Patents
Literature
84 results about "Hypothermia induced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
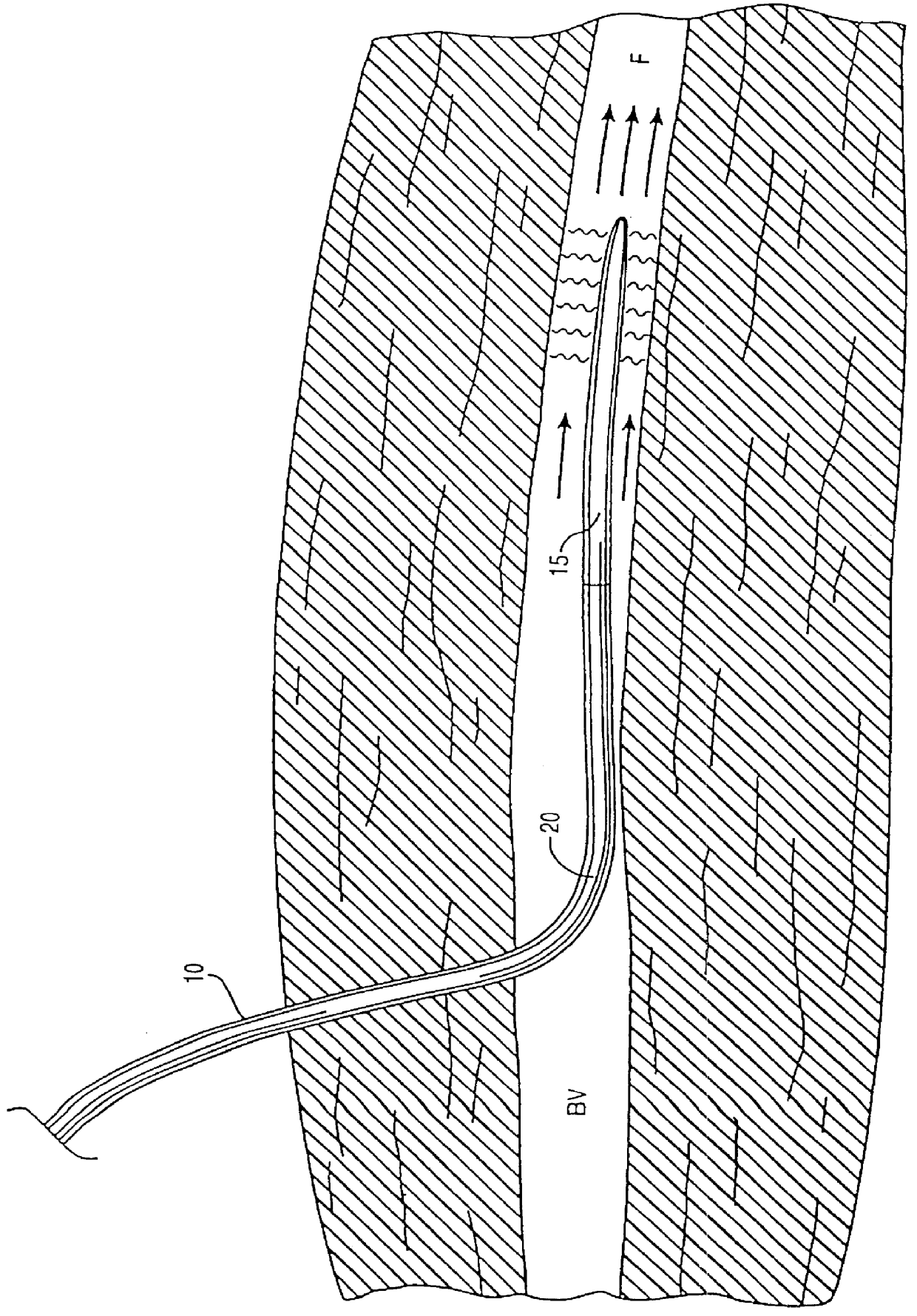
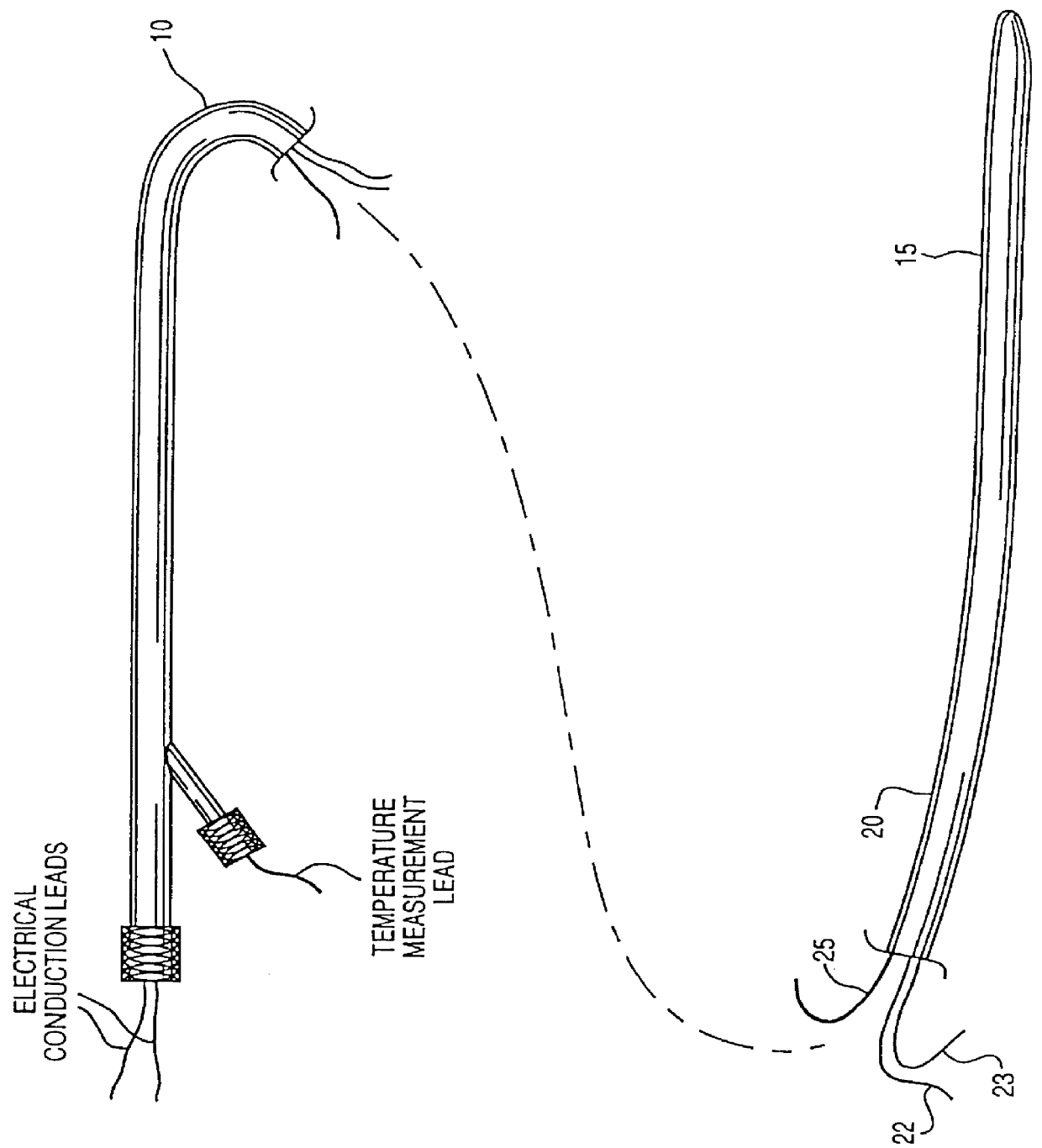
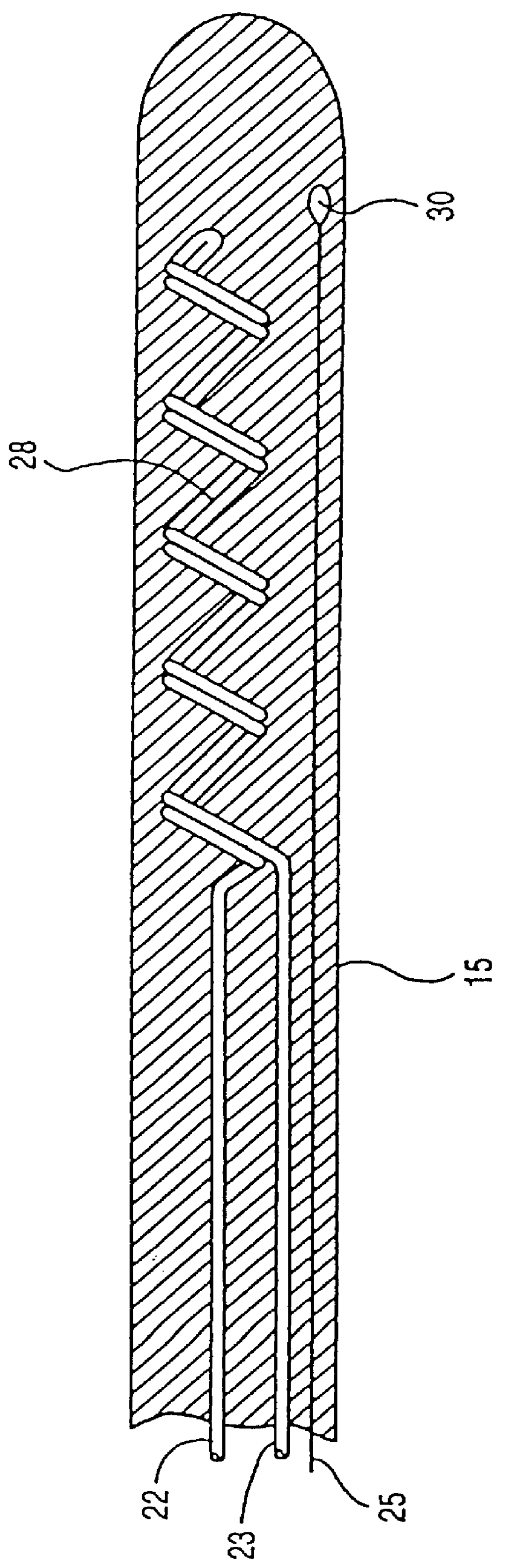
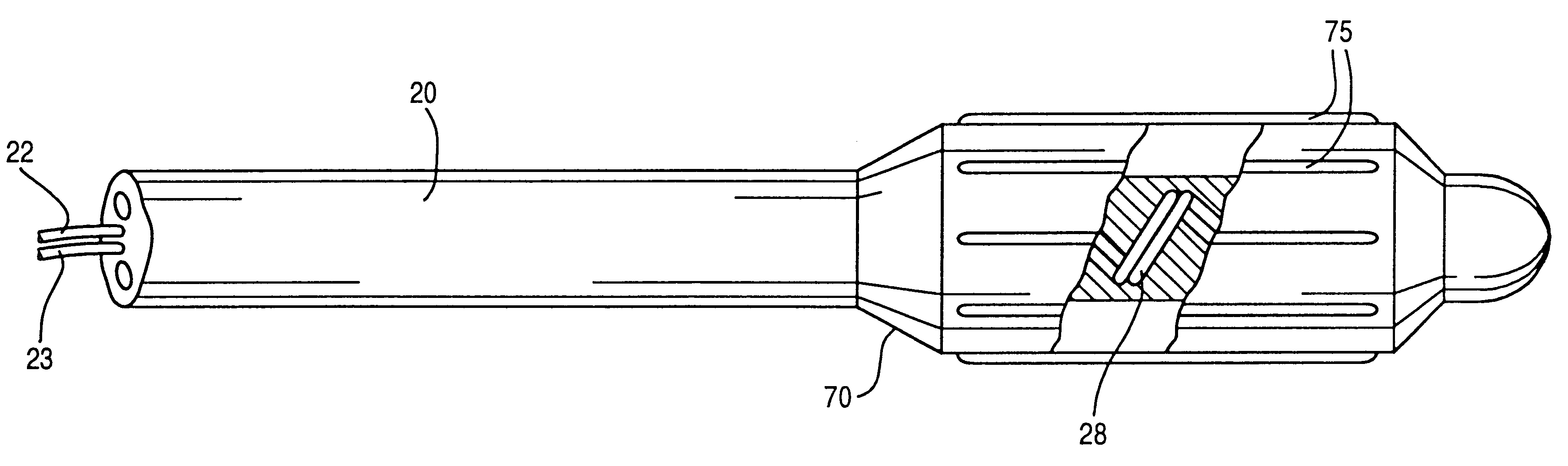
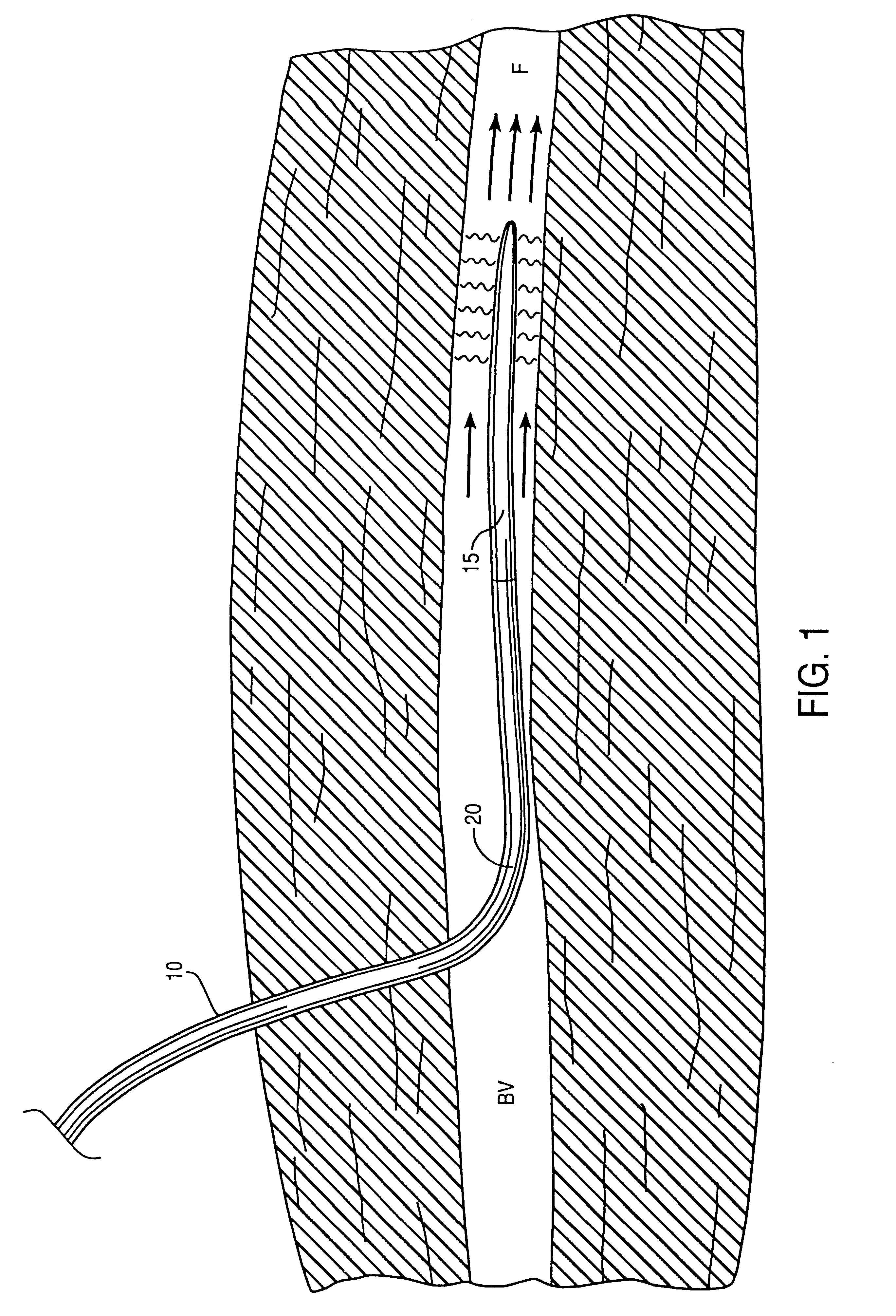
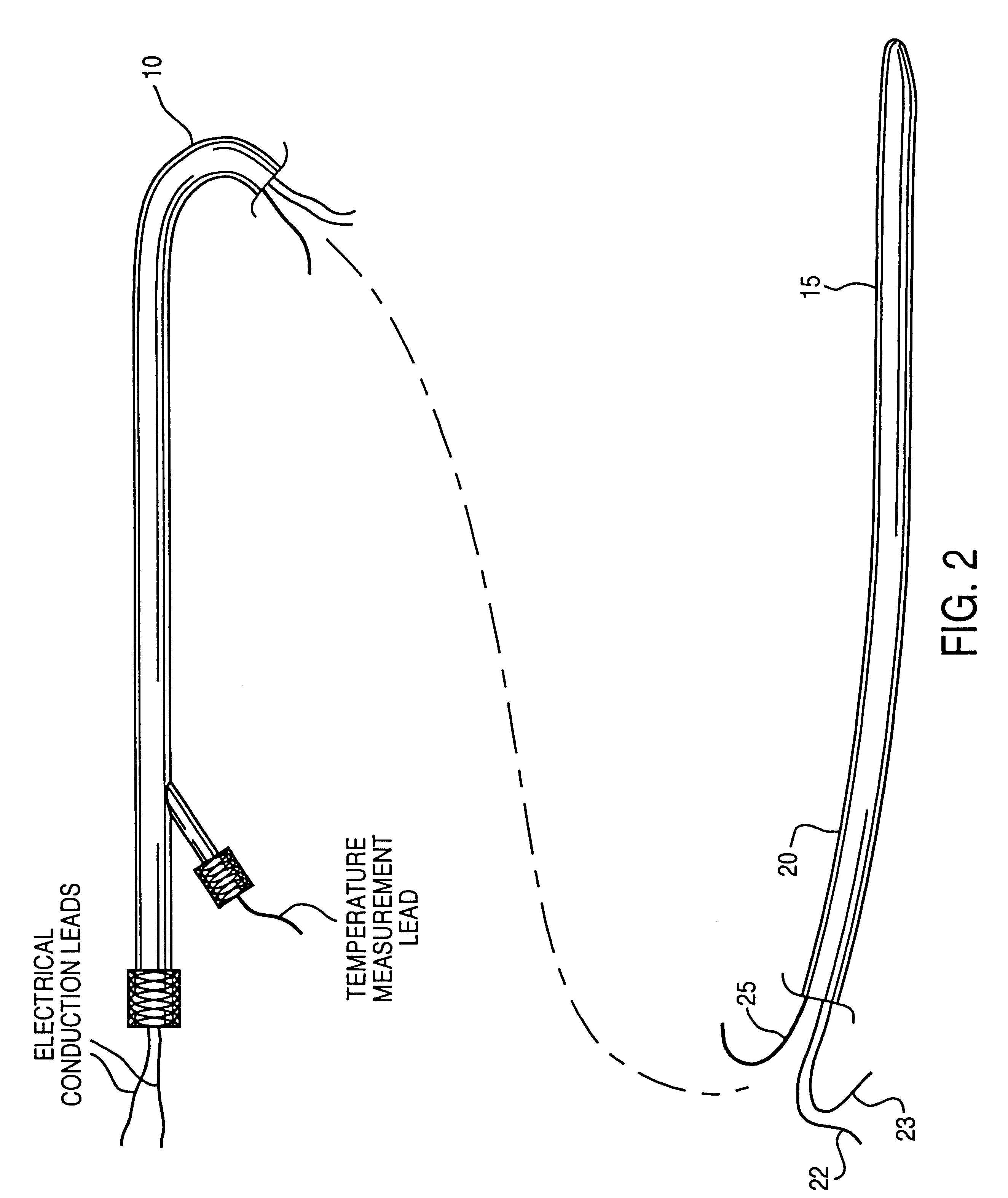
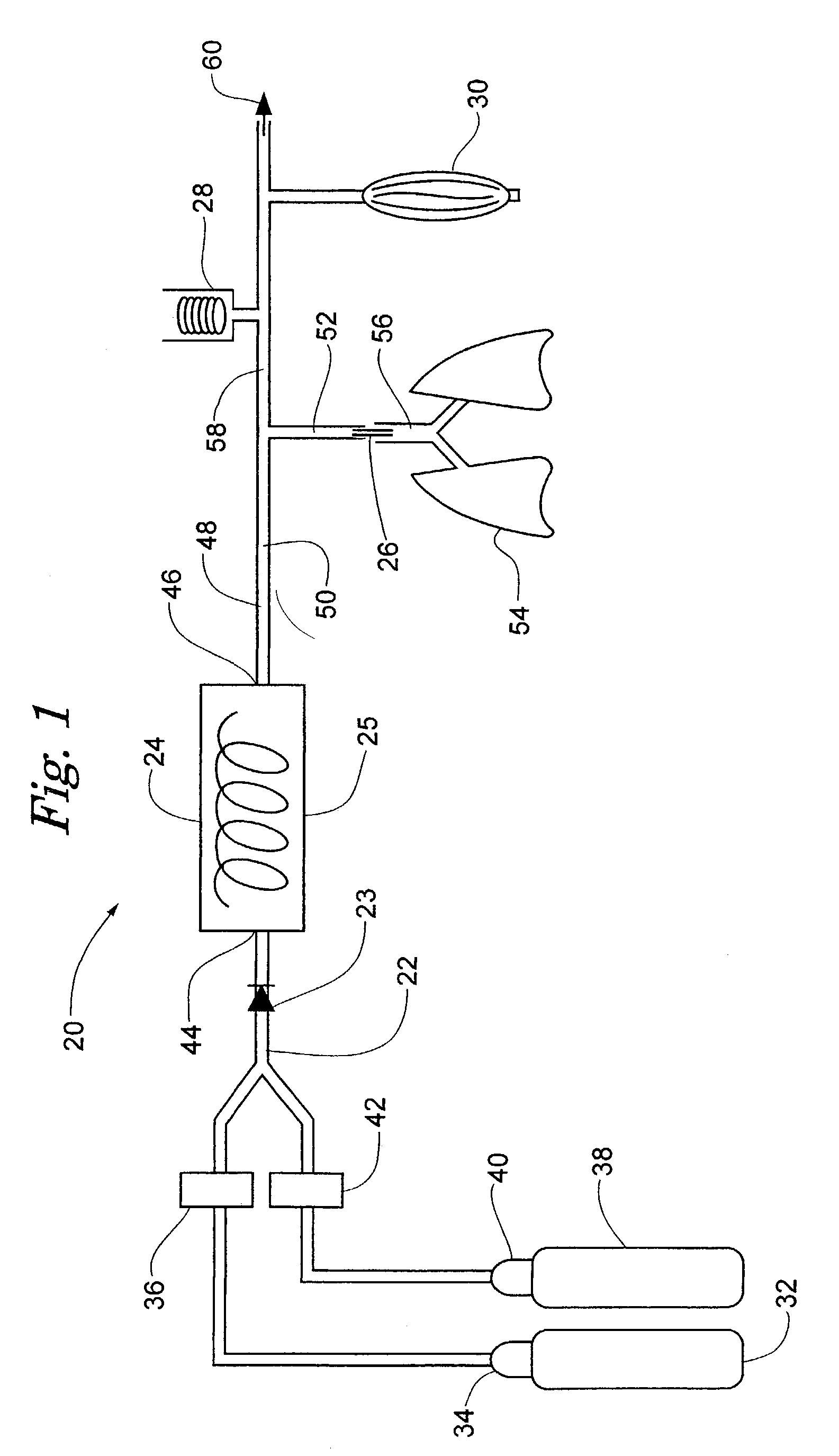
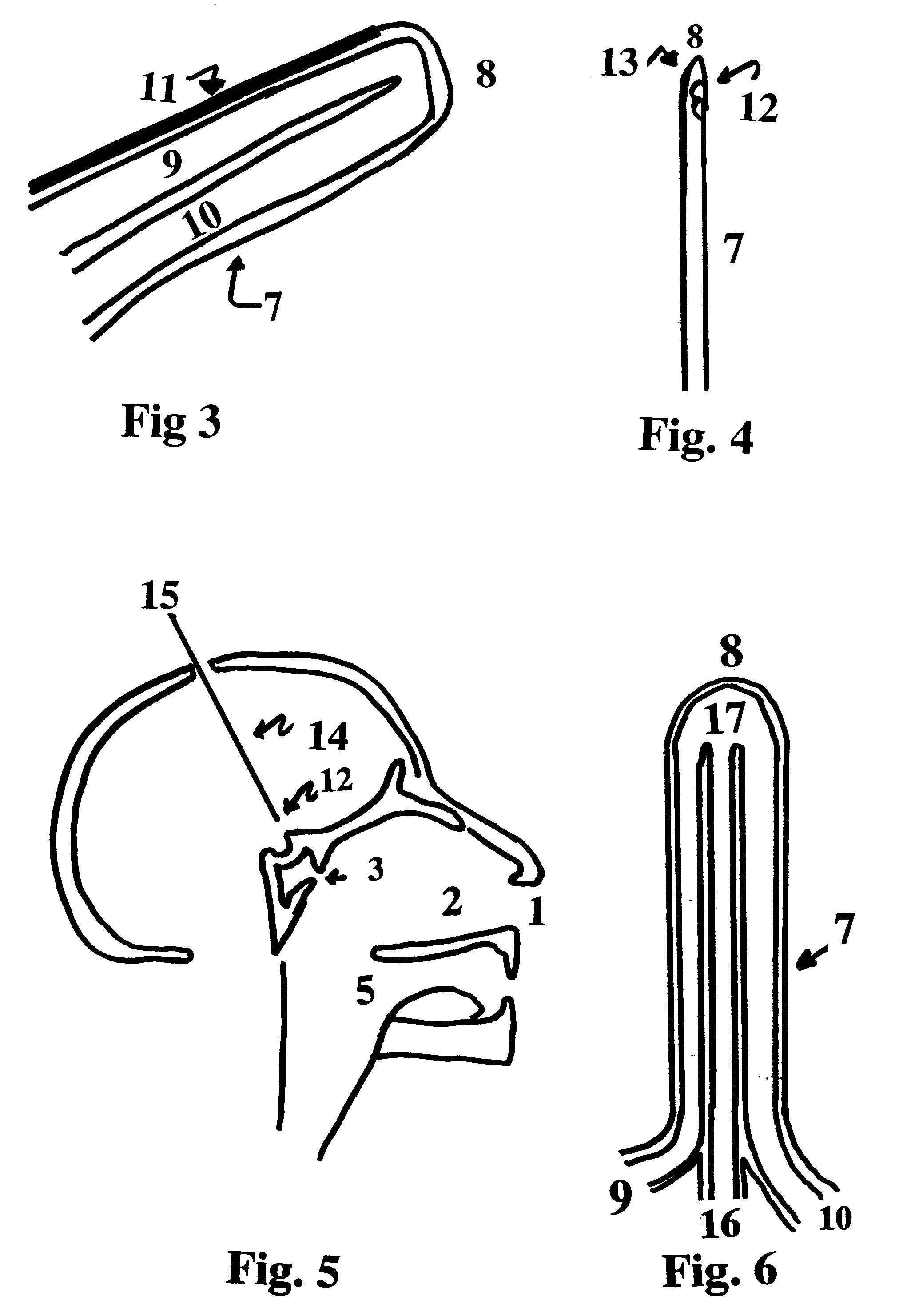
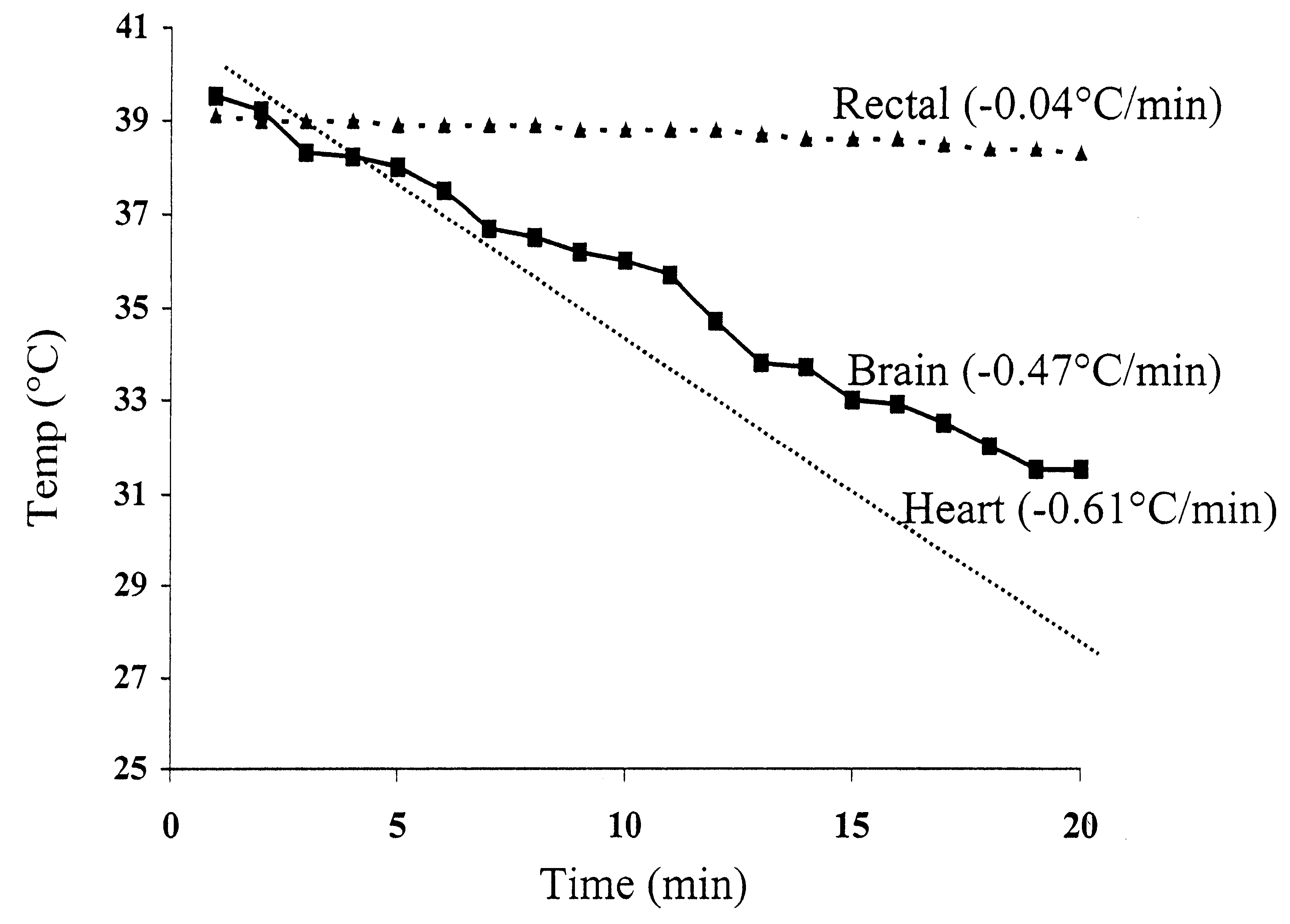
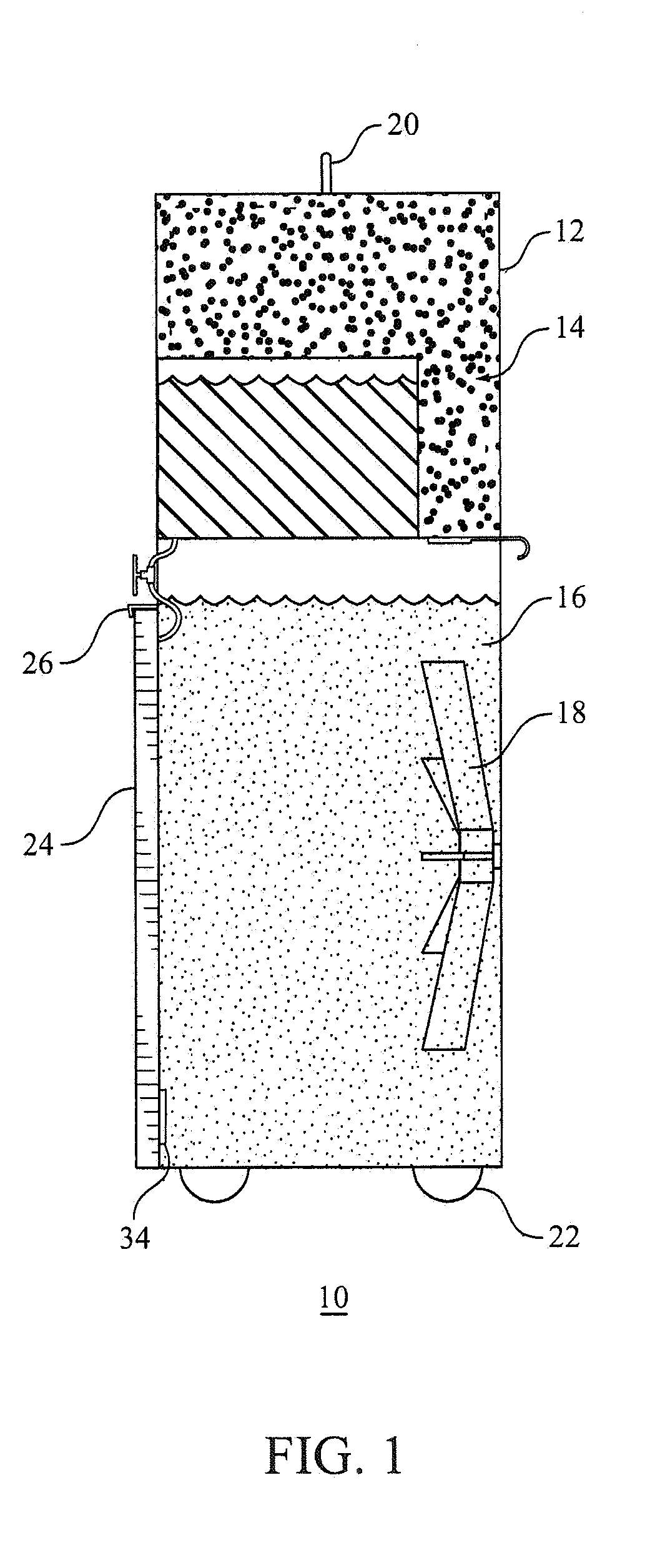
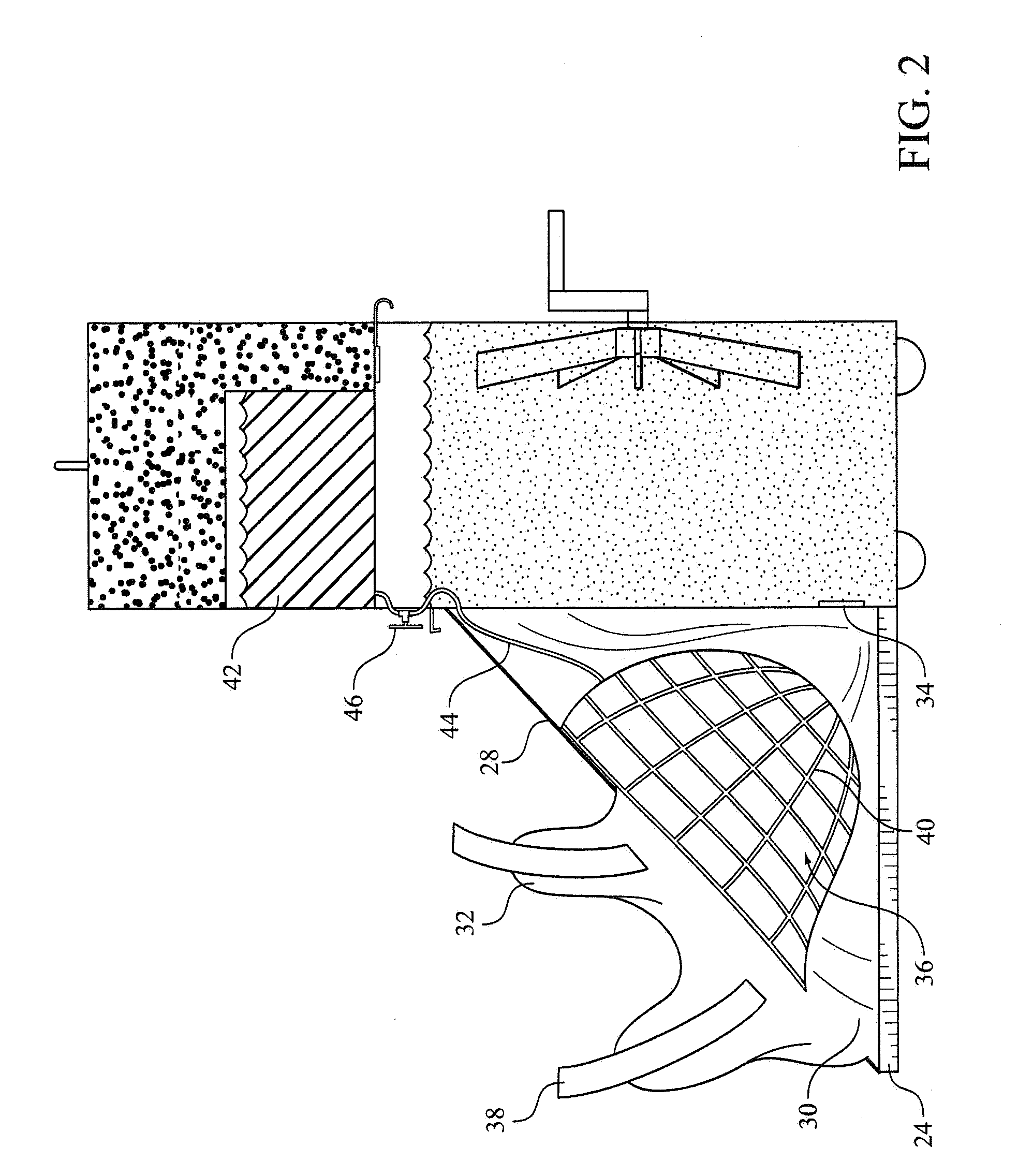
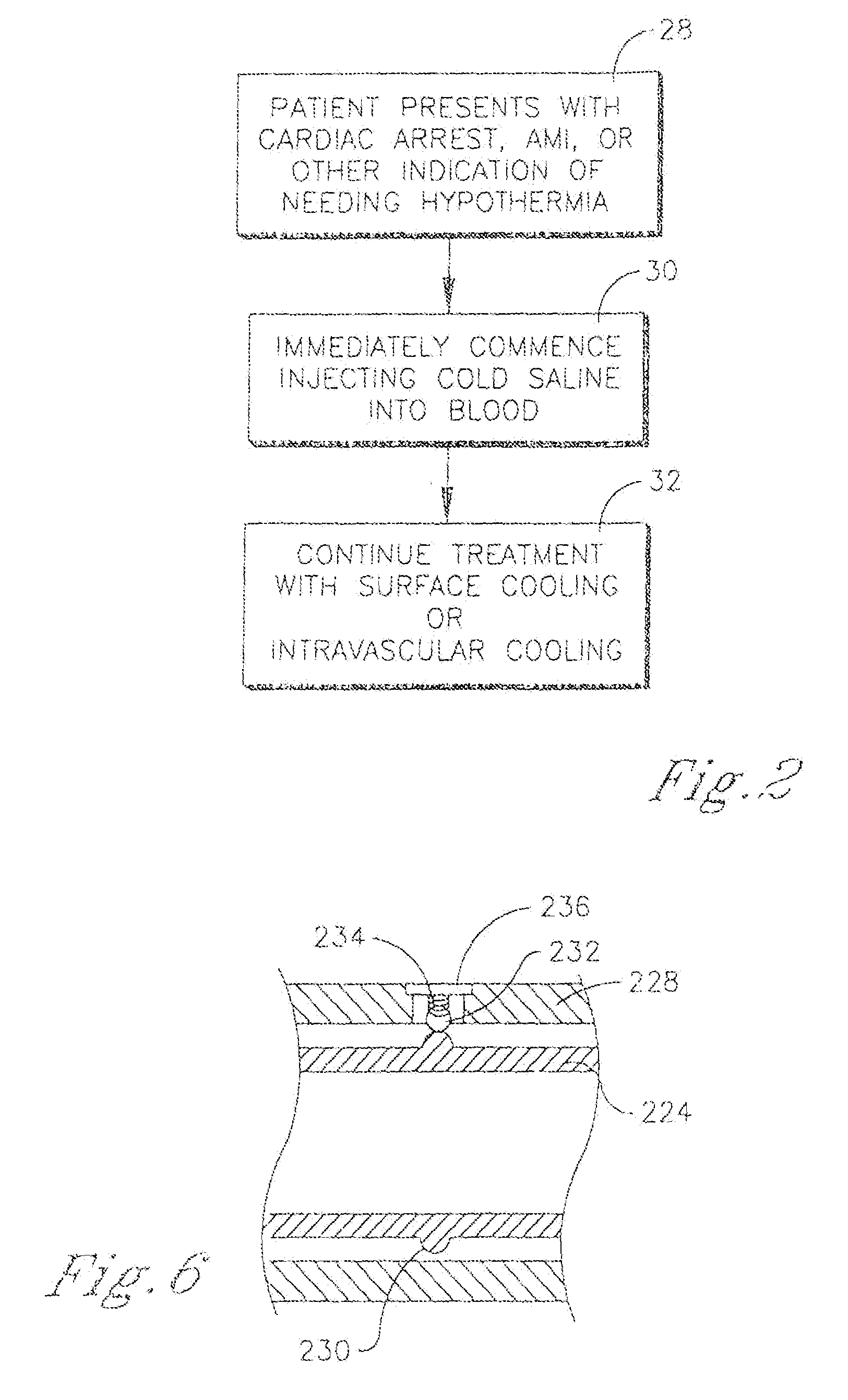
There are a variety of ways that hypothermia is induced, including intravascular cooling and water blankets. The former, an invasive procedure, involves a central venous catheter, which carries cold saline and is threaded through the femoral vein. The device serves as a heat exchange element,...
Phase change material thermal capacitor clothing
InactiveUS6855410B2Good thermal controlFast regenerationExothermal chemical reaction heat productionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSOCKSThermal insulation
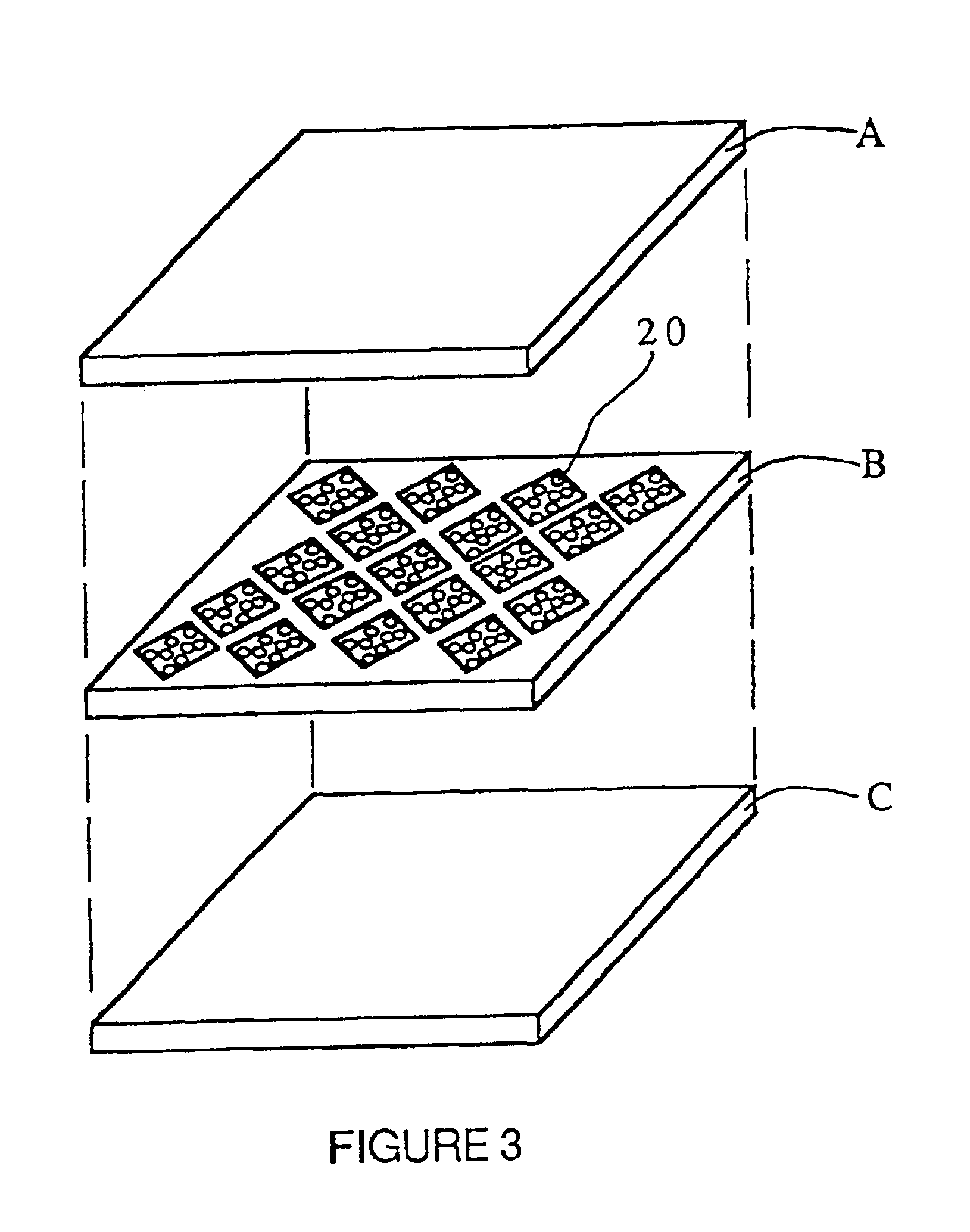
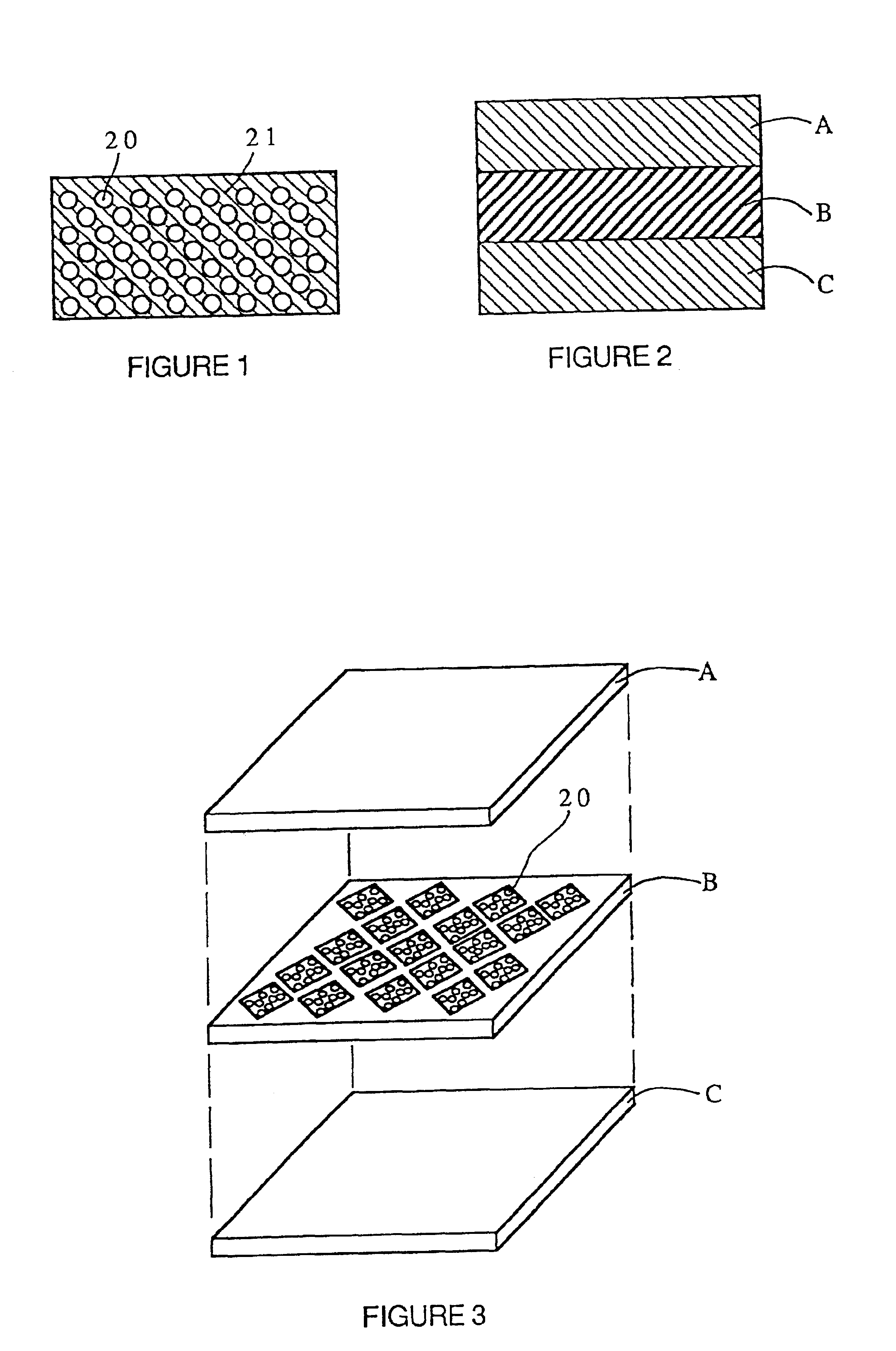
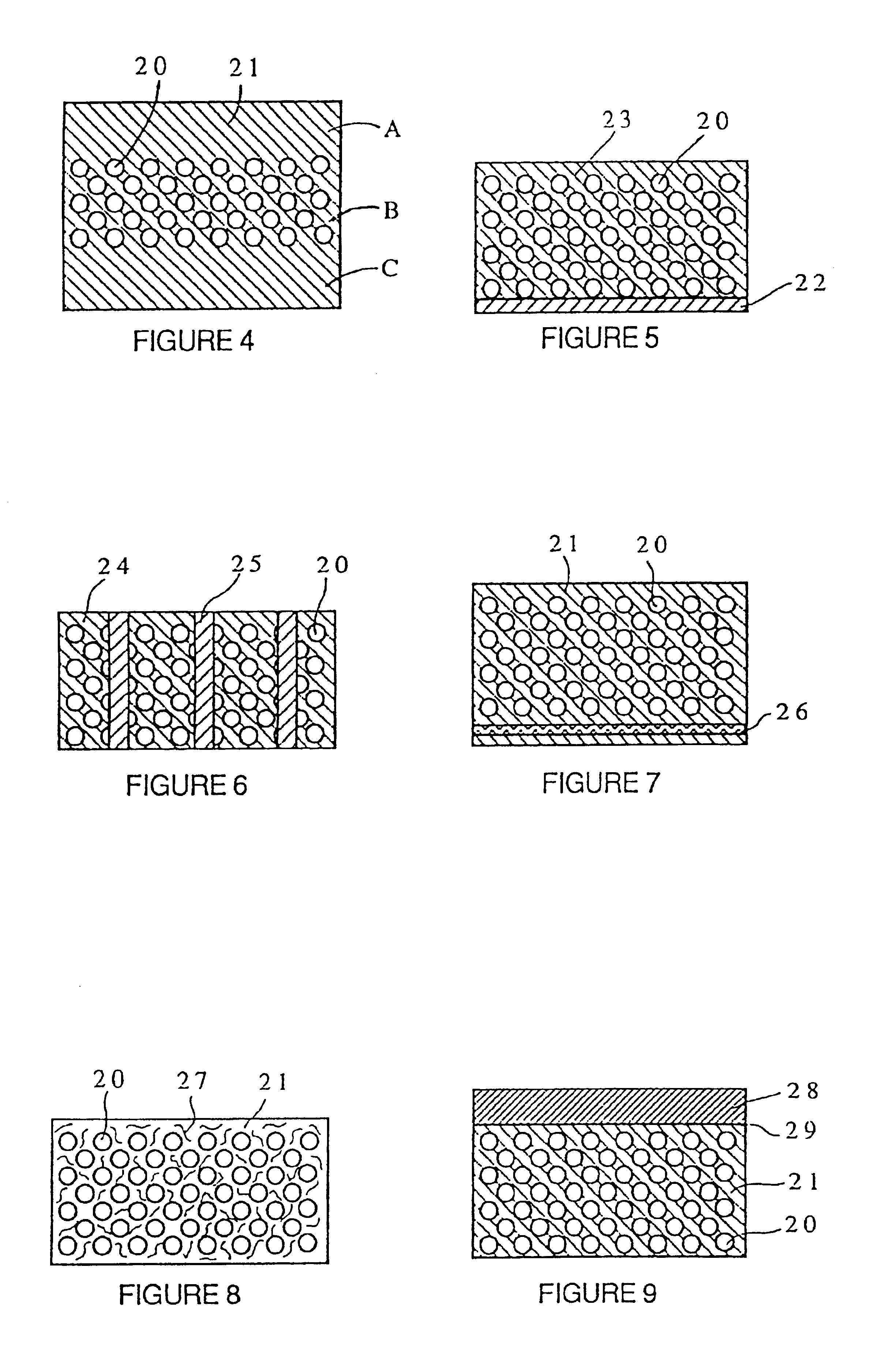
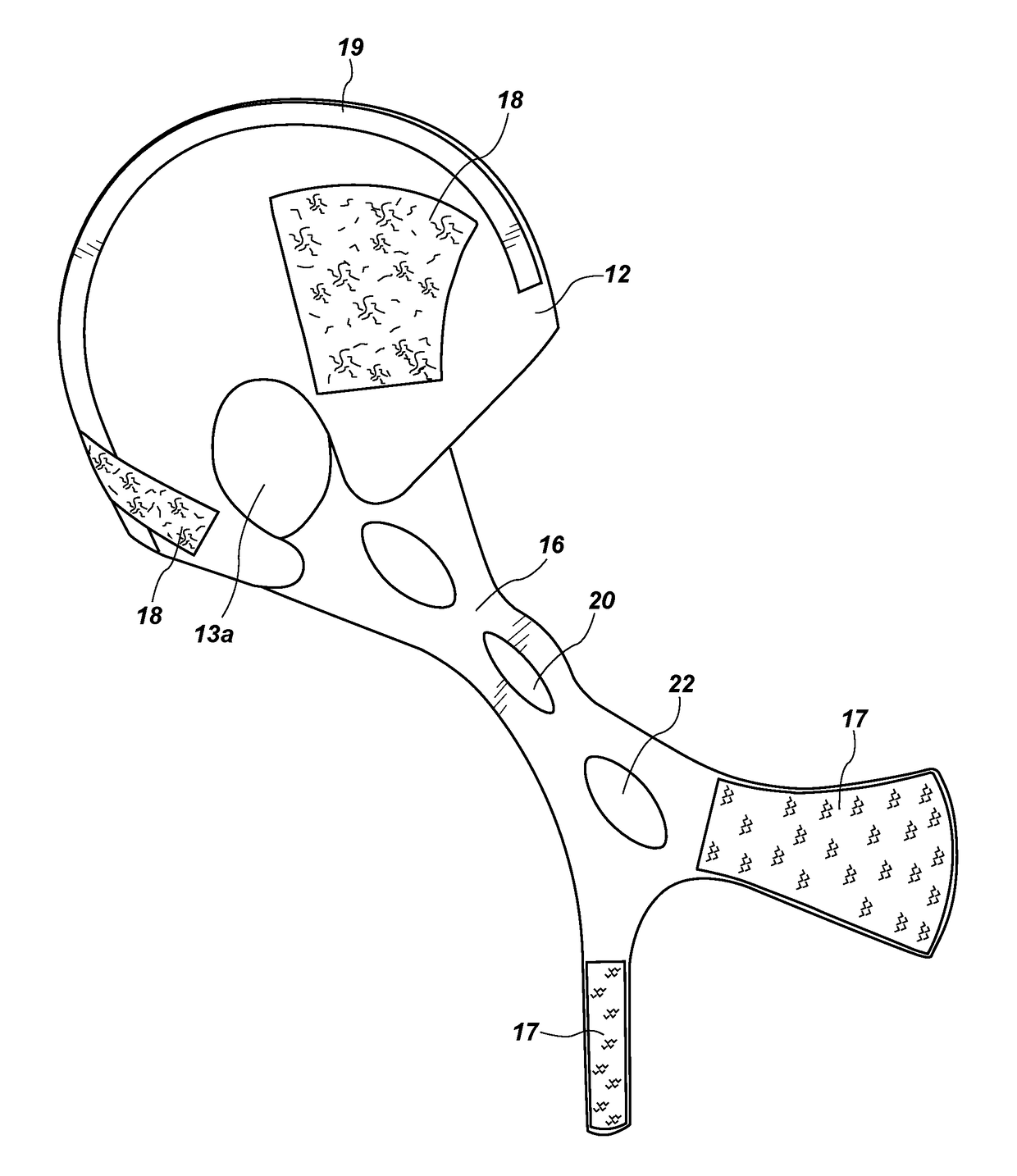
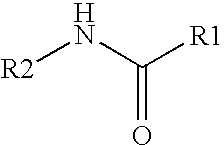
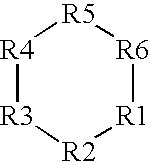
An apparatus and method for metabolic cooling and insulation of a user in a cold environment. In its preferred embodiment the apparatus is a highly flexible composite material having a flexible matrix containing a phase change thermal storage material. The apparatus can be made to heat or cool the body or to act as a thermal buffer to protect the wearer from changing environmental conditions. The apparatus may also include an external thermal insulation layer and / or an internal thermal control layer to regulate the rate of heat exchange between the composite and the skin of the wearer. Other embodiments of the apparatus also provide 1) a path for evaporation or direct absorption of perspiration from the skin of the wearer for improved comfort and thermal control, 2) heat conductive pathways within the material for thermal equalization, 3) surface treatments for improved absorption or rejection of heat by the material, and 4) means for quickly regenerating the thermal storage capacity for reuse of the material. Applications of the composite materials are also described which take advantage of the composite's thermal characteristics. The examples described include a diver's wet suit, ski boot liners, thermal socks, gloves and a face mask for cold weather activities, and a metabolic heating or cooling blanket useful for treating hypothermia or fever patients in a medical setting and therapeutic heating or cooling orthopedic joint supports.
Owner:BUCKLEY THERESA M
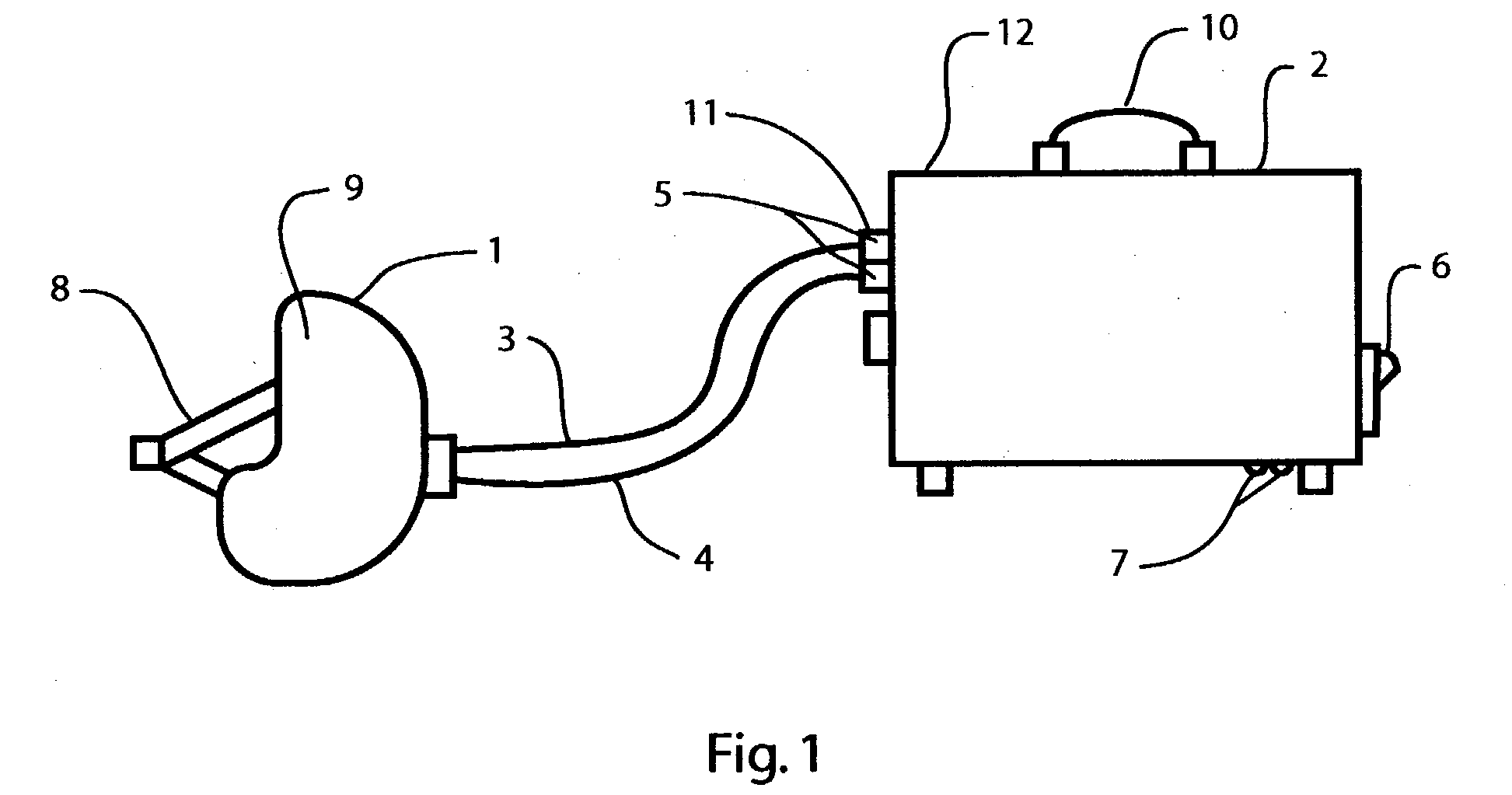
Method and apparatus for controlling a patient's body temperature by in situ blood temperature modifications
InactiveUS6110168AQuickly felt throughout the patient's bodyEliminate damageStentsBalloon catheterHypothermia inducedHigh body temperature
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the internal body temperature of a patient. According to the present invention, a catheter is inserted through an incision into a large blood vessel of a patient. By selectively heating or cooling a portion of the catheter lying within the blood vessel, heat may be transferred to or from blood flowing within the vessel and the patient's body temperature may thereby be increased or decreased as desired. The invention will find use in treating undesirable conditions of hypothermia and hyperthermia, or for inducing a condition of artificial hypothermia when desired.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
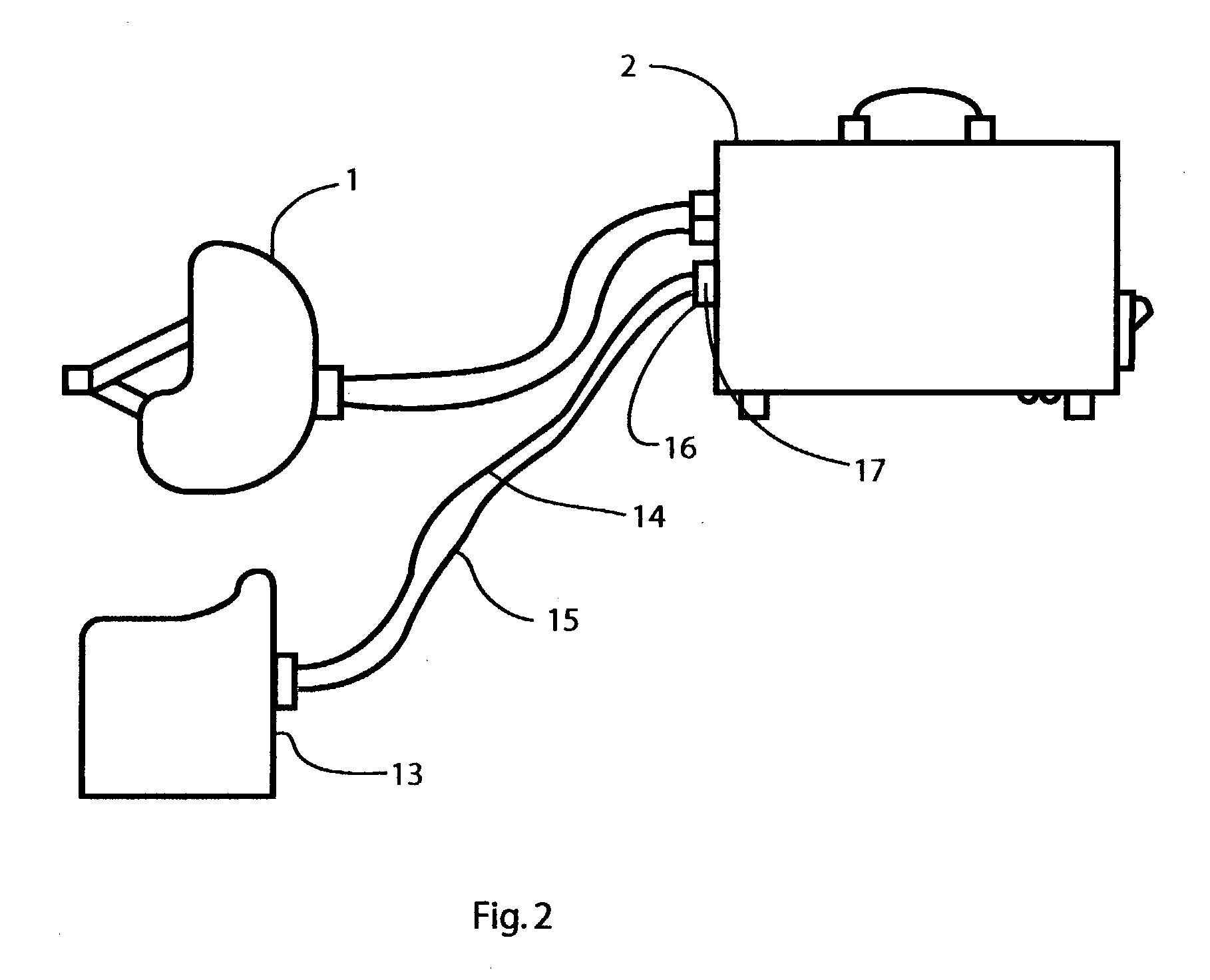
Method and Apparatus for Inducing Therapeutic Hypothermia
Methods and apparatus for delivering therapeutic hypothermia to a patient are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is a hypothermia system comprising a fluid source, a heat exchanger assembly, a catheter in fluid communication with the fluid source, and a pump system configured to infuse hypothermic fluid into a patient cavity and extract hypothermic fluid from the patient cavity. The hypothermia system can infuse and extract fluid automatically from the patient cavity. In one embodiment, the patient cavity is a peritoneal cavity. A safe access device to gain access to the patient cavity is also provided.
Owner:VELOMEDIX
Catheter system for controlling a patient's body temperature by in situ blood temperature modification
InactiveUS6306161B1Quickly felt throughout the patient's bodyEliminate damageStentsBalloon catheterMedicineHigh body temperature
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
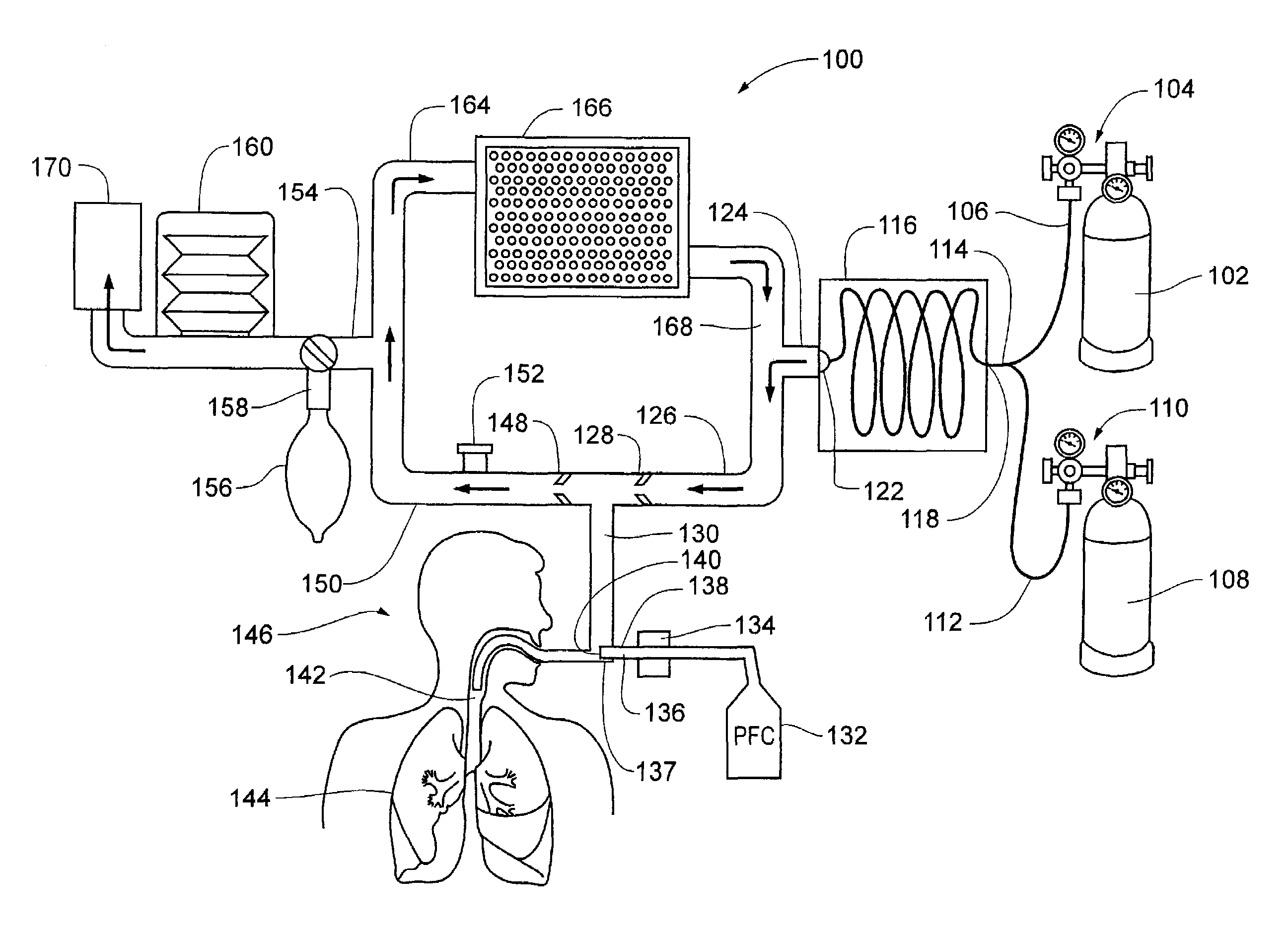
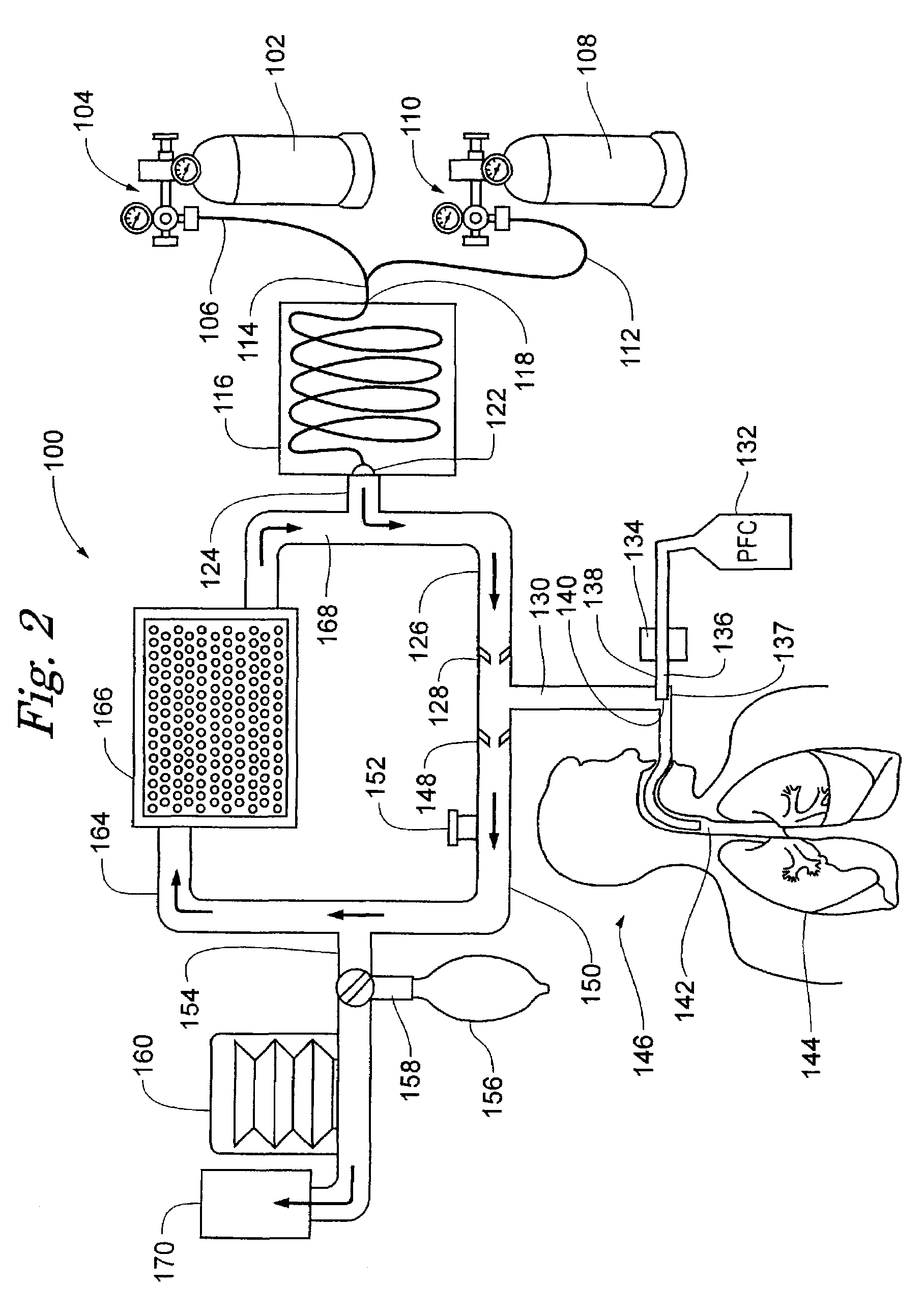
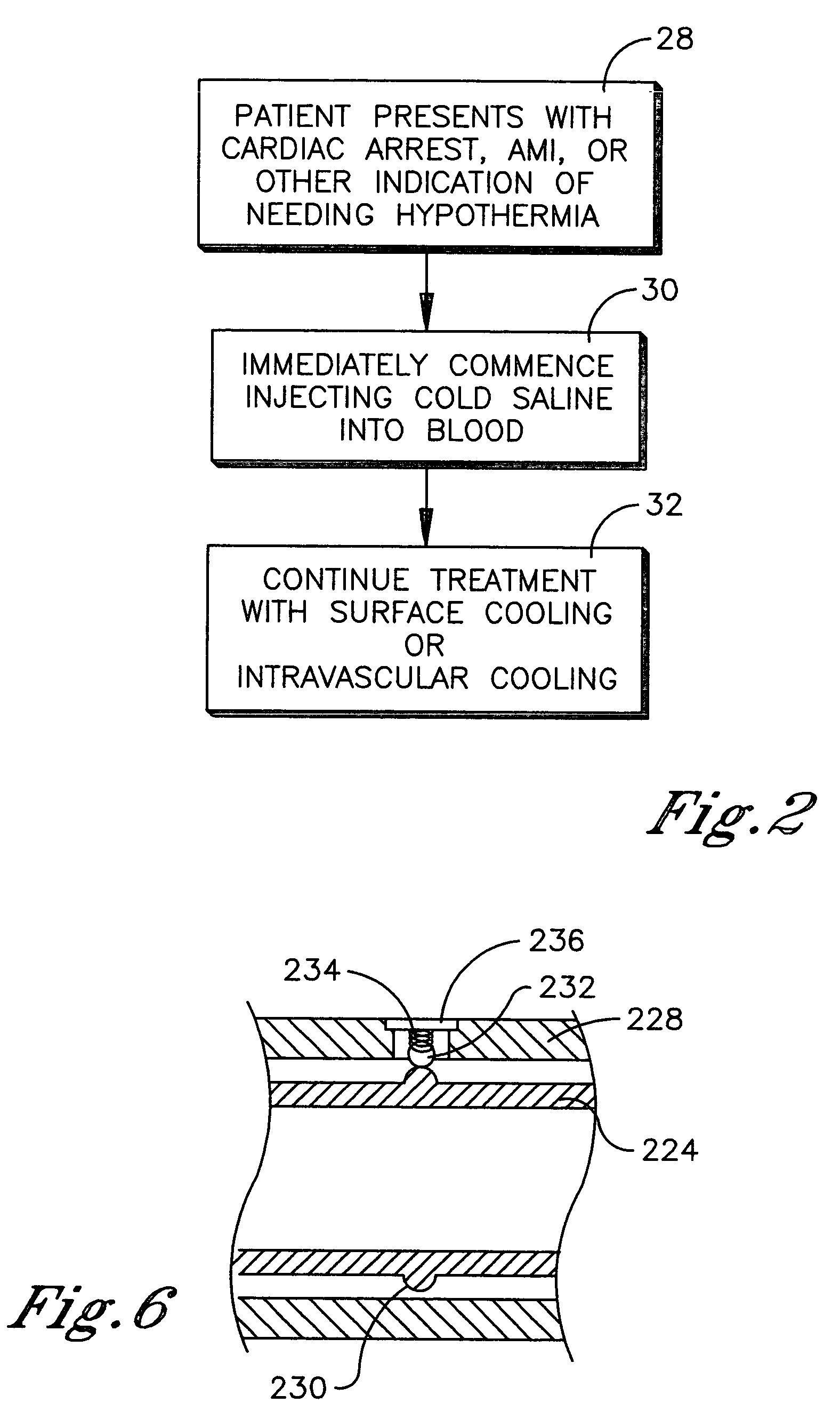
Inducing hypothermia and rewarming using a helium-oxygen mixture
ActiveUS6983749B2Mitigate warmingReduce coolingLighting and heating apparatusInorganic active ingredientsREFLEX DECREASEInspired gas temperature
Devices and methods to heat and cool human beings, including inducing and maintaining hypothermia in human patients. Methods include inducing hypothermia to treat ischemic events, including heart attack and stroke, to limit damage caused by the ischemic event. Methods can include: using the lungs for heat exchange; using cooled gases for ventilation; using helium in the ventilation gas mixture, using medications to control reflex heat production; and injecting a perfluorocarbon mist into the gas stream to increase the cooling rate. The high thermal conductivity and diffusivity of helium results in greater inspired gas temperature equalization toward body temperature. Due to the latent heat of vaporization, addition of even small quantity of phase-change perfluorocarbon dramatically increases the heat carrying capacity of the respiratory gases. Hypothermia may be terminated by discontinuing the medications and warming the patient using a warmed helium-oxygen mixture.
Owner:MINNESOTA HIGH TECH RESOURCES
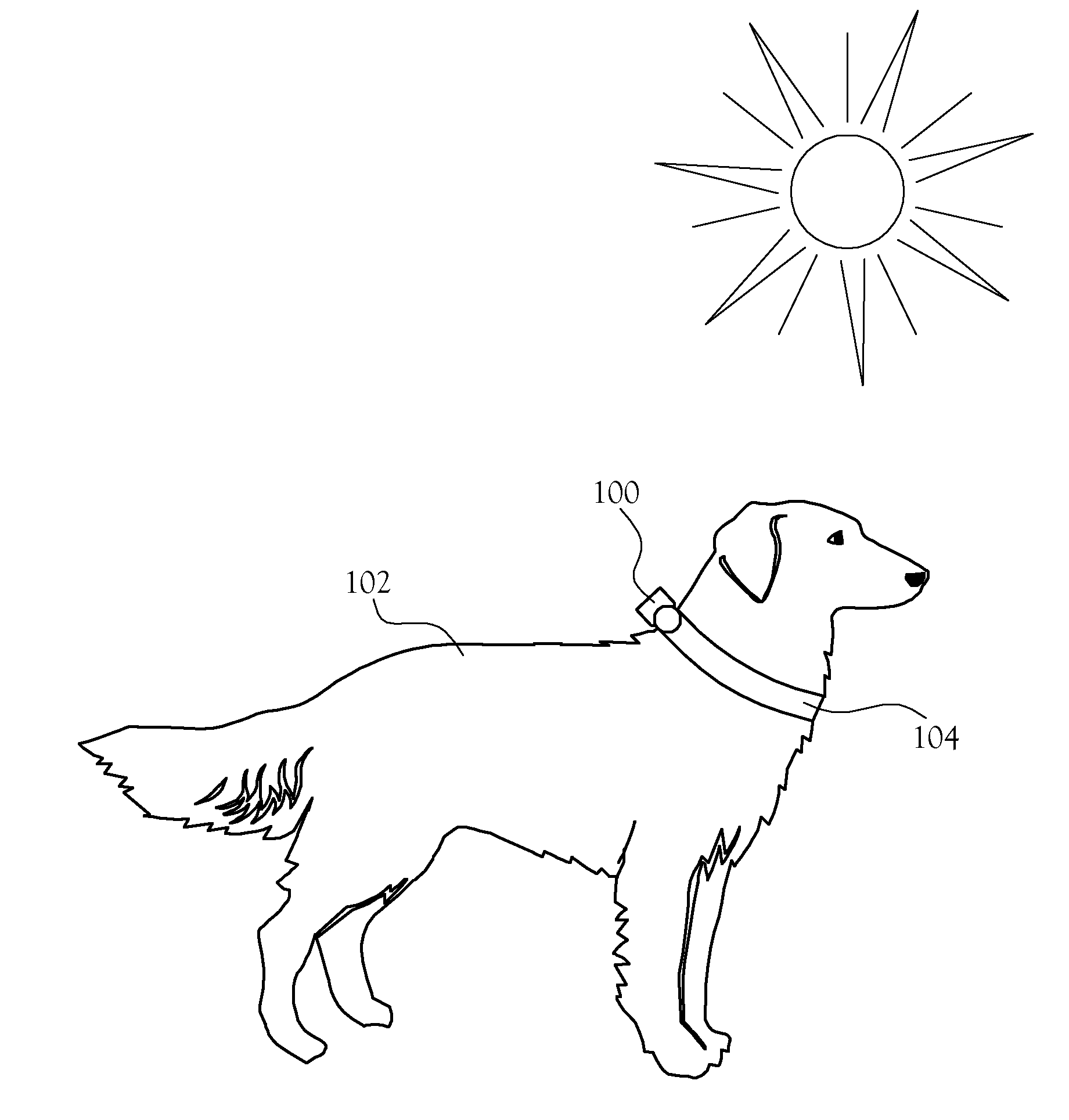
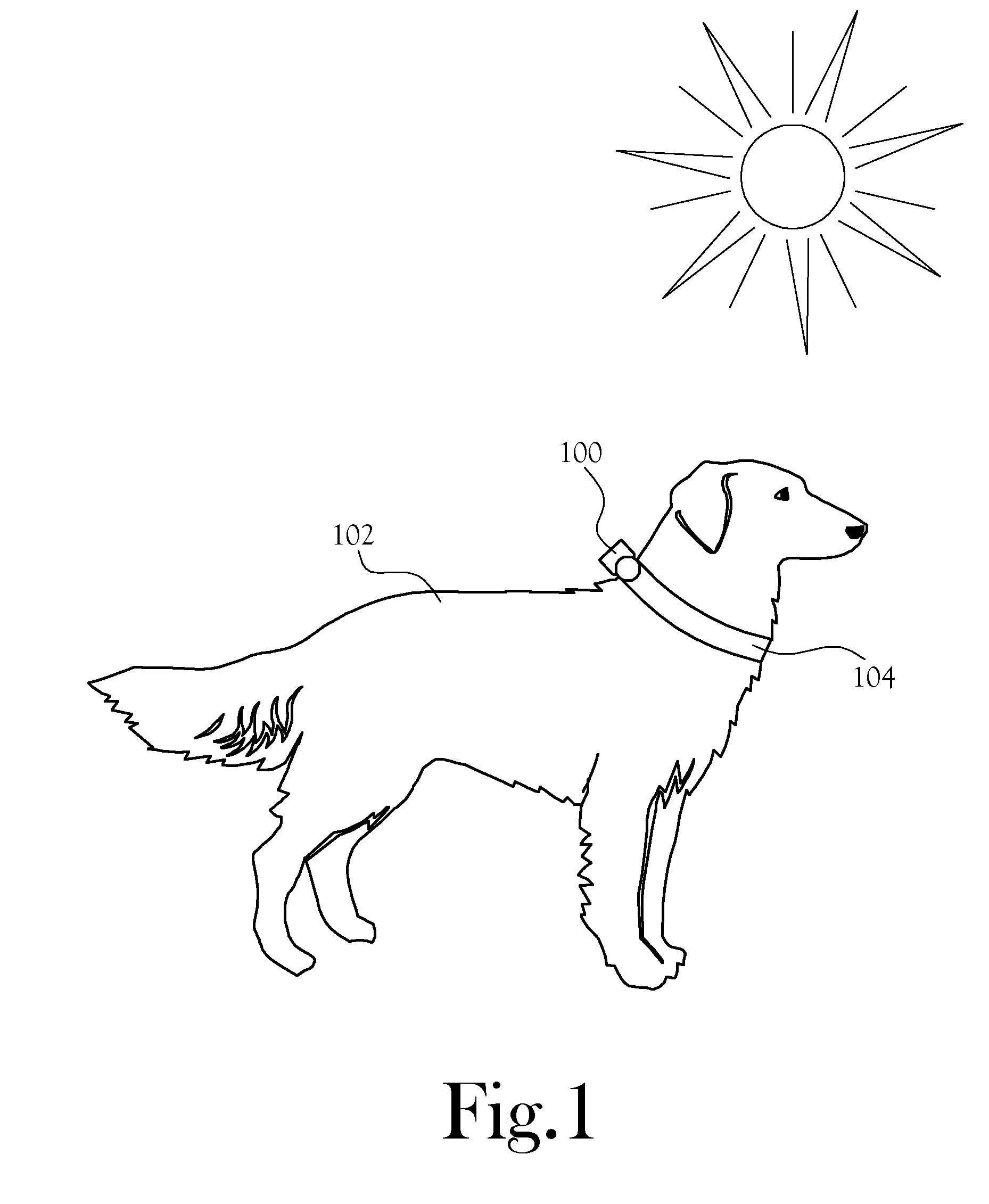
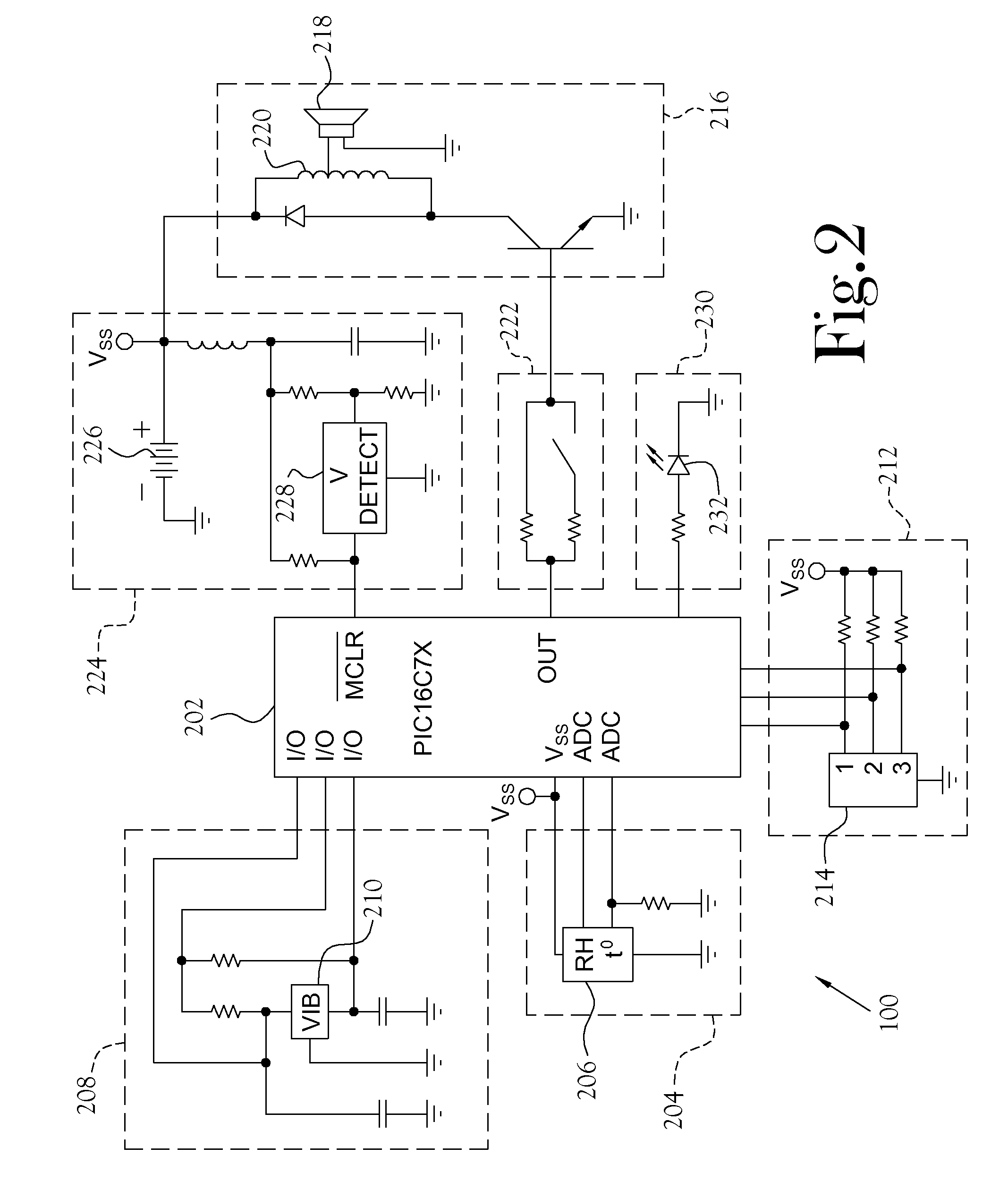
Animal Condition Monitor
An animal condition monitor. The animal condition monitor measures diagnostic parameters from the animal and determines whether the parameters indicate that the animal is at risk of a specified condition, such as heat stroke, heat exhaustion, hypothermia, or hyperthermia. The condition assessment is considered in light of a profile containing information about the age / health of the animal. When warranted, the animal condition monitor provides notification of the condition of interest.
Owner:RADIO SYST CORP
Method for inducing hypothermia for treating neurological disorders
InactiveUS6736837B2Increase body temperatureInsignificant coolingSurgeryTherapeutic coolingDiseaseRadical radiotherapy
The invention relates generally to methods of treating cancer and other diseases by modulating body temperature. Heat may directed to the hypothalamus of a warm-blooded animal to cool the animal, utilizing the physiological mechanisms that regulate body temperature to effect a compensatory cooling response, thereby lowering body temperature (hypothermia), and rendering other methods of lowering body temperature more effective. Heat may be withdrawn from the hypothalamus of an animal, cooling the hypothalamus, inducing a compensatory increase in body temperature (hyperthermia), and rendering other methods of raising body temperature more effective. Body temperature may be directly modulated by heat-exchange catheter positioned within a blood vessel of a patient. The invention relates generally to methods of treating cancer by inducing hypothermia by directing heat to the hypothalamus, optionally maintaining cancerous tissue at or near to normal body temperature, and optionally applying another cancer treatment. This other cancer treatment may be radiation therapy, chemotherapy, a combination of radiation and chemotherapy, or some other cancer treatment. The invention relates generally to methods of treating diseases including cancer, viral infections, and other diseases, comprising inducing hyperthermia by cooling the hypothalamus, and optionally applying another treatment, for example radiation, chemotherapy, antiviral therapy, or a combination of therapies.
Owner:FOX JAMES A
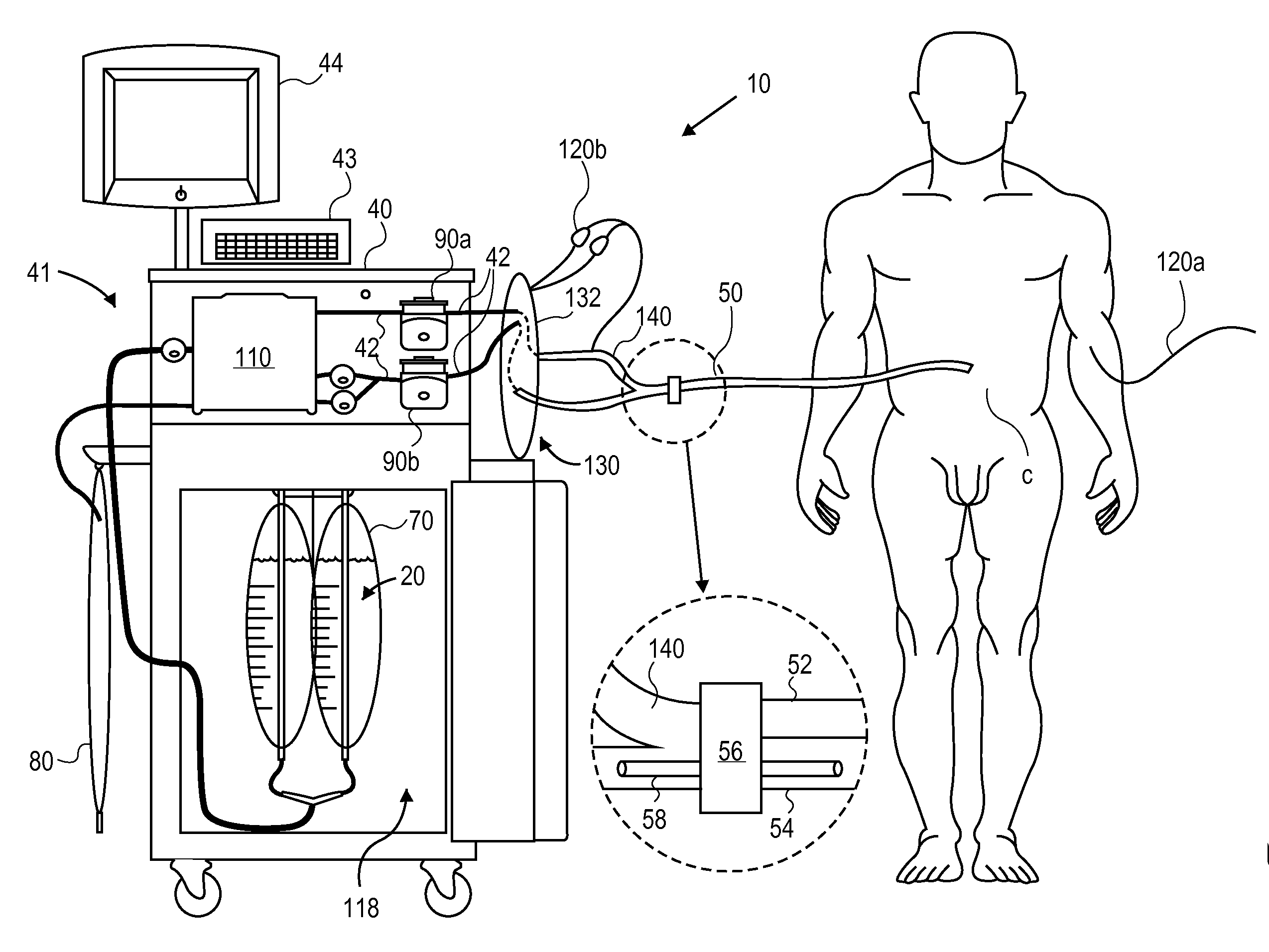
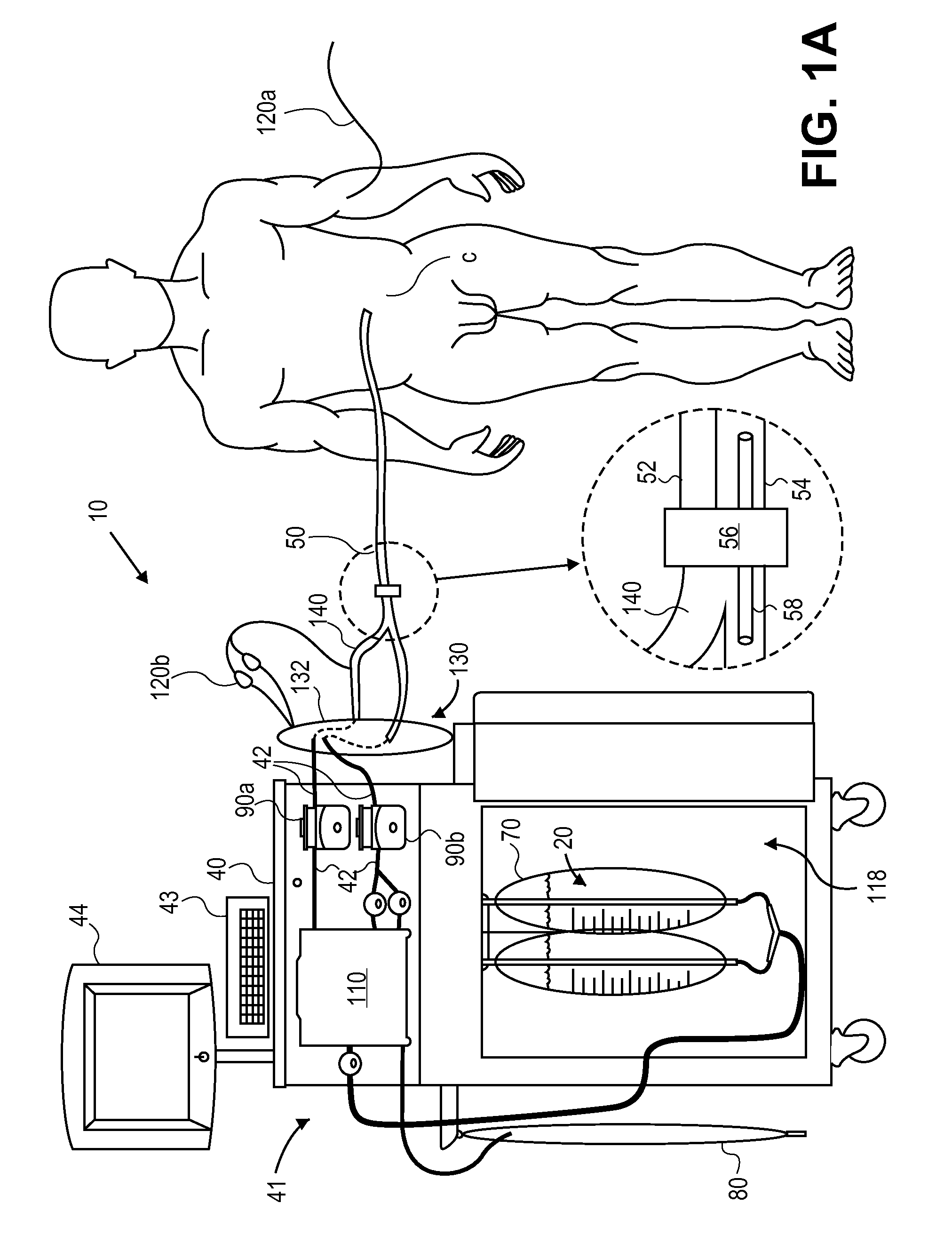
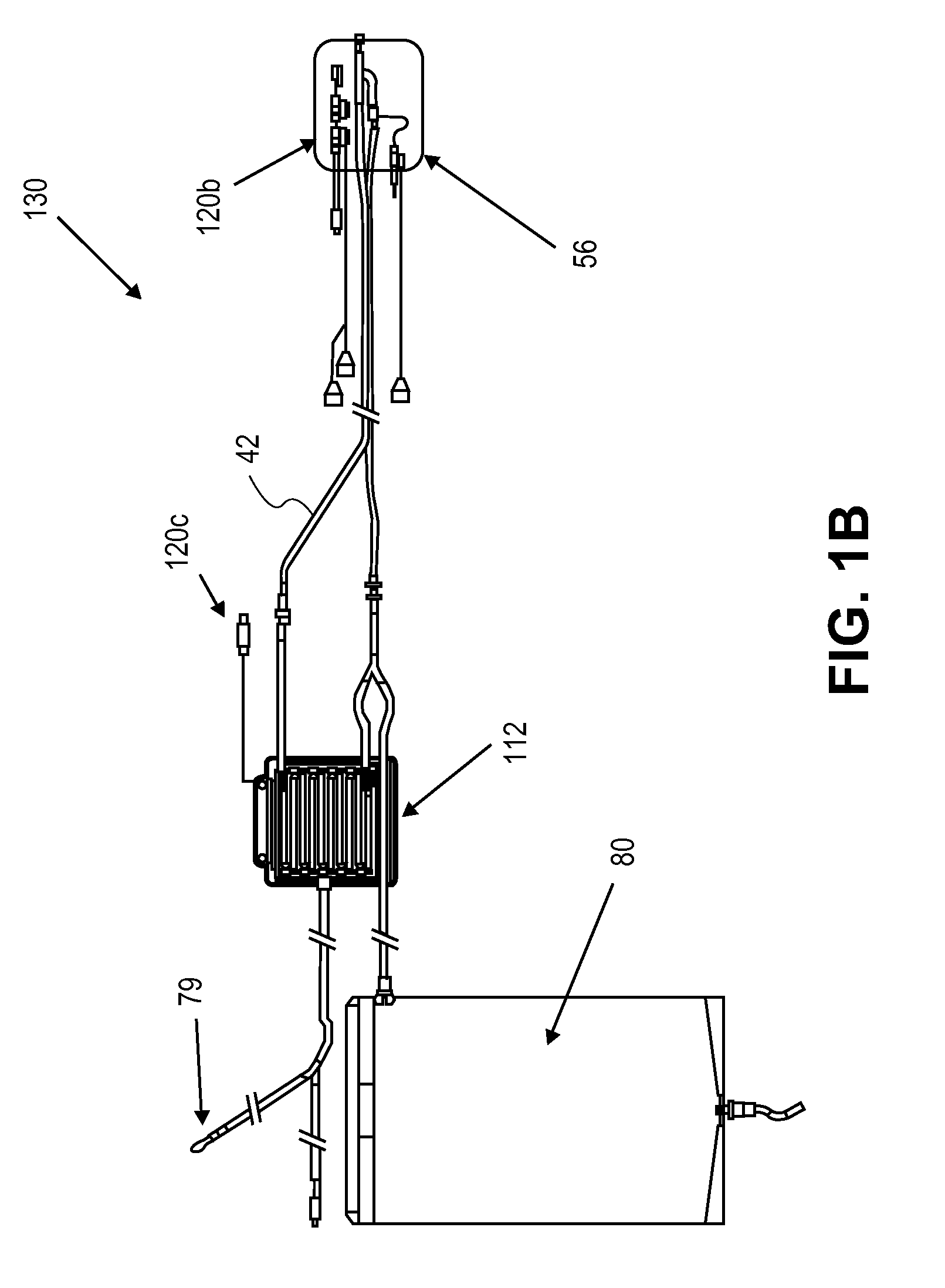
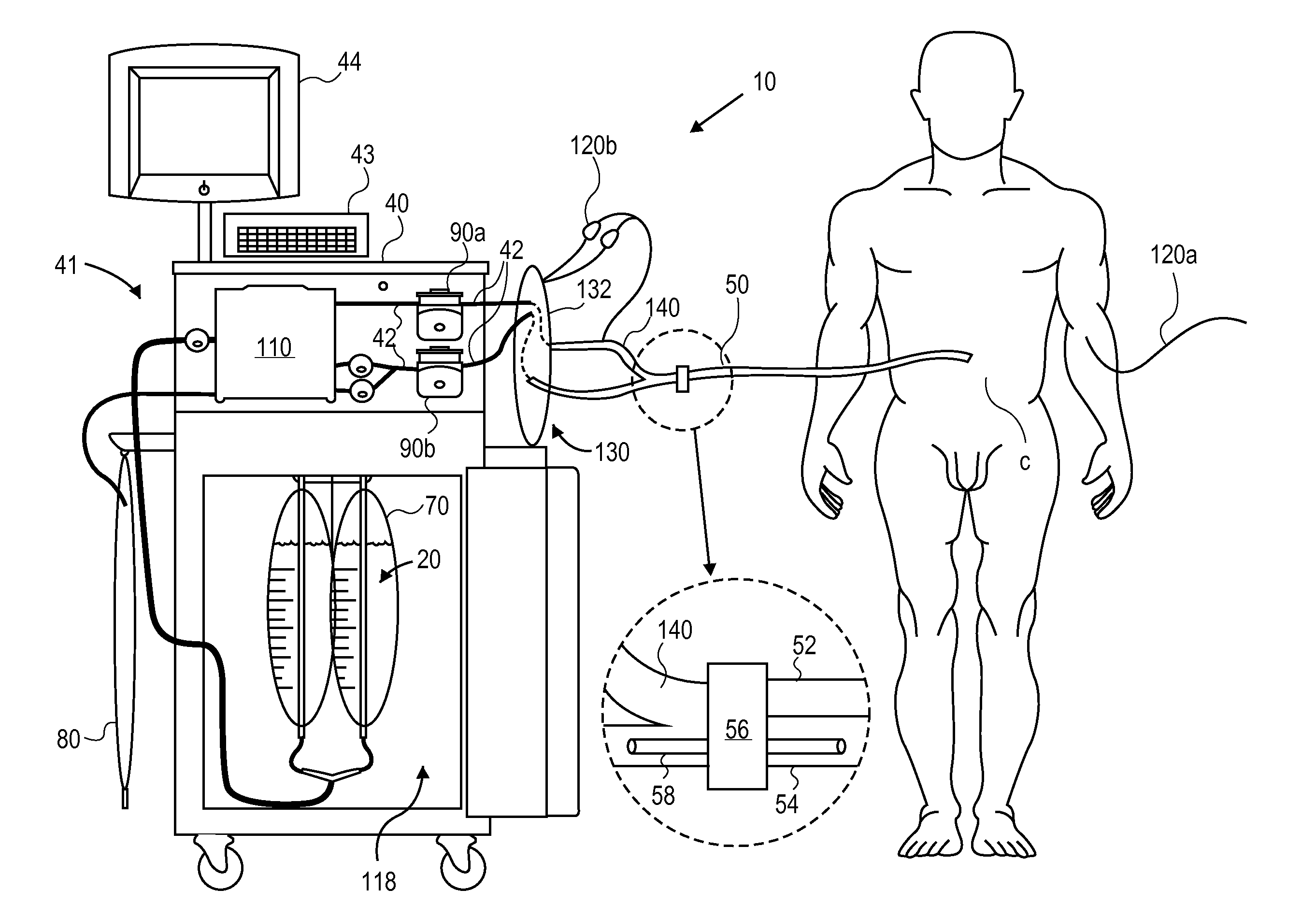
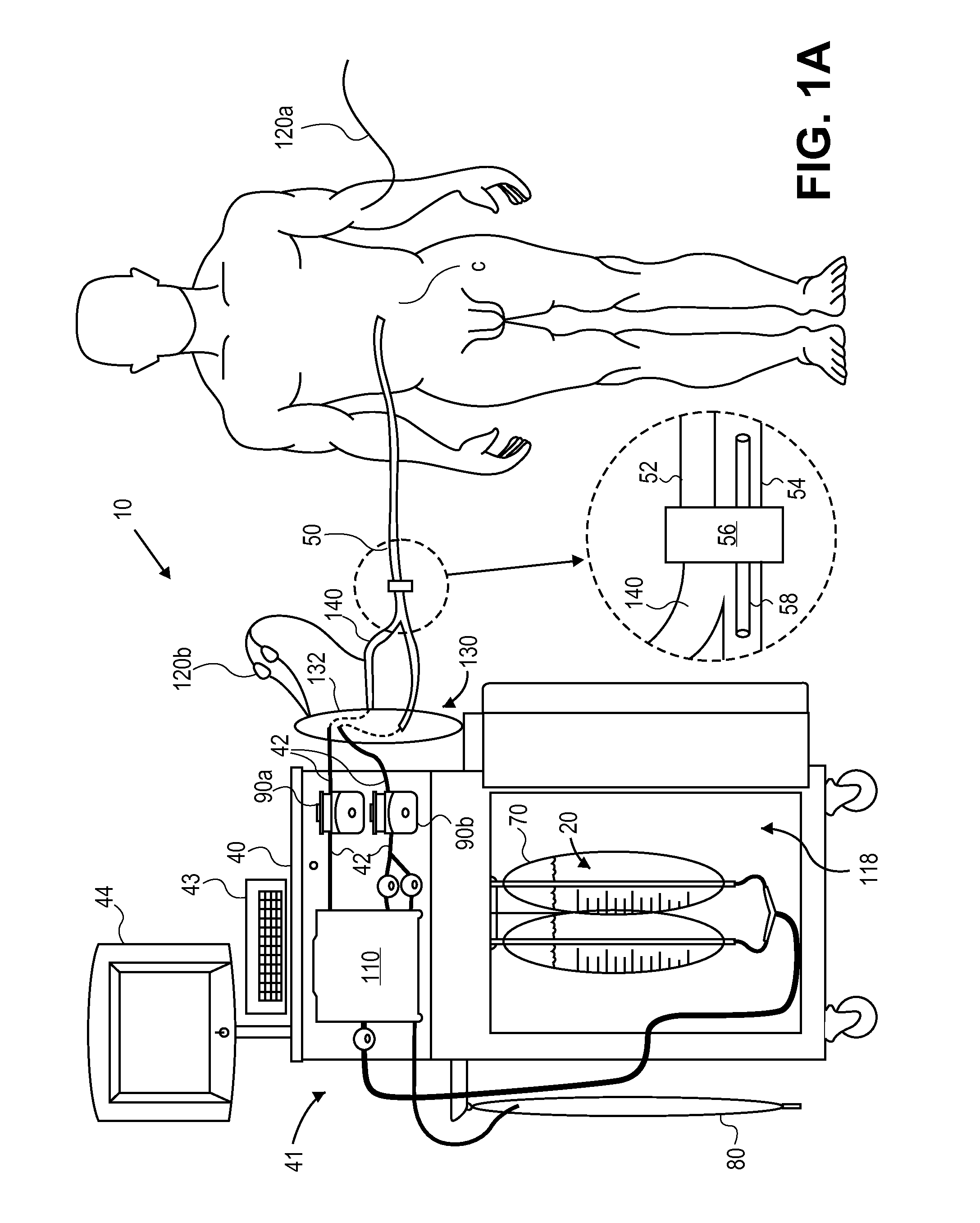
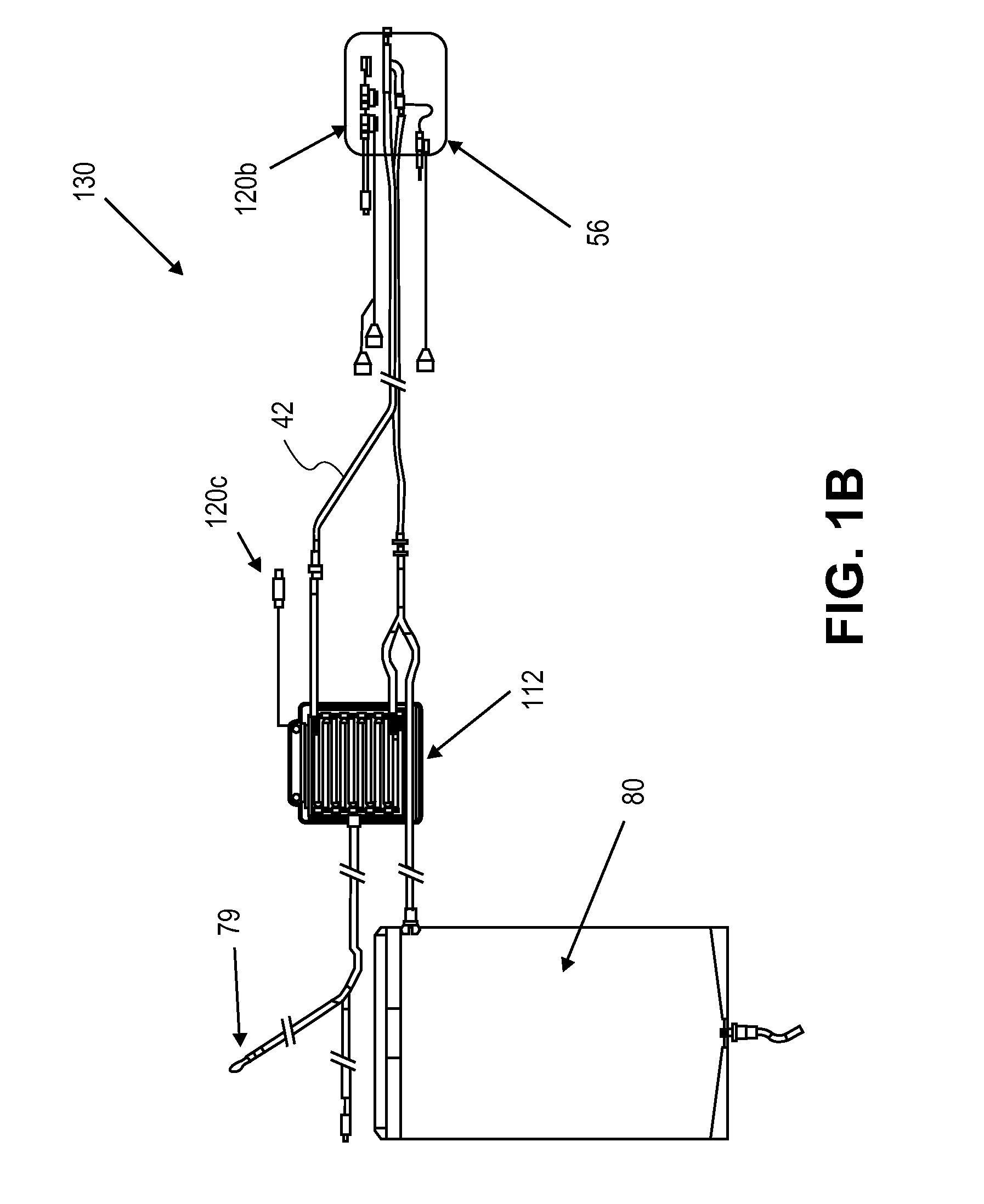
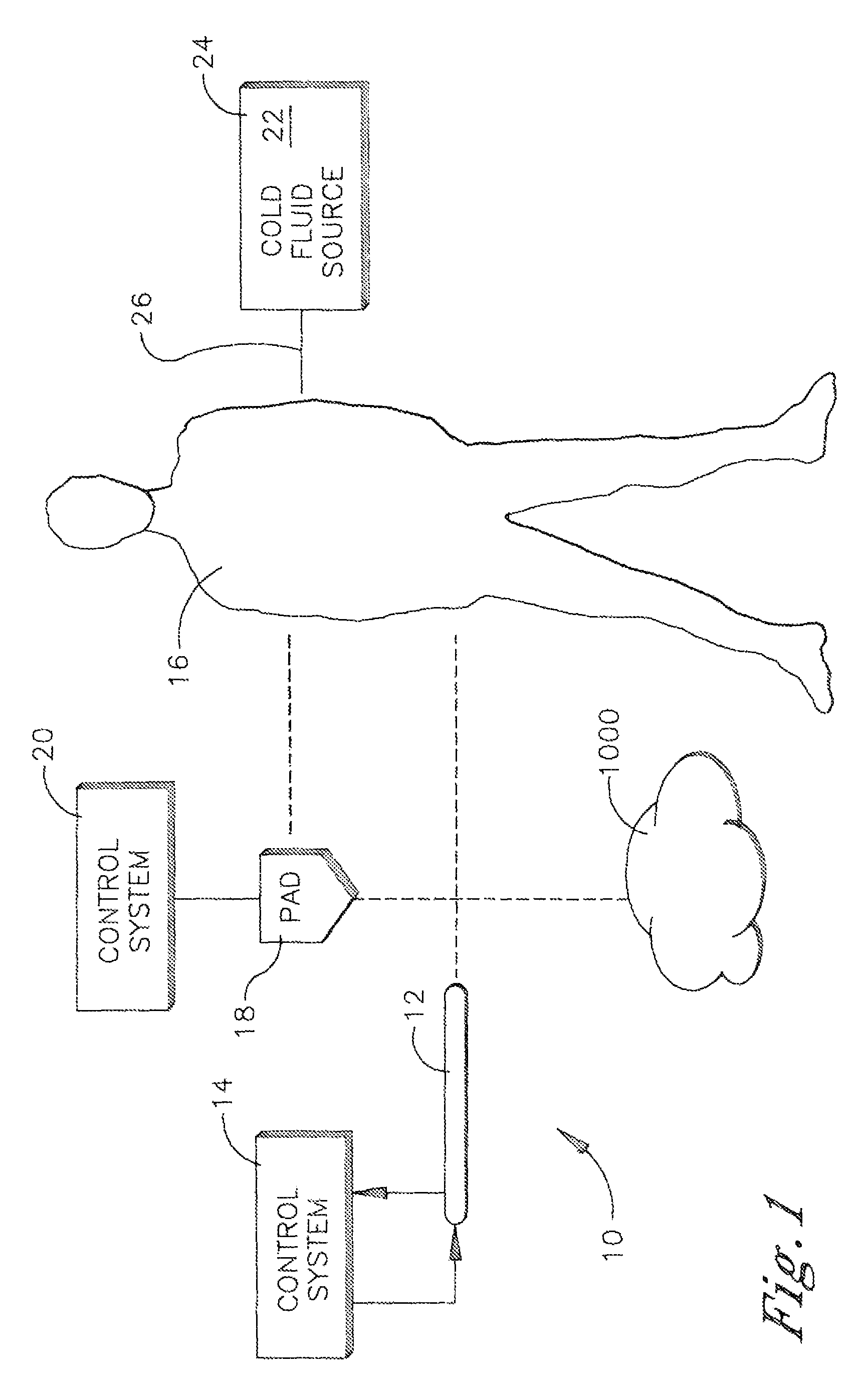
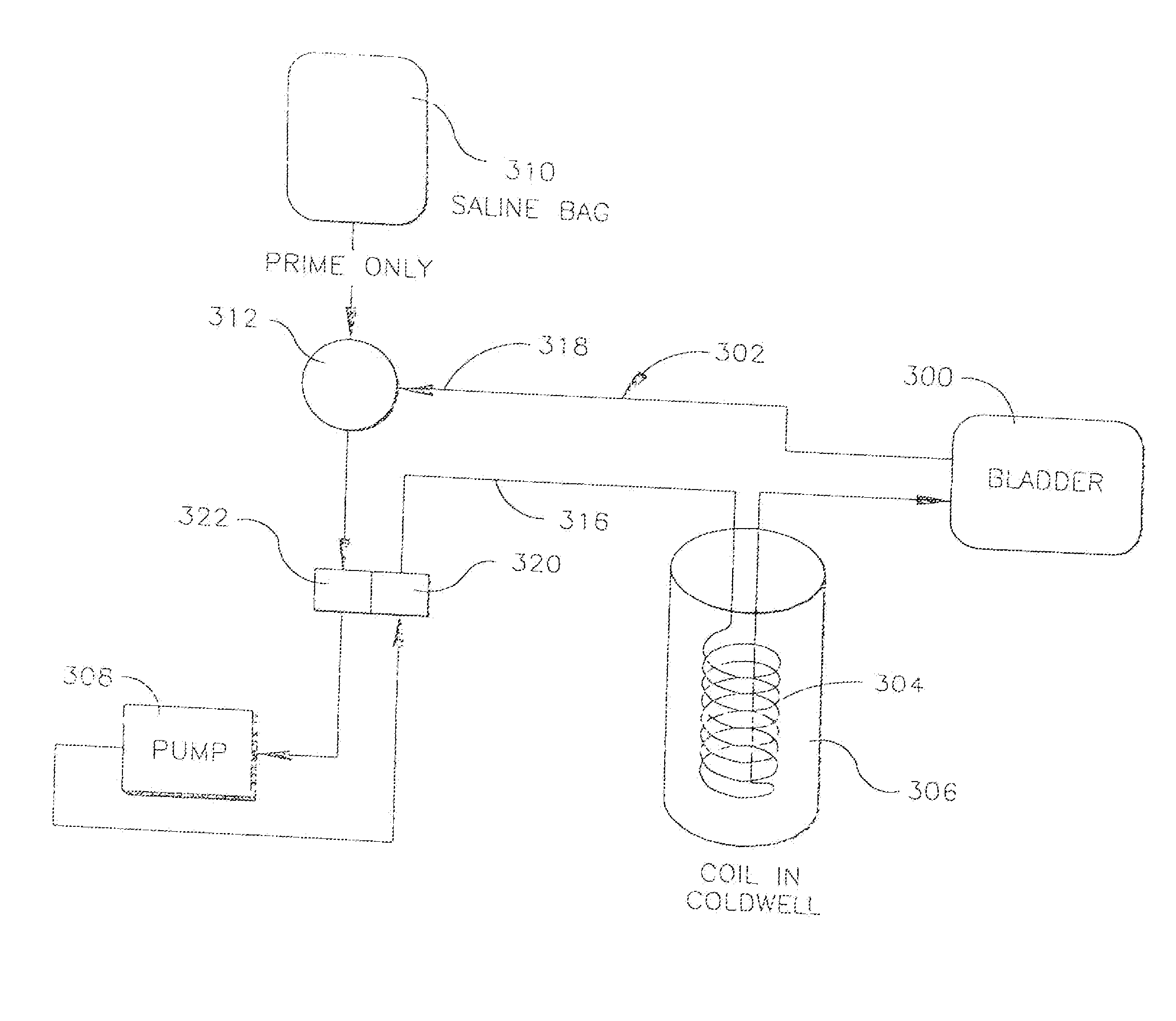
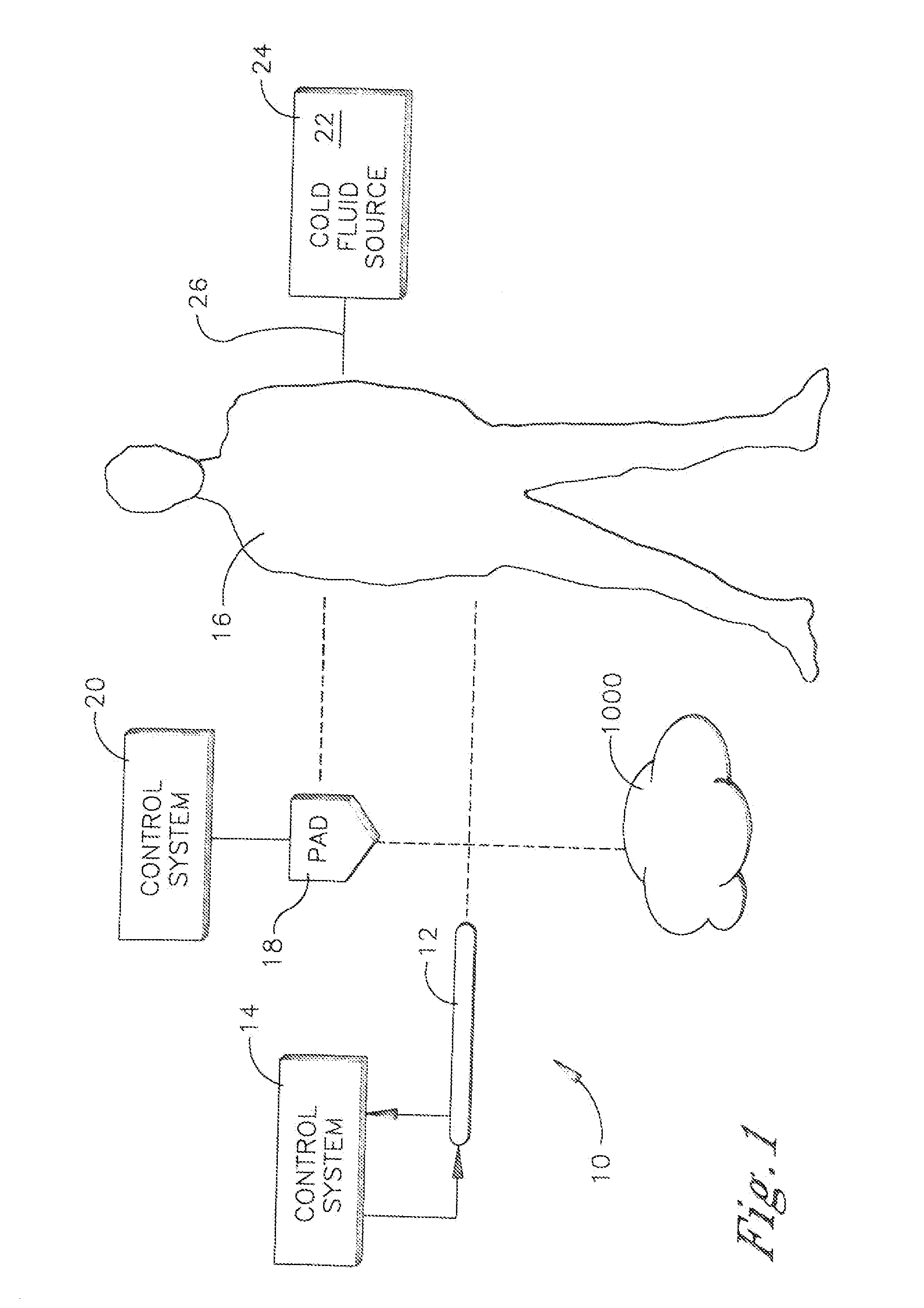
System and method for bringing hypothermia rapidly onboard
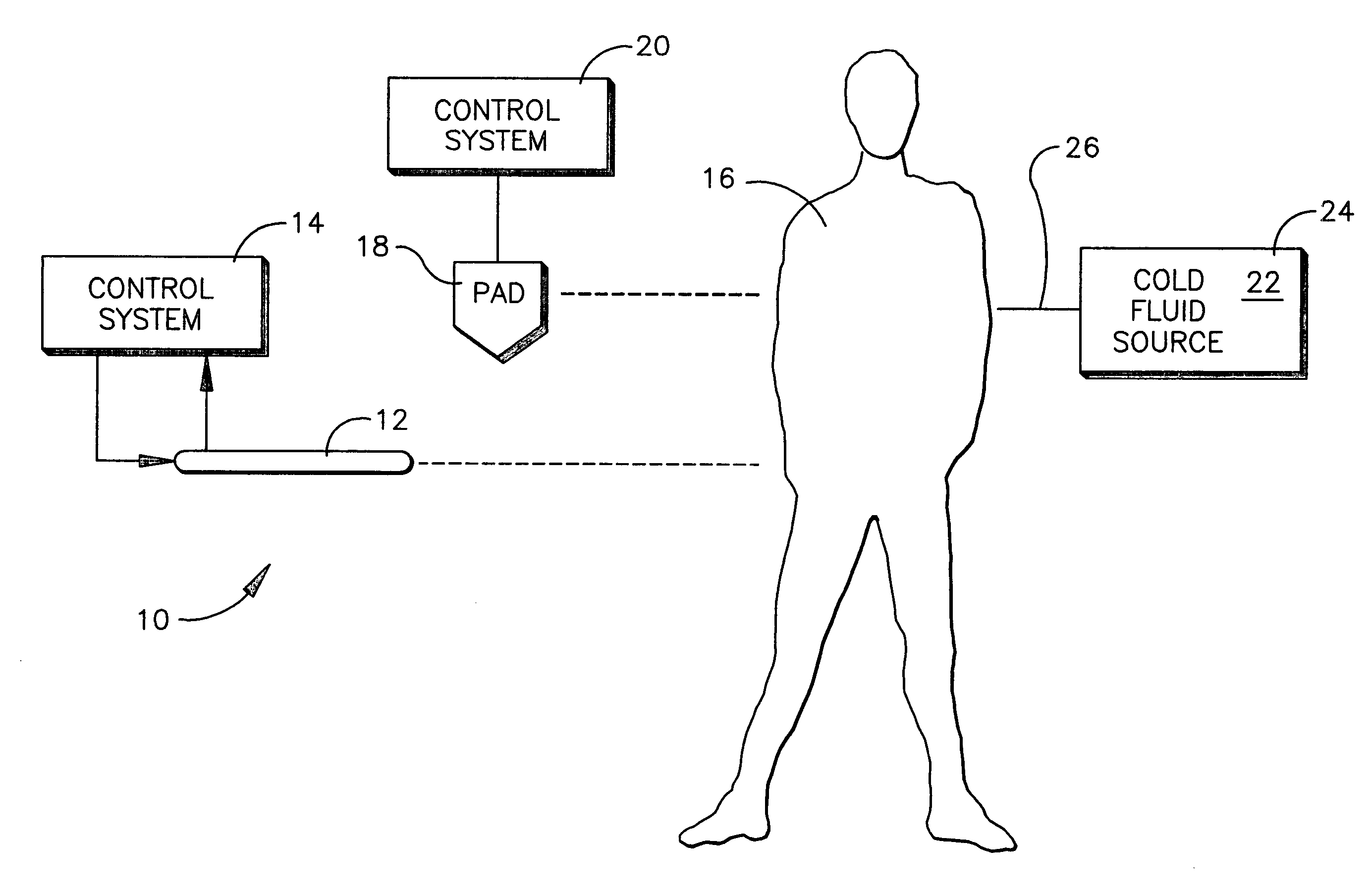
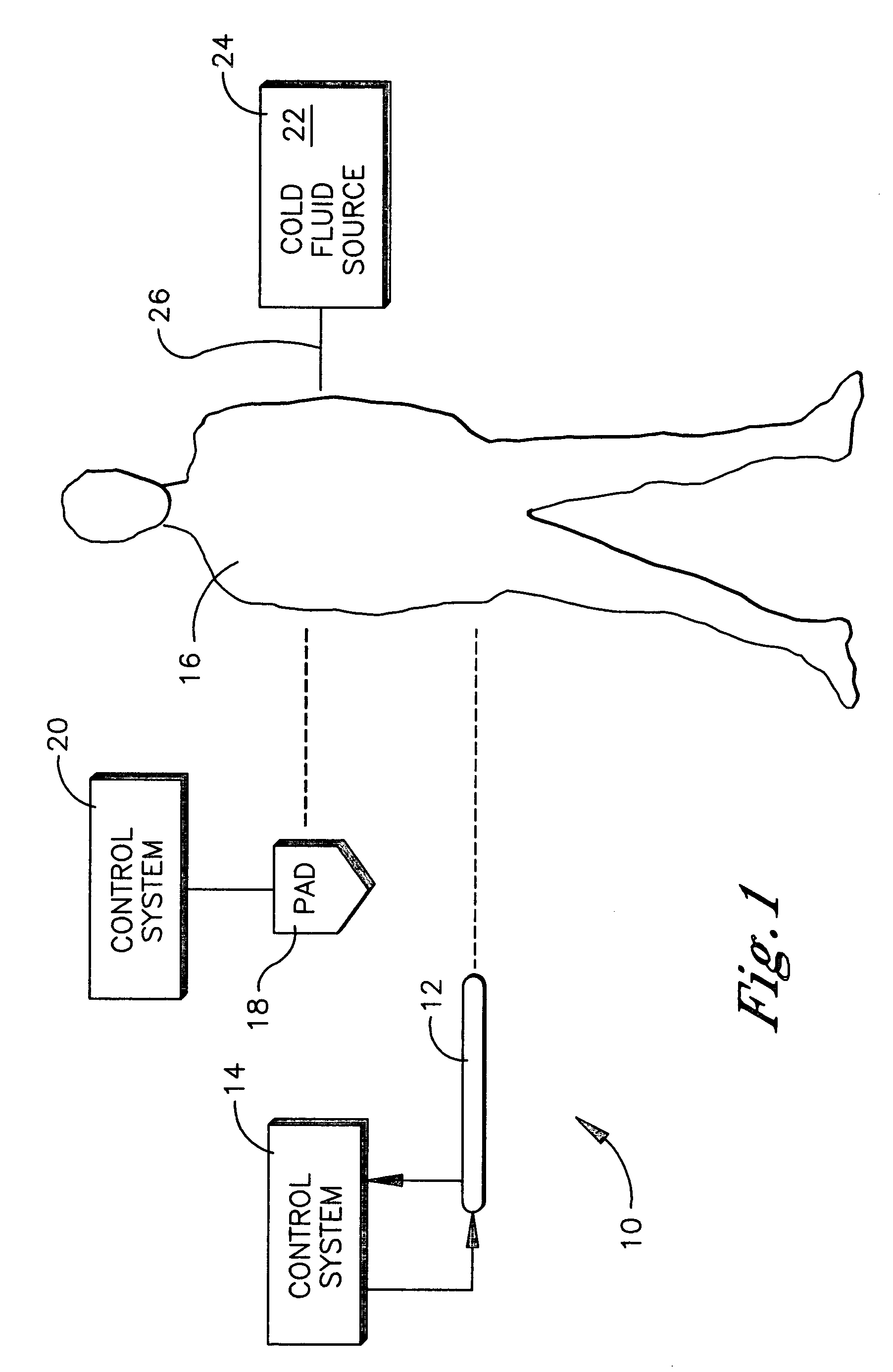
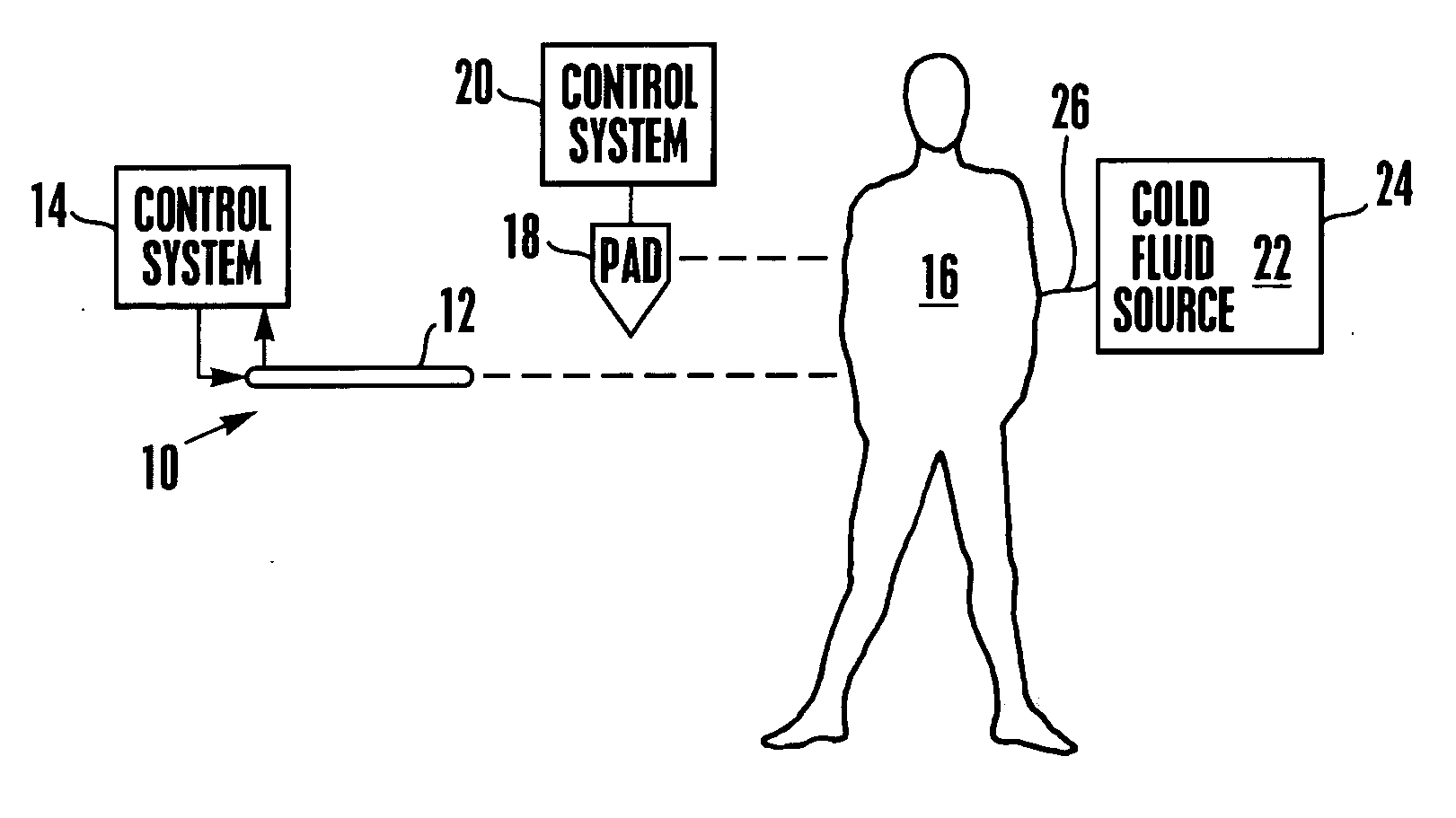
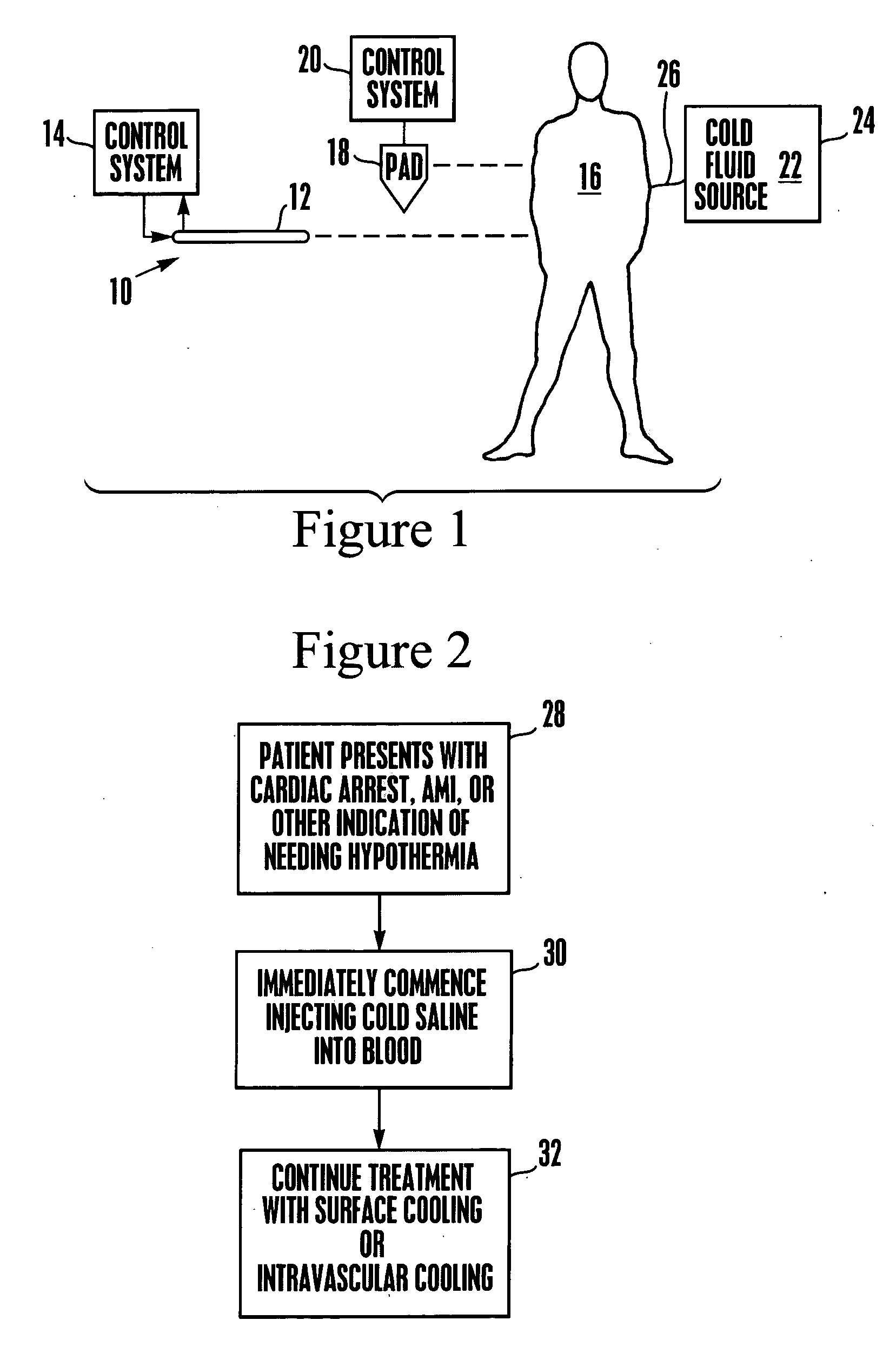
An intravenous heat exchange catheter and / or an external cooling pad / bladder can be used to maintain hypothermia in, e.g., a cardiac arrest patient, but to accelerate the cooling process the patient first can be infused with cold saline before the opportunity arises to connect the catheter or pad to the patient.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method for inducing hypothermia
InactiveUS6962601B2Simple methodImprove the protective effectOther chemical processesLighting and heating apparatusParticulatesSlurry
Systems for phase-change particulate slurry cooling equipment and methods to induce hypothermia in a patient through internal and external cooling are provided. Subcutaneous, intravascular, intraperitoneal, gastrointestinal, and lung methods of cooling are carried out using saline ice slurries or other phase-change slurries compatible with human tissue. Perfluorocarbon slurries or other slurry types compatible with human tissue are used for pulmonary cooling. And traditional external cooling methods are improved by utilizing phase-change slurry materials in cooling caps and torso blankets.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Apparatus and method for preventing brain damage during cardiac arrest, cpr, or severe shock
InactiveUS20090276018A1Rapid coolingImprove hypothermiaTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingInjury brainCardiorespiratory arrest
Apparatuses and methods for the cooling of the cranial and extracranial portions of a patient in need thereof. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention preferably employ a head cooling apparatus which includes a watertight shroud for the head and which needs no refrigeration. In certain preferred embodiments, the apparatuses of the present invention are collapsible and possess a reduced profile. In some presently preferred embodiments, the present invention includes a hammock that supports the head. In some embodiments, the present invention includes a shroud that lies behind the head with optional portions that may be drawn over the patient's neck and cranial area. The apparatuses and methods of the present invention also provide an improved mechanism for cooling the cranial and extracranial areas through the use of a novel distribution of endothermic solids (e.g. ammonium nitrate). The present invention provides a novel distribution of ammonium nitrate pellets that preferably includes multiple populations solid ammonium nitrate, preferably including small diameter (e.g., powdered) and larger diameter (e.g., 7 millimeter) ammonium nitrate to allow water initially to be cooled very quickly, thereby facilitating the rapid cooling of the cranial and extracranial areas, while at the same time producing extended hypothermia.
Owner:BRADER ERIC WILLIAM
Methods, Compositions and Articles of Manufacture for Enhancing Survivability of Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organisms
InactiveUS20080171726A1Improve survivabilityPrevent and reduce damageBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsSurvivabilityIn vivo
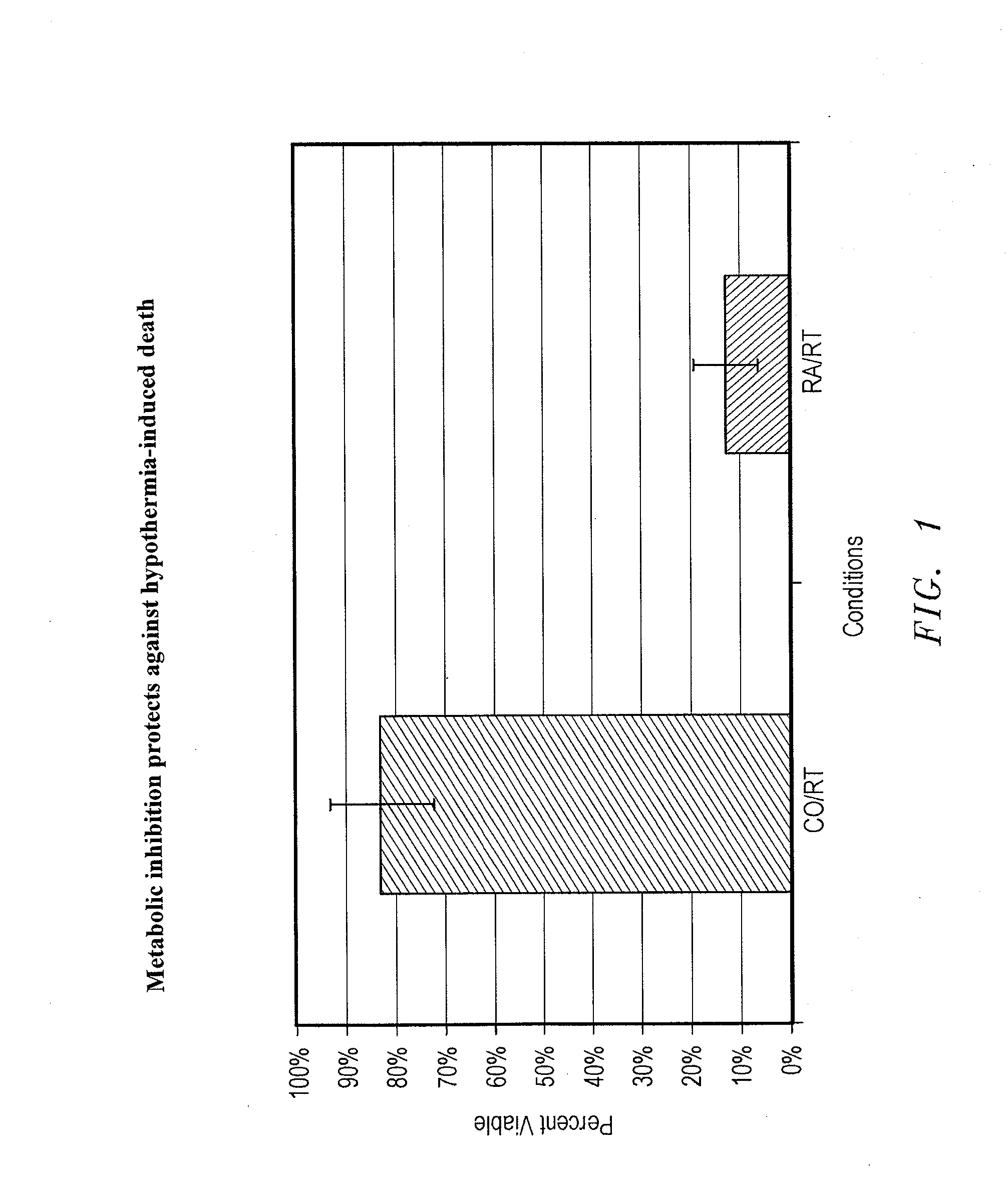
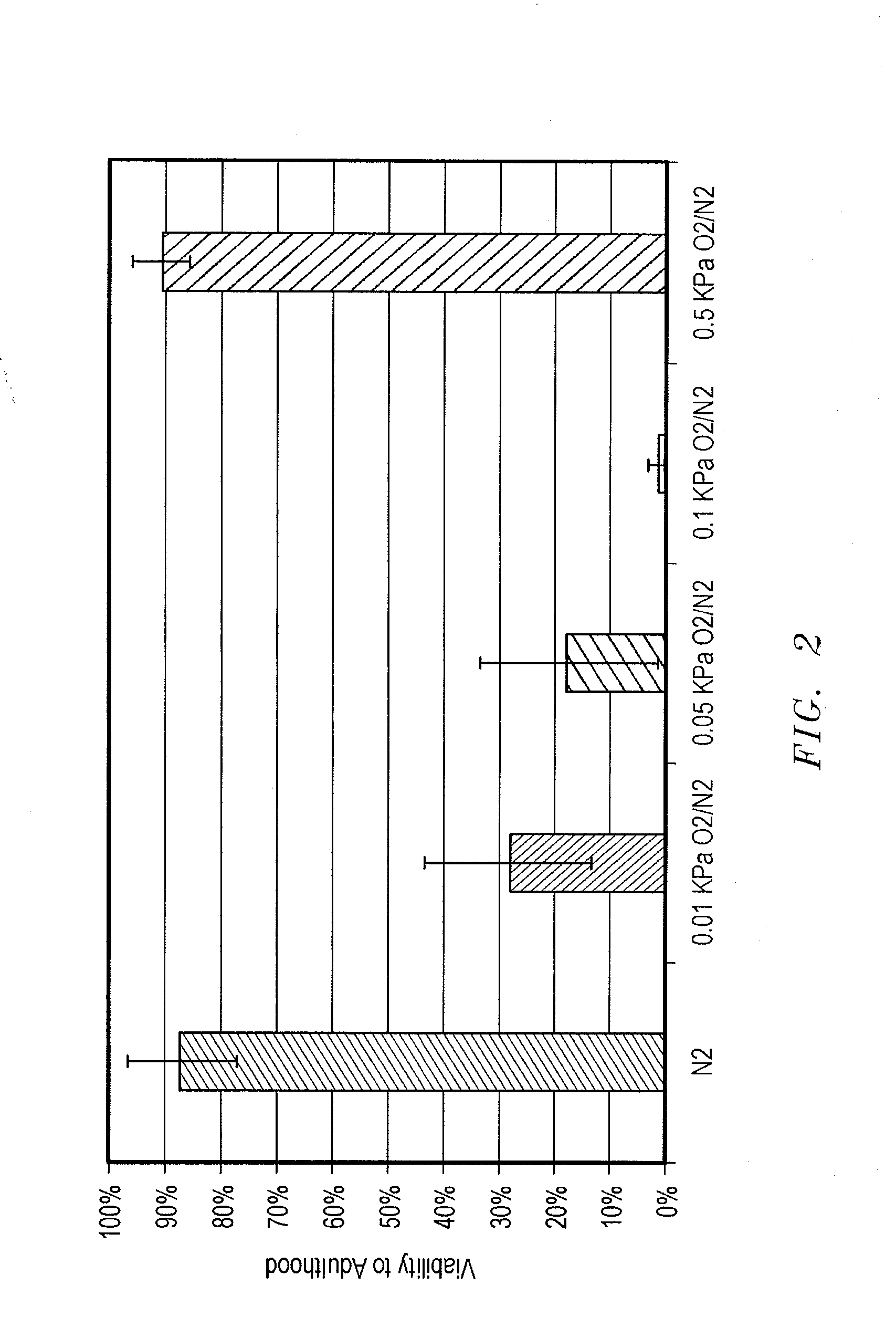
The present invention concerns the use of oxygen antagonists and other active compounds for inducing stasis or pre-stasis in cells, tissues, and / or organs in vivo or in an organism overall, in addition to enhancing their survivability. It includes compositions, methods, articles of manufacture and apparatuses for enhancing survivability and for achieving stasis or pre-stasis in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, there are also therapeutic methods and apparatuses for organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer using the active compounds described.
Owner:ROTH MARK B +3
Apparatus, system and methods for extracorporeal blood processing for selectively cooling the brain relative to the body during hyperthermic treatment or to induce hypothermia of the brain
InactiveUS20120029408A1Reduce adverse reactionsReduce riskOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesTherapeutic treatmentBlood processing
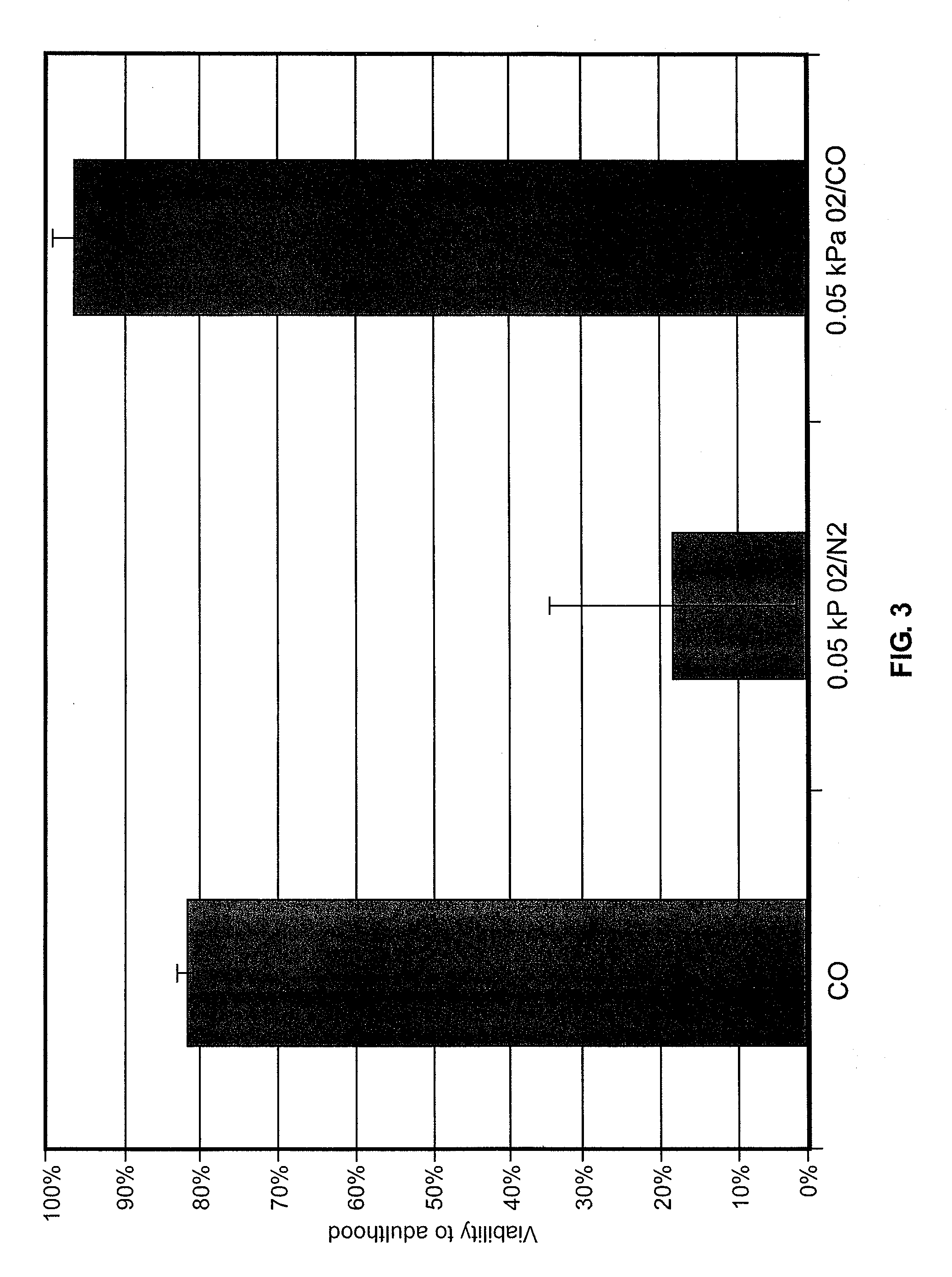
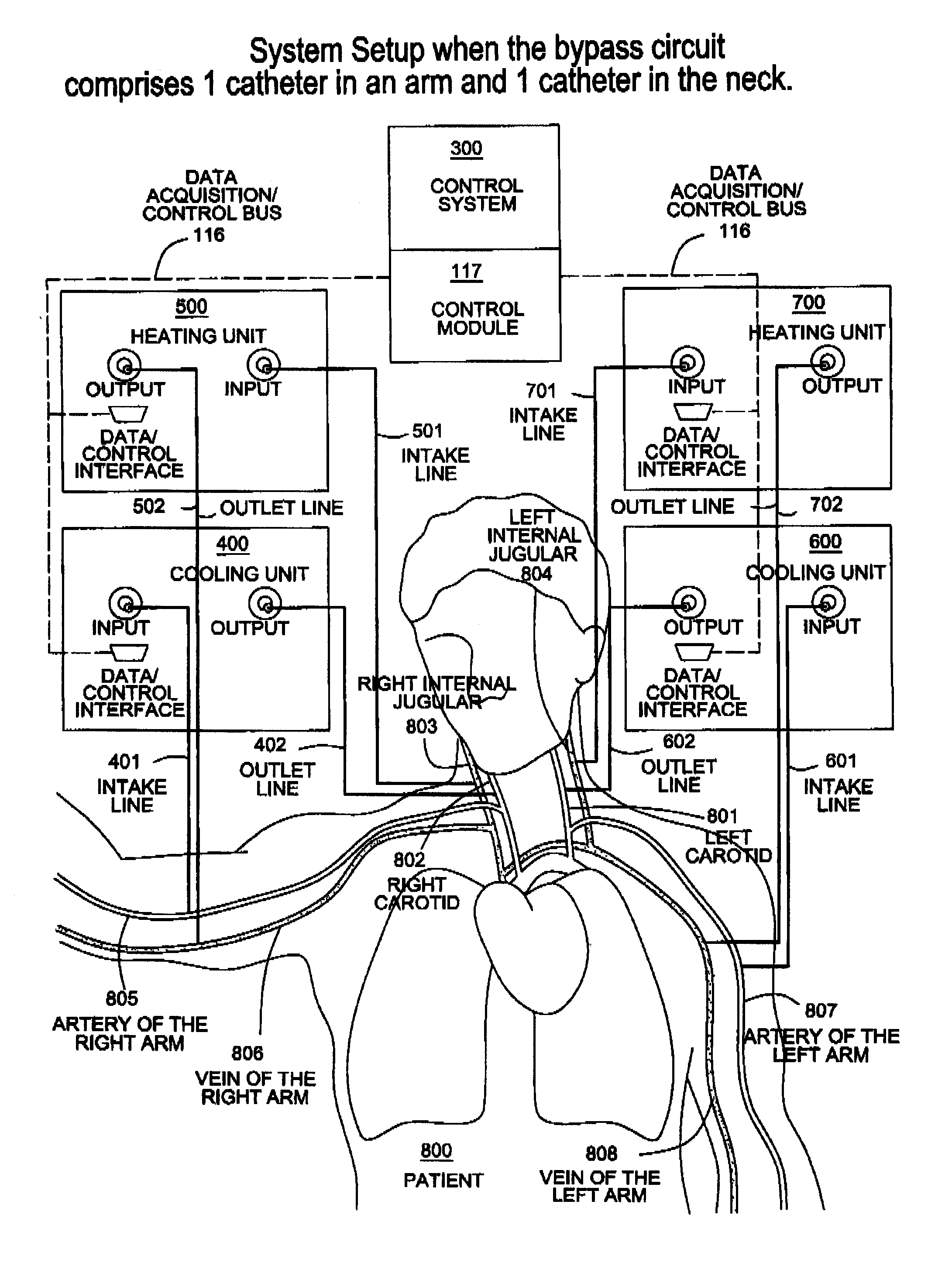
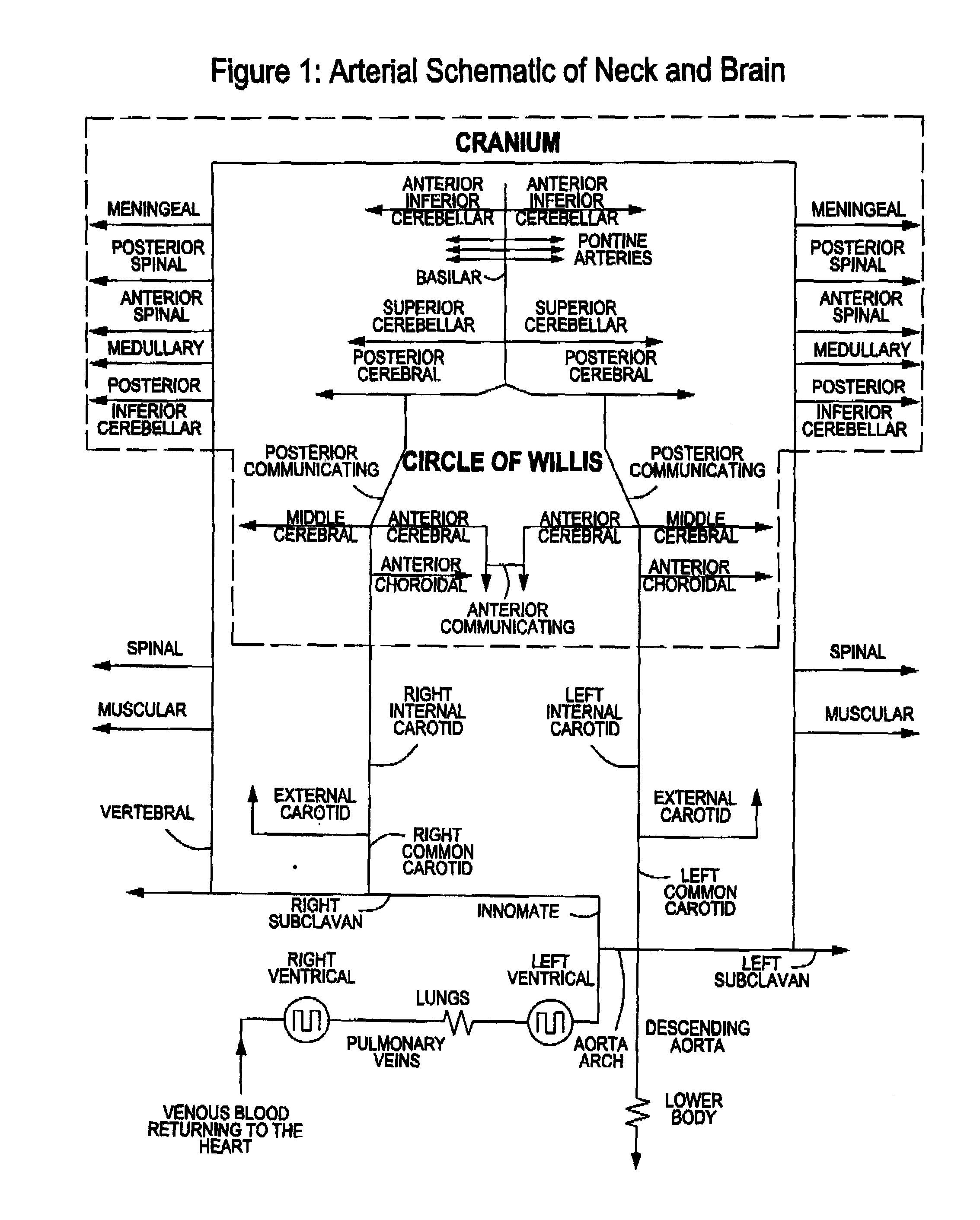
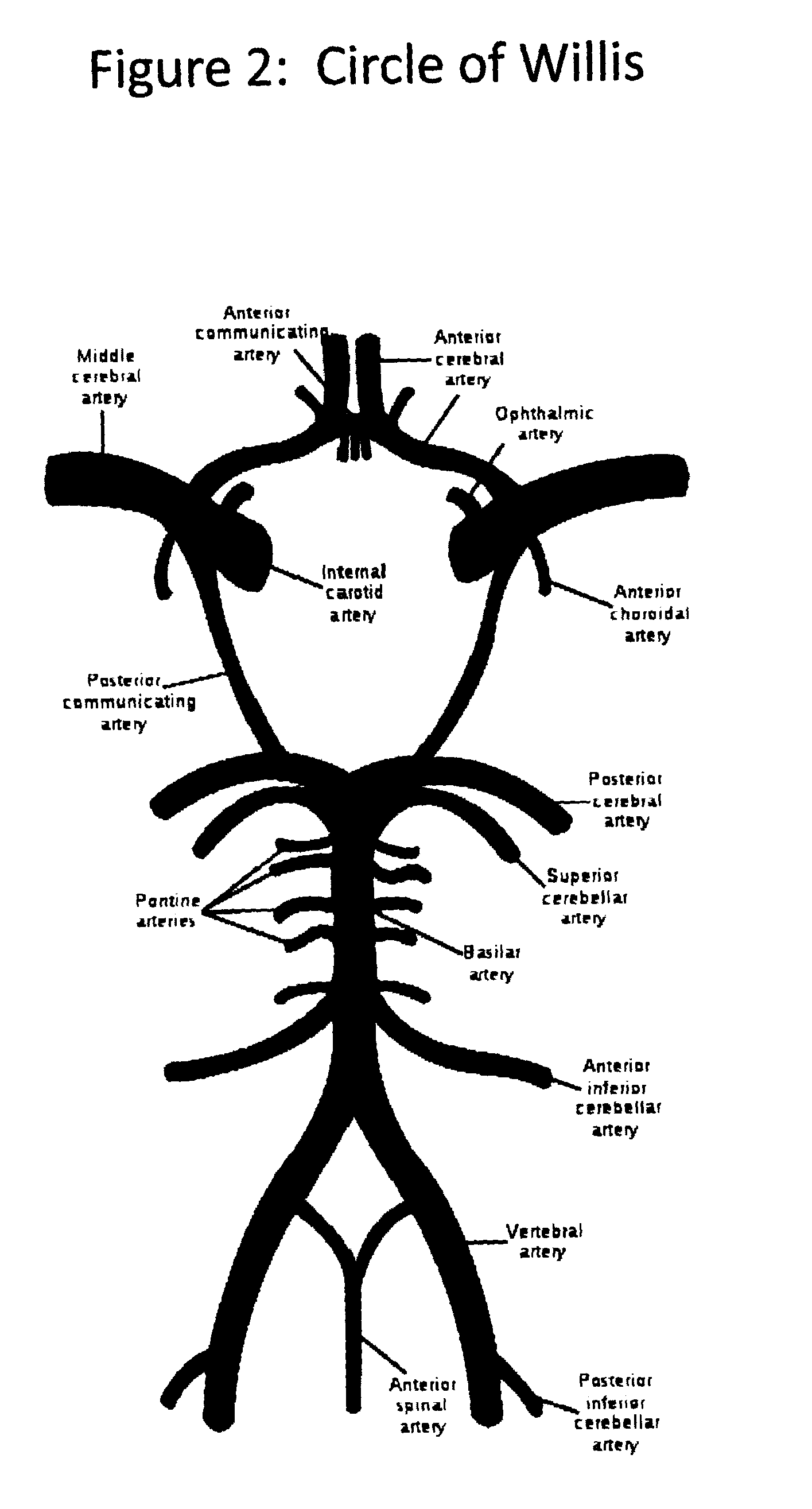
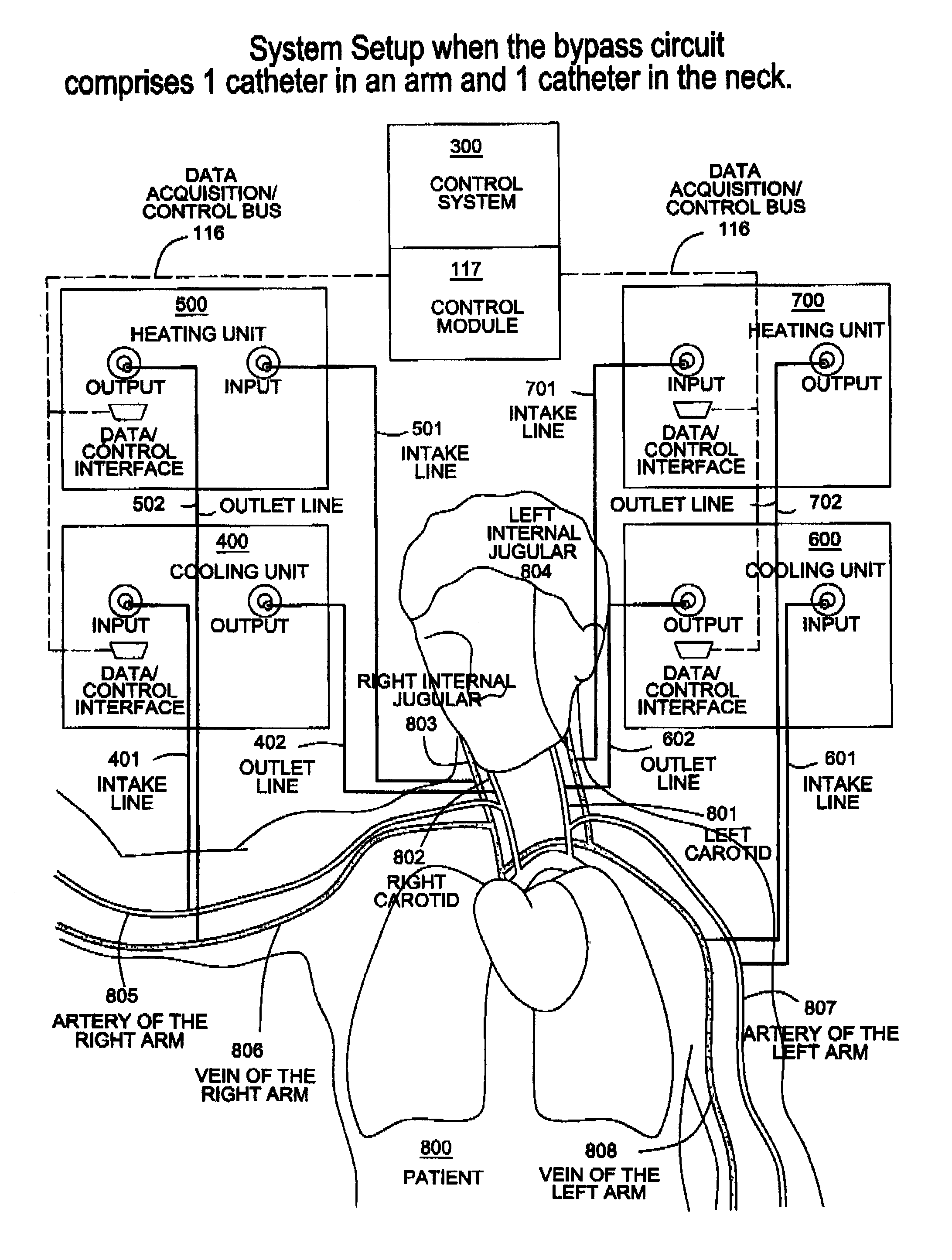
A system, apparatus and methods are provided for extra-corporeal blood treatment, and in particular for establishing and maintaining a neck down differential body temperature, while maintaining near normal brain temperatures, to protect the brain from extended or extreme hypothermia or hyperthermia. A blood treatment apparatus and system is provided for differential control of brain temperature and body temperature below the neck. For example, a first bypass circuit with heat exchanger for brain blood circulation maintains a near normal blood temperature, while a second bypass circuit for below the neck blood circulation provides for thermal treatment to induce a temperature differential, e.g. hyperthermia or hypothermia, relative to brain circulation. Such systems and apparatus have application, for example, for diagnostic and therapeutic treatments using hyperthermia, particularly for treatments of extended duration or at elevated temperatures above 42° C., for example, hyperthermia for treatment of cancer, infectious bacterial or viral diseases.
Owner:BEAUDIN STEVE ANDRE
Method and Apparatus for Inducing Therapeutic Hypothermia
Methods and apparatus for delivering therapeutic hypothermia to a patient are provided which may include any number of features. One feature is a hypothermia system comprising a fluid source, a heat exchanger assembly, a catheter in fluid communication with the fluid source, and a pump system configured to infuse hypothermic fluid into a patient cavity and extract hypothermic fluid from the patient cavity. The hypothermia system can infuse and extract fluid automatically from the patient cavity. In one embodiment, the patient cavity is a peritoneal cavity. A safe access device to gain access to the patient cavity is also provided.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Method for inducing hypothermia
InactiveUS7422601B2Rapid and safeStart fastLighting and heating apparatusIce productionParticulatesSlurry
Systems for phase-change particulate slurry cooling equipment and methods to induce hypothermia in a patient through internal and external cooling are provided. Subcutaneous, intravascular, intraperitoneal, gastrointestinal, and lung methods of cooling are carried out using saline ice slurries or other phase-change slurries compatible with human tissue. Perfluorocarbon slurries or other slurry types compatible with human tissue are used for pulmonary cooling. And traditional external cooling methods are improved by utilizing phase-change slurry materials in cooling caps and torso blankets.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
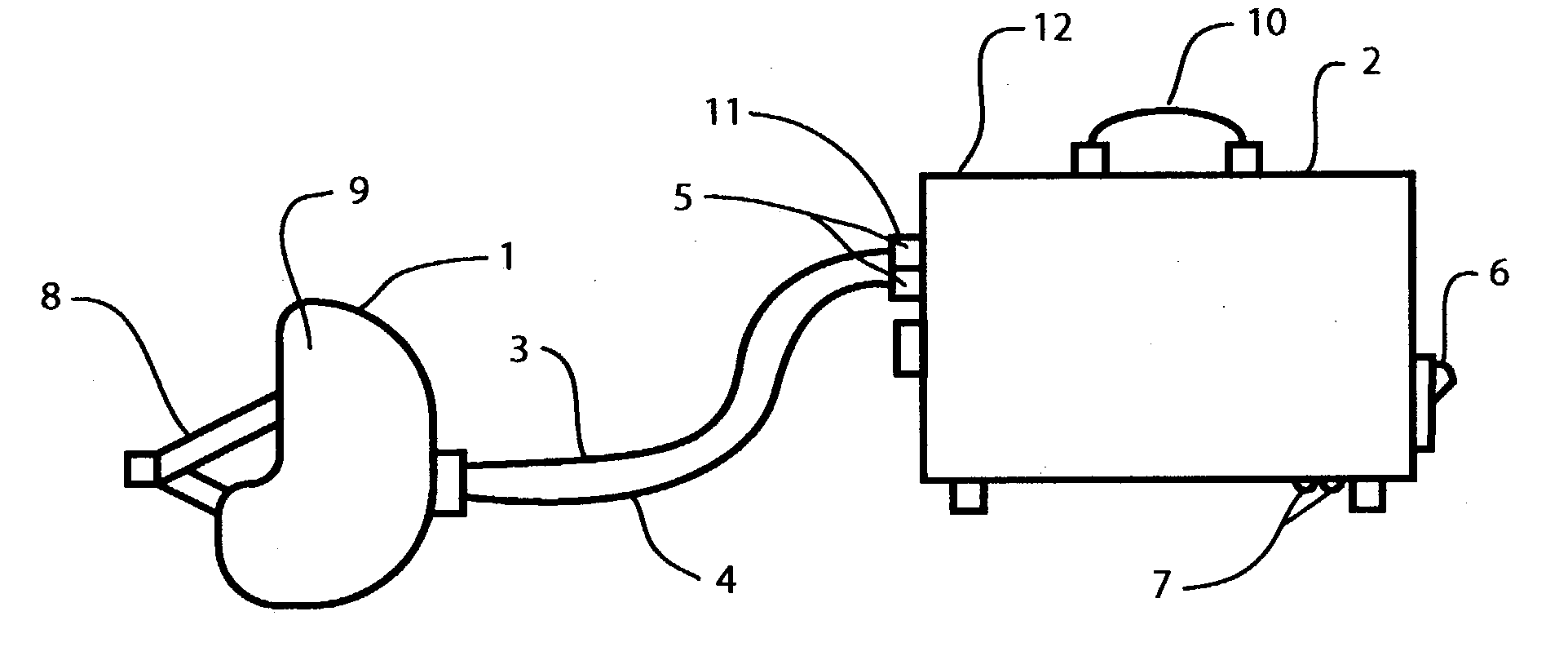
Patient heat transfer device
InactiveUS20090228082A1Controlled and rapid induced hypothermiaQuick controlIndirect heat exchangersTherapeutic coolingLiquid stateMedicine
To rapidly induce hypothermia to a patient, in the event the patient has a stroke, hyperthermia or some other temperature related heath problems which requires prompt action to regulate the temperature of the patient, a flat flexible structure conformable to the body of the patient is placed into contact with the patient. The structure has at least two heat transfer portions. One of heat transfer portions is positioned in contact with the body of the patient. The structure is hermetically sealed and a fluidized medium responsive to temperature change is provided in the structure between the heat transfer portions. The fluid is changeable between a liquid state and a gaseous state, when it is exposed to heat and cold. The heat absorbed by the heat transfer portion in contact with the patient is carried by the fluidized medium, as latent heat in the gas that results when the liquid is vaporized to its gaseous state, to the heat transfer portion layer not in contact with the patient, so that the latent heat in the gaseous vapor is dissipated. Upon dissipation, the gaseous vapor is condensed and the fluidized medium returns to its liquid state. The structure may be formed from a flat flexible heat pipe and may also be configured as a rib cage shaped jacket to embrace the torso of the patient. A cooling circuit or mechanism may be added to the structure to facilitate the removal of heat therefrom. The structure may also be used to raise the core temperature of a patient.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL ASD INC
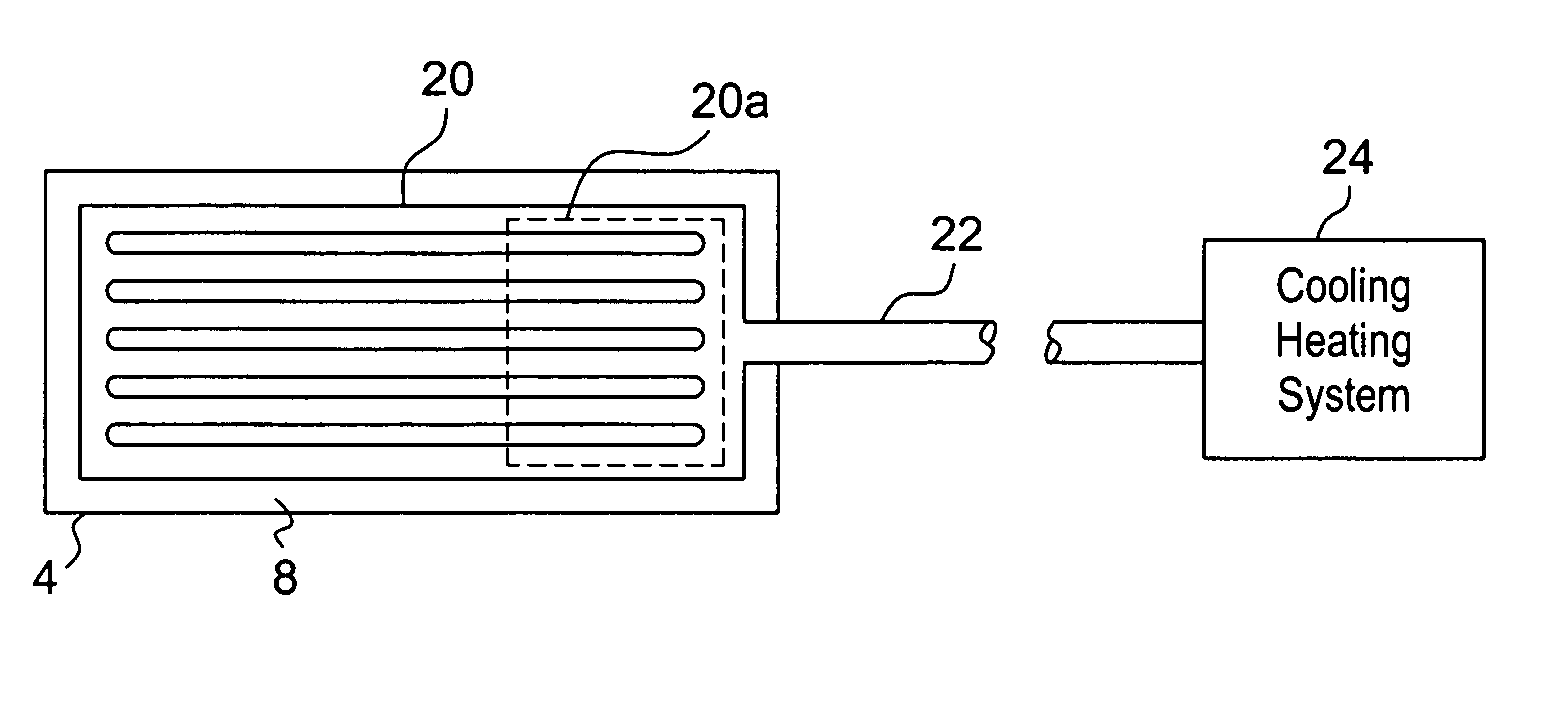
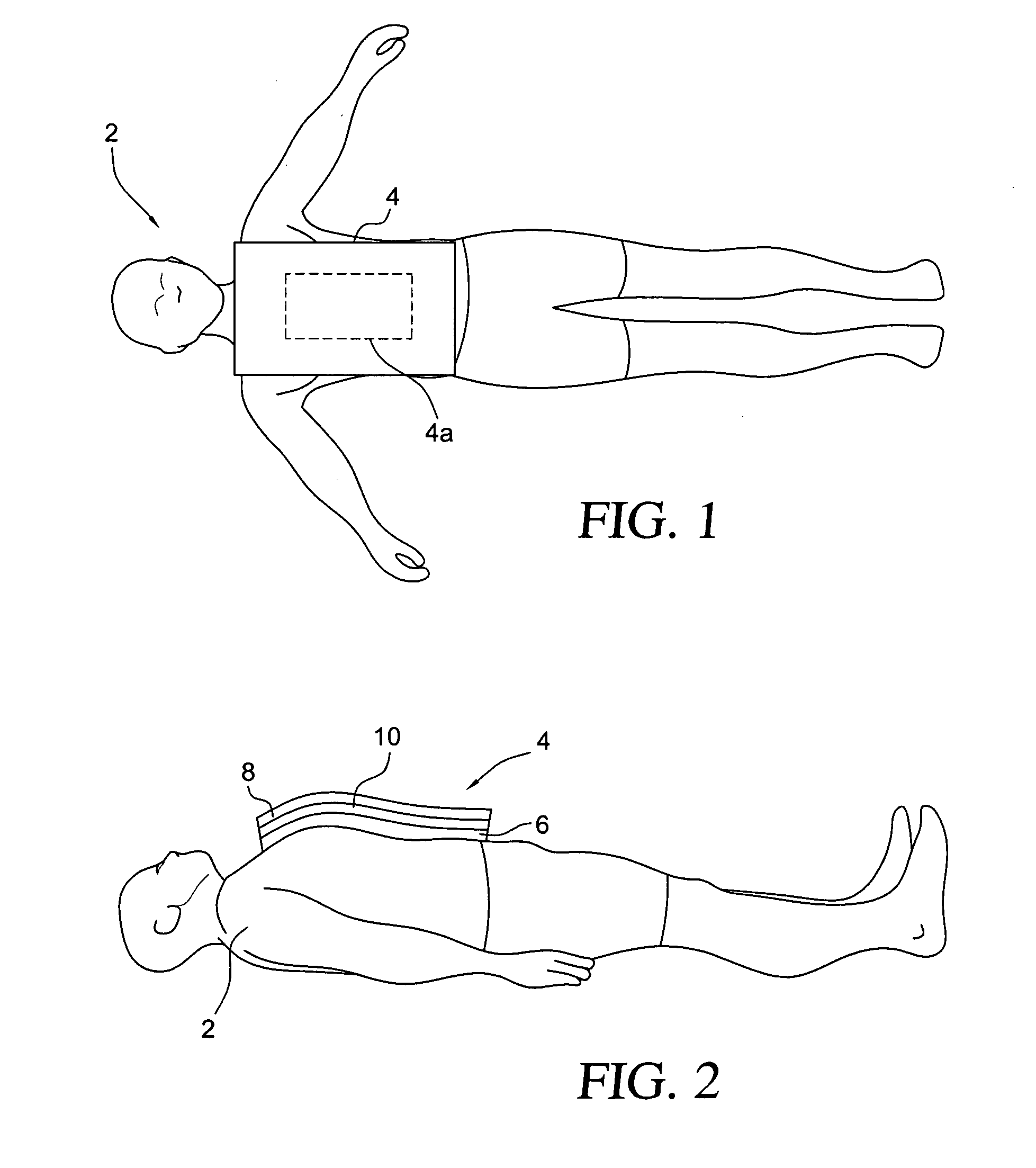
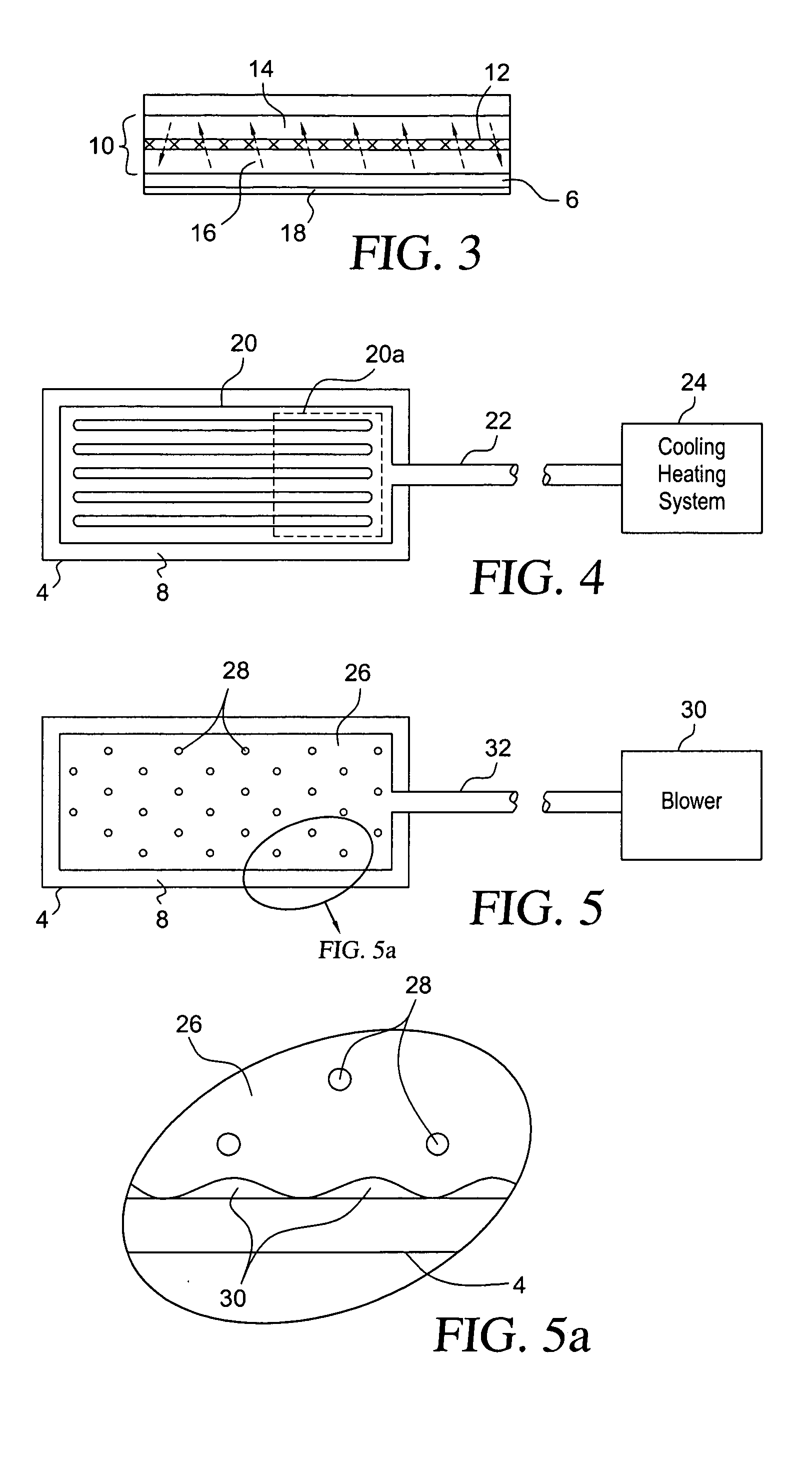
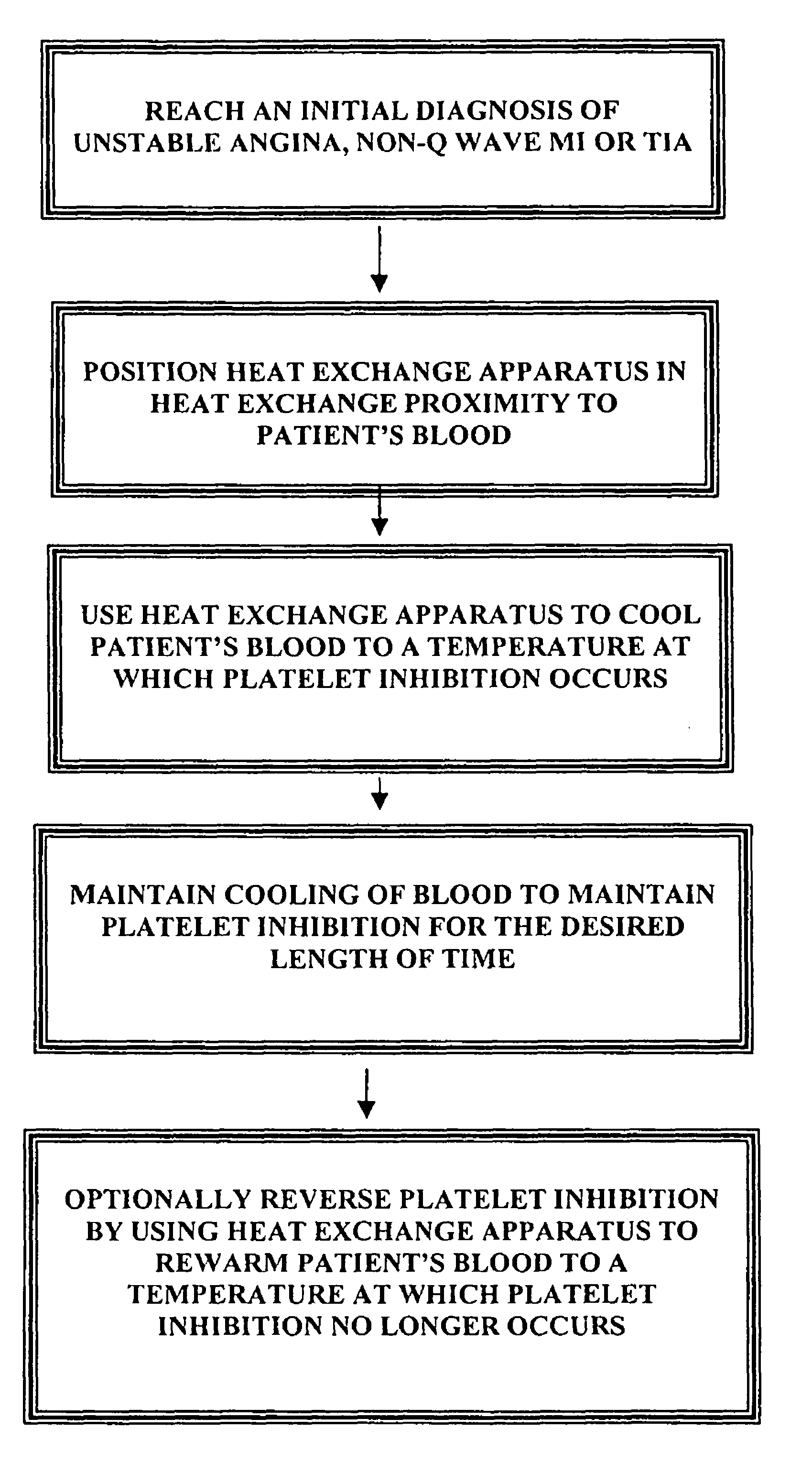
Inhibition of platelet activation, aggregation and/or adhesion by hypothermia
InactiveUS7846193B2Faster clearanceQuick effectTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingInstabilityACS - Acute coronary syndrome
A method for treating acute coronary syndromes (i.e., unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI) or transient ischemic attacks in a human or animal patient by placing a heat exchange apparatus in the patient's vasculature and using that heat exchange apparatus to cool the patient to a temperature (e.g. 30-36° C.) at which platelet inhibition (i.e., inhibition of platelet activation and / or aggregation and / or adhesion) occurs. Anti-shivering drugs or anesthesia may be administered to patients whose body temperature is cooled below that patient's shivering threshold (typically approximately 35.5 C). If it is determined that platelet inhibition is no longer desirable, such as when the patient is about to undergo a surgical or interventional procedure wherein bleeding could be problematic, the hypothermia-induced platelet inhibition may be rapidly reversed by using the intravascular heat exchange apparatus to re-warm the patient's body to normothermia or near normothermia.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Method for inducing hypothermia
InactiveUS20090125087A1Rapid and safeStart fastLighting and heating apparatusIce productionParticulatesSlurry
Systems for phase-change particulate slurry cooling equipment and methods to induce hypothermia in a patient through internal and external cooling are provided. Subcutaneous, intravascular, intraperitoneal, gastrointestinal, and lung methods of cooling are carried out using saline ice slurries or other phase-change slurries compatible with human tissue. Perfluorocarbon slurries or other slurry types compatible with human tissue are used for pulmonary cooling. And traditional external cooling methods are improved by utilizing phase-change slurry materials in cooling caps and torso blankets.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Apparatus, system and methods for extracorporeal blood processing for selectively cooling the brain relative to the body during hyperthermic treatment or to induce hypothermia of the brain
InactiveUS8834404B2Reduce adverse reactionsReduce riskOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesTherapeutic treatmentBlood processing
Owner:BEAUDIN STEVE ANDRE
External heat exchange pad for patient
An intravenous heat exchange catheter and / or an external cooling pad / bladder can be used to maintain hypothermia in, e.g., a cardiac arrest patient, but to accelerate the cooling process the patient first can be infused with cold saline before the opportunity arises to connect the catheter or pad to the patient.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
System and method for bringing hypothermia rapidly onboard
An intravenous heat exchange catheter and / or an external cooling pad / bladder can be used to maintain hypothermia in, e.g., a cardiac arrest patient, but to accelerate the cooling process the patient first can be infused with cold saline before the opportunity arises to connect the catheter or pad to the patient.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods of treating cerebral ischemia
The present invention provides methods of treating cerebral ischemia in mammals comprising inducing hypothermia in a mammal before, during, or following cerebral ischemia in the mammal. The hypothermia is induced by administering to the mammal an effective dose of a neurotensin analog that is capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier and that comprises neo-tryptophan.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
System and method for bringing hypothermia rapidly onboard
InactiveUS20060190066A1Therapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingHypothermia inducedIntensive care medicine
An intravenous heat exchange catheter and / or an external cooling pad can be used to maintain hypothermia in, e.g., a cardiac arrest patient, but to accelerate the cooling process the patient first can be infused with cold saline before the opportunity arises to connect the catheter or pad to the patient.
Owner:ALSIUS
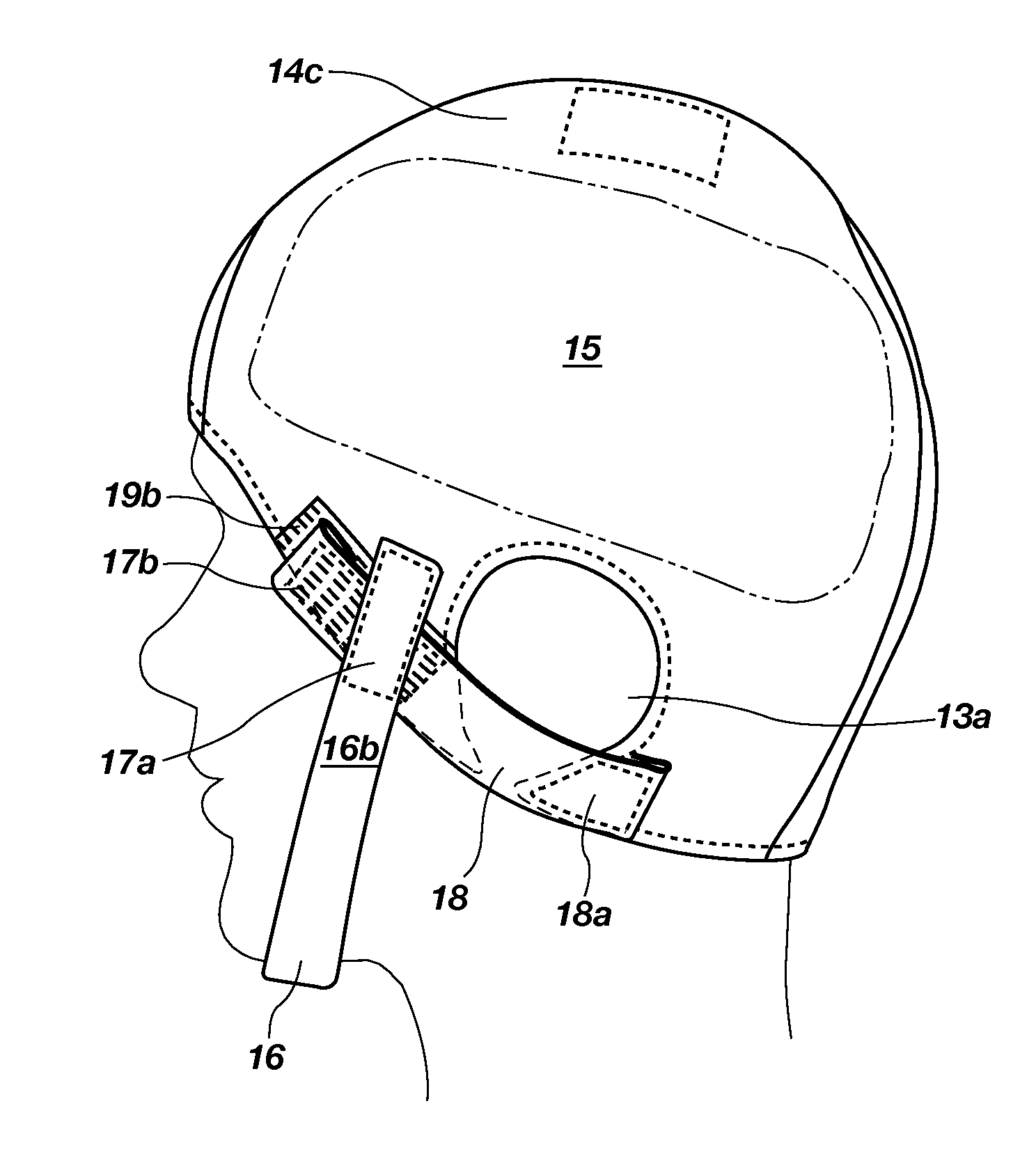
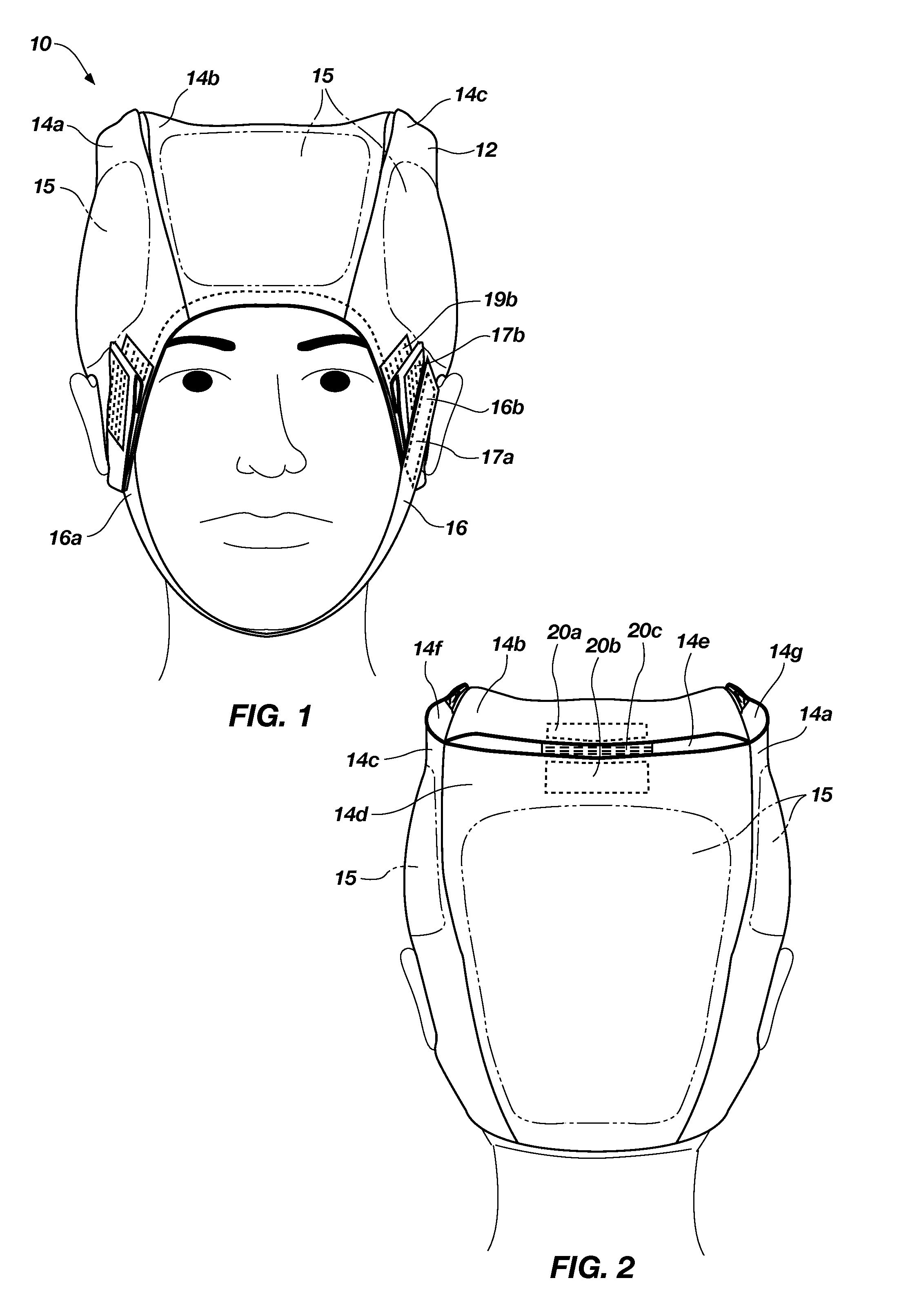
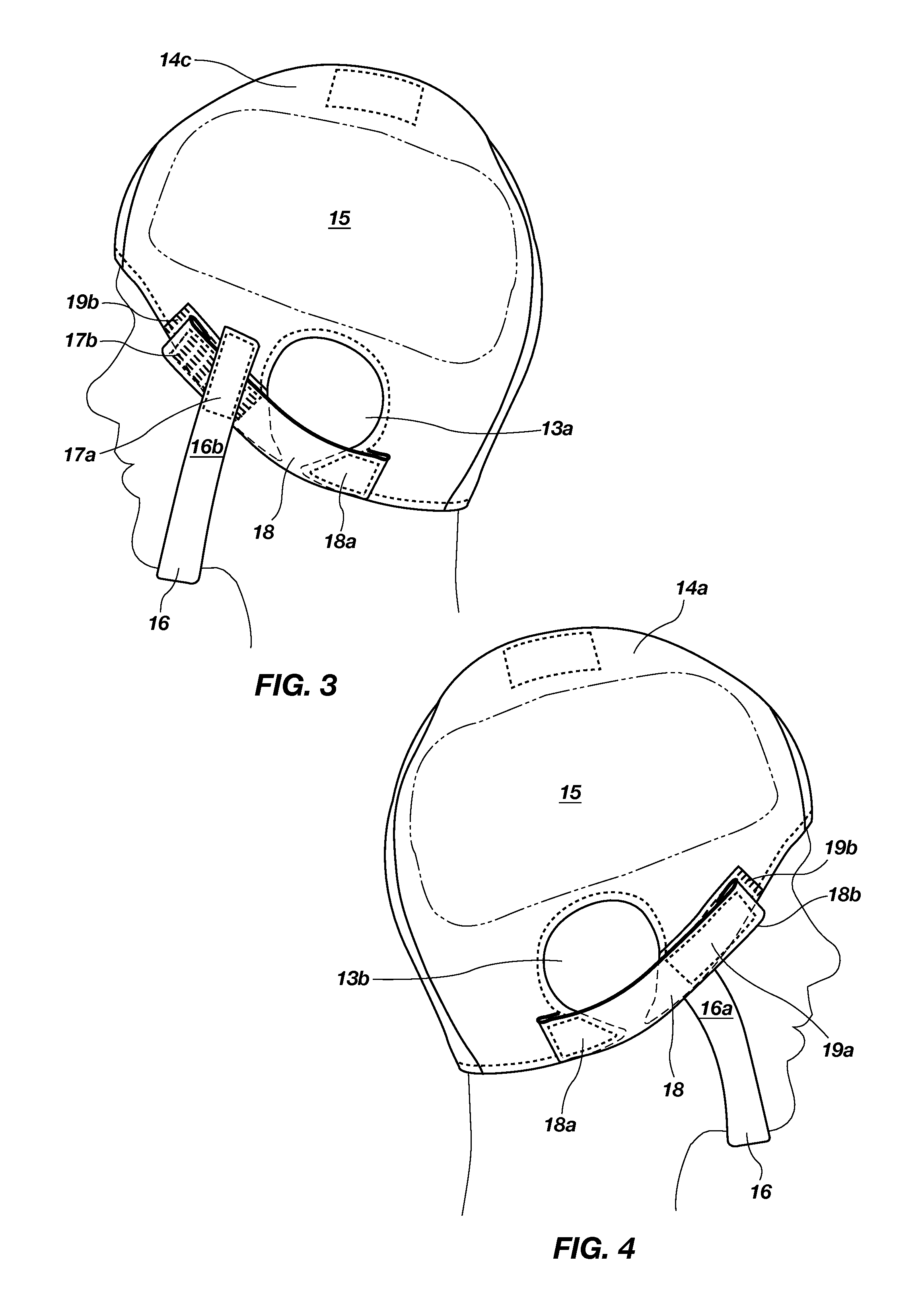
Head Trauma Bandage Cap and Method
ActiveUS20120296252A1Control bleedingMinimize movementHead bandagesNeck bandagesCervical spine immobilizationCold packs
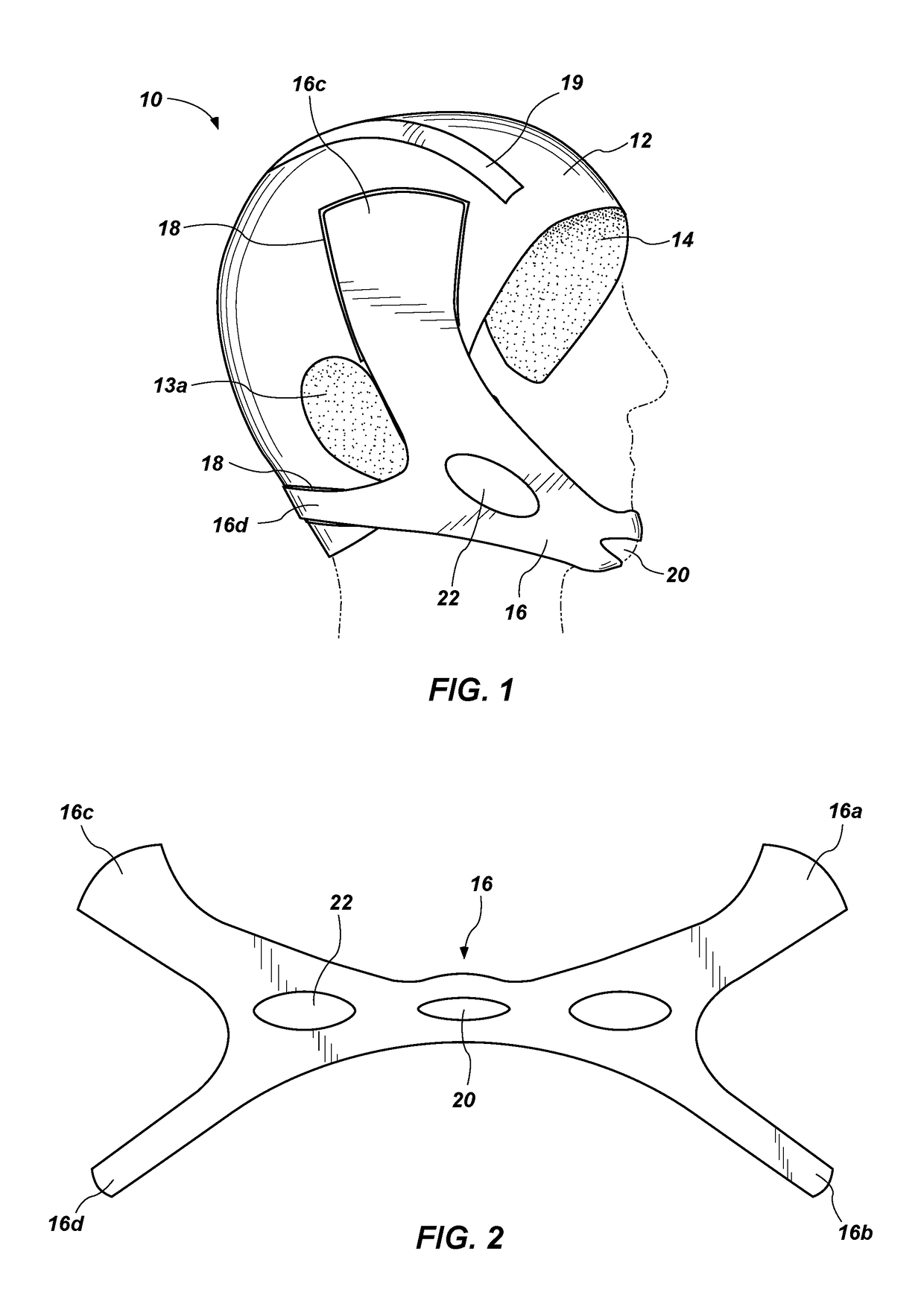
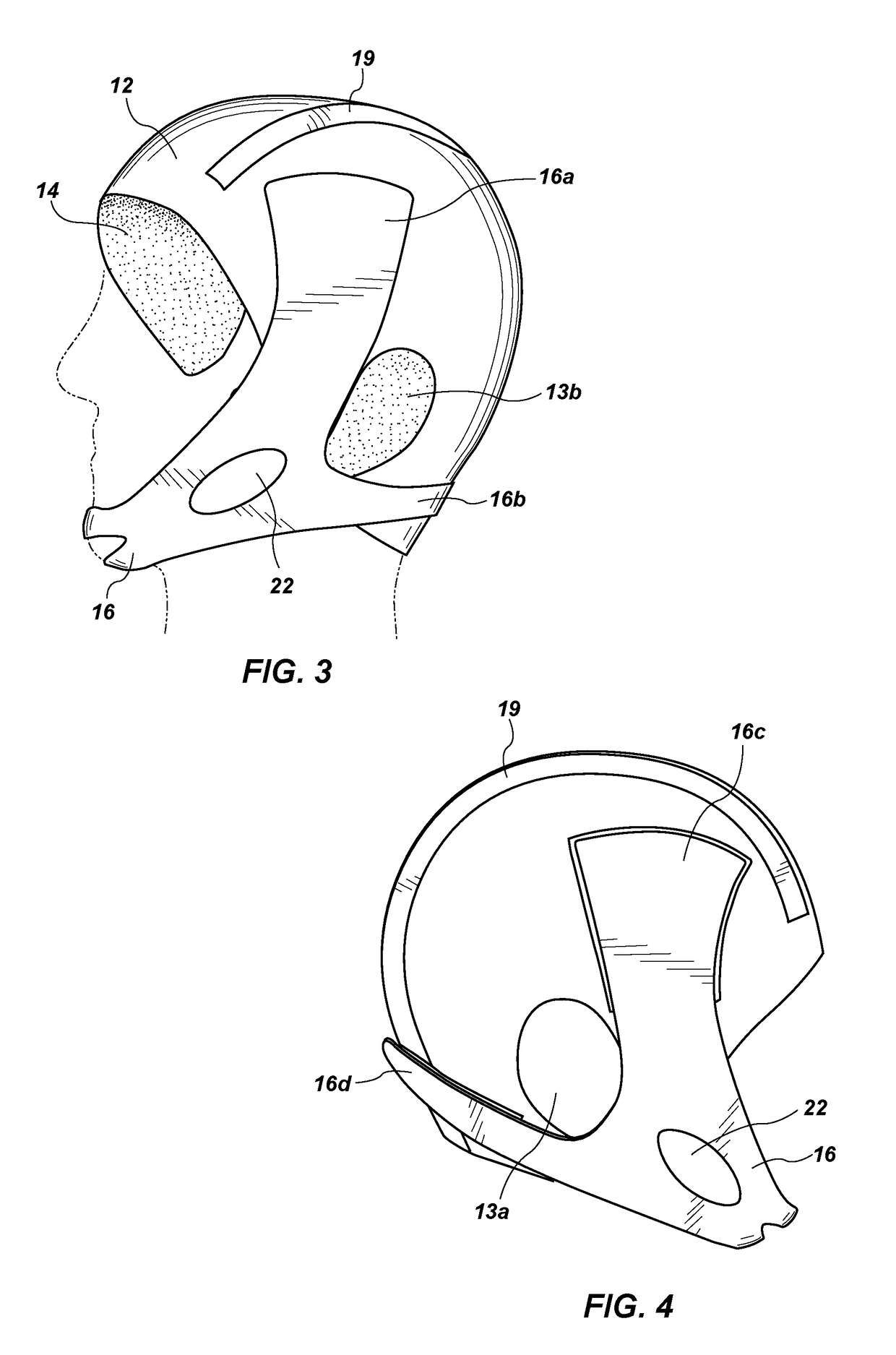
An emergency head trauma bandage cap with a detachable strap system and method of use, which, when applied to the head, delivers minimal pressure to control bleeding, doesn't compromise cervical spine immobilization, allows for fast and effective application of cold packs to control intracranial / internal swelling or hot packs to prevent hypothermia in non-trauma situations, doesn't come apart during treatment and transport, and doesn't require a caregiver to re-wrap the dressing.
Owner:EQUALIZER TECHNOLOGY LLC
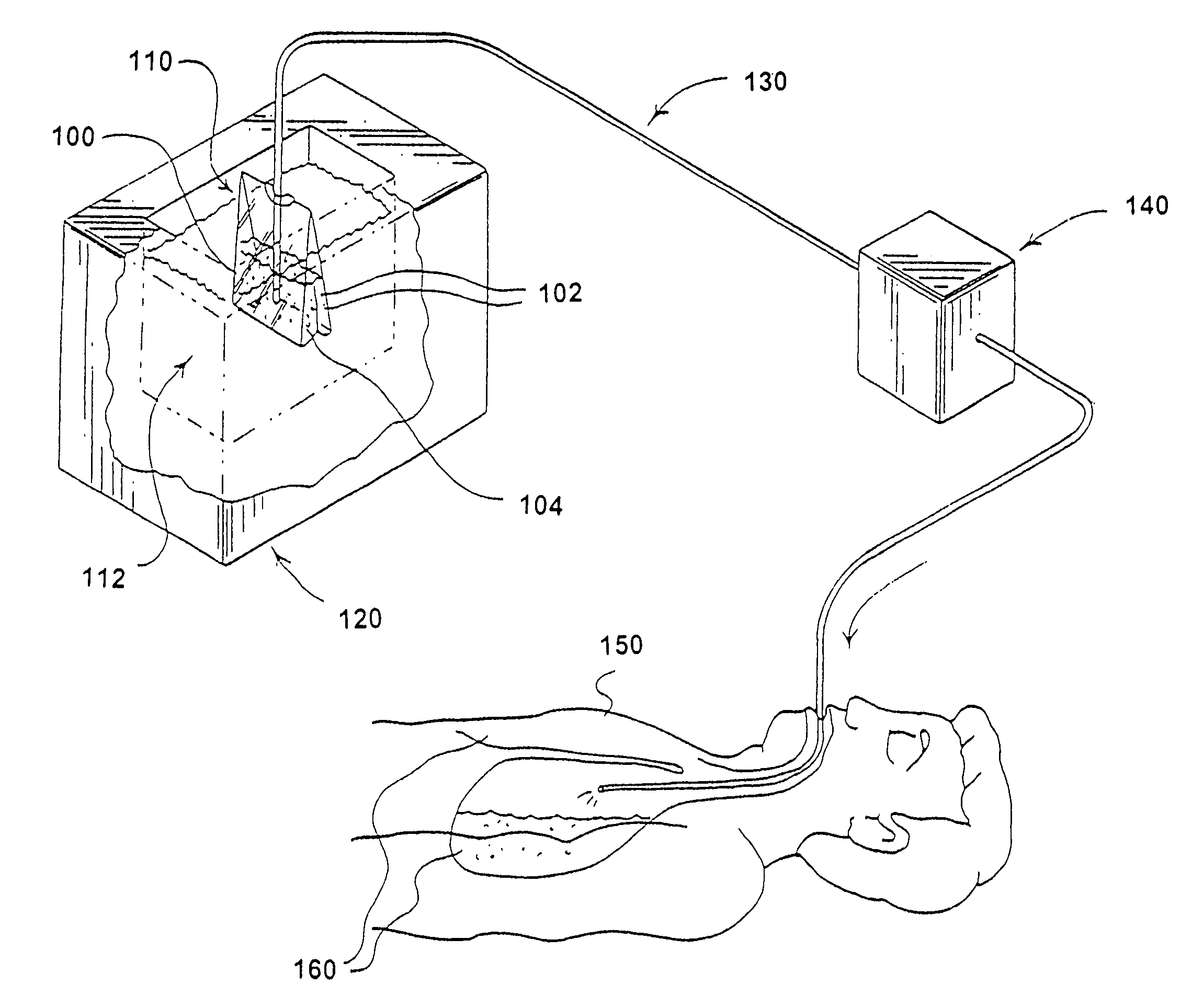
Method and device for rapidly inducing hypothermia
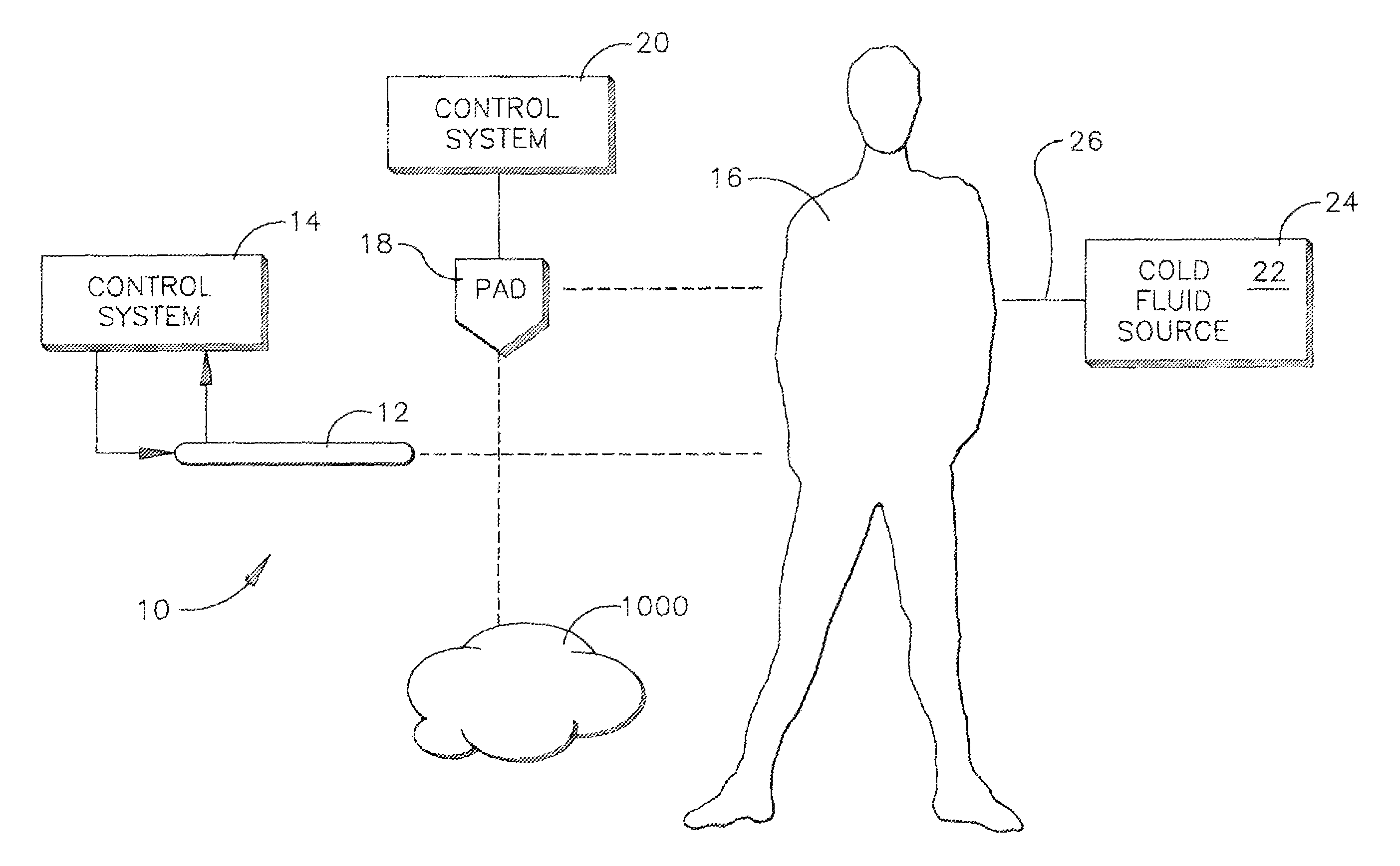
Disclosed is a system and method for inducing therapeutic levels of hypothermia in a patient in the emergent care setting. The system consists of a small battery operated console and one or more garments. The garments are connected to the console by one or more umbilicals. The console provides cold fluid to the garments under pressure and the garment cools the surface of the body. Fluid returns from the garment back to the console in a closed loop fashion. The console contains an electrical battery and a thermal battery that provides operation of the system for more than one hour. The cooling capacity of the system is sufficient to induce therapeutic levels of hypothermia in approximately 30 to 90 minutes in most patients. Use of the system does not preclude any therapeutic or diagnostic interventions that are commonly performed in the emergent care setting.
Owner:MEDCOOL
Methods and compositions for enhancing lifespan involving sirtuin-modulating compounds and chalcogenides
InactiveUS20120135091A1Extend your lifeImprove survivabilityBiocideOrganic chemistrySurvivabilityBiological materials
The present invention concerns the use of active compounds, including chalcogenides and sirtuin-modulating compounds, either alone or in combination for increasing or enhancing survivability and / or longevity in biological matter. In general aspects, the chalcogenides and other active compounds may modulate one or more sirtuin proteins. It includes compositions, methods, articles of manufacture and apparatuses for enhancing survivability in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, there are also therapeutic methods and apparatuses for aging or stress, diabetes, obesity, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease, blood clotting disorders, inflammation, cancer, organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer using the active compounds described.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Methods, Compositions and Devices for Inducing Stasis in Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organisms
InactiveUS20080085329A1Effective in inducing stasisReduces and eliminates amount of oxygenBiocideSulfur/selenium/tellurium active ingredientsIn vivoBiological materials
The present invention concerns the use of oxygen antagonists for inducing stasis in cells, tissues, and / or organs in vivo or in an organism overall. It includes methods and apparatuses for achieving stasis in any of these biological materials, so as to preserve and / or protect them. In specific embodiments, therapeutic methods and apparatuses for organ transplantation, hyperthermia, wound healing, hemorrhagic shock, cardioplegia for bypass surgery, neurodegeneration, hypothermia, and cancer is provided.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Anti-osteoarthritis and anti-hypothermia garment and device
InactiveUS6996848B2Relieve painRelieve swellingGarment special featuresFinger bandagesMedicineTherapeutic effect
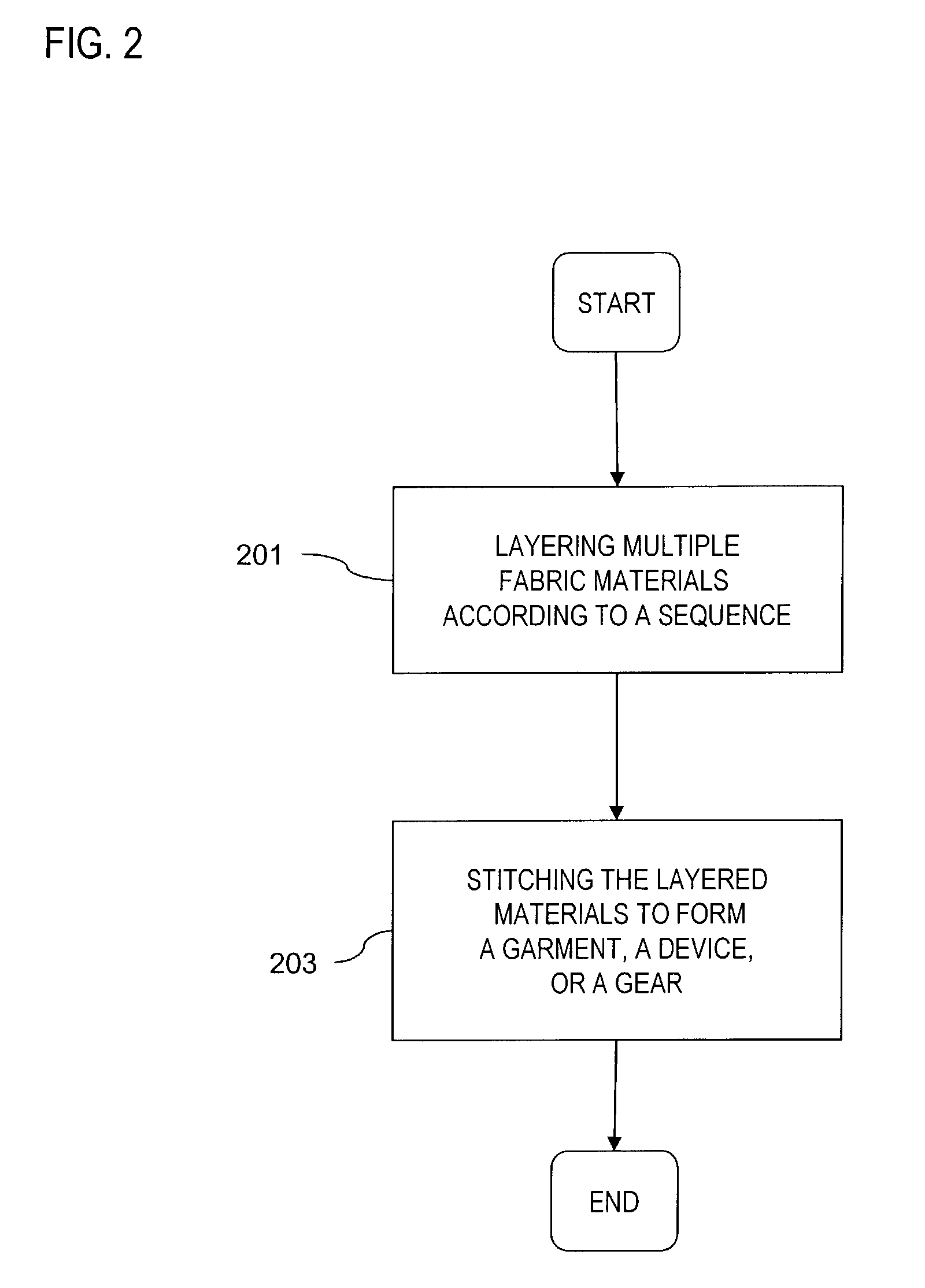
A multilayered material is provided that exhibits therapeutic effects for relieving the pain and swelling of various forms of arthritis (particularly osteoarthritis), delaying the onset of osteoarthritis, or preventing hypothermia or alleviating conditions caused by hypothermia. The flexible, breathable multilayered material includes a first layer of soft and hypoallergenic material (e.g., cotton, silk, linen), a second layer of soft, heat retentive material (e.g., wool, cashmere) contacting the first layer, and a third layer of water repellent material contacting the second layer. Additionally, the multilayered material provides a thin, flexible, breathable fabric that can be used to construct various garments, devices, and gears to combat harsh weather conditions.
Owner:DONALDSON ARCHIE R
Detection of flu using thermal imaging
InactiveUS20190192010A1Increase clinical relevanceRaise the possibilityHealth-index calculationSurgeryDiseaseDisplay device
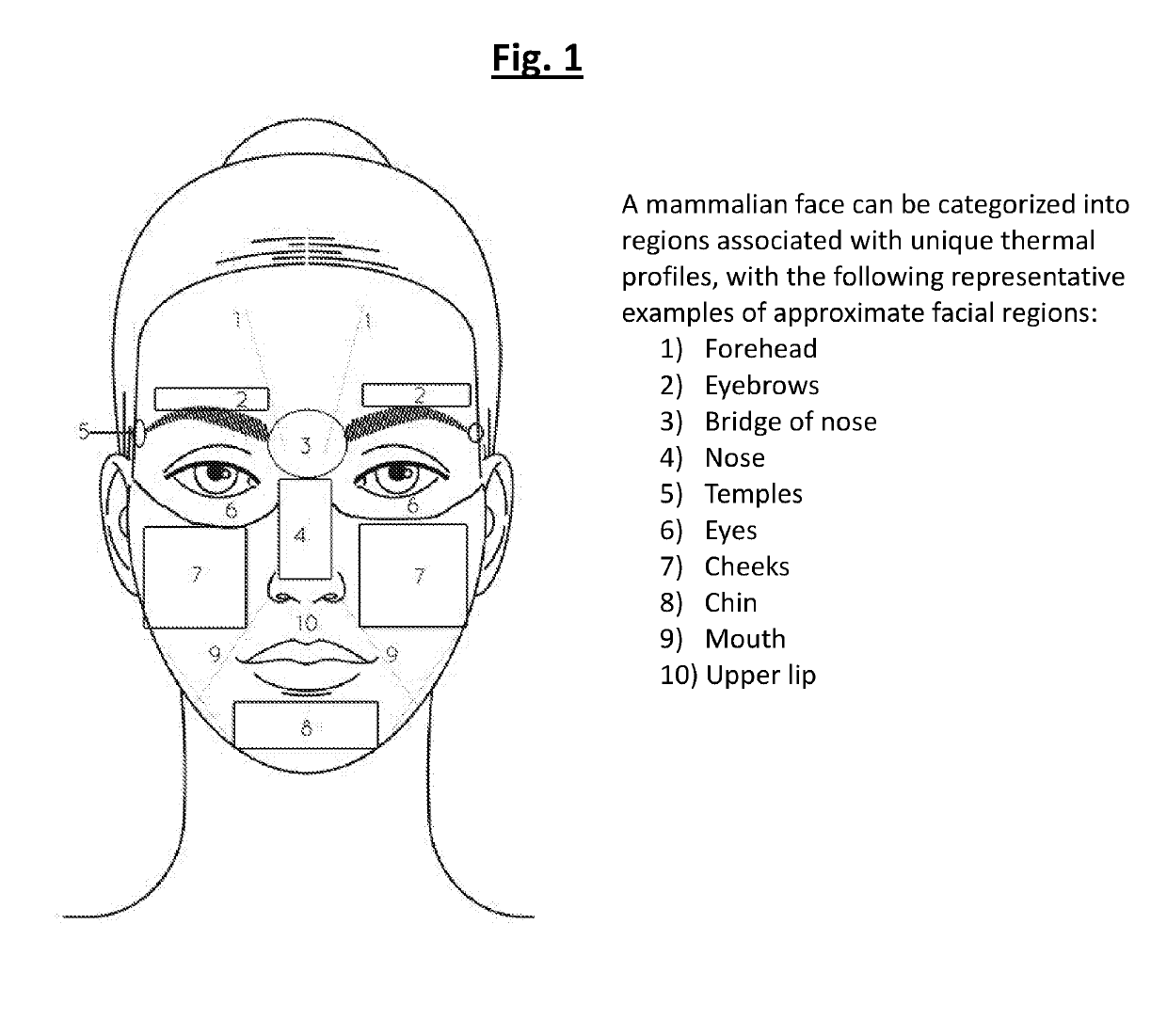
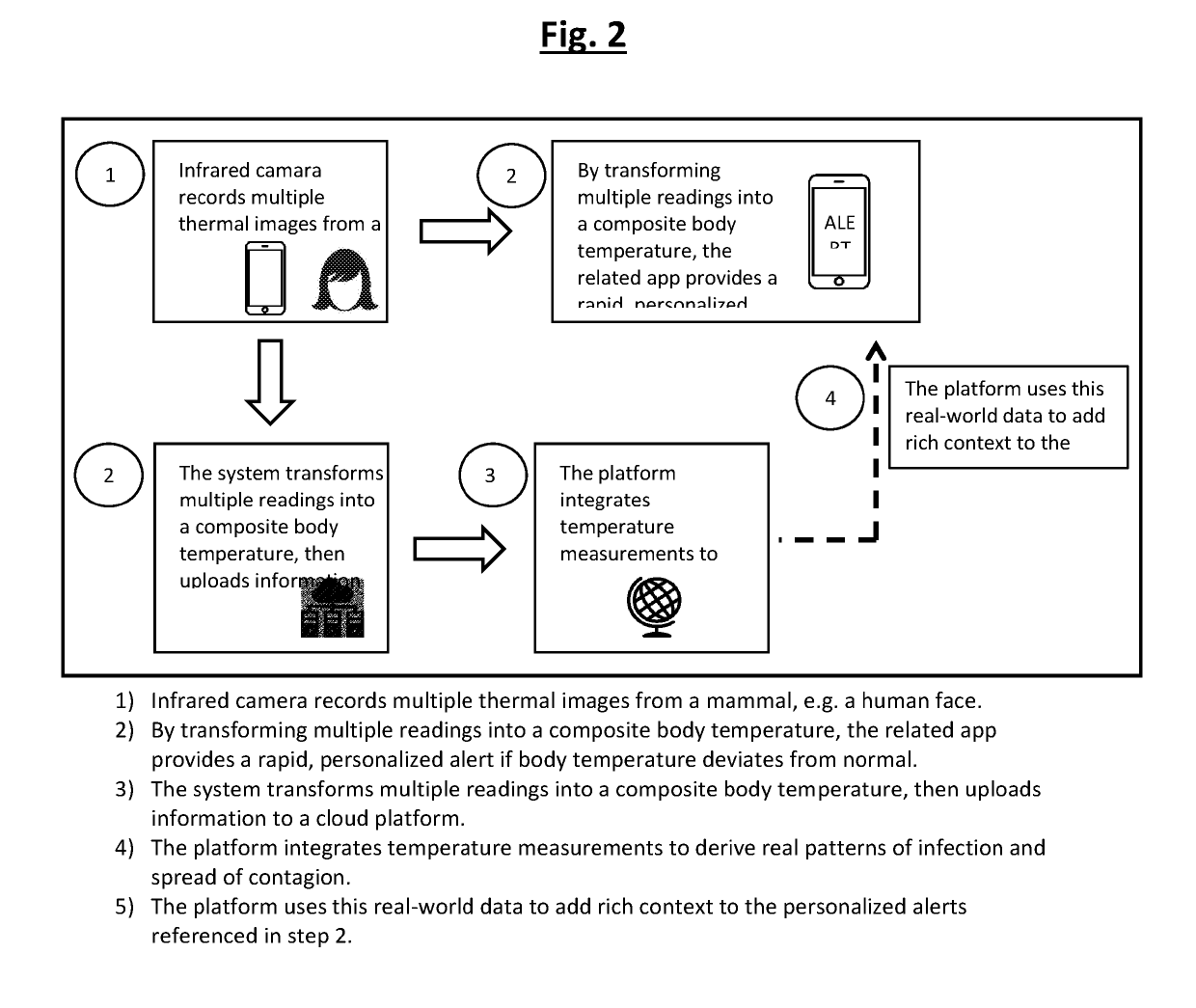
Methods for determining change in physical condition or illness of a mammal by obtaining a thermal image of the subject and determining the body temperature of the mammal based on the thermal image are described. An example method is implemented on a first electronic device having a first display and a thermal imaging hardware. The method includes obtaining the thermal image of a mammal using the first electronic device; comparing said thermal image to a reference thermal image of the subject at healthy state with no symptoms or characteristics of the physical condition or illness such as by way of example, flu, fever, hypothermia, ovulation, heat stress, cardiac condition; comparing the intensity of said thermal image to the reference thermal image; and in response to such comparison, determining whether the subject shows symptoms or hallmarks of a certain illness or condition marked by a change in body temperature and associated intensity of the thermal image; and displaying information regarding said determination on the first display of the first electronic device. The method includes first obtaining a reference thermal image of a mammal in a “normal” and / or “healthy” condition, then later obtaining additional image(s) for comparison to the reference image; and in response to such comparison, determining whether the subject shows symptoms of a certain illness or condition marked by a change in body temperature and associated intensity of the thermal image.
Owner:MANE VIRAJ +1
Head trauma bandage cap and method
ActiveUS20170246041A1Sufficient flexibilityMinimal pressureHead bandagesNon-adhesive dressingsCervical spine immobilizationHot pack
An emergency hemostatic head trauma bandage cap with a strap system and method of use, which, when applied to the head, delivers minimal pressure to control bleeding, doesn't compromise cervical spine immobilization, allows for fast and effective application of cooling gel to control intracranial / internal swelling or hot packs to prevent hypothermia in non-trauma situations, doesn't come apart during treatment and transport, and doesn't require a caregiver to re-wrap the dressing.
Owner:EQUALIZER TECHNOLOGY LLC
Use of Hypothermia Inducing Drugs
The present invention relates to the induction of hypothermia in humans in a predictable and dose responsive fashion by use of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a vanilloid receptor agonists, capsaicinoid or capsaicinoid-like agonist capable of inducing hypothermia, thereby benefiting patients suffering from illnesses characterized by tissue anoxia.
Owner:HJERTEFORSKNINGSFONDEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com