Patents
Literature
39 results about "Cortex motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
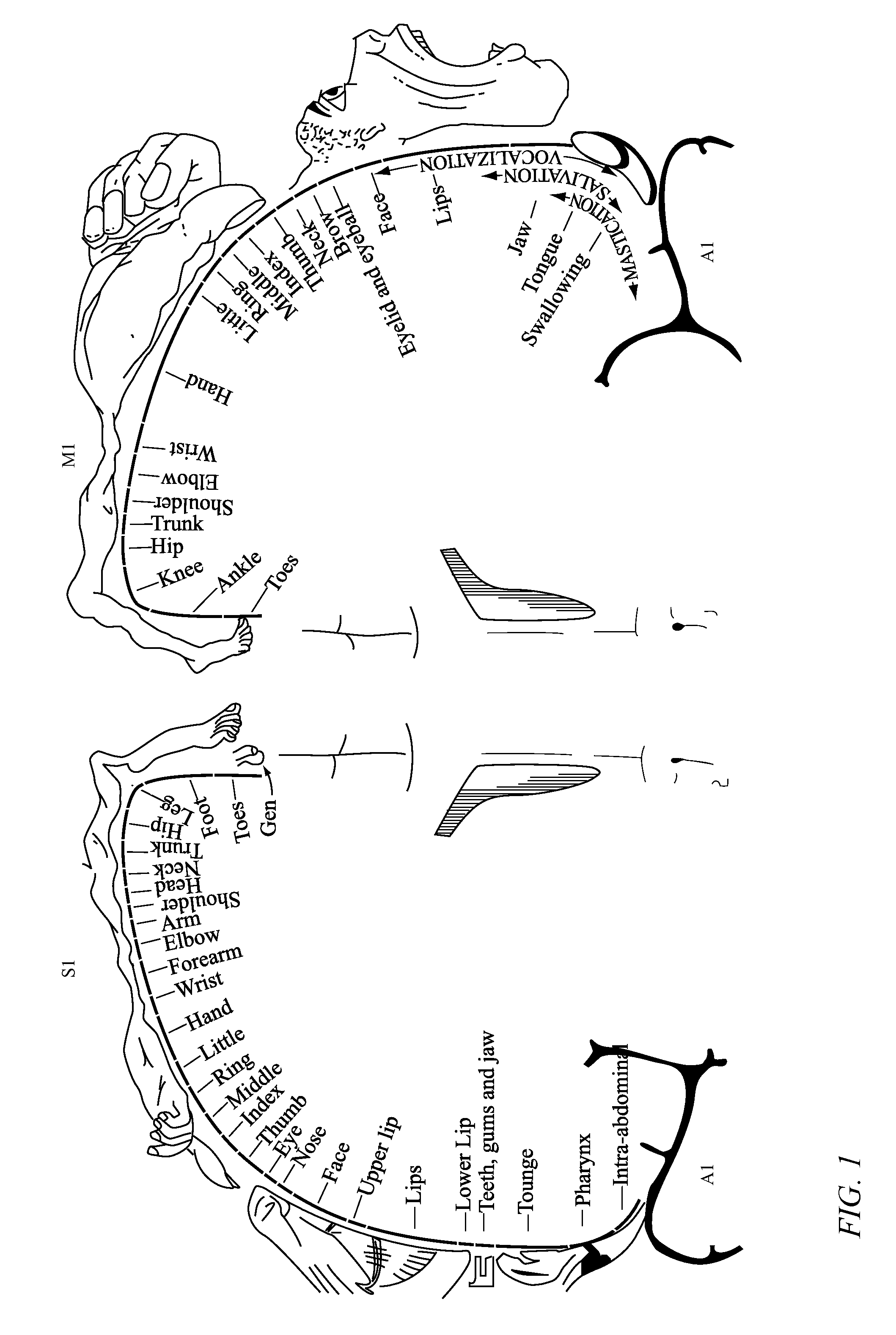
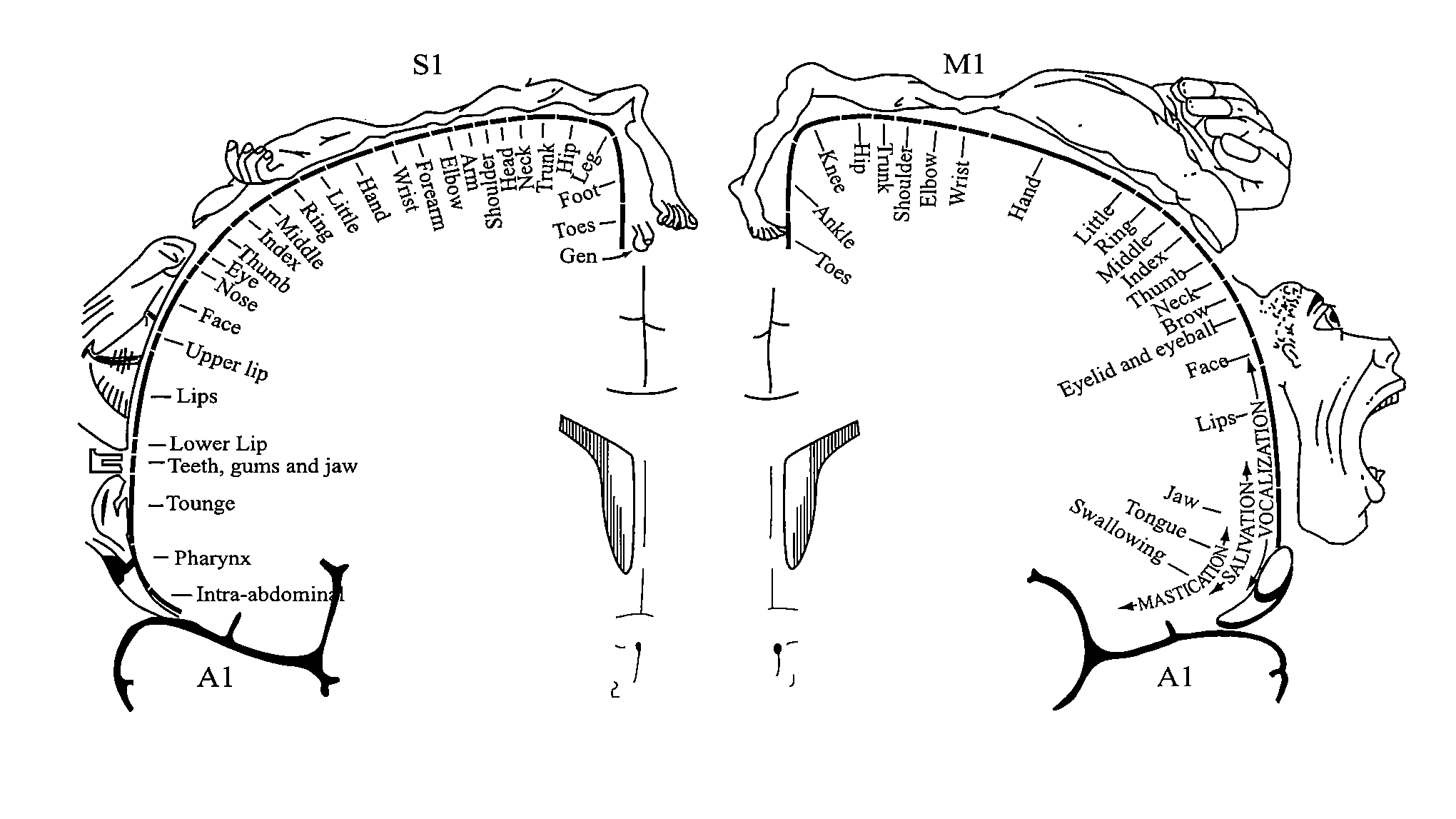
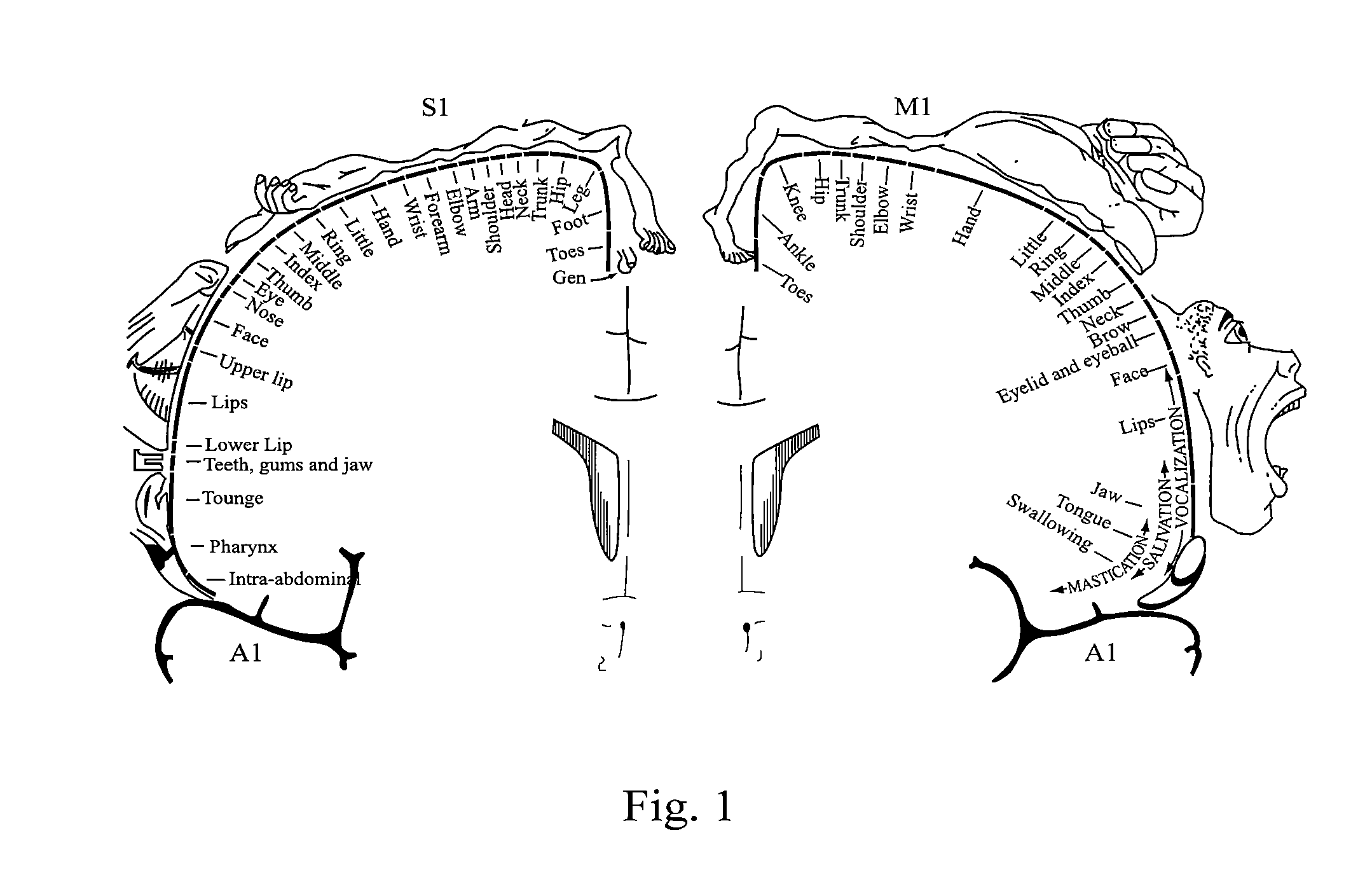
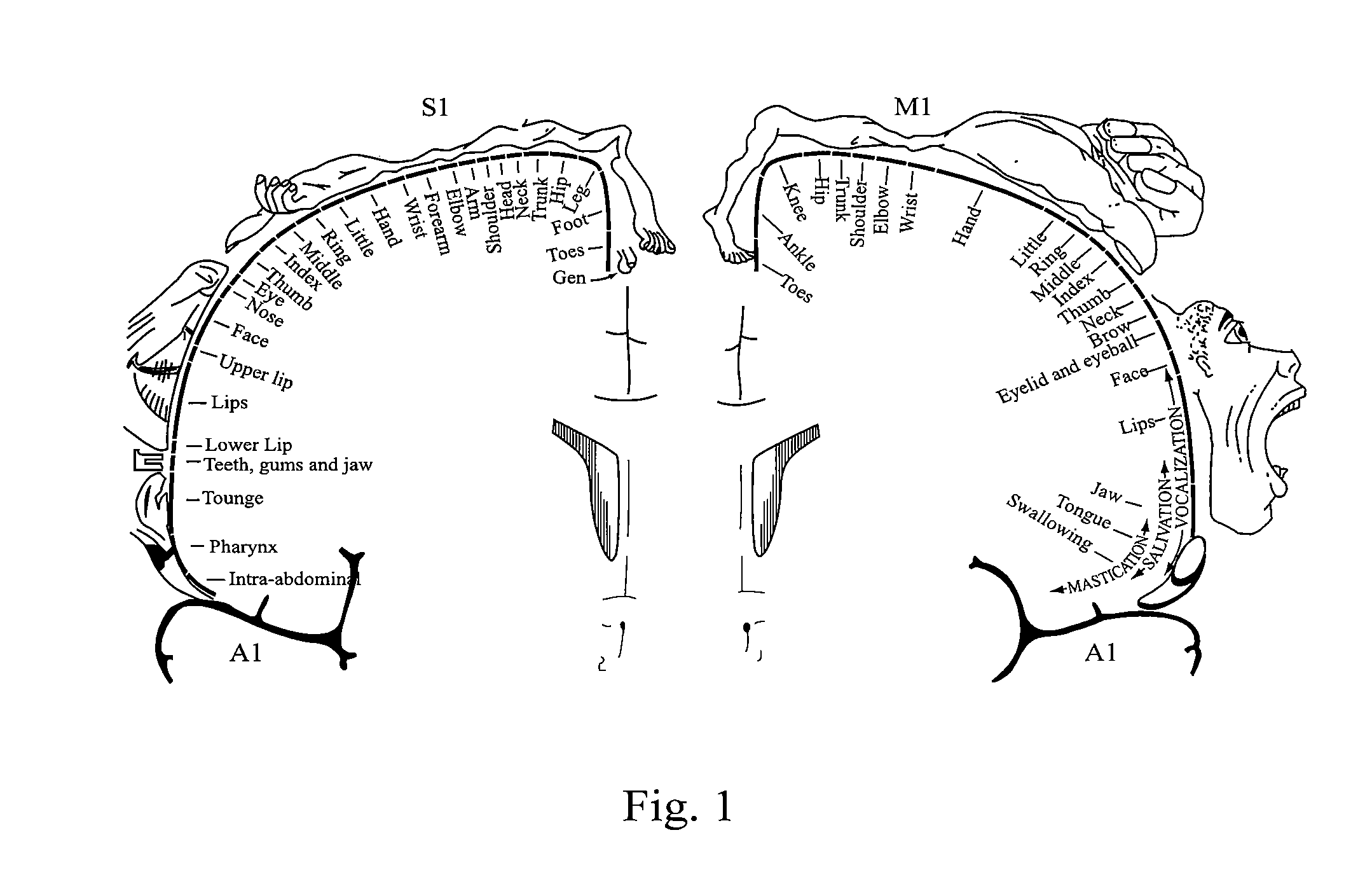
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. Classically the motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus.
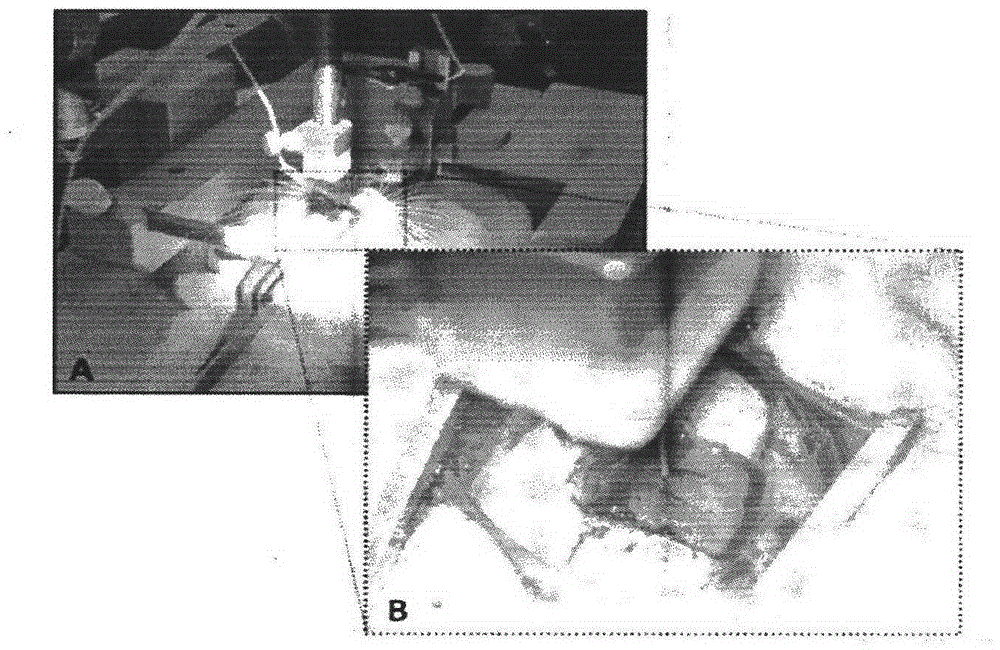
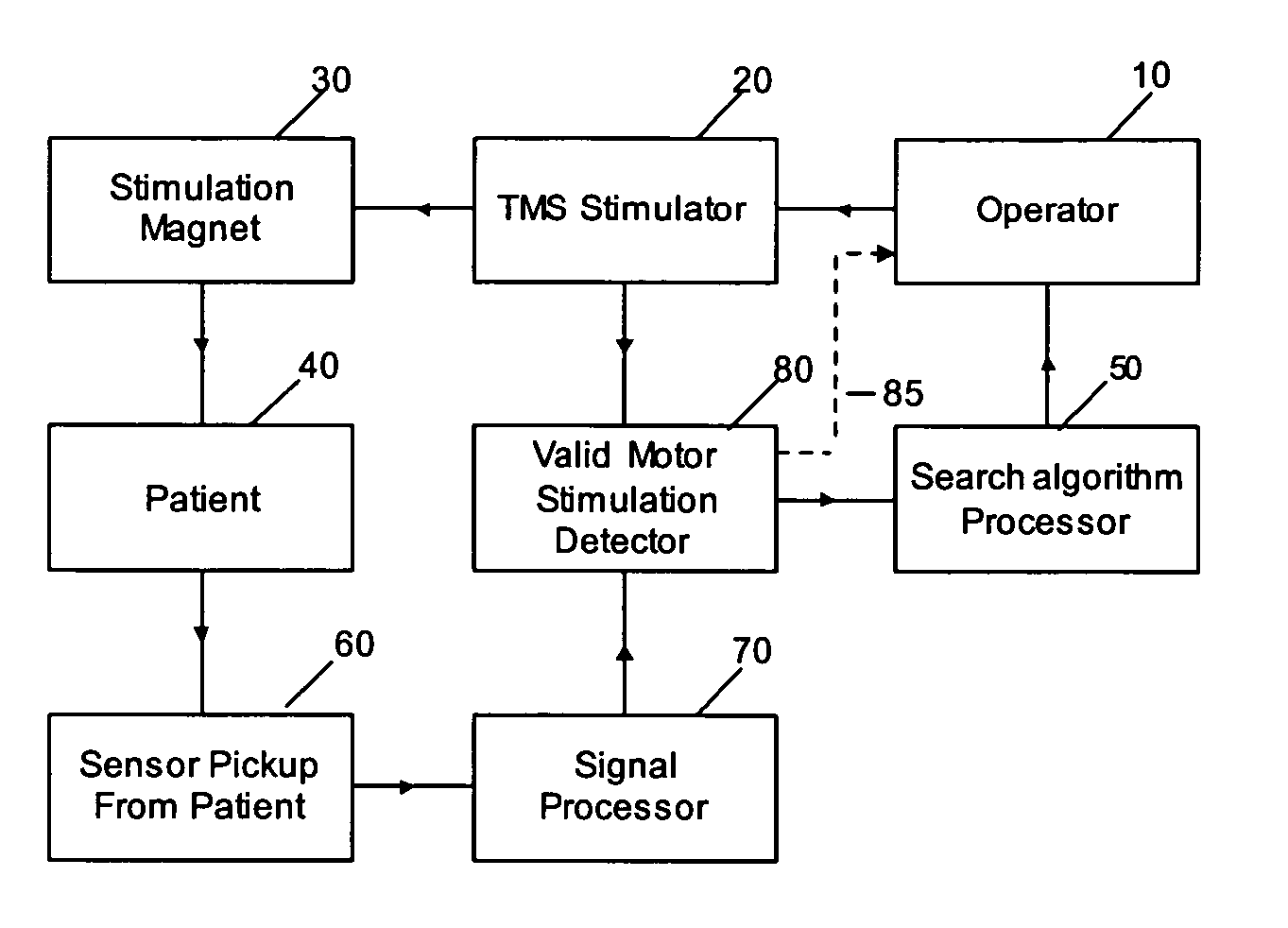
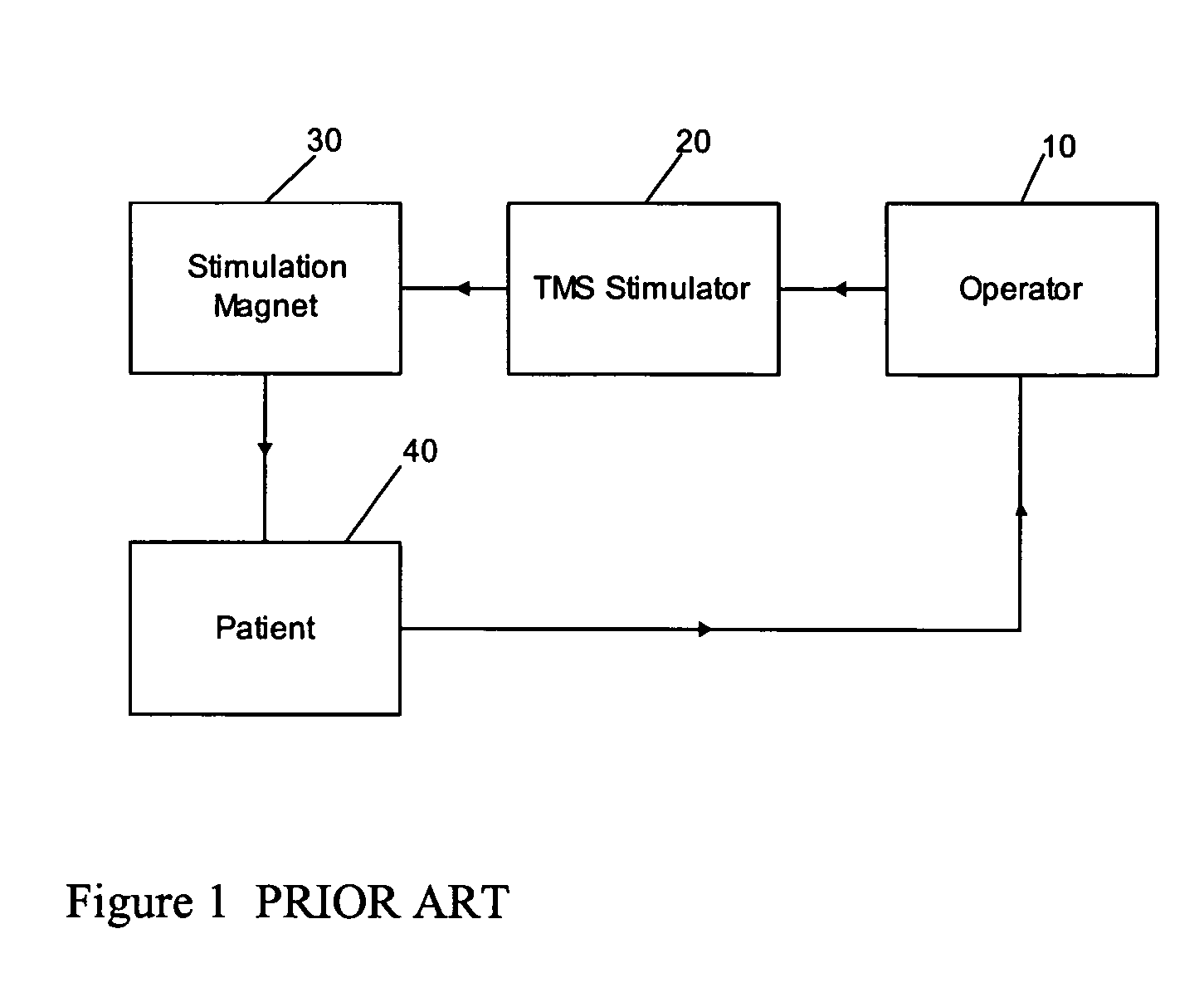
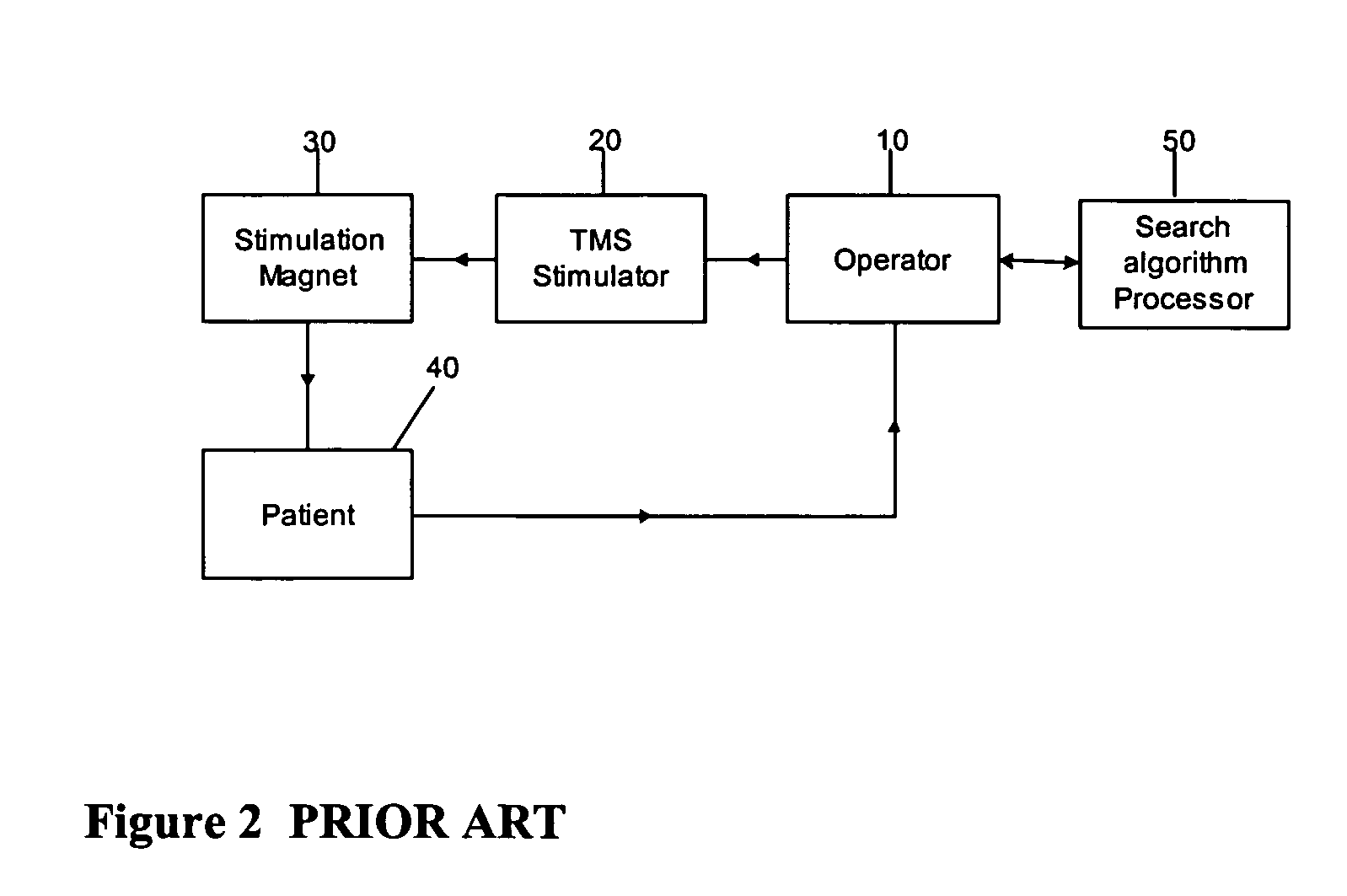
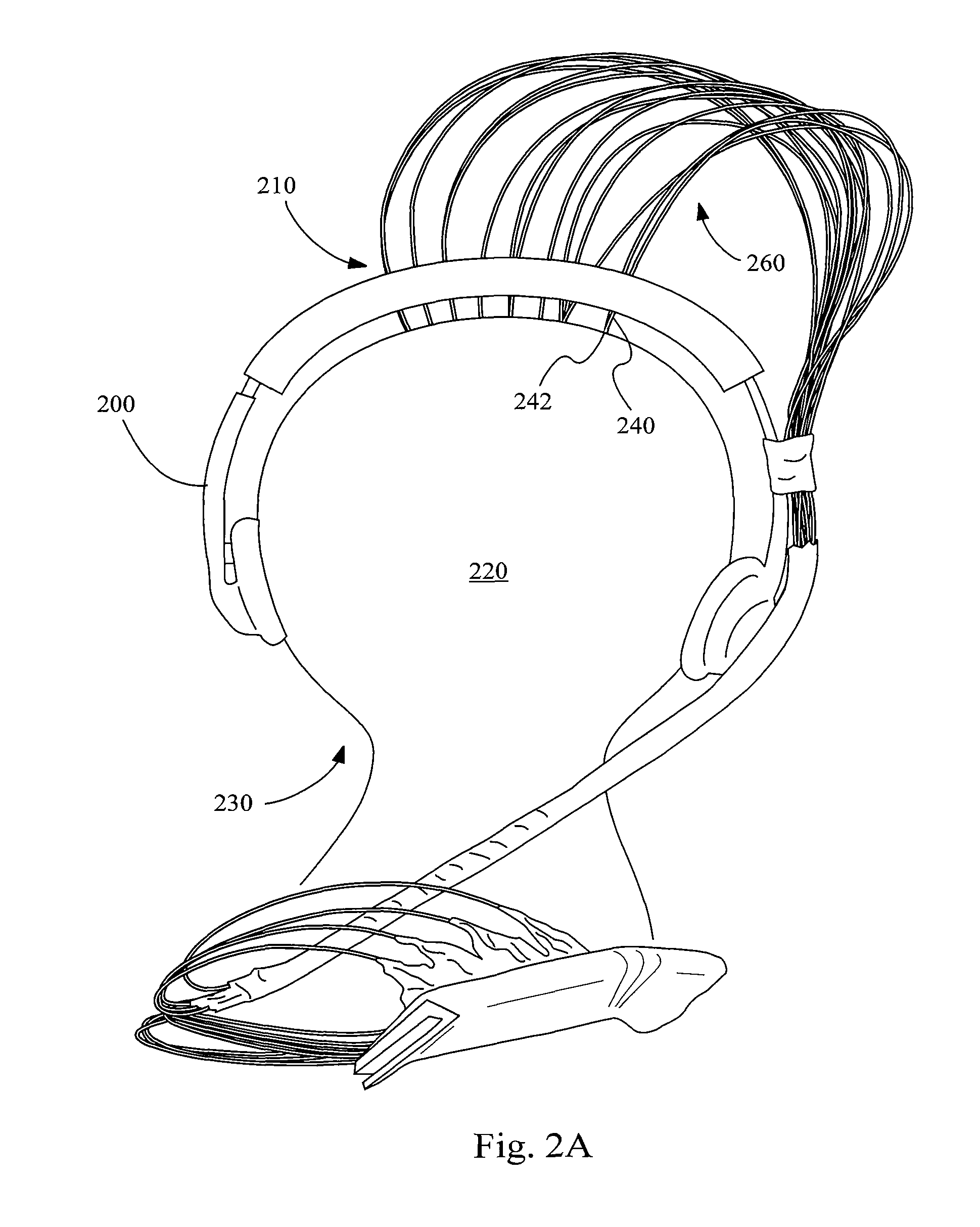
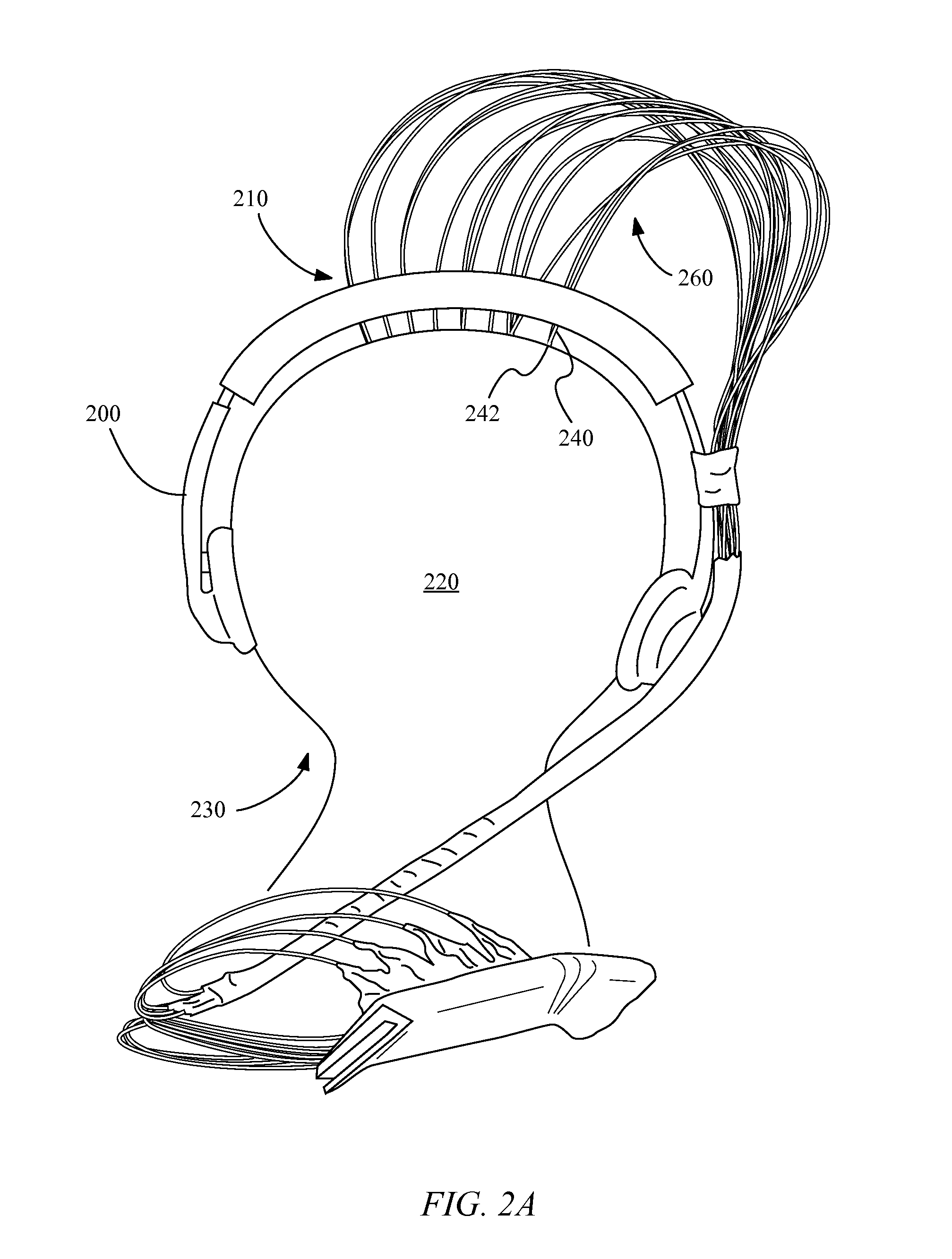
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
Methods and systems for controlling body parts and devices using ipsilateral motor cortex and motor related cortex
A system for controlling a body part includes a number of sensing devices that sense signals from a hemisphere of a brain. A signal translating unit translates the signals into a command signal for controlling the body part, which is on a same side of the body as the hemisphere of the brain. A prosthetic device receives the command signal from the signal translating unit and manipulates the body part in response to the command signal.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
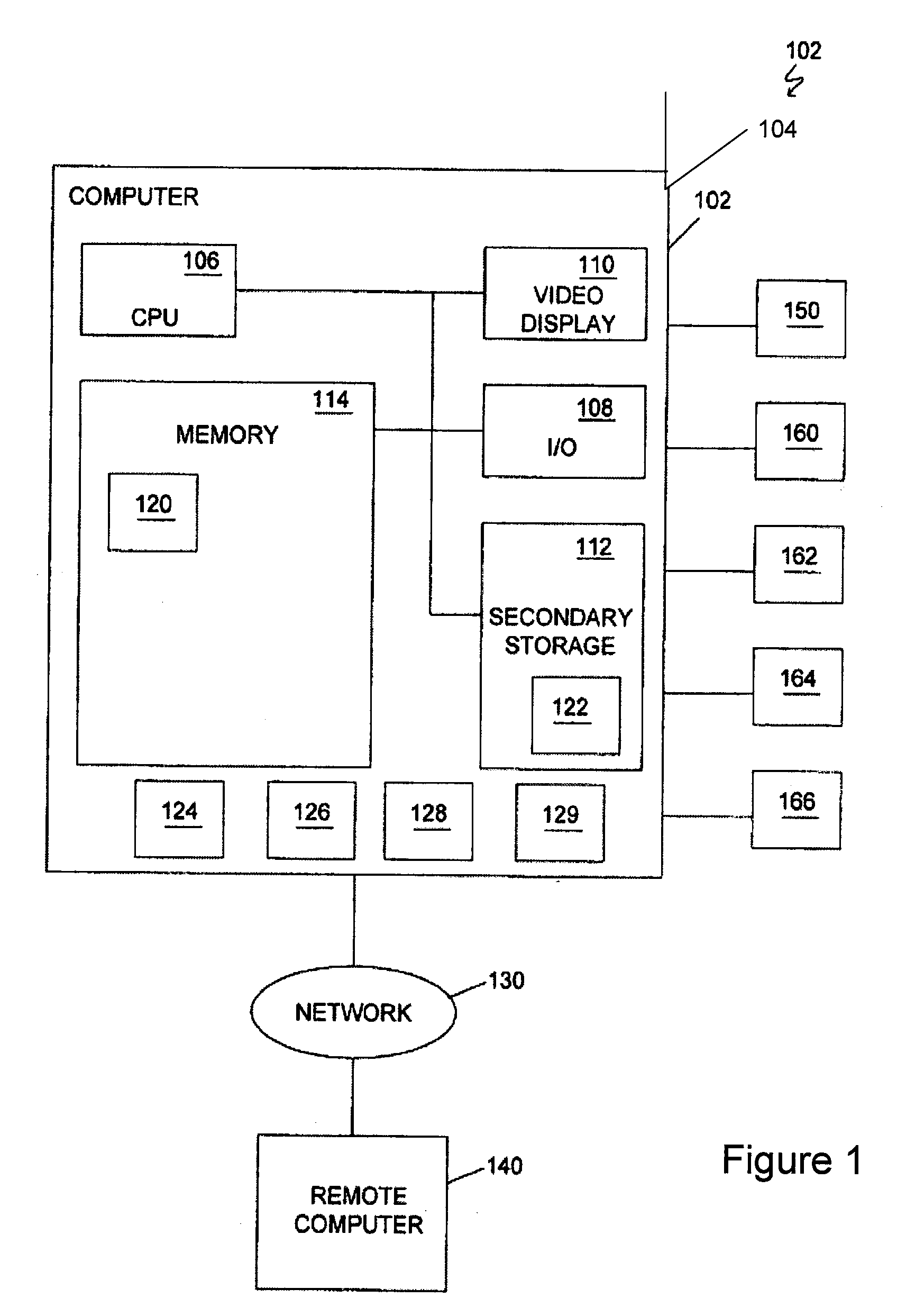
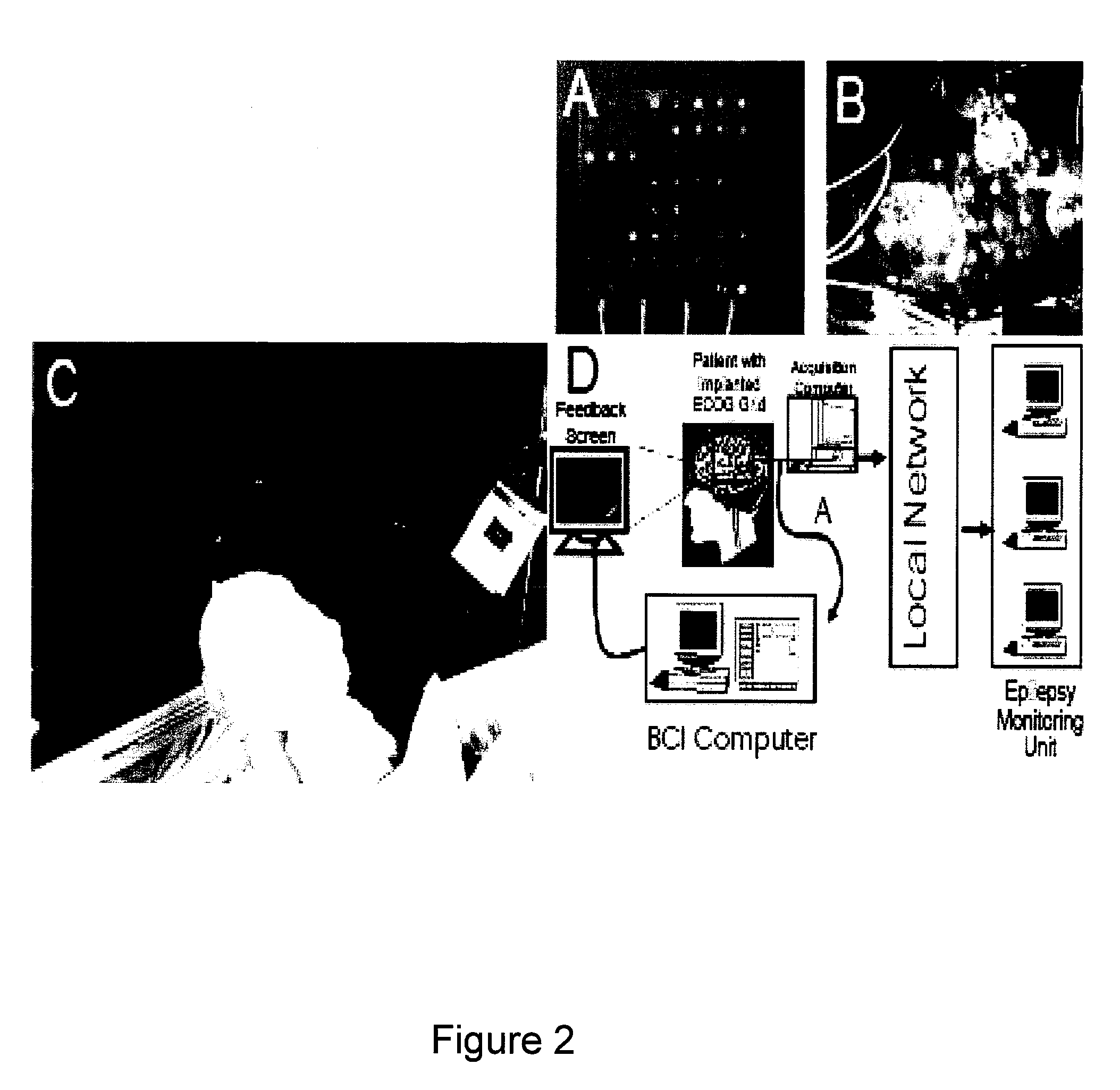
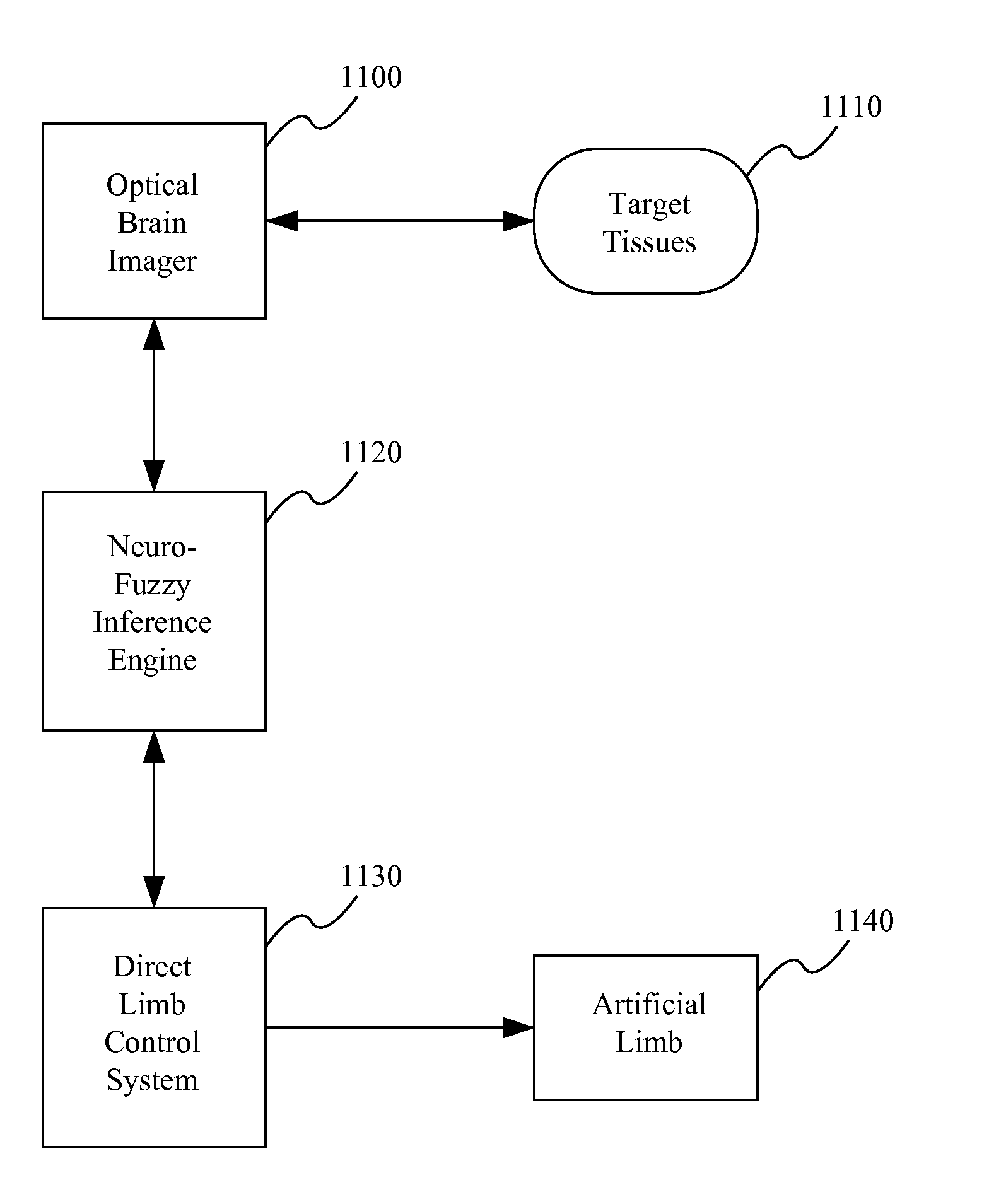
Brain imaging system and methods for direct prosthesis control
Methods and systems for controlling a prosthesis using a brain imager that images a localized portion of the brain are provided according to one embodiment of the invention. For example, the brain imager can provide motor cortex activation data using near infrared imaging techniques and EEG techniques among others. EEG and near infrared signals can be correlated with brain activity related to limbic control and may be provided to a neural network, for example, a fuzzy neural network that maps brain activity data to limbic control data. The limbic control data may then be used to control a prosthetic limb. Other embodiments of the invention include fiber optics that provide light to and receive light from the surface of the scalp through hair.
Owner:COLORADO SEMINARY
Method and system for treatment of neuromotor dysfunction
ActiveUS9011310B2Modulates associative plasticityLong recoverySurgeryMedical devicesMedicineBody region
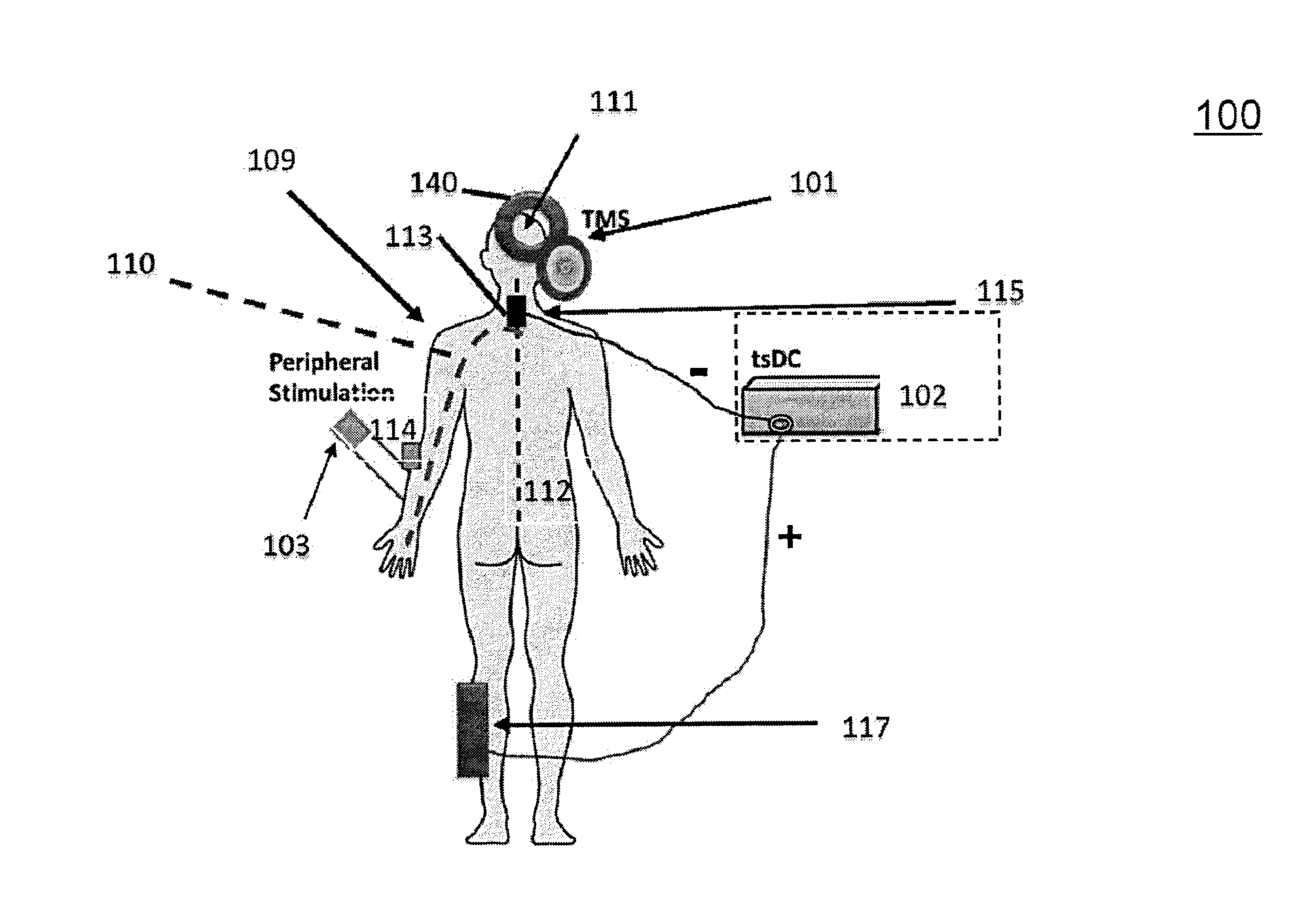
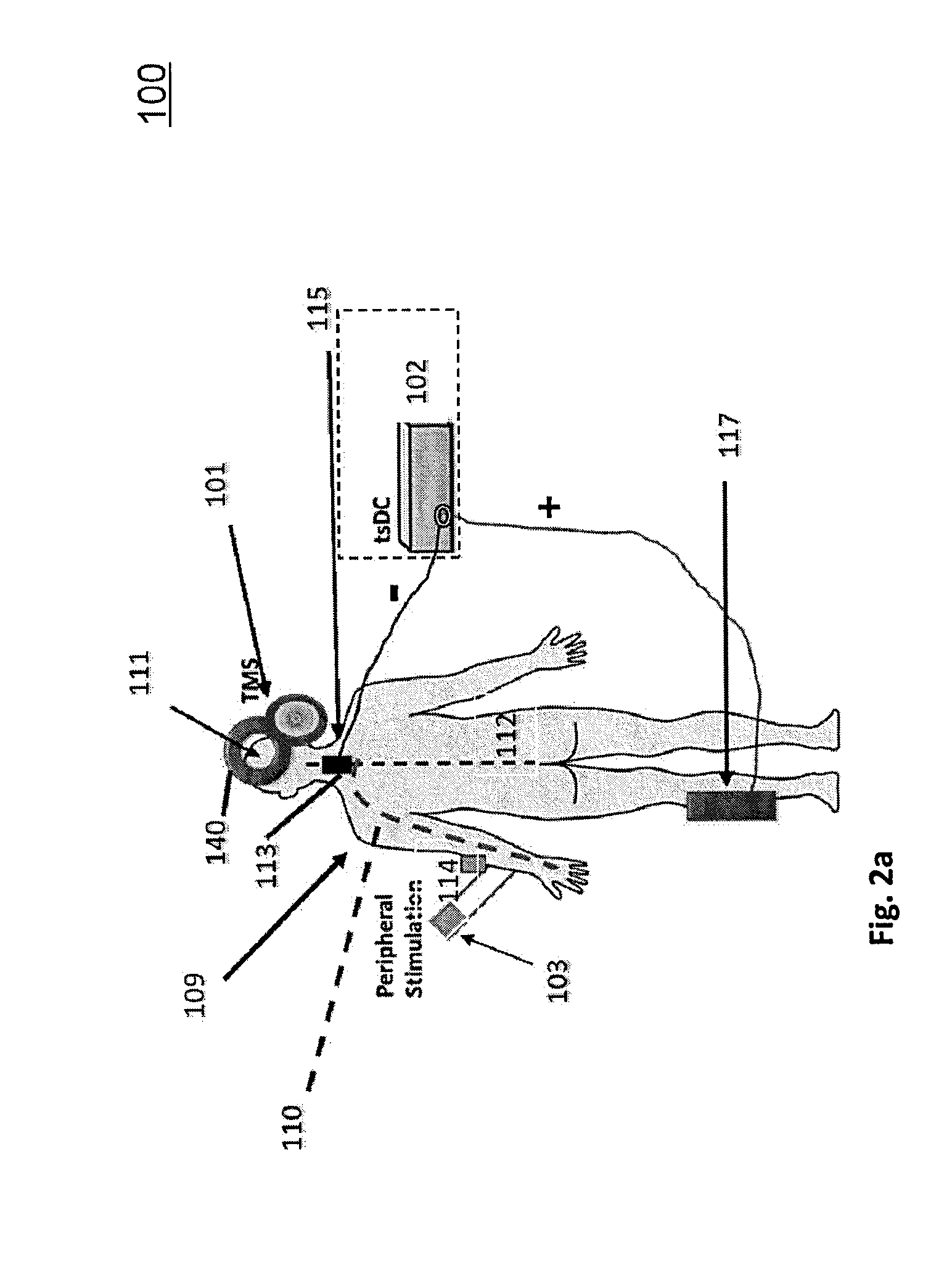
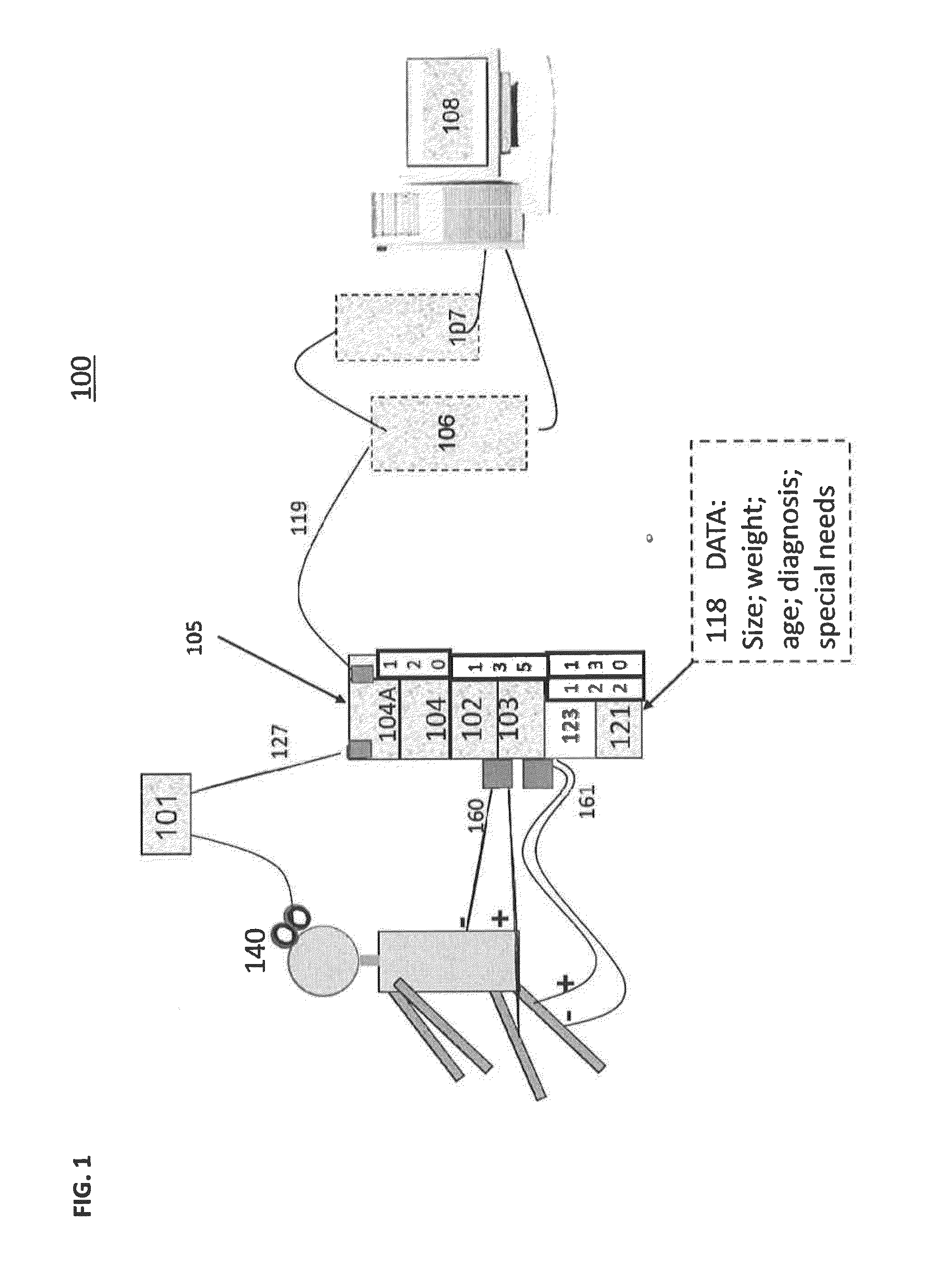
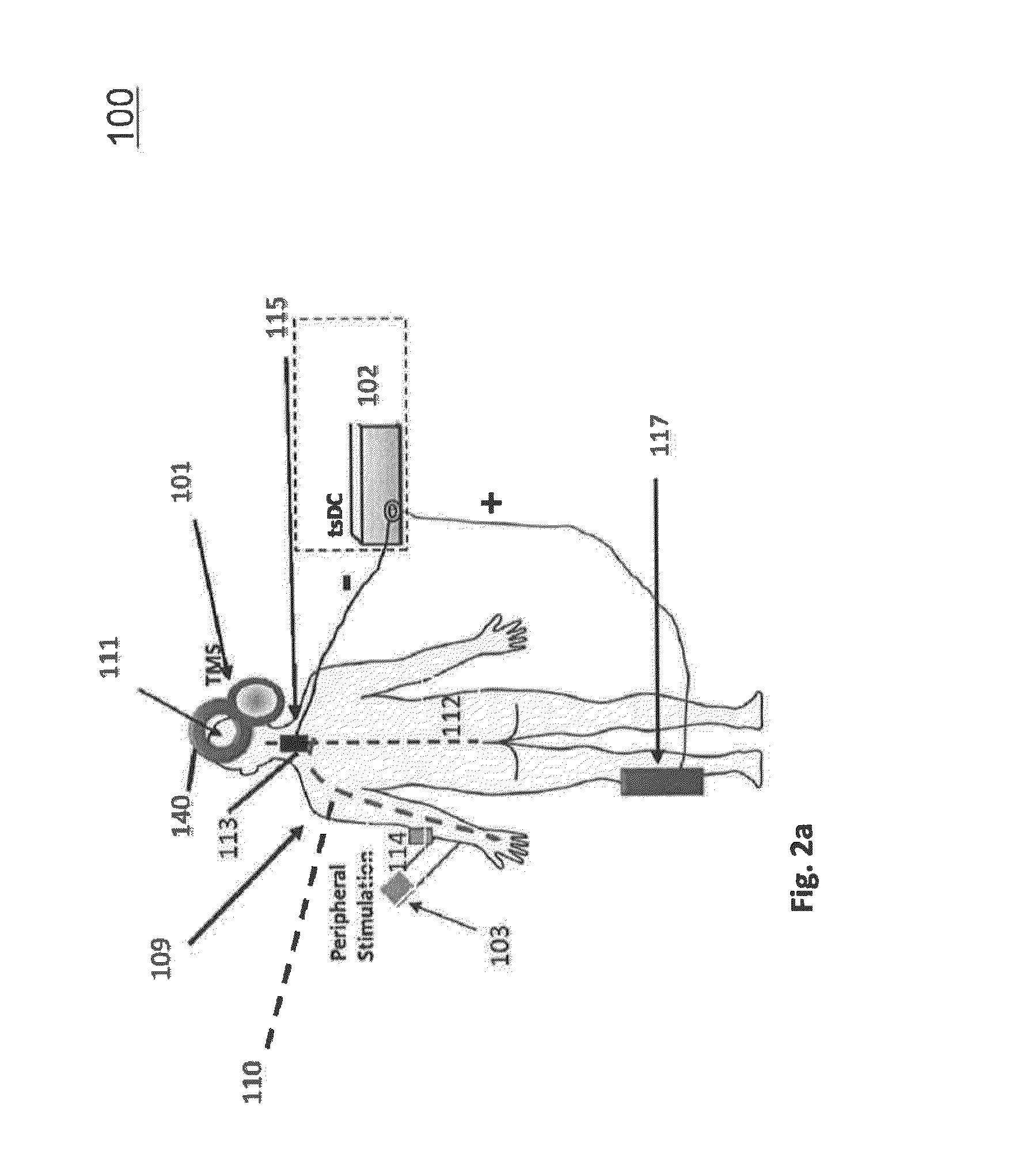
Effective systems and methods for improving neural communication impairment of a vertebrate being and affecting motor activity of a peripheral body part including a first signal-providing component configured to provide pulsed peripheral stimulation signals at the peripheral body part, a second signal-providing component configured to provide a pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal to a motor cortex area, a substantially DC signal-providing component configured to provide direct current spinal stimulation signal at a neural spinal junction and a controller component configured to control timing of the pulsed peripheral stimulation signals and the pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and system for treatment of mobility dysfunction
ActiveUS9008781B2Modulates associative plasticityLong recoveryMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsExternal electrodesMedicineDirect current
Effective systems and methods for improving neural communication impairment of a vertebrate being and affecting motor activity of a peripheral body part including a first signal providing component configured to provide pulsed peripheral stimulation signals at the peripheral body part, a second signal providing component configured to provide a pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal to a motor cortex area, a substantially DC signal providing component configured to provide direct current spinal stimulation signal at a neural spinal junction and a controller component configured to control timing of the pulsed peripheral stimulation signals and the pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Brain imaging system and methods for direct prosthesis control
Methods and systems for controlling a prosthesis using a brain imager that images a localized portion of the brain are provided according to one embodiment of the invention. The brain imager provides motor cortex activation data by illuminating the motor cortex with near infrared light (NIR) and detecting the spectral changes of the NIR light as passes through the brain. These spectral changes can be correlated with brain activity related to limbic control and may be provided to a neural network, for example, a fuzzy neural network that maps brain activity data to limbic control data. The limbic control data may then be used to control a prosthetic limb. Other embodiments of the invention include fiber optics that provide light to and receive light from the surface of the scalp through hair.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DENVER
Multimodal closed-loop brain-computer interface and peripheral stimulation for neuro-rehabilitation
InactiveUS20200038653A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectrotherapyStatistical analysisCerebral damage
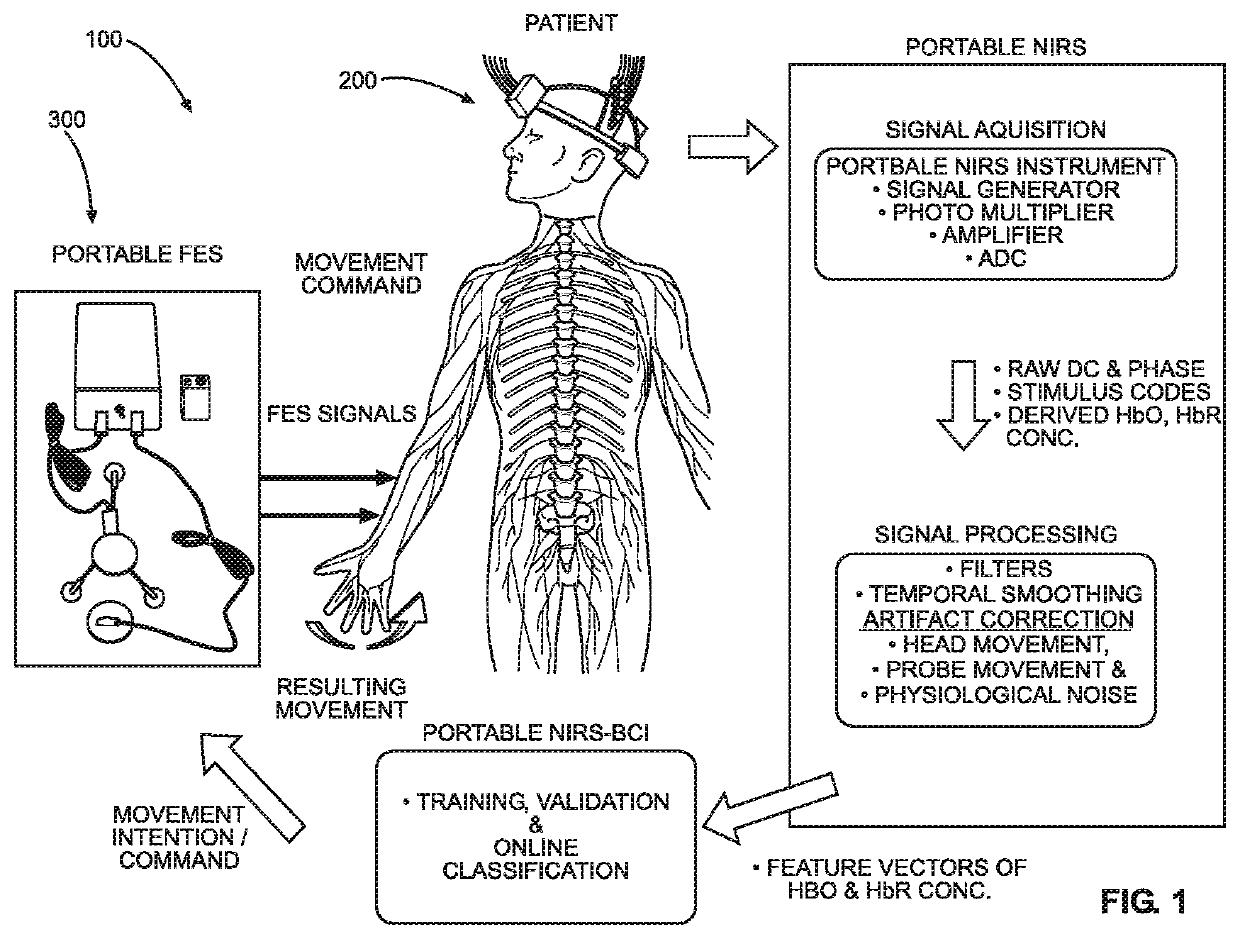
Brain impairment, for example due to stroke, is corrected in order to improve body movement. An fNIRS device is positioned over the motor cortex of non-impaired individuals, and blood oxygen in locations of the brain is analyzed to determine brain activity corresponding to a particular body movement. The movements are statistically analyzed, and are compared with fNIRS data gathered from a movement impaired individual attempting the same movement. A weighted value corresponding to the desired brain activity is generated using the statistical analysis, and is graphically displayed to the movement impaired individual during the attempts. This produces a feedback loop relating to the movement which can be repeated to produce brain plasticity in the impaired individual to facilitate the movement. Additionally, correct brain activity can be used to cause the application of an electrical signal to muscles of the body to produce the desired movement.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Methods and systems for controlling body parts and devices using ipsilateral motor cortex and motor related cortex
A system for controlling a body part includes a number of sensing devices that sense signals from a hemisphere of a brain. A signal translating unit translates the signals into a command signal for controlling the body part, which is on a same side of the body as the hemisphere of the brain. A prosthetic device receives the command signal from the signal translating unit and manipulates the body part in response to the command signal.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
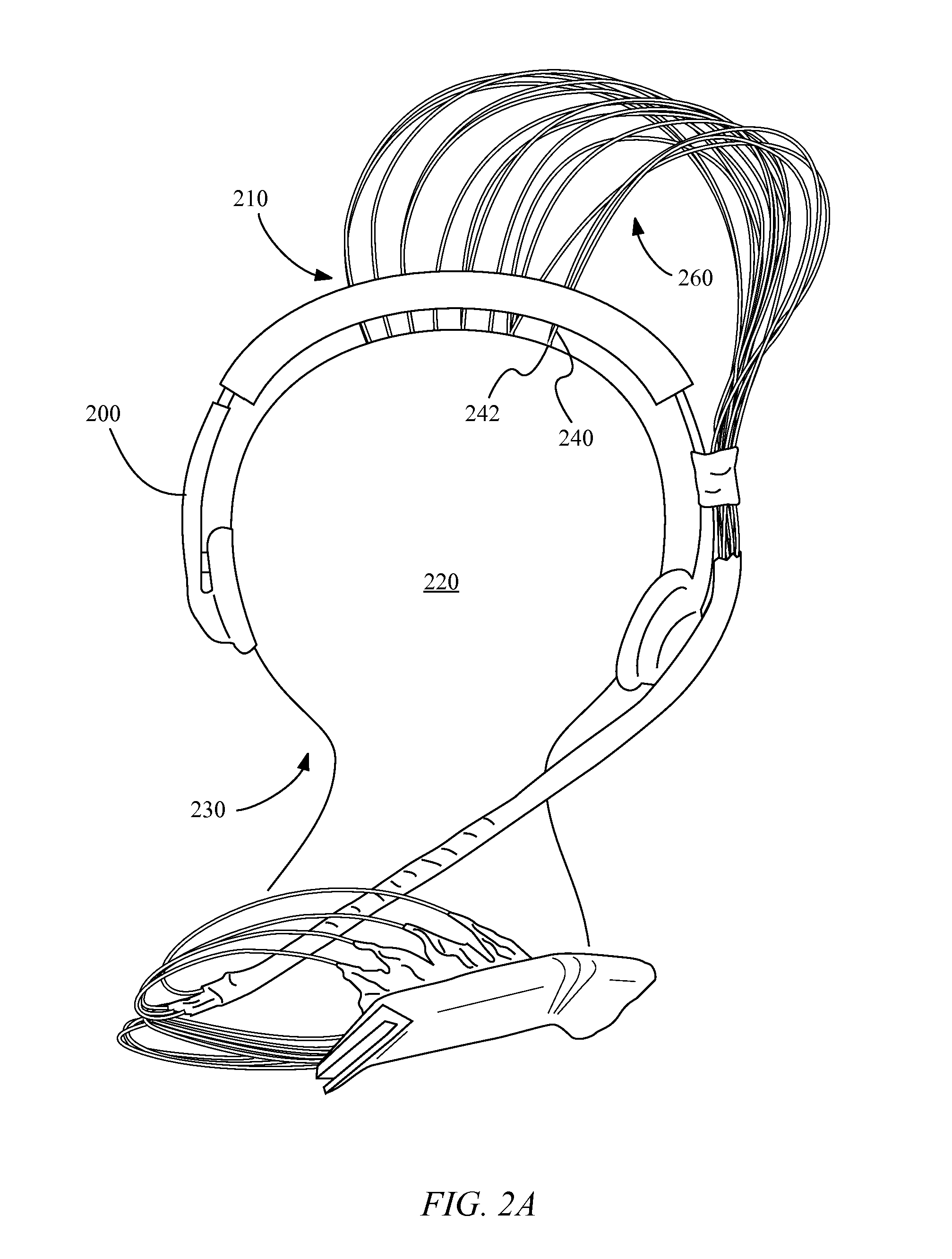
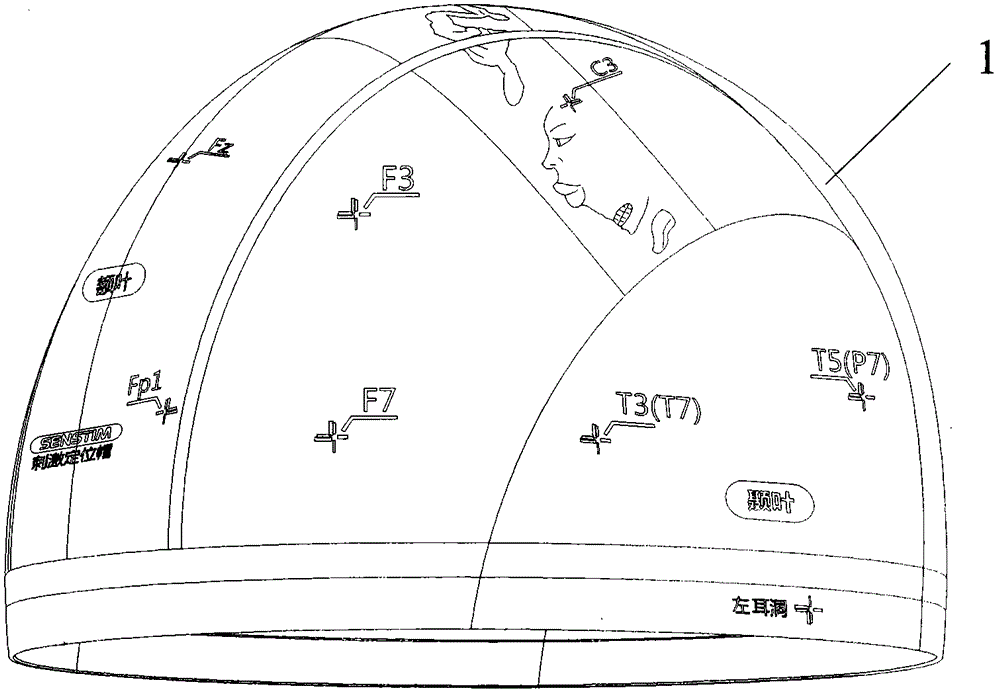
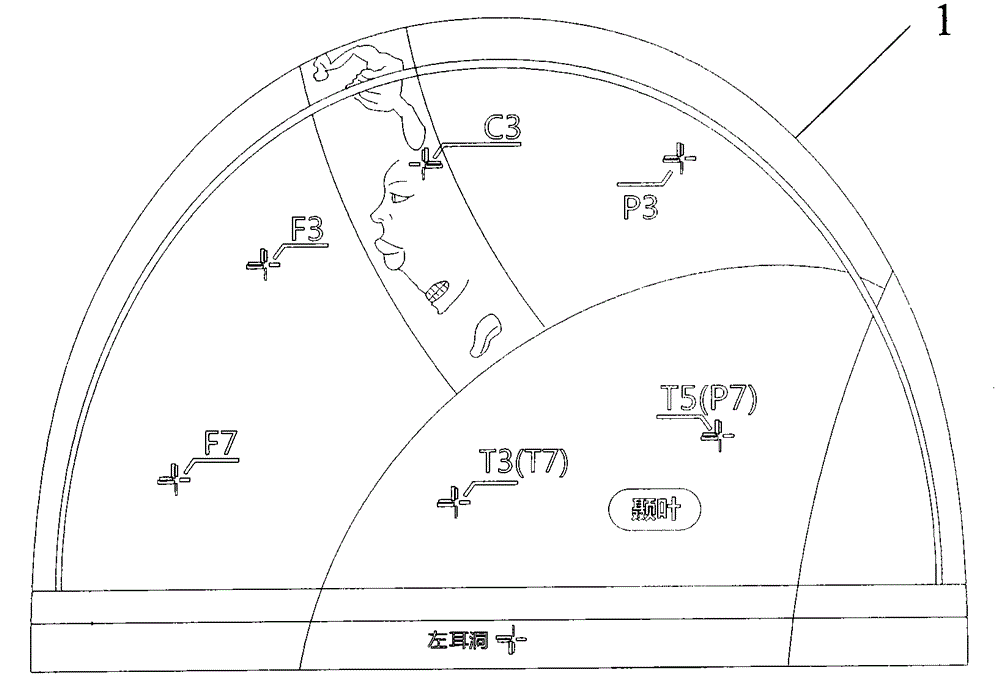
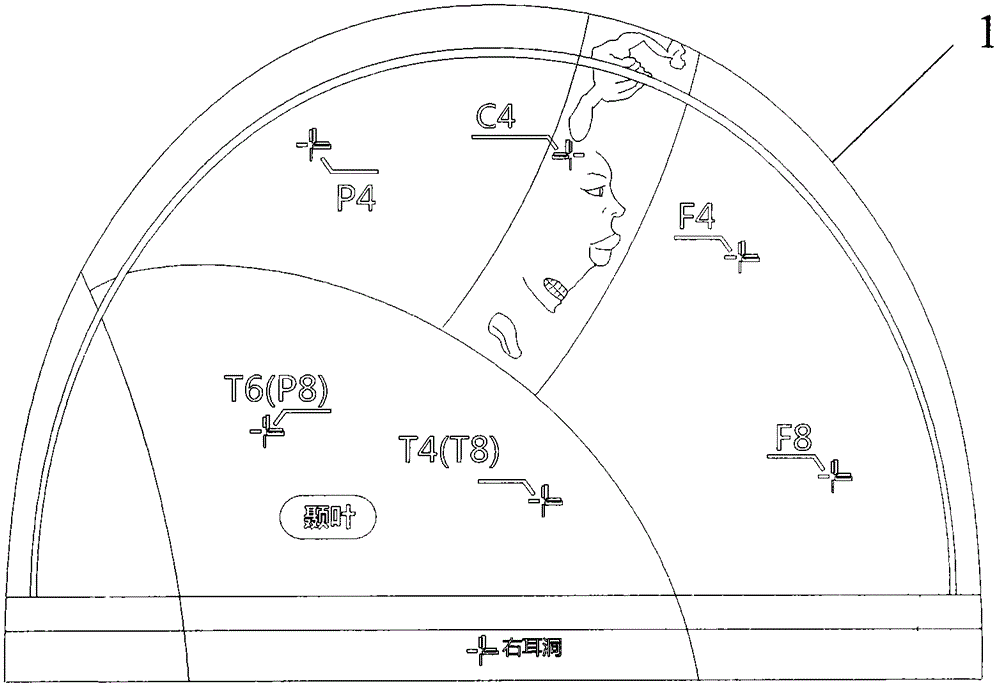
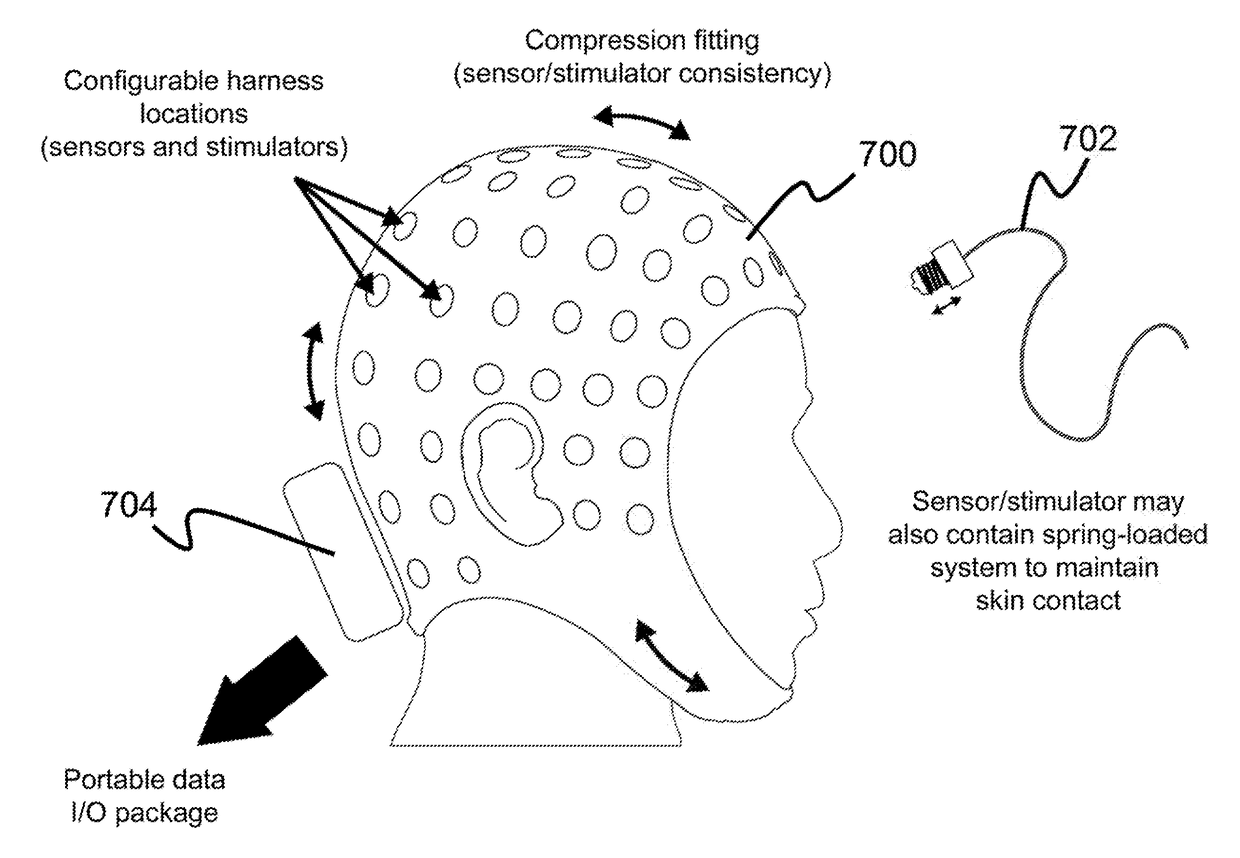
Transcranial magnetic stimulation positioning cap and marking method thereof
ActiveCN105879231AReduce medical costsSimple structureElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyCerebral hemisphereTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a transcranial magnetic stimulation positioning cap, which comprises a shell body adapt to the shape of a human brain, wherein the shell body is correspondingly provided with marking portions used for making two cerebral hemispheres, four brain lobes, EEG electrode parts, a motor cortex functional area, earholes for capping positioning and occipito posterior tuberosity. The transcranial magnetic stimulation positioning cap and the marking method thereof are low in implementation costs, thus medical expenses of patients are reduced; and the operation is convenient, time and effort are saved, and utilization rate of the equipment is increased. Multi-part marking information in the positioning cap makes stimulation parts accurate, the positioning description and repetitive stimulation of the stimulation parts are facilitated in scientific research. The uncertainty of traditional stimulation positioning relying on visual observation and experience is eliminated, and function modulation and therapeutic effect of stimulation nerves can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINGZHI TECH
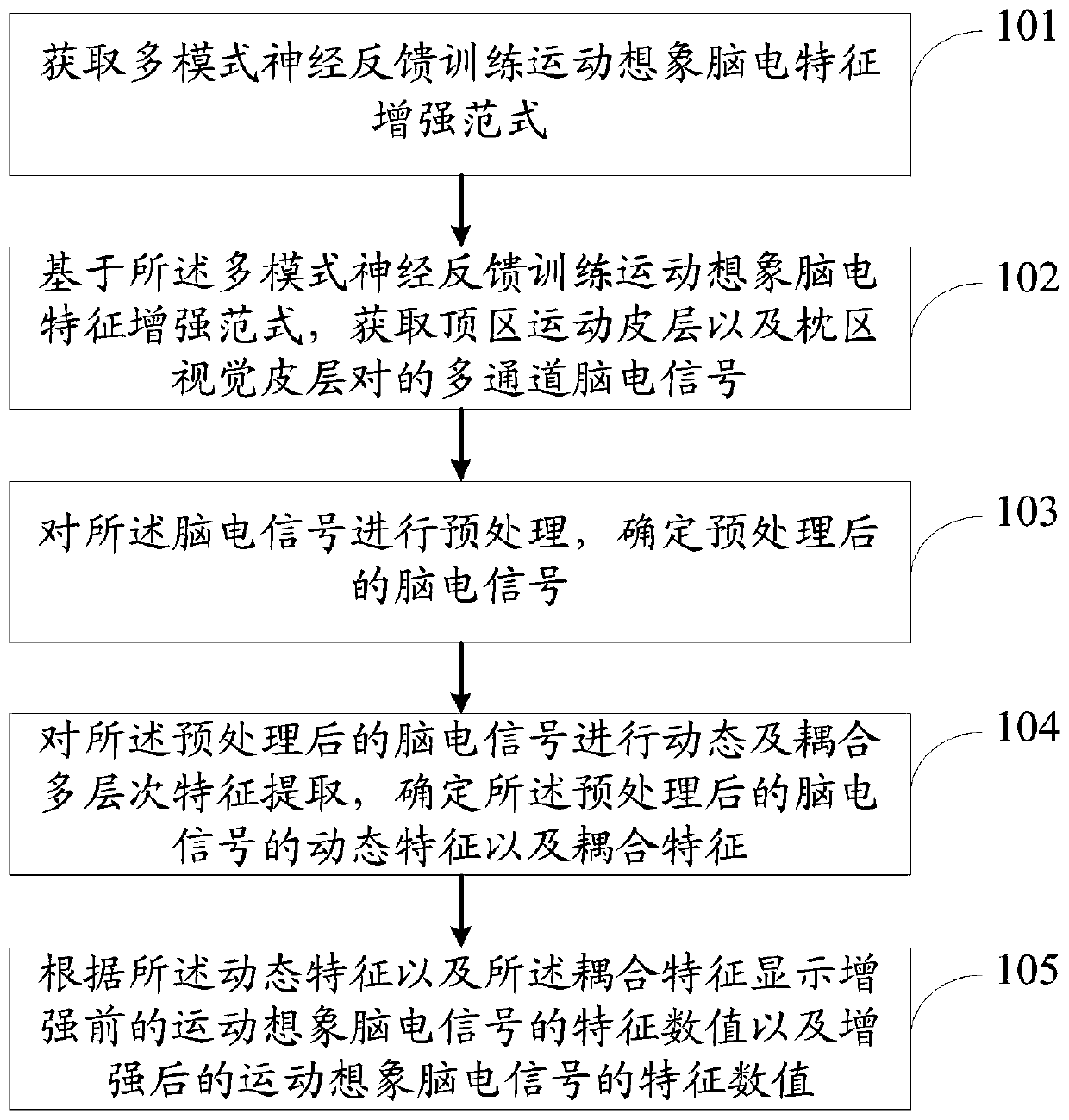
Motor imagery electroencephalogram feature enhancement method and system
InactiveCN111110230AImprove recognition rateComprehensiveDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVisual cortexElectroencephalogram feature
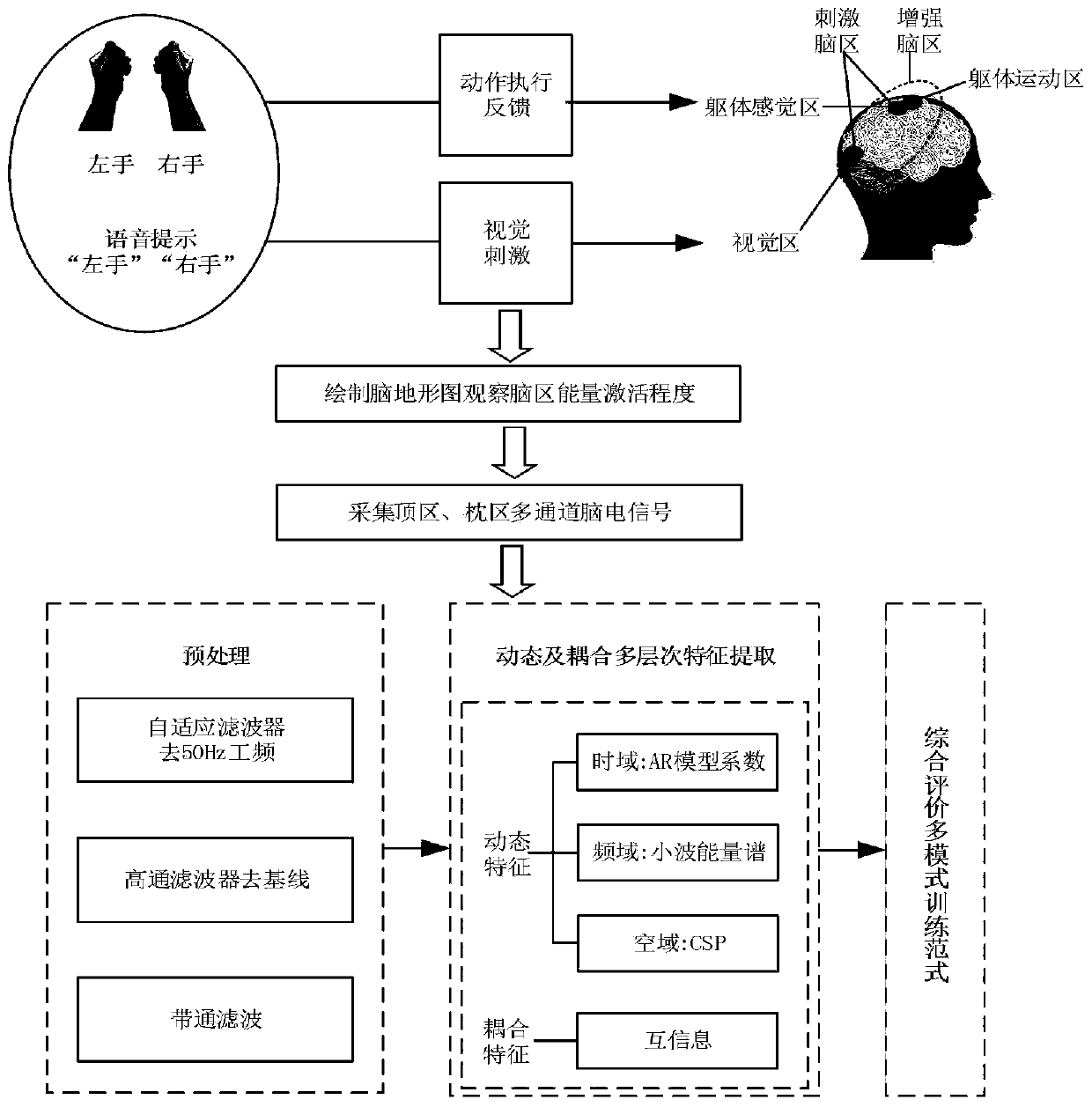
The invention relates to a motor imagery electroencephalogram feature enhancement method and system. The enhancement method comprises the following steps: acquiring a multi-mode neural feedback training motor imagery electroencephalogram feature enhancement paradigm; based on the multi-mode neural feedback training motor imagery electroencephalogram feature enhancement normal form, acquiring multi-channel electroencephalogram signals of a pair of a parietal region motor cortex and an occipital region visual cortex; preprocessing the electroencephalogram signals, and determining the preprocessed electroencephalogram signals; conducting dynamic and coupled multi-level feature extraction on the preprocessed electroencephalogram signals, and determining dynamic features and coupling features of the preprocessed electroencephalogram signals; and according to the dynamic features and the coupling features, displaying feature values of the motor imagery electroencephalogram signals before enhancement and feature values of the motor imagery electroencephalogram signals after enhancement. By adopting the enhancement method and system provided by the invention, the recognition rate of effective scalp electroencephalogram signals can be improved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Brain imaging system and methods for direct prosthesis control
Methods and systems for controlling a prosthesis using a brain imager that images a localized portion of the brain are provided according to one embodiment of the invention. The brain imager provides motor cortex activation data by illuminating the motor cortex with near infrared light (NIR) and detecting the spectral changes of the NIR light as passes through the brain. These spectral changes can be correlated with brain activity related to limbic control and may be provided to a neural network, for example, a fuzzy neural network that maps brain activity data to limbic control data. The limbic control data may then be used to control a prosthetic limb. Other embodiments of the invention include fiber optics that provide light to and receive light from the surface of the scalp through hair.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DENVER
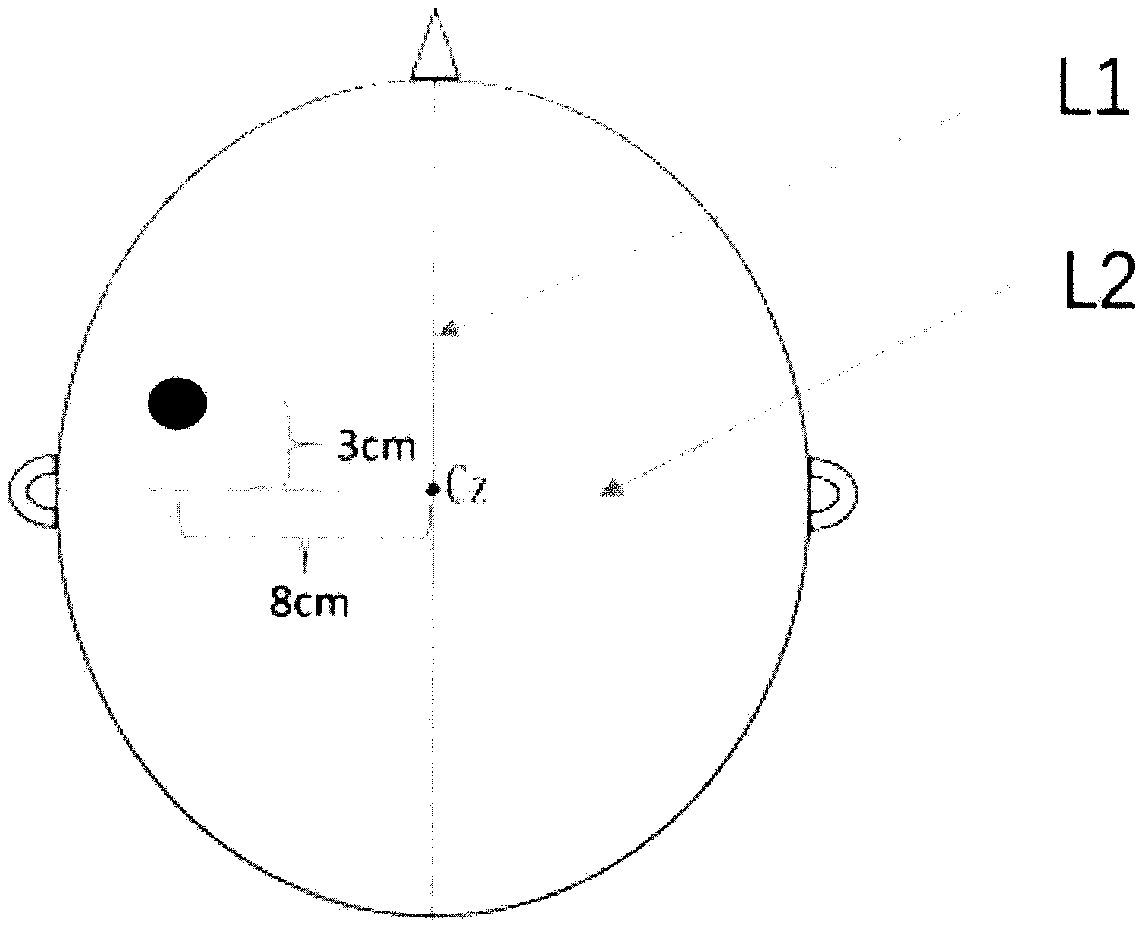
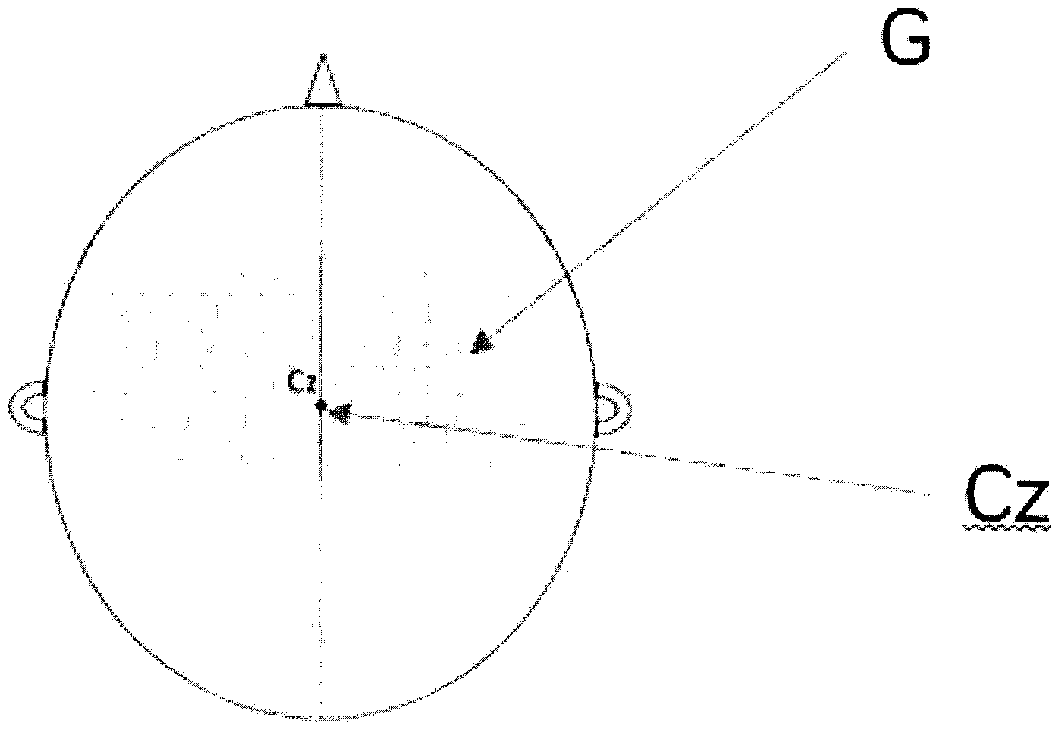
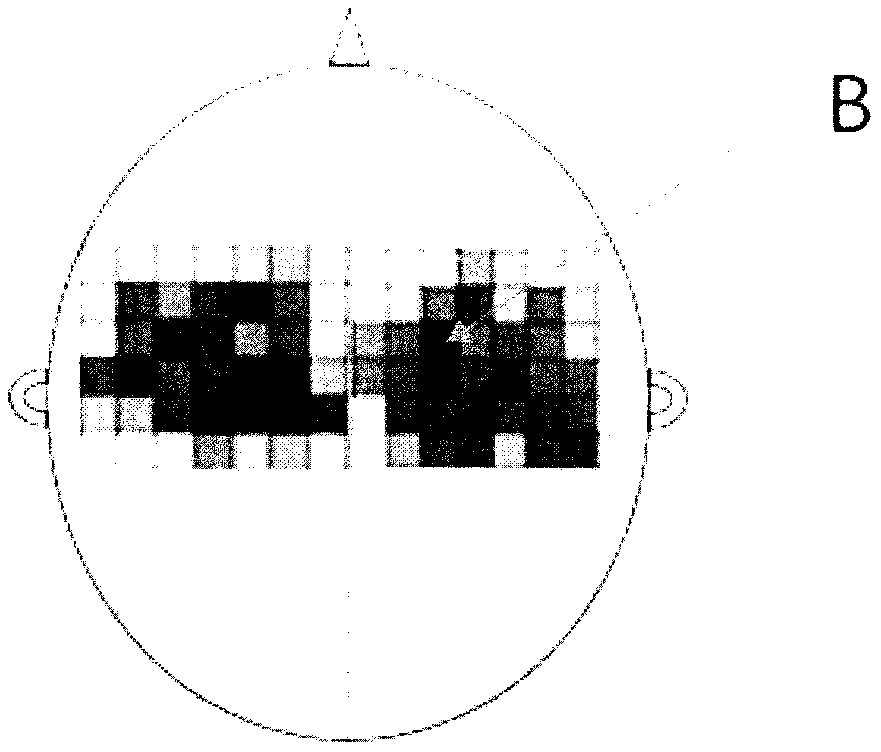
Drawing method for MEP topographic map of pharyngeal motor cortex area
InactiveCN109620222AAvoid detectionDrawn preciselyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNasal cavityHuman body
The invention provides a drawing method for an MEP topographic map of a pharyngeal motor cortex area, and further relates to a method for an MEP location map of the pharyngeal motor cortex area. According to the method, an electrode in the pharyngeal cavity is utilized to be inserted into the pharynx of the human body through the nasal cavity and the oral cavity to achieve the effect of accuratelyrecording electromyographic signals of the deep muscle of the pharynx, a positioning cap provided with multiple lattices of smaller sizes is utilized to cover the corresponding brain area to finallyachieve the effect of accurately drawing the MEP topographic map of the pharyngeal motor cortex area, and the drawing method is utilized to measure and draw multiple subjects to finally obtain the MEPlocation map of the pharyngeal motor cortex area of healthy people.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL (GUANGZHOU DIGESTIVE DISEASE CENT GUANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH)
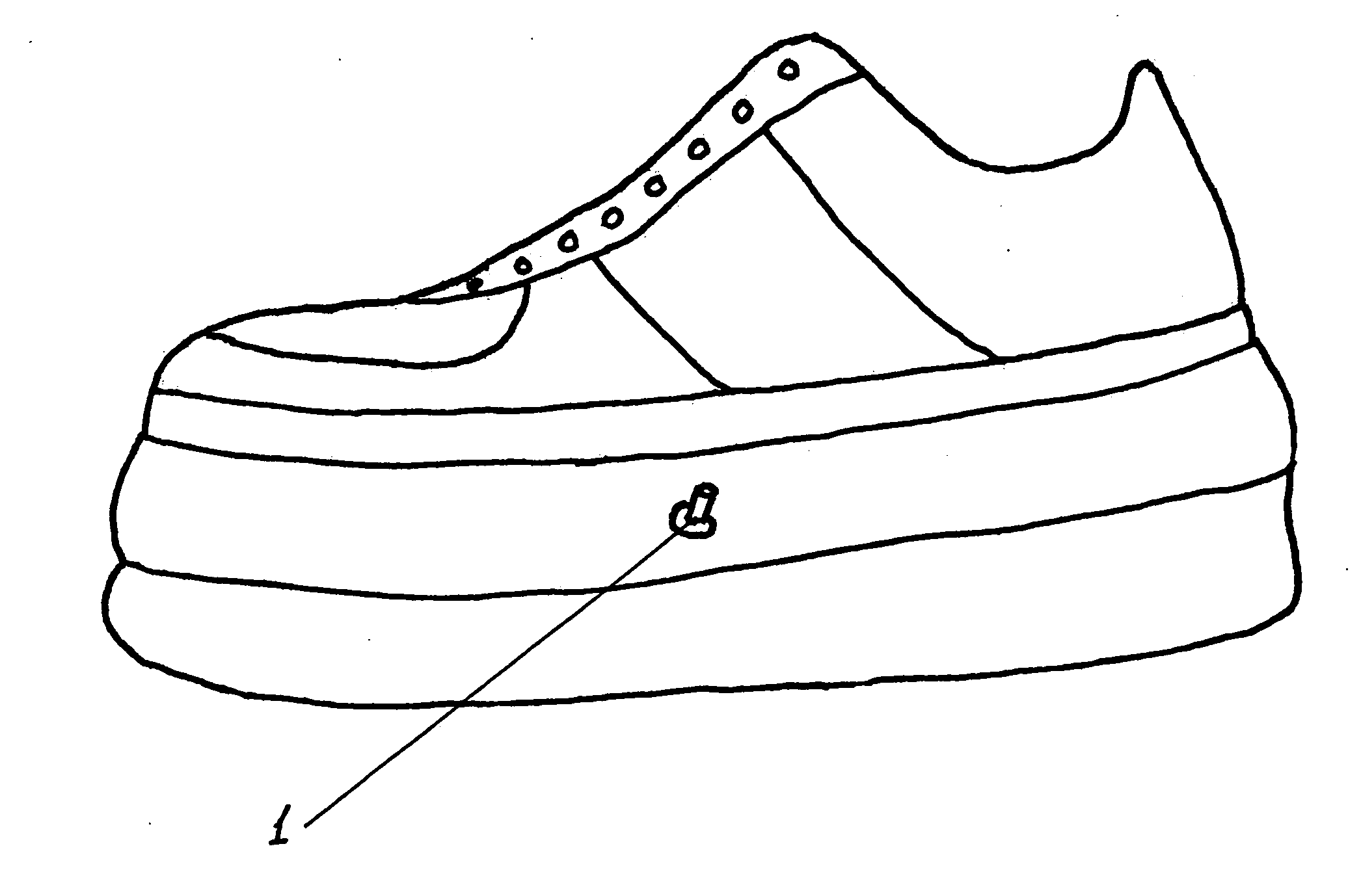
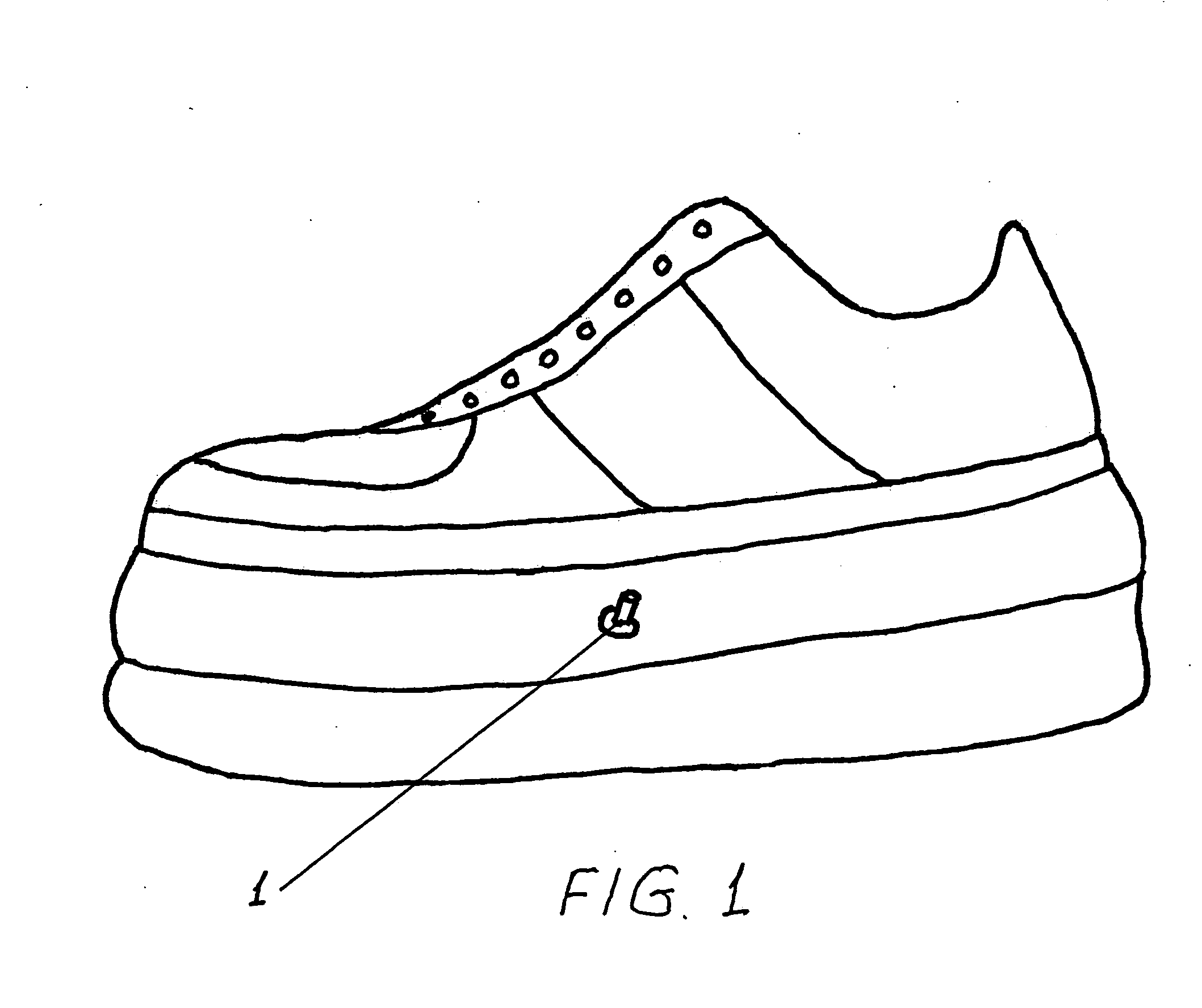
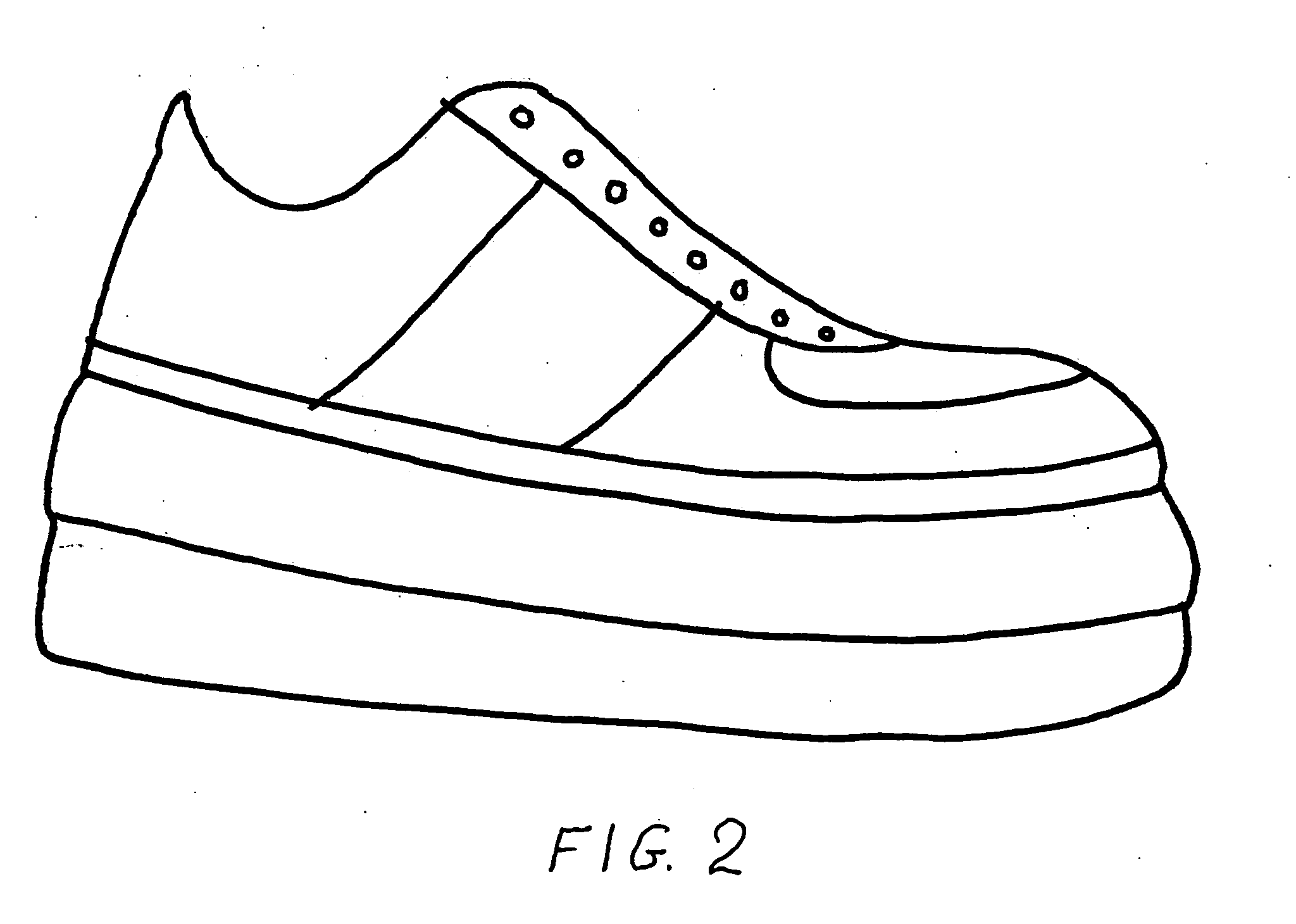
Hollow pneumatic sole sneaker
The hollow pneumatic sole sneaker creates an unstable condition, forcing the user to employ balance and equilibrium which is controlled and executed automatically by the brain through the core and leg muscles without conscious thinking. In an unstable position the human body's censoring systems (vestibular system, visual system, muscle, tendon and joints censoring system) create and send continuous signals to the brain of the body's position and movements. The signals are analyzed, interpreted and integrated in the brain and then the motor cortex creates a plan to execute the necessary muscle contractions to automatically maintain balance and equilibrium through the core and primary muscles of the body. Thus the unstable position of the human body has created the natural unconscious automatic possibilities to train the brain and muscles of the sneaker user.
Owner:YEFREMOV VALERIY IVANOVICH
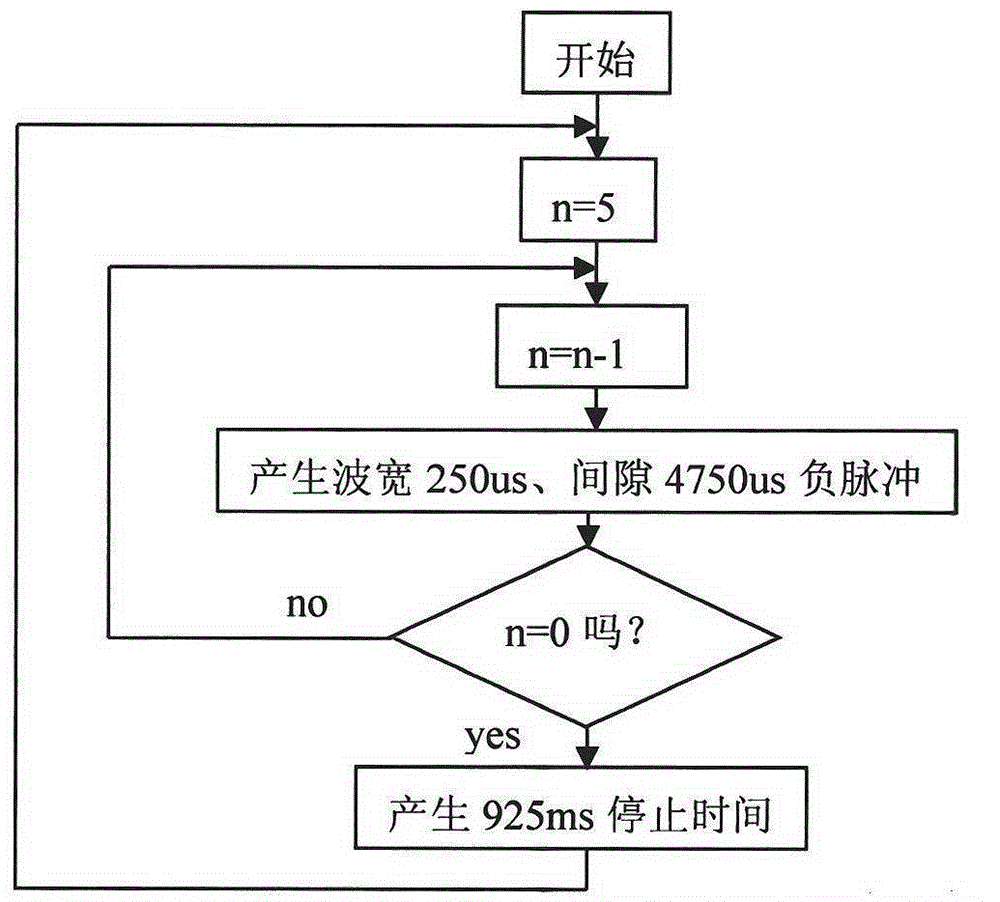
Electrical stimulation method for observing rat craniotomy motor cortex with adjustable waveform and amplitude
InactiveCN104825164AVoltage amplitude controllableEfficient outputSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringPrimary motor neuronBody movement
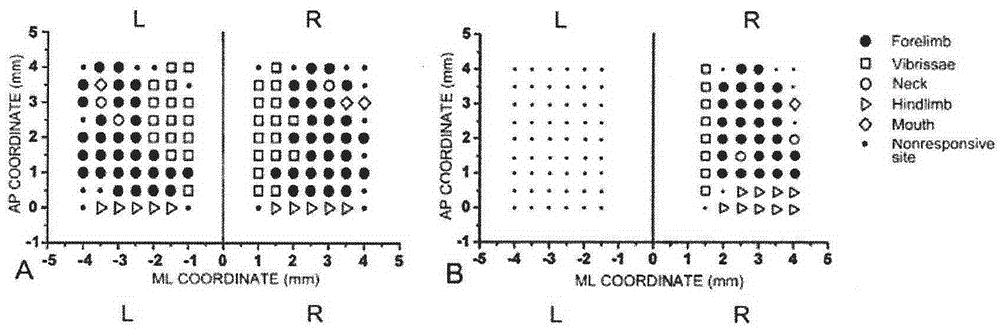
The present invention discloses an electrical stimulation method for observing rat craniotomy motor cortex with the adjustable waveform and amplitude. The method is characterized in that: the motor area of the cerebral cortex is an advanced nerve center for regulating the body motor function, and, through the downward pathway of the pyramidal and extrapyramidal system, controls activities of the brain stem and spinal motor neurons, so as to control muscle movement. Corresponding effects occur after cortical electrical stimulation, experimenters attempt to, through the electrical stimulation of the motor area of the cerebral cortex, cause the effect of body movement, and observe the phenomenon of functional localization of the motor area of the cortex. The rat is fixed to a stereotaxic apparatus, the bone windows are opened, a cortical electrical stimulation using microelectrode is performed, and the electrode is inserted vertically into the position 1.8 mm below the cortex, and adjusted within a range of + / - 200 um so as to cause the maximum movement of the contralateral forelimb, facial hair and neck corresponding to the stimulation points. An electrical stimulator with the adjustable waveform and amplitude is further produced, is capable of accurately completing the experimental observation of electrical stimulation predetermined by experimenters, and provides technical support for the experiment.
Owner:杨旭明 +1
Montage design for closed loop sensing and neurostimulation of the dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex and/or motor cortex
Described is a system for automatic adjustment of neurostimulation. The system controls stimulation of specific neural regions through a neural device positioned on a human subject, while simultaneously performing recordings from the neural device using a targeted arrangement of stimulating electrodes and distinct types of recording electrodes of the neural device. Stimulation of the specific neural regions is adjusted in real-time based on the recordings from the neural device.
Owner:HRL LAB
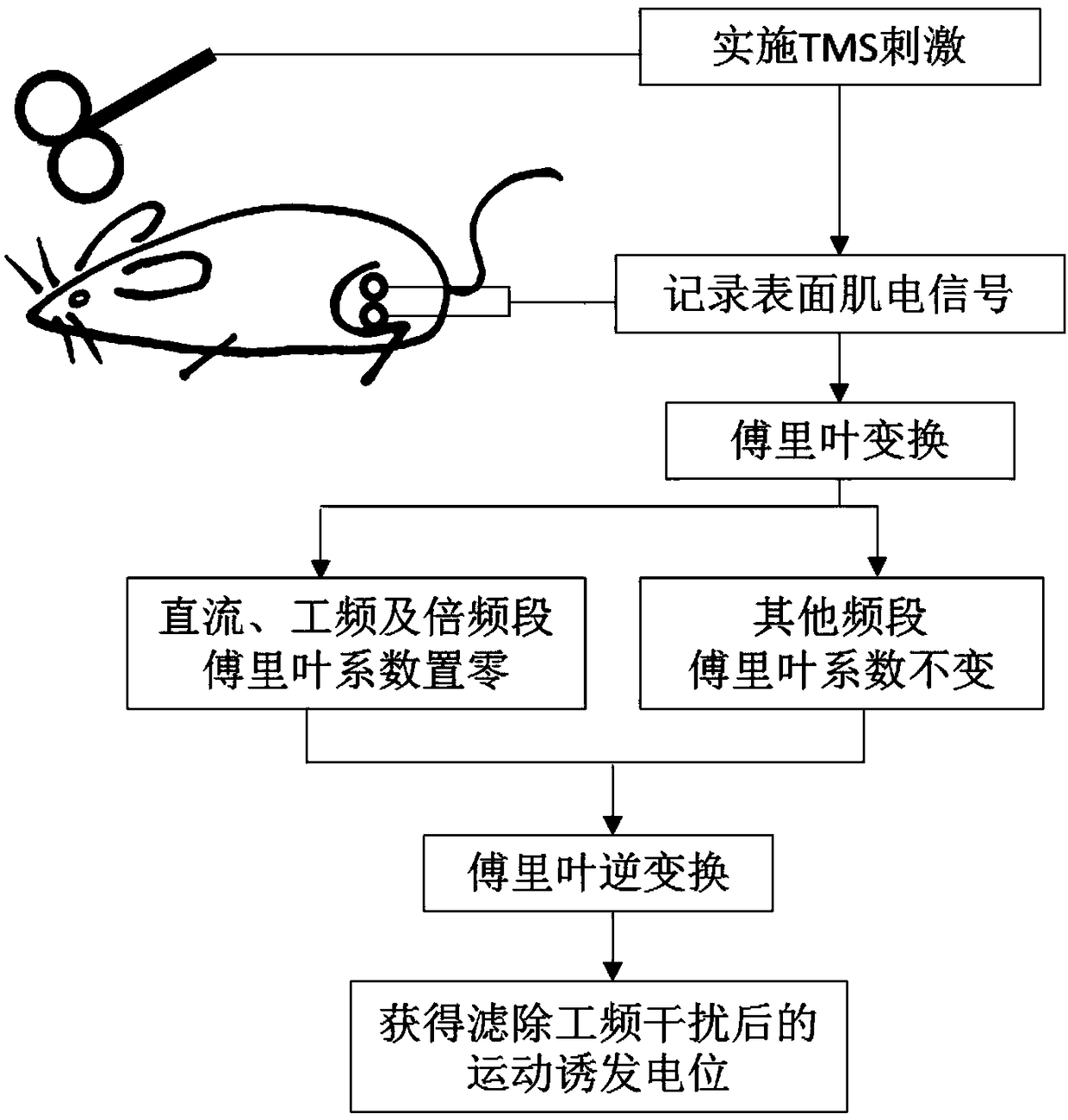
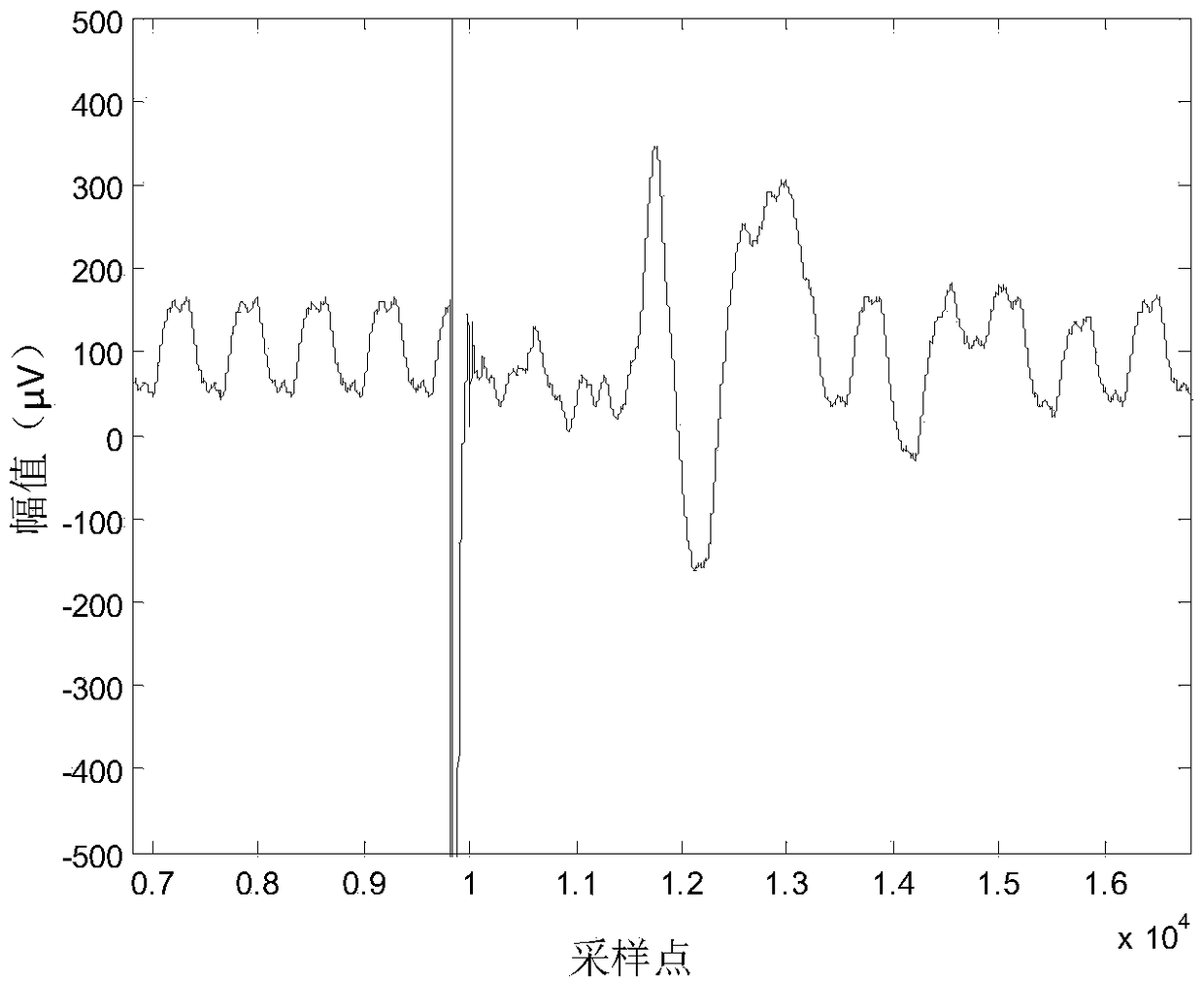
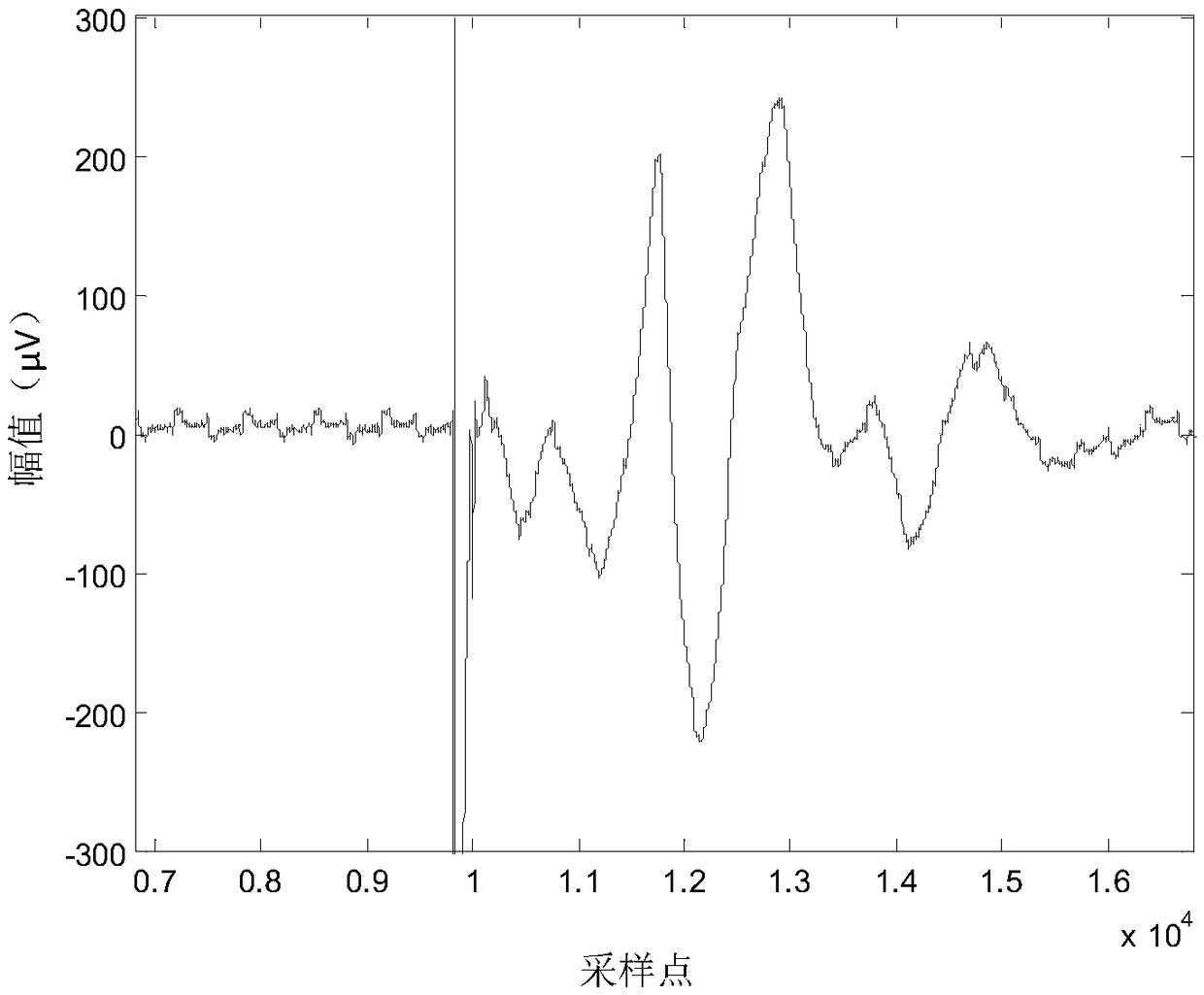
Power frequency filtering-away method for reducing influences of TMS electromagnetic pulses on rat motor evoked potential
ActiveCN108888266AReduce the impactRetain its own characteristicsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectromagnetic pulseMotor evoked potentials monitoring
The invention discloses a power frequency filtering-away method for reducing influences of TMS electromagnetic pulses on a rat motor evoked potential. The method includes the steps that the one-time TMS pulses act on a rat motor cortex, and a surface electromyogram signal of hind limbs of a rat in a waking state is recorded by the adoption of sampling frequency above 1,000 Hz; Fourier transformation conversion is performed on the electromyogram signal, Fourier coefficients corresponding to power frequency interference and a direct current component are subjected to zero setting, other Fouriercoefficients are kept unchanged, Fourier inverse conversion is performed, smoothing of power frequency interference is realized, and an electromyogram signal after smoothing is obtained; the motor evoked potential is extracted from the smoothed electromyogram signal, and a motor evoked potential is obtained after power frequency interference is filtered away. The method adopting Fourier inverse conversion for filtering away power frequency interference does not need establishment of a digital wave trap, the influences of the TMS electromagnetic pulses on the motor evoked potential can be reduced greatly during smoothing, self-characteristics of the motor evoked potential can be kept well, and the method has important meanings for accurate extraction of the motor evoked potential waveform,amplitude value and latent period of a rat under the effect of a TMS.
Owner:SHENZHEN DELICA MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Gene therapy for spinal disorders
InactiveCN101208108AImproves symptoms of motor neuron disorderGenetic material ingredientsVector-based foreign material introductionMedicineSpinal cord
This disclosure provides methods and compositions for treating disorders or injuries that affect motor function and control in a subject. In one aspect, the invention provides a method to deliver a transgene to a subject's spinal cord by administering a recombinant neurotropic viral vector containing the transgene. The viral vector delivers the transgene to a region of the deep cerebellar nuclei region of the brain. Also provided are compositions and methods to deliver a transgene to a subject's spinal cord by administering a recombinant neurotropic viral vector containing the transgene to the motor cortex region of the subject's brain.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Brain imaging system and methods for direct prosthesis control
Methods and systems for controlling a prosthesis using a brain imager that images a localized portion of the brain are provided according to one embodiment of the invention. For example, the brain imager can provide motor cortex activation data using near infrared imaging techniques and EEG techniques among others. EEG and near infrared signals can be correlated with brain activity related to limbic control and may be provided to a neural network, for example, a fuzzy neural network that maps brain activity data to limbic control data. The limbic control data may then be used to control a prosthetic limb. Other embodiments of the invention include fiber optics that provide light to and receive light from the surface of the scalp through hair.
Owner:COLORADO SEMINARY
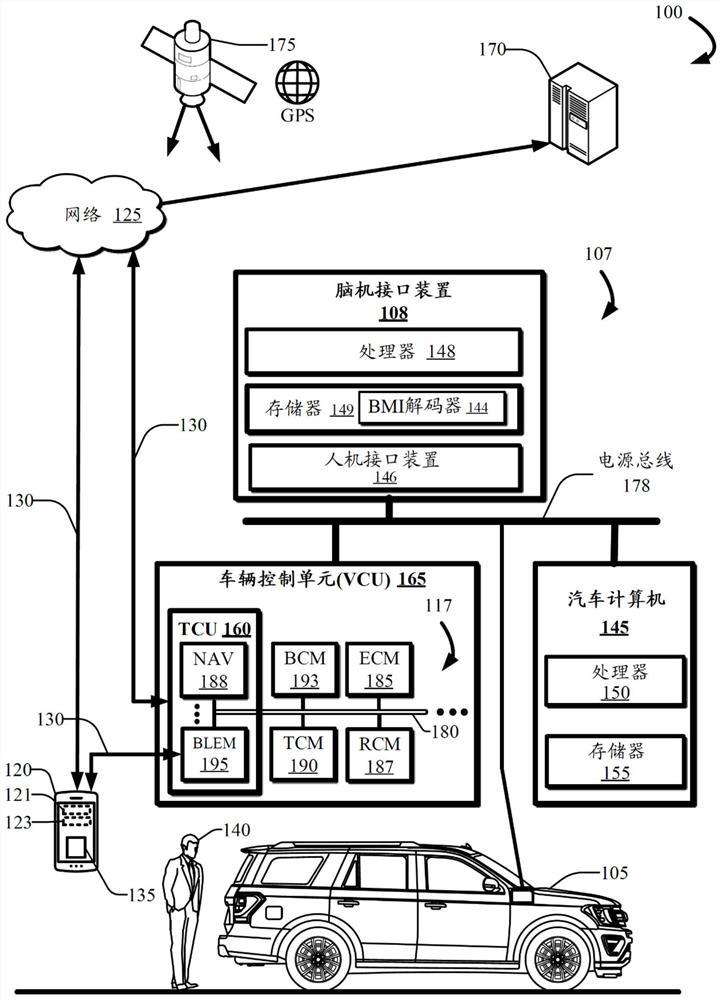
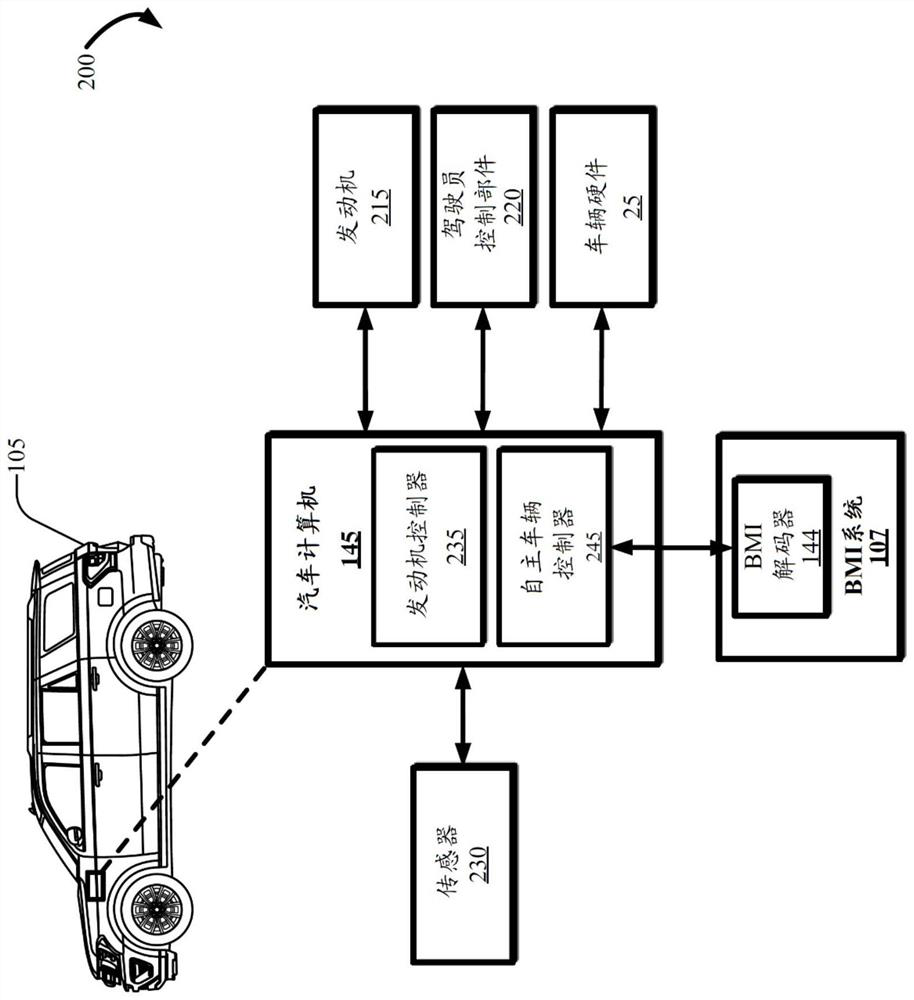
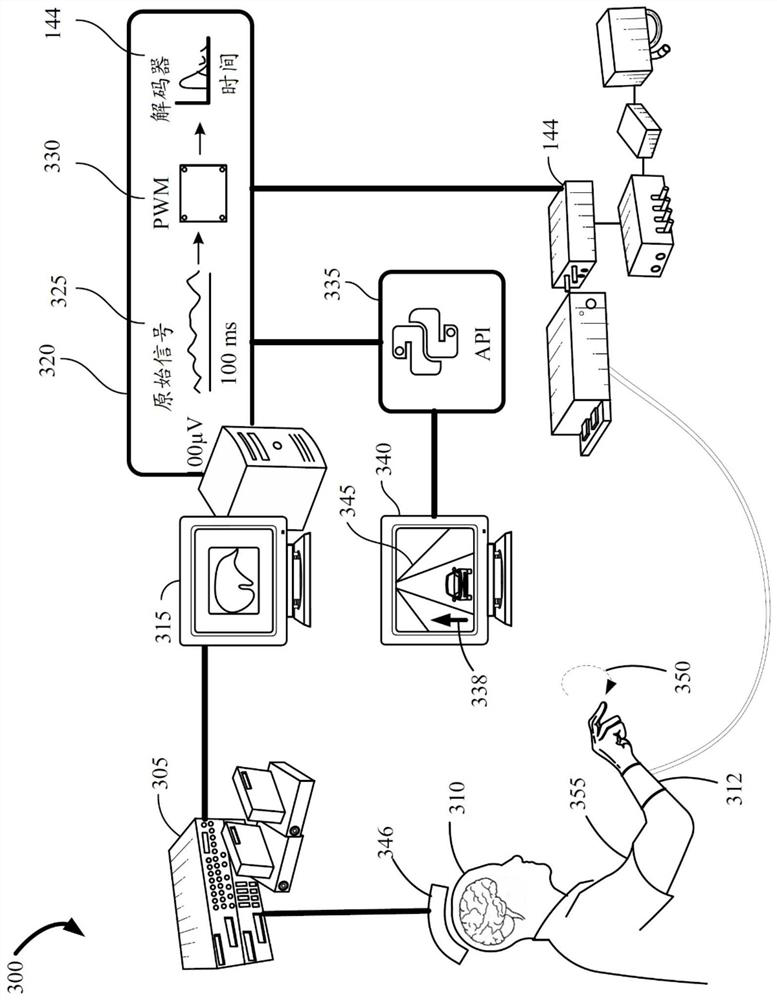
Analog driving feature control brain machine interface
The invention provides an analog driving feature control brain machine interface. Embodiments describe a system configured with a brain machine interface (BMI) system implemented in a vehicle for performing vehicle functions using electrical impulses from motor cortex activity in a user's brain. The system uses fuzzy states for increased robustness. The fuzzy states are defined by sets of Gaussian kernel-type membership functions that are defined for steering and velocity action function states. The membership functions define fuzzy states that provide overlapping control tiers for increasing and decreasing vehicle functionality. An autonomous vehicle may perform control and governance of transitions between membership functions that may overlap, resulting in smooth transitioning between the states.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
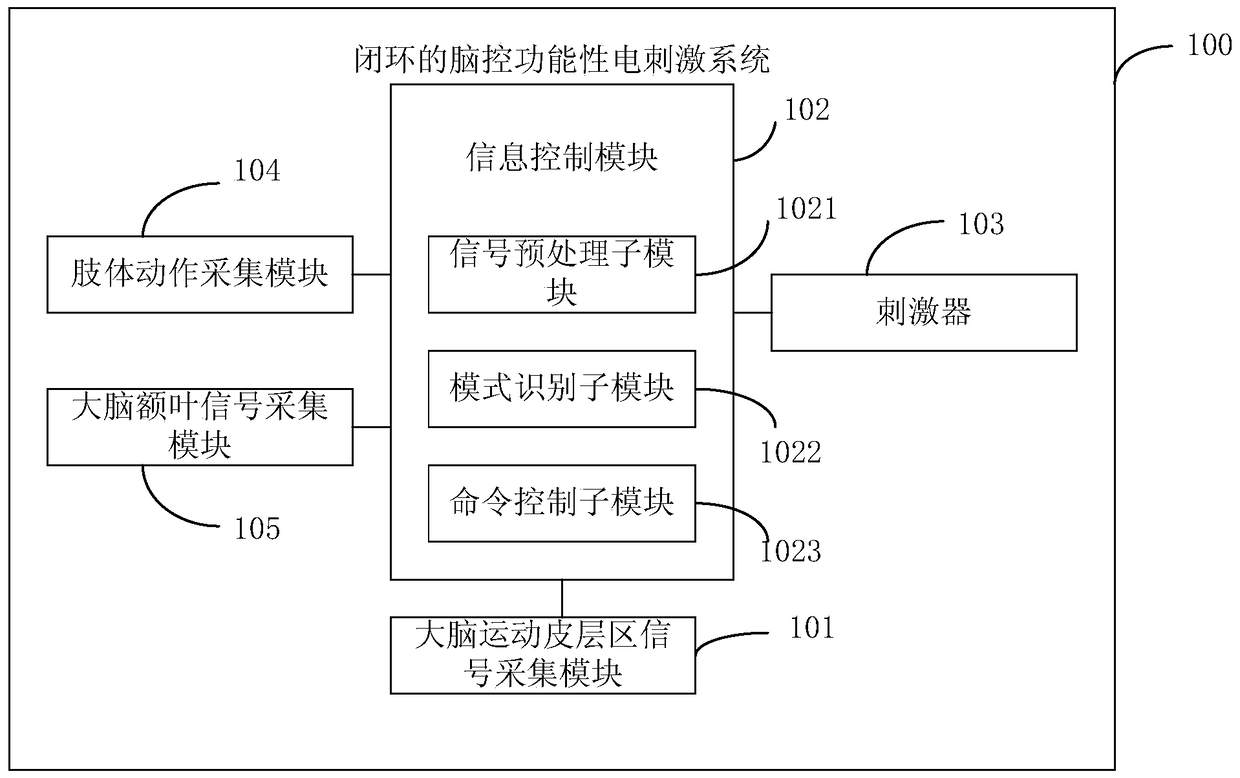
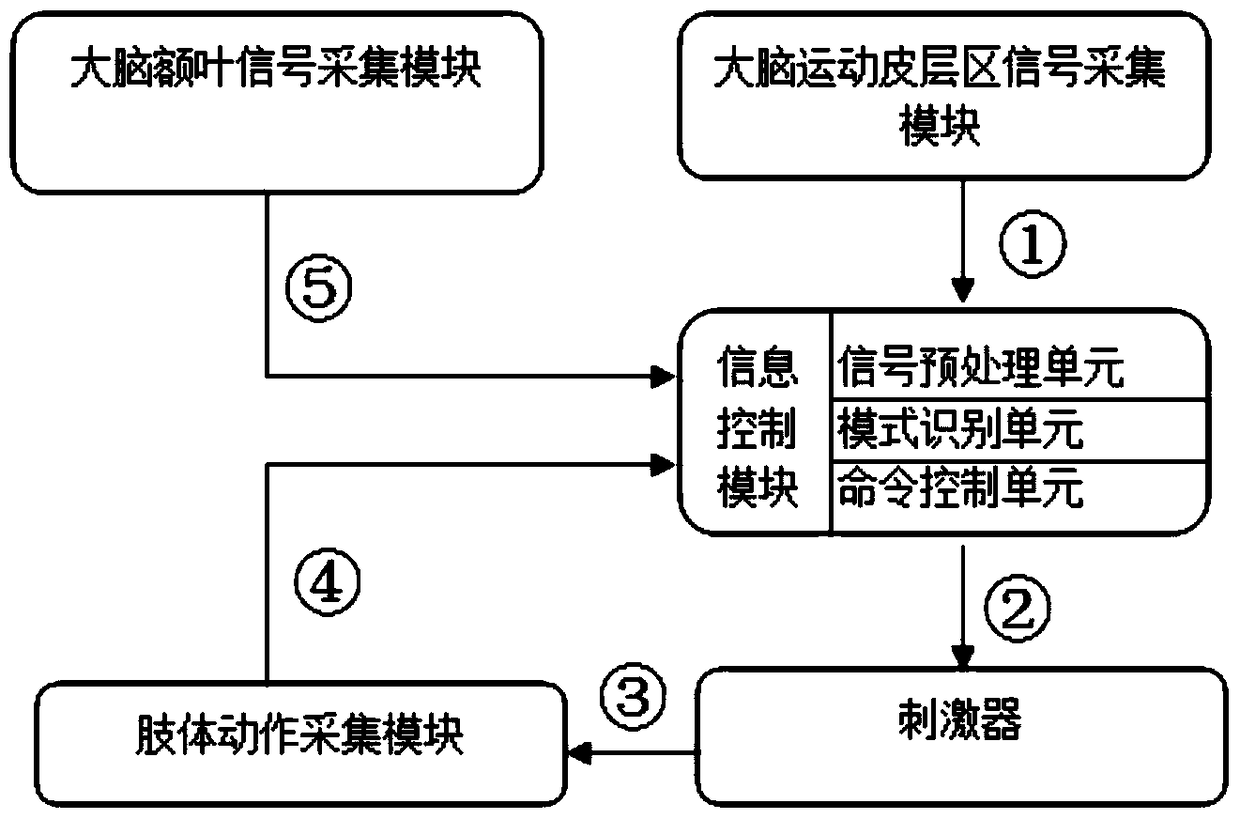
Closed-loop brain-controlled functional electrical stimulation system
ActiveCN105727442BImprove the effect of rehabilitation treatmentGuaranteed accuracyElectrotherapyDiagnostic signal processingClosed loopBody movement
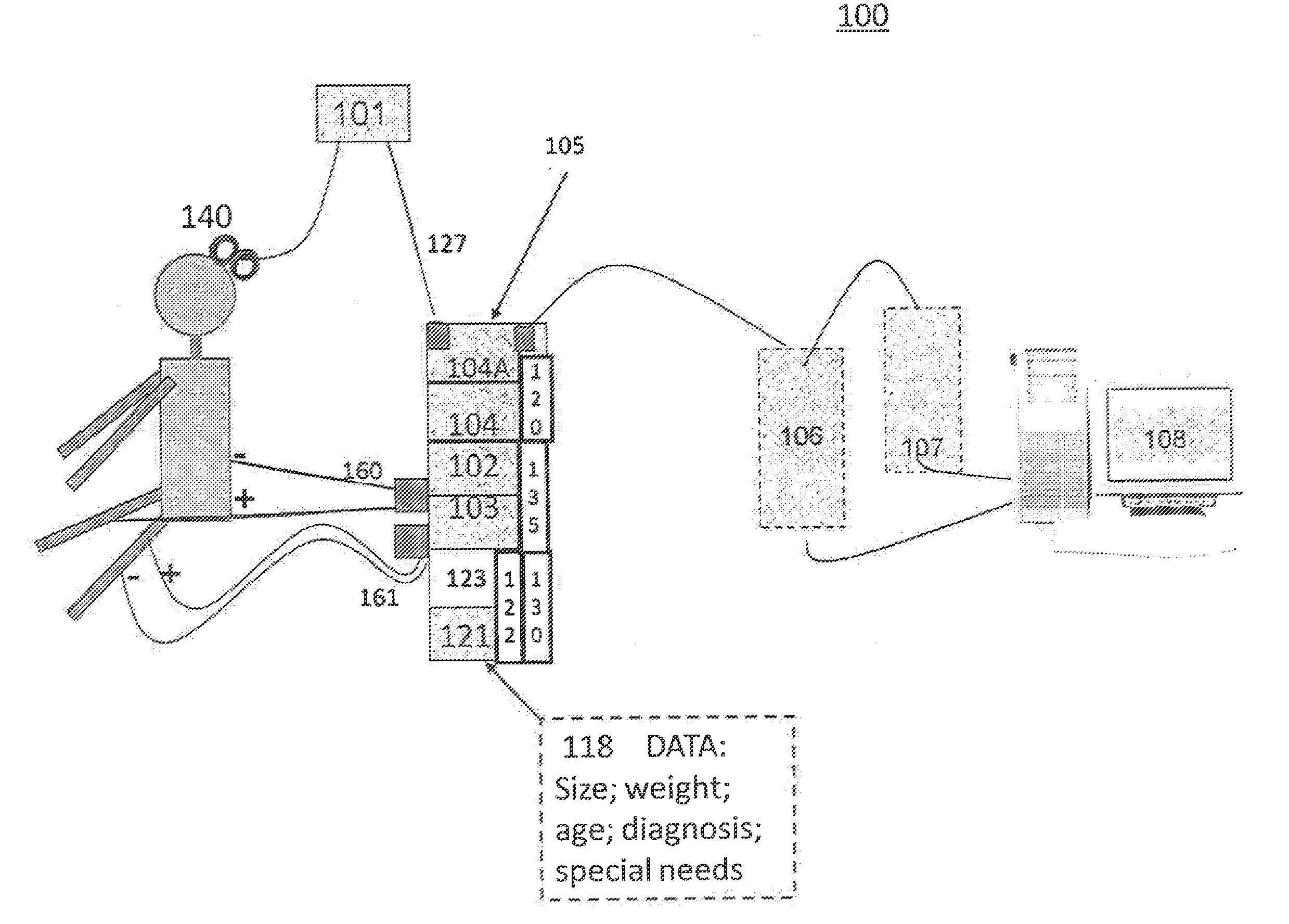
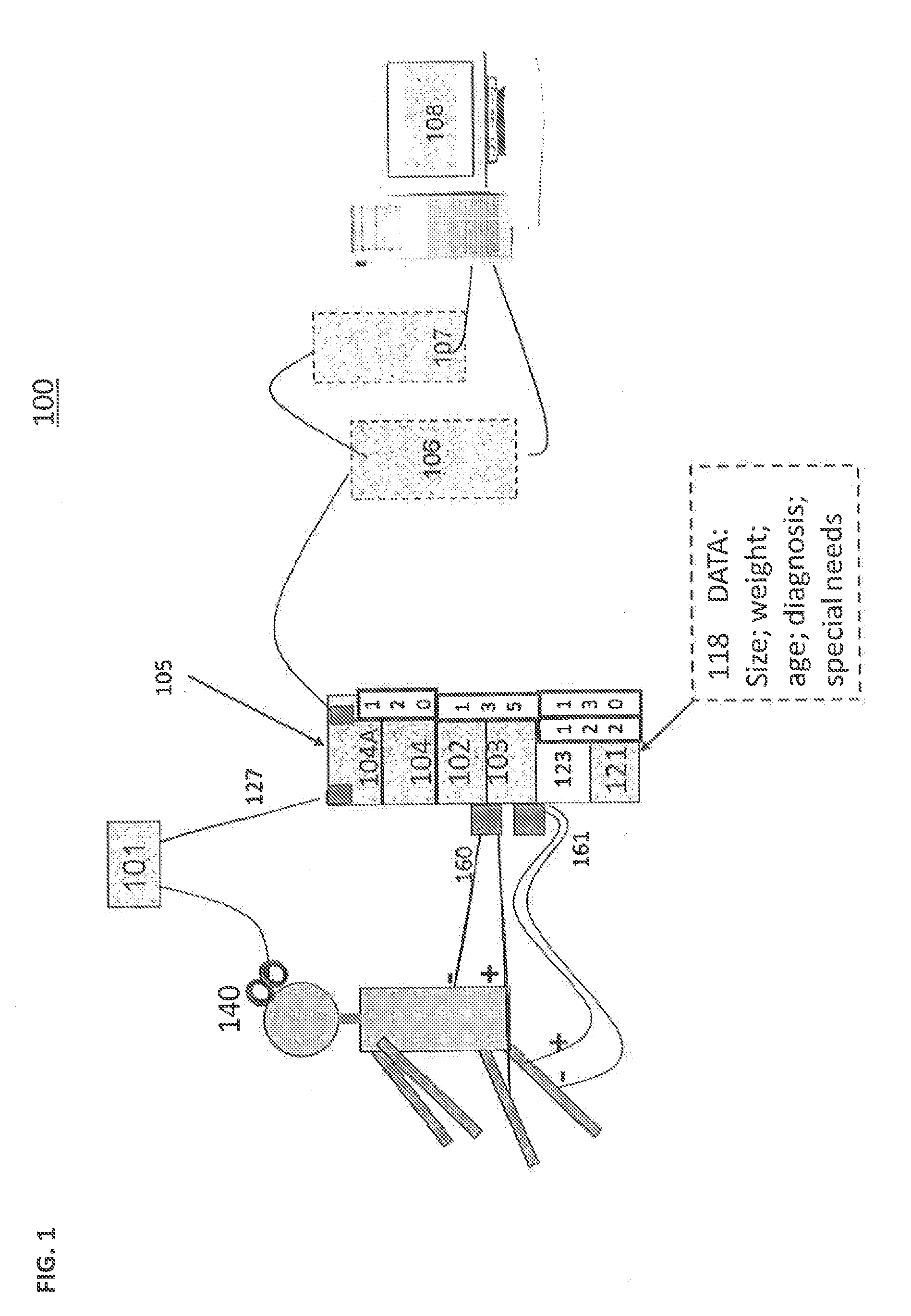
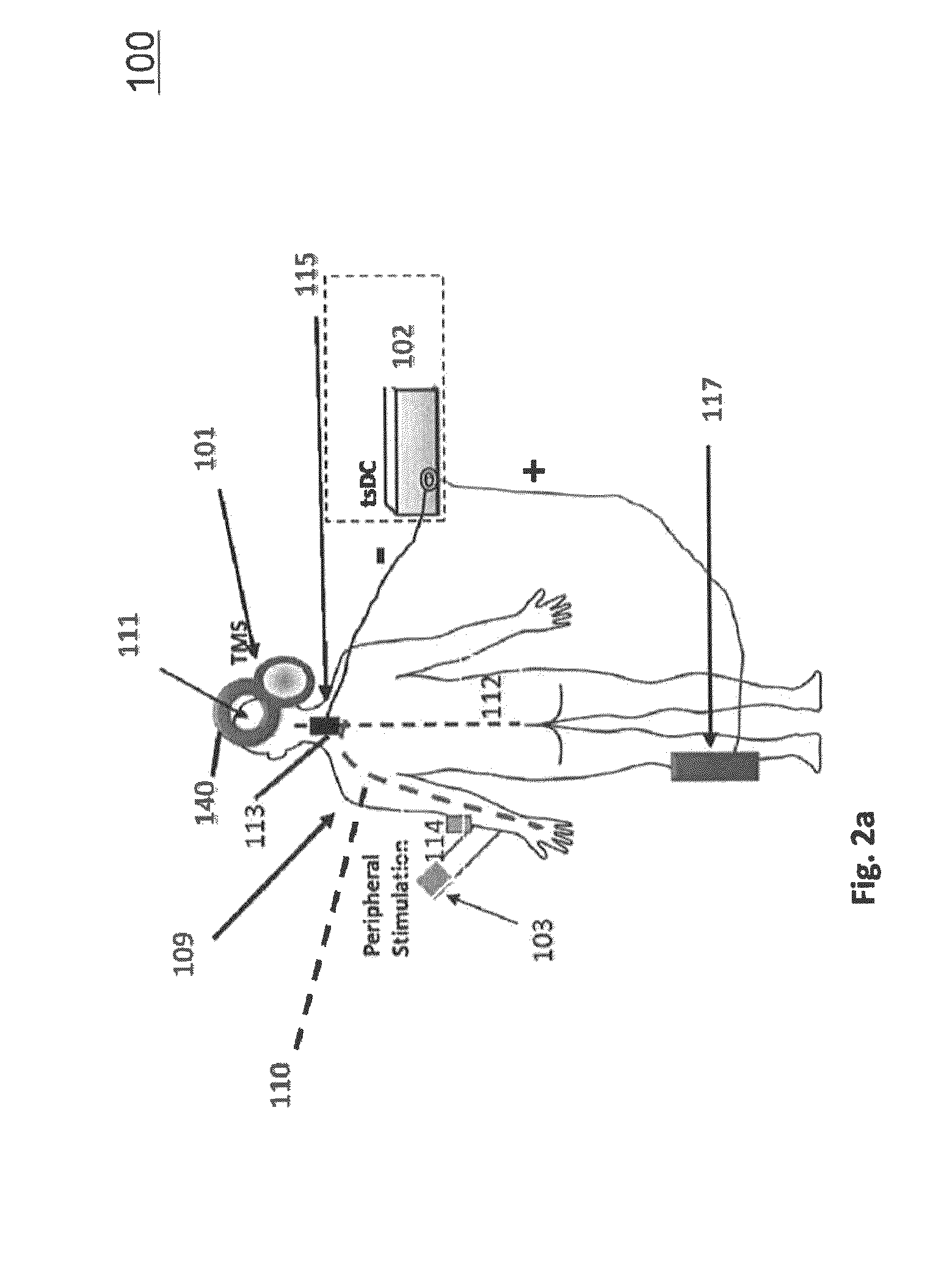
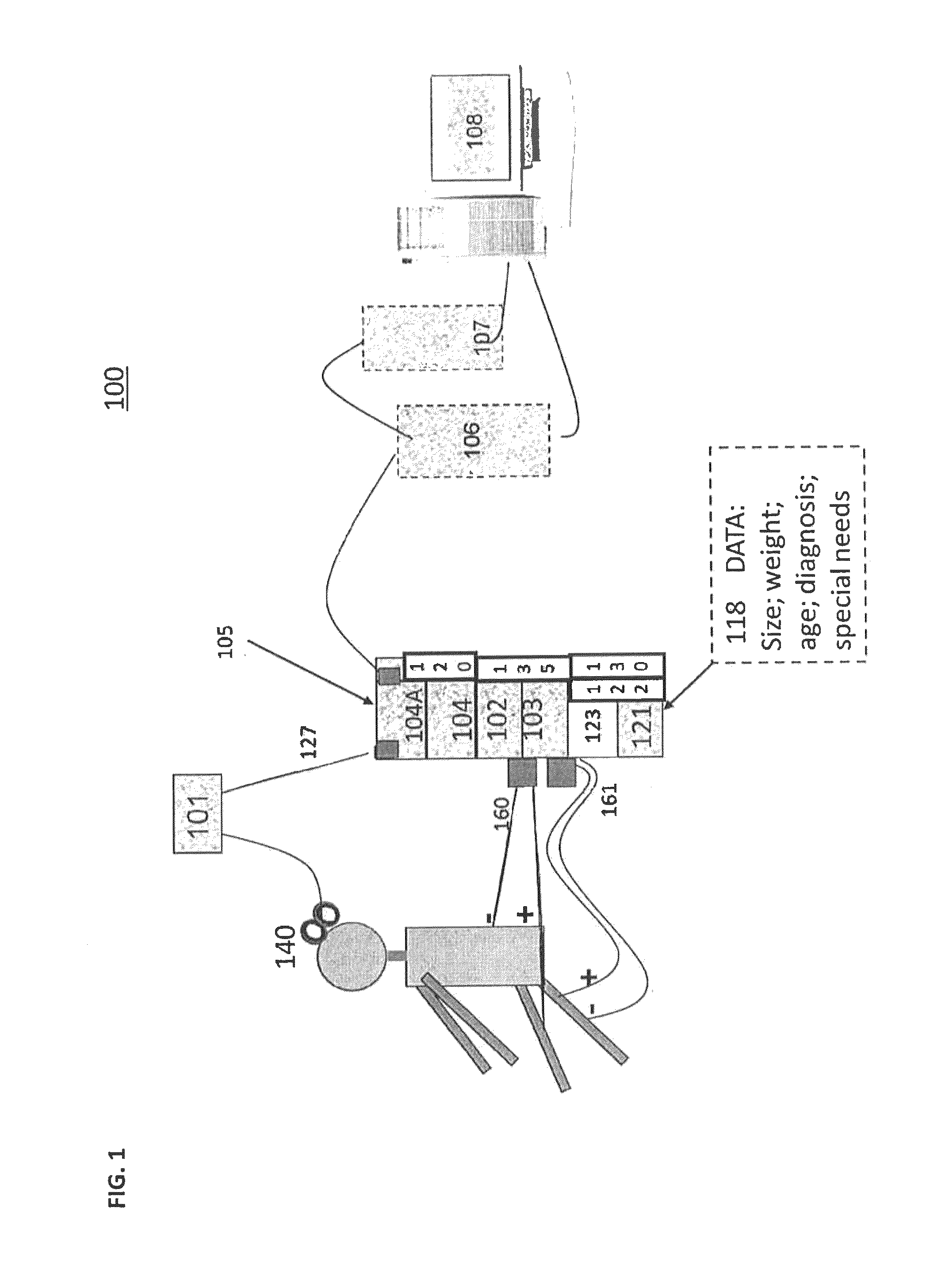
A closed-loop brain control functional electrostimulation system in the field of medical devices. The system comprises: a brain motor cortex area signal acquisition module (101), an information control module (102), a stimulator (103), a body movement acquisition module (104) and a brain frontal lobe signal acquisition module (105). The information control module (102) comprises a signal pre-processing sub-module (1021), a mode recognition sub-module (1022) and a command control sub-module (1023). The system has the advantages of ensuring the accuracy of body movement recognition and improving the rehabilitation treatment effect of paralysed patients.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method and system for treatment of neuromotor dysfunction
Effective systems and methods for improving neural communication impairment of a vertebrate being and affecting motor activity of a peripheral body part including a first signal-providing component configured to provide pulsed peripheral stimulation signals at the peripheral body part, a second signal-providing component configured to provide a pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal to a motor cortex area, a substantially DC signal-providing component configured to provide direct current spinal stimulation signal at a neural spinal junction and a controller component configured to control timing of the pulsed peripheral stimulation signals and the pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
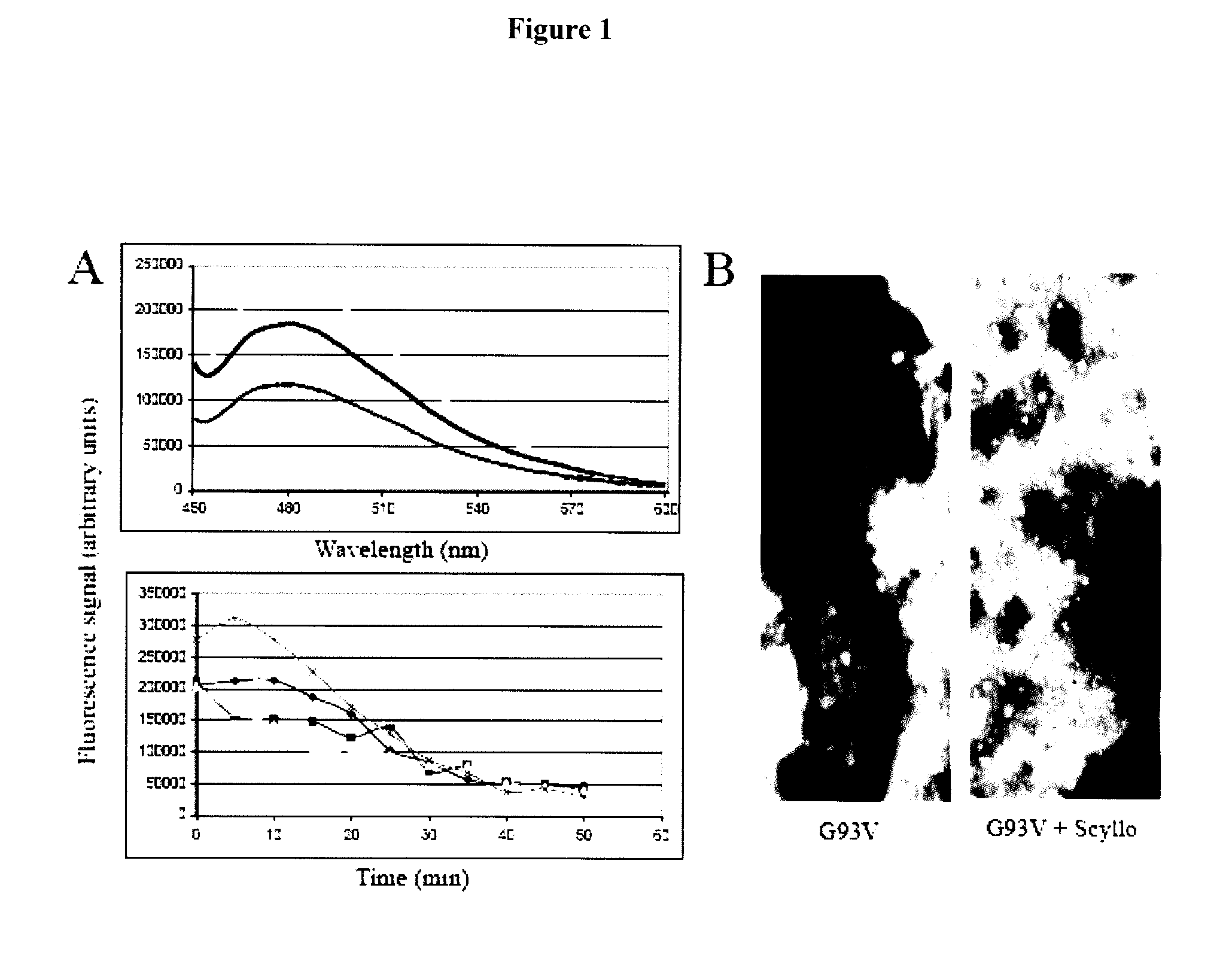
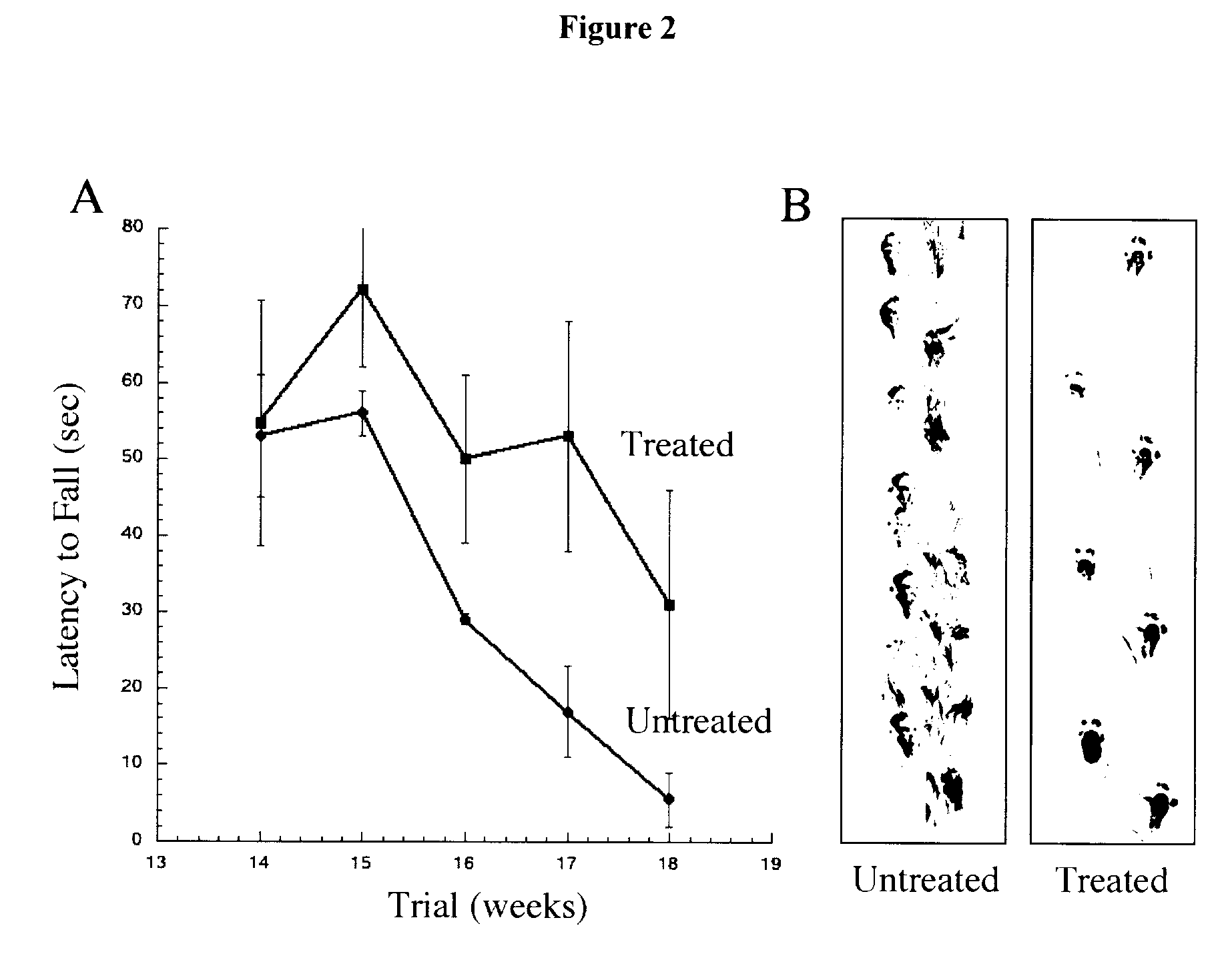
Use of cyclohexanehexol derivatives in the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
InactiveUS20100144891A1Minimize occurrenceEnhancing motor neuronBiocideNervous disorderNosePrimary motor neuron
The present invention relates to methods for modulating, disrupting or enhancing the clearance of copper / zinc superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) aggregates in astrocytes or motor neurons in a subject, by administering a medicament comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a cyclohexanehexyl derivative. In another aspect, the invention provides a medicament comprising at least one cyclohexanehexyl derivative of formula III or IV useful in preventing or treating amyothropic lateral sclerosis (ALS), improving motor neuron function and slowing the degeneration or death of motor neurons in brain stem, spinal cord or motor cortex. These medicaments may be administered orally, intravenously, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intranasal or transdermal.
Owner:MCLAURIN JOANNE
Method and system for treatment of mobility dysfunction
ActiveUS20140200387A1Long recoveryReduced dysfunctionSurgeryMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMedicineBody region
Effective systems and methods for improving neural communication impairment of a vertebrate being and affecting motor activity of a peripheral body part including a first signal providing component configured to provide pulsed peripheral stimulation signals at the peripheral body part, a second signal providing component configured to provide a pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal to a motor cortex area, a substantially DC signal providing component configured to provide direct current spinal stimulation signal at a neural spinal junction and a controller component configured to control timing of the pulsed peripheral stimulation signals and the pulsed motor cortex stimulation signal.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Encephalophone
Owner:DEUEL THOMAS ANDREW
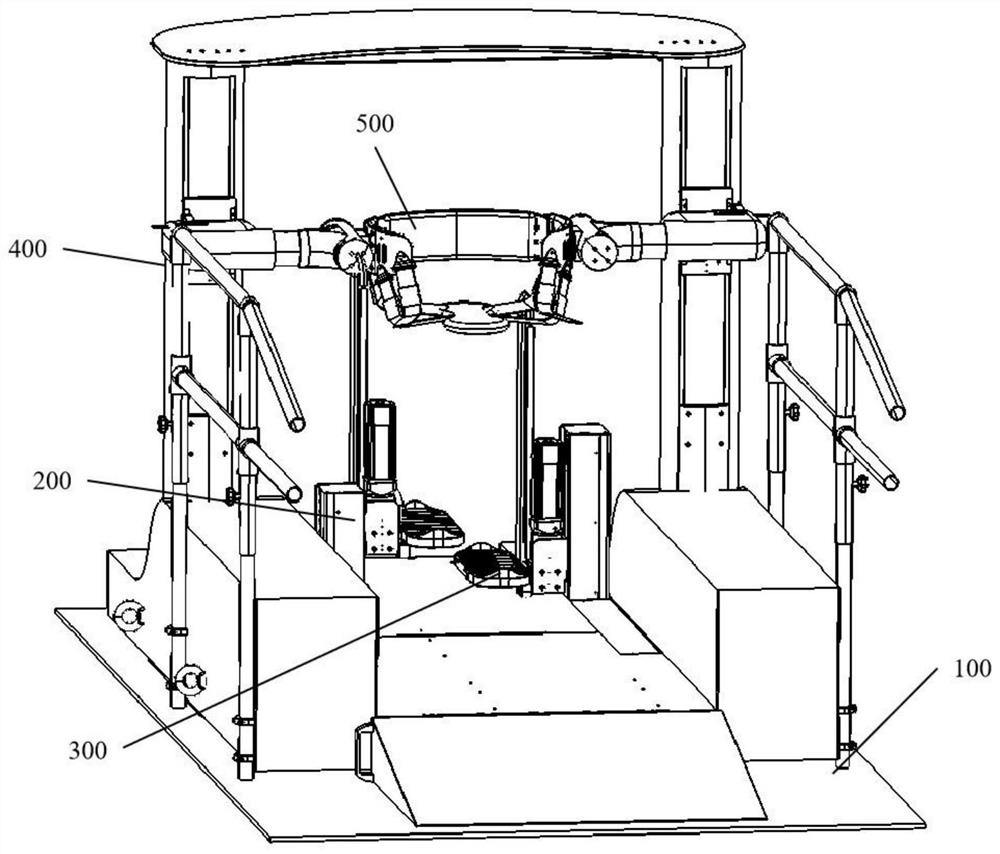
Three-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm for lower limb rehabilitation training device
PendingCN112826696ASolving activitySolve functionChiropractic devicesLinear motionPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides a three-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm for a lower limb rehabilitation training device, which comprises a fixed base arranged on a base supporting mechanism; an advancing mechanism fixedly connected to the fixed base and comprising a first linear motion module fixedly arranged on the fixed base; a lifting mechanism fixedly connected to the welding rectangular steel frame, wherein the welding rectangular steel frame is connected with the first linear motion module through a mounting base, and the lifting mechanism comprises a second linear motion module arranged on the welding rectangular steel frame; a rotating mechanism fixedly connected to the second linear motion module through an L-shaped adapter plate; and a guide rail supporting mechanism comprising a guide rail and a guide rail supporting block, wherein the guide rail is installed on the guide rail supporting block, and the guide rail supporting block is fixed to the top end of the first right-angle speed reducer of the lifting mechanism. The product can help a patient to perform lower limb exercise rehabilitation training, and can help to solve major clinical problems such as reactivation of a brain motor cortex and functional reconstruction of a motor sense network recovered after a nerve displacement operation clinically.
Owner:阁步(上海)医疗科技有限公司
A rat spinal cord signal detection and evaluation system and method
ActiveCN109173056BSolve the problem of implantationImplantable neurostimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringConduction pathwaySpinal nerve
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Montage design for closed loop sensing and neurostimulation of the dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex and/or motor cortex
Described is a system for automatic adjustment of neurostimulation. The system controls stimulation of specific neural regions through a neural device positioned on a human subject, while simultaneously performing recordings from the neural device using a targeted arrangement of stimulating electrodes and distinct types of recording electrodes of the neural device. Stimulation of the specific neural regions is adjusted in real-time based on the recordings from the neural device.
Owner:HRL LAB
Robot behavior learning system based on striated body structure and learning method thereof
ActiveCN112558605AQuick navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsAutonomous behaviorThalamus
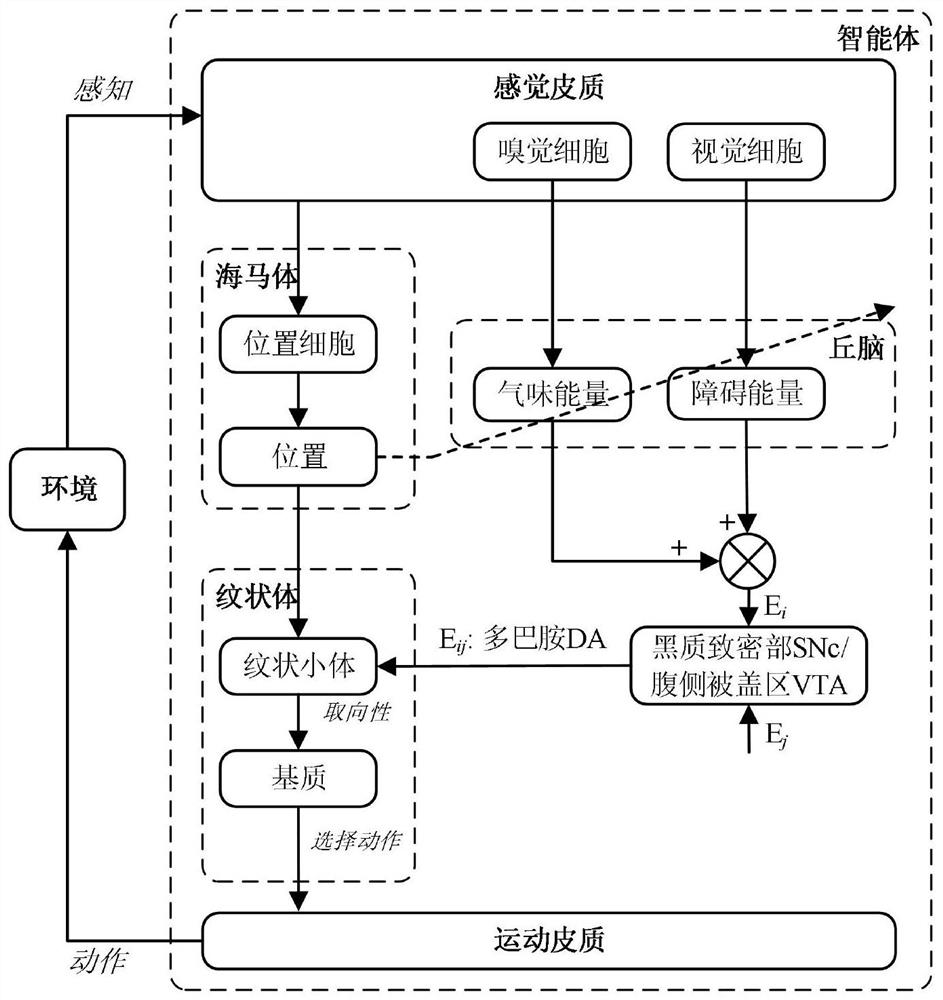
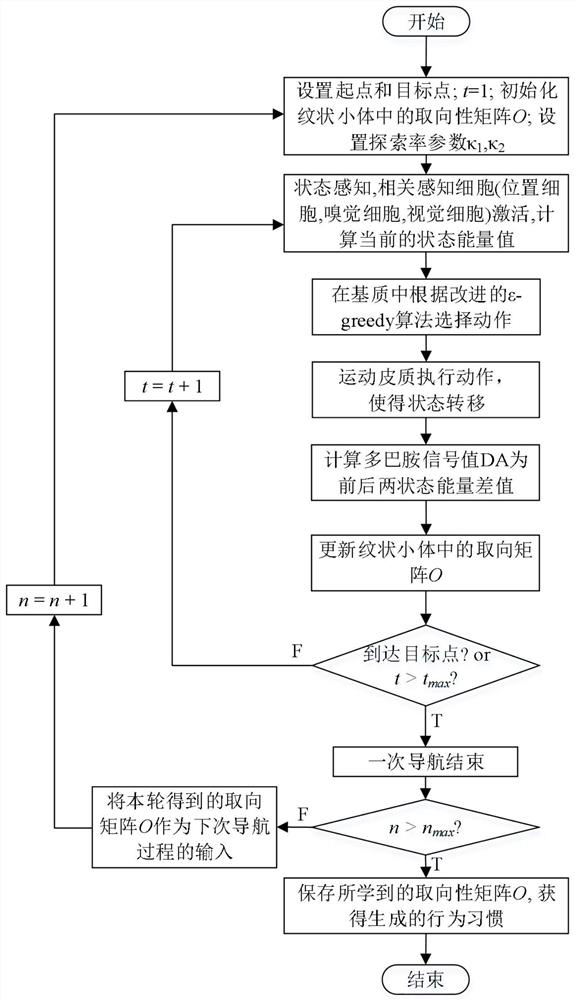
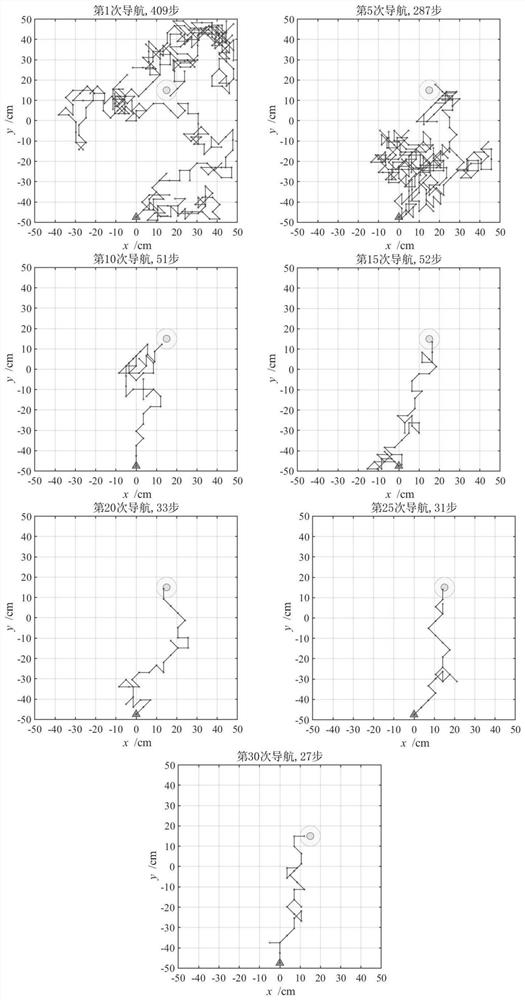
The invention discloses a robot behavior learning system based on a striated body structure and a learning method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bionics. The robot behavior learning system is composed of sensory cortex, motor cortex, hippocampus, thalamus, a black compact part, an abdominal side quilt area and a striated body, wherein the striated body comprises striated corpusclesand a matrix. The striped corpuscles receive positioning information generated by hippocampus position cells and dopamine information generated by a black compact part and an abdominal covered area,and update orientation information of the robot according to an operation conditioned reflex mechanism. The matrix receives orientation information of the striped corpuscles and performs action selection according to an improved epsilon-greedy algorithm. Behavior habits can be formed after the robot interacts with the environment for a period of time. According to the method, a possible explanation of animal habitual behavior generation is given, and robot autonomous behavior learning can be guided. The method can be applied to the fields of robot navigation, physiology, animal behavioristicsand the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
A communicative dual-arm rehabilitation training robot
ActiveCN109846673BAvoid injurySolve major clinical problems such as functional reconstructionChiropractic devicesMotor rehabilitationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a communicative dual-arm rehabilitation training robot. The communicative dual-arm rehabilitation training robot comprises the following parts: a supporting mechanism; a cooperative mechanical arm, a first end of which is mounted on the supporting mechanism; a control system, which is used for controlling the action of the cooperative mechanical arm; an end executing mechanism, which includes a connecting portion, a grip portion and a limit switch, wherein the connecting portion is mounted on a second end of the cooperative robot arm, the grip portion and the connectingportion are magnetically connected and can be separated from each other, and the limit switch is electrically connected with the control system. When the grip portion is separated from the connectingportion, the control system can obtain a sensing signal of the limit switch and control the stopping action of the cooperative arm. The communicative dual-arm rehabilitation training robot of the invention can help the patient to perform sports rehabilitation training based on large joints, and can help resolve major clinical problems including the reactivation of the brain motor cortex and the functional reconstruction of the motor sensory network after the clinical nerve transposition recovery.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
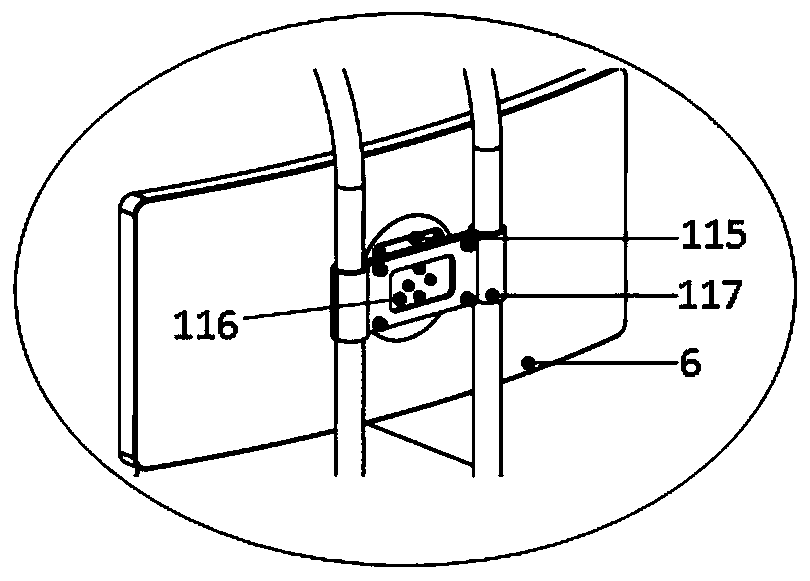
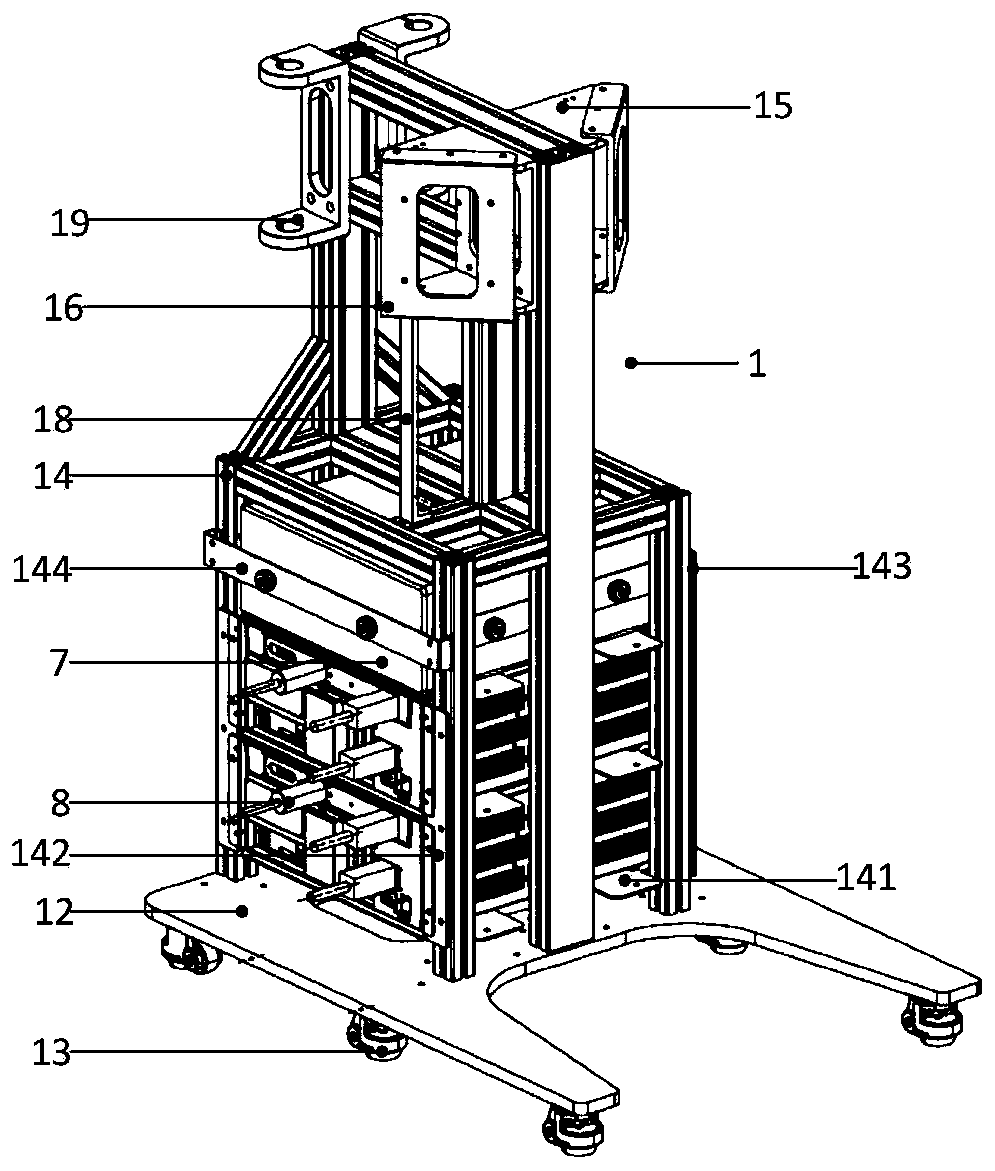
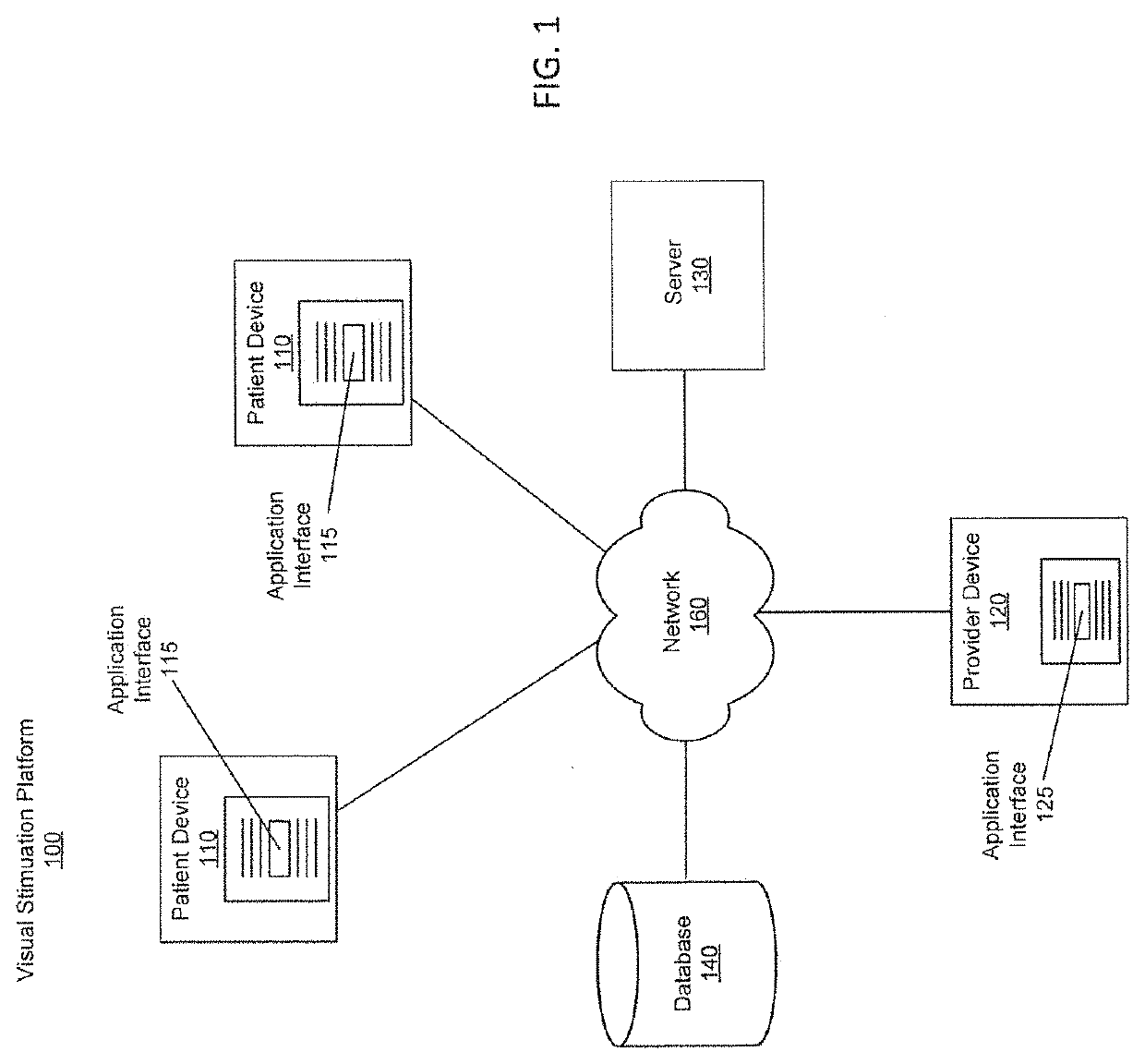
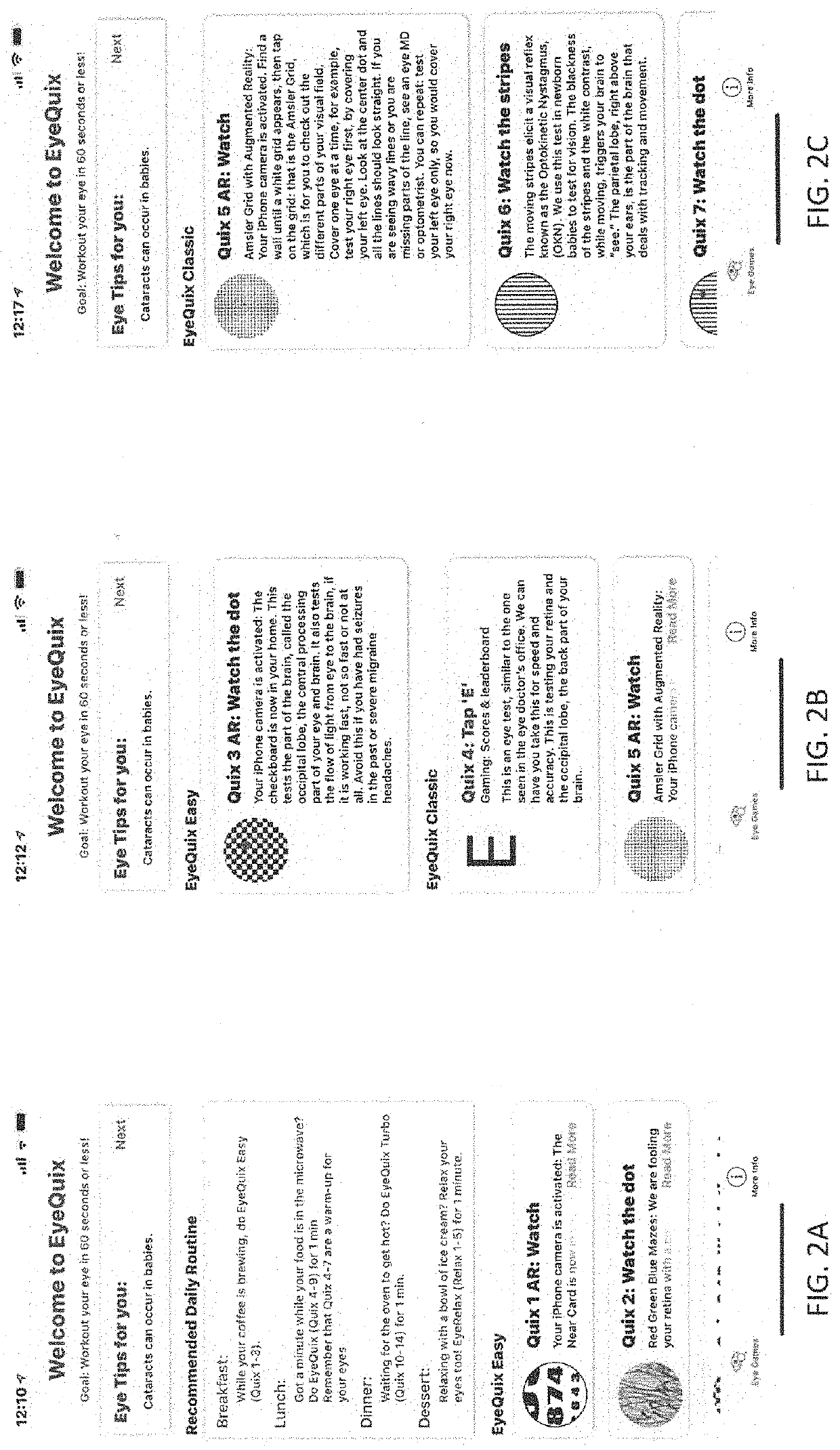
Stimulation of brain pathways and retinal cells for vision training
PendingUS20220351638A1Increase eye functionReduced activityDrawing from basic elementsTexturing/coloringStroke treatmentAnimation
A vision stimulation platform is designed for stimulation of brain pathways and retinal cells for vision training and enhancement. Modules of eye exercises are provided to a user, where each module includes an ordered sequence of eye exercises to be performed by the user. The eye exercises comprise one or more screens showing an animated display for the user to view for a time period less than a threshold time (e.g., 10 seconds). The animated display has a color, movement, or pattern designed to stimulate a specific visual pathway of the brain or the retina of the user, and the set of displays is designed to achieve a purpose (e.g., eye relaxation, vision precision, stroke treatment, etc.). At least one of the eye exercises comprises an interactive portion for the user to interact with one or more items on the screen to test the motor cortex of the user.
Owner:EYE QUIX LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com