Routing method for module-expansion-based data center network topology system
A data center network and basic module technology, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as huge routing table entries, lagging routing decision-making, and large system overhead, so as to improve transmission rate and data throughput, improve network transmission efficiency, and realize traffic flow balanced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: The source server and the destination server are in the same basic module, and are connected by different edge layer switches in the same Pod structure.
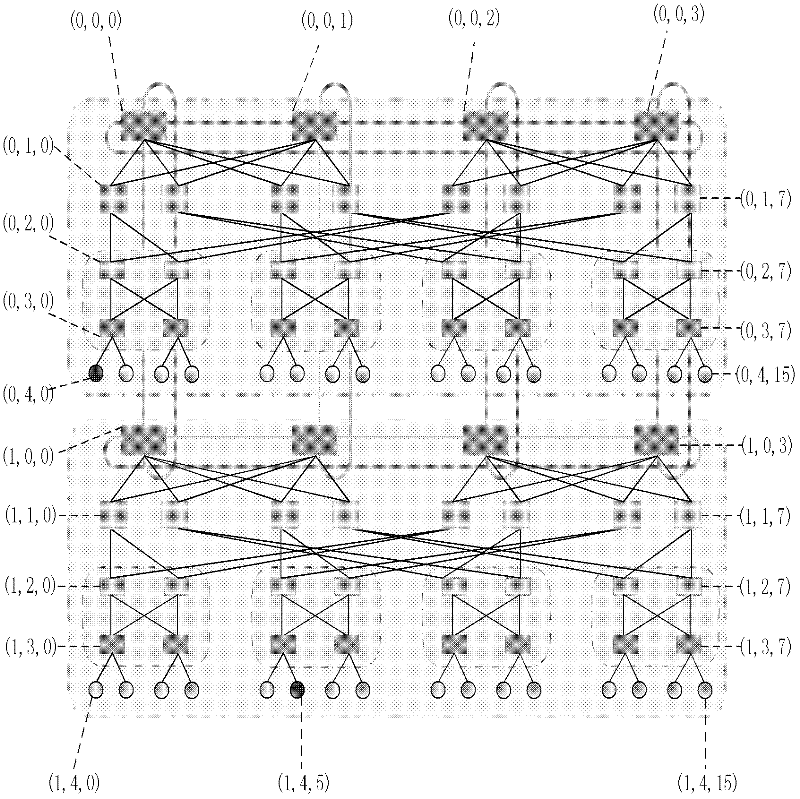
[0044] refer to Figure 4 , the routing method of the present invention, its implementation steps are as follows:
[0045] Step 1. Identify each network device in the topology system.
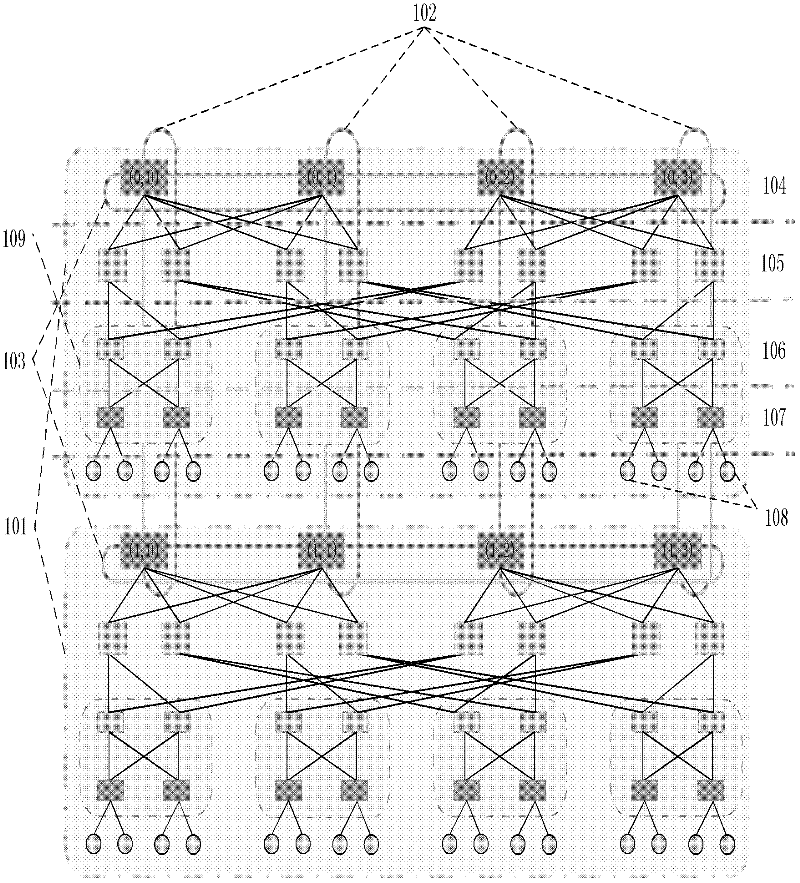
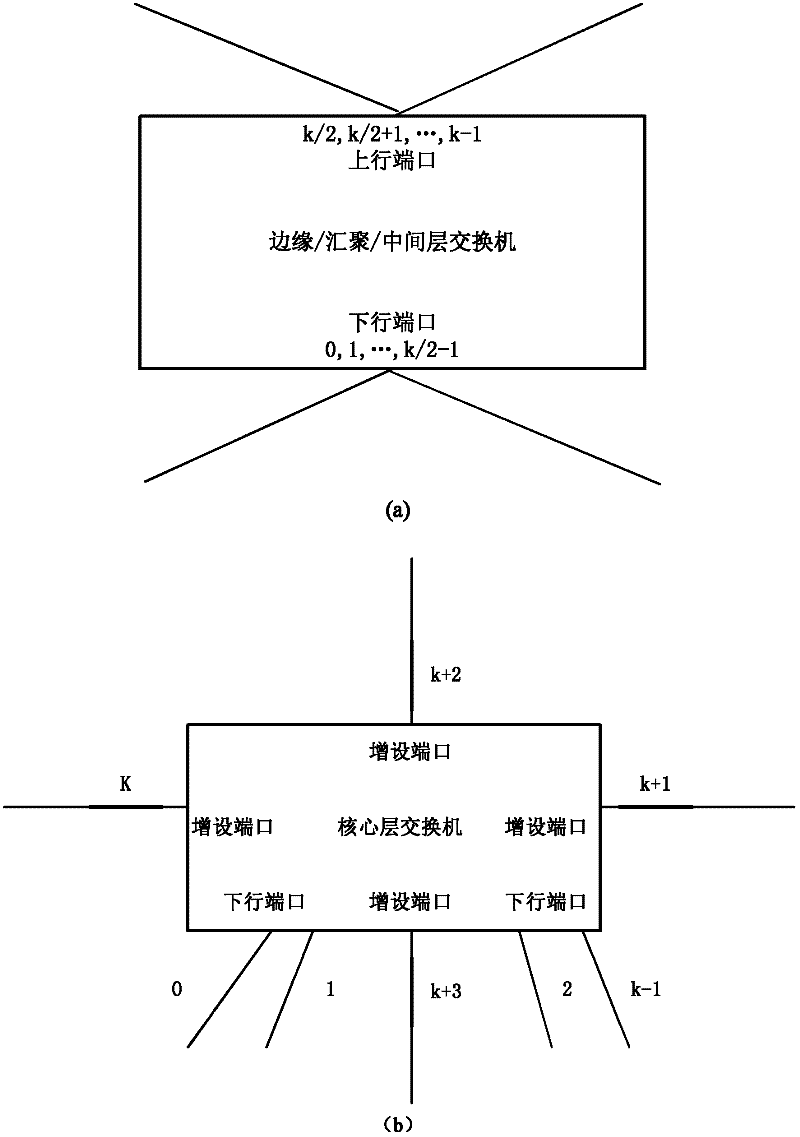
[0046] 1.1) The data center network topology system based on module expansion used by the present invention is as follows: figure 2 , it includes m basic modules, and each basic module includes k Pod structures, where m=2, k=4, but not limited to this value, using three-dimensional coordinates to address each network device in the topology system:
[0047] The address information of the source server S is used (S x , S y , S z ) representation, the address information of the destination server D is represented by (D x ,D y ,D z ) representation, the address information of the core layer switch C is represented by...
Embodiment 2
[0082]Embodiment 2: The source server and the destination server are located in the same basic module, and are connected by edge layer switches in different Pod structures.
[0083] refer to Figure 4 , the routing method of the present invention, its implementation steps are as follows:
[0084] Step 1. is the same as step 1 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0085] Step 2. is the same as step 2 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0086] Step 3. is the same as step three in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0087] Step 4. Determine the source and destination servers, and send the data packets generated by the source server to the directly connected edge layer switch.
[0088] 4a) Set the source server S as (0, 4, 4), and the destination server D as (0, 4, 11);
[0089] 4b) The source server generates a data packet, and encapsulates the address information of the destination server into the data packet;
[0090] 4c) According to the address information of the sou...
Embodiment 3
[0126] Embodiment 3: The source server and the destination server are in different basic modules.
[0127] refer to Figure 4 , the routing method of the present invention, its implementation steps are as follows:
[0128] Step A. is the same as step one in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0129] Step B. is the same as step two in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0130] Step C. is the same as step two in the above-mentioned embodiment 1.
[0131] Step D. Determine the source and destination servers, and send the data generated by the source server to the directly connected edge switch.
[0132] D1) Let the source server S be (0, 4, 0), and the destination server D be (1, 4, 5);
[0133] D2) The source server generates a data packet, and encapsulates the address information of the destination server into the data packet header;
[0134] D3) According to the address information of the source server S: S z =0=k 2 / 4*i+k / 2*j+p, get the intermediate variable i=0, j=0, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com