Patents
Literature
890results about How to "Small section" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
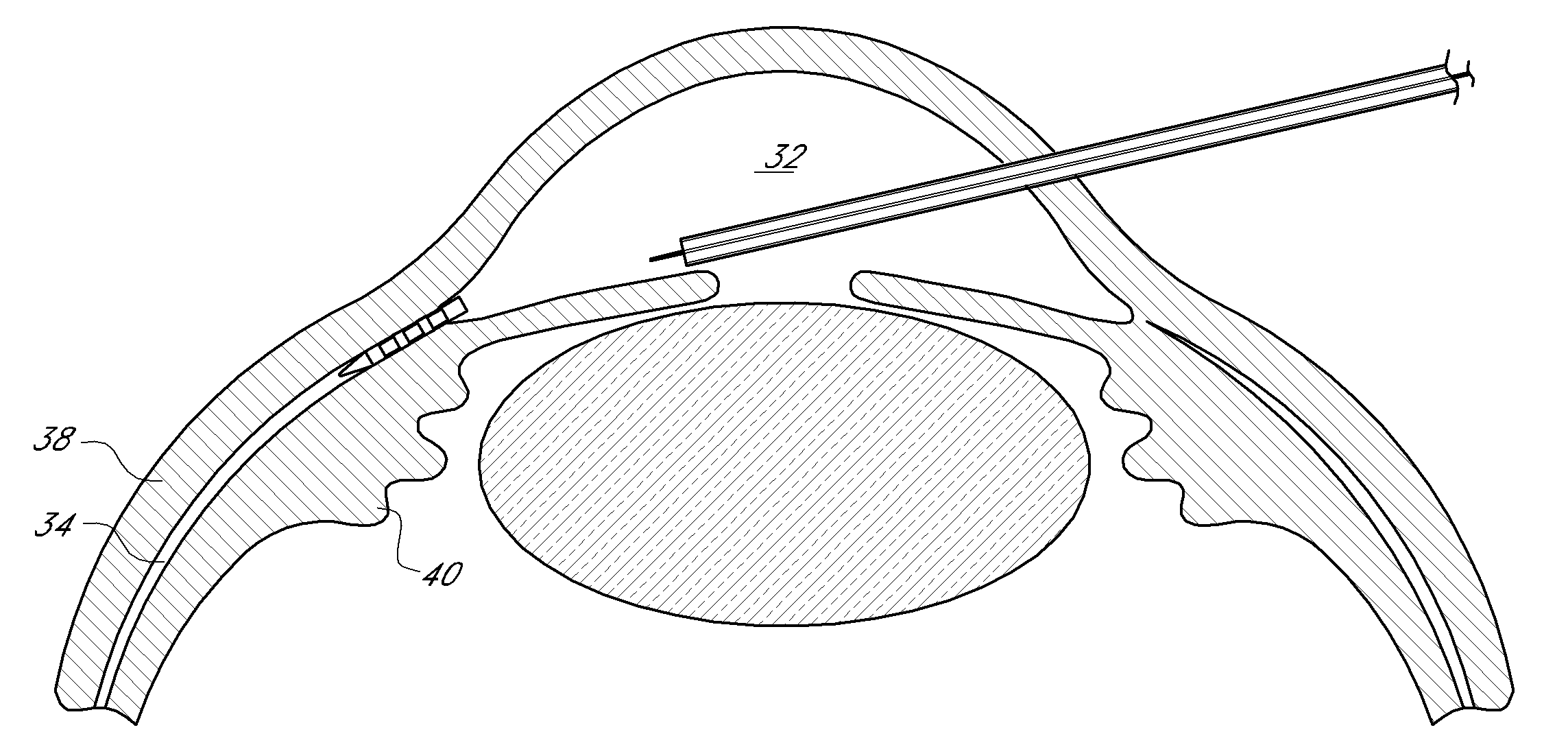
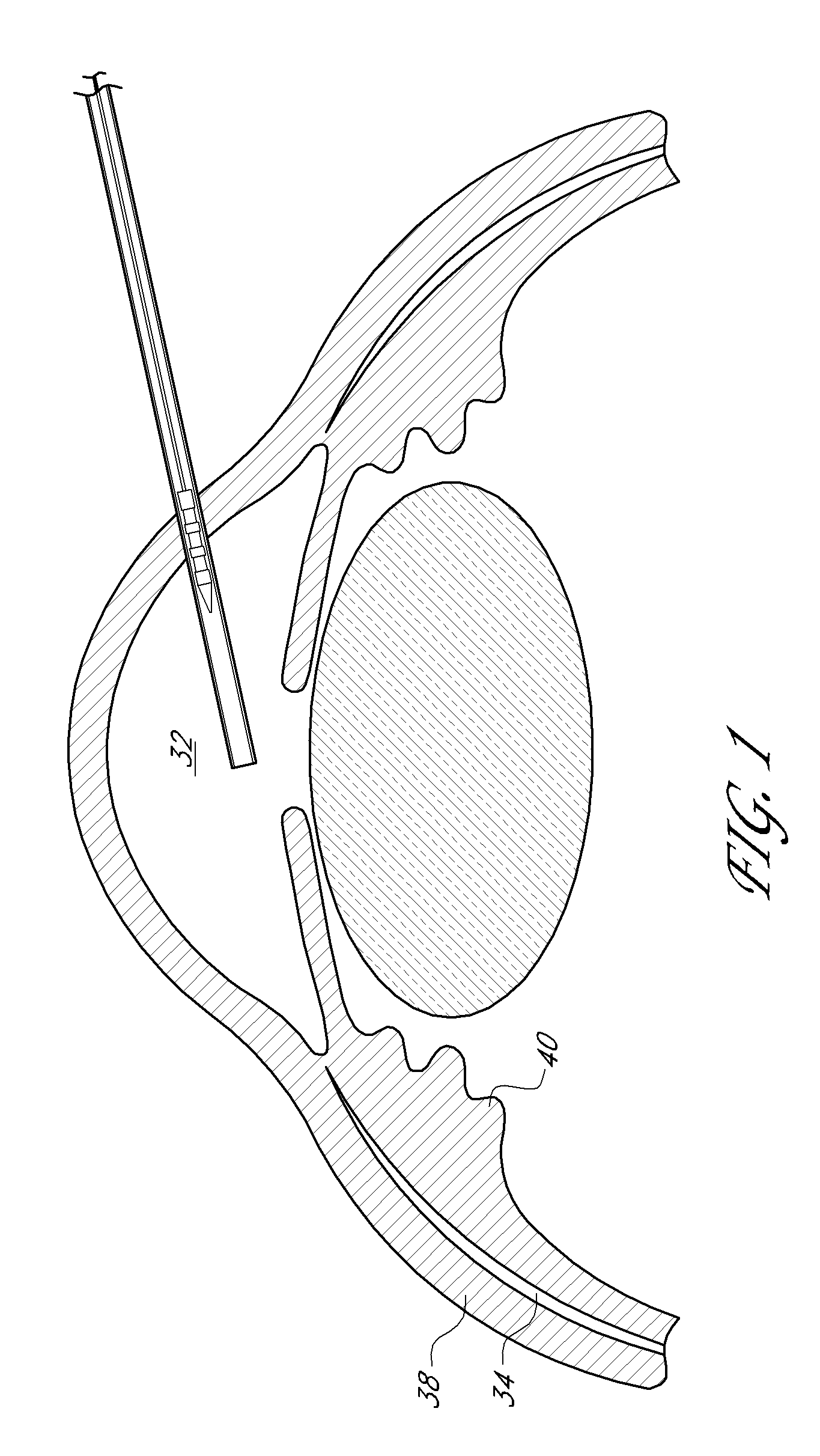
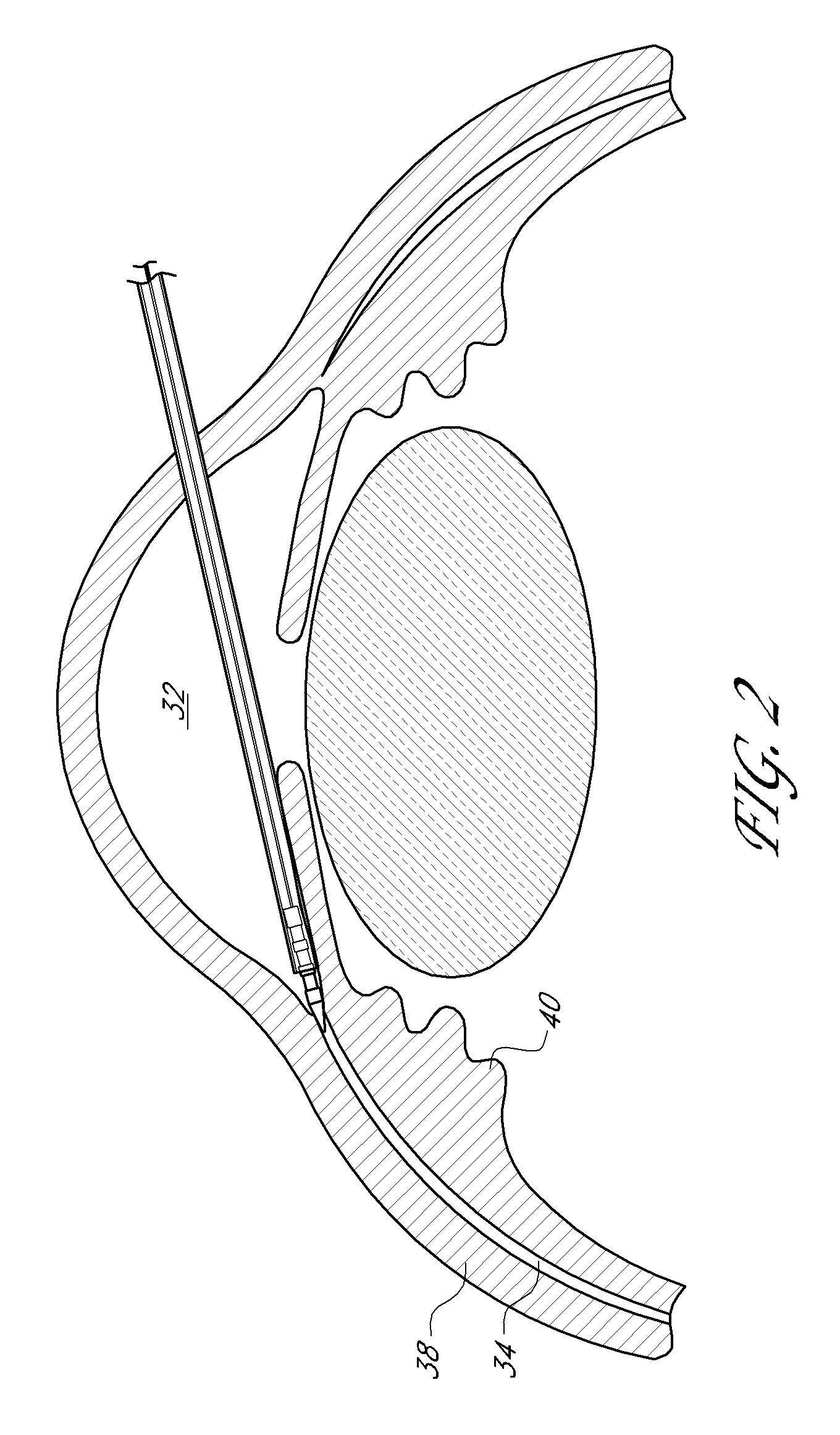
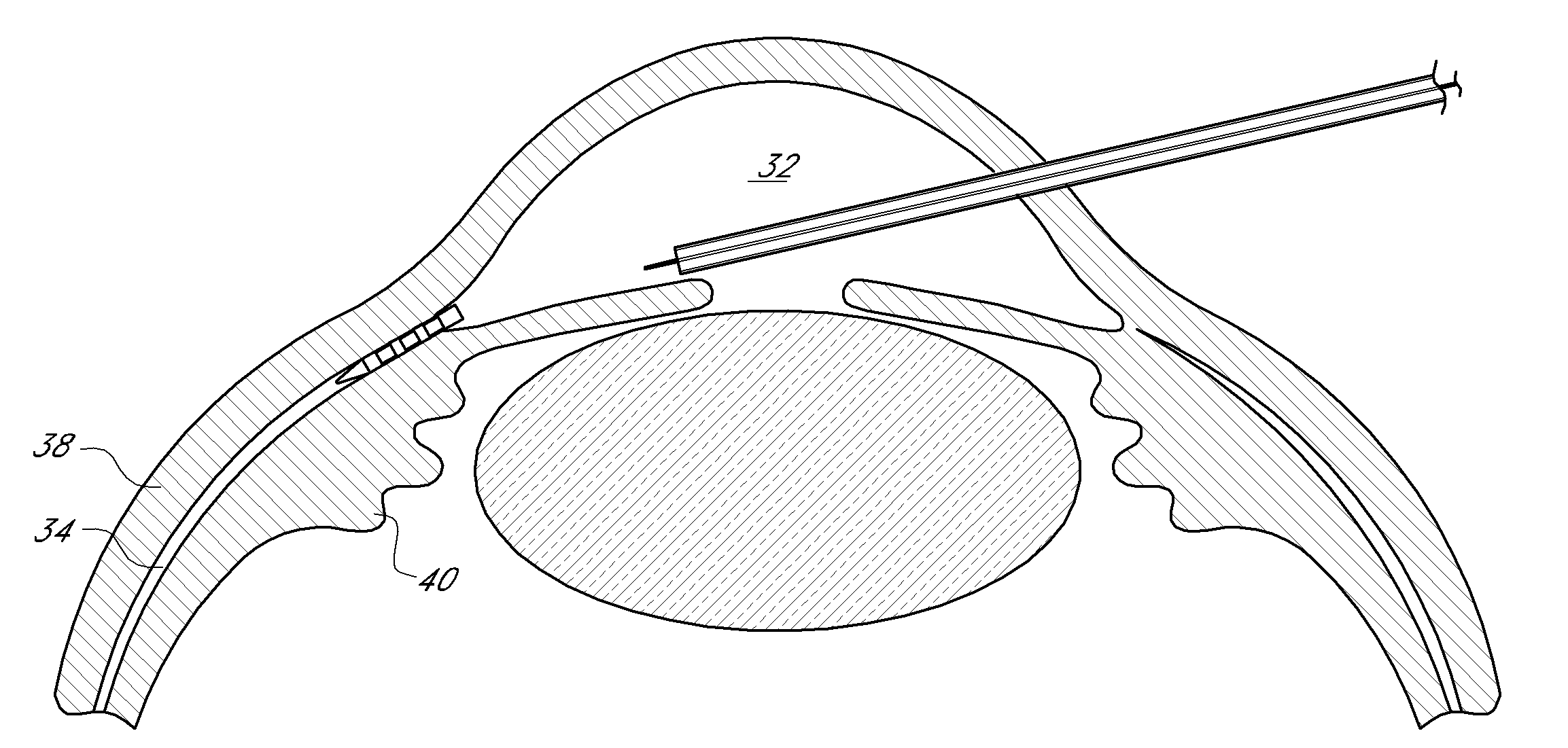
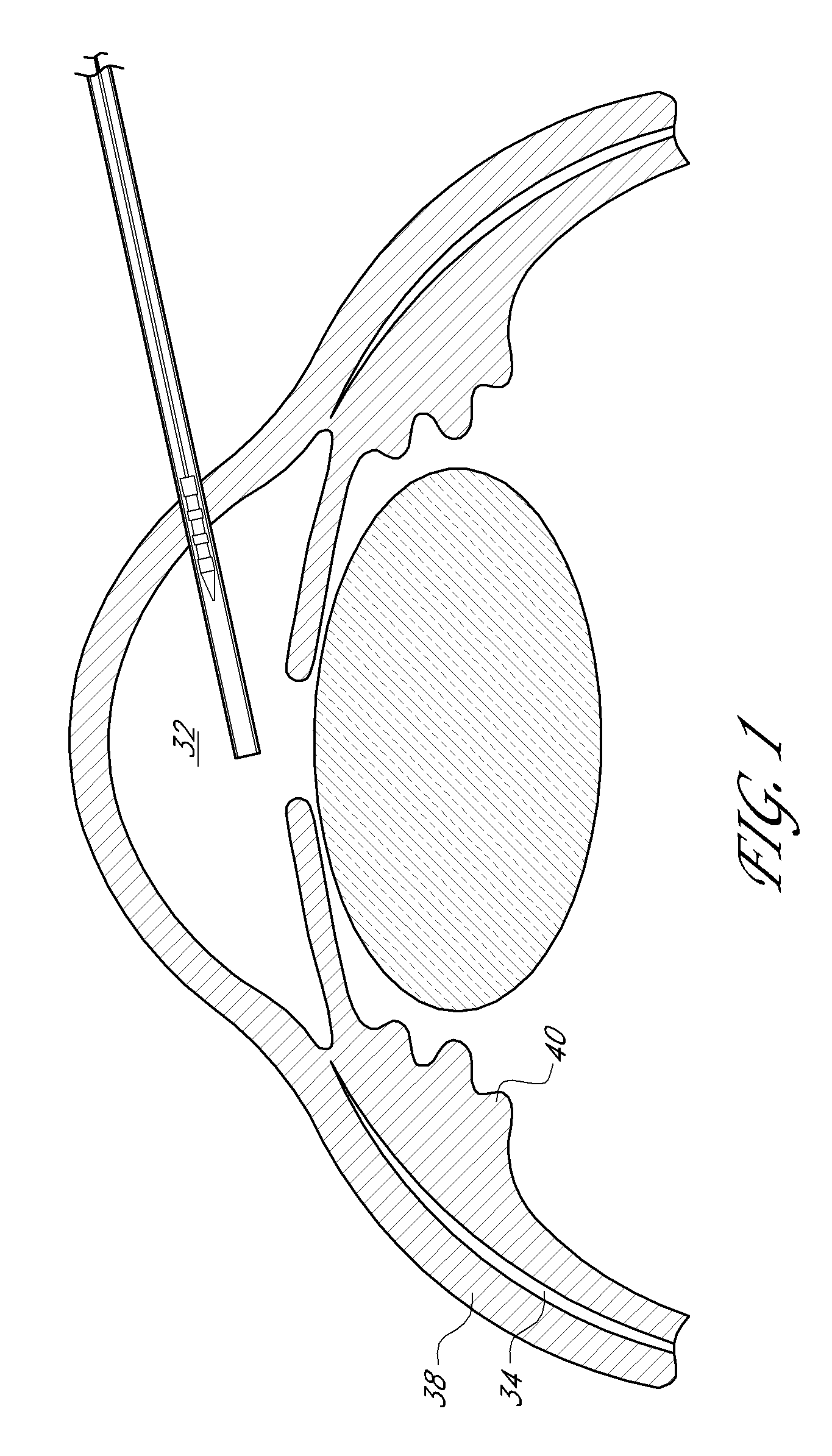
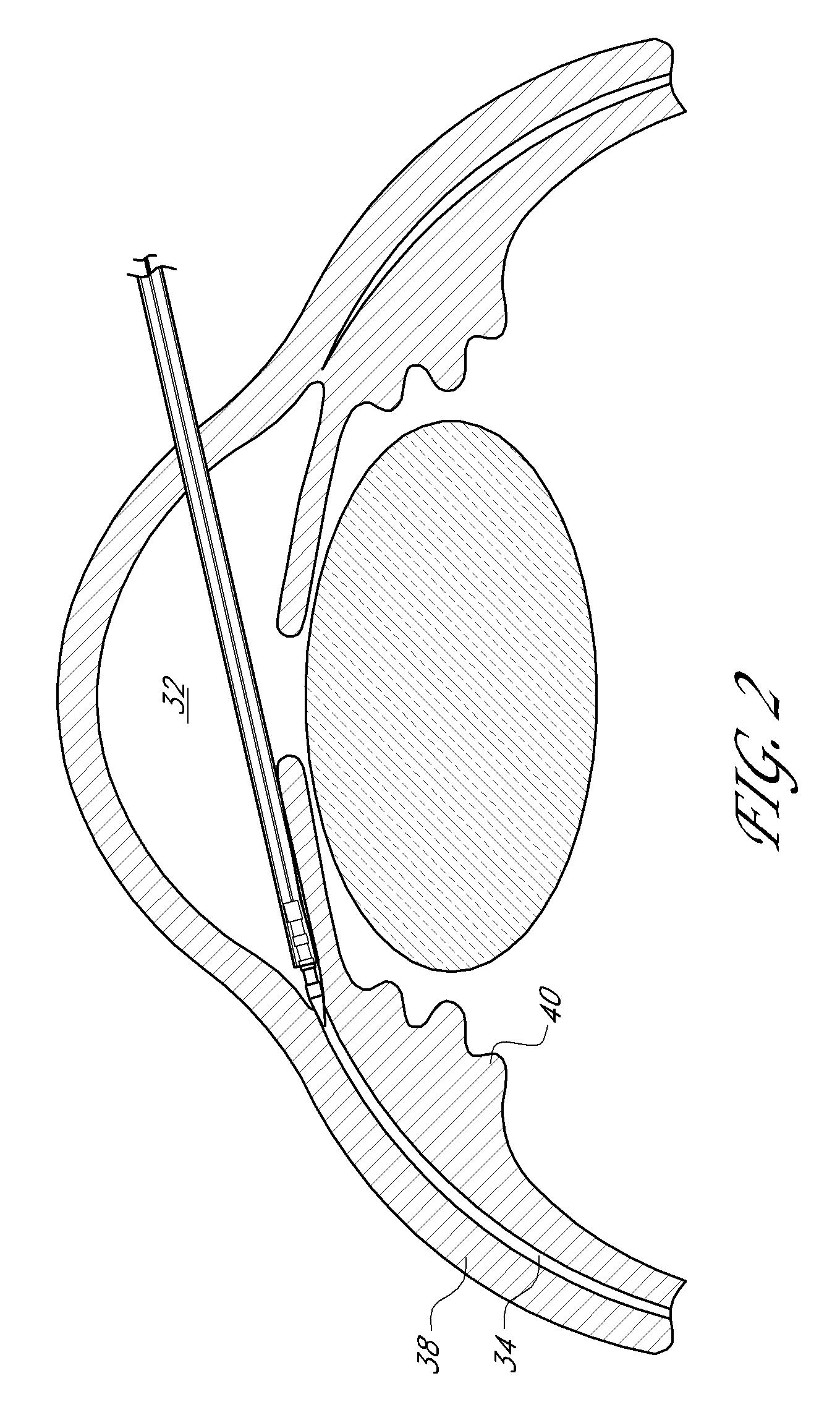
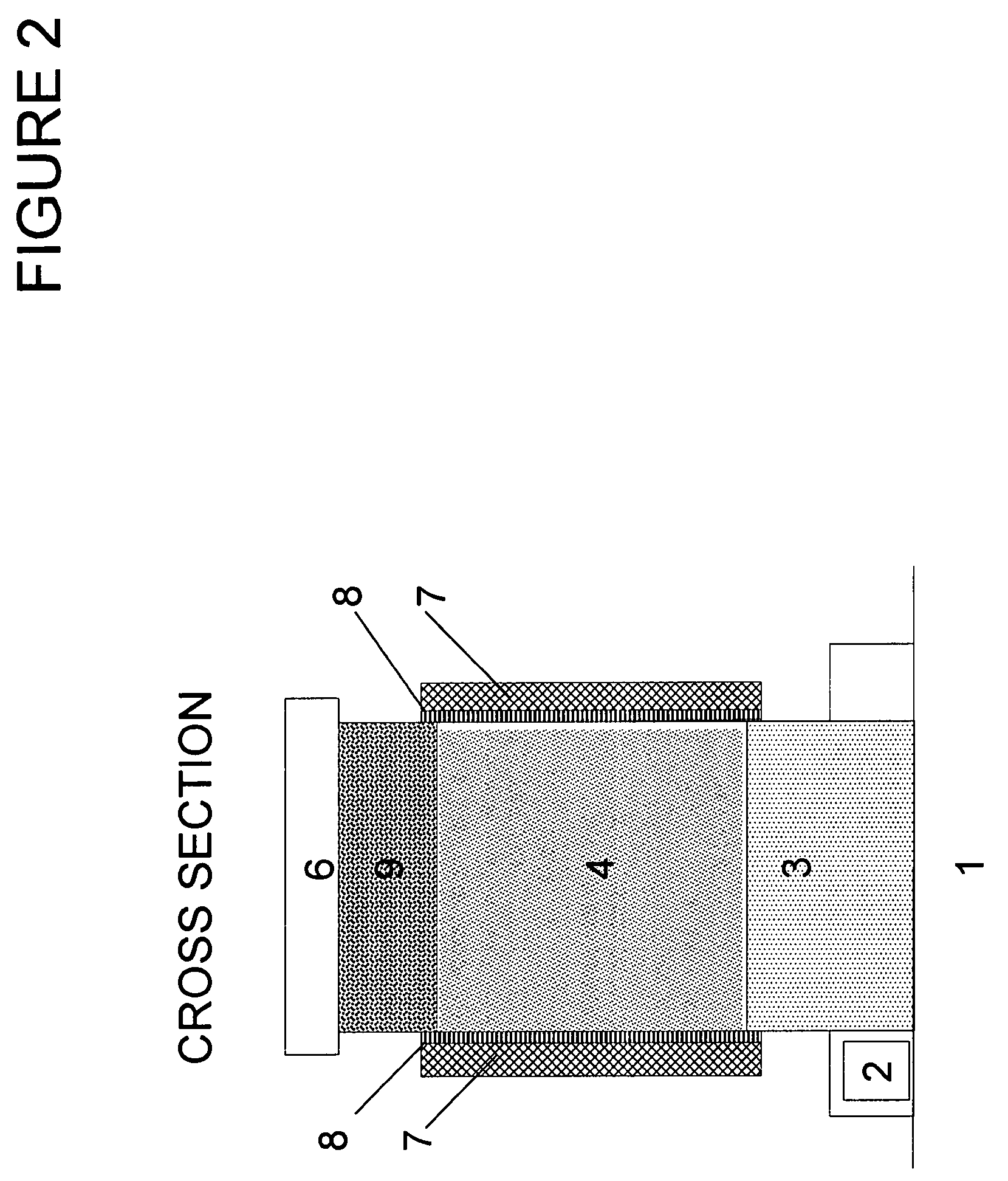
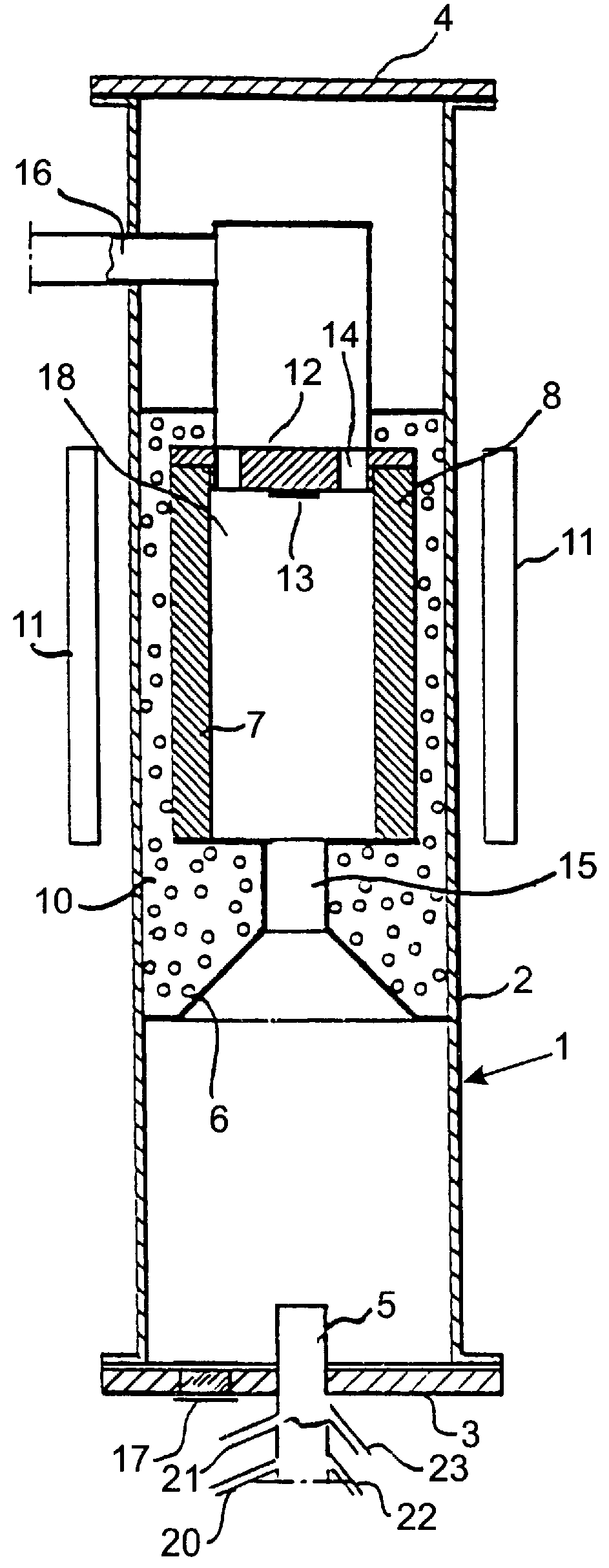
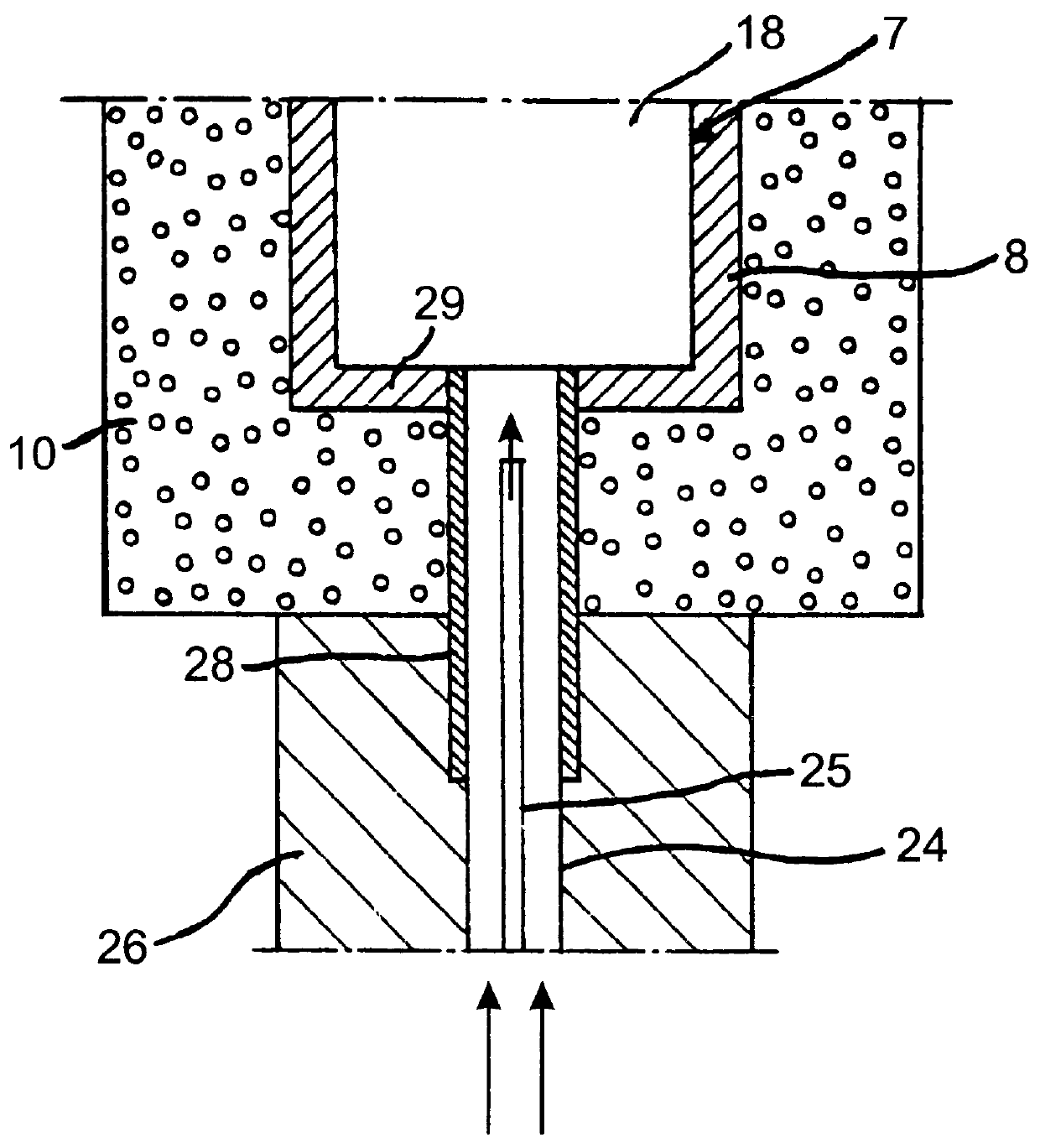
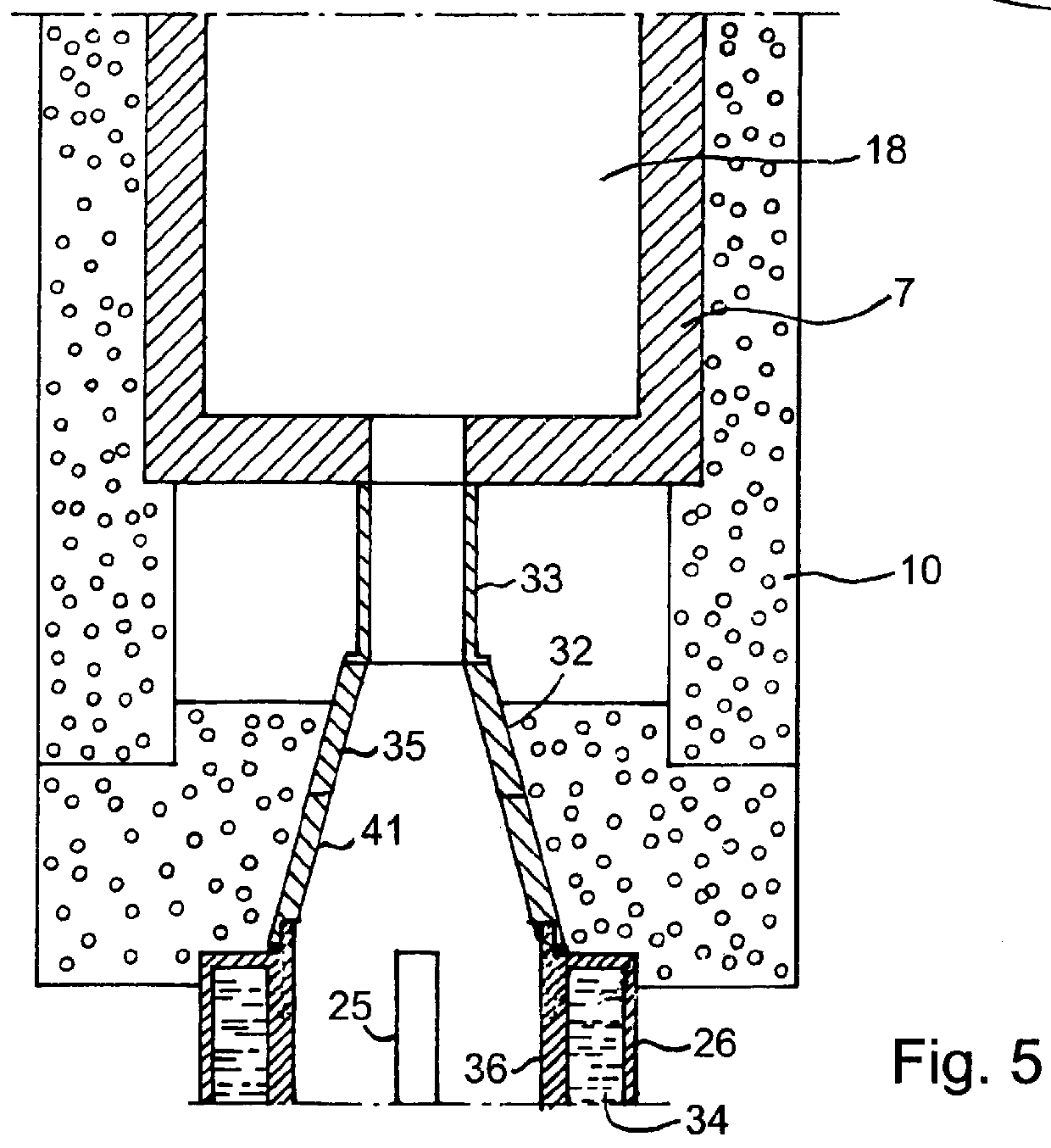
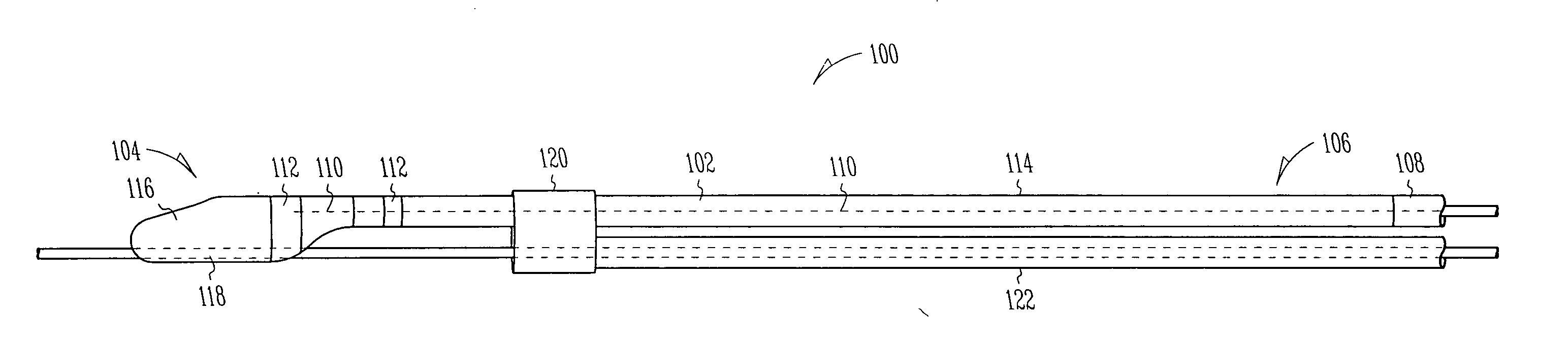
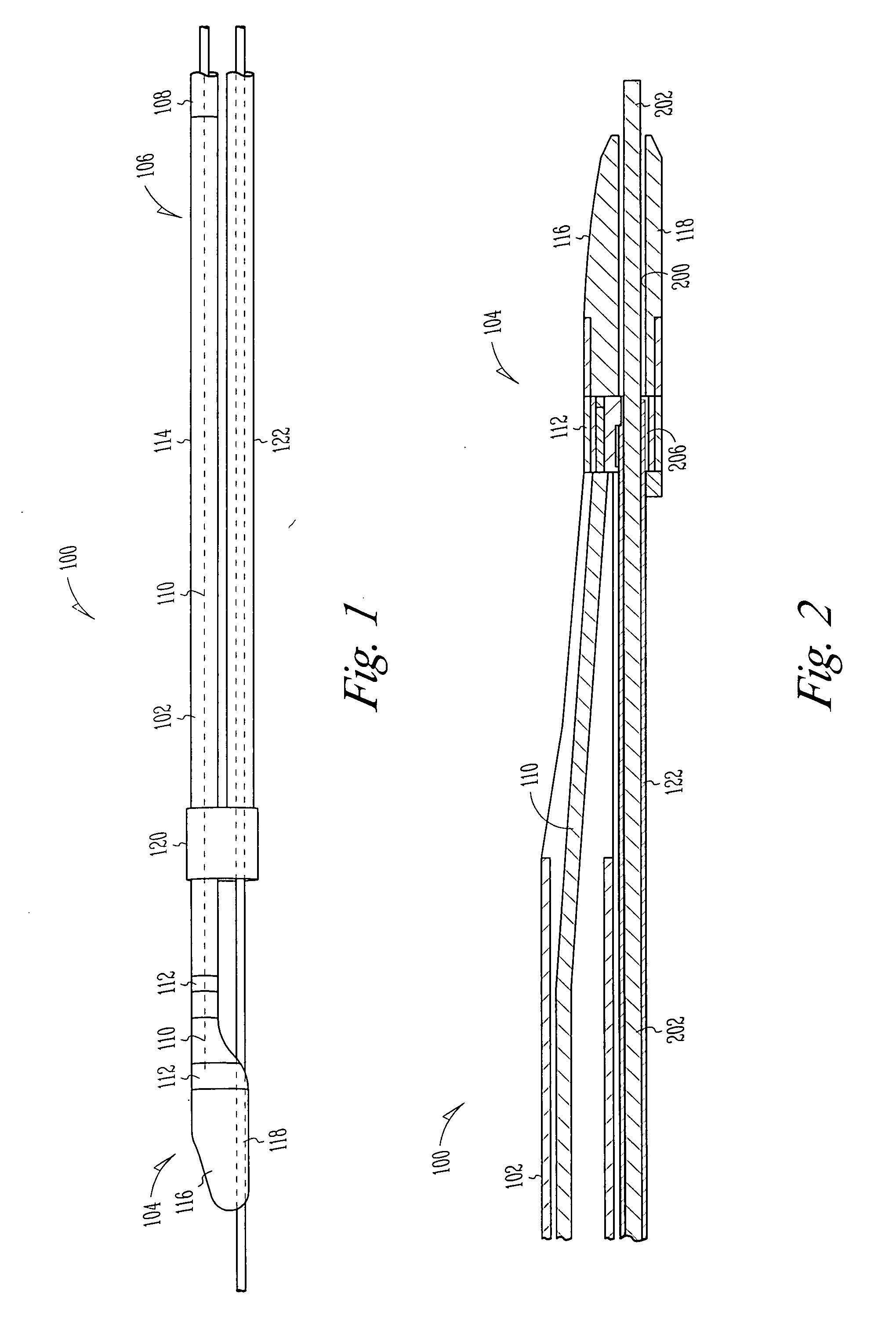
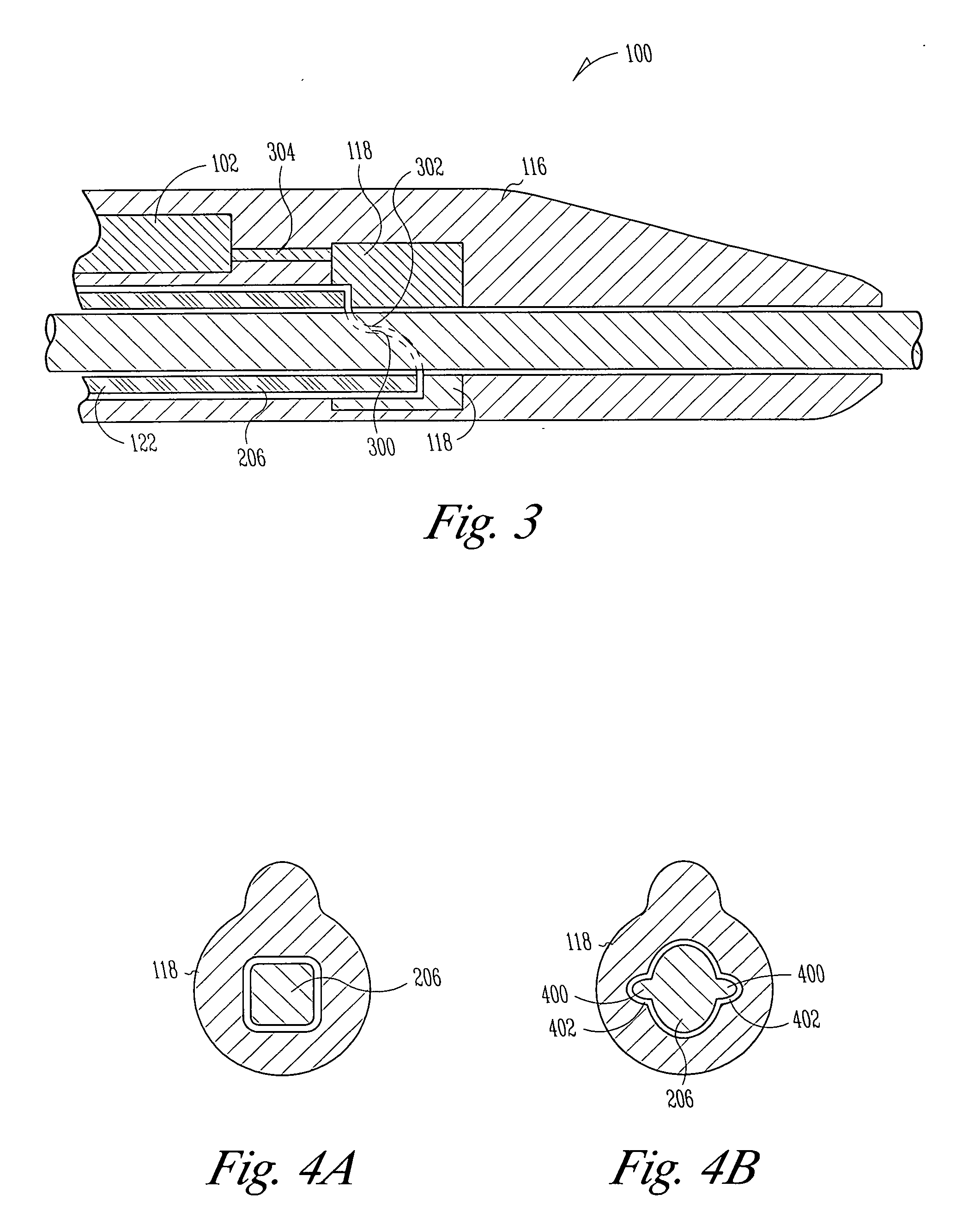
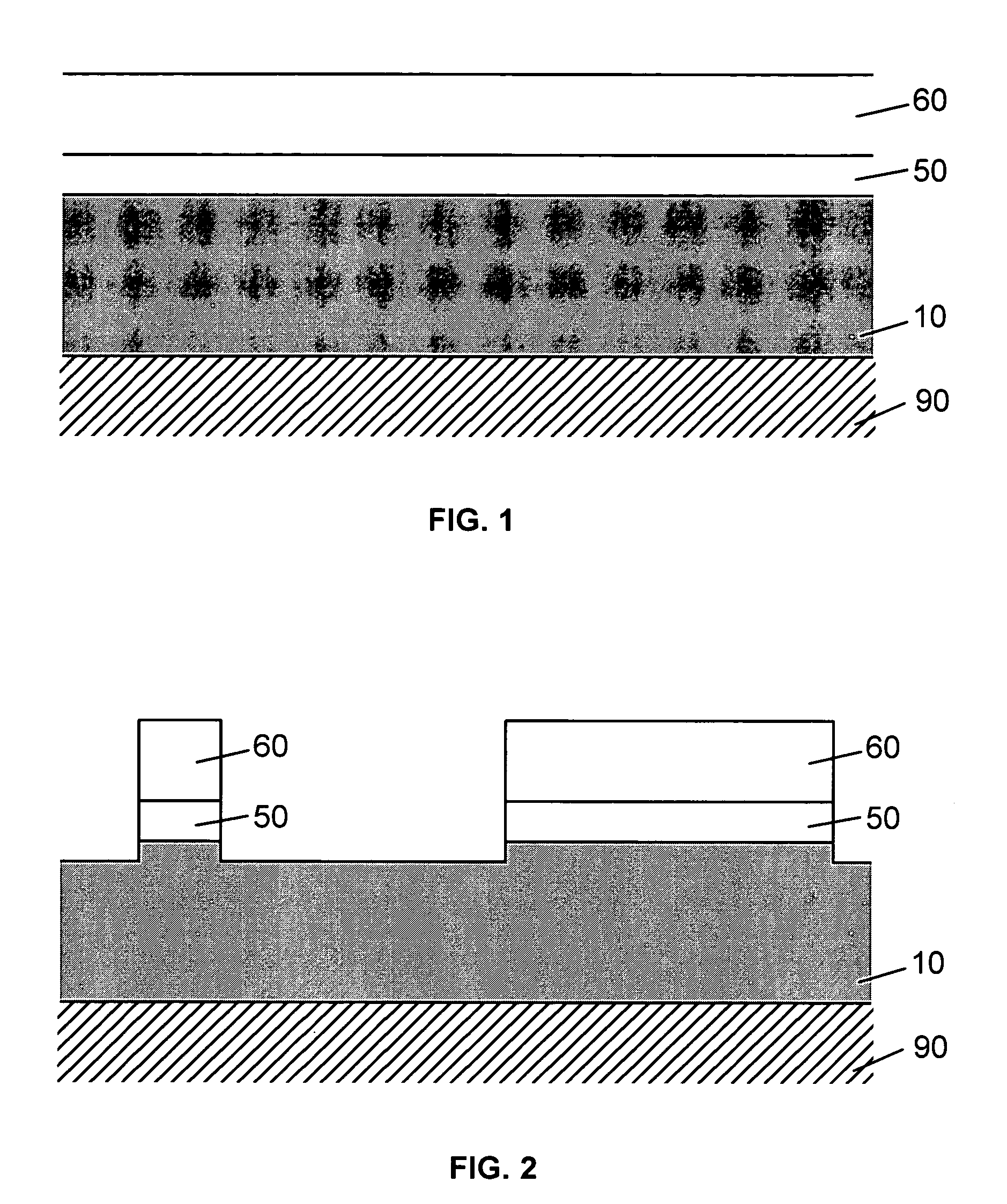
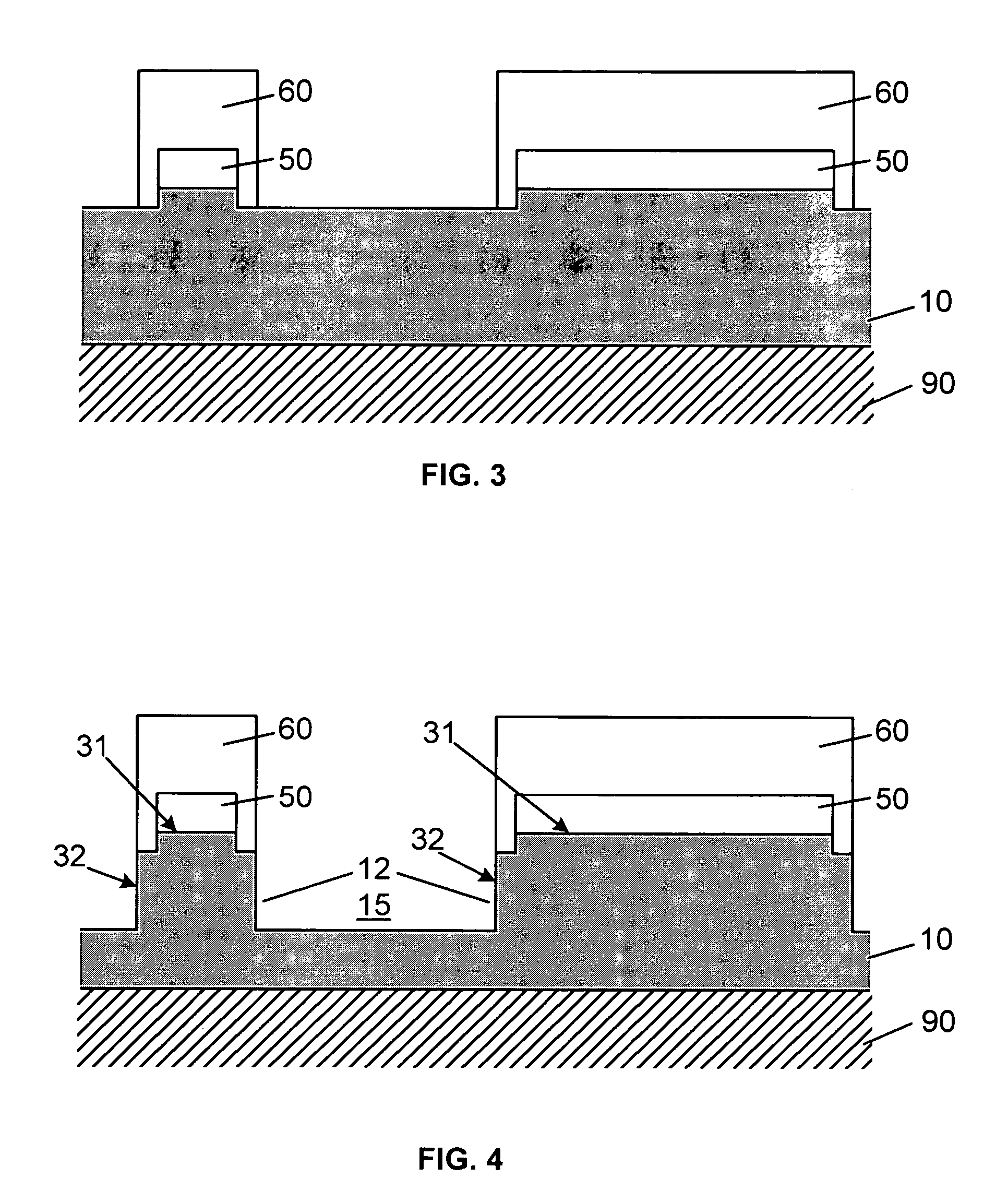
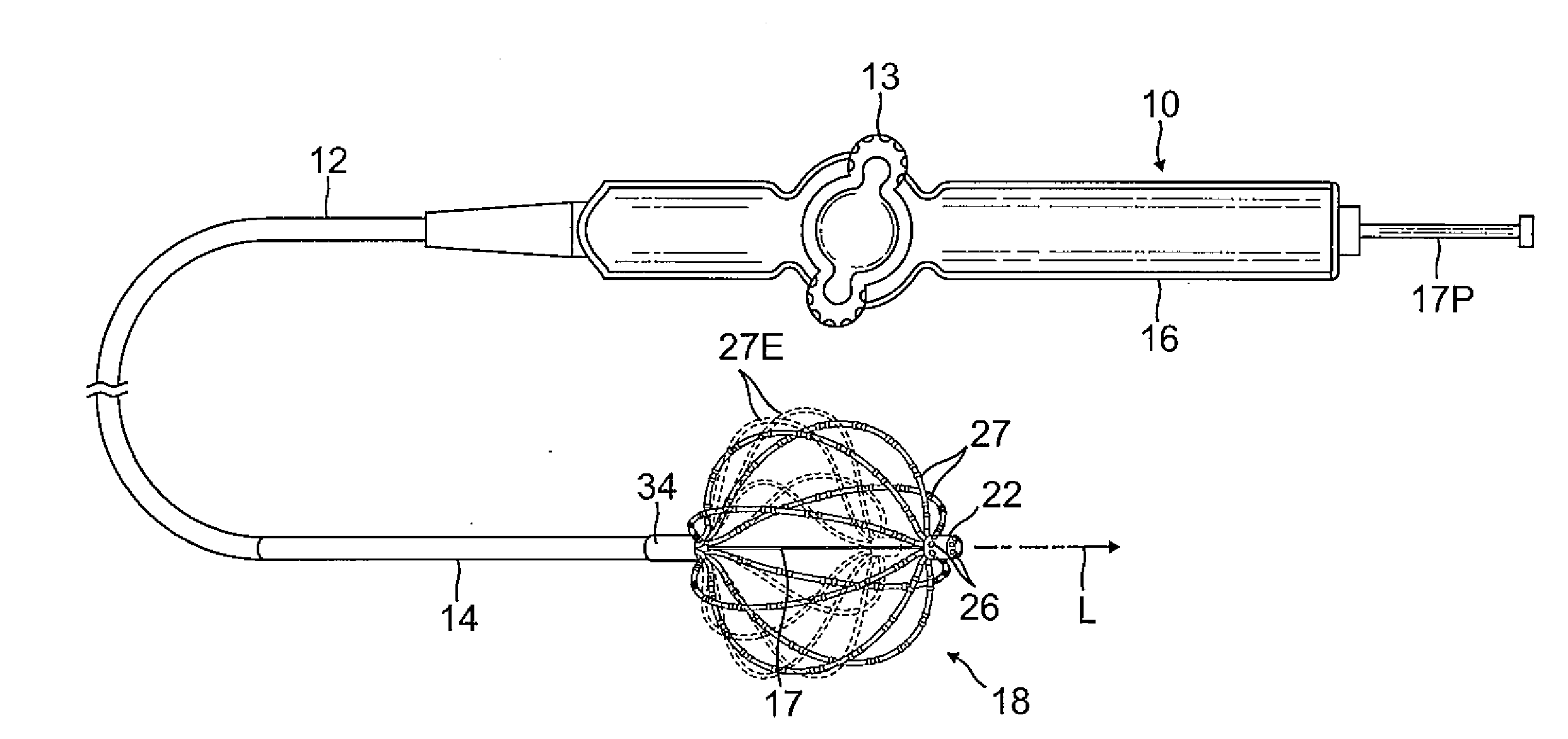
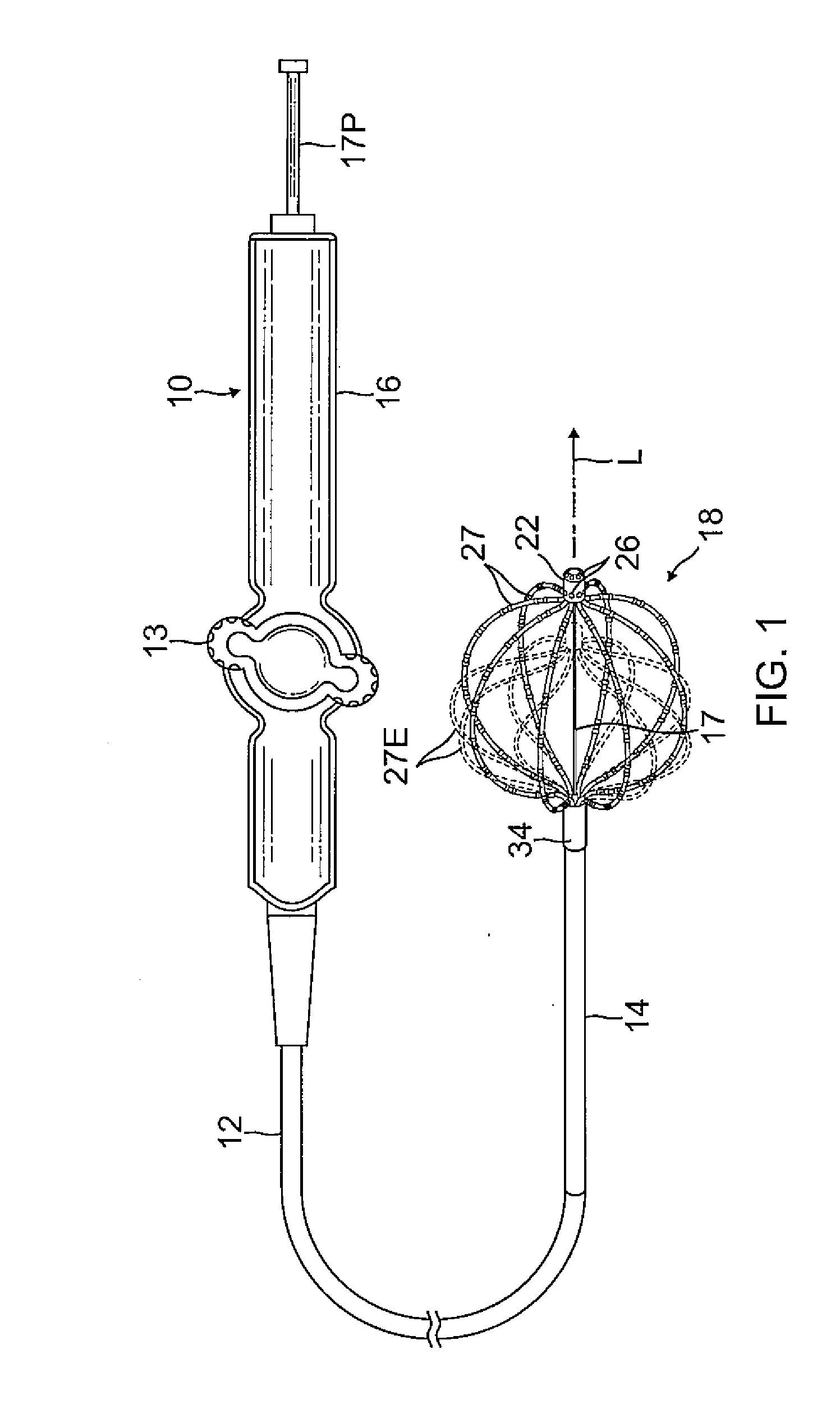
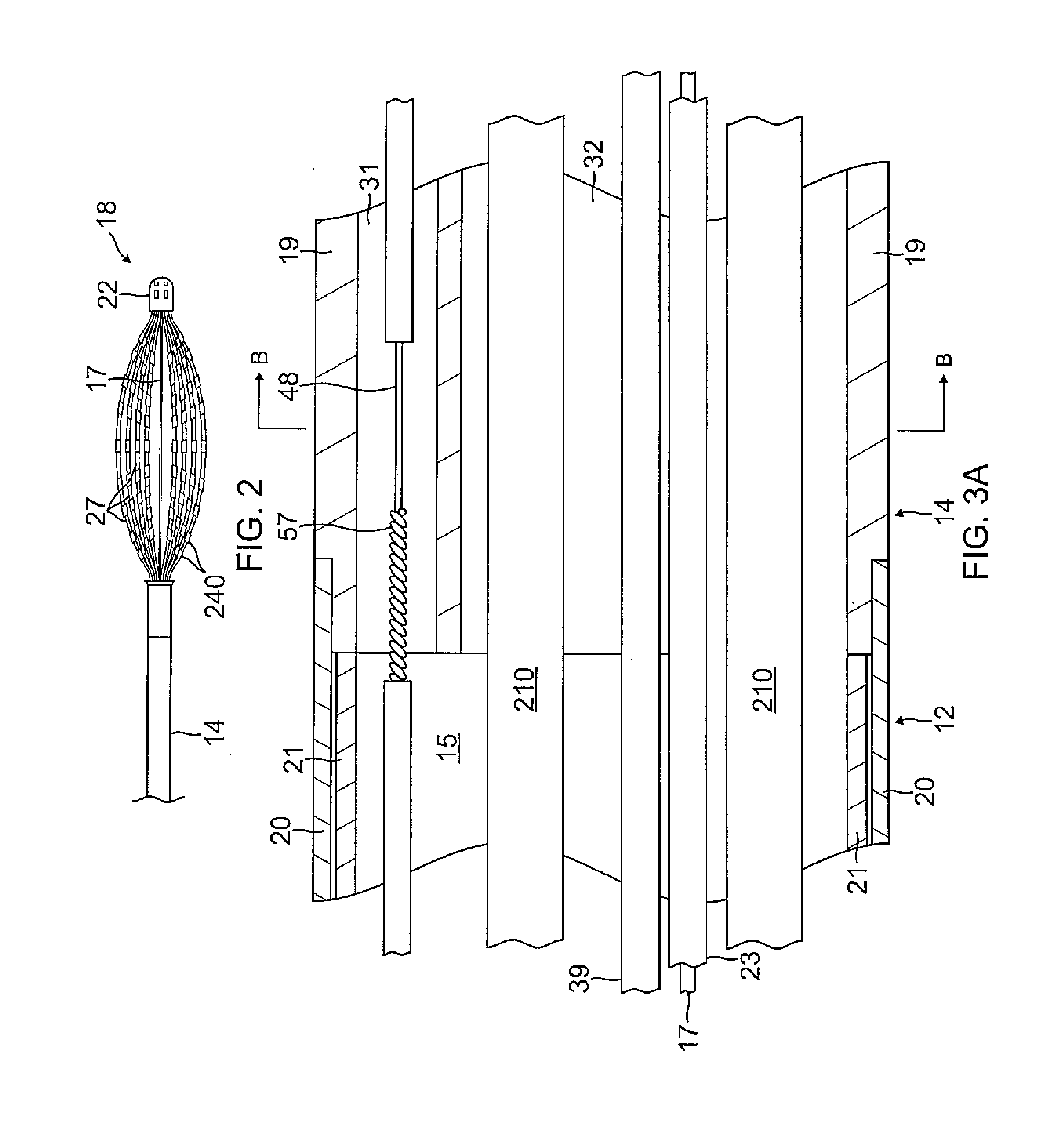
Uveoscleral shunt and methods for implanting same
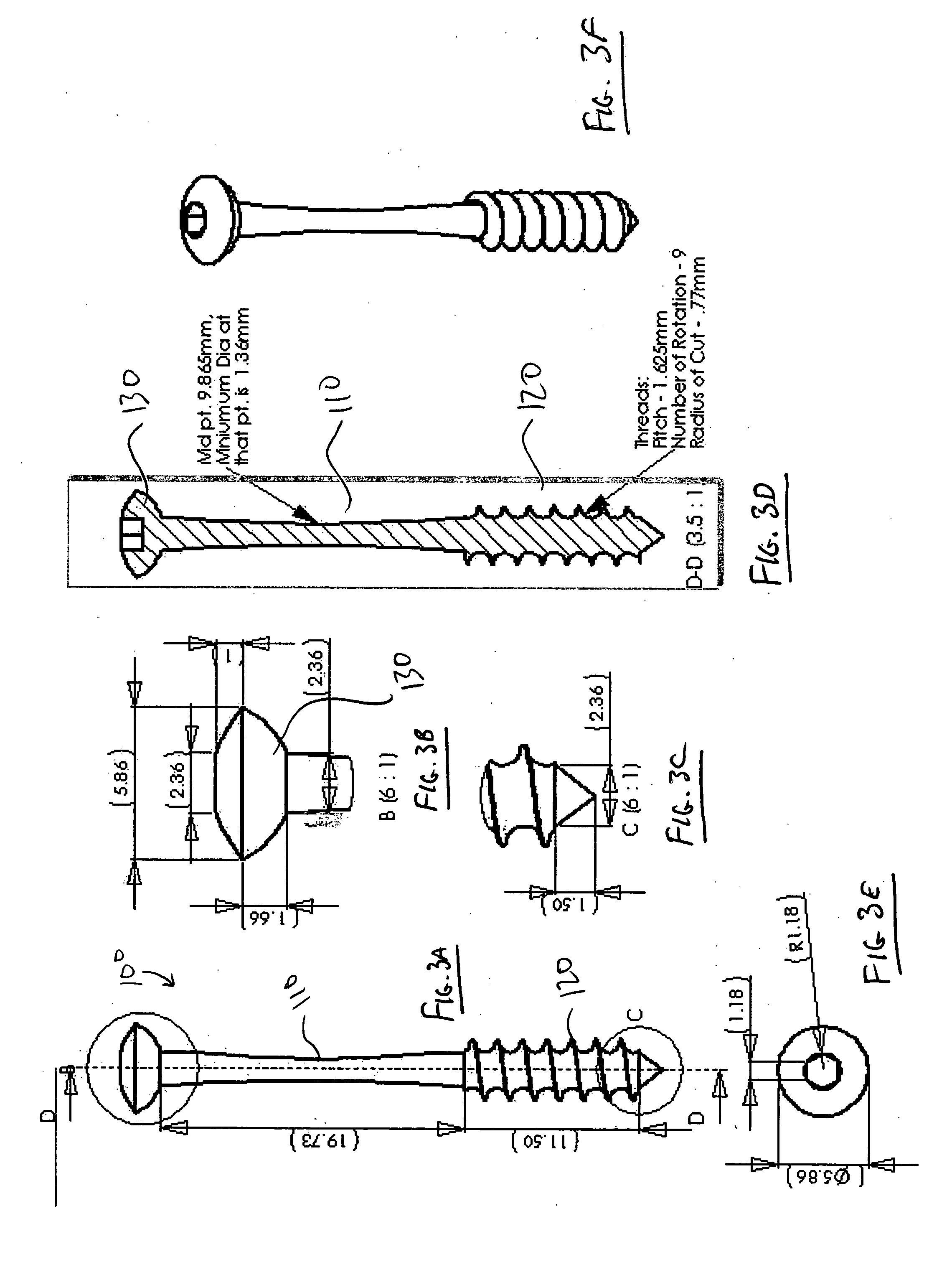
ActiveUS20080228127A1Small sectionAvoid passingSenses disorderEar treatmentCiliary bodySuprachoroidal space
Devices and methods for treating intraocular pressure are disclosed. The devices include shunts for draining aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to the uveoscleral outflow pathway, including the supraciliary space and the suprachoroidal space. The shunts are preferably implanted by ab interno procedures.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
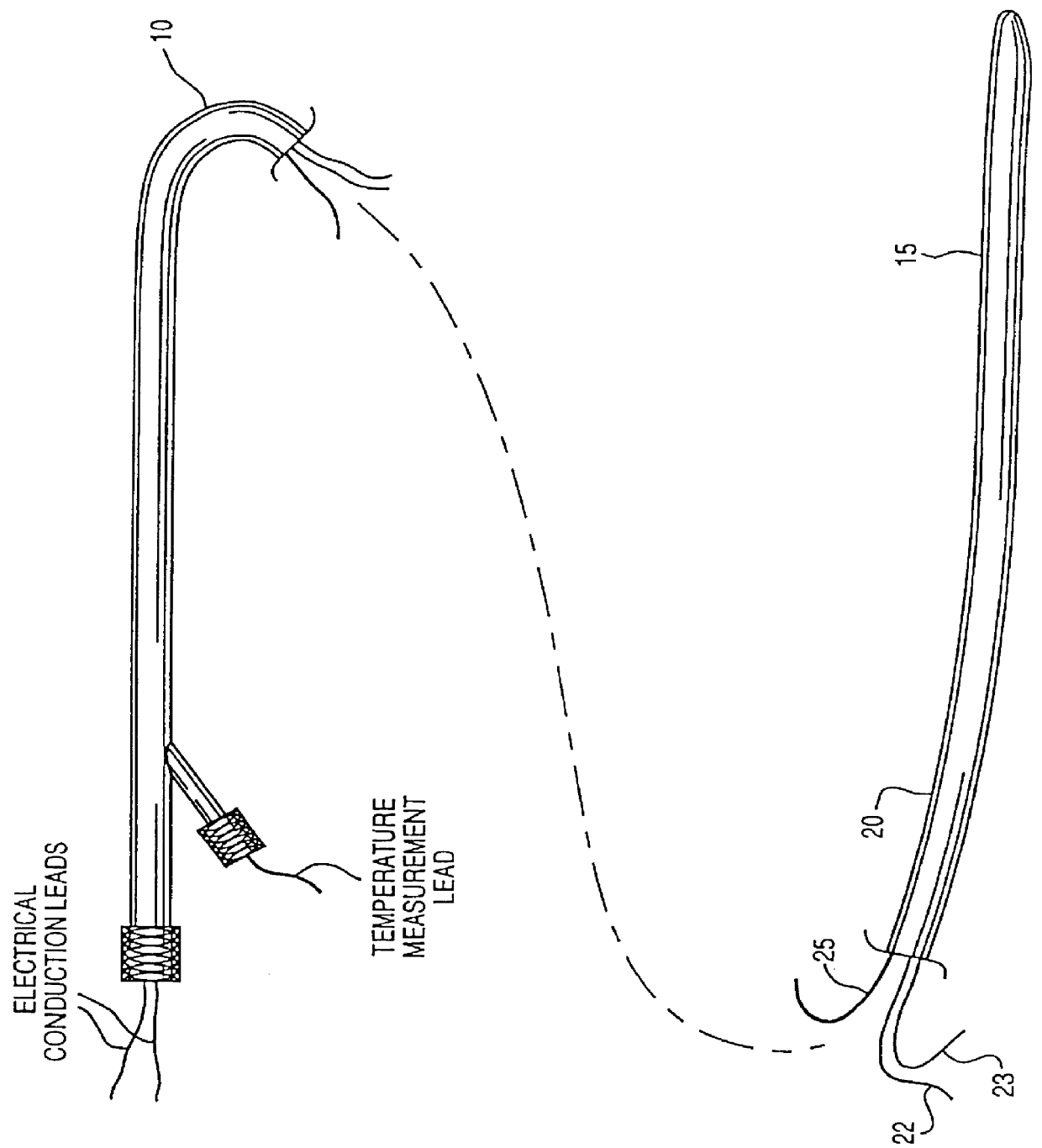
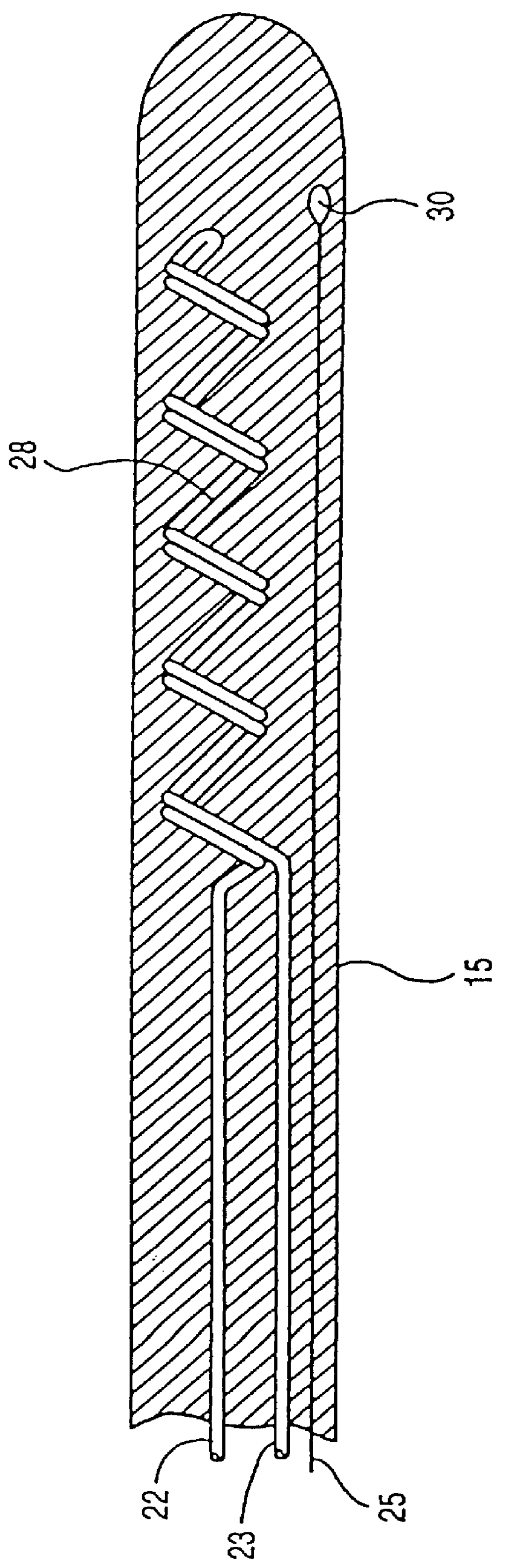
Method and apparatus for controlling a patient's body temperature by in situ blood temperature modifications
InactiveUS6110168AQuickly felt throughout the patient's bodyEliminate damageStentsBalloon catheterHypothermia inducedHigh body temperature
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the internal body temperature of a patient. According to the present invention, a catheter is inserted through an incision into a large blood vessel of a patient. By selectively heating or cooling a portion of the catheter lying within the blood vessel, heat may be transferred to or from blood flowing within the vessel and the patient's body temperature may thereby be increased or decreased as desired. The invention will find use in treating undesirable conditions of hypothermia and hyperthermia, or for inducing a condition of artificial hypothermia when desired.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Neuro-thrombectomy catheter and method of use
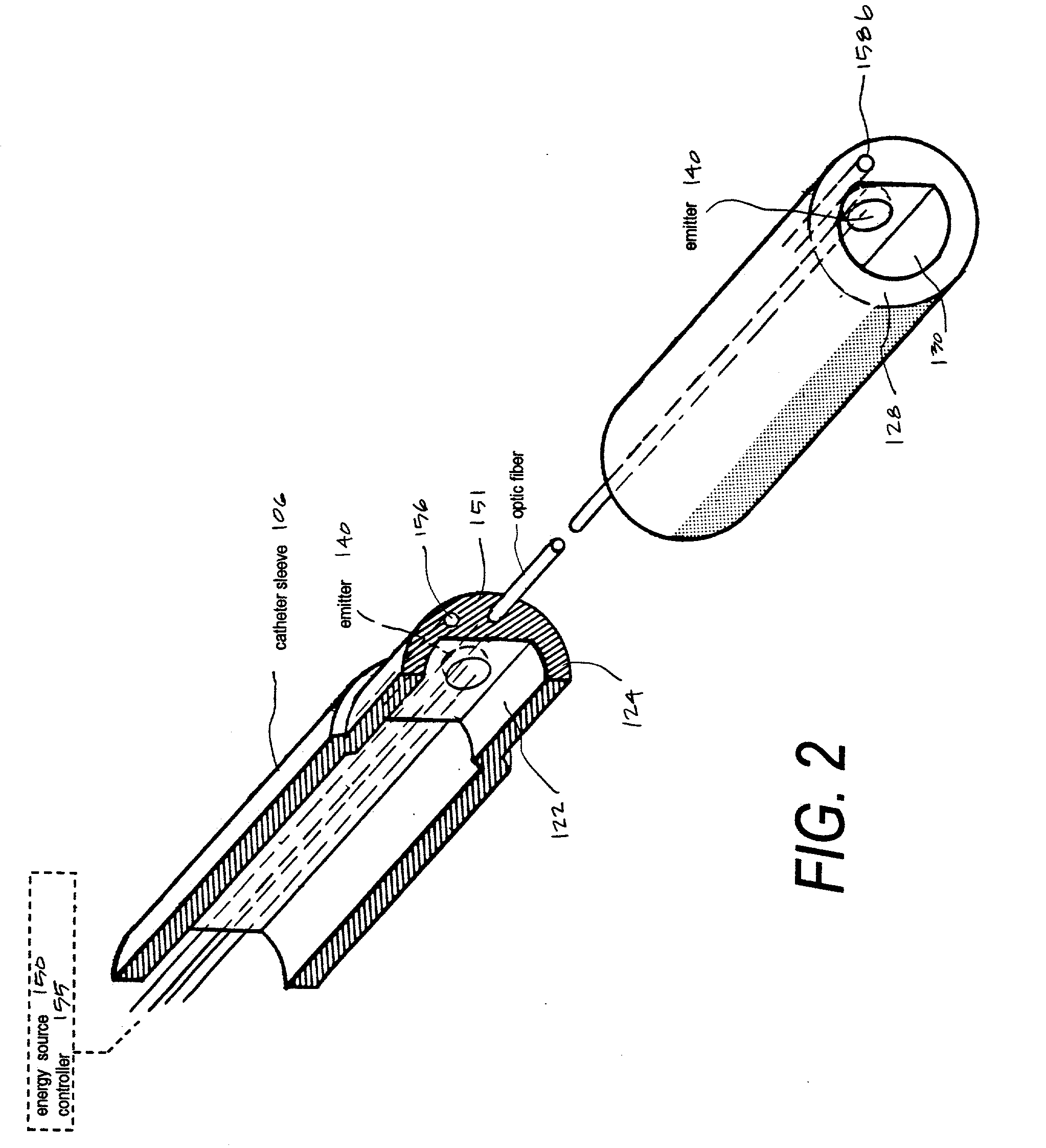
A microcatheter for removing thromboemboli from cerebral arteries in patients suffering from ischemic stroke. The microcatheter provides an extraction lumen that can be scaled to a very small diameter that is still capable of extracting and emulsifying thrombus without clogging the channel. The microcatheter of the invention uses a series of spaced apart energy application mechanisms along the entire length of the catheter's extraction lumen to develop sequential pressure differentials to cause fluid flows by means of cavitation, and to contemporaneously ablate embolic materials drawn through the extraction lumen by cavitation to thereby preventing clogging of the lumen. The catheter system thus provides a functional high-pressure extraction lumen that is far smaller than prior art catheter systems. Preferred mechanisms for energy delivery are (i) a laser source and controller coupled to optic fibers in the catheter wall or (ii) an Rf source coupled to paired electrodes within the extraction lumen. Each energy emitter can apply energy to fluid media in the extraction channel of the catheter-wherein the intense energy pulses can be sequentially timed to cause fluid media flows in the proximal direction in the channel.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
Cardiac mapping catheter
ActiveUS8103327B2Small and to manufactureStable configurationLine/current collector detailsElectrocardiographyNon contact mappingCardiac mapping catheter
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Implant
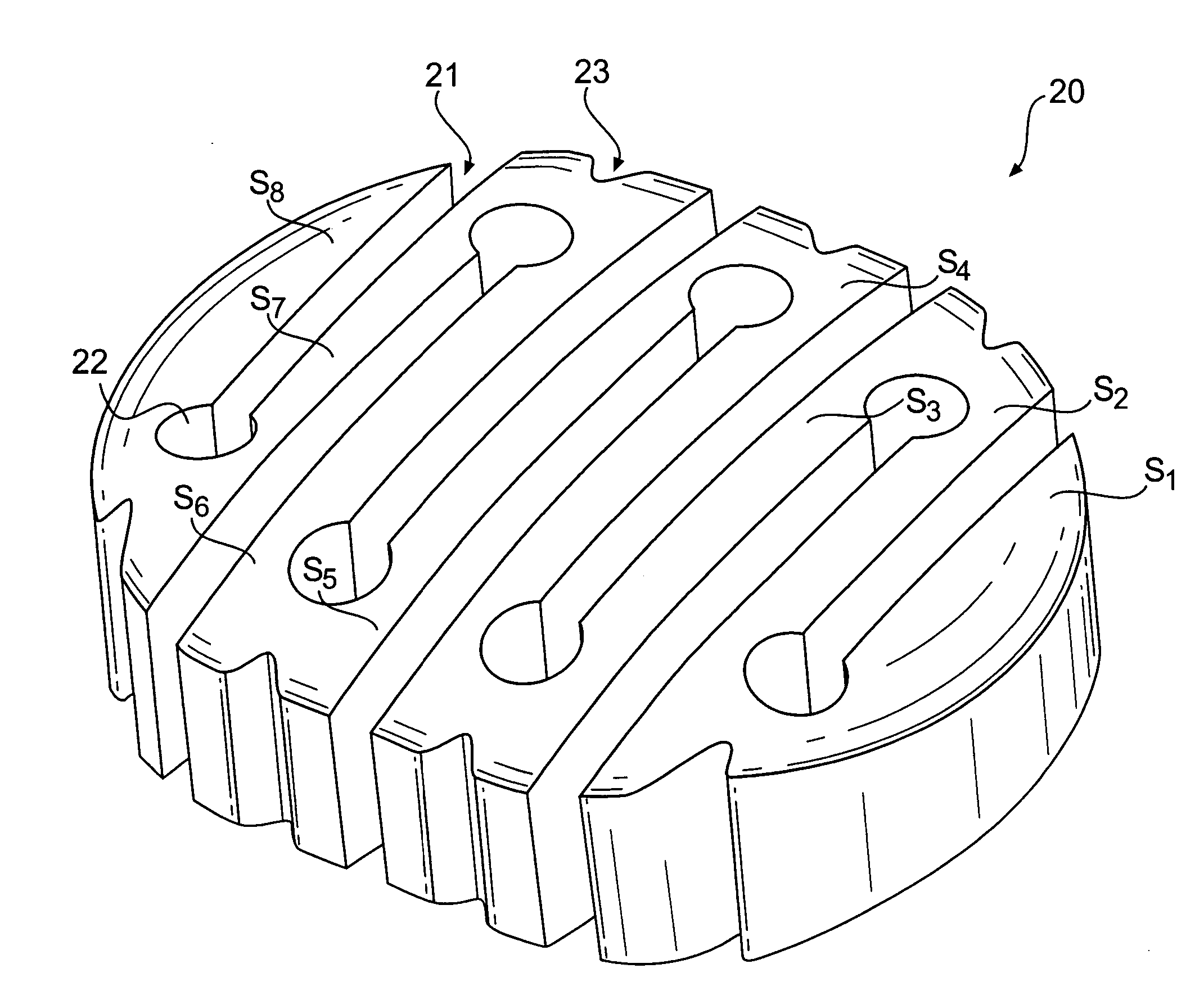
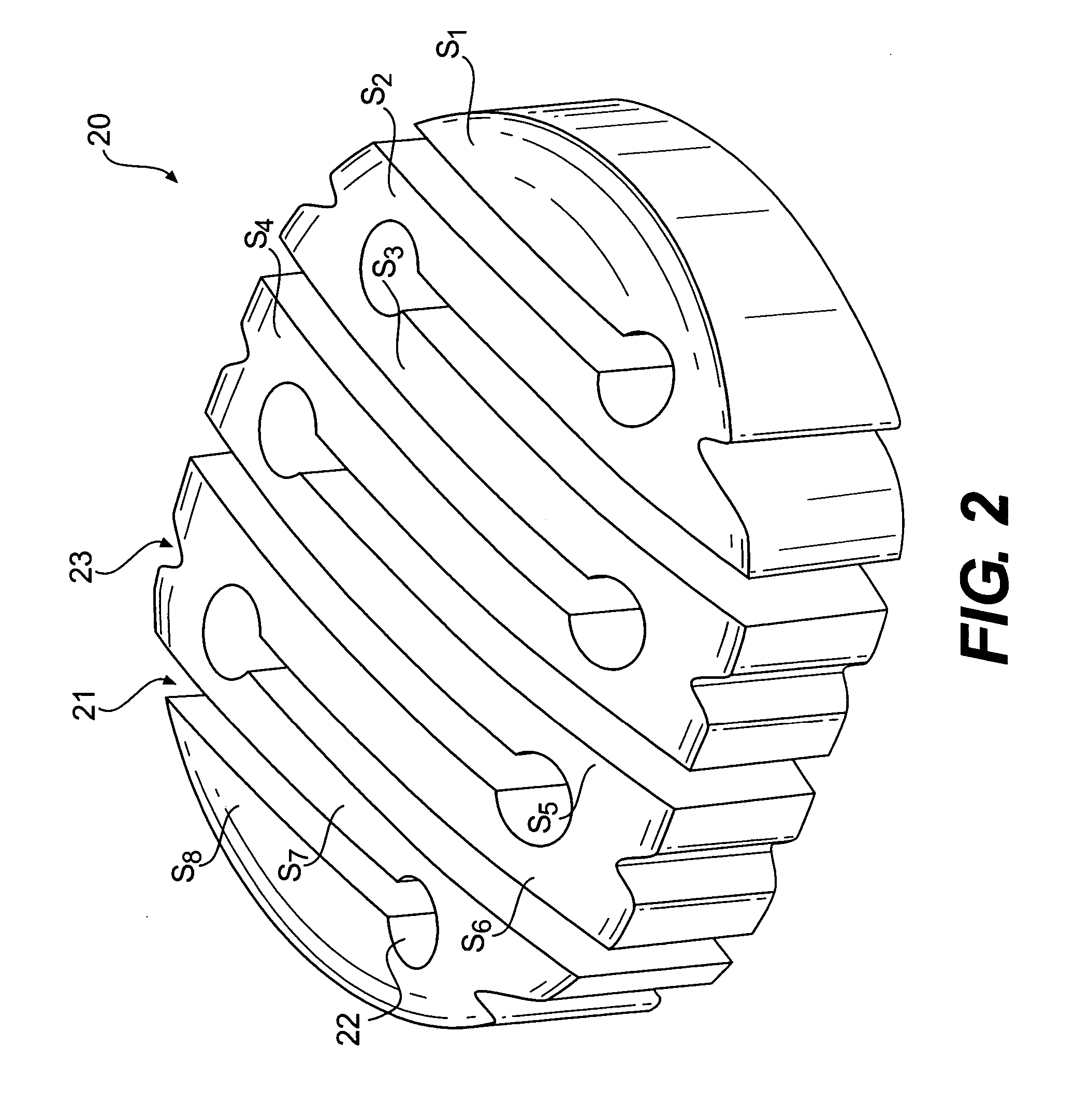
InactiveUS20060247781A1Small cross sectionPromoting functional performanceBone implantJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringIntervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc nucleus replacement is provided that is configurable into a first configuration to be assumed while the replacement is implanted in the nuclear cavity and a second configuration to be assumed during the procedure of inserting the replacement into the nuclear cavity. The first configuration may have an accordion-like structure formed by a plurality of sections folded in an alternating, zigzag-like manner, and may be sized and shaped to conform to the nuclear cavity. The second configuration may be formed by straightening the plurality of folded sections into an unfolded, elongated, linear member, thereby affording a smaller effective cross-section. The nucleus replacement may be made of an elastic material having shape memory and may be formed so that the first configuration is an unmanipulated or relaxed configuration and the second configuration is a manipulated or unrelaxed configuration.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Locking nail for the repair of femur shaft fractures
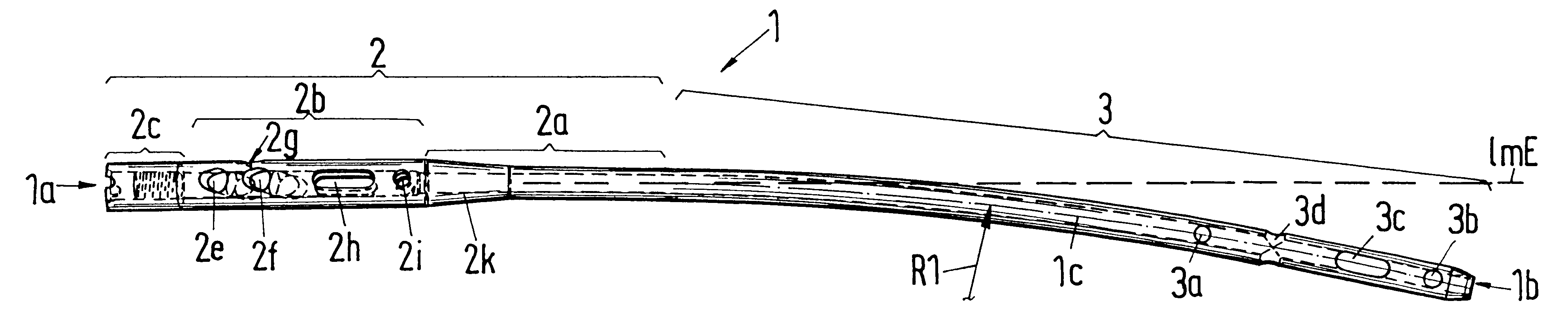
InactiveUS6461360B1Great exertionGood mechanical holdInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFEMUR SHAFTBone screws
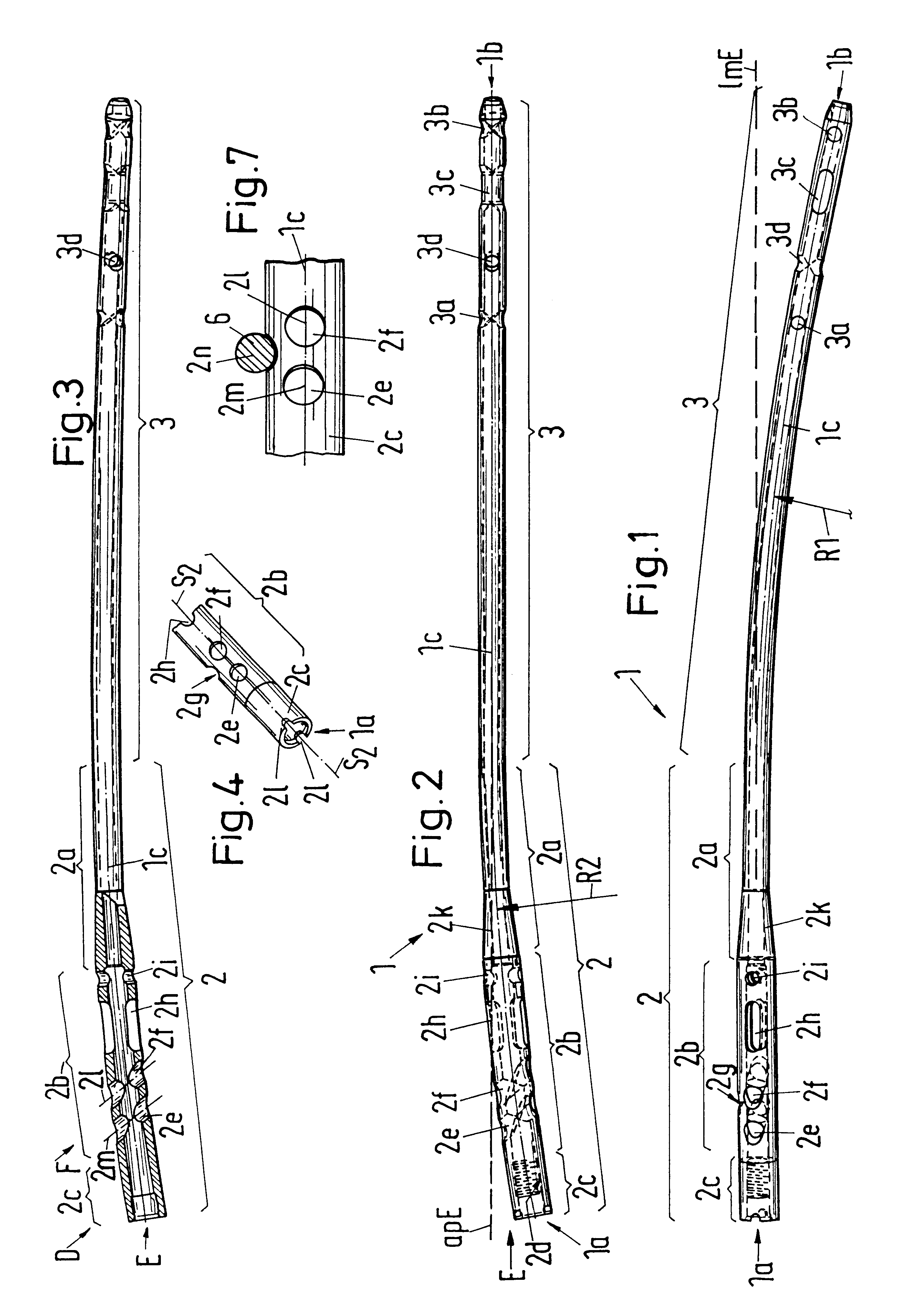
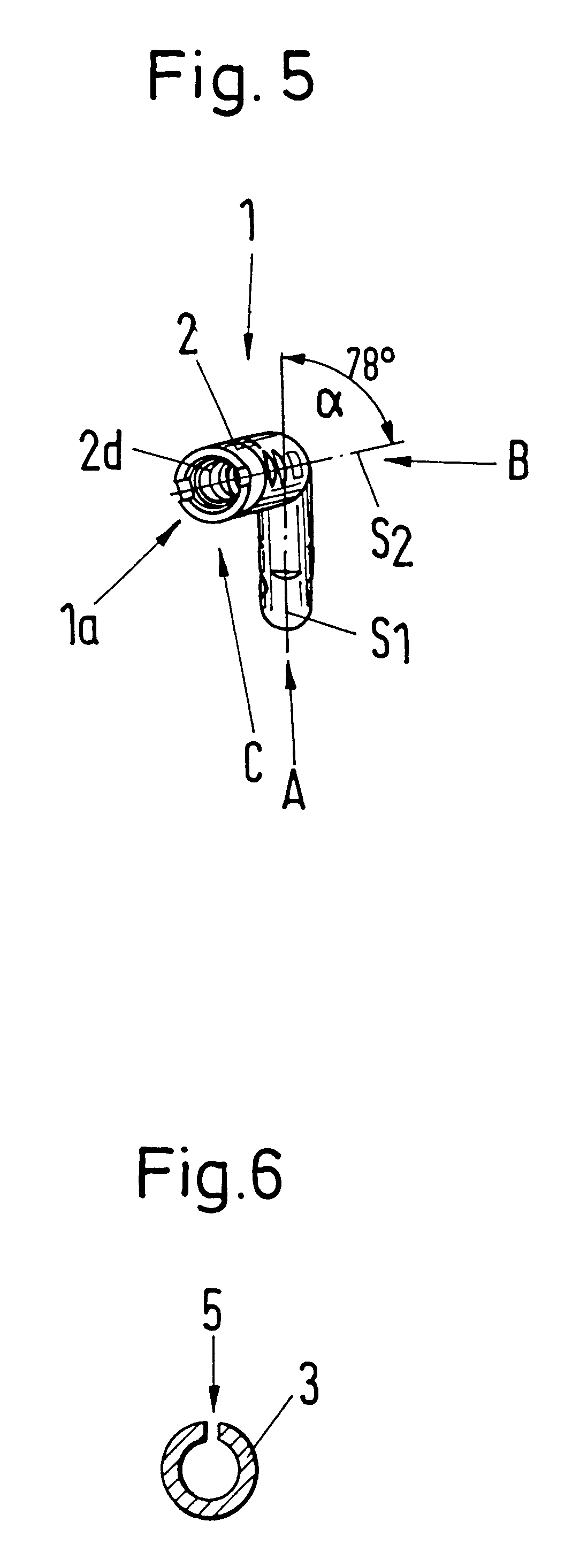
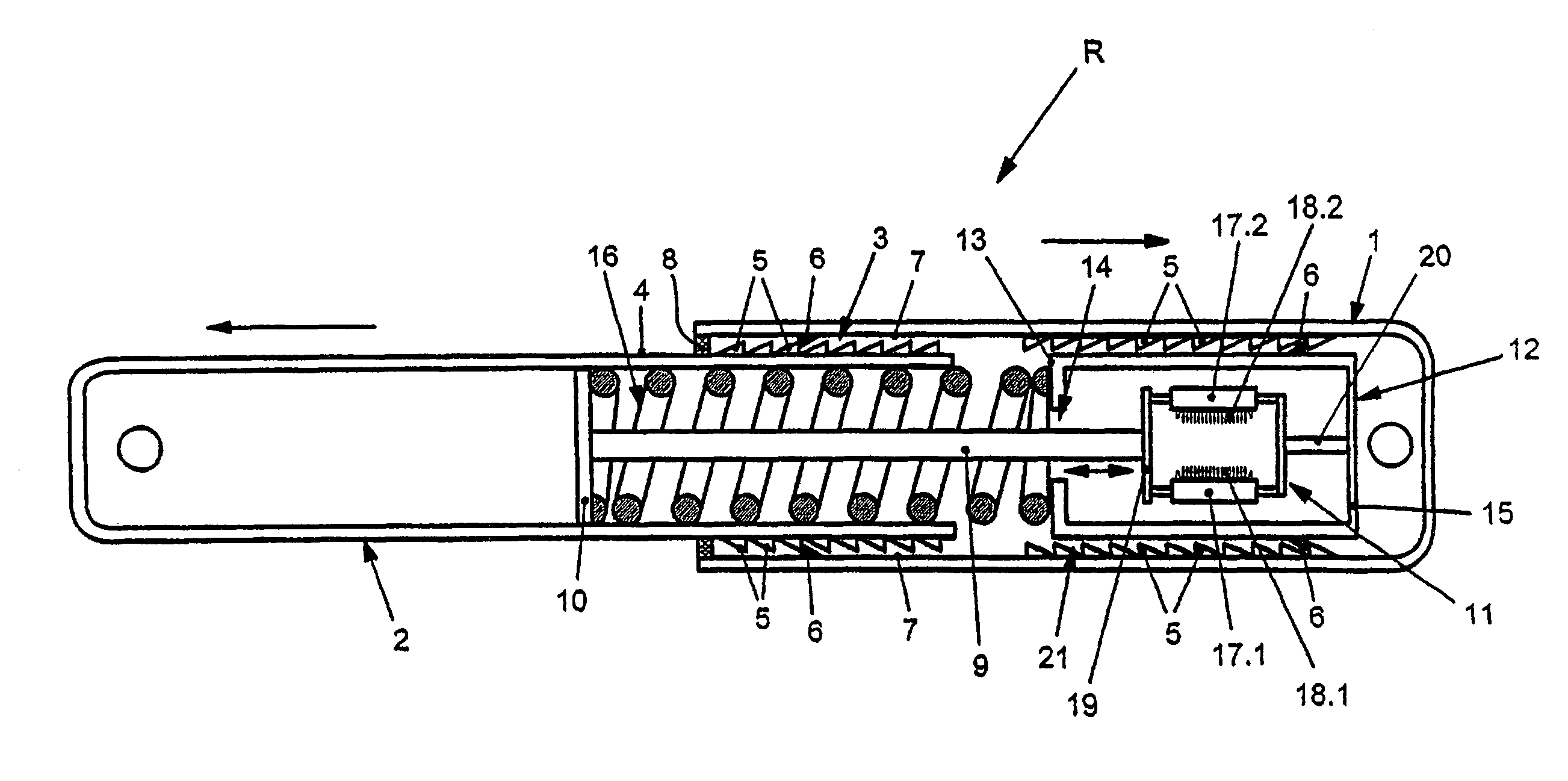
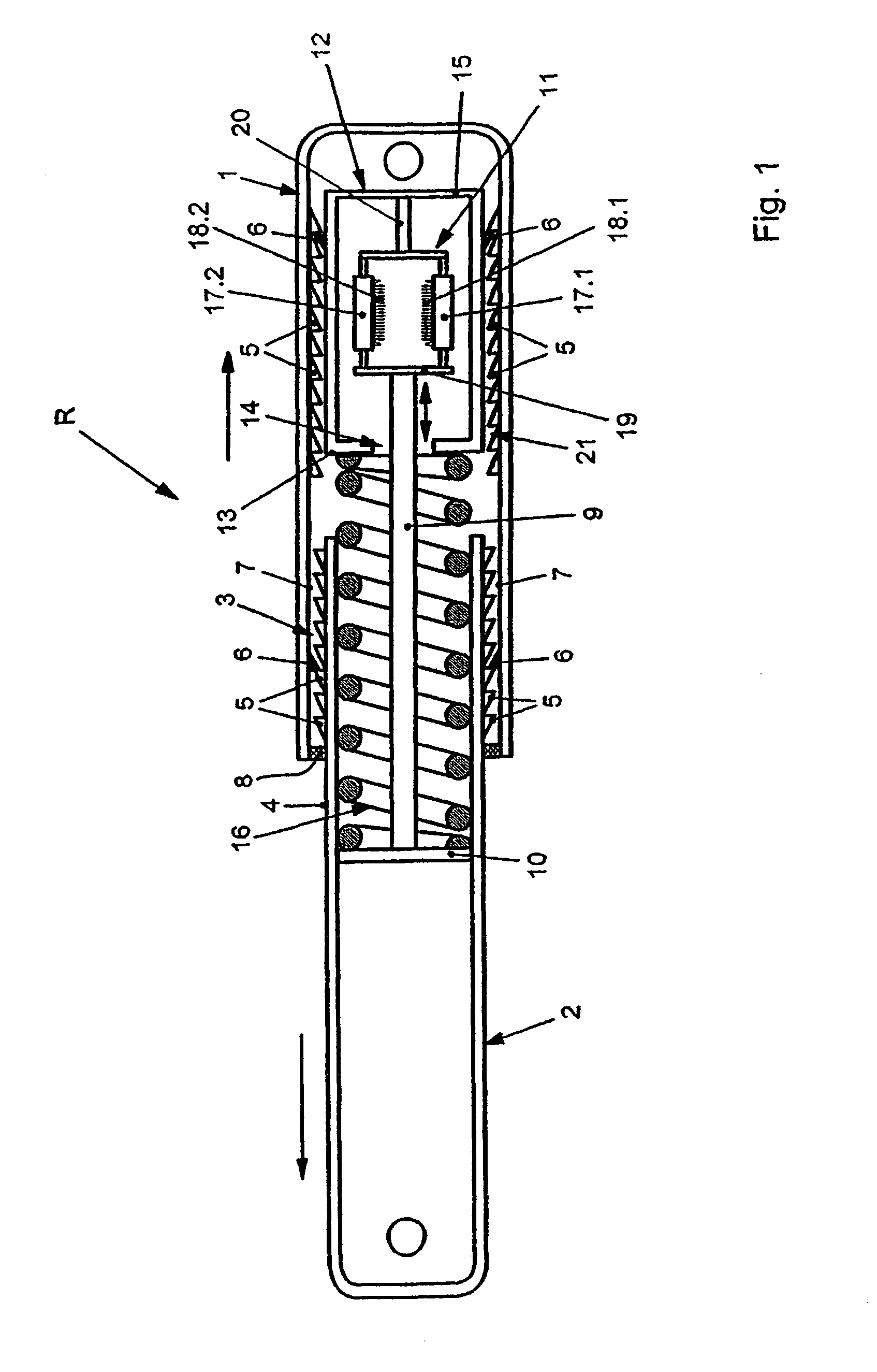
The locking nail for the repair of femur shaft fractures, also in connection with trochanteric femur fractures, comprises a proximal nail section (2) and a distal nail section (3) adjoining the latter, with the nail sections (2, 3) having bores (2e, 2f, 2h, 2i, 3a, 3b, 3c) for the reception of bone screws, and with the distal nail section (3) having a curvature extending in an anterior-posterior plane (apE) and corresponding substantially to the antecurvature of the femur, with the proximal nail section (2) having at least over a partial section (2a, 2b) a continuous curvature, in particular with constant radius of curvature (R2), extending in a lateral-medial plane (lmE).
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Osteosynthetic implants and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS20050240190A1Promote repairSmall sectionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone fixation devicesBiomedical engineering
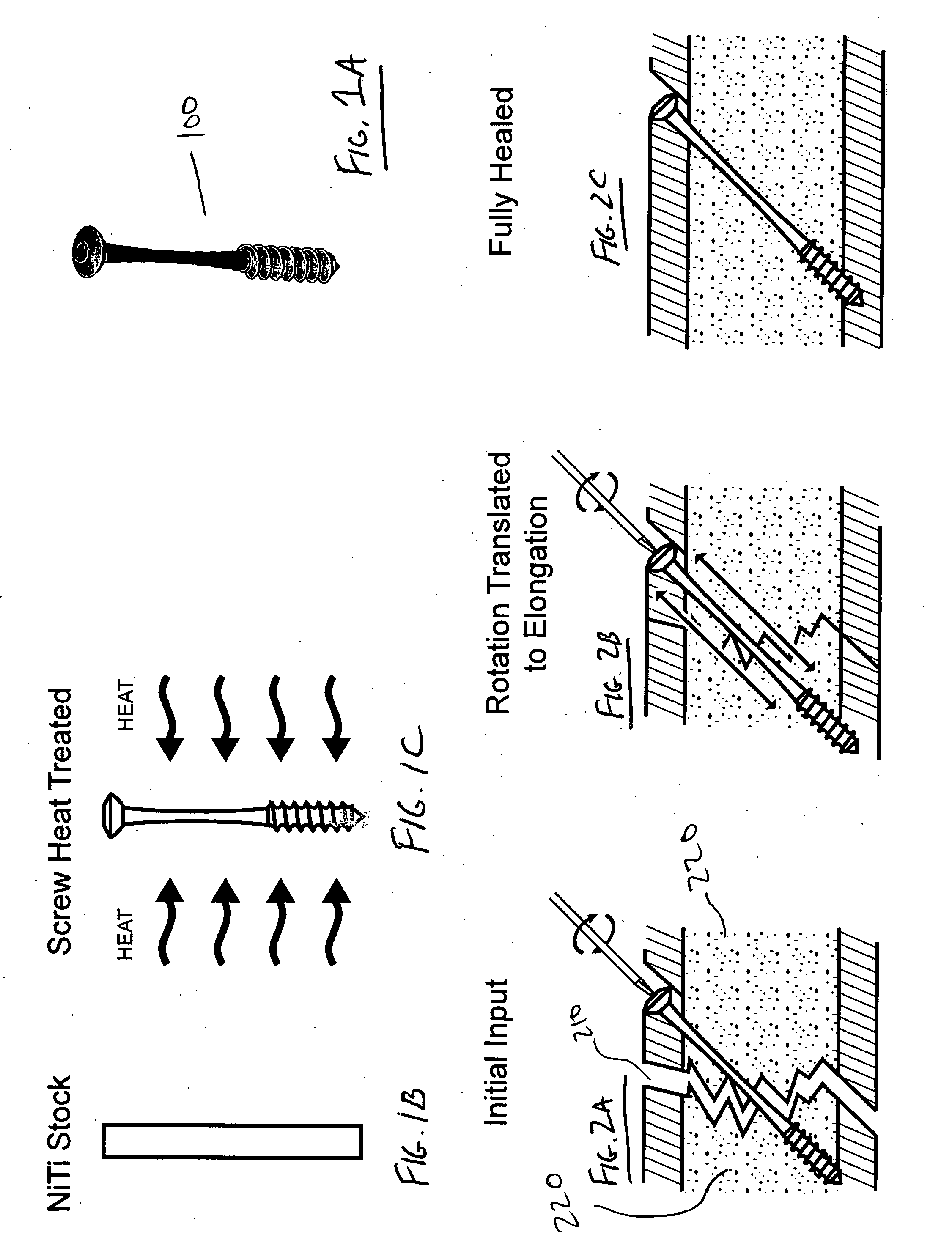
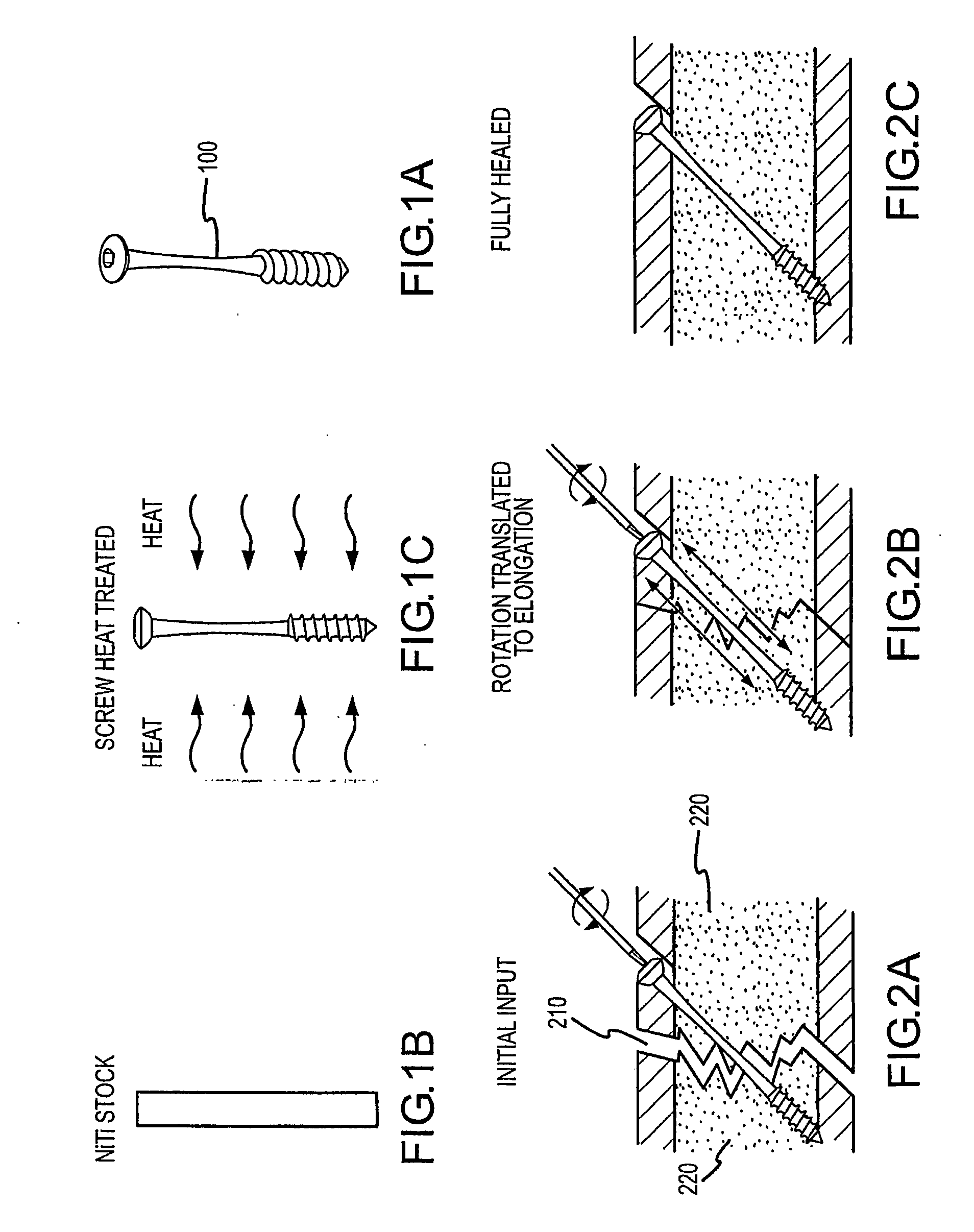
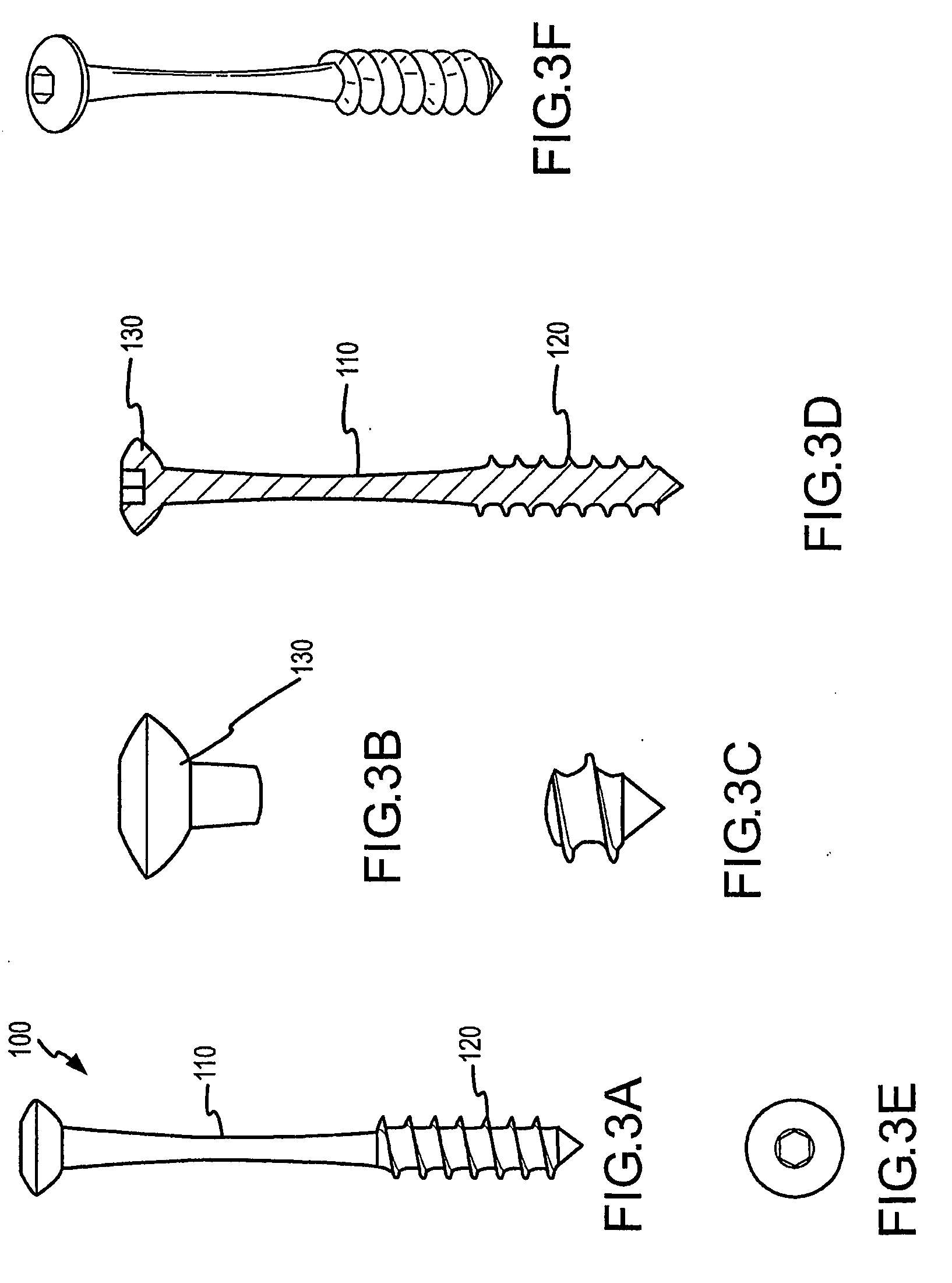
The present invention provides bone fracture fixation devices, systems and methods of use and manufacture. One such bone fixation device includes an elongate element having a responsive zone. The element is adapted to be coupled to the bone so that the responsive zone is positioned adjacent a fracture site in the bone. The responsive zone is adapted to apply a desired pressure to the bone when coupled thereto. In some embodiments, the responsive zone comprises a shape memory material, which may be nickel titanium or Nitinol, to apply compressive pressure across the fracture site for longer periods of time than standard bone screws.
Owner:MEDSHAPE
Catheter system for controlling a patient's body temperature by in situ blood temperature modification
InactiveUS6306161B1Quickly felt throughout the patient's bodyEliminate damageStentsBalloon catheterMedicineHigh body temperature
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Distraction device
InactiveUS7063706B2High constantSmall overall lengthInternal osteosythesisProsthesisDistractionDetent
A distraction device for moving a one-part or two-part or separated bone apart in order to extend or bridge a bone gap. The device is optionally provided in the form of an intramedullary pin, which can be inserted into a medullary space of a bone and which has at least two elements that can be axially moved in relation to one another. The first element is joined to the second element via at least one detent device for securing a distraction movement, and a pushing module for distracting the first element is assigned to the second element and is joined to the second element in a manner that enables it to be locked.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN GROUP
Tunnel effect transistors based on silicon nanowires
InactiveUS20080067495A1Optimize architectureReduce power consumptionTransistorNanoinformaticsMOSFETLattice mismatch
Tunnel field-effect transistors (TFETs) are regarded as successors of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), but silicon-based TFETs typically suffer from low on-currents, a drawback related to the large resistance of the tunnel barrier. To achieve higher on-currents a nanowire-based TFET with a germanium (Ge) tunnel barrier in an otherwise silicon (Si) channel is used. A nanowire is introduced such that the lattice mismatch between silicon and germanium does not result in a highly defective interface. A dynamic power reduction as well as a static power reduction can result, compared to conventional MOSFET configurations. Multiple layers of logic can therefore be envisioned with these nanowire Si / Ge TFETs resulting in ultra-high on-chip transistor densities.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Multi bridge channel field effect transistors with nano-wire channels and methods of manufacturing the same
A field effect transistor (FET) includes spaced apart source and drain regions disposed on a substrate and at least one pair of elongate channel regions disposed on the substrate and extending in parallel between the source and drain regions. A gate insulating region surrounds the at least one pair of elongate channel regions, and a gate electrode surrounds the gate insulating region and the at least one pair of elongate channel regions. Support patterns may be interposed between the semiconductor substrate and the source and drain regions. The elongate channel regions may have sufficiently small cross-section to enable complete depletion thereof. For example, a width and a thickness of the elongate channel regions may be in a range from about 10 nanometers to about 20 nanometers. The elongate channel regions may have rounded cross-sections, e.g., each of the elongate channel regions may have an elliptical cross-section. The at least one pair of elongate channel regions may include a plurality of stacked pairs of elongate channel regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Uveoscleral shunt and methods for implanting same
ActiveUS8506515B2Lower eye pressureSmall sectionSenses disorderEar treatmentCiliary bodySuprachoroidal space
Devices and methods for treating intraocular pressure are disclosed. The devices include shunts for draining aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to the uveoscleral outflow pathway, including the supraciliary space and the suprachoroidal space. The shunts are preferably implanted by ab interno procedures.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Osteosynthetic Implants and Methods of Use and Manufacture
ActiveUS20080269808A1Promote repairSmall sectionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone fixation devicesBiomedical engineering
Owner:MEDSHAPE
Tunnel effect transistors based on elongate monocrystalline nanostructures having a heterostructure
ActiveUS20080067607A1Optimize architectureReduce power consumptionTransistorNanoinformaticsMOSFETSemiconductor materials
Tunnel field-effect transistors (TFETs) are regarded as successors of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), but silicon-based TFETs typically suffer from low on-currents, a drawback related to the large resistance of the tunnel barrier. To achieve higher on-currents an elongate monocrystalline nanostructure-based TFET with a heterostructure made of a different semiconducting material (e.g. germanium (Ge)) is used. An elongate monocrystalline nanostructure made of a different semiconducting material is introduced which acts as source (or alternatively drain) region of the TFET. The introduction of the heterosection is such that the lattice mismatch between silicon and germanium does not result in a highly defective interface. A dynamic power reduction as well as a static power reduction can result, compared to conventional MOSFET configurations. Multiple layers of logic can therefore be envisioned with these elongate monocrystalline nanostructure Si / Ge TFETs resulting in ultra-high on-chip transistor densities.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +1
Device for epitaxially growing objects and method for such a growth
InactiveUS6039812AVelocity increasesImprove economyPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesGas phaseReactive gas
A device for epitaxially growing objects of for instance SiC by Chemical Vapor Deposition on a substrate has a first conduit (24) arranged to conduct substantially only a carrier gas to a room (18) receiving the substrate and a second conduit (25) received in the first conduit, having a smaller cross-section than the first conduit and extending in the longitudinal direction of the first conduit with a circumferential space separating it from inner walls of the first conduit. The second conduit is adapted to conduct substantially the entire flow of reactive gases and it ends as seen in the direction of the flows, and emerges into the first conduit at a distance from said room.
Owner:NORSTEL
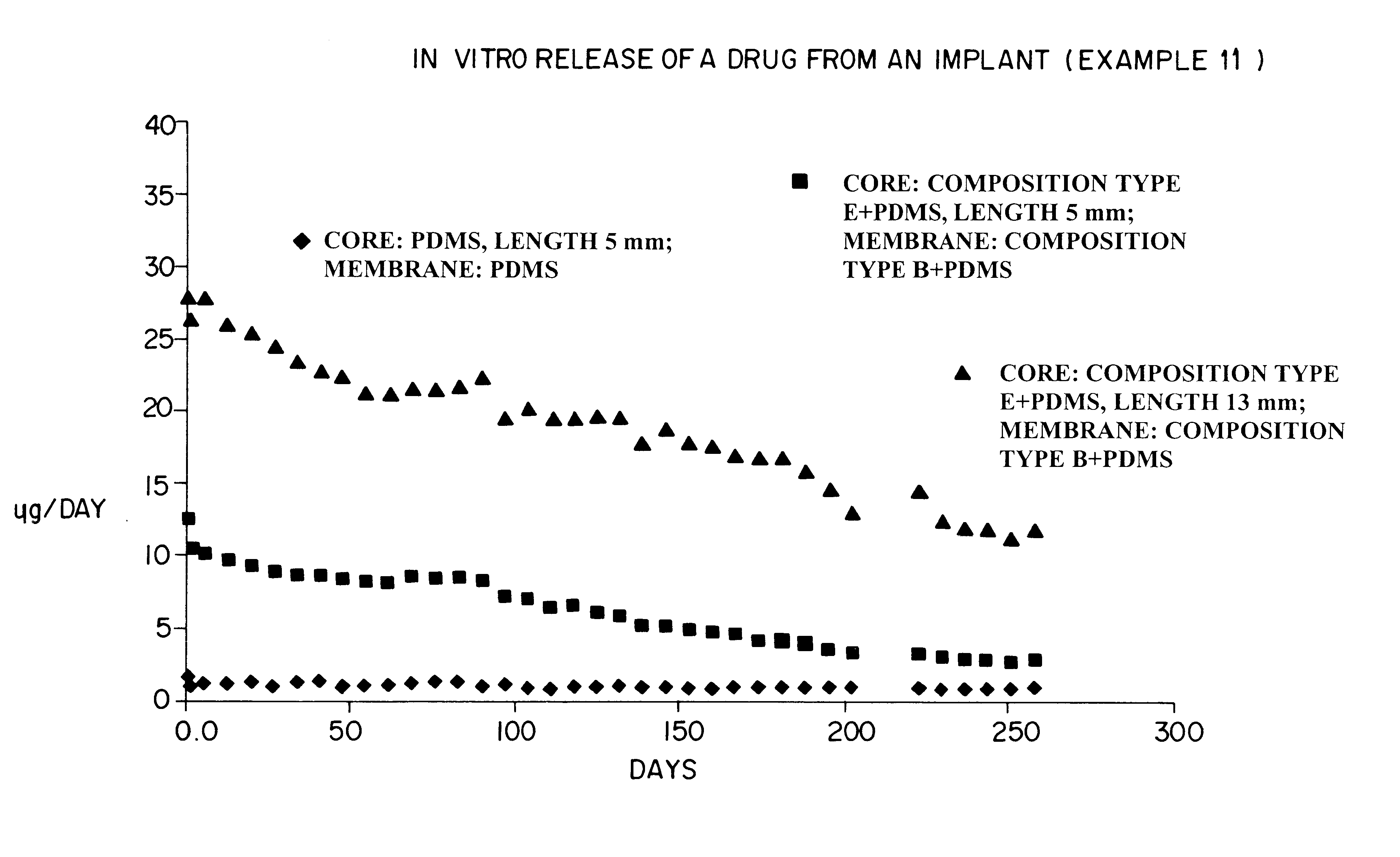
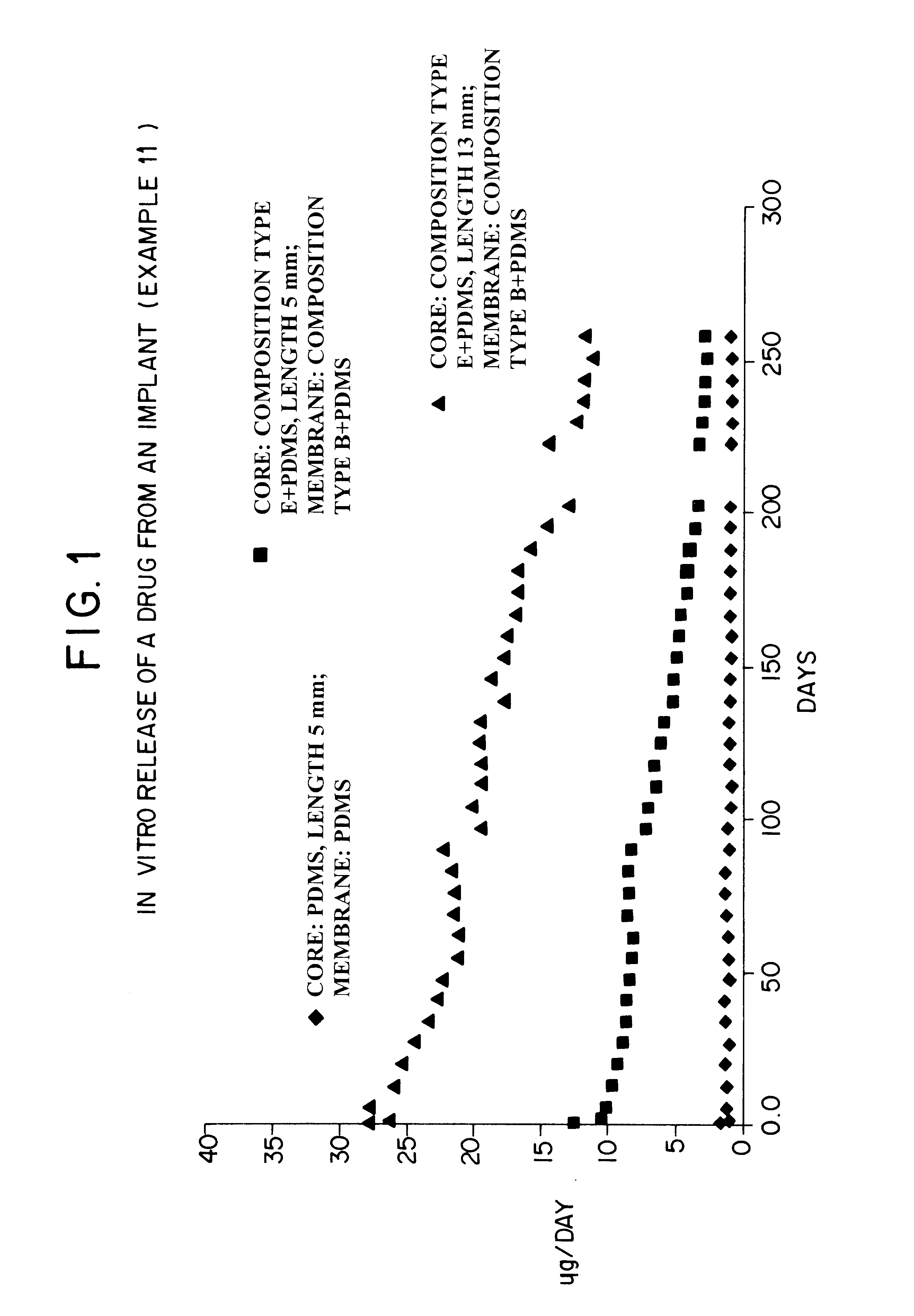
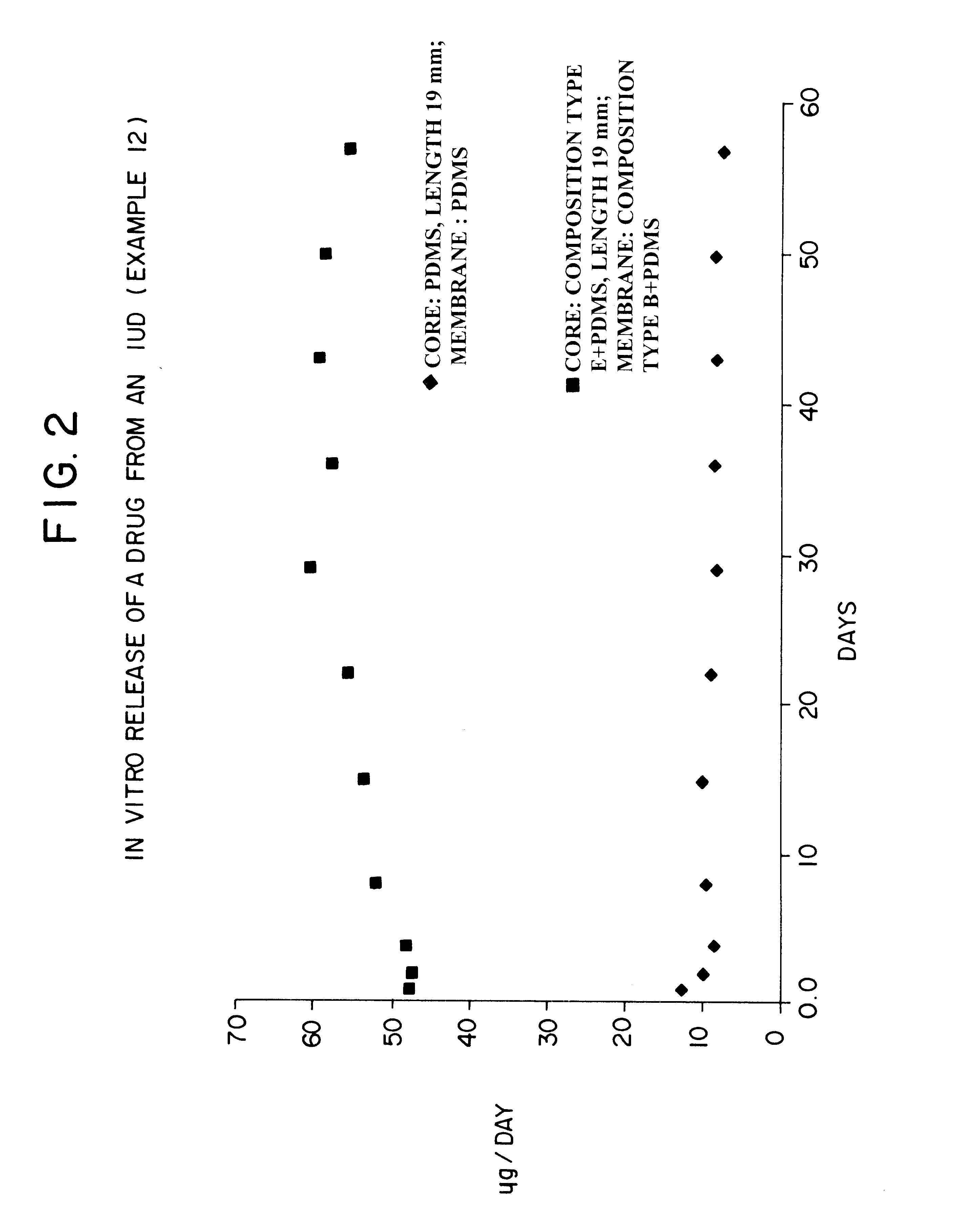
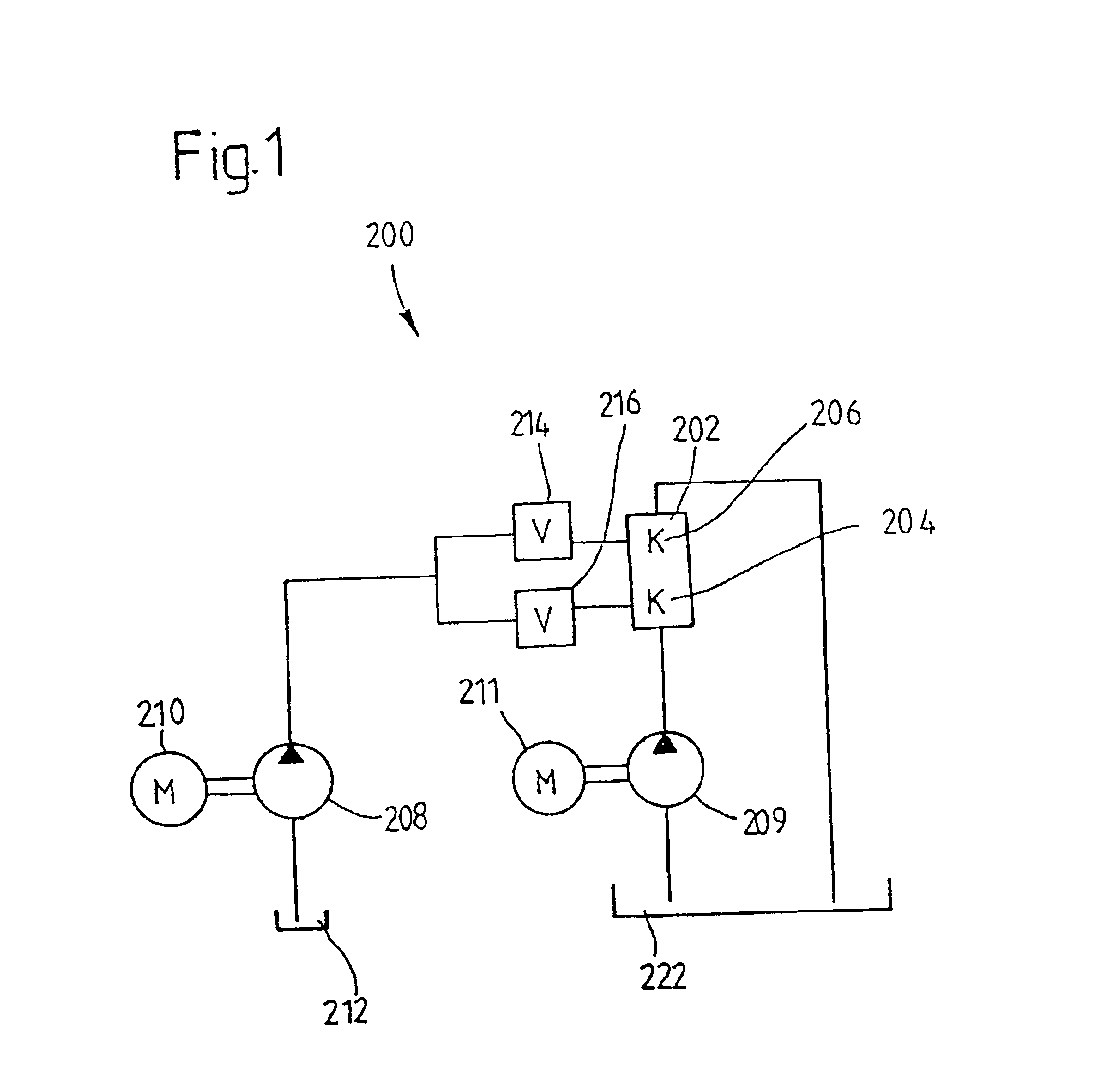
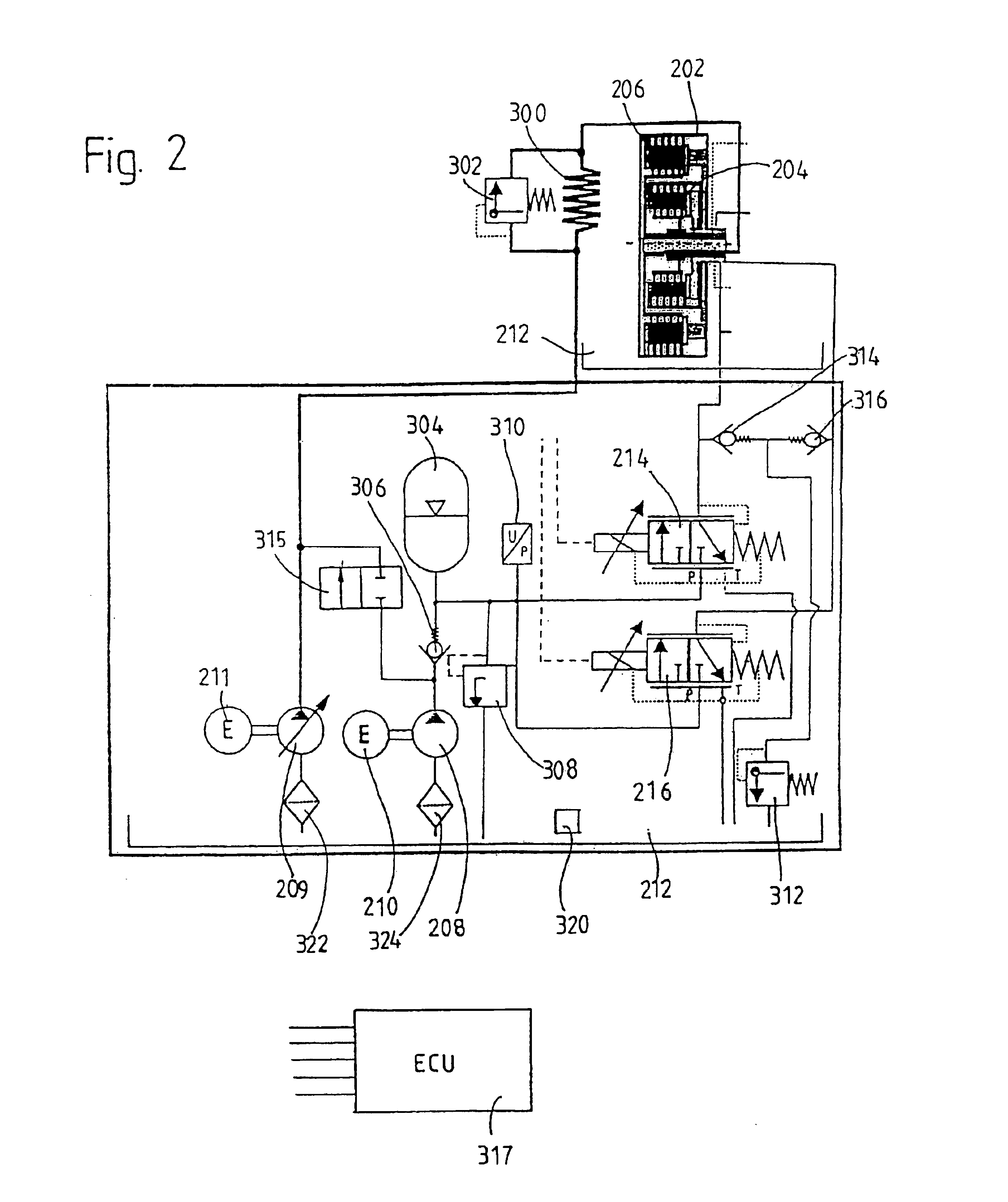
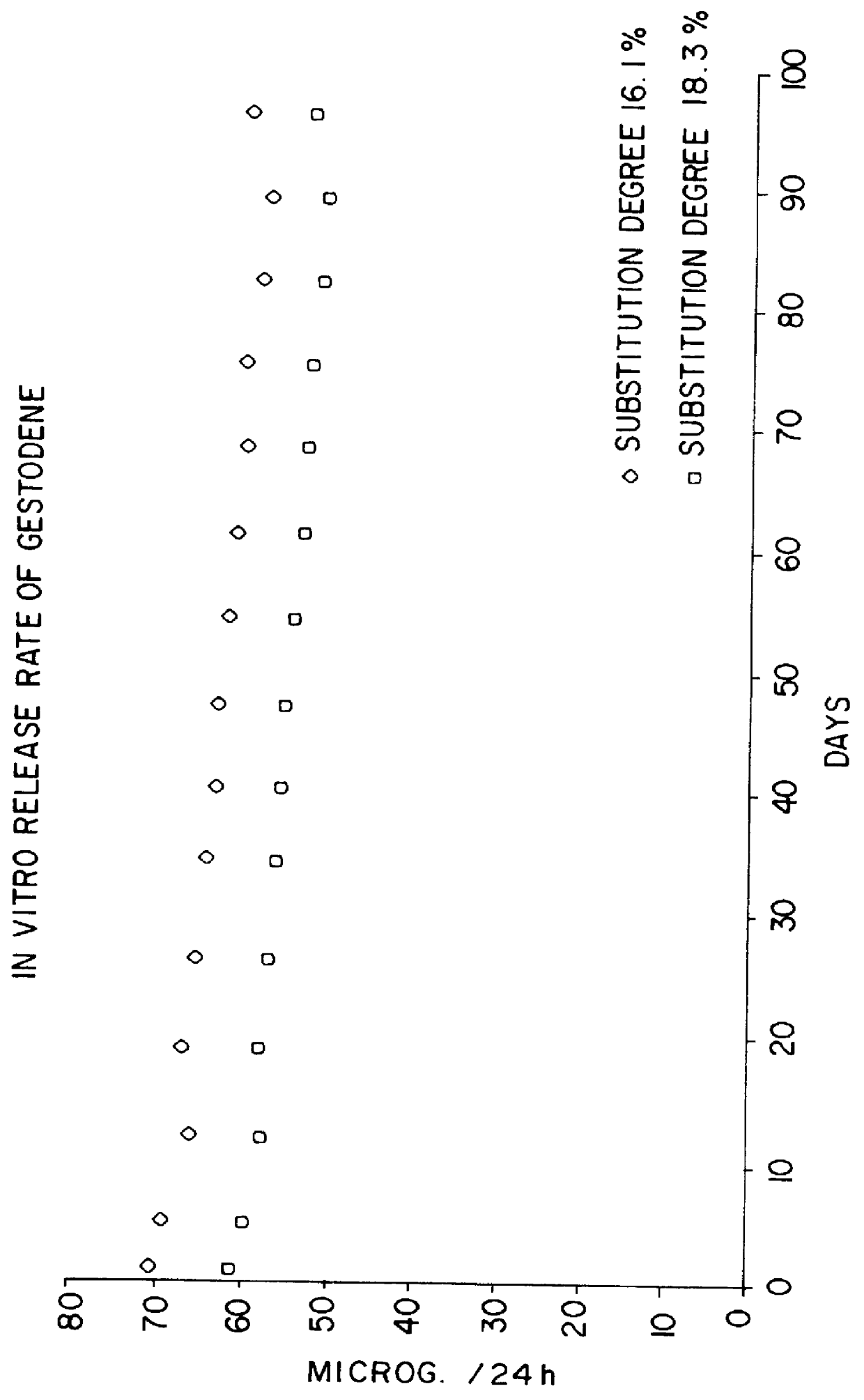
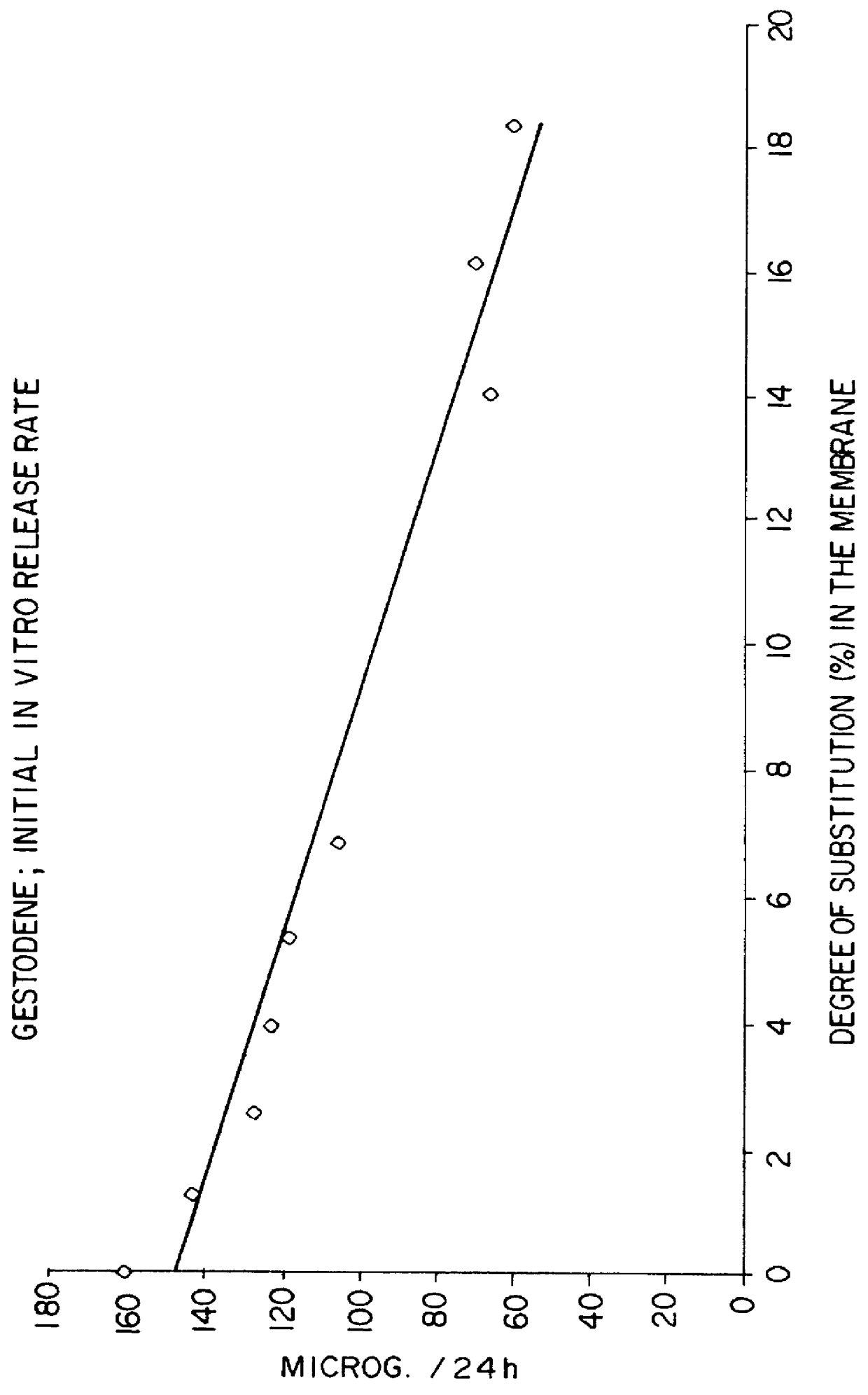
Devices for the delivery of drugs having antiprogestinic properties
InactiveUS6476079B1Small sectionEasy to insertPowder deliverySuppositories deliveryControlled releaseElastomer
A device for the controlled release over a prolonged period of time of a drug having antiprogestinic properties, the device including a core containing the drug, optionally a membrane encasing the core, where at least one of the core and membrane, when present, is made of a siloxane-based elastomer composition including at least one elastomer and optionally a non-crosslinked polymer. The device is characterized in that the elastomer composition includes poly(alkylene oxide) groups and that the poly(alkylene oxide) groups are present in the elastomer or polymer as alkoxy-terminated grafts of polysiloxane units, or as blocks, the grafts or blocks being linked to the polysiloxane units by silicon-carbon bonds, or as a mixture of these forms.
Owner:LEIRAS +1
Clutch system
InactiveUS6789658B2Lower the volumeShort switching timeMechanical actuated clutchesFluid actuated clutchesMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Drug delivery device especially for the delivery of progestins and estrogens
InactiveUS6063395AEasy to adjustSmall sectionOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryElastomerControl release
The invention relates to a delivery device for the controlled release of a therapeutically active agent, especially a progestin or an estrogen, over a prolonged period of time, said device including a core which contains the therapeutically active agent, and a membrane encasing the core wherein said membrane is made of an elastomer. According to the invention, the elastomer is a siloxane-based elastomer which includes 3,3,3-trifluoropropyl groups attached to the Si-atoms of the siloxane units.
Owner:OY SCHERING +1
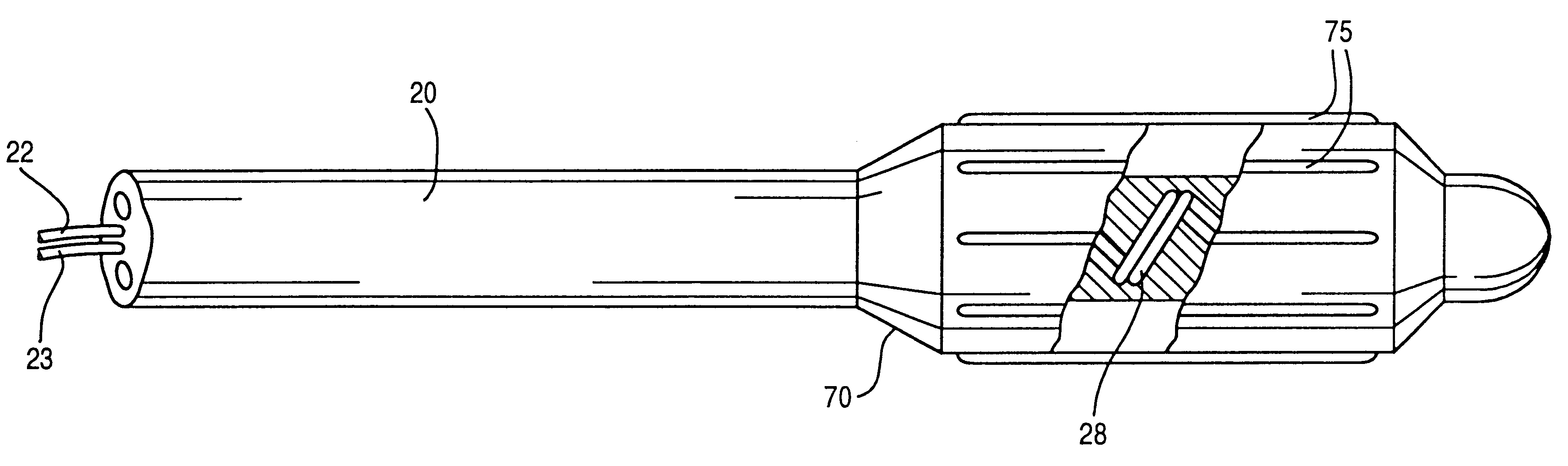
Lead assembly and methods including a push tube
InactiveUS20060036307A1Easy to browseSmall sectionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
A lead assembly includes an elongate body having a conductor electrically coupled with an electrode coupled to the elongate body. The lead assembly includes a push tube extending along at least a portion of the elongate body. A distal tip is coupled to the elongate body substantially adjacent to the distal end of the elongate body. The distal tip is sized and shaped to couple with a push tube distal end. In one option, the distal tip includes a seat to receive the push tube distal end. In another option, the seat is a side rail seat and a guide wire extends along the elongate body and is slidably coupled with the side rail seat. The lead assembly includes, optionally, an active fixation device slidably coupled with a portion of the elongate body, and the active fixation device is sized and shaped to couple with the push tube.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
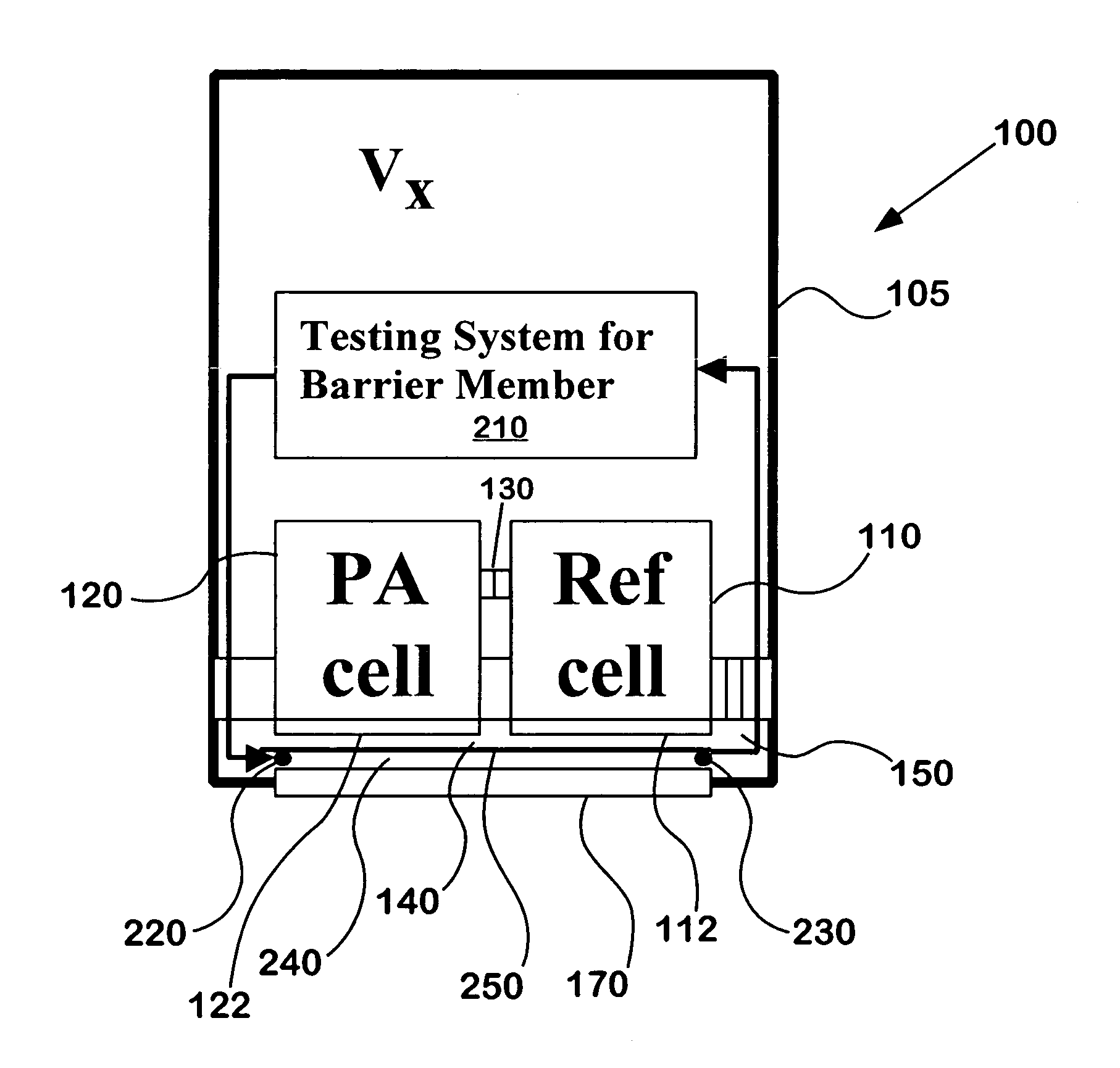
Gas sensors
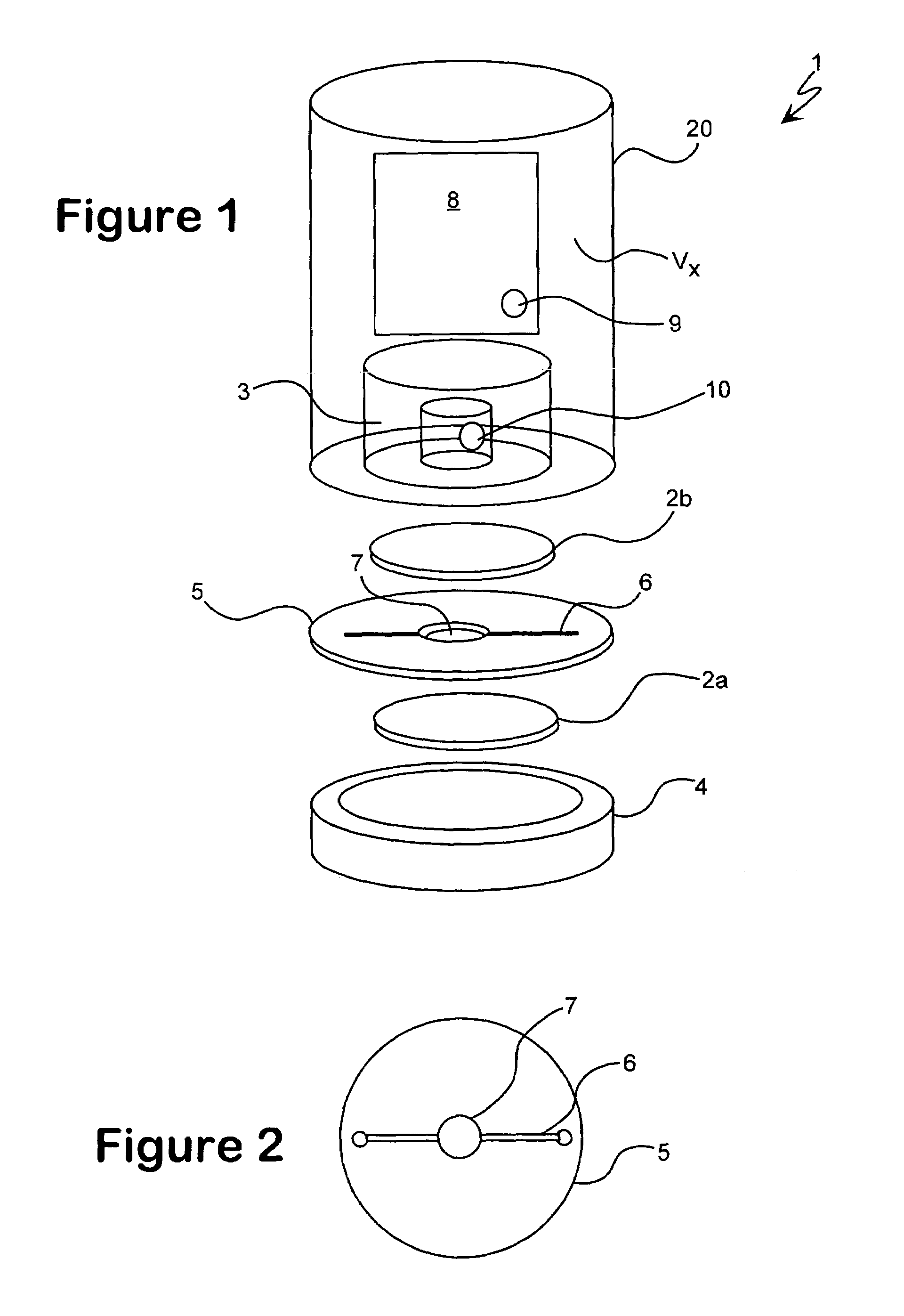
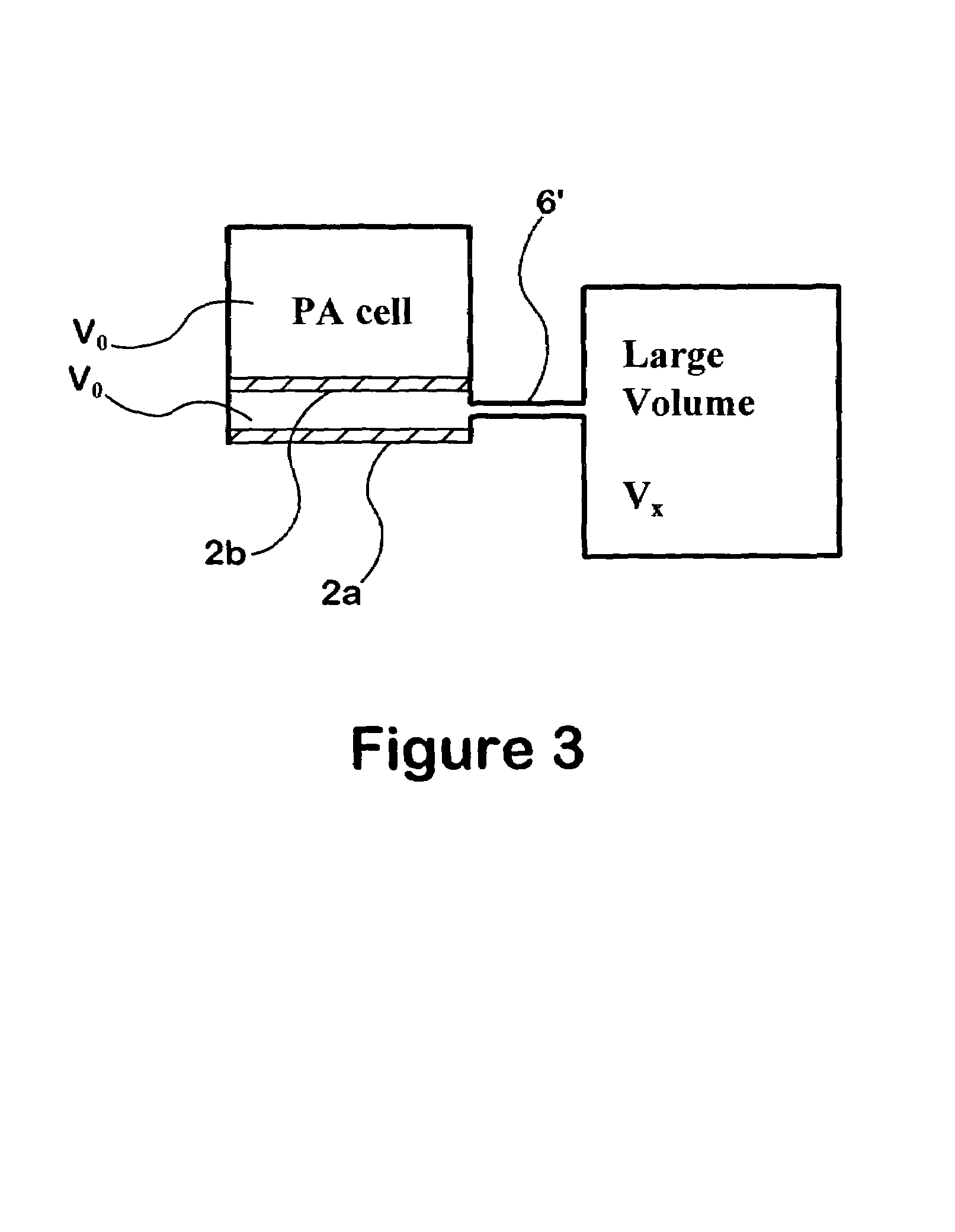
InactiveUS7034943B1Reduces externalAdequate response timeOptical radiation measurementOrganic active ingredientsDiffusionAnalyte
The present invention relates to a device for accomplishing noise reduction in a photoacoustic gas detector using a sound damping element and / or a background or reference microphone where a preferably larger external volume that acts as a sound damping element (SDE) is coupled to a smaller volume through which the gas diffuses. The coupling is accomplished in such a way that the externally generated sound waves incident upon the photoacoustic detector are adequately attenuated by the larger volume SDE without adversely affecting diffusion of the gaseous species of interest through the smaller volume for measurement by the detector. Preferably this is accomplished by coupling the larger SDE volume to the smaller gas diffusion volume by a long and thin pressure channel. Another photoacoustic detector includes a measuring system to measure the photoacoustic excitation of analyte gas entering the photoacoustic detector, a reference system to measure the effect of pressure waves in the environment, and a system for offsetting an output from the measuring system with an output from the reference system to reduce noise resulting from pressure waves in the environment in an output signal of the photoacoustic detector. The present invention also relates to a device for testing the integrity of a porous member and includes a source of pressure waves and a sensor for measuring a signal resulting from the transmittal of pressure waves from the transmitter. The signal is proportional to pressure losses through the porous member. The pressure losses through the porous member are, in turn, a measure of the degree to which the porous member has become clogged.
Owner:MSA TECH +1
Method and device for producing bristle products and bristle products
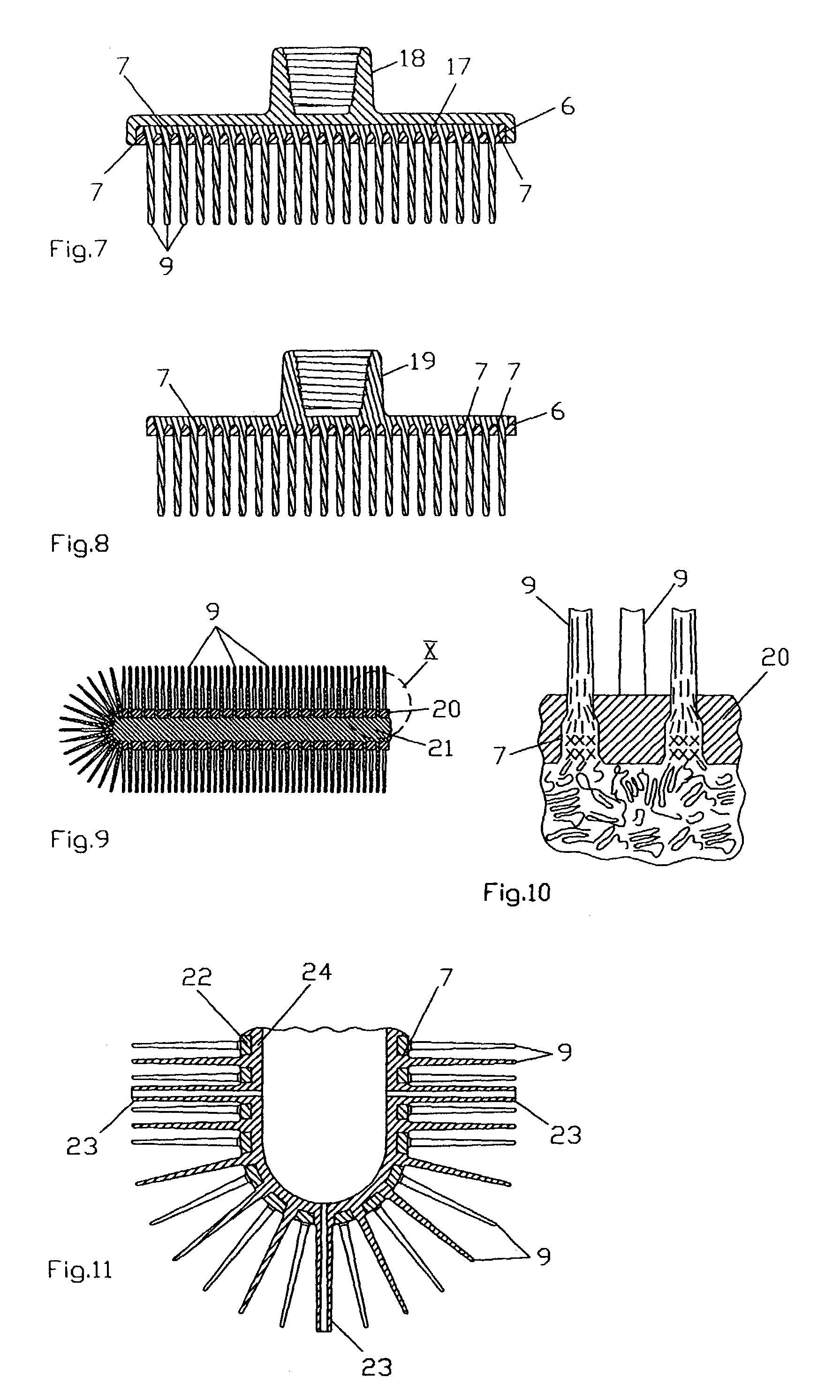
InactiveUS7503093B2Improve abilitiesEasy to disassembleBrush bodiesBristle carriersBristlePlastic materials
Brush ware comprising at least one carrier and bristles made from a moldable plastic material disposed thereon, is produced by providing the carrier with through holes acting like spinning nozzles, to which bristle-shaped molding channels join and a plastic melt for the bristles is injected from at least one side of the carrier—the feed side of the melt—through the holes into the channels thereby forming the bristles, wherein the through holes have a minimal width along at least a portion of their length which is ≦3 mm and the ratio between this width and the flow path of the melt resulting from the depth of the through holes plus the length of the channels is ≦1:5. A device for carrying out the method and brush ware produced in accordance with the method is also described.
Owner:GEKA
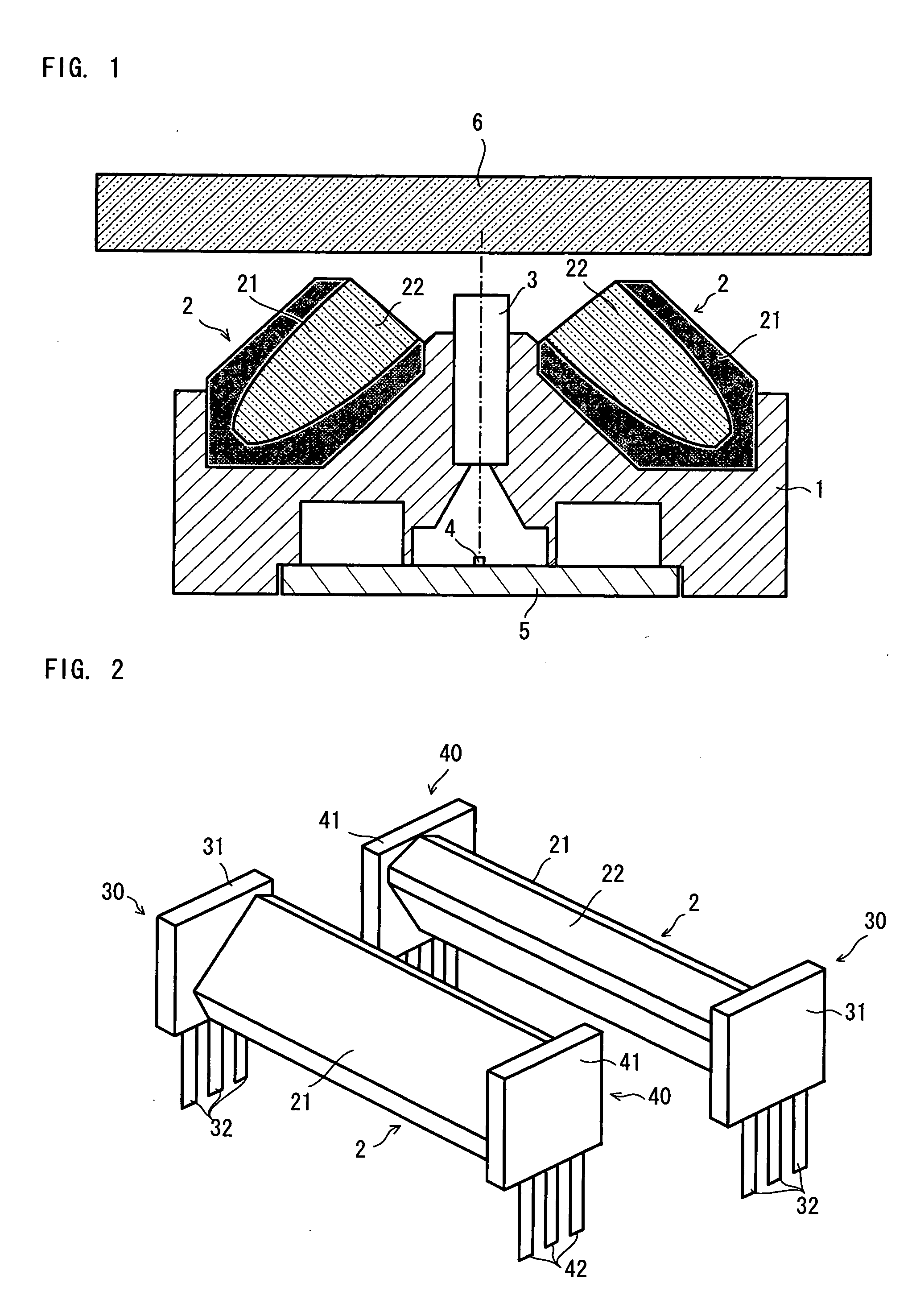
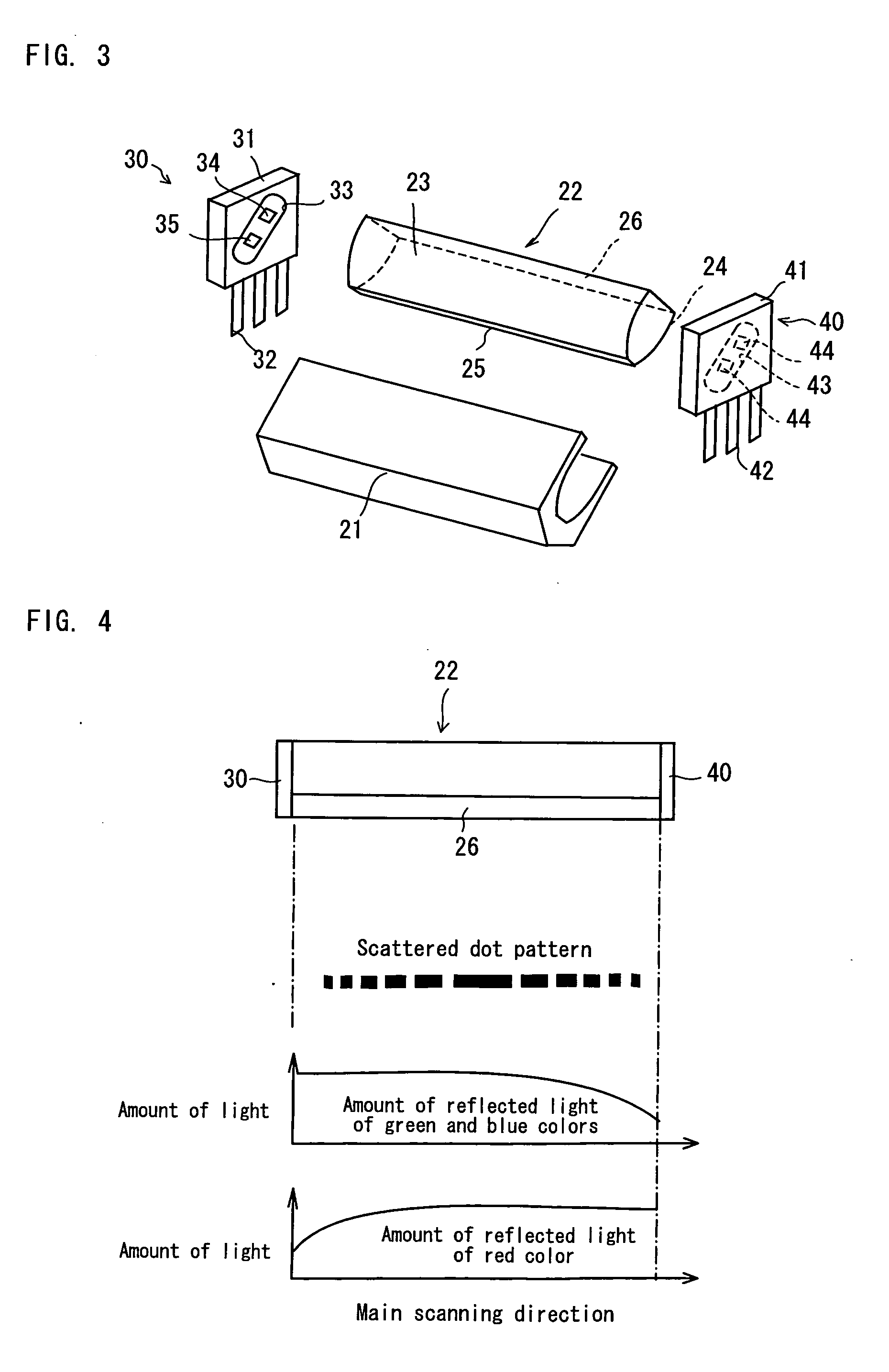
Line-illuminating device and image-scanning device
InactiveUS20050150956A1Improve accuracyHigh densityMechanical apparatusPattern makingLight guideEngineering
A line-illuminating device comprises a white casing, a bar-shaped light guide housed within the casing, and light-emitting units provided on opposite ends of the bar-shaped light guide. The light-emitting unit has a substrate forming a circuit on which a lead wire for power supply is installed. Formed on a surface of the substrate facing the bar-shaped light guide is a window for coupling in which a green-color light-emitting diode and a blue-color light-emitting diode are installed. Likewise, the light-emitting unit has a substrate on which a lead wire for power supply is installed. Formed on a surface of the substrate facing the bar-shaped light guide is a window for coupling in which two red-color light-emitting diodes are installed.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Crushable structure manufactured from mechanical expansion
A crush member for a vehicle having frame rails comprising a tube having a first end configured to be connected to the frame rails of the vehicle and a second end configured to be connected to a bumper. The tube has a constant thickness from the first end to the second end. The tube further has a taper along a axial direction from the first end to the second end, the tube having a larger cross section at the first end and a smaller cross section at the second end. The tube is configured to crush to absorb impact energy upon an axial or near axial load.
Owner:SHAPE CORP
Device fabrication by anisotropic wet etch
InactiveUS7410844B2Reduce capacitanceSmall sectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceBody contact
A method of fabrication and a field effect device structure are presented that reduce source / drain capacitance and allow for device body contact. A Si based material pedestal is produced, the top surface and the sidewalls of which are oriented in a way to be substantially parallel with selected crystallographic planes of the pedestal and of a supporting member. The pedestal is wet etched with an anisotropic solution containing ammonium hydroxide. The sidewalls of the pedestal become faceted forming a segment in the pedestal with a reduced cross section. The dopant concentration in the reduced cross section segment is chosen to be sufficiently high for it to provide for electrical continuity through the pedestal.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Waveguide based light source
InactiveUS6843590B2High emissionHigh excitationMechanical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorFluorescence
A wave guide based light source having a phosphor film with a large two-dimensional extent and a small thickness. The phosphor film is excited by an excitation means.
Owner:QUANTUM VISION
Clutch system
InactiveUS20030047410A1Lower the volumeShort switching timeMechanical actuated clutchesFluid actuated clutchesMobile vehicleEngineering
A clutch system includes a clutch device with at least one clutch arrangement for installation in a motor vehicle drive train between a drive unit and a transmission. The at least one clutch arrangement is actuated by a slave cylinder using a pressure medium which is supplied to the clutch device by a first pump. A further medium is also supplied to the clutch device by a second pump arrangement as an operating medium used during operation of the clutch device. The further medium is selectively supplied as a pressure medium to the slave cylinder.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
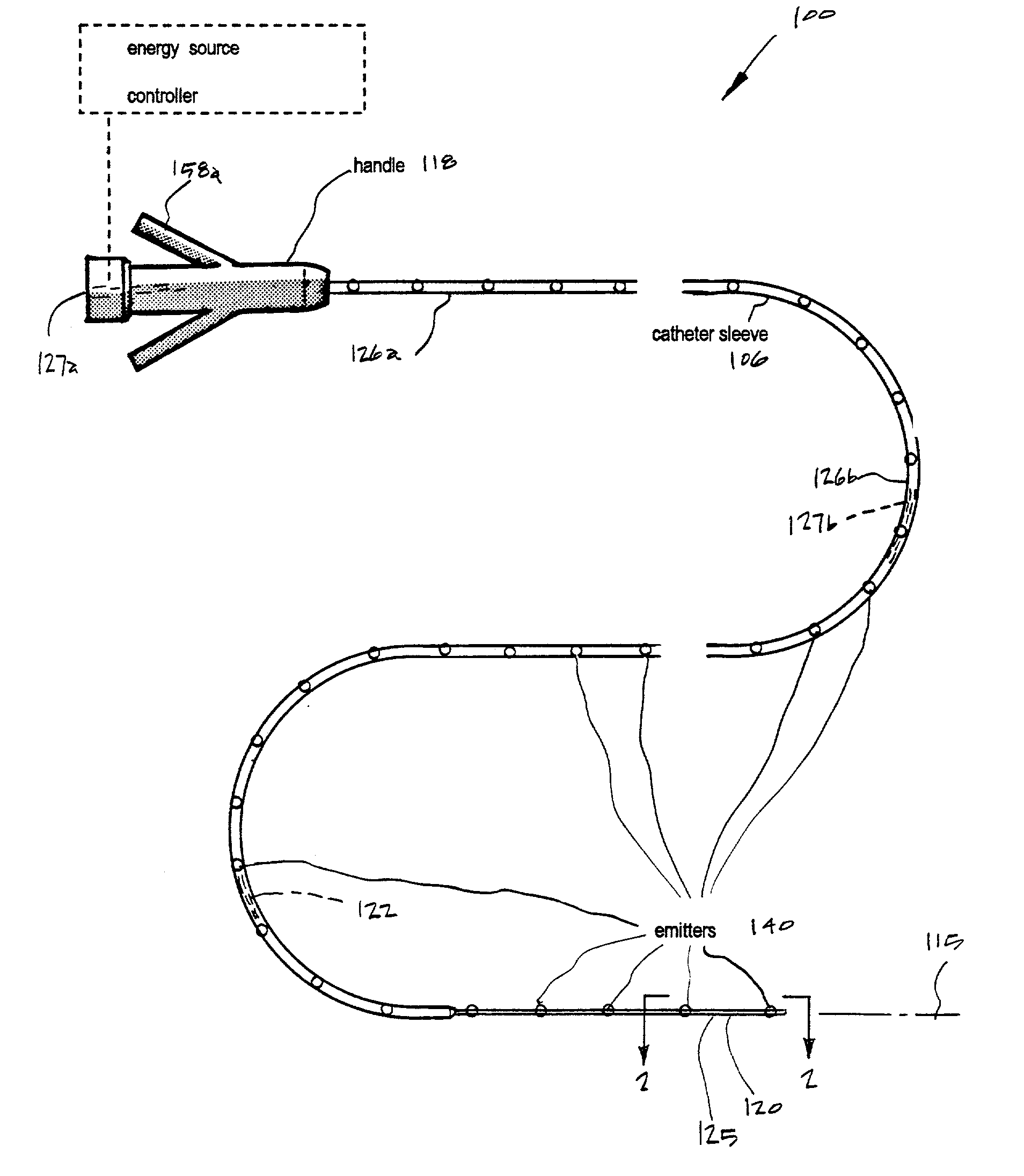
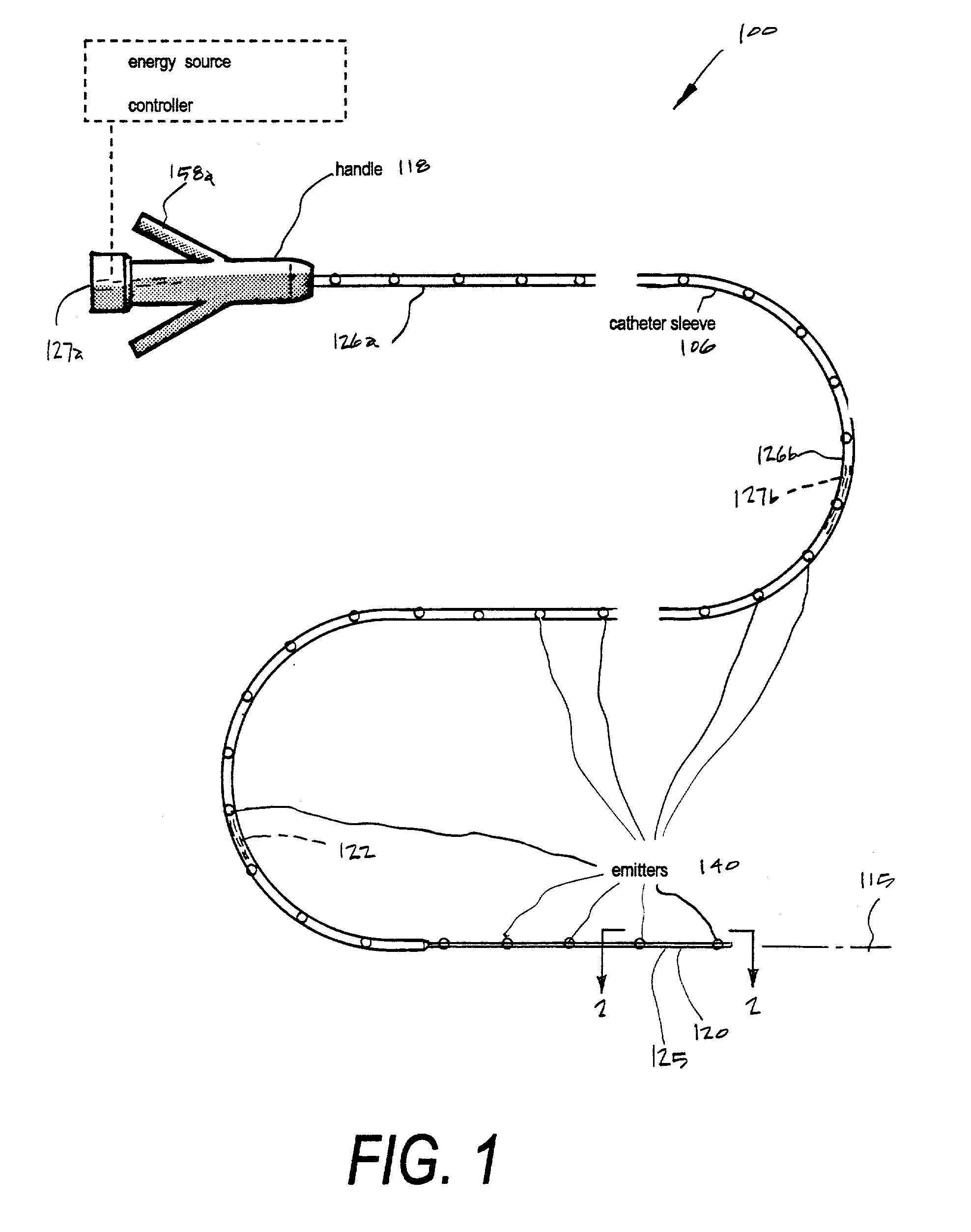
Basket catheter with improved spine flexibility
ActiveUS20160183877A1Reduce riskEasy to bendElectrocardiographyMedical devicesBasket catheterGuide tube
A catheter with basket-shaped electrode assembly with spines configured for hyper-flexing in a predetermined, predictable manner when a compressive force acts on the assembly from either its distal end or its proximal end. At least one spine has at least one region of greater (or hyper) flexibility that allows the electrode assembly to deform, for example, compress, for absorbing and dampening excessive force that may otherwise cause damage or injury to tissue wall in contact with the assembly, without compromising the structure and stiffness of the remaining regions of the spine, including its distal and proximal regions. The one or more regions of greater flexibility in the spine allow the spine to flex into a generally V-shape configuration or a generally U-shape configuration.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
Rail transportation system of small vehicle
ActiveCN1526596ASave construction investmentReduce operating costsRailway componentsRailway stationLight railRail transit
The rail transportation system of small vehicles is used to replace available underground railway and light rail system, and has small driverless vehicles running in closed rail. The system consists of vehicles, closed rails and stations, the vehicles are computerized automatic ones, the closed rails is provided with vehicle controlling equipment, and the vehicles are started from stations randomly for express service from station to station. The present invention has the advantages of great traffic amount similar to that of main stem transportation, personalized service, low construction investment and low running expensive. It may be used for both passenger transport and cargo transport, and municipal rail transportation network may be constructed.
Owner:沈涌
Absorbent articles comprising biodegradable PHA copolymers
InactiveUS6160199AProtect and promote and control plant growthRaise the ratioSynthetic resin layered productsBaby linensBiodegradable copolymersPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to biodegradable PHA copolymers comprising at least two randomly repeating monomer units. The present invention further relates to a plastic article comprising a biodegradable copolymer, wherein the biodegradable copolymer comprises at least two randomly repeating monomer units (RRMU) wherein the first RRMU has the structure wherein R1 is H, or C1 or C2 alkyl, and n is 1 or 2; the second RRMU has the structure and wherein at least 50% of the RRMUs have the structure of the first RRMU. The present invention further relates to an absorbent article comprising a liquid pervious topsheet, a liquid impervious backsheet comprising a film comprising a PHA of the present invention and an absorbent core positioned between the topsheet and the backsheet.
Owner:DANIMER IPCO LLC
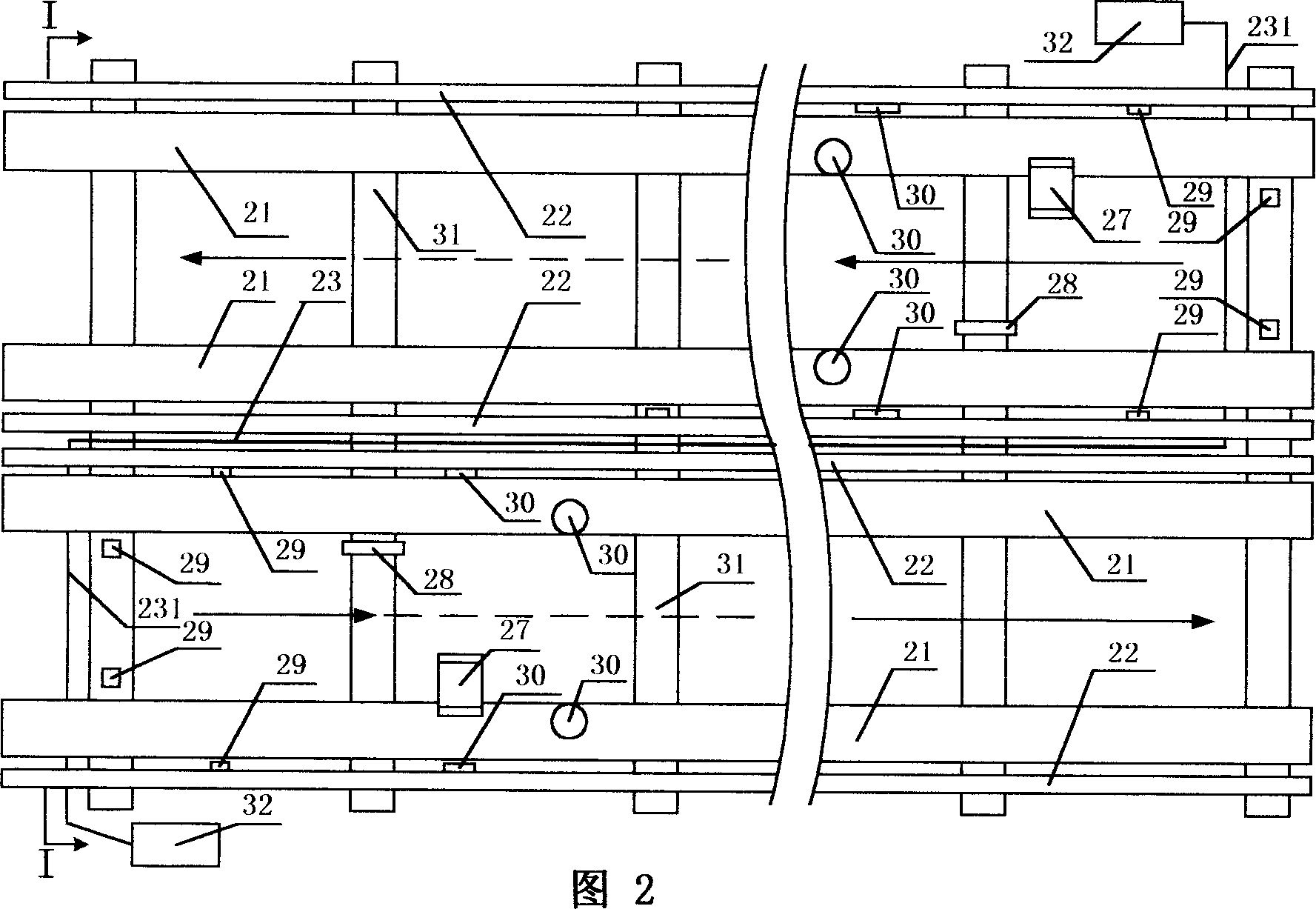
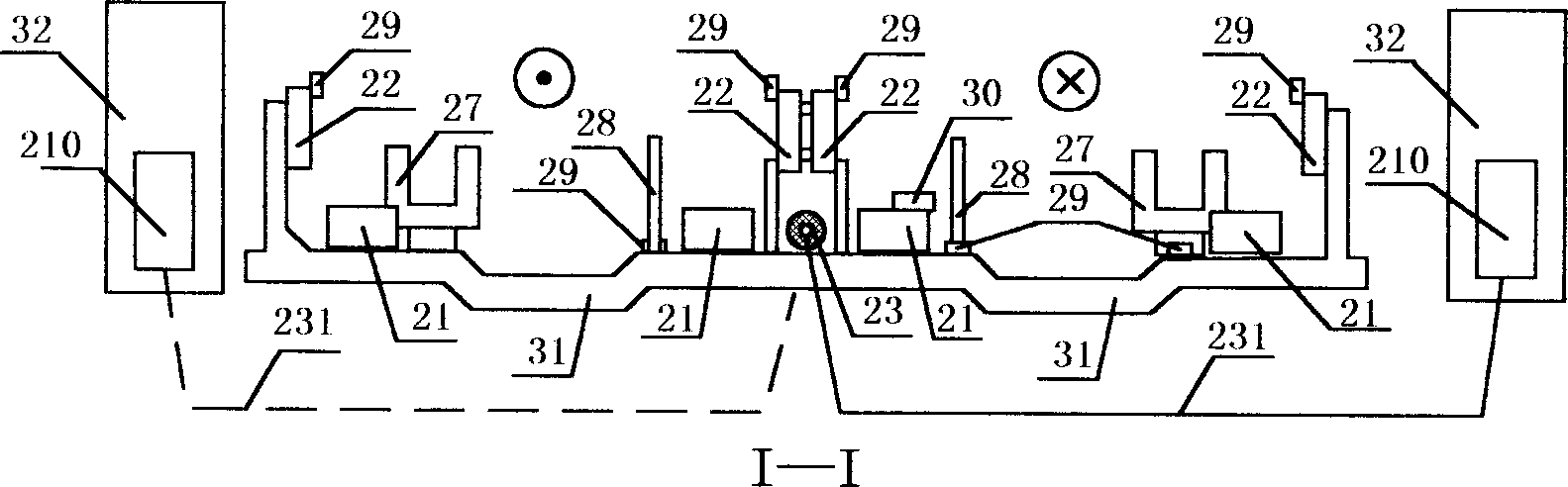
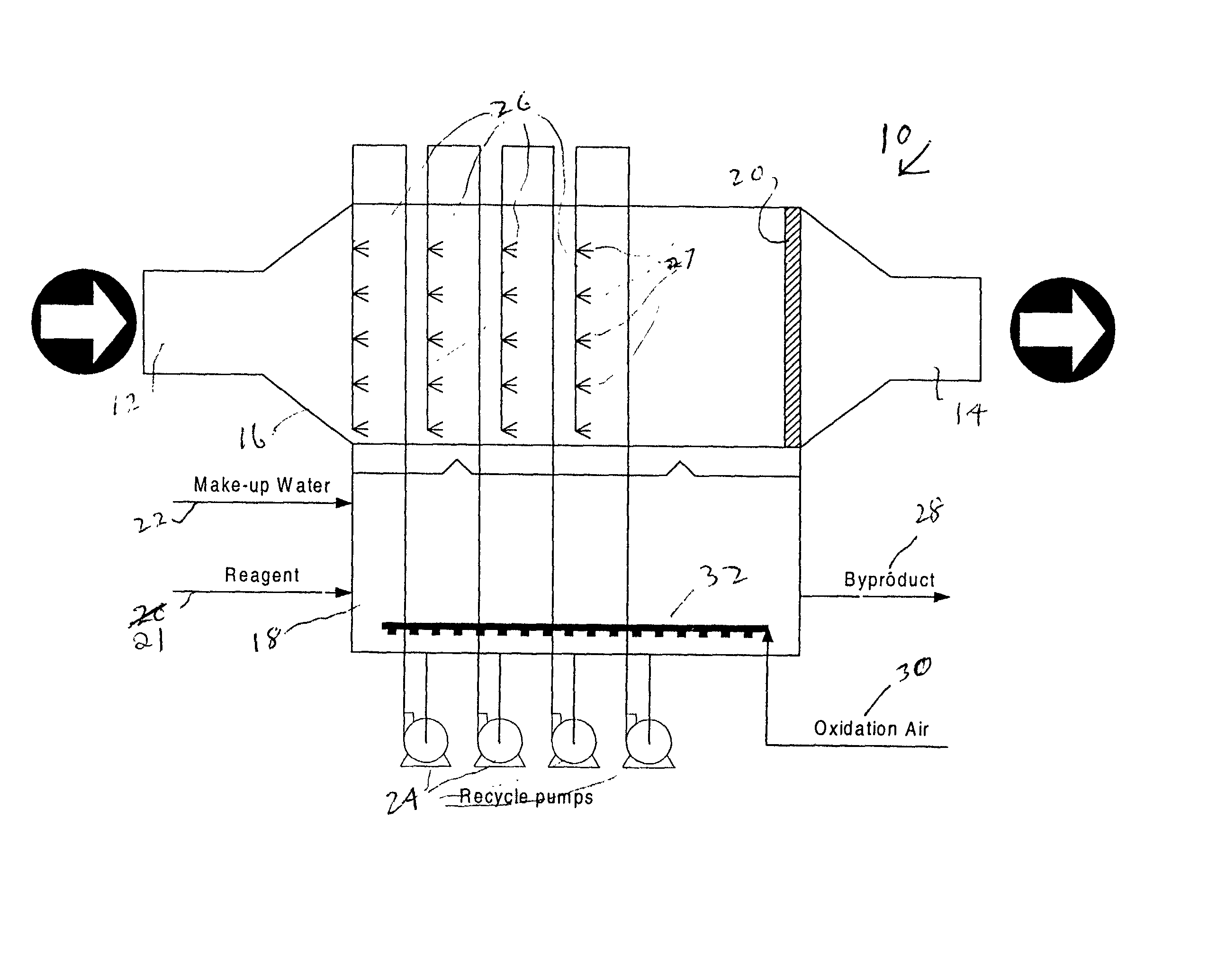
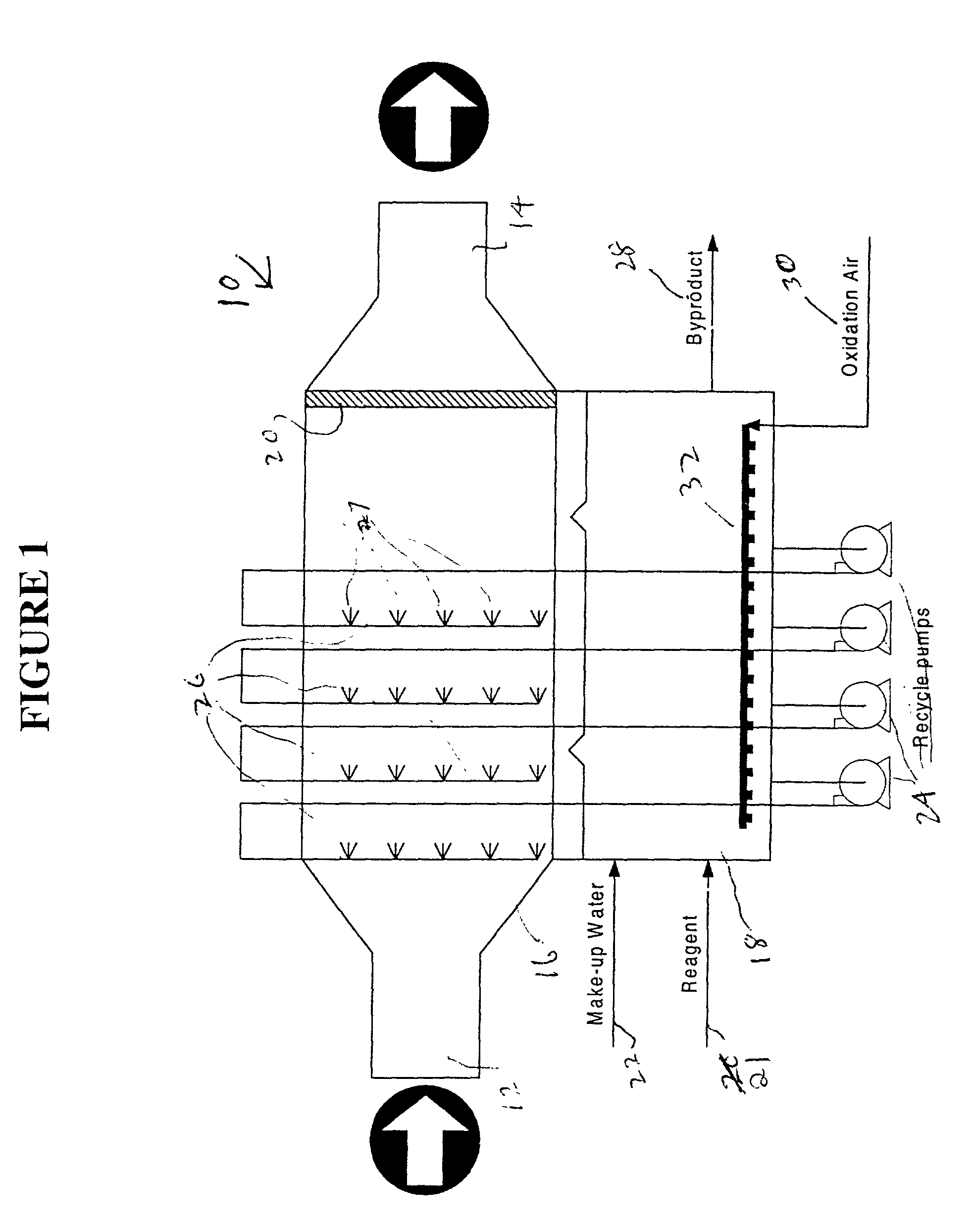
Horizontal scrubber system
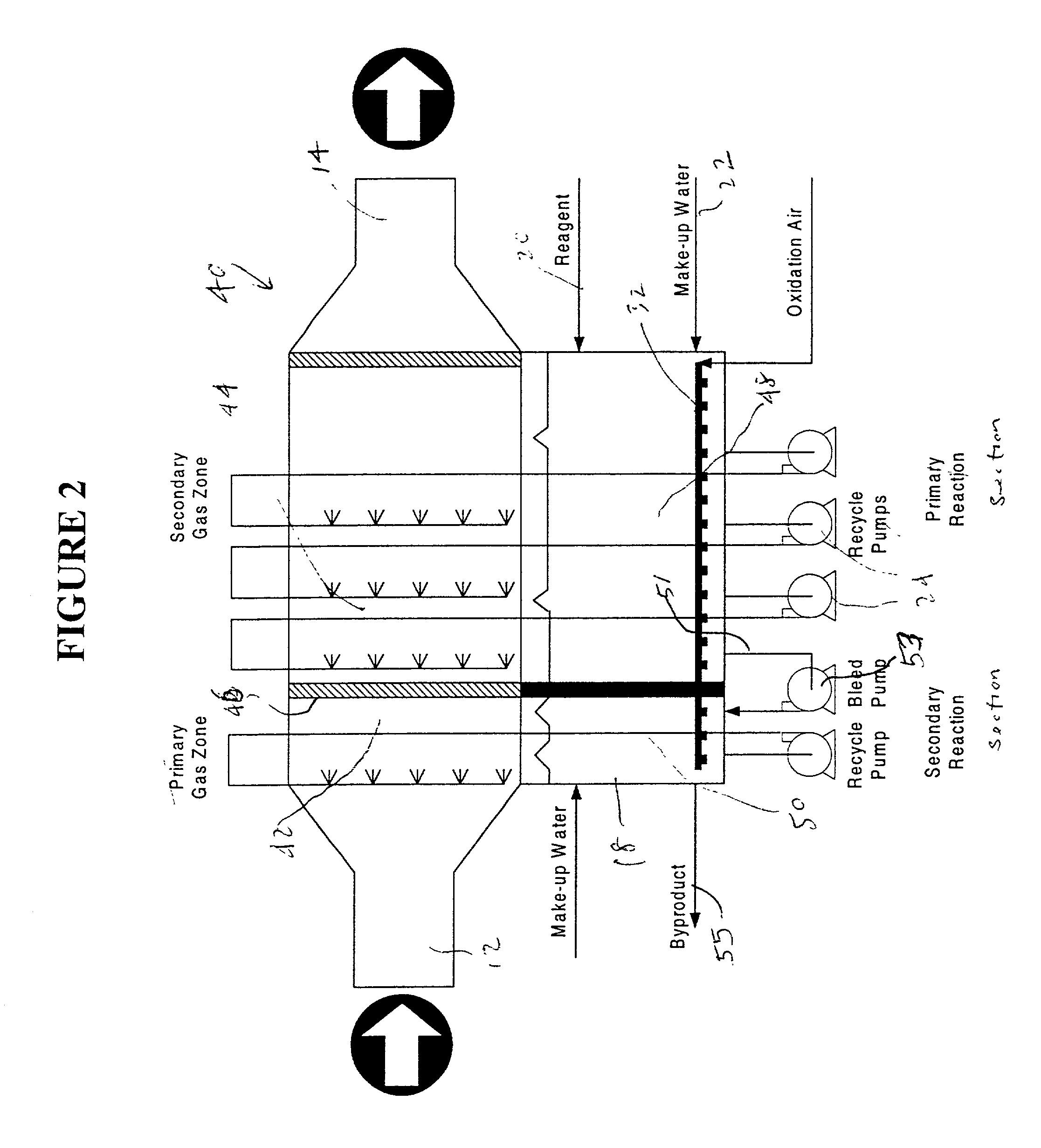
InactiveUS20020110511A1Eliminate needHigh gas velocityElectrostatic separationUsing liquid separation agentDifferential pressureProduct gas
A scrubber system is provided which enables a substantially horizontal flow path for the gas which is being subjected to scrubbing. Among other advantages, this permits operation of the absorber with a differential pressure of zero or less. Scrubber composition spray means are positioned in the horizontal gas flow path for spraying an aqueous scrubber composition in a direction which is generally cocurrent with said gas flow. The system is free of means which spray the scrubber composition in directions countercurrent to said gas flow.
Owner:URS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com