Network-wide inter-cell interference minimization via coordinated multipoint cell scheduling coordination
A technology for inter-cell interference minimization, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, allocation between users/terminals, signaling allocation, etc., can solve problems such as infeasibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
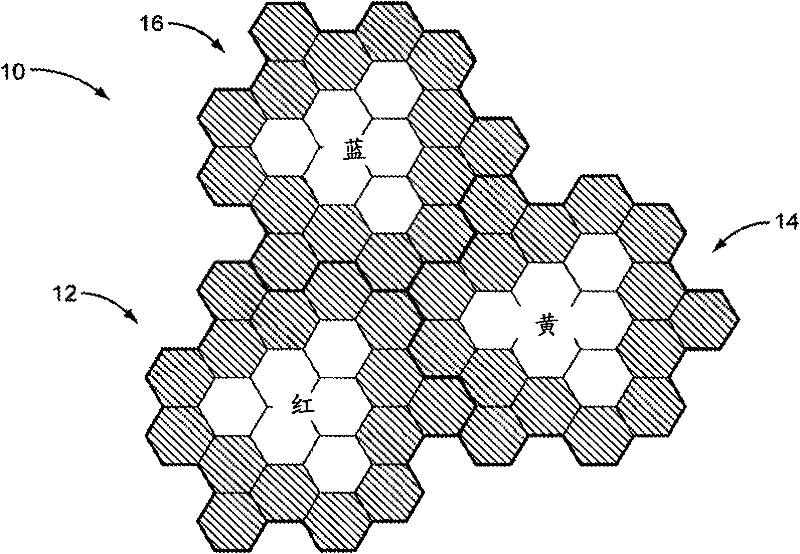
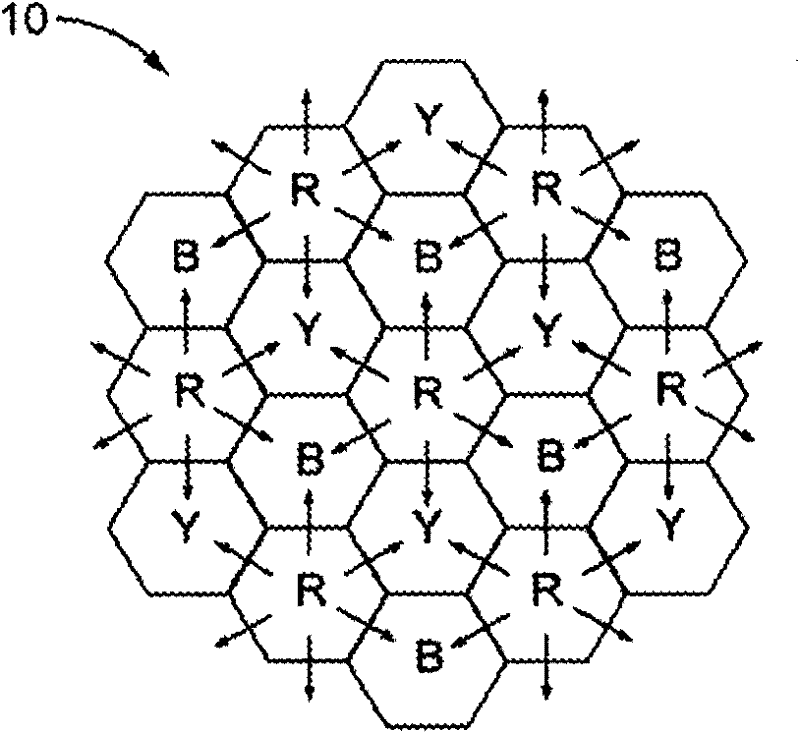
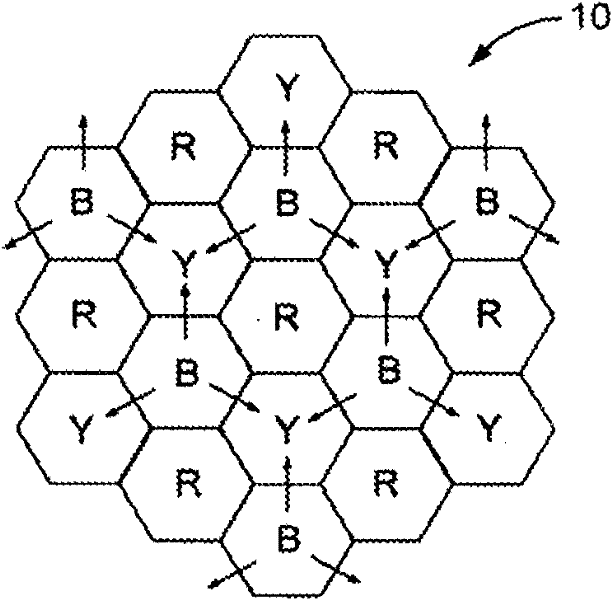
[0015] FIG. 2 shows two larger views of the network 10 . The network 10 is divided into a plurality of CoMP cells, each cell comprising a plurality of sub-cells (not shown). CoMP cells are grouped into sets, shown by the colors red (R), blue (B) and yellow (Y) CoMP cells. CoMP cell set groups are geographically dispersed, similar to traditional cellular network frequency reuse patterns, to geographically separate all CoMP cells per set or color. Due to this separation, transmissions to UEs in each set or color of CoMP cells can be scheduled independently since they do not cause interference to each other.
[0016] Starting from a set of red CoMP cells such as those in Figure 2, under the assumption that border subcells in adjacent blue and yellow CoMP cells do not cause interference, transmissions to UEs in red CoMP cells are scheduled to minimize the inter-subcell interference. Subsequently, if figure 1 As indicated by the outward arrows in , the red CoMP cell controller ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com