Patents
Literature
2156 results about "Whitelist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
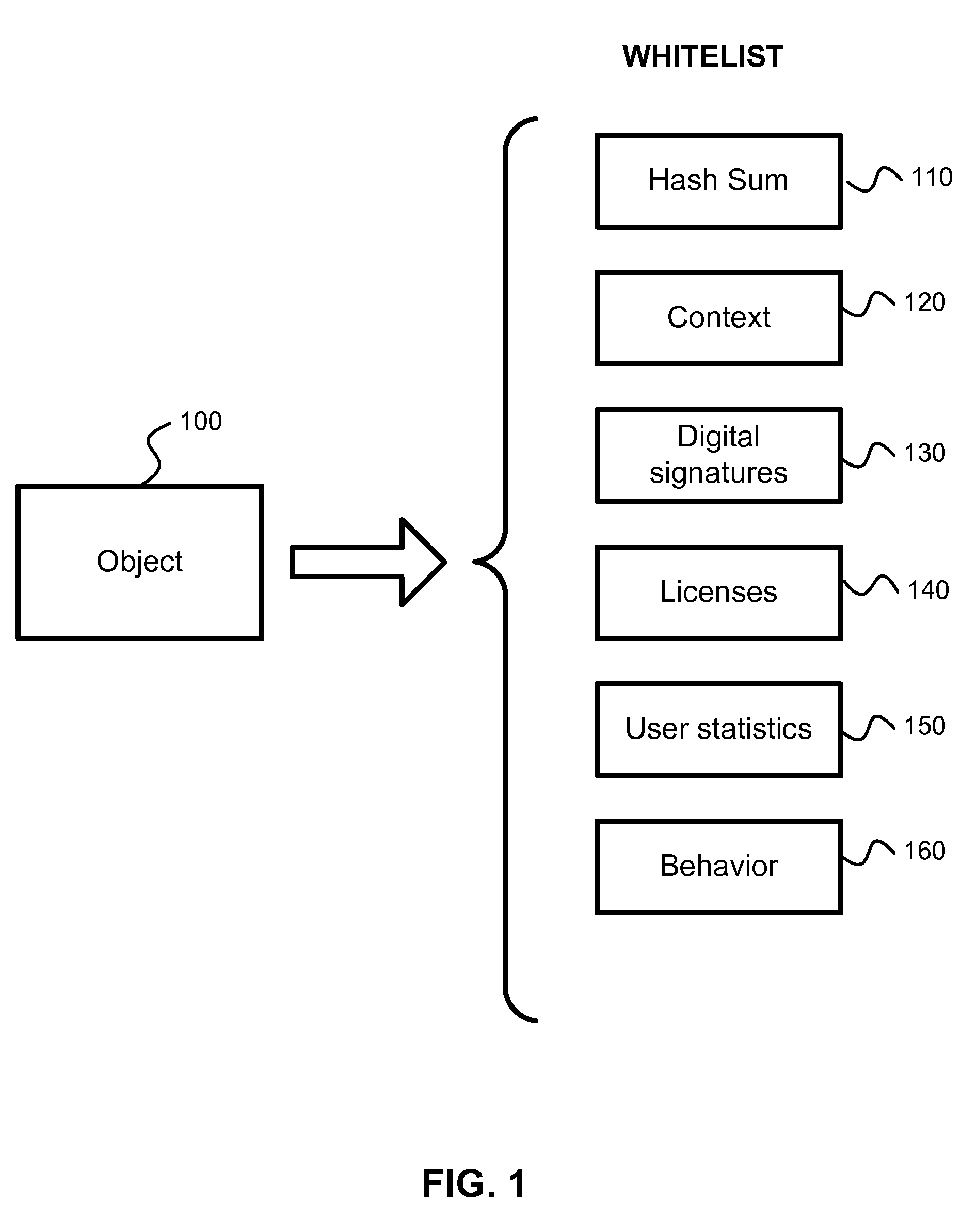
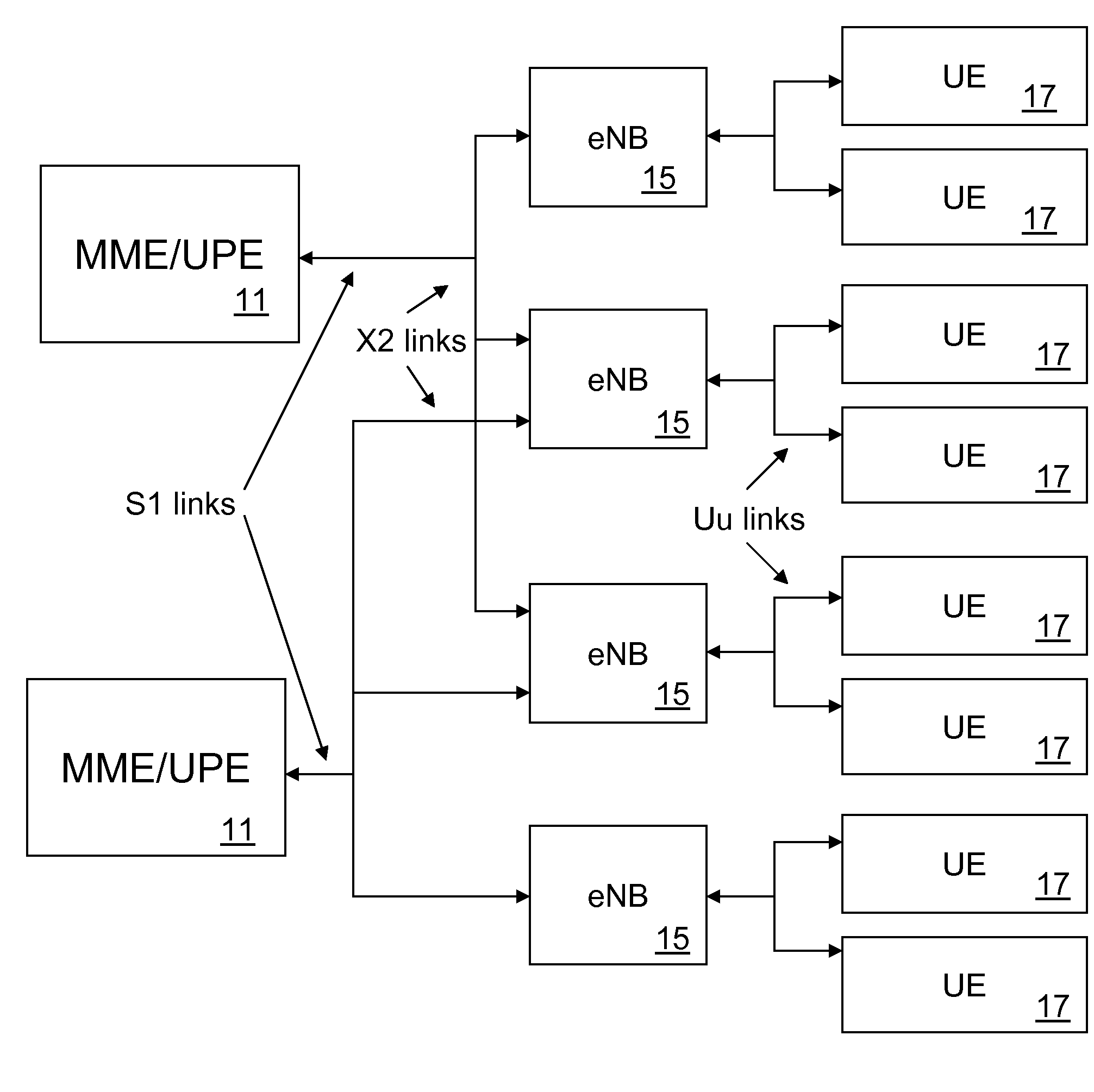
Whitelisting is the practice of explicitly allowing some identified entities access to a particular privilege, service, mobility, access or recognition. It is the reverse of blacklisting.
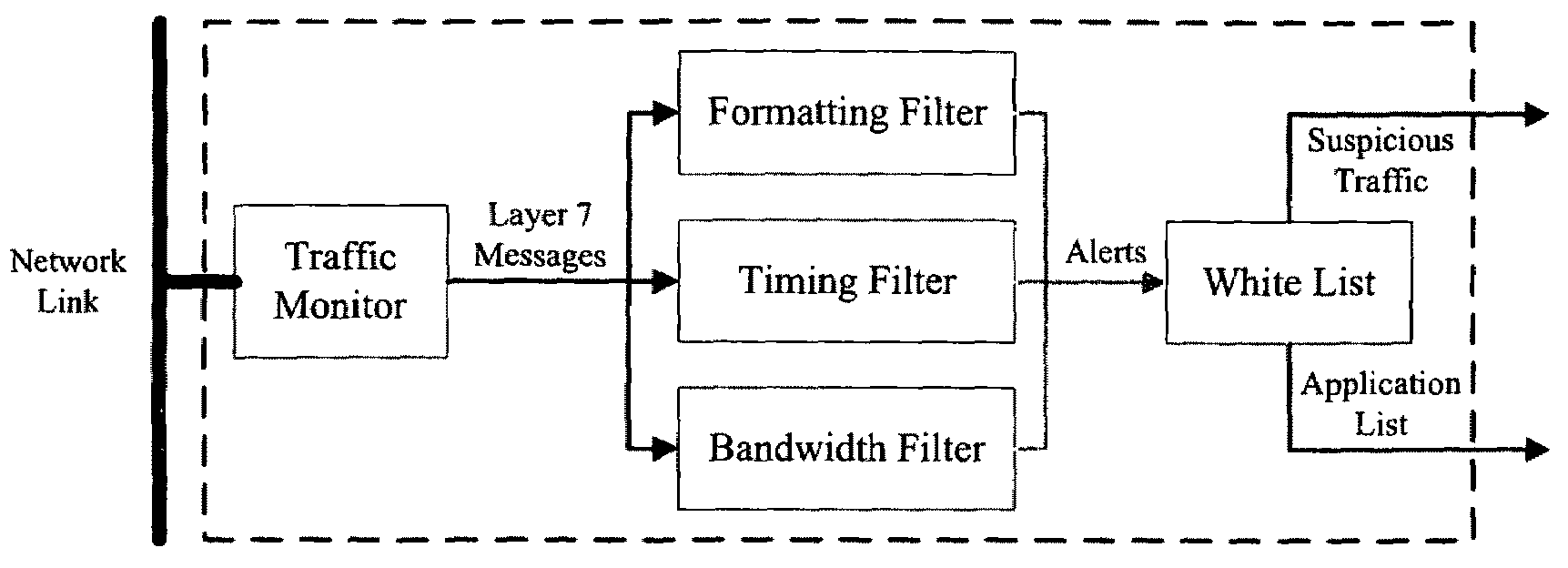
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files
Method, system and computer program product for detecting at least one of security threats and undesirable computer files are provided. A first method includes receiving a data stream which represents outbound, application layer messages from a first computer process to at least one second computer process. The computer processes are implemented on one or more computers. The method further includes monitoring the data stream to detect a security threat based on a whitelist having entries which contain metadata. The whitelist describes legitimate application layer messages based on a set of heuristics. The method still further includes generating a signal if a security threat is detected. A second method includes comparing a set of computer files with a whitelist which characterizes all legitimate computer files. The whitelist contains one or more entries. Each of the entries describe a plurality of legitimate computer files.
Owner:SYROWIK DAVID R
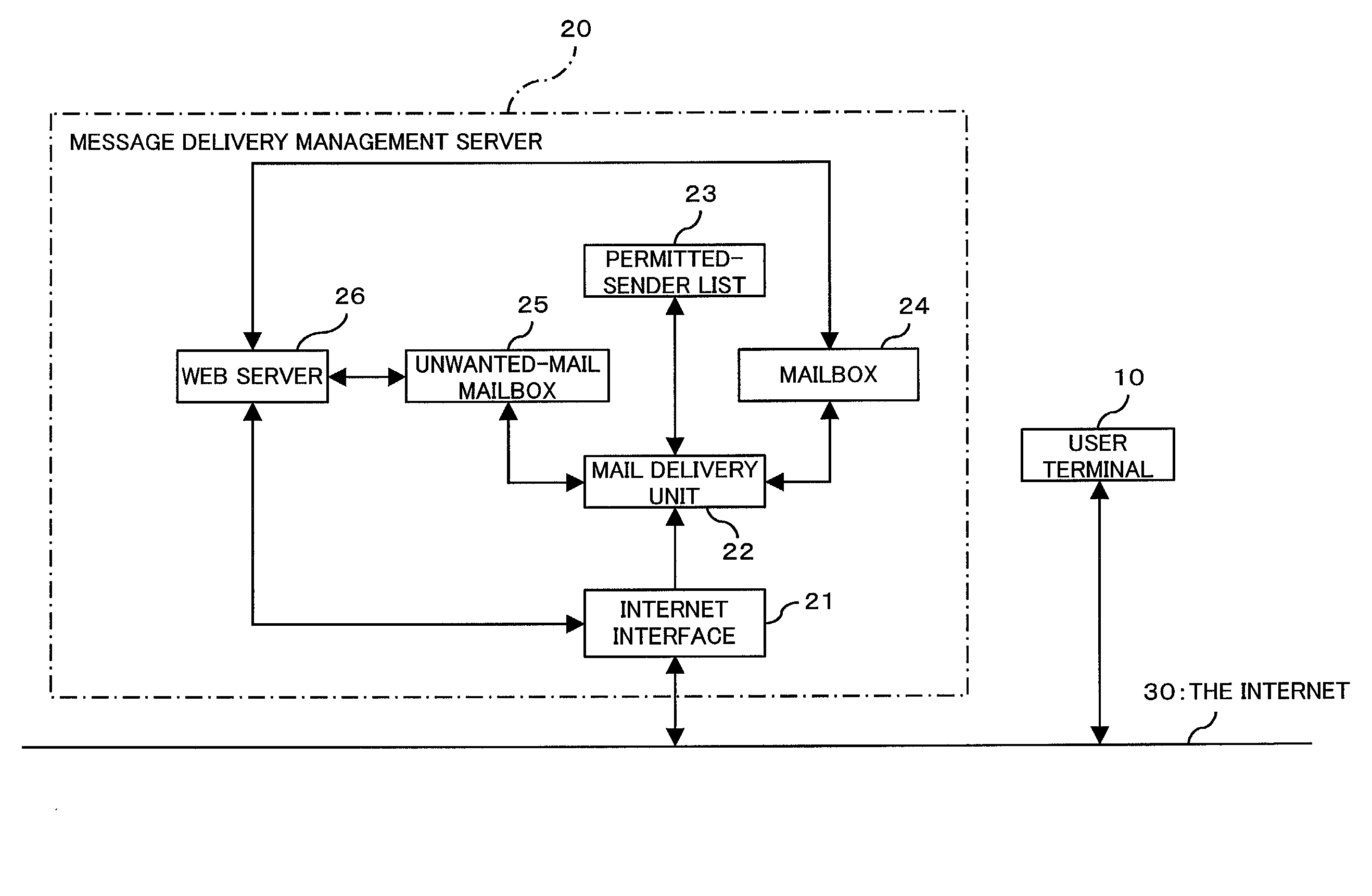
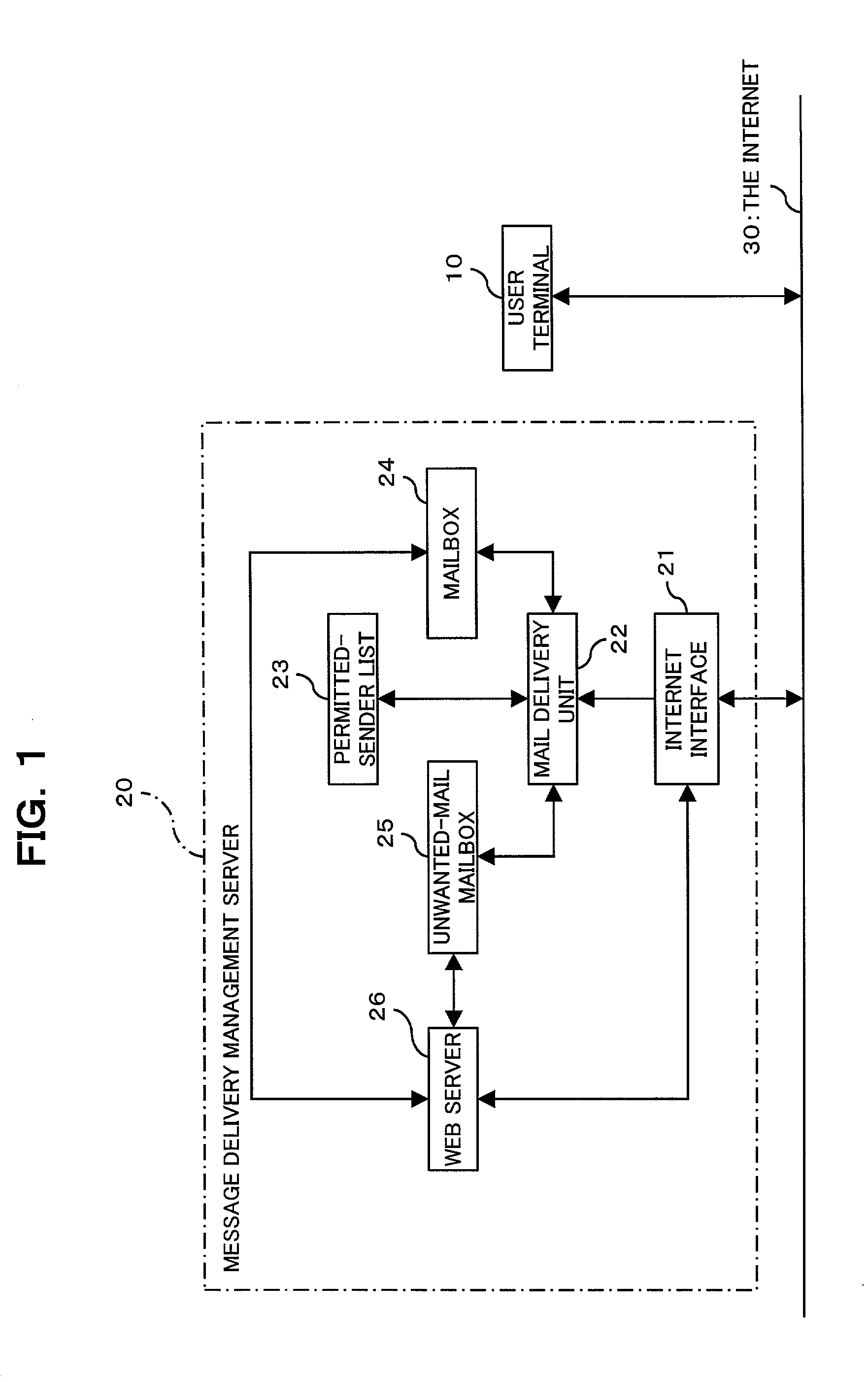
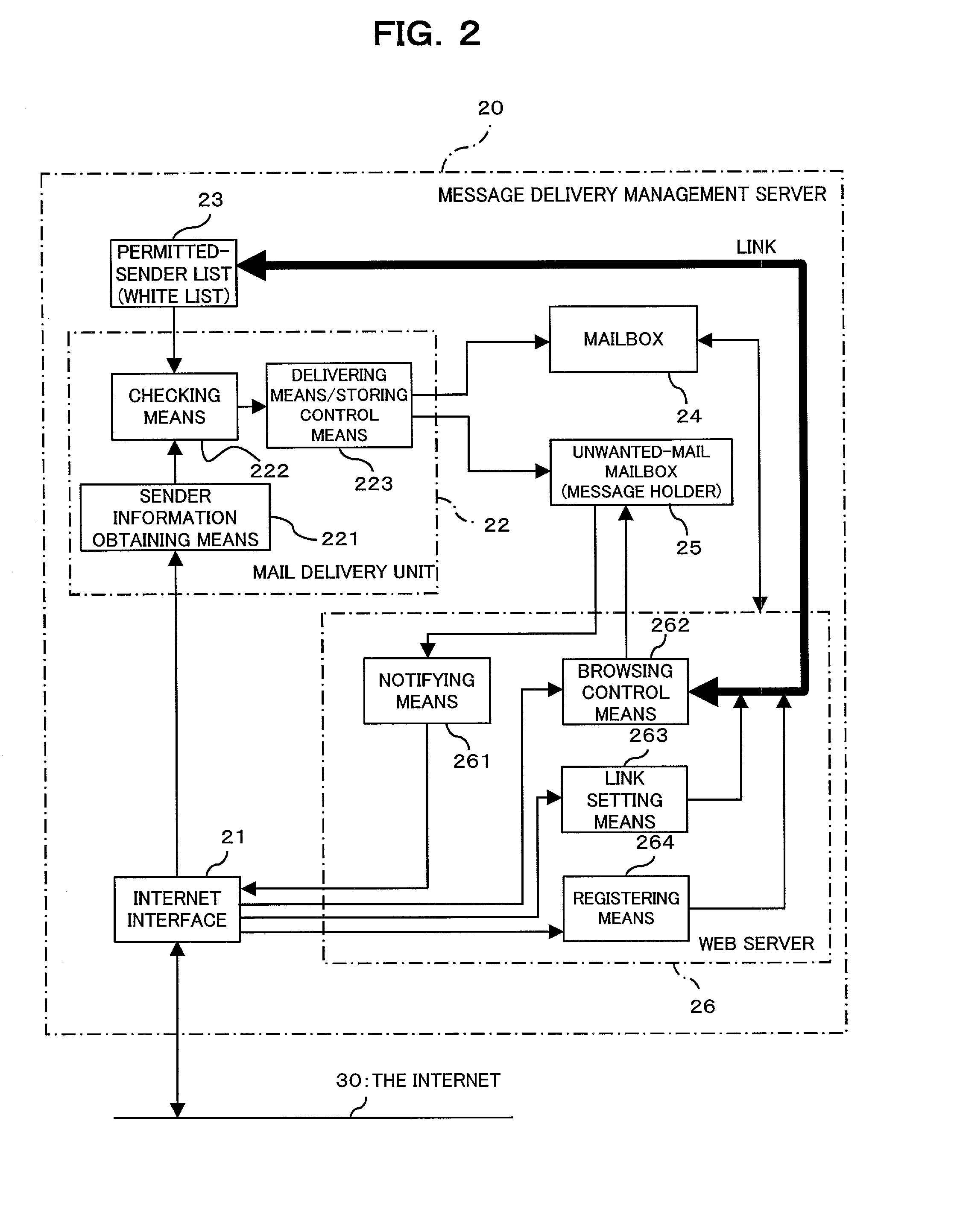
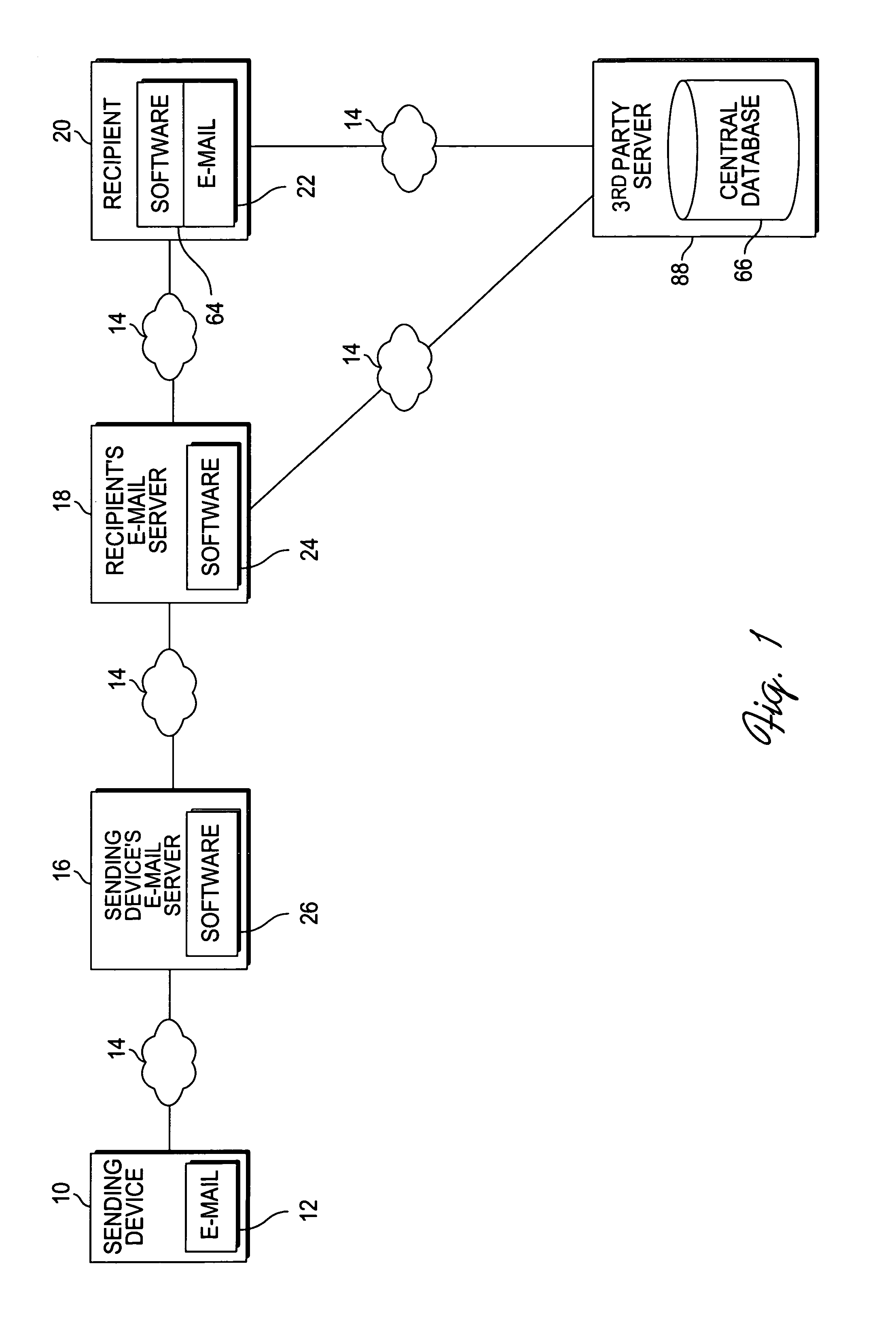
Electronic message delivery system, electronic message delivery managment server, and recording medium in which electronic message delivery management program is recorded
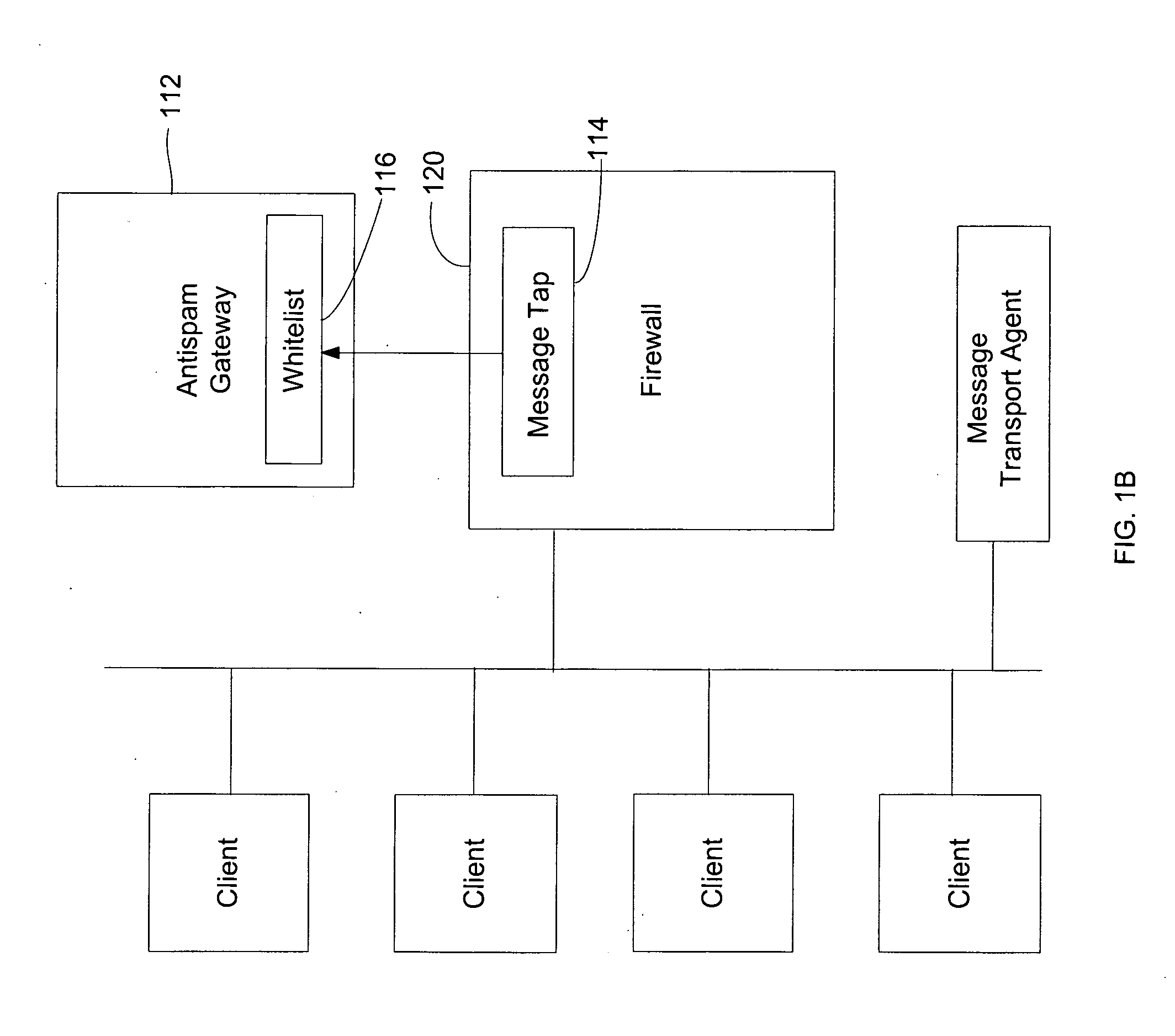
InactiveUS20030023692A1Easy constructionIncrease costMultiple digital computer combinationsAutomatic exchangesMessage deliveryComputer terminal
An apparatus is provided which allows a user, while surely rejecting unwanted electric messages with a white list, to browse the rejected messages so as to check their contents. Electric messages from persons unlisted on the permitted-sender list are accumulated in the message holder, and upon receipt of a browsing request from a user terminal, the messages stored in the message holder are permitted to be browsed by the user. While the user is browsing the messages on the user terminal, a link is established between the sender information and the permitted-sender list, and the sender information is added / registered to the permitted-sender list, in response to the user selecting the sender information of the electronic message on the user terminal. This apparatus is applicable to a system for electronically delivering electronic mail such as e-mail and voice mail that is sent directly to mobile telephones.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
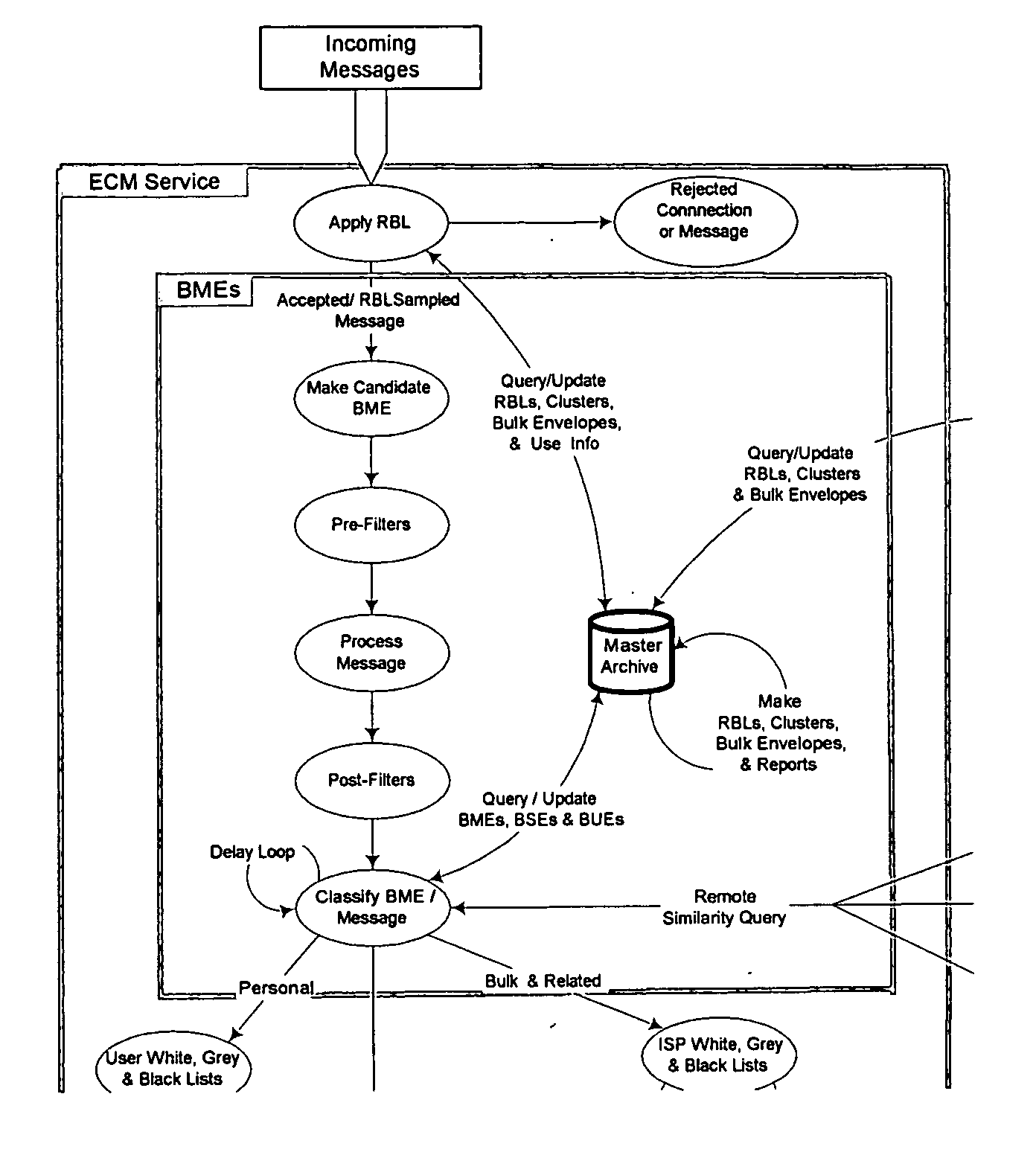
Dynamic message filtering
ActiveUS20050076084A1Reduce in quantityMake fastError detection/correctionGenetic modelsSpammingWhitelist
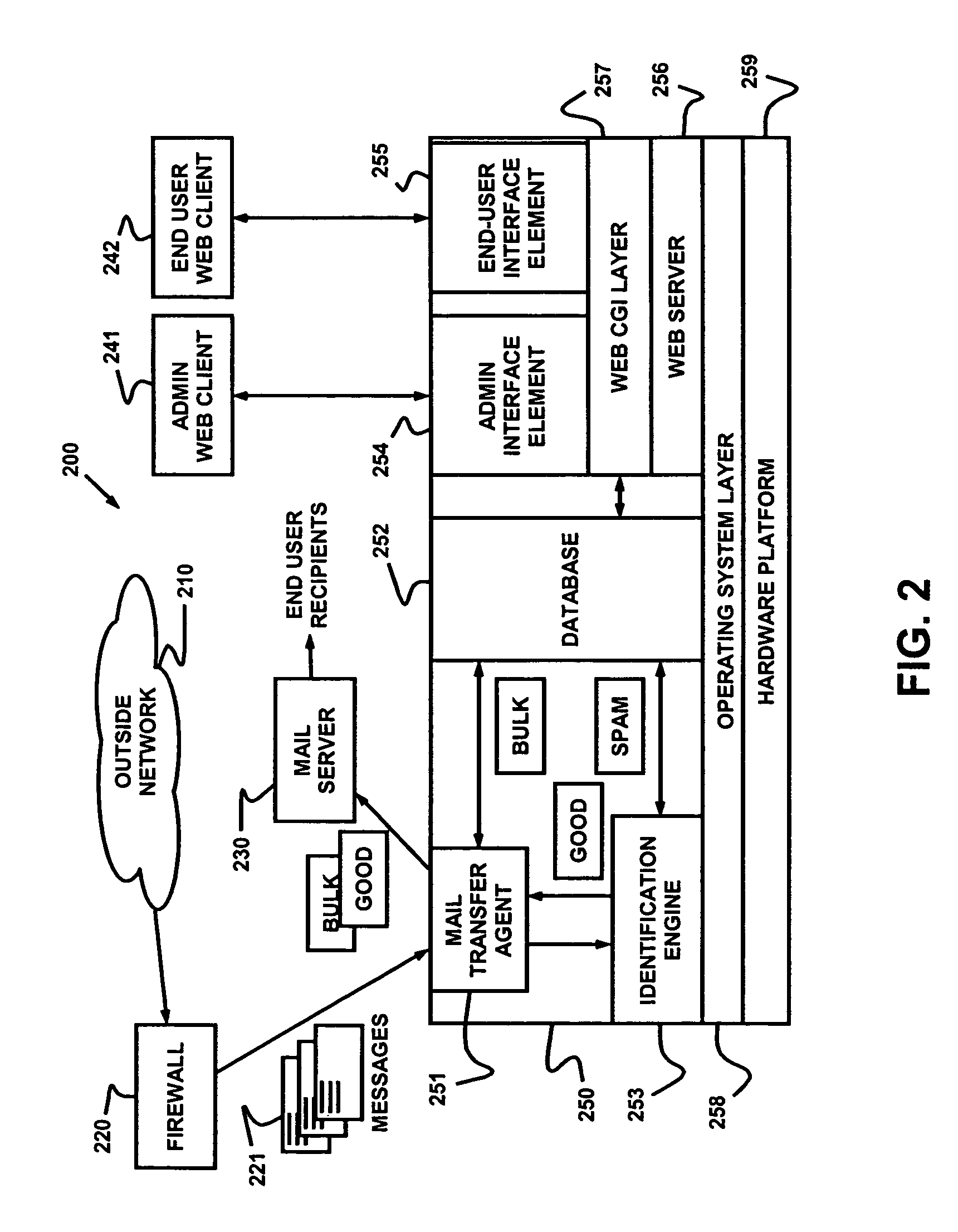
Dynamically filtering and classifying messages, as good messages, bulk periodicals, or spam. A regular expression recognizer, and pre-trained neural networks. The neural networks distinguish “likely good” from “likely spam,” and also operate at a more discriminating level to distinguish among the three categories above. A dynamic whitelist and blacklist; sending addresses are collected when the number of their messages indicates the sender is good or a spammer. A dynamically selected set of regular expressions input to the neural networks.
Owner:MAILGATE LLC
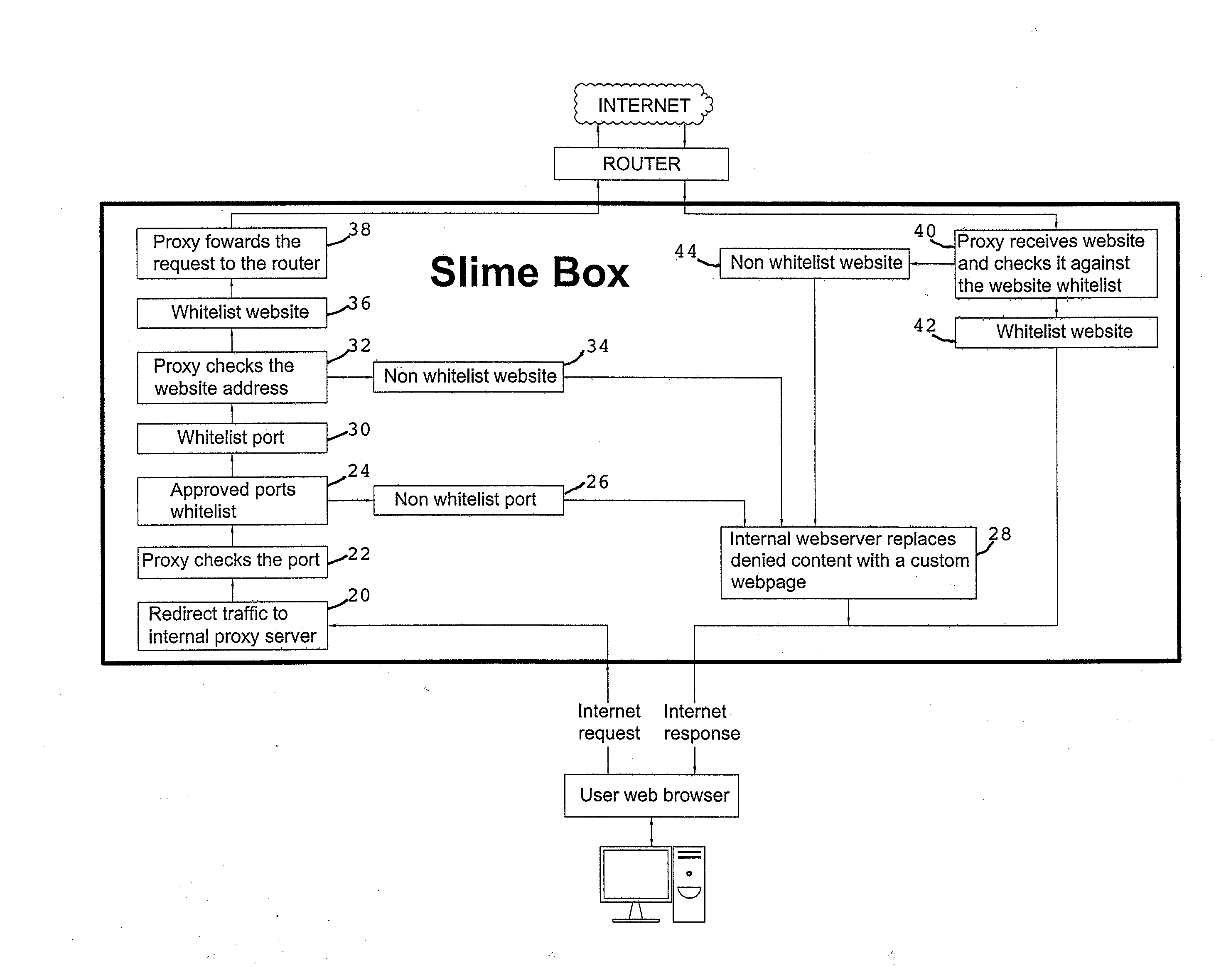
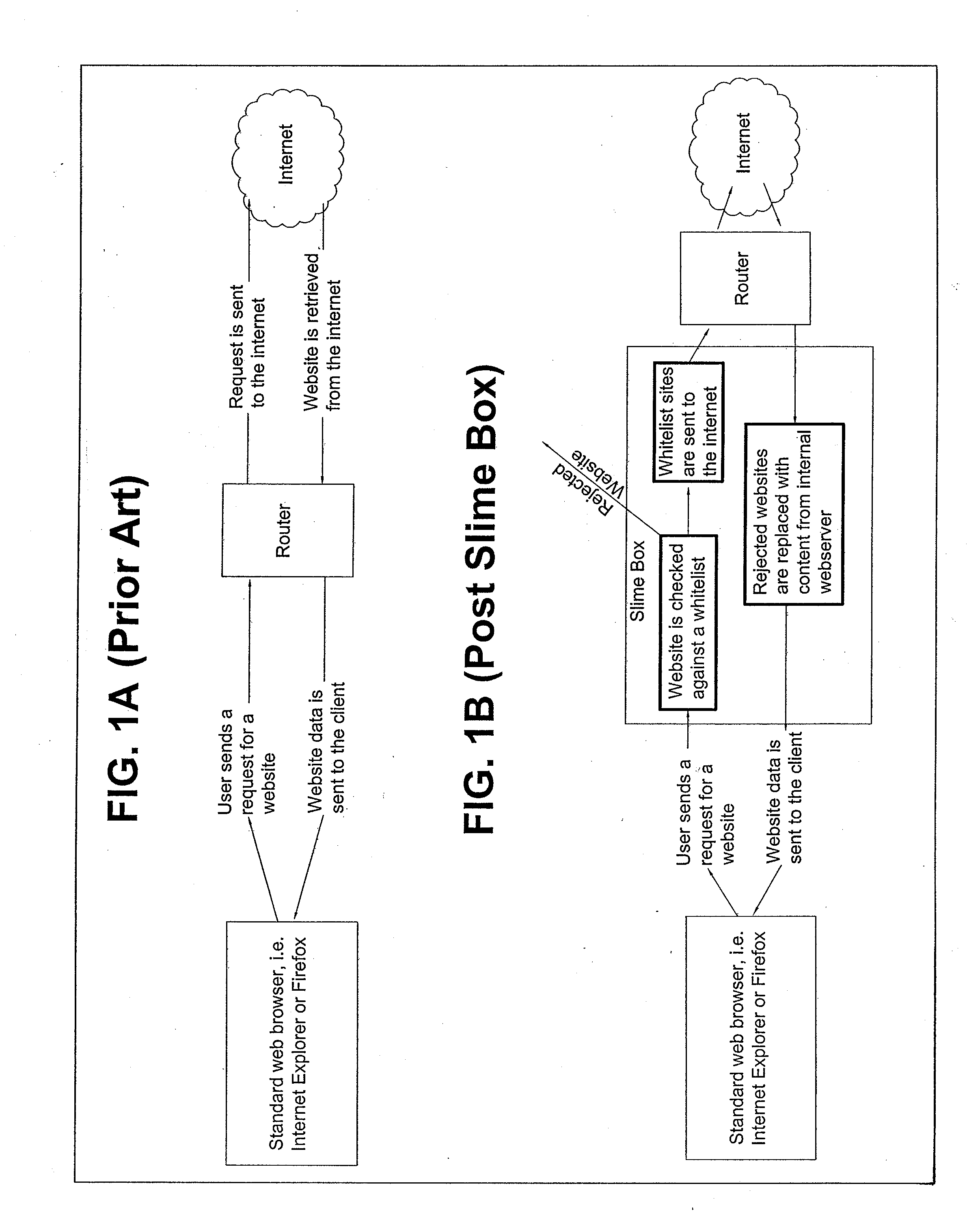
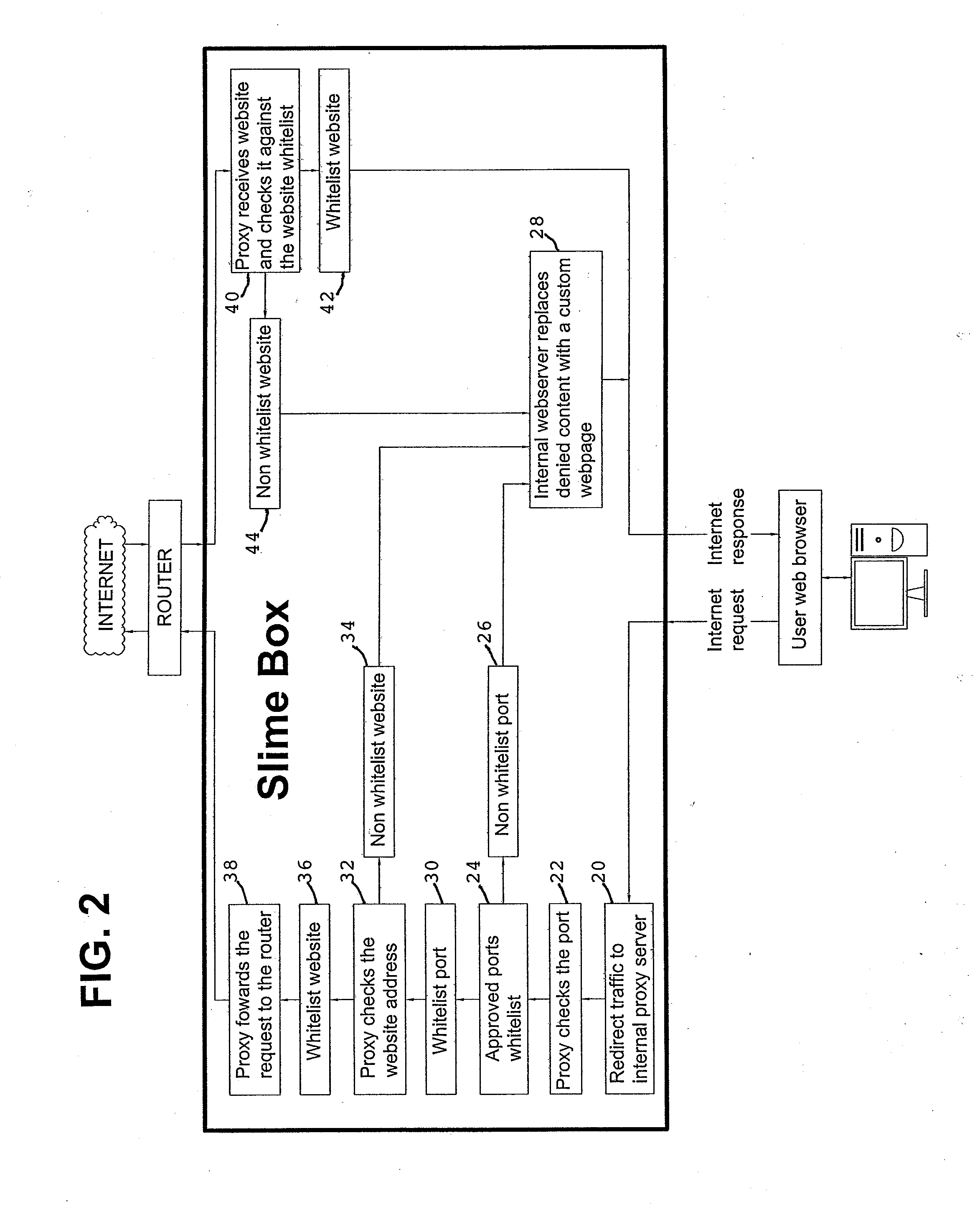
System and method for filtering internet content & blocking undesired websites by secure network appliance
InactiveUS20120023593A1Harder to hackDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb browserInternet content
Owner:PUDER GEORGE +1
System and method for the classification of electronic communication
InactiveUS20060168006A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksElectronic communicationSpamming
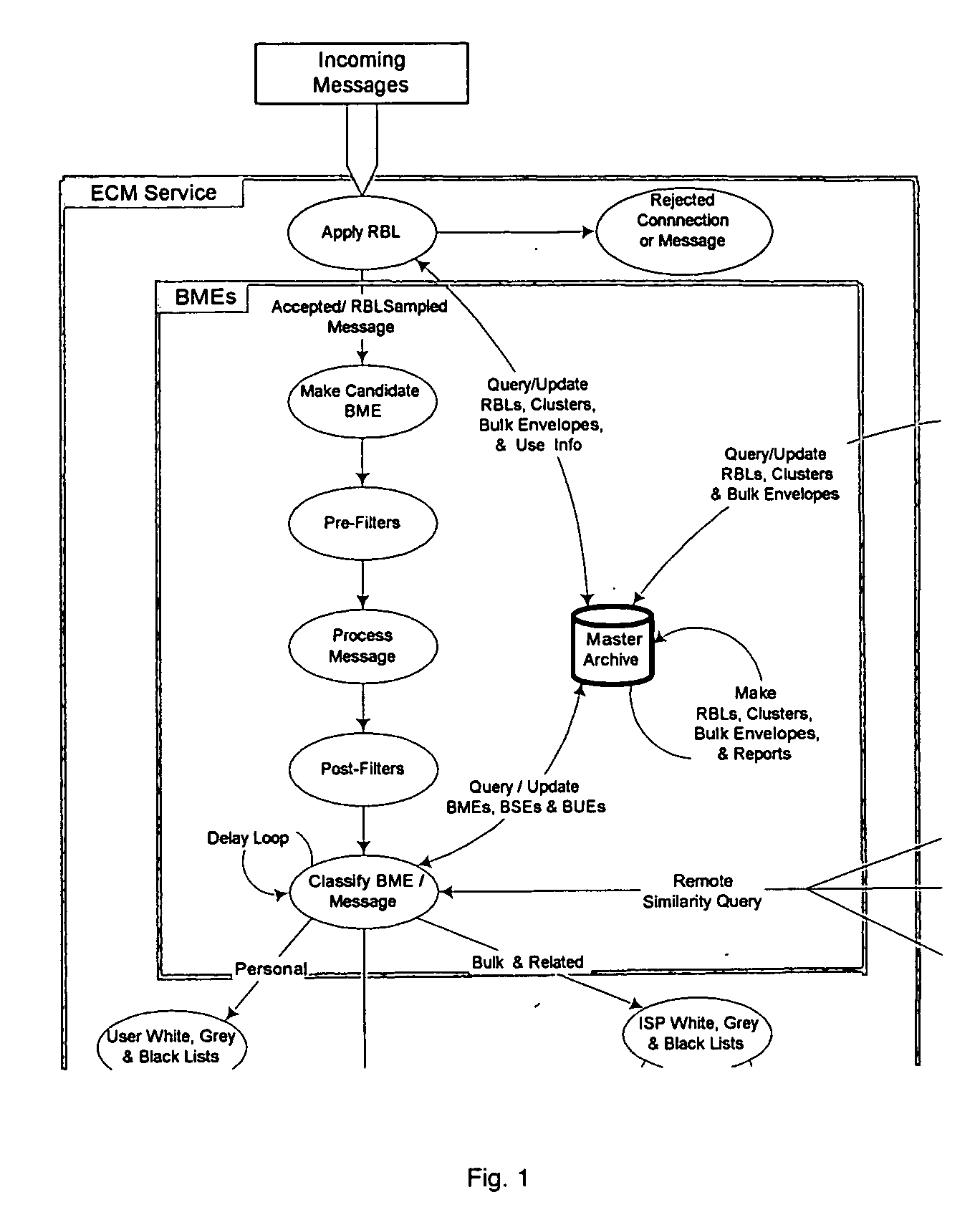
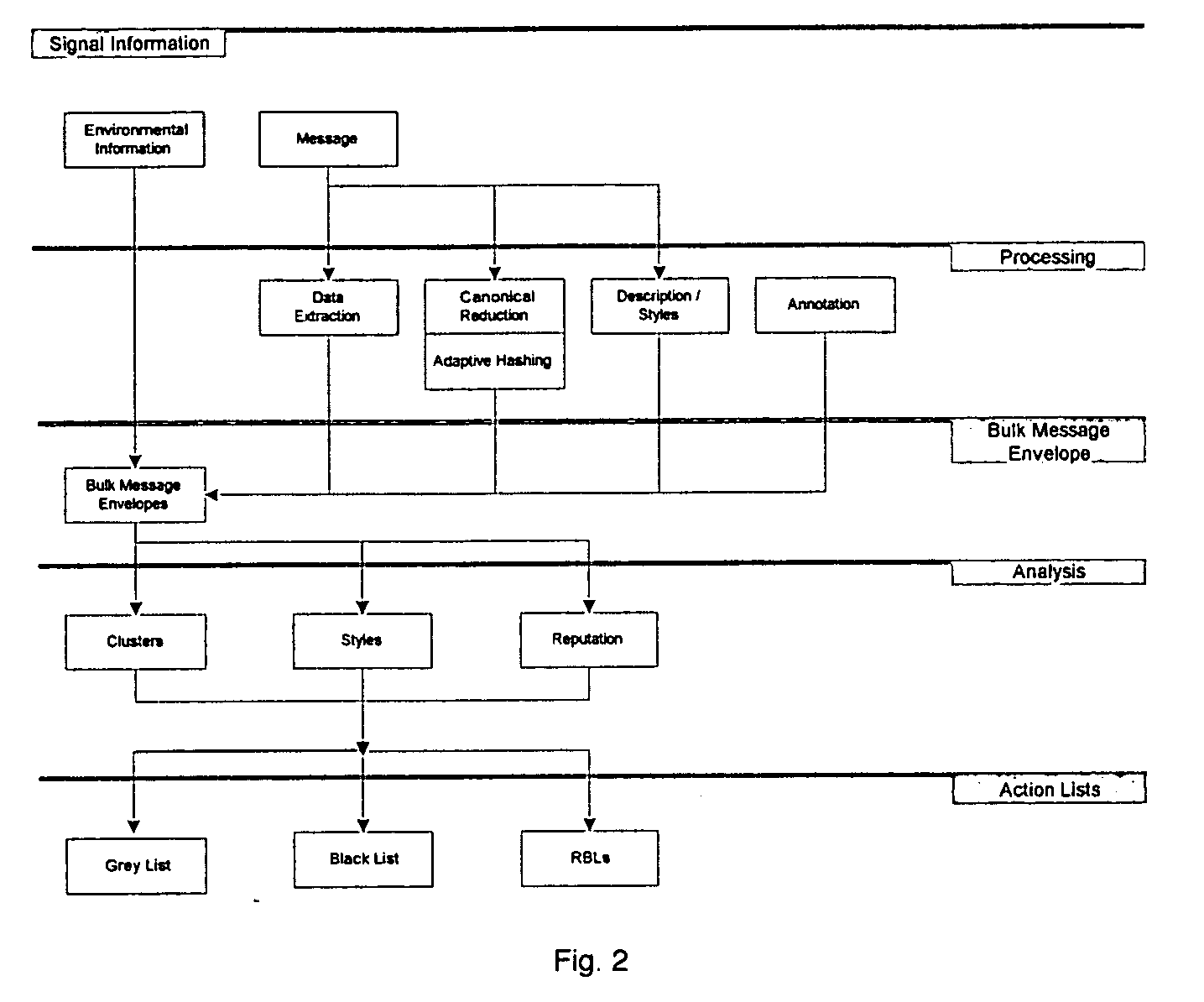
From an electronic message, we extract any destinations in selectable links, and we reduce the message to a “canonical” (standard) form that we define. It minimizes the possible variability that a spammer can introduce, to produce unique copies of a message. We then make multiple hashes. These can be compared with those from messages received by different users to objectively find bulk messages. From these, we build hash tables of bulk messages and make a list of destinations from the most frequent messages. The destinations can be used in a Real time Blacklist (RBL) against links in bodies of messages. Similarly, the hash tables can be used to identify other messages as bulk or spam. Our method can be used by a message provider or group of users (where the group can do so in a p2p fashion) independently of whether any other provider or group does so. Each user can maintain a “gray list” of bulk mail senders that she subscribes to, to distinguish between wanted bulk mail and unwanted bulk mail (spam). The gray list can be used instead of a whitelist, and is far easier for the user to maintain.
Owner:METASWARM INC
Online privacy management
ActiveUS9003552B2Simple processDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDashboardClient-side scripting
A privacy management system (PMS) is disclosed for a Chief Privacy Officer (CPO) or other user to use in monitoring and / or controlling in realtime the flow of data (e.g., outflow) about the user and his / her online experience. The PMS may employ pattern recognition software to evaluate analytics data and potentially block private information from being sent within the analytics data. The PMS may provide a dashboard displaying a whitelist and / or blacklist indicating what destinations / sources are blocked or allowed as well as private information settings indicating what types of private information should be blocked. The PMS includes browser-client scripting code and may also include a PMS-certified verification icon and / or lock and unlock icons for display on webpages being monitored / controlled in realtime by the PMS.
Owner:ENSIGHTEN
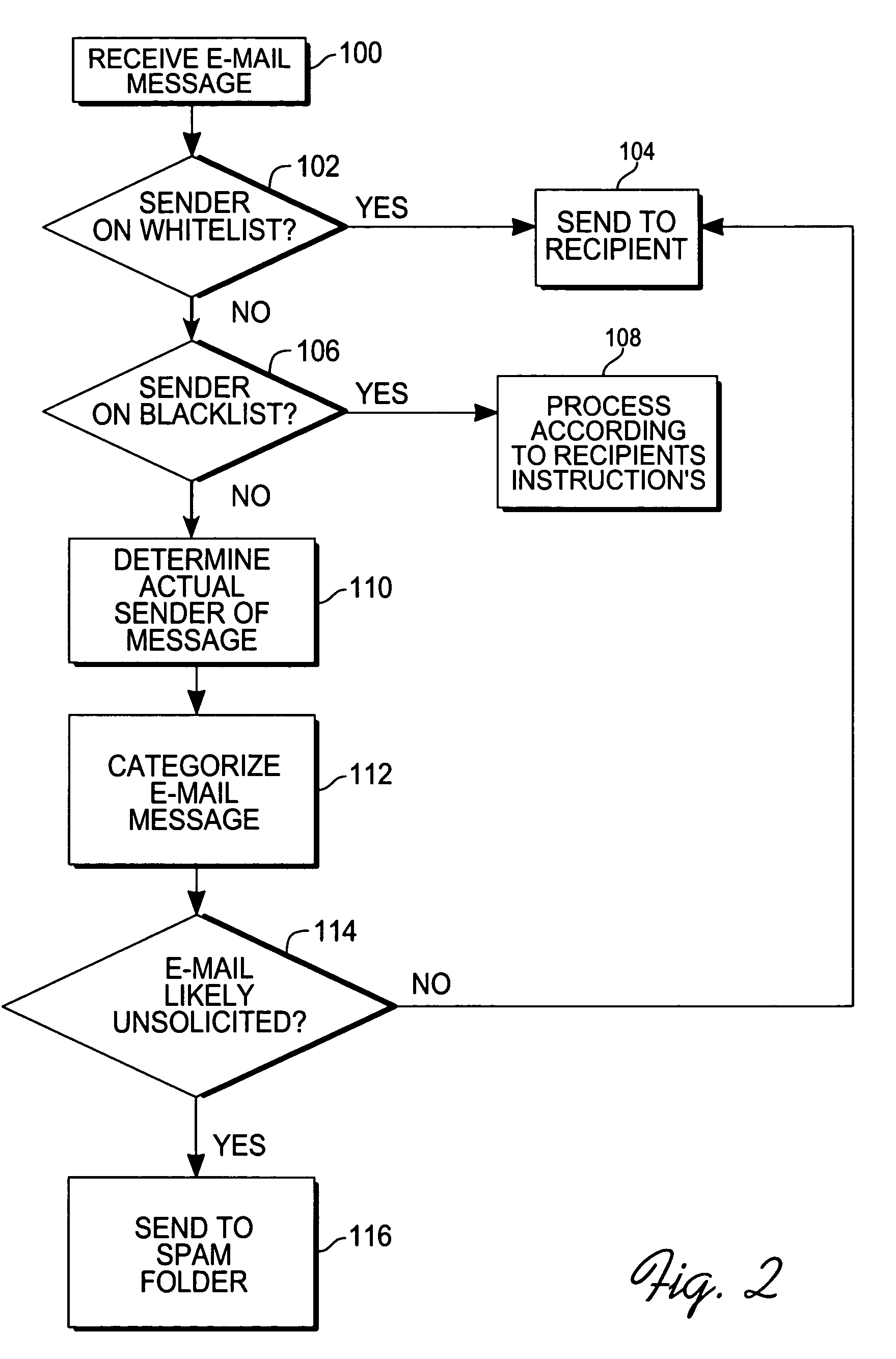
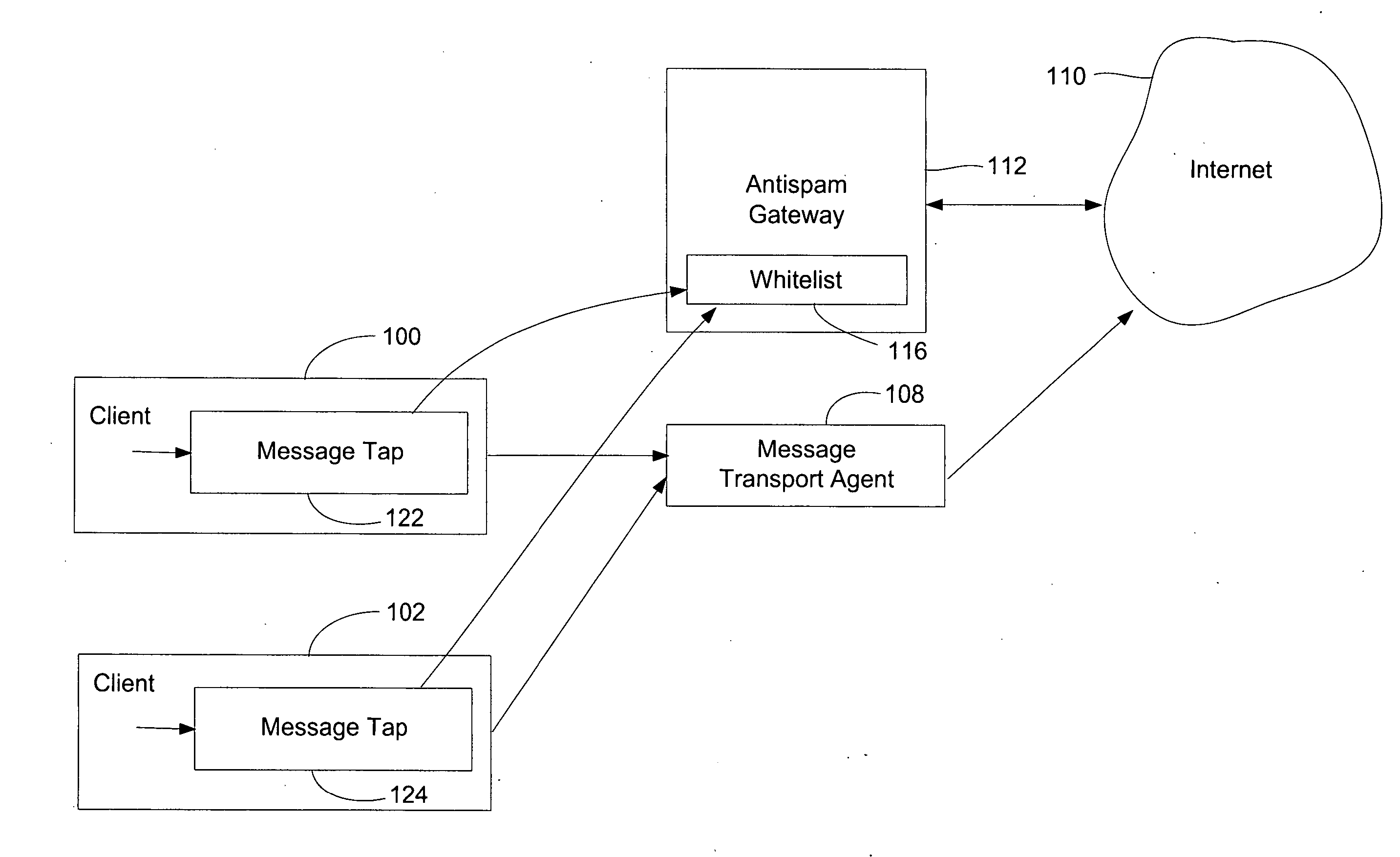
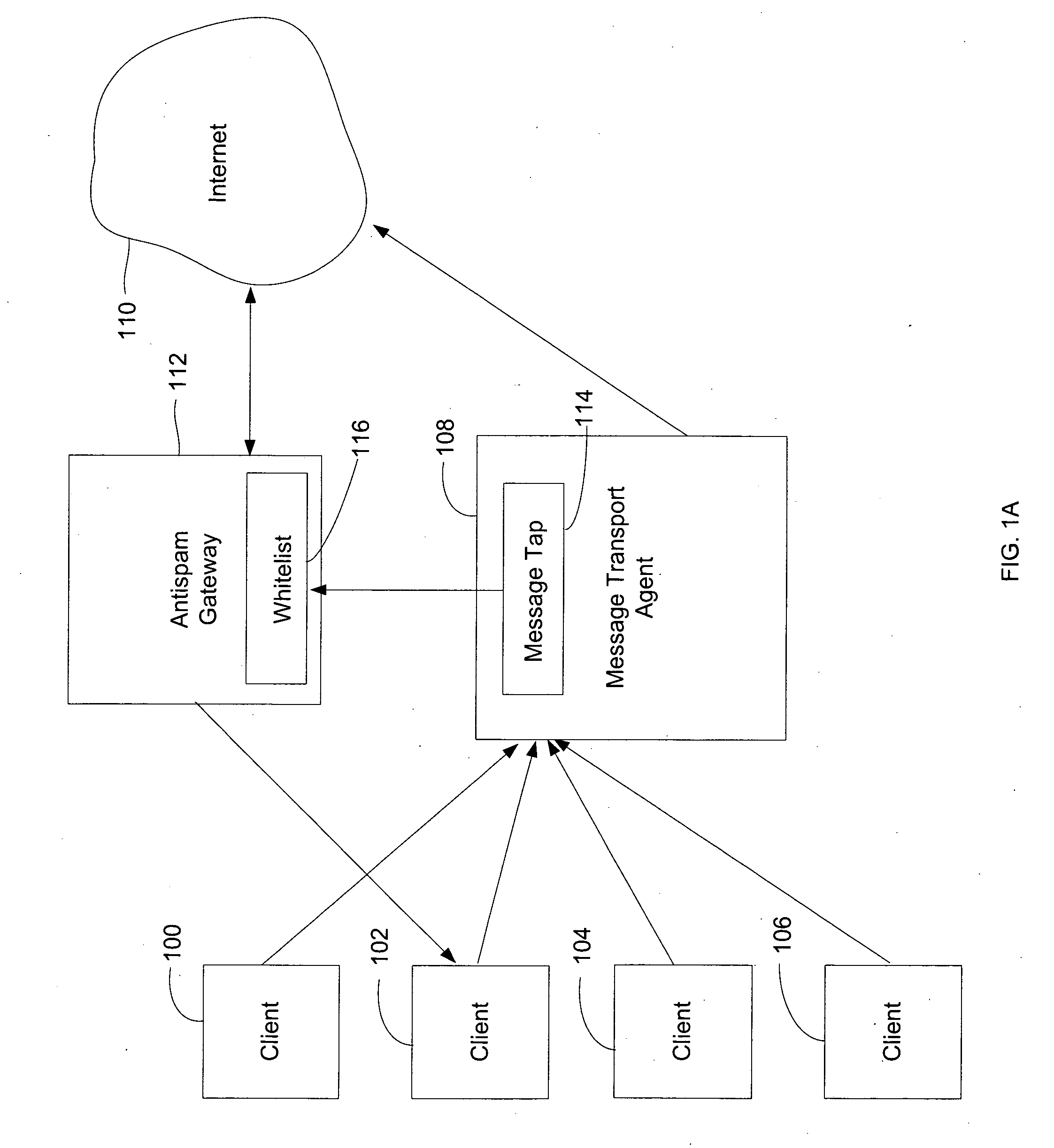
Method for creating a whitelist for processing e-mails
ActiveUS20050080855A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksEmail addressAddress book
A method of creating a whitelist for processing received e-mail messages. A whitelist is created by software running at an e-mail recipient's computer. The whitelist is constructed using e-mail addresses stored by the recipient (for instance, in an “address book”) as well as using the To:, Cc:, and Bcc: information of e-mails sent by the recipient. The subject line of a received message is also checked to see if it matches the subject line of a message recently sent by the user. If so, the sender is added to the whitelist.
Owner:PROOFPOINT INC
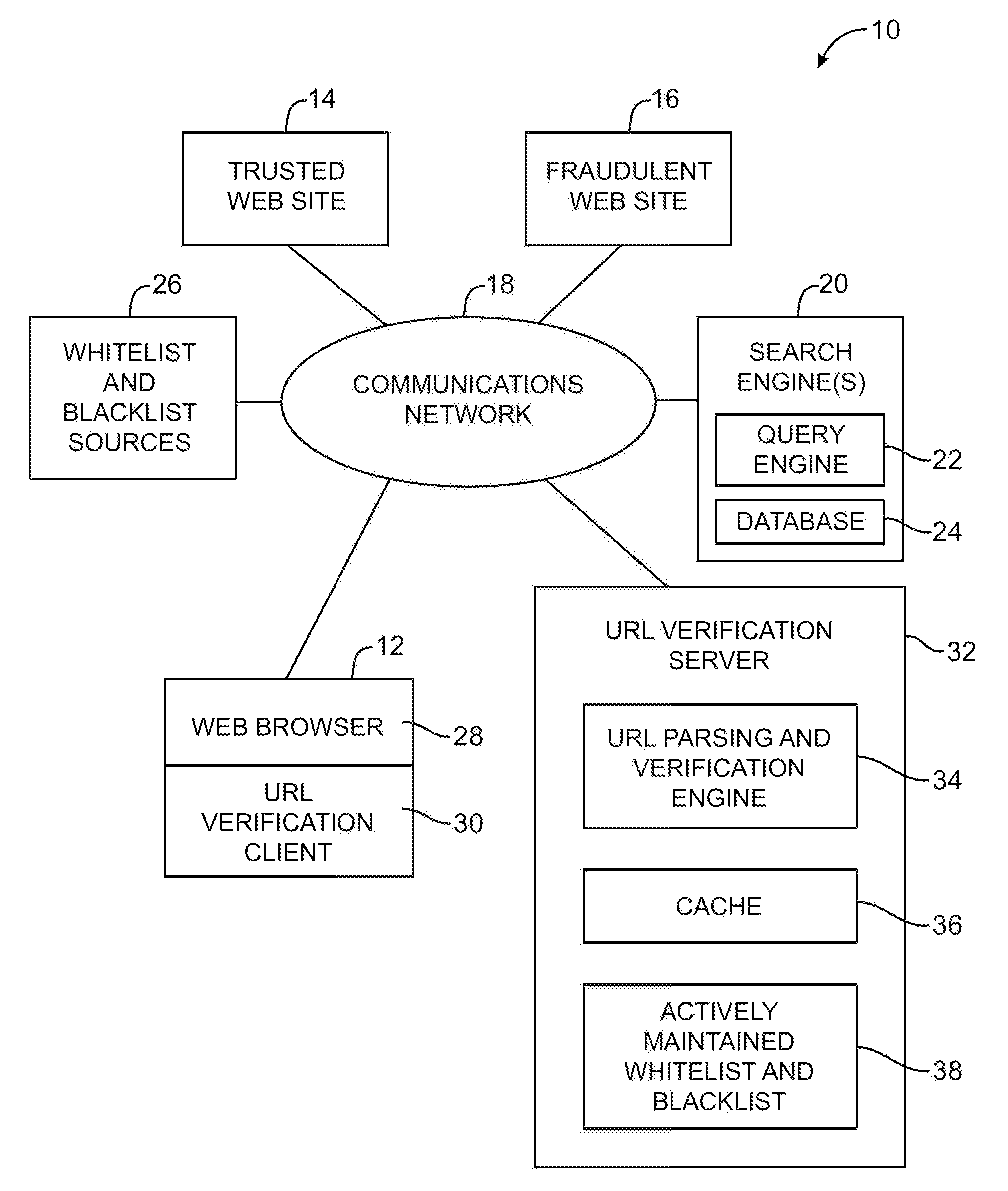
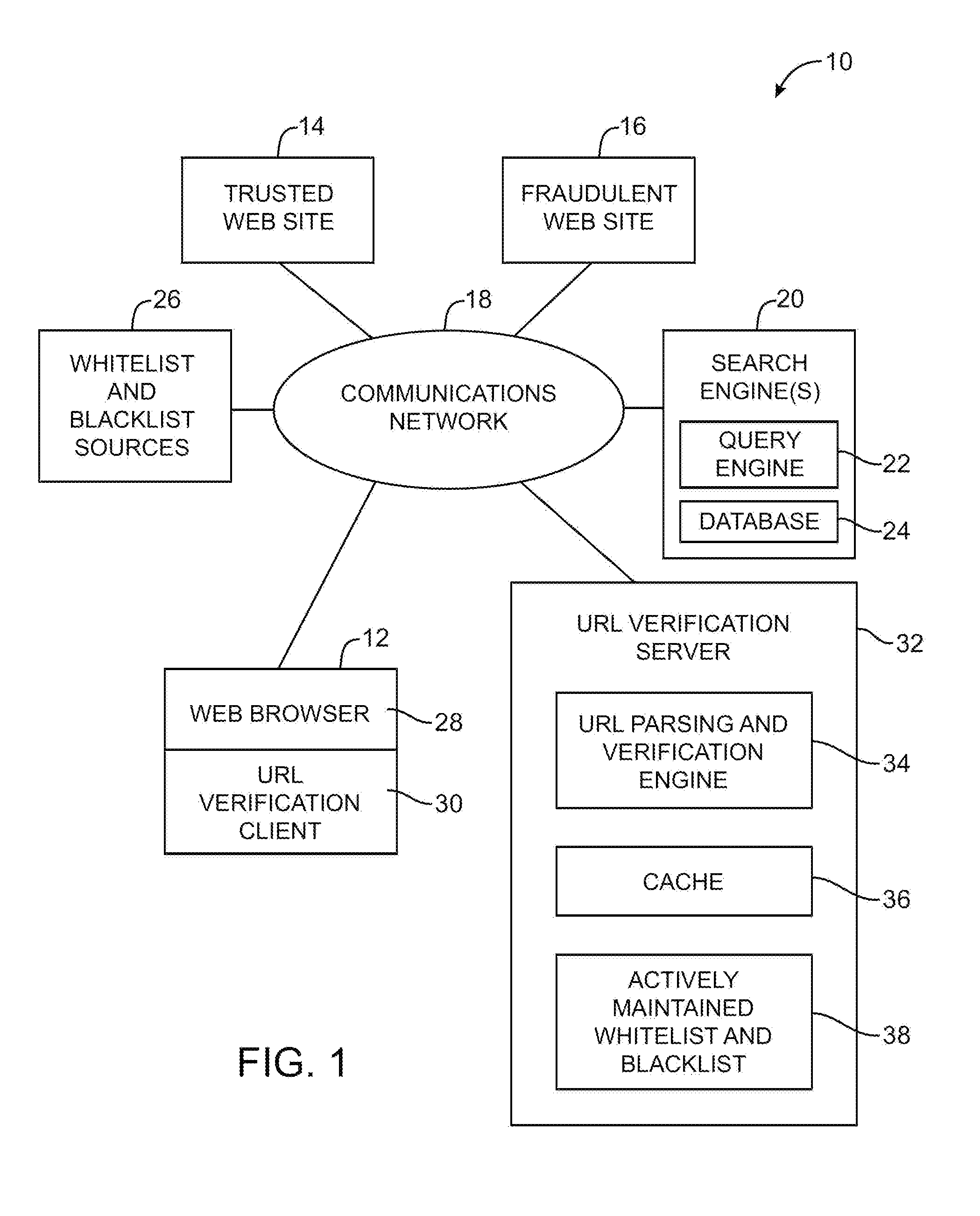
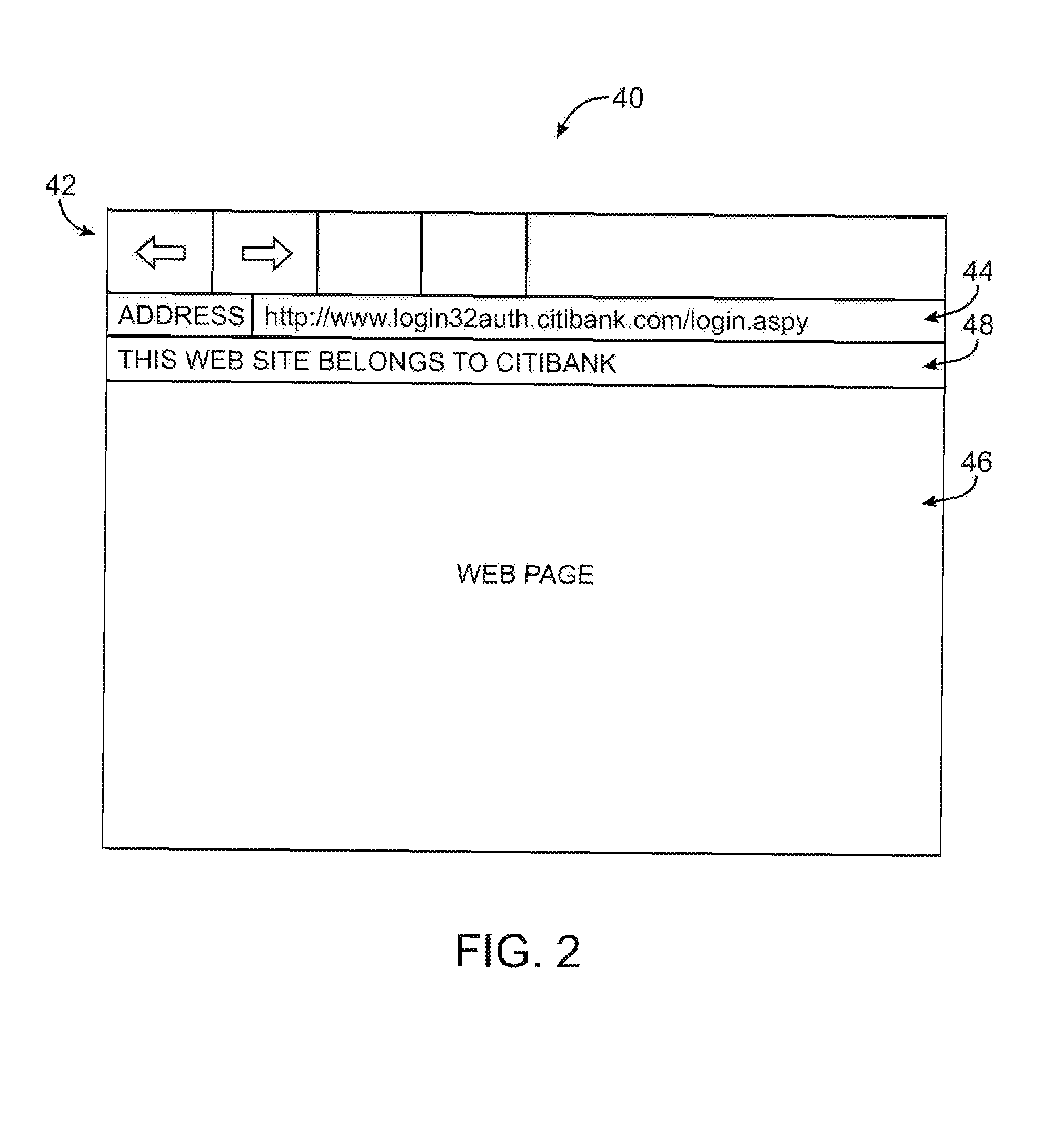
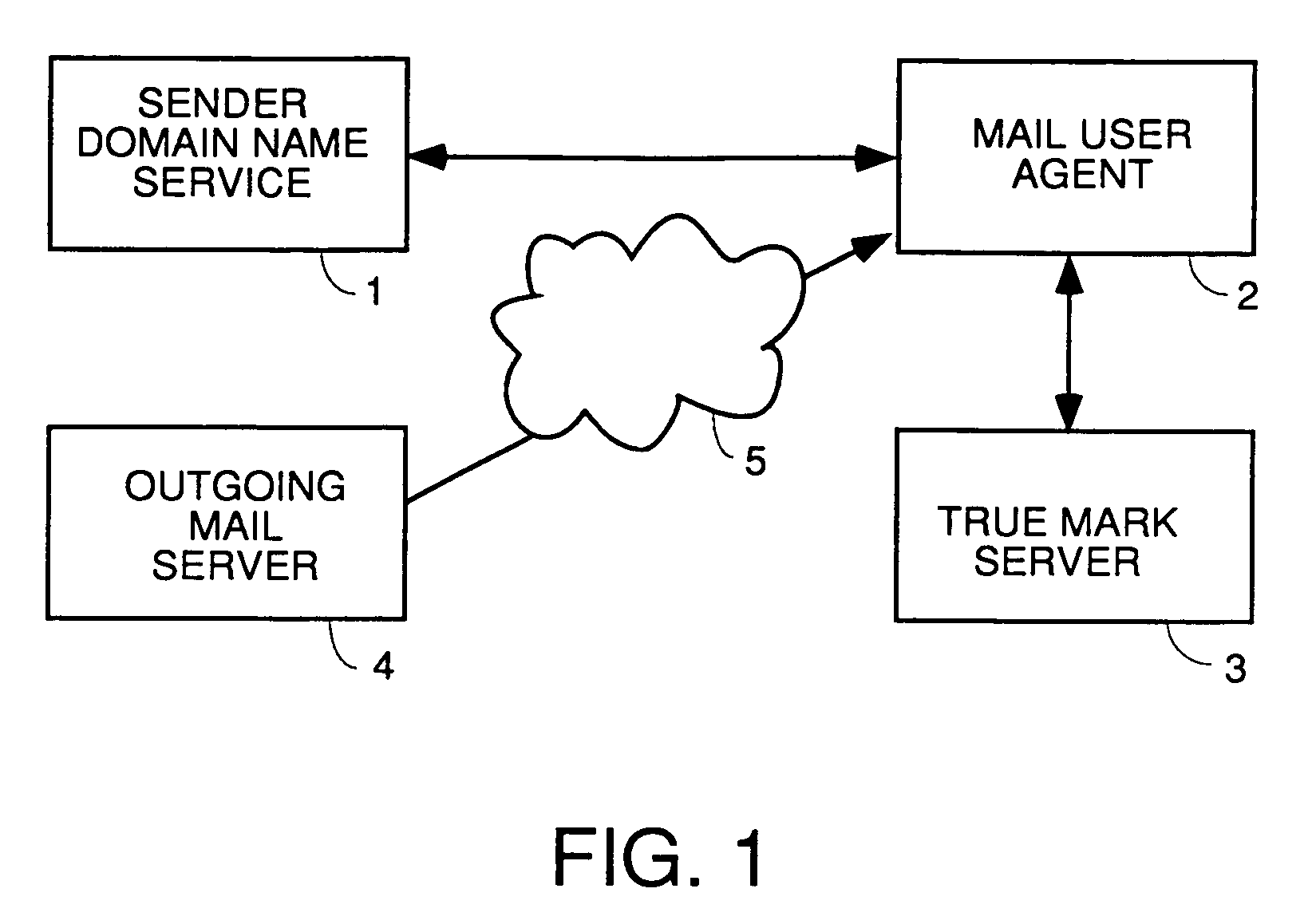
Server-based universal resource locator verification service
A URL verification service is provided that is used to evaluate the trustworthiness of universal resource locators (URLs). As a user browses the world wide web, a URL verification client captures a URL associated with a web page of unknown authenticity. The URL verification client transmits the captured URL to a URL verification server. The URL verification server compares the URL to actively maintained whitelist and blacklist information. The server also uses the URL and a user-supplied or automatically-extracted brand to query a search engine. The URL verification server processes the response of the search engine to the search engine queries and the results of cache and whitelist and blacklist comparisons to determine whether the captured URL is legitimately associated with the brand. The results of the URL evaluation process are transmitted from the URL verification server to the URL verification client, which notifies user.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
User interface for email inbox to call attention differently to different classes of email
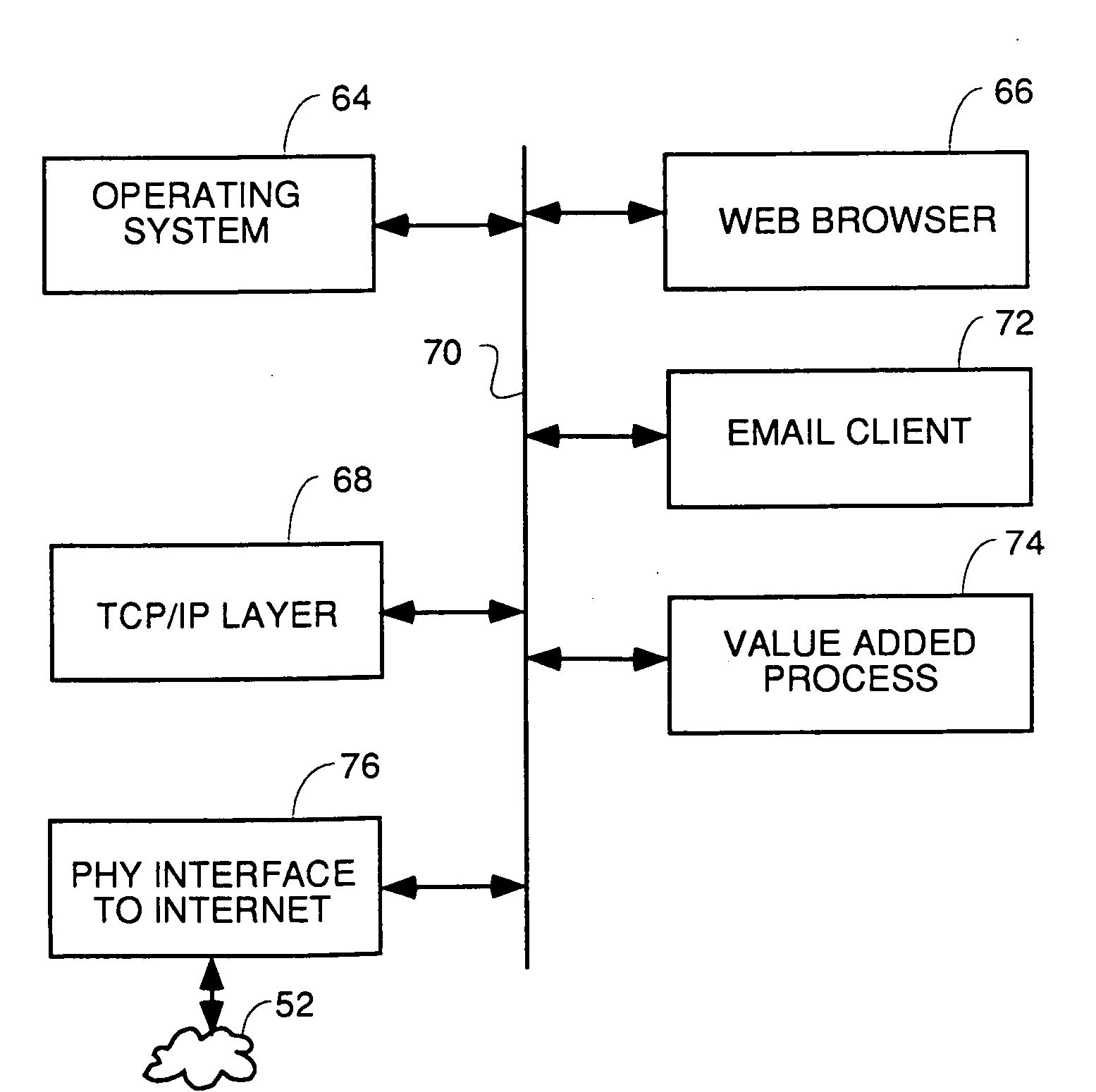
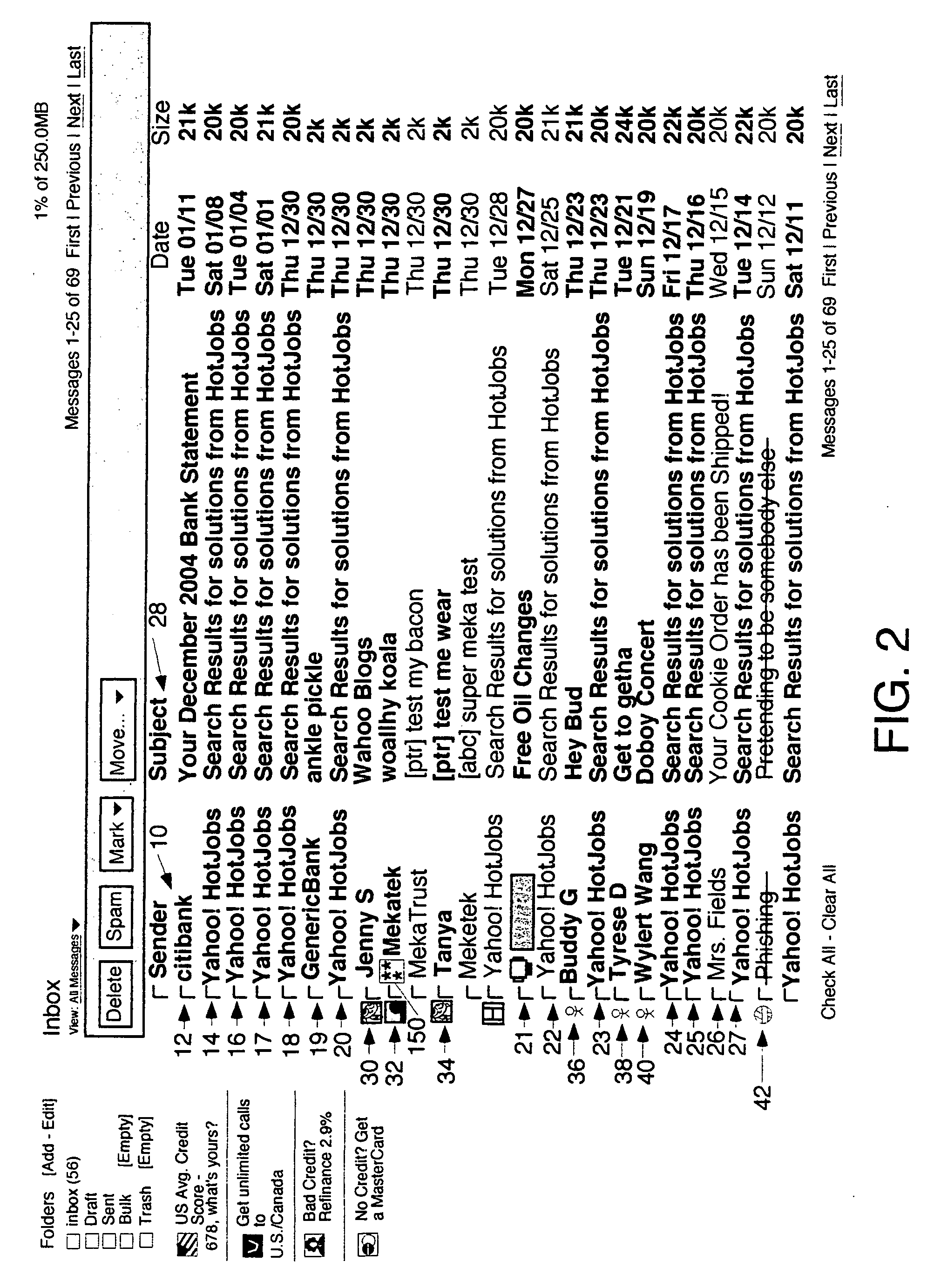
InactiveUS20070005702A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksGraphicsPhishing
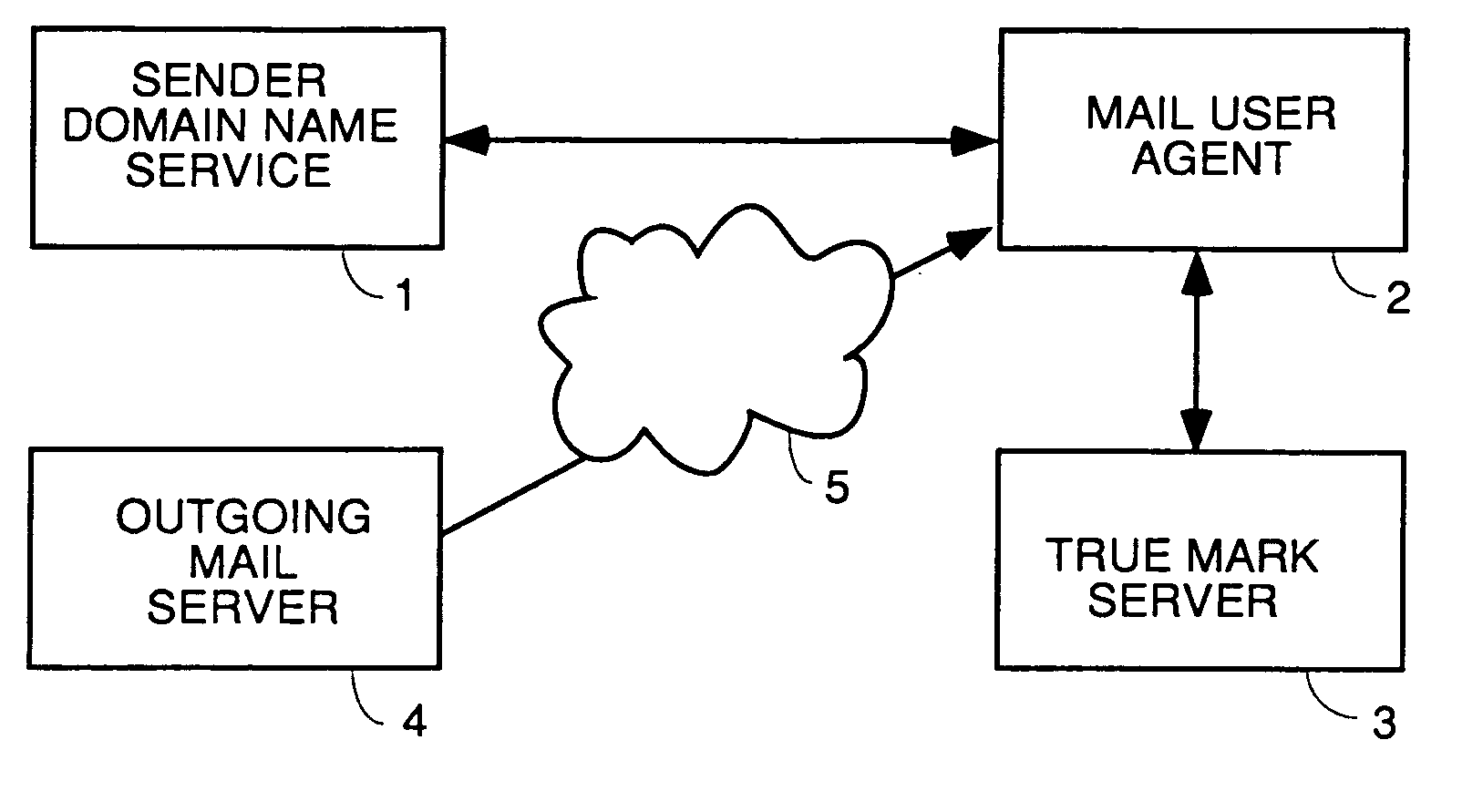
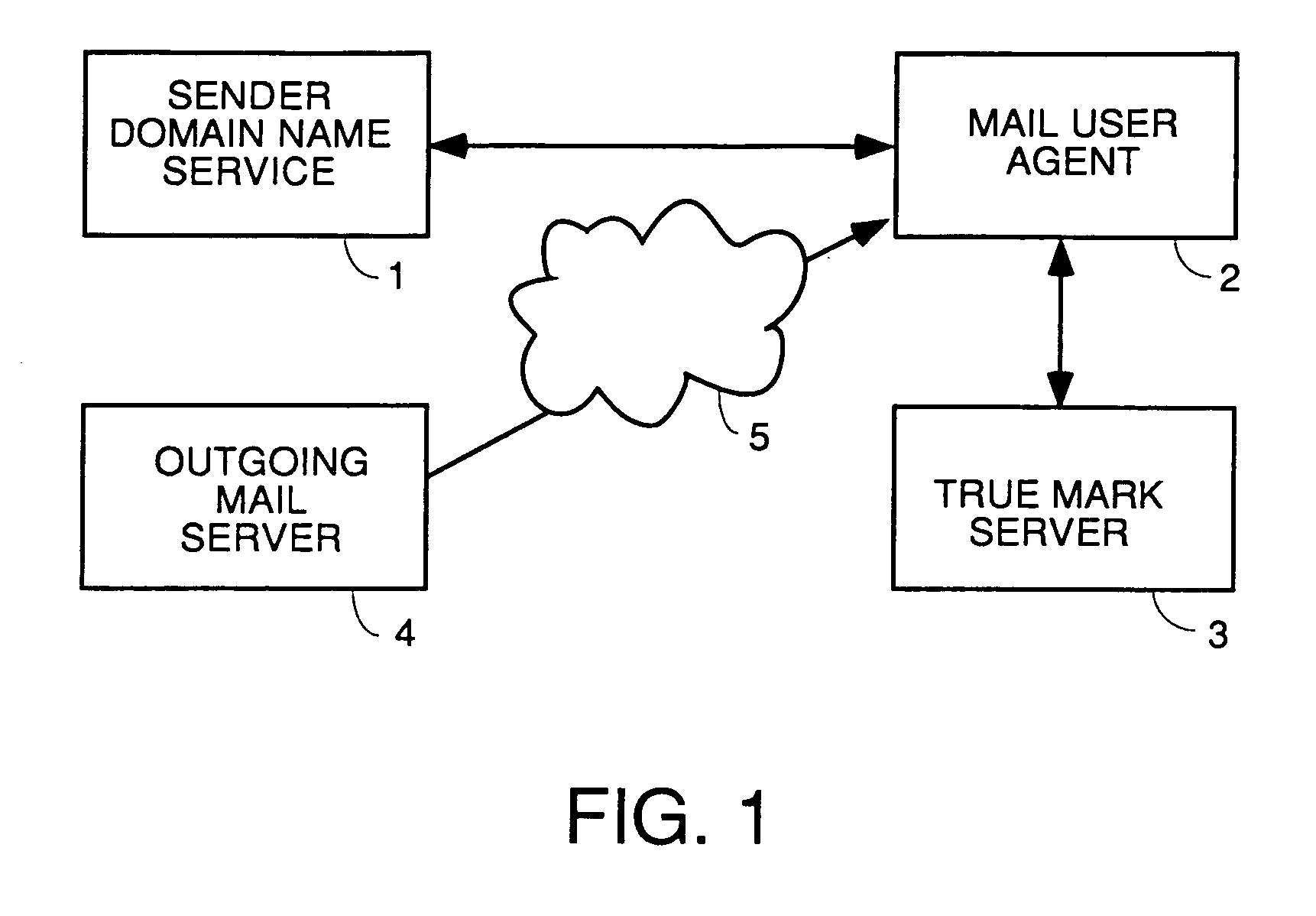
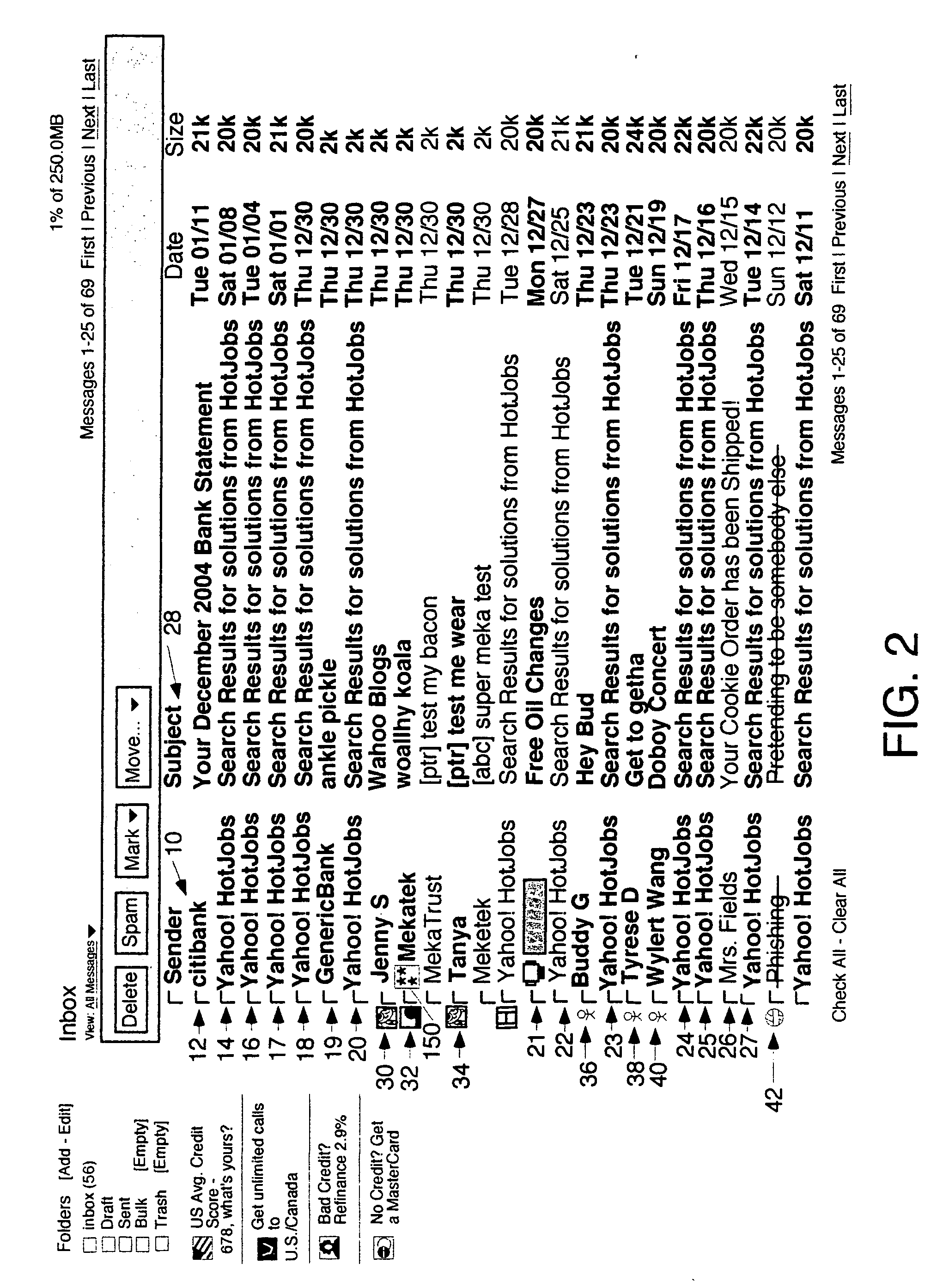
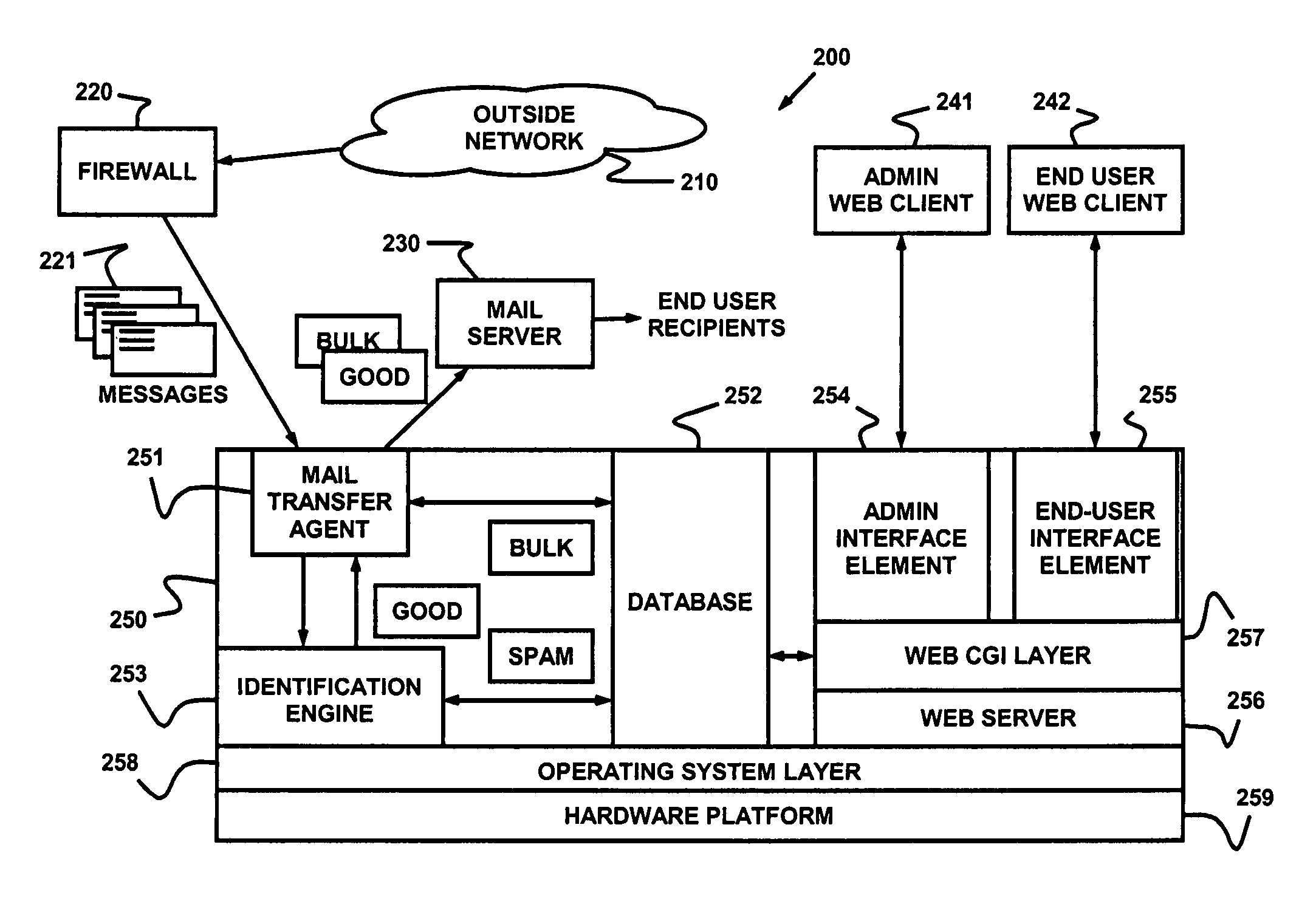
A user interface for email users which calls attention to one or more categories of emails in different ways. In some species, at least three categories are used: branded senders with Trumarks; white list buddies; and fraudulent emails which are either not from the domain they purport to be from or in which the content was tampered. The preferred embodiment authenticates emails from branded senders and displays them with the sender's Truemark. Branded sender emails have their Truemarks displayed in the sender column of a list view in the preferred embodiment. In a preferred embodiment, white list senders have either an icon or other graphic or photo they choose displayed to the left or right of the sender column with their name in the sender column. In a preferred embodiment, fraudulent emails have a fraud icon displayed to the left or right of the sender column with a warning in the sender column. Antiphishing processing is also disclosed.
Owner:ICONIX INC
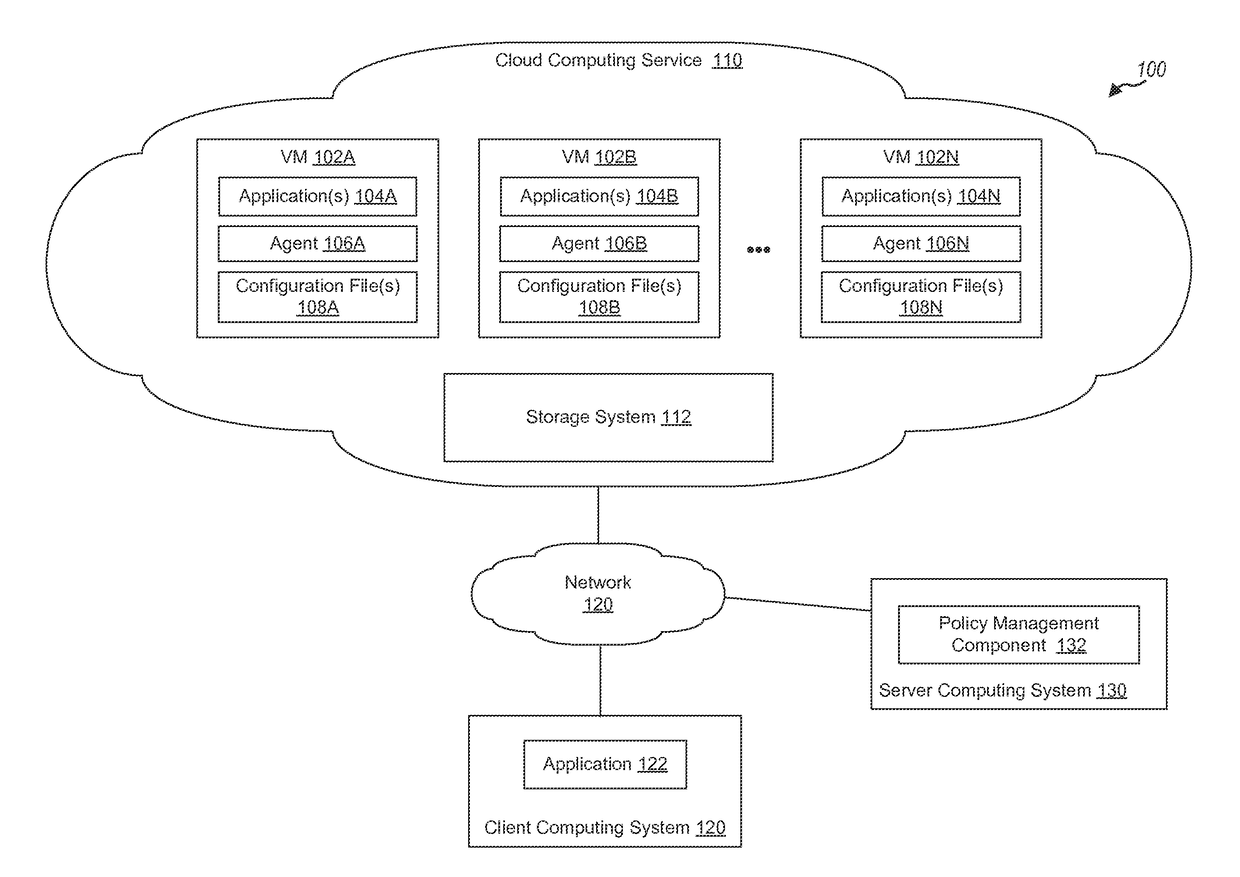
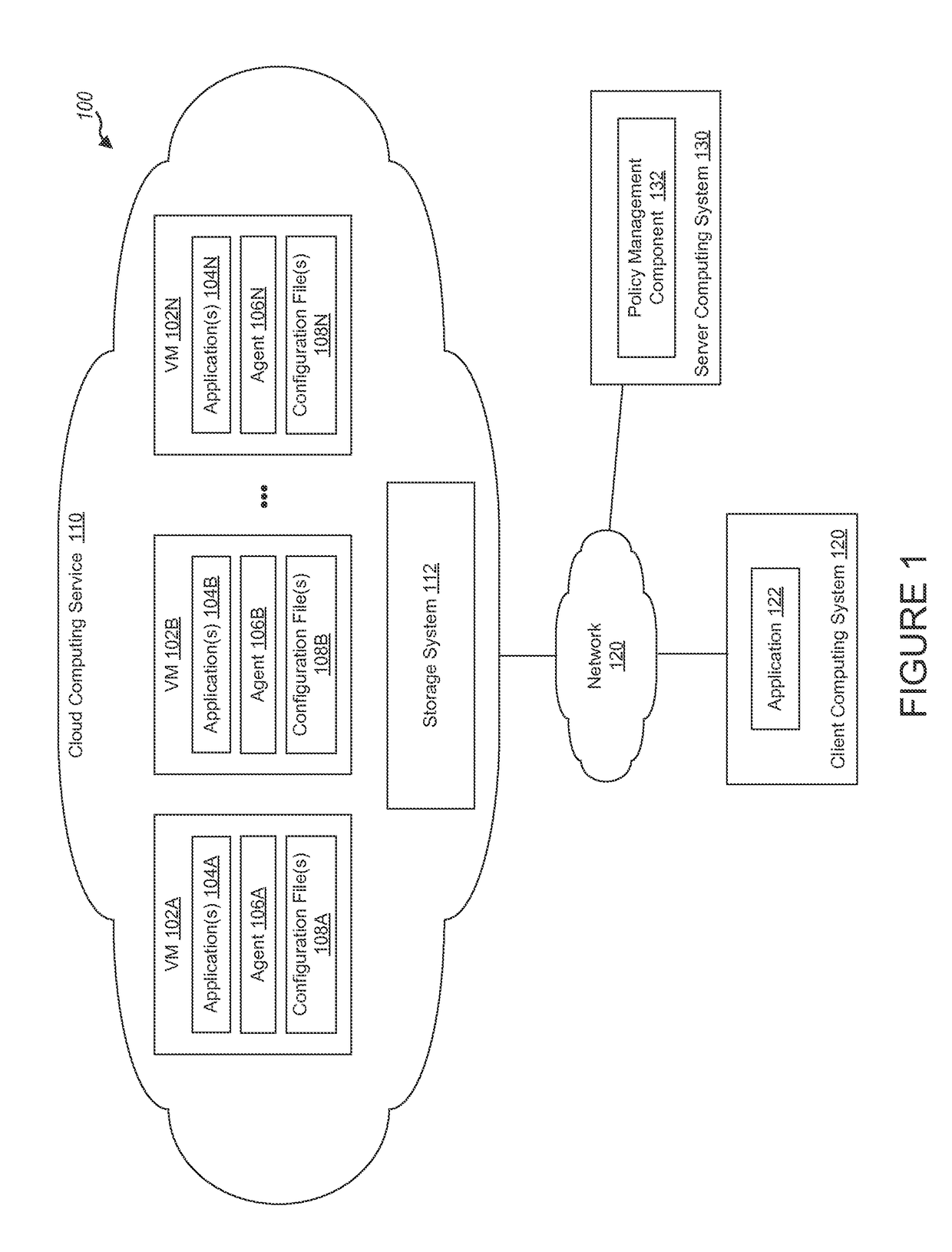
Cloud over IP session layer network
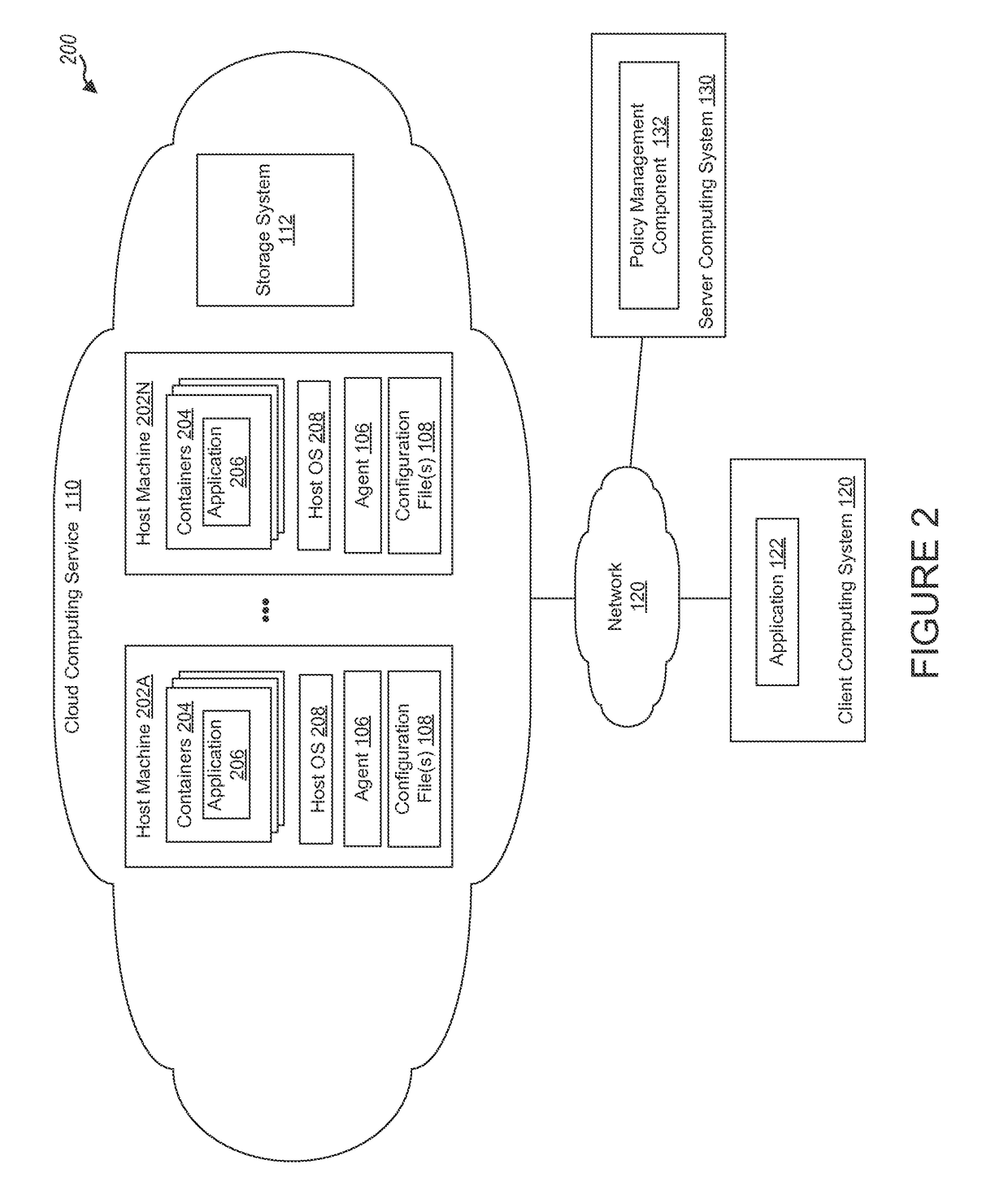
Cloud endpoints are secured using agents and a controller connected to the agents. A whitelist identifies components and processes of an authorized multi-tiered application for the cloud. An application profile for the application specifies valid computing flows between components of a tier and components of another tier, where components of the tier are executed at an endpoint and the other components of the other tier are executed at another endpoint. Endpoints are provisioned with static routing tables identifying at least one subnet destination. A request is received at a first endpoint to connect to a second endpoint. If the second endpoint falls within the at least one subnet destination, the controller performs one or more further security checks including checking the application profile flow, whitelist, and endpoint quarantine list. A network kernel table at an endpoint that includes the static routing table may be periodically checked to detect tampering.
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Disambiguating conflicting content filter rules
A content filtering mechanism is enhanced to resolve conflicts in filtering rules (e.g., those created by a whitelist, on the one hand, and a blacklist, on the other hand). Preferably, a conflict between or among content filtering rules is resolved by selecting among conflicting rules based on a notion of “risk” associated with the rules. According to this risk-based approach, when two or more rules conflict with one another, the particular rule whose risk value has a predetermined relationship (e.g., aligns most closely) with a risk level associated with the application (applying the rules) then takes precedence. By selecting among conflicting rules based on risk, the potential or actual conflicts are disambiguated, with the result being that the content is filtered appropriately.
Owner:IBM CORP
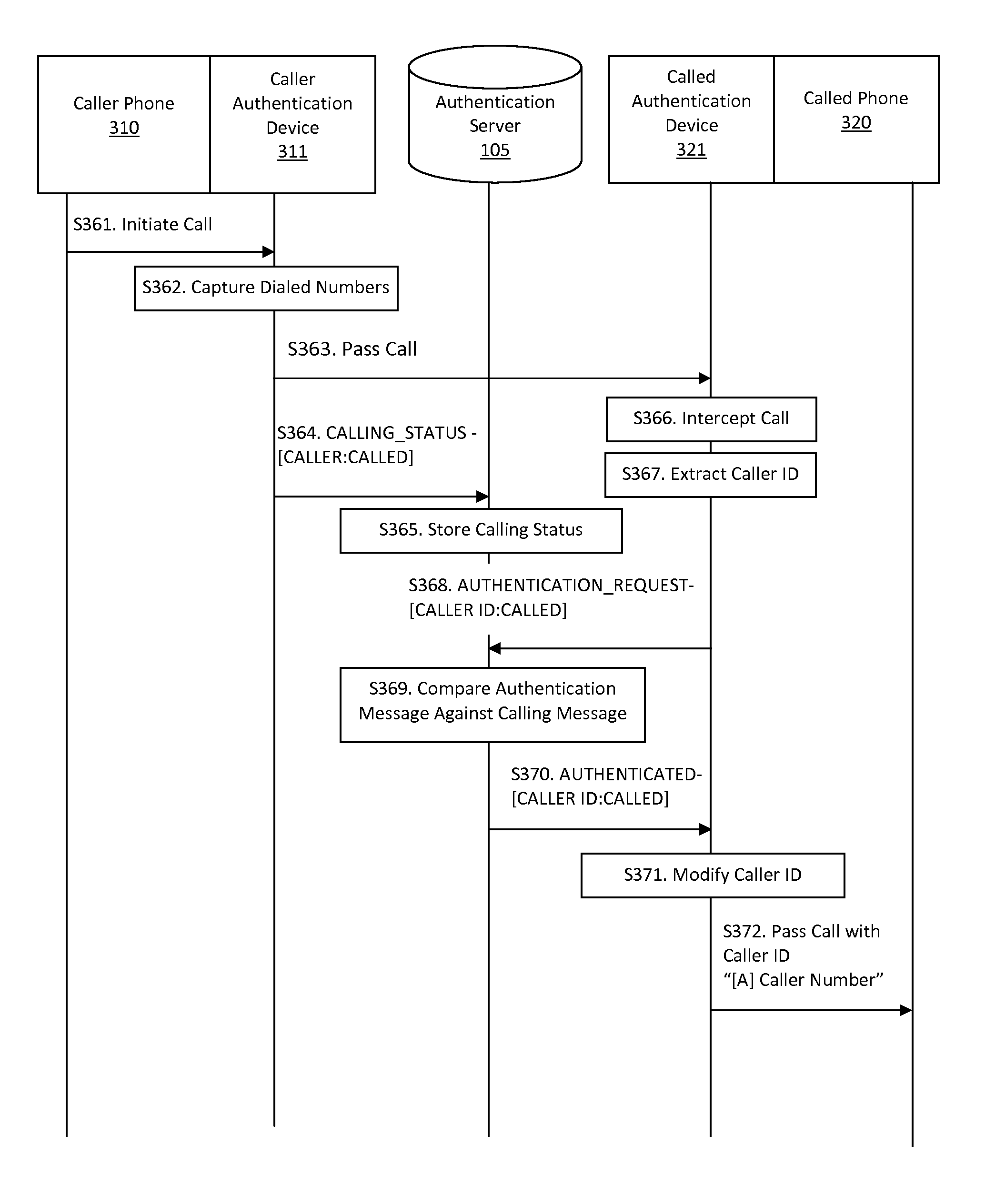
Systems and methods for caller ID authentication, spoof detection and list based call handling
ActiveUS9060057B1Special service for subscribersCalled number recording/indicationBase callingCommunication source
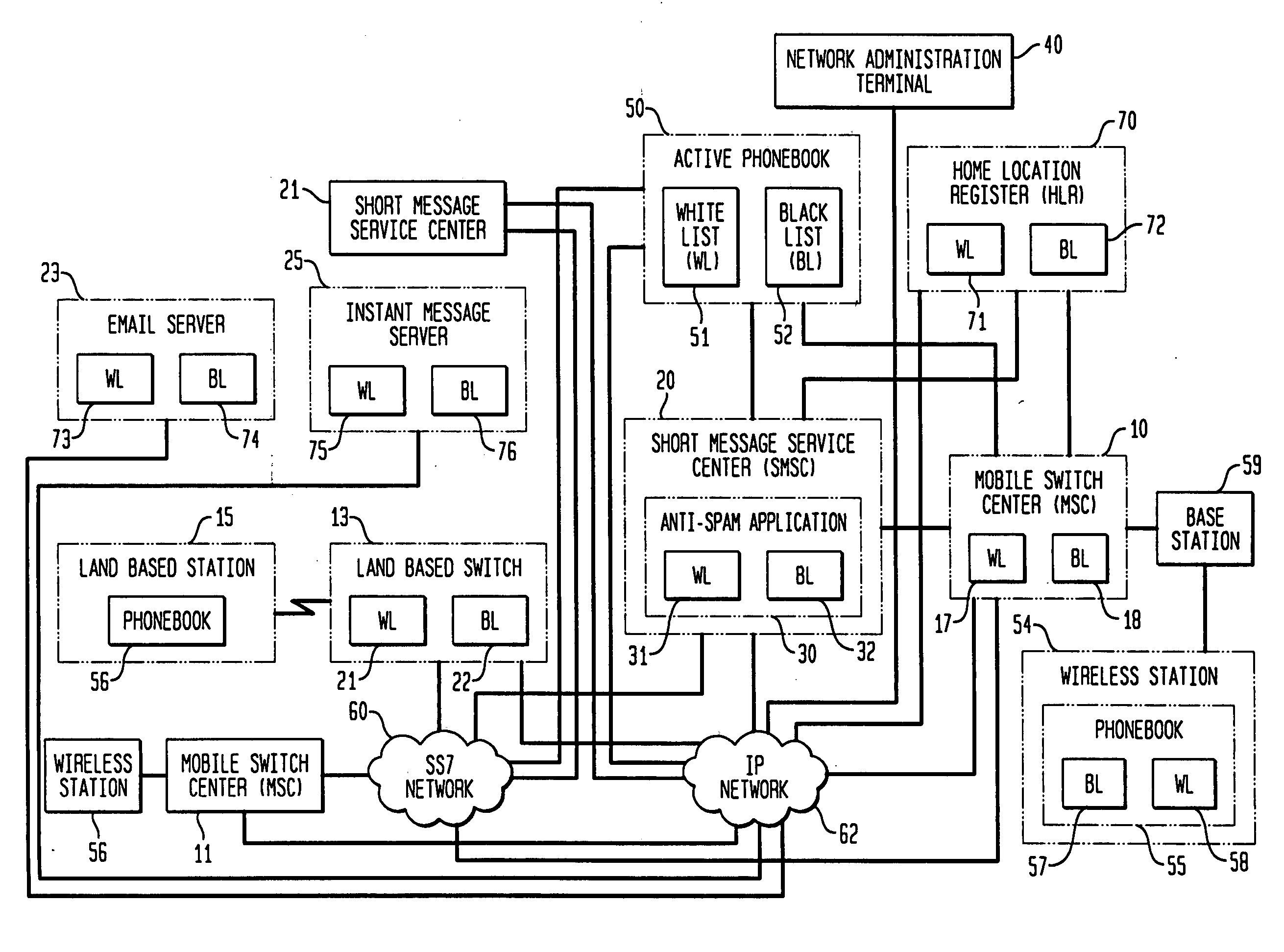
Systems and methods for caller id authentication, spoof detection and list based call handling are disclosed. The caller ID authentication is performed by an authentication device connected to the calling party telephone transmitting the source and destination telephone numbers of the call to an authentication server. The called party authentication device extracts the caller ID of the incoming call and transmits the caller ID of the caller and the telephone number of the called party to the authentication server. The authentication server analyzes the transmitted information from both devices and replies with the authentication status of the caller ID to the called party authentication device. Other embodiments are disclosed where the authentication server is not available and caller ID authentication is performed in a peer-to-peer manner. In another embodiment, the concepts of active and passive certification passwords are used to maintain the integrity of the system. Other embodiments allow for authenticating blocked caller ID's, reveling blocked caller ID's, VoIP implementations, legitimate caller ID spoofing, and placing a blocked caller ID on private white or black lists. Another embodiment combines the described caller ID authentication system within a call handling system utilizing internal, global and private white and black lists. Applications of caller ID authentication methodology to other forms of communication source address authentication, such as email, SMS, and postal mail are envisioned.
Owner:DANIS SERDAR ARTUN
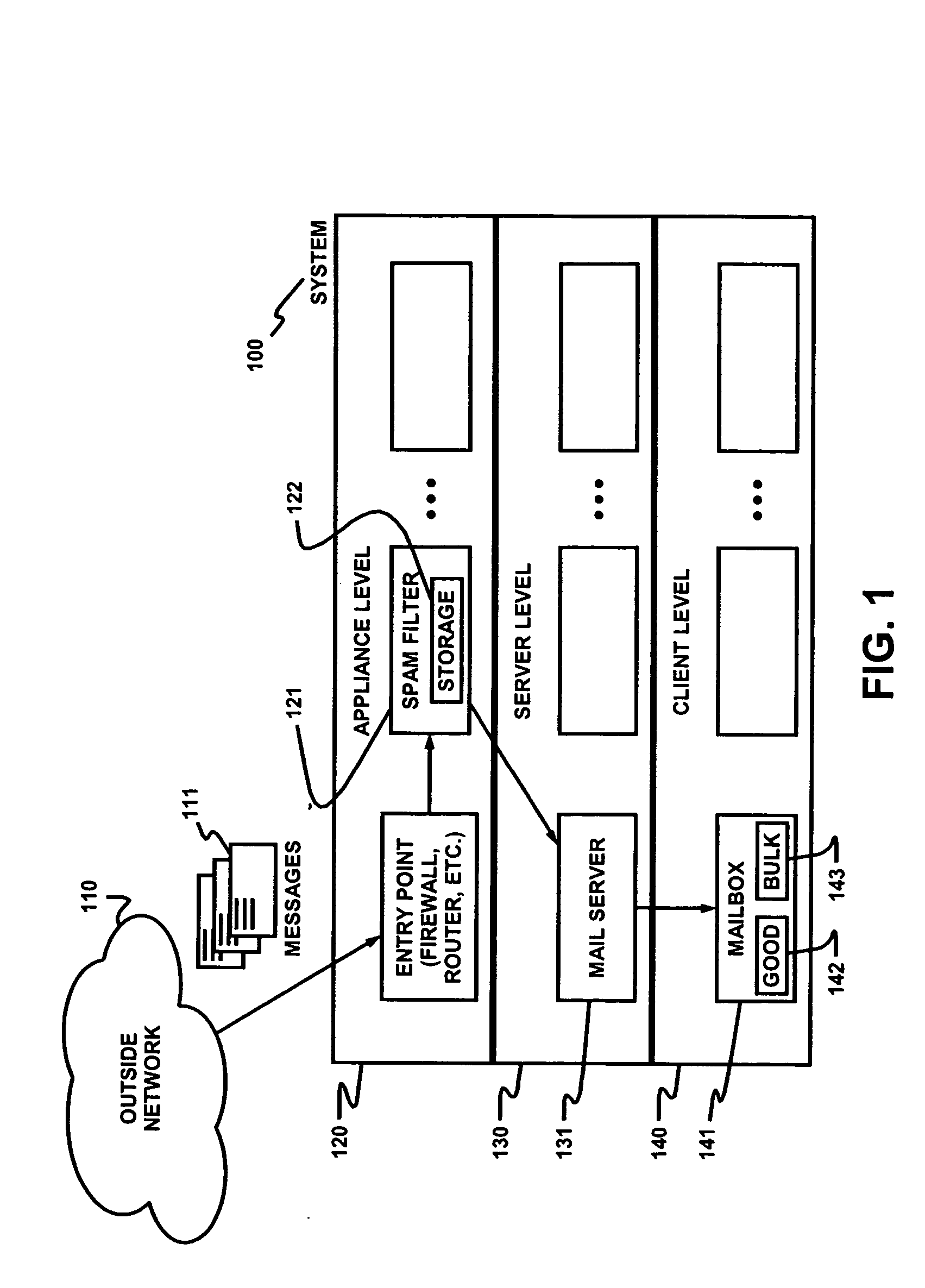
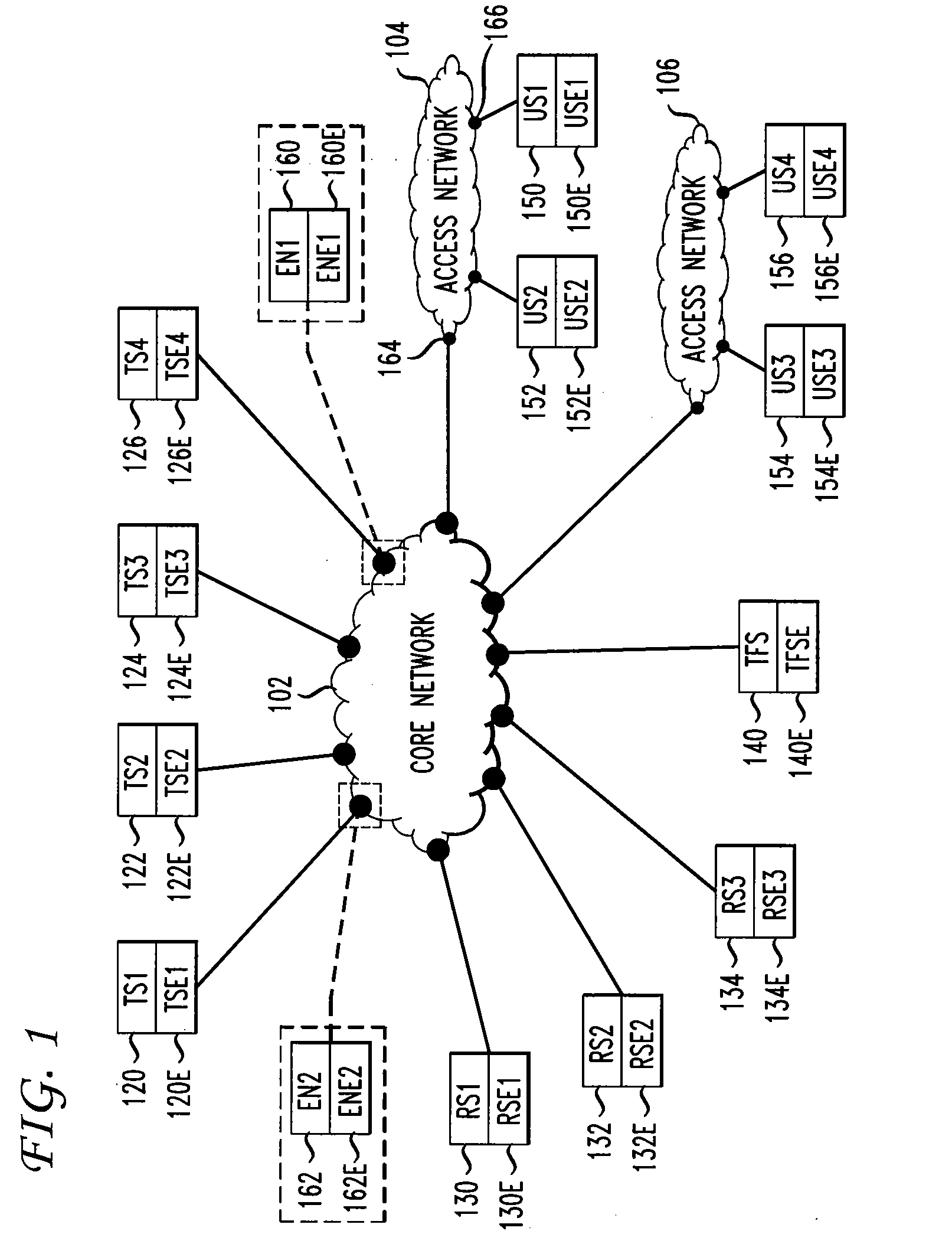
Filtering unwanted data traffic via a per-customer blacklist
ActiveUS20100082811A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityIp address
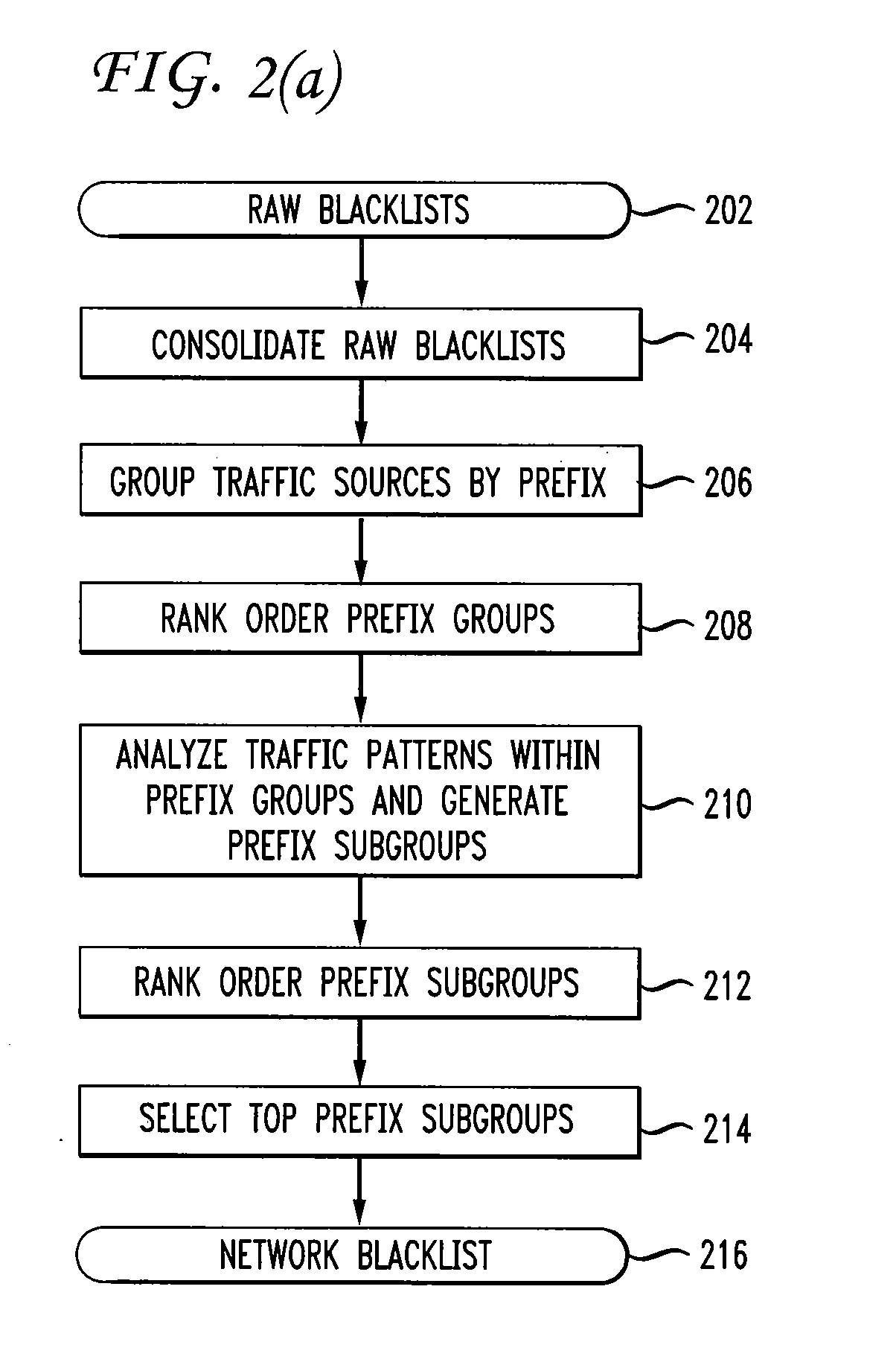
Traffic flow from a traffic source with a source IP address to a customer system with a destination IP address is filtered by comparing the source IP address to a customer blacklist. If the source IP address is on the customer blacklist, then traffic to the customer system is blocked; else, traffic to the customer system is allowed. The customer blacklist is generated from a network blacklist, comprising IP addresses of unwanted traffic sources, and a customer whitelist, comprising IP addresses of wanted traffic sources. The customer blacklist is generated by removing from the network blacklist any IP address also on the customer whitelist. The network blacklist is generated by acquiring raw blacklists from reputation systems. IP addresses on the raw blacklists are sorted by prefix groups, which are rank ordered by traffic frequency. Top prefix groups are selected for the network blacklist.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Automated construction of network whitelists using host-based security controls
Techniques are disclosed for constructing network whitelists in server endpoints using host-based security controls. Once constructed, the network whitelists are used to detect unauthorized communications at the server endpoints. In one embodiment, a method is disclosed for constructing a network whitelist. The method includes identifying at least a first application hosted on a computing system. The method also includes inspecting one or more configuration files associated with the first application to identify one or more configuration settings that specify how the first application communicates with one or more second applications. The method further includes generating a whitelist that specifies expected network communications activity for the first application, based on the configuration settings.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method and apparatus for detecting phishing attempts solicited by electronic mail
InactiveUS20090089859A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationKeyword analysisHeuristic
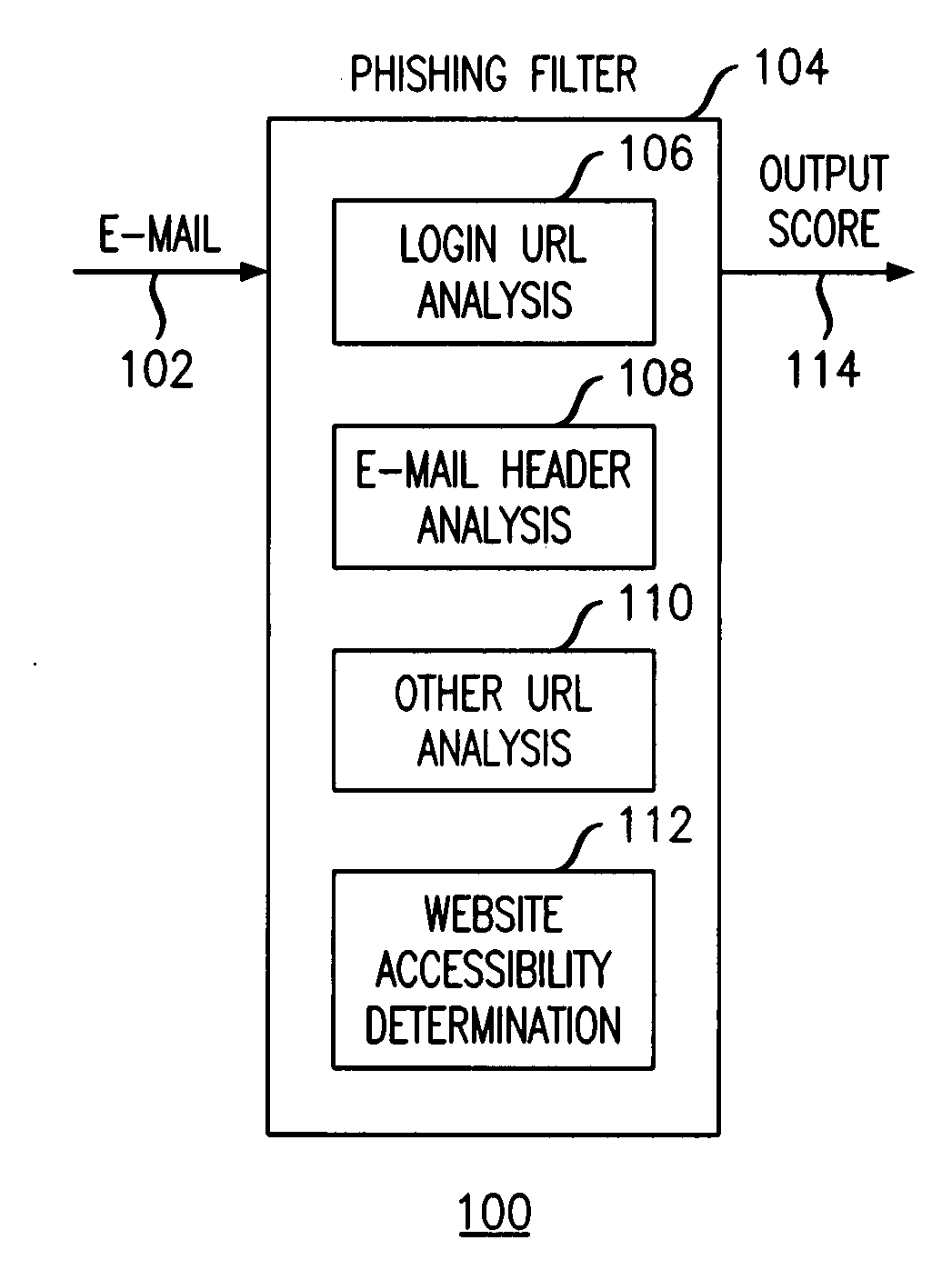
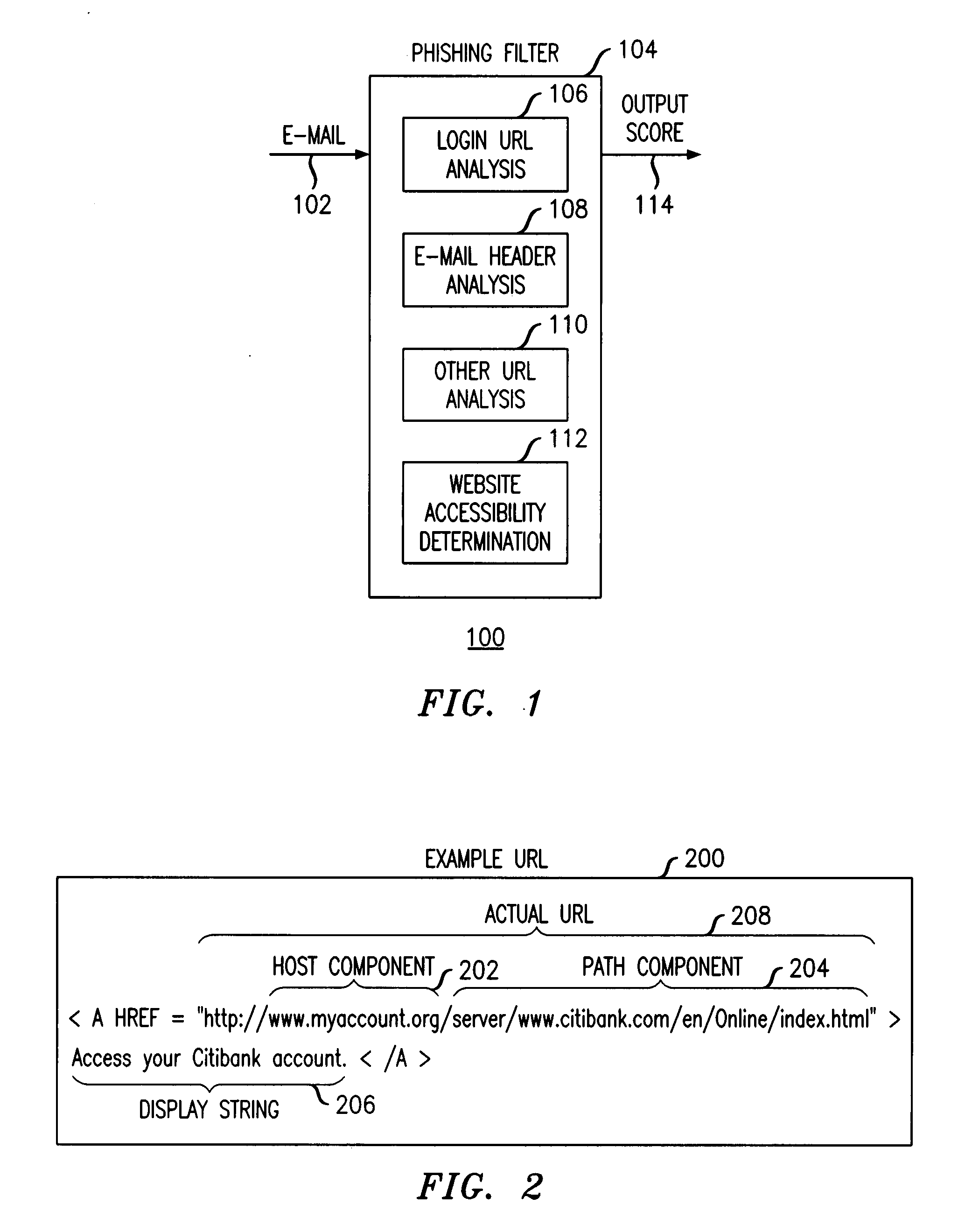
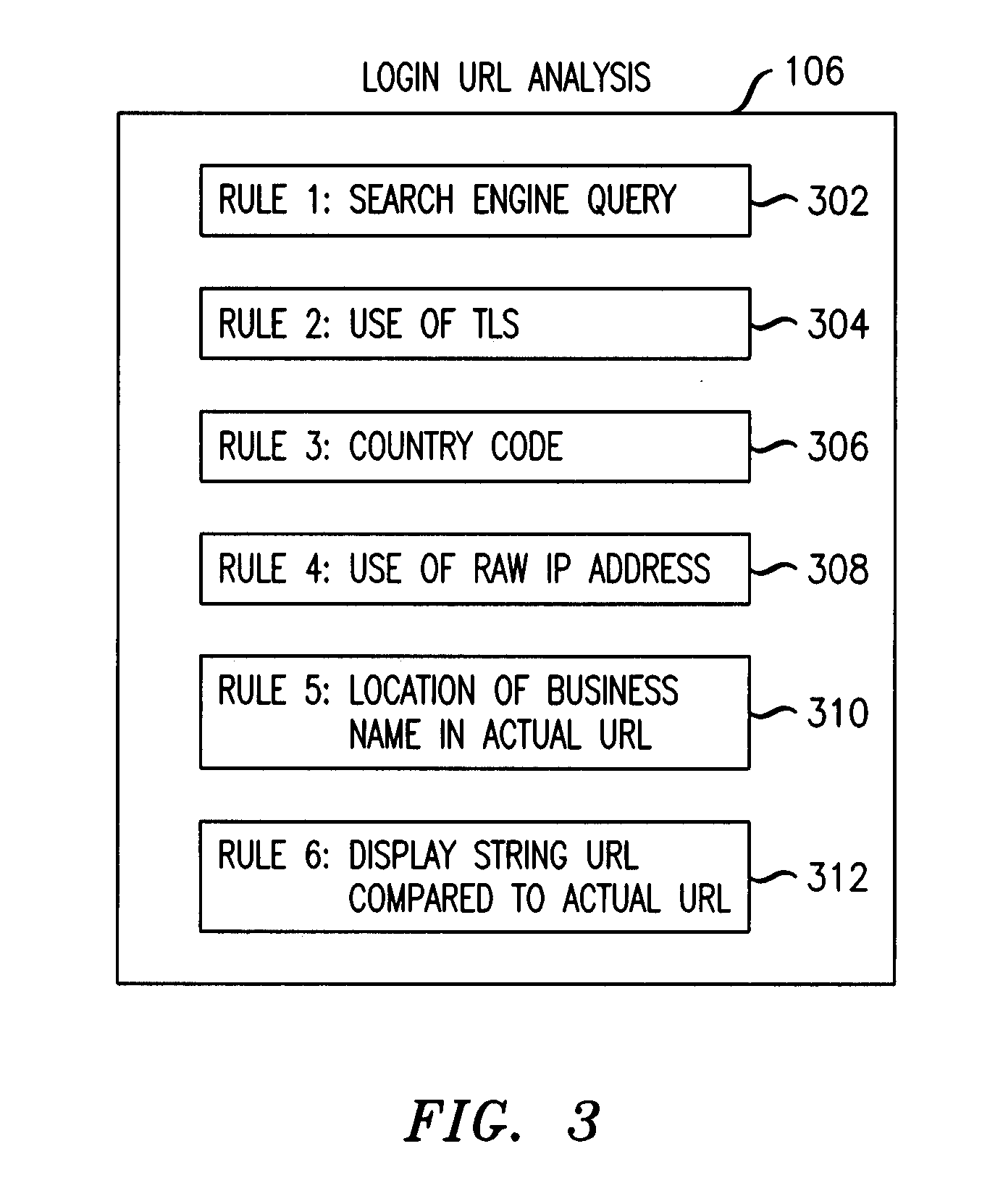
A phishing filter employs a plurality of heuristics or rules (in one embodiment, 12 rules) to detect and filter phishing attempts solicited by electronic mail. Generally, the rules fall within the following categories: (1) identification and analysis of the login URL (i.e., the “actual” URL) in the email, (2) analysis of the email headers, (3) analysis across URLs and images in the email other than the login URL, and (4) determining if the URL is accessible. The phishing filter does not need to be trained, does not rely on black or white lists and does not perform keyword analysis. The filter may be implemented as an alternative or supplemental to prior art spam detection filters.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
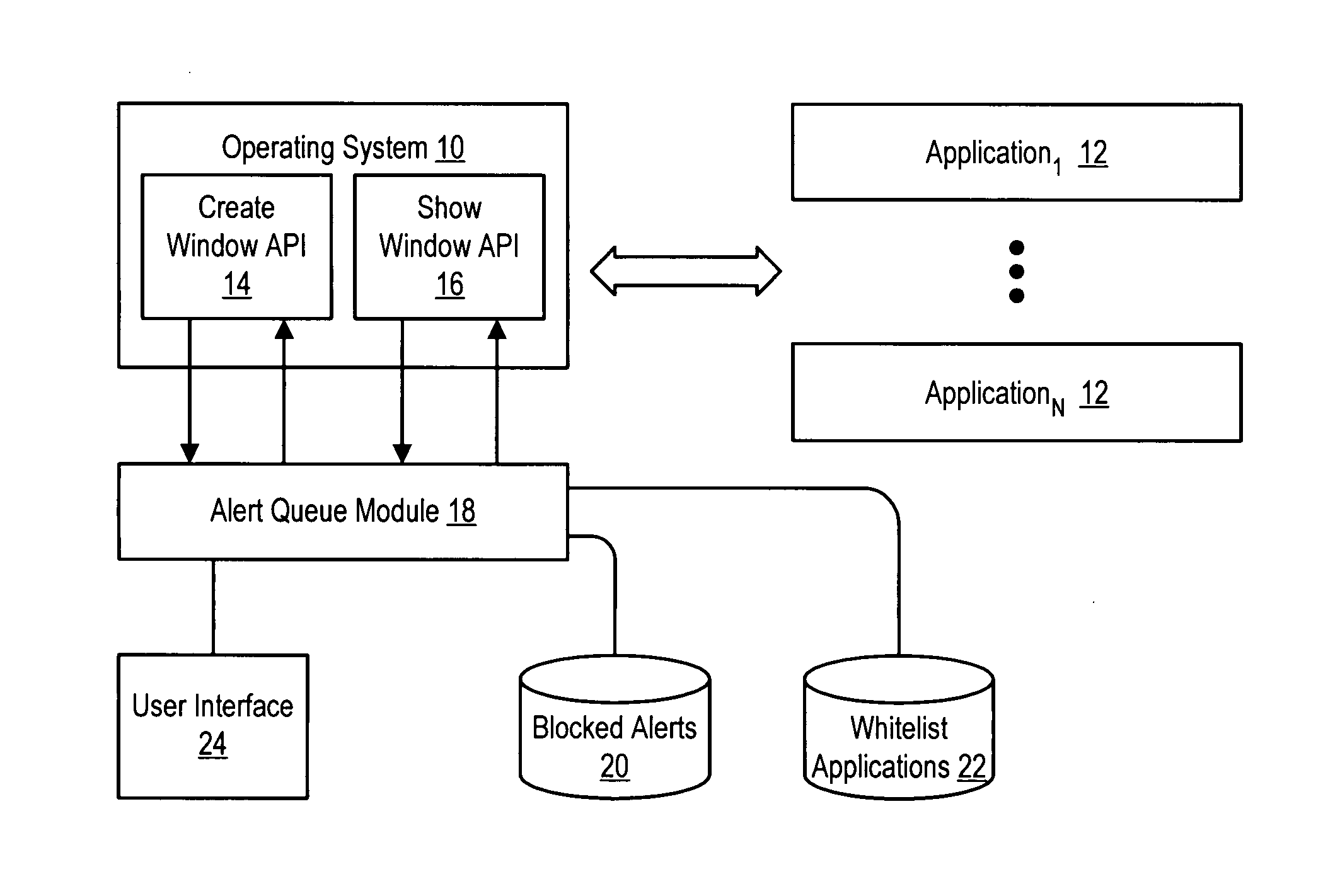
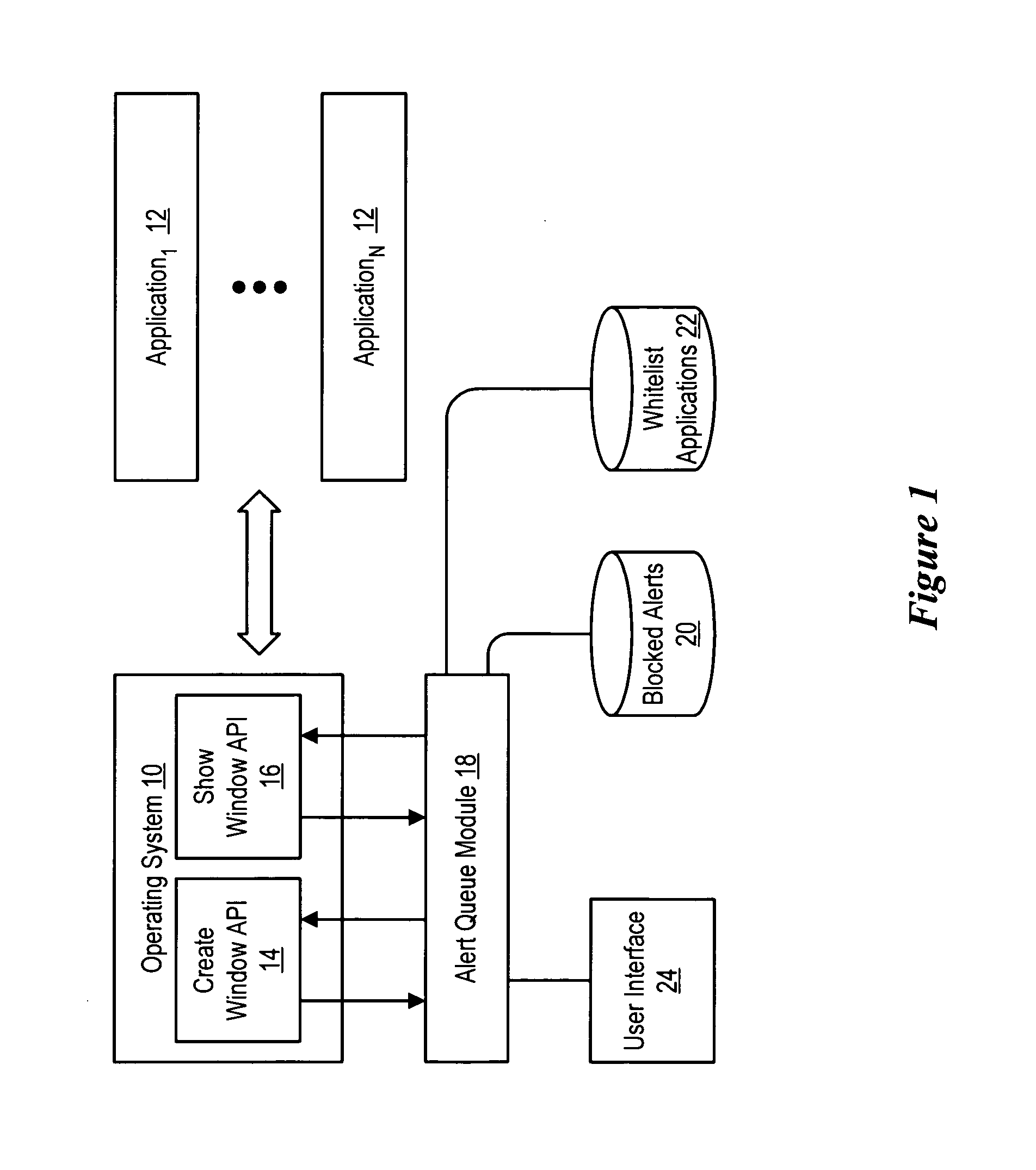
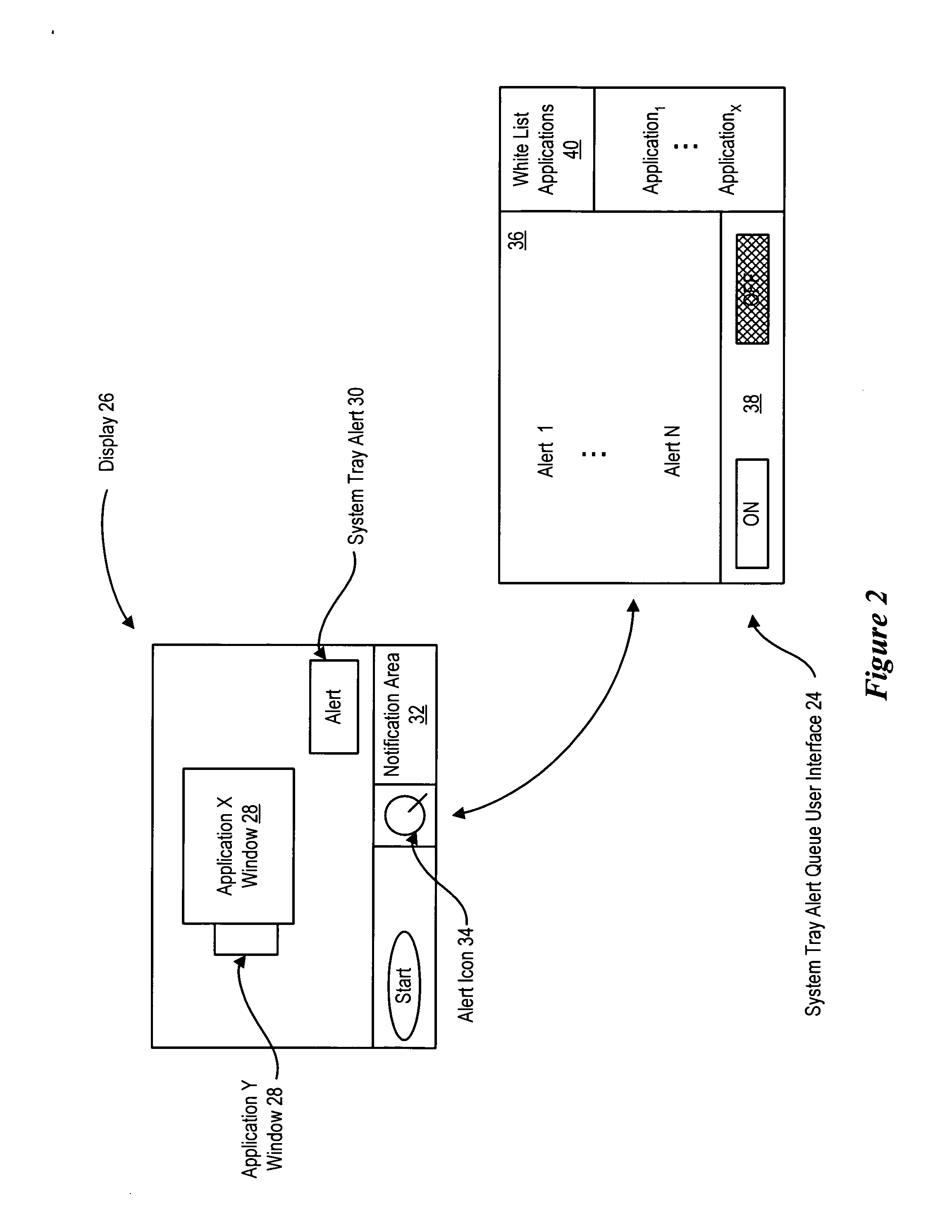
System and method for managing application alerts
InactiveUS20070214429A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsProgram controlMemory systemsInformation processingDisplay device
An alert queue module reduces presentation of alerts generated by applications running on an information handling system, such as system tray alerts, for selective subsequent viewing by an end user. For instance, inactive applications that are operating but not in focus at an information handling system display have their alerts suppressed unless the applications are on a white list of applications approved for presenting alerts. An icon presented at the display indicates that alerts have been suppressed and is selectable by an end user to present a list of suppressed alerts.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Method for creating a whitelist for processing e-mails
ActiveUS7366761B2Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksAddress bookEmail address
A method of creating a whitelist for processing received e-mail messages. A whitelist is created by software running at an e-mail recipient's computer. The whitelist is constructed using e-mail addresses stored by the recipient (for instance, in an “address book”) as well as using the To:, Cc:, and Bcc: information of e-mails sent by the recipient. The subject line of a received message is also checked to see if it matches the subject line of a message recently sent by the user. If so, the sender is added to the whitelist.
Owner:PROOFPOINT INC
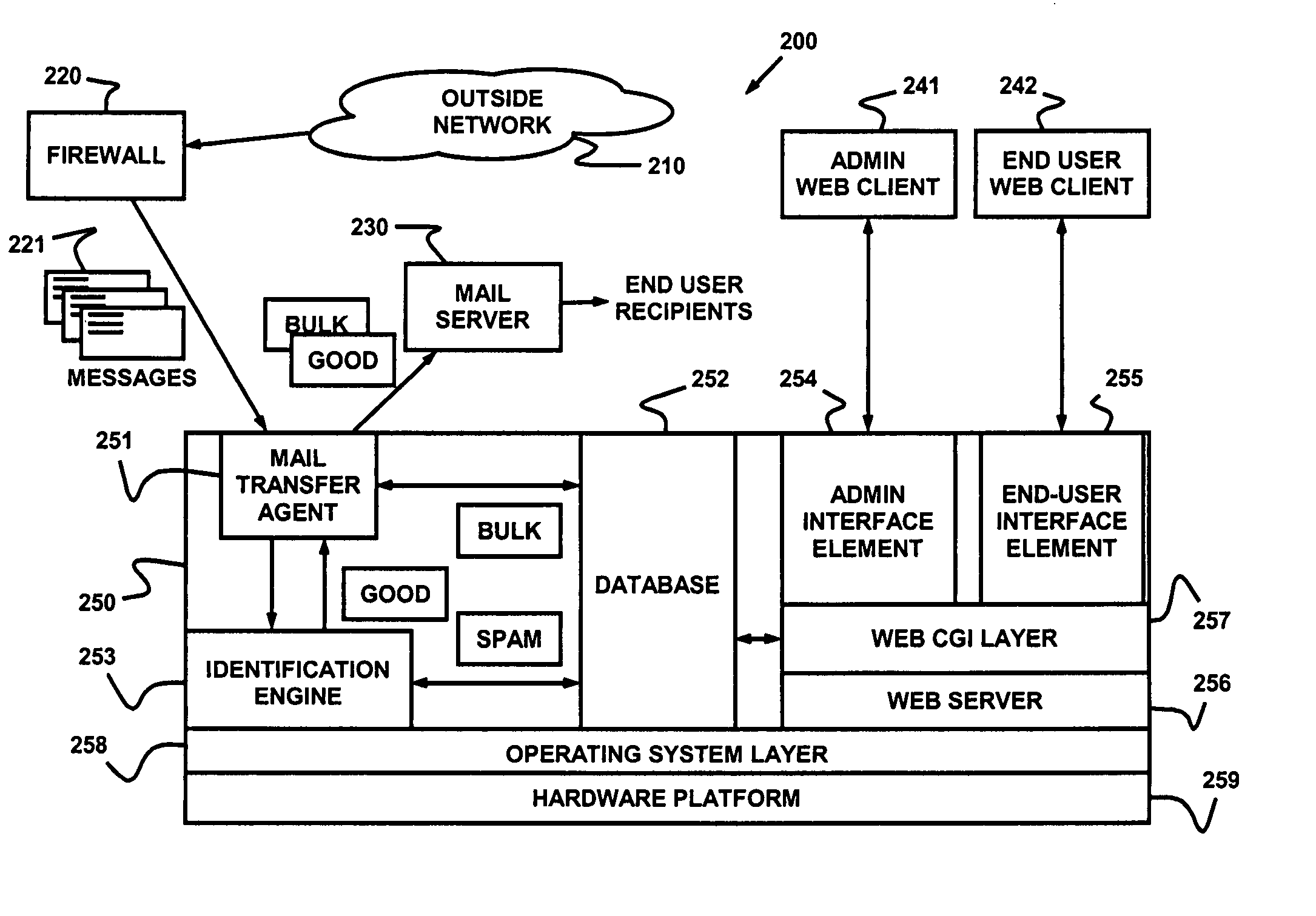
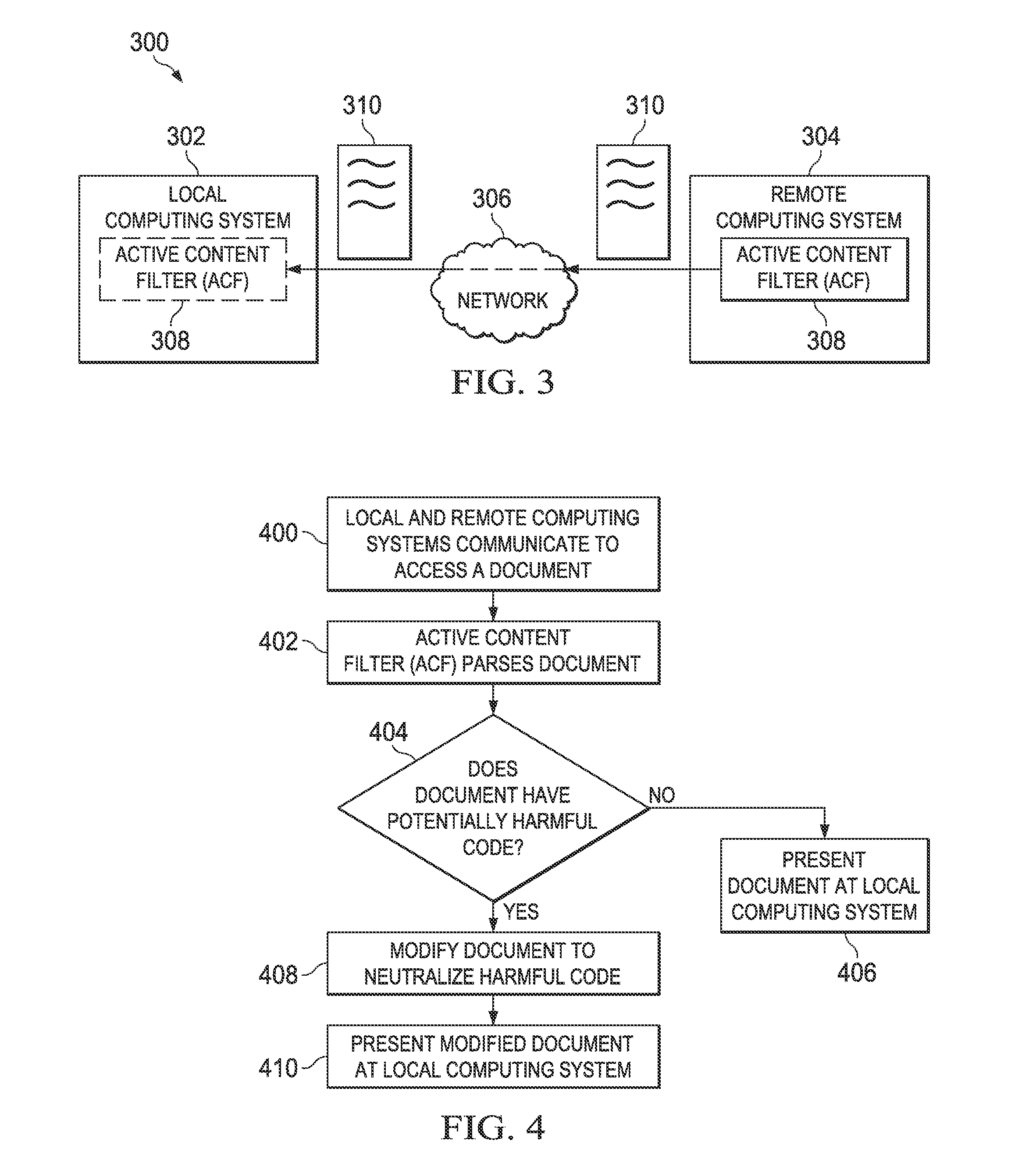
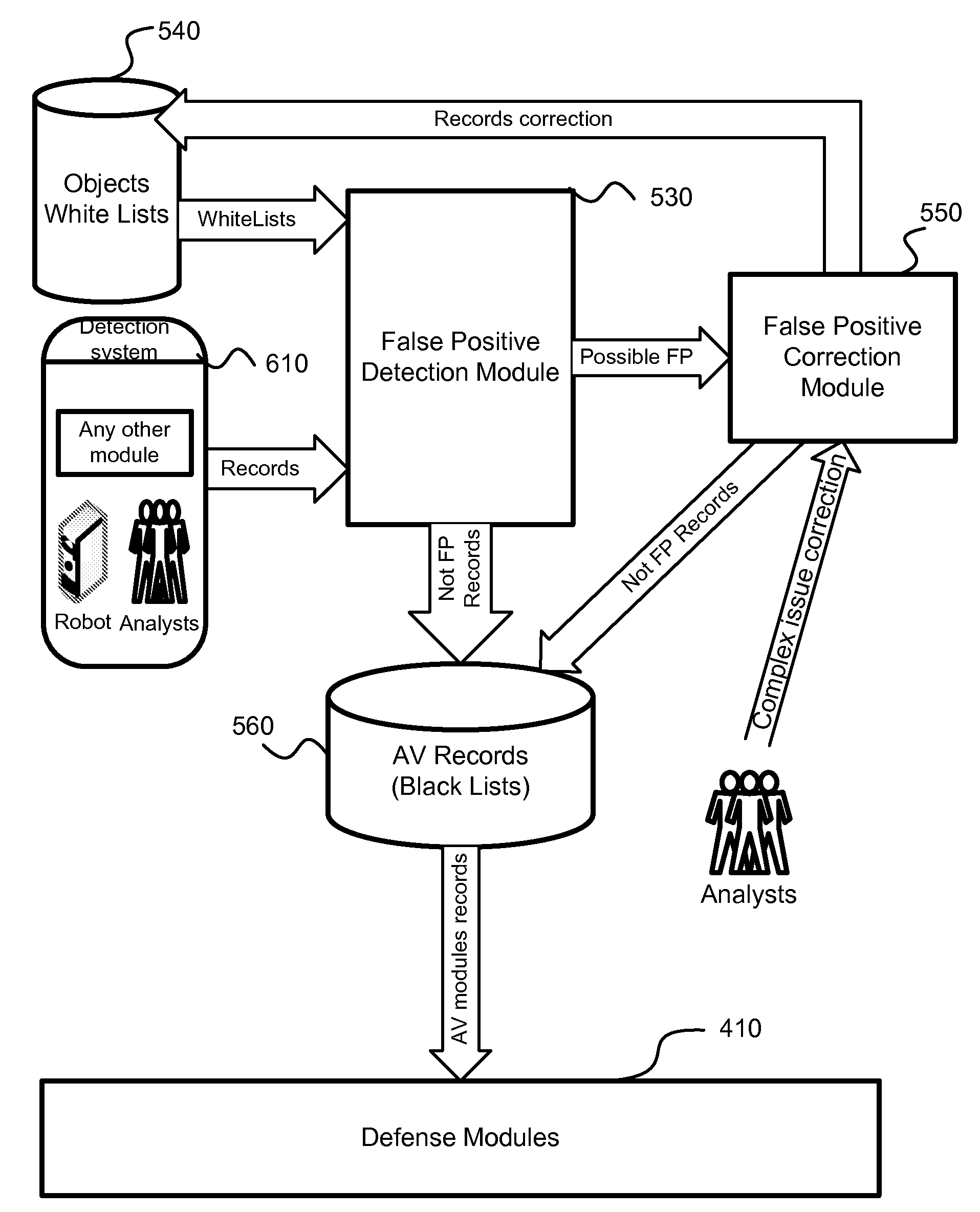
Detection and minimization of false positives in anti-malware processing
ActiveUS7640589B1Eliminate disadvantagesMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnti virusMalware
A system, method and computer program product for detection of false positives occurring during execution of anti-malware applications. The detection and correction of the false positives is implemented in two phases, before creation of new anti-virus databases (i.e., malware black lists) or before creation of new white lists, and after the anti-virus databases or new white lists are created and new false positives are detected. The system calculates a probability of detection of a certain potential malware object. Based on this probability, the system decides to either correct a white list (i.e., a collection of known clean objects) or update a black list (i.e., a collection of known malware objects). A process is separated into a several steps: creation and update (or correction) of white lists; creation and update of black lists; detection of collisions between these lists and correction of black lists or white lists based on the detected collisions.
Owner:AO KASPERSKY LAB
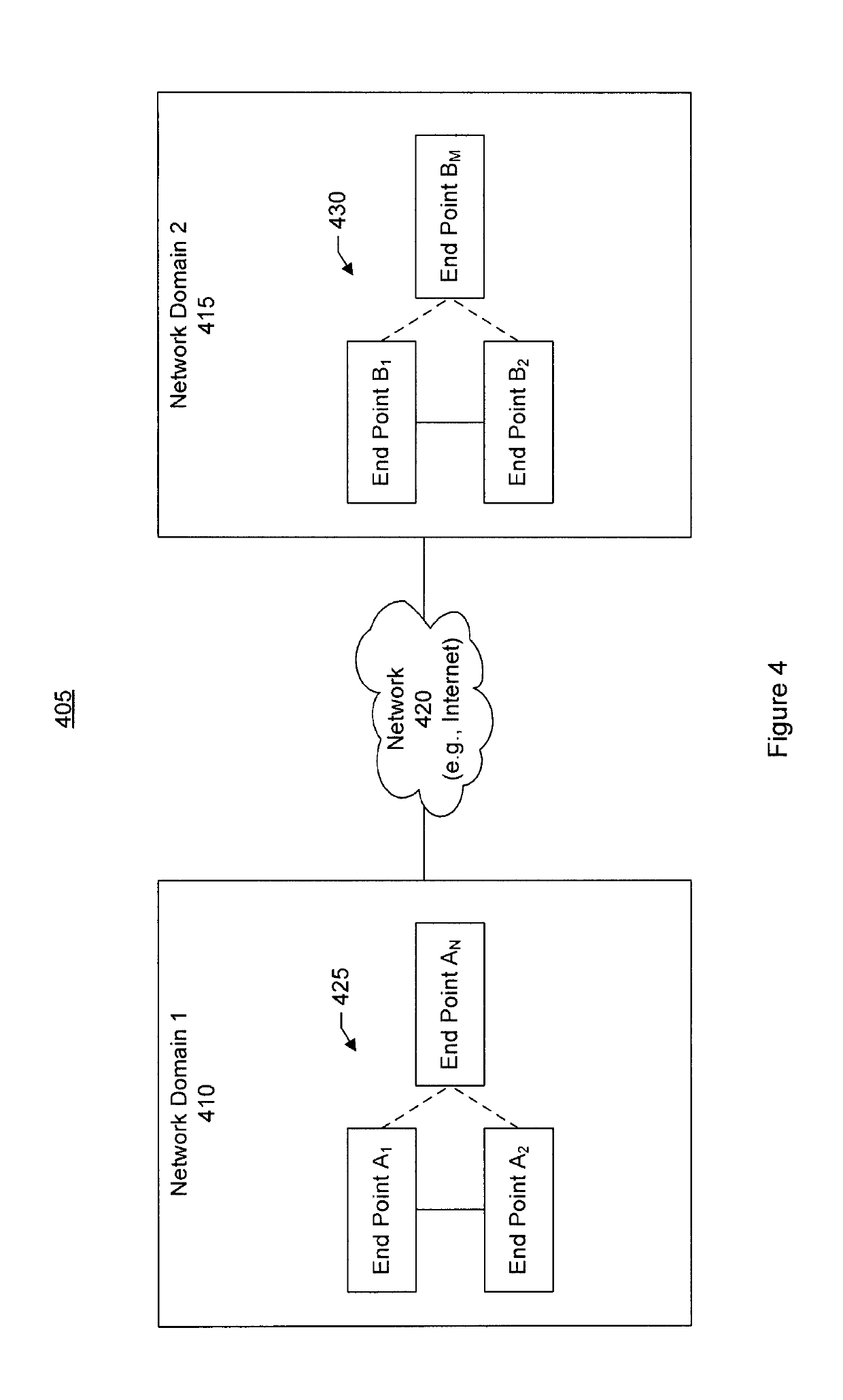
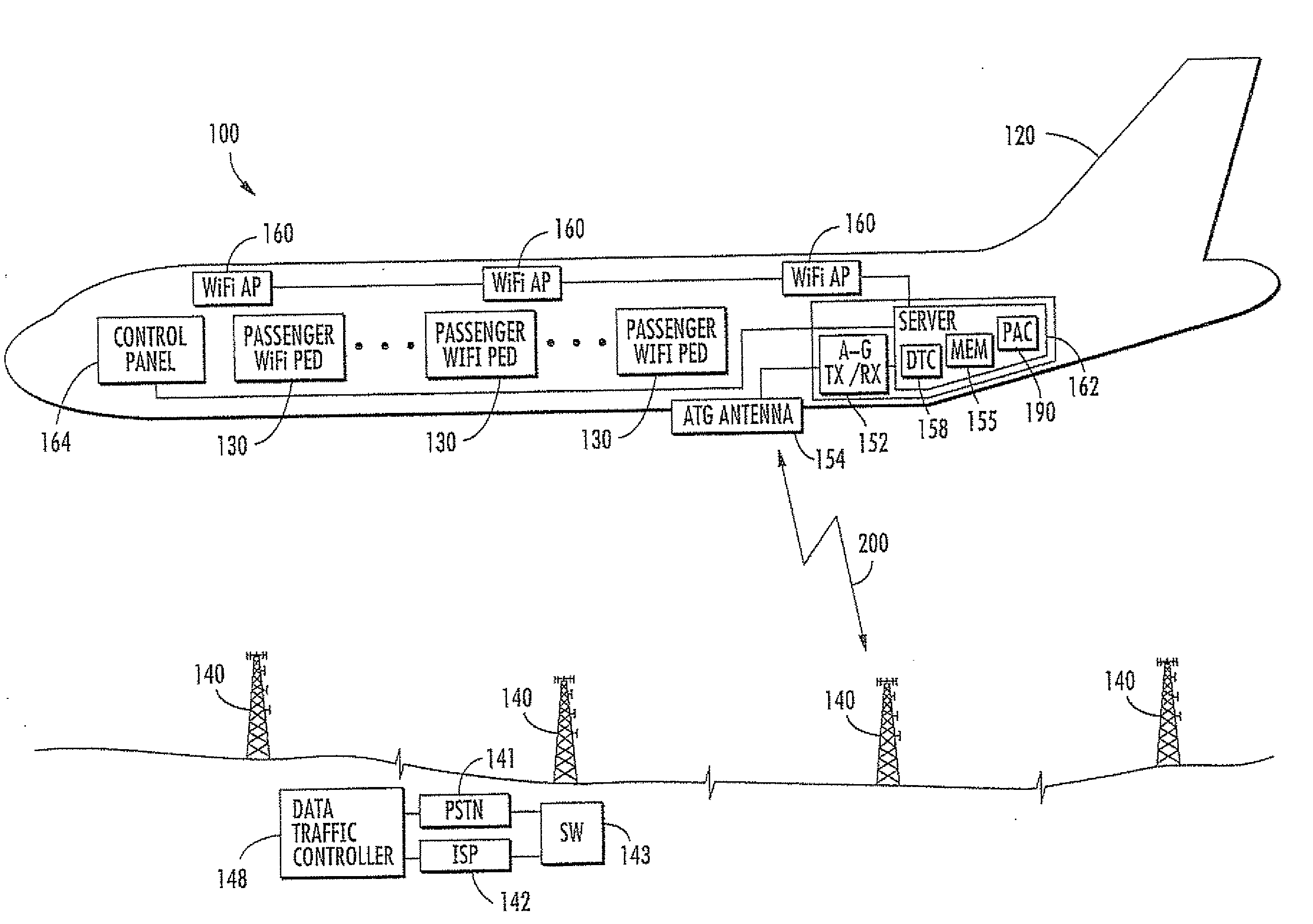
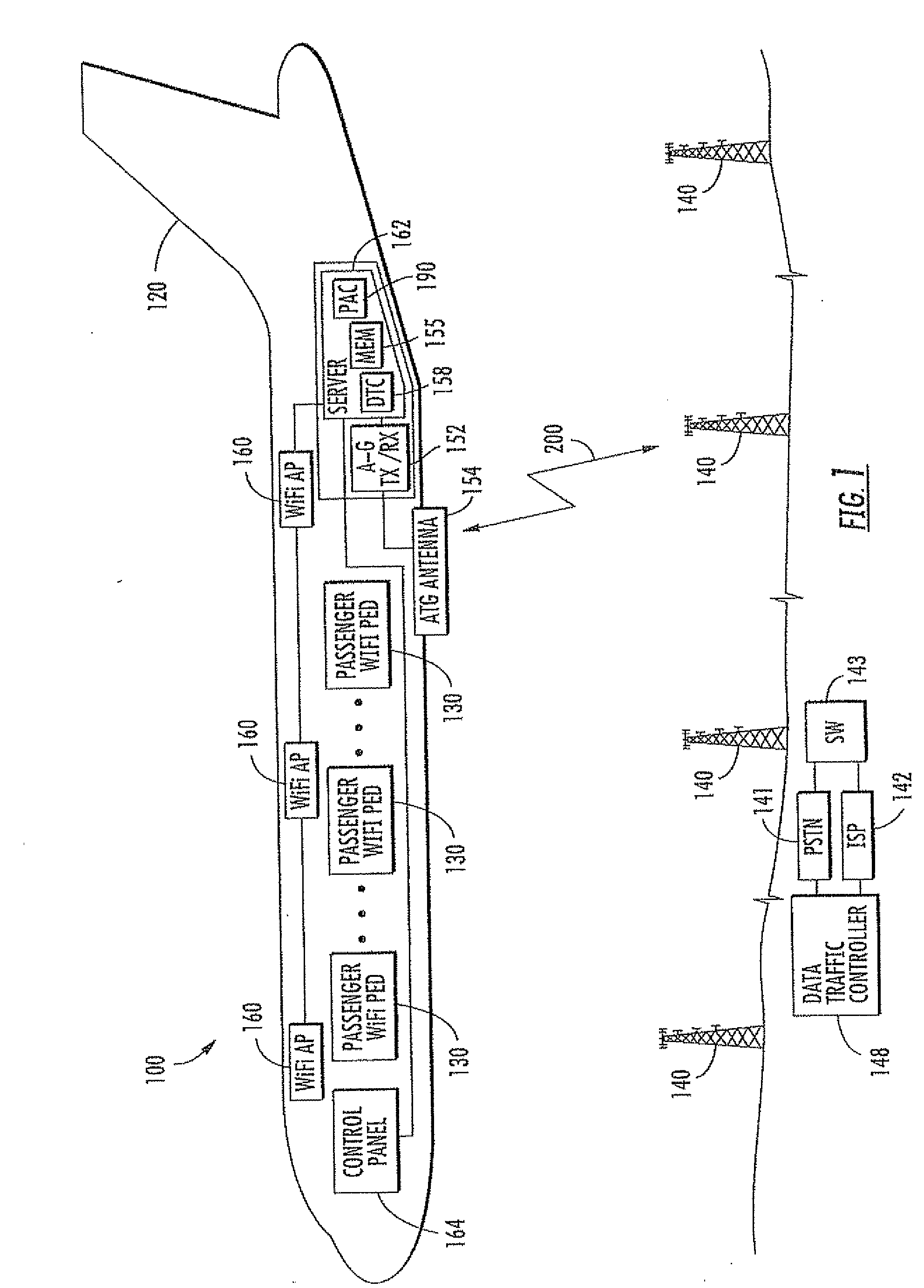
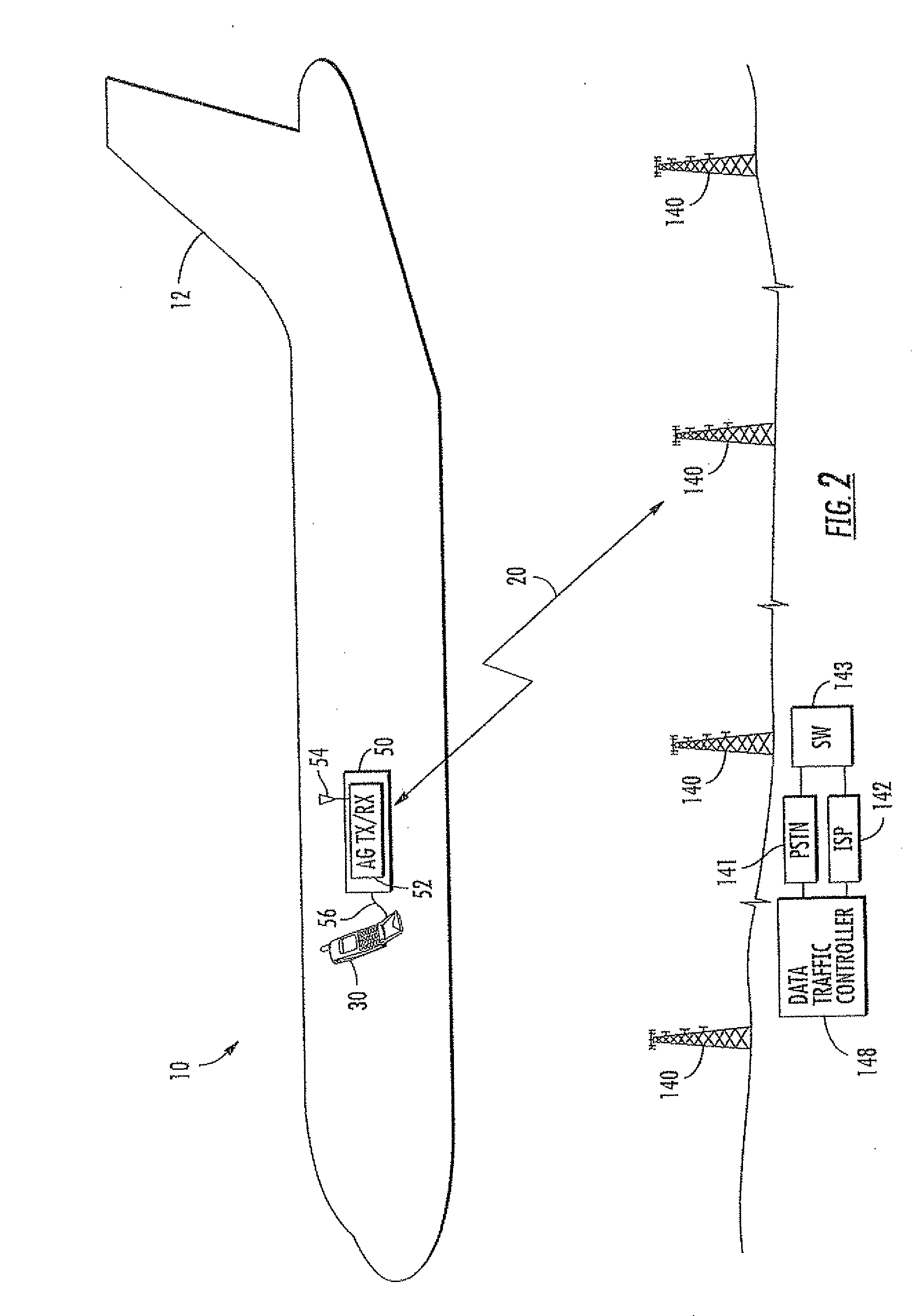
Aircraft communications system using whitelists to control access and associated methods
ActiveUS20090282469A1Digital data processing detailsNetwork topologiesTransceiverCommunications system
A communications system for an aircraft carrying personnel having personal electronic devices (PEDs) includes a wireless access device in the aircraft for the PEDs, and an aircraft server in the aircraft cooperating with the wireless access device for determining airborne validation of a ground server address entered via a corresponding PED. An air-to-ground transceiver in the aircraft cooperates with the aircraft server for communicating over an air-to-ground interface the airborne validated ground server address. A ground server on the ground receives the airborne validated ground server address over the air-to-ground interface, determines ground validation of the airborne validated ground server address, and provides ground access for the corresponding PED for which the entered ground server address has both airborne and ground validation.
Owner:LIVETV
System and method for providing closed subscriber groups in a packet-based wireless communication system
ActiveUS20100110945A1Save battery powerTimely controlAssess restrictionSubstation equipmentTransceiverCommunications system
Systems and methods for providing radio frequency transceiver user equipment in a packet based radio frequency signaling communication system are disclosed. User equipment is provided with closed subscriber group “CSG” capability including permanent storage for a CSG whitelist, the whitelist including identifiers of CSGs the user equipment is a member of. Base stations transmit signals including identifiers corresponding to CSGs the base station supports. The base station or cell selection process performed by the user equipment includes selecting cells that are part of the CSG whitelist. In additional embodiments, the user equipment includes user alterable storage for a user controlled CSG whitelist. The user alterable storage may further be partitioned into permanent and temporary portions. In an exemplary method, the user controls the cell selection process using the CSG whitelist information stored in the user equipment. Methods for managing the CSG whitelist are described.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
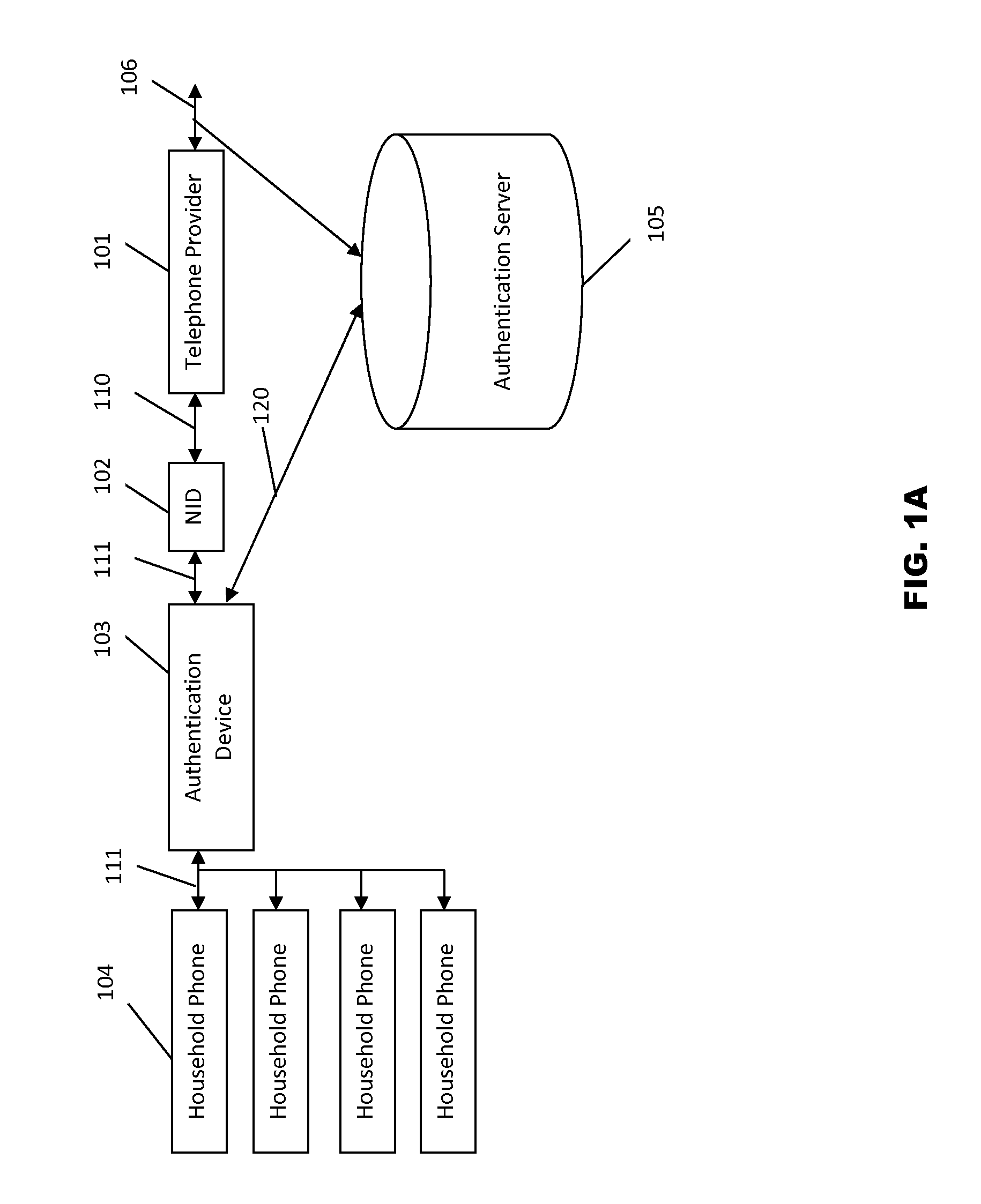
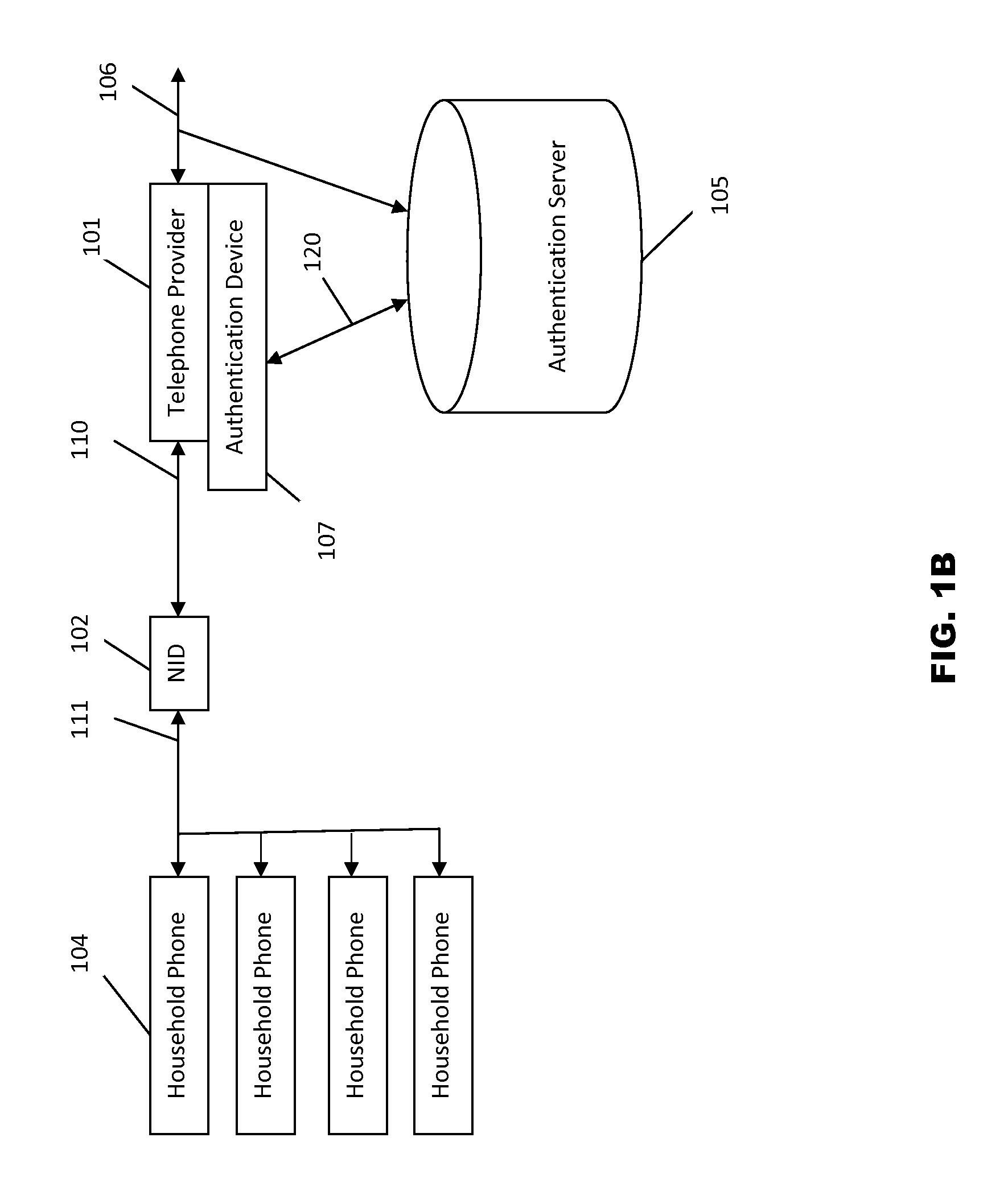
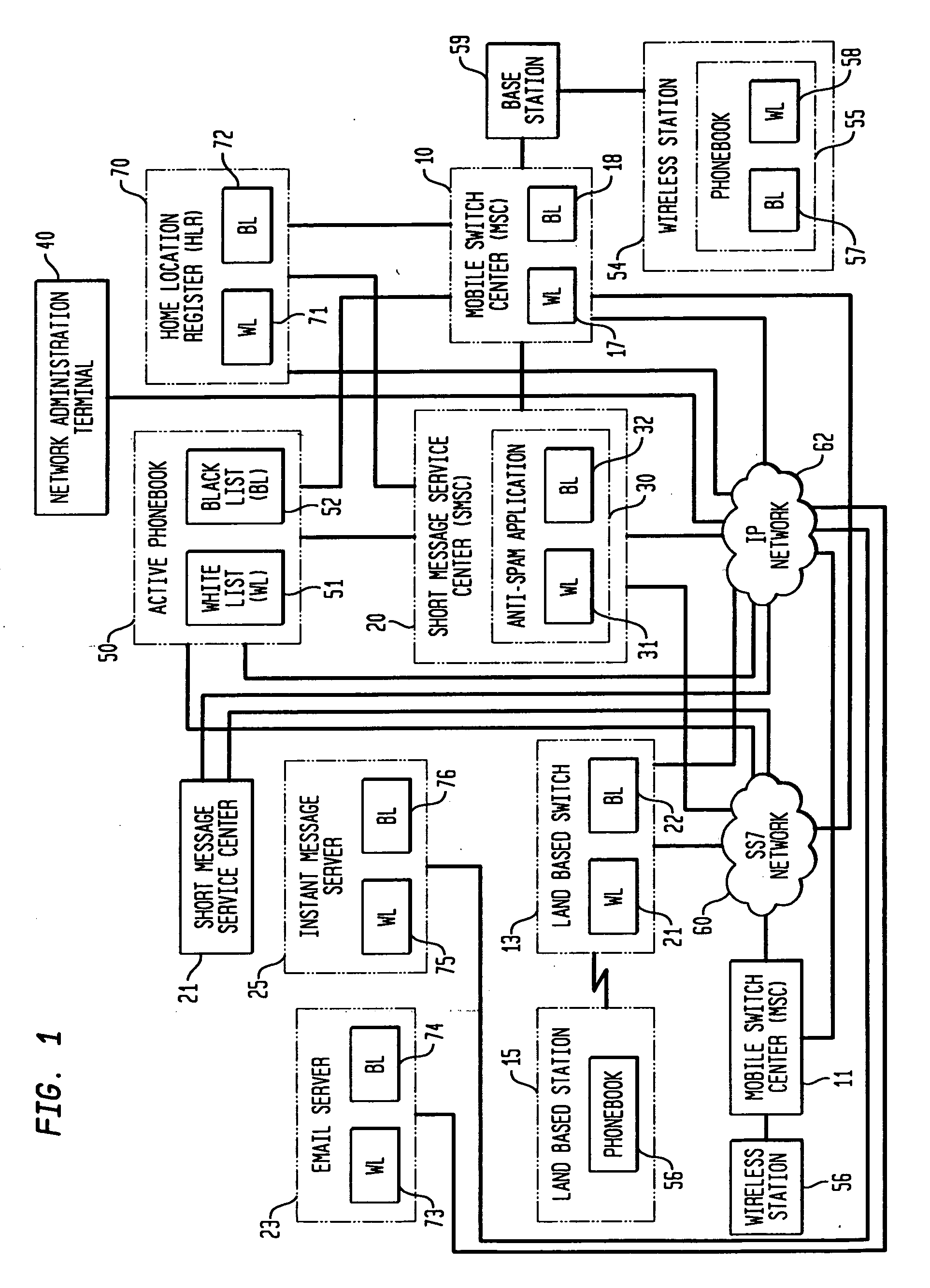
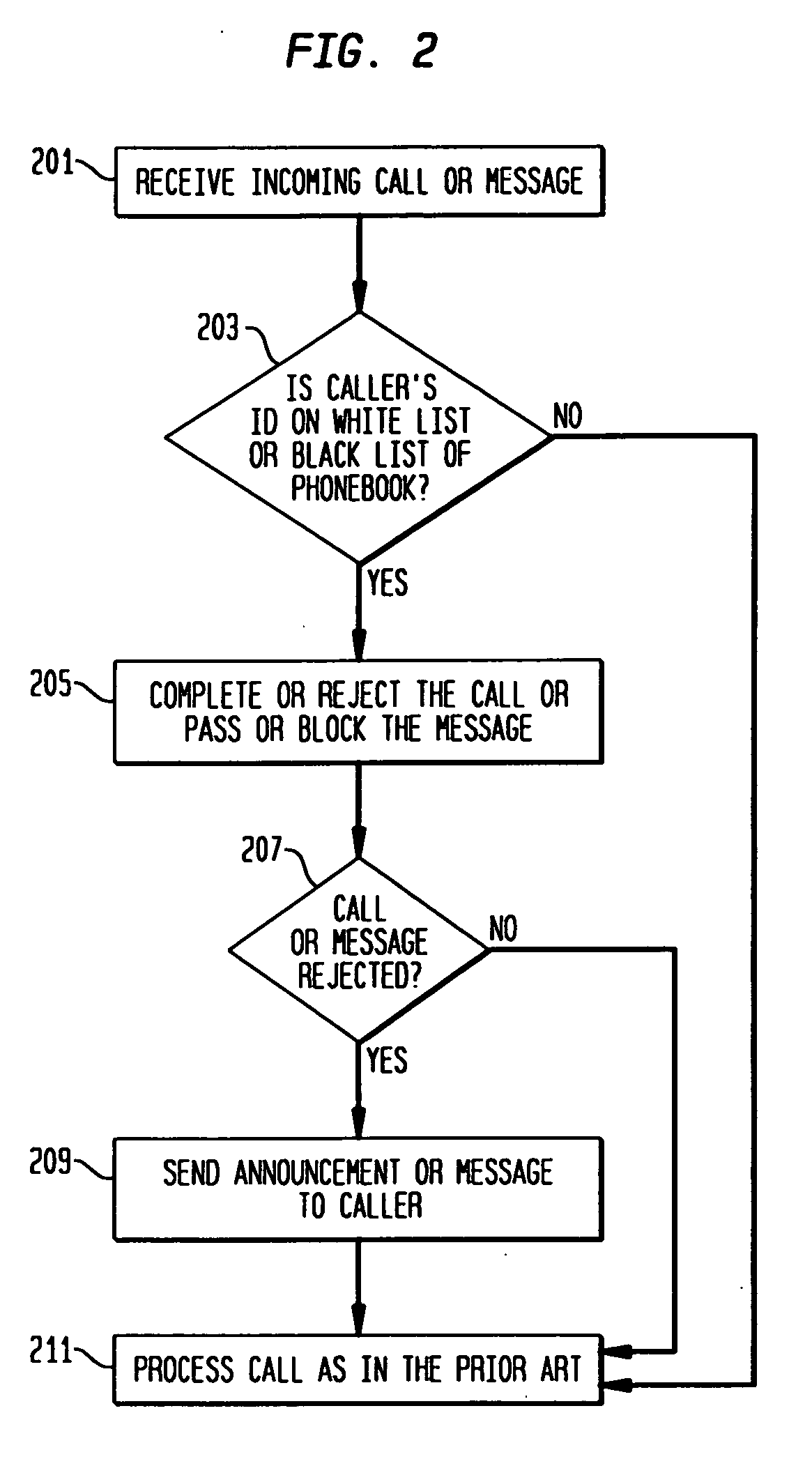
Phonebook use to filter unwanted telecommunications calls and messages
InactiveUS20070143422A1Minimizes and eliminates processingImprove network efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsSubstation equipmentTelecommunicationsWhitelist
This invention relates to the use of a customer phonebook feature for storing white lists and black lists for filtering unwanted voice calls or data messages. It also relates to the automatic population of a customer phonebook of identifications of a destination of outgoing calls. Advantageously, the phonebook can be rapidly and effortlessly populated with white lists and black lists to reduce processing for determining whether incoming calls or messages should be blocked or passed to the called destination.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Access admission control method and system for mobile communication system
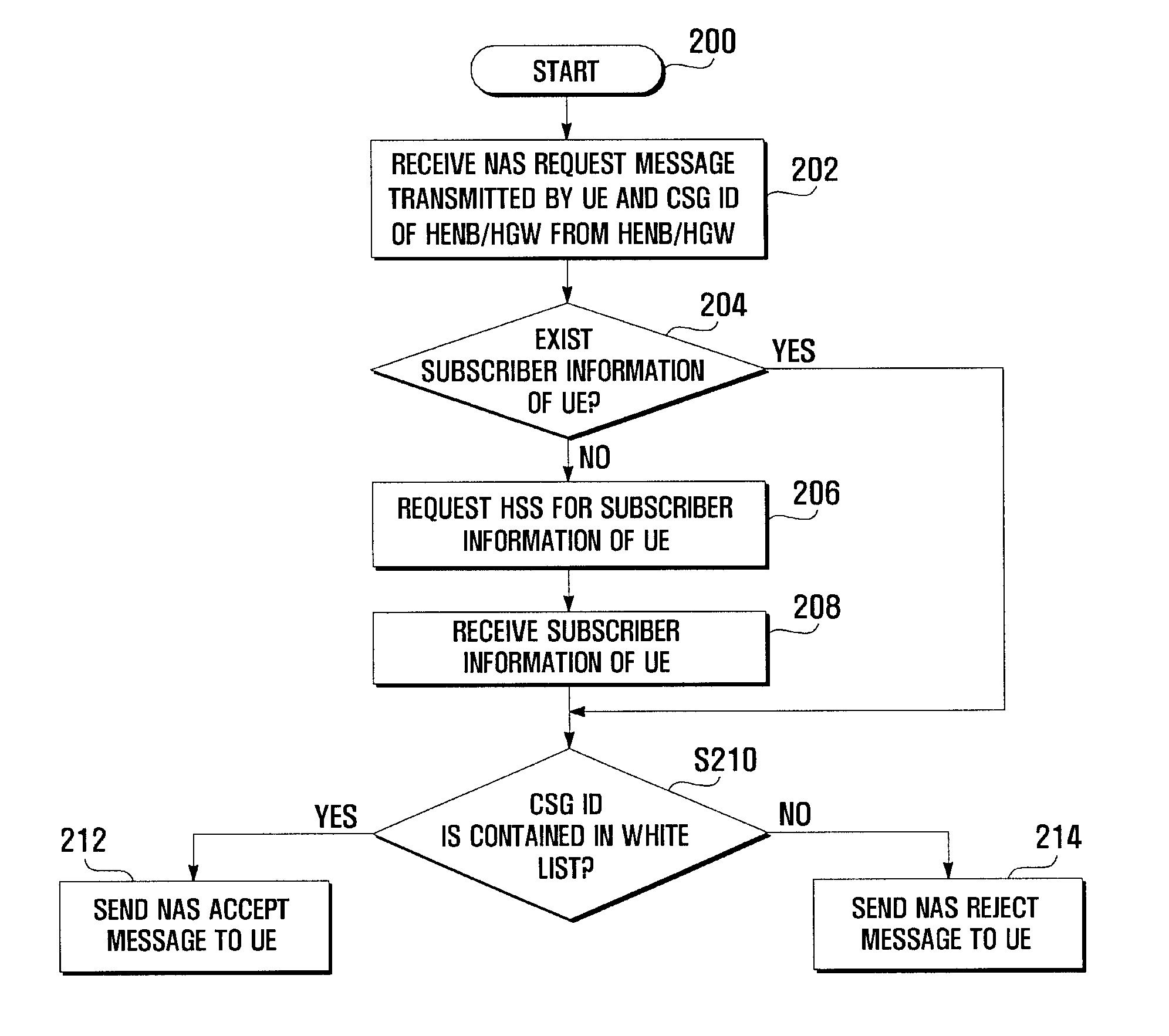
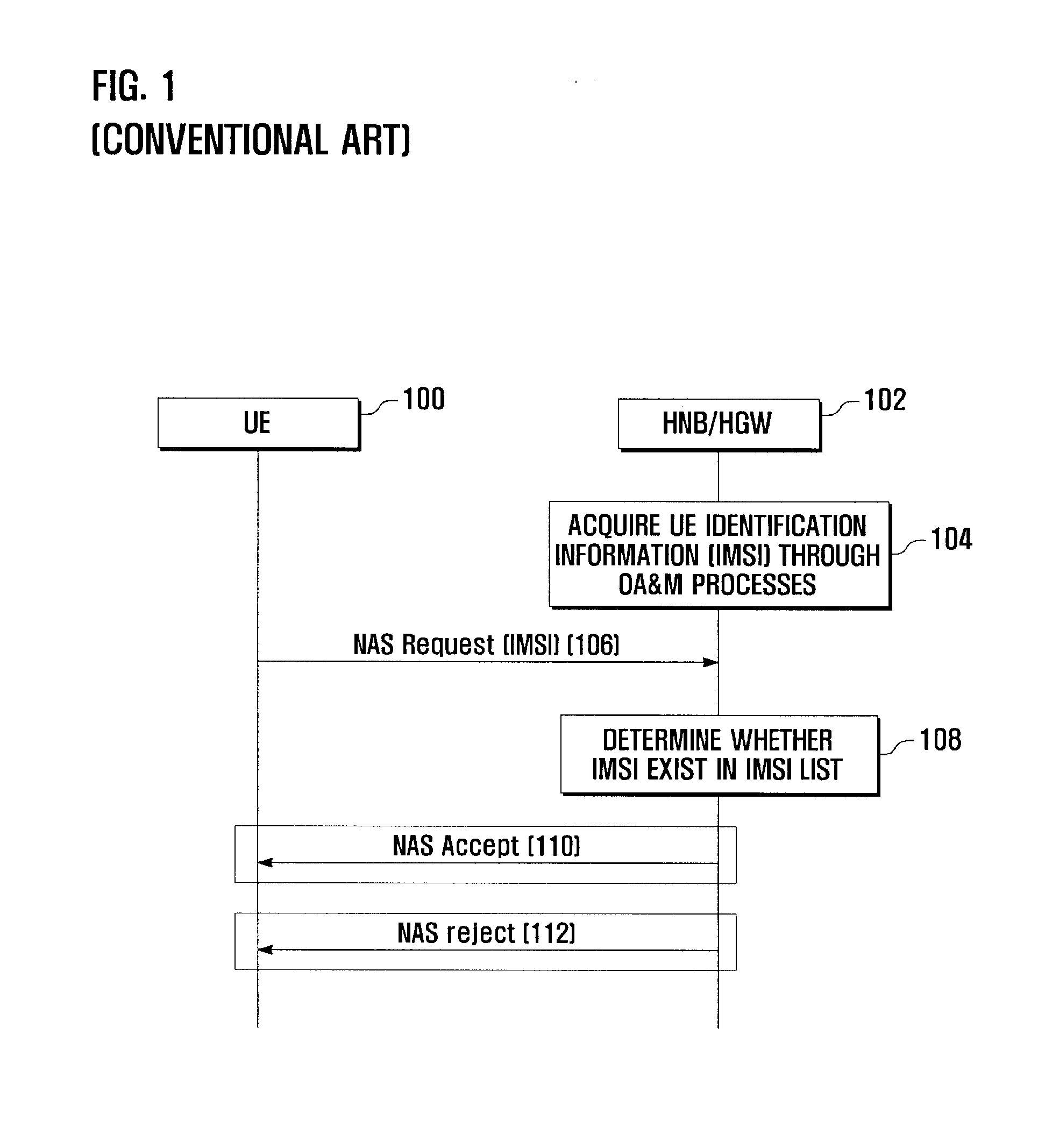
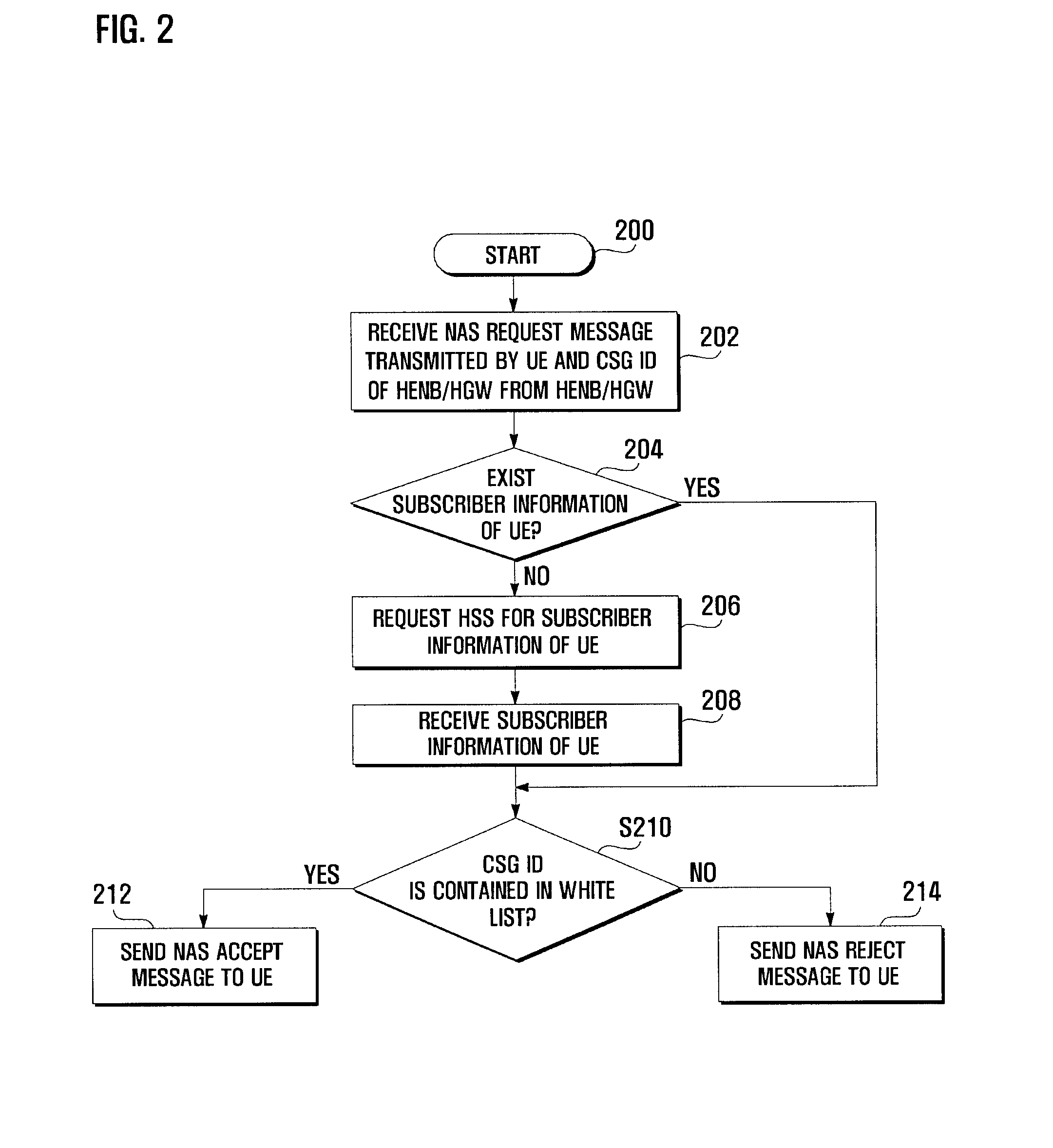
ActiveUS20100075635A1Effective controlUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionAssess restrictionMobile communication systemsWhitelist
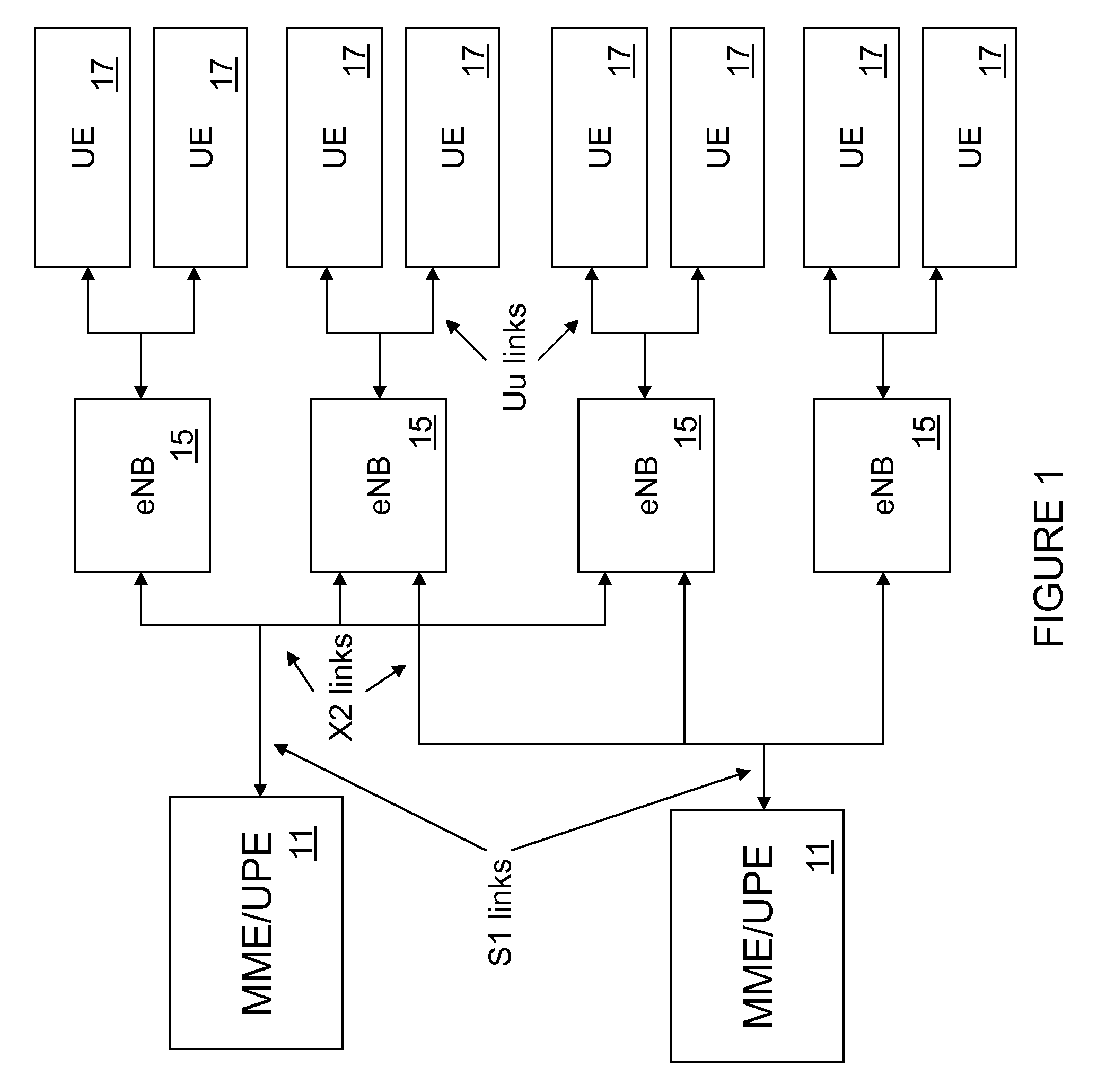
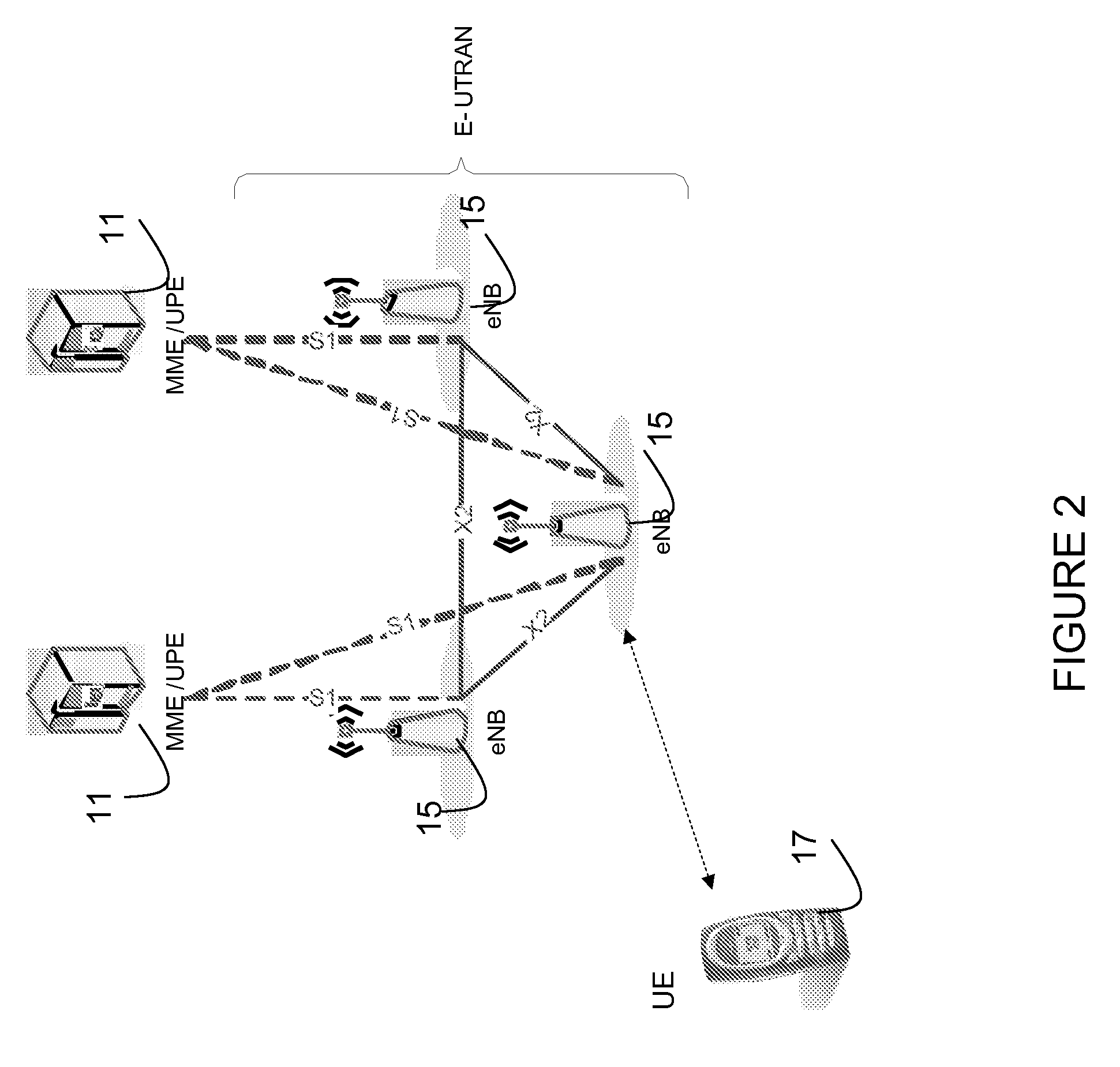
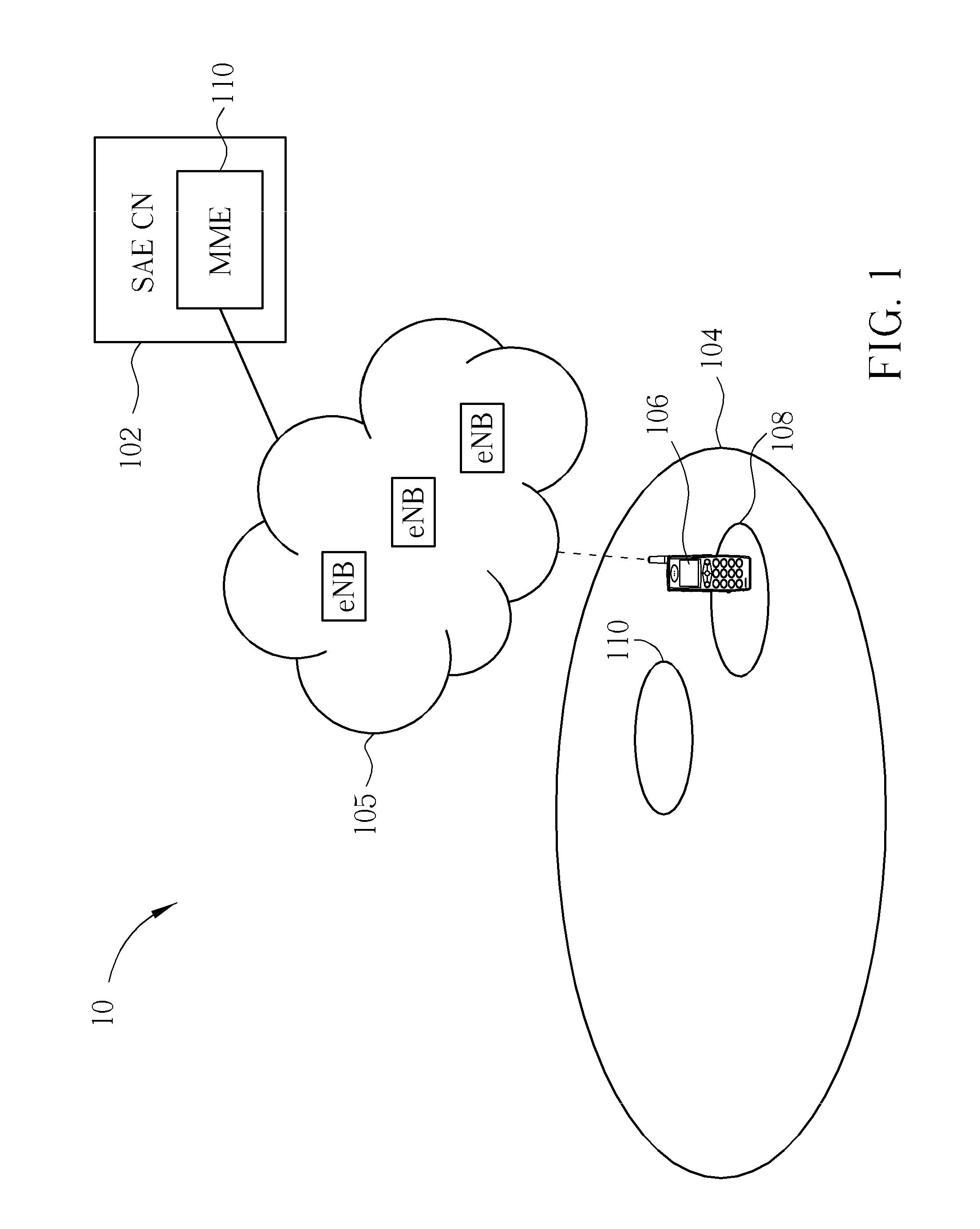
An access admission control method and system for and SAE / LTE system is provided for determining whether to accept or reject an access of a User Equipment (UE) to a Home evolved Node B (HeNB) based on the subscriber information of the UE. In an access admission control method according to the present invention, a HeNB or HeNB Gateway (HGW) transmits, when an access request message is received from a UE, the access request message to a Mobility Management Entity (MME) together with a CSG ID of the HeNB, and the MME determines, whether to accept or reject the access of the UE to the HeNB based on whether the CSG ID is contained in a white list associated with the UE.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
User interface for email inbox to call attention differently to different classes of email
A user interface for email users which calls attention to one or more categories of emails in different ways. In some species, at least three categories are used: branded senders with Trumarks; white list buddies; and fraudulent emails which are either not from the domain they purport to be from or in which the content was tampered. The preferred embodiment authenticates emails from branded senders and displays them with the sender's Truemark. Branded sender emails have their Truemarks displayed in the sender column of a list view in the preferred embodiment. In a preferred embodiment, white list senders have either an icon or other graphic or photo they choose displayed to the left or right of the sender column with their name in the sender column. In a preferred embodiment, fraudulent emails have a fraud icon displayed to the left or right of the sender column with a warning in the sender column. Antiphishing processing is also disclosed.
Owner:ICONIX INC
Online privacy management
ActiveUS8261362B2Simple processDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsData streamClient-side scripting
A privacy management system (PMS) is disclosed for a Chief Privacy Officer (CPO) or other user to use in monitoring and / or controlling in realtime the flow of data (e.g., outflow) about the user and his / her online experience. The PMS may provide a dashboard displaying a whitelist and / or blacklist indicating what destinations / sources are blocked or allowed. The PMS includes browser-client scripting code and may also include a PMS-certified verification icon for display on webpages being monitored / controlled in realtime by the PMS.
Owner:ENSIGHTEN
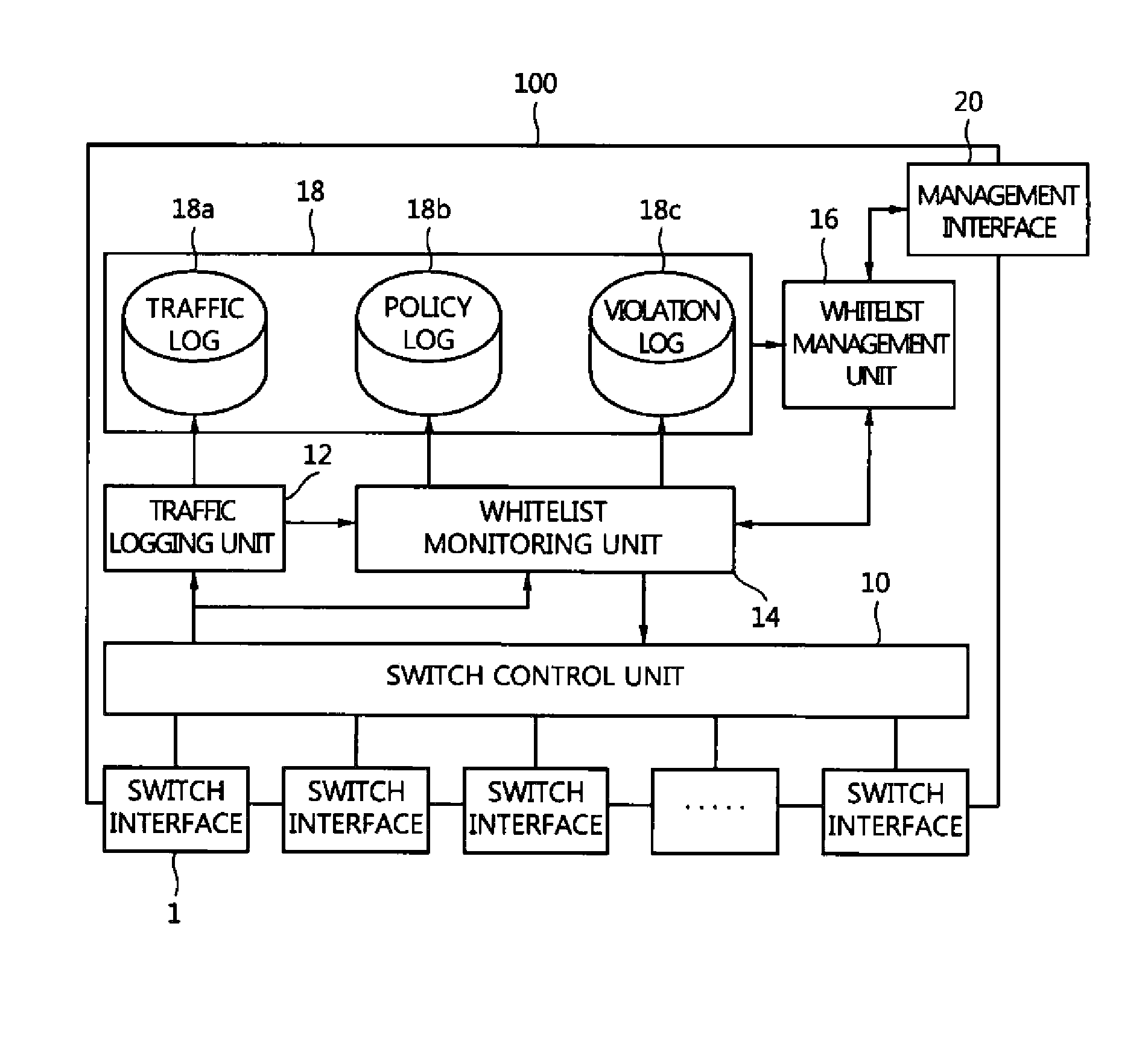
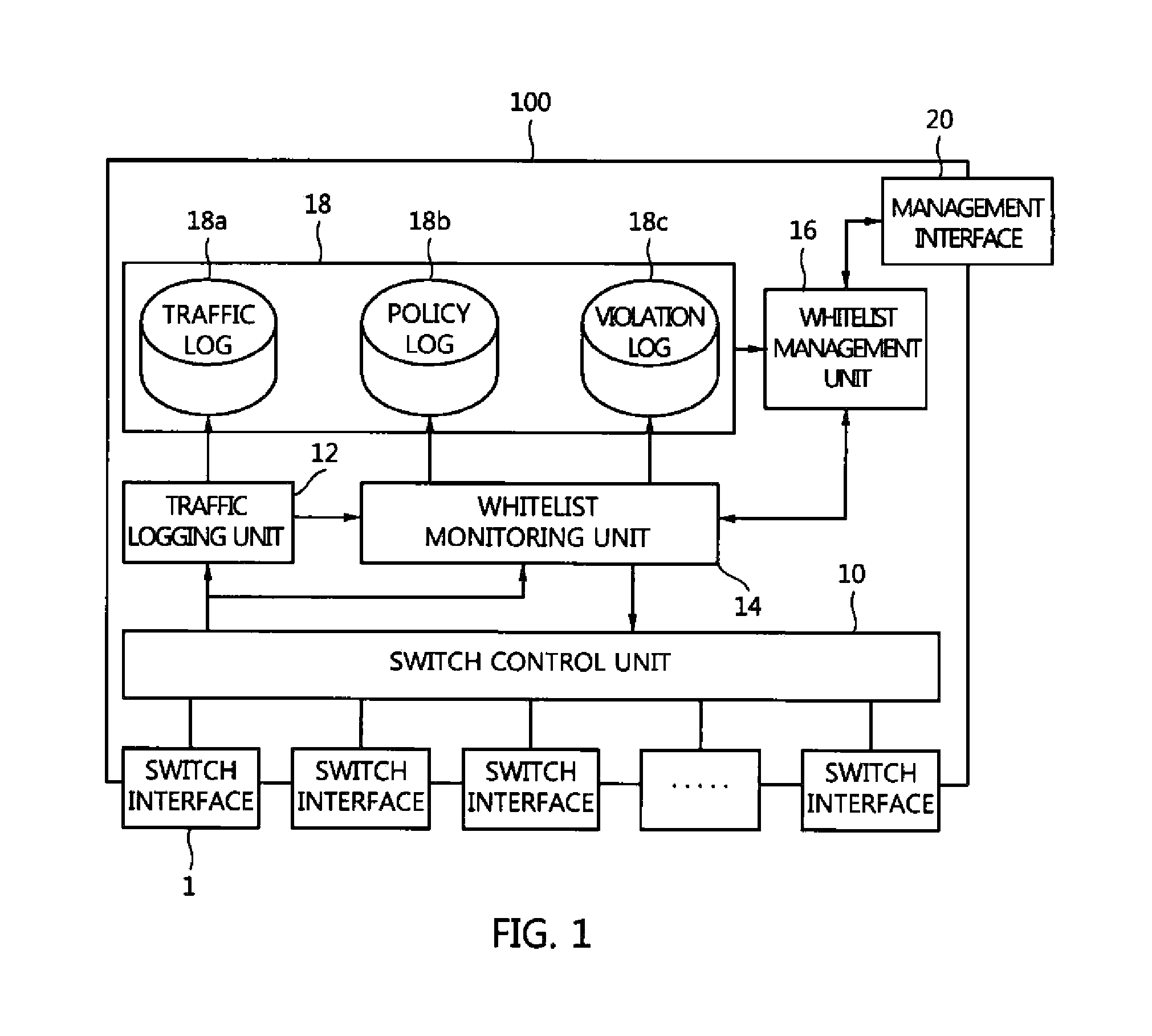
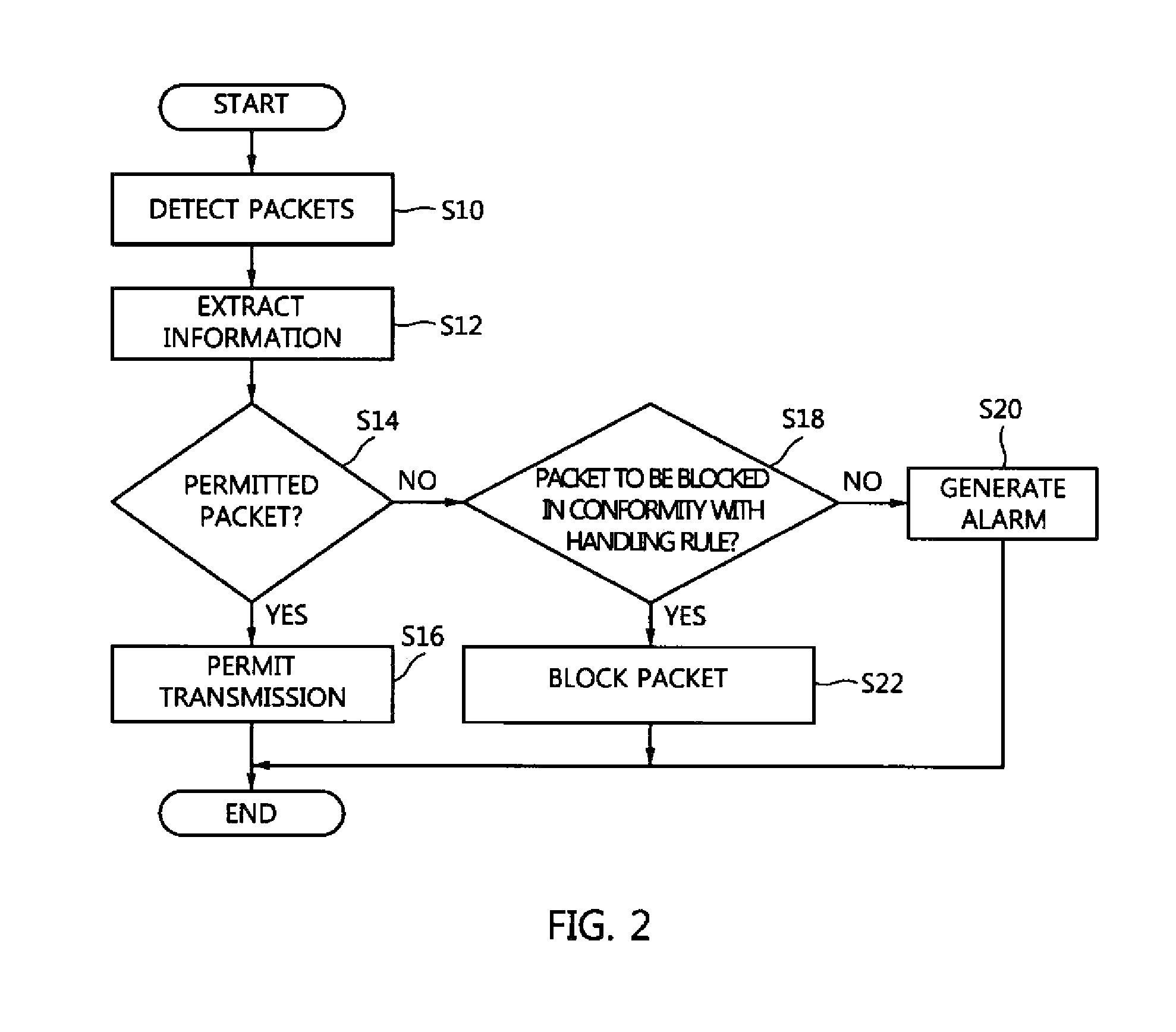
Whitelist-based network switch
A whitelist-based network switch defines a whitelist and a handling rule based on an access control list, security policies, etc., and monitors and blocks network traffic based on the whitelist and the handling rule. The whitelist-based network switch includes a whitelist monitoring unit for storing a whitelist including permitted communication rules, monitoring one or more packets input through a plurality of switch interfaces based on the whitelist, and permitting communication of each packet conforming to the whitelist, and a whitelist management unit for updating the whitelist and transmitting an updated whitelist to the whitelist monitoring unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
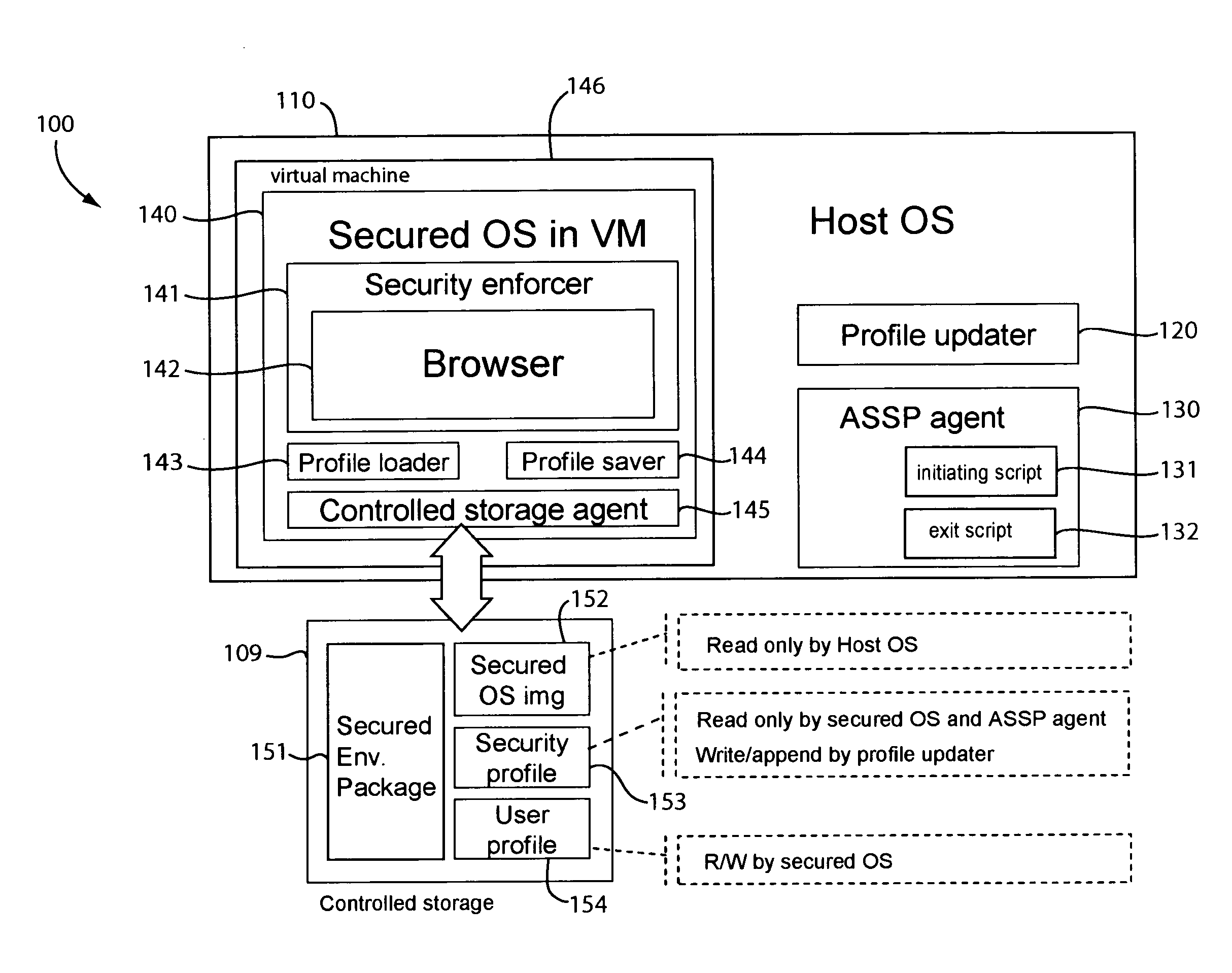
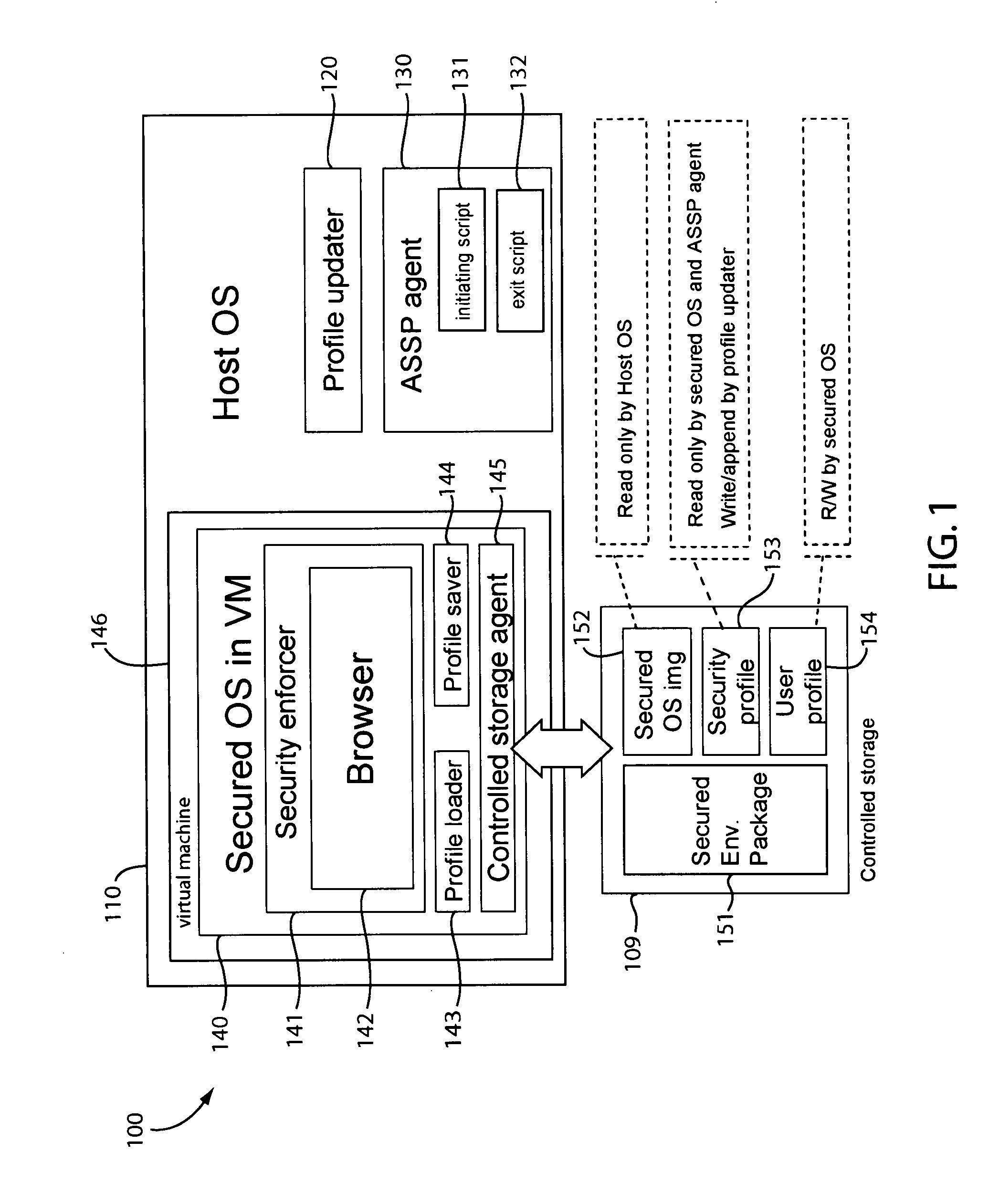
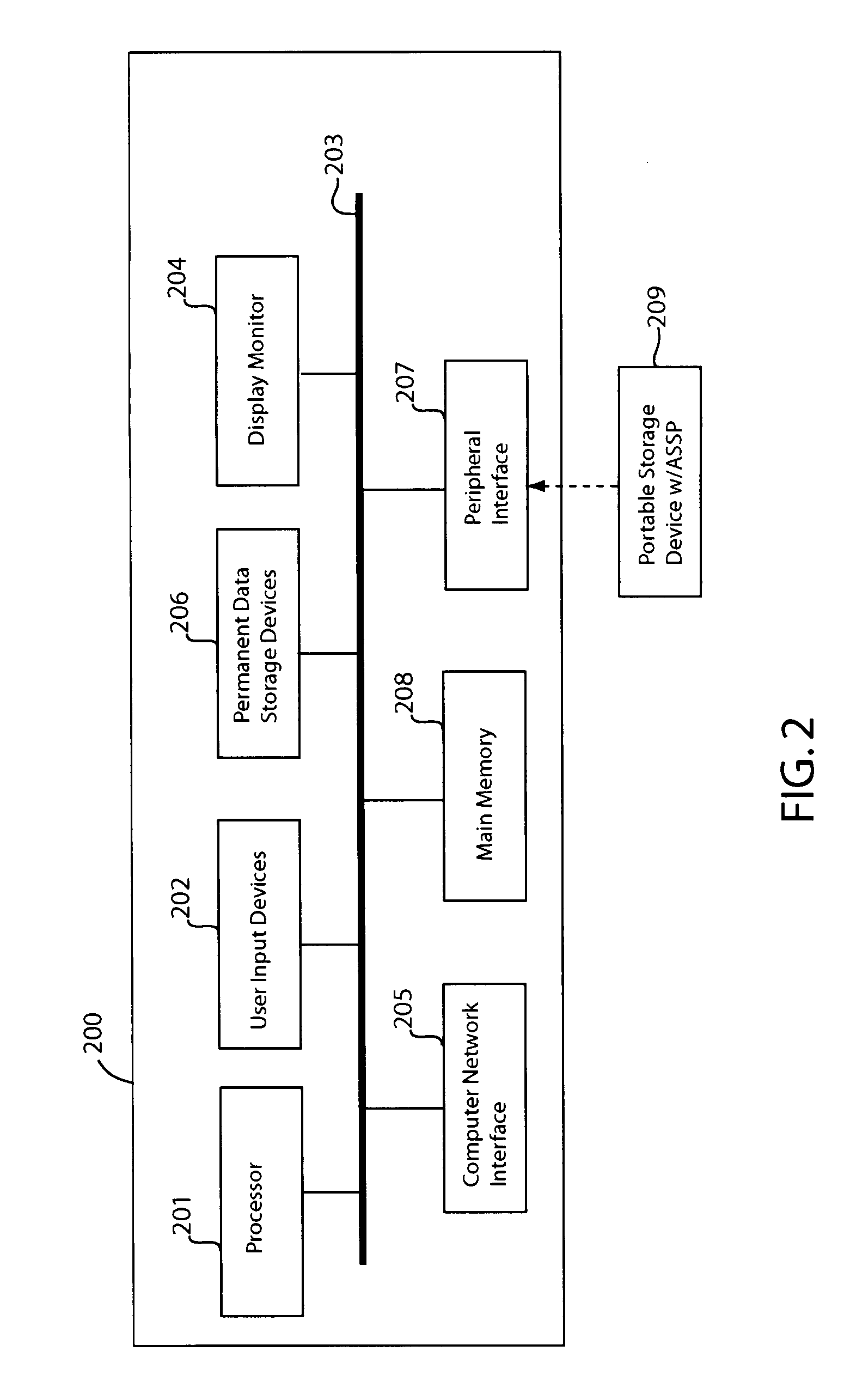
Portable secured computing environment for performing online confidential transactions in untrusted computers
ActiveUS20080256536A1Readily apparentMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsAccess networkOperational system
A portable secured computing environment for performing online confidential transactions in an untrusted host computer. The secured computing environment may be loaded from a portable storage device, such as a USB stick, plugged into a peripheral port of the host computer. The secured computing environment may include a virtual machine running under a host operating system of the host computer. A secured operating system may be running in the virtual machine. An online application, such as a web browser in communication with an online service, may be run under the secured operating system. Operation of the online application may be restricted by a security profile. For example, the online application may only access network addresses specifically indicated in a whitelist of the security profile.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
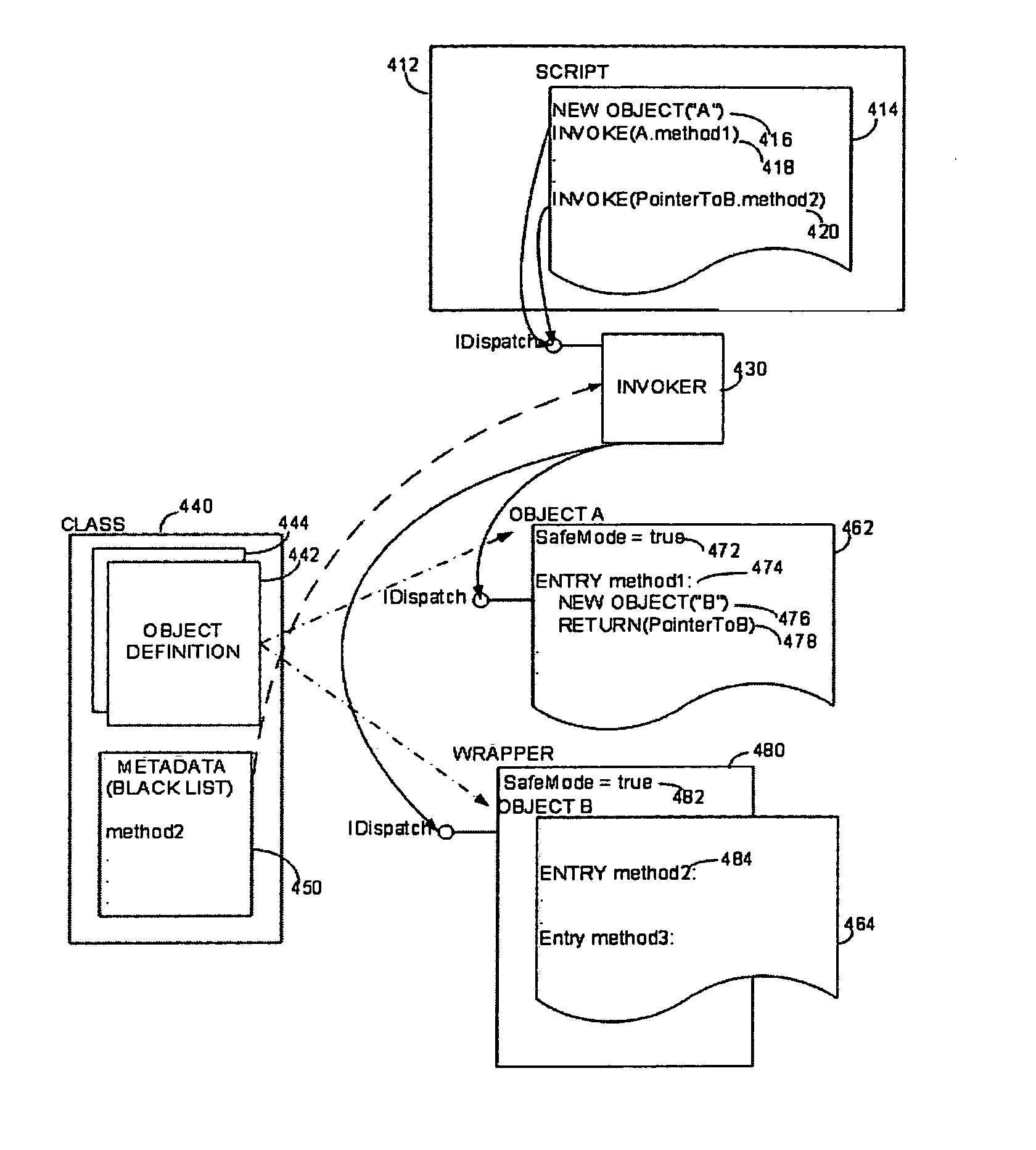
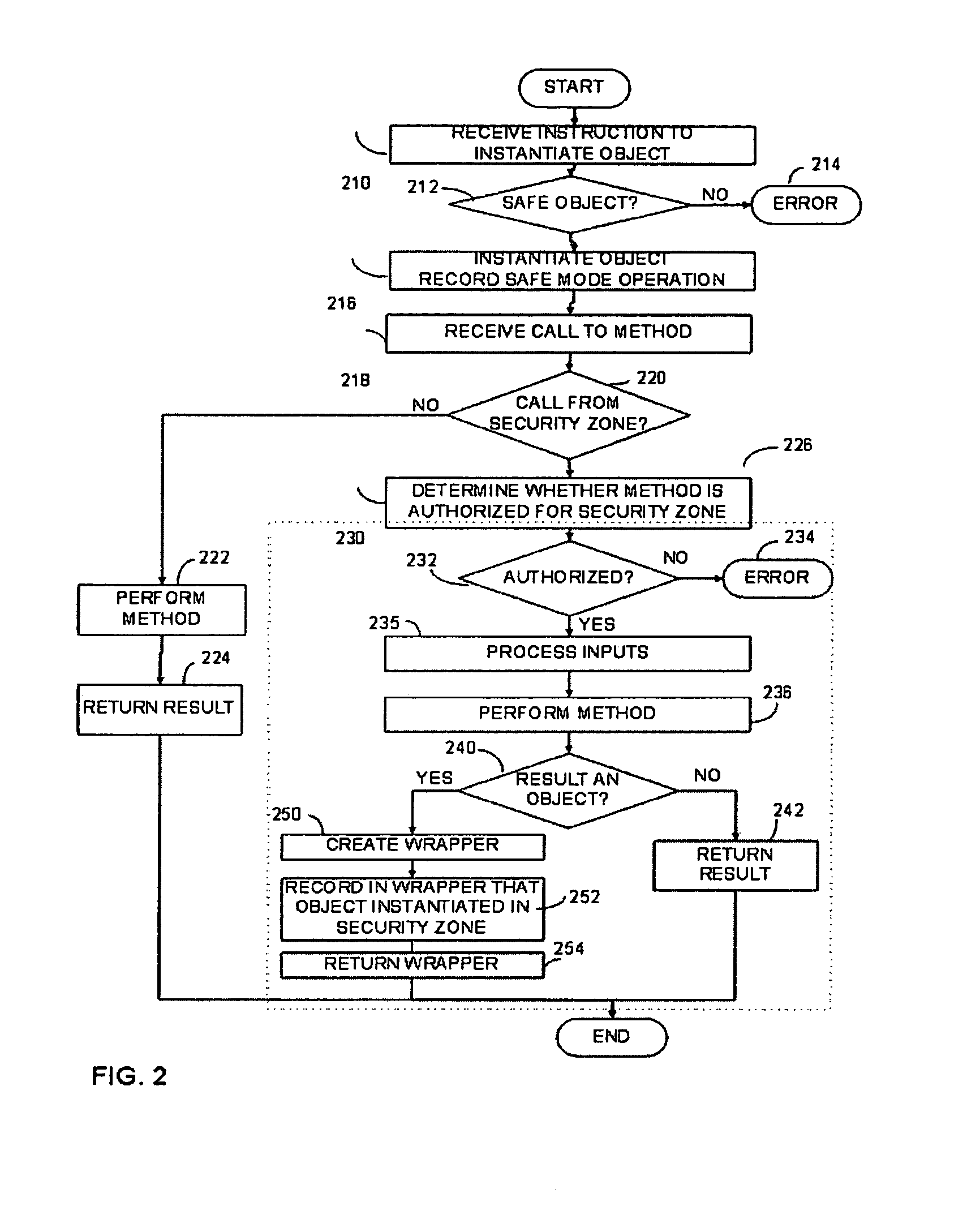
Software system with controlled access to objects
ActiveUS20070199000A1Easy to useImprove developmentSpecific access rightsProgram control using stored programsSoftware systemWhitelist
A computer system configured to intercept method calls placed on an object. By intercepting method calls, processing may be performed on a method call-by-method call basis. As part of the processing, metadata for an object is consulted to partition the methods for that object into subsets. The processing performed in response to any specific method call may be based on the subset to which the method belongs. The type of metadata may depend on the desired operation of the computer system. Metadata representing a white list or black list may be used in a computer system that implements a security zone that allows access to methods deemed to be safe or to deny access to methods deemed to be unsafe. In a performance monitoring system, metadata may identify methods to be logged or methods for which execution cost are to be measured. Values returned by a method call may also be processed when the method calls are intercepted. The returned value may be wrapped with a wrapper that holds data useful in implementing a security zone or for performing other processing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method of controlling cell selection for a wireless communication system and related device
ActiveUS20100075670A1Assess restrictionBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemCell selection
A method of controlling CSG, known as closed subscriber group, cell selection for a wireless communication system is provided. The wireless communication system includes a network and a user equipment including a whitelist capable of providing a list of accessible CSG cells. The method includes updating the whitelist when the user equipment subscribes to a CSG cell that is not included in the whitelist or does not subscribe to a CSG cell in the whitelist.
Owner:HTC CORP
Dynamic message filtering
ActiveUS7257564B2Reduce in quantityMake fastError detection/correctionGenetic modelsWhitelistData mining
Dynamically filtering and classifying messages, as good messages, bulk periodicals, or spam. A regular expression recognizer, and pre-trained neural networks. The neural networks distinguish “likely good” from “likely spam,” and also operate at a more discriminating level to distinguish among the three categories above. A dynamic whitelist and blacklist; sending addresses are collected when the number of their messages indicates the sender is good or a spammer. A dynamically selected set of regular expressions input to the neural networks.
Owner:MAILGATE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com