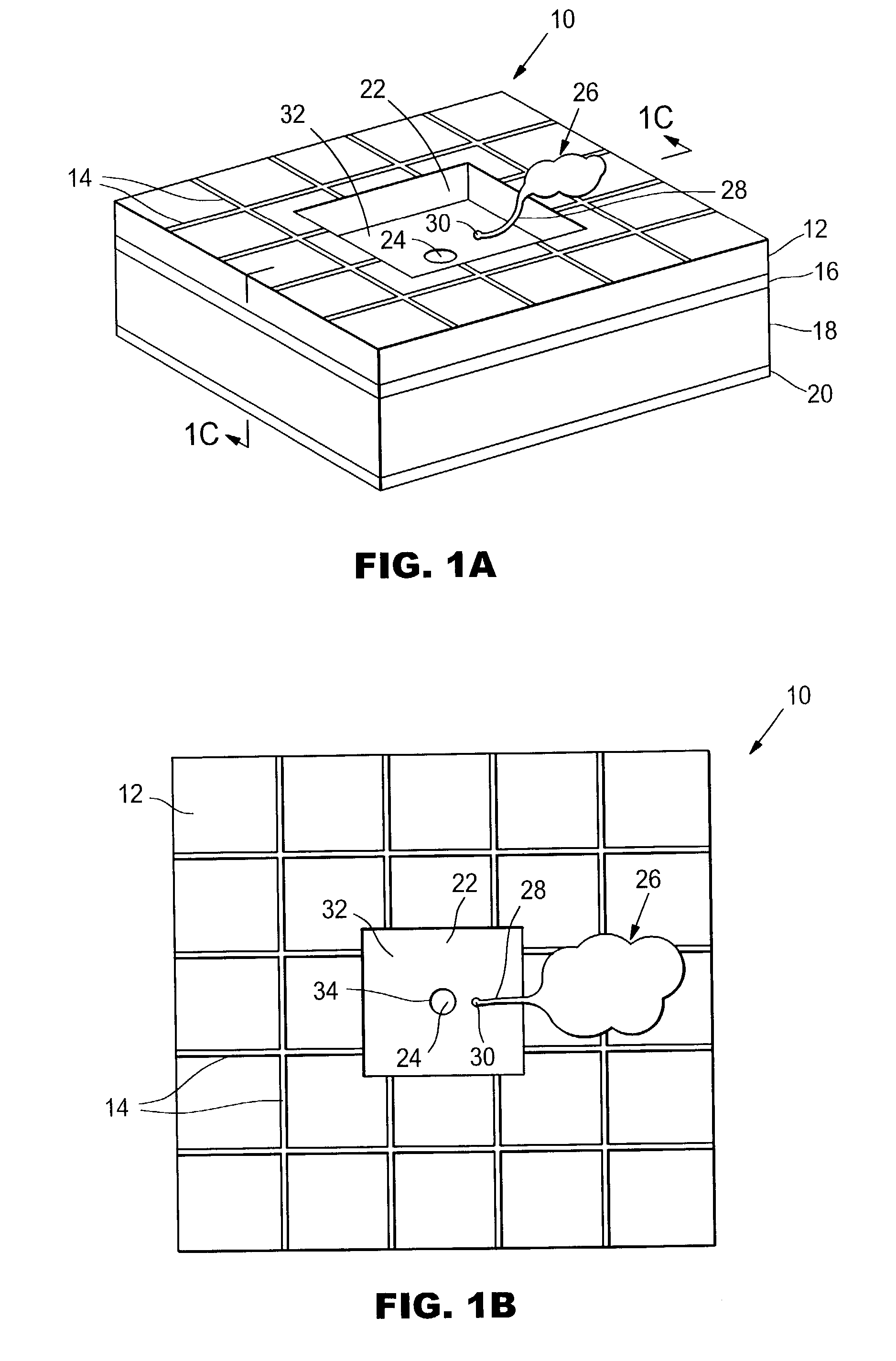
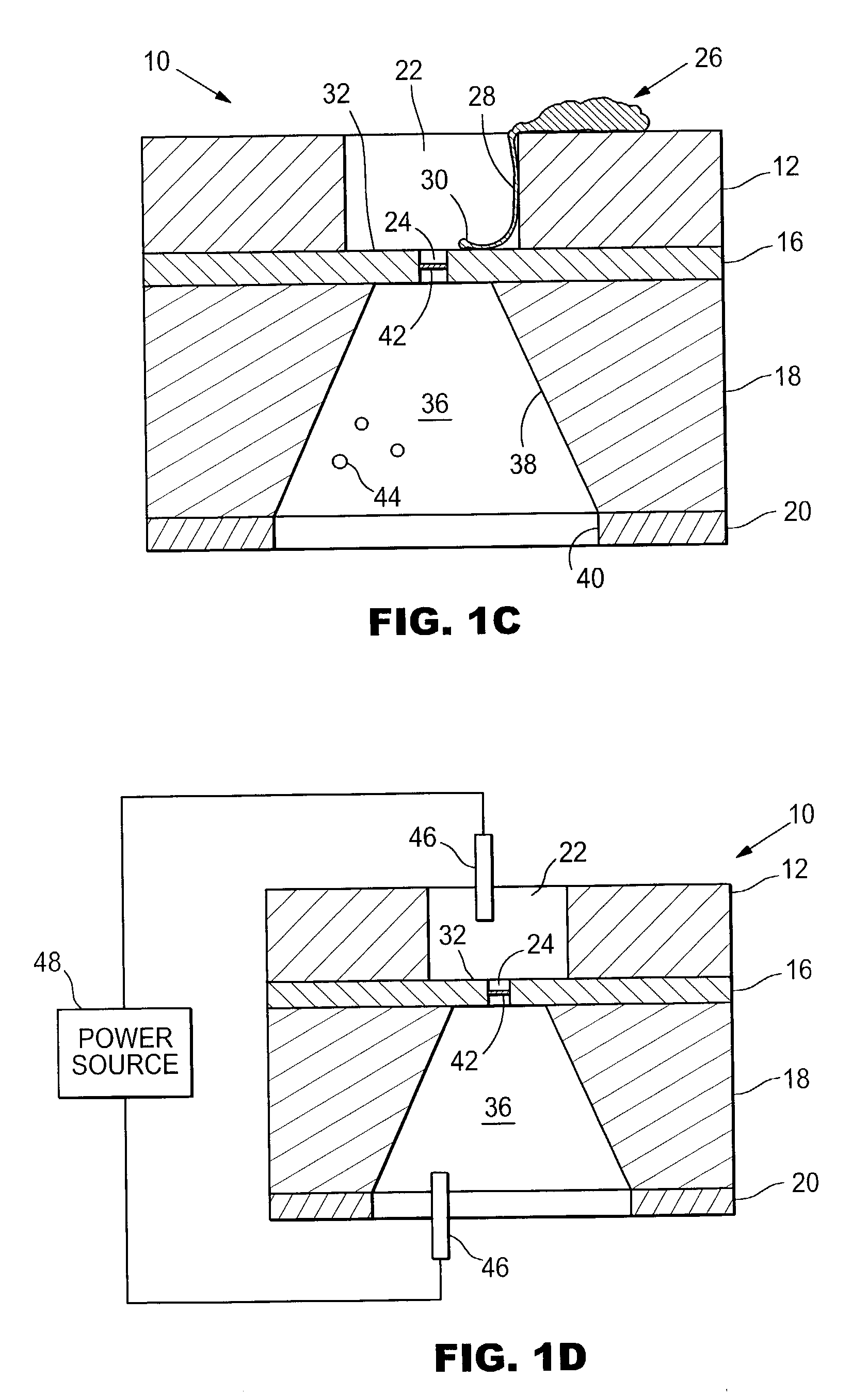
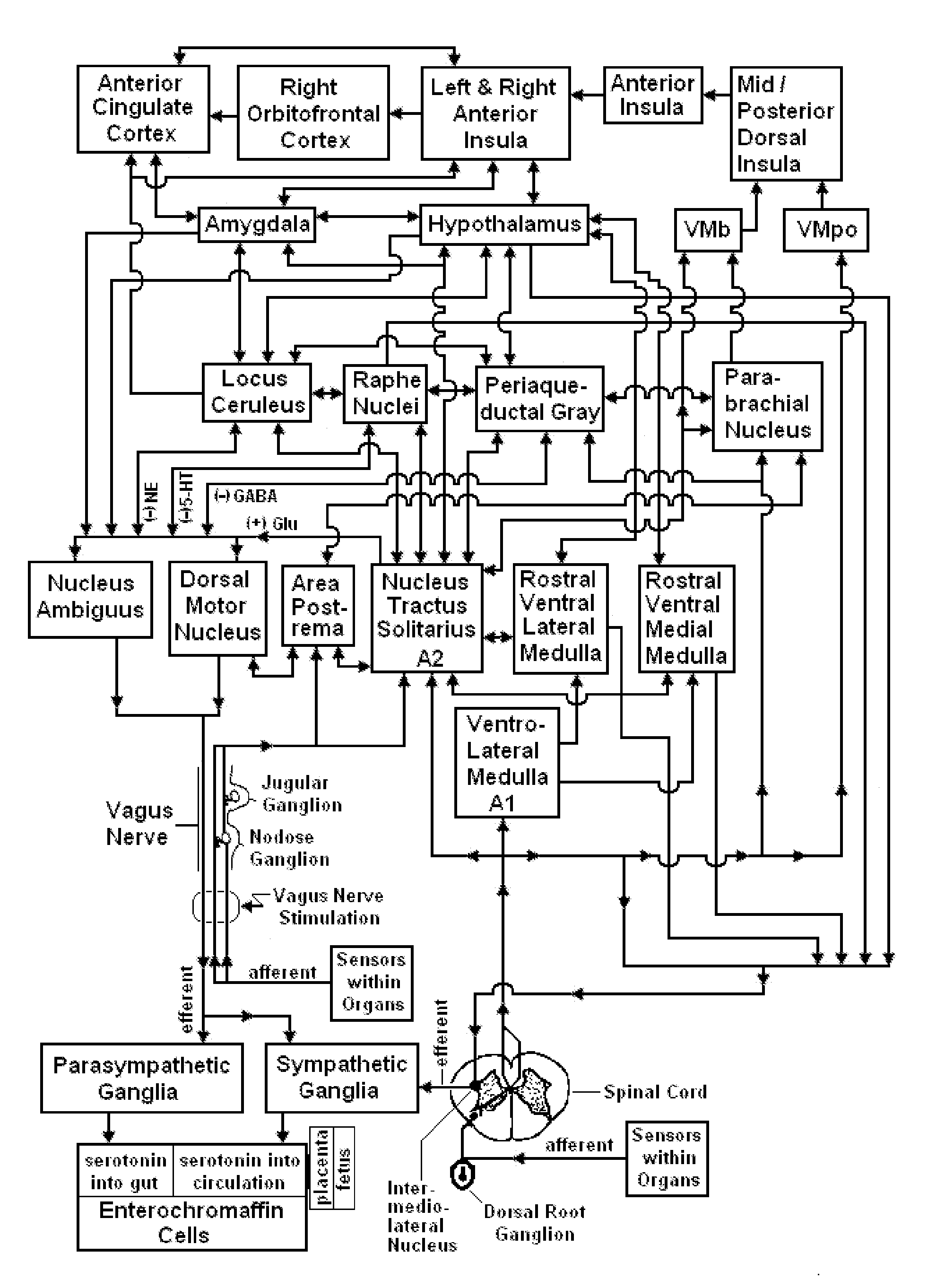
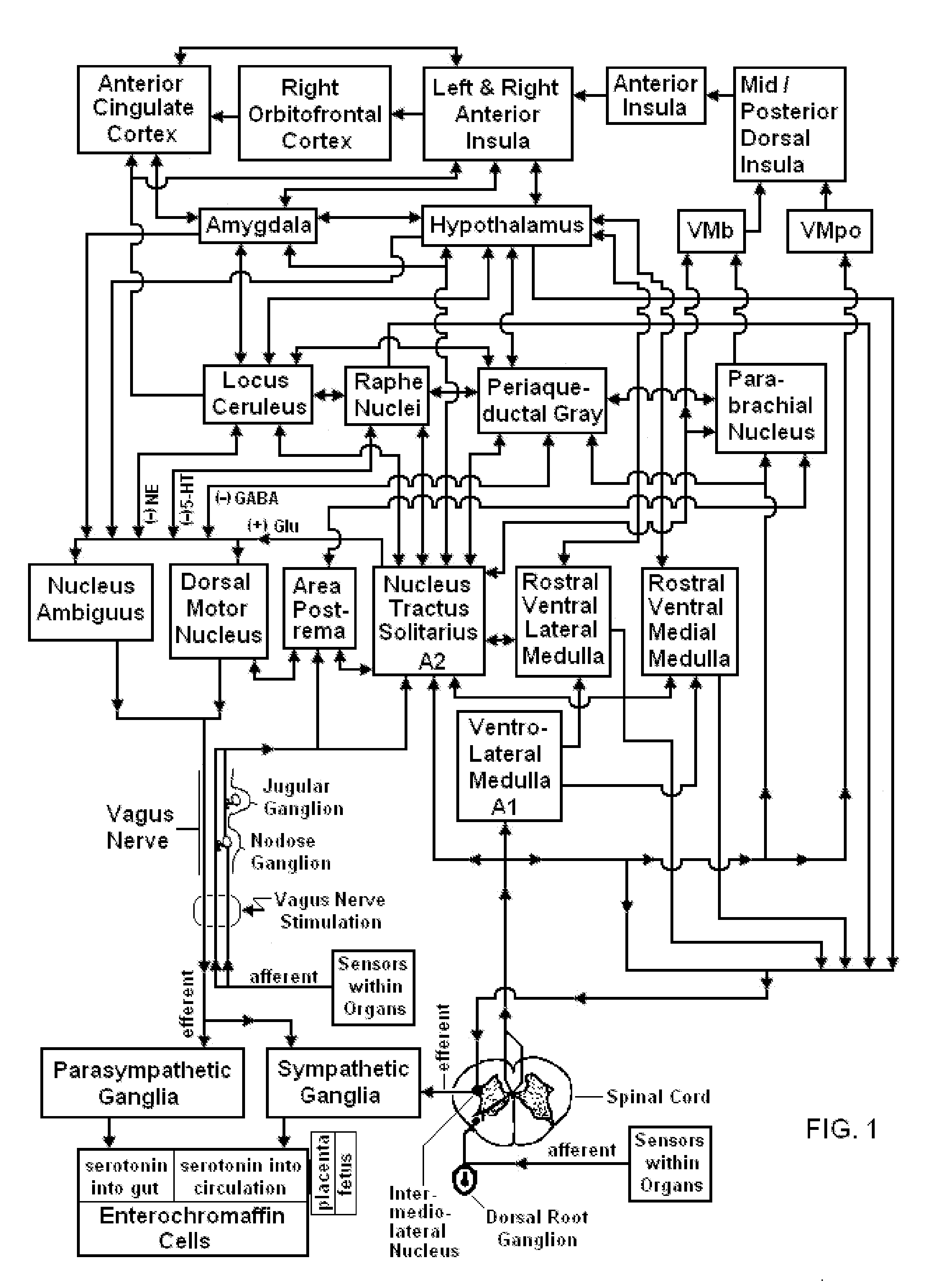
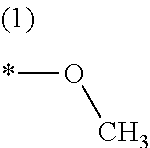
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Neuronal excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
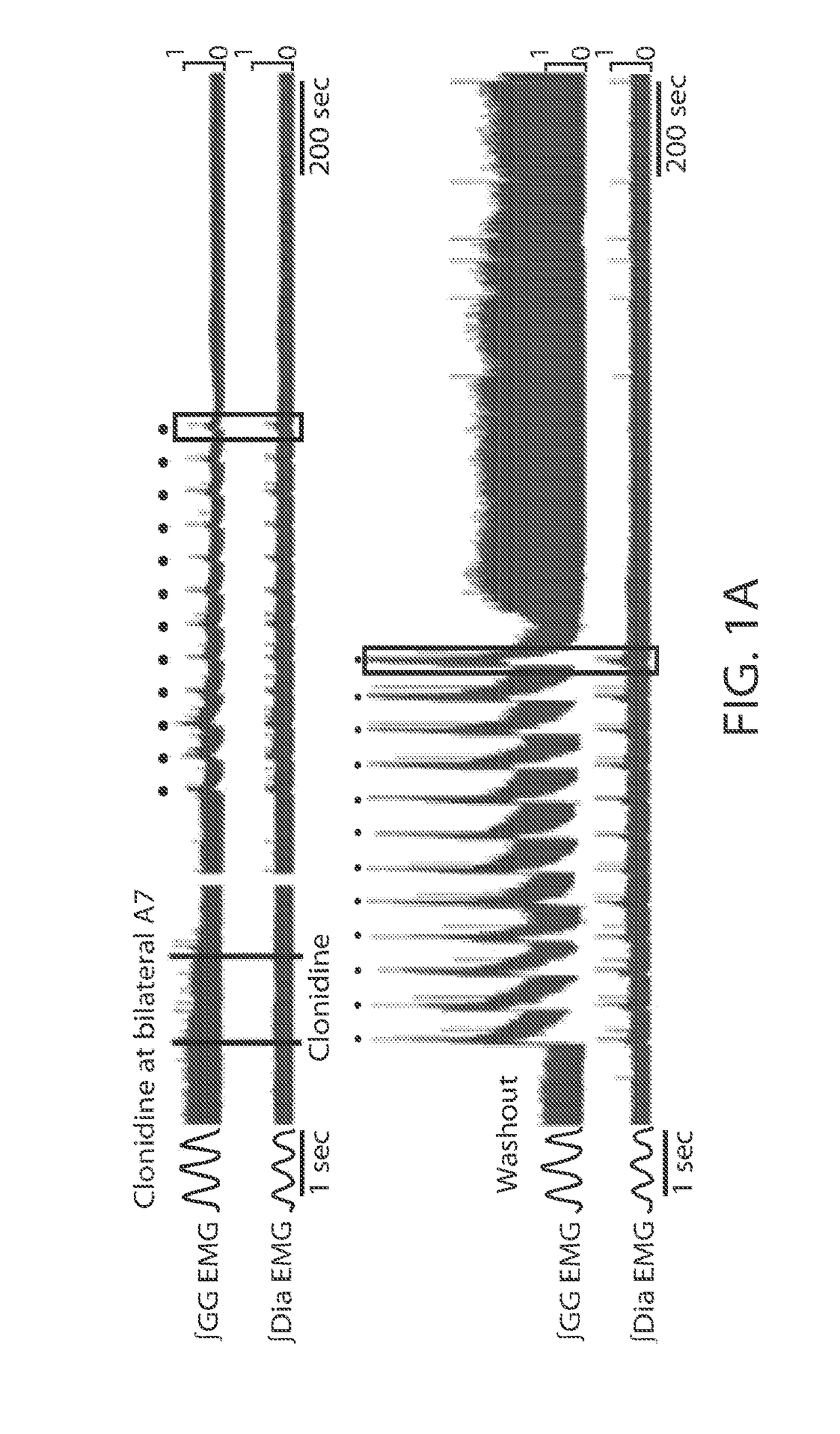
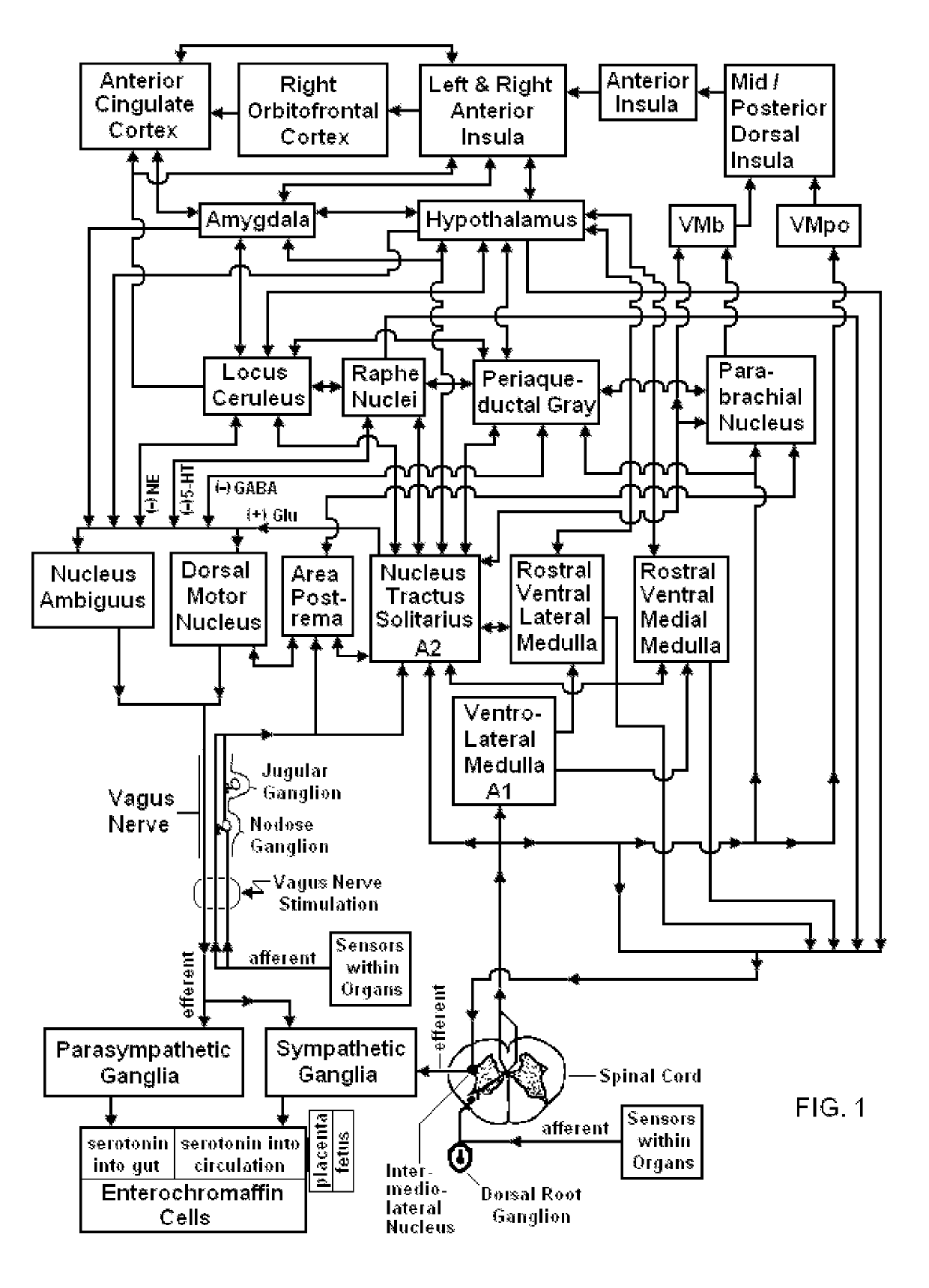
Neural oscillation. A series of rhythmic waves of neuronal excitation in the CNS, sustained either by reverberation of electrical activity in neuronal loops or dependent on increases in membrane excitability. Segen's Medical Dictionary.
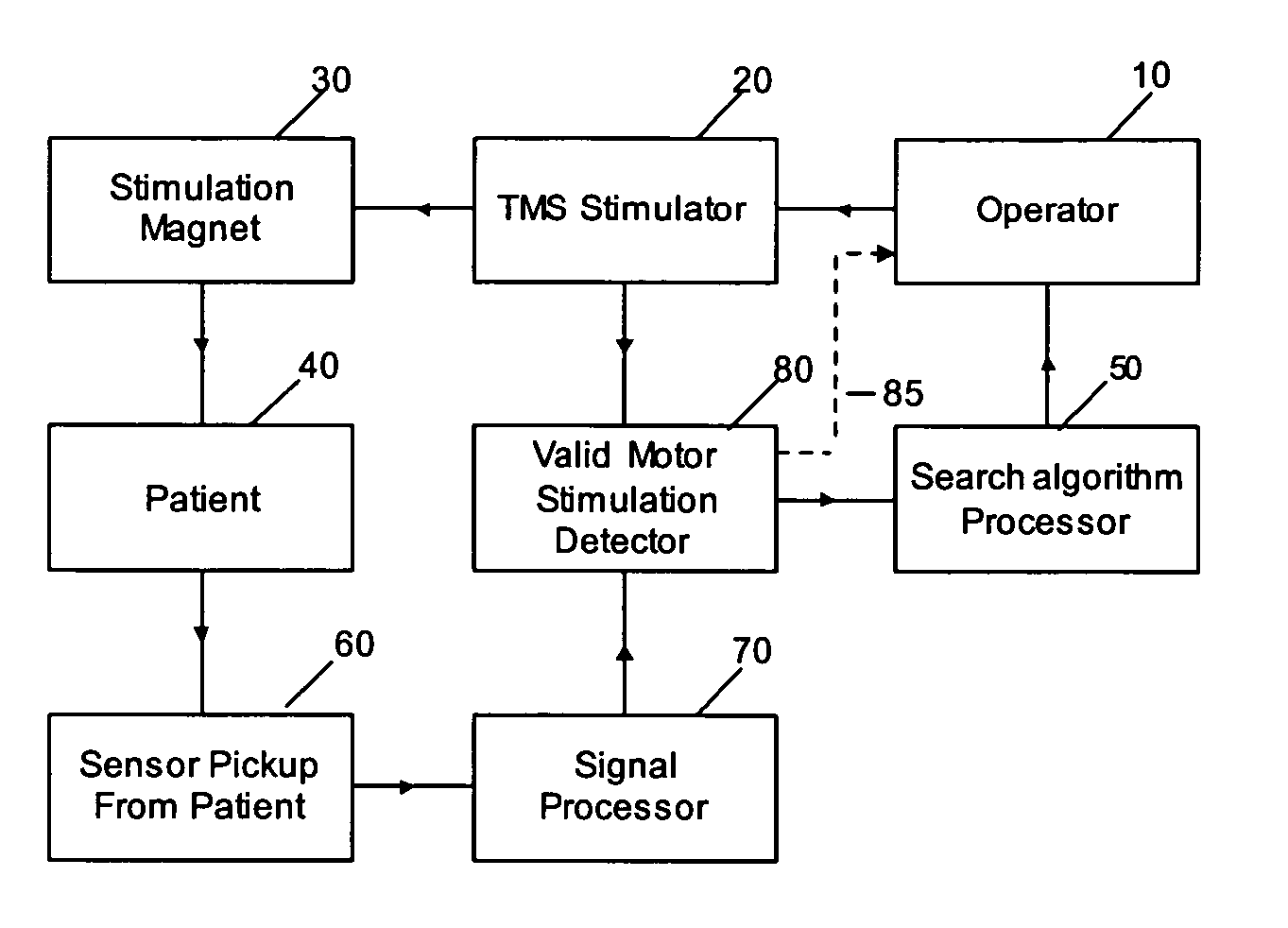
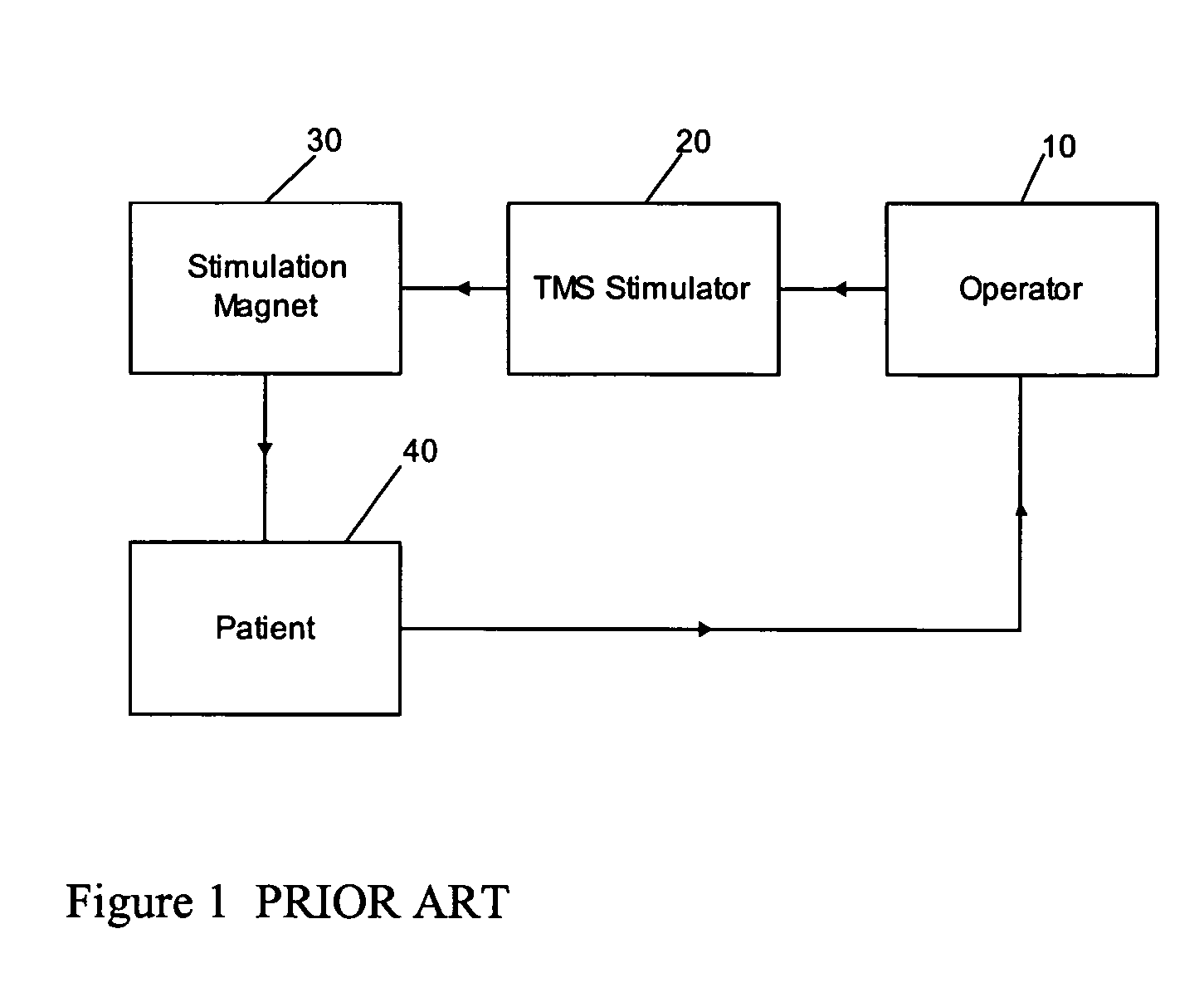
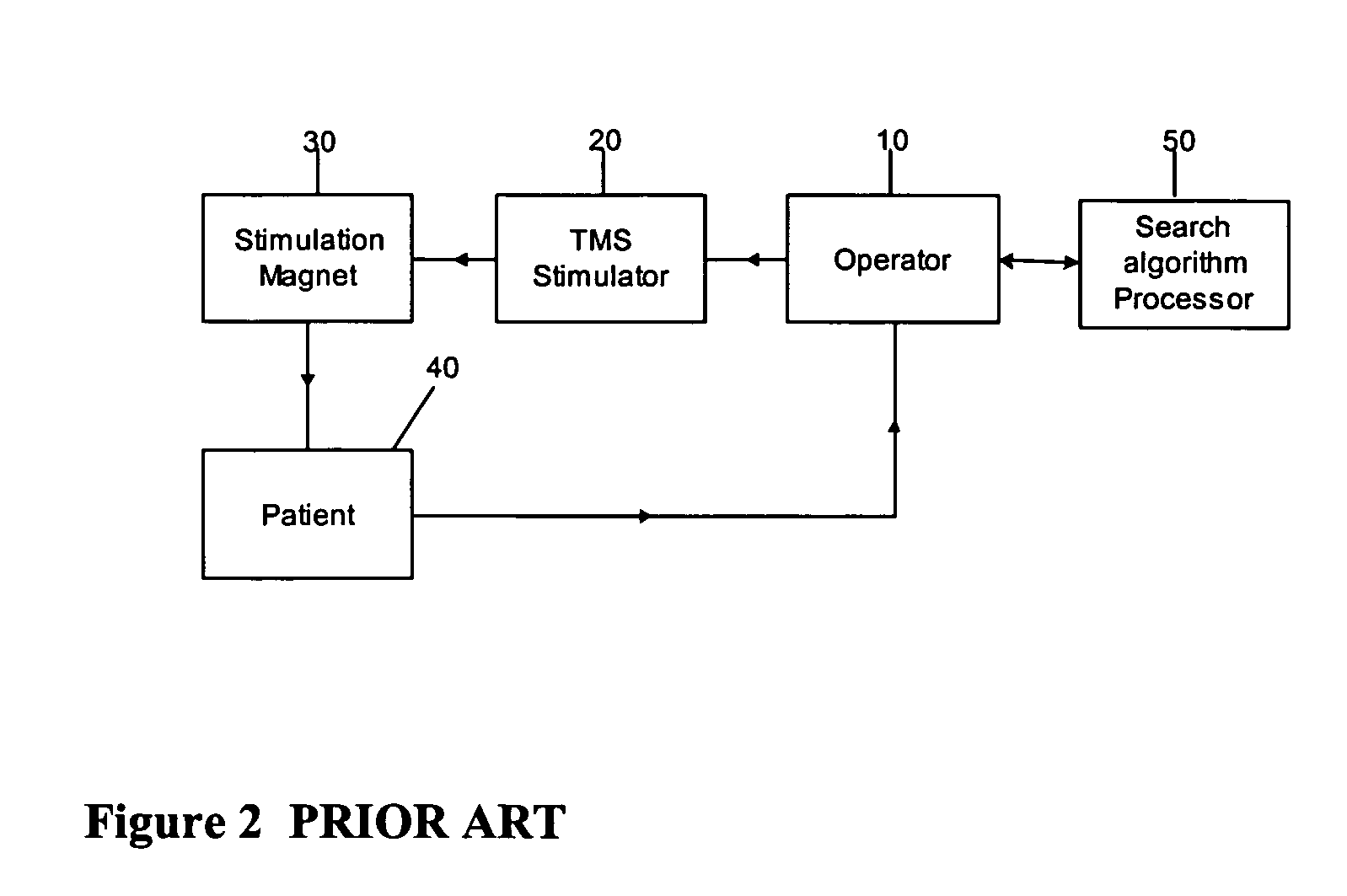
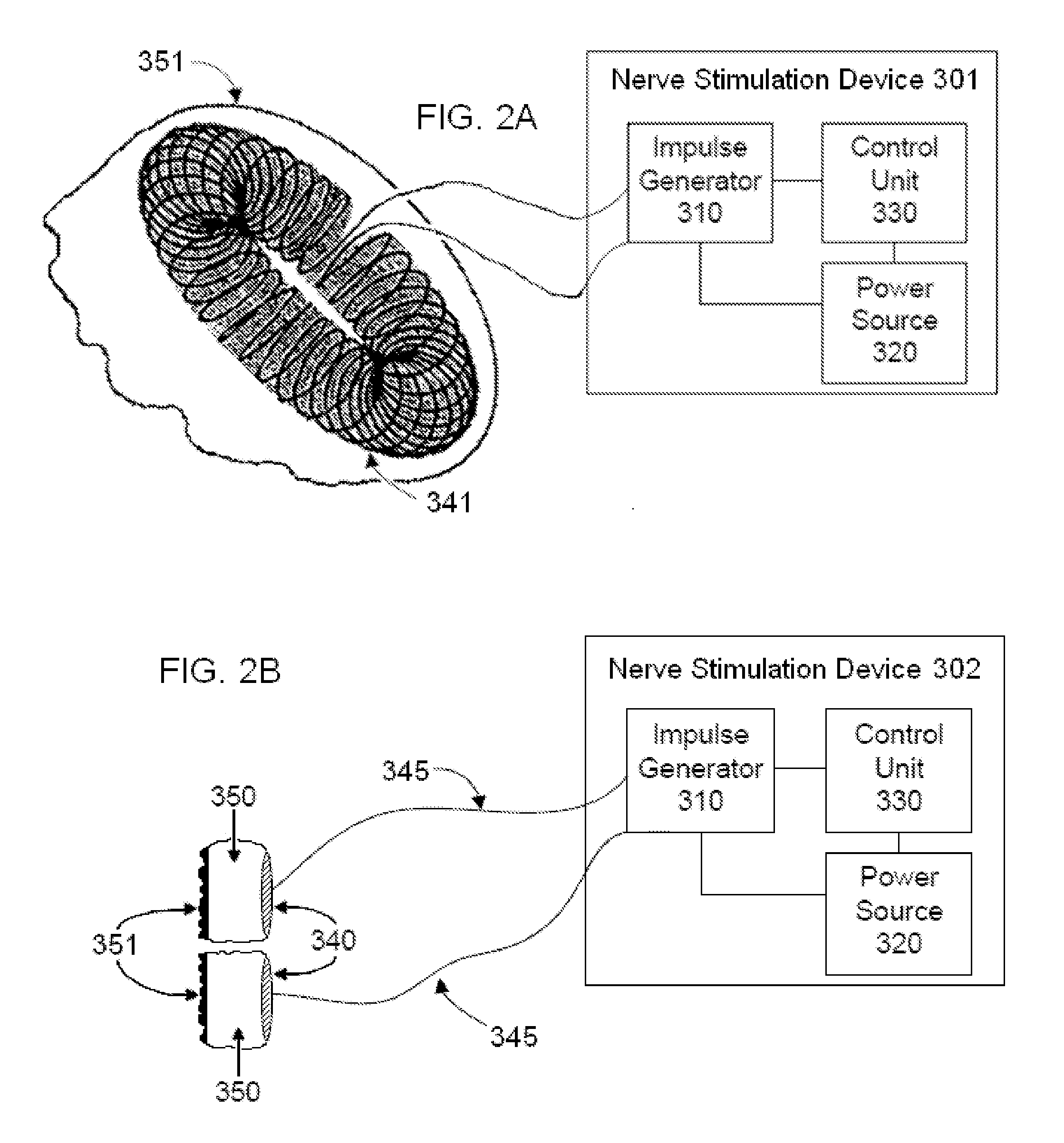
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
Topical management of ocular and periocular conditions
Chronic glaucoma, cataract, ocular and periocular aging are treated and prevented by the administration of agents that affect metabolic subsystems such as (i) mitochondrial bioenergetics, (ii) free radical moderation and glutathione maintenance, (iii) constitutive nitric oxide / endothelin-1 balance, and (iv) calcium wave signaling and associated neuronal excito-toxicity. Included among the agents are tetrahydrobiopterin, R-alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10, 17 alpha-estradiol, and glutathione.
Owner:CHRONORX
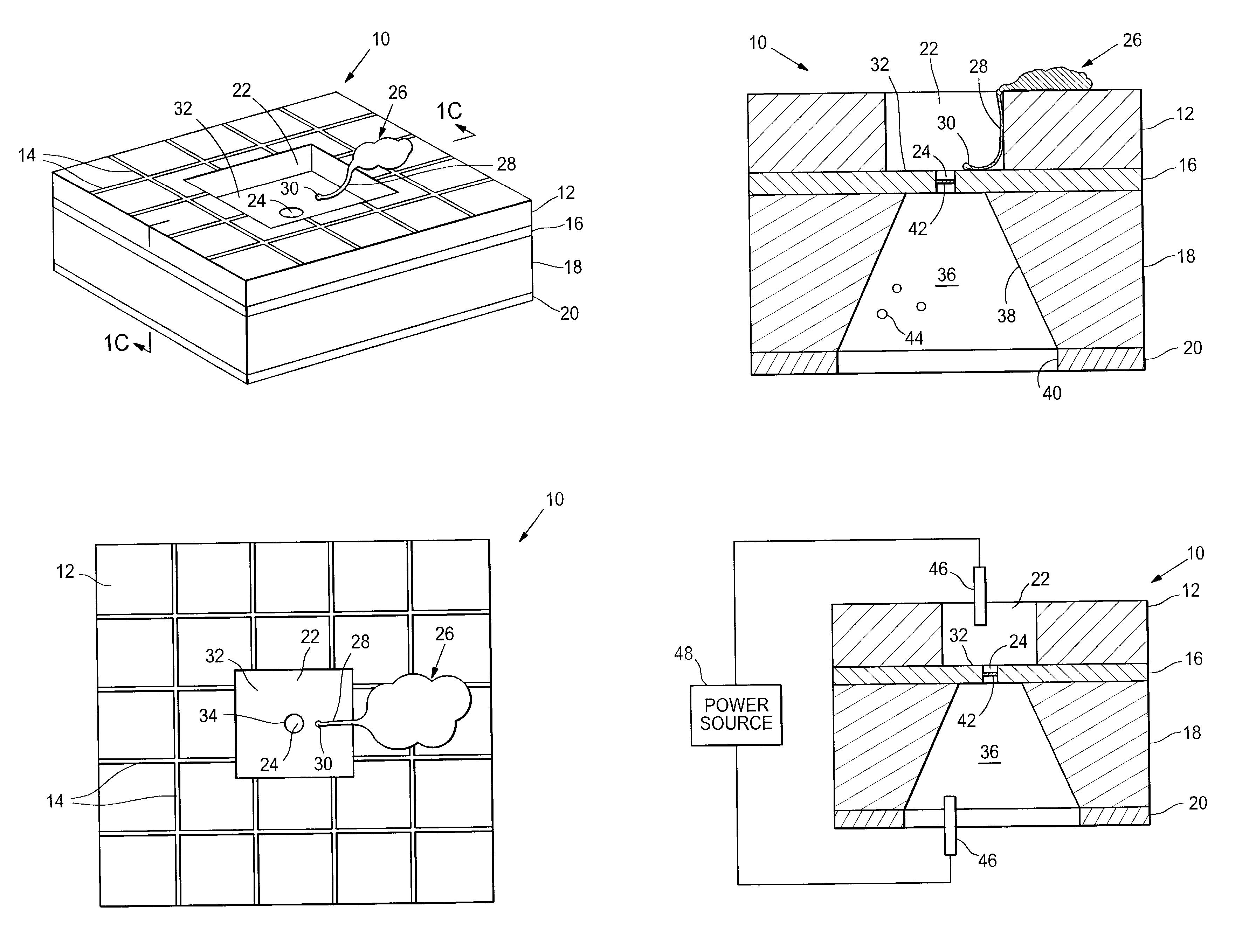
Artificial synapse chip interface for electronic prosthetic retina
InactiveUS7001608B2Efficient deliveryRecovery functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoElectron
The invention provides microfabricated devices and methods for directing the growth of a cell process to form an artificial synapse. The devices are called artificial synapse chips. The artificial synapse comprises a nanofabricated aperture (about 50–100 nm in size) that connects the cell process to a chemical or electrical means of neuronal excitation. Such an aperture width mimics the length scales of a natural synapse and thus emphasizes the localized spatial relationship between a neuron and a stimulation source. The invention further provides devices and methods for regenerating a nerve fiber into an electrode. The invention thus provides a regeneration electrode that uses a novel neural interface for stimulation and that uses novel surface methods for directing neuronal growth making possible in vivo connection of the devices to neural circuitry in a retina and other anatomical locations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
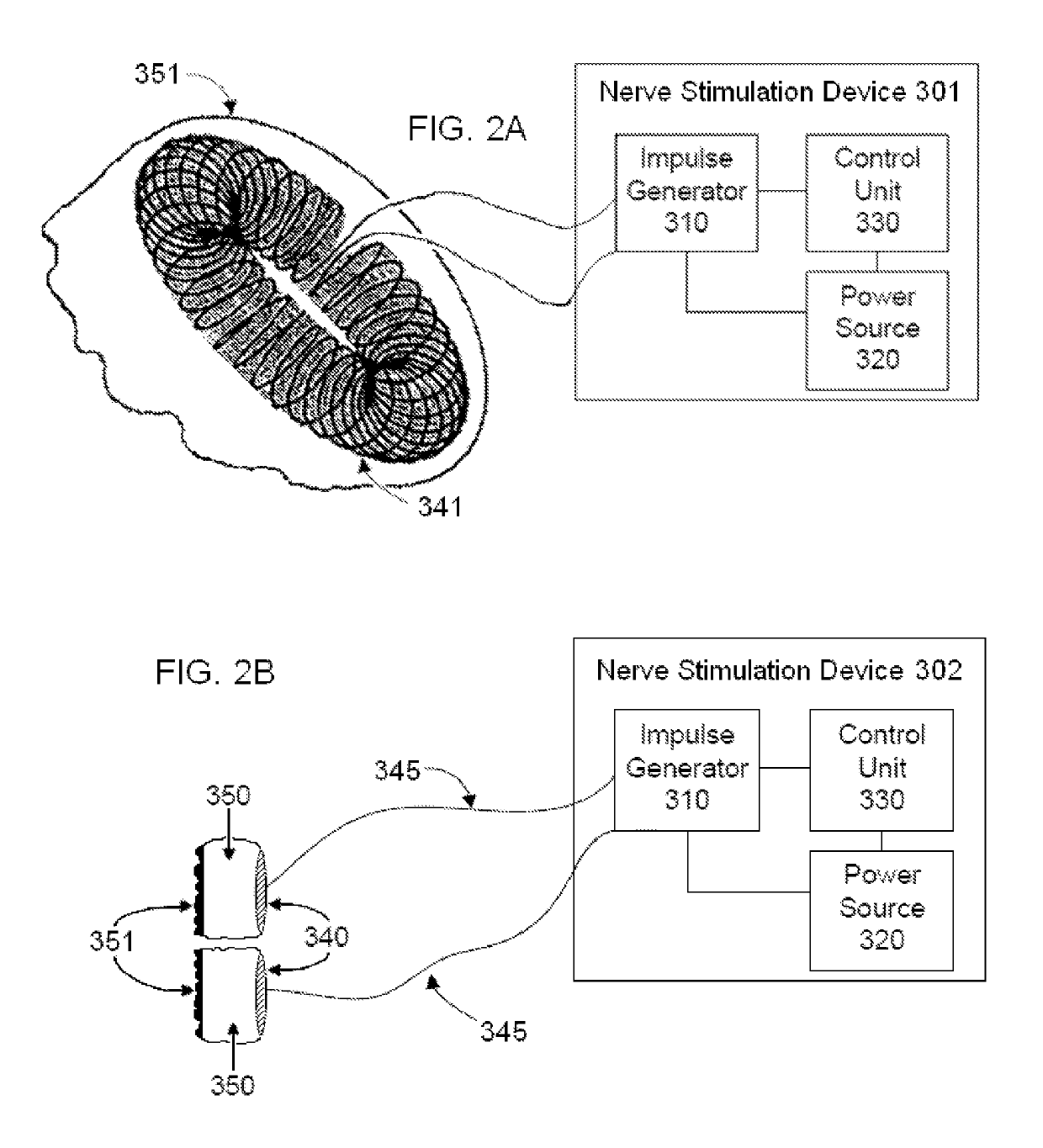
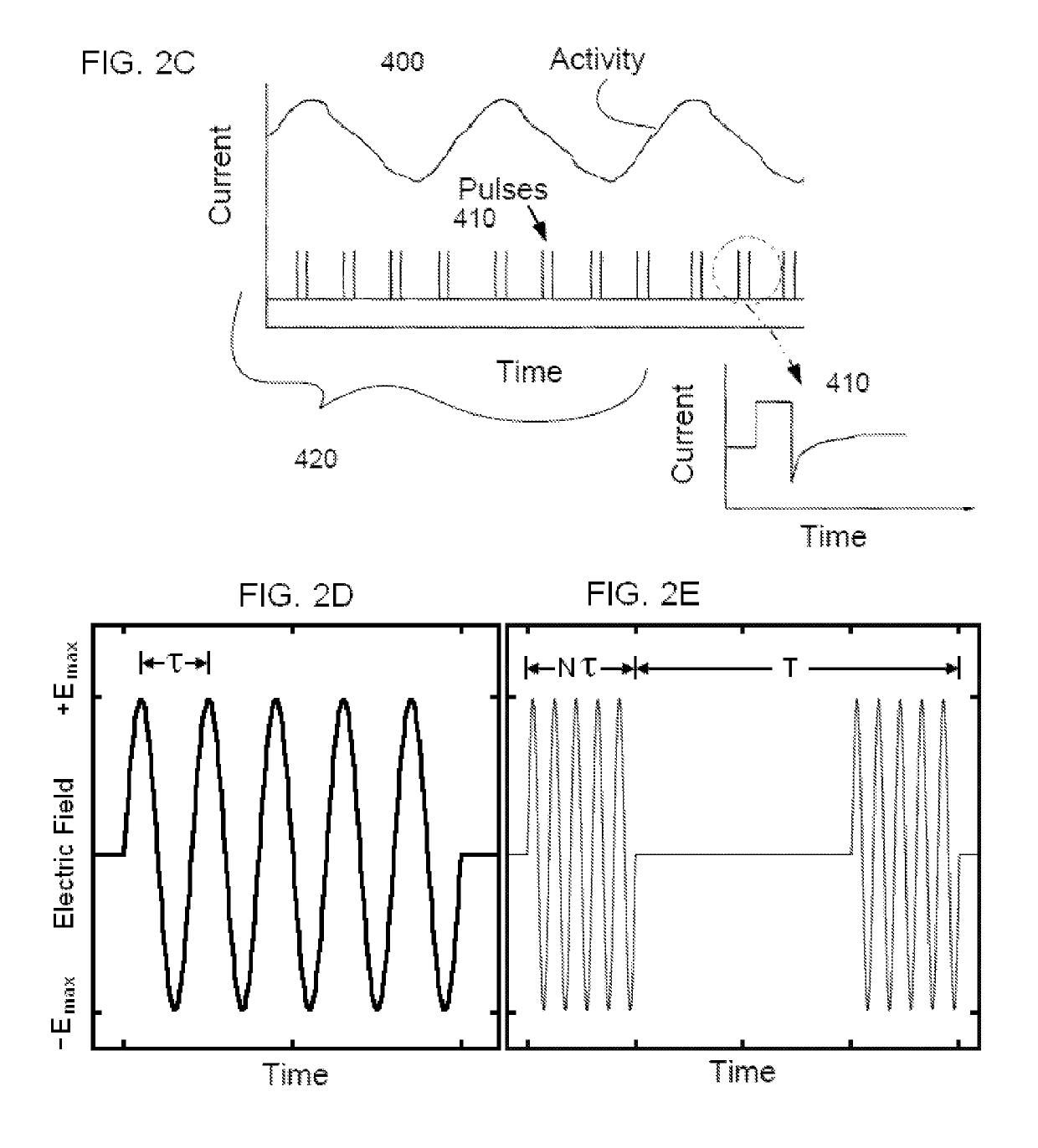
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat or prevent autism spectrum disorders and other disorders of psychological development
ActiveUS20130184792A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsExternal electrodesPervasive developmental disorderArrhythmia sinus
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing an autism spectrum disorder, a pervasive developmental disorder, or a disorder of psychological development. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. The nerve stimulation may be used as a behavior conditioning tool, by producing euphoria in an autistic individual. Vagus nerve stimulation is also used to modulate circulating serotonin levels in a pregnant woman so as to reduce the risk of having an autistic child; modulate the levels of growth factors within a child; promote balance of neuronal excitation / inhibition; modulate the activity of abnormal resting state neuronal networks; increase respiratory sinus arrhythmia; and avert episodes of motor stereotypies with the aid of forecasting methods.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC +1
Compositions and methods for controlling neuronal excitation
InactiveUS9486447B2High activityReduce functionOrganic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsAgonistElectromagnetic radiation
Embodiments of the technology described herein relate, at least in part, to methods of modulating the activity of a neuron by contacting the neuron with a photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonist and then illuminating the neuron with electromagnetic radiation. Also described herein are photo-sensitive TrpA1 agonists.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
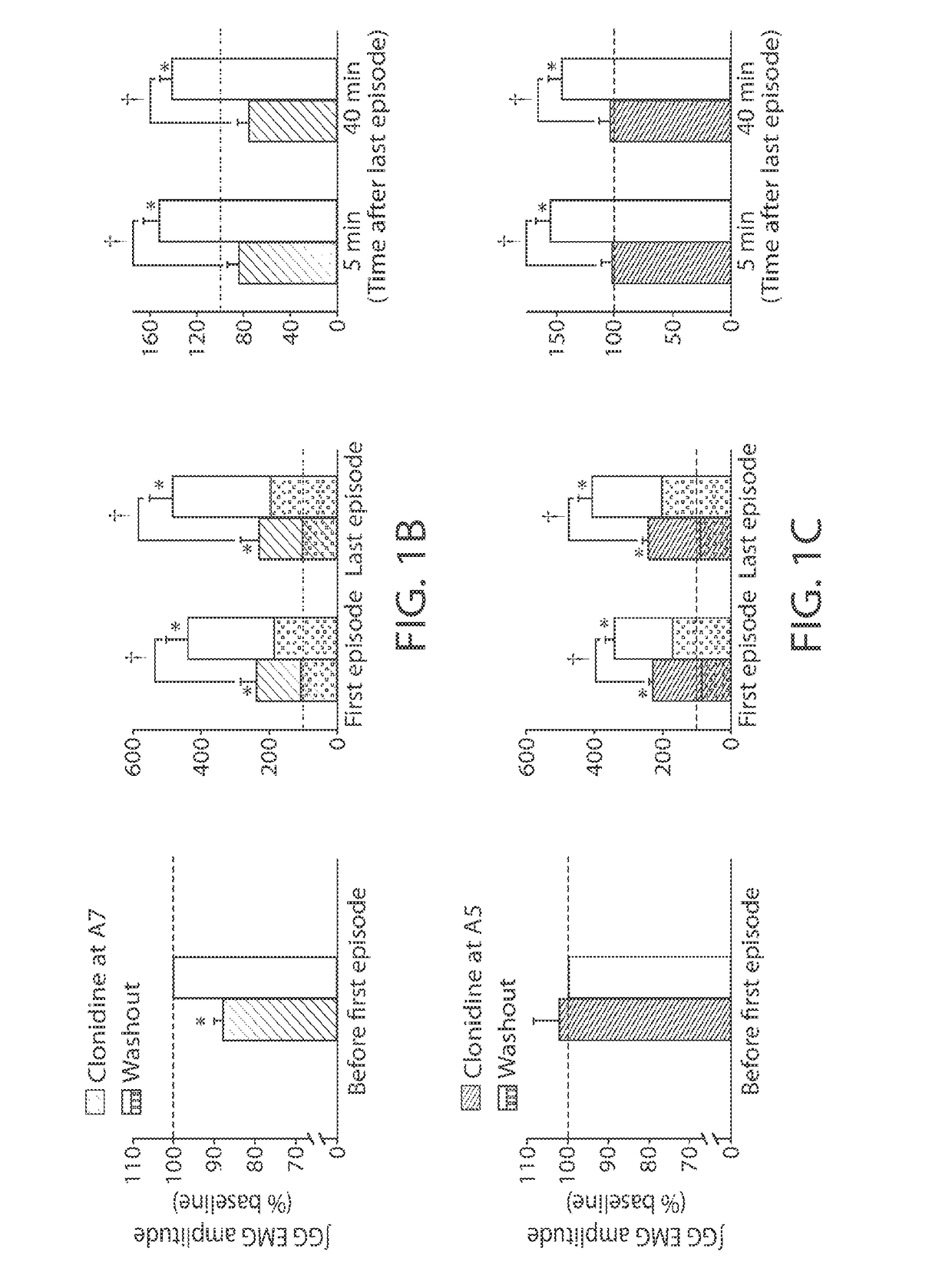
Method and system for detecting epileptogenesis
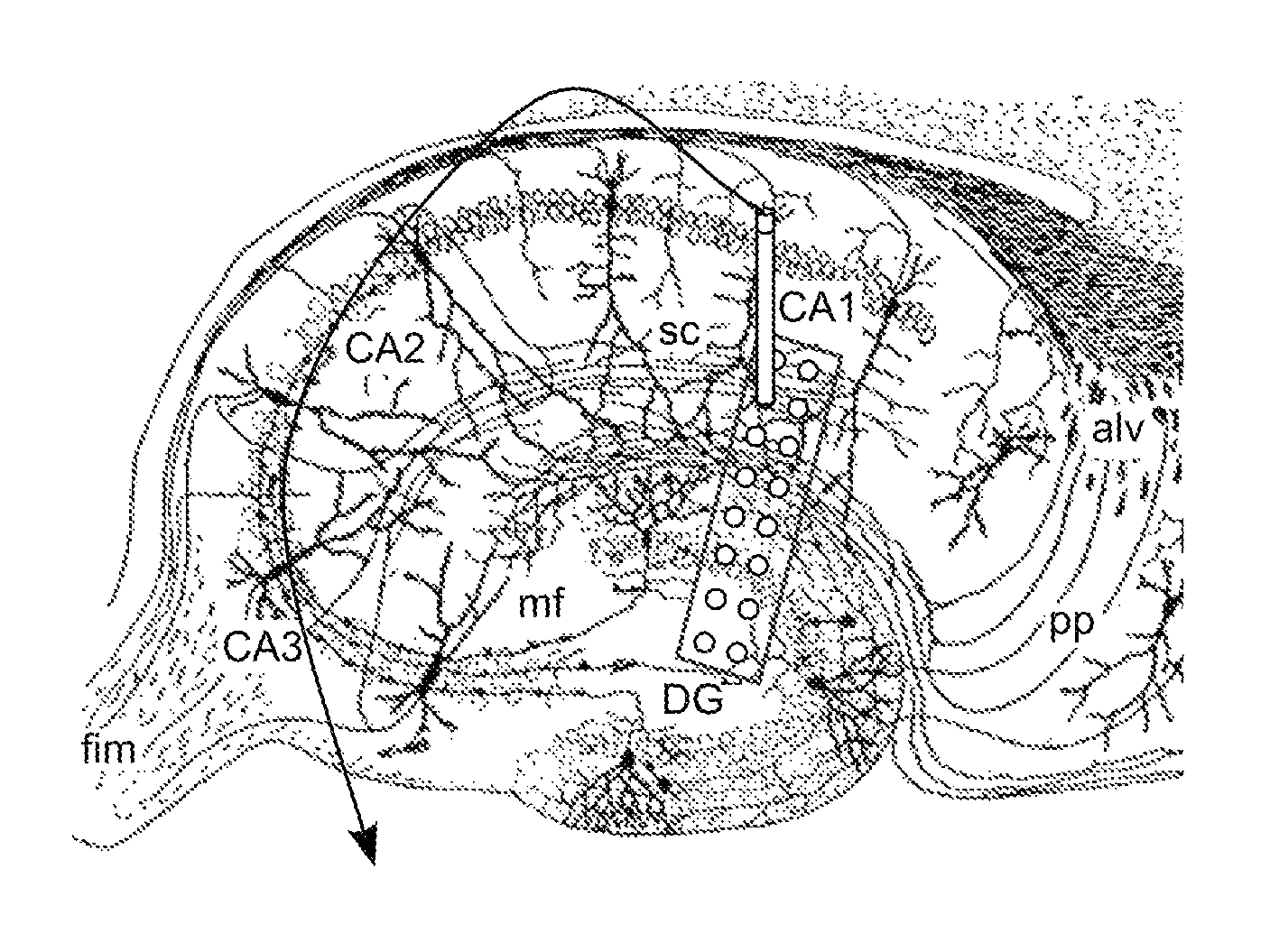
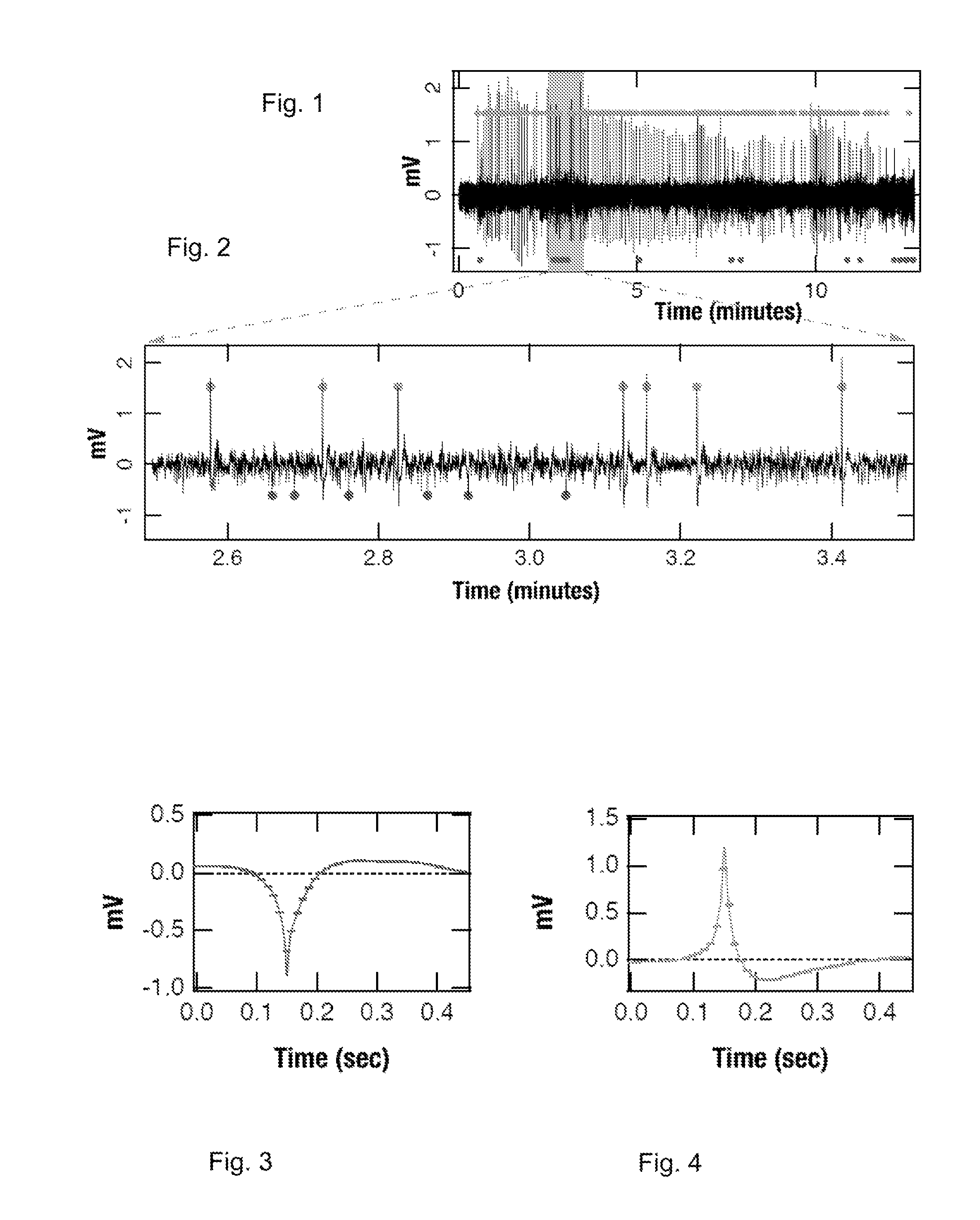
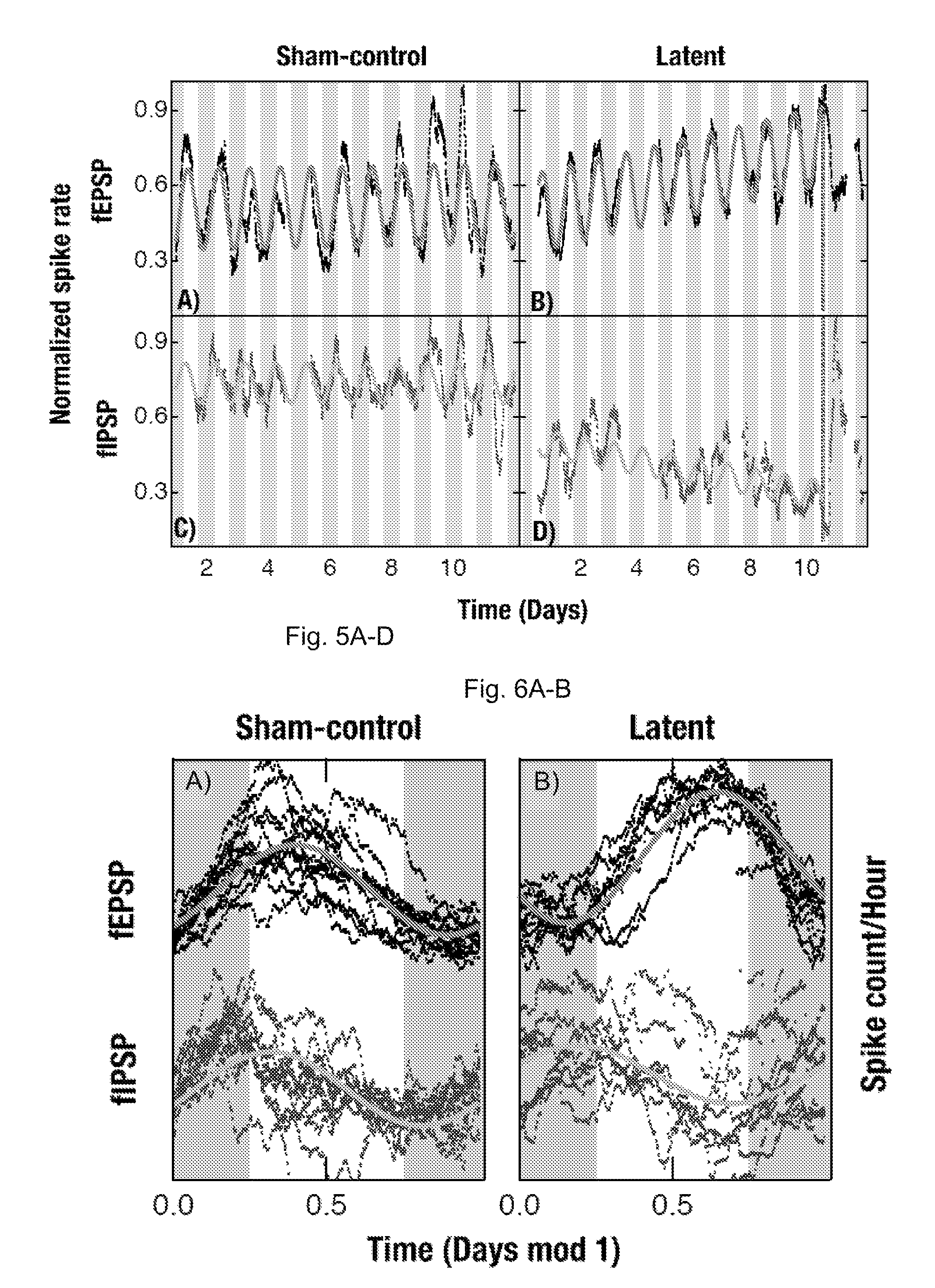
Neuronal excitation and inhibition of the brain is tracked in the hippocampal CA1 network during a latent period, wherein biomarkers are observed which include a sustained increase in the firing rate of the excitatory postsynaptic field activity, paired with a subsequent decrease in the firing rate of the inhibitory postsynaptic field activity; the mean amplitude profiles of both fEPSP and fEPSP field potential activity during the latent period have characteristic shapes; both excitatory and inhibitory CA1 field activity firing rates are observed to follow a circadian rhythm that drifts during epileptogenesis; the circadian rhythms described are in-phase in controls and anti-phase during epileptogenesis; and the fEPSP rate drifts from a circadian rhythm to a greater extent than the fEPSP rate. An additional biomarker is a change in a circadian rhythm of core body temperature. Therapeutic measures can include thermal, chemical, or electrical modulation, in an open or closed loop process.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Noradrenergic drug treatment of obstructive sleep apnea
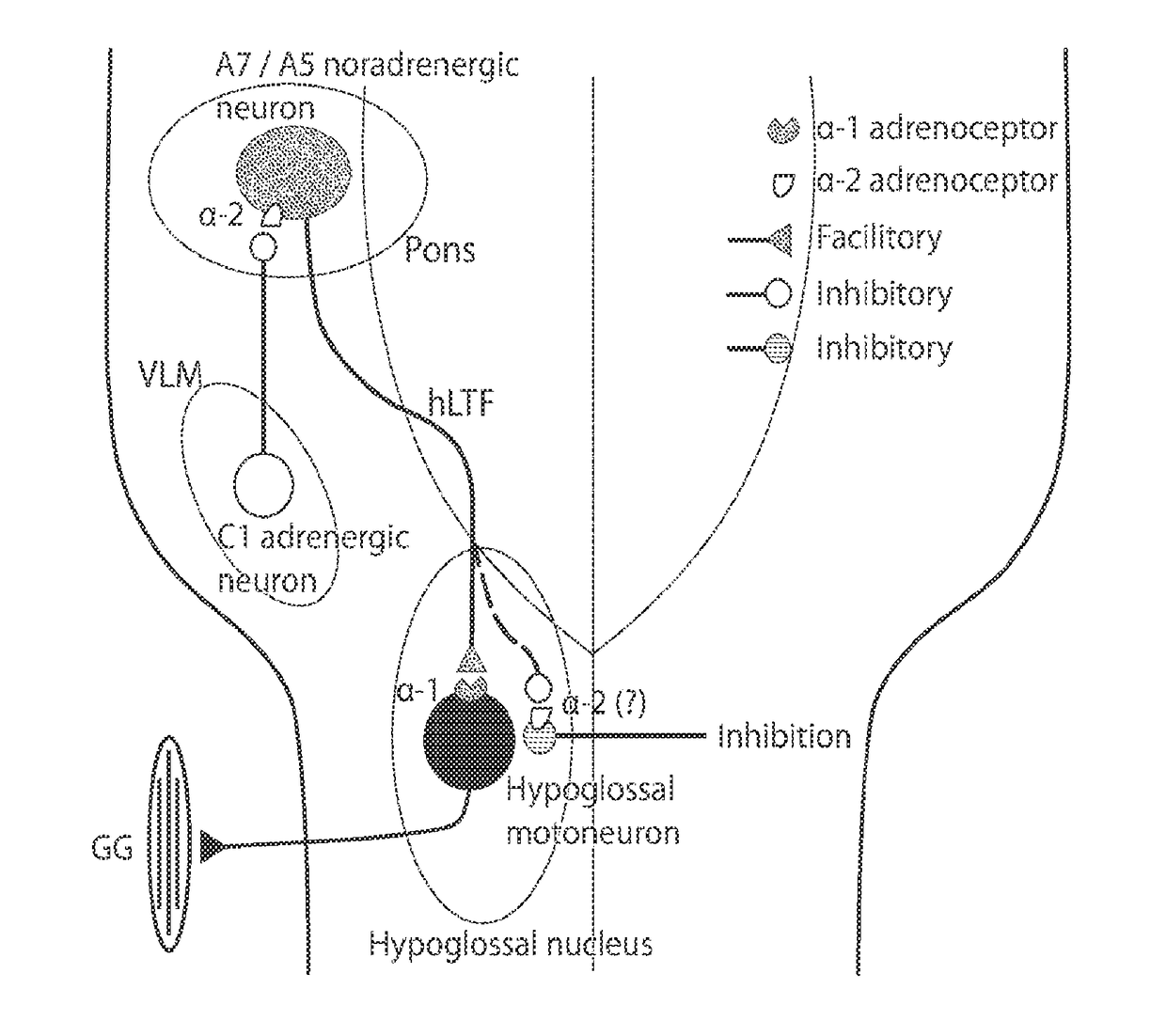
InactiveUS20180235934A1Promoting hypoglossal motoneuron excitabilityPromotes baseline excitabilityCapsule deliveryRespiratory disorderDiseaseCataplexy
Aspects of the disclosure relate to methods for treating disorders using agents for promoting hypoglossal motoneuron excitability. In some instances the disorders include obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), cataplexy, attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), attention deficit disorder (ADD) or depression. Related products are also included within the invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
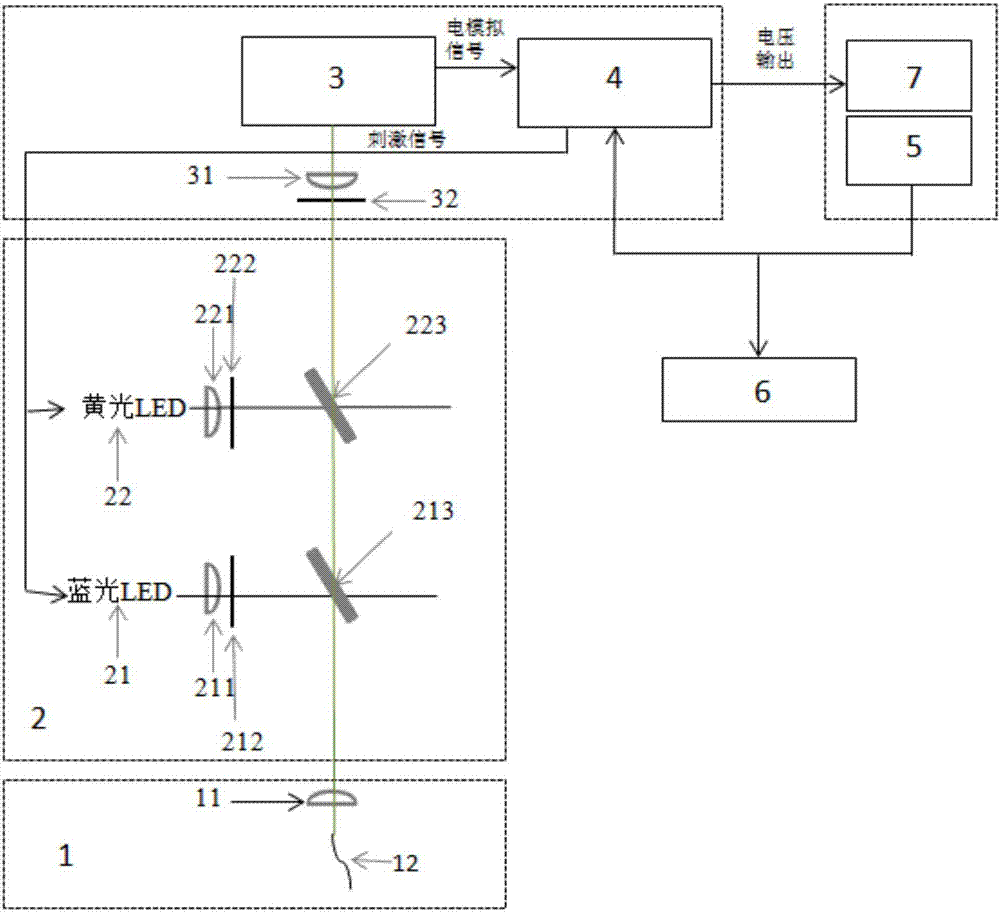
Two-channel animal nerve cell signal recording and synchronous irritation system
ActiveCN107334471AShort cycleGuaranteed accuracyDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionOptogeneticsIrritation
The invention belongs to the fields of biology, neuroscience, medicine and the like, and particularly relates to the field of photogenetics technology application, in particular to a two-channel animal nerve cell signal recording and synchronous irritation system. The photogenetics excitation and inhibition experiments can be realized at the same time in the process of recording the activity of animal nerve cells doing free activities. The system starts from the recording and the illumination of the relationship between target nerve cell self-activating signals and target behaviors through nerve cell self-activating signals; then, the verification is respectively performed from positive and negative points of view through nerve cell excitation experiments and inhibition experiments; and the scientificity and the accuracy of the experiment results are fully ensured. One optical fiber can be used for realizing the recording and stimulation functions; the process of switching recording and stimulation devices in the experiment process is avoided; the experiment time is reduced; and the experiment steps are simplified, so that the whole experiment period is greatly shortened.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
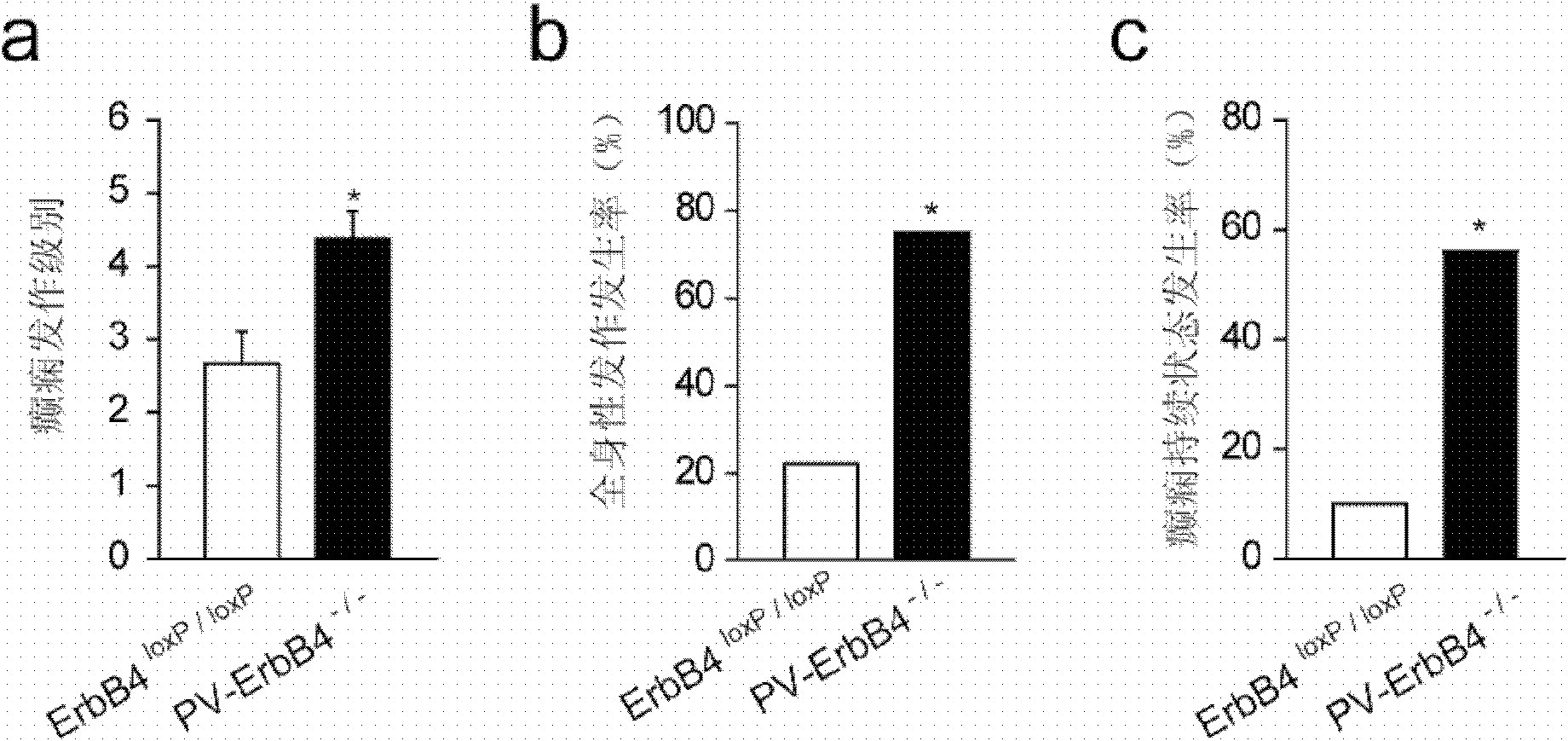
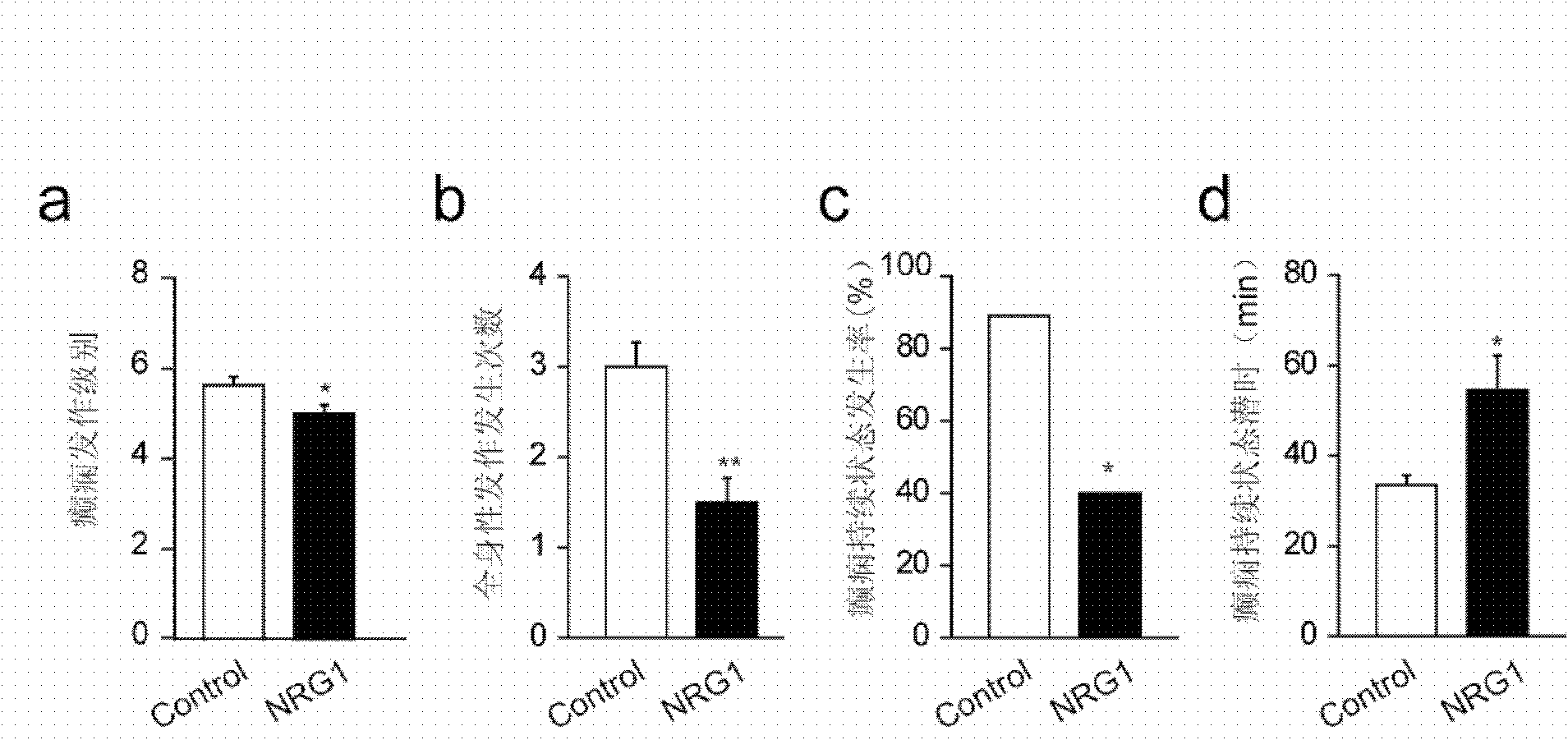
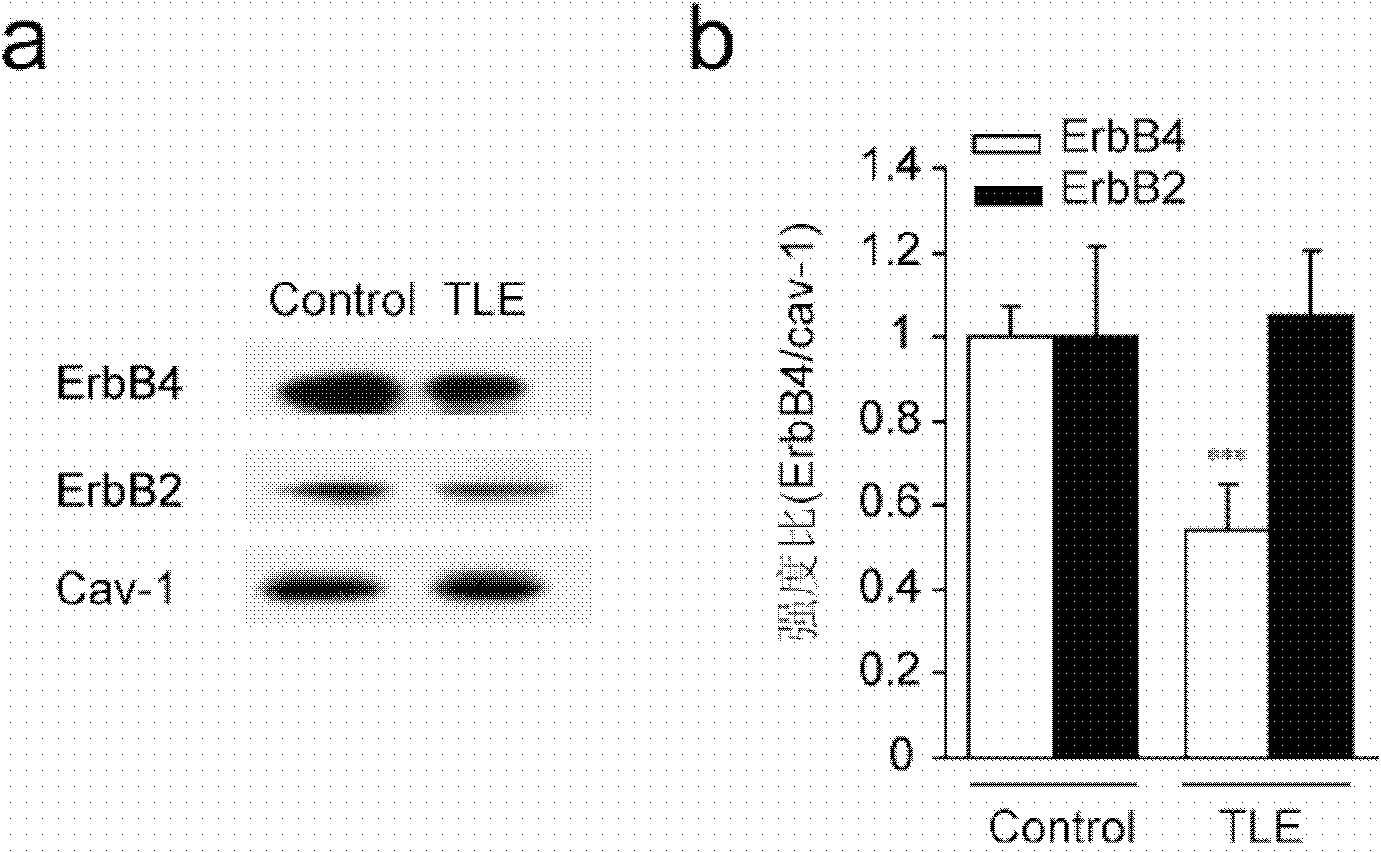
Application of ErbB receptor stimulant to preparation of medicament for treating epilepsy
The invention provides application of an ErbB receptor stimulant to preparation of a medicament for treating epilepsy. The ErbB receptor stimulant has the advantages: the inhibiting effect of the ErbB4 stimulant NRG1 on epilepsy is disclosed, the organism of epilepsy is studied intensively, a research direction for studying a novel effective 'target' and a molecule of an epilepsy inhibiting medicament is provided, and a basis is laid for the screening of a novel medicament for treating brain diseases based on neuronal excitability changes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
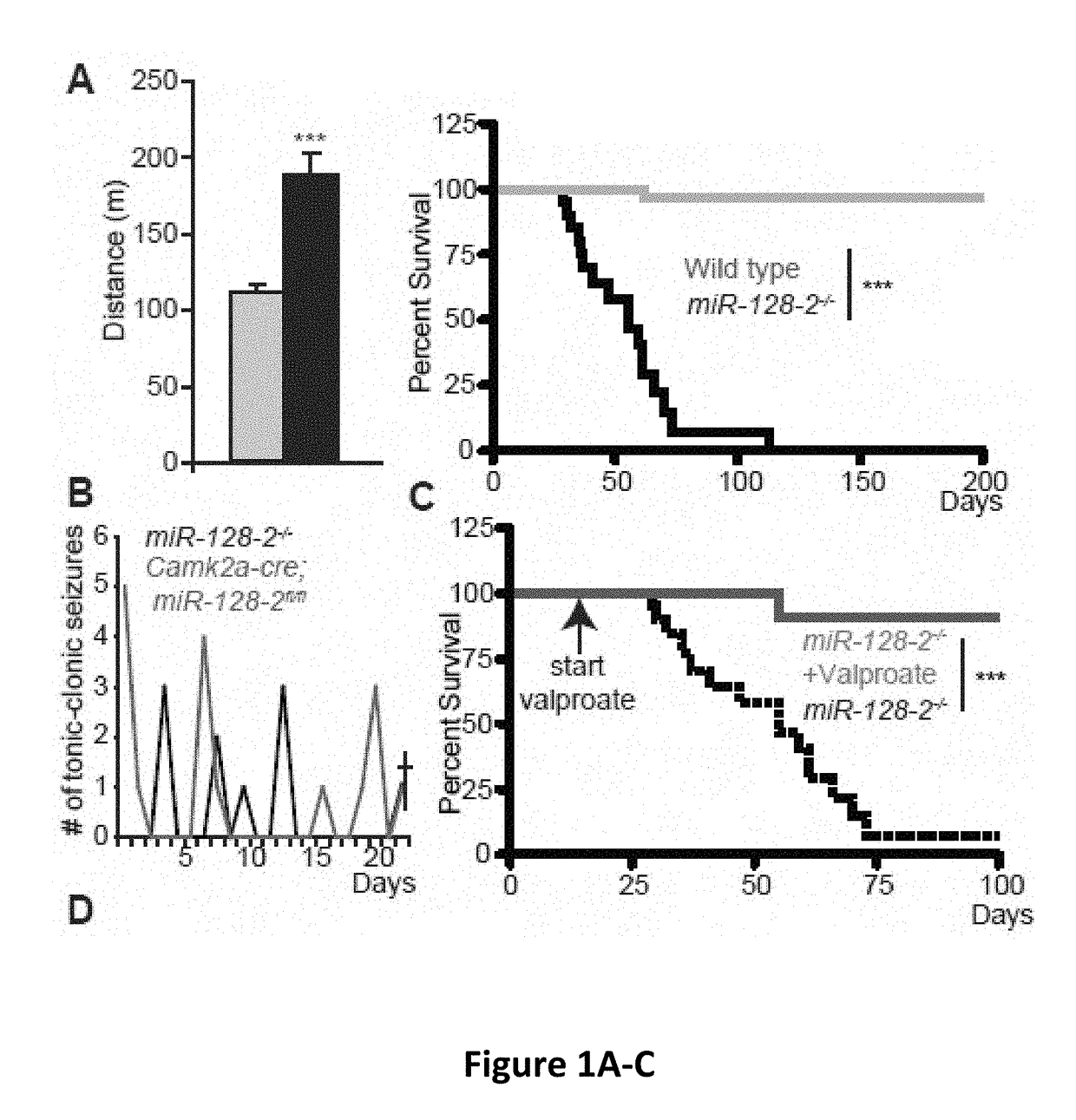
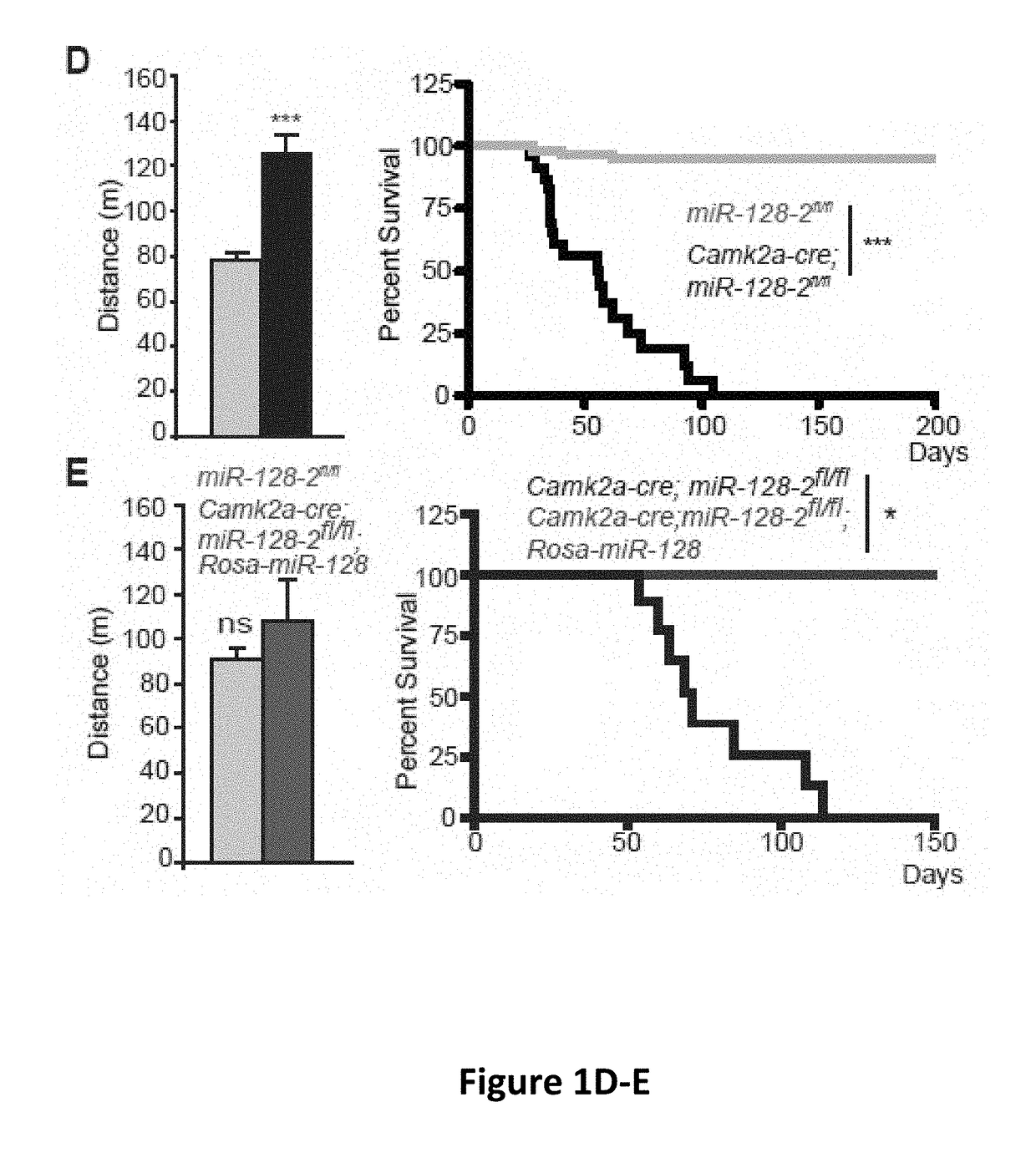
Compositions and methods for modulating neuronal excitability and motor behavior
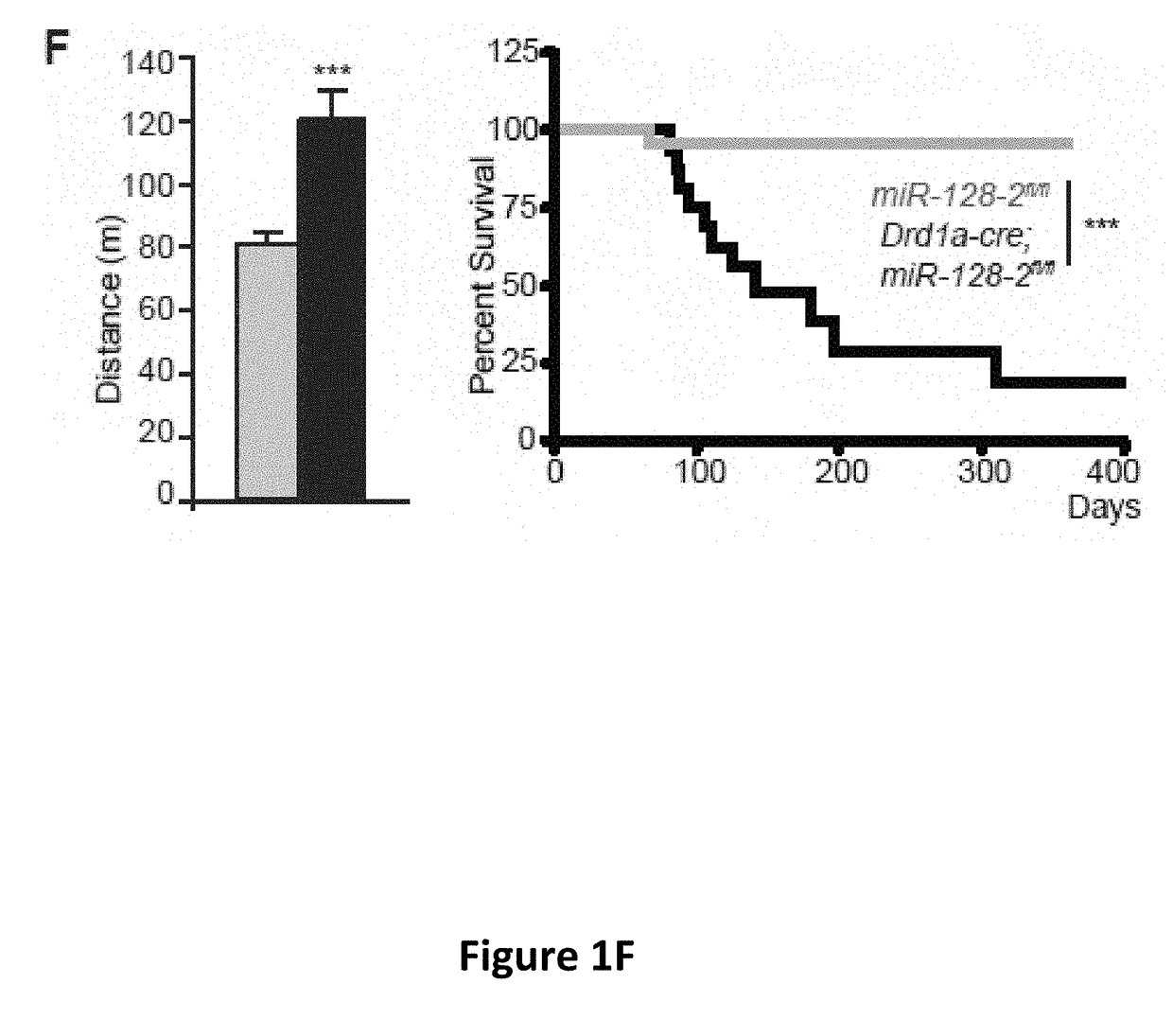
ActiveUS10087443B2Increasing expression and activityReduce the possibilityCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderNeuronEpileptic disorder
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for treating or reducing the likelihood of the development of epilepsy in an individual. The method comprises administering to the central nervous system of an individual in need of such treatment a therapeutically effective amount of an agent capable of increasing the expression and / or activity of miR-128.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV +1
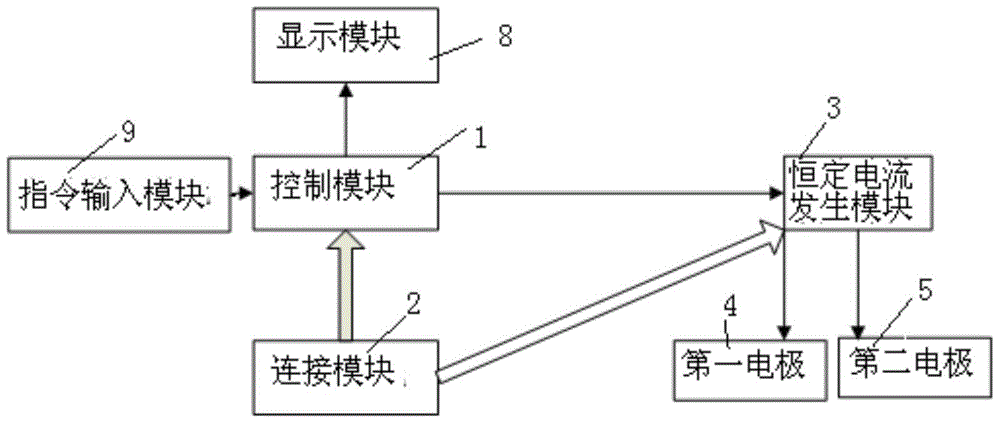
Device for treating insomnia
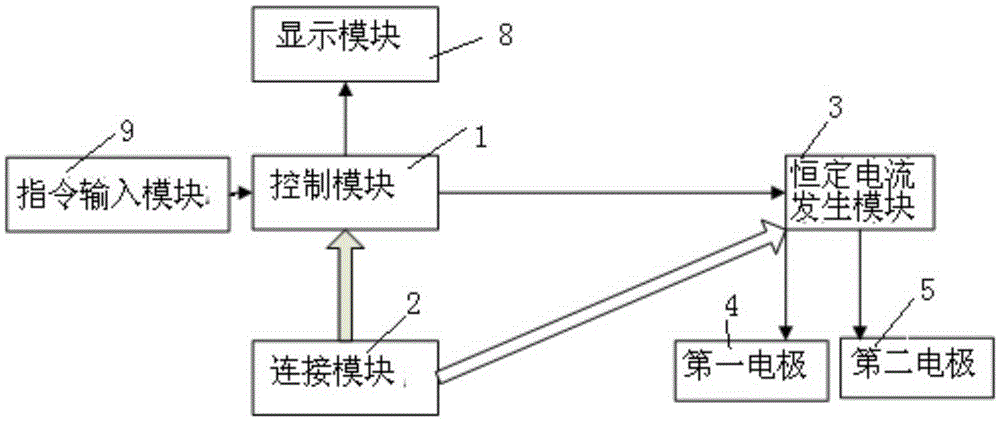
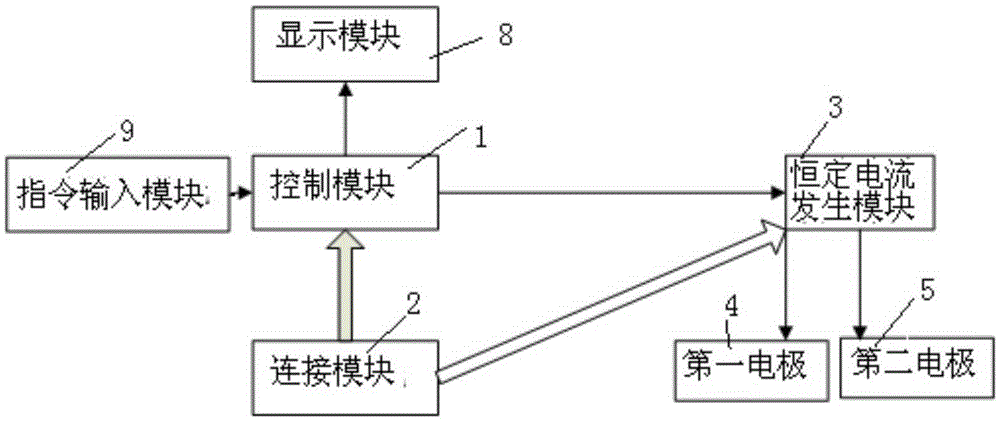
InactiveCN105311743AReduce corrosionEffective stimulationElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringInsomnia
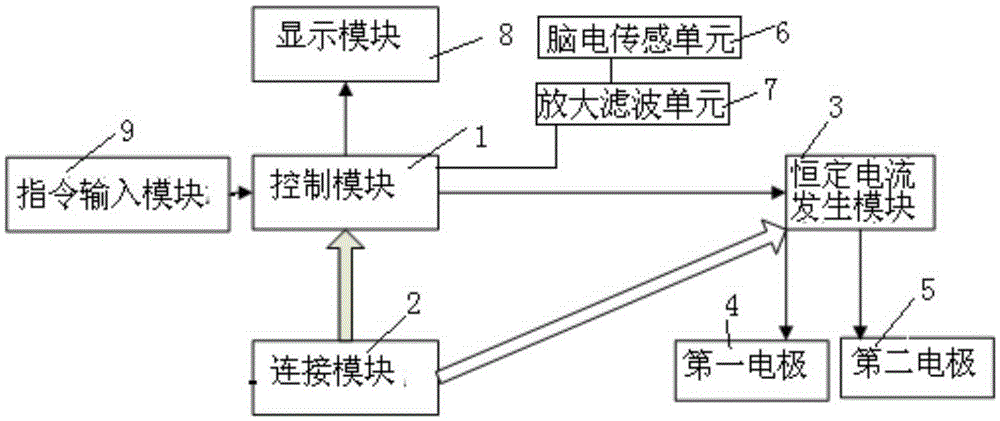
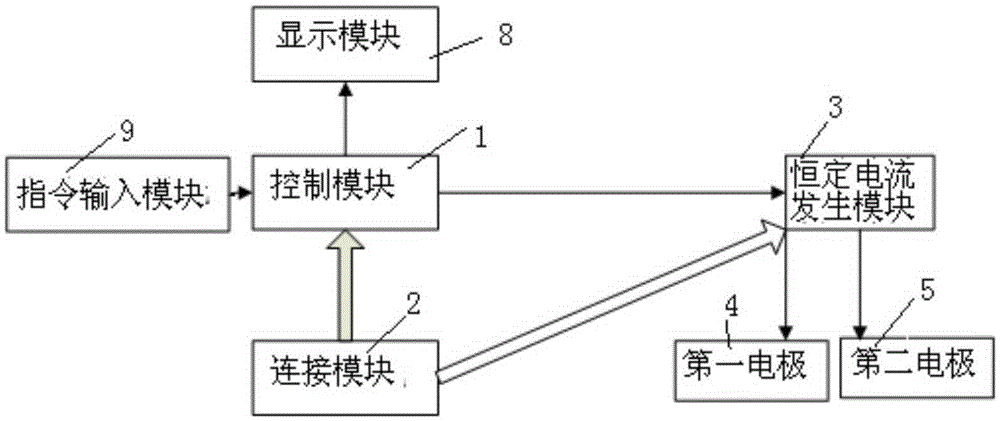
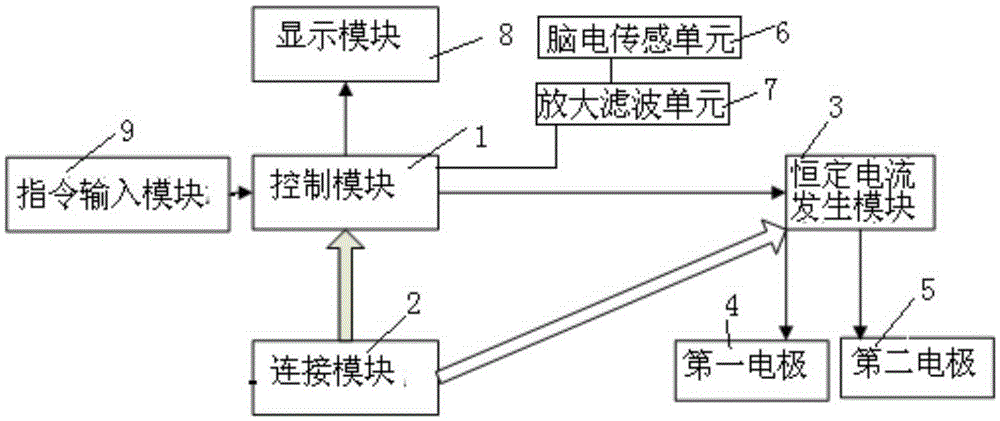
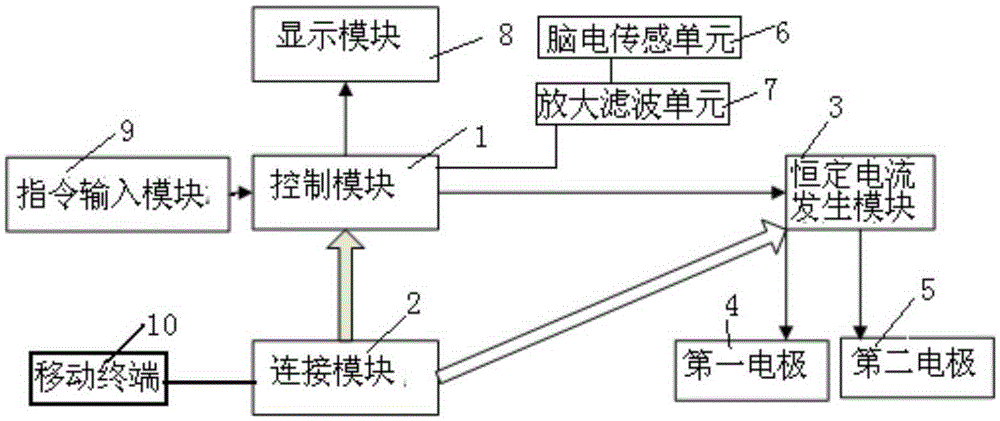
The invention relates to a device for treating insomnia. A constant current generating module is connected to a control module and a power module; the control module is used for controlling the constant current generating module to generate constant current; a first electrode and a second electrode are connected to the constant current generating module; the first electrode is a positive electrode and the second electrode is a negative electrode; power-on currents of the first electrode and the second electrode are more than 0mA and less than 5mA; and power-on durations of the first electrode and the second electrode range from 15min to 40min. Through DC electrical simulation, electroencephalogram signal detection and insomnia diagnosis, and in accordance with the neural electrophysiological characteristics of the insomnia, the insomnia treating device provided by the invention, according to an intensity-duration curve and biological effects of an electrical simulation waveform, can design the electrical simulation waveform which is capable of effectively inducing neurons excitation, and is low in electrode corrosion and free from tissue injury.
Owner:深圳市太赫兹科技有限公司
Methods and composition for treatment of inflammatory pain
The present invention relates to the field of pain management, and in particular, the management of inflammatory pain without inducing overt sedation. The present invention features compositions and treatments for inflammatory pain comprising the administration of an amount of an neurokinin (NK) antagonist in combination with a neuronal excitation inhibitor.
Owner:CNSBIO PTY LTD
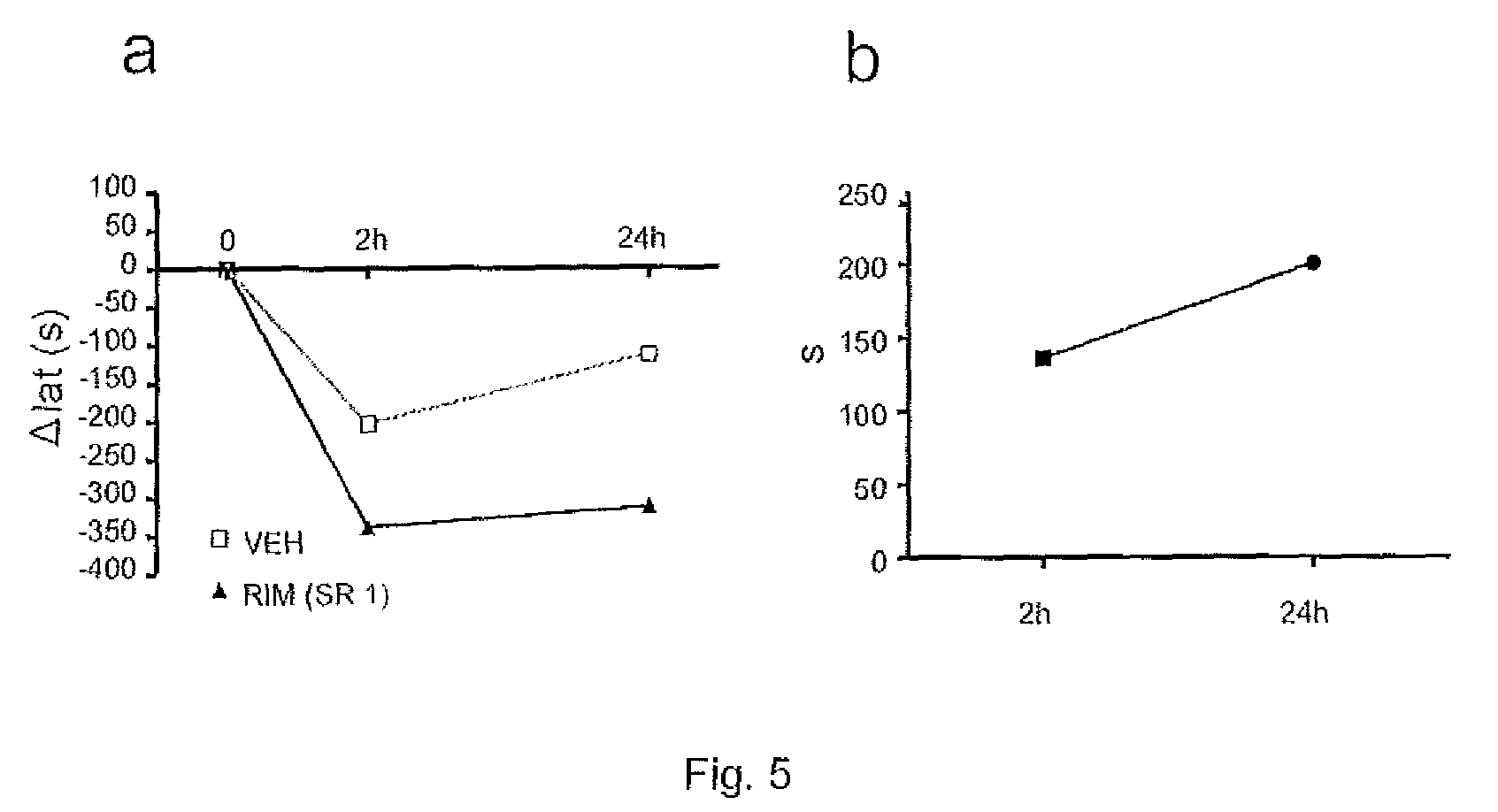
Use of CB1 antagonists and/or inverse agonists for the preparation of drugs that increase motor neuron excitability
ActiveUS9238027B2Reduction of excessive daytime sleepinessReduction of bradykinesiaBiocideNervous disorderSmall brainstemSpinal level
Use of a CB1 receptor antagonist and / or inverse agonist, preferably rimonabant, for the preparation of drugs useful for increasing motor neuron excitability in the cerebral cortex and / or in the brain stem and / or at the spinal level, as well as a method for increasing motor neuron excitability through the administration of a CB1 antagonist / inverse agonist receptors, and to the use of a pharmaceutical composition which comprises a CB1 receptor antagonist and / or inverse agonist, preferably rimonabant, for increasing motor neuron excitability in the cerebral cortex and / or in the brain stem and / or at the spinal level.
Owner:FUNDACION HOSPITAL NACIONAL DE PARAPLEJICOS PARA LA INVESTIGACION & LA INTEGRACION FUHNPAIIN
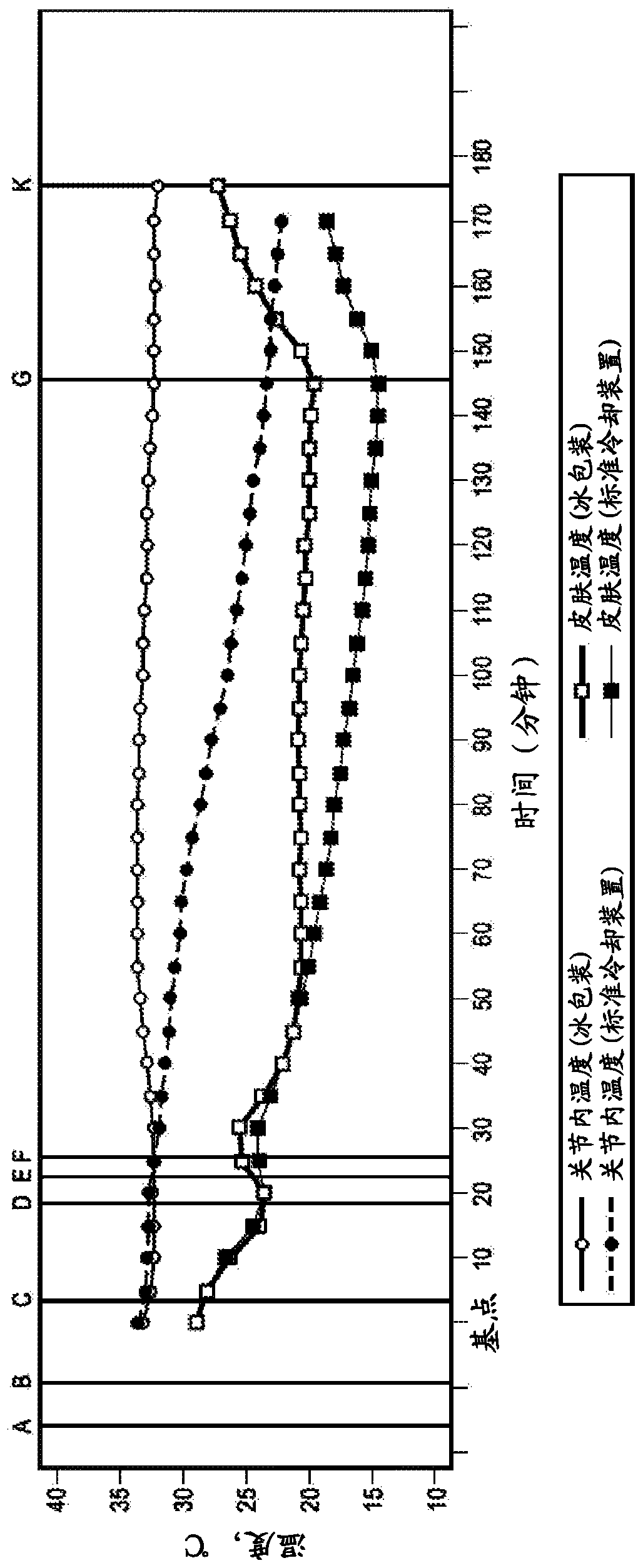
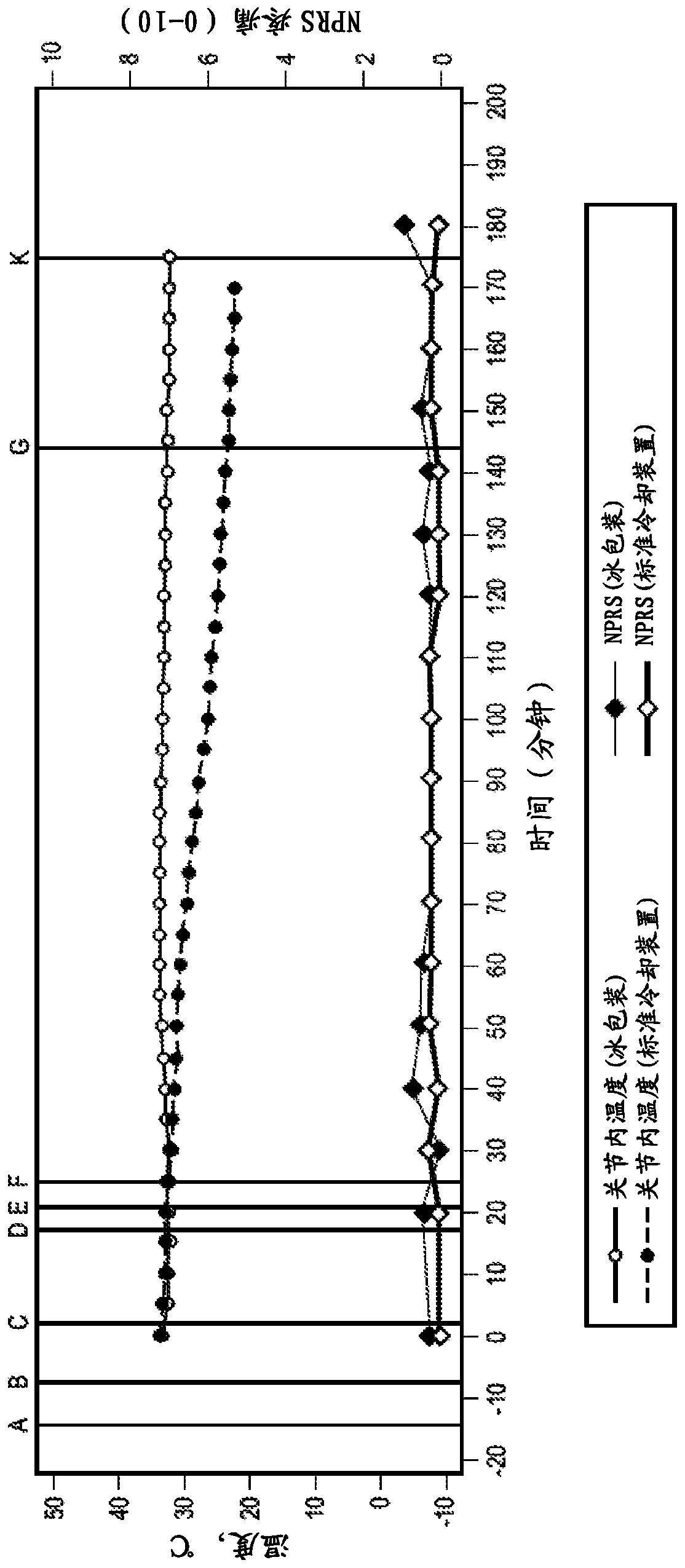
Methods and compositions for treatment of pain using capsaicin
The invention provides methods and compositions for treatment of pain, such as joint pain, using capsaicin in a procedure that attenuates transient burning sensation experienced by patients due to capsaicin administration. The methods desirably provide relief from joint pain, such as osteoarthritic knee joint pain, for an extended duration, such as at least about 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, or 1year. To attenuate the adverse side effect of a transient burning sensation caused by capsaicin-induced neuronal excitation, the methods utilize a cooling article, such as a material wrap cooled viaa circulating fluid, to reduce the temperature of tissue to be exposed to capsaicin to within a certain range for certain durations of time, optionally in combination with administering a local anesthetic agent, resulting in the substantial reduction or even elimination of transient burning sensation caused by capsaicin.
Owner:中枢疗法公司
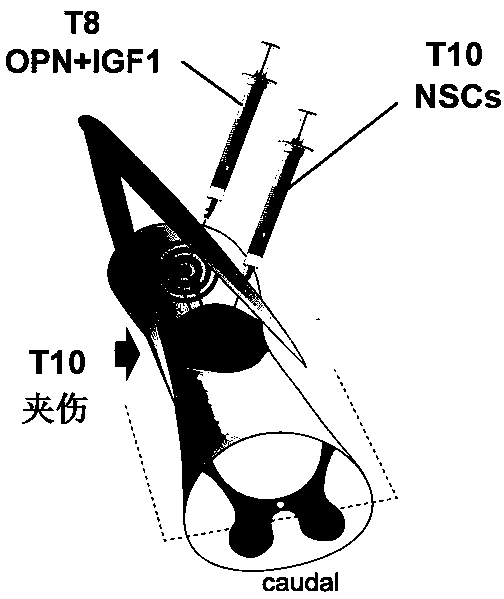
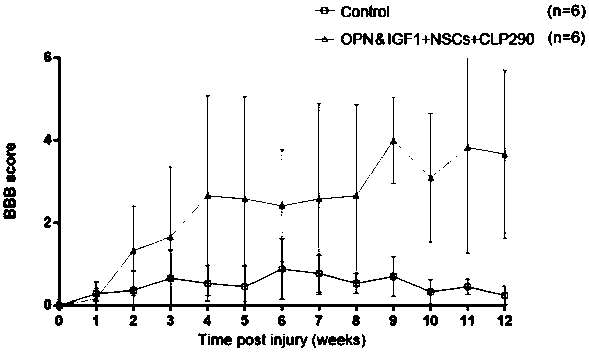
Medicine for treating spinal cord injury, medicine kit and method
PendingCN111388654AImprove regenerative abilityPromote functional recoveryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSpinal cord lesionSpinal nerve
The invention discloses application of growth promoting factor (OPN and IGF1) overexpression in combination with embryo spinal nerve stem cell (NSCs) transplantation and a small molecule compound (CLP290) in preparation of a medicine for treating spinal cord injury. A medicine kit for treating spinal cord injury comprises AAV-OPN, AAV-IGF1, NSCs and CLP290. The invention also discloses applicationof OPN and IGF1 overexpression in combination with NSCs transplantation and the small molecule CLP290 in treatment of spinal cord injury. OPN and IGF1 overexpression, NSCs transplantation and small molecule CLP290 intervention are combined for treating spinal cord injury, the intrinsic regeneration capacity of neurons is enhanced, meanwhile, interrupted upstream and downstream neural loops are rebuilt, the excitability of inhibitory neurons is adjusted, and functional recovery after spinal cord injury is promoted.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Device for treatment of cognitive disorder
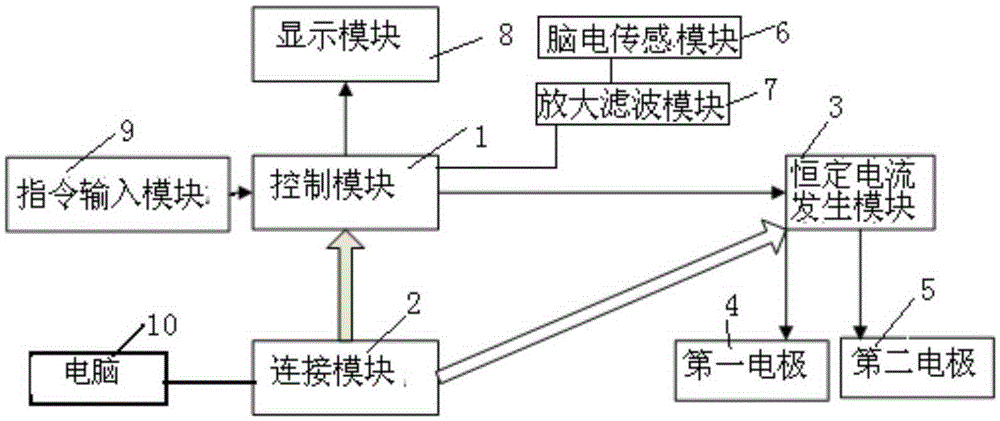
InactiveCN105944229AReduce corrosionEffective stimulationExternal electrodesEngineeringElectrical stimulations
The present invention relates to a device for treatment of cognitive disorder. A constant current generation module is connected with a control module and a power supply module; the control module controls the constant current generation module to generate constant current; a first electrode and a second electrode are connected with the constant current generation module; the first electrode is an anode, and the second electrode is a cathode; the power-on current of the first electrode and the second electrode is larger than 0mA and smaller than 5mA; and the power-on time of the first electrode and the second electrode is from 15 min to 40 min. The device for treatment of cognitive disorder is subjected to direct current electrical stimulation, EEG signal detection and cognitive disorder diagnosis, designs the electrical stimulation waveform capable of effectively inducing the Neuron excitement and with small electrode corrosion and nondestructive organization aiming at the cognitive disorder nerve electrophysiology characteristic according to the intensity-duration curve and the electrical stimulation waveform biology effect.
Owner:深圳市太赫兹科技有限公司
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat or prevent autism spectrum disorders and other disorders of psychological development
ActiveUS10512769B2Promote balance between supply and demandIncrease the number ofMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsExternal electrodesSerotoninPervasive developmental disorder
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing an autism spectrum disorder, a pervasive developmental disorder, or a disorder of psychological development. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. The nerve stimulation may be used as a behavior conditioning tool, by producing euphoria in an autistic individual. Vagus nerve stimulation is also used to modulate circulating serotonin levels in a pregnant woman so as to reduce the risk of having an autistic child; modulate the levels of growth factors within a child; promote balance of neuronal excitation / inhibition; modulate the activity of abnormal resting state neuronal networks; increase respiratory sinus arrhythmia; and avert episodes of motor stereotypies with the aid of forecasting methods.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC +1
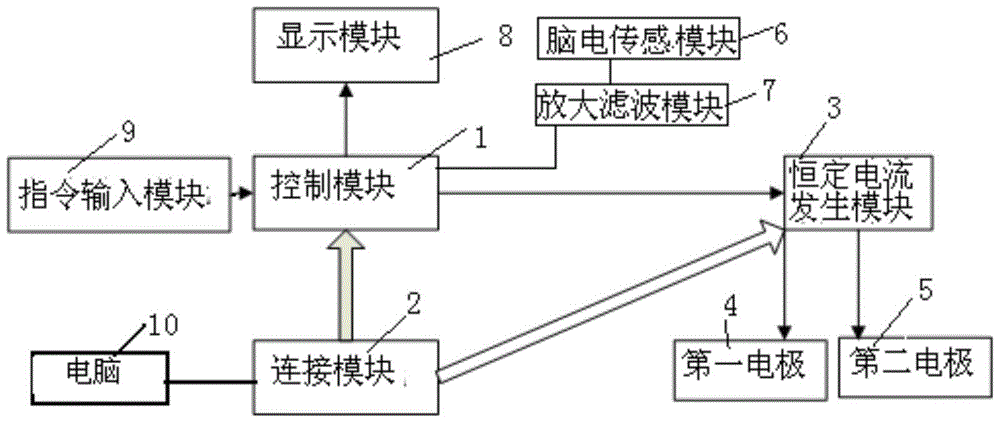
Mobile terminal based treatment device and treatment system for treating cognitive disorder
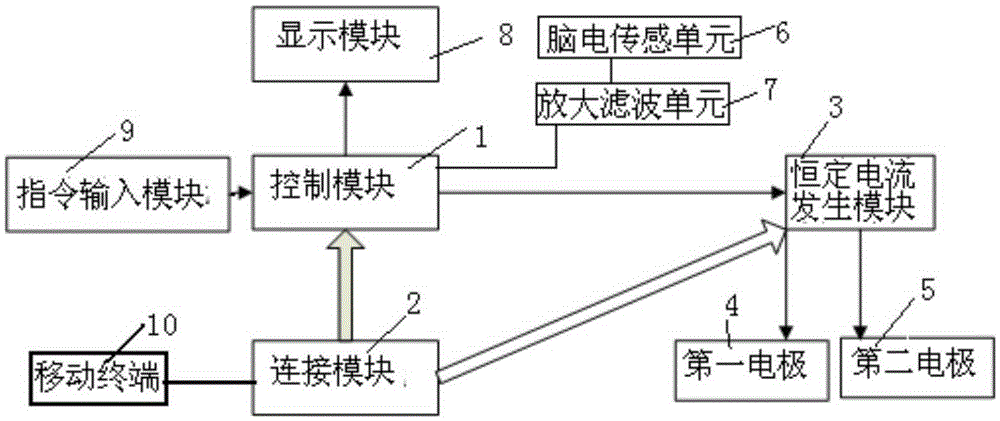
InactiveCN105311742AEffective stimulationEffectively induce excitementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringNeuronal excitation
The invention relates to a mobile terminal based device and a mobile terminal based system for treating cognitive disorder. A constant current generating module is connected to a control module and a power module; the control module is used for controlling the constant current generating module to generate constant current; a first electrode and a second electrode are connected to the constant current generating module; the first electrode is a positive electrode and the second electrode is a negative electrode; power-on currents of the first electrode and the second electrode are more than 0mA and less than 5mA; and power-on durations of the first electrode and the second electrode range from 15min to 40min. Through DC electrical simulation, electroencephalogram signal detection and cognitive disorder diagnosis, and in accordance with the neural electrophysiological characteristics of the cognitive disorder, the mobile terminal based device for treating the cognitive disorder provided by the invention, according to an intensity-duration curve and biological effects of an electrical simulation waveform, can design the electrical simulation waveform which is capable of effectively inducing neurons excitation, and is low in electrode corrosion and free from tissue injury.
Owner:深圳市太赫兹科技有限公司
Combination product for the induction and/or maintenance of general anesthesia
PendingUS20210186927A1Induce general anesthesiaOrganic active ingredientsAnaestheticsSide effectGeneral anaesthesia
The state of general anesthesia (GA) is essential to many surgical and medical procedures. This state is characterized by loss of consciousness, deep analgesia and suppression of movements. GA is rarely achieved with a single drug, usually requiring the combination of various pharmacological agents. Each drug can interact with one or more molecular targets affecting neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission in multiple regions of the CNS. Agonists of the μ-opioid receptor are commonly used in GA to cause analgesia, but not to induce or maintain loss of consciousness or movement suppression. Additionally, agonists of the μ-opioid receptor can cause serious unwanted side effects, e.g. respiratory depression. The present invention provides alternative combination products based on K-opioid receptor agonists. These combination products unexpectedly induced loss of consciousness, and were able to achieve and maintain GA. Furthermore, the combination products suppressed pain perception without the need of a μ-opioid receptor agonist. The combination of Salvinorin A, a selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, with Diazepam or Medetomidine surprisingly led to rapid consciousness, deep analgesia and movement suppression. This combination was found to effectively induce and maintain a state of general anesthesia.
Owner:TERRAN BIOSCIENCES INC
Novel fusion polypeptide with anti-cerebral ischemia effect and application thereof
InactiveCN109293743AHigh-speed and efficient entryGood treatment effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseMedicine
The invention relates to a novel polypeptide with anti-cerebral ischemia effect and application thereof. The peptide chain fragment sequence of the polypeptide is YGRKRRQRRRGESV. The polypeptide provided by the invention can enter cells under high speed and high efficiency, significantly inhibits glutamate-induced neuron excitotoxicity injury by interfering the signal transduction of NOS1AP, and effectively resists the cerebral ischemic injury of MCAO model rats. The polypeptide has good application prospects in preparation of drugs treating cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Fusion polypeptide with cerebral ischemia resistant effect and application thereof
ActiveCN106928322AGood at crossing the blood-brain barrierPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseMedicine
The invention provides a fusion polypeptide with a cerebral ischemia resistant effect and application thereof. The fusion polypeptide has a peptide chain fragment sequence of YGRKKRRQRRRGDPV. The polypeptide provided by the invention can rapidly and effectively enter cells; through interfering with the signal conduction of CAPON, the neuron excitatory toxicity injury induced by glutamic acid is obviously inhibited; the cerebral ischemia injury of MCAO model rats can be effectively resisted. The polypeptide has good application prospects in the preparation of medicine for treating cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
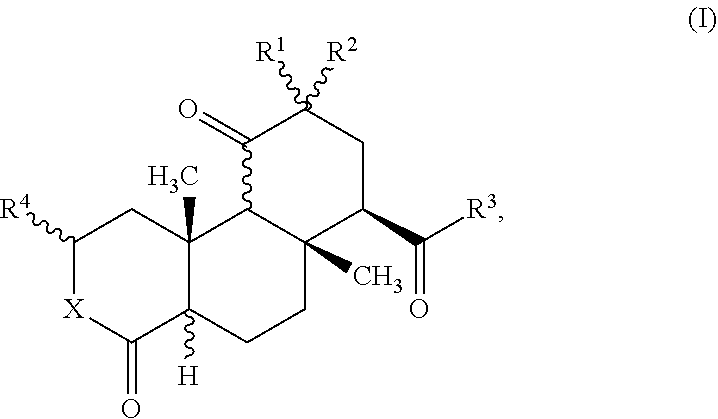
Phthalide isoquinoline alkaloid as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112940001ASignificantly inhibits neuropathic pain activityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDepressantQuinoline
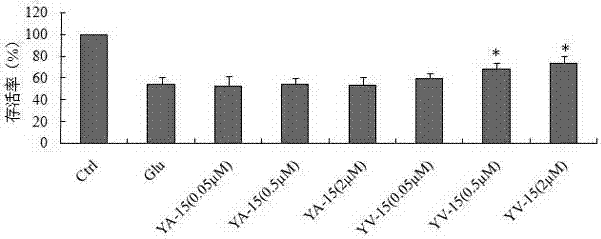
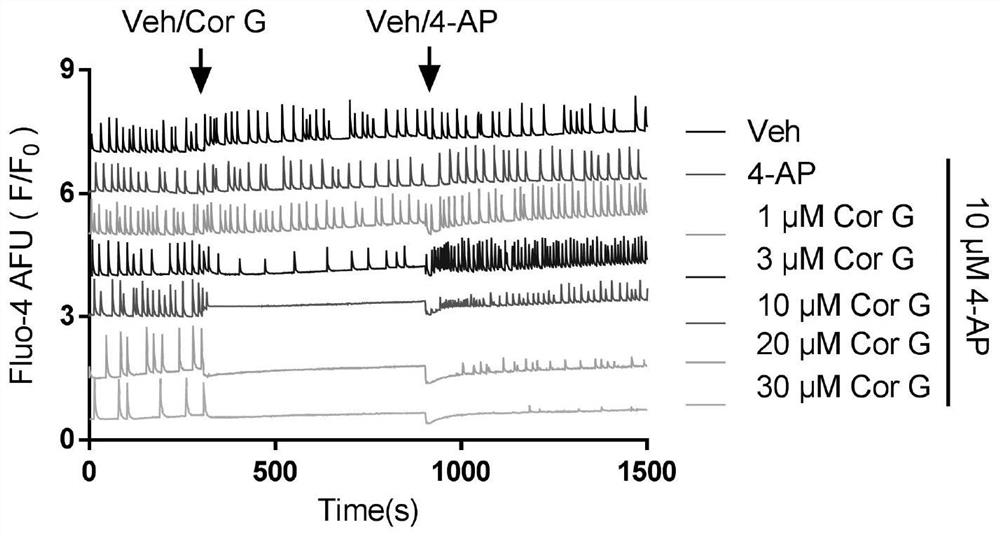
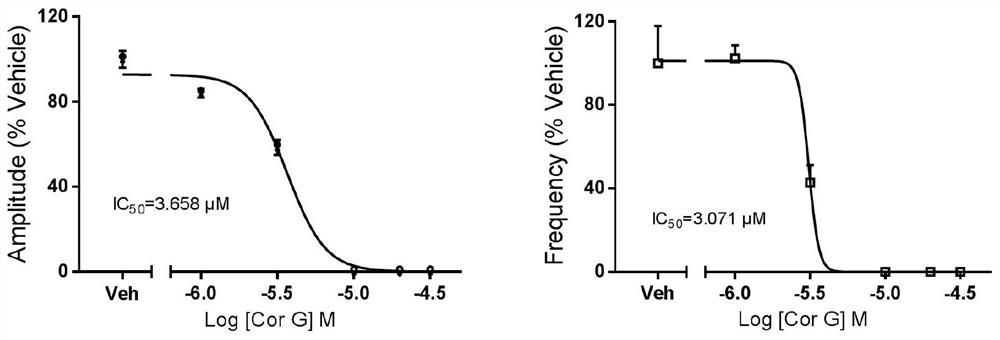
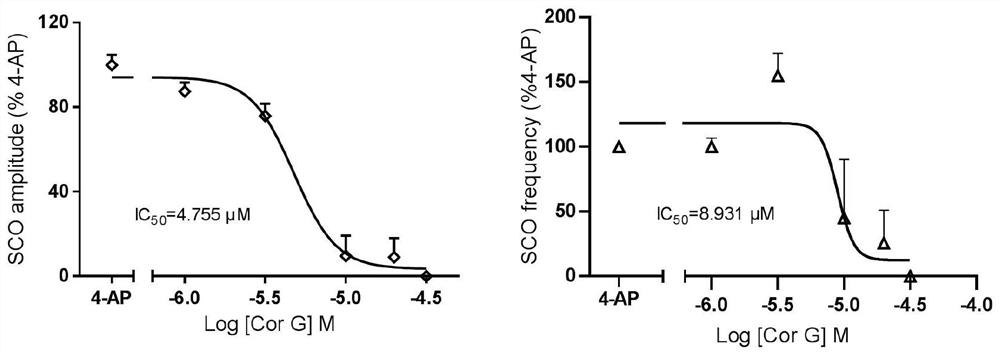
The invention discloses a phthalide isoquinoline alkaloid as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, the phthalide isoquinoline alkaloid is a new natural product extracted and separated from a traditional Chinese medicine corydalis amabilis, and is named as corydecumbine G, and the structural formula is shown as formula (I). The phthalide isoquinoline alkaloid corydecumbine G is a brand new inhibitor developed based on inhibition of neuronal excitability, and experiments prove that the phthalide isoquinoline alkaloid corydecumbine G can significantly inhibit neuronal excitability and improve neuropathic pain, can be used as a lead compound, and can be used for preparation of drugs for inhibiting neuronal excitability and research and development of drugs for treating neuropathic pain.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Application of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in preparing medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction
PendingCN111840519ASignificant anti-addictive effects of propofolAddiction PreventionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBrain-derived neurotrophic factorEffective treatment
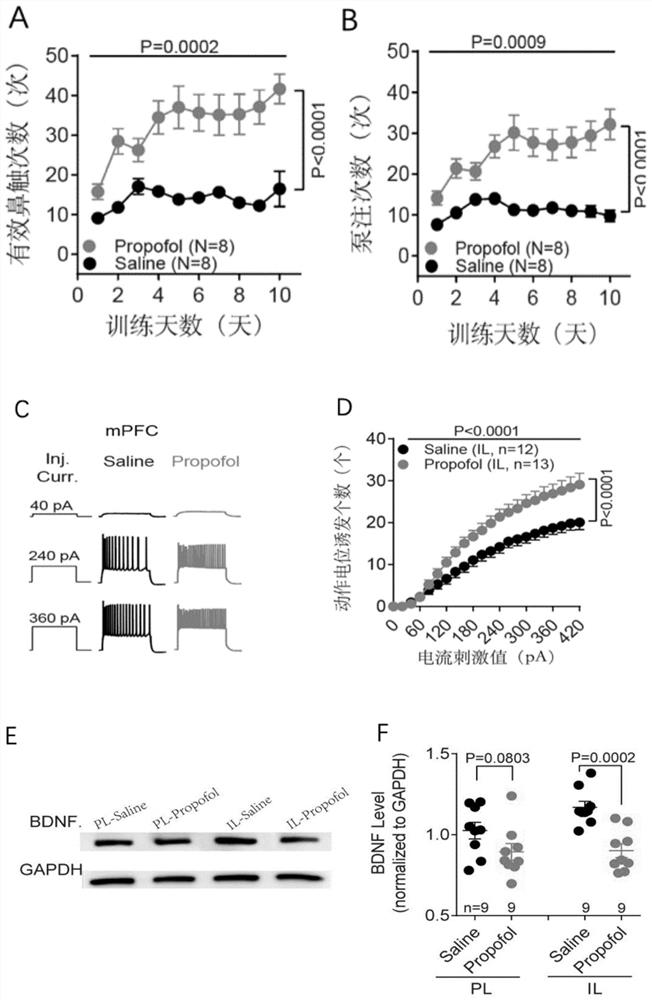
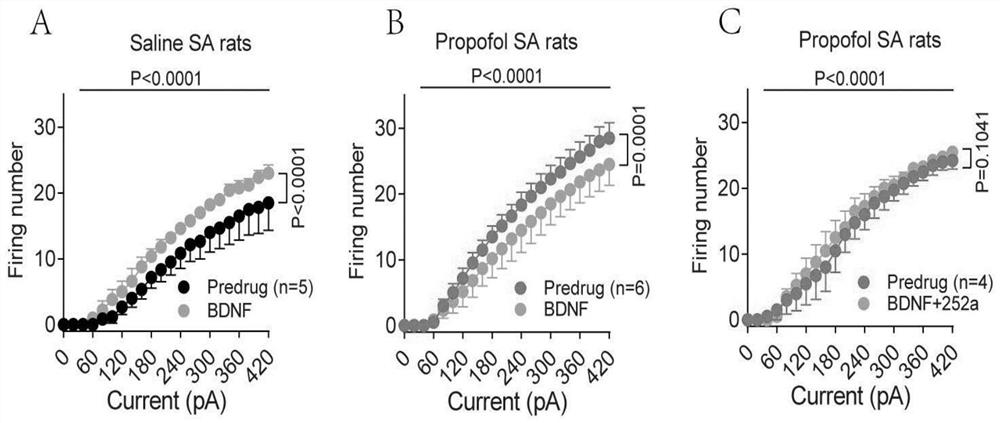
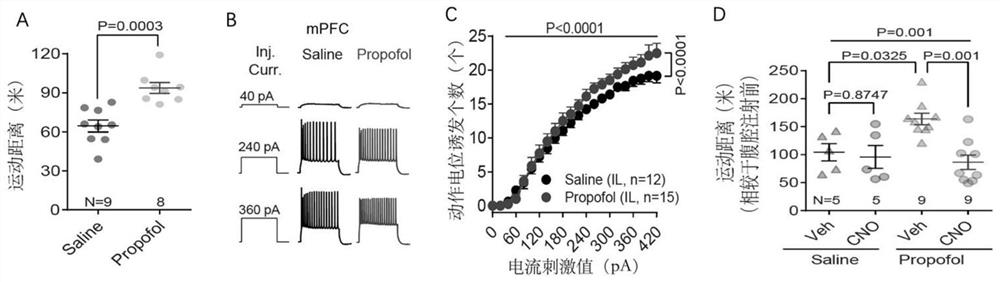
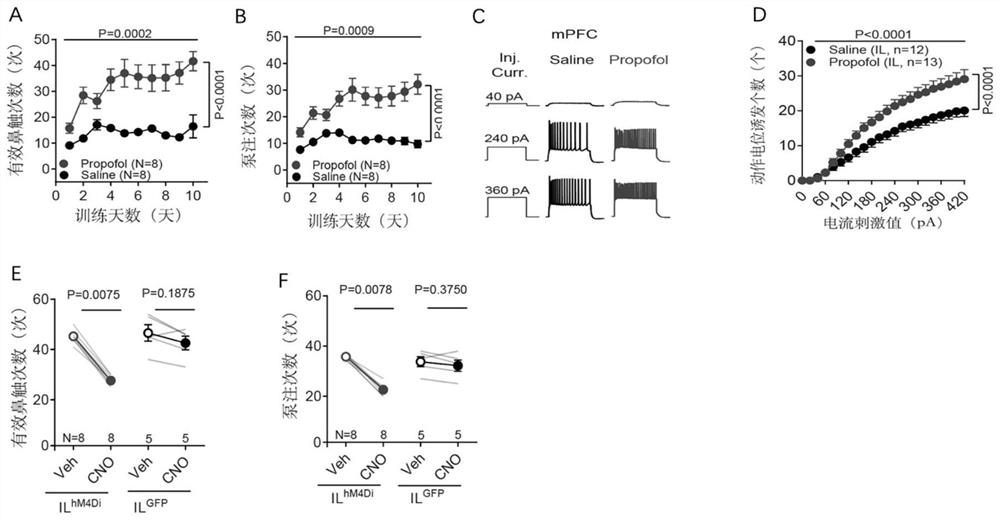
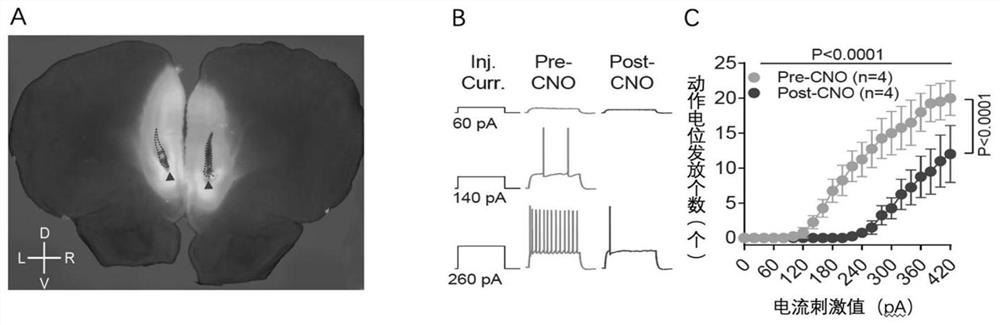
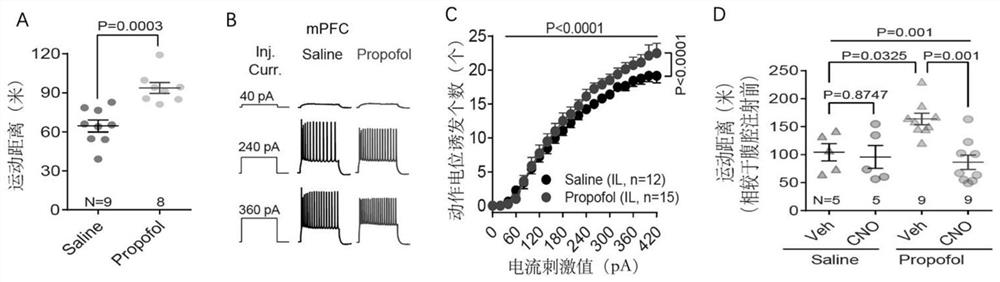
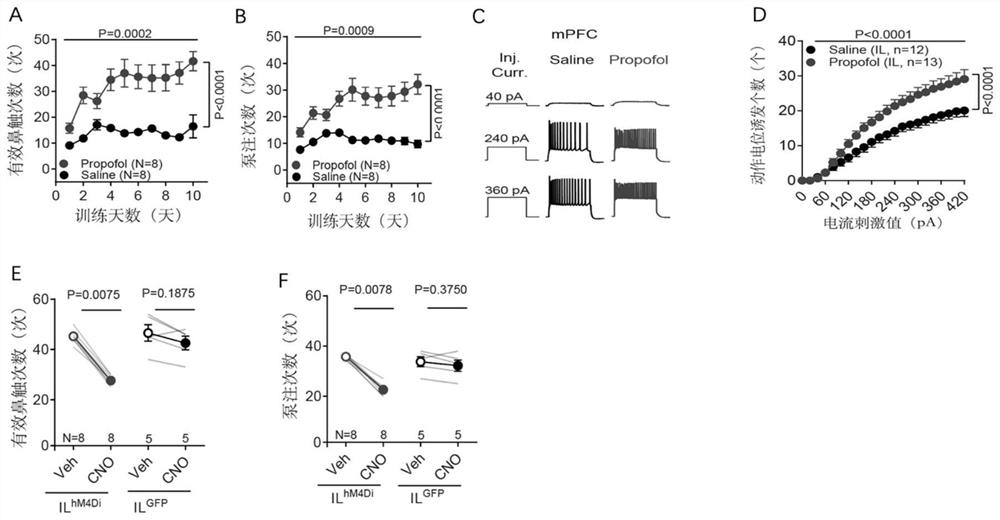
The invention discloses an application of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction. The invention fully proves that SD rats can generate addiction behaviors after long-term repeated use of propofol, and the addiction behaviors are mainly caused by increased excitability of neurons of the forehead cortex of the brain, especially the forehead cortex of the inner side (mPFC area); and the BDNF can effectively inhibit the highly excited state of cells in the mPFC region of the cortex caused by propofol, thereby inhibiting the propofol addiction behavior of rats. The invention provides an effective treatment means for treating the symptoms of addiction and excitability of propofol addiction, has a good effect, and isexpected to fundamentally treat propofol addiction behaviors.
Owner:连庆泉
System and method for simulating biological neuron dynamics to realize logical operation
The invention discloses a system and a method for simulating biological neuron dynamics to realize logical operation. The system for simulating biological neuron dynamics to realize logical operation comprises an input module, an electric coupling module, a laser response module and an output module. The system for simulating biological neuron dynamics to realize logical operation is based on the Fano laser, on one hand, compared with a traditional laser, the system has more stable characteristics, so that the excitability of simulated neurons can be more stable through an electric signal modulation injection technology, and unnecessary relaxation oscillation phenomena cannot be generated; and thus, the information processing speed is increased. Meanwhile, on the basis of avoiding extra light injection, the structure simplification is realized, especially in a large neural network for realizing complex tasks. And secondly, the Fano laser is extremely small in size, extremely low in energy consumption, higher in speed, simple in structure, low in cost and easy to control.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
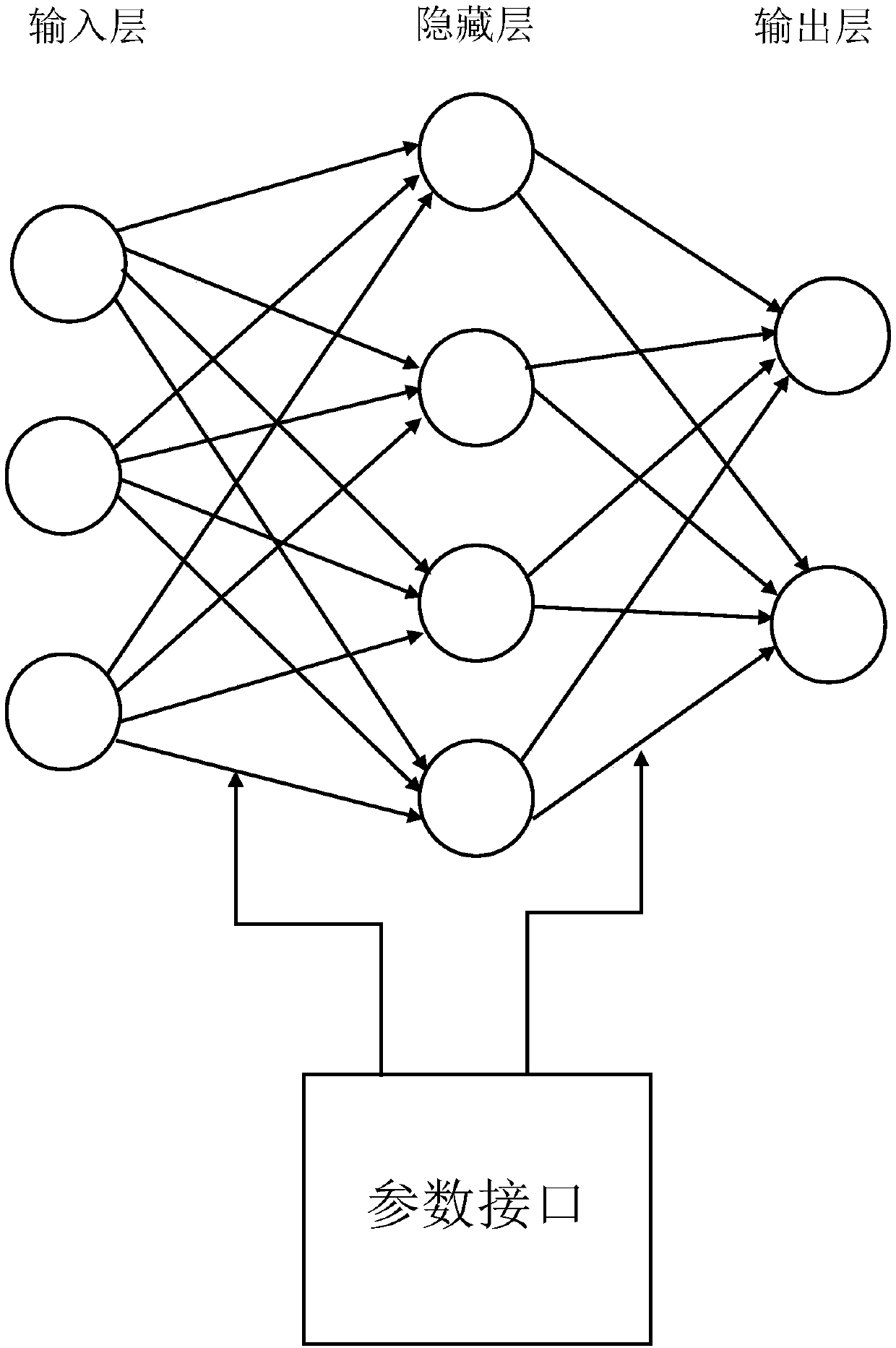
Neural network circuit structure capable of changing nerve cell excitement
InactiveCN109657785AAdequate approximation to the nonlinear stateApproximate nonlinear statePhysical realisationNeural learning methodsNetwork structureUncertain systems
The invention discloses a neural network circuit structure capable of changing nerve cell excitement, which comprises a neural network structure and a parameter interface module, and is characterizedin that the neural network structure is connected with the parameter interface module. According to the invention, the nonlinear state of neuronal excitement during learning of people can be fully approximated; The self-learning capability is achieved, and unknown or uncertain systems can be learned; All quantitative or qualitative information is equipotential distributed and stored in each neuronin the emotional neural network, so that the robustness and the fault tolerance are very high; And a parallel distribution processing method is adopted, so that the high-speed solution searching andoptimizing capability is achieved, the high-speed operation capability of a computer can be exerted, a large number of operations can be carried out quickly, and the learning efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Application of chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction
ActiveCN111658677BSignificant anti-addictive effects of propofolAddiction PreventionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAddictive behaviorPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses the application of a chemical genetic drug composition in preparing a drug for preventing and treating propofol addiction. The propofol addiction mainly involves two classic addictive behaviors, behavioral sensitization and self-administration. The present invention fully proves that after long-term repeated use of propofol in rats, addictive behavior will be produced, which is mainly caused by the excitation of neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC area) of the cortex; Inhibits the hyperexcitable state of mPFC region induced by propofol, thereby inhibiting propofol-addictive behavior in rats. The chemical genetic drug composition provided by the invention has the advantages of good effect, strong controllability and the like, and provides a new therapeutic drug for the treatment, research, development and prevention of propofol addiction.
Owner:连庆泉 +1
Therapeutic device and system used for treatment of insomnia based on mobile terminal
InactiveCN105344006AEffective stimulationEffectively induce excitementElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTherapeutic DevicesEngineering
The invention relates to a device and system used for treatment of insomnia based on a mobile terminal. A constant current generation module is connected with a control module and a power supply module. The control module controls the constant current generation module to generate constant current. A first electrode and a second electrode are connected with the constant current generation module. The first electrode is a positive electrode. The second electrode is a negative electrode. Electrifying current of the first electrode and the second electrode is greater than 0mA and less than 5mA. Electrifying time of the first electrode and the second electrode is from 15min to 40min. According to the device used for treatment of insomnia based on the mobile terminal, electrical stimulation waveforms which can effectively induce neuron excitation and are low in electrode corrosion without tissue damage can be designed through direct current stimulation, electroencephalogram signal detection and insomnia diagnosis by aiming at neural electrophysiological characteristics of insomnia according to a strength-duration curve and the biological effect of the electrical stimulation waveforms.
Owner:深圳市太赫兹科技有限公司
A fusion polypeptide with anti-cerebral ischemia effect and its application
ActiveCN106928322BGood at crossing the blood-brain barrierPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesMedicinePharmaceutical drug
The invention provides a fusion polypeptide with a cerebral ischemia resistant effect and application thereof. The fusion polypeptide has a peptide chain fragment sequence of YGRKKRRQRRRGDPV. The polypeptide provided by the invention can rapidly and effectively enter cells; through interfering with the signal conduction of CAPON, the neuron excitatory toxicity injury induced by glutamic acid is obviously inhibited; the cerebral ischemia injury of MCAO model rats can be effectively resisted. The polypeptide has good application prospects in the preparation of medicine for treating cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Application of chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction
ActiveCN111658677ASignificant anti-addictive effects of propofolAddiction PreventionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAddictive behaviorPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses an application of a chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction. The propofol addiction mainly relates to two classic addiction behaviors of behavior sensitization and self-administration. The invention fully proves that the addiction behaviors are generated after propofol is repeatedly used for along time for a rat, and the addiction behaviors are mainly caused by excitation of neurons of the prefrontal cortex (mPFC region) on the inner side of the cortex; and the mPFC region high excitationstate caused by the propofol can be effectively inhibited by utilizing the chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition, so that the propofol addiction behaviors of the rat is inhibited. The chemicalgenetics pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention has the advantages of good effect, strong controllability and the like, and provides a new therapeutic medicine for treating, researchingand developing and preventing propofol addiction.
Owner:连庆泉 +1
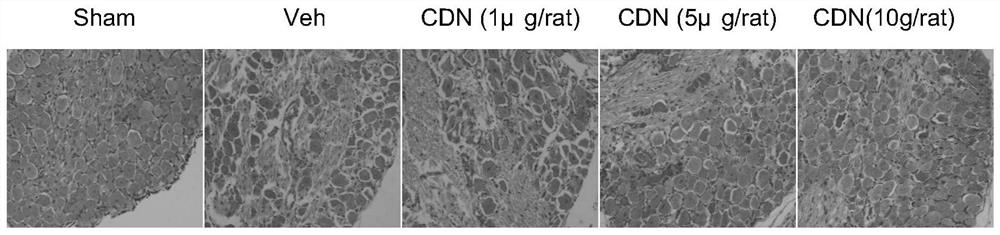
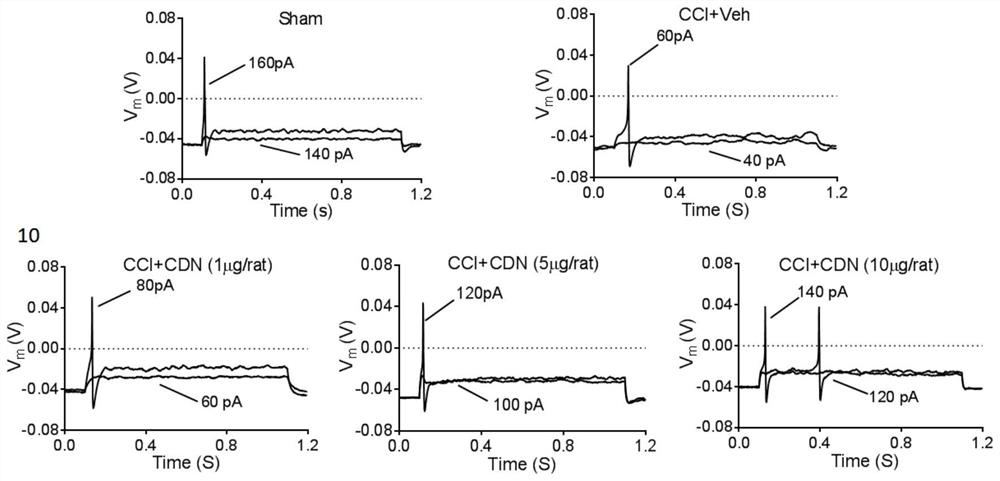
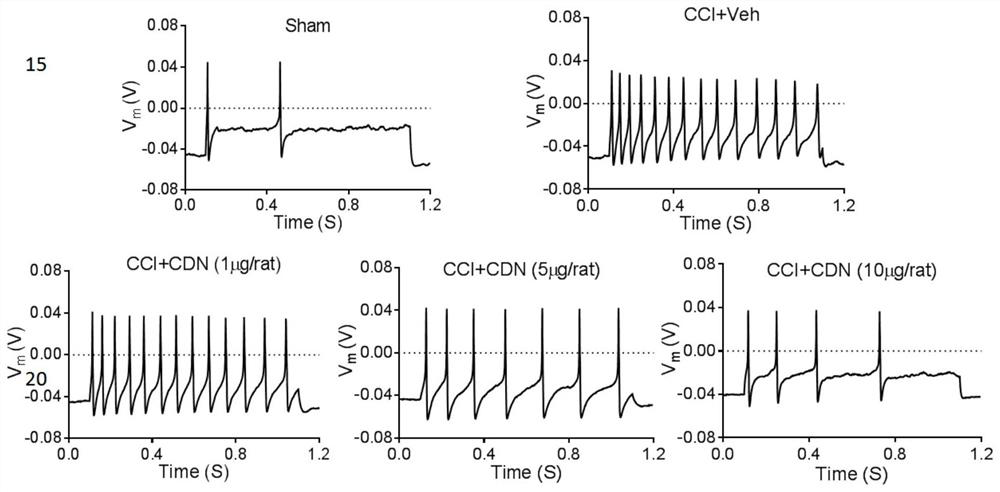
Application of cdn1163 in the preparation of drugs for alleviating or treating neuropathic pain
ActiveCN112716953BPromote activationInhibition of elevated excitabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDrug withdrawalNeural foramen
The invention discloses the application of CDN1163 in preparing a medicine for relieving or treating neuropathic pain. The CDN1163 can act on neuropathic pain including one or more of central neuropathic pain and peripheral neuropathic pain, and improve chronic sciatic nerve compression in rats. Mechanical pain sensitivity and thermal pain sensitivity caused by sexual injury, improve neuronal shrinkage and astrocyte activation in lumbar intervertebral foramen 5 dorsal root ganglia, inhibit neuronal excitation in lumbar intervertebral foramina 4-6 dorsal root ganglia It can effectively reduce the symptoms of neuropathic pain, and repeated injections can significantly reverse mechanical hyperalgesia and thermal hyperalgesia, and there is no sign of tolerance, and the therapeutic effect can be maintained after drug withdrawal. and difficult-to-treat neuropathic pain medications.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com