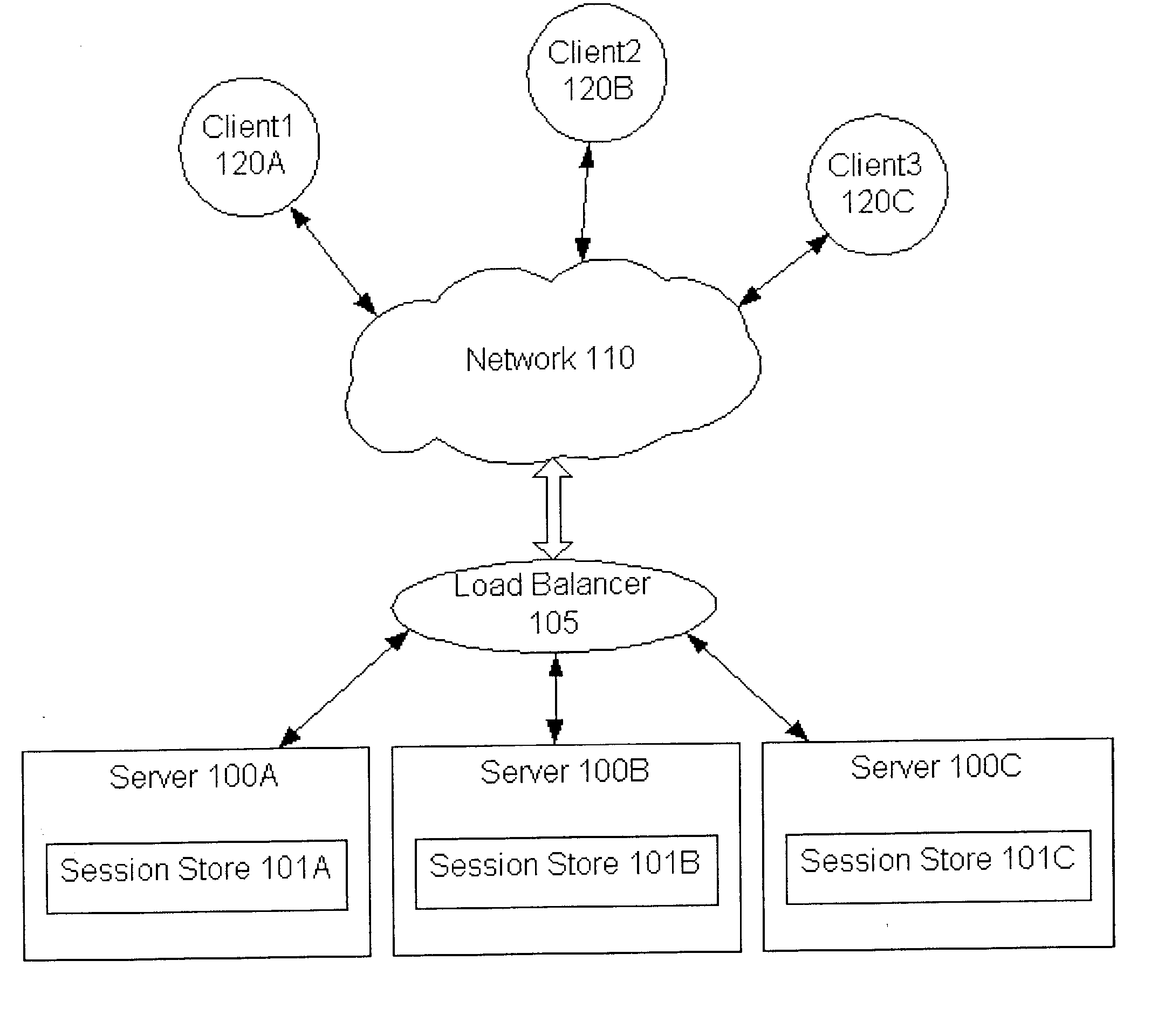
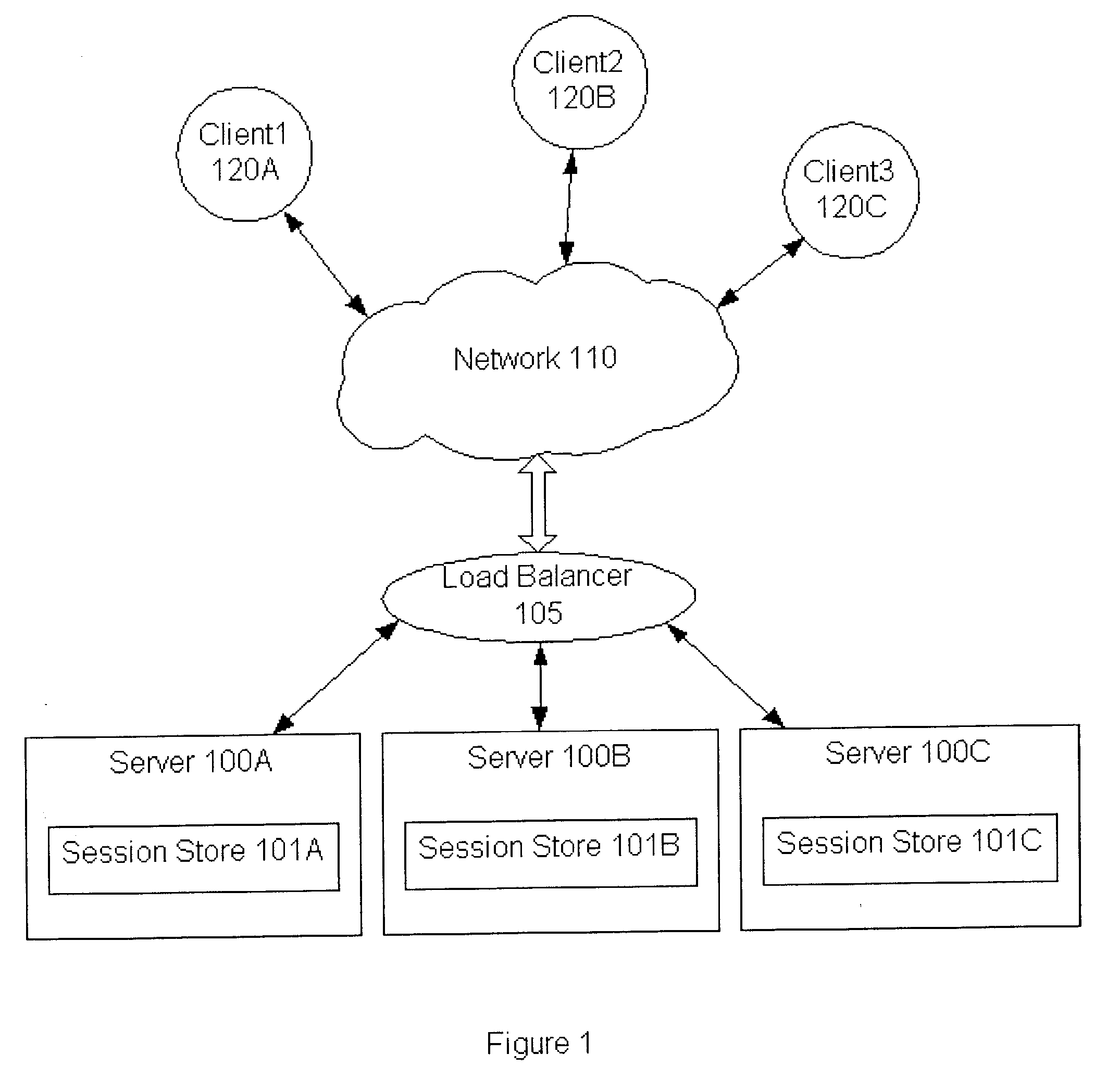
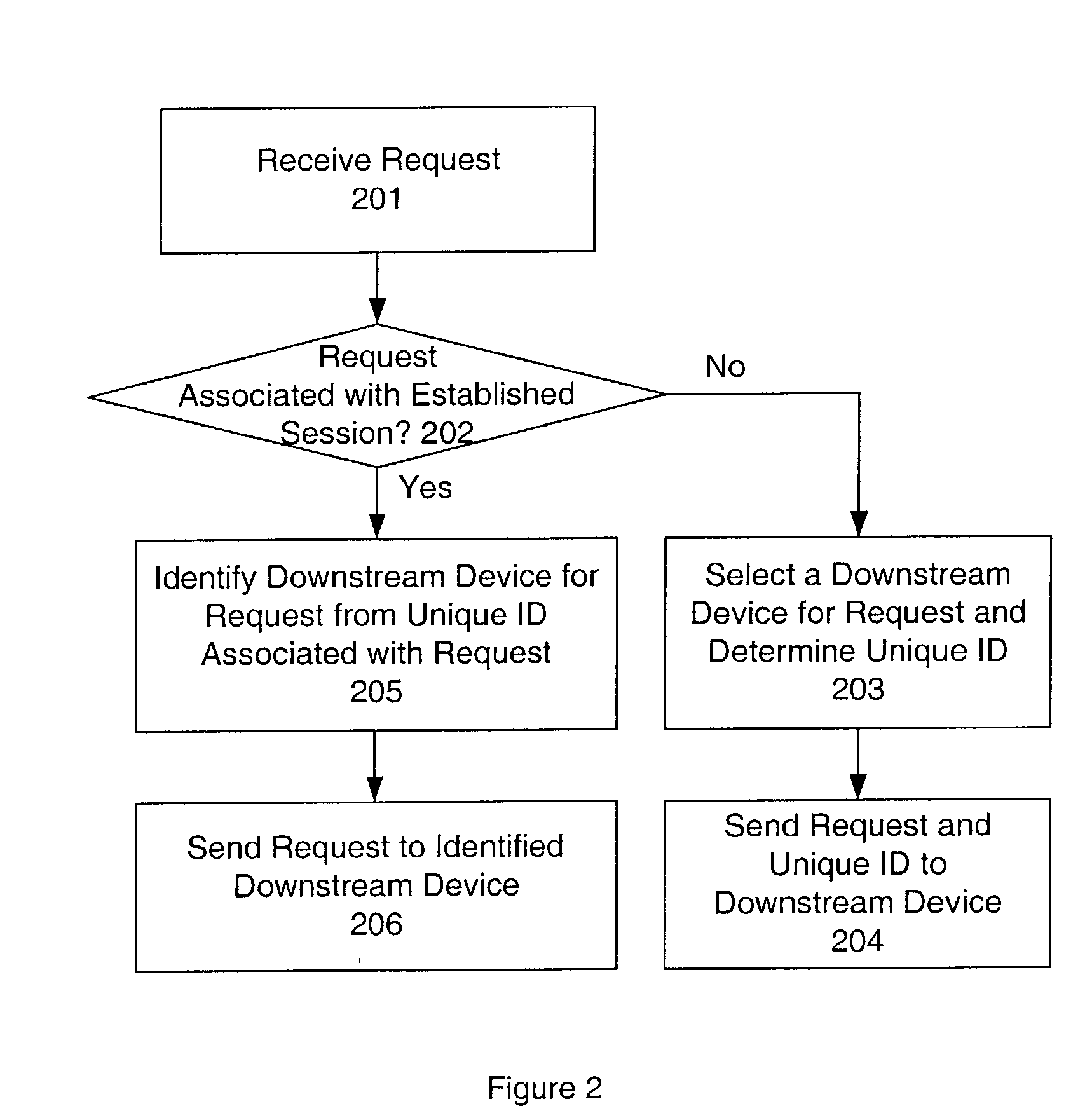
System and method for sticky routing of requests within a server farm
An upstream device, such as a load balancer or router within a server farm, may perform sticky routing of session requests to the servers handling those sessions by generating unique ID(s) identifying how requests may be routed through the server farm. Upstream devices through which travels a request that is not associated with a session on a server of the server farm may generate one or more unique IDs identifying how the request is routed through the server farm. The server handling the request may form a session ID and return that session ID and the unique ID(s) to the client that originated the new request and session. Clients may then send the session ID and unique IDs with clients requests for that session. Upon receiving requests corresponding to established sessions, the upstream devices may then identify routing information from the unique ID(s) and route the request accordingly.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
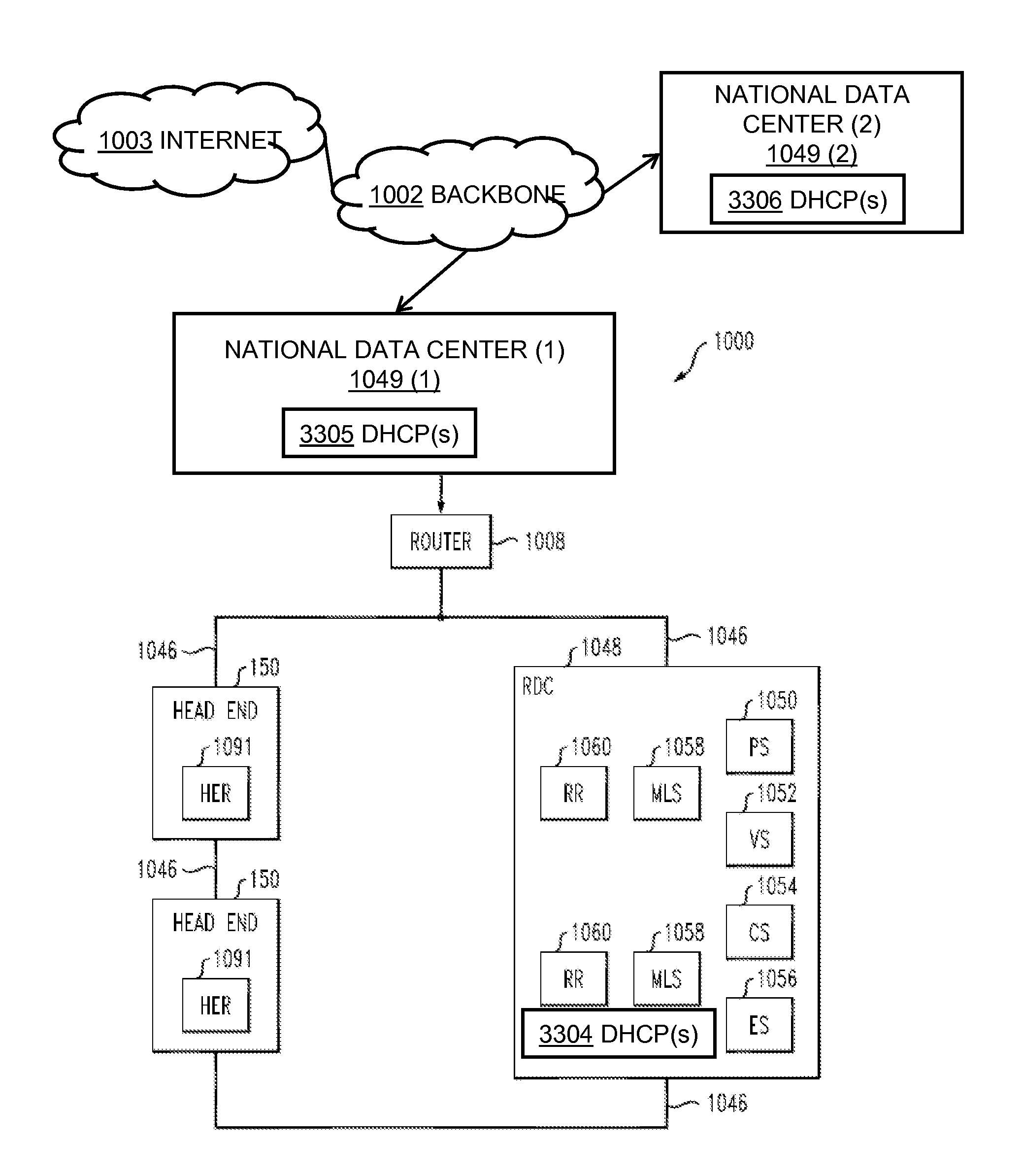
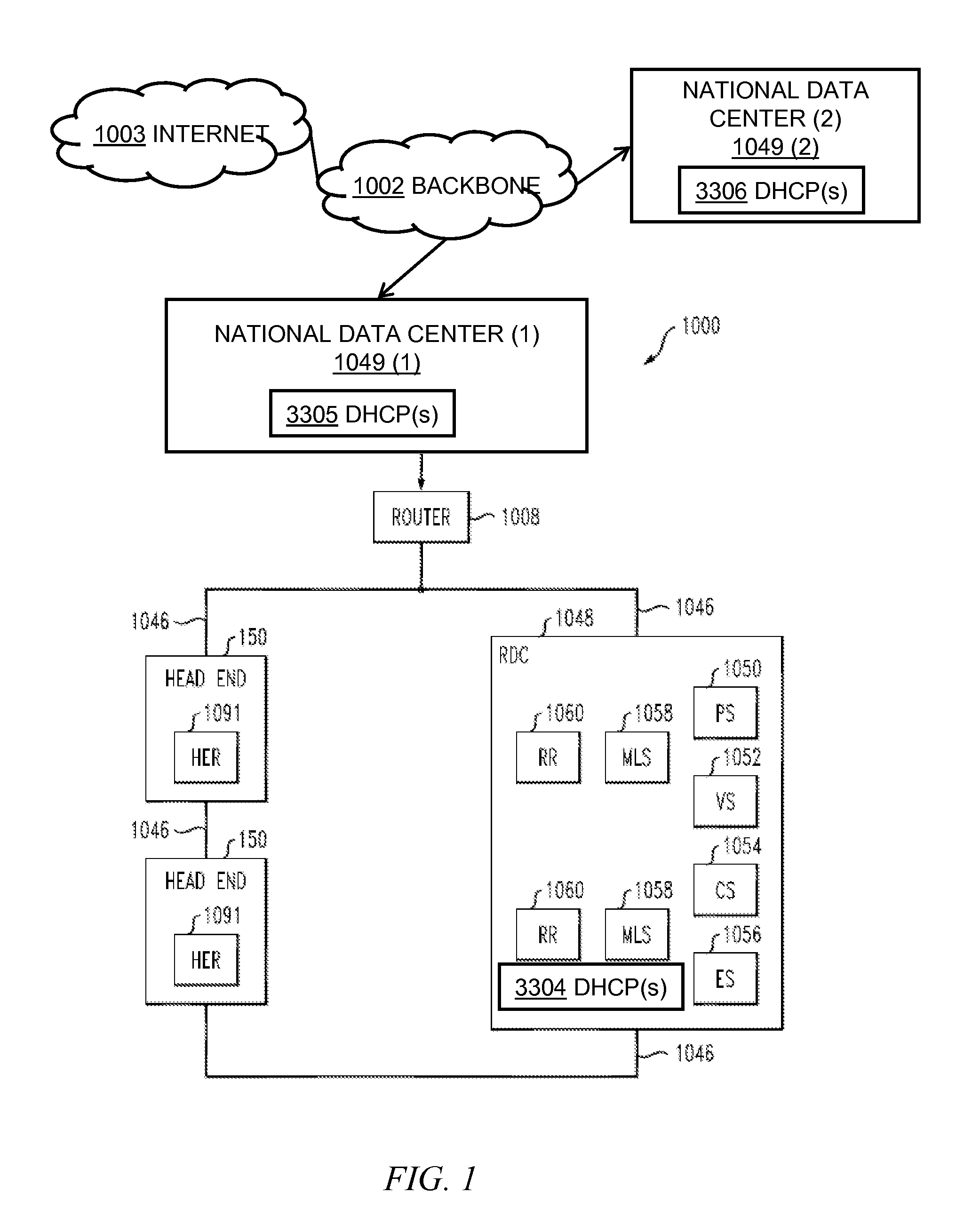
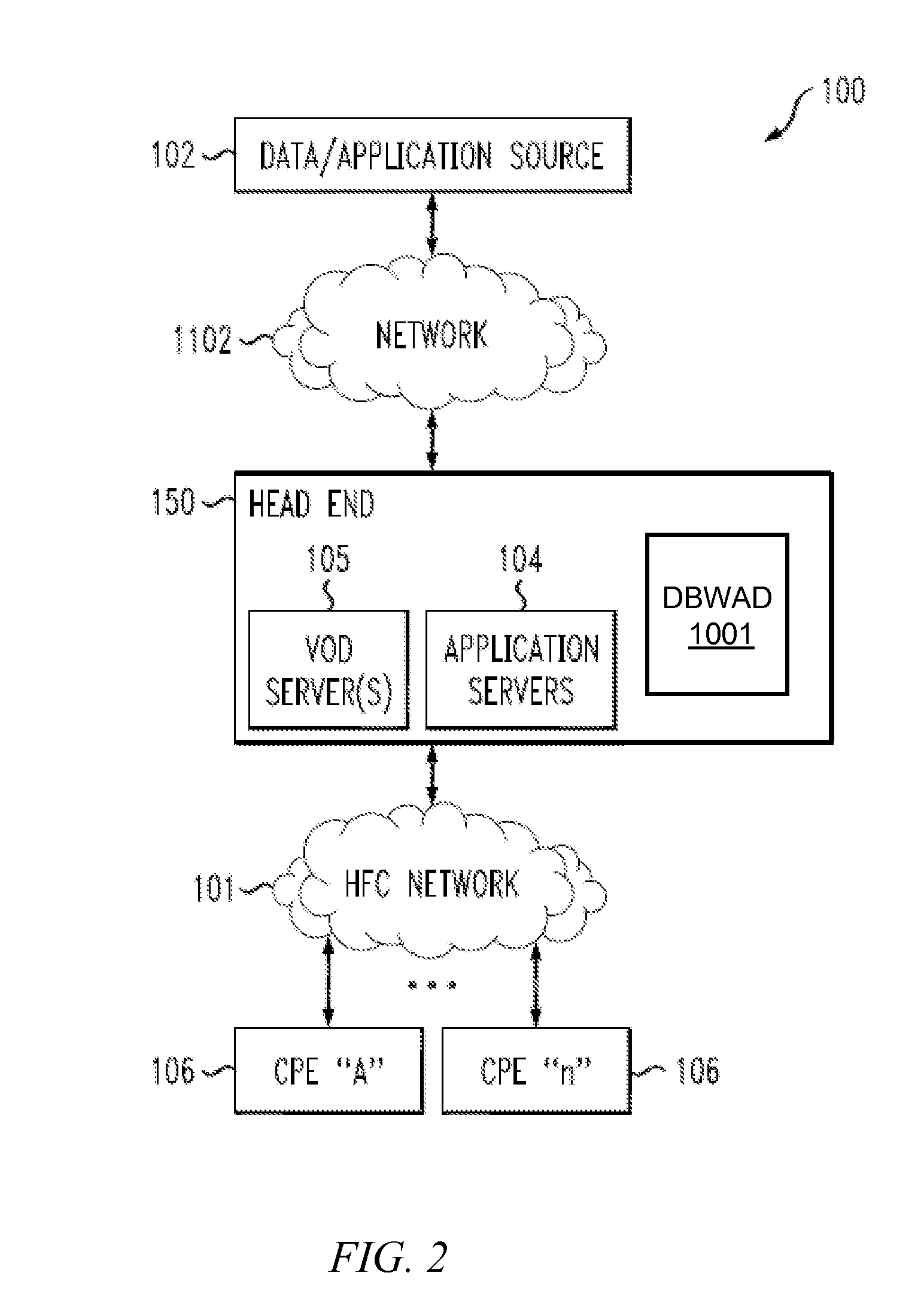
System and method for automatic routing of dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) traffic
ActiveUS20140281029A1Simple processEase in collecting metrics and/or statisticsMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityAutomatic routing
At an intermediary dynamic host configuration protocol relay device, over a network, a dynamic host configuration protocol message is obtained from one of a plurality of remote dynamic host configuration protocol relay devices in communication with the intermediary dynamic host configuration protocol relay device over the network. The intermediary dynamic host configuration protocol relay device accesses data pertaining to a plurality of dynamic host configuration protocol back-end servers logically fronted by the intermediary dynamic host configuration protocol relay device. Based on information in the dynamic host configuration protocol message and the data pertaining to the plurality of dynamic host configuration protocol back-end servers, the dynamic host configuration protocol message is routed to an appropriate one of the plurality of back-end dynamic host configuration protocol servers.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
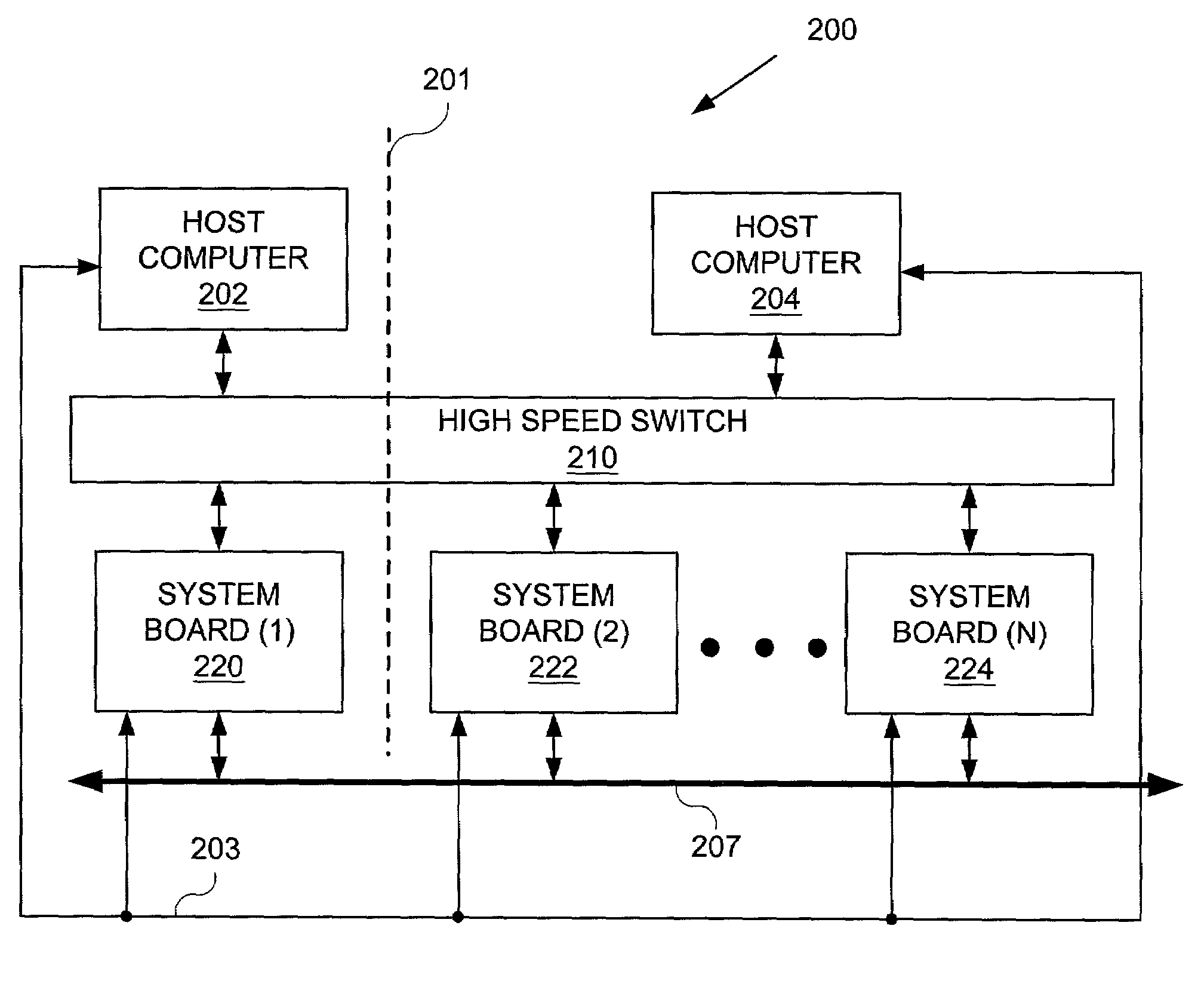
Method and apparatus for cycle-based computation
ActiveUS7036114B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designData connectionComputerized system
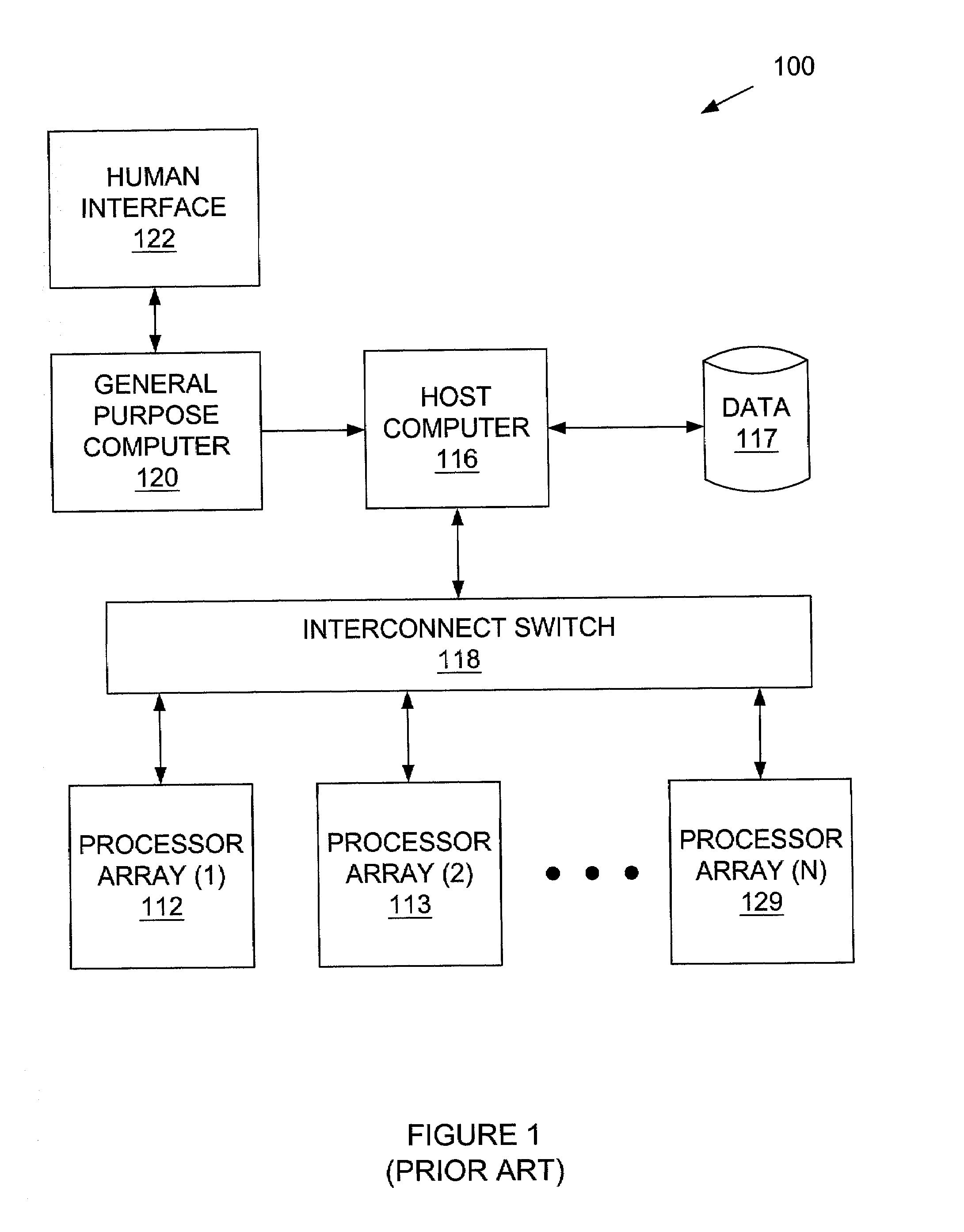
A computer system for cycle-based computation includes a processor array, a translation component adapted to translate a cycle-based design, a host computer operatively connected to the processor array and to the translation component, a data connection component interconnecting a plurality of members of the processor array using static routing, a synchronization component enabling known timing relationships among the plurality of members of the processor array, a host service request component adapted to send a host service request from a member of the processor array to the host computer, and an access component adapted to access a portion of a state of the processor array and a portion of a state of the data connection.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
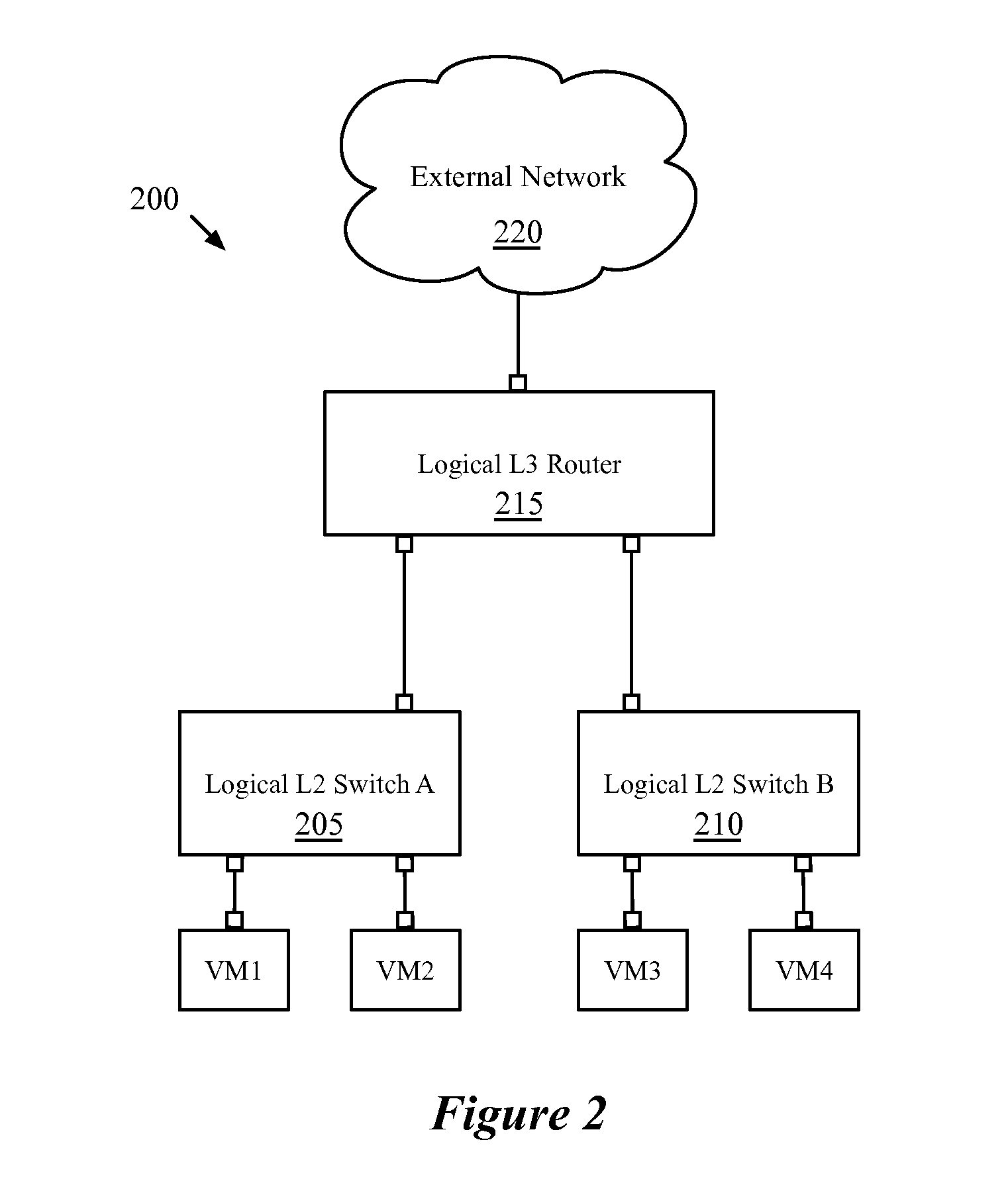
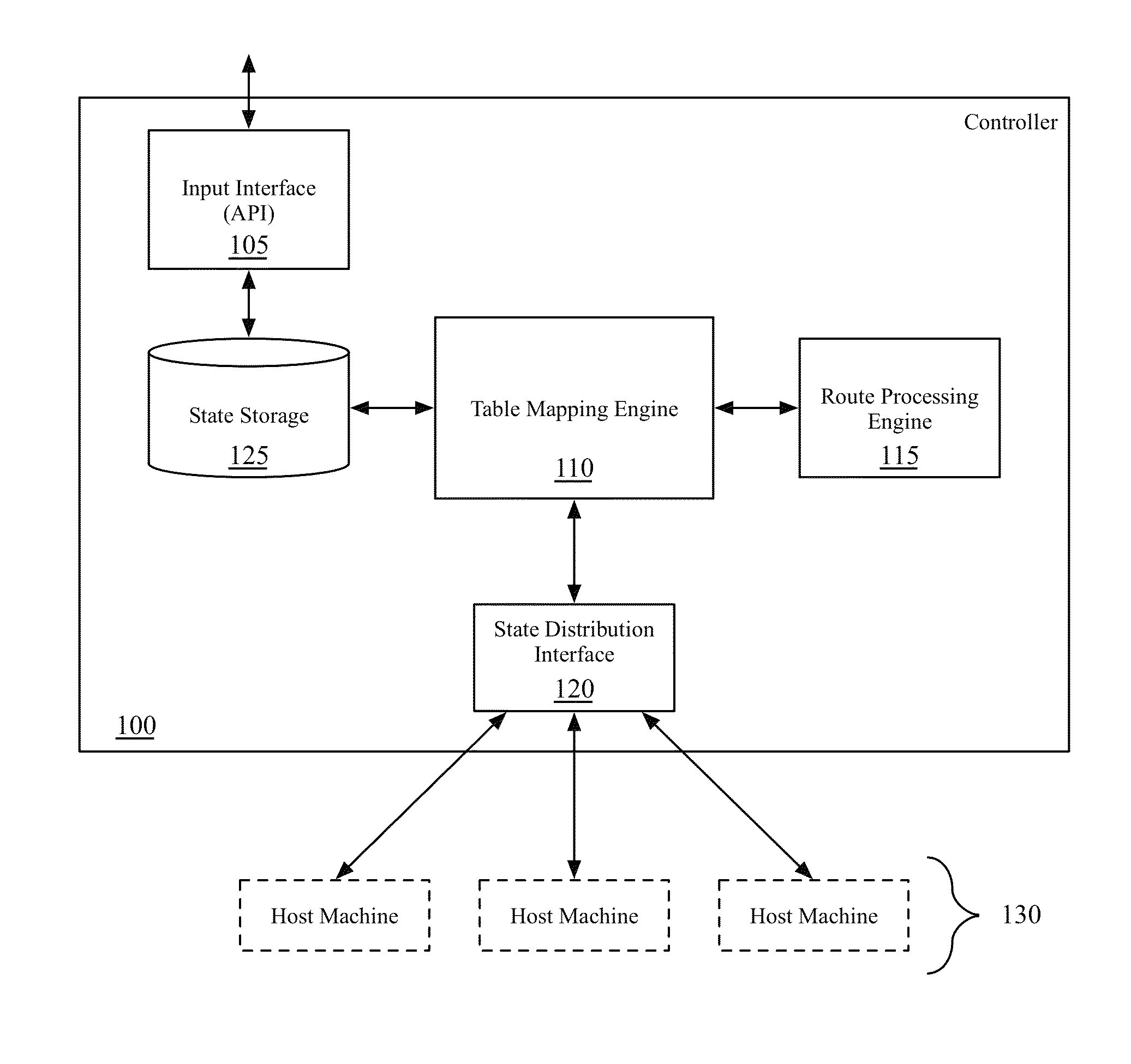
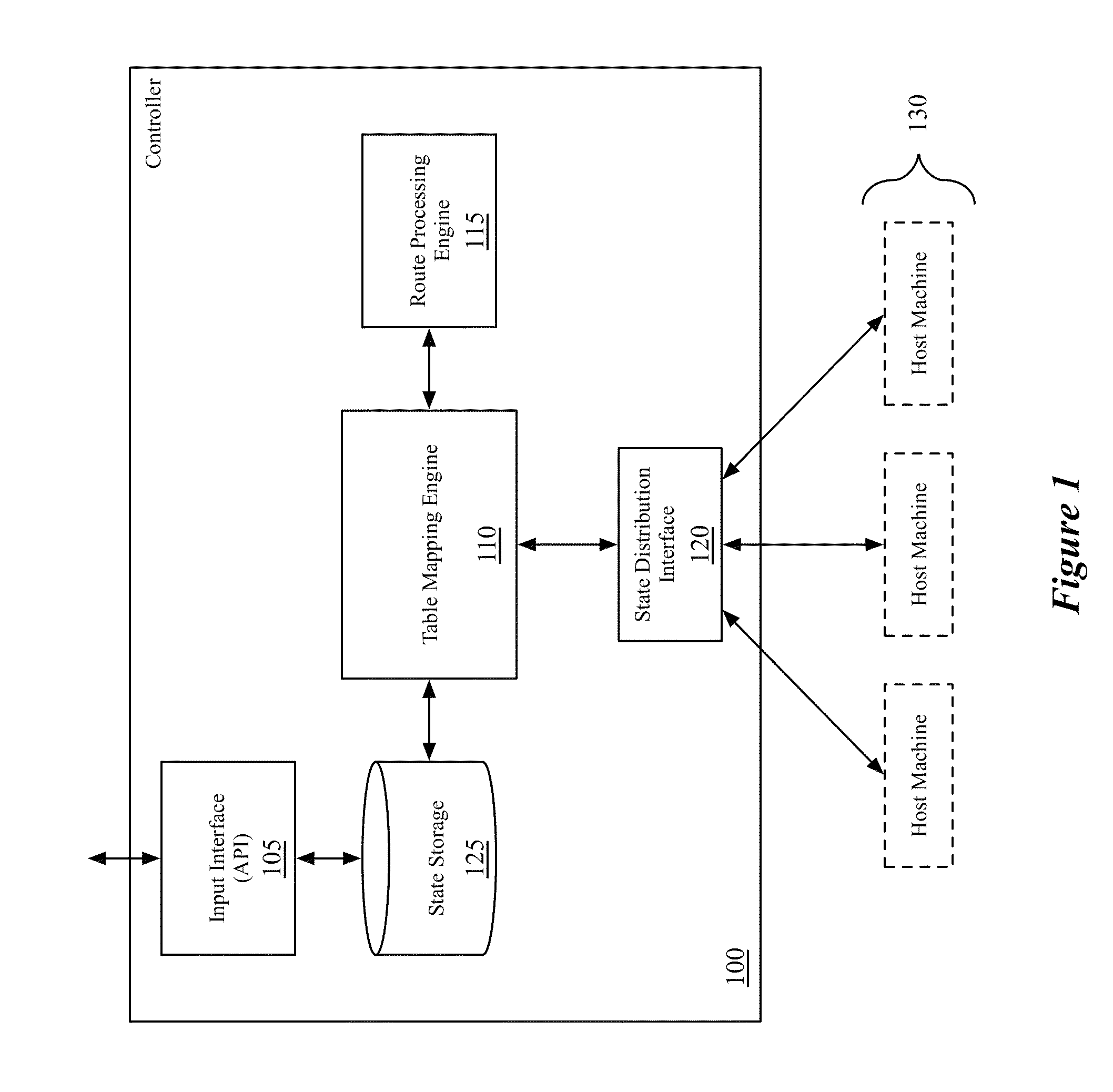
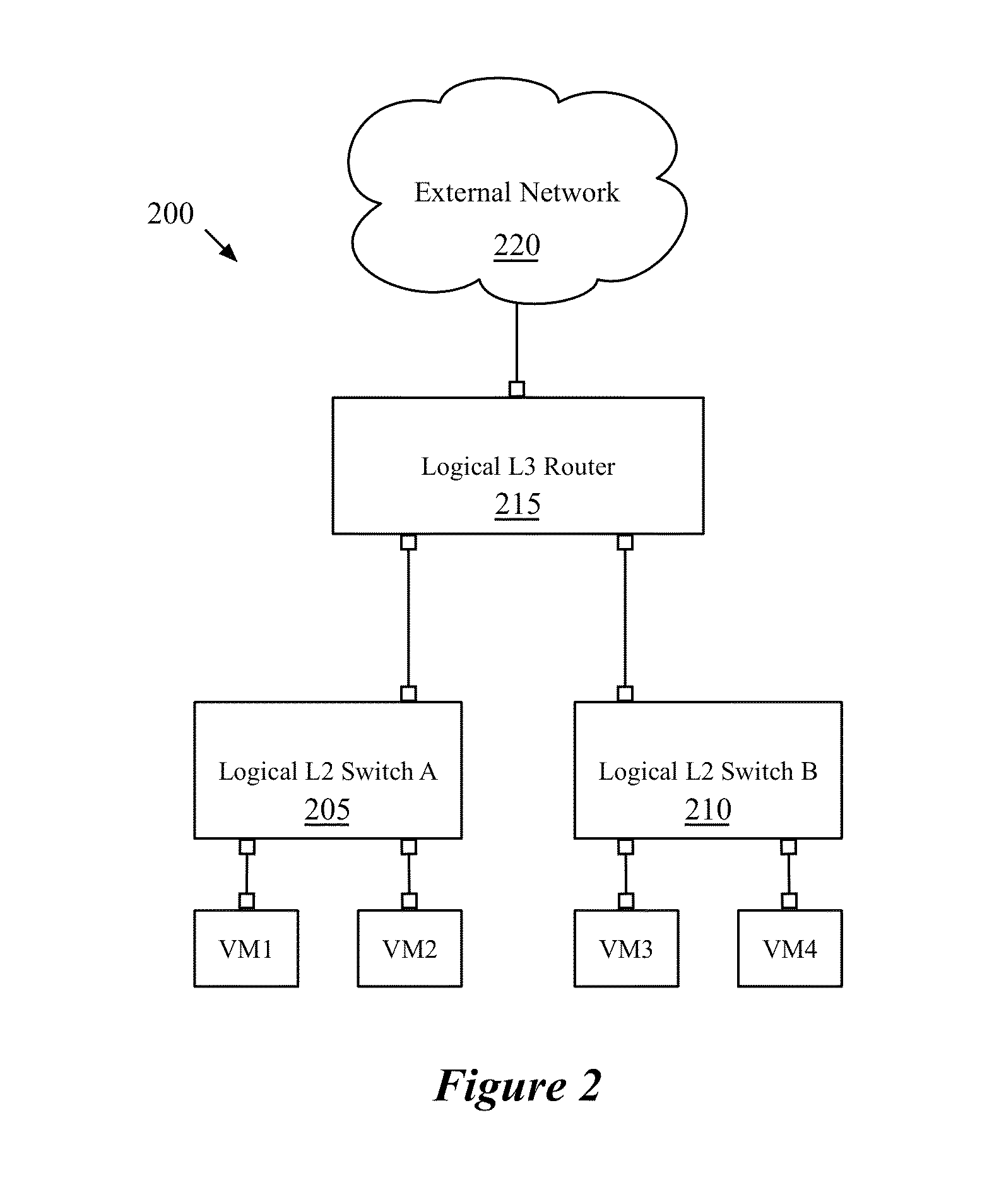
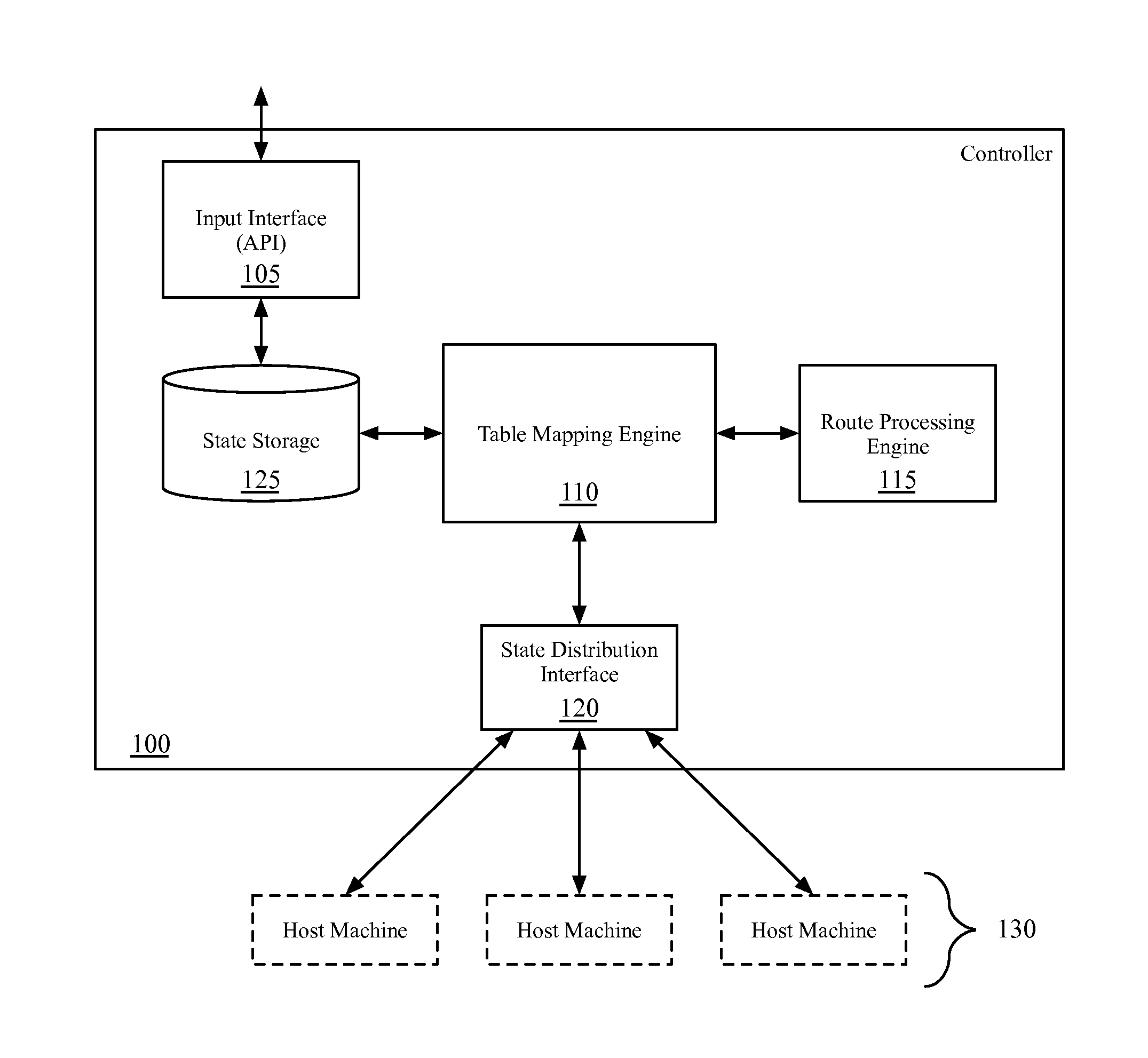
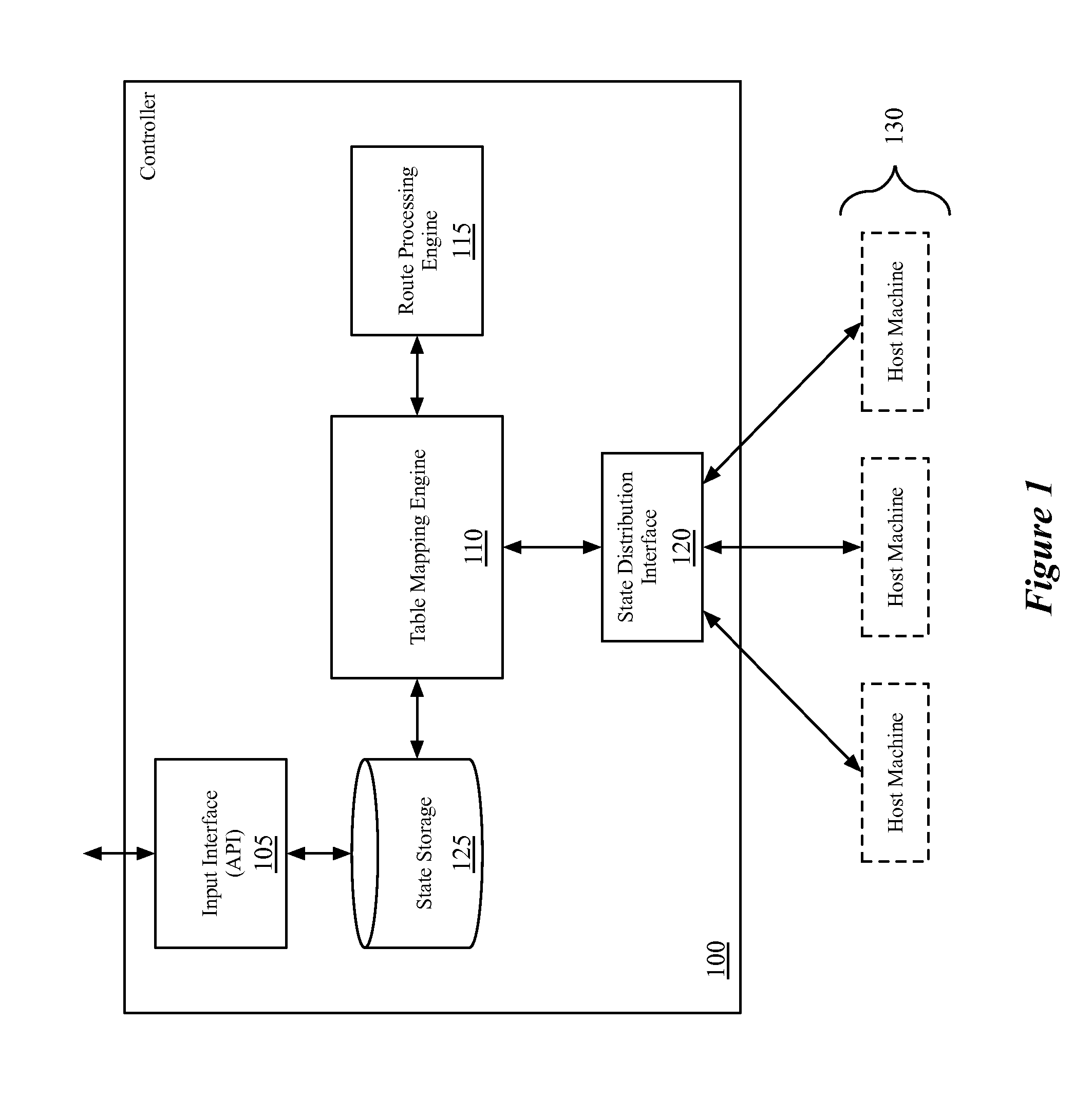
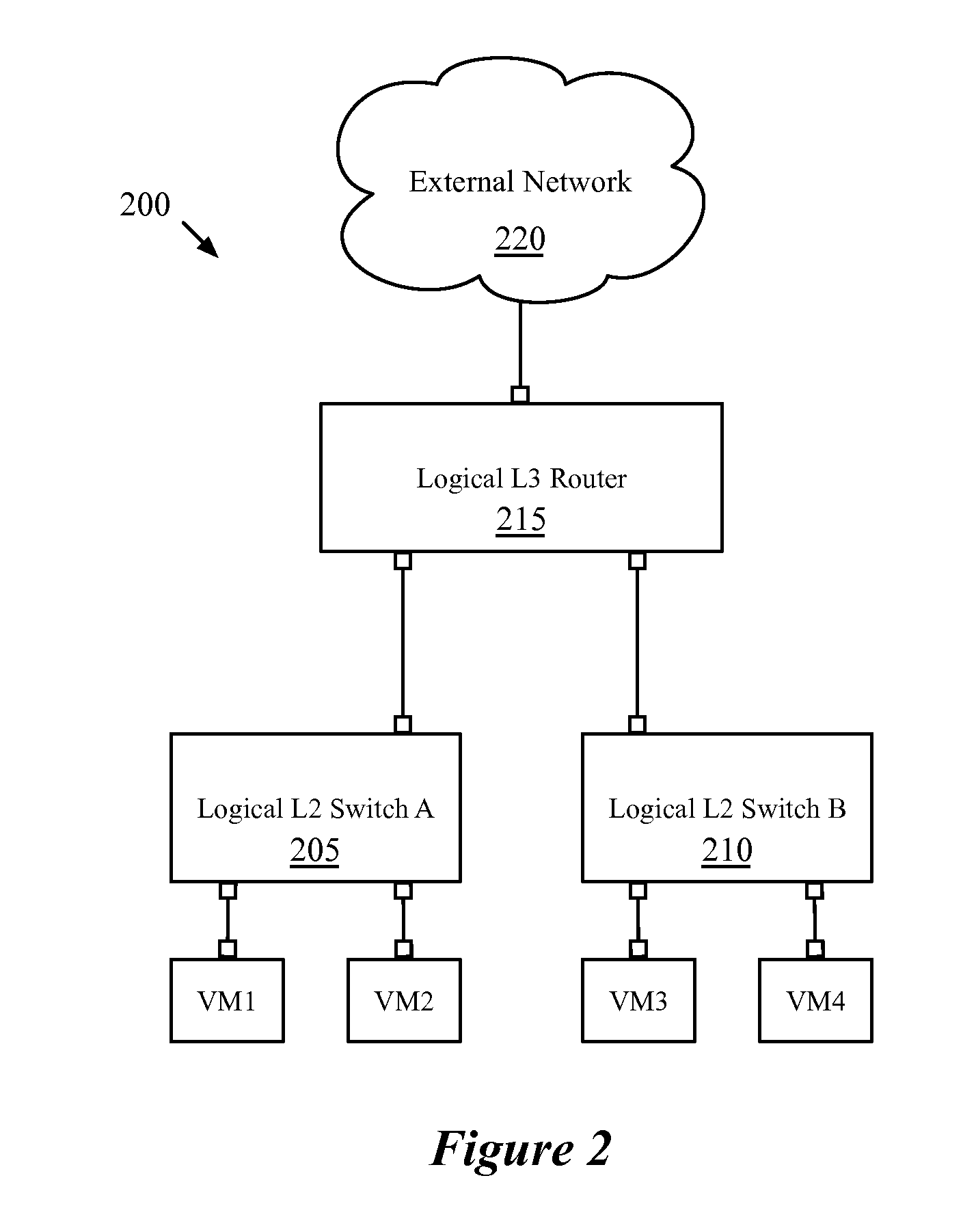
Static routes for logical routers
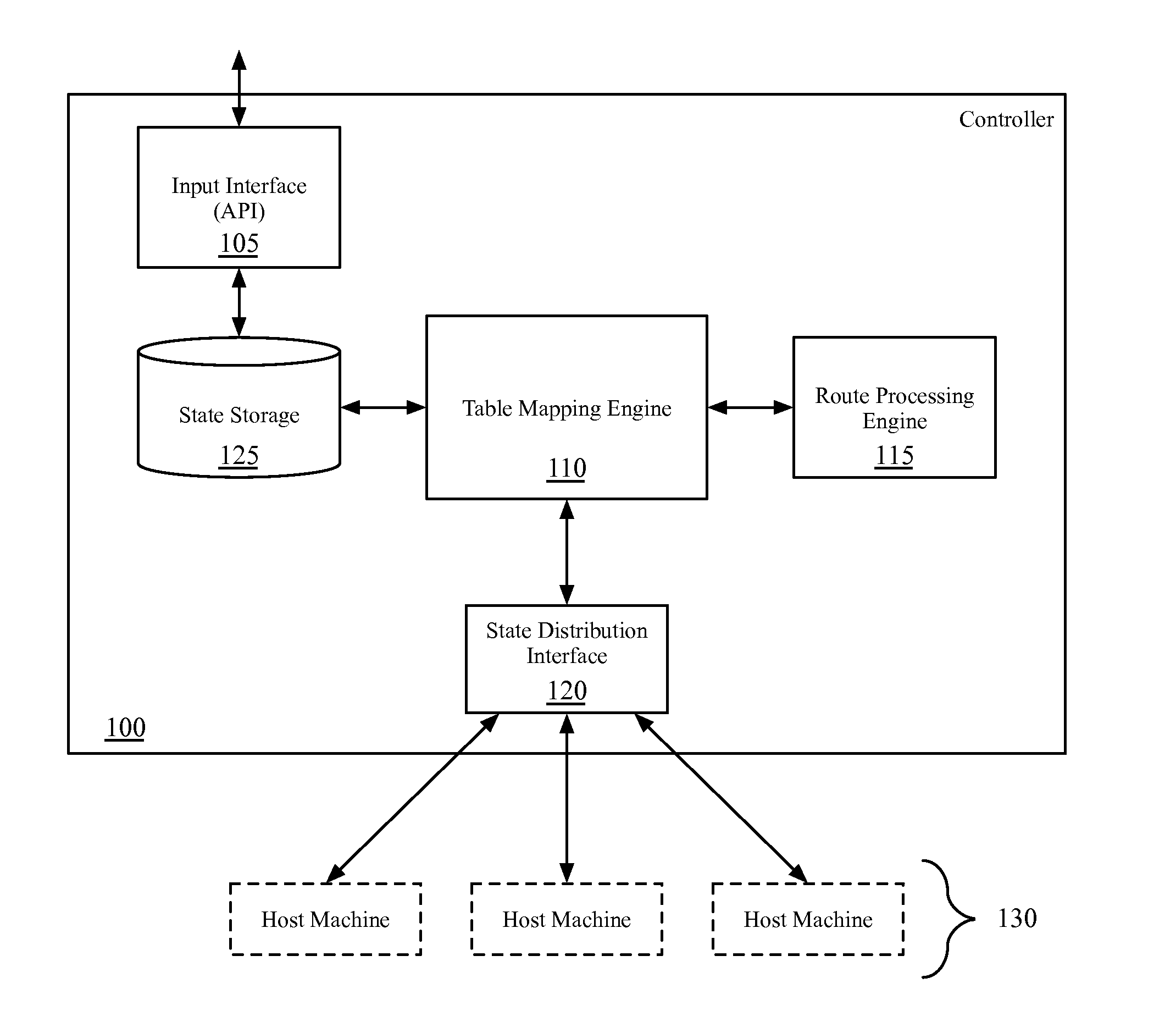
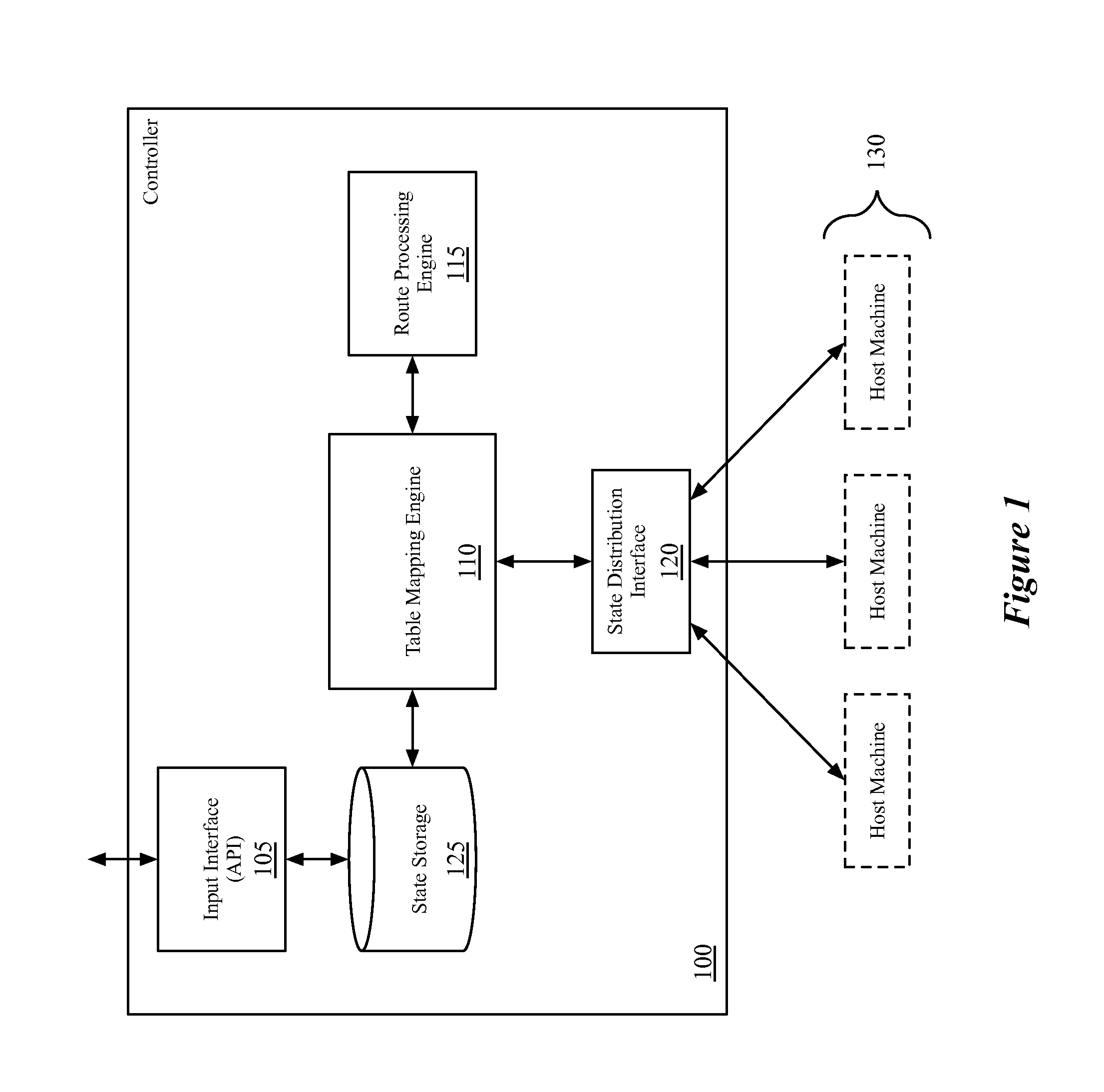
Some embodiments provide a method for a network controller. The method receives configuration data, for a logical router managed by the network controller, that specifies at least one logical port for the logical router. The method automatically generates connected routes for the logical router based on network address ranges specified for the logical ports of the logical router. The method receives a manually input static route for the logical router. The method generates data tuples, for distribution to several managed network elements, based on the connected and static routes for the logical router in order for the several managed network elements to implement the logical router.
Owner:NICIRA
Static routes for logical routers
Some embodiments provide a method for a network controller. The method receives configuration data, for a logical router managed by the network controller, that specifies at least one logical port for the logical router. The method automatically generates connected routes for the logical router based on network address ranges specified for the logical ports of the logical router. The method receives a manually input static route for the logical router. The method generates data tuples, for distribution to several managed network elements, based on the connected and static routes for the logical router in order for the several managed network elements to implement the logical router.
Owner:NICIRA
Label switched traffic routing and signaling in a label switched communication packet network
Label switched paths are installed in a label switched communications packet network. Paths are selected by defining and installing partial routes each having two or more paths such that an end-to-end route across the network can be defined as the concatenation of two partial routes. Signalling to select a path is effected by sending a path message from an end point to a first virtual router, determining a path from the end point to the virtual router, and forwarding an identity of the path to a second virtual router. The second virtual router determines a routing vector across the network, and returns information identifying the routing vector to the first virtual router.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Media gateway device and method for forwarding data frames
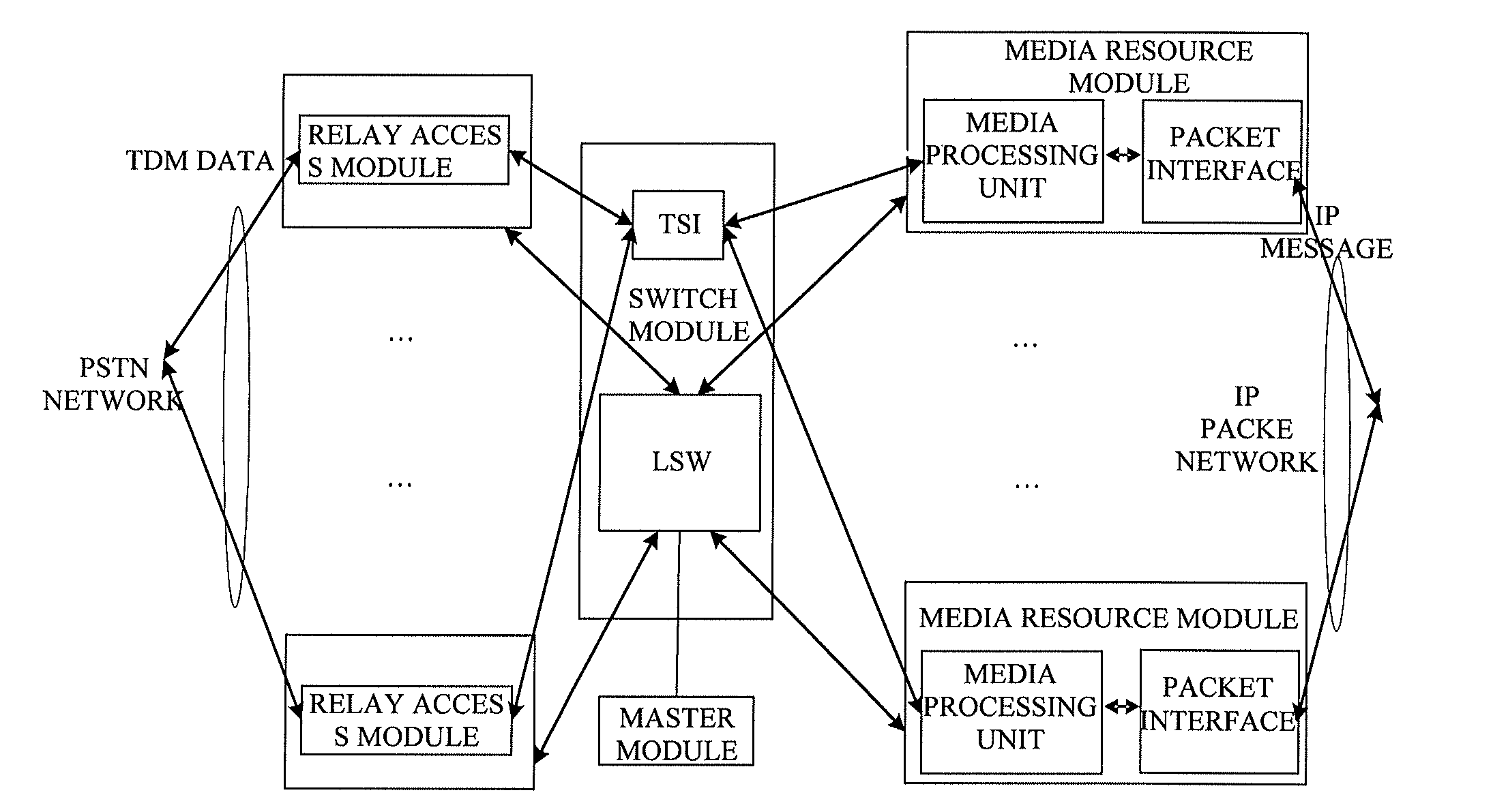
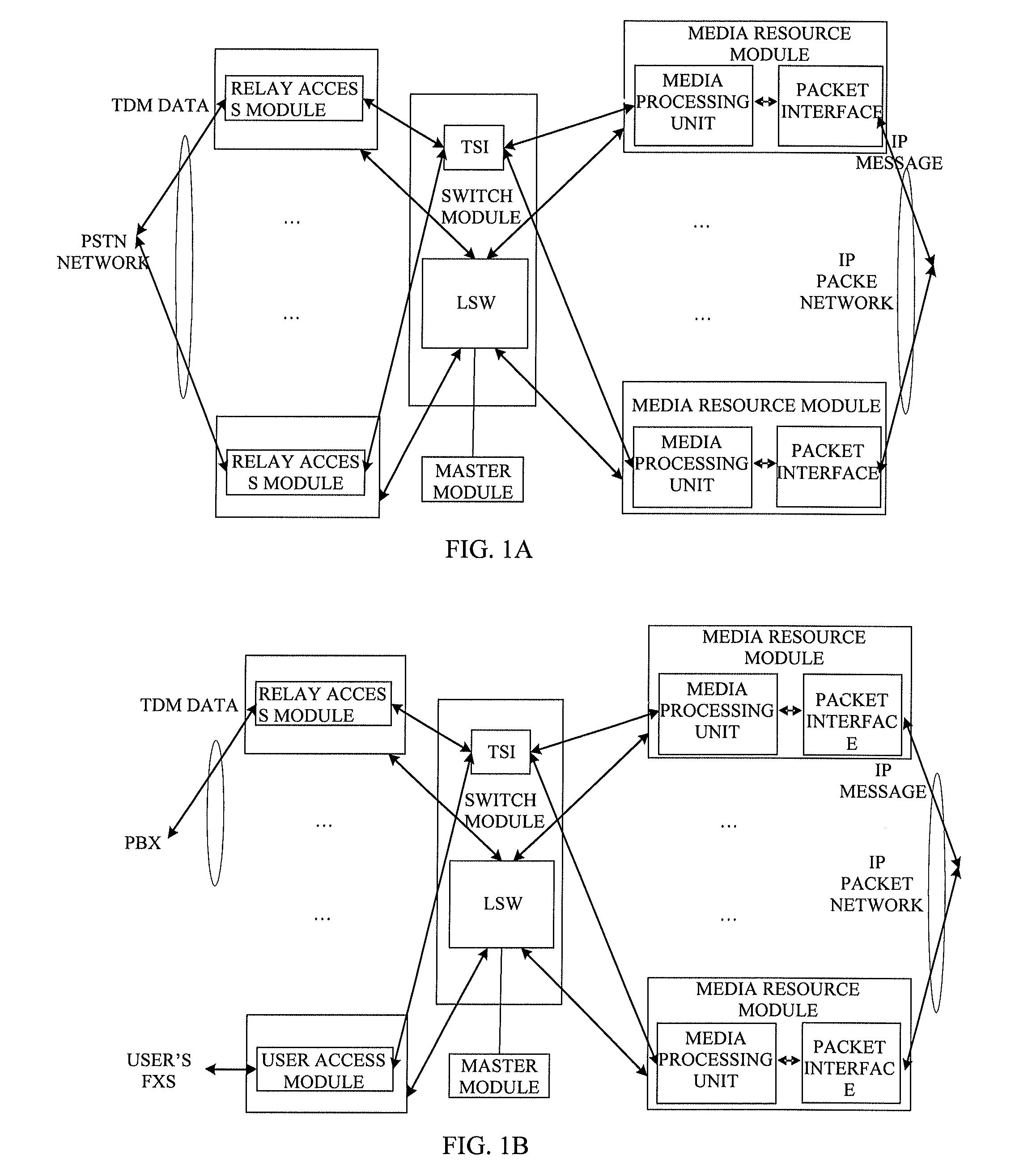
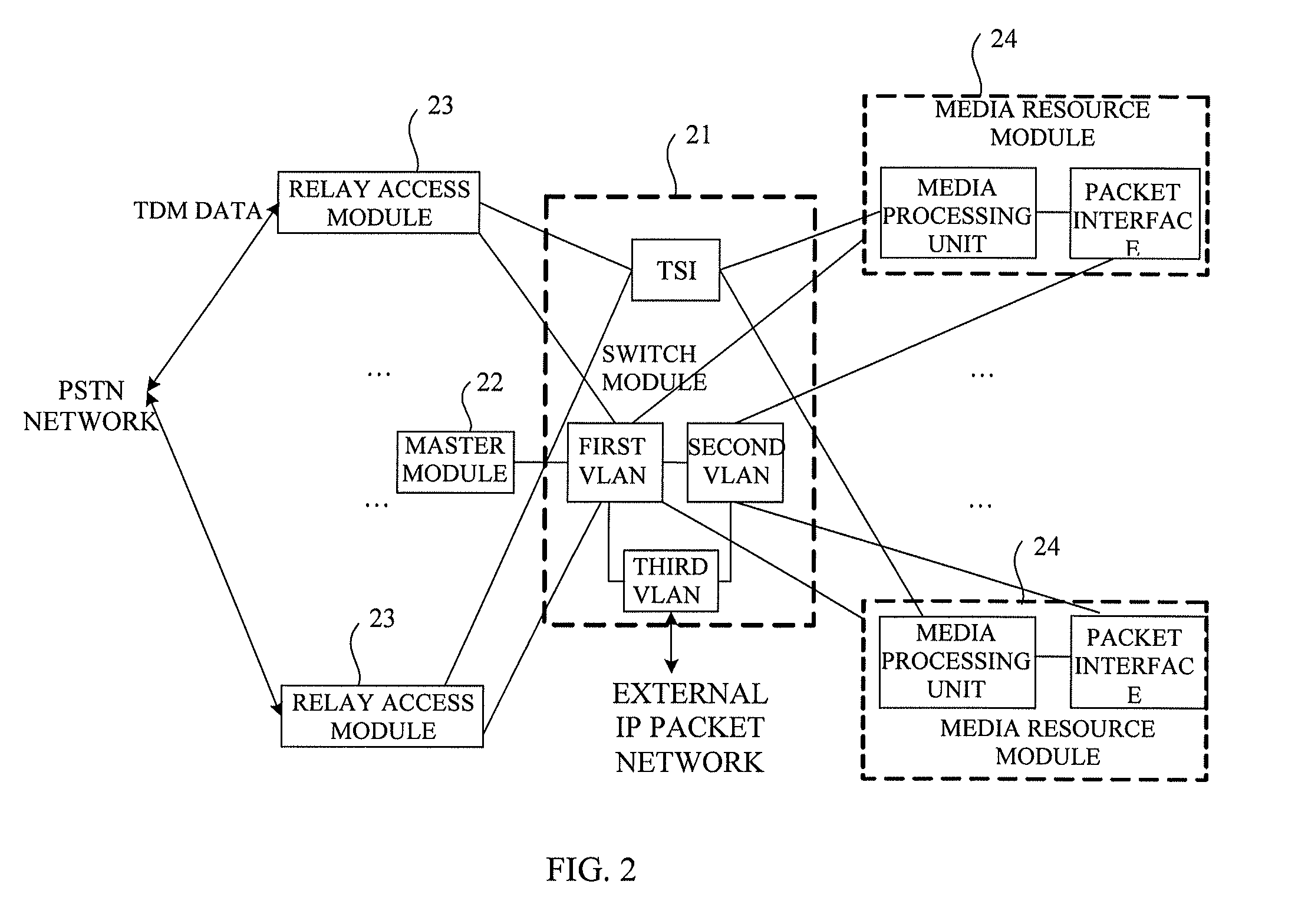
InactiveUS20140010239A1Reduce in quantityImprove securityData switching by path configurationVirtual LANNetsniff-ng
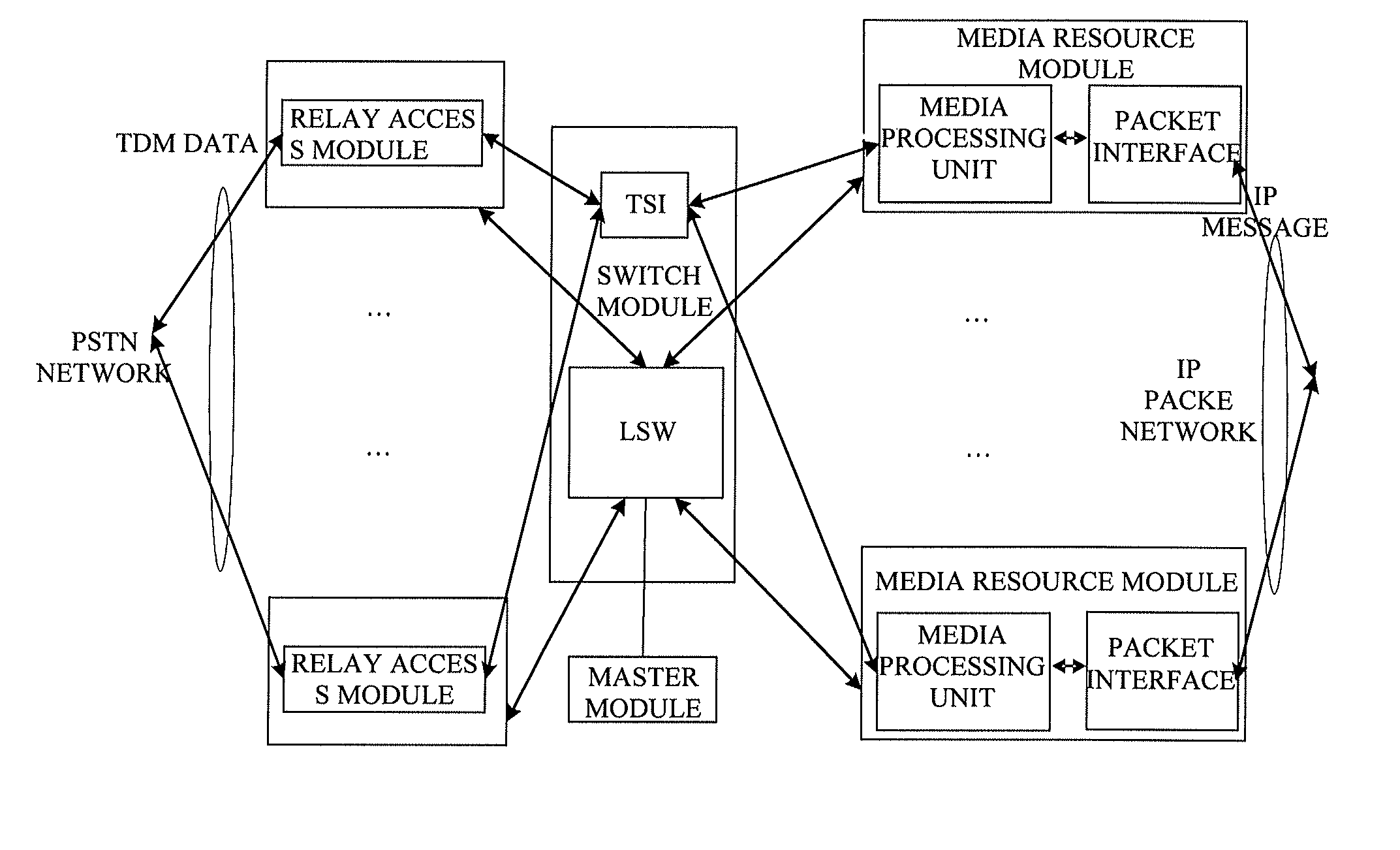
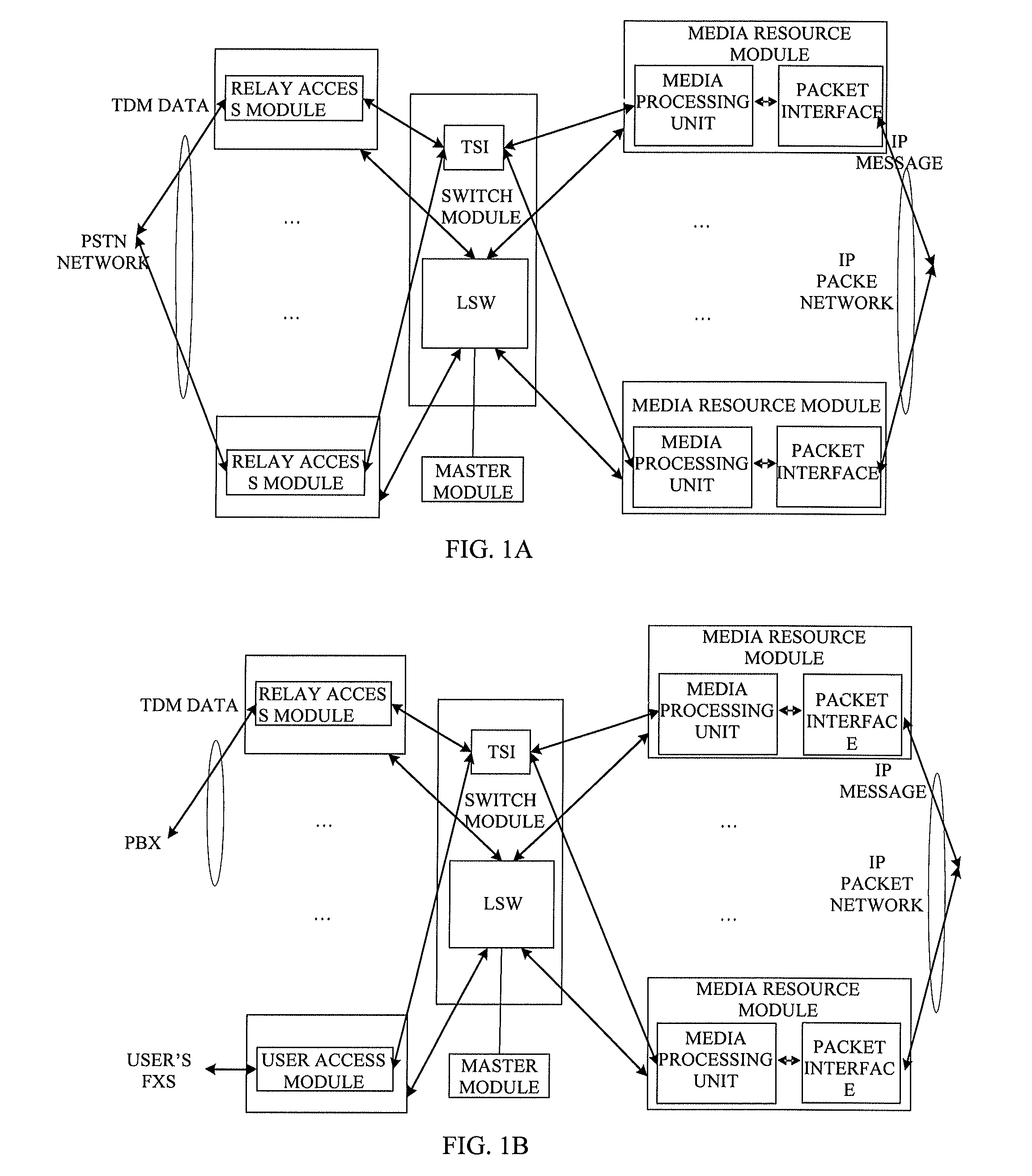
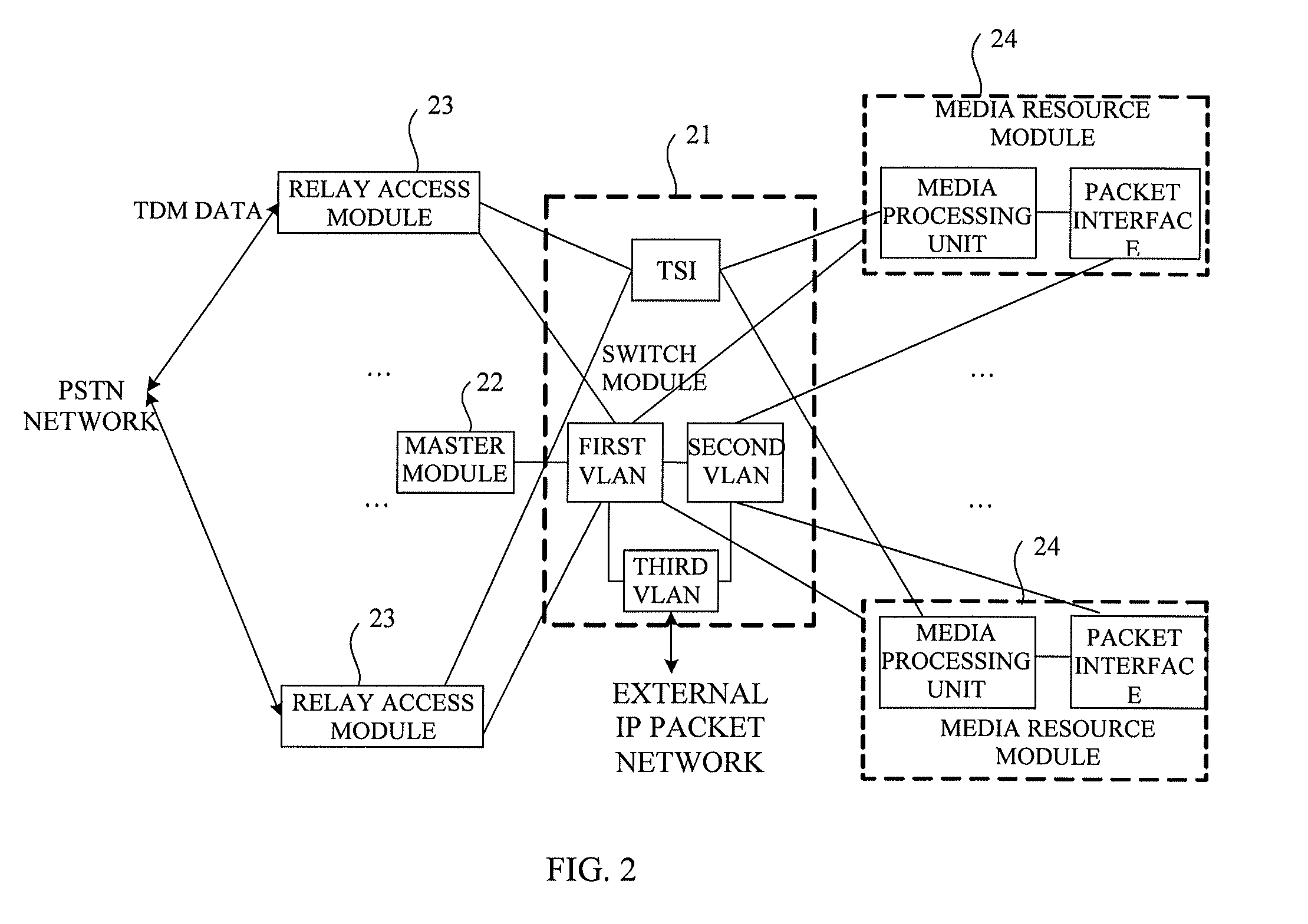
The present invention provides a media gateway device and a method for forwarding data frames. The media gateway device comprises: a master module, a switch module, a relay access module and a media resource module; the switch module comprises three independent Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), i.e., a first VLAN, a second VLAN and a third VLAN, respectively; the media resource module is connected to the switch module through the second VLAN, and the switch module is connected to an external Internet Protocol (IP) packet network through the third VLAN; the media gateway device further comprises a network layer static routing table. By using the media gateway device and the method for forwarding data frames according to the present invention, the number of the external interfaces of the media gateway device can be reduced, and the interface of the switch module can be managed by the VLAN.
Owner:APEX NET LLC
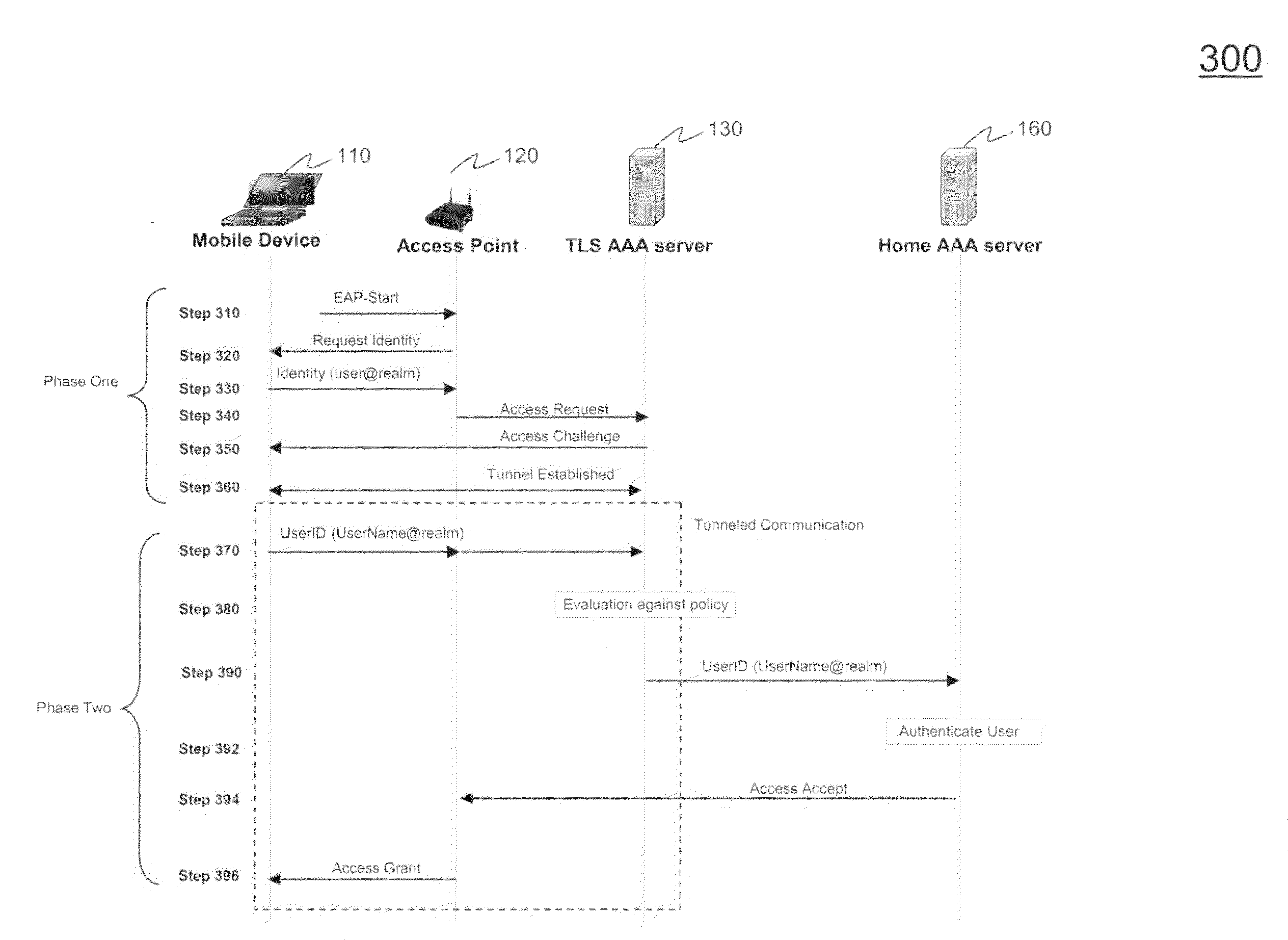
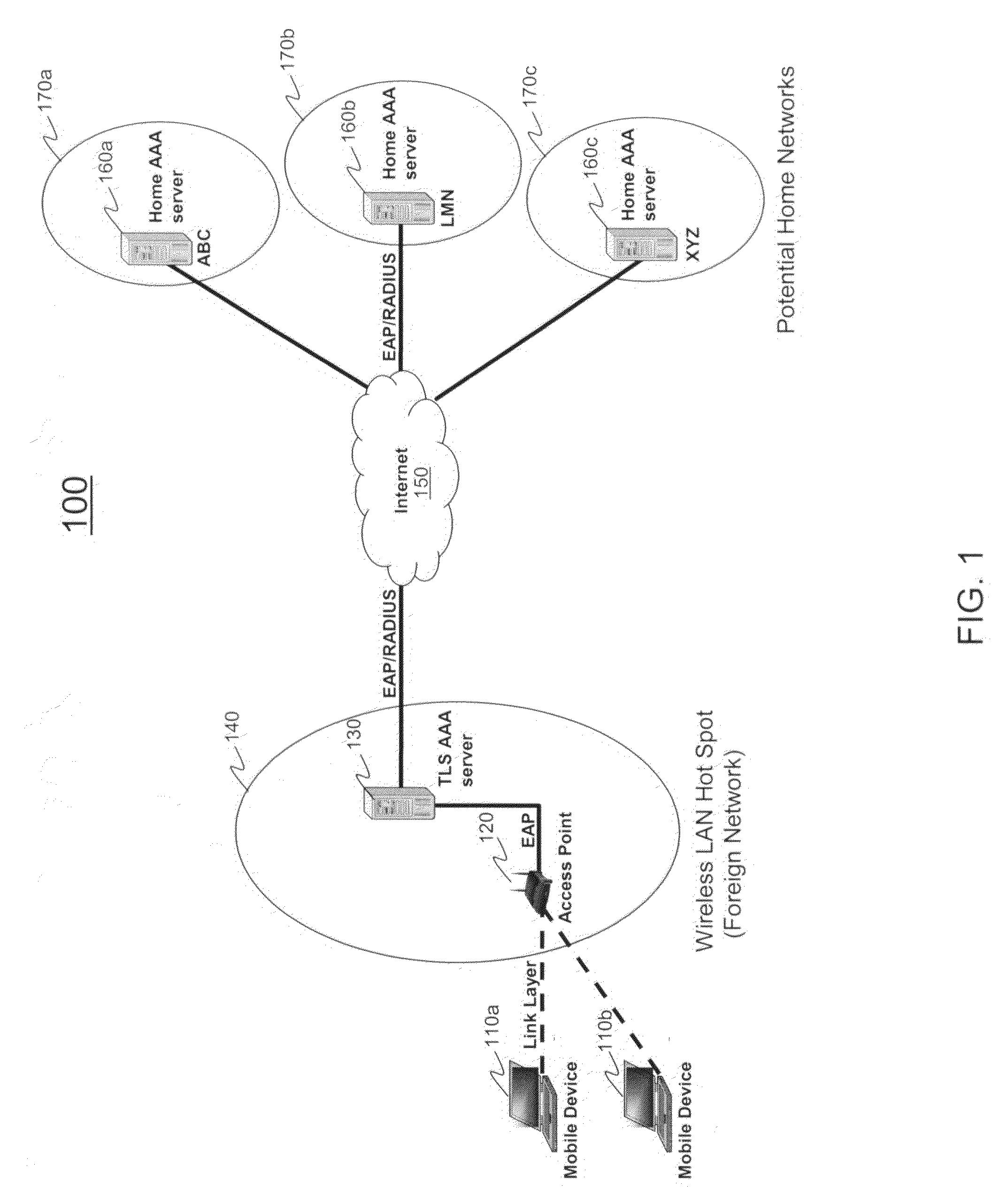
Methods for authenticating and authorizing a mobile device using tunneled extensible authentication protocol
ActiveUS20090119742A1Simplifies upfront EAPHighly flexible routingDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSecure communicationUser authentication
Methods for authenticating and authorizing a mobile device using tunneled extensible authentication protocol are provided. The methods include evaluating an inner user identifier against a policy engine to determine a home AAA server to route an access request for inner user authentication. Instead of having a static route configured based on an outer identifier / roaming identity, the policy engine can have multiple rules and actions for routing the request. The evaluation can be based on the conditions of the inner user identifier and or other AAA attributes received in the request. The request is transmitted within a secure communication tunnel. There are several embodiments of evaluating an inner user identifier against a policy engine.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
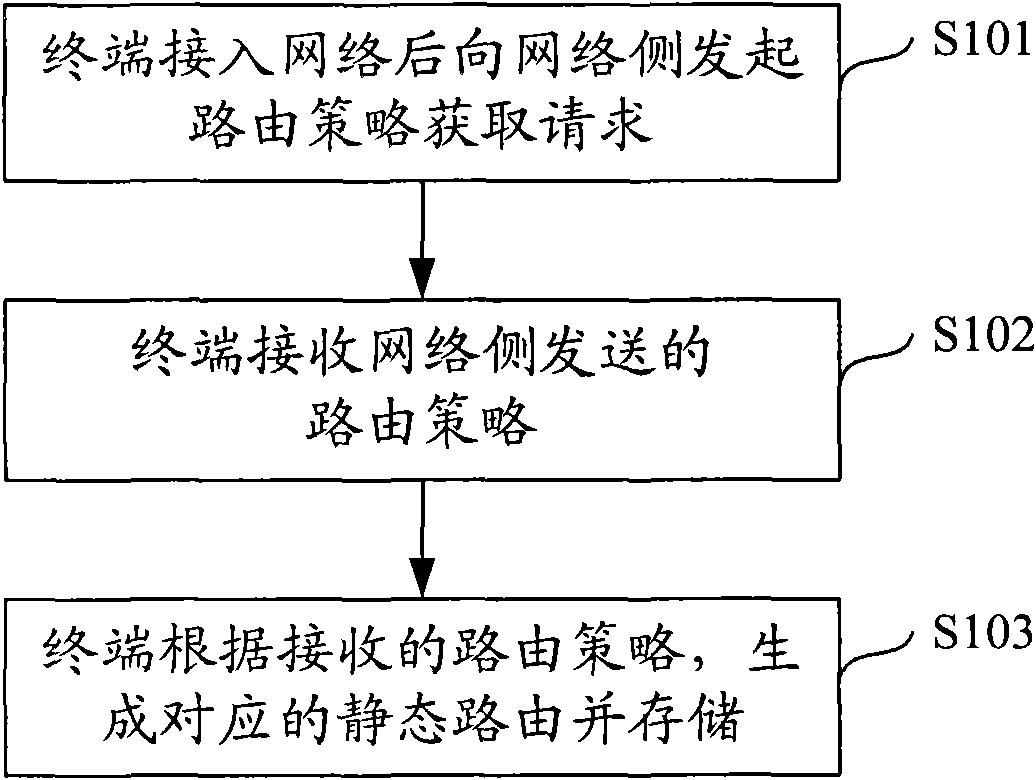
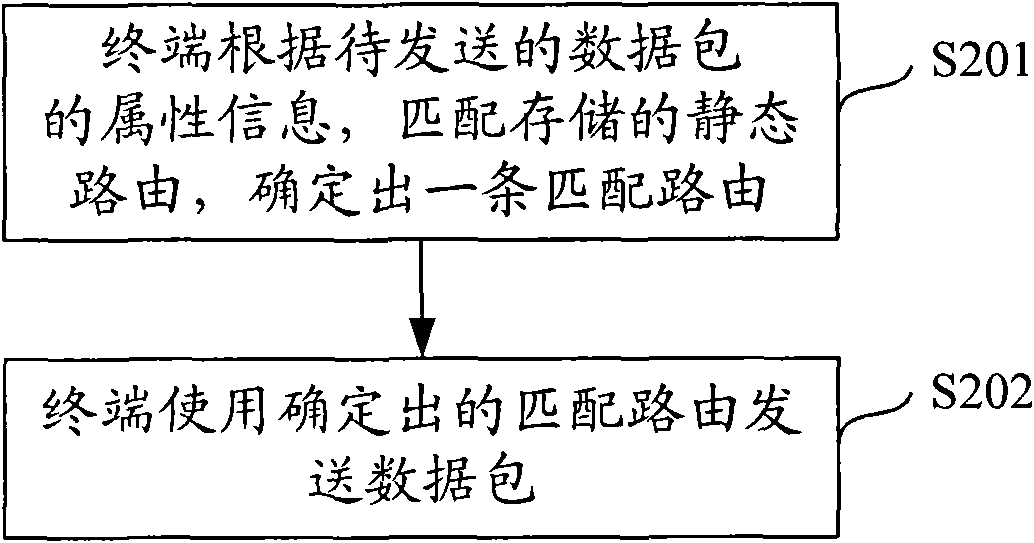
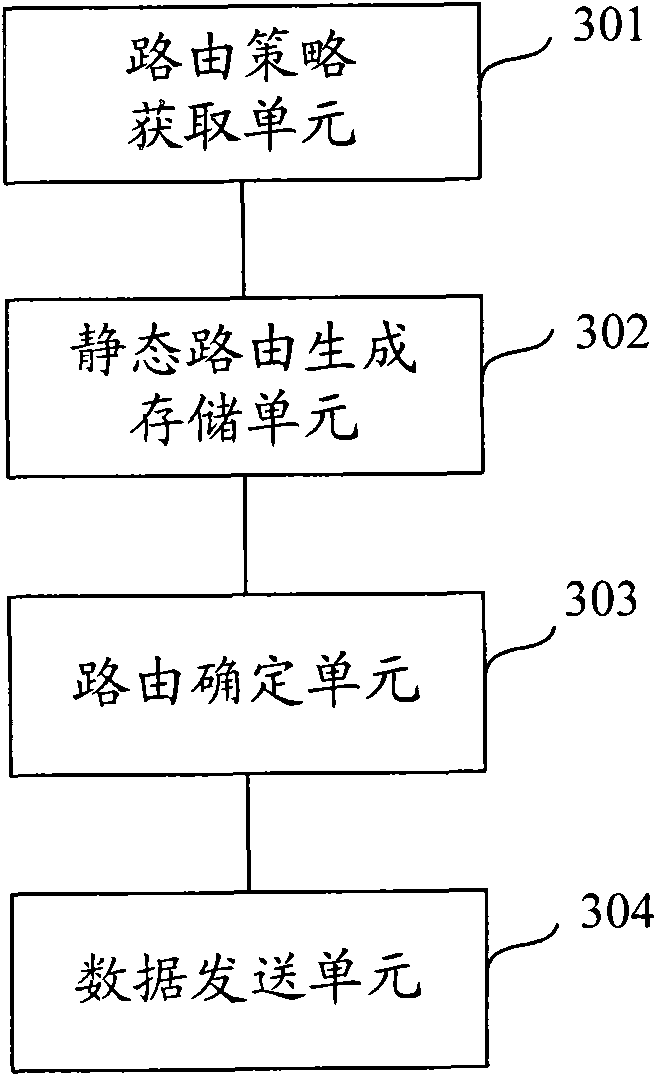
Static routing generation method, method and device for implementing terminal routing
InactiveCN101674221ASave computing resourcesTo achieve the purpose of multiple connectionsData switching networksStatic routingNetwork element
The invention discloses a static routing generation method, a method and a device for implementing terminal routing. The method for implementing the terminal routing comprises the following steps that: a network element device on a network side or a DHCP server transmits a routing policy to the terminal, and the terminal generates and stores a corresponding static routing according to the routingpolicy transmitted by the network element device or the DHCP server; and the terminal matches the stored static routing according to the attribute information about data packets to be transmitted to determine the matched routing and utilizes the determined matched routing to transmit the data packets. The scheme of the invention does not need a user to manually configure the static routing by acquiring various routing configuration parameters, can ensure that a plurality of networks are connected and the data packets pass through so as to implement the multi-connection of the terminal.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
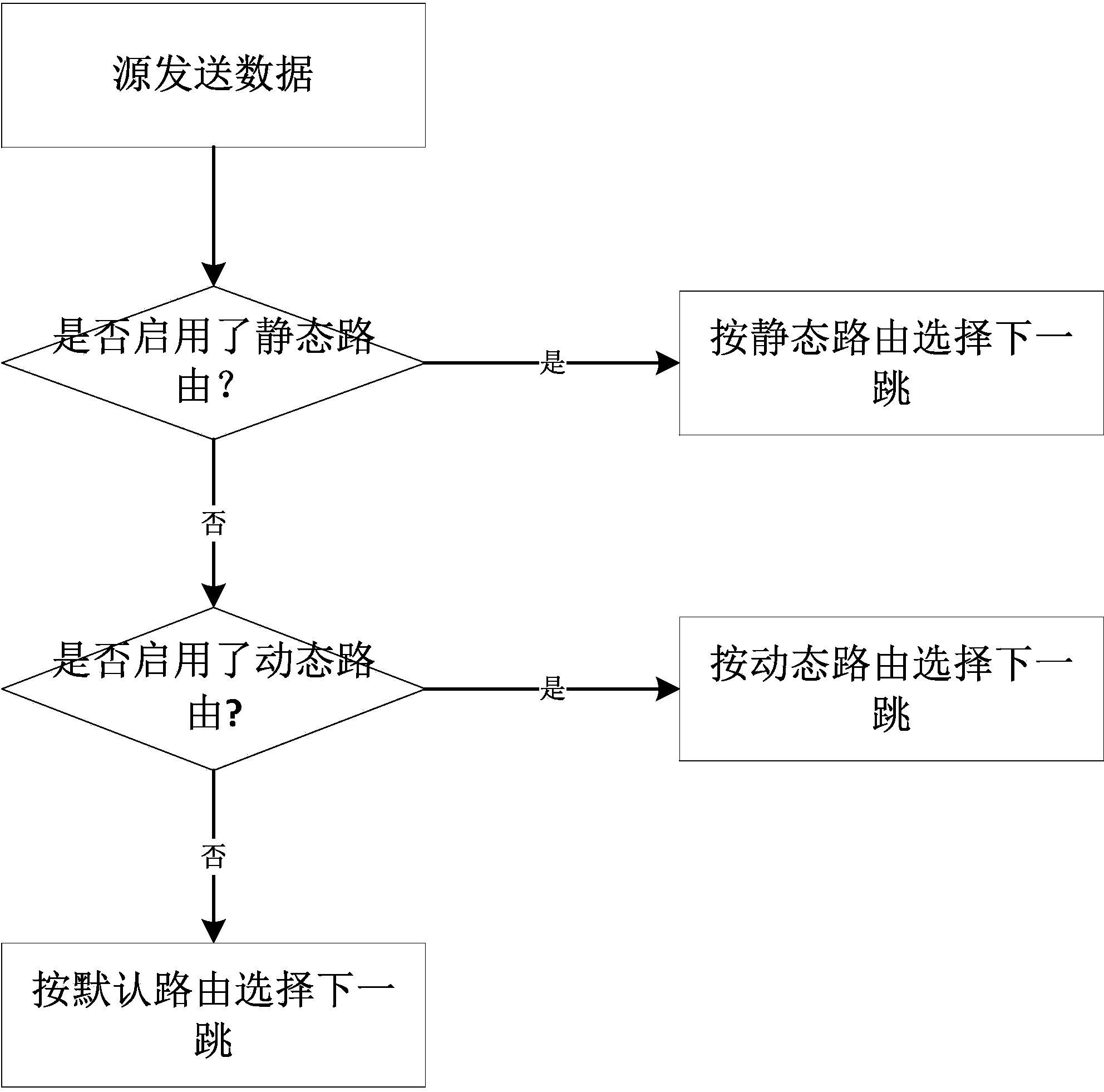
Data forwarding method based on different priorities in software-defined network
ActiveCN103825823AFlexible controlProminent permissionsData switching networksUser needsTraffic capacity
The invention discloses a data forwarding method based on different priorities in a software-defined network. Through the method, a routing flow table is divided into a static route, a dynamic route and a default route which respectively represent forwarding routes with different priorities. When a route is decided, an exchanger is used for detecting the route according to the priorities from the highest to the lowest and selecting the route with the highest priority to forward data. According to the route policy, the forwarding route can be selected by the data forwarding method according to real-time flow condition and user demand of the network, so that the data transmission efficiency is increased and the network jam is effectively relieved; therefore, the data forwarding method disclosed by the invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU INST FOR ADVANCED STUDY USTC
Communication device for selecting route of packet
InactiveUS7075932B2Securing reachabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsAdaptive routingCommunication device
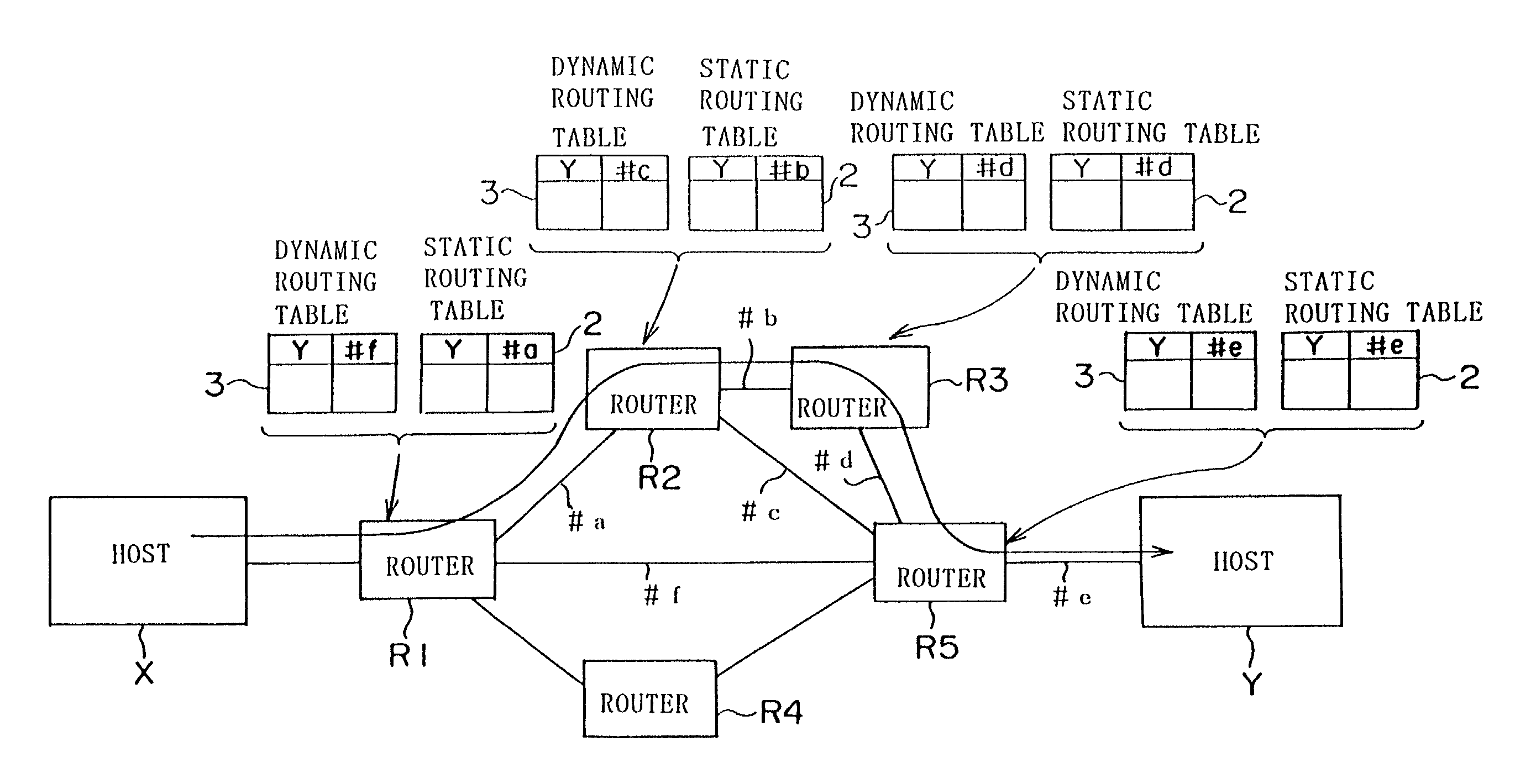
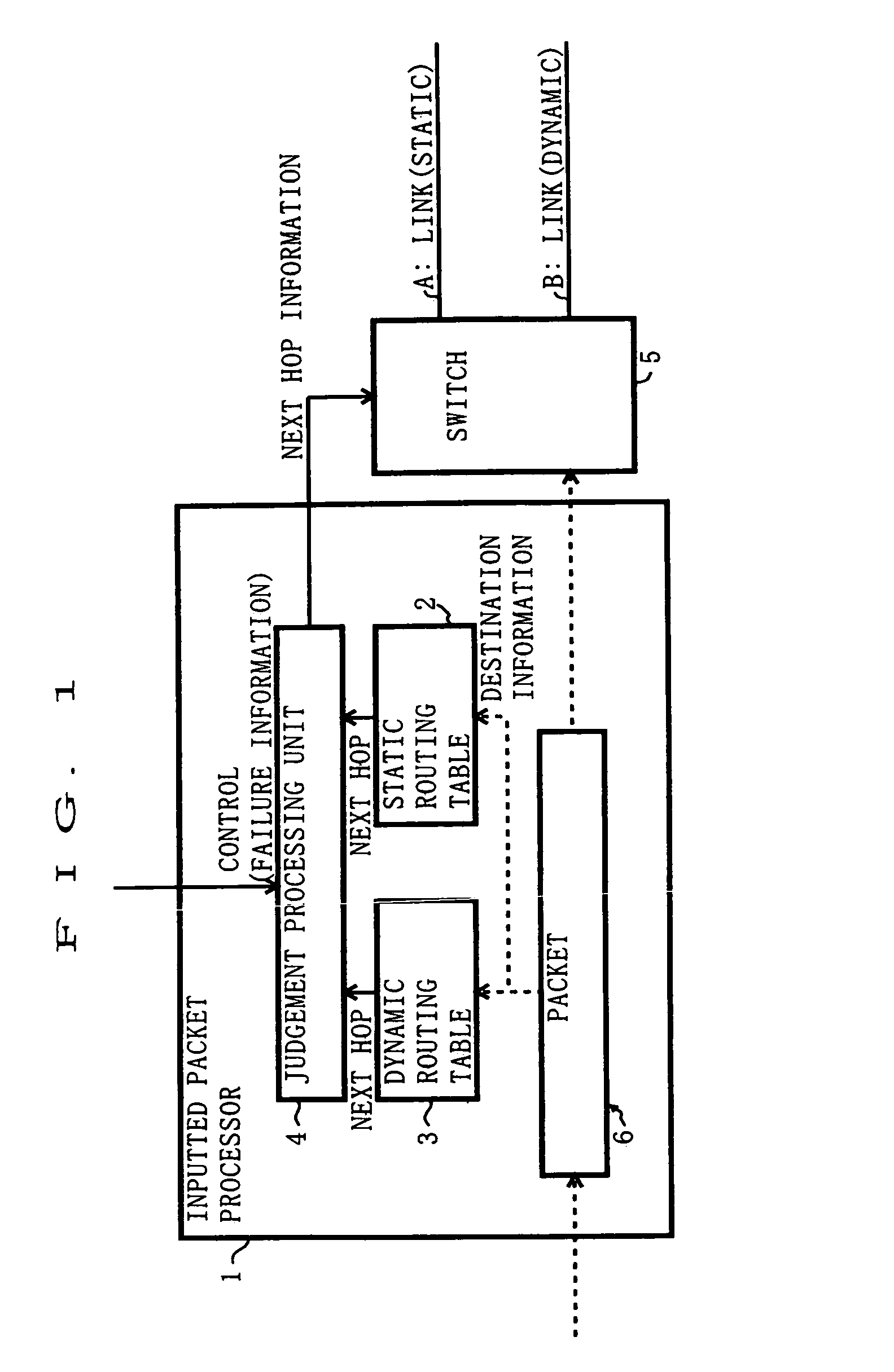
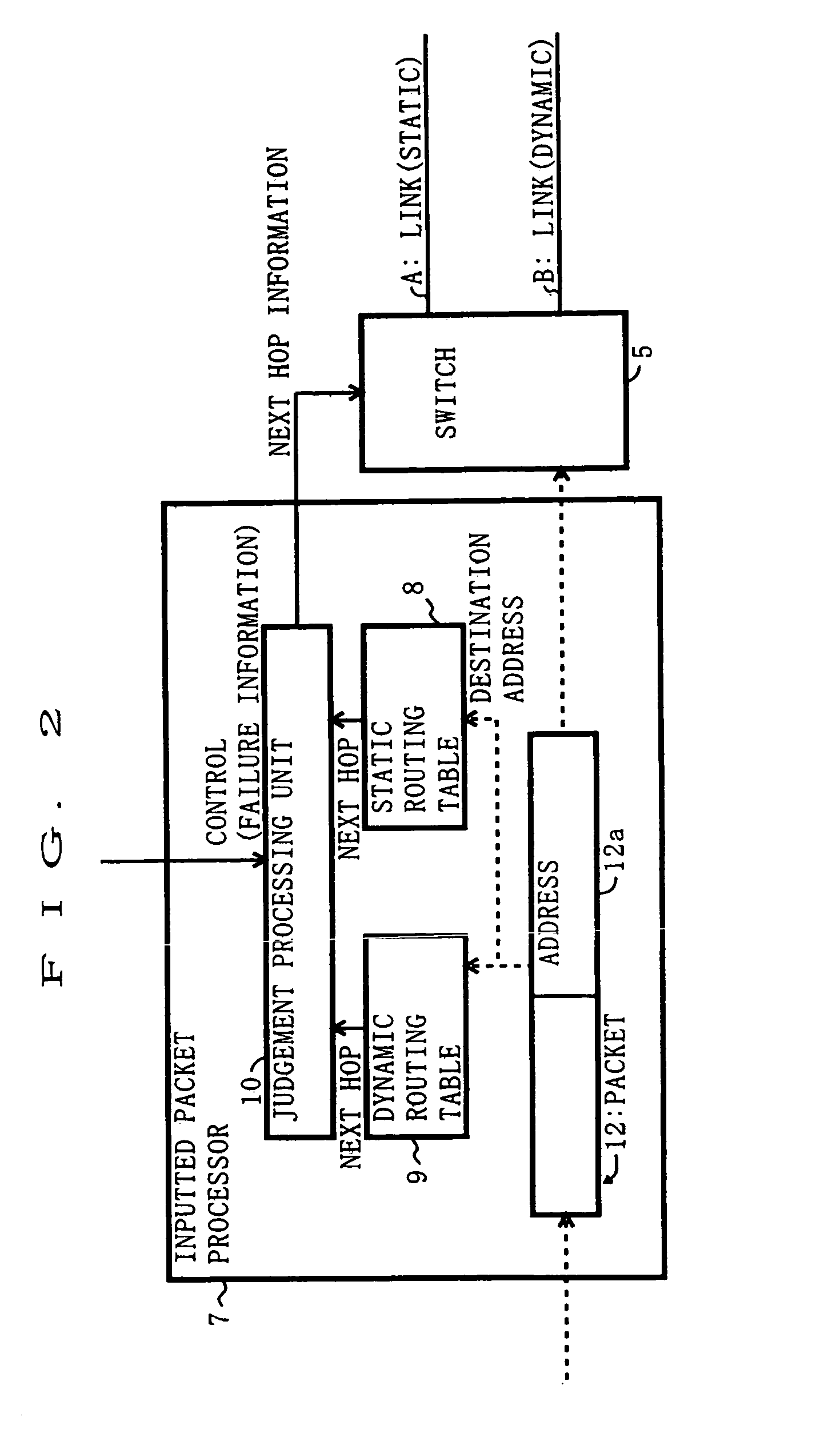
A communication device includes a static routing table, a dynamic routing table and a judging unit. The judging unit, if no failure occur in a static route, selects the static route based on routing information given from the static routing table as a route to which a packet should be forwarded. The judging unit, if the failure occurs in the static route, selects a dynamic route based on routing information given from the dynamic routing table as a route to which the packet should be forwarded.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Satellite internet communication system and method
InactiveUS20030204617A1Inexpensive and scalable solutionIncrease capacityMultiple digital computer combinationsRadio transmissionInternet communicationTTEthernet
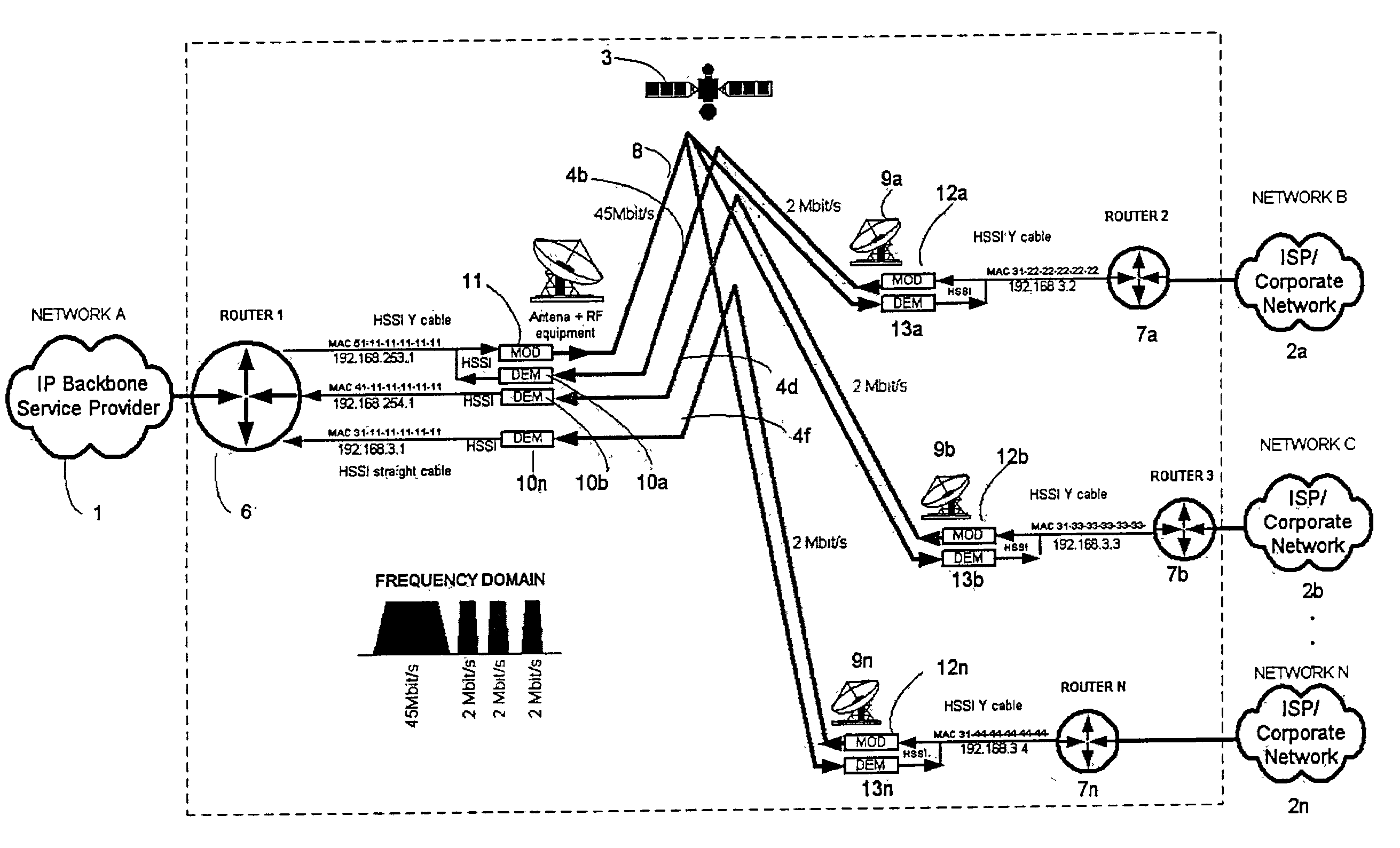
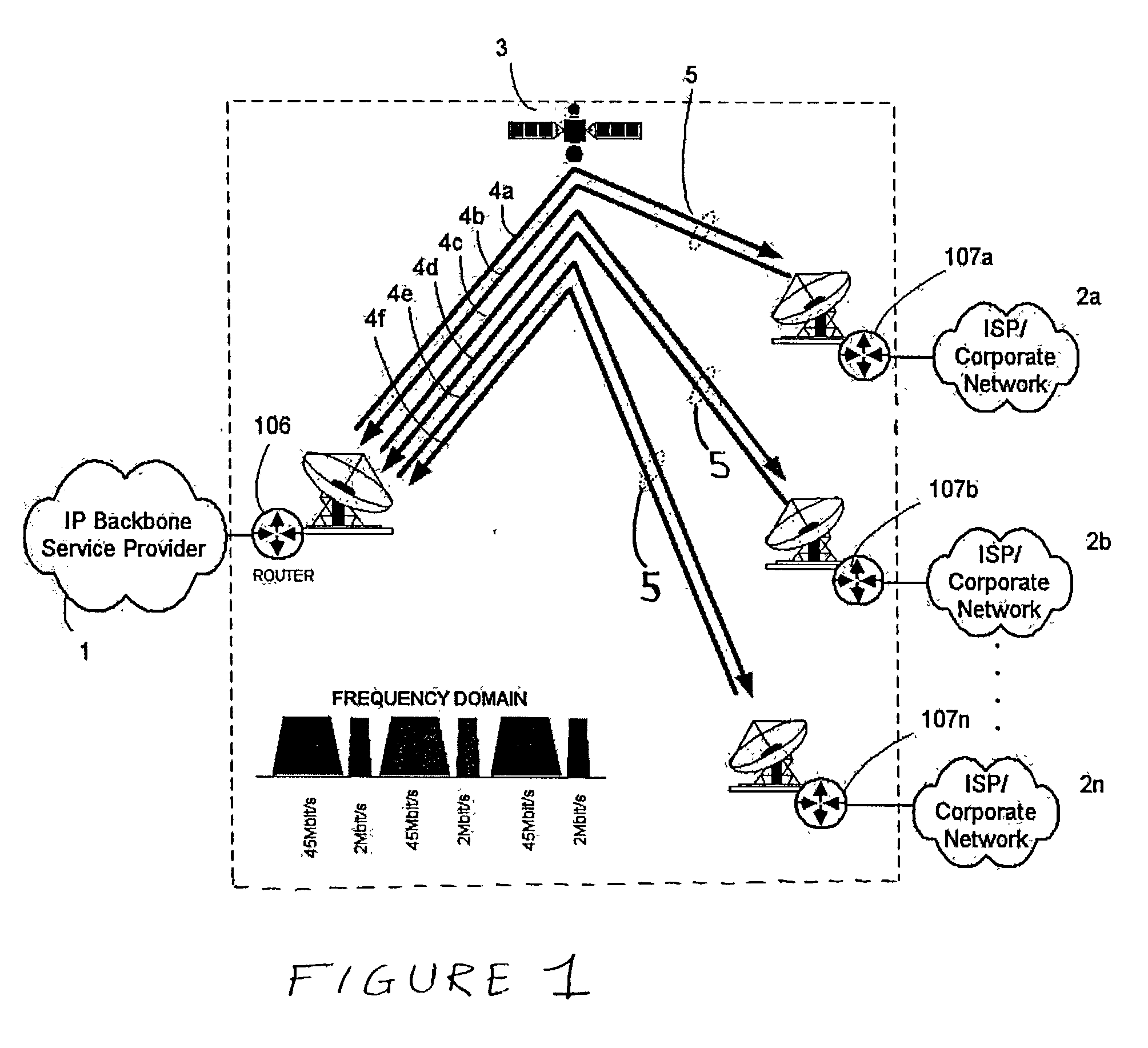
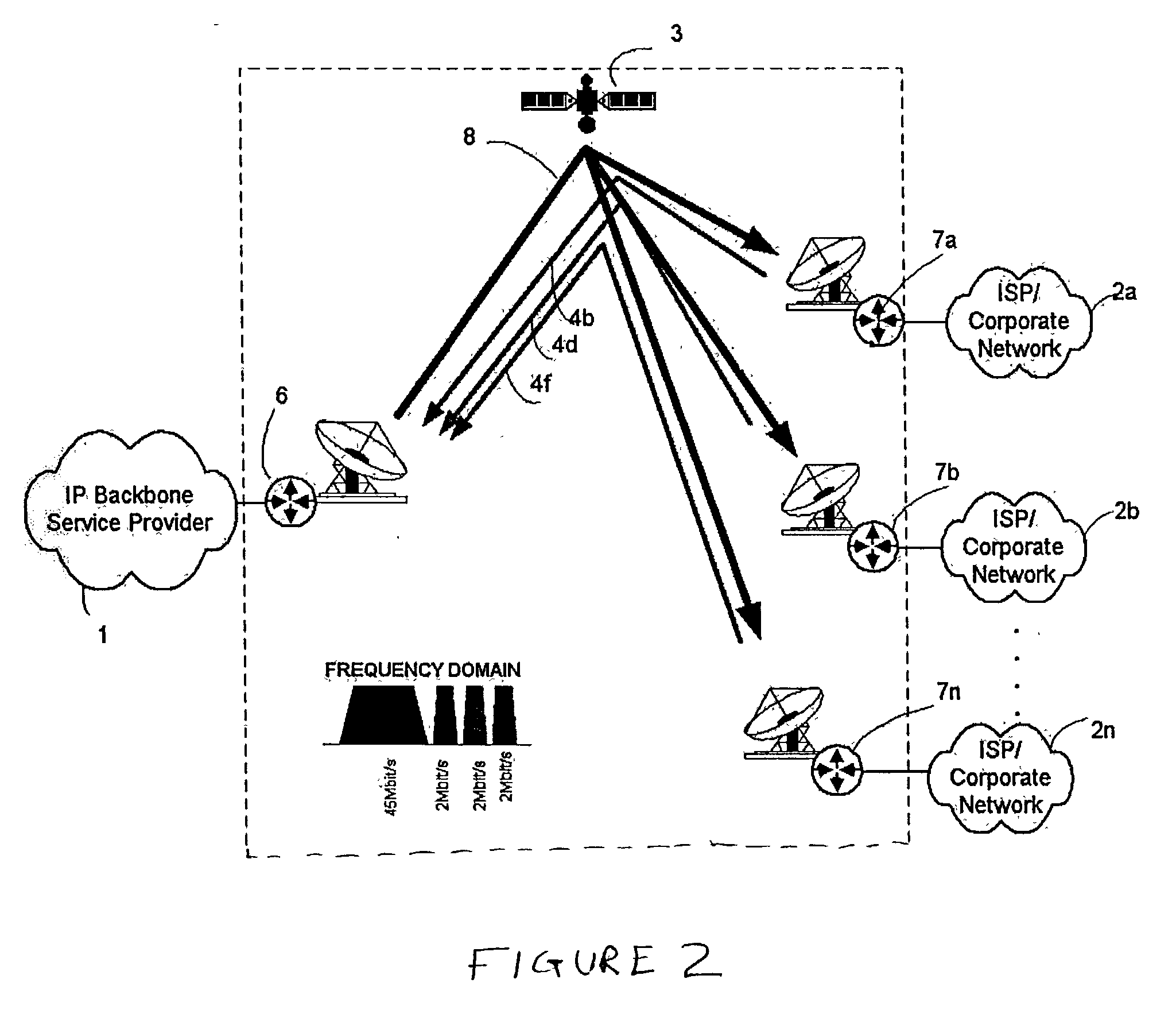
A method and system of communication between an IP backbone Internet Service Provider (ISP) and remote Internet service providers via a shared channel on a satellite is provided. At a first router coupled to the IP backbone ISP, a static route for an IP packet of the IP backbone ISP is determined based on a media access control (MAC) address of a destination router of the IP packet. The IP packet is encapsulated and transported in a frame having the MAC address of the destination router based on the static route. Next, the frame / IP packet is received in a second router coupled to the remote ISP, which either drops the IP packet prior to reaching the remote ISP, or transports the IP packet to a final destination in the remote ISP, based on the MAC address of the IP packet destination and a MAC address of the second router.
Owner:INTELSAT
Method of exchanging information between two networks operating under different routing protocols
InactiveUS20100014537A1Reduce workloadSmall loadData switching by path configurationRouting tableAdaptive routing
A method of exchanging information between a first network implementing a routing protocol using static routing tables and a second network implementing a routing protocol using dynamic routing tables and including stages of exchanging identification messages and of exchanging routing table update messages, the method comprising the steps of: a first routing element associated with the first network issuing to a second routing element associated with the second network identification messages containing identifiers of network elements to which the first routing element knows it is connected either directly or indirectly, and in the second routing element updating the routing table from the identification messages coming from the first routing element.
Owner:SAFRAN ELECTRONICS & DEFENSE
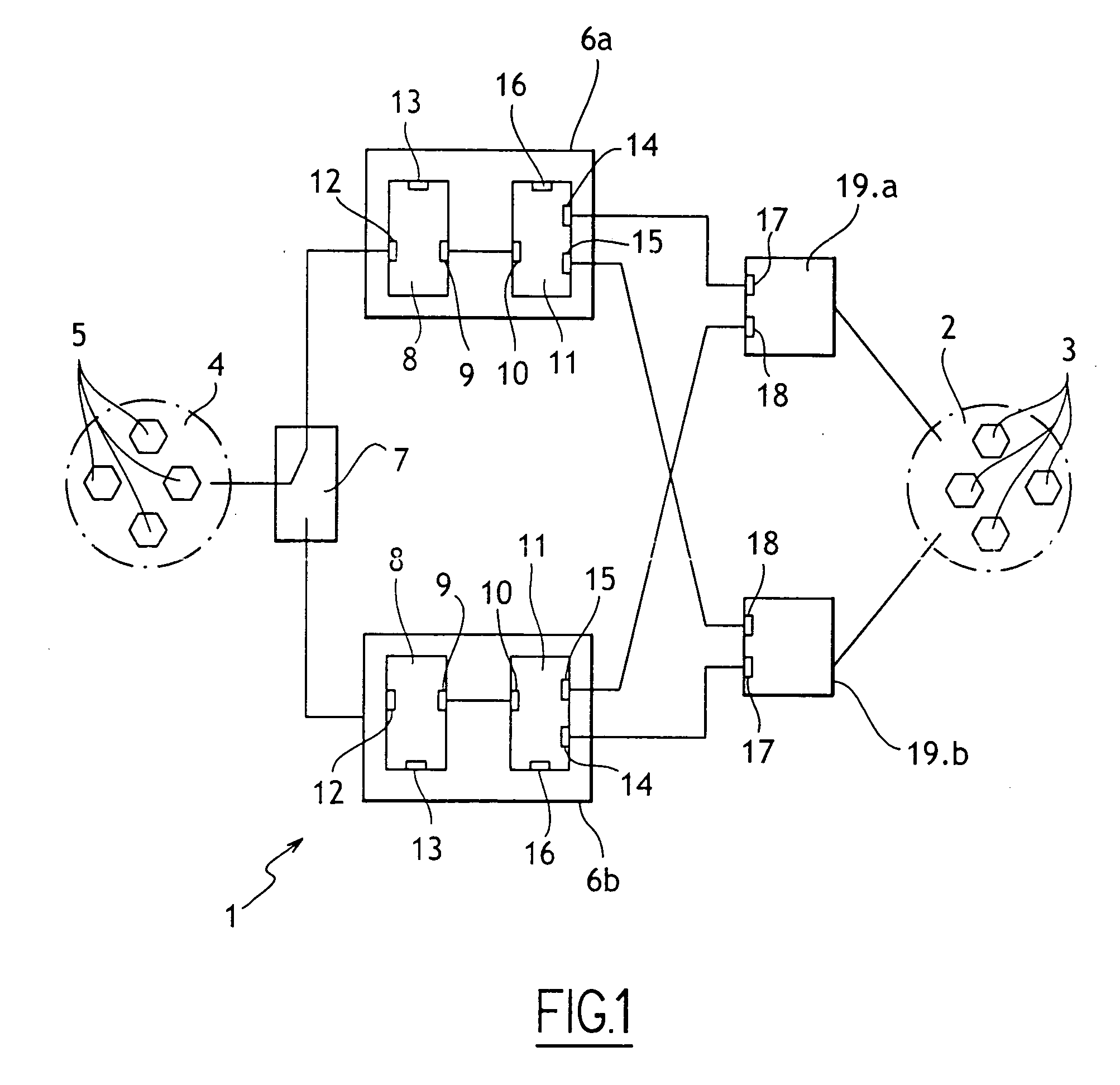
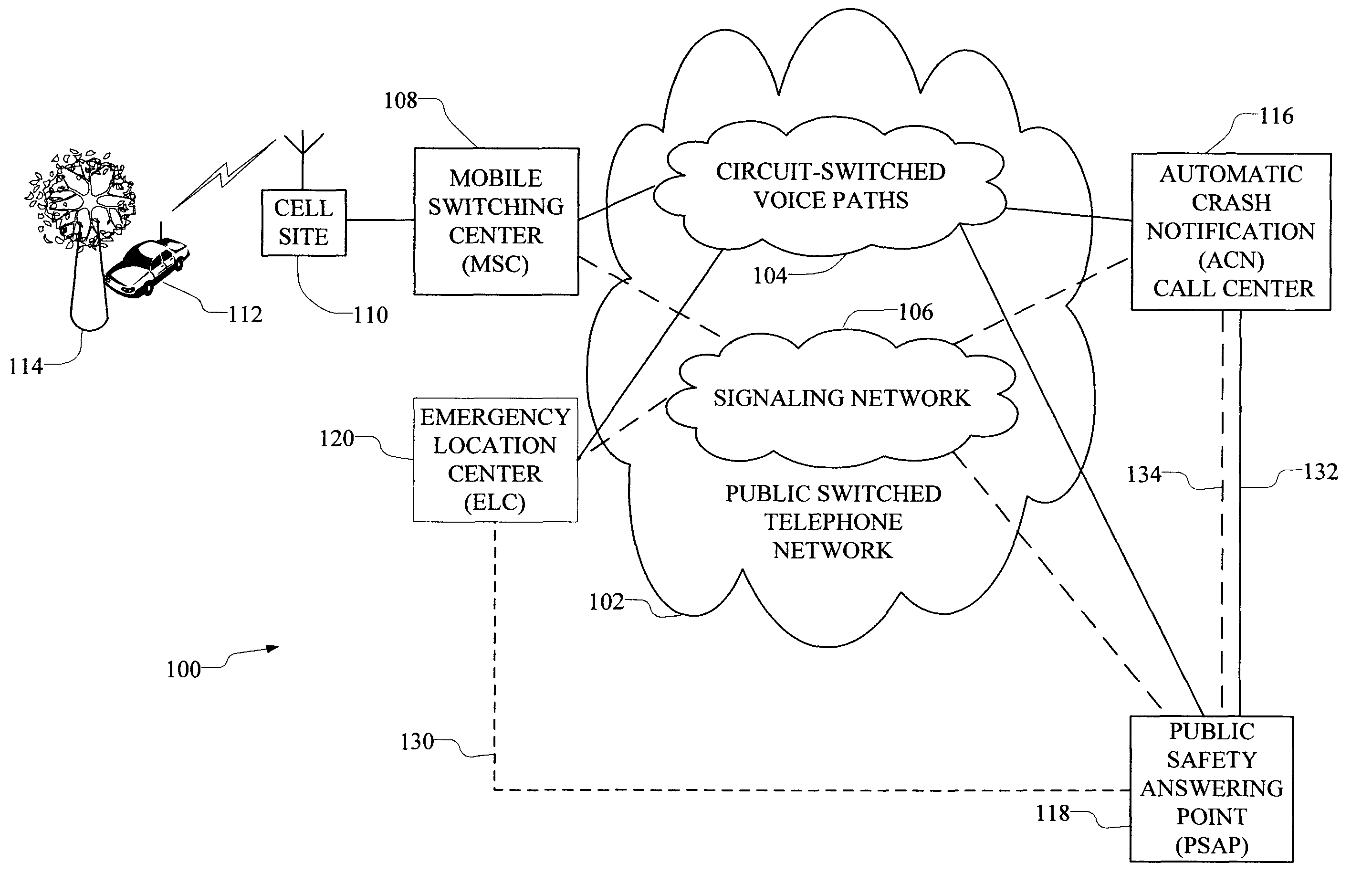
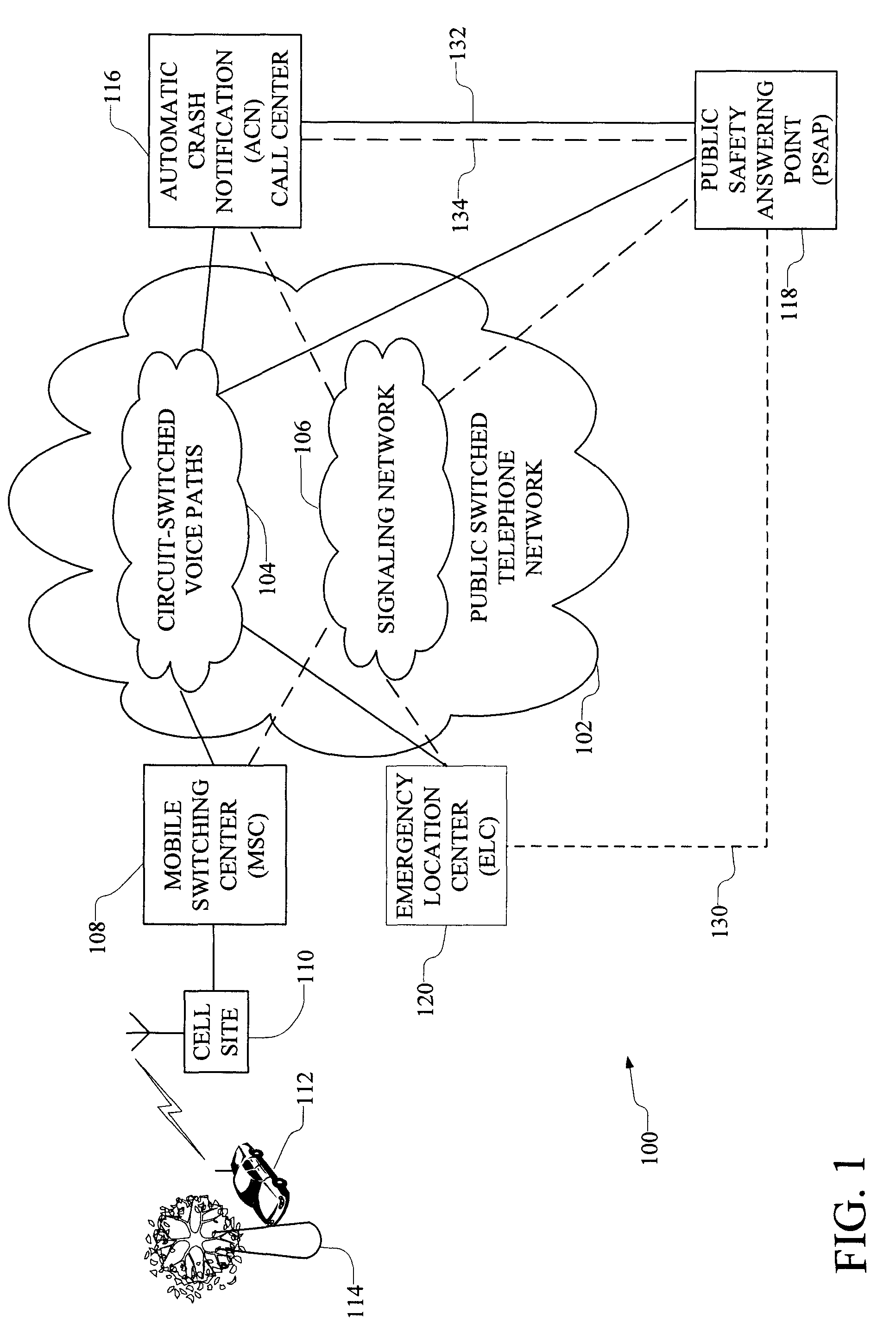
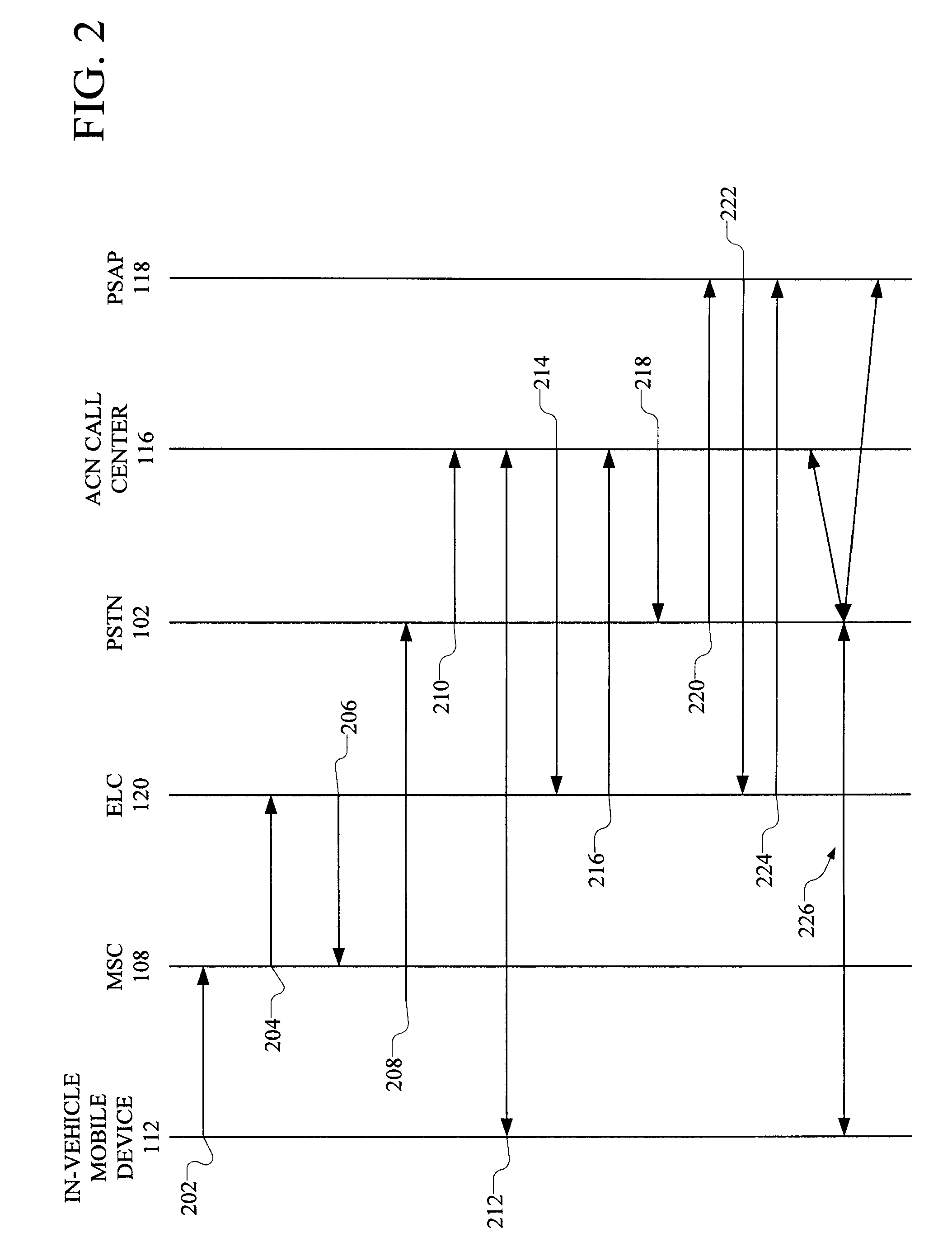
Automatic routing of in-vehicle emergency calls to automatic crash notification services and to public safety answering points
ActiveUS8180316B2Shorten call setup timeSpecial service for subscribersWireless communicationAutomated crash notificationIn vehicle
A system and method automatically routes in-vehicle emergency calls to an automatic crash notification (ACN) call center using information provided by the calling mobile device in the call set up message. An operator at the ACN call center is presented with an identification of a public safety answering point (PSAP) that serves the location of the vehicle. The ACN operator may then conference in the PSAP if needed. The provided information is displayed at both the ACN operator's position and at the PSAP. Alternatively, the call is routed to the PSAP first or to both the PSAP and the ACN call center simultaneously.
Owner:INTRADO LIFE & SAFETY INC
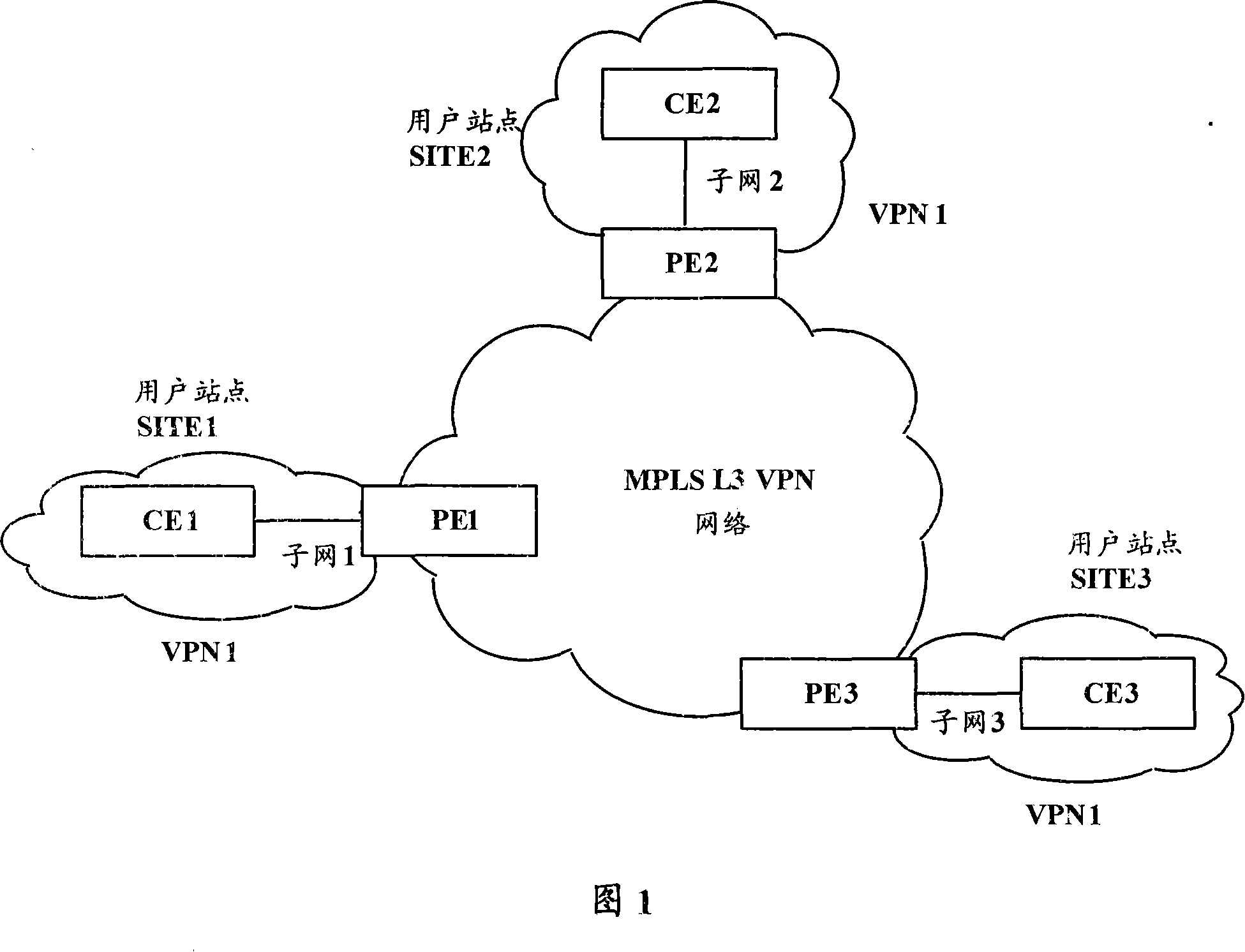
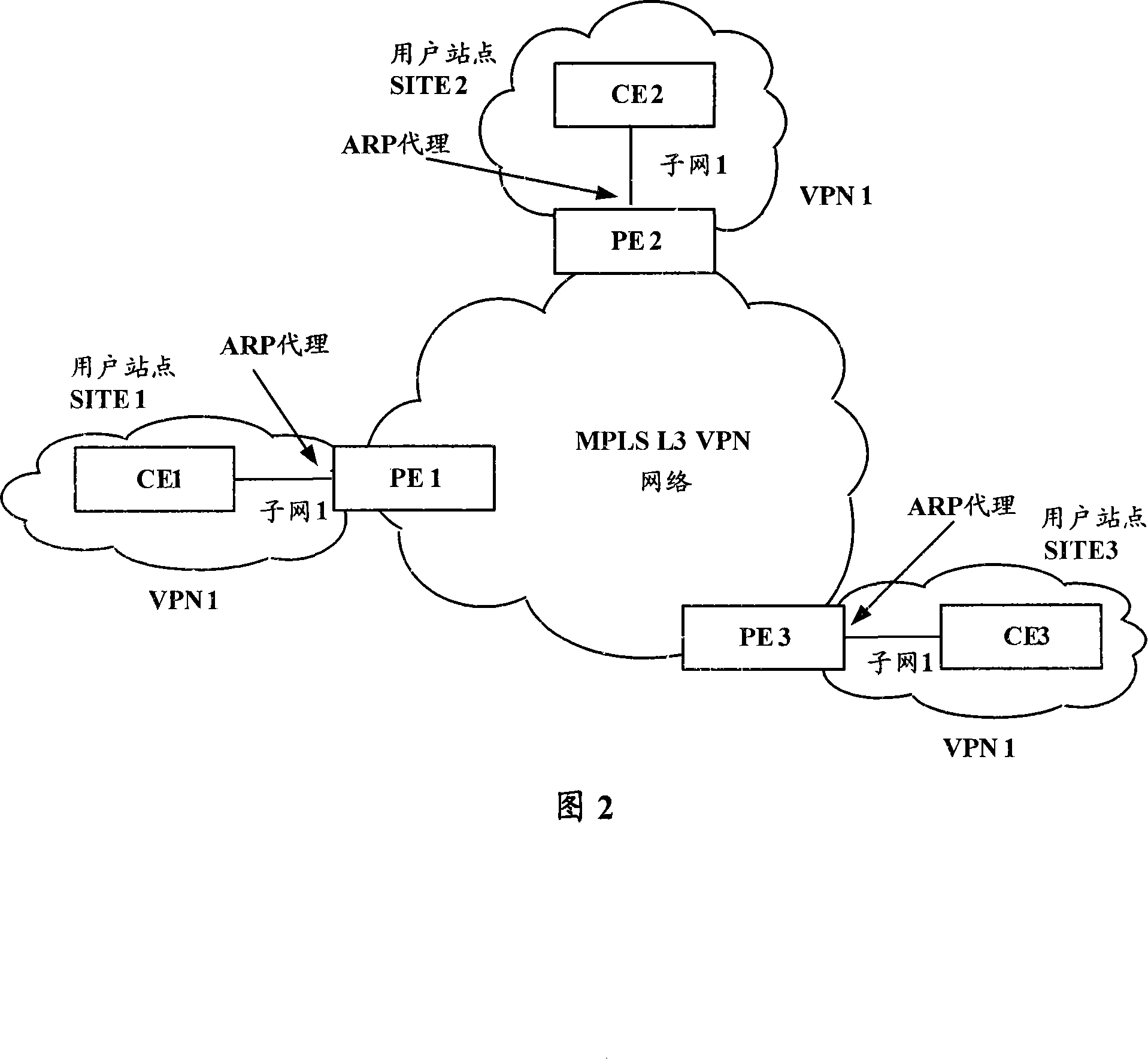
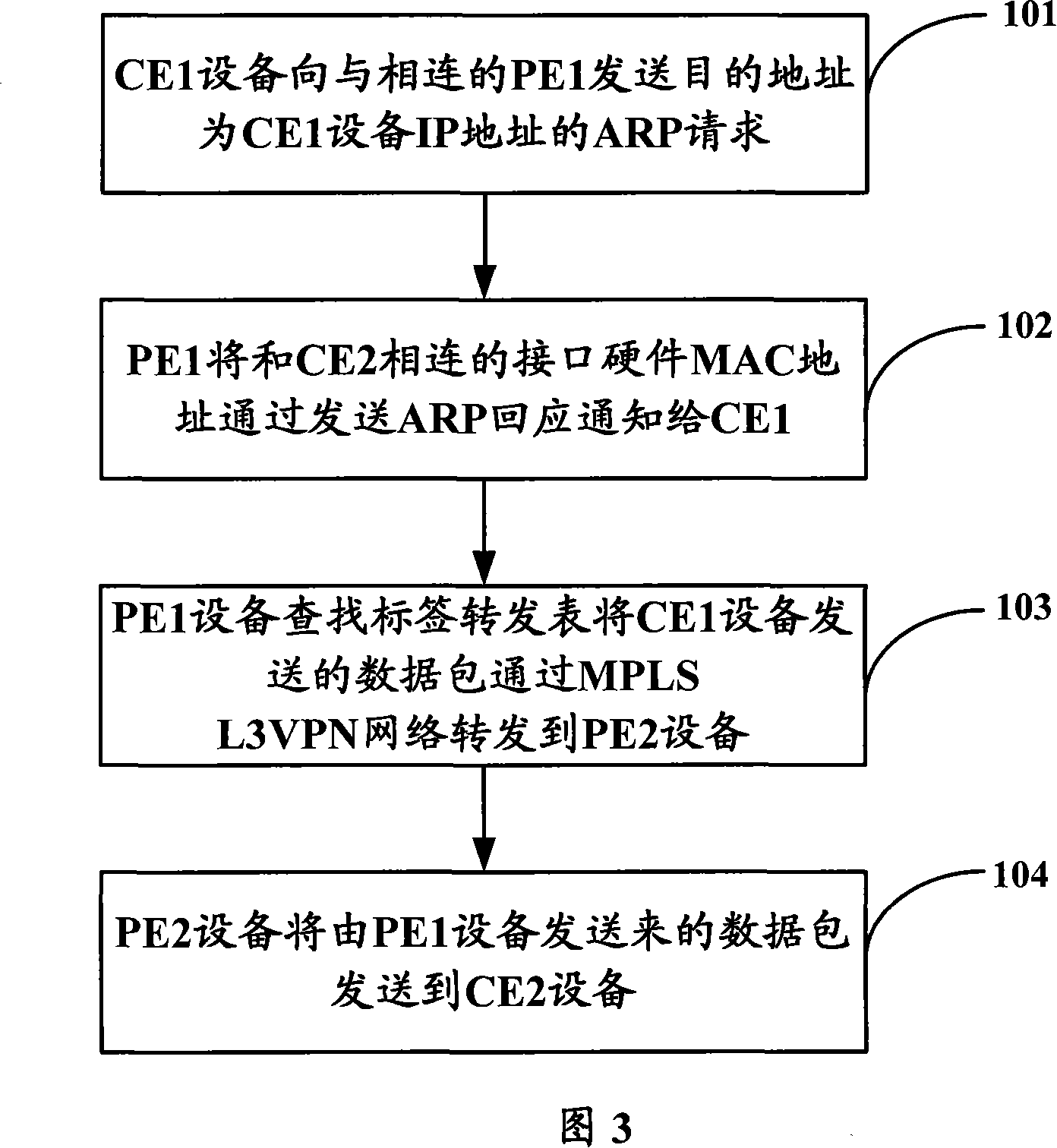
Method for realizing identical subnet communication for MPLS three-layer virtual special net
InactiveCN101072238ATo achieve mutual communicationReduce loadNetworks interconnectionNetwork packetIp address
The method includes following steps: (1) first consumer equipment CE1 sends ARP proxy request with destination address being as IP address of second consumer equipment CE2 to the connected first provider equipment PE1; (2) through sending ARP responses, PE1 informs CE1 the MAC address of interface hardware connected to CE1; (3) looking up label forwarding table, through static route setup by PE1 in advance, and MPLS three layers virtual private network L3VPN, CE1 forwards data packet sent by CE1 to second provider equipment PE2; (4) PE2 sends data packet sent from PE1 to CE2. The invention realizes intercommunication among VPN consumers in same IP sub network distributed at different sites in MPLS L3VPN network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Distributed network apparatus
ActiveCN104811400AEasy to manageConserve management IP addressesData switching networksIp addressDistributed computing
The invention provides a distributed network apparatus. The distributed network apparatus includes a main control board card, service board cards and an inter-board channel; the CPU of the main control board card is used for generating network forwarding table entries for the service board cards, and issuing the network forwarding table entries to the service board cards, and issuing corresponding flow-splitting strategy table entries to flow-splitting hardware and CPUs of the service board cards according to flow control strategies issued by a management side; and the flow-splitting hardware of the service board cards is used for storing the flow-splitting strategy table entries in flow-splitting strategy tables of the flow-splitting hardware, and transmitting messages which enter from network ports to the CPUs of corresponding service board cards according to the flow-splitting strategy tables of the flow-splitting hardware; and the CPUs of the service board cards are used for storing the flow-splitting strategy table entries in flow-splitting strategy tables of the CPUs, and performing application processing and network forwarding processing on the messages according to the flow-splitting strategy tables of the CPUs. With the distributed network apparatus of the invention adopted, problems brought about by requirements for configuring static routing or strategy routing for flow guiding can be solved, management is simpler, and management IP addresses can be saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DPTECH TECH
Logical Router Processing by Network Controller
Owner:NICIRA INC
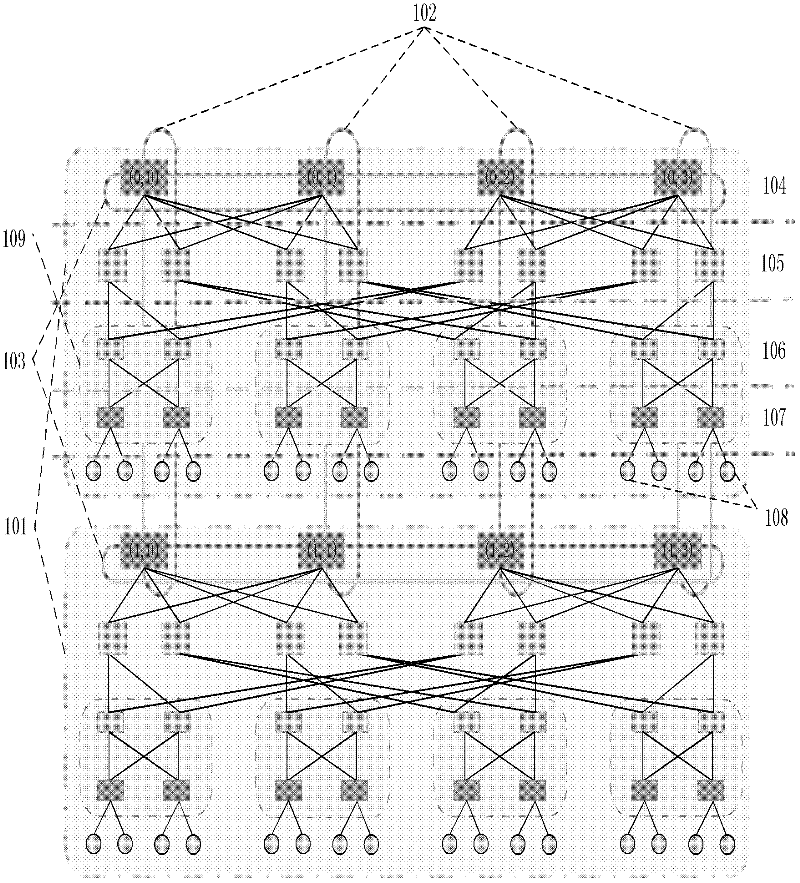
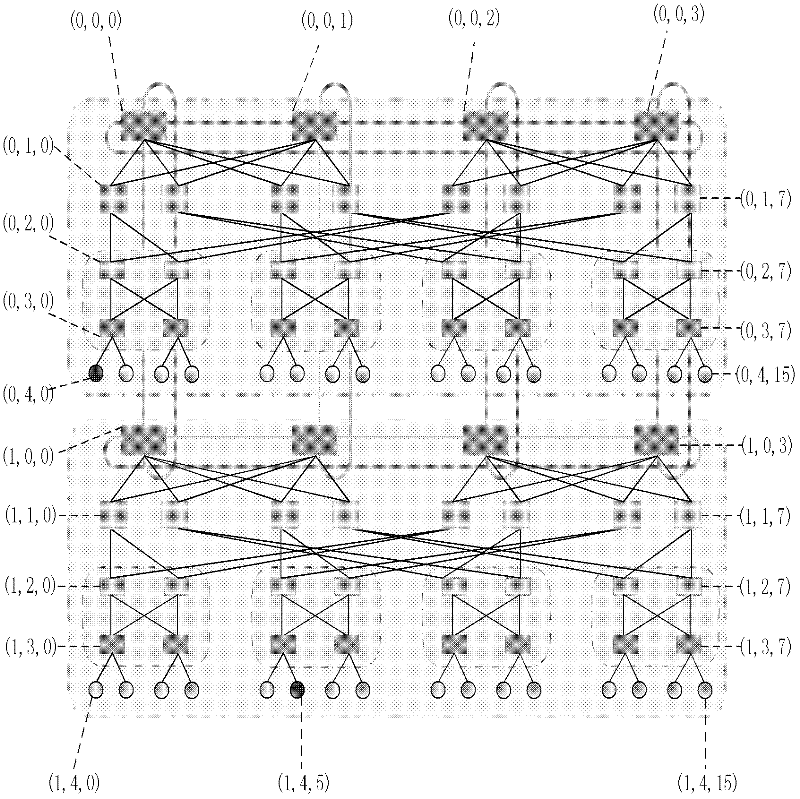
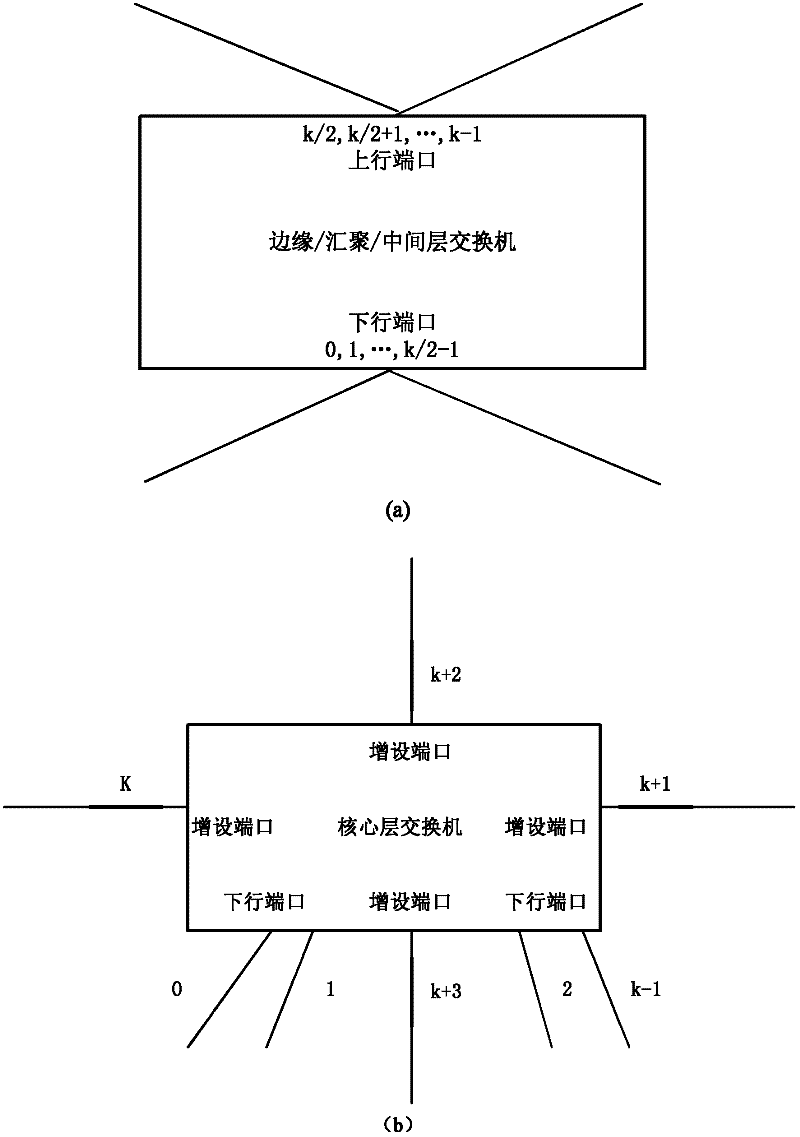
Routing method for module-expansion-based data center network topology system
InactiveCN102420775AImprove addressing efficiencySave storage spaceData switching networksTraffic capacityData center
The invention discloses a routing method for a module-expansion-based data center network topology system, and mainly aims to solve the problem that the conventional routing methods in the Ethernet and a data center tree network cannot be well applied to the module-expansion-based data center network topology system. The method is implemented by the following steps of: (1) performing initialization, and identifying each piece of network equipment in the topology system by adopting a hierarchical addressing mechanism; (2) reading the addressing information of current network equipment, and judging the type of the current network equipment; (3) generating data, and transmitting the data to edge layer switches by using a source server; (4) determining data output ports according to the destination address of the data and a port with the data by using the edge layer switches, convergence layer switches and intermediate layer switches; and (5), determining a data output port according to the destination address of the data, the hop number of a path hop number and the cache information of the port by using core layer switches. The method has the advantages that: network throughput is improved; traffic balancing is realized; the method can be used for the path selection of a data center network and the provision of high-efficiency data transmission service; and the shortcomings of static routing are overcome.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
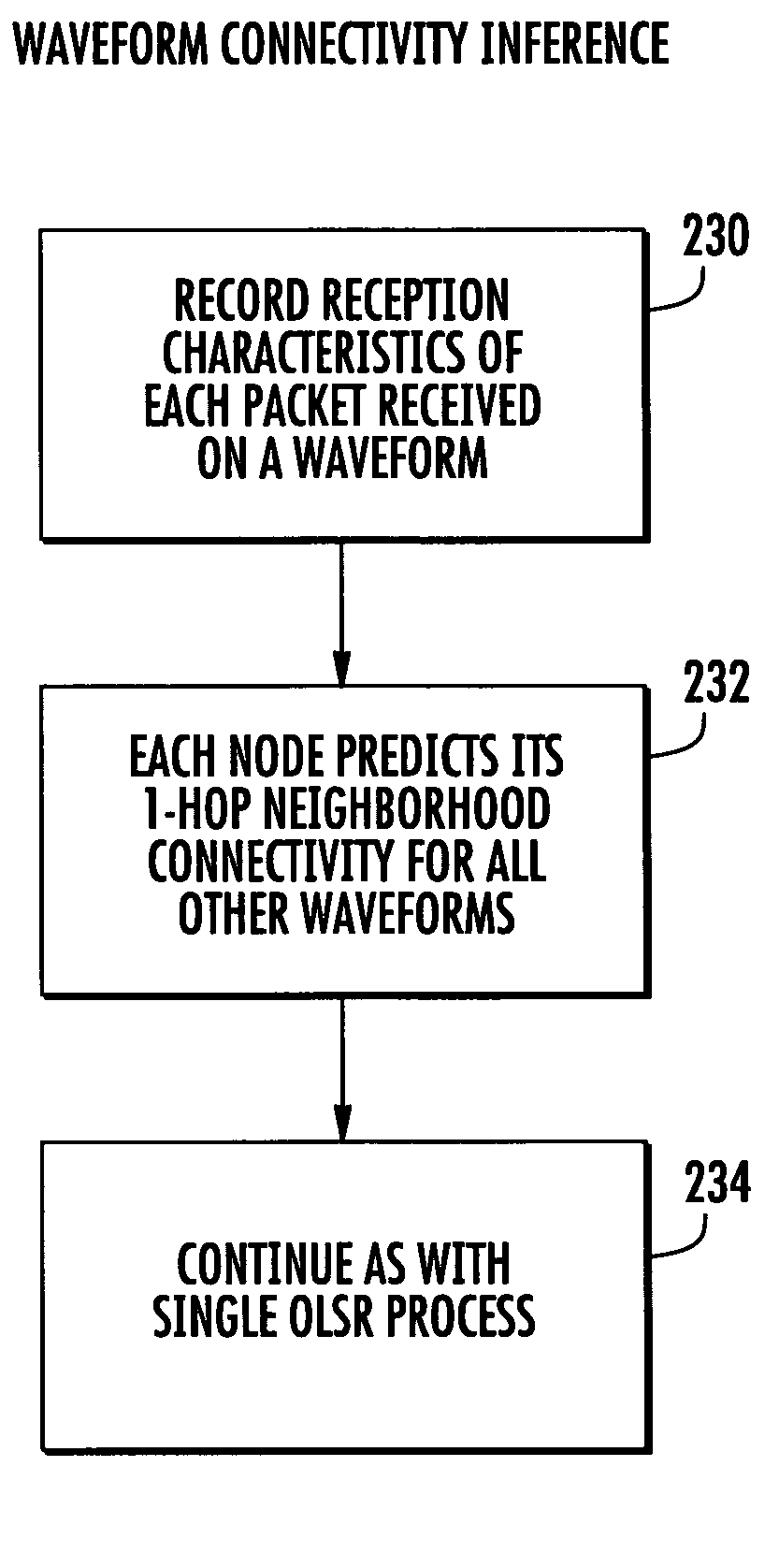
System and method for communicating over mesh networks using waveform-enhanced, link-state routing
ActiveUS8213409B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A communication system includes a plurality of mobile nodes forming a mesh network. A plurality of wireless communication links connect the mobile nodes together. Each mobile node is formed as a communications device and operative for transmitting data packets wirelessly to other mobile nodes via the wireless communications link from a source mobile node through intermediate neighboring mobile nodes to a destination mobile node using a link state routing protocol and multiple waveforms.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Inter-area exit route dynamic selection method and system
InactiveCN102780605AReduce management and maintenance costsShort response timeData switching networksQuality of serviceRouting table
The invention provides an inter-area exit route dynamic selection method and system. The method comprises the following steps that each area exit router collects self information regularly; the transmission performance evaluated value of each area exit router is calculated; an inter-area router acquires the transmission performance evaluated value; priority levels are generated; the inter-area router carries out priority level sequencing on the area exit routers according to the transmission performance evaluated values; and the inter-area router selects the router with the maximal transmission performance evaluated value as the next-hop address of the exit router, wherein the area exit routers refer to routers which are used for connecting an inter-area network and an extra-area network and have direct communication capability, and the inter-area router refers to a router which is directly connected with the exit routers but does not have capability of directly communicating with the extra-area network. According to the method and the system which are provided by the invention, an existing route protocol is not required to be changed, the allocation of a static route table is automatically completed by the system, and the defect that the QoS (Quality of Service) is not considered in a traditional method is effectively overcome.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
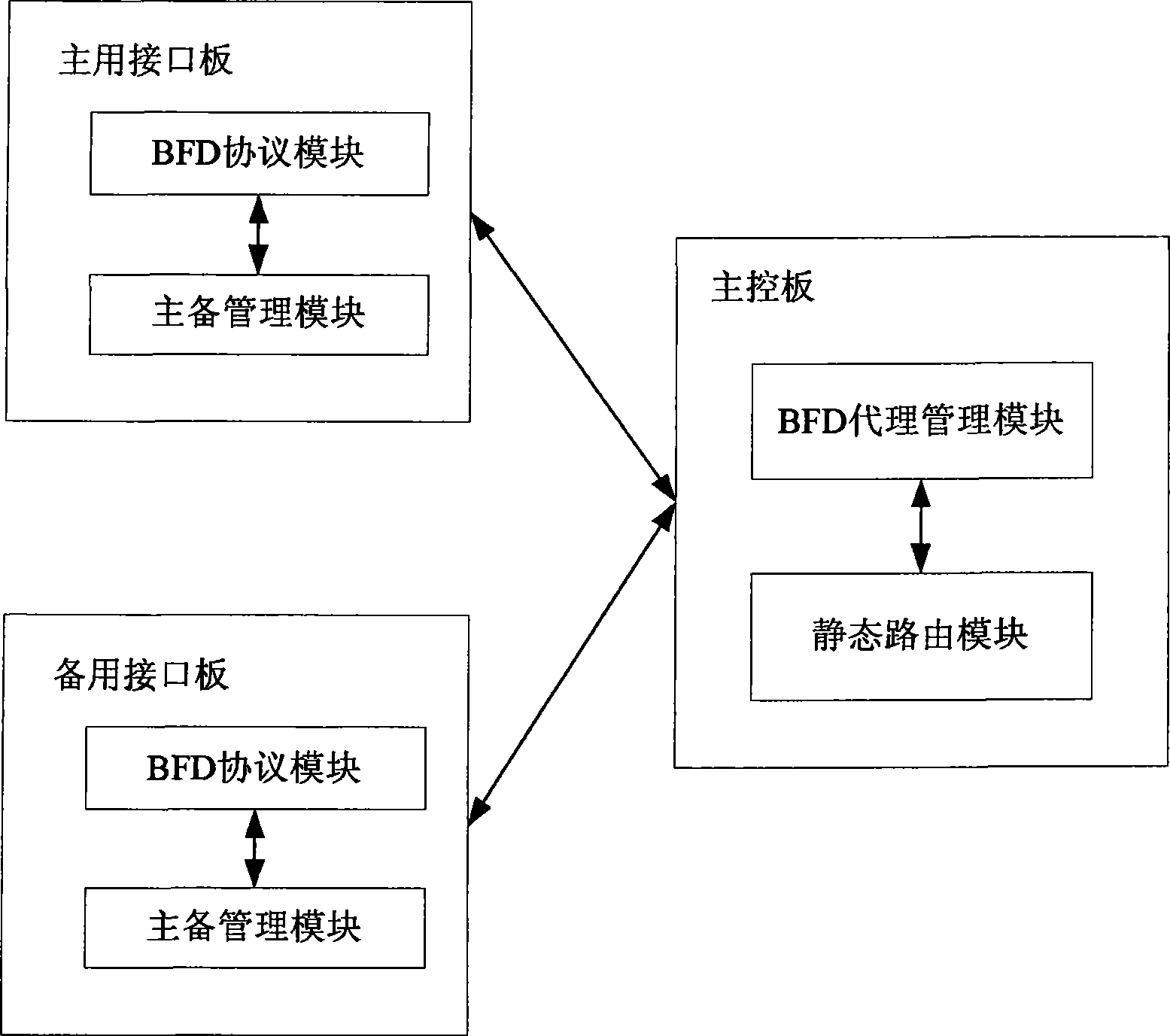
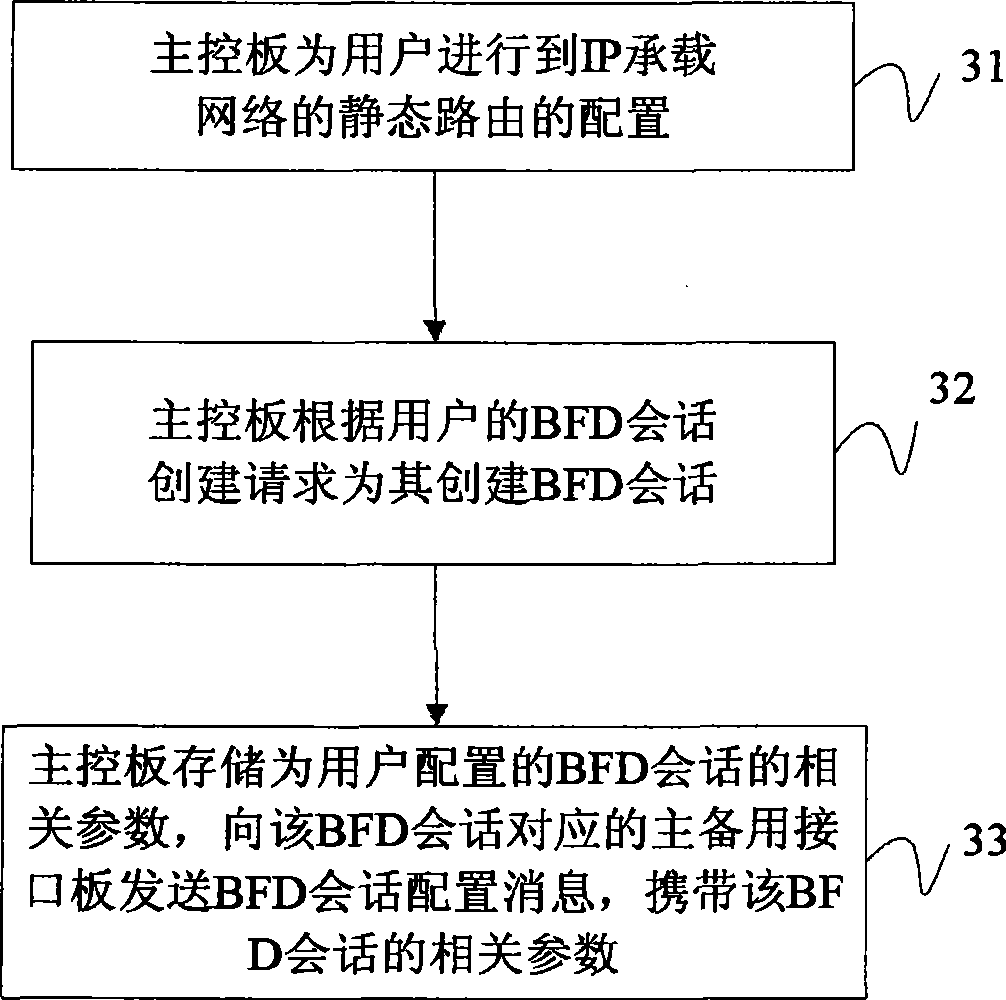
Method and device for triggering main and standby interface board inverse switch
ActiveCN101465859AShorten the switching timeSame convergence timeData switching networksNetwork ConvergenceBidirectional Forwarding Detection
The invention provides a method and a device for triggering the switching of main and standby interface boards, including that: a bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD)conversation is established between a 3G device and an IP carrier network; when the main interface board detects the occurrence of fault, switching of the main and the standby interface boards is carried out, and the original standby interface board is switched to a new main interface board. With the method, the time of switching the single boards can be greatly reduced; the fault detection time of the whole network can be unified, and the network convergence time is consistent; a user can combine the function with the bidirectional forwarding detection of multi next hop based on static routing and can realize double-back-up effect when gaining an access to the carrier network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
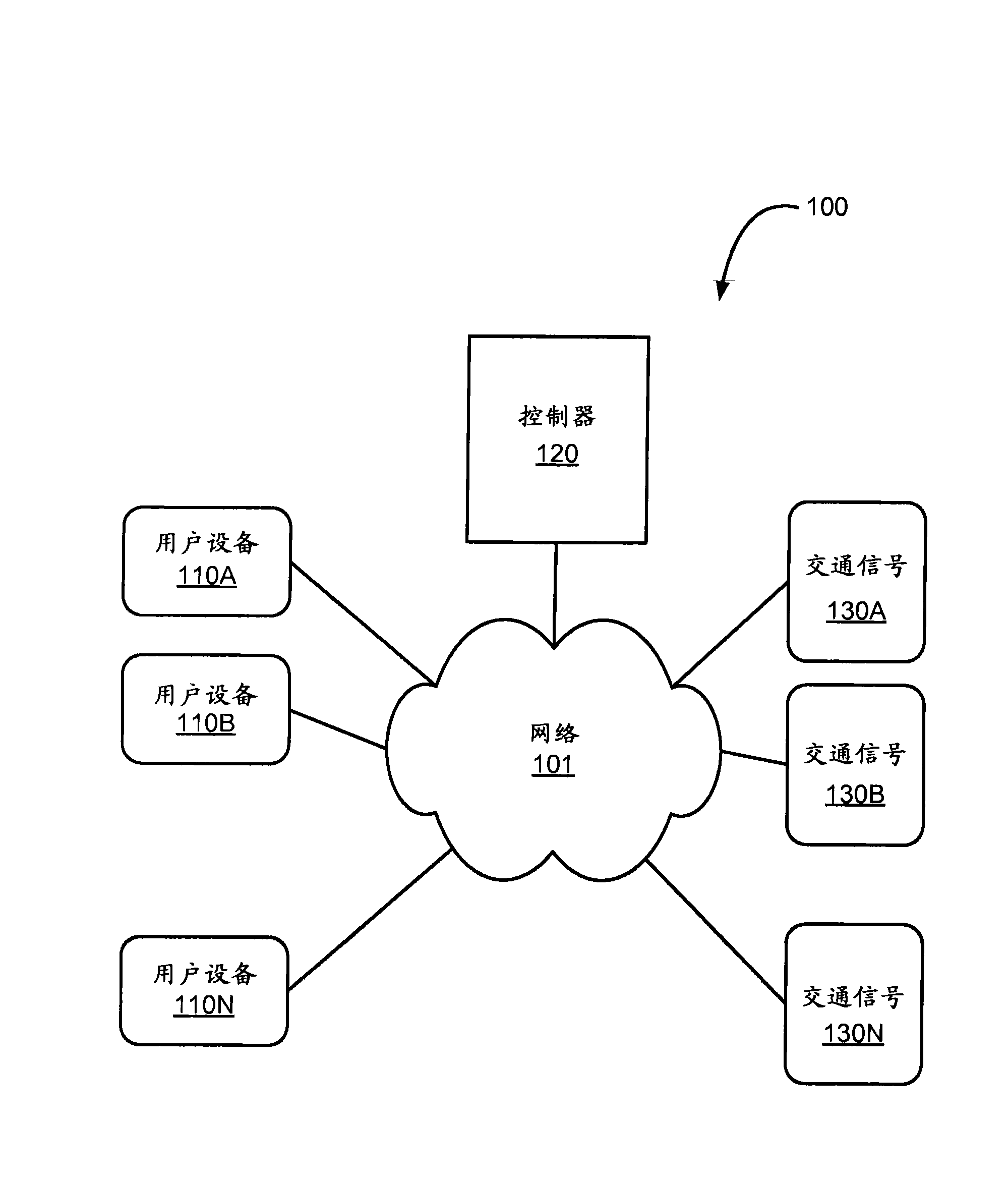
Traffic routing using intelligent traffic signals, GPS and mobile data devices
A traffic routing system reduces emissions from commuter and other traffic, eases congestion on roadways, and decreases transit time by use of communications among vehicles and traffic controls, such as traffic lights. In one aspect, a traffic light receives a signal that a vehicle is approaching and in response turns green to allow the vehicle to pass without impairment. In another aspect, a vehicle receives a signal to adjust a current rate of speed to arrive when a traffic signal allows vehicles to pass. In still another aspect, a combination of congestion, emergency traffic, roadwork and similar factors influence proposed routes sent to vehicles.
Owner:TIME SYST
Routing method for data transmission in space delay/disruption tolerant network
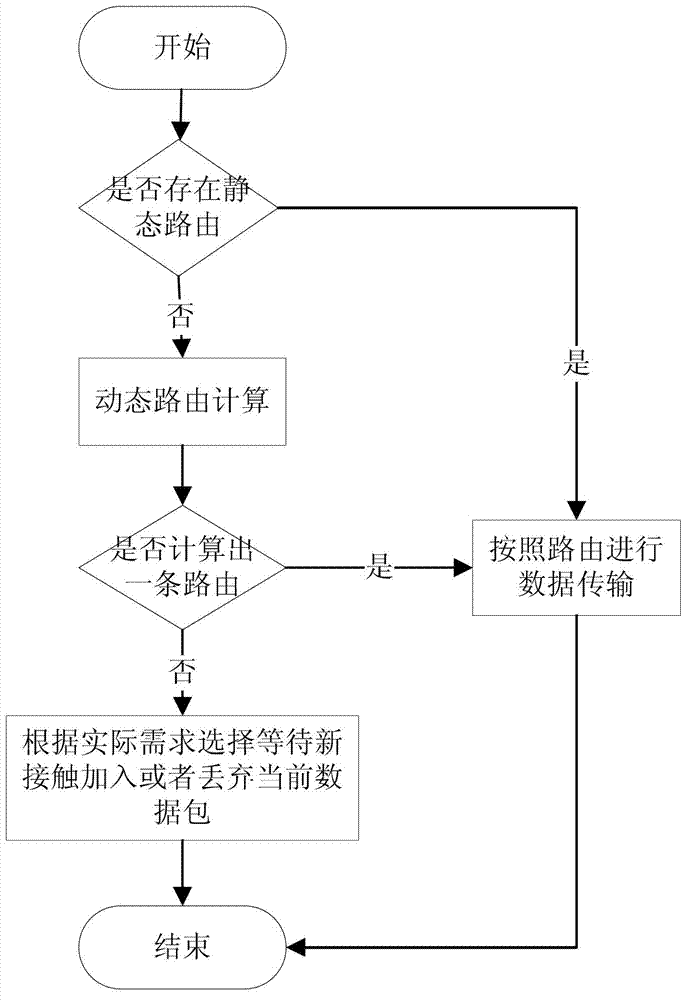
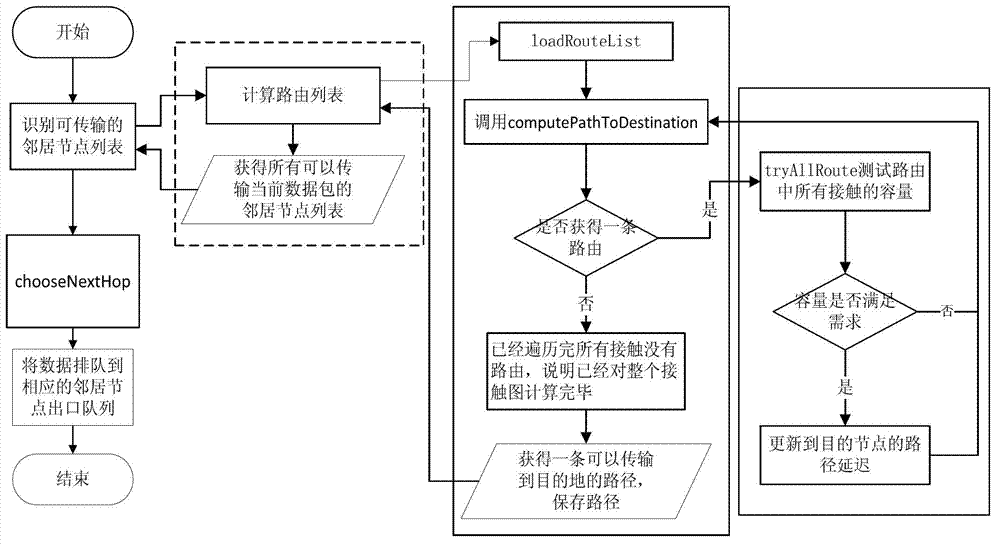
ActiveCN102780637AGuaranteed normal transmissionExcellent throughputData switching networksStatic routingData transmission
The invention discloses a routing method for data transmission in a space delay / disruption tolerant network. The routing method comprises the following steps: (1) searching for a static route: if no static route exists, executing dynamic route calculation; and (2) calculating a dynamic route: calculating the dynamic route according to a source node for transmitting data and a destination node by the following substeps: (2.1) calculating the minimum delay route; (2.2) testing the capacity of the route; and (2.3) selecting a next-hop node: comparing delays of all the selected routes, and selecting the minimum delay route. According to the invention, the routing method is based on space delay / disruption tolerant network capacity constraints of a node contact relational graph in the network, and the minimum delay route from the source node to the destination node can be calculated by precognizing a contact relation graph among nodes in the running process of the whole network and data streams among node pairs, so that the throughput of the whole network can be increased, the space node resources can be saved, and higher network performance can be obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
System and method for improving traffic analysis and network modeling
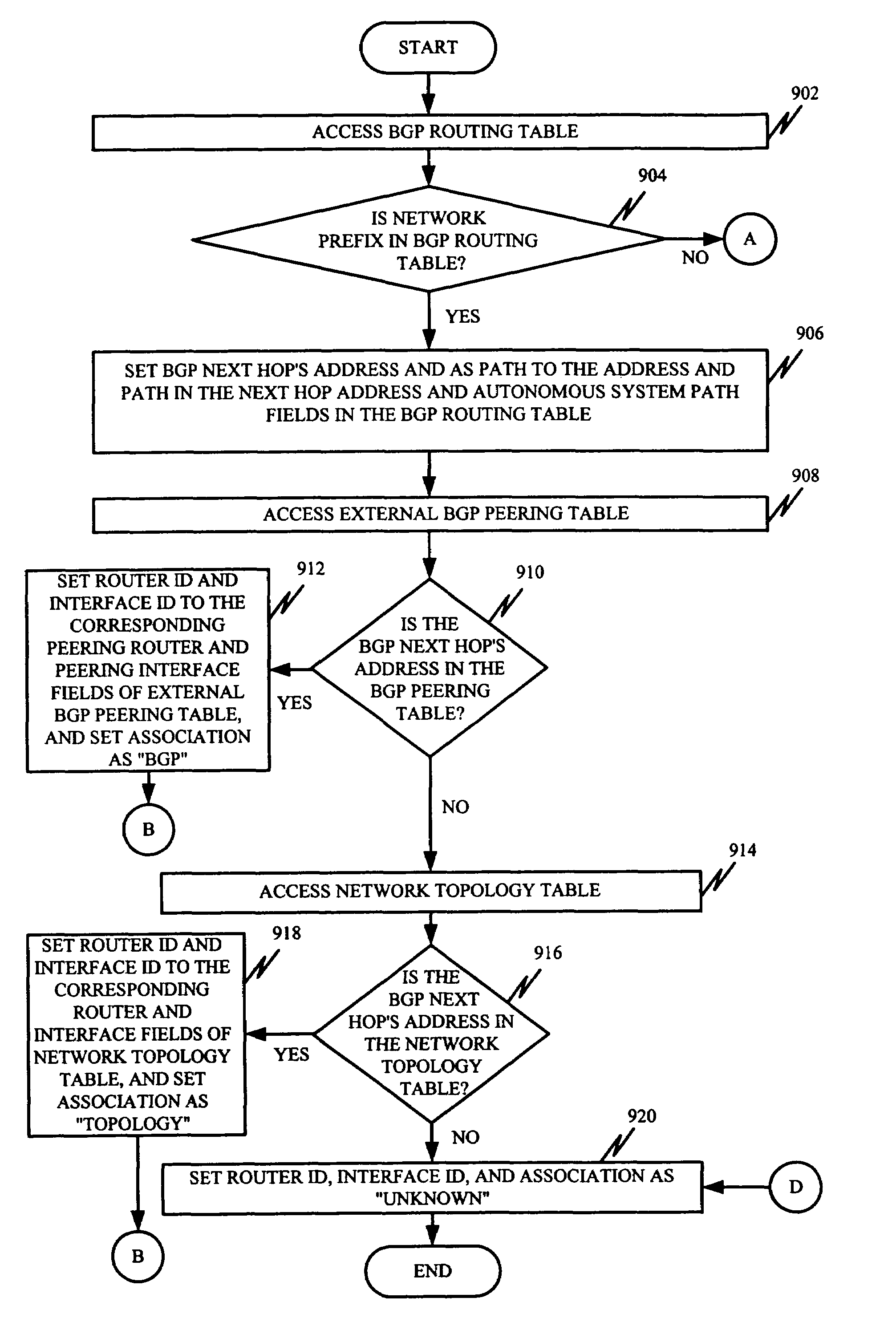
InactiveUS7035934B1Improve analysisImprove networkingData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityAnalysis data
A system (800) improves a network designer's ability to analyze a data network having several routers. The system (800) accesses static routing information and / or open shortest path first route summarization information, determines an identity of a network prefix using the accessed information, and analyzes the data network using the determined identity. The network designer can use this determined identity for traffic analysis or modeling of the data network.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC +2
Method for traffic grooming, wavelength assignment and spectrum allocation
InactiveUS8873962B2Better optimizedIncrease the number ofWavelength-division multiplex systemsTraffic groomingMultiplexing
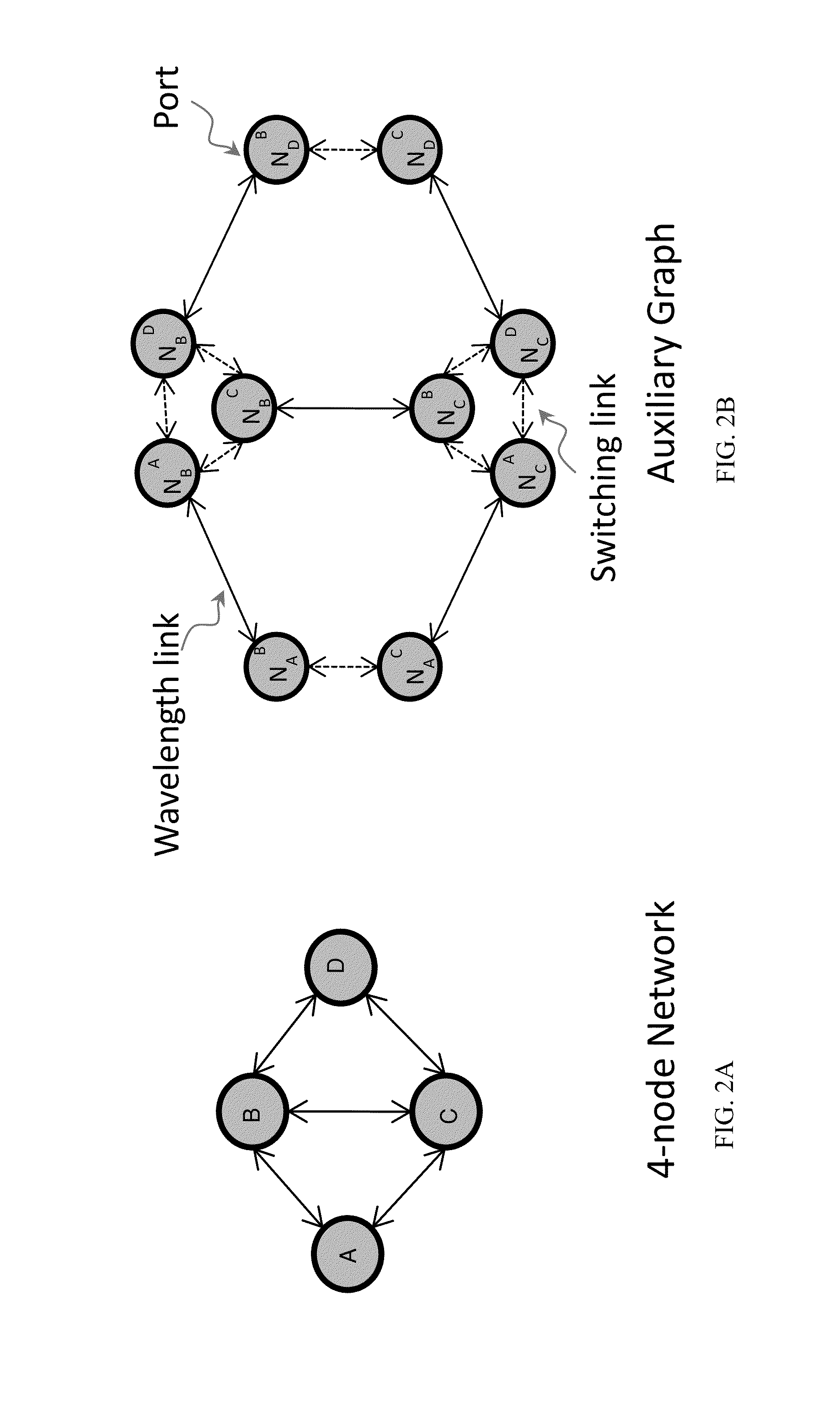
A method includes determining a line rate selection for a flexible optical wavelength-division-multiplexing WDM network, determining a traffic routing in said network, and determining simultaneously a channel routing, wavelength assignment and spectrum allocation in said network based on an auxiliary graph.
Owner:NEC CORP
Media gateway device and method for forwarding data frames
InactiveUS9356833B2Reduce in quantityImprove securityNetworks interconnectionVirtual LANExternal interface
The present invention provides a media gateway device and a method for forwarding data frames. The media gateway device comprises: a master module, a switch module, a relay access module and a media resource module; the switch module comprises three independent Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), i.e., a first VLAN, a second VLAN and a third VLAN, respectively; the media resource module is connected to the switch module through the second VLAN, and the switch module is connected to an external Internet Protocol (IP) packet network through the third VLAN; the media gateway device further comprises a network layer static routing table. By using the media gateway device and the method for forwarding data frames according to the present invention, the number of the external interfaces of the media gateway device can be reduced, and the interface of the switch module can be managed by the VLAN.
Owner:APEX NET LLC
A method for automatic configuration of network equipment in an ipv6 network, network equipment and system
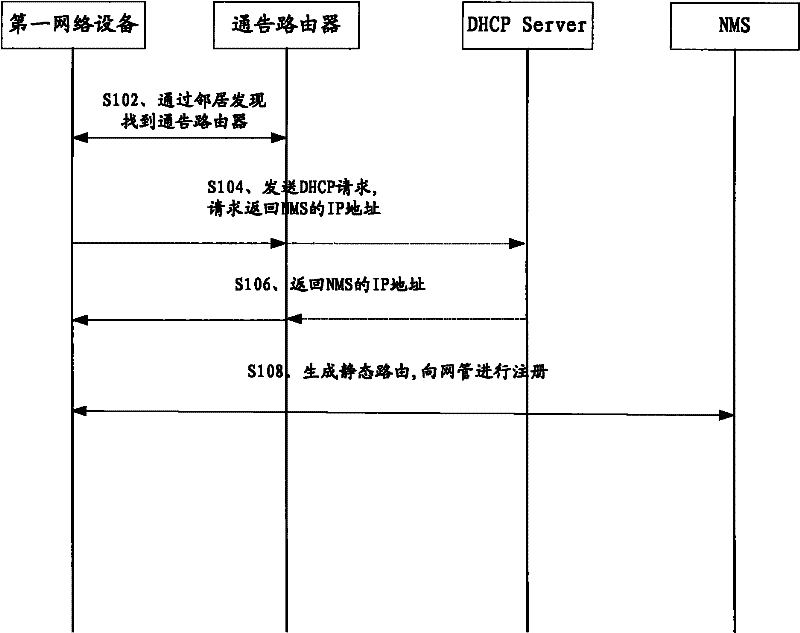
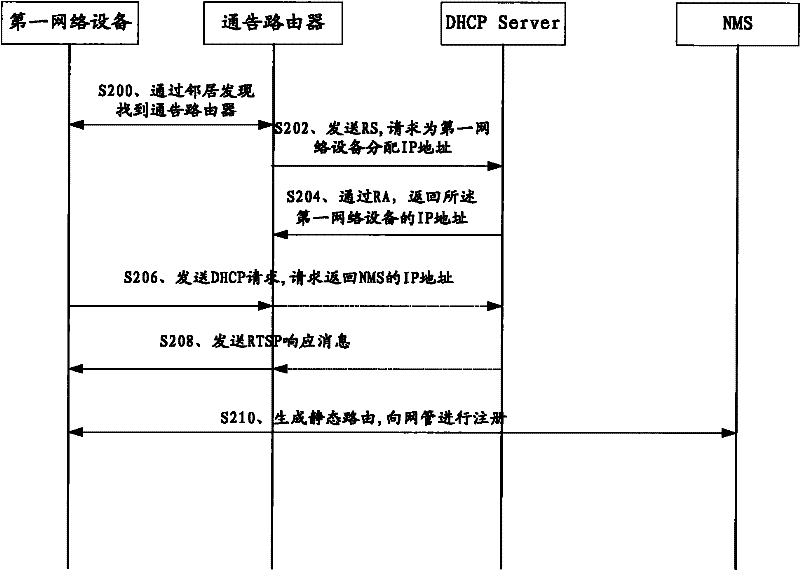
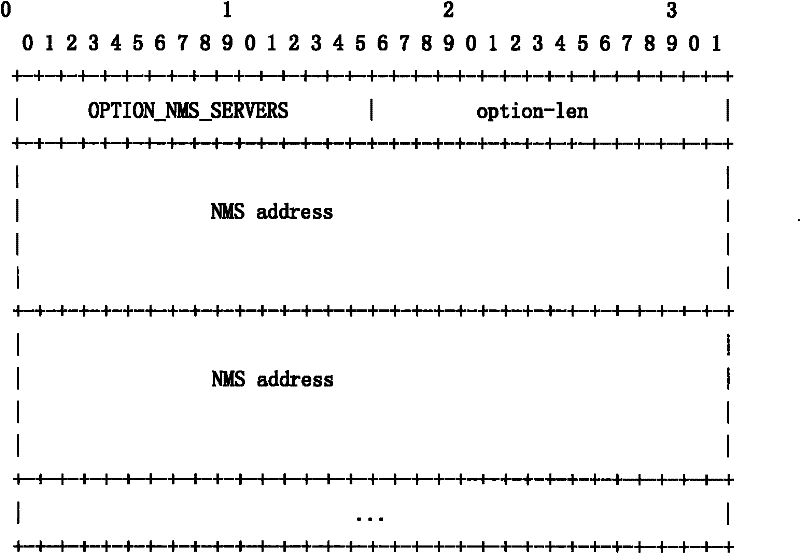
InactiveCN102271050AImprove deployment efficiencyImplement auto-discoveryData switching networksNetwork deploymentAuto-configuration
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a system for automatically configuring network equipment in an Internet protocol version 6 (IPv6) network, and corresponding network equipment. The technical scheme is that: the method comprises the following steps of: transmitting router solidification to an advertising router by using the network equipment to acquire an IP address of the network equipment; acquiring the IP address of a network management system by transmitting a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) request to a DHCP sever; generating a static route according to the IP addresses of the network equipment, the network management system and the advertising router; and performing registration in the network management system according to the generated static route. The network equipment realizes automatic discovery between the network management system and newly added IP equipment in the IPv6 network by adopting the method to reduce the workload of configuring network management equipment and the network equipment on the spot by an operator and improve network deployment efficiency.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com