Patents
Literature
428results about How to "Avoid discarding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
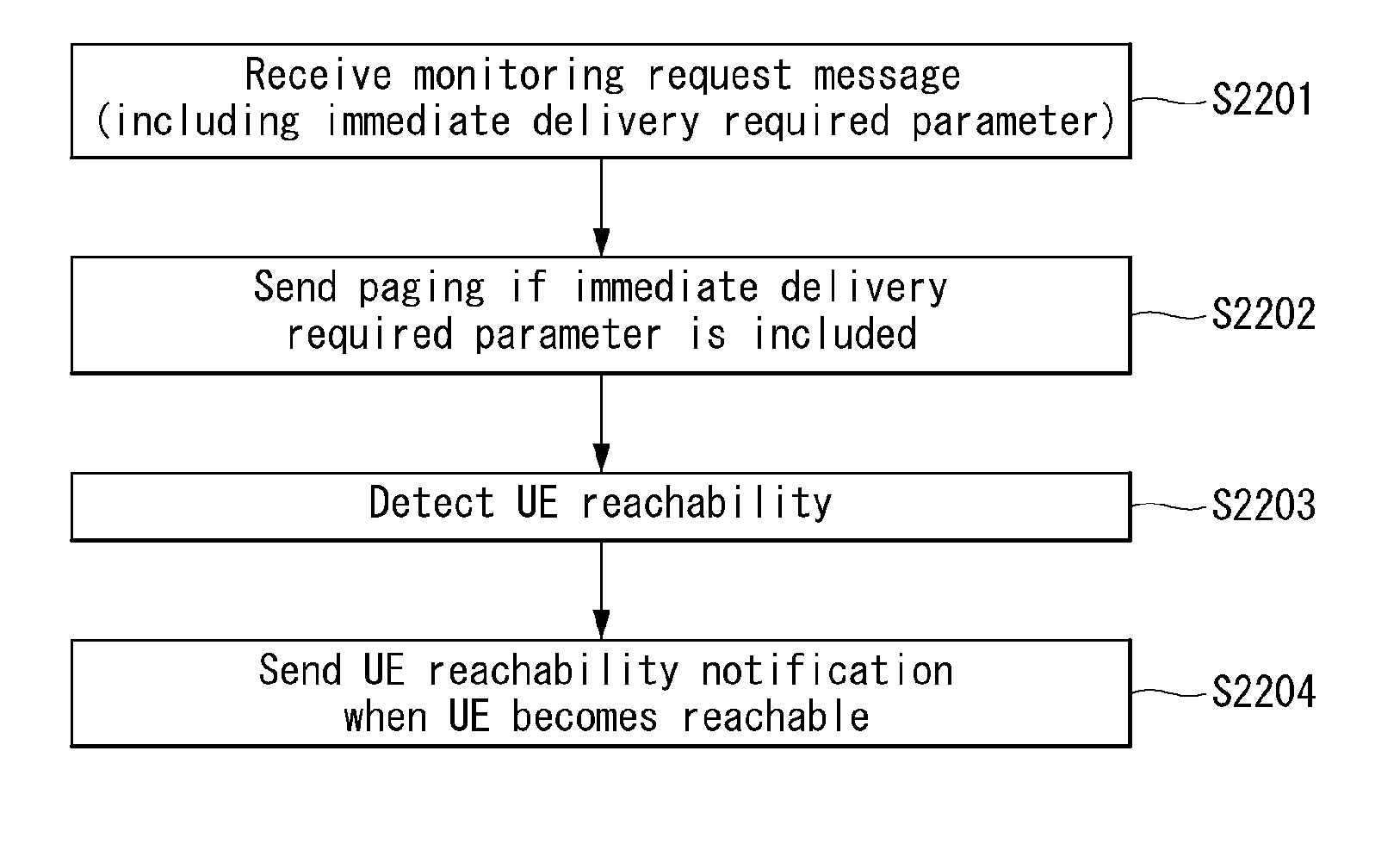
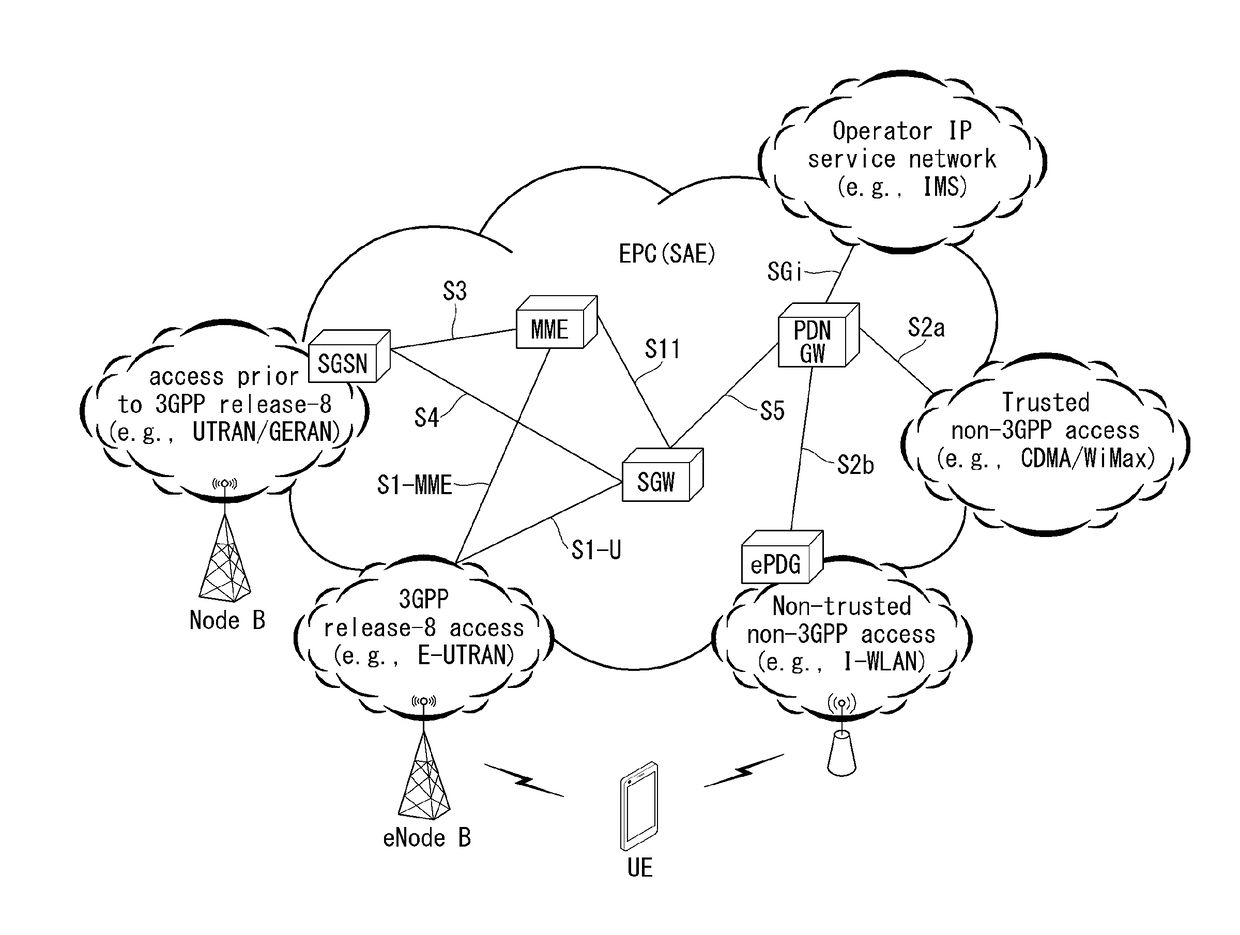
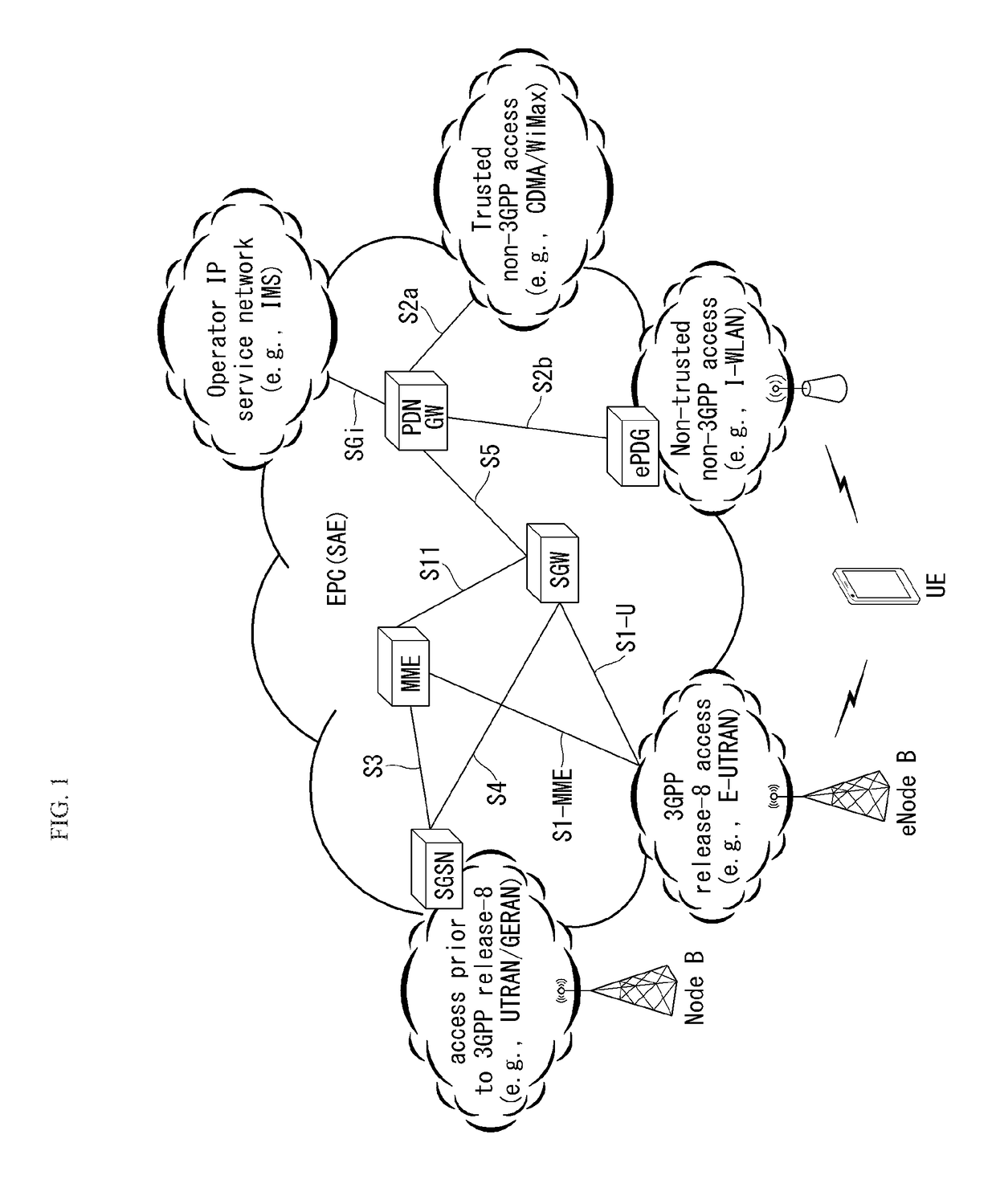
Method and apparatus for monitoring user equipment reachability in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20160286385A1Effective serviceExtended Discontinuous ReceptionConnection managementNetwork data managementCommunications systemReachability
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for monitoring UE reachability in a wireless communication system. A method for monitoring UE reachability may include receiving, by a Mobility Management Entity, a monitoring request message for UE reachability including a maximum response time from a Home Subscriber Server, detecting, by the MME, the UE reachability if it is expected that paging is able to be transmitted to UE when extended Discontinuous Reception is applied to the UE, and sending, by the MME, a UE reachability notification to a Service Capability Exposure Function before a next paging occasion of the UE, wherein the maximum response time may indicate a time during which the UE maintains a reachable state so that downlink data is reliably delivered to the UE, and wherein an occasion when the UE reachability notification is transmitted may be determined by taking into consideration the maximum response time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Data transmission method and data transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20050157696A1Degradation of data transmission efficiency can be preventedEfficient data transmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsData transmissionRadio wave
When retransmission requests are issued based on the results of error-correction decoding of received data packets to perform data transmission, statistical information indicating whether received data packets have been successfully decoded or have not been decoded is acquired, and based on the rate at which correct decoding has been made or the rate at which correct decoding has not been made, which is obtained from the statistical information, a request is transmitted to the transmission source to change the window size, which is the number of data units handled in a predetermined layer, so that when for example the communication environment is not excellent, processing can be performed at a small window size, and the occurrence of circumstances in which data retransmission and the discarding of received data are repeated can be efficiently prevented. Accordingly, data transmission efficiency in a wireless transmission system performing high-speed data transmission is improved under conditions of a poor radio wave environment.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
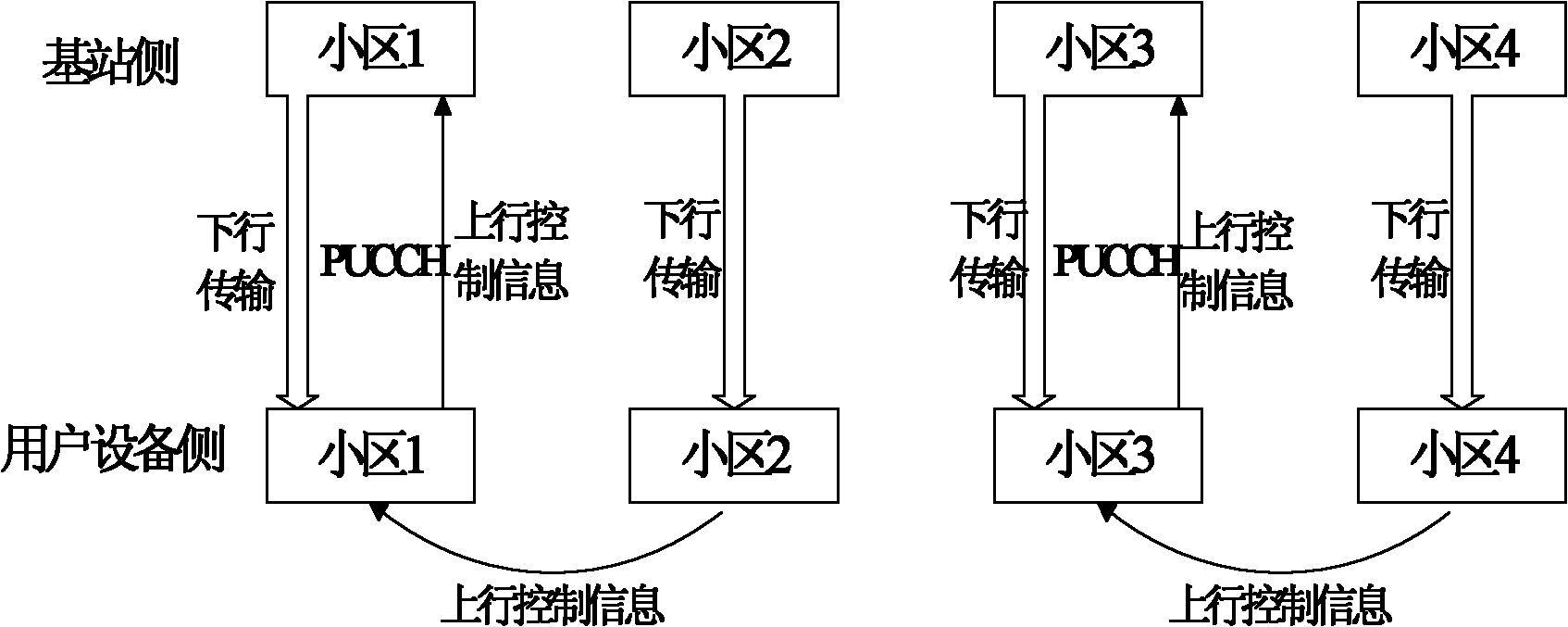
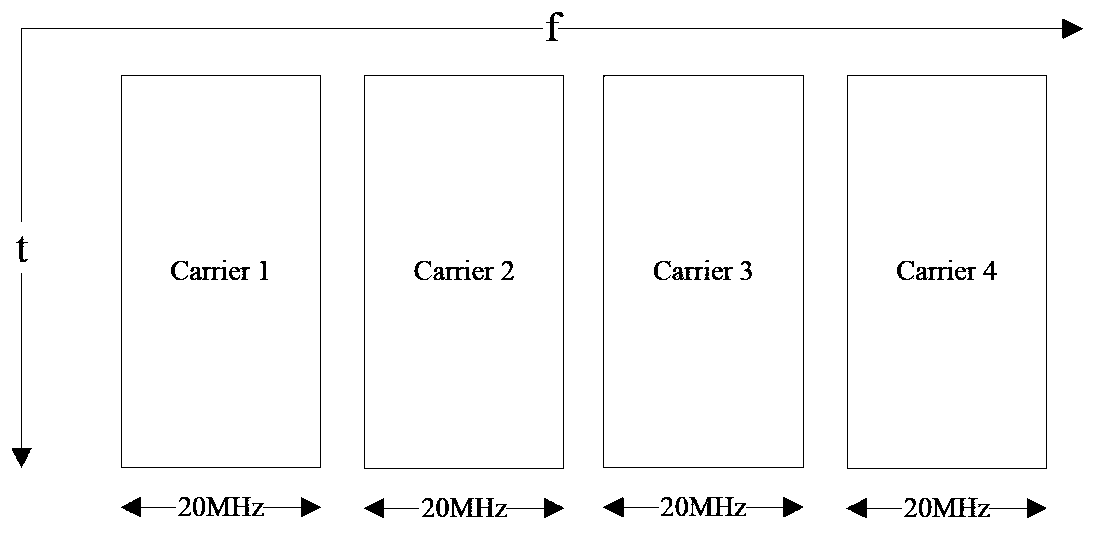
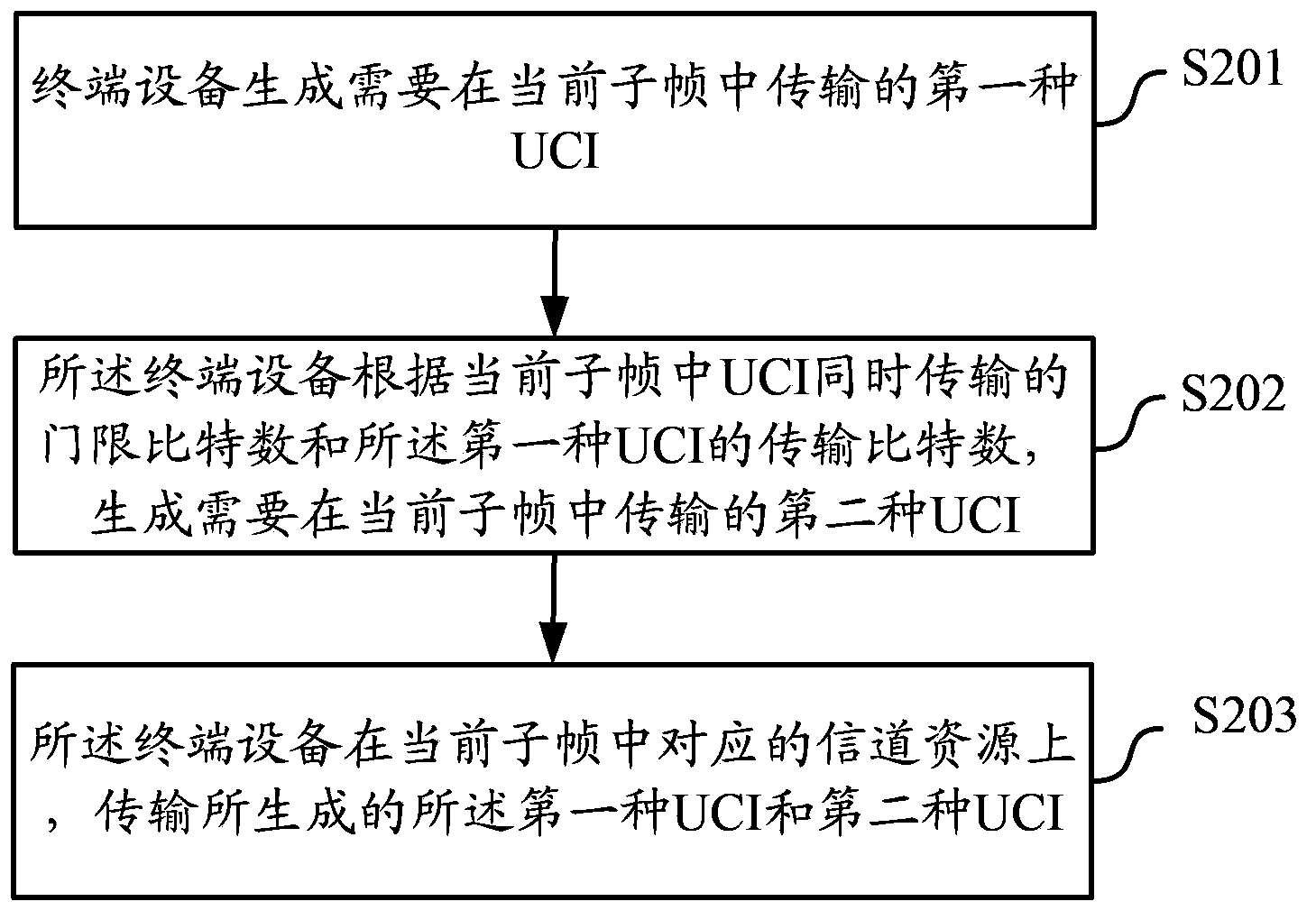
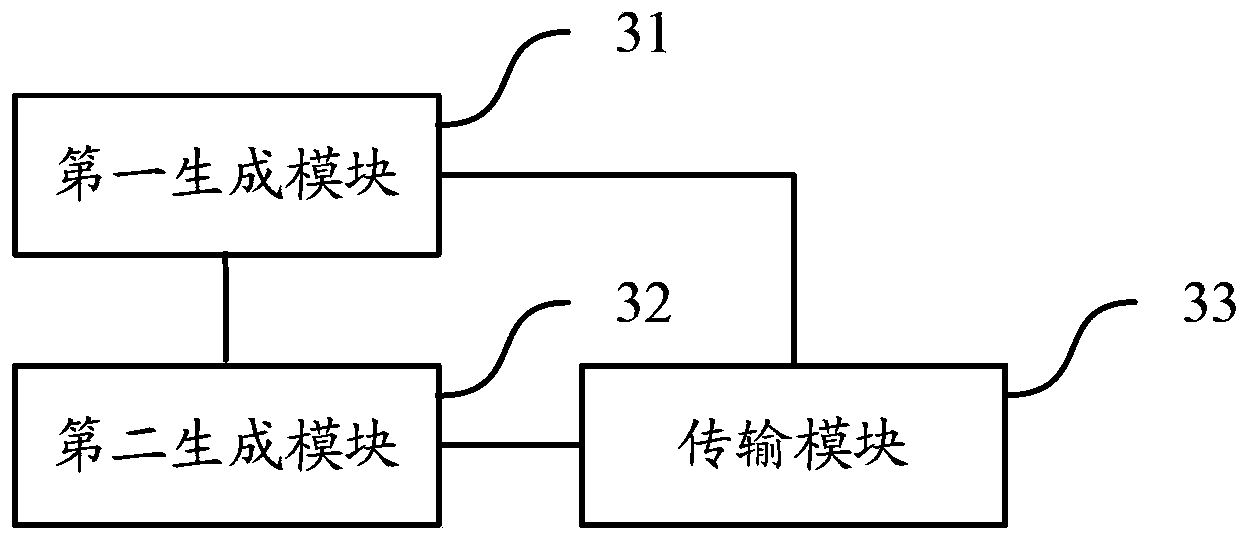
Uplink control information UCI transmitting and receiving method and device
ActiveCN102377537AAvoid discardingGuaranteed transmission reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal allocationChannel state informationTelecommunications
The invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, and discloses a UCI transmitting and receiving method and device. The method comprises the steps that: a piece of UE (User Equipment) determines an uplink carrier wave of a PUCCH (Physical Unlink Control Channel) for transmitting the UCI and an uplink carrier wave of a PUSCH (Physical Unlink Share Channel) for transmitting the UCI; the UE transmits ACK(acknowledgement) / NACK (negative acknowledgement) information at the uplink carrier wave of the PUCCH for transmitting the UCI by the PUCCH; and the UE transmits channel state information at the uplink carrier wave of the PUSCH for transmitting the UCI by the PUSCH. In the invention, the scheme, which is suitably applied to a LTE-A (Long Term Evolution-Access) system and is compatible with a LTE system and supports the synchronous transmission of the UCI on the PUCCH and the PUSCH, is provided; and the scheduling accuracy is provided while the transmission reliability is ensured.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Communication node and packet transfer method
InactiveUS6850519B1Reliable transmissionStrong error correction abilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionTime-division multiplexReal-time computingPayload
A communication node which can reliably transfer a packet with a payload including data having error resistance in radio environments is disclosed. A packet to be transmitted is divided into segments to form a plurality of packet segments. From among a plurality of error correction schemes that have been prepared in advance, the scheme to be employed is selected for each of the packet segments in accordance with predetermined criteria, and the selected error correction scheme is applied to each packet segment. Subsequently, the processed packet segment is transmitted to the network. Packet segments are received from the network. From among a plurality of error correction schemes prepared in advance, the scheme to be employed is selected for each of the received packet segments based on predetermined information contained in each received packet segment, and the selected error correction scheme is applied to the received packet segment. An original packet is formed from the plurality of processed packet segments.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
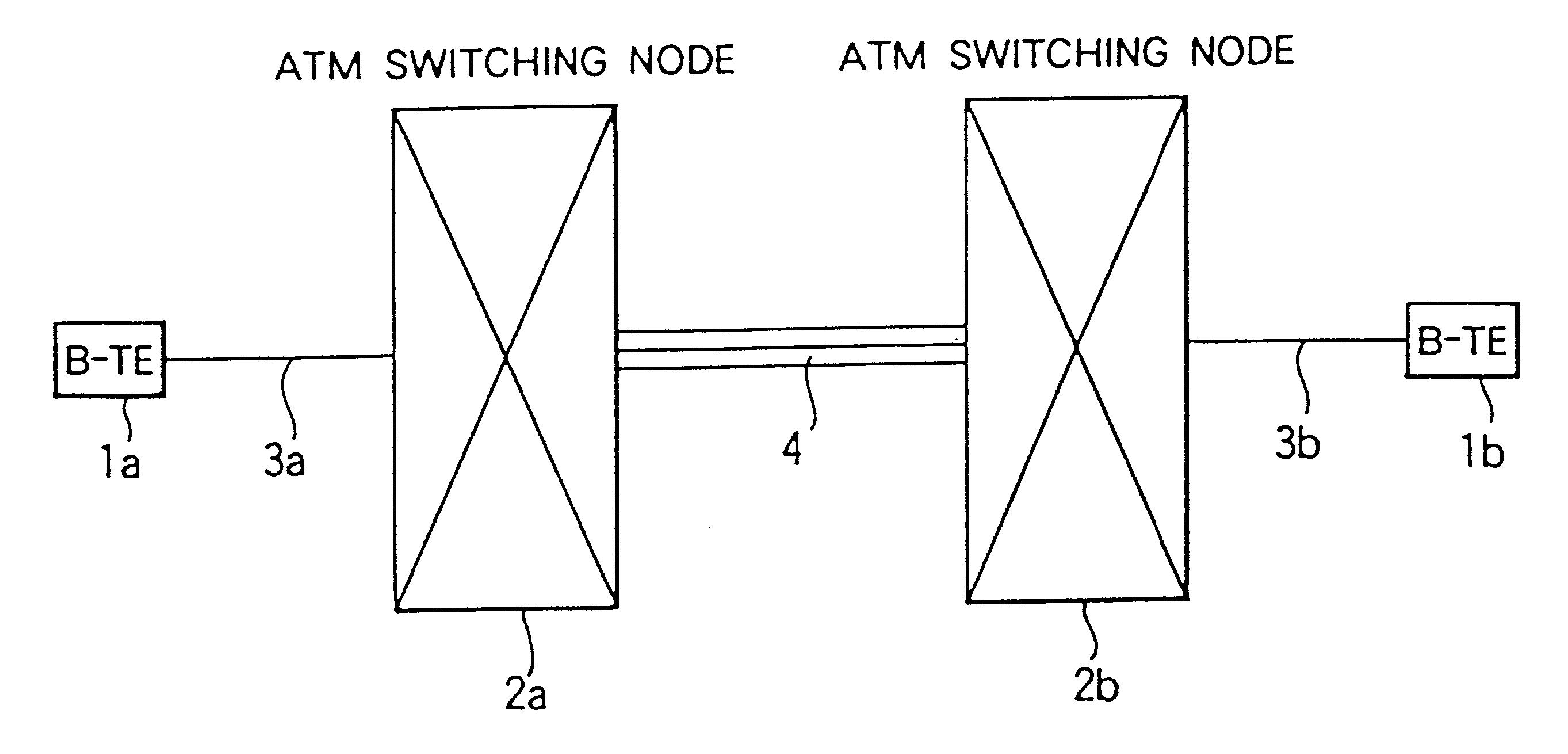
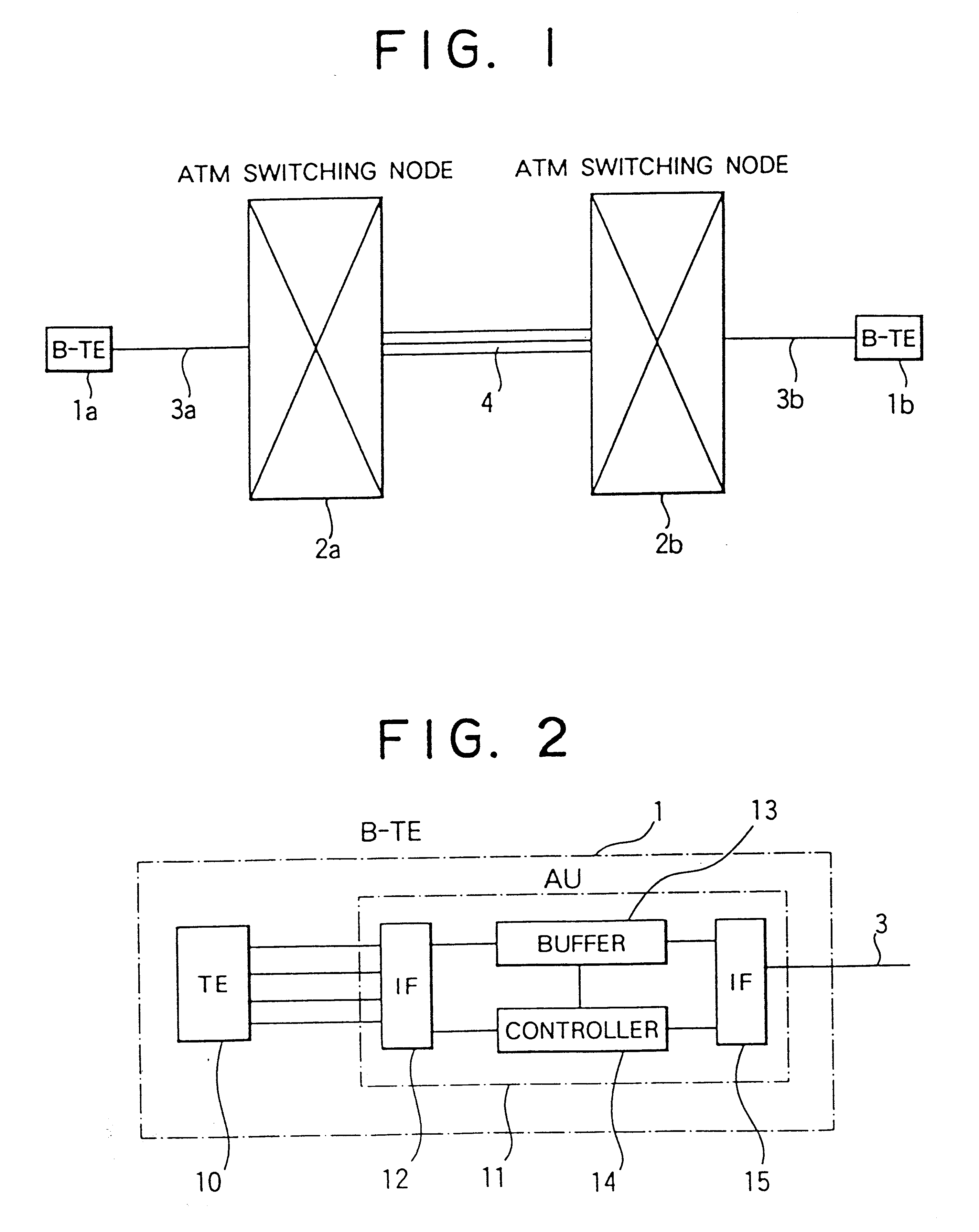
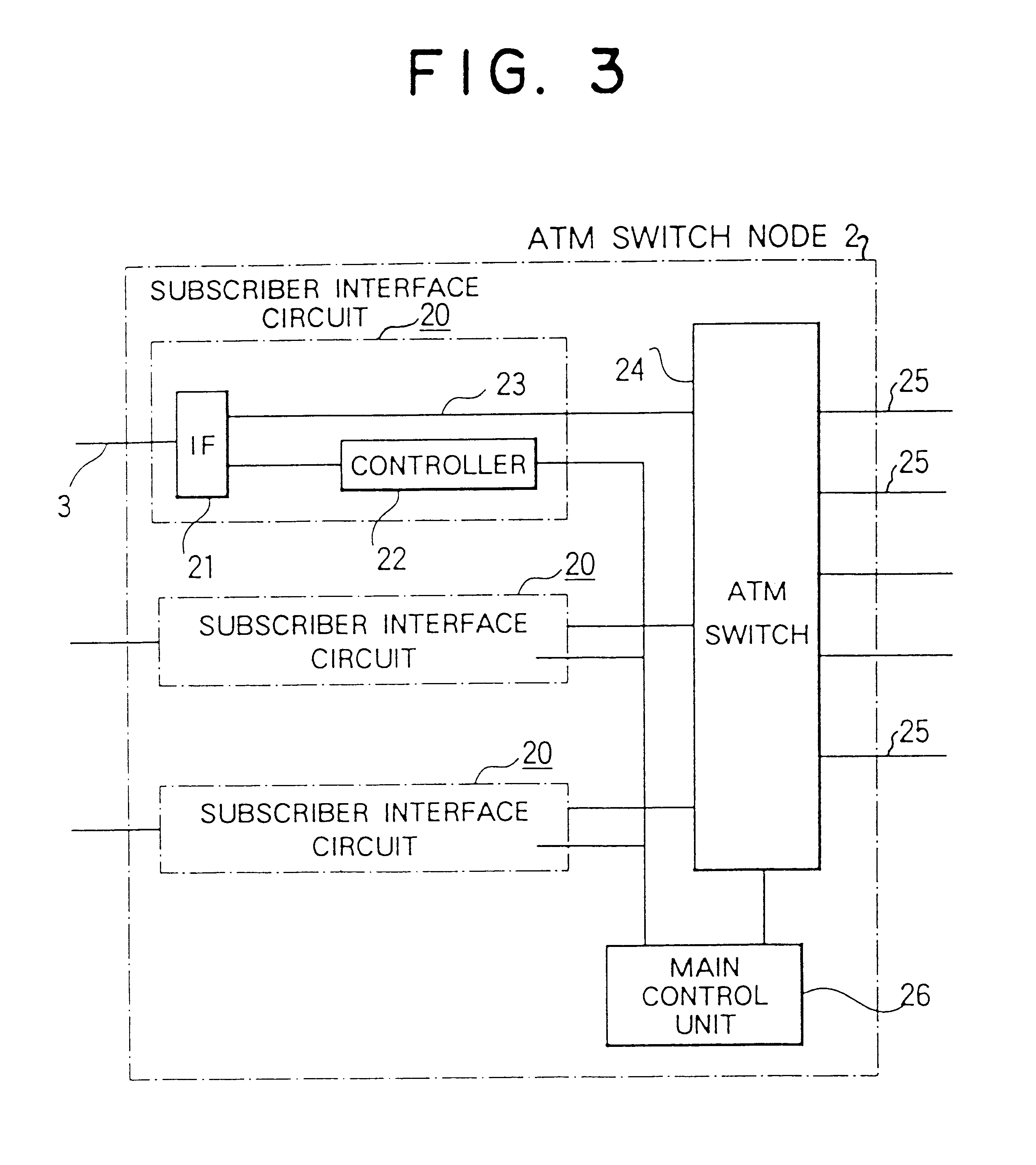
Broadband switching networks
InactiveUS6219349B1Avoid discardingEasy to controlData switching by path configurationTime-division multiplexing selectionBroadbandBit rate
Broadband switching networks are disclosed, which has a plurality of broadband switch nodes and a broadband switch inter-node transmission line for connecting the plurality of broadband switch nodes, information being transmitted by cells, each of which comprises a header and an information field, wherein the broadband switch node comprises a broadband input and output port for inputting and outputting the cells to and from the broadband inter-node transmission line, and a switch for separating the cells being input through the broadband input and output port and for multiplexing the cells so as to output them, wherein data composed of the plurality of cells is transmitted and received through the broadband switch node by constant bit rate transmission, variable bit rate transmission, or a combination of the constant bit rate transmission and the variable bit rate transmission.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Communication node and packet transfer method
InactiveUS20050147053A1Reliable transmissionStrong error correction abilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsReal-time computingPayload
A communication node which can reliably transfer a packet with a payload including data having error resistance in radio environments is disclosed. A packet to be transmitted is divided into segments to form a plurality of packet segments. From among a plurality of error correction schemes that have been prepared in advance, the scheme to be employed is selected for each of the packet segments in accordance with predetermined criteria, and the selected error correction scheme is applied to each packet segment. Subsequently, the processed packet segment is transmitted to the network. Packet segments are received from the network. From among a plurality of error correction schemes prepared in advance, the scheme to be employed is selected for each of the received packet segments based on predetermined information contained in each received packet segment, and the selected error correction scheme is applied to the received packet segment. An original packet is formed from the plurality of processed packet segments.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
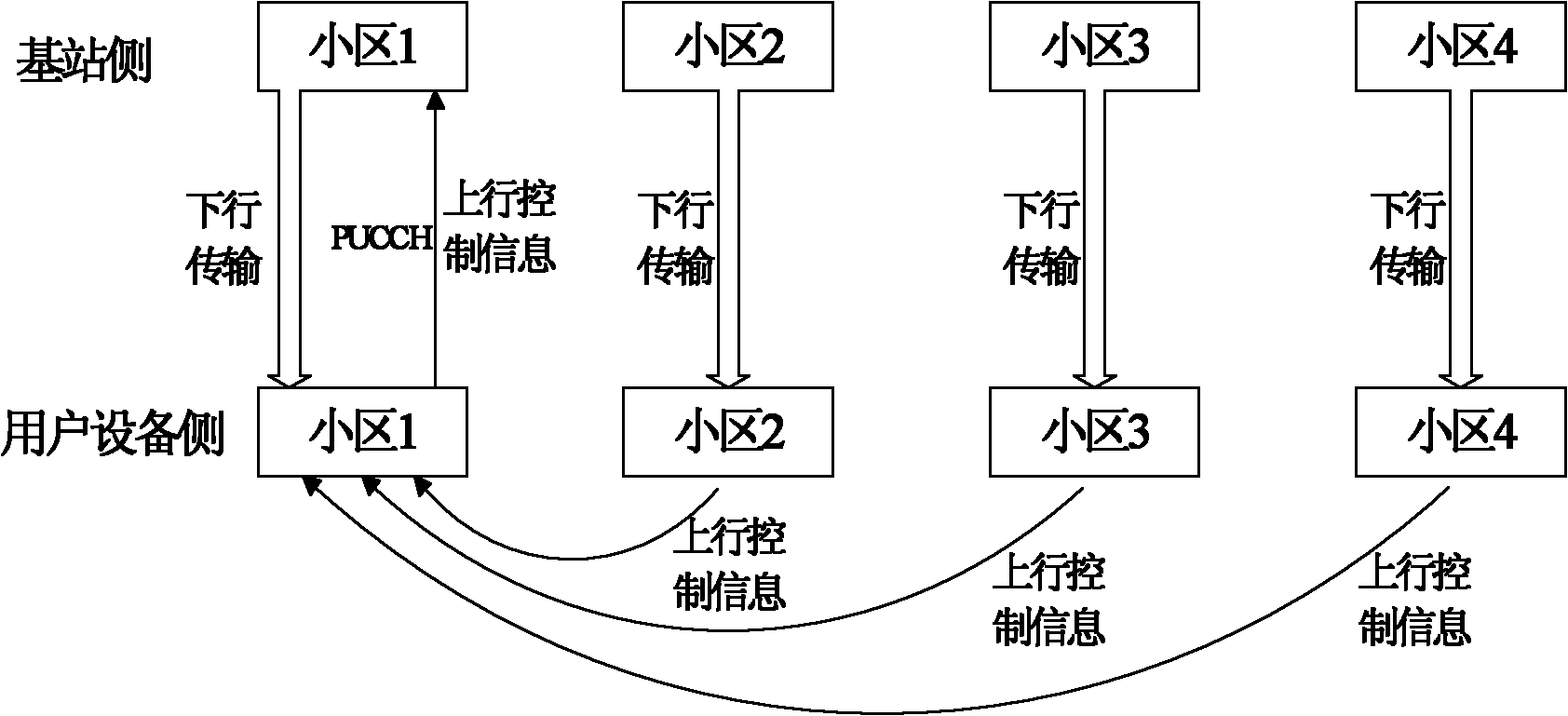
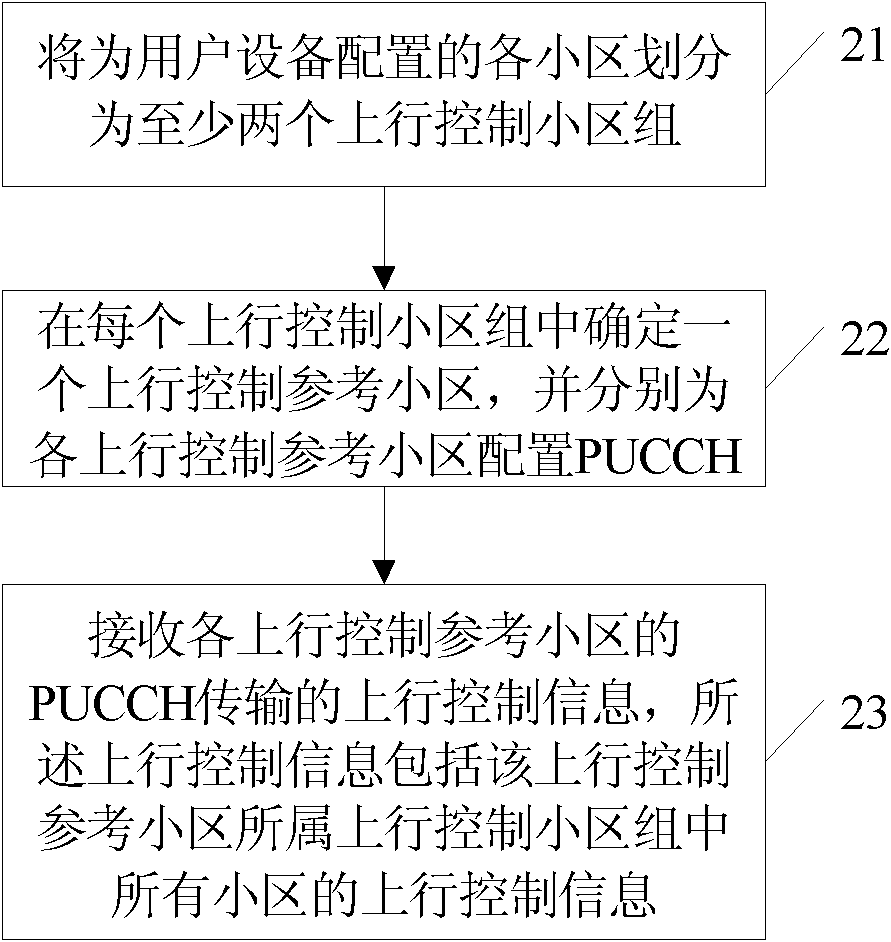
Transmission method and device for uplink control information in carrier aggregation system
The invention discloses a transmission method and device for uplink control information in a carrier aggregation system, relates to the technical field of wireless communication, can ensure that all cell uplink control information is transmitted to a base station in time, better meets the low time-delay characteristic of high speed data transmission, improves the data throughput of a system, and enhances the user experience. The embodiment of the invention provides the transmission method for the uplink control information in the carrier aggregation system, and the transmission method comprises the steps as follows: each cell equipped for UE is divided into at least two uplink control cell groups; one uplink control reference cell is determined in each uplink control cell group, and is equipped with a PUCCH (physical uplink control channel); the uplink control information transmitted by the PUCCH of each uplink control reference cell is received, and comprises the uplink control information of all of the cells in the uplink control cell group to which the uplink control reference cell belongs.
Owner:北京万海云科技有限公司
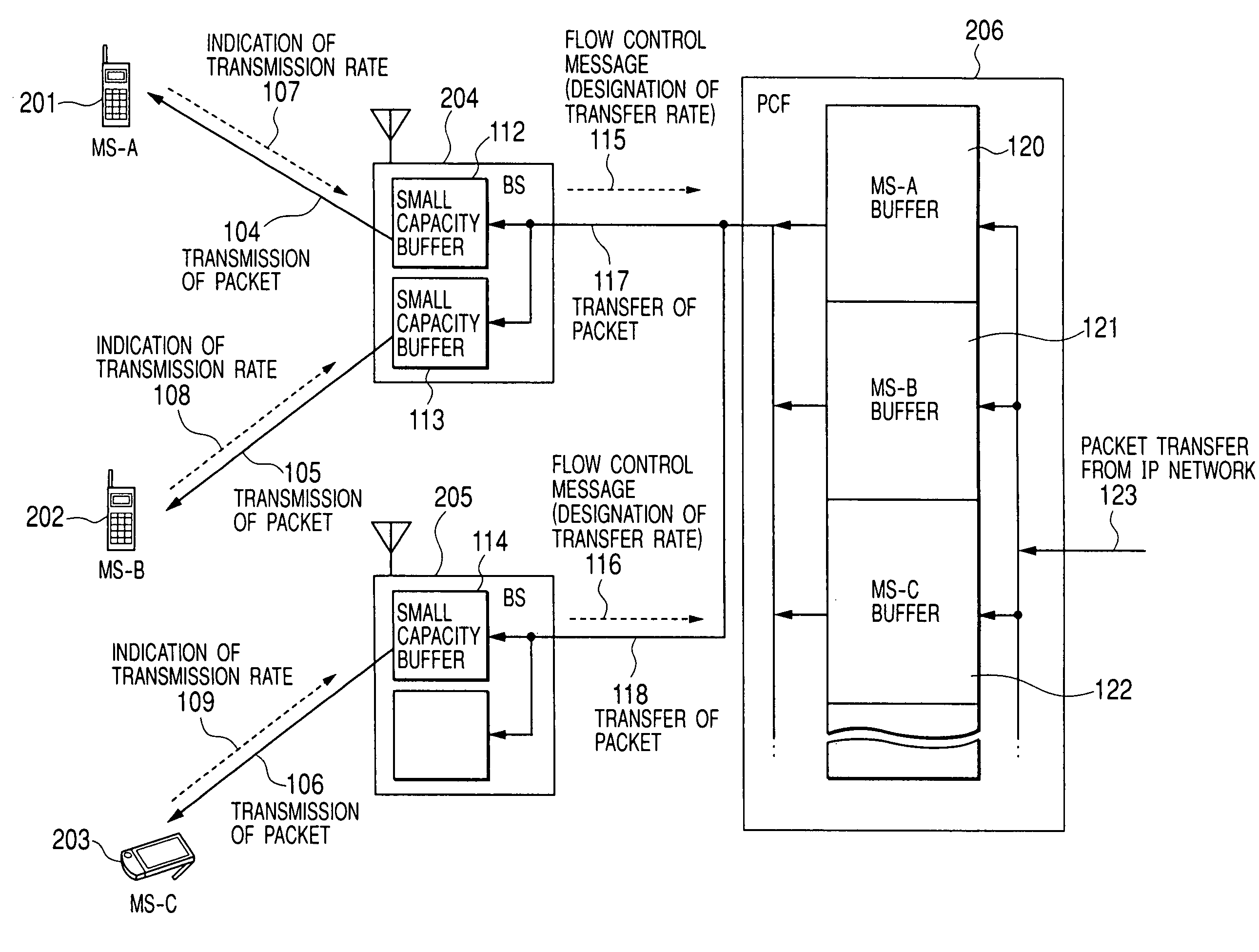
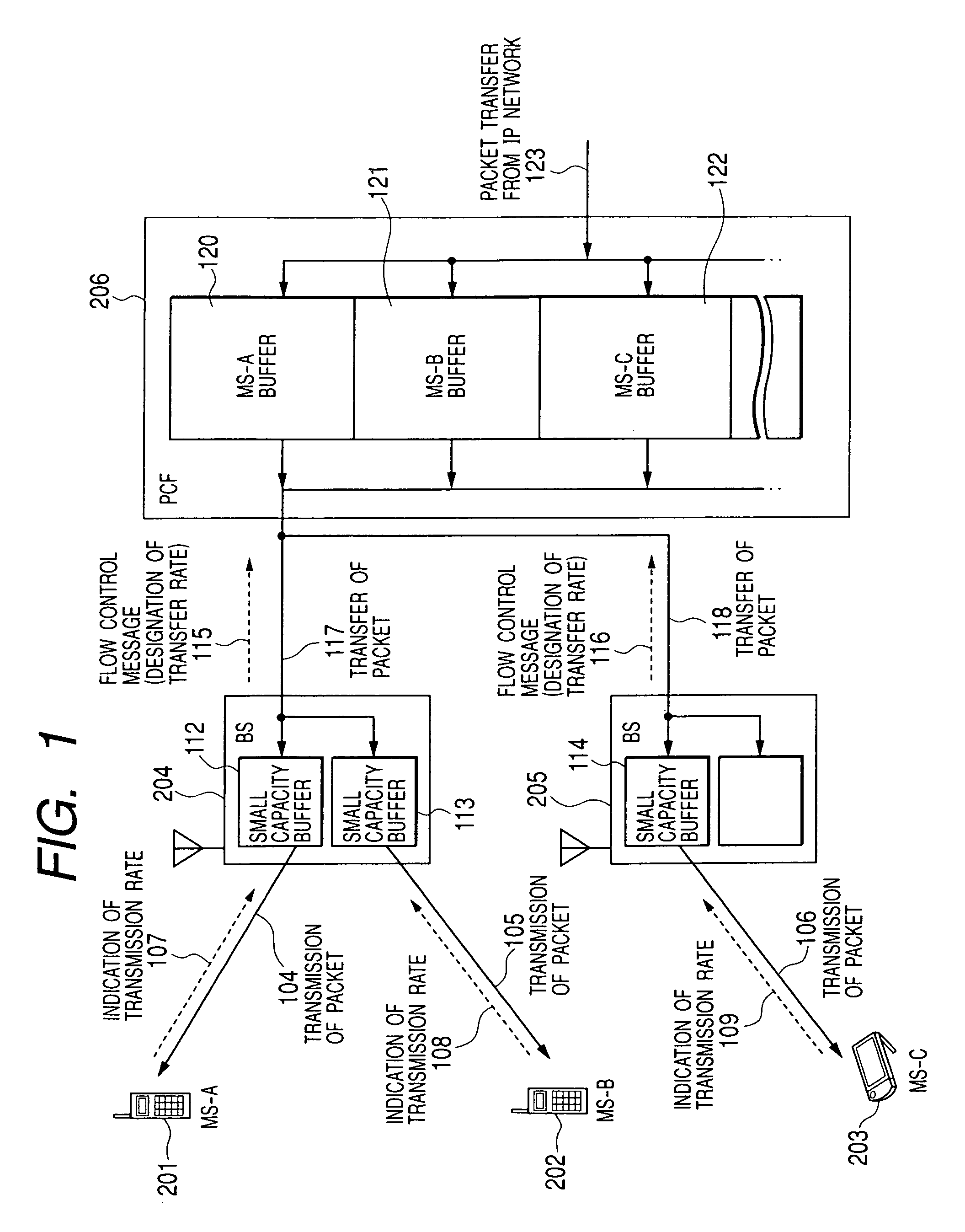
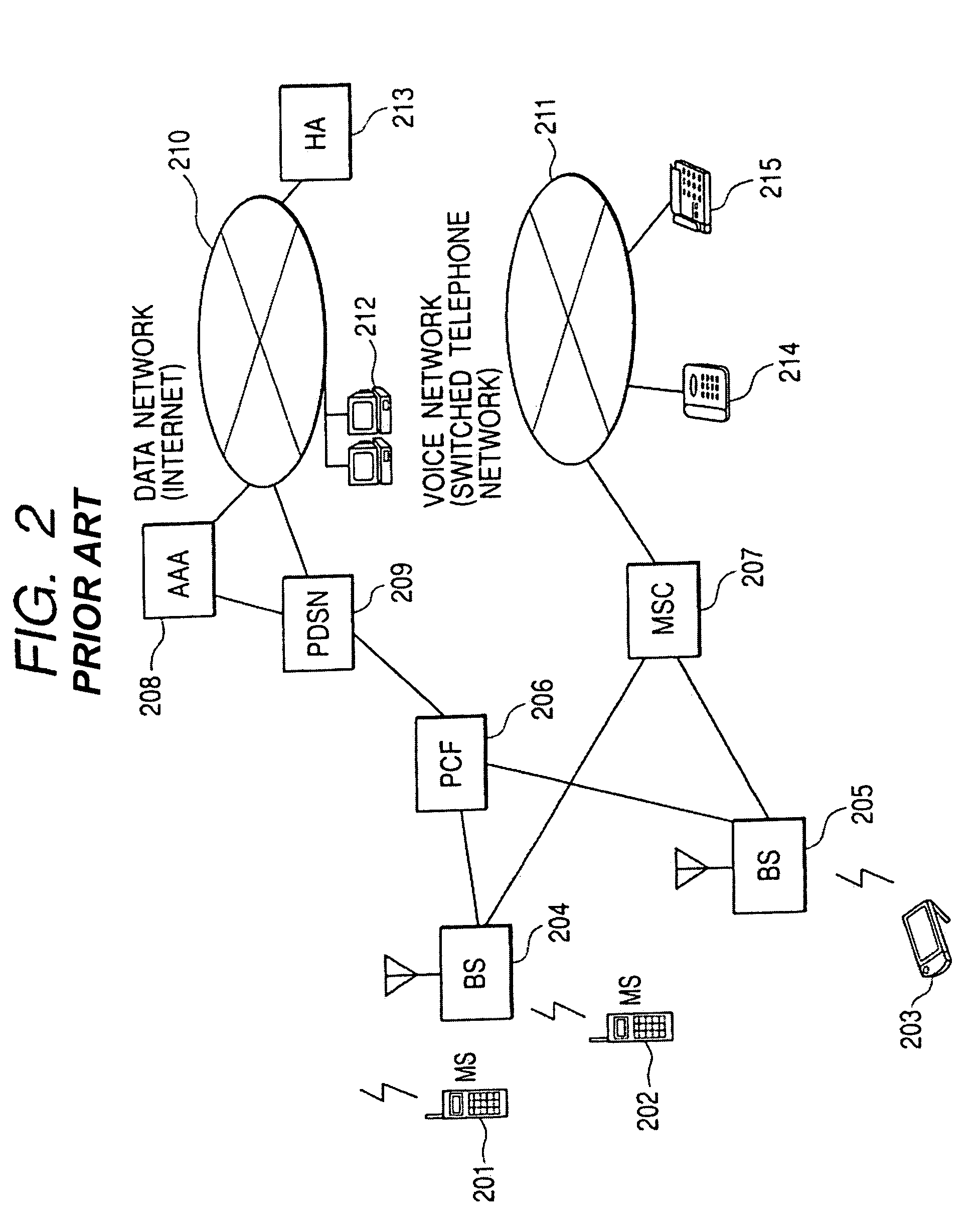
Wireless base station and packet transfer apparatus for dynamically controlling data transmission rate
InactiveUS7003302B2Maximally utilizedAvoid discardingFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching by path configurationControl dataRadio channel
In a mobile communication system in which a plurality of base stations are connected to a communication network via a packet transfer node and a transmission rate of a forward link radio channel between a base station and a mobile station dynamically changes, each of the base stations designates a packet transmission rate in accordance with the status of a radio channel of each of mobile stations under control for the packet transmission node, and the packet control node transfers packets destined for each of mobile stations to the base station at the designated transfer rate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Uplink control information transmission method and device
ActiveCN103384183AAvoid discardingImprove accuracyError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless communicationCarrier signalDownlink scheduling
The invention discloses an uplink control information transmission method and device. A UE side method comprises the steps that when UE is configured to use a PUCCH format 3 for transmitting ACK / NACK information and does not receive a PDCCH used for indicating a PUCCH format 3 channel resource corresponding to ACK / NACK, or when more than one carrier is configured on the UE and the UE is configured to use a PUCCH format 1b with channel selection for transmitting the ACK / NACK information, the UE generates the ACK / NACK information; period channel state information (CSI) is generated; the period CSI and the ACK / NACK information are transmitted on a channel resource corresponding to the period CSI through the same uplink subframe. The uplink control information transmission method and device prevent the period CSI from being discarded and improve the accuracy of downlink scheduling of a base station.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Reducing or eliminating routing microloops in networks having a clos topology, such as data center clos networks employing the exterior border gateway protocol (EBGP) for example
ActiveUS20190363975A1Avoid discardingAvoids otherwise droppingData switching networksBorder Gateway ProtocolEngineering
The problem of routing micro-loops in networks having a CLOS topology, such as data center CLOS networks employing the exterior border gateway protocol (eBGP) for example, is solved by: (a) receiving, on an interface of one of the nodes, a datagram, the datagram including destination information; (b) determining a next hop and an egress interface using (1) an identifier of the interface on which the datagram was received, (2) the destination information of the received datagram, and (3) stored forwarding information such that a routing micro-loop is avoided without discarding the datagram; and (c) forwarding the datagram via the egress interface. For example, this problem may be solved by (a) receiving, on an interface a node of the CLOS network, a datagram, the datagram including destination information; (b) looking up, using the destination information of the received datagram and stored forwarding information, a next hop egress interface on the node; (c) determining whether or not the next hop egress interface on the node is the same as the interface on which the datagram was received; and (d) responsive to a determination that the next hop egress interface on the node is the same as the interface on which the datagram was received, (1) replacing the next hop egress interface with a safe multipath next hop egress interface, and (2) forwarding the datagram via the safe multipath next hop egress interface, and otherwise, responsive to a determination that the next hop egress interface on the node is not the same at the interface on which the datagram was received, simply forwarding the datagram via the next hop egress interface.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method for preventing stack system from generating loop and member equipment in stack system
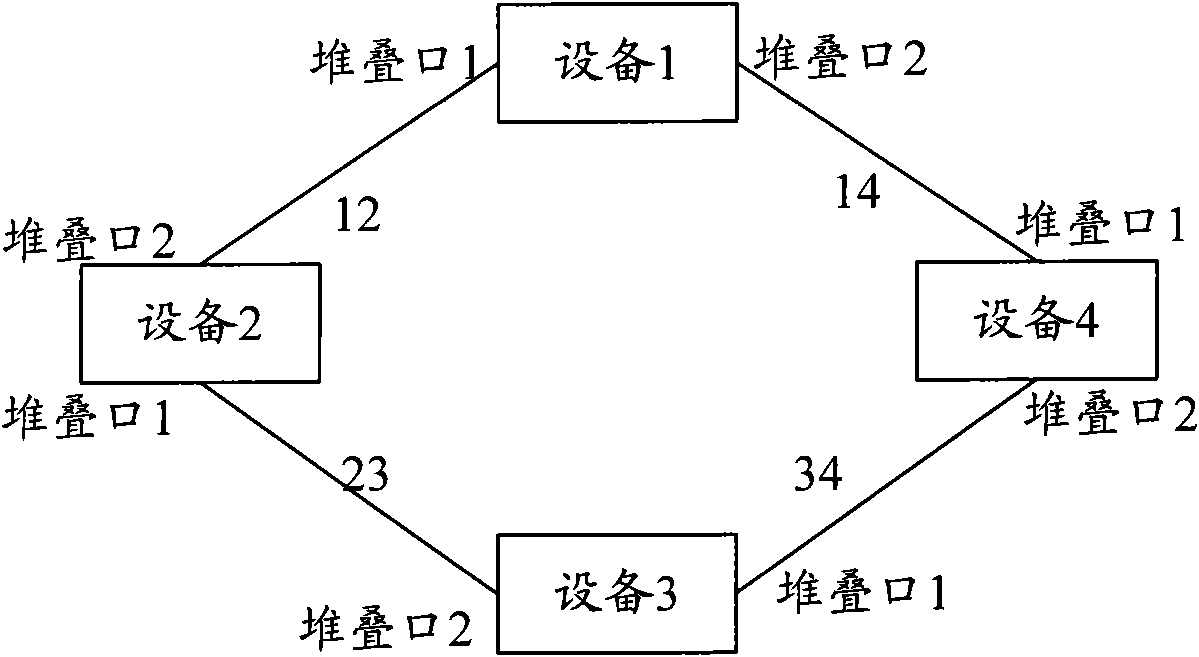
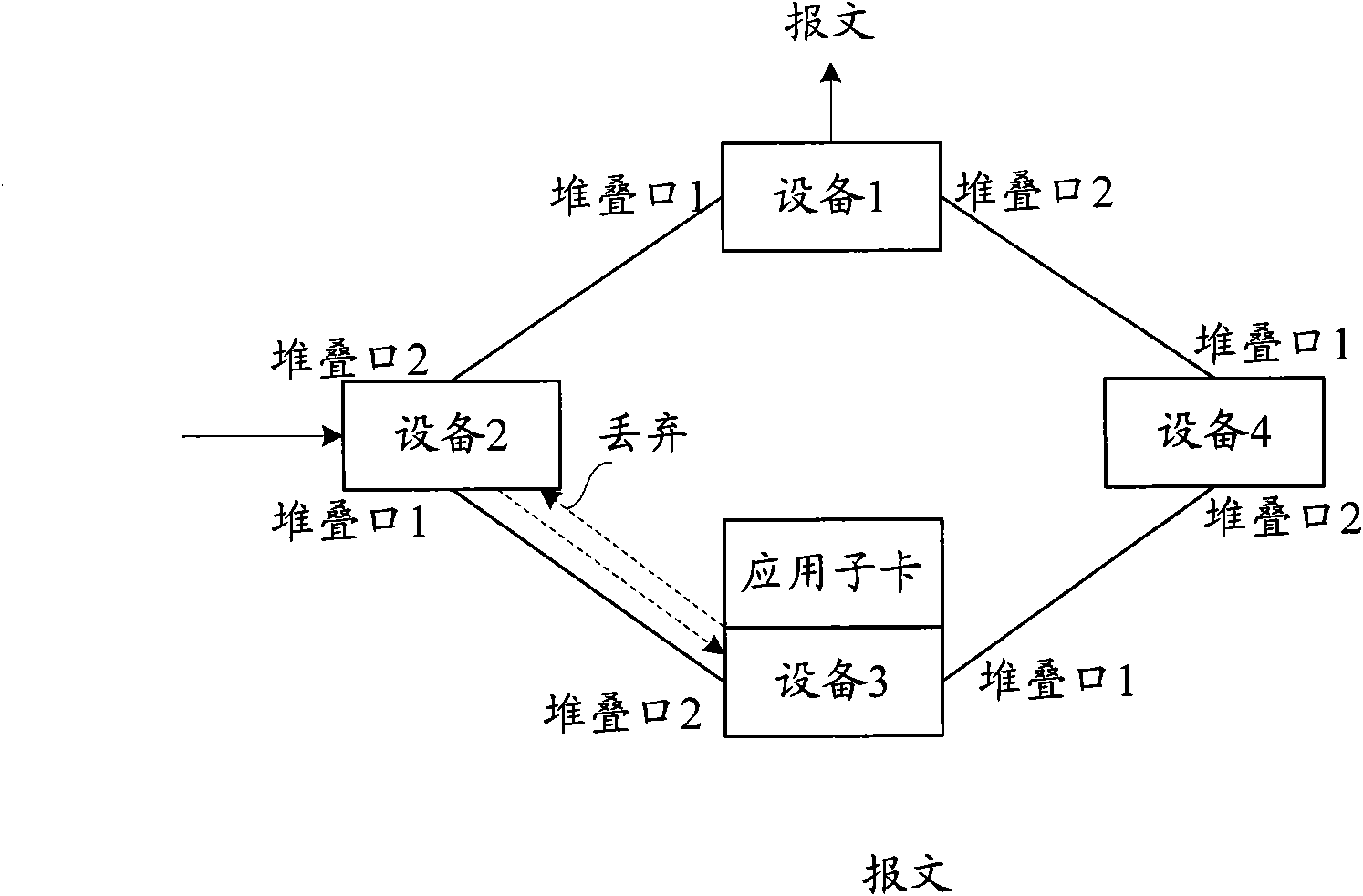
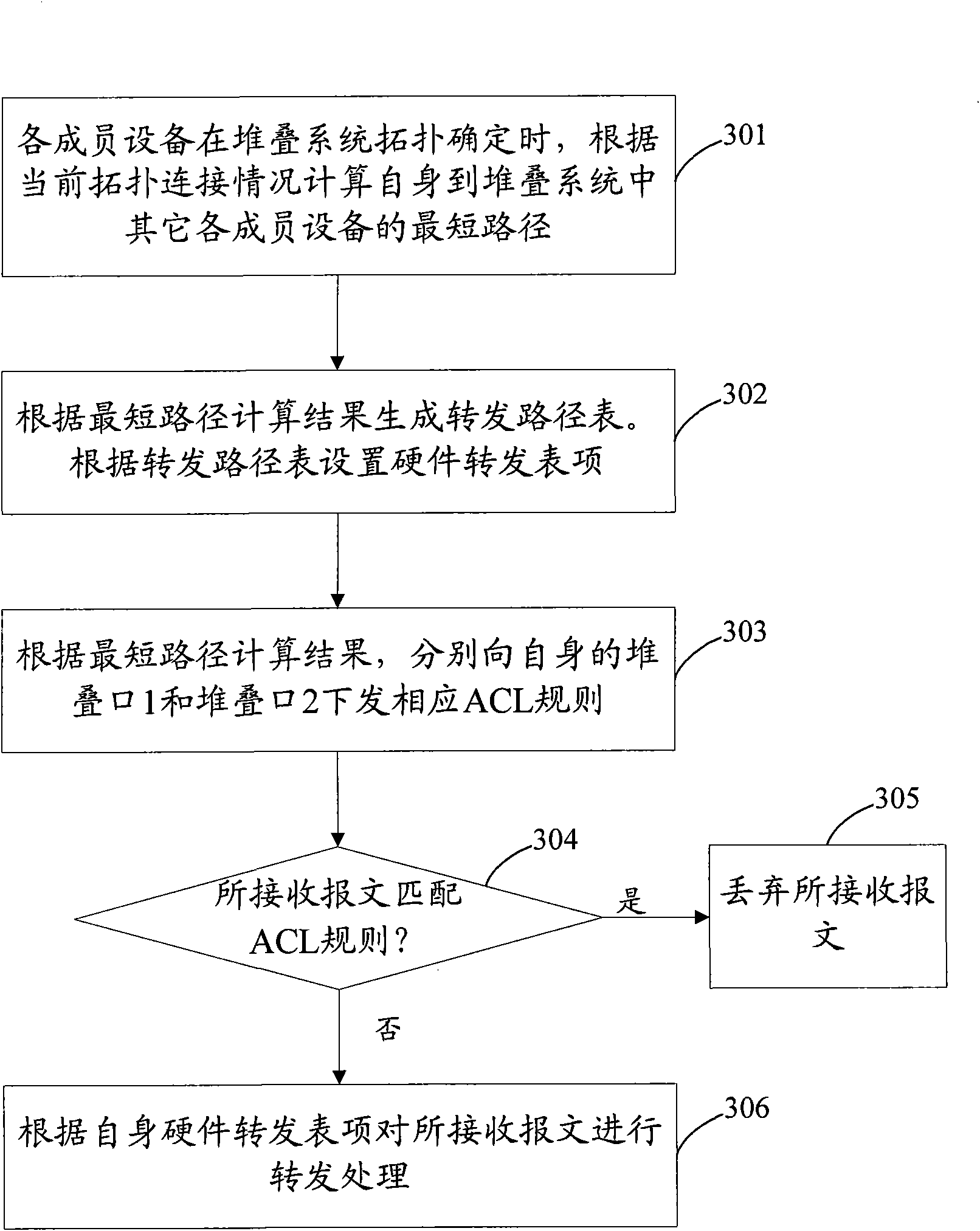
ActiveCN101594304AAvoid discardingWill not affect the inspection effectData switching networksEmbedded system
The invention discloses a method for preventing the stack system from generating a loop and member equipment in the stack system. The method comprises the following steps that: the member equipment in the stack system receives a message from a stack port and judges whether the received message is a known unicast message; if the received message is a known unicast message, the member equipment in the stack system forwards the message; and otherwise, the member equipment in the stack system detects the loop in the received message and discards the received message if loop generation is detected or forwards the received message if loop generation is not detected. The method can prevent a reoriented message from being discarded by mistake when the reoriented message receives the loop detection and avoid influences on the effect of loop detection.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Decoupling storage controller cache read replacement from write retirement
InactiveCN1967507AAvoid discardingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLeast recently frequently usedData store
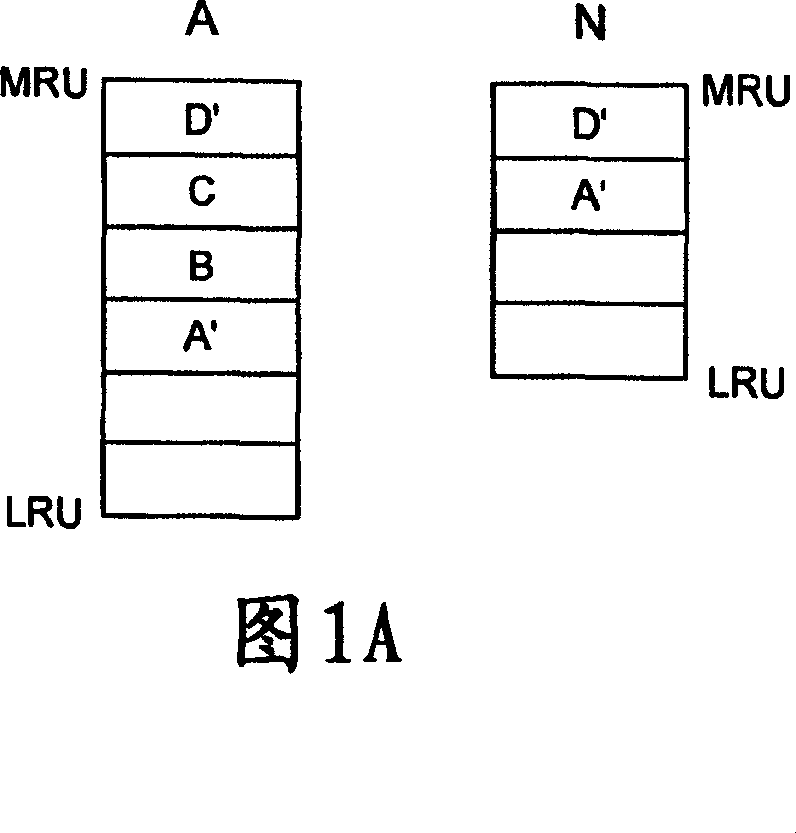
In a data storage controller, accessed tracks are temporarily stored in a cache, with write data being stored in a first cache and a second cache and read data being stored in a second cache . Corresponding least recently used (LRU) lists are maintained to hold entries identifying the tracks stored in the caches. When the list holding entries for the first cache (the A list) is full, the list is scanned to identify unmodified (read) data which can be discarded from the cache to make room for new data. Prior to or during the scan, modified (write) data entries are moved to the most recently used (MRU) end of the list, allowing the scans to proceed in an efficient manner and reducing the number of times the scan has to skip over modified entries. Optionally, a status bit may be associated with each modified data entry. When the modified entry is moved to the MRU end of the A list without being requested to be read, its status bit is changed from an initial state to a second state, indicating that it is a candidate to be discarded. If the status bit is already set to the second state, then it is left unchanged. If a modified track is moved to the MRU end of the A list as a result of being requested to be read, the status bit of the corresponding A list entry is changed back to the first state, preventing the track from being discarded. Thus, write tracks are allowed to remain in the first cache only as long as necessary.
Owner:IBM CORP
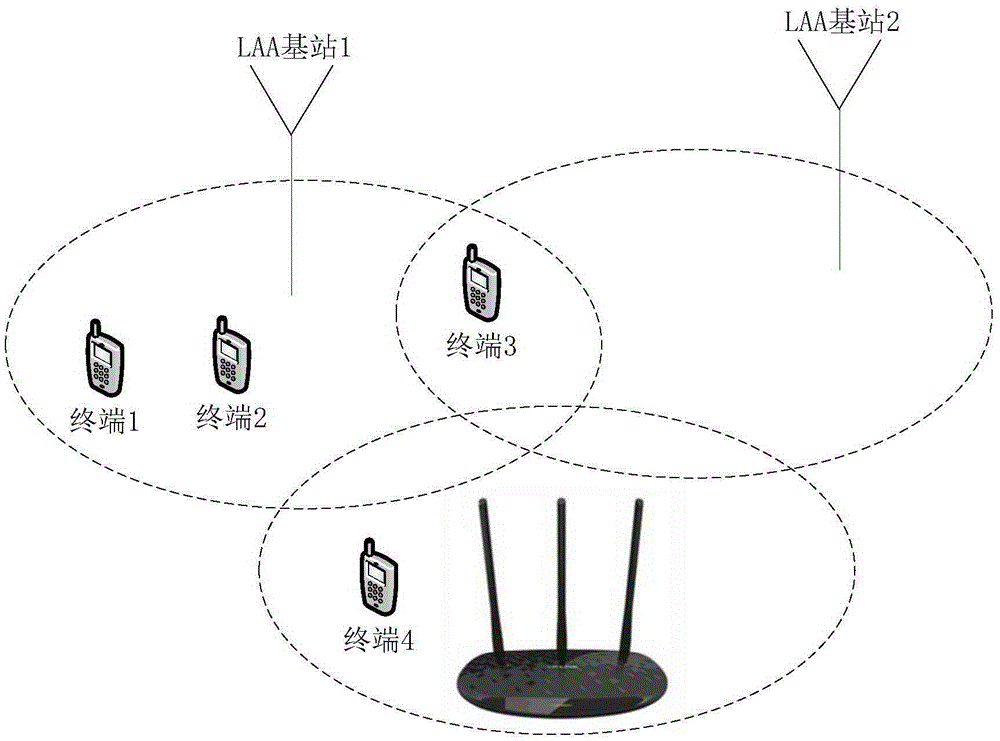
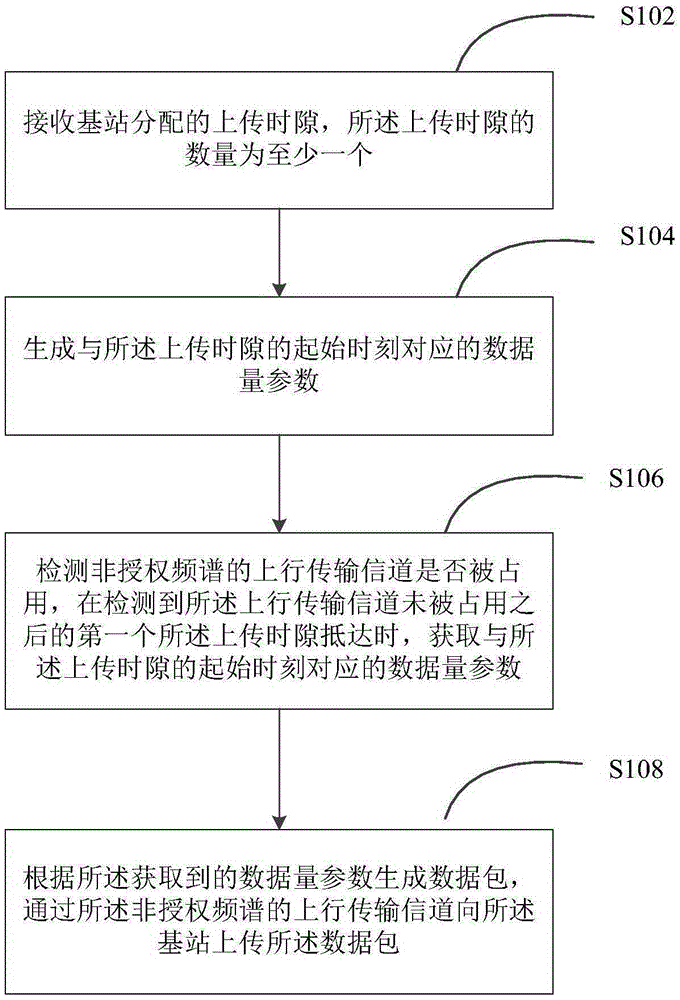
Data transmission method and device based on LAA (Licensed-Assisted Access) system
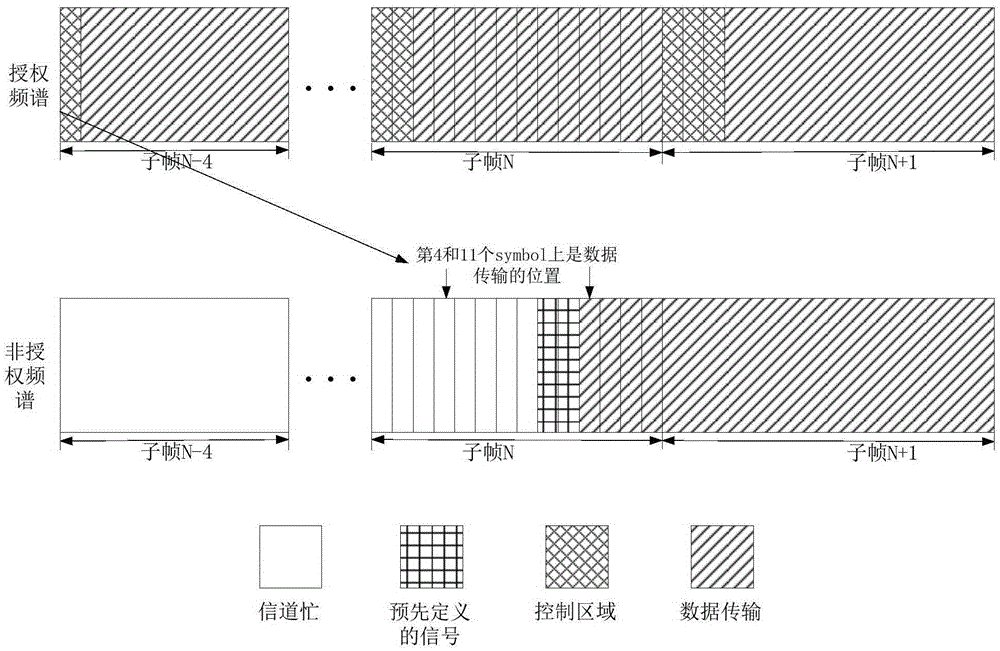
ActiveCN105307180AAvoid discardingIncrease profitNetwork planningFrequency spectrumResource utilization
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission method based on an LAA (Licensed-Assisted Access) system. The method comprises the following steps: receiving an upload time slot allocated by a base station, wherein at least one upload time slot is allocated; generating a data volume parameter corresponding to a starting moment of the upload time slot; detecting whether an uplink transmission channel of an unauthorized frequency spectrum is occupied or not, and acquiring the data volume parameter corresponding to the starting moment of the upload time slot at the arrival of a first upload time slot after the upload transmission channel is detected to be not occupied; and generating data packets according to the acquired data volume parameter, and uploading the data packets to the base station through the uplink transmission channel of the unauthorized frequency spectrum. The invention also discloses a data transmission device based on the LAA system. Through adoption of the data transmission method and device based on the LAA system, the resource utilization ratio of channel resources can be increased.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Mechanism for Controlling Data Transmission in Fragmentation Transmission Mode
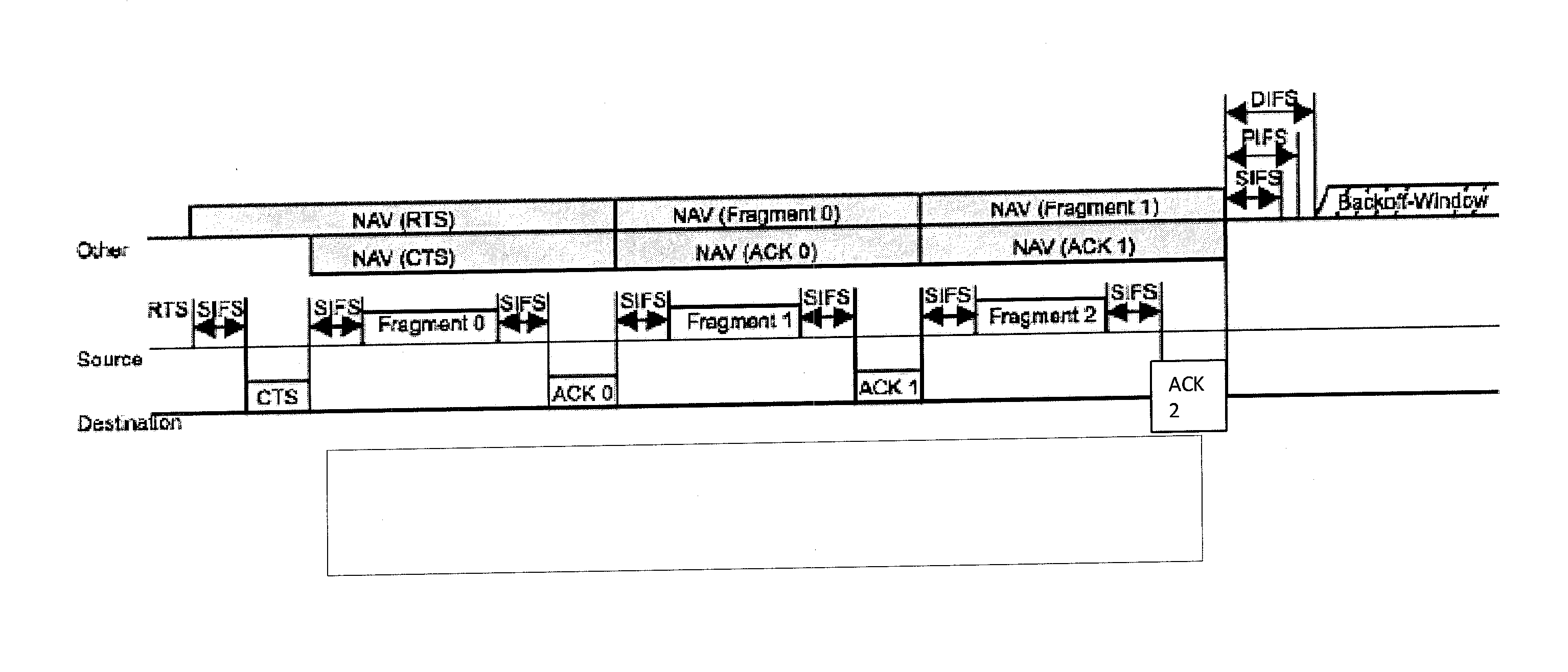
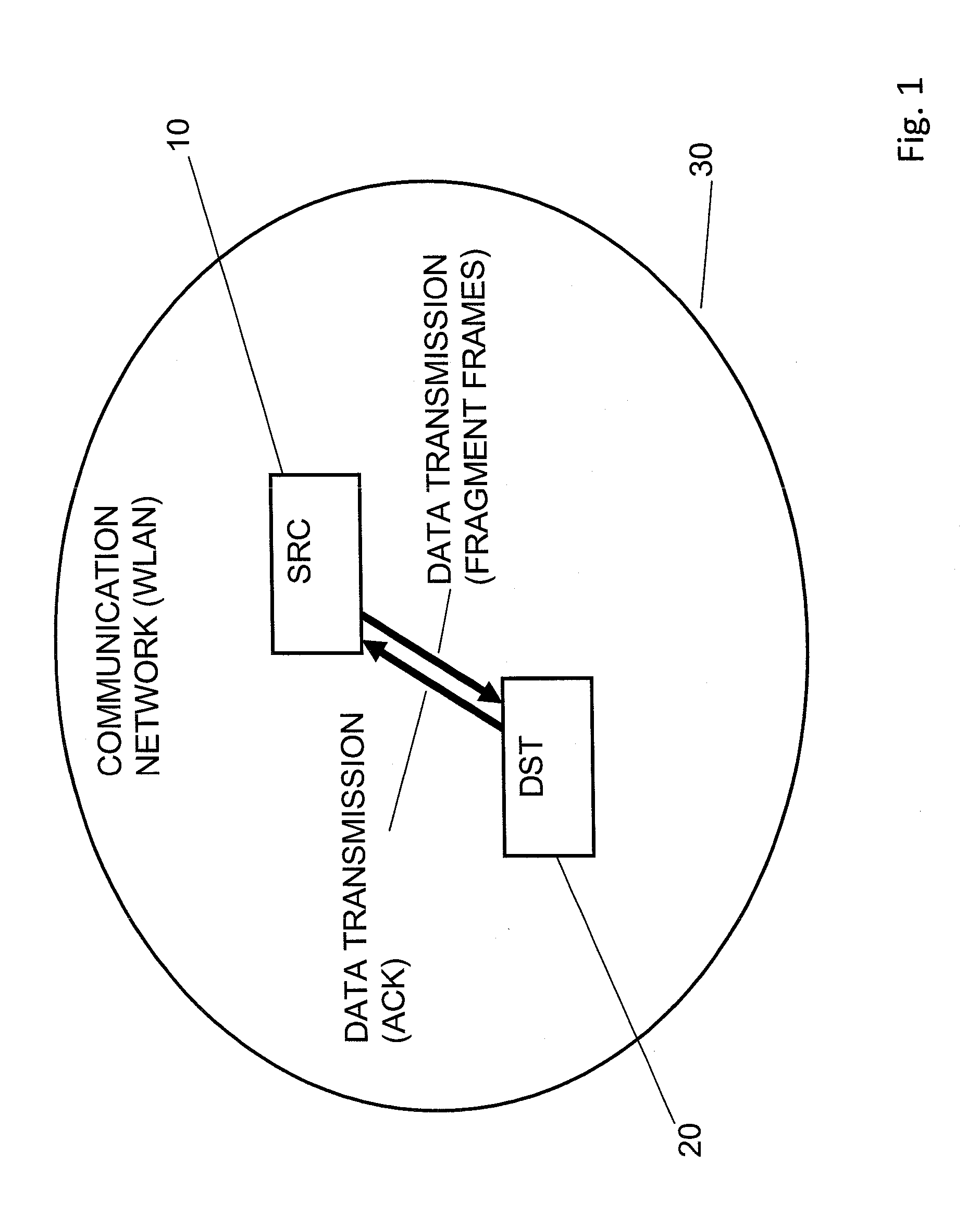
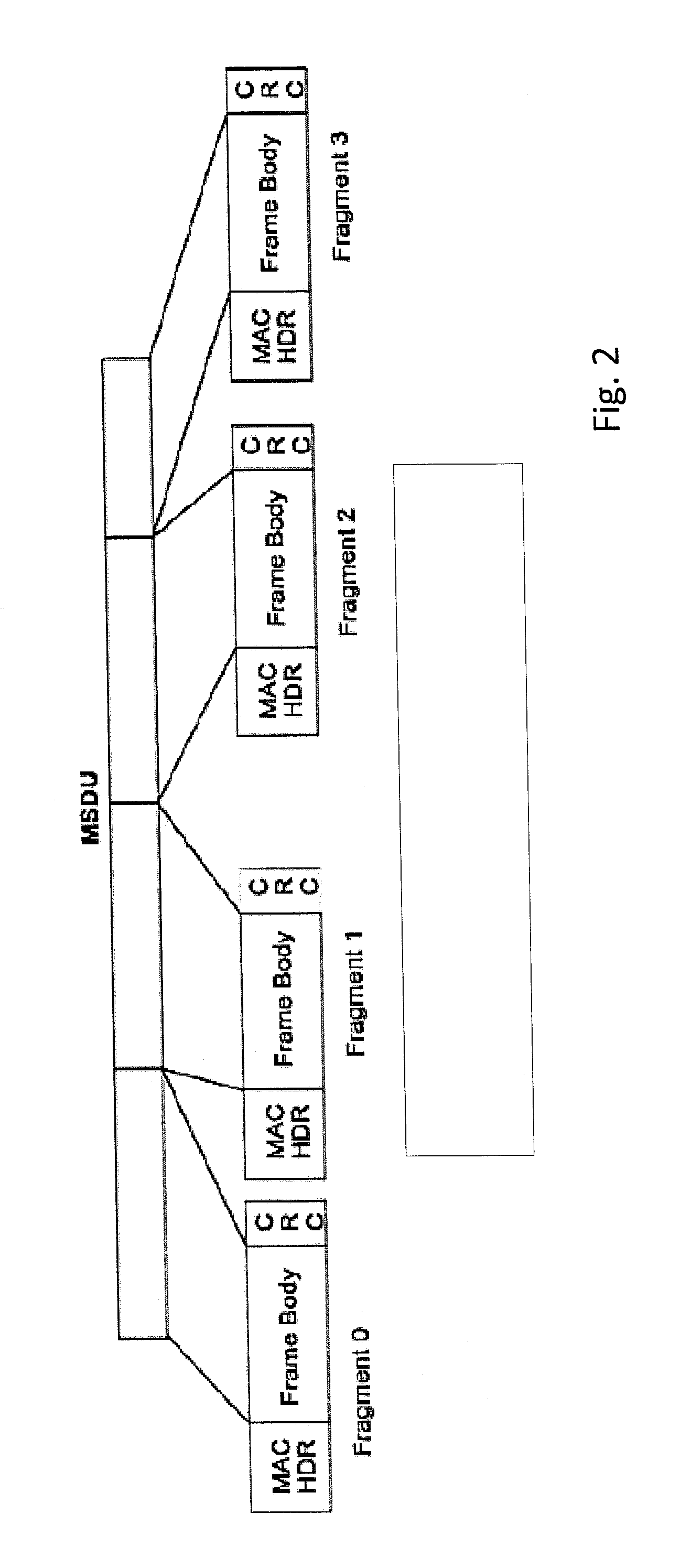
InactiveUS20130148640A1Communication performanceOptimization mechanismError preventionNetwork topologiesSuccessful transmissionControl data
There is provided a mechanism for controlling a transmission of data in a fragmentation transmission mode. When fragments are transmitted in a fragmentation transmission mode, it is determined whether the fragment frame is received successfully or whether an acknowledgment message for confirming a successful transmission of the fragment frame is received. In case the acknowledgment for the successful transmission of the one fragment frame is not received, or the fragment is frame is not successfully received, the fragmentation transmission mode is maintained and a retransmission of the fragment frame is initiated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
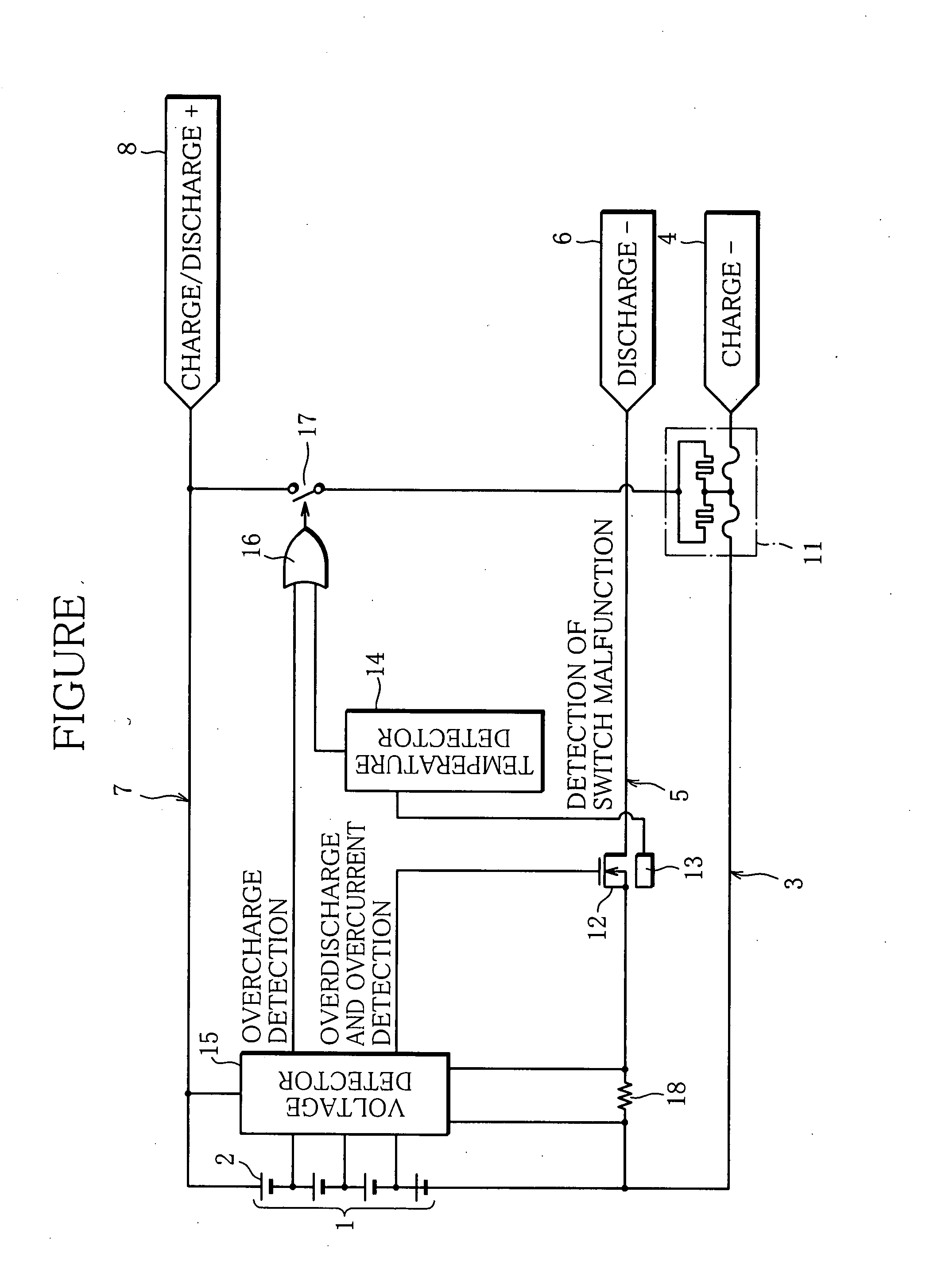
Rechargeable battery device
InactiveUS20070216351A1Not wastefully useDeterioration of characteristicBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingCharge and dischargeElectricity
Charging and discharging lines for a rechargeable battery are arranged independently from each other, and as a protection circuit for the rechargeable battery, there are provided a nonreturn-type switch (for example, thermo-fuse with an internal heater) that is interposed in the charging line in series and interrupts the charging line by blowout and a semiconductor switch (for example, MOS-FET) that is interposed in the discharging line in series and electrically continues or interrupts the discharging line. The switch control circuit turns off the semiconductor switch element when detecting overdischarge of the rechargeable battery, and blows out the nonreturn-type switch when detecting overcharge of the rechargeable battery or a malfunction of the semiconductor switch element.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
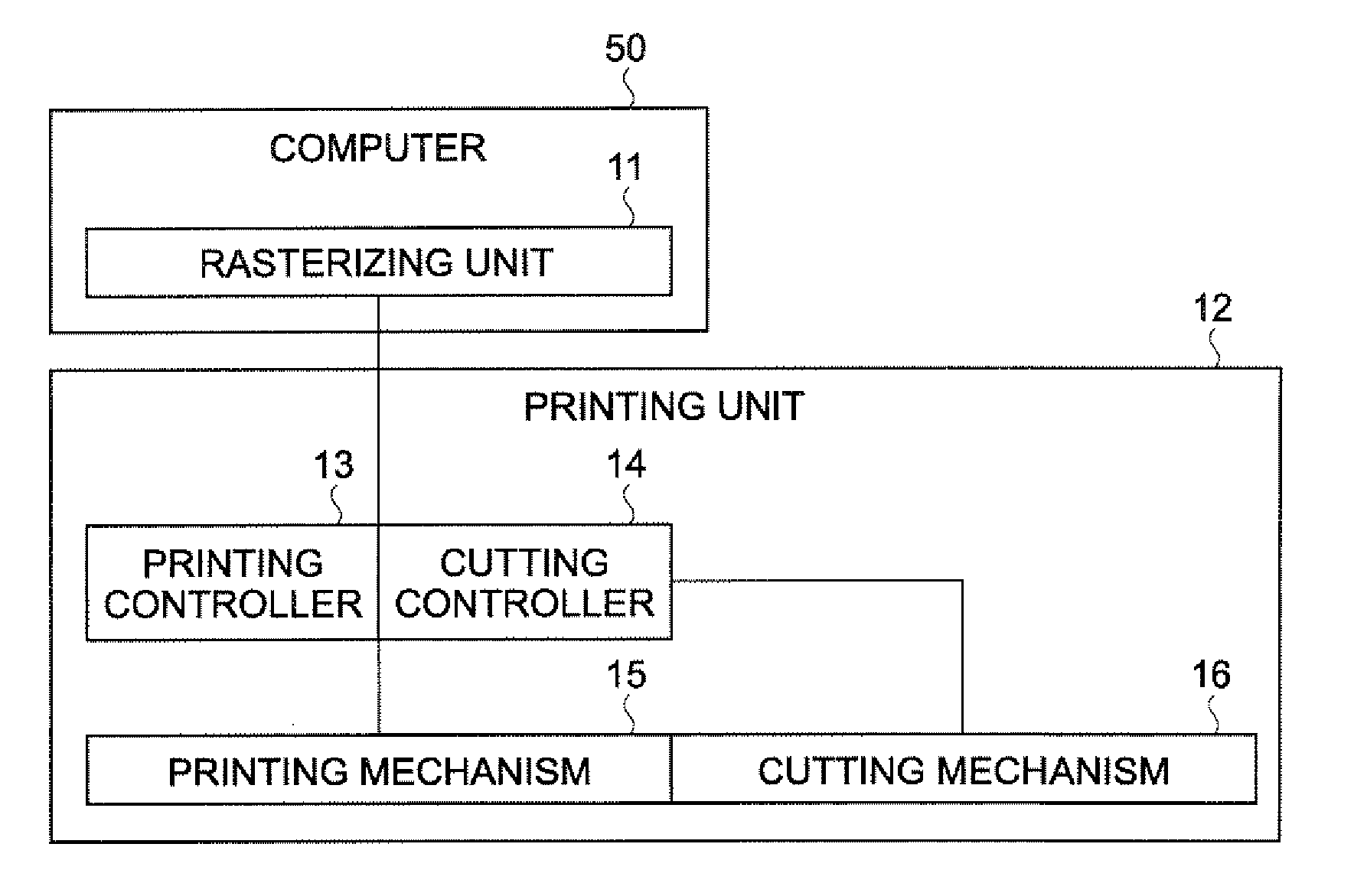
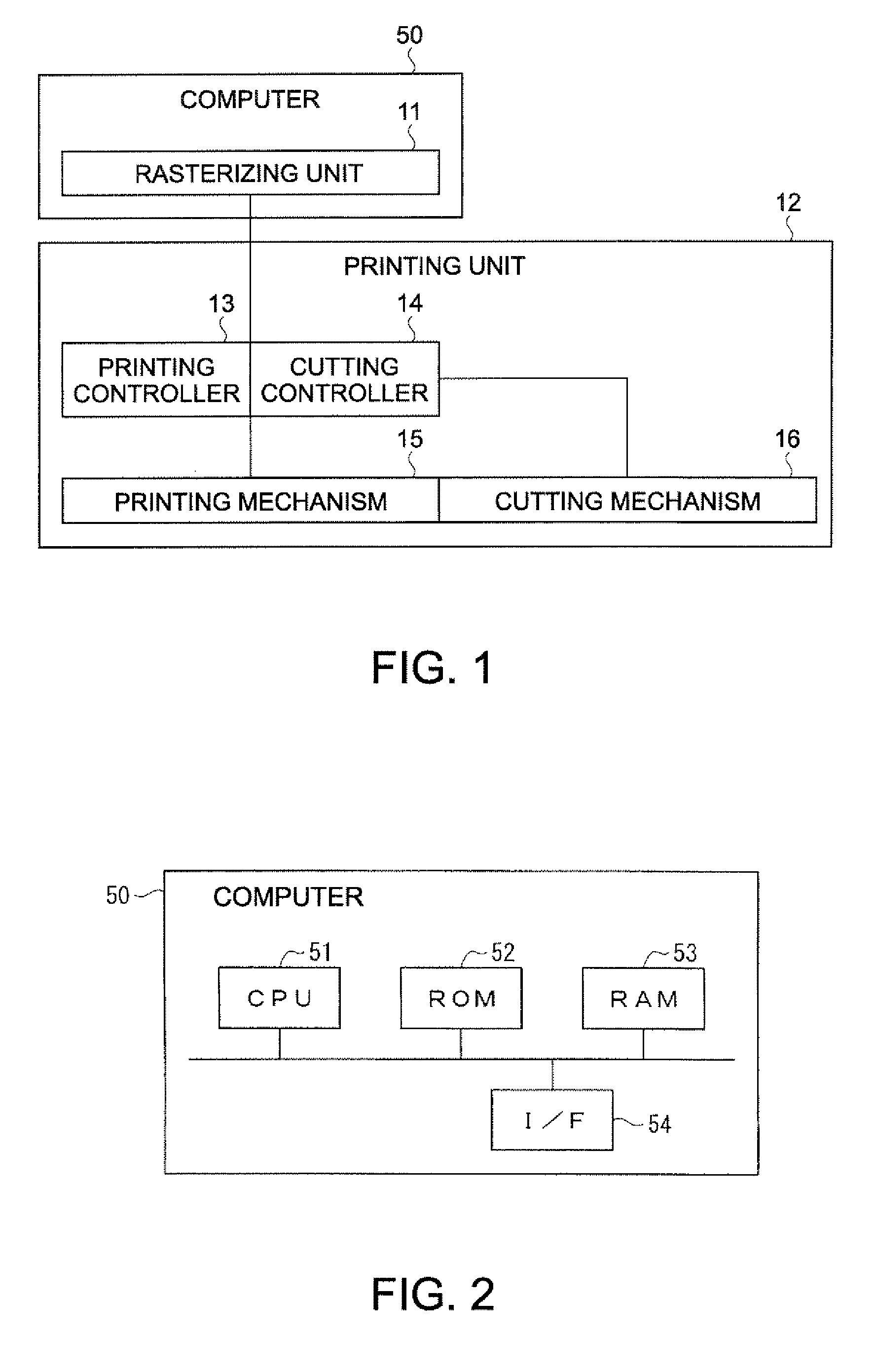
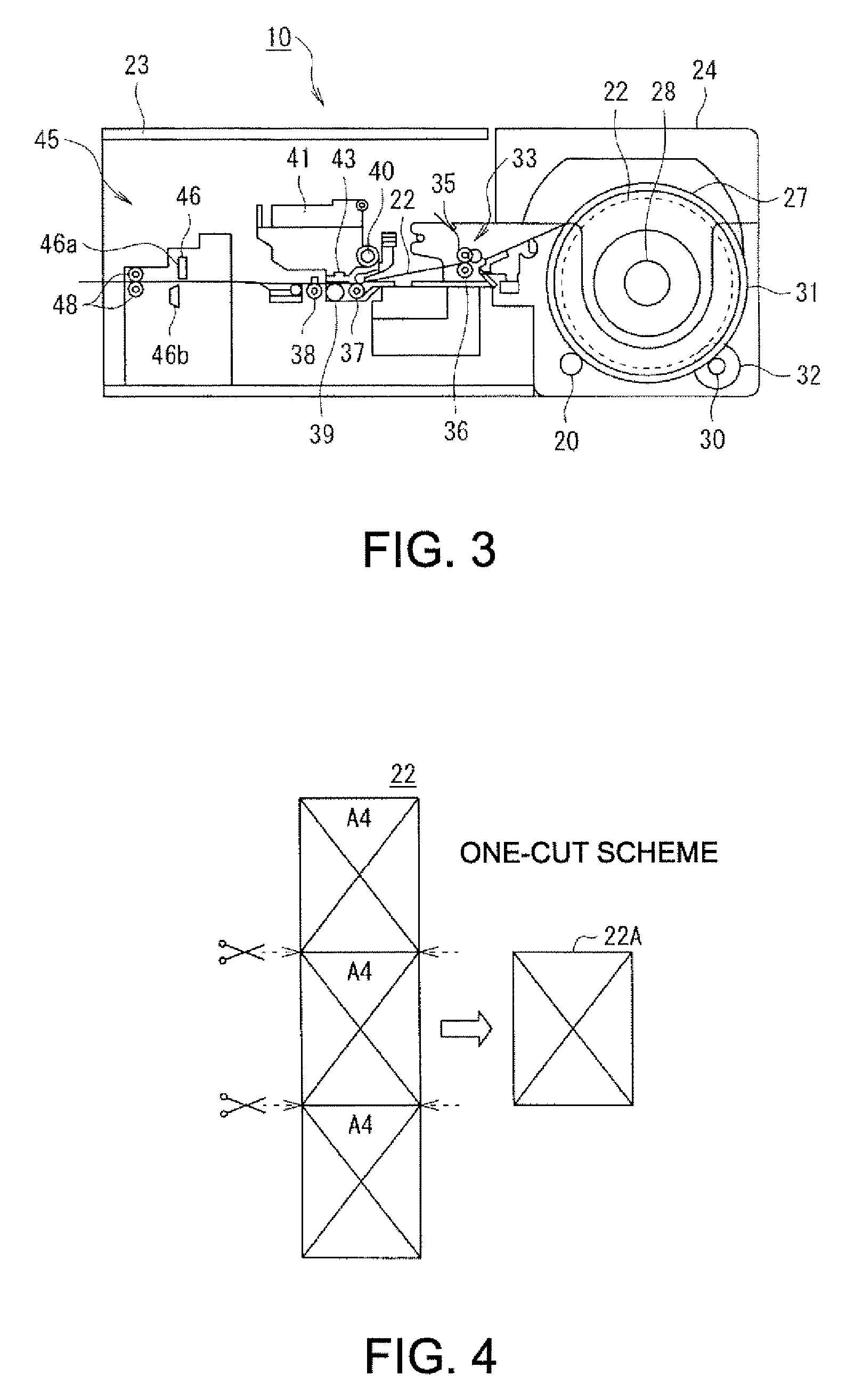
Printing system, printing apparatus, printing data generating apparatus and program, cutting indicating data generating apparatus and program, printing program, and printing method
InactiveUS20070013959A1Avoid paper wasteAvoid discardingVisual presentation using printersOther printing apparatusImaging dataComputer engineering
A system includes: a unit printing on a medium; a unit cutting the medium; a unit comparing data of two adjacent images on the medium; a unit selecting, based on the comparison, a first process adjacently printing the two images or a second process printing the two images with a cutting region therebetween; and a unit generating, for each cutting position, cutting indicating data indicating a cutting process of the cutting unit by corresponding a first cutting process to a cutting position corresponding to the first printing process and corresponding a second cutting process to a cutting position corresponding to the second printing process; and a unit generating printing data based on image data and the selection, wherein the printing unit selects the first or second printing process and prints, and the cutting unit selects the first or second cutting process and cuts.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Scheduling apparatus and method for real-time service
InactiveCN101340390AGuaranteed Latency RequirementsAvoid discardingData switching networksTime delaysReal time services
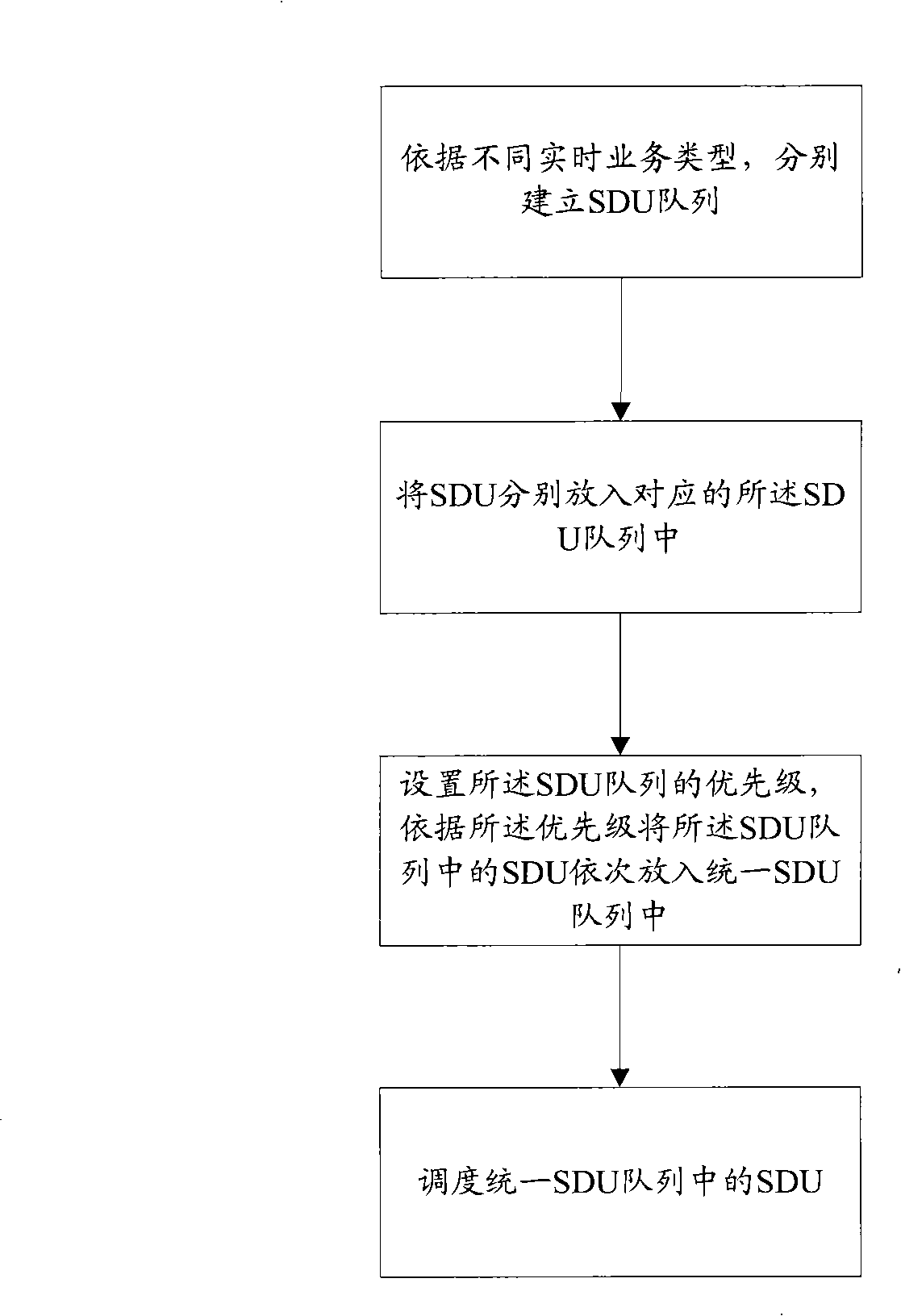
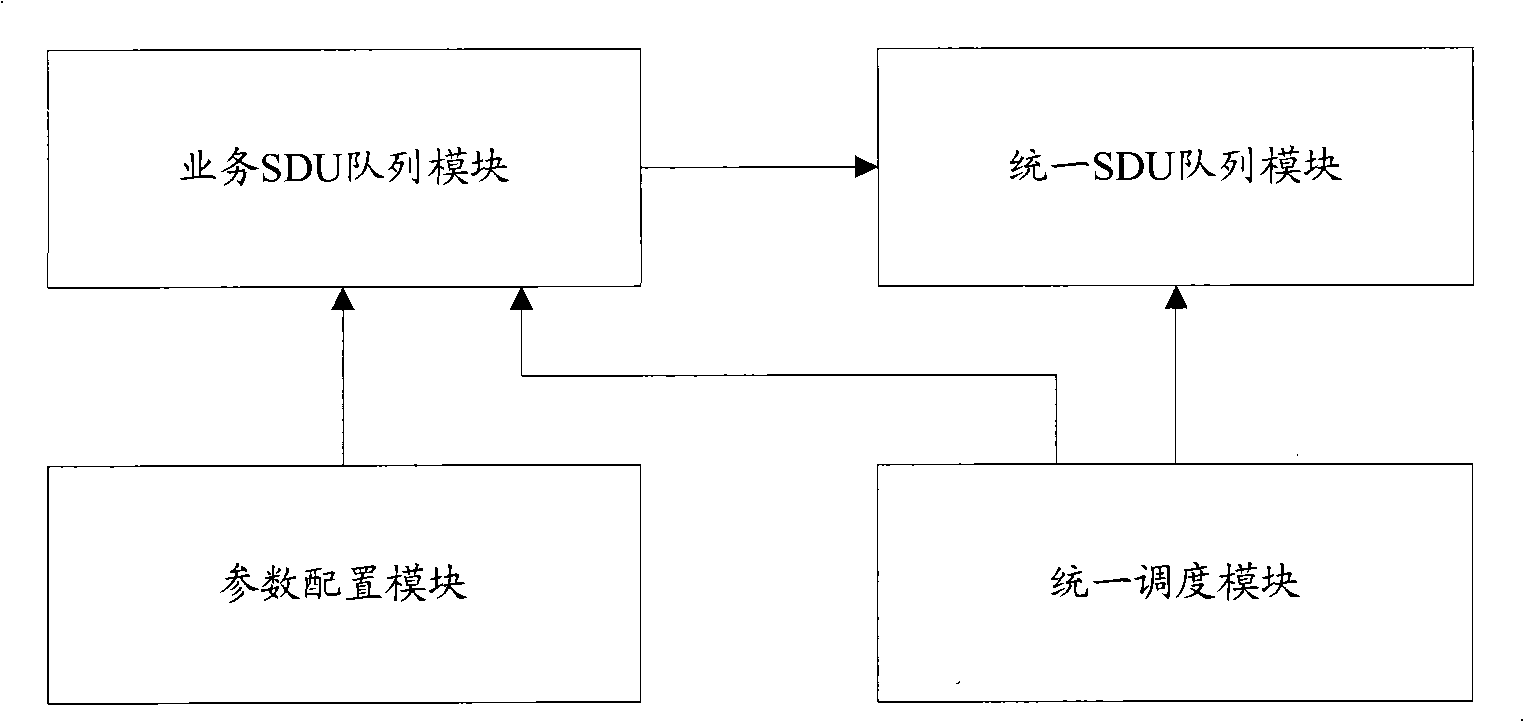
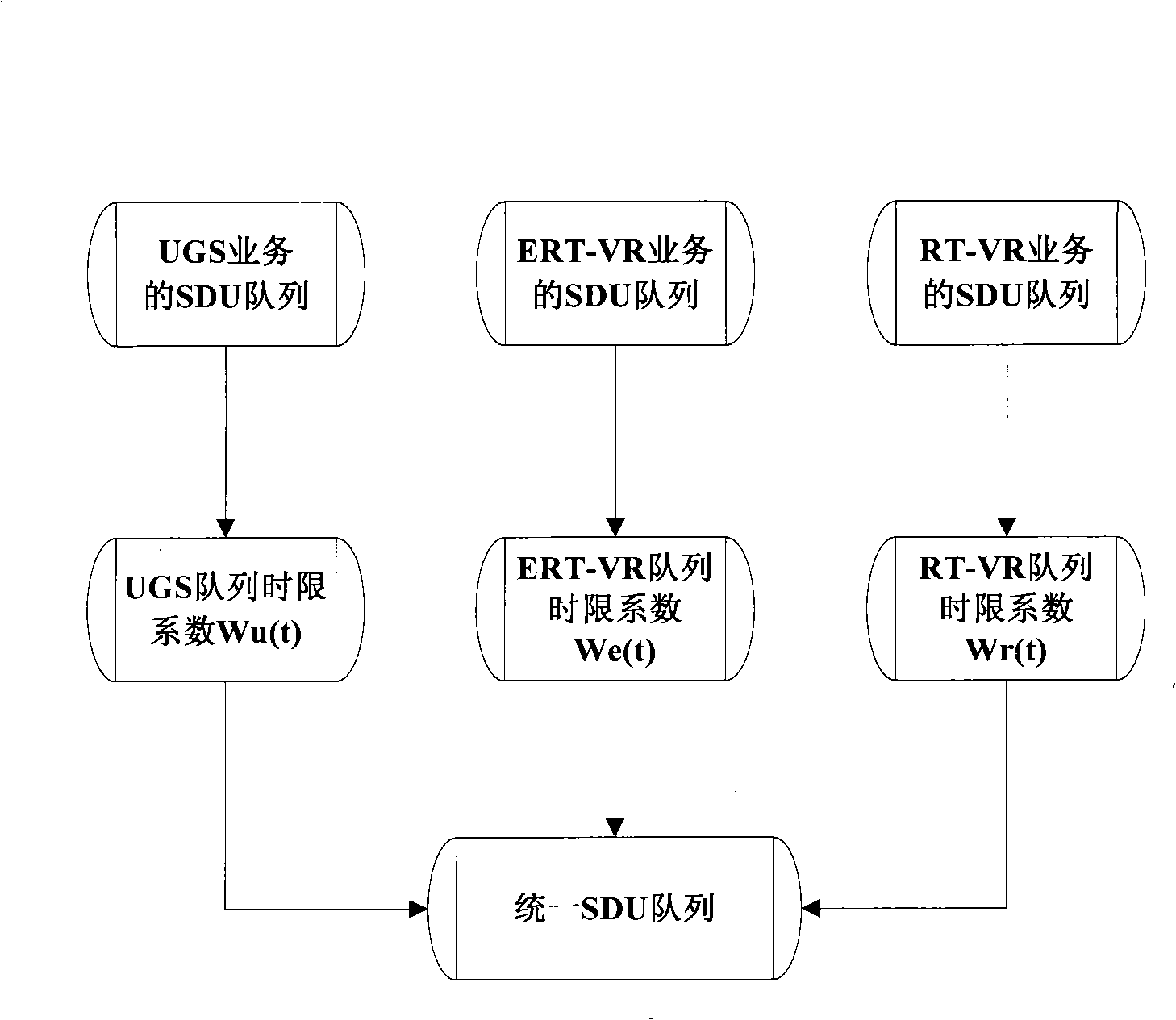
The invention discloses a device for dispatching a real-time service and a method thereof, which comprises: according to the types of different real-time services, SDU queues are established respectively; the SDU is put in the corresponding SDU queues respectively; priority of the SDU queues is set, and the SDU in the SDU queues is uniformly put in the SDU queues in sequence according to the priority; and the SDU in the SDU queues is dispatched uniformly. In the dispatching method of the invention, time limit coefficient and the uniform SDU queues are introduced, SDU which has pressing time requirement can be guaranteed to be dispatched in time, being lost can be avoided for overtime of dispatching, better time guaranteeing performance is provided, and the effects can be realized that the rate of losing packet is lowered and time delay requirement can be guaranteed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for initialization of integrity protection
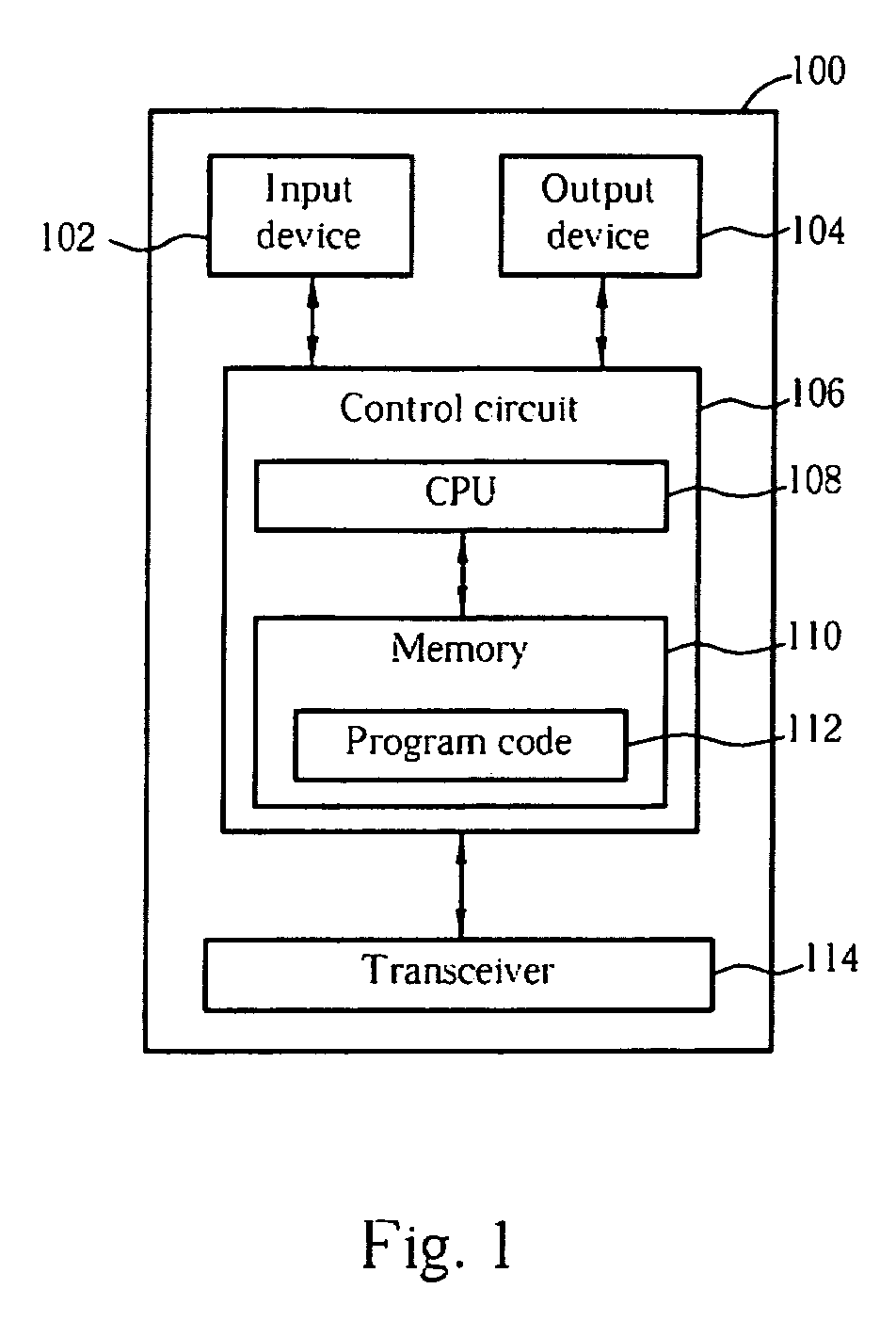
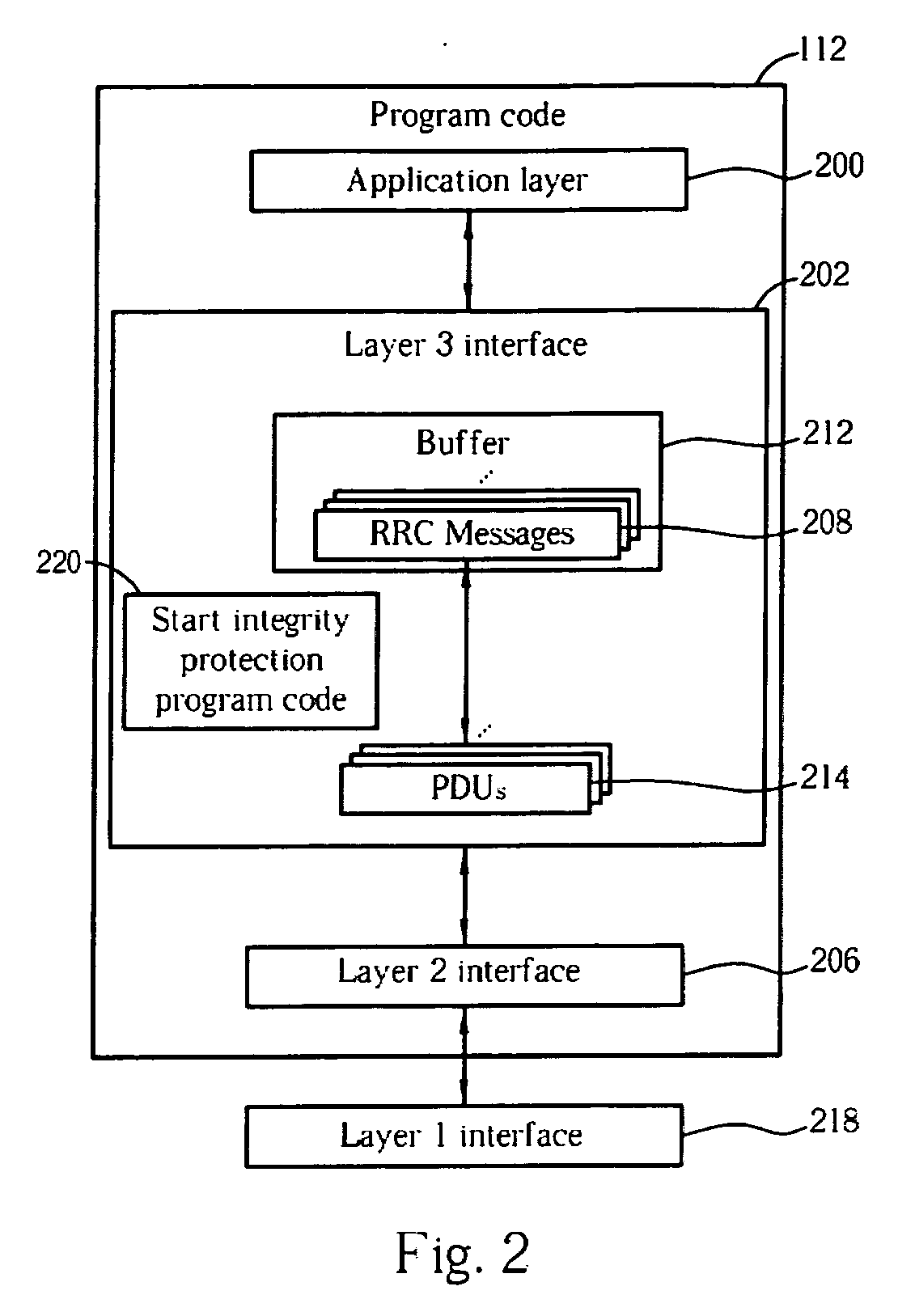
InactiveUS20070155339A1Avoid discardingTransmissionSecurity arrangementCommunications systemRadio communications
A method of starting Integrity Protection in a receiving end of a radio communications system starts with receiving a first Radio Resource Control (RRC) message for starting Integrity Protection. Then, a first Signaling Radio Bearer (SRB) is used to output a second RRC message to a network end of the radio communications system for indicating completion of starting Integrity Protection. Finally, a second SRB is prohibited from transmitting a third RRC message before receiving a confirmation message from the network end acknowledging successful receipt of the second RRC message.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
Method for determining type of data packet and device thereof
InactiveCN101547070AAvoid discardingImprove reception qualityError prevention/detection by using return channelData switching networksNetwork packetInvalid Data
The invention discloses a method for determining the type of a data packet. The method comprises the following steps: setting a determination timer; and determining the type of a newly received data packet according to the operation state of the determination timer and a sequence number of the newly received data packet when the newly received data packet drops in a reordering window, thereby distinguishing that whether the newly received RLC PDU is a repeated invalid data packet or a new effective data packet. The invention also discloses a device for determining the type of the data packet, which avoids the problem that the effective data packet is abandoned in the prior technical proposal, and improves the receiving quality of a receiving terminal.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmission method and device of uplink control information
ActiveCN103580797AAvoid CSI dropGuaranteed accuracy and completenessError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path divisionInformation transferChannel resource
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
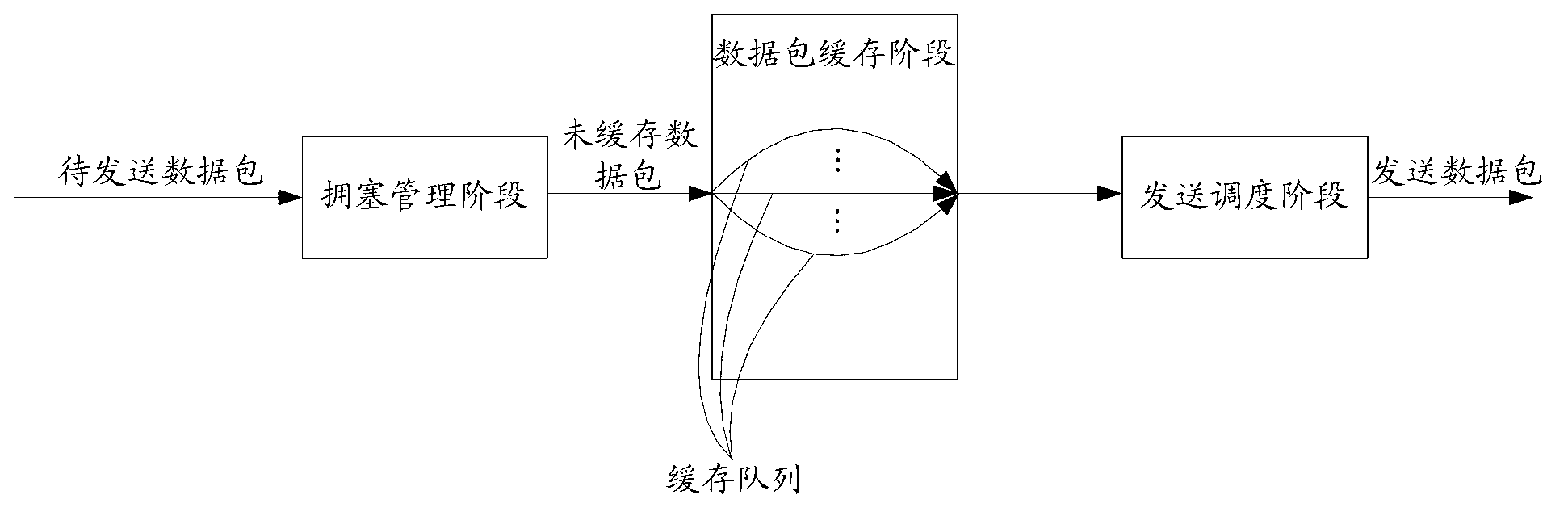
Data packet transmission method and device
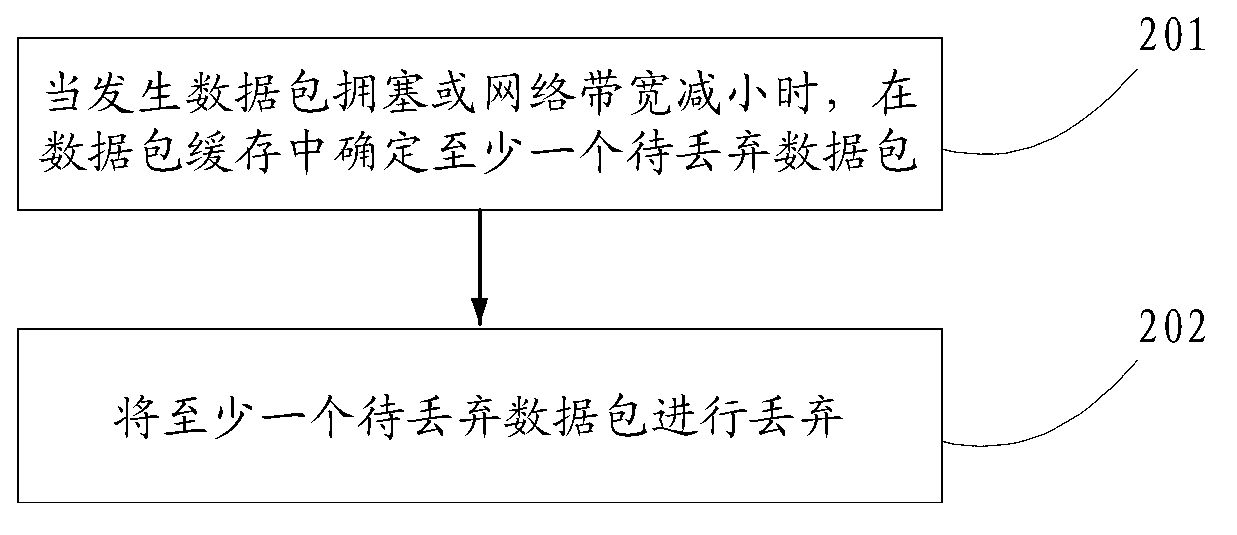
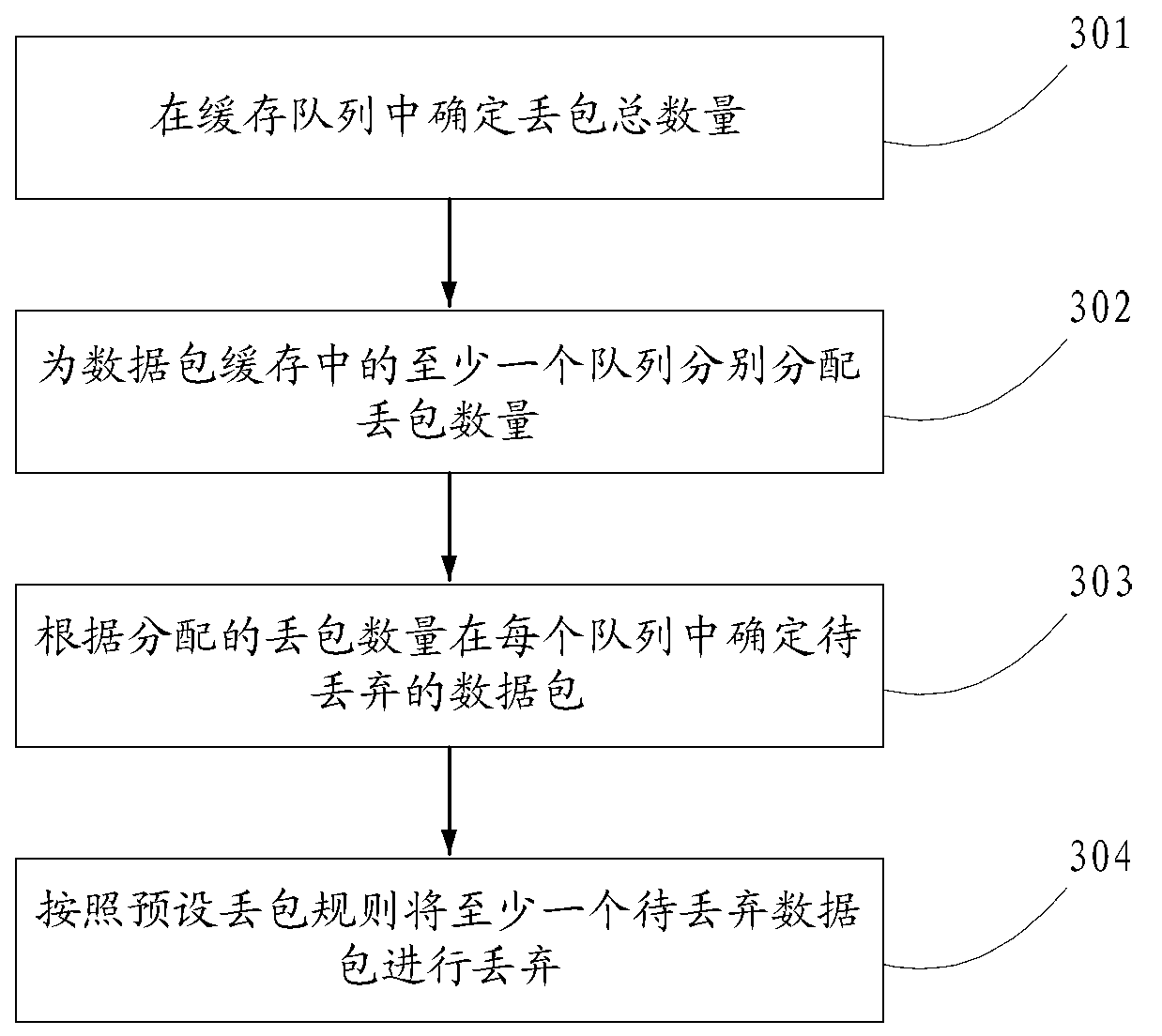
ActiveCN103229466AAlleviate packet loss pressureAvoid discardingData switching networksPacket transmissionReal-time computing
The invention discloses a data packet transmission method and device. The data packet transmission method and device relate to the technical field of communication and enable the phenomenon that too many data packets are lost in a congestion management period when congestion suddenly occurs between devices or between modules of the devices to be improved. The method includes: when data packet congestion occurs when or a network bandwidth is reduced, determining at least one data packet to be abandoned in a data caching; abandoning the at least one data packet to be abandoned so that at least one data packet which is not cached enters the data packet caching and thus preventing too many data packets, which are not cached, from being abandoned, wherein the data packets which are not cached are the data packets which do not enter the data caching. The data packet transmission method and device are mainly applicable to the data packet caching process.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Negotiation method of maximum segmentation parameters and network forwarding equipment
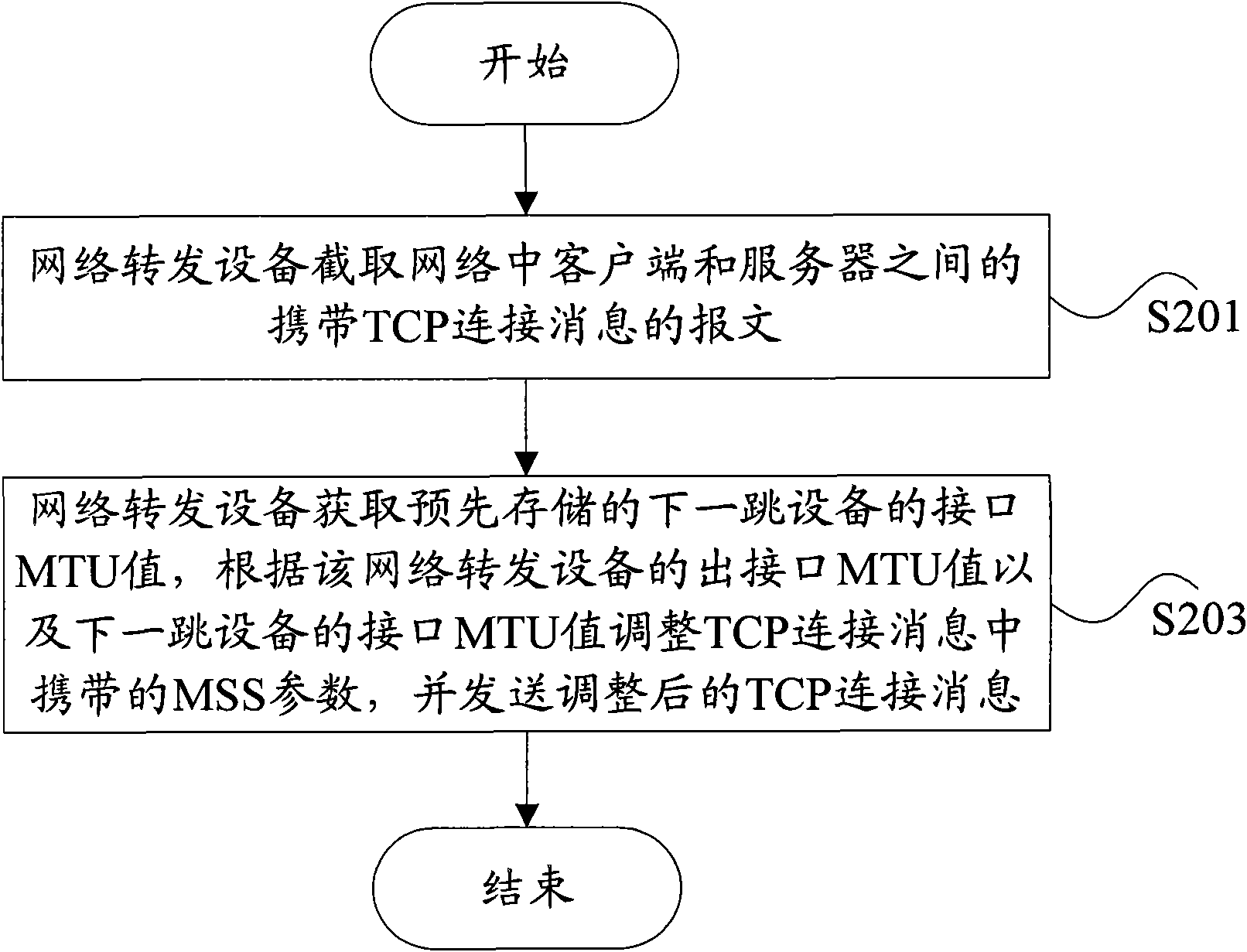
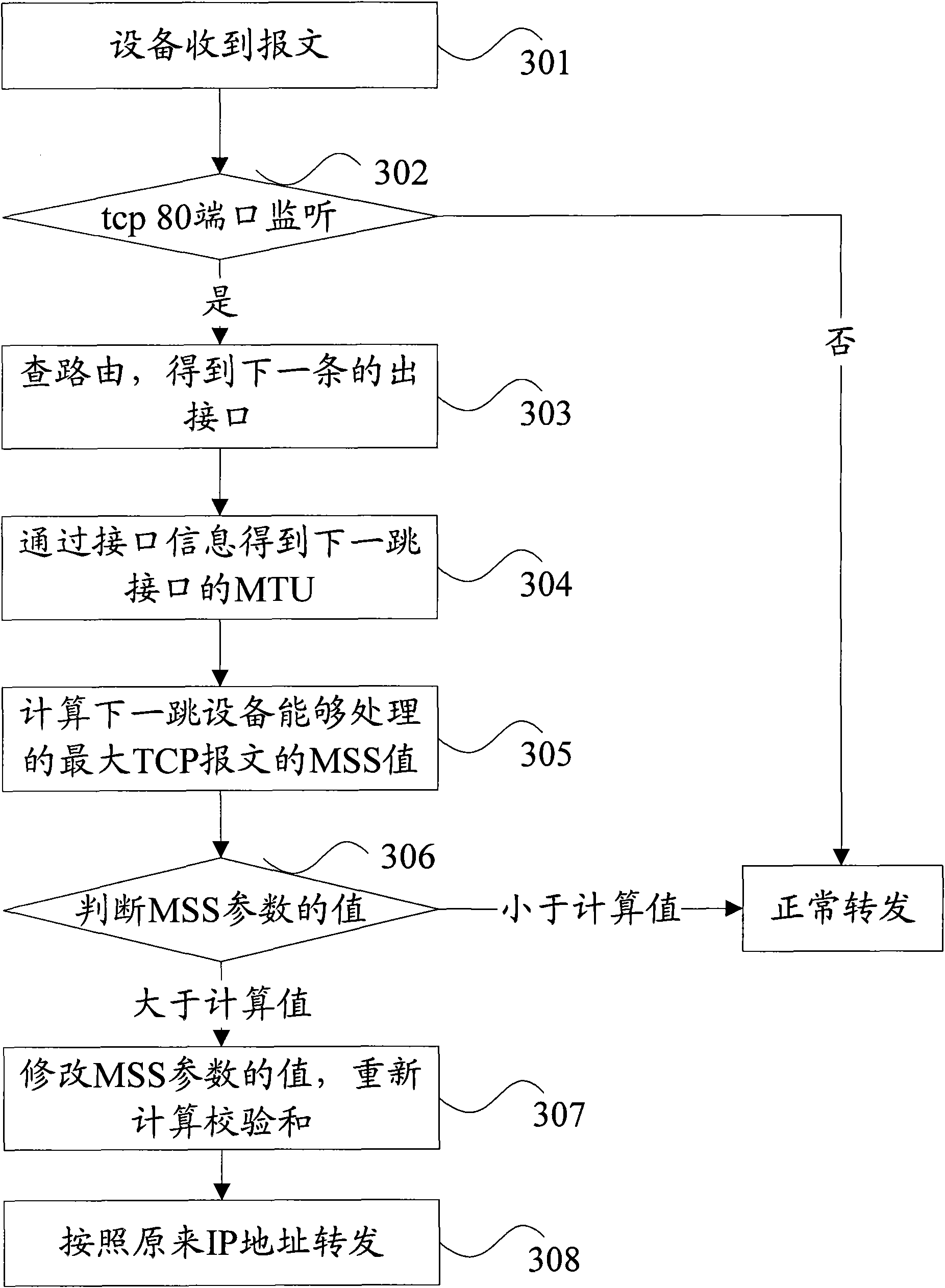
InactiveCN101924689AIncrease success rateAvoid discardingData switching networksClient-sideMaximum segment size
The invention discloses a negotiation method of maximum segmentation parameters and network forwarding equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: intercepting a message carrying a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection message between a client and a server in a network by the network forwarding equipment; acquiring a preliminarily stored interface MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value of next hop equipment by the network forwarding equipment; and adjusting an MSS (Maximum Segment Size) parameter carried in the TCP connection message according to the interface MTU value of the network forwarding equipment and the interface MTU value of the next hop equipment and sending the adjusted TCP connection message. The invention can avoid the occasion of data packet discarding since the messages are beyond the processing capacity of the equipment and improve the success ratio of message forwarding.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Packet forwarding apparatus and method for multicast packets
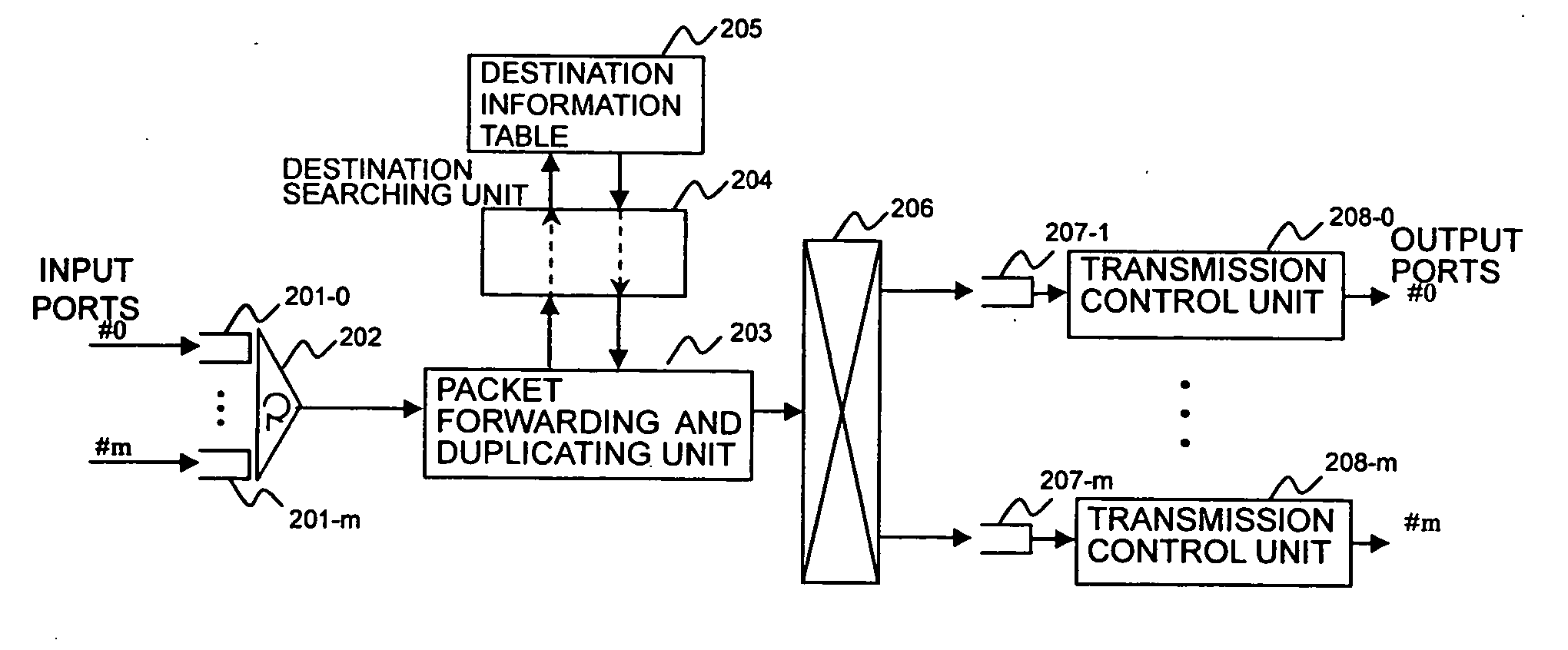
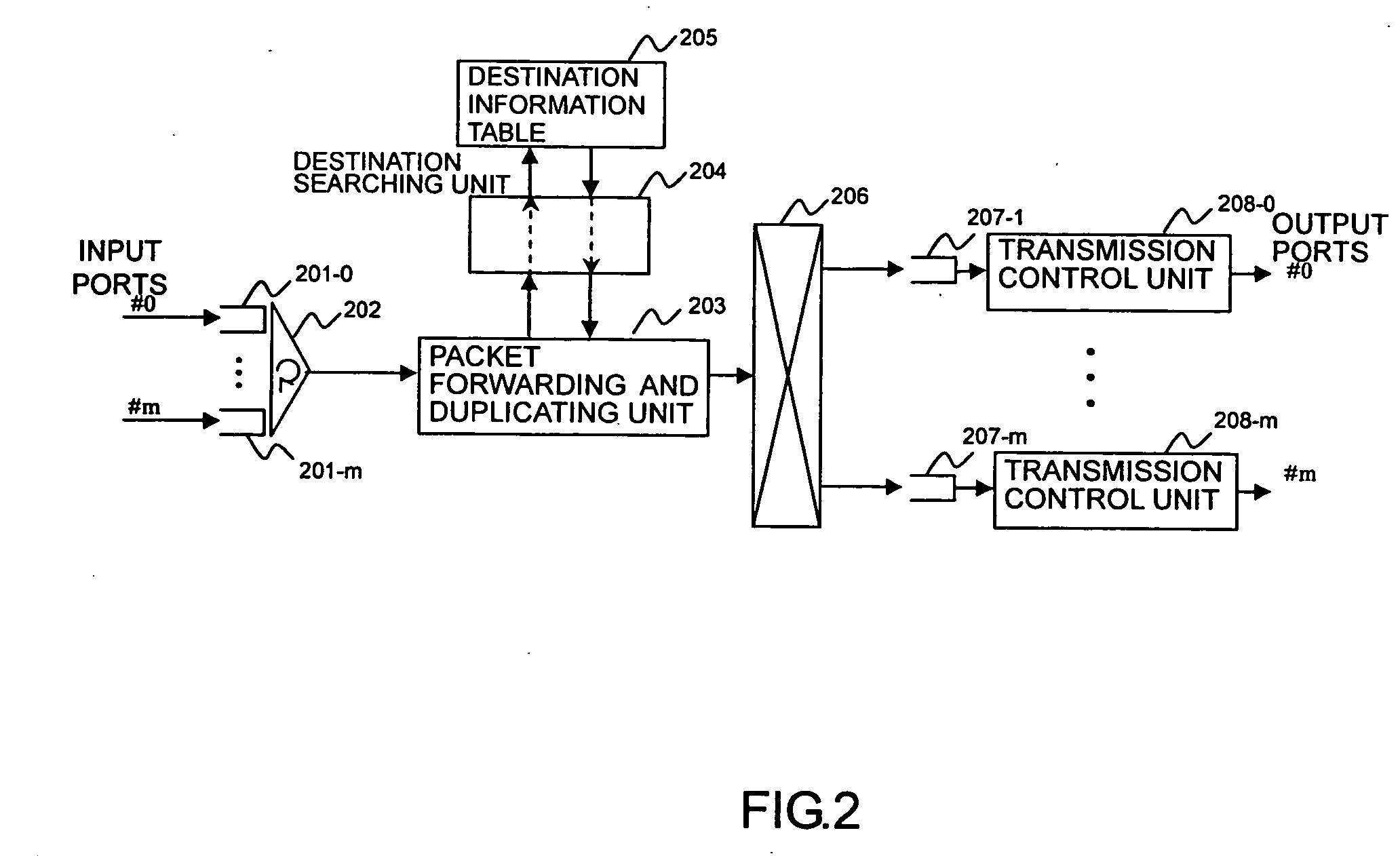
InactiveUS20070133531A1Increase the number ofReduce delaysTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMulticast packetsDistributed computing
The present invention provides a technology for processing packets, such as VoIP packets, with priority. A priority-designating unit designates priority information based on header information. A pointer searching unit refers to a pointer table to obtain pointer information corresponding to a destination address. A sorting unit sorts the pointer information into a high-priority queue and a low-priority queue according to the priority information. A next queue holds pointer information obtained from a destination information table. A scheduler extracts and outputs the pointer information from each queue in the following order of priority: the next queue, a high-priority queue, and a low-priority queue. A destination-information-table searching unit obtains destination information and / or the pointer information from the destination information table based on the pointer information, and outputs the destination information to a packet forwarding and duplicating unit and outputs the pointer information to the next queue.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
Bandwidth resource saving method
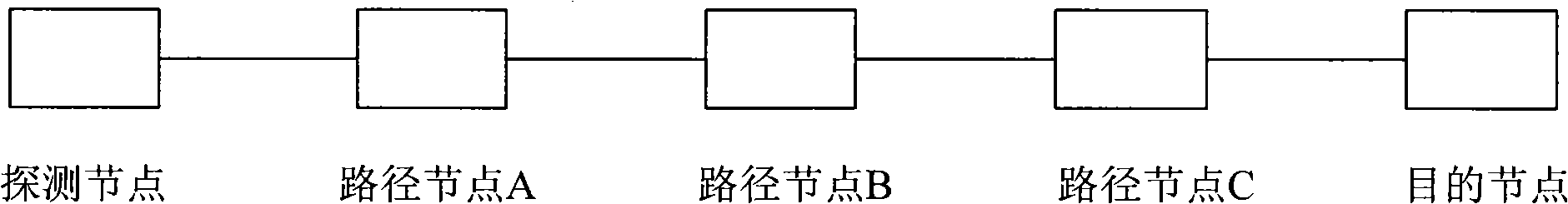
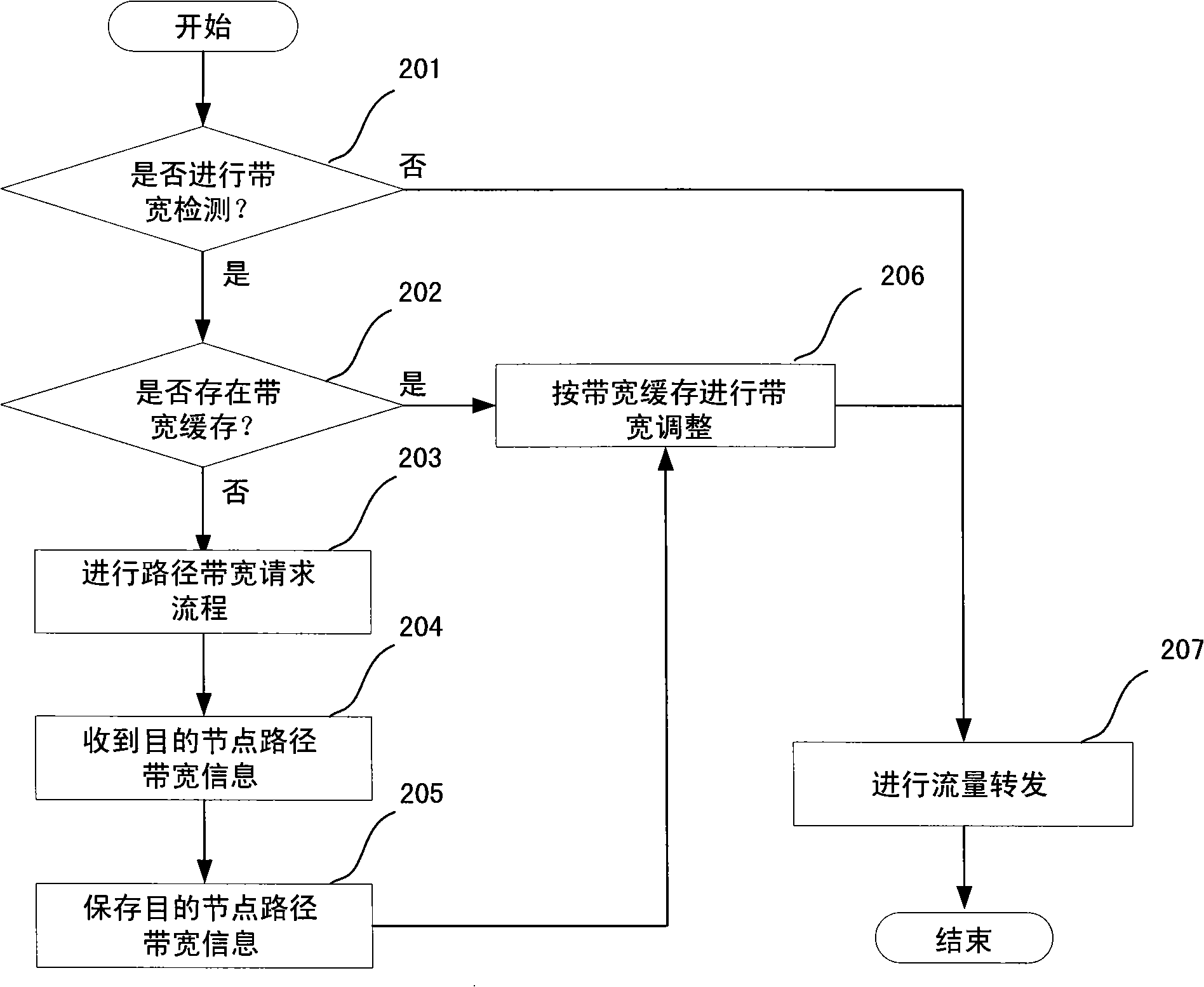
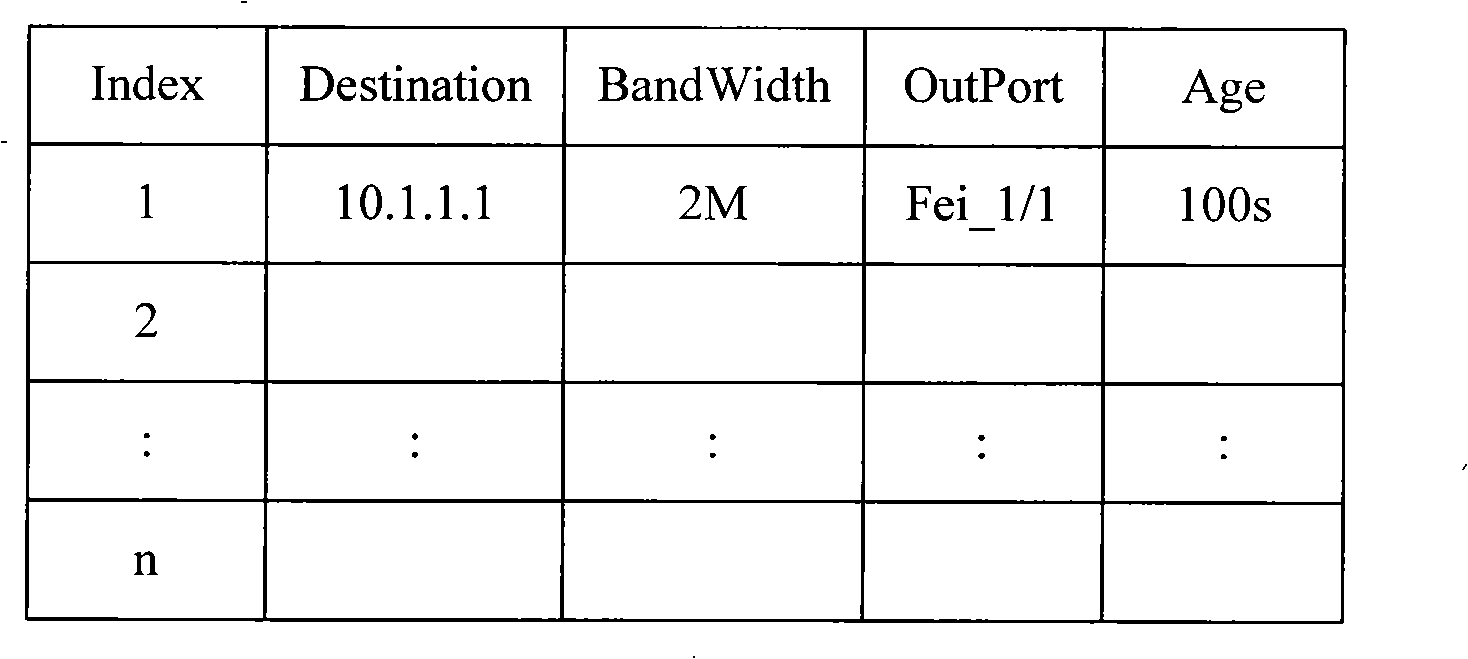
InactiveCN101360046AAvoid discardingSave bandwidth resourcesData switching networksNetwork linkResource saving
The invention discloses a method of saving the bandwidth resource, comprising the following: a source node or an access node constructs a path detection requesting message carrying information according to the maximum available bandwidth from a local node to the inyoite interface link of a destination node, and sends the message to a middle node on a path from the local node to the destination node; after the middle node receives the path detection requesting message, the middle node compares the maximum available bandwidth from the local node to the inyoite interface link of the destination node with that in the requesting message to replace the maximum available bandwidth value or directly forwards the maximum available bandwidth value to a next node; and after the destination node receives the path detection requesting message, the destination node constructs a path detection reversion message, carries the maximum available bandwidth in the requesting message, and sends the reversion message to the source node or the access node. The invention perceives the path bandwidth in advance, controls the flow bandwidth at the source node or the access node, and saves the bandwidth resource of the middle node, thereby making the flow on the network link reach the optimum rate of utilization and throughput and improving the availability and the safety of the network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
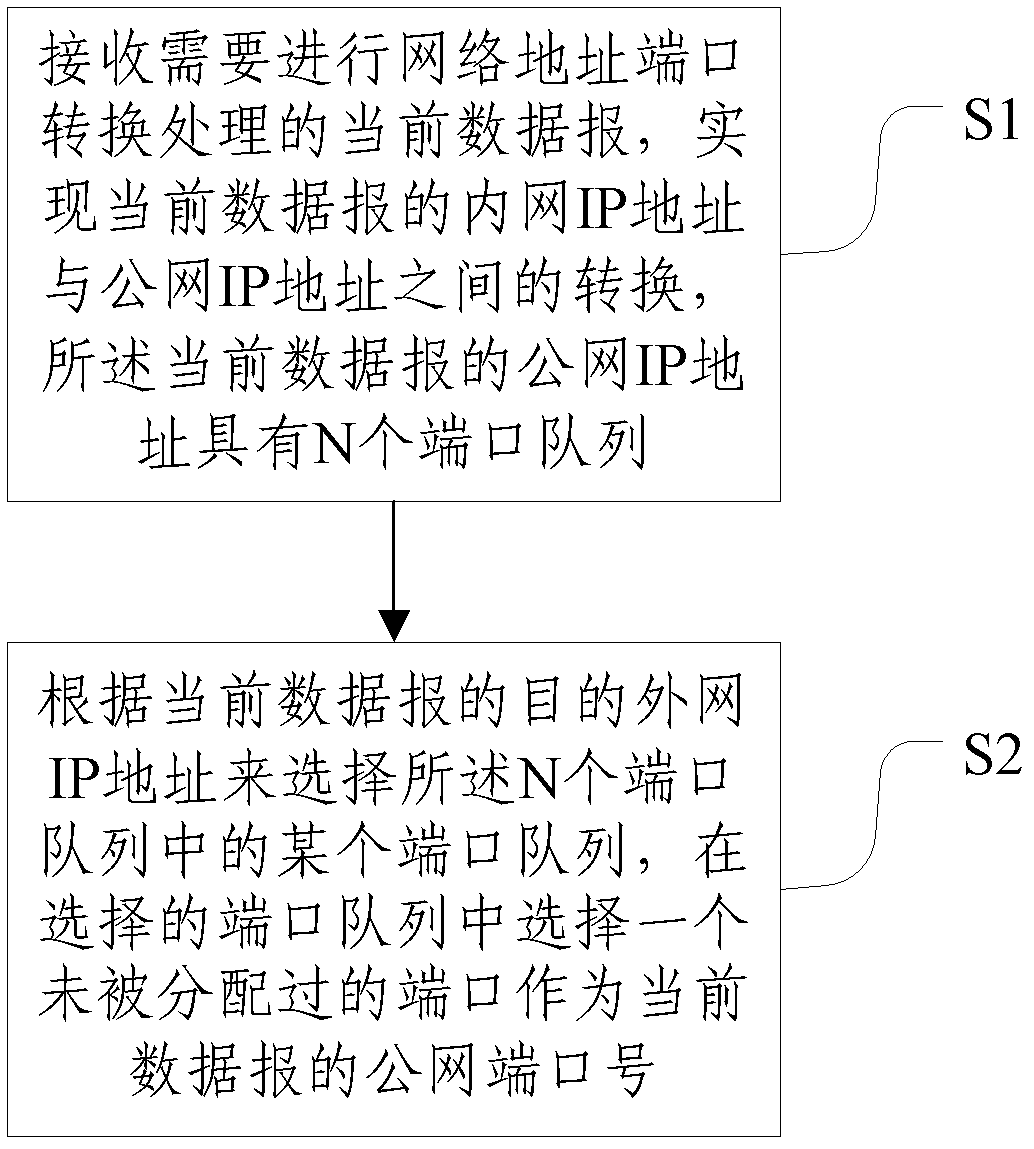
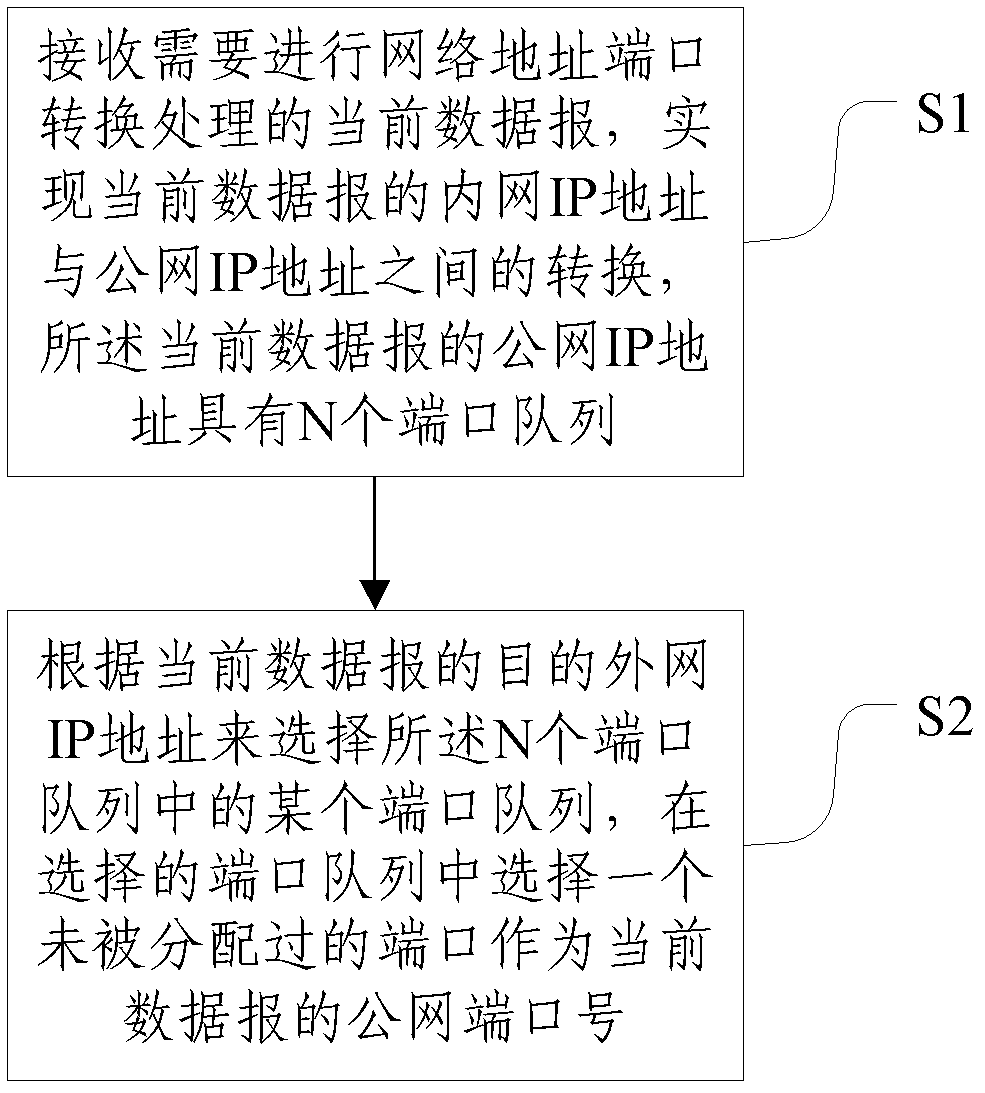
Method and system for achieving network address translation
The invention discloses a method and a system for achieving network address translation, which relates to the technical field of network communication. The method comprises the steps of: S1, receiving a current datagram requiring network address port translation, achieving translation of an inner network IP (internet protocol) address and a public network IP (internet protocol) address of the current datagram, wherein the public network IP address of the current datagram comprises N port queues, and N is an integer greater than 1; S2, selecting one port sequence in the N port queues according to an outer network IP address of the current datagram, and selecting a port which is not distributed in the selected port queue as a public network port number of the current datagram. According to the invention, judgment of a target IP is increased on a conversion method of PAT (port address translation); the same port number can be adopted as to different resources; multiplexing of the port is achieved; the different resources are expanded for N times relatively to the port resource, and the datagram is prevented from being abandoned due to exhausting of the port resource.
Owner:OPZOON TECH
Method for generating call ticket
InactiveCN101409877AImprove robustnessAvoid discardingMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesSerial codeBilling system
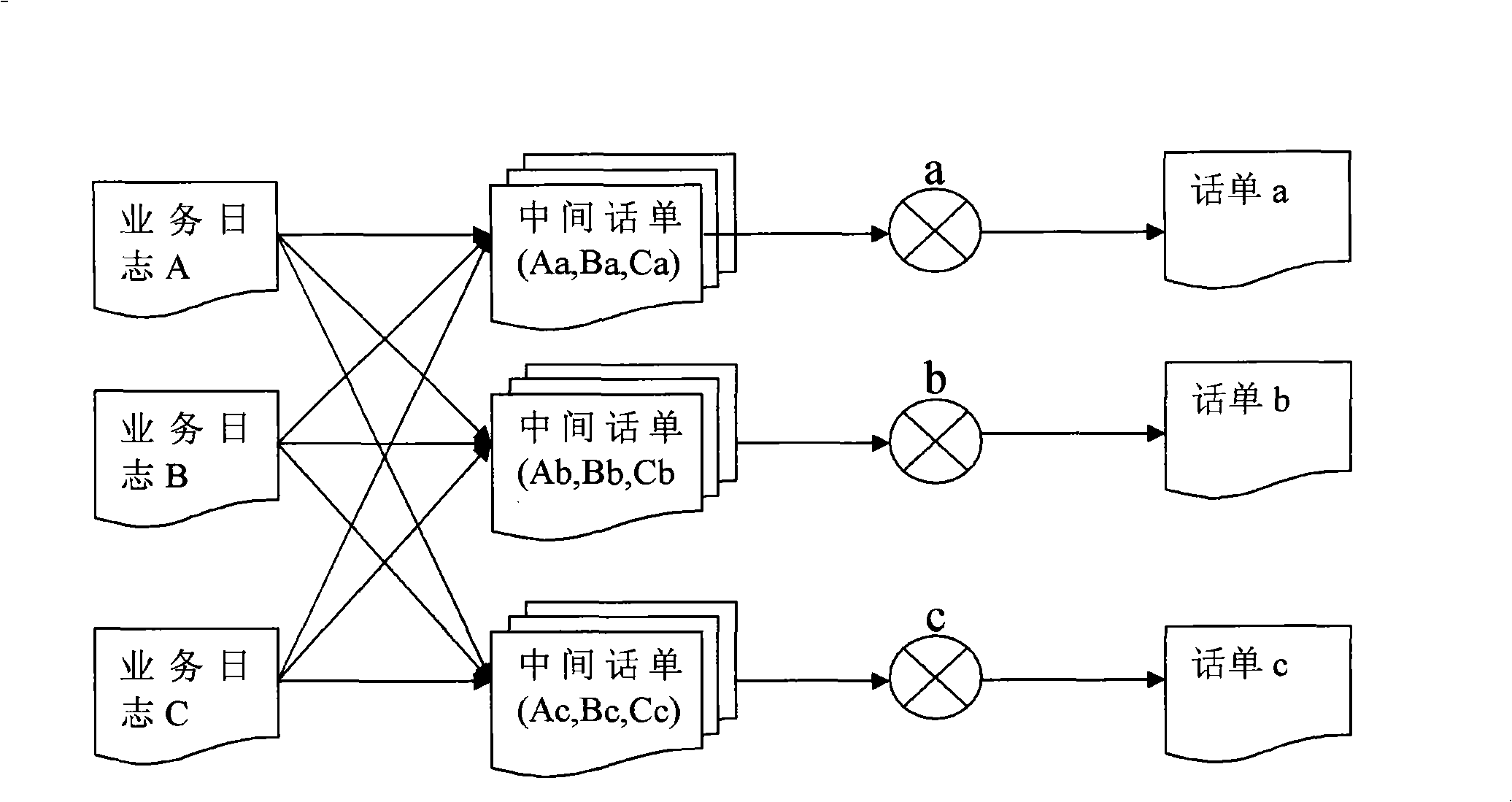
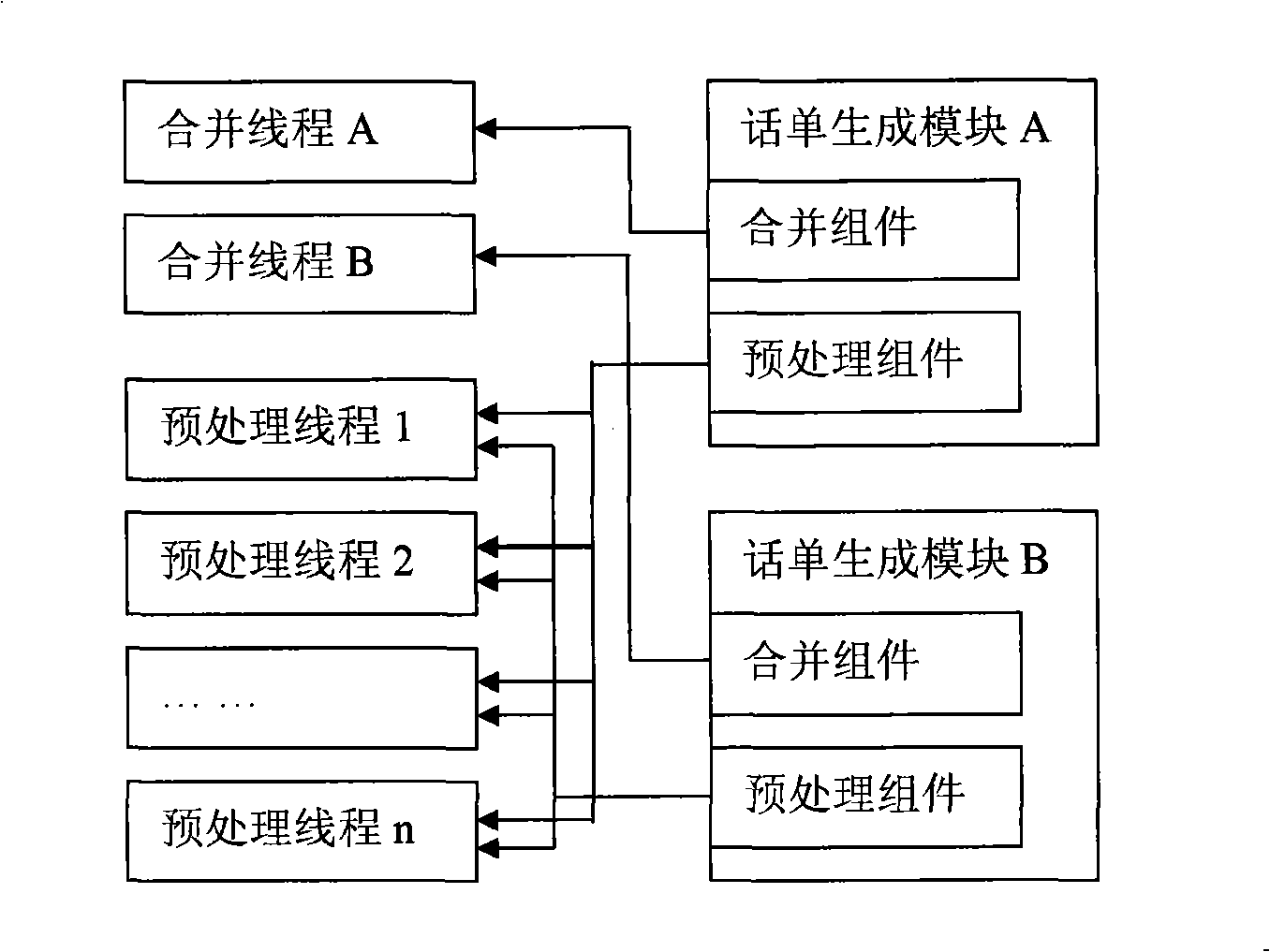
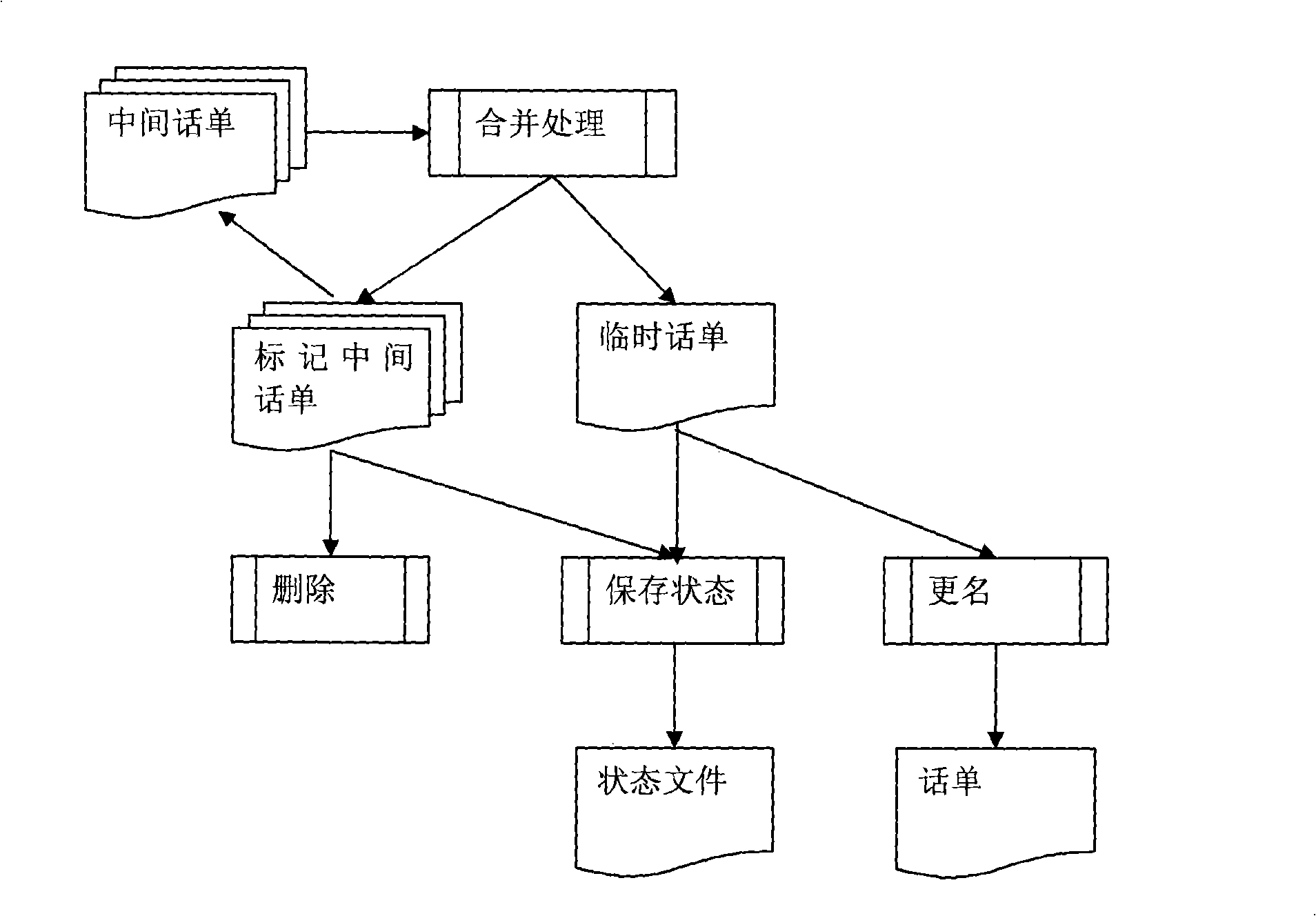
The invention discloses a phone bill generating method, which is applied in a charging system of communication field. The generating method includes a pre-processing process and a phone bill combination process; wherein, in the pre-processing process, the charging system adopts a plurality of threads to carry out the pre-processing to multiple service logs, each service log generates one or a plurality of intermediate phone bills after pre-processing and the information in the service logs is needed to be converted into the required information in the phone bill in the pre-processing; the phone bill combination process adopts a single thread for processing to gradually generate the required phone bills and in the generating process of each phone bill, the charging system collects and combines the intermediate phone bills required by the phone bill generation and then completes the coding of serial numbers and the document serial numbers, thus generating a phone bill. The invention reduces the treatment complexity while ensuring the processing ability of the system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Feedback information and multi-path routing based wireless sensor network data transmission method
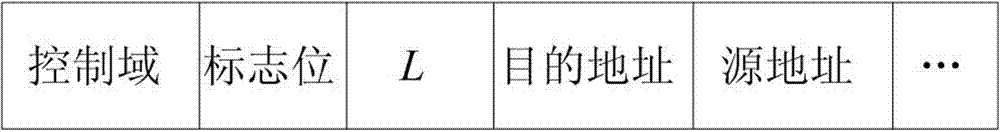
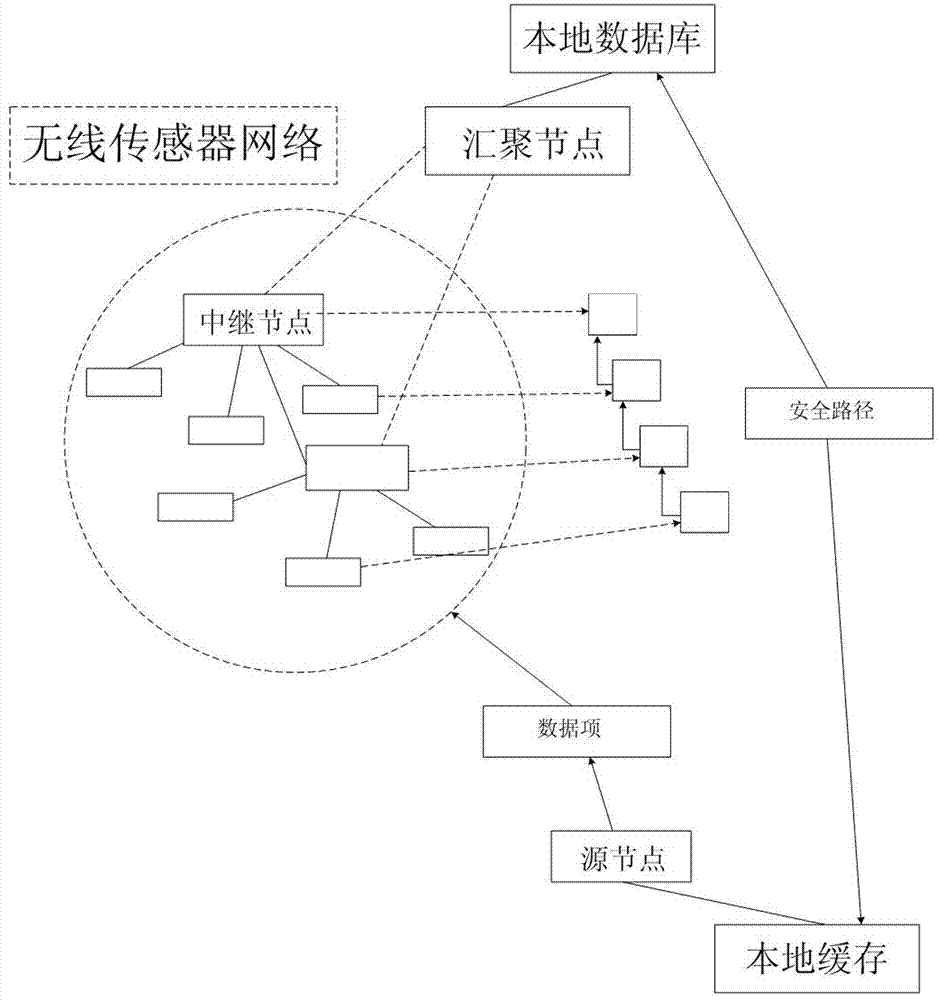
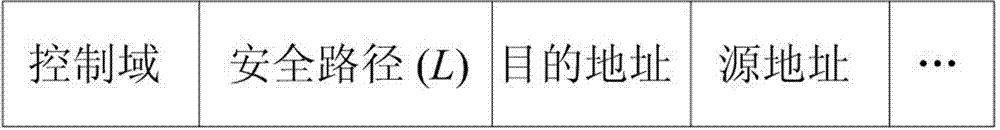
InactiveCN103037465AReduce chances of interception and theftImprove efficiency and qualityKey distribution for secure communicationNetwork topologiesMulti path routingData transmission
The invention discloses a feedback information and multi-path routing based wireless sensor network data transmission method which comprises a feedback information based safety routing structure, multi-path routing establishment and multi-path routing transmission application. According to the feedback information and multi-path routing based wireless sensor network data transmission method, in the multi-path routing aspect, the multi-path routing protocol of on-demand routing is mainly adopted, and multiple maximum disjoint routing paths are established, and therefore network congestion is prevented, and available wireless sensor network resources are effectively initialized. Through the feedback information based safety routing structure, feedback paths can be obtained from Sink node for an originating node of data transmission. When the originating node receives enough feedback paths from the Sink node, the paths can be utilized for multi-path data transmission with combination of multi-path routing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing safety mode and radio network controller
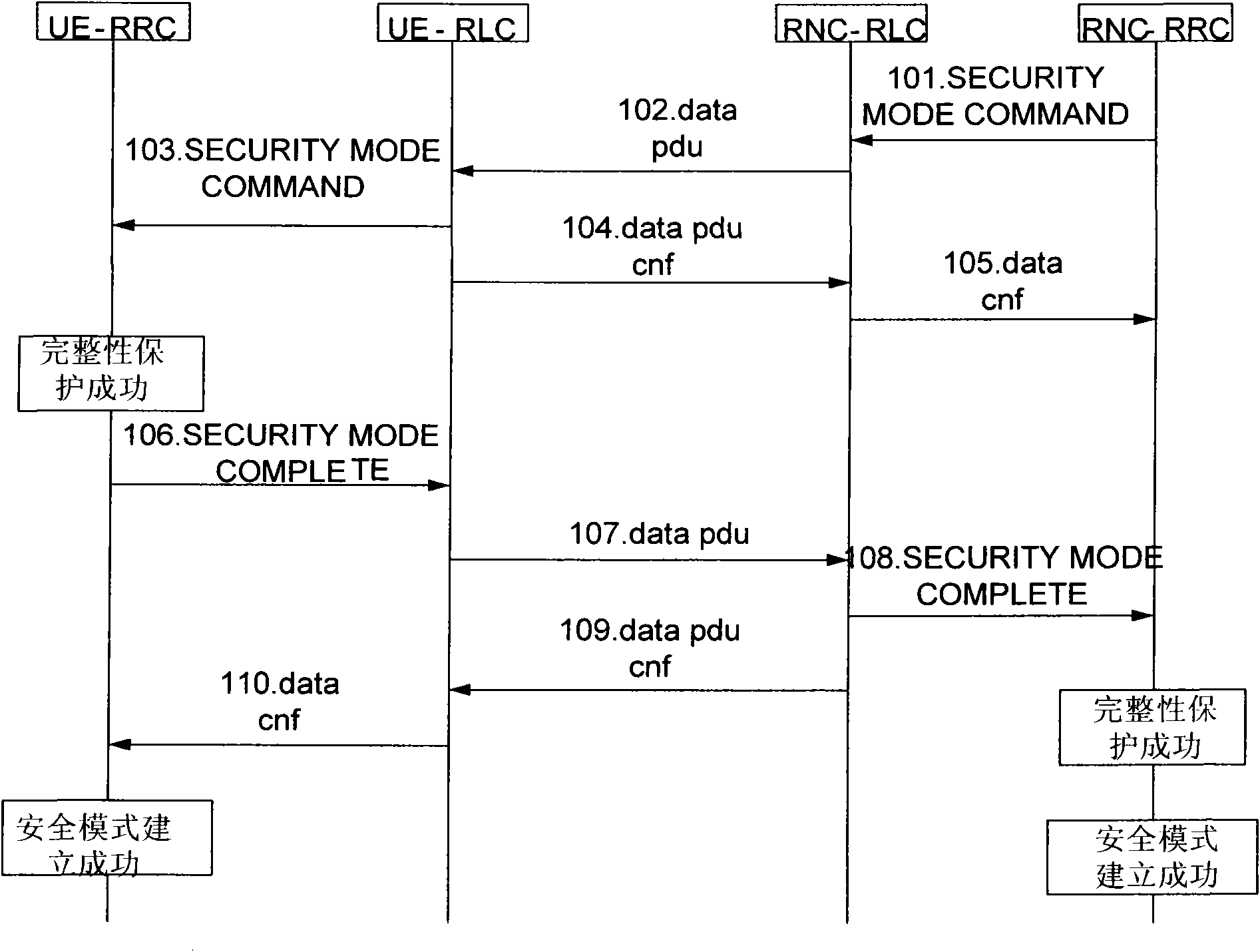
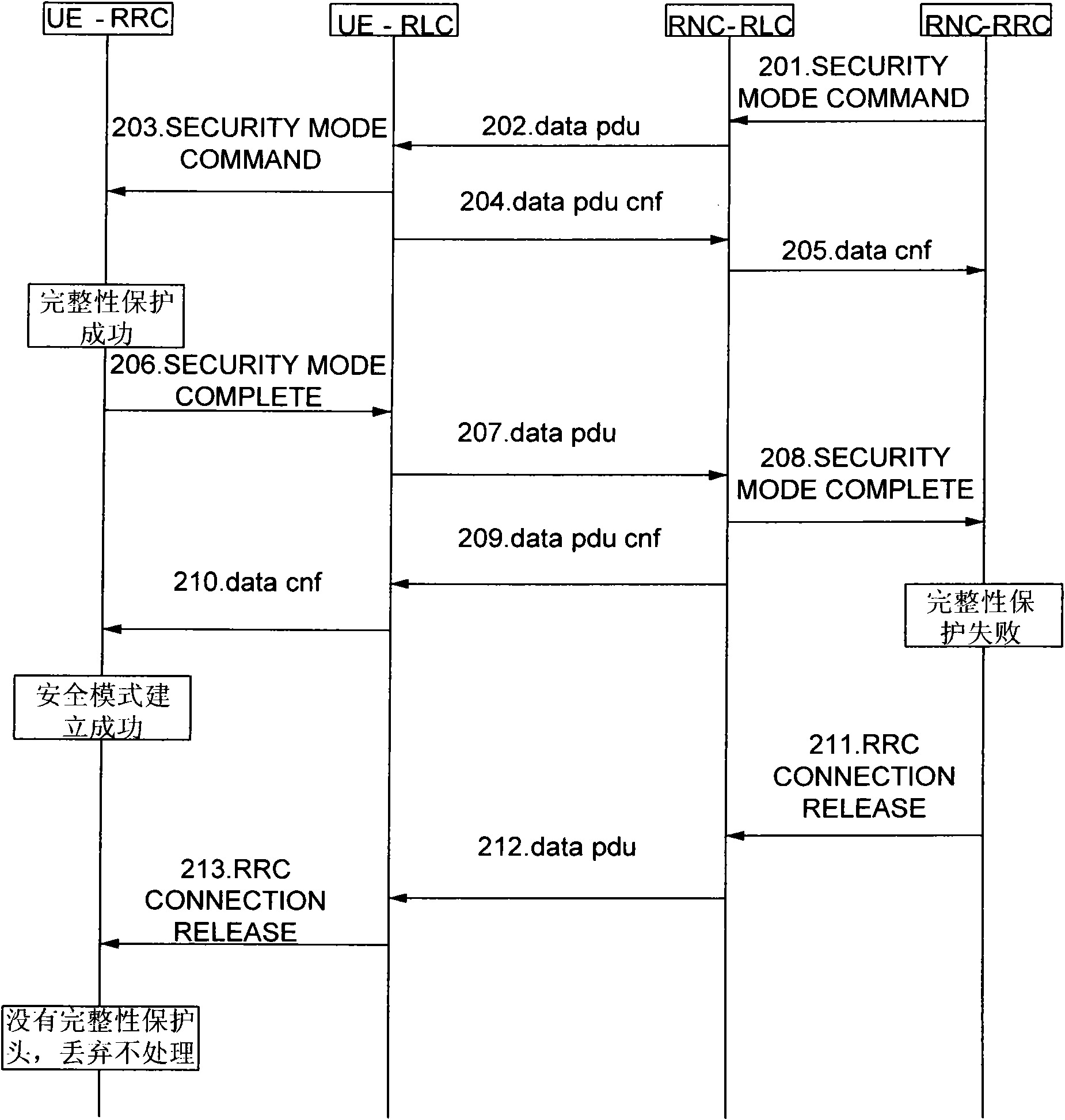
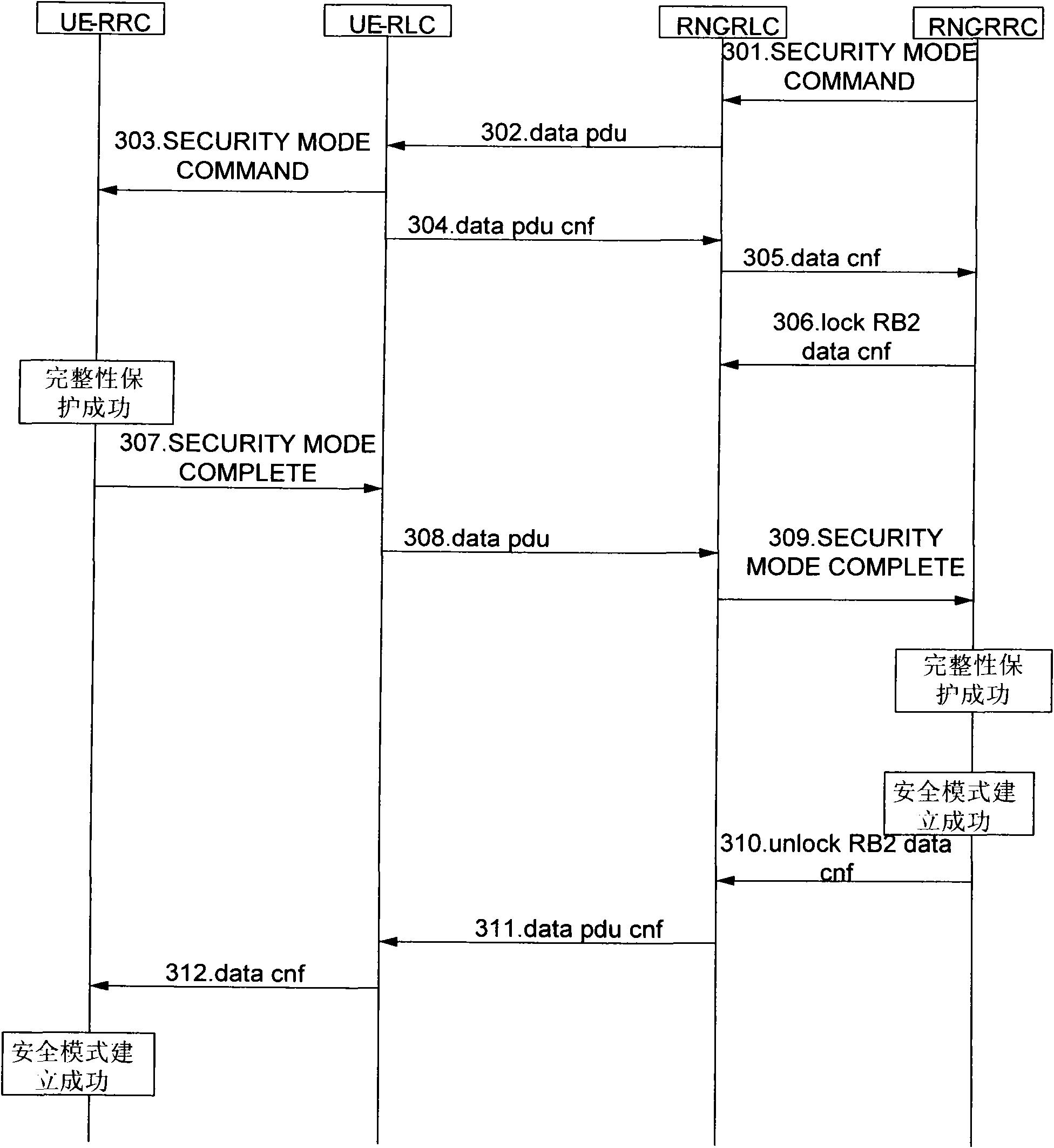
ActiveCN101651949AAvoid discardingConnection managementSecurity arrangementTelecommunicationsEngineering
The invention discloses a method for establishing a safety mode, comprising the following steps: locking the information confirming function of a radio link controller (RLC) of a radio network controller (RNC) to user equipment (UE) after a radio resource controller (RRC) of the RNC confirms that safety mode control information is successfully transmitted to the UE; transmitting safety mode finishing information to the RNC in a confirming mode after the integral protecting inspection of the safety mode control information is passed by the UE, and carrying out the integral protecting inspectionon the information after the RRC of the RNC receives the safety mode finishing information. If the integral protection fails, after a district update request of the UE is received, RRC connection release information is transmitted to the UE for notifying the UE to release the RRC connection. The method can avoid repeatedly transmitting the RRC CONNECTION RELEASE information because a network sidecannot obtain the confirmation of the connection release of the UE side, so that the signaling connection cannot be released to get into deadlock.
Owner:ZTE CORP
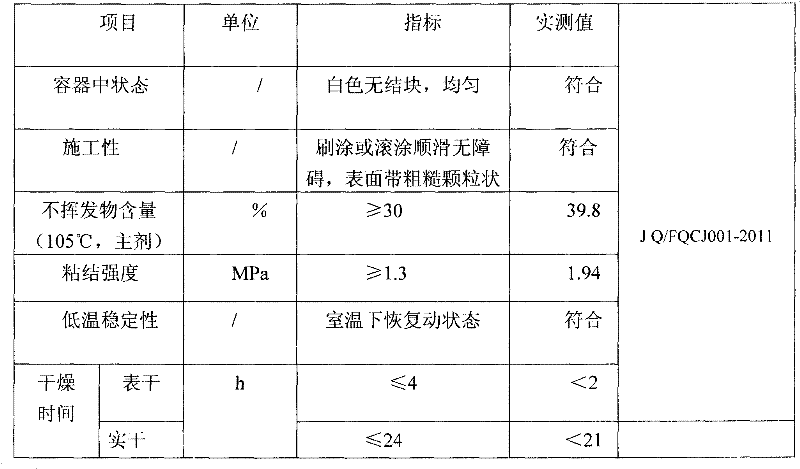
Polymer emulsion interface agent for base layer coating treatment and preparation method thereof
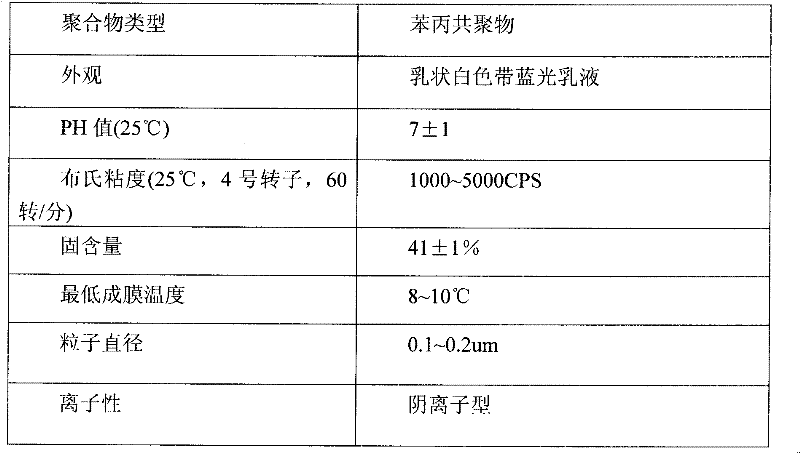
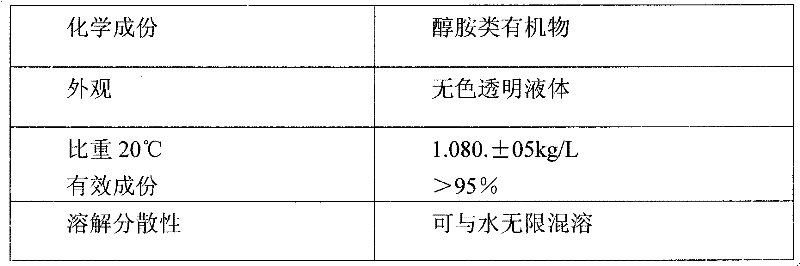
The invention discloses a polymer emulsion interface agent for base layer coating treatment and a preparation method thereof. The polymer emulsion interface agent for base layer coating treatment comprises a component A and a component B. In use, the component A and the component B are mixed according to a weight ratio of 1: 1. The mixture of the component A and the component B is white paint. The component A comprises 0.1 to 0.5% of hydroxyethylcellulose, 0.2 to 0.9% of a dispersing wetting agent, 12 to 19% of quartz powder, 48 to 65% of styrene-acrylic acid ester polymer emulsion, 0.05 to 0.35% of an antiseptic, 0.01 to 0.2% of a mildew inhibitor, 0.05 to 0.25% of a multifunctional auxiliary agent, 0.05 to 0.55% of a thickening agent, 0.1 to 0.5% of an antifoaming agent, 0.2 to 0.7% of a film forming auxiliary agent and 18 to 35% of water. The component B comprises 20 to 38% of wollastonite powder, 15 to 35% of quartz powder and 38 to 55% of quartz sand. Through combining the component A and the component B according to a ratio, the polymer emulsion interface agent for base layer coating treatment has the characteristics of good cohesion and adhesion, high bonding intensity, good closeness, rough surface layer and good adhesiveness with putty.
Owner:FUZHOU QICAIJU BUILDING MATERIAL
Method and apparatus for monitoring user equipment reachability in wireless communication system
ActiveUS9668236B2Easy to receiveSending downlink data to user equipment rapidly and efficientlyConnection managementWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemReachability
Disclosed herein are a method and apparatus for monitoring UE reachability in a wireless communication system. A method for monitoring UE reachability may include receiving, by a Mobility Management Entity, a monitoring request message for UE reachability including a maximum response time from a Home Subscriber Server, detecting, by the MME, the UE reachability if it is expected that paging is able to be transmitted to UE when extended Discontinuous Reception is applied to the UE, and sending, by the MME, a UE reachability notification to a Service Capability Exposure Function before a next paging occasion of the UE, wherein the maximum response time may indicate a time during which the UE maintains a reachable state so that downlink data is reliably delivered to the UE, and wherein an occasion when the UE reachability notification is transmitted may be determined by taking into consideration the maximum response time.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com