Patents
Literature
302results about How to "Width minimized" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
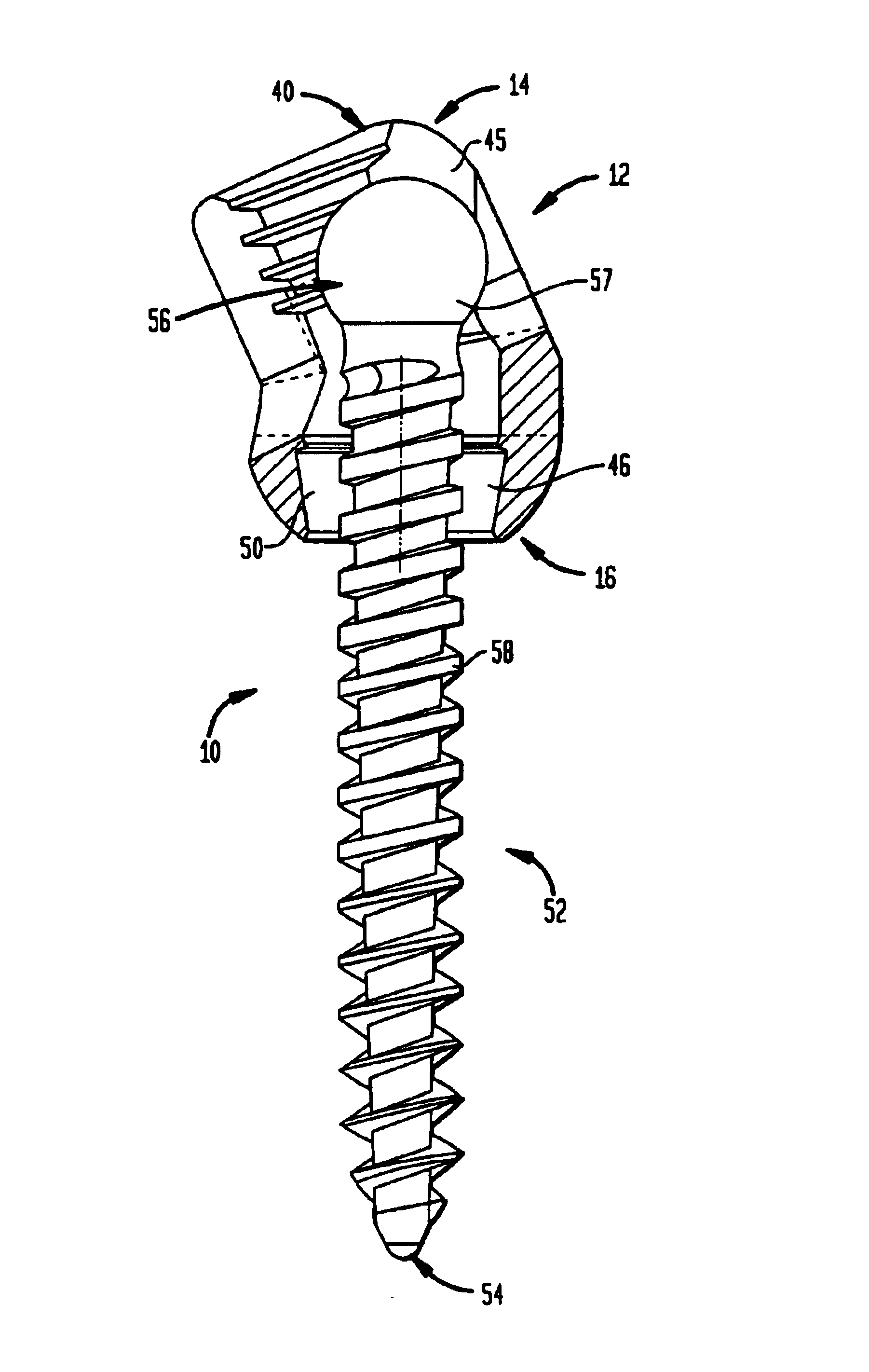
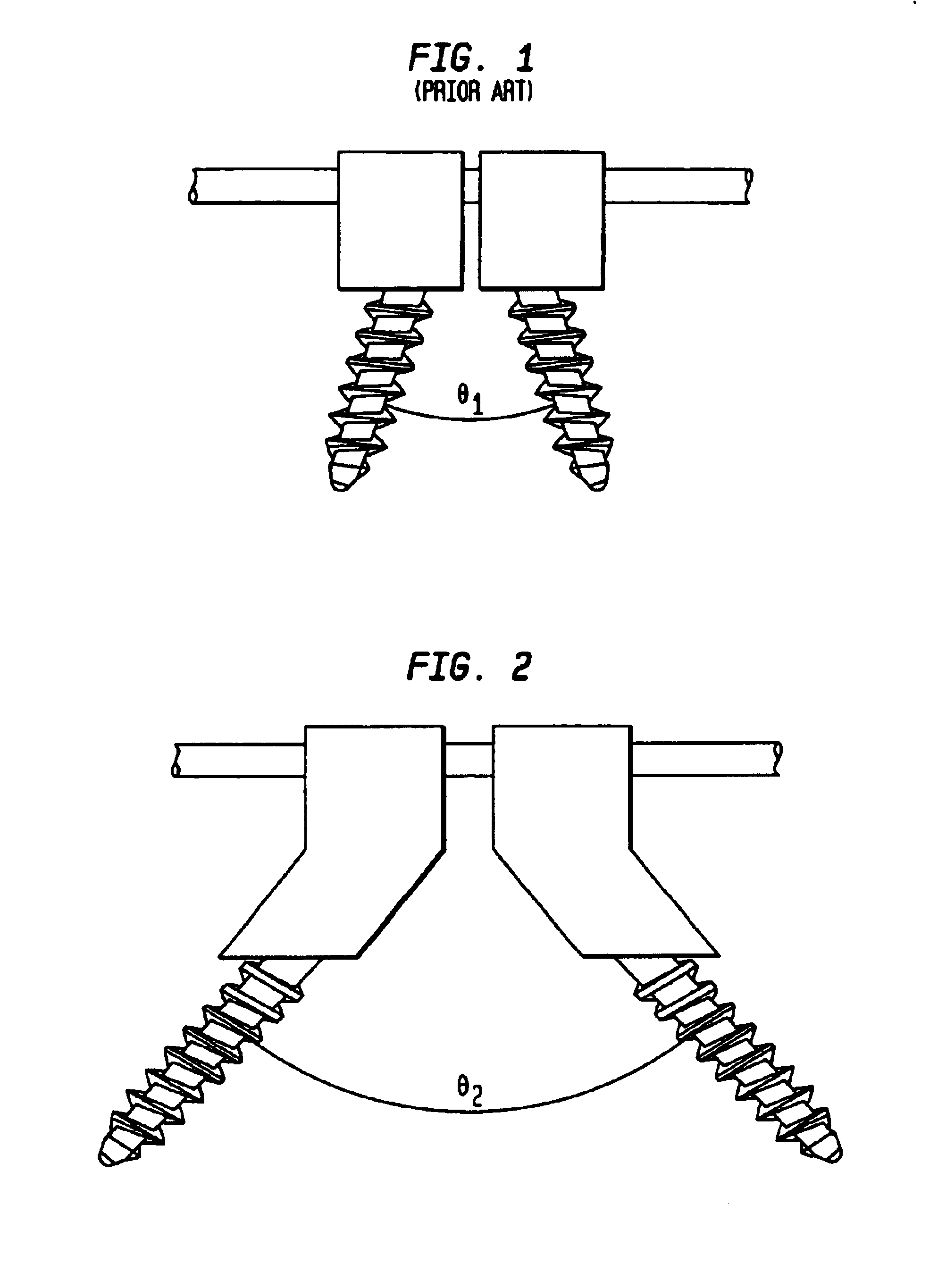
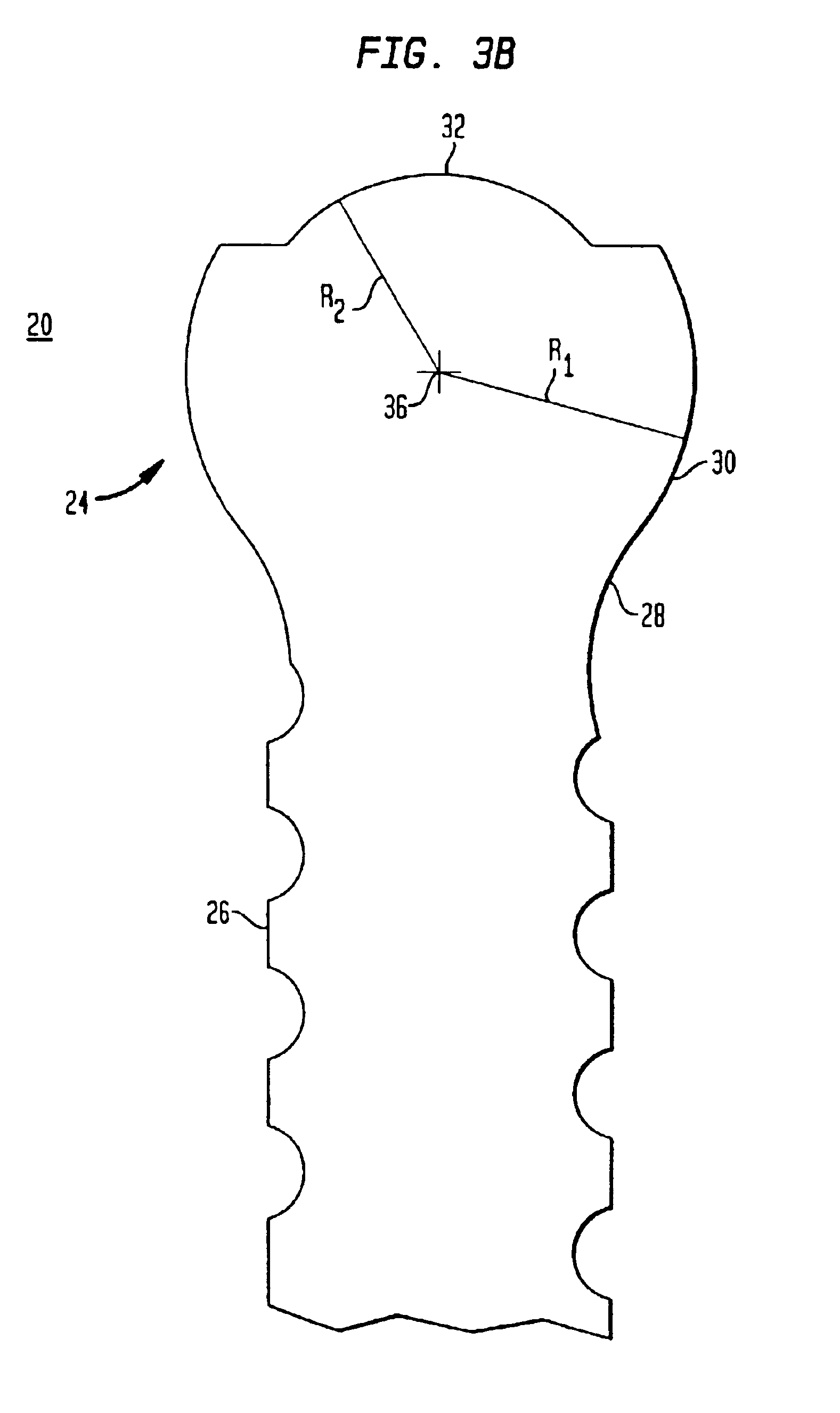
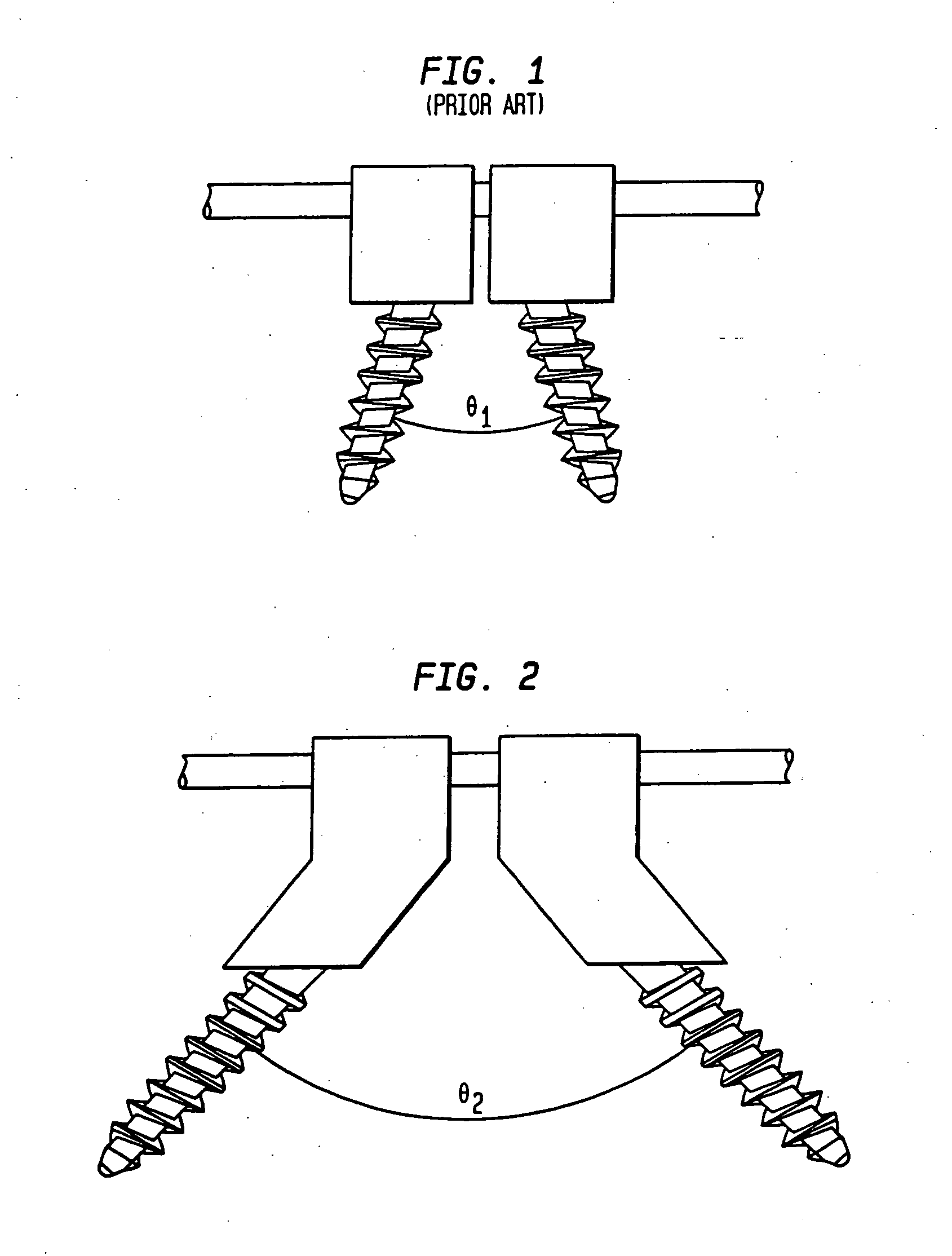
Biased angulation bone fixation assembly
InactiveUS6974460B2Reduce the overall diameterFacilitate pivotal movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCouplingPlastic surgery
A bone fixation assembly including a coupling element having an inner surface defining a first bore coaxial with a first longitudinal axis, and a second bore coaxial with a second longitudinal axis, whereby the second longitudinal axis intersects the first longitudinal axis. The coupling element has a seat adjacent the lower end of the coupling element, the seat being defined by the inner surface of the coupling element. The assembly includes an anchoring element assembled with the coupling element, the anchoring element having a first end for insertion into bone and a head spaced from the first end, the head being in contact with the seat of the coupling element. The assembly provides sufficient angulation between adjacent anchoring elements securing a common orthopedic rod, and is particularly useful for assemblies mounted in spines having abnormal curvatures and in the cervicothoracic region of the spine.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
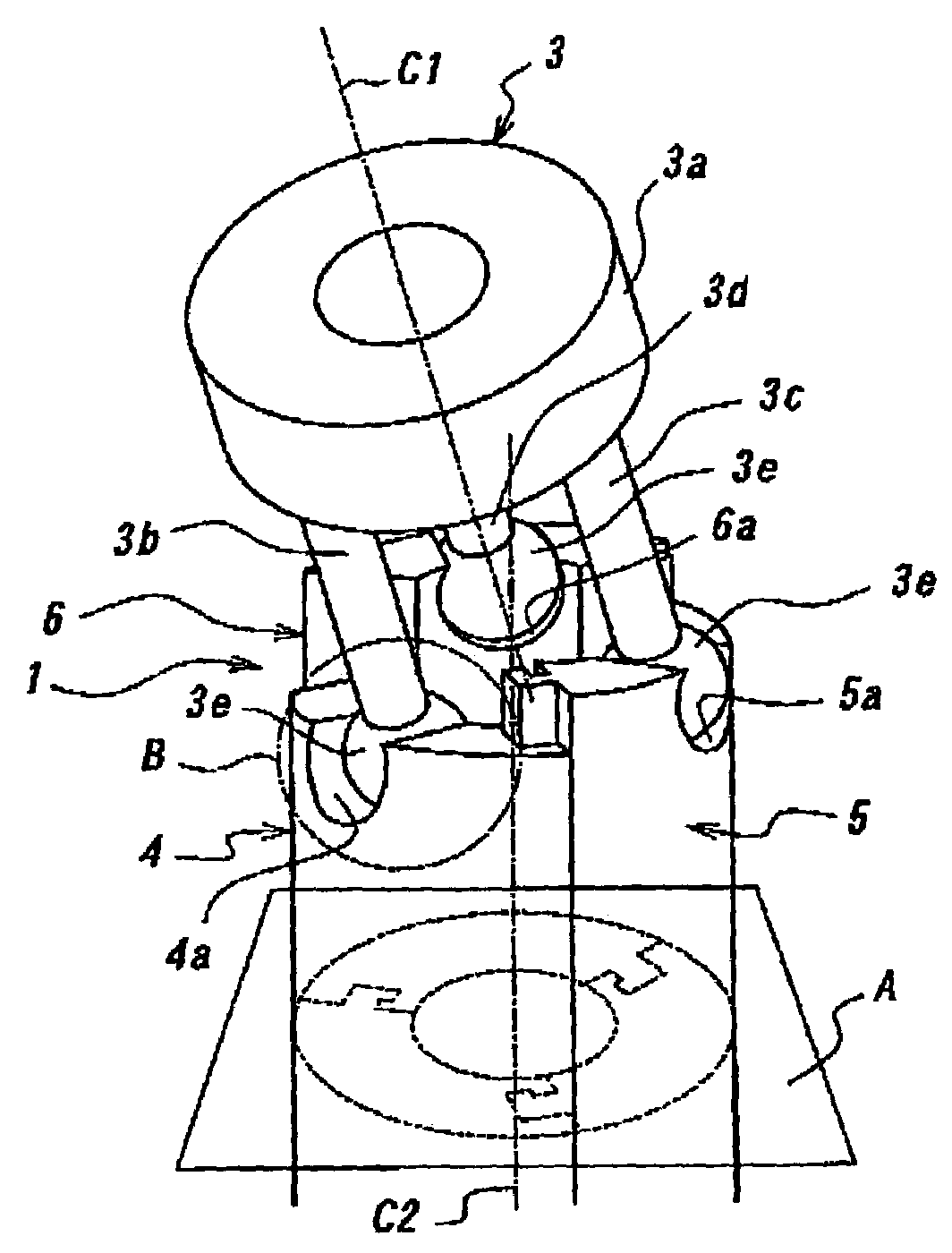
High-rigidity forceps tip assembly for active forceps and active forceps equipped with the same
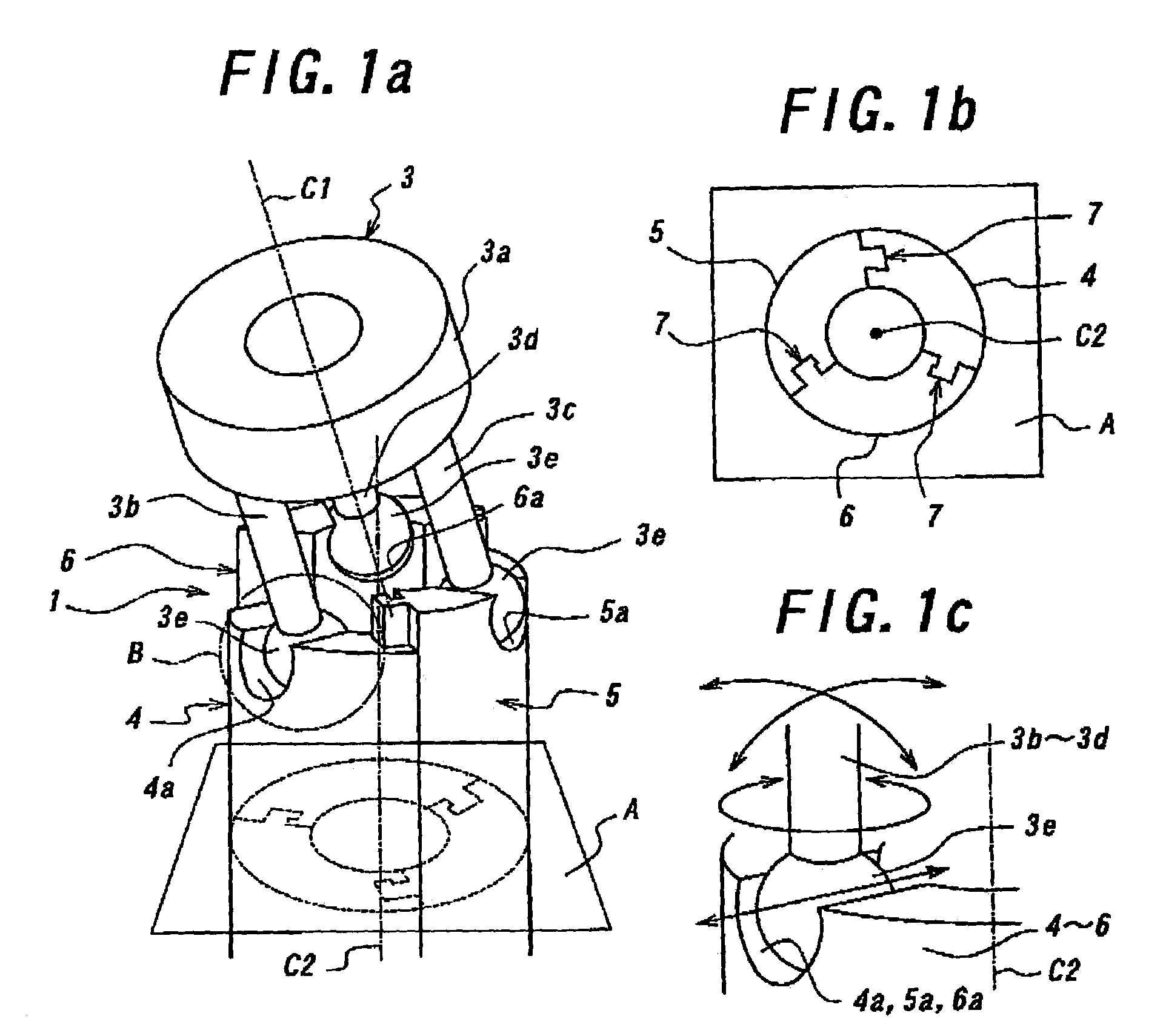
InactiveUS7273488B2Efficiently transmitHigh rigidityMechanical apparatusJointsLaparoscopic surgeryForceps
Provided is a forceps tip assembly capable of supporting a forceps tip with high rigidity in order to realize a laparoscopic surgery requiring a significant power with the forceps tip, such as an organ removal surgery which has been heretofore difficult to be performed by a robot for medical use. The forceps tip assembly includes: a forceps tip supporting member which has a supporting part for supporting a forceps tip and three leg parts which are disposed at even intervals in a circumferential direction around a central axis line C1 and fixed to the supporting part so as to protrude backward from the supporting part; and three back-and-forth moving members which are disposed at even intervals in a circumferential direction around a predetermined central axis line C2 extending in a front-to-rear direction, which have their front end portions coupled with the three leg pads swingably and slidably in a direction orthogonal to the predetermined central axis line C2 and which are mutually coupled together as relatively movable in the extending direction of central axis line C2.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
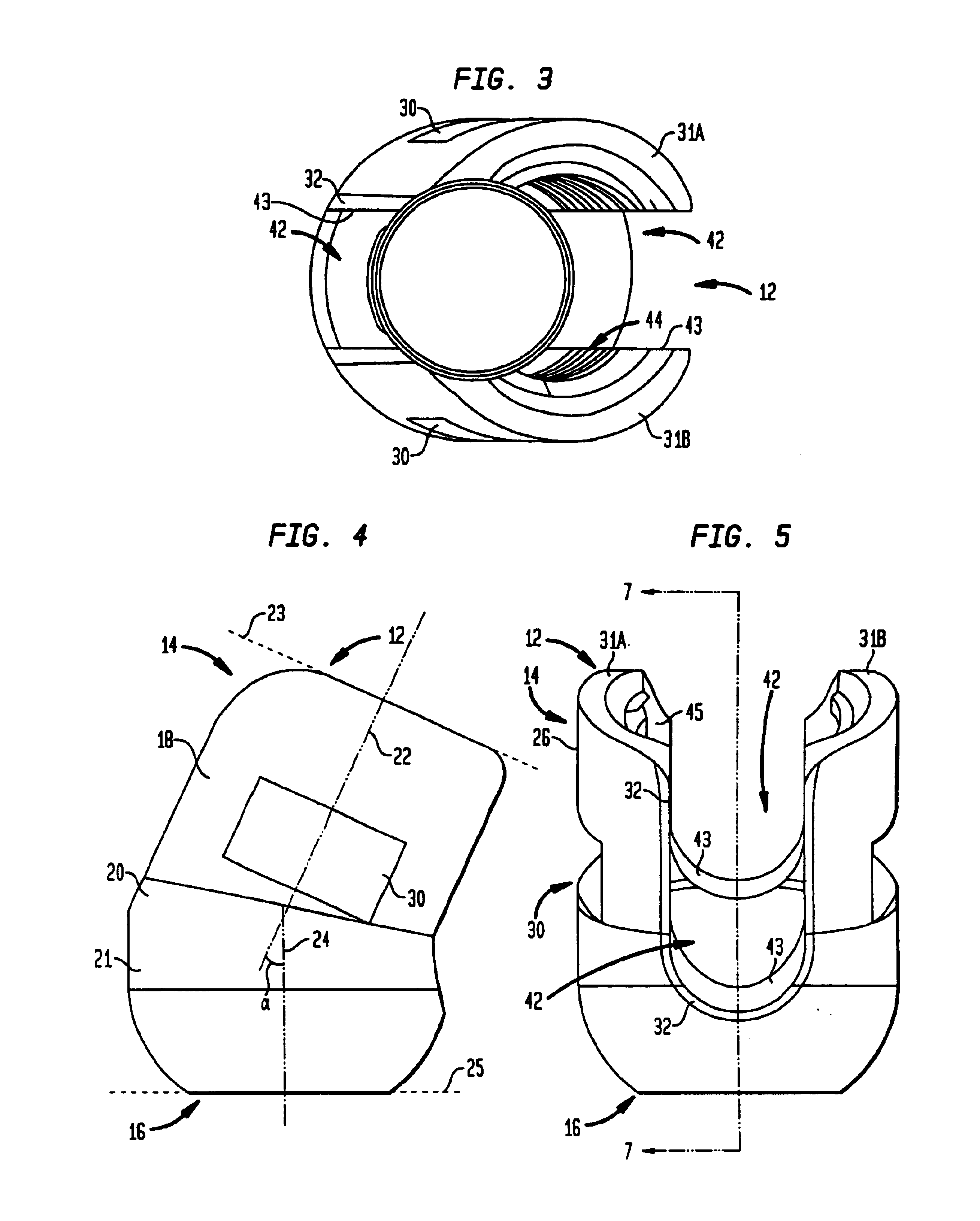
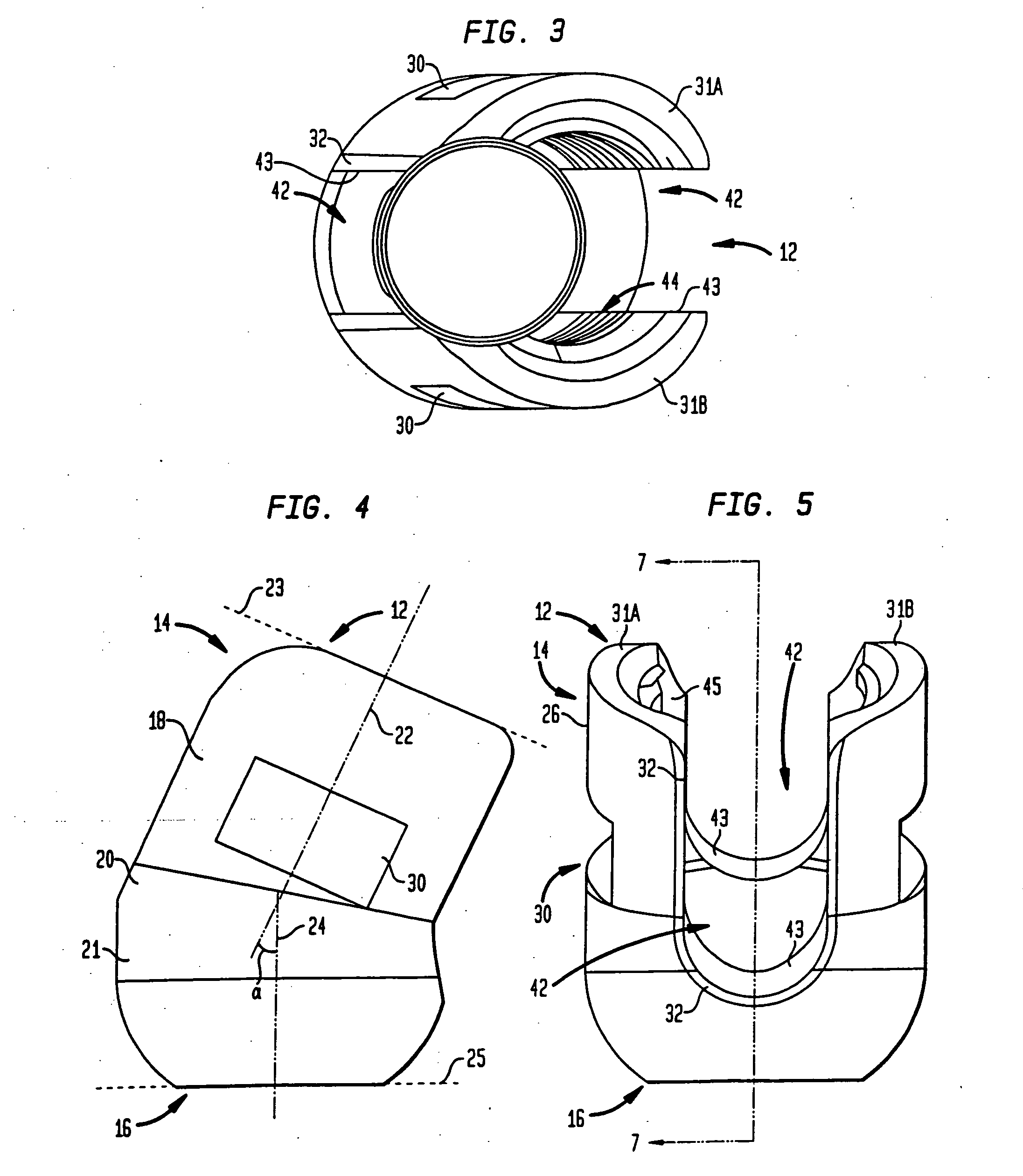
Pedicle screw assembly and methods therefor
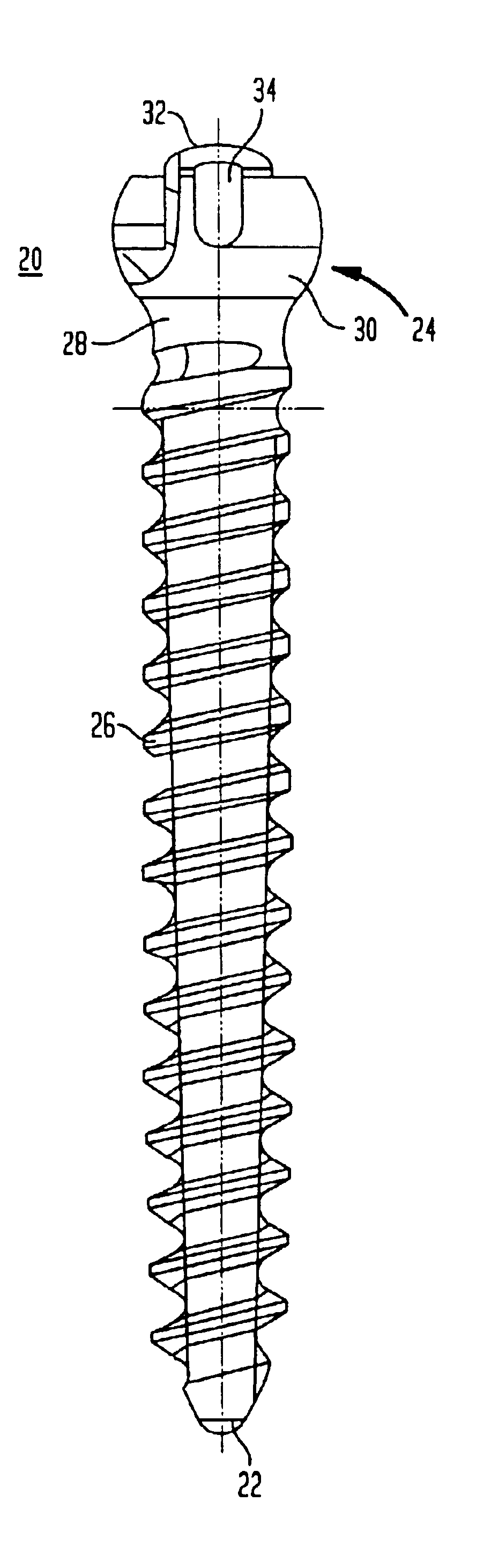
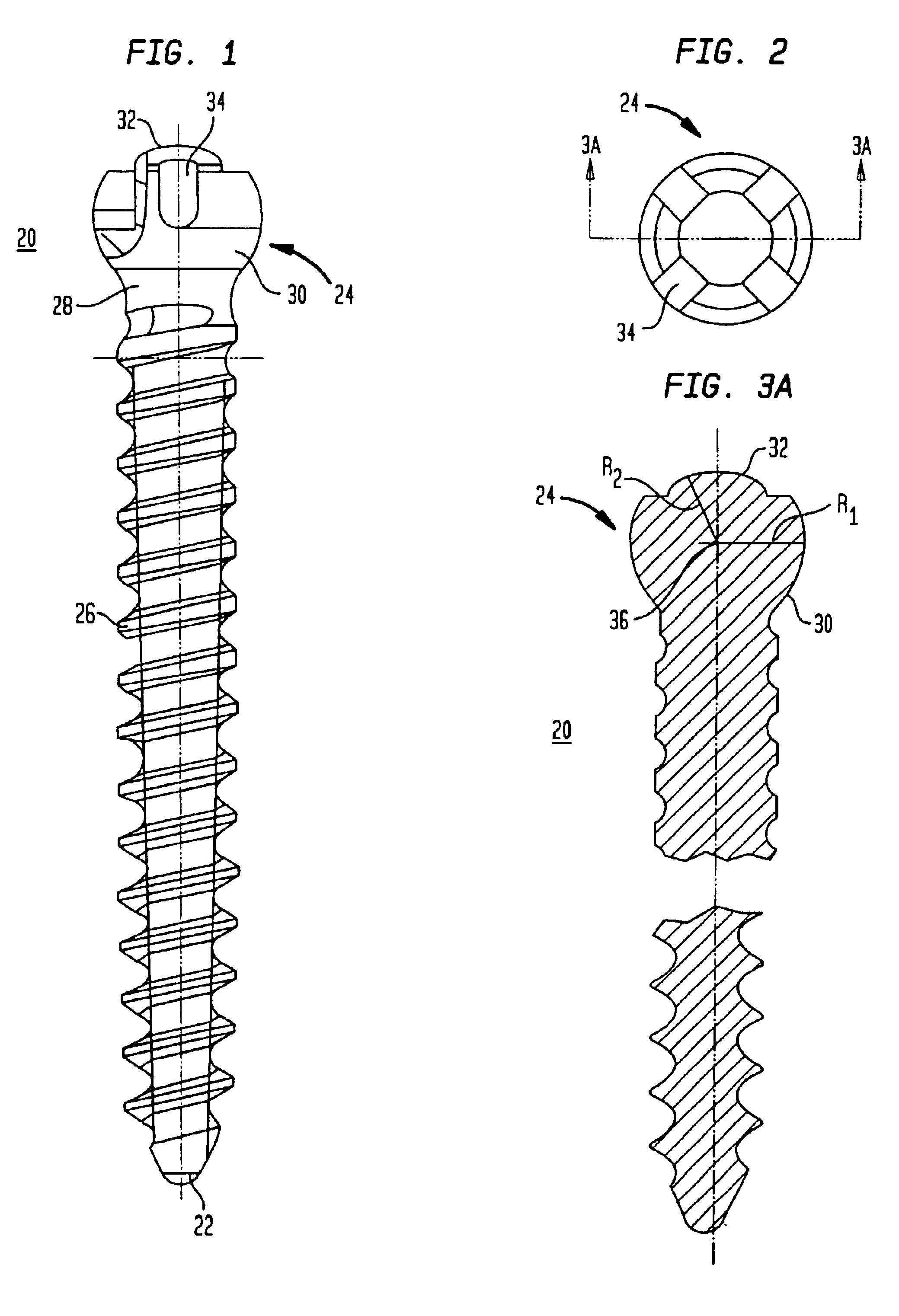
InactiveUS6858030B2Improve compactnessLow profileInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCouplingEngineering
A method for stabilizing a spine includes providing a coupling element having upper and lower ends, a rod receiving opening adapted to receive an elongated stabilizing rod, a bore extending through the lower end and a conical-shaped seat surrounding the bore adjacent the lower end; providing a fastener having upper and lower ends, a head having a radial surface, and at least one anchoring element between the lower end of the fastener and the head; assembling the fastener with the coupling element so that the lower end of the fastener passes through the bore of the coupling element and the radial surface of the head engages the conical-shaped seat. The method also includes anchoring the fastener to bone; moving the coupling element relative to the fastener for capturing the elongated stabilizing rod in the rod receiving opening; and urging the captured stabilizing rod toward the head of the fastener so that the rod contacts the head and forces the radial surface of the head against the conical-shaped seat of the coupling element for locking the coupling element from further movement relative to the fastener.
Owner:STRYKER SPINE
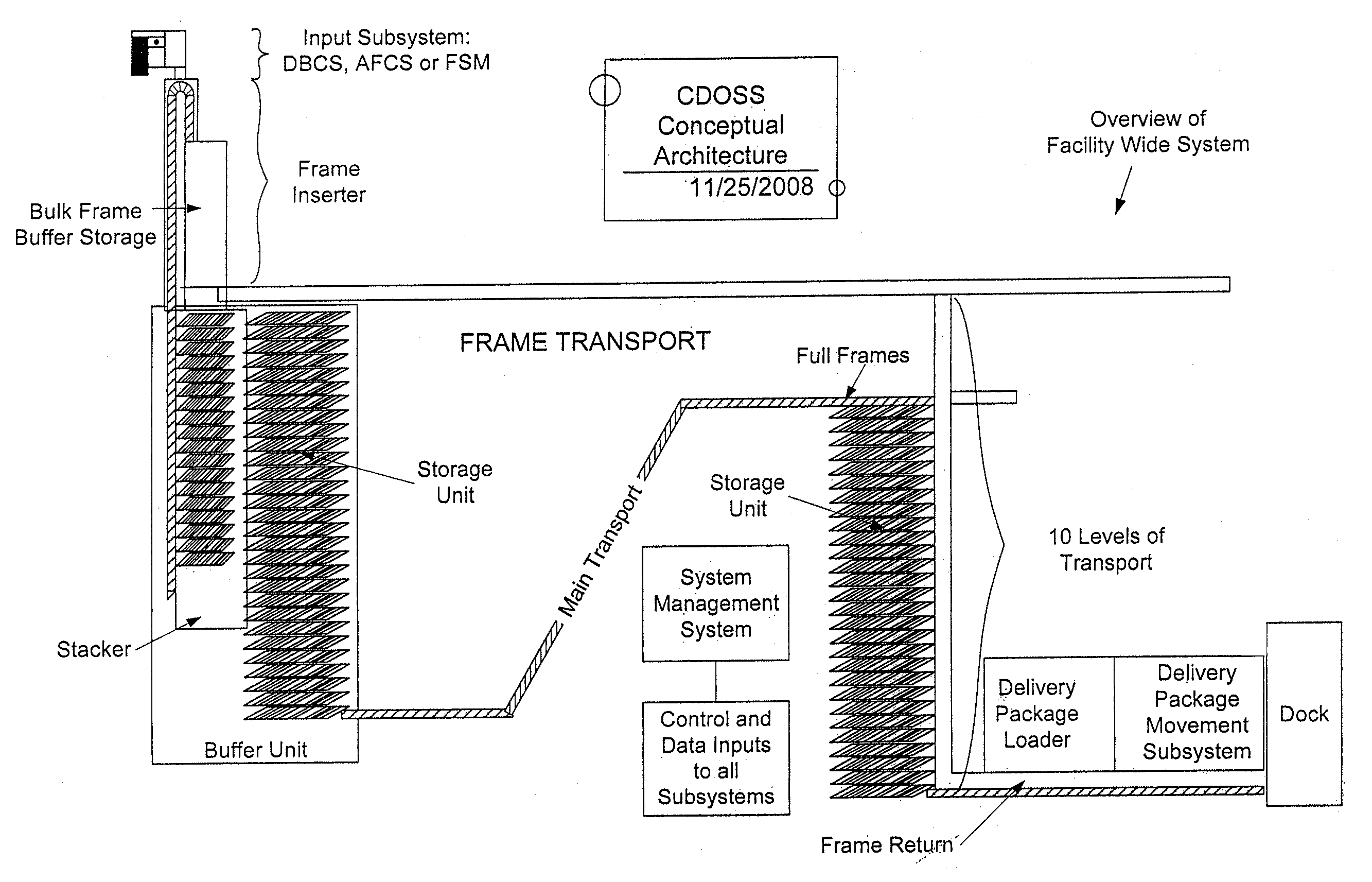
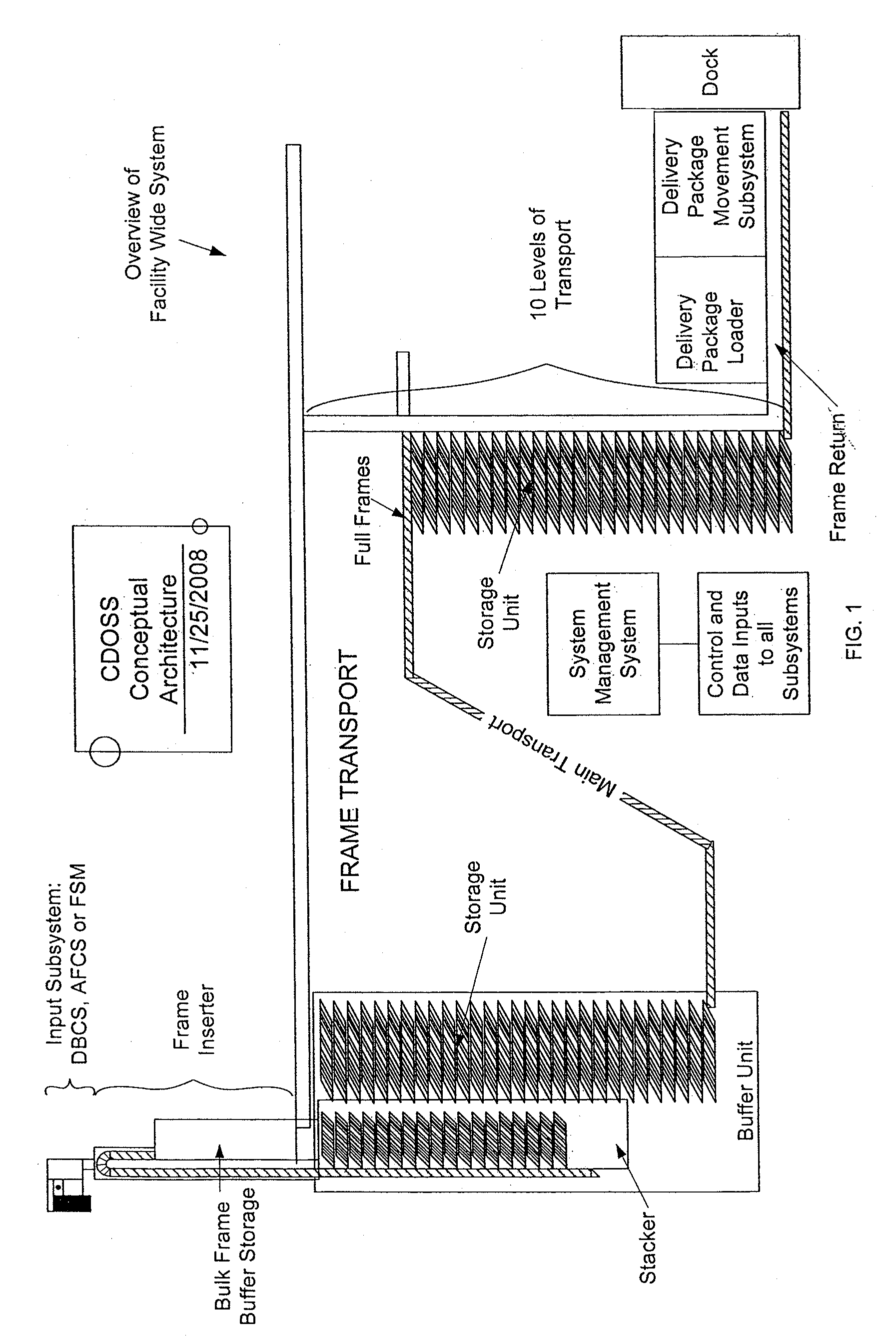
Facility Wide Mixed Mail Sorting and/or Sequencing System and Components and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110046775A1Reduce network congestionWidth minimizedConveyorsData processing applicationsEngineeringProduct processing
The invention generally relates to a facility wide sorting and / or sequencing system for improving product processing operations and, more particularly, to a facility wide system and related functionality for simultaneously sorting and sequencing mixed mail pieces such as, for example, flats and letter mail pieces. The flats and letter mail pieces are placed in frames so that all types of mail pieces can be sorted and / or sequenced simultaneously through merging and diverting a stream of filled trays into and out of different streams at a full or substantially full transport speed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method of forming a pattern in a semiconductor device and method of forming a gate using the same
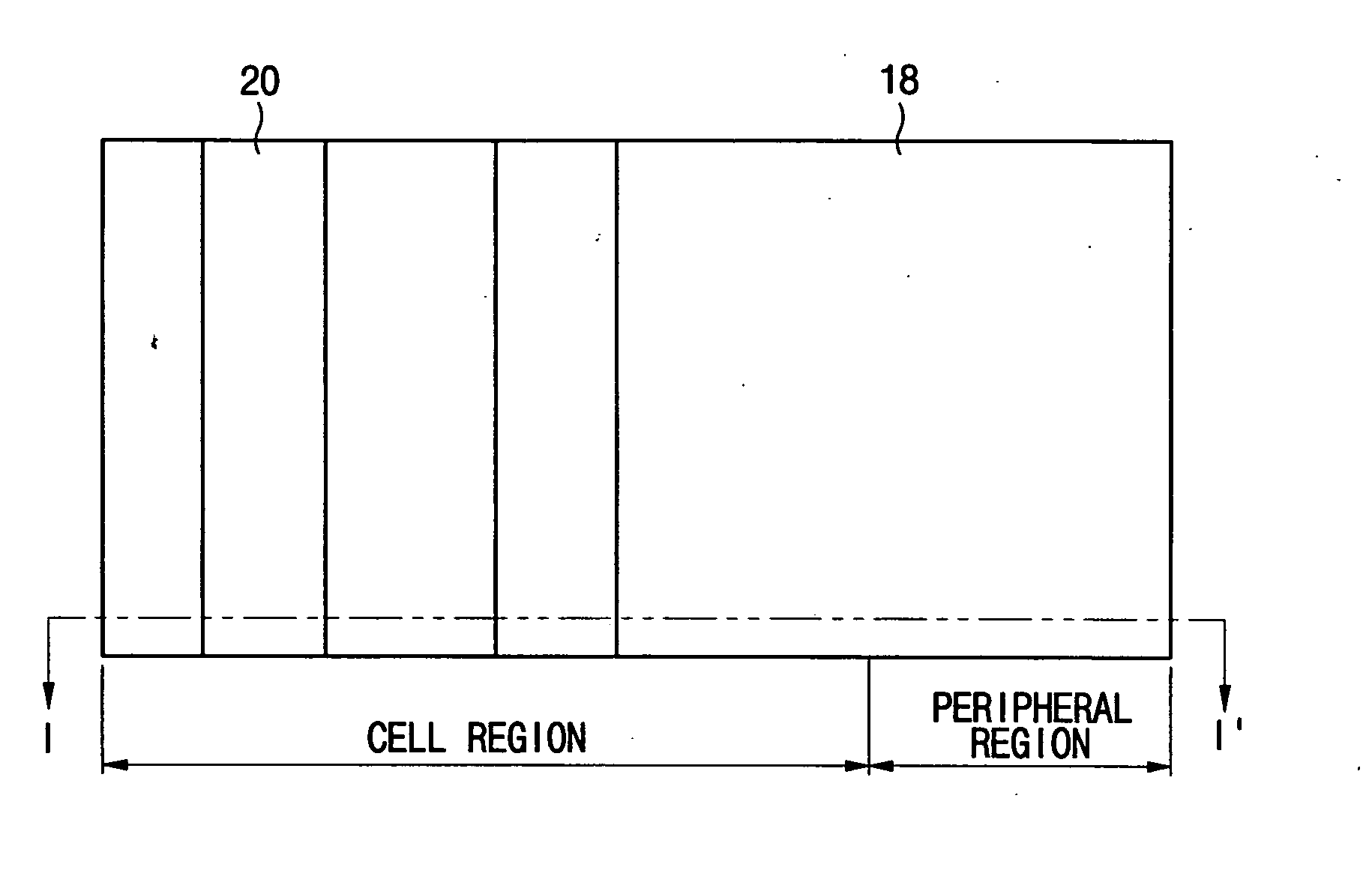
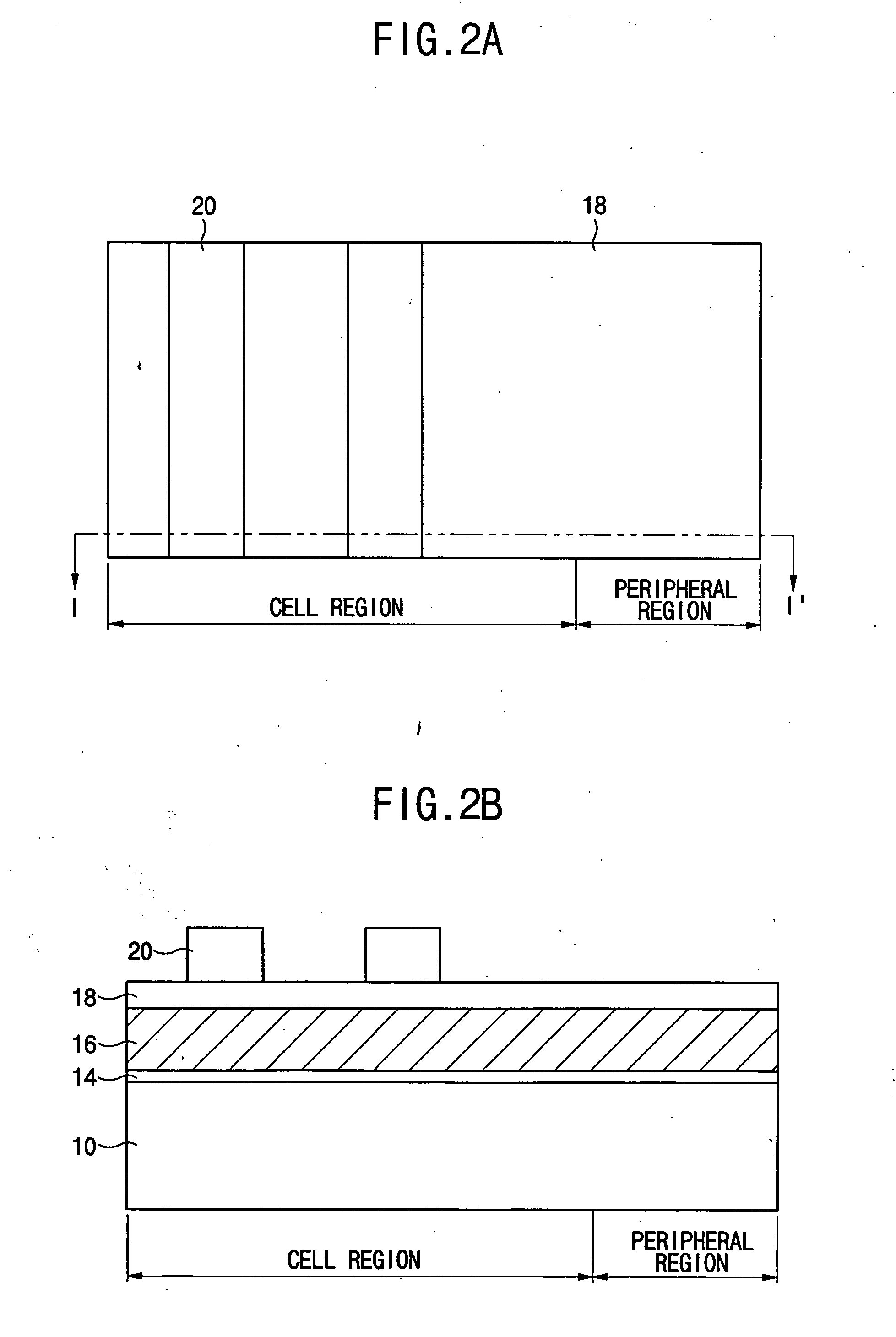
InactiveUS20050142497A1Small line widthLine width variationPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialCell region
A method of forming a pattern in a semiconductor device is described. A substrate divided into cell and peripheral regions is provided, and an object layer is formed on a substrate. A buffer pattern is formed on the object layer in the cell region along a first direction. A spacer is formed along a sidewall of the buffer pattern in the cell region, and a hard mask layer remains on the object layer in the peripheral region. The buffer layer is removed, and the spacer is separated along a second direction different from the first direction, thereby forming a cell hard mask pattern. A peripheral hard mask pattern is formed in the peripheral region. A minute pattern is formed using the cell and peripheral hard mask patterns in the substrate. Therefore, a line width variation or an edge line roughness due to the photolithography process is minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for a folded optical element waveguide for use with light based touch screens
InactiveUS20060001653A1Minimum widthWidth minimizedCathode-ray tube indicatorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesDisplay deviceWaveguide
A folded optical element waveguide that allows a minimum width bezel to be used around the perimeter of a light-based touch screen display. The apparatus and method includes a touch screen and a waveguide substrate provided adjacent the touch screen. The waveguide substrate includes a plurality of waveguides and a plurality of optical elements provided adjacent the touch screen. The waveguides include an internally reflective surface to reflect light perpendicular to the surface of the touch screen. The emitting and detecting waveguides are thus folded and provided around the side edges of the display. As a result, the width of the bezel around the display can be minimized.
Owner:POA SANA LIQUIDATING TRUST
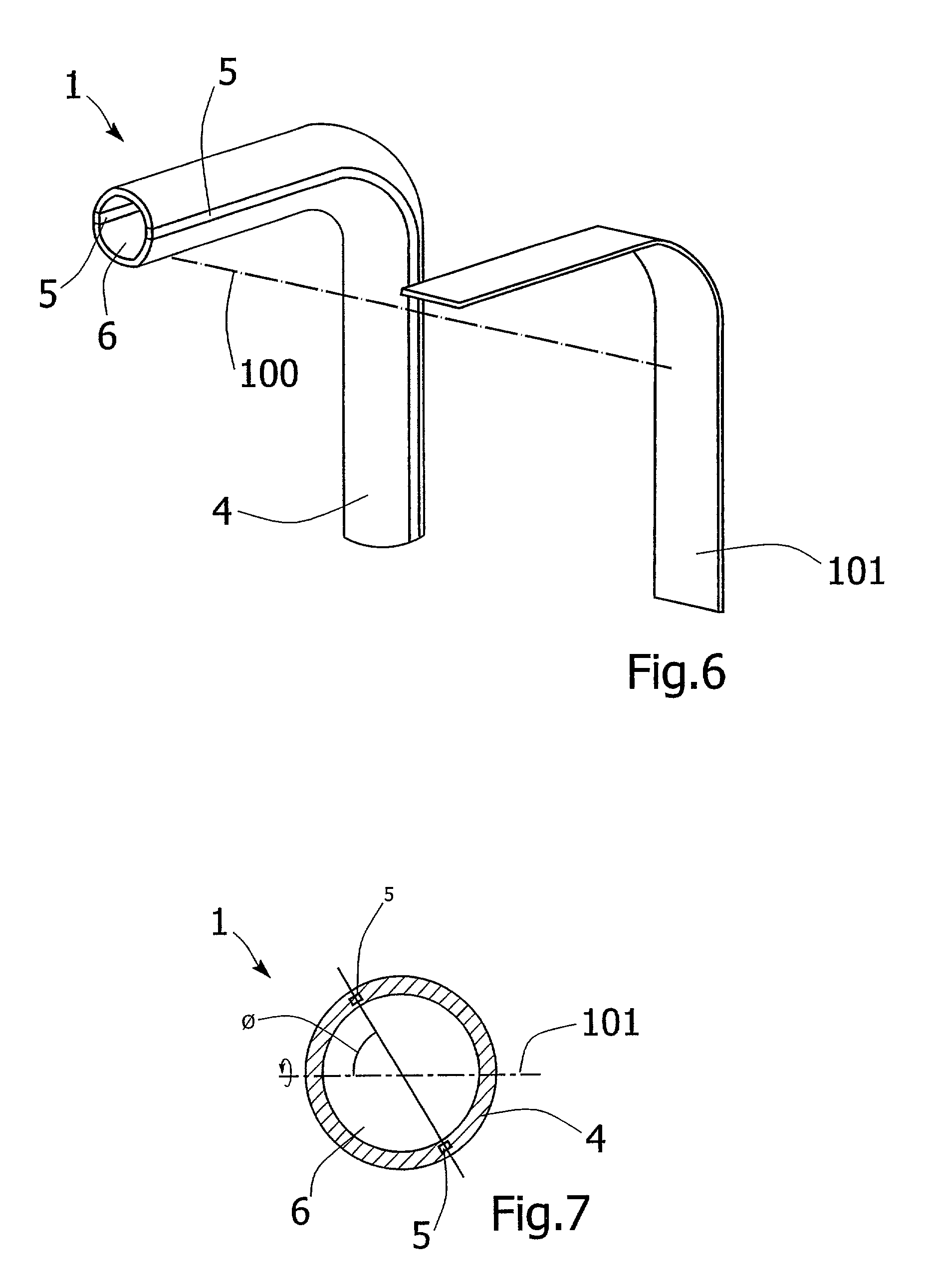
Catheter
InactiveUS7018372B2Maintaining trackabilityDrag minimizationCatheterIntravenous devicesCatheter device
A catheter 1 suitable for advancement through a body passageway of a patient. The catheter 1 comprises a catheter body 4 which is flexible to provide the necessary trackability for the catheter 1 to advance through a body passageway, and two stainless steel reinforcement wires 5 extending along the catheter body 4 which provide the necessary pushability to advance the catheter 1 through the passageway. The reinforcements 5 are positioned diametrically opposed to one another by approximately 180 degrees on opposite sides of the longitudinal axis of the catheter 1, and the catheter body 4 is relatively soft and twistable. This configuration enables the entire catheter 1 to spontaneously twist during advancement so that the reinforcements 5 orientate themselves along a plane of neutral bending during advancement of the catheter 1. In this way, any resistance to the trackability of the catheter 1 due to the stiff reinforcements 5 is minimized.
Owner:SALVIAC +1
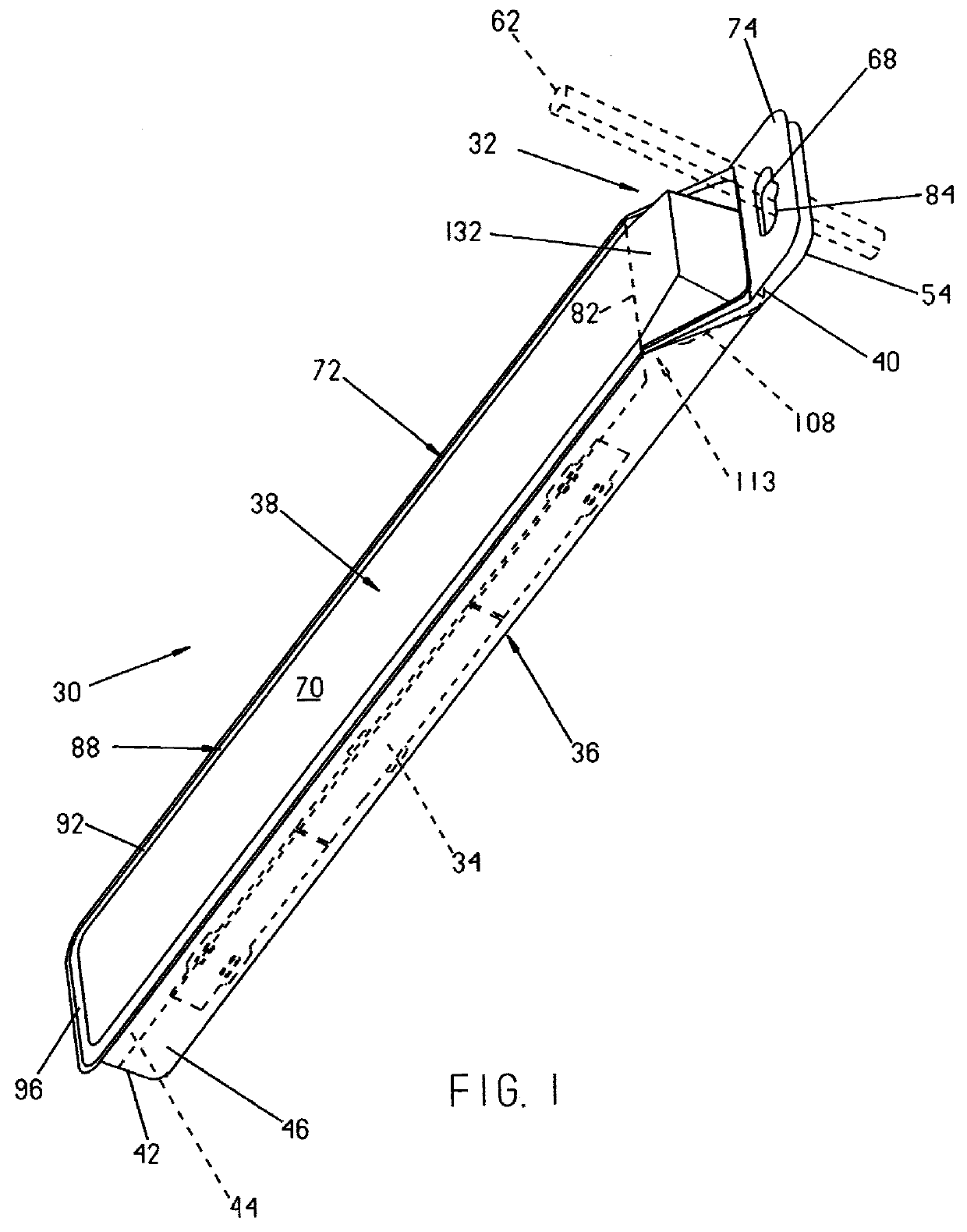
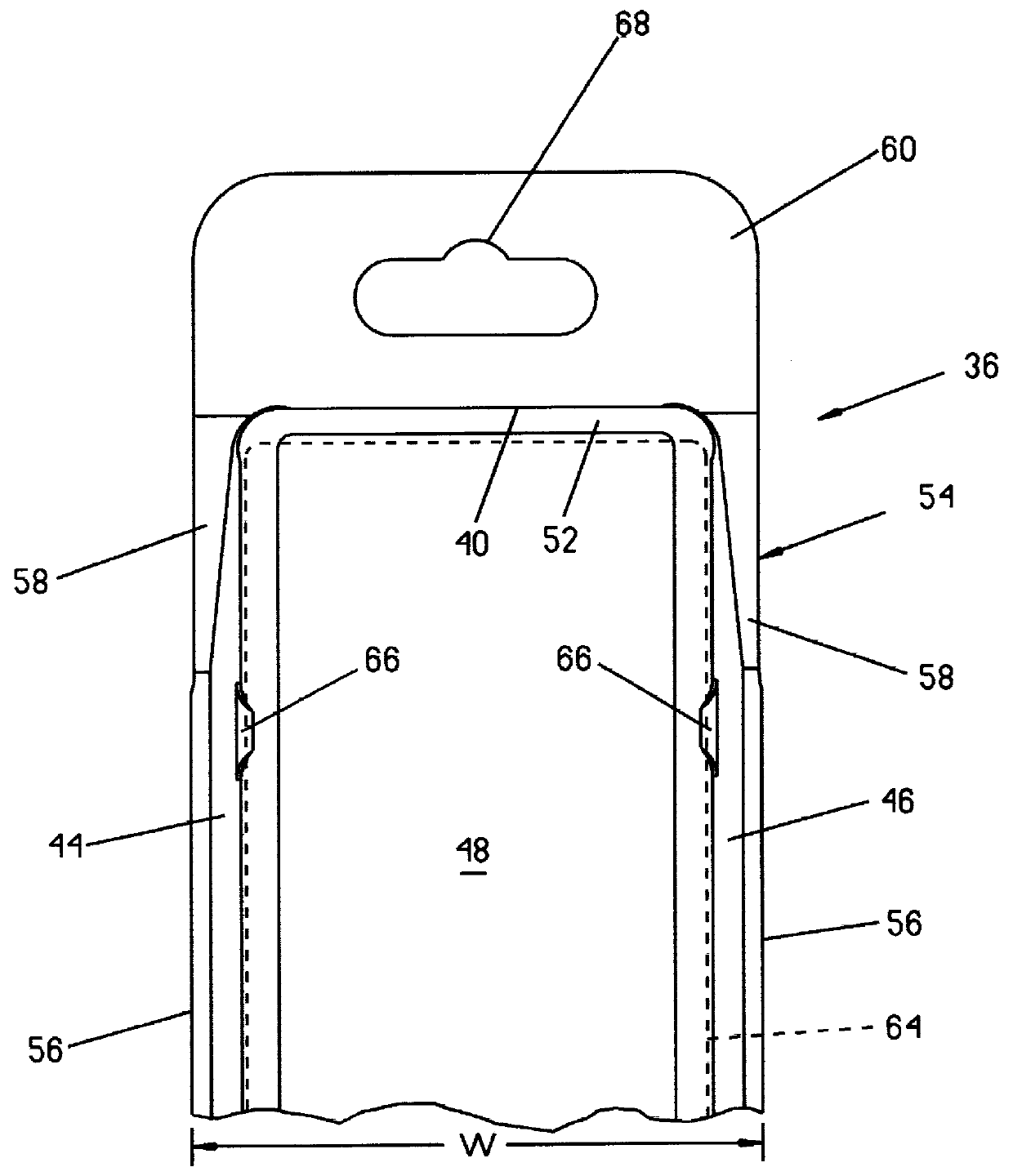
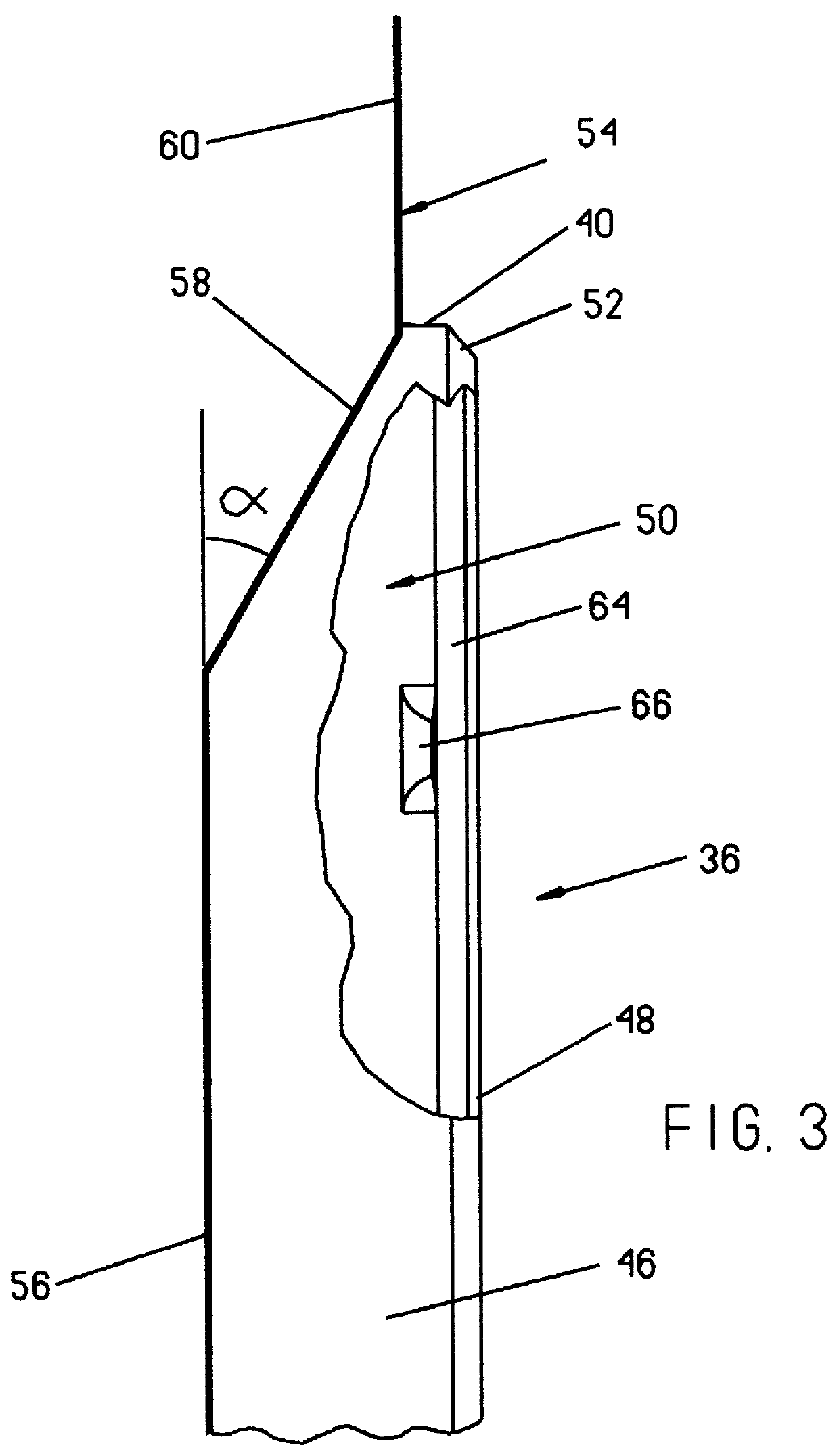
Reclosable package and method
InactiveUS6070723AWidth minimizedMaximizing usable package volumePackaging vehiclesContainers for machinesEngineeringBlisters
A reclosable package and method having an integral reclosable door adjacent one end that permits article removal from the end of the package. The package is comprised of a thermoformed blister body joined to a thermoformed backing body. The blister body has sidewalls, endwalls and a peripheral flange broken into a first section adjacent the door where the height of the sidewalls decrease and a second section opposite the door with the first section angled relative to the second section. The backing body carries the door and has an integral peripheral rib inboard of a peripheral flange with the flange having a first section about the door and a second section disposed away from the door. The rib has a pair of longitudinally-extending sections divided by a notch that preferably is a transverse rib that causes the door to bend about a desired fold line that runs generally through or adjacent the ribs or notches when urged away from a closed position. In a preferred method, after performing a multilevel trim operation to trim the multiplanar flanges of one or both the blister body and the backing body, the two bodies are joined at the flange sections about a portion of the periphery to adjacent the fold line using an energy welding process, preferably RF welding, that produces a narrow tear seam that enables finished package flange width to be minimized to thereby also minimize package width.
Owner:PORTAGE PLASTICS
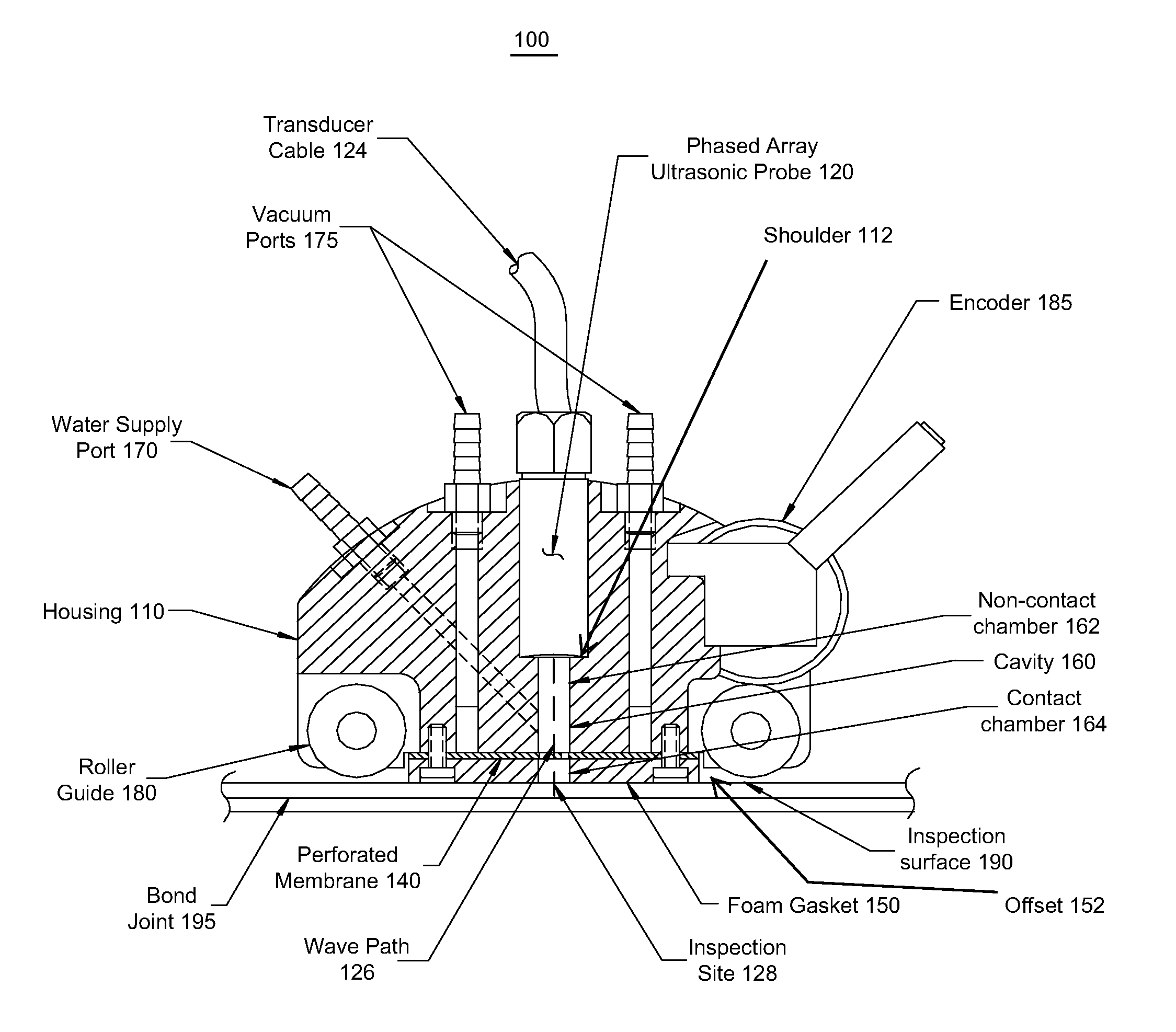
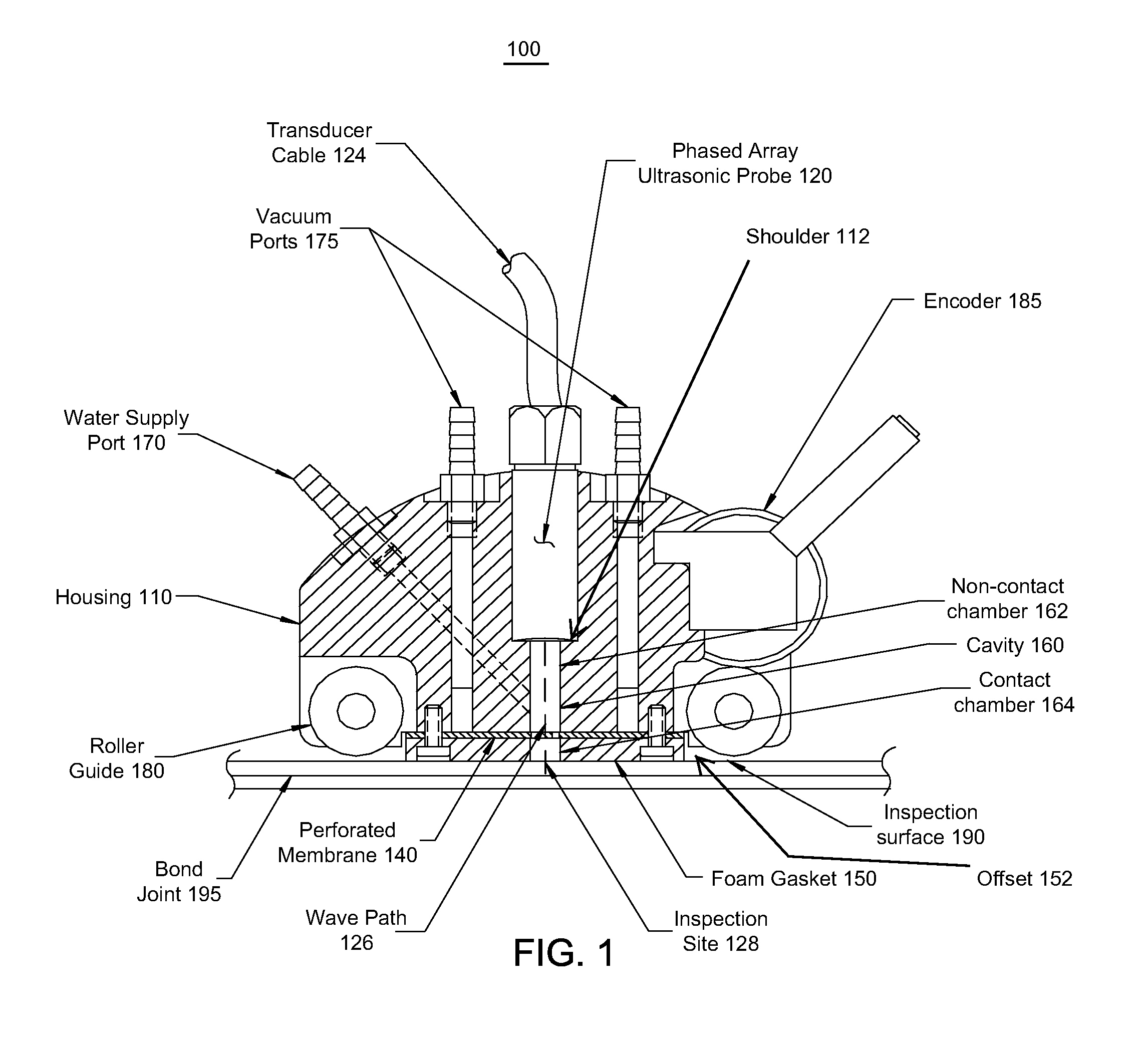
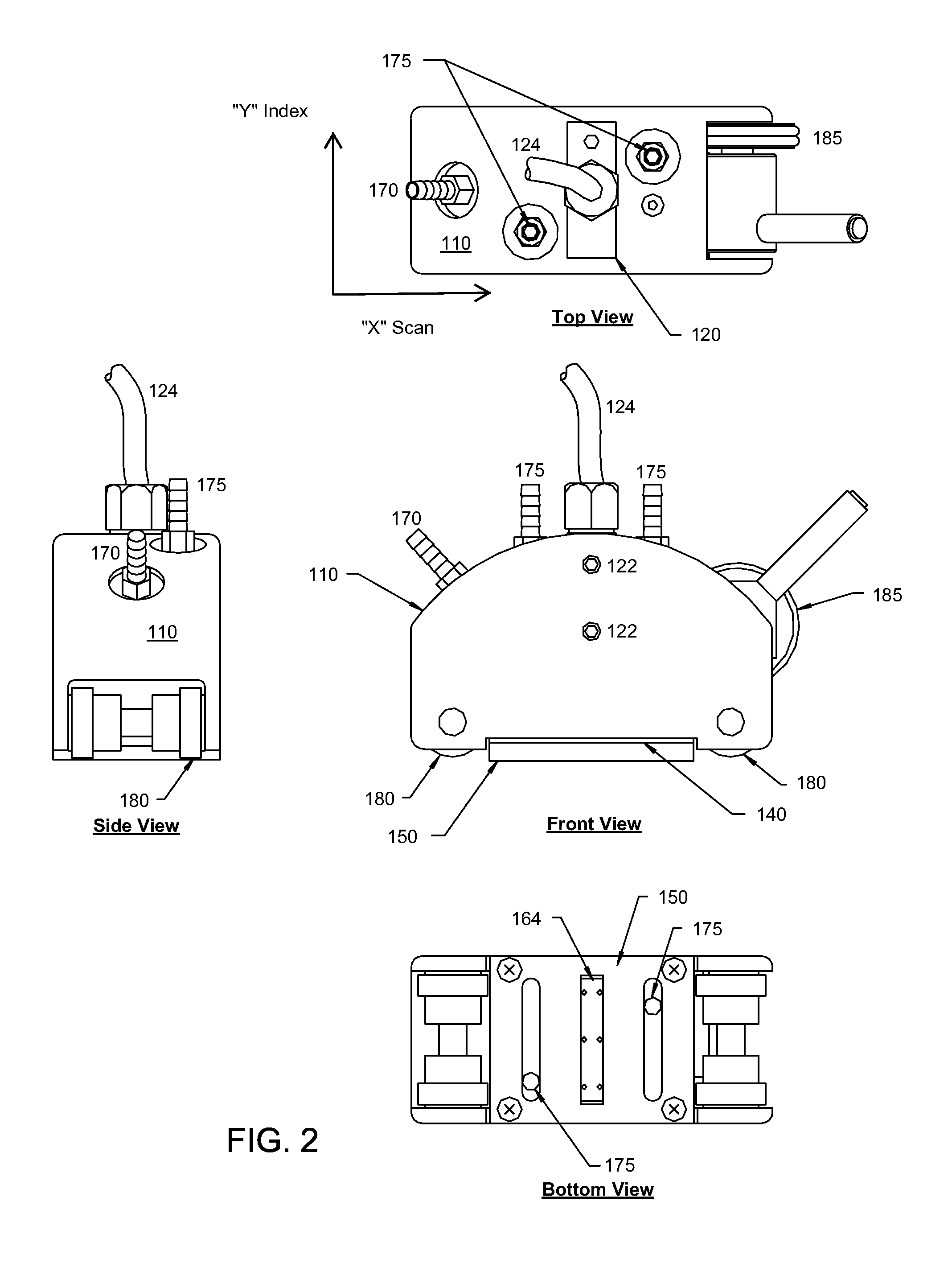
Ultrasonic probe deployment device for increased wave transmission and rapid area scan inspections
ActiveUS8087298B1Maximize effectivenessOvercome limitationsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEngineeringUltrasonic transmission
An ultrasonic probe deployment device in which an ultrasound-transmitting liquid forms the portion of the ultrasonic wave path in contact with the surface being inspected (i.e., the inspection surface). A seal constrains flow of the liquid, for example preventing the liquid from surging out and flooding the inspection surface. The seal is not rigid and conforms to variations in the shape and unevenness of the inspection surface, thus forming a seal (although possibly a leaky seal) around the liquid. The probe preferably is held in place to produce optimum ultrasonic focus on the area of interest. Use of encoders can facilitate the production of C-scan area maps of the material being inspected.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Robotic cart pulling vehicle
ActiveUS20050029029A1Minimize contact patch widthMinimize variationAutomatic initiationsNon-deflectable wheel steeringCartLow load
A robotic cart pulling vehicle includes a positioning error reducing system for reducing accumulated error in the ded-reckoning navigational system. The positioning error reducing system including at least one of a low load transfer point of the cart attaching mechanism, a floor variation compliance structure whereby the drive wheels maintain a substantially even distribution of load over minor surface variations, a minimal wheel contact surface structure, a calibration structure using at least one proximity sensor mounted on the robot body, and a common electrical and mechanical connection between the cart and the robot vehicle formed by a cart attaching post.
Owner:ST ENG AETHON INC
Display apparatus and tiled display apparatus
ActiveUS20170148374A1Satisfactory qualitySpace be limitedCathode-ray tube indicatorsPrinted circuit manufactureEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A display apparatus includes a display panel, a display panel driver and a first connection wire. The display panel includes a substrate and a display layer disposed on a first surface of the substrate. The display panel driver applies a driving signal to the display panel. The display panel driver is disposed on a second surface opposite to the first surface of the substrate. The first connection wire is disposed at a first side surface connecting the first and second surfaces of the substrate. The first connection wire connects electrically the display panel with the display panel driver.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
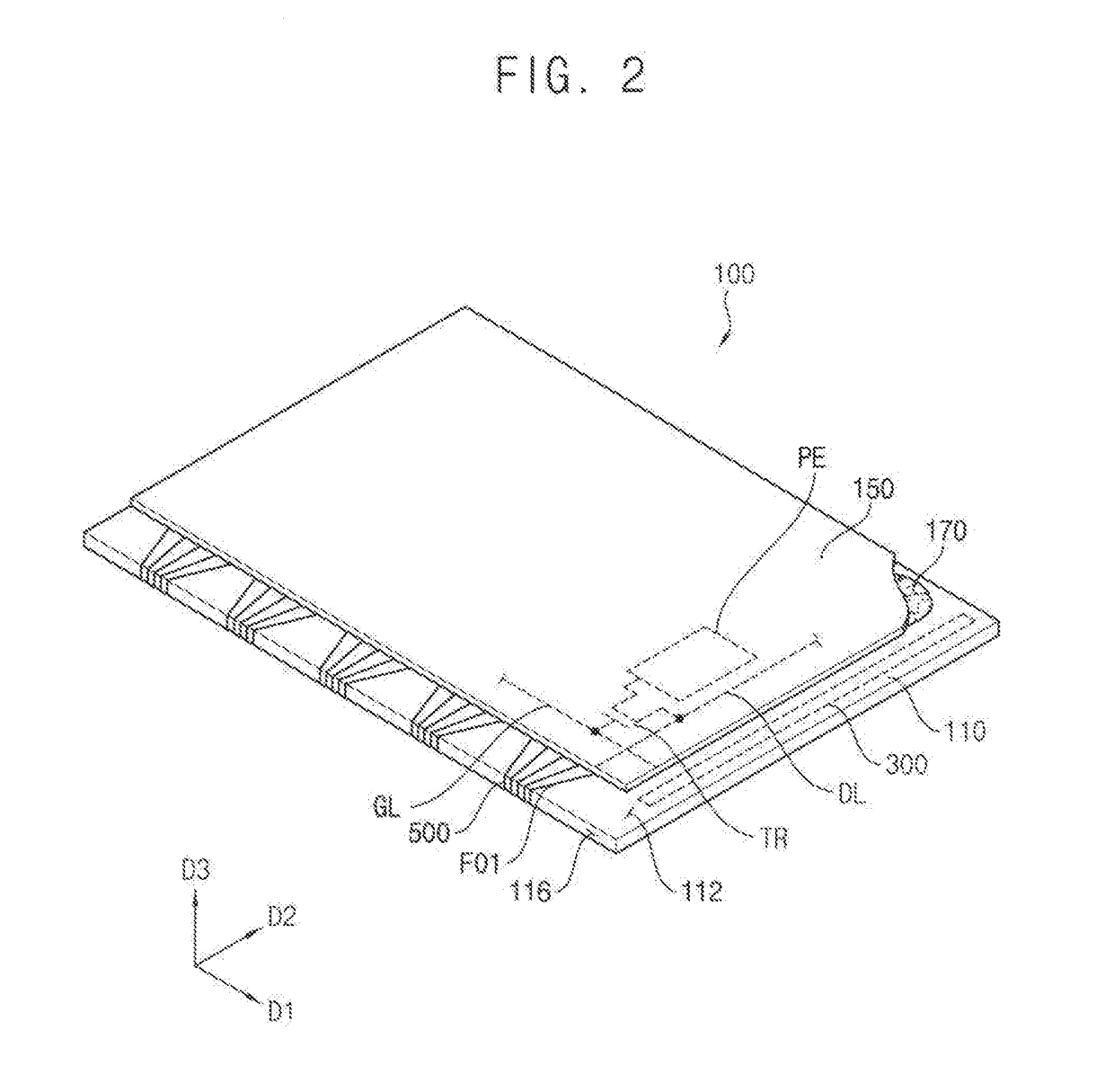
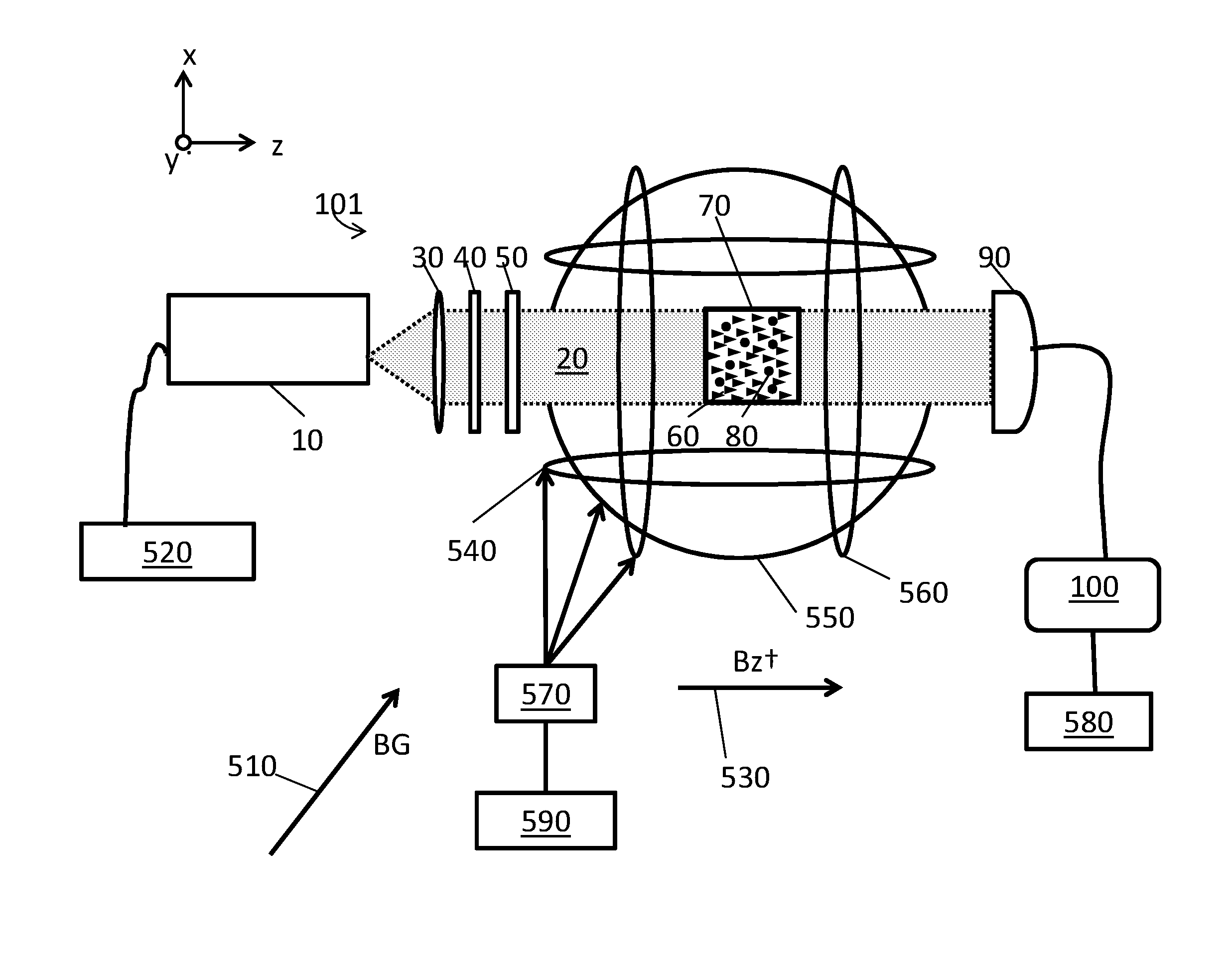
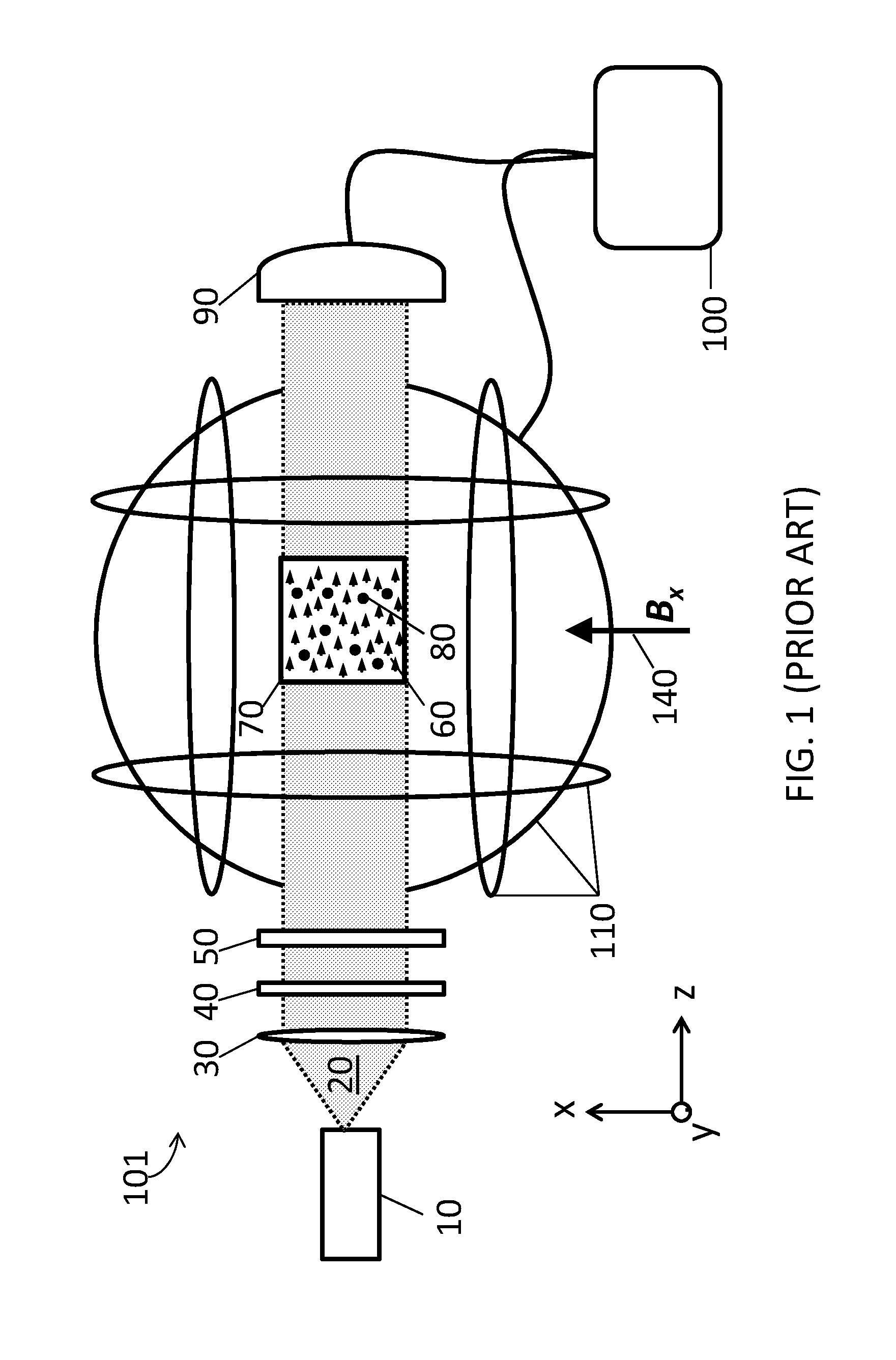
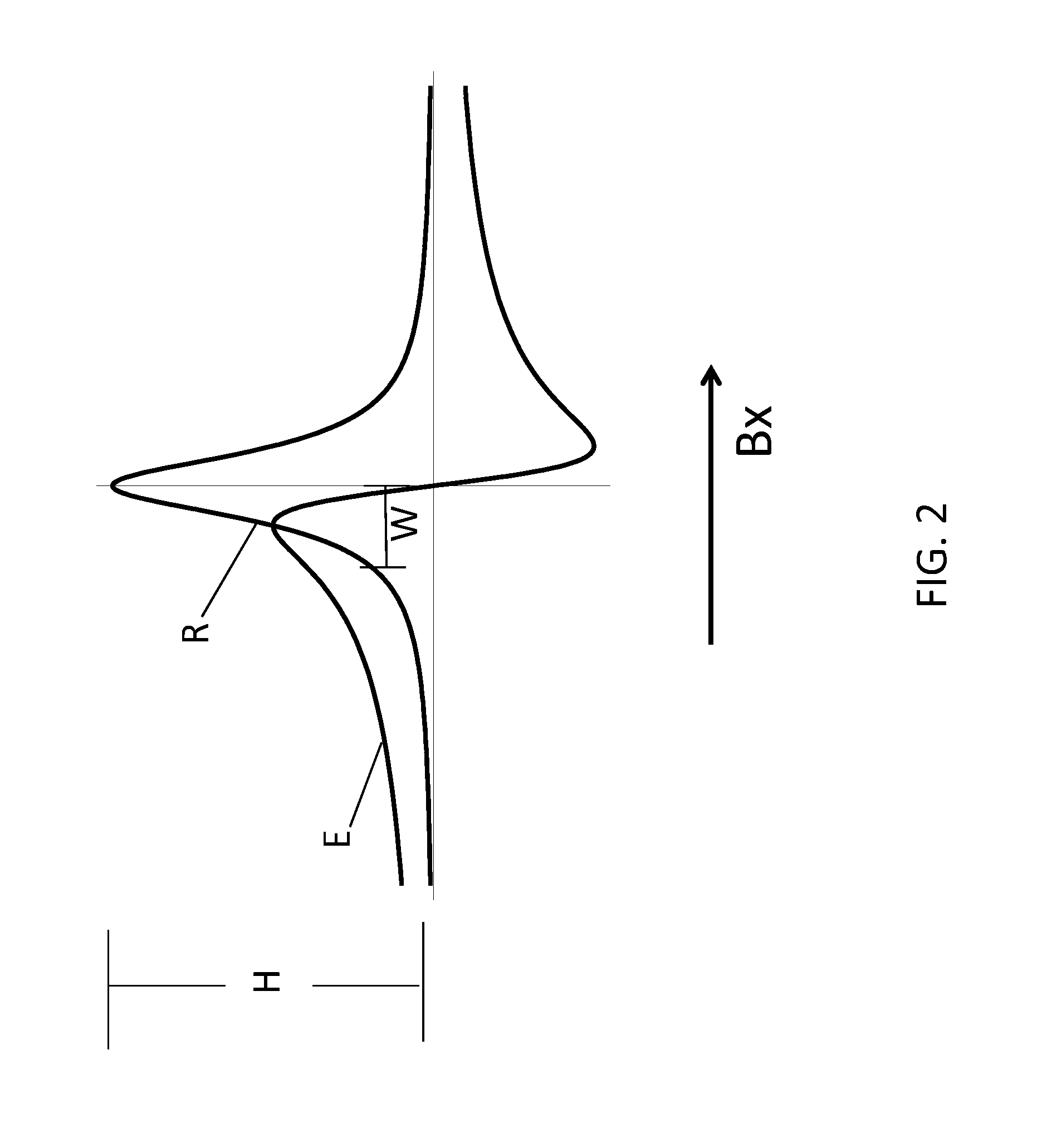
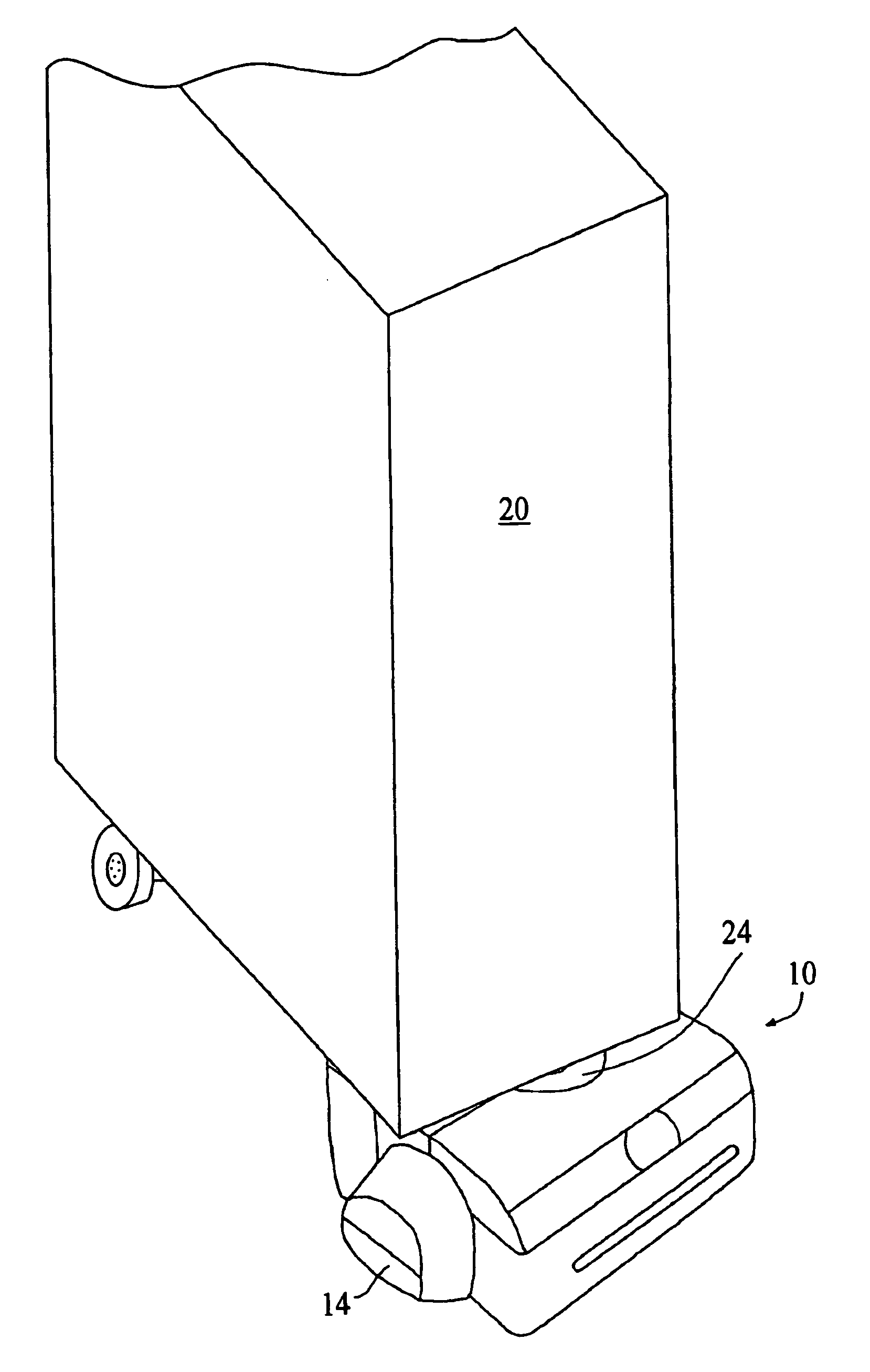
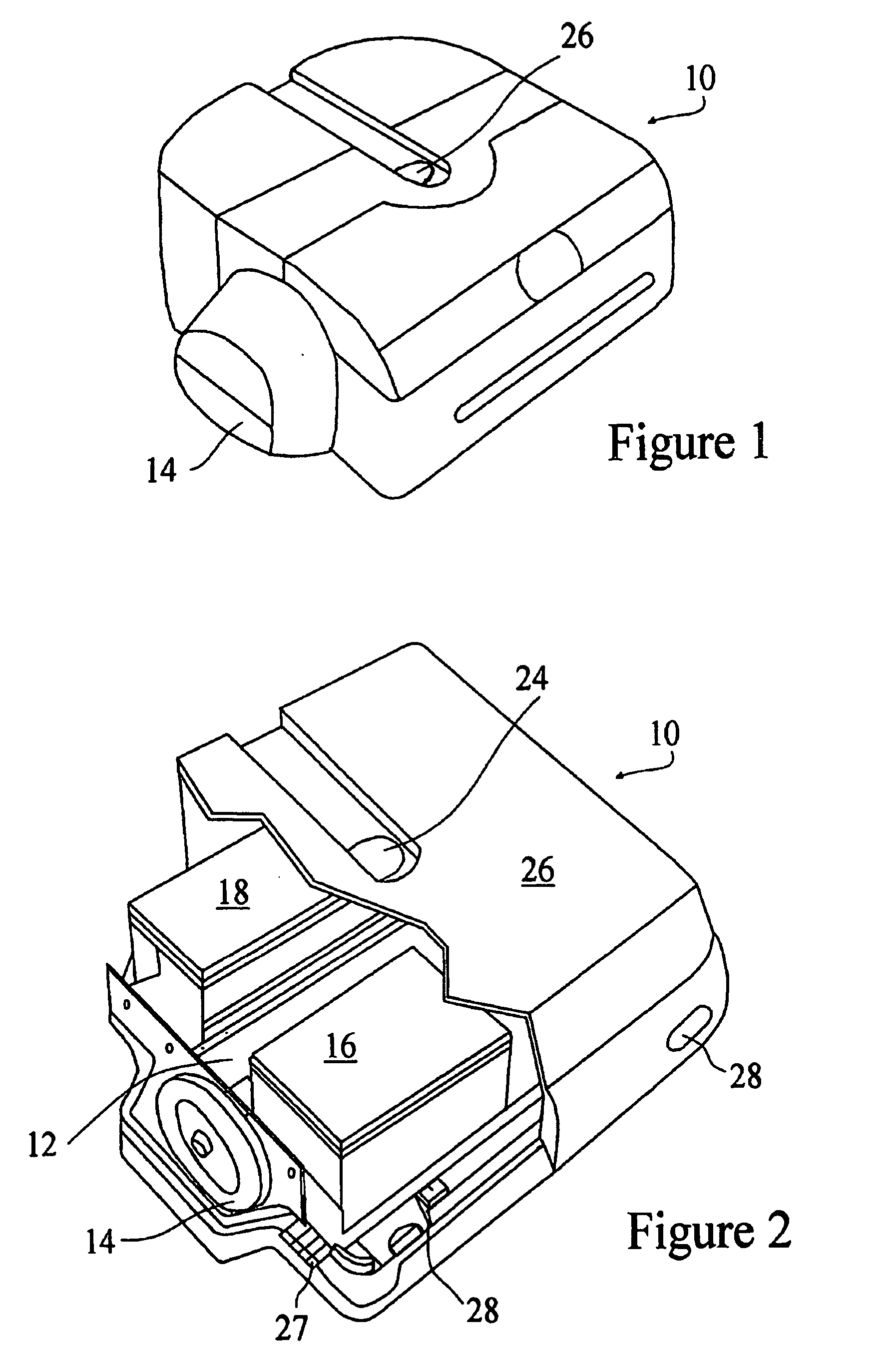
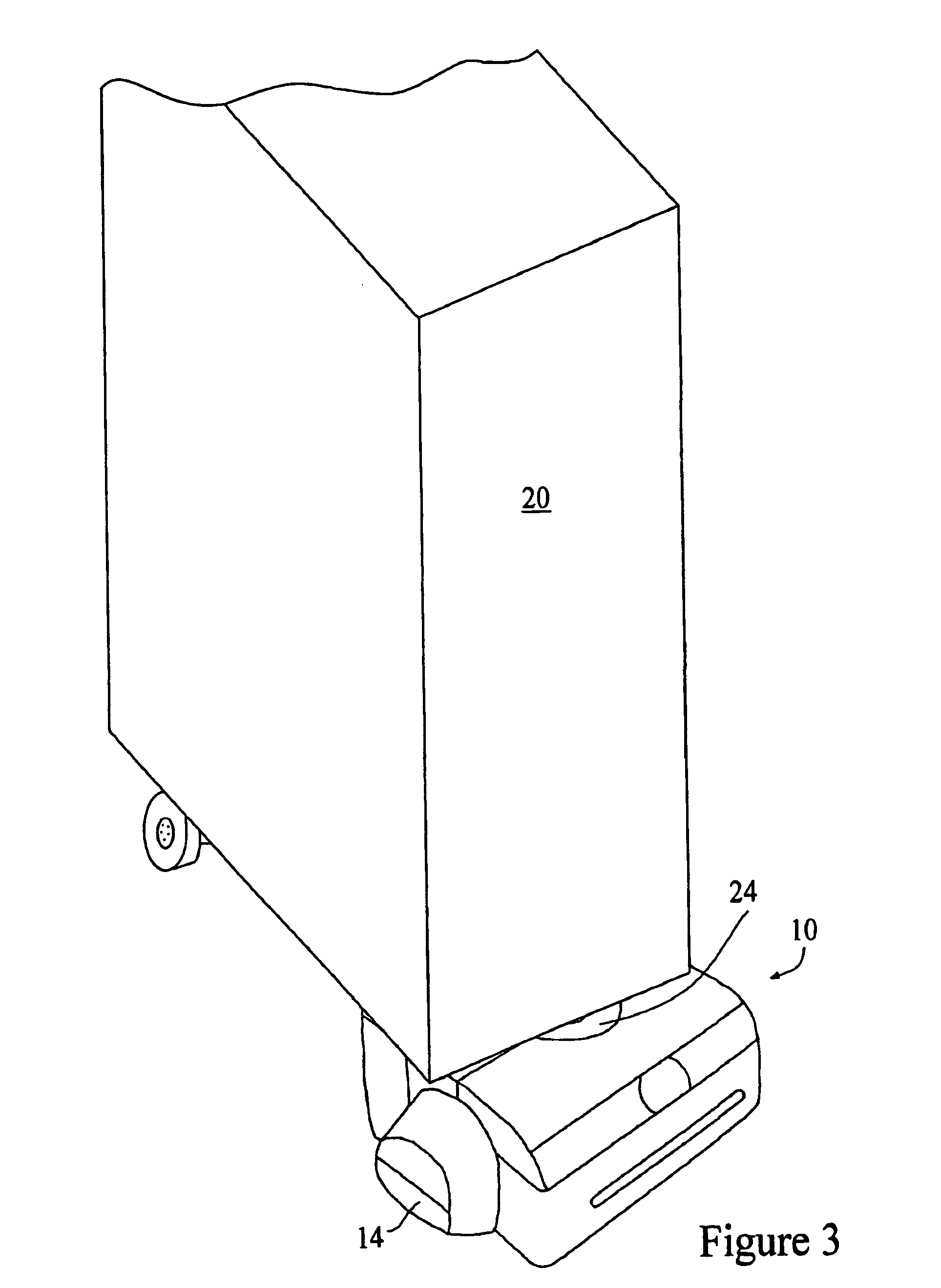
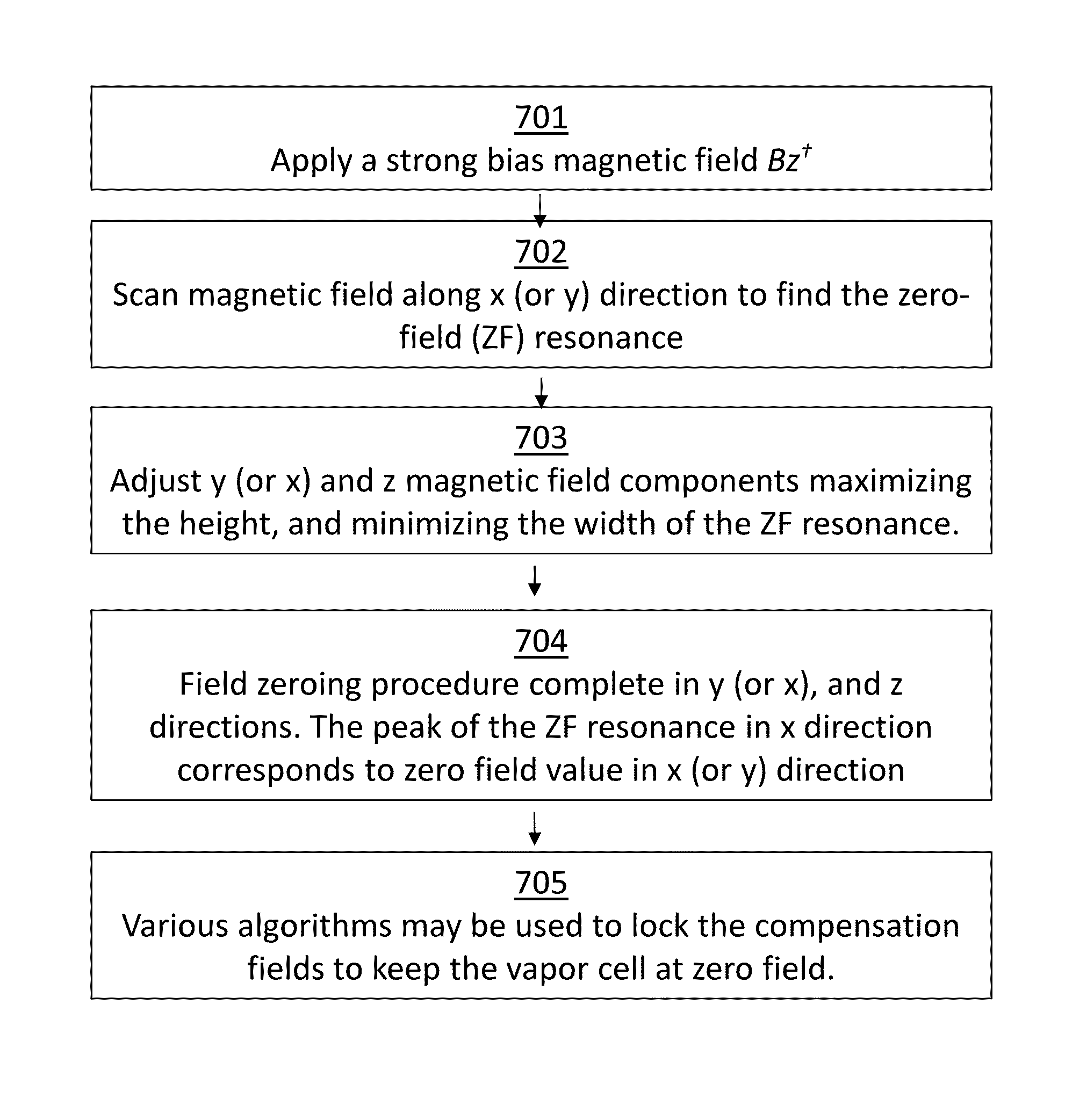
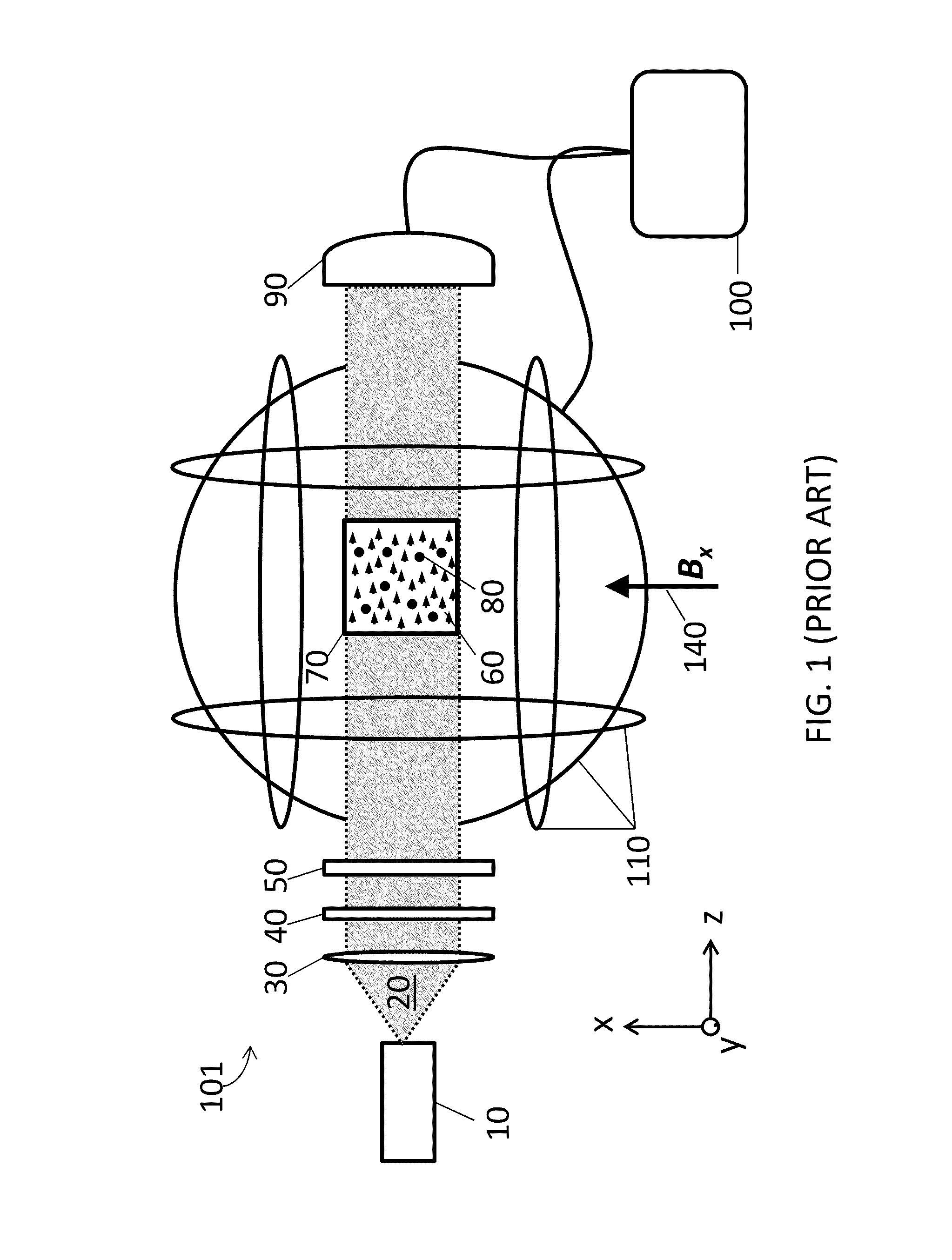
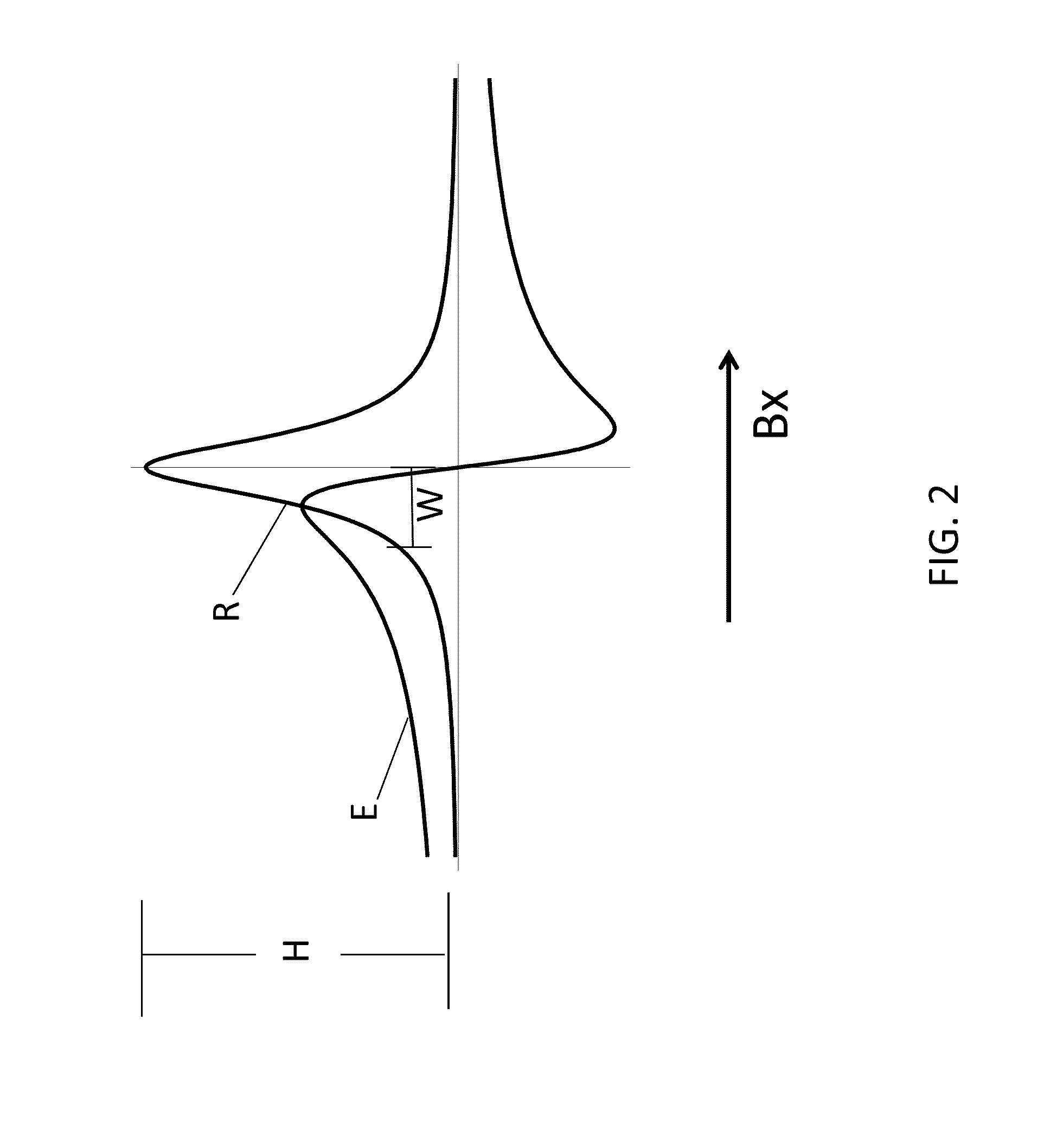
System for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS20160223627A1Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Robotic cart pulling vehicle
ActiveUS7100725B2Reduce accumulated errorsWidth minimizedAutomatic initiationsNon-deflectable wheel steeringProximity sensorNavigational system
A robotic cart pulling vehicle includes a positioning error reducing system for reducing accumulated error in the ded-reckoning navigational system. The positioning error reducing system including at least one of a low load transfer point of the cart attaching mechanism, a floor variation compliance structure whereby the drive wheels maintain a substantially even distribution of load over minor surface variations, a minimal wheel contact surface structure, a calibration structure using at least one proximity sensor mounted on the robot body, and a common electrical and mechanical connection between the cart and the robot vehicle formed by a cart attaching post.
Owner:ST ENG AETHON INC
Method for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS9116201B2Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
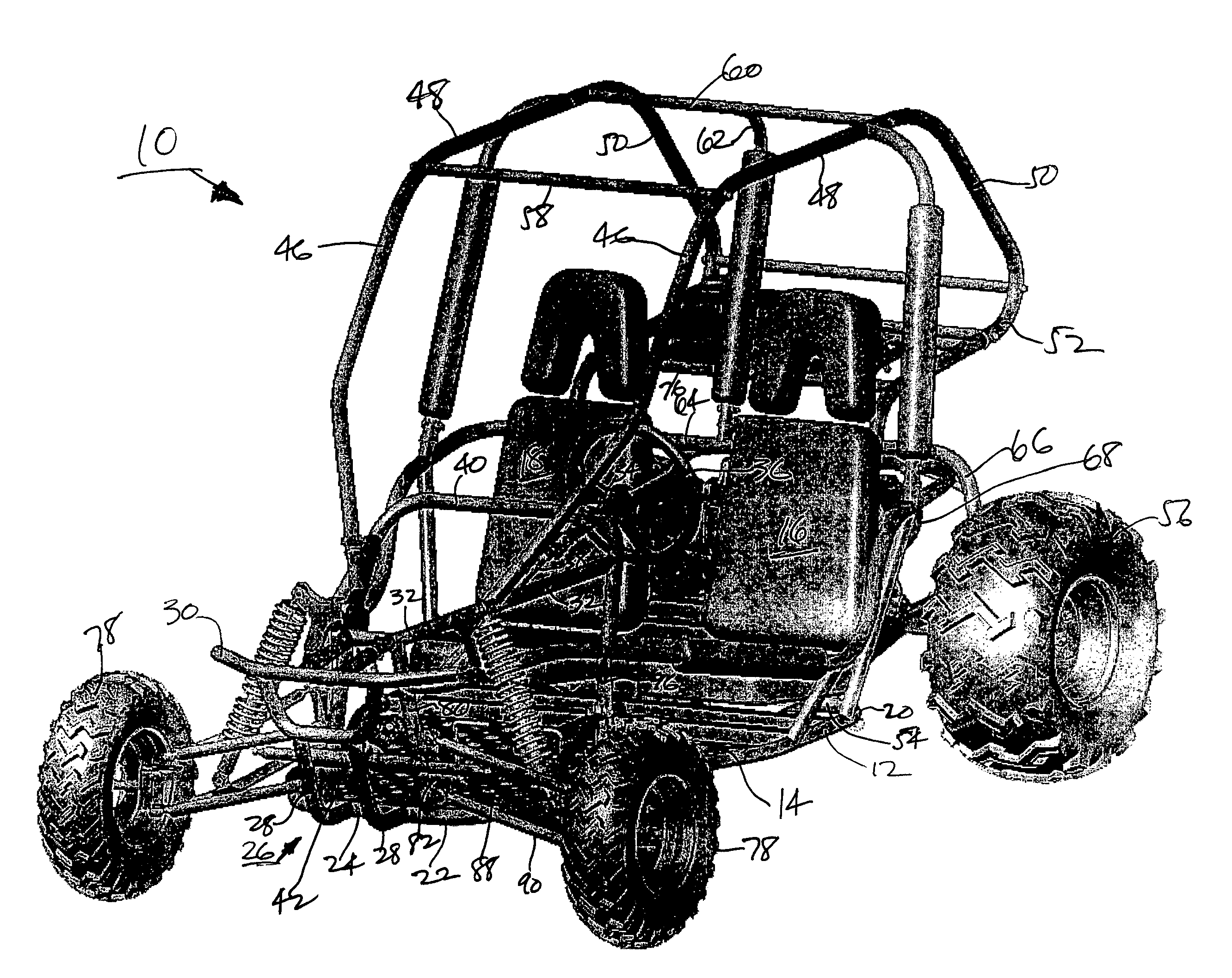
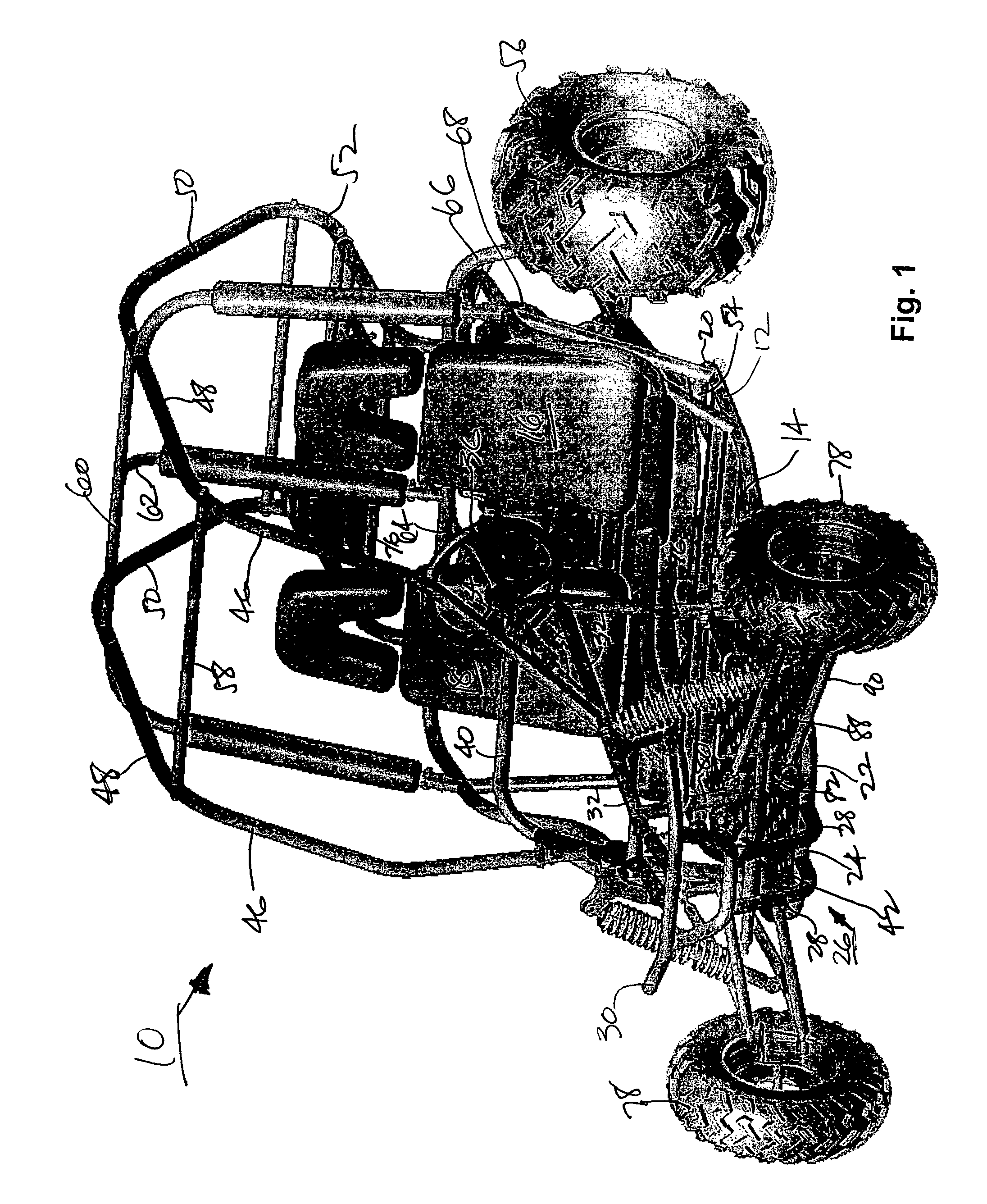
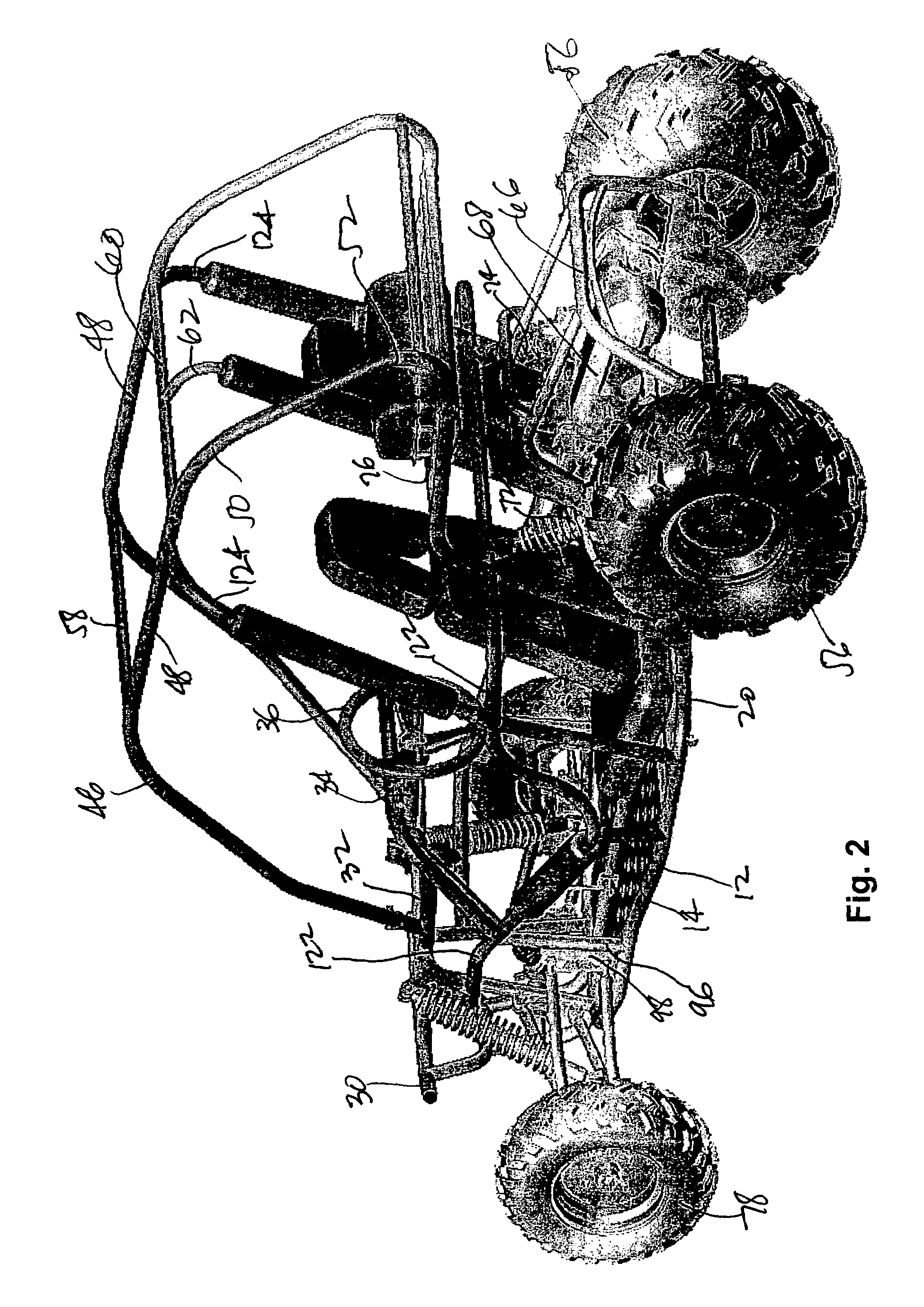
Go-cart
InactiveUS7380805B1Great vertical front wheel travelLong legroomResilient suspensionsPivoted suspension armsTerrainControl arm
A four-wheeled recreational vehicle in the form of a go-cart having an open body without doors or windows. The body is formed from interconnected tubular members to define a chassis and frame. The vehicle includes a front suspension having V-shaped, parallel upper and lower control members including forward and rear control arms. The forward control arms are substantially perpendicular to the chassis centerline and the rear control arms incline inwardly and rearwardly from the front wheels. Greater vertical front wheel travel is provided for improved ride comfort and stability over rough terrain. The accelerator and brake pedals are placed closer to the front wheel pivot axis for greater legroom.
Owner:ASIAN VENTURES
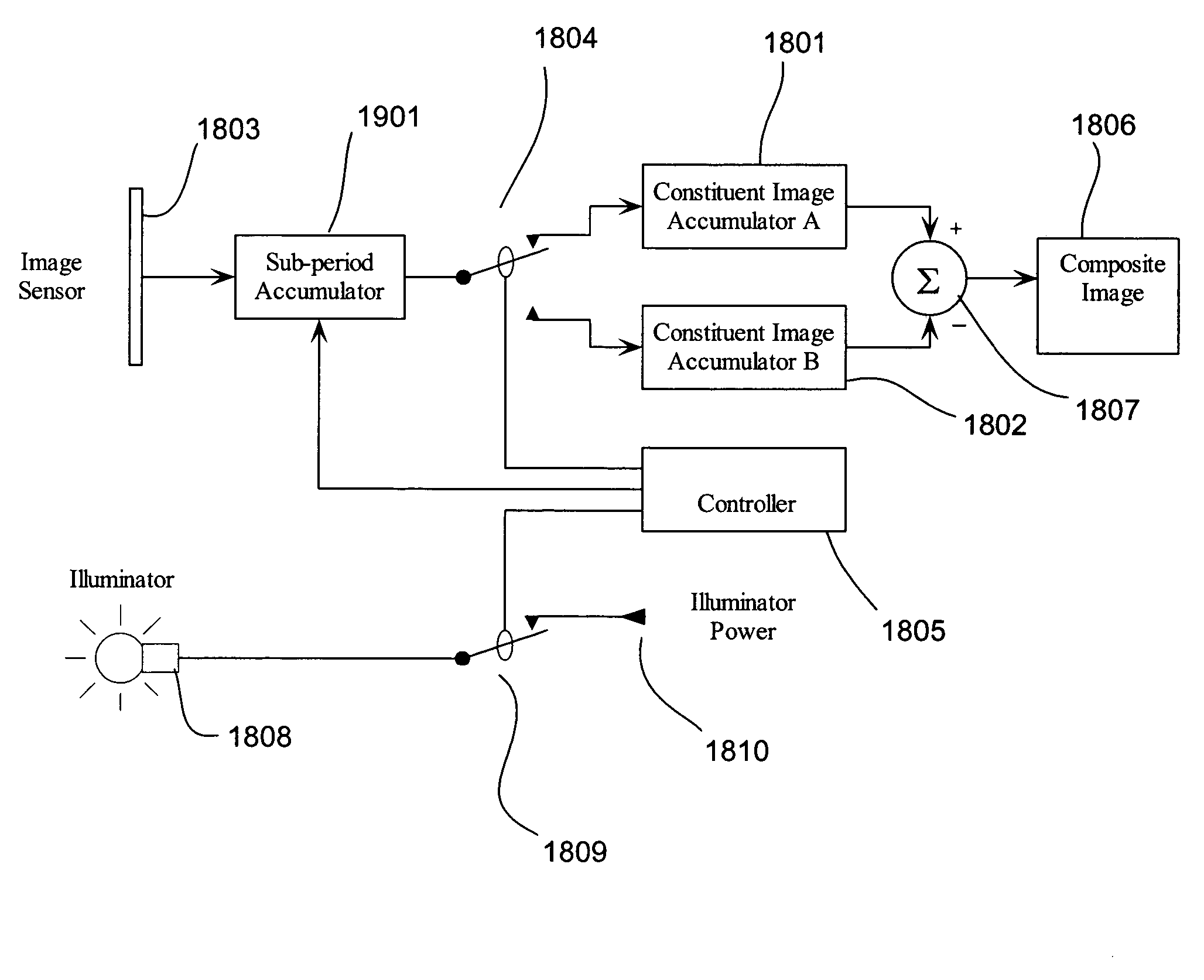
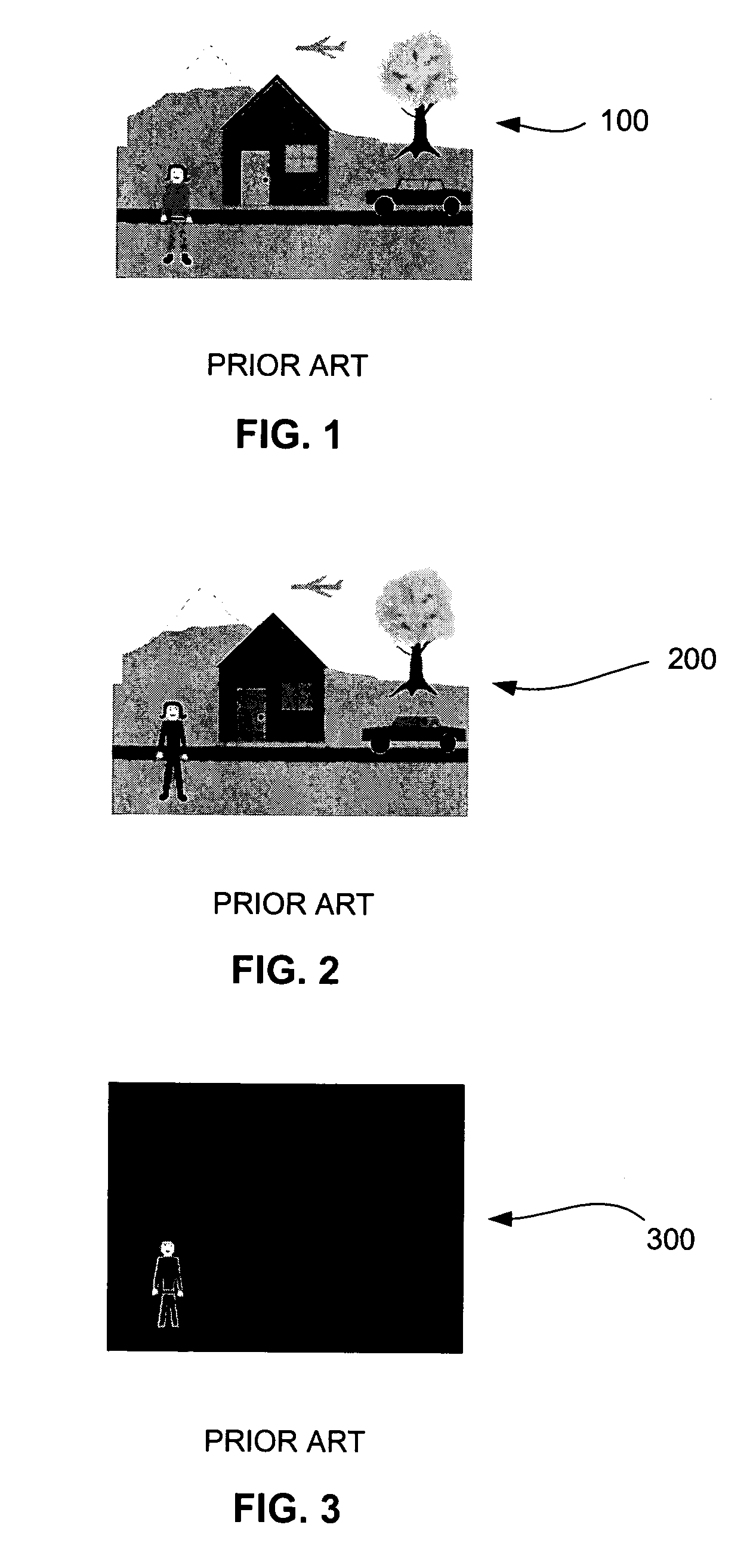
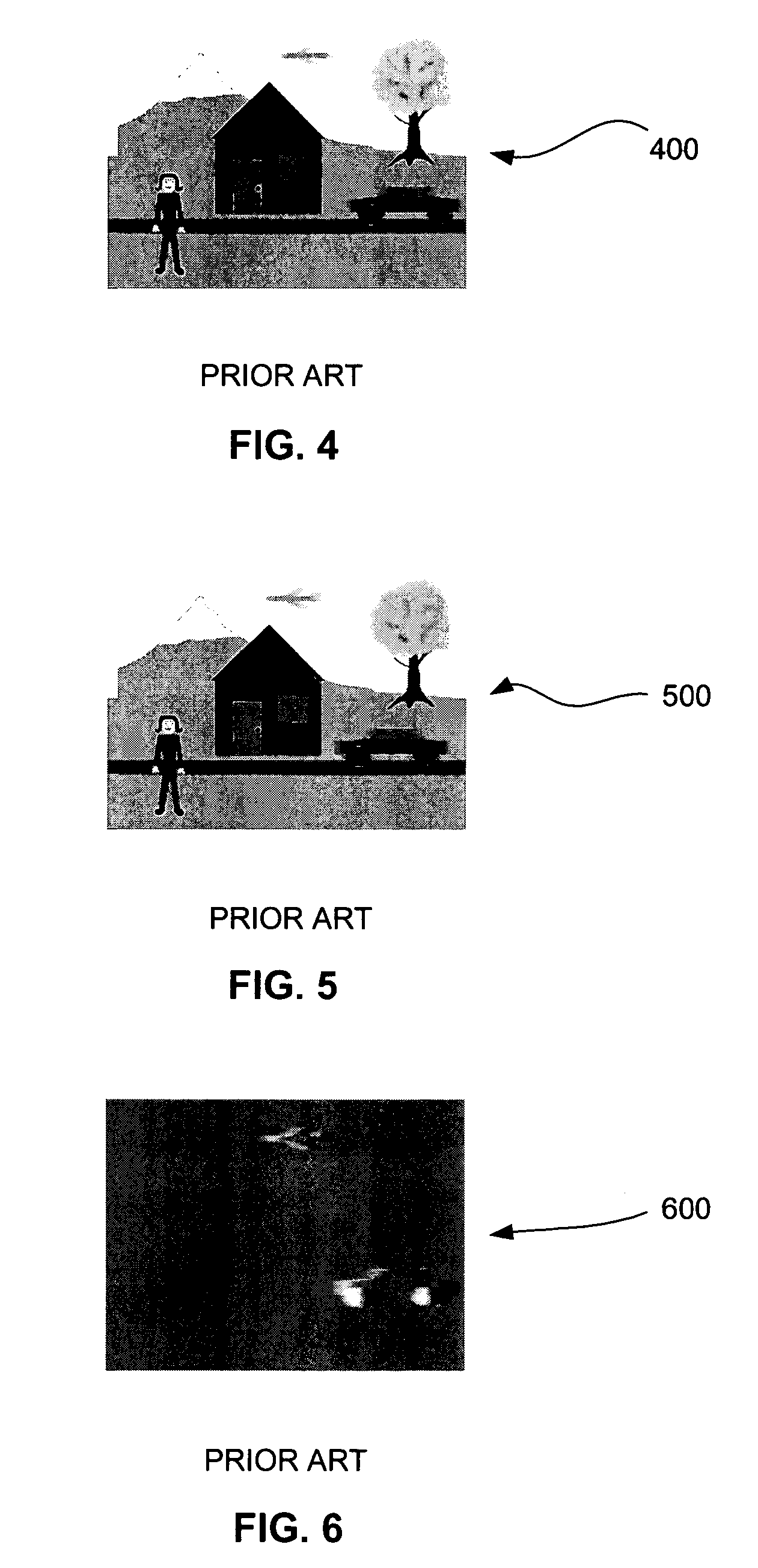
Motion clutter suppression for image-subtracting cameras
ActiveUS7315324B2Magnitude is minimisedWidth minimizedTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage subtractionElectronic chip
Embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for minimizing motion clutter in image-generation devices. Temporally-interleaved image-subtraction reduces the magnitude of motion clutter and has no adverse effect on the desired ambient-light cancellation of static images. Embodiments of image-generation devices employing temporally-interleaved image-subtraction include single, double, triple, and series accumulator configurations. All four embodiments allow synchronization with scene illuminators and may be implemented on a single electronic chip. Temporally-interleaved image-subtraction is particularly well suited for use in video eyetracking applications where ambient light and scene motion can cause significant problems.
Owner:EYEGAZE INC
Semiconductor device structure and methods of making
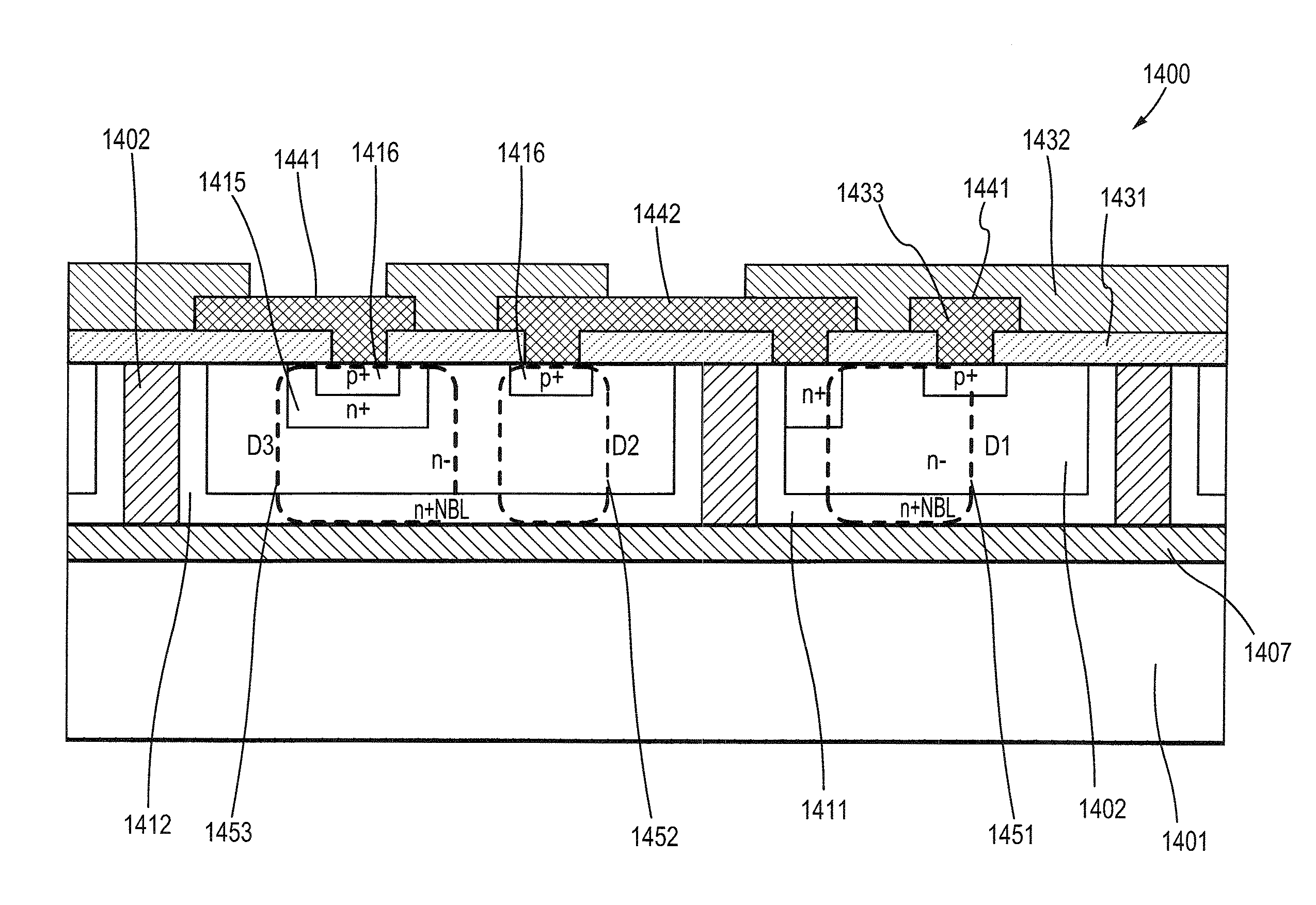
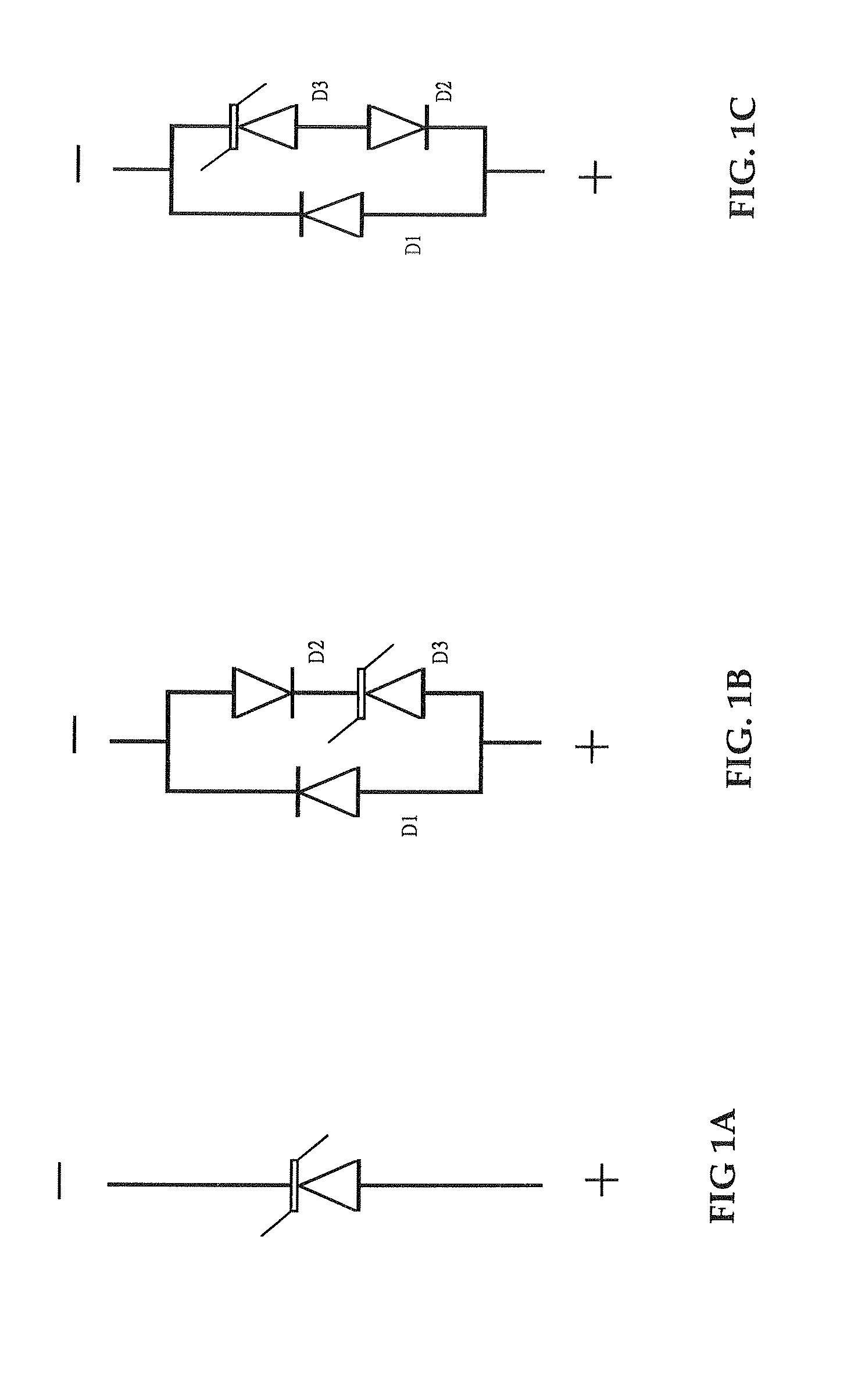
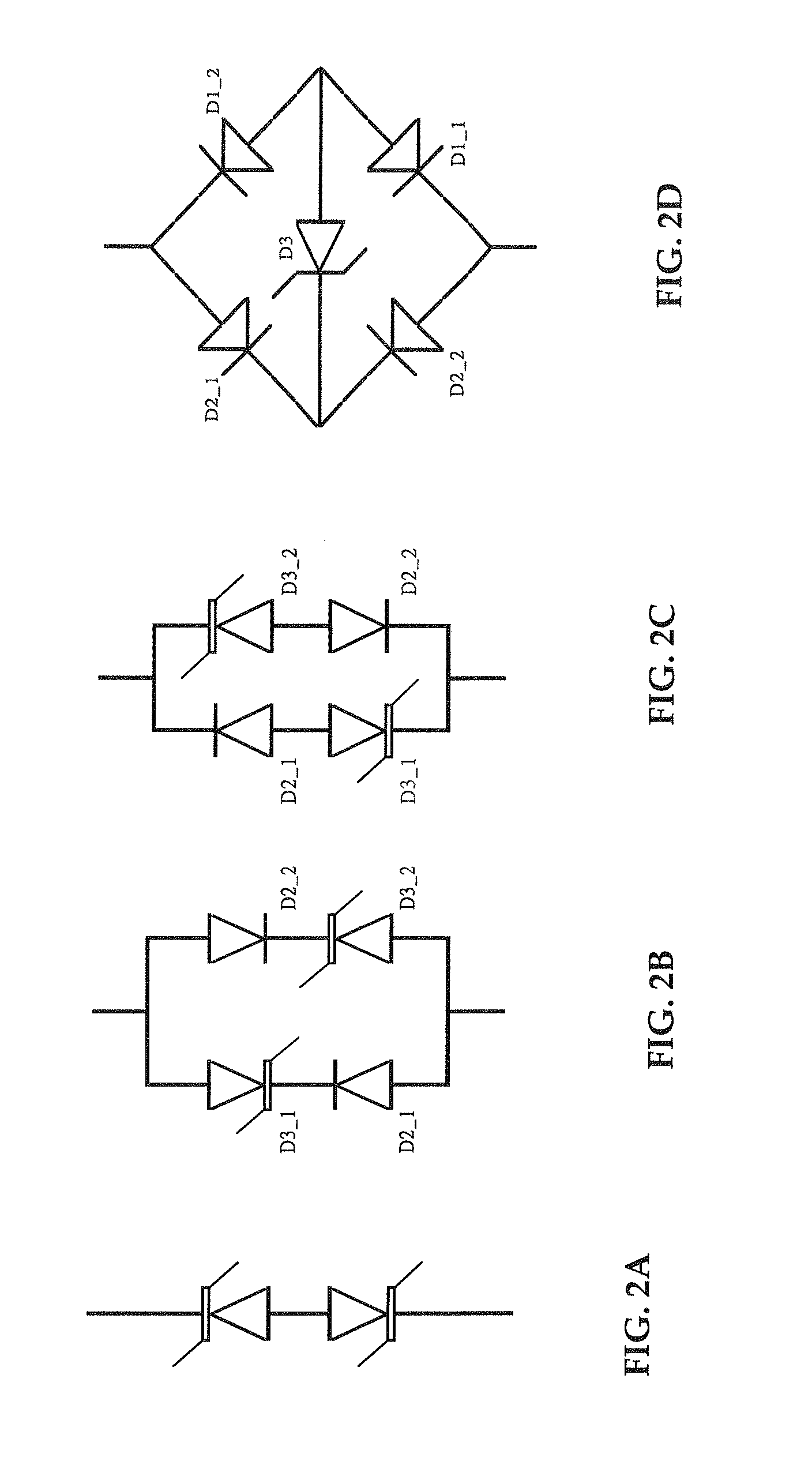
InactiveUS20110212595A1Reduce doping concentrationReduce thermal cyclesThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceGas phase
A process for fabricating a semiconductor device having reduced capacitance for high frequency circuit protection is disclosed that comprises first forming an n+ buried layer in a p-type substrate by depositing n-type dopant on the top surface of the substrate and then drive in or by implanting n-type material into the substrate, and then growing an n-type epitaxial layer atop the n+ buried layer as the device layer. Trenches that surrounds the device region with depth extending from the top surface, going through the n+ buried layer and reaching down to the substrate are then formed and then an n+ layer on the sidewalls of the trenches is formed by diffusion or ion implantation. The trenches are then filled by growing a layer of thermal oxide on the sidewalls of the trenches and followed by deposition of plasma enhanced oxide, nitride, TEOS oxide CVD oxide, or polysilicon into the trenches and then planarizing the top surface by plasma etch back or polishing. Then n+ region of the device is formed by forming an oxide layer on the top surface of the device layer and then etching the oxide by photolithography, then depositing n-type dopant material and then driving in by high temperature diffusion. Finally p+ region of the device is formed by etching the oxide using photolithography, then depositing p-type dopant material by solid or gas phase deposition or ion implantation and then driving in by high temperature diffusion so that the breakdown voltage between cathode and anode of the device is set to a targeted voltage for high frequency circuit protection.
Owner:HU JERRY +2
Electrode assembly and pouch type lithium rechargeable battery having the same
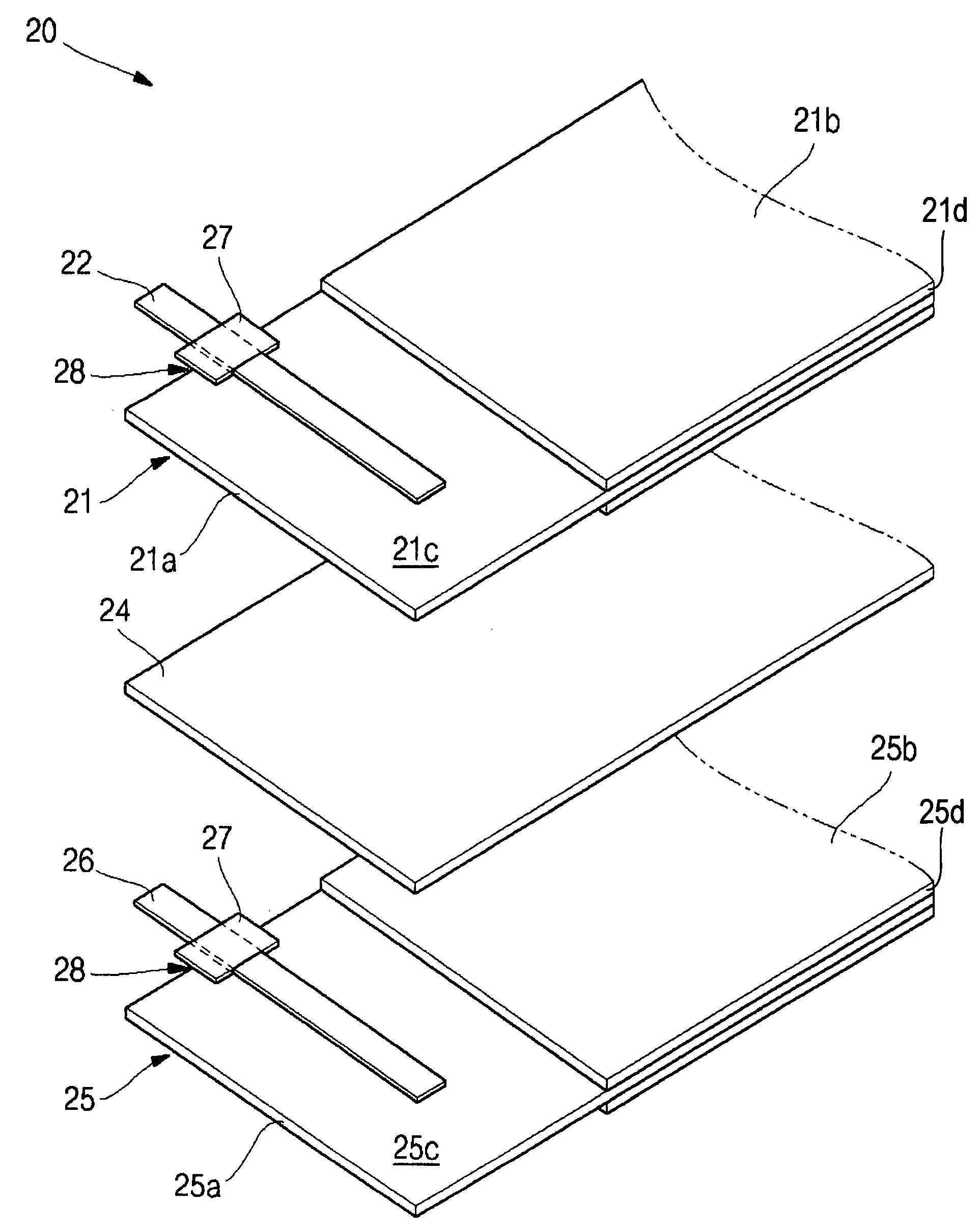
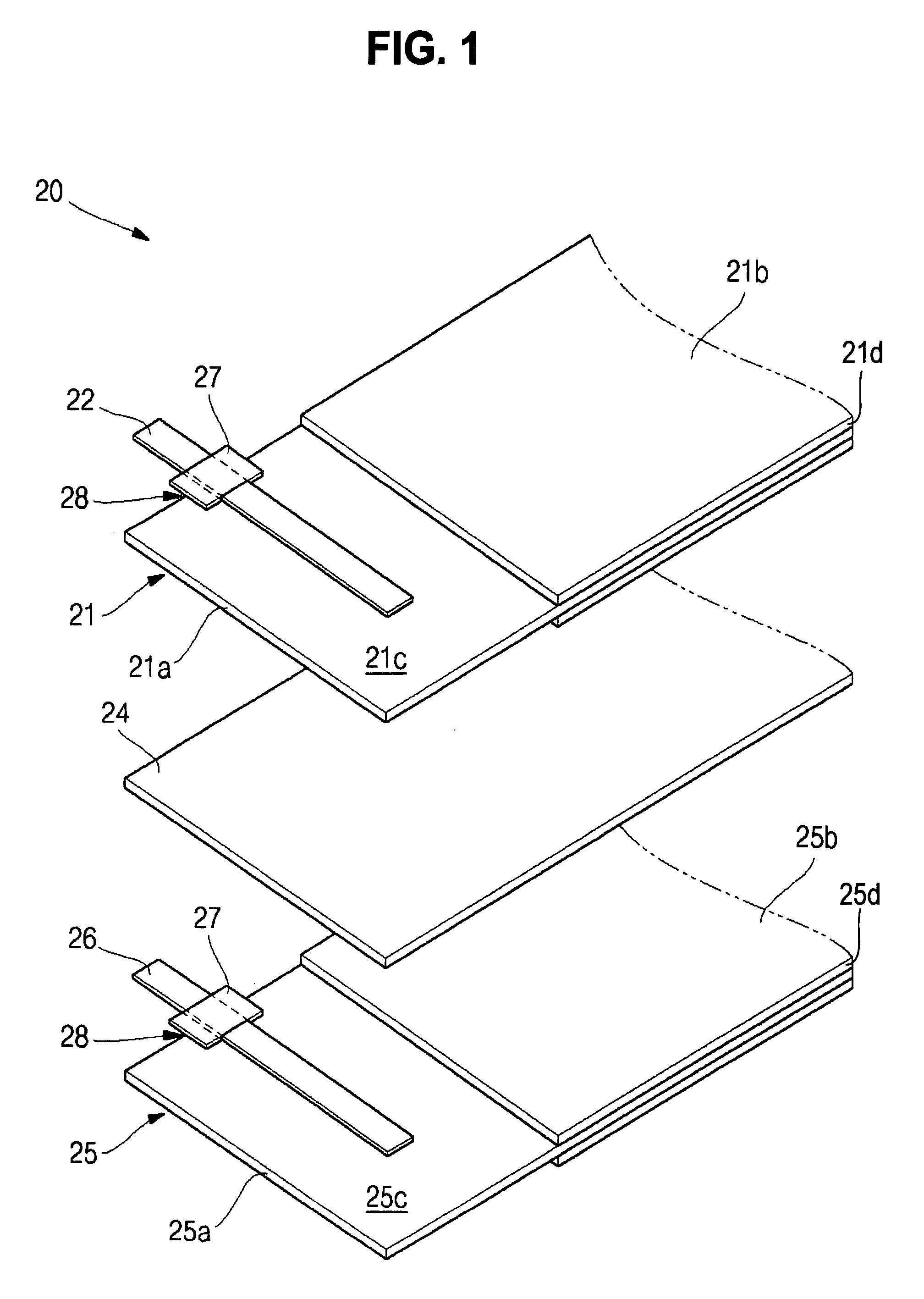
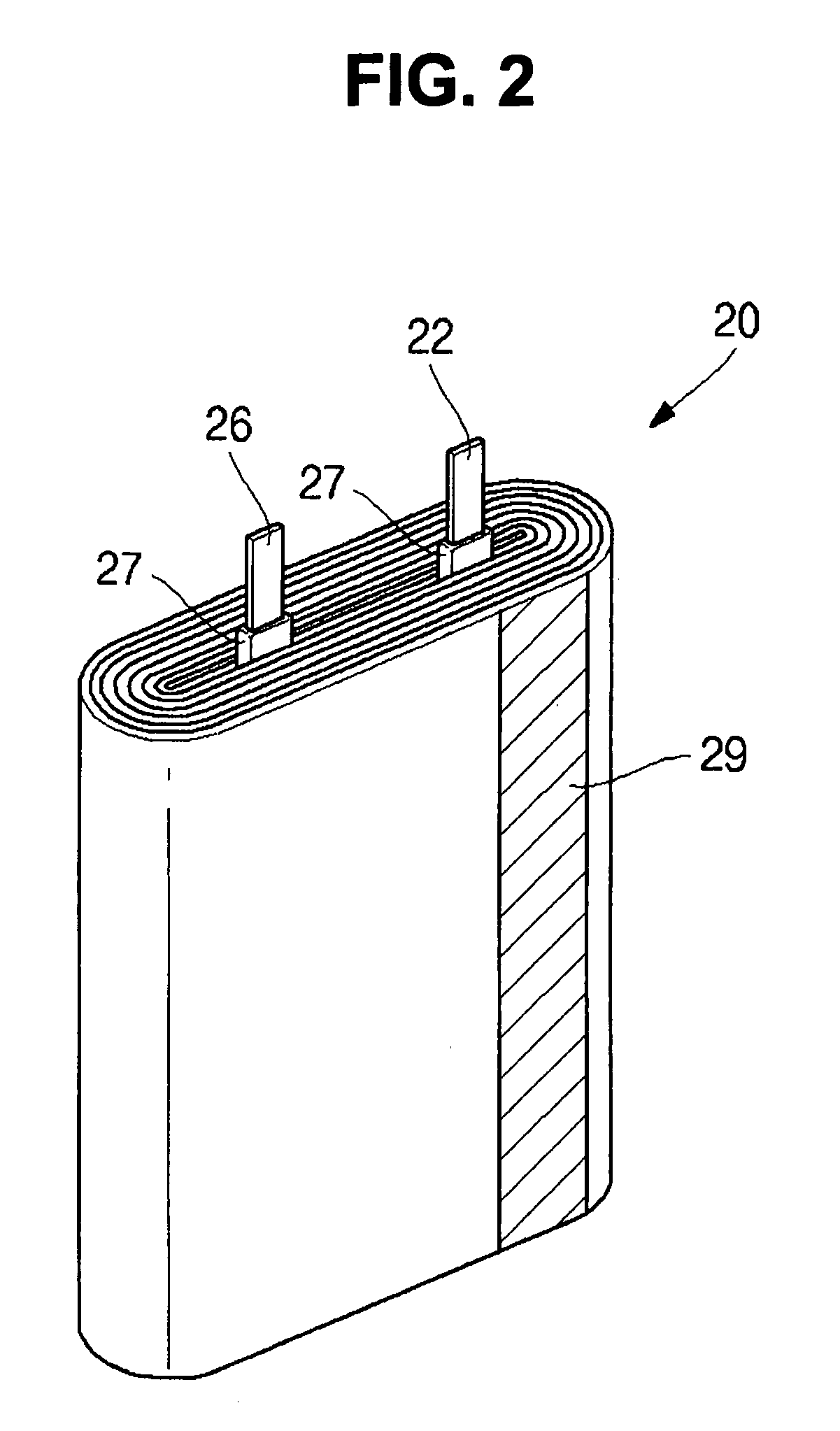
ActiveUS20070231701A1Width minimizedMaximize distanceCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureLithiumElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention relates to an electrode assembly and a pouch type lithium rechargeable battery having the same, which can minimize the total volume of a battery while maximizing a distance between electrode tabs. Insulation members cover portions of electrode tabs to prevent contact of an electrode tab with another electrode tab and electrode plate with opposite polarity. The shape of the insulation member is changed to effectively increase the distance between electrode tabs and to reduce overall thickness or width of the battery.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Painting system
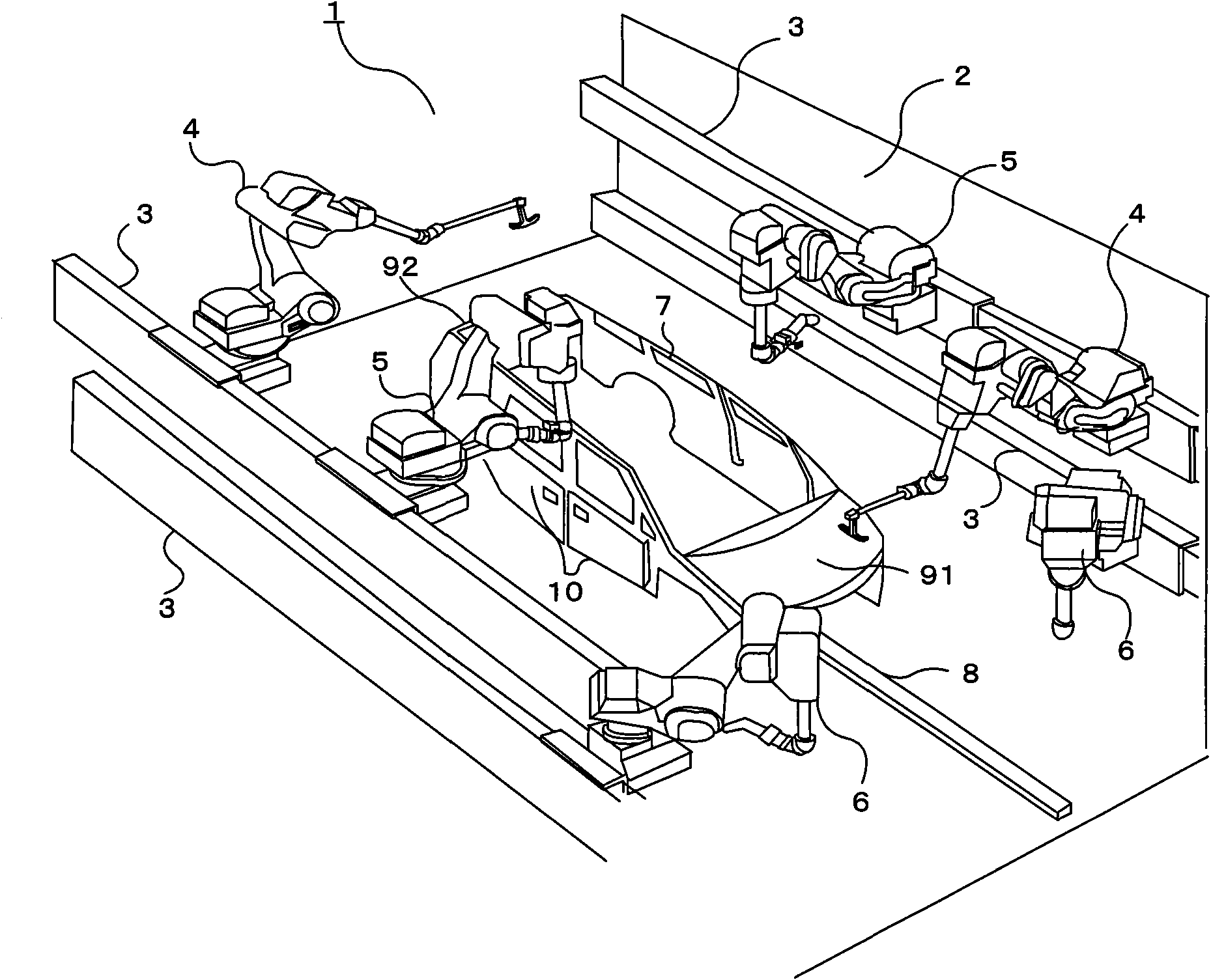
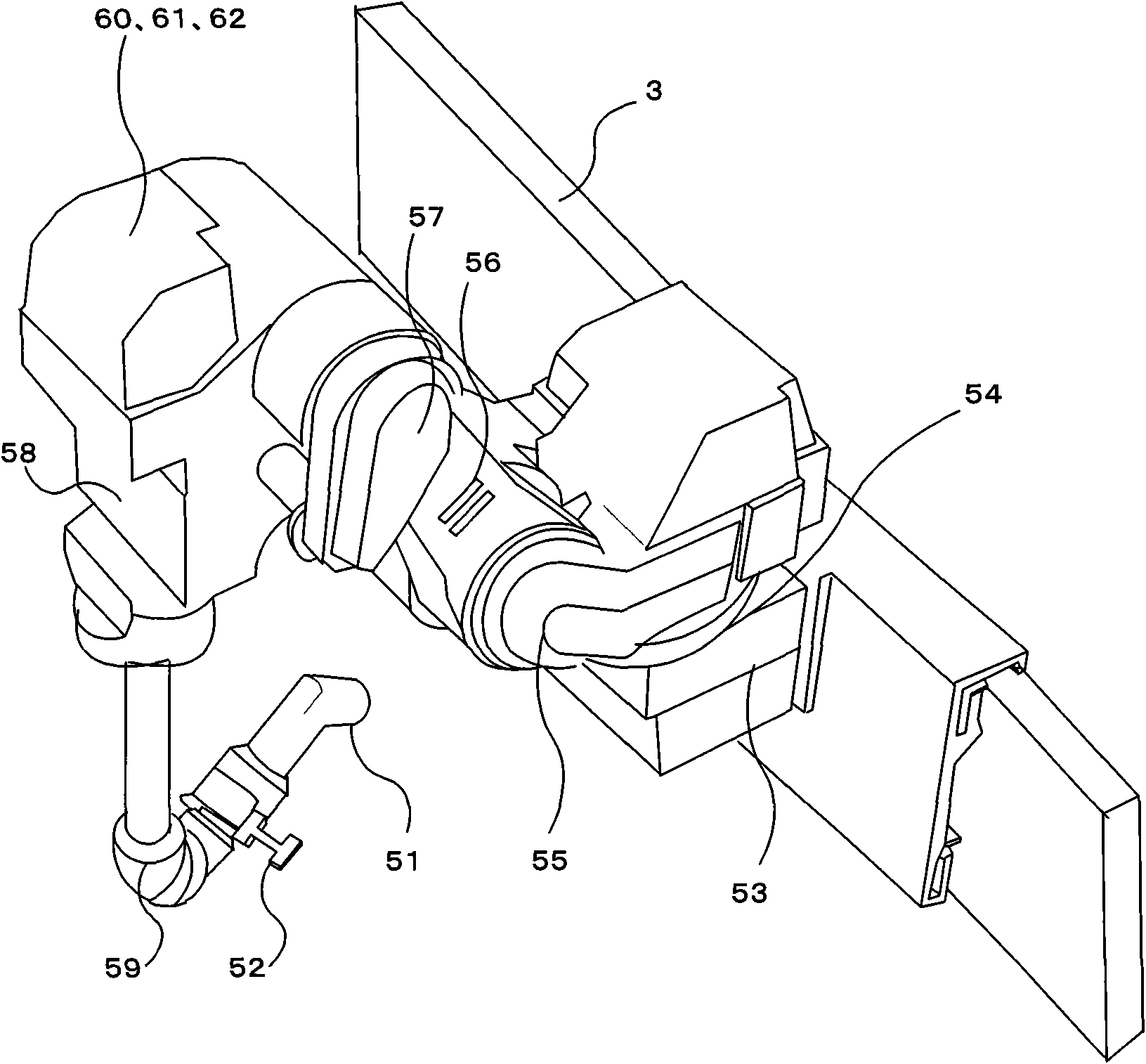
ActiveCN101657264AAbnormal color does not occurRealize continuous coatingProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpray boothsControl theoryRobot
The present invention relates to a painting system having improved productivity achieved by optimizing the number and arrangement of robots in a painting booth. A painting system (1) in which a painting robot (6) and an opener robot (4) can pass each other without interference on a first travel guide rail (3) and a second travel guide rail (3). The first travel guide rail (3) is placed at a lower position than the second travel guide rail (3). The painting robot (6) is placed on the first travel guide rail (3), and the opener robot (4) is placed on the second travel guide rail (3).
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK +1
Insulation for storage or transport of cryogenic fluids
InactiveUS20100146992A1Reduce and eliminate requirementImprove efficiencyGas handling applicationsMachines using refrigerant evaporationAmbient pressureEngineering
A vessel storing or transporting a low temperature fluid includes an insulating material disposed between an inner tank and an outer shell. The insulating material is volumetrically compressed so that it exerts a reaction force that is equal to or exceeds an ambient pressure at the outer shell and / or supports at least some of the weight of the inner tank. Manufacturing processes and methods of using the vessel also are described.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Expandable intervertebral device, and systems and methods for inserting same
ActiveUS20150100130A1Width minimizedEasy to insertBone implantJoint implantsIntervertebral spaceBiomedical engineering
An expandable interbody device for implantation within an intervertebral space is provided, together with methods and tools for use therewith. The interbody devices include a leading first and trailing second bearing member configured to expand laterally via connecting portions disposed at the trailing end of the first being member and at least the leading end of the second bearing member. In some forms, the connecting portions have an arcuate configuration. The insertion tool is configured expand the interbody device by holding the first bearing member while shifting the second bearing member.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Method and apparatus for cutting off glass panes from a continuously produced glass sheet
InactiveUS20050023337A1High yieldWidth minimizedProgramme controlMaterial testing goodsEngineeringGlass sheet
The method for cutting off glass panes from a continuously produced glass sheet includes continuously testing the glass sheet for glass faults prior to the cutting off process and determining glass sheet regions to be discarded containing the glass faults. Based on the test results for the glass faults an optimized cutting pattern for a predetermined glass sheet section is calculated in a cutting optimization device, which is a plan for cutting the glass sheet section into crosscut pieces, in which glass panes of respective sizes are arranged next to each other in corresponding crosscut pieces. In order to reduce waste, the cutting lines for the glass panes to be cut away within each crosscut piece are placed sufficiently close to the fault-containing glass sheet regions, so that widths (BS) of the glass sheet regions to be discarded are minimized or the glass sheet regions to be discarded are minimized, while accounting for a largest possible number of usable glass panes. The crosscut pieces are subsequently cut according to the optimized cutting pattern and the glass panes are formed. An appropriate apparatus for performing the method is described.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Conductors Having Polymer Insulation On Irregular Surface
InactiveUS20090233052A1Increase in sizeSmall sectionLayered productsConfectioneryElectrical conductorThermoplastic polymer
A communications cable is provided comprising a conductor and polymer insulation encasing said conductor, the polymer insulation having a foamed interior and having an exterior surface formed from longitudinally running rounded peaks and valleys. A process is also provided for producing this polymer insulation or unfoamed polymer insulation having the same or similar peak / valley exterior surface by extruding molten thermoplastic polymer through an orifice to coat a conductor passing through the orifice, thereby forming polymer insulation on the conductor, said orifice defining the exterior surface of said polymer insulation comprising longitudinally running rounded peaks and valleys, said peaks covering at least about 30% of said exterior surface and having a height that is at least 50% of the width of said peaks.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Expandable intervertebral device, and systems and methods for inserting same
ActiveUS9408717B2Width minimizedEasy to insertBone implantJoint implantsIntervertebral spaceBiomedical engineering
An expandable interbody device for implantation within an intervertebral space is provided, together with methods and tools for use therewith. The interbody devices include a leading first and trailing second bearing member configured to expand laterally via connecting portions disposed at the trailing end of the first being member and at least the leading end of the second bearing member. In some forms, the connecting portions have an arcuate configuration. The insertion tool is configured expand the interbody device by holding the first bearing member while shifting the second bearing member.
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
Switching transistor driver circuit
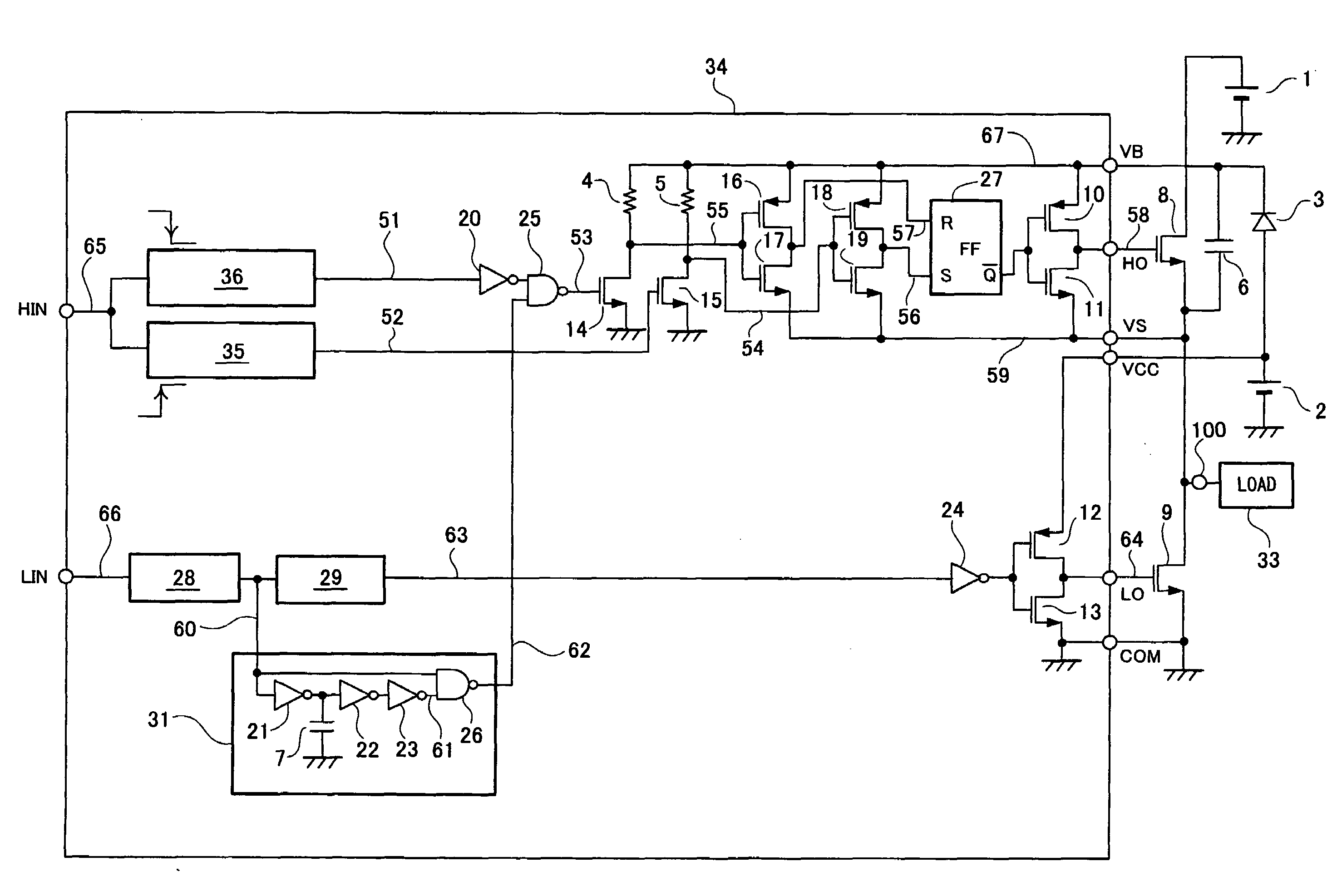
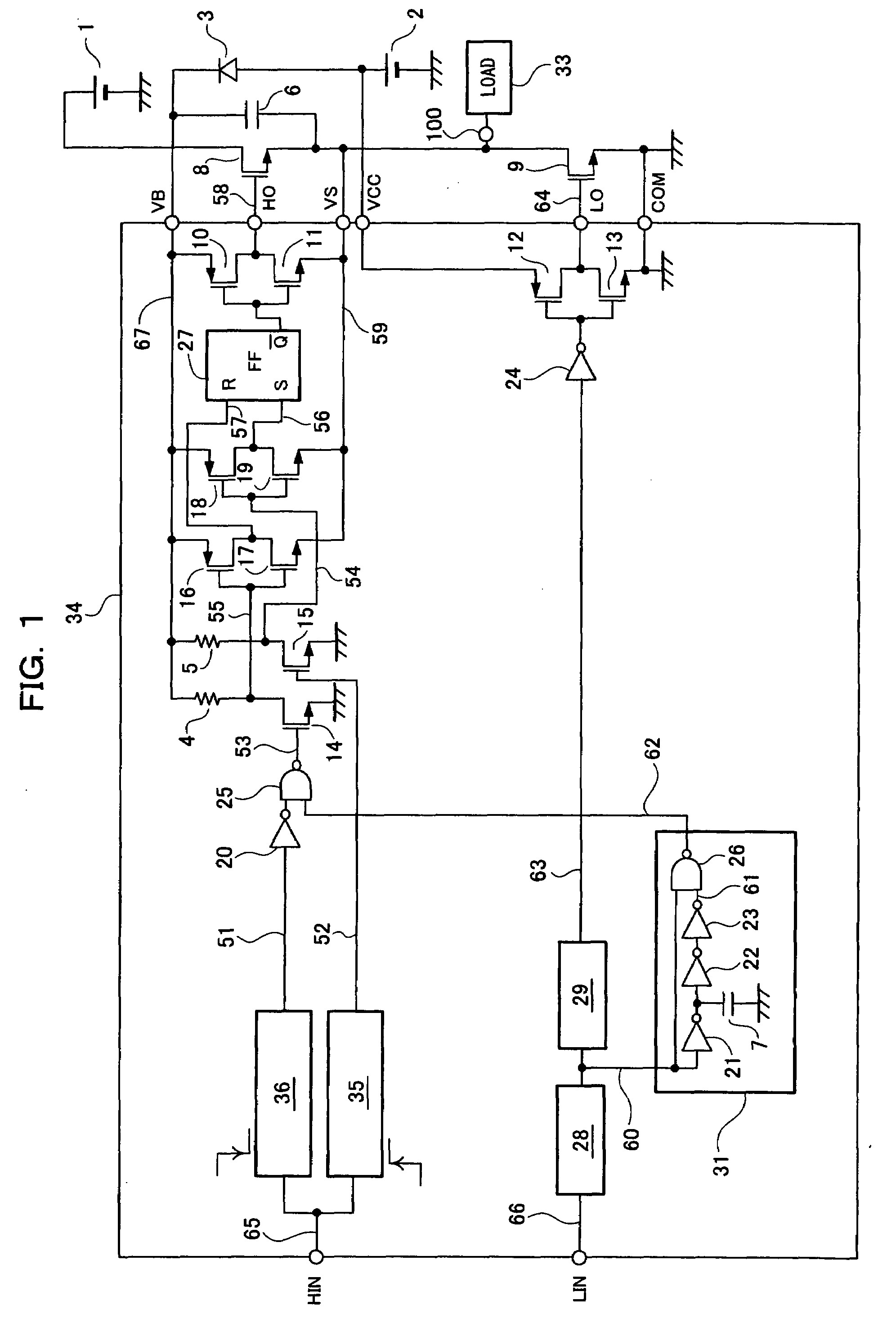
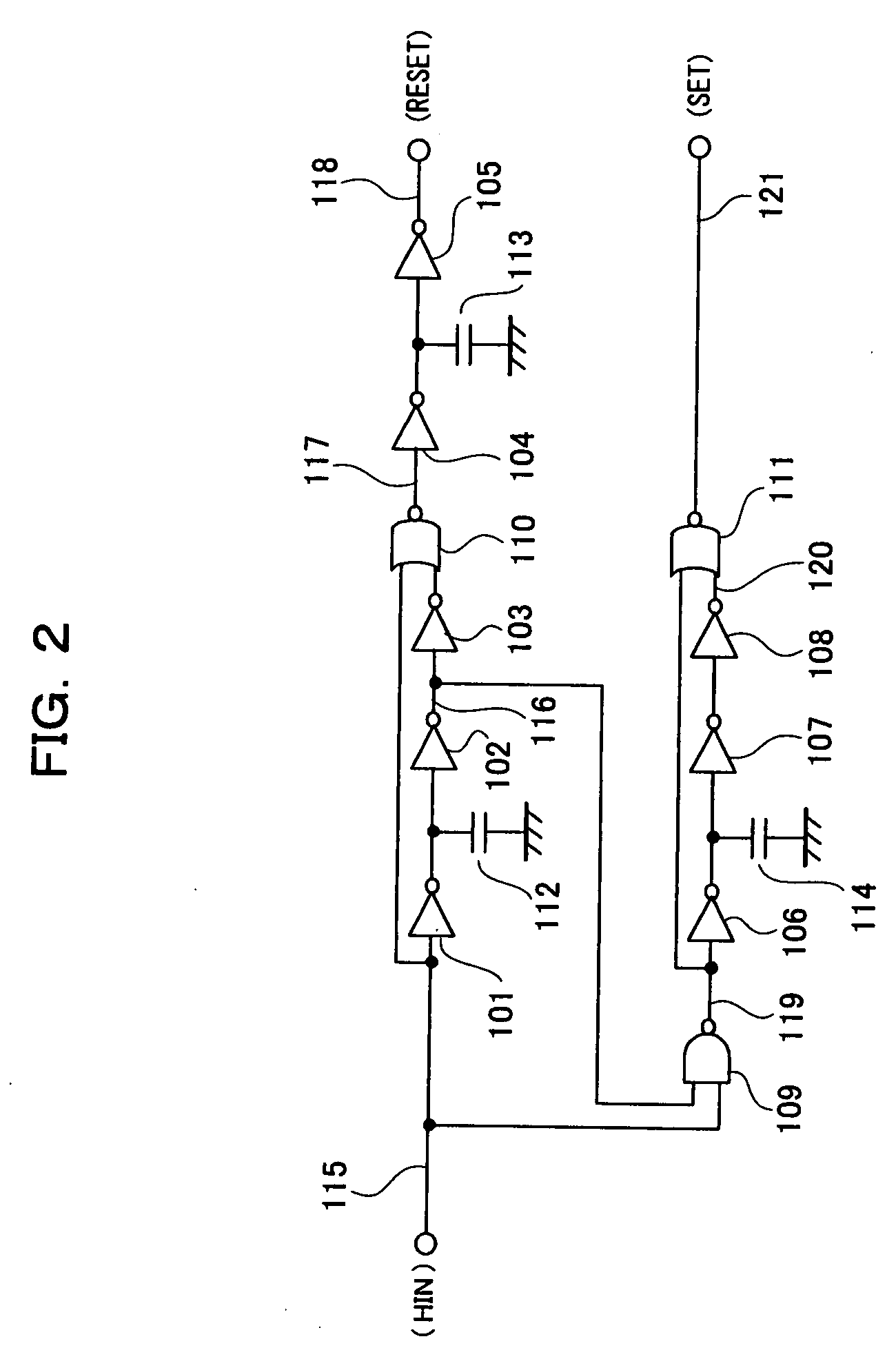
InactiveUS20070210780A1Prevent large power consumptionWidth minimizedPower reduction in field effect transistorsAc-dc conversionHigh potentialHigh pressure
Of a pair of switching transistors connected in series between a high voltage power source and the ground, when the switching transistor on the high potential side is controlled by an RS flip-flop in response to an input signal, in order to prevent a malfunction caused by the influence of dv / dt transient phenomena of an output terminal for driving a load, a latch circuit is reset using an input signal from a low side input terminal LIN in a period during which the voltage of the output terminal for driving the load abruptly decreases.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Methods for stabilizing bone using spinal fixation devices
InactiveUS20080132953A1Width minimizedAvoid excessive widthSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCouplingBiomedical engineering
A method of stabilizing bone, such as a spine, includes providing a coupling element having first and second sections that are angled relative to one another, the coupling element having rod receiving openings for securing an elongated member such as an orthopedic rod, and assembling the coupling element with an anchoring element. The method includes securing the anchoring element in bone, moving the coupling element relative to the anchoring element to align the rod receiving openings with the orthopedic rod, securing the orthopedic rod in the rod receiving openings, and after the securing step, locking the coupling element from further movement relative to the anchoring element.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
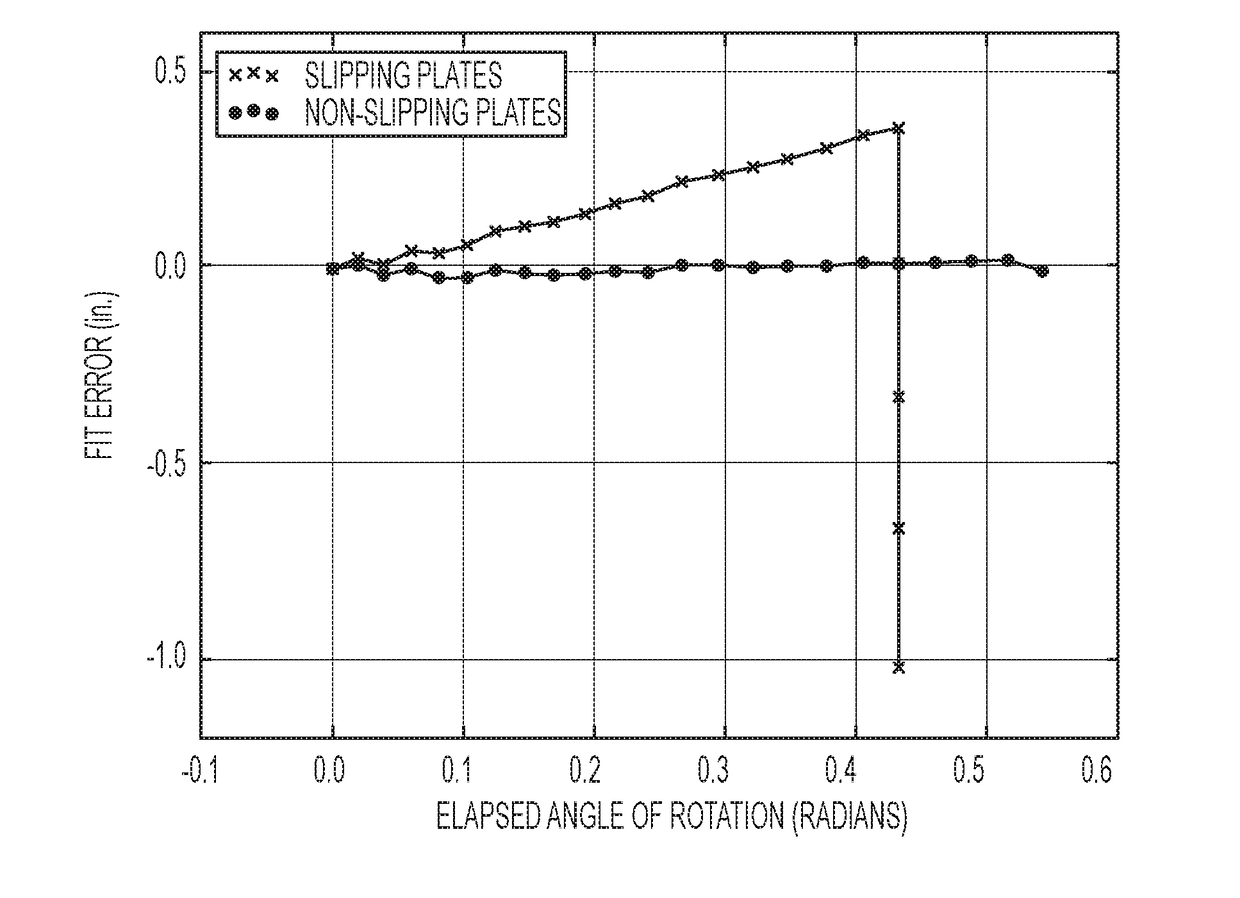
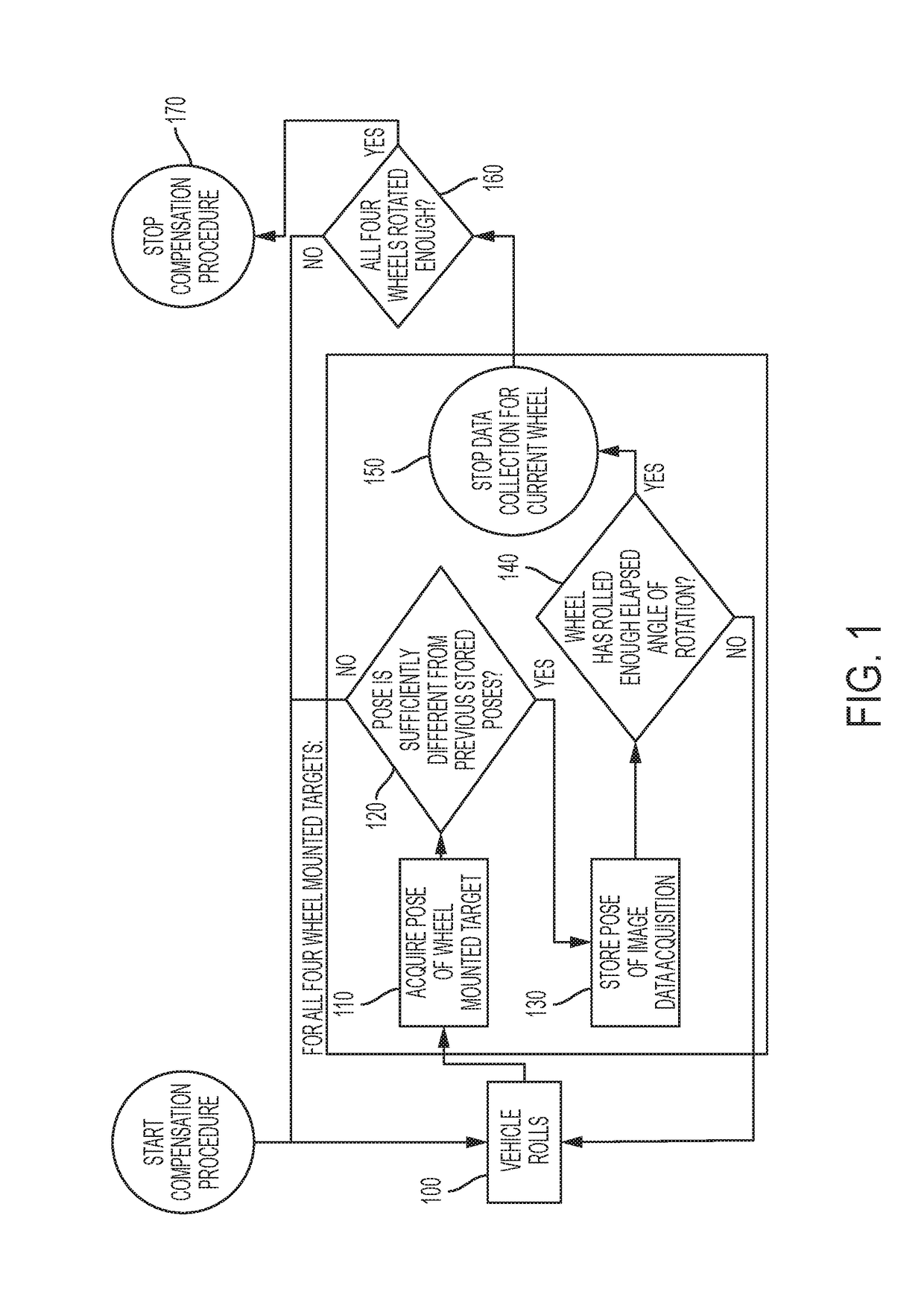
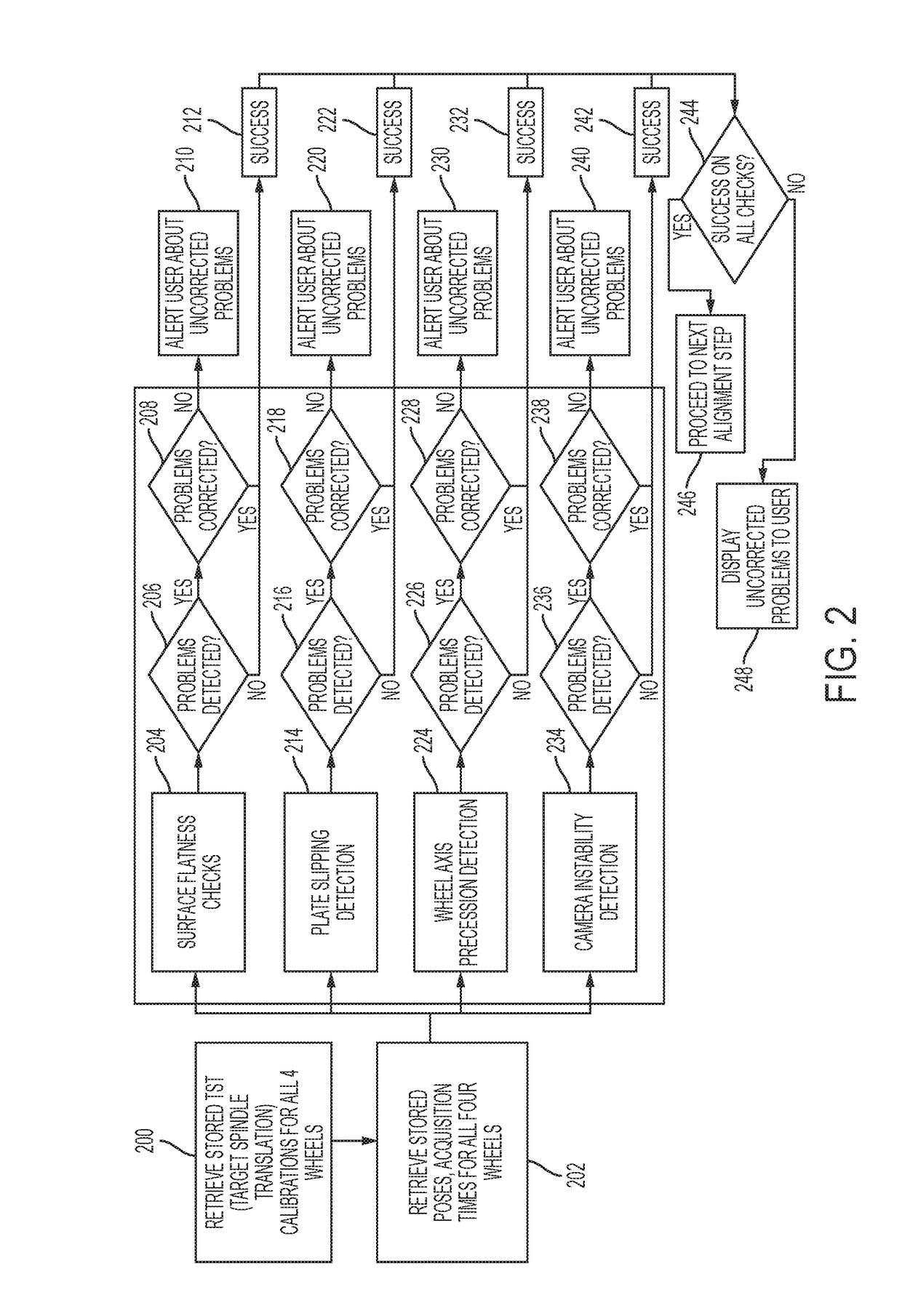
Wheel aligner with advanced diagnostics and no-stop positioning
InactiveUS20170097229A1Reduce weightLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementEngineeringImaging data
A vehicle wheel alignment system has a plurality of cameras, each camera for viewing a respective target disposed at a respective wheel of the vehicle and capturing image data of the target as the wheel and target are continuously rotated a number of degrees of rotation without a pause. The image data is used to calculate a minimum number of poses of the target of at least one pose for every five degrees of rotation as the wheel and target are continuously rotated the number of degrees of rotation without a pause. At least one of the cameras comprises a data processor for performing the steps of preprocessing the image data, and calculating an alignment parameter for the vehicle based on the preprocessed image data.
Owner:SNAP ON INC
Photodetector in germanium on silicon
ActiveUS8148794B2Maximize efficiencyEfficient collectionPhotovoltaic energy generationOptical light guidesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A photodetector structure includes a silicon-based waveguide in which optical signals to be detected travel in a given direction and are confined therein and a germanium layer disposed in contact with a portion of the silicon-based waveguide so that an evanescent tail of the propagating optical signal in the waveguide is coupled into the germanium layer. In addition, the germanium layer includes a mesa having a length along the signal propagating direction and a width in a direction substantially perpendicular to the propagating direction, in which the width of said mesa is smaller than its length. The photodetector also comprises a first and a second metal contacts, the first metallic contact being located on the germanium layer, the said second metallic contact being located on the silicon-based waveguide, the first and second contacts being used to collect electrons generated by light absorption to obtain an output electric signal.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
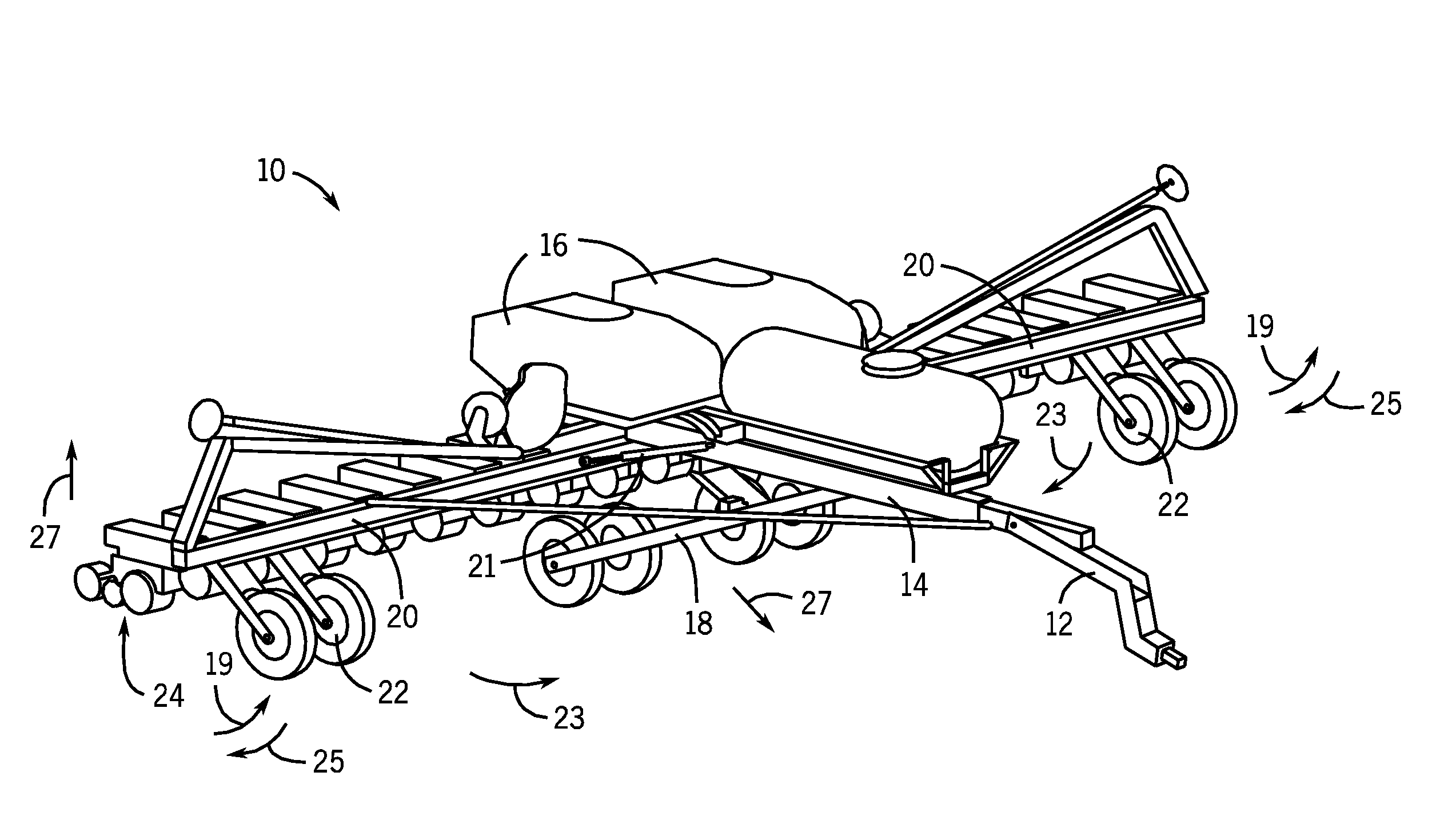
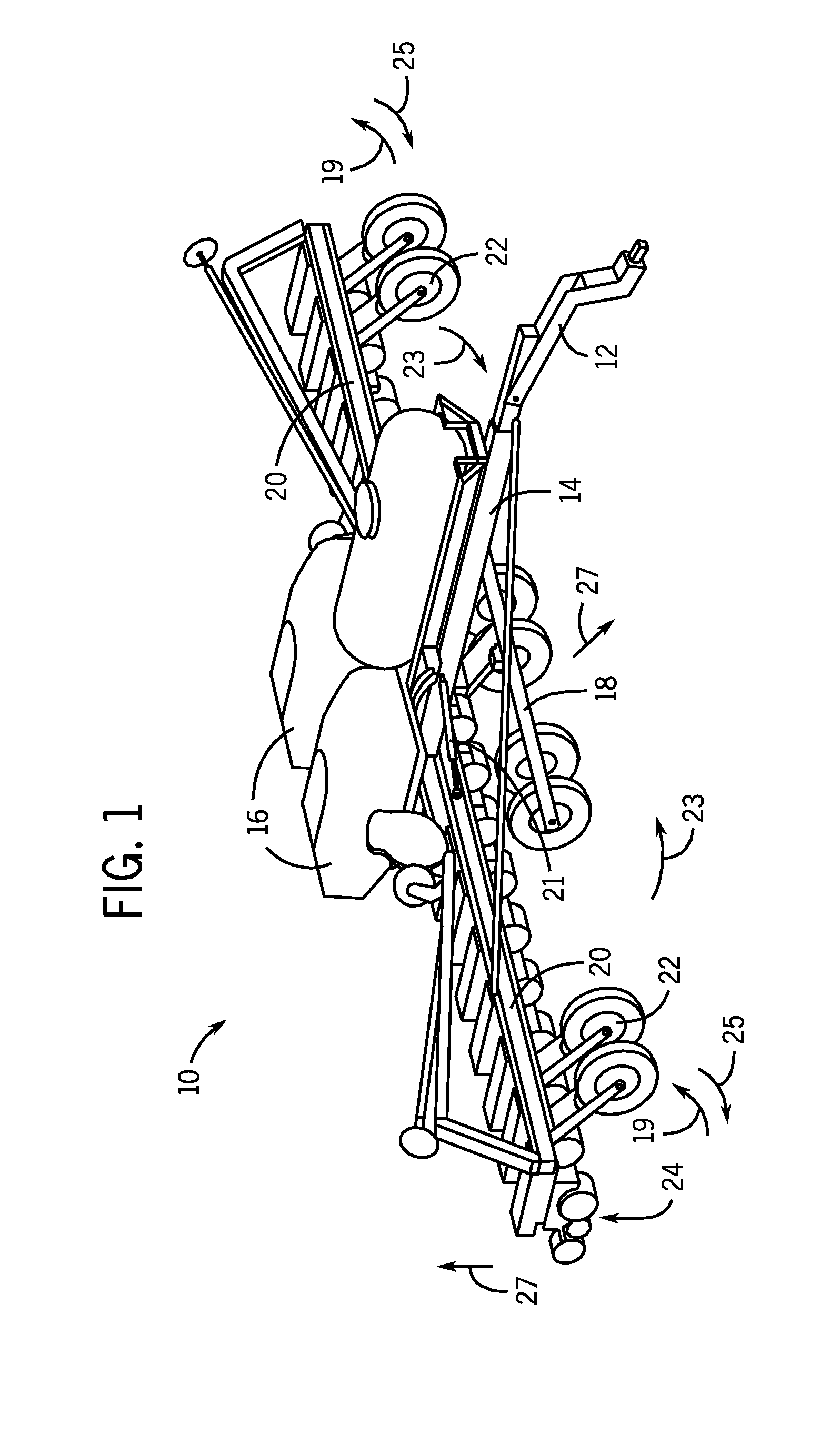
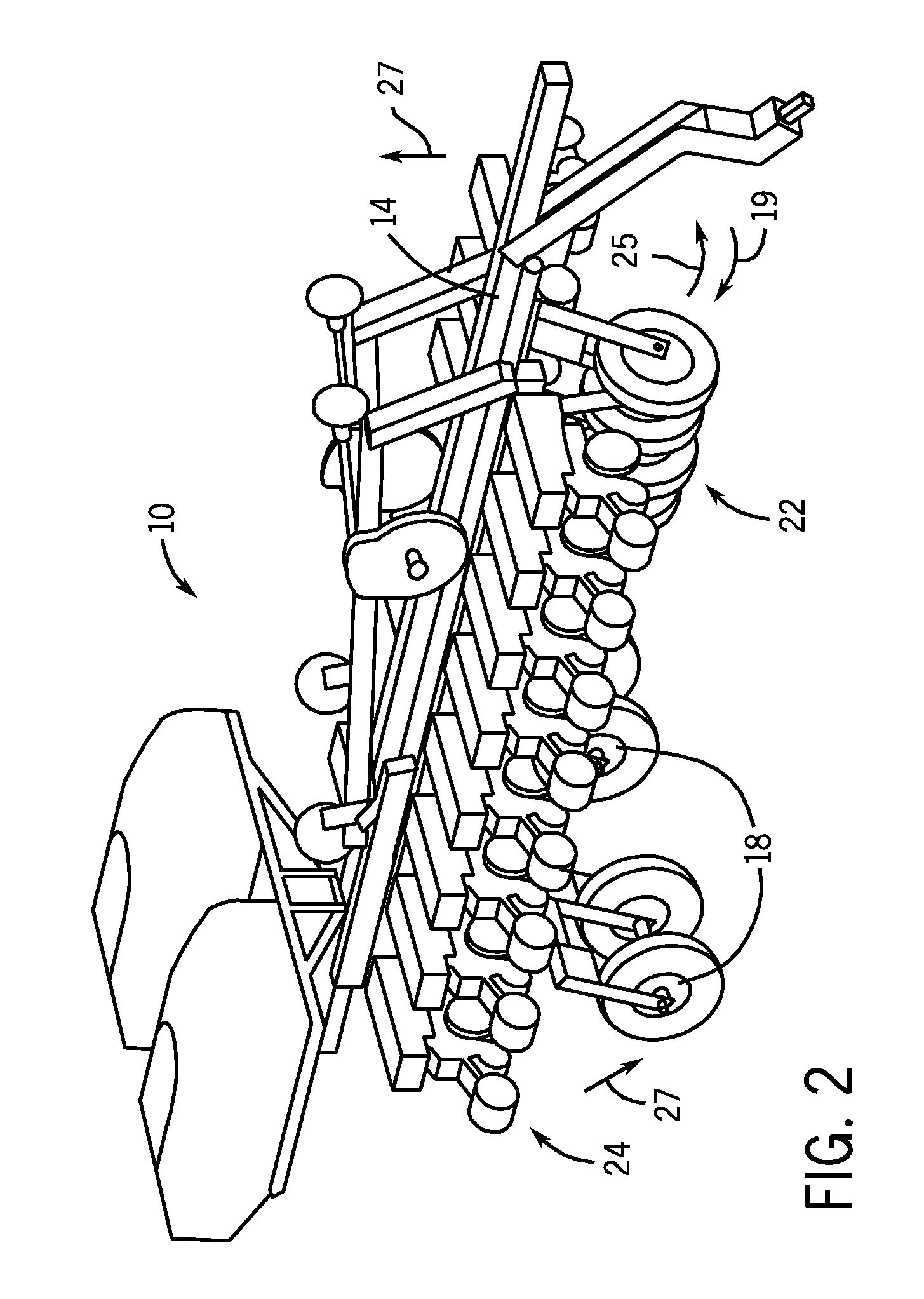
Implement frame with front folding wings and transport wheels
An agricultural implement arrangement is disclosed that may provide wheel assemblies that are stored in front of wing assemblies and row units mounted thereon. The arrangement may include actuators to extend the wheel assemblies in order to lift the row units off the ground to move to a transport position. When in a fully-folded position, the wing wheel assemblies may interleave. The arrangement may also shift the weight of the wing assemblies while in transport position to the hitch of the tractor and center the rearward weight over the central wheel assembly.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
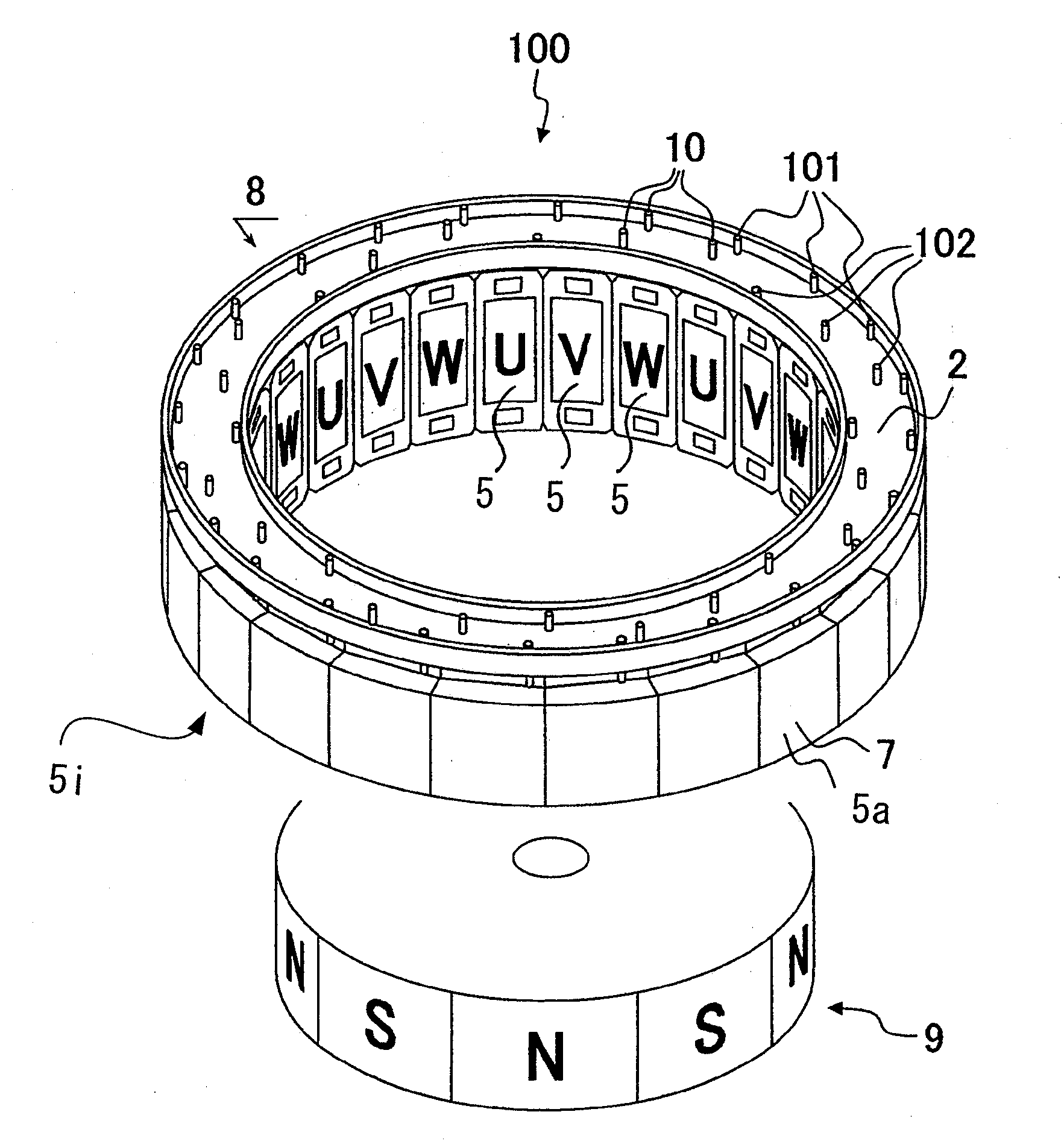
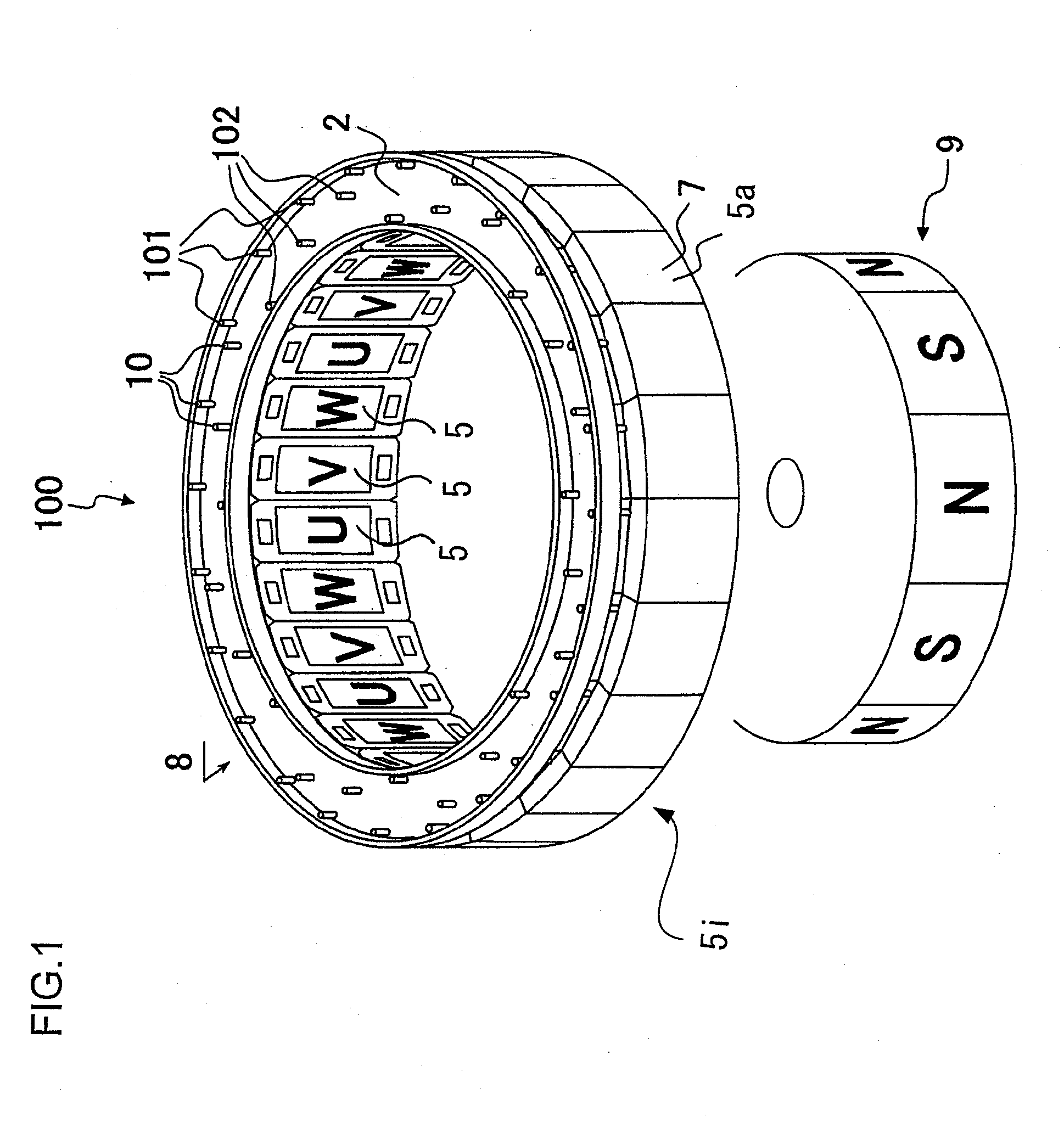
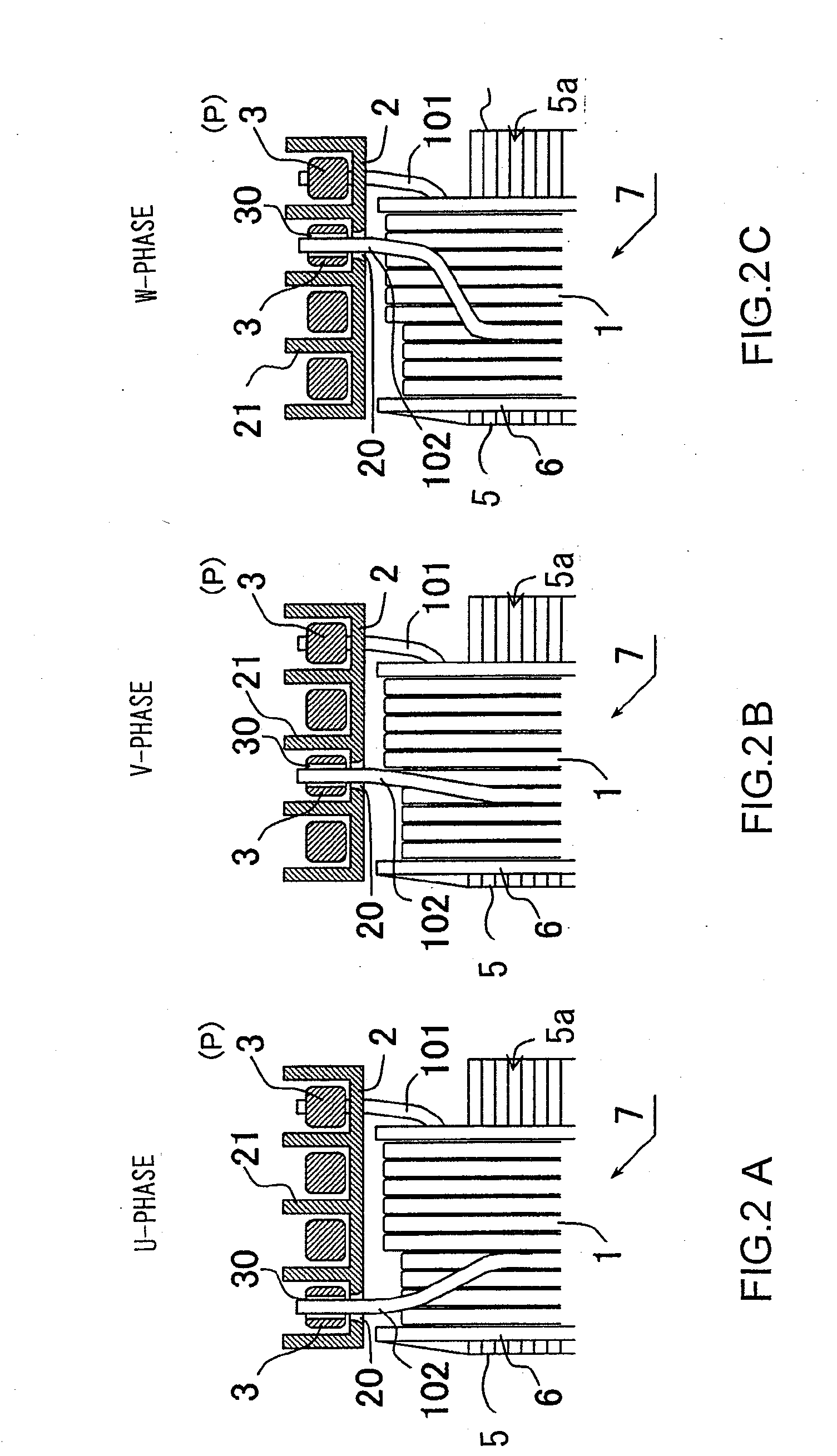
Stator for Rotating Machine and Rotating Machine Using the Same
InactiveUS20090140595A1Width minimizedReduce widthSynchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectrical conductorEngineering
The stator includes a plurality of concentrated winding coils disposed coupled into an annular form through yokes, and a plurality of conductors that couple the coil ends of the concentrated winding coils to each other in a multi-phase connection fashion. Conductors for a U-phase, a V-phase, a W-phase, and neutral points P are each formed of a plurality of holes for inserting therethrough coil ends and are substantially circular with different diameters, and are disposed on the same plane. A connection plate provided with a wall is inserted between the conductors and the concentrated winding coils. A rotating machine includes the above-mentioned stator and a rotor that is rotatable within the stator.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com