Communication node and packet transfer method
a packet transfer and communication node technology, applied in data switching networks, two-way working systems, frequency-division multiplexes, etc., can solve the problems of reducing system throughput and increasing the demand for radio communications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
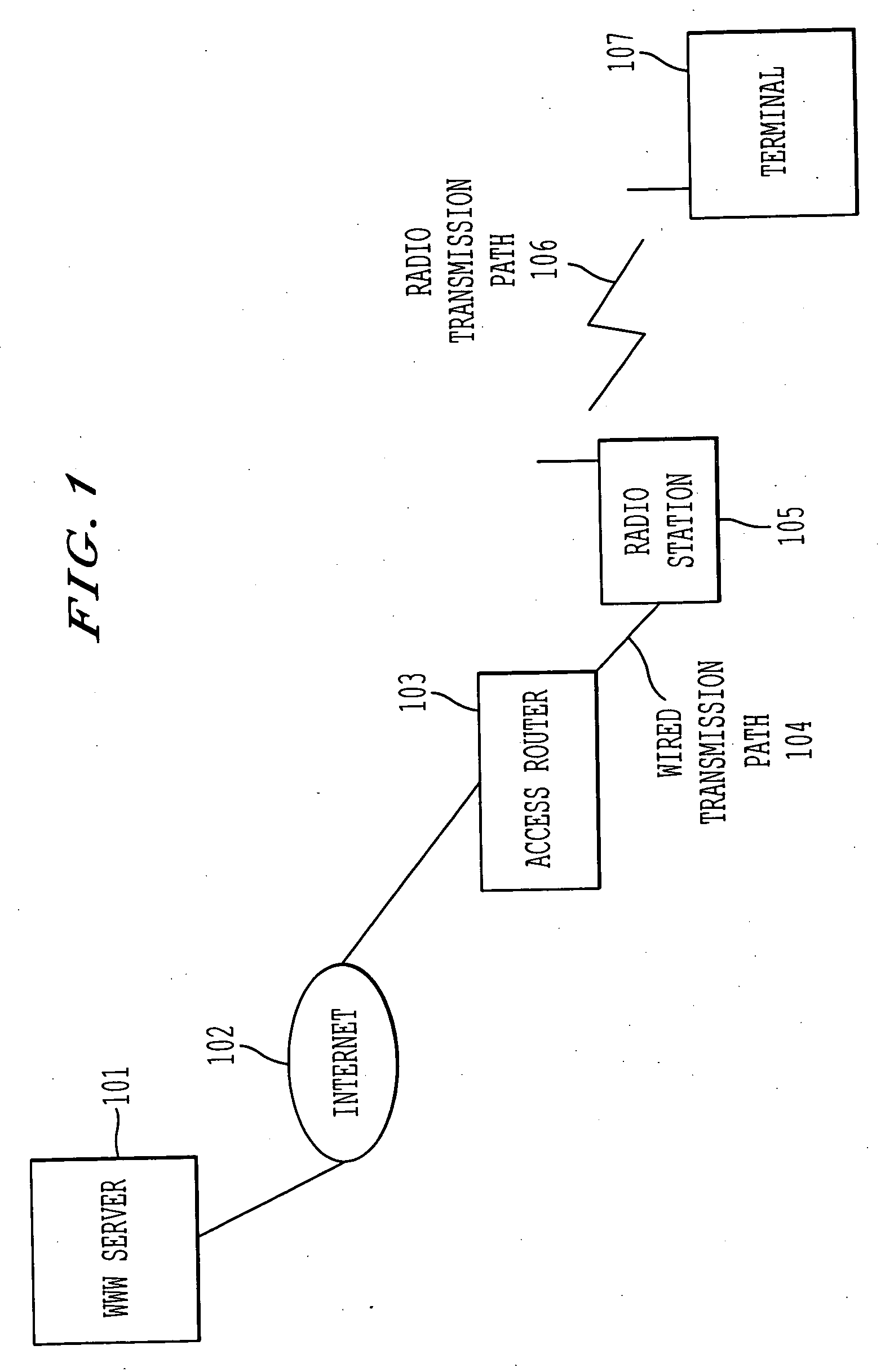
[0052]FIG. 1 shows one example of an overall configuration of a network system according to the present invention.
[0053] Referring to FIG. 1, a terminal 107 communicates with a WWW server 101 via a radio transmission path 106, such as a radio public network. Here, the WWW server 101, an access router 103, and the terminal 107 are nodes that are connected to the Internet 102.
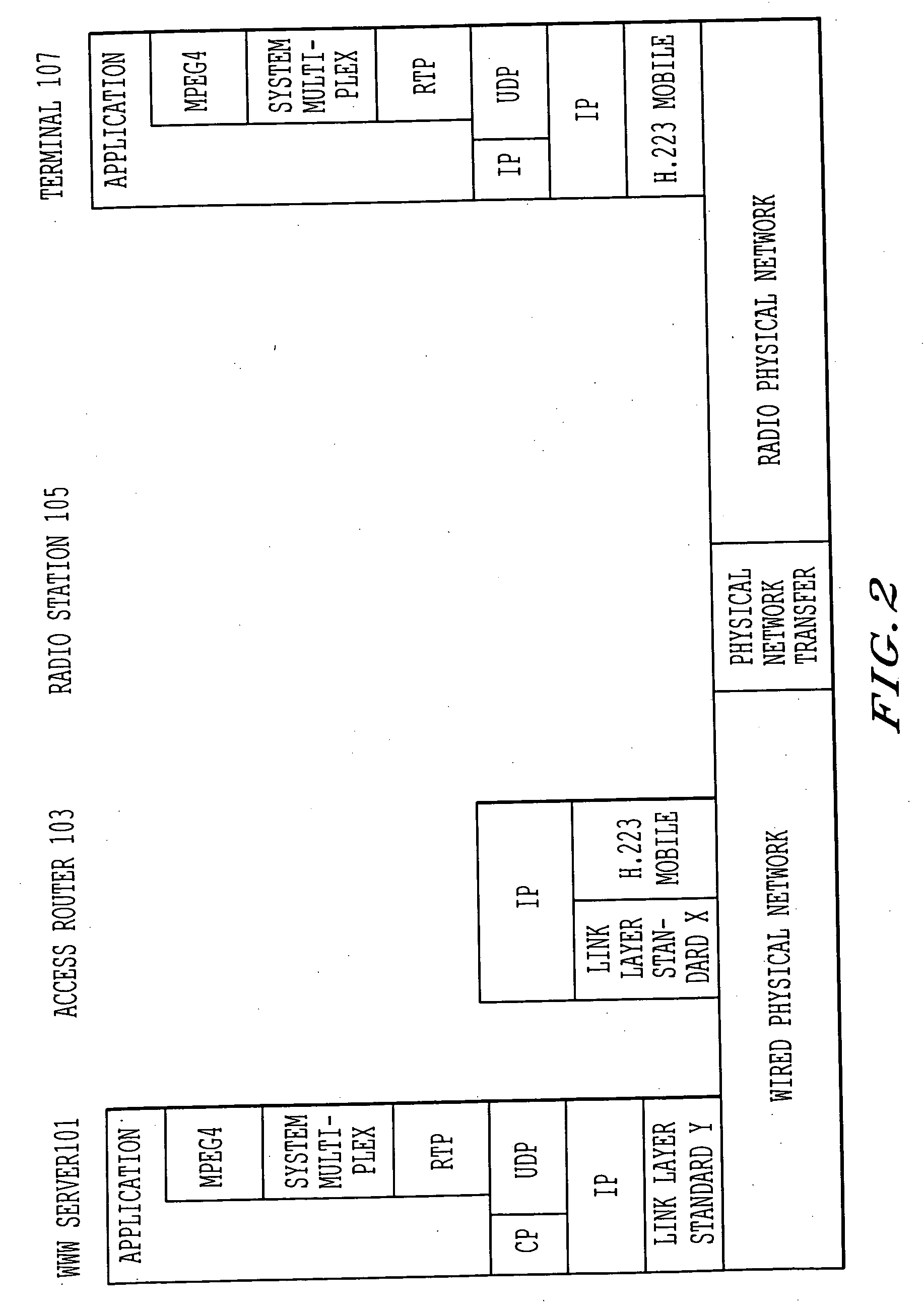
[0054] In the Internet communication system shown in FIG. 1, transmission paths between the access router 103 and the terminal 107 (i.e., a wired transmission path 104 and the radio transmission path 106) are considered part of the Internet 102, beyond just the wired network. However, for purposes of explanation, the transmission paths 104 and 105 are considered separate from the Internet 102 to highlight the present invention, which focuses on the differences in transmission properties (e.g., a transmission error) between those transmission paths 104 and 105 and the Internet 102.
[0055] The terminal 107 securel...
second embodiment
[0121]FIG. 14 shows one example of an entire sequence of the negotiation between the access router 103 and the terminal 107 according to the
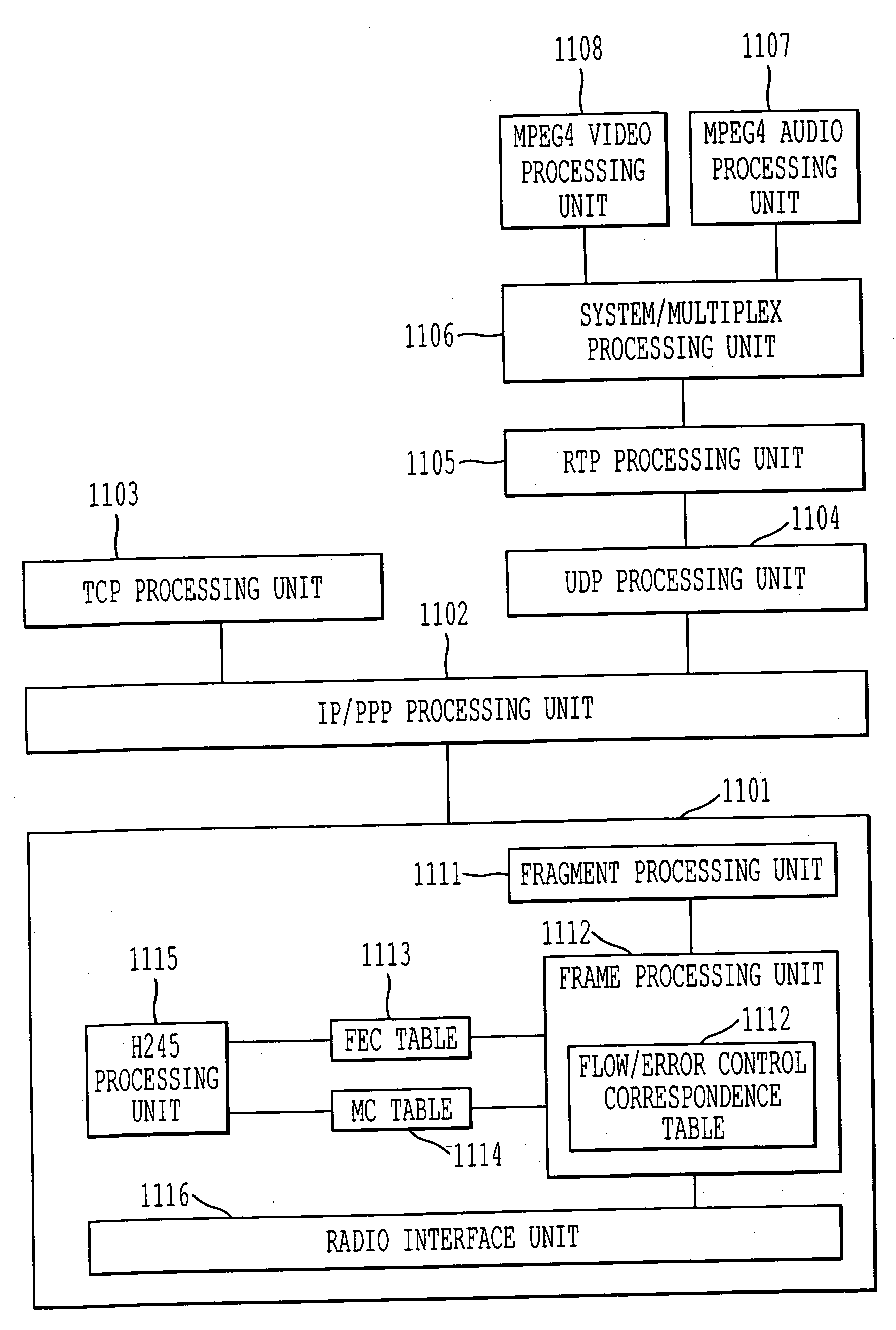
[0122] In the first embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, the type of FEC to be used and other information regarding data are negotiated using separate codes (i.e, the FEC code and the MC code). In this second embodiment, the FEC code is not used, and the value of the MC code, including the type of FEC to be used, is decided during the H.245 negotiation (i.e., what the value of the MC code means is decided through the negotiation). In other words, the negotiation is performed such that both the transmitting and receiving sides can recognize the type of FEC to be used from the MC value. Results of the negotiation are reflected in the MC table shown in, by way of example, in FIG. 15. The MC table is held in both nodes, i.e., the access router 103 and the terminal 107.
[0123] It is negotiated, for example, that in the case of MC=1 and MC=2, data that hav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com