Patents
Literature
31 results about "Prefrontal cortex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
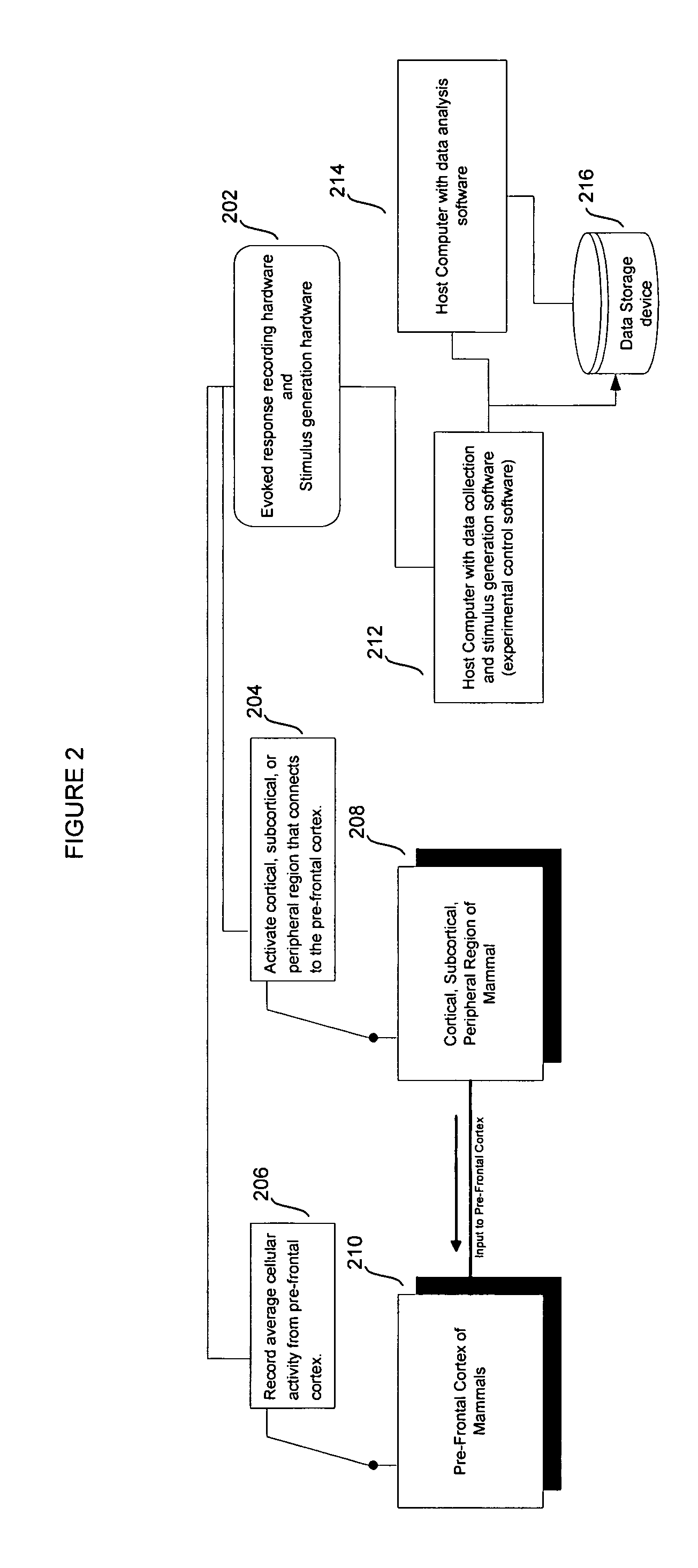
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) is the cerebral cortex which covers the front part of the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47.
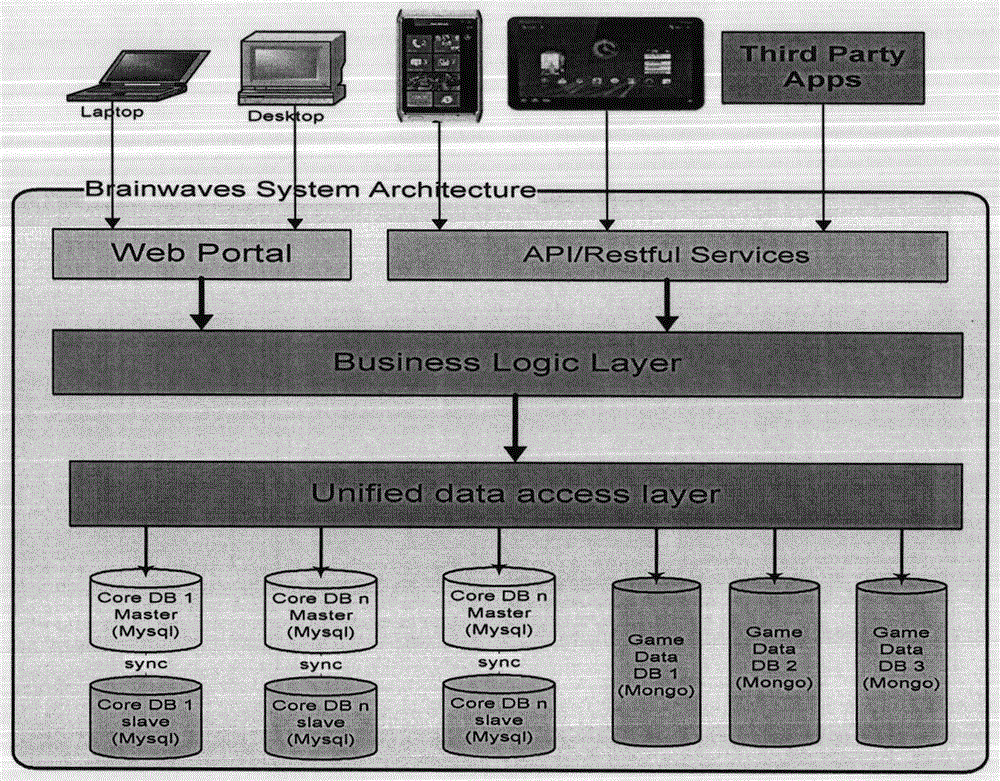
Human brain health training system based on SAAS platform
InactiveCN103226665AGood for healthRealize the establishmentSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyData access
The invention relates to a human brain health training system which is based on the SAAS (Software as a Service) platform. The system comprises a user interactive interface layer, a business logic service layer and a data access interface, wherein the user interactive interface layer comprises a client which is based on the Web platform or a mobile platform and provides data service; the business logic service layer comprises an account service module, a brain stimulation implementation module, a brain data collection module, an assessment service module, a course service module, a brain index analysis module and a system report service module; and the data access interface comprises a core data interface, a user data interface and a cognitive ability index data interface. The system provided by the invention can improve the cranial nerve circuitry junction in the memory area, is beneficial to the improvement of the memory storage capacity, can further strengthen the capability of the executive function area positioned at the prefrontal cortex, and finally adjusts the advanced function of human body, coordinates all kinds of neural activities of the function, and improves brain advanced functions such as brain health, emotion and the like.
Owner:BEIJING LOVE WISDOM SCI & TECH DEV
Electrophysiological screens for cognitive modulators
InactiveUS8396545B2Increase awarenessCognitive impairmentElectroencephalographySensorsMedicineStimulant
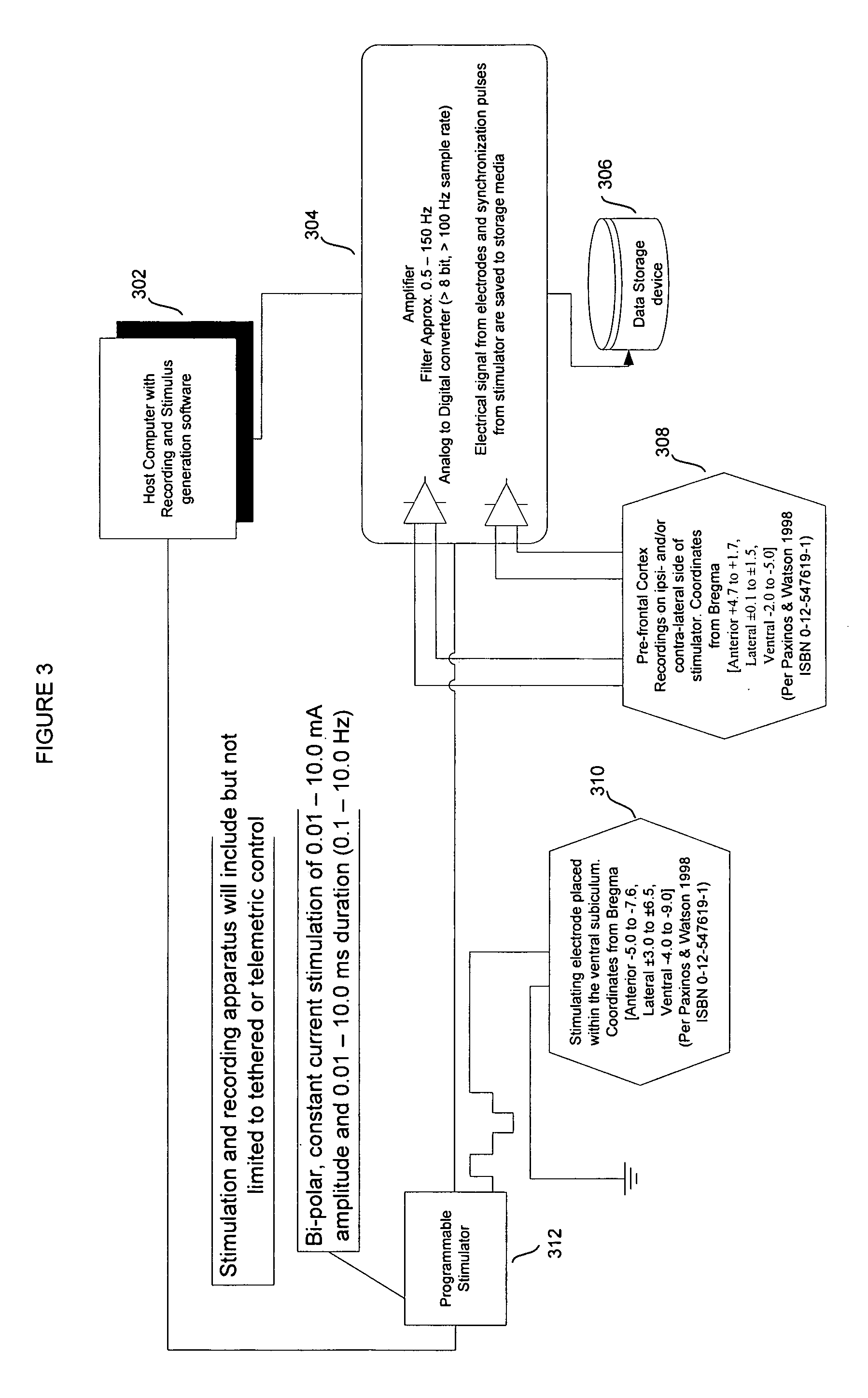
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for analysis of electromagnetic activity of prefrontal cortex neurons in subjects are provided. The methods, apparatuses, and systems of the present invention can be used as a means to screen for cognitive modulators. They can be used to predict the effects of compounds such as psychostimulants and other drugs on prefrontal cortex-dependent cognition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
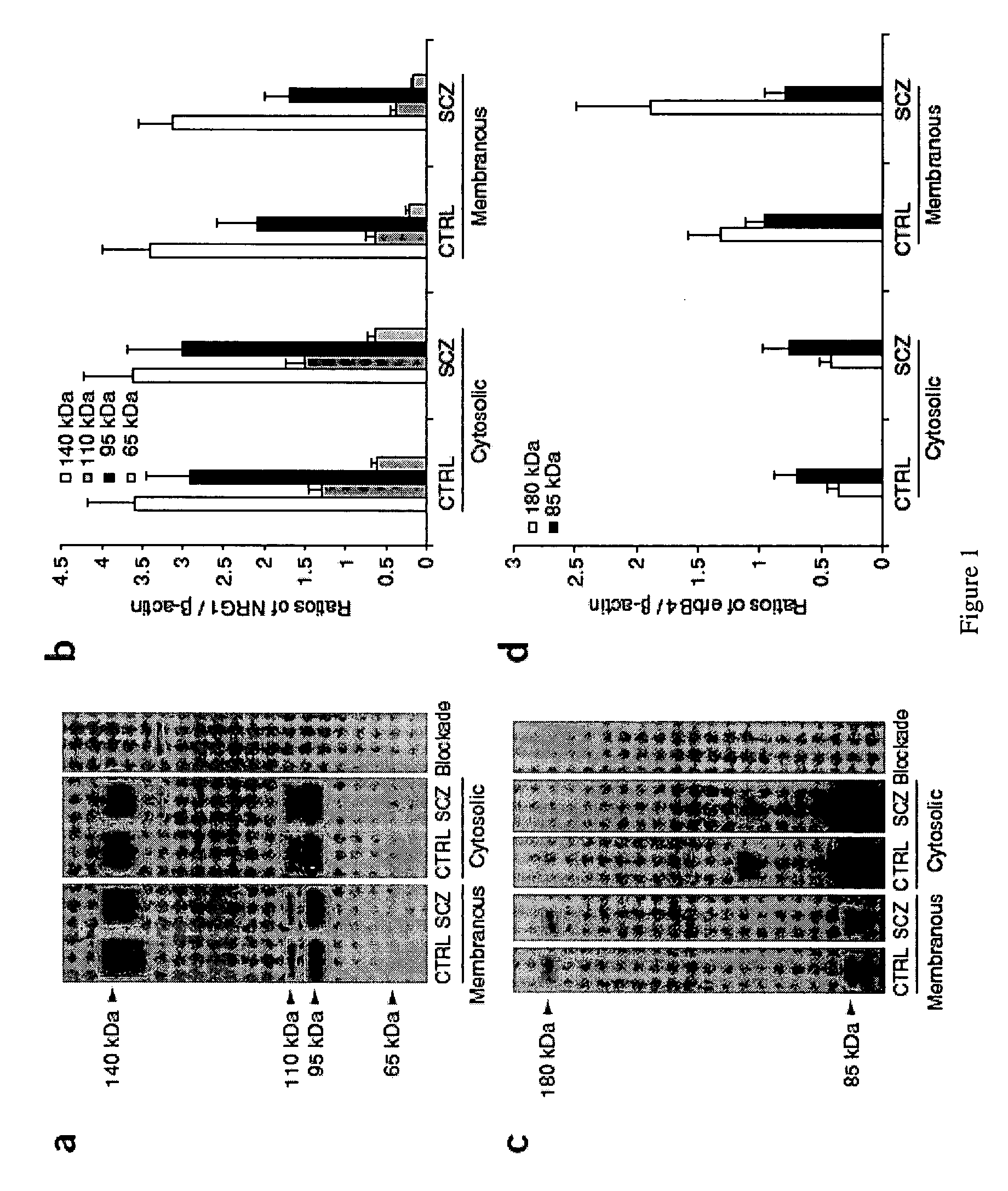
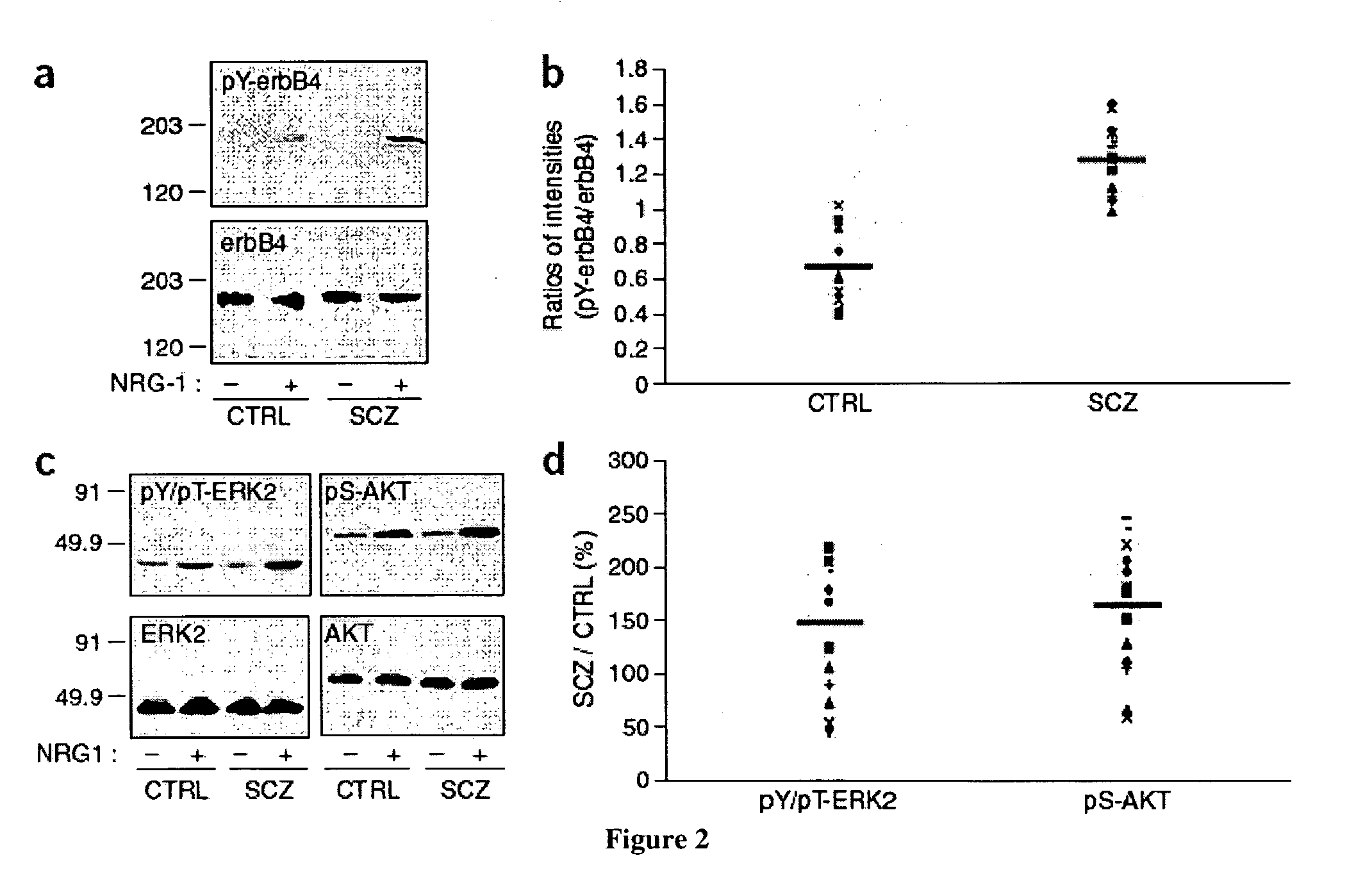
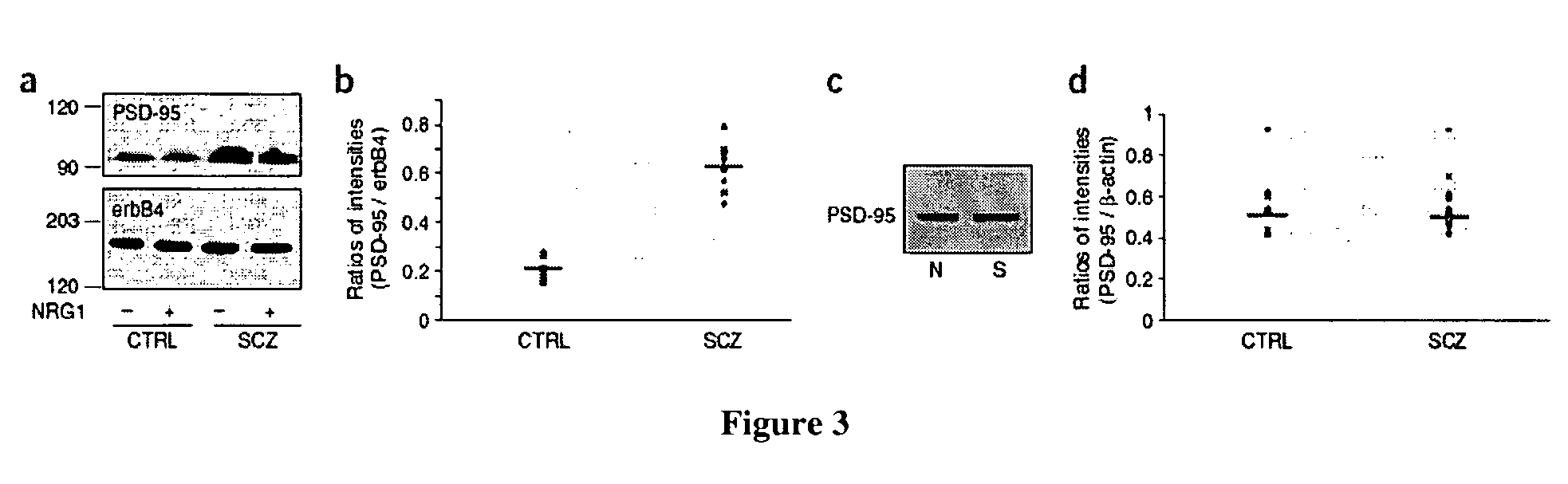
Neurgulin 1 (NRG1) - ErbB4 signaling as a target for the treatment of schizophrenia
InactiveUS20080181882A1Enhancing tyrosine phosphorylationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeuregulinErbB
This invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment of schizophrenia. Specifically, provided herein are methods and compositions for the treatment of schizophrenia by modulating the effect of Neuregulin-1 on the stimulation of erbB and its subsequent effect on schizophrenic prefrontal cortex.
Owner:THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods of treating cognitive impairment associated with neurodegenerative disorders
InactiveUS20150313903A1Increase awarenessCognitive declineBiocideOrganic active ingredientsExcipientPrefrontal cortex
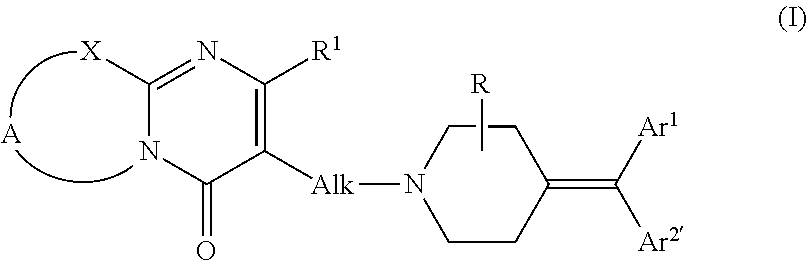
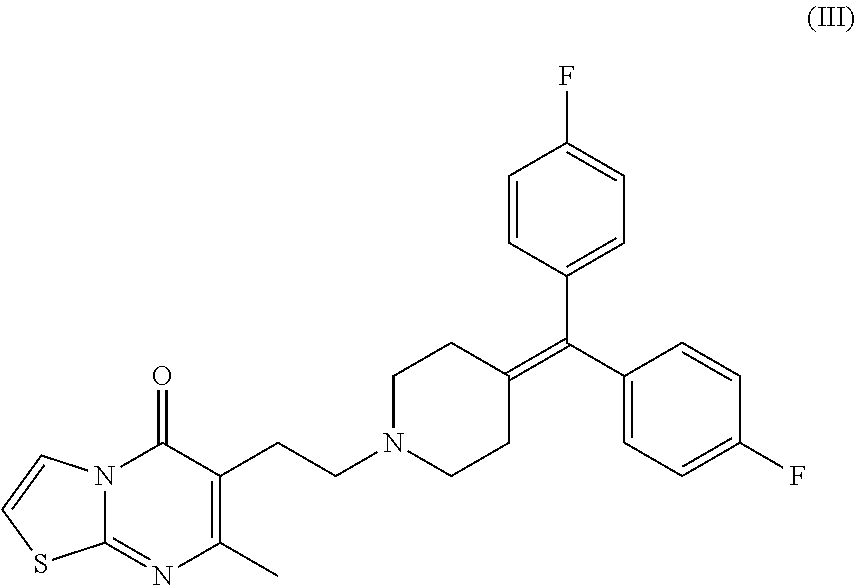
Methods of treating cognitive impairment, and / or reducing or preventing one or more neuropsychiatric morbidities in a subject with a neurodegenerative disease or disorder are disclosed. The methods can include administering the subject an effective amount of a (1-piperidinylalkyl)pyrimidinone derivative, preferably ritanserin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, to increase slow wave sleep; to increase dopamine signaling, preferably in the brain, more preferably in the prefrontal cortex; to increase the expression of BDNF preferably in the brain, more preferably in the hippocampus; or a combination thereof. Typically, the compound is administered in a pharmaceutical composition including a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or excipient. In some embodiments, the subject has not been clinically diagnosed with neurodegenerative disease based on physical symptoms.
Owner:OVID THERAPEUTICS
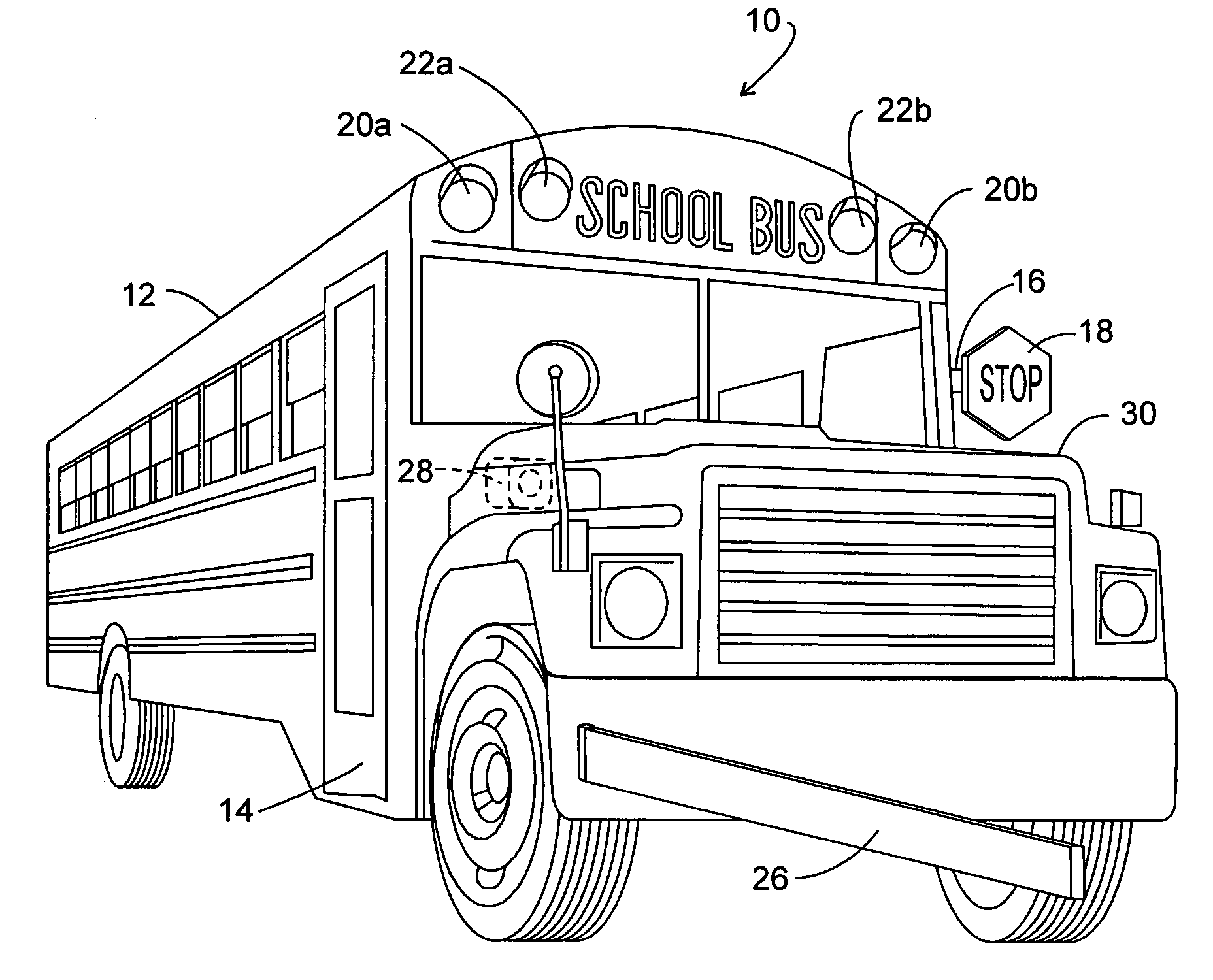
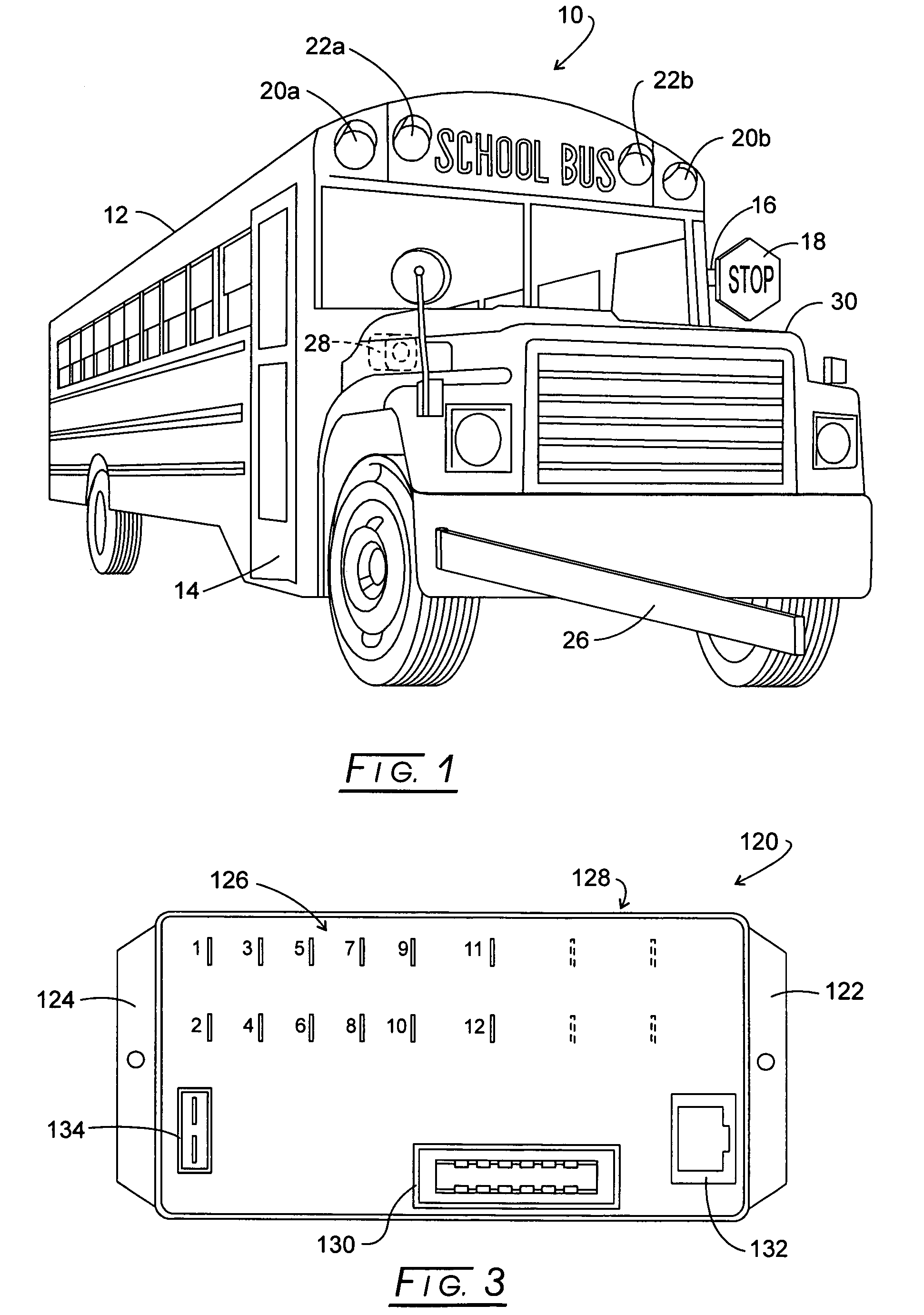
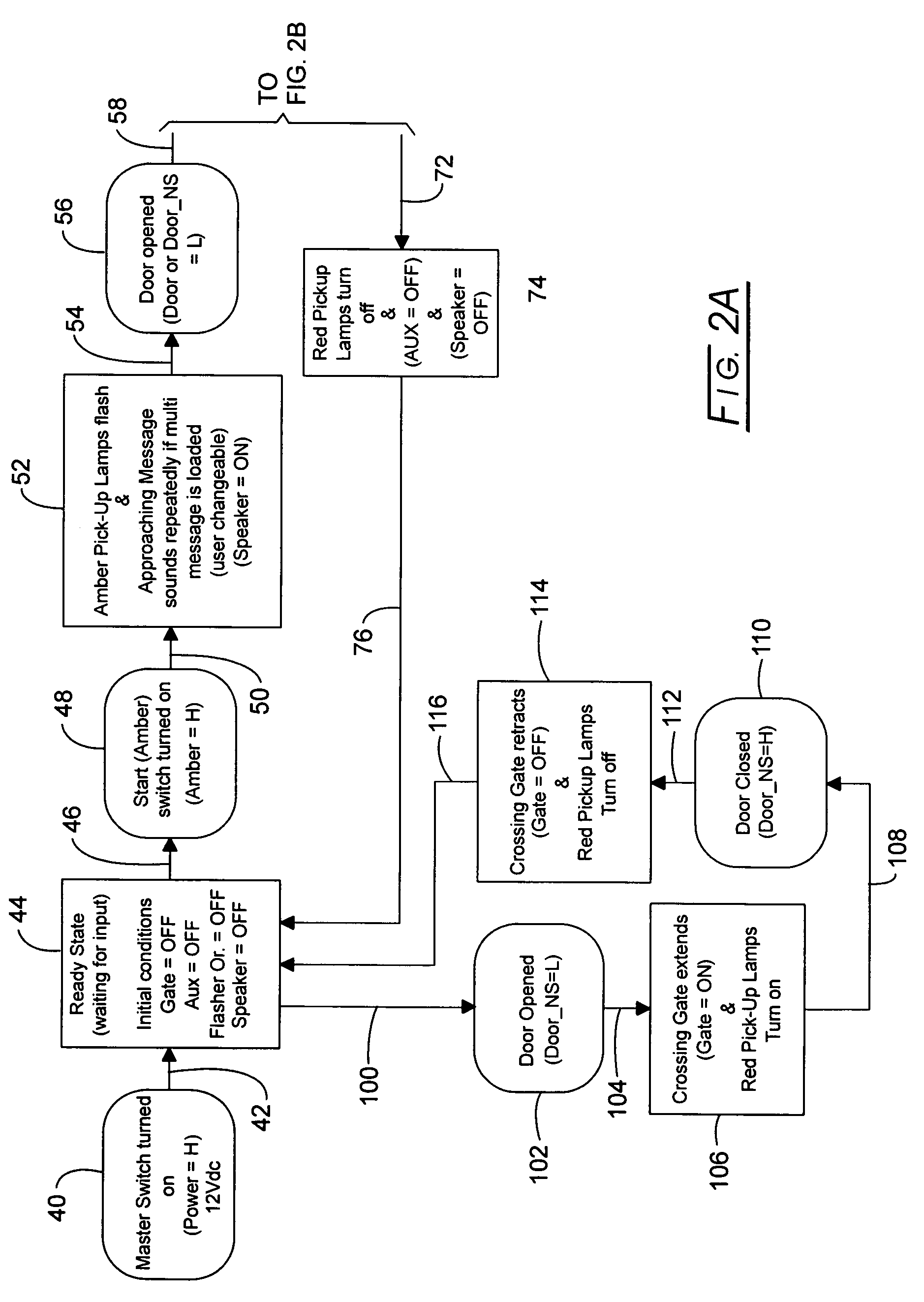
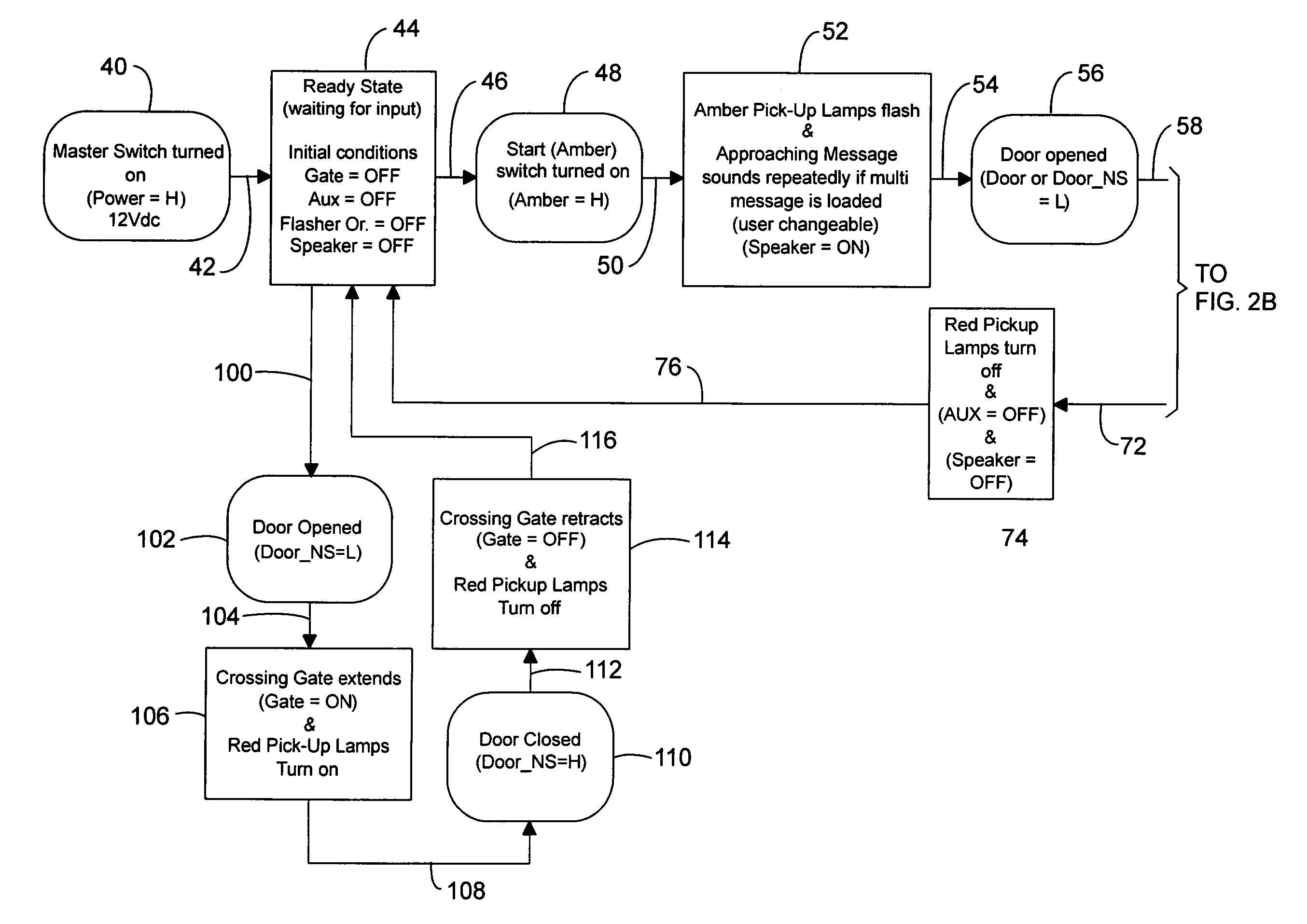
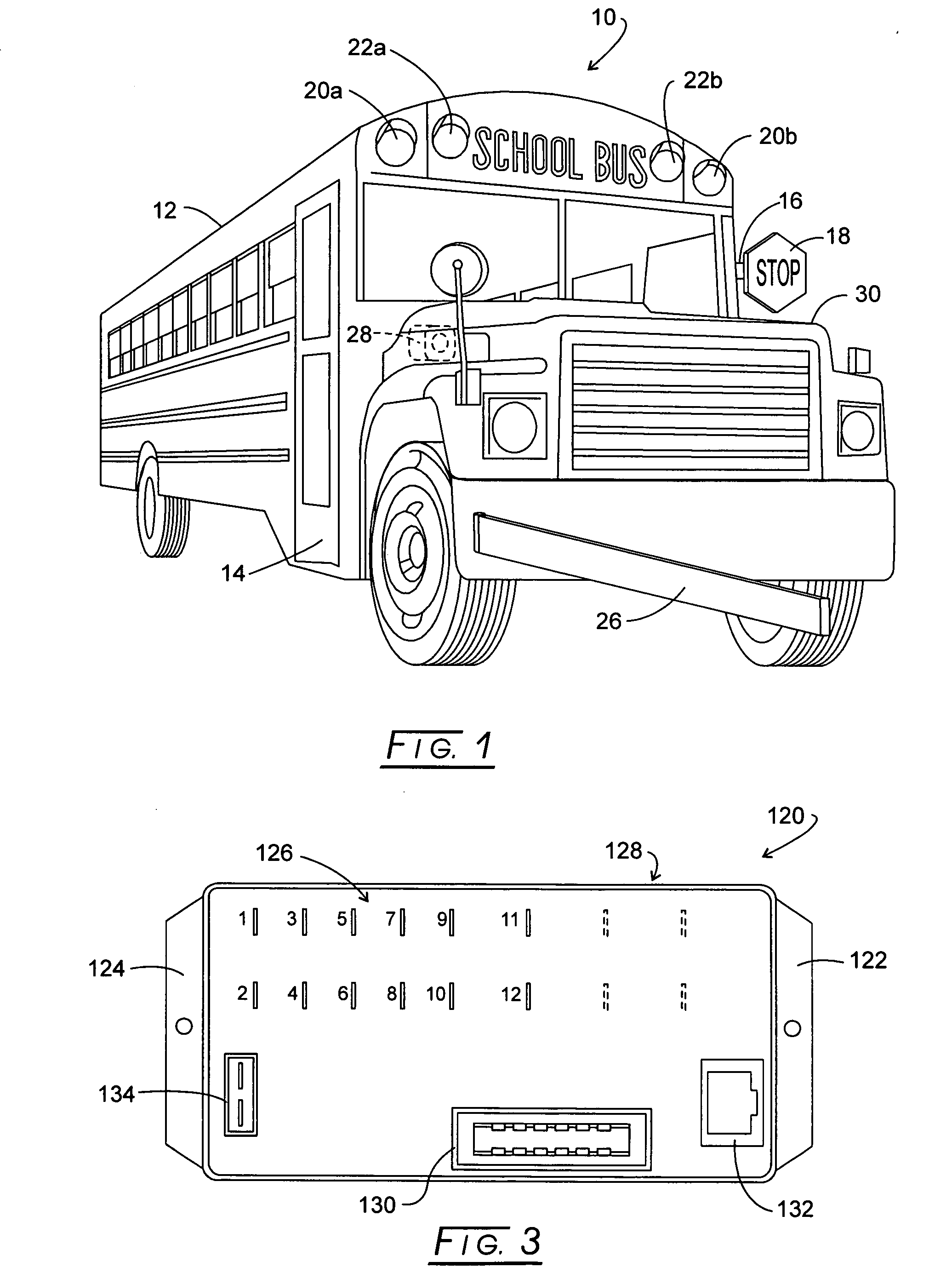
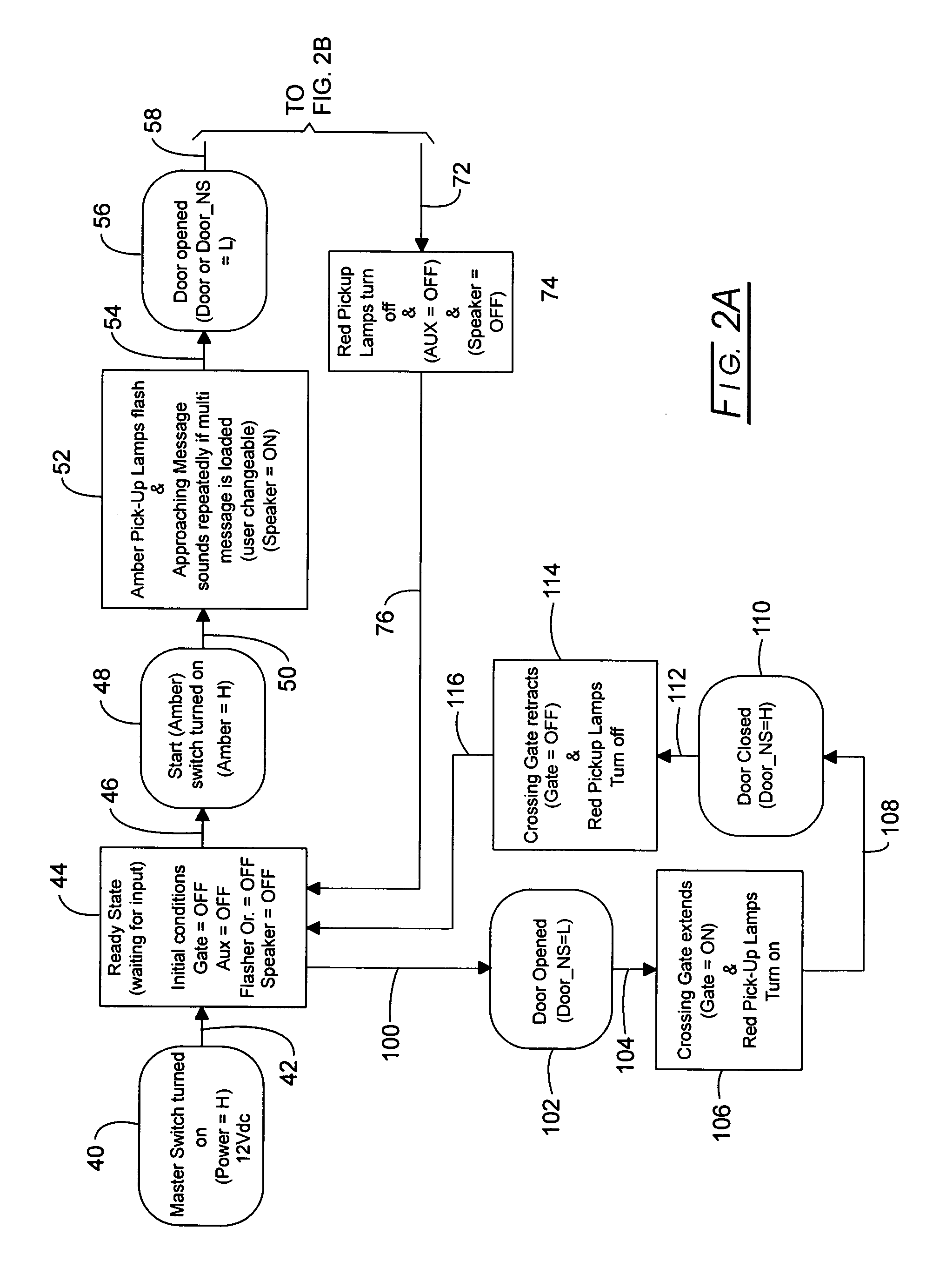
Bus safety controller method and system
Owner:TRANSPORTATION SAFETY PRODS
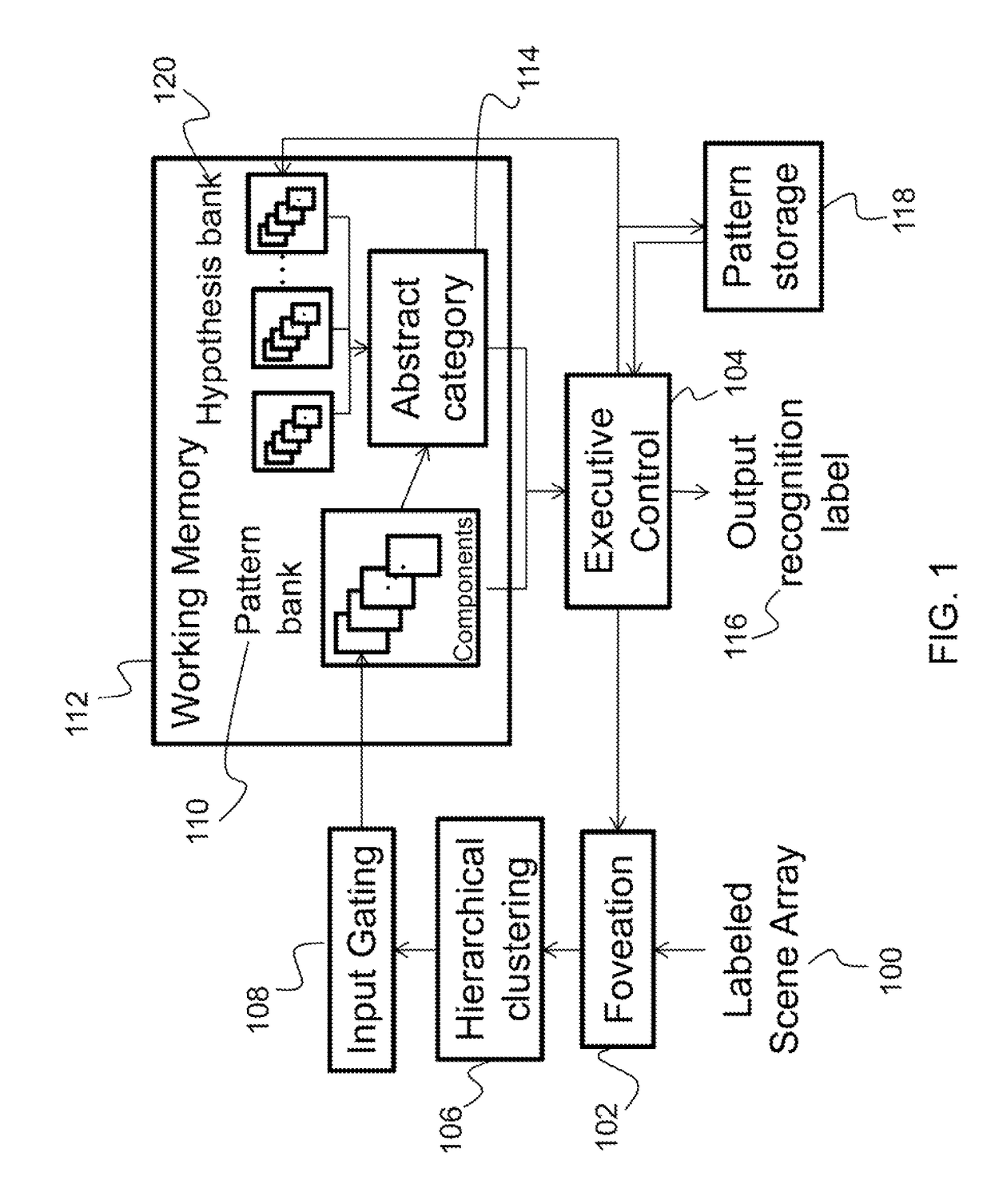
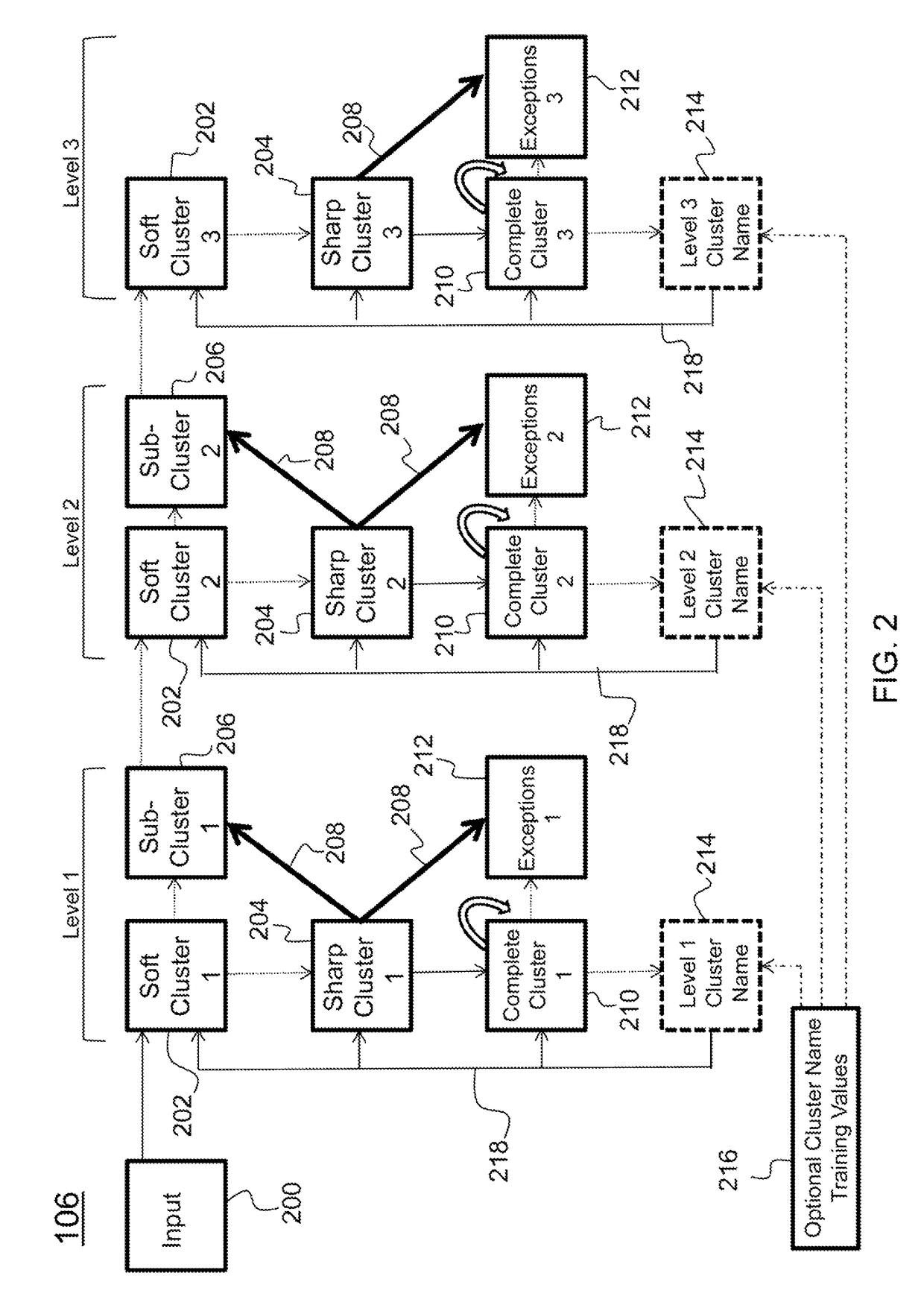
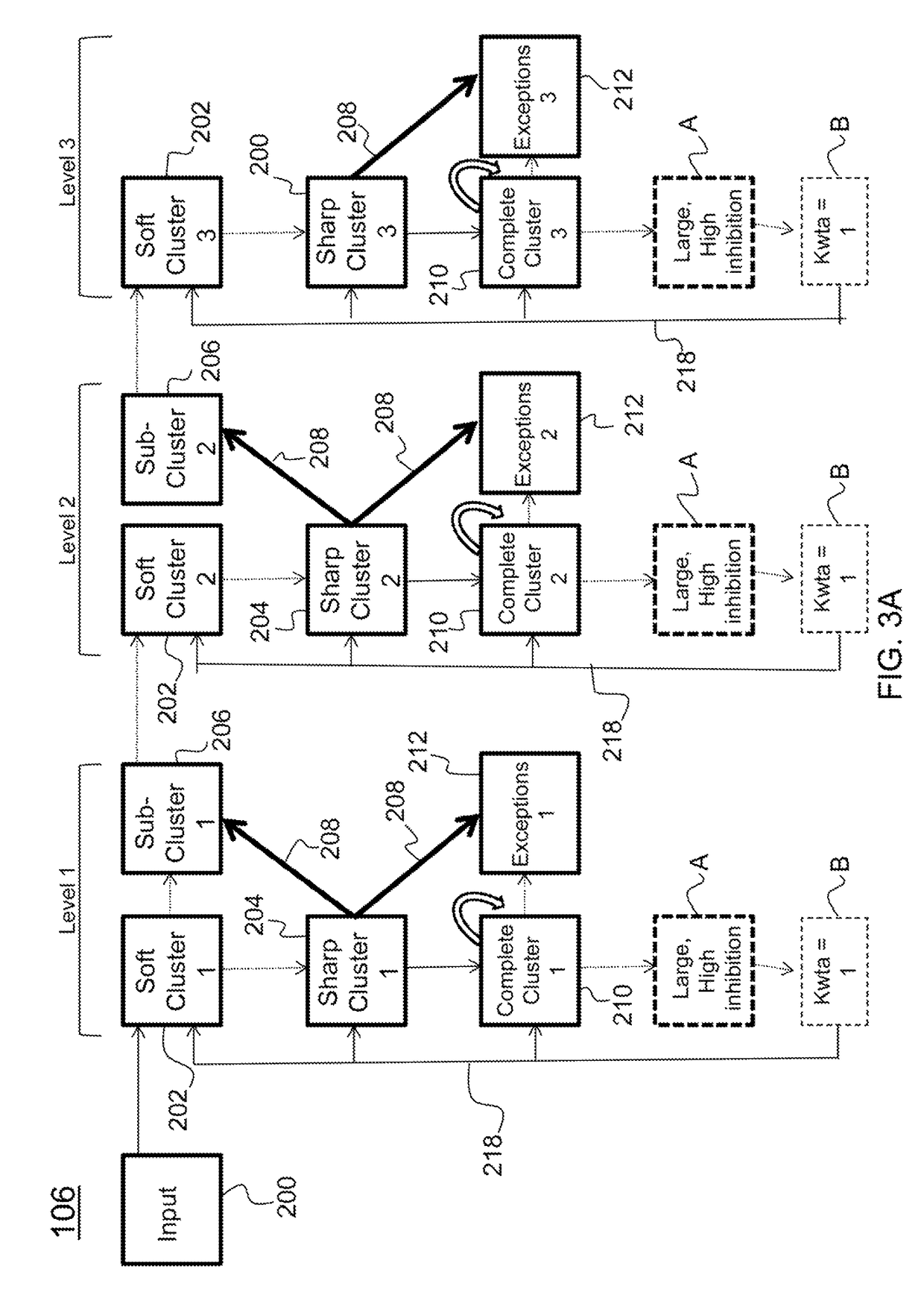
Hierarchical clustering method and apparatus for a cognitive recognition system based on a combination of temporal and prefrontal cortex models
Described is system and method for cognitive recognition. The system receives a multi-dimensional scene array as input data. A foveation module divides the multi-dimensional scene array into a plurality of sub-arrays and outputs contents of a currently selected sub-array. The contents are clustered with a hierarchical clustering module to generate a spatially invariant hierarchical cluster of the contents comprising a plurality of components which are based on a statistical distribution of co-occurrence of features across the currently selected sub-array. Task-relevant components are selectively gated and robustly maintained into a component memory location of a pattern bank with a working memory module with an input gating module. If the task-relevant components activate an abstract category module based on pattern matching, then a category recognition label is generated for the contents of the currently selected sub-array with an executive control module.
Owner:HRL LAB
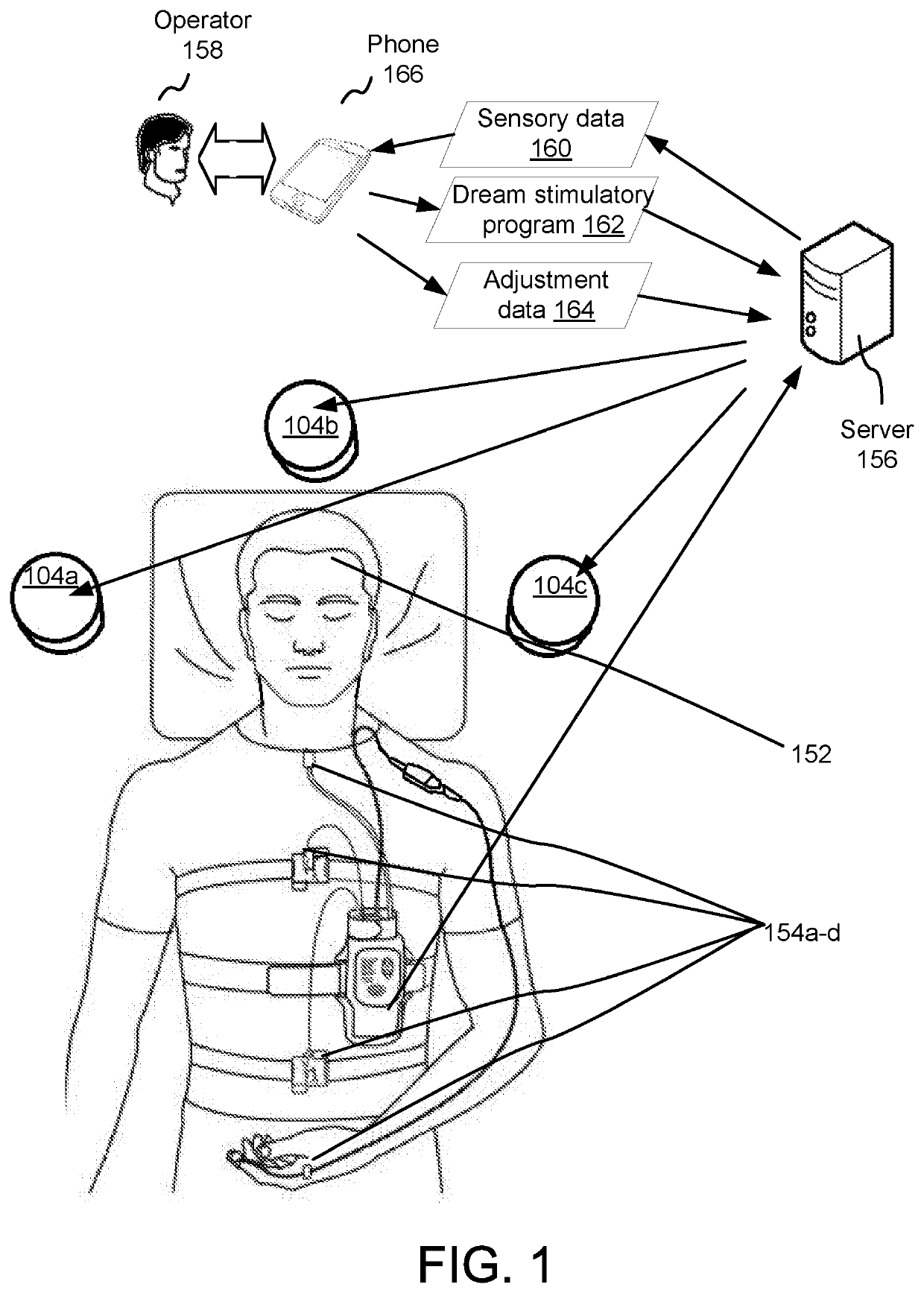
Low-powered electromagnetic brain stimulation dreaming apparatus and method
A brain stimulation apparatus and method making use of electromagnetics in the form of solenoids, in some embodiments, to stimulate brain function during sleep using oscillating low-powered electromagnetic fields to activate select regions of the brain of a subject which interact weakly with said regions, including, in some embodiments, the prefrontal cortex, the hippocampus, visual cortex, and posterior cortical hot zone.
Owner:JORGENSEN MITCHELL DART
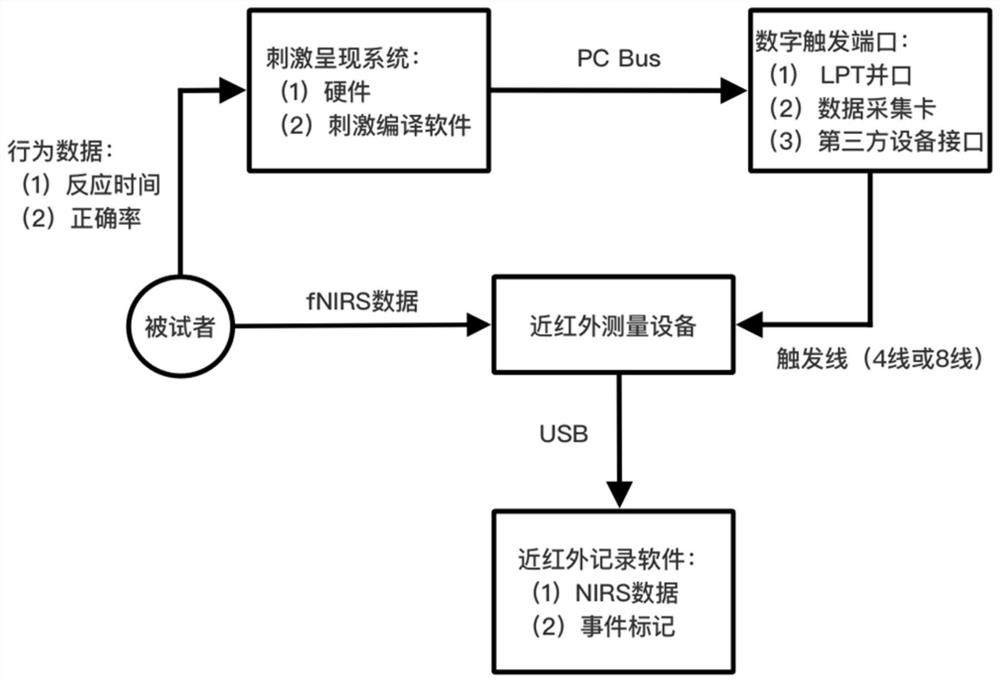
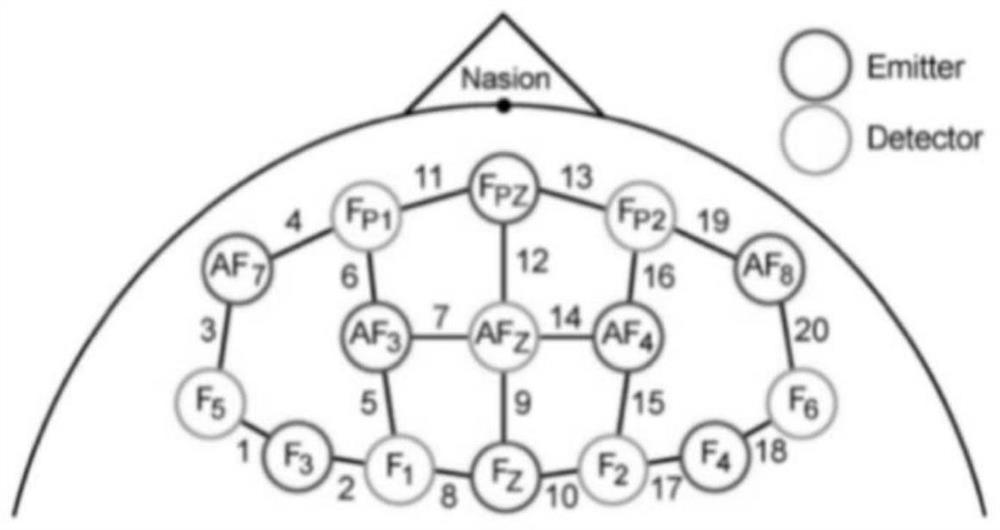
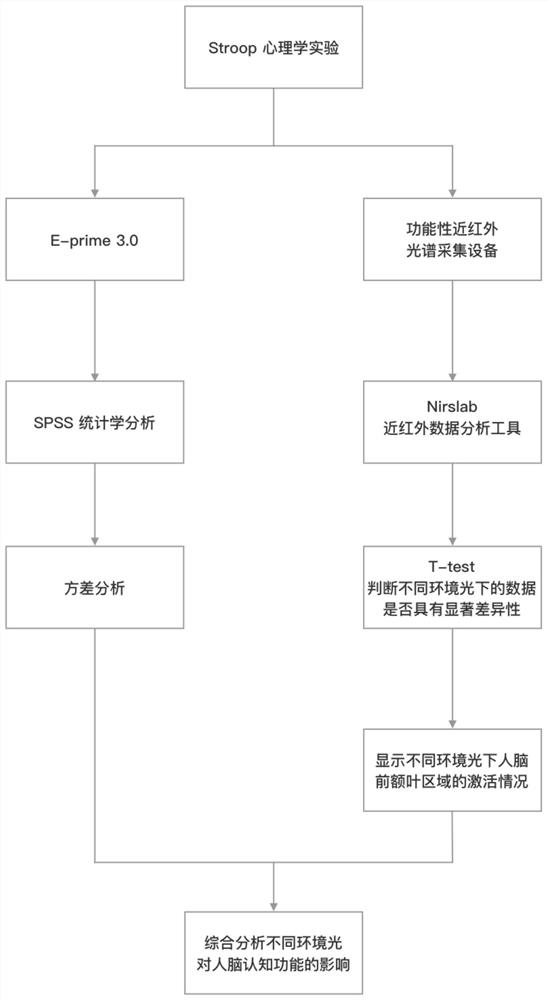
Near-infrared spectroscopy detection method of ambient light modulated brain cognitive function
ActiveCN112450879ADiagnostic signal processingDiagnostics using spectroscopyPrefrontal cortexLight modulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of brain science cognition, and particularly relates to a near-infrared spectroscopy detection method of an ambient light modulated brain cognition function. According to the method, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is utilized, a classical paradigm Stroop of cognitive behavioral psychology is combined, and the influence of ambient light change on the cognitive function of a human brain is explored for a prefrontal cortex (PFC) area with high correlation with the cognitive function of the human brain; The near-infrared spectroscopy detection method comprises the steps of designing an experiment environment; designing psychological Stroop experiment stimulation rules; designing an experiment process; building an experiment system; configuring a detection channel; combining a Stroop psychological test method with the fNIRS for testing; and finally, carrying out fNIRS data processing. Brain activation area images under different illumination conditions are obtained, and brain area channels with significant difference (P is smaller than 0.05) under different illumination conditions are obtained through t test, which proves thatthe channels are activated due to ambient light change.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
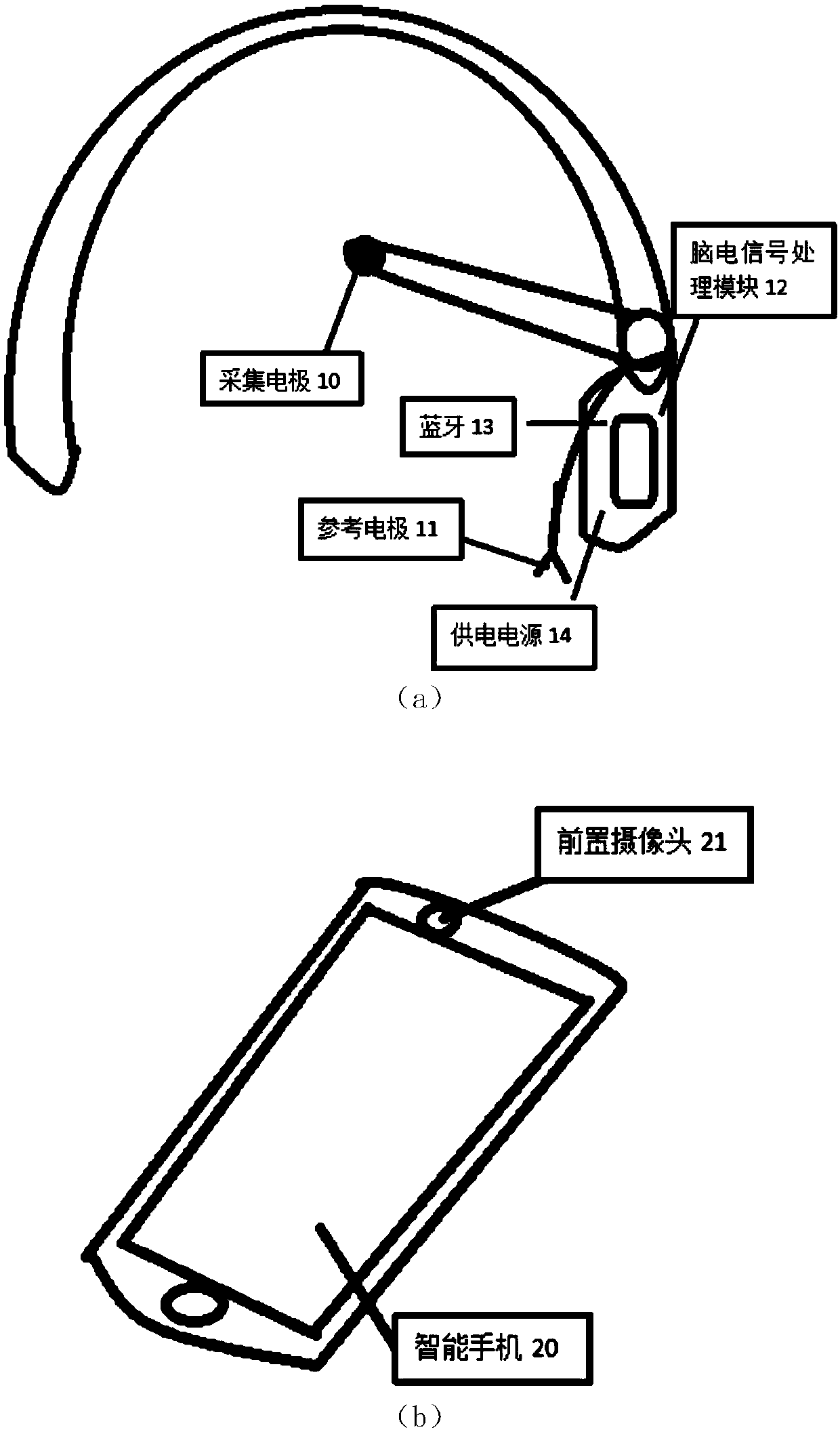
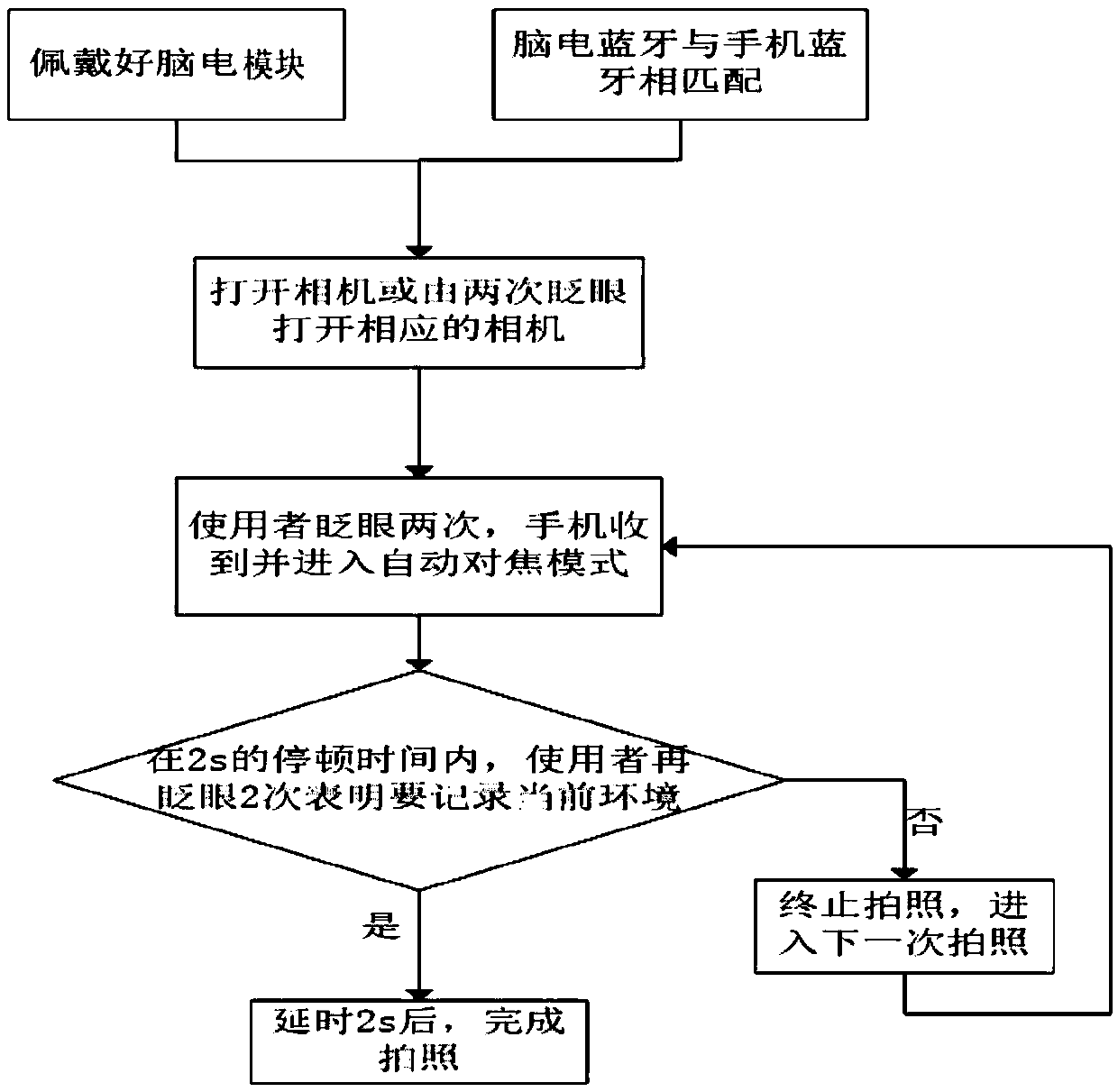
Mobile terminal intelligent photographing system and method based on brain wave control
InactiveCN108683804AHigh speedImprove experienceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer scienceEnd user
The invention discloses a mobile terminal intelligent photographing system and method based on brain wave control, and relates to the technical field of brain waves. The mobile terminal intelligent photographing system includes an EEG module and a mobile terminal. The EEG module includes a brain wave acquisition module, an EEG signal processing module, a Bluetooth communication module, and a powersupply. The brain wave acquisition module is configured to acquire a potential signal of a human prefrontal cortex. The EEG signal processing module is used for processing the acquired potential signal of the human prefrontal cortex to extract an effective blink signal. The Bluetooth communication module is configured to transmit the extracted effective blink signal to the mobile terminal. The mobile terminal, according to the transmitted effective blink signal, forms a control command for automatic photographing. The system and method can improve the photographing speed and experience of a mobile terminal user, improve the interest, and simplify the user operation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Bus safety controller method and system
InactiveUS20070132561A1Supplementing executive brain functionEfficient qualityRoad vehicles traffic controlPublic address systemsBroadcastingSpeech sound
System and method for automatically broadcasting voice-based prompt warnings toward an embarkation and / or disembarkation location at which passengers such as students and others may or will be present. The method is multi-model providing voice messages during an approach mode, a stop mode and a standby mode. Recorded human voice messages are employed for the prompt and are the recorded voices of one or more people having voice characteristics generally recognizable by the passengers to an extent effective to supplement the function of the immature prefrontal cortex.
Owner:TRANSPORTATION SAFETY PRODS
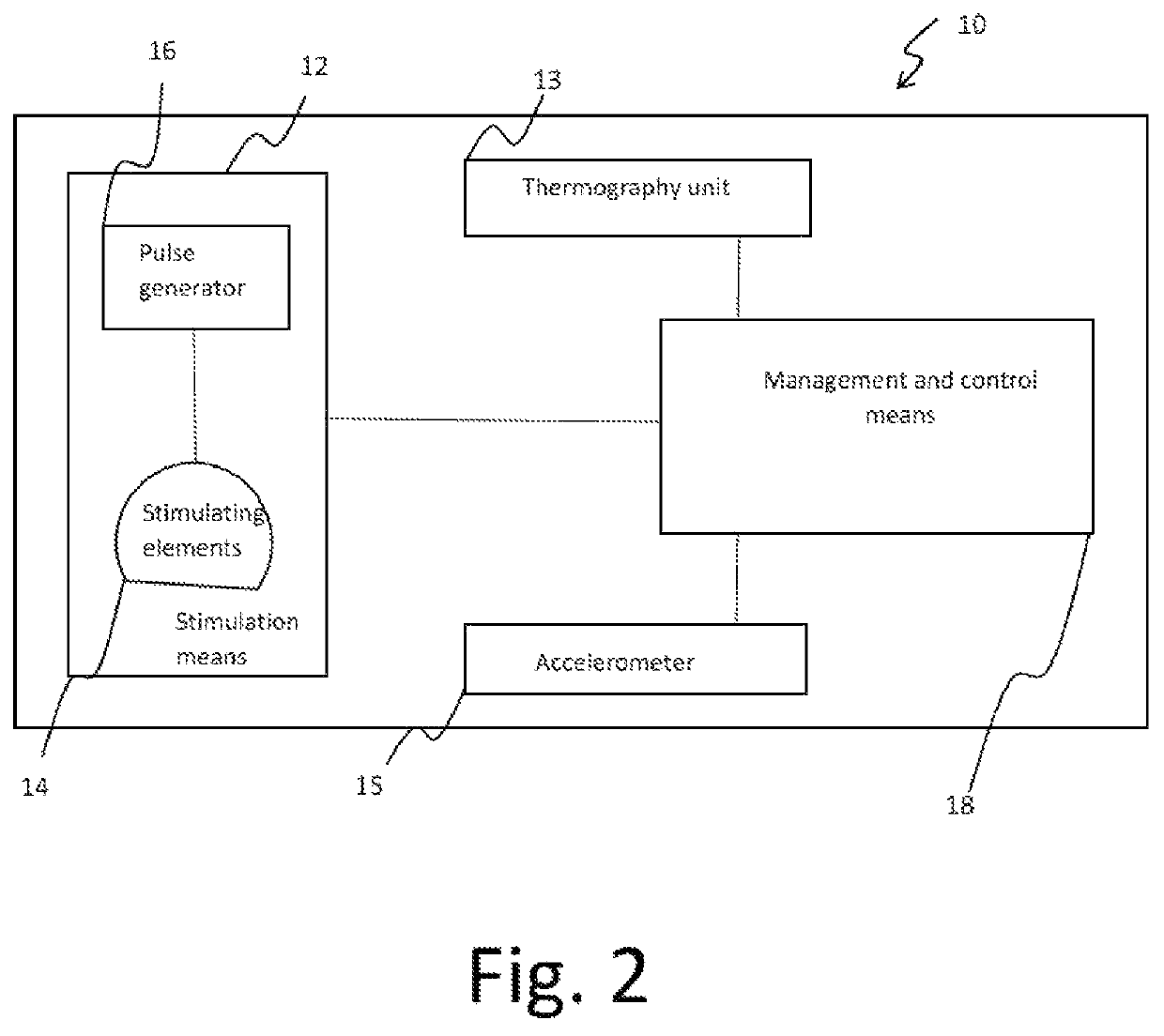
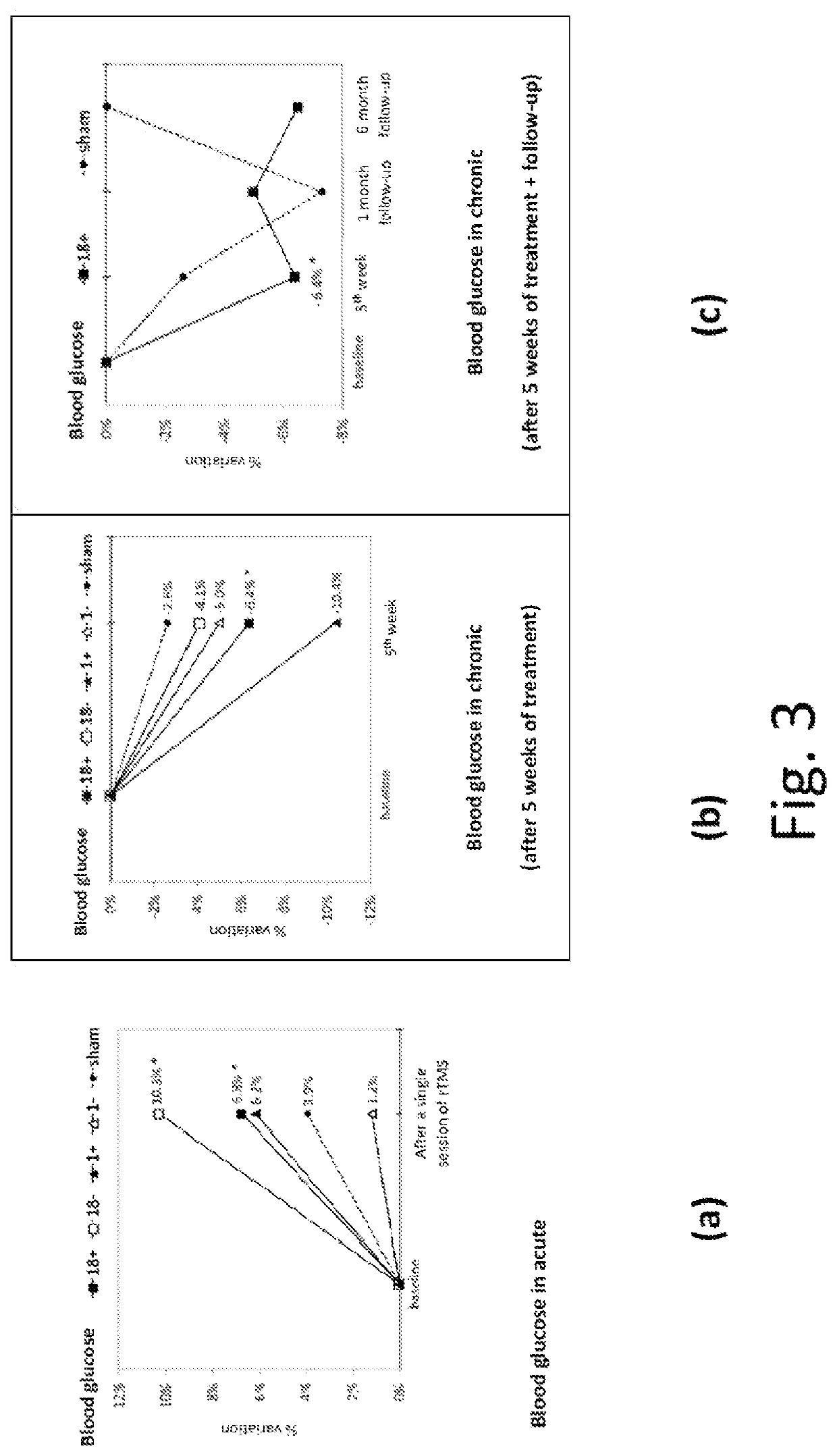
Method and system for modulating the brain electrical activity
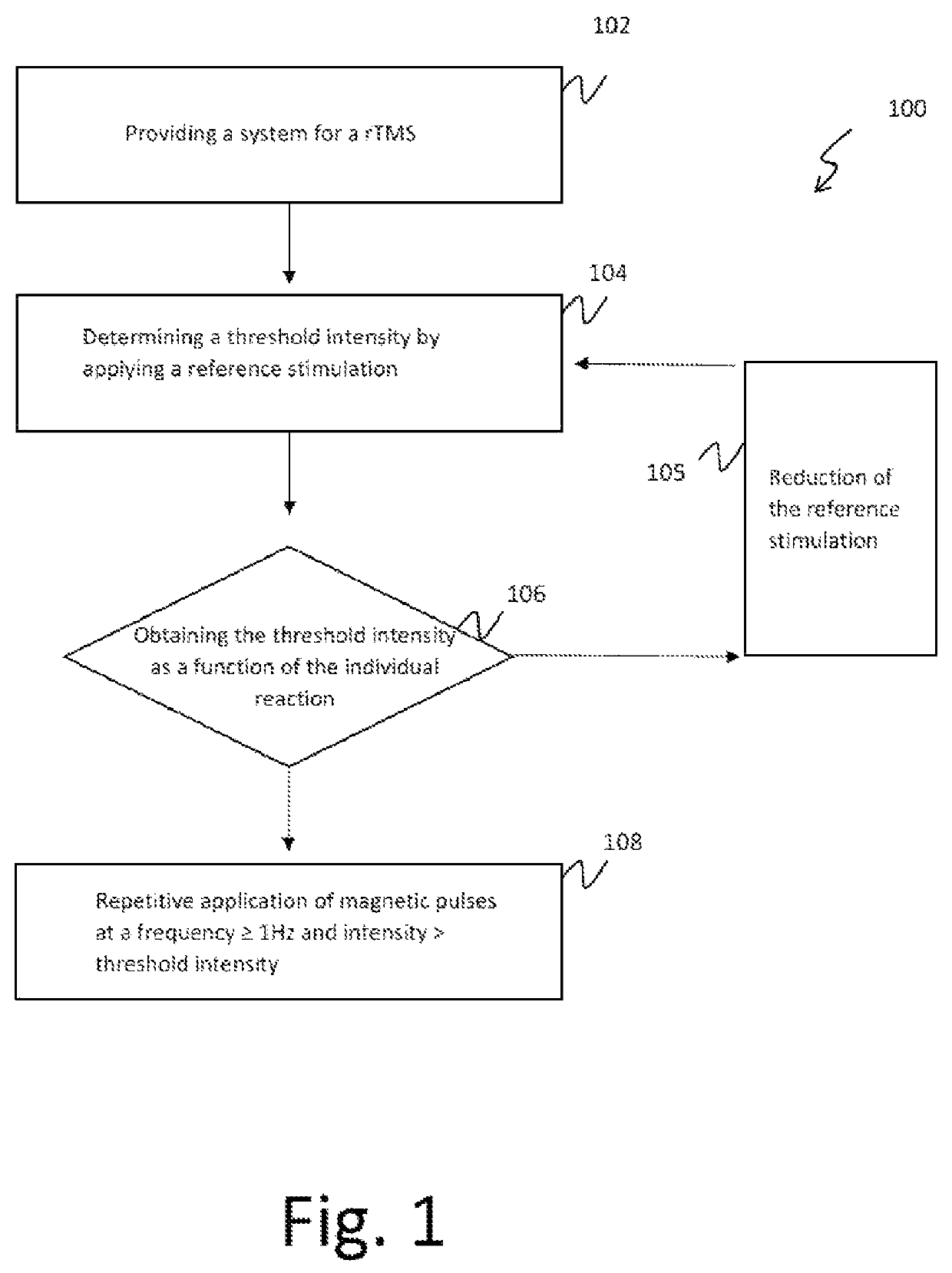
ActiveUS20190217114A1Reduce addictionIncreased activationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsFrontal lobeUltimate tensile strength
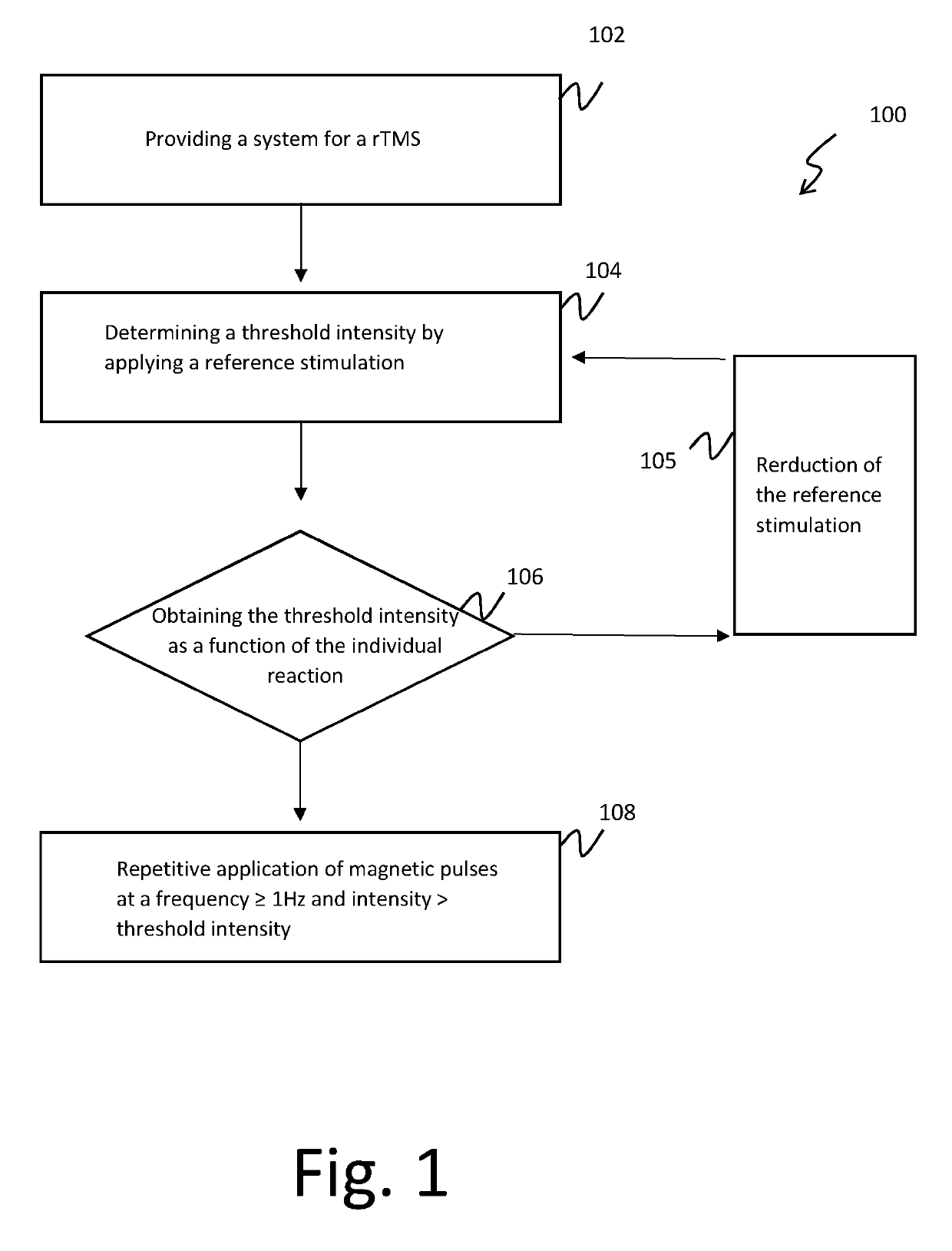
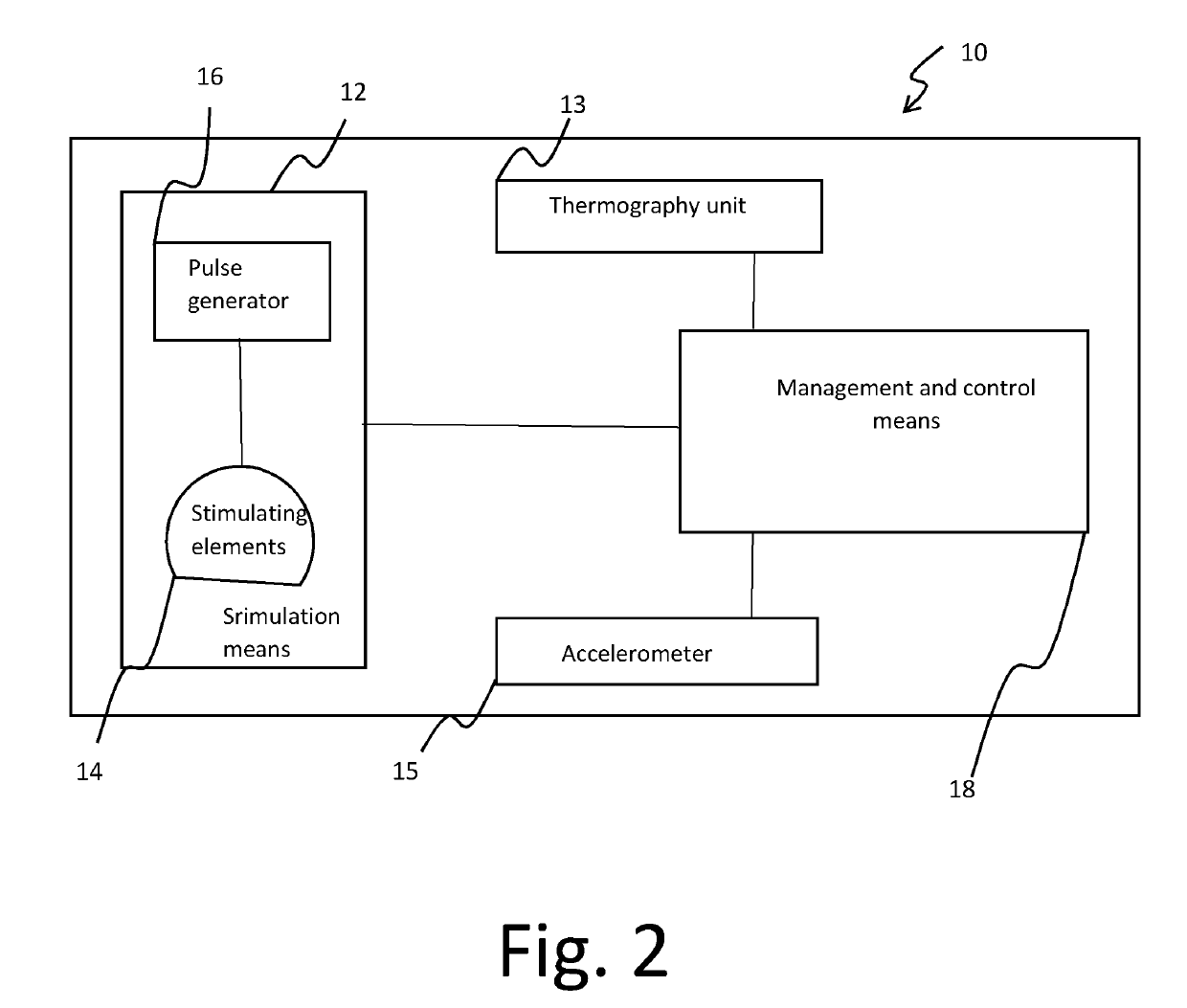
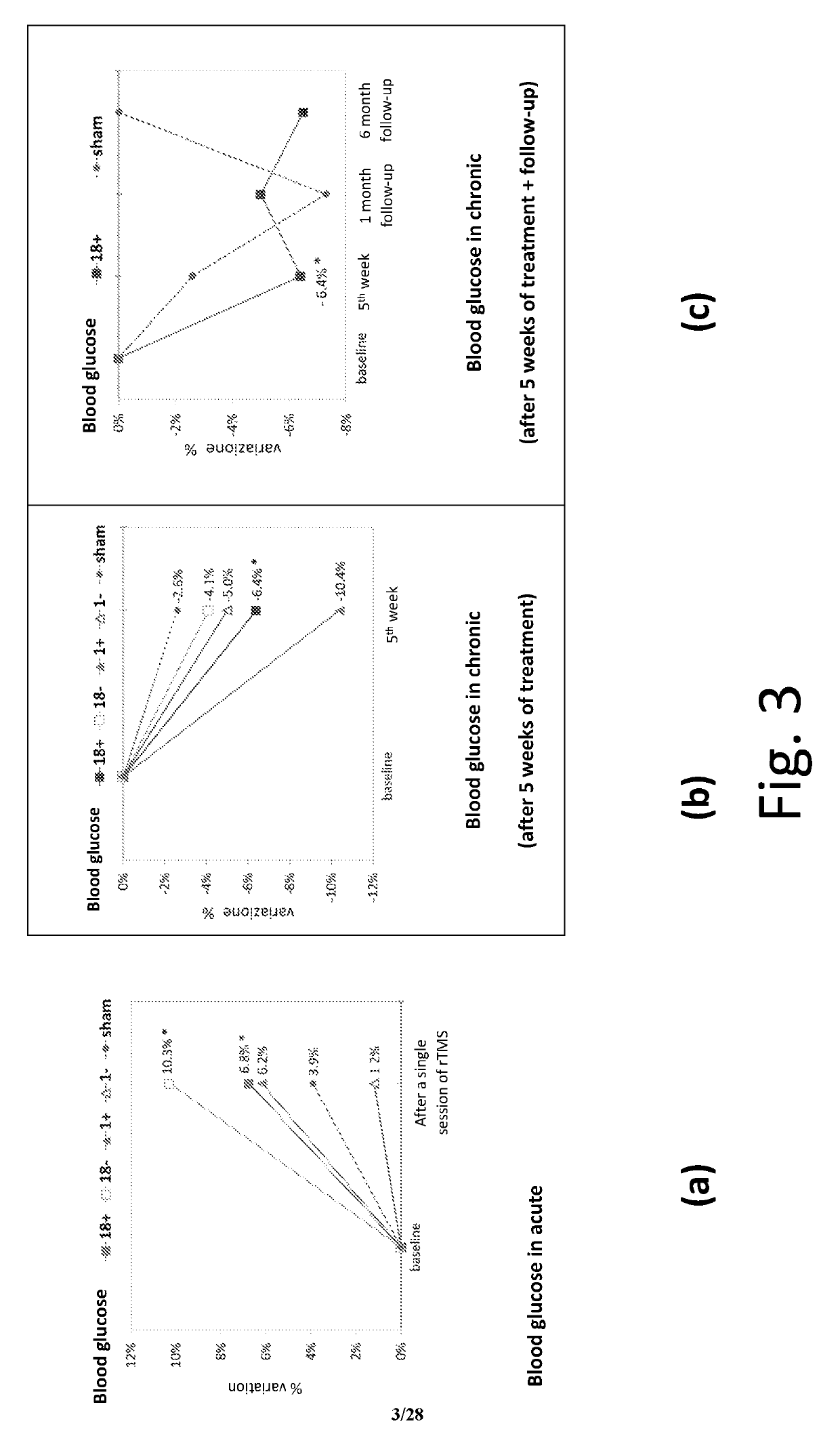
Method for a deep and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of an individual by means of magnetic pulses applied at least to a region of the scalp of the individual, said region being at least the bilateral prefrontal cortex, preferably the bilateral prefrontal cortex and the insula, the method comprising the steps of determining a threshold intensity of said magnetic pulses by applying to the individual one or more reference magnetic stimulations and determining a reaction of the individual to said reference stimulation, wherein said reaction corresponds to a right thumb movement and repeatedly applying a magnetic stimulation for at least 80 trains per session for a duration not exceeding 2 seconds each with a time interval between a train application and the next one not less than 20 seconds, wherein said magnetic stimulation has a frequency of at least 18 Hz with an intensity of stimulation at least 120% of the threshold intensity.
Owner:MULTIMEDICA
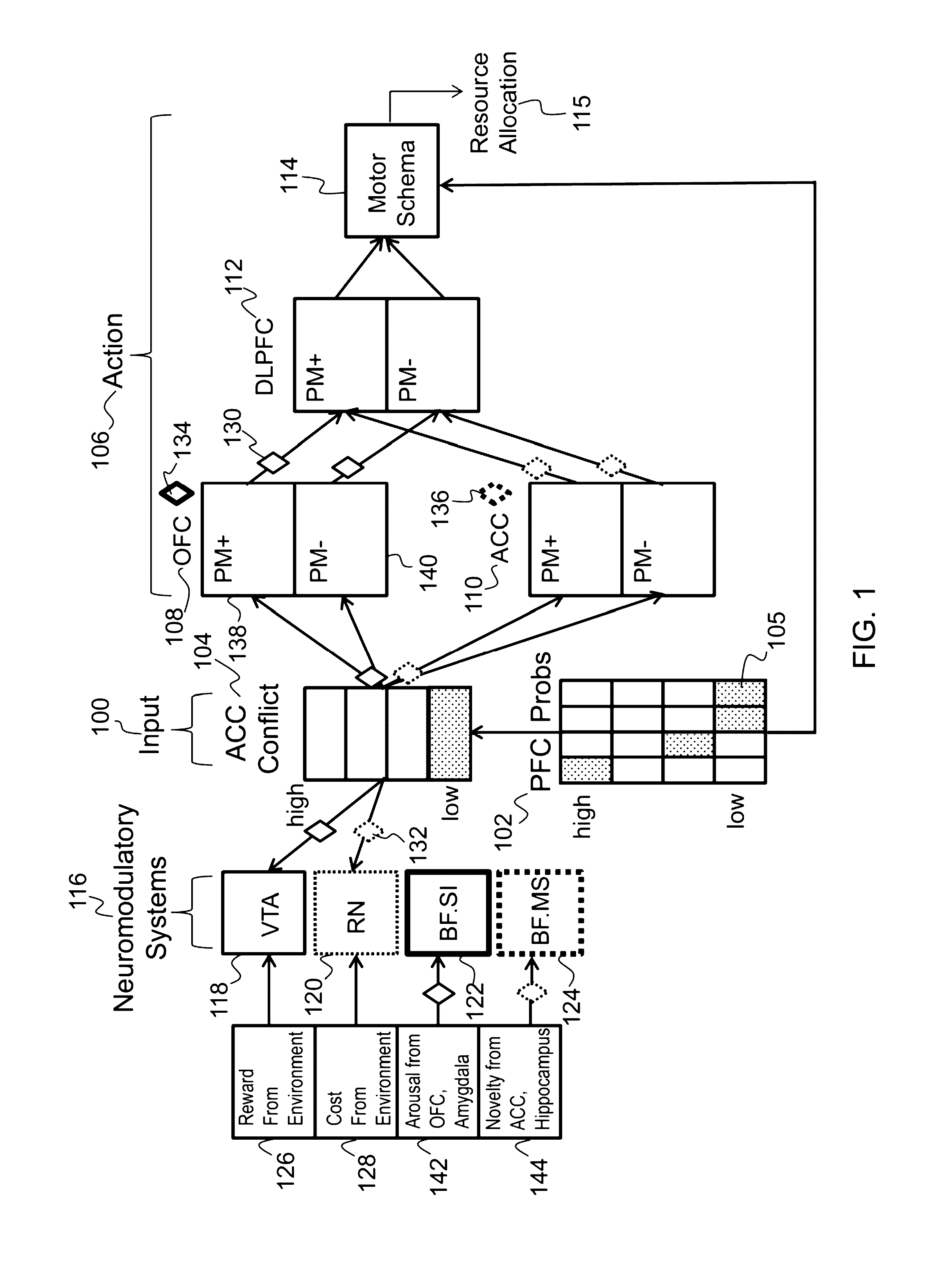
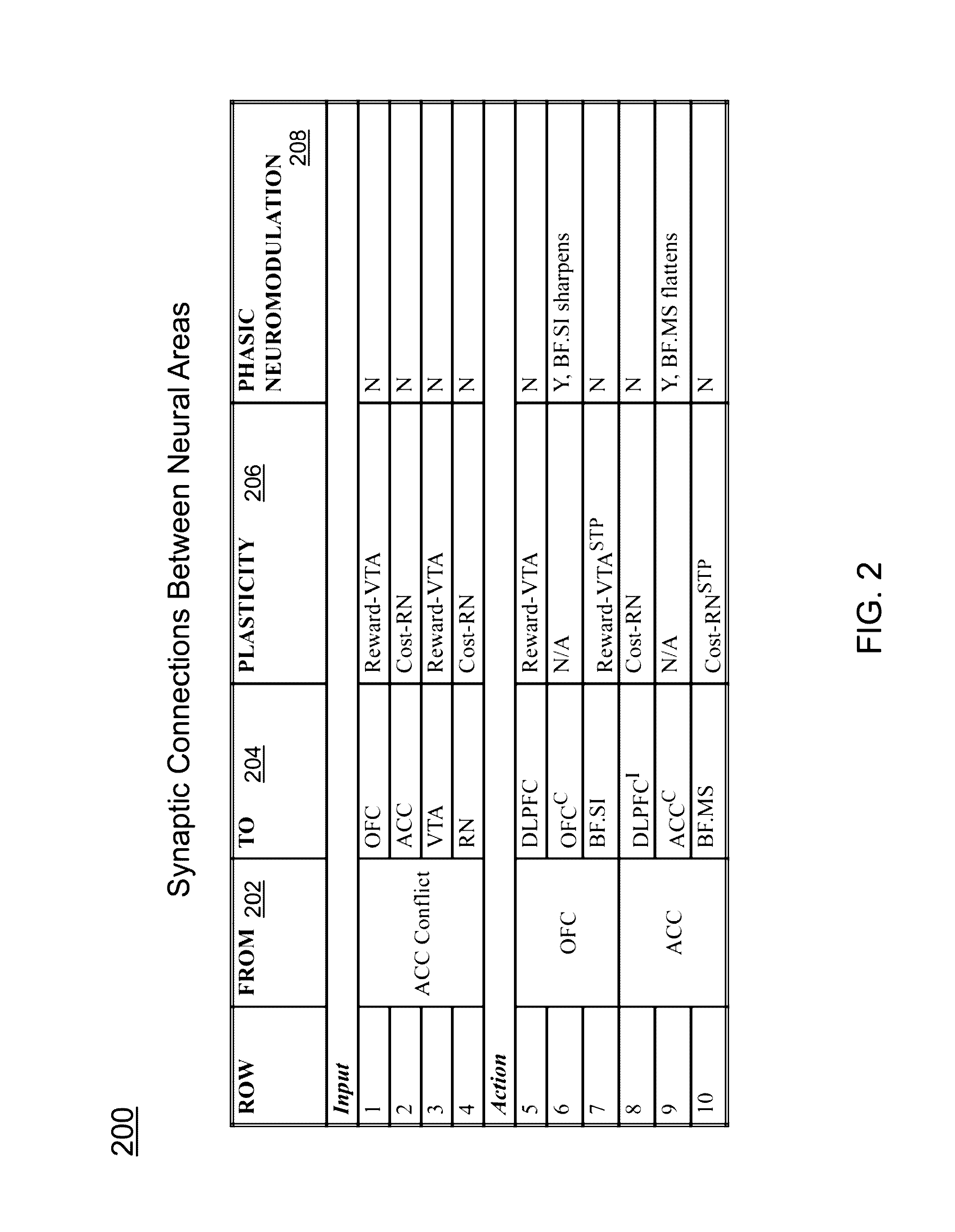
Method and apparatus for an action selection system based on a combination of neuromodulatory and prefrontal cortex area models
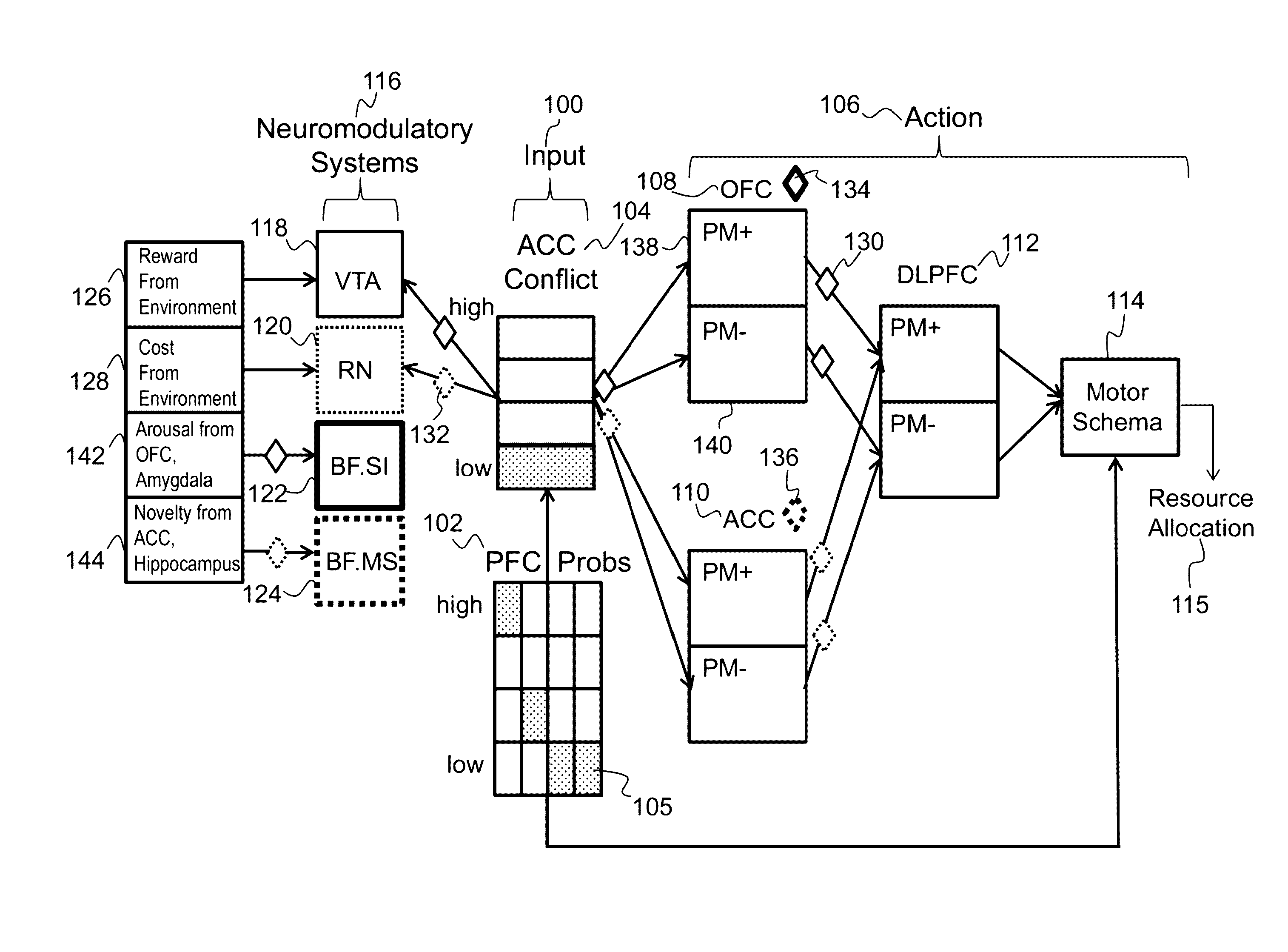
Described is a system for action selection based on a combination of neuromodulatory and prefrontal cortex models. The system inputs group attack probability estimates for multiple groups in a prefrontal cortex (PFC) input area of a model instance. The system encodes a dispersion of the group attack probability estimates in an anterior cingulated cortex (ACC) conflict input area of the model instance, resulting in activation of the ACC conflict input area. The activation is propagated to an action area and a neuromodulatory area of the model instance. An action strategy is selected in the action area. The action strategy is implemented, and a reward and a cost is generated for the implemented action strategy. An assessment of possible action strategies is updated based on the generated reward and cost. Each model instance modulates its subsequent action strategy selection based on the updated assessment of the possible action strategies.
Owner:HRL LAB
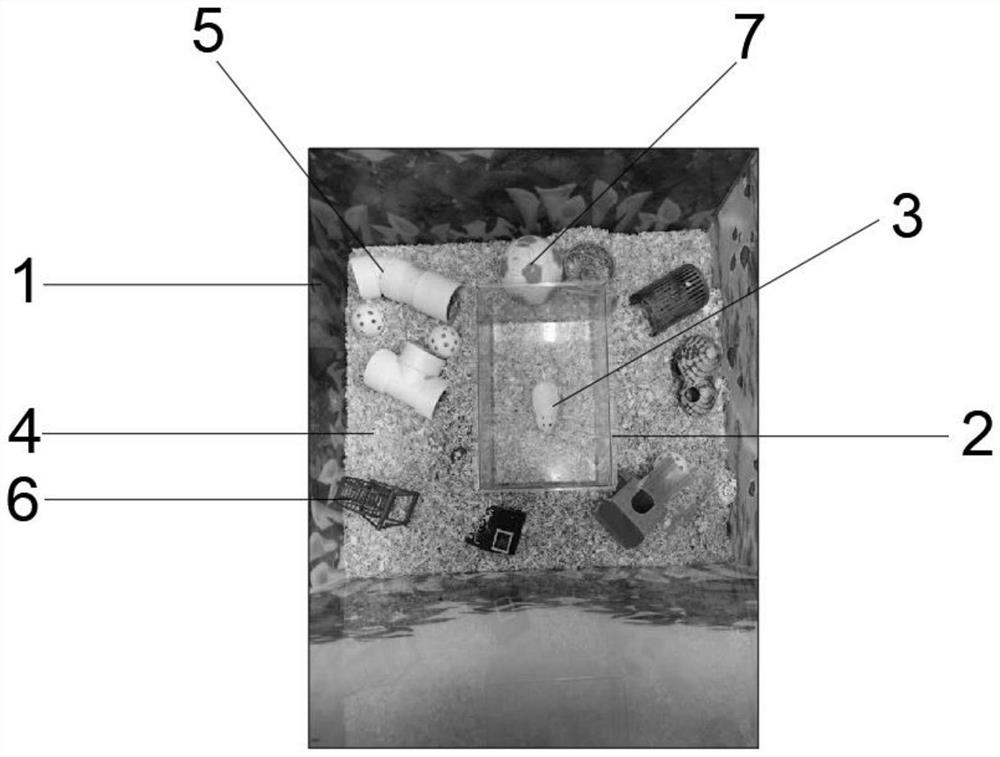
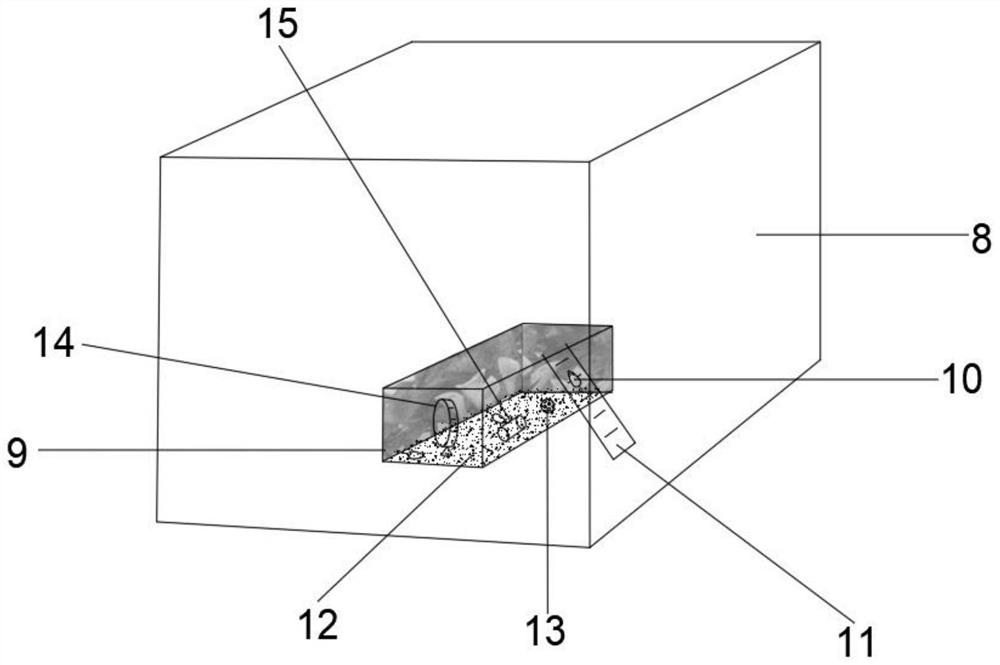
Comprehensive testing method for rat cognitive behaviors
ActiveCN111742852AWeaken the disturbing factorsIntervention changeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsInstinctCranial nerves
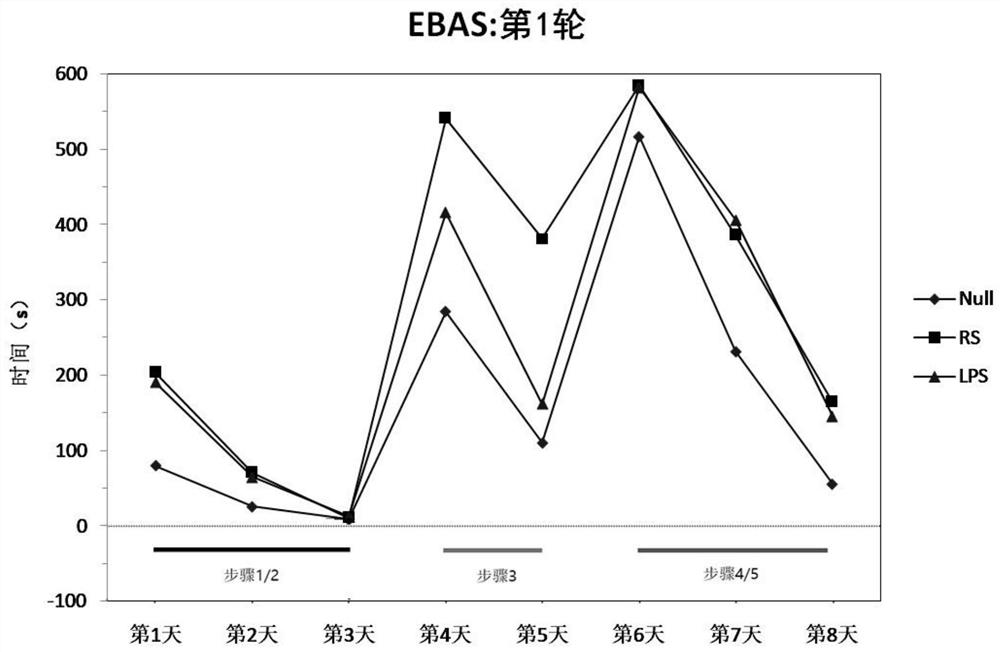
The invention provides an EBAS (Environmental Enrichment Based Acquisition System) evaluation system and discloses a comprehensive testing method for rat cognitive behaviors. The method is a comprehensive testing method for cognitive behaviors such as emotions, anxiety, society and the like of rats on the basis of EE (Environmental Enrichment), the testing is carried out under the condition of weakening the external stress environment without artificial separation, the rat cognitive behaviors are completely instinctive exploratory behaviors, and the method can be used for exploring material basis of neural circuit of hippocampus CA1 / CA3 and prefrontal cortex (PFC), is scientific for evaluating animal behavior change under actions of various drugs and medical intervention and can offer assistance for investigation of influence of drugs or medical intervention on change of cranial nerve or synaptic transmitter.
Owner:JIUJIANG UNIVERSITY
Pre-frontal cortex processing disorder, gait and limb impairment treatment
A methylphenidate, particularly including dextro-threo-methylphenidate, is administered to a subject to treat a gait or limb impairment secondary to a genetically acquired pre-frontal cortex processing disease or disorder, particularly including multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, Angelman syndrome, Rett syndrome and Fragile-X syndrome.
Owner:GILROSE PHARMA
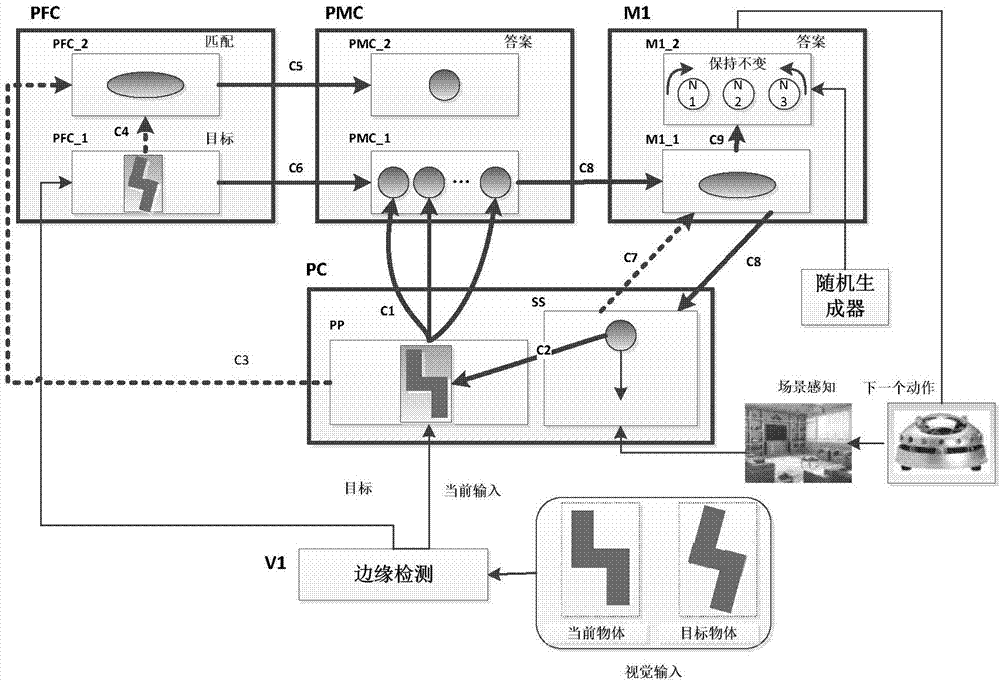
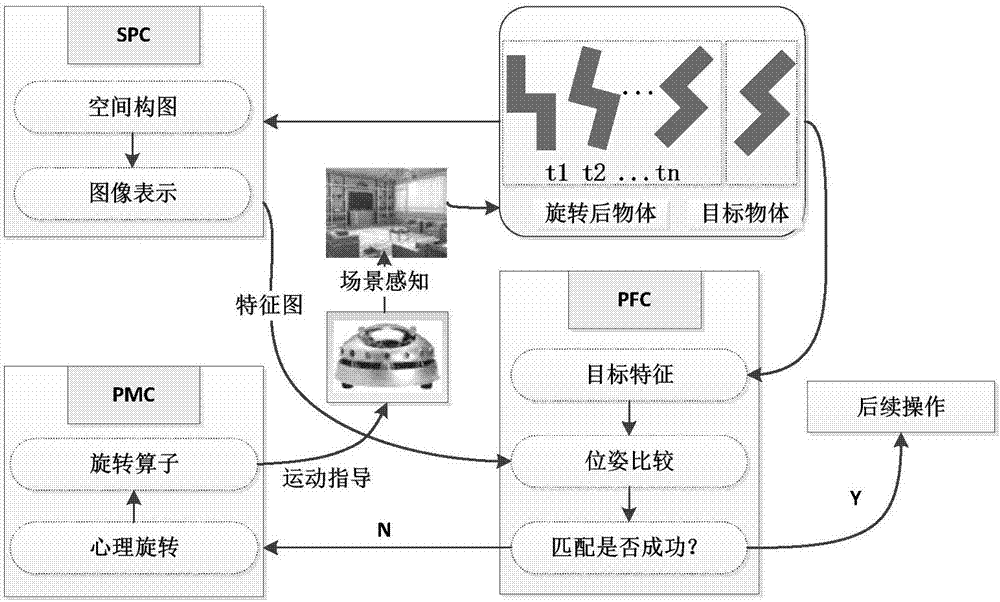
Four-dimensional space translation and rotation-based mental rotation mechanism realization model
InactiveCN107194332AOvercoming training troublesOvercome the shortcomings of poor learning abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionPrimateMental rotation
The invention discloses a four-dimensional space translation and rotation-based mental rotation mechanism realization model, and aims at exploring application prospect of the model in mobile robot navigation. According to the model, the main brain region functions involved in the mental rotation process of primates are expressed in a quantification manner, such as a superior parietal cortex (SPC), a prefrontal cortex (PFC) and a premotor cortex (PMC). The model is implemented through the following steps of carrying out map construction and image expression by an SPC module; carrying out feature and posture matching by a PFC module, comparing image features obtained by the SPC with a specified threshold value so as to decide whether objects are the same or not and whether postures are the same or not; and carrying out simulated rotation on the current object by the PMC, comparing dot cloud feature maps of the current object and a target object, calculating a rotation matrix, carrying out simulated rotation on the current object, and repeating the step to ensure that the difference between the objects is minimum, so as to obtain a time-related four-dimensional rotation operator, wherein the rotation operator is used for instructing navigation tasks of a mobile robot. According to the model, the defects such as bad learning ability, strong dependency on environment and high training cost of the traditional navigation algorithms are overcome.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
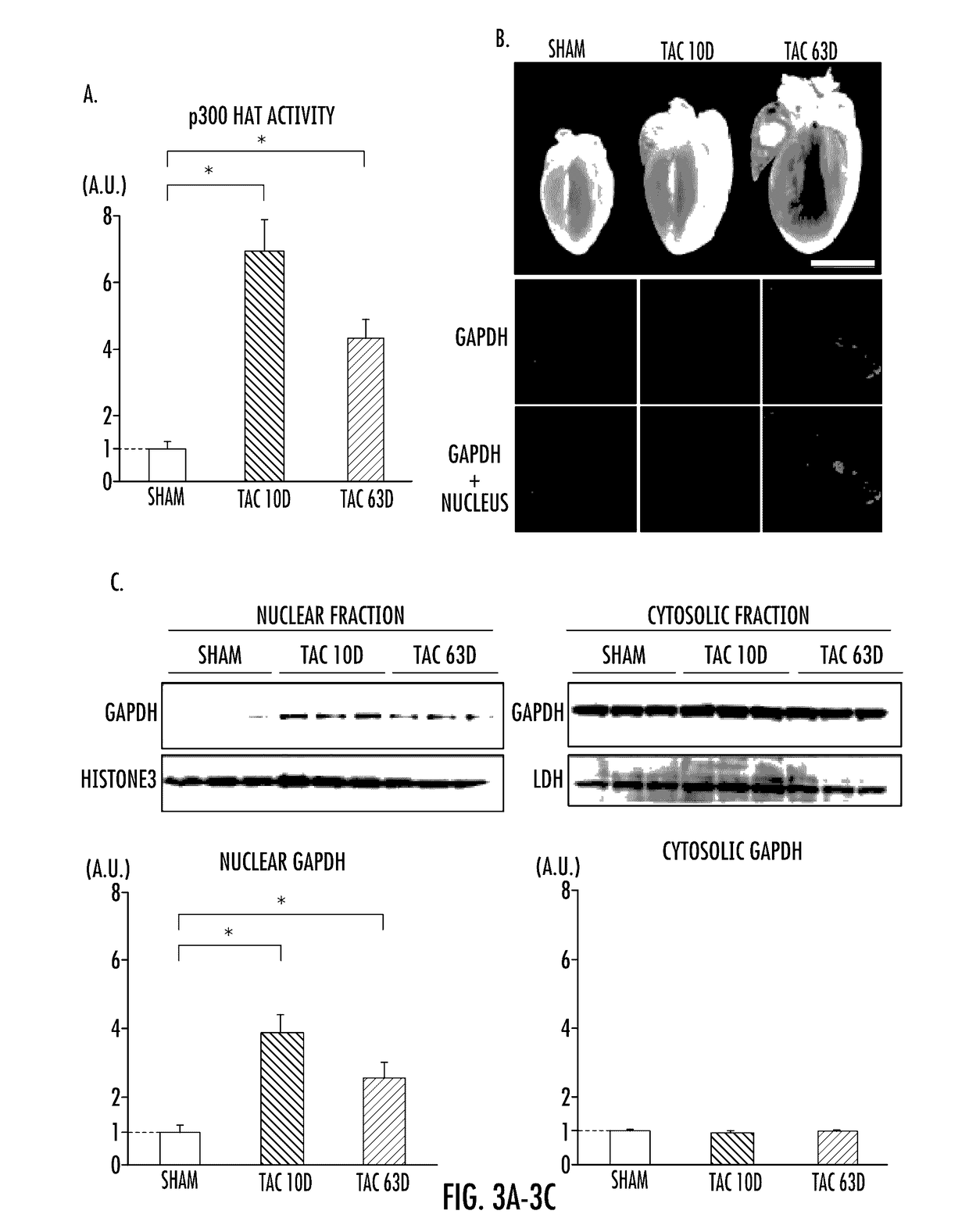
Gapdh cascade inhibitor compounds and methods of use and treatment of stress induced disorders including mental illness
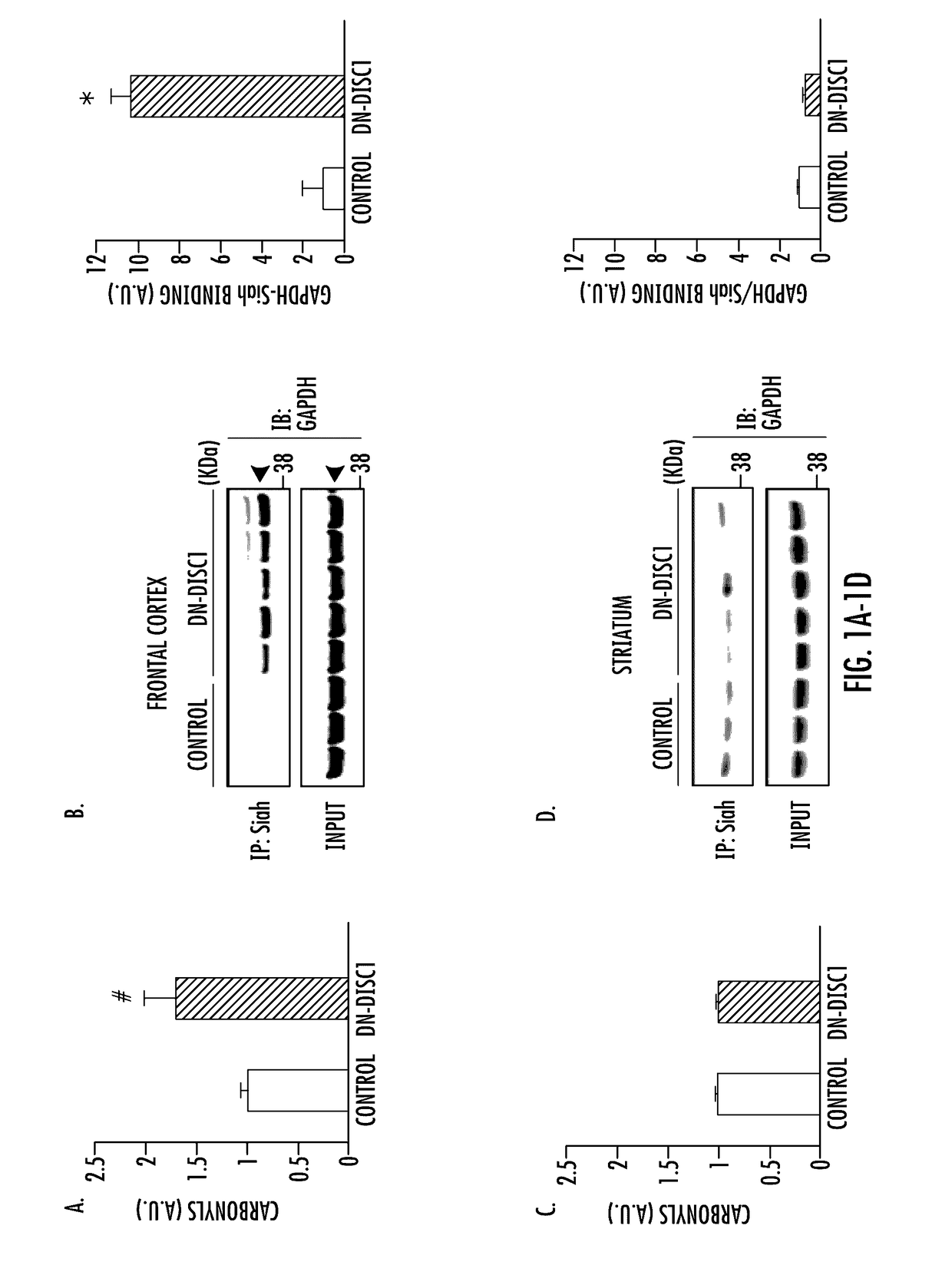
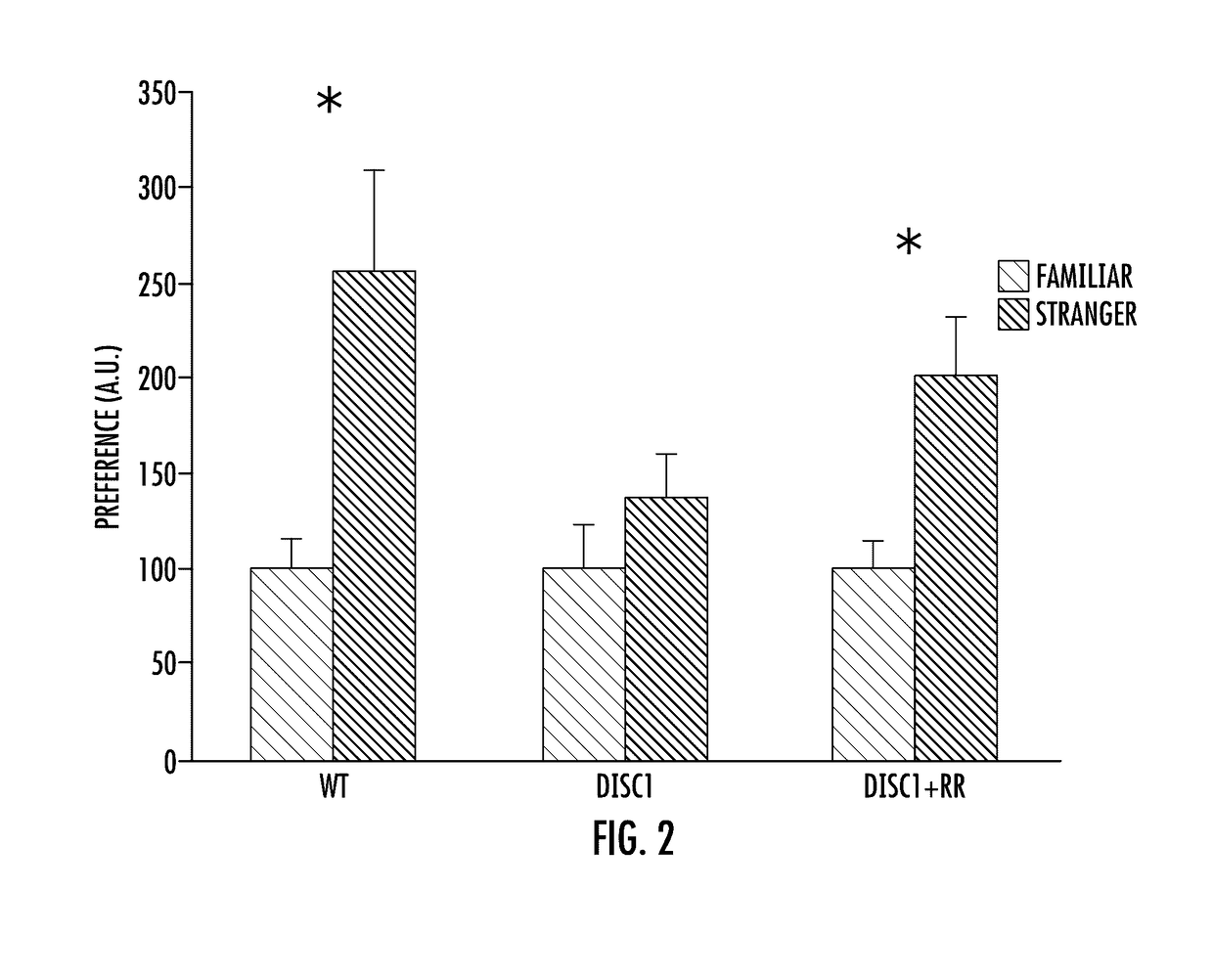
In DN-DISC1 mice, a mouse model for major mental illnesses, the model that expresses pathological phenotypes relevant to schizophrenia, mood disorders, and addiction simultaneously, the inventors of the present invention found pronounced levels of oxidative stress in the prefrontal cortex, but not in the striatum. These mice also displayed greater amounts of GAPDH-Siah1 binding, a protein-protein interaction that is activated under exposure to oxidative stress. The present inventors investigated the role of oxidative stress in other organ systems. As detailed herein, the inventors found that GAPDH-Siah1 binding was increased in mouse models of cardiac failure. It was also found, that certain novel analogs of deprenyl, significantly inhibited GAPDH-Siah1 binding in cardiac tissue. Thus, with experimental data provided herein, it is clear that this GAPDH-Siah1 binding cascade is a crucial mechanism involved in major mental illness, such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and addiction, as well as in stress-associated diseases involving other organs where GAPDH is expressed.The present invention provides compounds and composition comprising analogs of deprenyl and their use in the inhibition of nuclear GAPDH-Siah1 binding and the activation of p300 and MEF2. Also provided herein are methods of prevention and treatment of stress induced disorders of the body, including, for example, major mental illness, such as schizophrenia, mood disorders, and addiction, as well as in stress-associated diseases involving other organs, such as cardiac hypertrophy, in vivo, comprising administering to a mammal a therapeutically effective amount of analogs of deprenyl.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Prefrontal cortex processing disorders, gait and limb disorders treatment
Owner:GILROSE PHARMA
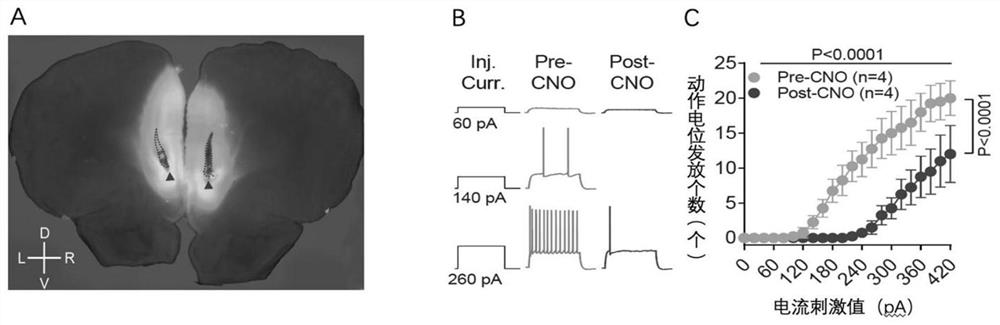
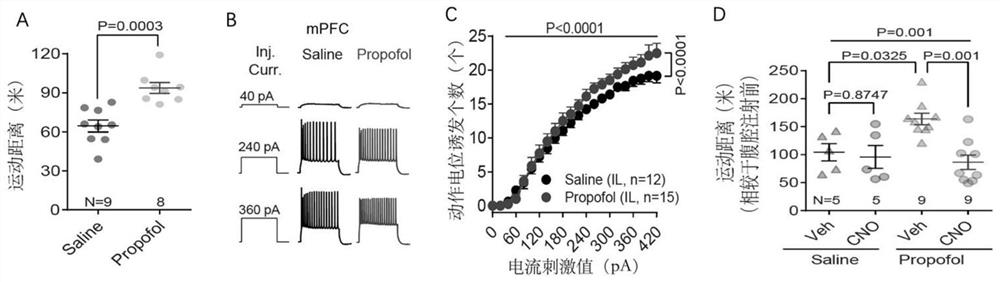
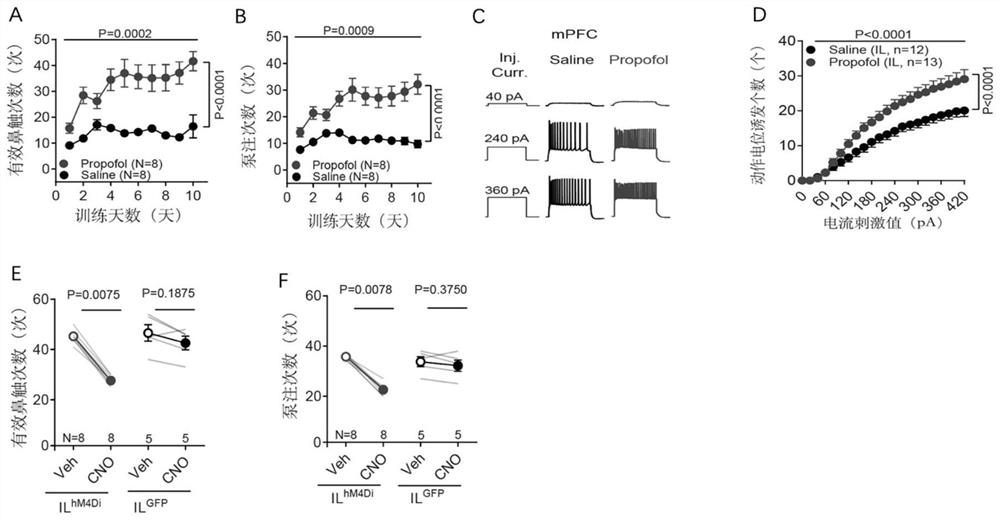
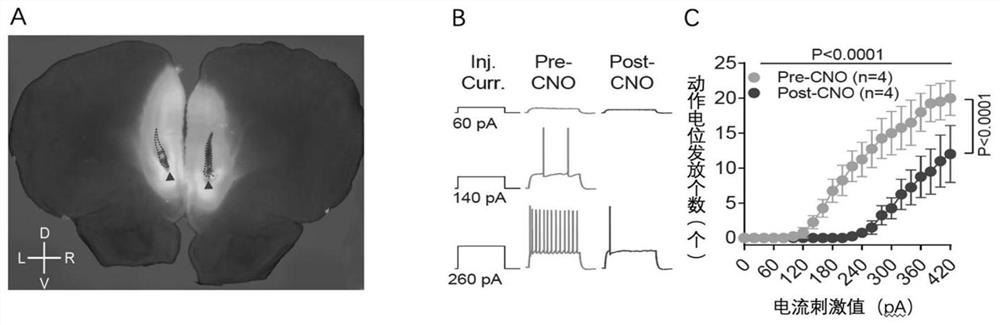
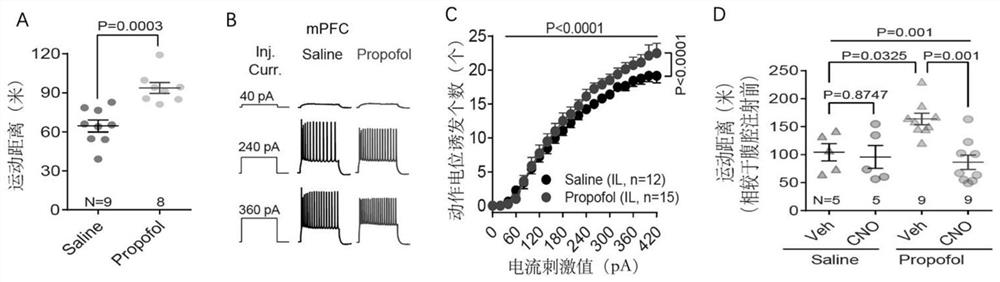
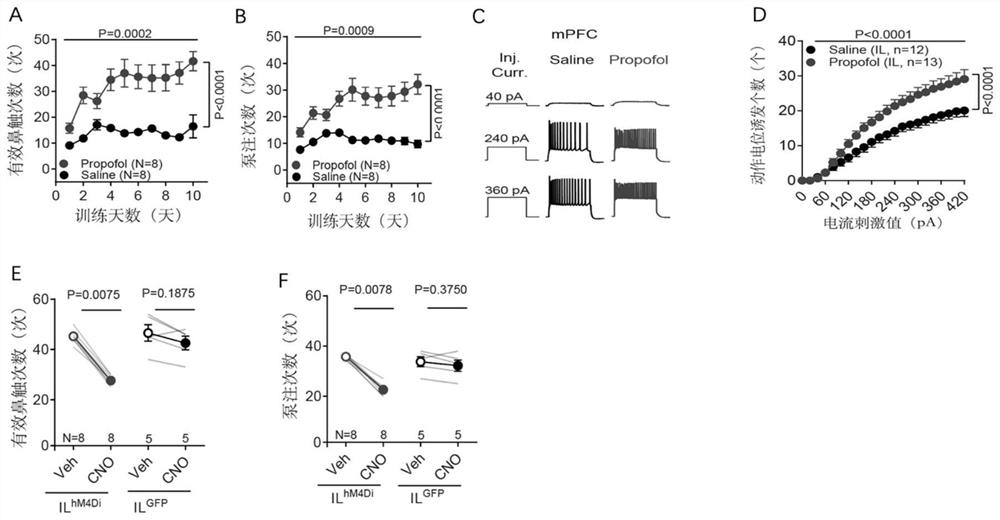
Application of chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction
ActiveCN111658677BSignificant anti-addictive effects of propofolAddiction PreventionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAddictive behaviorPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses the application of a chemical genetic drug composition in preparing a drug for preventing and treating propofol addiction. The propofol addiction mainly involves two classic addictive behaviors, behavioral sensitization and self-administration. The present invention fully proves that after long-term repeated use of propofol in rats, addictive behavior will be produced, which is mainly caused by the excitation of neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC area) of the cortex; Inhibits the hyperexcitable state of mPFC region induced by propofol, thereby inhibiting propofol-addictive behavior in rats. The chemical genetic drug composition provided by the invention has the advantages of good effect, strong controllability and the like, and provides a new therapeutic drug for the treatment, research, development and prevention of propofol addiction.
Owner:连庆泉 +1
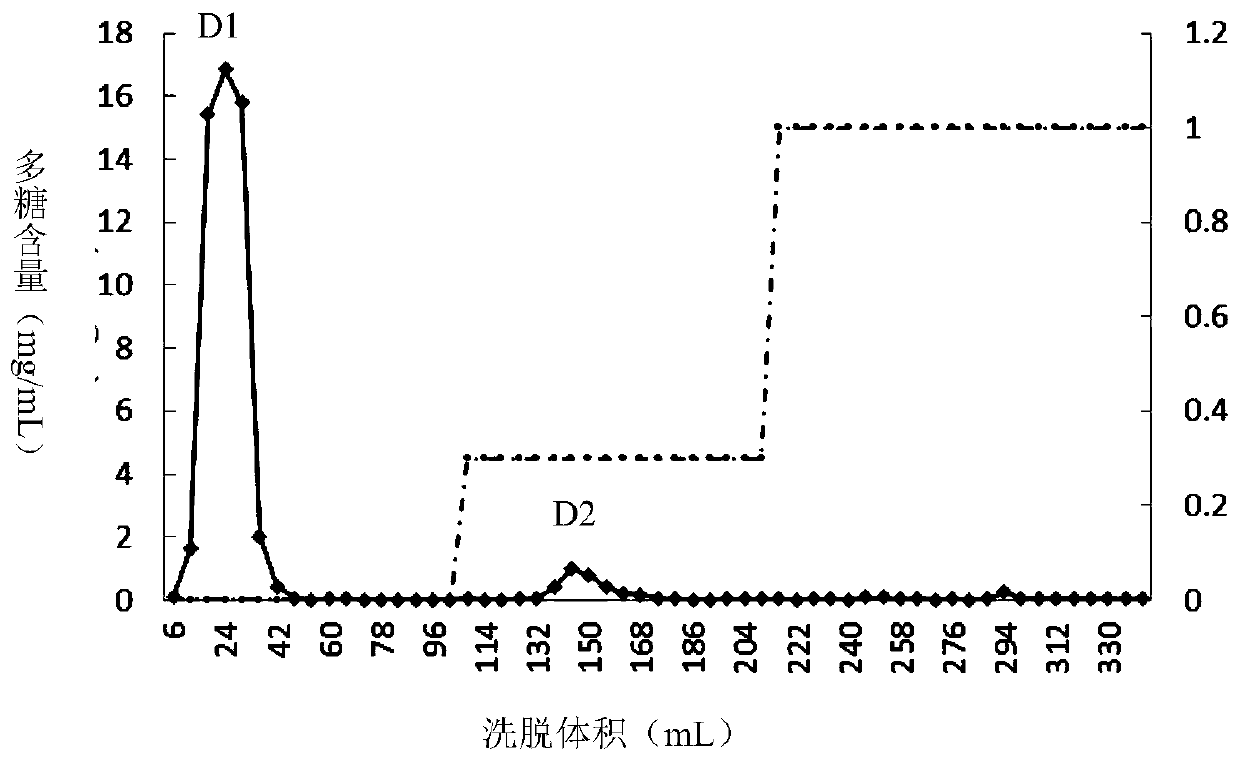
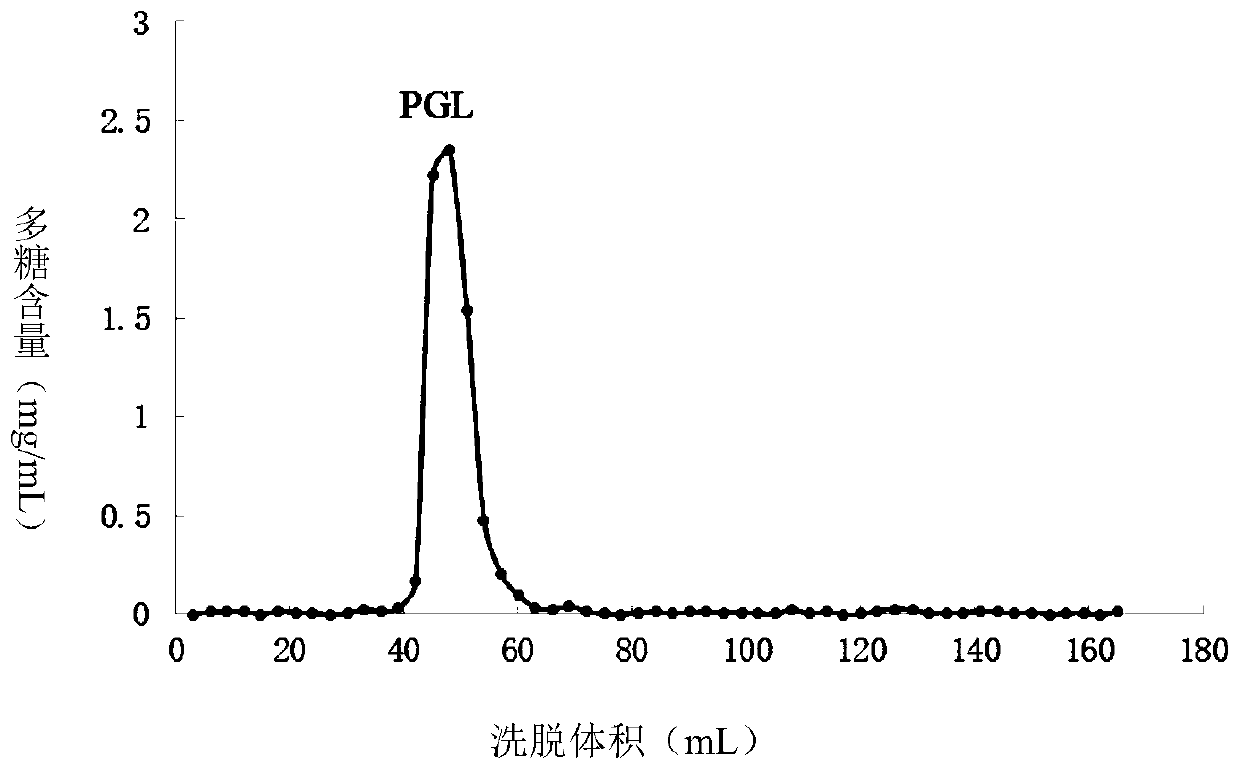
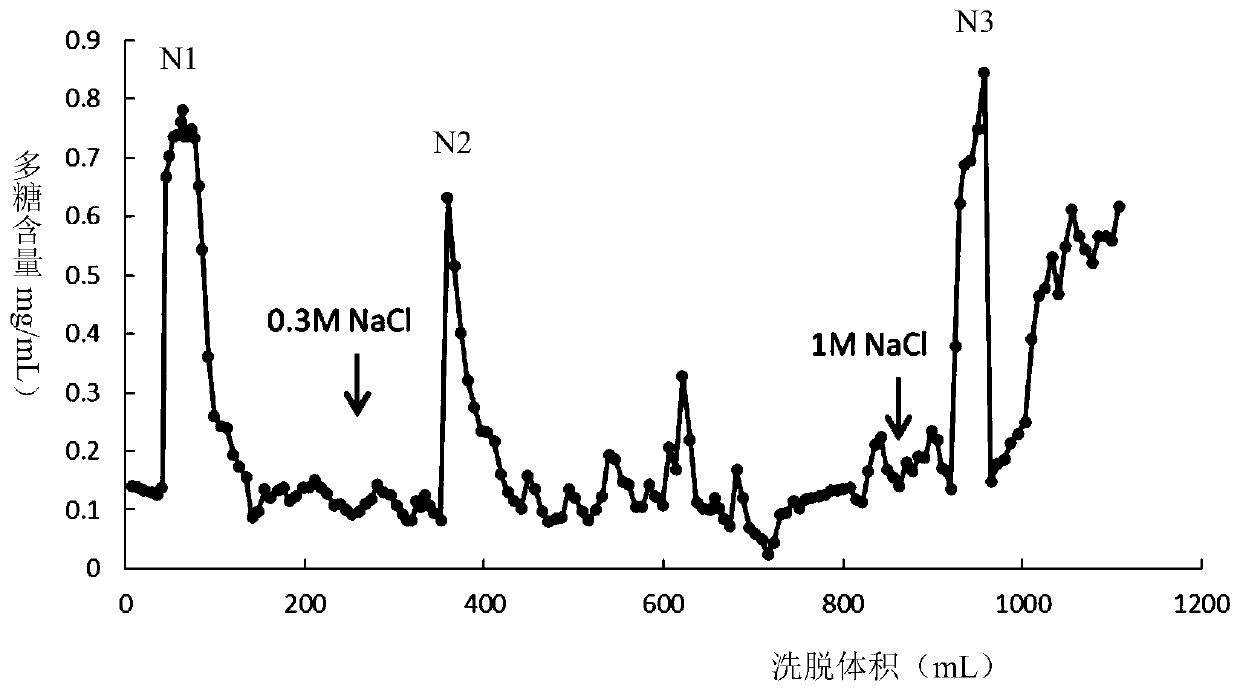
A kind of glycopeptide with antidepressant function and its preparation method and application
The invention discloses glycopeptide having the function of resisting depression and a preparation method and application of the glycopeptide. The glycopeptide having the function of resisting depression is from glossy ganoderma, the N-terminal sequence of the glycopeptide is as shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and the glycopeptide has 4 peptide segments as shown in 1-4 in the sequence table. The glycopeptide can reduce the tail suspension fixing time of mice, reduce the swimming dead time of the mice, increase the sucrose preference ratio of depression mice, increase the level of 5-hydroxytryptamine in prefrontal cortex of the depression mice, increase the level of noradrenaline in the prefrontal cortex of the depression mice, increase the expression level of BDNF protein in theprefrontal cortex of the depression mice and reduce the content of corticosterone of the depression mice. The glycopeptide can be used for preventing and / or treating depression.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Human brain health exercise system based on saas platform
The invention relates to a human brain health training system which is based on the SAAS (Software as a Service) platform. The system comprises a user interactive interface layer, a business logic service layer and a data access interface, wherein the user interactive interface layer comprises a client which is based on the Web platform or a mobile platform and provides data service; the business logic service layer comprises an account service module, a brain stimulation implementation module, a brain data collection module, an assessment service module, a course service module, a brain index analysis module and a system report service module; and the data access interface comprises a core data interface, a user data interface and a cognitive ability index data interface. The system provided by the invention can improve the cranial nerve circuitry junction in the memory area, is beneficial to the improvement of the memory storage capacity, can further strengthen the capability of the executive function area positioned at the prefrontal cortex, and finally adjusts the advanced function of human body, coordinates all kinds of neural activities of the function, and improves brain advanced functions such as brain health, emotion and the like.
Owner:BEIJING LOVE WISDOM SCI & TECH DEV
Application of chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction
ActiveCN111658677ASignificant anti-addictive effects of propofolAddiction PreventionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAddictive behaviorPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses an application of a chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating propofol addiction. The propofol addiction mainly relates to two classic addiction behaviors of behavior sensitization and self-administration. The invention fully proves that the addiction behaviors are generated after propofol is repeatedly used for along time for a rat, and the addiction behaviors are mainly caused by excitation of neurons of the prefrontal cortex (mPFC region) on the inner side of the cortex; and the mPFC region high excitationstate caused by the propofol can be effectively inhibited by utilizing the chemical genetics pharmaceutical composition, so that the propofol addiction behaviors of the rat is inhibited. The chemicalgenetics pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention has the advantages of good effect, strong controllability and the like, and provides a new therapeutic medicine for treating, researchingand developing and preventing propofol addiction.
Owner:连庆泉 +1
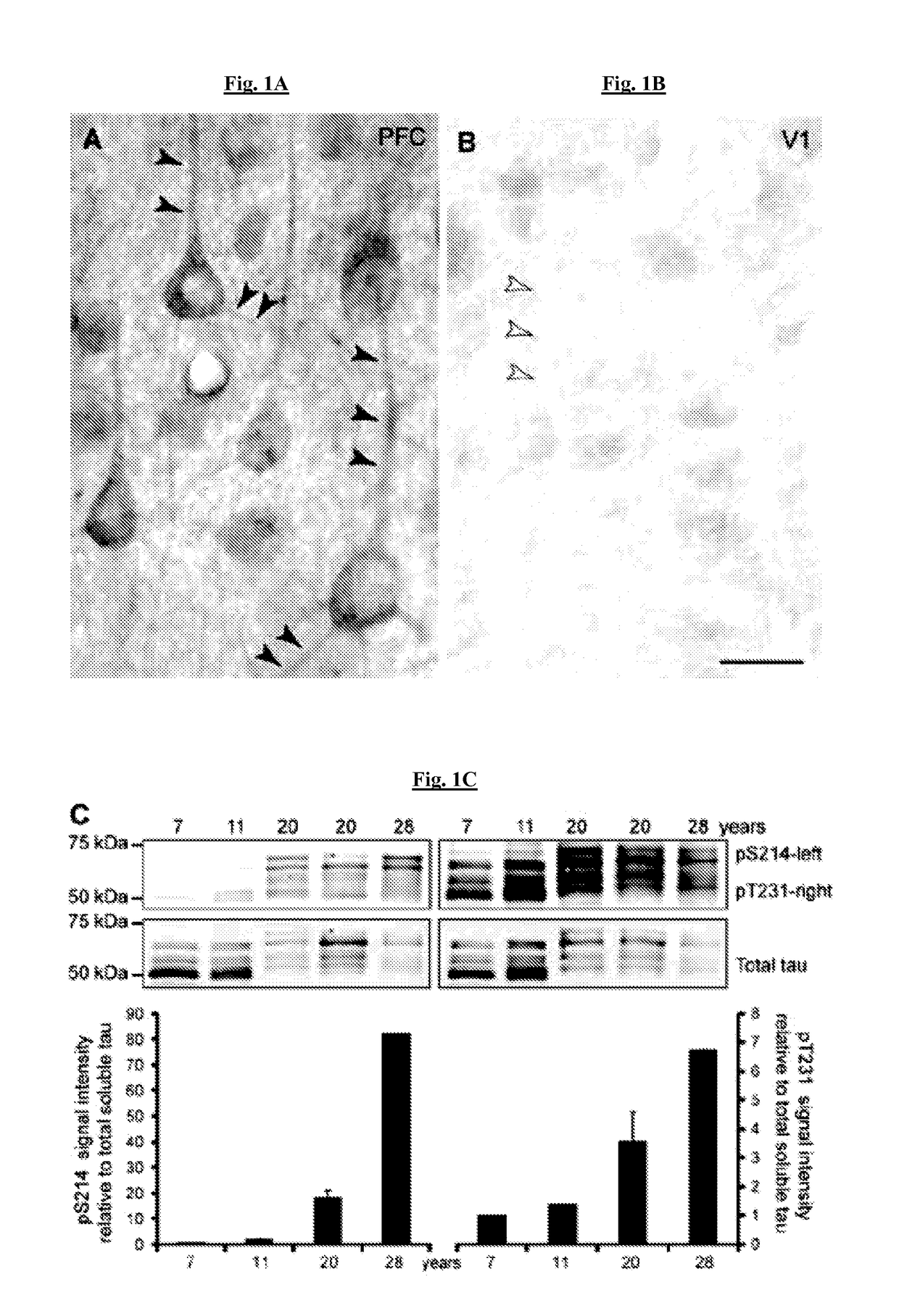
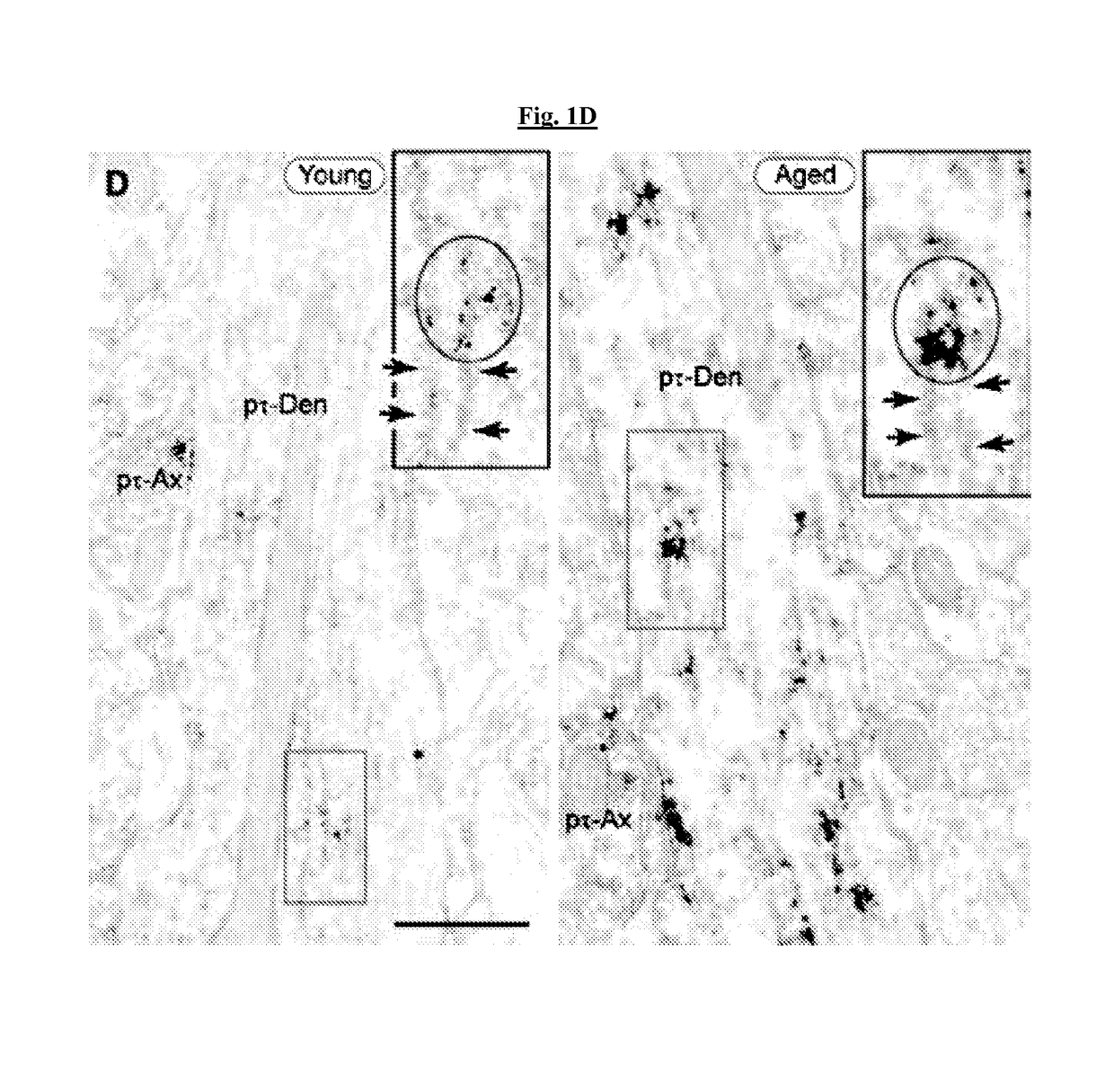
Methods of preventing neurodegeneration of association cortex in a mammal
ActiveUS20170360724A1Prevent and reduce riskPrevent degradationNervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPhosphorylationAdrenergic receptor agonists
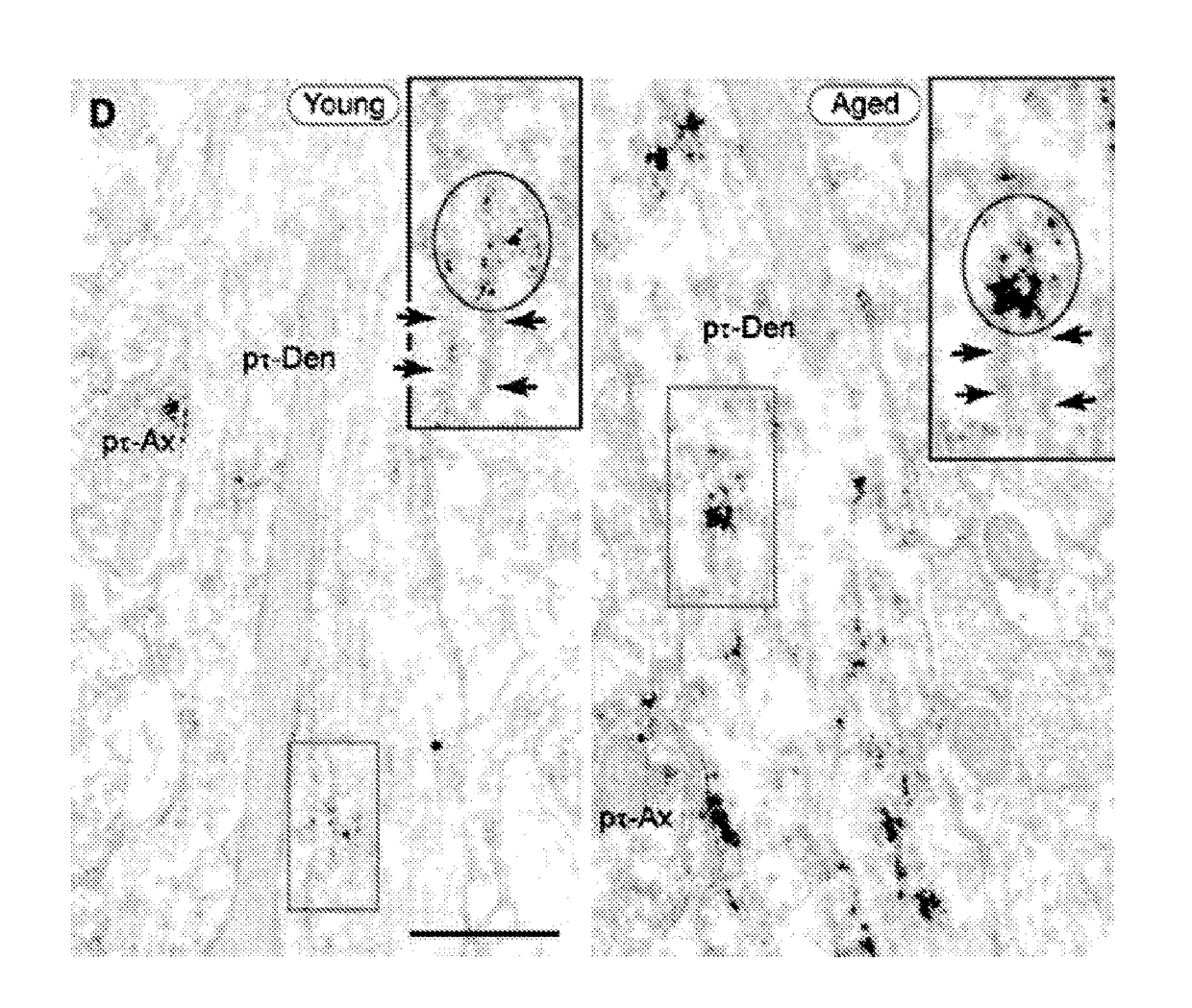
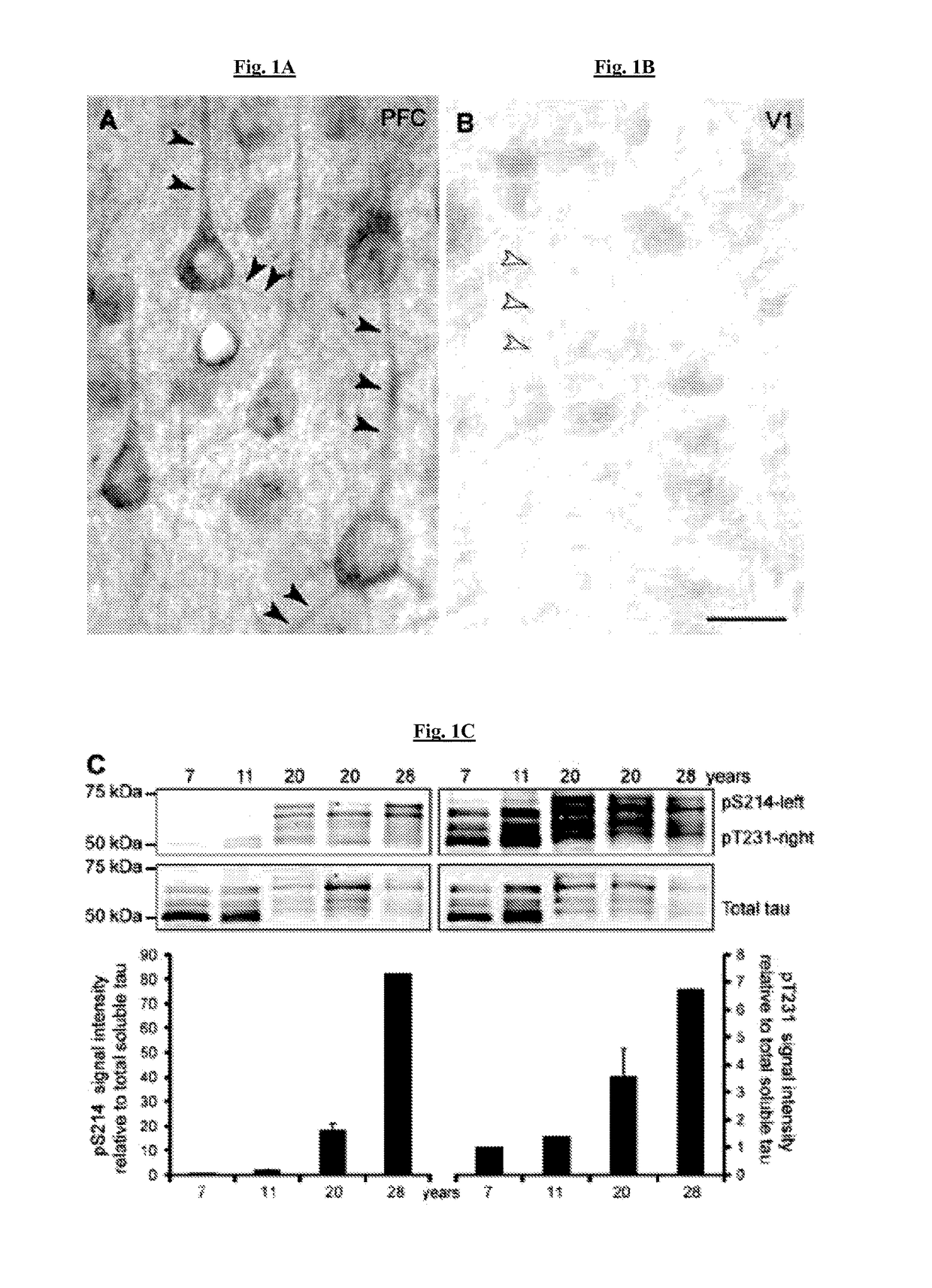
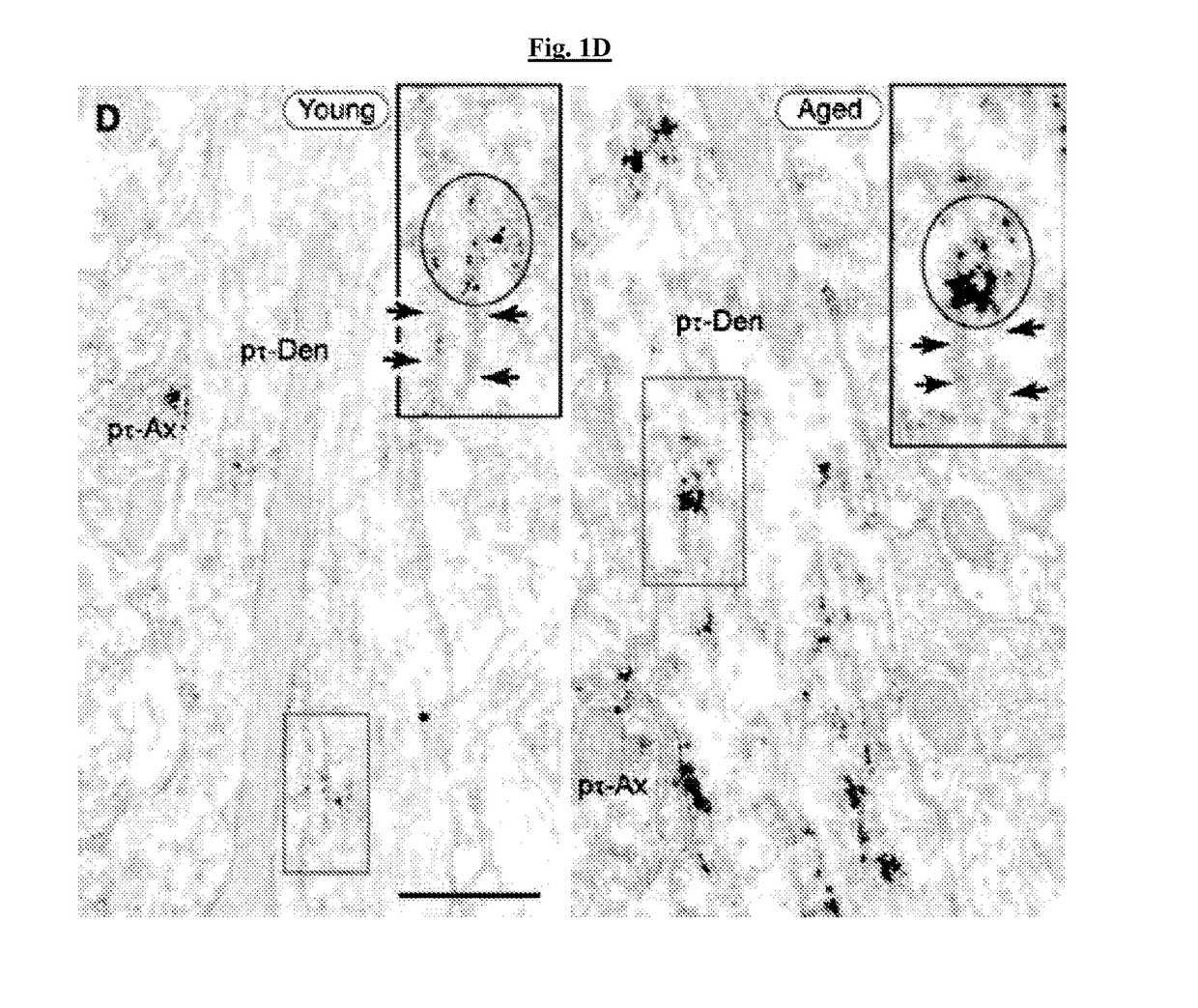
The present invention provides methods of preventing and / or reducing risk of neurodegeneration of association cortex, and / or inhibiting or reversing formation of phosphorylated tau or COXIV in the prefrontal cortex of a mammal in need thereof. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist.
Owner:YALE UNIV
A kind of pharmaceutical composition and its application
ActiveCN104055759BHigh activityProtectiveNervous disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsAtomoxetine hydrochloridePharmaceutical drug
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Medicine composition and application thereof
ActiveCN104055759AReduce spontaneous hyperactive behaviorIncrease SOD activityNervous disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsTyrosine hydroxylaseTaurine
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and in particular relates to a medicine composition and an application thereof. The medicine composition comprises atomoxetine hydrochloride and taurine, wherein the synergy can be generated via the combination of the atomoxetine hydrochloride and the taurine. The experiment finds that compared with the single application of the atomoxetine hydrochloride, according to the medicine composition prepared by the combination of the atomoxetine hydrochloride and the taurine, the SOD (Superoxide Dismutase) activity and the GSH (Glutathione) content of the brain tissue of an ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) model rat at a juvenile stage can be obviously increased while the MDA (Methane Dicarboxylic Aldehyde) content (P is less than 0.01) in the brain tissue of the ADHD model rat is decreased, thereby performing an antioxidation function, improving the expressions of DBH (Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase) and TH (Tyrosine Hydroxylase) in the brain of the ADHD model rat at the juvenile stage and improving the expression (P is less than 0.01) of Fos protein in the prefrontal cortex of the ADHD model rat. Compared with the single application of the medicine, the medicine composition provided by the invention has obvious effects. Thus, the medicine composition can serve as a candidate medicine for treating pediatric hyperactivity.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Systems and methods for preventing, mitigating, and/or treating dementia
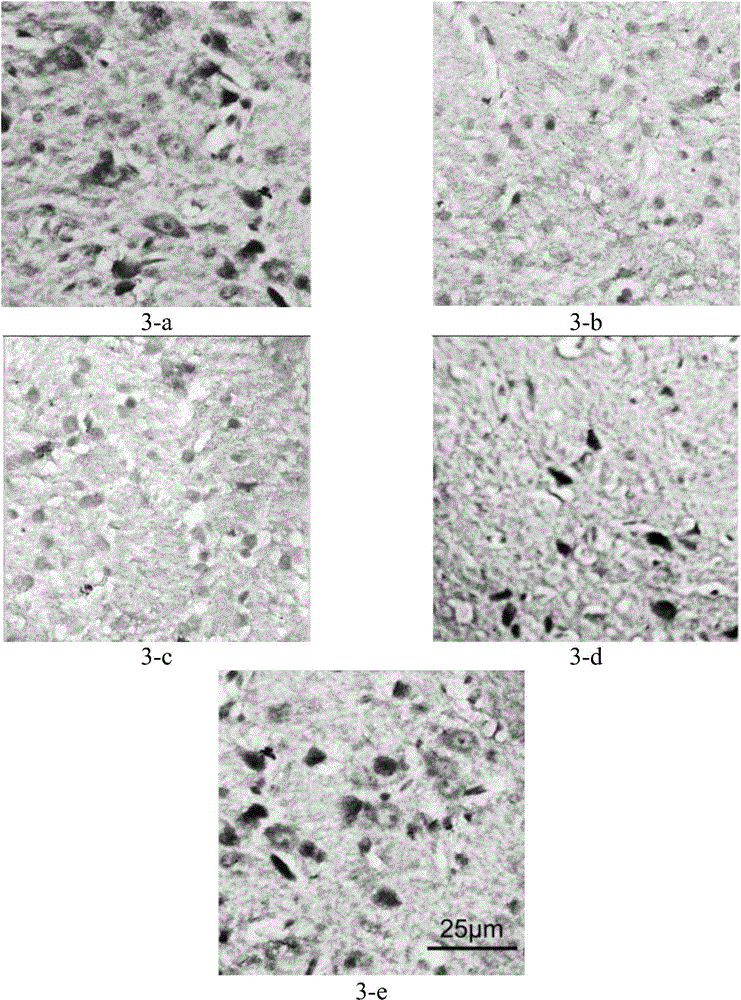
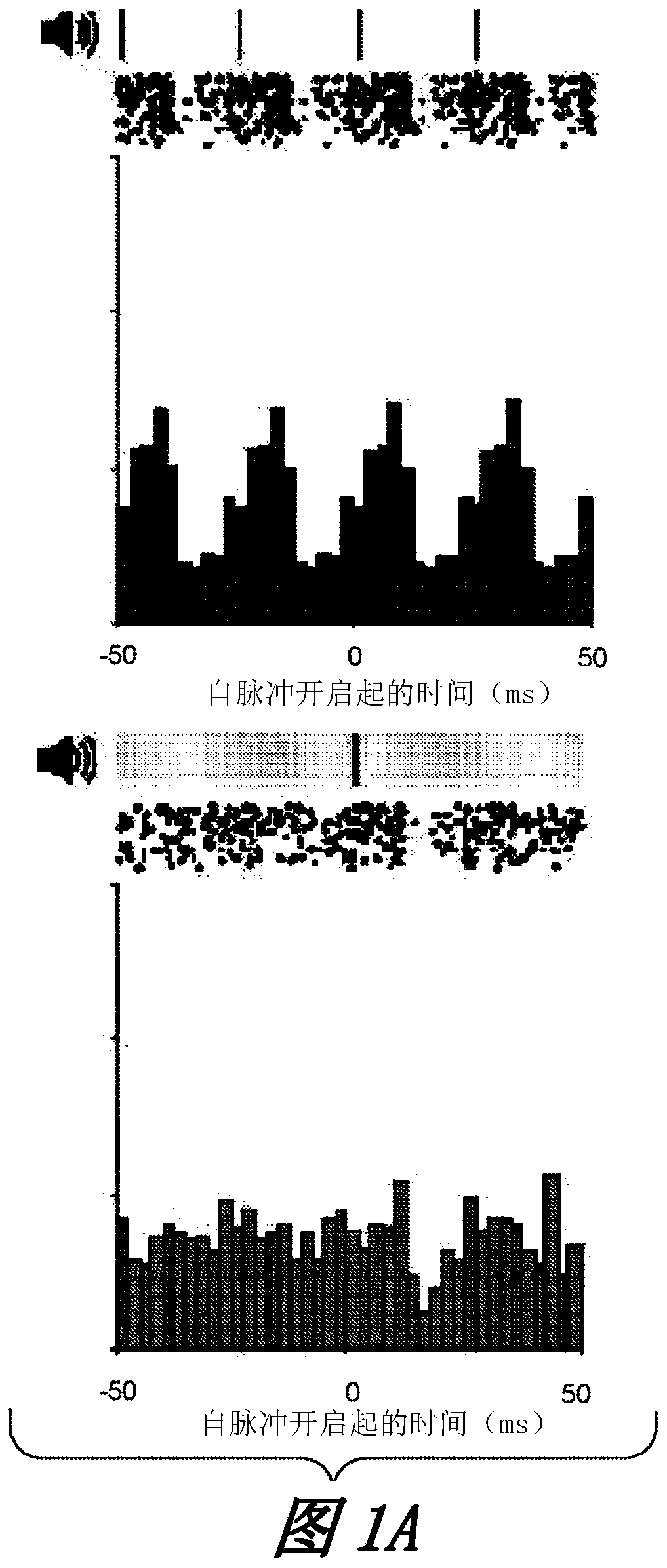
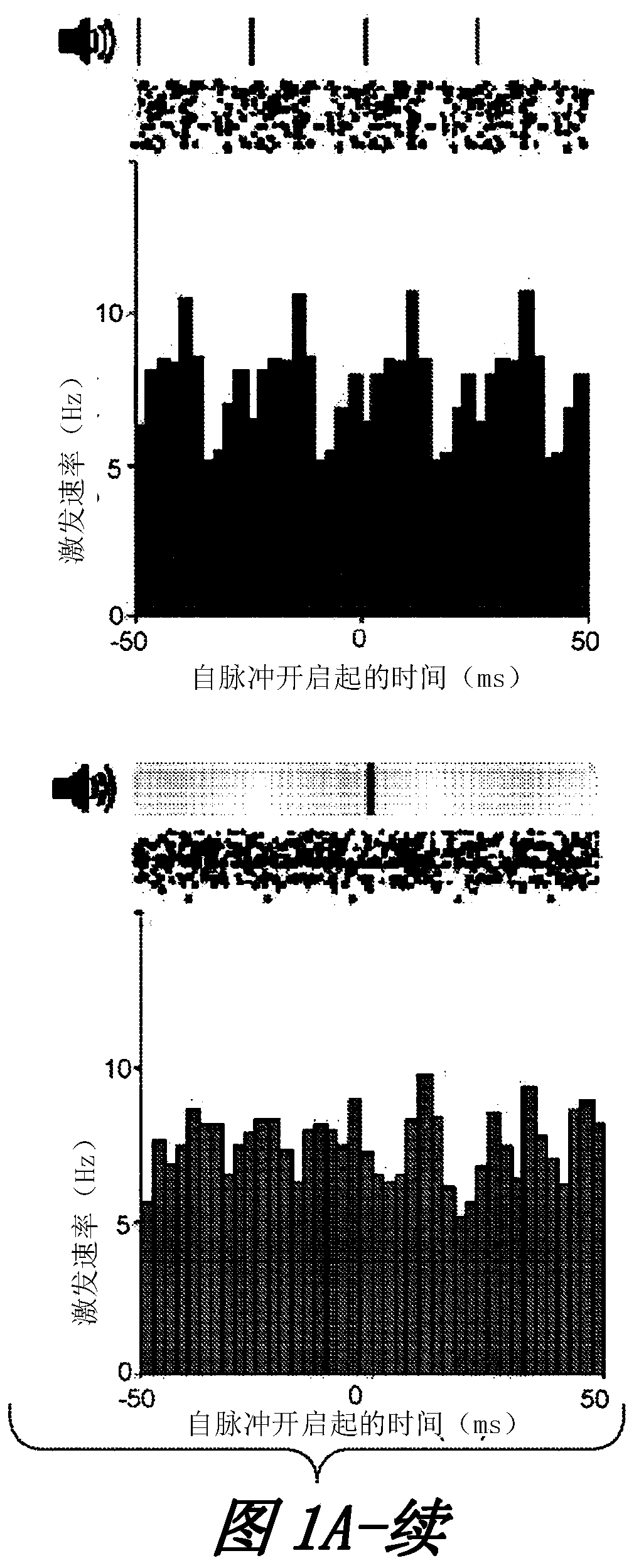
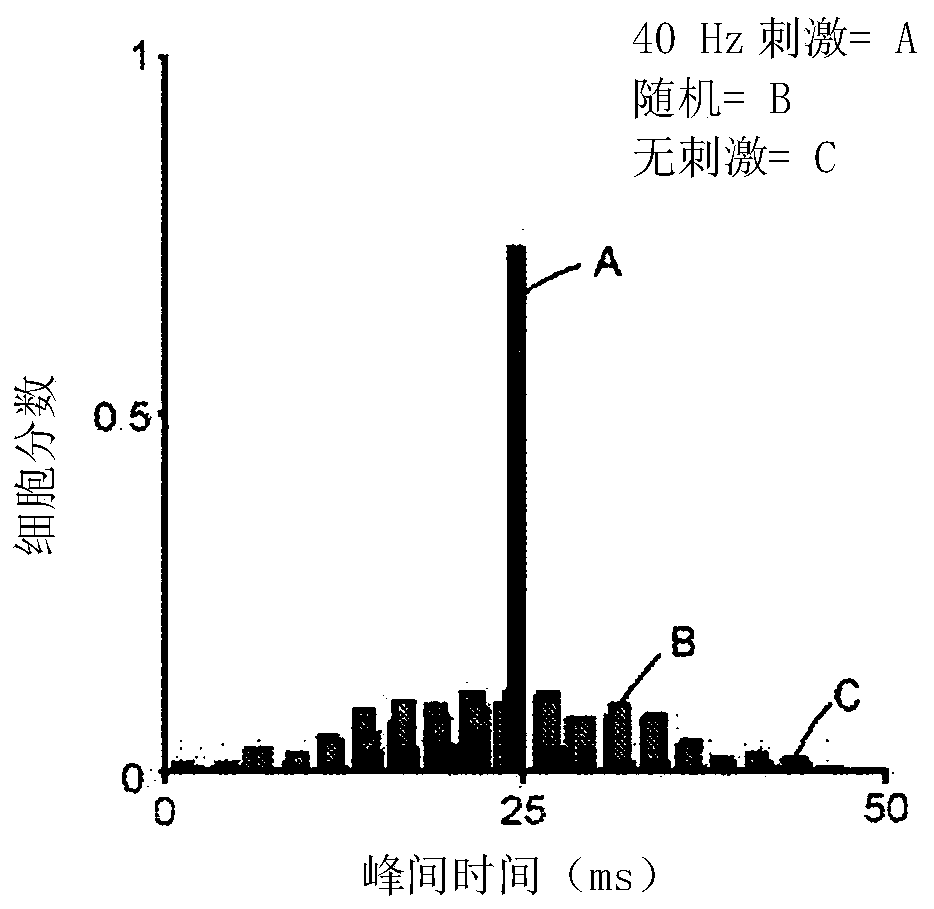
Devices, systems, and methods for a treating dementia or Alzheimer's disease in a subject in need thereof. In one example, combined auditory and visual stimuli having a frequency of about 20 Hz to about 60 Hz, and more specifically about 40 Hz, are non-invasively delivered to the subject to induce synchronized gamma oscillations in at least one brain region of the subject. In particular, pursuantto various treatment and exposure protocols, combined auditory and visual stimulation (as opposed to auditory or visual stimulation alone) promotes a microglia response in the medial prefrontal cortex(mPFC). More generally, combined auditory and visual stimulation induces an extended microglia clustering response in the auditory cortex, the visual cortex, and the mPFC.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Glycopeptide having function of resisting depression and preparation method and application of glycopeptide
ActiveCN110183522AReduce contentNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCorticosteroneGlycopeptide
The invention discloses glycopeptide having the function of resisting depression and a preparation method and application of the glycopeptide. The glycopeptide having the function of resisting depression is from glossy ganoderma, the N-terminal sequence of the glycopeptide is as shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and the glycopeptide has 4 peptide segments as shown in 1-4 in the sequence table. The glycopeptide can reduce the tail suspension fixing time of mice, reduce the swimming dead time of the mice, increase the sucrose preference ratio of depression mice, increase the level of 5-hydroxytryptamine in prefrontal cortex of the depression mice, increase the level of noradrenaline in the prefrontal cortex of the depression mice, increase the expression level of BDNF protein in theprefrontal cortex of the depression mice and reduce the content of corticosterone of the depression mice. The glycopeptide can be used for preventing and / or treating depression.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method and system for modulating the brain electrical activity
ActiveUS11077315B2Reduce addictionIncreased activationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsRight thumbMedicine
A deep and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of an individual is performed by applying magnetic pulses at least to a region of the scalp of the individual, the region being at least the bilateral prefrontal cortex, and can include preferably the bilateral prefrontal cortex and can include the insula. A threshold intensity of the magnetic pulses is determined by applying to the individual one or more reference magnetic stimulations, and a reaction of the individual to the reference stimulation is determined. The reaction corresponds to a right thumb movement. A magnetic stimulation is repeatedly applied for at least 80 trains per session for a duration not exceeding 2 seconds each with a time interval between a train application and the next one not less than 20 seconds, wherein the magnetic stimulation has a frequency of at least 18 Hz with an intensity of stimulation at least 120% of the threshold intensity.
Owner:MULTIMEDICA
Methods of preventing neurodegeneration of association cortex in a mammal
ActiveUS10022341B2Prevent and reduce riskPrevent degradationNervous disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsPhosphorylationAdrenergic receptor agonists
The present invention provides methods of preventing and / or reducing risk of neurodegeneration of association cortex, and / or inhibiting or reversing formation of phosphorylated tau or COXIV in the prefrontal cortex of a mammal in need thereof. In certain embodiments, the method comprises administering to the mammal a therapeutically effective amount of an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Human milk oligosaccharides for use in enhancing executive function
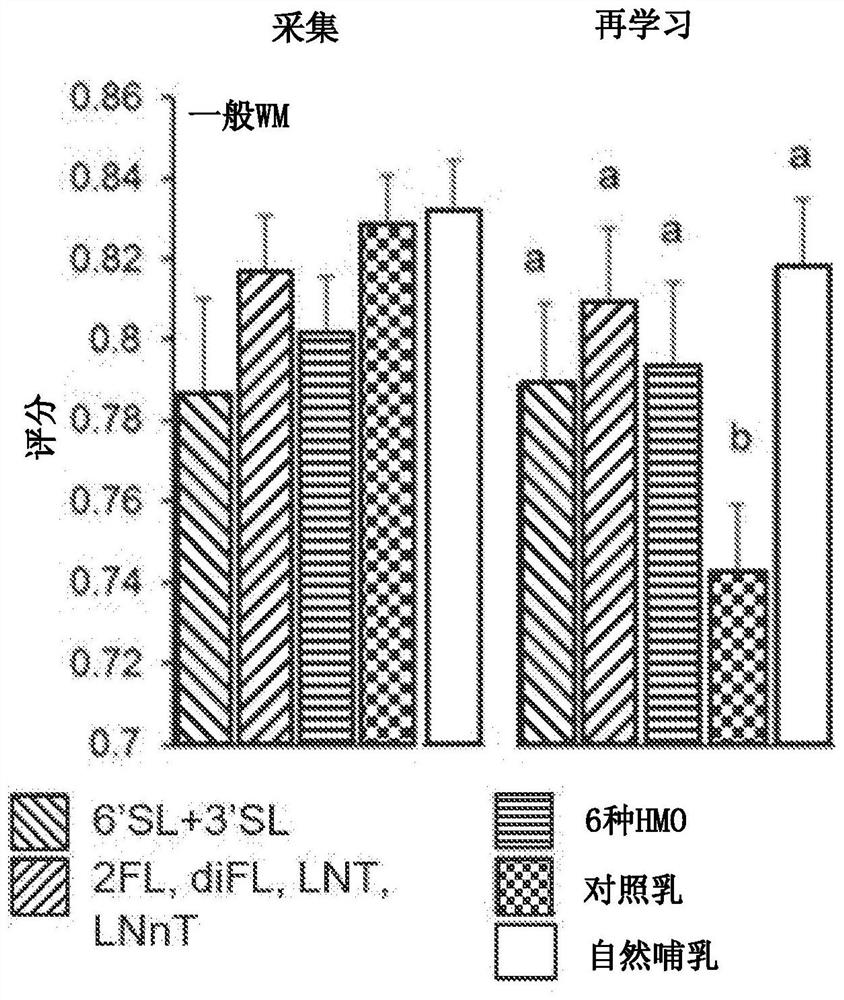
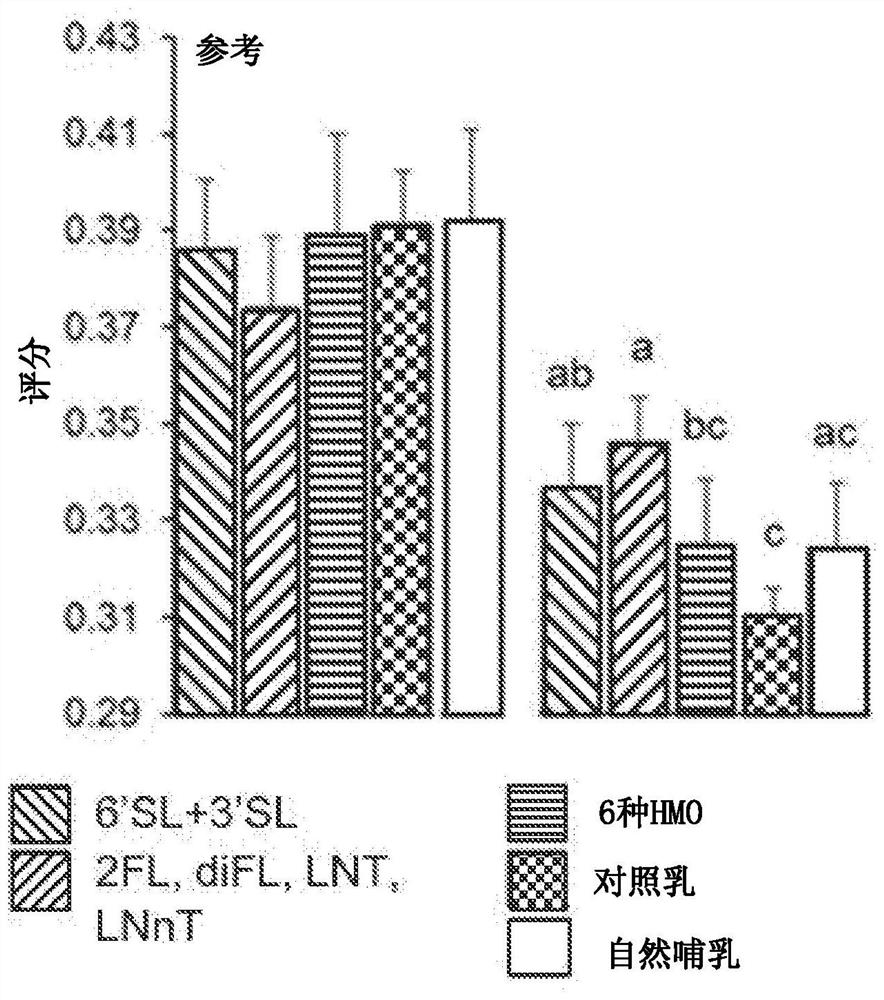
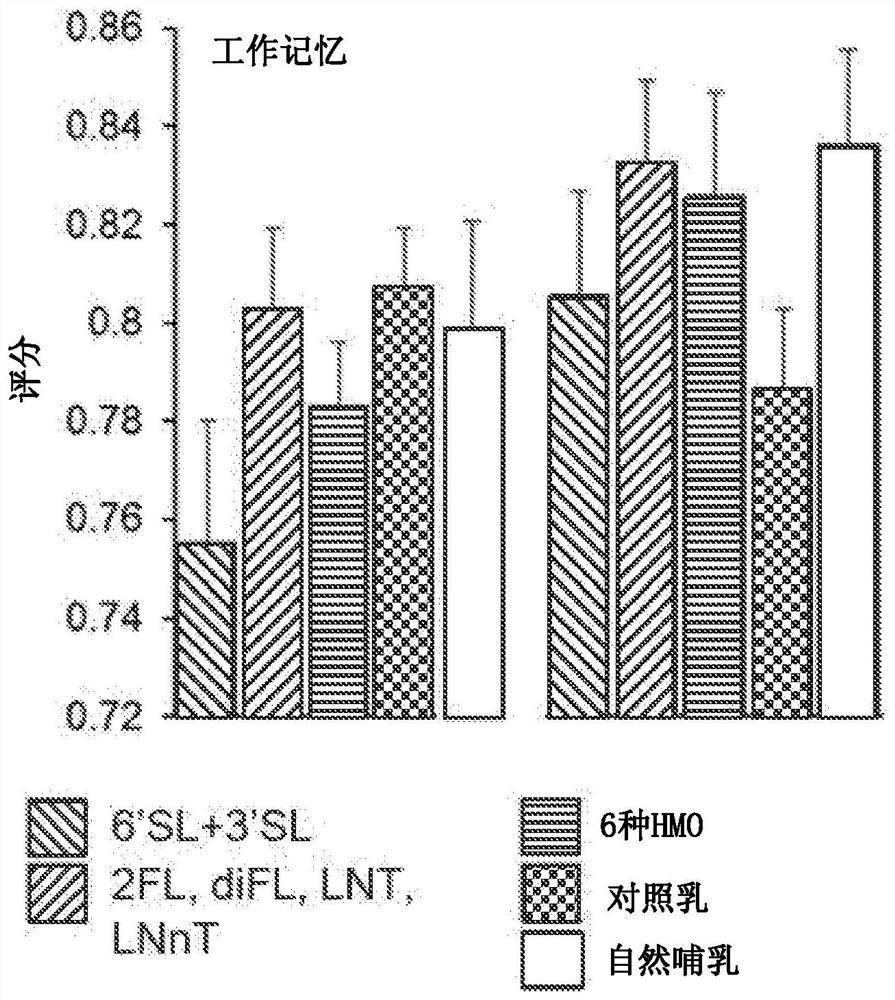
The invention discloses use of a human milk oligosaccharide (HMO), or a nutritional composition comprising a human milk oligosaccharide, to enhance executive function in a non-infant, to prevent and / or reduce the risk of sub-optimal executive function in a non-infant, to manage sub-optimal executive functioning in a non-infant, and / or to improve myelination to mature the pre-frontal cortex region of the brain in a non-infant, as well as synthetic compositions of HMOs and packs comprising at least 14 individual daily doses of an effective amount of at least one HMO for such a use.
Owner:GLYCOM AS
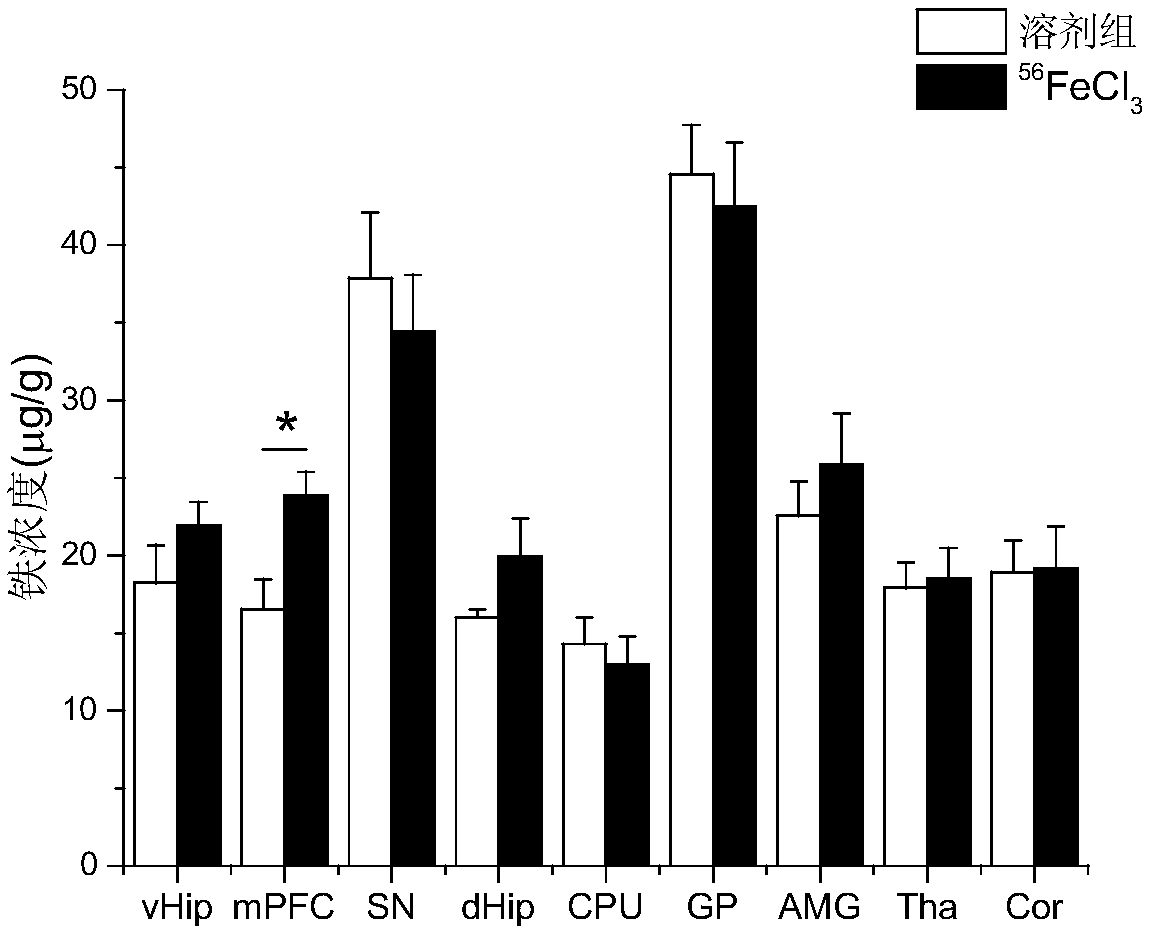
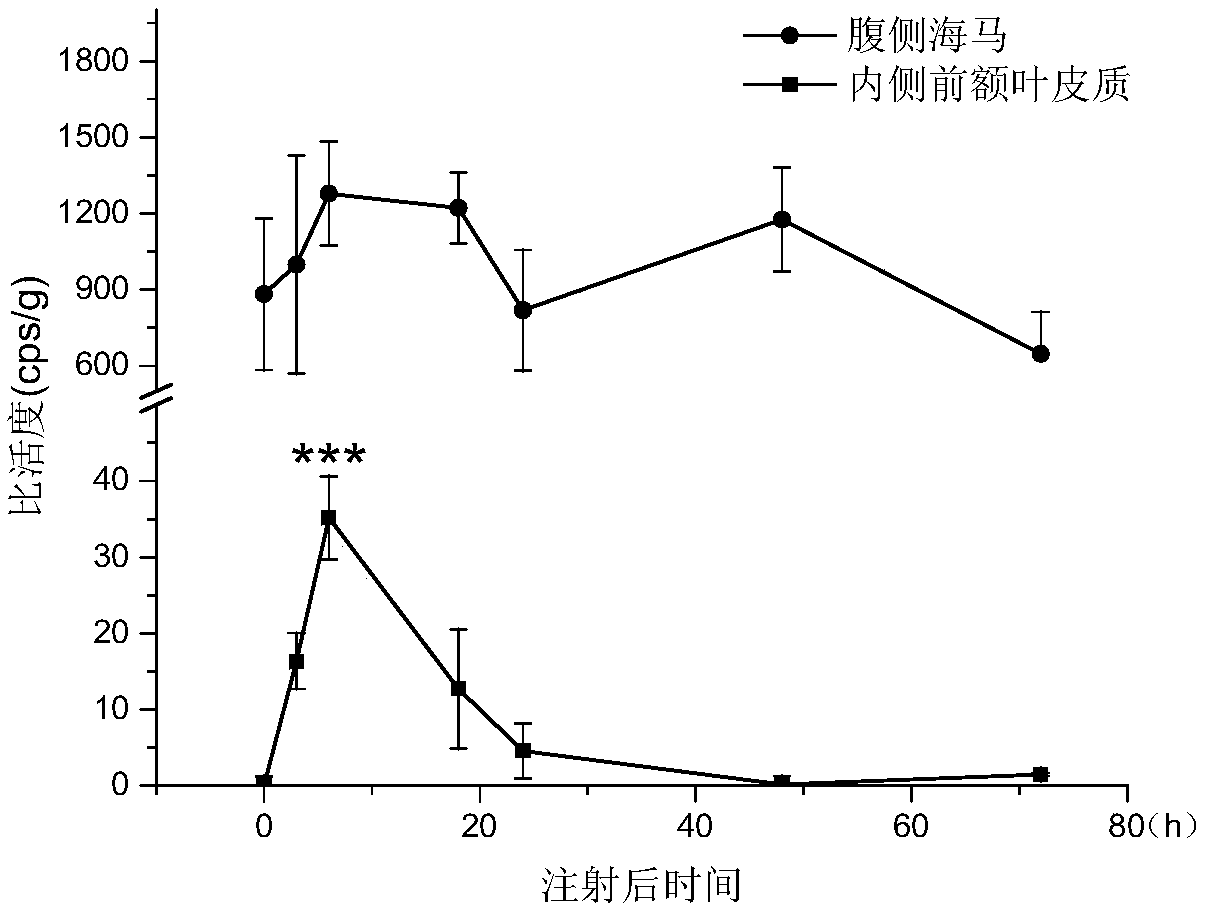
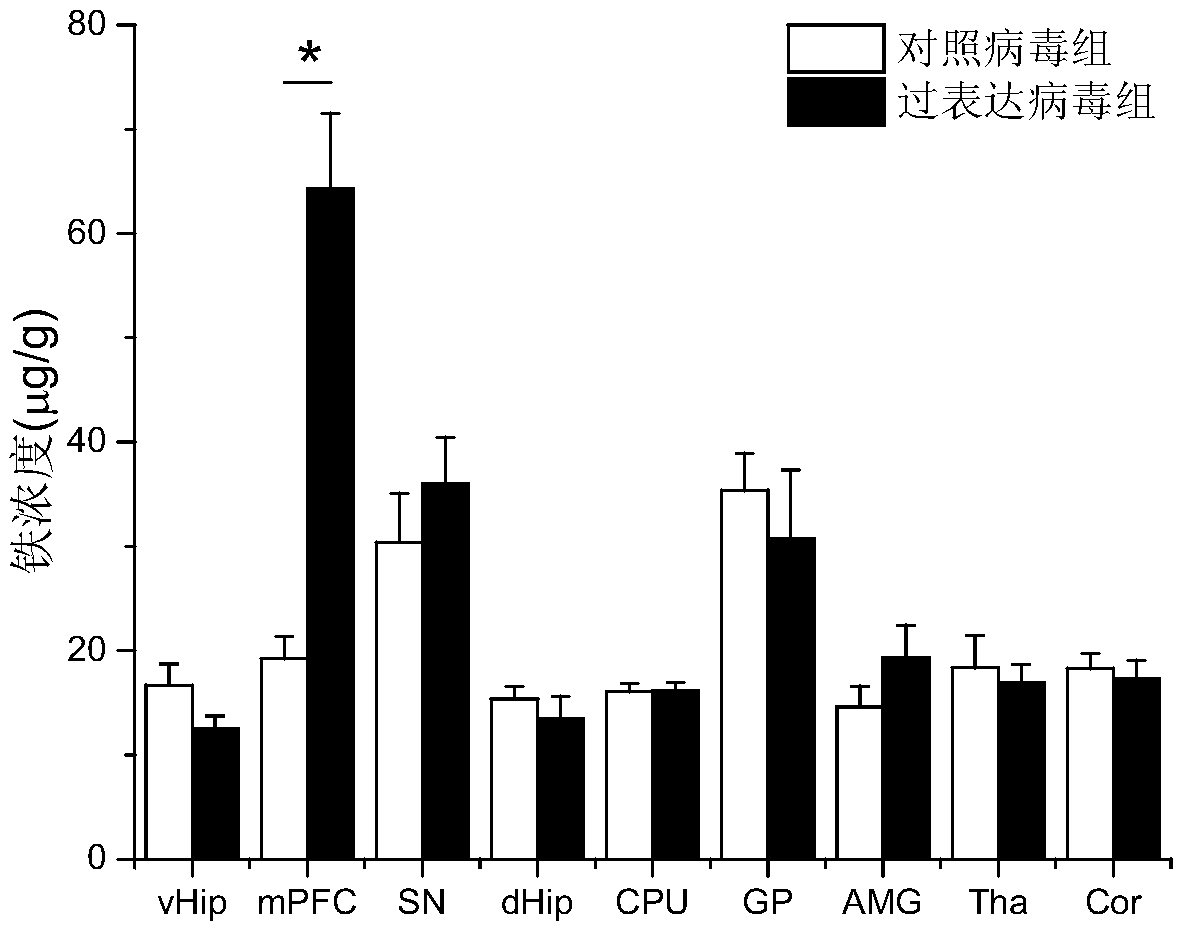
Application of drug for increasing iron transport from ventral hippocampus to medial prefrontal cortex in preparation of drugs for treating neuropsychiatric diseases
ActiveCN110179984AEffective treatmentNervous disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsPhysiologyNeuropsychiatric disease
The present invention discloses an application of a drug for increasing iron transport from ventral hippocampus to medial prefrontal cortex in preparation of drugs for treating neuropsychiatric diseases. Inventors enable human-source ferroportin to be over-expressed in neurons projected to the ventral hippocampus of the medial prefrontal cortex. Results show that iron concentration in the medial prefrontal cortex is significantly increased after 14 days of overexpression of viruses, suggesting that the method can increase the iron transport from the ventral hippocampus to the medial prefrontalcortex. Compared with control mice, the over-expression mice are increased in total motion distance, increased in time in a middle of an open field, decreased in time in a black box, and increased intime on elevated open arm, and have anti-anxiety behaviors. After successful modeling, compared with the normal control, the mice with the increased iron transport after an injection of deferiprone are increased in the time on the elevated open arm and increased in number of times entering the open arm, and have the anti-anxiety behaviors. In summary, the increase of the iron transport from the ventral hippocampus to the medial prefrontal cortex has effects of preventing and treating anxiety.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com