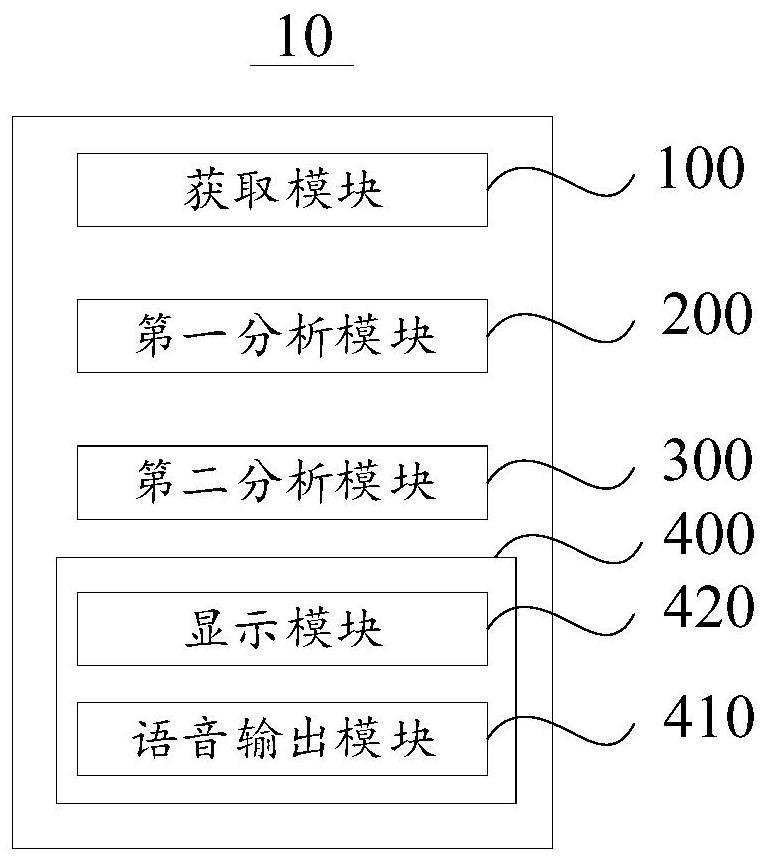
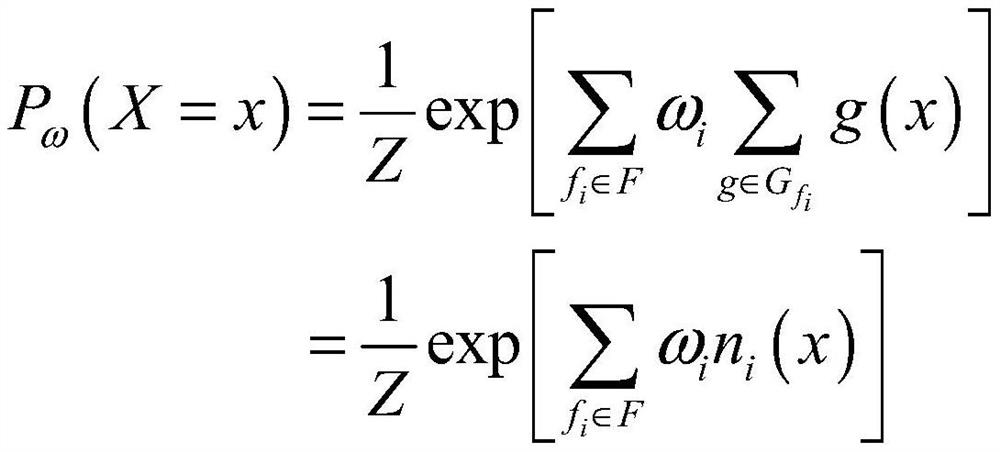Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Adequate response time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gas sensors
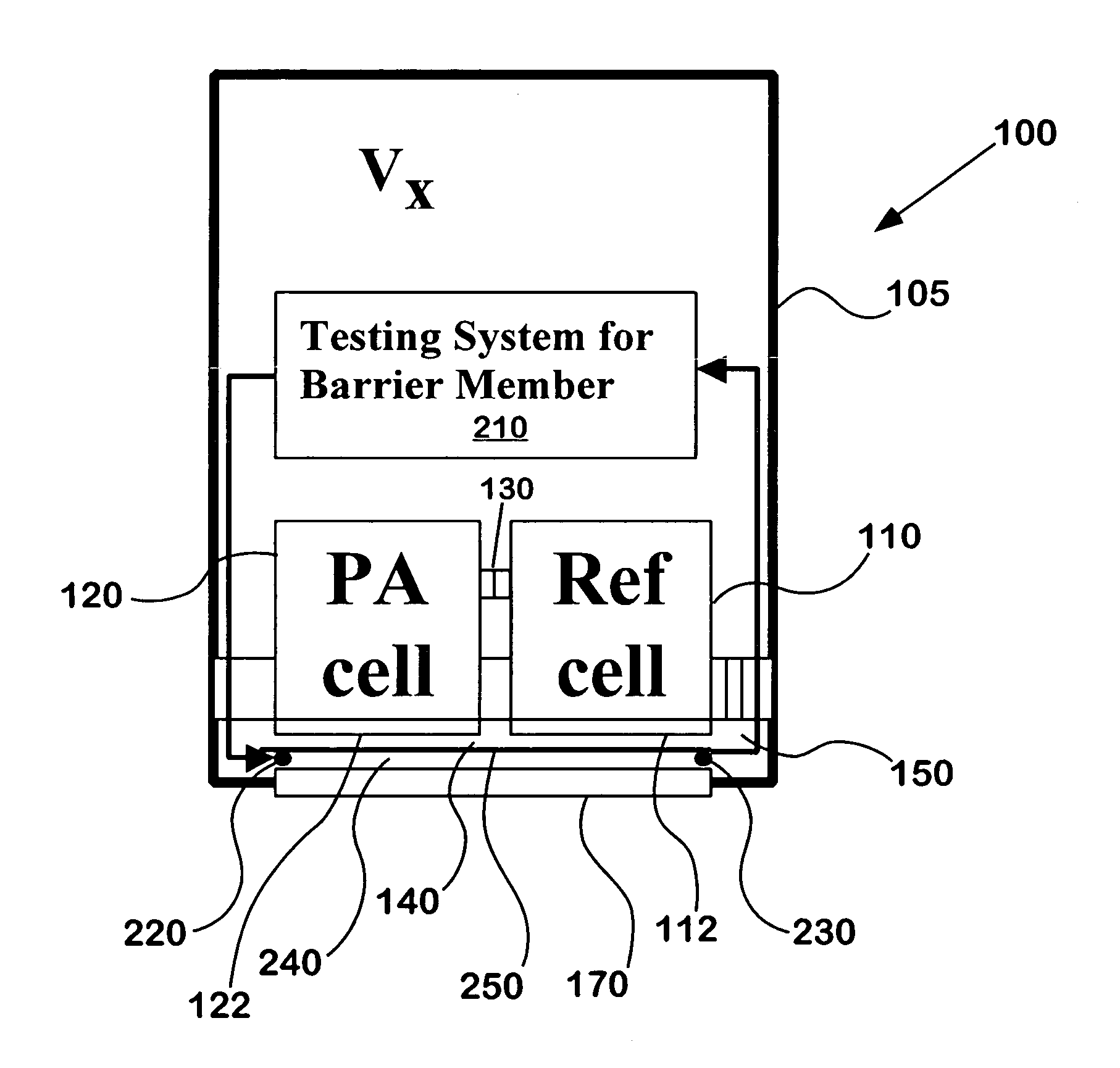
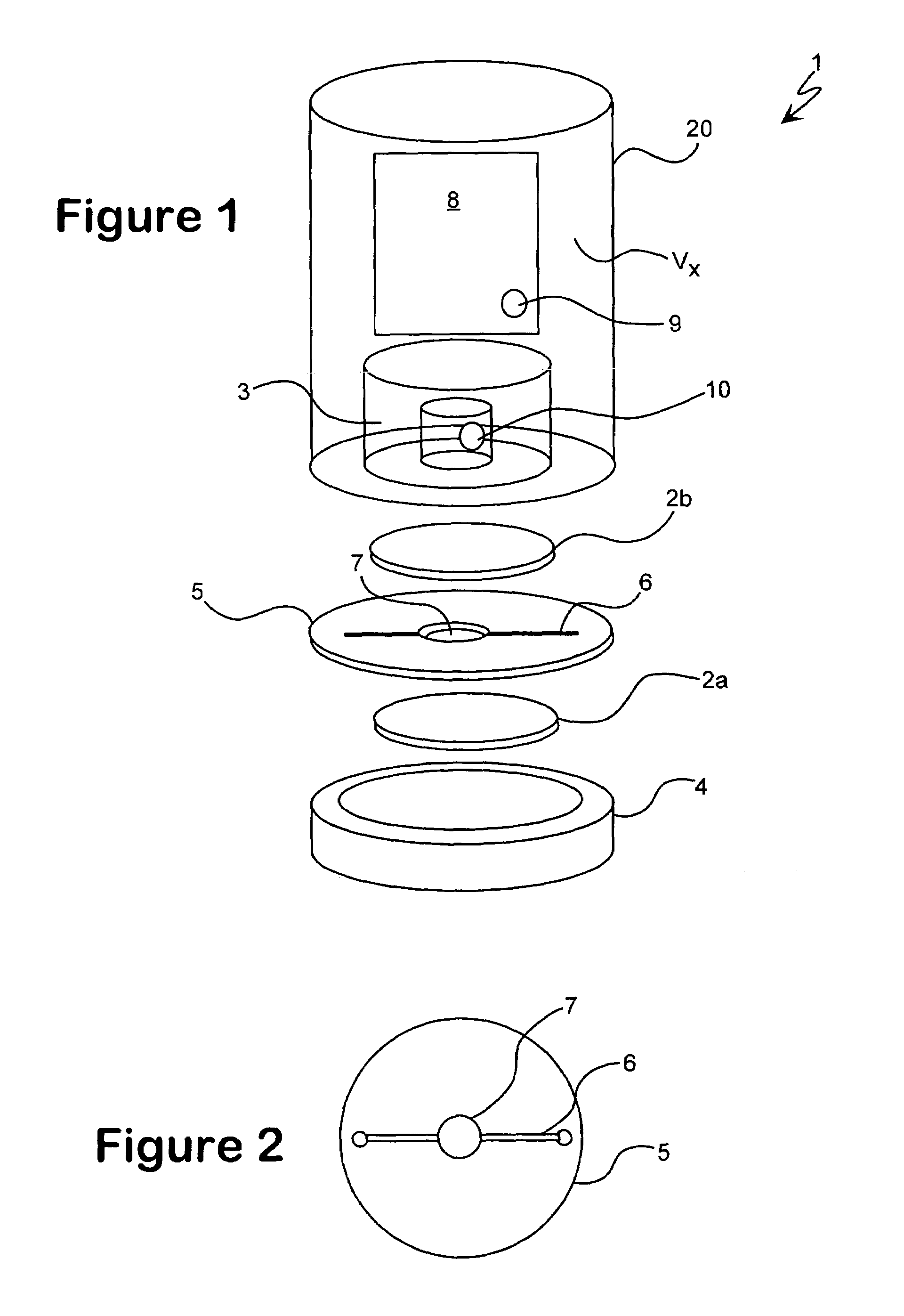
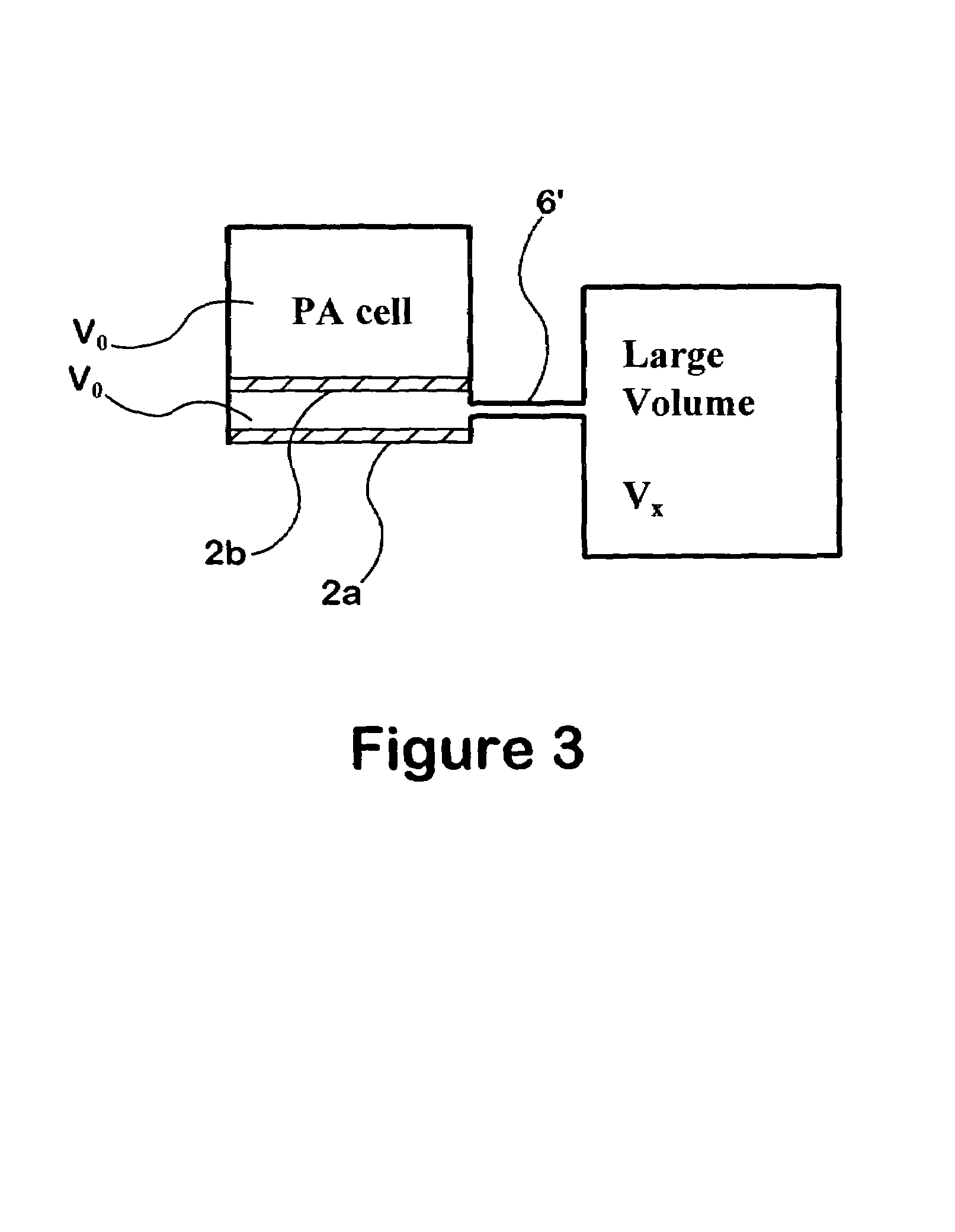
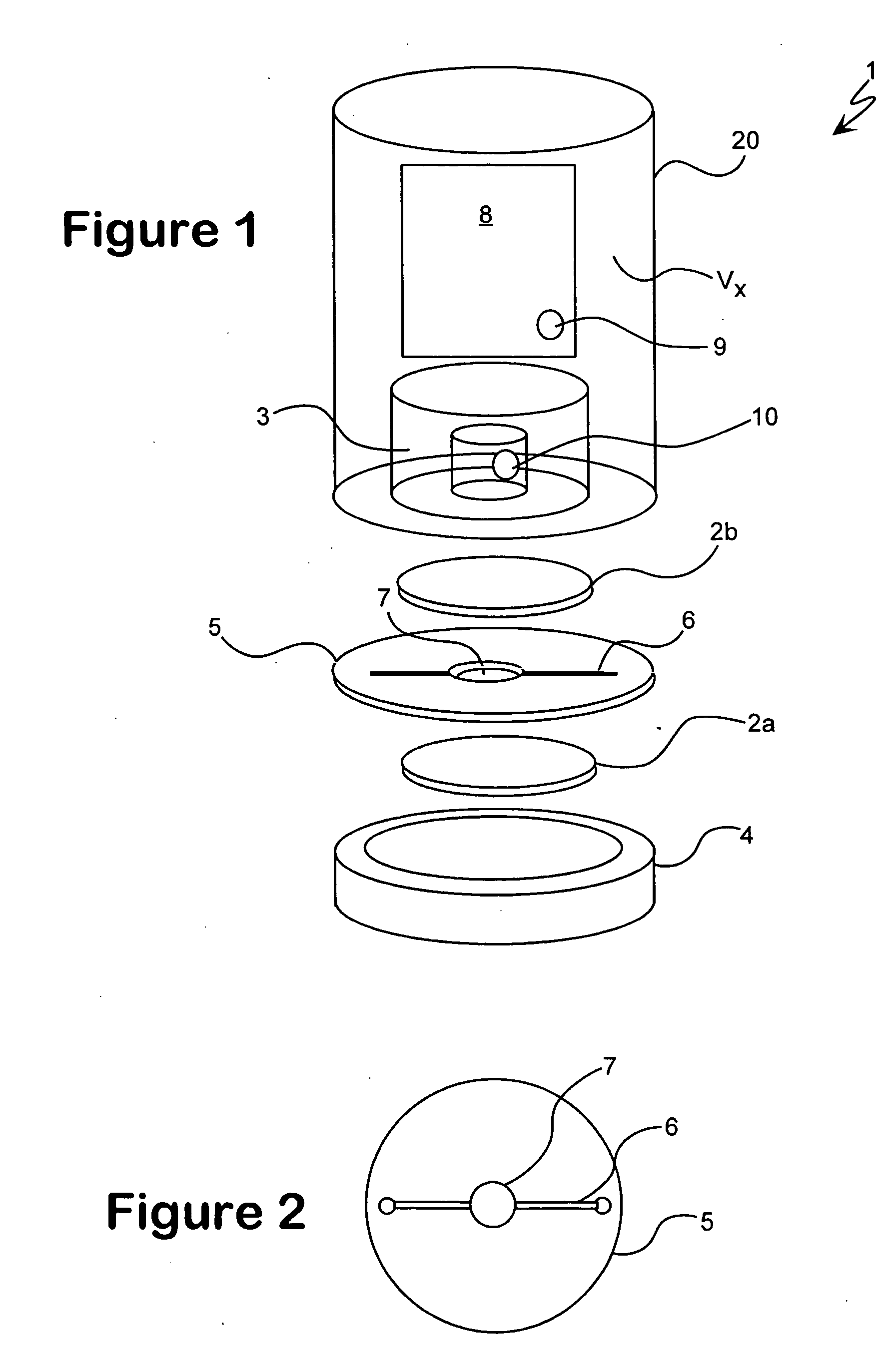
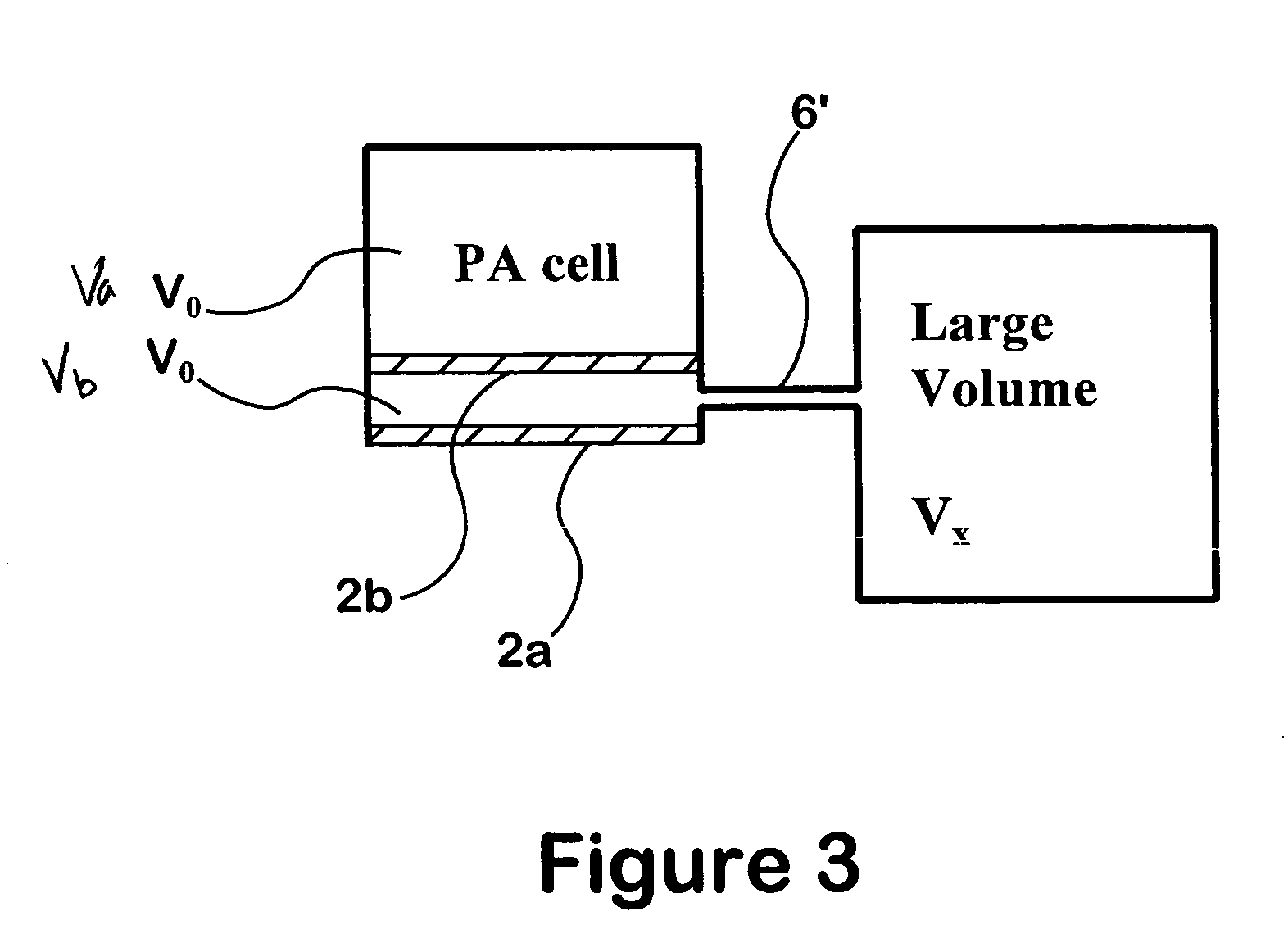
InactiveUS7034943B1Reduces externalAdequate response timeOptical radiation measurementOrganic active ingredientsDiffusionAnalyte
The present invention relates to a device for accomplishing noise reduction in a photoacoustic gas detector using a sound damping element and / or a background or reference microphone where a preferably larger external volume that acts as a sound damping element (SDE) is coupled to a smaller volume through which the gas diffuses. The coupling is accomplished in such a way that the externally generated sound waves incident upon the photoacoustic detector are adequately attenuated by the larger volume SDE without adversely affecting diffusion of the gaseous species of interest through the smaller volume for measurement by the detector. Preferably this is accomplished by coupling the larger SDE volume to the smaller gas diffusion volume by a long and thin pressure channel. Another photoacoustic detector includes a measuring system to measure the photoacoustic excitation of analyte gas entering the photoacoustic detector, a reference system to measure the effect of pressure waves in the environment, and a system for offsetting an output from the measuring system with an output from the reference system to reduce noise resulting from pressure waves in the environment in an output signal of the photoacoustic detector. The present invention also relates to a device for testing the integrity of a porous member and includes a source of pressure waves and a sensor for measuring a signal resulting from the transmittal of pressure waves from the transmitter. The signal is proportional to pressure losses through the porous member. The pressure losses through the porous member are, in turn, a measure of the degree to which the porous member has become clogged.
Owner:MSA TECH +1
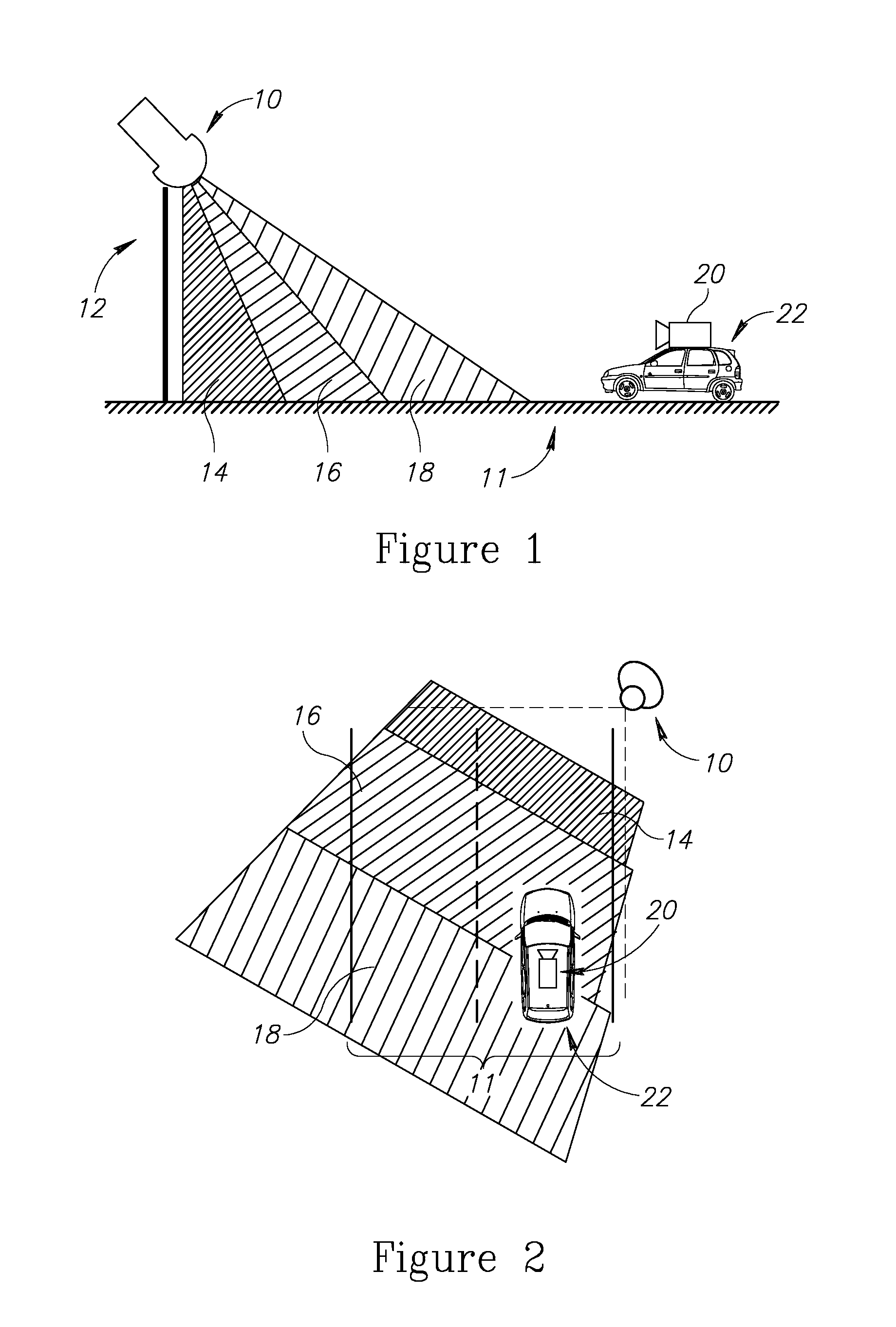
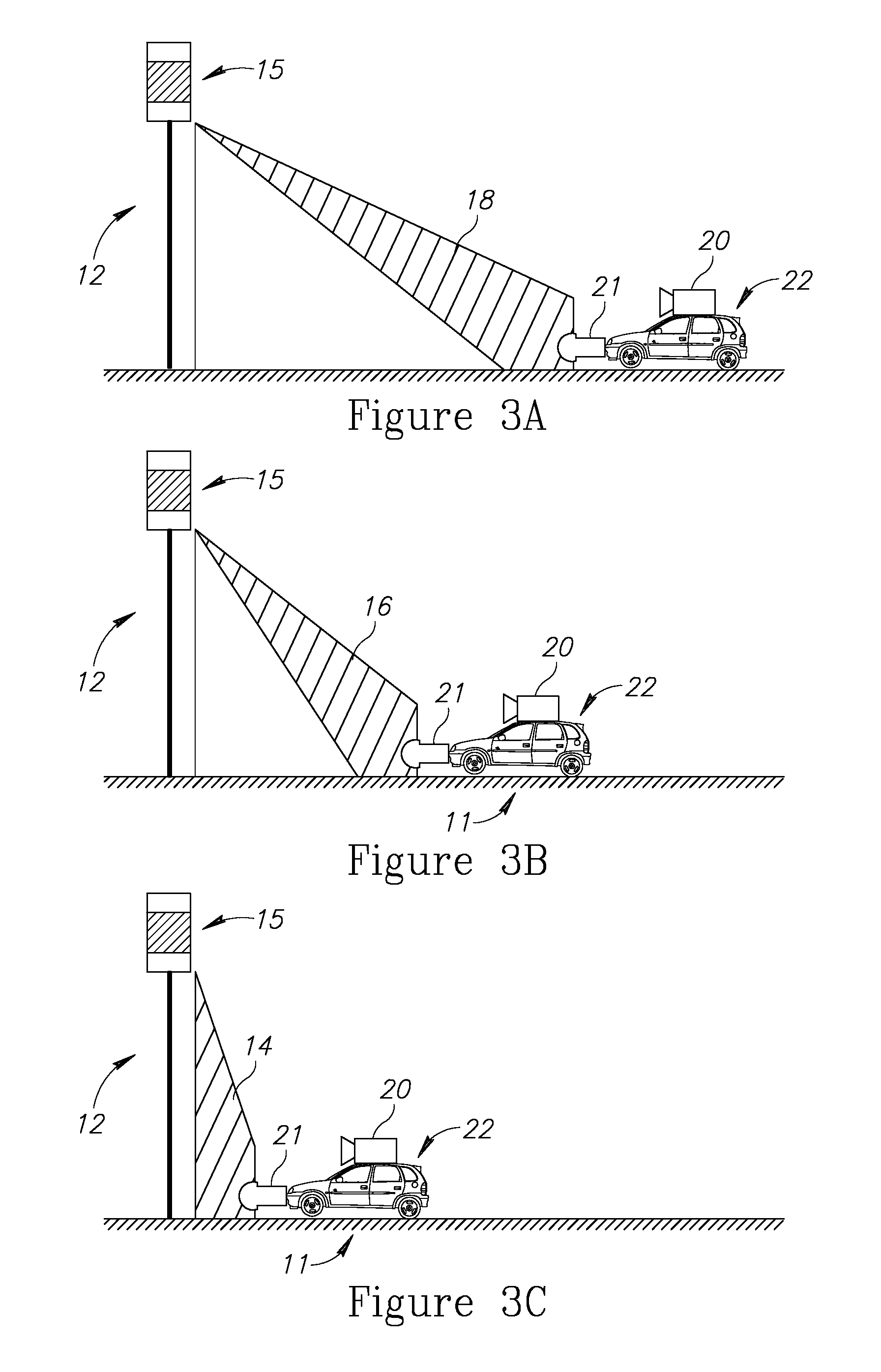
Smart traffic sign system and method
ActiveUS9214084B2Short processAdequate response timeArrangements for variable traffic instructionsAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorEngineering
A system for increasing awareness of a driver to traffic-signs on the road is provided herein. The system includes: a sensor attached to a vehicle and configured to determine a type of one or more traffic-signs that are present in a scene containing the vehicle, wherein at least some of the traffic-signs are time-variant traffic-signs which present time-variant visual indicators; and a controller configured to: monitor and analyze, in real time: relative metrics indicative of one or more spatial relations between the vehicle and the one or more detected traffic-signs; and temporal data associated with the time-variant visual indicators of the time-variant traffic-signs; apply one or more decision functions to at least two of: the detected one or more traffic-signs and to the monitored relative metrics, and the temporal data associated with the time-variant visual indicators, so as invoke an action selected from a predefined set of actions.
Owner:BRIGHTWAY VISION
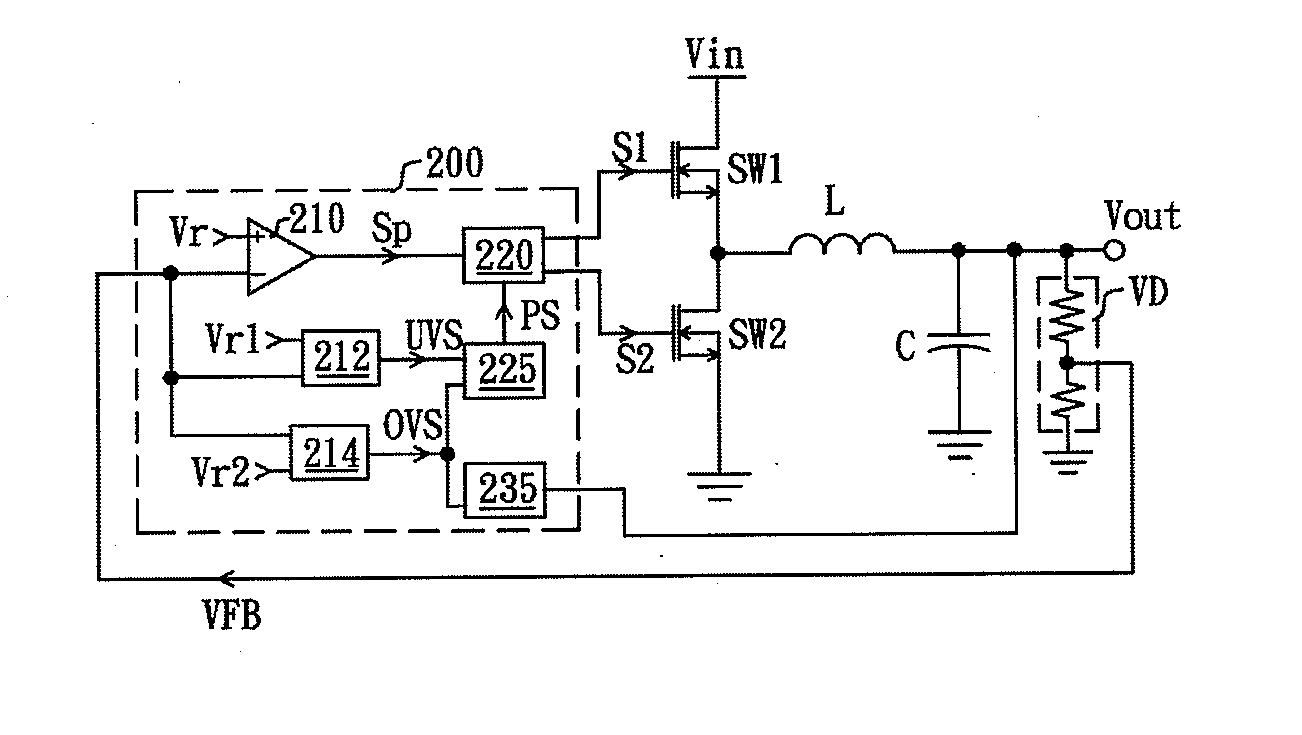
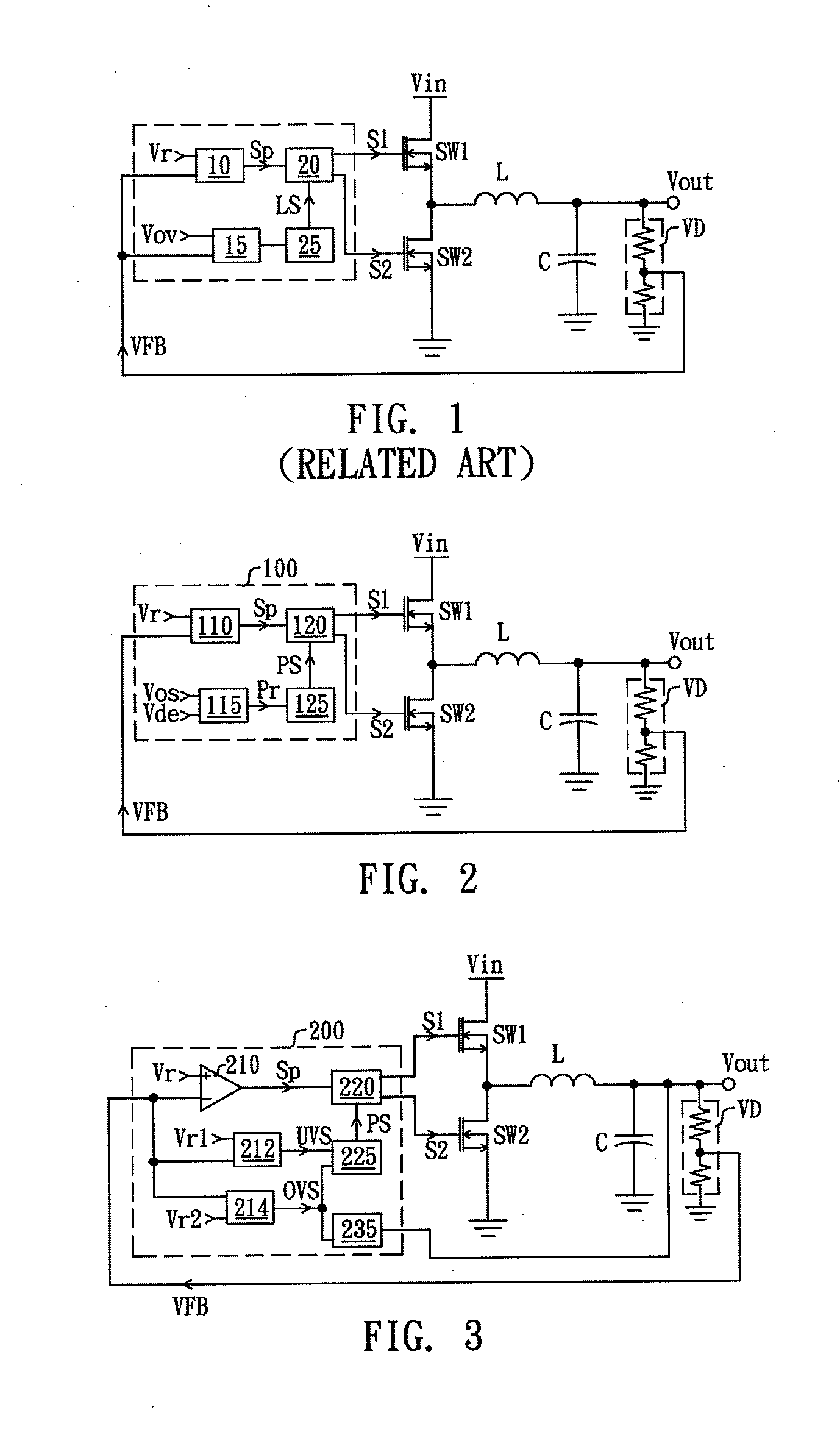
Controller with protection function
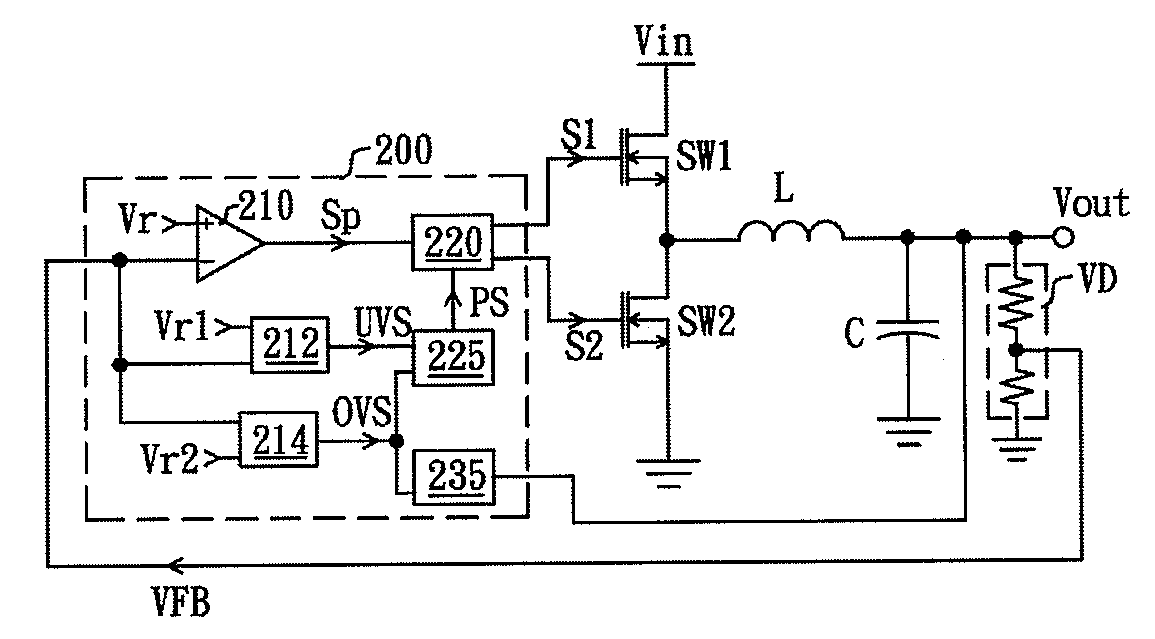
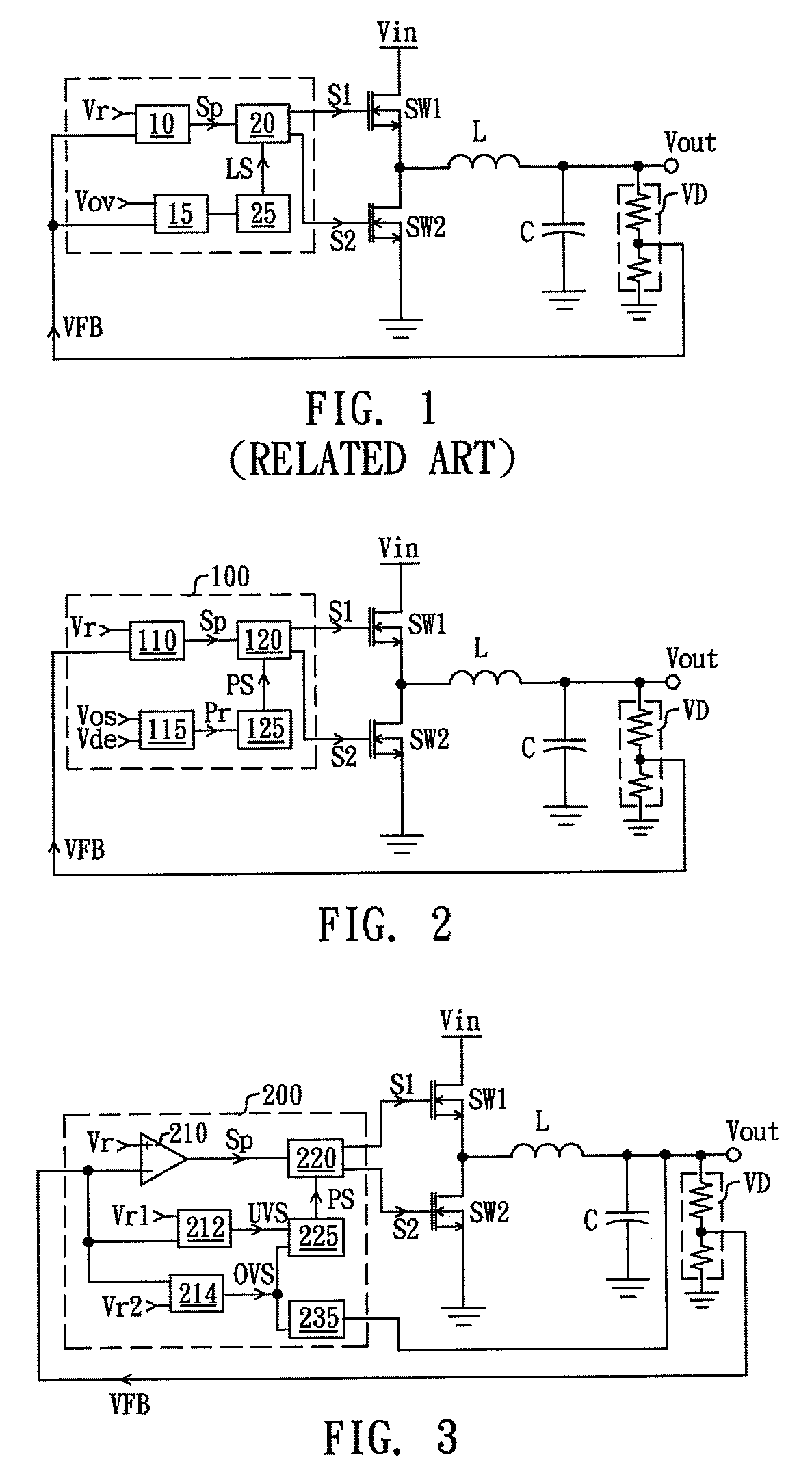
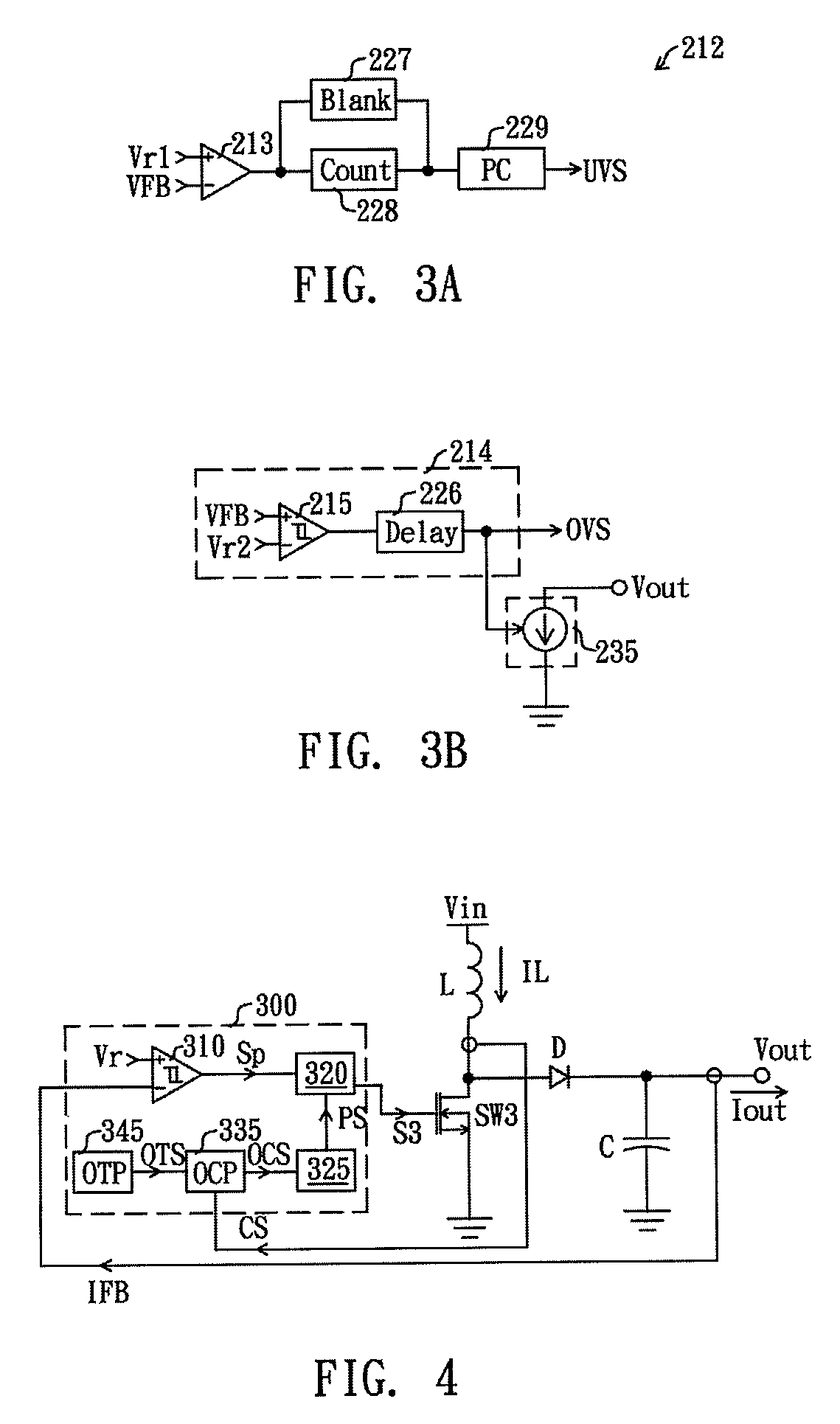
ActiveUS20140152274A1Effective protectionProtection from damageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFeedback circuitsEngineering
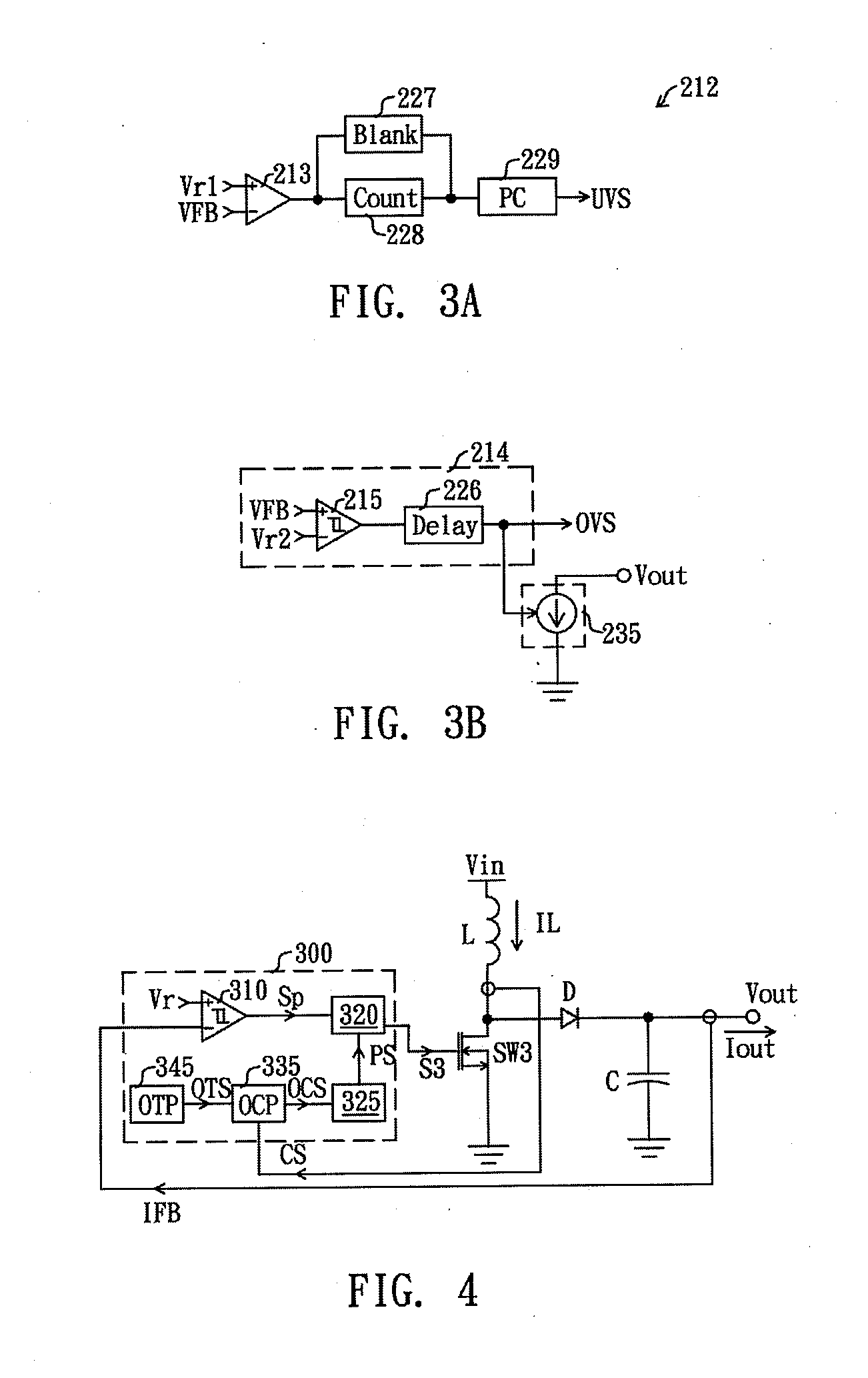
A controller with protection function, comprising a feedback circuit, a logic control circuit, an over-state judgment circuit, and a protection control circuit, is disclosed. The feedback circuit generates a modulation signal according to an output of a converting circuit. The logic control circuit is coupled to the feedback circuit and controls the converting circuit according to the modulation signal for stabilizing the output of the converting circuit. The over-state judgment circuit receives an over-state reference signal and a detecting signal, and generates a protection signal in response to levels of the detecting signal and the over-state reference signal. The protection control circuit is coupled to the logic control circuit and the over-state judgment circuit and controls the logic control circuit to lower the output of the converting circuit when receiving the protection signal.
Owner:GREEN SOLUTION TECH CO LTD
Smart traffic sign system and method
ActiveUS20140320317A1Short processAdequate response timeArrangements for variable traffic instructionsElectromagnetic wave reradiationDriver/operatorEngineering
A system for increasing awareness of a driver to traffic-signs on the road is provided herein. The system includes: a sensor attached to a vehicle and configured to determine a type of one or more traffic-signs that are present in a scene containing the vehicle, wherein at least some of the traffic-signs are time-variant traffic-signs which present time-variant visual indicators; and a controller configured to: monitor and analyze, in real time: relative metrics indicative of one or more spatial relations between the vehicle and the one or more detected traffic-signs; and temporal data associated with the time-variant visual indicators of the time-variant traffic-signs; apply one or more decision functions to at least two of: the detected one or more traffic-signs and to the monitored relative metrics, and the temporal data associated with the time-variant visual indicators, so as invoke an action selected from a predefined set of actions.
Owner:BRIGHTWAY VISION
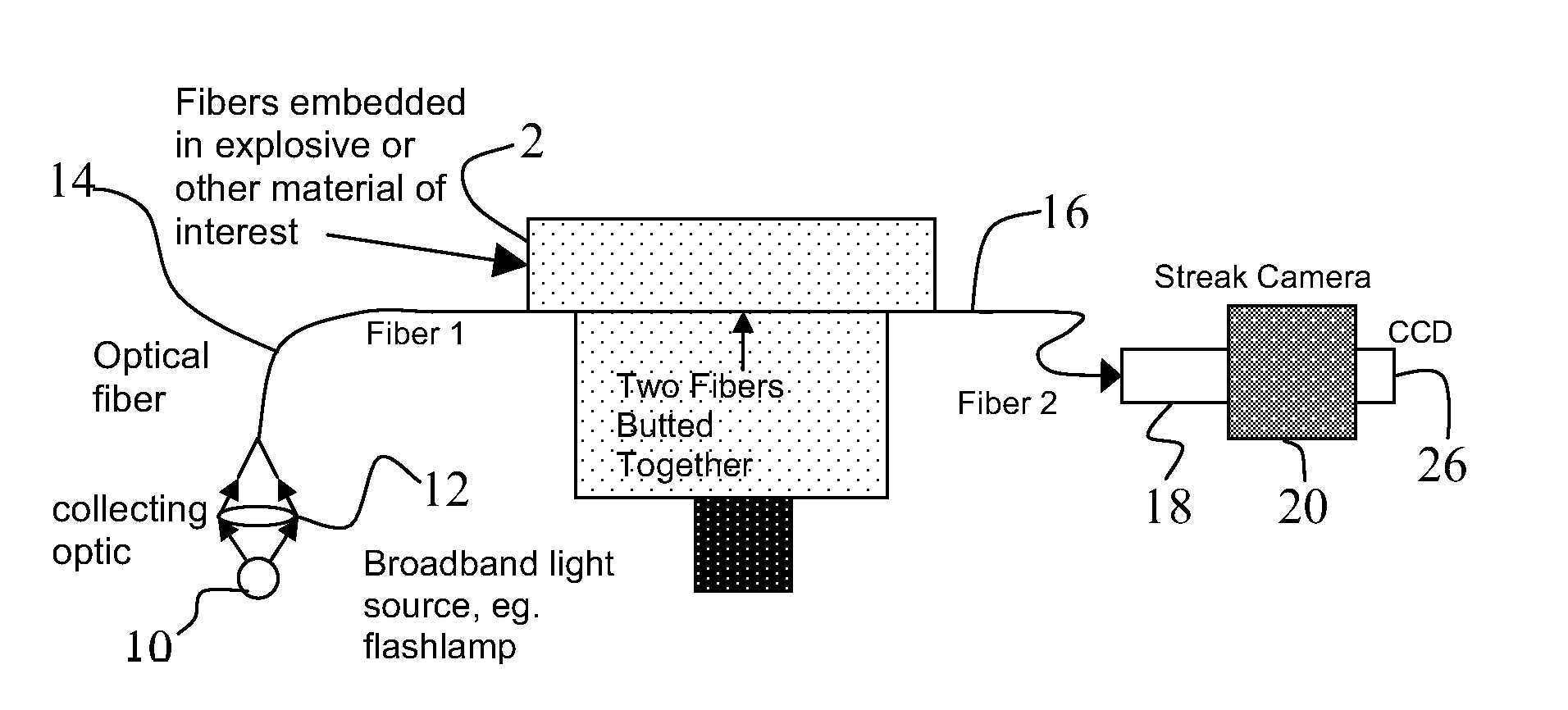
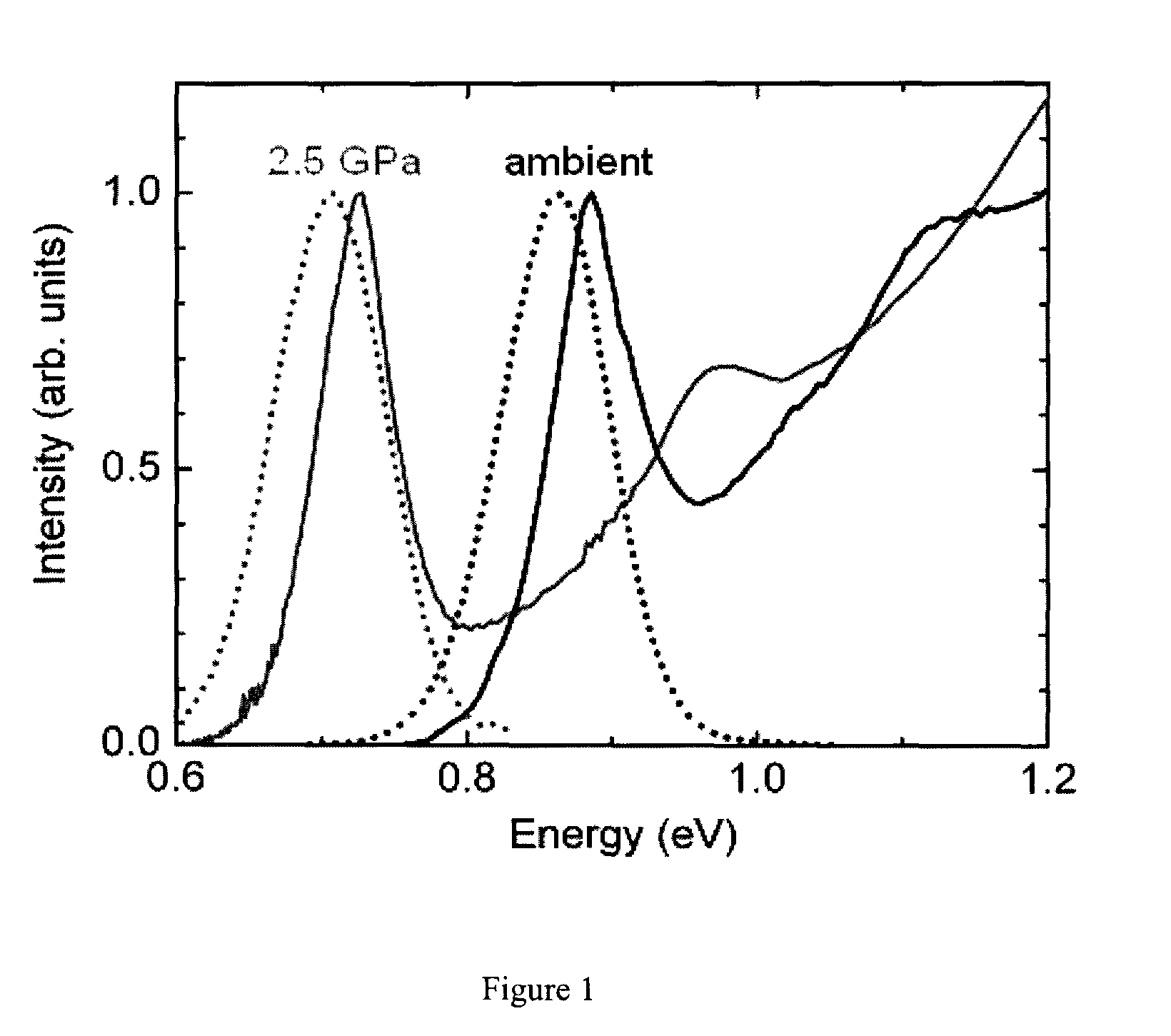
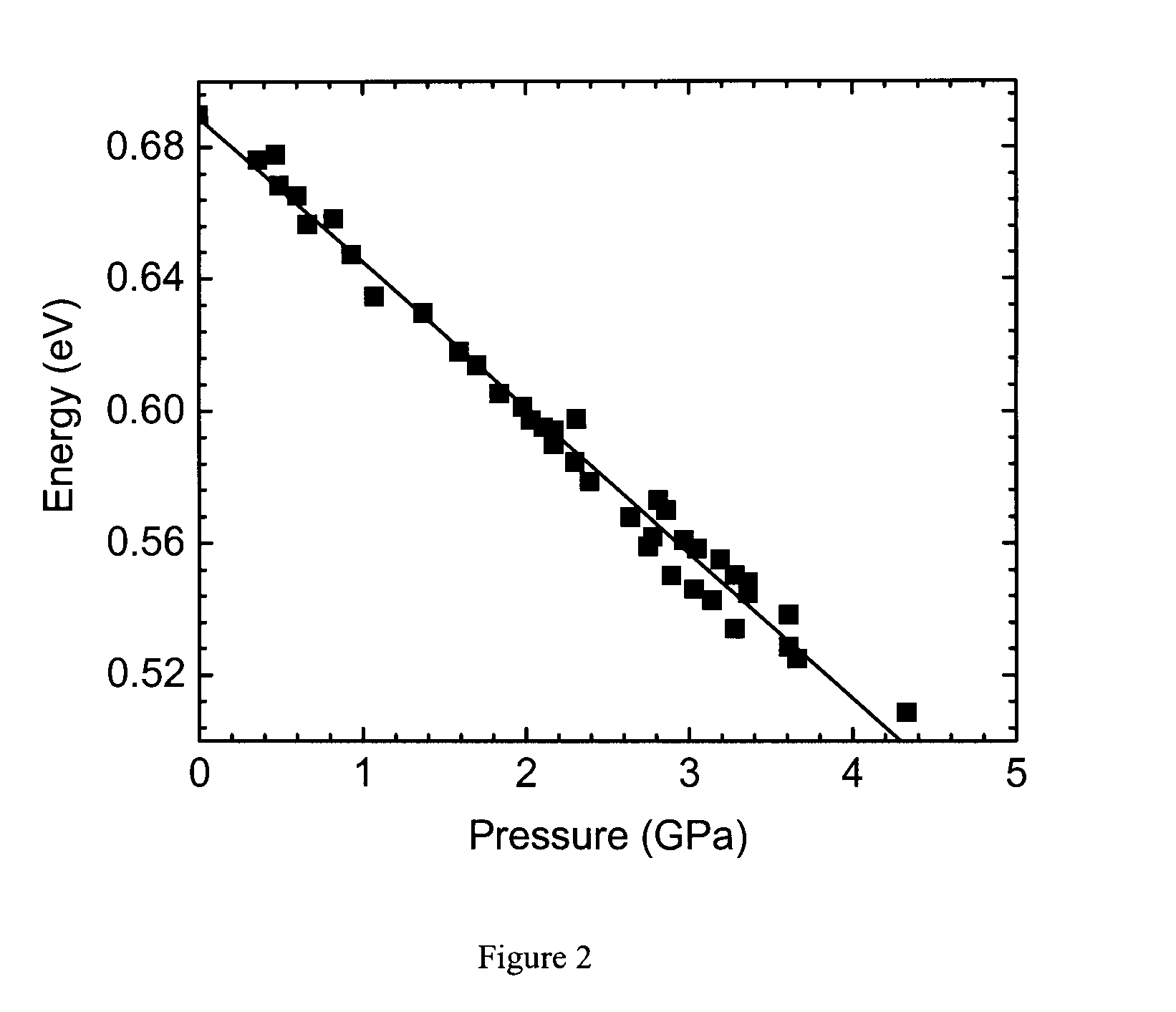
Real time measurement of shock pressure
InactiveUS8135244B1Strong of band gapAdequate response timeRadiation pyrometryForce measurementShock wavePhotoluminescence
A fiber-based optical pressure-sensor, made using semiconductor nanocrystal quantum dots (NQDs) as the active transducing material, provides response time fast enough for shock wave measurements. For NQDs, the shift in band gap as a result of applied pressure can be observed as a shift of the photoluminescence (PL) peak. Further, the shift of the principal absorbance feature allows pressure measurements faster than those obtainable by following the PL peak.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
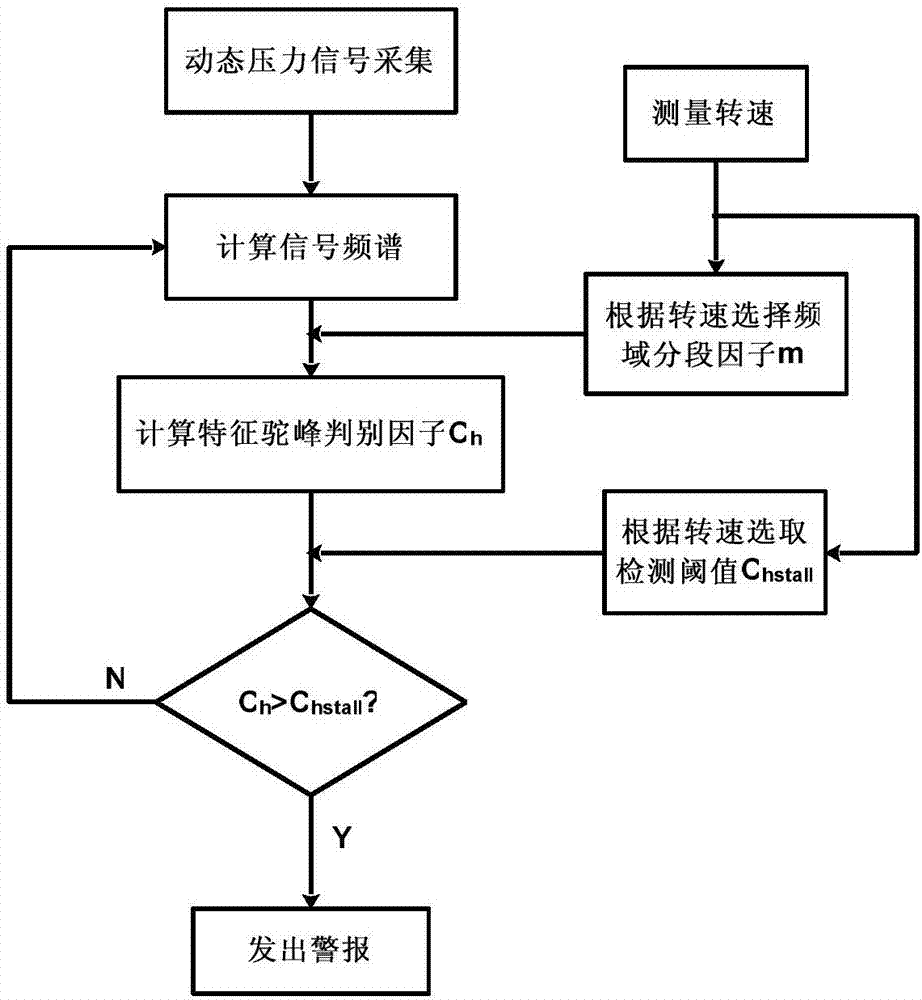
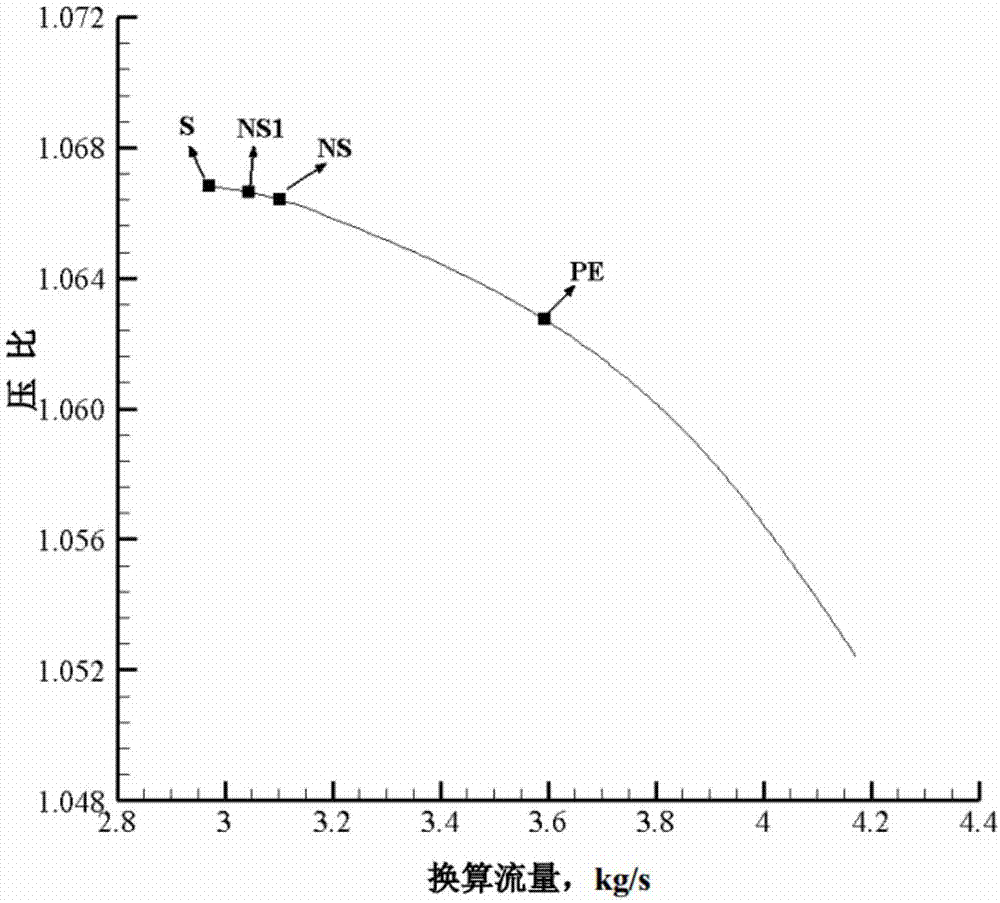
Early warning method for rotating stall of axial-flow air compressor based on frequency domain hump identification
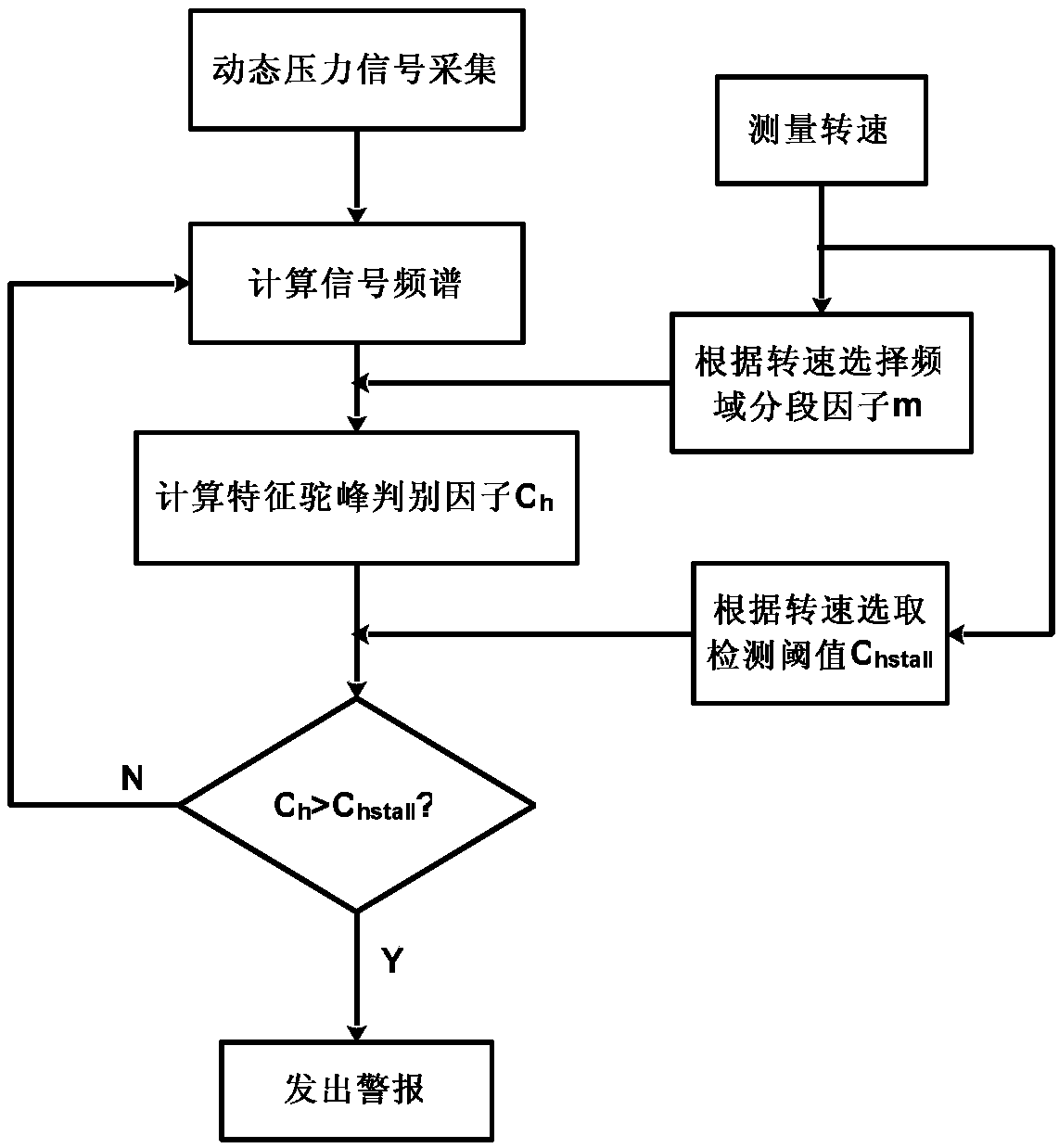
ActiveCN107165850ACalculation speedReduce intermediate processCharacter and pattern recognitionPump controlFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an early warning method for rotating stall of an axial-flow air compressor based on frequency domain hump identification. The method comprises the following steps: continuously and dynamically acquiring a pressure signal; continuously calculating the frequency spectrum of the pressure signal within one air compressor rotation period by utilizing fast Fourier transform; calculating a characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch corresponding to the frequency spectrum; and judging whether the air compressor is close to the rotating stall boundary by comparing the characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch with a detection threshold value Chsta11. The characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch defined by the early warning method for rotating stall of the axial-flow air compressor has definite physical significations and is used for implementing real-time on-line detection on a frequency domain hump appearing earlier than rotating stall so as to give an early warning when the work situation of the air compressor is close to the rotating stall boundary, and the early warning method is reliable. By requiring a simplex signal sensor only and adopting fast Fourier transform, the early warning method for rotating stall of the axial-flow air compressor has few middle procedures, realizes high calculation speed and provides sufficient response time for active control.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
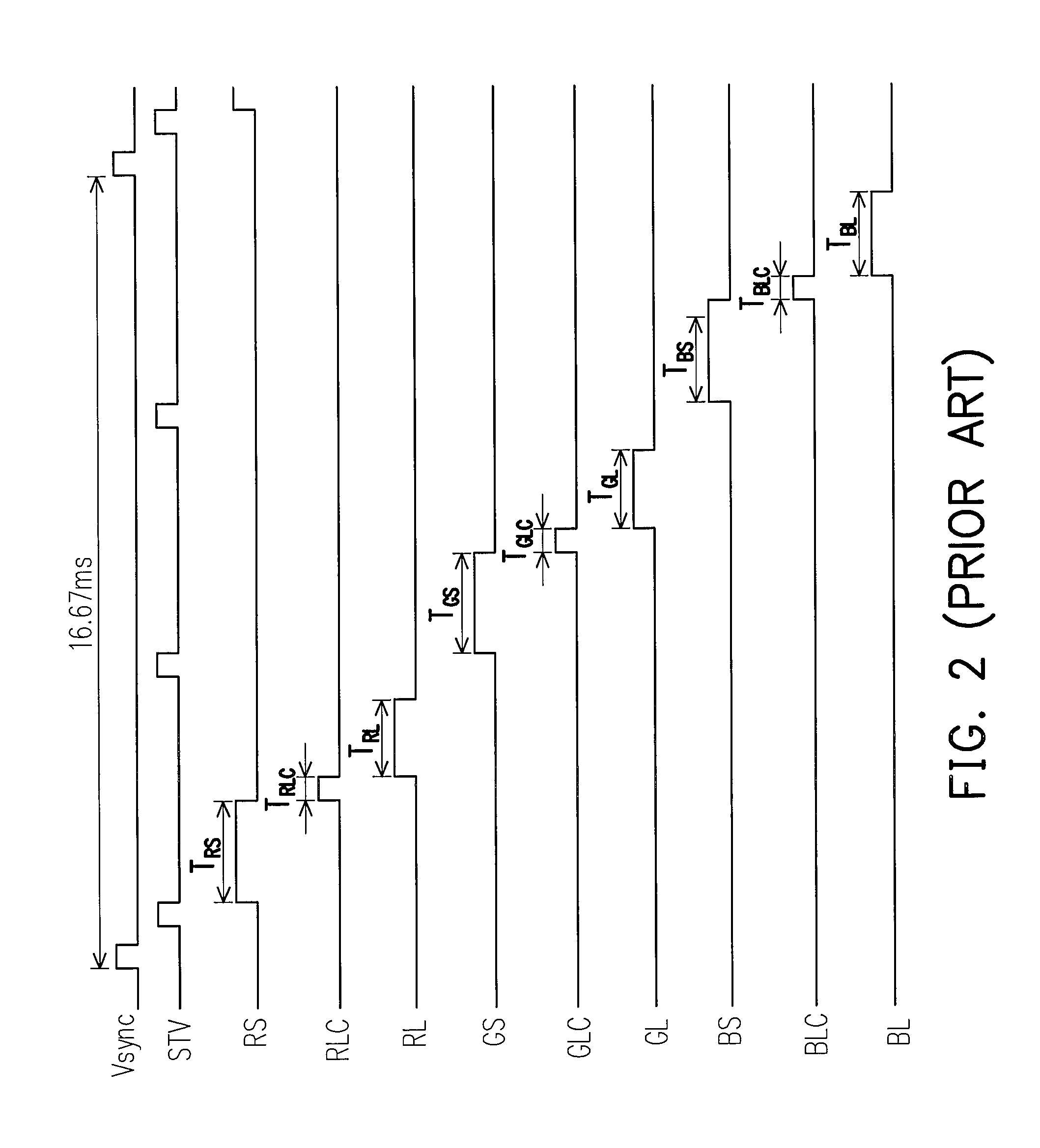
Color sequential liquid crystal display and liquid crystal display panel driving method thereof
InactiveUS20100013755A1Reduce scan timeExtension of timeStatic indicating devicesLighting-up timeMonochromatic color
A color sequential liquid crystal display (color-sequential-LCD) and an LCD panel driving method thereof are disclosed. By changing the arrangement of the pixel array in the LCD panel and turning on several rows of pixels in the LCD panel at the same time, so that the color sequential LCD of the present invention not only respectively reduces the scanning time of red, green and blue video data to make the liquid crystal molecules of all the pixels on the LCD panel have enough response time but also respectively increases the lighting-up time of the red, green and blue light emitting diodes of the back light module to promote the display brightness of the entire LCD panel. Therefore, the color sequential LCD of the present invention displays a single color or a full color image without the bottom color mixing phenomenon, and furthermore, the display brightness thereof can be promoted.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Gas sensors
InactiveUS20060192966A1Adequate response timeReduces externalAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOrganic active ingredientsDiffusionAnalyte
Owner:MINE SAFETY APPLIANCES CO +1
Image display system and image display methods
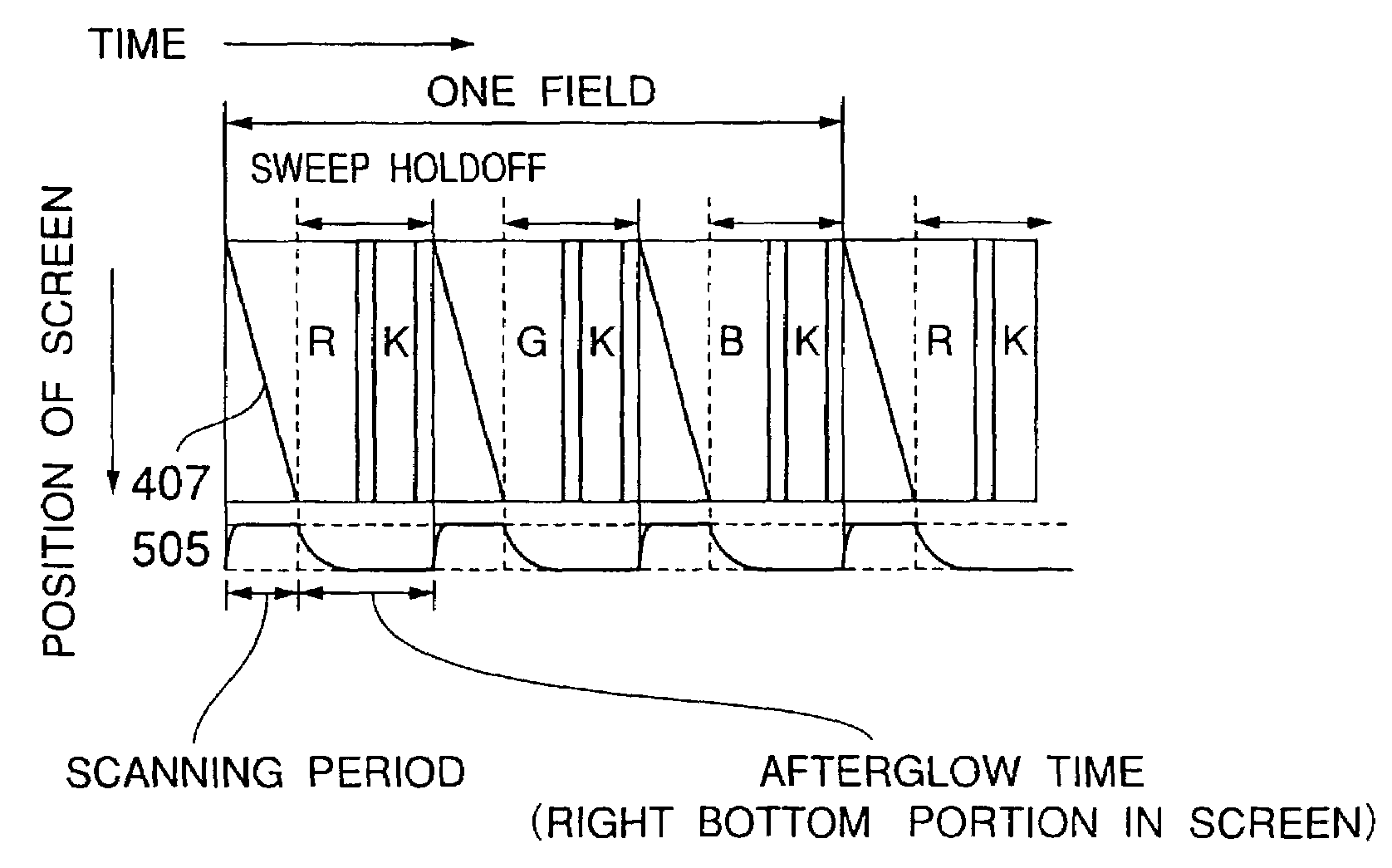
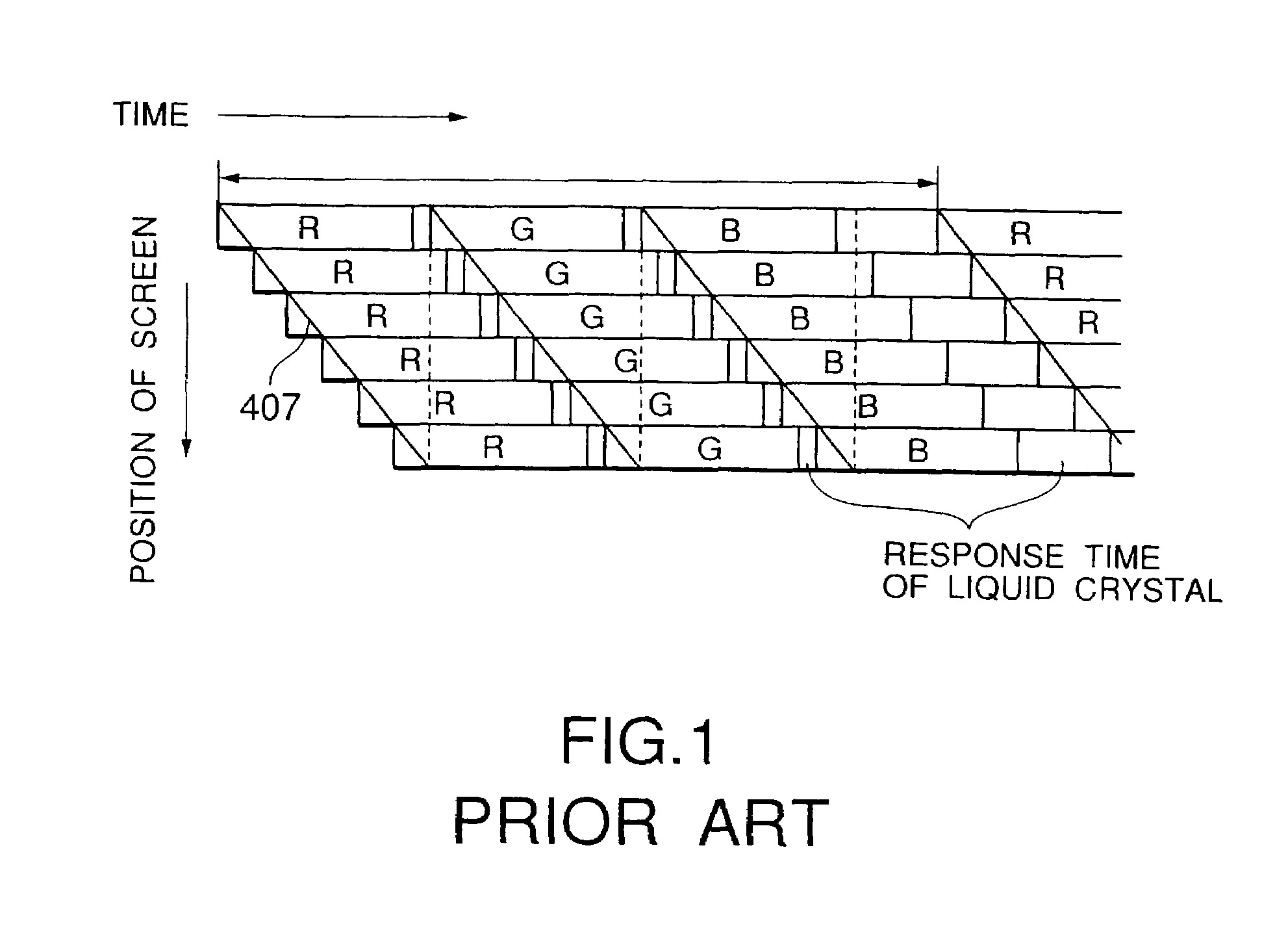
InactiveUS7079098B2Improve processing speedAdequate response timePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
An image display system produces a color image by arranging a color shutter capable of time-divisionally switching a plurality of colors to be displayed, in front of a monochrome image display. This image display system comprises: a self-luminous image display part for time-divisionally displaying monochrome images corresponding to three primary colors; and a color display part for time-divisionally coloring and outputting the monochrome images which formed on the side of the light outgoing surface of the self-luminous image display part and which correspond to the three primary colors. The color display part further comprises: a liquid crystal cell driven by carrying out an optical switching on the basis of the inversion between positive and negative polarities; a transparent electrode formed by dividing the liquid crystal cell into a plurality of parts; and a liquid crystal color shutter capable of optionally setting display colors for a plurality of display regions by means of the transparent electrode, the liquid crystal color shutter displaying different display colors for at least two display regions in an optional time in a driving condition.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
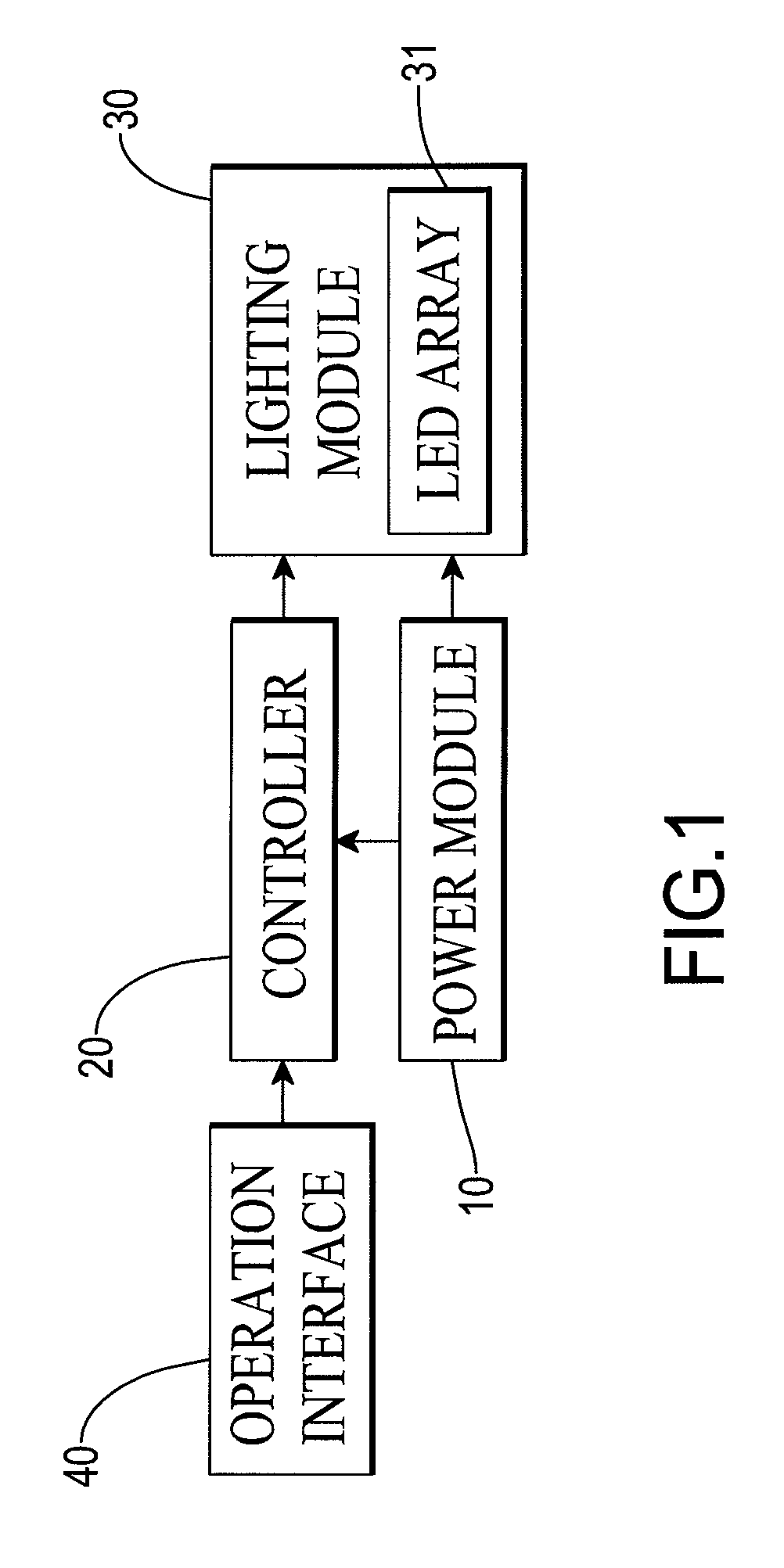
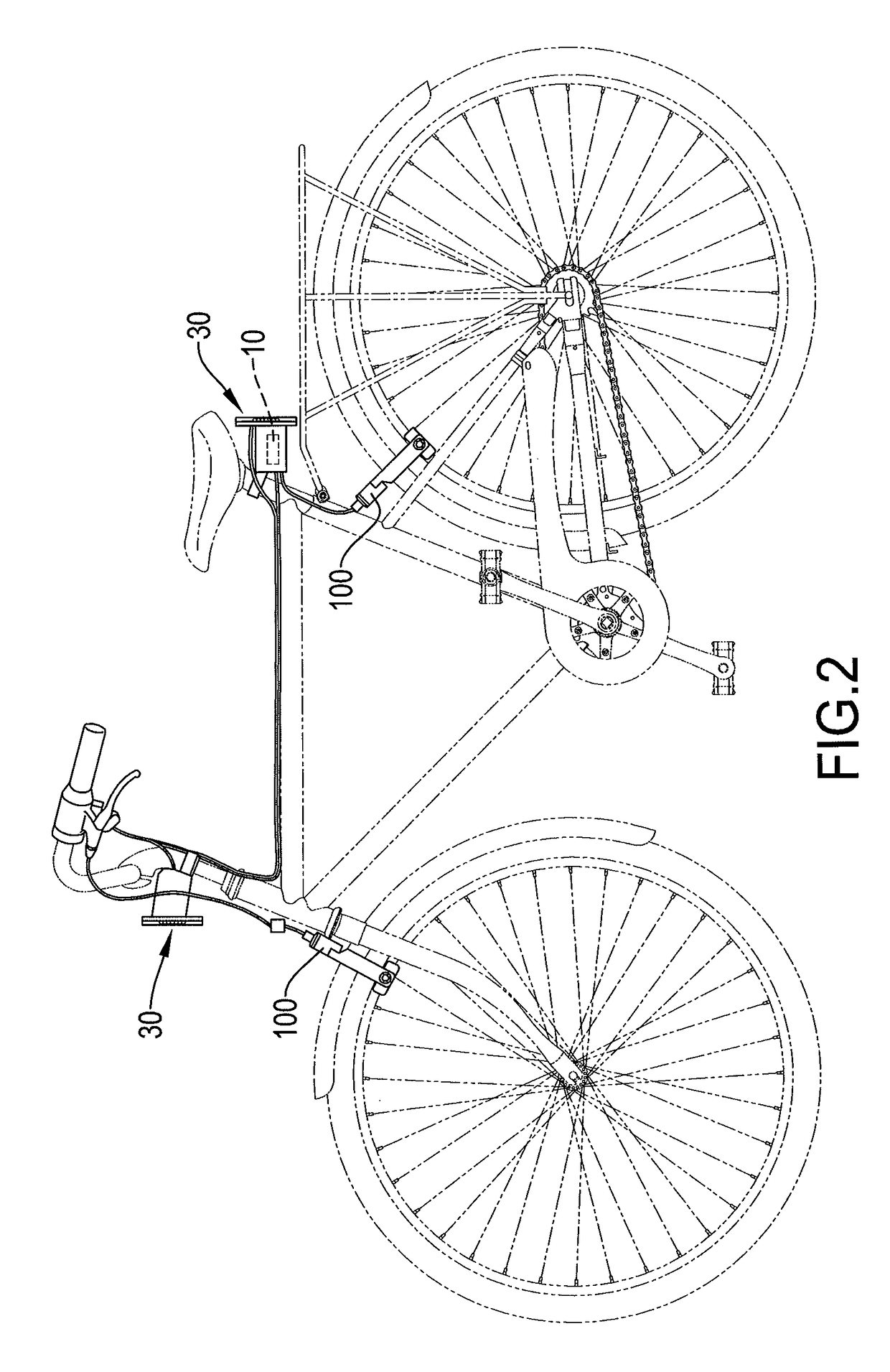
LED signaling device for a bicycle
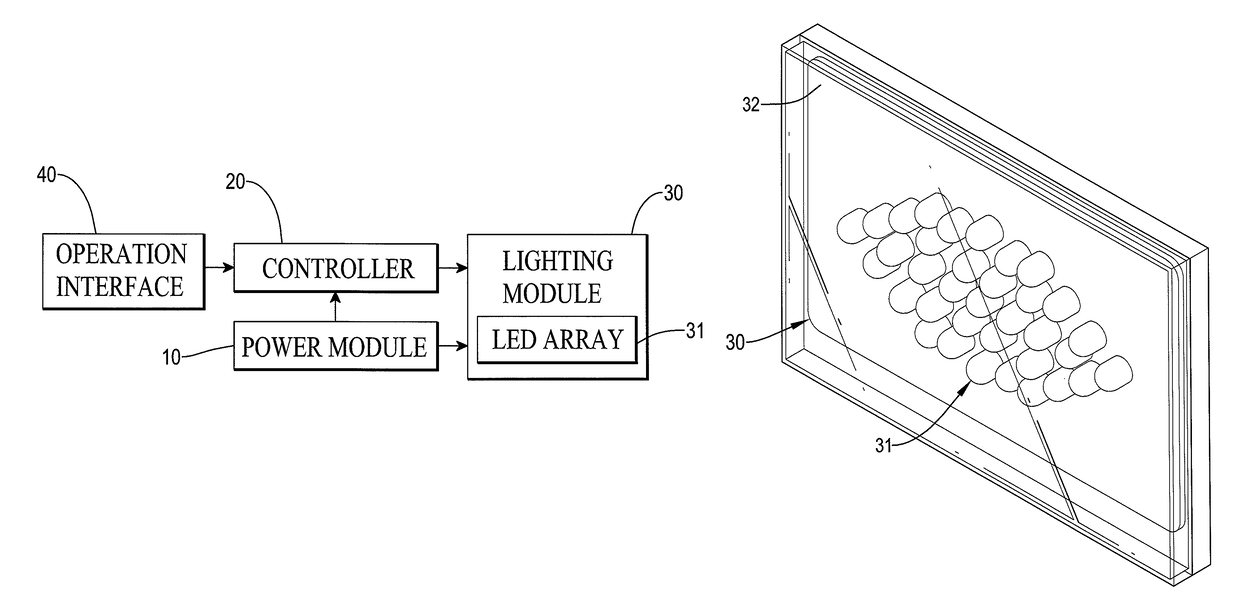
ActiveUS9637191B2Reduce chanceAdequate response timeAnti-theft cycle devicesOptical signalLed arrayEffect light
A bicycle LED signaling device for a bicycle includes a lighting module with at least one array of light emitting diodes (LEDs), a power source, an operation interface, and a controller connected to the power source and the operation interface to receive an operation command to control the LED array to display a corresponding signal.
Owner:TENNUS IND
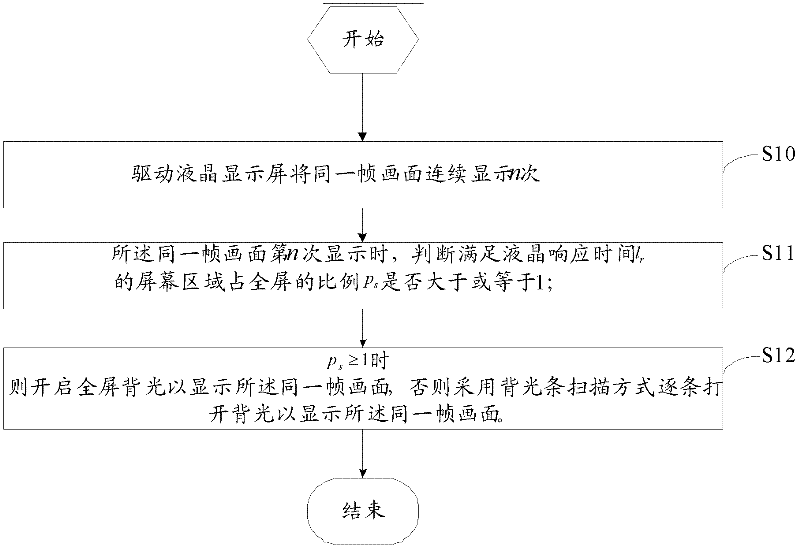
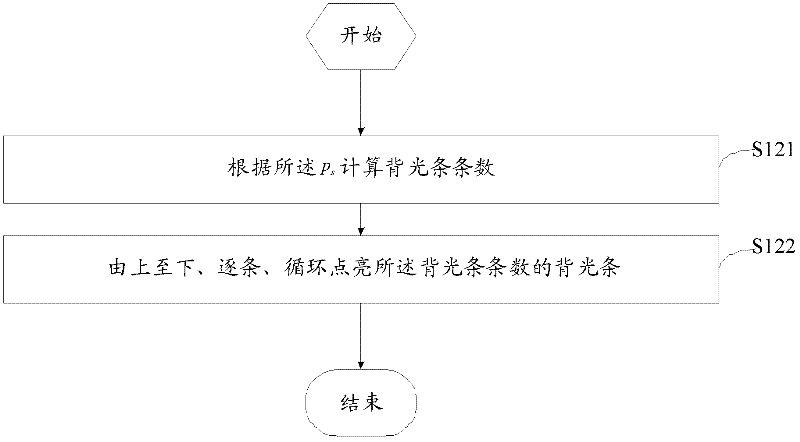
Method and device for reducing 3D TV ghost interference
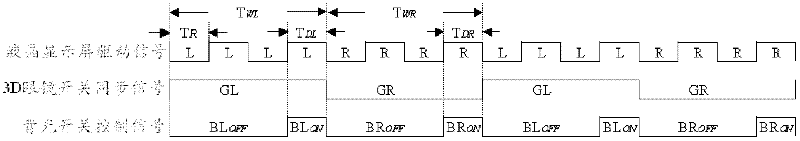
ActiveCN102270441AReduce ghost crosstalkAdequate response timeTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayGlasses type
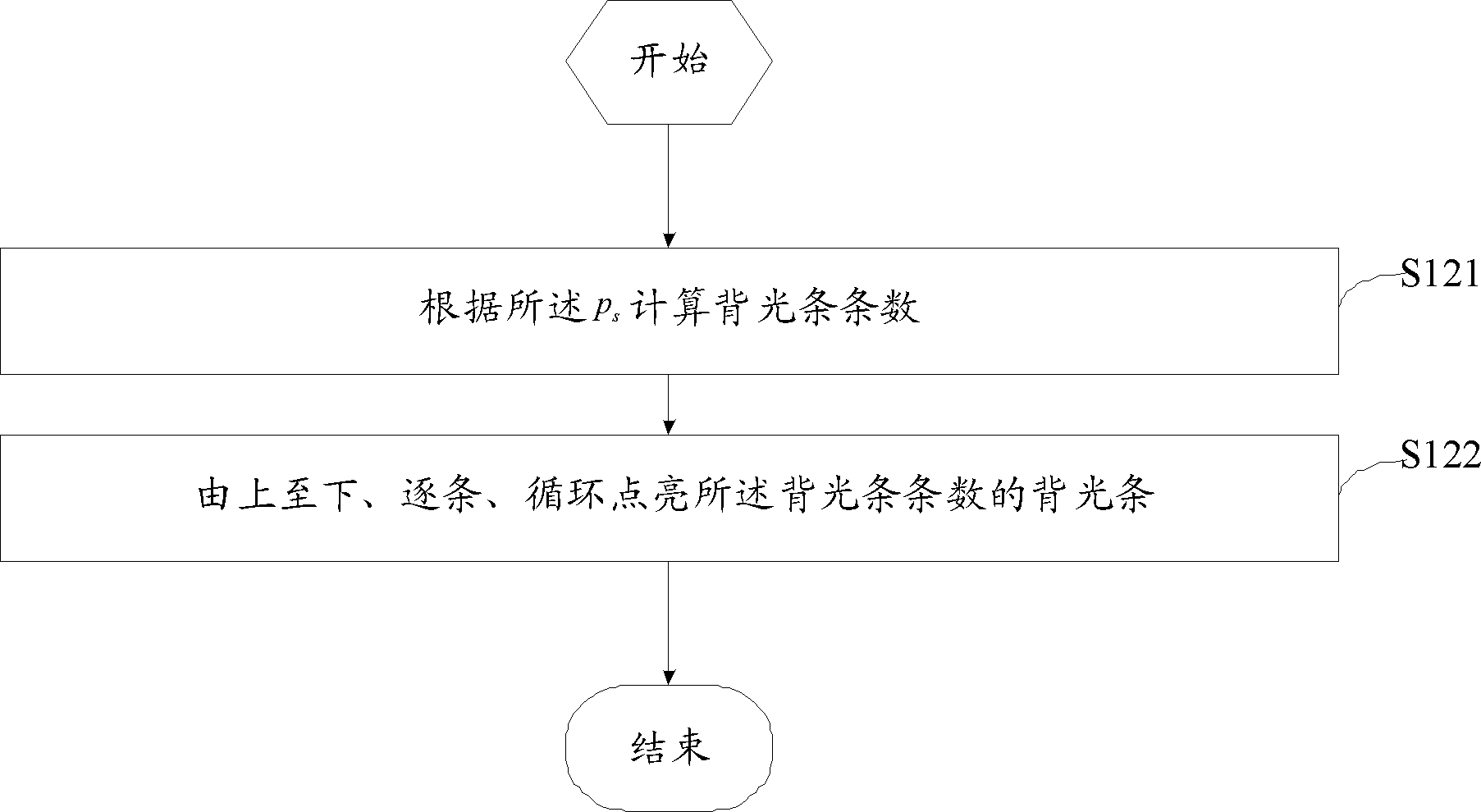
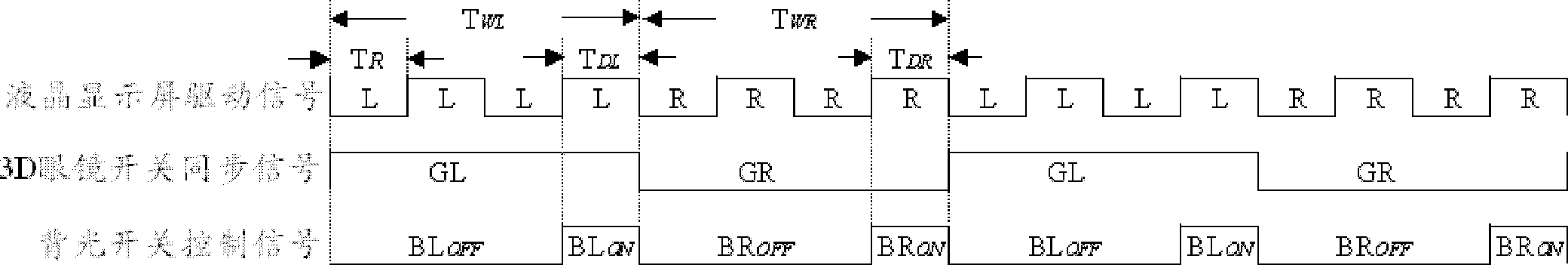
The invention discloses a method for reducing ghost images and crosstalk of a 3D television. The method comprises the steps of: driving a liquid-crystal screen to continuously display a same frame picture for n times; judging whether the proportion ps of a screen area, which meets liquid-crystal display response time 1r, occupying a full screen is larger than or equal to 1 or not when the same frame picture is displayed for n times; and turning on a full-screen backlight to display the same frame picture when ps is larger than or equal to 1, or else, turning on the backlight in a strip-by-strip way by adopting a backlight strip scanning approach so as to display the same frame picture. The invention further provides a corresponding device. According to the method and the device for reducing the ghost images and the crosstalk of the 3D television, provided by the invention, the ghost images and the crosstalk of a shutter glass type 3D television can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
Controlling a parking lot sensor
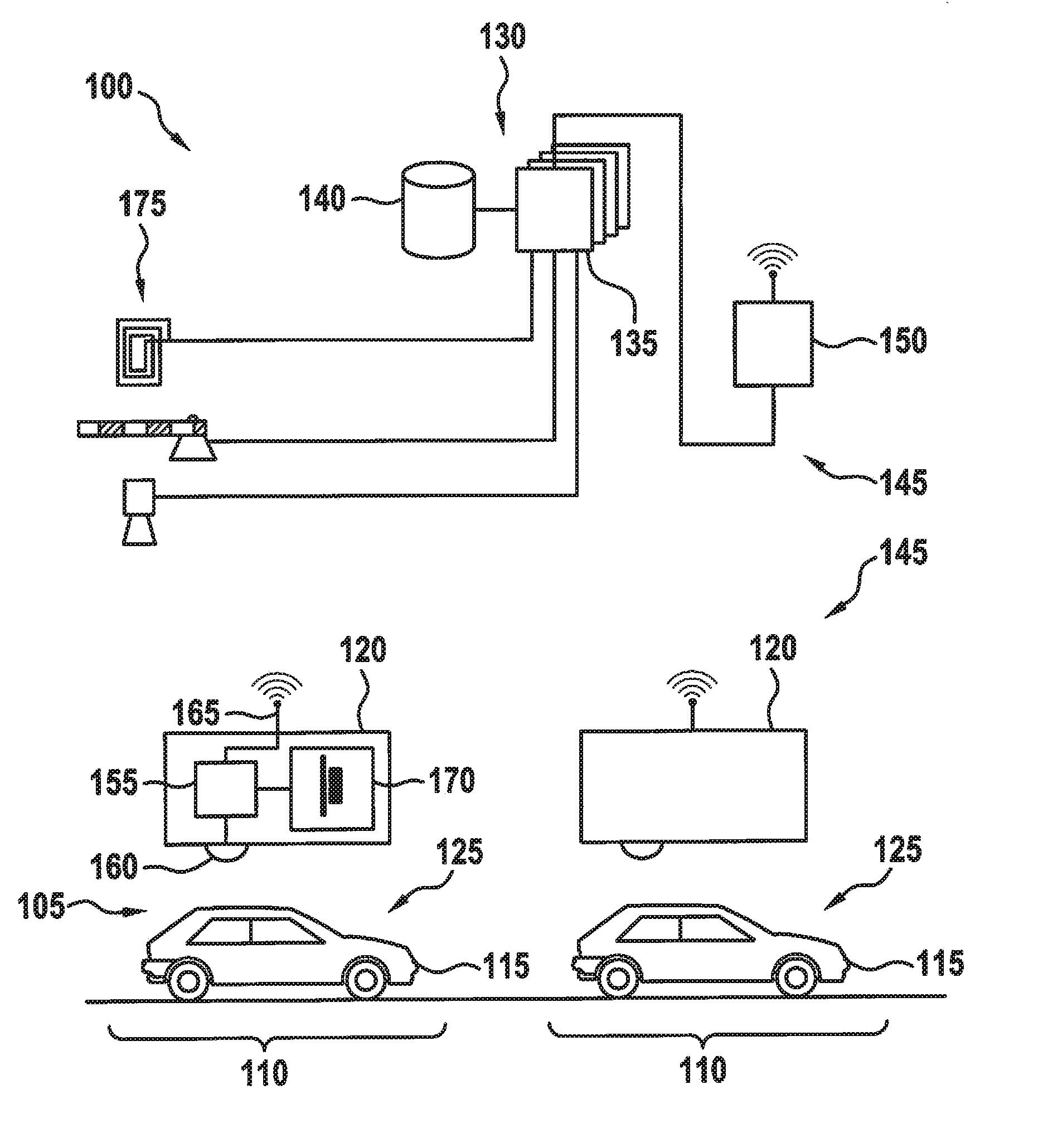
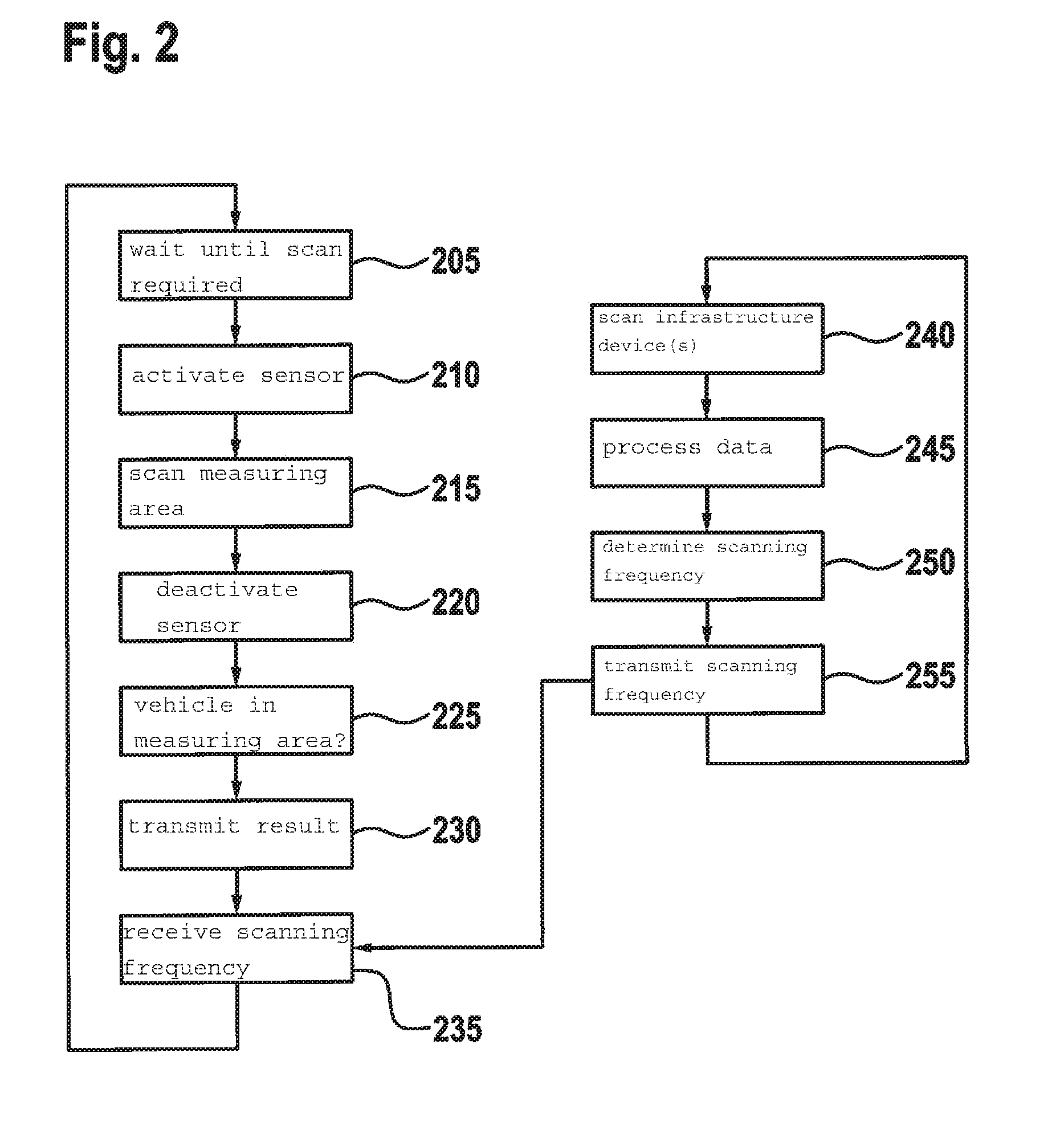
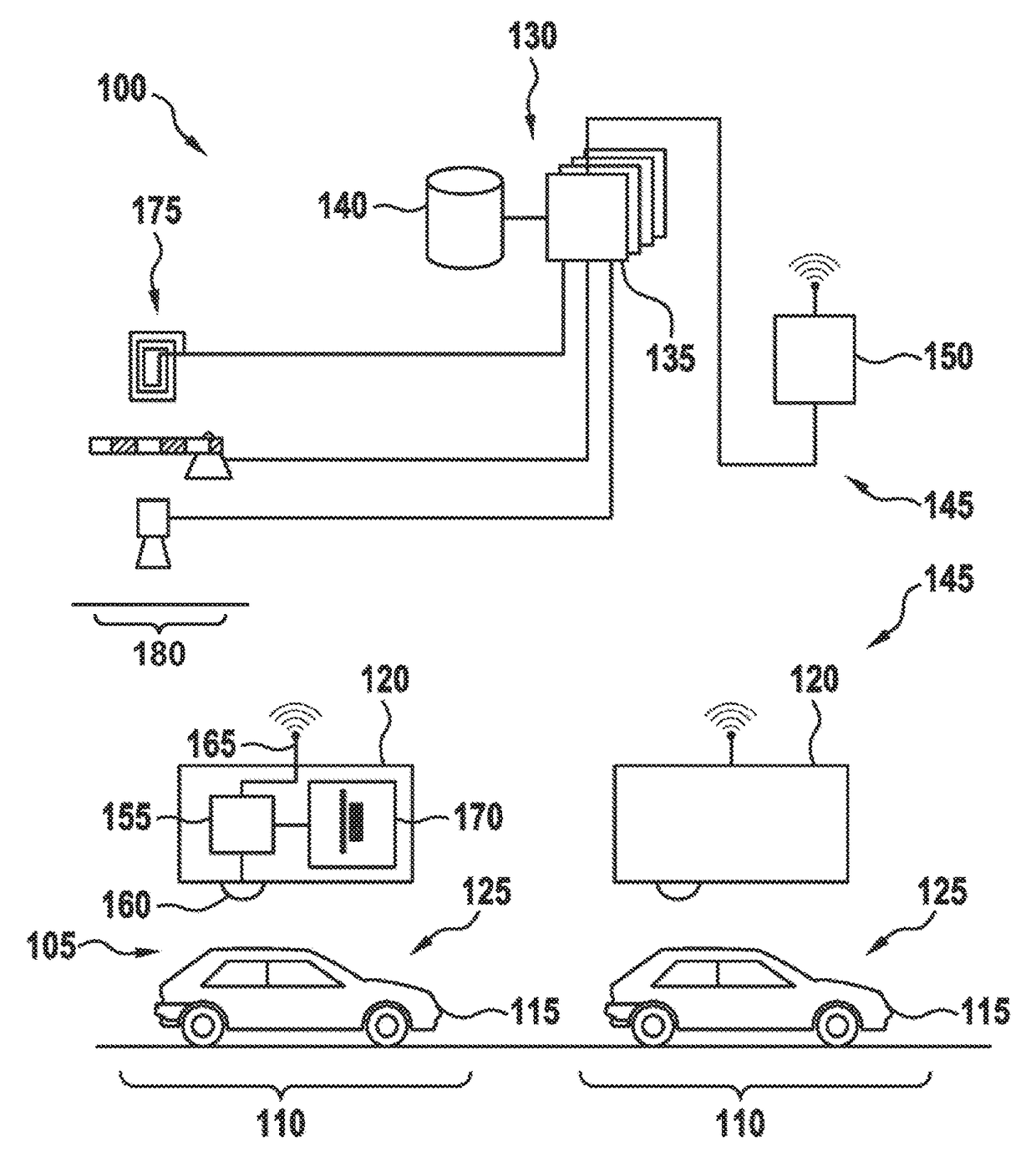
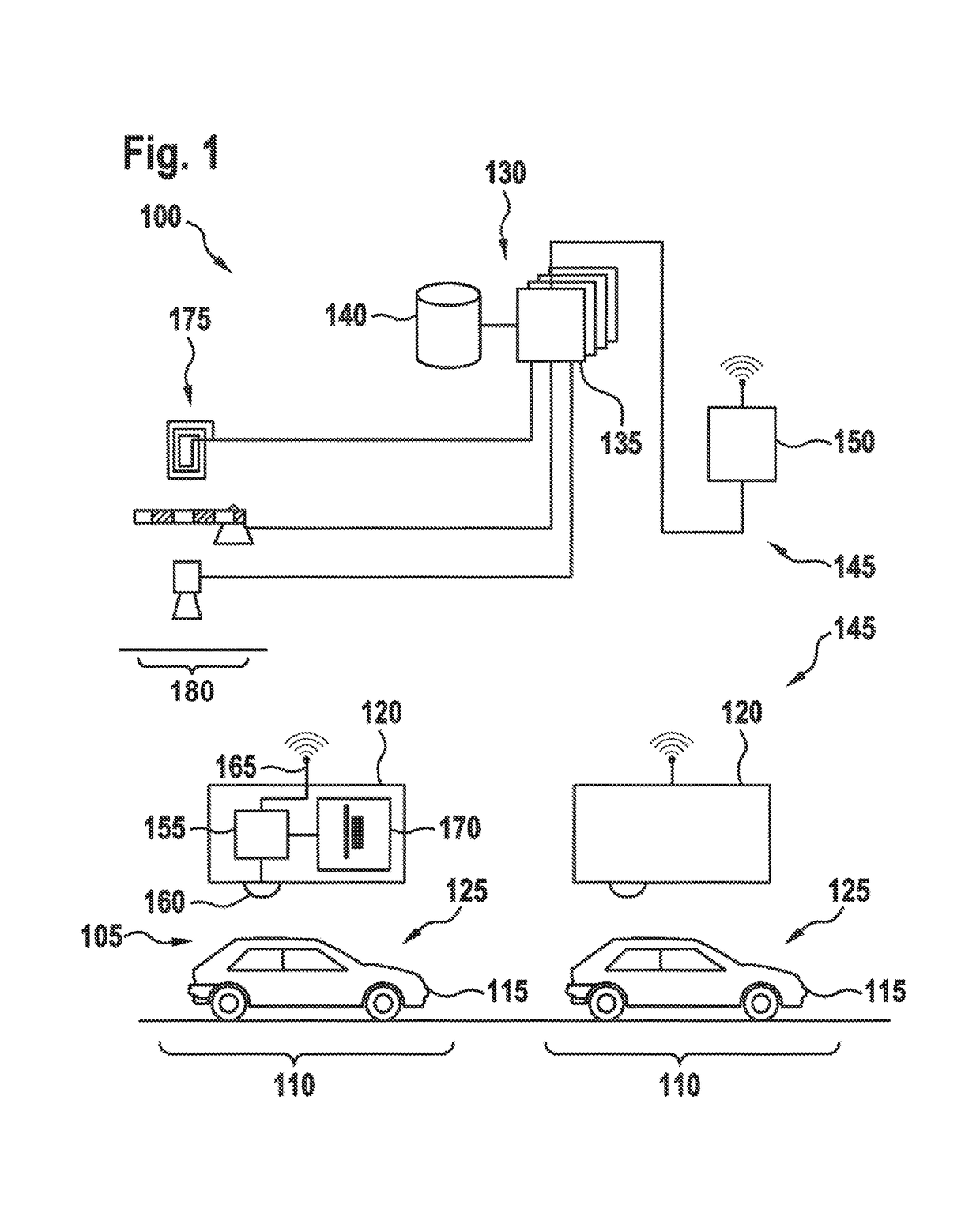
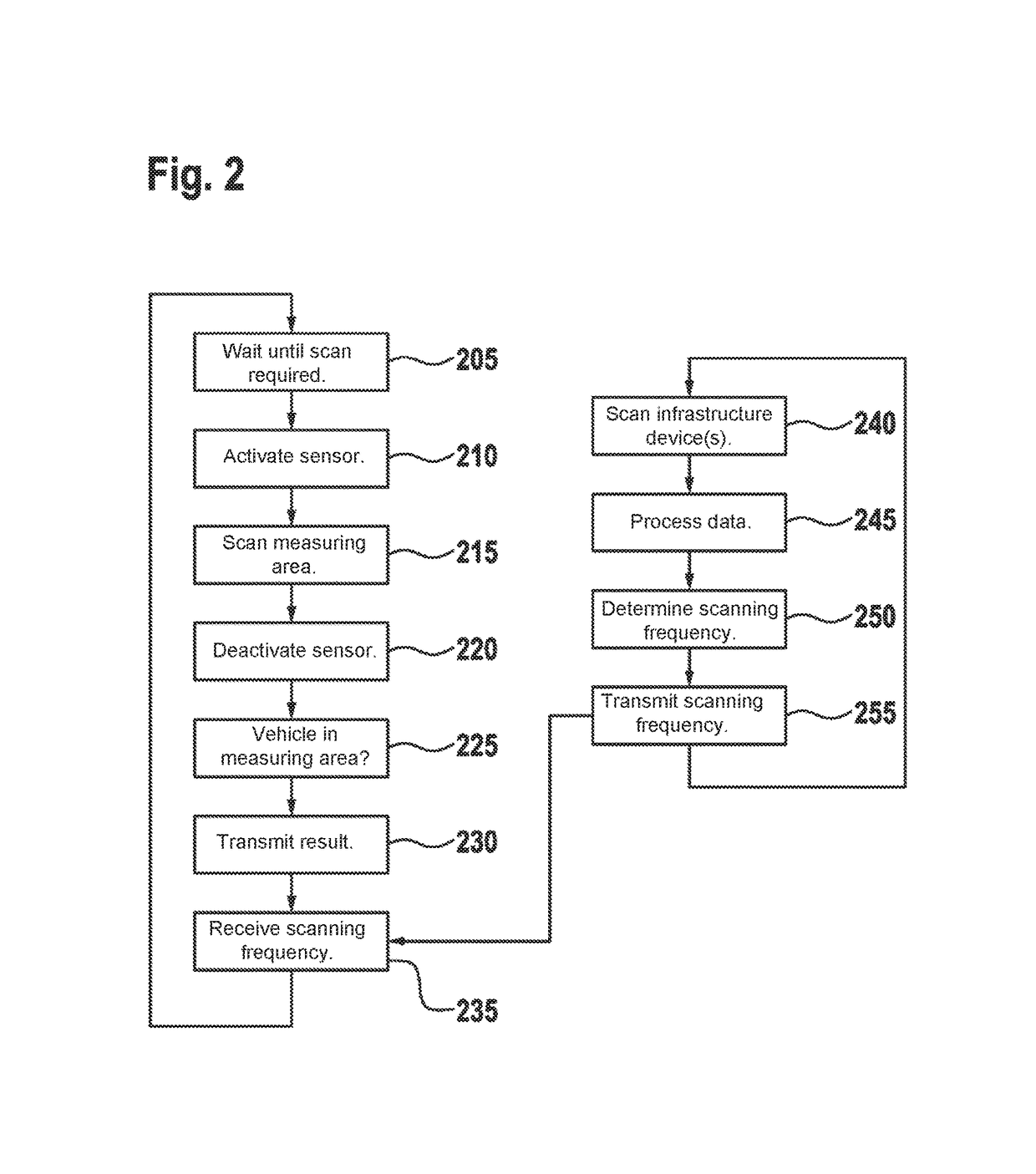
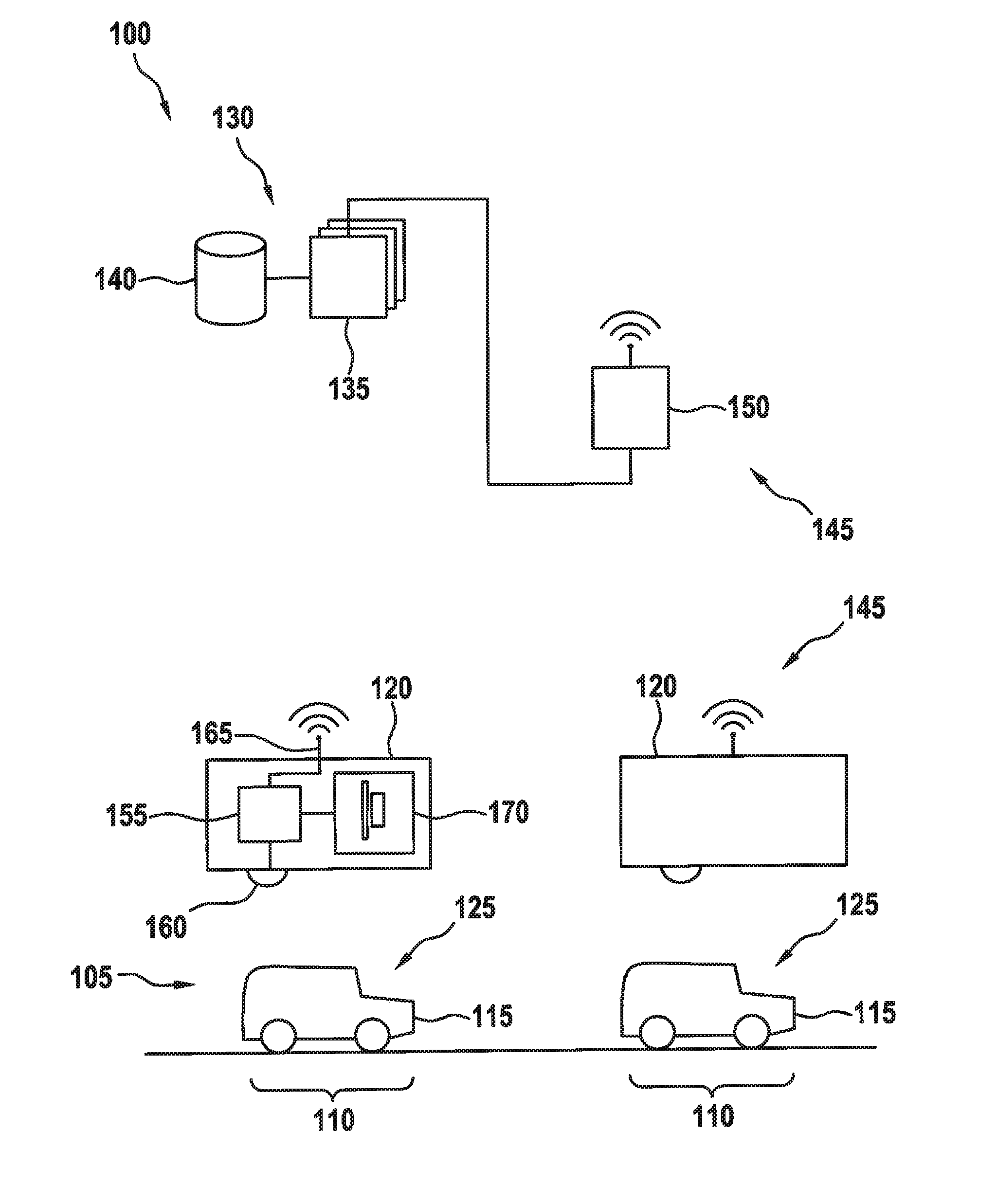
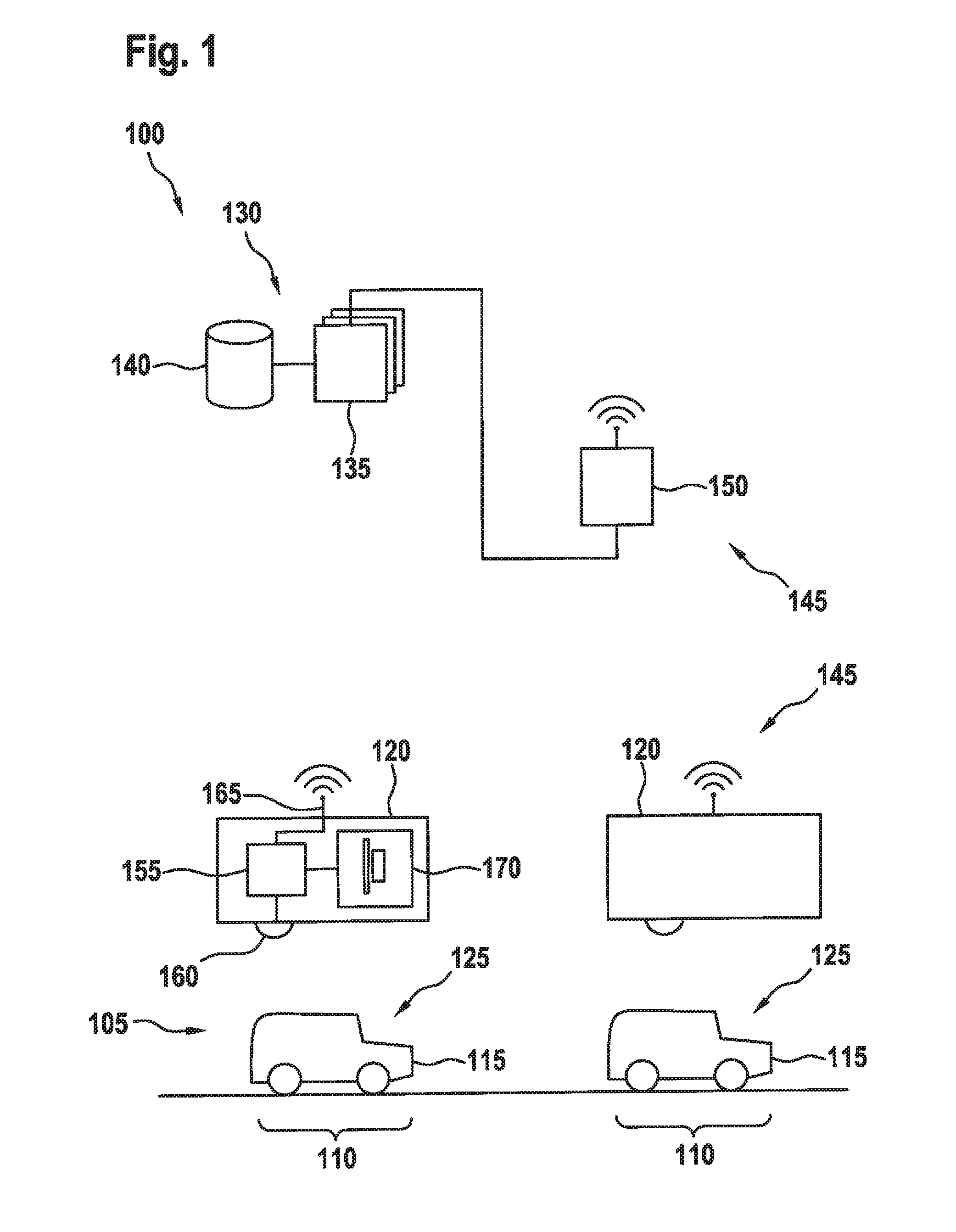
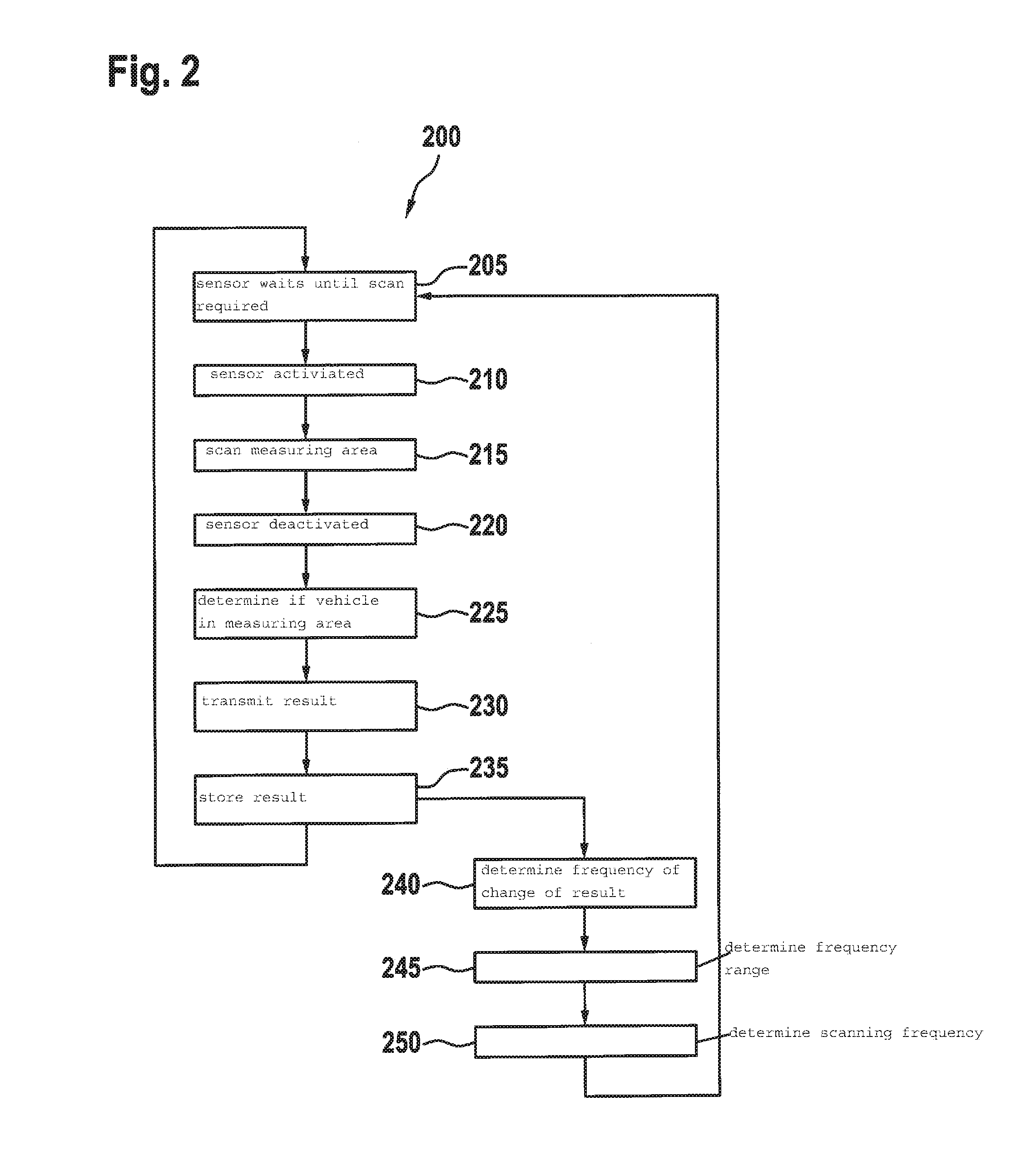
ActiveUS20160371974A1Reduce servicingReduce maintenance costsDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesParking areaParking space
A parking lot sensor includes a sensor for scanning a parking space for a vehicle. A method for controlling the parking lot sensor includes steps of determining an activity of vehicles in the parking lot, of determining a scanning frequency on the basis of the activity and of controlling, as a function of the scanning frequency, the sensor respectively for carrying out a scan.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Refrigerant cooling system with high temperature stability
ActiveCN108458509AStable temperatureAddressing Insufficient Temperature StabilityMechanical apparatusHeat storage plantsWorking temperatureMetallic materials
The invention relates to the technical field of heat exchange, and relates to a refrigerant cooling system with high temperature stability. The system comprises a variable-frequency compressor, a condenser, a radiator and a phase-change energy storage unit, wherein the radiator is in contact with heat generating components, and the phase-change energy storage unit is arranged on the radiator; thephase change energy storage unit comprises a high-temperature phase-change material, a medium-temperature phase-change material and a low-temperature phase-change material which are not less than three phase change points in different temperature areas; the high-temperature, the medium-temperature and low-temperature phase-change materials are made of non-metal materials and are correspondingly and independently arranged on the radiator; the phase-change temperature of the medium-temperature phase-change material is the working temperature of the radiator; and a refrigerant pipeline and a coldmedium flowing through the refrigerant pipeline are arranged in the radiator. According to the refrigerant cooling system with high temperature stability, the refrigerant cooling technology and the phase change energy storage technology are organically combined, phase change materials with three or more than three phase change points in different temperature zones are used, multiple temperature buffering and temperature control signals are provided, the temperature runaway risk is reduced, and the problem that a traditional refrigerant cooling system is insufficient in temperature stability when the loss is changed is solved.
Owner:CSR ZHUZHOU ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE RES INST
Controller for protectively reducing an output of a converting circuit
InactiveUS9007041B2Effective protectionProtection from damageDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringFeedback circuits
A controller for protectively reducing an output of a converting circuit includes a feedback circuit, a logic control circuit, an over-state judgment circuit, and a protection control circuit, is disclosed. The feedback circuit generates a modulation signal according to an output of a converting circuit. The logic control circuit is coupled to the feedback circuit and controls the converting circuit according to the modulation signal for stabilizing the output of the converting circuit. The over-state judgment circuit receives an over-state reference signal and a detecting signal, and generates a protection signal in response to levels of the detecting signal and the over-state reference signal. The protection control circuit is coupled to the logic control circuit and the over-state judgment circuit and controls the logic control circuit to lower the output of the converting circuit when receiving the protection signal.
Owner:GREEN SOLUTION TECH CO LTD
Inertia load mechanism of a reciprocating exercise equipment
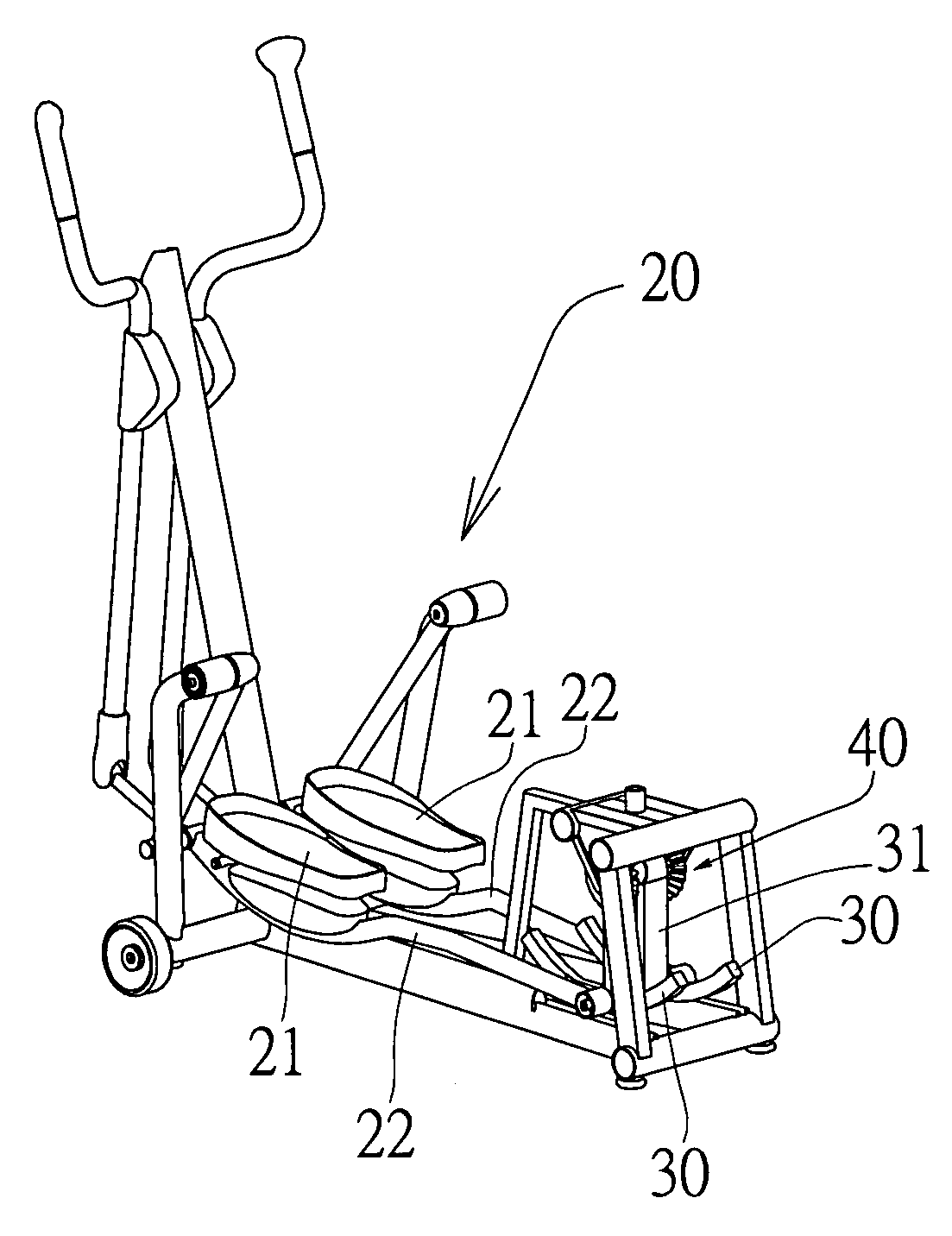
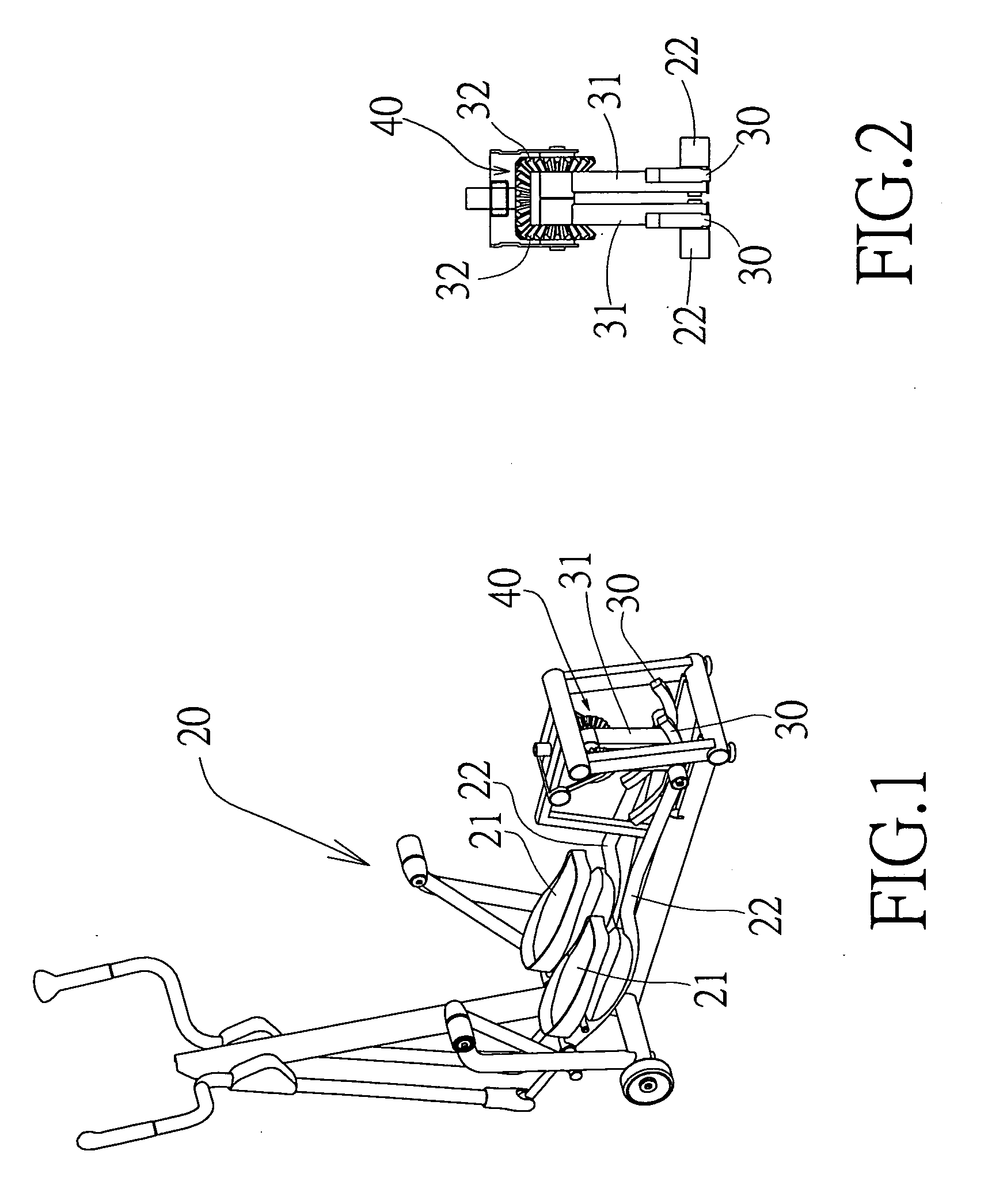
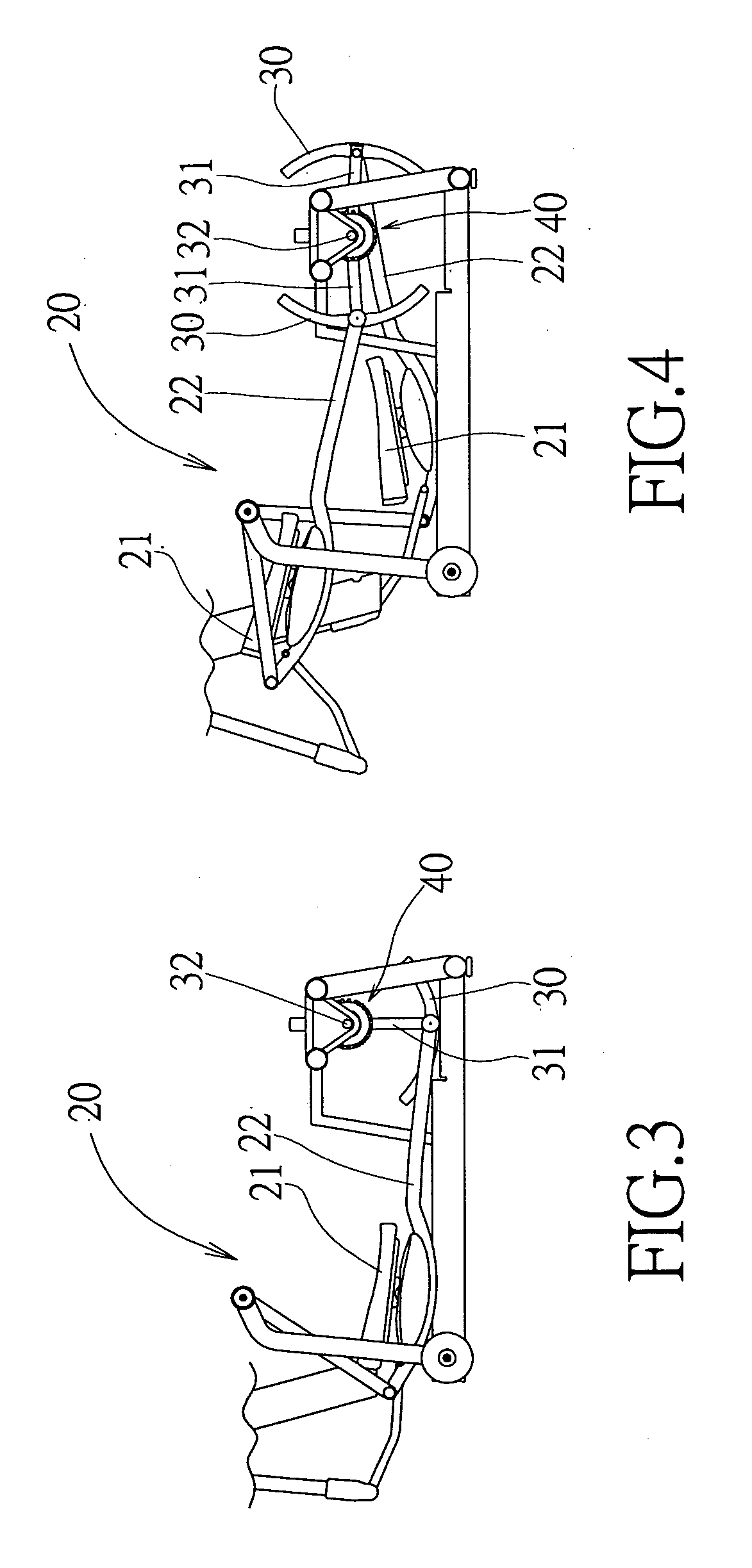
InactiveUS20100022356A1Eliminate damageAdequate response timeMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesReciprocating motionGravitational force
In an inertia load mechanism of a reciprocating exercise equipment, a pendulum load mechanism is installed to an exercise link rod of a reciprocating exercise equipment, such that the pendulum load mechanism forms an inertia link and gives an exercise resistance. If the moving link rod of the reciprocating exercise equipment is at a moment of changing its exercise direction, the speed of changing direction of the pendulum load mechanism will be slowed down by the gravitational force, so that an exerciser's muscle has sufficient response time for the change of the exercise direction to eliminate a possible sport injury.
Owner:WANG LEAO
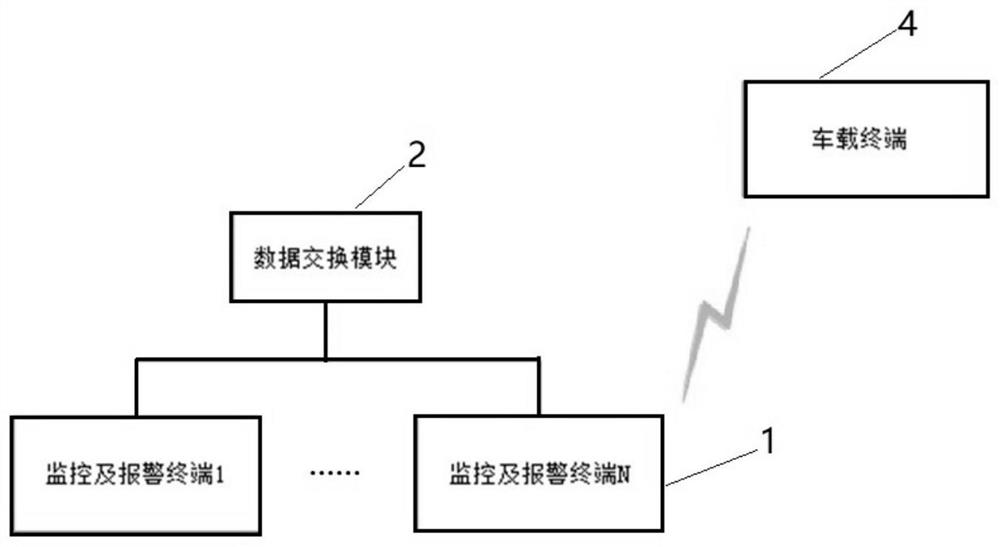
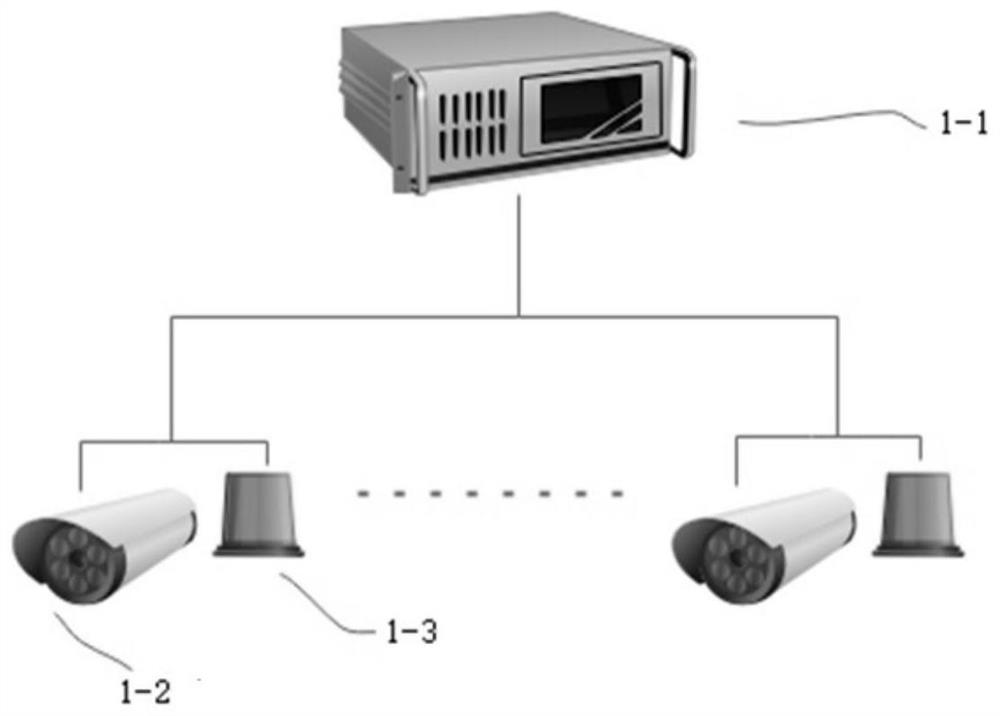
Rail transit monitoring system and method
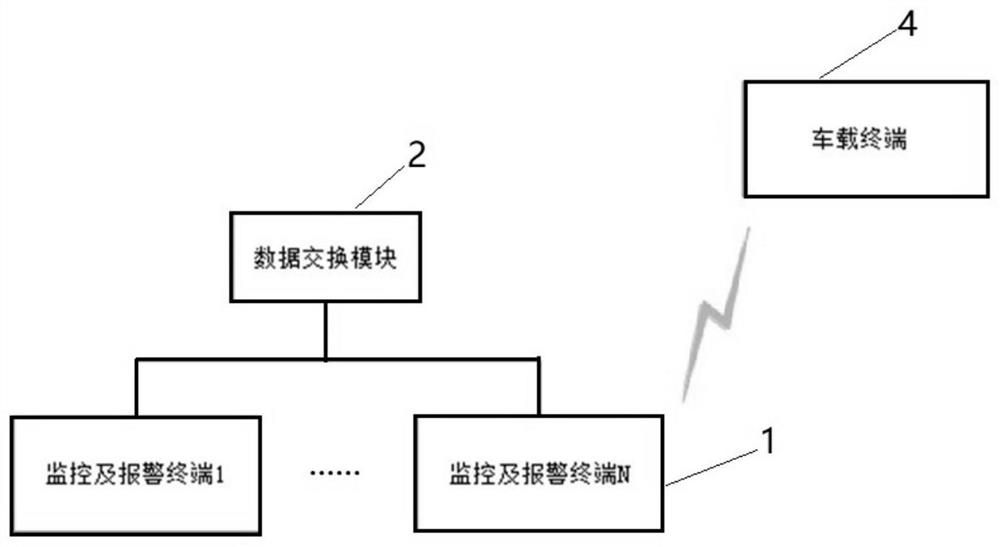
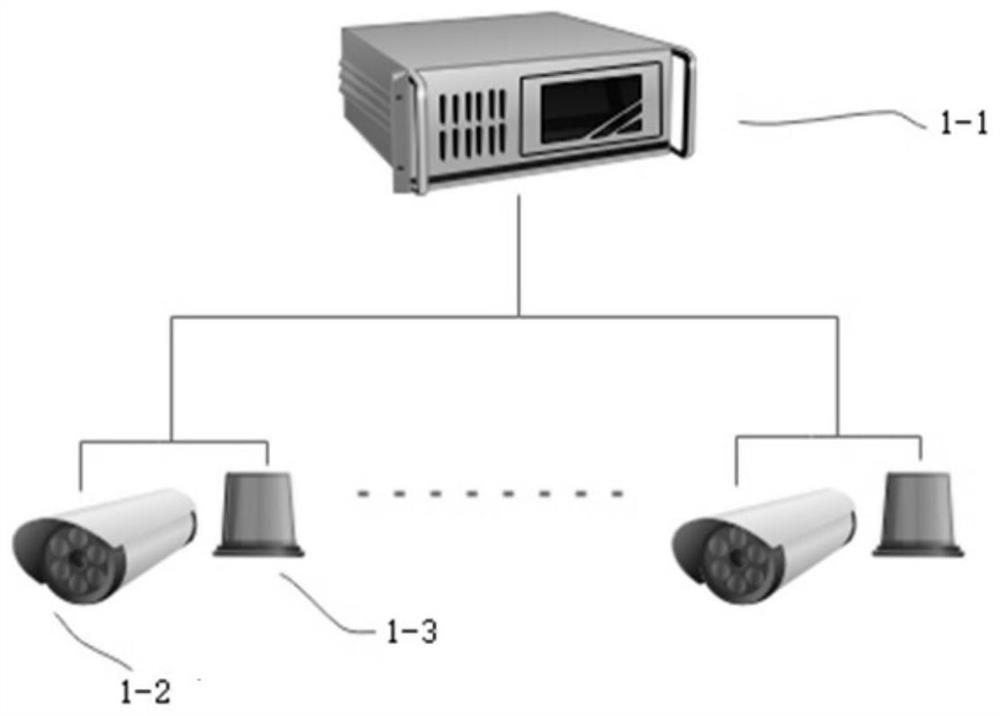
ActiveCN111717243AGuarantee operational safetyExtended viewing distanceRailway signalling and safetyIn vehicleDriving safety
The invention provides a rail transit monitoring system and method. The system comprises a plurality of monitoring alarm terminals, a data exchange module and a vehicle-mounted terminal which are arranged along a track; each monitoring alarm terminal comprises a plurality of image acquisition modules, a plurality of light alarm modules and a first processing module; all the first processing modules are connected and communicated through the data exchange module; each first processing module is used for identifying whether foreign matter invasion exists in the image output by an image acquisition module or not, and transmitting an alarm signal to the first processing module of the monitoring alarm terminal in front of or behind the monitoring alarm terminal when the foreign matter invasionexists, so that the light alarm module in a first distance range in front of or behind the monitoring alarm terminal sends a light alarm signal; the vehicle-mounted terminal comprises an optical receiver located at the head of the train and a second processing module. The system sends out a light alarm signal through each light alarm module, does not depend on a signal system to transmit the alarmsignal, and can still effectively transmit the alarm signal and improve the driving safety when a signal communication system breaks down or in a tunnel or other scenes with poor communication quality.
Owner:成都希格玛光电科技有限公司
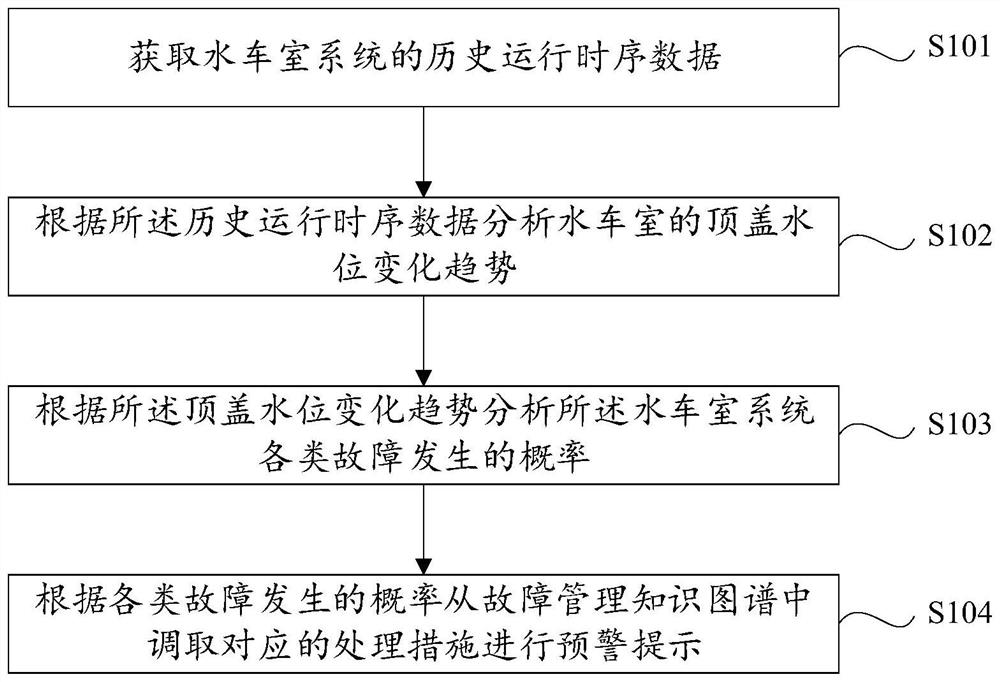
Water flooded waterwheel chamber early warning method and system based on knowledge graph
The invention provides a water flooded waterwheel chamber early warning method and system based on a knowledge graph. The method comprises the steps of acquiring historical operation time sequence data of a waterwheel chamber system; analyzing the top cover water level change trend of the waterwheel chamber according to the historical operation time sequence data; analyzing the occurrence probability of various faults of the waterwheel chamber system according to the top cover water level change trend; and calling corresponding processing measures from a fault management knowledge graph according to the occurrence probability of various faults to carry out early warning prompt. Through the mode, the fault type and reason can be autonomously judged while early warning is carried out in advance, and enough response time is provided for timely fault processing.
Owner:GUODIAN DADUHE ZHENTOUBA HYDROPOWER CONSTR CO LTD
An obstacle avoidance method for unmanned aerial vehicle inspection and safe return
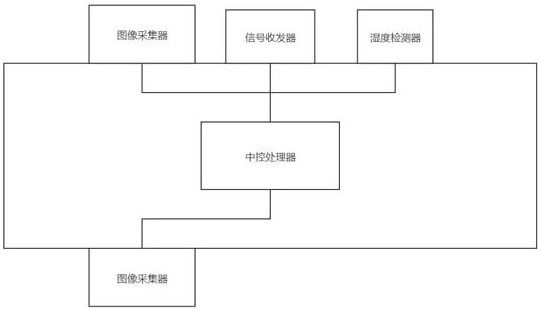
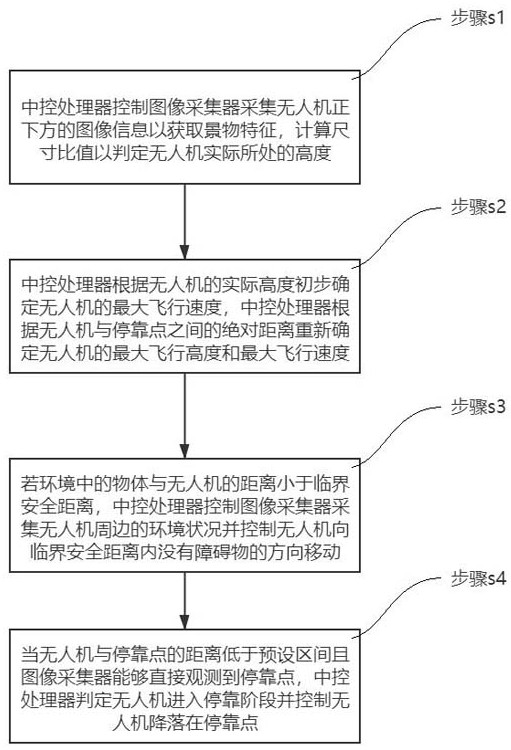
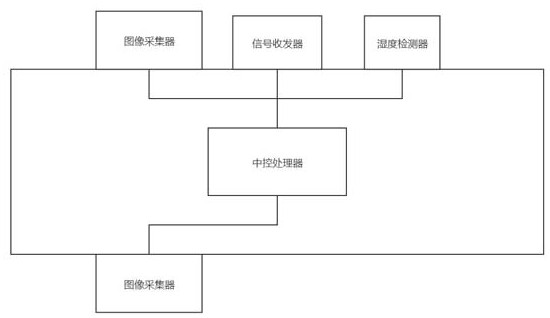
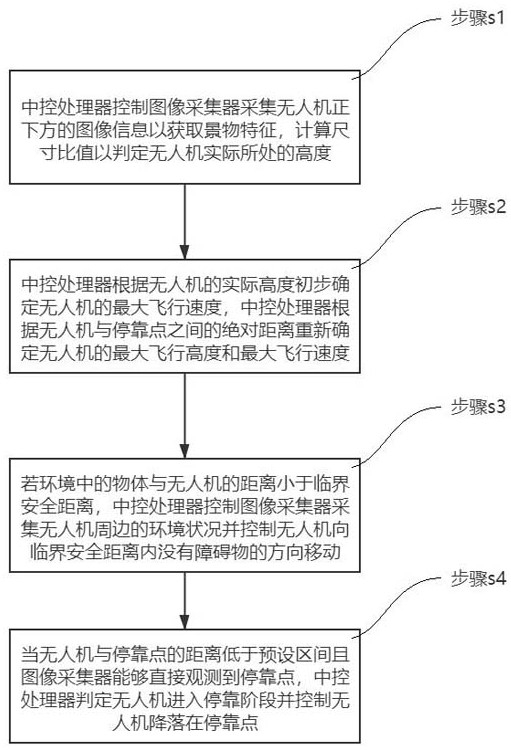
ActiveCN113253762BAvoid damageImprove inspection efficiencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsSimulationUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to an obstacle avoidance method for safe return of unmanned aerial vehicles, including: collecting image information to determine the actual height of the unmanned aerial vehicle; readjusting the maximum flight height and the maximum Flight speed; if the distance between the object in the environment and the drone is less than the critical safety distance, the central control processor controls the movement of the drone; when the drone enters the docking stage, the central control processor controls the drone to land at the docking point. The present invention can quickly obtain the surrounding environment information of the UAV by collecting the image information of the surrounding environment of the UAV, so that the central control processor can quickly obtain the flight height and flight speed of the UAV according to the actual situation. The obstacles that will appear during the flight of the UAV can be predicted in advance, which can effectively avoid the damage or crash of the UAV caused by the collision between the UAV and the obstacle, and effectively improve the inspection efficiency of the UAV.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KETENG INFORMATION TECH
Controlling a parking lot sensor
ActiveUS9852623B2Reduce power consumptionIncrease relative volatilityDetection of traffic movementIndication of parksing free spacesParking spaceEngineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Controlling a parking lot sensor
ActiveUS20160370495A1Saving maximum amount of energyMaximum response timeIndication of parksing free spacesGeological measurementsEngineeringParking lot
A method for controlling a parking lot sensor, which includes a sensor for scanning a predetermined measuring area, includes steps of determining an expected fluctuation of vehicles in the measuring area, of determining a scanning frequency on the basis of the expected fluctuation and of controlling, as a function of the scanning frequency, the sensor respectively for carrying out a scan.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Obstacle avoidance method for unmanned aerial vehicle routing inspection safe return
ActiveCN113253762AAvoid damageImprove inspection efficiencyPosition/course control in three dimensionsUncrewed vehicleFlight velocity
The invention relates to an obstacle avoidance method for unmanned aerial vehicle routing inspection safe return. The method comprises the steps of collecting image information to judge the actual height of an unmanned aerial vehicle; readjusting the maximum flight height and the maximum flight speed according to the absolute distance between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the stop point; if the distance between the object in the environment and the unmanned aerial vehicle is smaller than the critical safety distance, enabling the central control processor to control the unmanned aerial vehicle to move; and when the unmanned aerial vehicle enters the parking stage, enabling the central control processor to control the unmanned aerial vehicle to land at the parking point. According to the invention, by collecting the image information of the surrounding environment of the unmanned aerial vehicle, the surrounding environment information of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be quickly obtained, so that the central control processor can quickly obtain the flight height and the flight speed of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the actual situation, and meanwhile, obstacles appearing in the flight process of the unmanned aerial vehicle are predicted in advance, the situation that the unmanned aerial vehicle is damaged or crashed due to collision between the unmanned aerial vehicle and the obstacle can be effectively avoided, and the inspection efficiency of the unmanned aerial vehicle is effectively improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KETENG INFORMATION TECH
Temperature sensor as flip chip on a printed circuit board
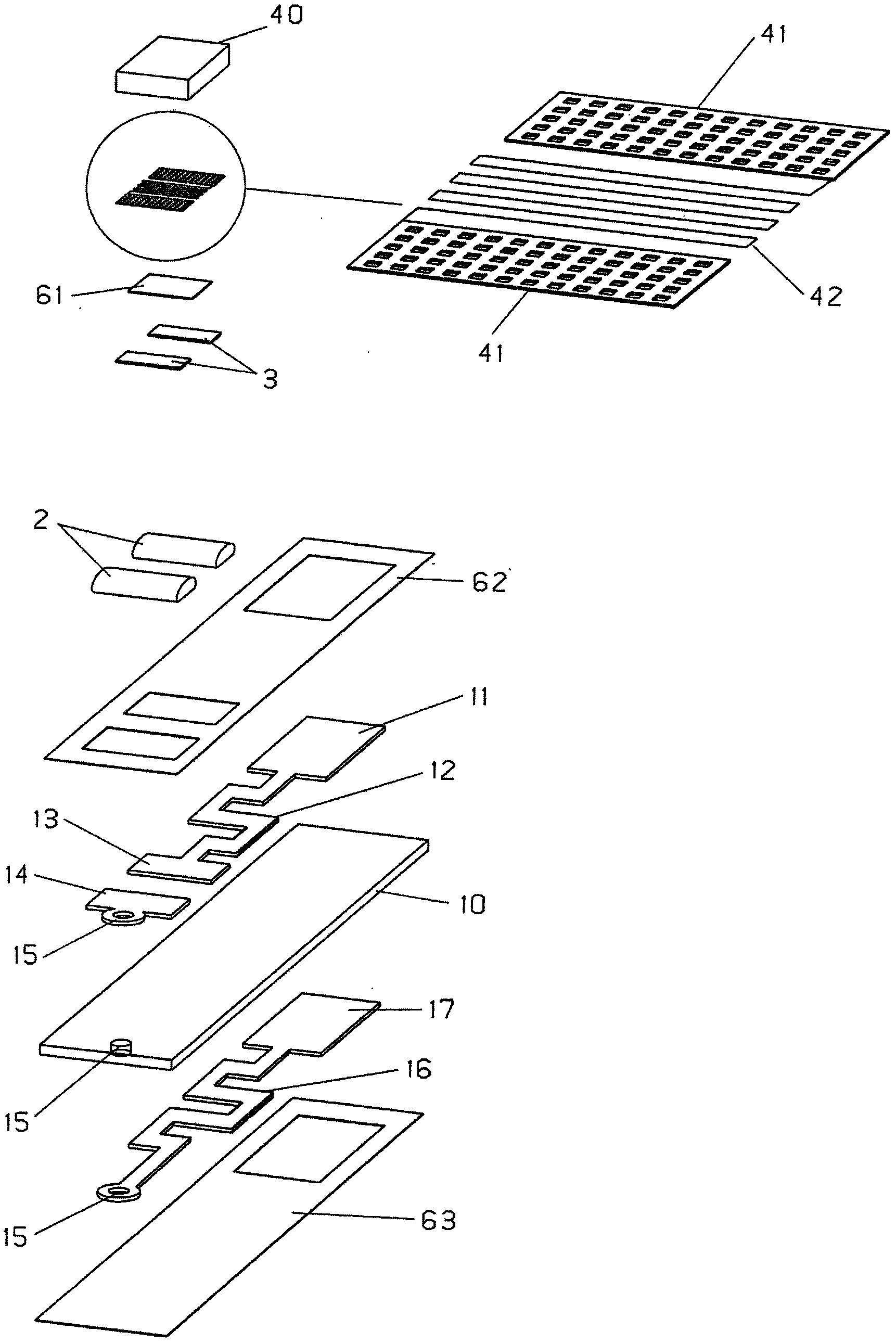
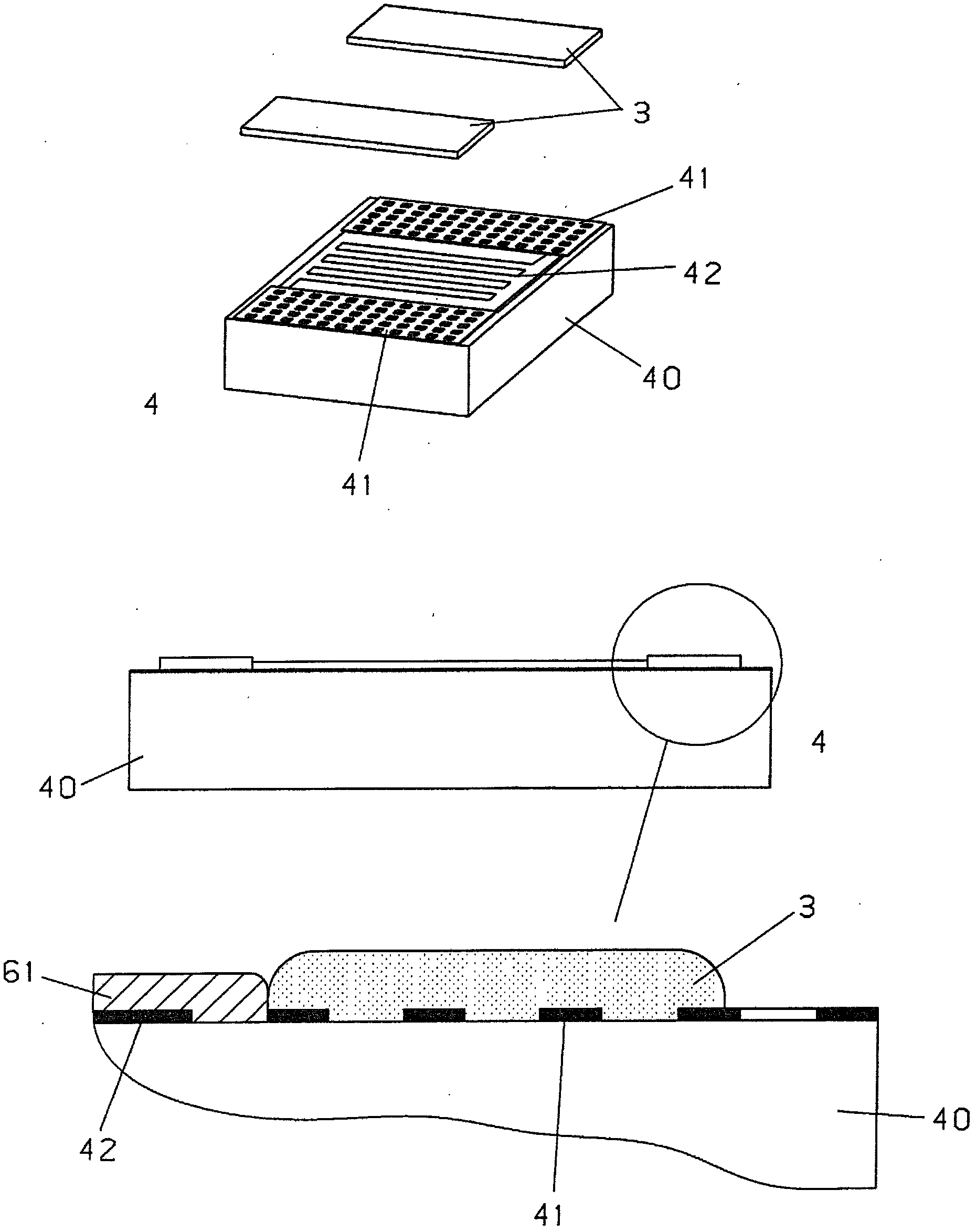
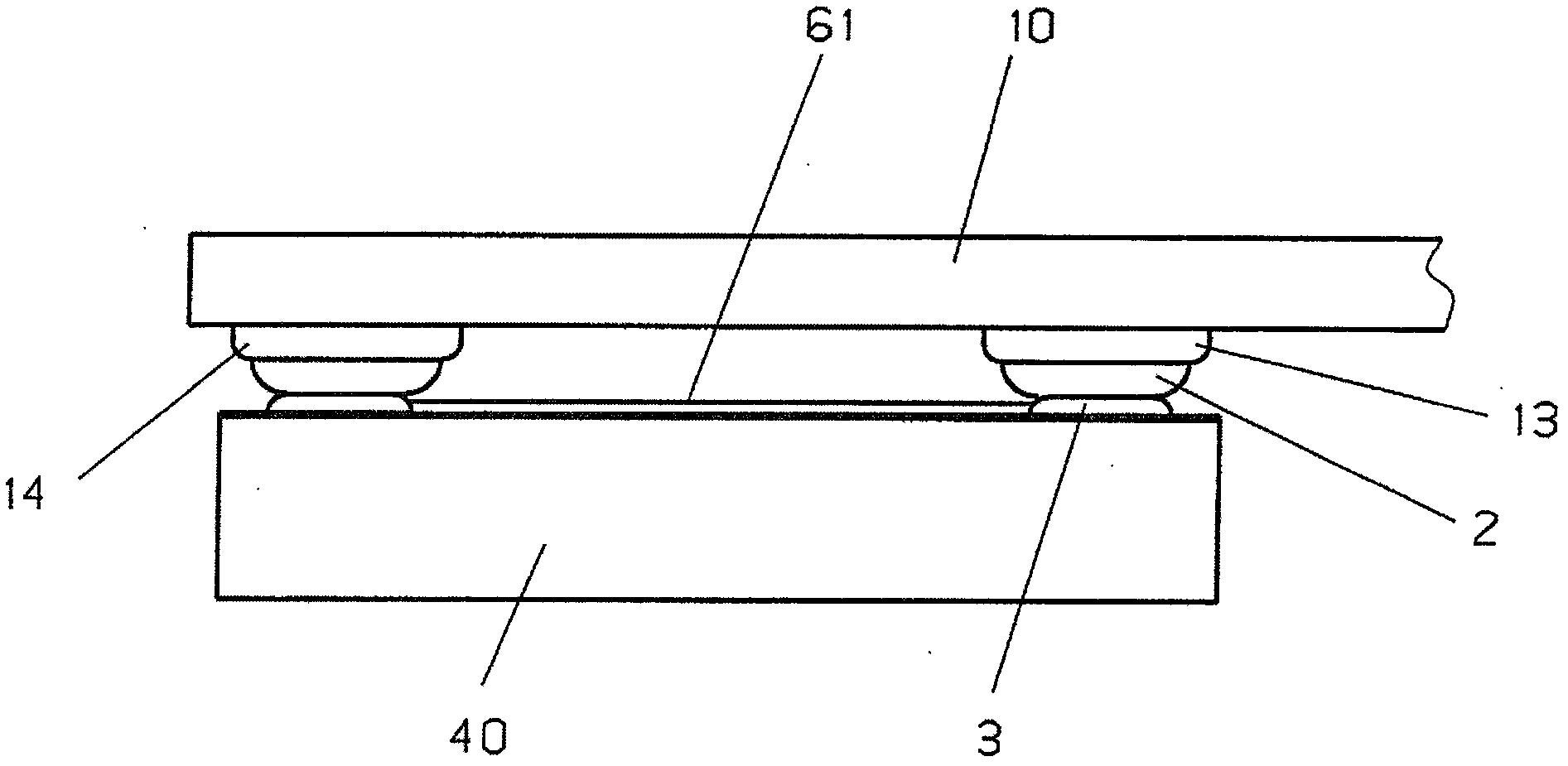
ActiveCN102809441AMechanically stable installationAdequate response timeThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansPlatinumCopper
To produce a temperature sensor, in which a conductor track (42), which has at least 100 Ohm and is made of platinum, is connected via contact fleids (41) to two conductor tracks (12, 16) made of copper, and in which the conductor track (42) made of platinum, which is implemented ifl thin-film technology as a platinum track that is at least 10 mm long, 3 to 50 pm wide and 0.1 to 5 pm thick on a rectangular surface area measuring 1 to 10 mm of a 0.1 to 1 mm thick ceramic plate (40), transitions at its two ends into contact fleids (41) that are 20 to 500 times wider, according to the invention these two widened fields (41) ifl the interior of these fleids (41) are structured, a metal paste is applied to the two internally structured flelds, and the metal paste is burned ifl, whereby the thick film (3) / pad, which is generated from the paste, contains an oxidic component and is fixed to the oxidic surface of the ceramic plate (40) which is freely accessible due to the internal structure of the contact fields (41).
Owner:HERAEUS SENSOR NITE
Sequential mold opening lock catch mechanism and sequential mold opening injection mold
The invention provides a sequential mold opening lock catch mechanism and a sequential mold opening injection mold. The sequential mold opening lock catch mechanism comprises a buckle machine base, abuckle machine block, a buckle machine shifting rod and a buckle machine hook, and the buckle machine block is movably mounted on the buckle machine base so as to have a locking position locked on thebuckle machine hook and a releasing position for releasing the buckle machine hook; the button machine block is defined as a locking direction from a releasing position to a locking position; a shifting rod groove is formed in the buckle machine base, the buckle machine shifting rod is inserted into the shifting rod groove, and an abutting part for fixing the buckle machine block at the locking position is further arranged on the buckle machine shifting rod; and the tail end, away from the locking direction, of the buckle machine shifting rod is bent to form an elbow structure. The buckle machine block is fixed at the locking position through the abutting part of the buckle machine shifting rod, the buckle machine block is released through the elbow structure at the end part in the mold opening process, the unlocking is realized, the locking state of a buckle mechanism has no play gap, and the problems of poor stability and prone to running failure of an existing buckle mechanism aresolved.
Owner:XIAMEN WAIN ELECTRICAL
Anti-shaking buffer device
PendingCN107882916AIncrease resistanceImprove the effect of intelligent anti-shakeTelevision system detailsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringControl theory
The invention belongs to the field of anti-shaking devices and discloses an anti-shaking buffer device. The anti-shaking buffer device comprises a connector, a mounting joint and a joint for connecting the mounting joint with the connector; the connector is hinged to the upper end of the joint through a first pivot; the mounting joint is hinged to the lower end of the joint through a second pivot;and the first pivot and the second pivot are arranged horizontally and are distributed in a crossed manner in respective axial directions in space. Thus, under the bumpy condition, when the upper endof the joint is inclined upwards around the first pivot, the mounting joint can rotate downwards around the second pivot under the gravity effect of external equipment and can be kept downward, so that the transient stability of the equipment can be realized; and the first pivot and the second pivot are distributed in the crossed manner, thus the angle of the joint and the angle of the mounting joint are inconsistent, the swinging resistance is further increased, the mounting joint is better kept in the vertical state, and the intelligent anti-shaking effect of the front-end equipment is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INFINOVA
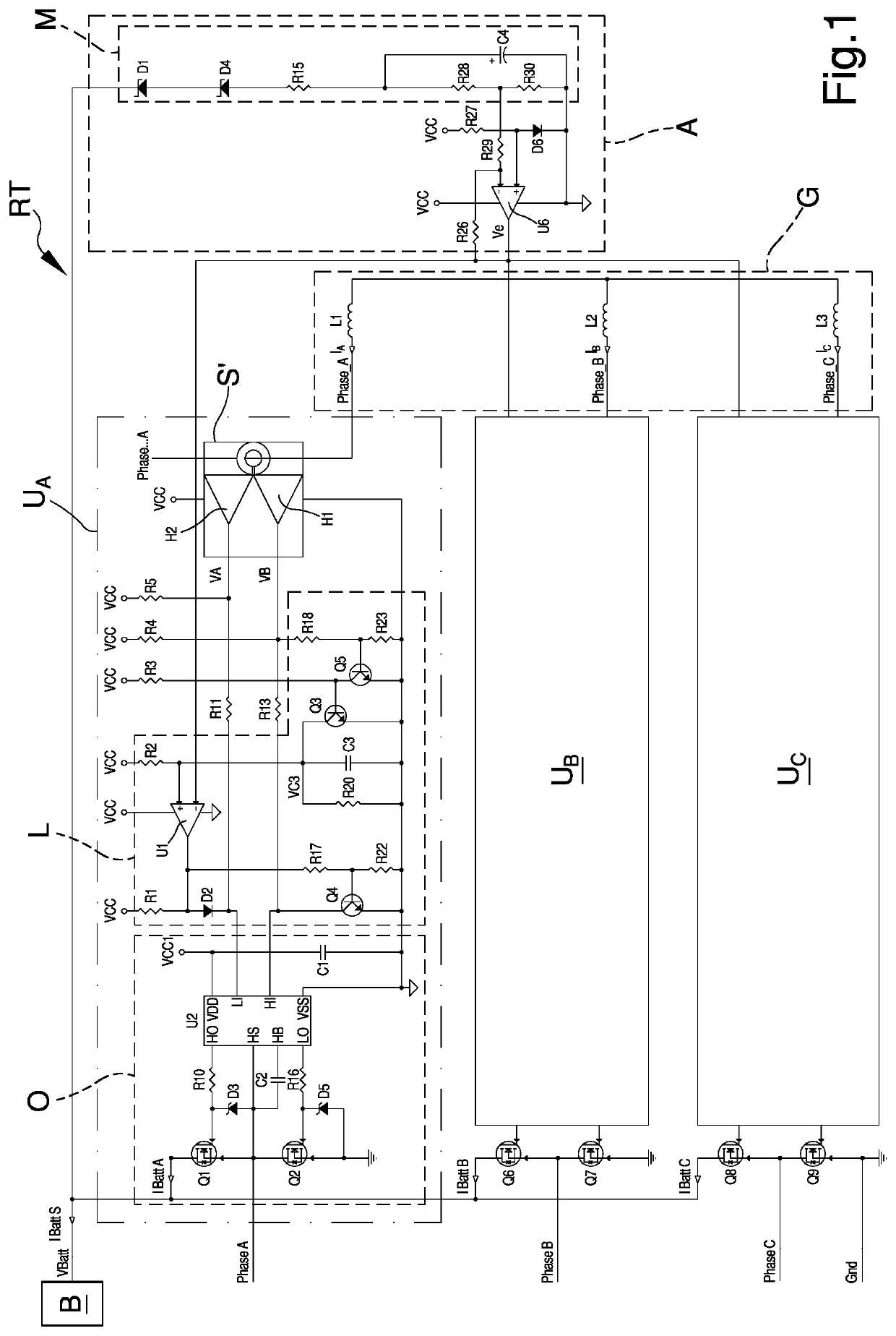
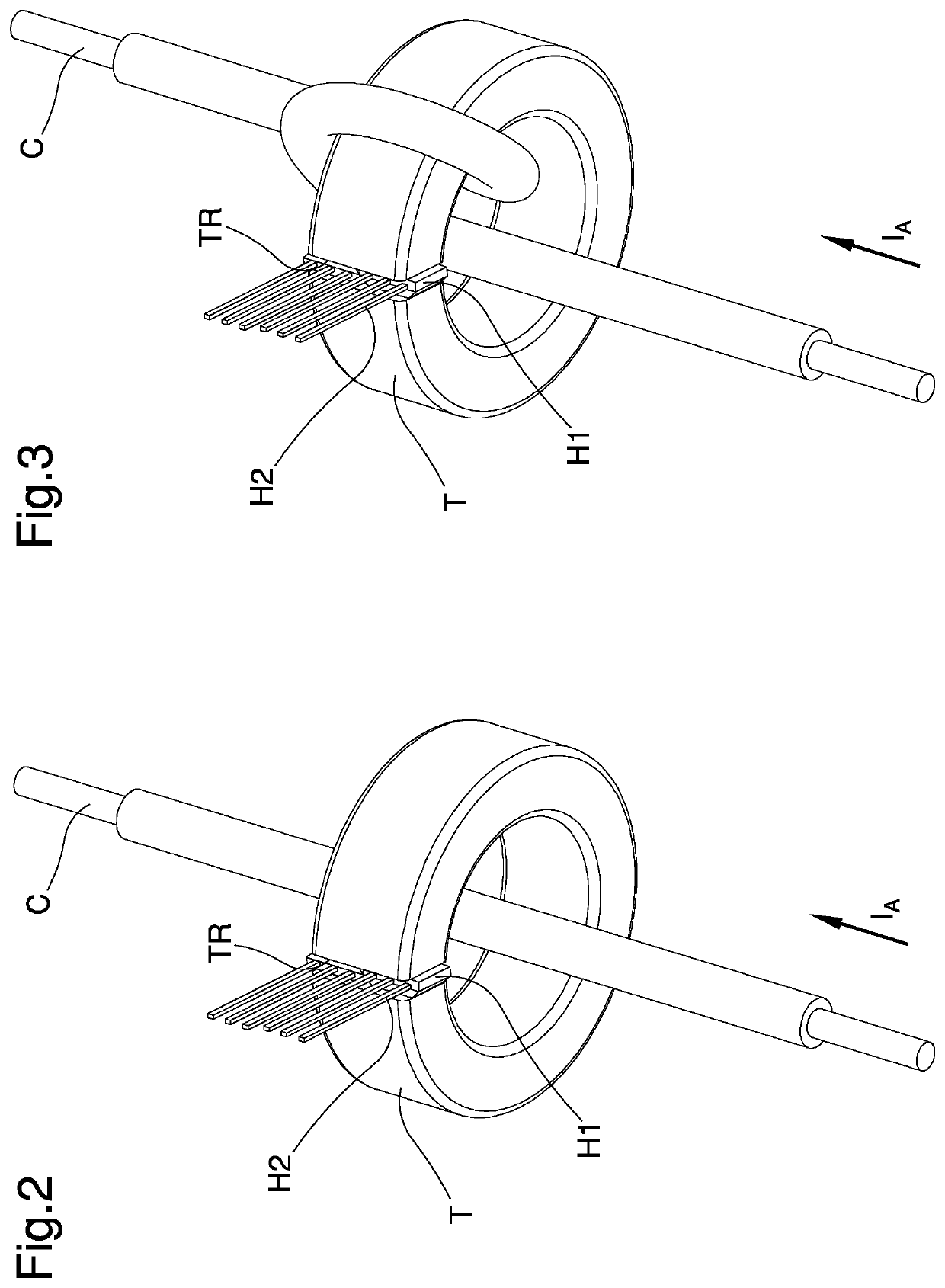
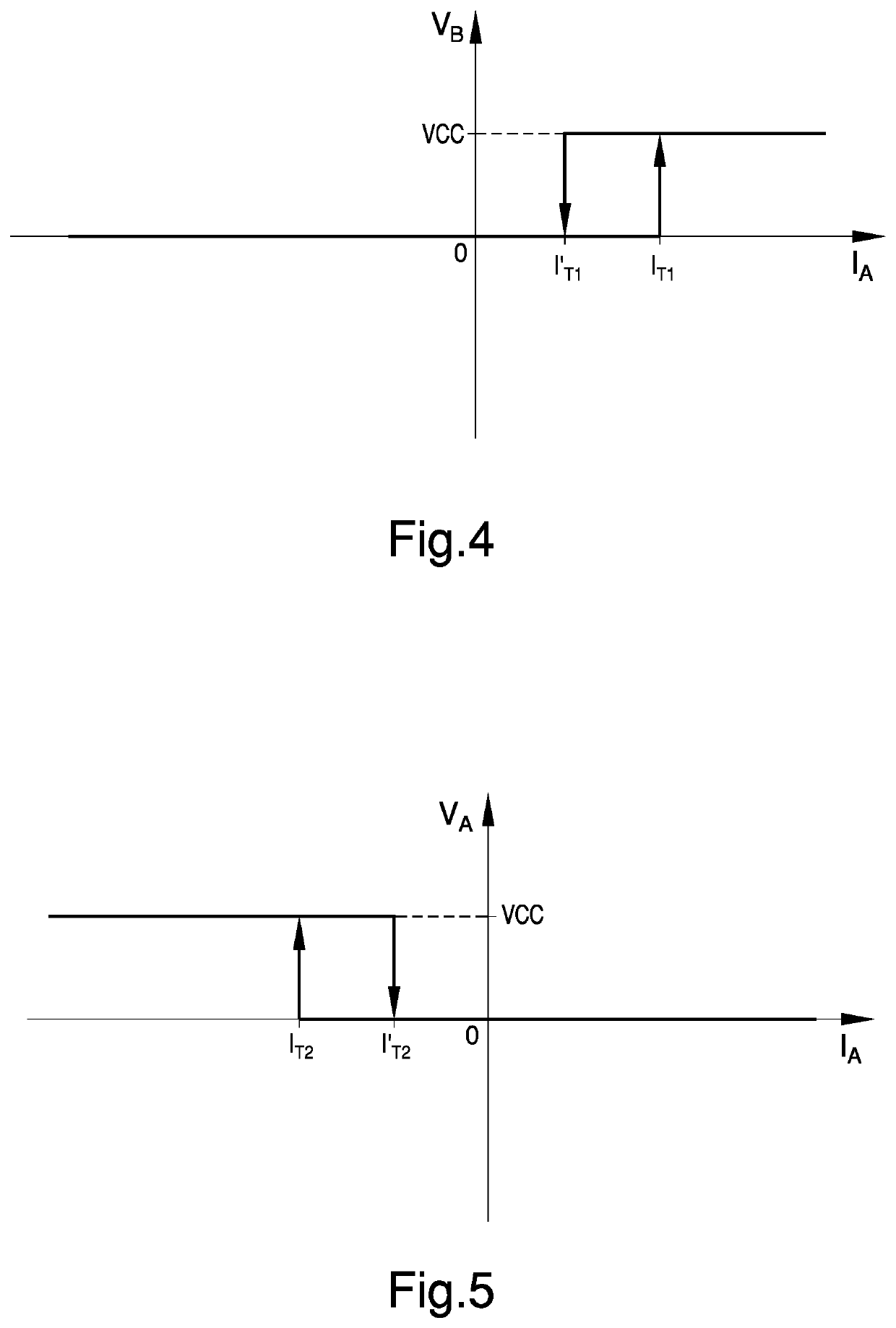
Three-phase synchronous rectifier for battery charger on board vehicle
ActiveUS20210057931A1Accurate detectionAdequate response timeCircuit monitoring/indicationCurrent/voltage measurementCurrent transducerPhase currents
The three-phase synchronous rectifier for battery charger on board vehicle comprises: three rectification units provided with respective inputs connected to respective phases of a permanent magnet generator and with respective outputs connected to a battery of a vehicle; wherein the rectification units are configured to receive at input respective phase currents of the generator and to supply at output rectified currents; and wherein each of the rectification units comprises a current sensor connected to a respective phase of the generator and a respective output circuit connected to the battery and operatively connected to said current sensor; the current sensor being configured to receive at input a respective phase current and the output circuit being configured to be piloted by means of the current sensor to generate the rectified currents; wherein the current sensor comprises at least one toroidal element made of a magnetic material crossed by a lead which conveys the phase current and at least one Hall effect sensor connected to the toroidal element and to the output circuit.
Owner:DUCATI ENERGIA
Method and device for reducing ghost images and crosstalk of 3D (Three-dimensional) television
ActiveCN102270441BReduce ghost crosstalkAdequate response timeStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsLiquid-crystal displayGlasses type
The invention discloses a method for reducing ghost images and crosstalk of a 3D television. The method comprises the steps of: driving a liquid-crystal screen to continuously display a same frame picture for n times; judging whether the proportion ps of a screen area, which meets liquid-crystal display response time 1r, occupying a full screen is larger than or equal to 1 or not when the same frame picture is displayed for n times; and turning on a full-screen backlight to display the same frame picture when ps is larger than or equal to 1, or else, turning on the backlight in a strip-by-strip way by adopting a backlight strip scanning approach so as to display the same frame picture. The invention further provides a corresponding device. According to the method and the device for reducing the ghost images and the crosstalk of the 3D television, provided by the invention, the ghost images and the crosstalk of a shutter glass type 3D television can be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL NEW-TECH CO LTD
A real-time elimination method of laser powder bed melting near-surface forming defects
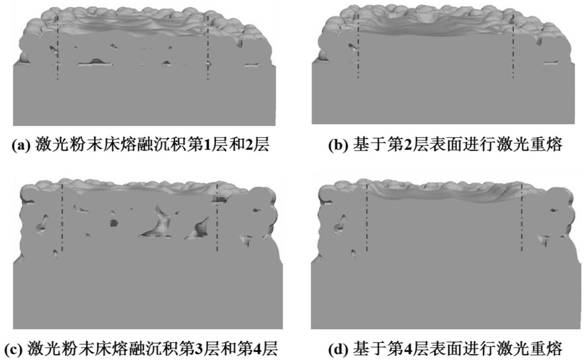
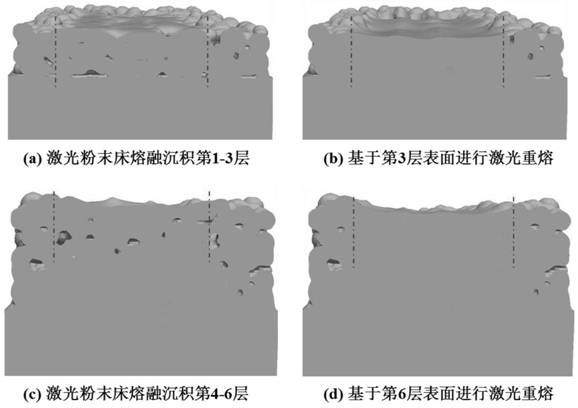
ActiveCN113042749BReduce surface roughnessPore defects are eliminated in timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMetallurgyPowder bed
The invention proposes a real-time elimination method of laser powder bed melting near-surface forming defects. First, the distance h between the laser powder bed melting and forming defects and the surface of the deposition layer is monitored in real time through an external acquisition system; then the position of the defect is determined, and when h > When the thickness of N deposition layers is reached, laser remelting is performed immediately; when h≤N thicknesses of deposition layers, powder spreading and laser powder bed melting are performed, and so on and so forth until the cumulative printing height H reaches the specified height, and the surface of the deposition layer is re-melted. Perform laser remelting. Compared with the existing forming technology, the present invention can not only reduce the surface roughness of the formed part, but also realize the timely elimination of pore defects. The forming efficiency is greatly improved, and at the same time, a more abundant response time is obtained for the online feedback adjustment of defects.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A rail transit monitoring system and method
ActiveCN111717243BRealize monitoringAccurate monitoringRailway signalling and safetyComputer hardwareEmbedded system
The invention provides a rail traffic monitoring system and method. It includes multiple monitoring and alarm terminals, data exchange modules and vehicle-mounted terminals arranged along the track; the monitoring and alarm terminal includes multiple image acquisition modules, multiple optical alarm modules, and the first processing module; all first processing modules are connected and communicated through the data exchange module The first processing module identifies whether there is a foreign object in the image output by the image acquisition module, and when there is a foreign object intrusion, the first processing module of the monitoring and alarm terminal at the front or the rear transmits an alarm signal, so that the first distance range at the front or the rear The optical alarm module in the vehicle sends out an optical alarm signal; the vehicle-mounted terminal includes an optical receiver located at the front of the train and a second processing module. The system sends out an optical alarm signal through the optical alarm module, and does not rely on the signal system to transmit the alarm signal. When the signal communication system fails, or in scenarios with poor communication quality such as tunnels, the alarm signal can still be effectively transmitted to improve driving safety.
Owner:成都希格玛光电科技有限公司
HF/VHF frequency-range ultra wide band electromagnetic pulse protection module
ActiveCN102403702BExtend the rise timeIncrease reflectionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentLow-pass filterPulse energy
The invention provides an HF / VHF frequency-range ultra wide band electromagnetic pulse protection module comprising a coaxial cavity low-pass filter, a gas discharge tube, a high-power TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressors) tube and a low-power TVS tube, wherein the two ends of the coaxial cavity low-pass filter are connected to coaxial ports through copper leads, respectively; the gas discharge tube and the high-power TVS tube are connected in series and then connected between the copper lead at one end of the coaxial cavity low-pass filter and a ground wire; and the low-power TVS tube is connected between the copper lead at the other end of the coaxial cavity low-pass filter and the ground wire. In the coaxial connection manner, the module can be conveniently mounted on a coaxial signal wire between an outdoor cable (including an antenna) and an indoor electronic device so as to discharge ultra wide band electromagnetic pulses coupled to the signal cable; therefore, the module is capable of protecting HF / VHF frequency-range sensitive devices from the damage of the pulse energy.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
An early warning method for axial compressor rotating stall based on frequency domain hump recognition
ActiveCN107165850BCalculation speedReduce intermediate processCharacter and pattern recognitionPump controlAxial compressorFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses an axial flow compressor rotating stall early warning method based on frequency-domain hump identification. The method continuously calculates the frequency spectrum of the pressure signal within a compressor rotation cycle through continuous dynamic pressure signal collection and fast Fourier transform. The characteristic hump discriminant factor Ch corresponding to the frequency spectrum is calculated, and by comparing the characteristic hump discriminant factor Ch with the detection threshold Chstall, it is judged whether the compressor is close to the rotating stall boundary. The characteristic hump discriminant factor Ch defined by the axial flow compressor rotating stall early warning method has a clear physical meaning, and is used for real-time on-line detection of the frequency domain hump that occurs prior to the rotating stall, so that when the working condition of the compressor is close to the boundary of the rotating stall, it will send out Early warning, early warning method is reliable. The axial compressor rotating stall early warning method only needs a single signal sensor, adopts fast Fourier transform, has few intermediate processes and fast calculation speed, and provides sufficient response time for active control.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com