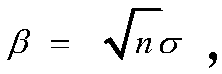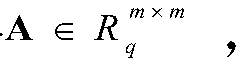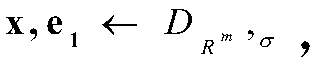Improved lattice-based key exchange protocol algorithm
A key exchange protocol and algorithm technology, applied in key distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] In this invention, we not only point out the reasons why this Bi-ISIS-based key exchange protocol is insecure. In order to avoid the shared key attack, we propose an improved KE algorithm based on Bi-ISIS, whose security can be reduced to (M-LWE: Learning With Error problem over Modules) learning with errors.
[0021] Through the cryptographic analysis of the existing Bi-ISIS-based key exchange protocol and its simple variant protocol, it can be found that the attacker mainly uses the fact that the key vector and the noise vector are orthogonal. Therefore, to avoid such attacks, we need to apply new noise methods. That is, the secret vector and the noise vector are no longer orthogonal.
[0022] The present invention improves the existing KE scheme by introducing the general paradigm (Generation) BI-GISIS of Bi-ISIS. This improved security relies on the difficult assumption of DBi-GISIS, which is equivalent to cracking the Modulus Difficult Learning with Errors (M-DLW...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com