Bandwidth resource saving method
A bandwidth resource and bandwidth technology, applied in the field of bandwidth resource saving, can solve the problems of inability to deploy resource reservation protocols in large numbers, complex implementation of resource reservation protocols, heavy burden on intermediate nodes, etc., to improve network availability and optimal utilization. and throughput, easy-to-achieve effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
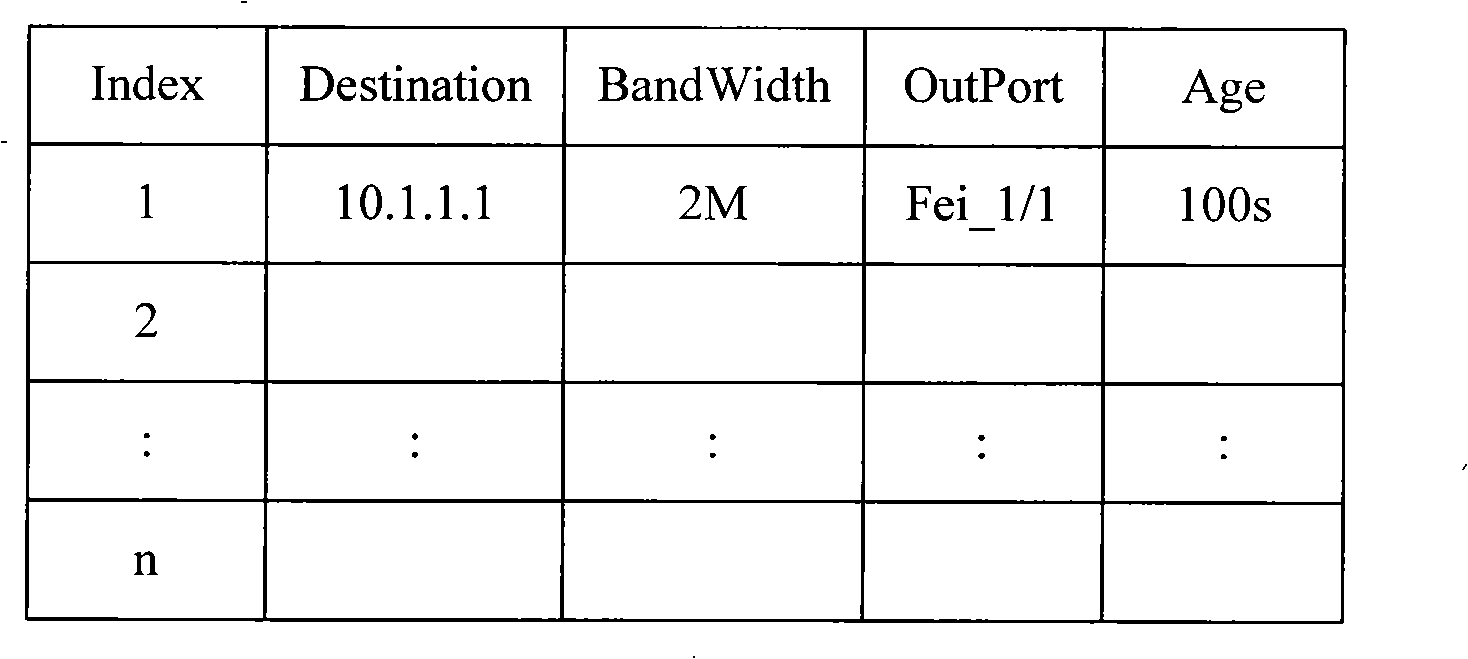
[0039]The core idea of the present invention is: before the detection node (which can be a source node or an access device) sends traffic, through a detection mechanism, the maximum available bandwidth of the path between it and the destination node is accurately known, and according to the detection The maximum available bandwidth of , and the detection node implements a bandwidth control strategy for the corresponding traffic locally.
[0040] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
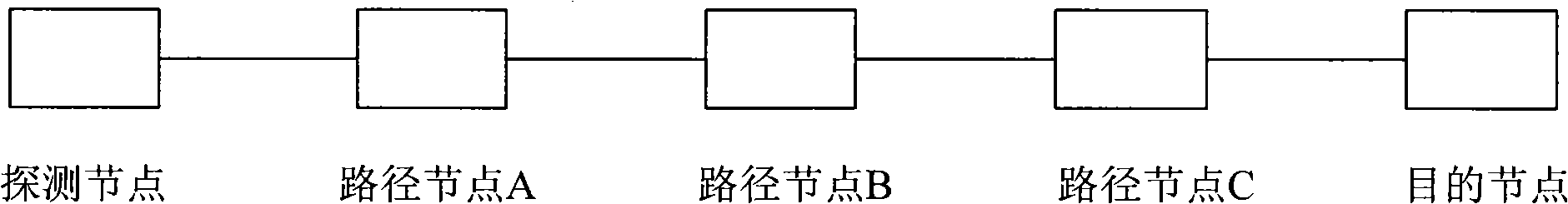
[0041] figure 1 It is a simple schematic diagram, pointing out the location and connection mode of the detection node, the intermediate node of the path and the destination node in the current IPv6 network. The detection node in the present invention may be an access device or a source node in practice.
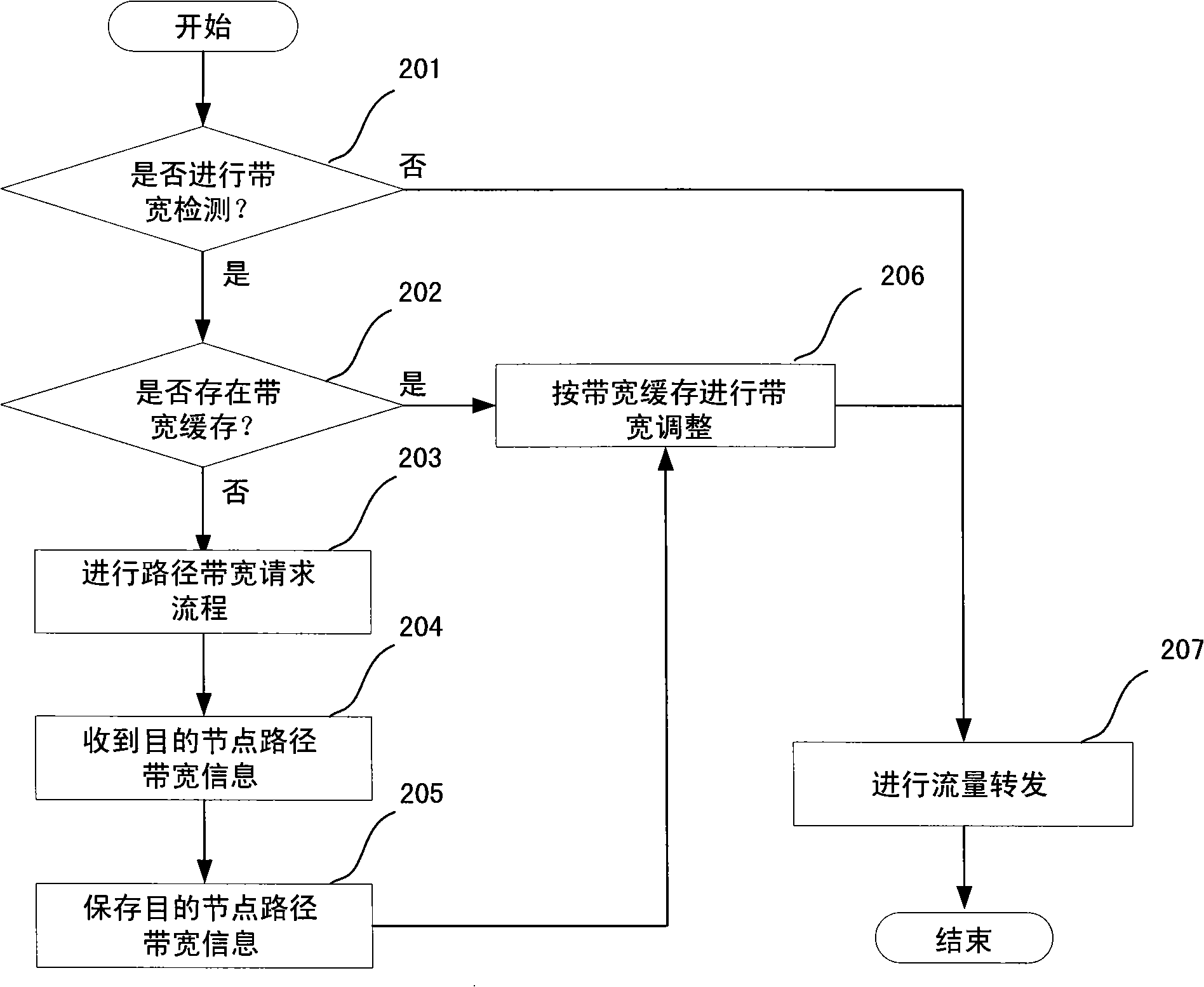
[0042] figure 2 It is the processing steps of the detection node in the process of data packet forwar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com