Patents
Literature
430 results about "Data placement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
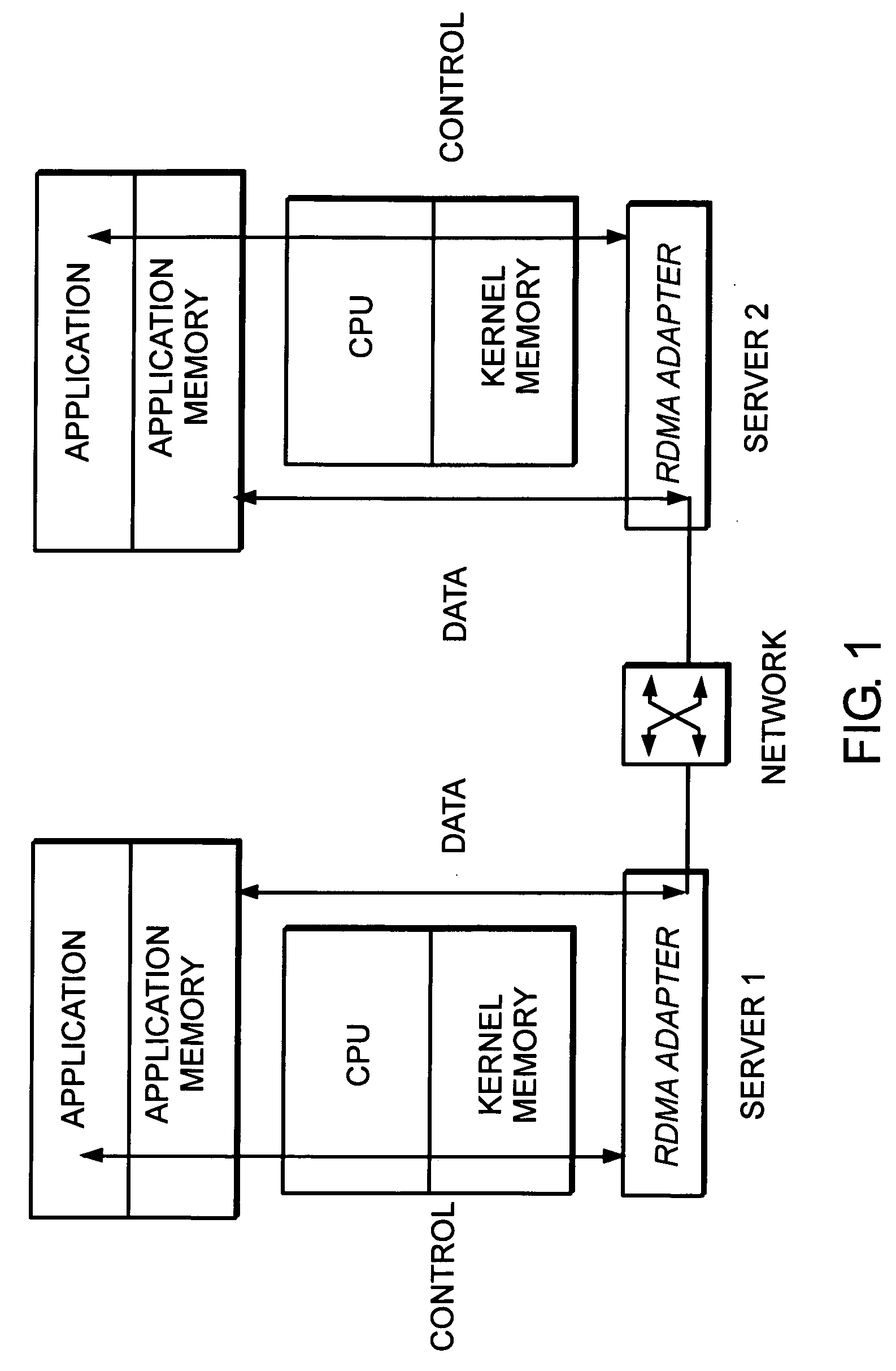
Method and apparatus for data communication
InactiveUS6094684AInterprogram communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
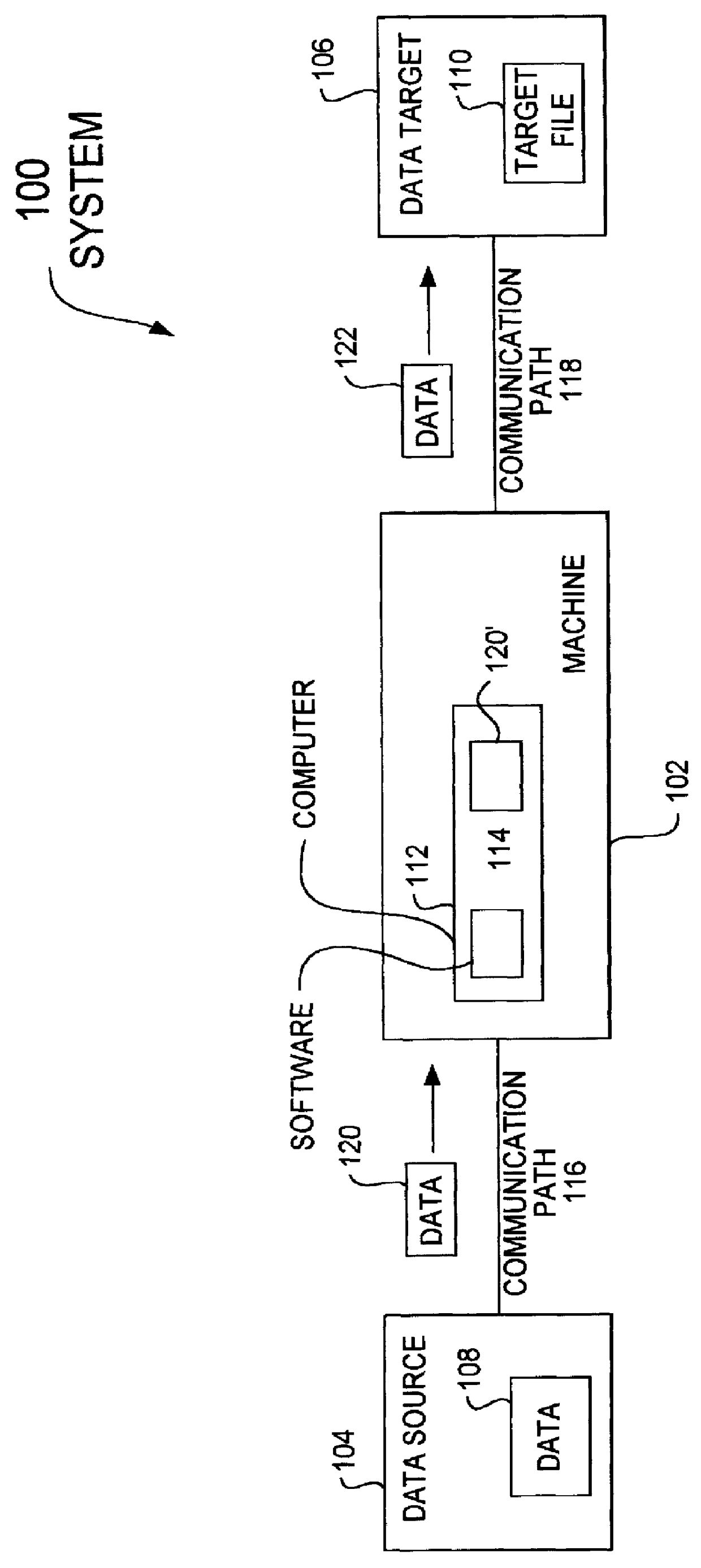
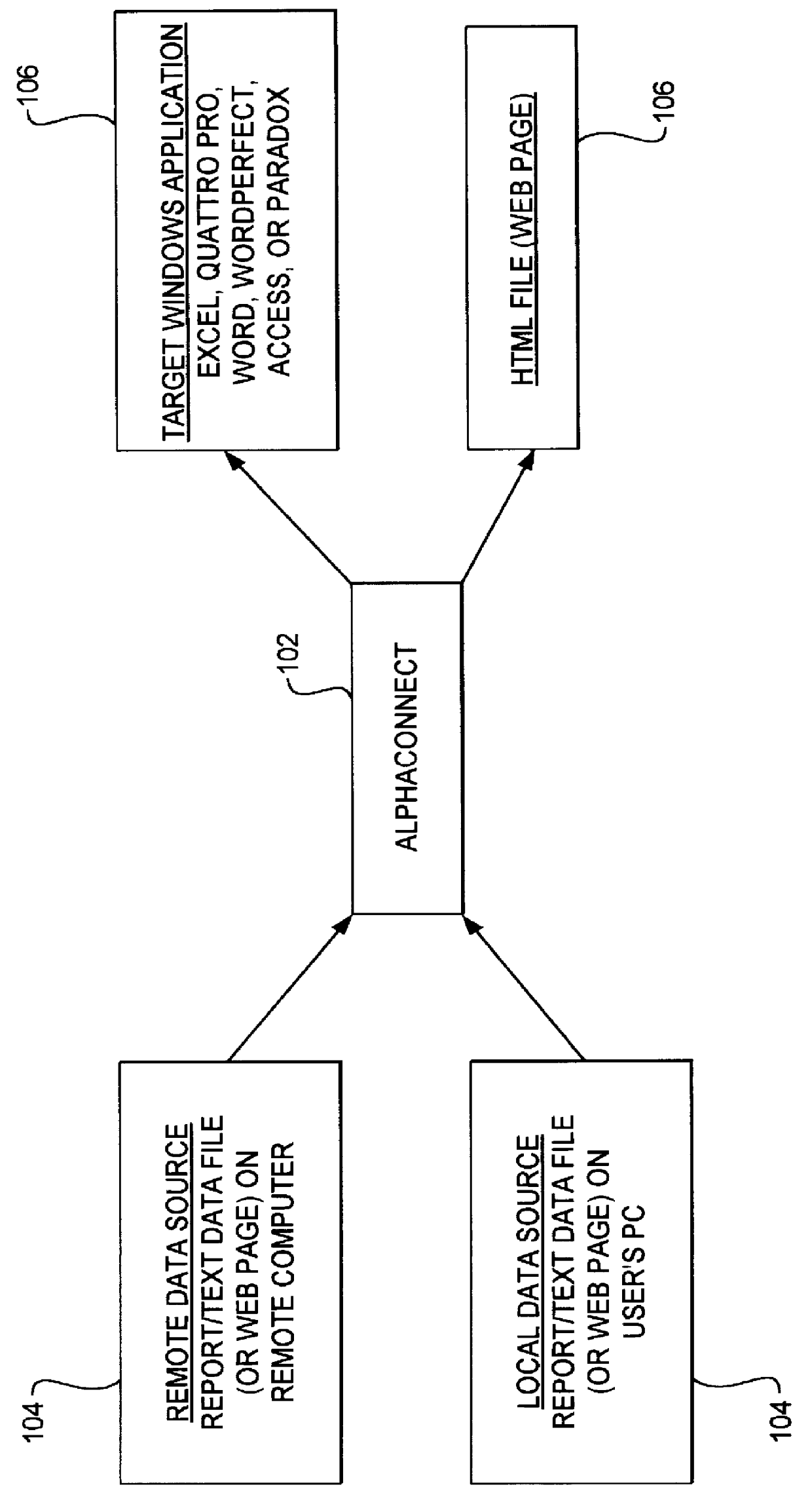
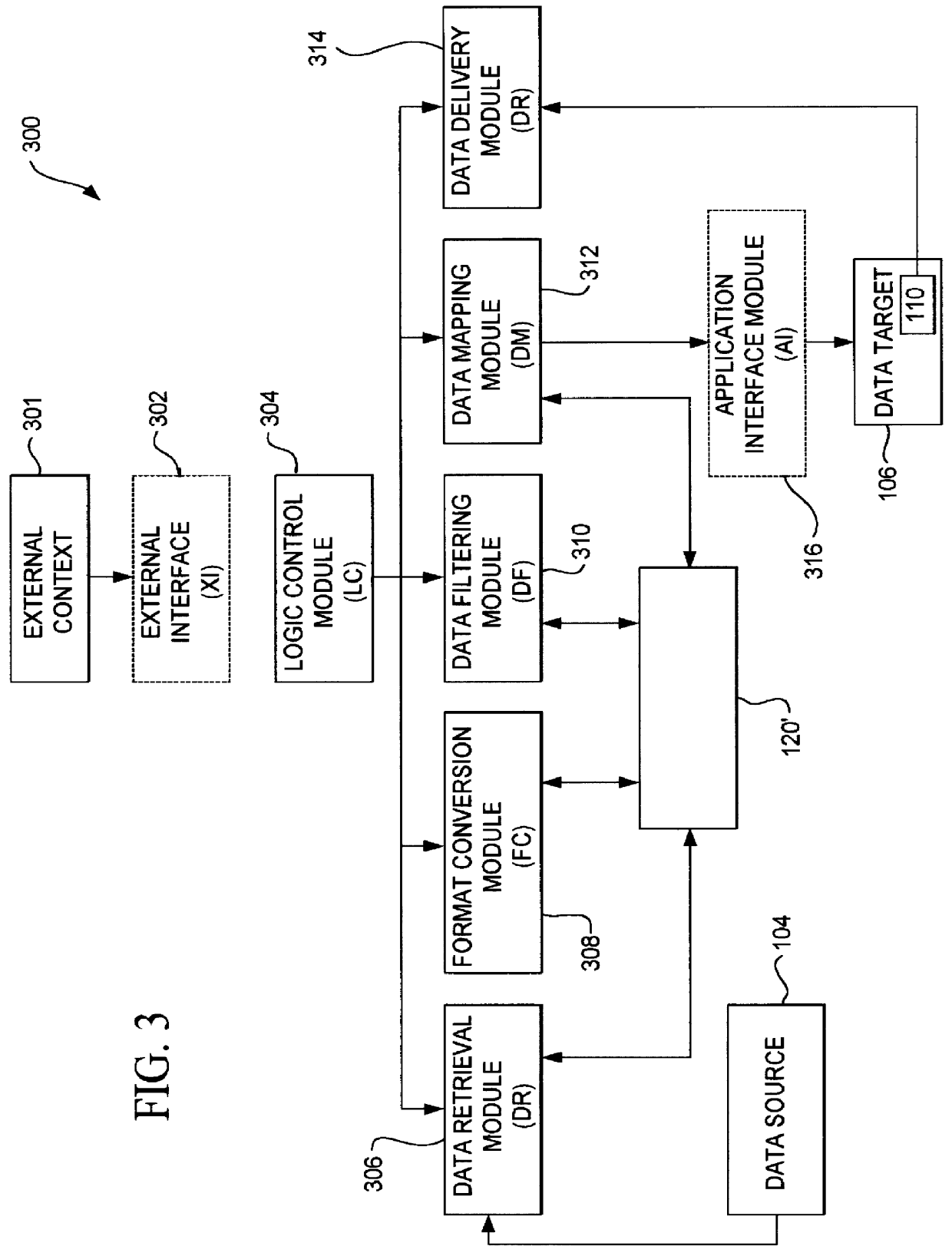
A data acquisition and delivery system for performing data delivery tasks is disclosed. This system uses a computer running software to acquire source data from a selected data source, to process (e.g. filter, format convert) the data, if desired, and to deliver the resulting delivered data to a data target. The system is designed to access remote and / or local data sources and to deliver data to remote and / or local data targets. The data target might be an application program that delivers the data to a file or the data target may simply be a file, for example. To obtain the delivered data, the software performs processing of the source data as appropriate for the particular type of data being retrieved, for the particular data target and as specified by a user, for example. The system can communicate directly with a target application program, telling the target application to place the delivered data in a particular location in a particular file. The system provides an external interface to an external context. If the external context is a human, the external interface may be a graphical user interface, for example. If the external context is another software application, the external interface may be an OLE interface, for example. Using the external interface, the external context is able to vary a variety of parameters to define data delivery tasks as desired. The system uses a unique notation that includes a plurality of predefined parameters to define the data delivery tasks and to communicate them to the software.
Owner:E BOTZ COM INC A DELAWARE +2
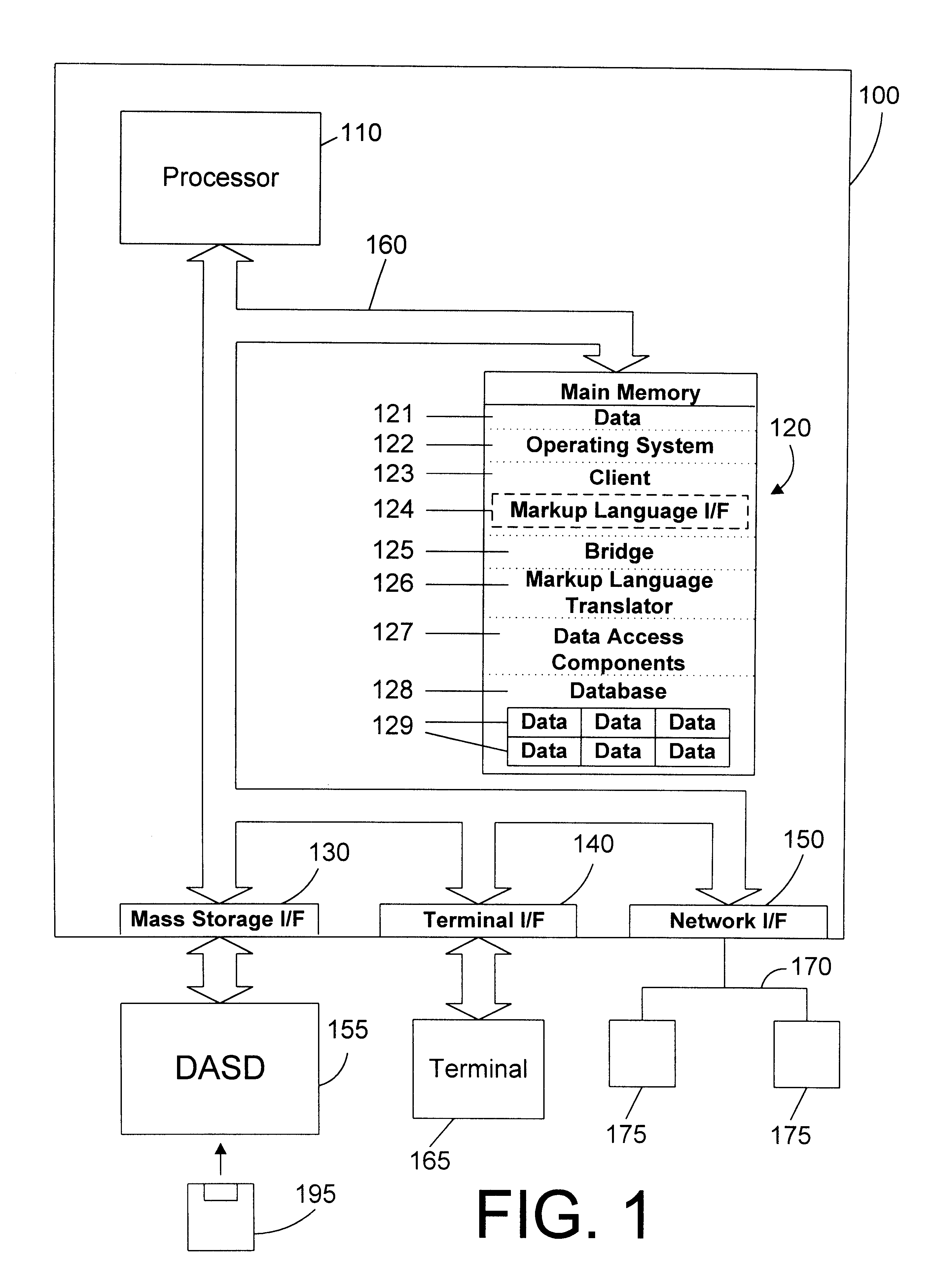
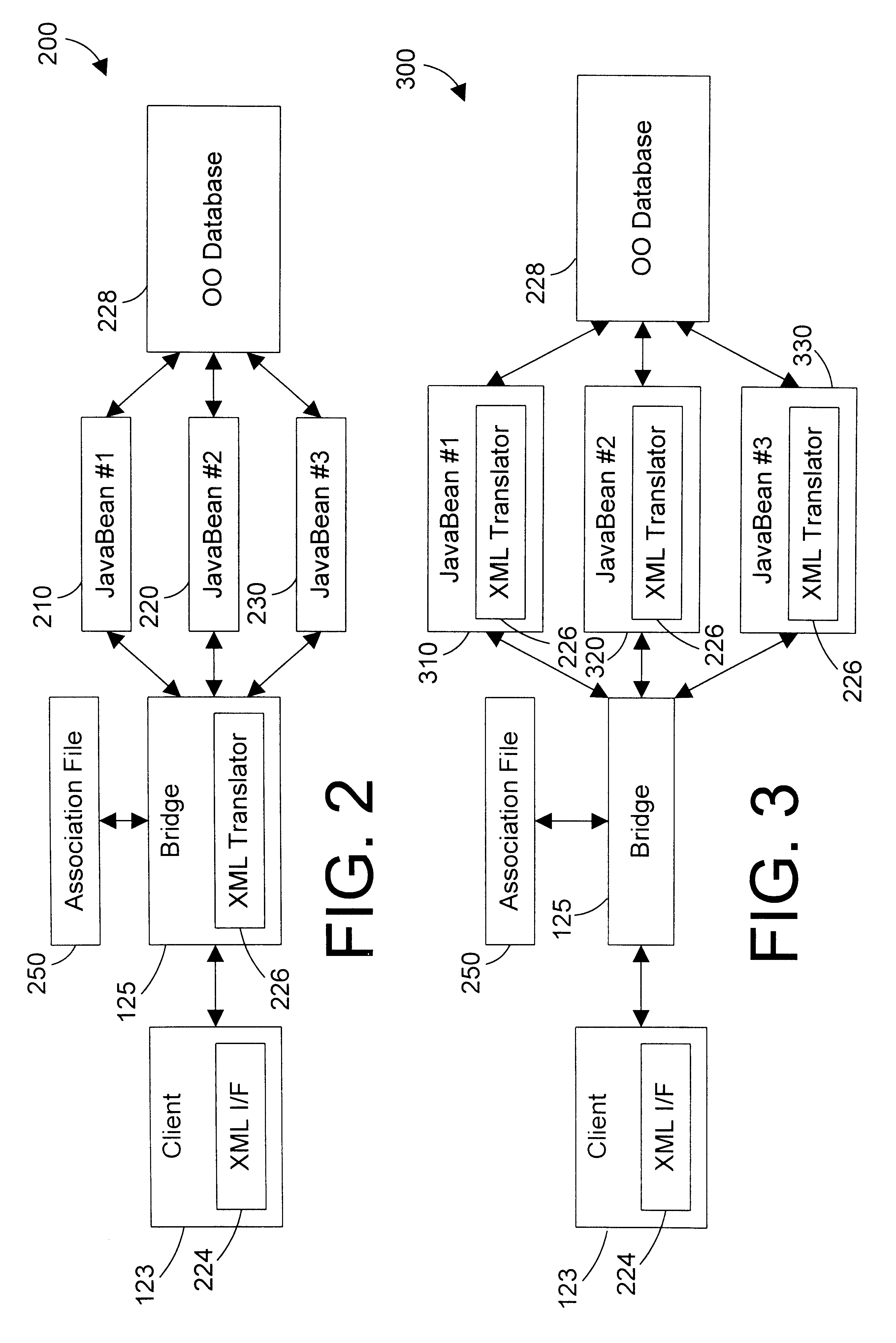
Tagged markup language interface with document type definition to access data in object oriented database
InactiveUS6480860B1Data processing applicationsWebsite content managementExtensible markupDocument preparation
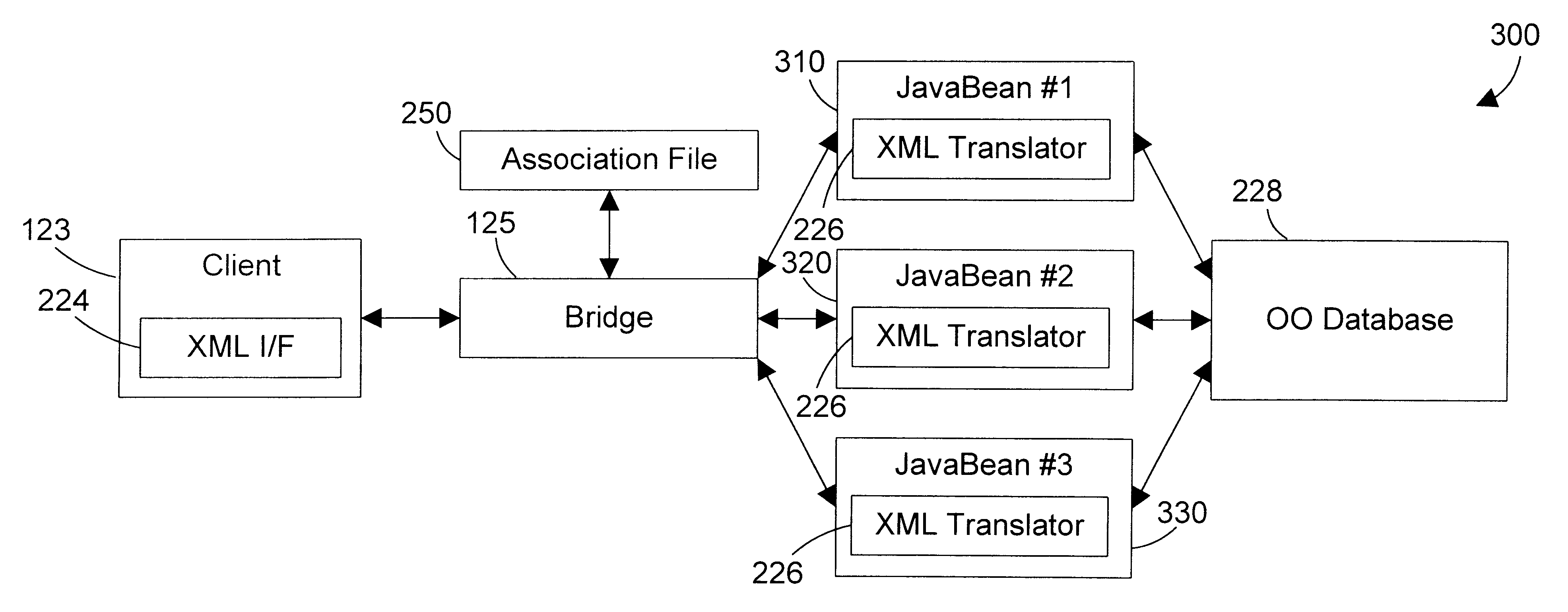
An apparatus and method defines a markup language for accessing data in a database. The markup language is preferably defined in extensible markup language (XML) by creating suitable document type definitions (DTDs), which define the grammar for accessing data in the database using the markup language. A bridge interprets the data request from the client in markup language format, a suitable database query for the database is formulated, and the data is then placed within a document for delivery in markup language format to the user. As new data types are added to the database, corresponding document type definitions (DTDs) may be dynamically generated, allowing a user to access new kinds of data in a database with a software tool that has a user-friendly graphical user interface without having to manually update the software tool for each new data type that is added to the database.
Owner:IBM CORP
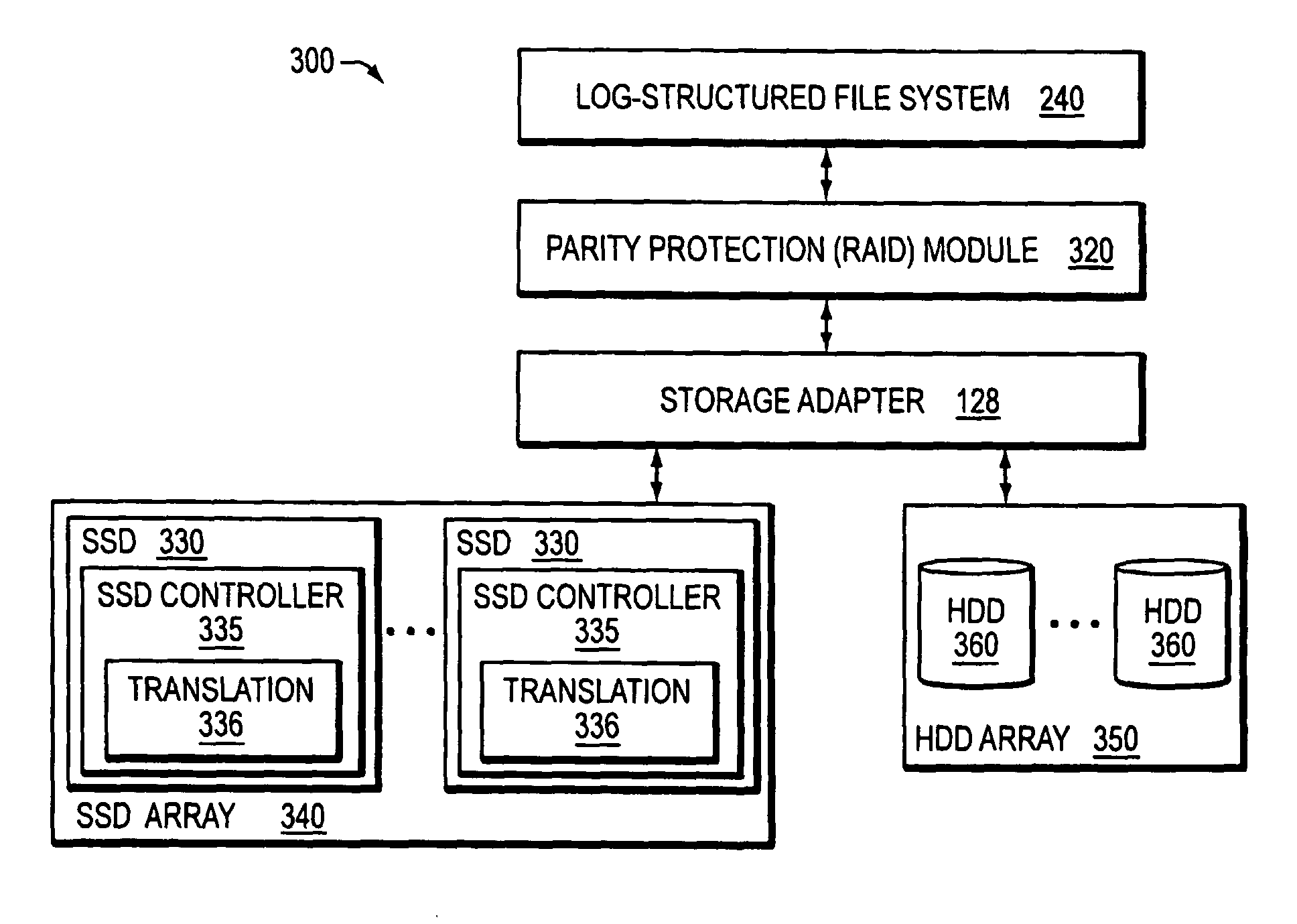
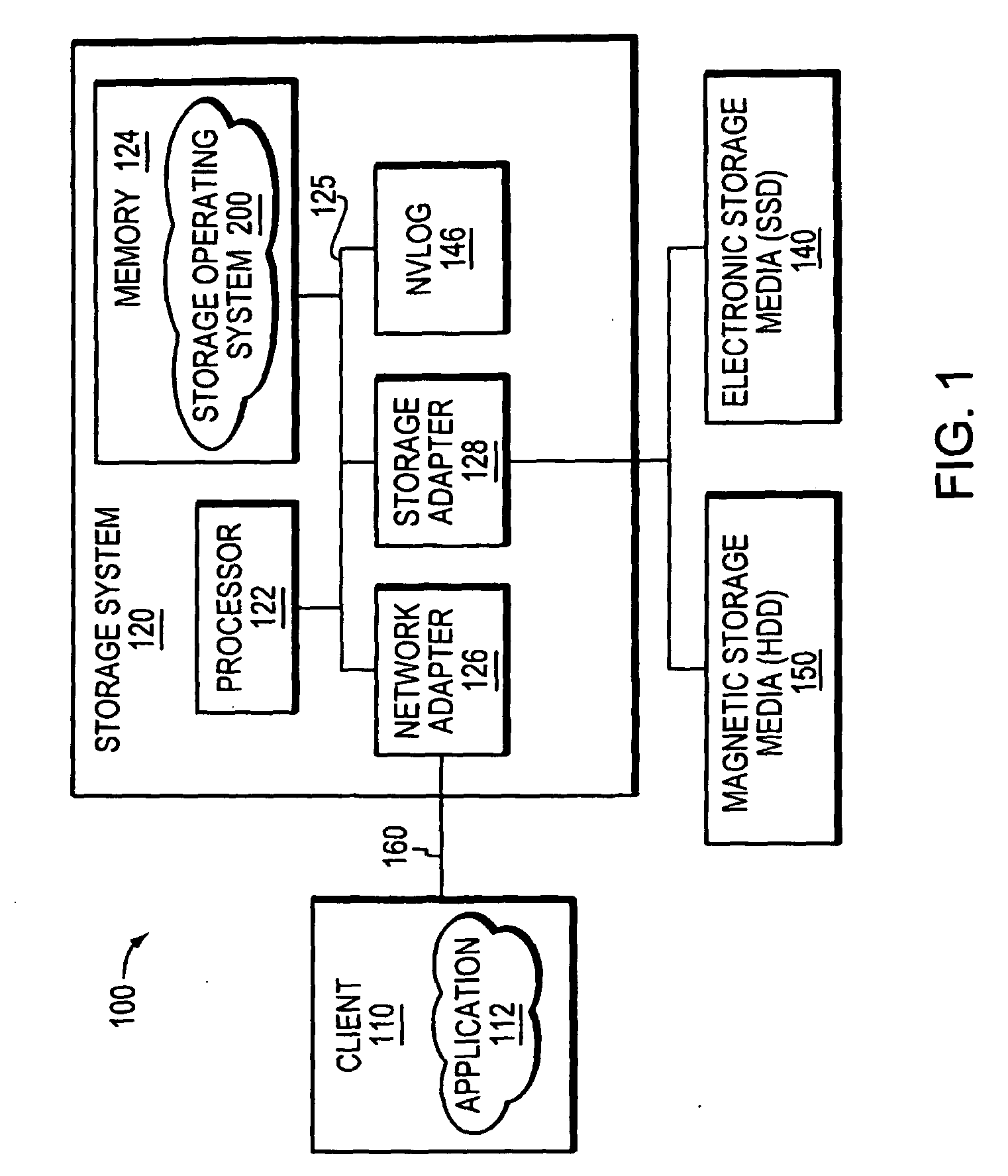
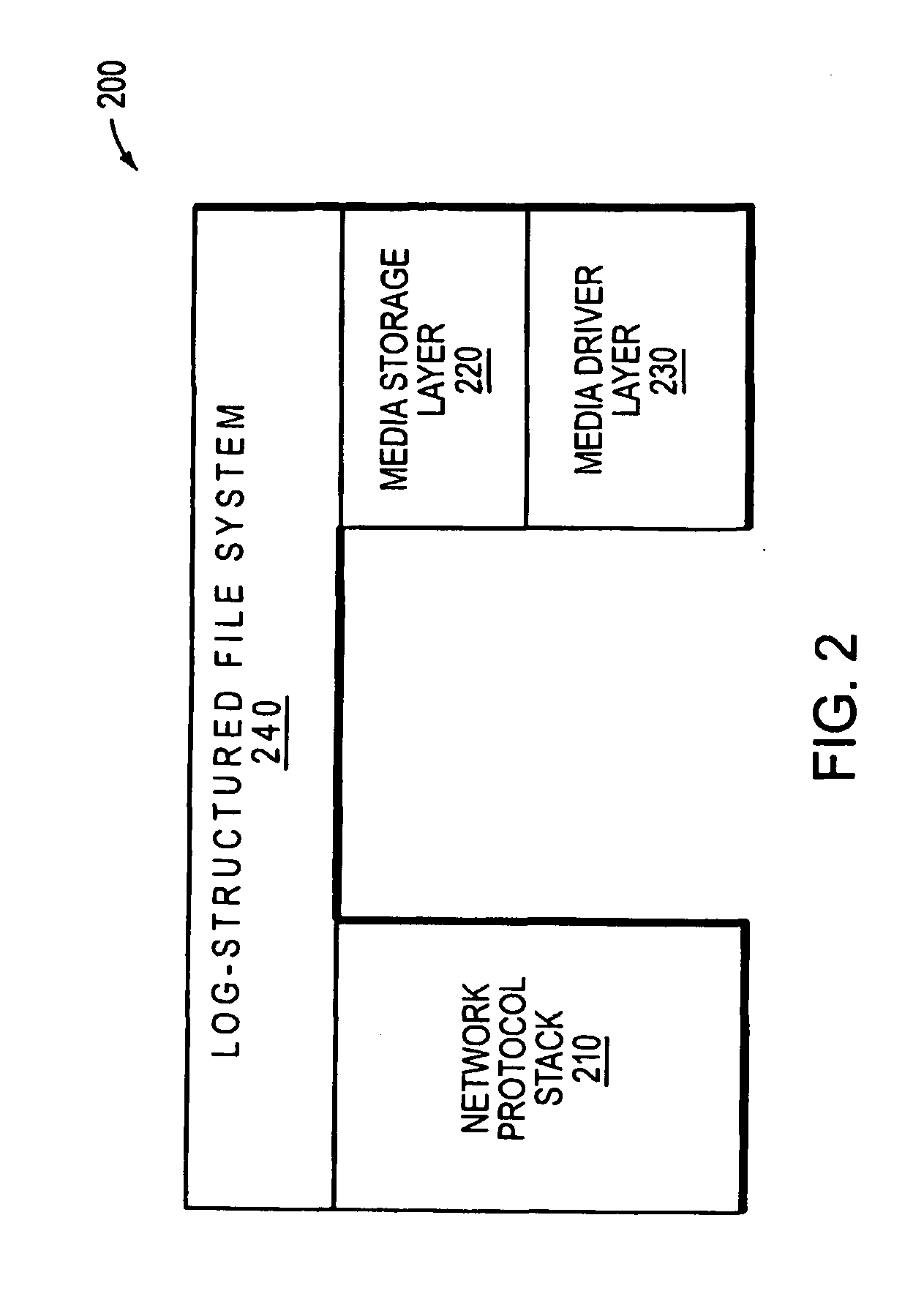
Hybrid media storage system architecture
ActiveUS20110035548A1Improved performance characteristicsOvercome disadvantagesDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionFile systemGranularity
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
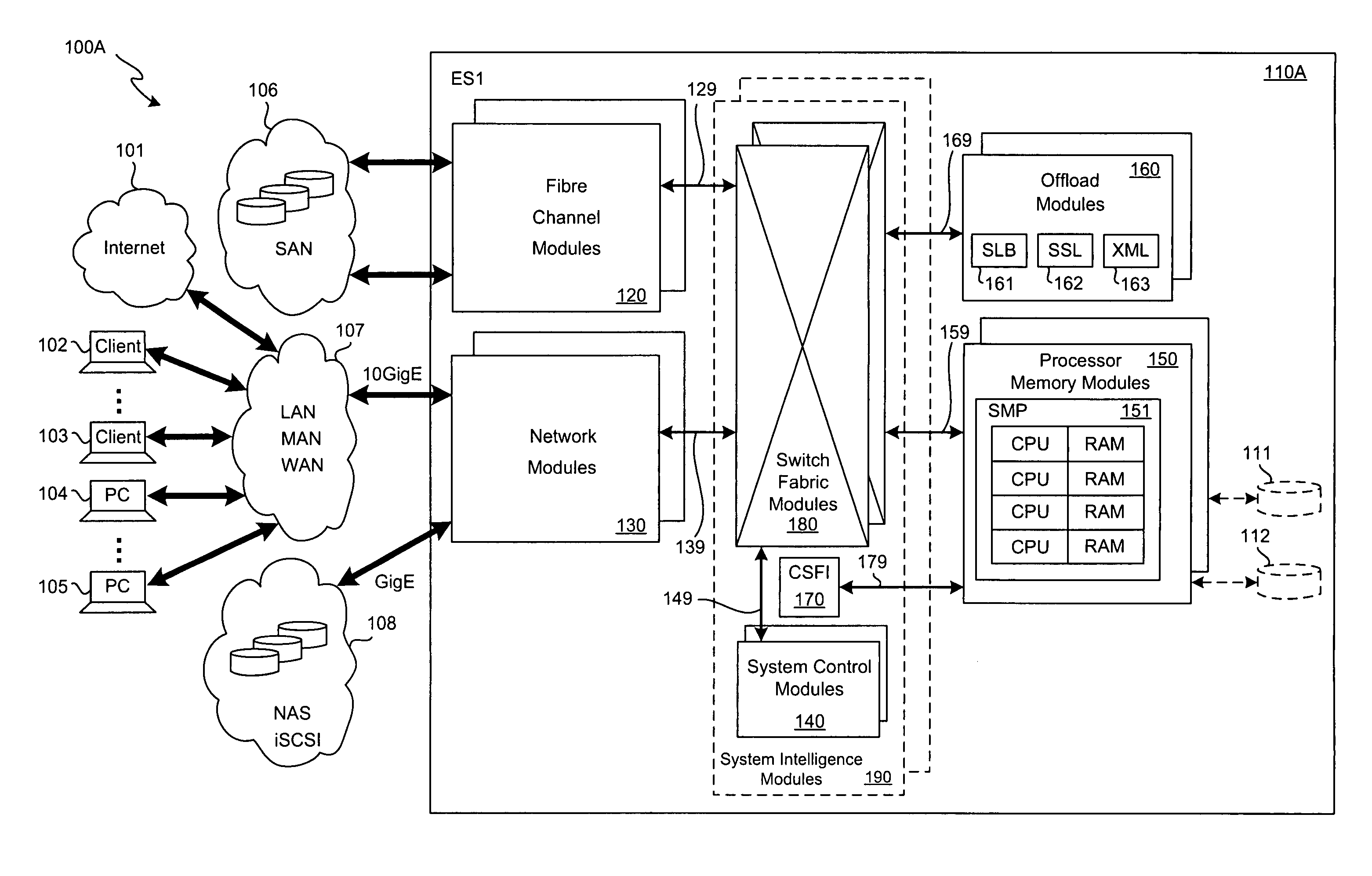
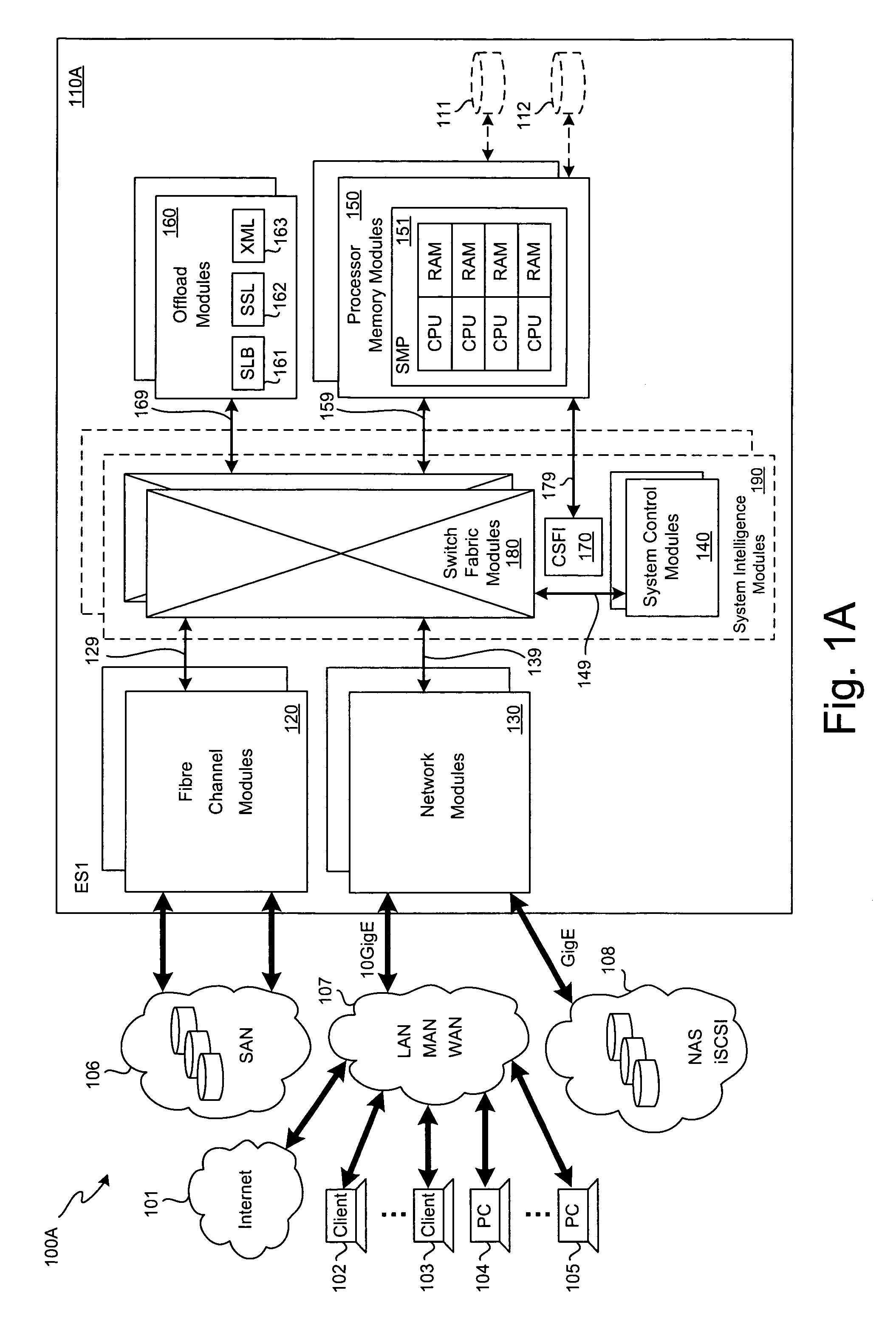
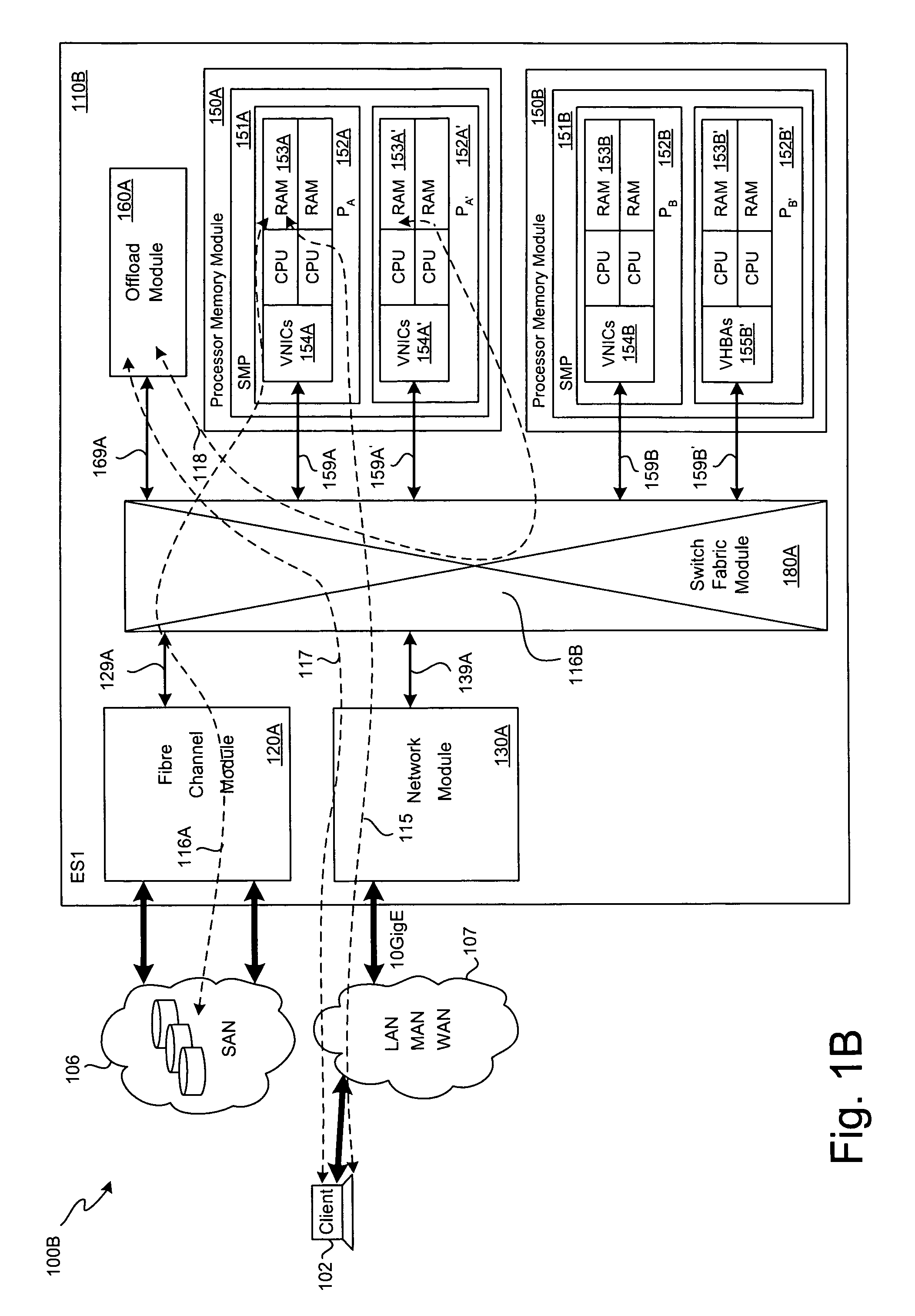
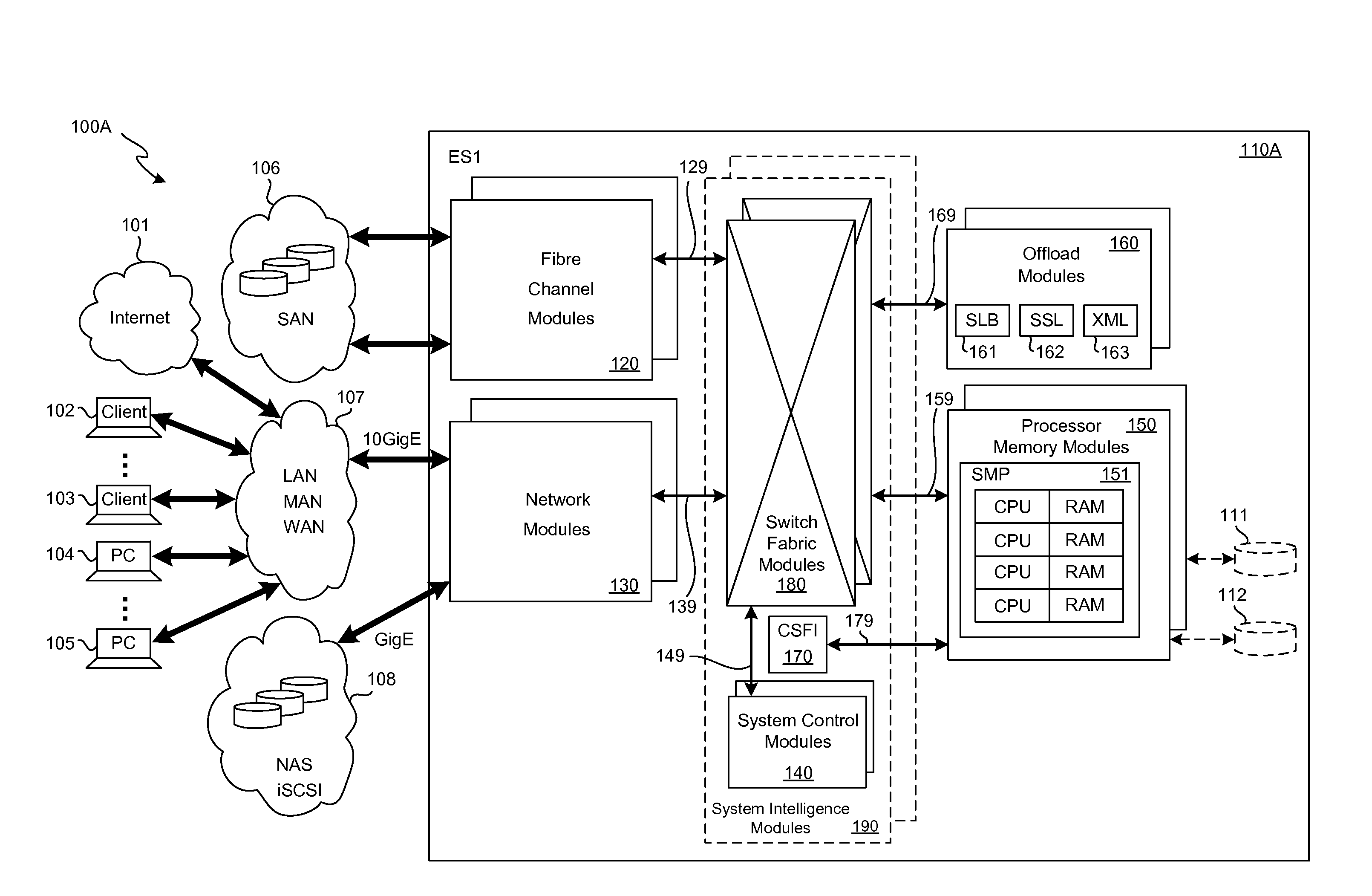
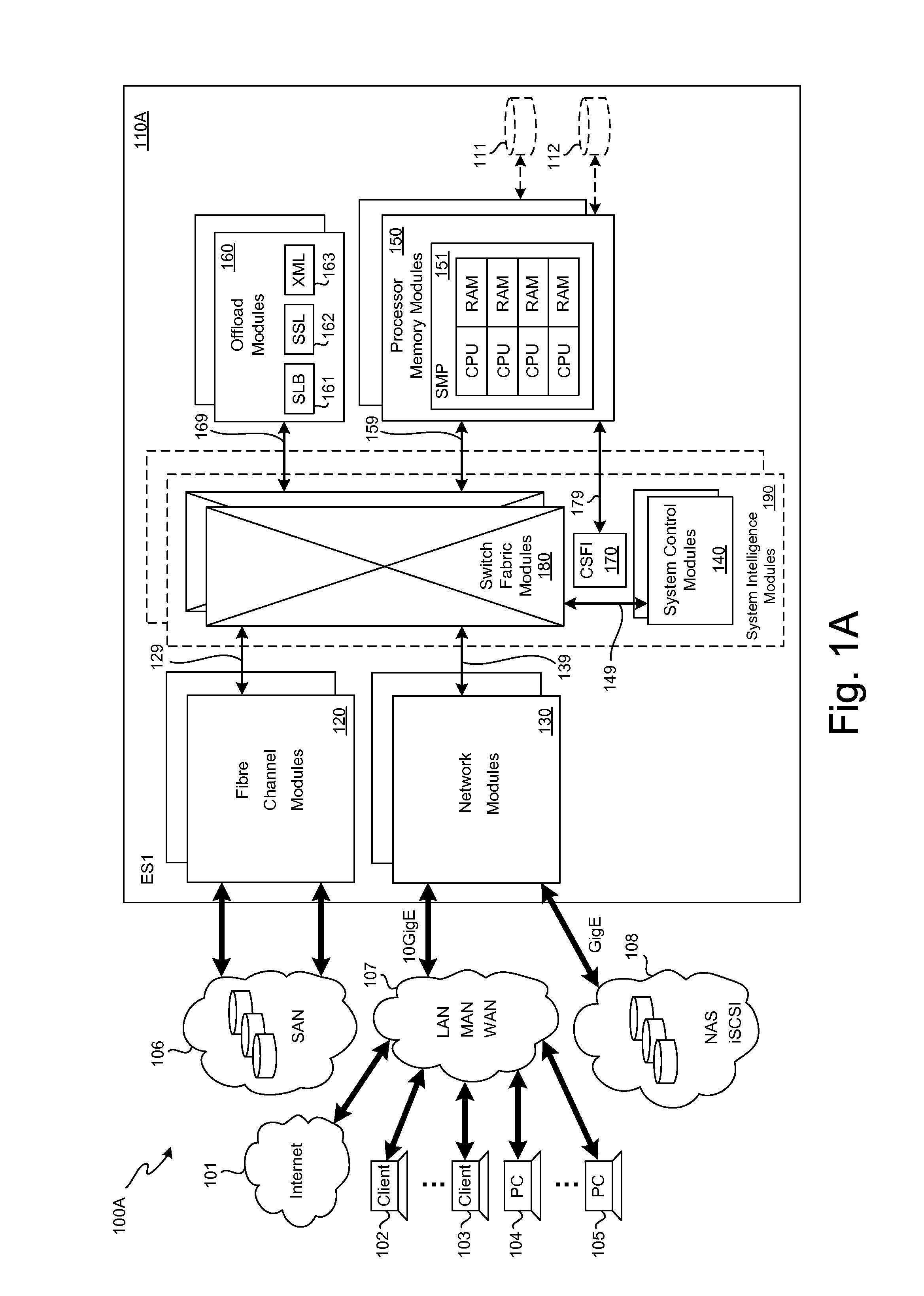
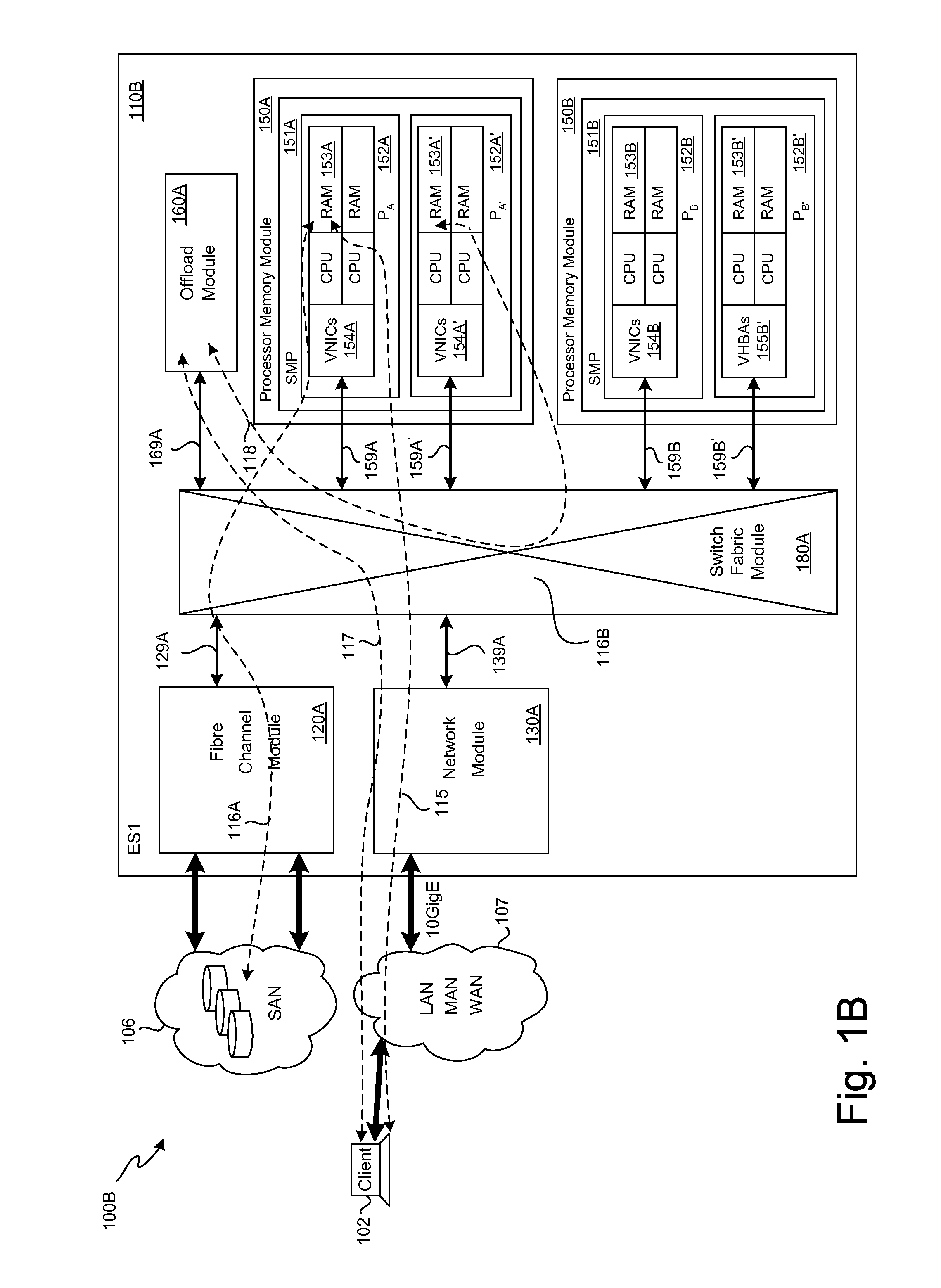
SCSI transport for fabric-backplane enterprise servers
ActiveUS7633955B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationSCSI initiator and targetFiber
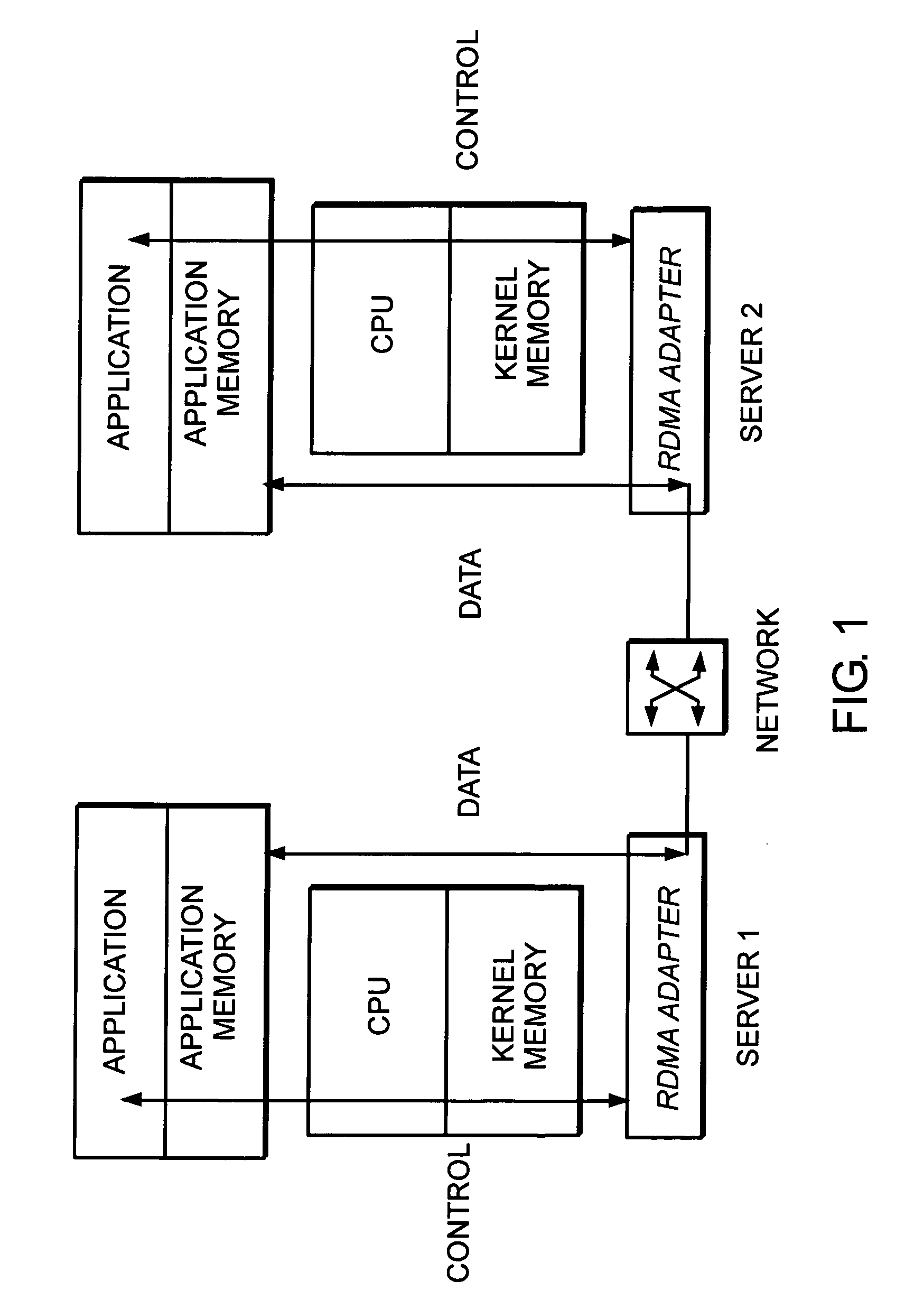
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) transport for fabric backplane enterprise servers provides for local and remote communication of storage system information between storage sub-system elements of an ES system and other elements of an ES system via a storage interface. The transport includes encapsulation of information for communication via a reliable transport implemented in part across a cellifying switch fabric. The transport may optionally include communication via Ethernet frames over any of a local network or the Internet. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Direct Data Placement (DDP) protocols are used to communicate the information (commands, responses, and data) between SCSI initiator and target end-points. A Fibre Channel Module (FCM) may be operated as a SCSI target providing a storage interface to any of a Processor Memory Module (PMM), a System Control Module (SCM), and an OffLoad Module (OLM) operated as a SCSI initiator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
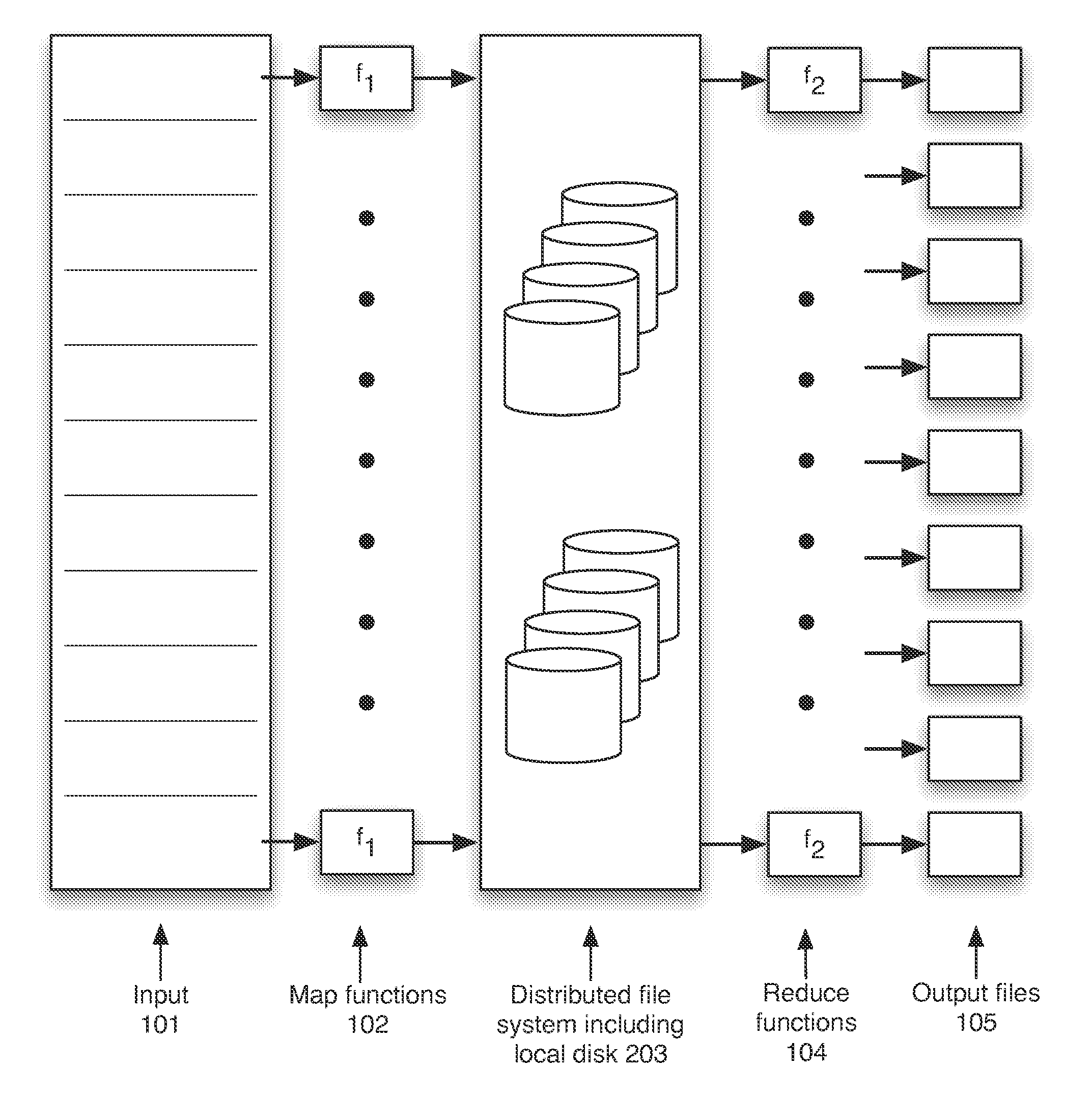
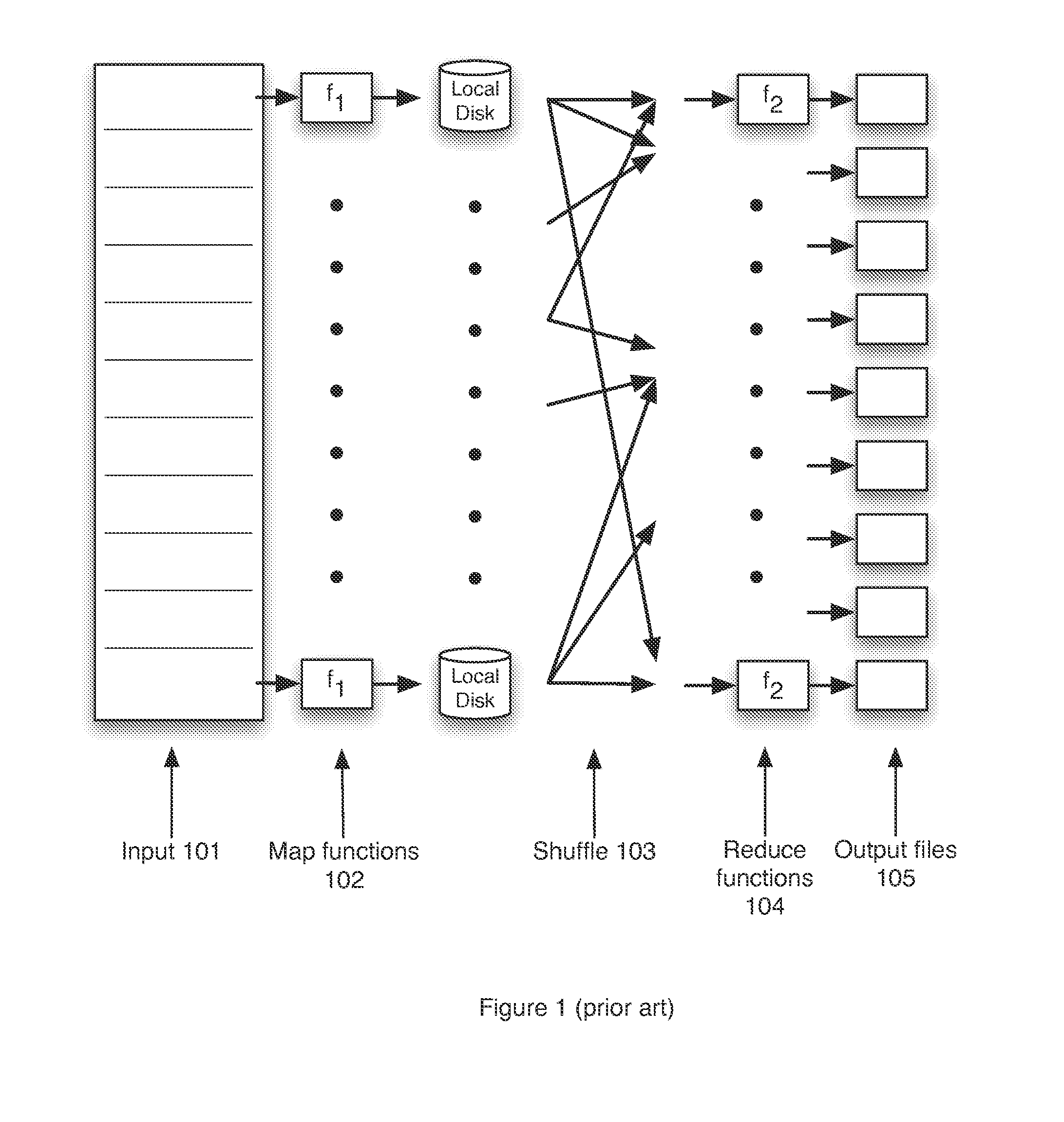
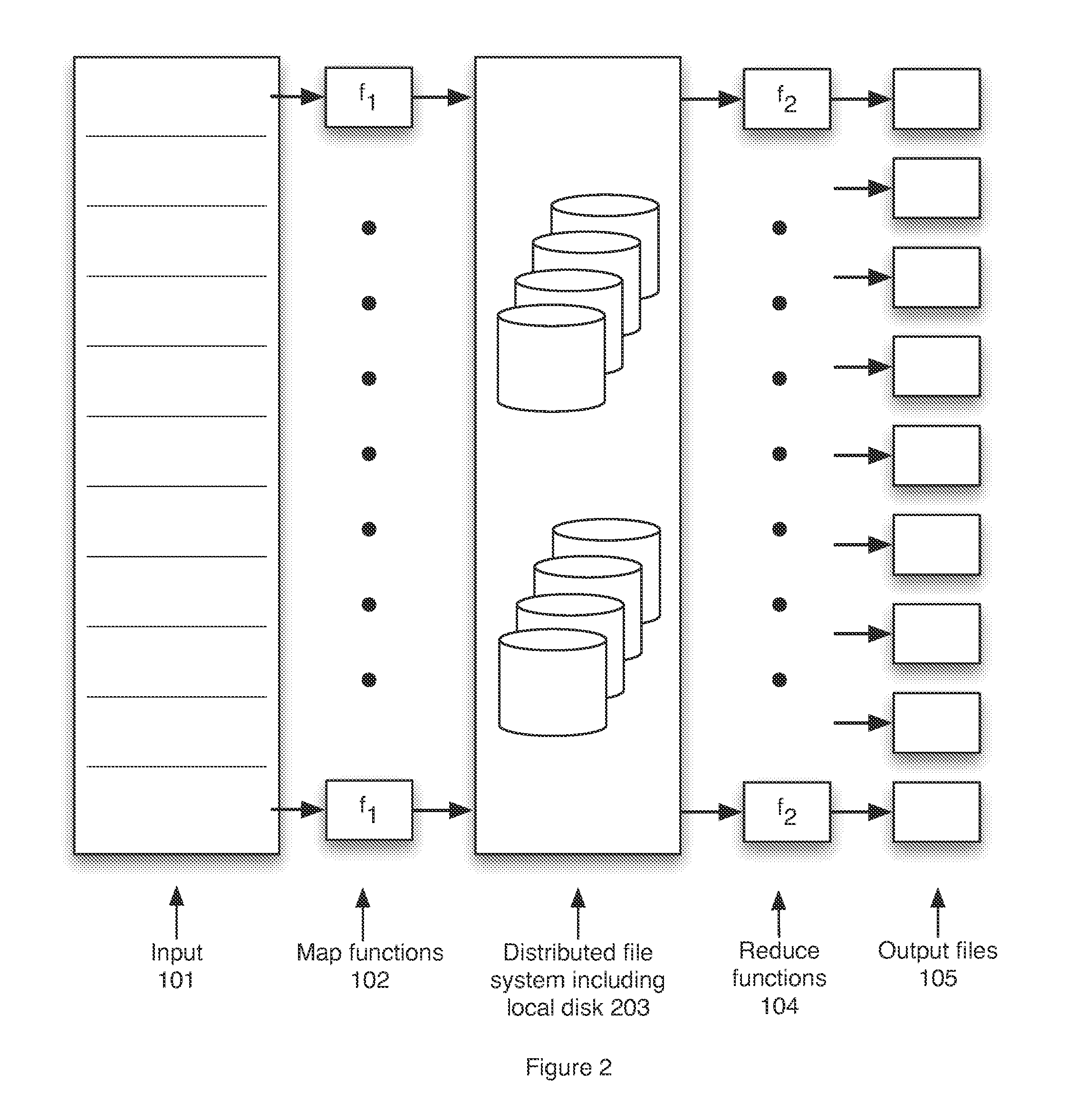
Map-Reduce Ready Distributed File System
A map-reduce compatible distributed file system that consists of successive component layers that each provide the basis on which the next layer is built provides transactional read-write-update semantics with file chunk replication and huge file-create rates. A primitive storage layer (storage pools) knits together raw block stores and provides a storage mechanism for containers and transaction logs. Storage pools are manipulated by individual file servers. Containers provide the fundamental basis for data replication, relocation, and transactional updates. A container location database allows containers to be found among all file servers, as well as defining precedence among replicas of containers to organize transactional updates of container contents. Volumes facilitate control of data placement, creation of snapshots and mirrors, and retention of a variety of control and policy information. Key-value stores relate keys to data for such purposes as directories, container location maps, and offset maps in compressed files.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
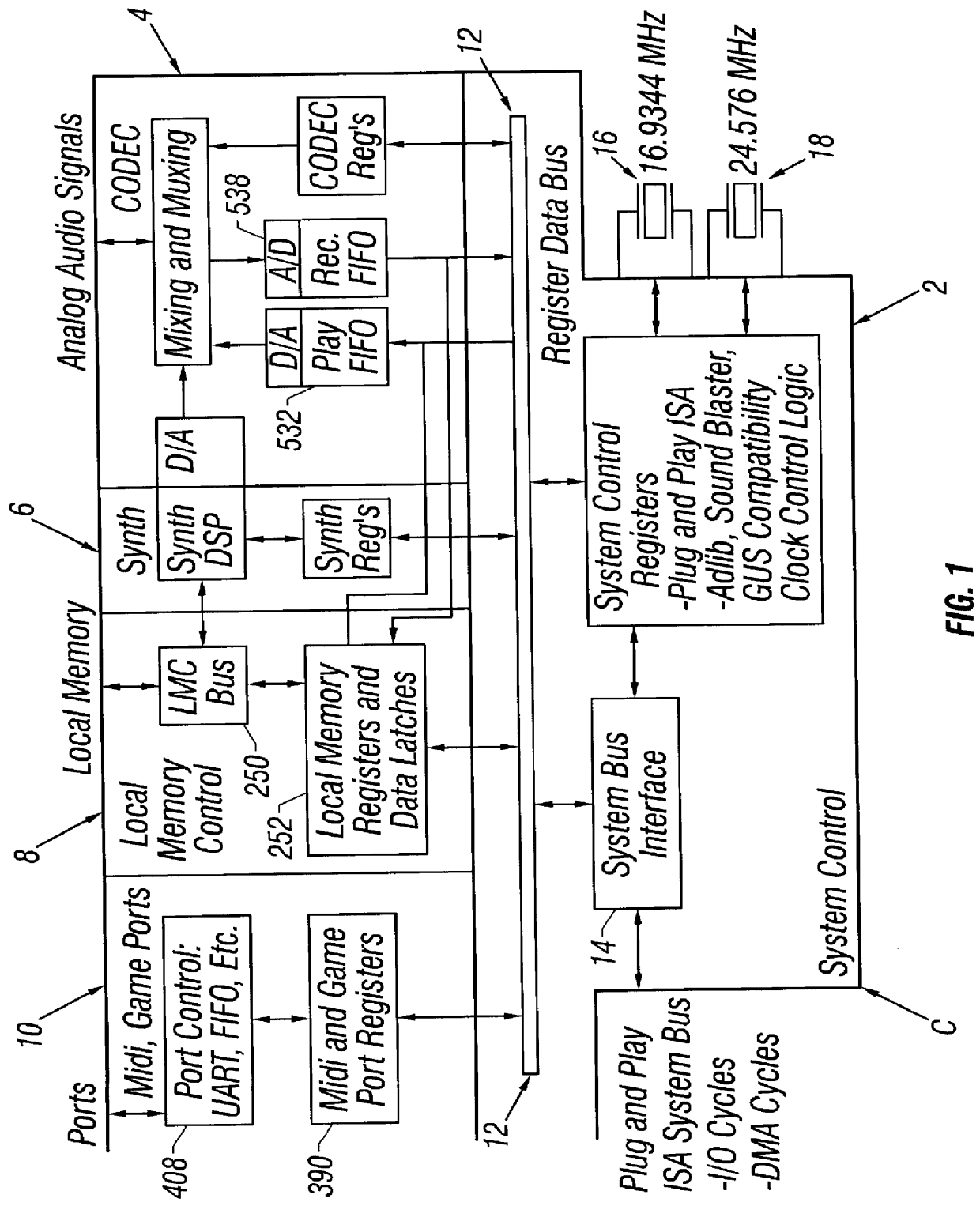
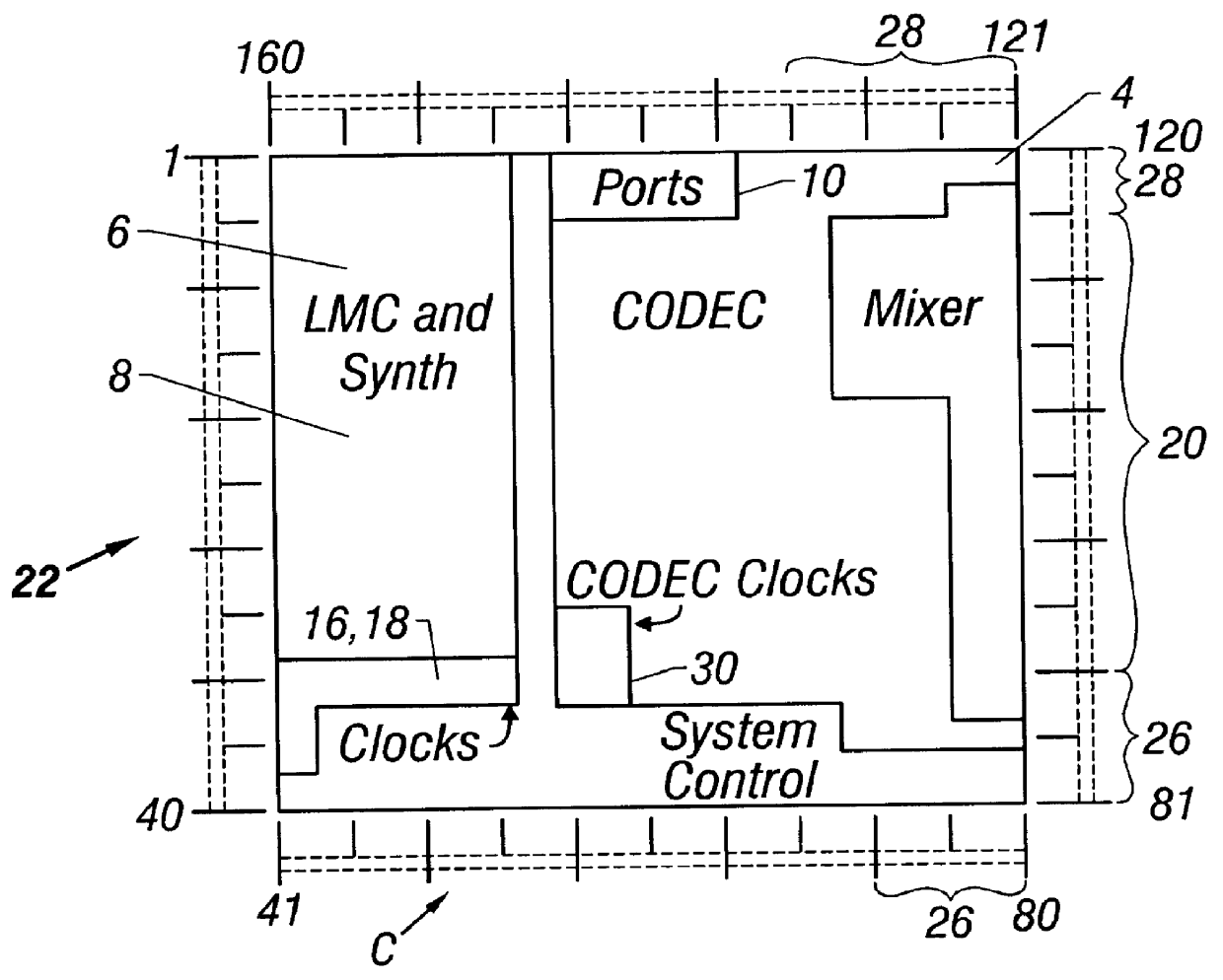
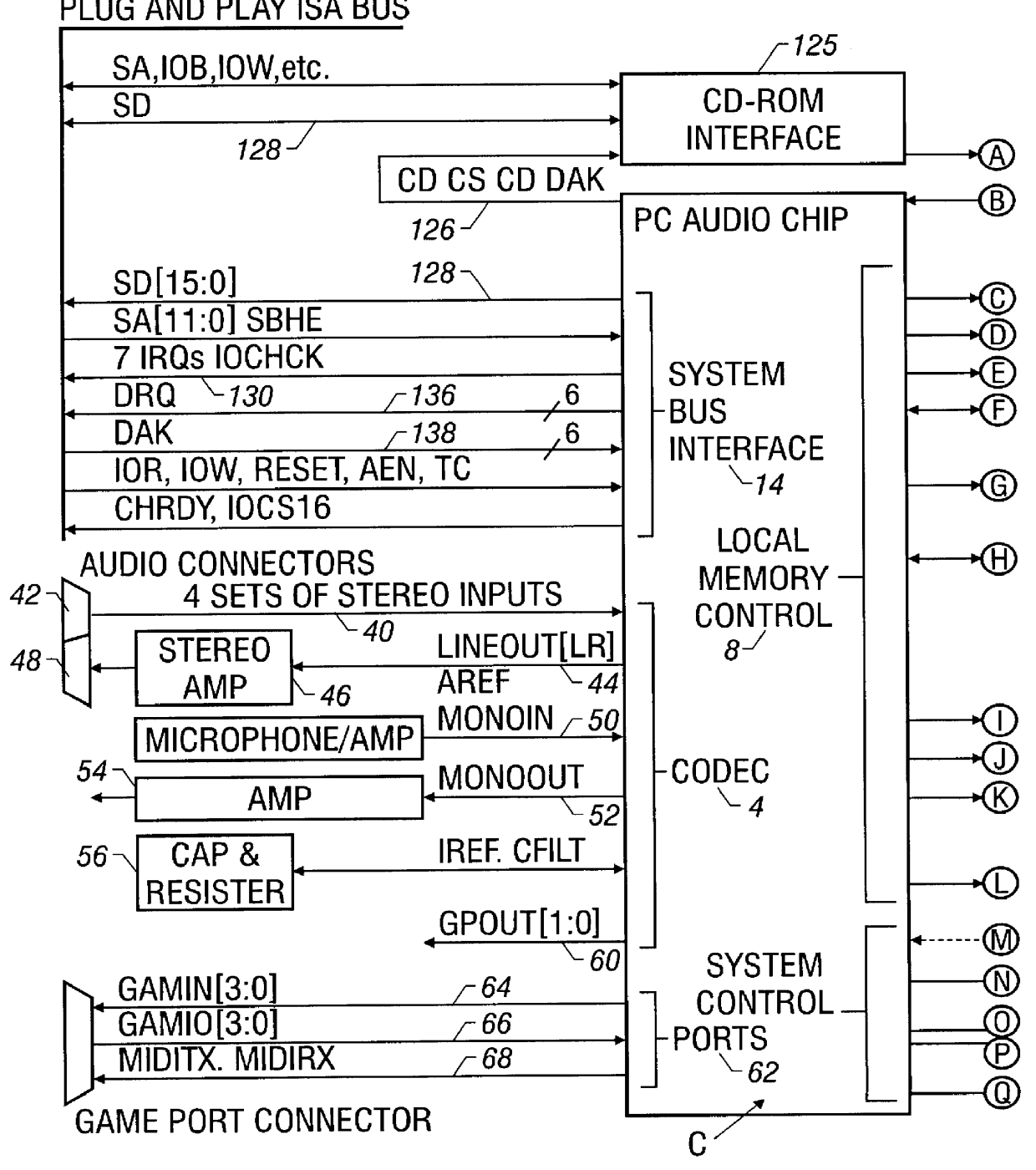
Digital wavetable audio synthesizer with delay-based effects processing
InactiveUS6047073AElectrophonic musical instrumentsCounting chain pulse countersAudio synthesisNoise
A digital wavetable audio synthesizer is described. The synthesizer can generate up to 32 high-quality audio digital signals or voices, including delay-based effects, at either a 44.1 KHz sample rate or at sample rates compatible with a prior art wavetable synthesizer. The synthesizer includes an address generator which has several modes of addressing wavetable data. The address generator's addressing rate controls the pitch of the synthesizer's output signal. The synthesizer performs a 10-bit interpolation, using the wavetable data addressed by the address generator, to interpolate additional data samples. When the address generator loops through a block of data, the signal path interpolates between the data at the end and start addresses of the block of data to prevent discontinuities in the generated signal. A synthesizer volume generator, which has several modes of controlling the volume, adds envelope, right offset, left offset, and effects volume to the data. The data can be placed in one of sixteen fixed stereo pan positions, or left and right offsets can be programmed to place the data anywhere in the stereo field. The left and right offset values can also be programmed to control the overall volume. Zipper noise is prevented by controlling the volume increment. A synthesizer LFO generator can add LFO variation to: (i) the wavetable data addressing rate, for creating a vibrato effect; and (ii) a voice's volume, for creating a tremolo effect. Generated data to be output from the synthesizer is stored in left and right accumulators. However, when creating delay-based effects, data is stored in one of several effects accumulators. This data is then written to a wavetable. The difference between the wavetable write and read addresses for this data provides a delay for echo and reverb effects. LFO variations added to the read address create chorus and flange effects. The volume of the delay-based effects data can be attenuated to provide volume decay for an echo effect. After the delay-based effects processing, the data can be provided with left and right offset volume components which determine how much of the effect is heard and its stereo position. The data is then stored in the left and right accumulators.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
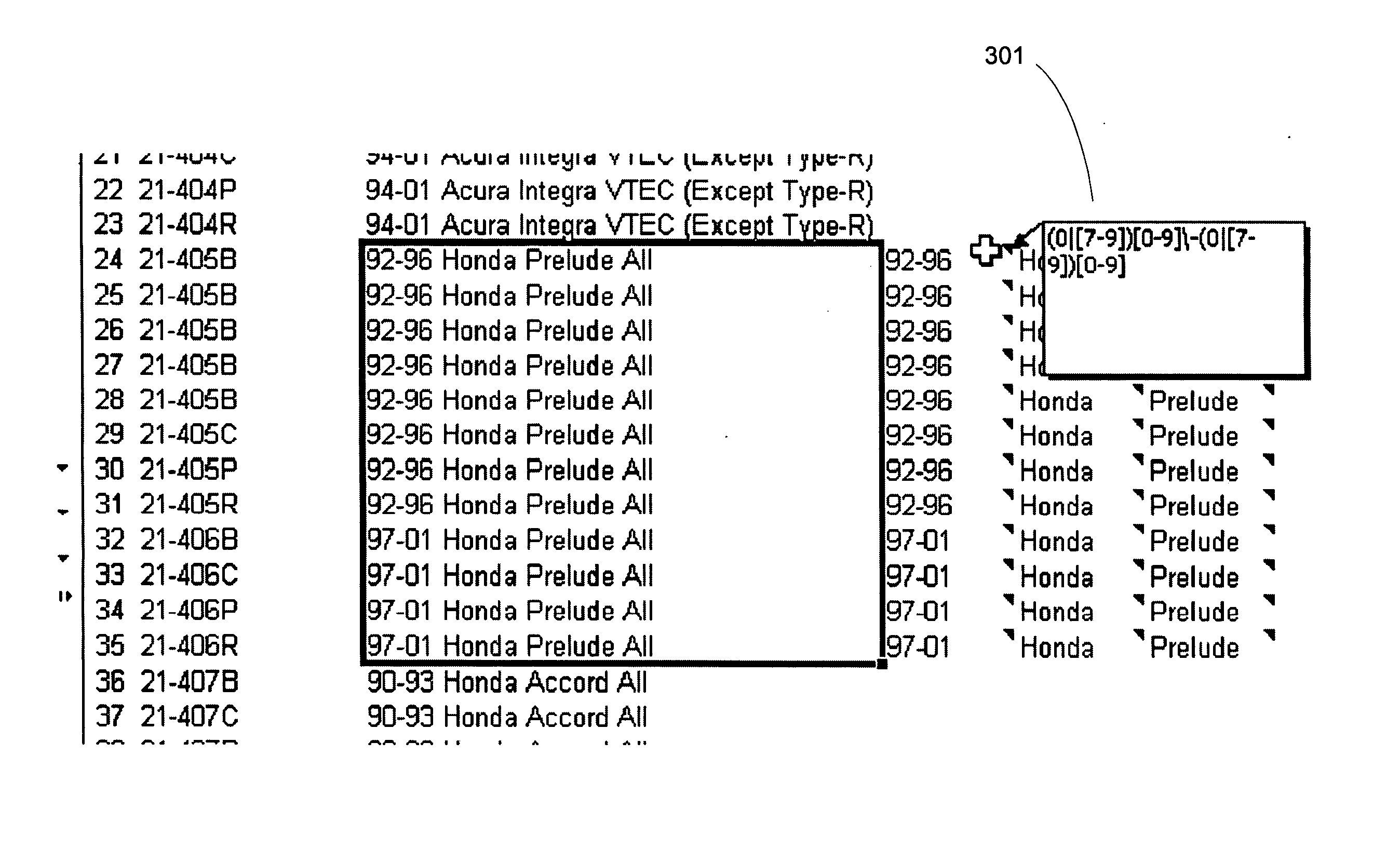
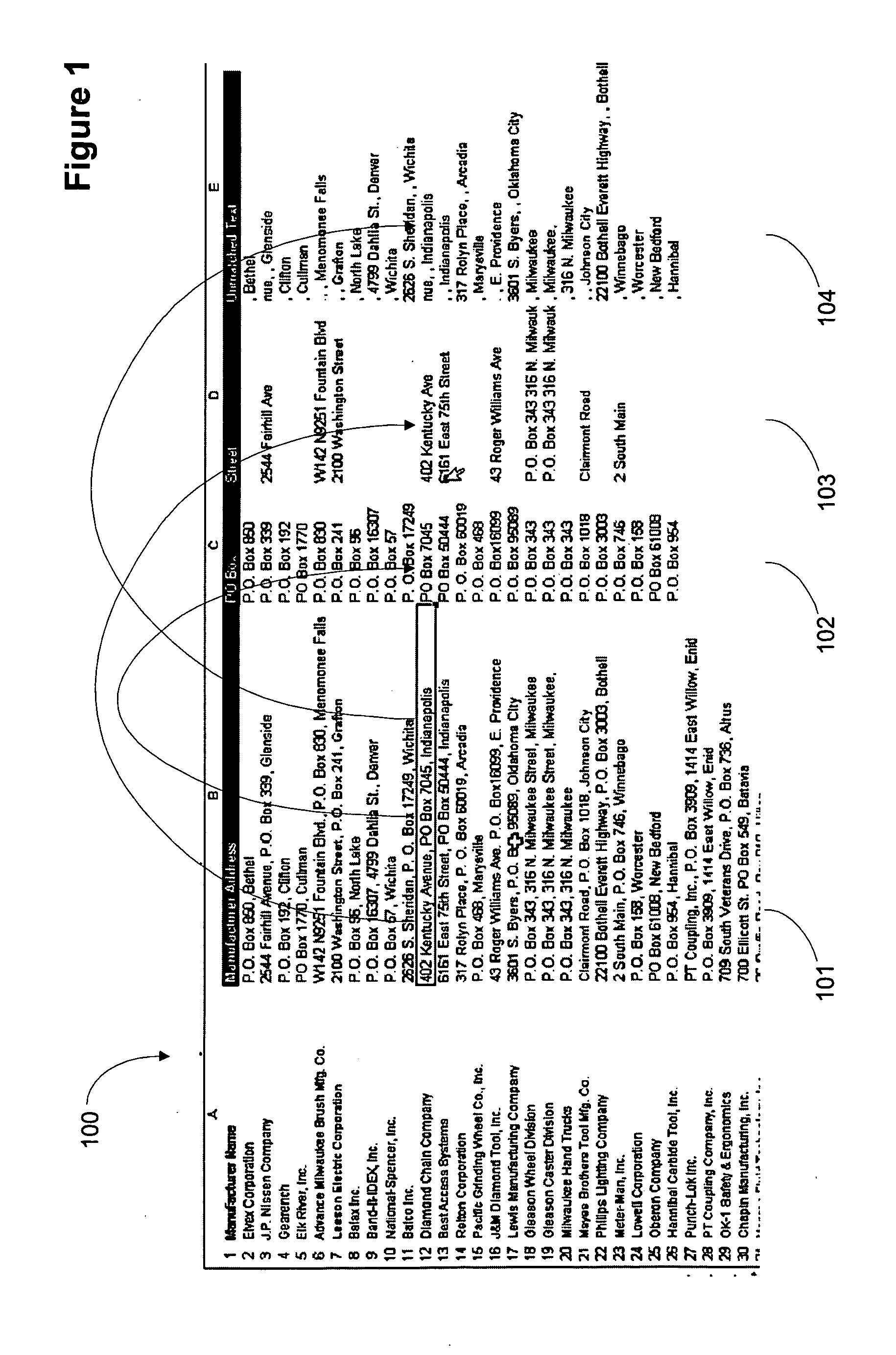
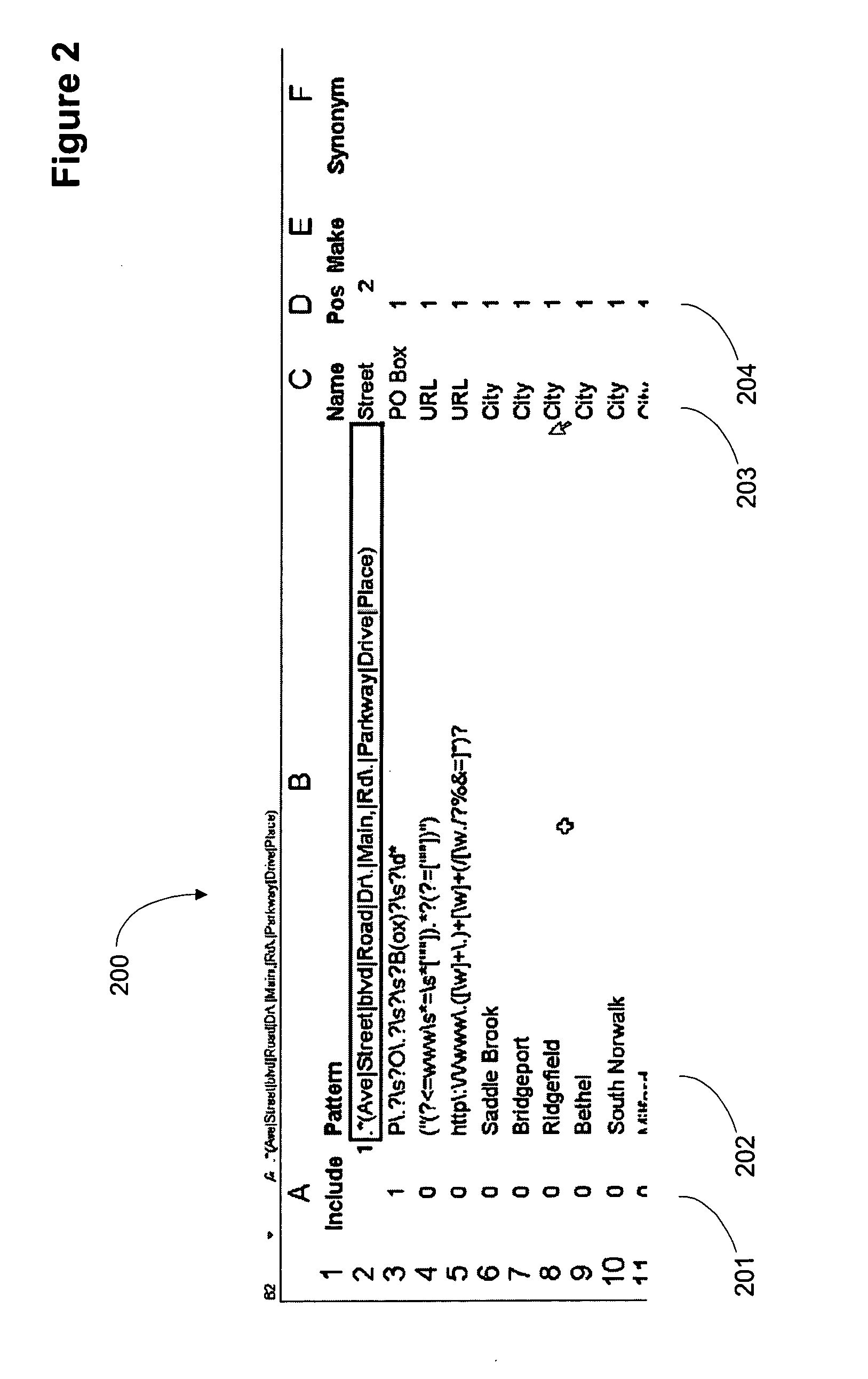
Apparatus and method for parsing unstructured data
ActiveUS20070078872A1Quick implementationEliminates more and more unmatched textDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPattern matchingPosition dependent
A user interface for parsing unstructured data using pattern recognition. The patterns used in parsing data are formed from regular expressions. The parsed data may be displayed in a first format and unmatched strings in the unstructured text may be displayed in a second format. A format may comprise a desired color, font or any other user interface parameter. In addition, the data that parses according to a pattern may be placed in a column associated with the pattern in a tabular user interface, for example a spreadsheet like Excel™. Associating a pattern with a position to display successful matches in allows for breaking unstructured text into pieces associated with a particular field or column. Modification of the patterns allows for more and more of the unstructured text to match the patterns and when the data has been parsed to the desired level, the data may be imported into a database.
Owner:REGIONAL RESOURCES LTD
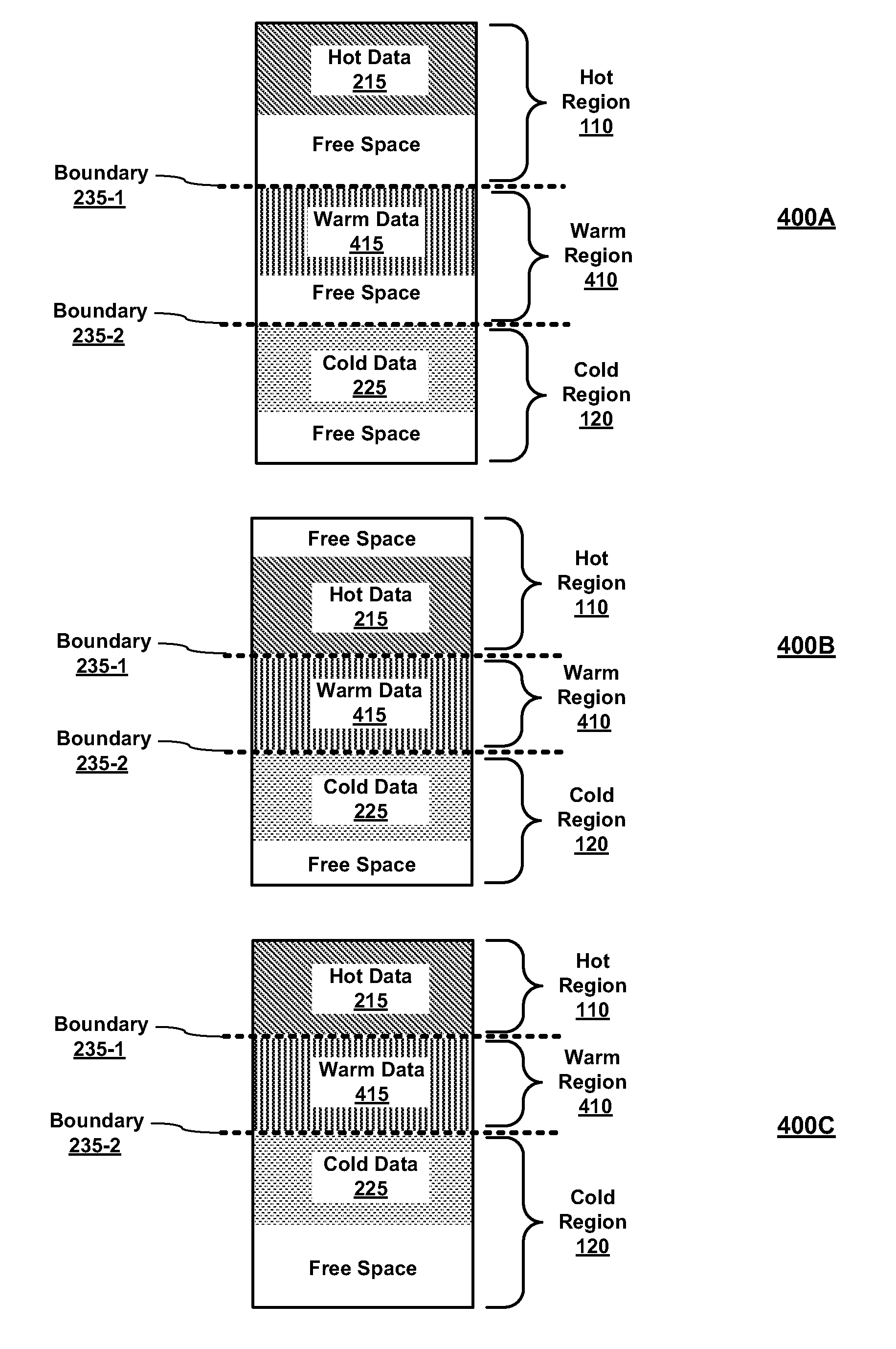
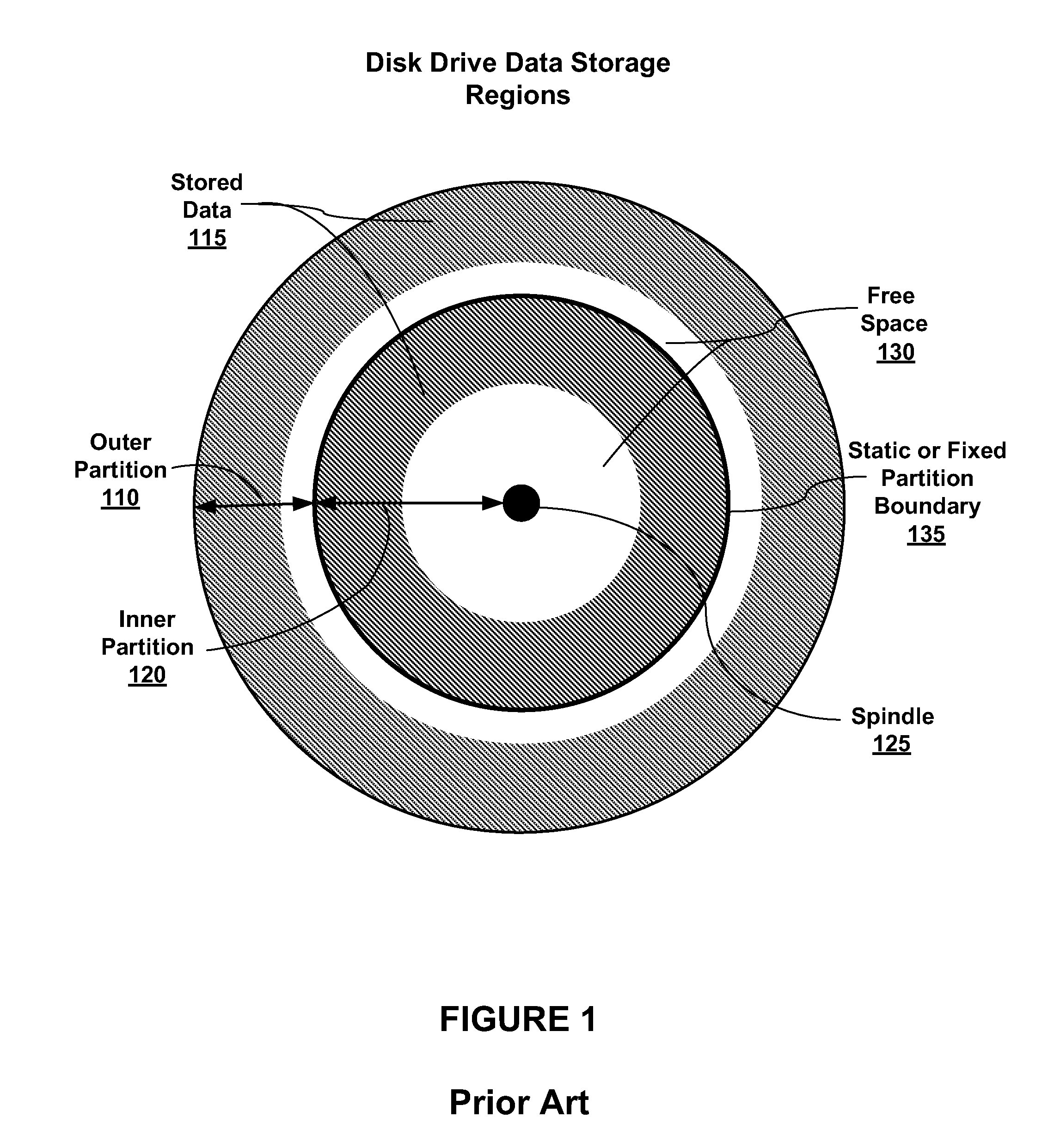
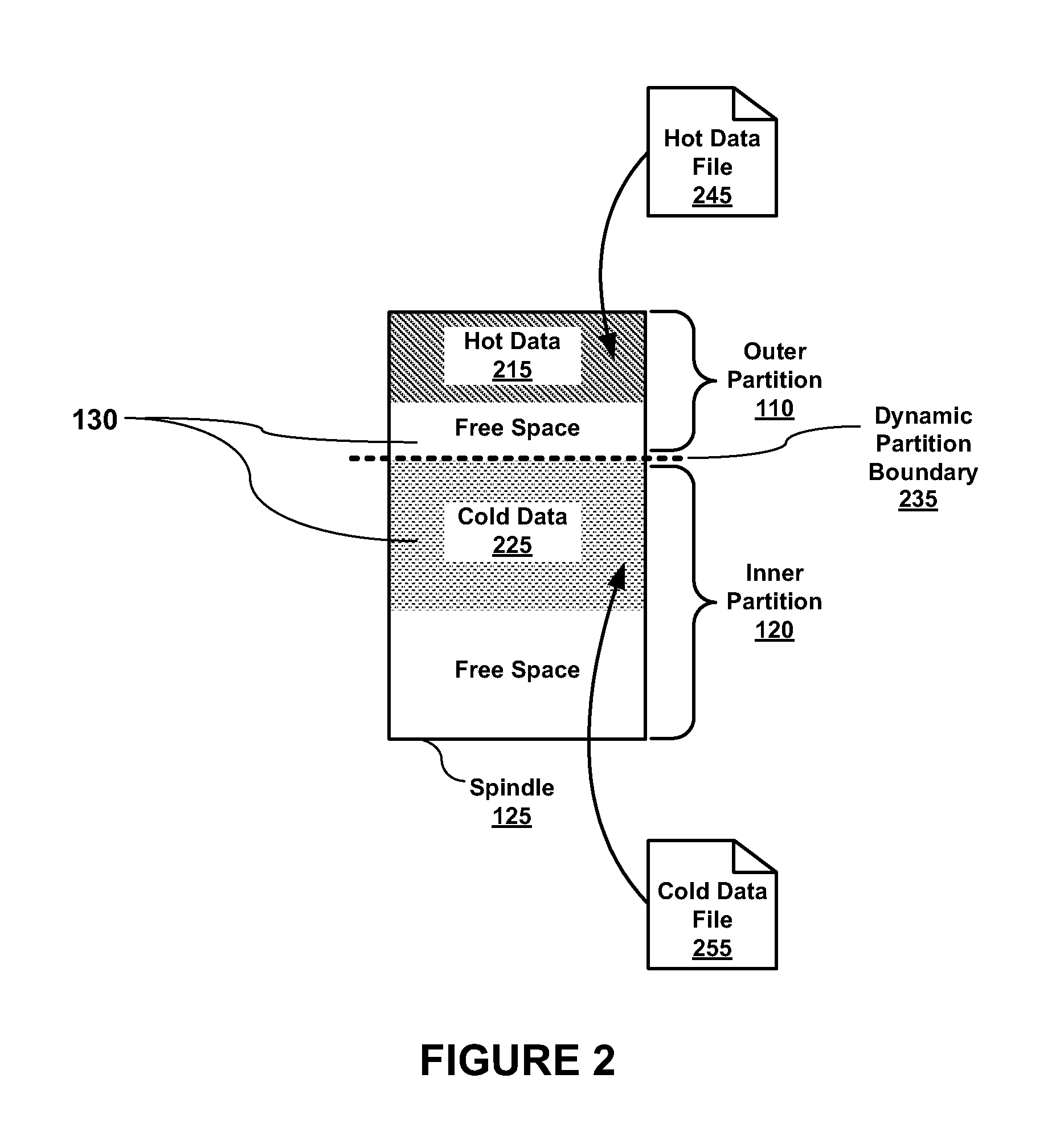
Dynamic Data Storage Repartitioning
ActiveUS20110138148A1High performance valueLow performance valueDigital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemStorage management
Embodiments of the present invention enable dynamic repartitioning of data storage in response to one or more triggers. In embodiments, a trigger may be a user-initiated action, a system-generated action, and / or an inference based on storage usage parameters. Applications of the present invention are its use in embodiments of a storage management system comprising a file system manager and a volume manager, where the placement of data into a partition (data storage region) may be specified by matching one or more disk region placement data attributes assigned to data with corresponding disk region attributes. In embodiments, dynamic repartitioning comprises adjustment of the location of the boundary between adjacent disk partitions and, if necessary, rebalancing of the data stored within the partitions by identifying mismatched data and relocating it to the partition with which it is associated.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
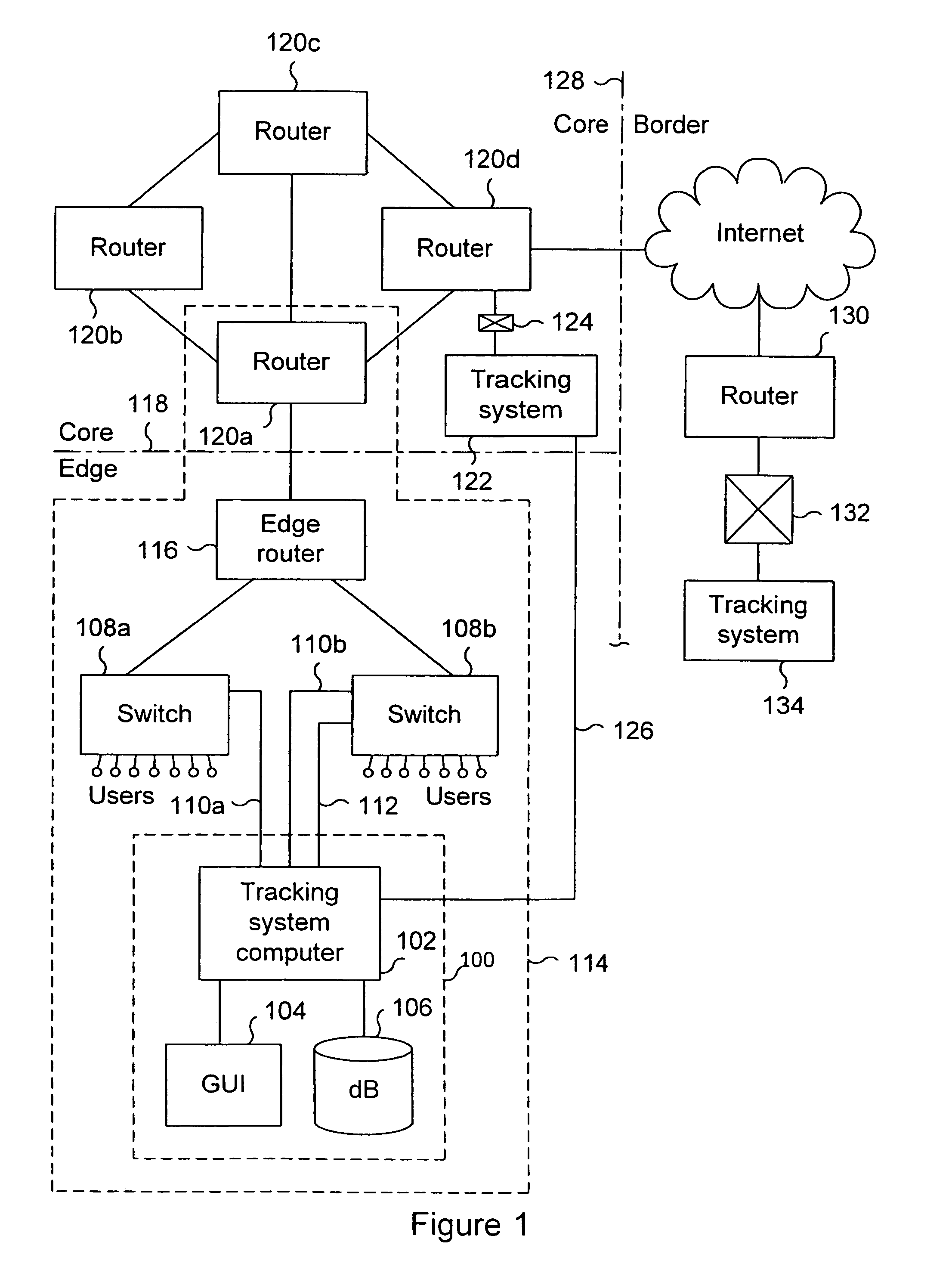
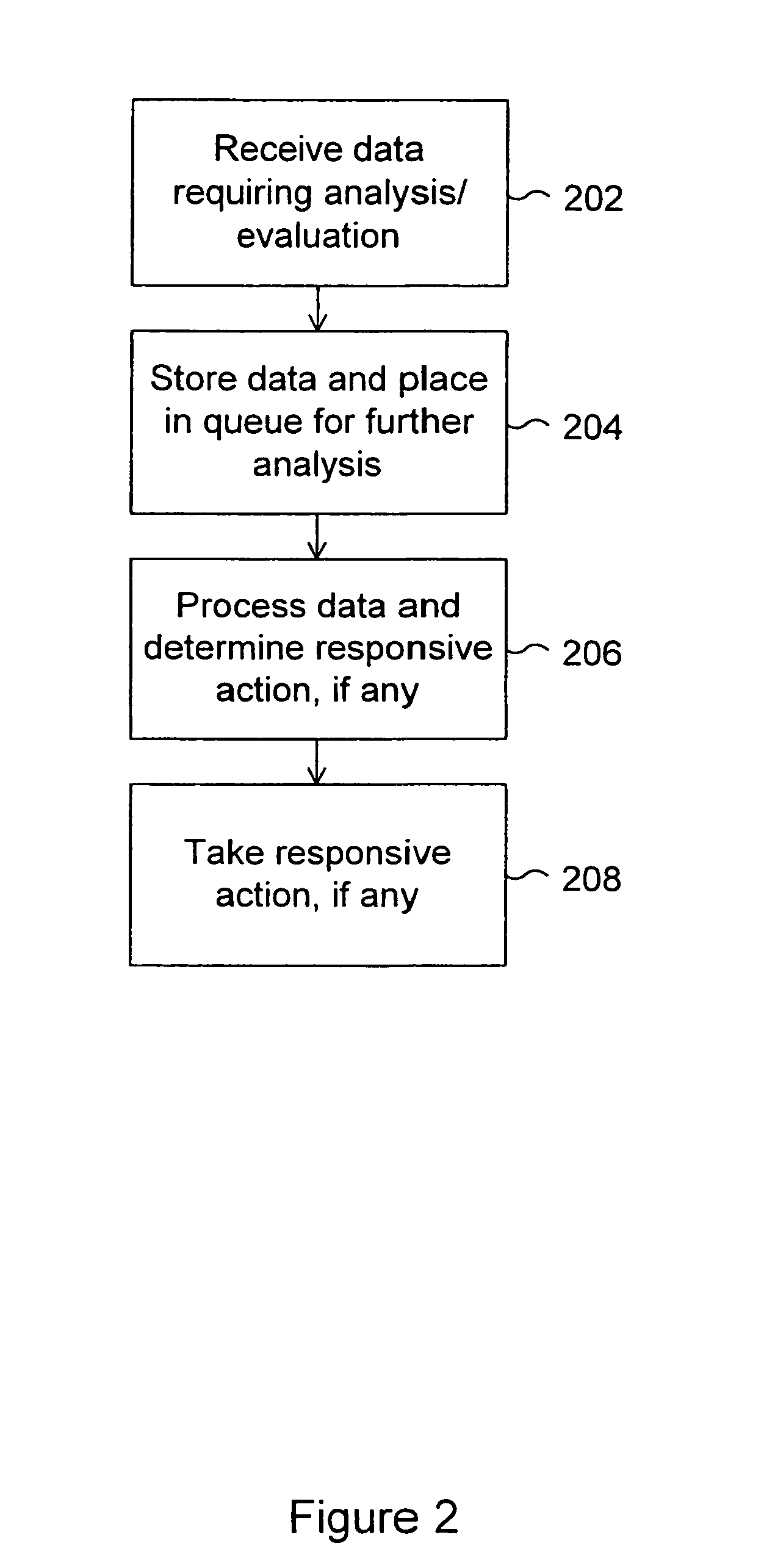
System and method for tracking the source of a computer attack
InactiveUS6971028B1Memory loss protectionDigital computer detailsAdministrative domainData placement
A system and method are disclosed for detecting and processing attacks on a computer network. Data indicating an attack may be taking place is received. The data is associated with an event. The data is placed in a selected one of a plurality of queues of data to be processed. The data in the queue is processed. Each queue is configured to store one or more sets of data, each set of data being associated with an event to be processed. An administrative domain may be notified that an attack may be taking place. The destination administrative domain may or may not be associated with other than the sending administrative domain. The source of an attack may be identified. Messages associated with an attack may be tracked back to identify a point of attack at which messages associated with the attack are entering a network.
Owner:CA TECH INC
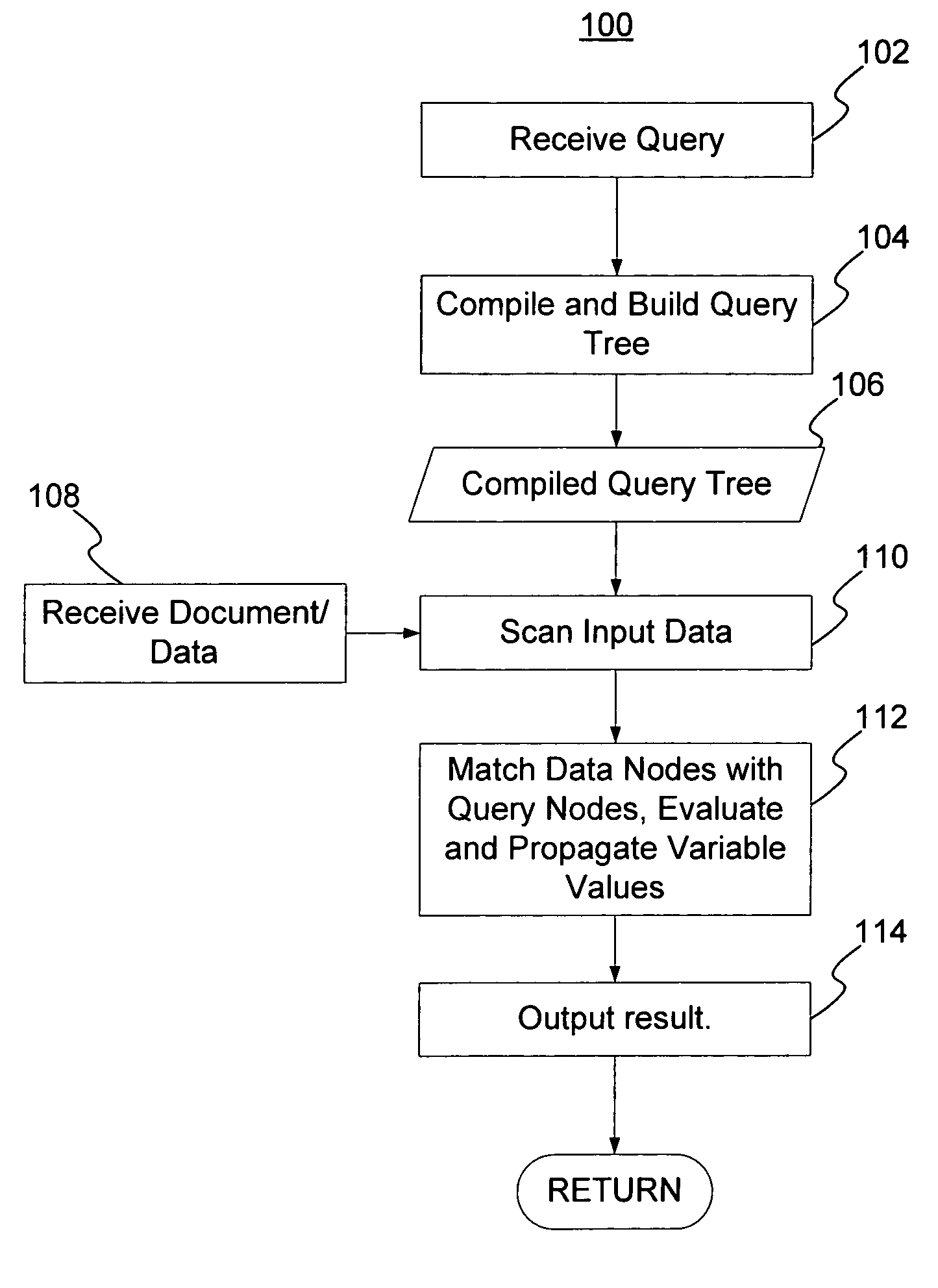
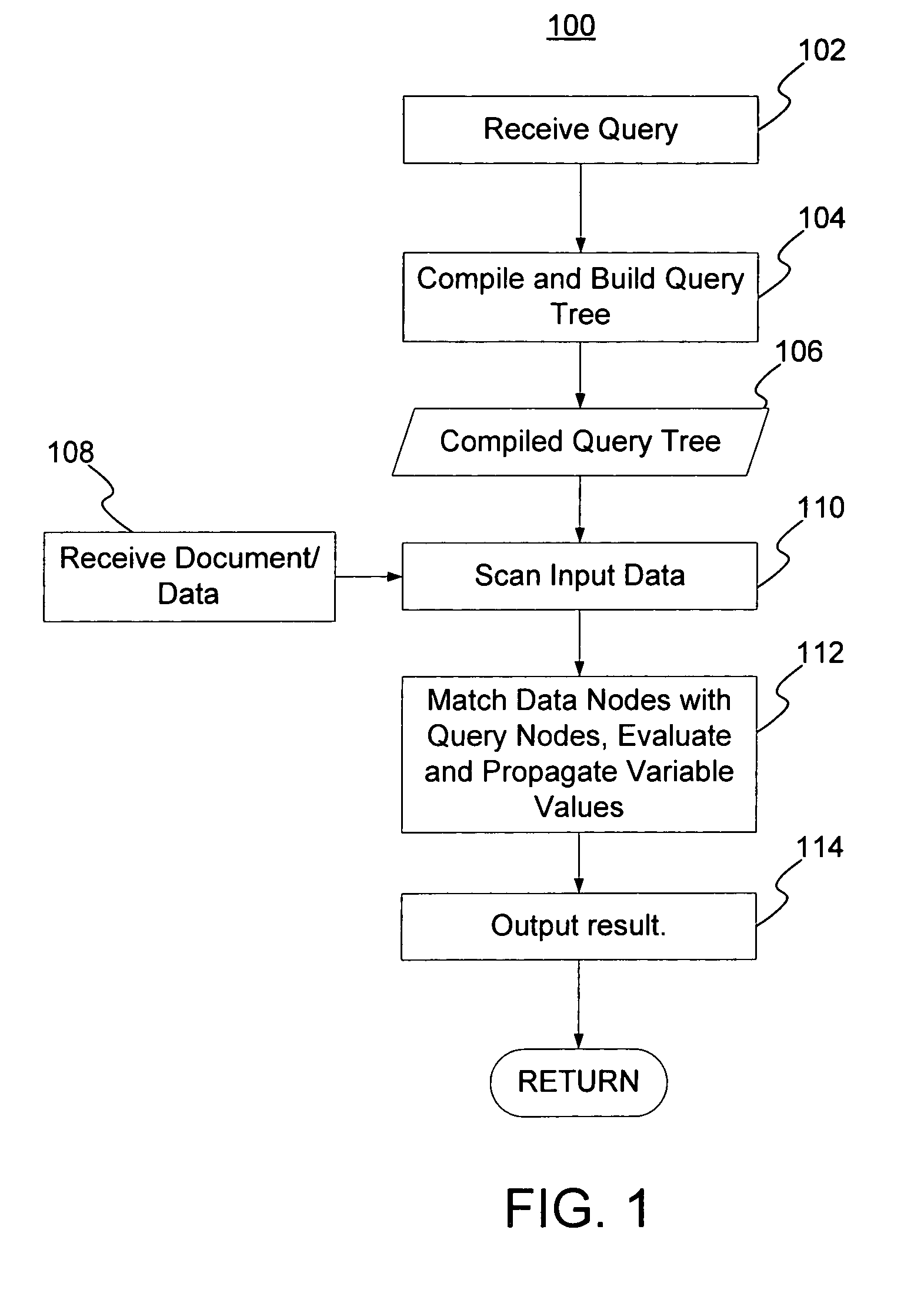
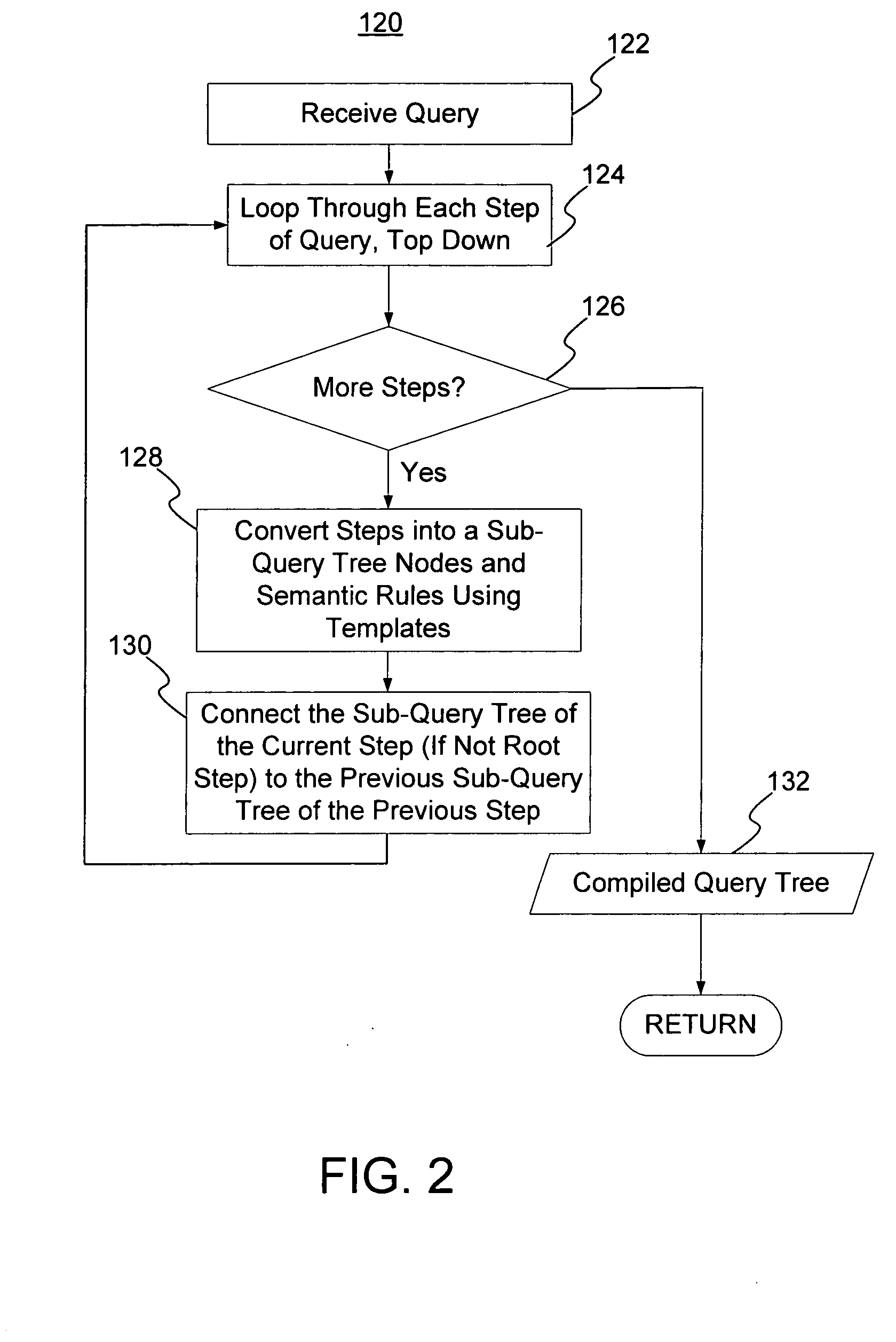
Streaming XPath algorithm for XPath expressions with predicates
InactiveUS20070198479A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsPaper documentData node
A method and system for evaluating a path query are disclosed. The path query corresponds to a query tree including a plurality of query nodes. At least one query node corresponds to at least one predicate and is at a level. The predicate(s) are evaluated for previous query node(s). The method and system include scanning data nodes of a document and determining if the data nodes match the query nodes. The method and system also include placing data related to the data node in match stacks corresponding to matched query nodes. The data for the query node(s) include attribute(s) corresponding to the predicate(s). The method and system further include propagating a matching of the at least one query node backward to a matching of the at least one previous query node.
Owner:IBM CORP
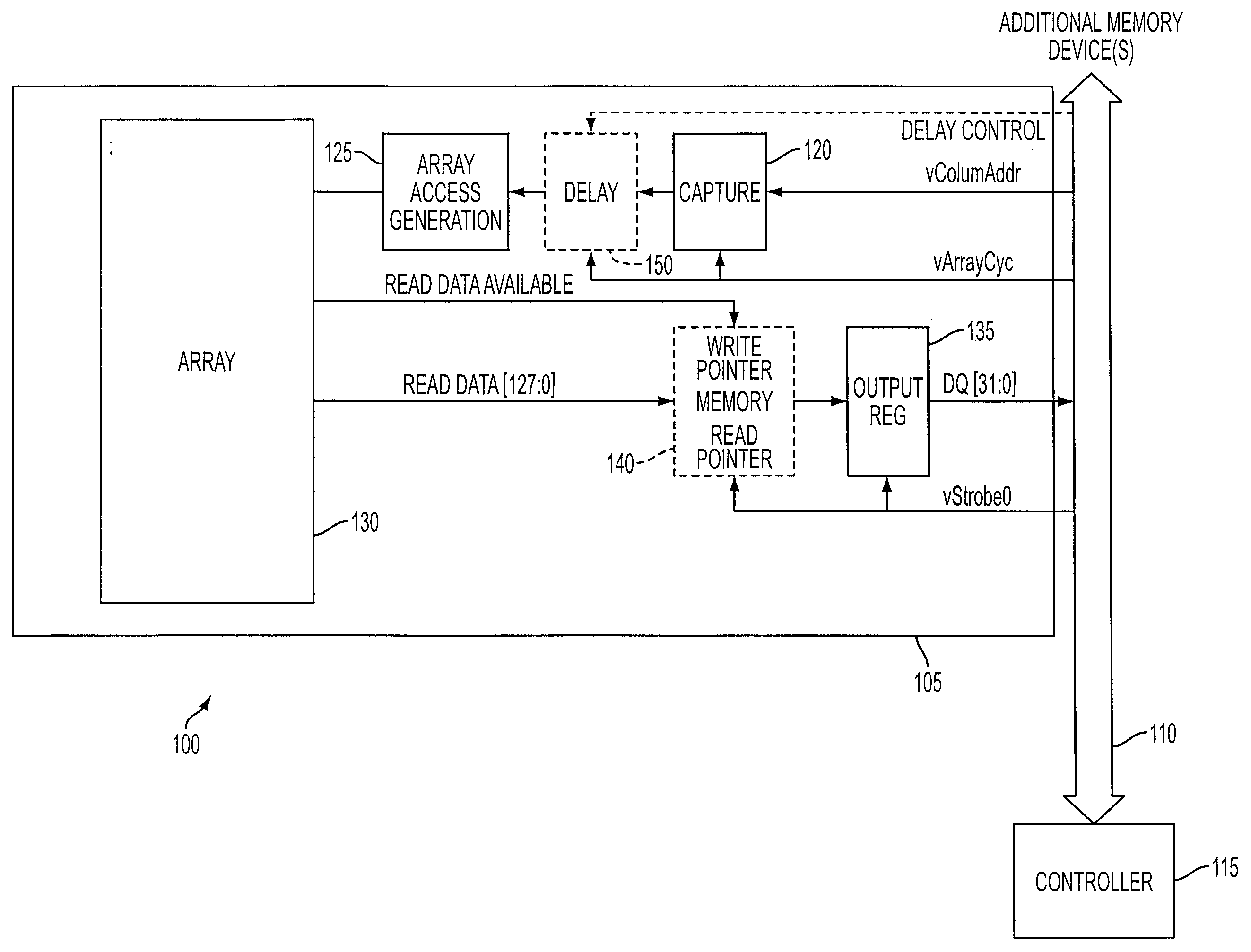
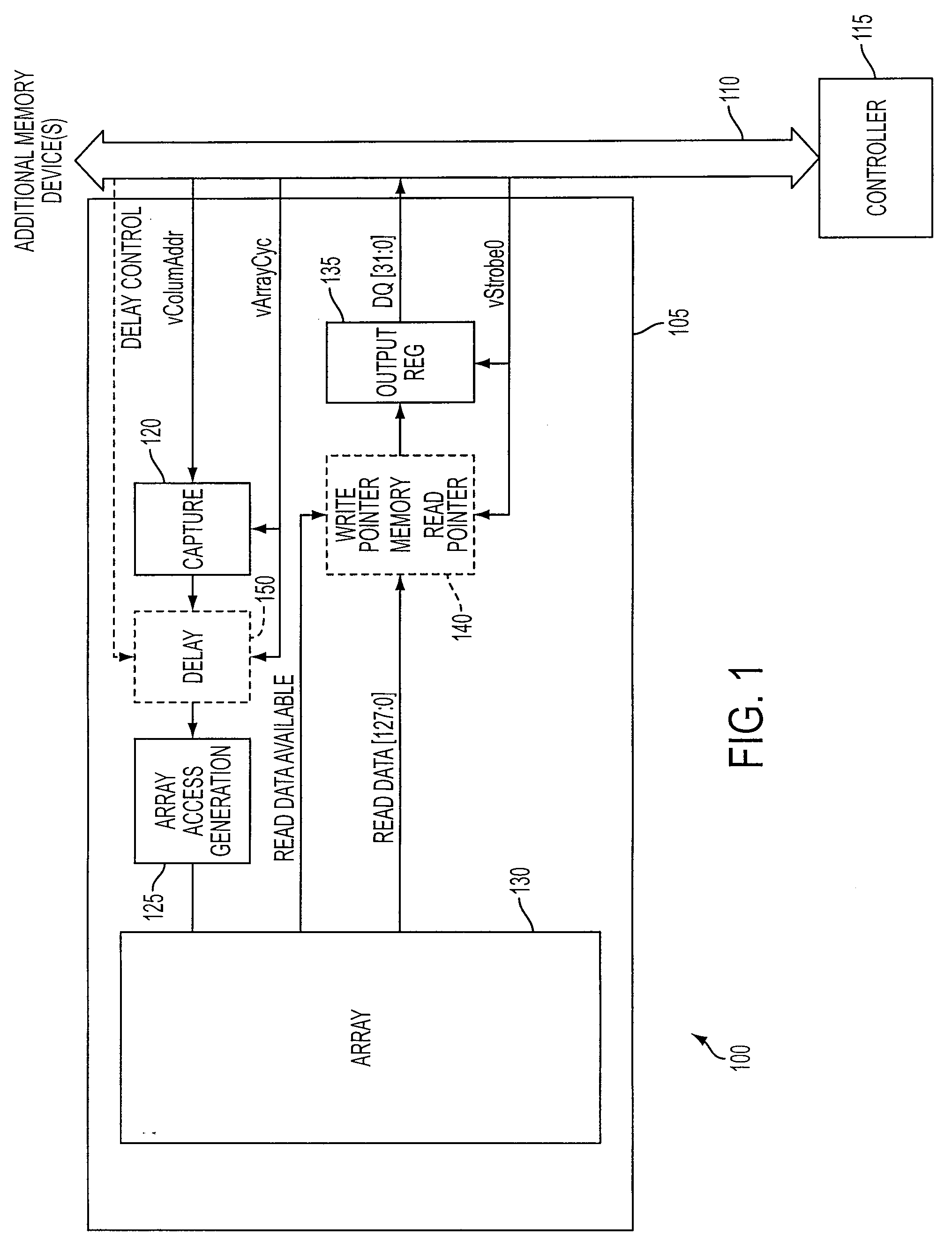
Memory systems and methods for controlling the timing of receiving read data
Embodiments of the present invention provide memory systems having a plurality of memory devices sharing an interface for the transmission of read data. A controller can identify consecutive read requests sent to different memory devices. To avoid data contention on the interface, for example, the controller can be configured to delay the time until read data corresponding to the second read request is placed on the interface.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Map-Reduce Ready Distributed File System
A map-reduce compatible distributed file system that consists of successive component layers that each provide the basis on which the next layer is built provides transactional read-write-update semantics with file chunk replication and huge file-create rates. Containers provide the fundamental basis for data replication, relocation, and transactional updates. A container location database allows containers to be found among all file servers, as well as defining precedence among replicas of containers to organize transactional updates of container contents. Volumes facilitate control of data placement, creation of snapshots and mirrors, and retention of a variety of control and policy information. Also addressed is the use of distributed transactions in a map-reduce system; the use of local and distributed snapshots; replication, including techniques for reconciling the divergence of replicated data after a crash; and mirroring.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
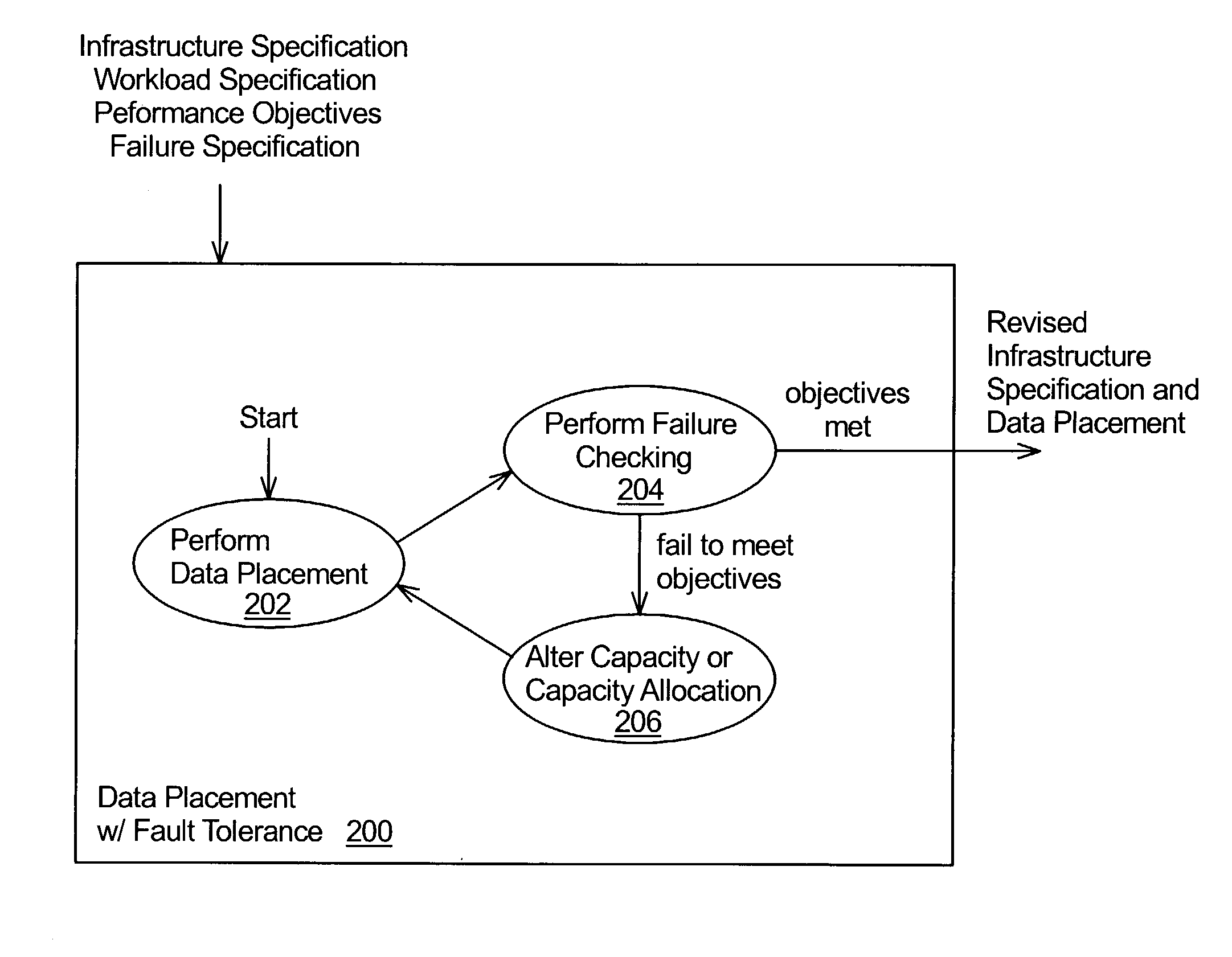
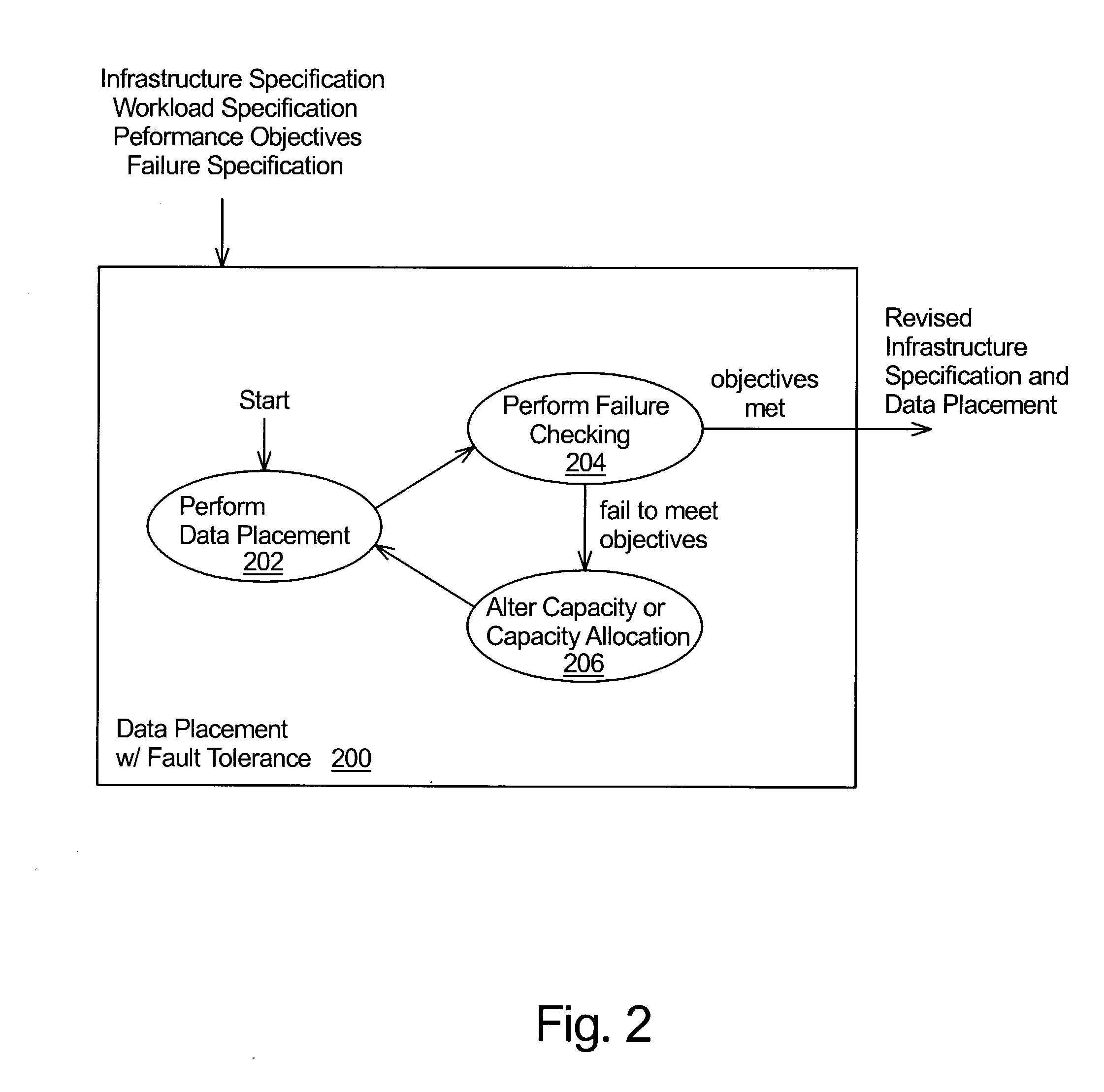
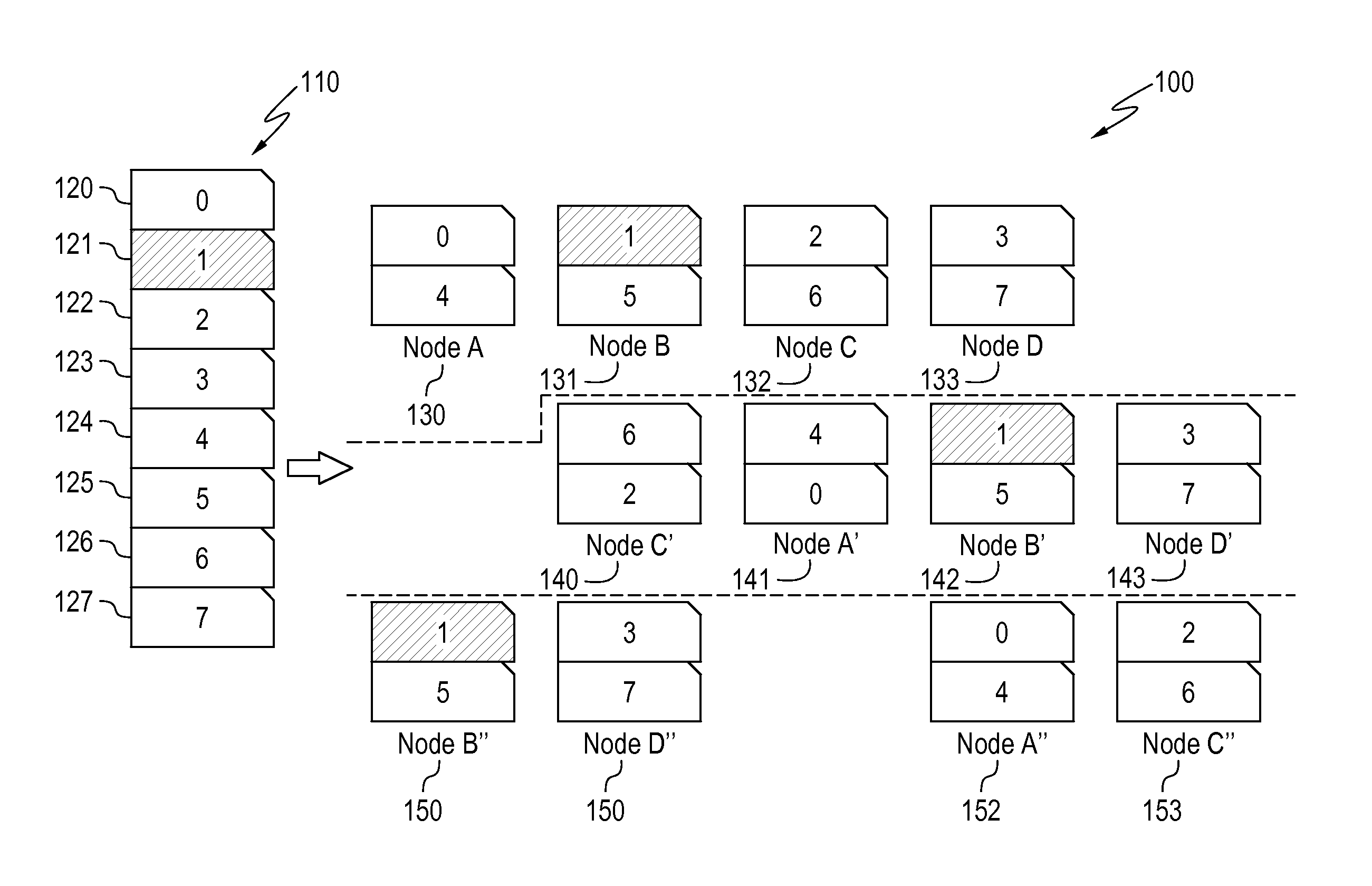
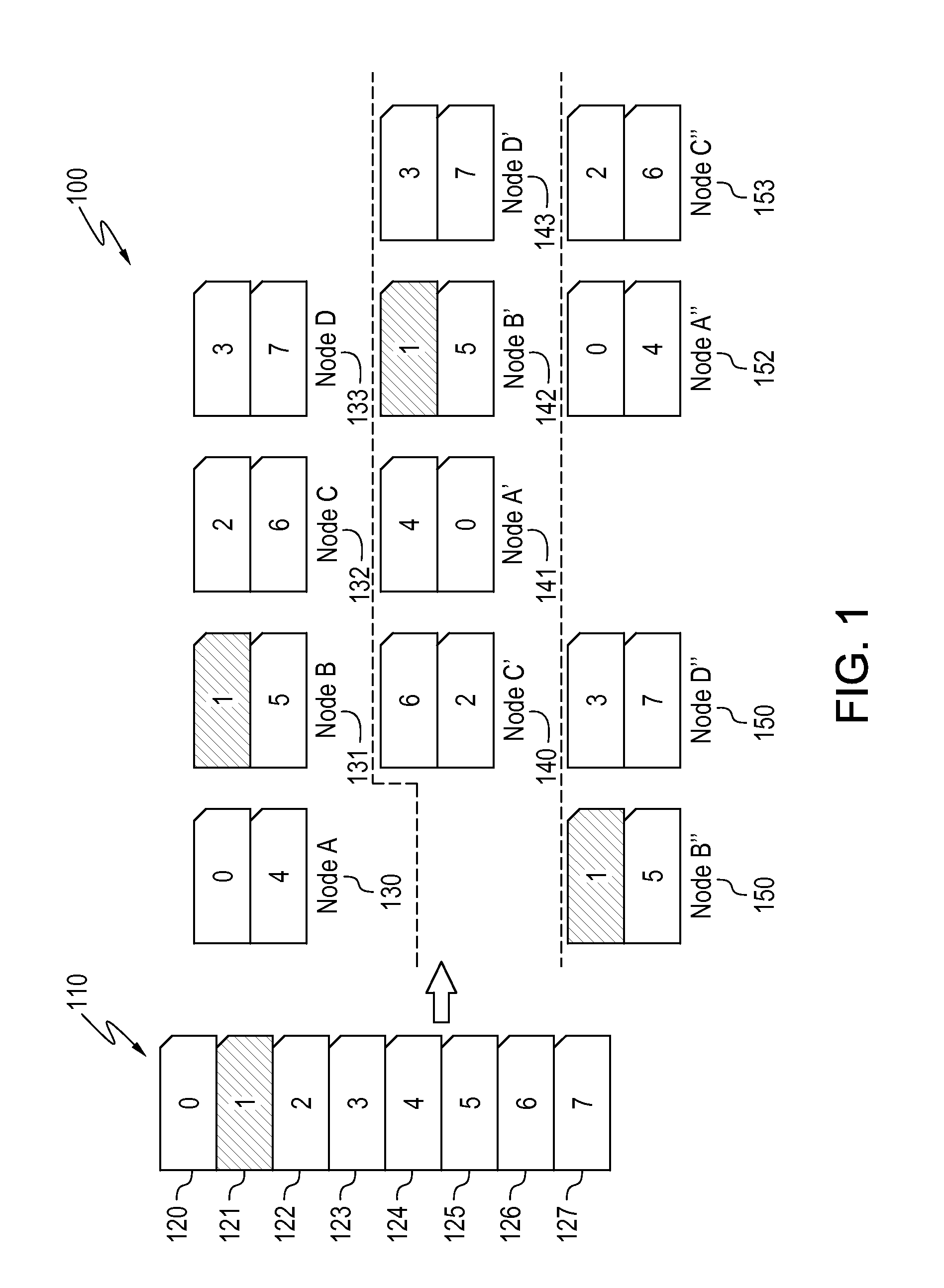
Data placement for fault tolerance
A technique for data placement in a distributed system that takes into account fault tolerance. Data placement is performed in which data objects, and possibly replicas thereof, are assigned to nodes within the distributed system. The resulting placement is then tested to determine whether the system provides desired performance under various different fault scenarios. If not, the distributed system is altered such as by altering its capacity or its capacity allocations. Performing data placement, testing for fault-tolerance and altering capacity or capacity allocations are performed repetitively, thereby increasing the system's ability to provide the desired performance under the fault scenarios. Preferably, a system and placement are eventually determined that provide the desired performance under the given fault scenarios.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
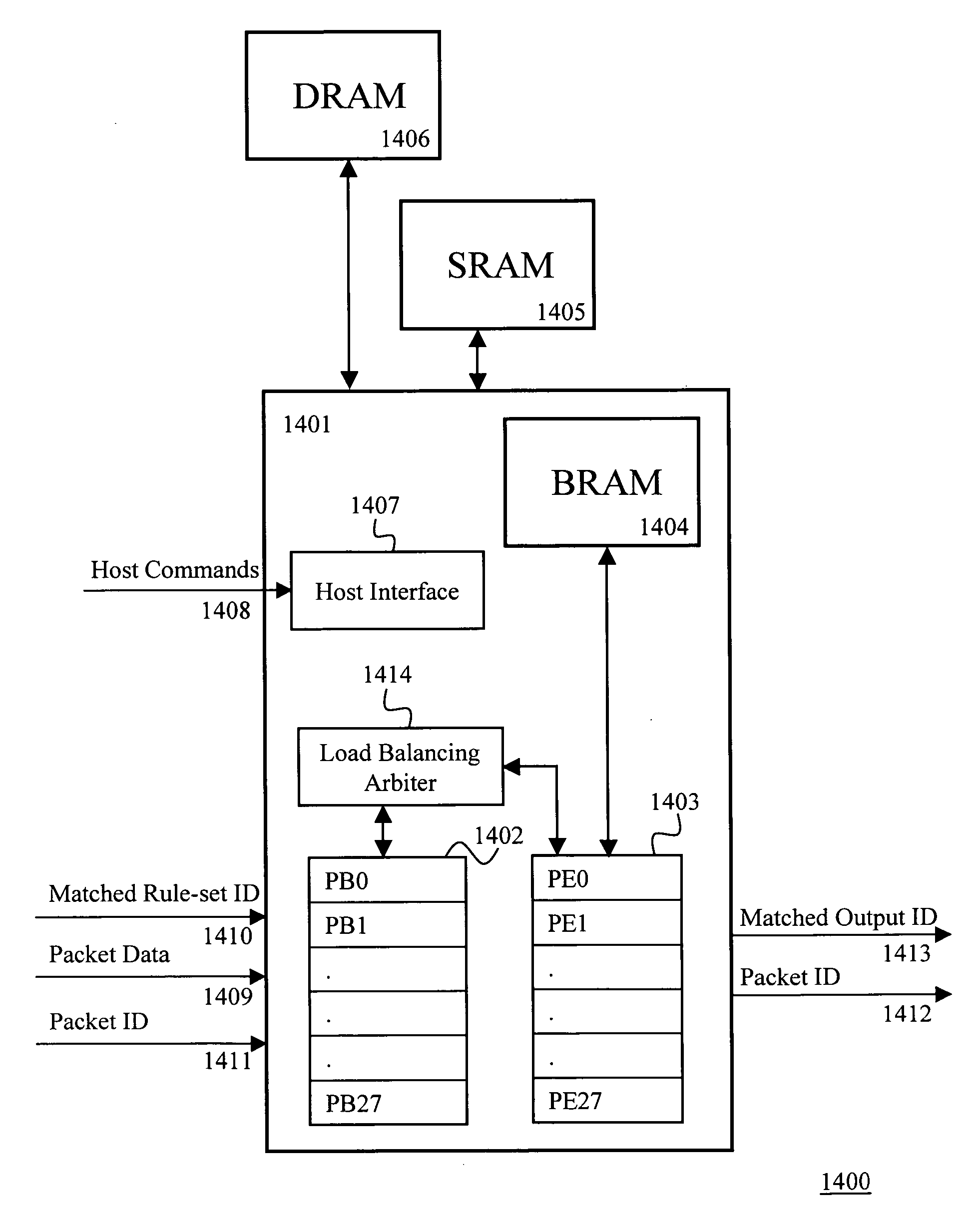
Layered memory architecture for deterministic finite automaton based string matching useful in network intrusion detection and prevention systems and apparatuses
ActiveUS20060101195A1Reduce decreaseTransmissionMemory systemsLine rateDeterministic finite automaton
Owner:FORTINET
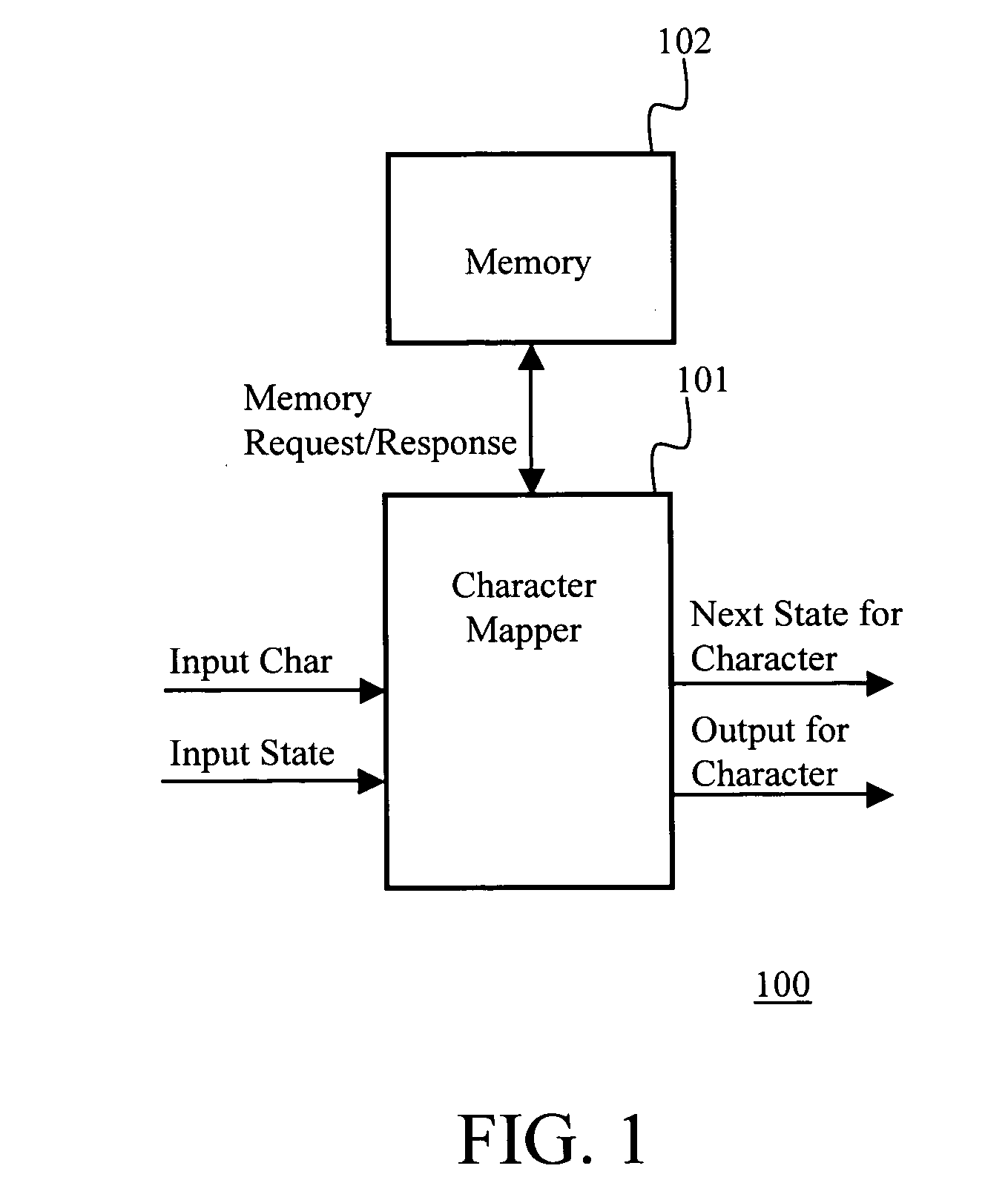
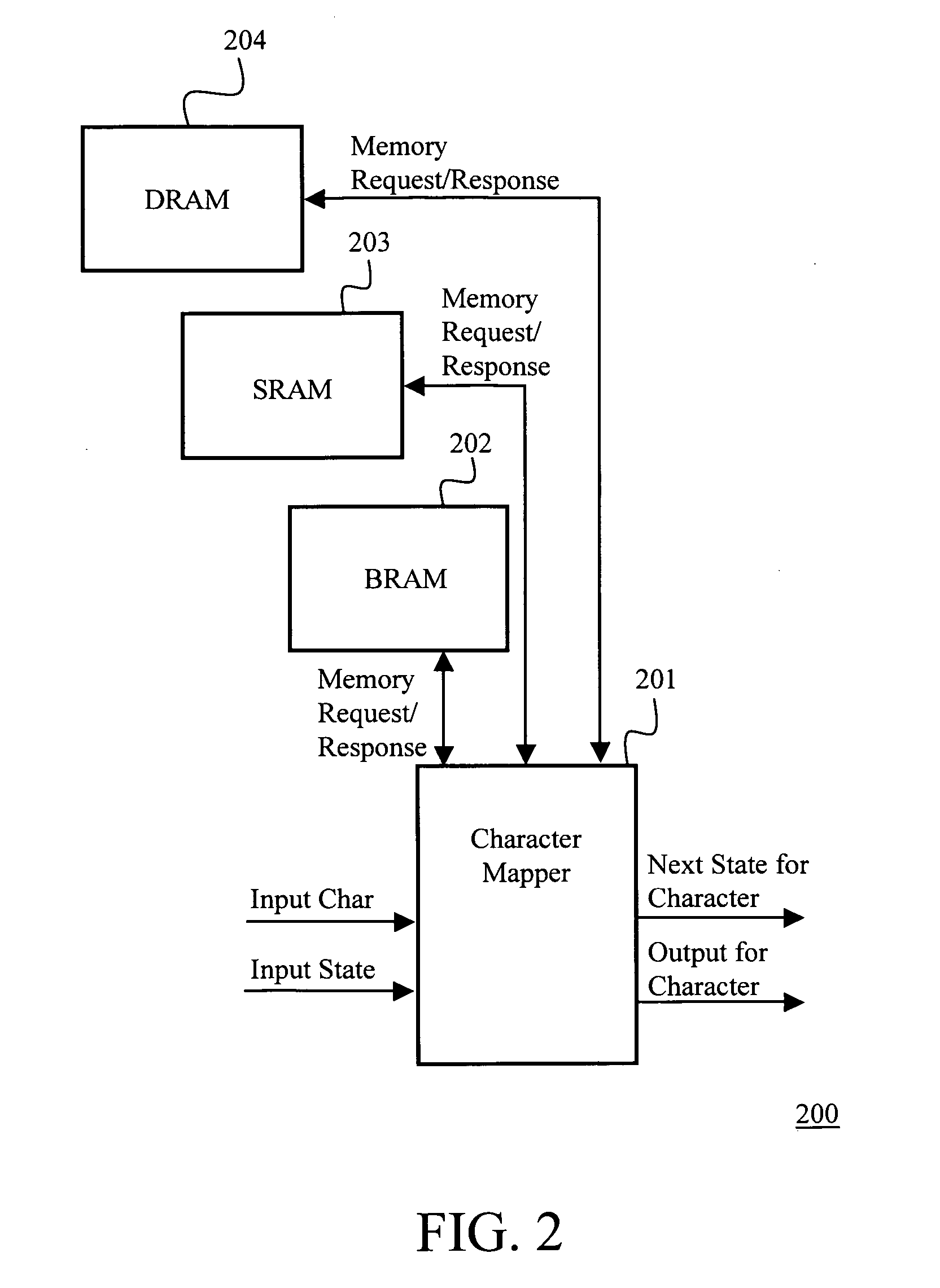
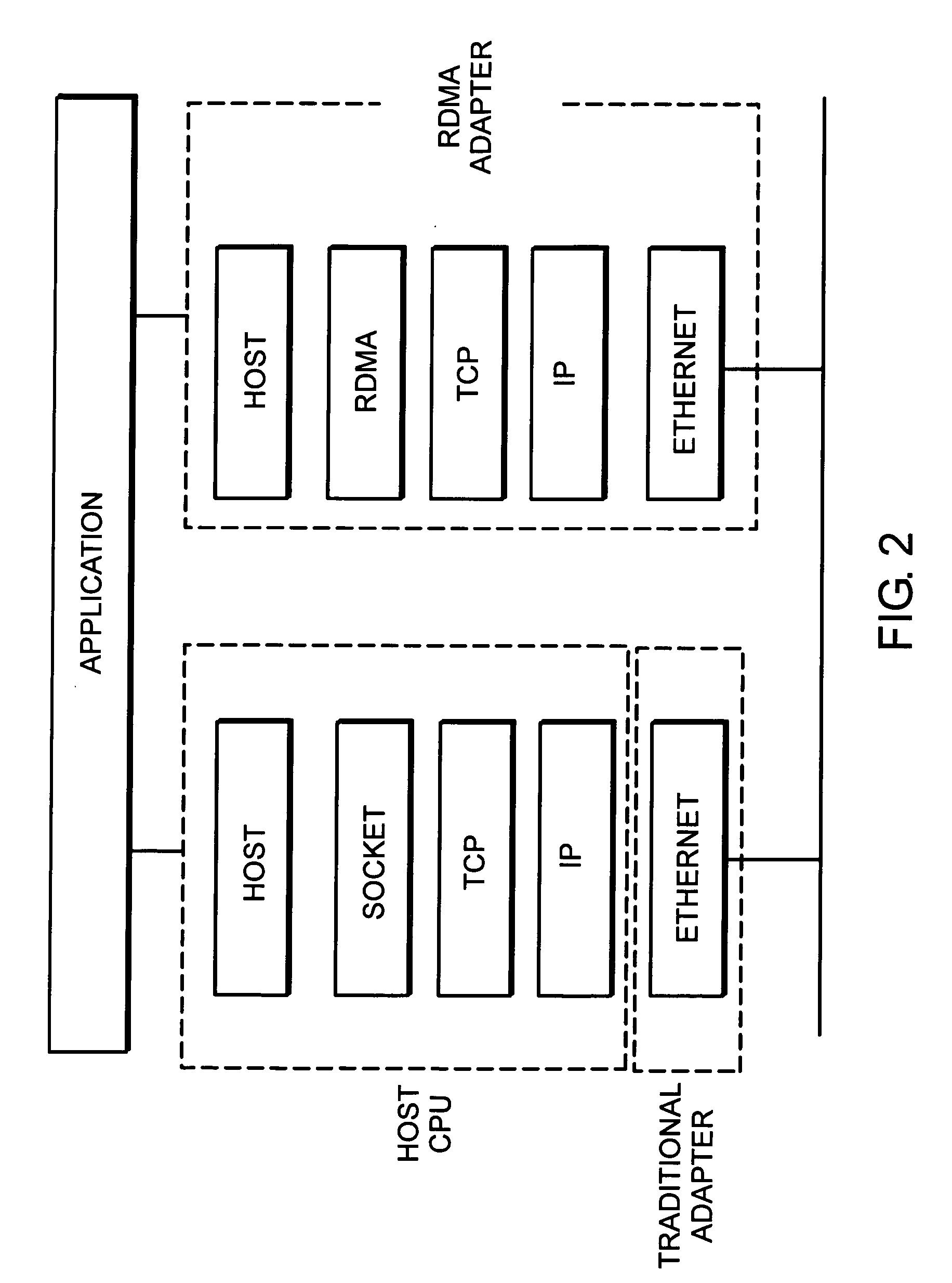
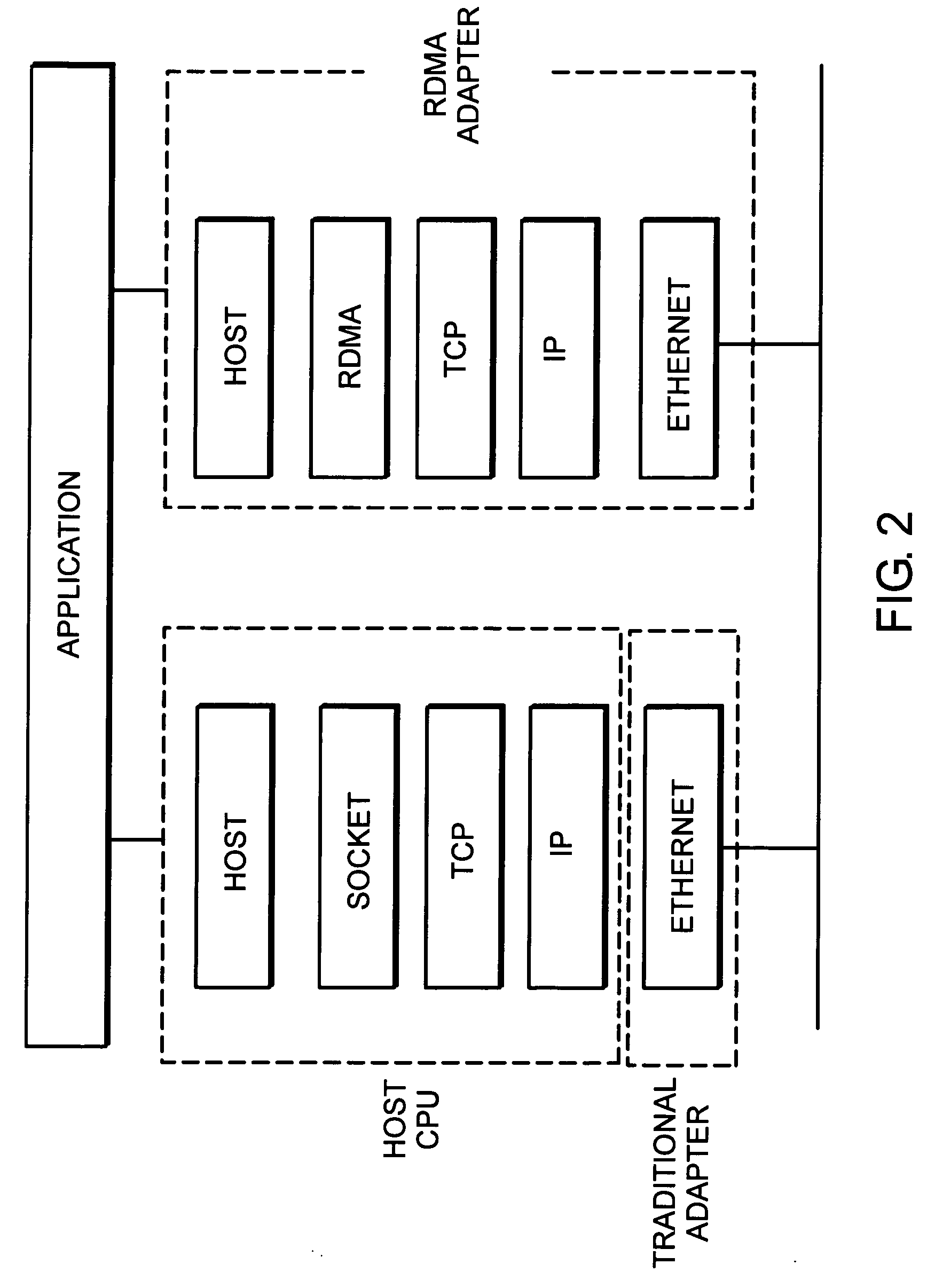
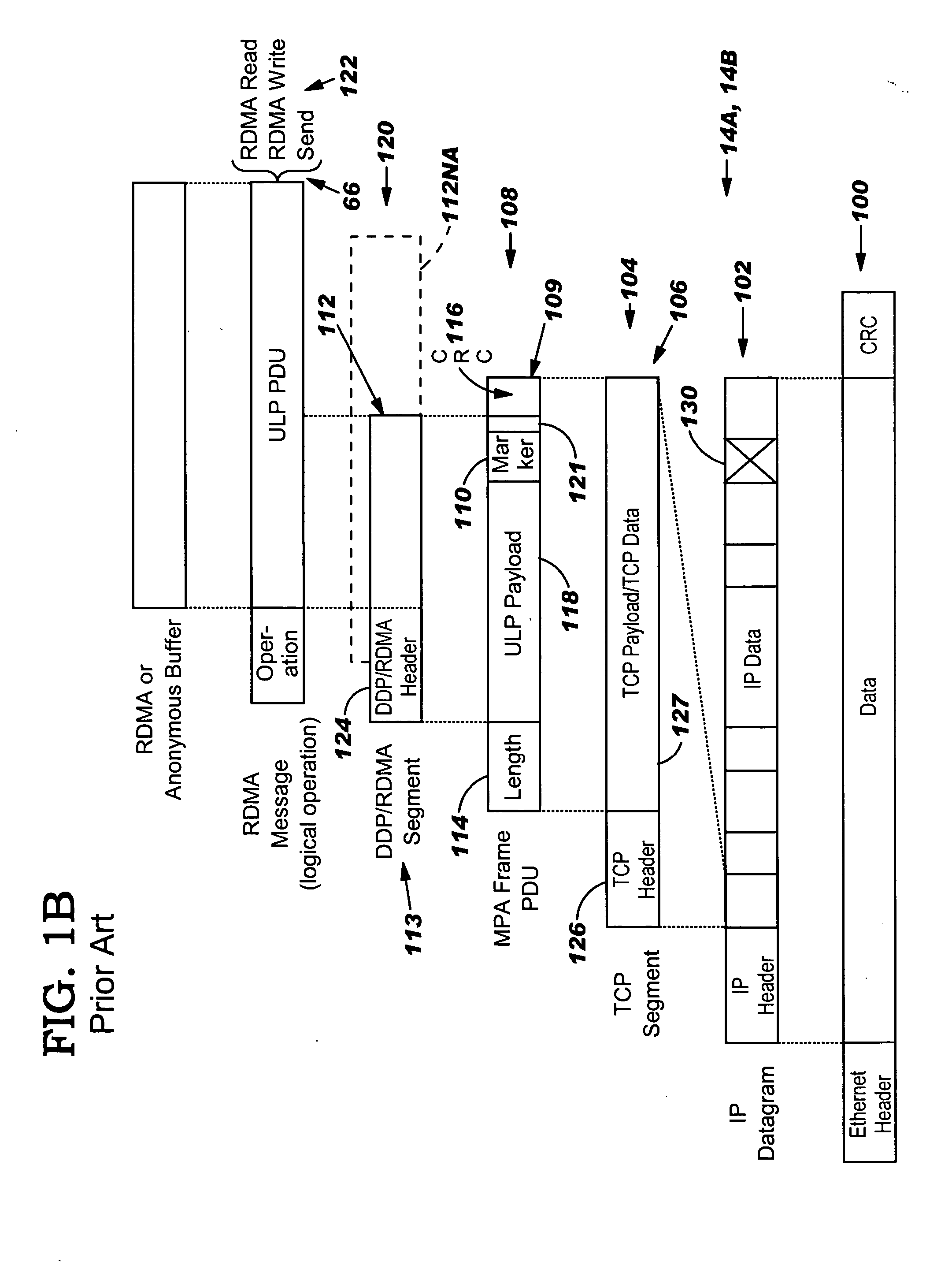
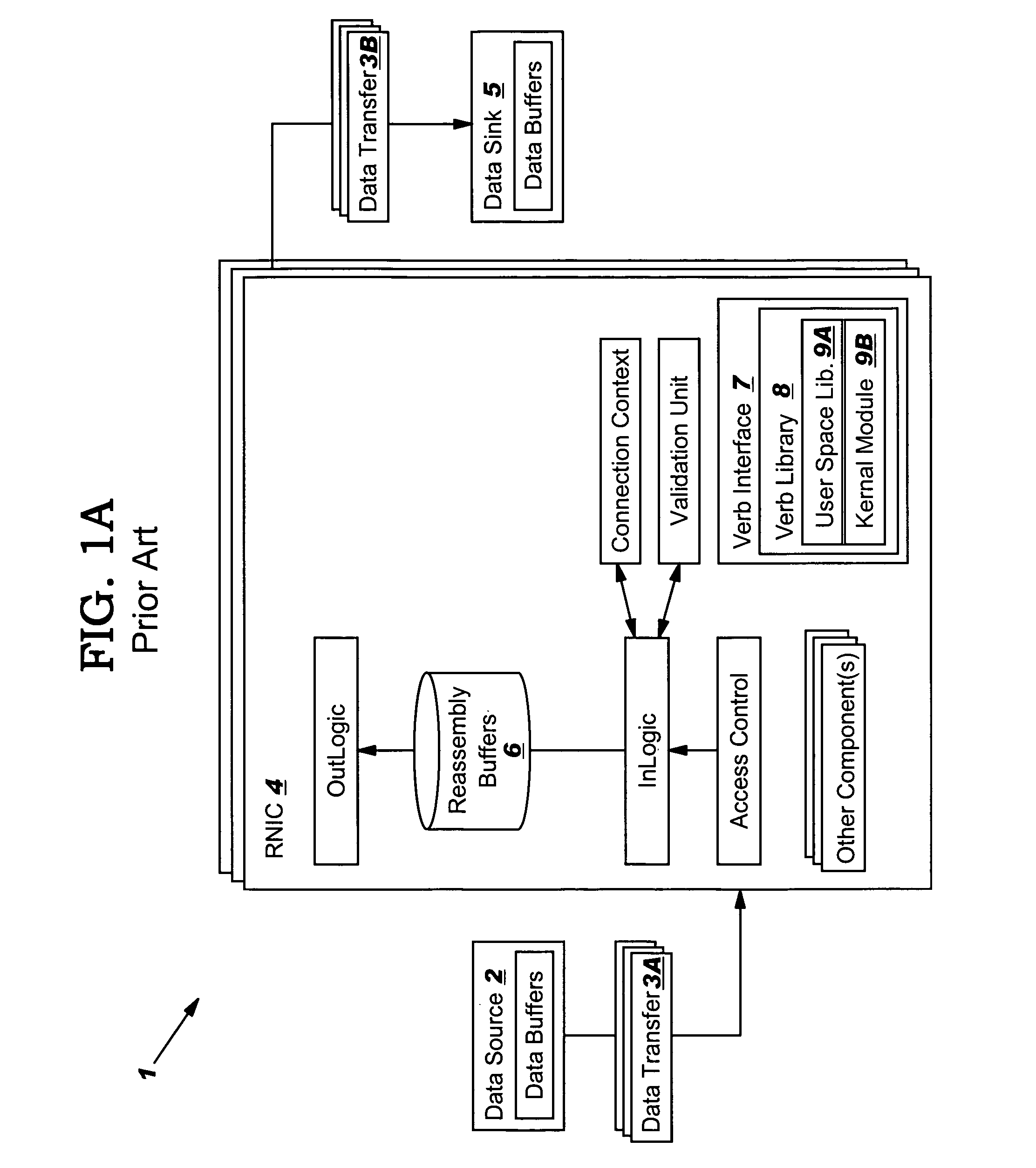
System and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication
InactiveUS20050223118A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual memoryPhysical address
A system and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication. According to one embodiment, a network adapter system for use in a computer system includes a host processor and host memory and is capable for use in network communication in accordance with a direct data placement (DDP) protocol. The DDP protocol specifies tagged and untagged data movement into a connection-specific application buffer in a contiguous region of virtual memory space of a corresponding endpoint computer application executing on said host processor. The DDP protocol specifies the permissibility of memory regions in host memory and specifies the permissibility of at least one memory window within a memory region. The memory regions and memory windows have independently definable application access rights, the network adapter system includes adapter memory and a plurality of physical buffer lists in the adapter memory. Each physical buffer list specifies physical address locations of host memory corresponding to one of said memory regions. A plurality of steering tag records are in the adapter memory, each steering tag record corresponding to a steering tag. Each steering tag record specifies memory locations and access permissions for one of a memory region and a memory window. Each physical buffer list is capable of having a one to many correspondence with steering tag records such that many memory windows may share a single physical buffer list. According to another embodiment, each steering tag record includes a pointer to a corresponding physical buffer list.
Owner:AMMASSO
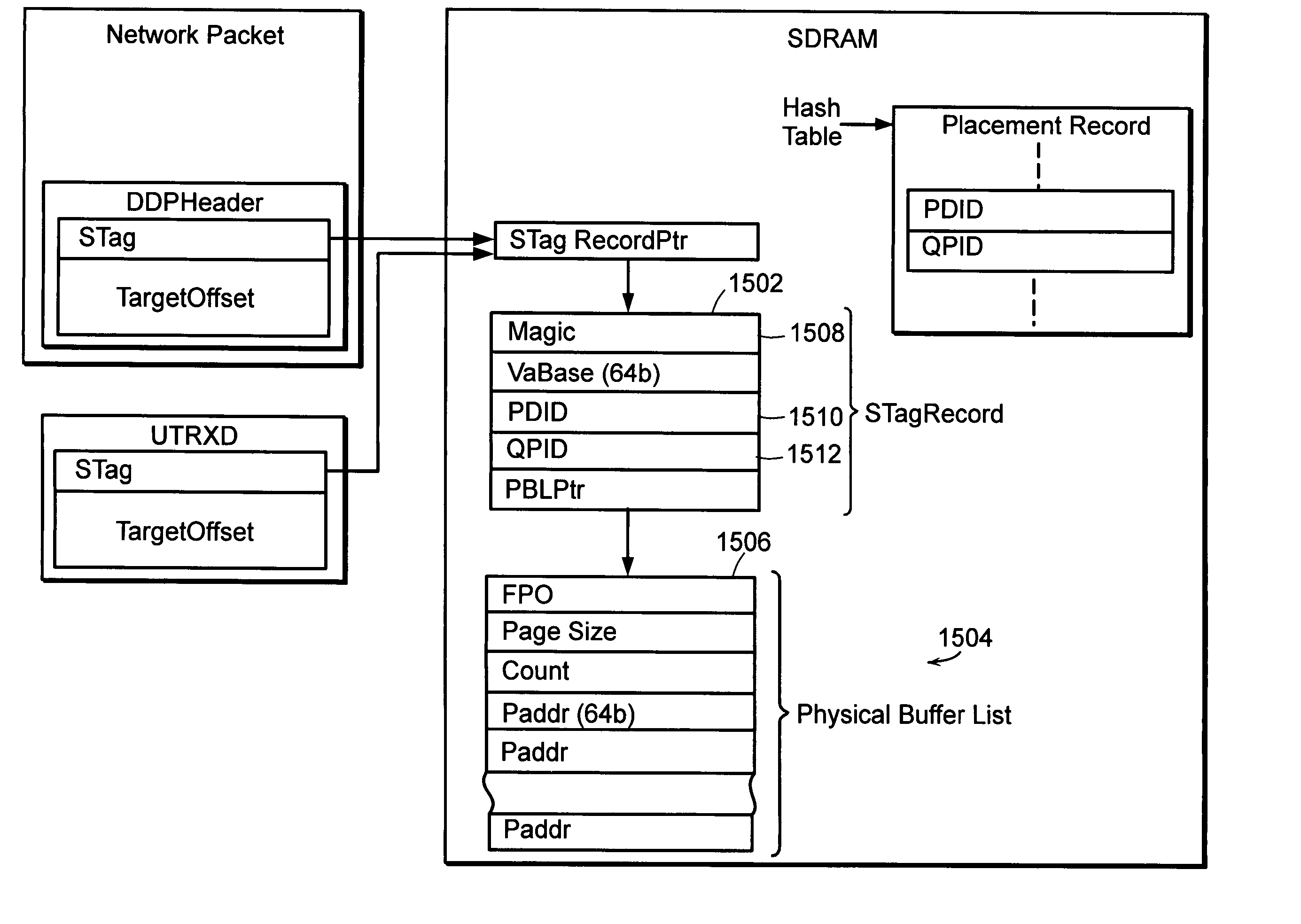
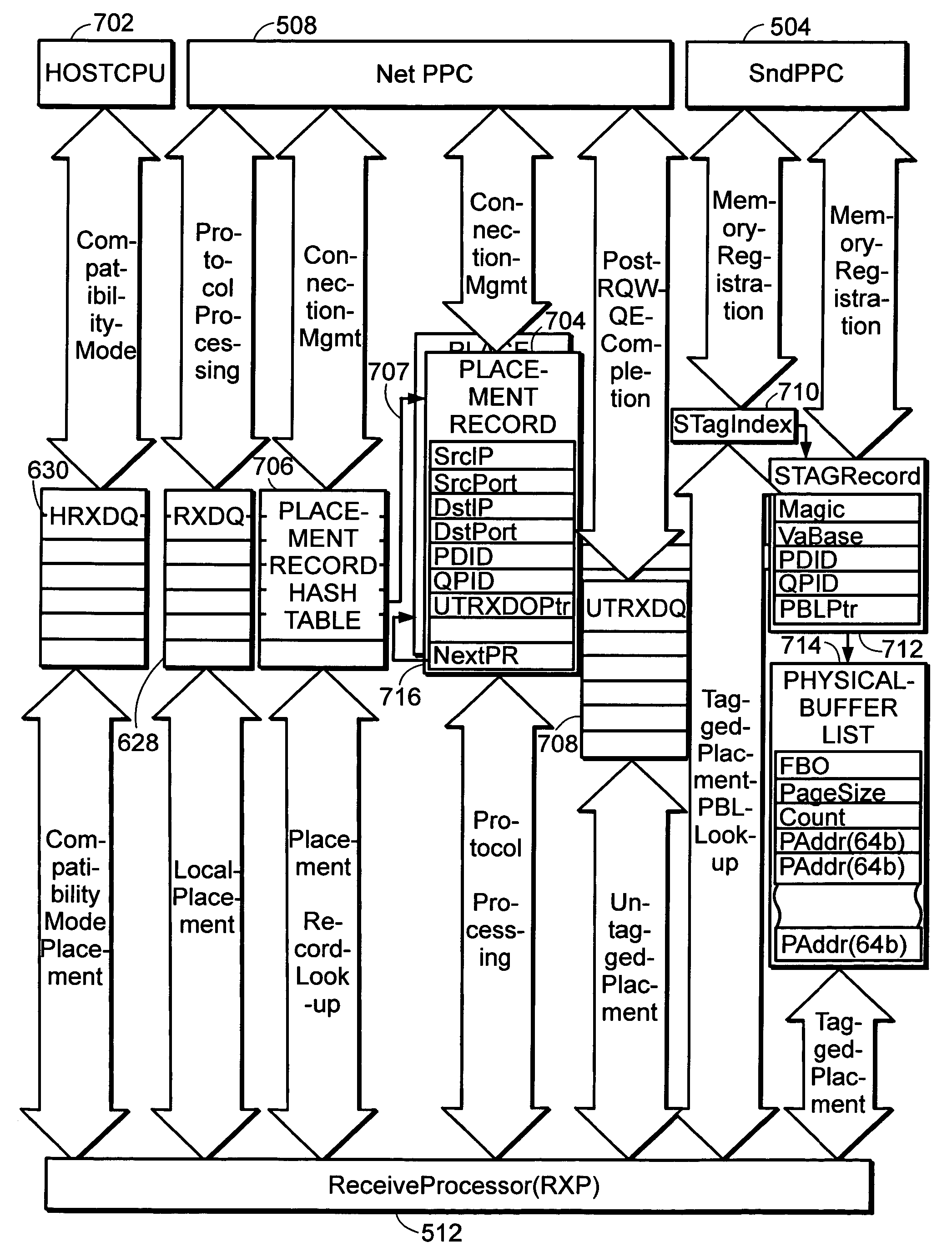
System and method for placement of RDMA payload into application memory of a processor system
InactiveUS20060067346A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationComputer hardwarePhysical address
A system and method for placement of RDMA payload into application memory of a processor system. Under one embodiment, a network adapter system is capable of use in network communication in accordance with a direct data placement (DDP) protocol, e.g., RDMA. The network adapter system includes adapter memory and a plurality of placement records in the adapter memory. Each placement record specifies per-connection placement data including at least network address information and port identifications of source and destination network entities for a corresponding DDP protocol connection. Placement record identification logic uniquely identifies a placement record from network address information and port identification information contained in a DDP message received by the network adapter system. Untagged message payload placement logic directly places the payload of the received untagged DDP message into physical address locations of host memory corresponding to one of said connection-specific application buffers. Tagged message payload placement logic directly places the payload of the tagged DDP message into physical address locations of host memory corresponding to the identifier in the received DDP message. According to one embodiment, the placement records are organized as an array of hash buckets with each element of the array containing a placement record and each placement record containing a specification of a next placement record in the same bucket. The placement record identification logic includes hashing logic to create a hash index pointing to a bucket in the array by hashing a 4-tuple consisting of a source address, a destination address, a source port, and a destination port contained in the received DDP message.
Owner:AMMASSO
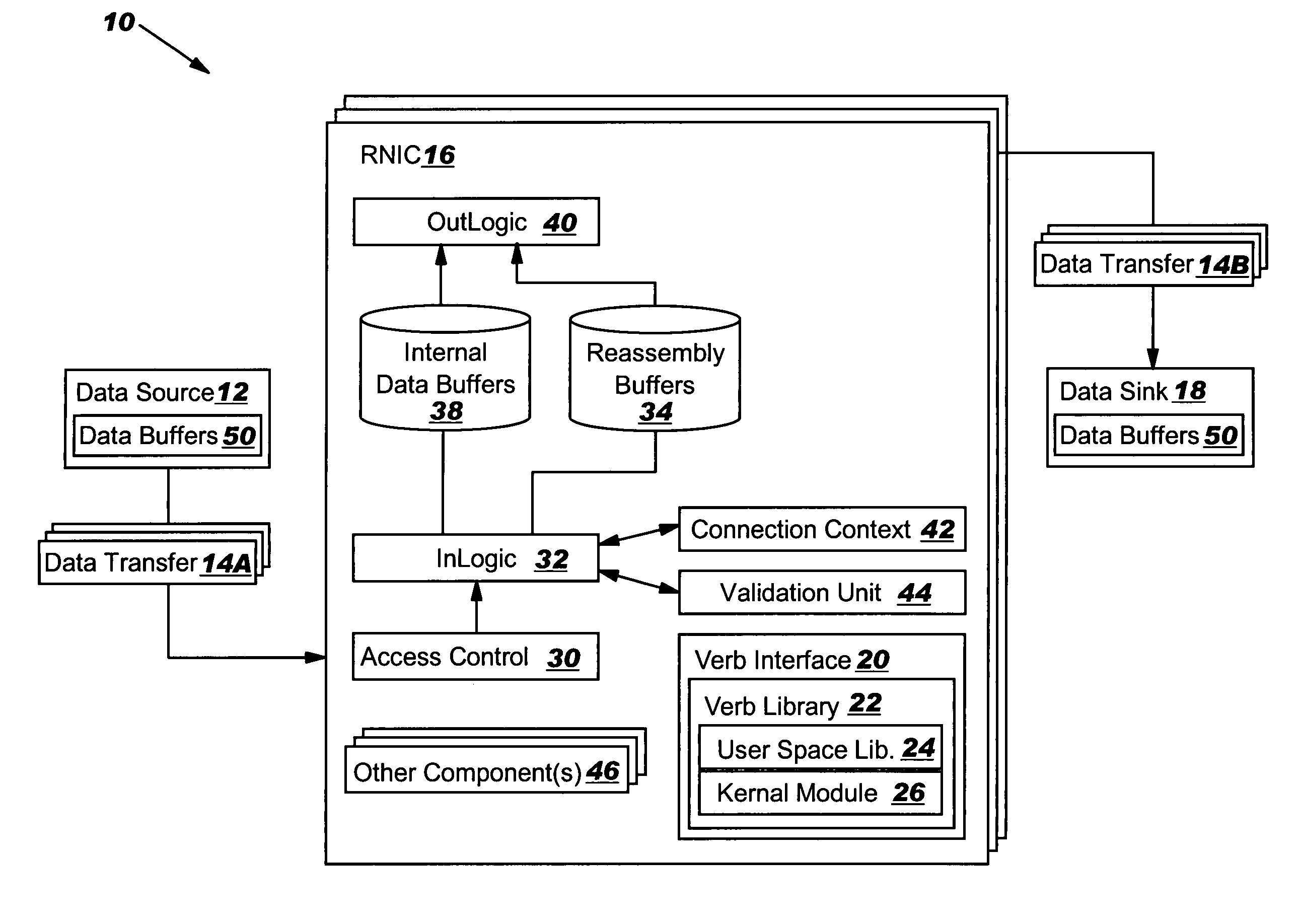
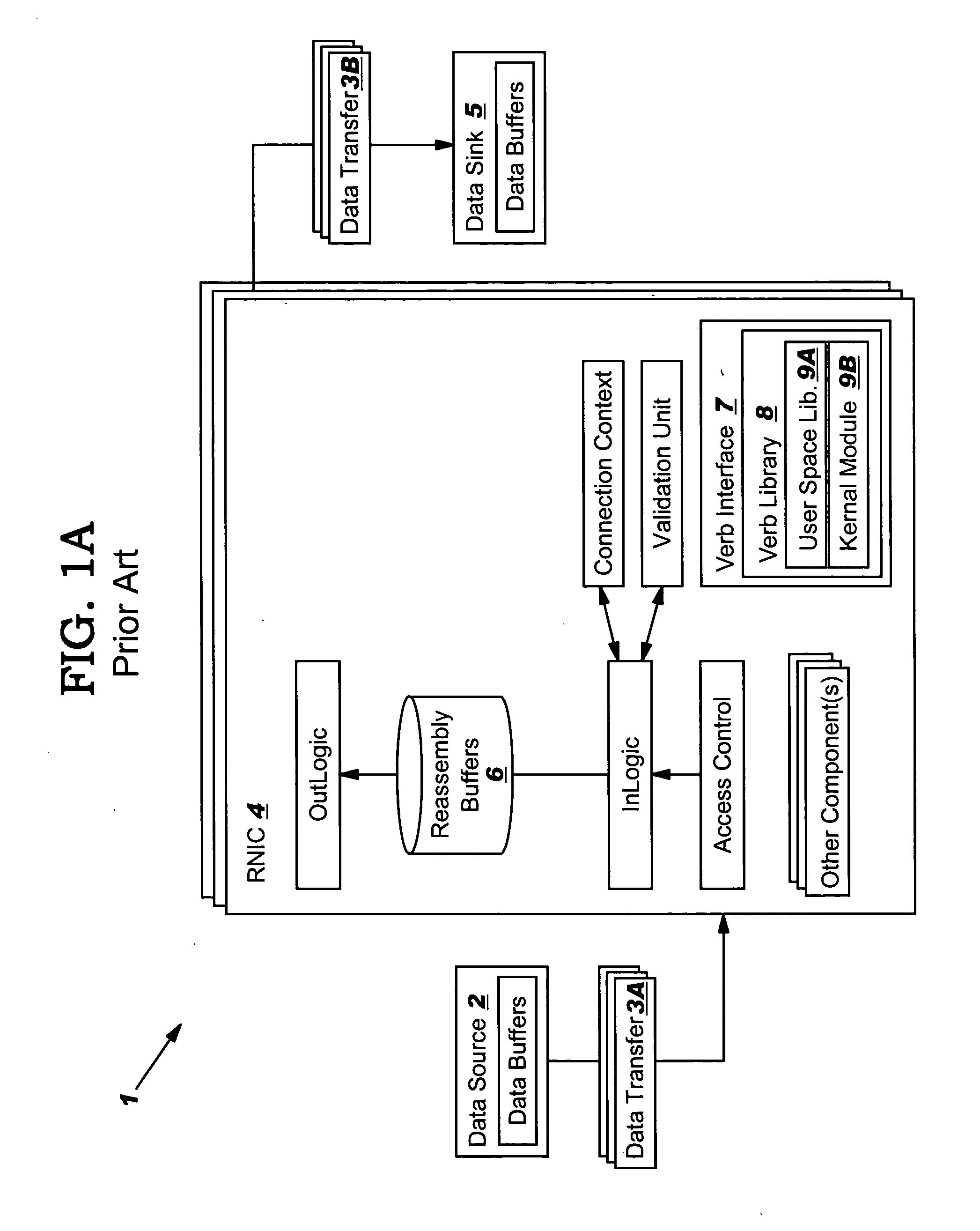
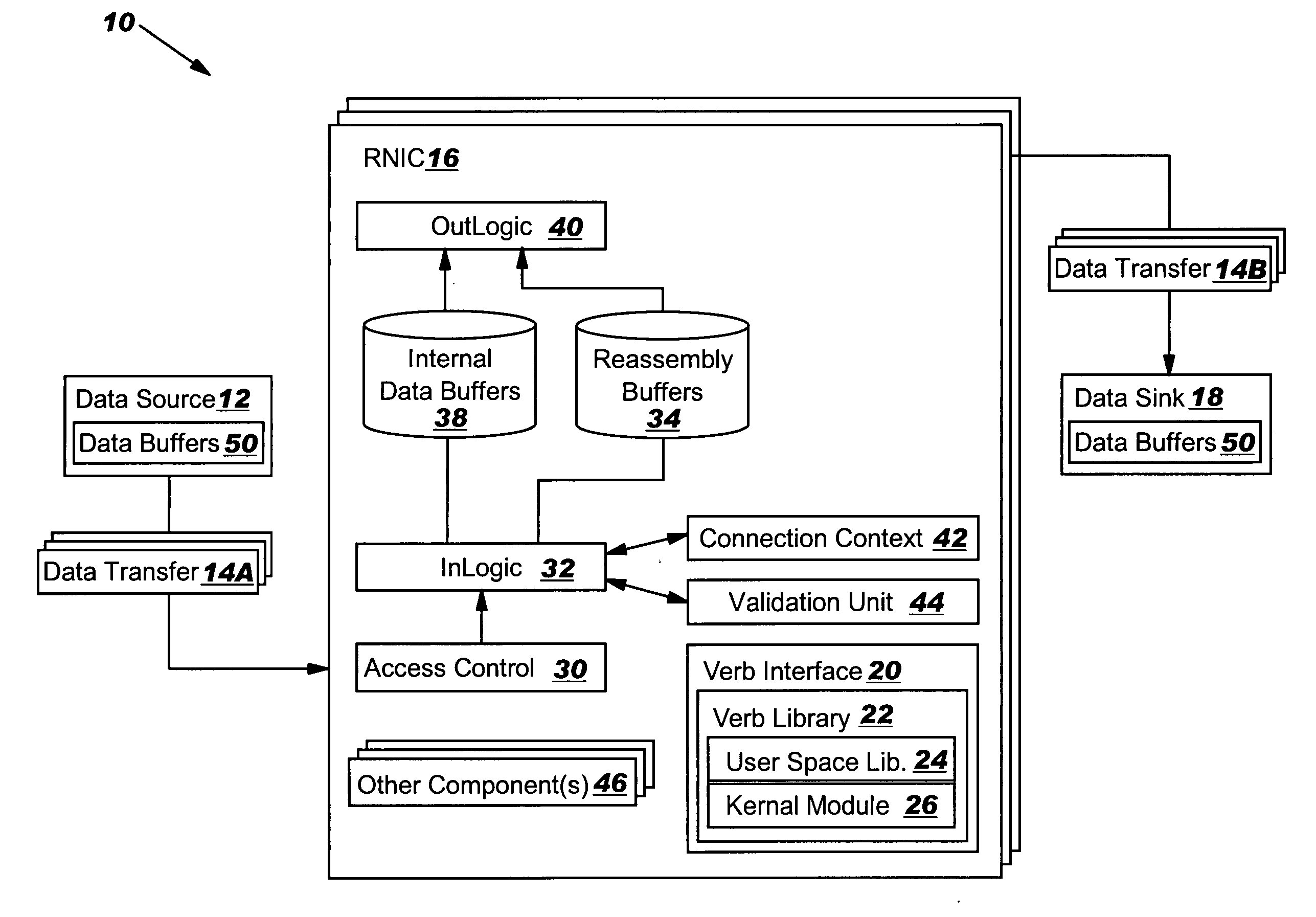
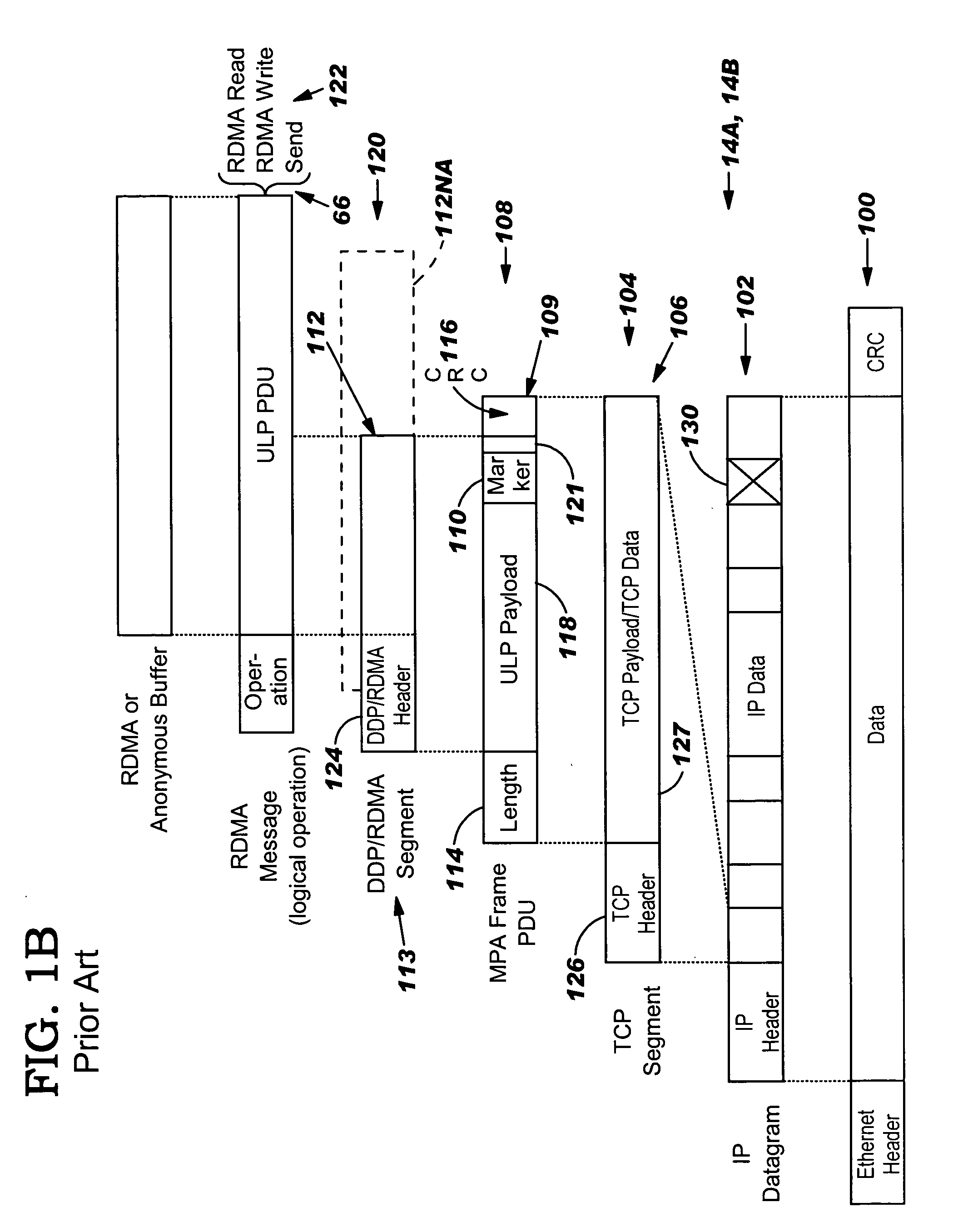
Data transfer error checking
InactiveUS20050149817A1Reduce memory bandwidthReduce latencyCode conversionError detection onlyConnection typeData placement
An RNIC implementation that performs direct data placement to memory where all segments of a particular connection are aligned, or moves data through reassembly buffers where all segments of a particular connection are non-aligned. The type of connection that cuts-through without accessing the reassembly buffers is referred to as a “Fast” connection because it is highly likely to be aligned, while the other type is referred to as a “Slow” connection. When a consumer establishes a connection, it specifies a connection type. The connection type can change from Fast to Slow and back. The invention reduces memory bandwidth, latency, error recovery using TCP retransmit and provides for a “graceful recovery” from an empty receive queue. The implementation also may conduct CRC validation for a majority of inbound DDP segments in the Fast connection before sending a TCP acknowledgement (Ack) confirming segment reception.
Owner:IBM CORP
SCSI transport for servers
ActiveUS20130117621A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsFiberSCSI initiator and target
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) transport for fabric backplane enterprise servers provides for local and remote communication of storage system information between storage sub-system elements of an ES system and other elements of an ES system via a storage interface. The transport includes encapsulation of information for communication via a reliable transport implemented in part across a cellifying switch fabric. The transport may optionally include communication via Ethernet frames over any of a local network or the Internet. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Direct Data Placement (DDP) protocols are used to communicate the information (commands, responses, and data) between SCSI initiator and target end-points. A Fibre Channel Module (FCM) may be operated as a SCSI target providing a storage interface to any of a Processor Memory Module (PMM), a System Control Module (SCM), and an OffLoad Module (OLM) operated as a SCSI initiator.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
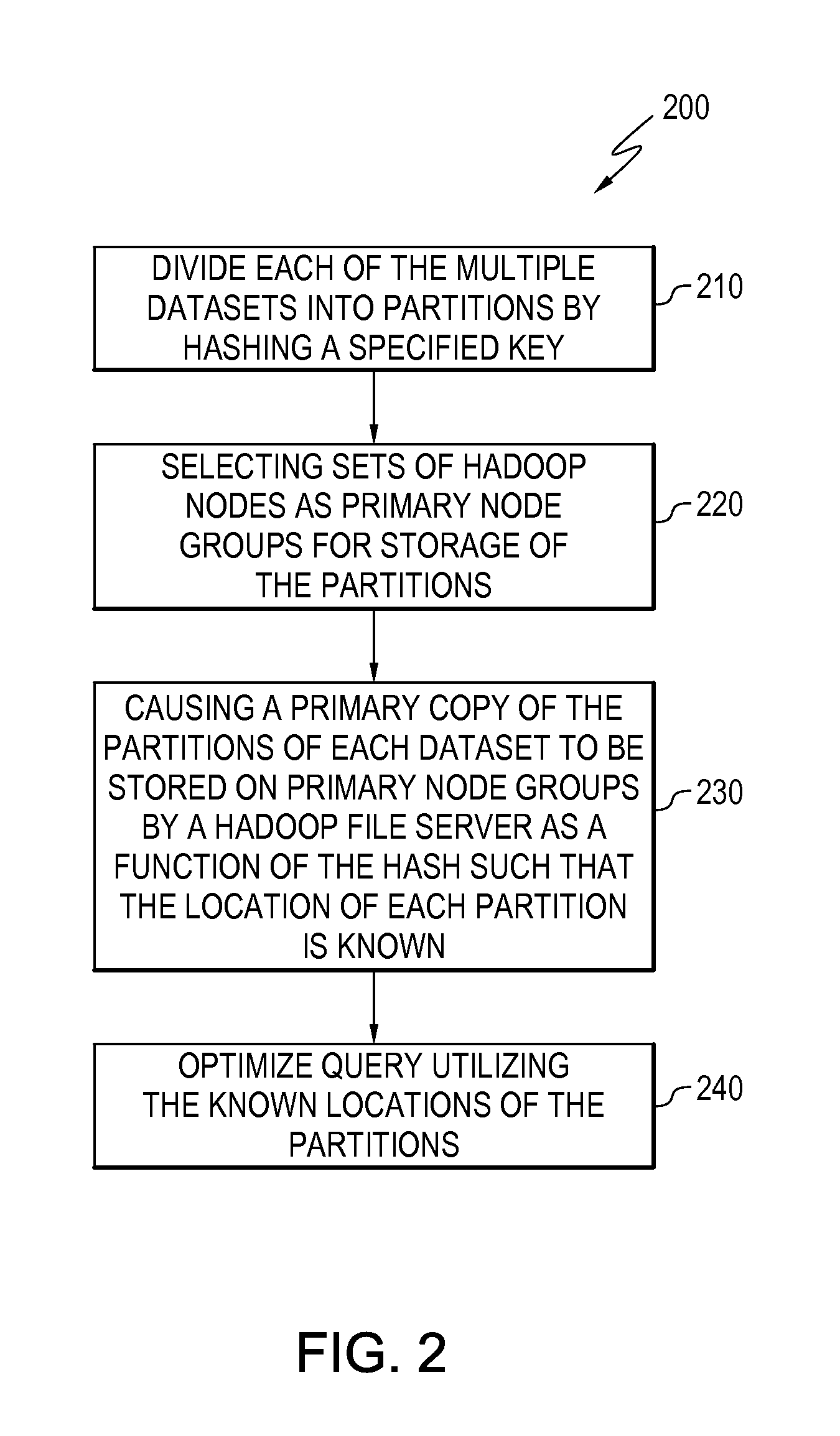
Data placement control for distributed computing environment
ActiveUS20170031988A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setDistributed File System
A method includes dividing a dataset into partitions by hashing a specified key, selecting a set of distributed file system nodes as a primary node group for storage of the partitions, and causing a primary copy of the partitions to be stored on the primary node group by a distributed storage system file server such that the location of each partition is known by hashing of the specified key.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
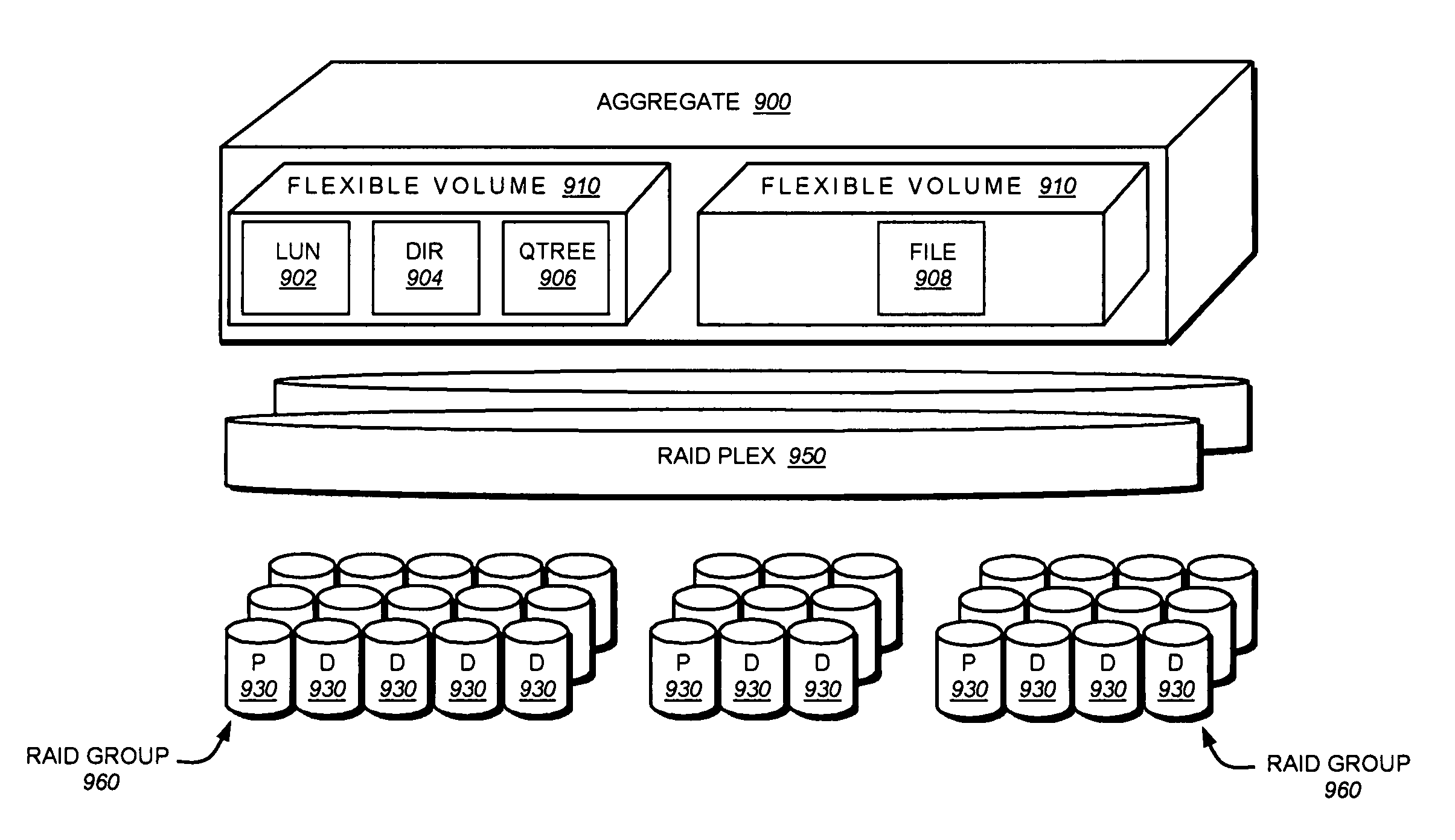
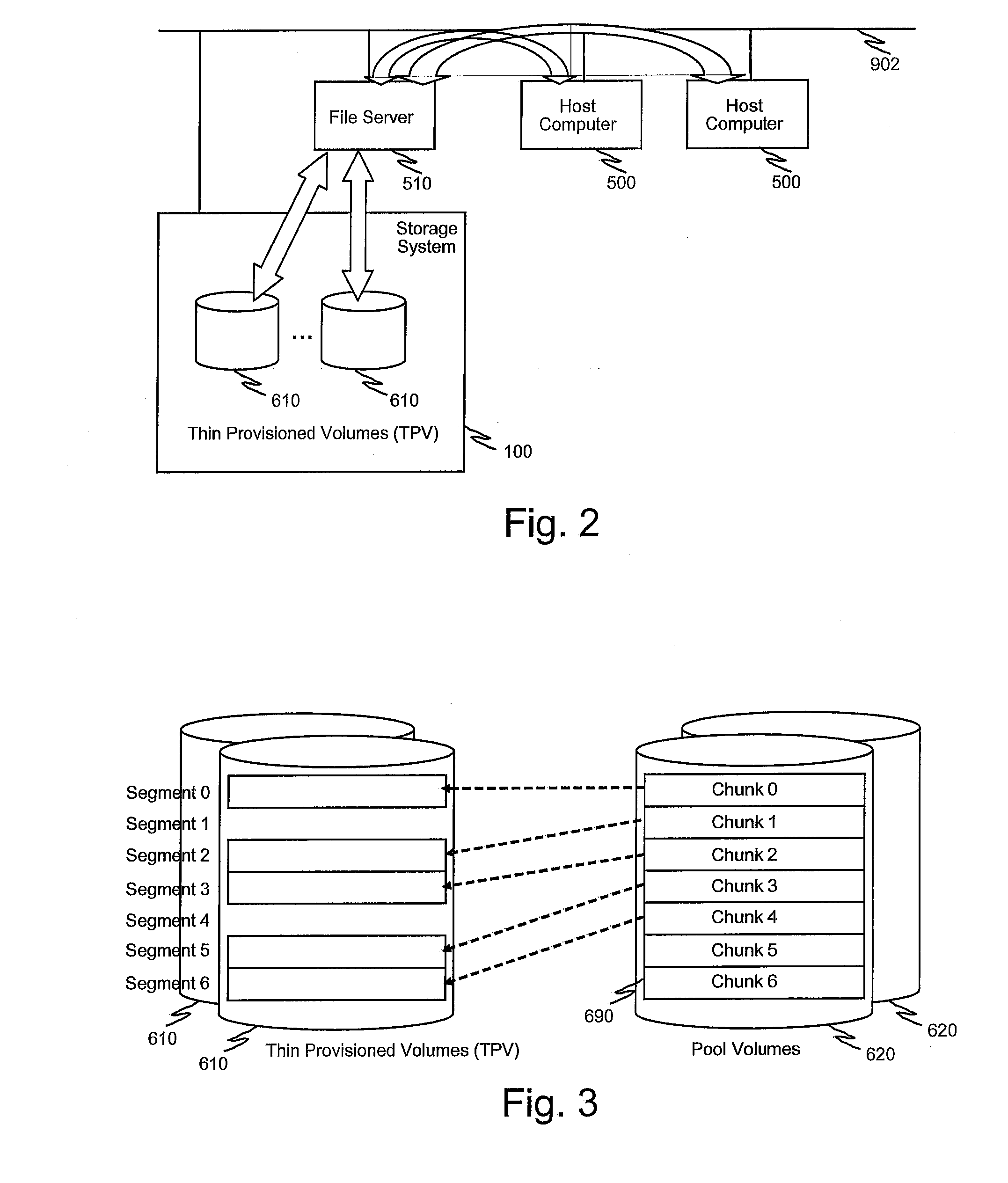
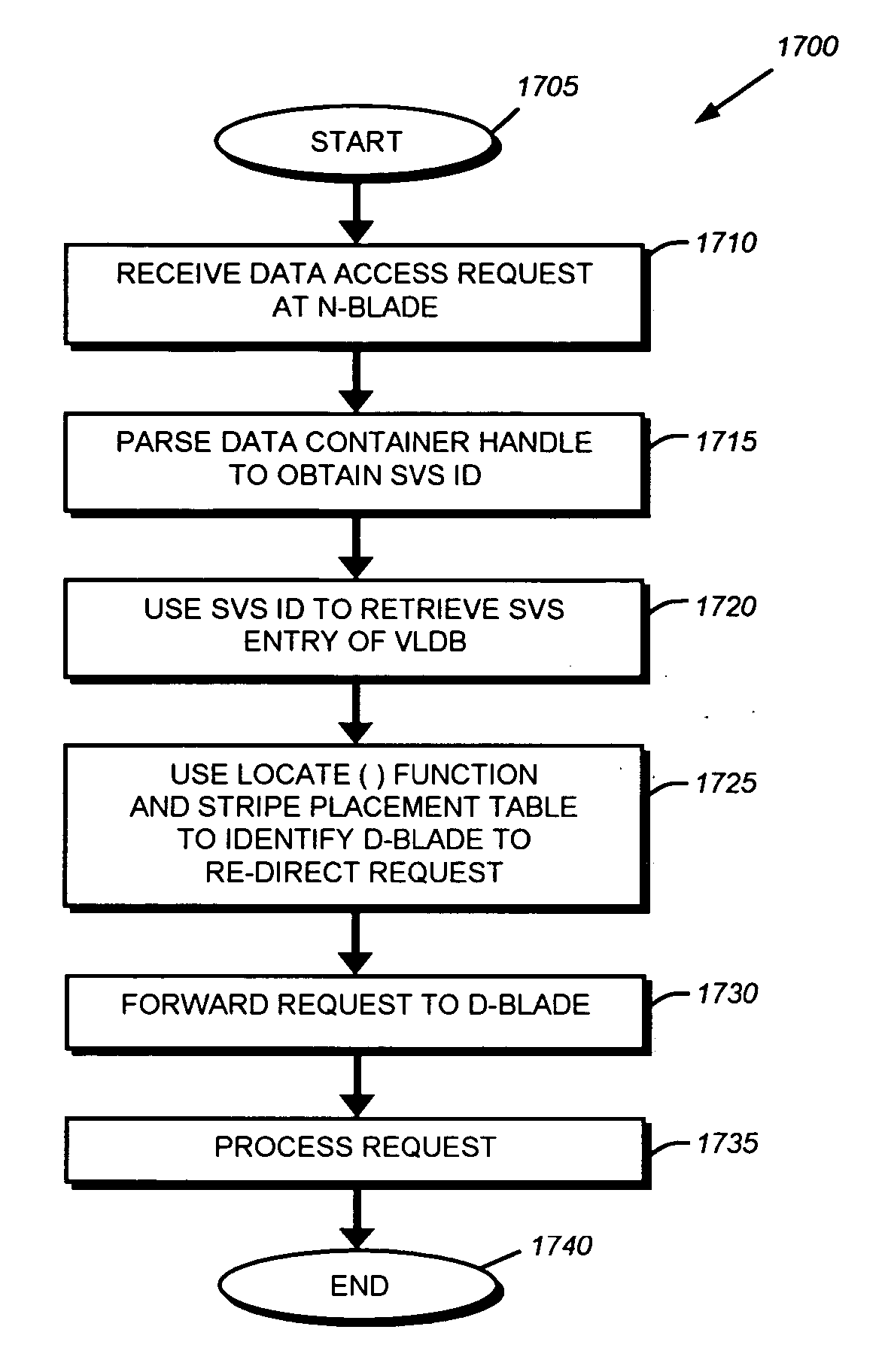
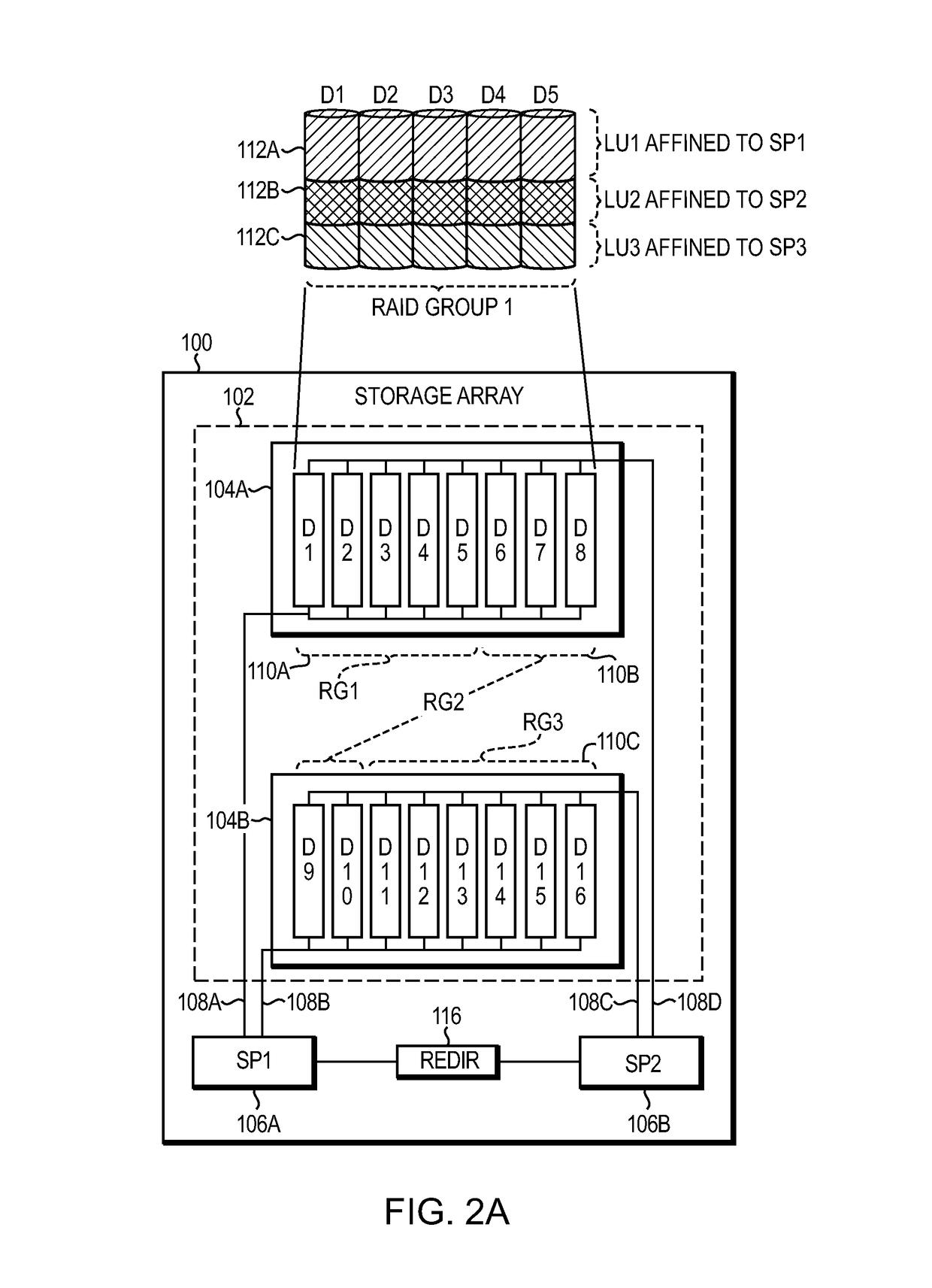
Data placement technique for striping data containers across volumes of a storage system cluster
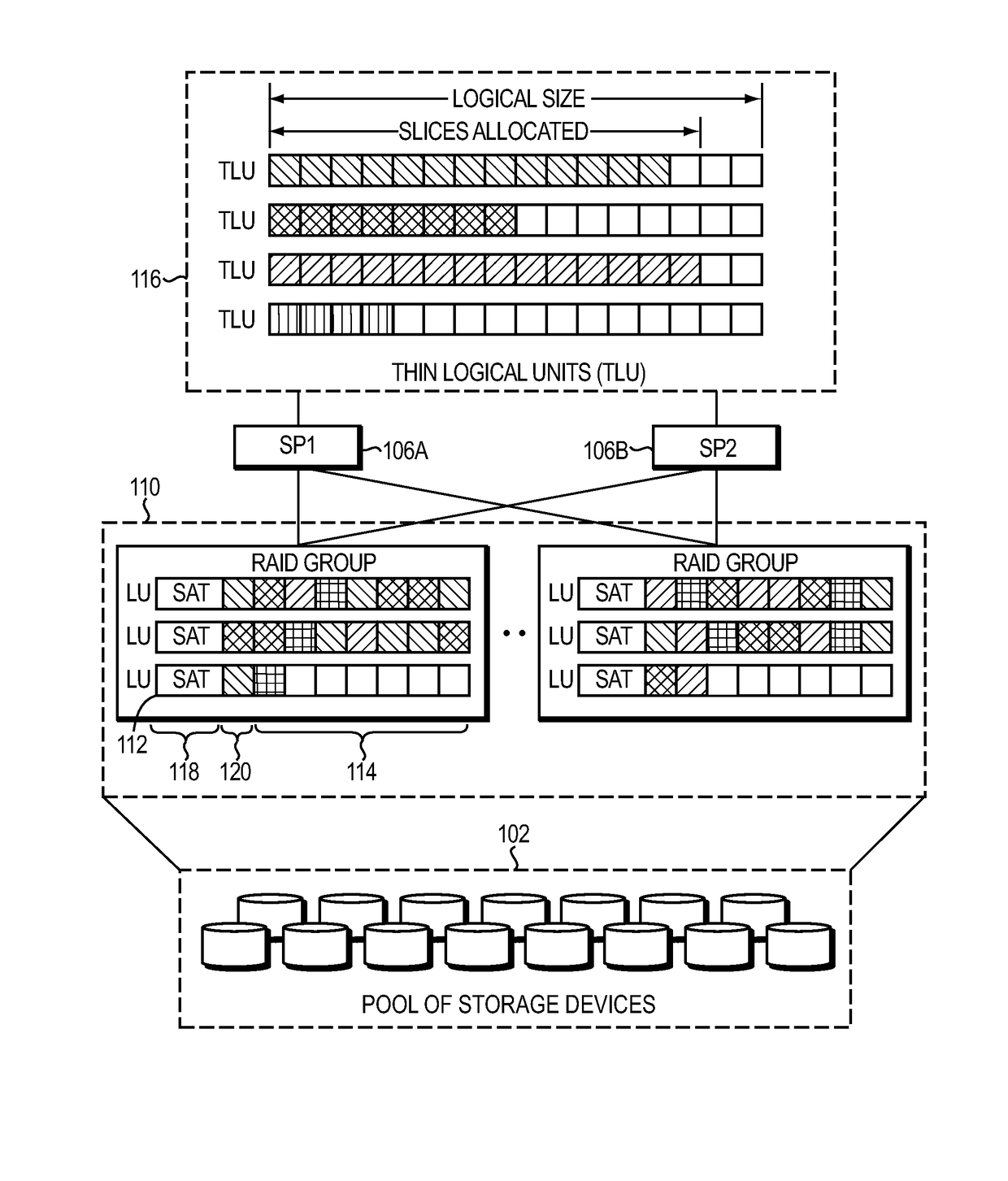
ActiveUS7366837B2Improve efficiencyOvercome disadvantagesRedundant data error correctionMemory systemsData placementFixed length
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
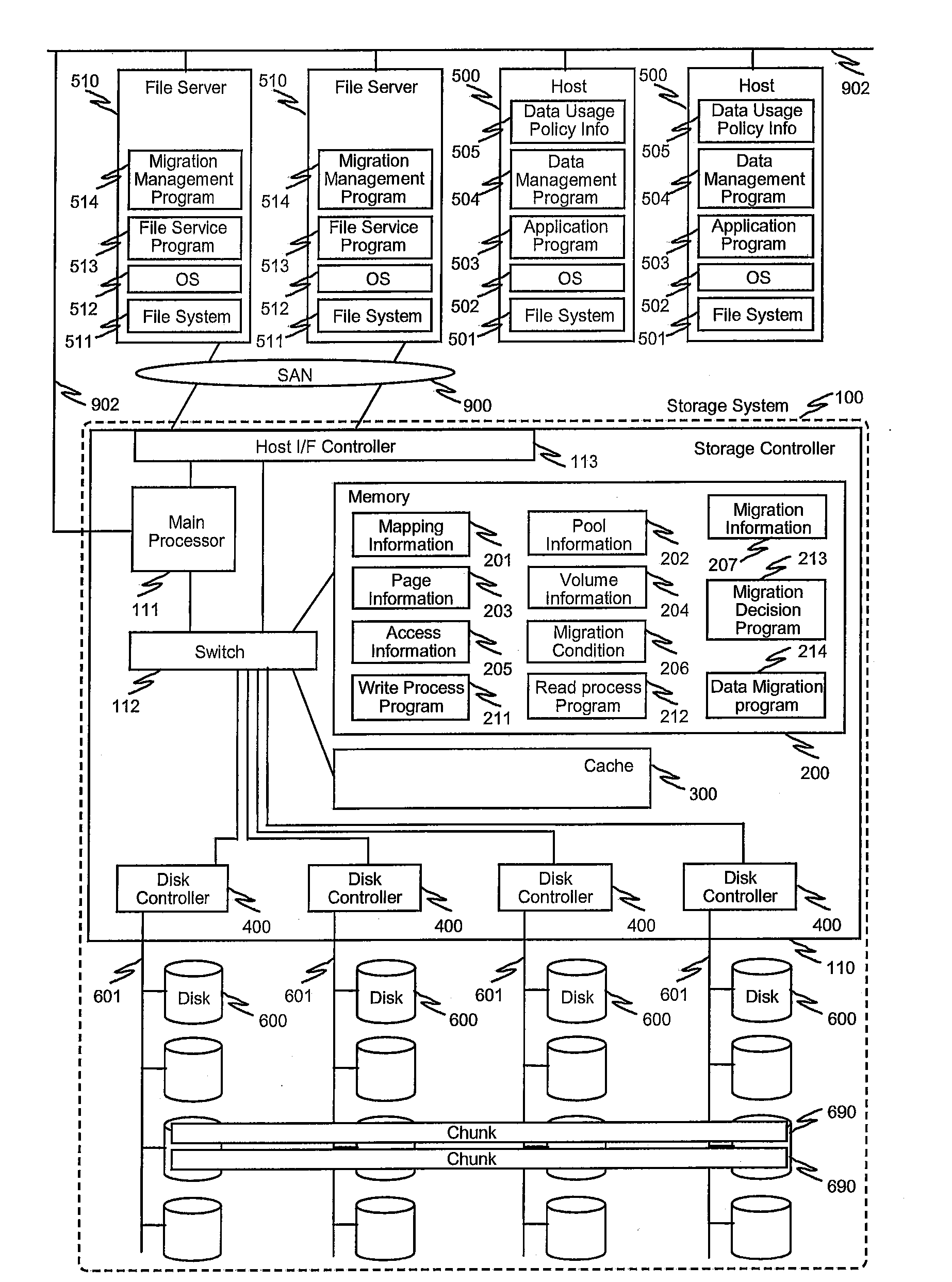
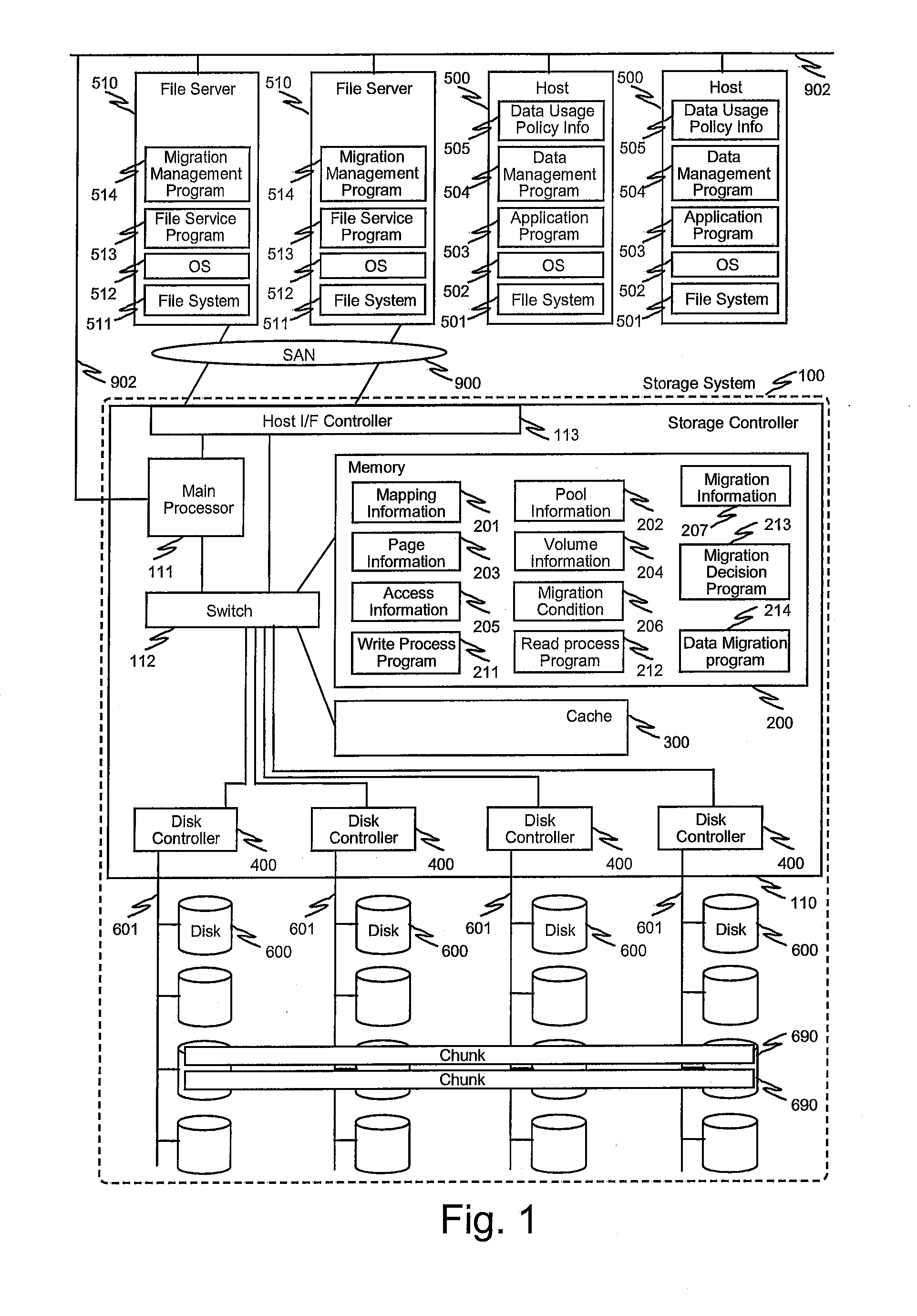
System and method for controlling automated page-based tier management in storage systems
ActiveUS20100077168A1Enabling changeError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData placementFile server
System and method for automated page-based management in storage systems. The system includes host computers, file servers and a storage system having automated page-based management means. The storage system interface receives instructions to change the condition for decision for migration regarding particular parts or the whole volume. The host computer can control execution of the migration performed by the storage system by specifying areas or volumes with the condition via the interface. Highly optimized, appropriate data placement and data relocation in computer system can be achieved when the application, host computer or management computer can recognize or predict the usage of the data or files. The storage system having automated page-based management may include compression / decompression and a control method for the compression and decompression process.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Limiting number of retransmission attempts for data transfer via network interface controller
ActiveUS20050129045A1Reduce memory bandwidthReduce latencyError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsConnection typeData placement
An RNIC implementation that performs direct data placement to memory where all segments of a particular connection are aligned, or moves data through reassembly buffers where all segments of a particular connection are non-aligned. The type of connection that cuts-through without accessing the reassembly buffers is referred to as a “Fast” connection because it is highly likely to be aligned, while the other type is referred to as a “Slow” connection. When a consumer establishes a connection, it specifies a connection type. The connection type can change from Fast to Slow and back. The invention reduces memory bandwidth, latency, error recovery using TCP retransmit and provides for a “graceful recovery” from an empty receive queue. The implementation also may conduct CRC validation for a majority of inbound DDP segments in the Fast connection before sending a TCP acknowledgement (Ack) confirming segment reception.
Owner:MELLANOX TECHNOLOGIES LTD
Method and system for handling out-of-order segments in a wireless system via direct data placement
InactiveUS20060007935A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementData placementComputer science
A method and system for handling or processing out-of-order TCP segments in a wireless system may comprise at least one of: placing a first TCP segment received by a wireless network processor in a host buffer and having a mapping between a TCP sequence number and a corresponding buffer address. It may be determined whether a second TCP segment received by the wireless network processor is one of an in-order TCP segment or an out-of-order TCP segment. If the second received TCP segment is an out-of-order TCP segment, then control information associated with at least the second TCP segment may be stored locally on the wireless network processor. The out-of-order TCP segment may be placed in a portion of the host buffer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Data placement technique for striping data containers across volumes of a storage system cluster
ActiveUS20060184731A1Minimize the numberReducing duration of operationMemory loss protectionRedundant data error correctionData placementFixed length
A technique places content, such as data, of one or more data containers on volumes of a striped volume set (SVS). The placement of data across the volumes of the SVS allows specification of a deterministic pattern of fixed length. That is, the pattern determines a placement of data of a data container that is striped among the volumes of the SVS. The placement pattern is such that the stripes are distributed exactly or nearly equally among the volumes and that, within any local span of a small multiple of the number of volumes, the stripes are distributed nearly equally among the volumes. The placement pattern is also substantially similar for a plurality of SVSs having different numbers of volumes.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
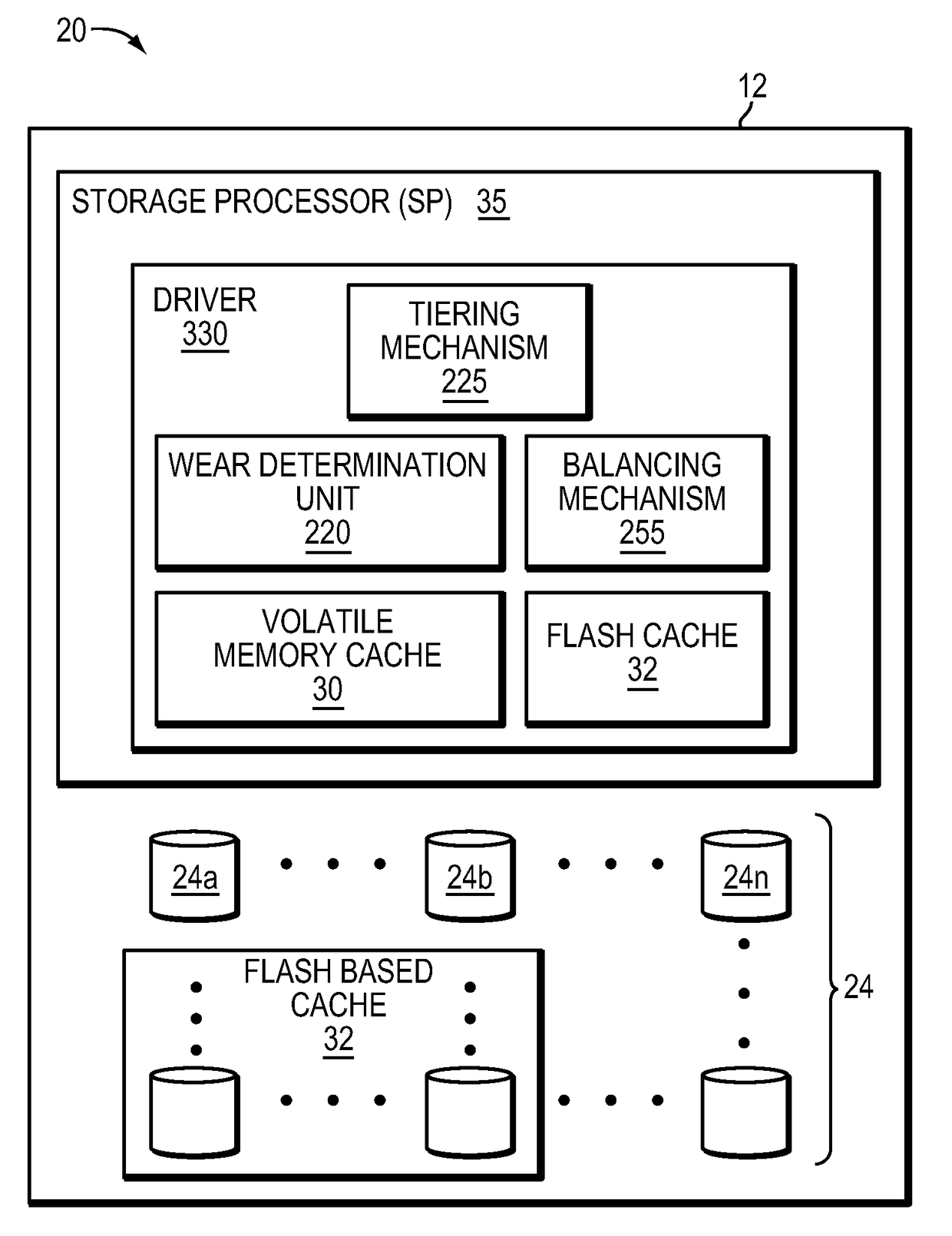
Managing data placement based on flash drive wear level
ActiveUS9811288B1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData placementHigh activity
A method is used in managing data in a data storage system. A tiered storage pool is identified wherein the storage pool includes multiple tiers having multiple storage units. A wear indicator for each of the multiple storage units is monitored. A first storage unit having a wear indicator greater than a second storage unit is identified. High activity data on the first storage unit is also identified. The identified high activity data is migrated from the first storage unit to the second storage unit.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
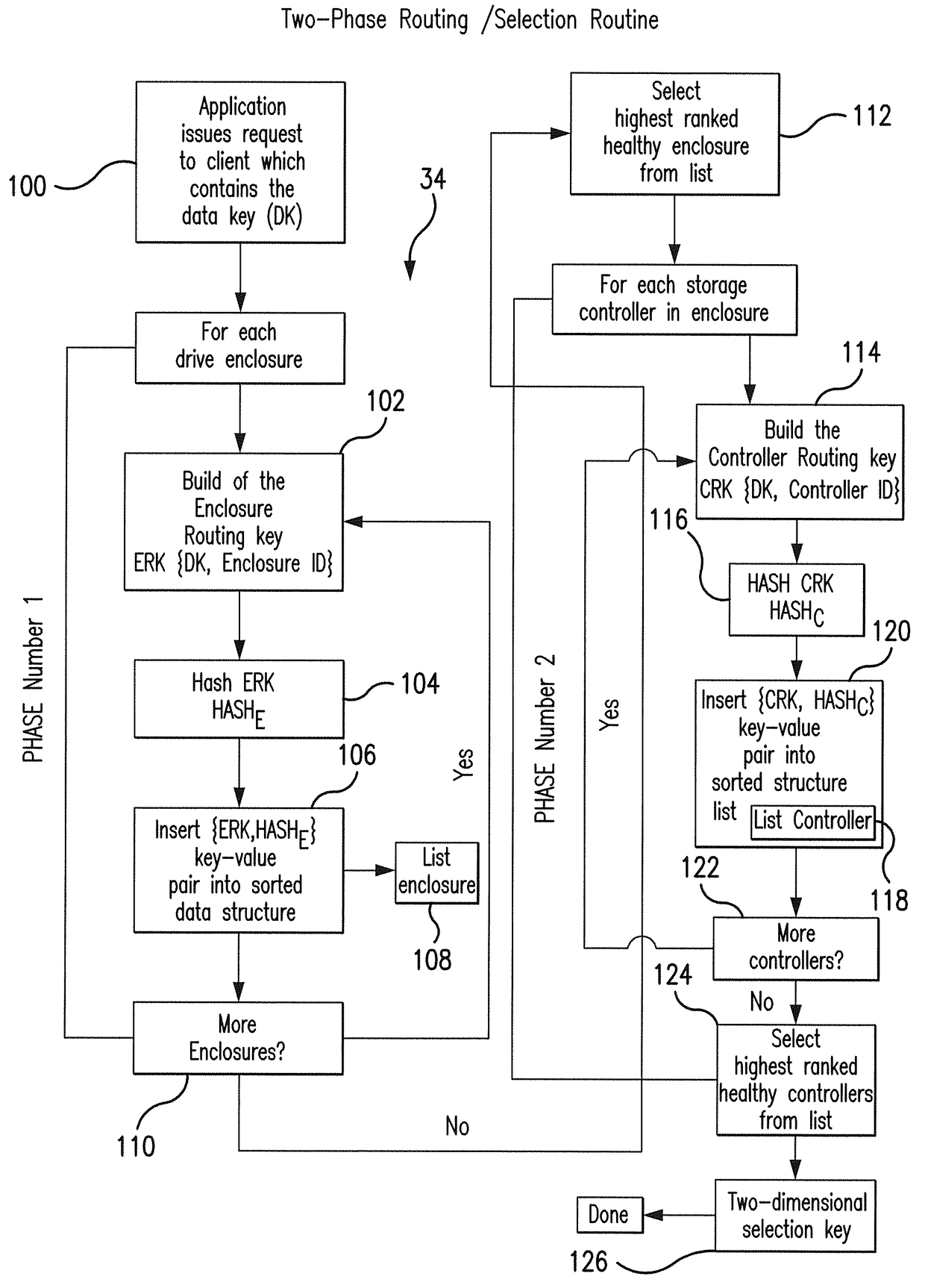
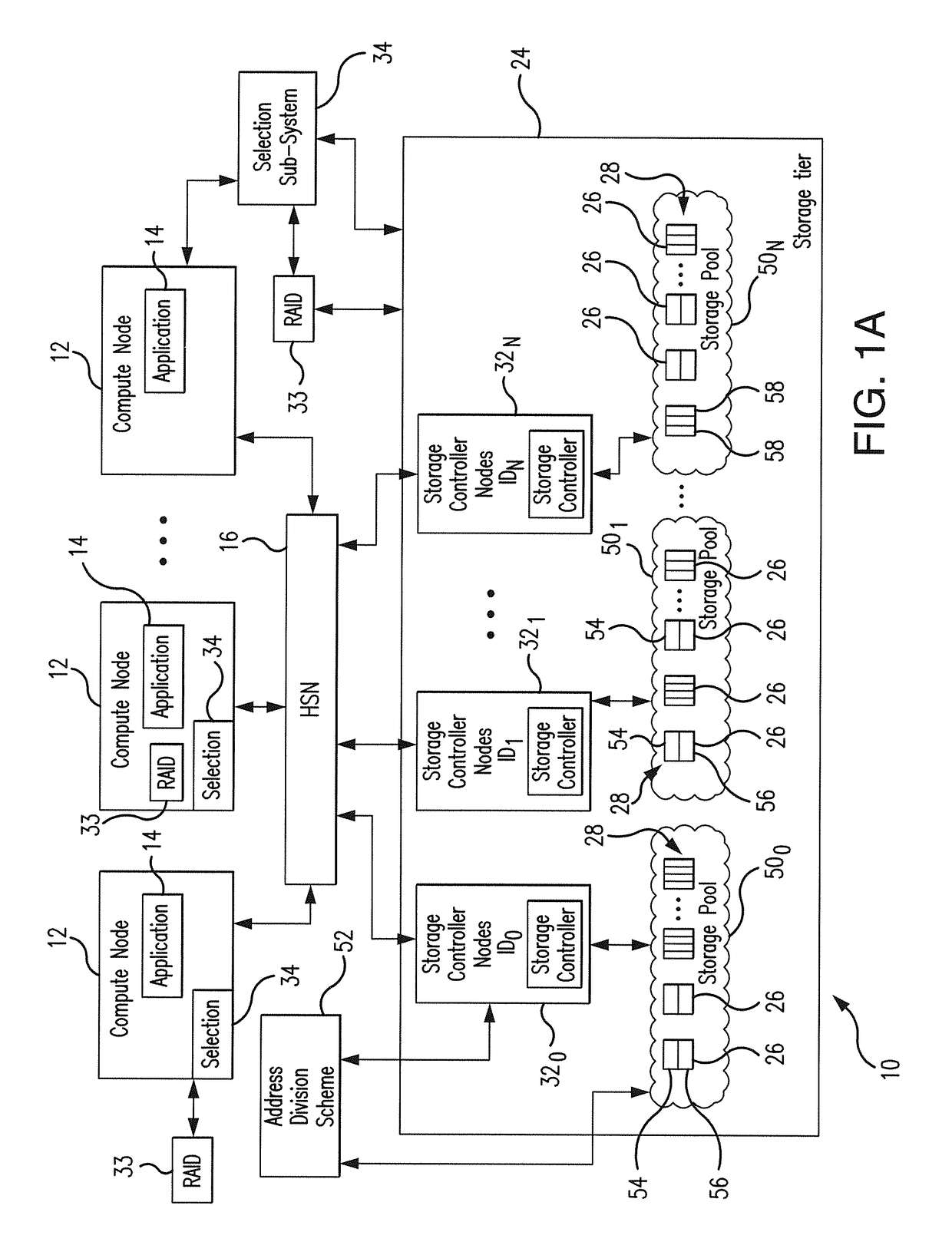
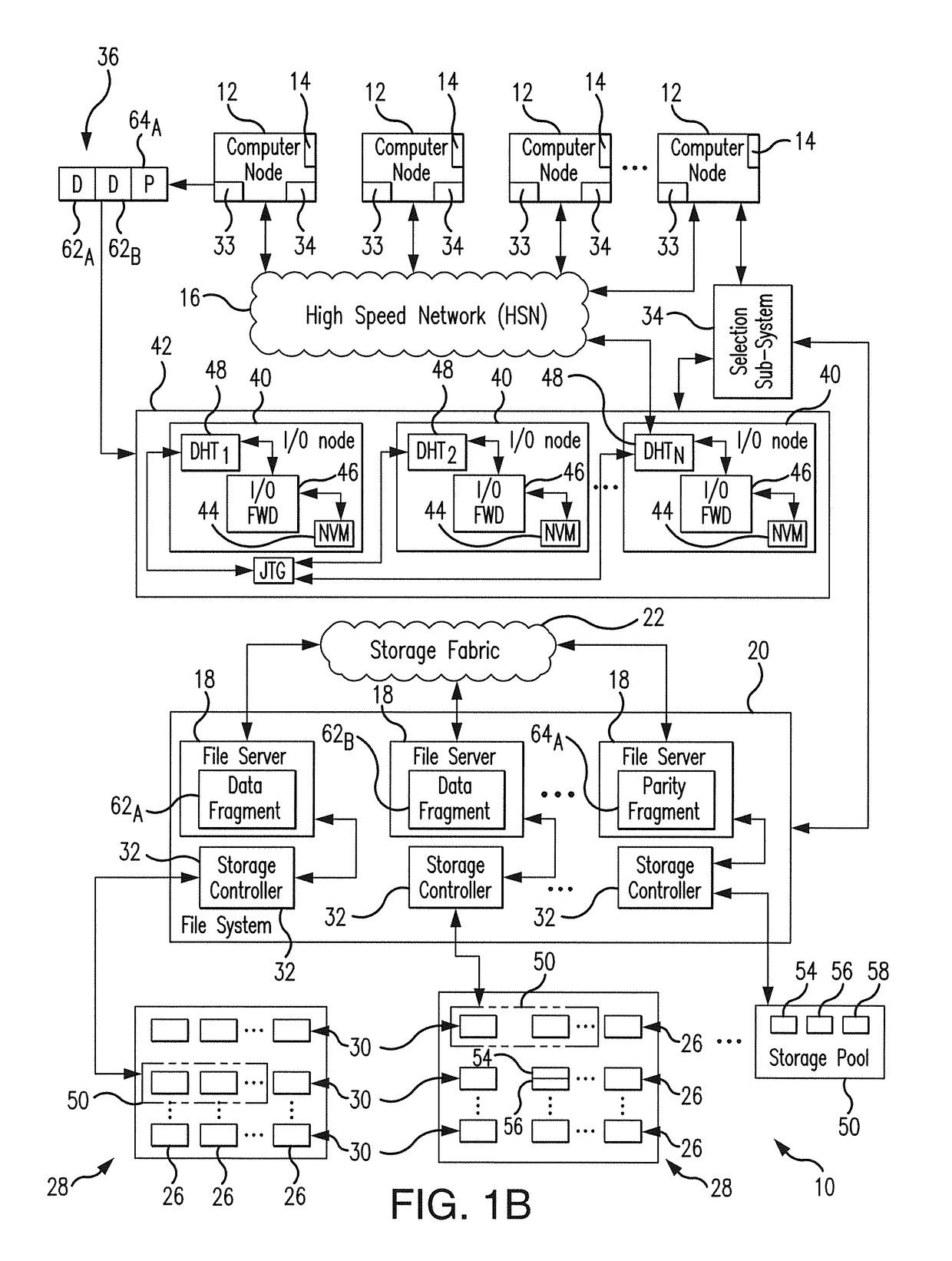
Low latency and reduced overhead data storage system and method for sharing multiple storage devices by high performance computing architectures
ActiveUS9959062B1Improve the level ofReliable rebuildInput/output to record carriersRedundant hardware error correctionData setPerformance computing
A data migration system supports a low-latency and reduced overhead data storage protocol for data storage sharing in a non-collision fashion which does not require inter-communication and permanent arbitration between data storage controllers to decide on the data placement / routing. The multiple data fragments of data sets are prevented from routing to the same storage devices by a multi-step selection protocol which selects (in a first phase of the selection routine) a healthy highest ranked drive enclosure, and further selects (in a second phase of the selection routine) a healthy highest-ranked data storage controller residing in the selected drive enclosure, for routing data fragments to different storage pools assigned to the selected data storage devices for exclusive “writing” and data modification. The selection protocol also contemplates various failure scenarios in a data placement collision free manner.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
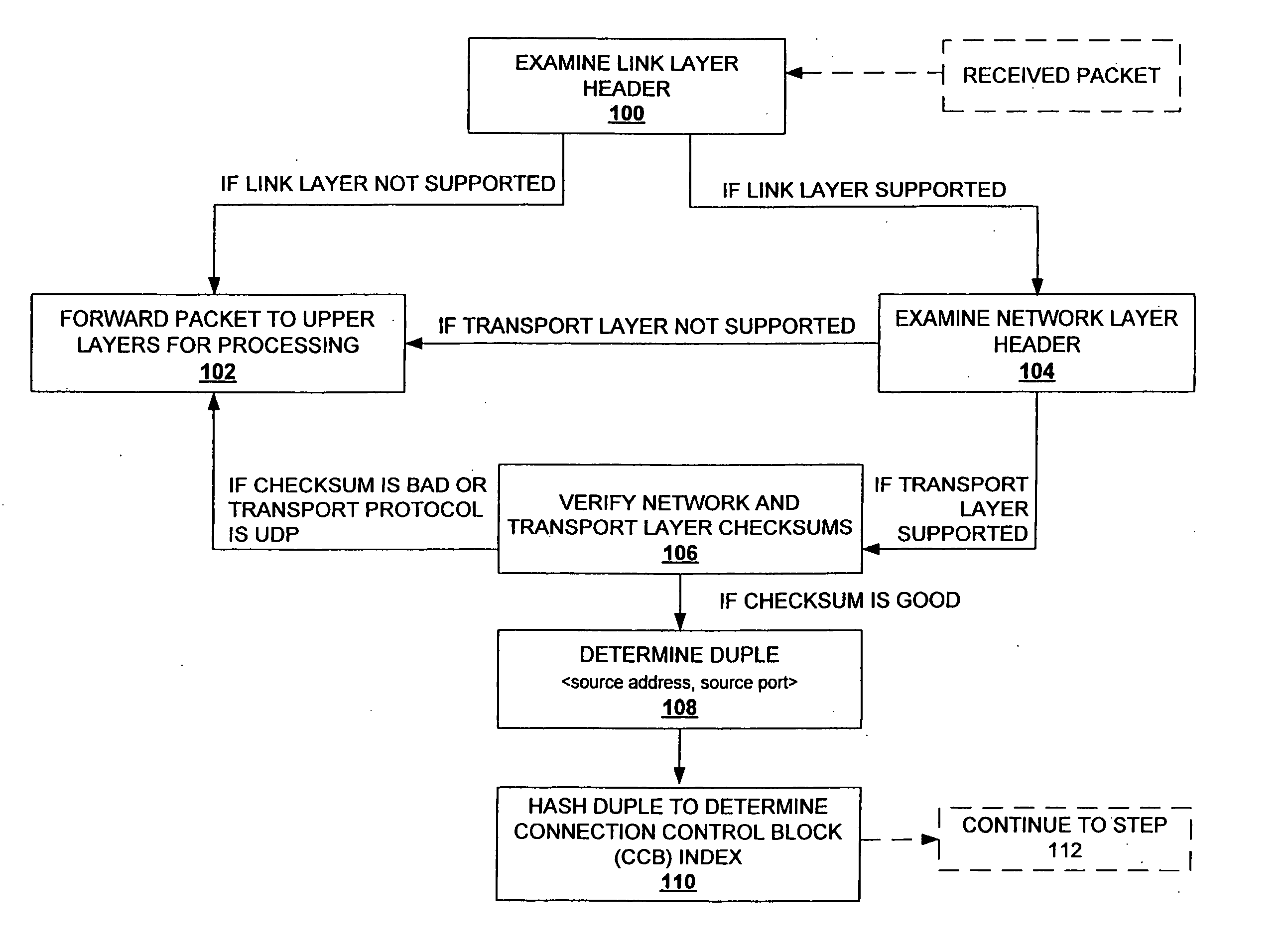
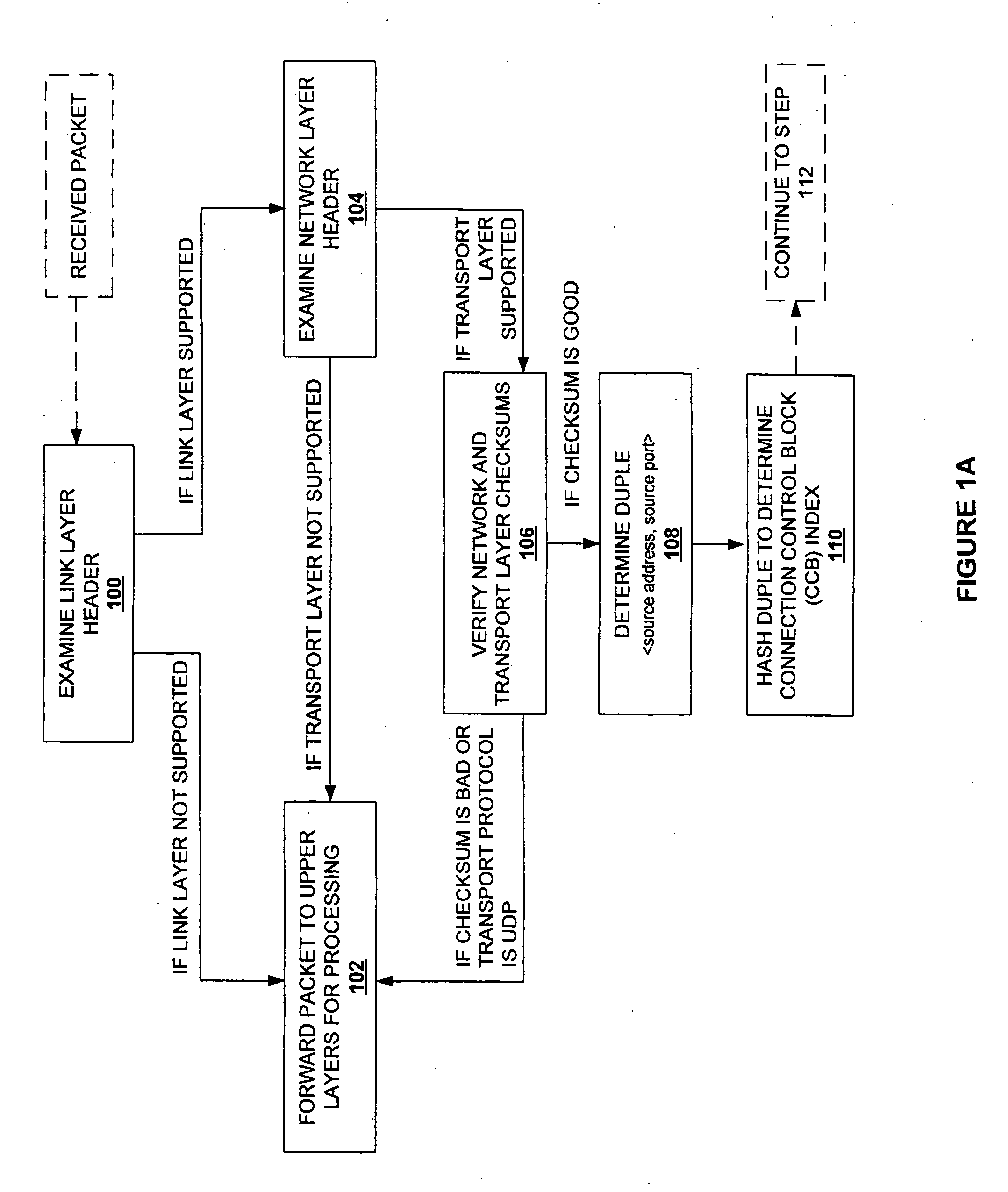
Method and system for providing direct data placement support
InactiveUS20060034283A1Reduction of CPU processing overheadReduced space requirementsTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationWire speedZero-copy
A system and method for reducing the overhead associated with direct data placement is provided. Processing time overhead is reduced by implementing packet-processing logic in hardware. Storage space overhead is reduced by combining results of hardware-based packet-processing logic with ULP software support; parameters relevant to direct data placement are extracted during packet-processing and provided to a control structure instantiation. Subsequently, payload data received at a network adapter is directly placed in memory in accordance with parameters previously stored in a control structure. Additionally, packet-processing in hardware reduces interrupt overhead by issuing system interrupts in conjunction with packet boundaries. In this manner, wire-speed direct data placement is approached, zero copy is achieved, and per byte overhead is reduced with respect to the amount of data transferred over an individual network connection. Movement of ULP data between application-layer program memories is thereby accelerated without a fully offloaded TCP protocol stack implementation.
Owner:IBM CORP
In-order delivery of plurality of RDMA messages
InactiveUS20050144310A1Increase probabilityAttenuation bandwidthMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionConnection typeData placement
An RNIC implementation that performs direct data placement to memory where all segments of a particular connection are aligned, or moves data through reassembly buffers where all segments of a particular connection are non-aligned. The type of connection that cuts-through without accessing the reassembly buffers is referred to as a “Fast” connection because it is highly likely to be aligned, while the other type is referred to as a “Slow” connection. When a consumer establishes a connection, it specifies a connection type. The connection type can change from Fast to Slow and back. The invention reduces memory bandwidth, latency, error recovery using TCP retransmit and provides for a “graceful recovery” from an empty receive queue. The implementation also may conduct CRC validation for a majority of inbound DDP segments in the Fast connection before sending a TCP acknowledgement (Ack) confirming segment reception.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and Method for Optimizing Data Storage in a Distributed Data Storage Environment
InactiveUS20140136571A1Optimize allocationLow costDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsHigh availabilityData access
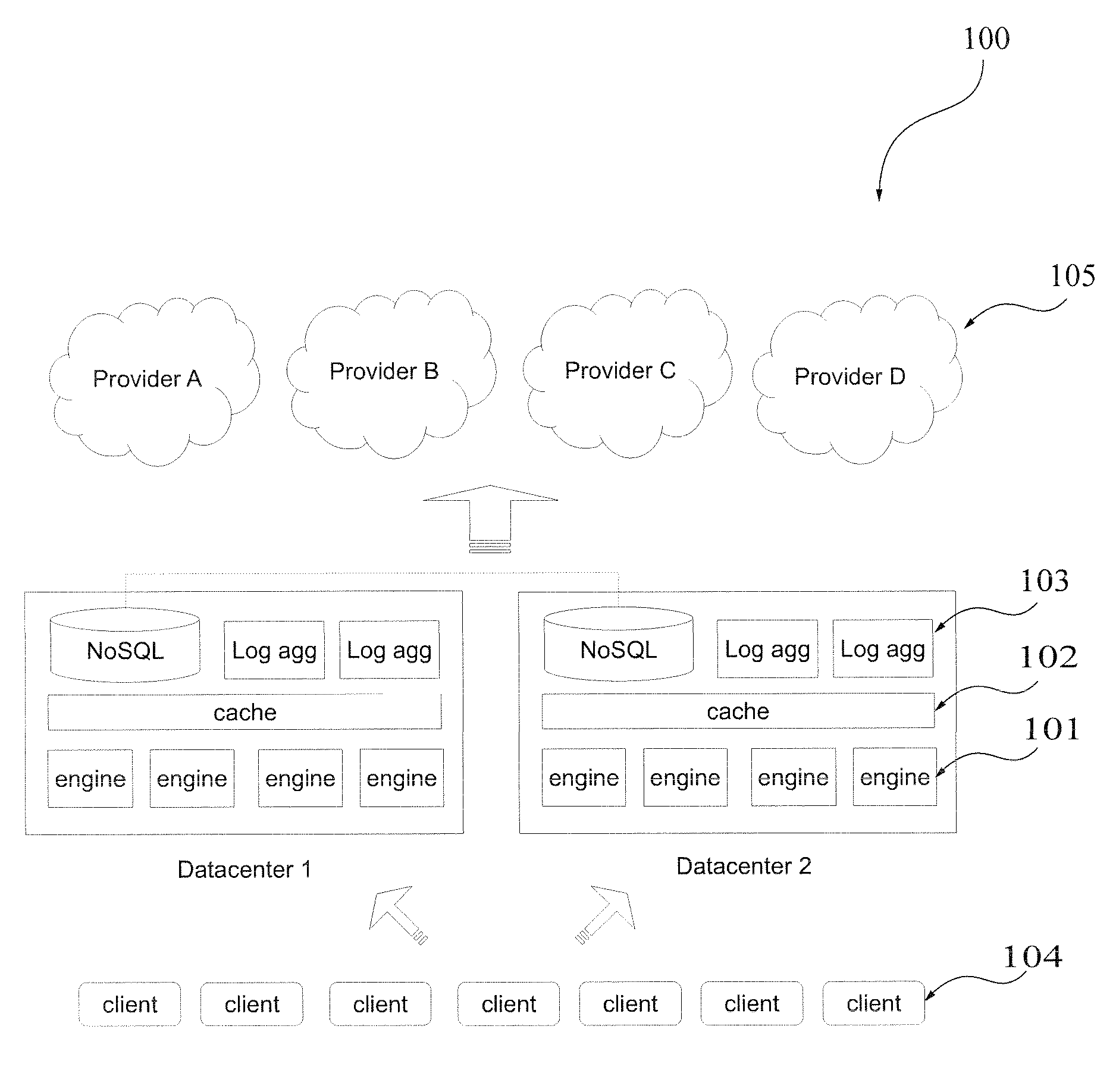
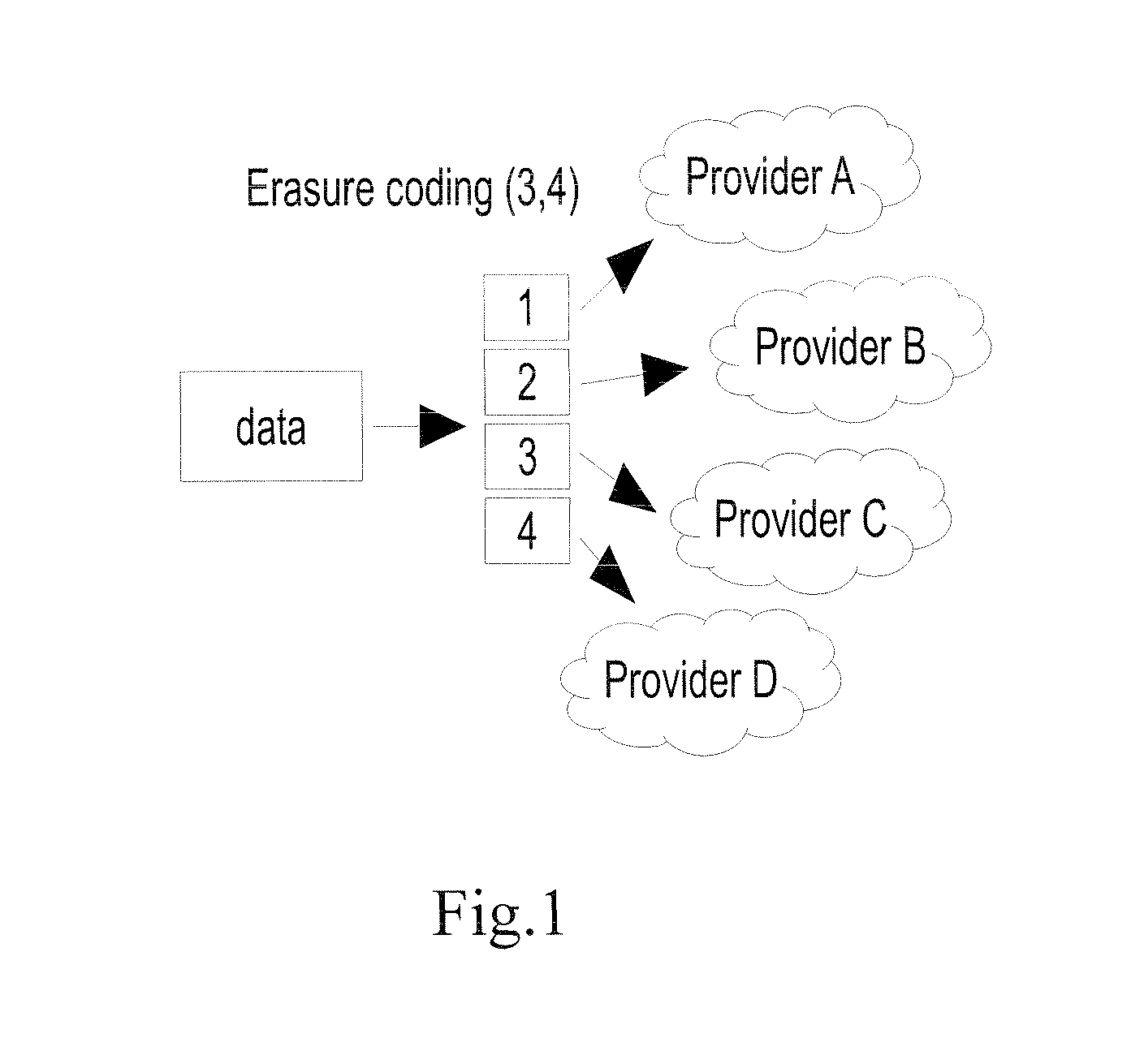
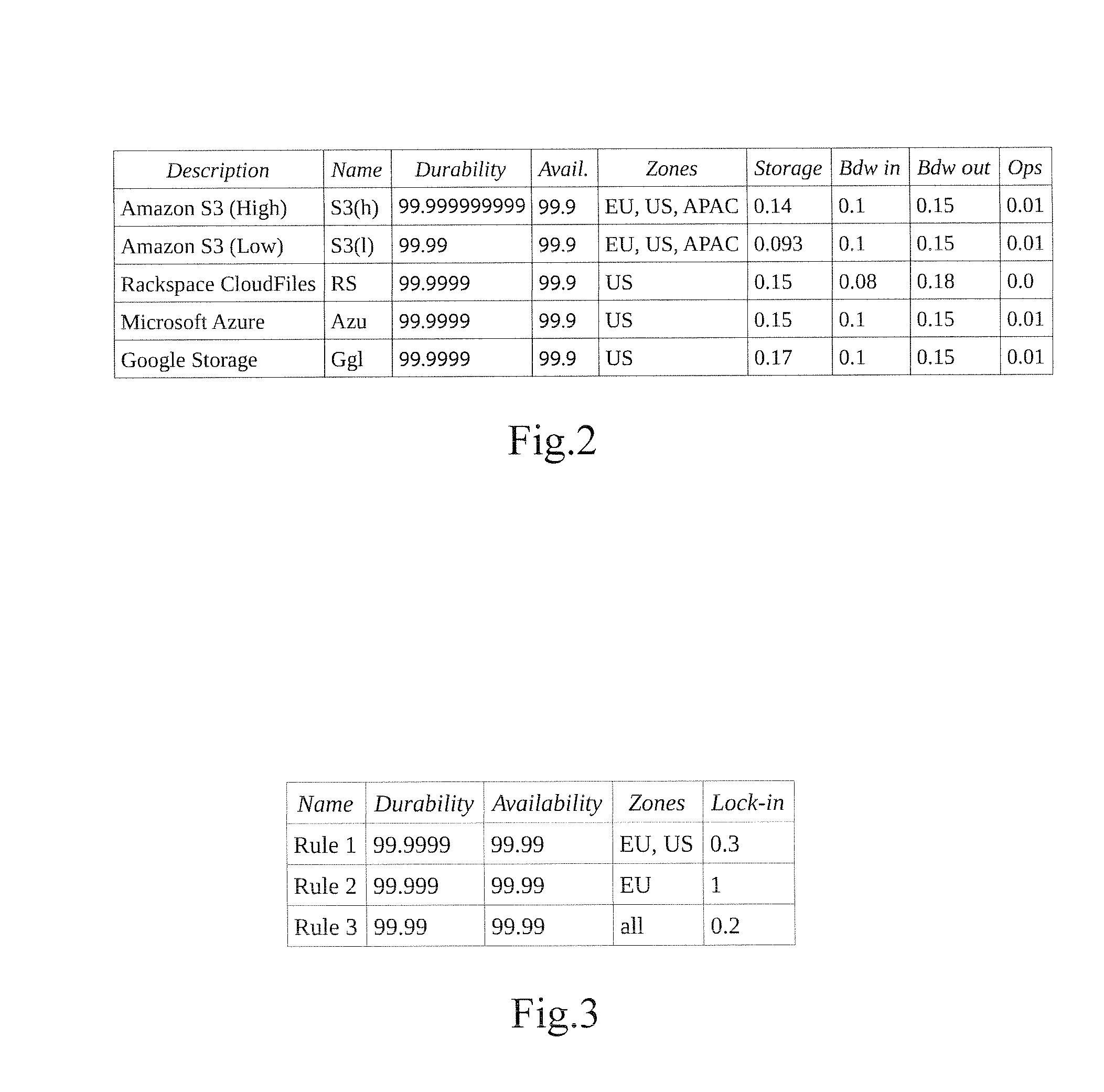
A growing amount of data is produced daily resulting in a growing demand for storage solutions. While cloud storage providers offer a virtually infinite storage capacity, data owners seek geographical and provider diversity in data placement, in order to avoid vendor lock-in and to increase availability and durability. Moreover, depending on the customer data access pattern, a certain cloud provider may be cheaper than another. In this respect is provided a method and a system that facilitates allocation of data objects in a distributed data storage environment. The system continuously adapts the placement of data based on its access patterns and subject to optimization objectives, such as storage costs. The system efficiently considers repositioning of only selected objects that may significantly lower the storage cost.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Managing data placement in storage systems
A method is used in managing data placement in storage systems. A portion of an allocated storage space is identified in a data storage system for managing data placement. The allocated storage space includes first and second set of slices. The first set of slices associated with the portion of the allocated storage space in the data storage system is identified. Data of the first set of slices is transferred to the second set of slices of the allocated storage space in the data storage system. The first set of slice is removed from the allocated storage space in the data storage system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com