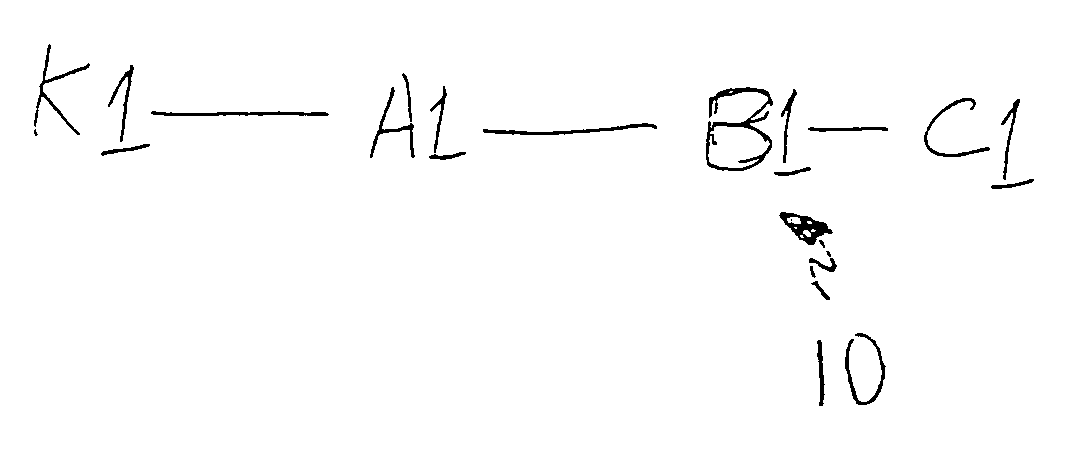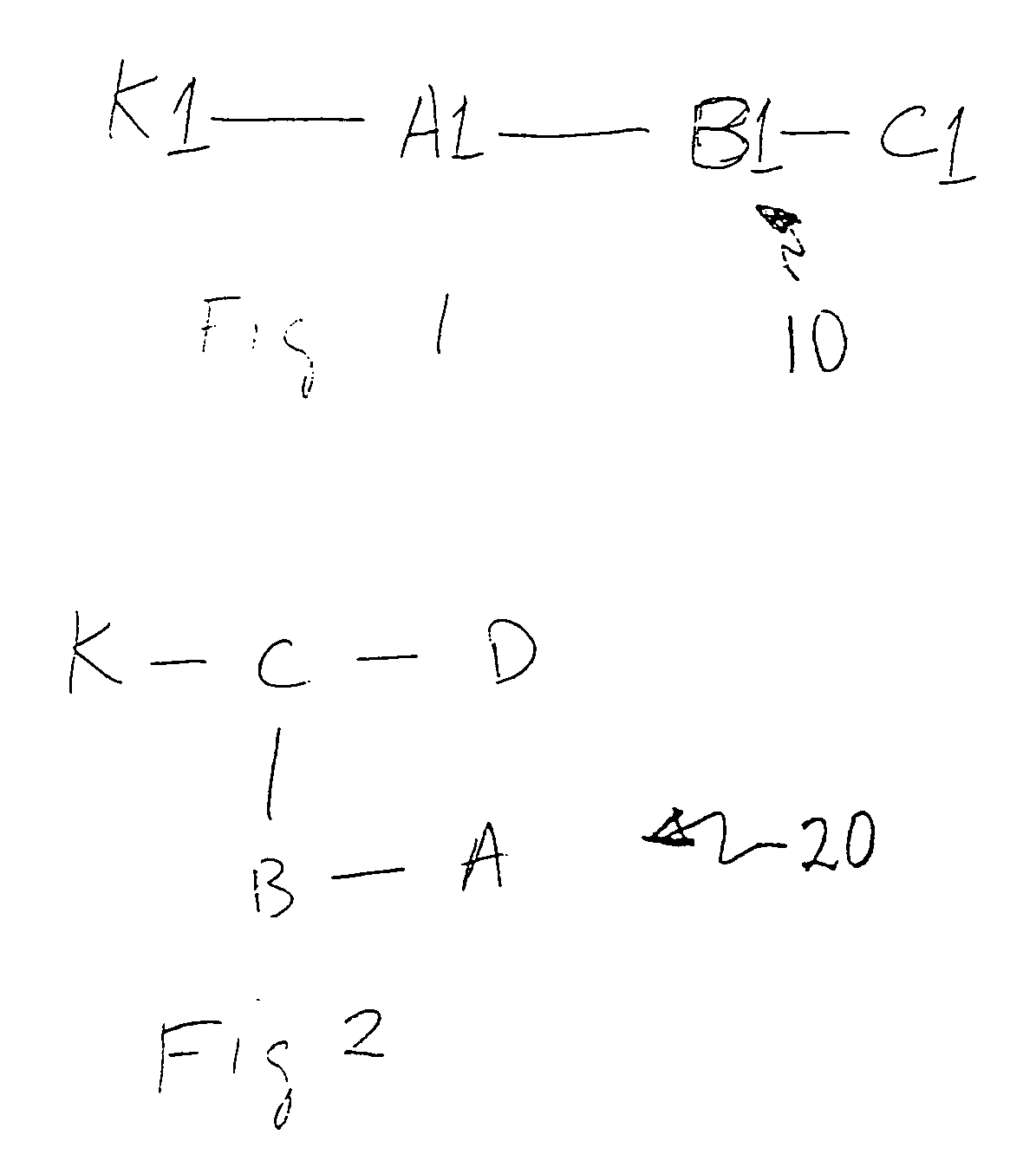Patents
Literature
194 results about "Transmission latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
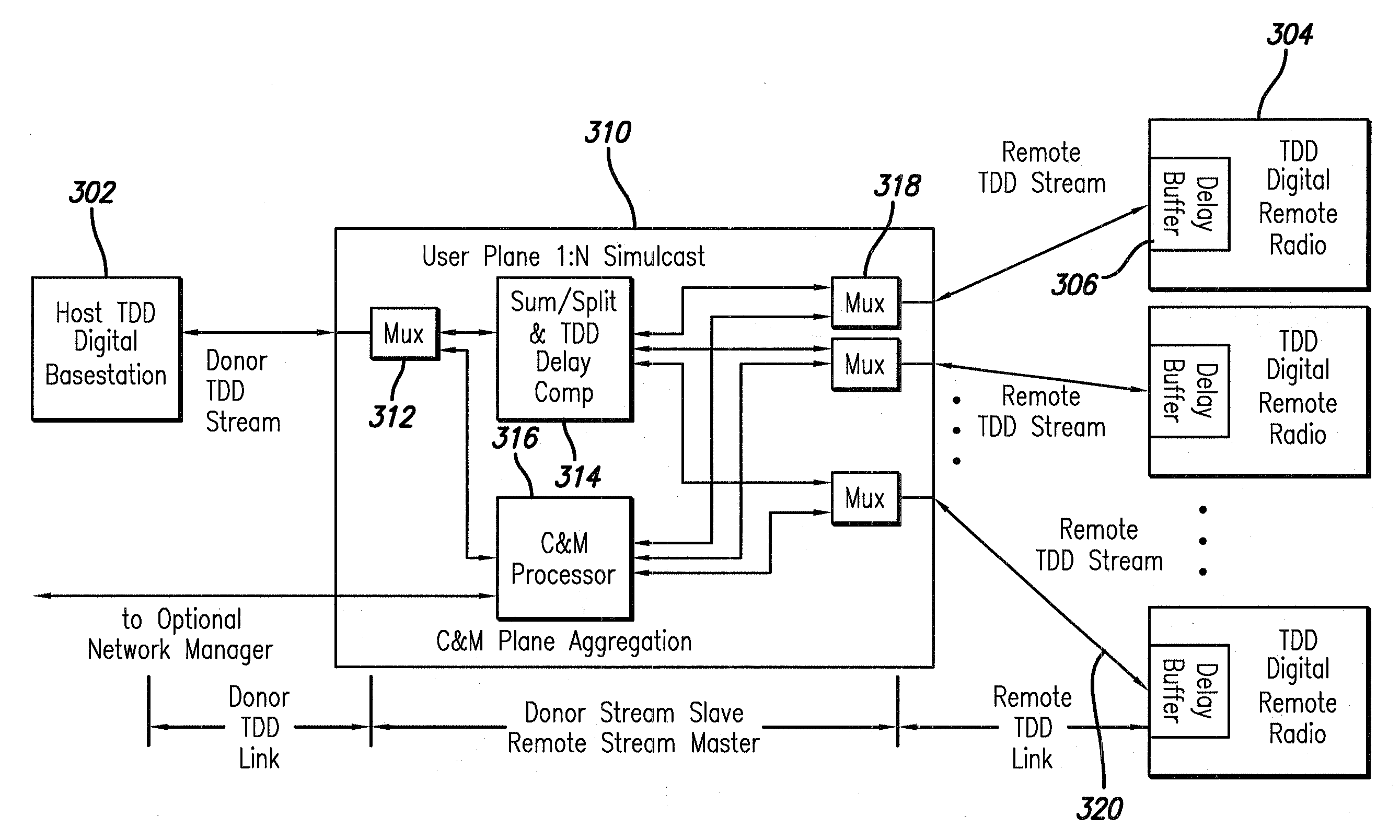
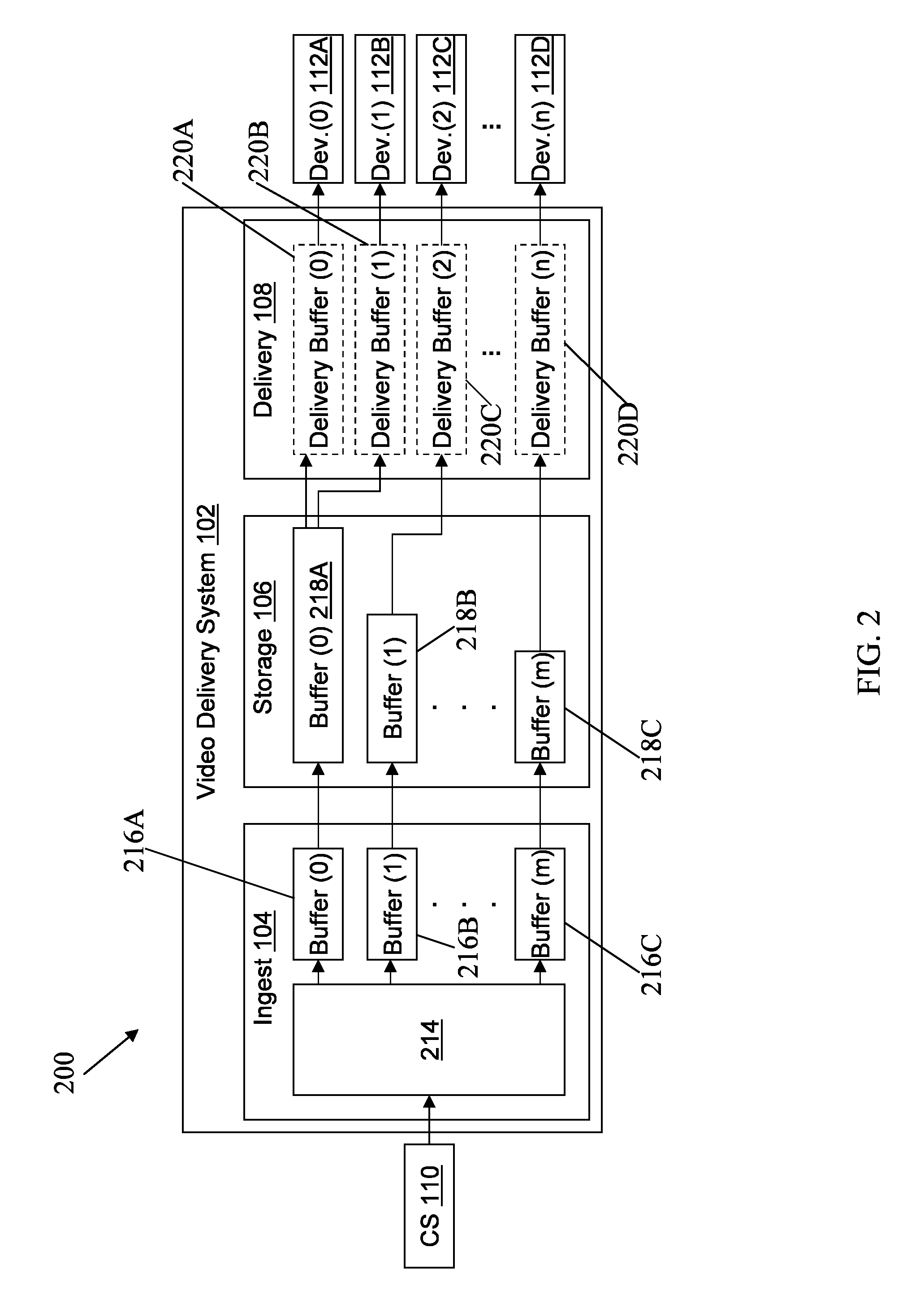
Time division duplexed digital distributed antenna system
A Time Division Duplexed (TDD) digital distributed antenna system (DDAS) that performs simulcast distribution to multiple simulcast groups while using TDD time advanced burst to negate the data rate reducing effects of transport delays. The User Plane data is adapted for eliminating time delay ambiguities across multiple simulcast digital radios. In addition, the Control and Management Plane is aggregated across multiple remote units to allow a non-modified donor digital base station to control simulcast groups.
Owner:INTEL CORP
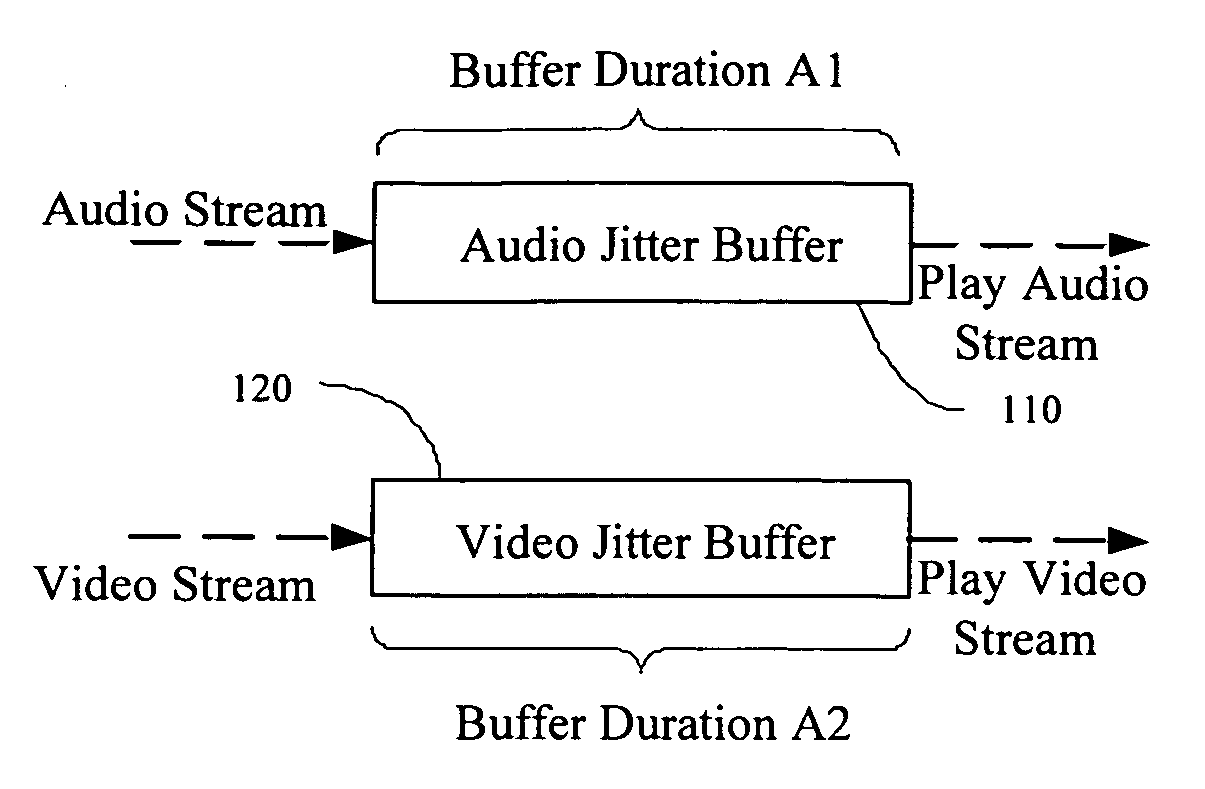
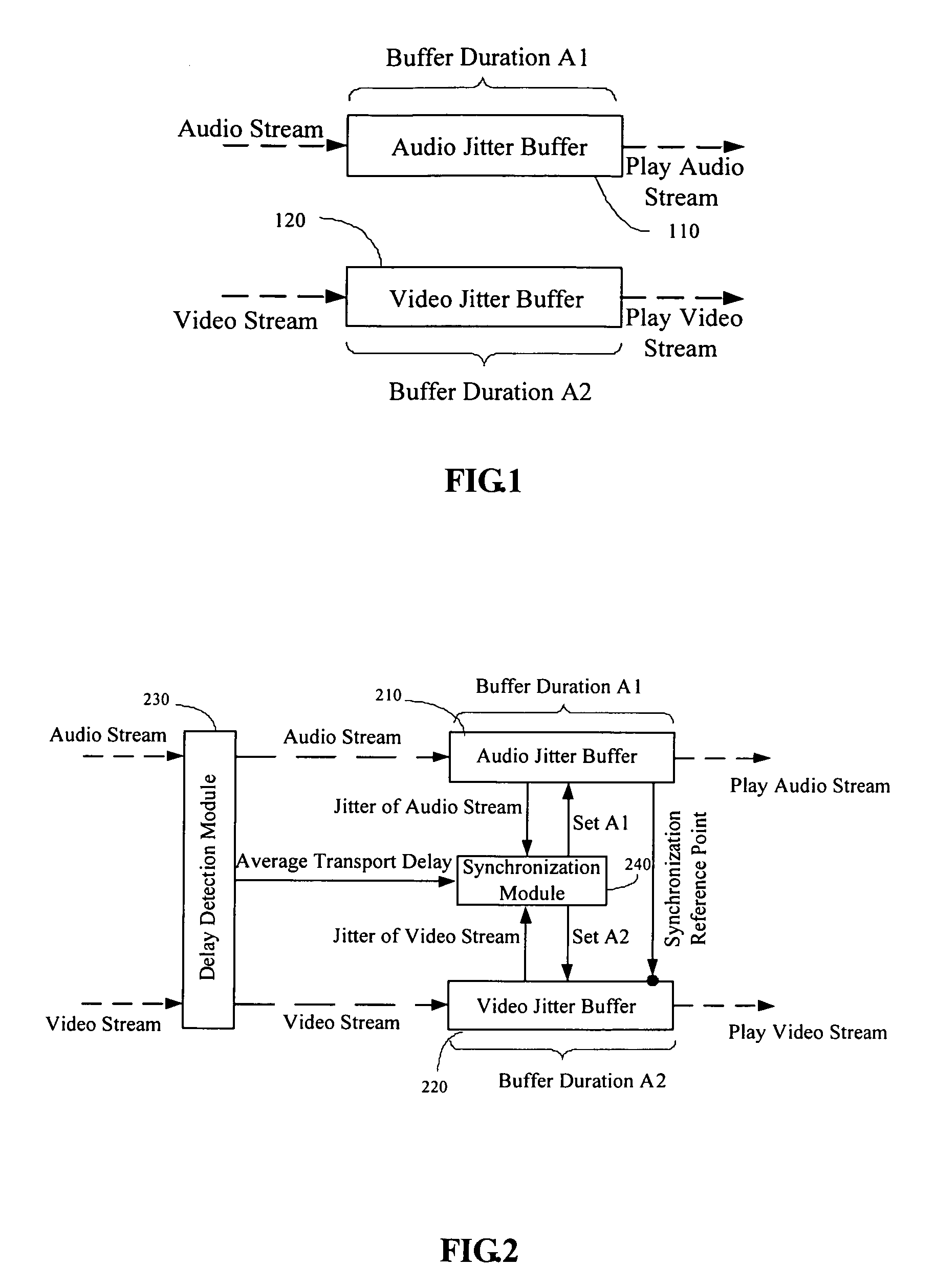
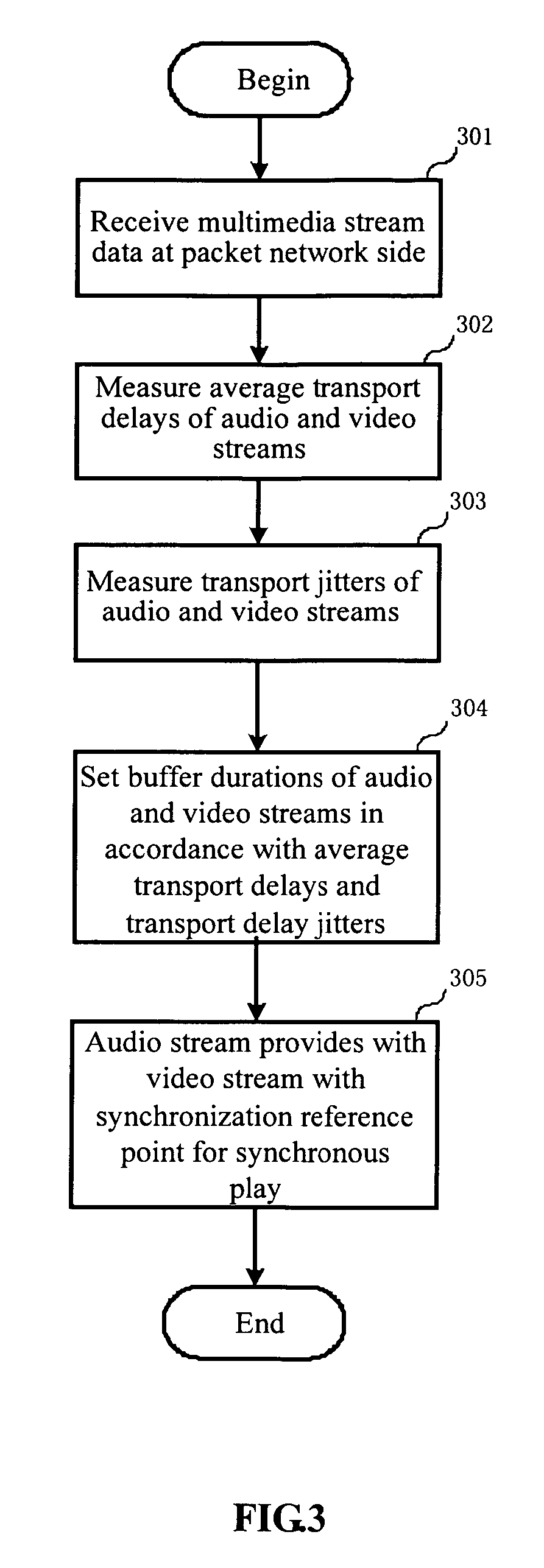
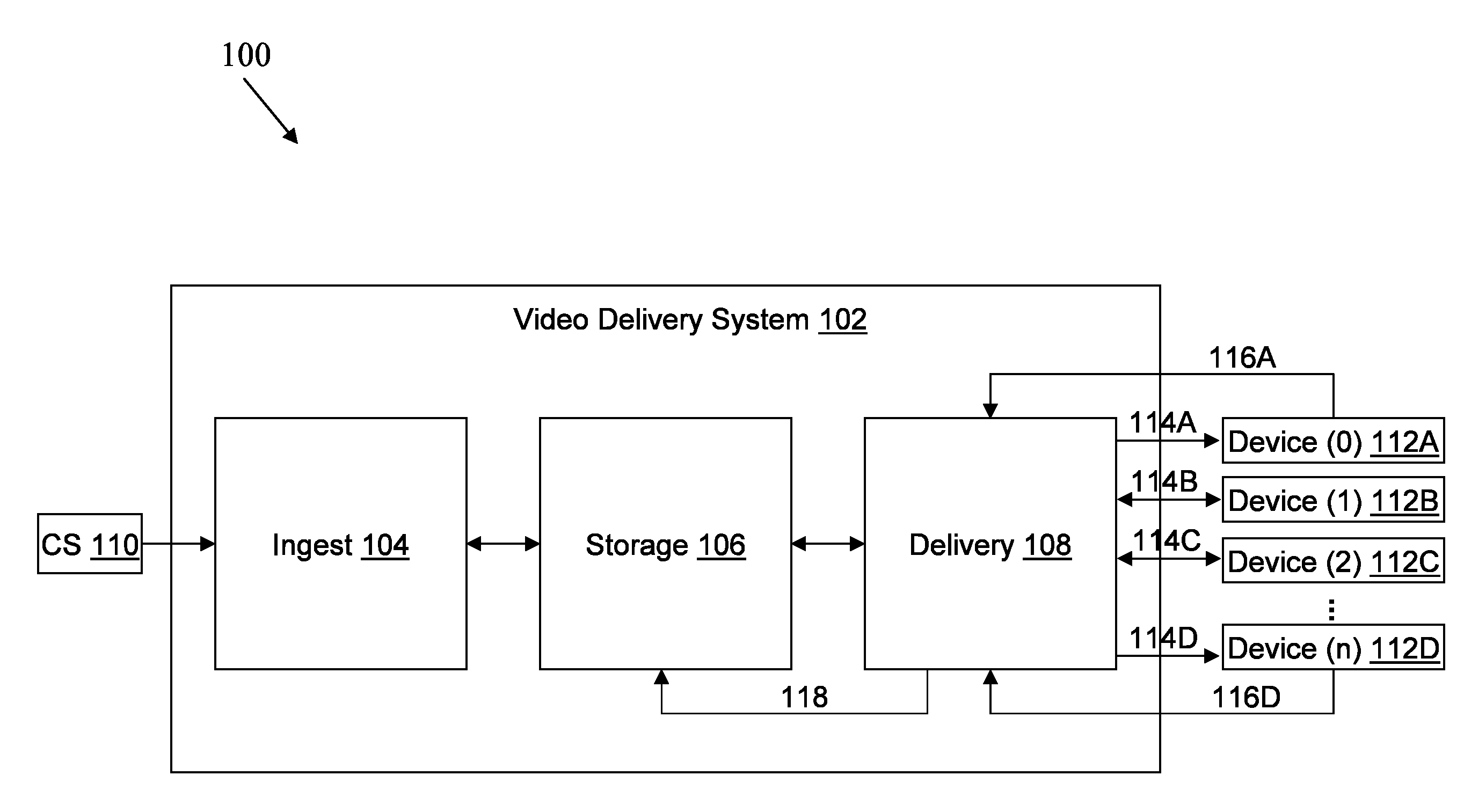
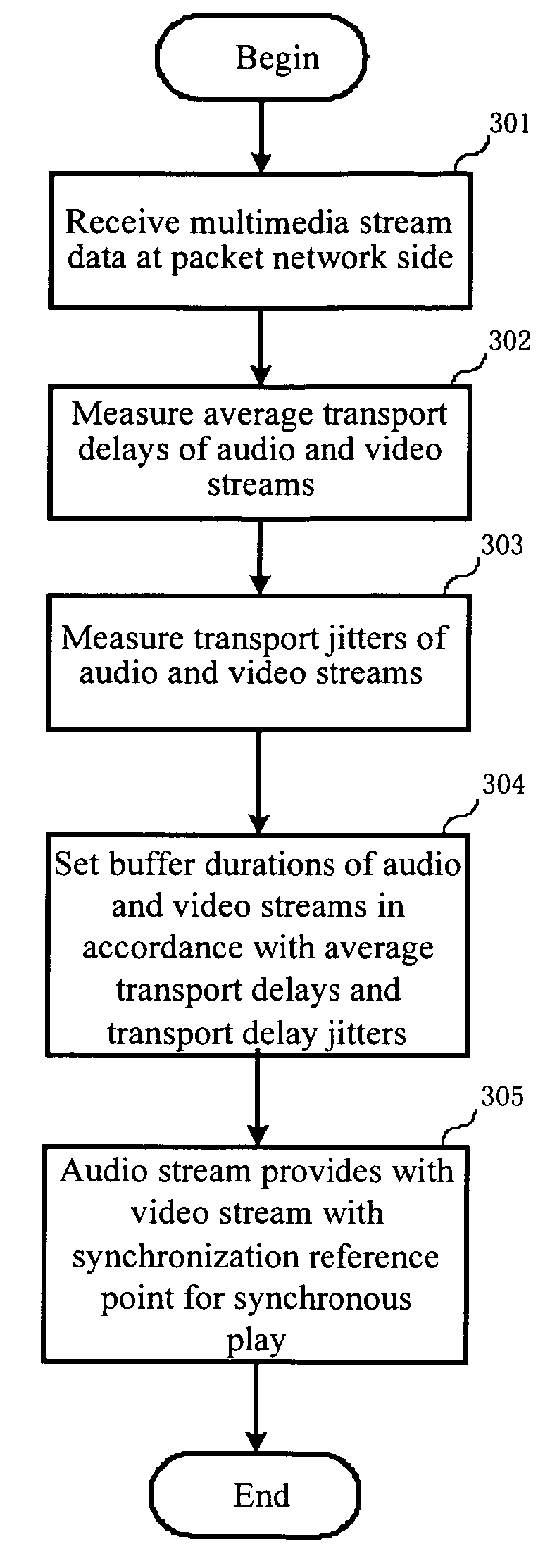
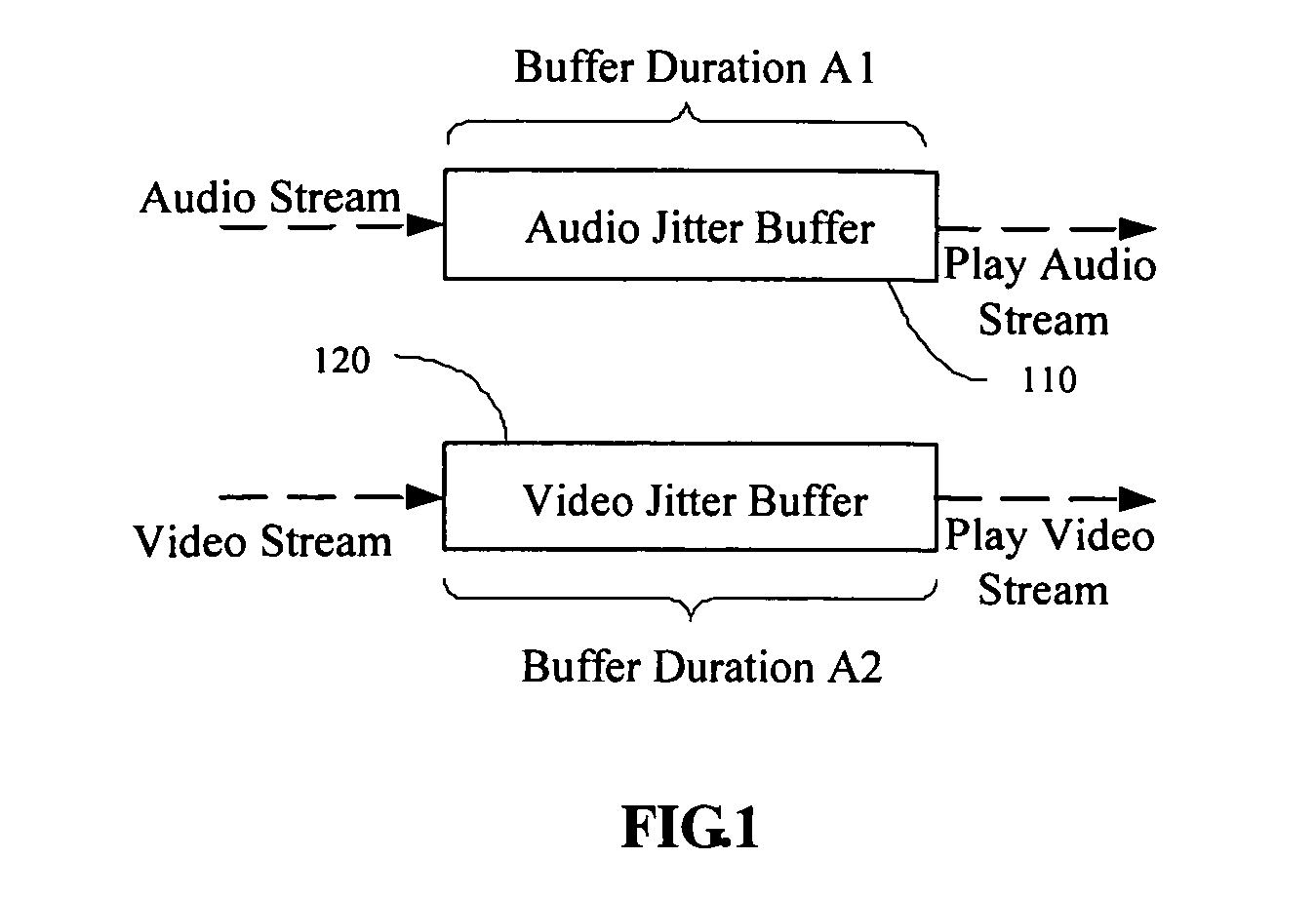
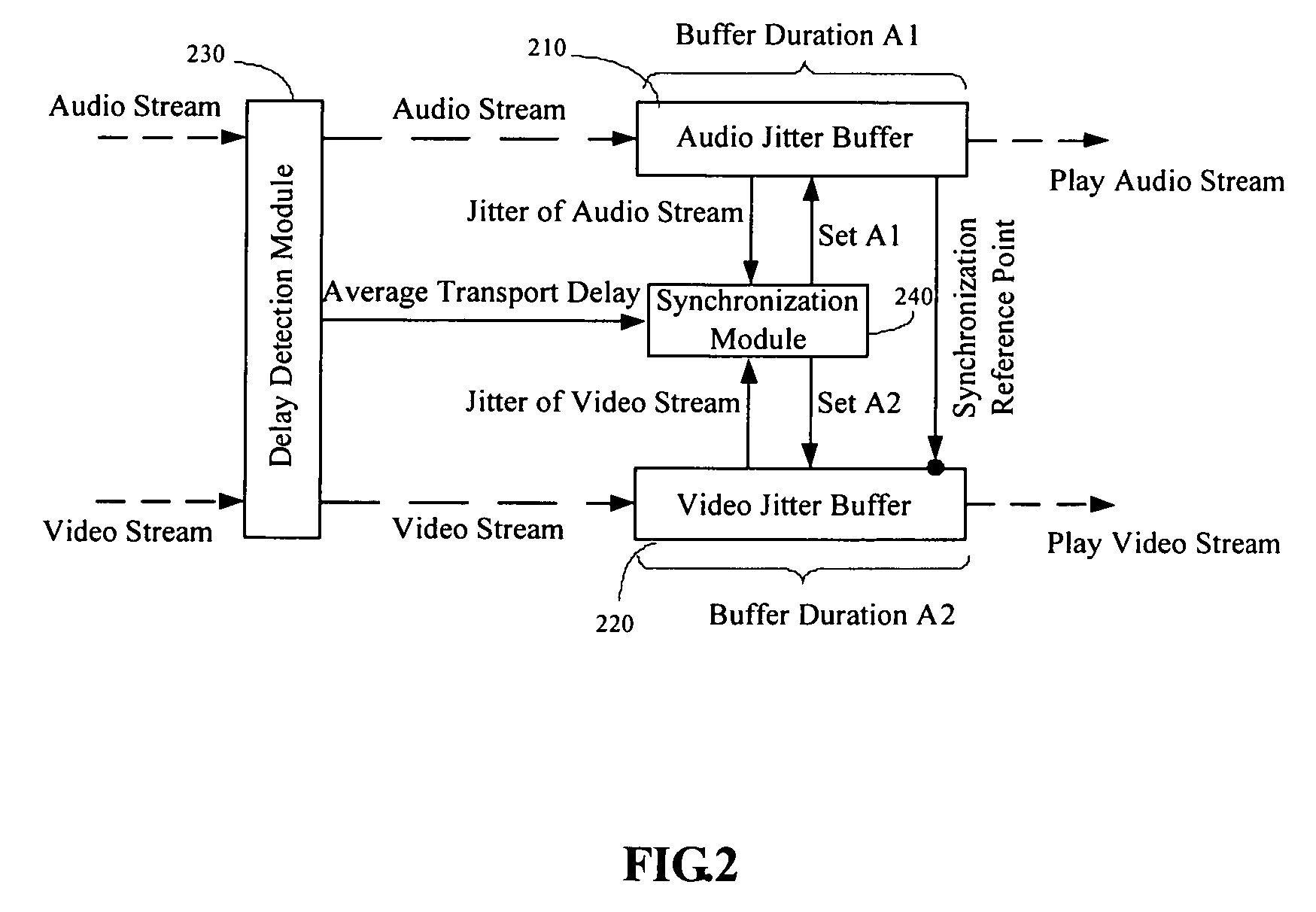
Method and device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over packet network
ActiveUS20070081562A1Transport resistantHigh precisionPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexTransport delayTransmission latency
A method for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network, in which the multimedia includes a first stream and a second stream which are buffered and played through buffers. The method includes: measuring average transport delays of the first and second streams; measuring transport delay jitters of the first and second streams; and calculating a delay difference between the first and second streams which corresponds to the average transport delays and the transport delay jitters of the first and second streams, and setting buffer durations. A device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network is also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Deterministically skewing transmission of content streams
ActiveUS20100218231A1Reducing peak bandwidth requirementReduce loadColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer networkTransmission latency
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for deterministically skewing transmission of content streams. A content stream comprising one or more video frames is received. The content stream is buffered in a buffer, wherein the buffer allows simultaneous read access to the content stream at a plurality of locations. One or more video frames of the content stream are transmitted from the buffer to a first device associated with a first subscriber beginning at a first location in the buffer based on a first transmission delay parameter. One or more video frames of the content stream are transmitted from the buffer to a second device associated with a second subscriber beginning at a second location in the buffer based on a second transmission delay parameter.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
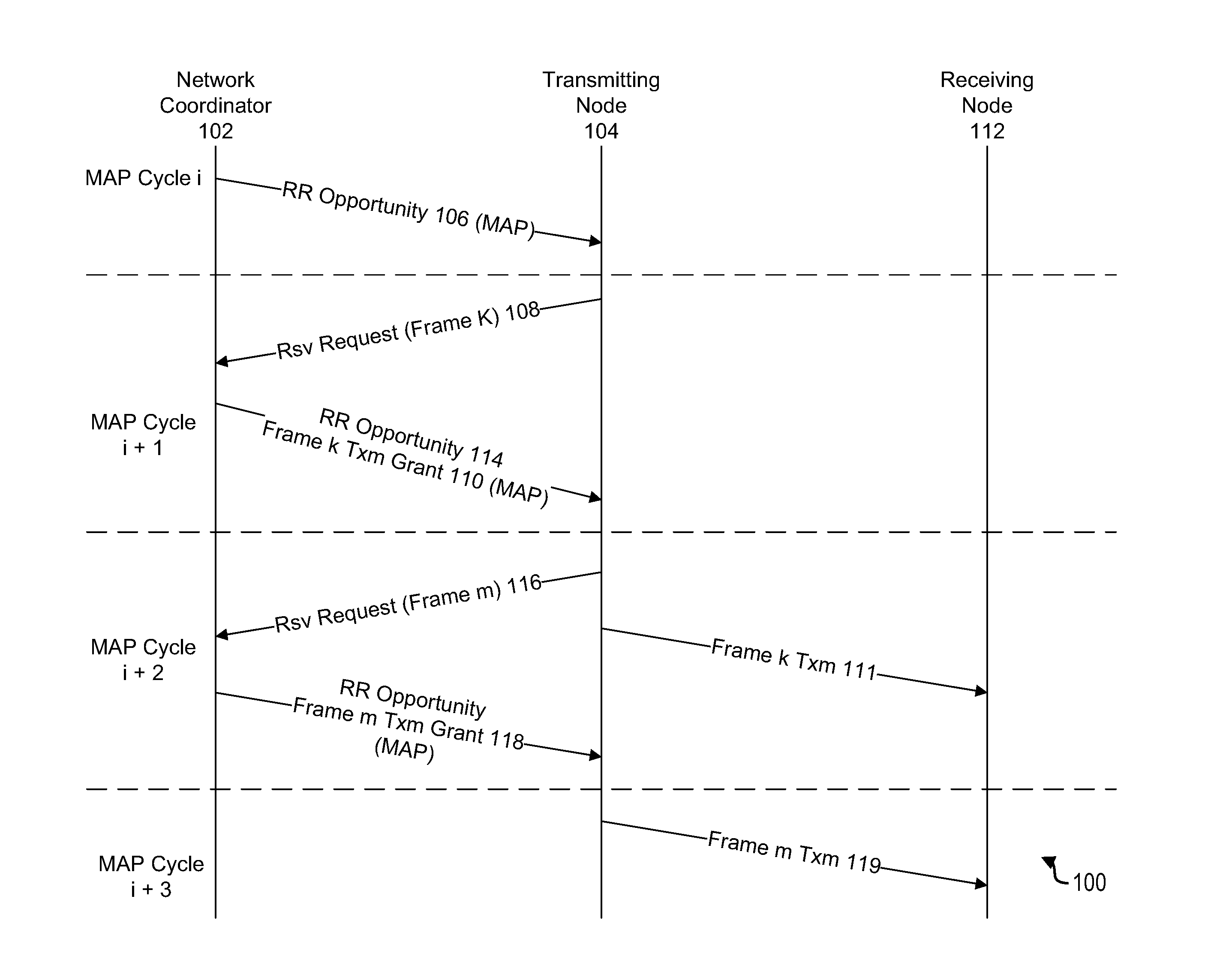
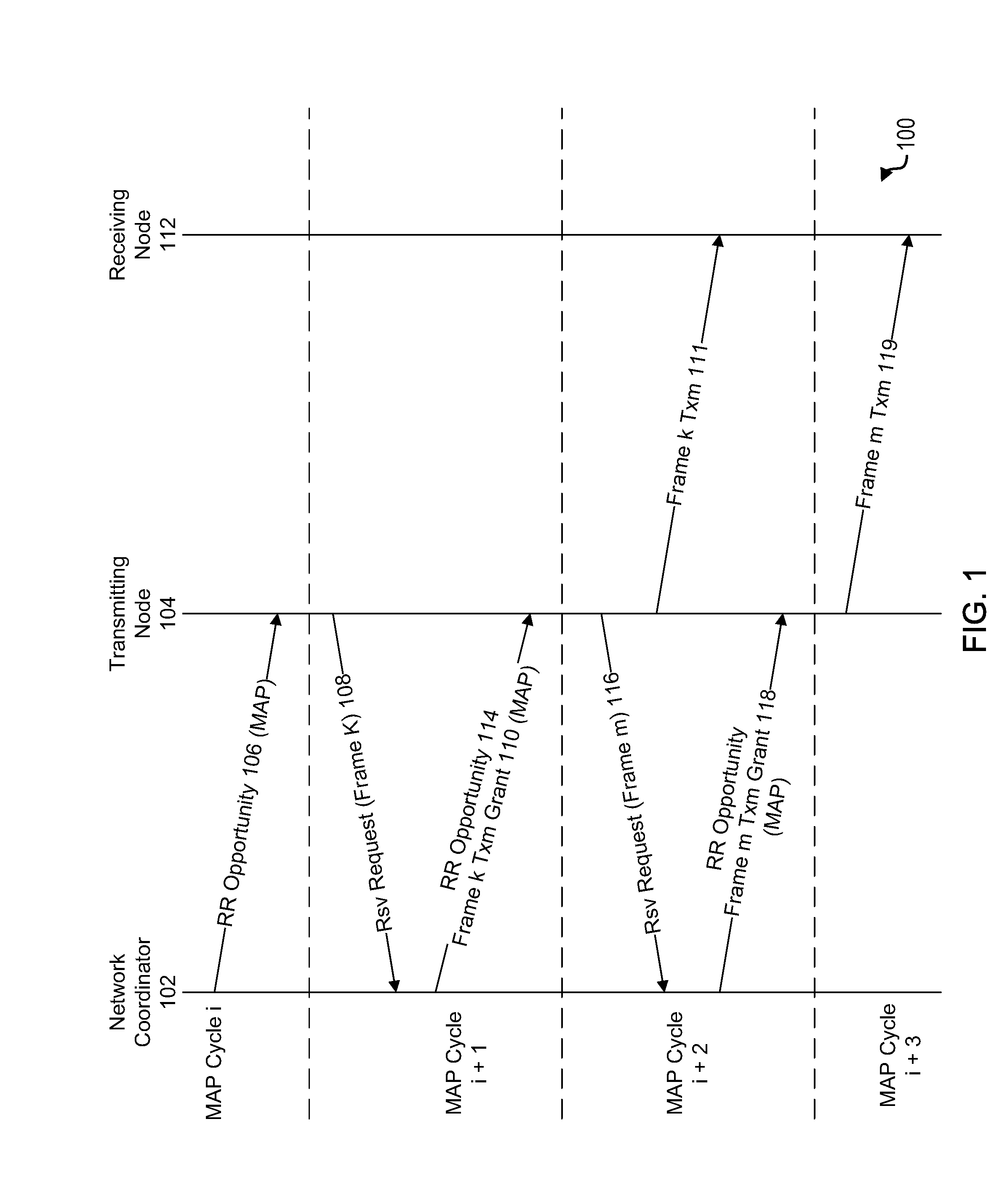
Apparatus and methods for reduction of transmission delay in a communication network
Apparatus and methods for reducing latency in coordinated networks. The apparatus and methods relate to a protocol that may be referred to as the Persistent Reservation Request (“p-RR”), which may be viewed as a type of RR (reservation request). p-RR's may reduce latency, on average, to one MAP cycle or less. A p-RR may be used to facilitate Ethernet audiovisual bridging. Apparatus and methods of the invention may be used in connection with coaxial cable based networks that serve as a backbone for a managed network, which may interface with a package switched network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
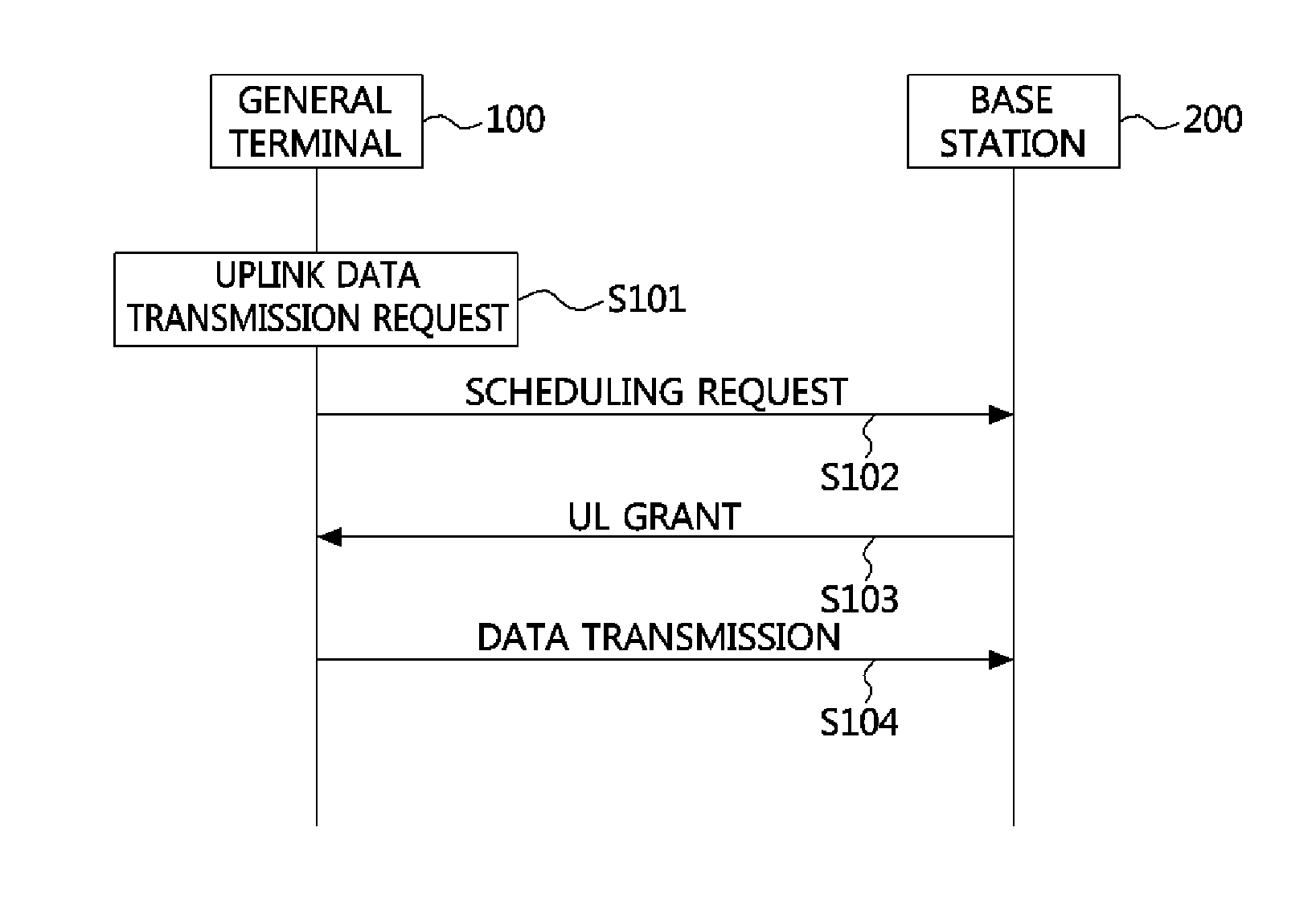
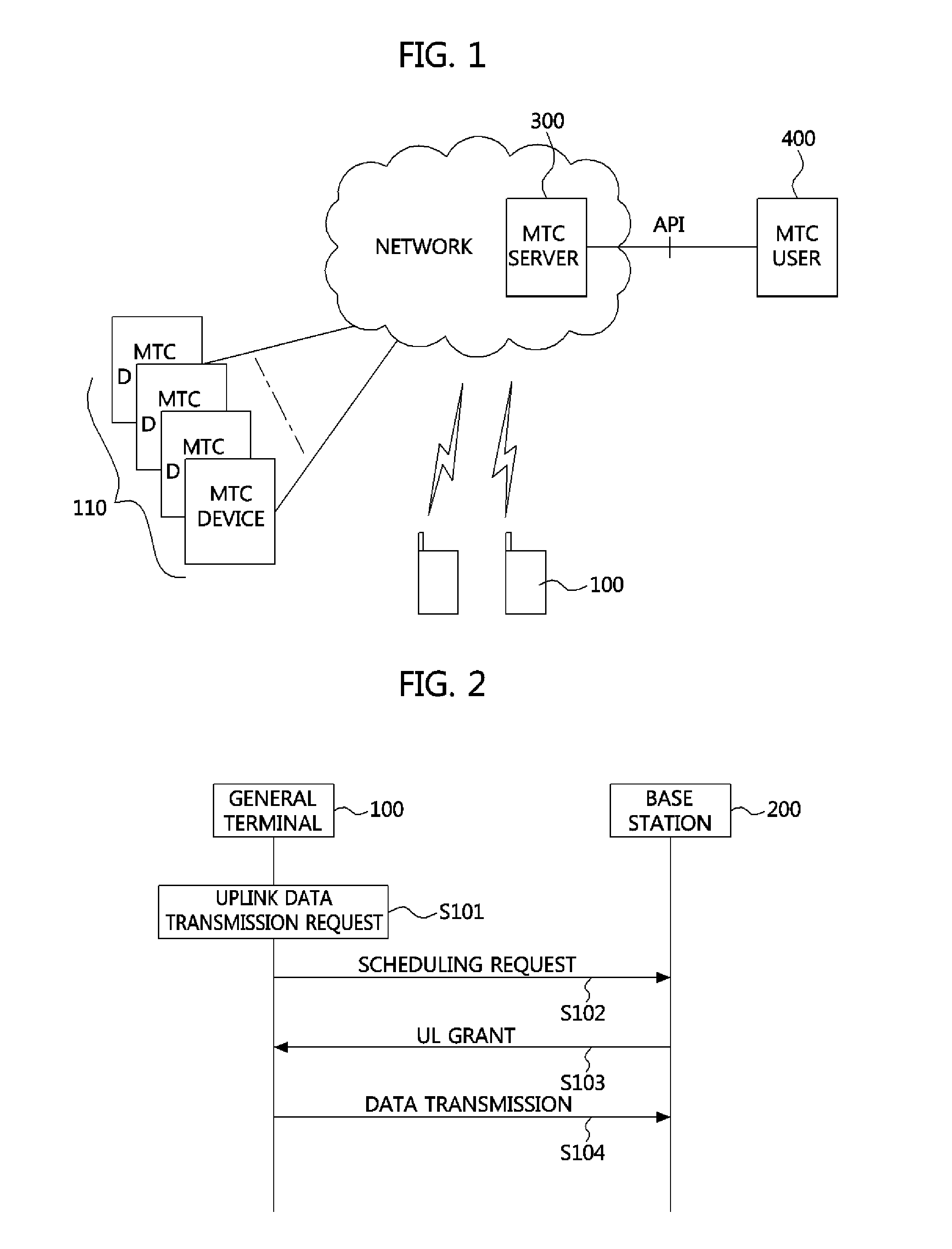
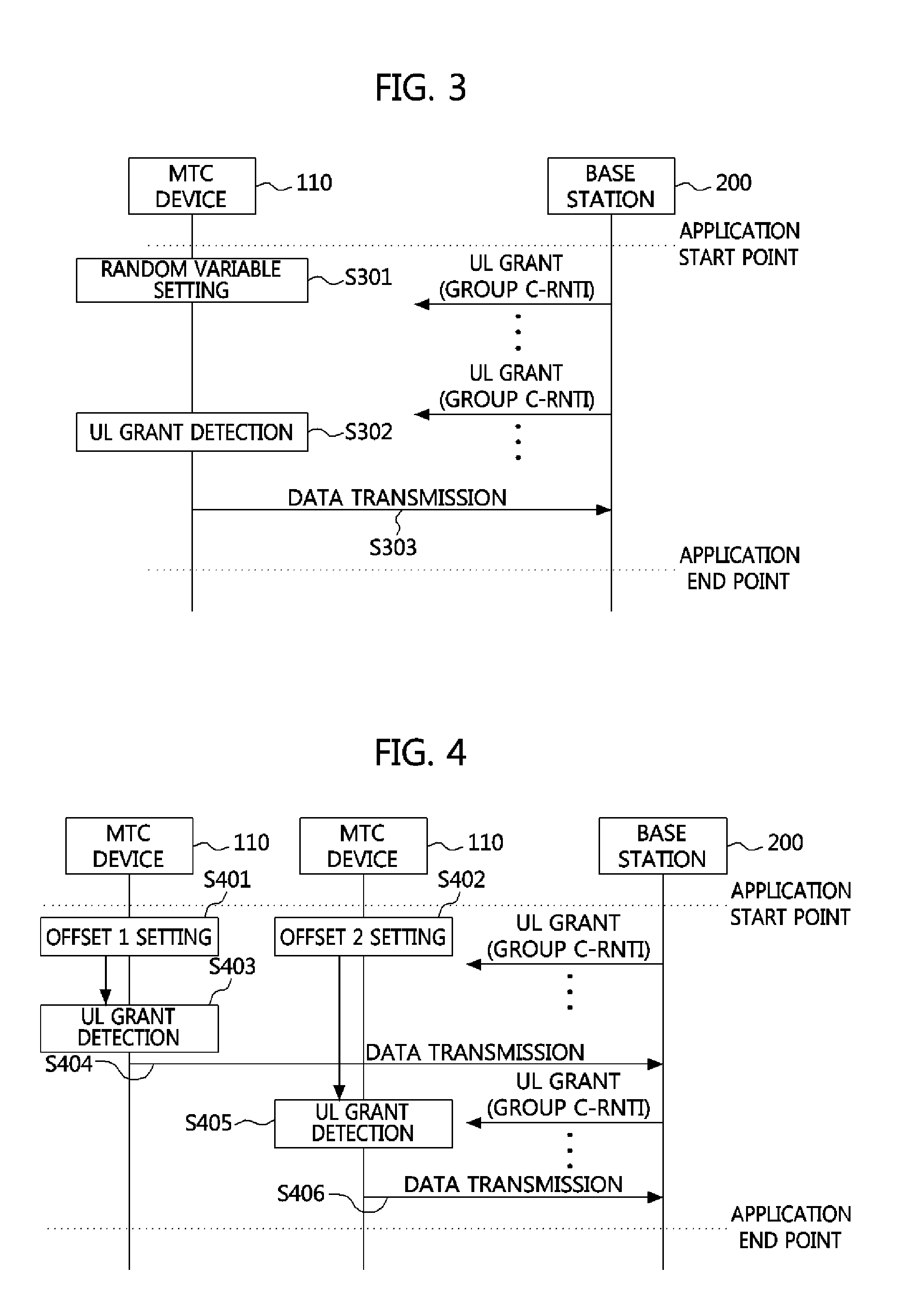
Method of transmitting data in machine type communication device and mobile communication system using the same
InactiveUS20120155406A1Smooth serviceSolve overloadWireless commuication servicesMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceTransmission latencyMobile communication systems
Provided is a method of transmitting data in at least one machine type communication (MTC) device belonging to an MTC group identified by a unique identity according to application features. The method includes setting, by at least one MTC device belonging to the MTC group, unique transmission latency; waiting, by the MTC device, for the set transmission latency and then receiving information on uplink resources allocated to each MTC group identity from a base station; and transmitting, by the MTC device, uplink data using the allocated uplink resources.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
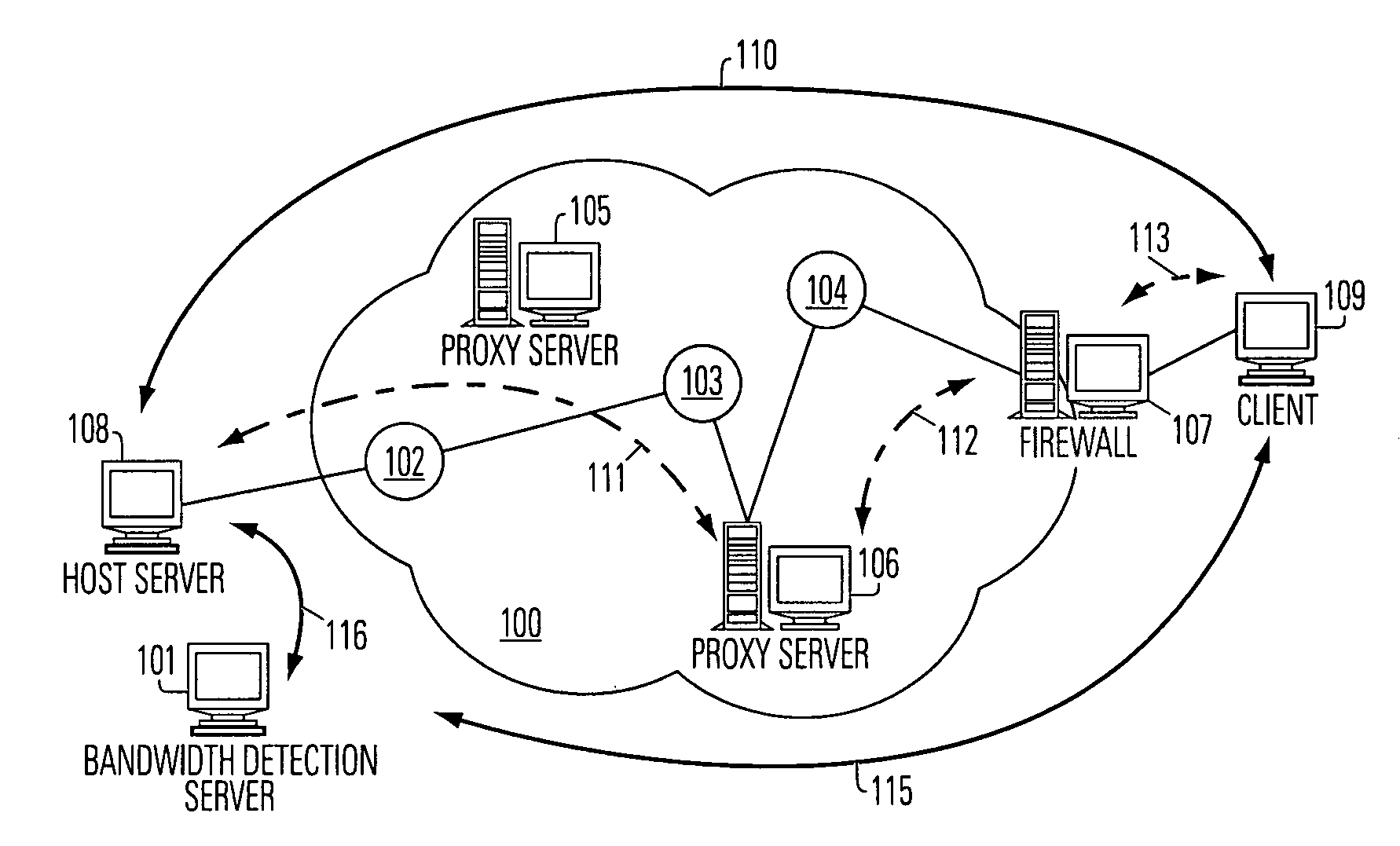
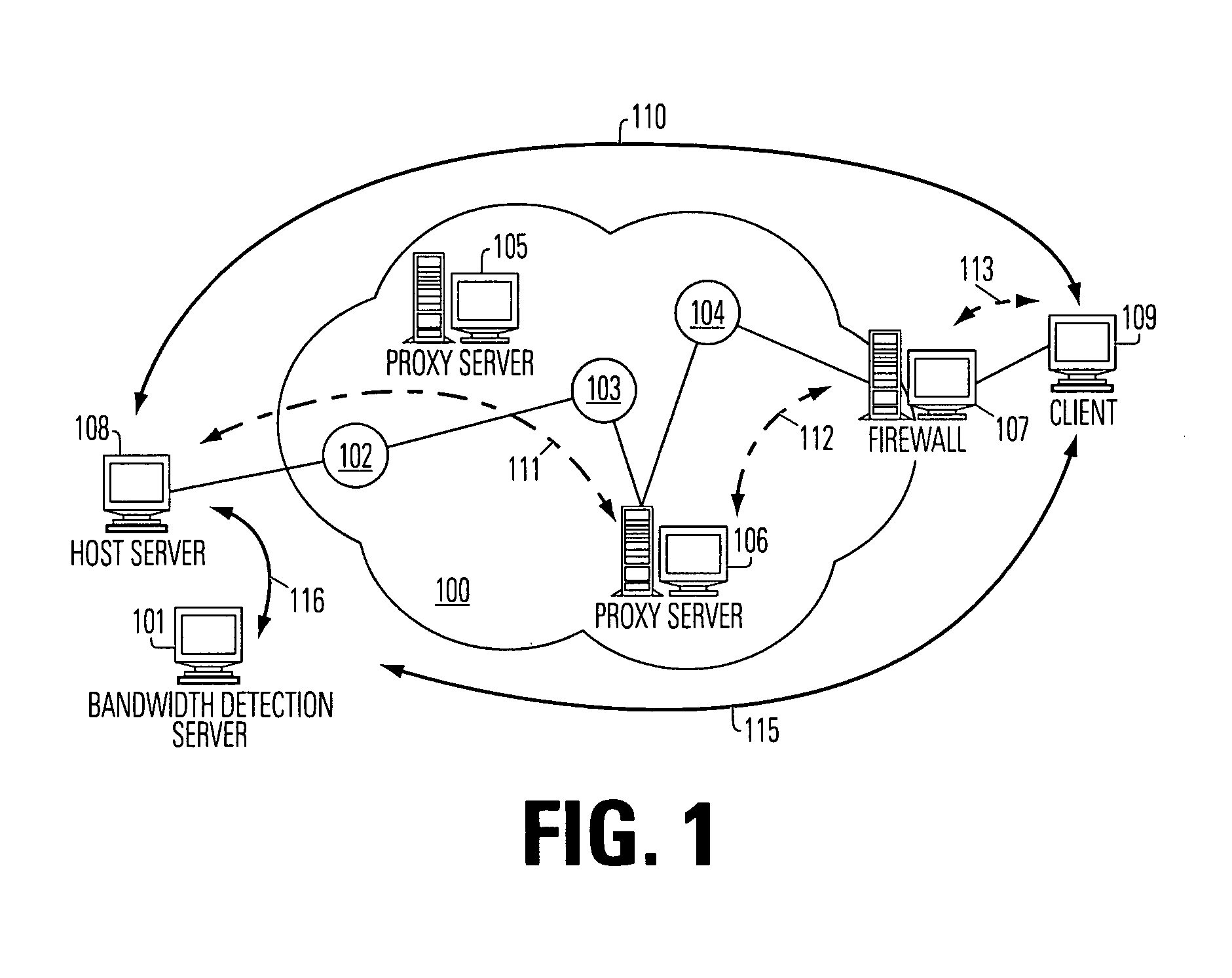
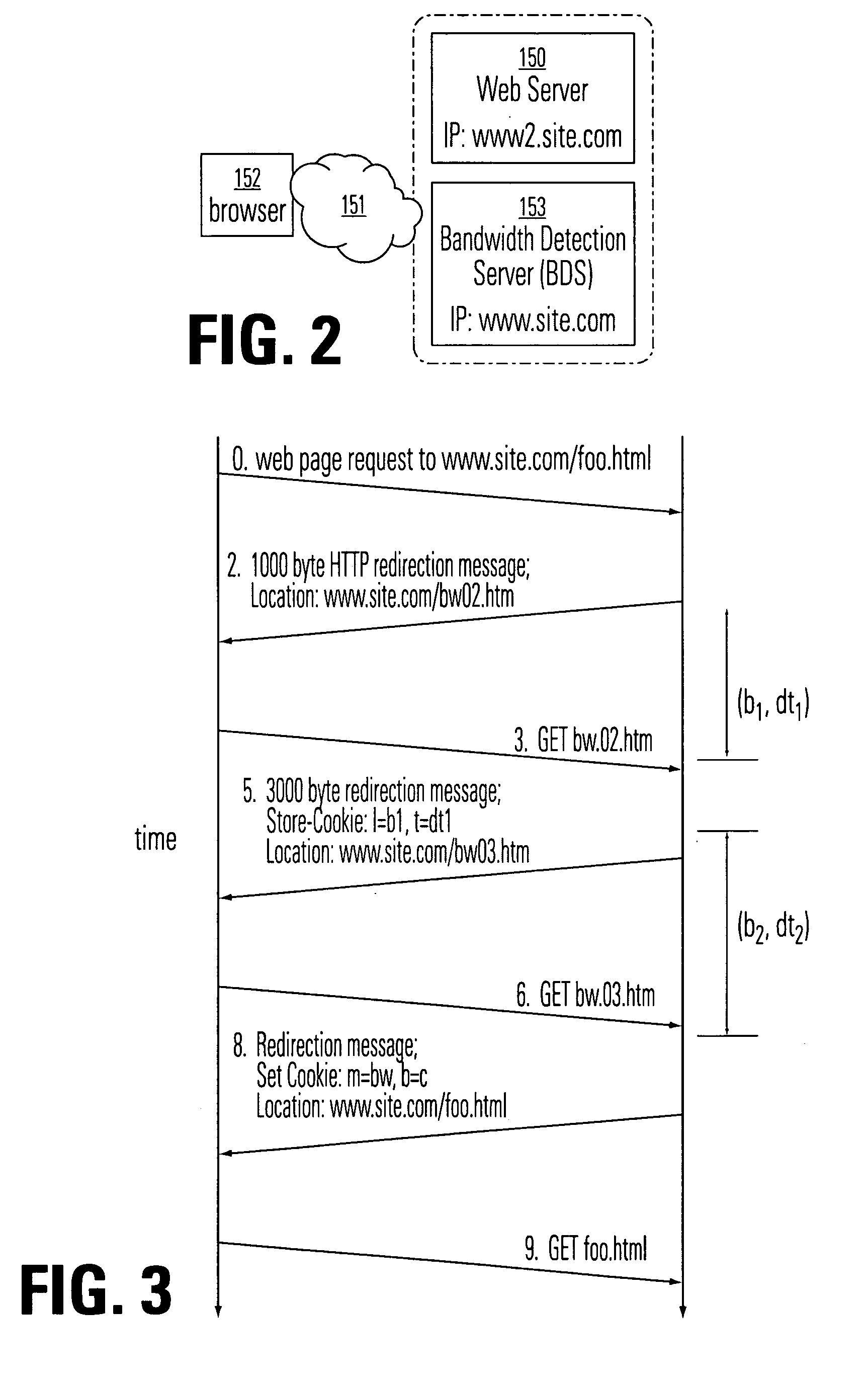
Bandwidth detection in a heterogeneous network with parallel and proxy modes
InactiveUS6992983B1QuicklyEnabling detectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTelecommunications linkData segment
Effective bandwidth of a communication link is determined in a heterogeneous, packet switched network between a source and a destination, where effective bandwidth is defined as the actual available bandwidth between the server and the client, minus the overhead of the various network protocols used to transmit the data. The method includes measuring transmission times between the source and a destination for a plurality data segments having different characteristics, such as different sized files or subfiles of data; processing the transmission times to cancel effects of transmission latencies other than the different characteristics of the data segments; and indicating a bandwidth based on said processing. The processing is done in parallel with the return of user resources to the destination, and using a bandwidth detection engine associated with a proxy server.
Owner:ADOBE INC
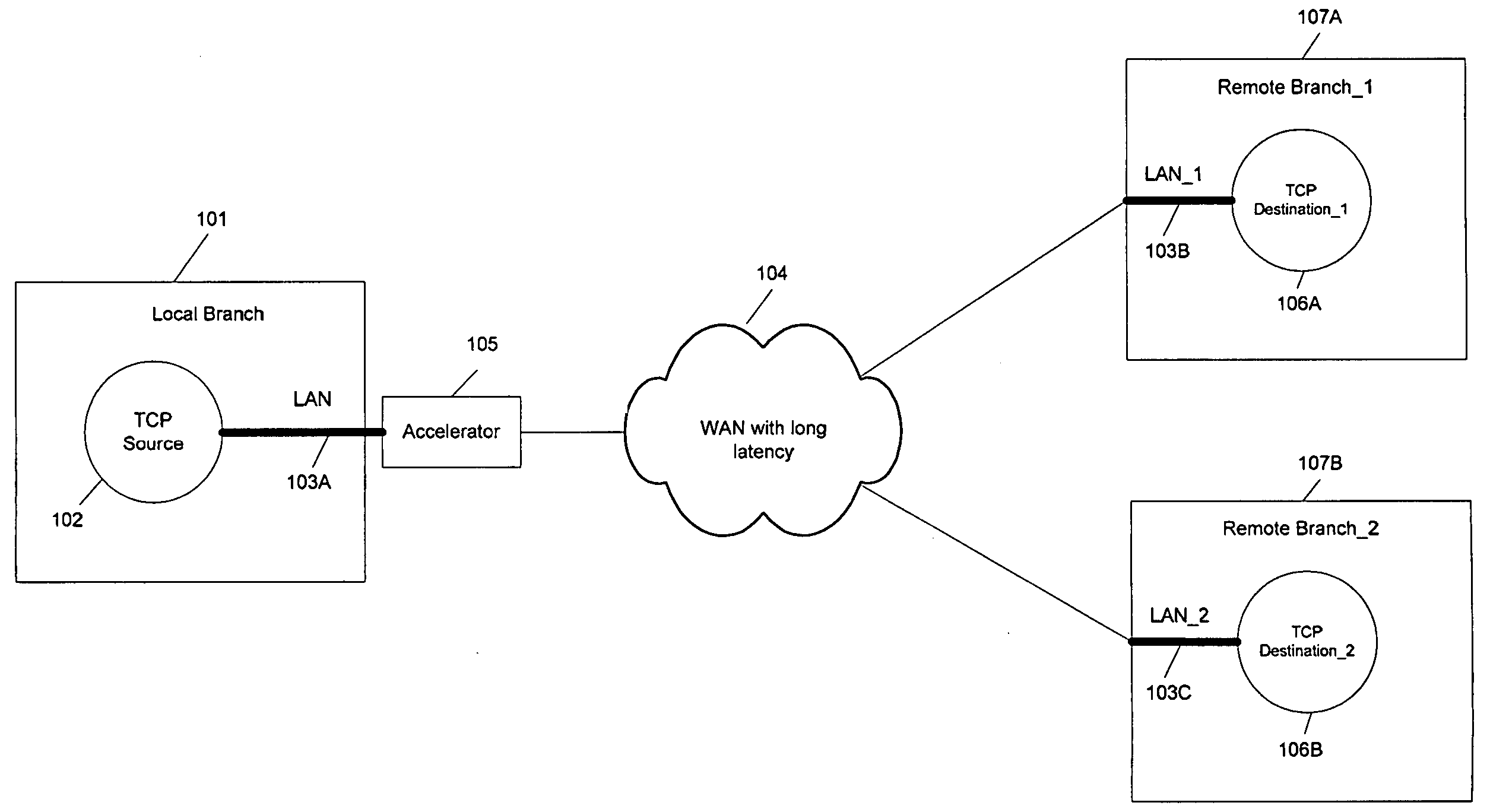
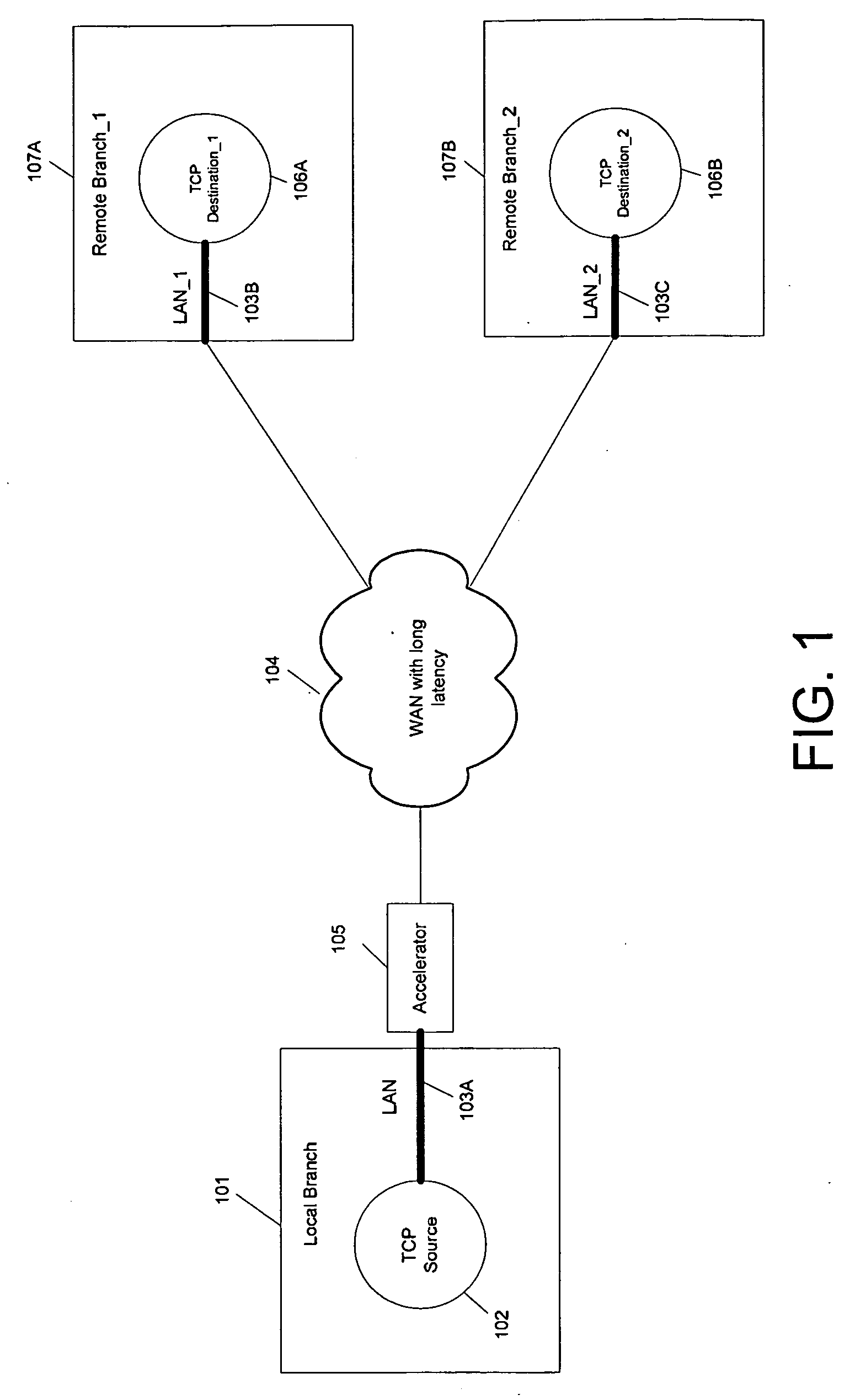
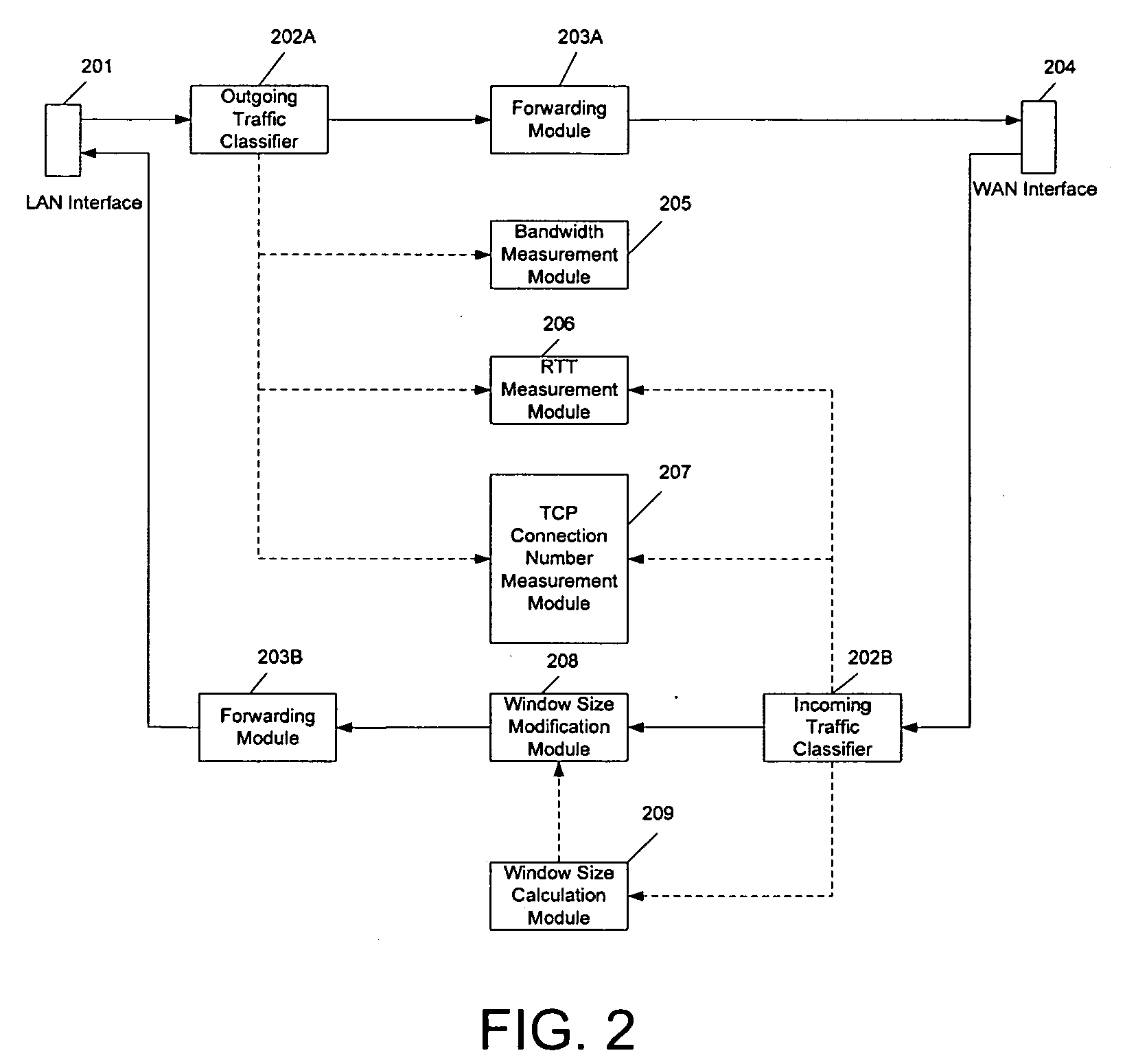
Method and device for hign utilization and efficient flow control over networks with long transmission latency
InactiveUS20100054123A1High network utilizationImprove overall utilizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityTransport control protocol
The present invention is to provide a method and device which can determine current available bandwidth for each Transport Control Protocol (TCP) connection and adjust window size dynamically according to the available bandwidth to achieve high network utilization and efficient flow control in the same time without the need to buffer any received TCP packets, which can work with and without support of large window option. The device classifies incoming traffic into several groups (public and private), monitors and allocates the available bandwidth for each group. To enable flow control, the device also records the initial window size value for each connection and compares it with the original window size value for a newly received TCP packet. If the original window size value received from TCP receivers changes, the device varies the modified window size accordingly to enable efficient flow control in the same device as well.
Owner:JITCOMM NETWORKS PTE
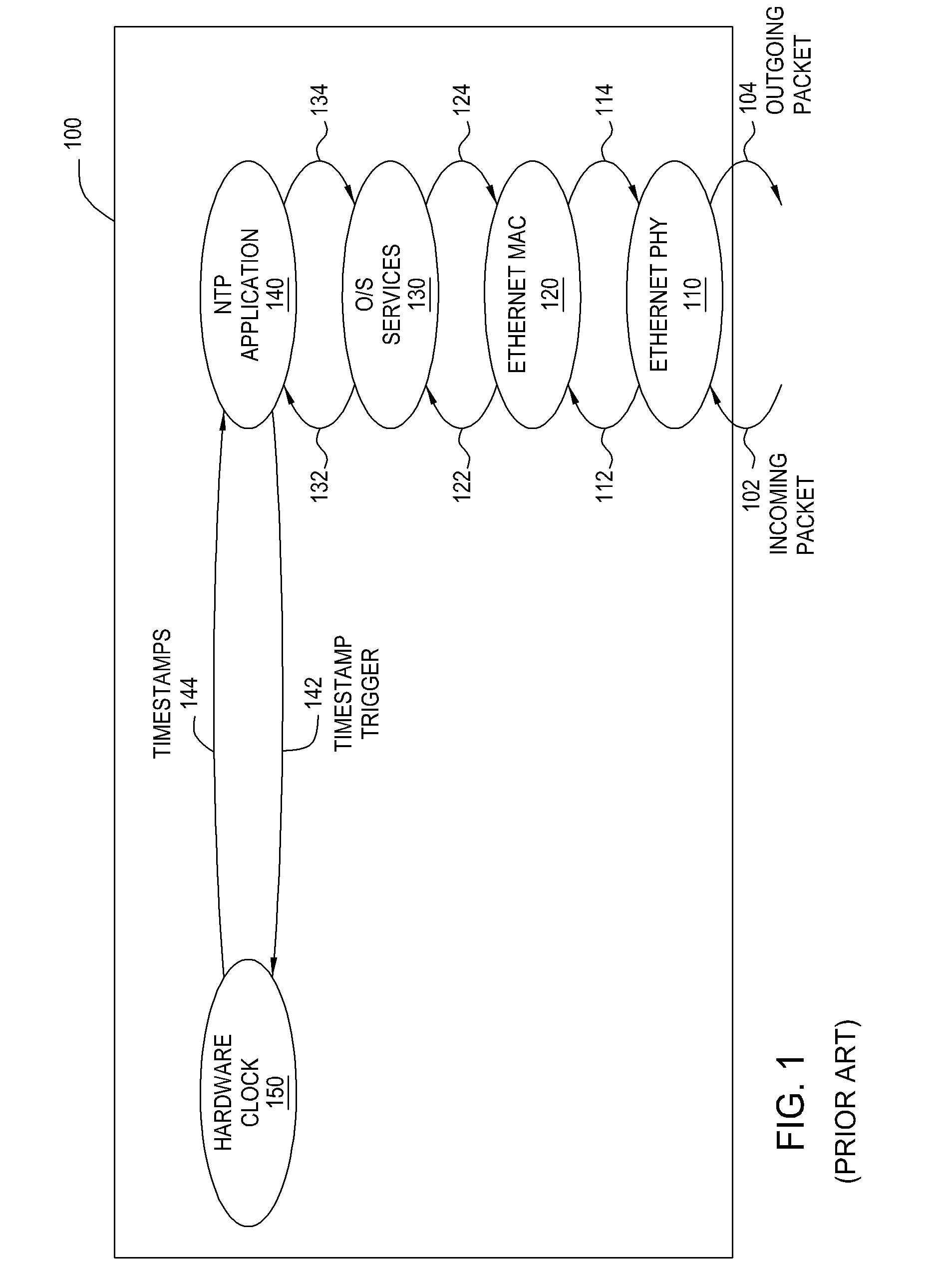
Network time protocol precision timestamping service
ActiveUS20070268938A1Easy to controlHigh precisionTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementTimestampTransmission latency
Embodiments of the present invention set forth a method and system for reducing uncertainty in receive and transmit timestamps created by an NTP server. The uncertainty in the receive timestamps is removed by recording the time-of-arrival in the hardware clock of the NTP server before the incoming packets may be delayed by traversing the various layers of software in a timestamping system. The uncertainty in the transmit timestamps is removed by giving the outgoing packets a timestamp in the future using an estimate of the transmission latency calculated by the latency estimator filter. Subsequently, the actual time-of-departure is used to re-calculate and update the estimate of the transmission latency. In this fashion, superior control of the timestamping function may be implemented in existing NTP servers in a manner that retains interworking compatibility with the current NTP standards.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
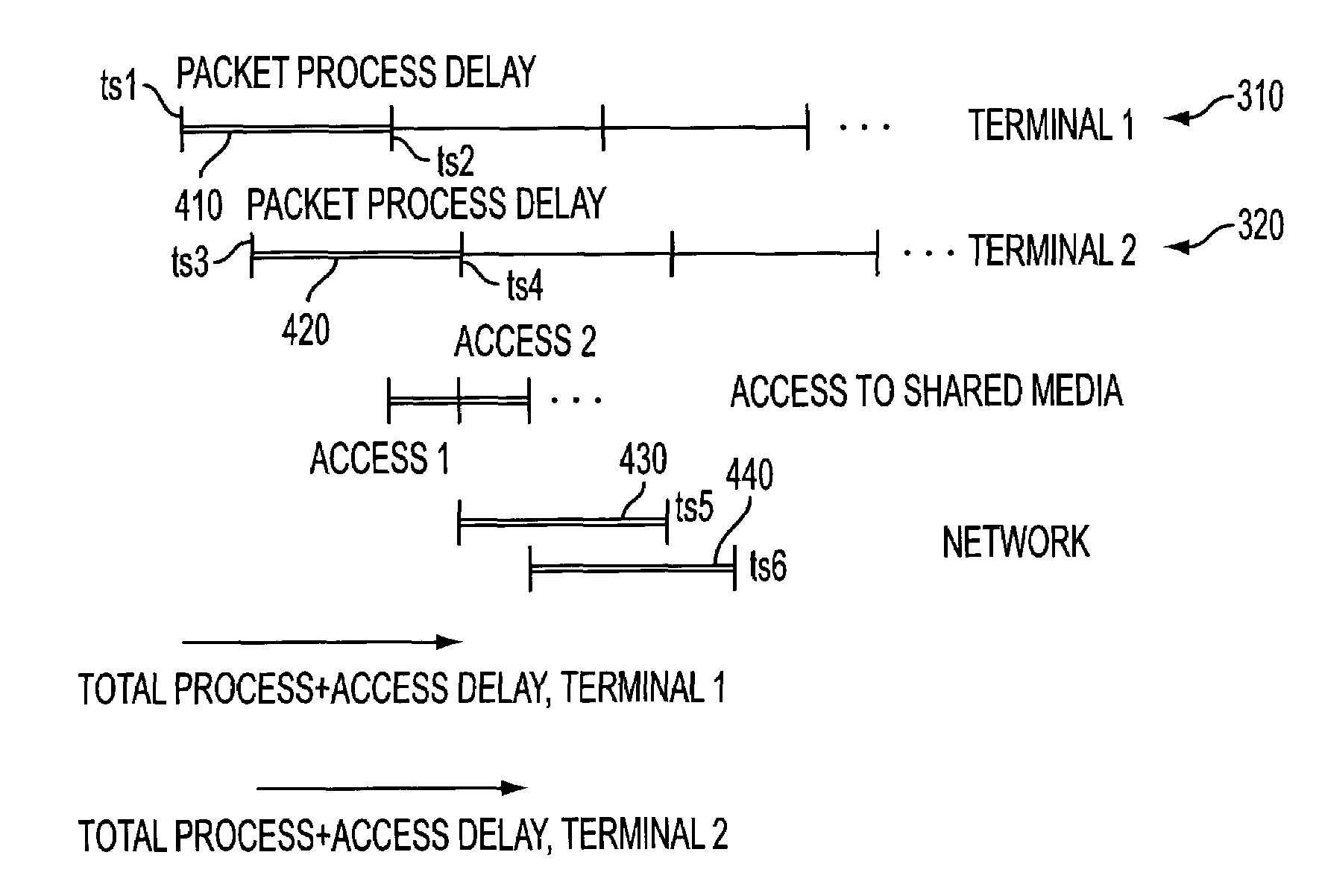
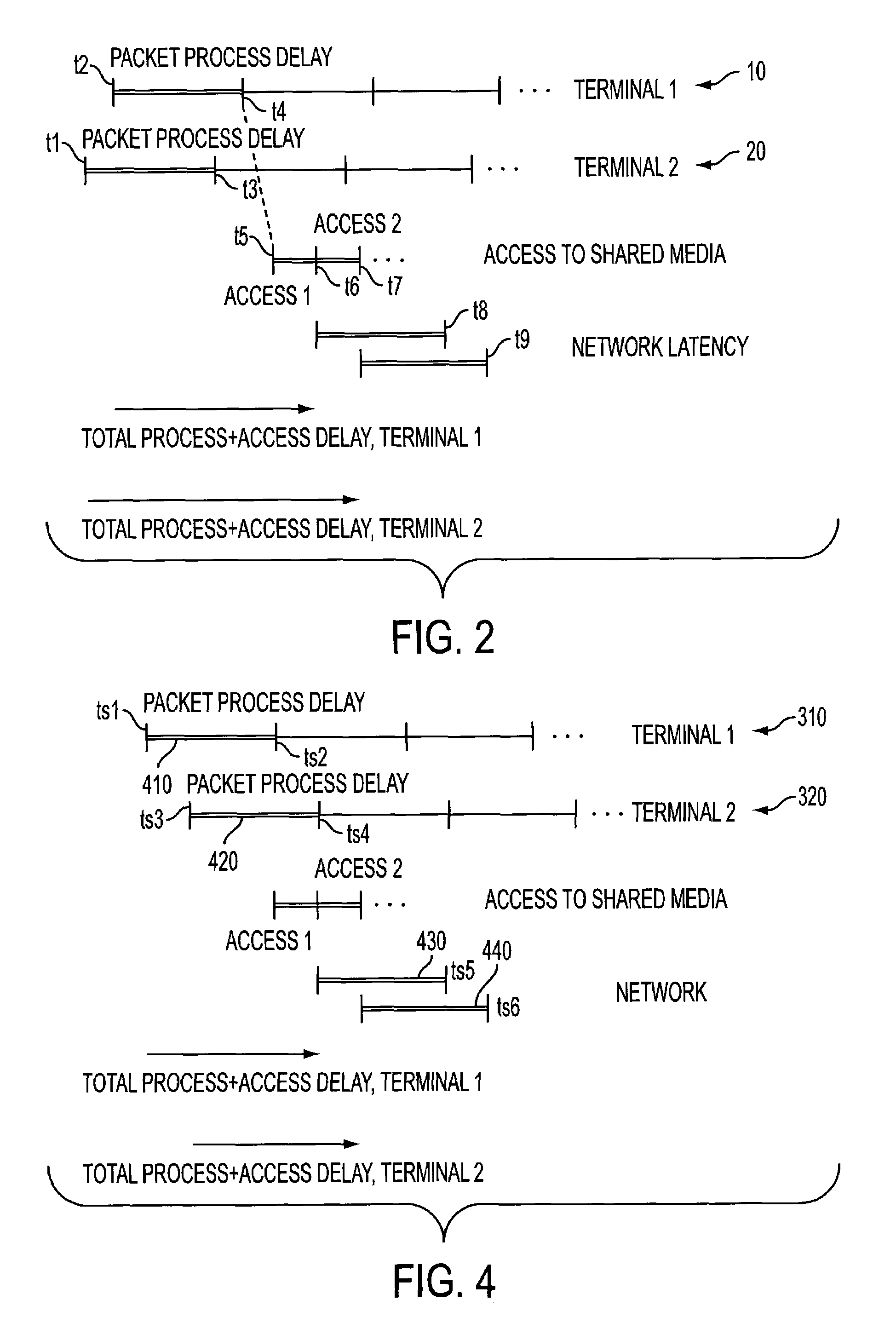
Reducing the access delay for transmitting processed data over transmission data
ActiveUS7243150B2Reducing access-delayReduce transmission latencyMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork terminationModem device
The present invention describes a method and apparatus for reducing the access-delay and transmission latency in a system where a network terminal modem terminates to a network over a transmission media. In a network the processing of input data to be transmitted as processed data on the transmission media is synchronized with a time period when the transmission media is to be allocated for transmitting the processed data. Synchronization is achieved by determining when access to the transmission media will be granted for transmitting the processed data and synchronizing the processing of the input data with the determined time. Thereby the synchronizing results in the processing being completed at a time relatively close to the time when access to the transmission media is granted. Thus the need to store the processed data awaiting transmission is significantly reduced and thereby reducing the access delay and transmission latency.
Owner:RADWIN
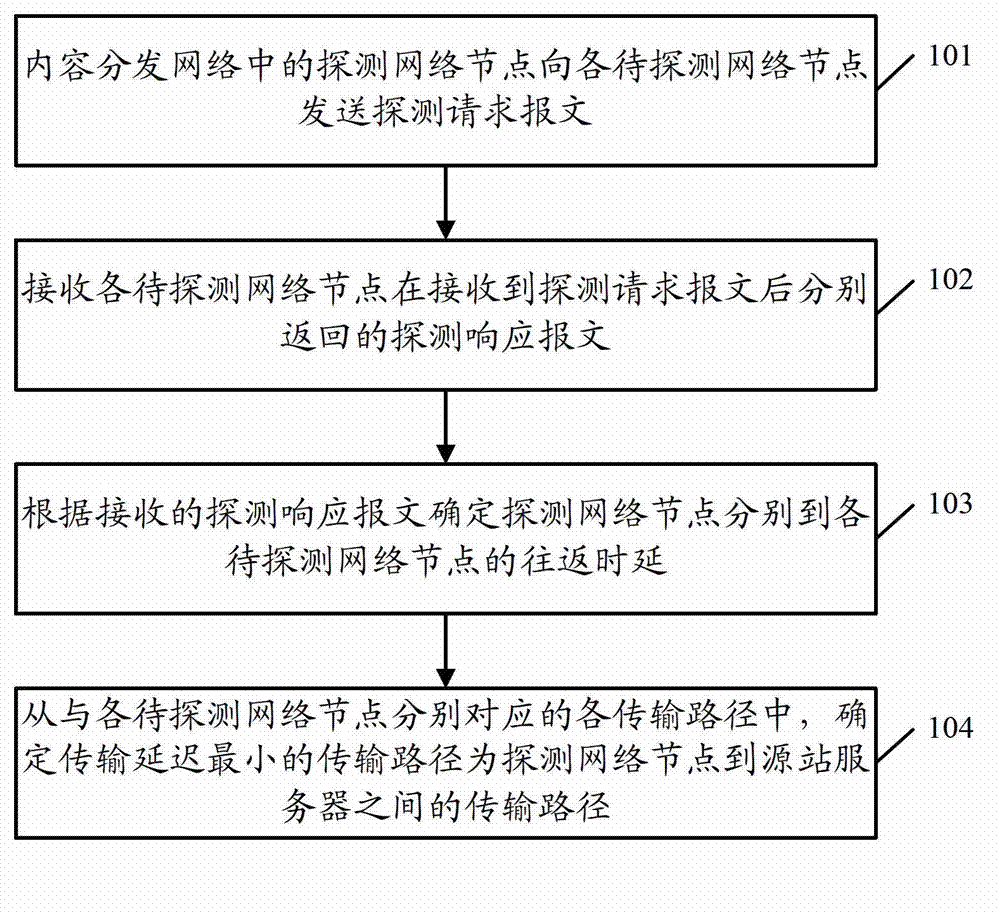
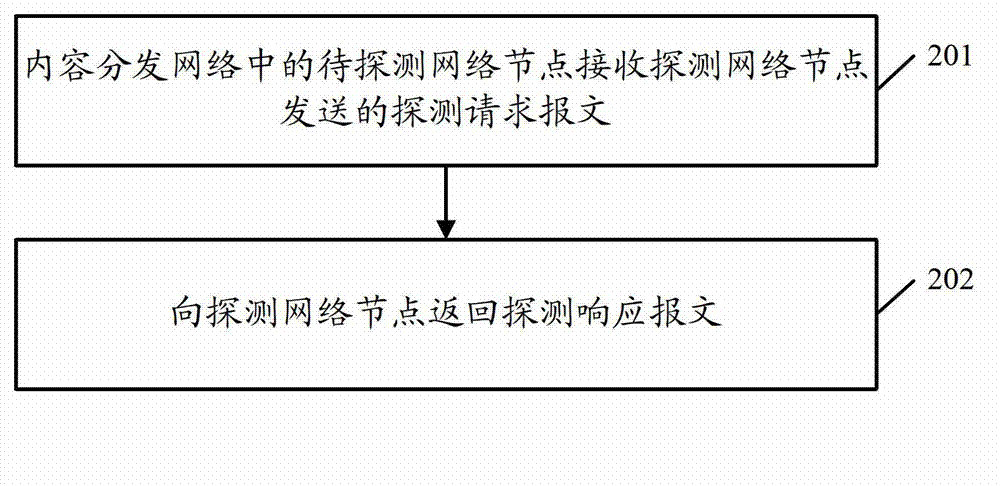
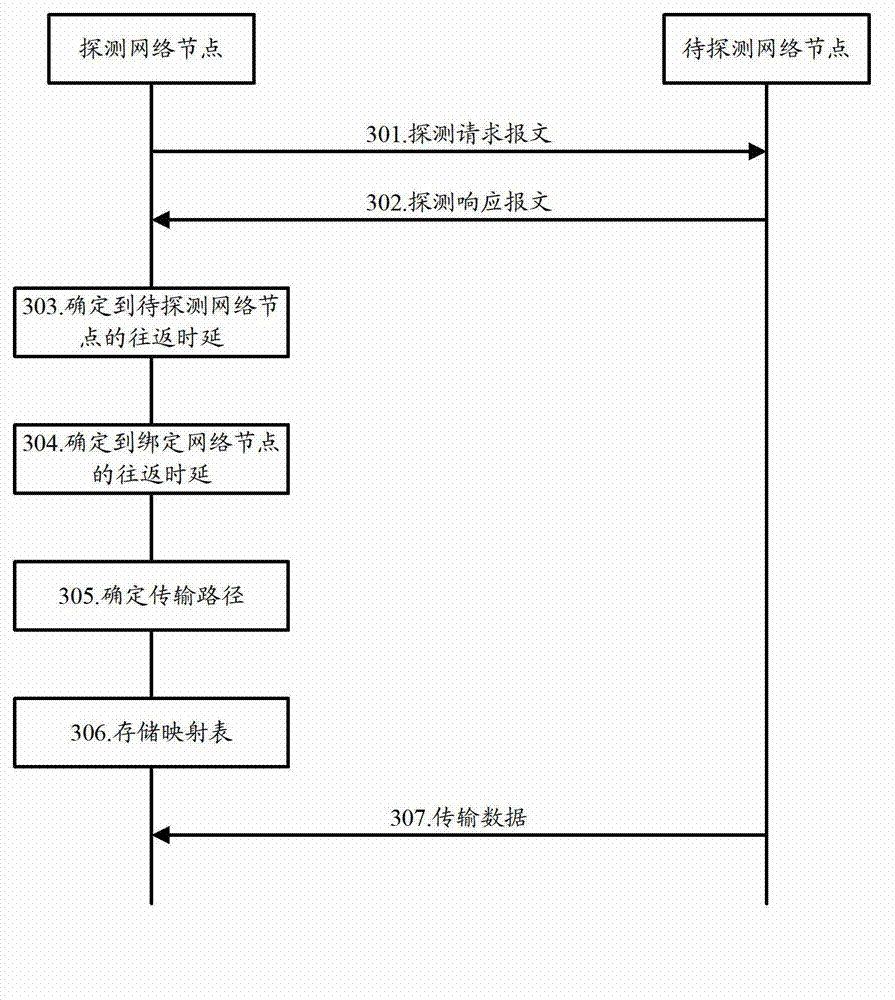
Data transmission path determination method, network node and content delivery network system
InactiveCN103051709AImprove data transfer efficiencyImprove transmission efficiencyData switching networksTime delaysTransmission latency
The invention discloses a data transmission path determination method, a network node and a content delivery network system. The method comprises the following steps of: transmitting a detection request message to each network node to be detected by using a detection network node in a content delivery network; receiving a detection response message from each network node to be detected after the network nodes to be detected receive the detection request messages, wherein each detection response message carries round-trip time delay from the corresponding network node to be detected to a bound network node bound with a source station server in the content delivery network; determining round-trip time delay from the detection network node to each network node to be detected according to the corresponding received detection response message; and selecting a transmission path with a minimum transmission delay as a transmission path from the detection network node to the source station server from transmission paths corresponding to the network nodes to be detected respectively. According to the scheme, the data transmission efficiency can be improved by determining the data transmission path with the minimum transmission delay.
Owner:SINA COM TECH (CHINA) CO LTD
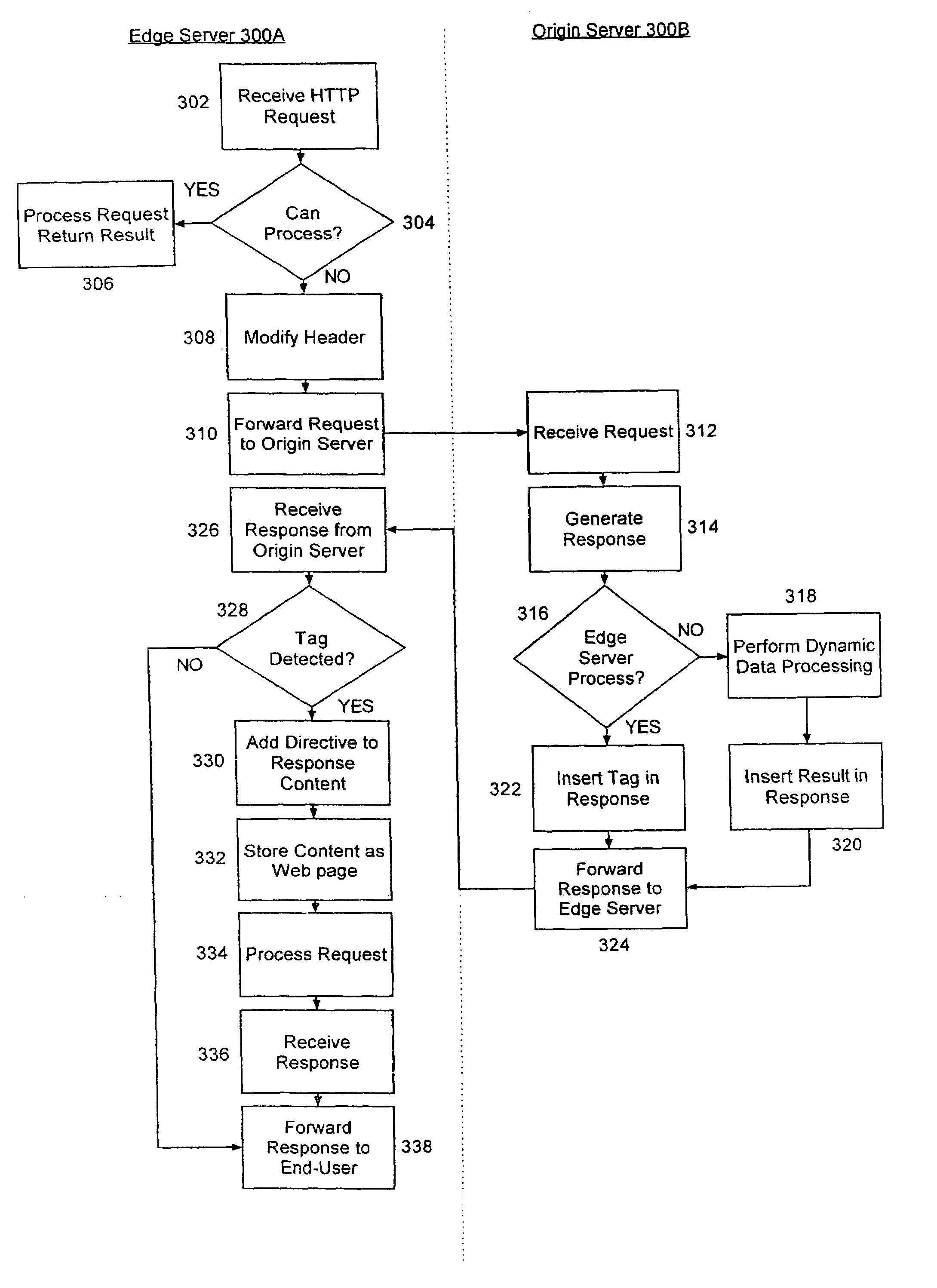
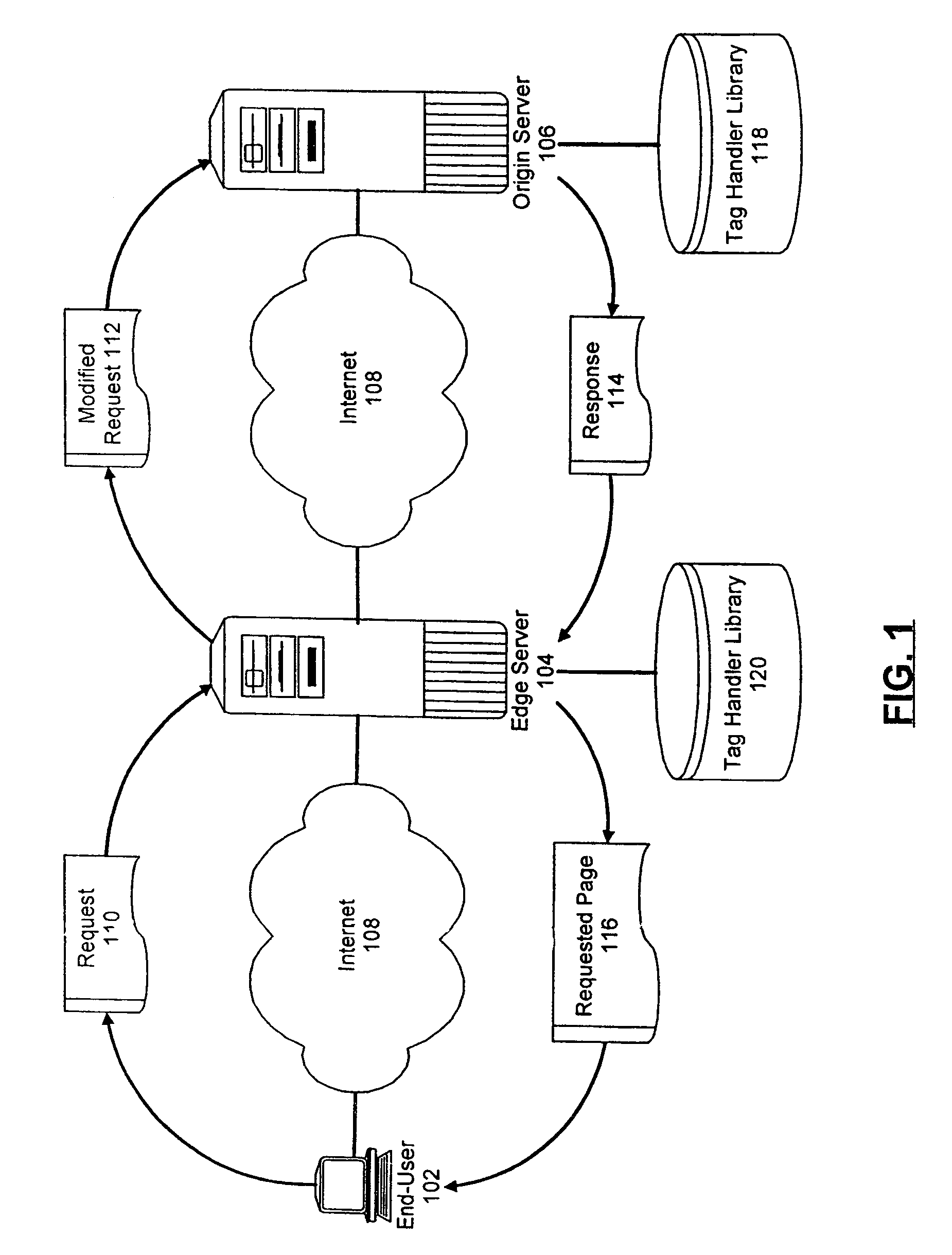
Selectively handling data processing requests in a computer communications network
InactiveUS7155478B2Blocking in networkNetwork latencyMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer networkEdge server
A system and method for selectively handling requests for dynamic data processing. In the system and method, requests for dynamic data processing can be received in an origin server, but the dynamic data processing can be deferred to an edge server in those circumstances where it is dynamically determined that the edge server is capable of performing such dynamic data processing. In this way, network transmission latencies can be avoided by performing dynamic data processing in those edge servers closest to the requesting user.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Estimating available bandwith and enhancing narrow link bandwith estimations in telecommunications networks using existing user traffic
ActiveUS20070242616A1Reduce uncertaintyError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPropagation delayTelecommunications network
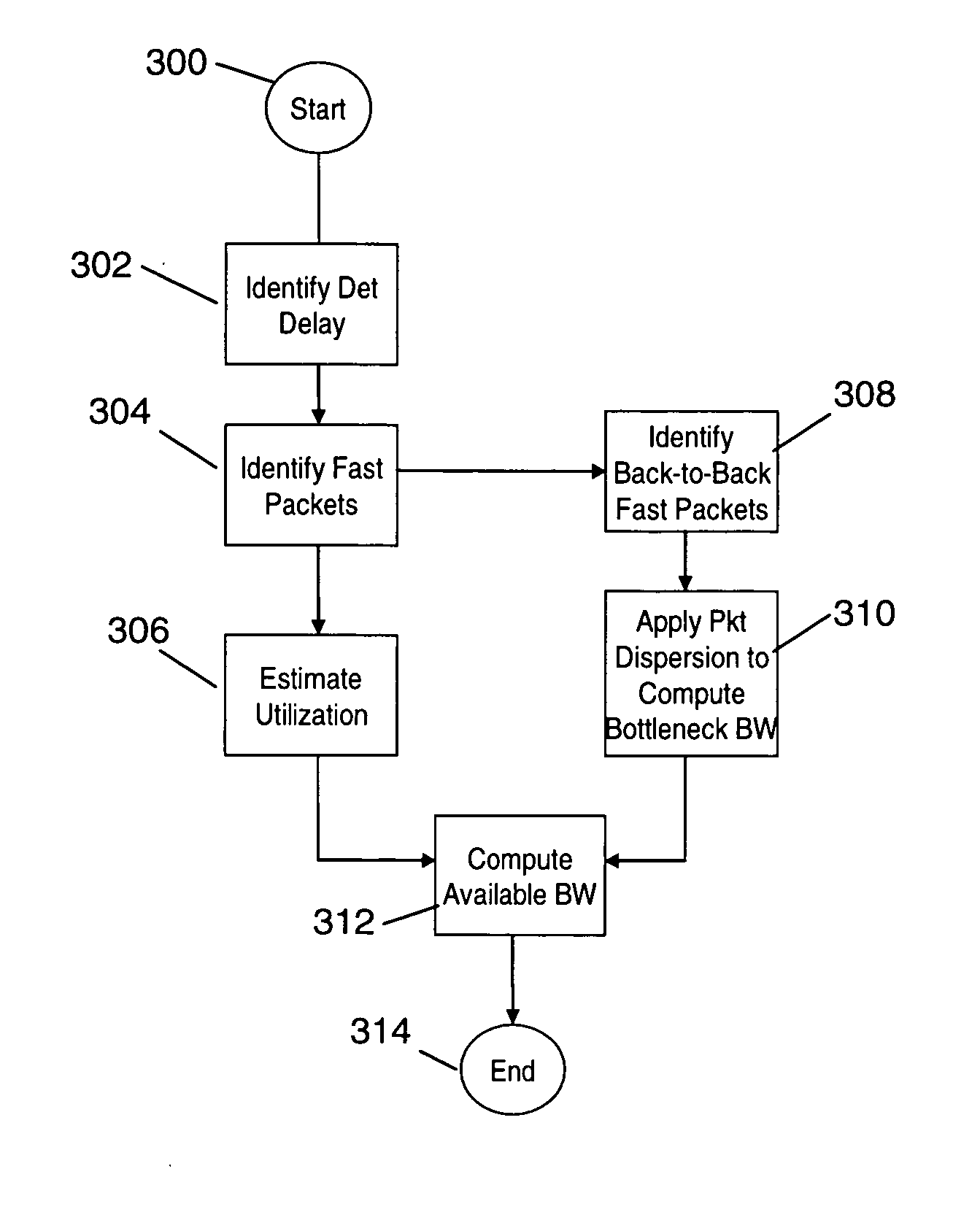
Without using additional probing packets, estimates of the narrow link bandwidth and available bandwidth of a network path are computed based on existing traffic. The network can be of different types such as a wireless battlefield network context or a wired or wireless commercial network environment. “Fast packets”, i.e. those packets which do not experience any queuing delay in the network, are identified. Fast packets are identified to resolve end-to-end packet delay into its constituent components (deterministic, transmission and queuing delays), estimate path utilization and eliminate the uncertainty (false alarms) that causes the prior art method to lose its effectiveness. An estimation algorithm computes end-to-end transmission delay and end-to-end deterministic delay of fast packets traveling along a path in a network. Examples of deterministic delay include satellite propagation delays and clock effects. Then, based on the results of the fast packet identifying algorithm, two logic branches are followed. A first branch calculates utilization and a second branch calculates narrow link bandwidth. The narrow link bandwidth is determined from the packet pair dispersion. The available bandwidth is obtained from the narrow link bandwidth and the utilization. Estimation of available bandwidth for an end-to-end network path allows traffic sources to judiciously regulate the volume of application traffic injected into the network.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Data transmission method and data trasmission system
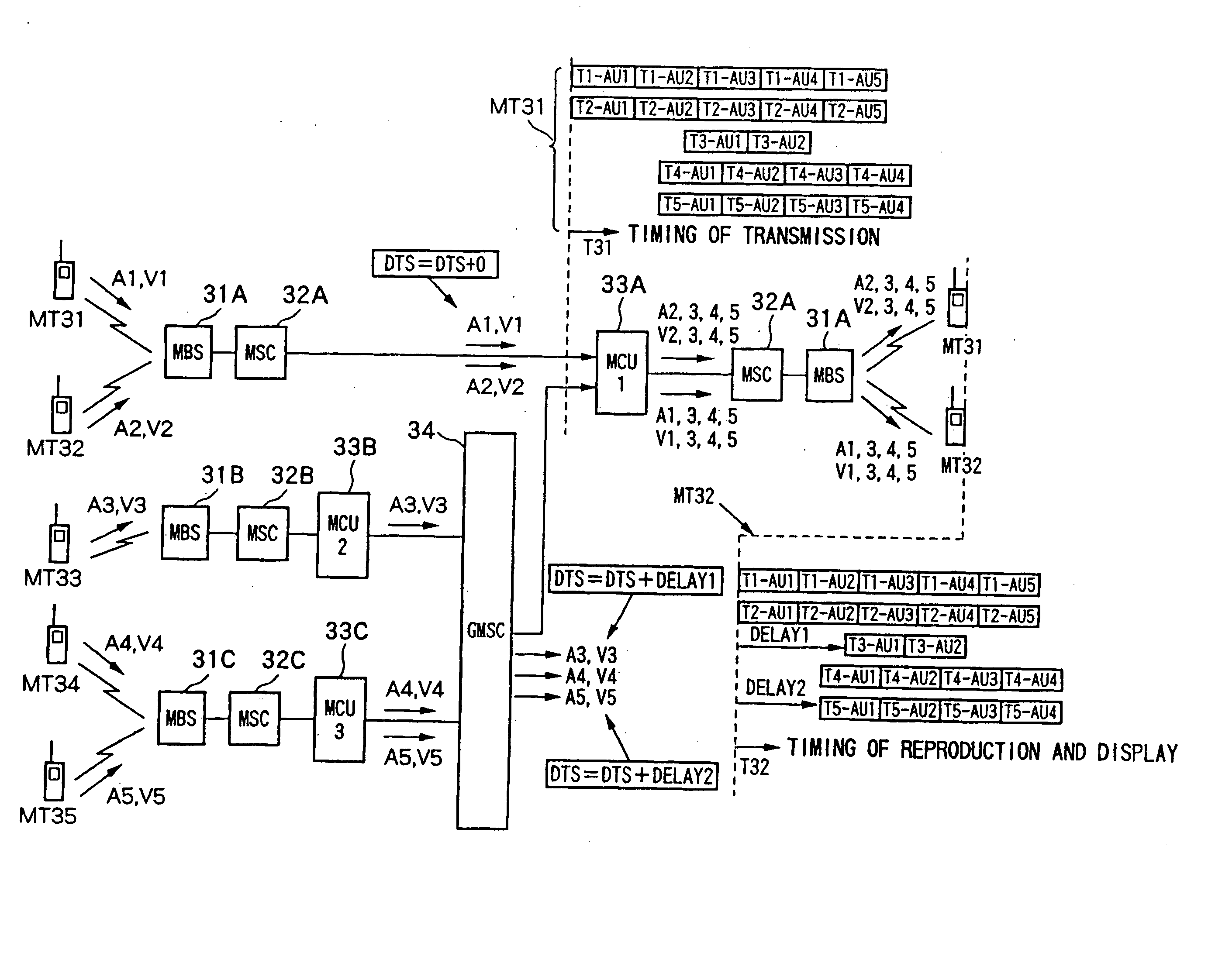
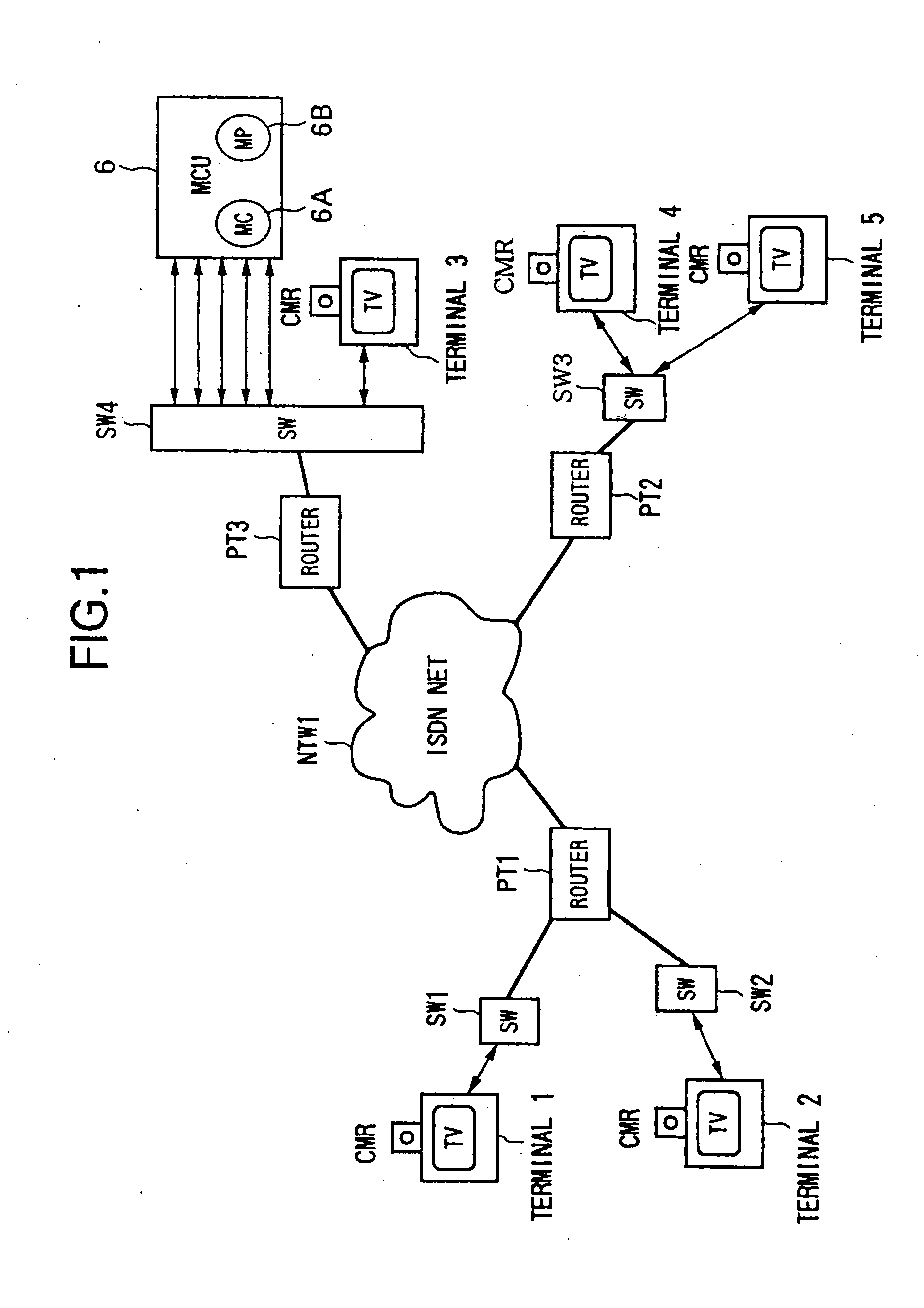
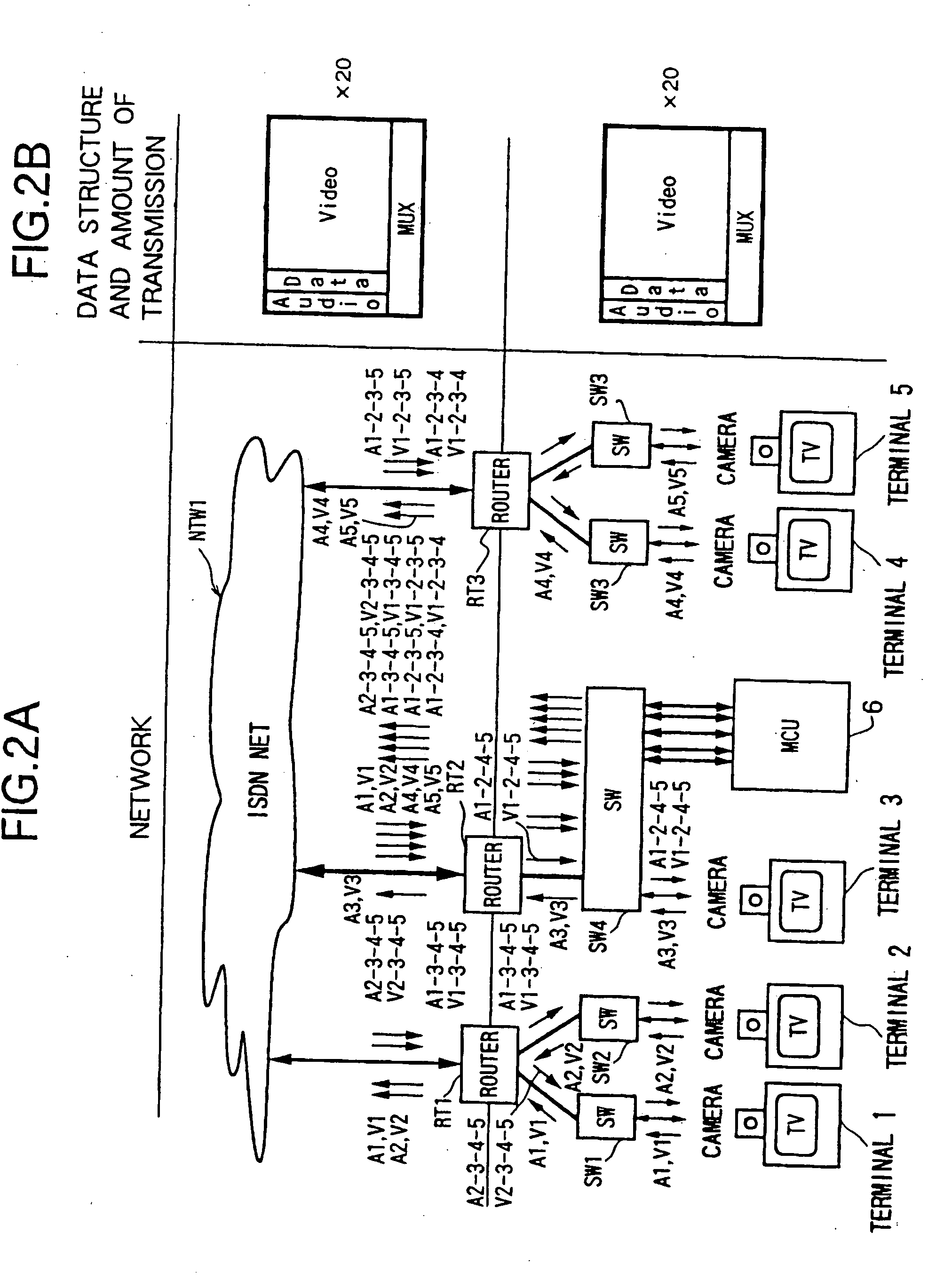
InactiveUS20060038878A1Reduce traffic problemsReduce hardware sizeSpecial service provision for substationTelevision conference systemsMultiplexingTransmission latency
A data transmission method and a data transmission system not requiring a large delay unit for multiplexing and composition and capable of reducing the hardware scale, wherein when transmitting data among multiple points from a plurality of terminals arranged in a network, when the data at multiple points are transmitted to the terminals, in the network, identical packets are added different time stamps in accordance with the transmission delays, whereby the data shifted in accordance with the transmission delays are transmitted.
Owner:TAKASHIMA MASATOSHI +4
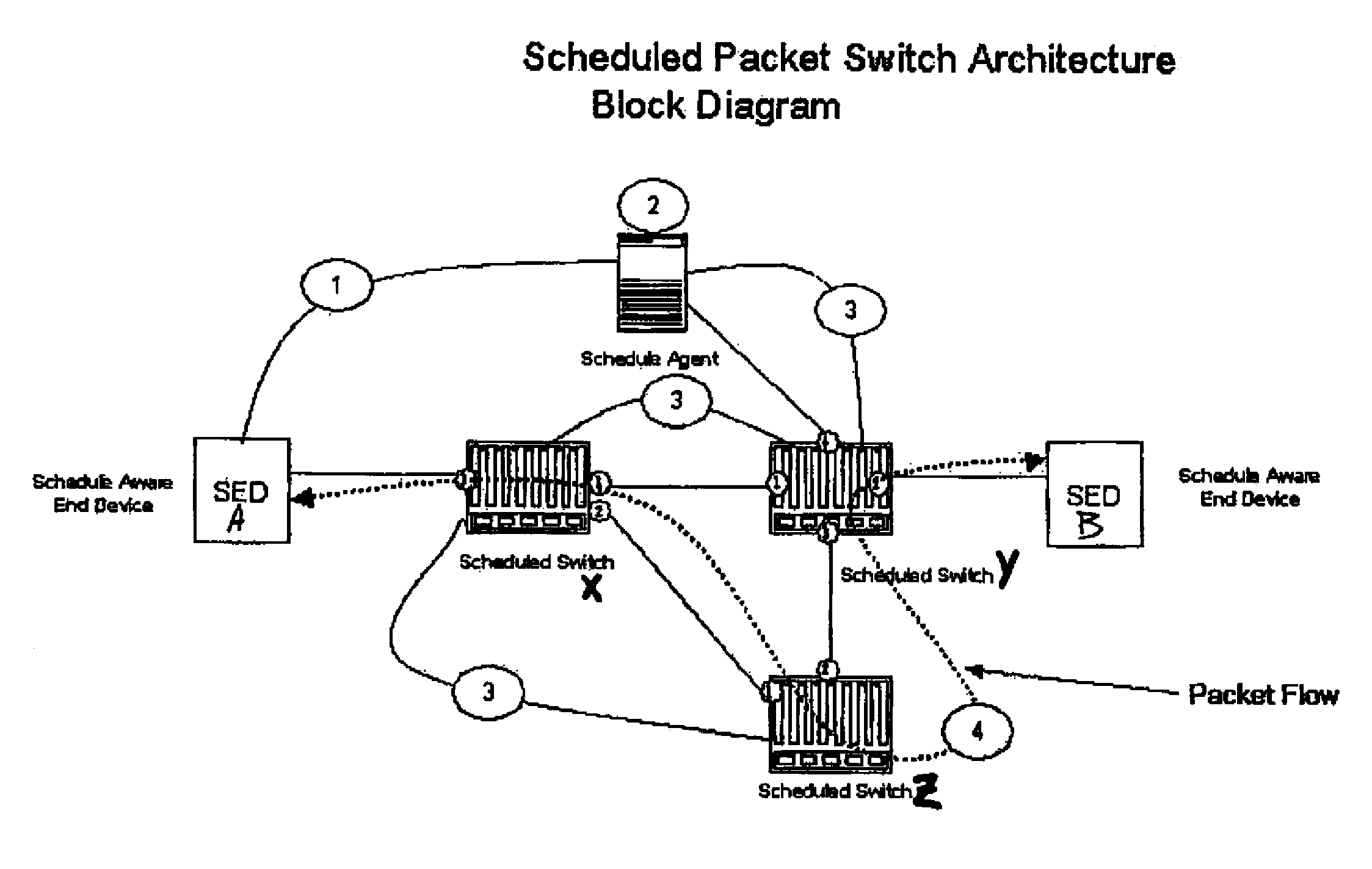
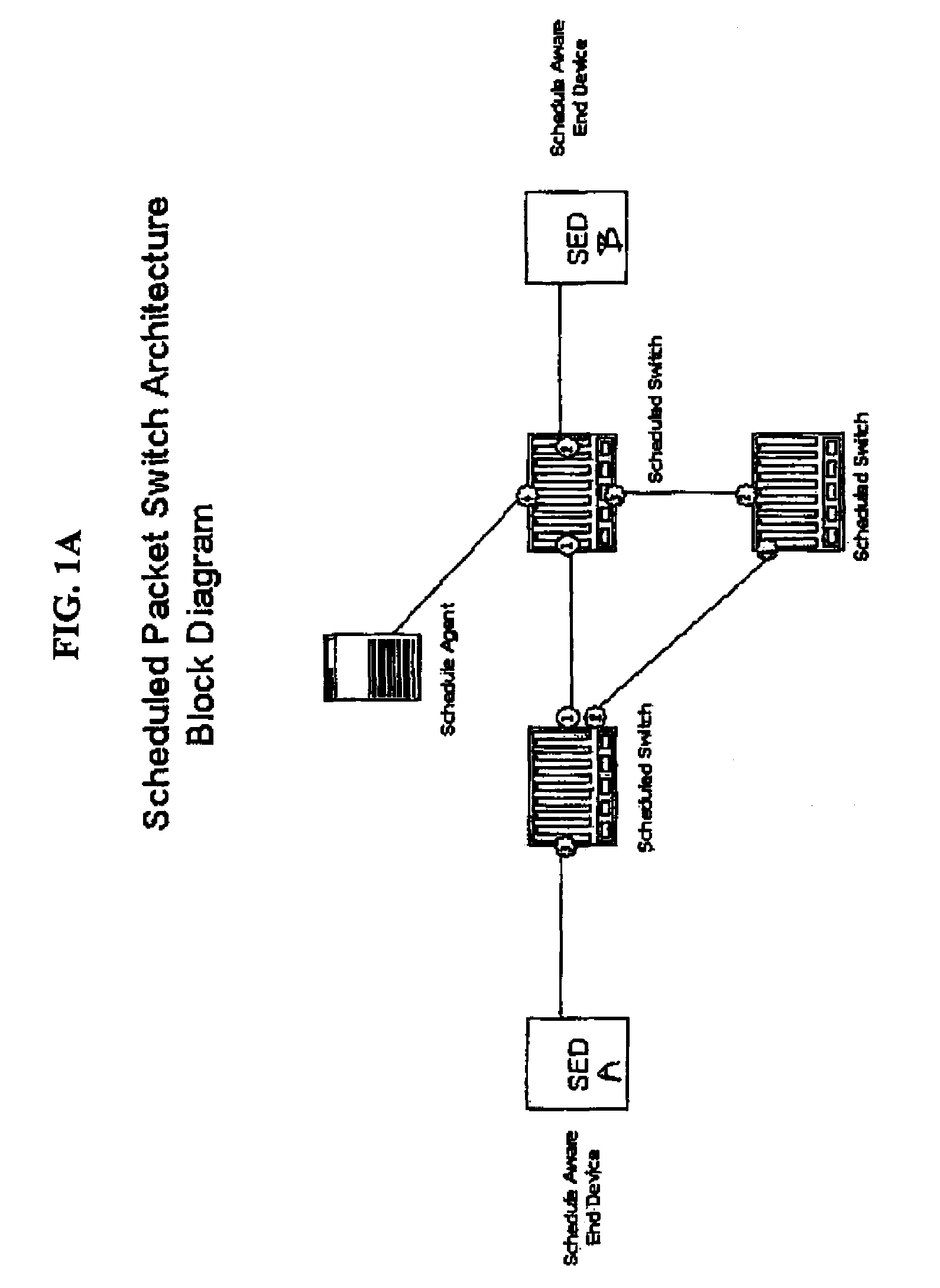
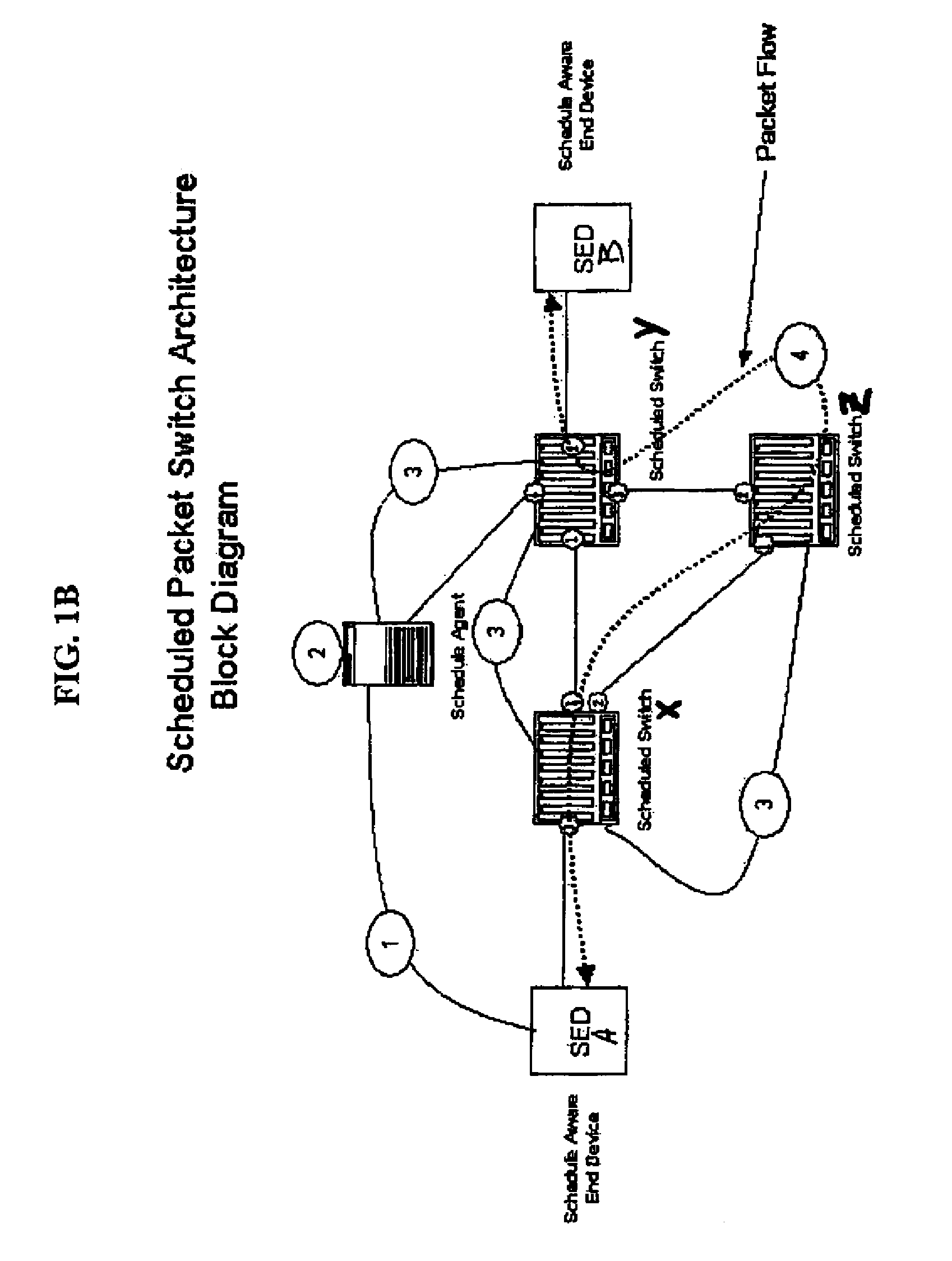
Method for achieving high-availability of itineraries in a real-time network scheduled packet routing system
ActiveUS8477616B1Reduce needGuaranteed bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsAppointment timeTopology information
A system using scheduled times for transmission at each link guarantees bandwidth for transmitting data across a packet network. A scheduling agent determines availability of data paths across a network according to pre-selected criteria and real-time network topology information. Precise schedules are determined for transmission and reception appointments for data packets to traverse each link and switch in the network including compensation for transmission delays and switch latencies, resulting in a fixed packet flow itinerary for each connection. Itineraries are communicated to schedule-aware switches and endpoints and appointment times are reserved for transmission of the scheduled data packets. Scheduled packets arriving at each switch are forwarded according to their predetermined arrival and departure schedules, rather than their headers or contents, relieving the switches from making real-time routing decisions. Any unscheduled transmission times remain available for routing of unscheduled packets according to their IP headers. Real-time transmission of data can be guaranteed in each scheduled path, and schedule selection criteria may be adjusted according to network utilization and tolerable setup delay and end-to-end delay.
Owner:AVAYA INC
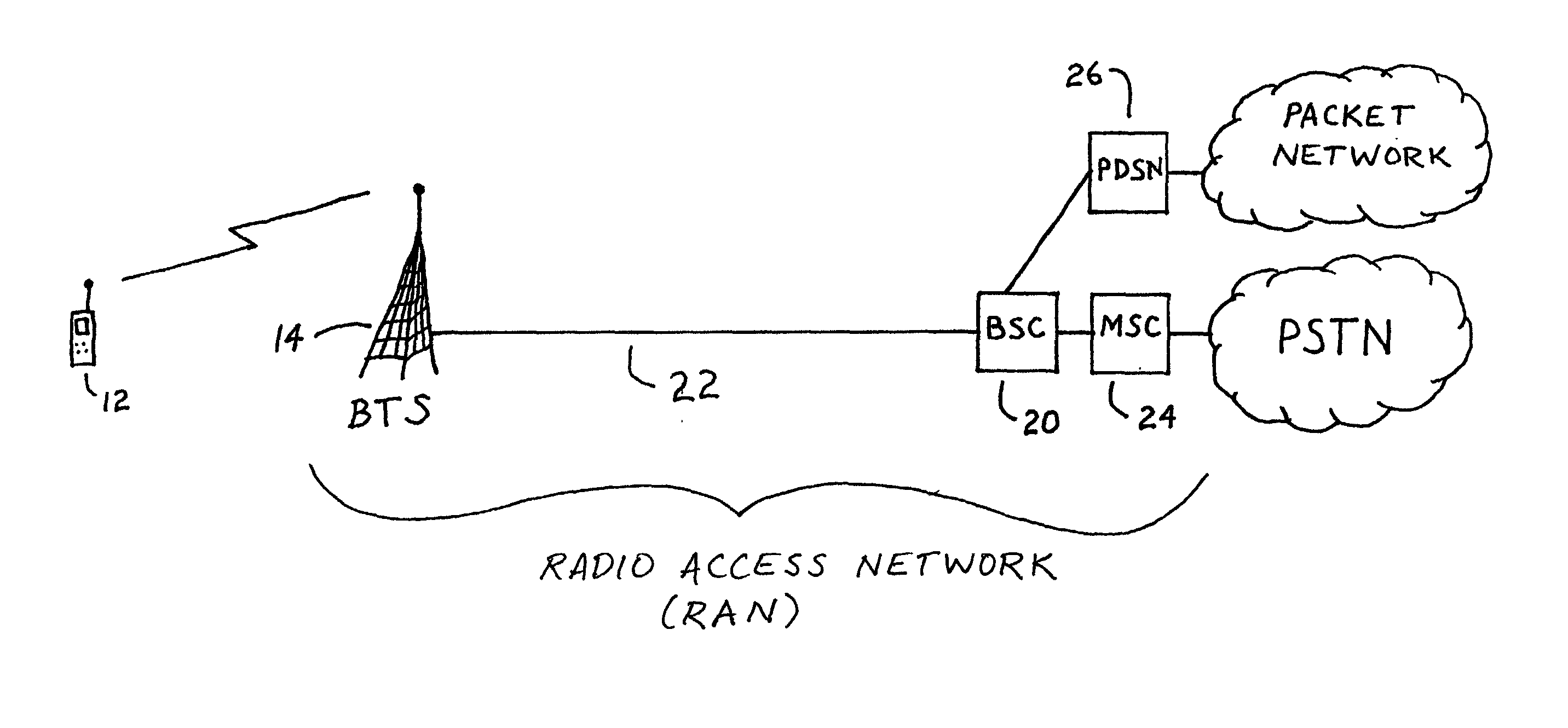
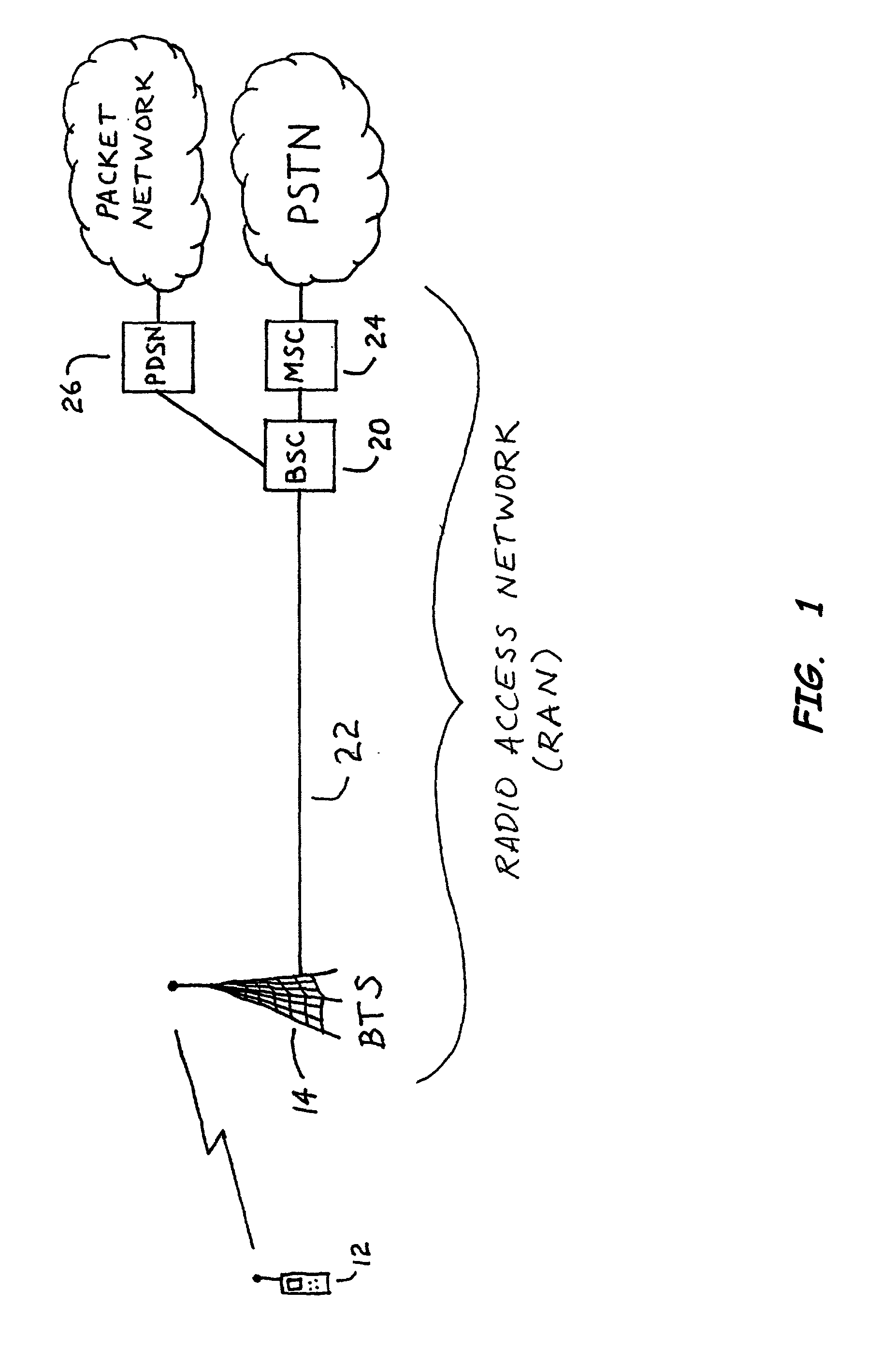
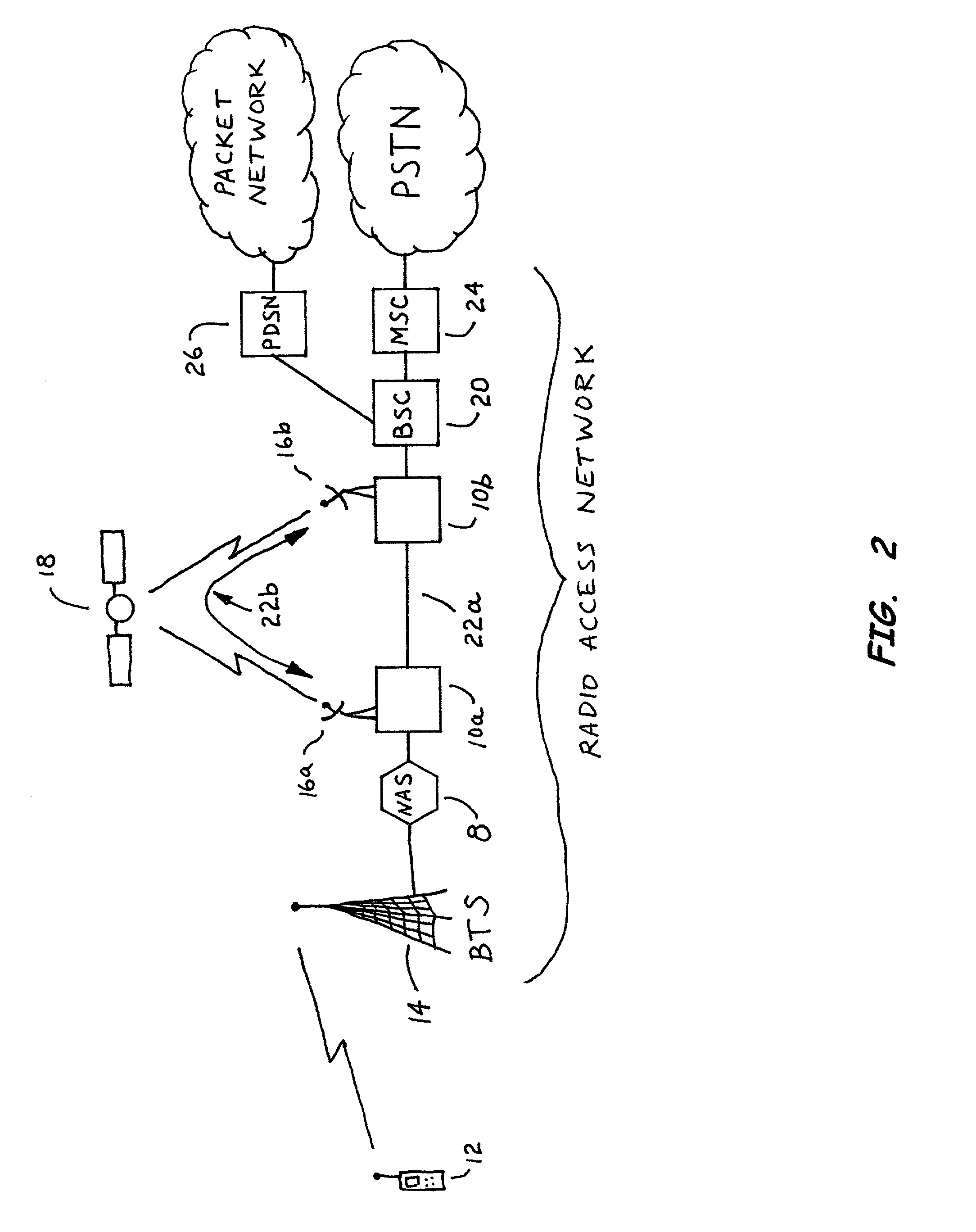
System and method for data routing for fixed cell sites
InactiveUS20040001439A1Improve real-time medium qualityImprove latencyError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkLeast cost
An intelligent switching system and method provides an alternate, least-cost telecommunications link (which may be a wireless link) between a base transceiver station (BTS) and a base station controller (BSC) in a radio access network (RAN). Signals may be routed via the alternate telecommunications link or via an existing telecommunications link based on the sensitivity of the signals to transmission latency. The switching system may determine the sensitivity of the signals to transmission latency.
Owner:SPRING SPECTRUM LP
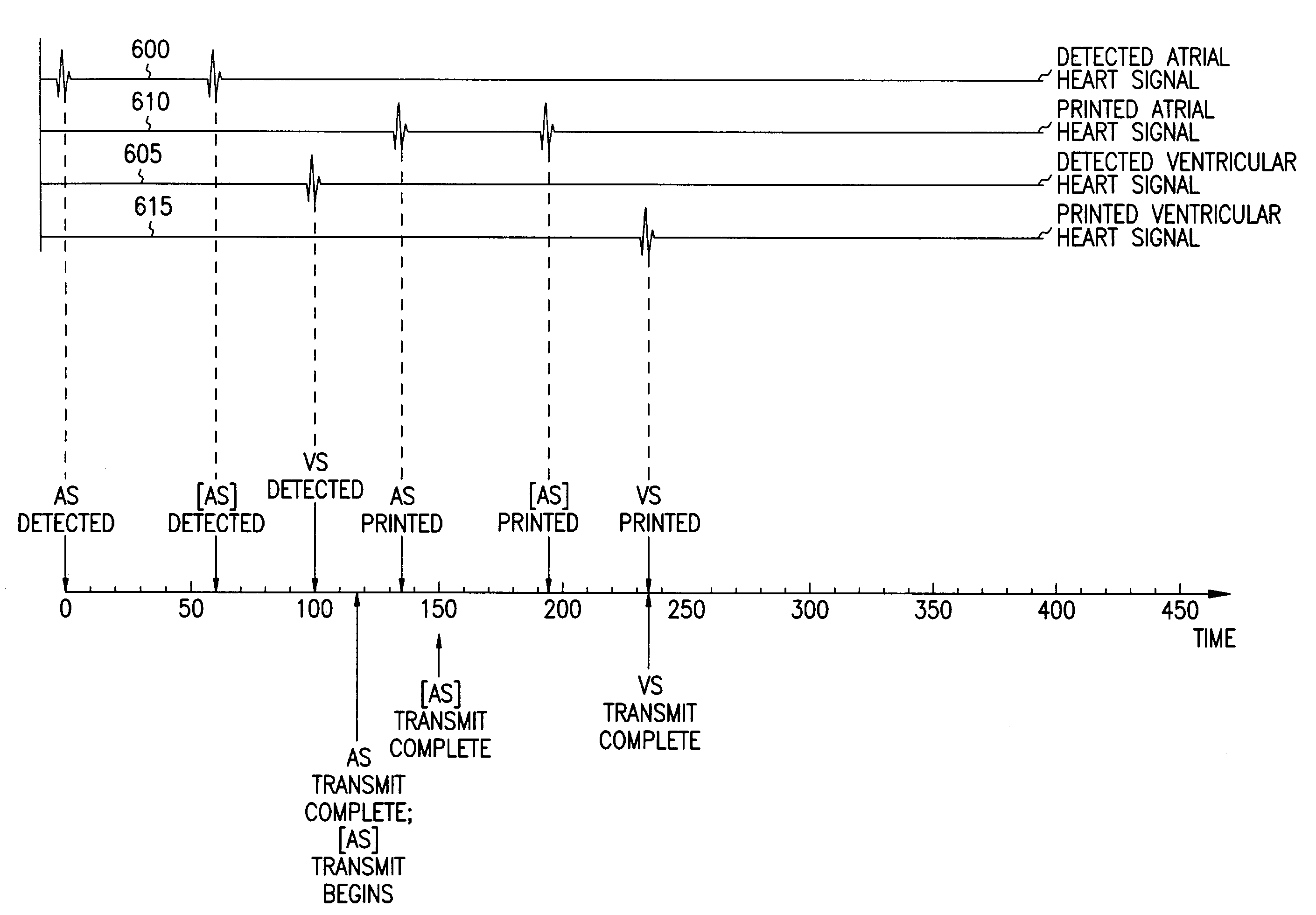
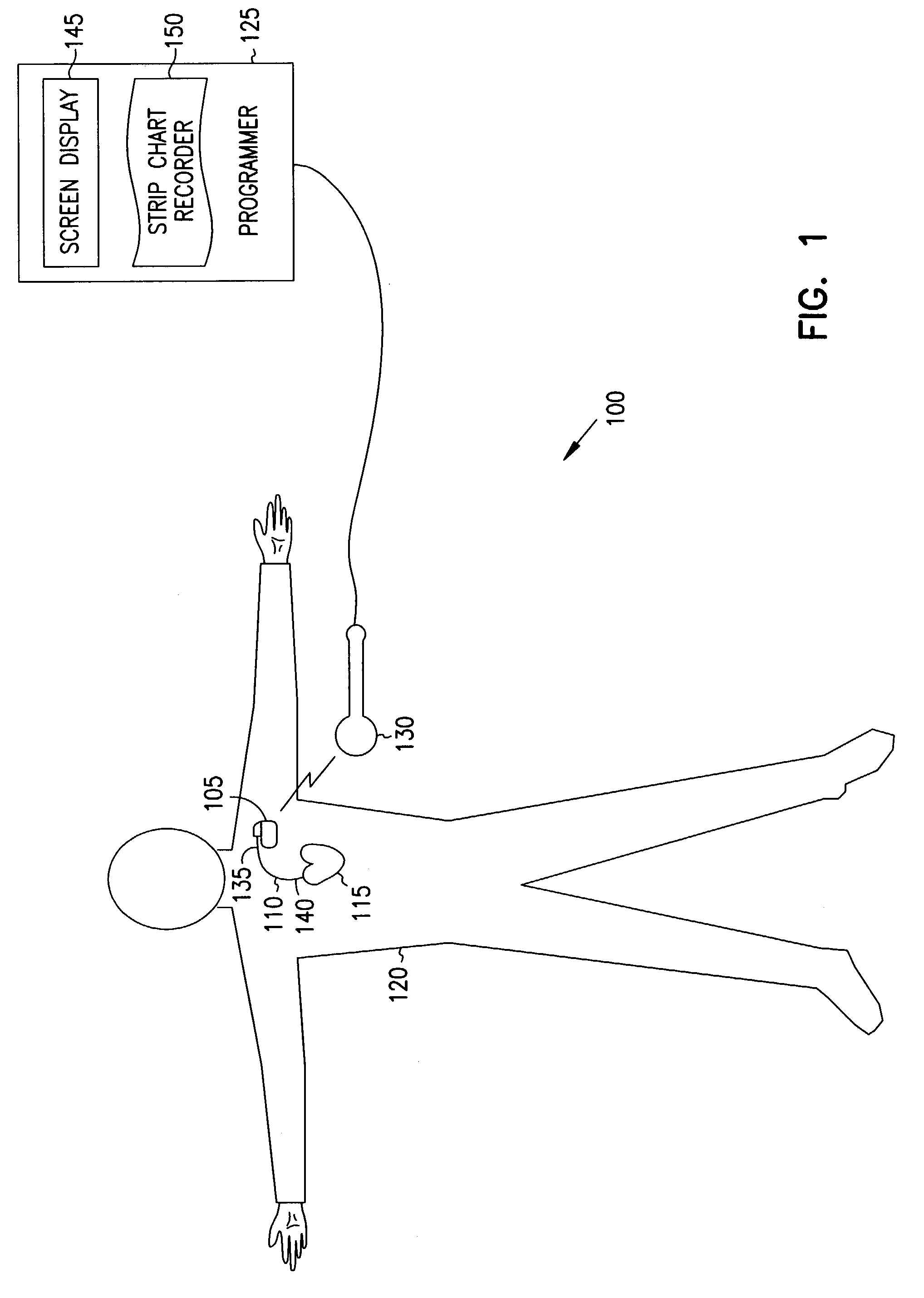
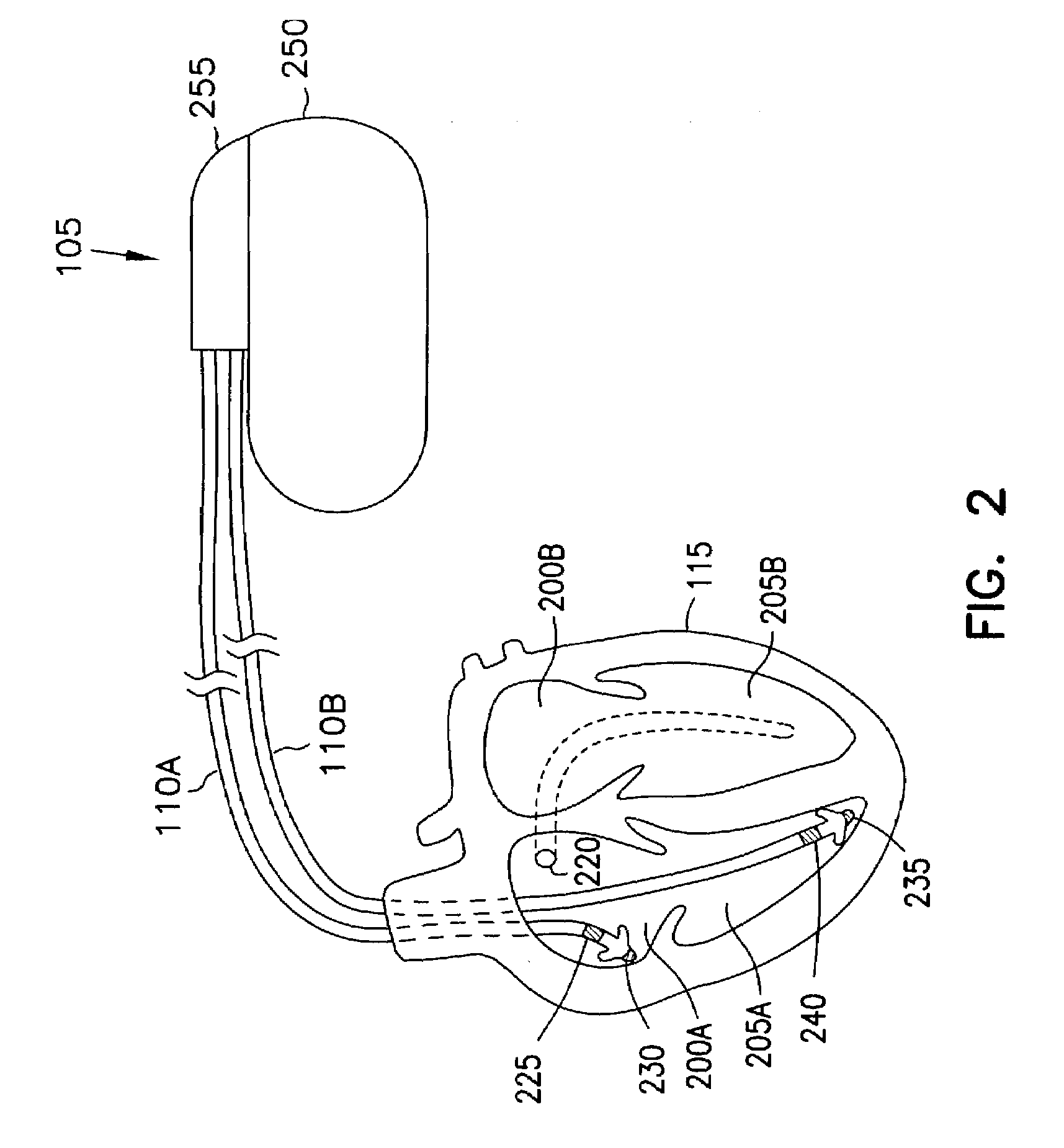
Event marker alignment by inclusion of event marker transmission latency in the real-time data stream
InactiveUS7117037B2Accurate informationHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringReal-time dataData stream
A cardiac rhythm management system transmits event markers from an implantable device to a remote user interface such as an external programmer. The event markers include timestamp information. A printed / displayed event marker representation is aligned to a printed / displayed heart signal representation based at least in part on the timestamp information. Proper alignment of the printed / displayed heart signal representation to the printed / displayed event marker, and proper alignment of the printed / displayed event markers with respect to each other, provides more accurate diagnostic information to the caregiver. This assists the caregiver in using the cardiac rhythm management system to provide a patient with proper cardiac rhythm management therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
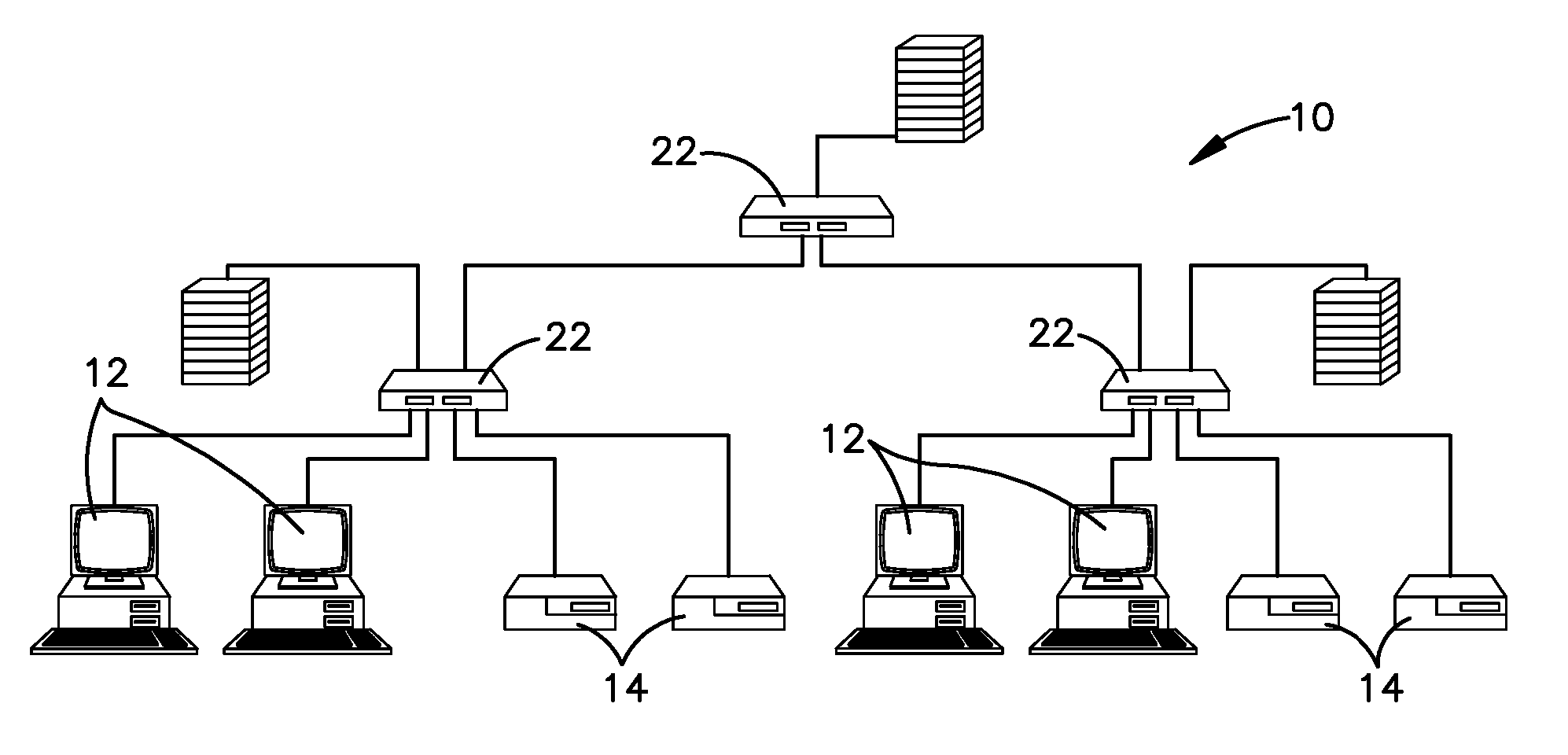
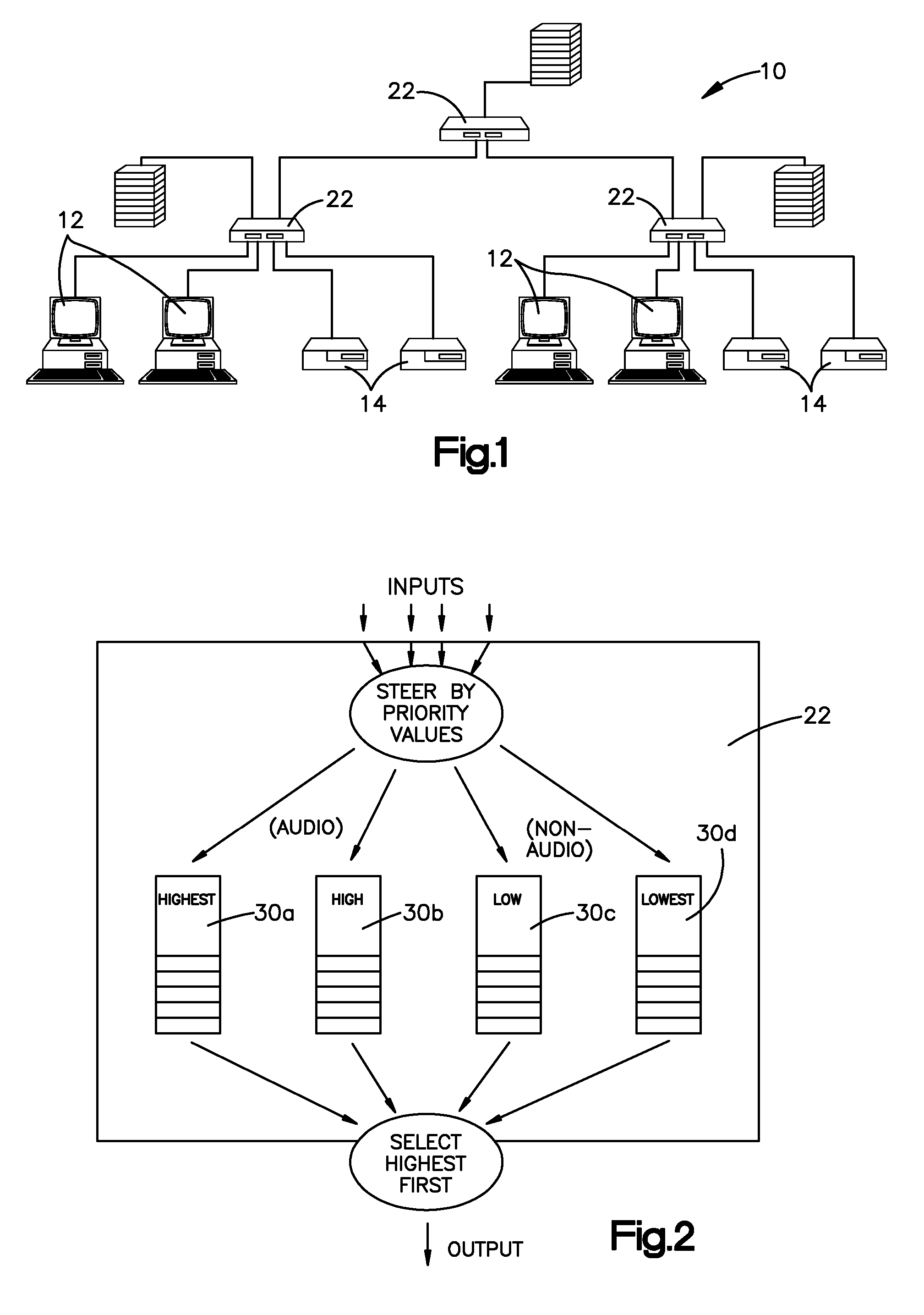
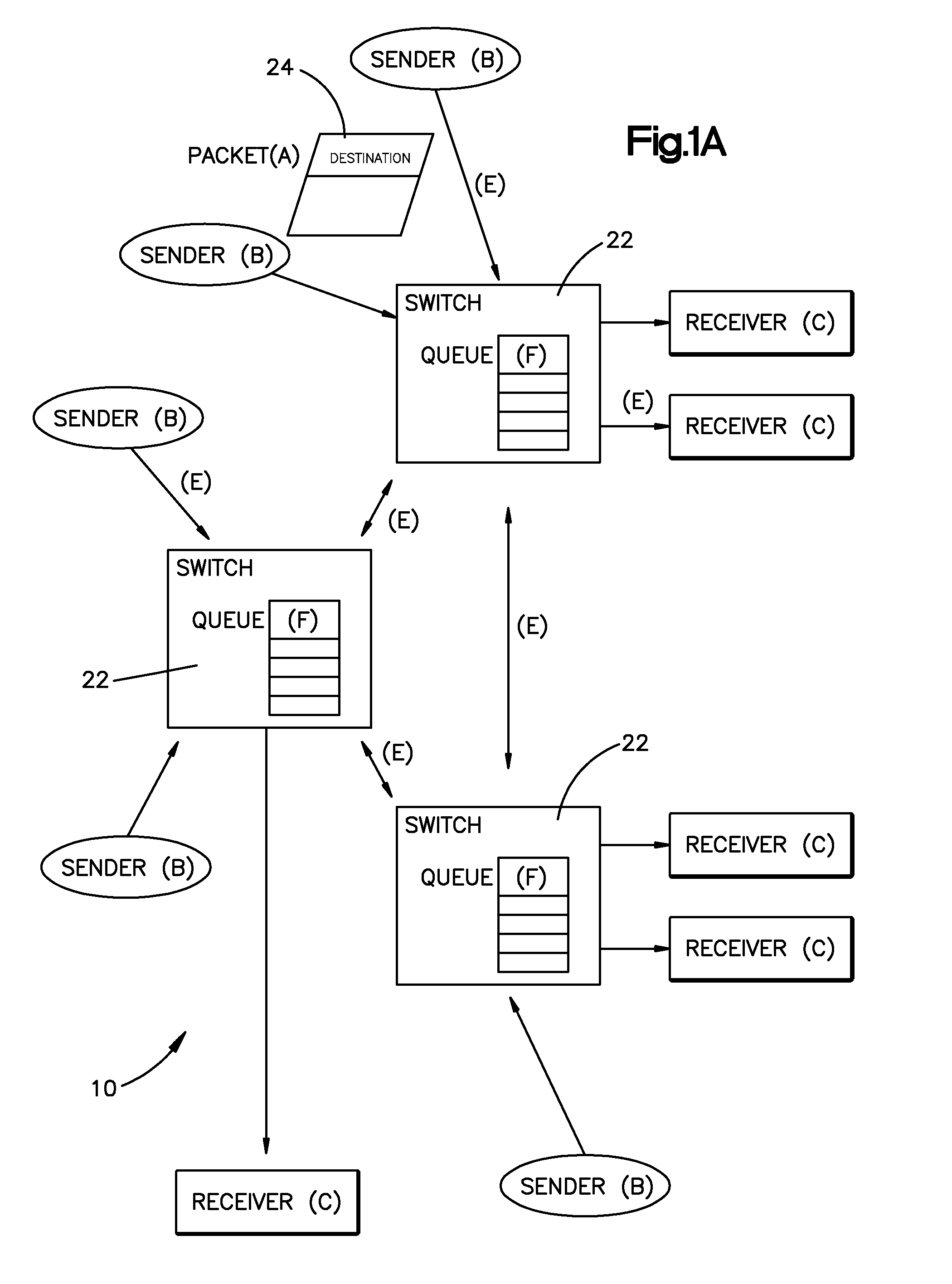
Low Latency Digital Audio over Packet Switched Networks
InactiveUS20070153774A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLatency (engineering)Transmission latency
Method and Apparatus for delivering audio signals from a source node to a destination node on a network. The apparatus uses a number of switches that transmit prioritized data on a packet network. The switches are coupled to a number of send / receive nodes for sending and receiving digital audio signals on the data network. The audio packet size and the receive buffers are sized to store a minimum possible number of audio samples to minimize latency in processing audio signals arriving at said receive node, but still ensure audio delivery without interruption due to packet data network delay. An additional feature of the invention is recovery of clock synchronization over the same data network by novel arrangement of transmission of timing packets on the network. By sending a multiplicity of packets at irregular intervals a minimum network transit delay can be determined by each of the receive nodes which allows the receive nodes to filter out packet network transit delay error and maintain accurate local clocks.
Owner:TLS CORP
Deferral of transmissions in wireless local area network
A wireless local area network comprising a plurality of computing entities communicating over a common communications frequency within a local area network operates a transmission deferral method whereby each computing entity defers its own transmissions if it receives a signal at said communications frequency which is above a threshold value set within said computing entity, and which is decodable. Each computing entity is capable of varying dynamically the value of its threshold level above which receipt of signals results in the computing entity deferring its own transmission. Received signals on the communications frequency which are less than the threshold value do not result in the computing entity deferring its transmissions, but are ignored by the computing entity. The threshold value is varied according to whether traffic from more remote signal sources are sufficiently intense that the local traffic cannot be decoded.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
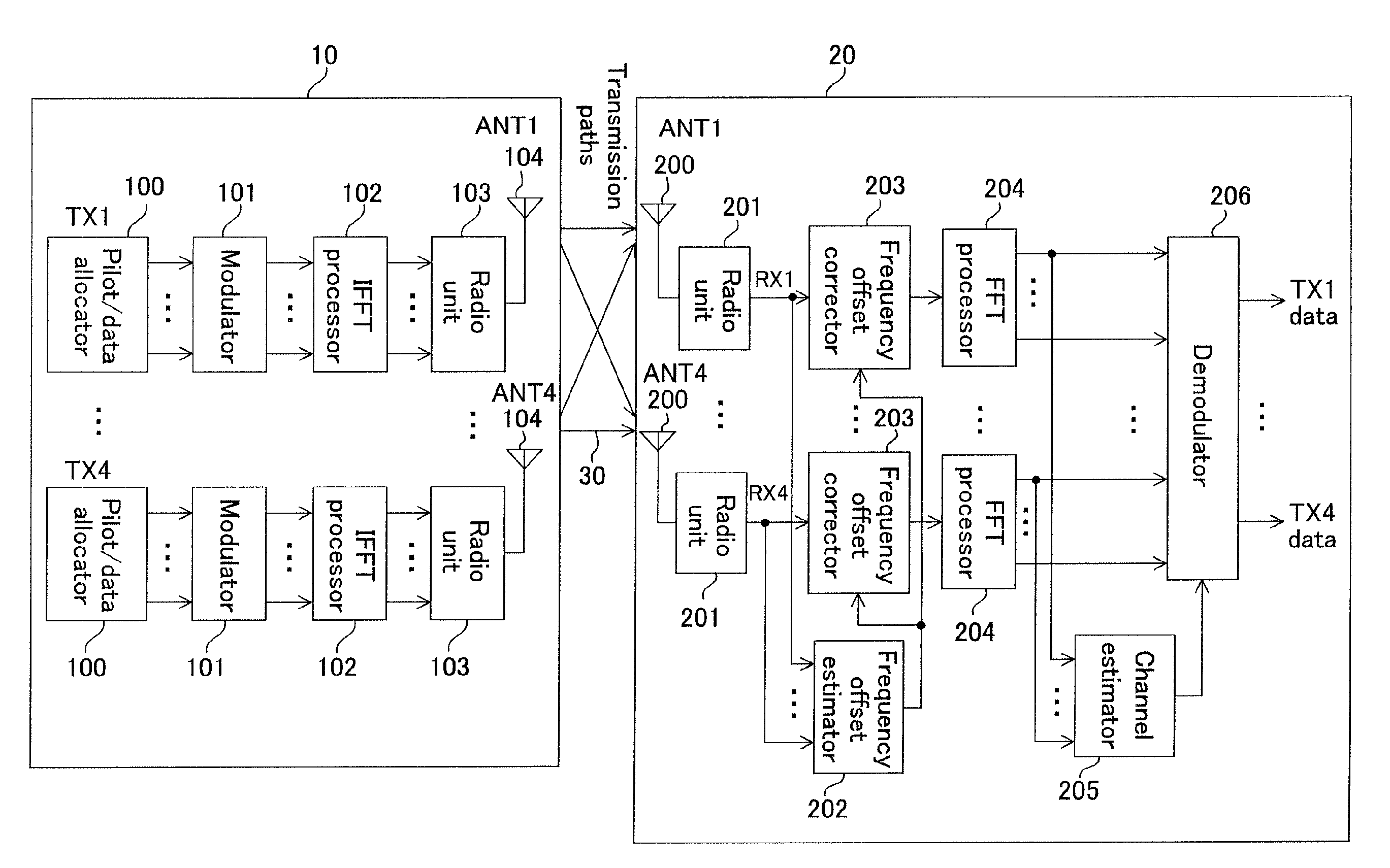
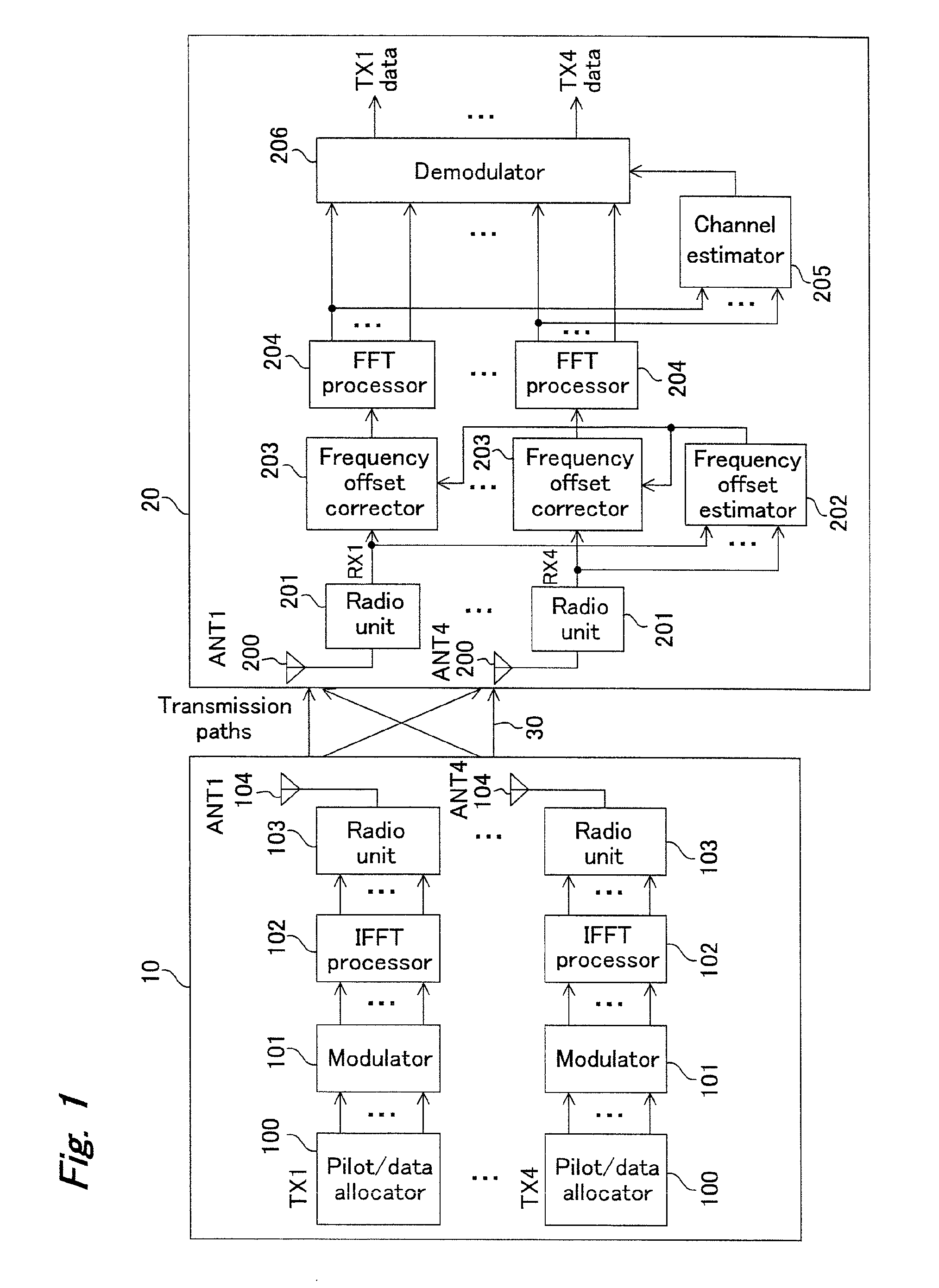
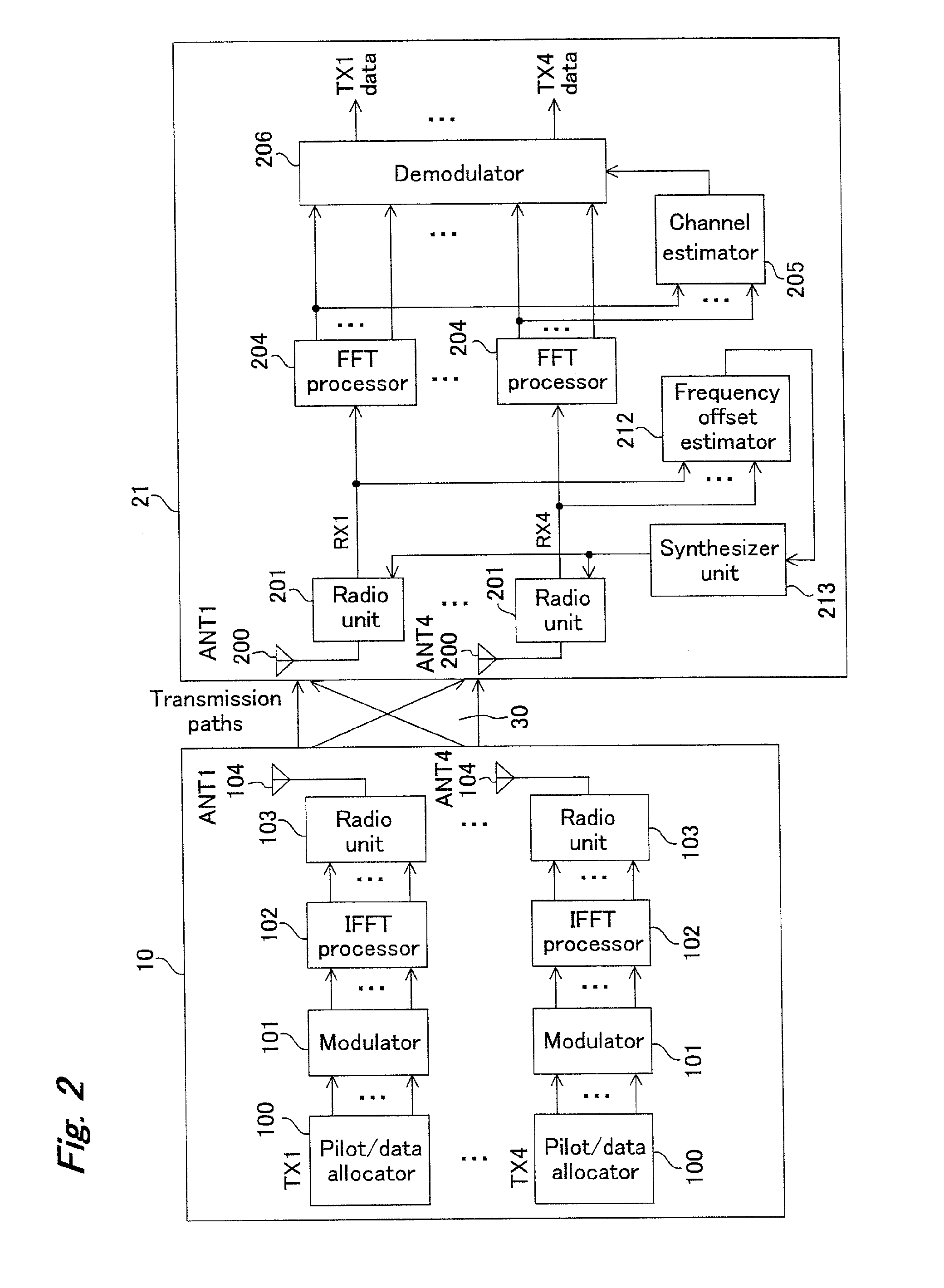
OFDM transmittter and OFDM receiver
InactiveUS20090323515A1Reduce errorsImprove accuracyModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionFrequency compensationTransmission latency
In an environment with large transmission delays, use of an OFDM transmitter which includes: a pilot / data allocator for allocating pilot / data symbols on OFDM symbols and an OFDM receiver which includes: an antenna for receiving the OFDM signals sent out from the antenna of this OFDM transmitter; a ratio unit for frequency transforming the OFDM signals received as RF signals to baseband signals; a frequency offset estimate for estimating an offset value; and a frequency offset corrector for performing frequency compensation by the amount of the frequency offset, improves data transmission efficiency while reducing interference of data between sub-carriers to prevent degradation of reception characteristics by performing appropriate frequency offset correction.
Owner:SHARP KK
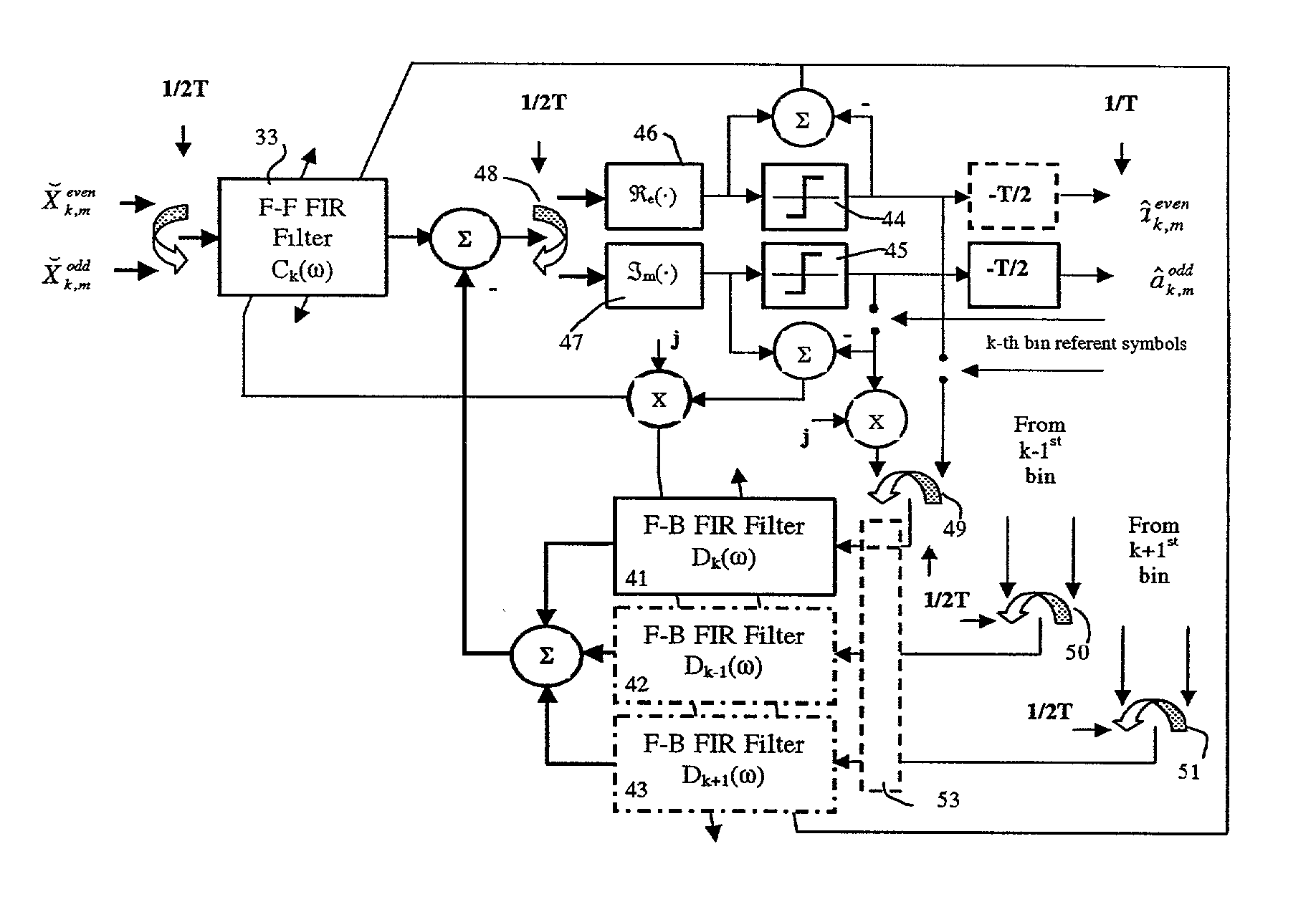
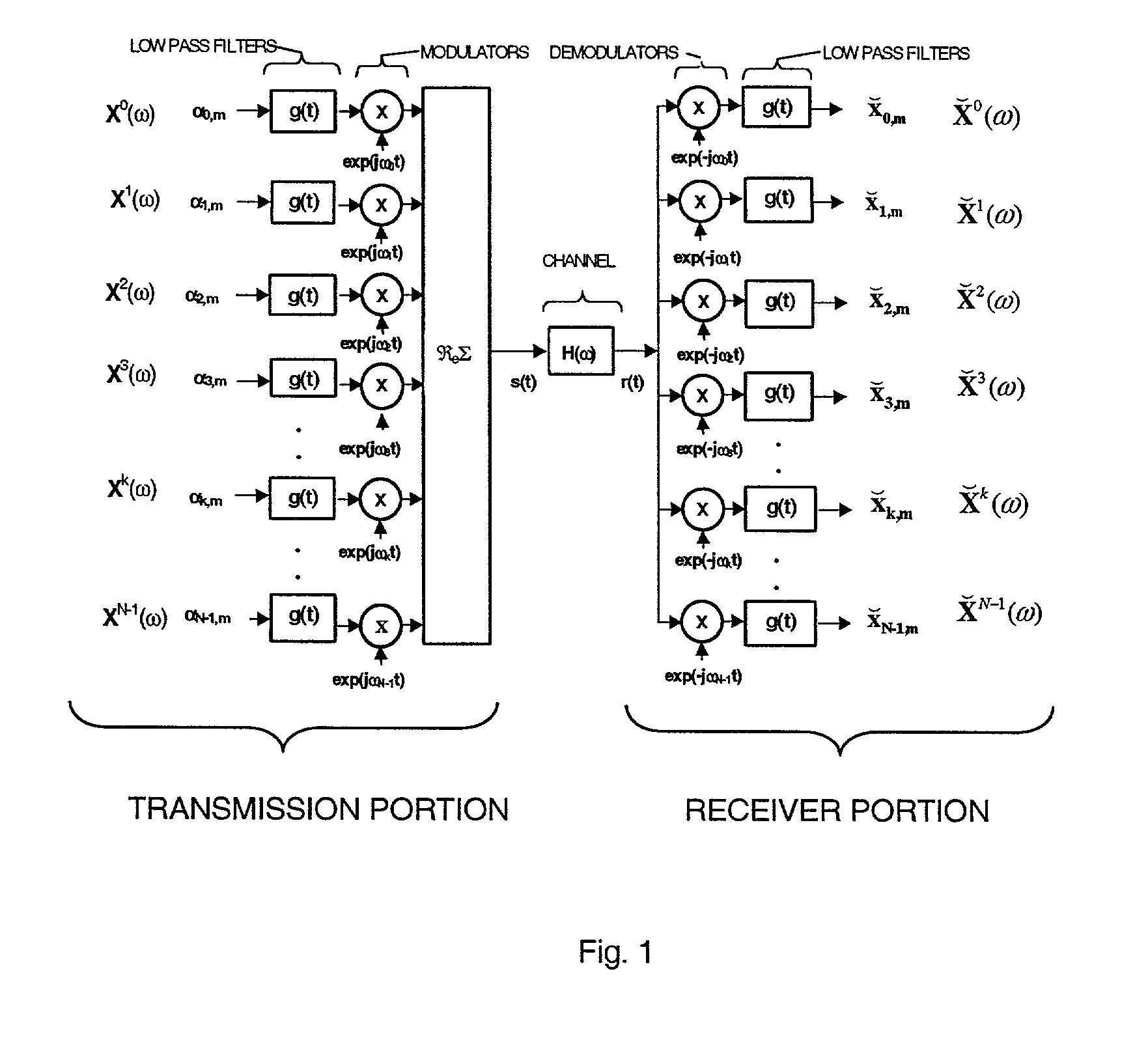
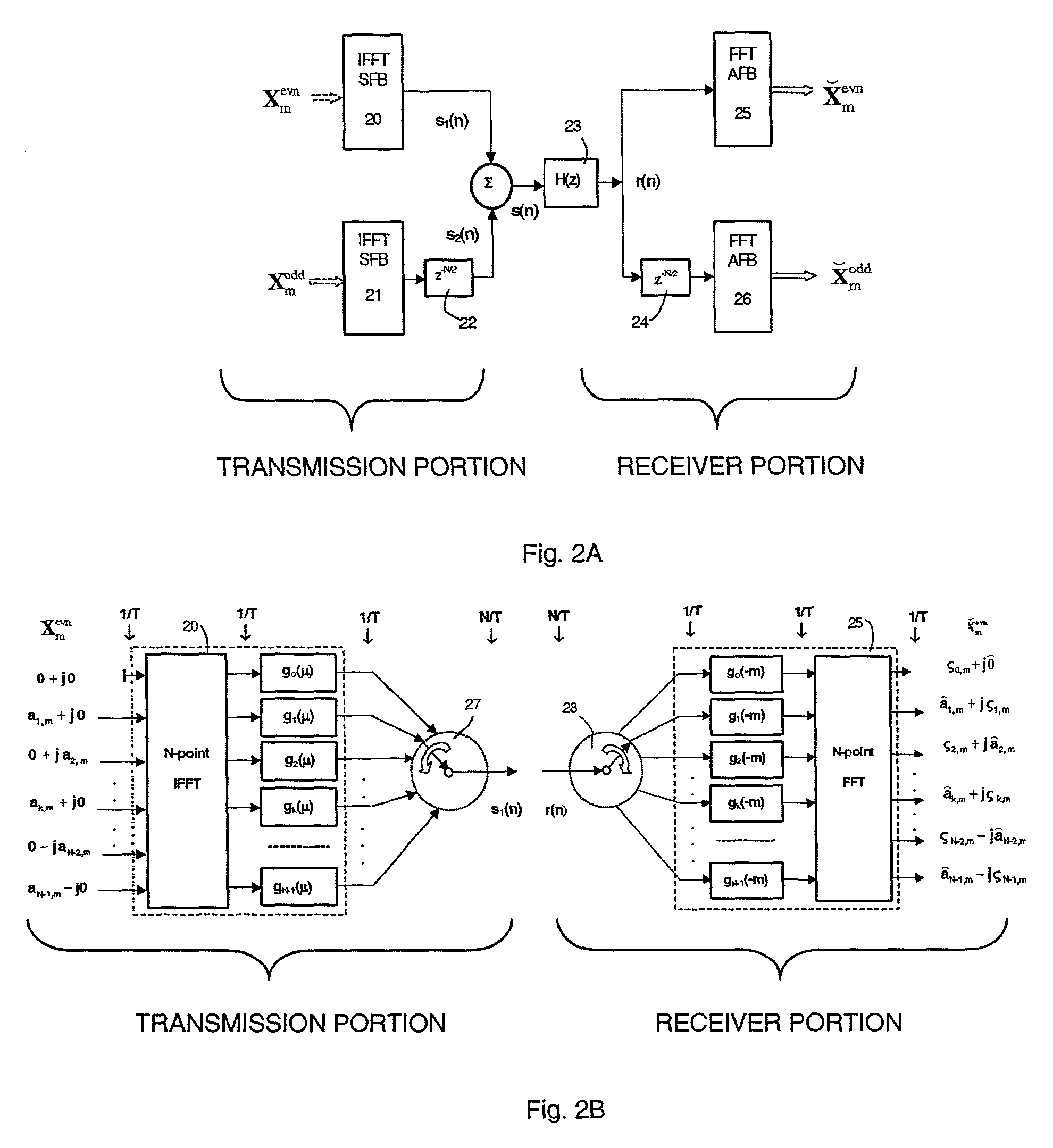
Per-bin DFE for advanced OQAM-based multi-carrier wireless data transmission systems
An Apparatus for non-linear per-bin adaptive equalization in orthogonal multi-carrier data transmission systems with the Nyquist sub-channel spectral shaping and T / 2 staggering of in-phase and quadrature components is disclosed. A previously introduced linear equalization embodiments are augmented by up to three, or more decision feed-back filters, to improve performance in presence of narrow-band interference (NBI) in wire-line and wire-less data transmission systems, and to enable exploitation of implicit diversity of multi-path fading channels, both with and without transmitter-end pre-coding. Adaptation properties of per-bin DFE equalization are analyzed by computer simulation for an intermediate number of constituent sub-channels. BER performance comparison between the conventional Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplication-(OFDM) and (Orthogonal Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (OQAM)-based multi-carrier systems of similar modulation / demodulation complexity and transmission latency is provided and the potential advantage of using spectrally well shaped orthogonal sub-channels in wireless applications is demonstrated.
Owner:NEC CORP
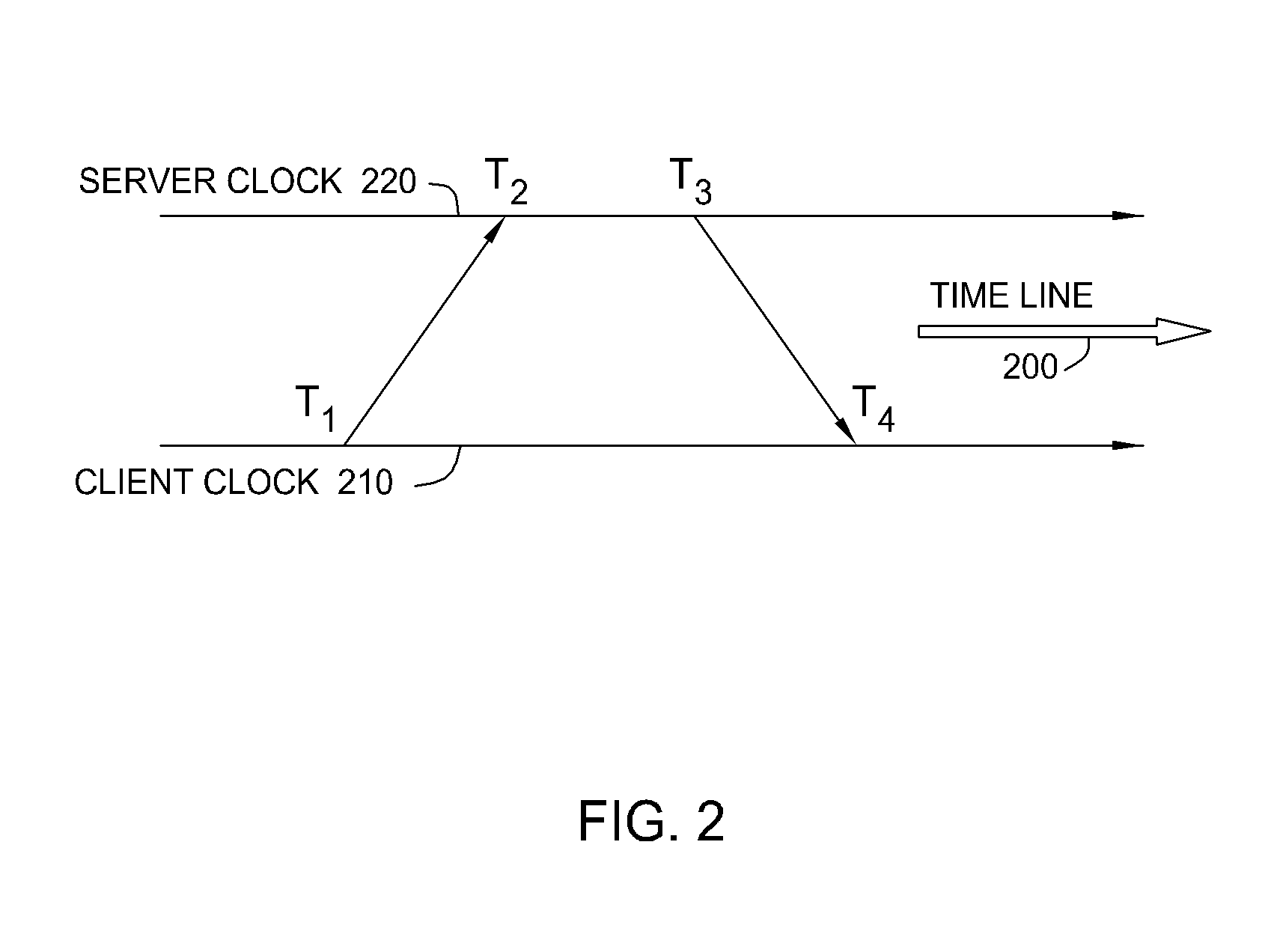
Method for determining the delay and jitter in communication between objects in a connected network
Methods which determine network performance by determining not only the transit delay between nodes in a network but also the variance, or jitter, of such transit delays. A common node, usually a network management computer (NMC), sends out a signal to a first node of interest and measures the time before it receives an acknowledgment from the first node. The NMC then sends out a similar signal to a second node of interest and similarly measures the time required to receive an acknowledgment. Based on these two measurements, the transit delay between the first and second nodes can be calculated if the first node lies on the path between the NMC and the second node or vice versa. For a multiple node communications path, the total transit delay between any two nodes is the sum total of the transit delays between adjacent nodes lying on the path. In the case of meshed networks, where a path to a node may be ambiguous, additional measurement nodes strategically positioned in the network can be used such a way that the transit delay between any adjacent pair of nodes can be calculated unambiguously from at least one of these measurement nodes, i.e., the portion of the network being measured will be reduced to a hierarchical one with respect to at least one of the measurement nodes.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Automatic web conference presentation synchronizer
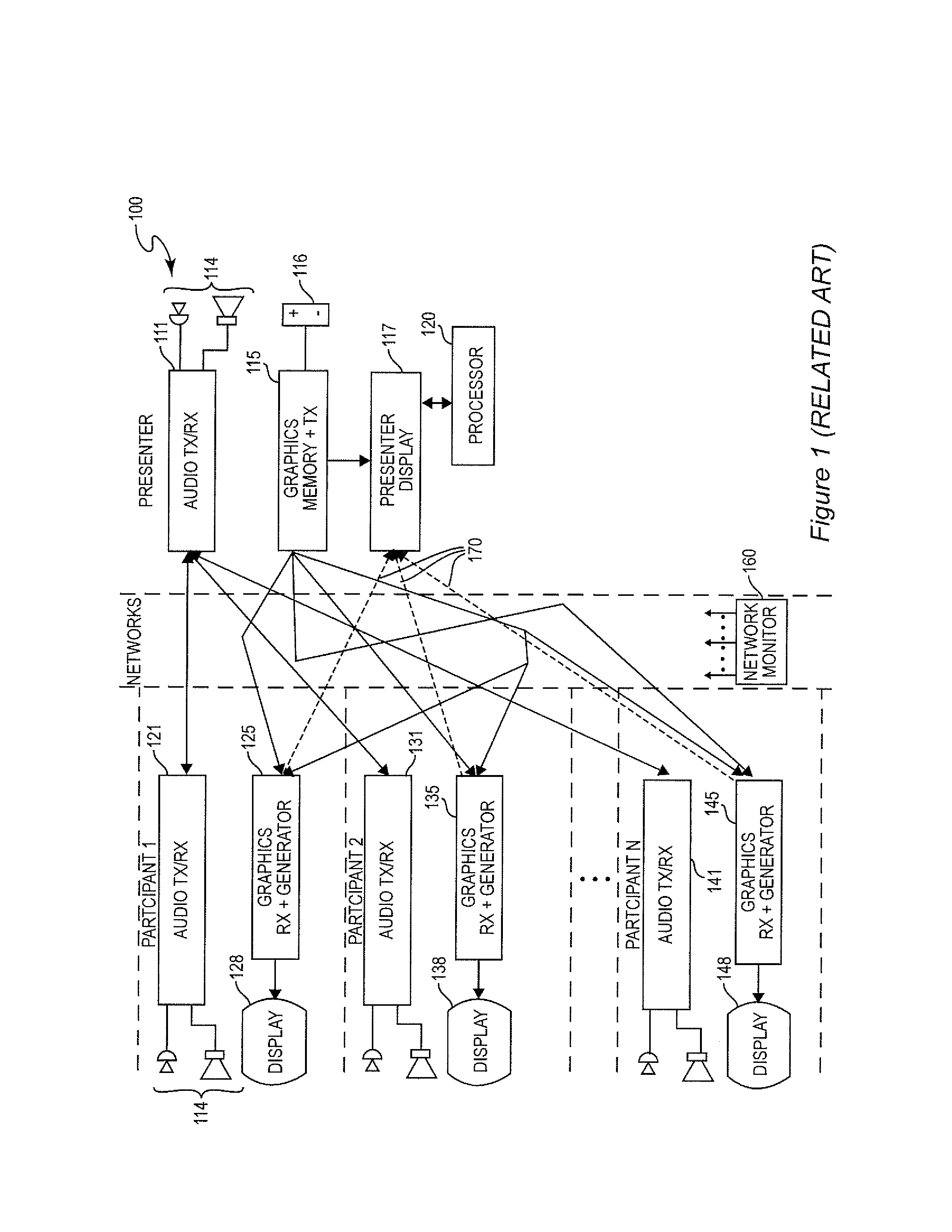
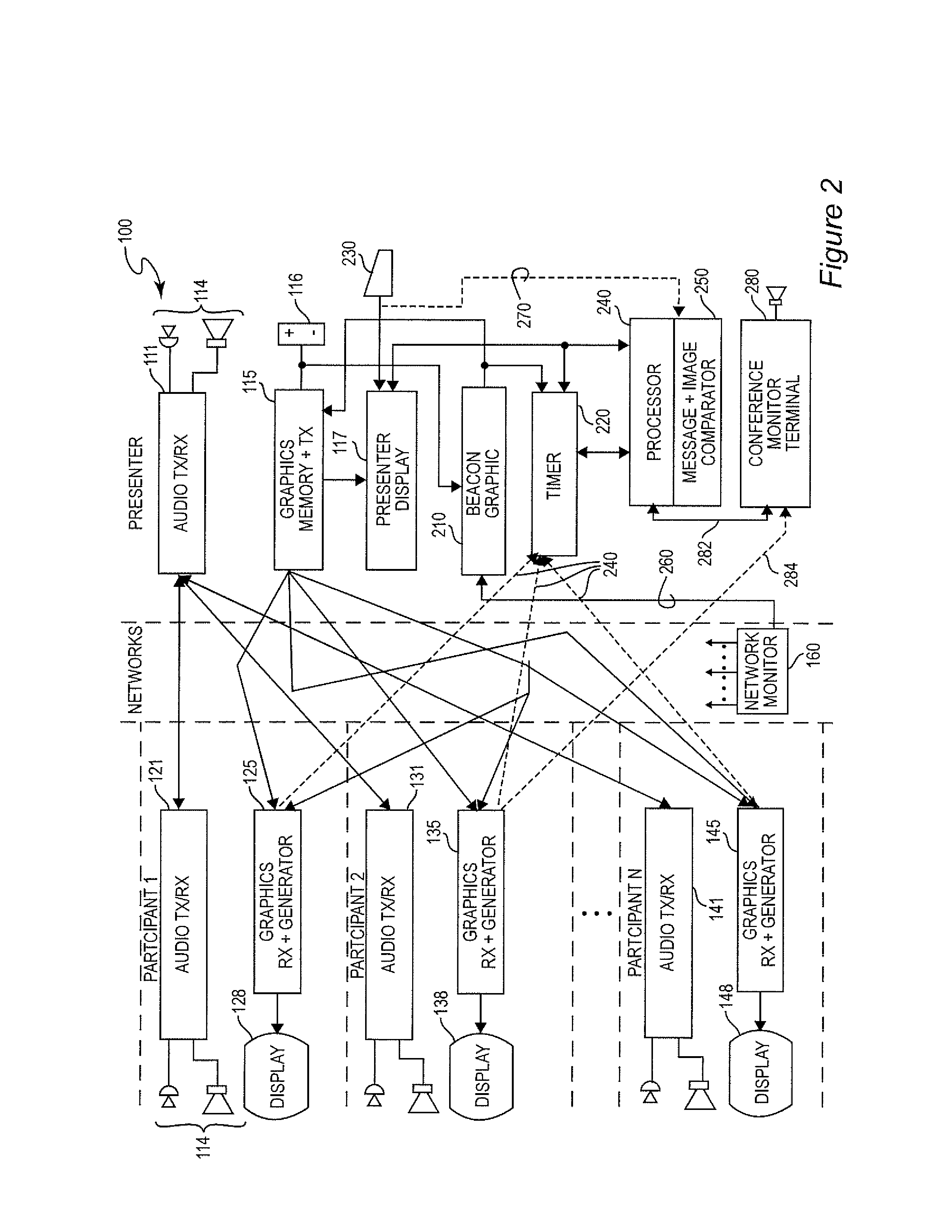
ActiveUS20130182063A1Reduce degradationReducing corresponding distractionTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsTelecommunications linkTransmission latency
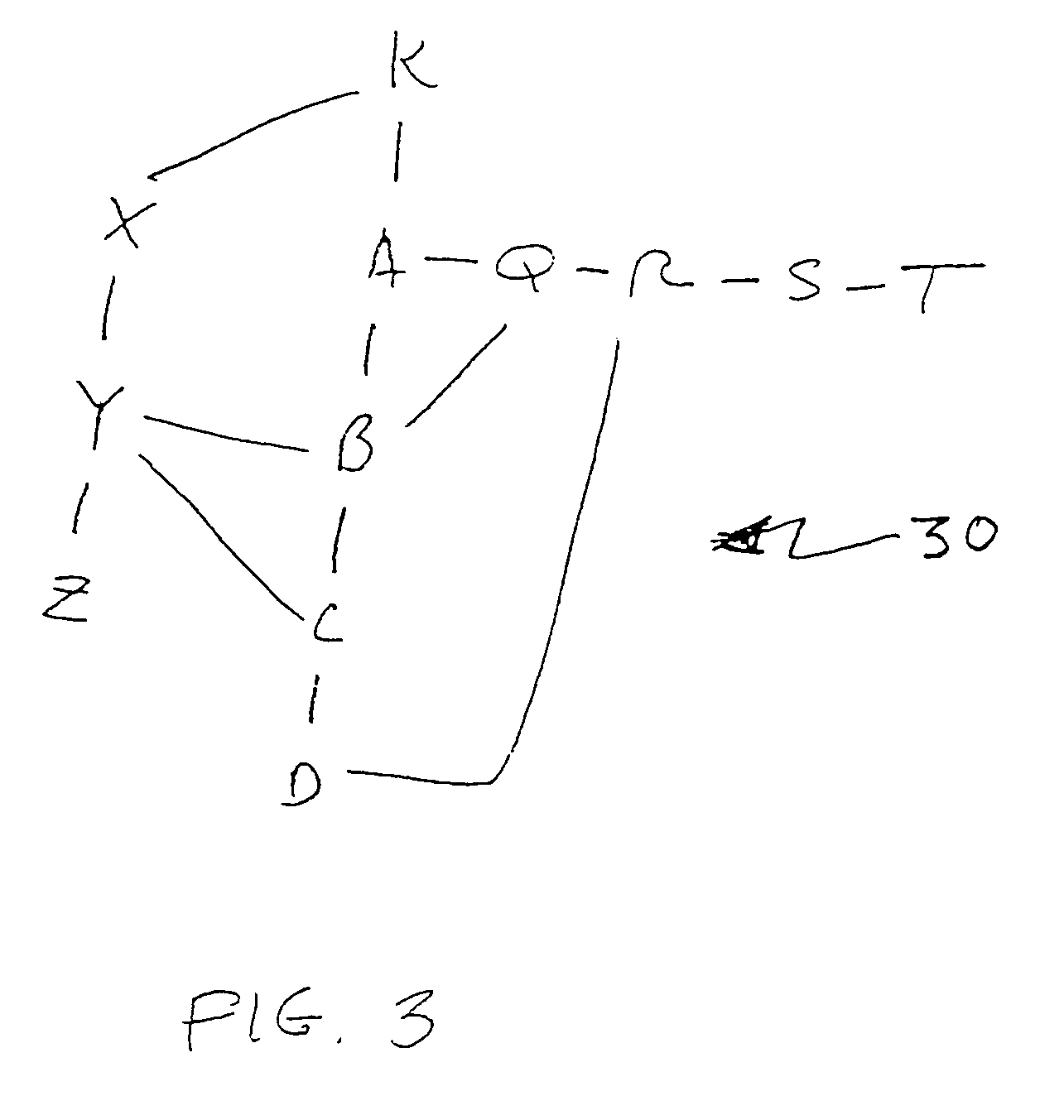
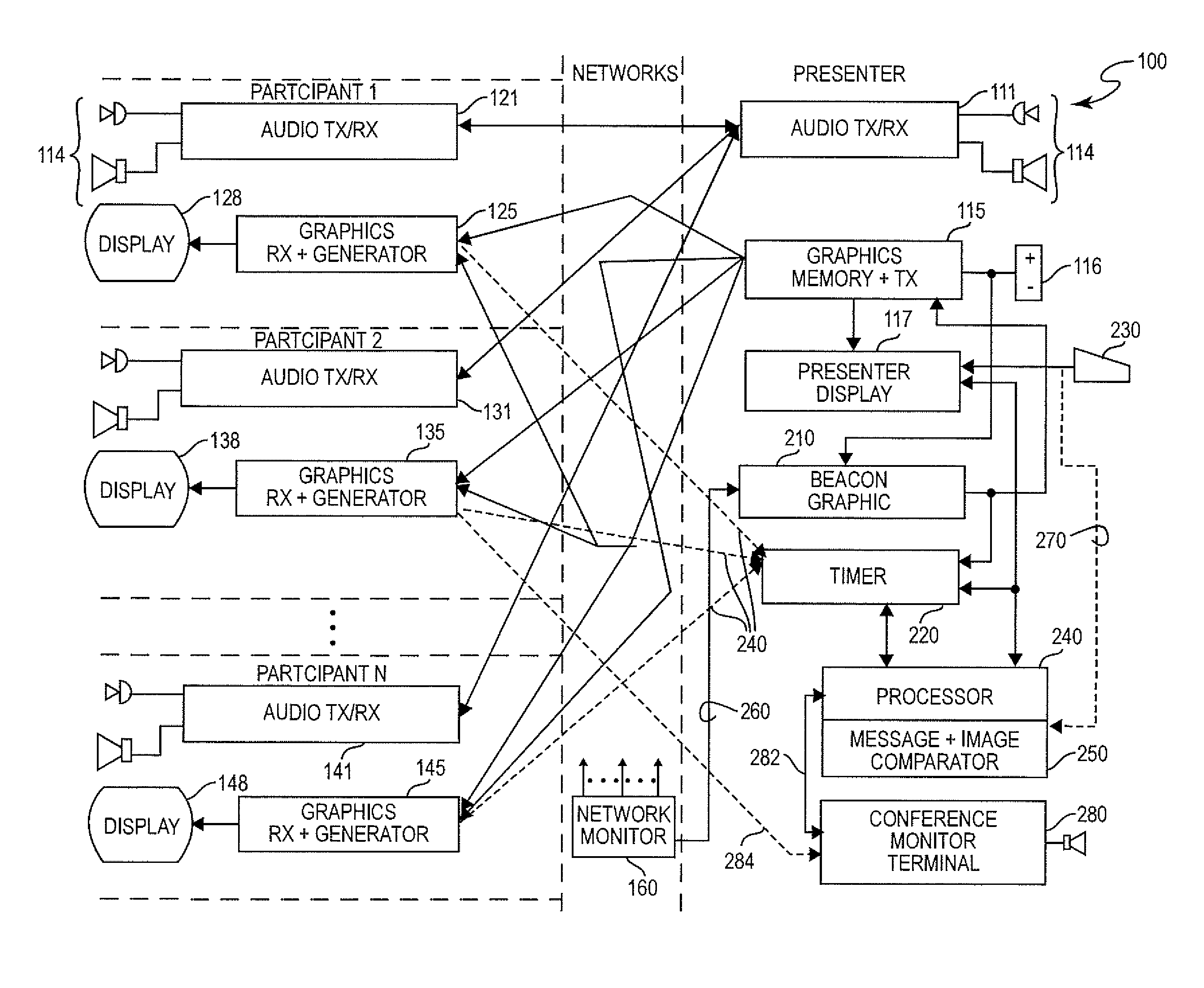
A beacon signal including image information and an application to cause acknowledgment of receipt of the beacon signal is transmitted in order to measure approximate latency in transmission over a communication link that exhibits latency such as a packet switched digital network. Transmission latency for image information for an image included in a web conference is then estimated and elapsed time after transmission of such image information is measured and an indication provided to a presenter or conference monitor when the image should be visible to a conference participant which can be easily selected by the presenter.
Owner:IBM CORP
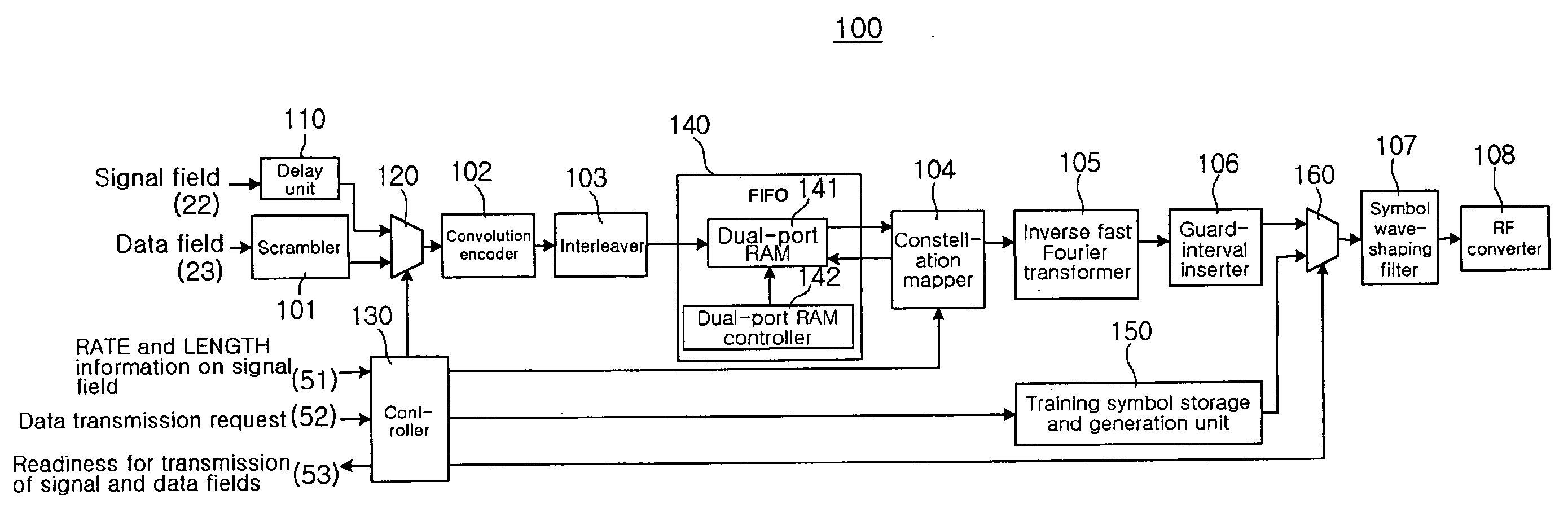
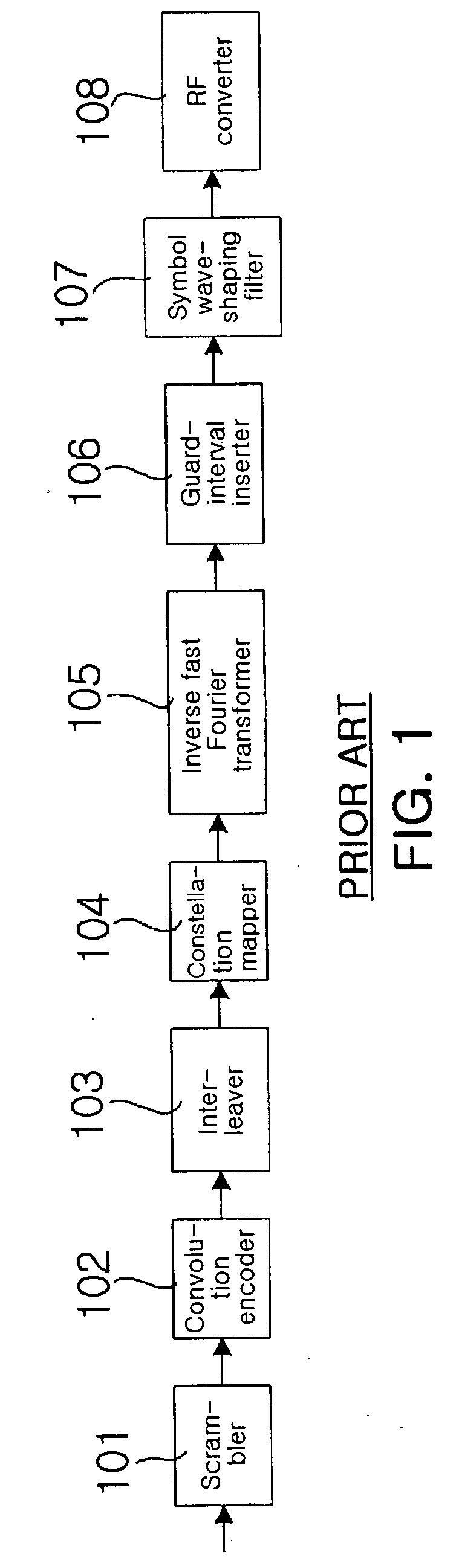
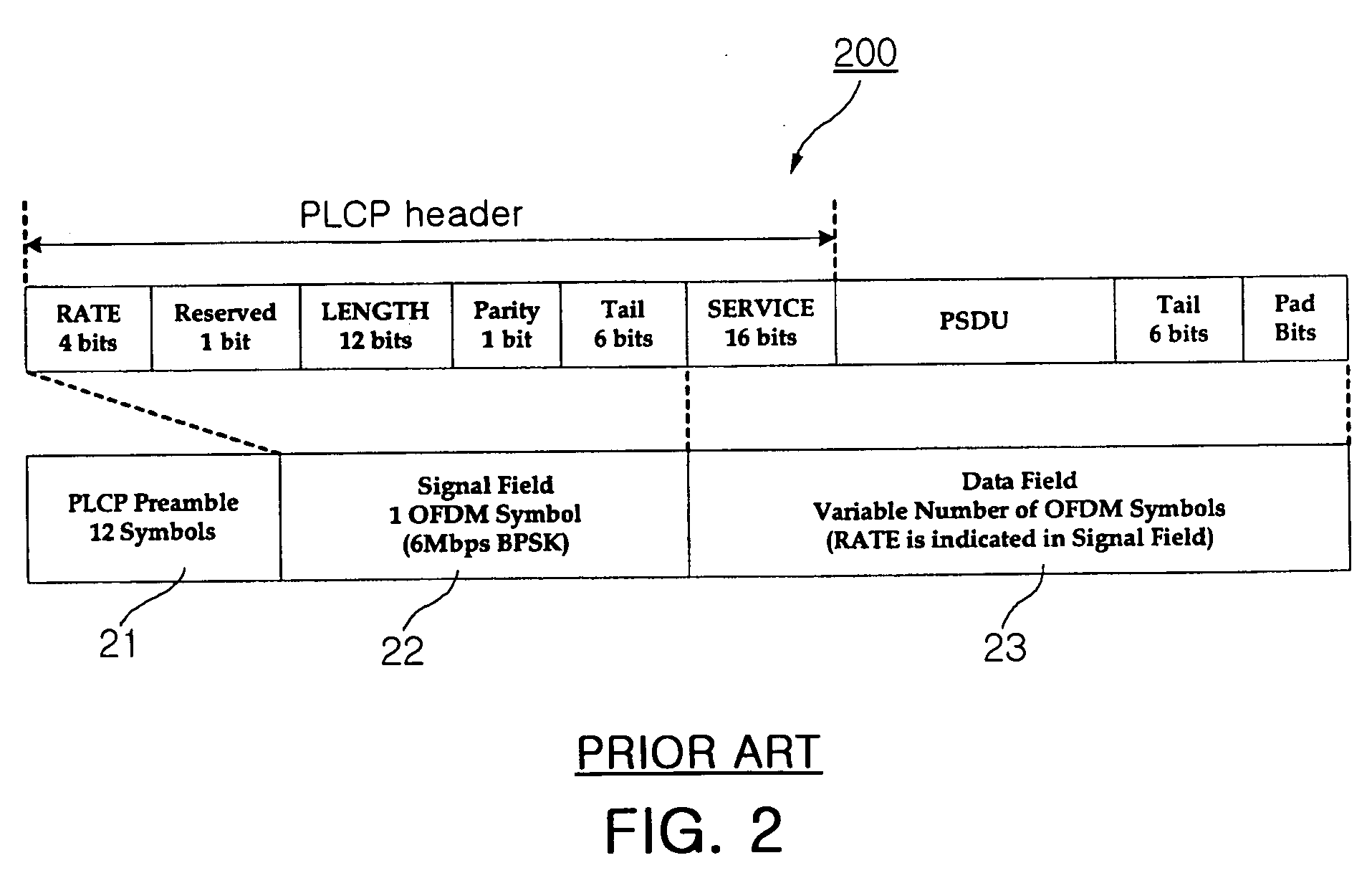
OFDM transmission apparatus and method having minimal transmission delay
ActiveUS20060092825A1Minimized transmission delayMinimal transmission delayFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsData fieldTransmission latency
An OFDM transmission apparatus having minimal transmission delay comprises a training symbol storage and generation unit, a delay unit and a controller. The training symbol storage and generation unit stores training symbols for the preamble, and outputs the stored training symbols when a training symbol output request signal is received. The delay unit receives data for the signal field from the MAC layer, delays the received data by the data processing time of the scrambler, and outputs the delayed data to the convolution encoder. The controller outputs the training symbol output request signal, requesting the preamble of the frame, to the training symbol storage and generation unit when a frame transmission request is received from the MAC layer, and outputs a data request signal, requesting the signal field and the data field, to the MAC layer in consideration of total data processing time (TPROCESS).
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
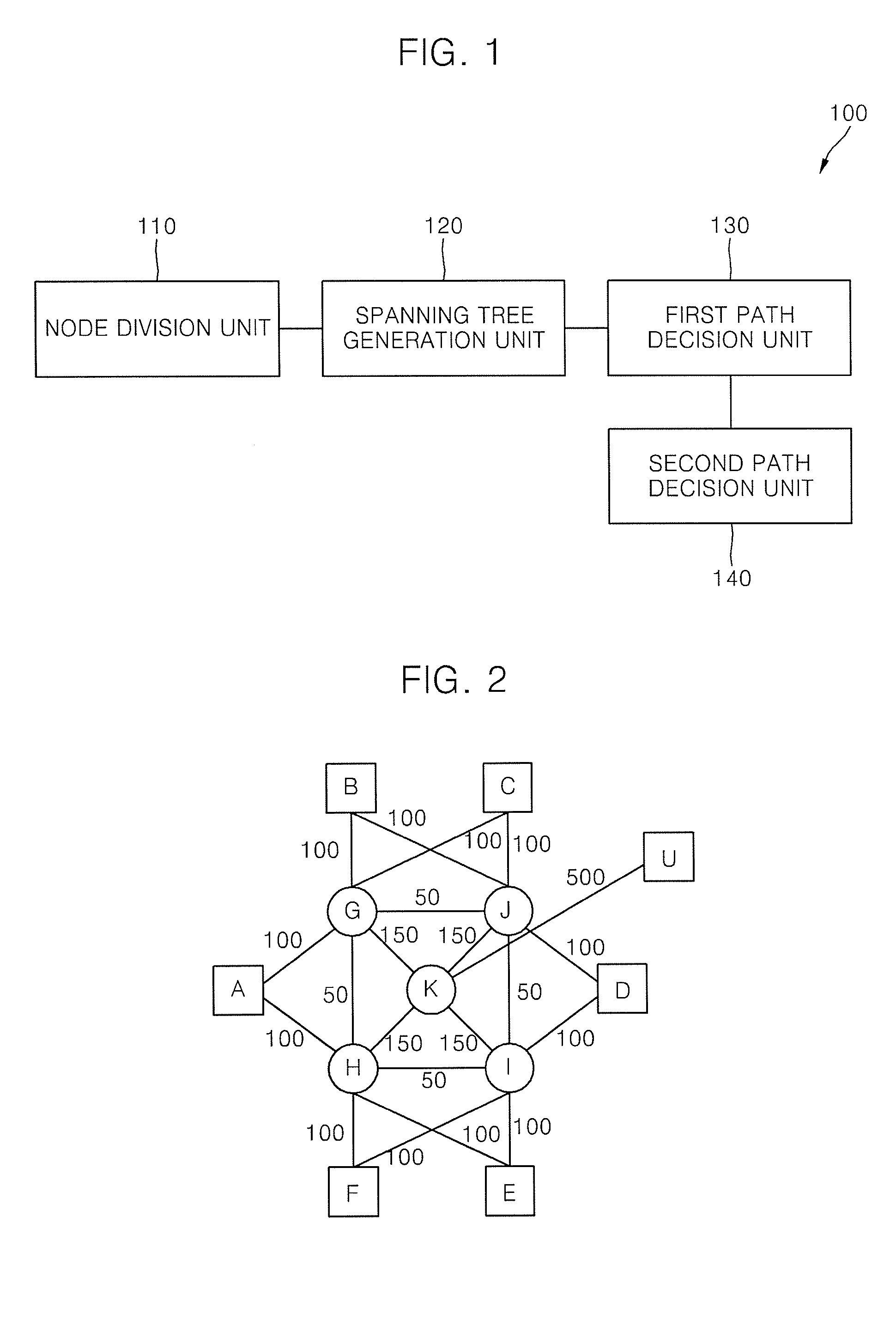
Node device and method for deciding shortest path using spanning tree
InactiveUS20100040070A1Improve performanceReduce delaysData switching by path configurationPacket lossTransmission latency
Provided are a node device and a method for deciding a shortest path using a spanning tree. The node device includes: a node division unit dividing the node device into sub-nodes as many as the number of nodes connected to the node device when the node device operates an edge node that is located at an end of a backbone network and is in charge of reformatting and routing frames; a spanning tree generation unit generating as many spanning trees as the number of sub-nodes, wherein each of the spanning trees comprises a shortest path to reach the other edge nodes constructing the backbone network from each of the sub-nodes; and a first path decision unit deciding a shortest path from a source node to a predetermined destination node, as a path to be used, based on the spanning trees that are generated by the spanning tree generation unit. The shortest path that is obtained based on the plurality of spanning trees is used as a path to be used such that throughput of traffic is 3 times and 1.5 times larger than in existing STP and SPB, respectively, and the transmission delay is smaller than in existing STP and SPB. In addition, packet loss is smaller than in STP and SPB, and the node device and the method for deciding a shortest path using a spanning tree are robust to the unbalanced traffic.
Owner:FOUND OF SOONGSIL UNIV IND COOP
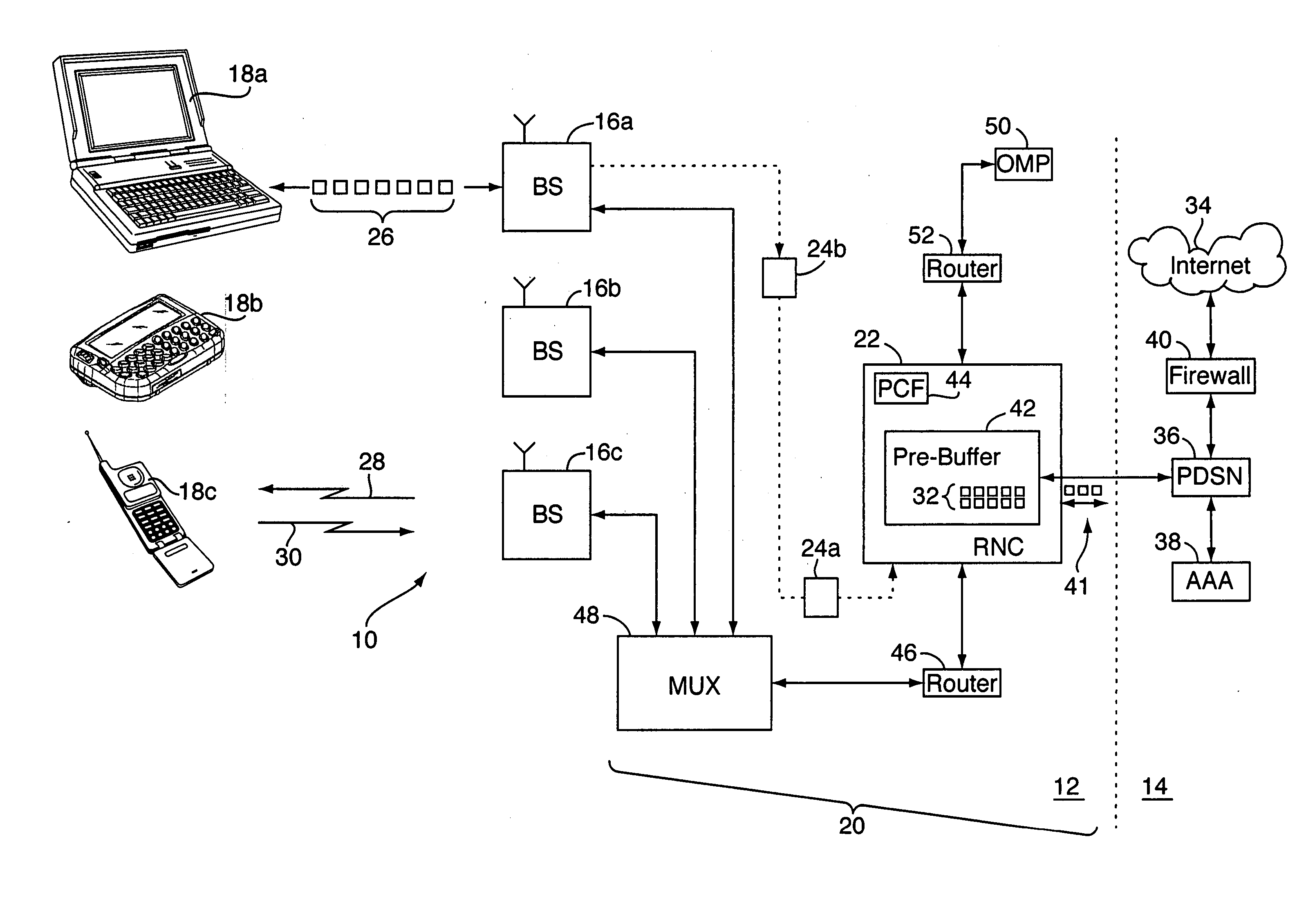
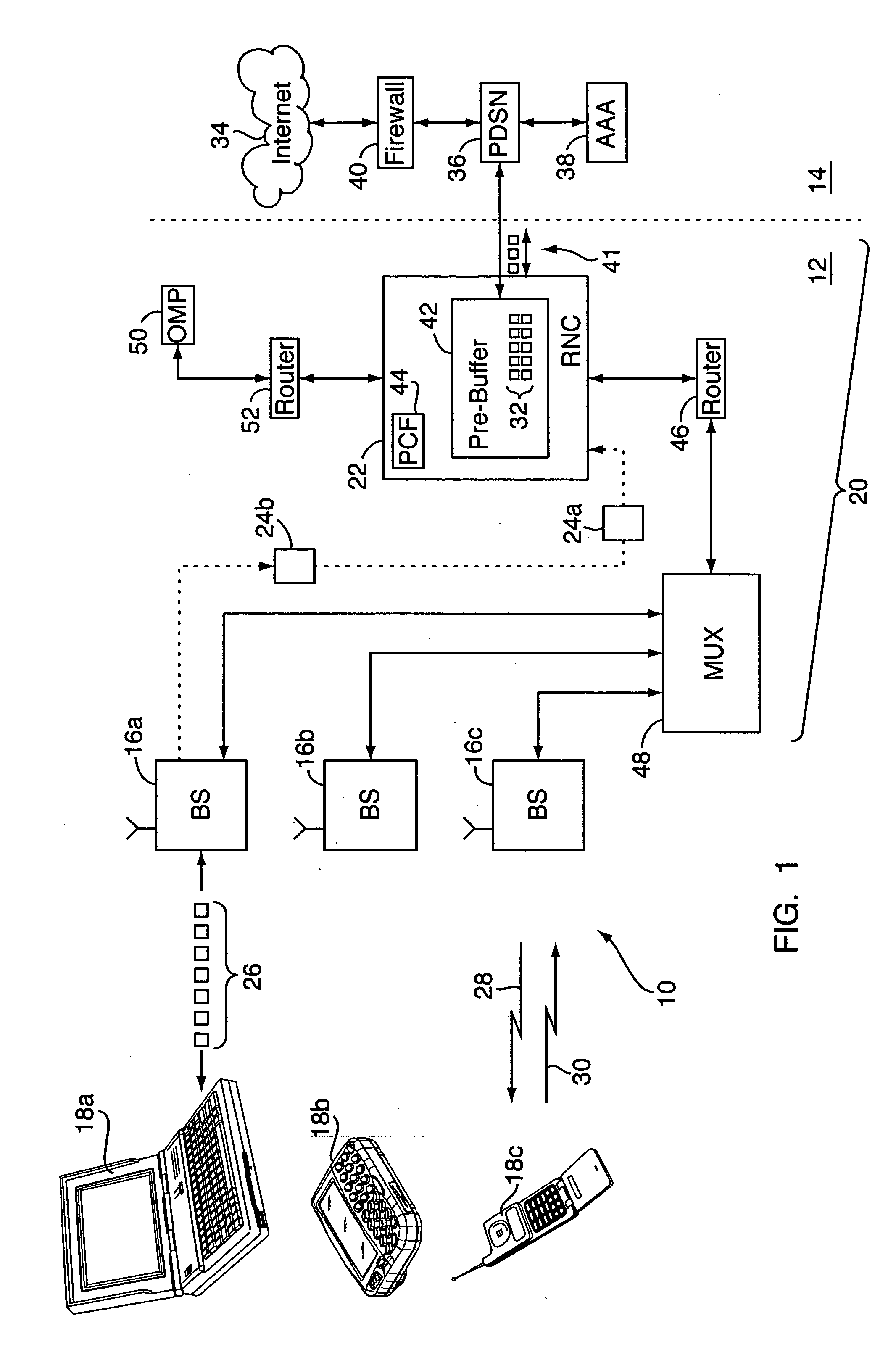
Method for measuring airlink transmission latency in a 1x-EVDO wireless network
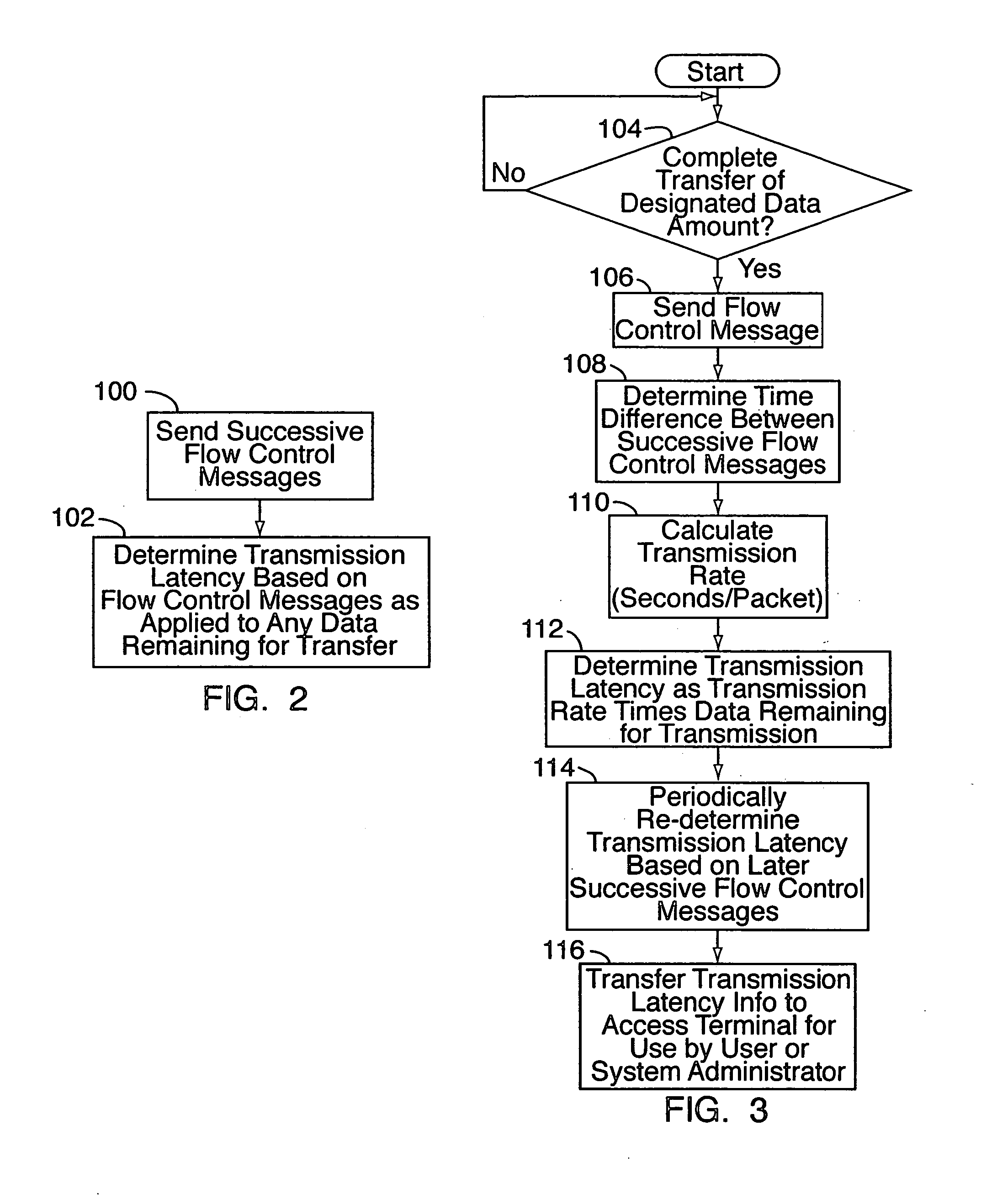
In a method for determining transmission latency in a wireless network, data packets addressed to a wireless unit are received at a radio network controller (RNC) and forwarded to a base station in communication with the wireless unit for transmission over the forward link. The RNC keeps track of when it receives the packets. Periodically, the base station sends messages back to the RNC. Each message identifies a data packet and the time it was transmitted to the wireless unit. The RNC uses the messages to calculate a data transfer rate, e.g., the number of packets between the first packet received by the RNC and the packet identified in the message, divided by the time difference between the message and when the first packet was received by the RNC. The RNC then applies the transfer rate to any data remaining for the wireless unit, to determine the transmission latency thereof.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Message board system and method
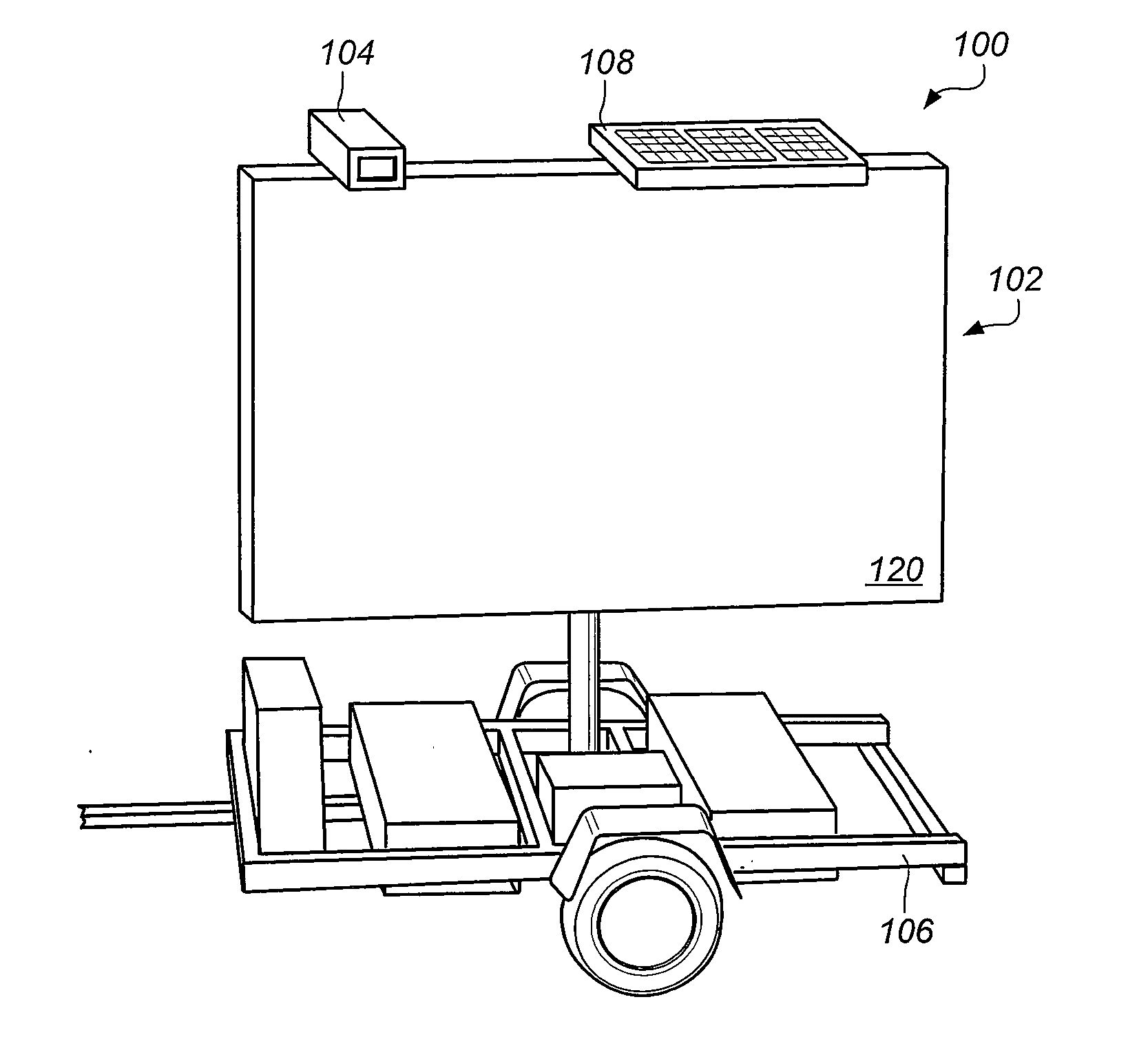
InactiveUS20110012751A1Electric signal transmission systemsArrangements for variable traffic instructionsMessage boardTransmission latency
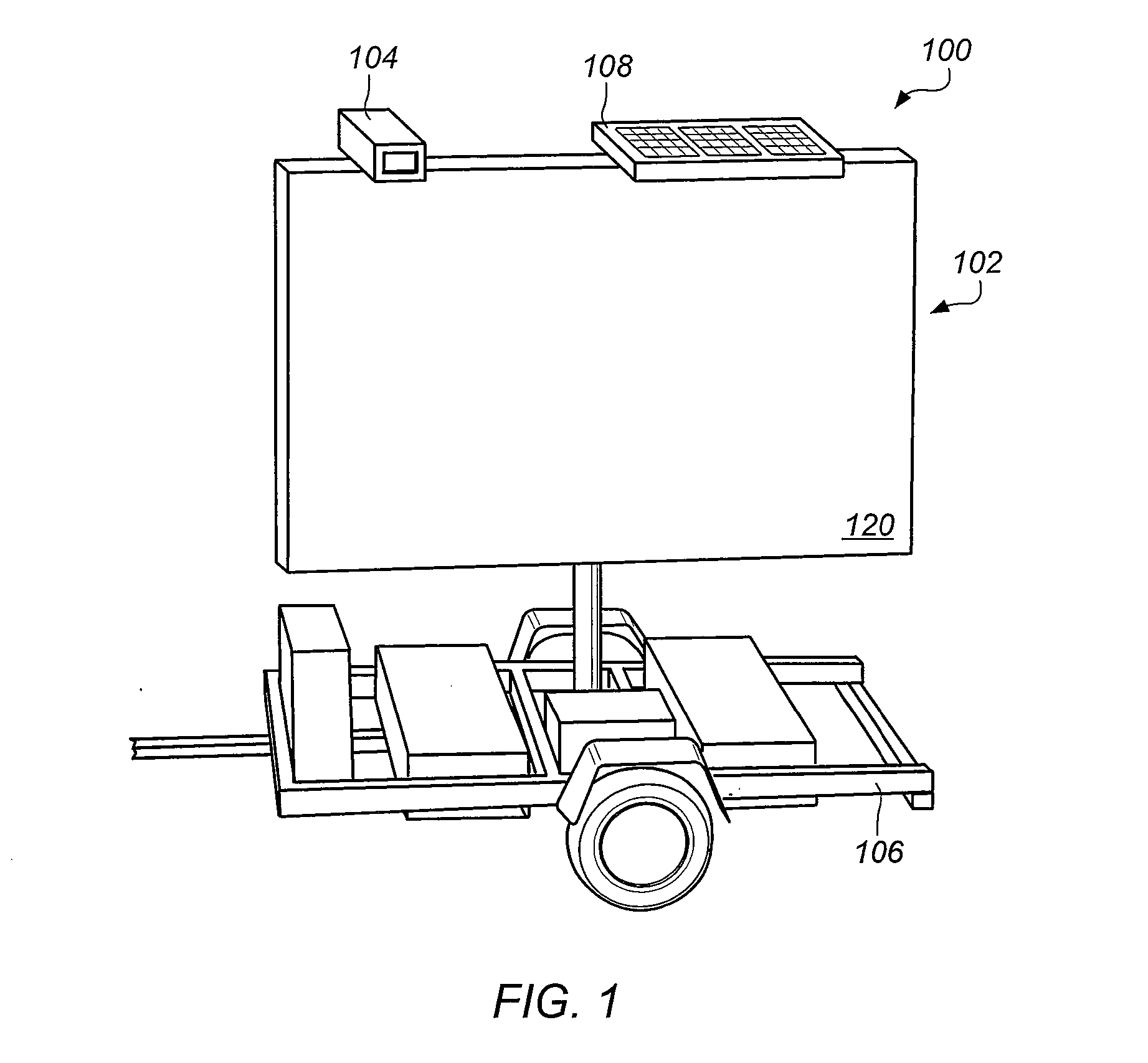
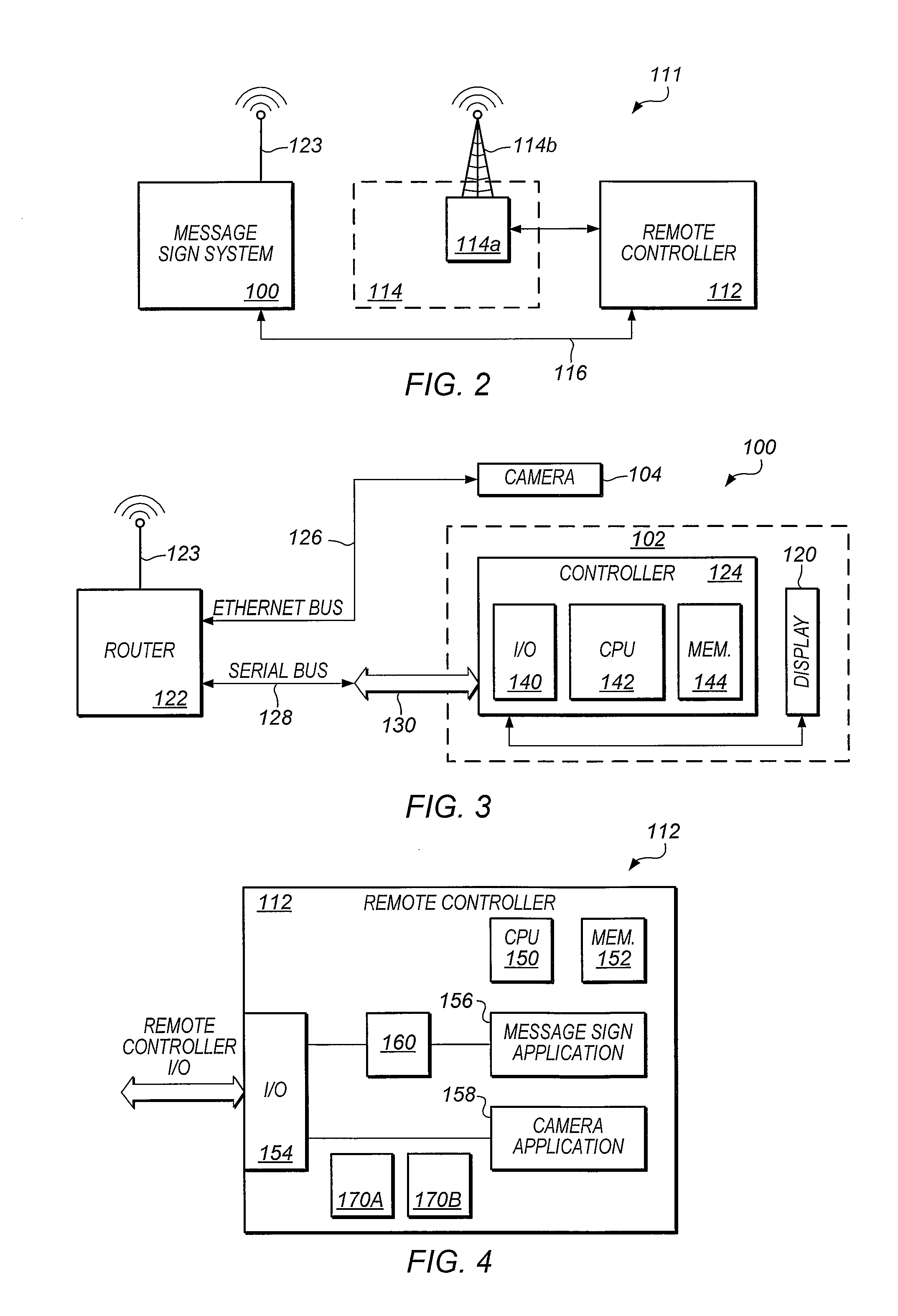
Provided is a messaging system that includes a highway message sign system. The message sign system includes a wireless cellular router having an Ethernet port and a serial port and being capable of communicating with a cellular wireless communication network. The message system also includes a camera coupled to the Ethernet port of the cellular router and a message sign. The message sign includes a message display and a message sign controller coupled to the serial port of the cellular router. The message sign controller is able to control operation of the message sign. Further provided is a method of operating message sign remote controller. The method includes receiving a request to communicate with a message sign system, executing an initialization file configured to initialize a communication port redirect, executing an initialization file configured to account for transmission latencies associated with use of the communication port redirect, generating a serial communication configured control operation of a message sign system, routing a serial communication from a message control application to the communication port redirect, converting the serial communication to an other communication protocol message receivable by a wireless cellular network, and routing the other communication to the message sign system via the wireless cellular network.
Owner:TEXAS DEPT OF TRANSPORTATION
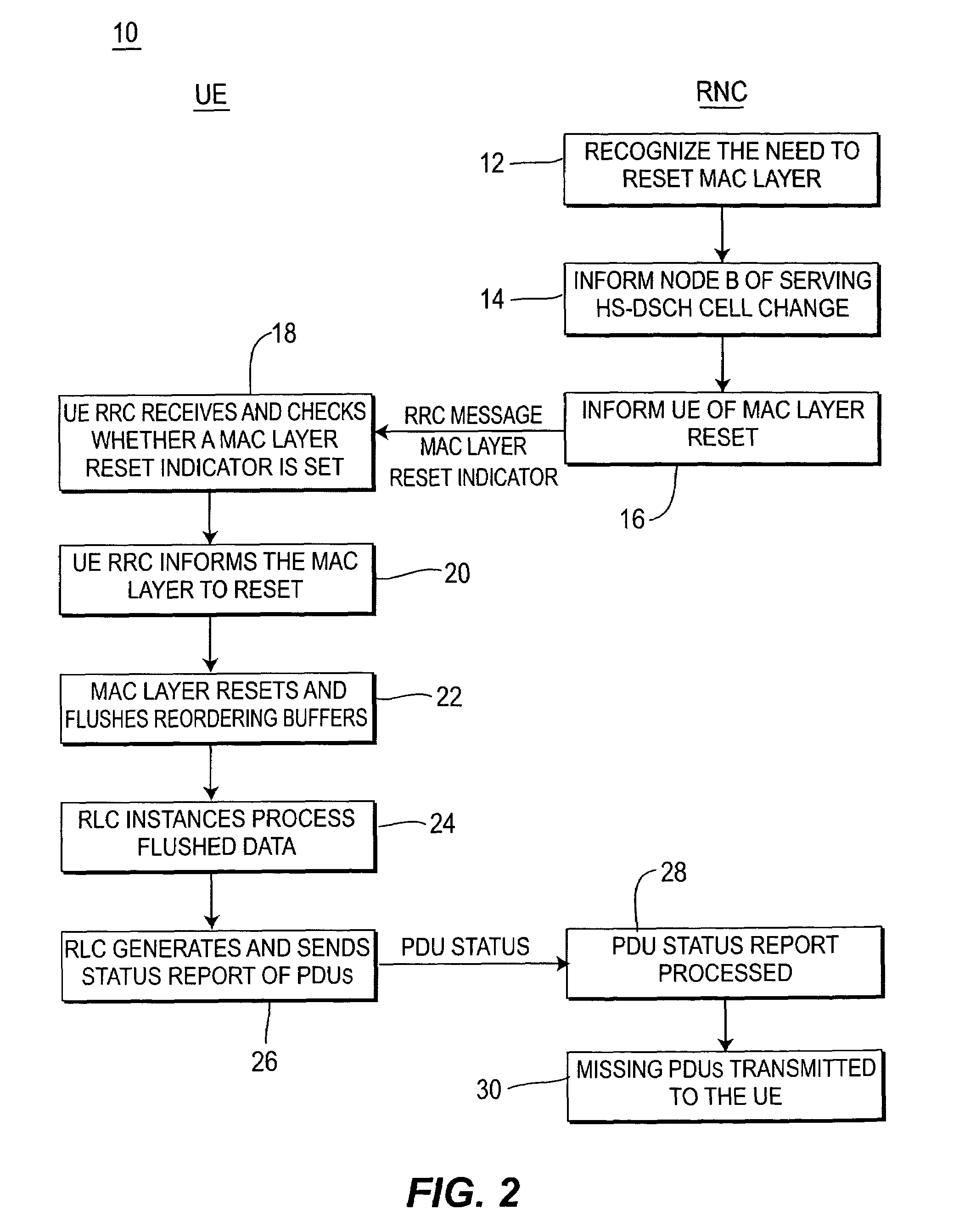
System for efficient recovery of Node-B buffered data following MAC layer reset
ActiveUS7706405B2Reduce transmission delayAvoid lostPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision system scanning detailsTransmission latencyEmbedded system
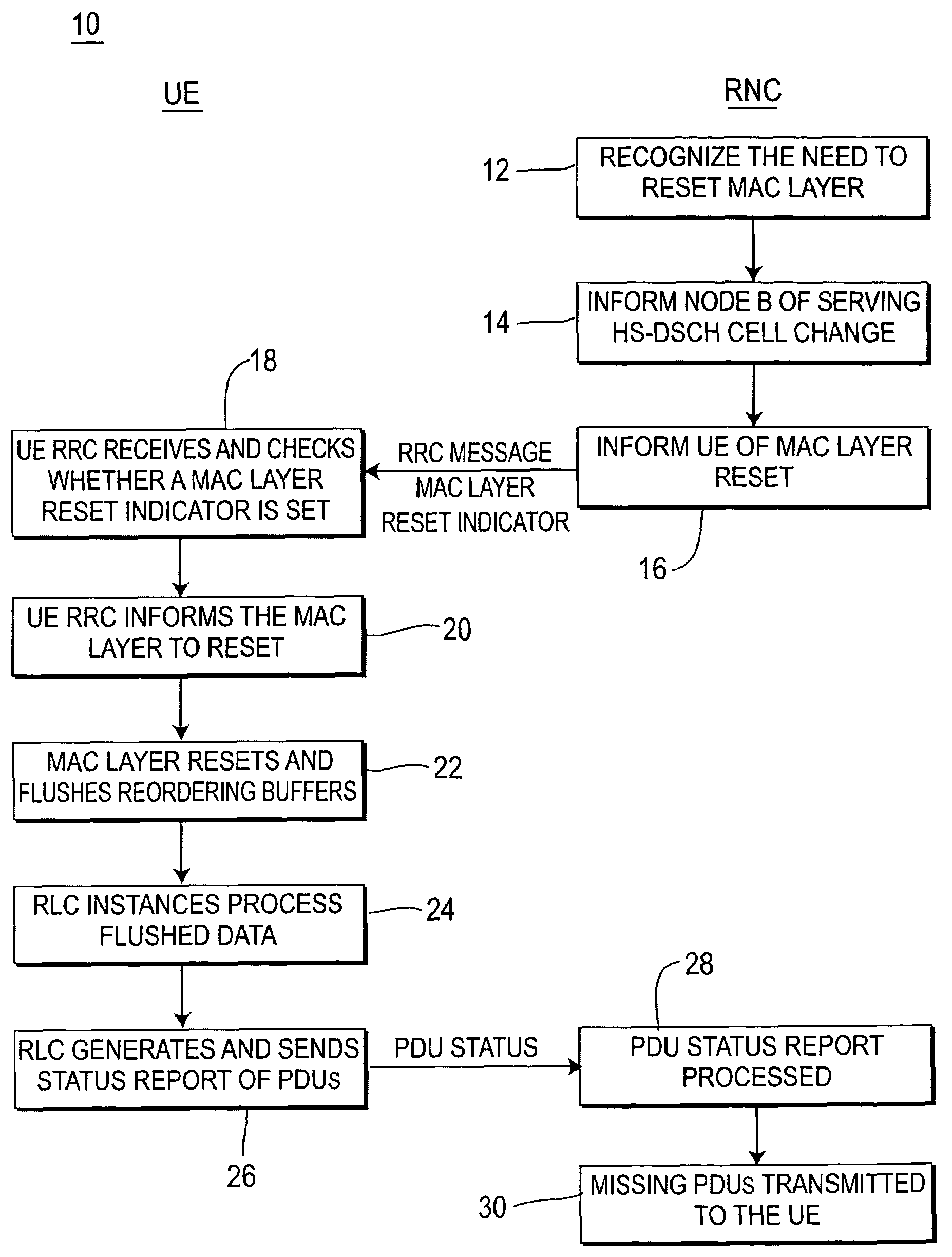
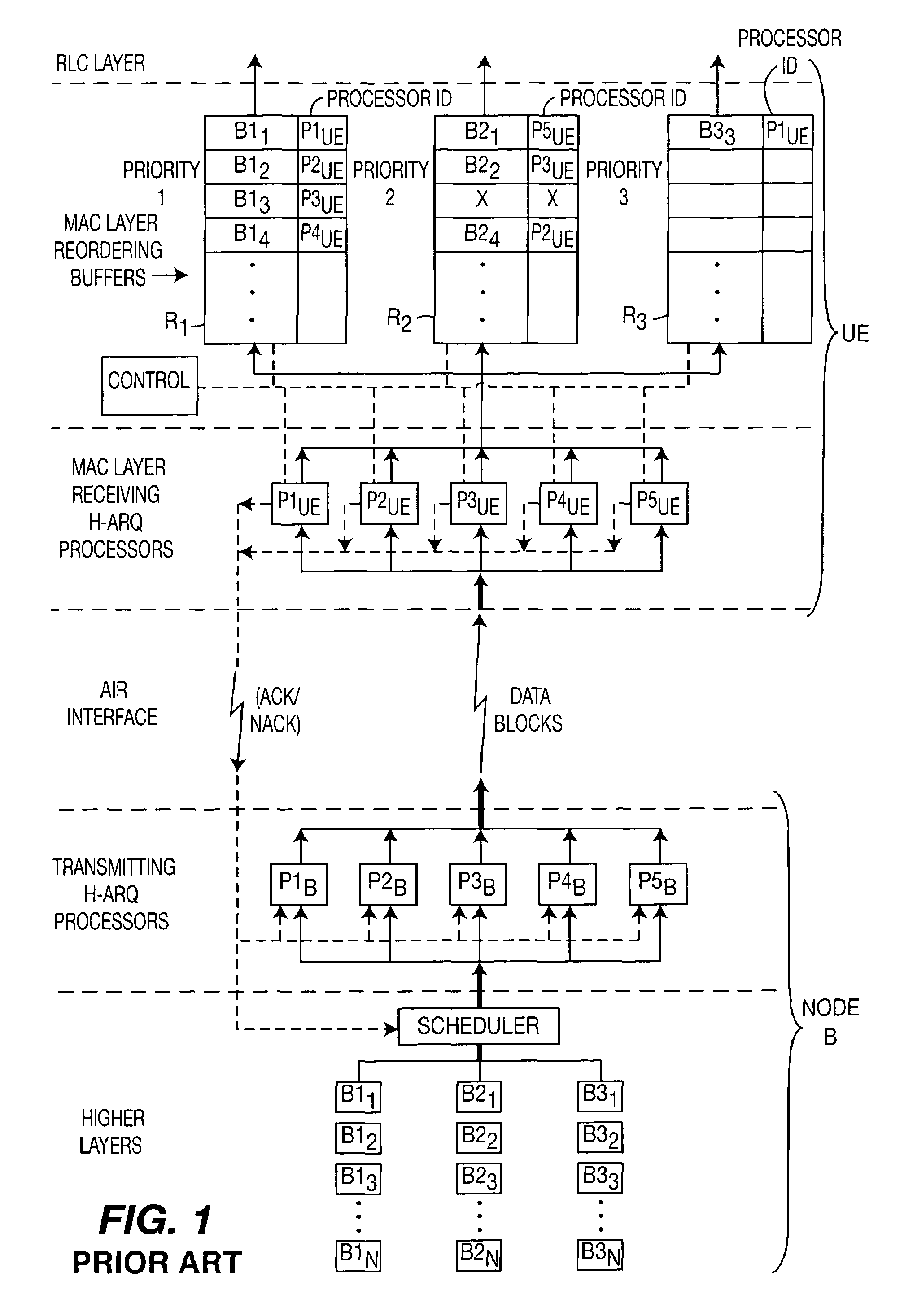
A method and system for the UE and RNC to reduce transmission latency and potentially prevent loss of PDUs upon a MAC layer reset. UE generation of the status PDU is coupled with the MAC layer reset. The RNC generates a message with a MAC reset indication. Following the MAC layer reset all PDUs stored in the UE MAC layer reordering buffers are flushed to RLC entities and then processed by RLC entities prior to the generation of a PDU status report. The PDU status report provides to the RNC the status of all successfully received PDUs. Upon reception of a PDU status report in the RNC, missing PDUs are realized and retransmitted to the UE.
Owner:APPLE INC
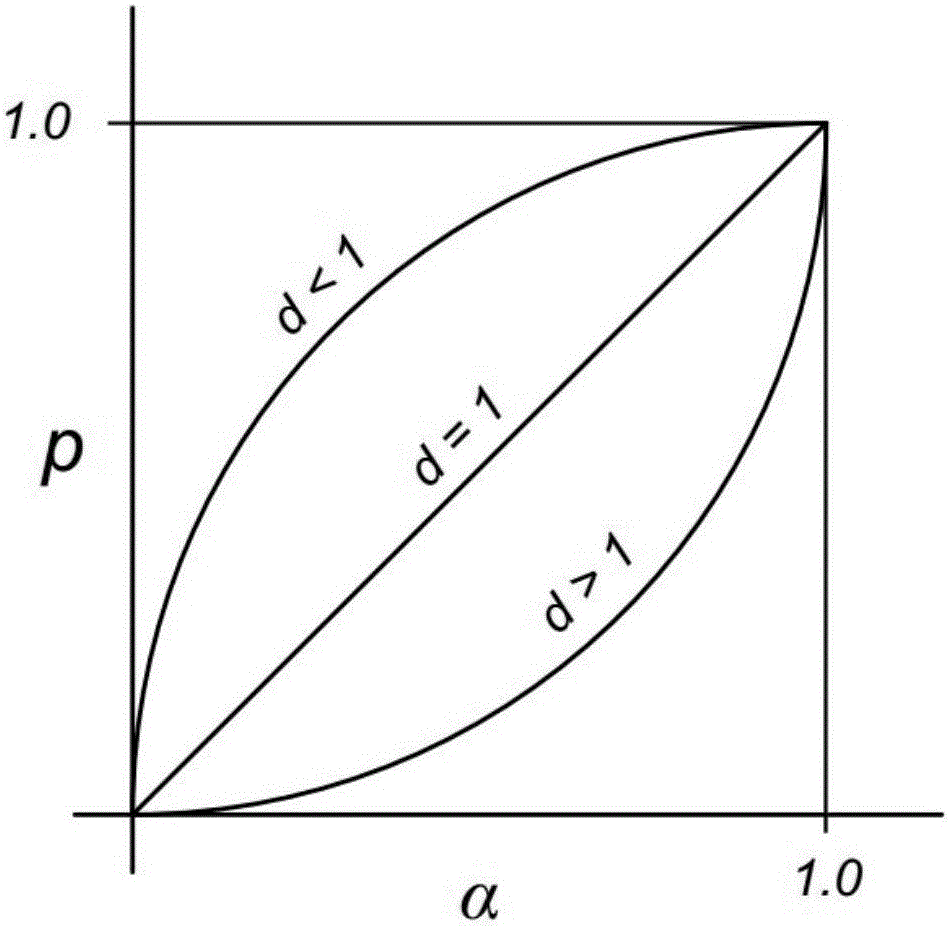
Data center network transmission layer stream data transmission method based on priority
InactiveCN105827540AImprove throughputReduce transmission delayData switching networksData streamData center
The invention discloses a data center network transmission layer stream data transmission method based on priority. The method comprises steps that S1, data flows transmitted by a data center network are classified into small data flows and large data flows; S2, the priority number pri of the small data flows is calculated; S3, weight w of the small data flows is calculated; S4, a congestion degree alpha of the present network is calculated; S5, whether the present network is in a congestion state is determined, if yes, a step S6 is actuated; if not, a step S7 is actuated; S6, results of the steps S2, S3 and S4 are substituted into a Gamma function formula to reduce the size of a data flow congestion degree window; S7, the result of the step S3 is substituted into the formula to enlarge the size of the data flow congestion degree window; and S8, the data flows are sent according to the updated window. Through the method, transmission delay of the small data flows can be not reduced on the condition that an application level is not required to prompt parameters such as the volume of the data flows, and the integral high throughput of the network can be further maintained.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
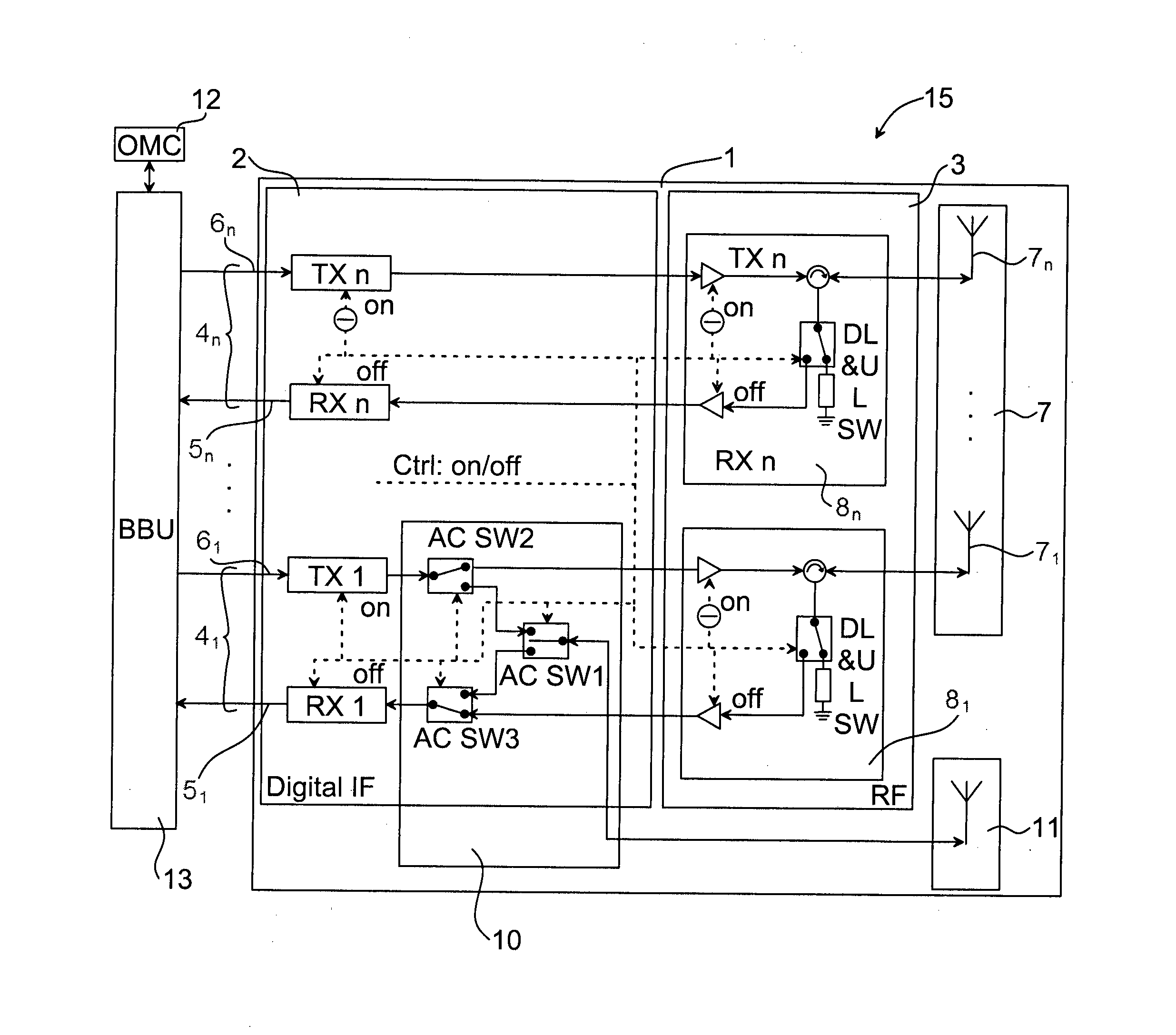
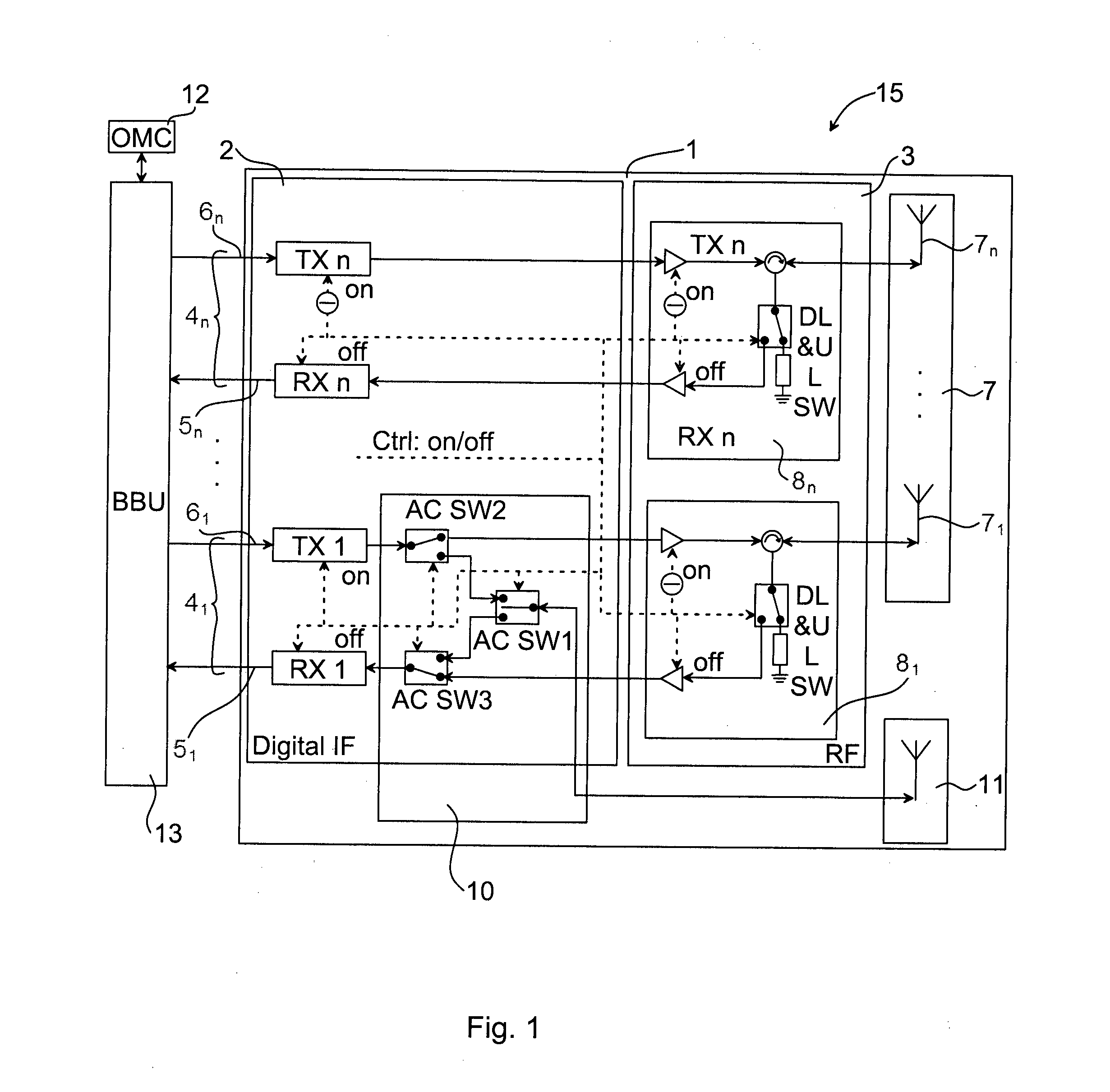
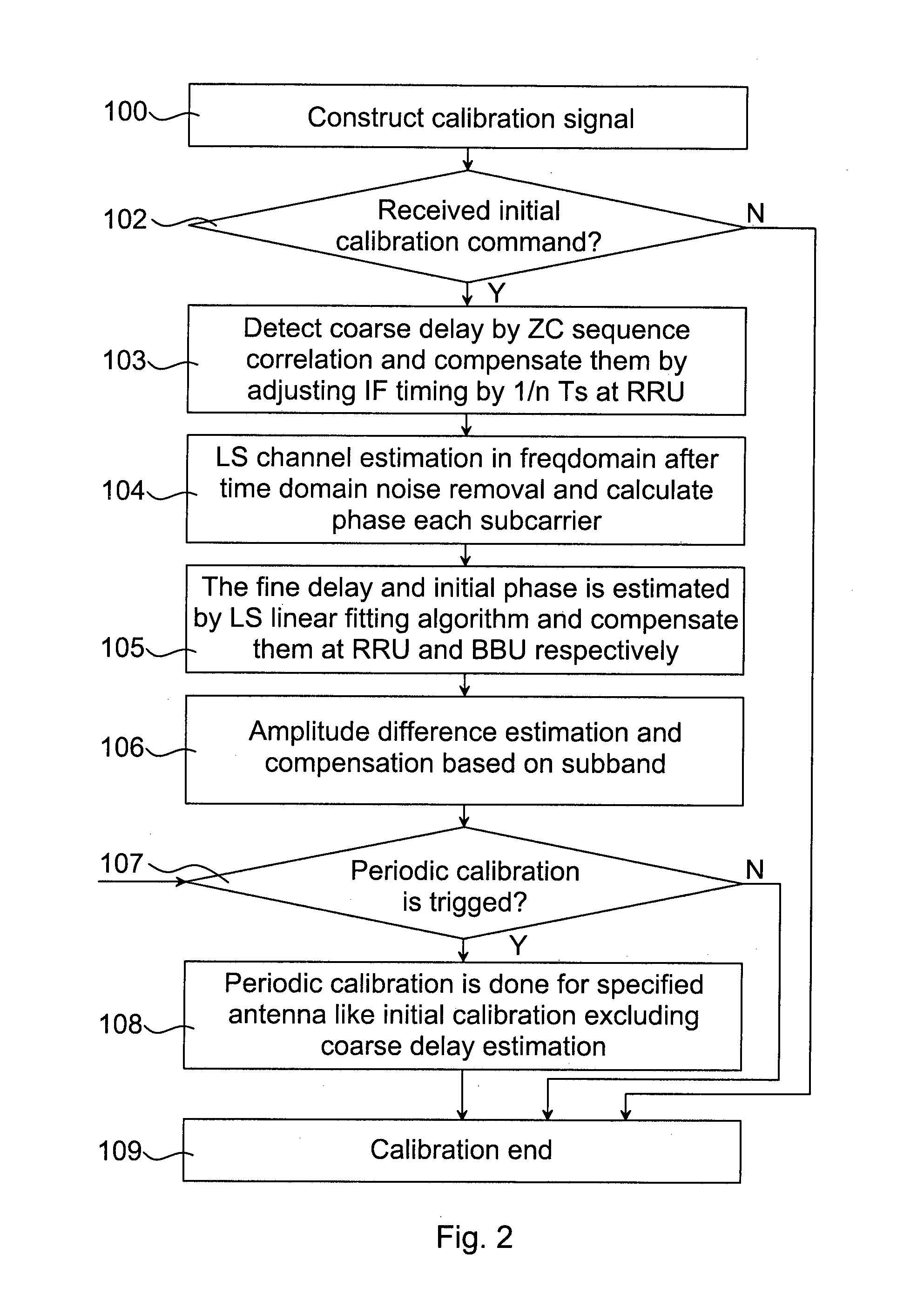
Methods, processing device, computer programs, computer program products, and antenna apparatus for calibration of antenna apparatus
InactiveUS20140370823A1Improved antenna calibrationLess processor loadTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringIntermediate frequencyTransceiver
The invention relates to a method 20 in an antenna array system 15 for calibration of an antenna apparatus 1. The method 20 comprises: estimating 21 coarse receive delays for the receive chains 51, . . . , 5n and coarse transmit delays for the transmit chains 61, . . . , 6n; adjusting 22 a timing of the receive chains 51, . . . , 5n based on the estimated coarse receive delays so that the receive chains 51, . . . , 5n align with the maximum coarse receive delay difference and adjusting a timing of the transmit chains 61, . . . , 6n based on the estimated coarse transmit delays so that the transmit chains 61, . . . , 6n align with the maximum coarse transmit delay difference; estimating 23 a fine delay and initial phase for the receive chains 51, . . . , 5n and the transmit chains 61, . . . , 6n based on their phase-frequency characteristics; adjusting 24 an intermediate frequency timing of the antenna apparatus 1 based on the estimated fine delay; compensating 25 initial phase and residual delay at base band frequency-domain signal; estimating 26 amplitude-frequency characteristics of the transceiver chains 41, . . . , 4n; and compensating 27 the estimated amplitude-frequency characteristics at base band frequency-domain signal.
Owner:OPTIS CELLULAR TECH LLC
Method and device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over packet network
ActiveUS7680153B2Overcome networkOvercome variationPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexTransport delayTransmission latency
A method for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network, in which the multimedia includes a first stream and a second stream which are buffered and played through buffers. The method includes: measuring average transport delays of the first and second streams; measuring transport delay jitters of the first and second streams; and calculating a delay difference between the first and second streams which corresponds to the average transport delays and the transport delay jitters of the first and second streams, and setting buffer durations. A device for stream synchronization of real-time multimedia transport over a packet network is also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com