Patents
Literature
1478 results about "Telenet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
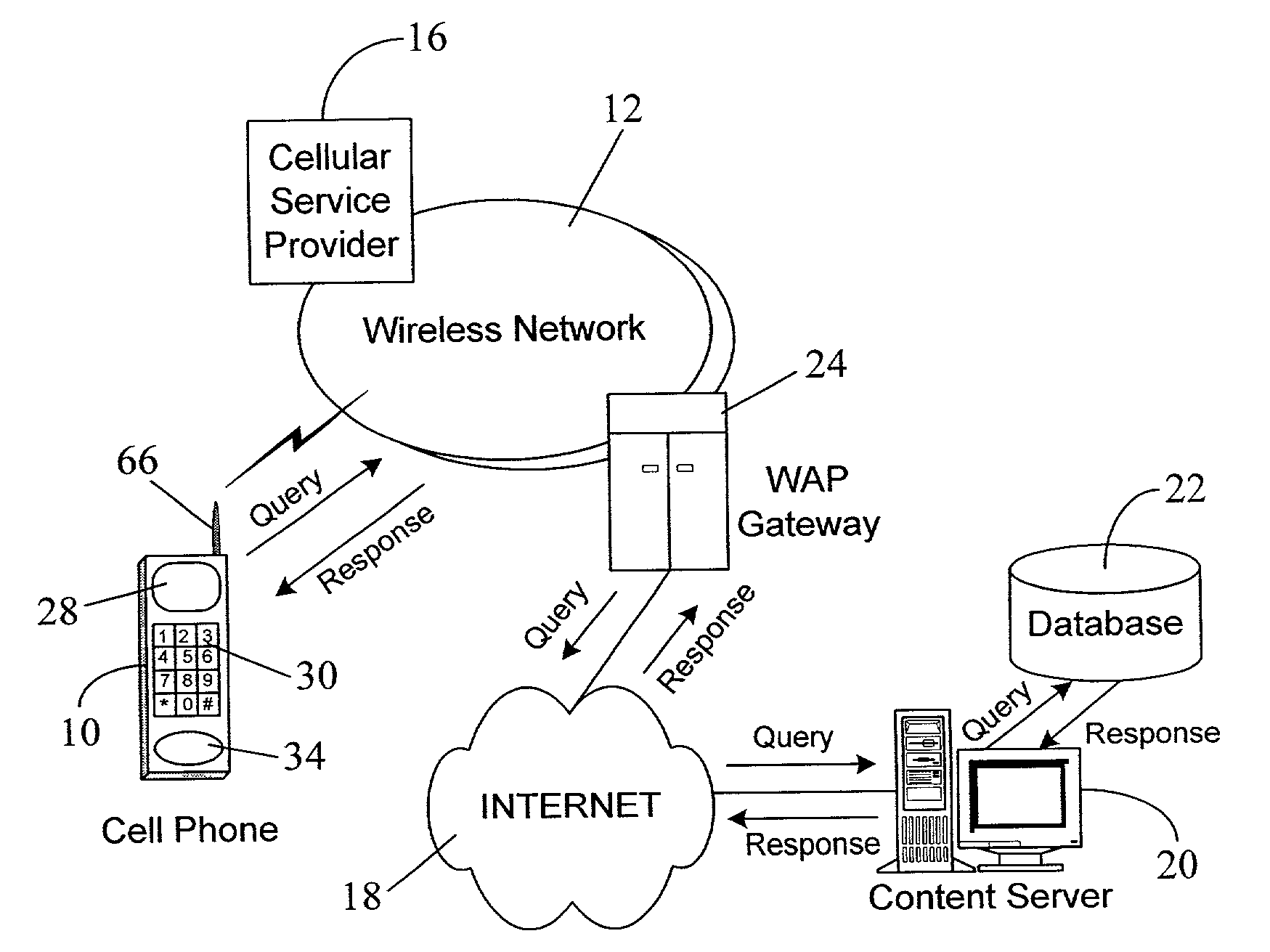
Telenet was an American commercial packet switched network which went into service in 1974. It was the first packet-switched network service that was available to the general public. Various commercial and government interests paid monthly fees for dedicated lines connecting their computers and local networks to this backbone network. Free public dialup access to Telenet, for those who wished to access these systems, was provided in hundreds of cities throughout the United States.
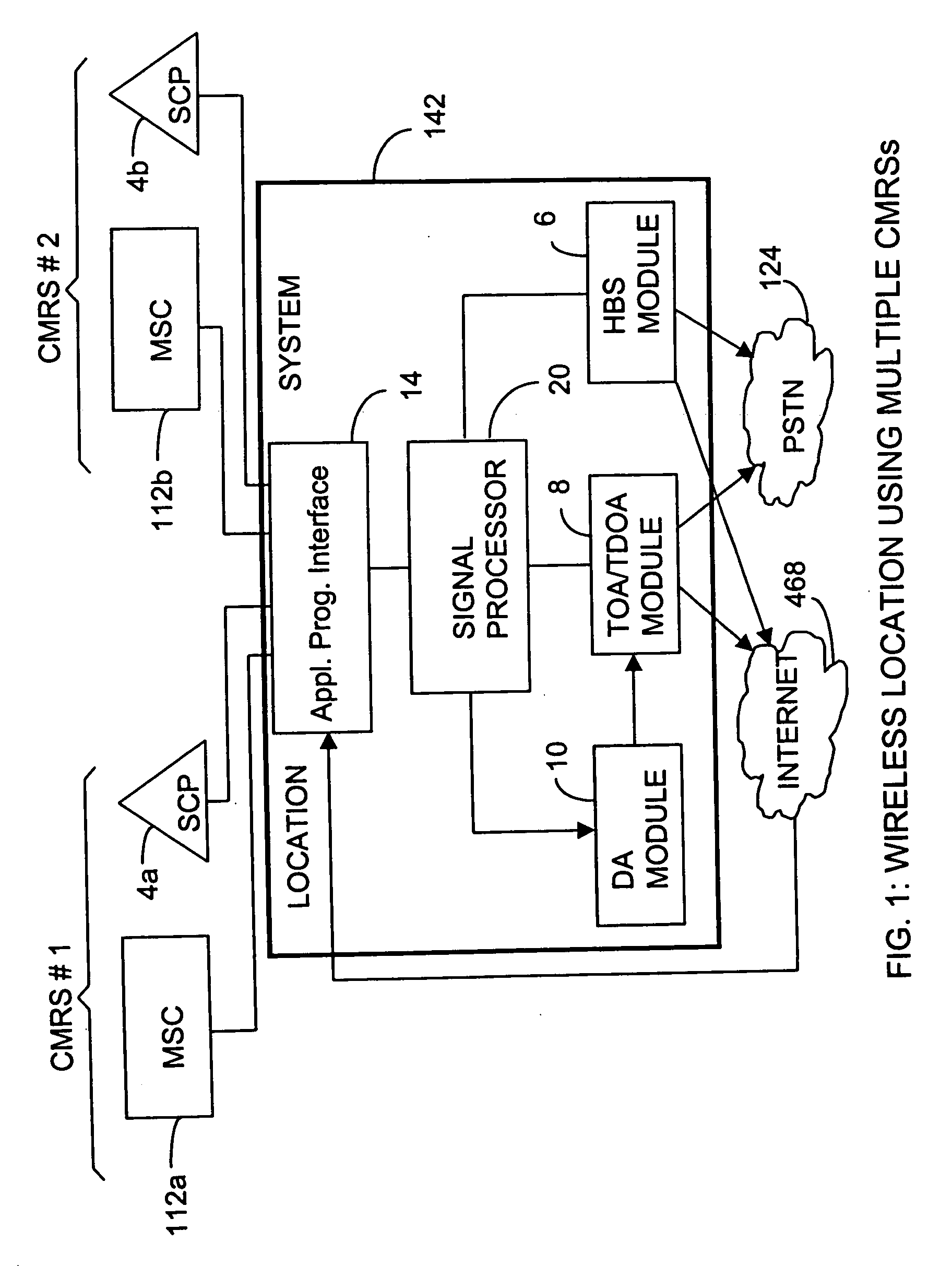
Wireless location using multiple location estimators
InactiveUS6249252B1Effectively and straightforwardly resolvedAmbiguity and conflictDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesTerrainHeuristic
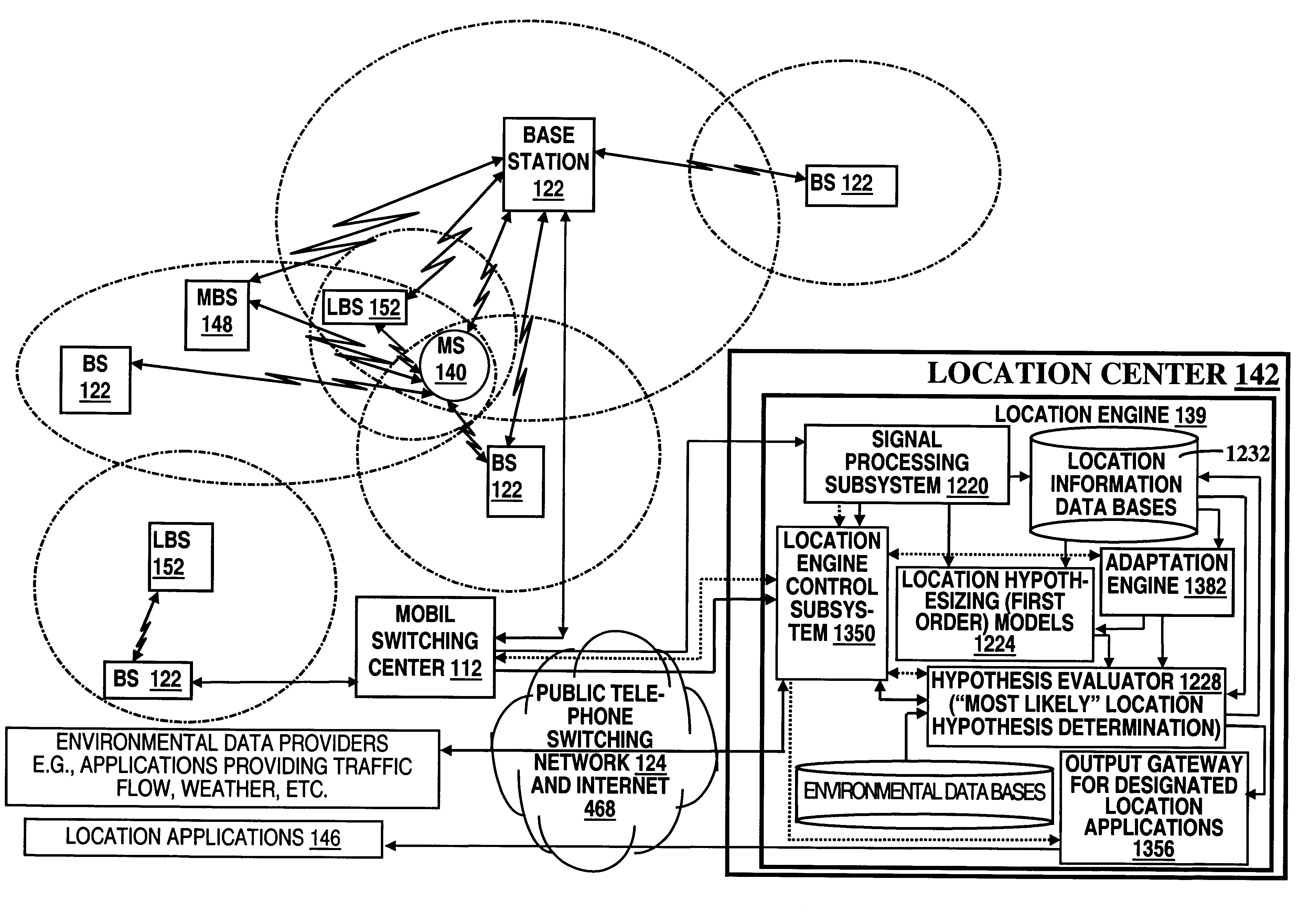
A location system is disclosed for commercial wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location centers for outputting requested locations of commercially available handsets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., CDMA, AMPS, NAMPS or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local MS location requests and more global MS location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location centers. The system uses a plurality of MS locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) pattern recognition; (3) distributed antenna provisioning; (5) GPS signals, (6) angle of arrival, (7) super resolution enhancements, and (8) supplemental information from various types of very low cost non-infrastructure base stations for communicating via a typical commercial wireless base station infrastructure or a public telephone switching network. Accordingly, the traditional MS location difficulties, such as multipath, poor location accuracy and poor coverage are alleviated via such technologies in combination with strategies for: (a) automatically adapting and calibrating system performance according to environmental and geographical changes; (b) automatically capturing location signal data for continual enhancement of a self-maintaining historical data base retaining predictive location signal data; (c) evaluating MS locations according to both heuristics and constraints related to, e.g., terrain, MS velocity and MS path extrapolation from tracking and (d) adjusting likely MS locations adaptively and statistically so that the system becomes progressively more comprehensive and accurate. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signing environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. Accordingly, the system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:TRACBEAM
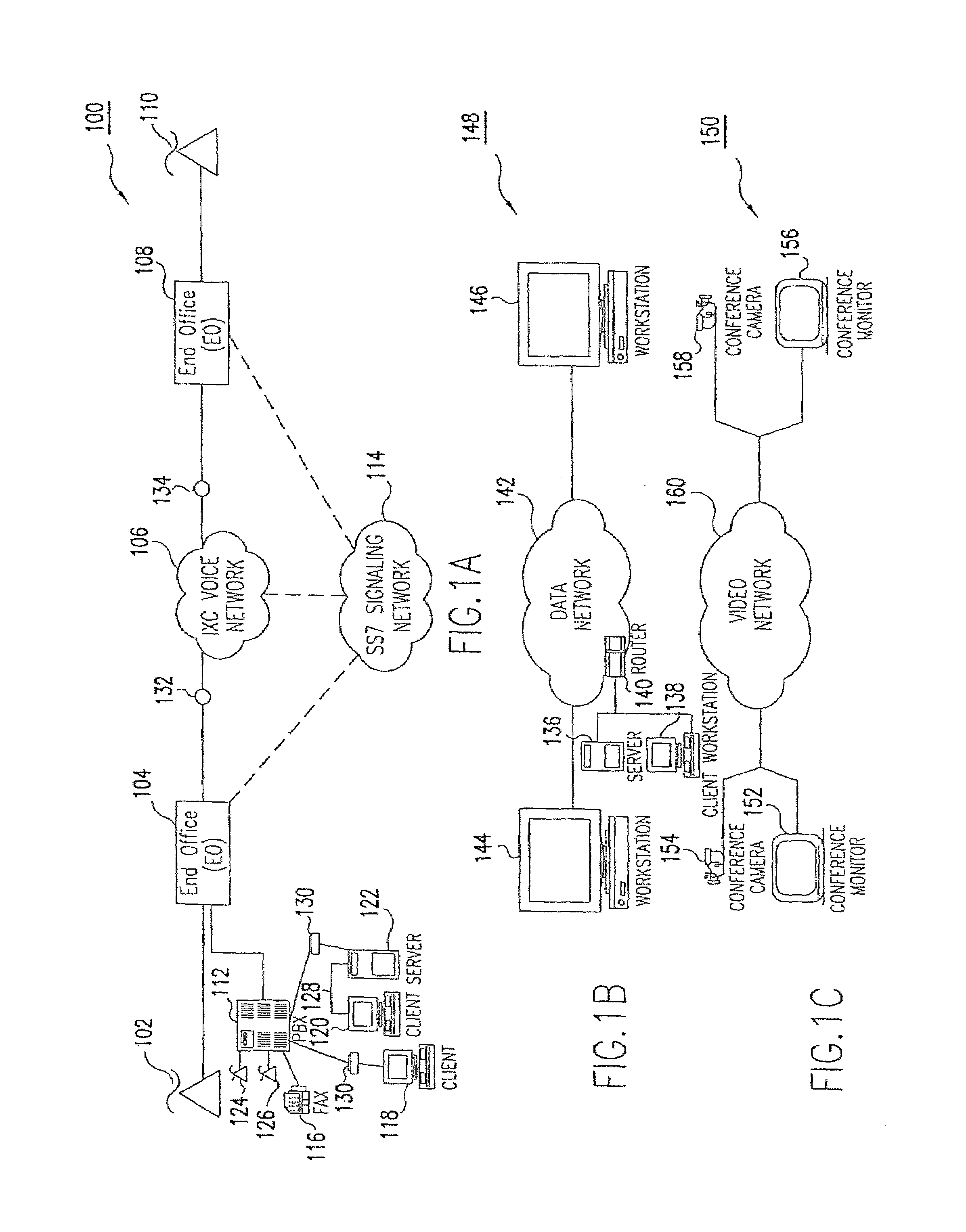
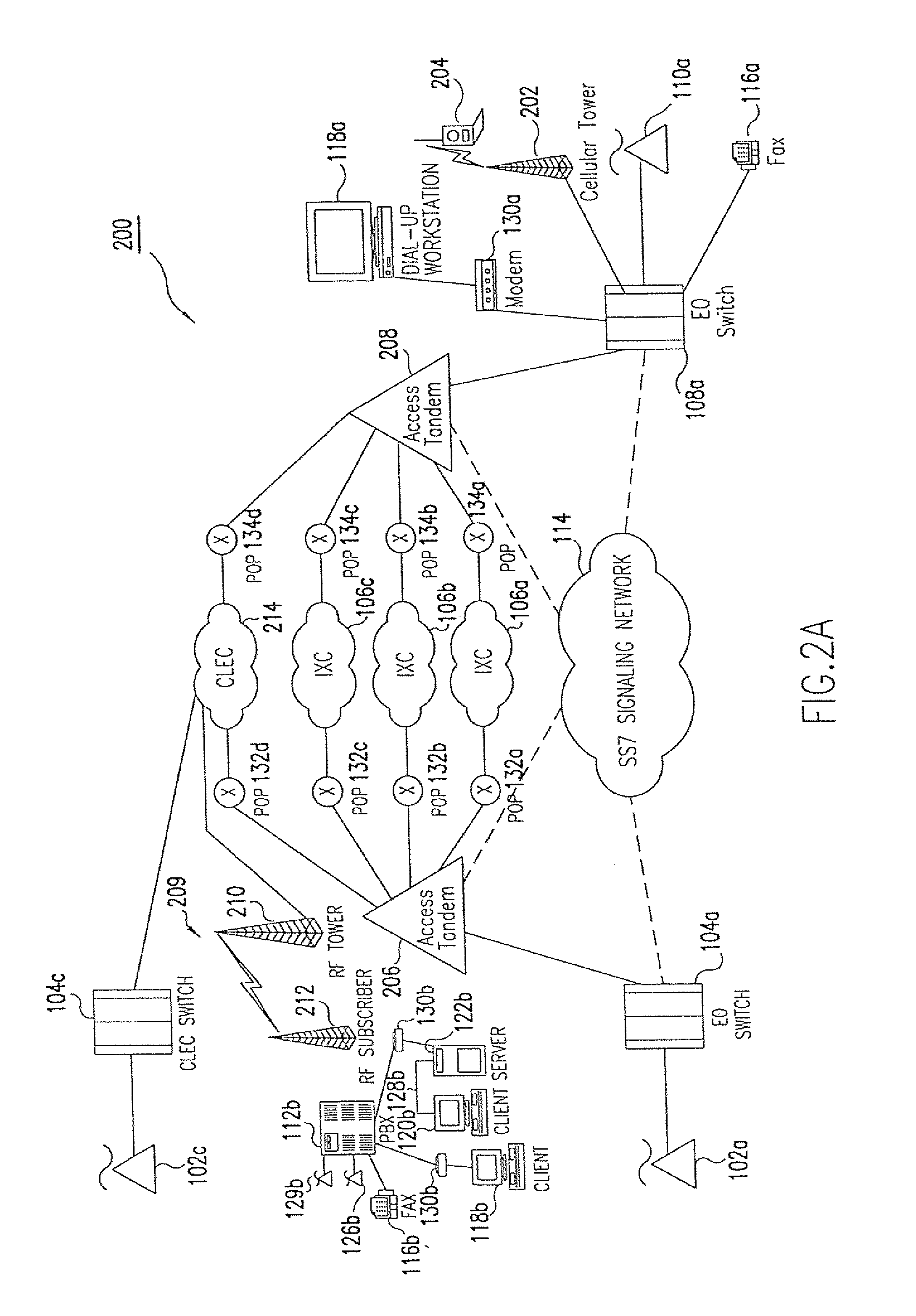
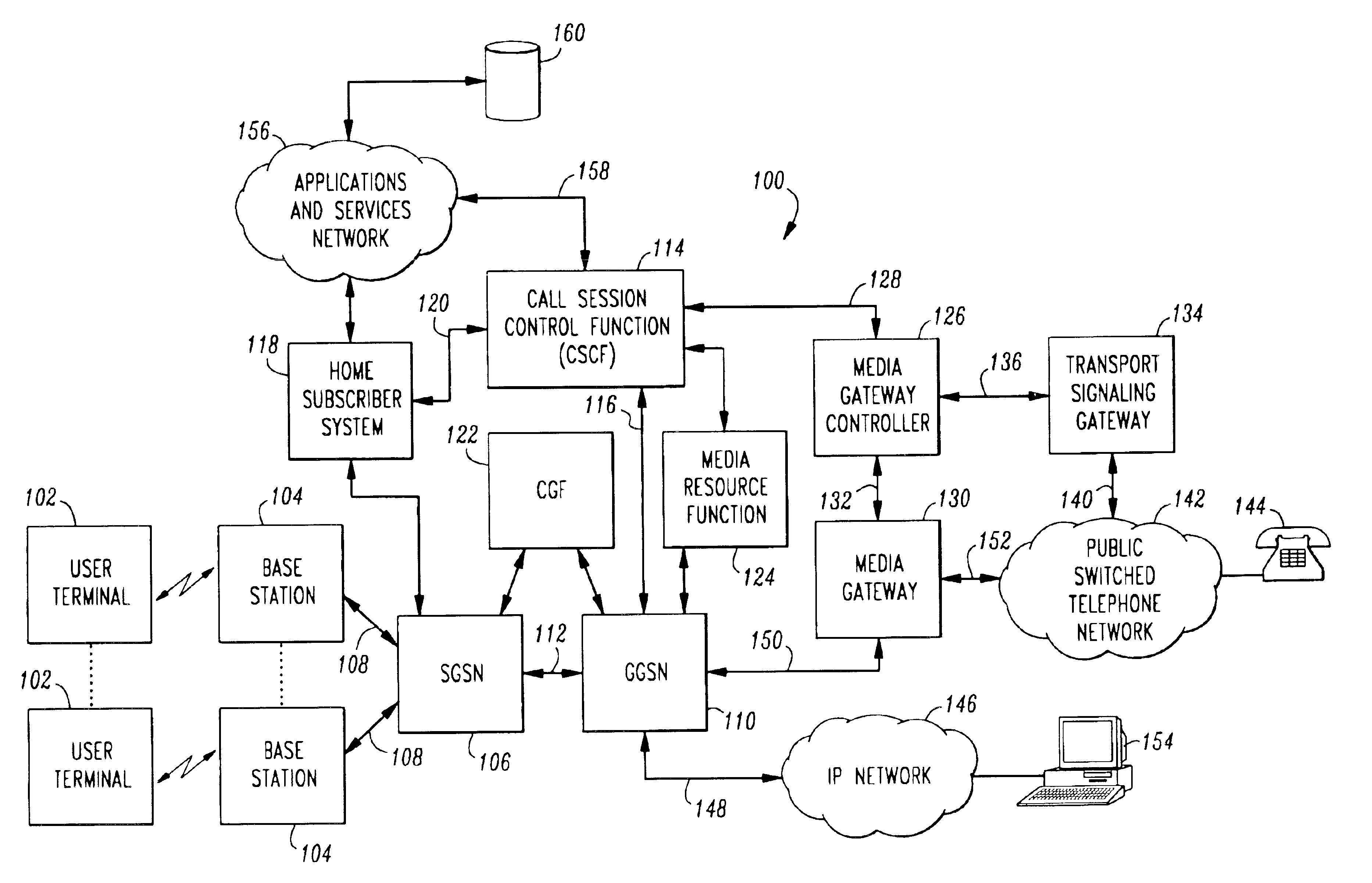
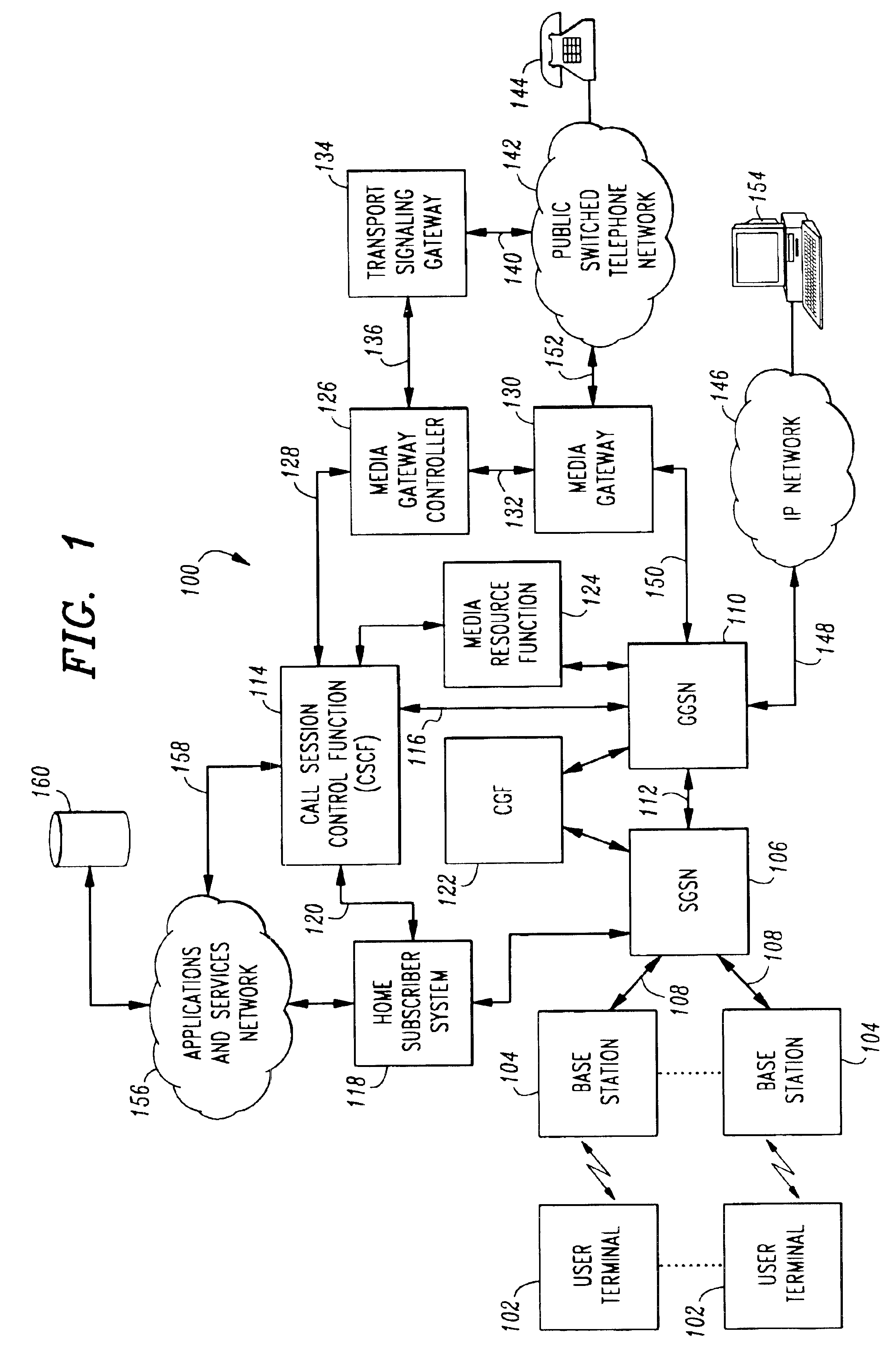
Voice over data telecommunications network architecture
InactiveUS6614781B1Interconnection arrangementsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNetwork operations centerNetwork architecture
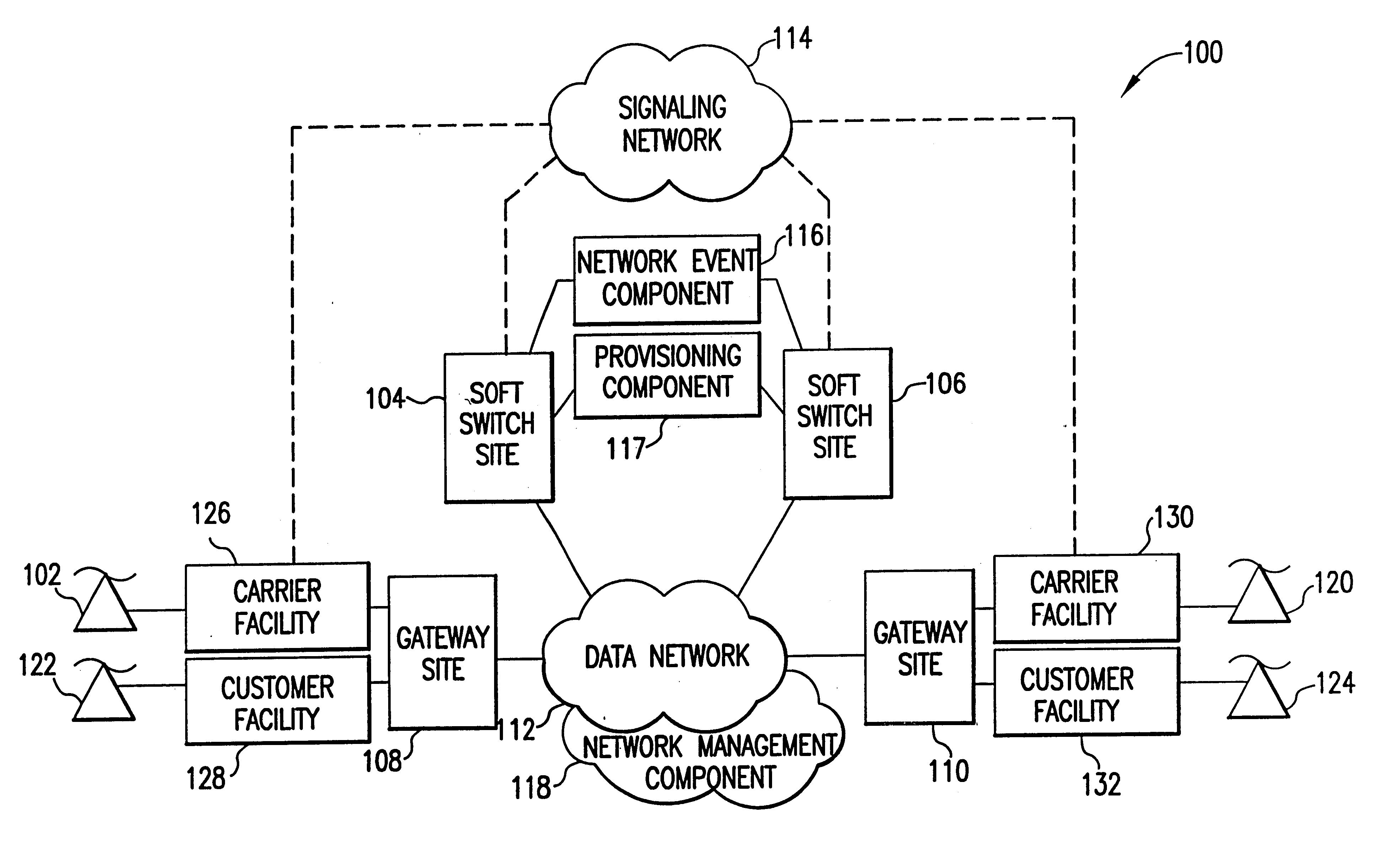
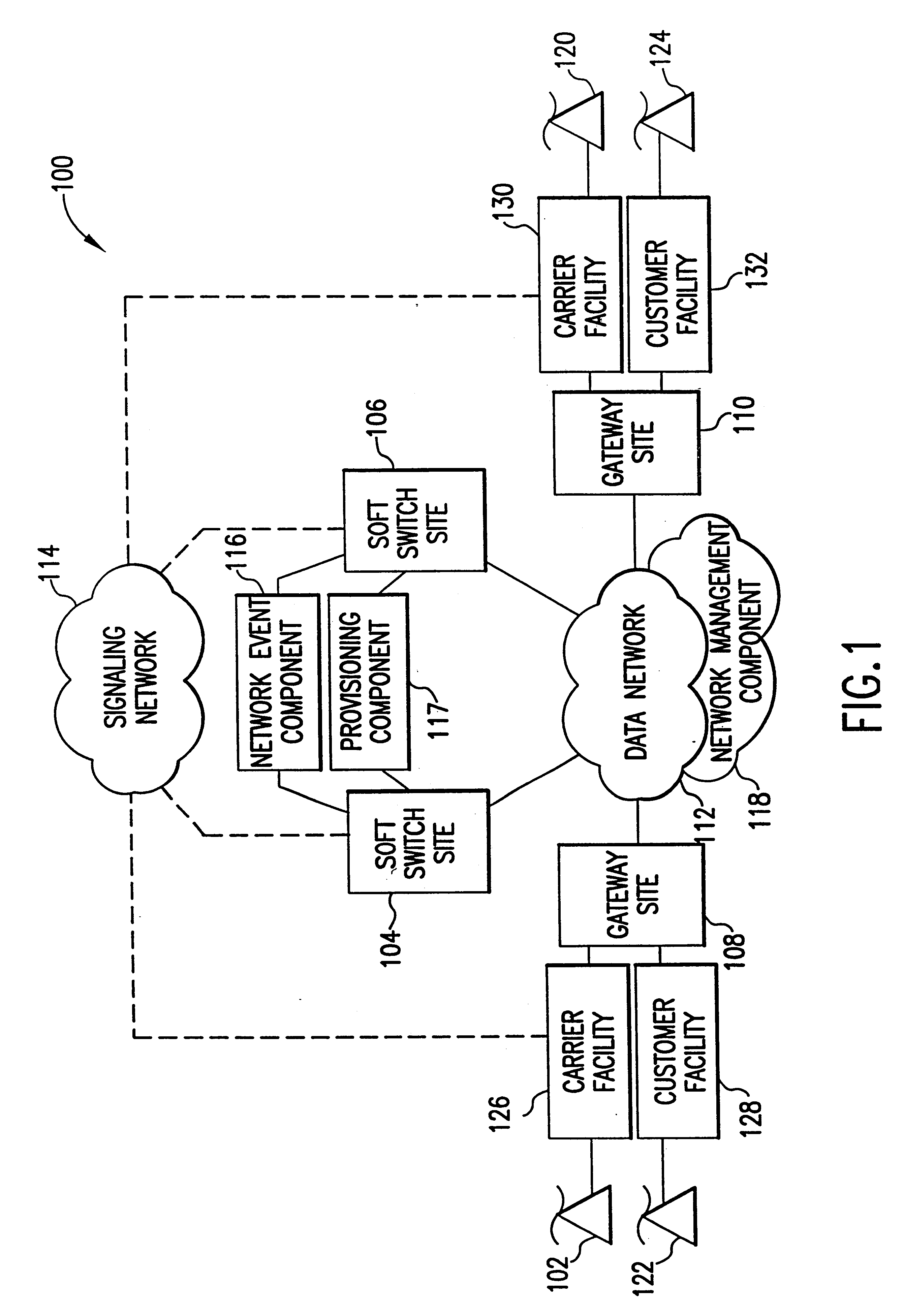
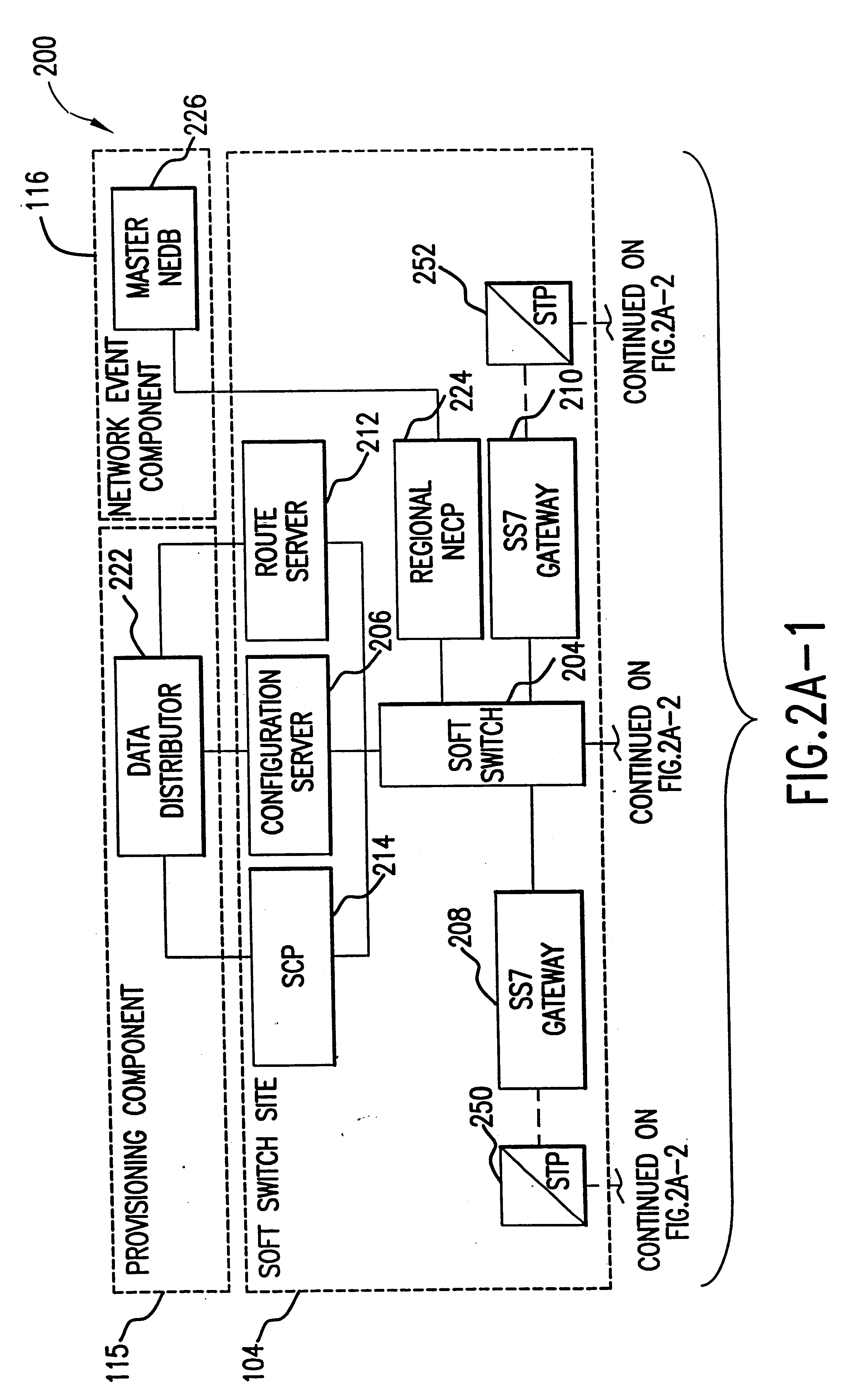
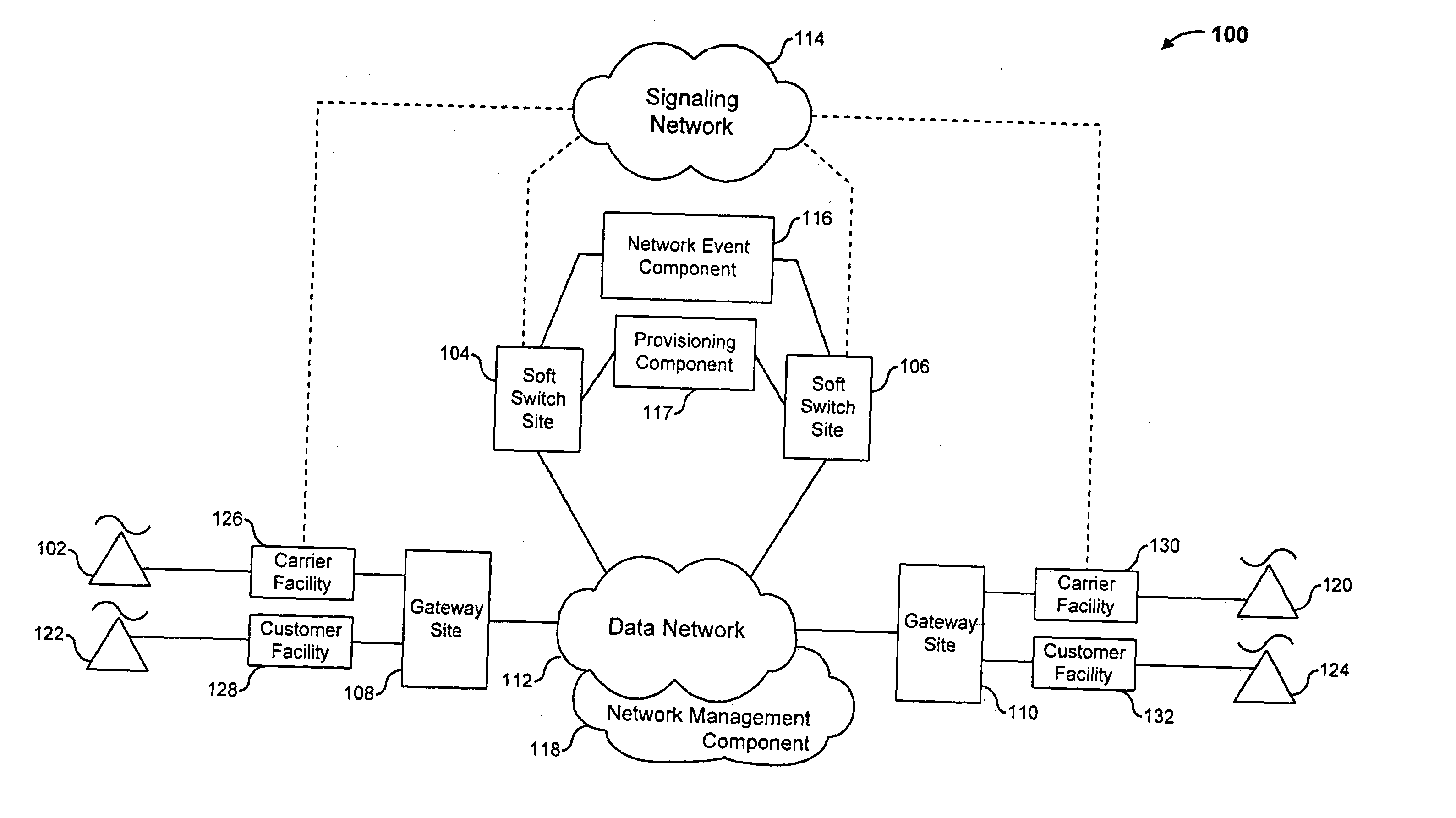
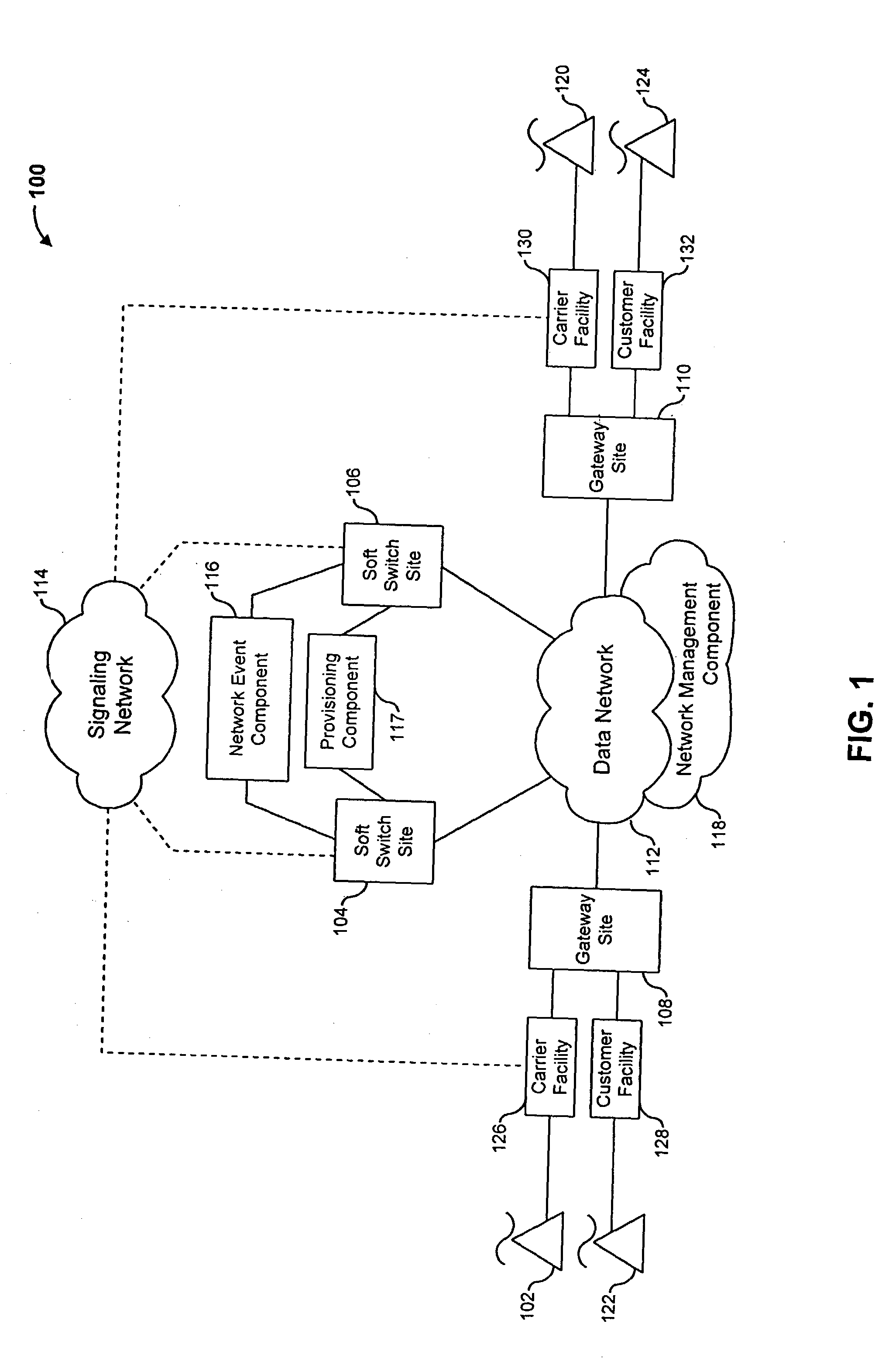
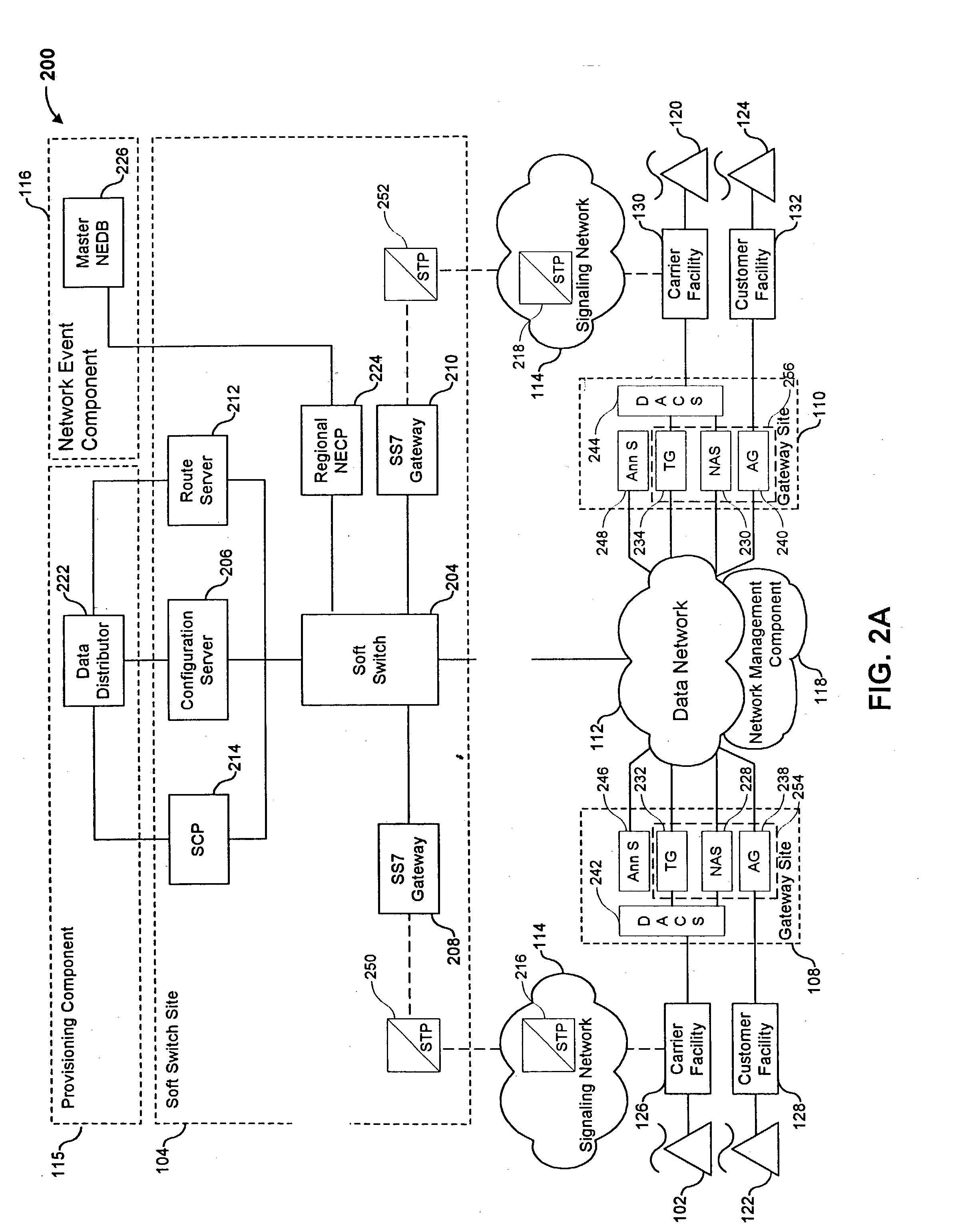
The present invention describes a system and method for communicating voice and data over a packet-switched network that is adapted to coexist and communicate with a legacy PSTN. The system permits packet switching of voice calls and data calls through a data network from and to any of a LEC, a customer facility or a direct IP connection on the data network. The system includes soft switch sites, gateway sites, a data network, a provisioning component, a network event component and a network management component. The system interfaces with customer facilities (e.g., a PBX), carrier facilities (e.g., a LEC) and legacy signaling networks (e.g., SS7) to handle calls between any combination of on-network and off-network callers.The soft switch sites provide the core call processing for the voice network architecture. The soft switch sites manage the gateway sites in a preferred embodiment, using a protocol such as the Internet Protocol Device Control (IPDC) protocol to request the set-up and tear-down of calls. The gateway sites originate and terminate calls between calling parties and called parties through the data network. The gateway sites include network access devices to provide access to network resources. The data network connects one or more of the soft switch sites to one or more of the gateway sites. The provisioning and network event component collects call events recorded at the soft switch sites. The network management component includes a network operations center (NOC) for centralized network management.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
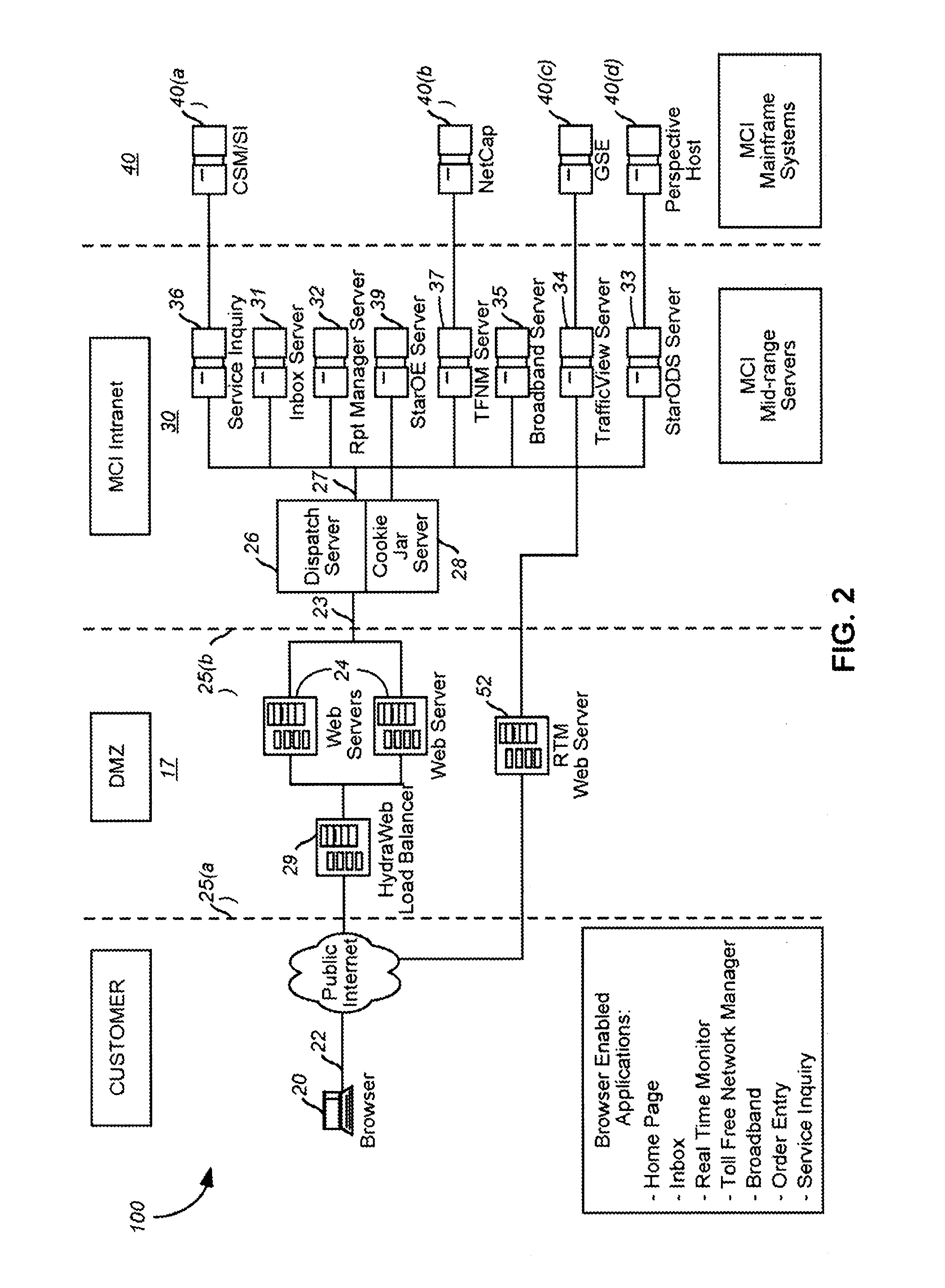
Integrated systems for providing communications network management services and interactive generating invoice documents
InactiveUS7225249B1Easy and convenient accessTelephonic communicationCathode-ray tube indicatorsWeb serviceInvoice
A integrated customer interface for providing telecommunications management to a customer at a browser involves a web server and a client application. The web server manages a client session supports communication of request messages received from the browser to a network management resource. The client application is integrated for use within the browser, downloadable from the web server in accordance with a predetermined customer entitlement, and programmed to be in interactive communications with the network management resource.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
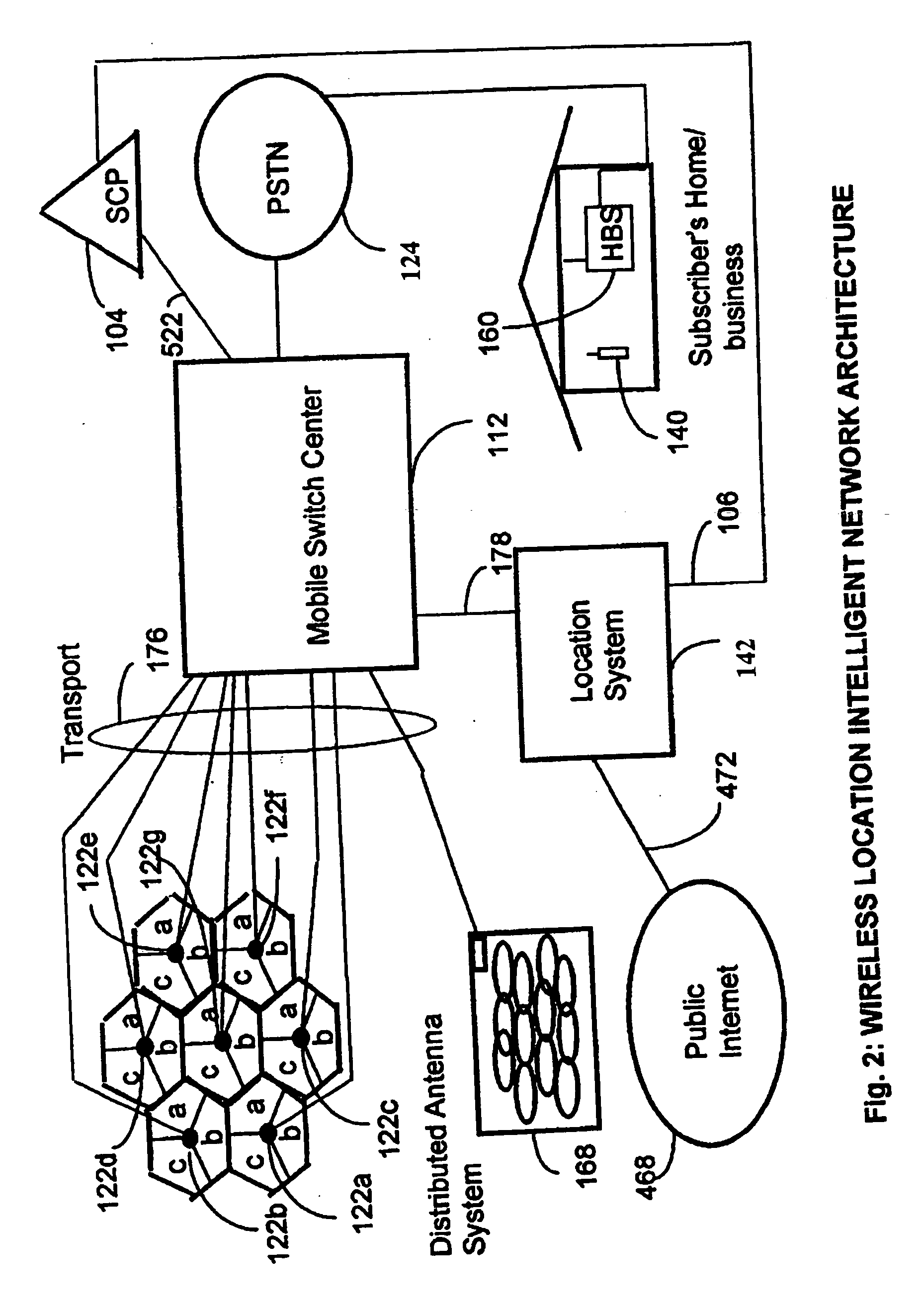
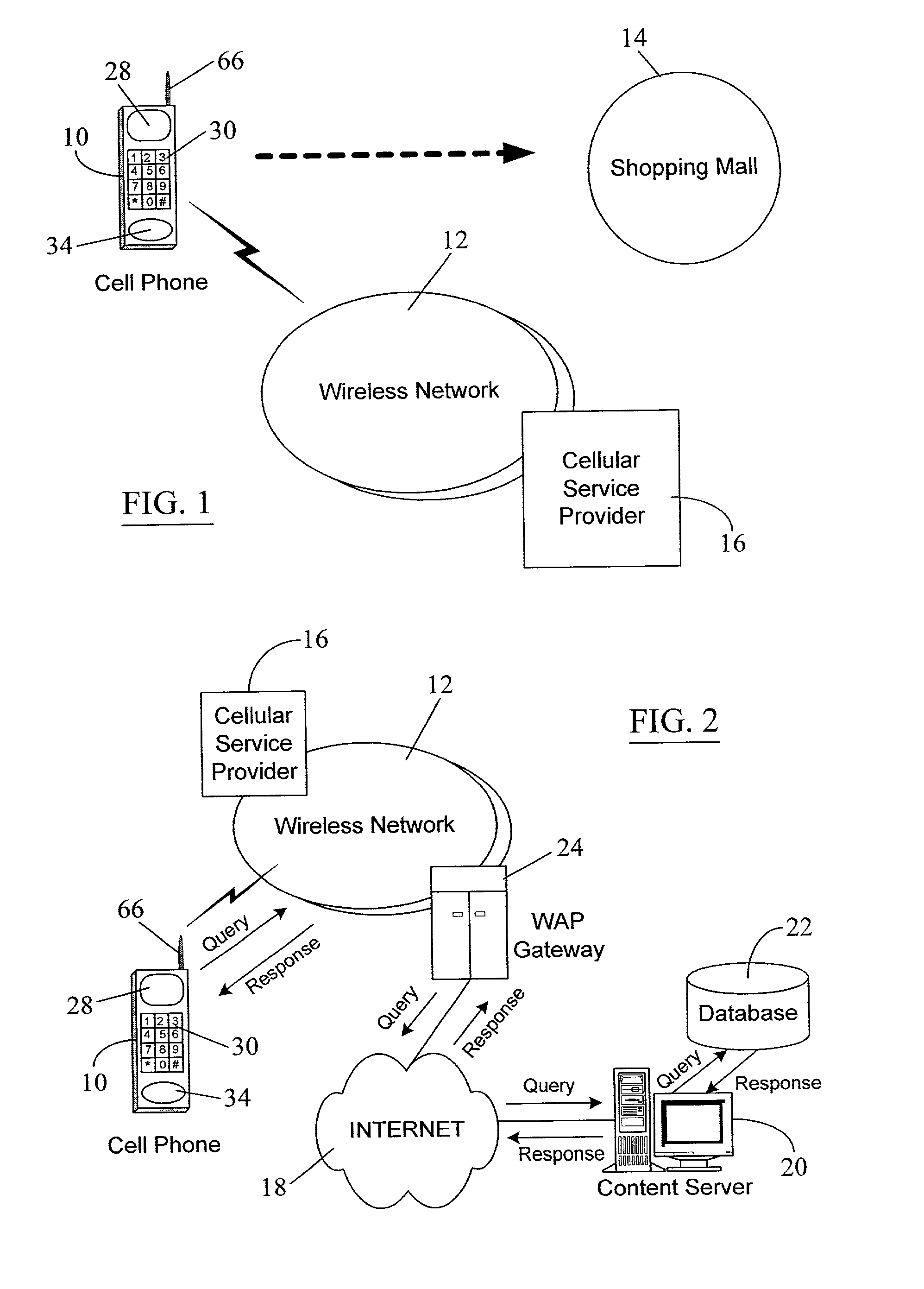
Locating a mobile station and applications therefor
InactiveUS20060025158A1Accurate locationEmergency connection handlingNetwork traffic/resource managementInternet communicationModularity
A location system is disclosed for wireless telecommunication infrastructures. The system is an end-to-end solution having one or more location systems for outputting requested locations of hand sets or mobile stations (MS) based on, e.g., AMPS, NAMPS, CDMA or TDMA communication standards, for processing both local mobile station location requests and more global mobile station location requests via, e.g., Internet communication between a distributed network of location systems. The system uses a plurality of mobile station locating technologies including those based on: (1) two-way TOA and TDOA; (2) home base stations and (3) distributed antenna provisioning. Further, the system can be modularly configured for use in location signaling environments ranging from urban, dense urban, suburban, rural, mountain to low traffic or isolated roadways. The system is useful for 911 emergency calls, tracking, routing, people and animal location including applications for confinement to and exclusion from certain areas.
Owner:FINETRAK LLC
Voice over data telecommunications network architecture
InactiveUS20040022237A1Interconnection arrangementsDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionNetwork operations centerNetwork architecture
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
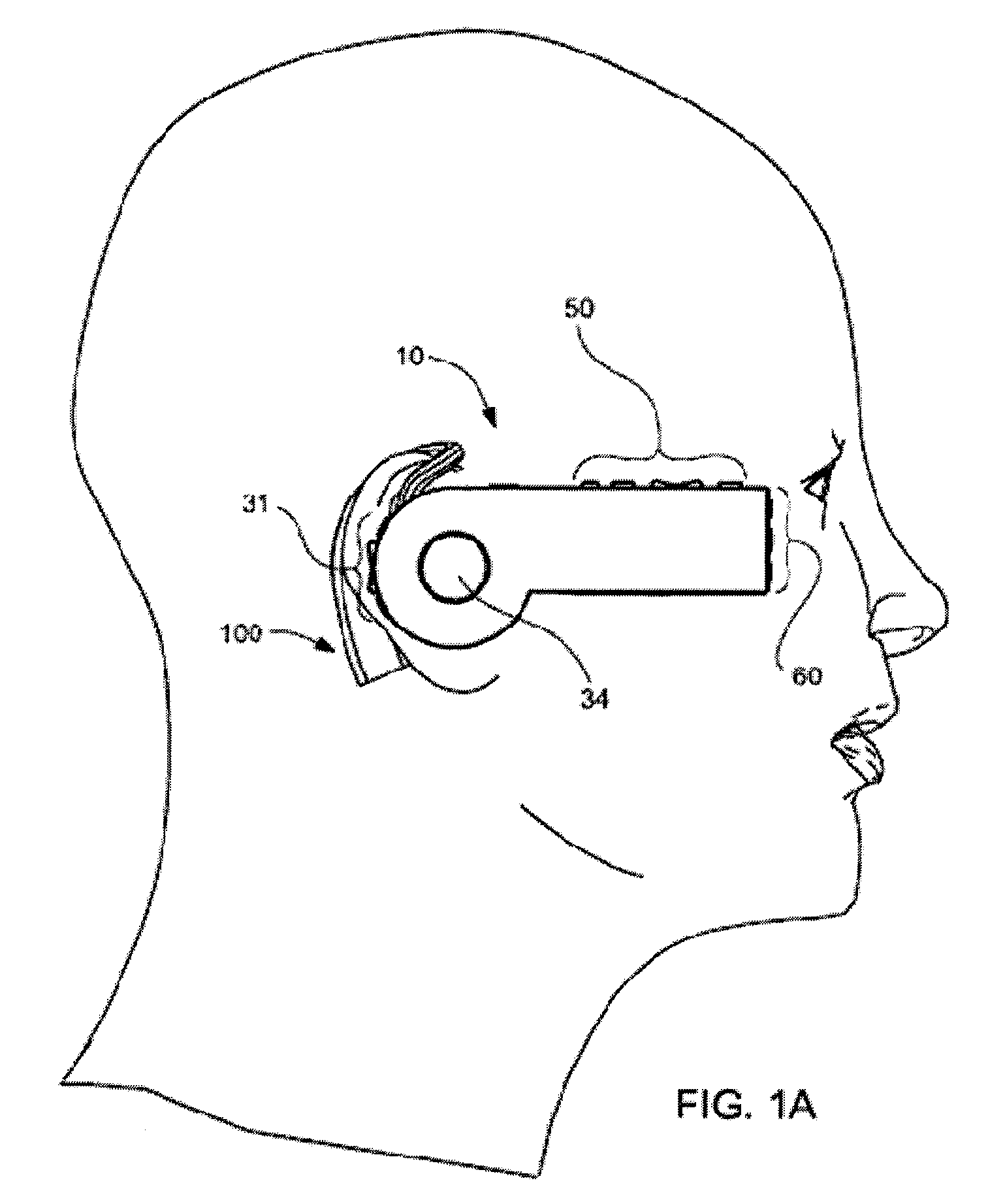
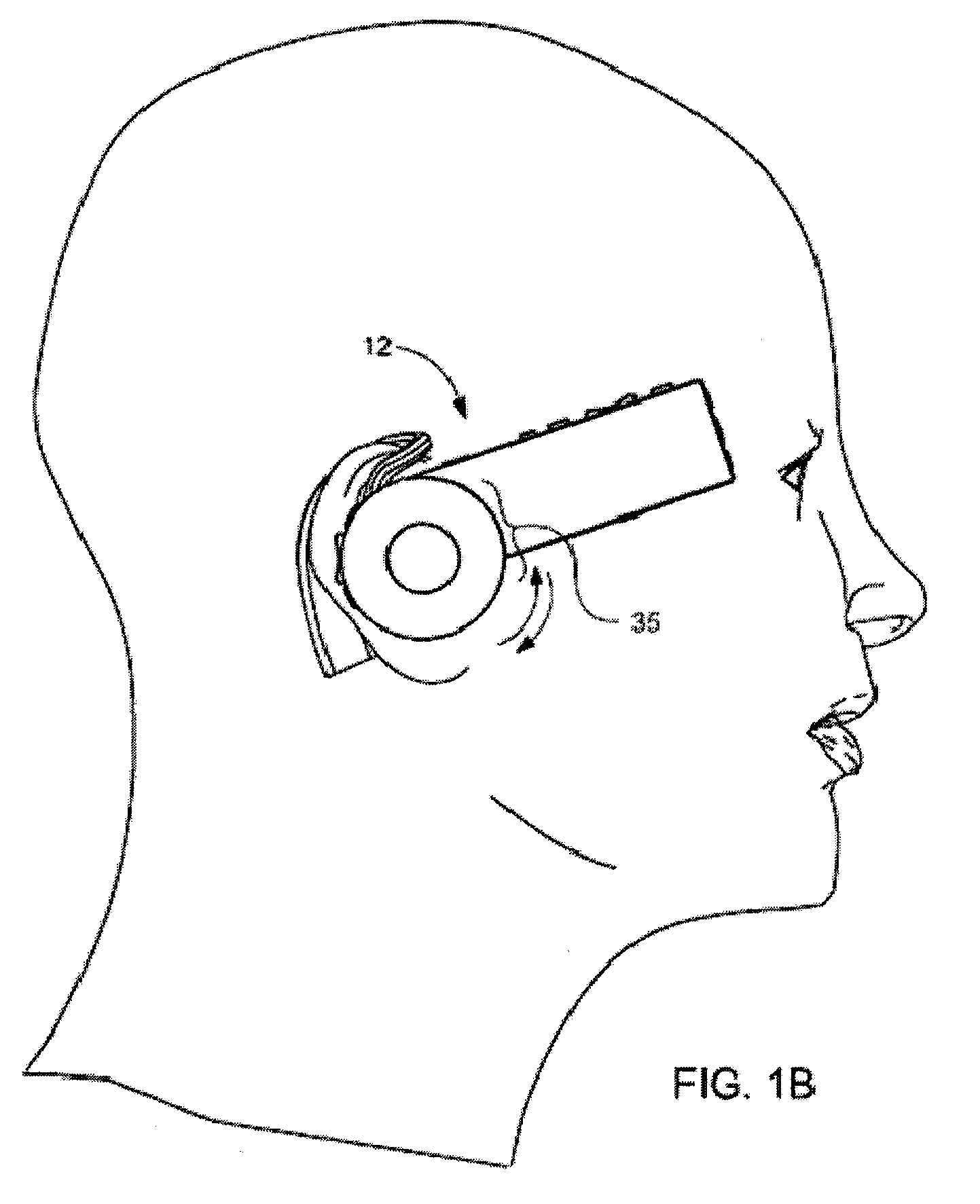
Headset-Based Telecommunications Platform
ActiveUS20100245585A1Extend battery lifeTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersData streamPeer-to-peer
A hands-free wireless wearable GPS enabled video camera and audio-video communications headset, mobile phone and personal media player, capable of real-time two-way and multi-feed wireless voice, data and audio-video streaming, telecommunications, and teleconferencing, coordinated applications, and shared functionality between one or more wirelessly networked headsets or other paired or networked wired or wireless devices and optimized device and data management over multiple wired and wireless network connections. The headset can operate in concert with one or more wired or wireless devices as a paired accessory, as an autonomous hands-free wide area, metro or local area and personal area wireless audio-video communications and multimedia device and / or as a wearable docking station, hot spot and wireless router supporting direct connect multi-device ad-hoc virtual private networking (VPN). The headset has built-in intelligence to choose amongst available network protocols while supporting a variety of onboard, and remote operational controls including a retractable monocular viewfinder display for real time hands-free viewing of captured or received video feed and a duplex data-streaming platform supporting multi-channel communications and optimized data management within the device, within a managed or autonomous federation of devices or other peer-to-peer network configuration.
Owner:EYECAM INC
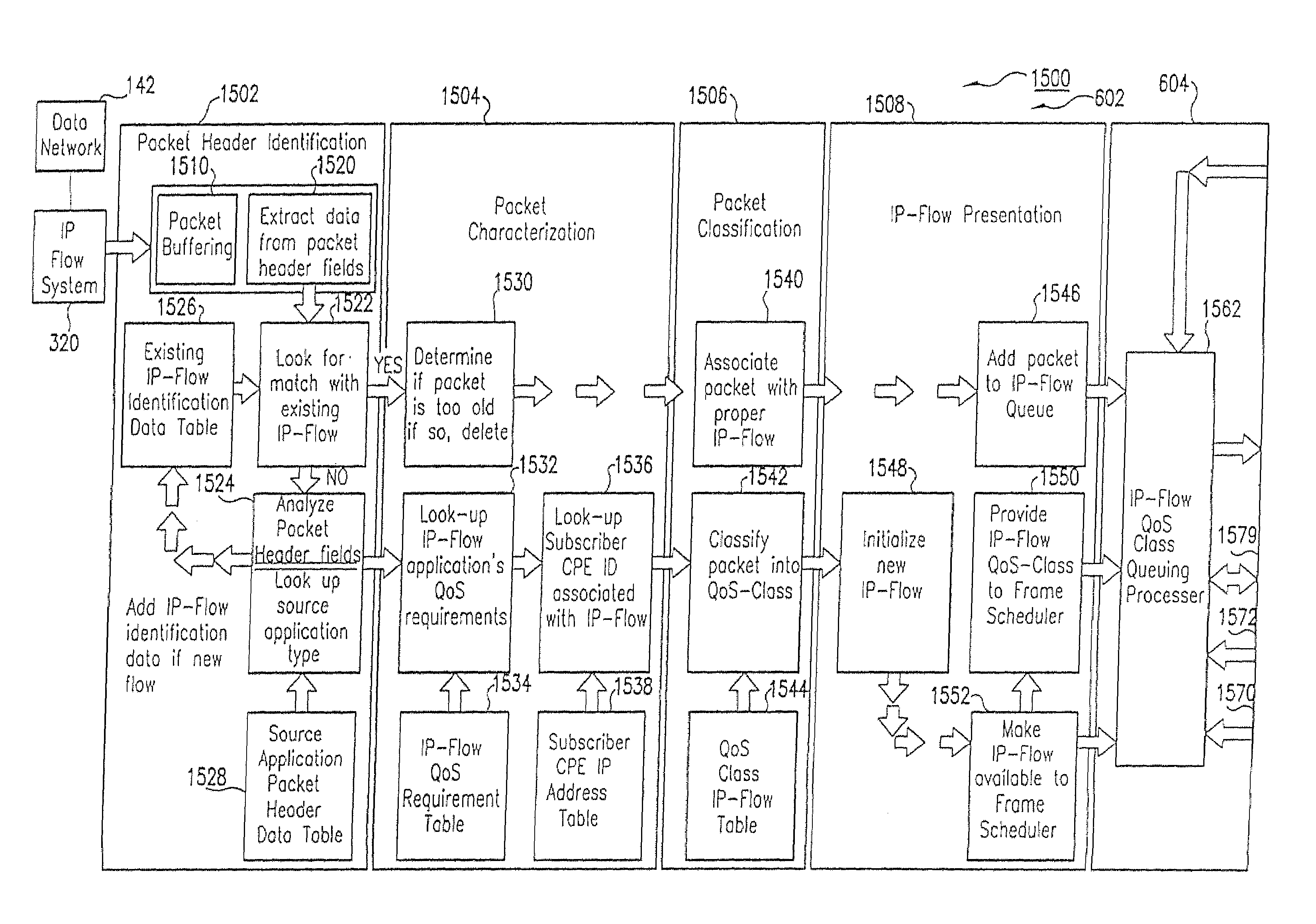
Method and computer program product for internet protocol (IP)-flow classification in a wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system
InactiveUS7251218B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceWireless access point
A system and method for Internet Protocol (IP) flow classification group IP flows in a packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system is disclosed. The method comprises analyzing an IP flow in a packet-centric manner, classifying the IP flow, scheduling the IP flow for transmission over a shared wireless bandwidth between a wireless base station and at least one subscriber customer premises equipment (CPE) station, allocating the shared wireless bandwidth to a communication of the IP flow between the wireless base station and a subscriber CPE station so as to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS) associated with the IP flow.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
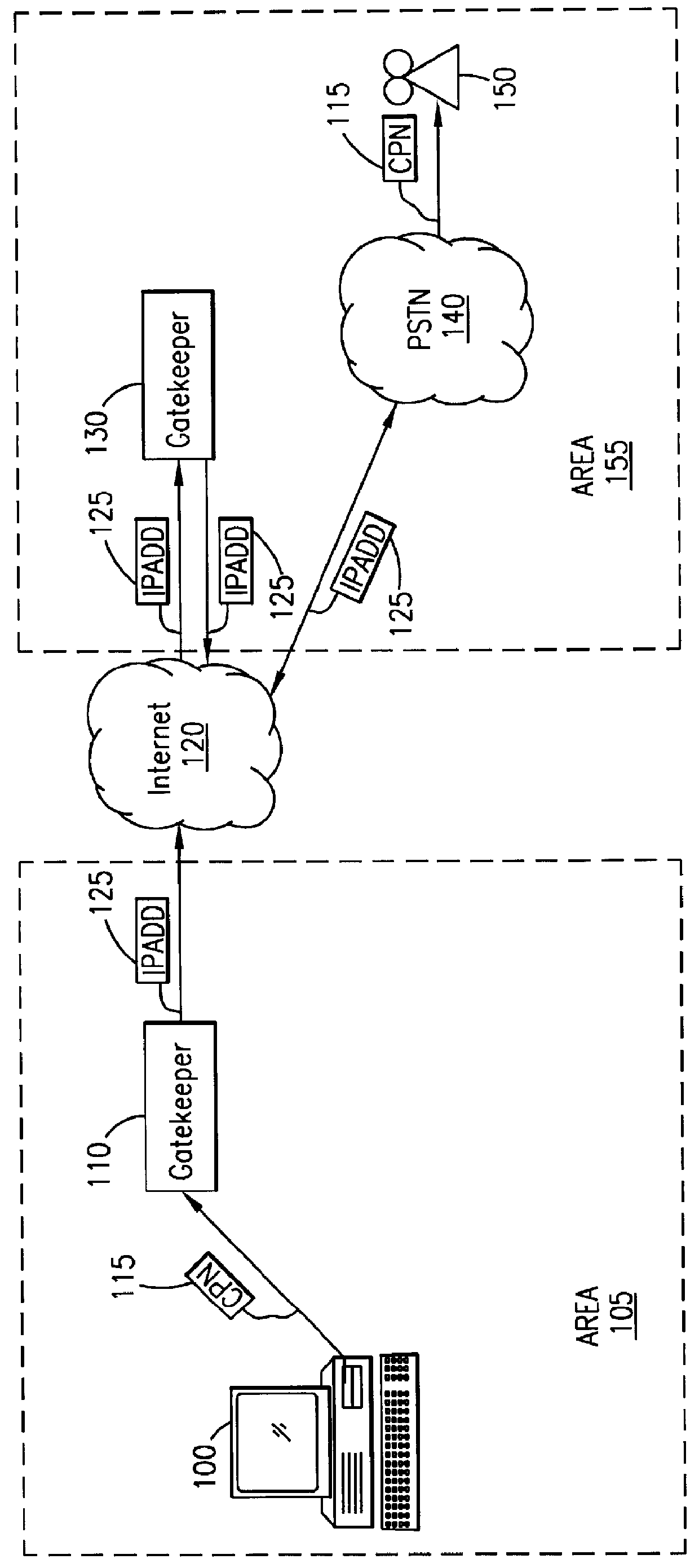
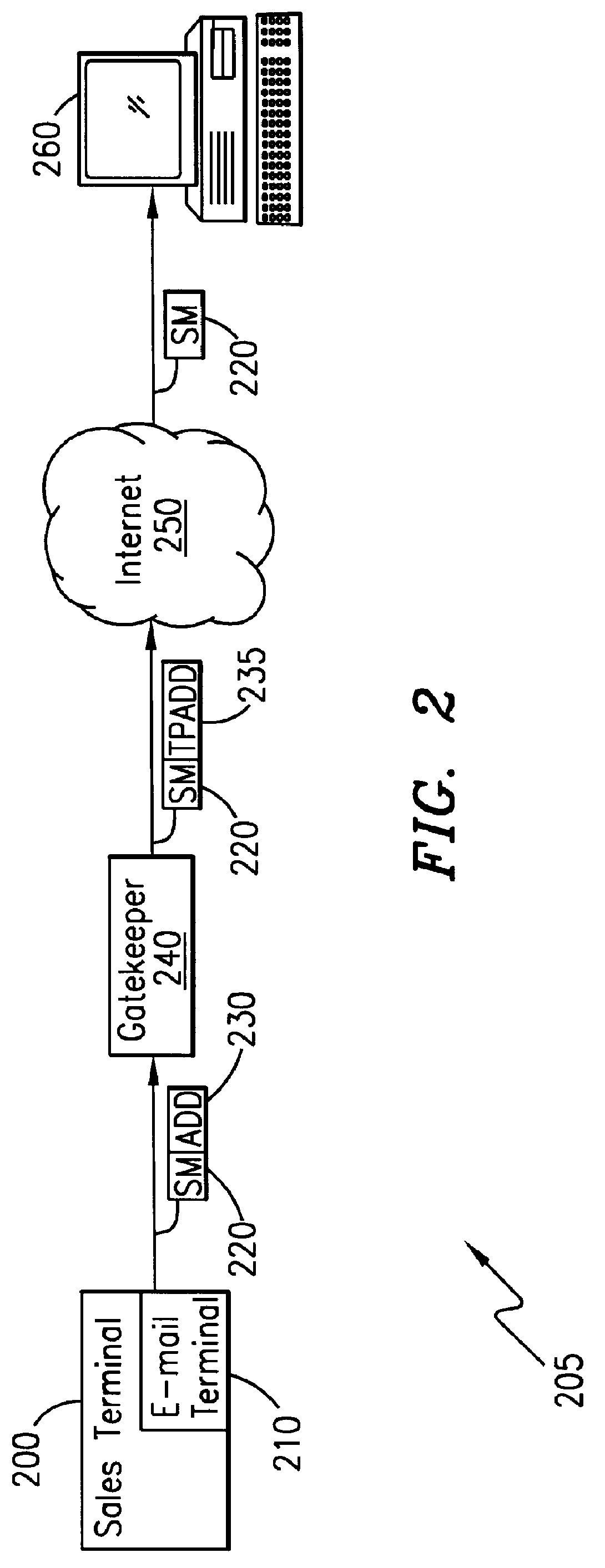
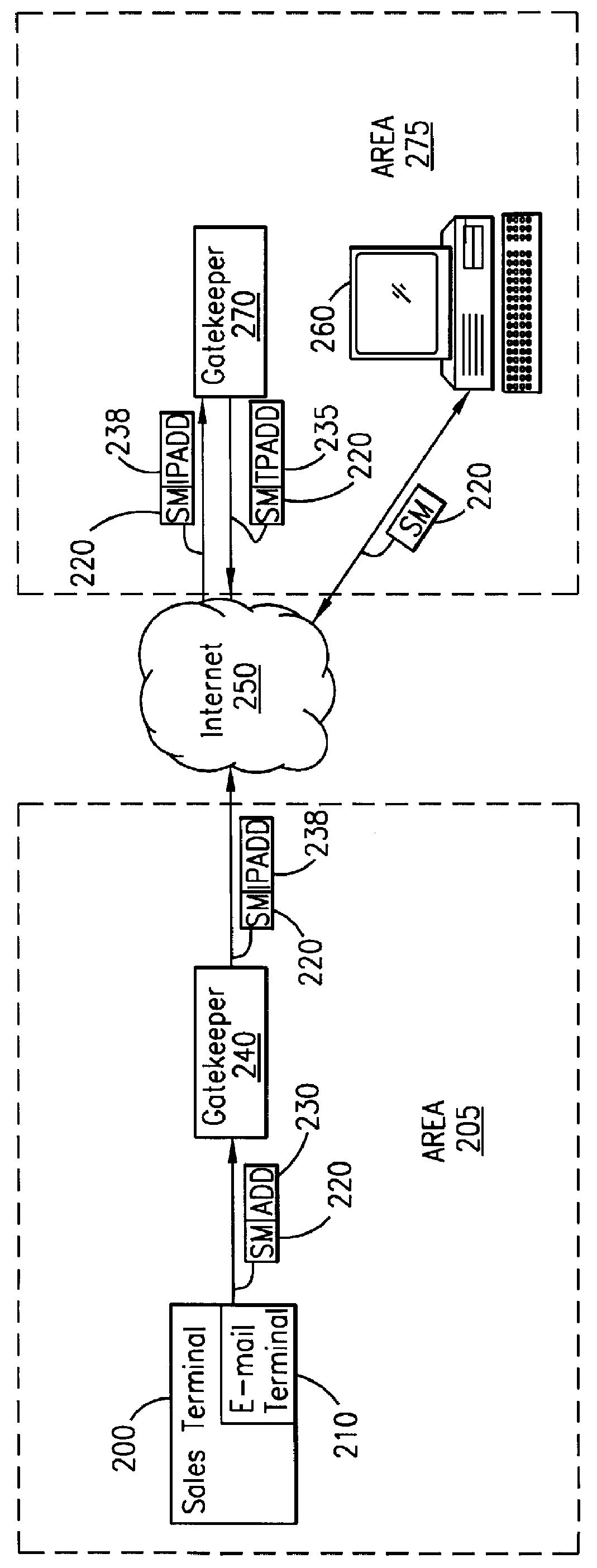
System and method for sending a short message containing purchase information to a destination terminal
InactiveUS6067529AEfficient and cost-effectiveReliable deliveryComplete banking machinesCash registersMulticast addressComputer terminal
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for providing a substantially immediate electronic receipt after a consumer has made a purchase. When a consumer makes a purchase, the sales terminal, which is attached with a short message / e-mail sending capable terminal, can generate and route a short message along with the detailed purchase information to a transport address or alias address associated with the consumer via a Gatekeeper for the Internet for the area that the sales terminal is located in. Upon receipt of the short message, the Gatekeeper can then convert the alias address to the transport address, if the alias address is given and the consumer does not want the short message sent to the alias address, and forward the short message through the Internet to that transport address (or alias address) as an Internet Protocol datagram for storage and retrieval of the short message by the consumer either immediately or at a later time.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Wireless multimedia player
InactiveUS6845398B1Network traffic/resource managementMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless mesh networkMultimedia servers
A wireless device, system and method for receiving and playing multimedia files streamed from a multimedia server over a wireless telecommunications network. A desired multimedia file is selected from one or more multimedia files stored in the multimedia server, which server is operatively connected to the wireless telecommunications network. Successive blocks of data from the desired multimedia file are streamed over the wireless telecommunications network in a digitized and compressed format and received by the wireless telecommunications device. The received blocks of data from the streamed multimedia file are temporarily stored in a buffer in the wireless device, decoded and decompressed, and successively played through an audio and / or video output in the wireless device. The wireless device monitors the blocks of data stored in the buffer and signals the wireless telecommunications network to increase the rate that the data blocks are transmitted over the wireless network in the event that the data stored in the buffer falls below a minimum threshold level.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Position determination system
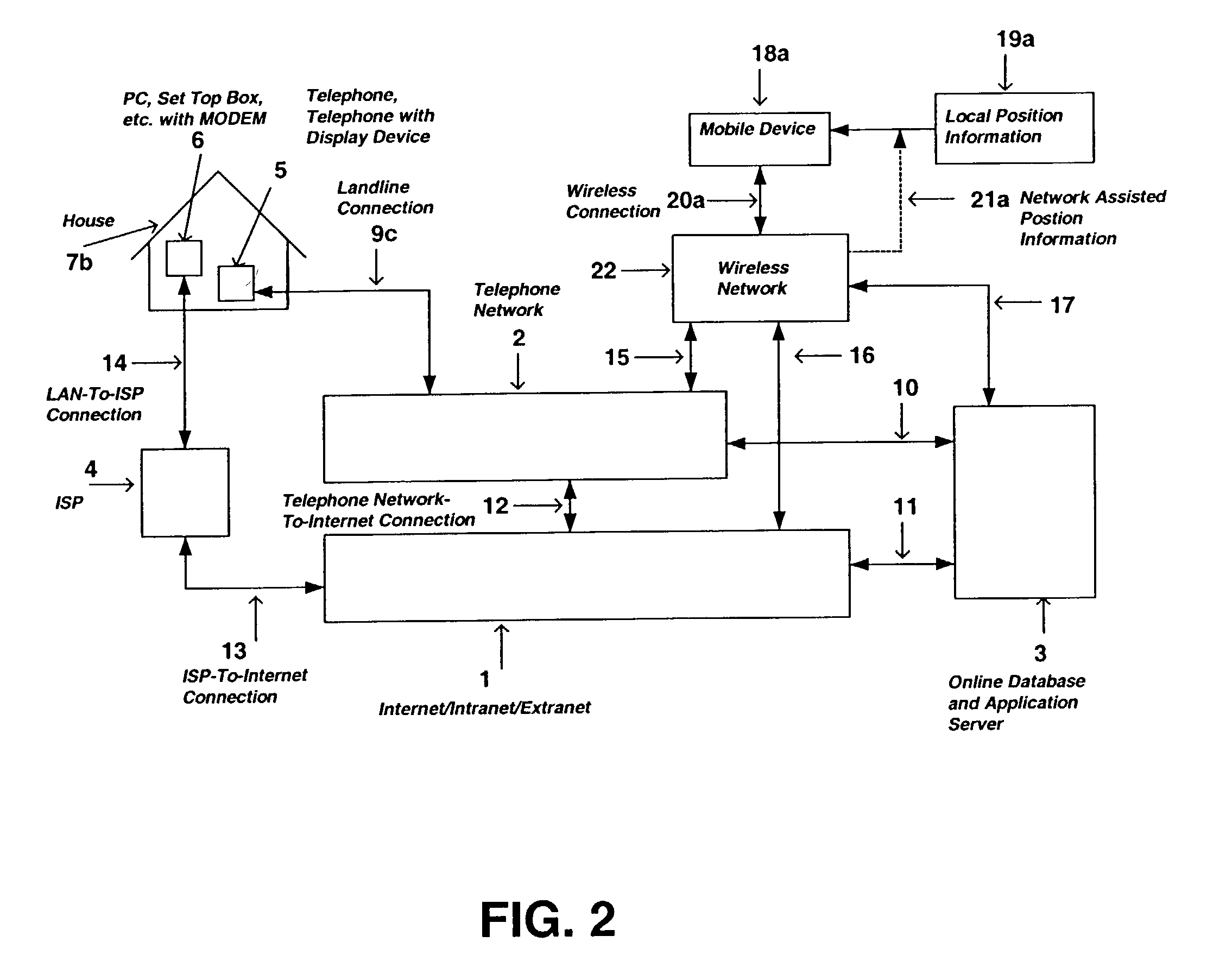
InactiveUS20030016804A1Limited resourceReduce areaInstruments for road network navigationDevices with GPS signal receiverTelecommunications networkThe Internet
The present invention is directed to a system and method for providing real-time position information of one party to another party by utilizing a conventional telecommunication network system such as the convention telephone network, a mobile telecommunications network, a computer network, or the Internet. More specifically, the preferred embodiments of the present invention allow a caller and a receiver of a telephone call to provide to and receive from each other position information related to the caller and / or receiver's physical location, including address information, GPS coordinates, nearby fixed locations such as a parking structure, etc. Additionally, the preferred embodiments of the present invention allow a caller and receiver to retrieve routing instructions or maps for traveling to or from each other. In another embodiment of the present invention, a party may locate the position of another party via the entry of the other party's unique identifier such as a phone number of the other party's mobile phone. In yet another embodiment of the present invention, the position information of a party may be concurrently delivered to another party's computer terminal whereby the other party can process the information in further detail.
Owner:ARTAX LLC
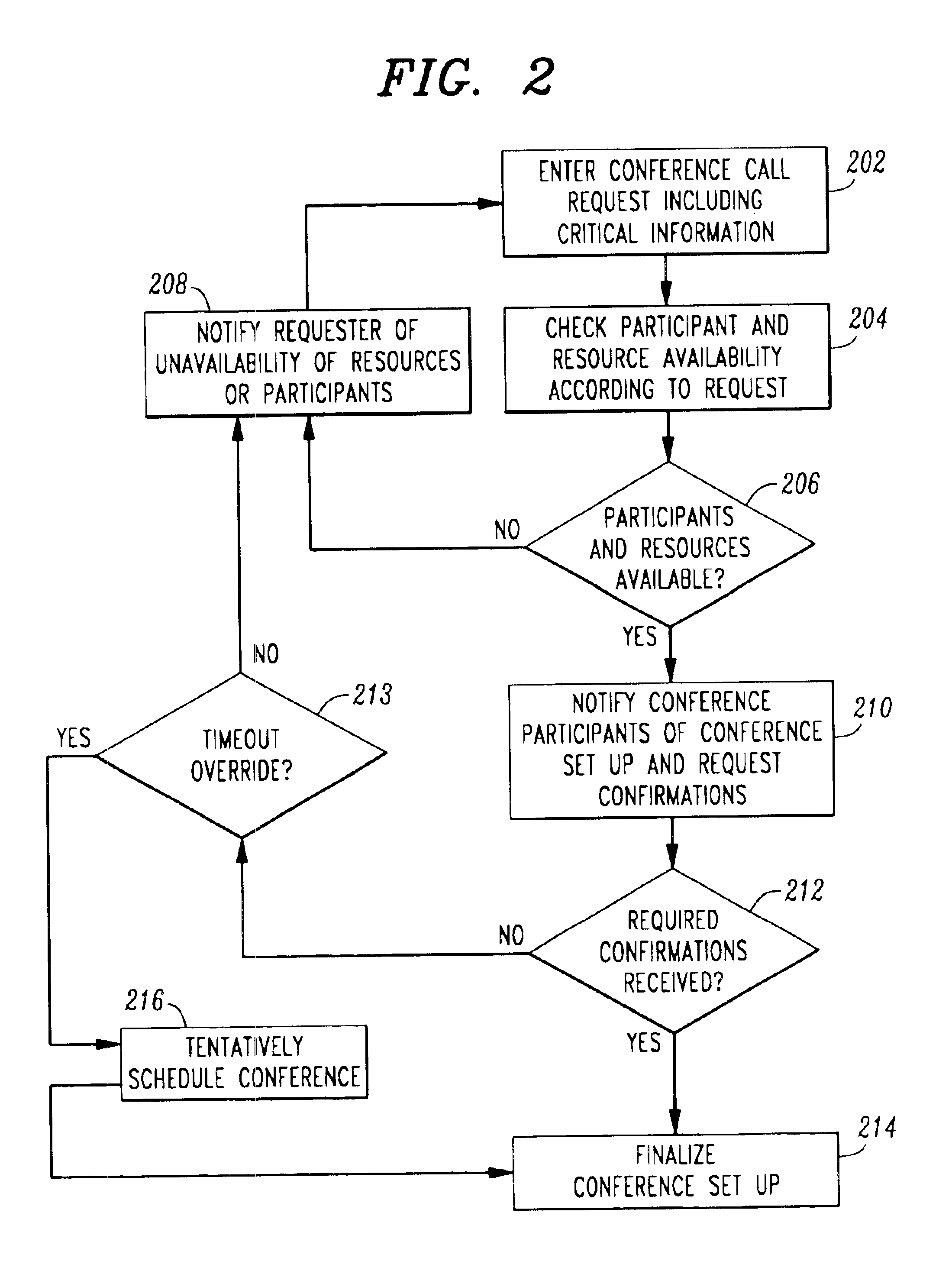
Targeted and intelligent multimedia conference establishment services
InactiveUS6870916B2Special service for subscribersCommmunication supplementary servicesCommunications systemTelecommunications network
In a multimedia communications system (100), a conference establishment server coordinates the scheduling of a conference call. The server receives request for conference calls (202). The request includes a list of participants and may include an indication of the resources necessary and any rules for the conference call. The request may indicate critical resources or participants that are required for the call. Based on the request, the server determines a conference time and notifies participants of the time (204, 206, 210). Prior to conference time, participants are reminded of the time and automatically connected to the call. The server may check the status of users on the telecommunications network to determine availability. If a critical participant or resource is unavailable at conference time, the conference may be cancelled with notification to the participants.
Owner:GEMPLU
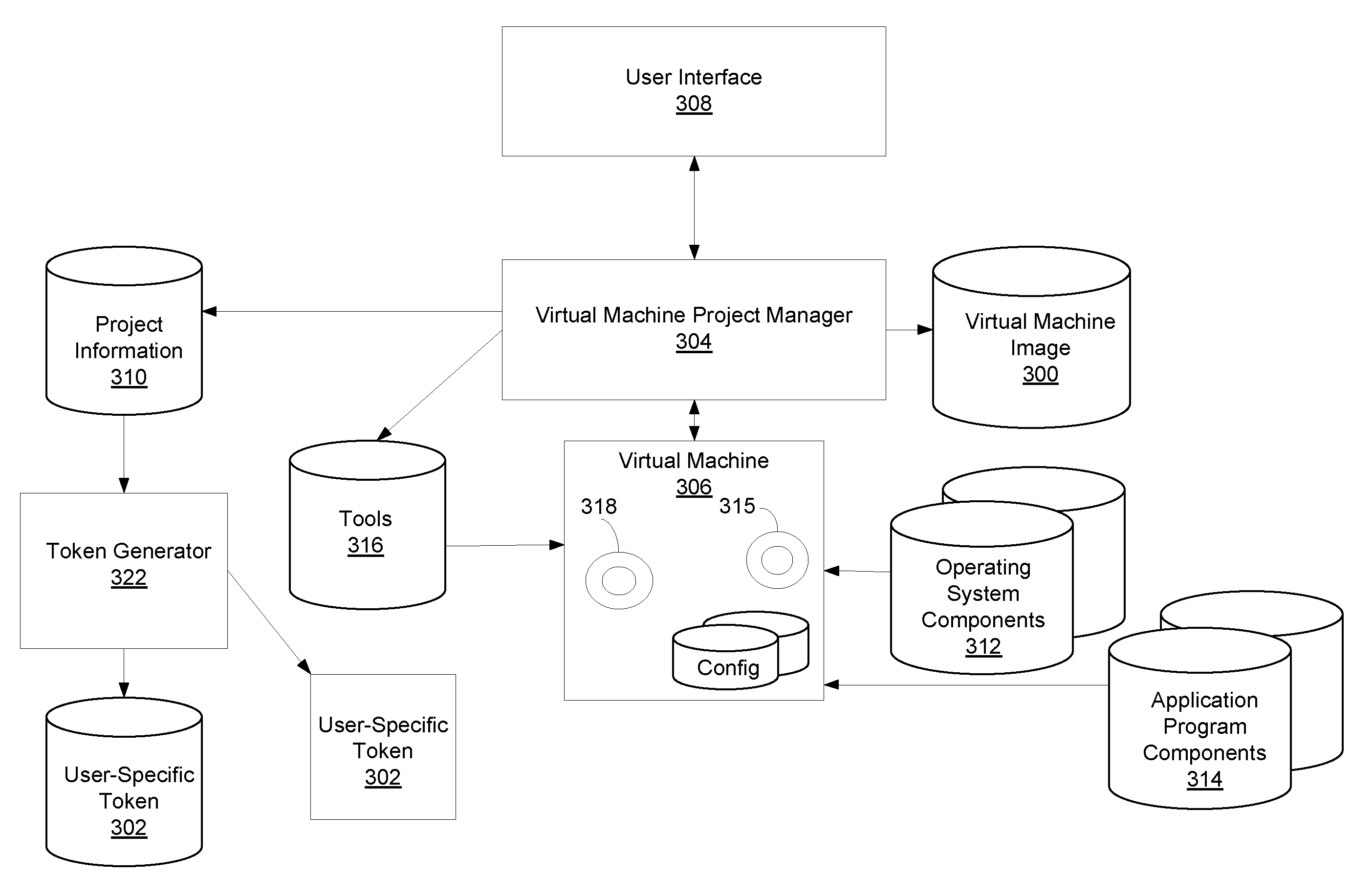
Remote Network Access Via Virtual Machine
ActiveUS20070300220A1User identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkSoftware engineering
A virtual machine project manager creates a generic, i.e., not user-specific, virtual machine image file. Copies of this image file may be distributed to one or more users, each of whom may then use an automated procedure to generate a user-specific virtual machine image file and, thus, a user-specific virtual machine on his / her remote host computer. The generic virtual machine image file may be distributed on computer-readable media, such as a DVD disks, or the file may be stored on a server and downloaded (such as via the Internet) by the users. Each user also receives or downloads a token, which contains a small amount of user-specific information that is used by the automated procedure to provision the generic virtual machine image file for the particular user. A virtual machine accesses a security token connected to a host computer to automatically authenticate or re-authenticate a user, such as when a virtual private network connection is restarted. Substantially identical session identifiers are used by a host computer and a virtual machine, or by two or more virtual machines and, when communicating with an integrated access server. A file server stores virtual machine images that are accessed by a plurality of host computers.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
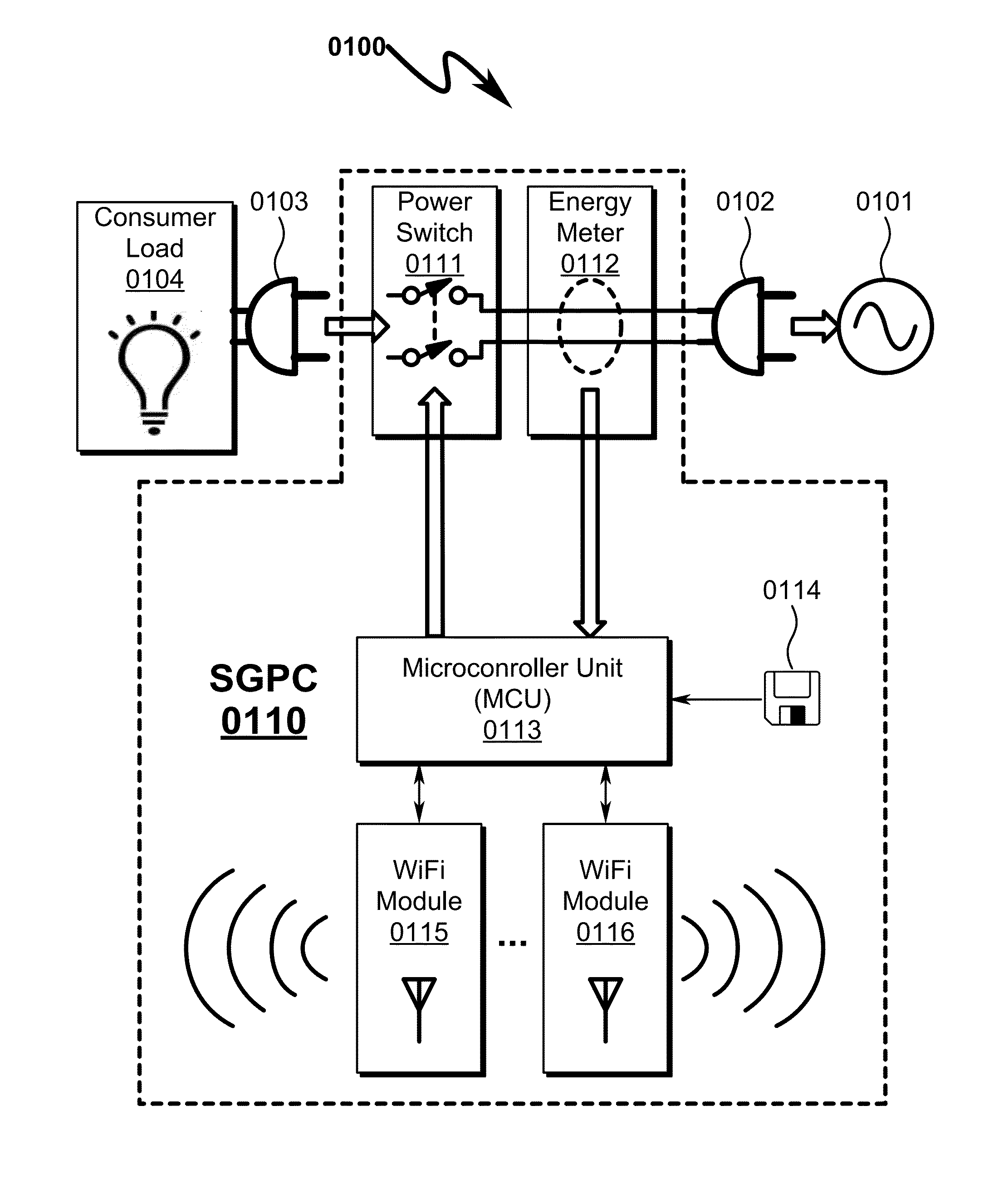
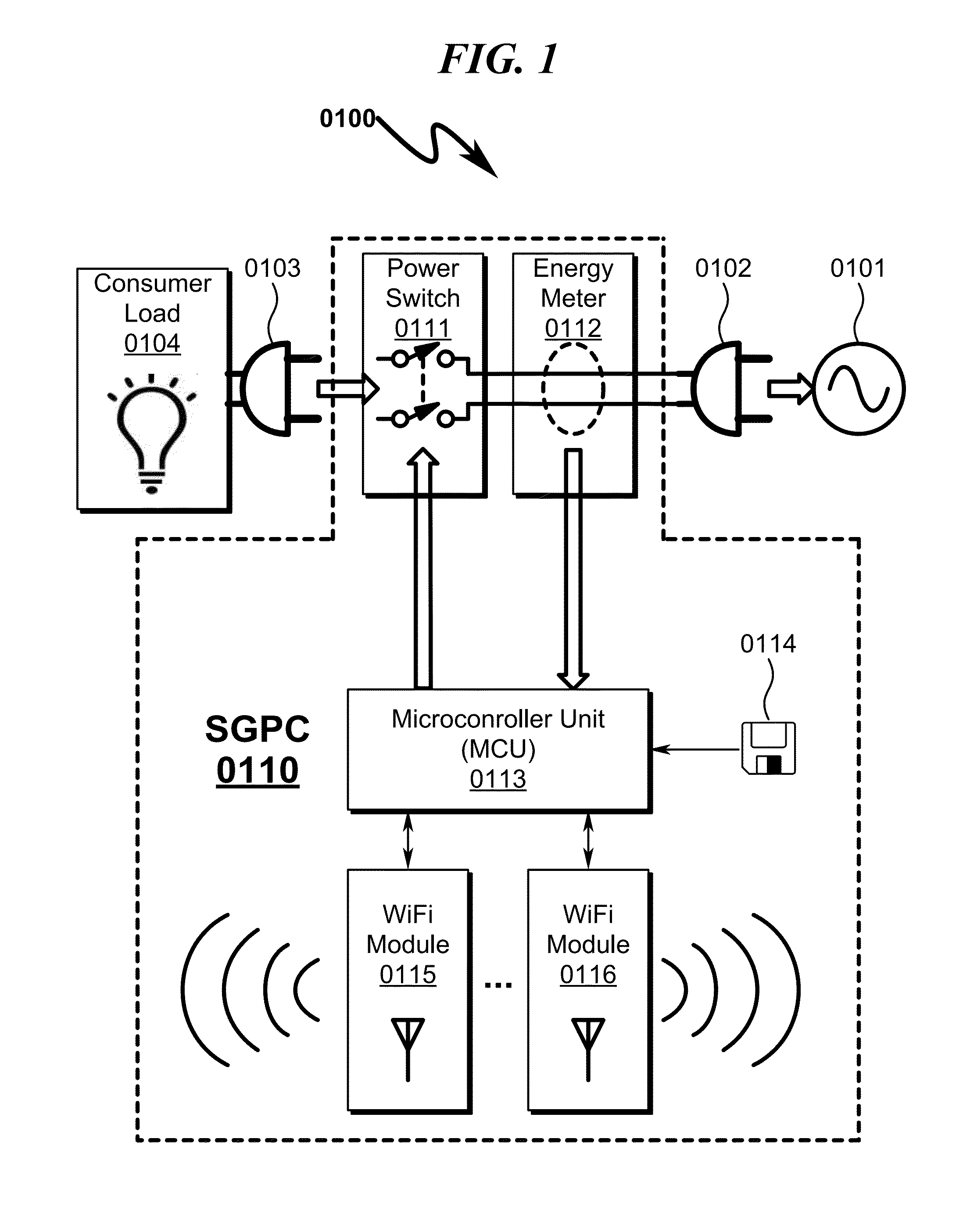
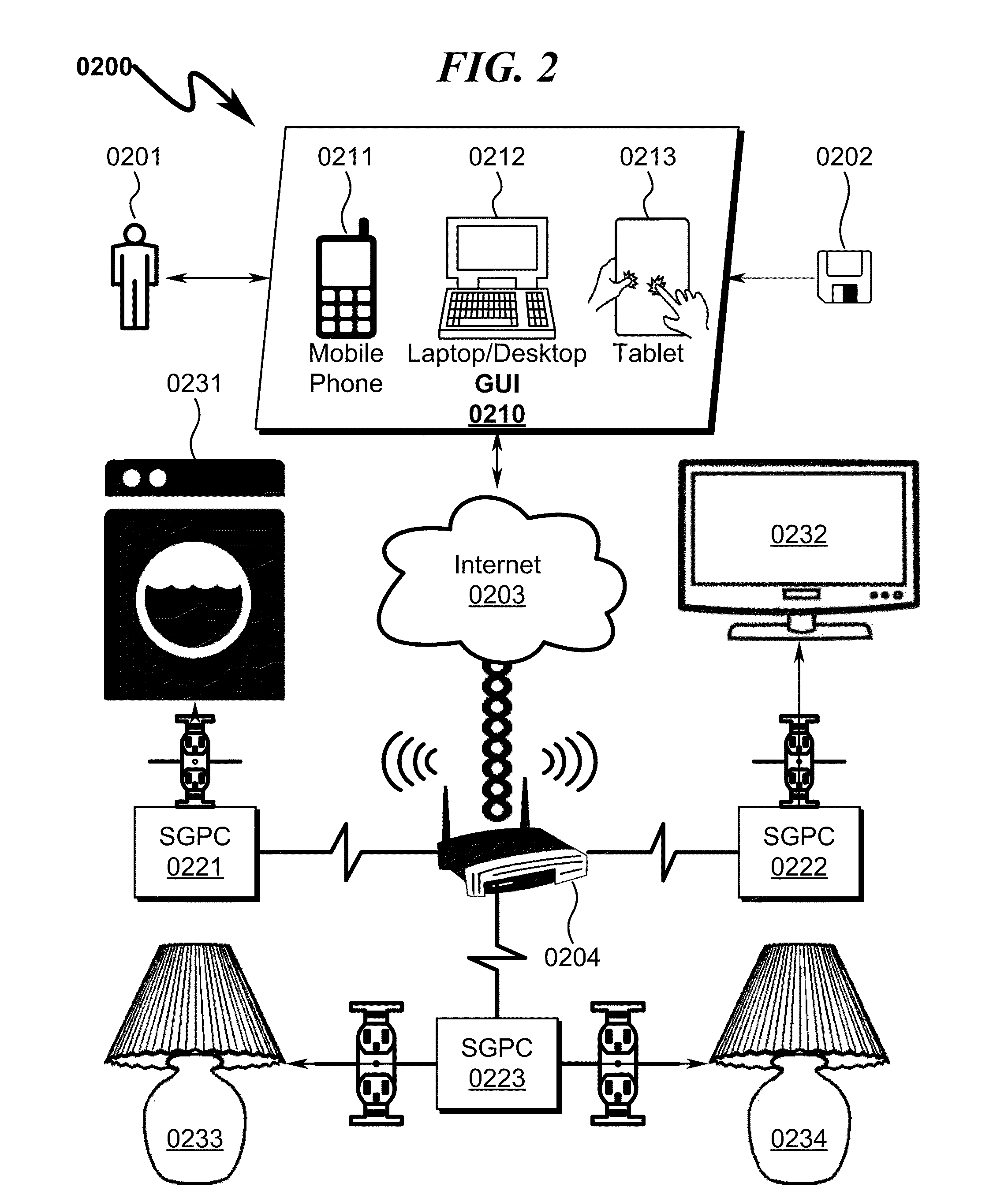
Power distribution system and method
ActiveUS20130261821A1Easy accessMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlTablet computerDistribution power system
A power distribution system / method implementing Internet based access to hybrid home automation networks is disclosed. The system utilizes a smart gateway power controller (SGPC) configured for single / multi-gang wallplate installation to selectively switch an AC power source to a load device under switched control and / or local / remote network commands that may be routed through a variety of network interfaces and protocols present within a home or other structure-local communications network. SGPC configurations may be nested within a home automation network to permit separation of control for load devices within a common home automation environment. Present invention methods may include routing protocols between disparate home automation networks as well as remote access protocols that permit control of disparate home automation networks via the Internet using a wide variety of remote access interfaces including mobile devices, tablet computers, laptops, desktop computers, and the like.
Owner:ADVANERGY
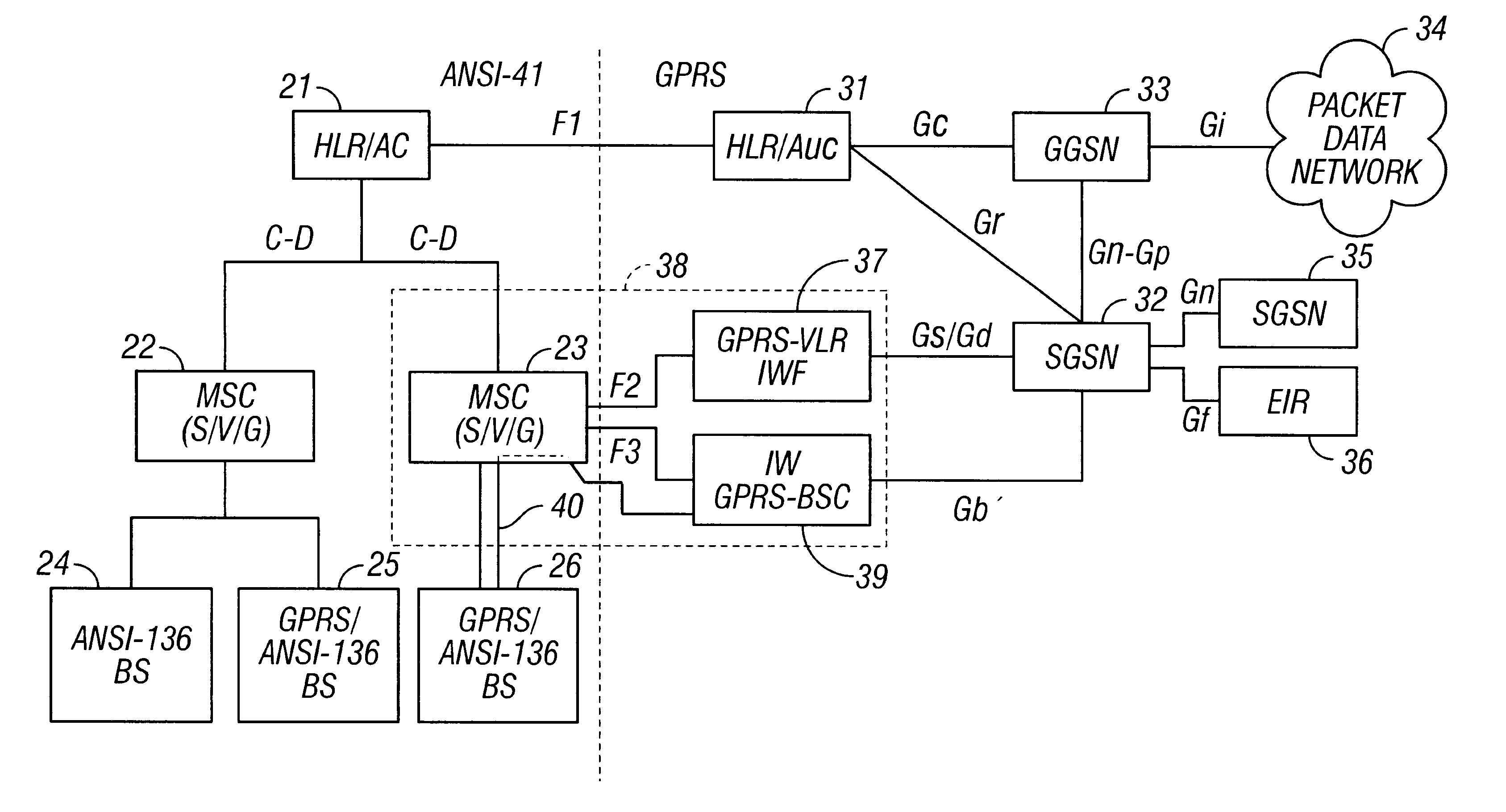
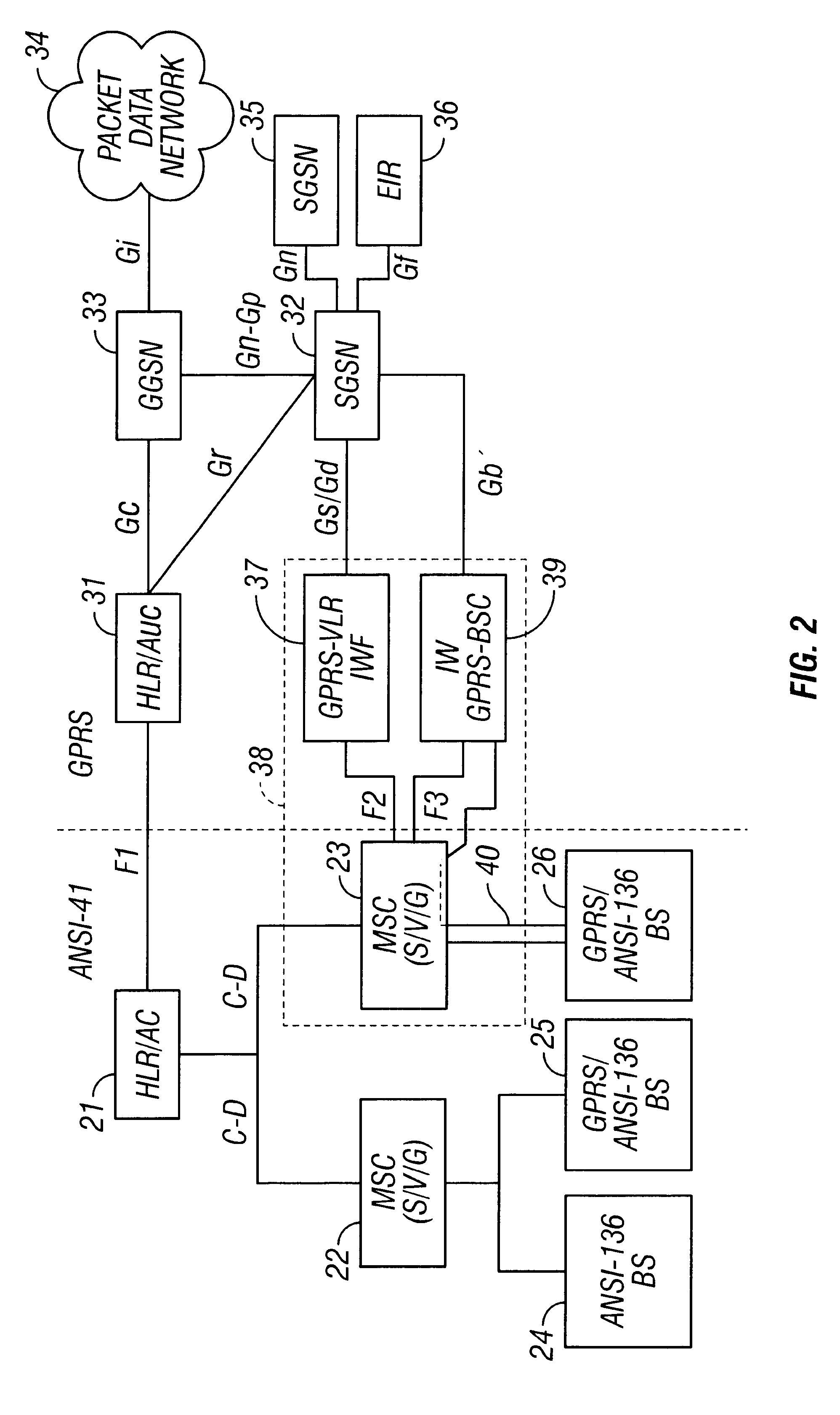
Integrated radio telecommunications network and method of interworking an ANSI-41 network and the general packet radio service (GPRS)
InactiveUS6463055B1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork connectionsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTelecommunications network
An integrated radio telecommunications network which integrates an ANSI-41 circuit switched network and a General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) packet data network to support a mobile station which operates in both the ANSI-41 network and the GPRS network. An interworking function interfaces a mobile switching center (MSC) in the ANSI-41 network with a serving GPRS switching node (SGSN) in the GPRS network by mapping circuit switched signaling utilized by the MSC into GPRS packet switched signaling utilized by the SGSN, and mapping GPRS packet switched signaling into circuit switched signaling. An interworking GPRS base station controller interfaces the SGSN with a GPRS / ANSI-136 base station which supports both ANSI-136 operations and GPRS operations. The interworking GPRS base station controller adapts the traffic signaling format utilized by the SGSN into an air interface traffic signaling format utilized by the GPRS / ANSI-136 base station. An authentication center interface passes the authentication state of the mobile station between an ANSI-41 home location register / authentication center (HLR / AC) in the ANSI-41 network, and a GPRS home location register / authentication center (HLR / AUC) in the GPRS network.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
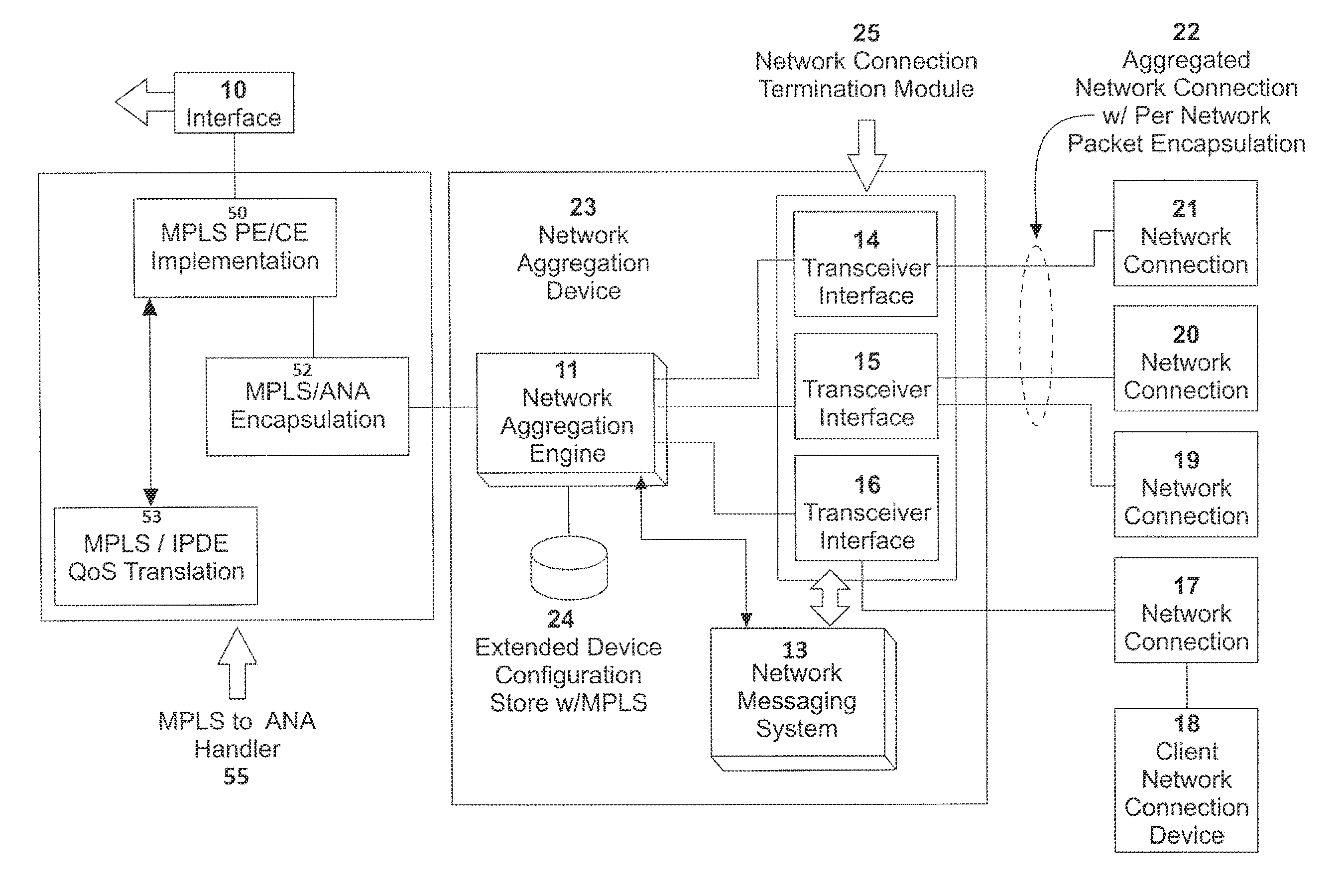
System, apparatus and method for providing a virtual network edge and overlay with virtual control plane
ActiveUS20160072669A1Improve communication performanceImprove throughputDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionTraffic capacityNetwork connection
A network system is provided between at least a first client site and a second client site. A client site network component is implemented at least at the first client site, the client site network component aggregating one or more diverse network connections so as to configure an aggregated connection that has increased throughput. At least one network server component may be configured to connect to the client site network component using the aggregated connection. A cloud network controller may be configured to manage the data traffic and a virtual edge providing transparent lower-link encryption for the aggregated connection between the client site network component and the network server component. The network server component includes a virtual control plane interface configured to establish a unicast path between the network server component and each of a plurality of remote network server components.
Owner:ADAPTIV NETWORKS INC
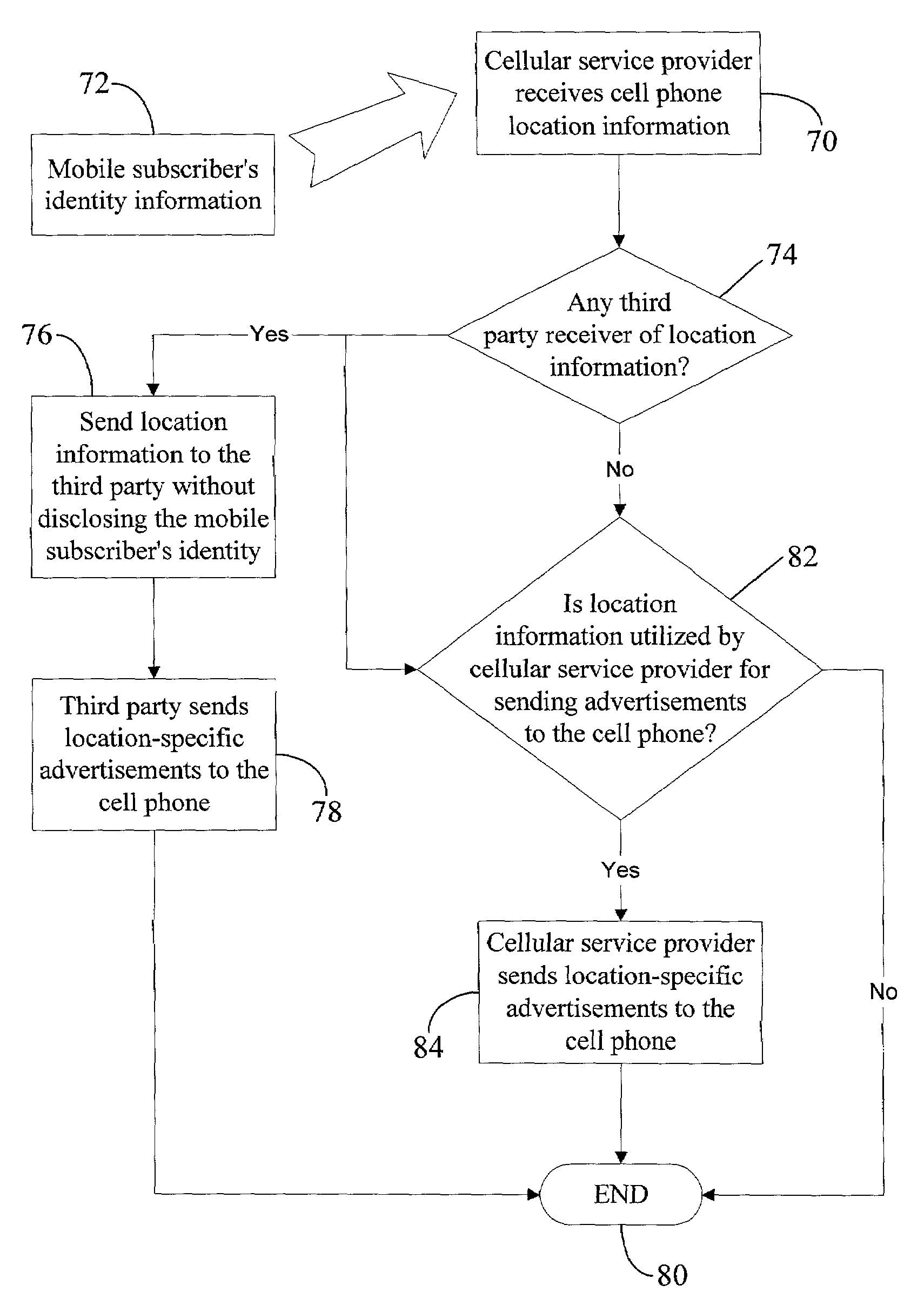
Location blocking service from a web advertiser
InactiveUS7085555B2Discounts/incentivesUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionThird partyOnline advertising
Location-blocking and identity-blocking services that can be commercially offered by a service promoter, e.g., a cellular service provider or a web advertiser. In the identity-blocking service, the service promoter may disclose the current physical location of a mobile subscriber (i.e., a cellular phone operator) to a third party (e.g., a web advertiser) subscribing to the identity-blocking service. However, the service promoter may not send any identity information for the mobile subscriber to the third party. On the other hand, in the location-blocking service, the service promoter may disclose the mobile subscriber's identity information to the third party, but not the current physical location of the mobile subscriber. Blocking of the mobile subscriber's identity or location information may be desirable for privacy reasons, to comply with a government regulation, or to implement a telecommunication service option selected by the mobile subscriber. However, in the case of the mobile subscriber requesting emergency help, the service promoter may not block identity and / or location information. Instead, the service promoter may send all such information to the emergency service provider (e.g., the police or a hospital).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
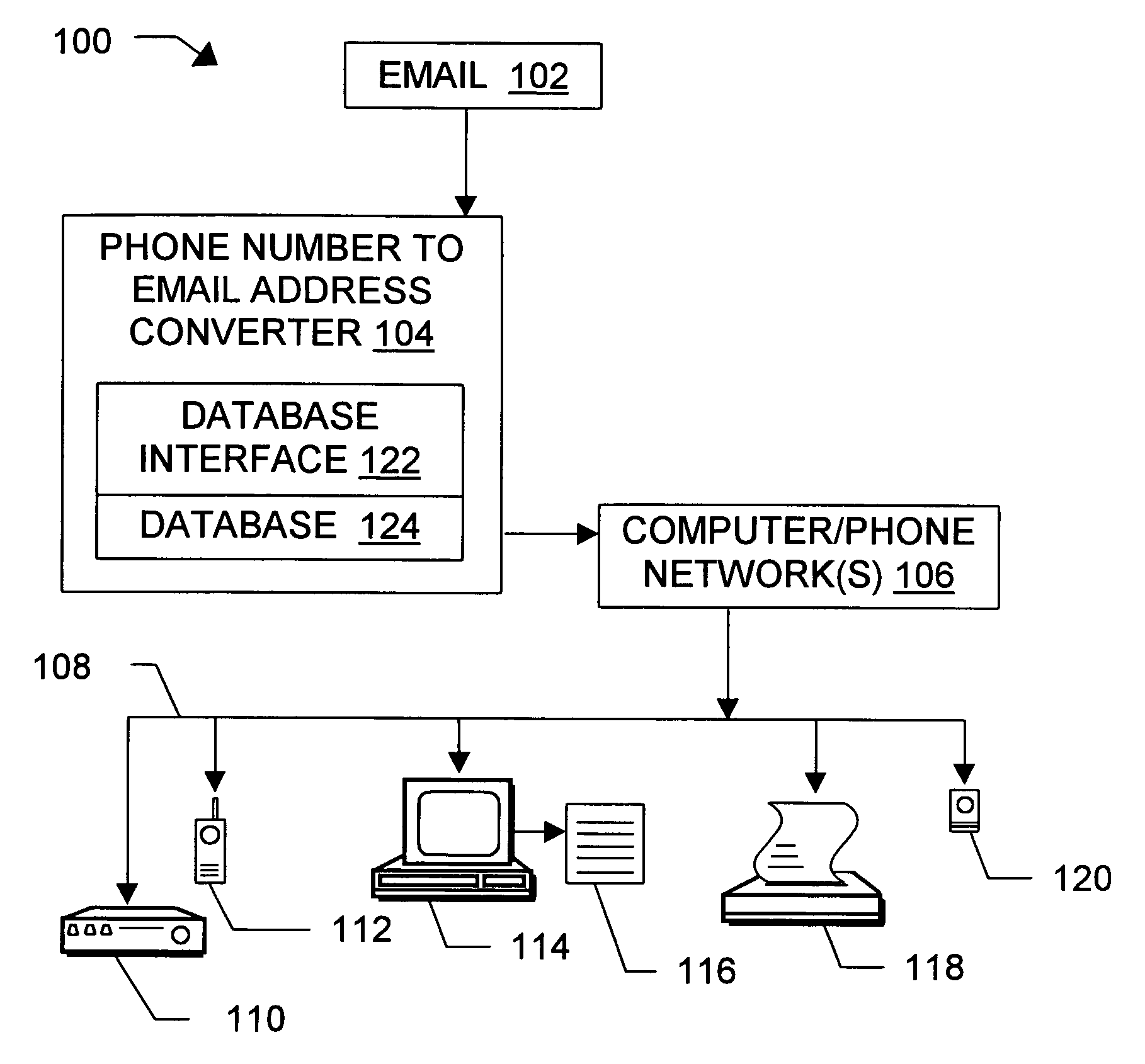
Message routing
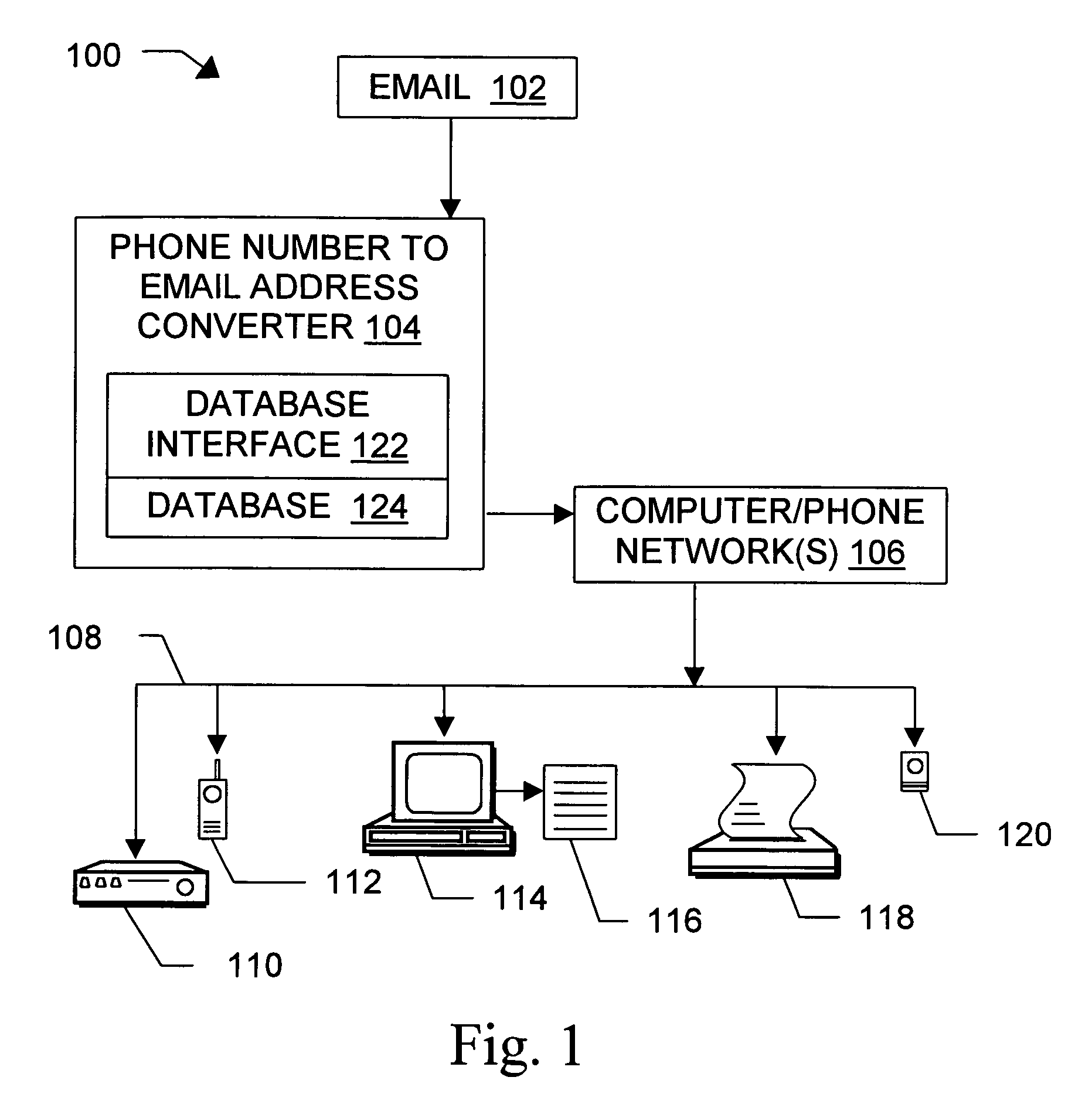
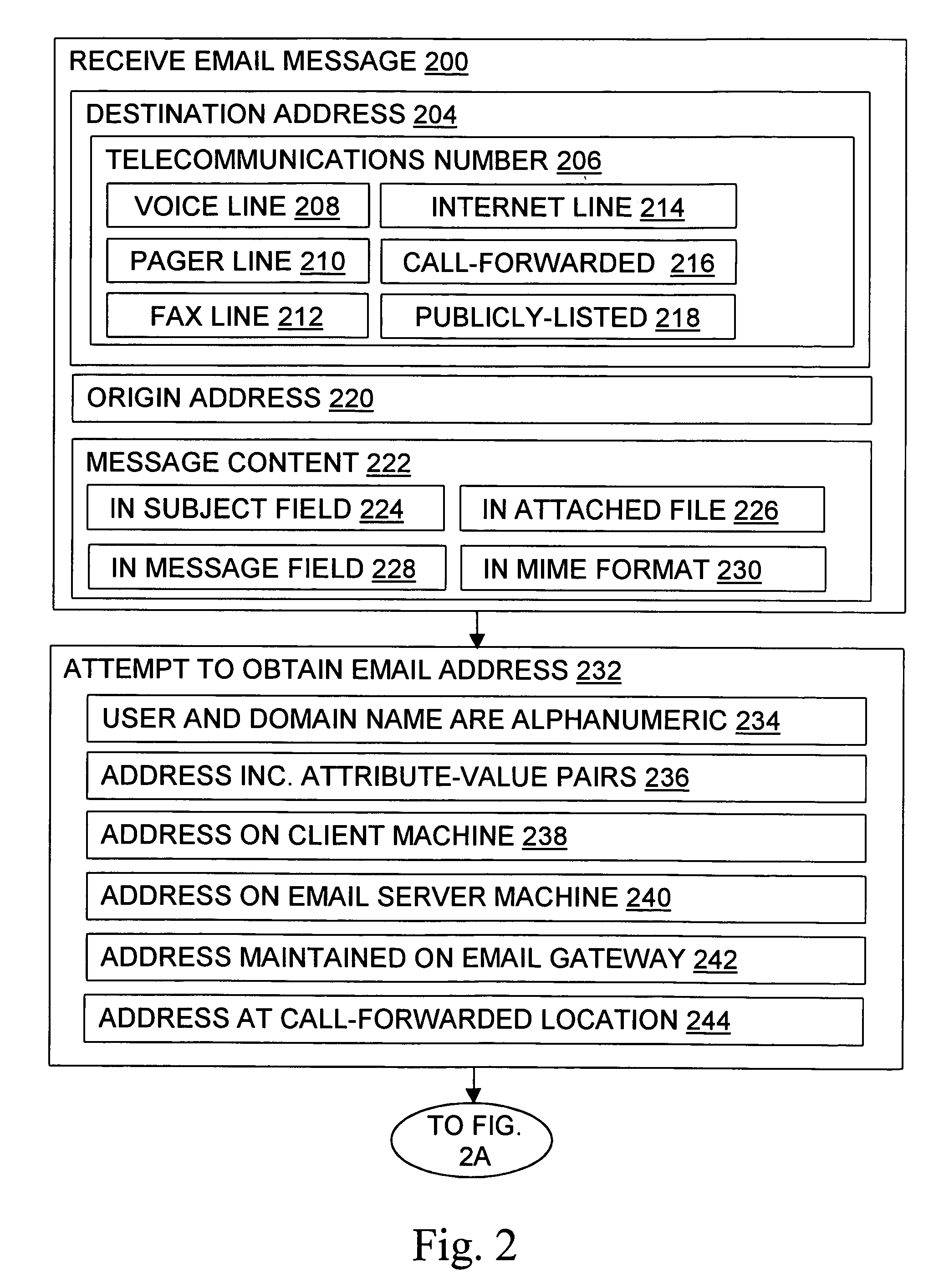
InactiveUS6981023B1Easy to getRemove the burdenInterconnection arrangementsPublic key for secure communicationEmail addressSelective calling
Methods, devices, signals, and systems are provided in a message routing architecture which provides improved capabilities for integrating “digital” communication through email messages with “analog” communication through voice and / or fax or pager messages. Email can be addressed using nothing more than a standard telephone or fax number. If the registered owner of the telephone or fax number has a corresponding email address, then the invention converts the telephone or fax number to the email address for delivery and uses standard email delivery systems to deliver the message. If no conventional delivery email address is known, or if the message sender or recipient specify multiple delivery modes, then the email message content is transformed into voice, pager and / or fax content and delivered to the recipient using the telephone or fax number which was specified as the email address. Familiar telecommunications services such as call forwarding and selective call blocking can also be used with messages that originate as email. The invention also supports use of telecommunications numbers as indexes into databases which contain public key certificates, to make it unnecessary for a proposed message recipient to provide its public key expressly in advance to each particular proposed message originator.
Owner:HAMILTON MICHAEL +1
Internet download systems and methods providing software to internet computer users for local execution
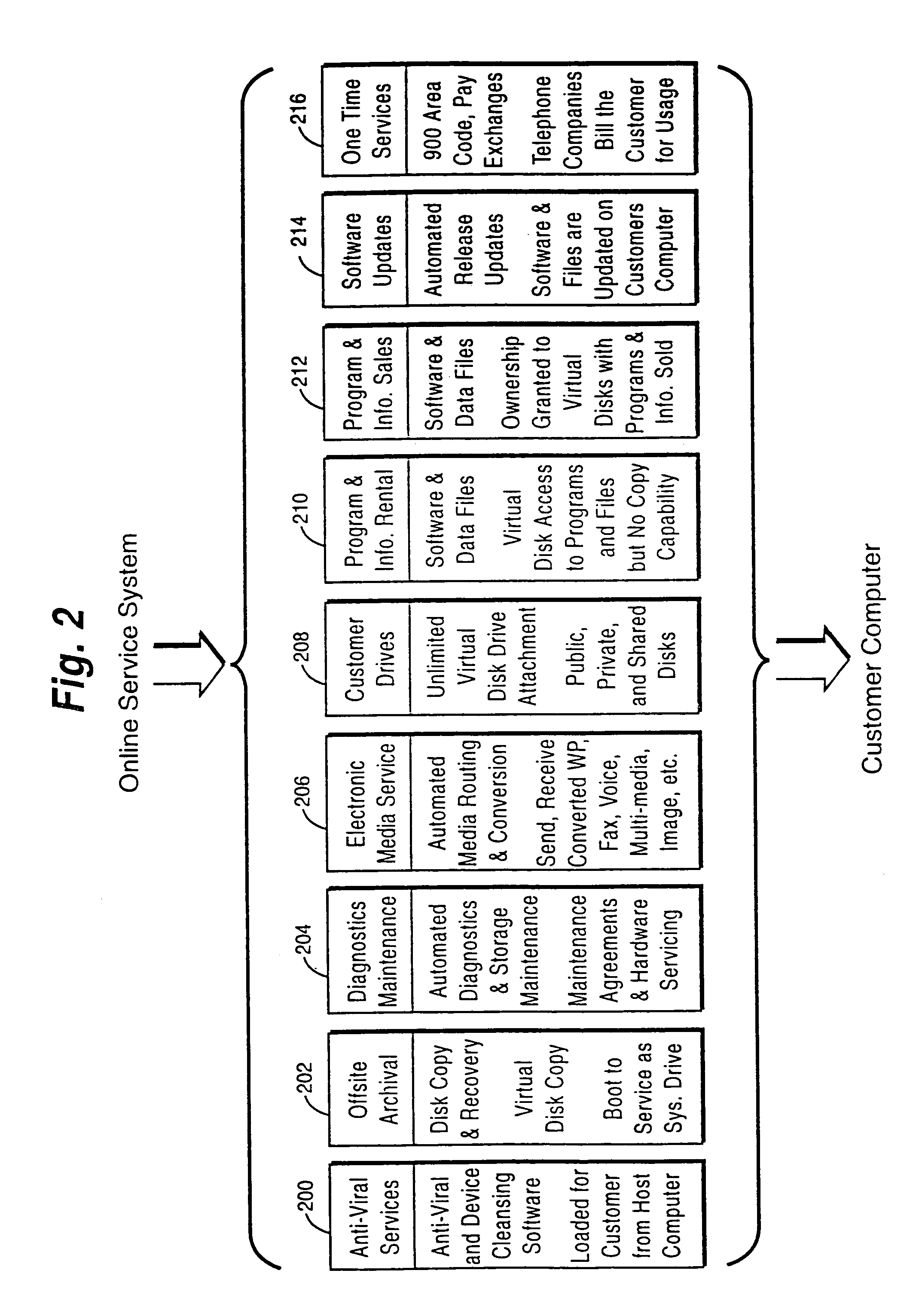
A customer computer connects to an online service provider by phone, Internet, or other telecommunications link. The link gives the customer access to additional processing and storage resources such as virtual storage, processing power and / or additional software or data through interaction between the customer computer and an online service provider computer over the link. The additional resources made available to the customer computer enhance the customers' local needs through access to virtual storage, a more powerful processor of similar type for program execution, and / or online support services such as software rental, software sales, release update services, anti-viral services, data backup and recovery services, diagnostic services and / or repair services.
Owner:OASIS RES +6
Method and system for network delivery of content associated with physical audio media
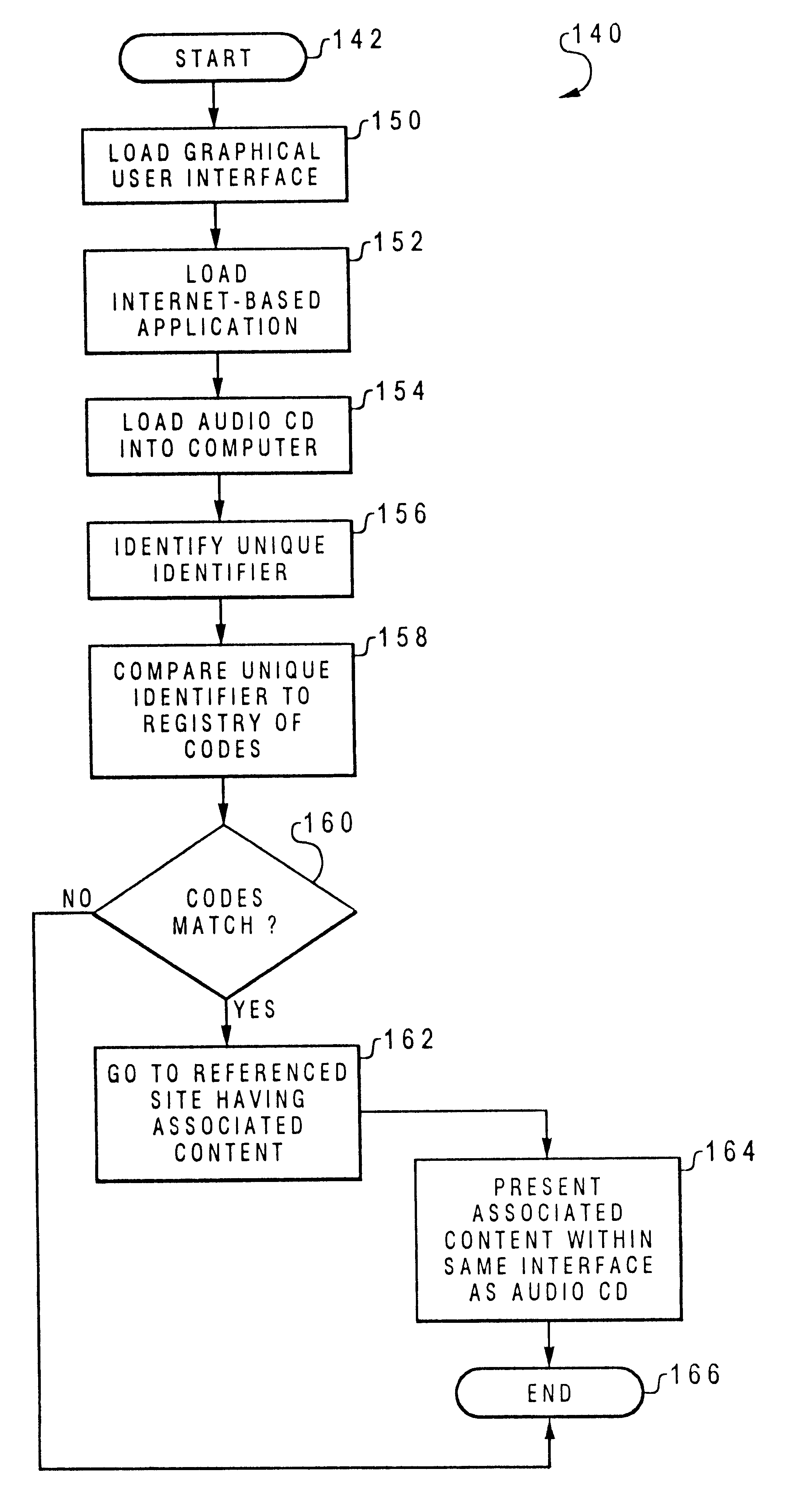
InactiveUS6195693B1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsAudio MediaComputer hardware
A method and system in a multimedia computer system for automatically retrieving and presenting data associated with an audio recording having unique identifying indicia therein. In response to playing an audio recording in a multimedia computer system, a unique identifying indicia associated with the audio recording is identified. A listing of codes within the multimedia computer system is automatically searched to find a code corresponding to the unique identifying indicia. In response to finding the code corresponding to the unique identifying indicia, multimedia data is retrieved which corresponds to the unique identifying indicia. The multimedia data can be retrieved from local storage or from a remote network site. The multimedia data corresponding to the unique identifying indicia is then presented in the multimedia computer system, while playing the audio recording in the multimedia computer system.
Owner:IBM CORP
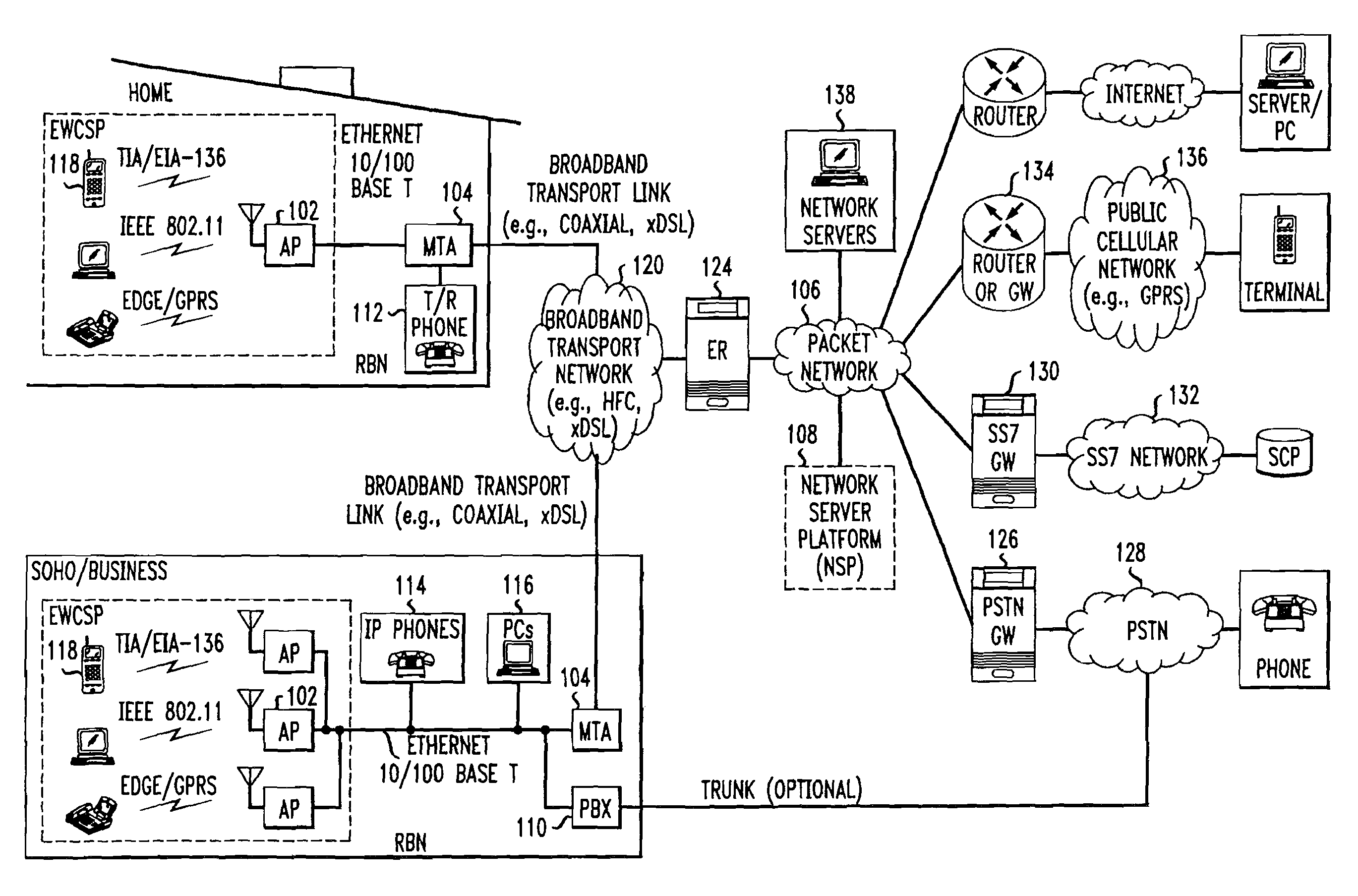
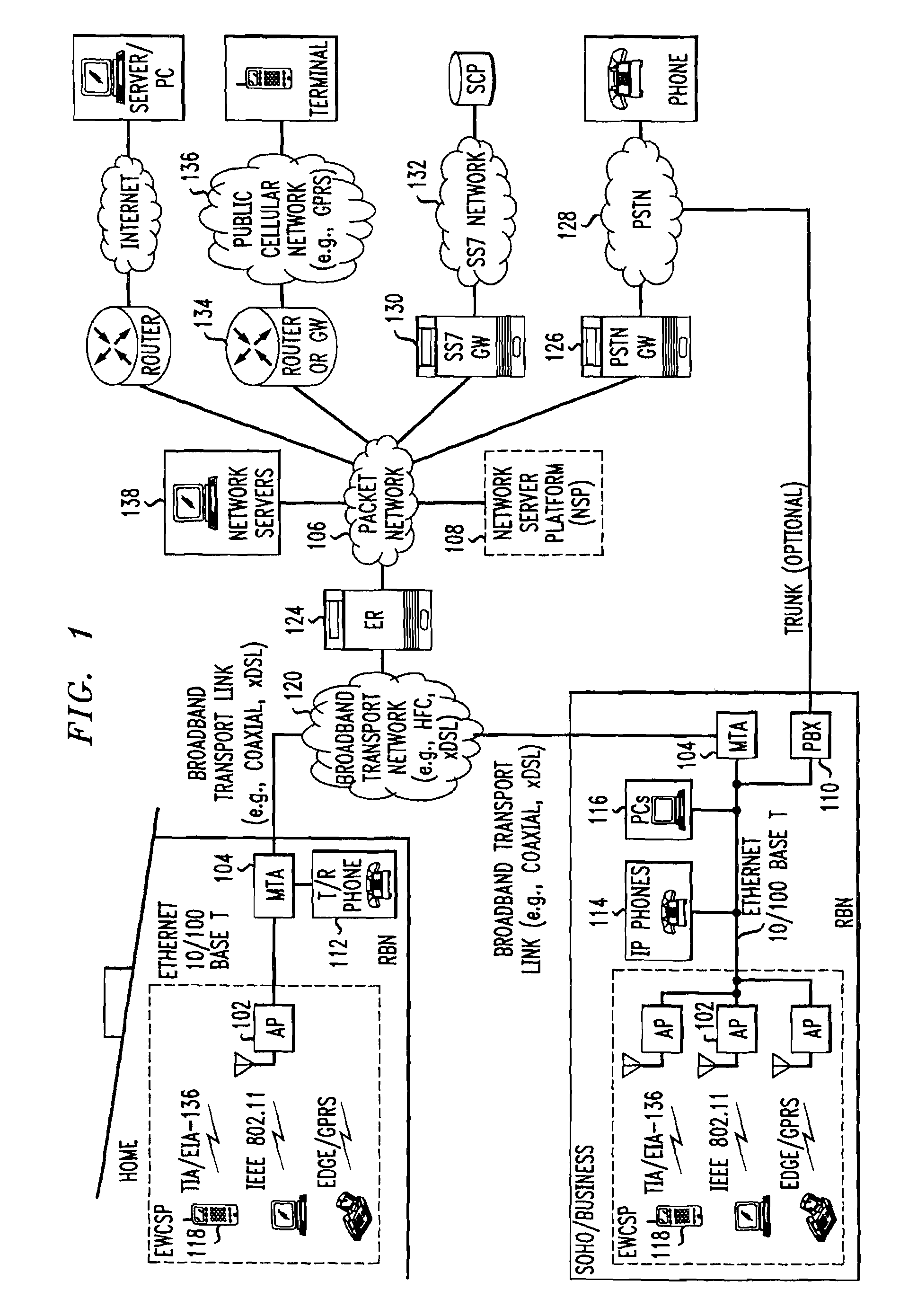
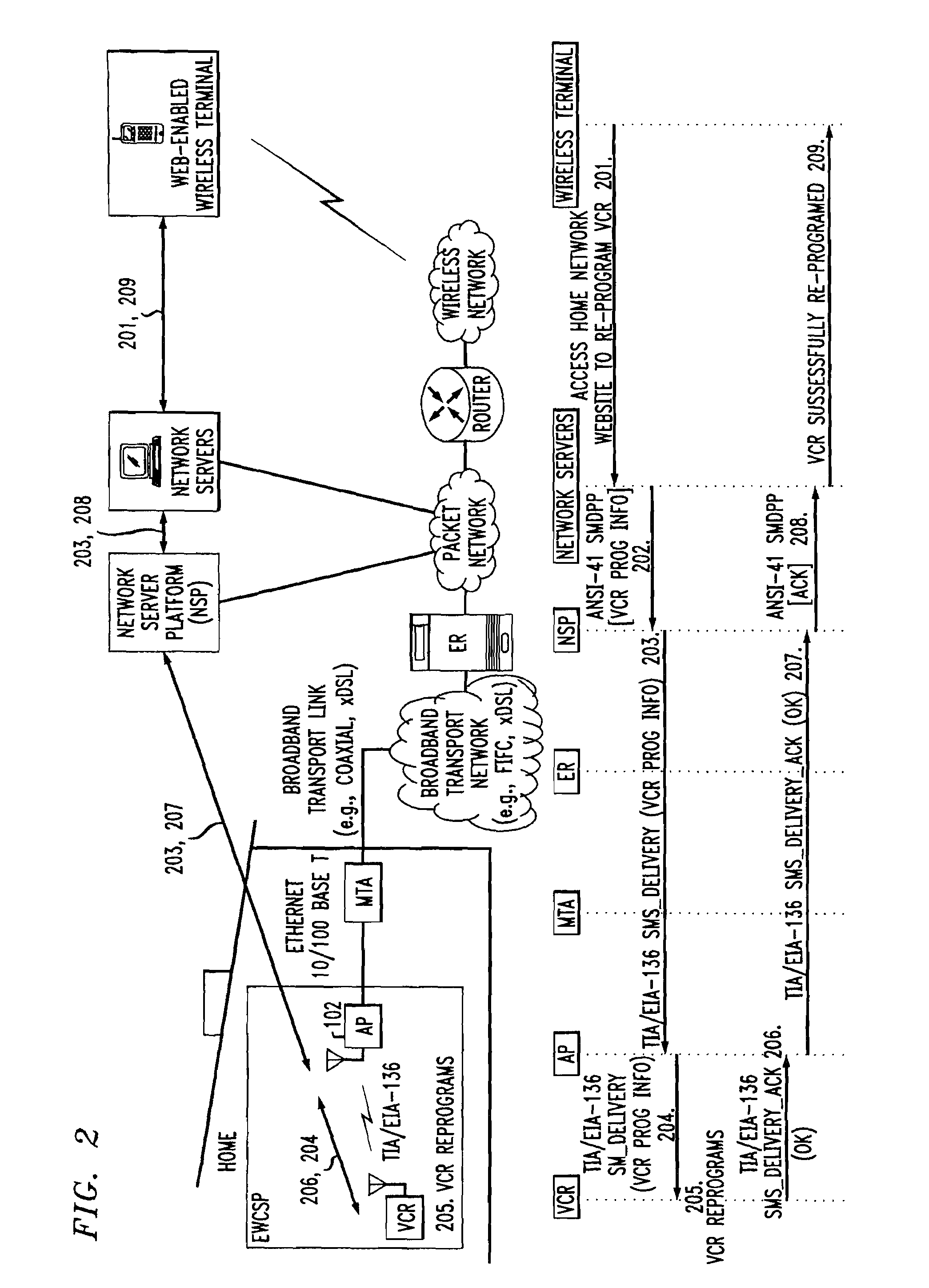
Computer readable medium with embedded instructions for providing communication services between a broadband network and an enterprise wireless communication platform within a residential or business environment
InactiveUS8155155B1Easy maintenanceCost-effectivelyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceBroadband transmission
The present invention sets forth computer-readable non-transitory medium having computer-executable instructions for providing network-centric service distribution method that integrates a wireless access system / service with conventional telecommunications services in the residence, SOHO, business or public environment through the use of a local broadband network, such as a Residential-Business Broadband Network (RBN). The RBN communicates with the service provider's broadband transport network and broadband packet network to facilitate end-to-end packet telecommunication services. Signals from a plurality of wireless devices are accepted and forwarded to an IEEE 802.11b interface for a wireless modem and / or to an Ethernet interface for a Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) / Ethernet Processor, where the forwarded signals comprise intranet telephony and data.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
Wireless device to manage cross-network telecommunication services
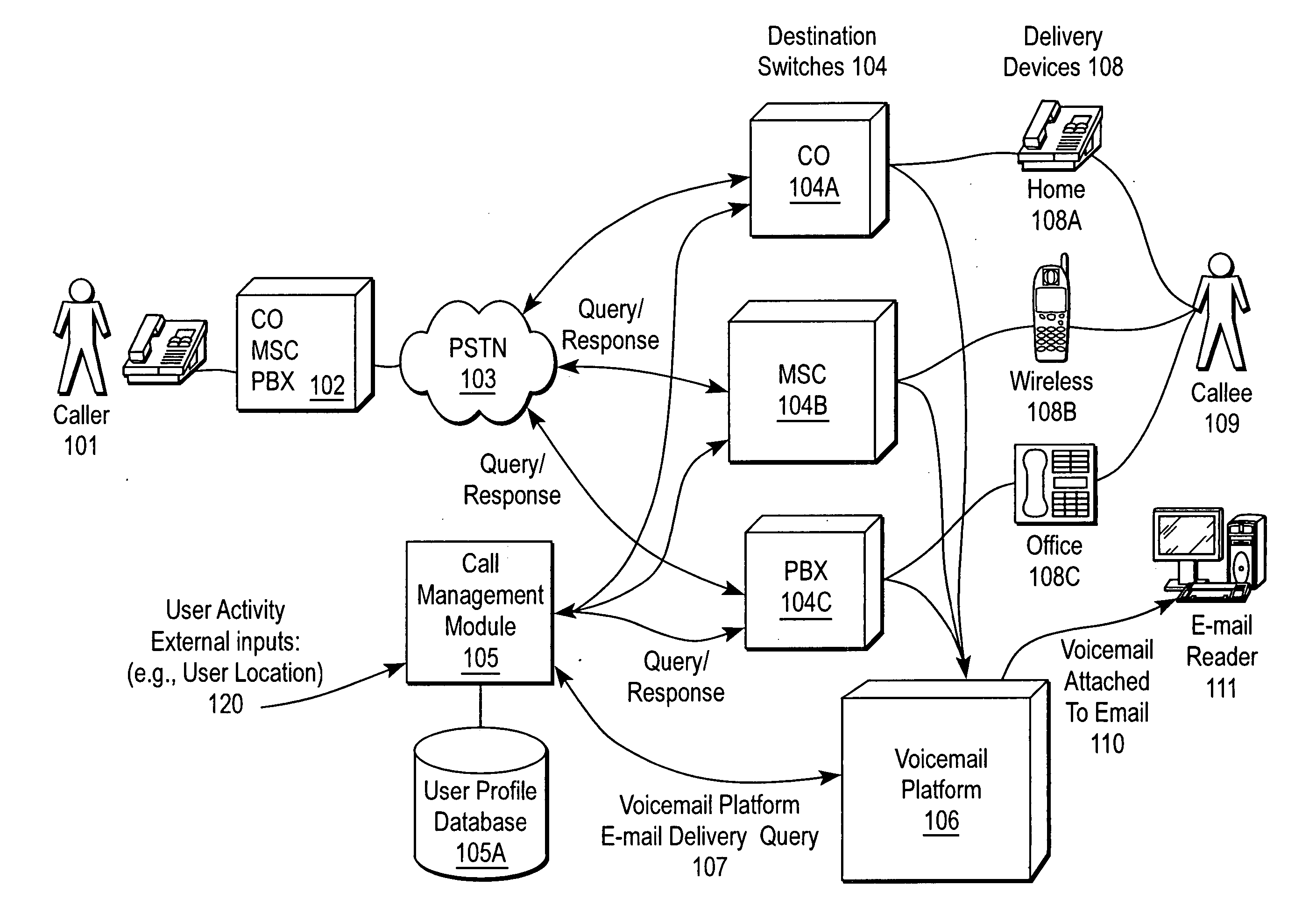
ActiveUS20060072726A1Special service for subscribersCommmunication supplementary servicesMode selectionCall management
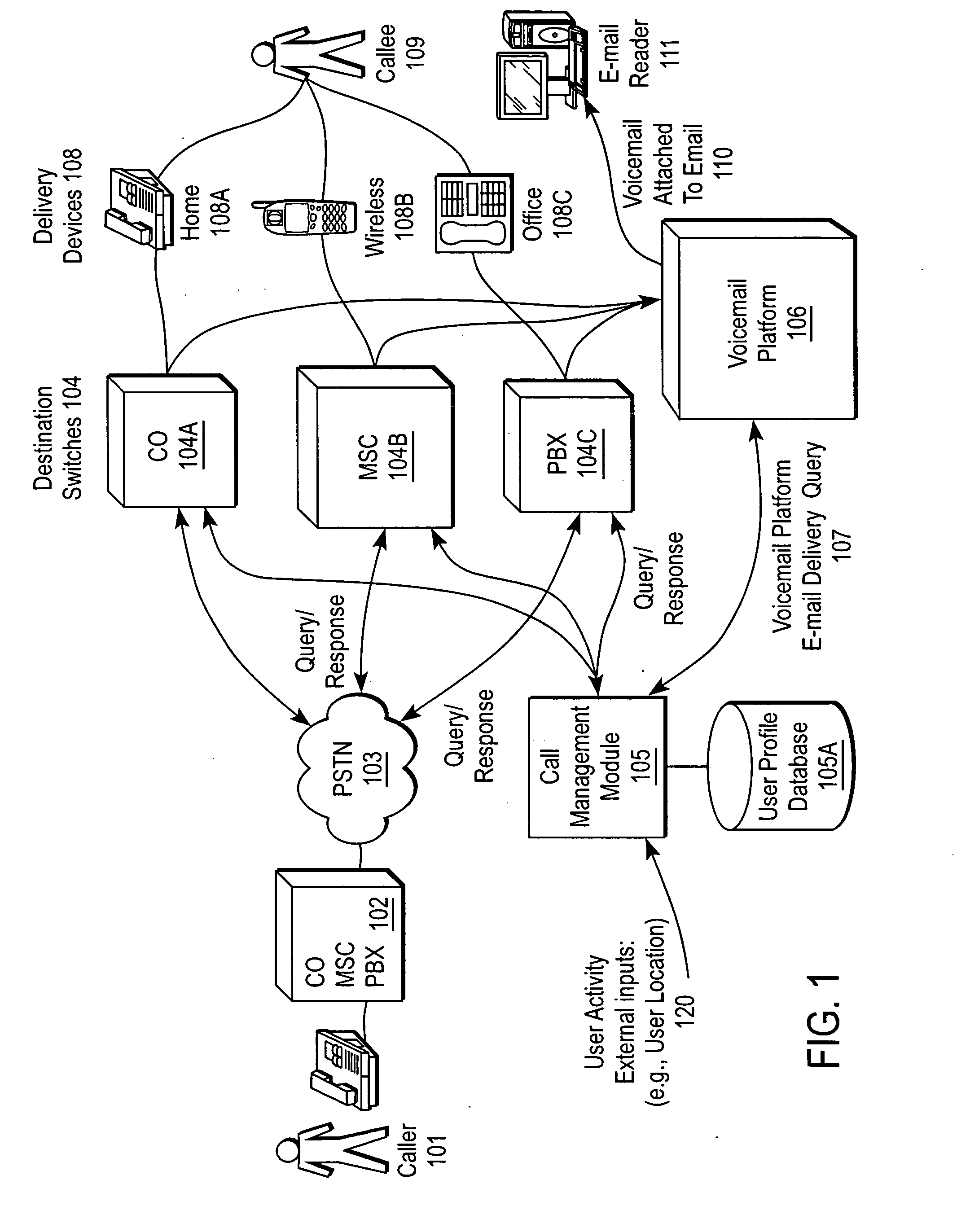
A communication remote control system allows a user to remotely configure call management functions across various phone networks using a client device. The communication remote control system centrally handles call management for the user's telephones. The communication remote control system may provide a centralized address book, call log, and voicemail. The user can specify various parameters including modes, filters, schedules, and the like, which are stored in the communication remote control system. The communication remote control system routes incoming calls made to the phone networks to the user's delivery device, which may be part of the client device. Incoming calls are routed to a specified telephone number, sent to voicemail, or otherwise disposed of or users can change modes manually or can specify automatic mode selection based on time of date, day of week, location, and / or other factors.
Owner:AVAYA INTEGRATED CABINET SOLUTIONS +1
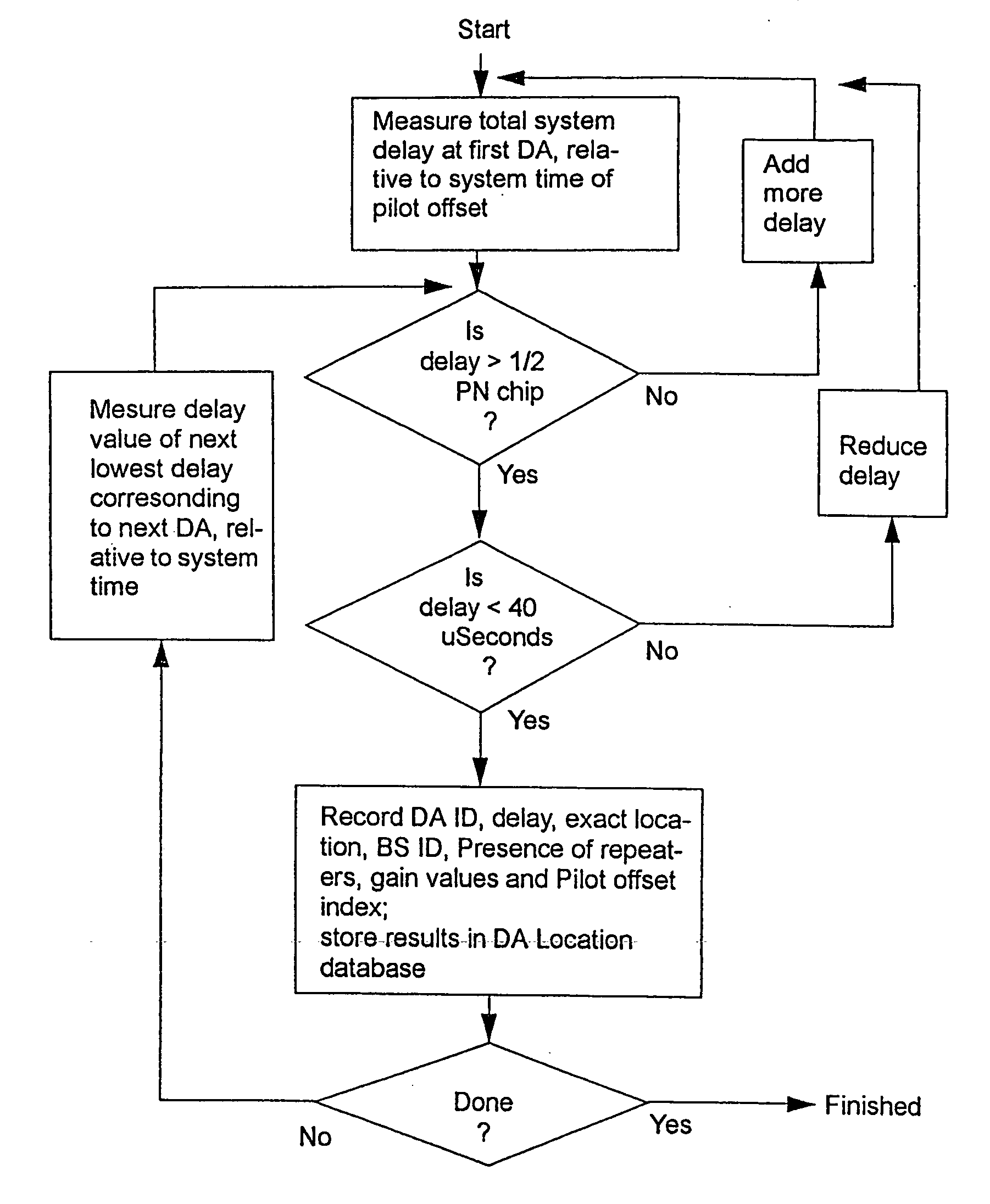
Location estimation in wireless telecommunication networks
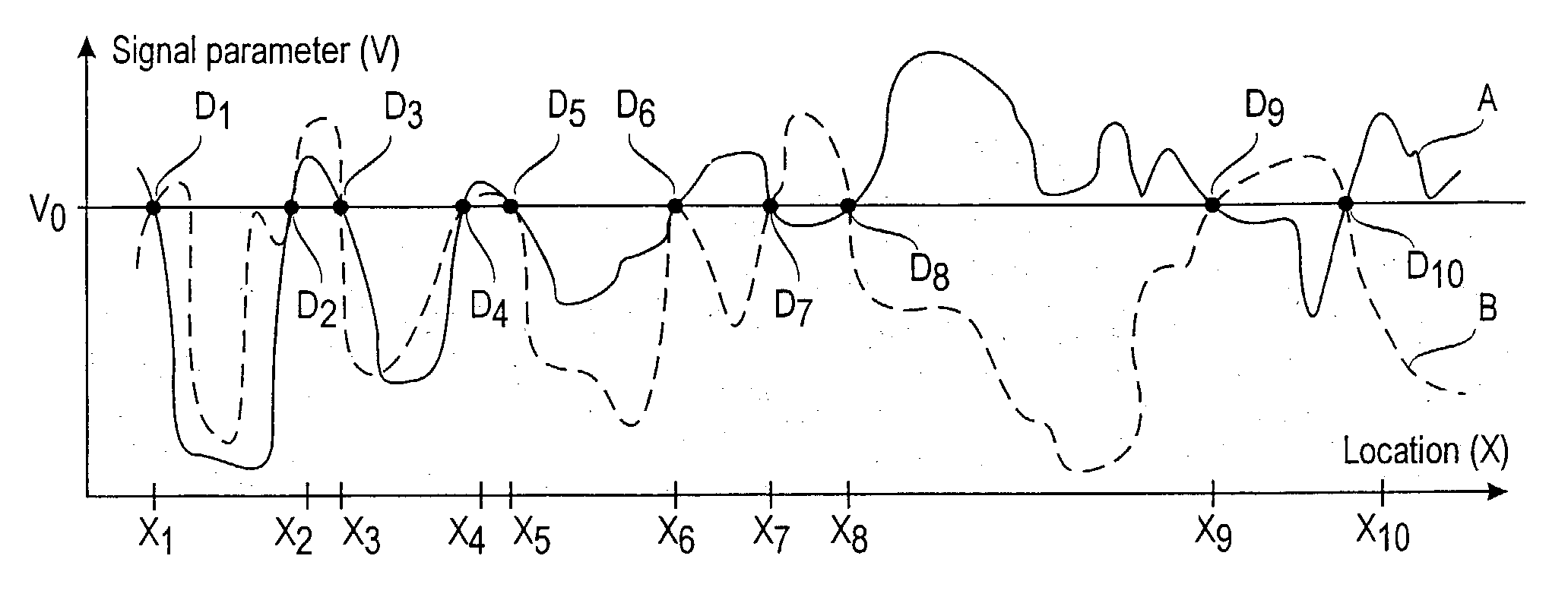
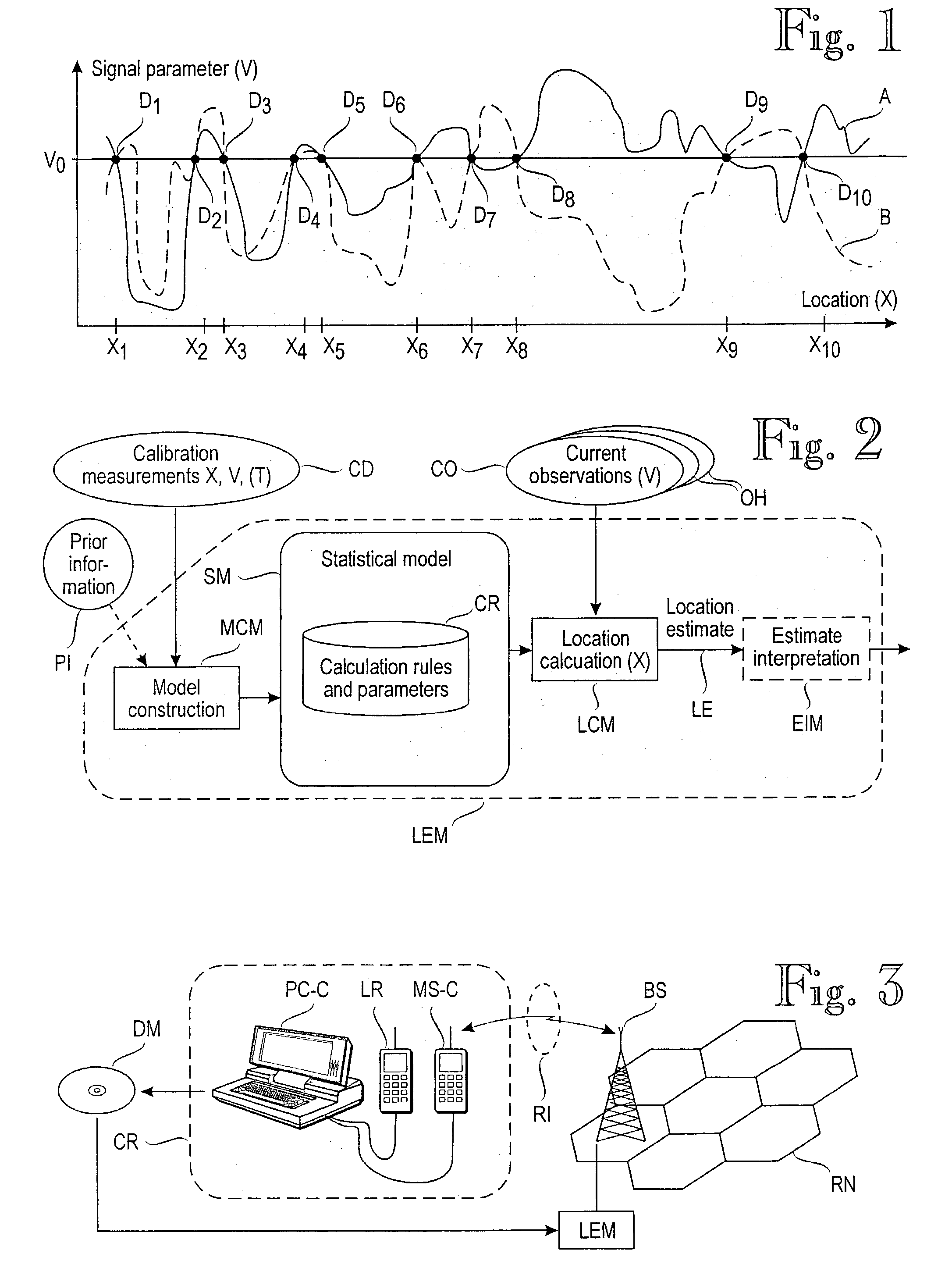
A method for estimating a receiver's location in a wireless communication environment having several channels. Each channel has at least one signal parameter that varies with location differently from the other channels. A set of calibration data is determined for each calibration point, each set including the location and at least one measured signal parameter for each of several channels. The calibration data serve as a basis for a statistical model of the signal parameters versus a receiver's location. A set of observed signal parameters is determined, the set including at least one signal parameter for each of several channels at the receiver's location. A location estimate approximating the location of the receiver is determined on the basis of the statistical model and the set of observed signal parameters.
Owner:AIRWAVE LOCATION TECH LLC
System, method, and computer program product for connecting or coupling analog audio tone based communications systems over a packet data network
ActiveUS8687650B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsInformation formatCommunication system softwareModem device
An automated telecommunications system includes a first system operable to receive PSTN compatible audio frequency signals, to decode and interpret said incoming signals according to the message format and a modem protocol being used, and transmit digital messages to a second system over a packet data network. Said second system receives and interprets digital messages incoming from the first system, encodes and regenerate outgoing audio frequency signals. The system may be bi-directional and operate over a packet based data network, such as for example an Internet protocol (IP) based network, a satellite based network, or an IP based cable or wireless network. The functionality of said first and second systems may be combined at a single location and operate with a VoIP network to allow modem signals to pass across the VoIP system.
Owner:NSGDATACOM
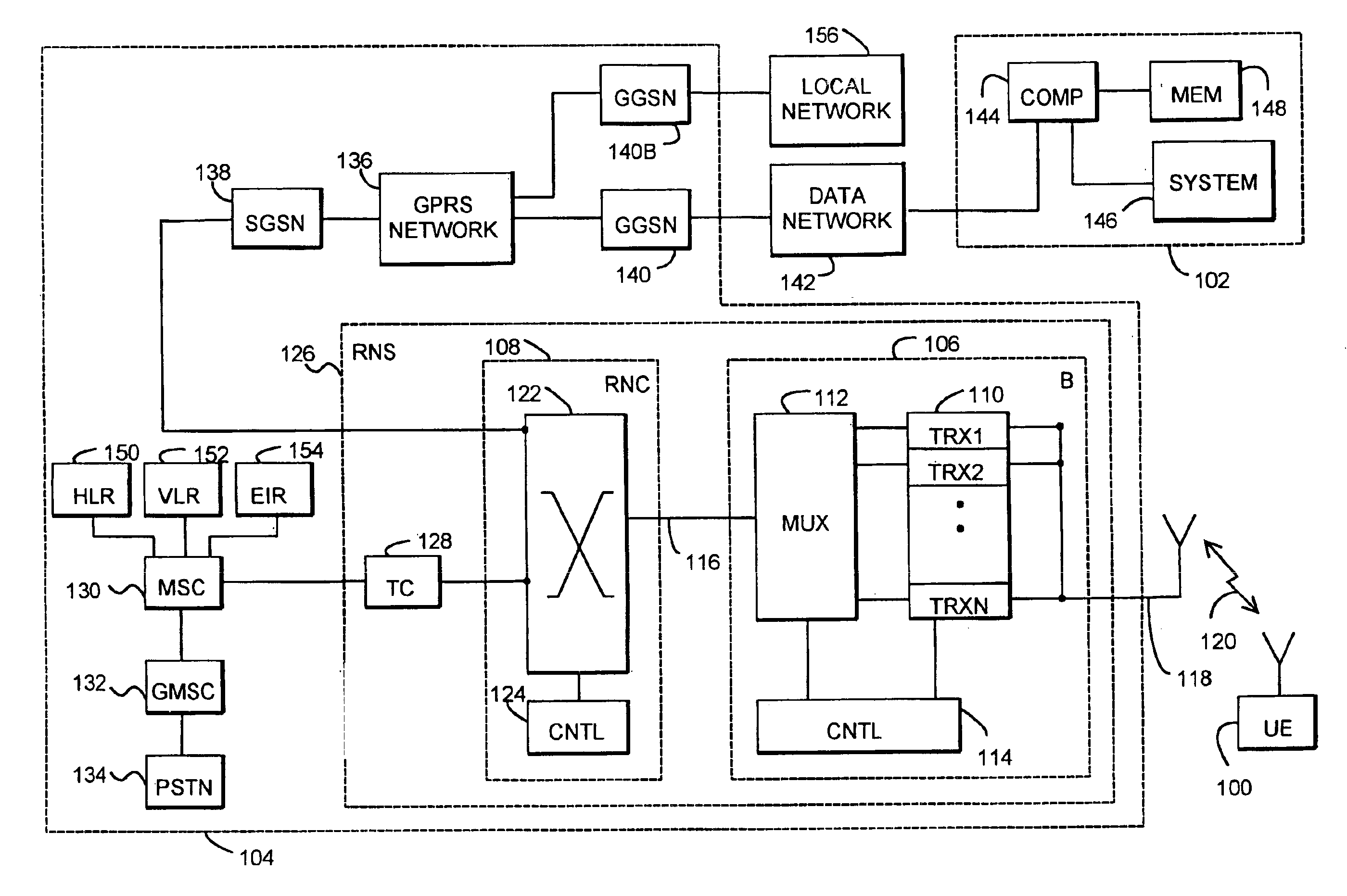
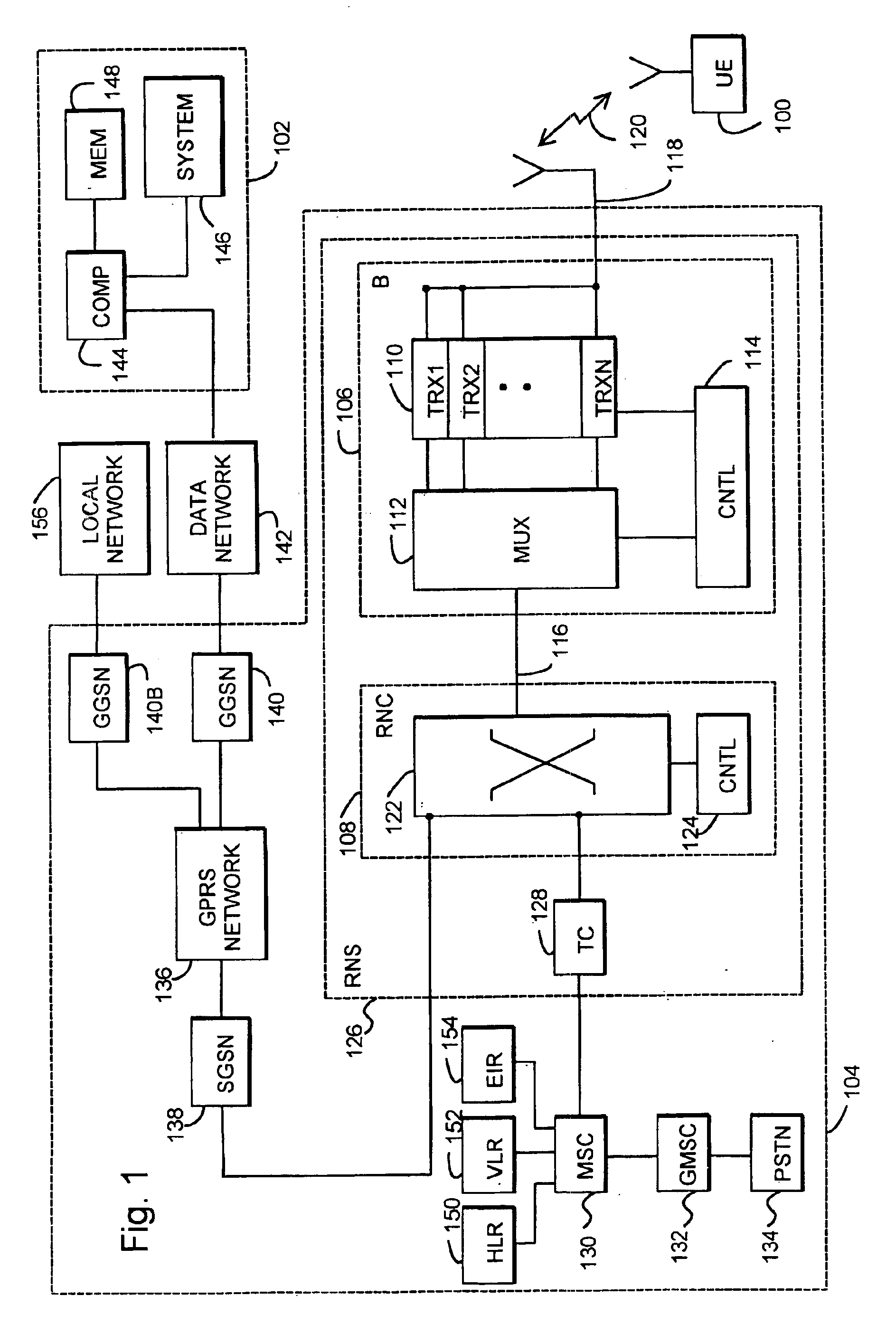
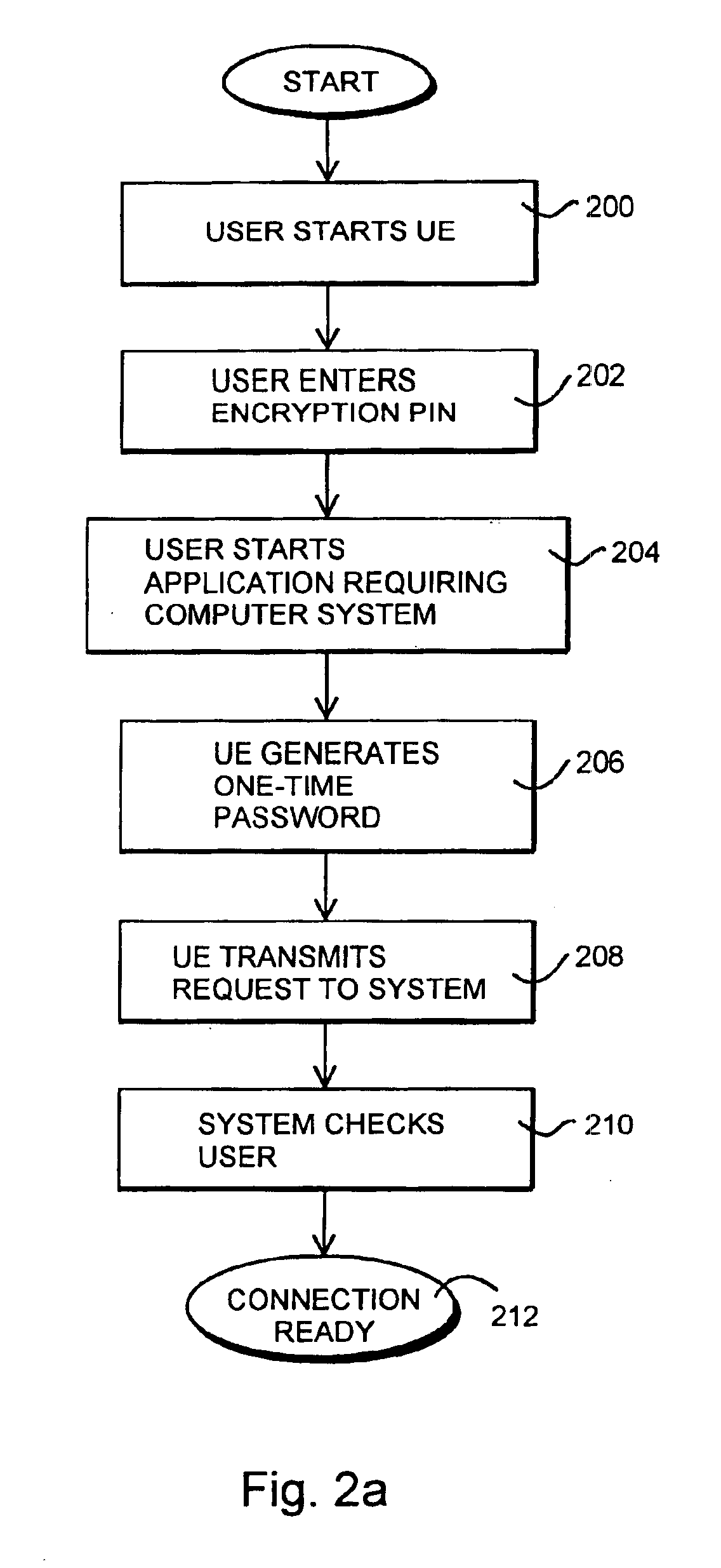
Method and arrangement for reliably identifying a user in a computer system
InactiveUS6928558B1Avoid disadvantagesReliable identificationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPersonal identification numberComputerized system
The invention relates to an arrangement and a method for reliably identifying a user in a computer system. The method utilizes a mobile station for communicating with the system. The method comprises generating a first one-time password in the mobile station by utilizing a known algorithm on the basis of the identification number of the user, subscriber-specific identifier, device-specific identifier of the mobile station, and time. The password obtained and the subscriber-specific identifier of the user are encoded and transmitted to an authentication server of the computer system, comprising identifying the user on the basis of the subscriber-specific identifier, searching a database for the personal identifier number of the user and the device-specific identifier of the mobile station associated with the user, generating a second password at the authentication server by utilizing the same predetermined algorithm on the basis of the personal identification number of the user, subscriber-specific identifier, device-specific identifier of the mobile station and time, comparing the first and the second passwords with each other at the authentication server, and if the passwords match, enabling the telecommunication connection between the mobile station and the computer system.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
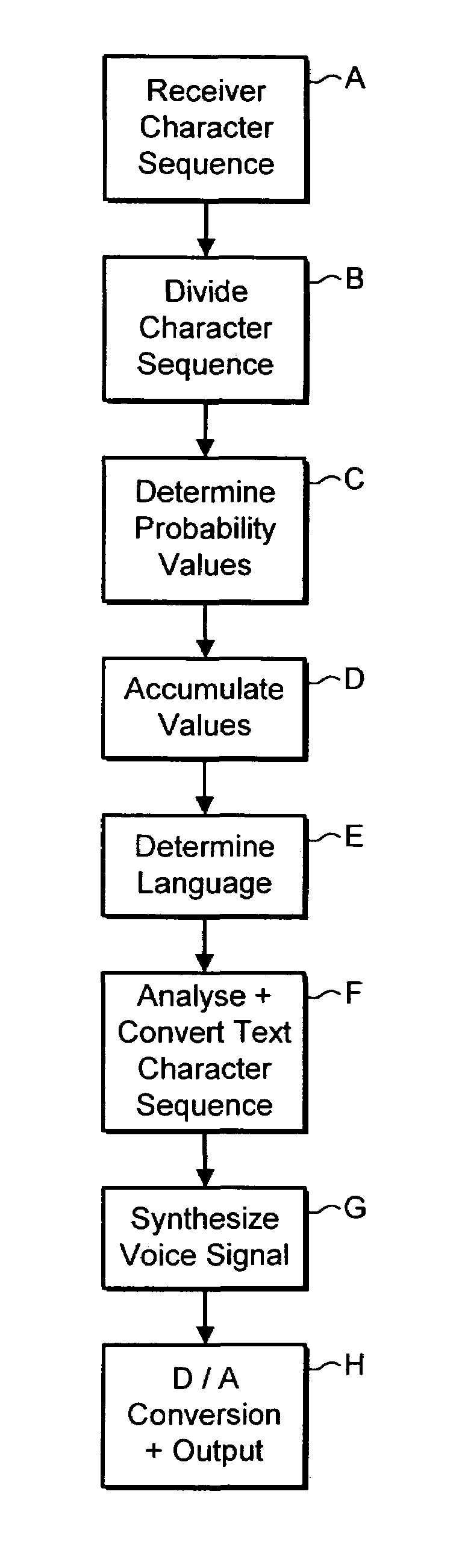
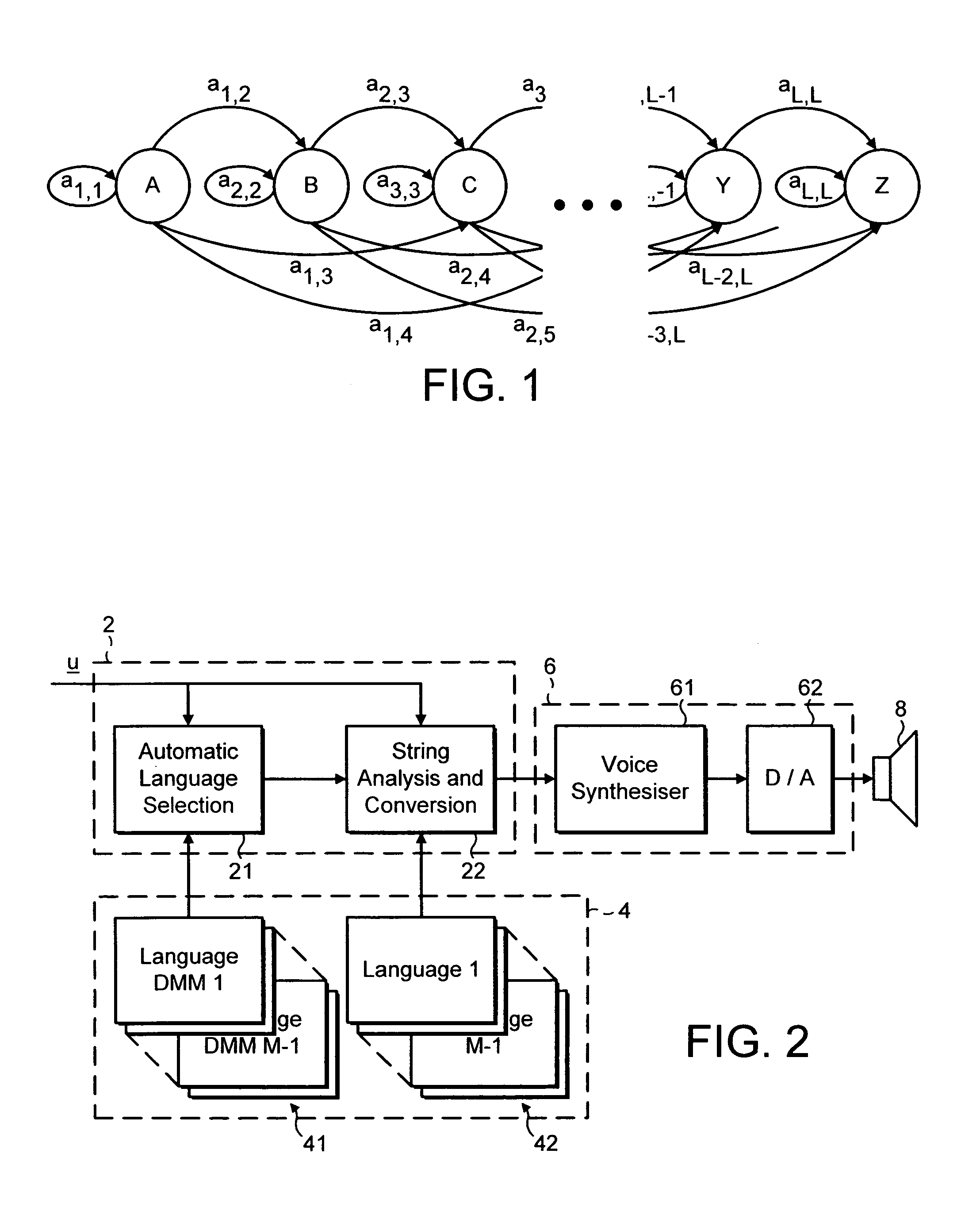
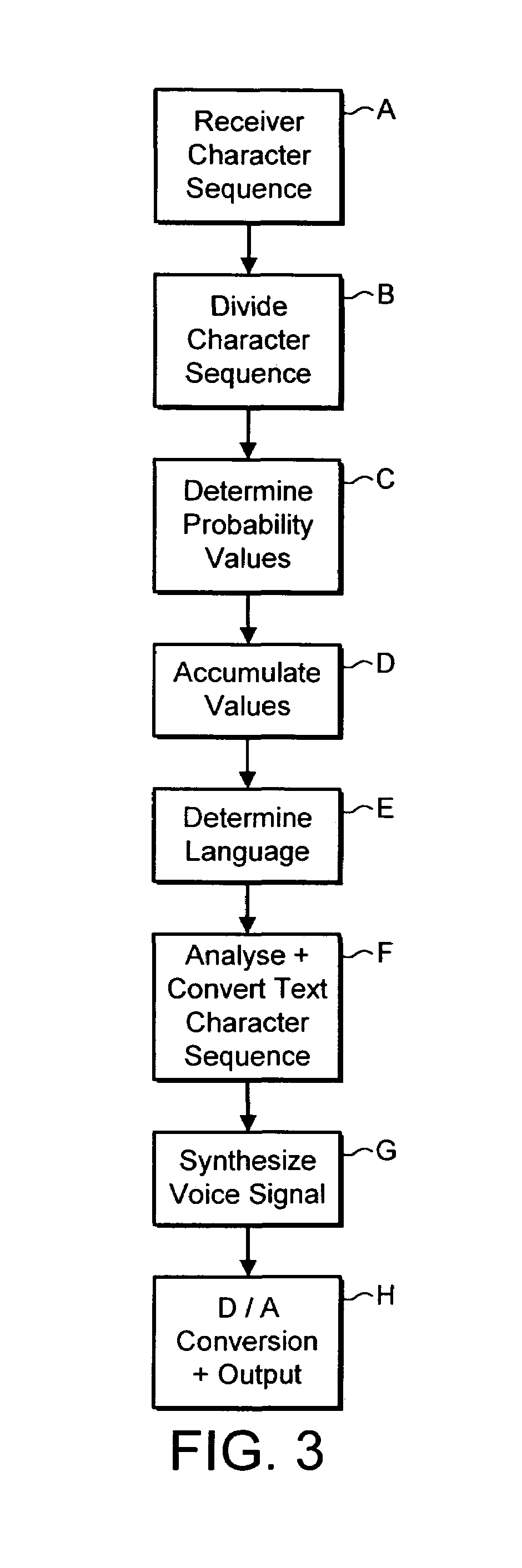
Text language detection
A method of determining the language of a text message received by a mobile telecommunications device indicates receiving an input text message at a mobile telecommunications device; analyzing the input text message using language information stored in the mobile telecommunications device; selecting, from a group of languages defined by the language information, a most likely language for the input text message; and outputting, from the mobile telecommunications device, speech signals corresponding to the input text message, in the selected language.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
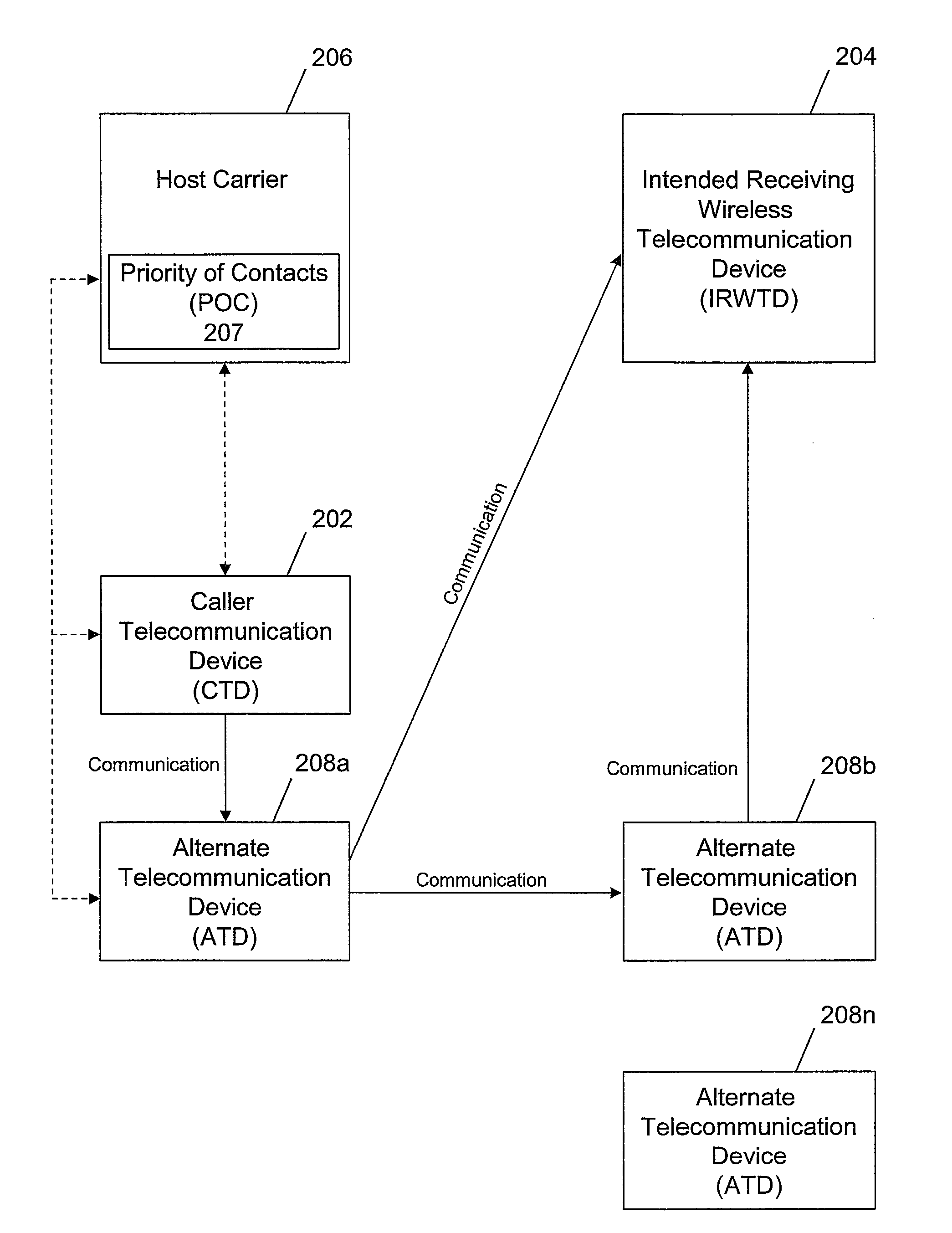
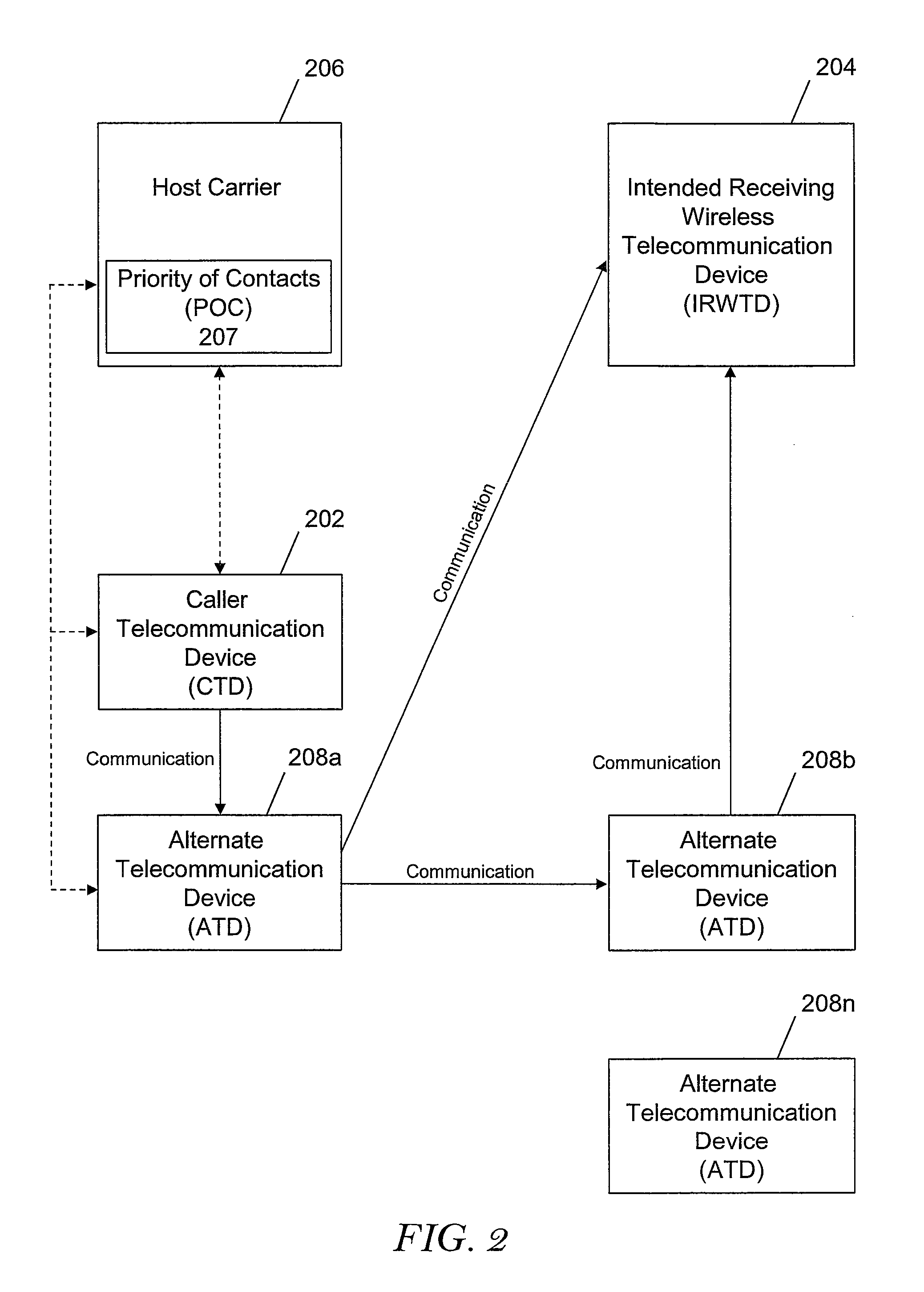
Performing routing of a phone call through a third party device
A method, system, and computer program for routing an outgoing communication in real time is presented. A communication is received from a caller to an intended receiving wireless telecommunication device. In response to the communication failing to connect to the intended receiving wireless telecommunication device, a host carrier initiated query of third party priority of contacts routing preferences of the intended receiving wireless telecommunication device is initiated to determine if other communication devices are available for receiving a re-route of the original communication. If third party routing preferences of the intended receiving wireless telecommunication device have previously been established, then the call is rerouted through one or more alternate telecommunication devices to the intended receiving wireless telecommunication device. The priority of contacts is stored with the host carrier.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Identity blocking service from a wireless service provider
InactiveUS7110749B2Special service provision for substationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionOnline advertisingCellular telephone
Location-blocking and identity-blocking services that can be commercially offered by a service promoter, e.g., a cellular service provider or a web advertiser. In the identity-blocking service, the service promoter may disclose the current physical location of a mobile subscriber (i.e., a cellular phone operator) to a third party (e.g., a web advertiser) subscribing to the identity-blocking service. However, the service promoter may not send any identity information for the mobile subscriber to the third party. On the other hand, in the location-blocking service, the service promoter may disclose the mobile subscriber's identity information to the third party, but not the current physical location of the mobile subscriber. Blocking of the mobile subscriber's identity or location information may be desirable for privacy reasons, to comply with a government regulation, or to implement a telecommunication service option selected by the mobile subscriber. However, in the case of the mobile subscriber requesting emergency help, the service promoter may not block identity and / or location information. Instead, the service promoter may send all such information to the emergency service provider (e.g., the police or a hospital).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
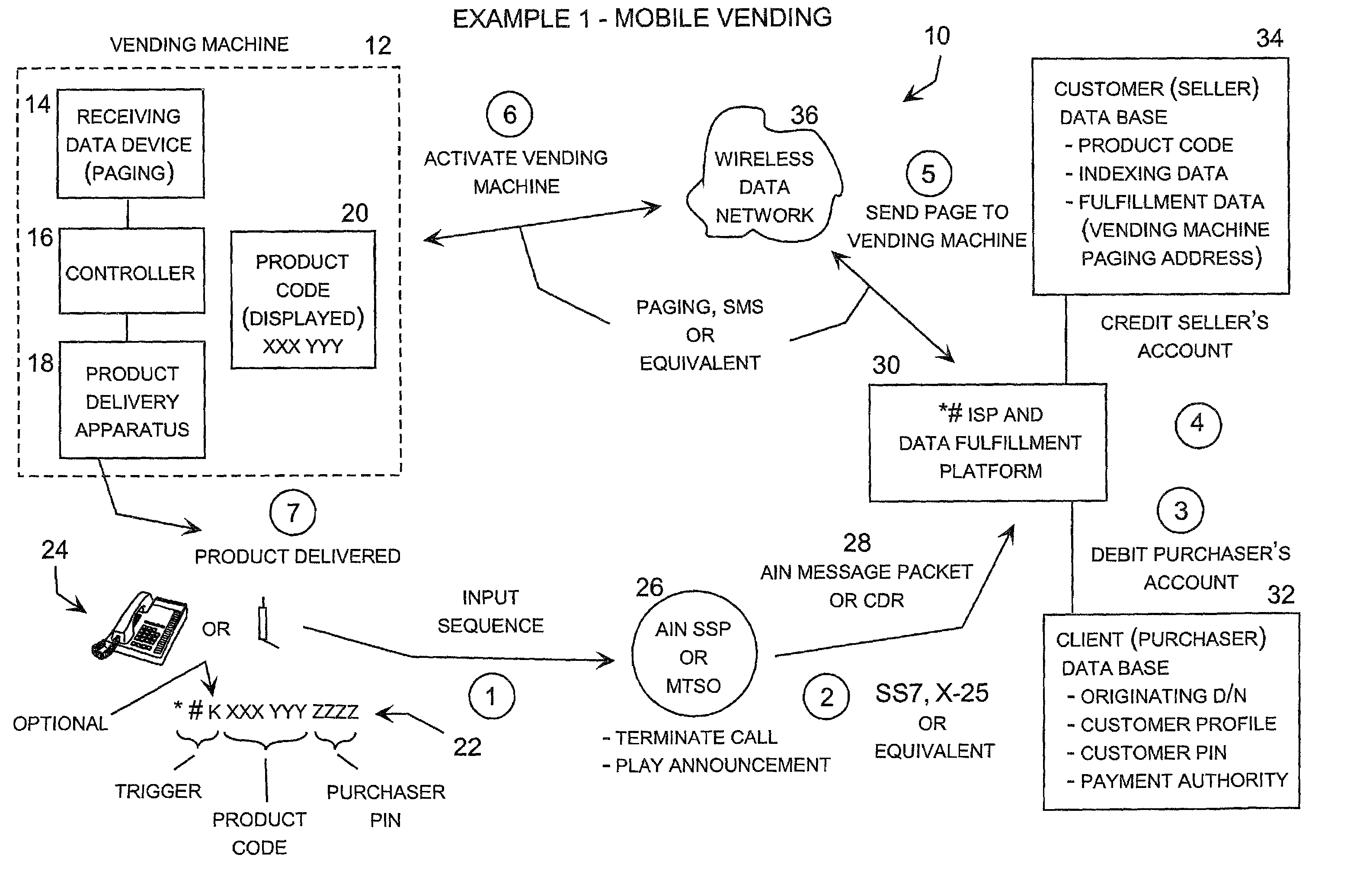
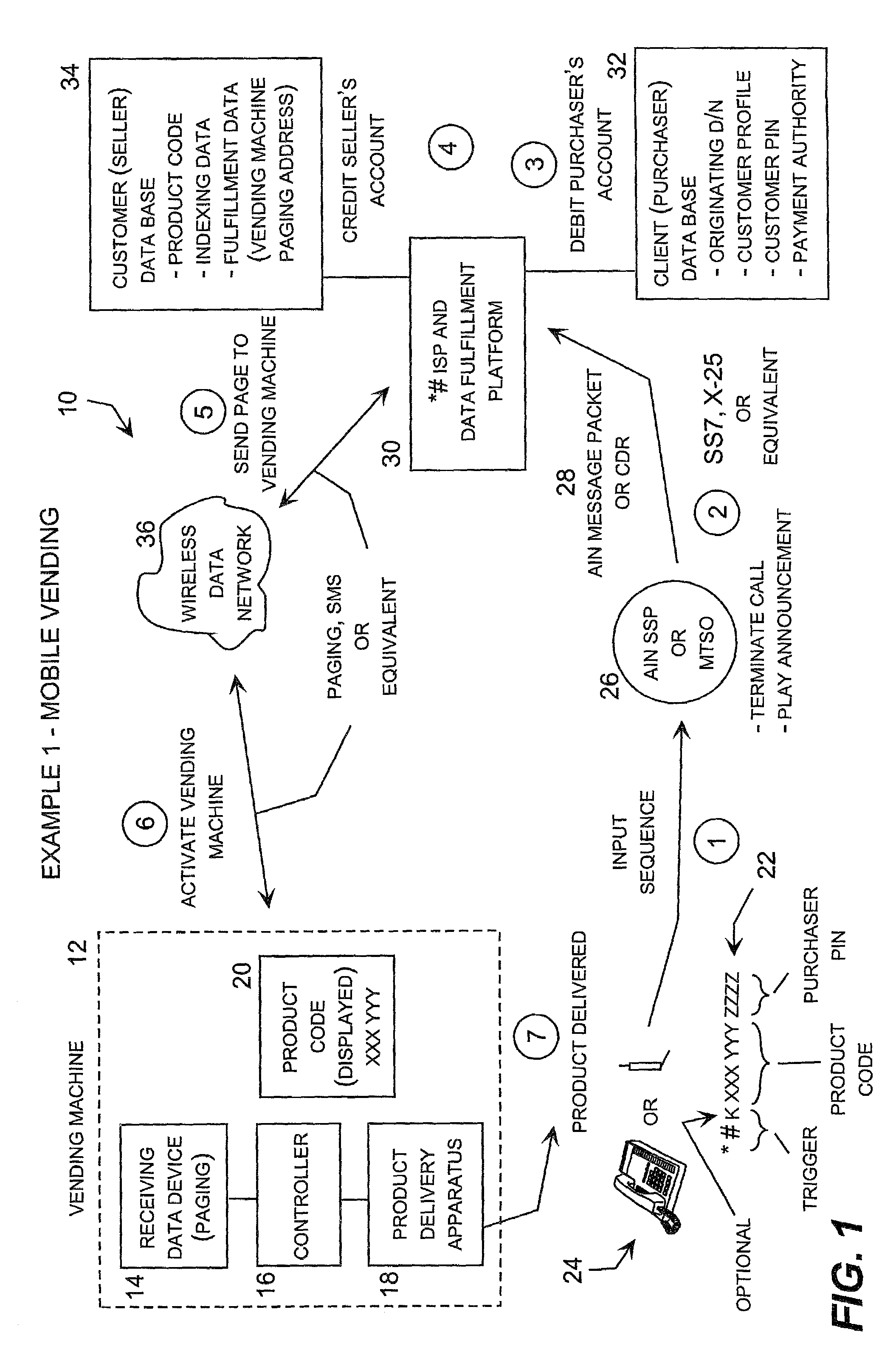
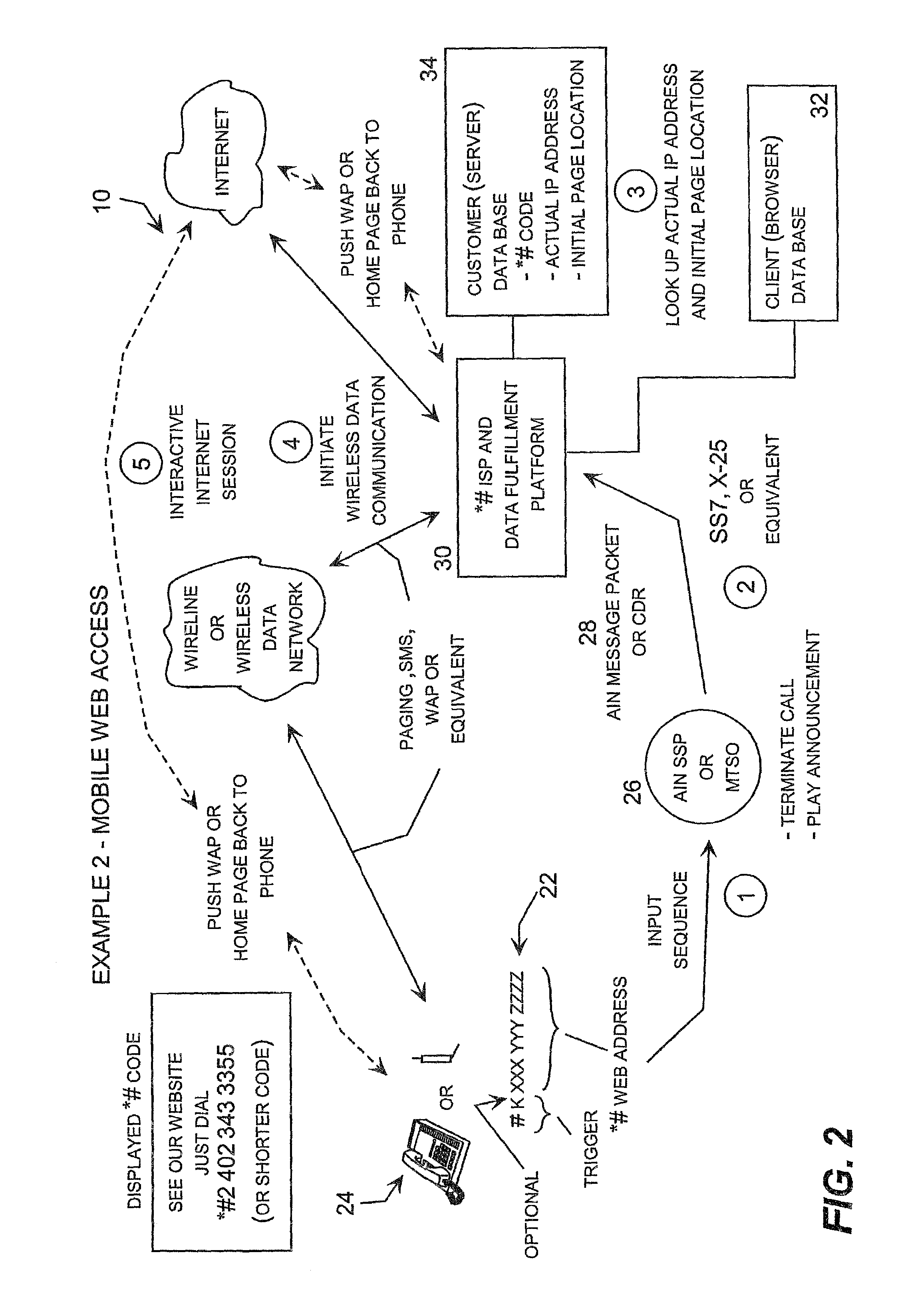
Telecommunications initiated data fulfillment system
InactiveUS6990472B2Allow reuseHighly integratedDiscounts/incentivesTelephonic communicationWireless dataThe Internet
A system for providing a wide range of telecommunications initiated data fulfillment services in which a multi-function code, such as “*#” (star, pound), input into an originating telecommunications device, such as a conventional land-line or wireless telephone, triggers the treatment of the input sequence as a multi-function code service request rather than a dialed directory number. The multi-function code is followed by an input data string to complete the multi-function code service request, which the user typically enters into the telecommunications device just like a conventional telephone call, except that the input string begins with the multi-function code. The telecommunications system recognizes the multi-function code as a trigger, and in response takes one or more actions, such as automatically terminating the call to an announcement and routing a data message to a data fulfillment center, which responds to the message by implementing a response action indicated by the multi-function code service request. For example, the data fulfillment center may respond by transmitting a message over a wireless data network or the Internet to implement a service, such as activation of a vending machine, remote control of device, delivery of a message over the Internet or wireless data network, initiation of an interactive Internet session with the originating device, or a wide range of other services. In addition, a charge for this service may be automatically charged to an account associated with the originating telecommunications device, which may be billed separately or incorporated on the user's conventional monthly telecommunications invoice.
Owner:STARPOUND
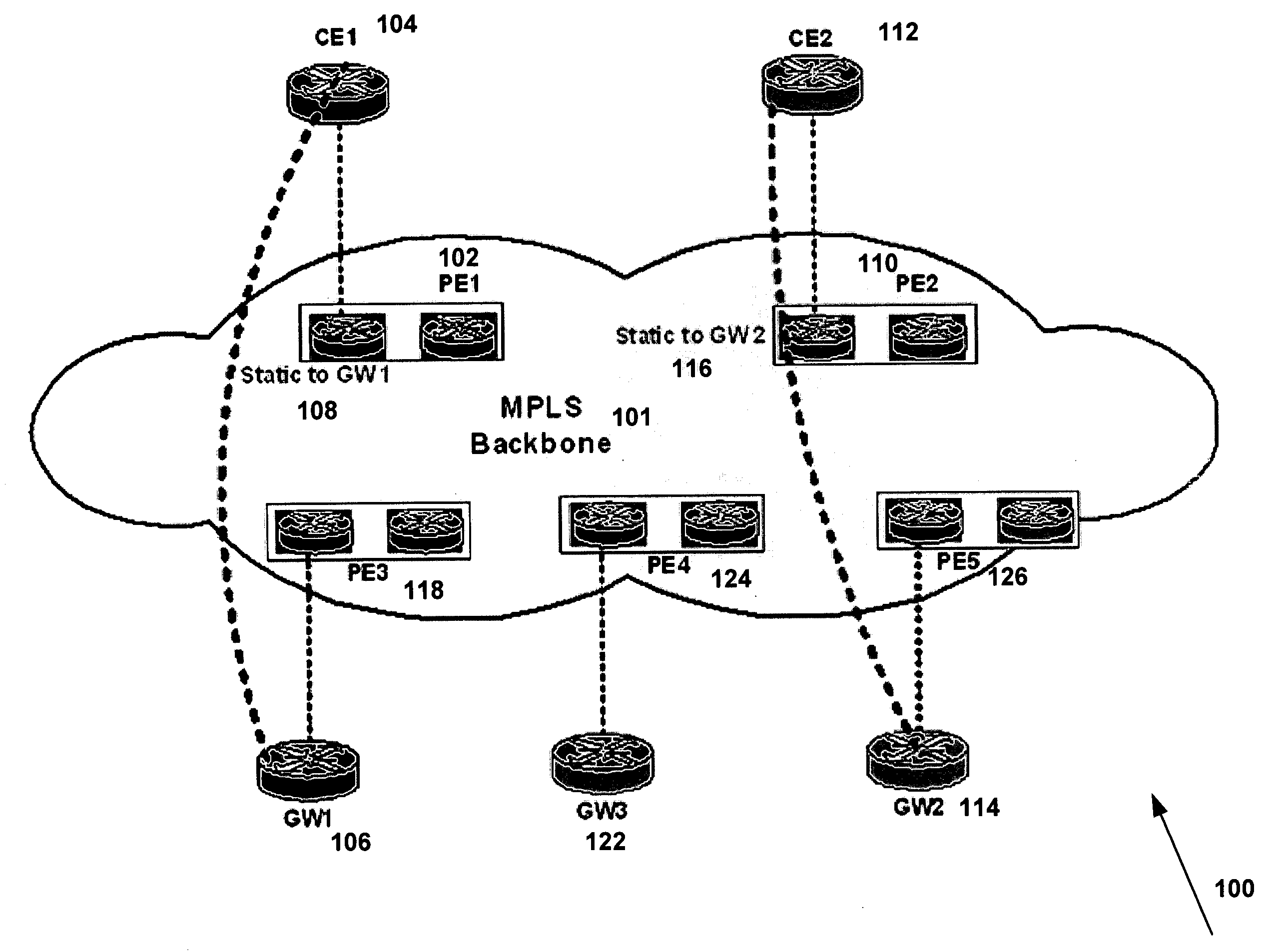
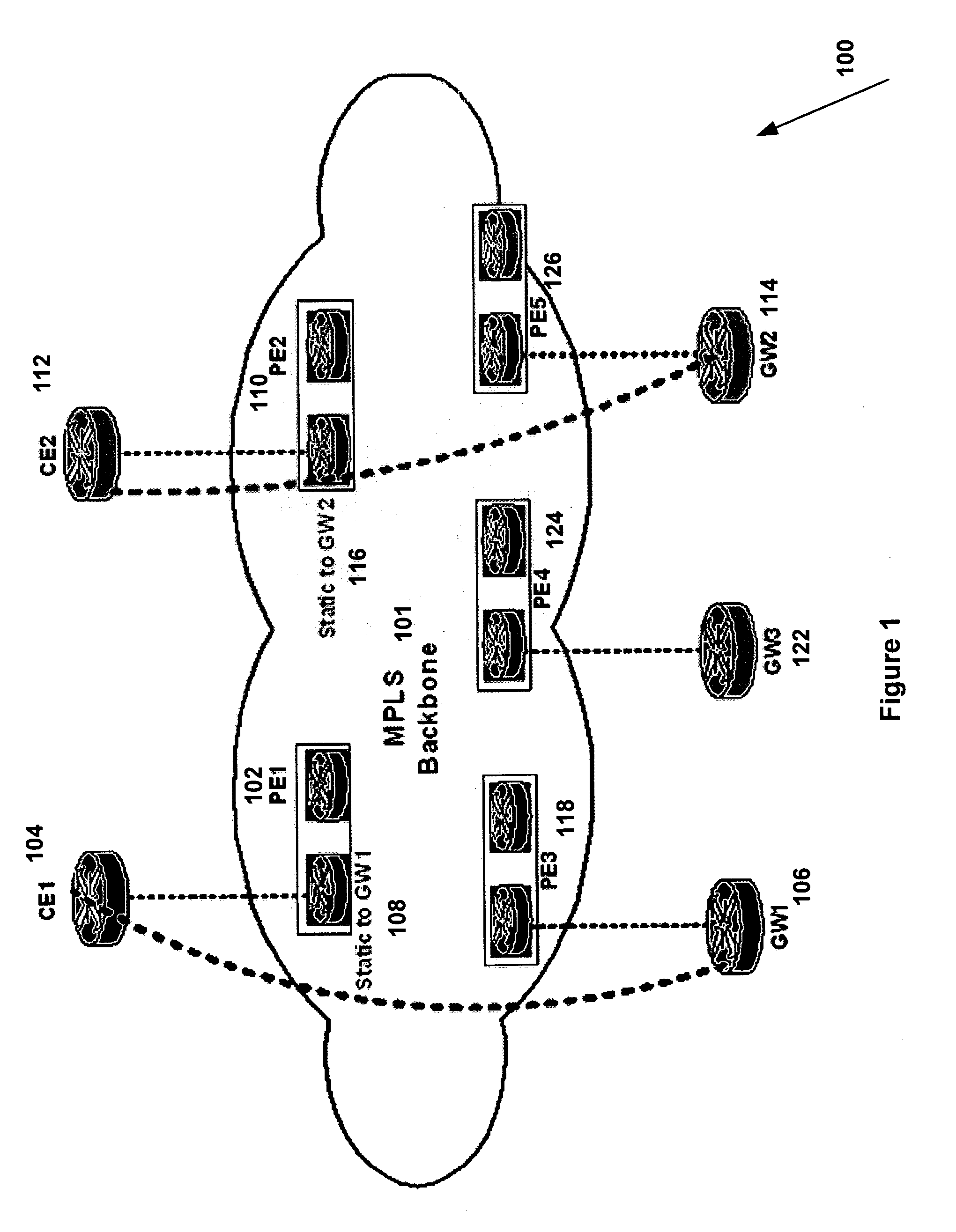
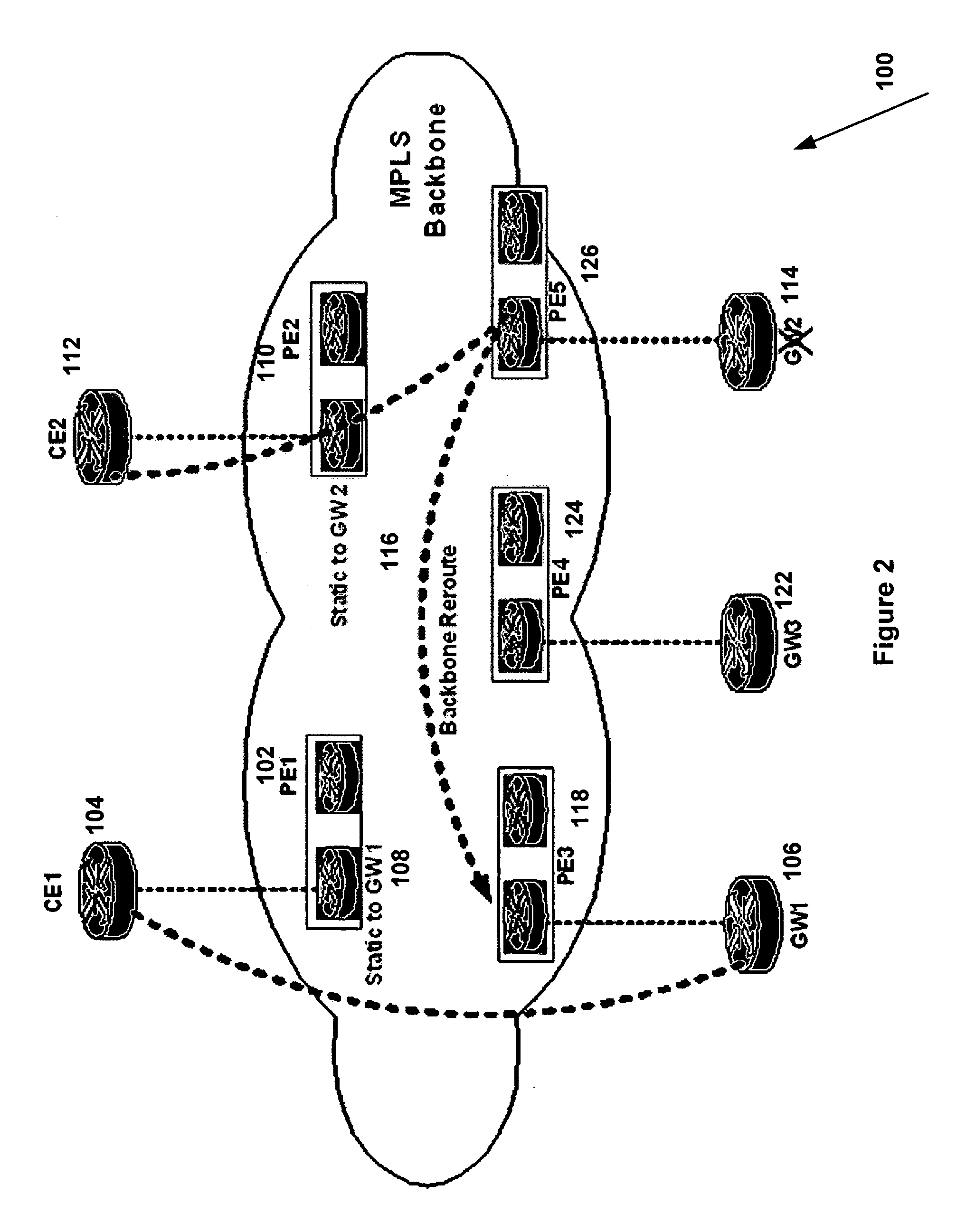
System and method for forwarding traffic data in an MPLS VPN
InactiveUS20080080517A1Data switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTelecommunications network
The present invention provides a system and method for forwarding traffic data in a MPLS VPN network within a telecommunications network. The method comprise a technique for gateway selection in the MPLS VPN by using a combination of recursive floating static routes in the PE routers and conditional route advertisements from the gateway CE routers. This method allows for choice of gateway on a per-PE per-VRF basis.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Age verification and content filtering systems and methods
ActiveUS20070260603A1Additional revenue opportunityRiskDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsThe InternetTelenet
A system and method is provided for age verification and content filtering (AV / CF) on a wireless telecommunications system capable of providing enhanced products such as Internet, WAP, messaging, games, video, music, applications, etc. A profile controls content that is accessible by a user depending upon the user's age or restrictions placed on accessible content in accordance with content categories. Rating information is obtained from content providers and mapped to content categories or content is rated dynamically. User's requests for access may be recorded whether access is provided or denied and used to provide reports including reports to account holders responsible for the user's account. In some instances, attempts to access banned information may be reported to law enforcement officials.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com