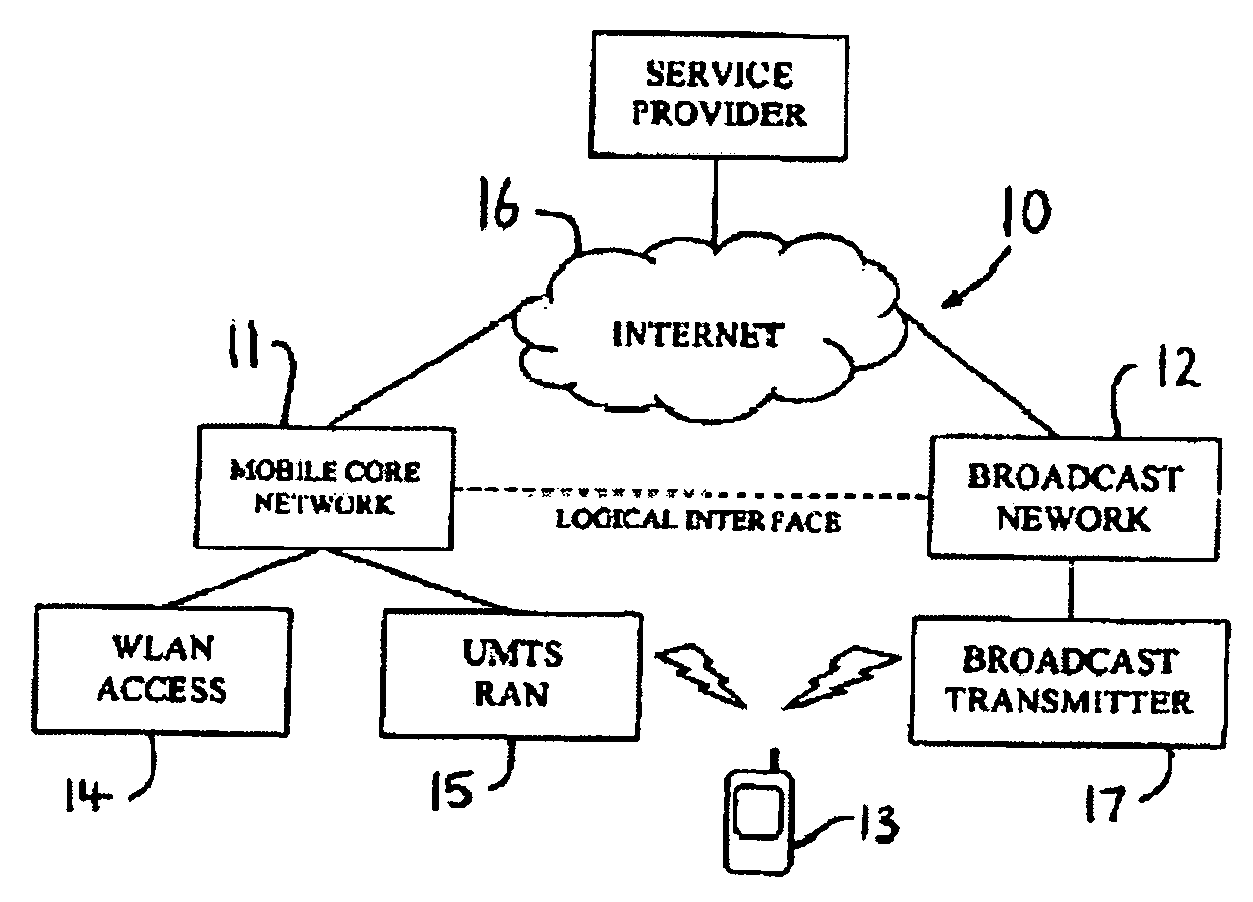
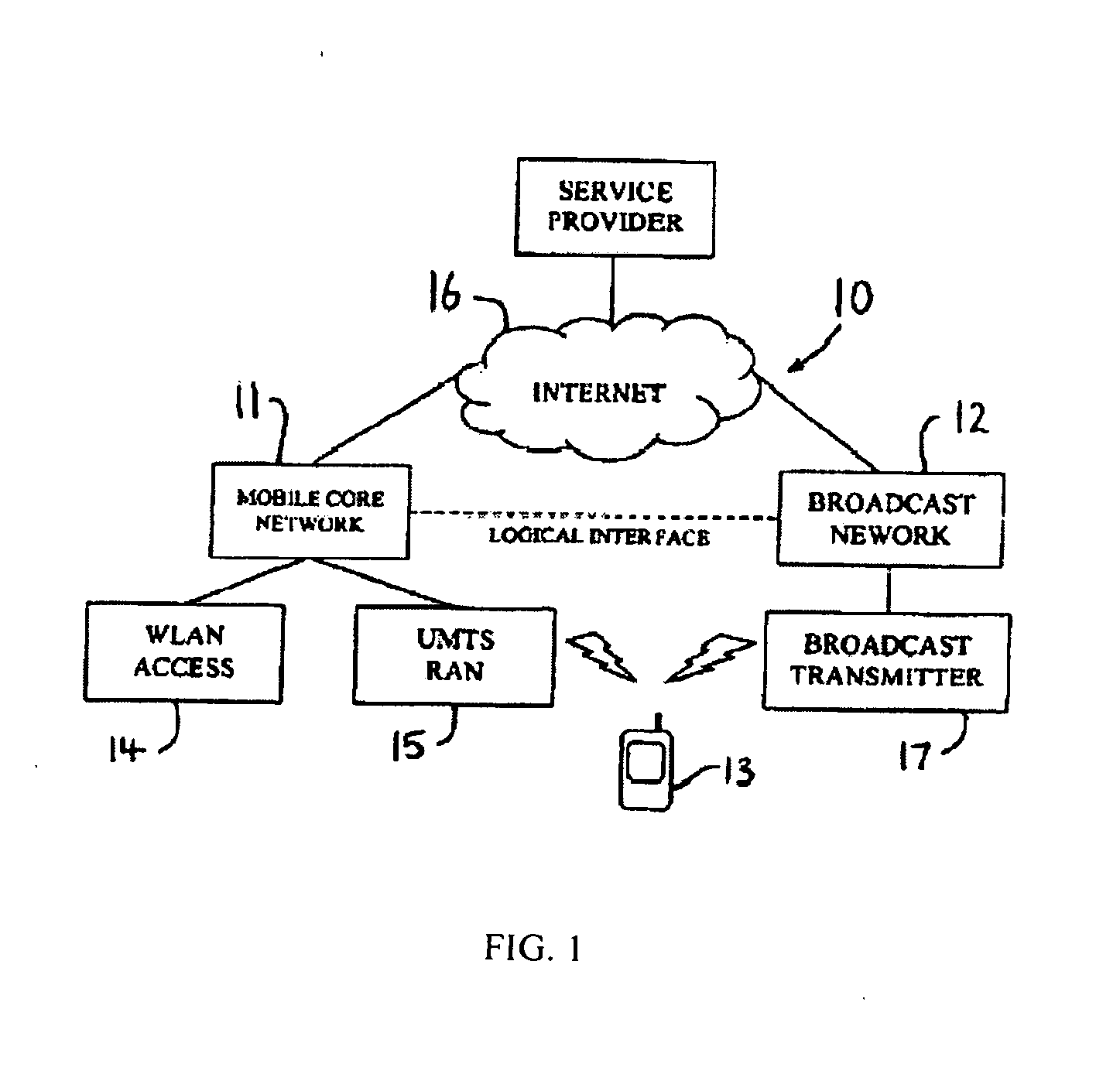
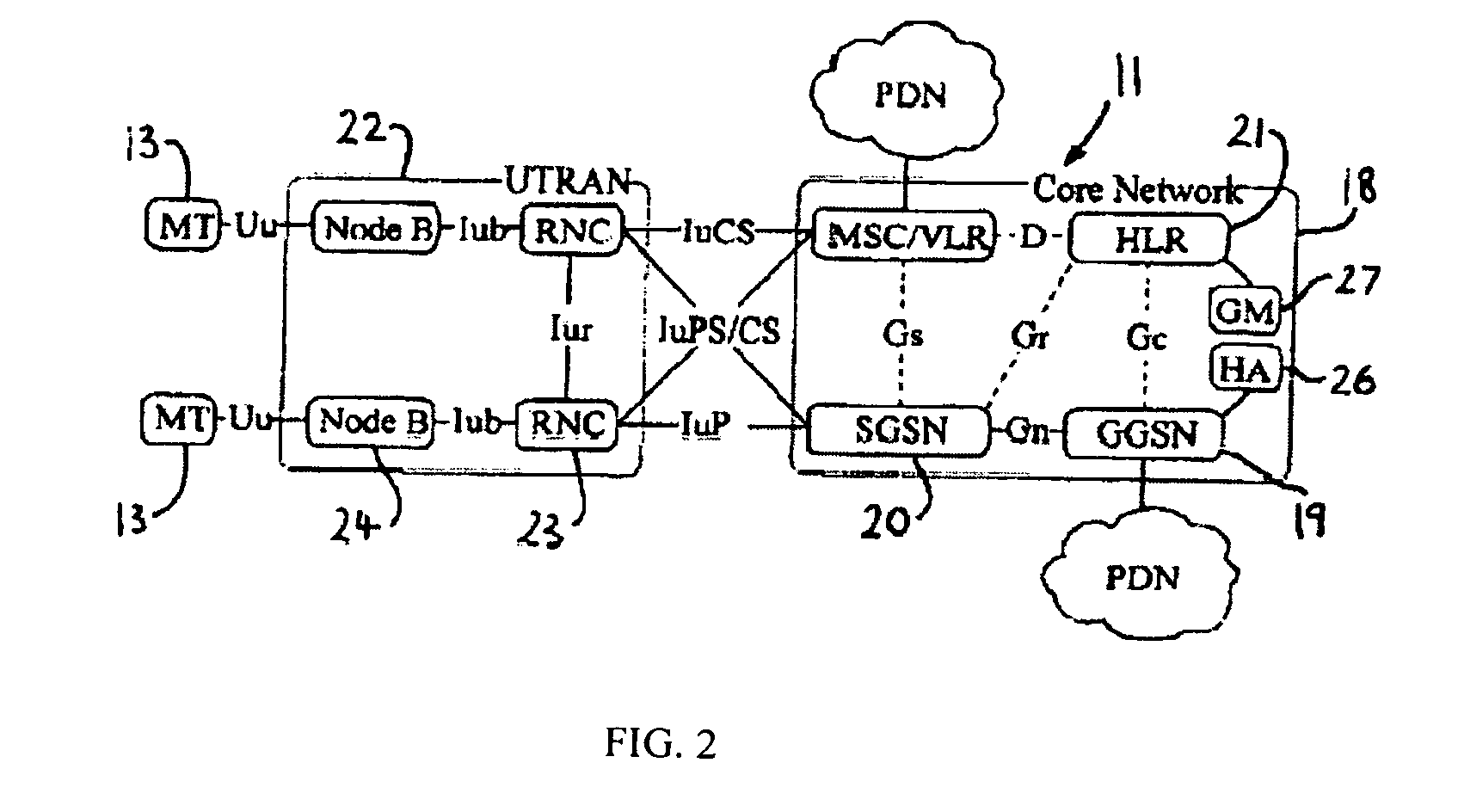
Patents
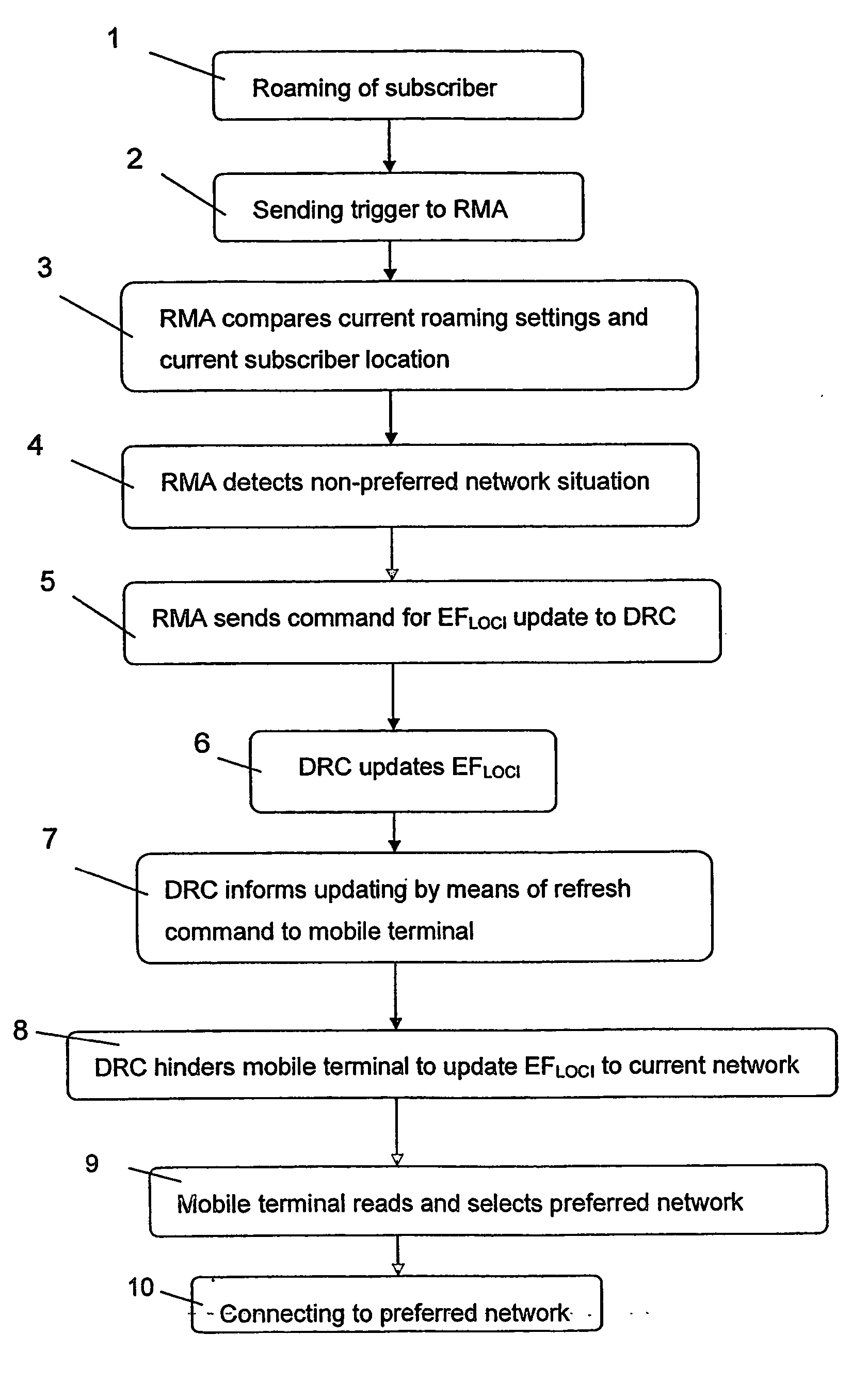
Literature
212 results about "Foreign network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
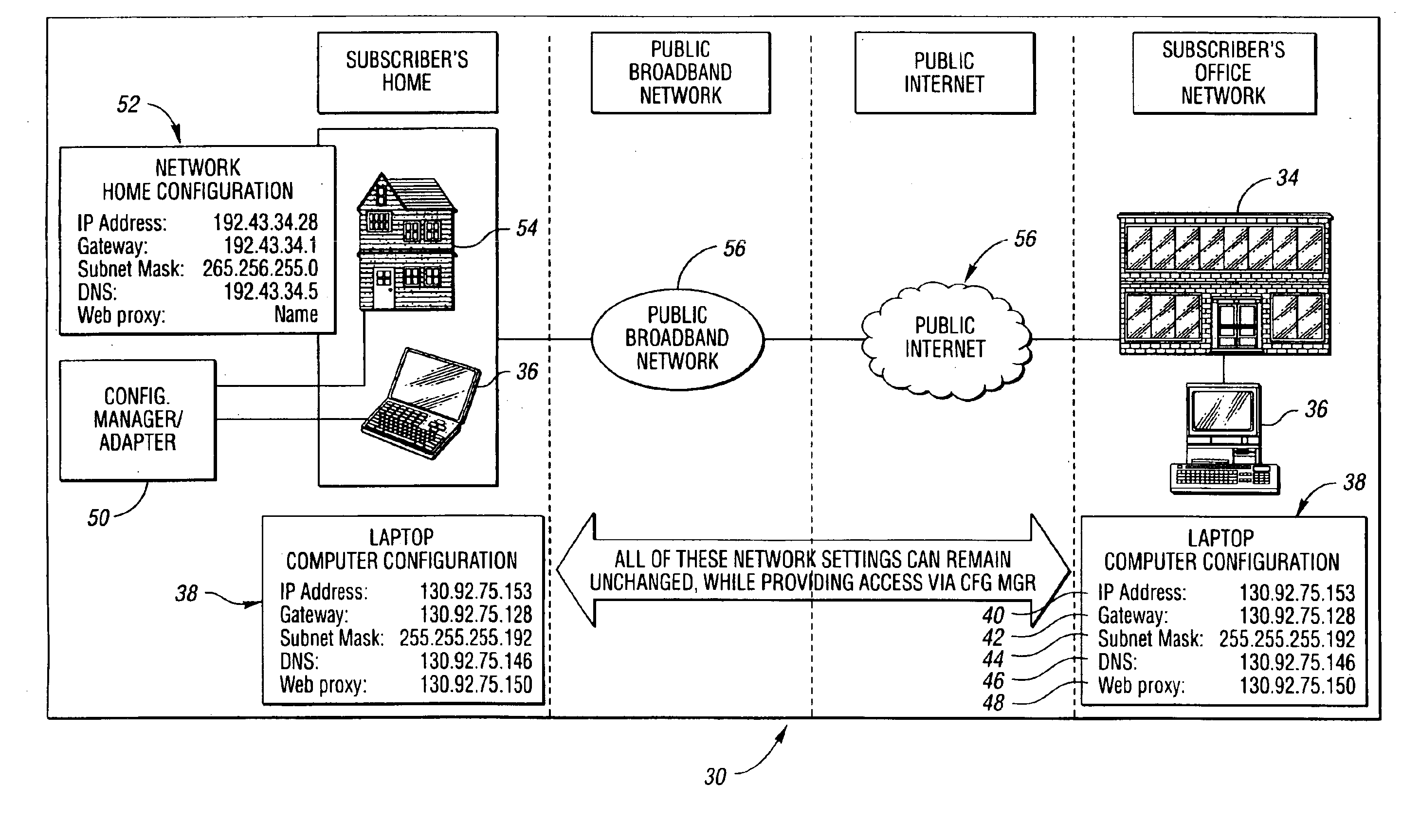
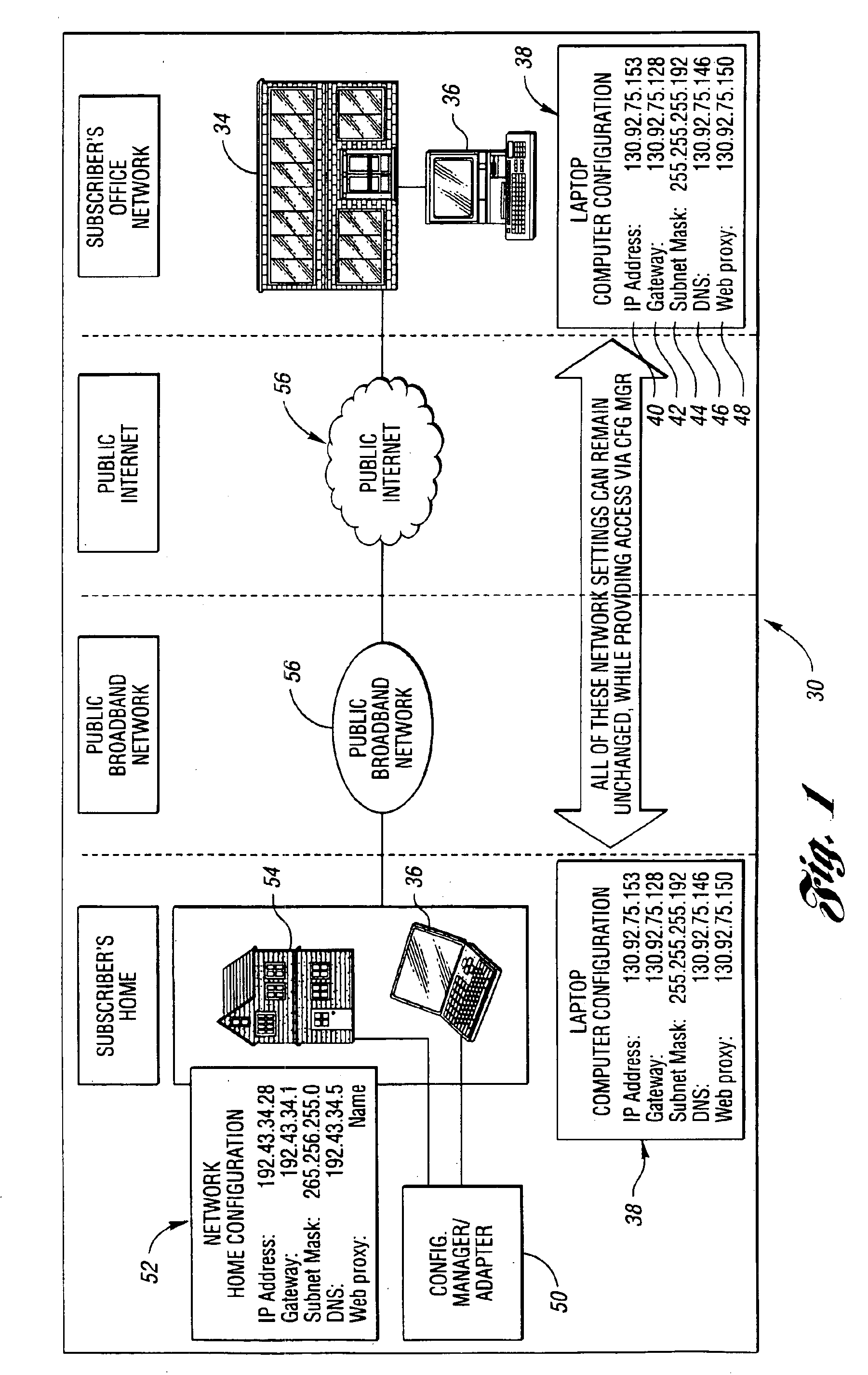
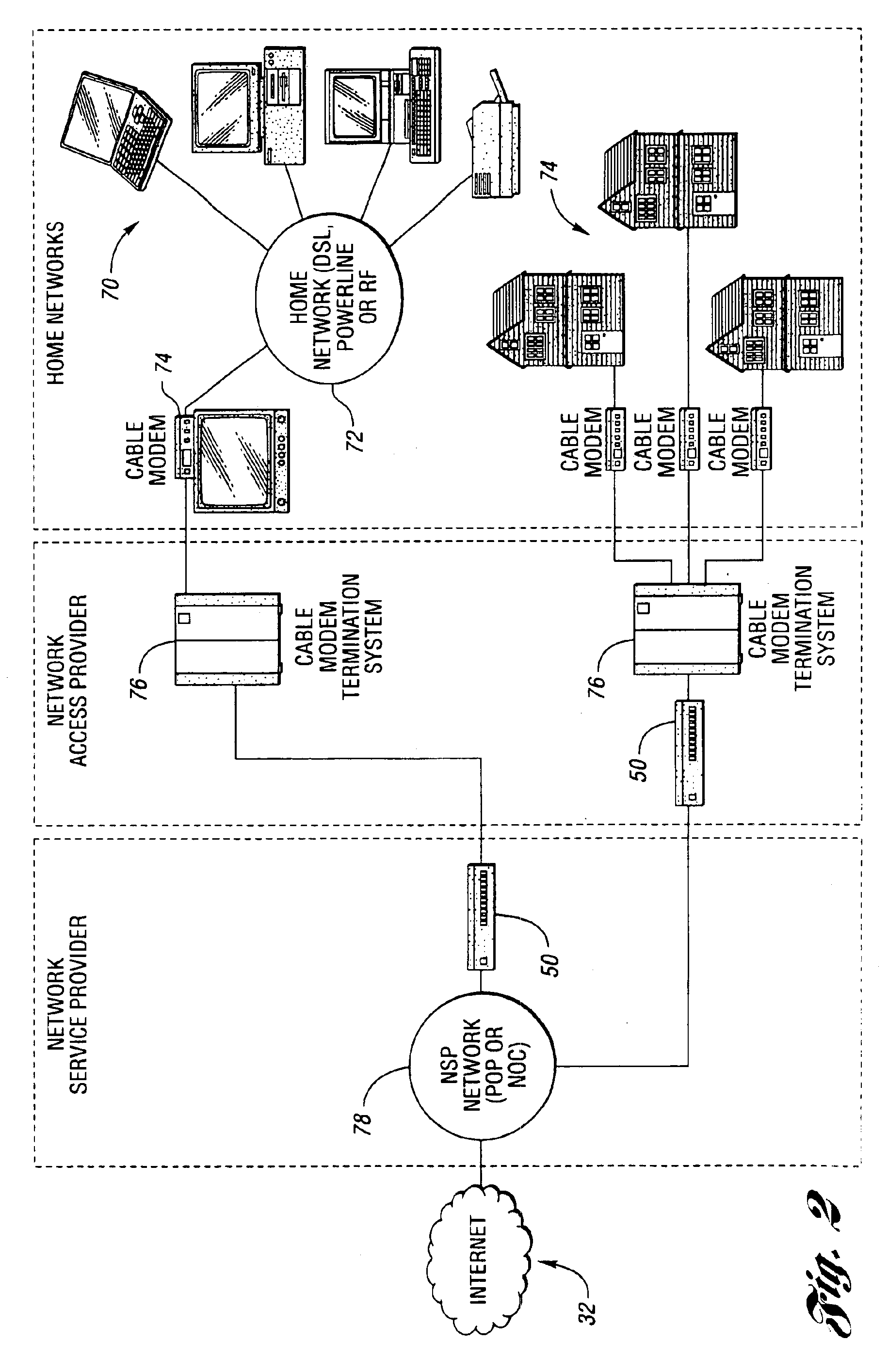
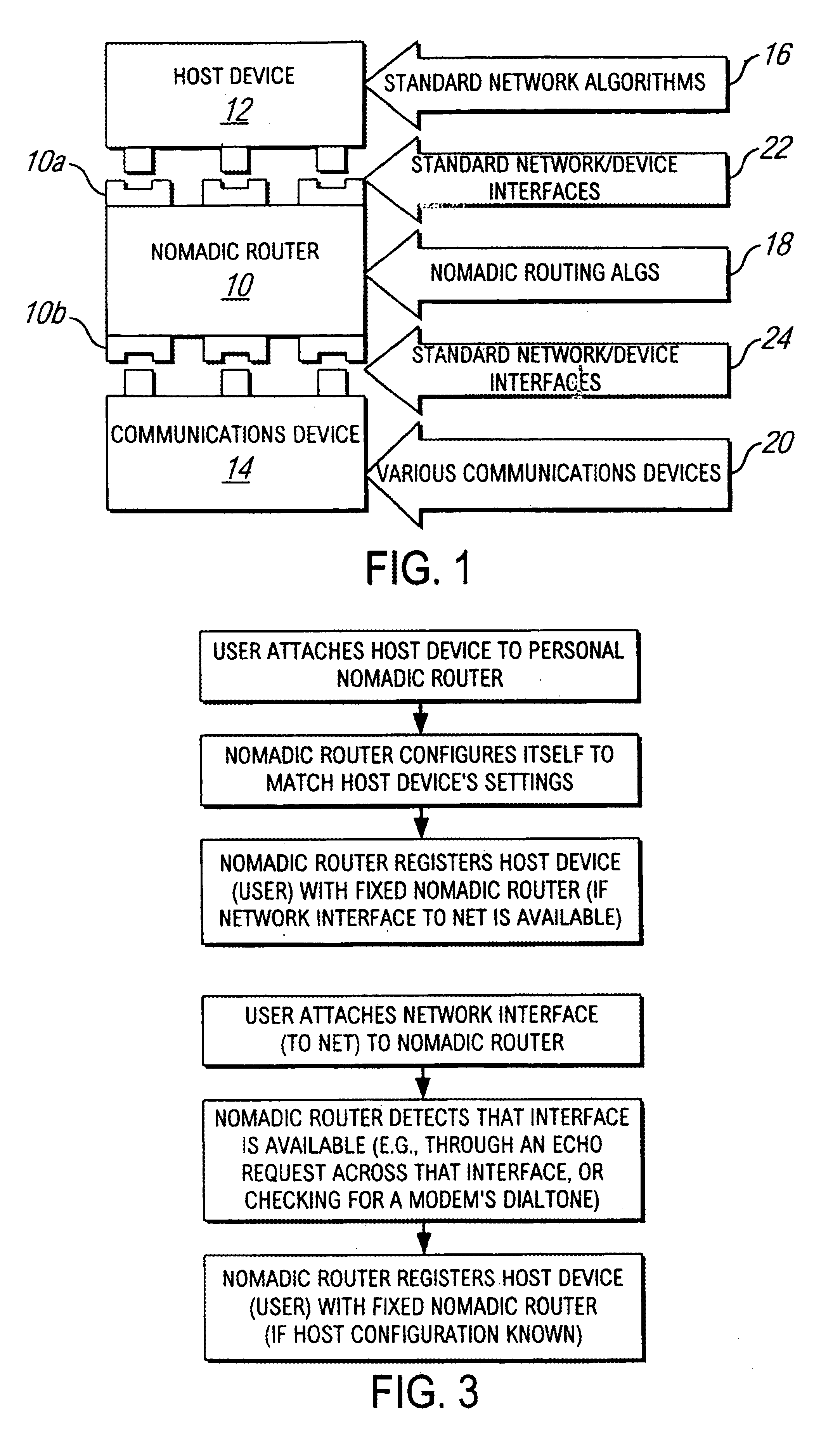
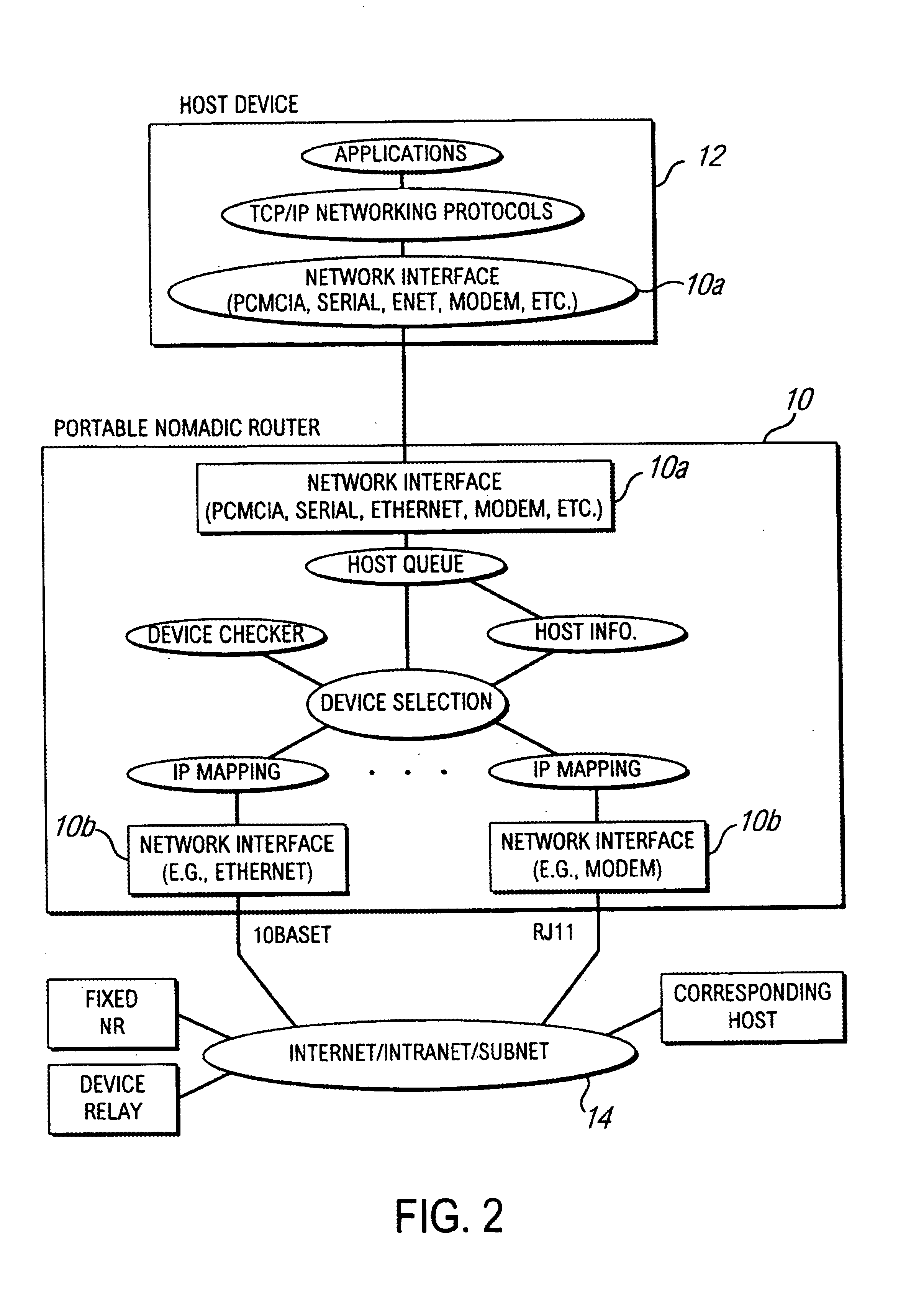
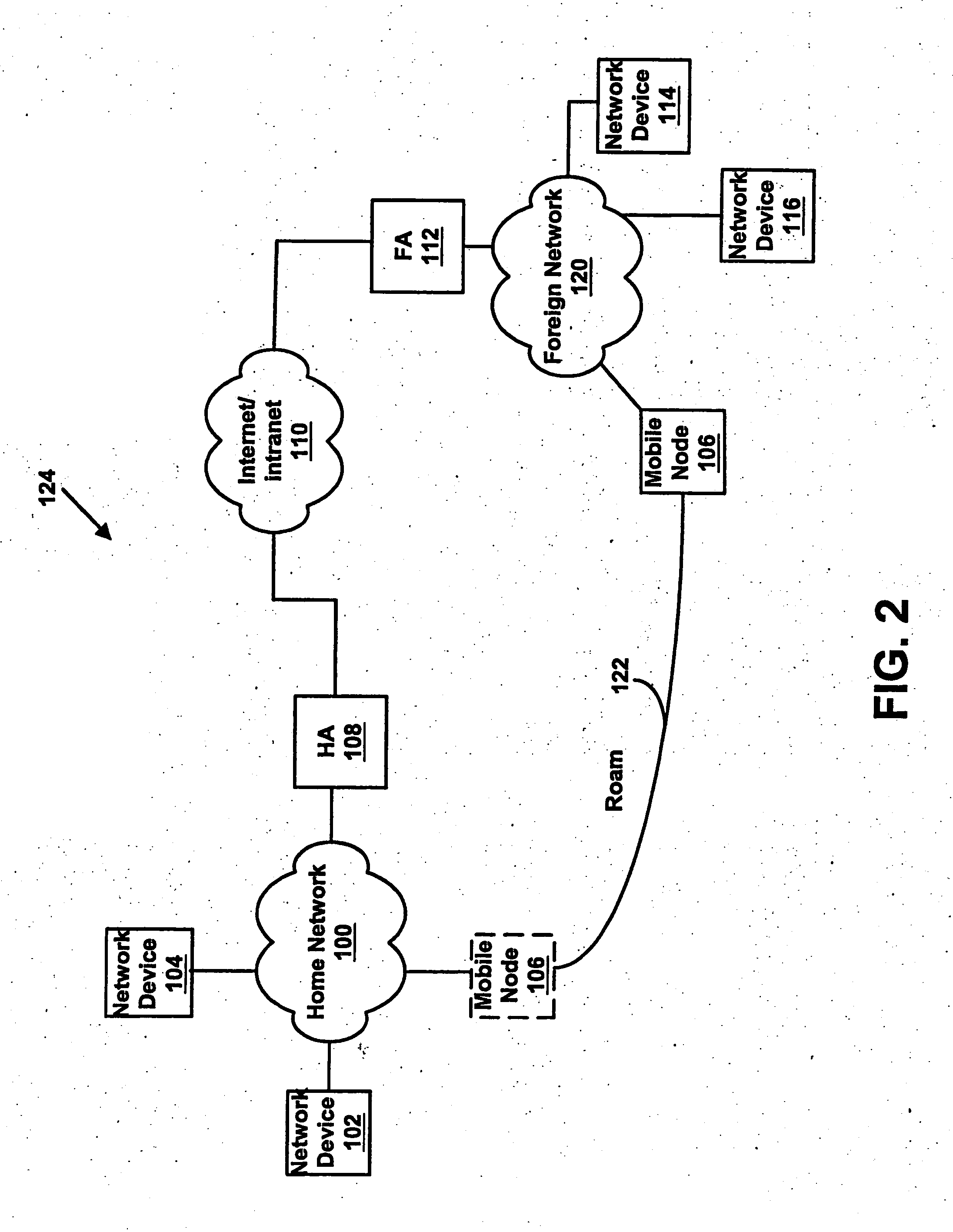
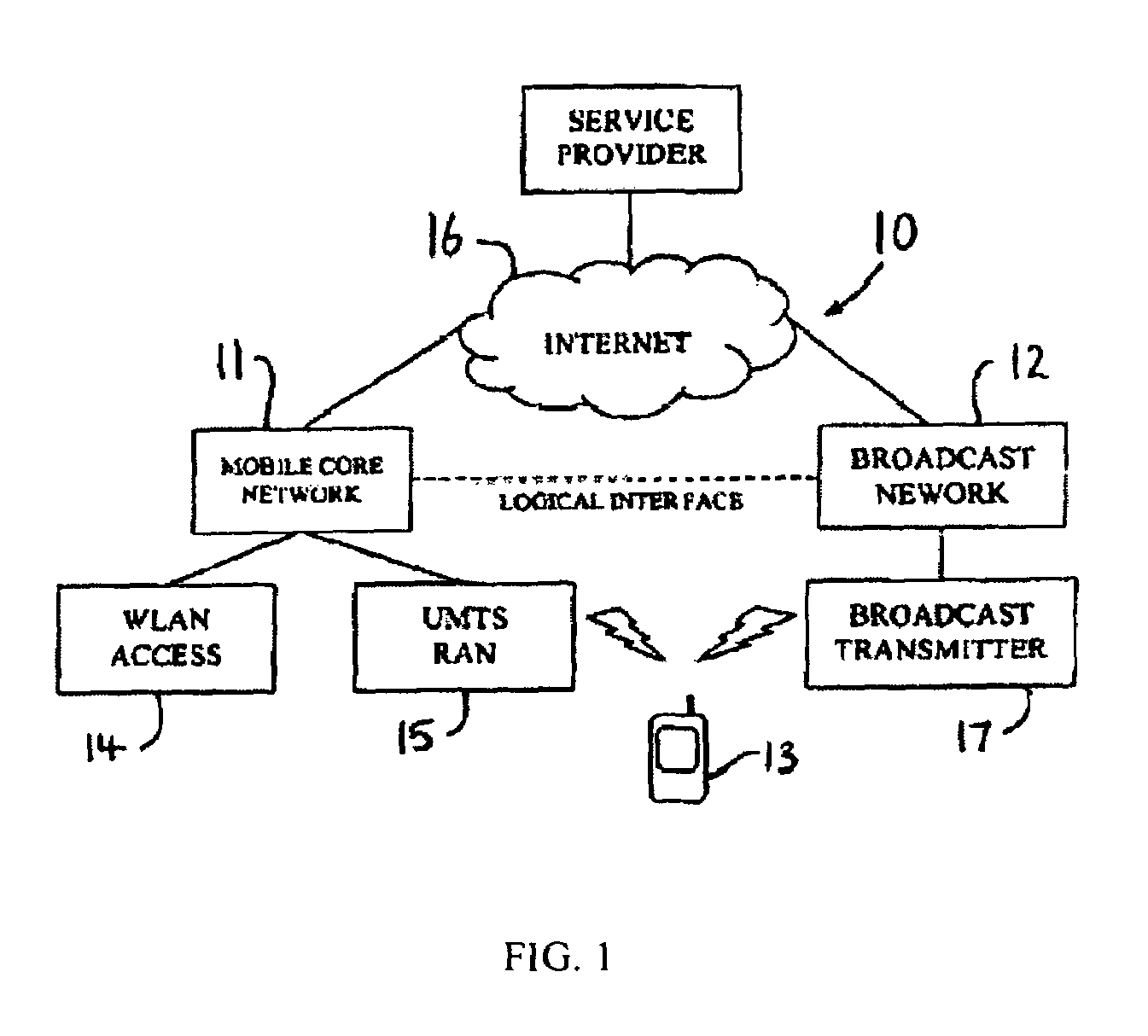
System and method for network access without reconfiguration
InactiveUS6857009B1Easy to addEasy to deleteTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationDomain nameComputer compatibility
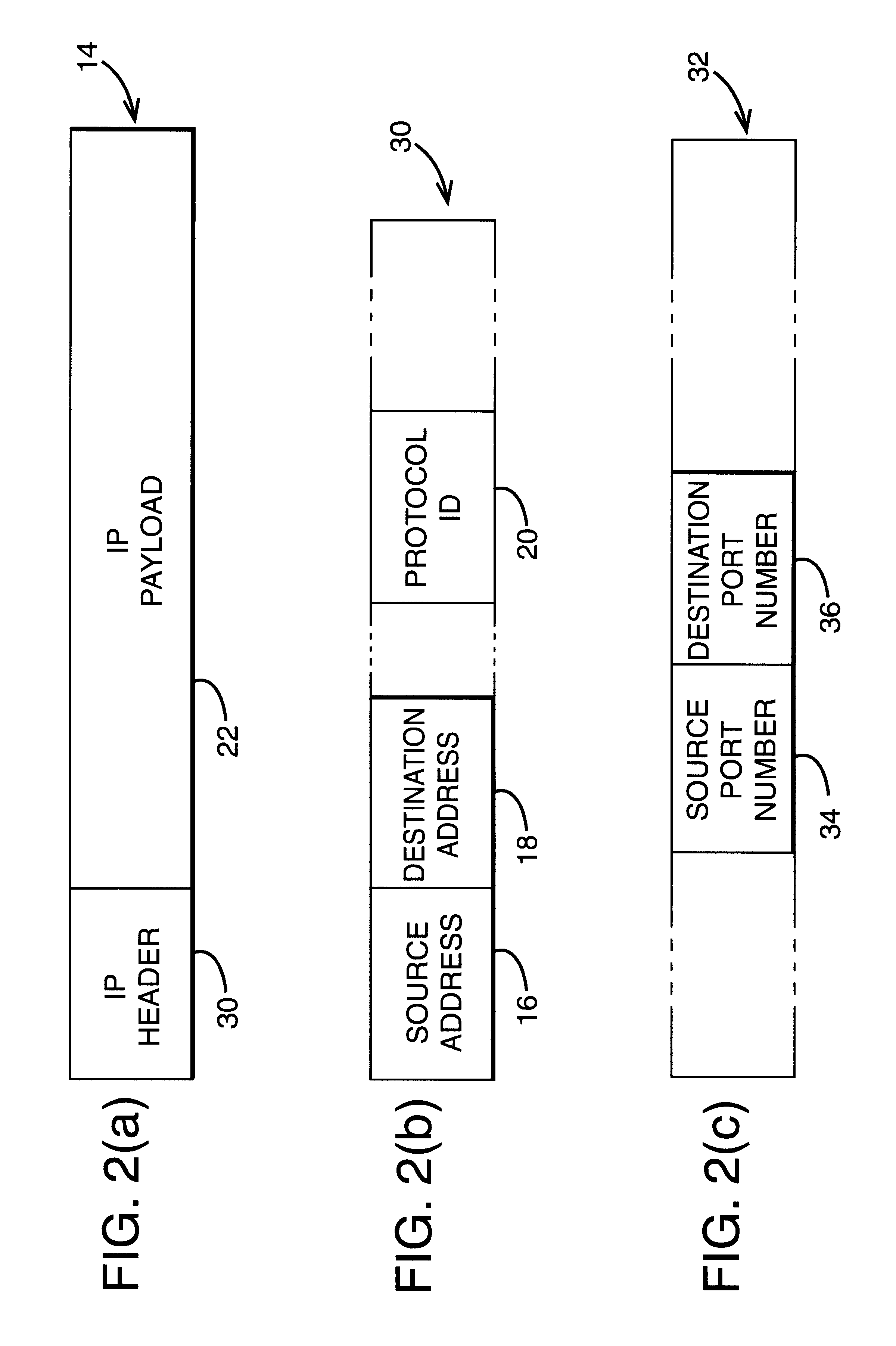
A system and method for providing connectivity to a foreign network for a device configured for communication over a home network without reconfiguring the device include intercepting packets transmitted by the device, selectively modifying intercepted packets which are incompatible with the foreign network to be compatible with network settings of the foreign network, and selectively providing network services for the device corresponding to network services available on the home network to reduce the delay associated with accessing the network services from the foreign network, or to provide network services otherwise inaccessible from the foreign network. Network services are provided by or through a configuration adapter connected to the device or to the foreign network. The configuration adapter accommodates incompatibilities resulting from proxy server requests, domain name server requests, and / or outgoing email service requests to provide transparent network access for mobile users without reconfiguration of the users computing device.
Owner:NOMADIX INC
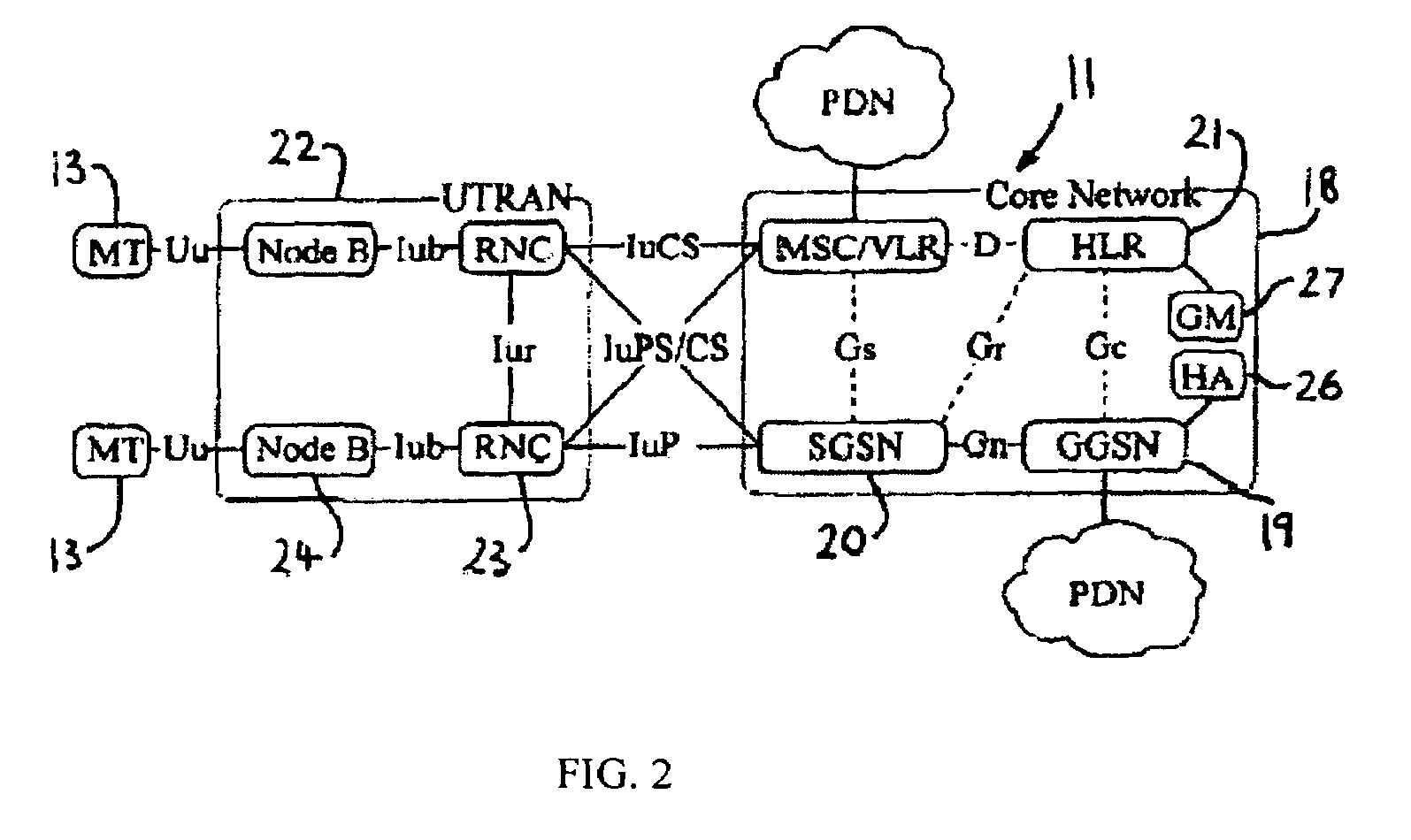
System and method for establishing network connection with unknown network and/or user device
InactiveUS7088727B1Soft handoffImprove throughputTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionNetwork addressing
Owner:NOMADIX INC
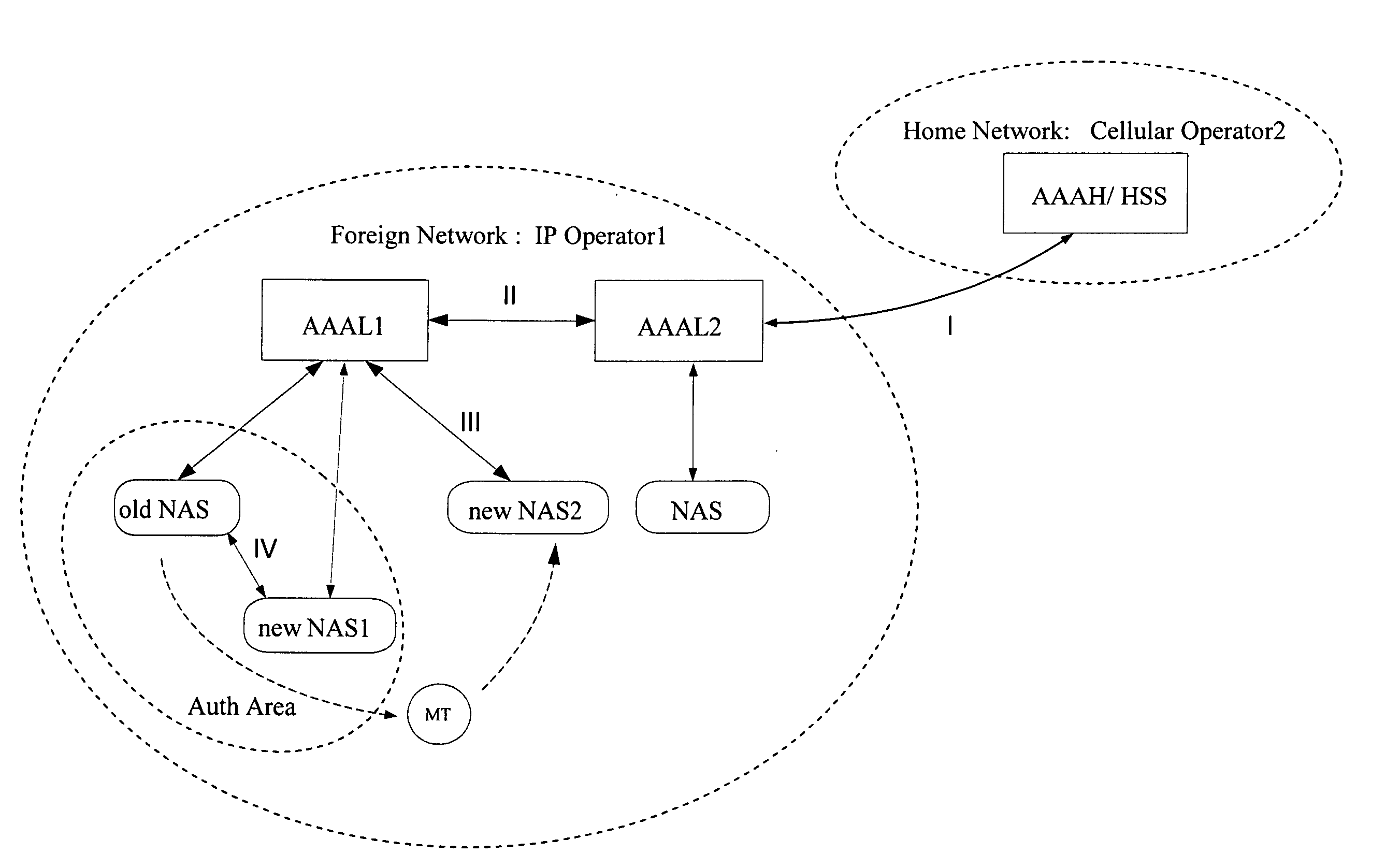
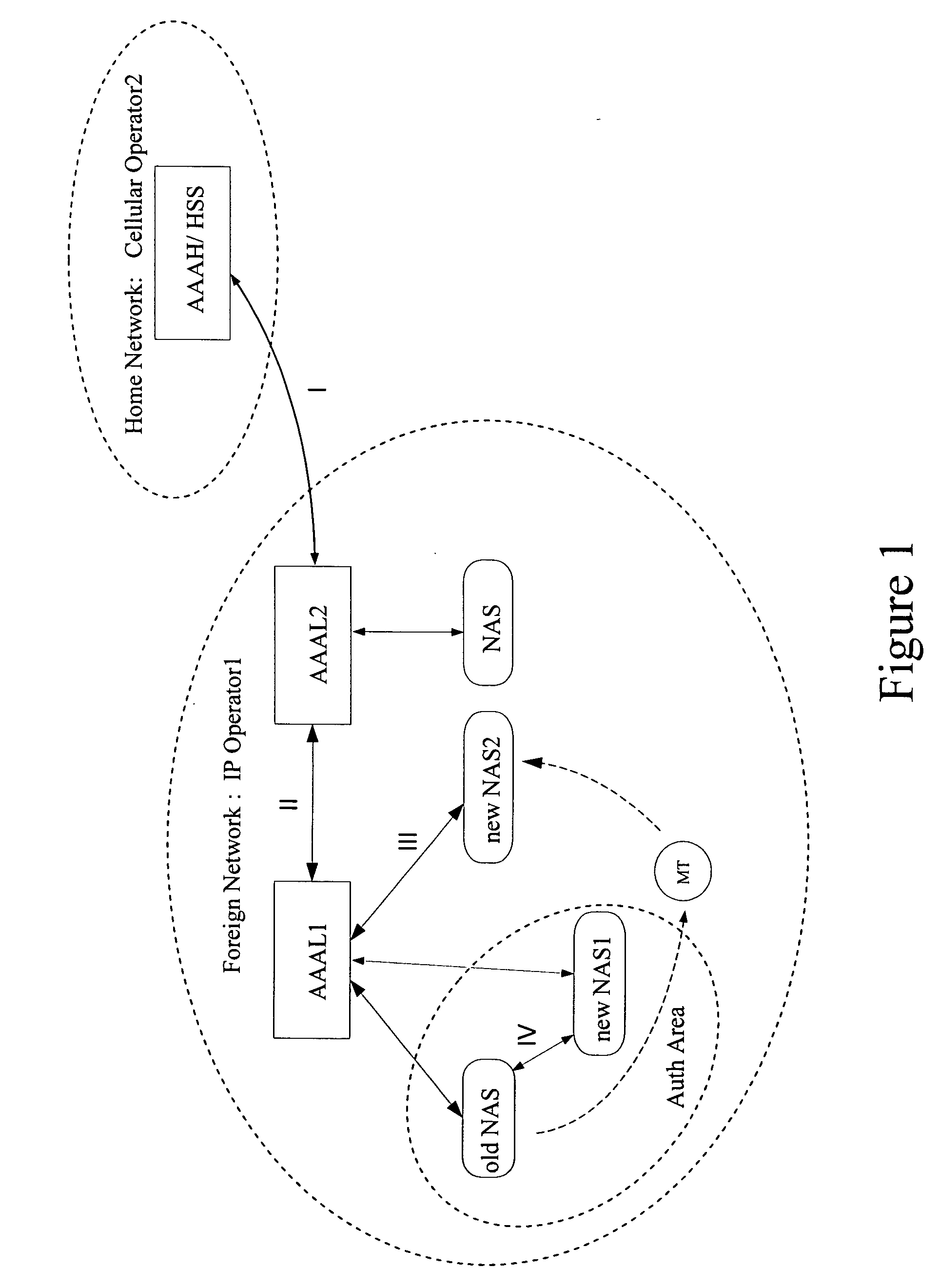
Authentication and authorization in heterogeneous networks
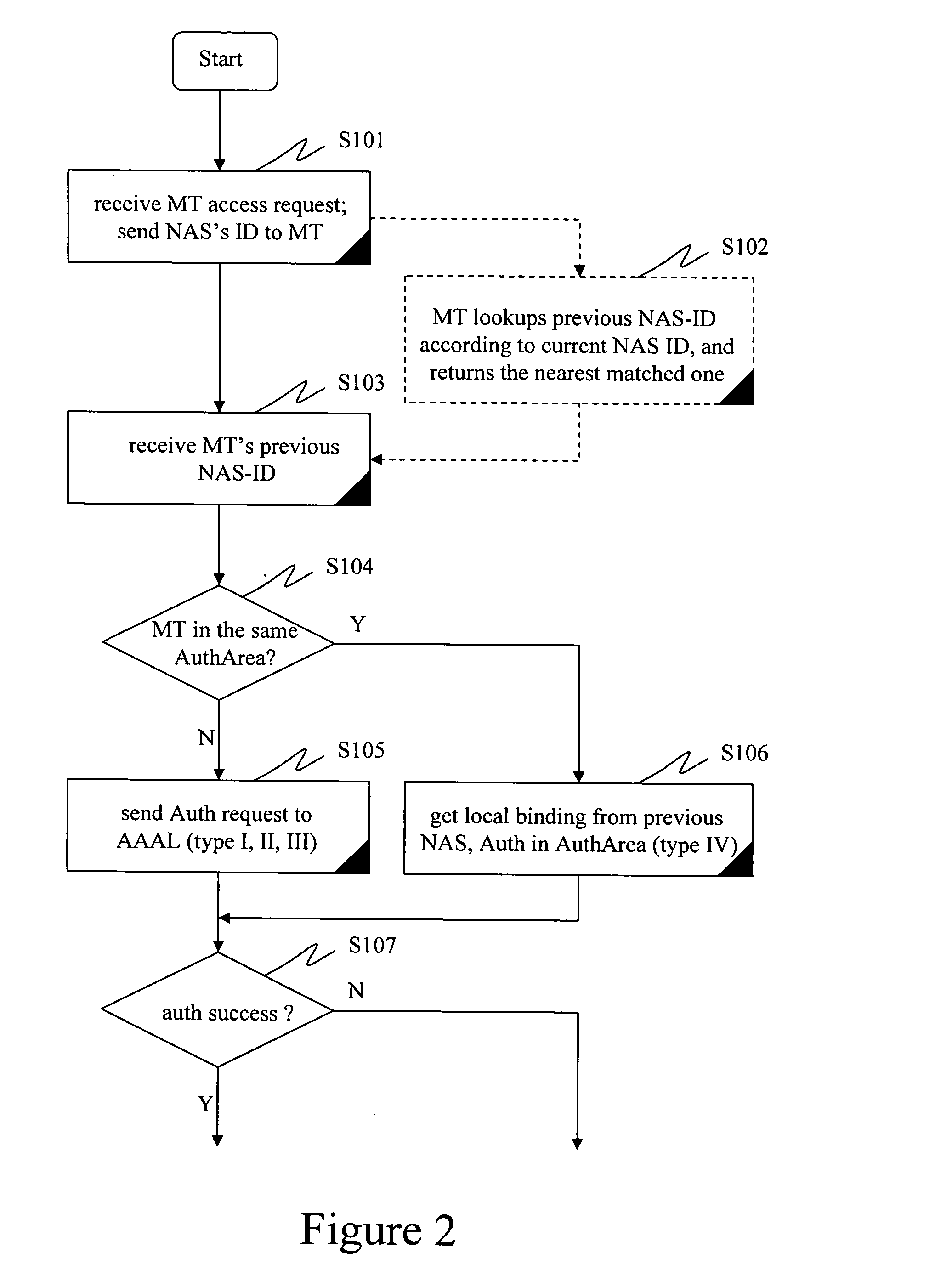
ActiveUS20050166043A1Optimized network access performanceImproved AAA performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksNetwork access serverHeterogeneous network
A method, system, and network elements for authentication and authorization of a mobile terminal (MT) roaming to or in a foreign network different from its home network is provided, the home network having an authentication and authorization home server (AAAH), and the foreign network having a plurality of domains each of which comprises at least one local server (AAAL1, AAAL2) for authentication, authorization and accounting, each of which local servers being connected to at least one network access server (NAS) for handling access for mobile terminals roaming to or in the foreign network, wherein an authentication and authorization of the mobile terminal is performed whenever the mobile terminal performs a roaming, wherein the authentication and authorization is performed according to a procedure pursuant to one of a plurality of hierarchy levels, whereby a combination of network elements involved in the roaming determines the hierarchy level to be used.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Roaming presence and context management
InactiveUS20060052113A1Freedom of movementWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsContext managementRoaming
Apparatus for mediating between a cellular telephony network and a wireless LAN, comprises a first adaptor for allowing signal exchange with the cellular telephony network, a second adaptor for allowing signal exchange with the wireless LAN; and a presence tracker associated with the adaptors for obtaining and storing a current location of a wireless device on any of the networks. The apparatus allows for mobile wireless devices to connect to wireless LANs and be able to register and receive services from their mobile operator, by treating the LAN in the same way as a foreign network in International roaming.
Owner:STARHOME GMBH
Roaming method
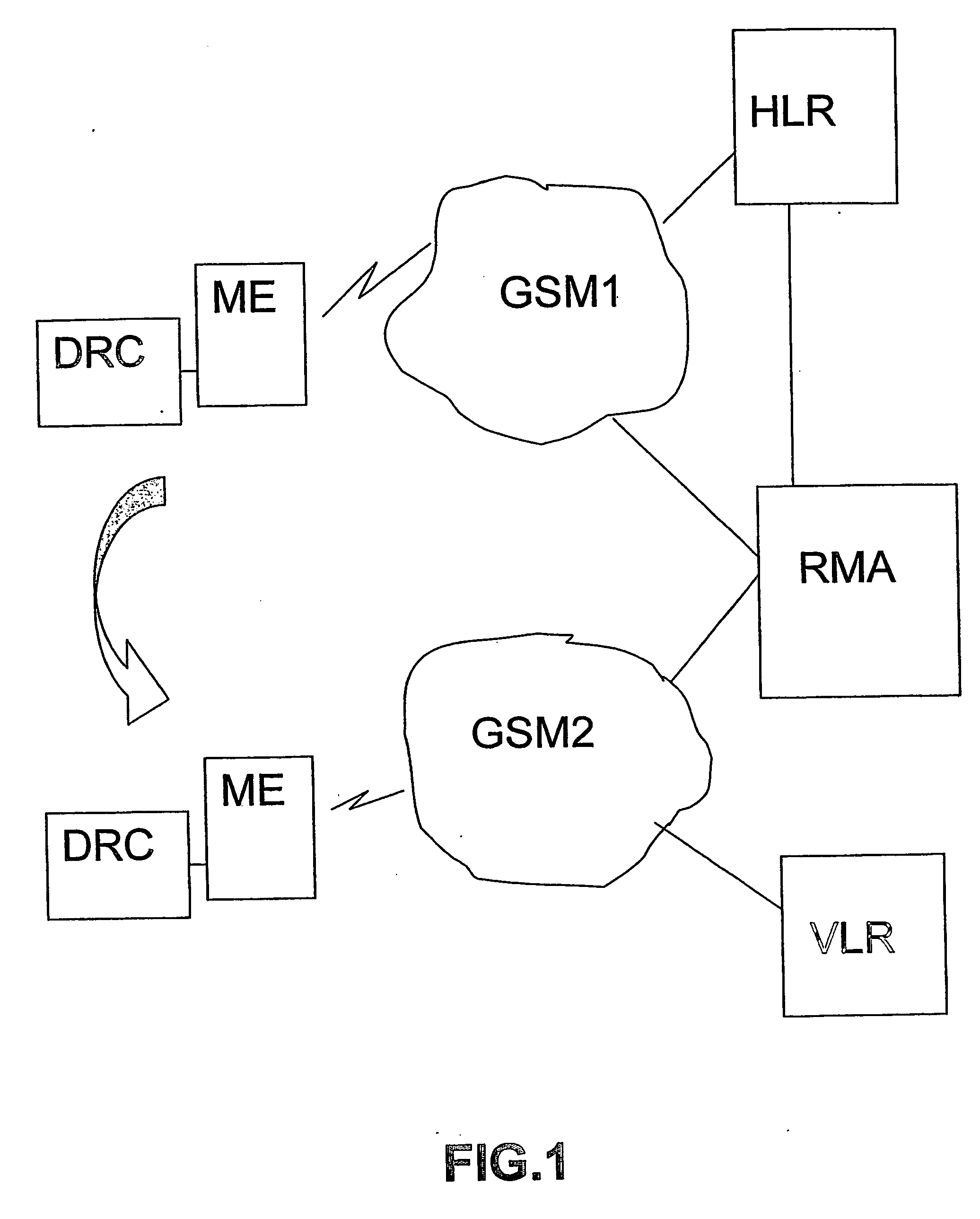
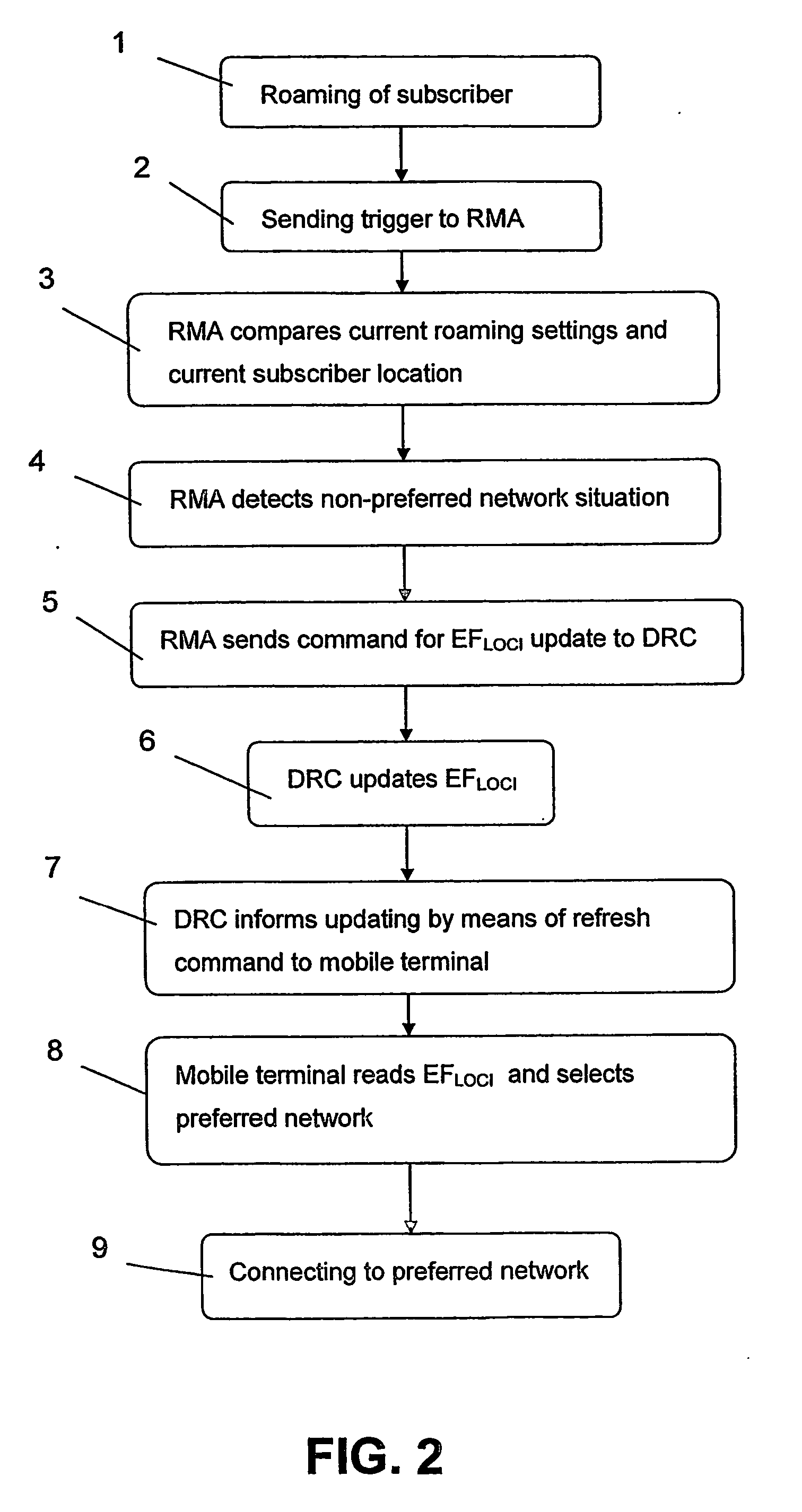
ActiveUS20060052100A1Intermediate rollback of EF<sub>LOCI </sub>can be avoidedSubstation equipmentRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsForeign network
The method relates to the management of roaming of mobile subscribers between a home network and foreign networks. The roaming behavior of a mobile terminal is based on roaming settings in the form of contents of different control files saved in the mobile terminal of the subscribers. A first file contains a list of networks to be used in a priority order in a roaming situation and a second file contains information about the last network the subscriber was registered in. The method starts with roaming of the subscriber from one network to another network, and checking the current roaming setting for the subscriber. If the network that the subscriber roamed into does not correspond to the highest priority network, the subscriber is moved to a preferred network corresponding to the priority order of said list.
Owner:GIESECKE & DEVRIENT MOBILE SECURITY GMBH
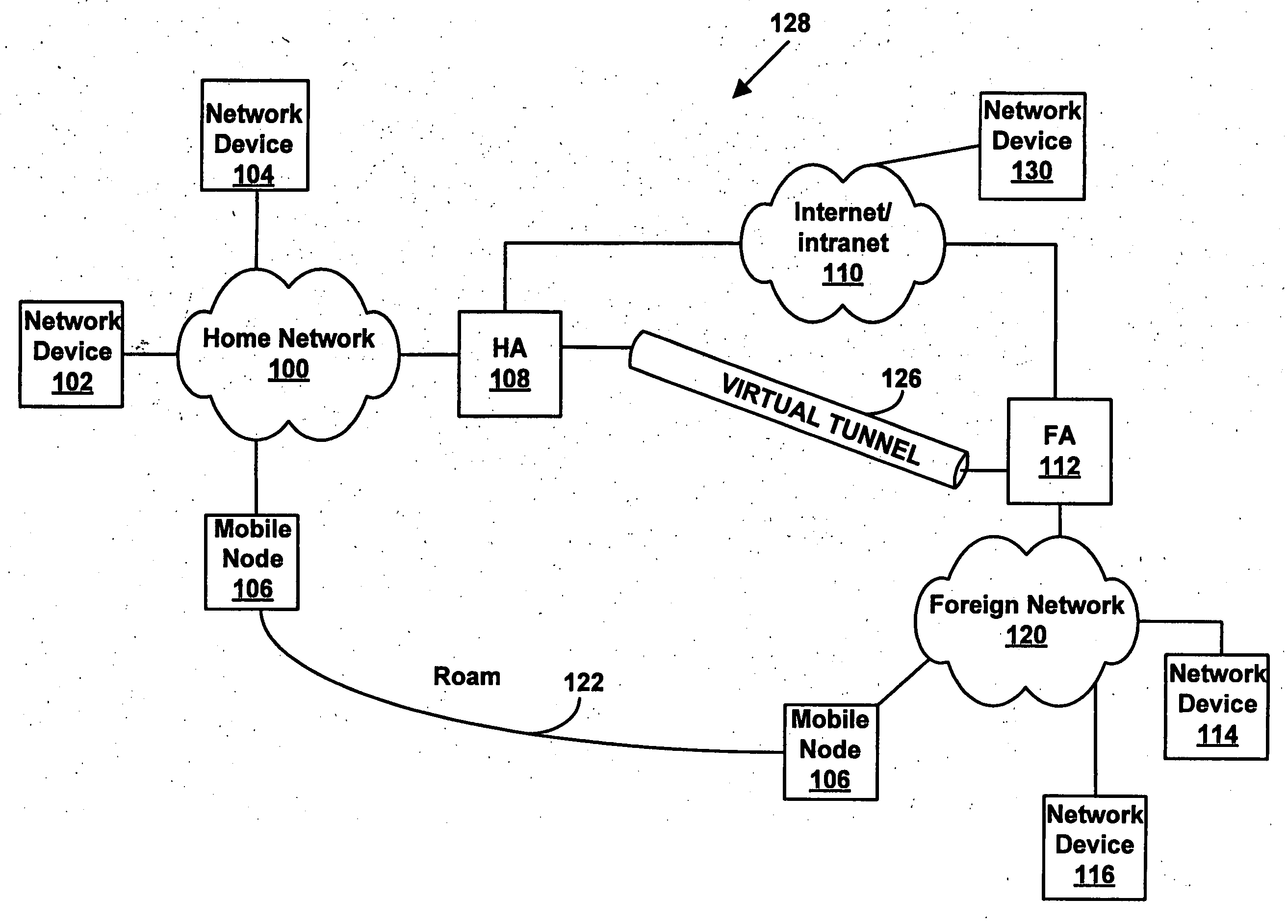
Method to provide dynamic internet protocol security policy service
InactiveUS6839338B1Overcome problemsWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInternet protocol suiteForeign agent
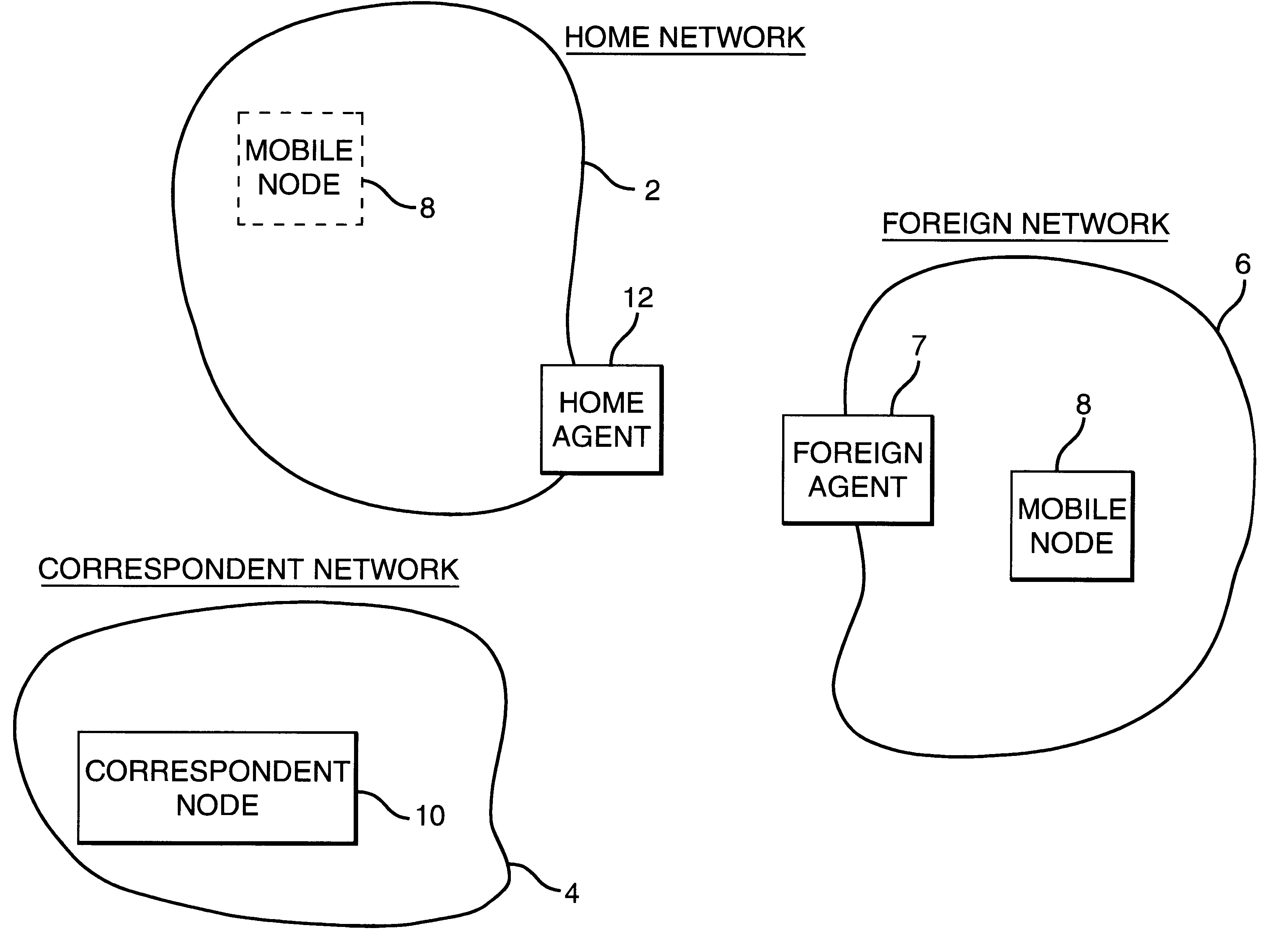
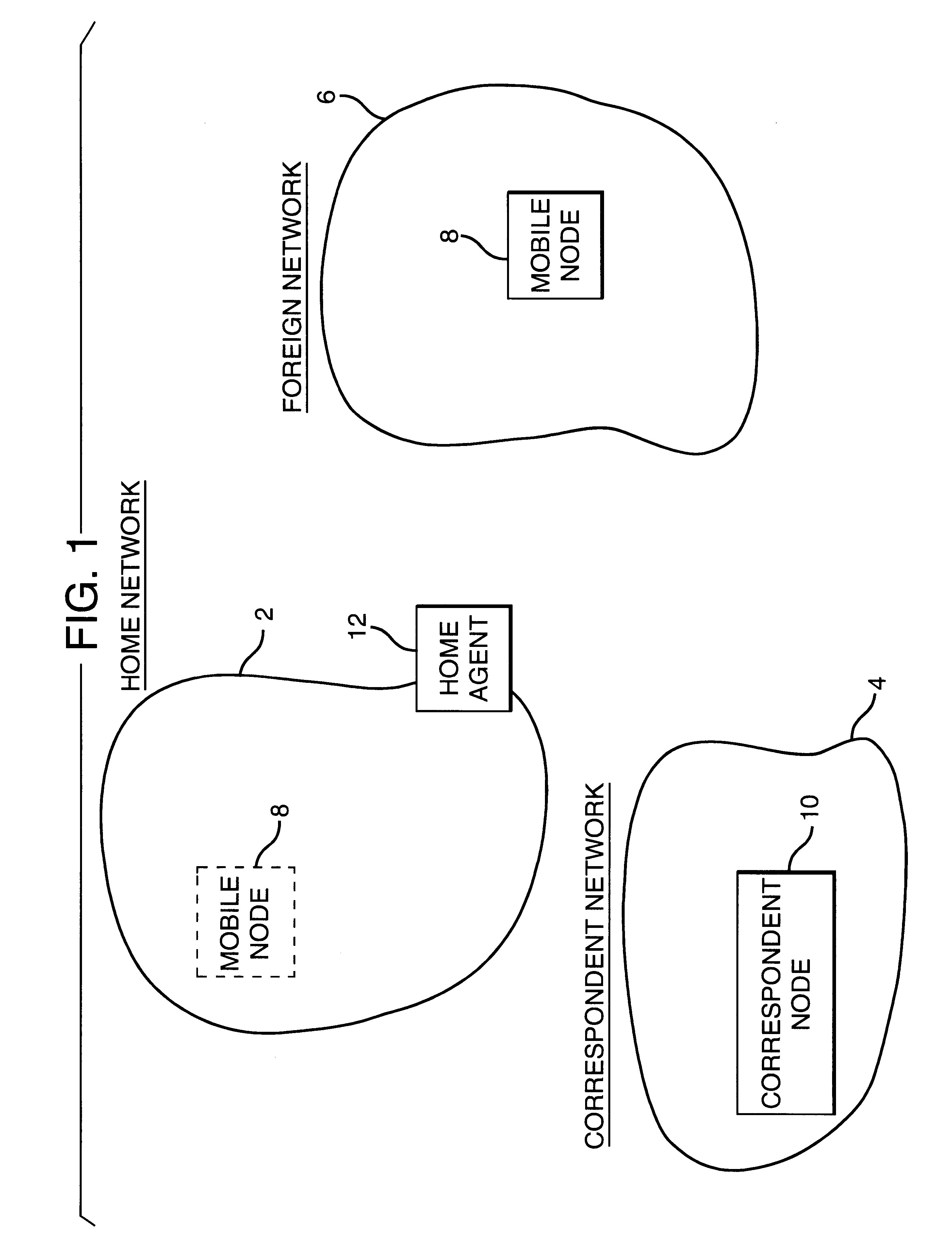
A mobile node may roam away from its home network to a foreign network. The mobile node may communicate using the Mobile Internet Protocol, and it may use Internet Protocol security to communicate with its home network. A foreign agent on the foreign network and a home agent on the home network may dynamically link a policy to be used for a Internet Protocol security session between the foreign agent and the home agent. The foreign agent and the home agent may dynamically create a filter to be used for the Internet Protocol Security session.
Owner:FORTINET
Roaming gateway for support of advanced voice services while roaming in wireless communications systems
ActiveUS7403775B2Connection managementBroadcast service distributionCommunications systemIt service providers
A roaming gateway for support of advanced voice services while roaming in wireless communications systems. The roaming gateway supports push-to-talk (P2T) calls, or other advanced voice services, when P2T subscribers roam from their home network (i.e., a network operated by their service provider where the subscriber's profile resides) into a foreign network (i.e., a network operated by another service provider). The roaming gateway is a specialized version of a real-time exchange that is located in the home network and is connected to mobile switching centers in foreign networks, so that the mobile switching centers in the foreign networks need not be programmed for the advanced voice services.
Owner:KODIAK NETWORKS
Security framework for an IP mobility system using variable-based security associations and broker redirection
InactiveUS7174018B1Improve securityPromote large-scale roamingWireless network protocolsSecret communicationService-level agreementSecurity association
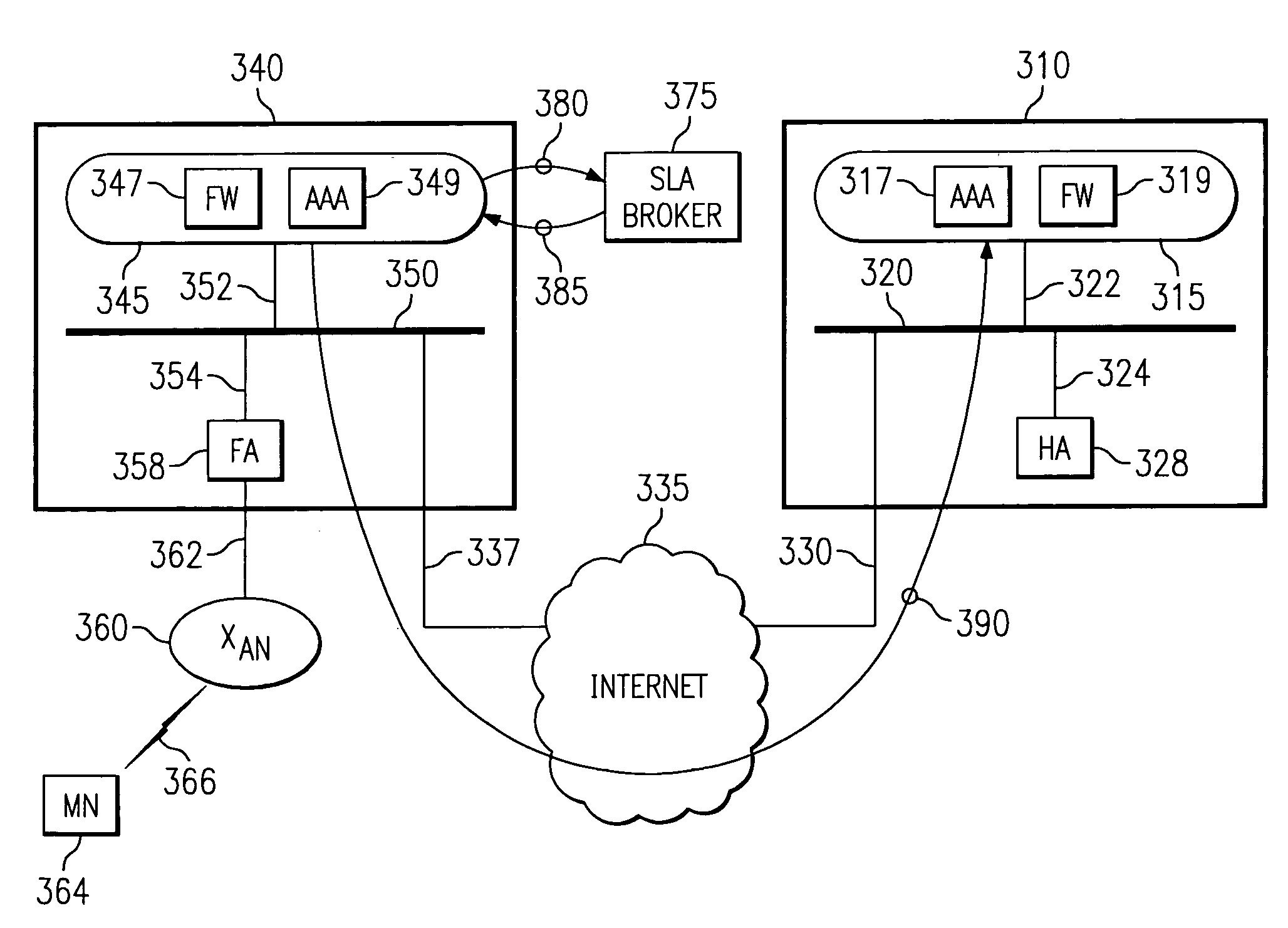
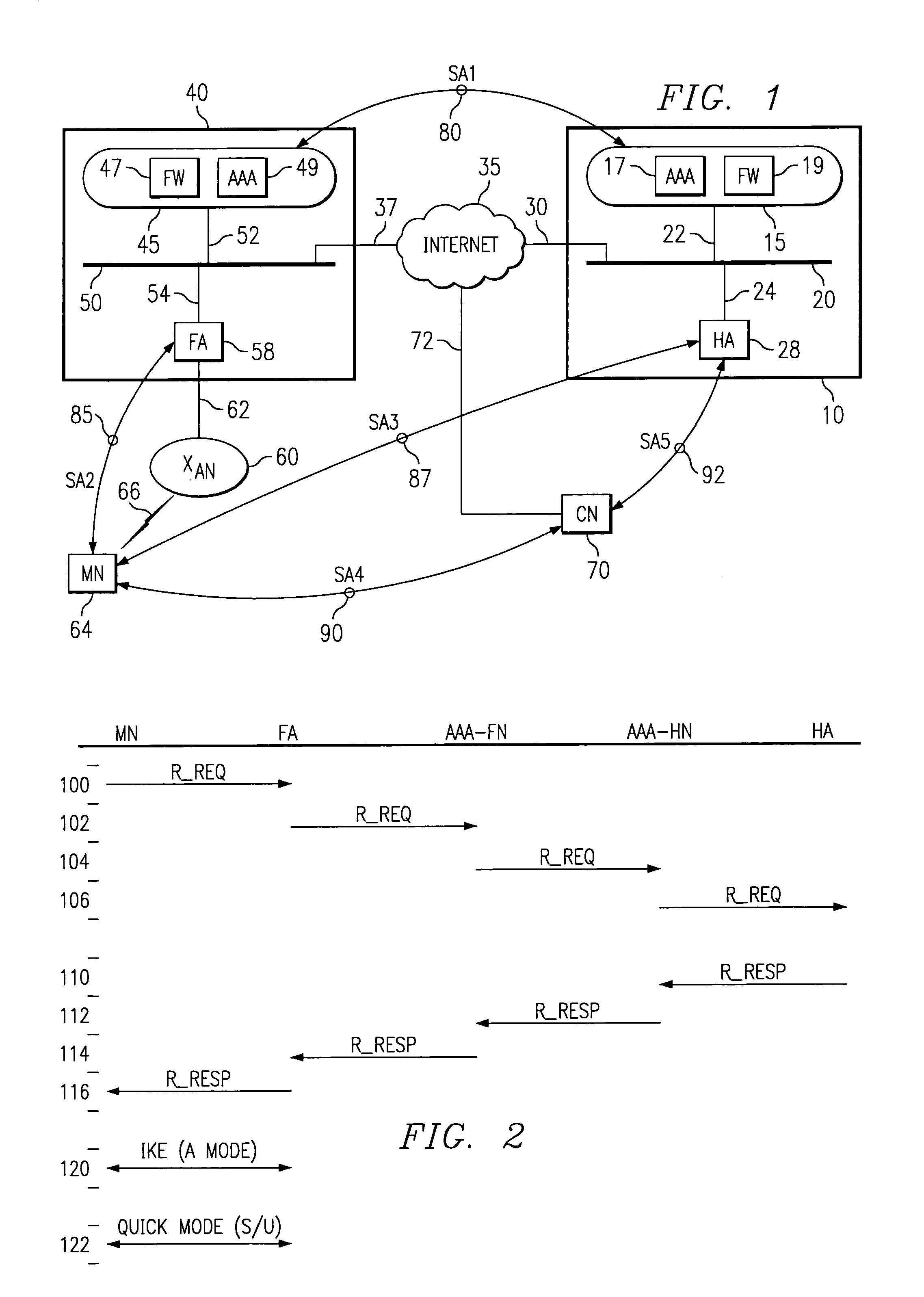
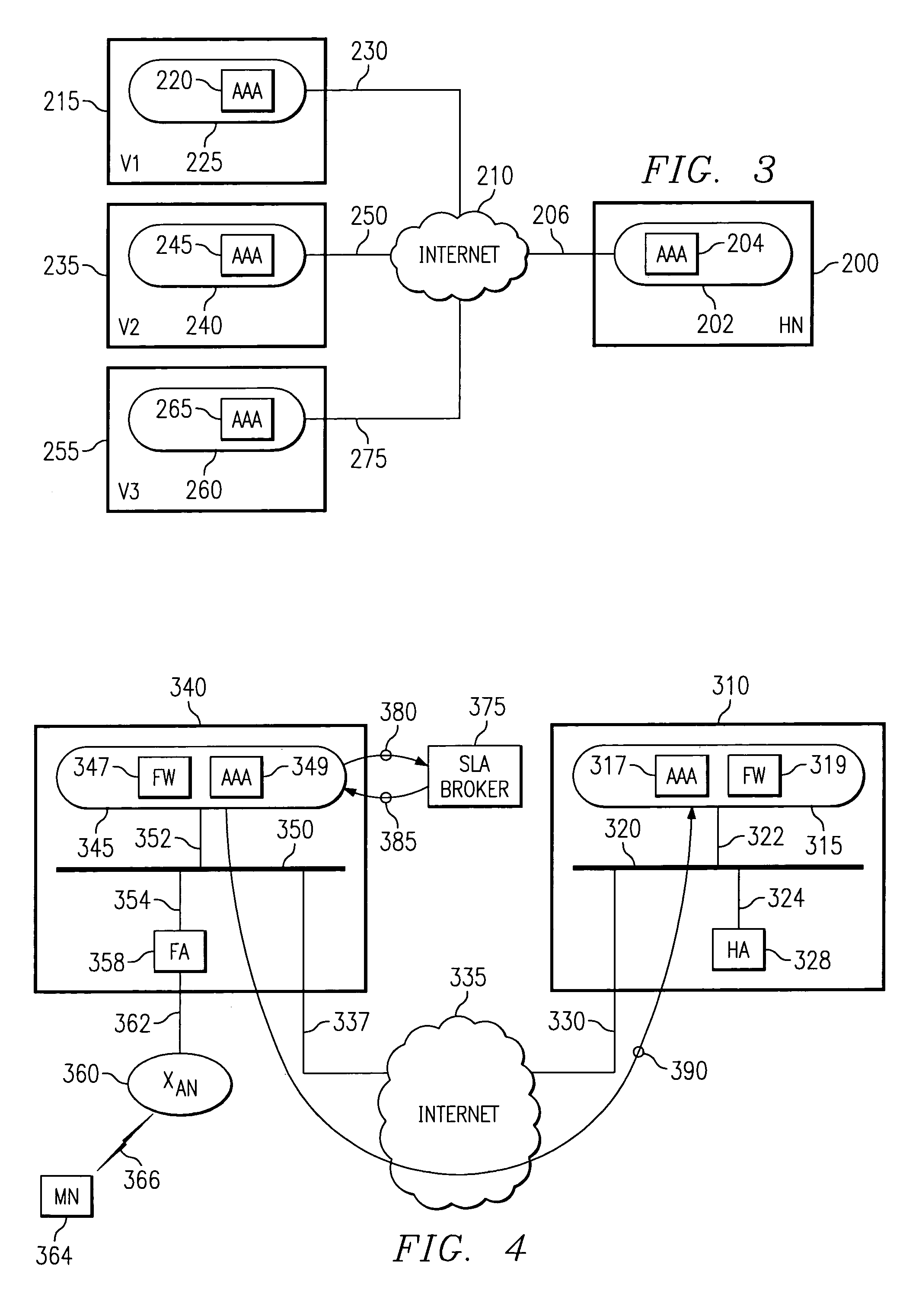
In an IP-based mobile communications system, the Mobile Node changes its point of attachment to the network while maintaining network connectivity. Security concerns arise in the mobile system because authorized users are subject to the following forms of attack: (1) session stealing where a hostile node hijacks session from mobile node by redirecting packets, (2) spoofing where the identity of an authorized user is utilized in an unauthorized manner to obtain access to the network, and (3) eavesdropping and stealing of data during session with authorized user. No separate secure network exists in the IP-based mobility communications system, and therefore, it is necessary to protect information transmitted in the mobile system from the above-identified security attacks.The present invention improves the security of communications in a IP mobile communications system by creating variable-based Security Associations between various nodes on the system, a Virtual Private Network supported by an Service Level Agreement between various foreign networks and a home network, and an SLA Broker to promote large-scale roaming among different SLAs supported by the SLA Broker or agreements with other SLA Brokers.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method of discovering multi-mode mobile terminals
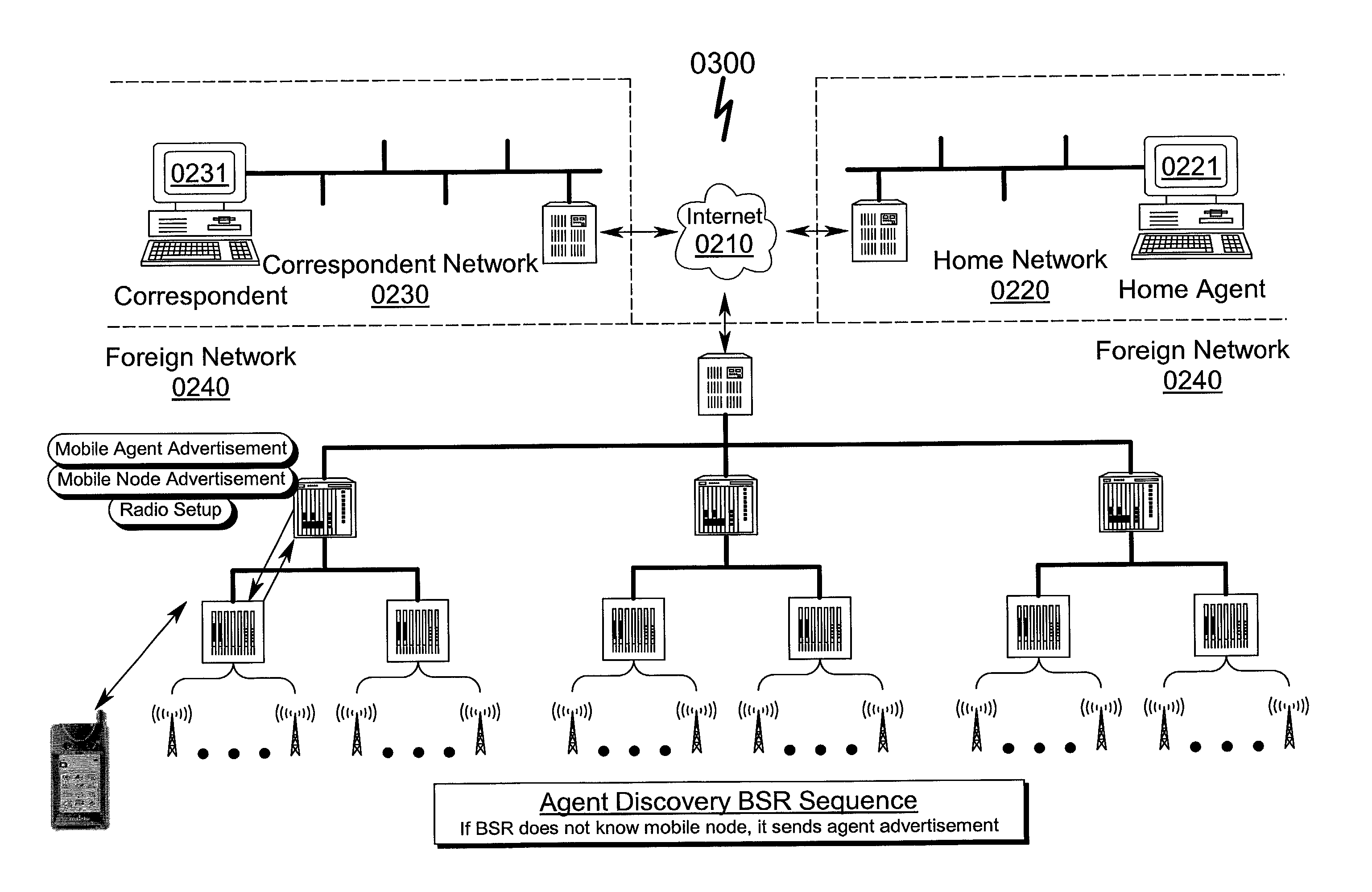
ActiveUS20060166699A1Convenient intercommunicationEasily informedNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsHeterogeneous network
A method of discovering multi-mode mobile terminals (13) in a heterogeneous network environment, each multi-mode mobile terminal (13) having at least one interface for sending packet data to and / or receiving packet data from a home radio communication network (11) and a foreign radio communication network (12), said home radio communication network having a different access technology from said foreign radio communication network, each multi-mode mobile terminal (13) performing the steps of: (a) listening to said foreign radio communication network (12); (b) receiving and storing a foreign network indicator for indicating presence of said foreign radio communication network (12); and (c) transmitting said foreign network indicator to said home radio communication network (11); whereby said home radio communication network (11) may store a database comprising a mapping between a multi-mode mobile terminal identity, a home network indicator and a foreign network indicator, to facilitate interworking of said home and foreign radio communication networks.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
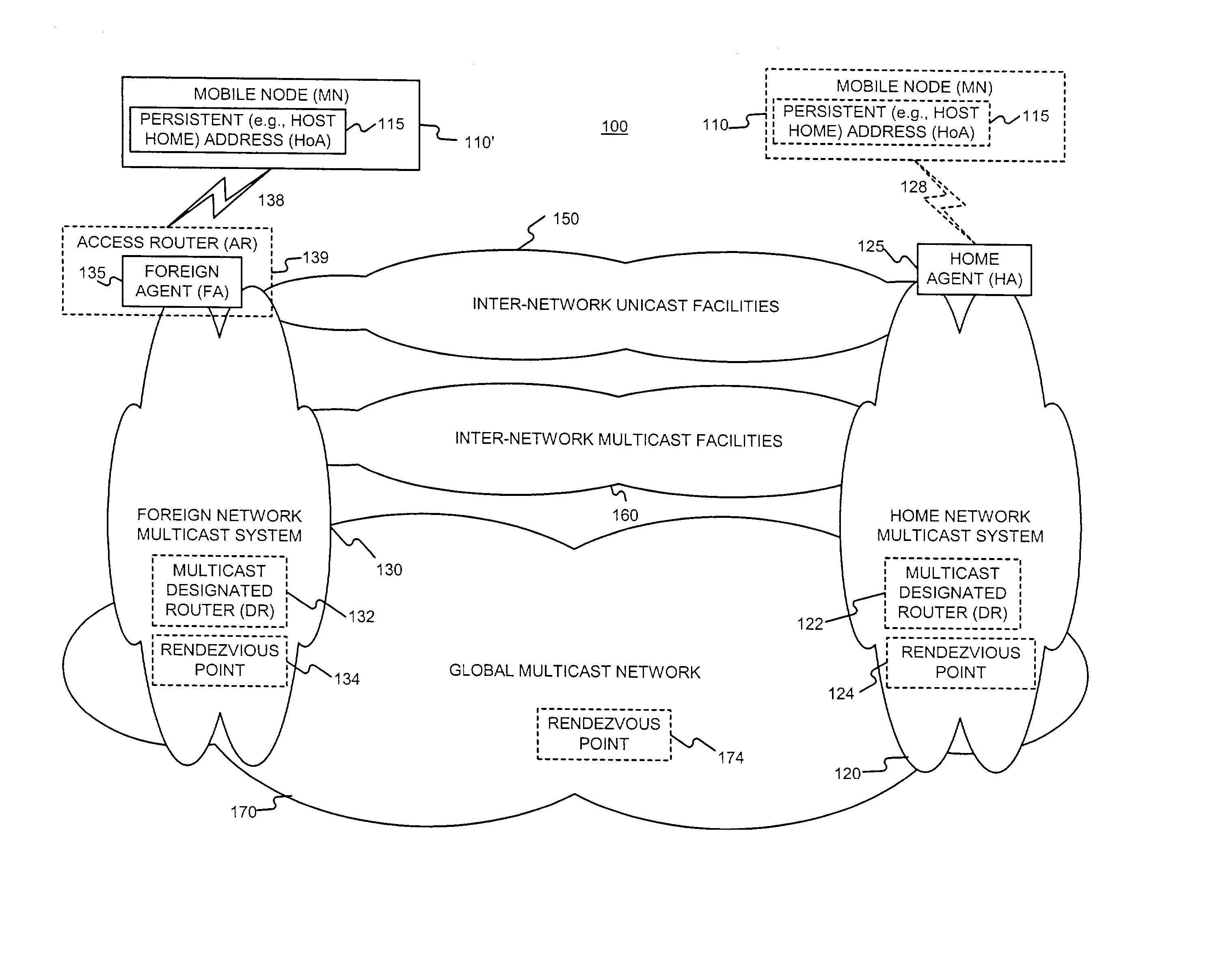
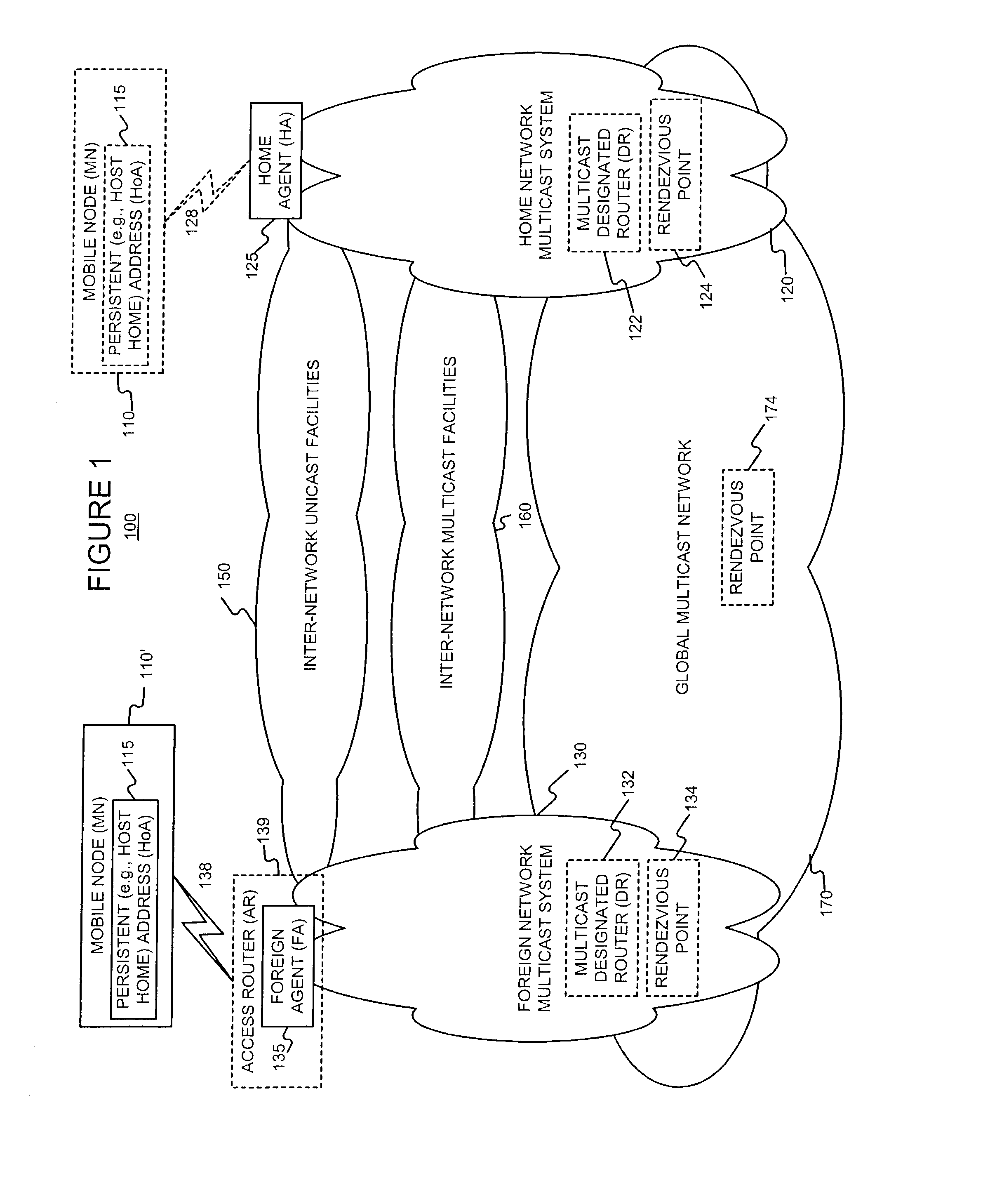
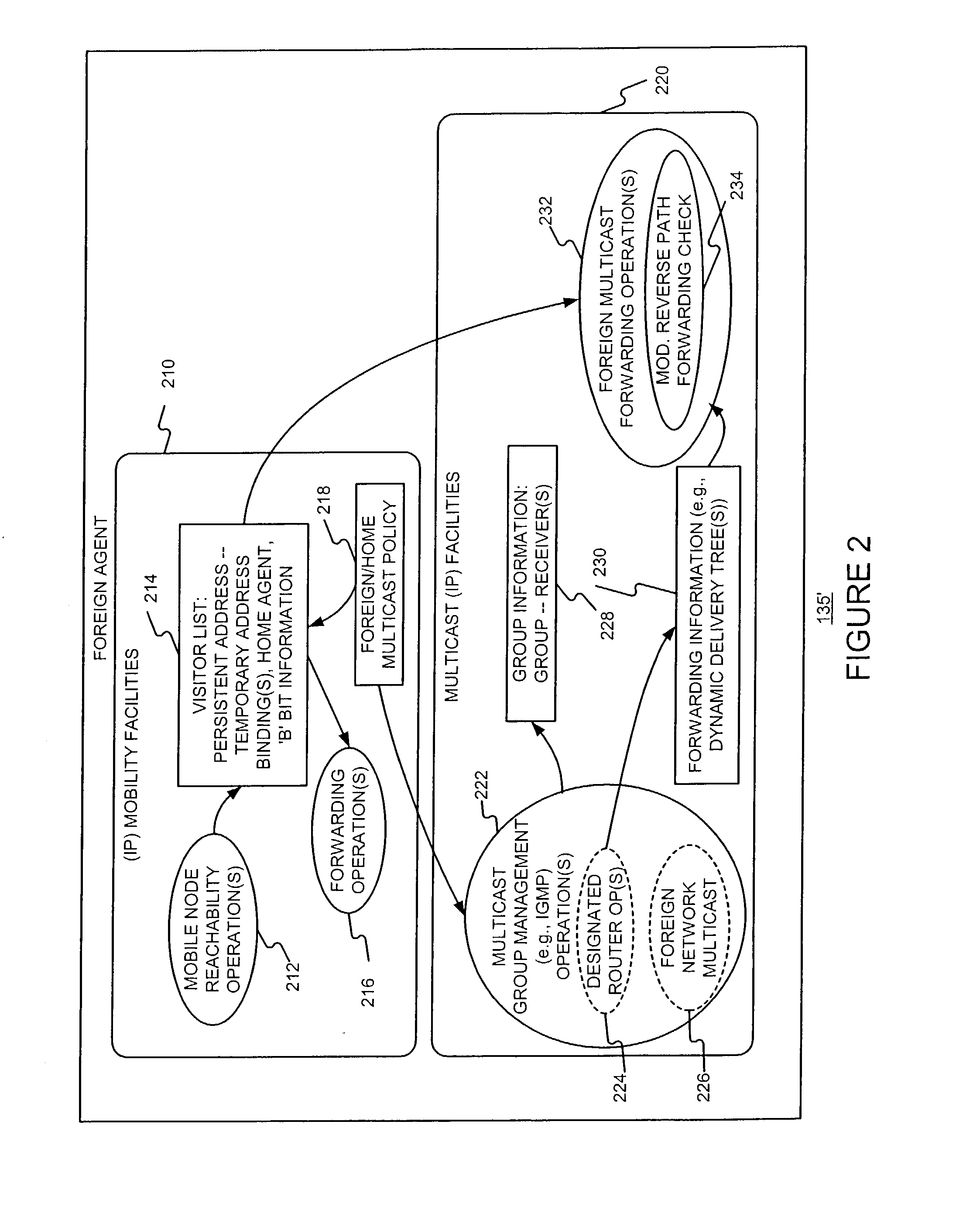
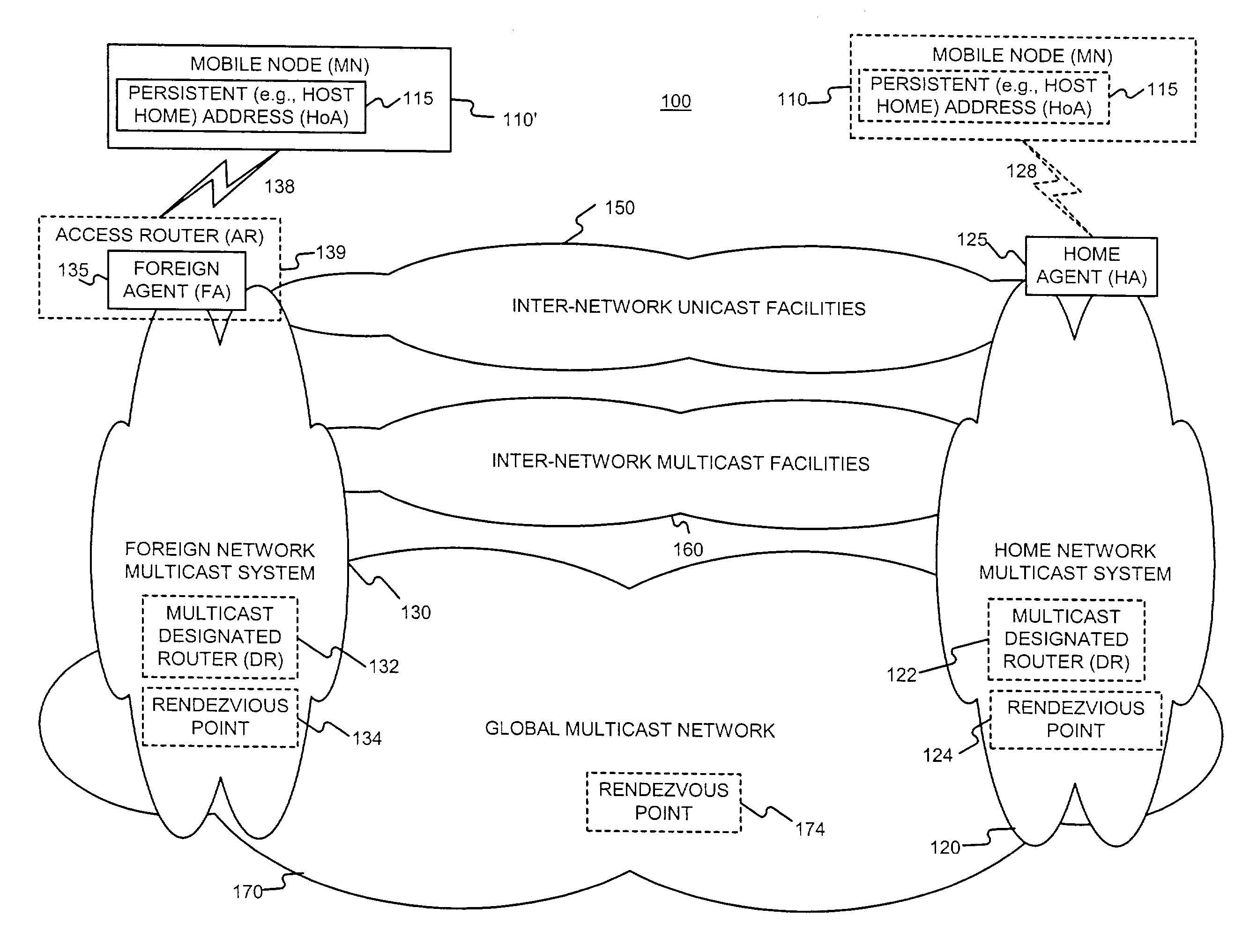
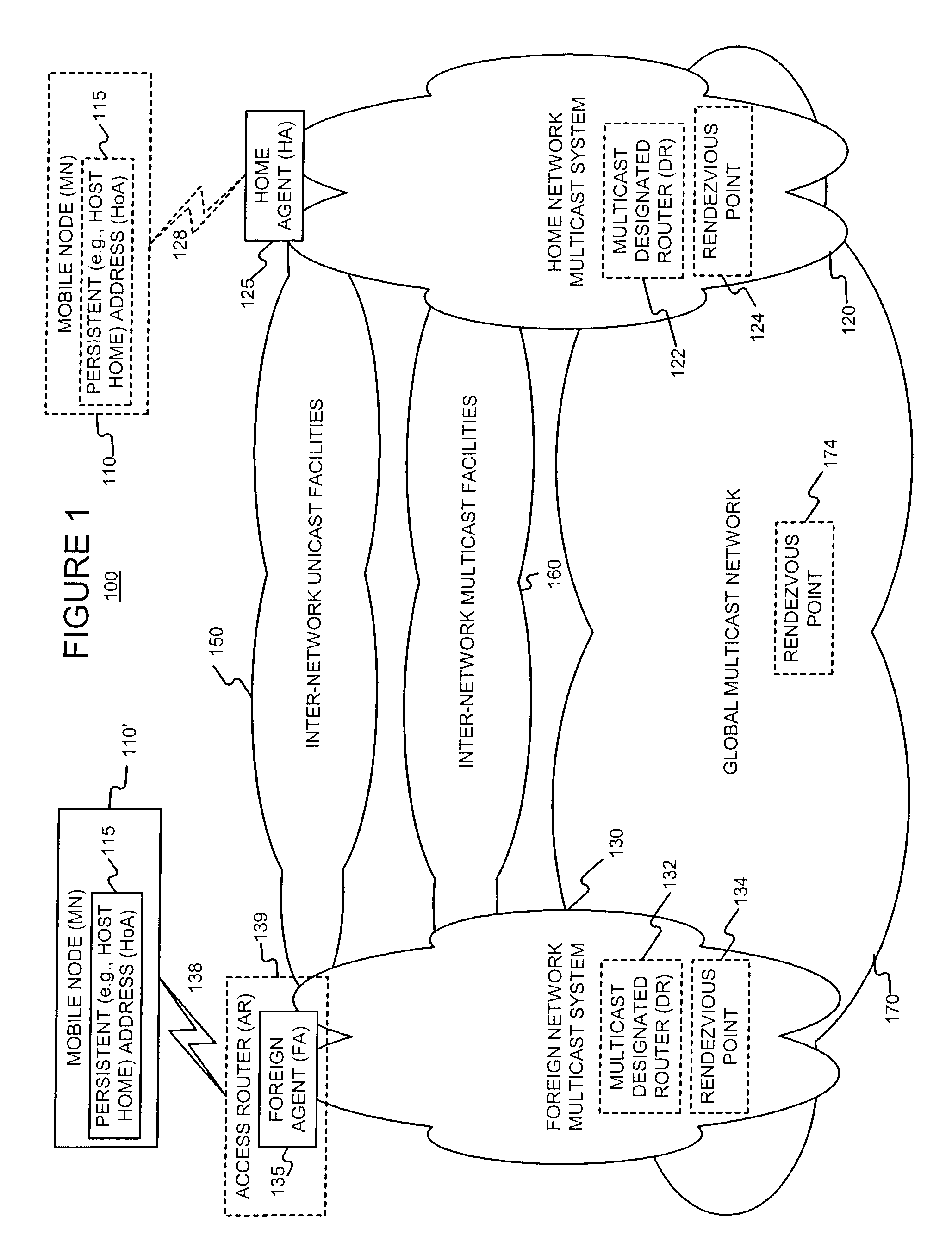
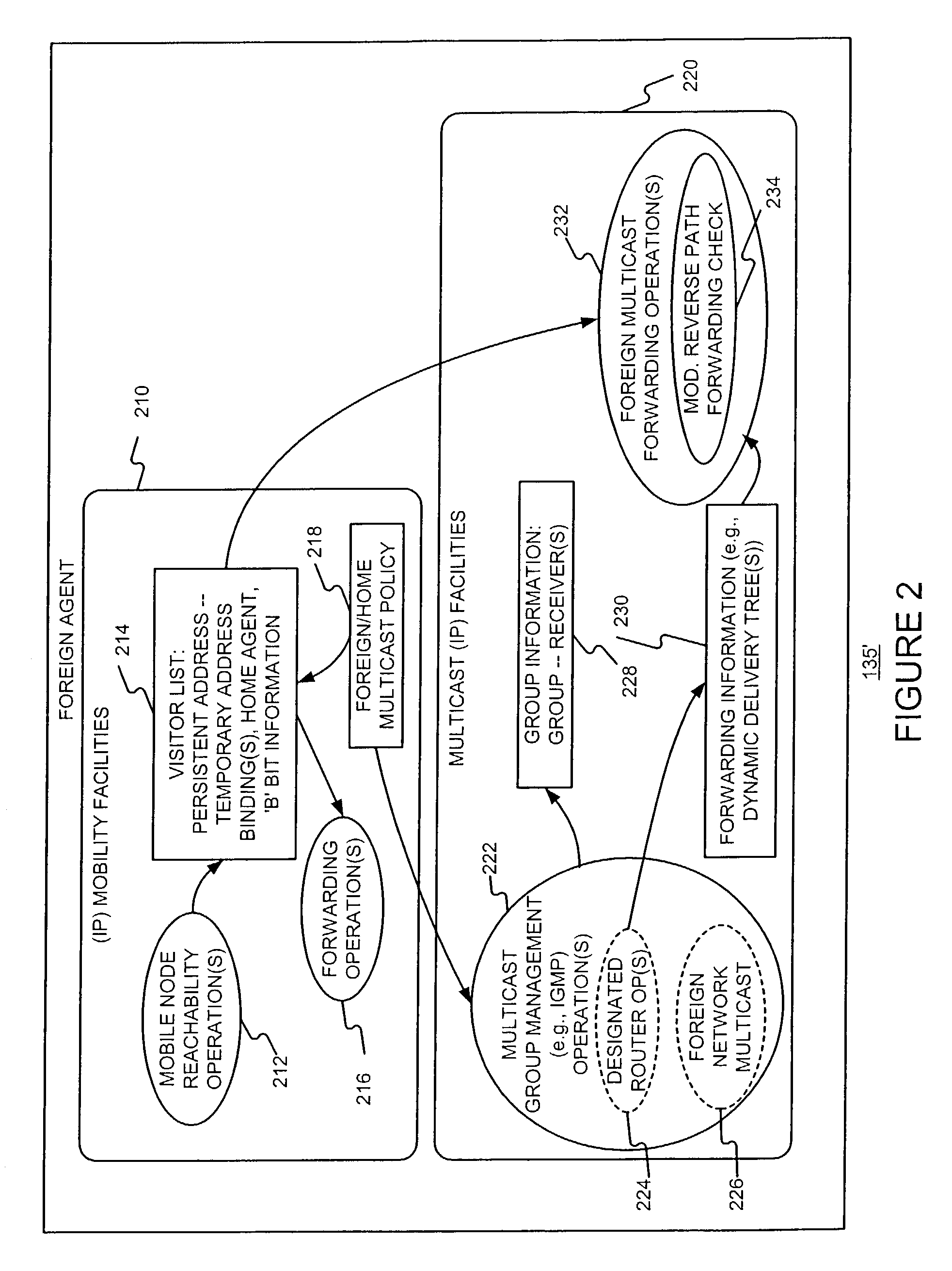
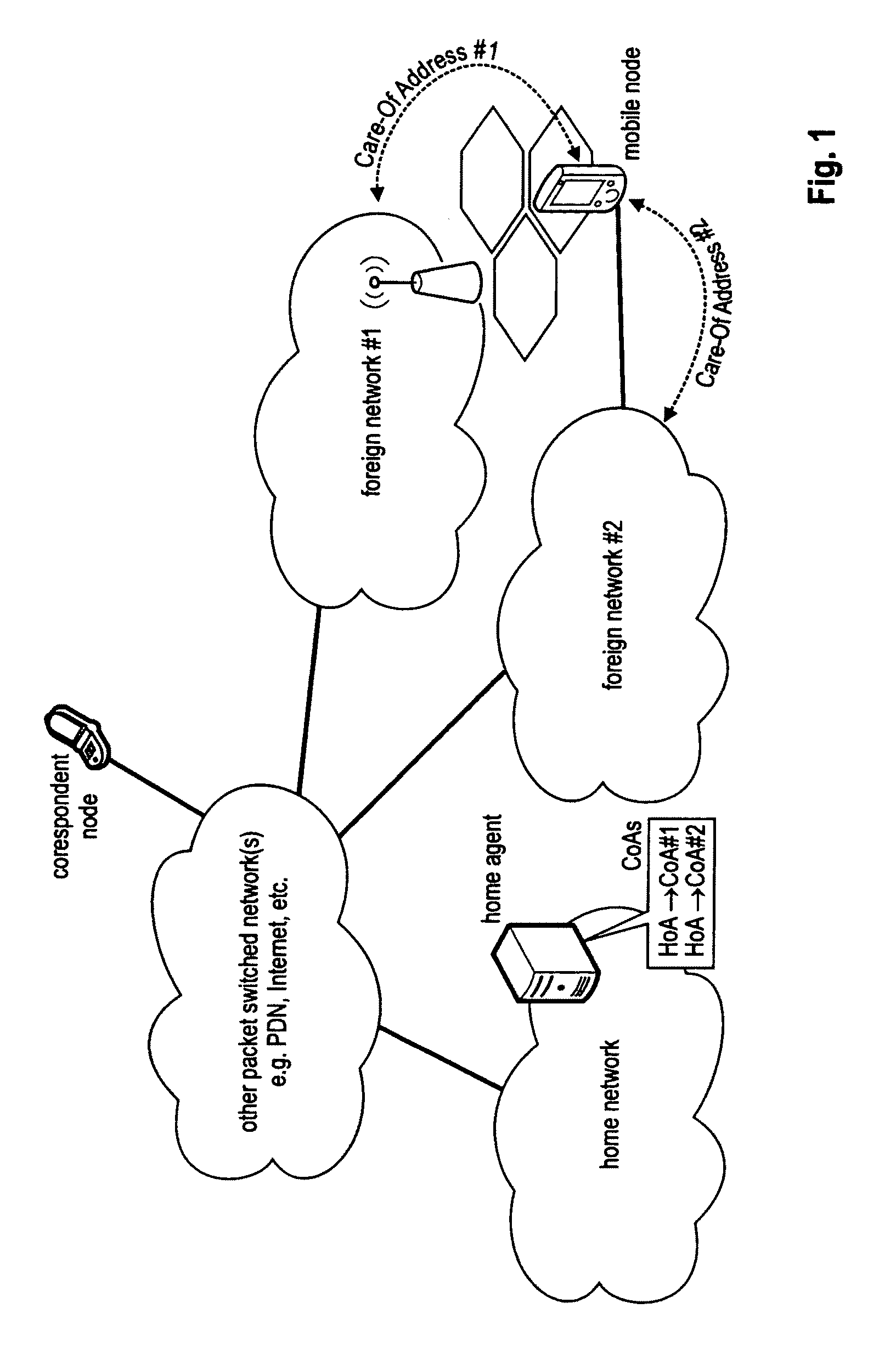
Enabling foreign network multicasting for a roaming mobile node, in a foreign network, using a persistent address
InactiveUS20030018715A1Special service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsReverse path forwardingForeign agent
Permitting a mobile host to roam in a foreign network, with multiple access node handoffs, while permitting foreign network multicasting by (i) having the mobile node (MN) use a persistent address, for purposes of multicasting, and (ii) relaxing or modifying reverse path forwarding checks, and (iii) modifying the forwarding of multicast packets sent from a non-local source address. The persistent address, used in mobile networks as the source address in the IGMP Membership reports and the multicast packets, may be the permanent and hence stable host home address (HoA). This enables the HoA to be supported as a source address by foreign agents (FAs) and multicast routing protocols in foreign networks.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Enabling foreign network multicasting for a roaming mobile node, in a foreign network, using a persistent address
InactiveUS7339903B2Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexReverse path forwardingForeign agent
Permitting a mobile host to roam in a foreign network, with multiple access node handoffs, while permitting foreign network multicasting by (i) having the mobile node (MN) use a persistent address, for purposes of multicasting, and (ii) relaxing or modifying reverse path forwarding checks, and (iii) modifying the forwarding of multicast packets sent from a non-local source address. The persistent address, used in mobile networks as the source address in the IGMP Membership reports and the multicast packets, may be the permanent and hence stable host home address (HoA). This enables the HoA to be supported as a source address by foreign agents (FAs) and multicast routing protocols in foreign networks.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Temporary unique private address
InactiveUS6856624B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPrivate IPTelecommunications
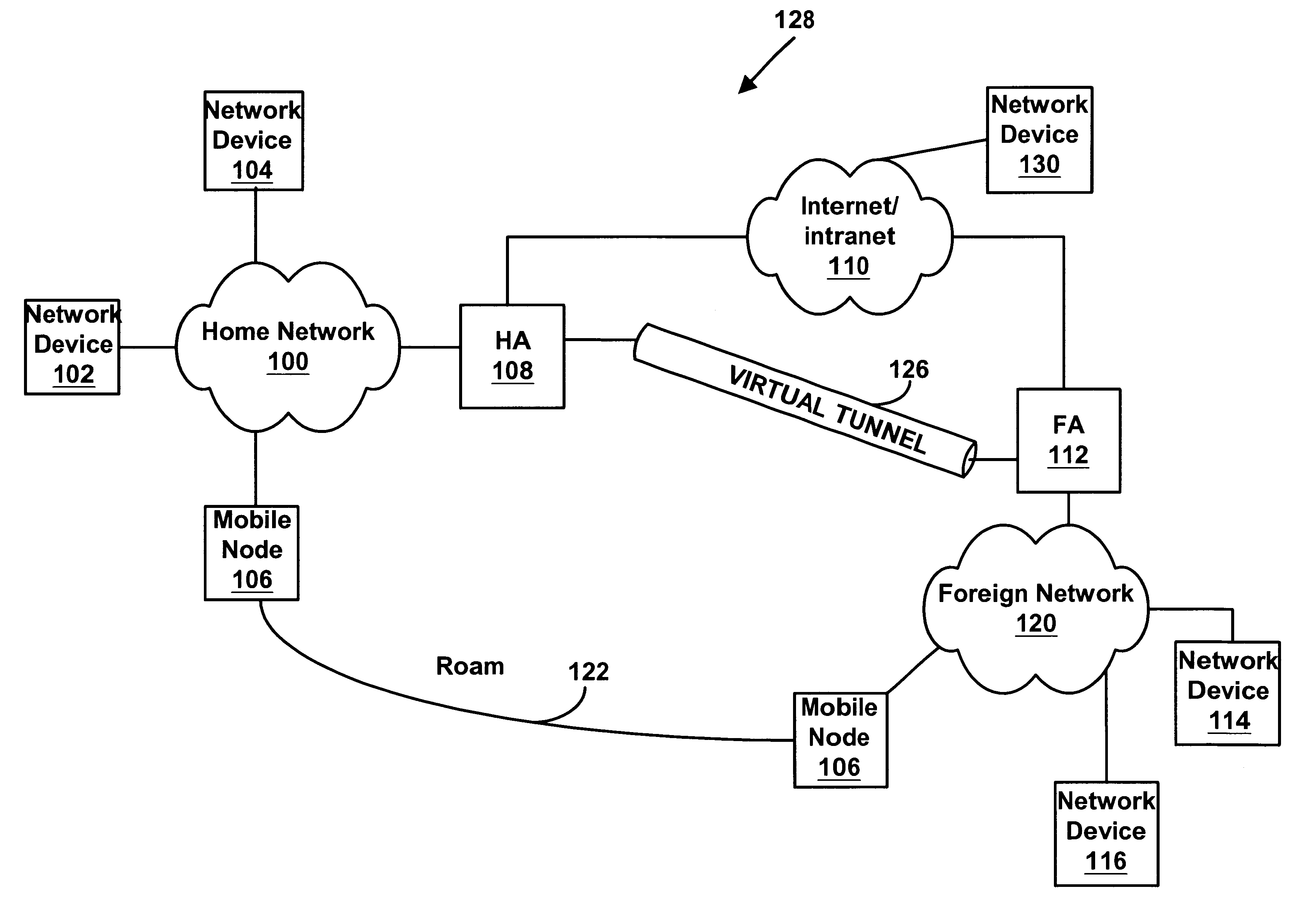
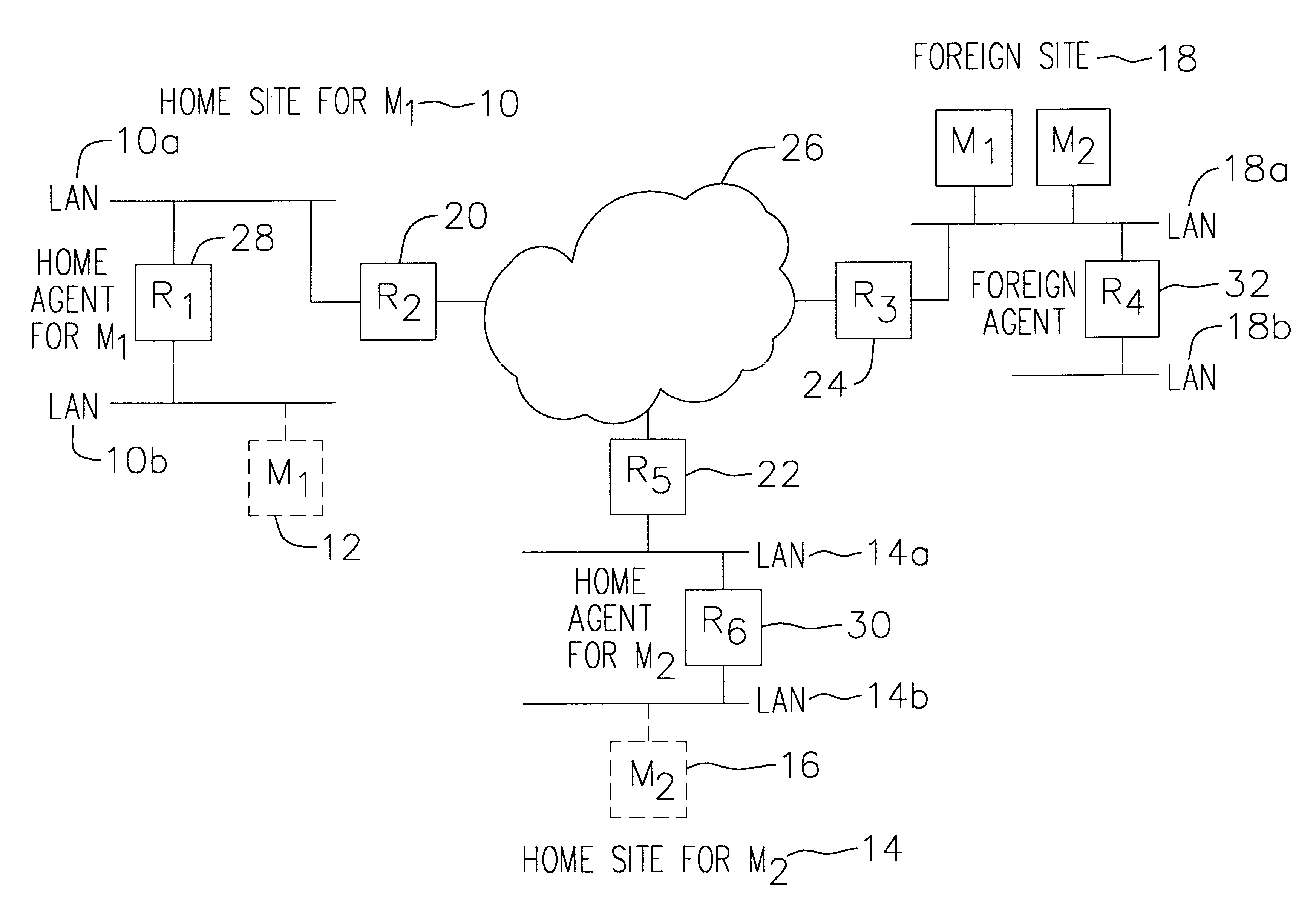
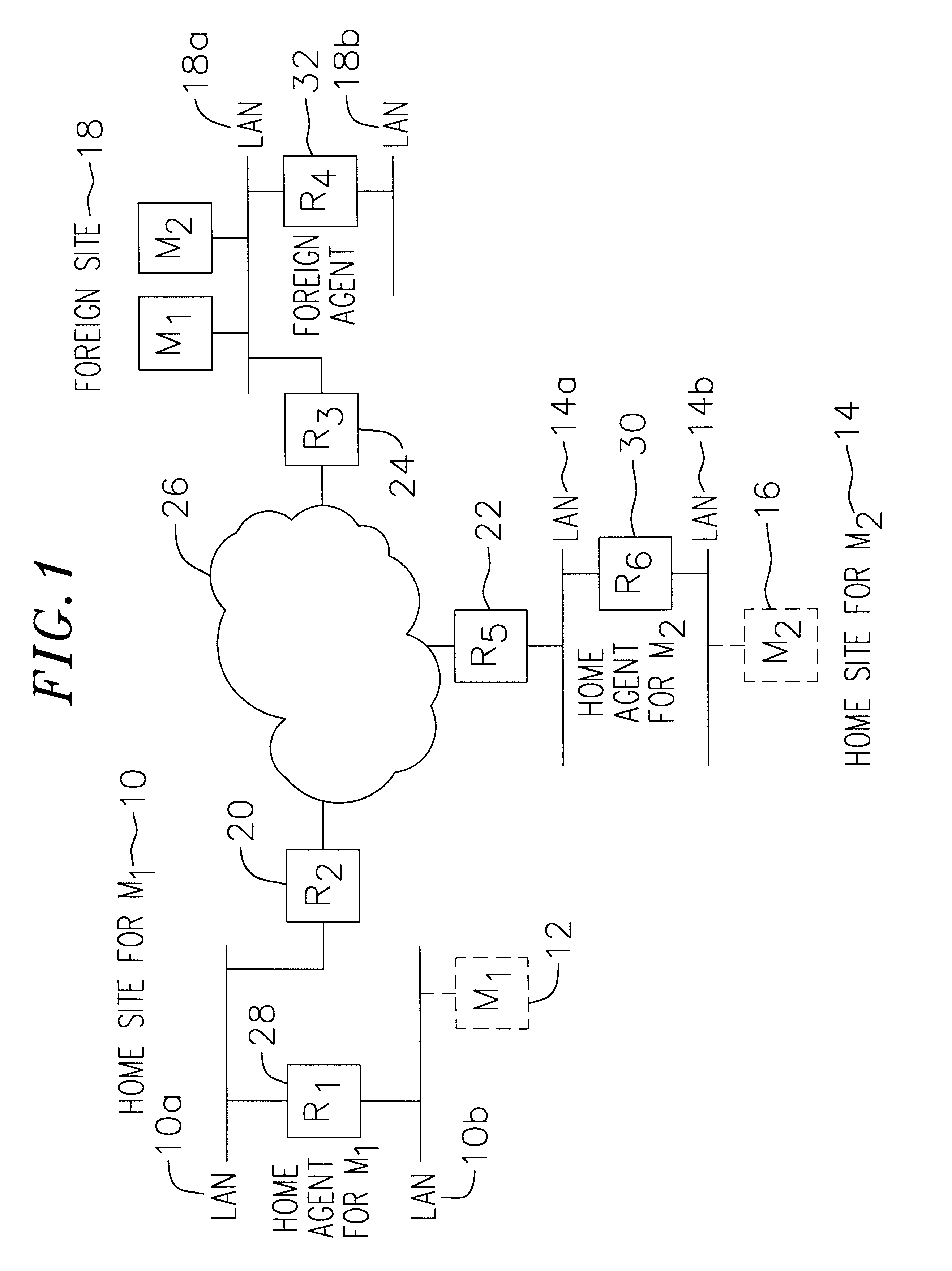
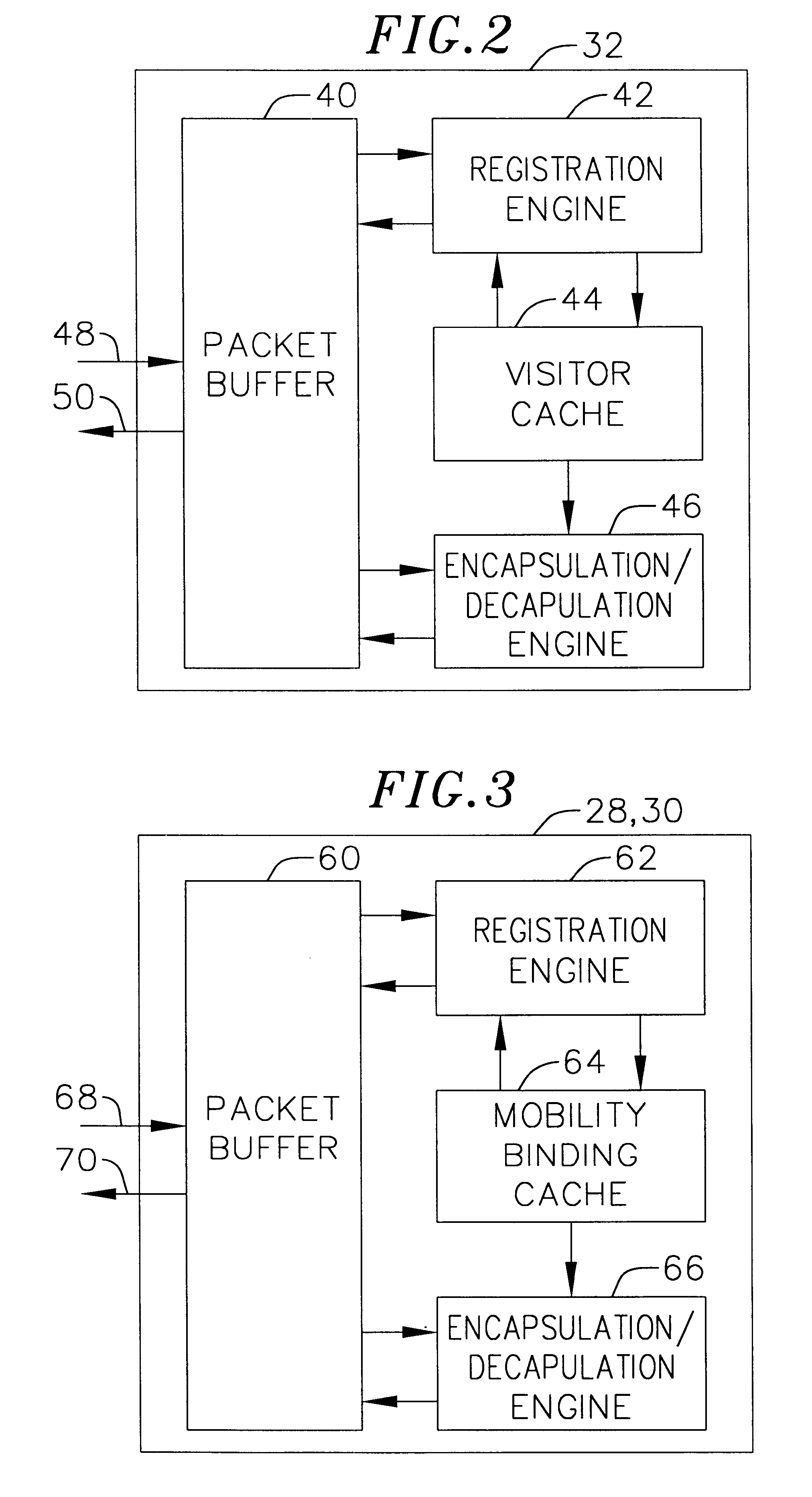
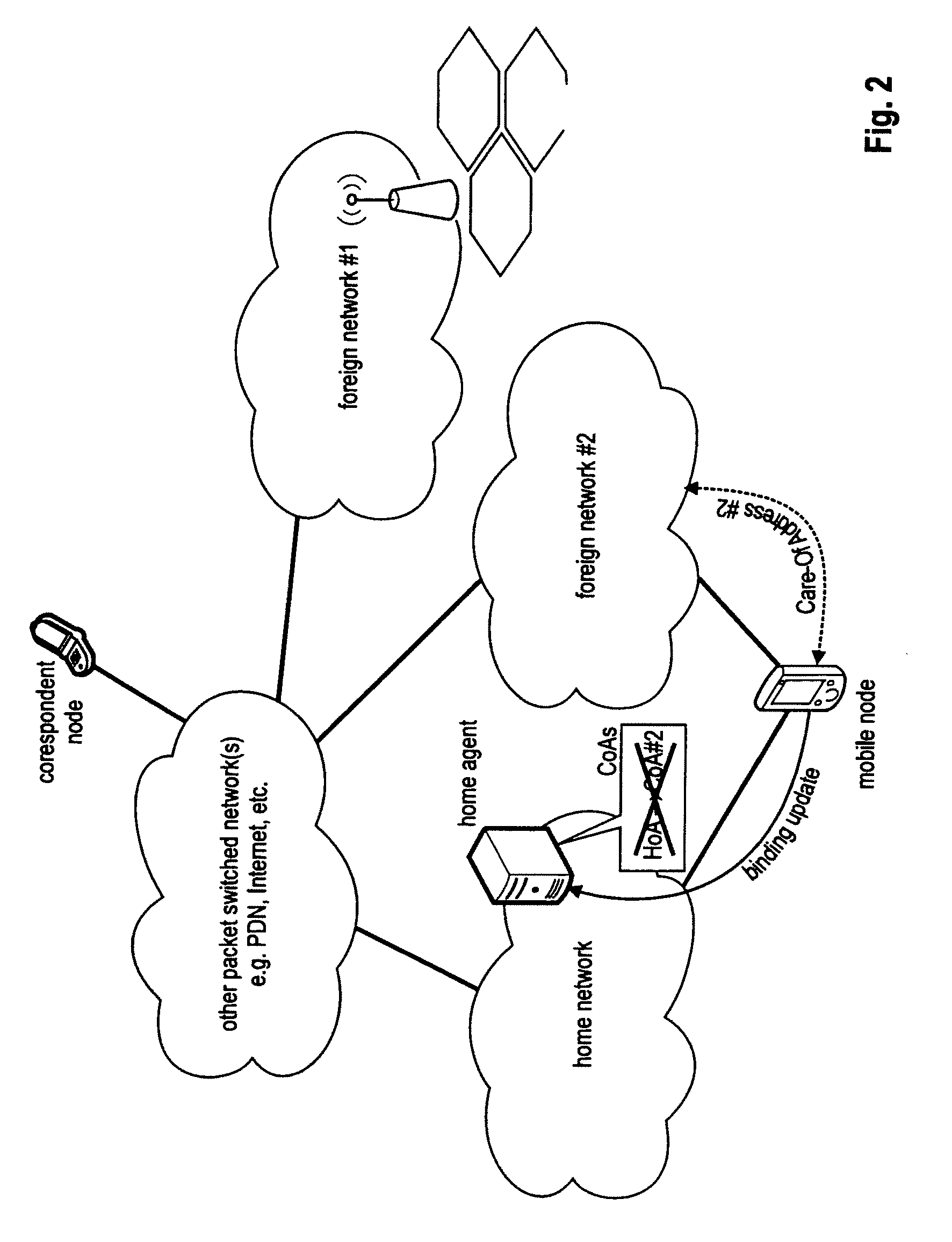
A communication network providing mobile IP services to mobile nodes sharing the same private IP address. A mobile node visits a foreign network from its home network and transmits a registration request including its private IP address to a foreign agent on the foreign network. If the foreign agent determines that another mobile node with a valid registration shares the same private IP address, the foreign agent requests the mobile node to use a temporary address. The temporary address is sent along with the registration request to the registering mobile node's home agent. When the home agent receives a packet addressed to its mobile node, it creates two tunnels. An outer tunnel is created using a care-of address associated with the foreign agent. An inner tunnel is created using the temporary address assigned to mobile node. The packet is then forwarded via the two tunnels. Upon receipt of the tunneled packet by the foreign agent, it de-tunnels the outer tunnel to uncover the inner tunnel, and forwards the inner tunnel to the mobile node. The mobile node de-tunnels the inner tunnel to recover the original packet.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
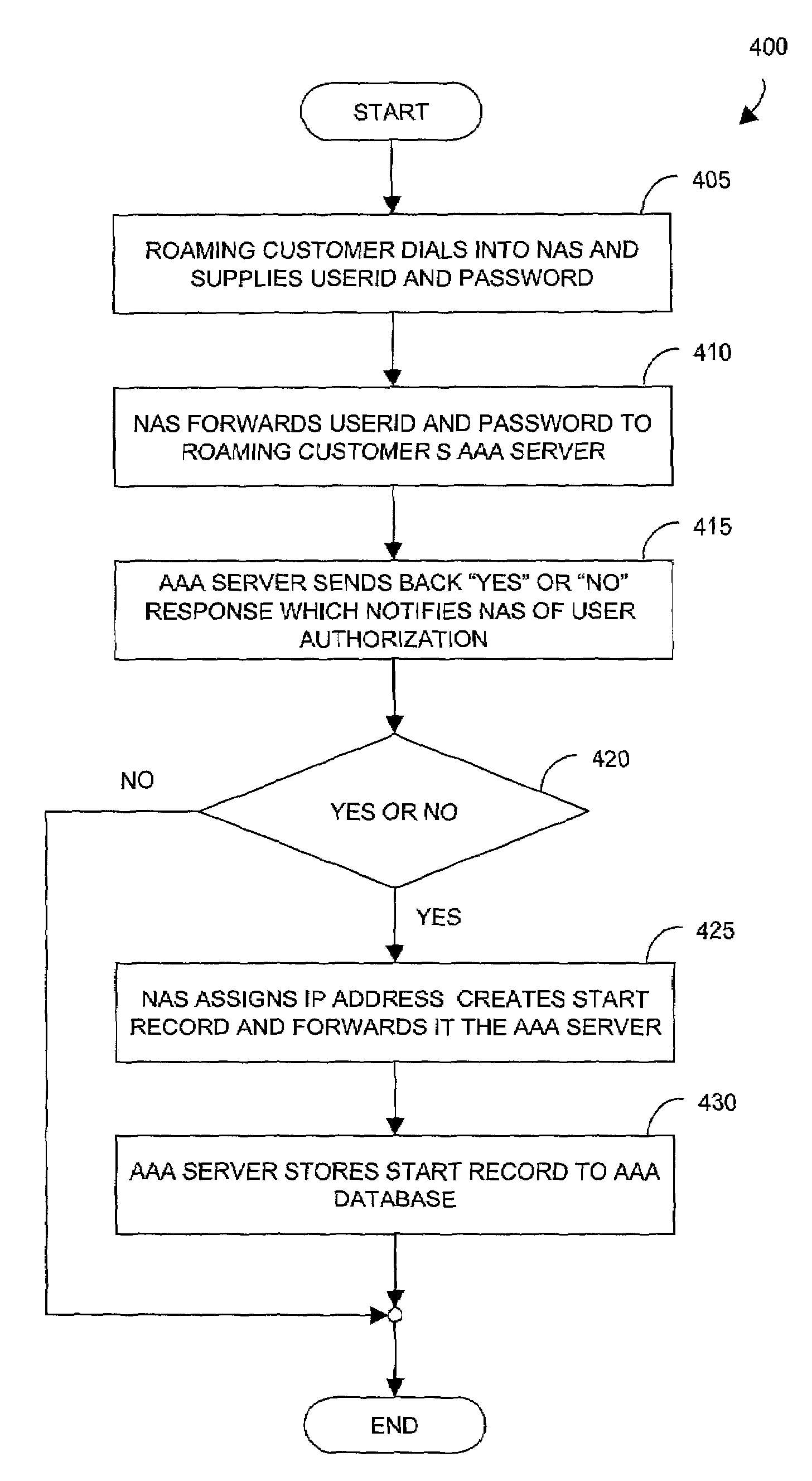
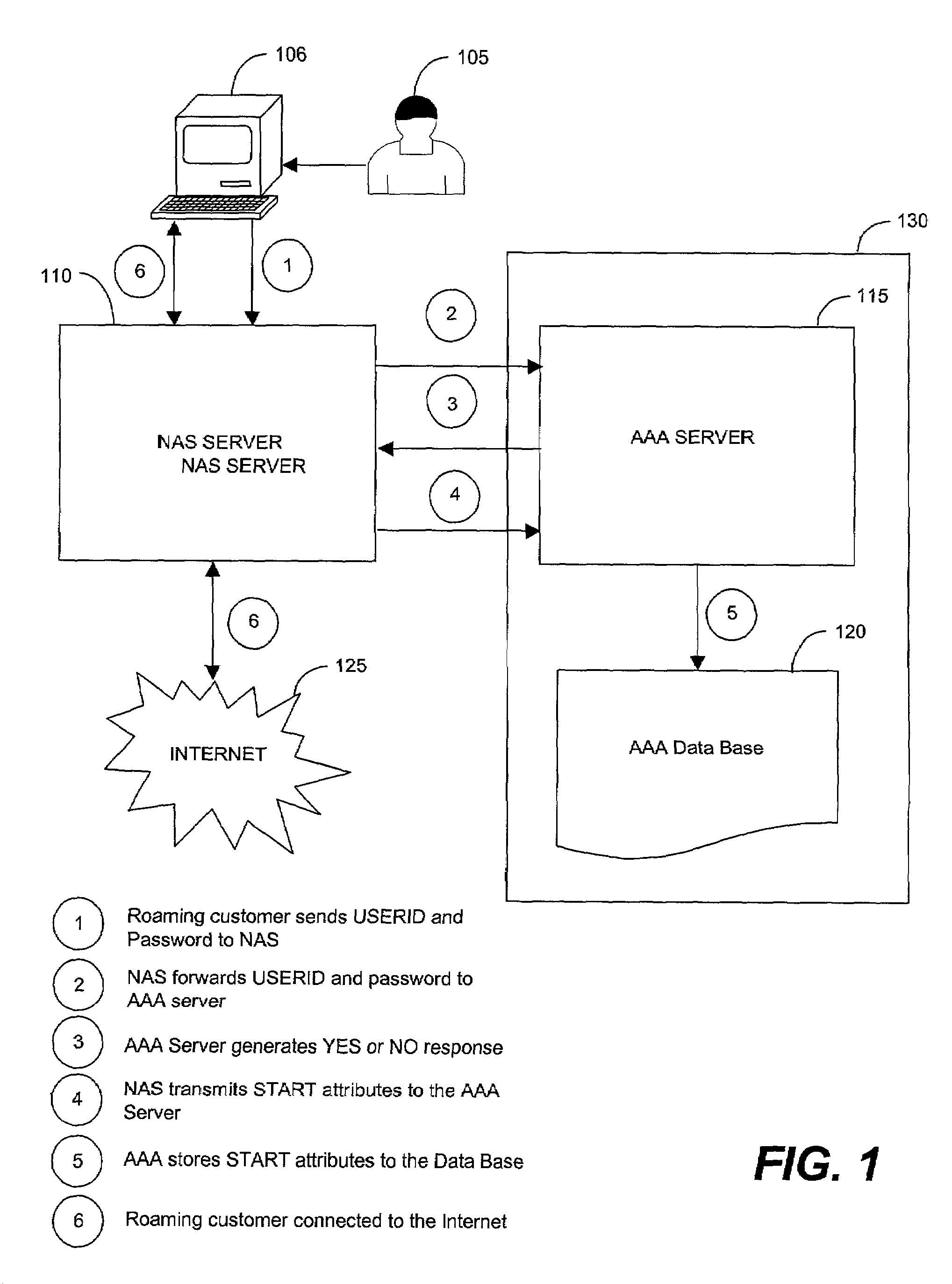
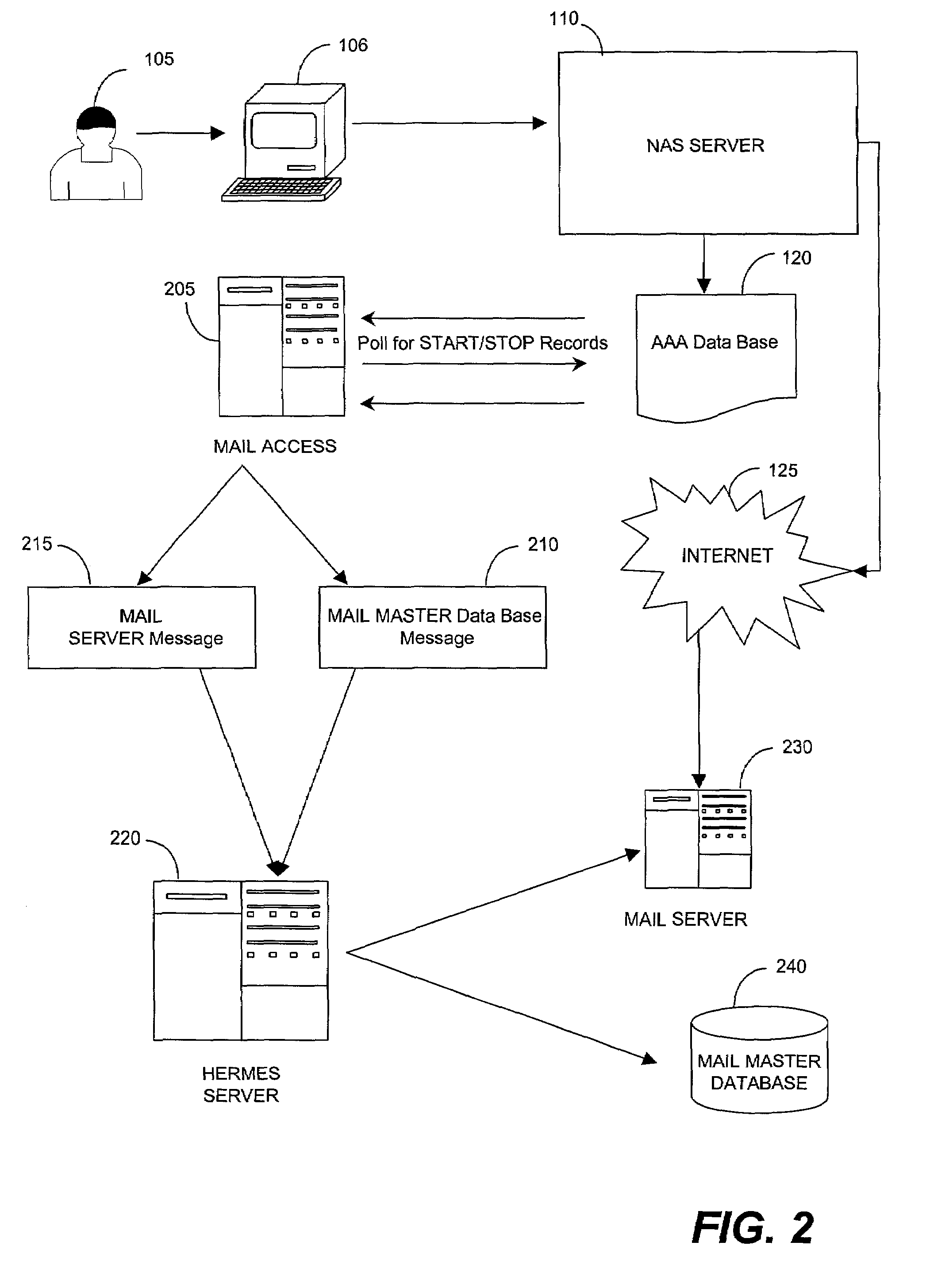
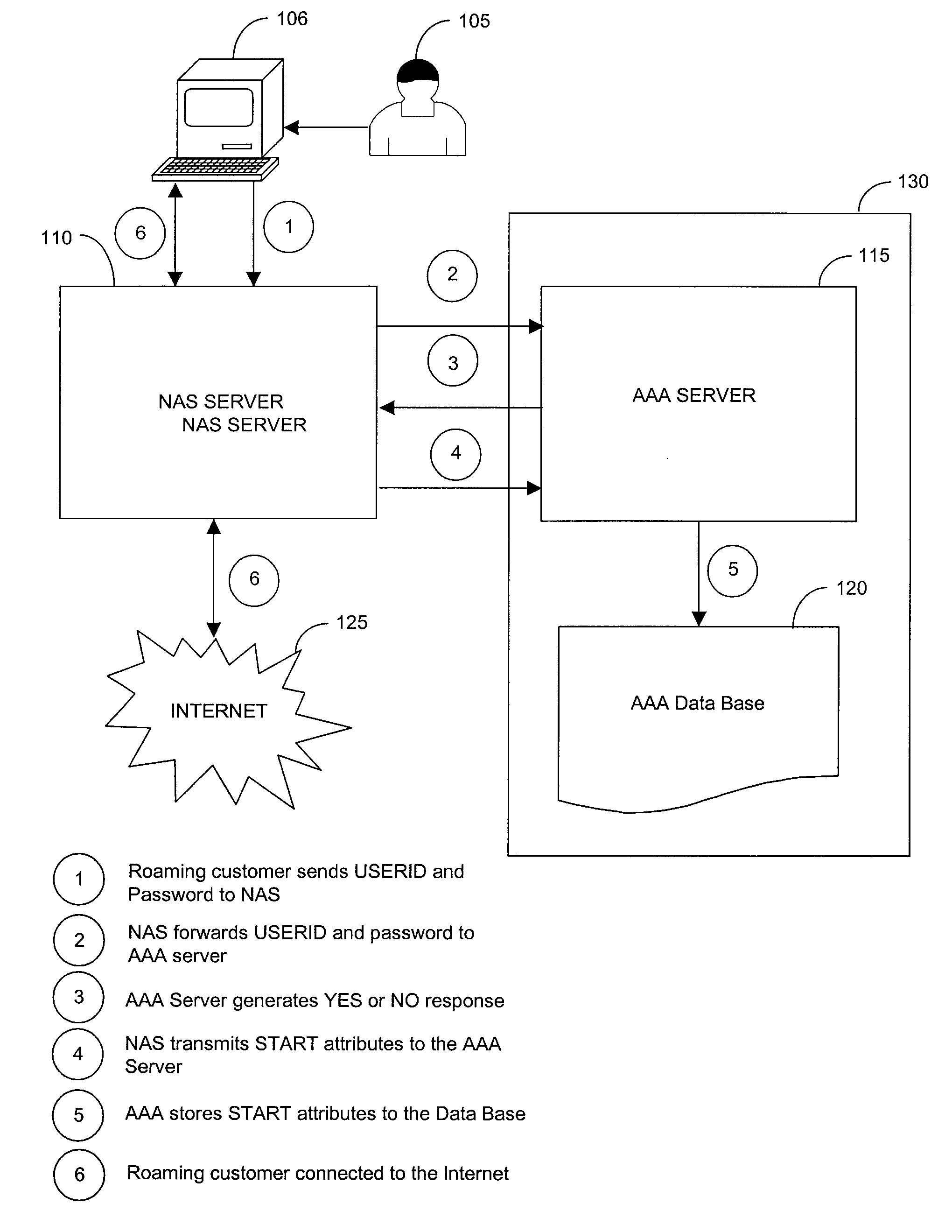
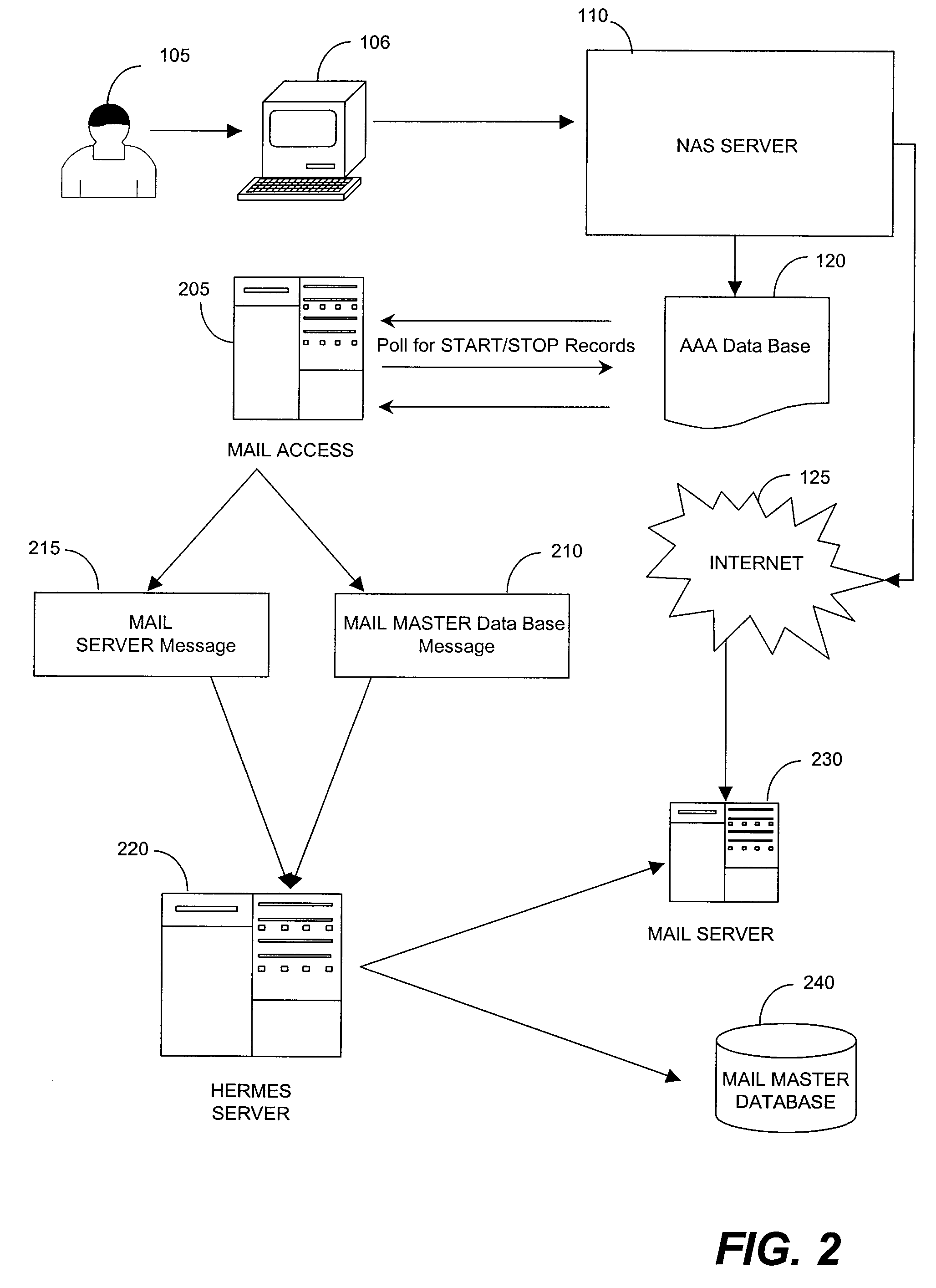
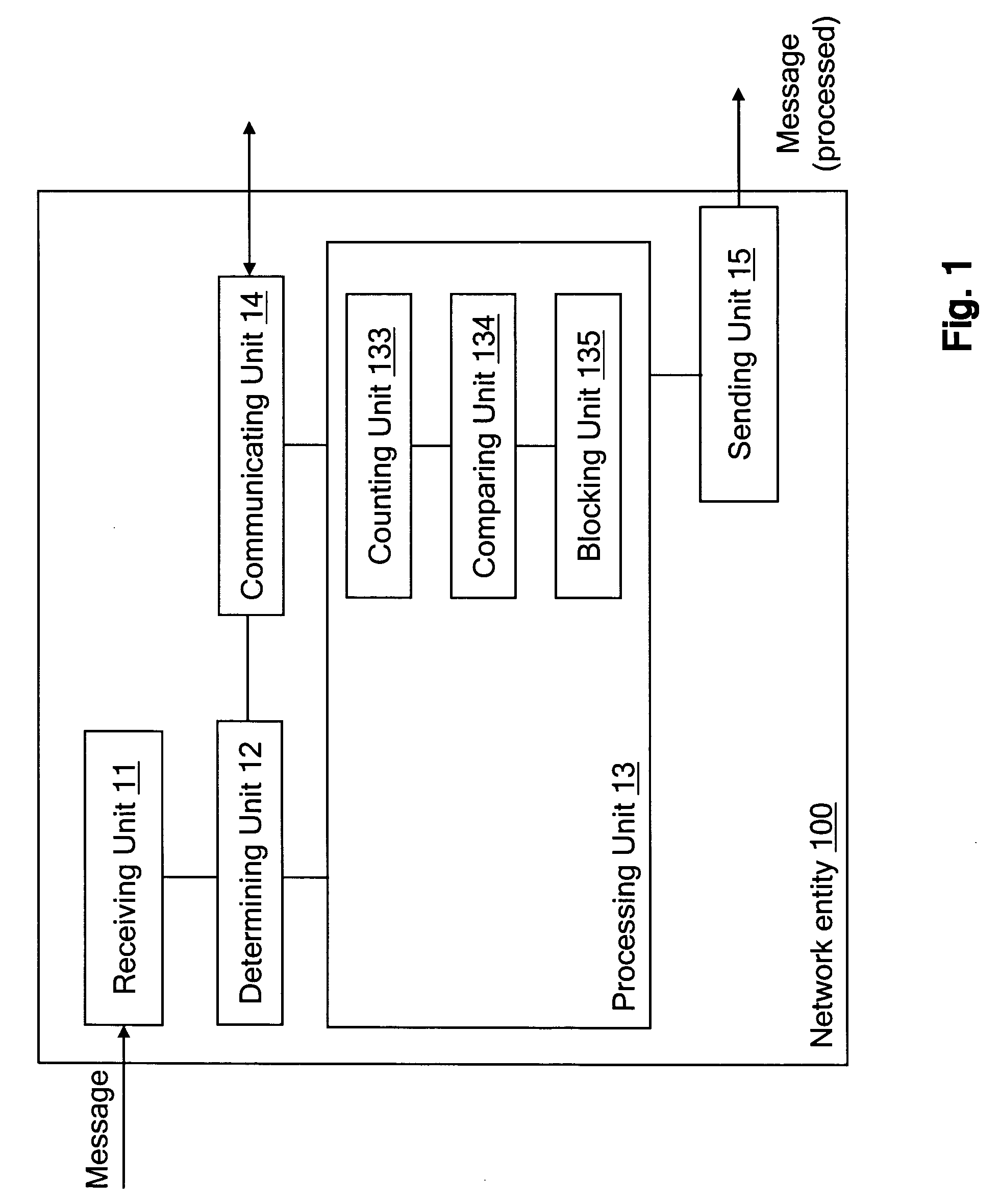
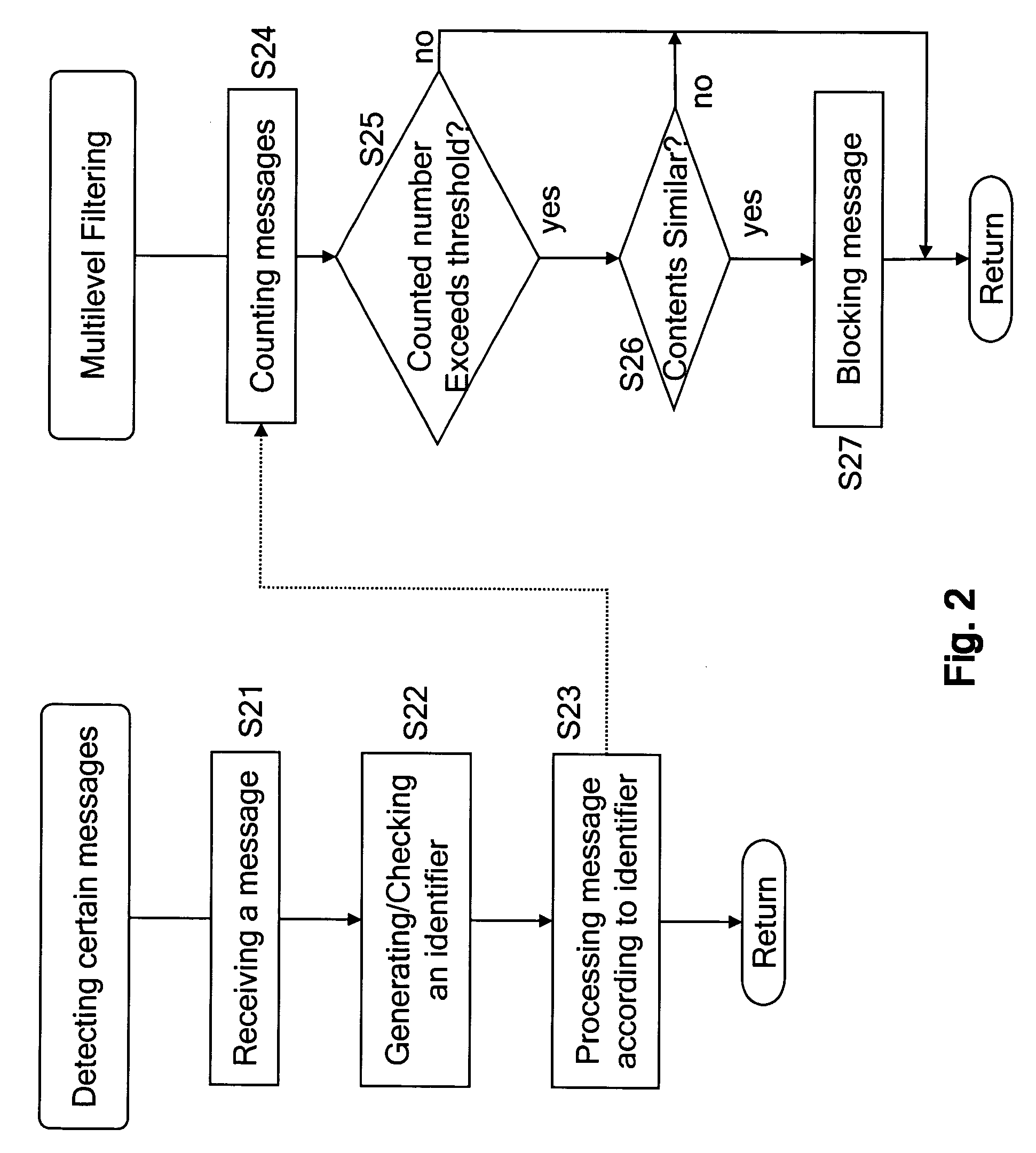
Foreign network SPAM blocker
A method involves blocking unsolicited e-mail being transmitted from a remote server when a roaming customer of the ISP logs onto the Internet through the foreign NAS. The roaming customer first logs onto the ISP through the foreign NAS by providing a user identification (USERID) and password, which are sent to the ISP. The ISP uses the USERID and the password to authenticate the roaming customer as a valid subscriber of the ISP. An IP address is assigned by the foreign NAS to the roaming customer and is dynamically added to a pool of IP addresses used by the mail server. The roaming customer can then log onto the mail server to send and receive email messages. Once the roaming customer terminates the session, the IP address assigned to the roaming customer is removed from the pool of valid IP address that can be used to access the mail server.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
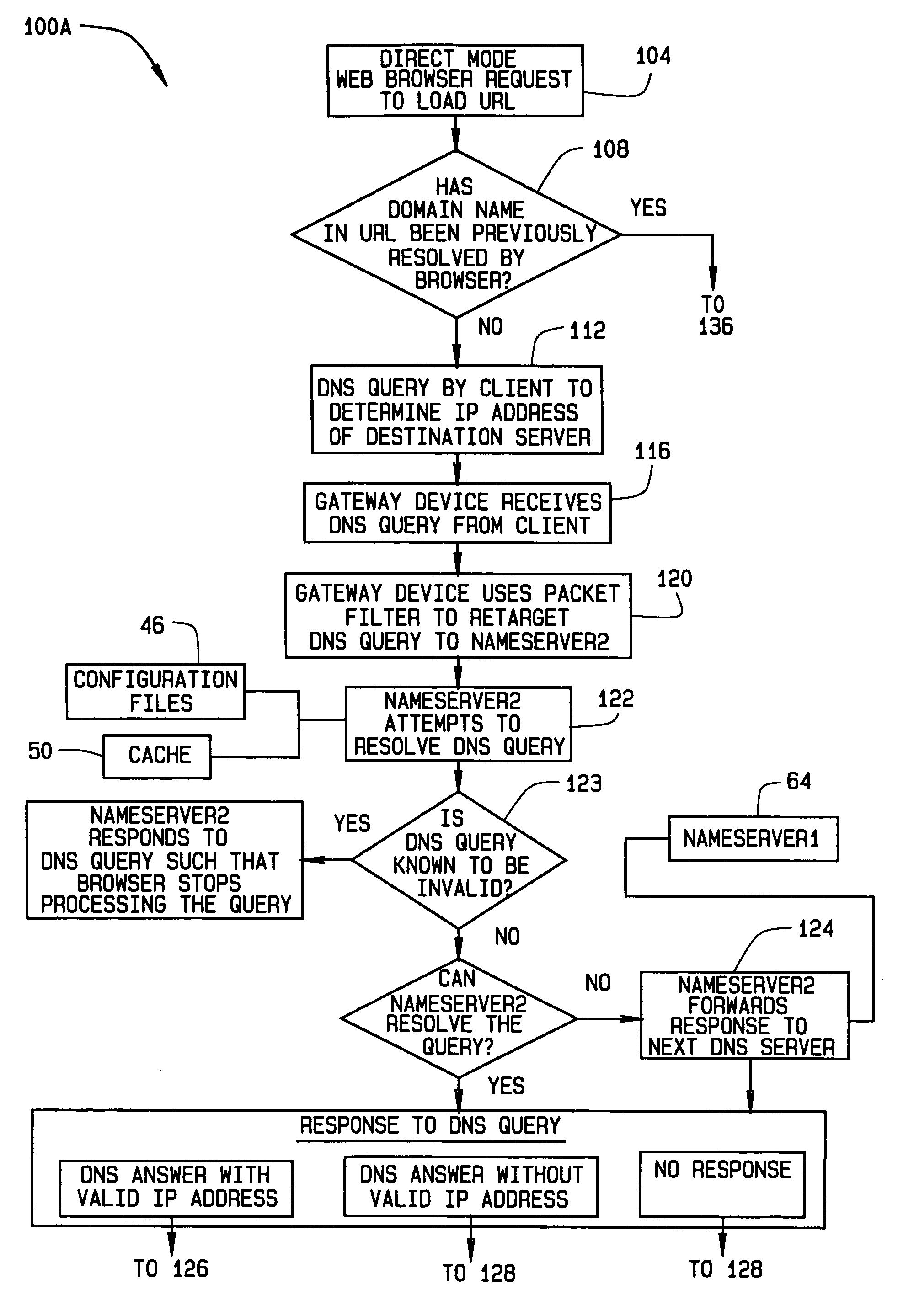
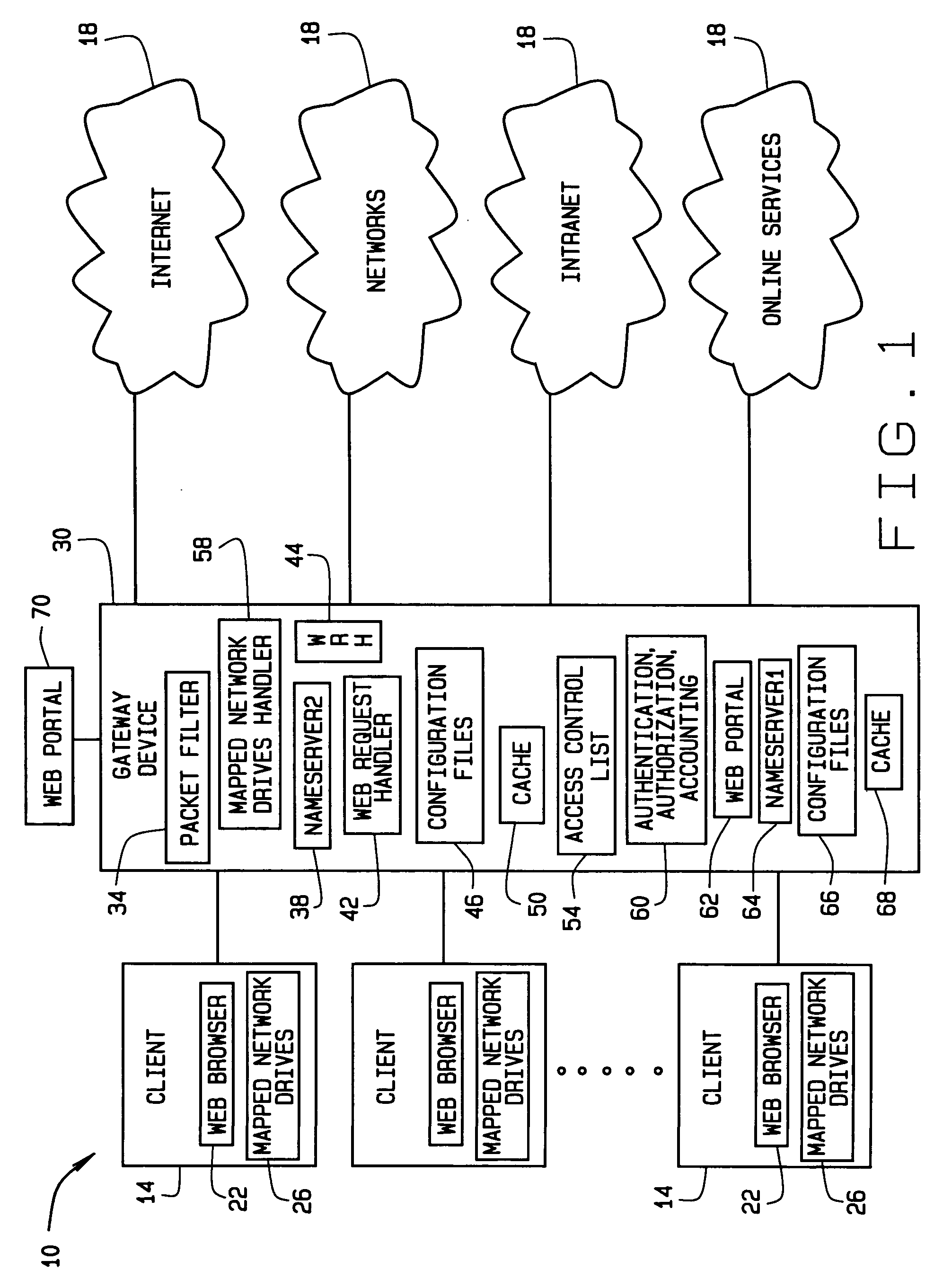
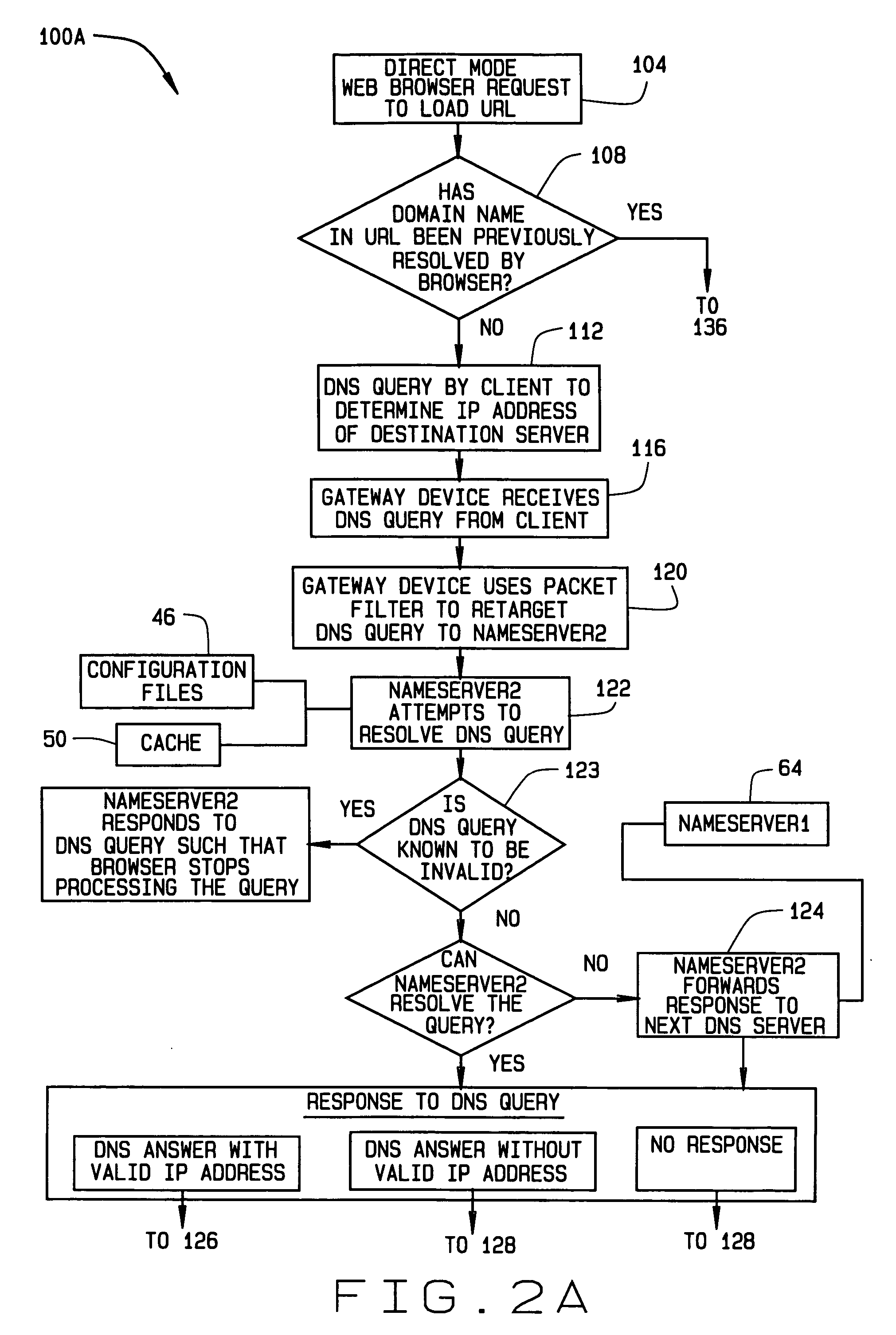
Apparatus and methods for transparent handling of browser proxy configurations in a network gateway device
InactiveUS20060031394A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb browserClient-side
A method of providing web browsers with access to a foreign network via a network gateway device. The browsers are installed on clients of the gateway device and have different proxy settings. Web requests from a browser are intercepted during a browser pre-login phase. Based on the intercepted web requests, the browser is accommodated in configuring a proxy mode. The method includes intercepting and redirecting web requests from the proxy-mode-configured browser to provide access to the network. These steps are performed for each of a plurality of browsers installed on a single client.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Method to provide dynamic Internet Protocol security policy service
InactiveUS20050063352A1Wireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer networkForeign agent
A mobile node may roam away from its home network to a foreign network. The mobile node may communicate using the Mobile Internet Protocol, and it may use Internet Protocol security to communicate with its home network. A foreign agent on the foreign network and a home agent on the home network may dynamically link a policy to be used for a Internet Protocol security session between the foreign agent and the home agent. The foreign agent and the home agent may dynamically create a filter to be used for the Internet Protocol Security session.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
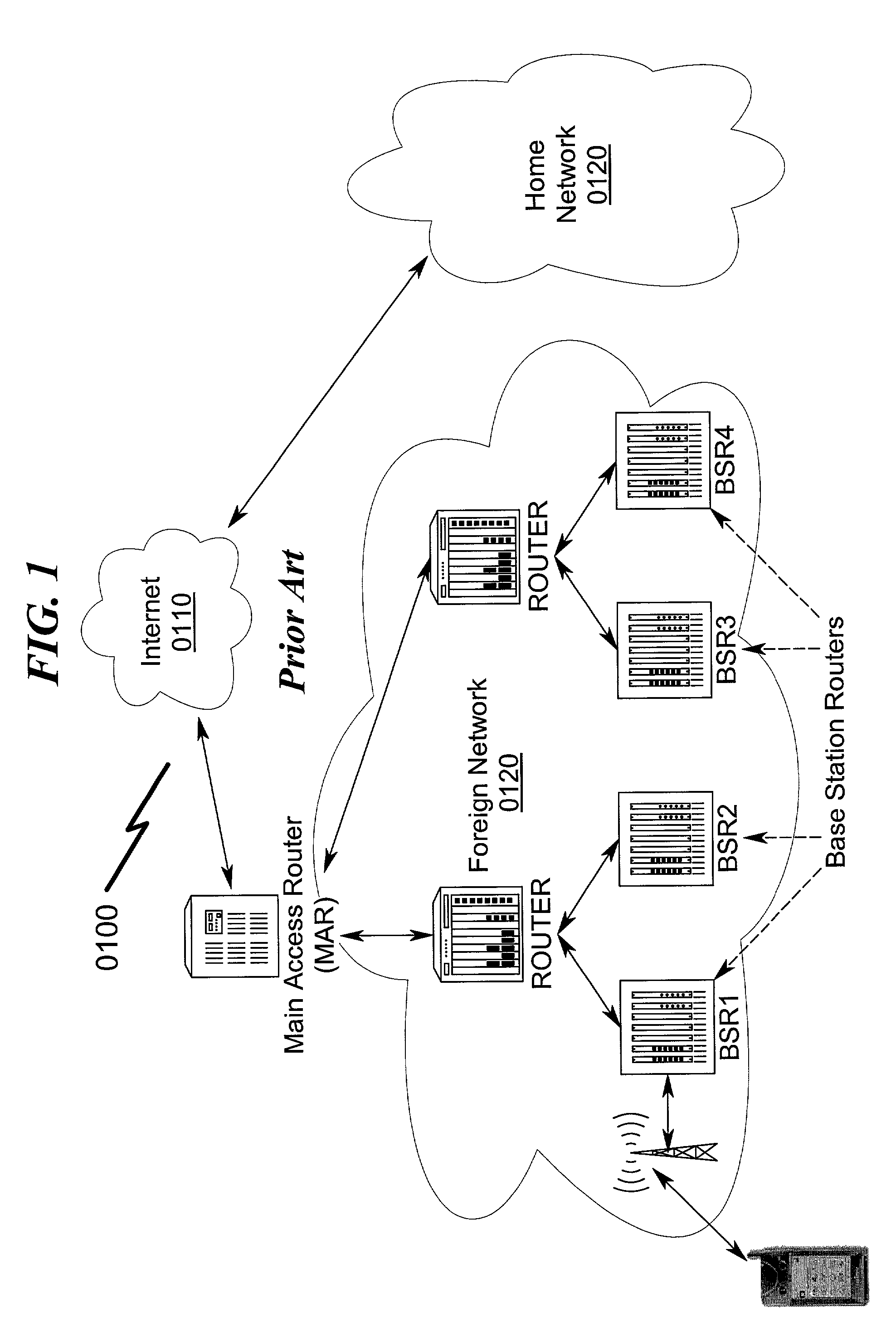
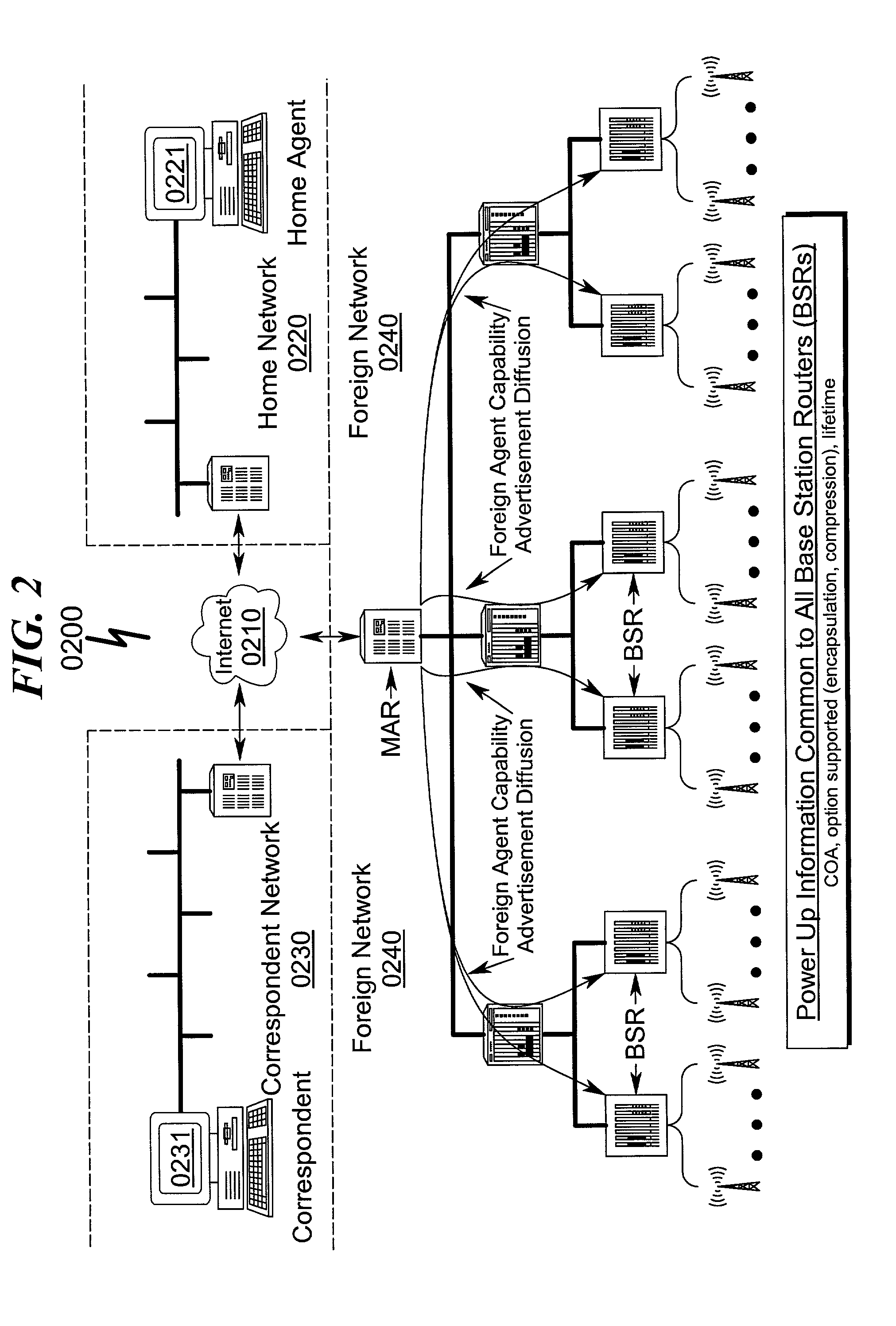
Micro-mobility network routing system and method
InactiveUS20050213545A1Lower latencyImprove smoothnessWireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMobile ip protocolIp address
A micro-mobility network routing system and method implementing a protocol that extends the macro mobility support of Mobile IP to support micro mobility is disclosed which permits a more efficient and easily implemented Internet routing protocol for network devices to be affected. The macro mobility feature herein refers to the notion in which the mobile node gains access to the Internet, while retaining the same IP address. This concept is used only once when the mobile node enters the coverage area of a foreign domain (eventually its home domain). The concept of micro mobility within this context eases routing packets to the mobile node while its moves within the foreign network. The present invention implements these new features via the use of message compositions and protocol extensions that extend the prior art Mobile IP protocols.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
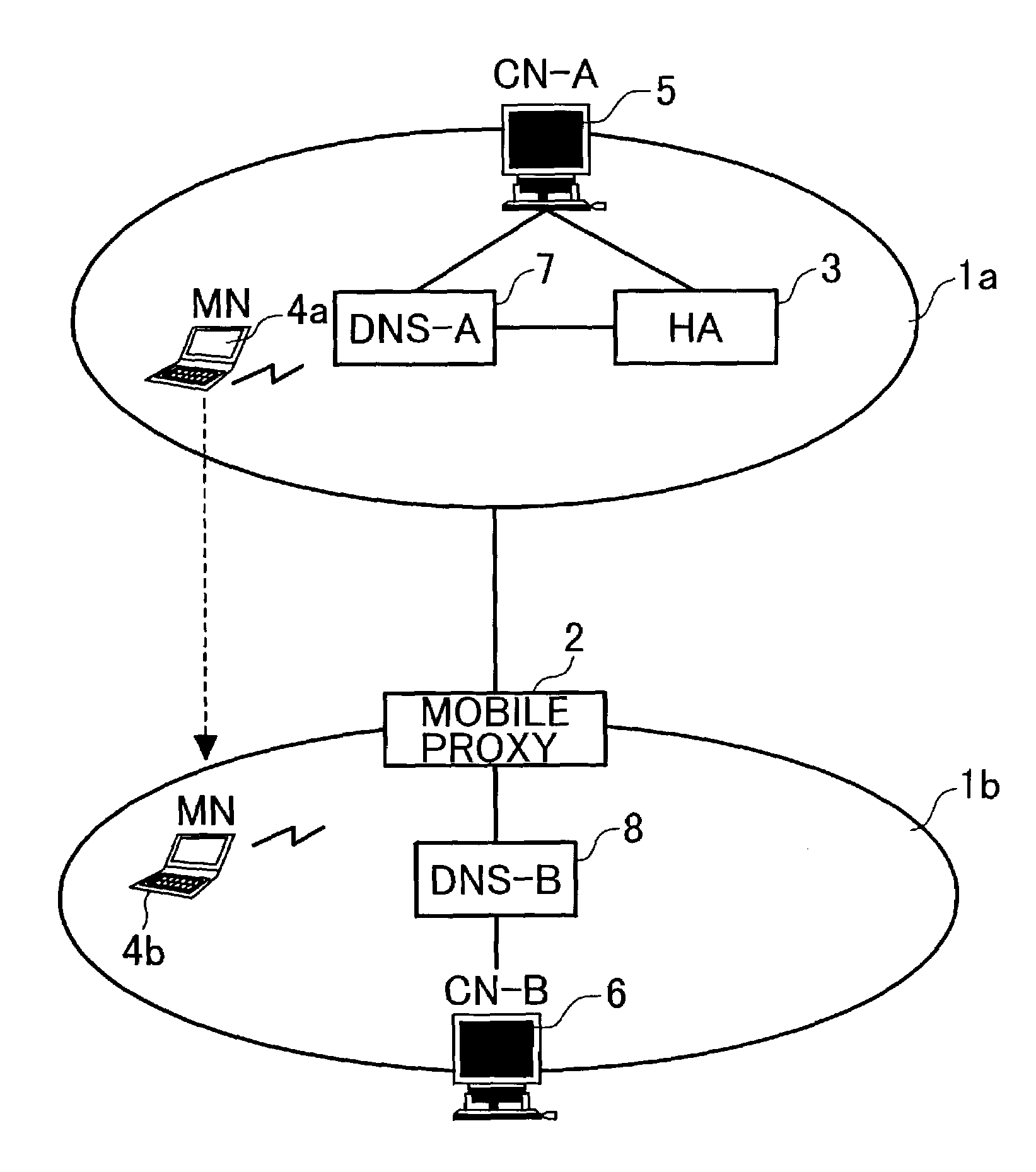
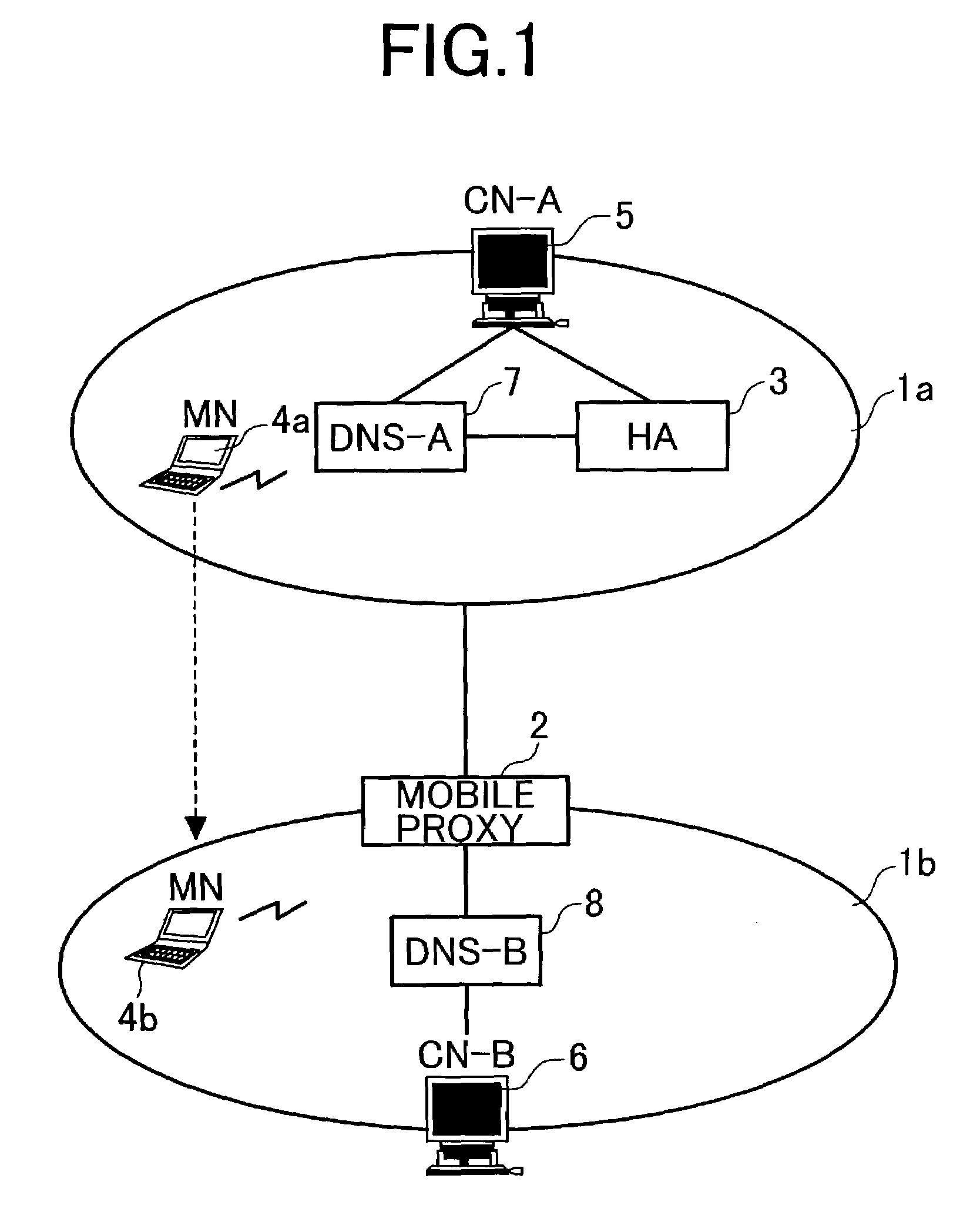
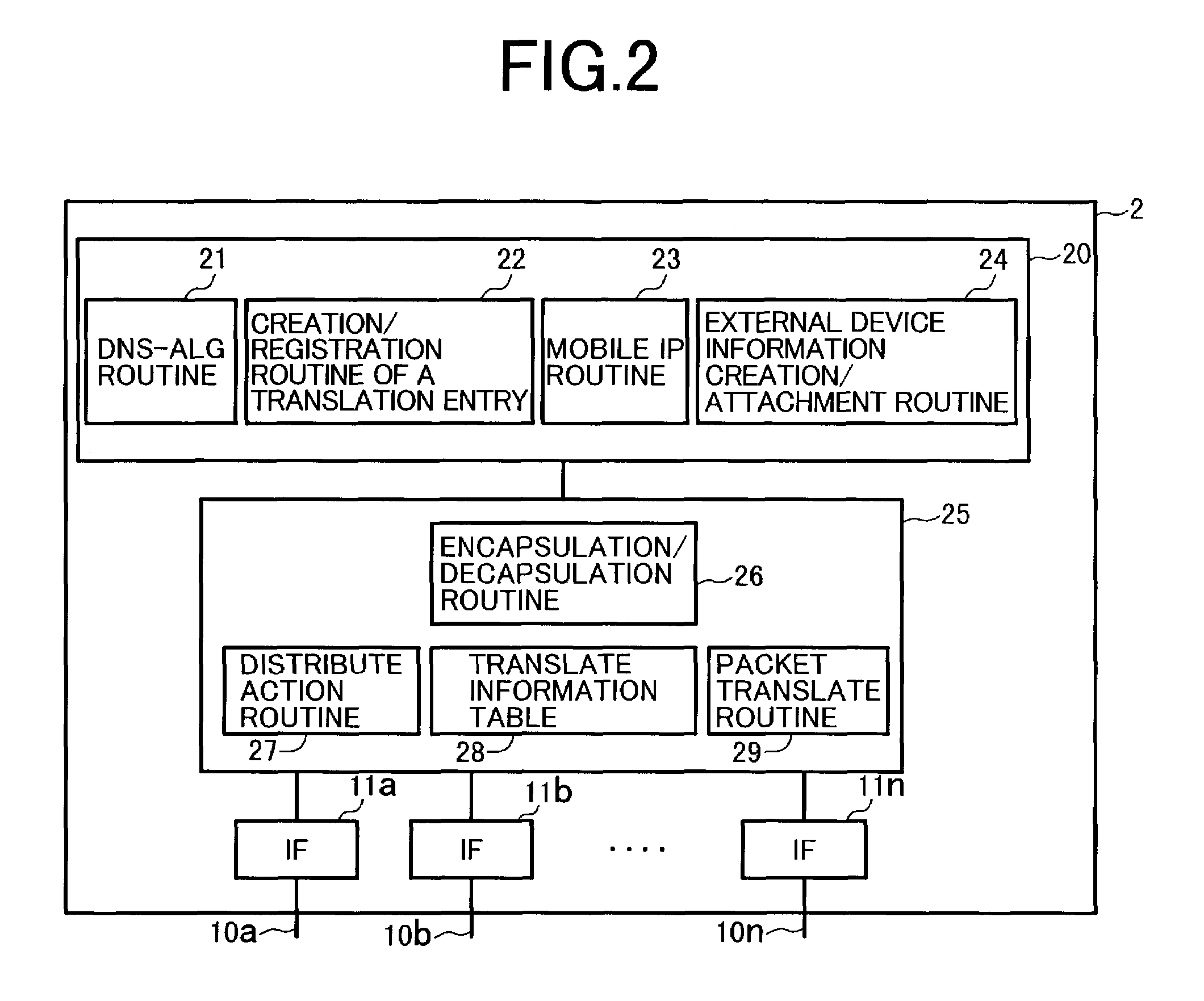
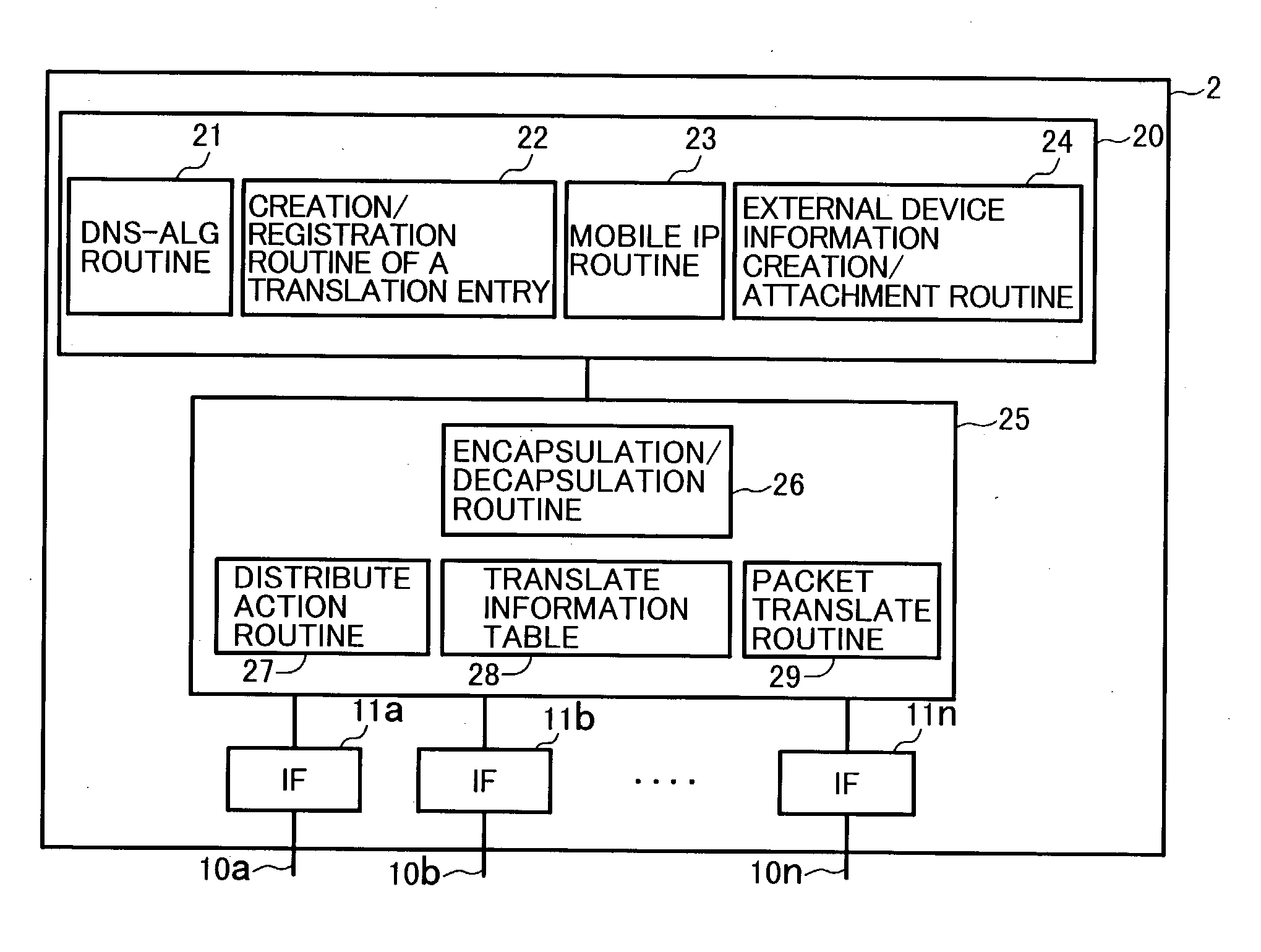
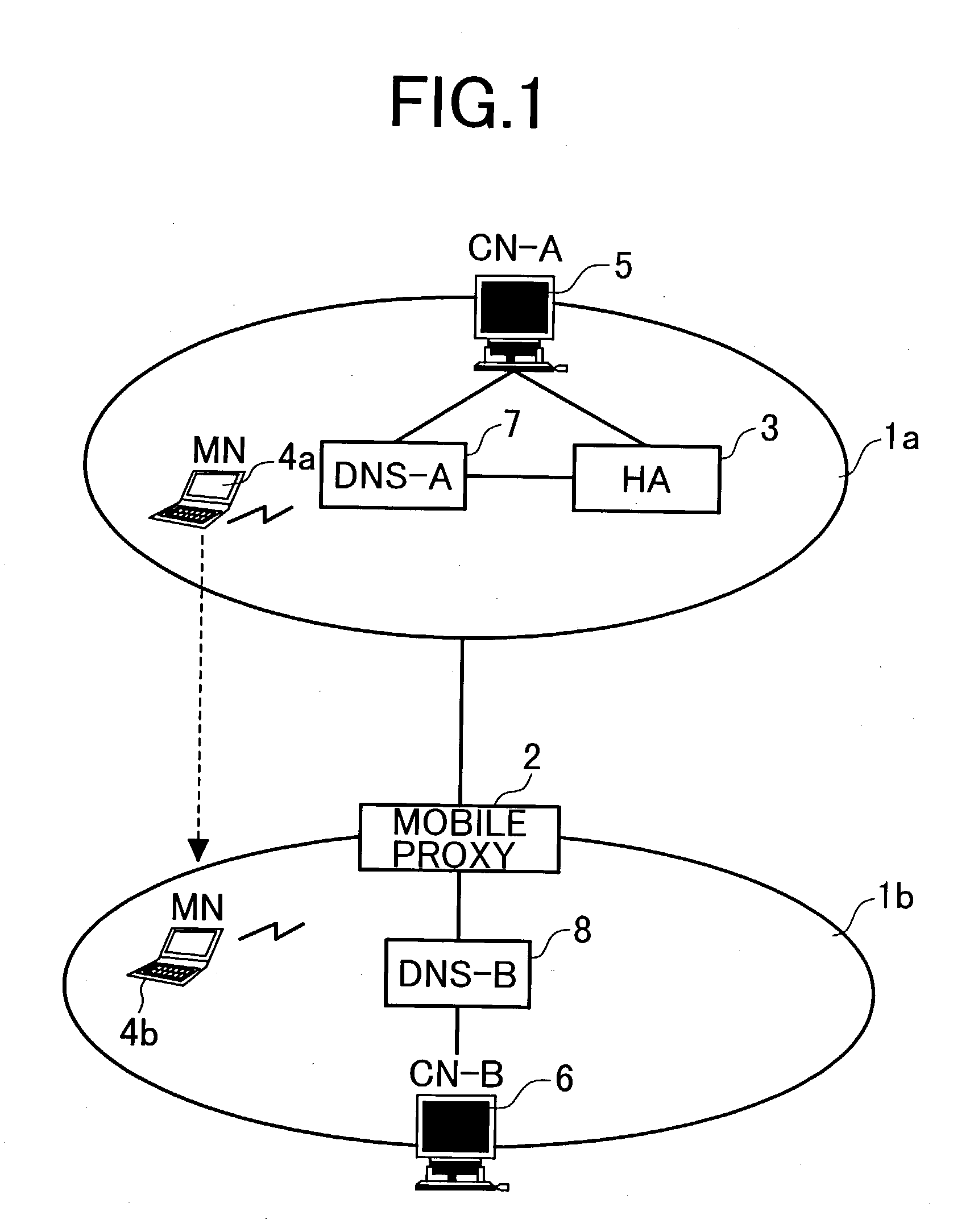
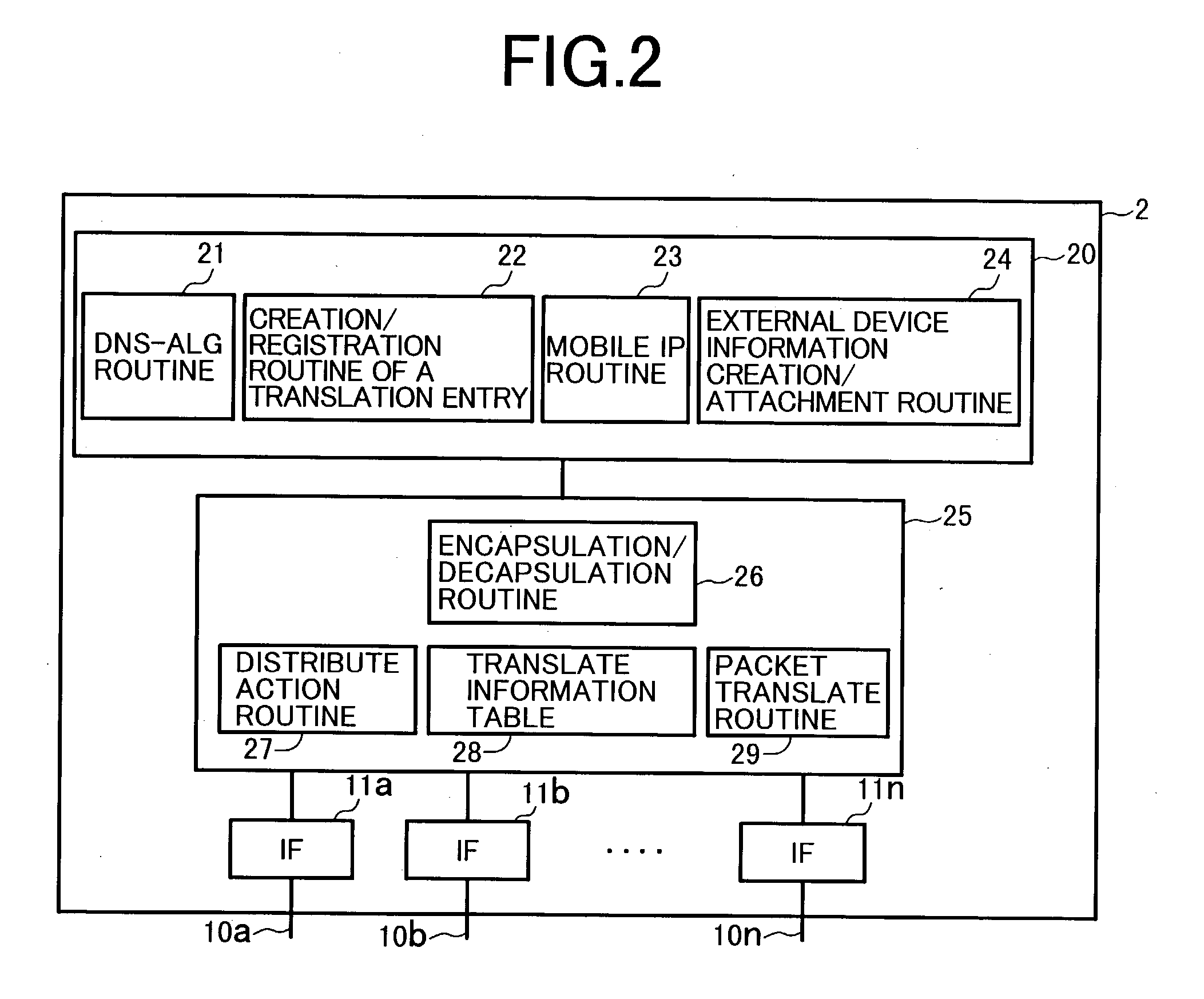
System using mobile proxy for intercepting mobile IP message and performing protocol translation to support multiple communication protocols between mobile networks
InactiveUS7162529B2Connection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork Communication ProtocolsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
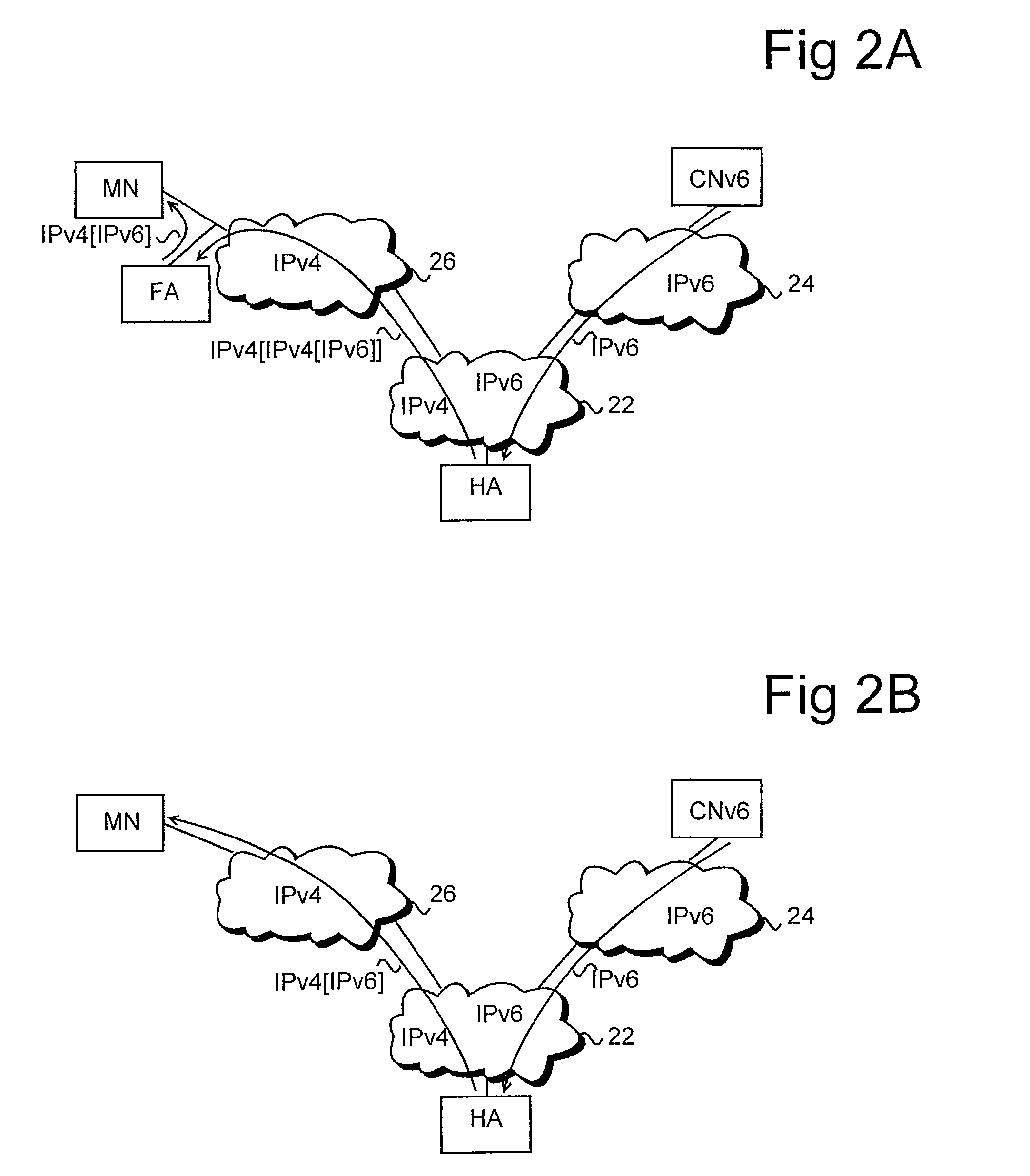
Since the Mobile IP is defined under the assumption that a mobile node roams between networks conforming to the same communications protocols, mobile communications between IPv4 and IPv6 are not possible. Further, a translation of the location registration messages also requires translating the format between different protocol layers. To solve this problem, a mobile proxy apparatus 2 is provided between a home network 1a and a foreign network 1b governed by different communications protocols. The mobile proxy apparatus 2 has a DNS-ALG function, a translator function and a Mobile IP function, and, by combining these functions, performs address translation and format translation on Mobile IP messages and user packets. The MN4 has Mobile IPv4 and Mobile IPv6 functions and executes communication suitable for the communications protocol governing the network to which it moves.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Enabling Simultaneous Use of Home Network and Foreign Network by a Multihomed Mobile Node
ActiveUS20080256220A1Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsTelecommunicationsFamily network
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
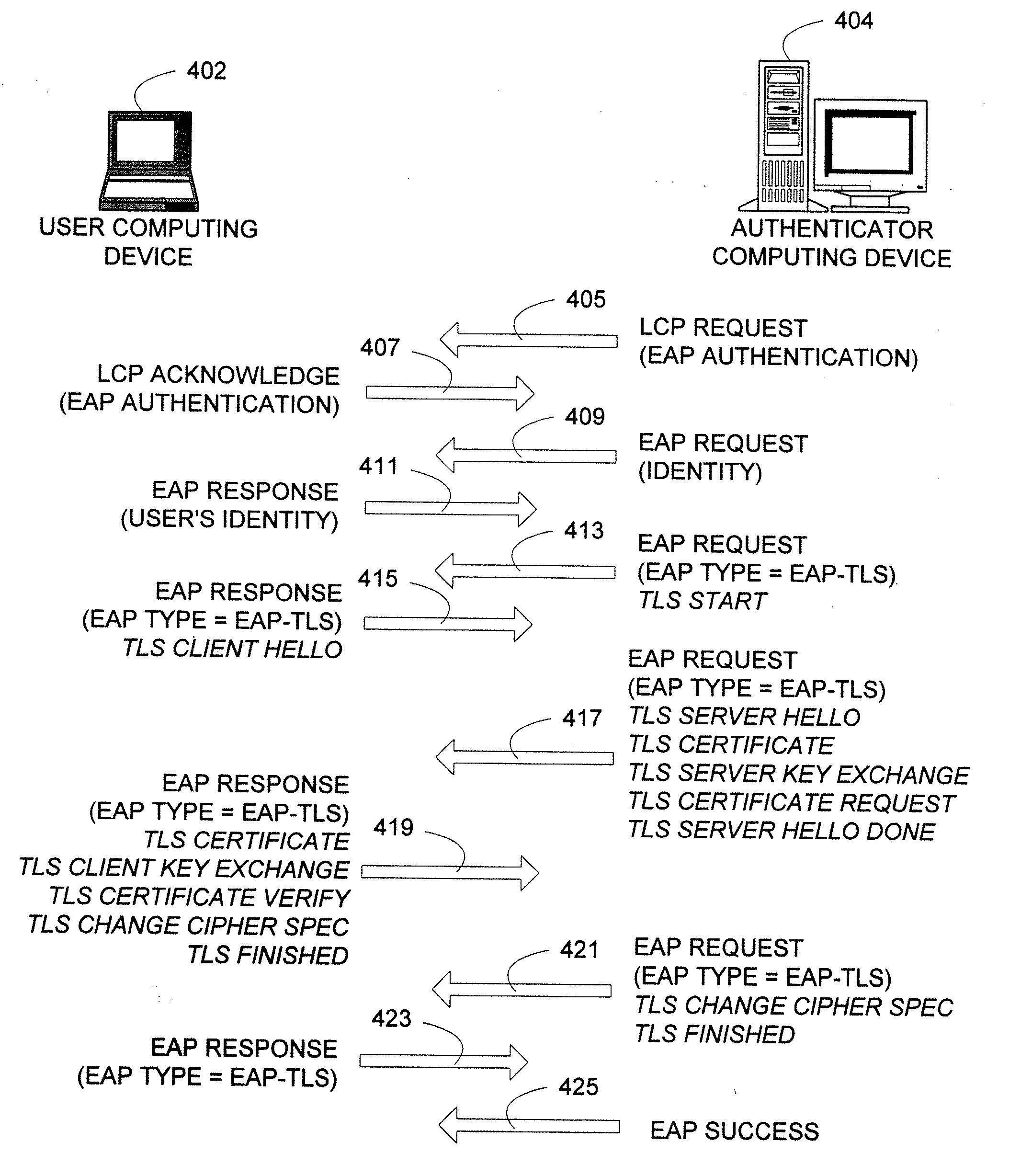
TLS tunneling
InactiveUS7529933B2Reduce interceptionProtect normal transmissionUser identity/authority verificationSecret communicationSecure communicationWireless mesh network
An authentication protocol can be used to establish a secure method of communication between two devices on a network. Once established, the secure communication can be used to authenticate a client through various authentication methods, providing security in environments where intermediate devices cannot be trusted, such as wireless networks, or foreign network access points. Additionally, the caching of session keys and other relevant information can enable the two securely communicating endpoints to quickly resume their communication despite interruptions, such as when one endpoint changes the access point through which it is connected to the network. Also, the secure communication between the two devices can enable users to roam off of their home network, providing a mechanism by which access through foreign networks can be granted, while allowing the foreign network to monitor and control the use of its bandwidth.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
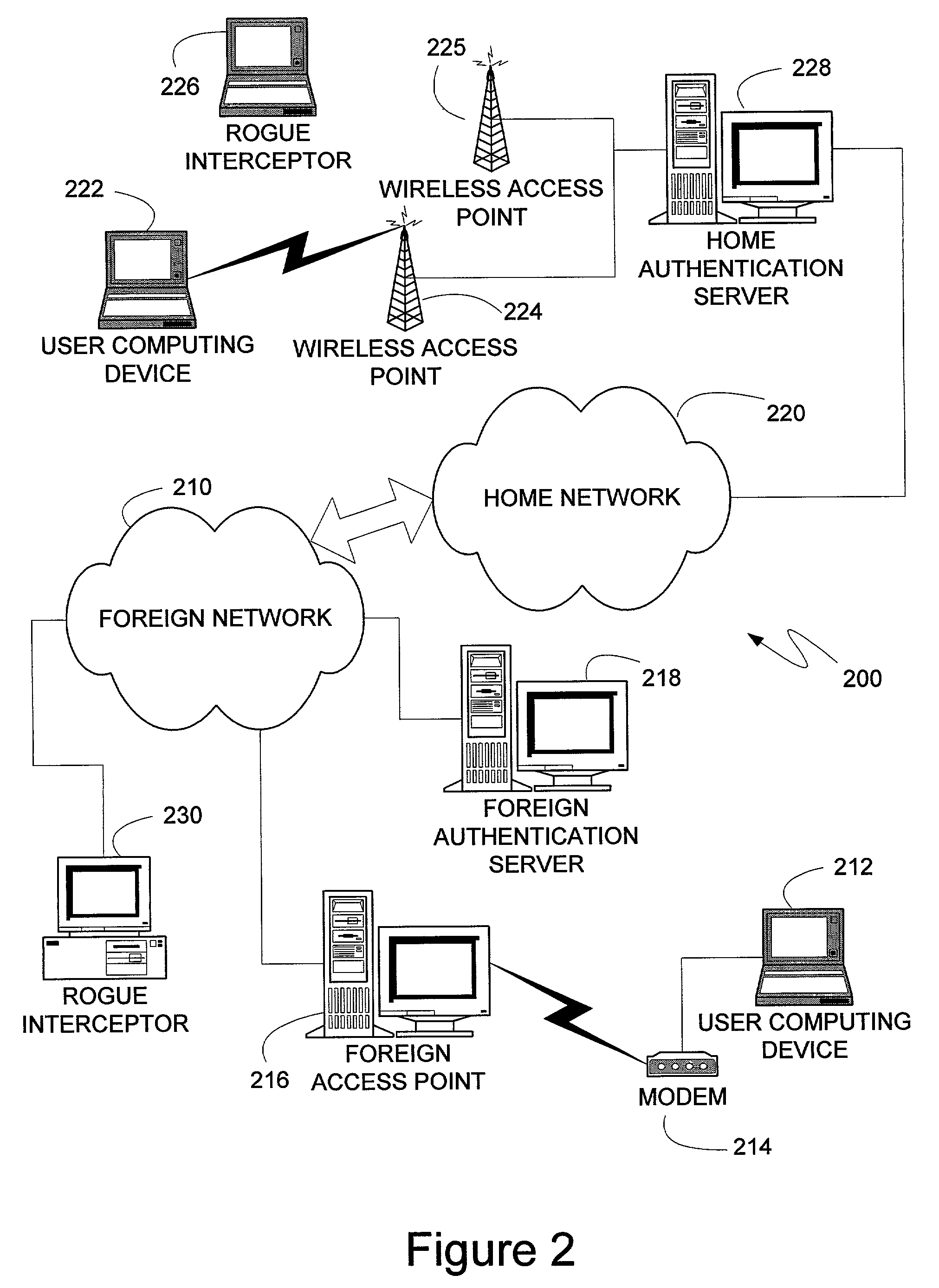
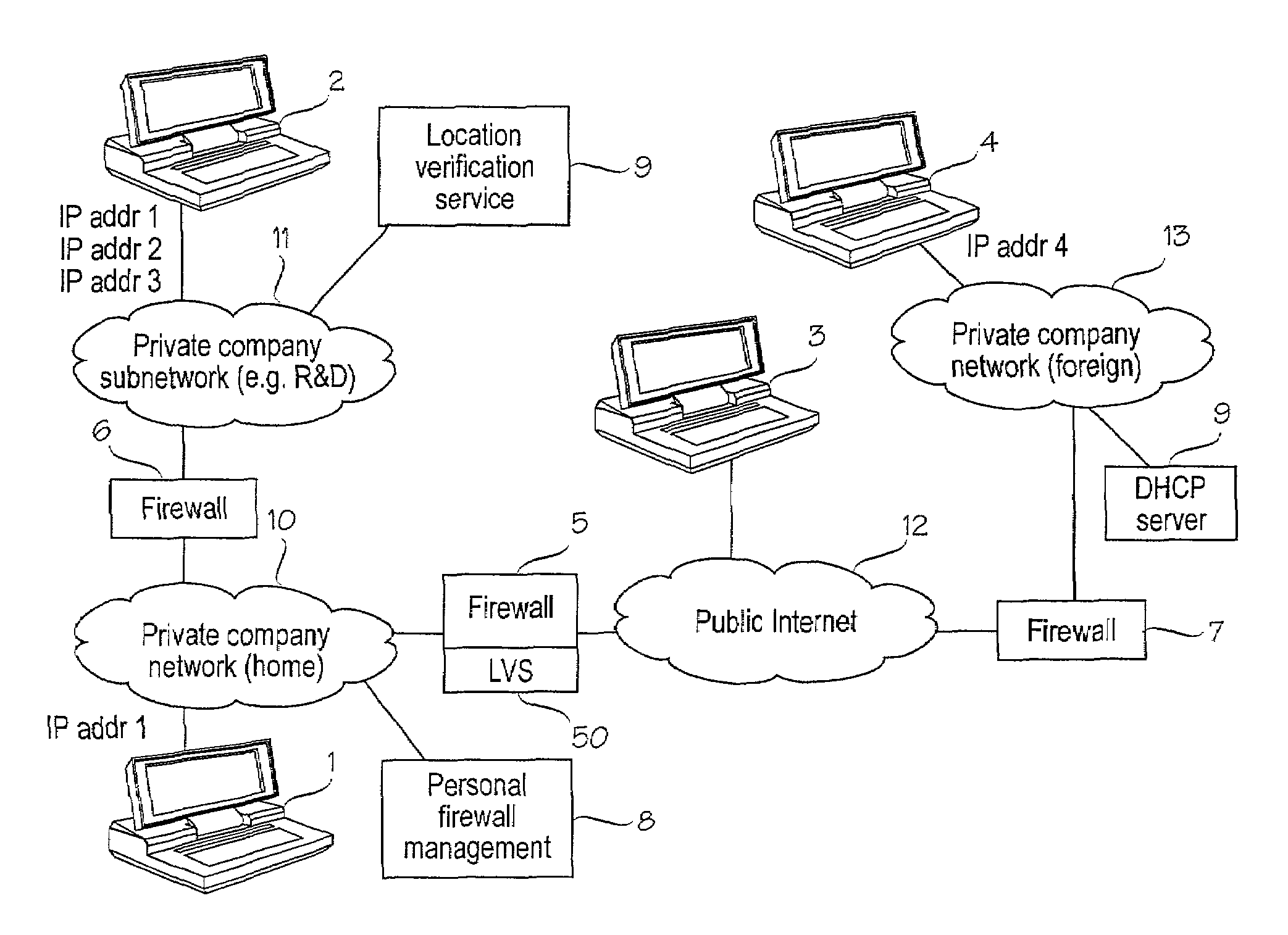
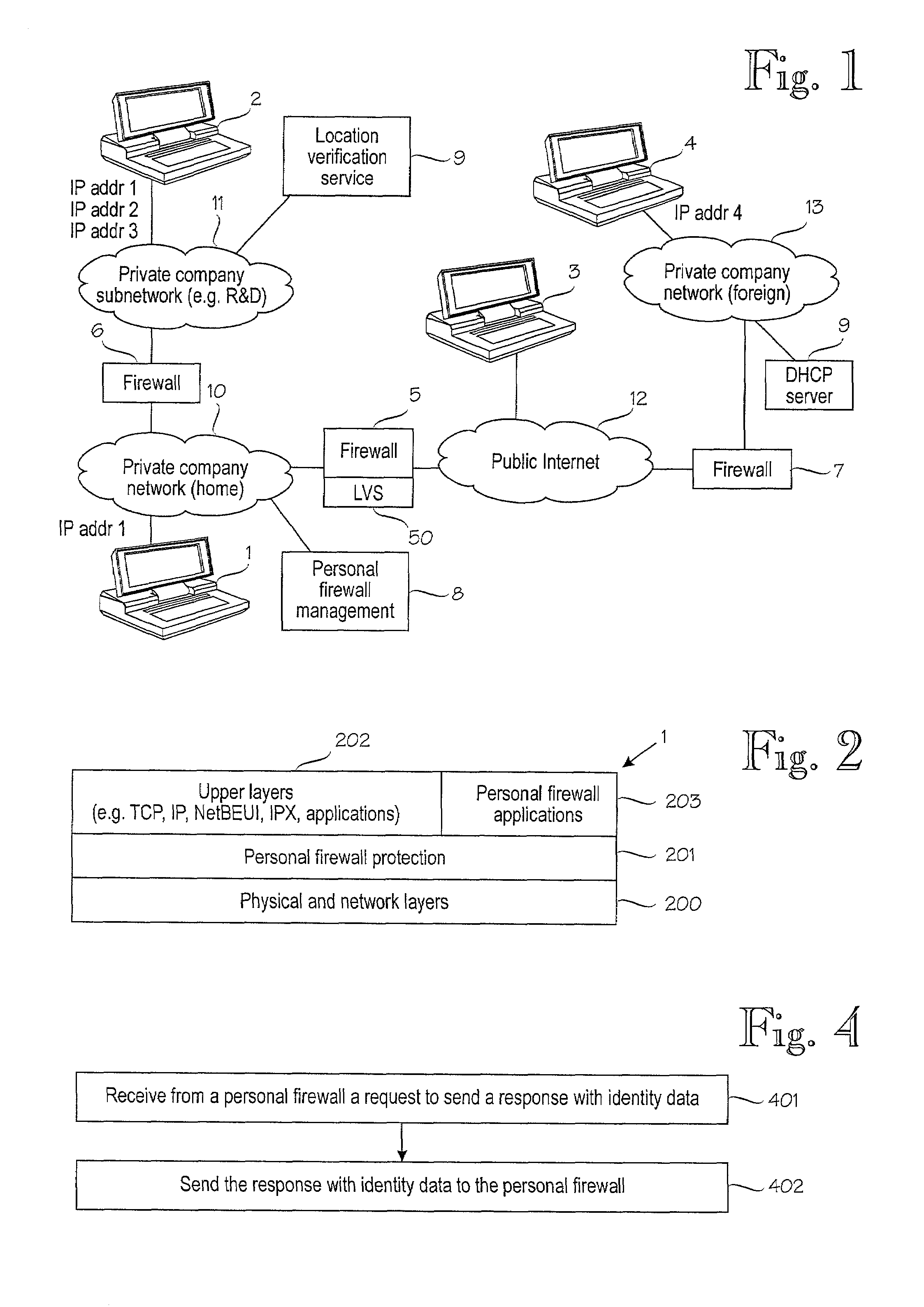
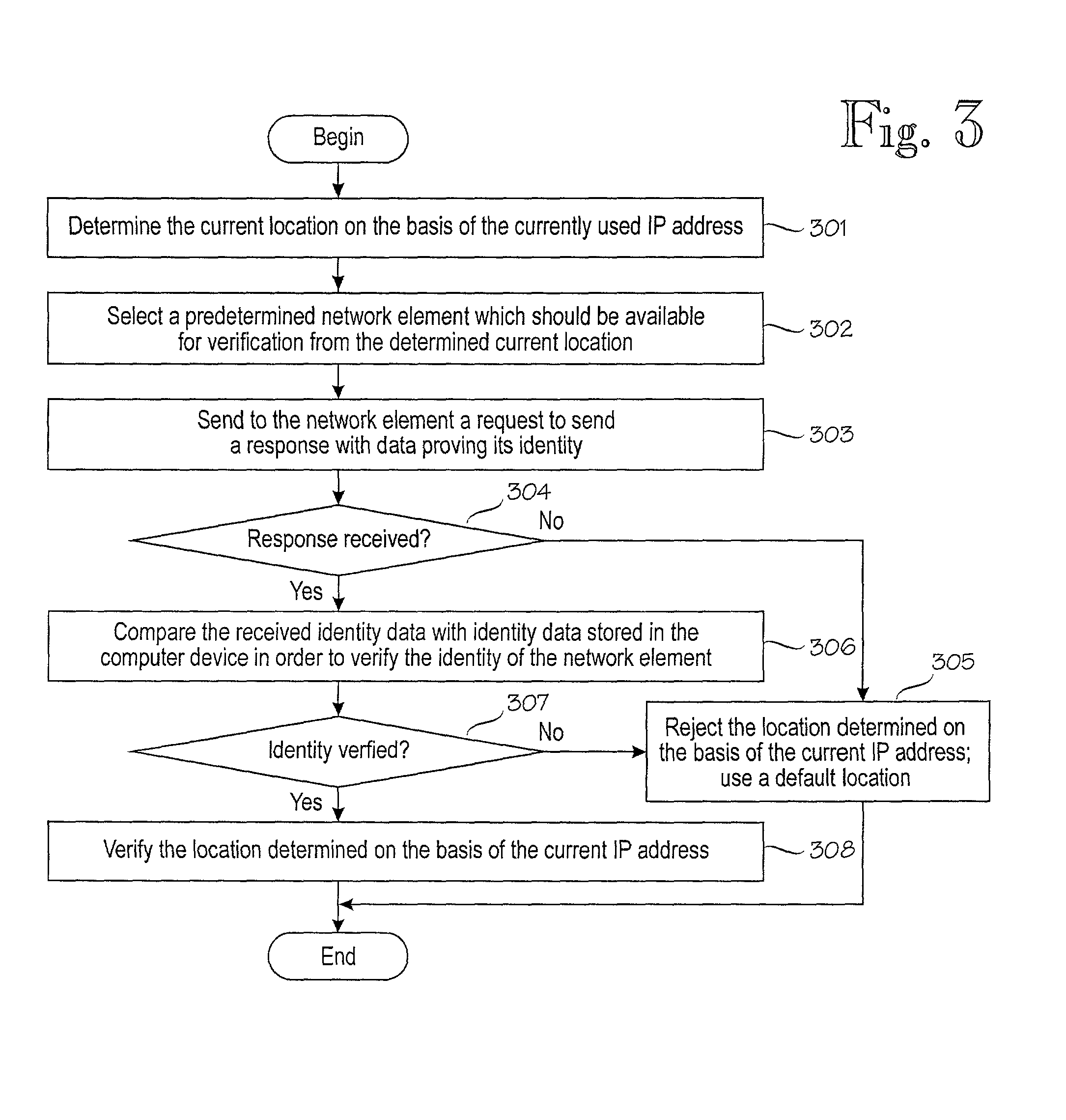
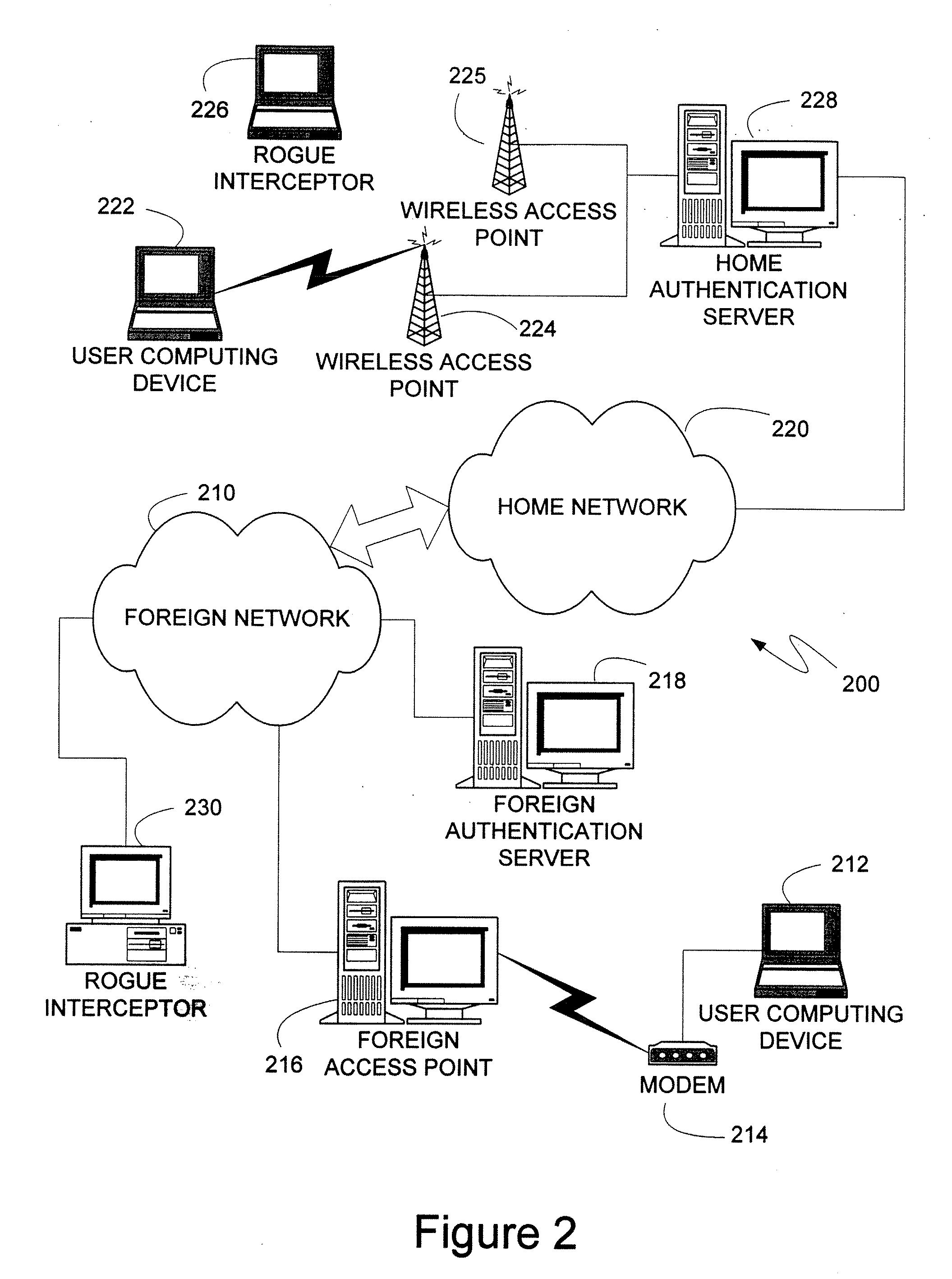
Personal firewall with location detection
A computer device which can be connected to a home network and to a foreign network is provided with a local security mechanism, called a personal firewall, for protecting the computer device from attacks from the foreign network, in addition to or instead of a firewall in the internal network which protects the computer when connected to the internal network. The personal firewall is arranged to detect its current location, i.e. to determine the network to which it is connected at each particular moment, and to control its operation accordingly. The current location of the computer device is first determined on the basis of a currently used IP address of the computer device. Then this location determined on the basis of the current IP address of the computer device is verified by carrying out an additional location verification procedure with a predetermined network element.
Owner:FORCEPOINT LLC
Mobile proxy apparatus and mobile communication method
InactiveUS20030225900A1Connection managementMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork Communication ProtocolsProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
Since the Mobile IP is defined under the assumption that a mobile node roams between networks conforming to the same communications protocols, mobile communications between IPv4 and IPv6 are not possible. Further, a translation of the location registration messages also requires translating the format between different protocol layers. To solve this problem, a mobile proxy apparatus 2 is provided between a home network 1a and a foreign network 1b governed by different communications protocols. The mobile proxy apparatus 2 has a DNS-ALG function, a translator function and a Mobile IP function, and, by combining these functions, performs address translation and format translation on Mobile IP messages and user packets. The MN4 has Mobile IPv4 and Mobile IPv6 functions and executes communication suitable for the communications protocol governing the network to which it moves.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
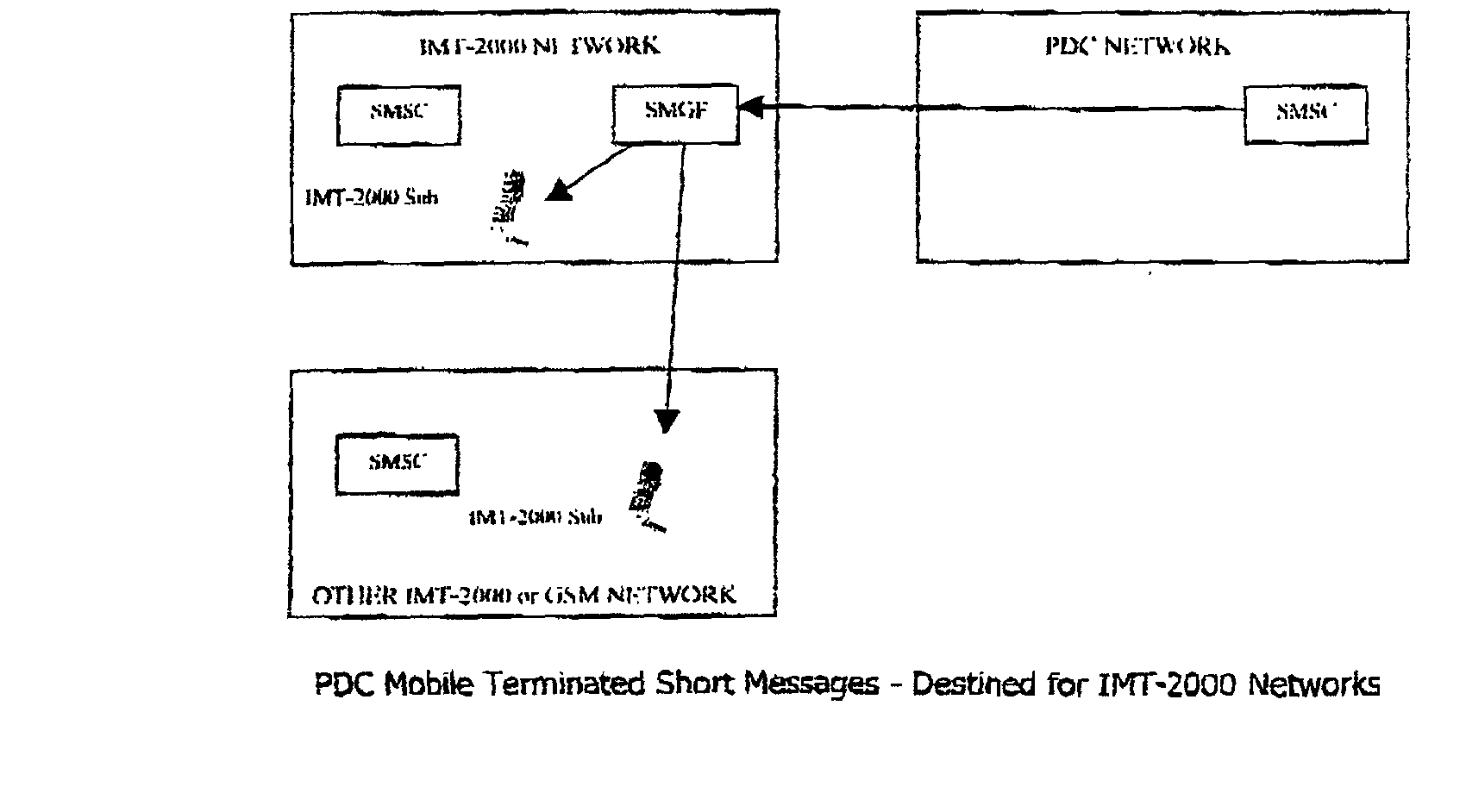
Short message gateway
InactiveUS20020173320A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentFamily networkText message
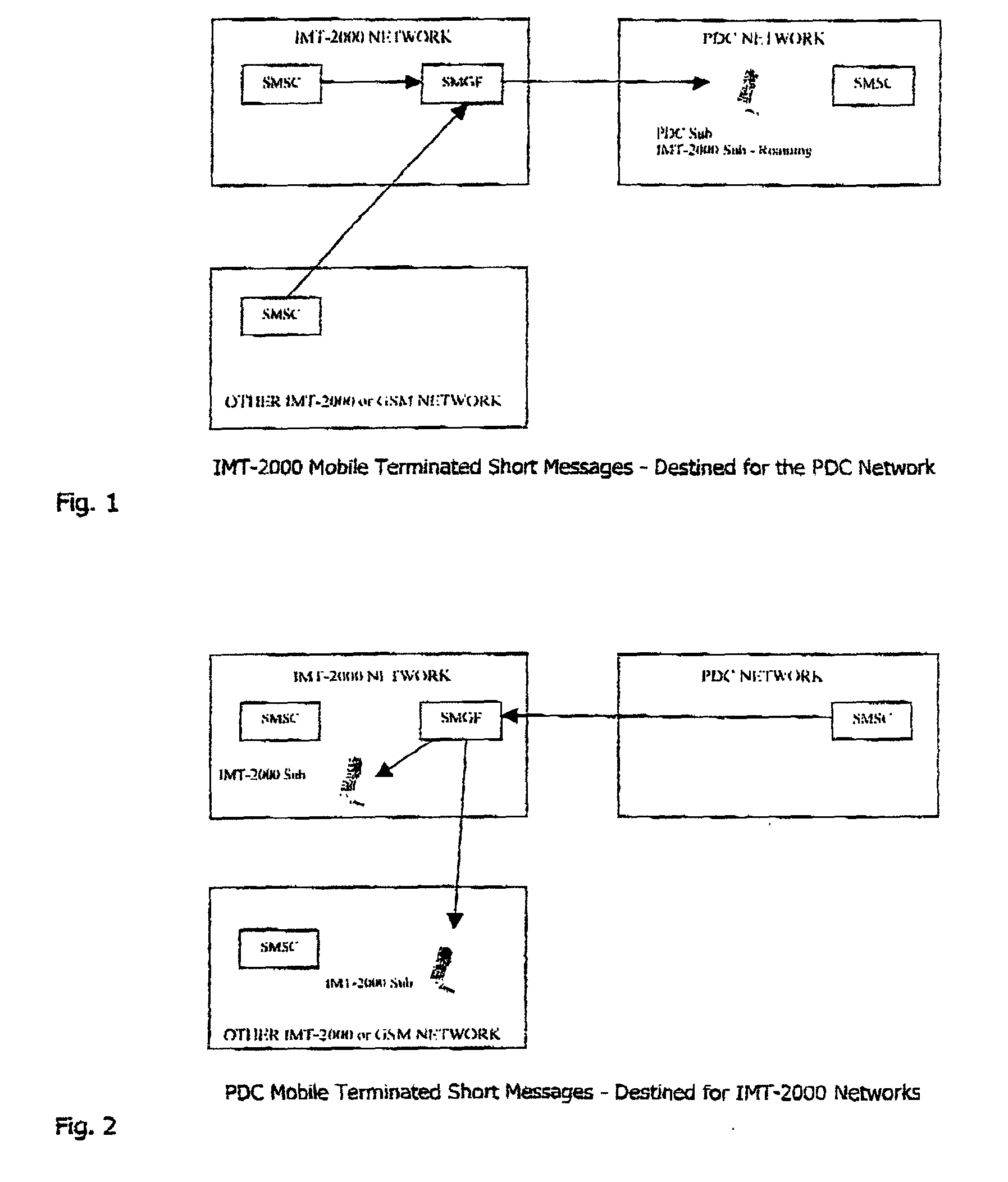
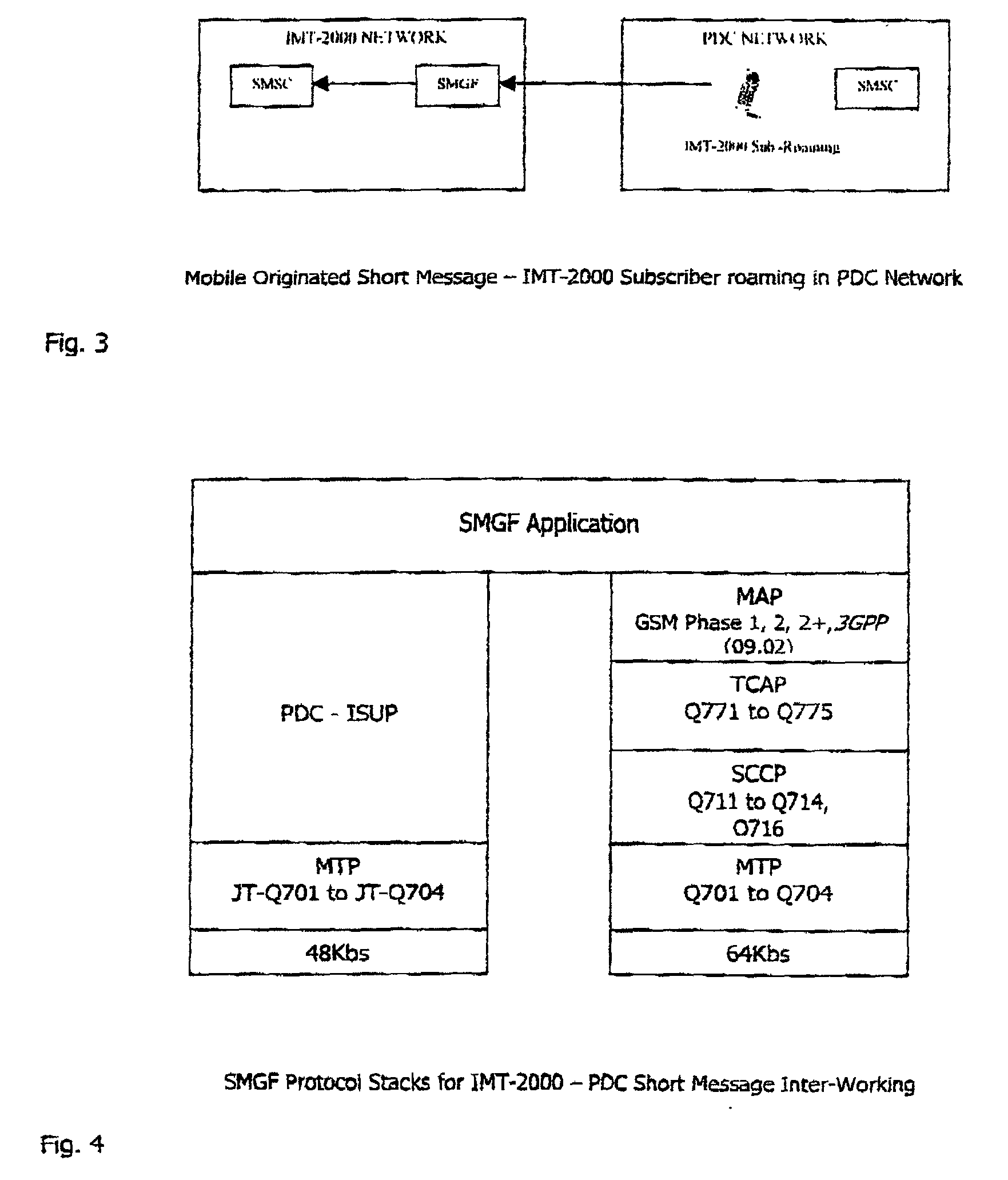
A short message gateway comprises a gateway function (SMGF) and programs in an HLR or a home network (IMT-2000). It does not have any physical impact on a foreign (PDC) network, and it converts short messages communicated between the home and foreign networks. The gateway function (SMGF) primarily inter-operates with an HLR and an SMSC of the home network, the GMSC providing the link to the foreign network. The gateway allows communication in a wide variety of scenarios for communication with subscribers in the home and foreign networks and roaming subscribers from one to the other.
Owner:MARKPORT LTD
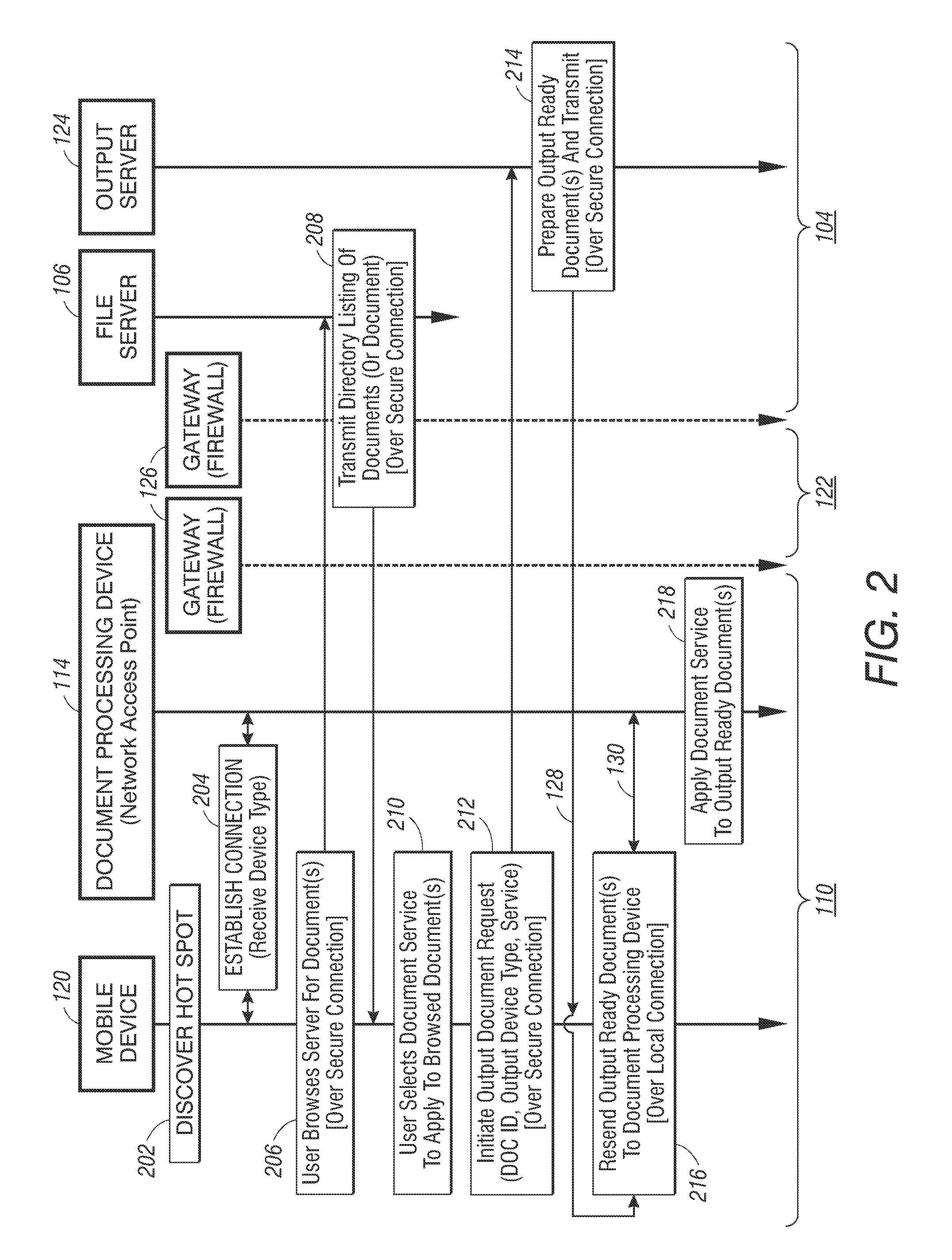
Method and apparatus for controlling document service requests from a mobile device
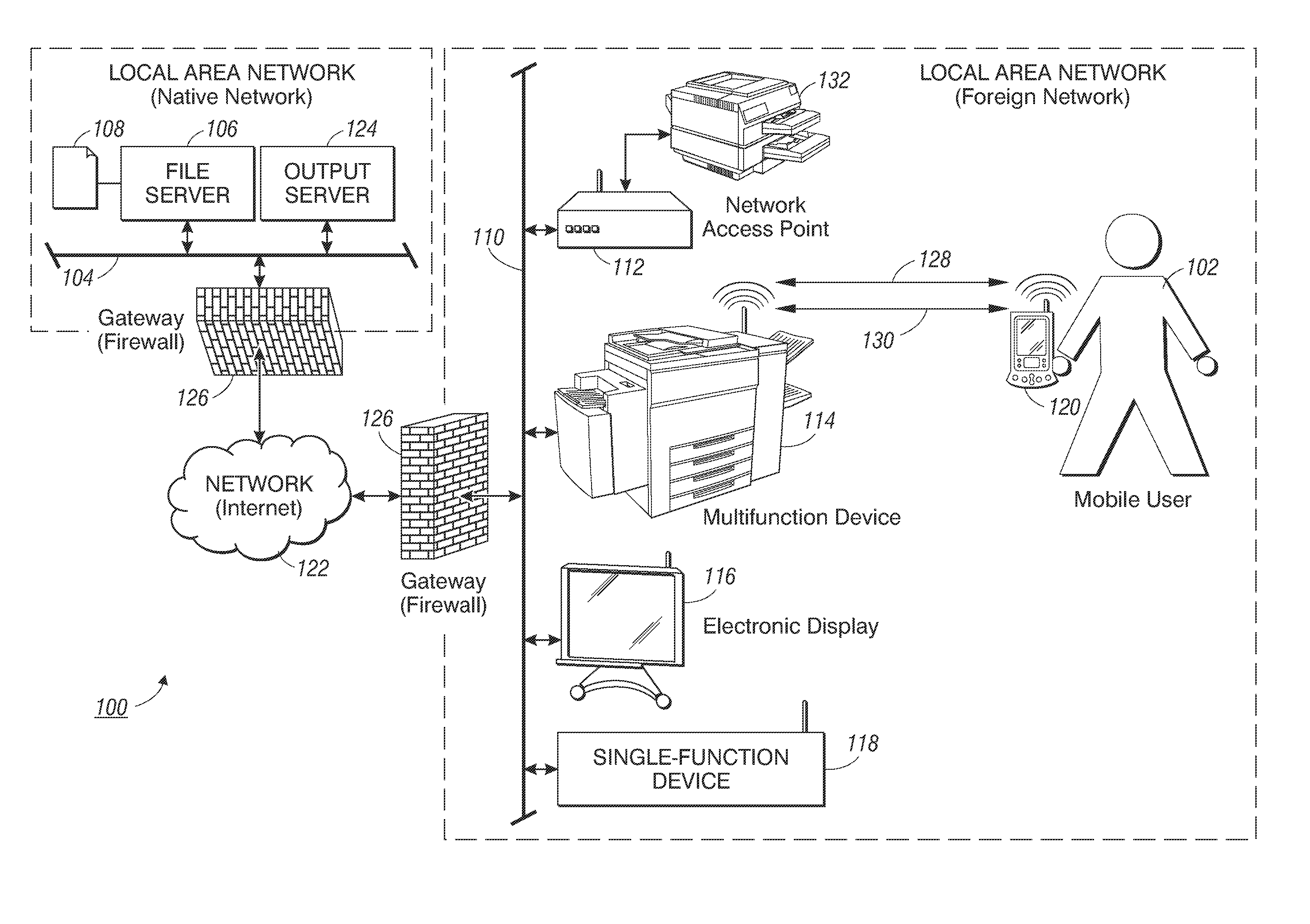
Methods for controlling a document service request involve defining a document service request workflow and redirecting document service requests from the mobile device. In one embodiment, through a short-range connection with a document processing device on a foreign network, a mobile device establishes a secure connection to the mobile device's native network to identify a document stored on a file server operating thereon. Once a document is identified, the mobile device over the secure connection initiates a document service request by requesting an output server operating on the native network to retrieve and convert the identified document into an output-ready format suitable for the document processing device. Upon receipt of the output-ready document, the mobile device resends the output-ready document over a local connection to the document processing device to carry out the document service request.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Tls tunneling
ActiveUS20070157027A1Reduce interceptionProtect normal transmissionUser identity/authority verificationMultiple digital computer combinationsSecure communicationRelevant information
An authentication protocol can be used to establish a secure method of communication between two devices on a network. Once established, the secure communication can be used to authenticate a client through various authentication methods, providing security in environments where intermediate devices cannot be trusted, such as wireless networks, or foreign network access points. Additionally, the caching of session keys and other relevant information can enable the two securely communicating endpoints to quickly resume their communication despite interruptions, such as when one endpoint changes the access point through which it is connected to the network. Also, the secure communication between the two devices can enable users to roam off of their home network, providing a mechanism by which access through foreign networks can be granted, while allowing the foreign network to monitor and control the use of its bandwidth.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Non-encapsulation mobile IP
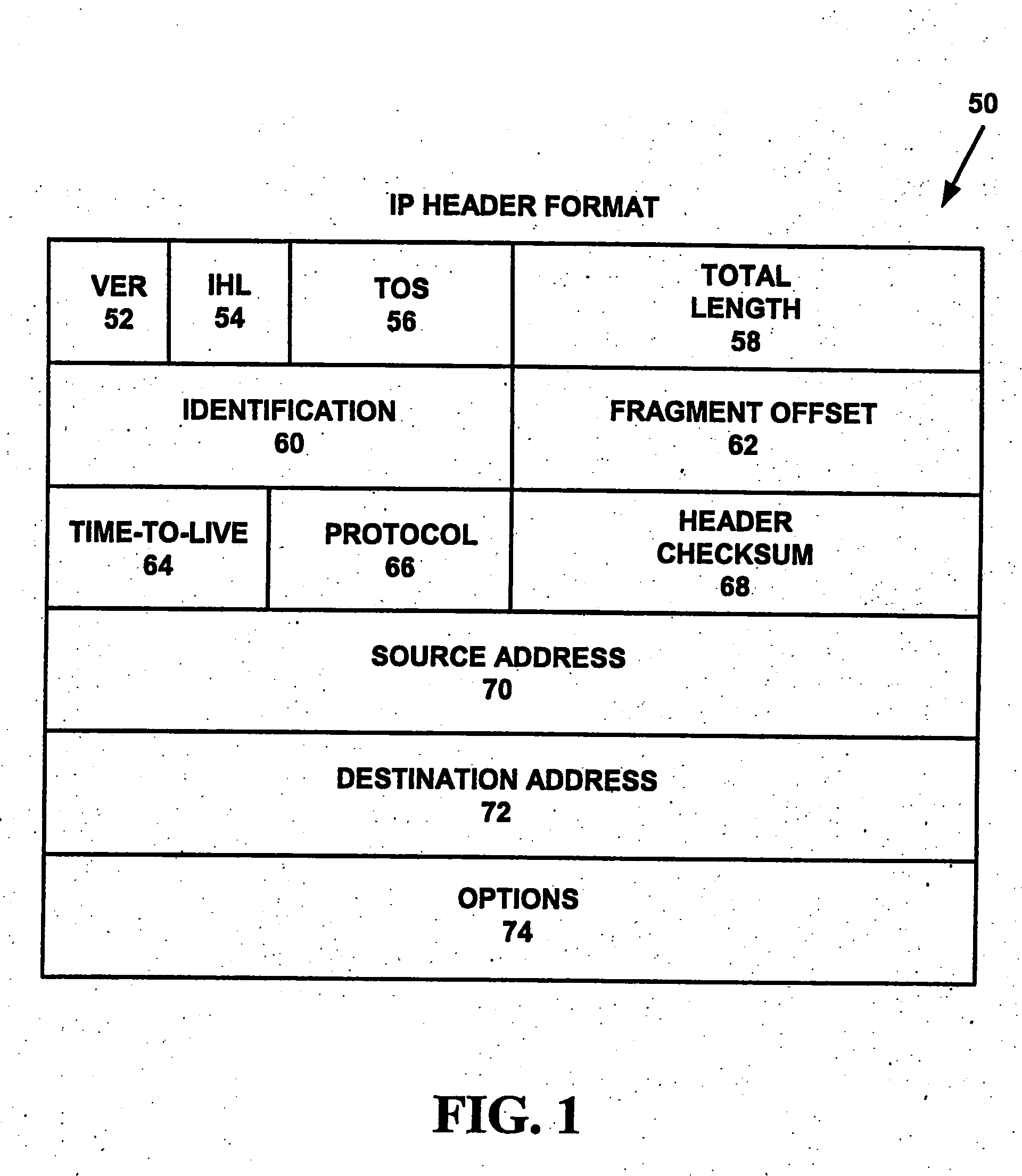
InactiveUS6842456B1Length minimizationIncrease the lengthTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer networkForeign agent
A method is provided of directing an internet protocol (IP) packet to a mobile node. The mobile node has a home address in a home network and is temporarily connectable in a foreign network having a foreign agent. The IP packet has a header portion including the destination address to which the IP packet is to be sent. The method comprises the steps of: receiving, in the home network, the IP packet including a destination address corresponding to the home address of the mobile node; modifying the IP packet by removing the home address of the mobile node from the header portion of the IP packet and replacing it with the foreign agent care-of address, and appending a mobile node identifier to the IP packet, and transmitting the modified IP packet.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method of discovering multi-mode mobile terminals
ActiveUS7596385B2Convenient intercommunicationEasily informedNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTelecommunicationsHeterogeneous network
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
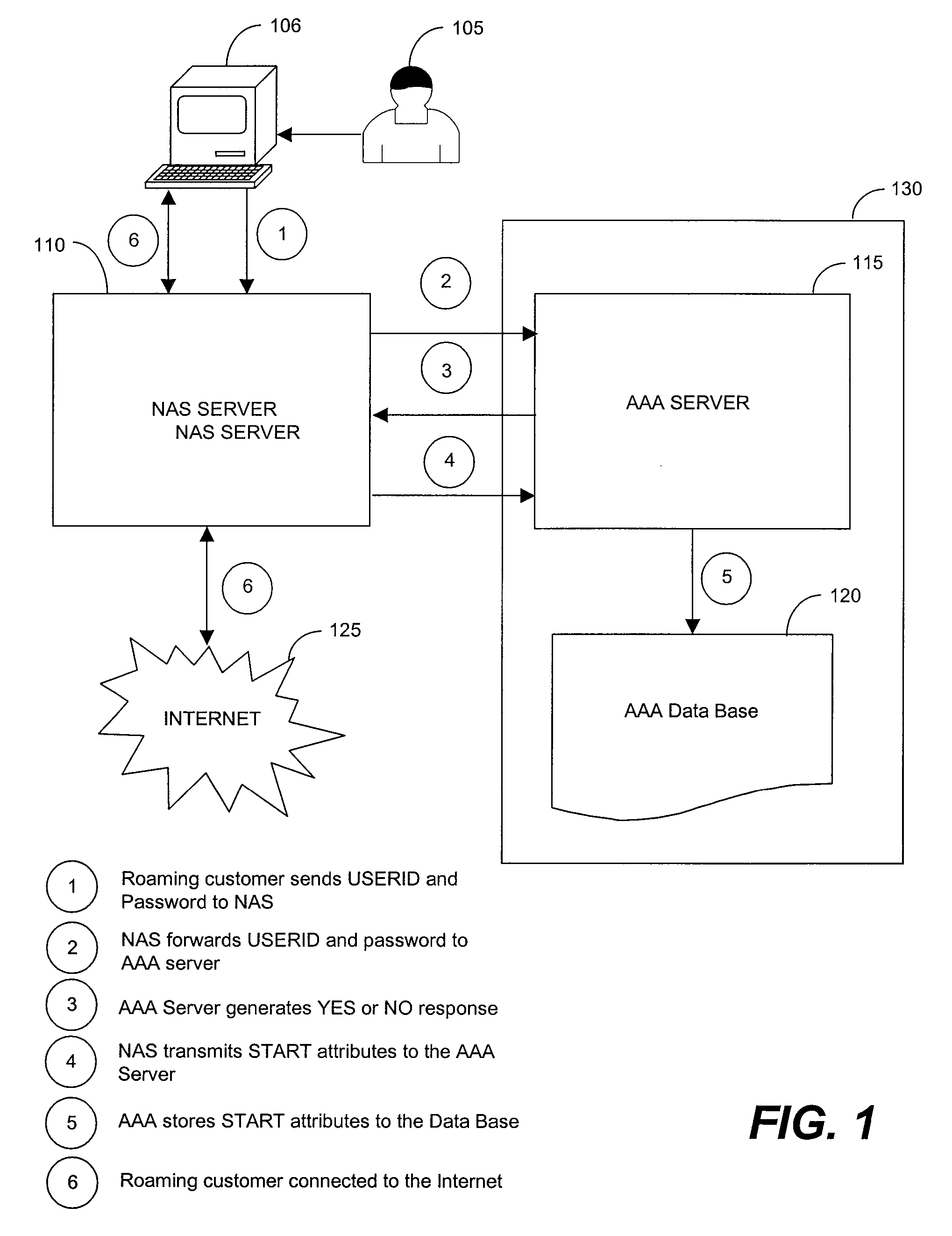
Foreign Network Spam Blocker
A method involves blocking unsolicited e-mail being transmitted from a remote server when a roaming customer of the ISP logs onto the Internet through the foreign NAS. The roaming customer first logs onto the ISP through the foreign NAS by providing a user identification (USERID) and password, which are sent to the ISP. The ISP uses the USERID and the password to authenticate the roaming customer as a valid subscriber of the ISP. An IP address is assigned by the foreign NAS to the roaming customer and is dynamically added to a pool of IP addresses used by the mail server. The roaming customer can then log onto the mail server to send and receive email messages. Once the roaming customer terminates the session, the IP address assigned to the roaming customer is removed from the pool of valid IP address that can be used to access the mail server.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
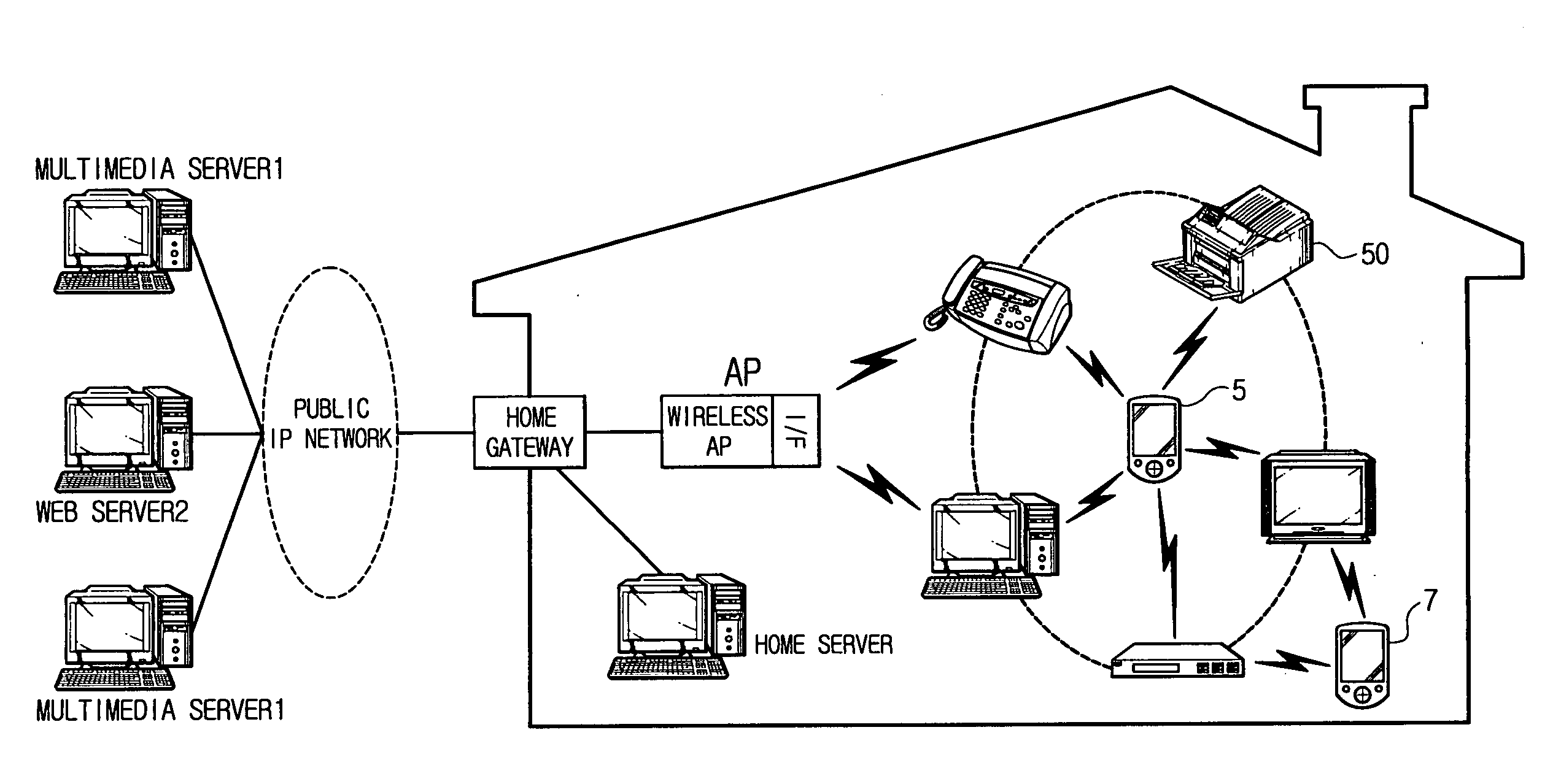
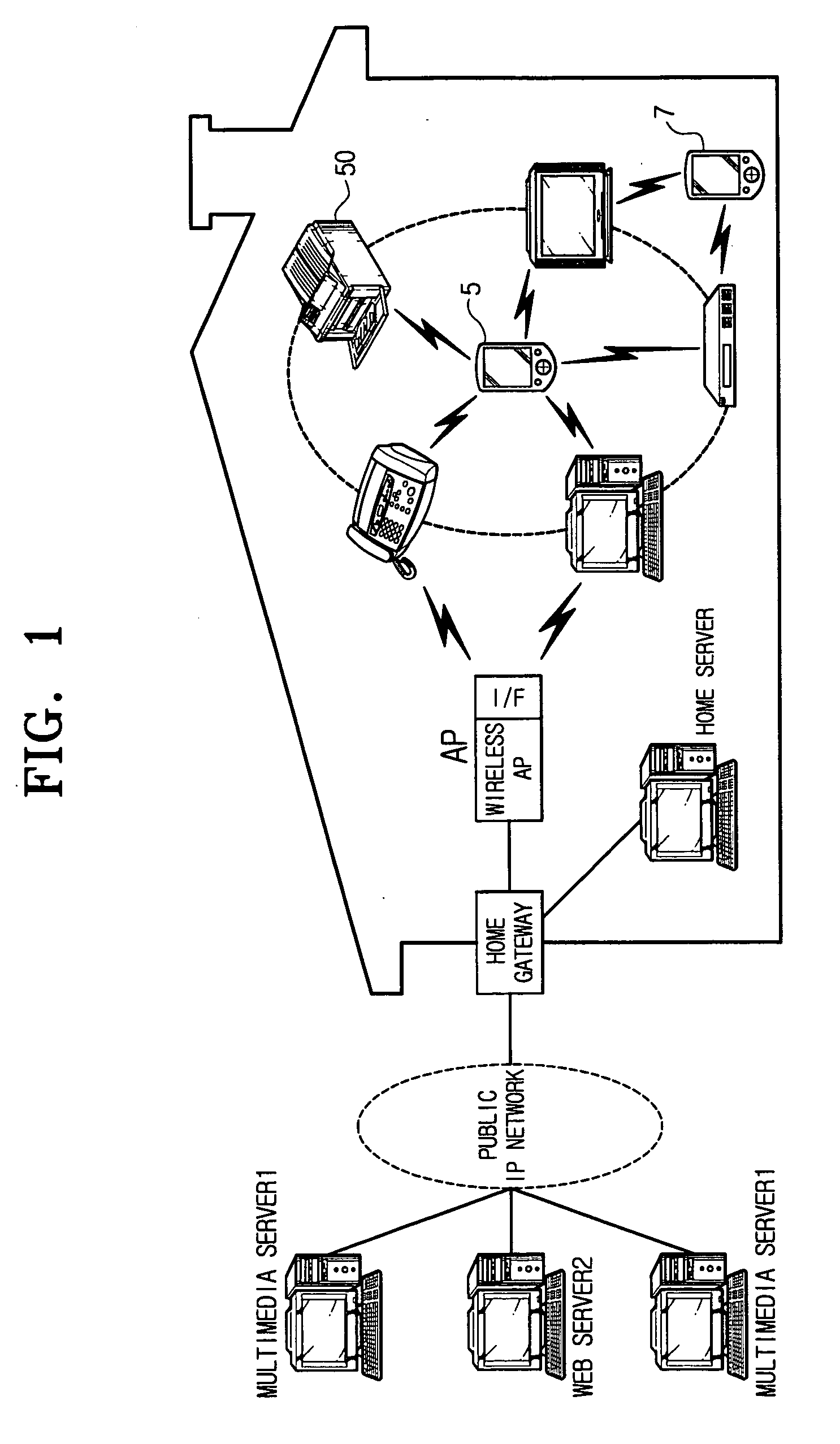
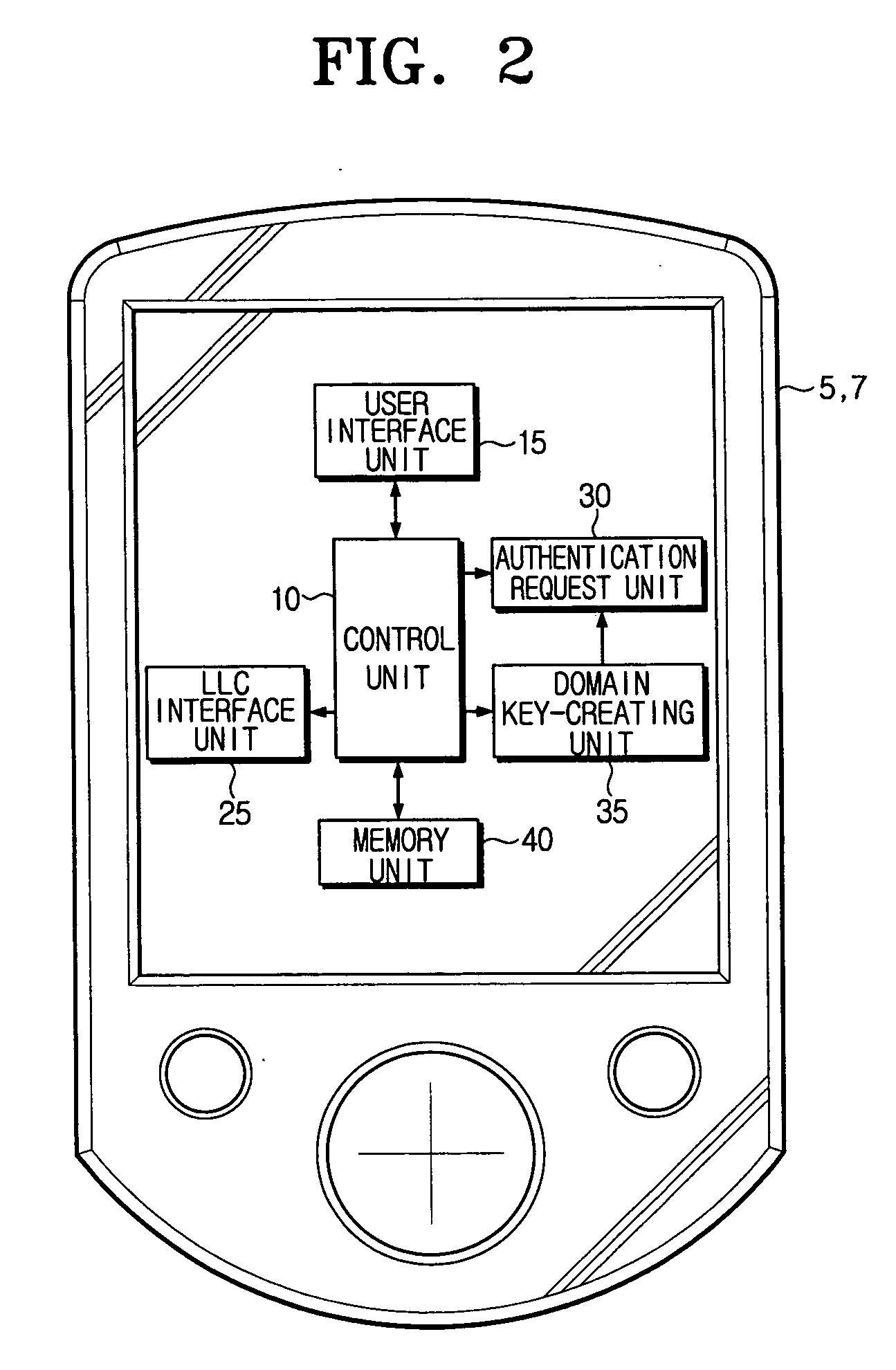
Network and domain-creating method thereof
ActiveUS20070177737A1Efficient managementSecurity and Privacy GuaranteedSpectales/gogglesDigital data processing detailsA domainAuthorization
A network capable of communicating with foreign networks and having a plurality of devices capable of mutually communicating with one another and a domain setup method thereof. The network includes at least one main remote controller for, out of the devices, setting up authorization to use the respective devices belonging to at least one main domain having at least one of the devices; and at least one subsidiary remote controller for receiving authentication for authorization to use the respective device belonging to a domain having the respective devices authorized to at least one user by the respective main remote controllers. Thus, the present network enables each user to efficiently administer whether to use the home devices as well as enables the home devices authorized to each user to be set up in one domain in order to keep security and privacy from foreign domains.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
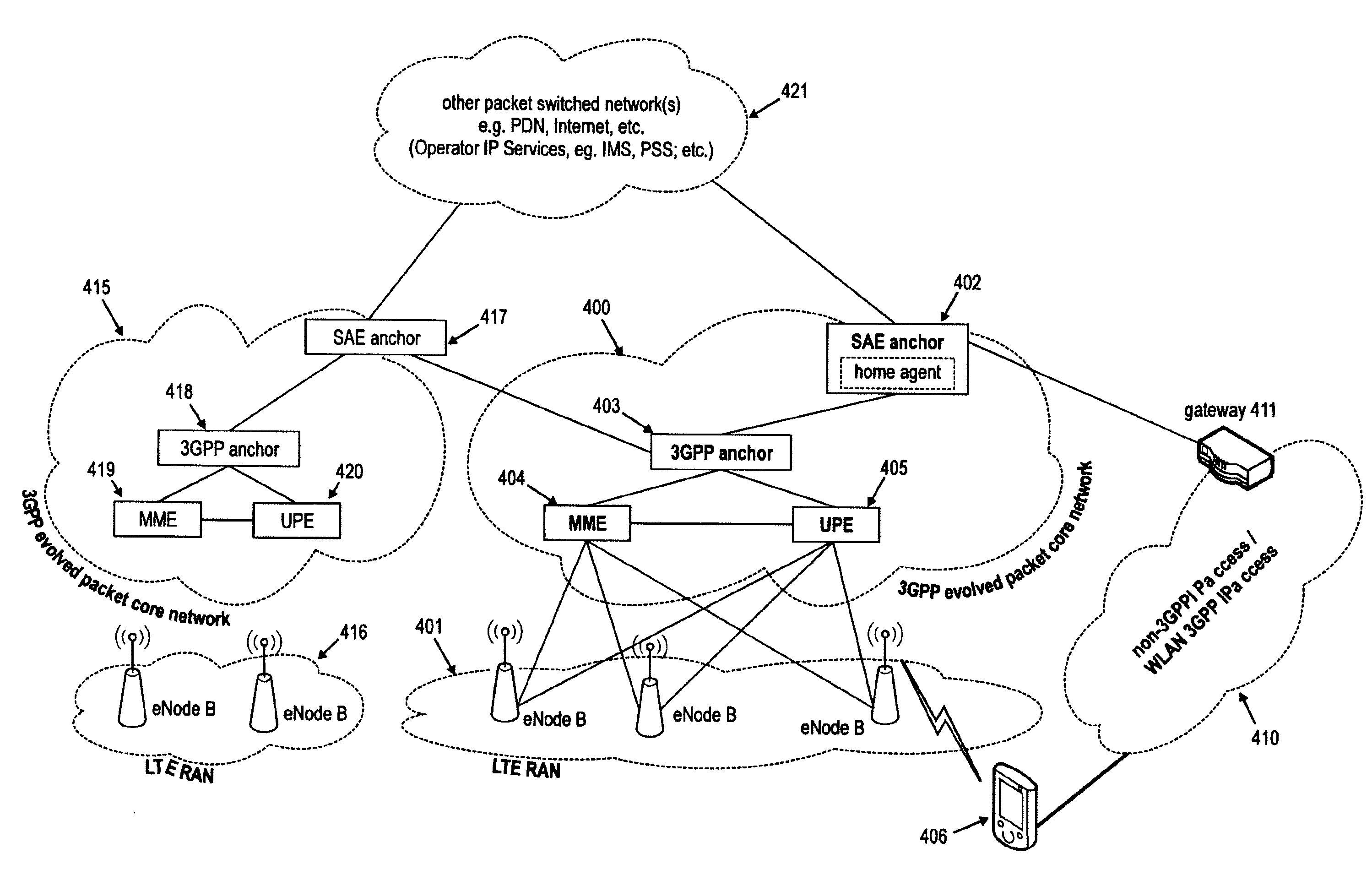
IP mobility in a communication system
InactiveUS7191226B2Increase employmentLittle overheadMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsCommunications systemProtocol stack
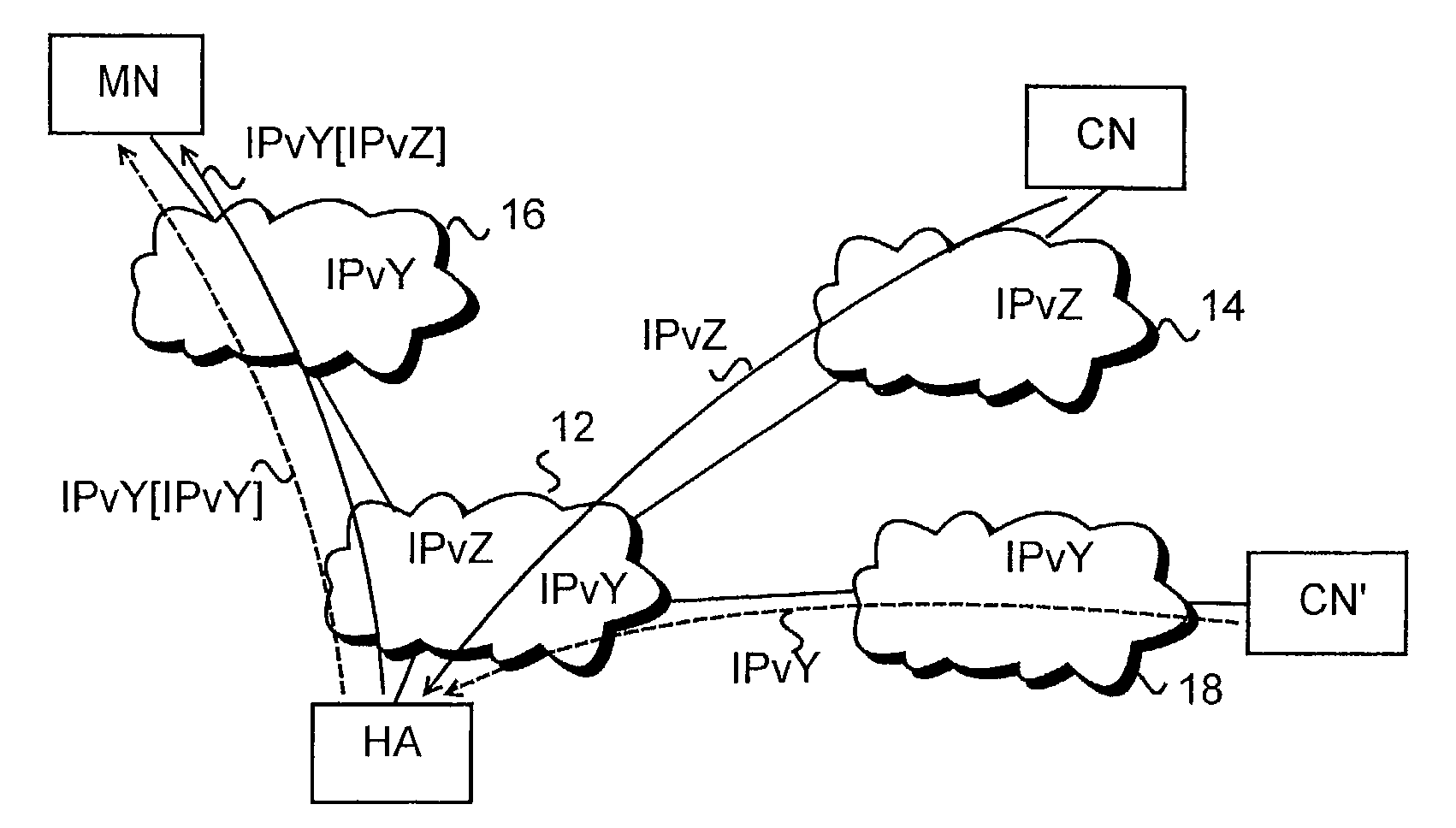
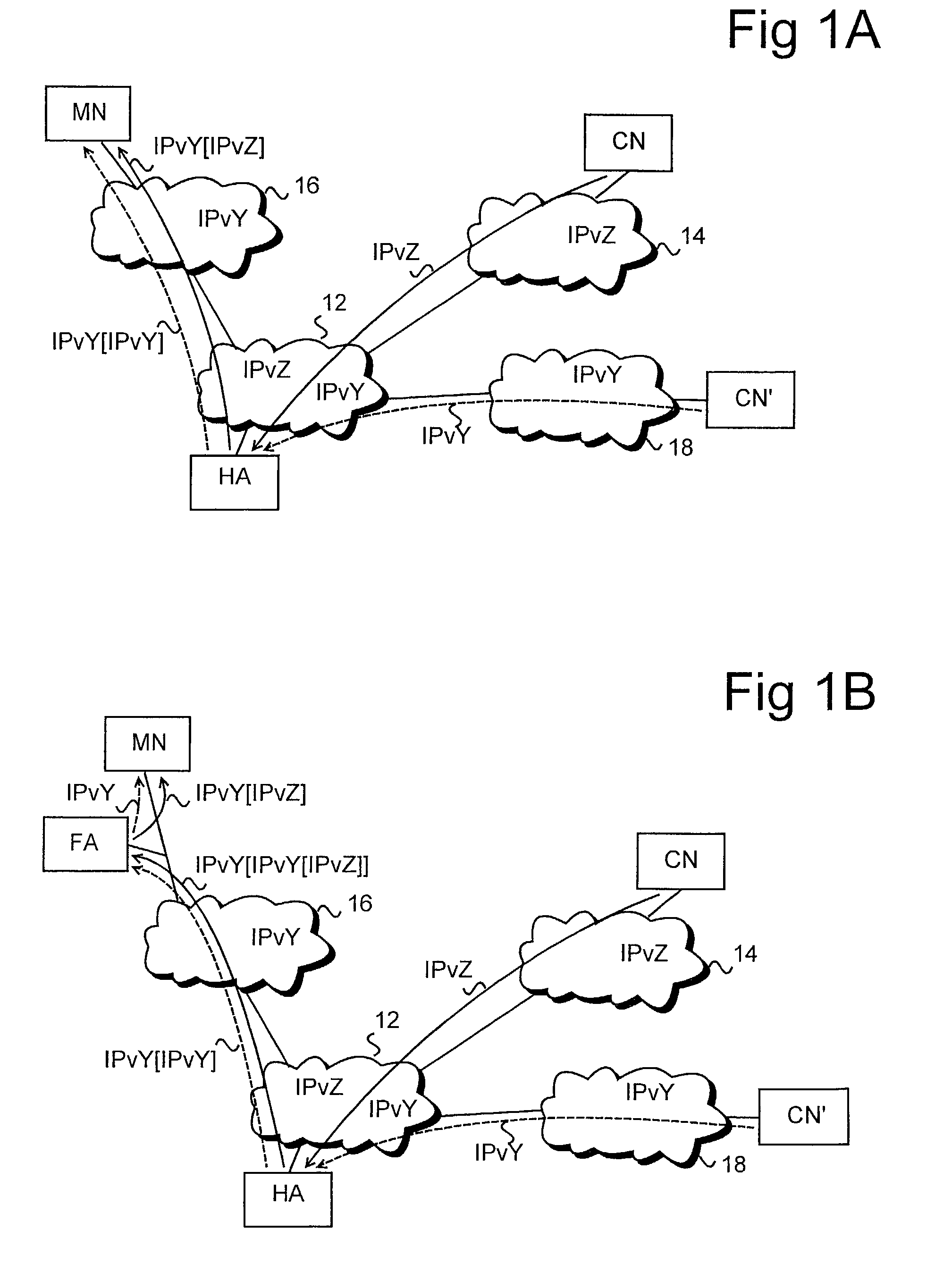
A method for routing data packets to a mobile node in a communication system which includes at least a first subnetwork of a first type supporting a first IP version and a second subnetwork of a second type supporting a second IP version. The mobile node is provided with a set of protocol stacks for handling data packets at least according to the first and the second IP version and with a home address at least according to the first and the second IP version. The home agent intercepts at least data packets addressed to the mobile node's home address according to the first or the second IP version and for encapsulating a data packet addressed to the mobile node in a packet according to the IP version of the foreign network to which the mobile node is attached, for routing the data packet to the mobile node.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Providing security for network subscribers
InactiveUS20060211406A1Avoid receivingUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer networkQuarantine
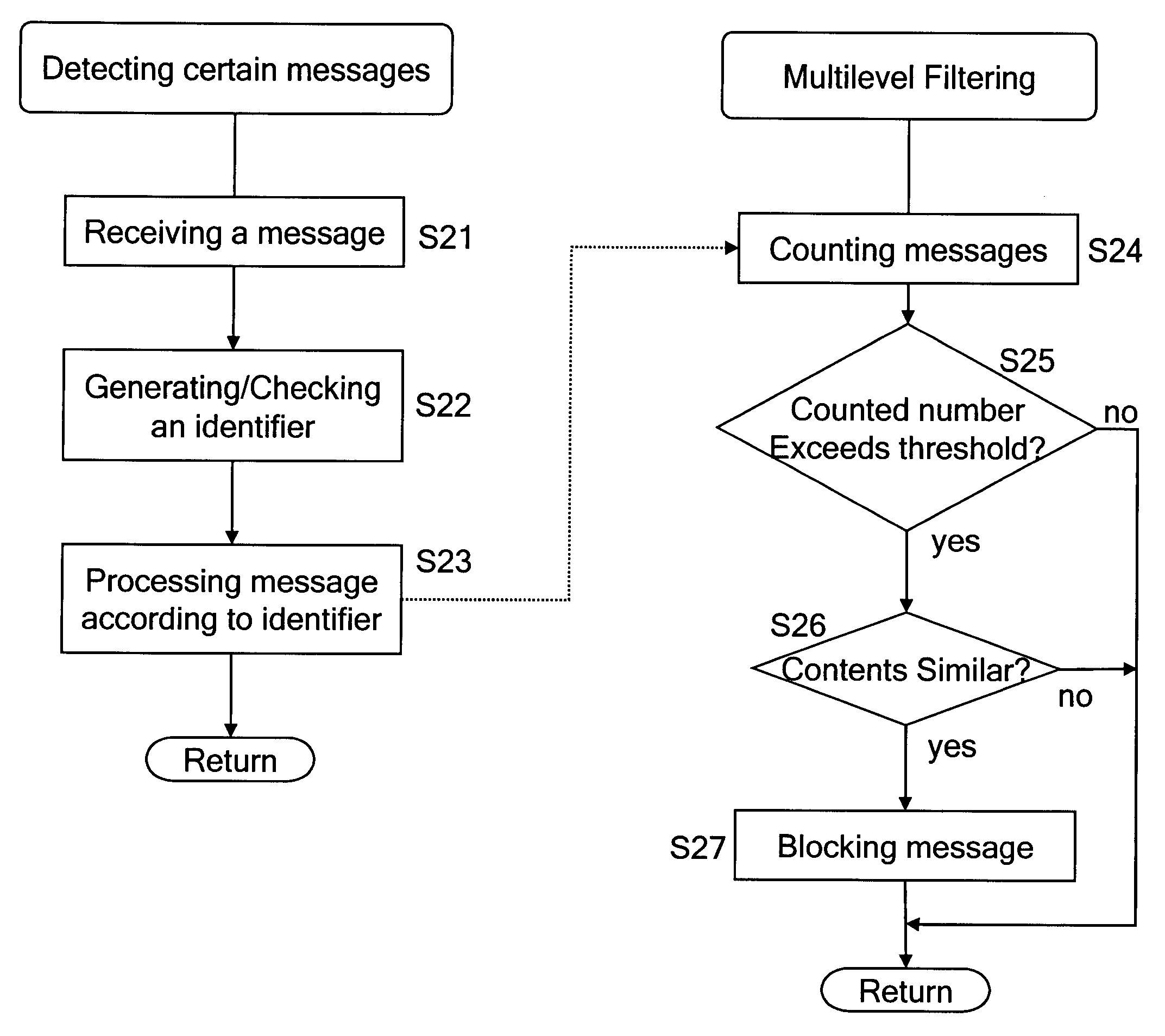
Messages are marked on the basis of whether they are originated in a home network or in a foreign network. Messages originated in the foreign network may be subjected to further filtering and may be put to ‘quarantine’ for further checking.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com