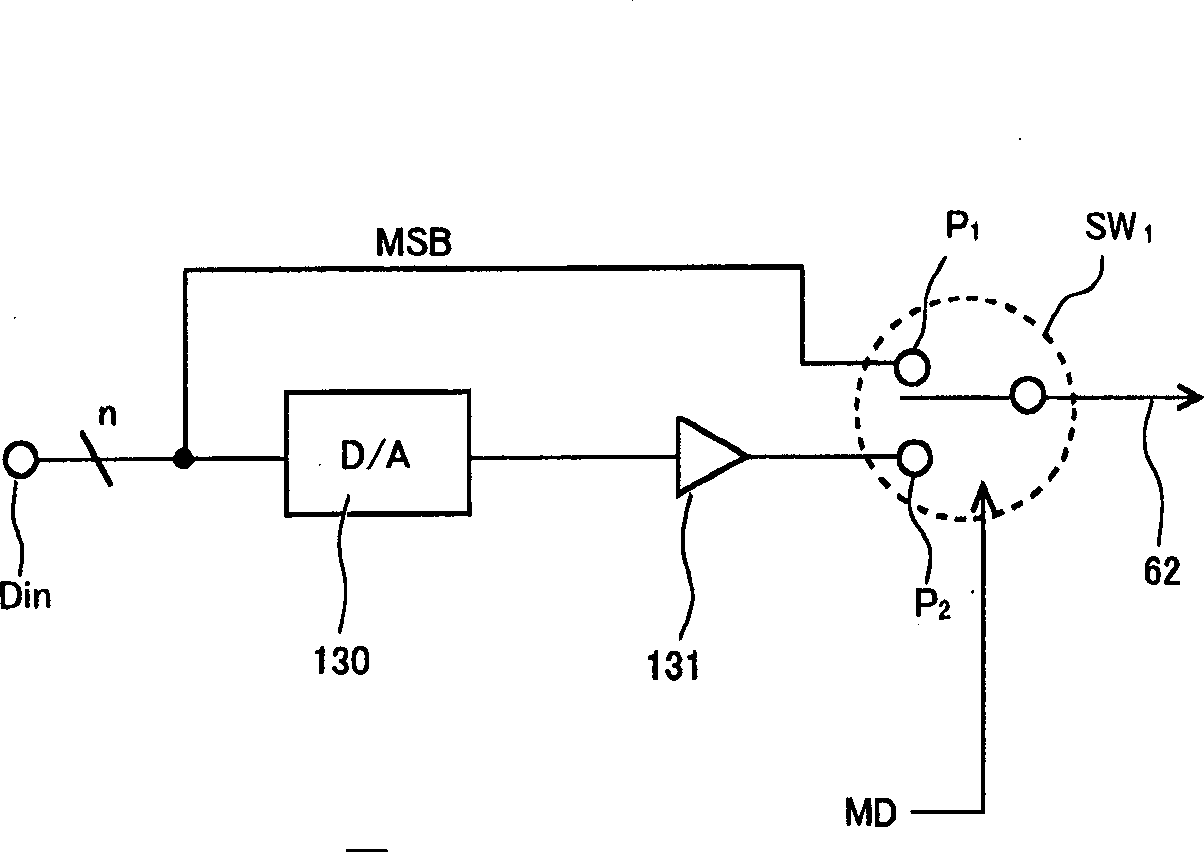
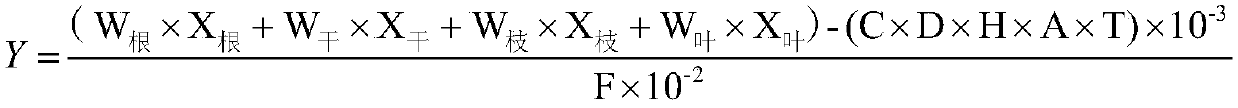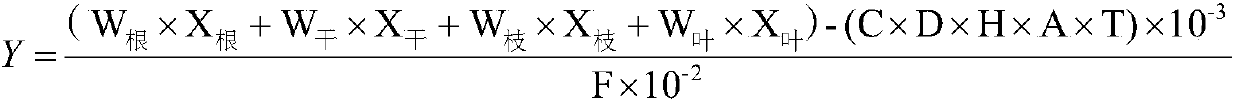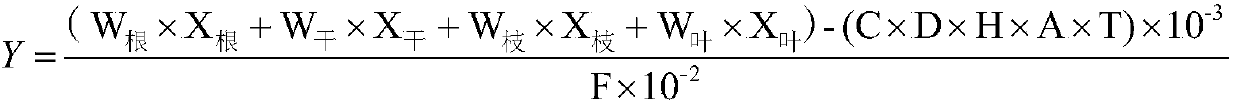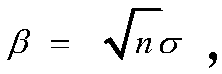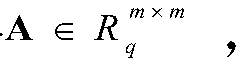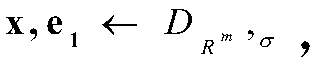Patents
Literature
58 results about "Absolute minimum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Absolute minimum. absolute minimum A value of a given function that is less than or equal to any value of the given function.
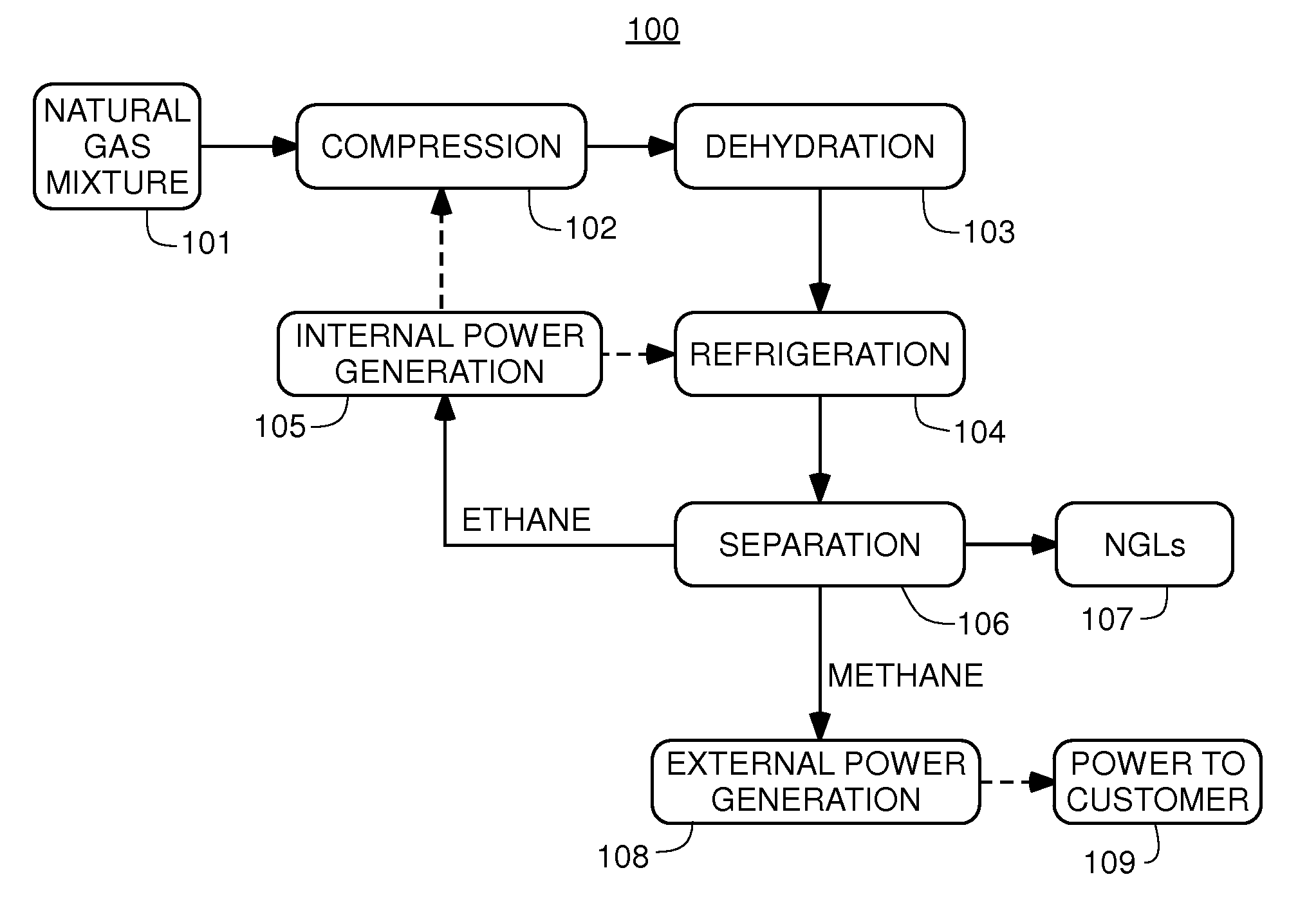
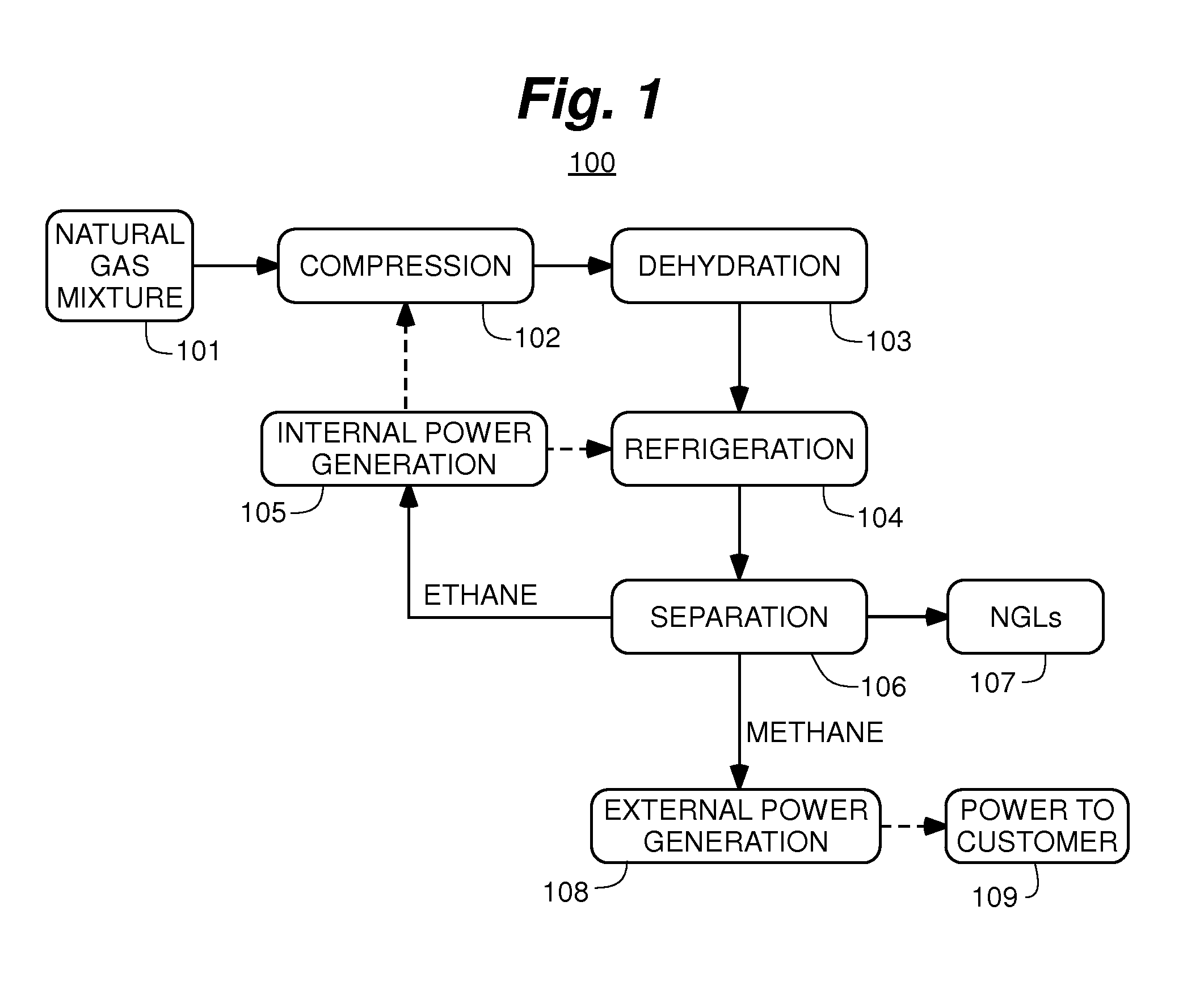
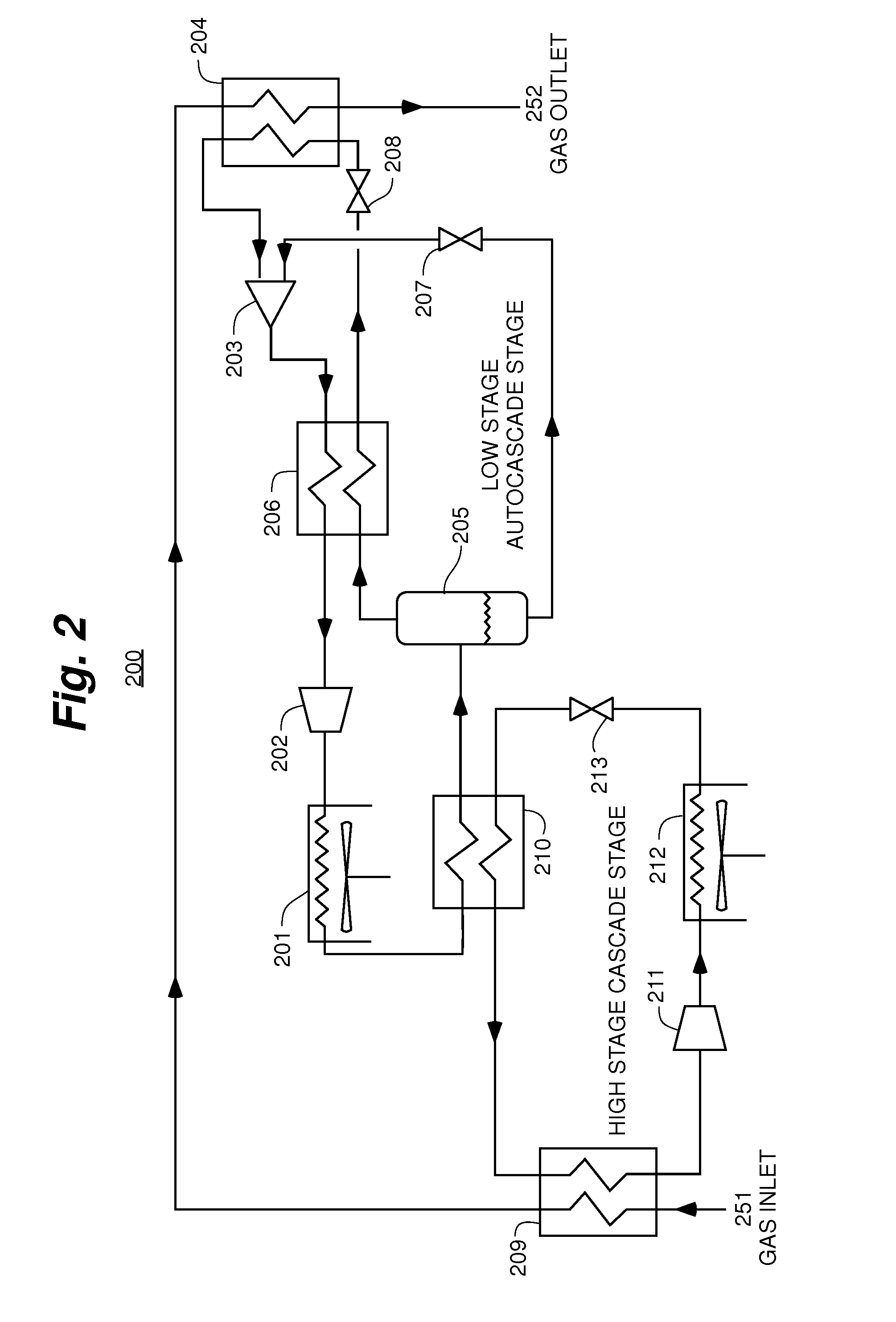
Systems and methods for separating alkane gases with applications to raw natural gas processing and flare gas capture
InactiveUS20140366577A1Reduce stepsHigh quality separationSolidificationLiquefactionAlkaneNatural-gas processing
The present invention is a field-deployable system for separating methane and natural gas liquids (NGLs) from a raw gas stream comprising a compressor; a dehydrator; a refrigerator having one or more stages; and a separation subsystem adapted to separate the raw gas stream into three product streams including a methane stream that is at least 80% methane, an ethane-rich stream, and a NGLs stream having a vapor pressure of no more than 250 psia at 38° C. The methane stream is sufficiently lean to be useable in existing natural gas engines without modification. The NGLs stream has a sufficiently low vapor pressure to be transportable in standard propane containers. The ethane-rich stream may be utilized within the system itself to power its own operations. The system can be utilized to reduce flaring from liquids-rich gas production sites to an absolute minimum, produce natural gas liquids for transport, and provide dry methane gas suitable for use in portable field generators.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
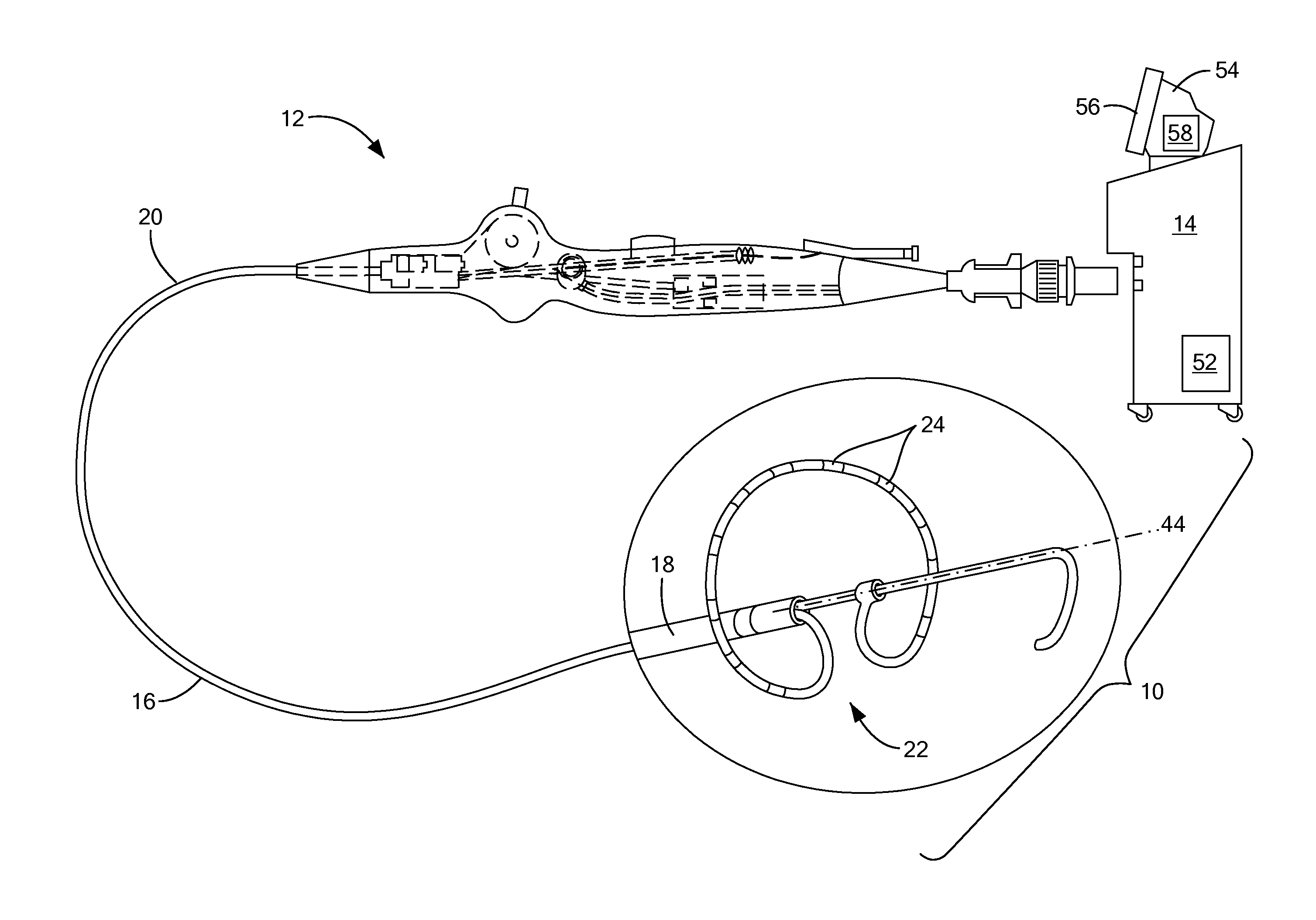
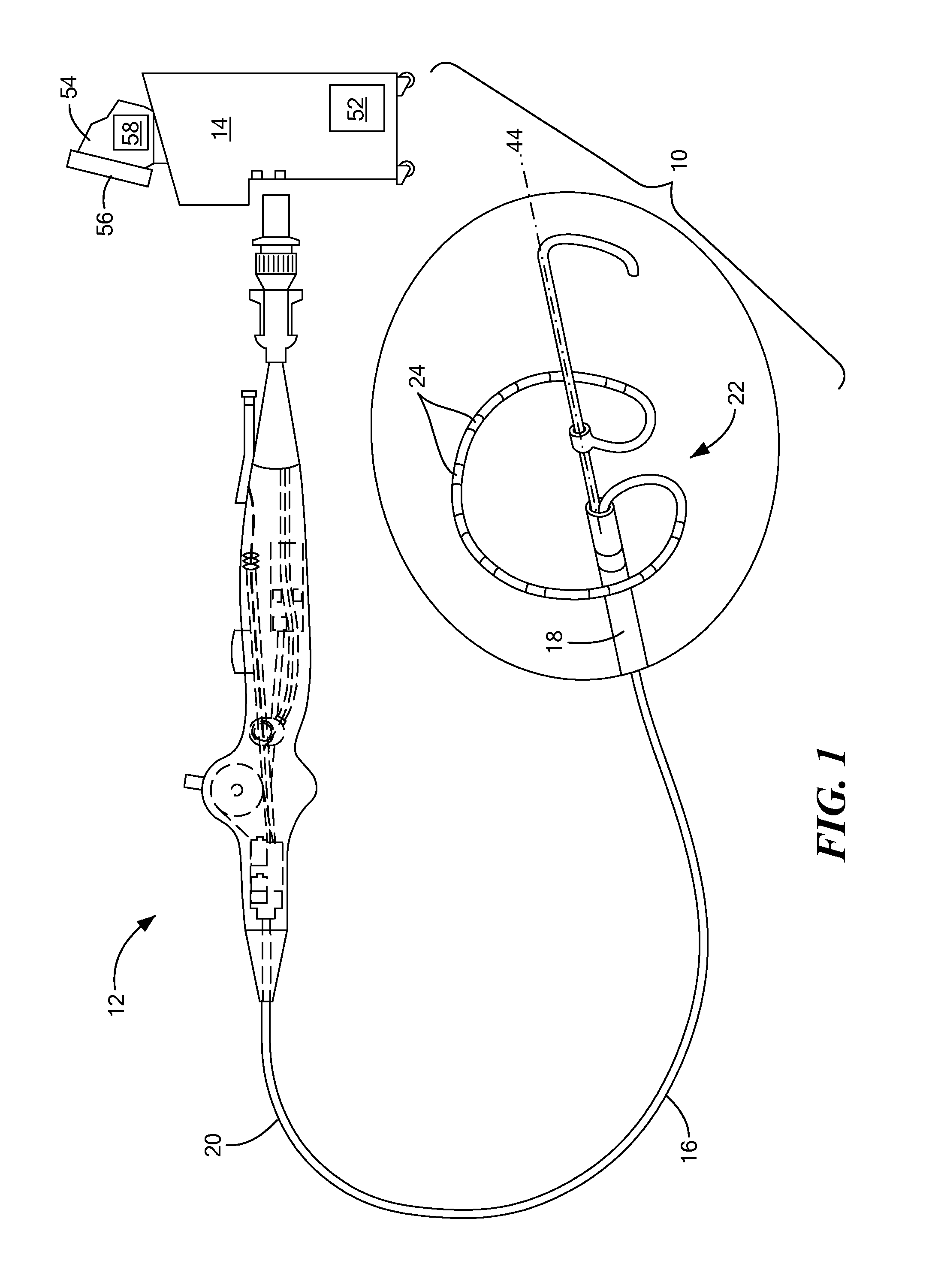
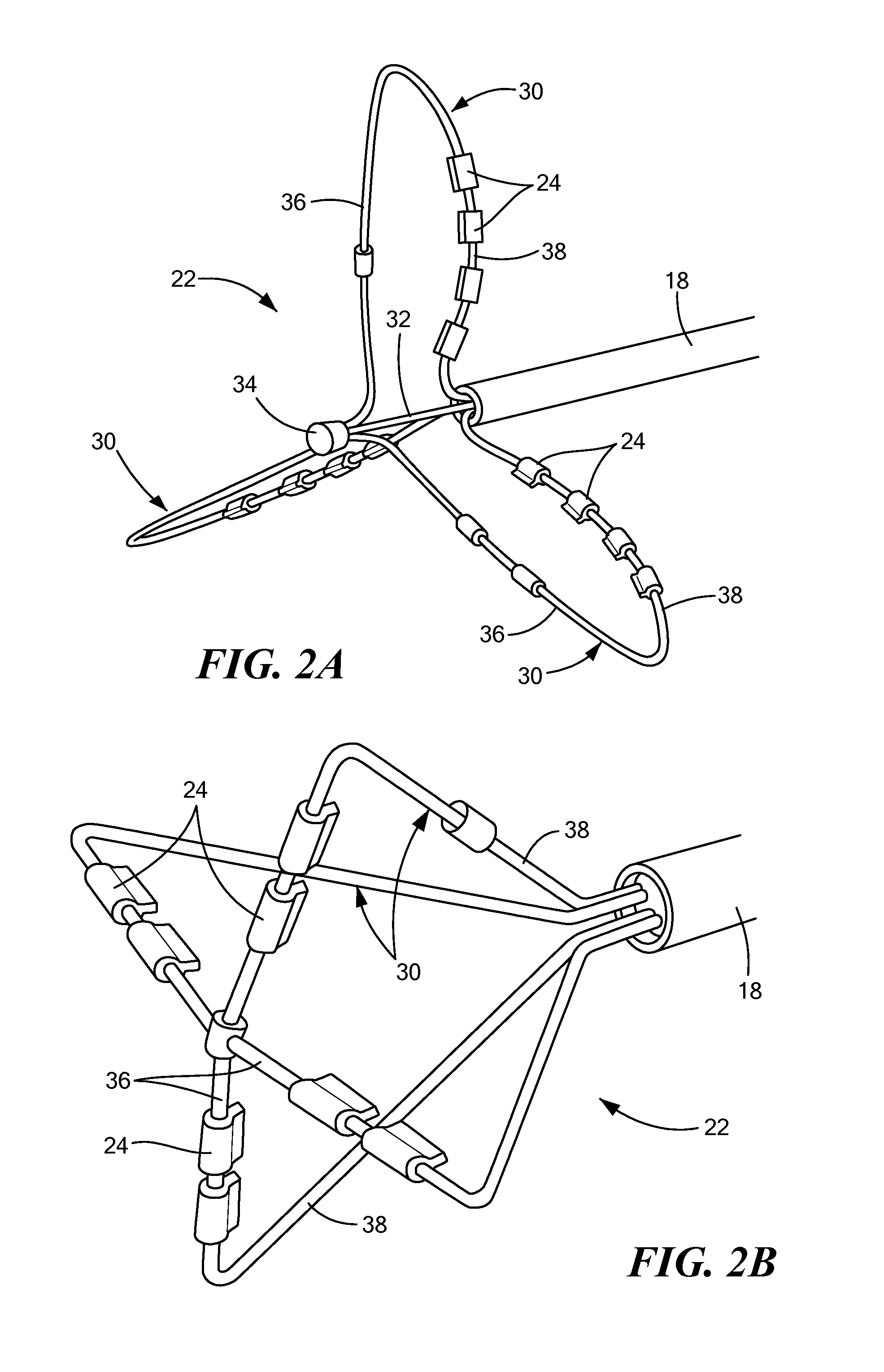
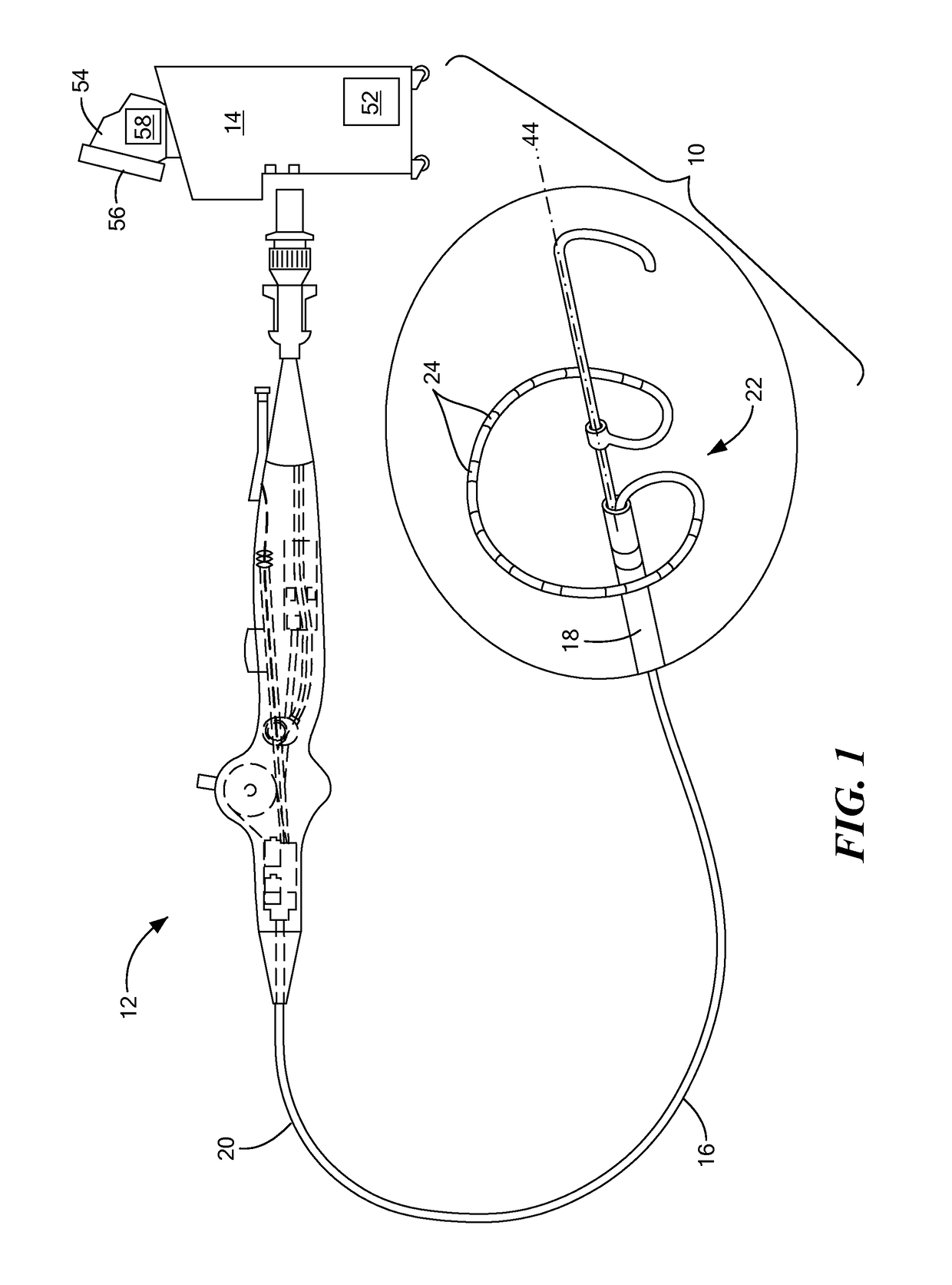
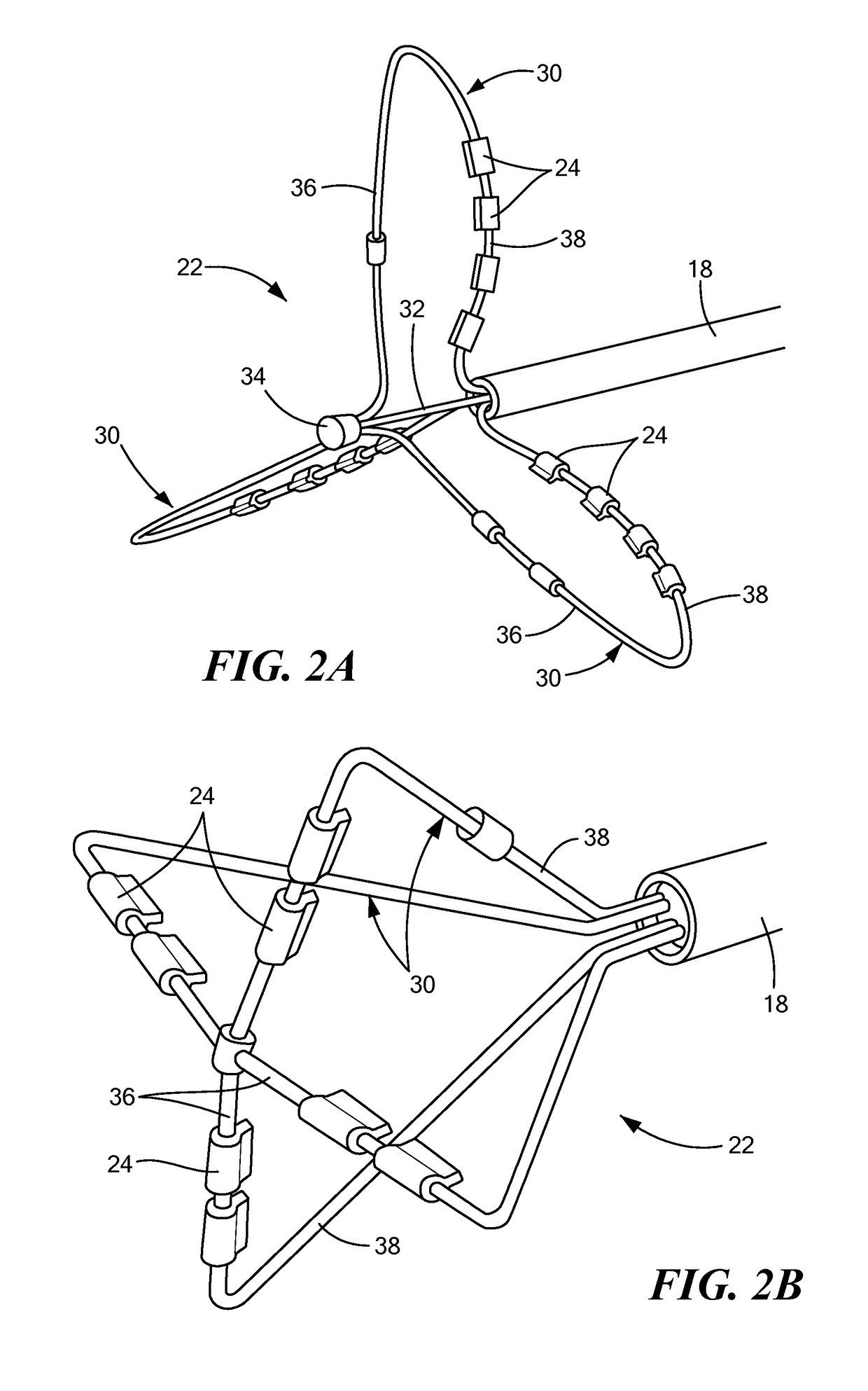
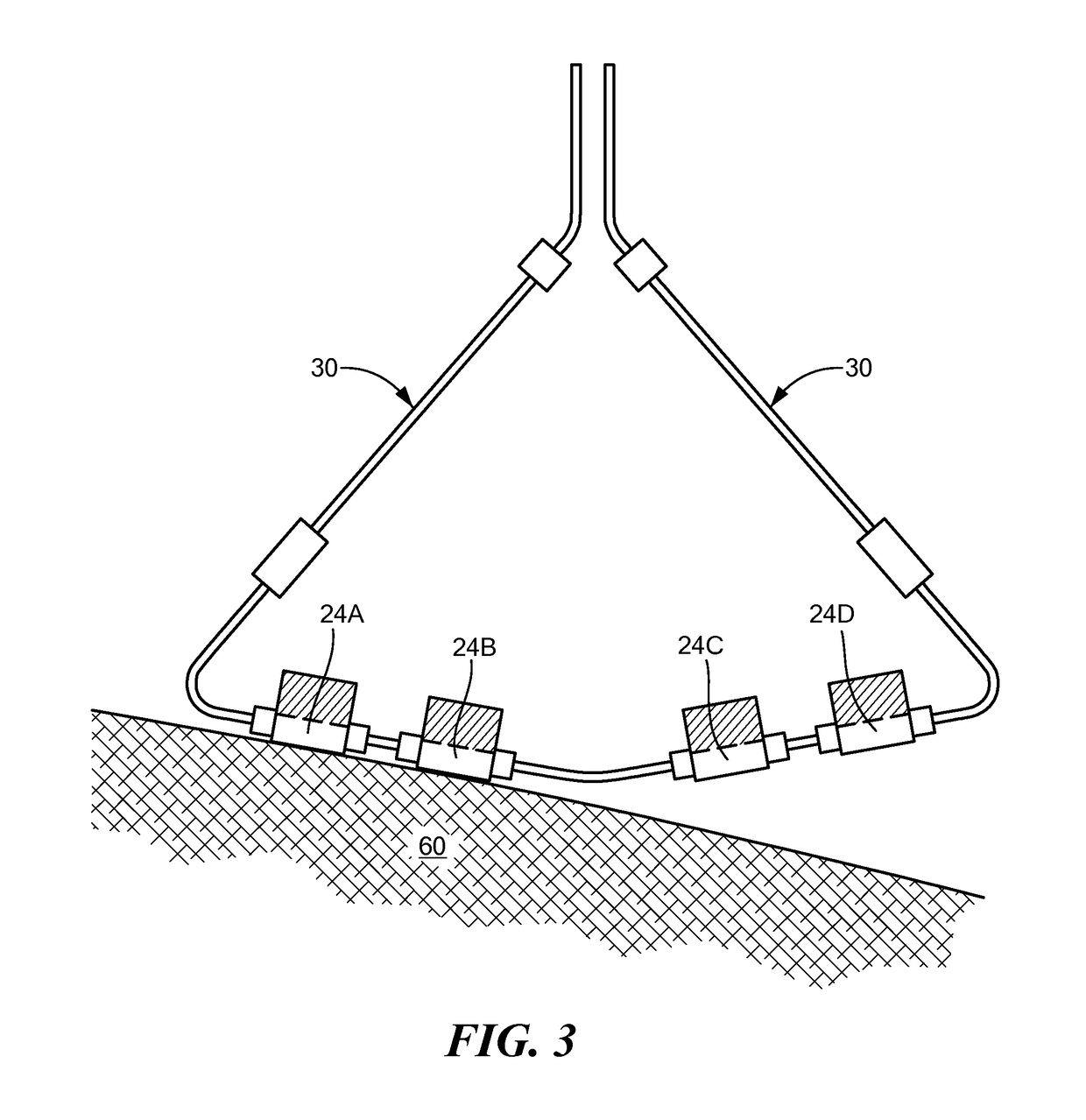
Tissue contact sensing with a multi electrode ablation catheter
A method and system for assessing electrode-tissue contact before the delivery of ablation energy. The method may generally include determining a difference between a maximum impedance magnitude at a low frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance magnitude at the low frequency across all electrodes, determining a difference between a maximum impedance magnitude at a high frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance magnitude at the high frequency across all electrodes, and determining a difference between a maximum impedance phase at the high frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance phase at the high frequency across all electrodes. These differences may be correlated to one another using a linear model, the results of which determining whether the given electrode is in contact or not in contact with tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
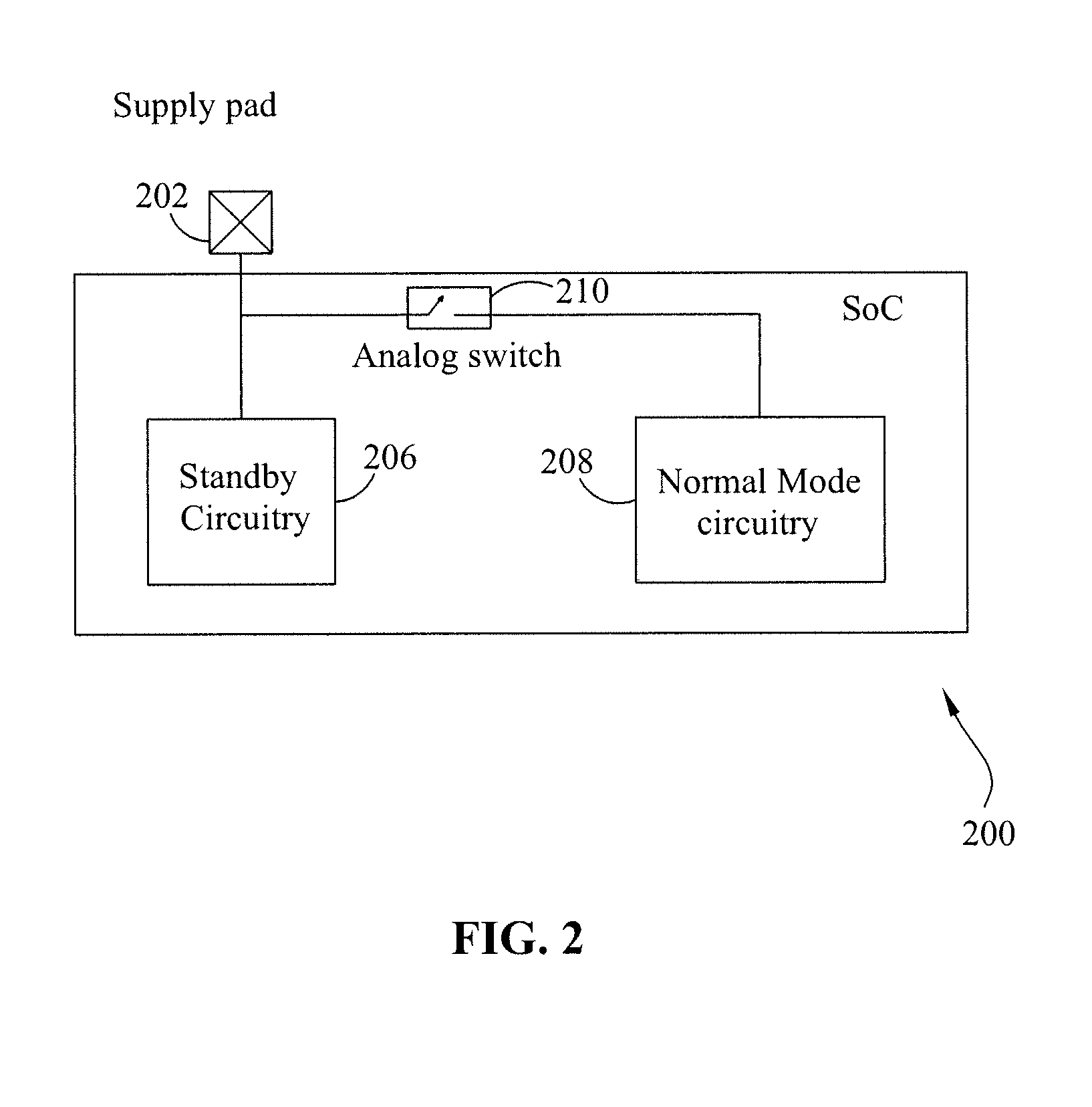
Architecture incorporating configurable controller for reducing on chip power leakage
InactiveUS20080313480A1Reduce leakageEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementAbsolute minimumLeakage power
The present invention provides a method and system for controlling leakage power consumption at a System on Chip (SoC) level during a normal run or a boot-up mode. The leakage power reduction is achieved by incorporating a central programmable controller in the SoC architecture and test structures of idle SoC peripherals to place them into an Absolute Minimum Power consumption state with respect to static and dynamic power.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
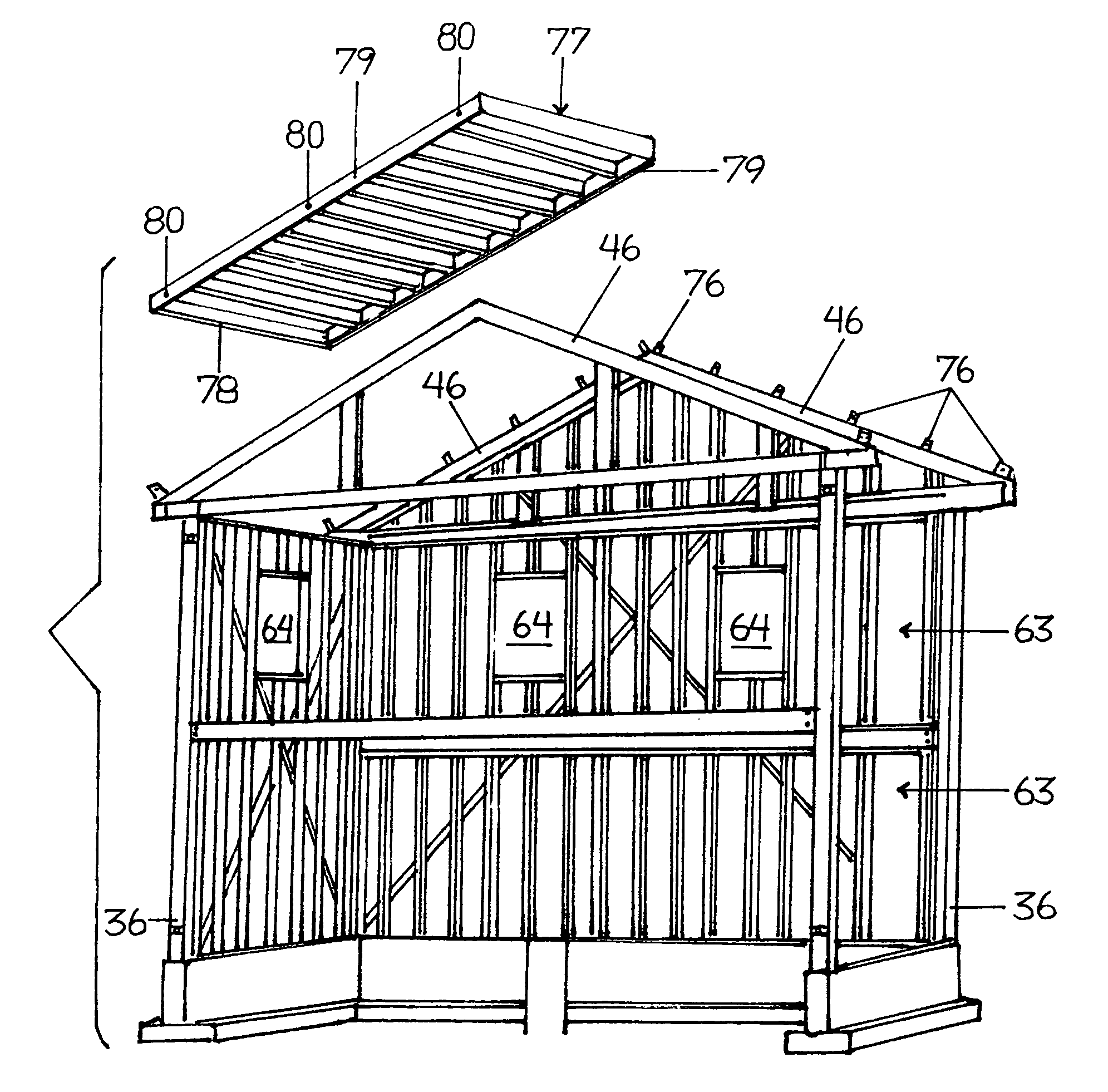
Structural steel framed houses with gable end frames, intermediate frames, and wall and roof panels having perimeters of C-shaped steel channels
InactiveUS7665251B1Easy to installEasy maintenanceBuilding roofsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsPurlinAbsolute minimum
Steel frames formed of rolled steel I-beams are connected by steel framed wall panels spanned by steel studs, and covered by steel framed roof panels spanned by steel purlins, making a structural frame completely formed of steel components bolted together. All components are precut and predrilled before transport to a construction site. A crane is used to raise steel frames and steel framed roof panels into position for bolted assembly, reducing construction times to absolute minimums. Entire structure is virtually lightning-proof, wind-proof, and earthquake resistant.
Owner:LANG STEVEN
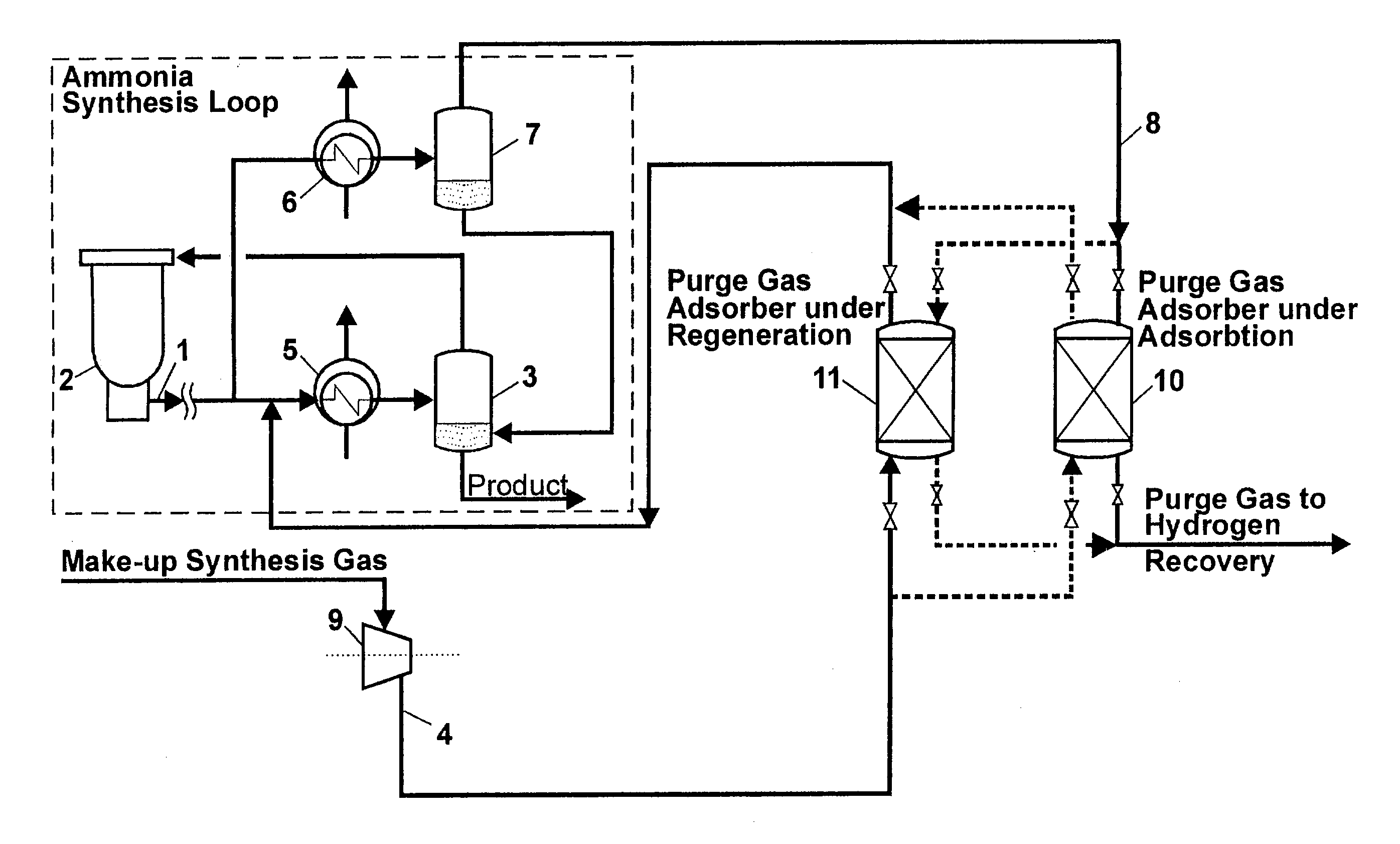
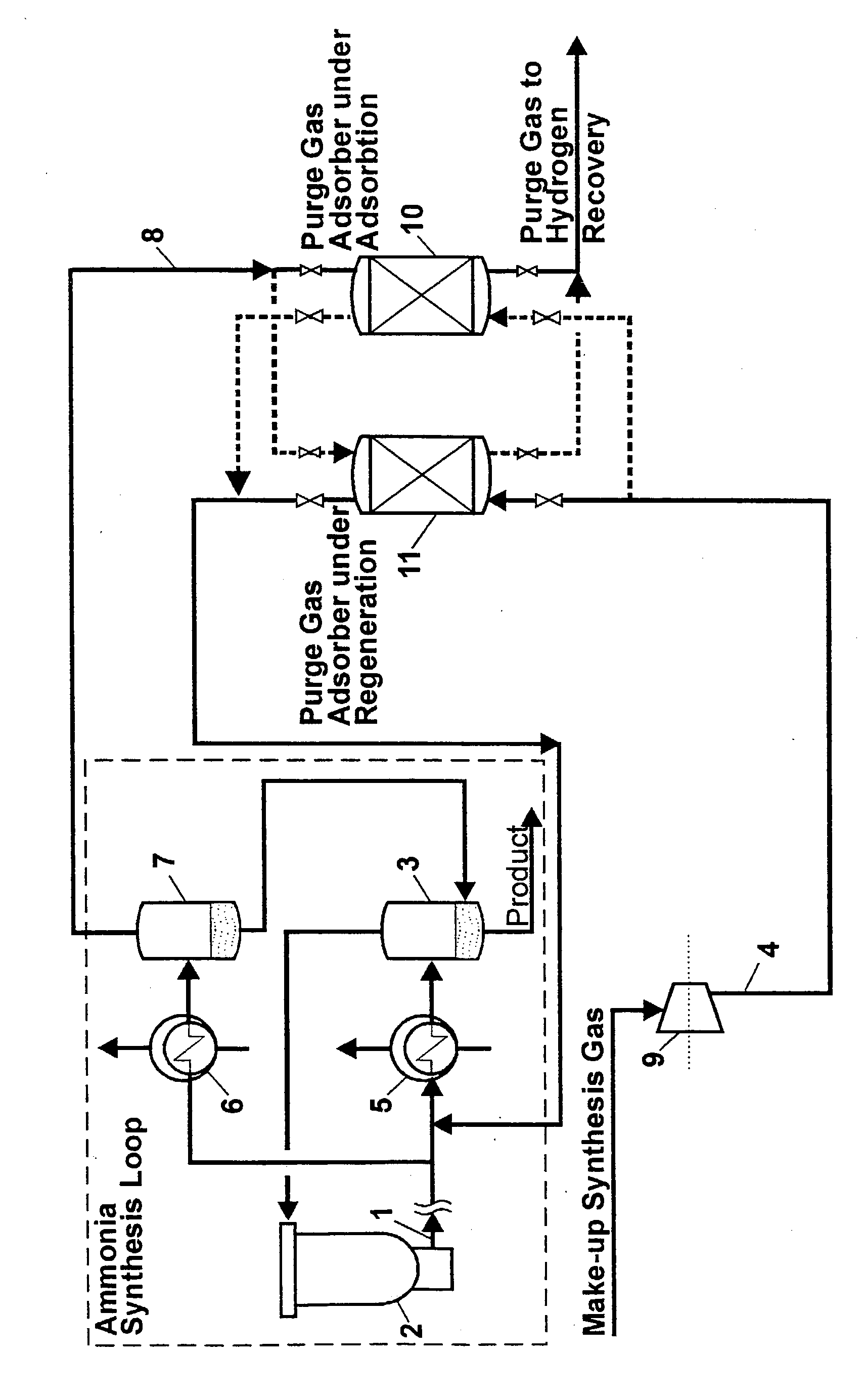
Ammonia recovery from purge gas
InactiveUS20030172809A1Cheap and effective regainHigh investment and costGas treatmentIsotope separationGas compressorSorbent
The invention relates to ammonia synthesis loops containing gasses, which do not react and would accumulate if they were not purged out. By the present invention ammonia in a purge gas is recovered by an adsorption agent operating at the full synthesis loop pressure. The adsorption agent is chosen in such a way that the ammonia can be removed again by passing a gas comprising hydrogen and nitrogen through it at the same elevated pressure as the loop pressure. This enables the adsorption agent to be regenerated by fresh synthesis gas coming from the synthesis gas compressor just before this gas enters the synthesis loop. Thereby, the regeneration requires an absolute minimum of energy consumption and equipment.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
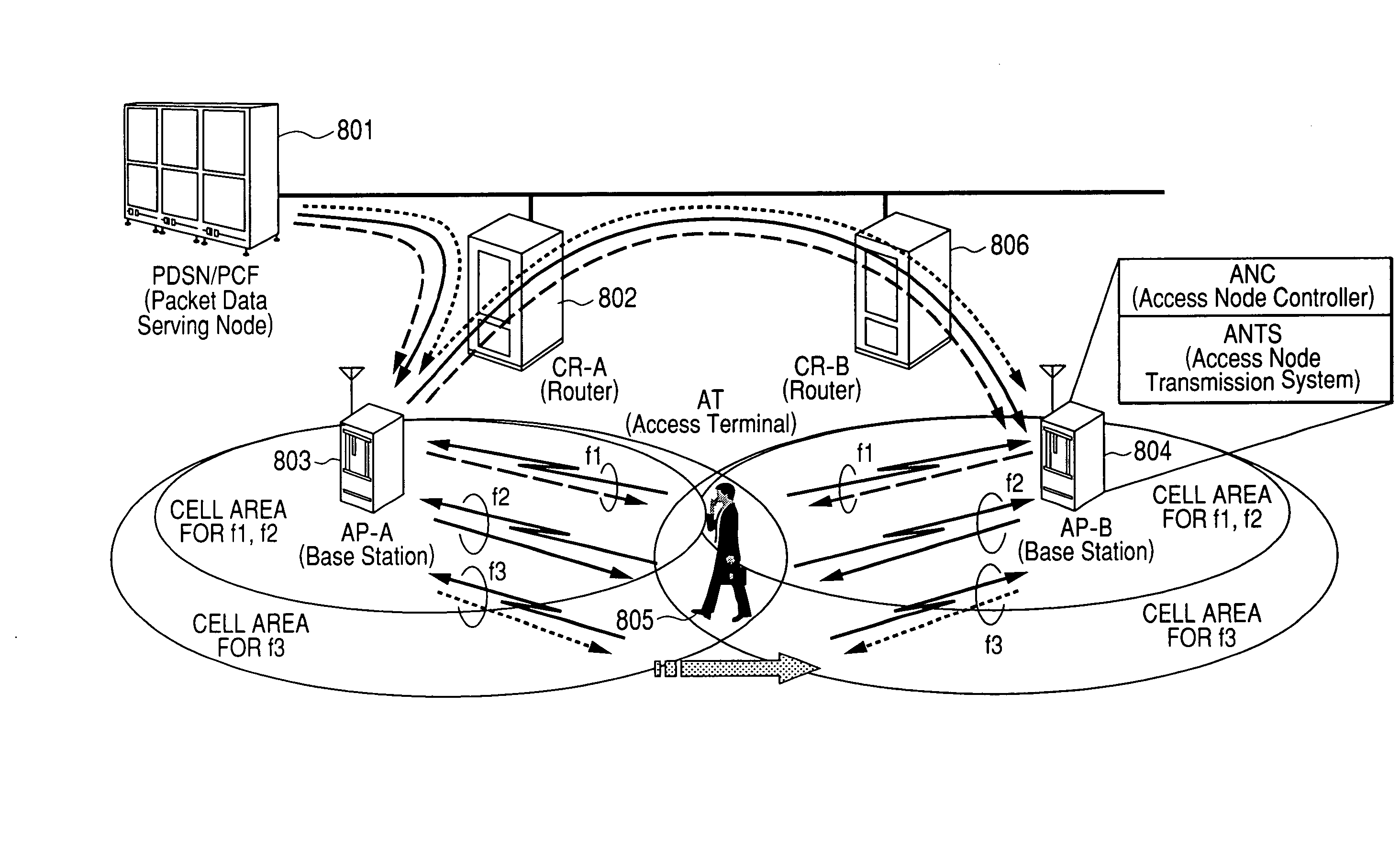
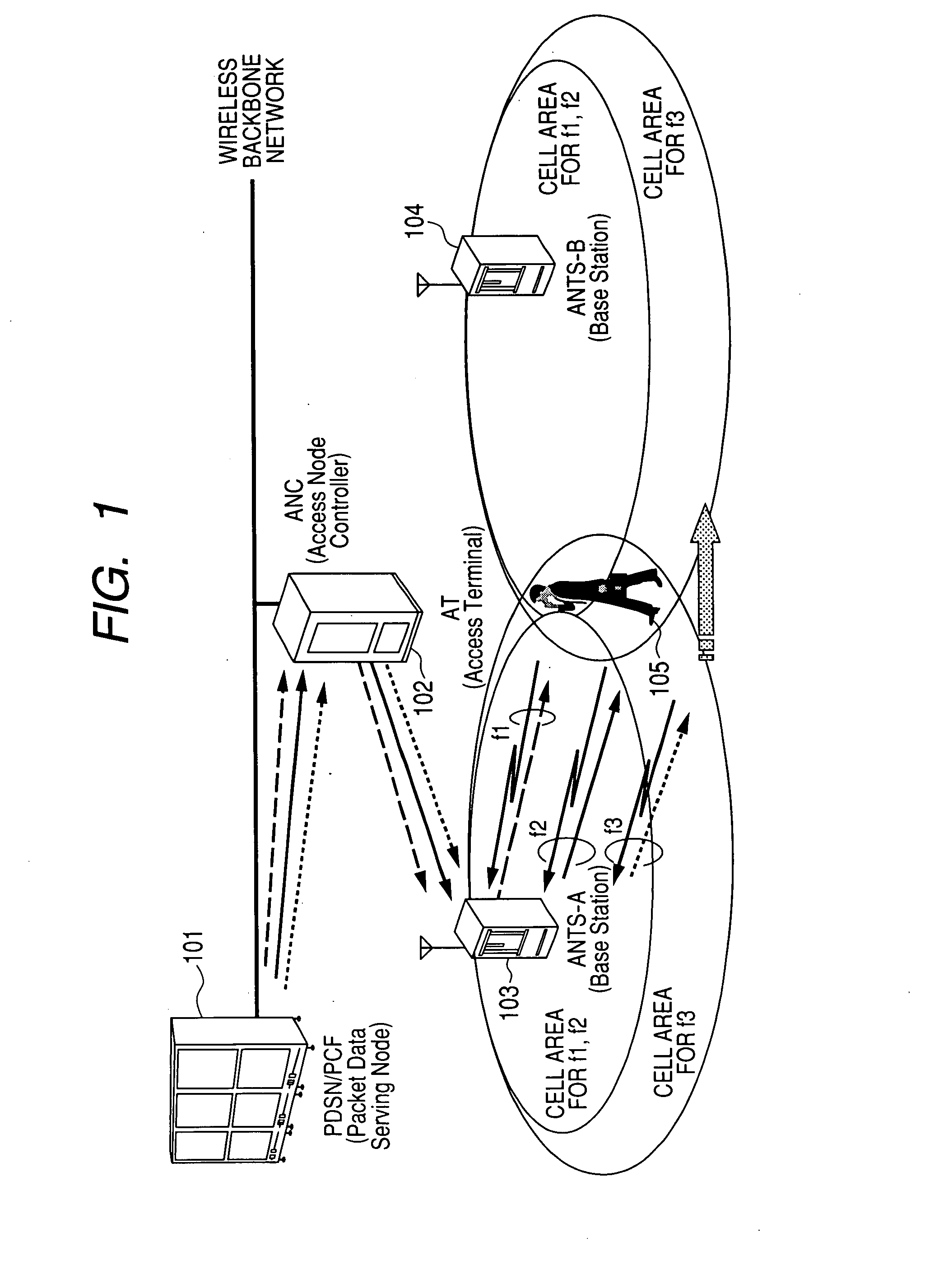
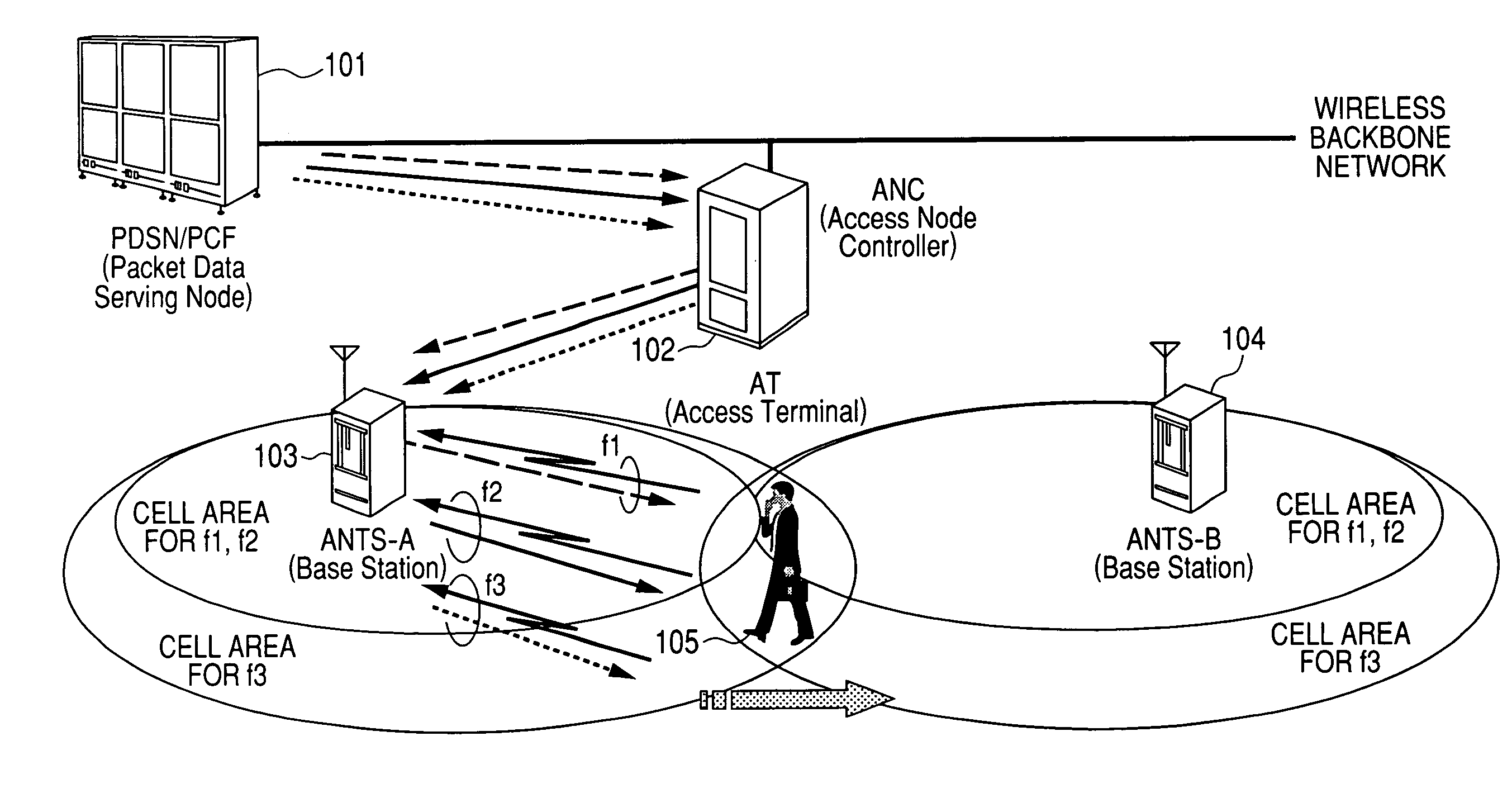
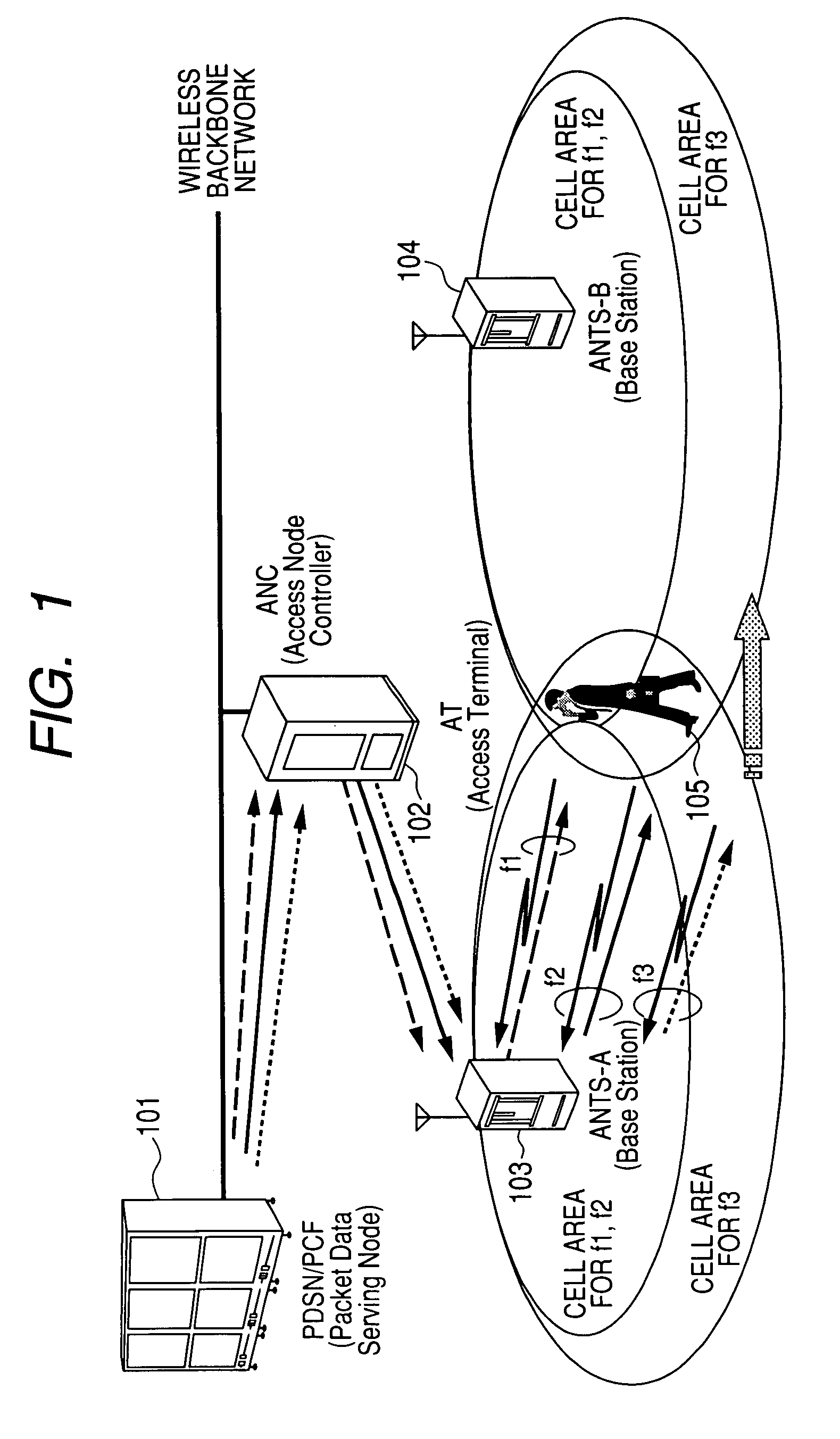
Handoff method for communication system using multiple wireless resources
InactiveUS20080057970A1Increase reception strengthGuaranteed mobilityError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemViewpoints
In a wireless communications system operating according to CDMA or the like, when one terminal simultaneously performs communication using multiple wireless resources (e.g., multiple carriers), there was a problem that when it was attempted to guarantee network mobility by the same soft handoff system as in the case where communication was performed using only one wireless resource, efficiency suffered from the viewpoint of network forwarding load, processing load and wireless resource occupancy time. Soft handoff termination is judged and soft handoff is forcibly terminated according to whether or not the data rate obtained for all resources on the network side satisfies a requested rate, based on a reception state notification from a terminal concerning wireless resources. By performing this processing, the soft handoff period is shortened, sufficient received strength in the terminal is maintained and terminal mobility is guaranteed, while at the same time network forwarding load, terminal processing load and wireless resource occupancy time are suppressed to the absolute minimum.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Measurement for eigenfrequency of interferometric type fiber-optic gyroscope by using asymmetrical square wave modulation method
InactiveCN1967146AAccurate measurementImplement automatic trackingResonant frequencySpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberGyroscope
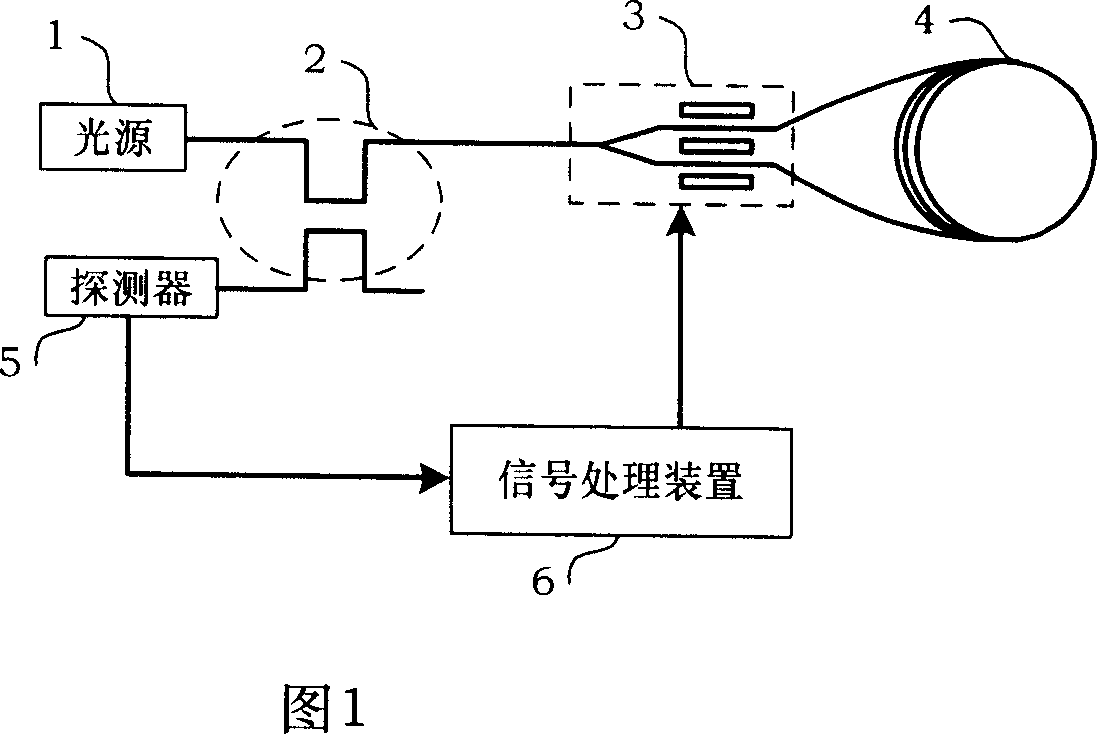
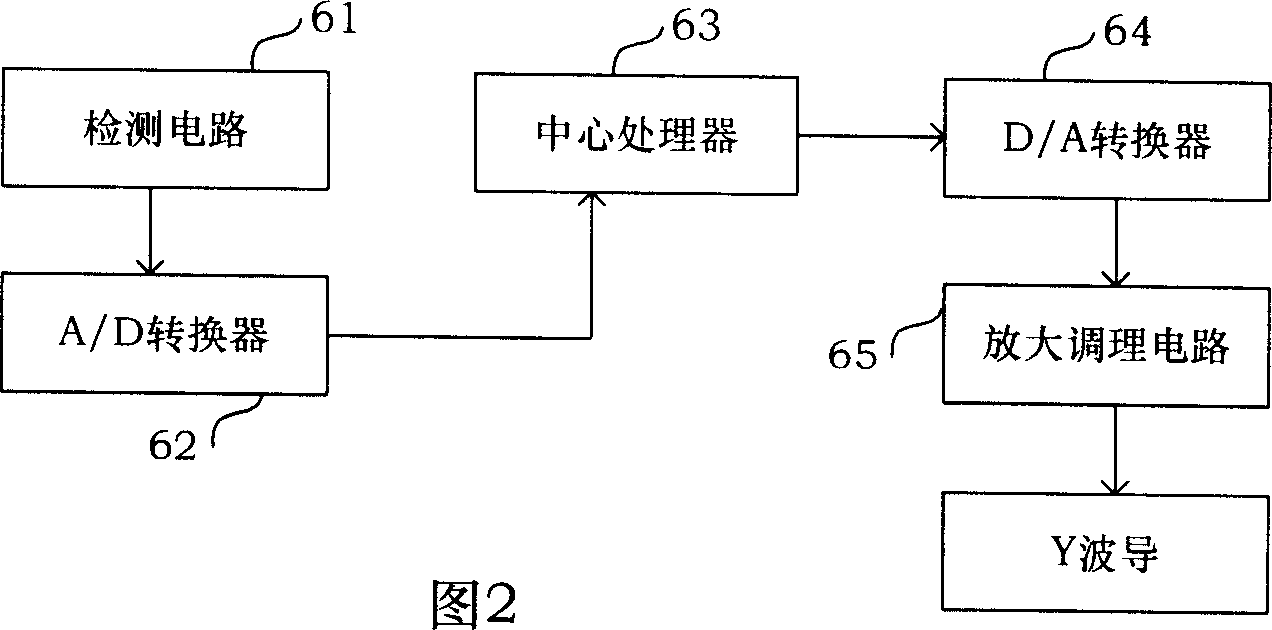
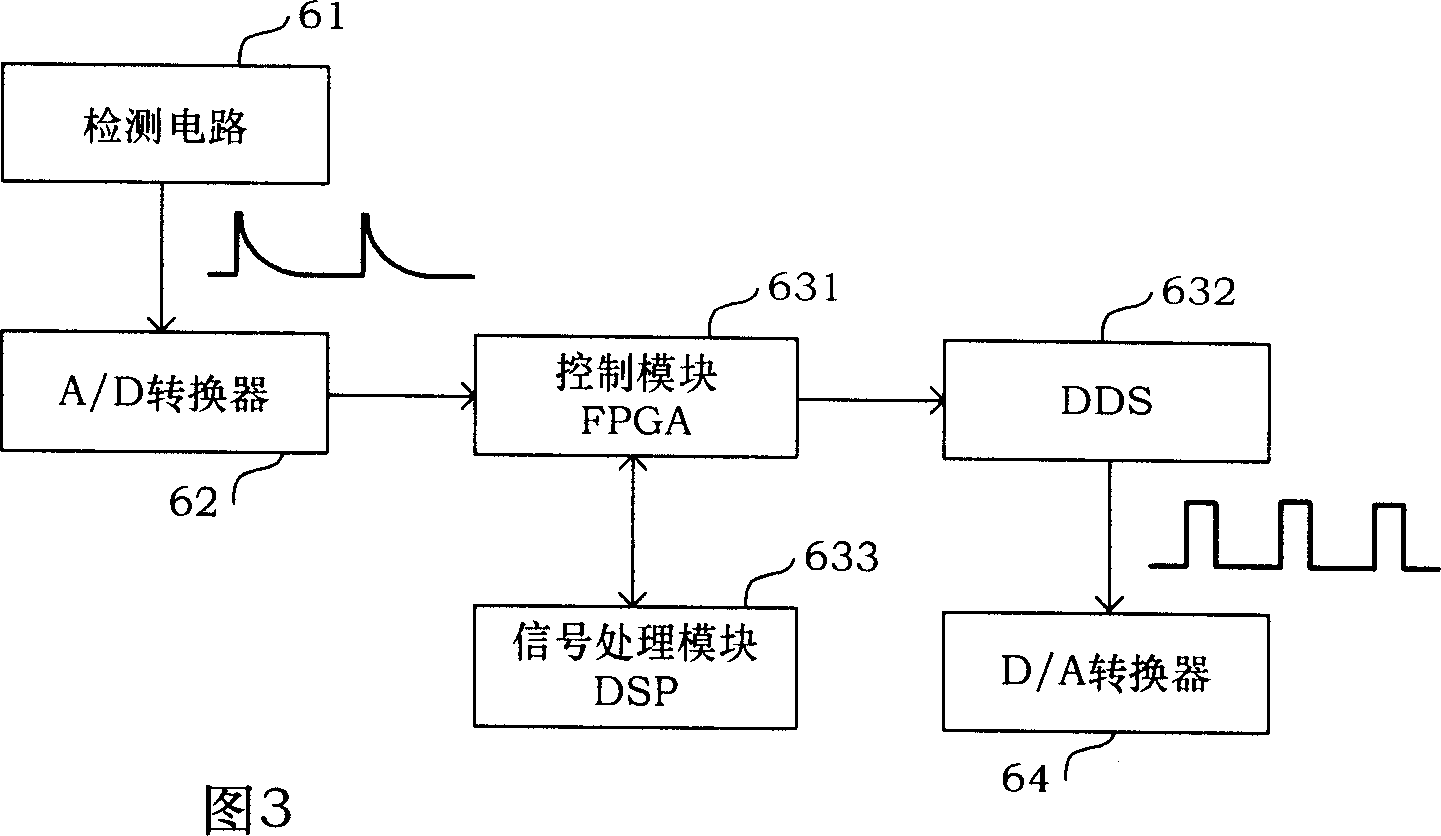
The invention discloses an asymmetric square wave modulation method to measure interference fiber gyro eigenfrequency. By controlling module FPGA, the method controls DDS to generate different frequency asymmetric square wave to process phase modulation to Y waveguide; and the signal processing module DSP real-time calculates the margin absolute DeltPd of the accumulation in A / D sampling time T, and processes the absolute minimum judgment to the said margin absolute DeltPd, and when the margin absolute DeltPd close to zero, gets the fiber gyro eigenfrequency fe equaling modulation frequency fd. Such measurement method measures the eigenfrequency Fe with high accuracy, and frequency tracking speed adjustment quick, and highly real-time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Flow-through pressure sensor apparatus
ActiveUS20100206046A1Dead space of flowIncreased durabilityVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsAbsolute minimumPressure sense
A flow-through pressure sensor apparatus that reduces the dead space of a flow tube utilized to provide fluid communication between a pressure sense die and a fluid and with an absolute minimum trapped volume. A cover (e.g., plastic) with two-molded ports can be added to one side of the pressure sense die utilizing molded-in solder pins to improve ruggedness and rigidity. A temperature and a humidity sensor can also be mounted to a substrate (e.g., ceramic) in the flow path and can be connected to a programmable compensation integrated circuit on the opposite side utilizing a clip end of mounting pins or by vias through the substrate outside a pressurized area.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
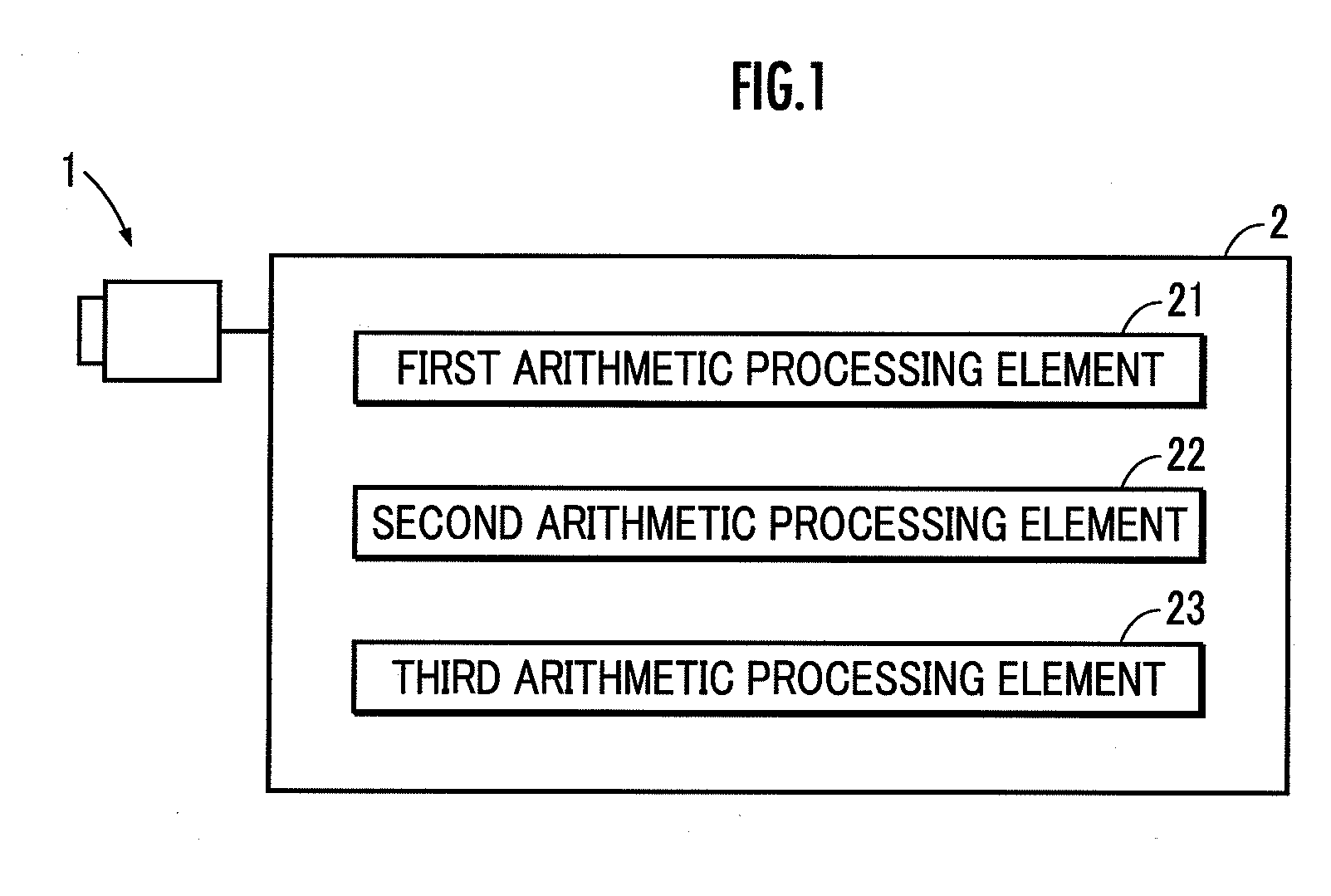
Arithmetic functions in torus and tree networks
InactiveUS7313582B2Accelerated programImprove efficiencyError preventionDigital data processing detailsNODALAbsolute minimum
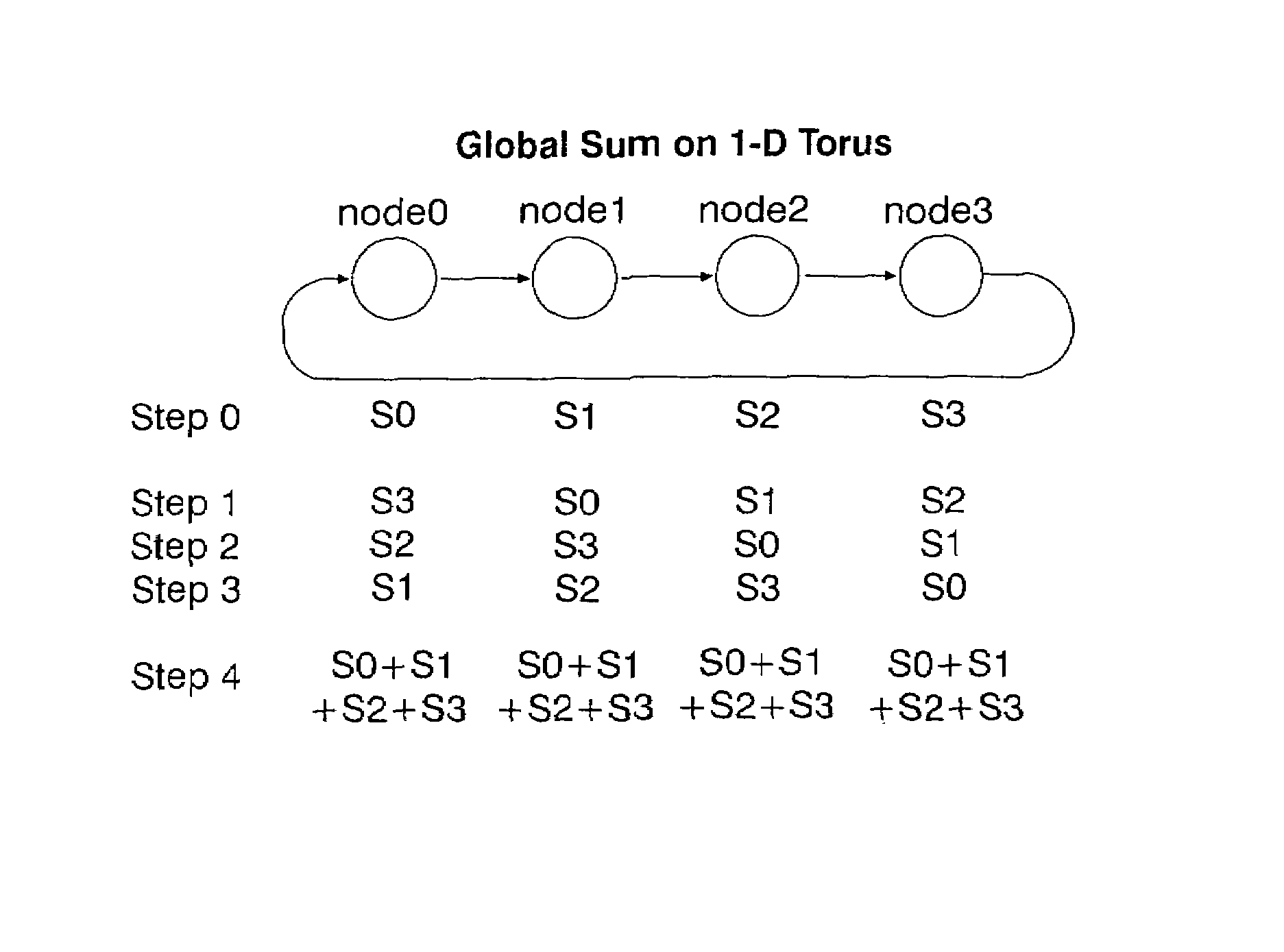
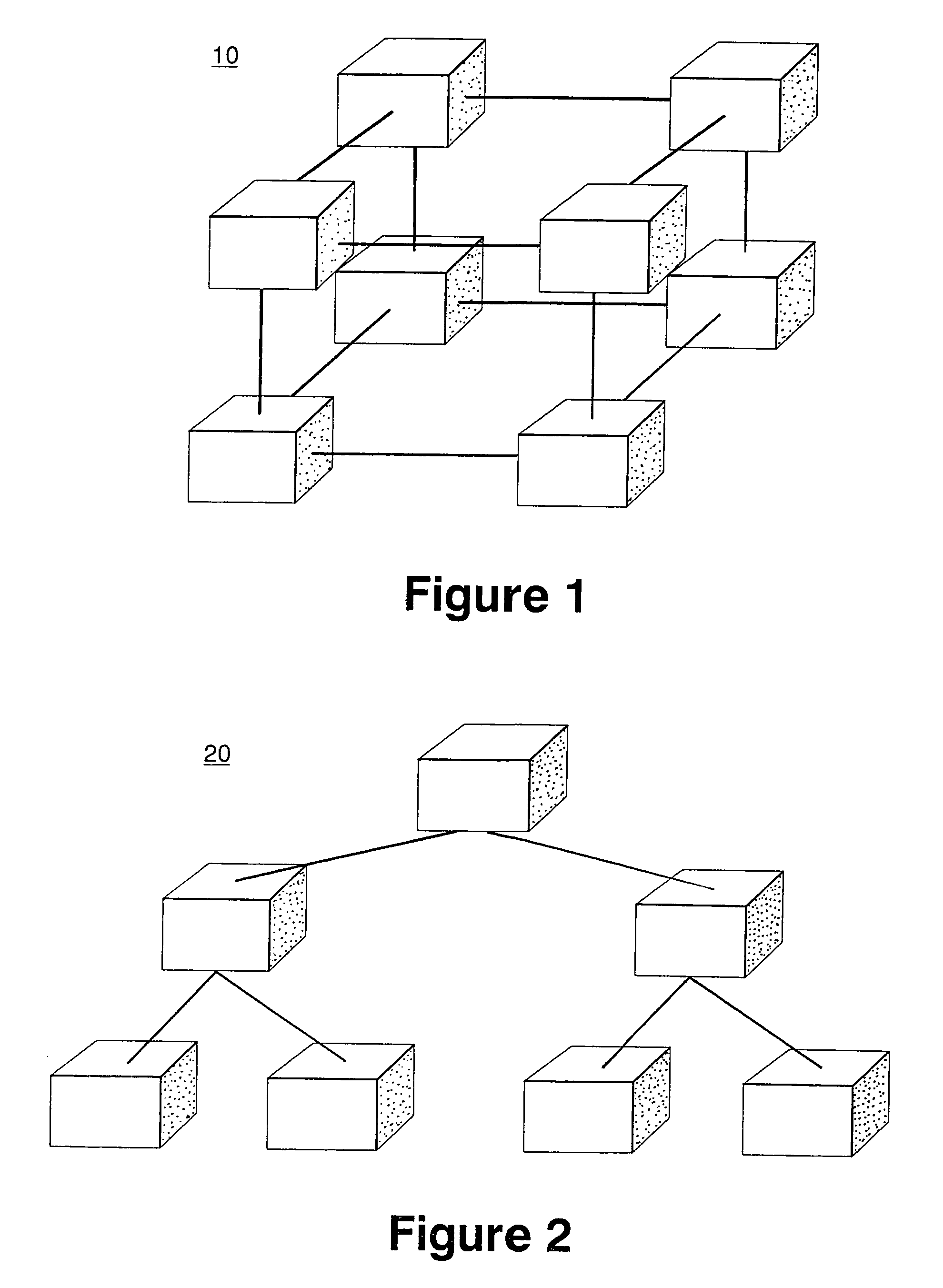
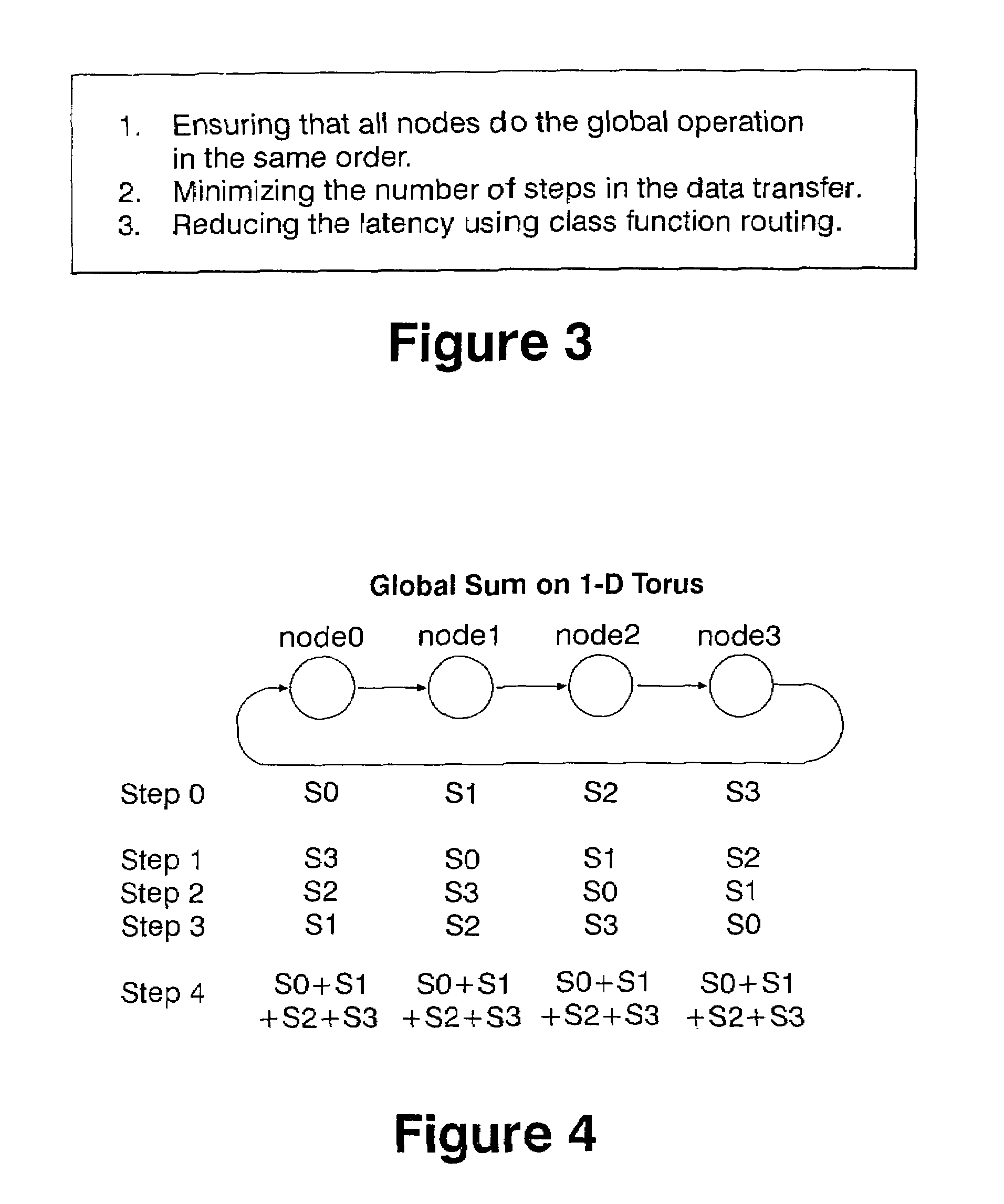
Methods and systems for performing arithmetic functions. In accordance with a first aspect of the invention, methods and apparatus are provided, working in conjunction of software algorithms and hardware implementation of class network routing, to achieve a very significant reduction in the time required for global arithmetic operation on the torus. Therefore, it leads to greater scalability of applications running on large parallel machines. The invention involves three steps in improving the efficiency and accuracy of global operations: (1) Ensuring, when necessary, that all the nodes do the global operation on the data in the same order and so obtain a unique answer, independent of roundoff error; (2) Using the topology of the torus to minimize the number of hops and the bidirectional capabilities of the network to reduce the number of time steps in the data transfer operation to an absolute minimum; and (3) Using class function routing to reduce latency in the data transfer. With the method of this invention, every single element is injected into the network only once and it will be stored and forwarded without any further software overhead. In accordance with a second aspect of the invention, methods and systems are provided to efficiently implement global arithmetic operations on a network that supports the global combining operations. The latency of doing such global operations are greatly reduced by using these methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for automatic on-line calibration of a process model
InactiveUS7359830B2Improve performanceConvenient closed-loop controlSimulator controlDigital computer detailsDead timeProcess quality
A method is disclosed for collecting and processing raw process data. The method includes processing the raw data through a process model to obtain a prediction of the process quality; processing this prediction through two dynamic transfer functions thus creating two intermediate signals; storing the two intermediate signals as a function of time; retrieving at the time of a real and validated measurement of the process quality from the history the absolute minimum value and maximum value of the two intermediate signals in the time period corresponding to a minimum and maximum specified deadtime, in which the absolute minimum value and maximum values define the minimum and maximum prediction possible; calculating the deviation as being the difference between the real and validated measurement and the uncertainty area encompassed between the minimum and maximum prediction possible; incorporating the deviation into the process model to calibrate the process model; and, repeating.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Scroll compressor differential pressure control during compressor shutdown transitions
ActiveCN103994618ARotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsCompression machines with non-reversible cycleHysteresisDifferential pressure
A method includes determining a pressure difference across a scroll compressor of a cooling system. The pressure difference is compared to a minimum differential pressure value. Pressure differences across the scroll compressor that are less than the minimum differential pressure value are associated with unloading the scroll compressor. Parameters including a pressure set point value and an absolute minimum pressure value are increased when the pressure difference is less than the minimum differential pressure value. Subsequent to the increasing of the parameters, the parameters are decreased when the pressure difference is greater than a sum of the minimum differential pressure value and a hysteresis value.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
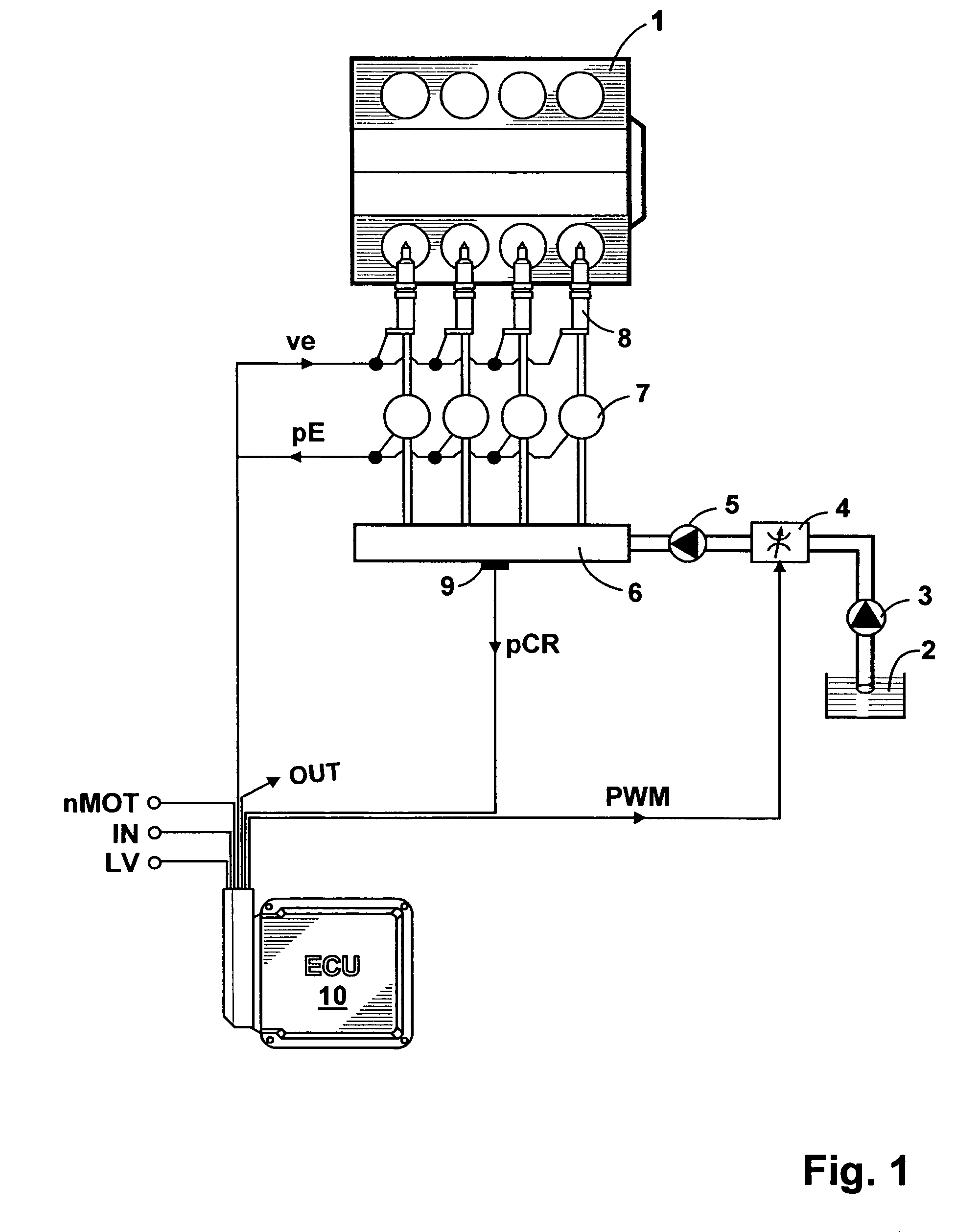
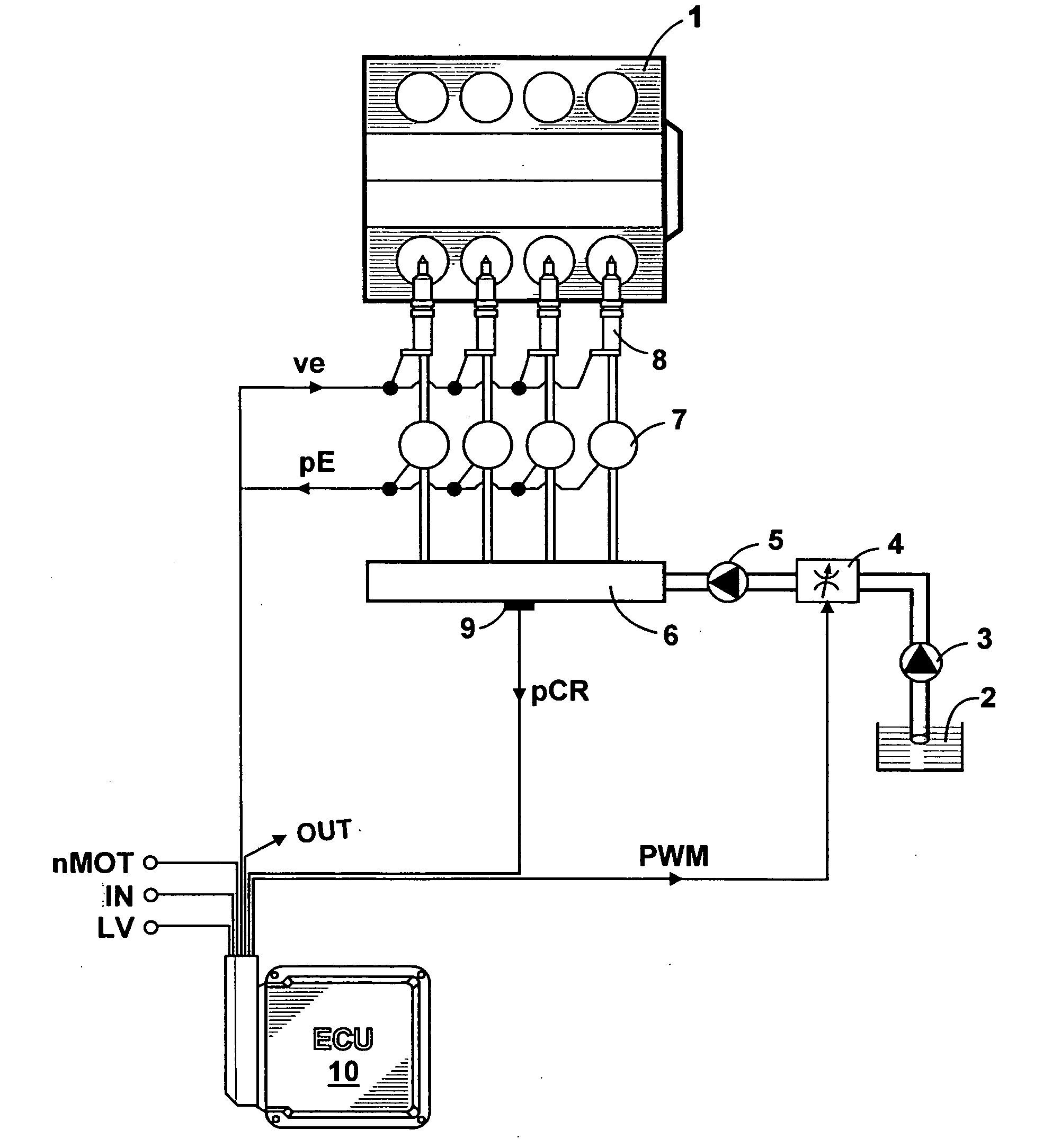
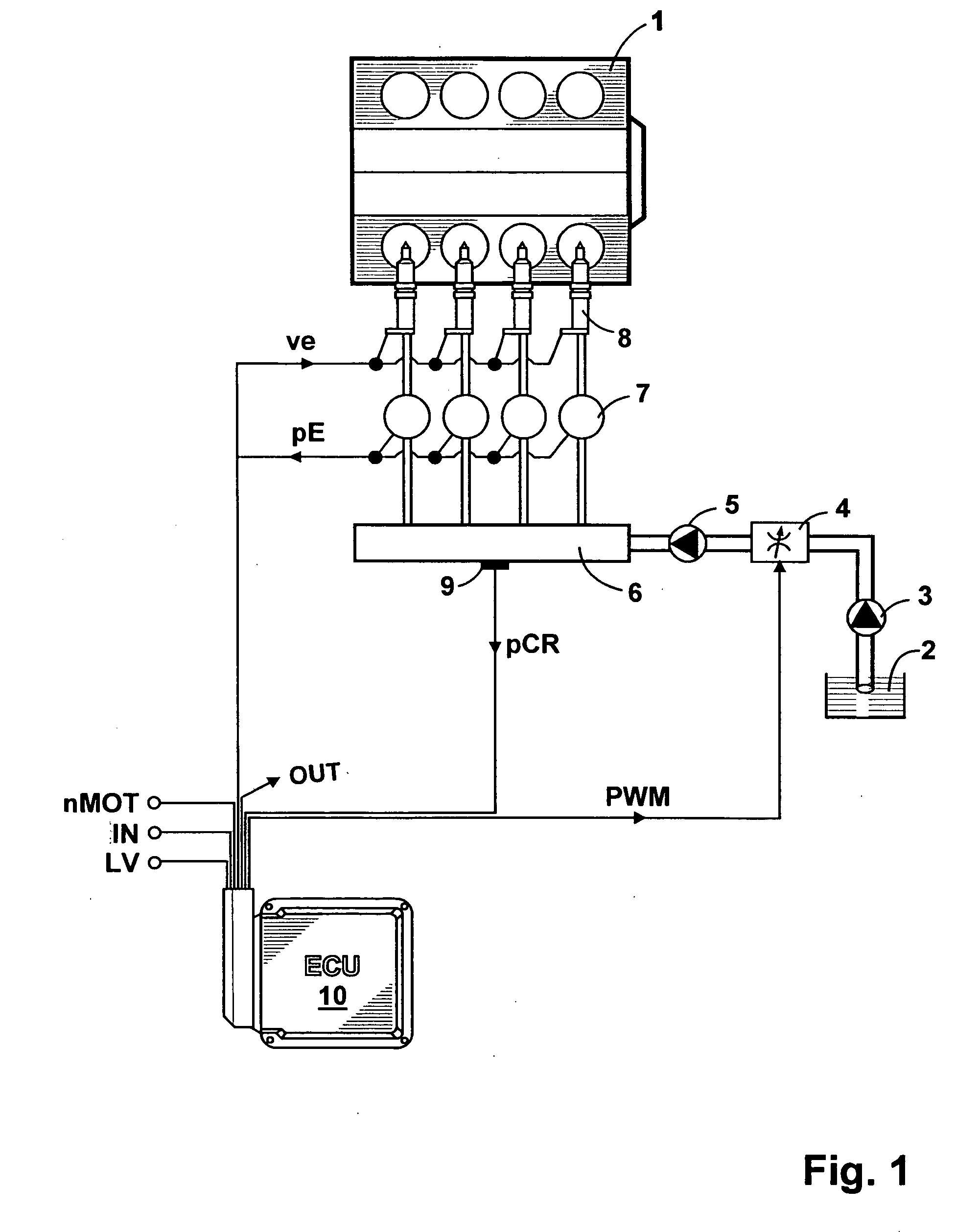
Process for the open-and closed-loop control of an internal combustion engine with a common rail system including individual accumulators
ActiveUS7769530B2Improve reliabilityEffect emission valueElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCommon railExternal combustion engine
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
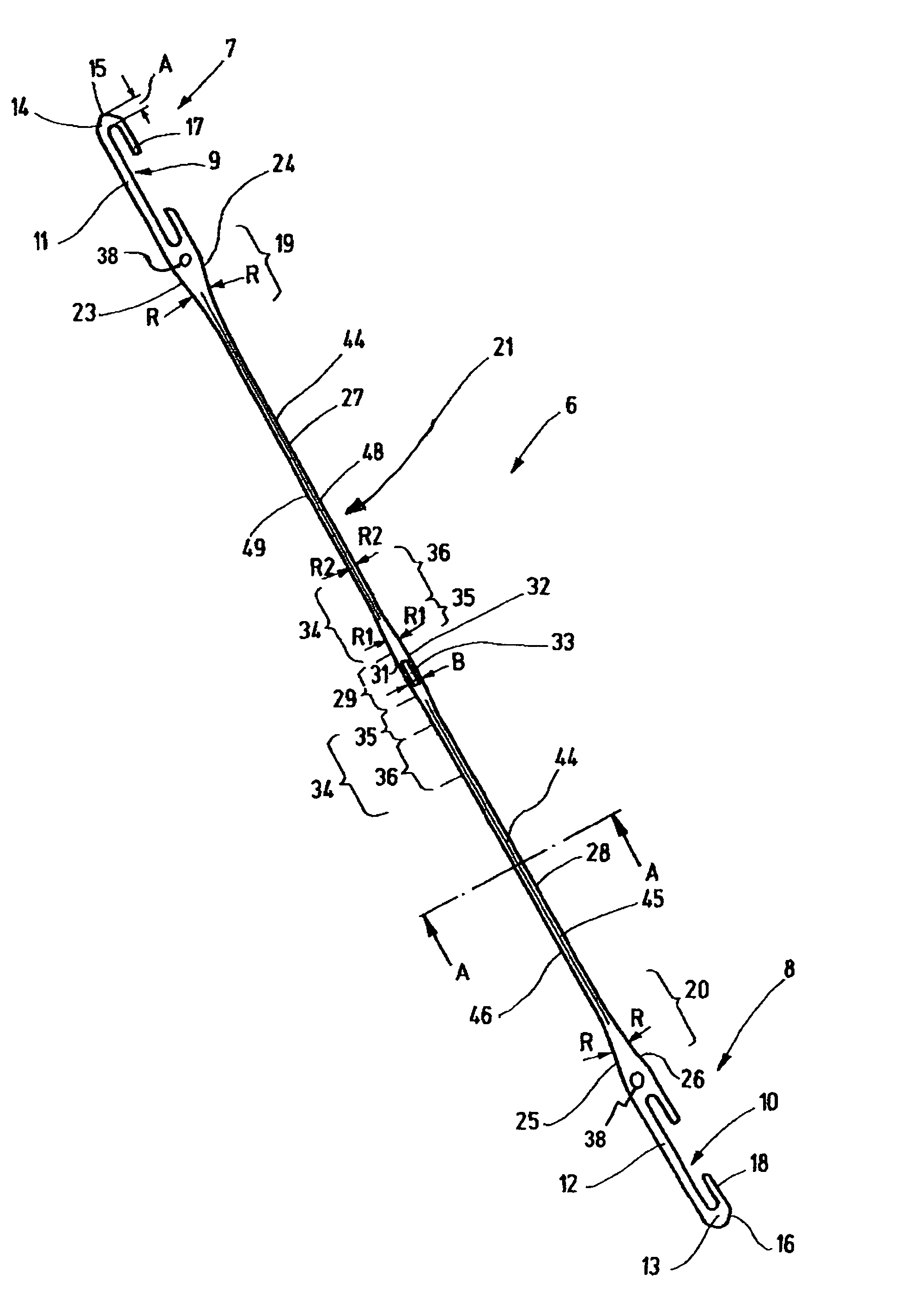
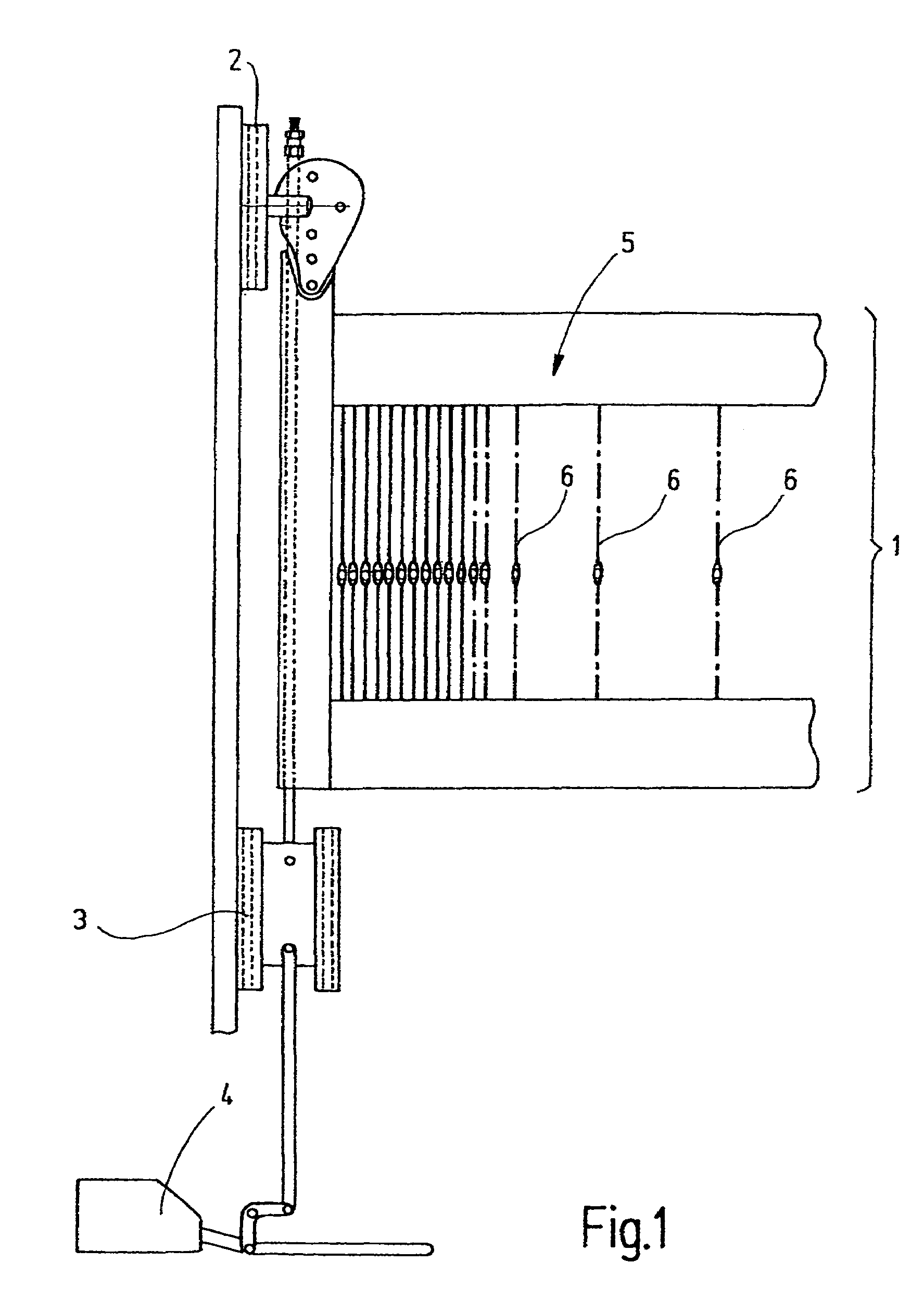
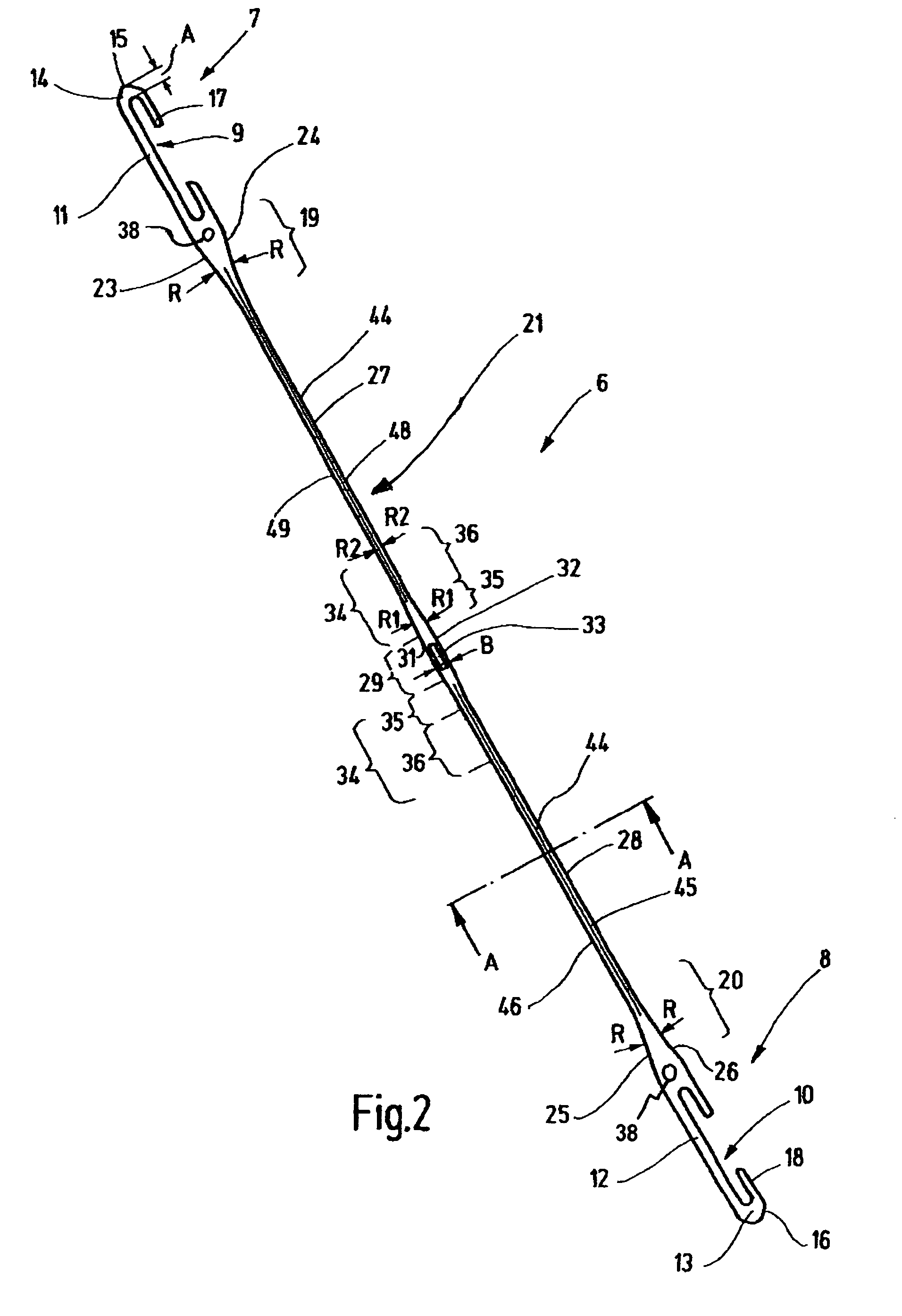
Heddle
In a heddle (6), the slender heddle shank (21) has been lengthened, at the cost of the end eyelets (7, 8) and the yarn eyelet region (29). This is accomplished on the one hand by shortening the end eyelet regions (7, 8) to their absolute minimum length and on the other by placing the auxiliary openings (38), which serve to transport the heddles, closer to the end eyelets (7, 8). The radii R in the region of the end eyelets (7, 8) are reduced. Instead of the usual 2 mm width, the heddle shank (21) still has a maximum width of 1.6 mm. The regions (14, 13) of the heddle (6) that protrude past the end openings still have, instead of the usual length of 4 mm, a length of 2.5 mm to 3 mm. Directly around the yarn eyelet (33), the heddle has a width which, as before, is equivalent to twice the width of the yarn eyelet (33). However, the length of this region is shortened to a maximum of twice to three times the yarn eyelet width. The transition from the narrowest zone (27, 28) of the heddle shank (21) to the comparatively wide zone (29) around the yarn eyelet (33) is characterized by an elongated transition region (34), which has a maximum width of 1.8 mm and serves to reinforce this region against mechanical stresses.
Owner:GROZ BECKERT KG
Dynamic minimum-memory interleaving
ActiveCN101204014ACode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesCell schedulingComputer architecture
Minimum-memory-implementation is available with any depth and period in DSL interleaving / deinterleaving, always allowing the minimum amount of memory to be used in both transmitter and receiver without loss of performance or of basic triangular structure, even if the interleaver / deinterleaver parameters change dynamically. A novel cell-scheduling process ensures availability of the minimum amount of memory (or any other desired memory usage) to implement an image of the perfect triangle and works for any co-prime depth and interleaver period. Minimal memory use may be further characterized by a simple off-line method that determines an addressing order for each of the memory cells in a minimum-memory (or other) implementation of an interleaver / deinterleaver according to the invention. Time variation of interleaver depth in operation can be accommodated easily with absolute minimum memory requirement at all time instants.
Owner:ADAPTIVE SPECTRUM & SIGNAL
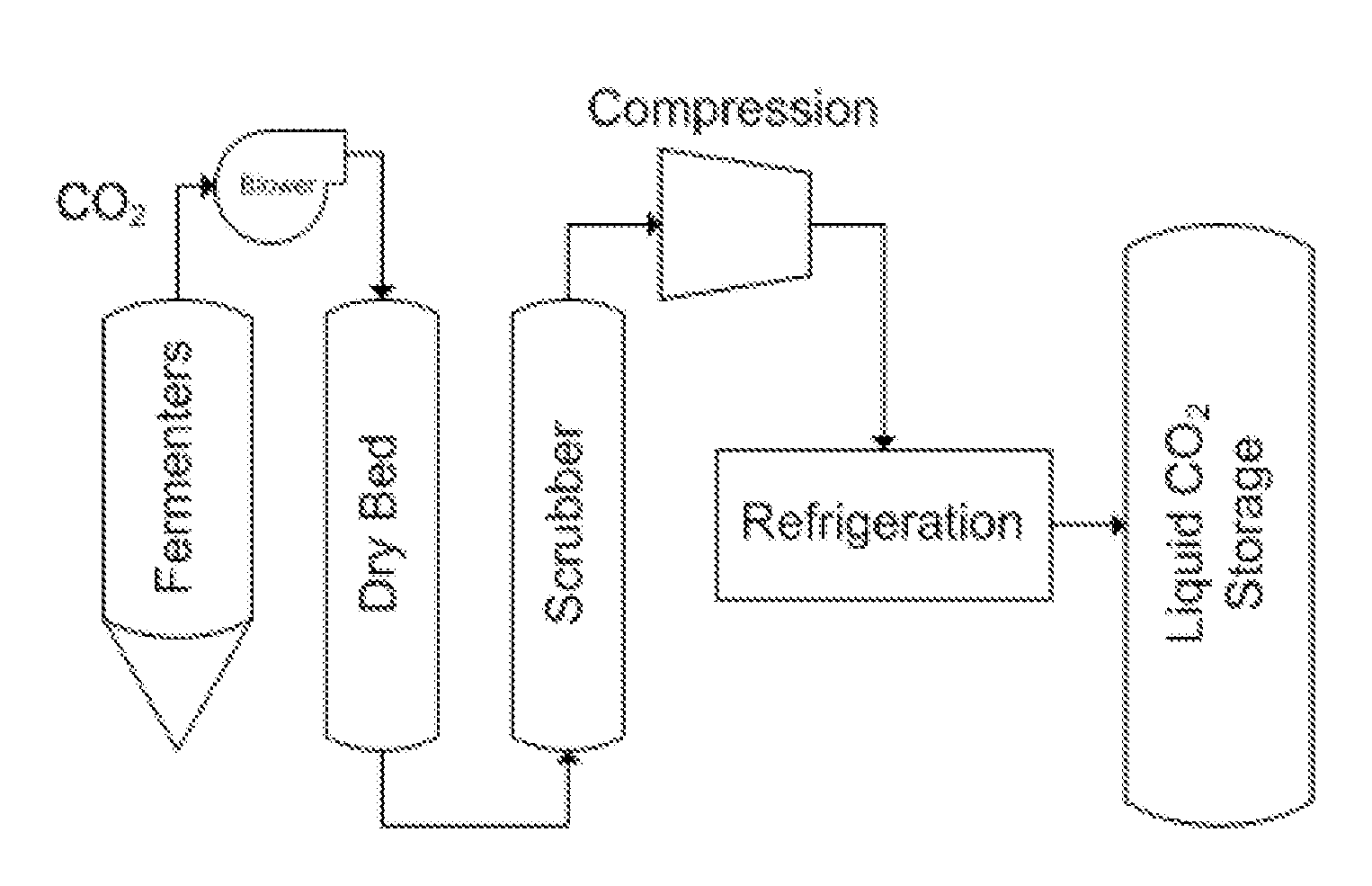
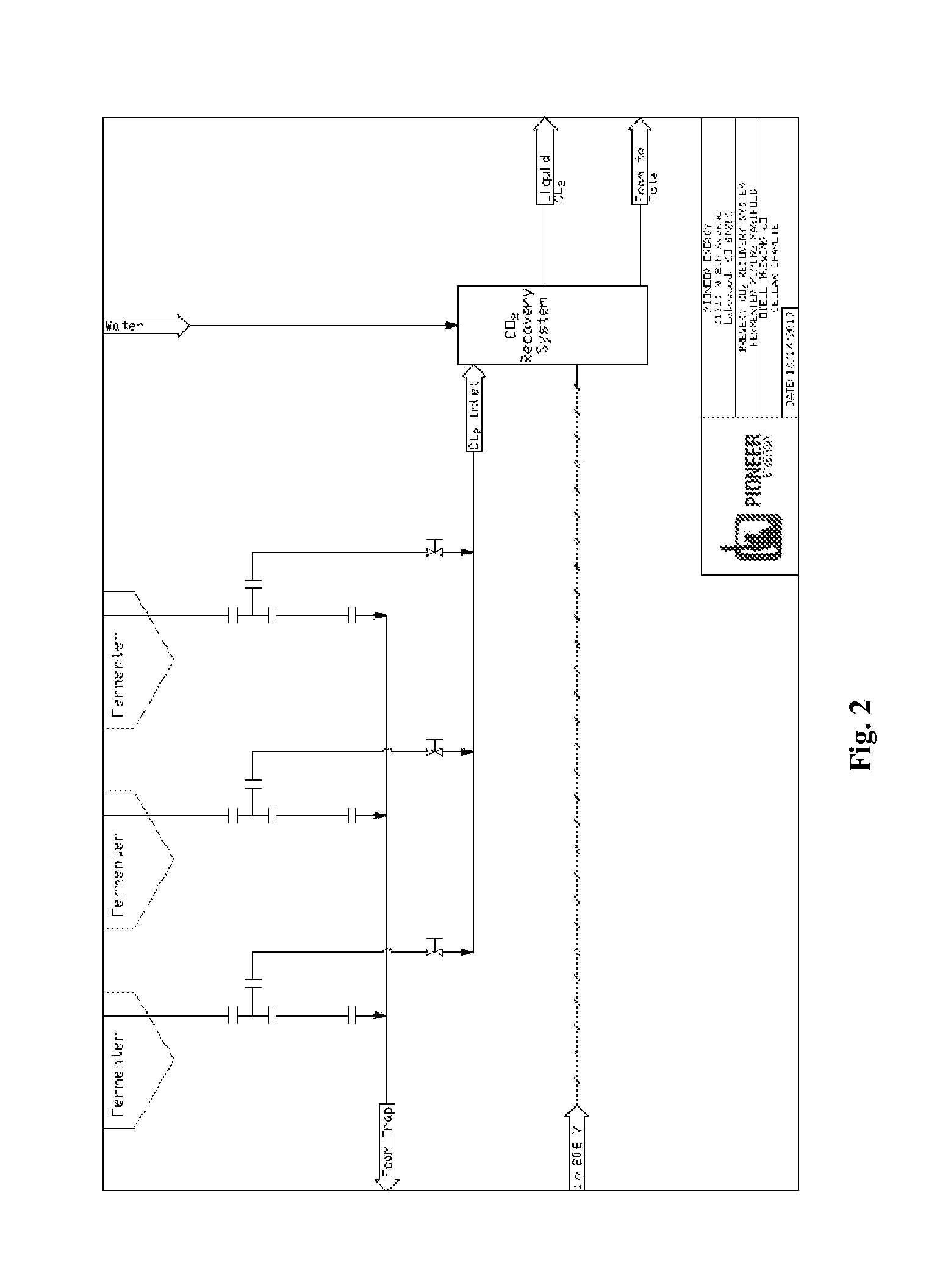
Systems and methods for recovering carbon dioxide from industrially relevant waste streams, especially ethanol fermentation processes, for application in food and beverage production
InactiveUS20160003532A1Easy to relocateReduce up-front capital costSolidificationLiquefactionWaste streamAbsolute minimum
A system for recovering CO2 via liquefaction and purification from a vented CO2 gas stream comprising a compressor; a dehydrator; a scrubber; a refrigerator having one or more stages; and a separation subsystem adapted to ensure non-condensable gas content in the final product meets industry standards. The liquid CO2 product is of sufficient purity to be used in applications requiring beverage-grade CO2. The system can be utilized as a single-brewery installation to reduce venting from ethanol fermenters to an absolute minimum, produce a high purity liquid CO2 product for use in-process or external sales, and offset the purchasing of expensive, industrial CO2 of inferior purity.
Owner:PIONEER ENERGY
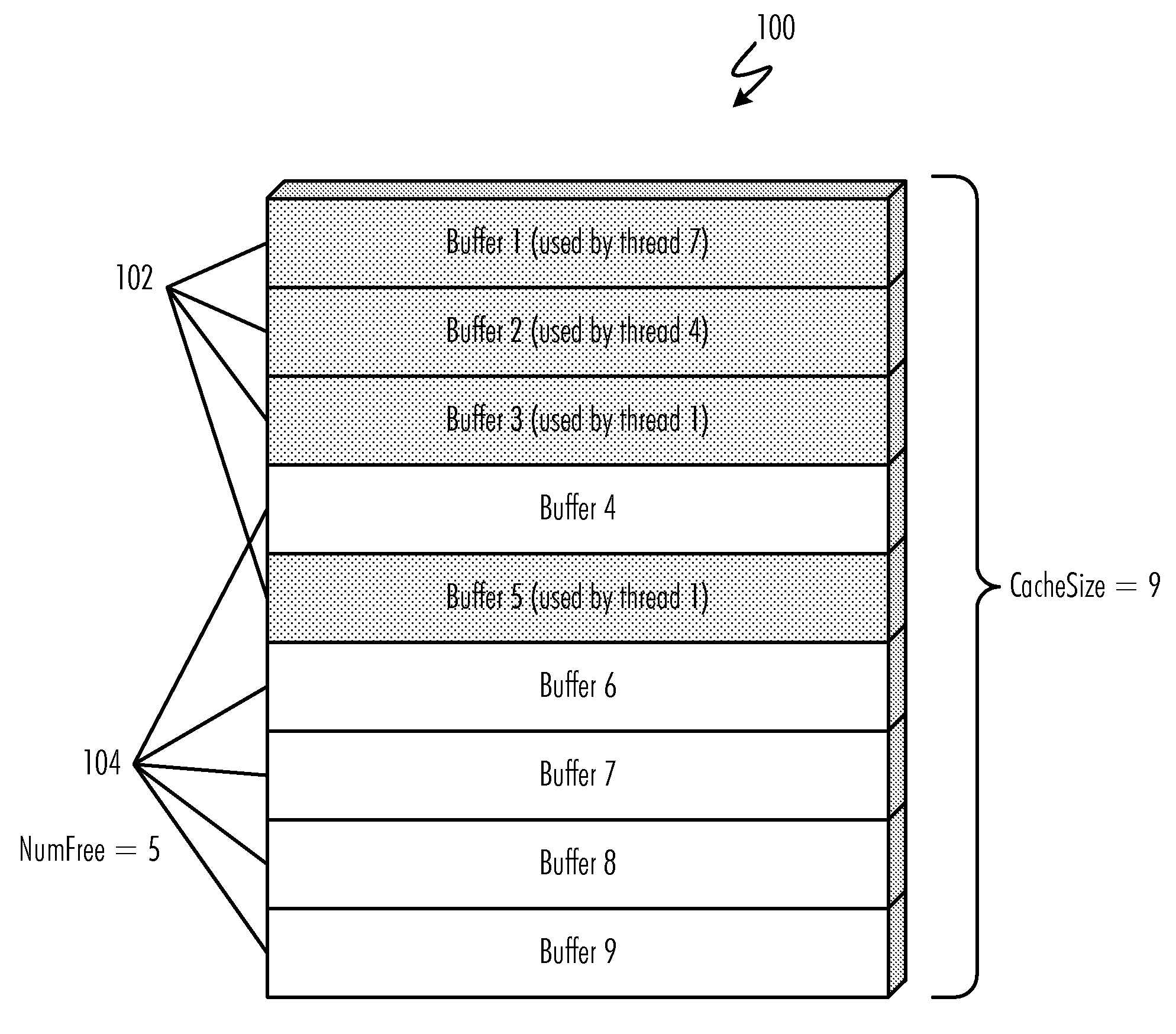
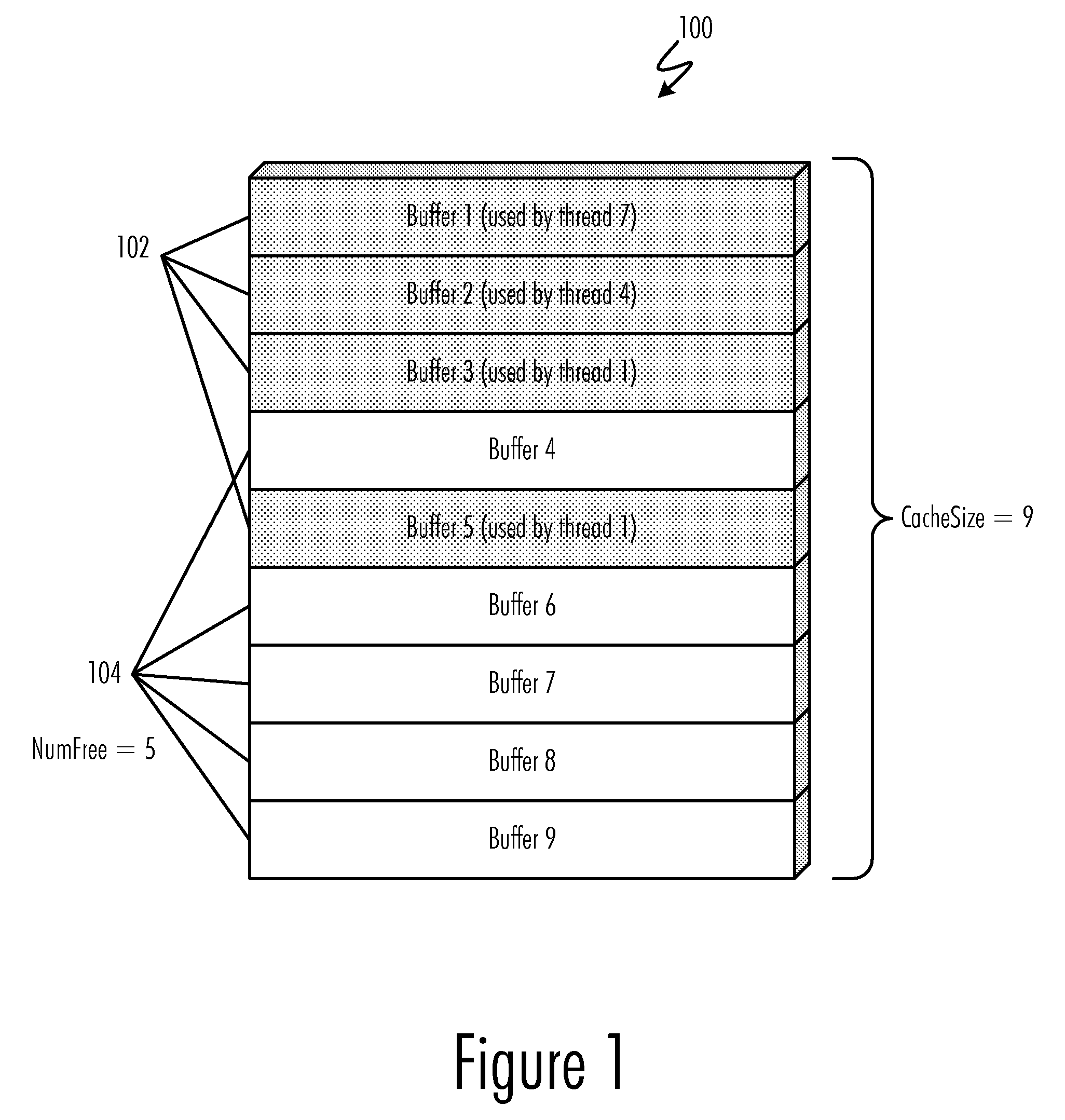
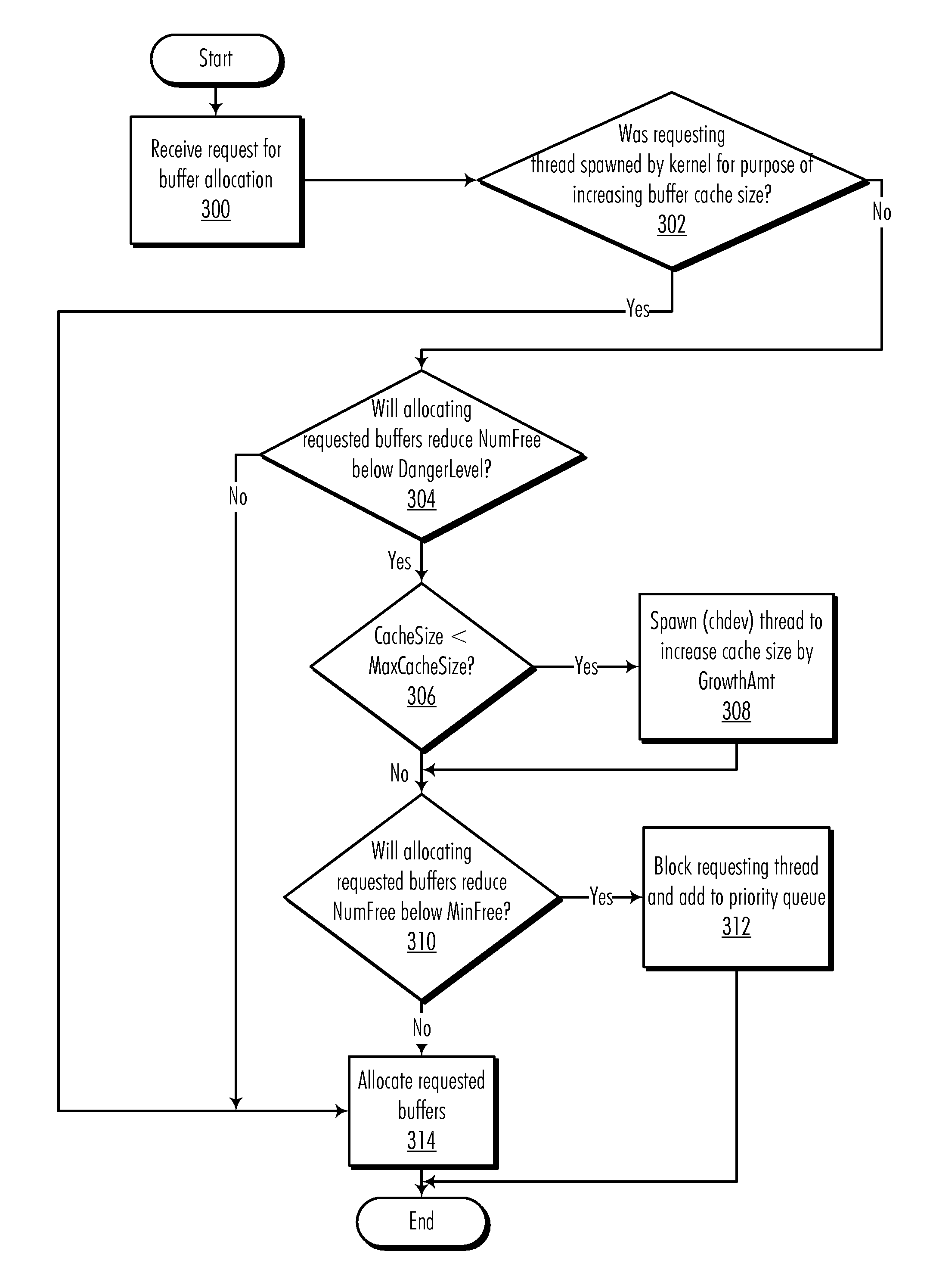
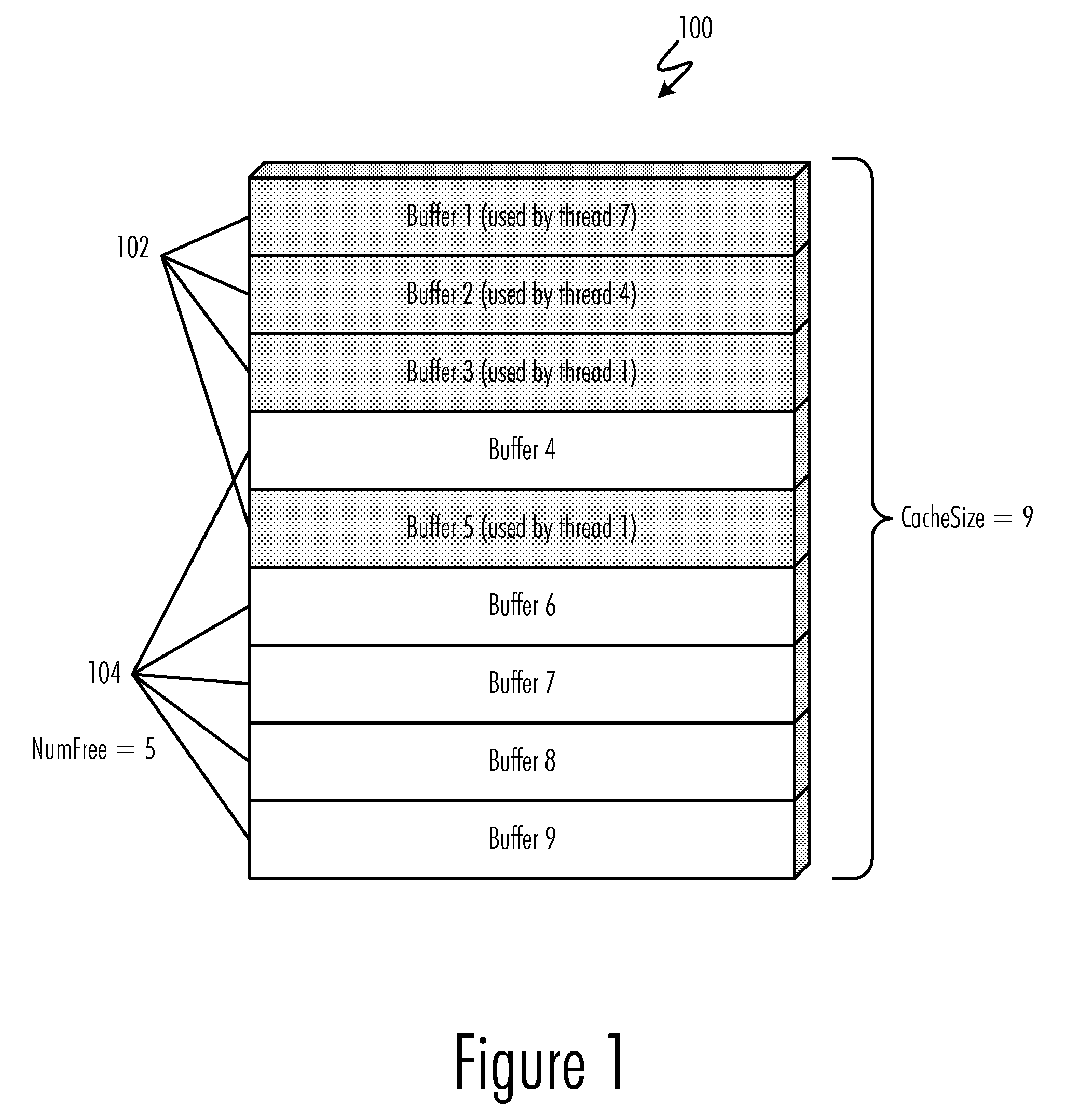
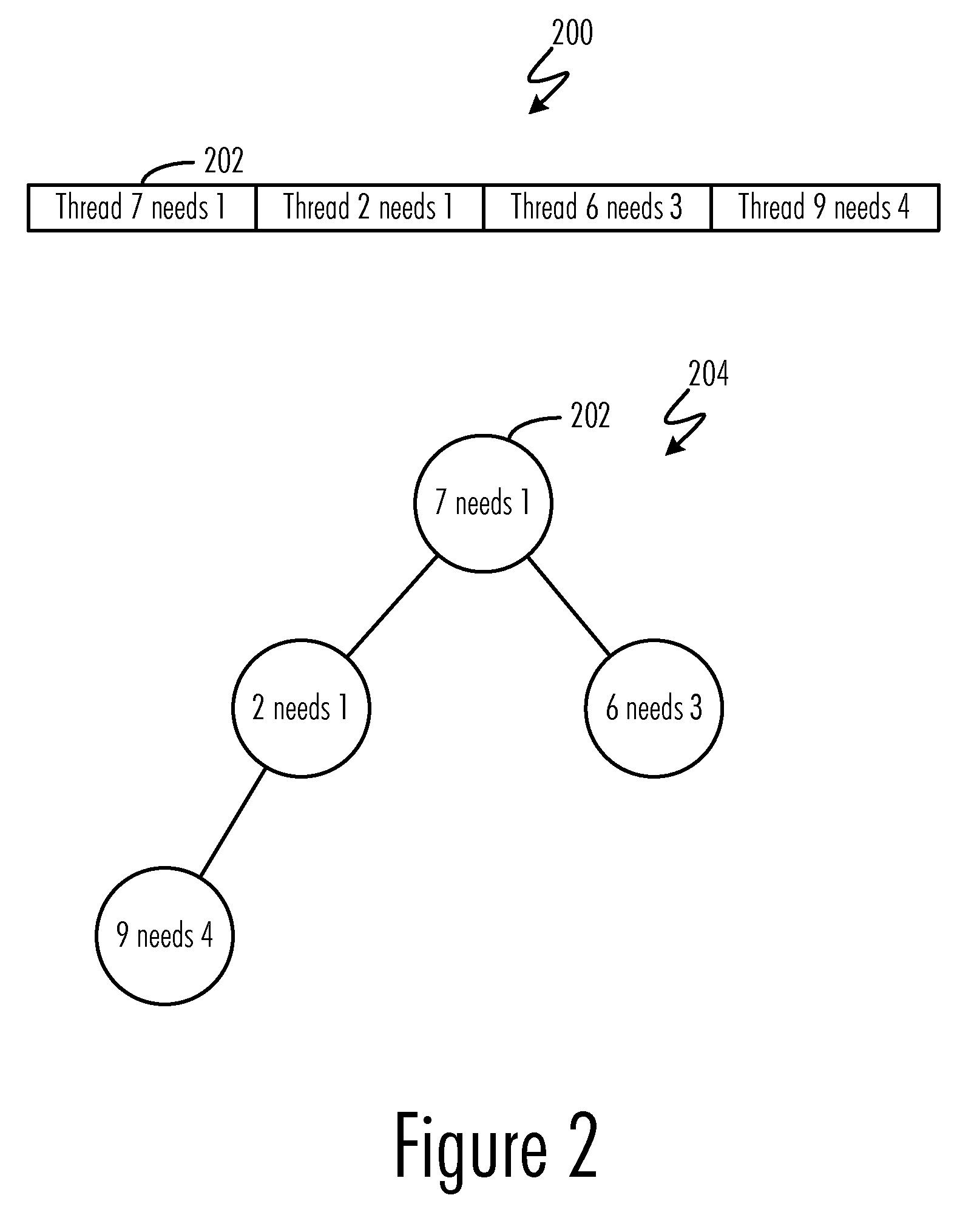
Buffer cache management to prevent deadlocks
InactiveUS20090157969A1Avoid deadlockProgress can be ensuredMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemAbsolute minimum
A method, computer program product, and data processing system for managing a input / output buffer cache for prevention of deadlocks are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, automatic buffer cache resizing is performed whenever the number of free buffers in the buffer cache diminishes to below a pre-defined threshold. This resizing adds a pre-defined number of additional buffers to the buffer cache, up to a pre-defined absolute maximum buffer cache size. To prevent deadlocks, an absolute minimum number of free buffers are reserved to ensure that sufficient free buffers for performing a buffer cache resize are always available. In the event that the buffer cache becomes congested and cannot be resized further, threads whose buffer demands cannot be immediately satisfied are blocked until sufficient free buffers become available.
Owner:IBM CORP
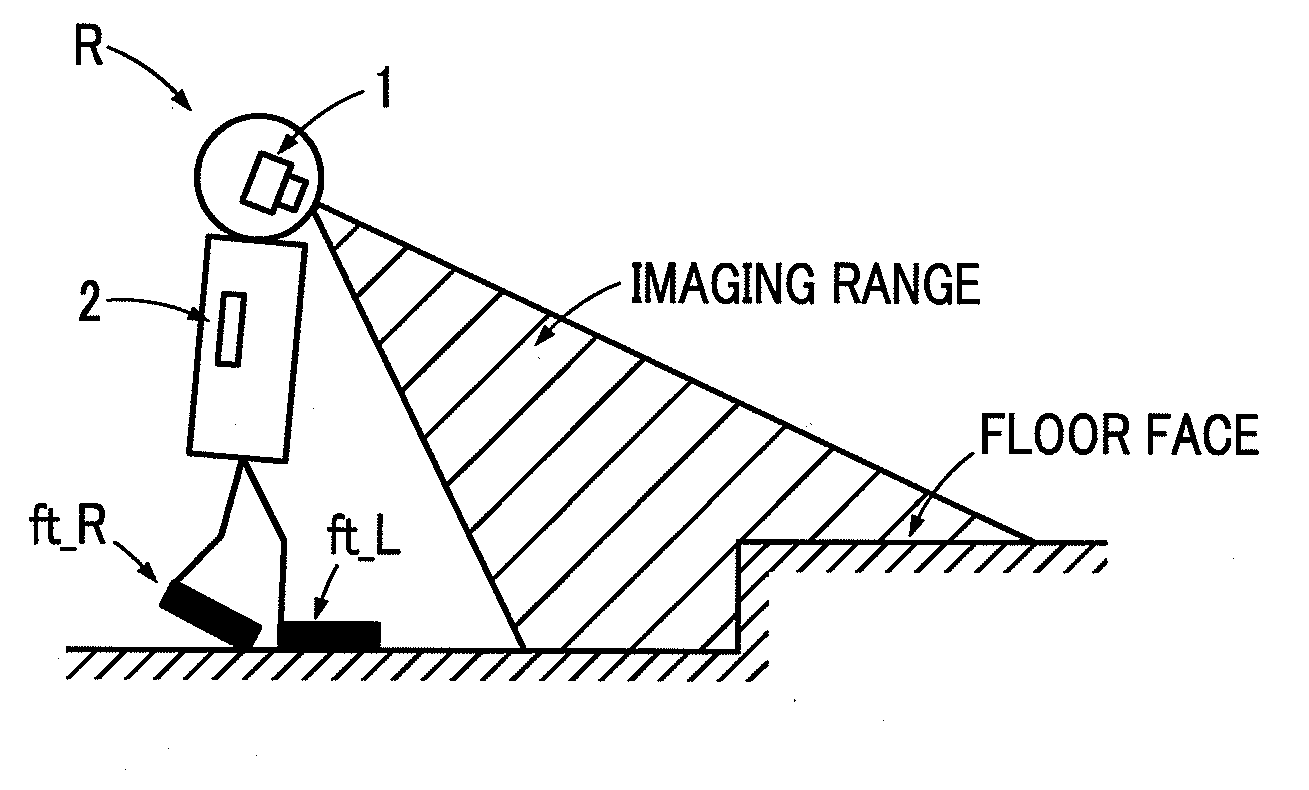
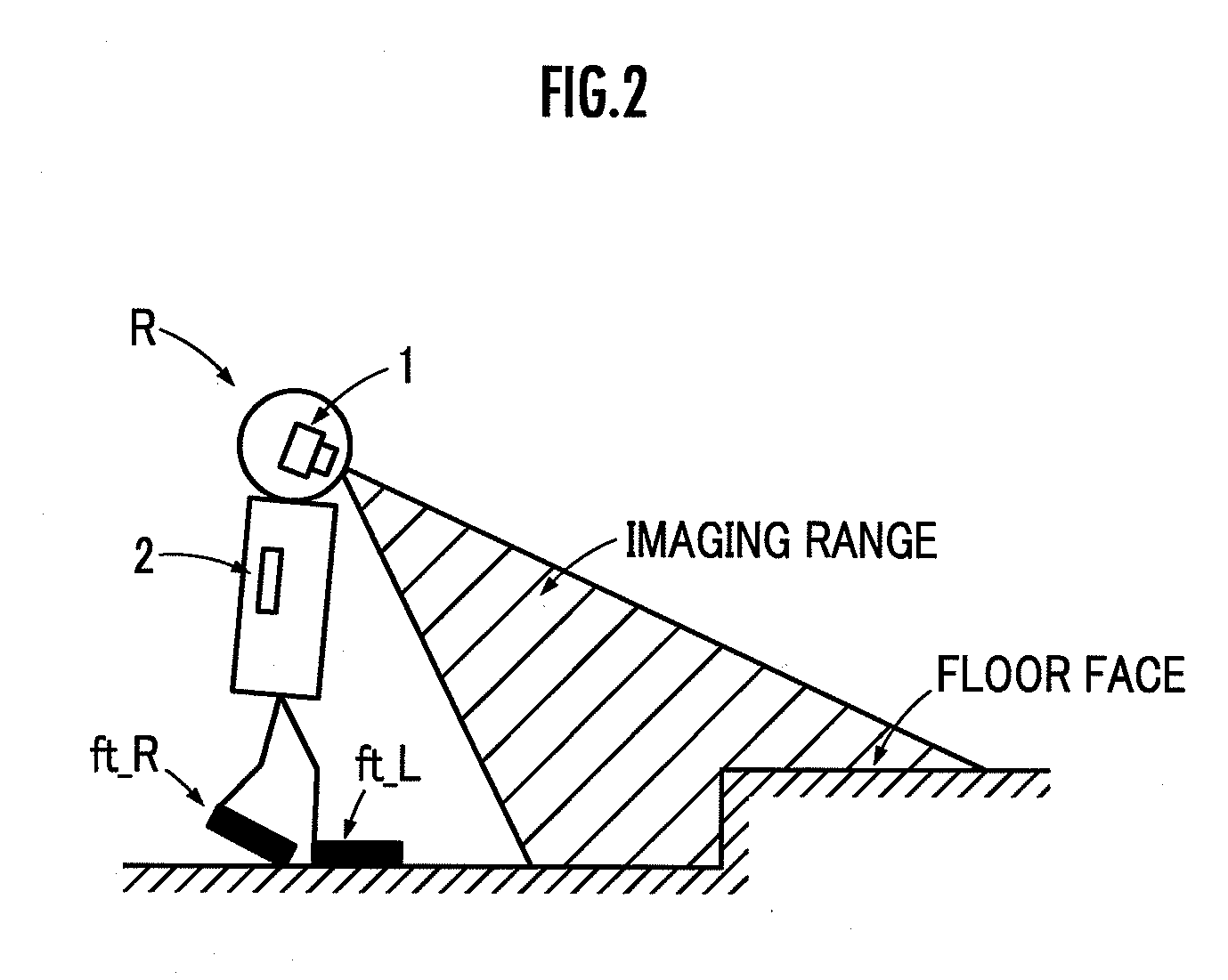
Contact state estimating apparatus and trajectory generation apparatus
ActiveUS20130058538A1Calculation loadAccurate estimateCharacter and pattern recognitionVehicle position/course/altitude controlAbsolute minimumSimulation
A state where at least a part of the virtual object (e.g., a foot of a robot) enters into the actual object (e.g., floor), i.e., a state where at least a part of a plurality of virtual points located on the surface of the virtual object is inside the actual object, can be assumed. At each of the inside and the outside of the actual object, as a virtual point is located at a deeper position inside and away from the surface or the skin part of the actual object and as a coordinate value difference ΔZi is larger, a higher value is calculated for the cost Ei as well. The combination Ẑ of coordinate values of virtual points, bringing the total cost E=ΣiEi closer to an absolute minimum or a local minimum, can be searched.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
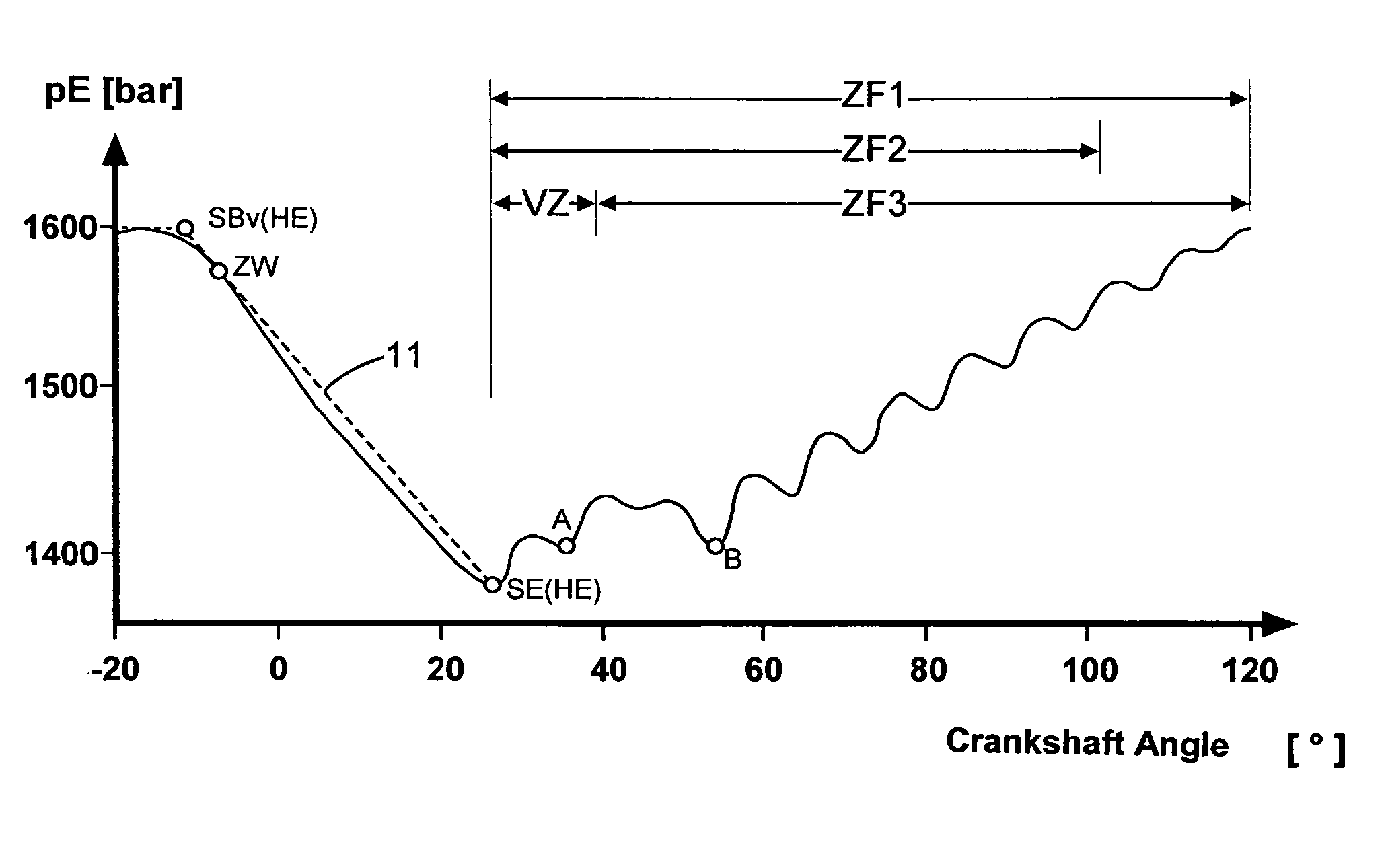
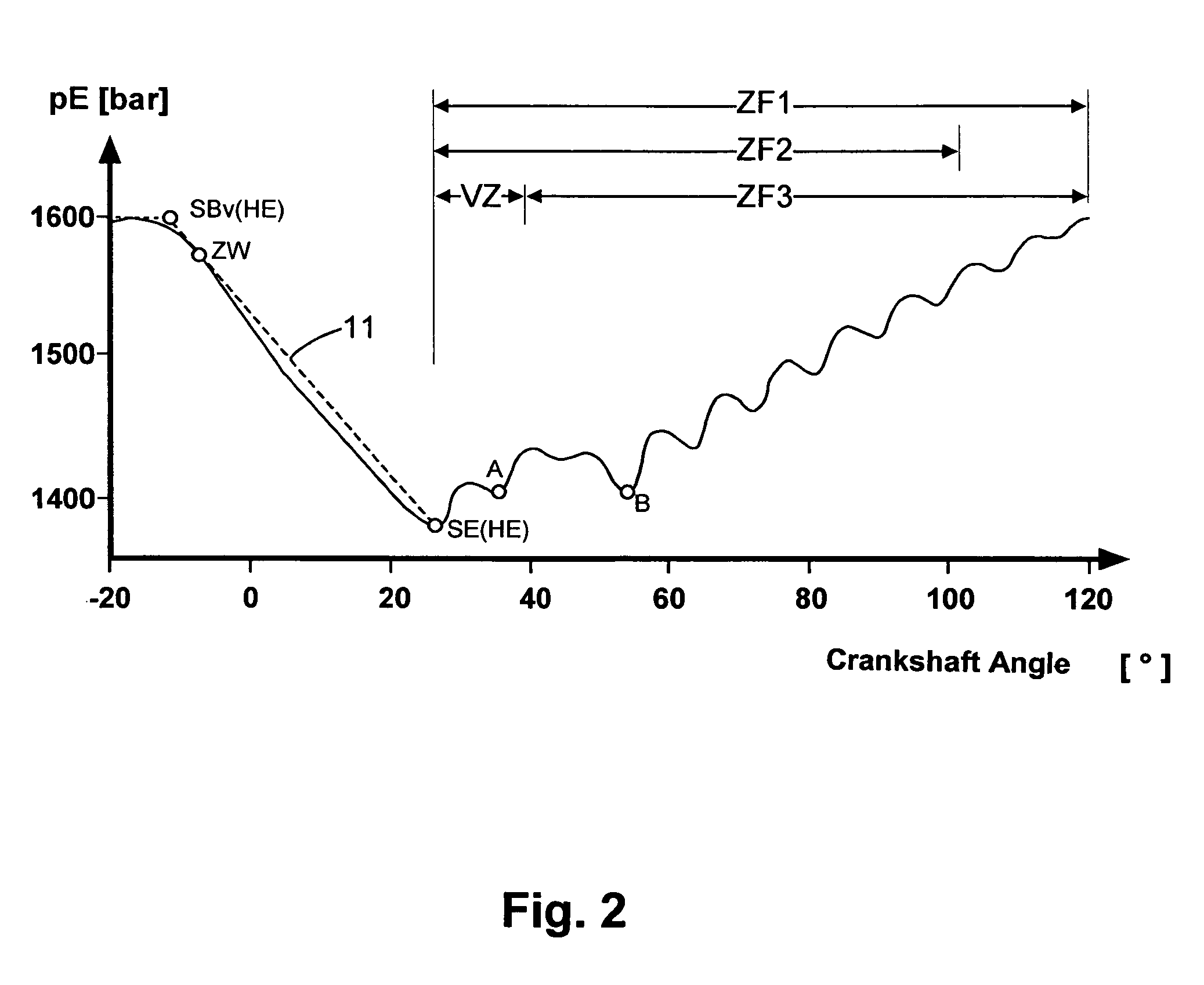
Process for the open-and closed-loop control of an internal combustion engine with a common rail system including individual accumulators
ActiveUS20100076665A1Improve reliabilityReduce decreaseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCommon railExternal combustion engine
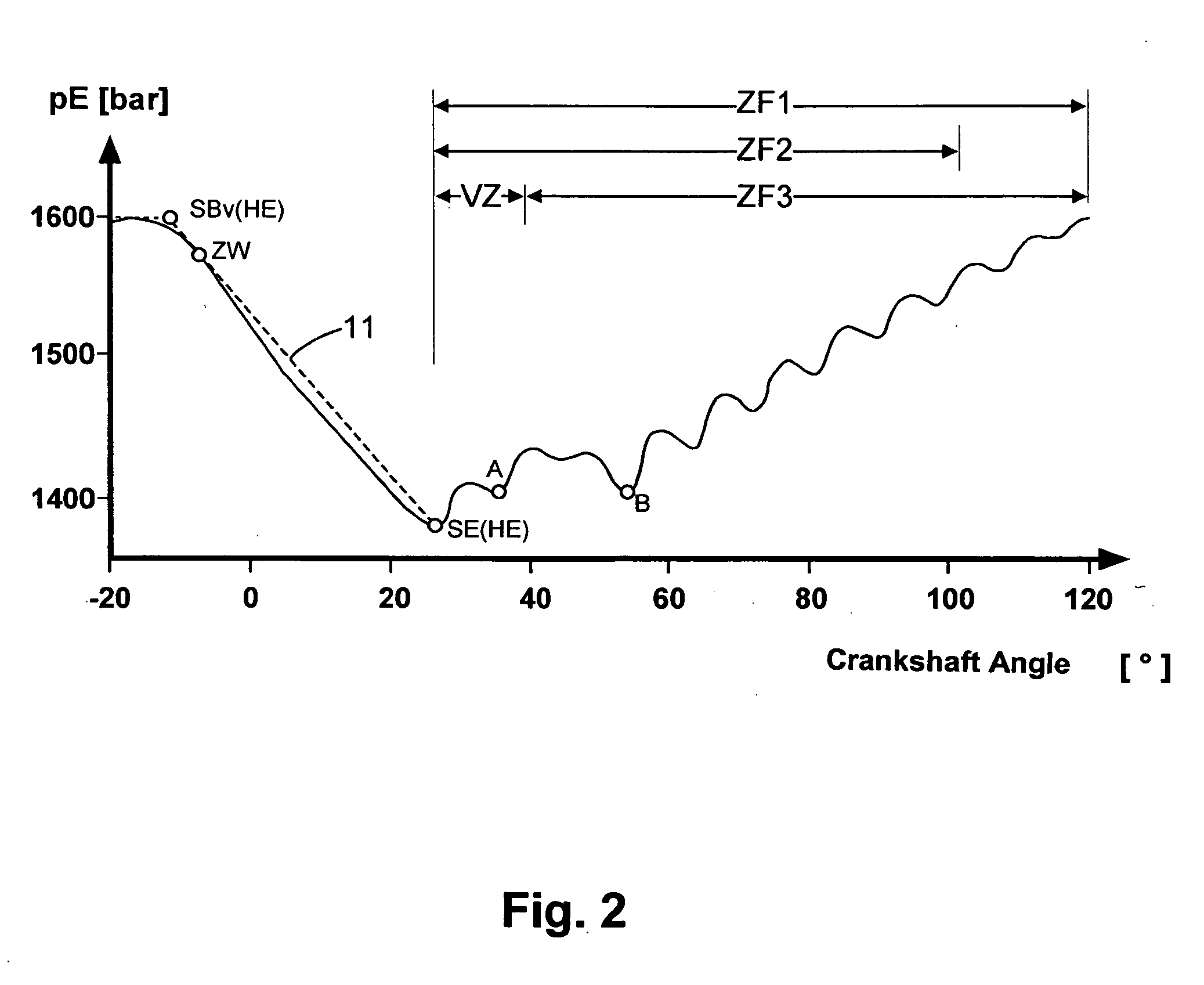
For an internal combustion engine with a common rail system including individual accumulators, a process for open- and closed-loop control is proposed, in which the individual accumulator pressure (pE) is detected within a measuring interval and stored, an absolute minimum value of the stored individual accumulator pressure (pE) is interpreted as the end of the main injection, and on the basis of the end of the main injection, a mathematical function is used to calculate a virtual starting time for the main injection. In the measuring interval after the end of the main injection, the individual accumulator pressure (pE) is filtered within a time window, a local minimum value of the filtered individual accumulator pressure is interpreted as the end of a post-injection, and a mathematical function is used to calculate a virtual start of the post-injection.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
Camellia oleifera planting method capable of increasing oil yield
ActiveCN109588198APromote formationMeet growth needsData processing applicationsAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserIllicium verumCamellia oleifera
The invention provides a camellia oleifera planting method capable of increasing oil yield. Formulated fertilization is performed according to content of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizerin each organ of camellia oleifera, the annual mean temperature of the camellia oleifera in the planting process is 16-17 DEG C, and the absolute minimum temperature is not lower than subzero 8 DEG C.According to the camellia oleifera planting method, biomass of the organs such as root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit and the like of each camellia oleifera body and the content of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in each organ are analyzed precisely by sampling according to nutrition absorption and utilization characteristics of the camellia oleifera and a forest all-tree nutrition method for soil, so that the absorption and accumulation absolute values and relative proportion of a large number of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the camellia oleifera bodies are calculated scientifically, the scientific ratio of macroelements (N, P and K) of nutrient fertilizer for fertilization of the camellia oleifera is calculated, and output and the oil yield are increased.
Owner:GUANGXI FORESTRY RES INST
Tissue contact sensing with a multi electrode ablation catheter
A method and system for assessing electrode-tissue contact before the delivery of ablation energy. The system may include a control unit programmed to determine a difference between a maximum impedance magnitude at a low frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance magnitude at the low frequency across all electrodes, determine a difference between a maximum impedance magnitude at a high frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance magnitude at the high frequency across all electrodes, and determine a difference between a maximum impedance phase at the high frequency for a given electrode and an absolute minimum impedance phase at the high frequency across all electrodes. Differences may be correlated to one another using a linear model, the results determining electrode-tissue contact status. The results may be displayed in a graphical format for easy communication to the user.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Flow-through pressure sensor apparatus
ActiveUS8312774B2Dead space of flowImprove rigidityVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsAbsolute minimumPressure sense
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
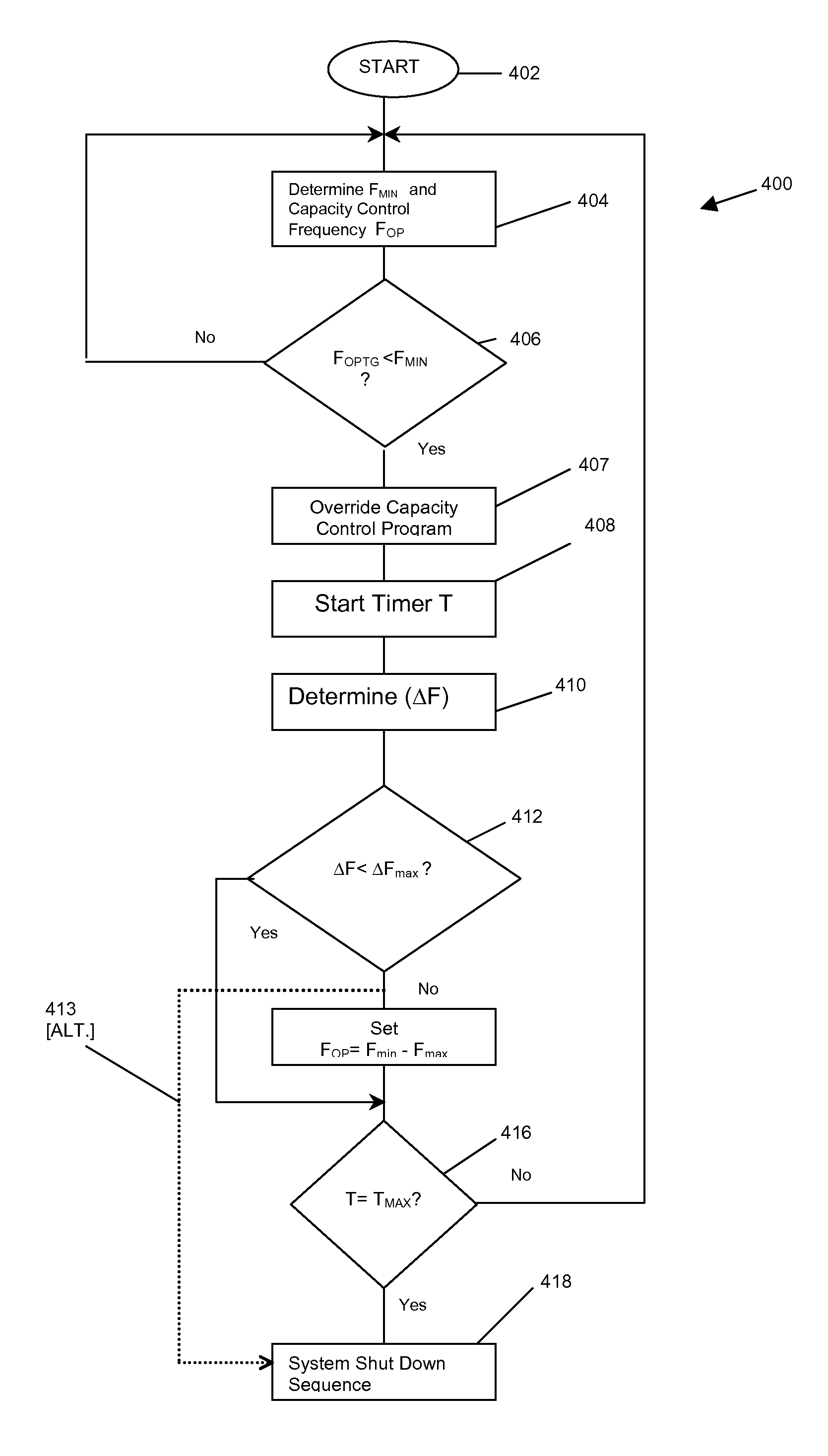
Reduced compressor capacity controls
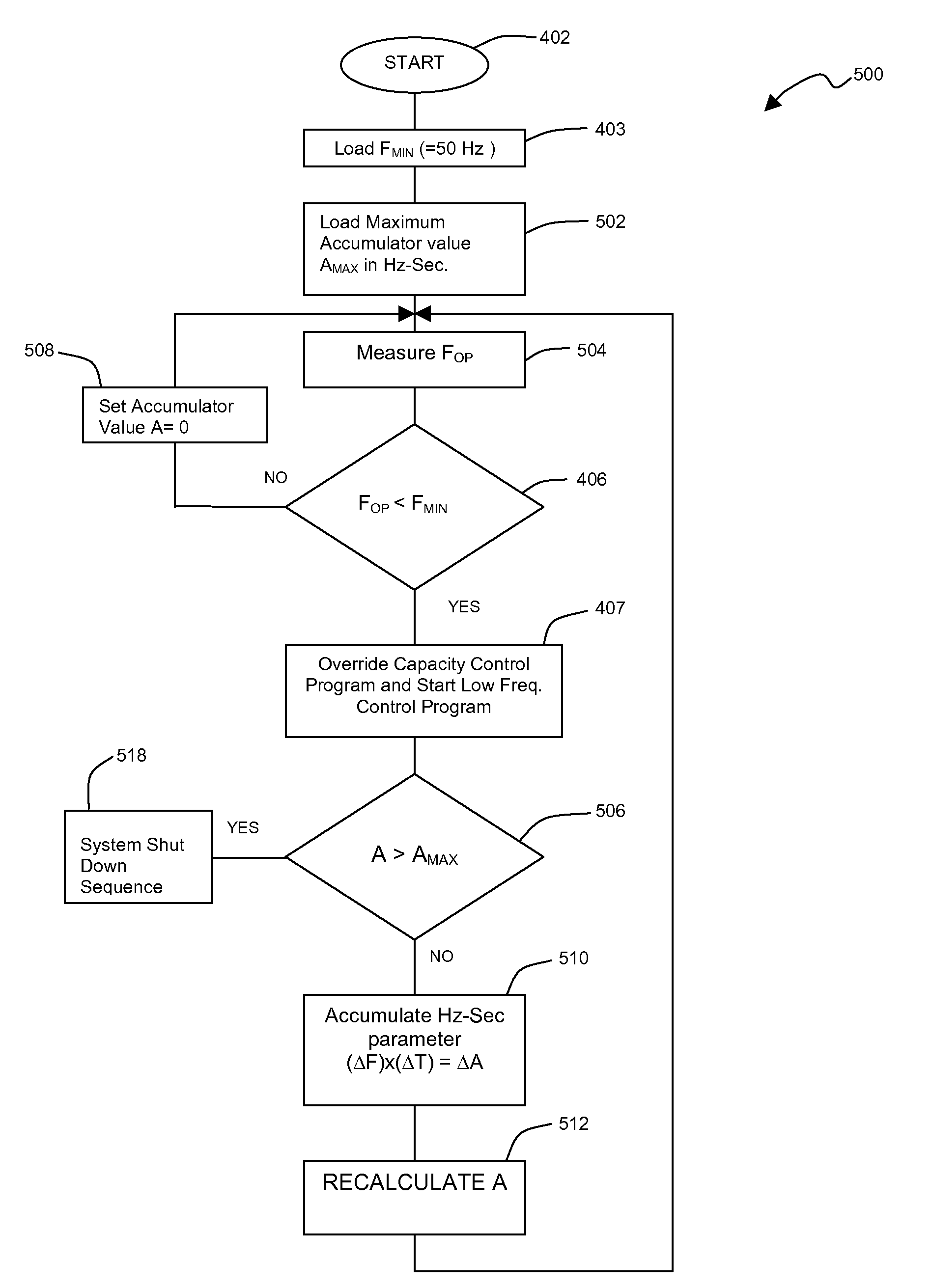
ActiveUS8079227B2Compression machines with non-reversible cycleAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesAbsolute minimumTime segment
A method of controlling the frequency of a compressor in a chiller system is disclosed. The method includes determining a nominal minimum frequency of a compressor, and providing a control algorithm for controlling the period of time and the deviation of the actual operating frequency below the nominal minimal frequency that the compressor may operate without shutting down the chiller system. The time period of operation below nominal minimum frequency may be predetermined as a fixed time period of operation below nominal minimum frequency, or as a variable time period based on the amount by which the frequency deviates below nominal minimum frequency. Also, an absolute minimum operating frequency is provided that results in the control algorithm shutting down the chiller system and the compressor.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO +1
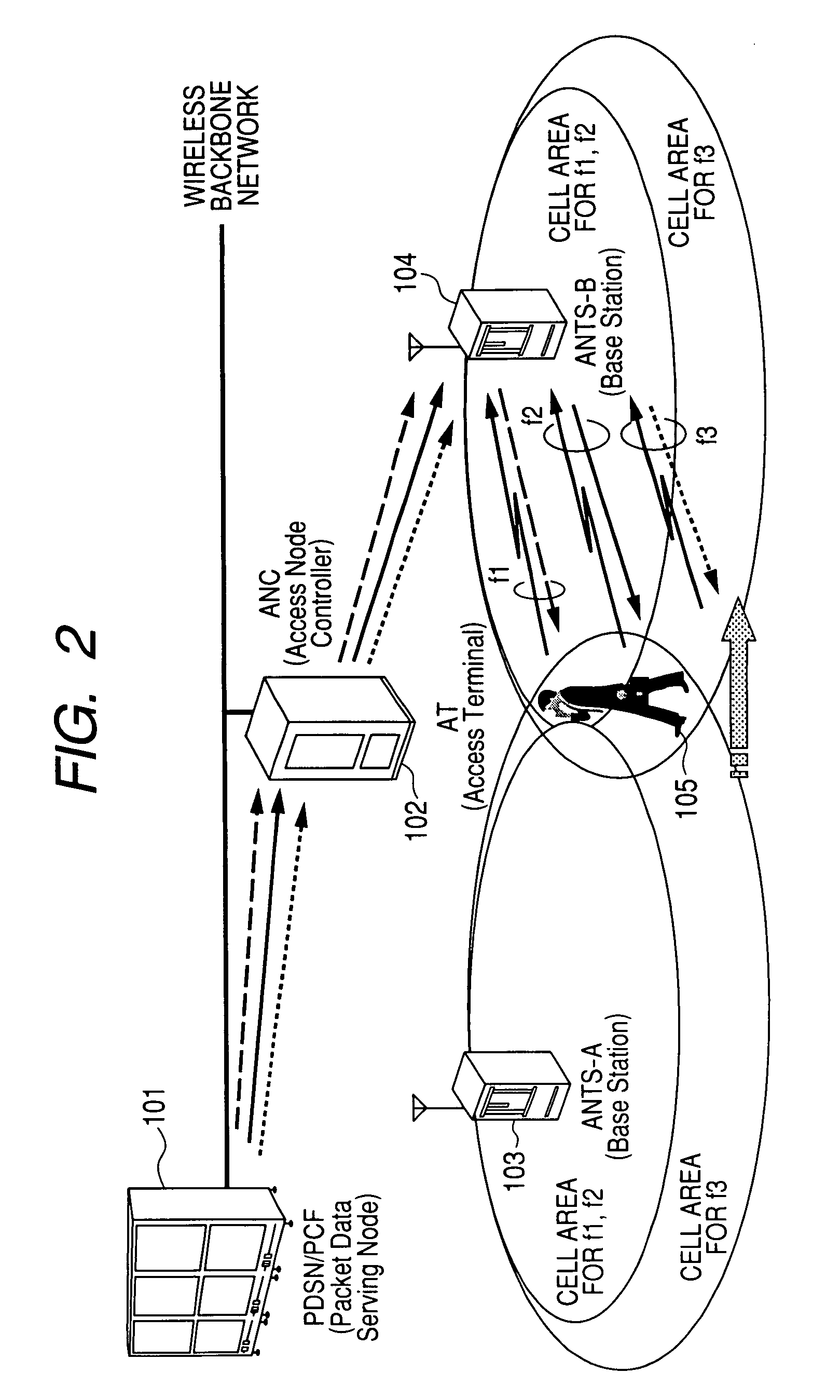
Communication system using multiple wireless resources during a soft handoff
InactiveUS7894817B2Network resourceShorten operation timeError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemViewpoints
In a wireless communications system operating according to CDMA or the like, when one terminal simultaneously performs communication using multiple wireless resources (e.g., multiple carriers), there was a problem that when it was attempted to guarantee network mobility by the same soft handoff system as in the case where communication was performed using only one wireless resource, efficiency suffered from the viewpoint of network forwarding load, processing load and wireless resource occupancy time. Soft handoff termination is judged and soft handoff is forcibly terminated according to whether or not the data rate obtained for all resources on the network side satisfies a requested rate, based on a reception state notification from a terminal concerning wireless resources. By performing this processing, the soft handoff period is shortened, sufficient received strength in the terminal is maintained and terminal mobility is guaranteed, while at the same time network forwarding load, terminal processing load and wireless resource occupancy time are suppressed to the absolute minimum.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
AC filter bank reactive power control method in high-voltage DC transmission system
InactiveCN106532732AControl switchingReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationPower exchangeAbsolute minimum
The invention discloses an AC filter bank reactive power control method in a high-voltage DC transmission system, which realizes the absolute minimum filter capacity limit, the highest / lowest voltage limit, the maximum reactive power exchange limit, the minimum filter capacity limit, and reactive power exchange control and voltage control. Switching of the filters can be controlled effectively in real time, and in each operation condition of the high-voltage DC transmission system, the reactive power exchanged between a converter station and the AC system can be kept in a given range, or the voltage of the AC bus in the converter station can be kept in a required range.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Buffer cache management to prevent deadlocks
InactiveUS7882285B2Avoid problemsProgress can be ensuredMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemAbsolute minimum
A method, computer program product, and data processing system for managing a input / output buffer cache for prevention of deadlocks are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, automatic buffer cache resizing is performed whenever the number of free buffers in the buffer cache diminishes to below a pre-defined threshold. This resizing adds a pre-defined number of additional buffers to the buffer cache, up to a pre-defined absolute maximum buffer cache size. To prevent deadlocks, an absolute minimum number of free buffers are reserved to ensure that sufficient free buffers for performing a buffer cache resize are always available. In the event that the buffer cache becomes congested and cannot be resized further, threads whose buffer demands cannot be immediately satisfied are blocked until sufficient free buffers become available.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for automatic calibration of a camshaft sensor for a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20180259365A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce variationAutomatic recalibrationConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyAbsolute minimumEngineering
A method for automatic calibration of a camshaft sensor for a motor vehicle, allowing reduction of the fluctuations on the output signal of the sensor. The method proposes comparing, on each target rotation, the new maximum values of the magnetic field of each tooth to the maximum values of the same teeth from the preceding target rotation. The switching thresholds are only calculated with the new maximum values if these differ from the maximum values of the preceding target rotation. Moreover, the invention proposes using a single minimum value of the magnetic field, i.e. the absolute minimum value on a target rotation in order to calculate the switching thresholds.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE FRANCE +1
Display and its drive method
InactiveCN1345023APrevent accidental writingReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDigital videoAbsolute minimum
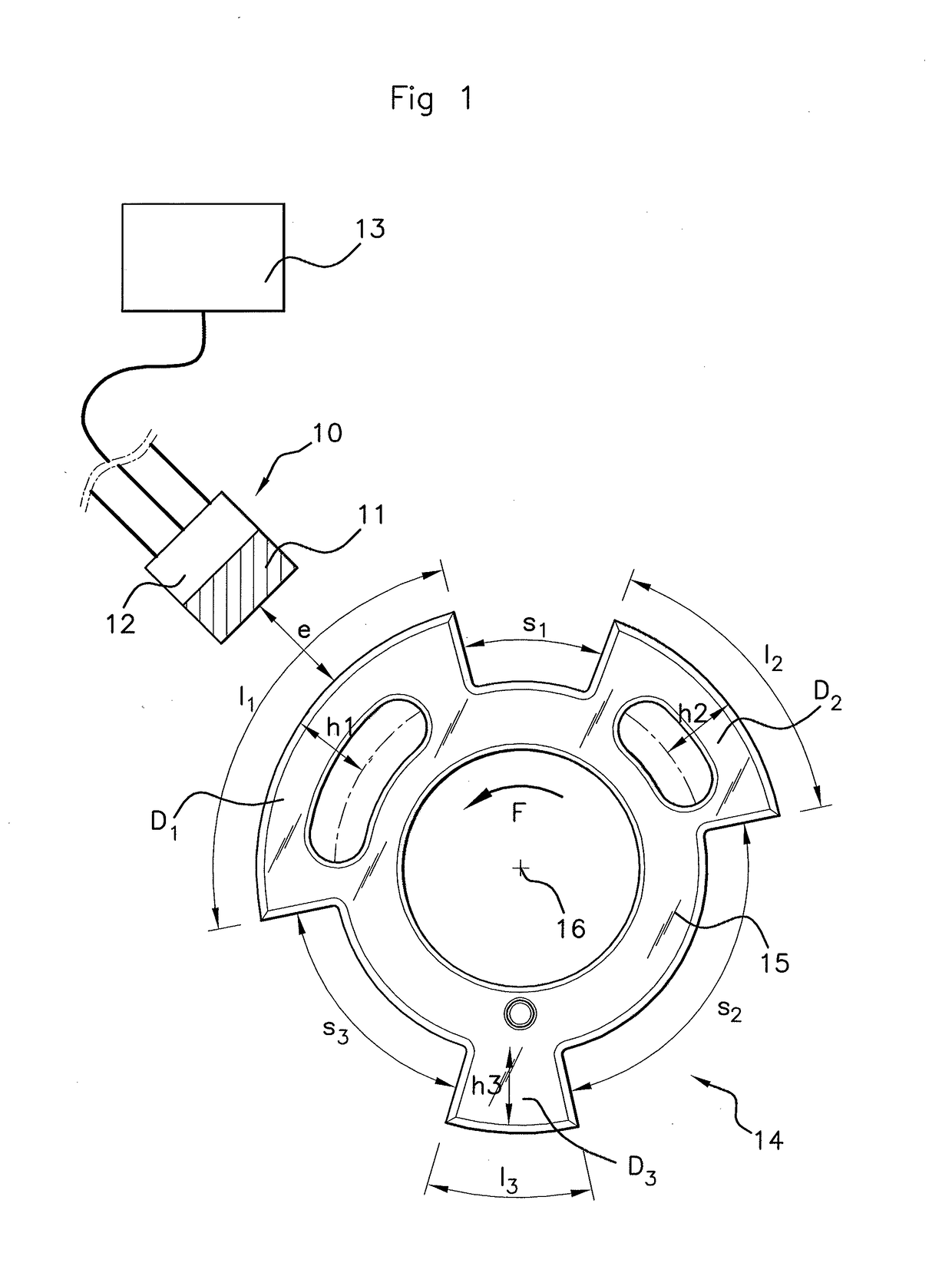
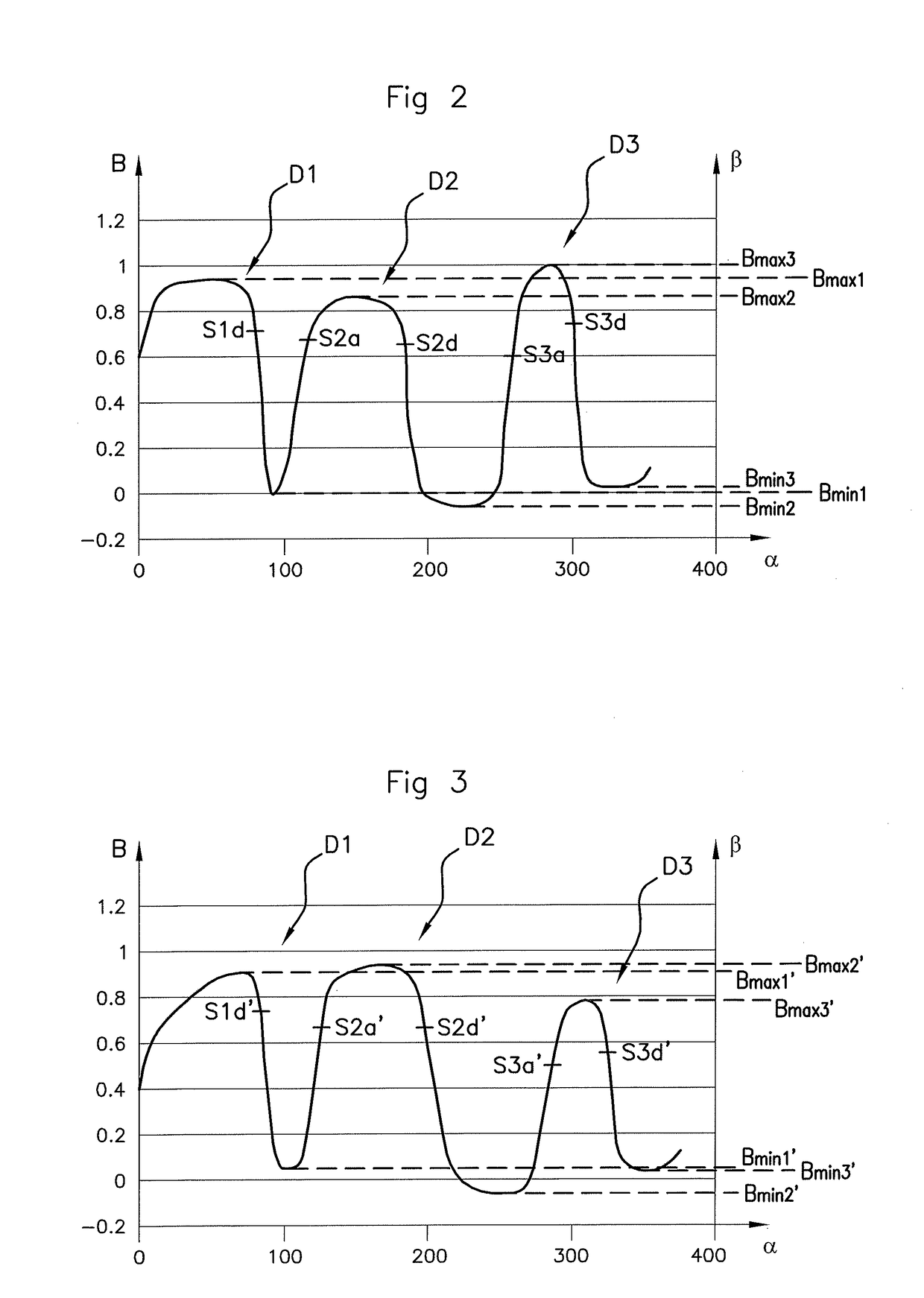
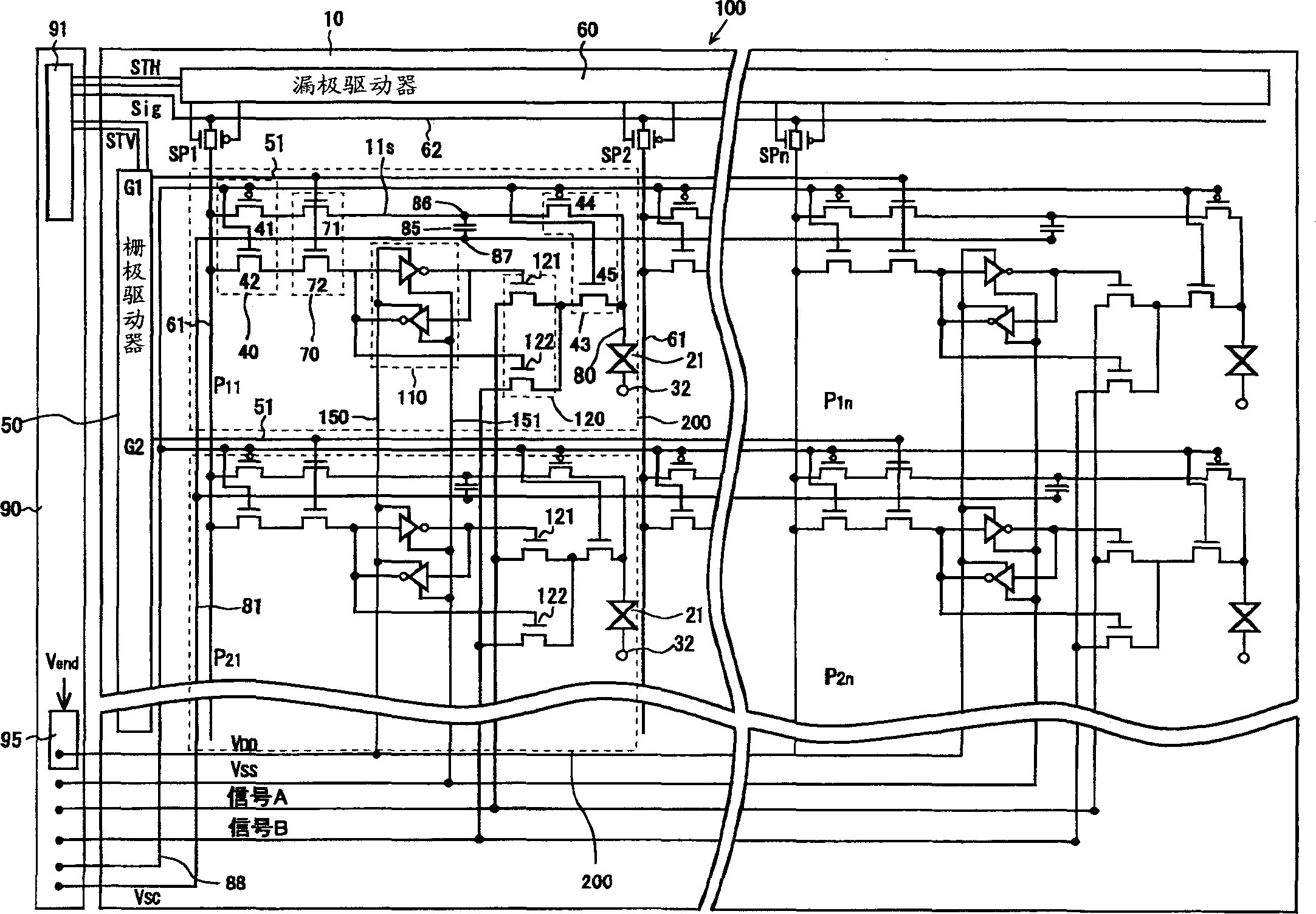
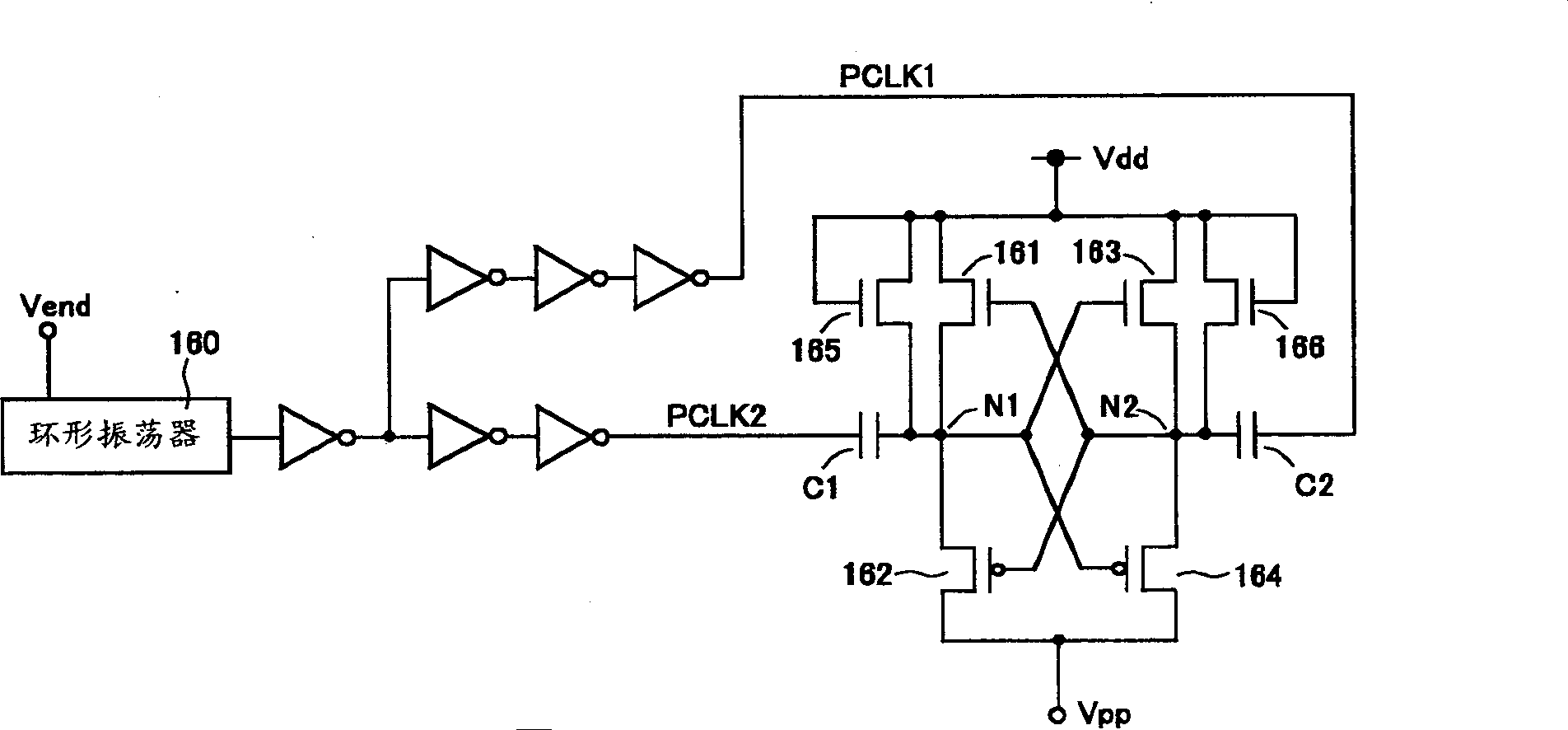
The present invention provides a display device and its driving method to prevent the occurrence of erroneous writing of data into a holding circuit 110, to reduce power consumption and to provide highly integrated display pixels. In a display device which is provided with holding circuits to sustain digital video data for display pixels, the power supply voltage supplied to the holding circuits 110 is set to a minimum level that is an absolute minimum for sustaining the data. The power supply voltage to be supplied to the circuits 110 is boosted by a boosting circuit 95 after completion of the writing. In accordance with the signals inputted from gate signal lines 51, digital video signals from drain signal lines 61 are written into the circuits 110 and the circuits 110 sustain the signals. Displaying is conducted in accordance with the signal sustained in the circuits 110.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Improved lattice-based key exchange protocol algorithm
InactiveCN109617686AQuantum resistantKey distribution for secure communicationKey exchangeAbsolute minimum
The invention relates to a protocol algorithm, specifically a lattice-based key exchange protocol algorithm improved through utilization of random Gaussian noises. The method comprises the steps that1, it is assumed that a constant m is greater than or equal to 2, lambda is equal to O(n), beta is equal to (square root of n)sigma, and q is equal to O(2<lambda>mn[beta]<2>, wherein the sigma is a security parameter in M-DLWE definition, it is assumed that X is equal to {z which is an element of a set R<m>:||z||<=the beta, wherein the i is the element of the set [m]}, wherein the z is the element of the set R, and the||z|| is a norm z of a coefficient vector, hereinafter, an absolute minimum residual system is employed for R<q>, namely, each coefficient a satisfies |a|<q / 2,wherein the a is the element of the set R<q>; S2, an m-order random matrix A is selected, wherein the A is the element of the set R<q><m _ x _ m>, and the A is accepted by a first communication partyand a second communication party, wherein; S3, information is issued, specifically, (1), the first communication party selects x,e<1><- D<R<m,sigma>>, computes a=(Ax+e<1>)mod q, and sends the a to thesecond communication party, and (2), the second communication party selects y,e<2><- D<R<m,sigma>>, computes b<T>=(y<T>A+e<2><T>)mod q and sends the b to the first communication party; and S4, sharedkeys are generated, specifically, (1), the first communication party generates the shared key k<1>=MSB(b<T>x mod q); and (2), the second communication party generates the shared key k2=MSB(y<T>a modq).
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Reduced compressor capacity controls
ActiveUS20070151264A1Compression machines with non-reversible cycleAuxillary controllers with auxillary heating devicesAbsolute minimumOperating frequency
A method of controlling the frequency of a compressor in a chiller system is disclosed. The method includes determining a nominal minimum frequency of a compressor, and providing a control algorithm for controlling the period of time and the deviation of the actual operating frequency below the nominal minimal frequency that the compressor may operate without shutting down the chiller system. The time period of operation below nominal minimum frequency may be predetermined as a fixed time period of operation below nominal minimum frequency, or as a variable time period based on the amount by which the frequency deviates below nominal minimum frequency. Also, an absolute minimum operating frequency is provided that results in the control algorithm shutting down the chiller system and the compressor.
Owner:JOHNSON CONTROLS TECH CO +1
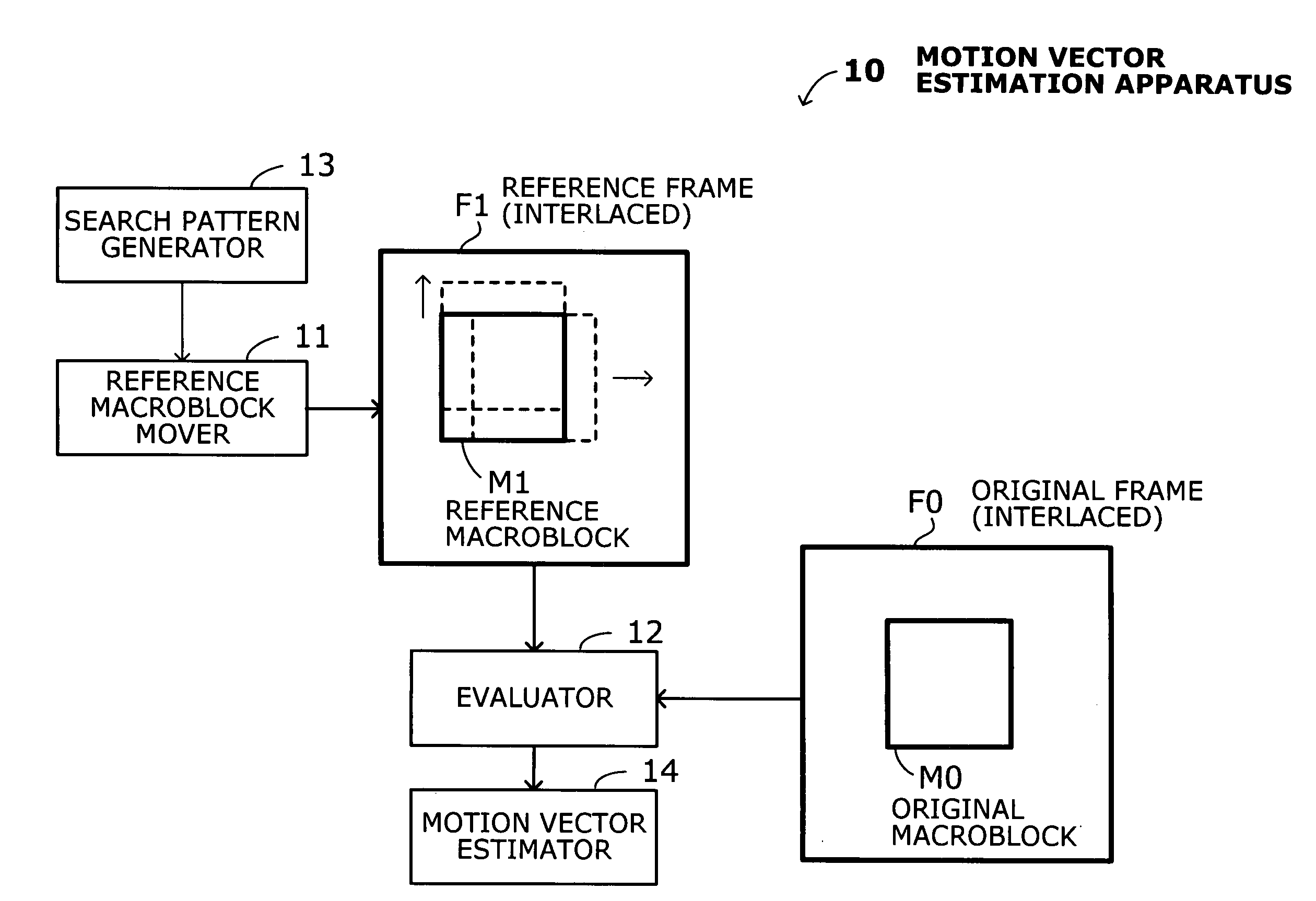
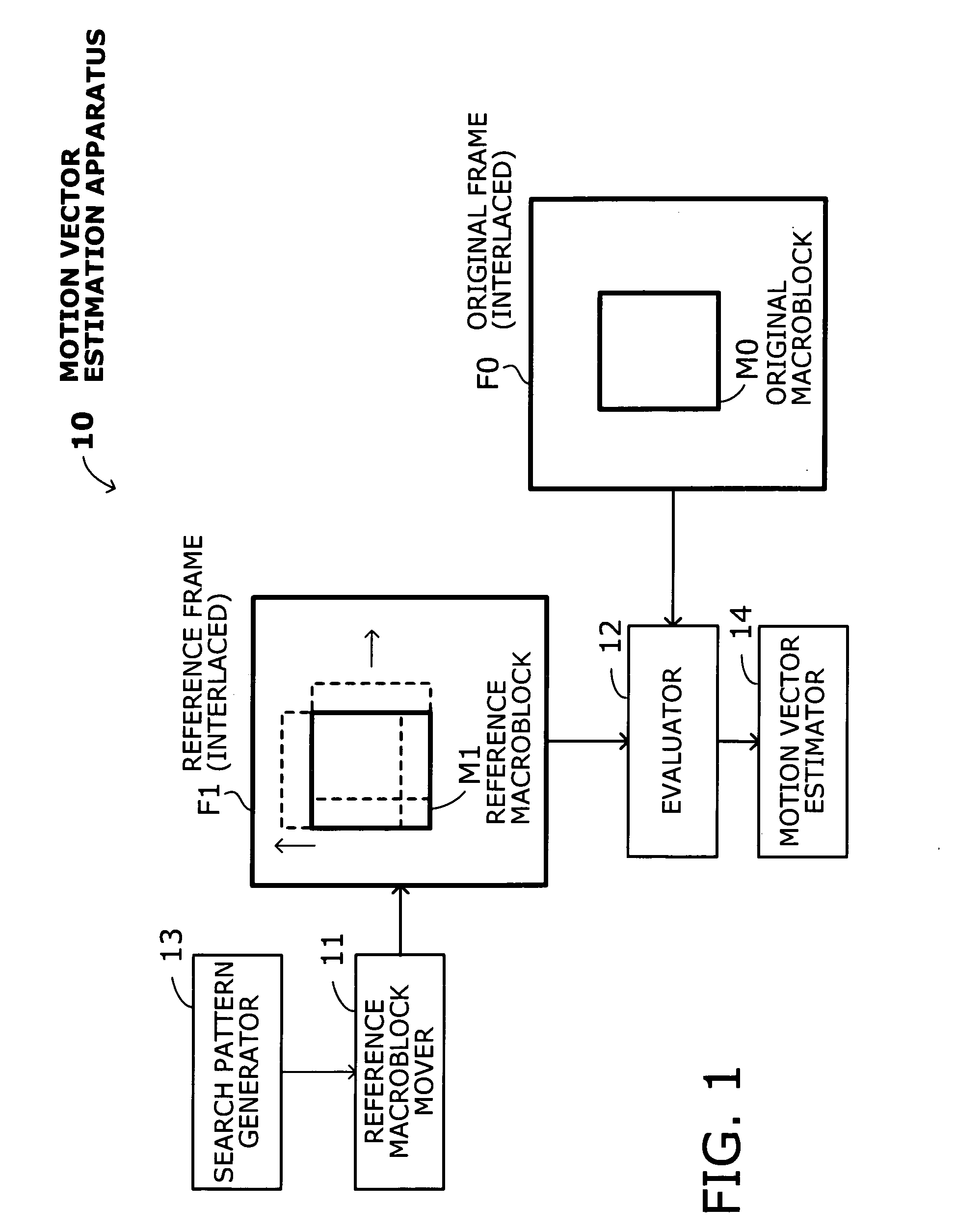
Apparatus for estimating motion vectors with extended search movement of reference macroblock
InactiveUS20070230577A1Increase the amount of calculationAccurate motion vectorColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorAbsolute minimum
A motion vector estimation apparatus that can produce motion vectors accurately with an adequately expanded search domain, without increasing computational load too much. A reference macroblock mover moves a reference macroblock in a given reference frame according to a current search pattern, starting from a point identified as a minimum point in a preceding evaluation step. An evaluation processor calculates evaluation values corresponding to specified search movements, thus extracting a minimum evaluation value among as many evaluation values as the number of search movements performed. The evaluation processor finally finds an absolute minimum point from the extracted minimum evaluation values. A search pattern generator provides search patterns specifying extended search movements in a vertical direction so as to move a reference macroblock across different field lines. A motion vector estimator calculates a motion vector representing a distance and direction of the original macroblock relative to the reference macroblock at the absolute minimum point.
Owner:FUJITSU KYUSHU NETWORK TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com