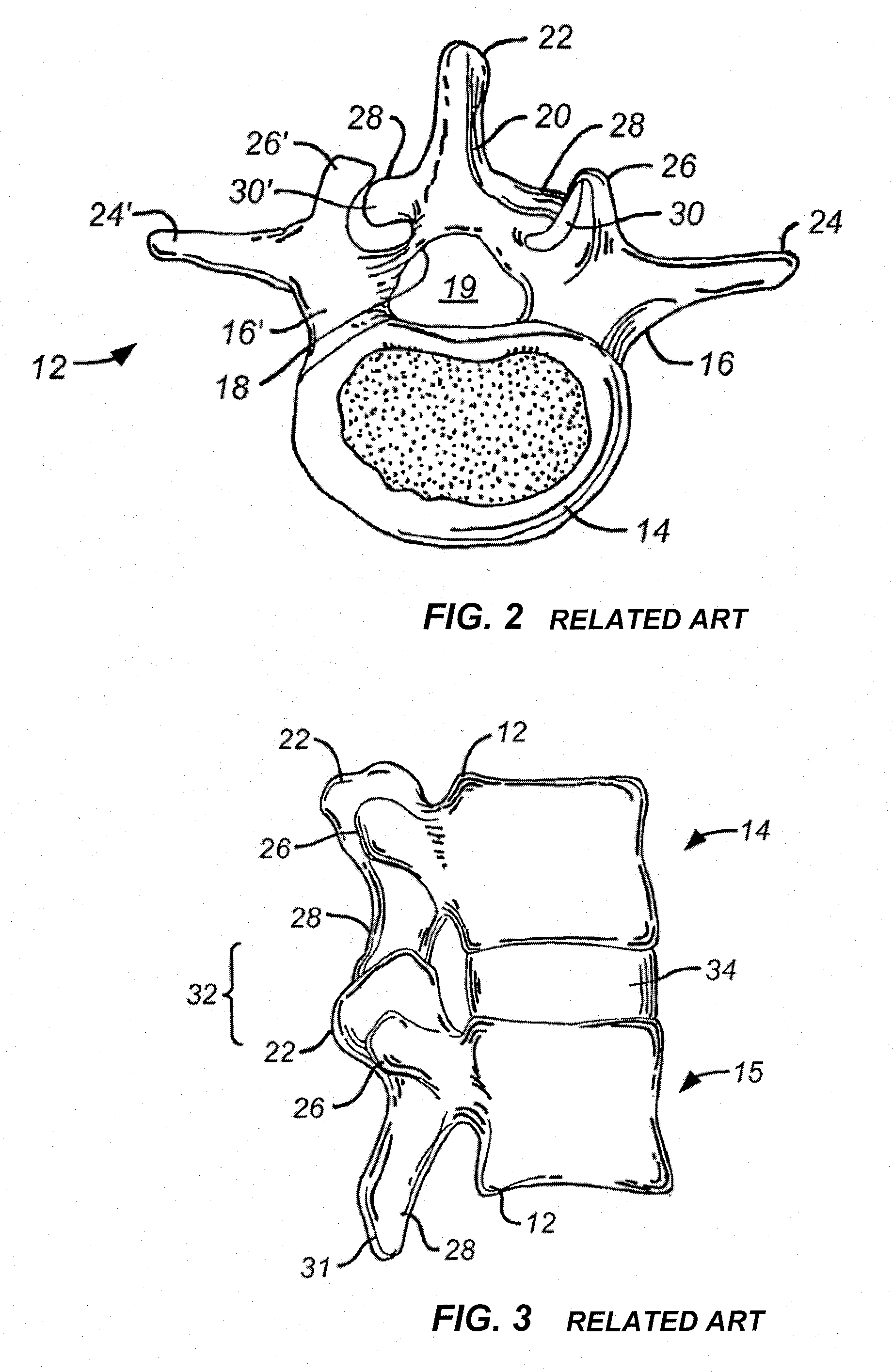
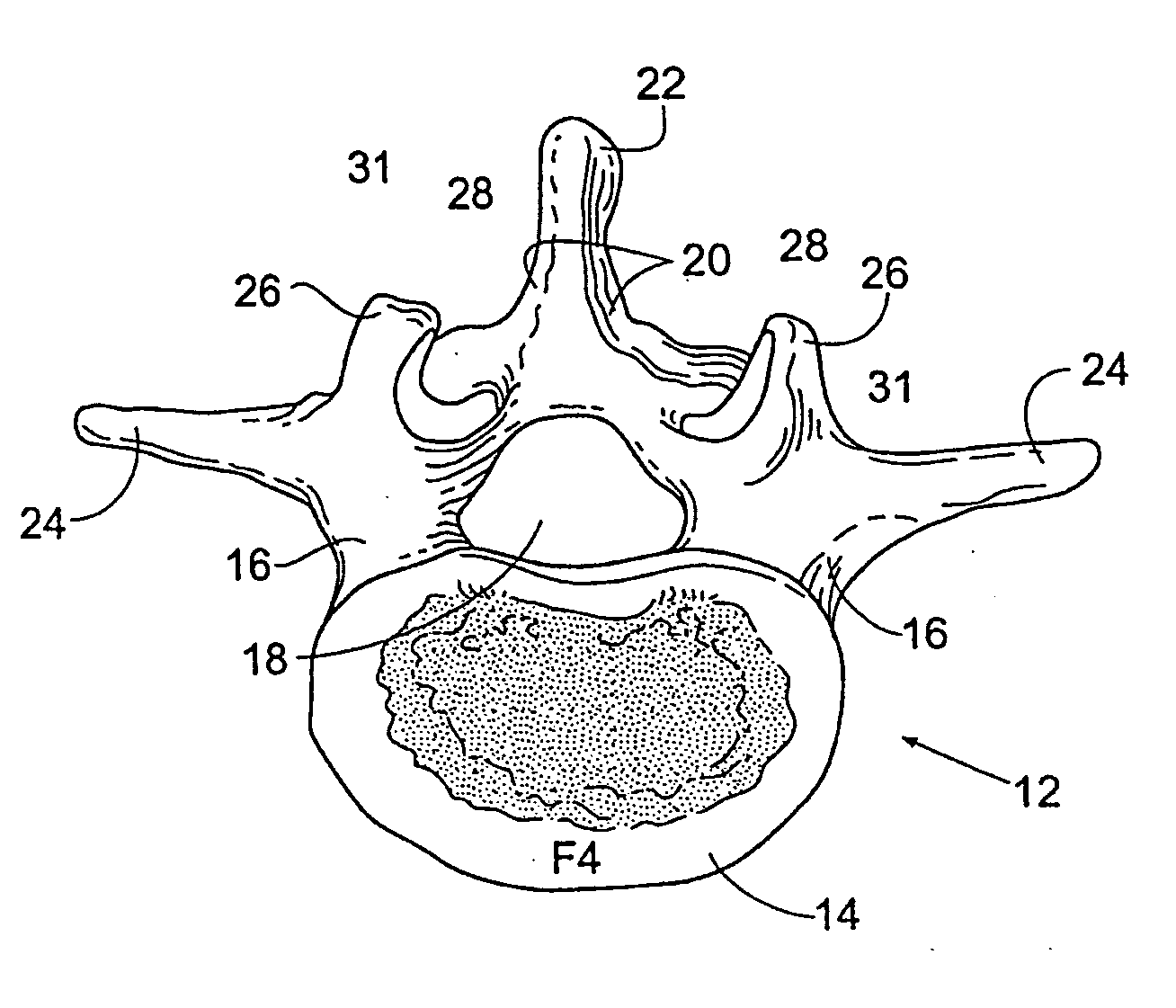
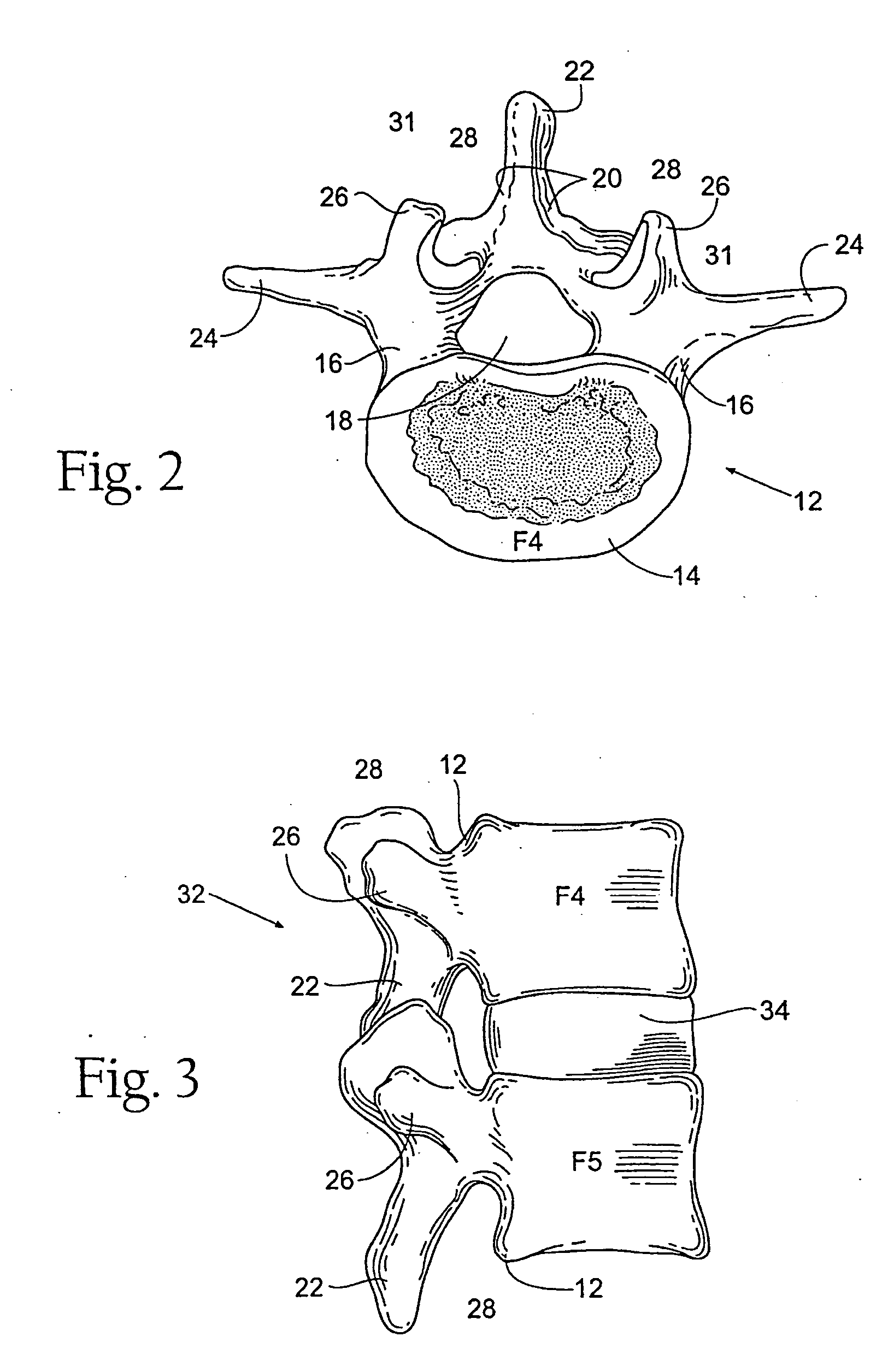
Patents
Literature
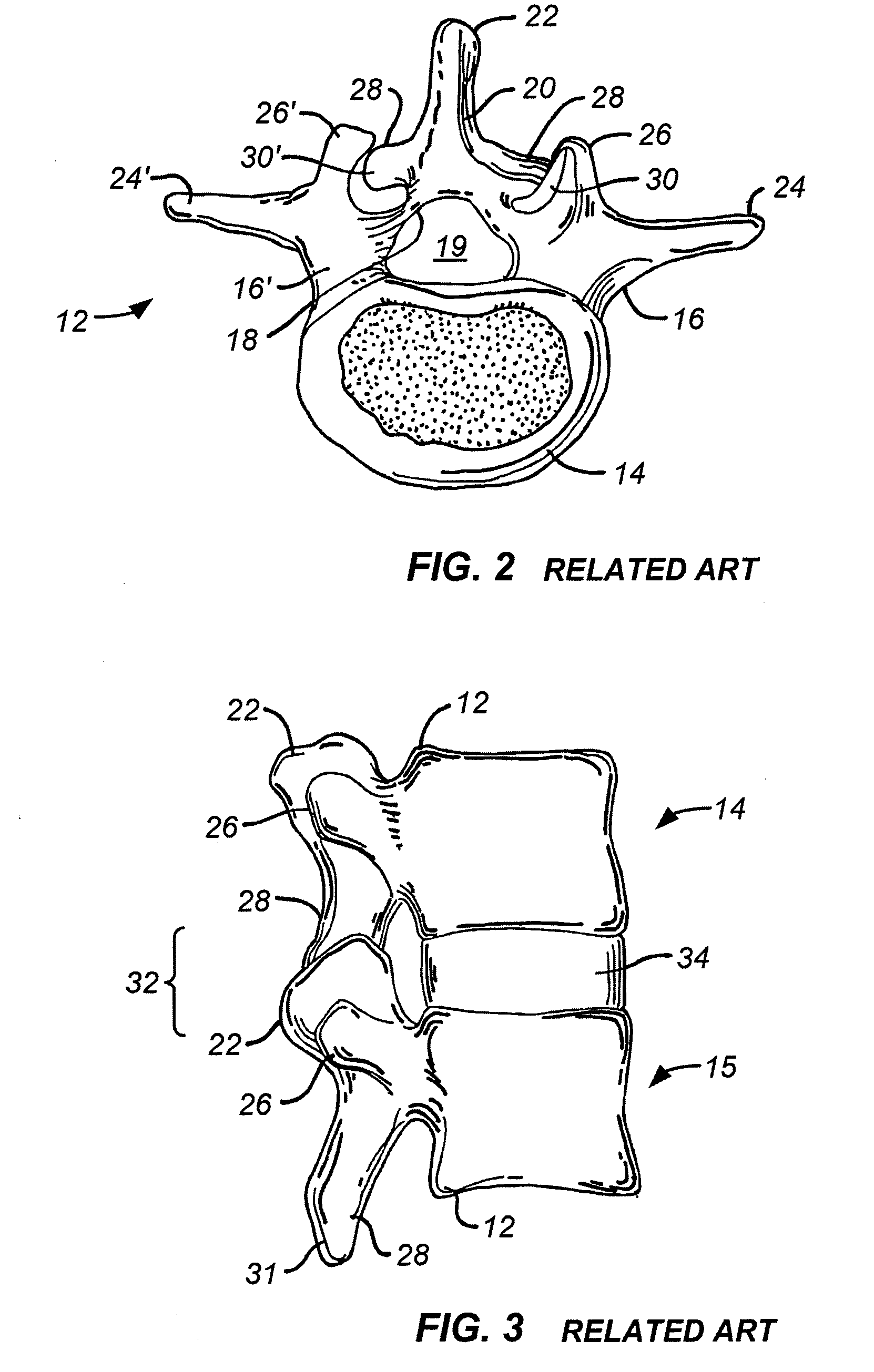
37 results about "Spinal level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
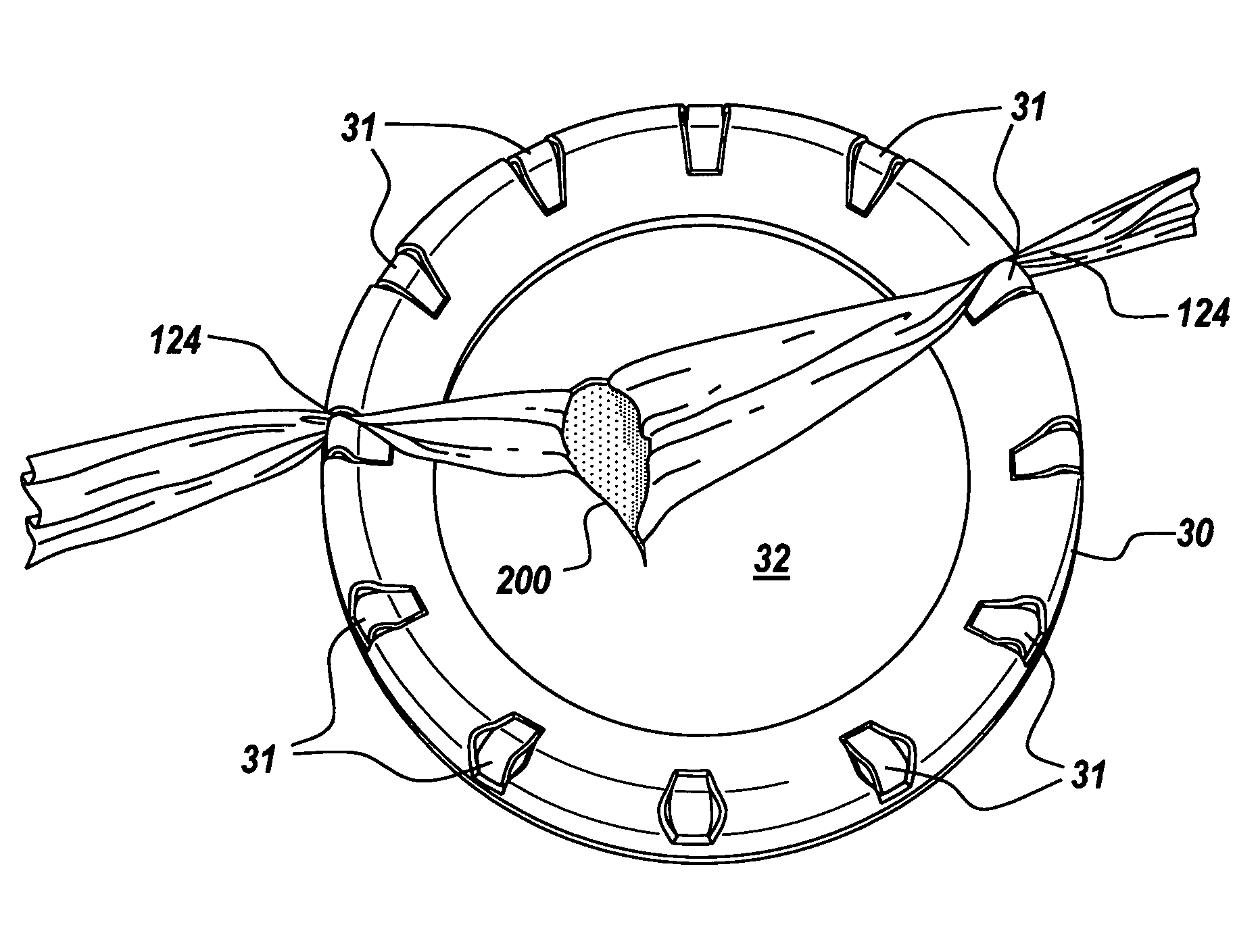
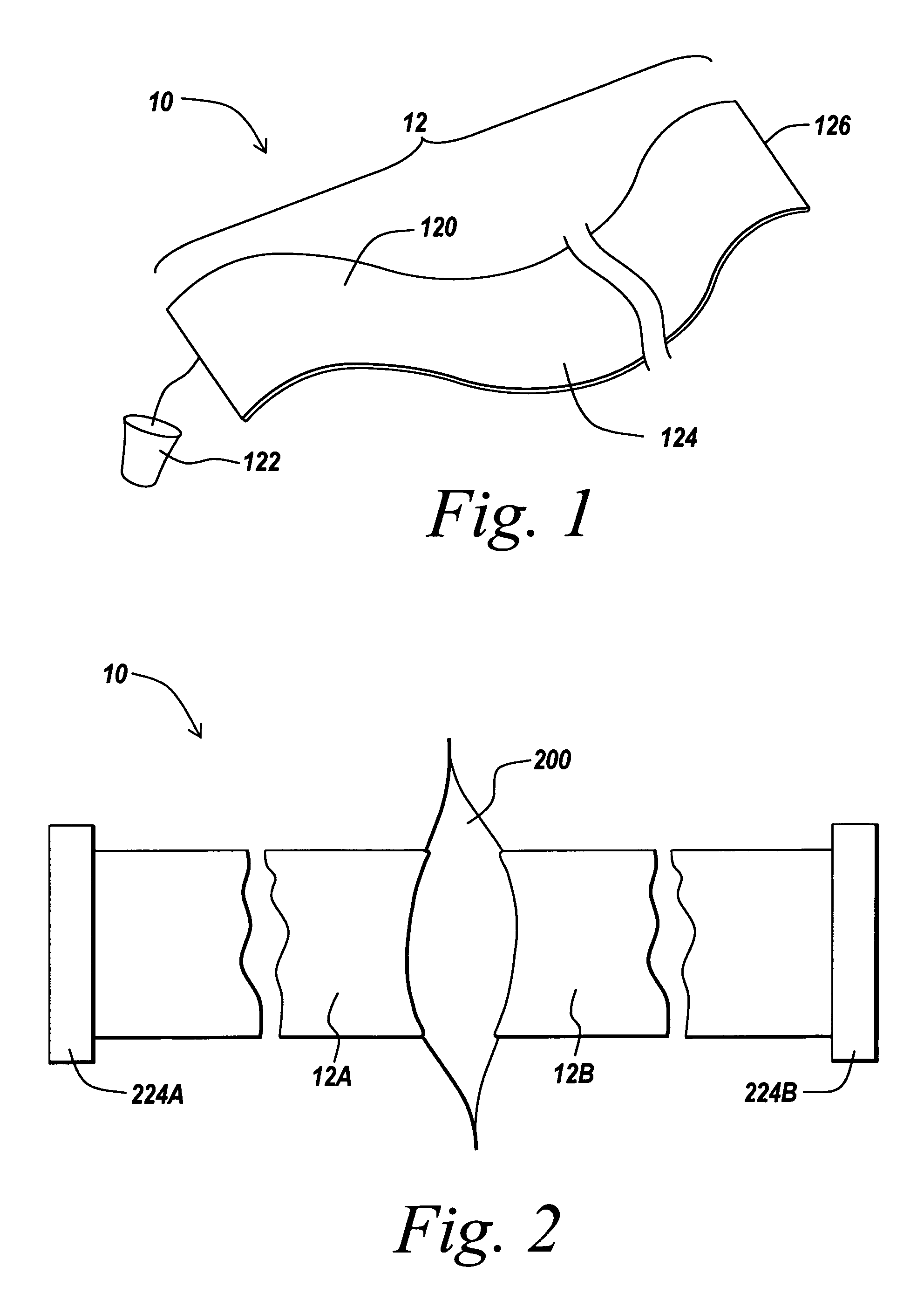
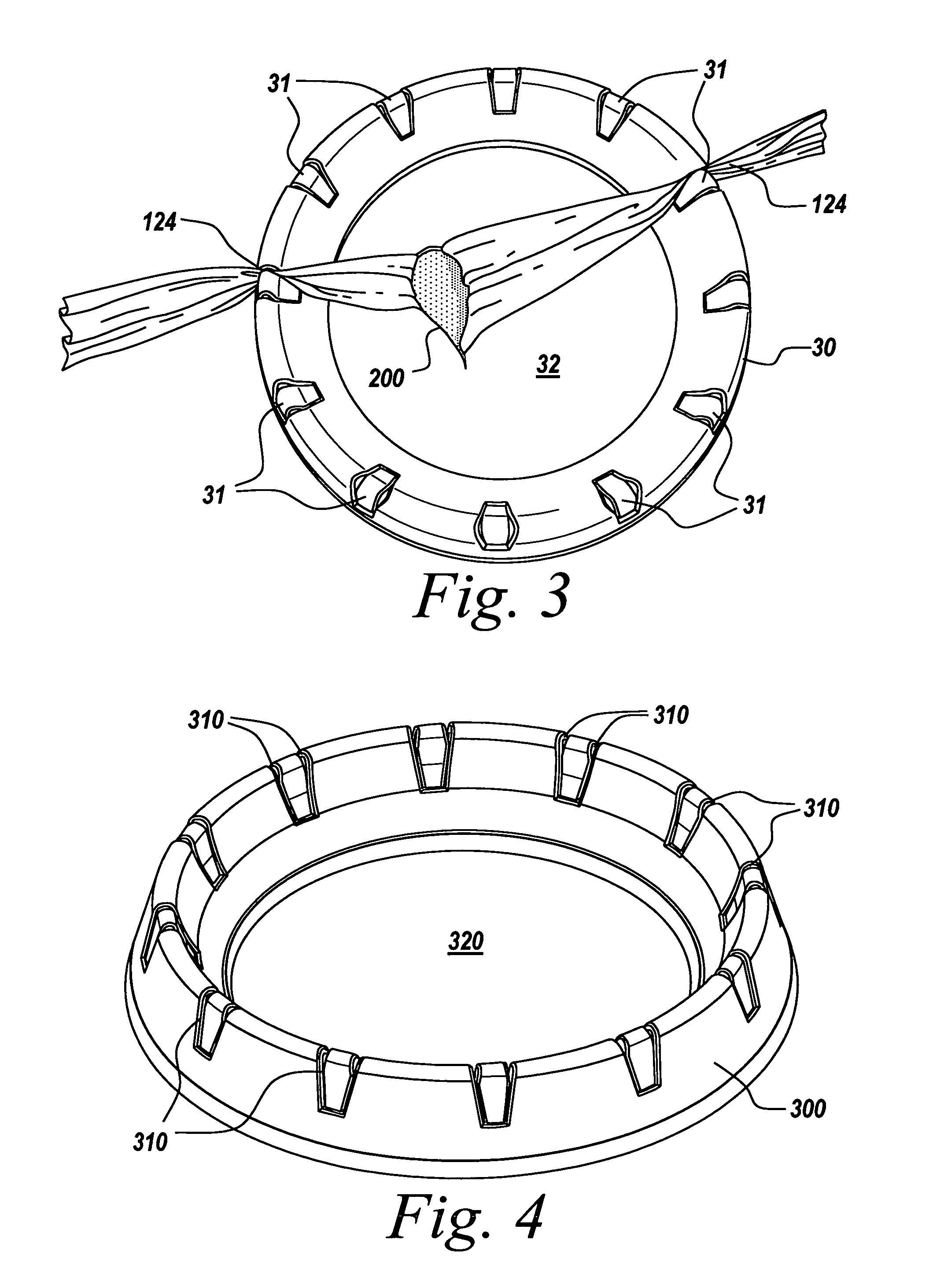
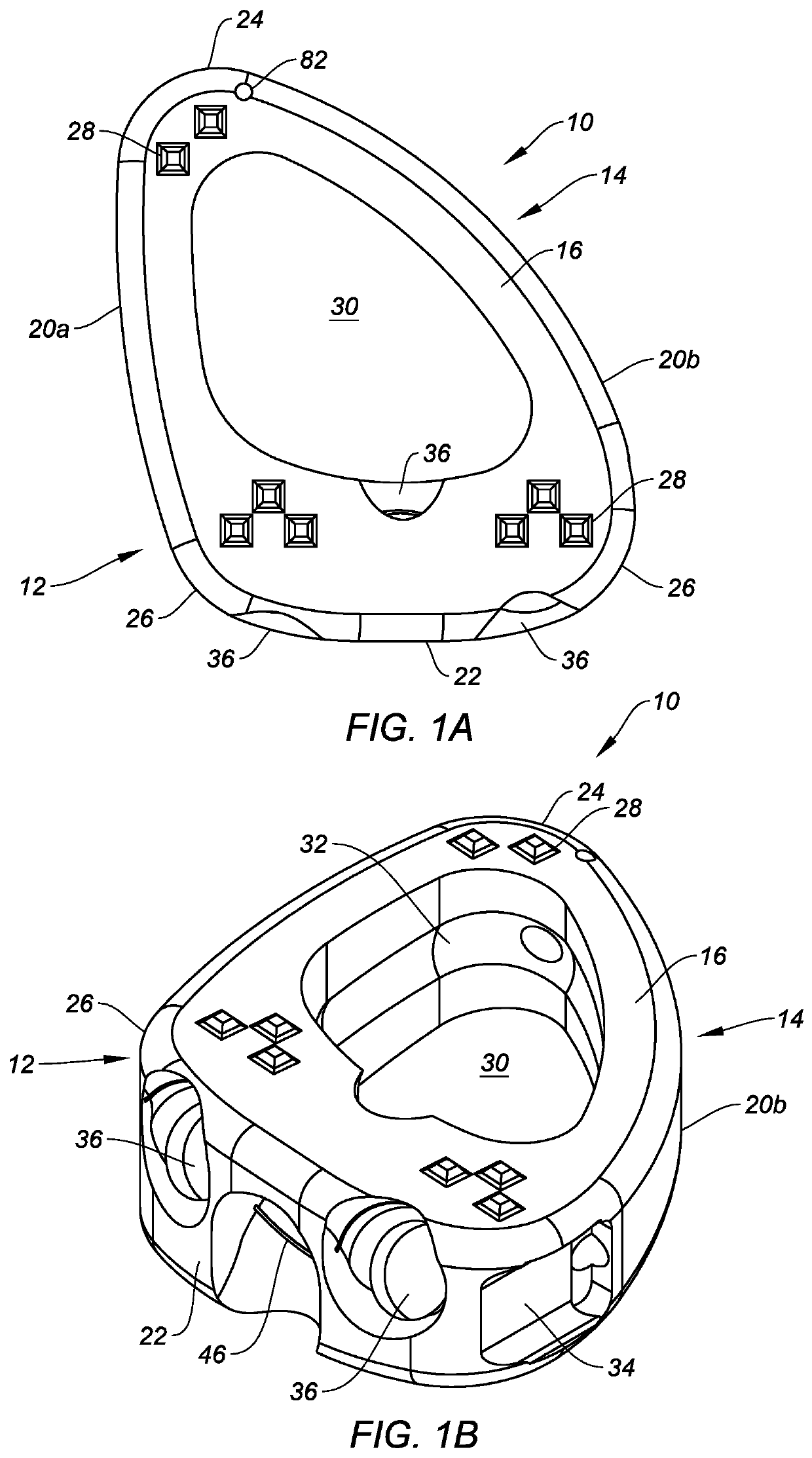
Non-rigid surgical retractor
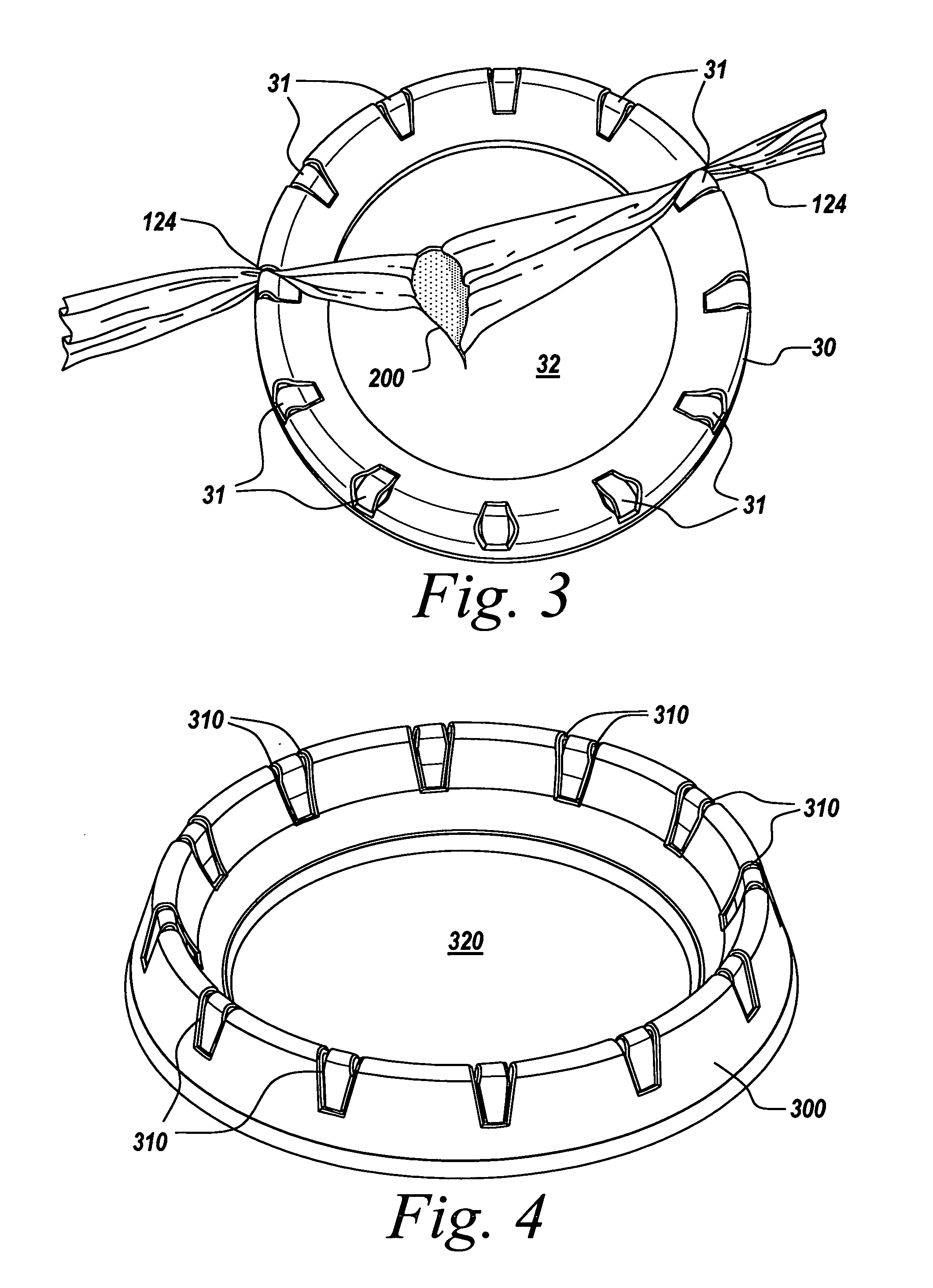
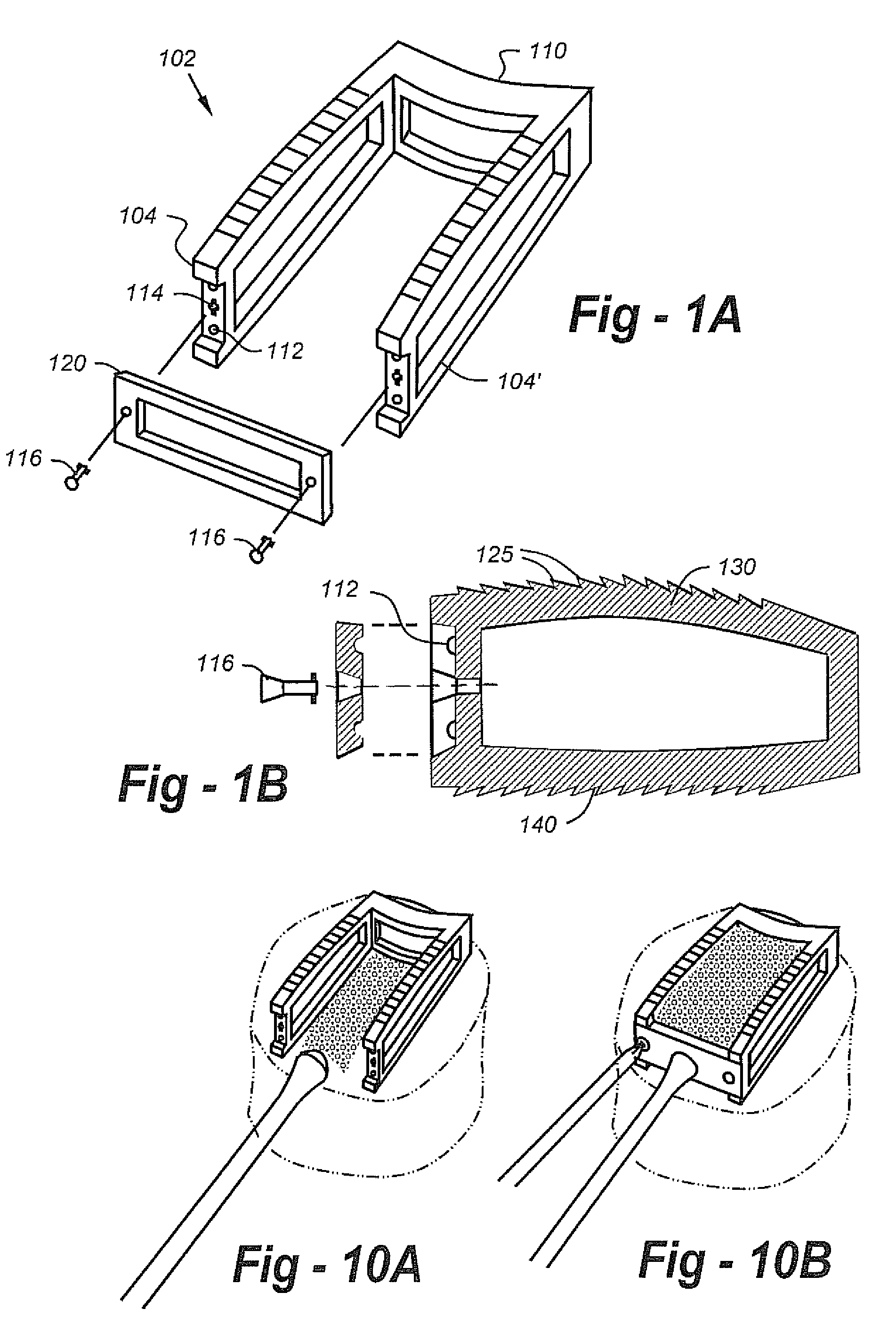
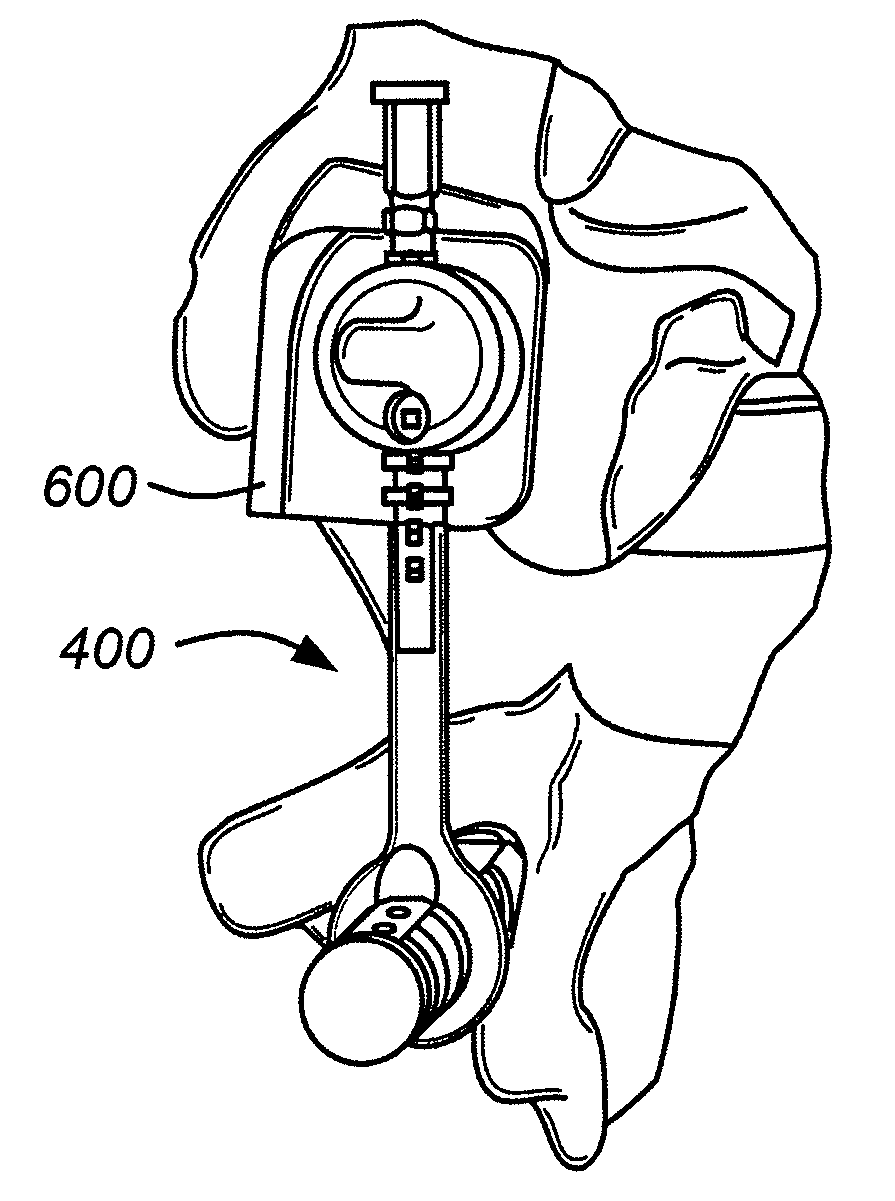
The present invention provides a non-rigid retractor for providing access to a surgical site, such as a patient's spine, during a surgical process. When used in spinal surgery, the non-rigid retractor allows a surgeon to operate on one or more spinal levels. The non-rigid retractor includes at least one flexible strap anchored at a first end to the spine or other internal body part at the surgical site. The body of the at least one flexible strap extends from a skin incision and is anchored at a second location external to the body to retract skin and muscle from the surgical site, allowing adequate visualization of the surgical site and providing access for implants and surgical instruments to pass through the retractor and into the surgical site.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
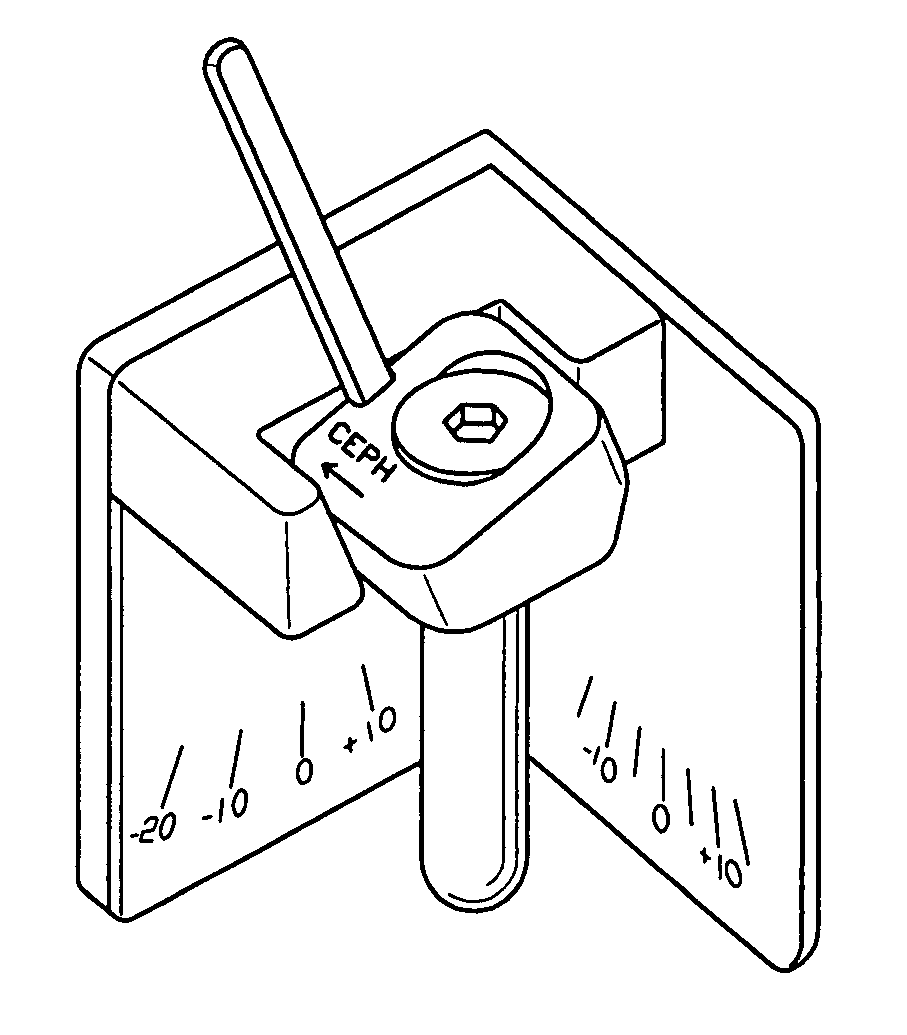
Facet joint prosthesis measurement and implant tools
ActiveUS7051451B2Easy to measureAngles/taper measurementsInternal osteosythesisFacet joint prosthesisProsthesis
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of facet joint prosthesis at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing a cephalad facet joint prosthesis including a fixation measurement element and a support arm element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a cephalad facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a measurement tool for installing a caudal facet joint prosthesis including a stem element and a trial caudal bearing surface element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a caudal facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Yet another aspect is a measurement tool holder including a measurement surface connected to a holder element. This tool holder assists in determining the measurements obtained with the caudal facet joint prosthesis measurement tool.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Implantable orthopedic device component selection instrument and methods
ActiveUS7406775B2Easy to measureInternal osteosythesisMeasurement devicesSpinal levelSacroiliac joint
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of artificial facet joints at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing an artificial cephalad facet joint including a fixation measurement element and a support arm element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of an artificial cephalad facet joint for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a measurement tool for installing a caudad facet joint including a stem element and a trial caudad bearing surface element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a caudad facet joint for implantation in a patient. Yet another aspect is a measurement tool holder including a measurement surface connected to a holder element. This tool holder assists in determining the measurements obtained with the caudad facet joint measurement tool.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
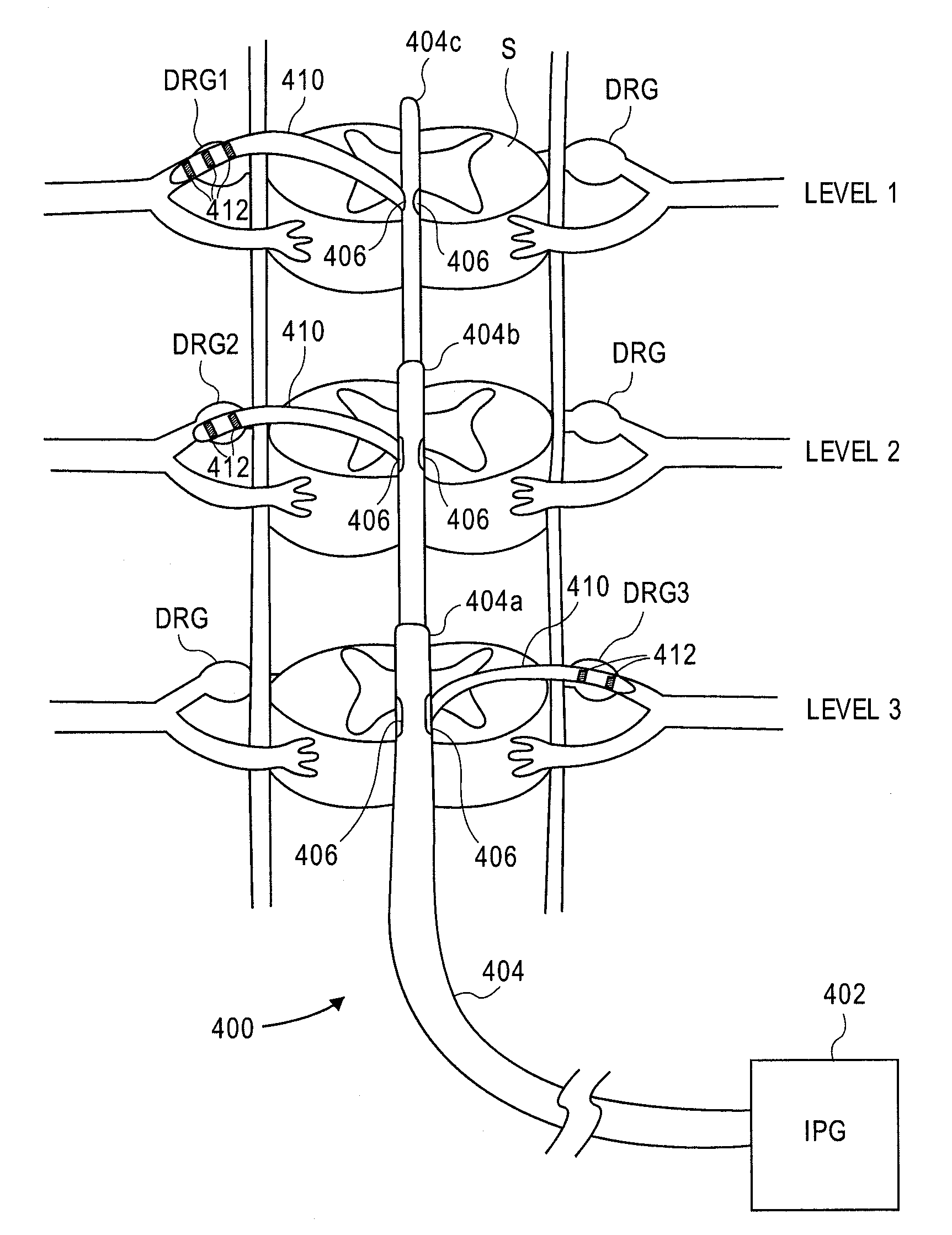
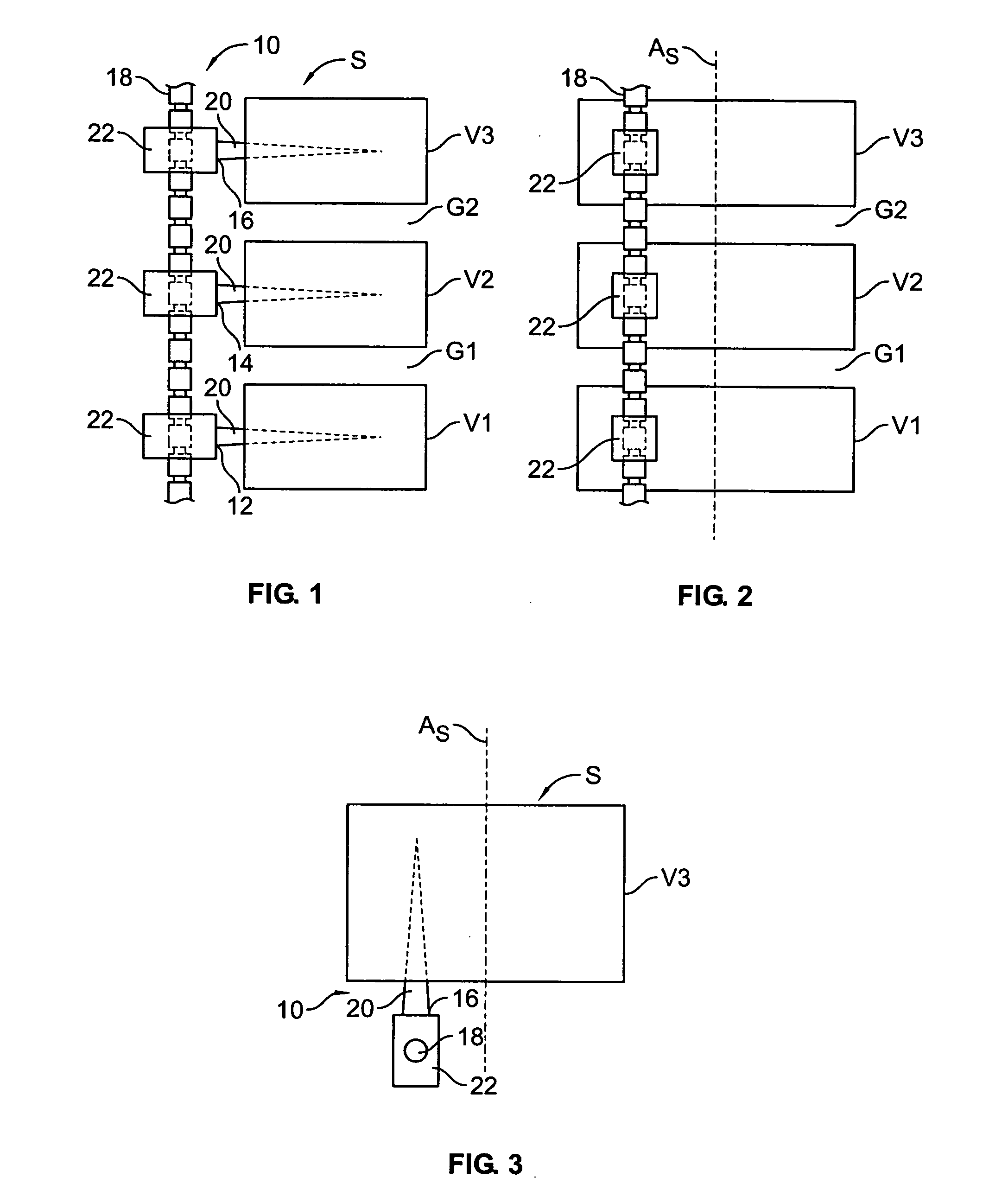
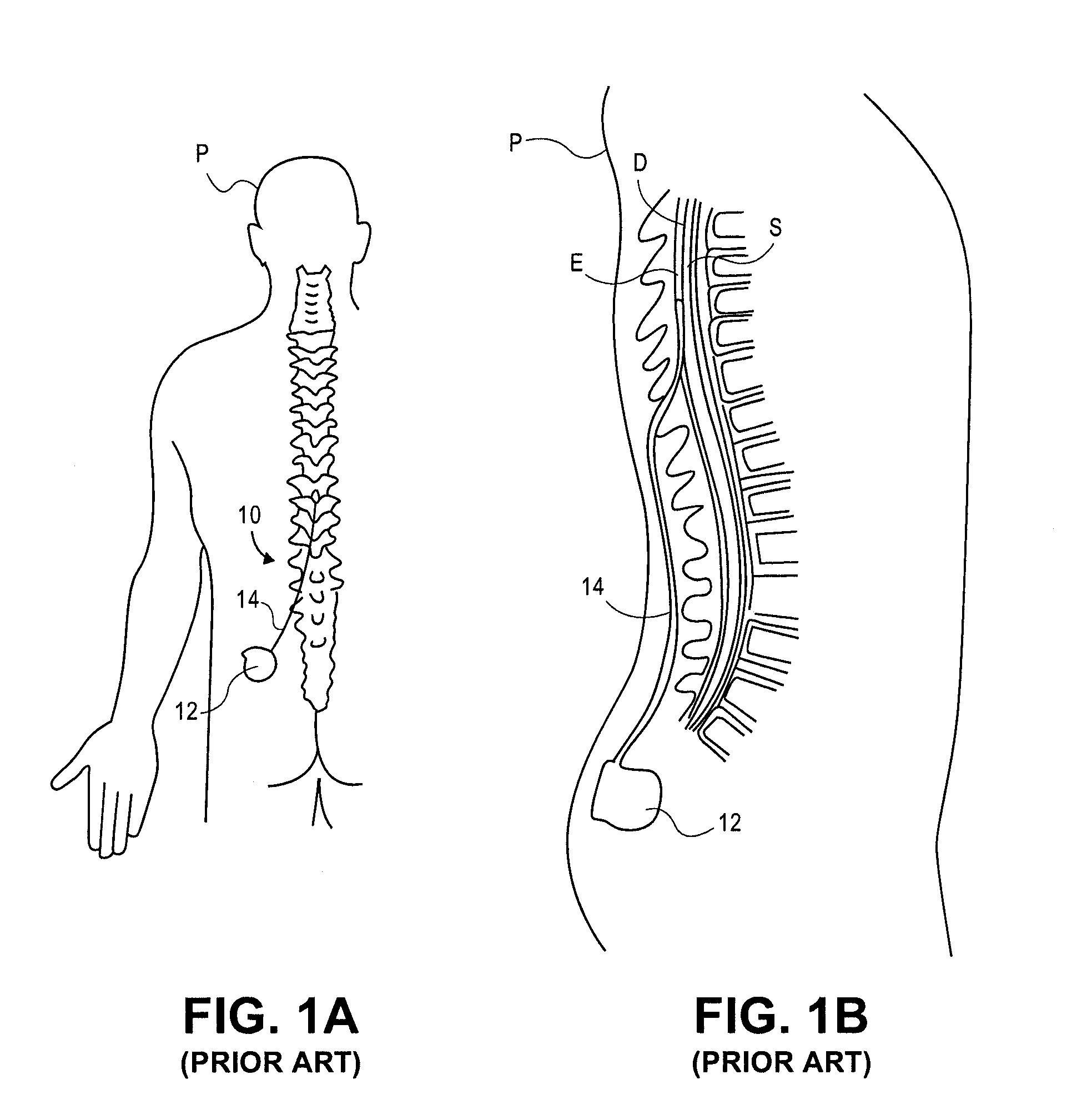
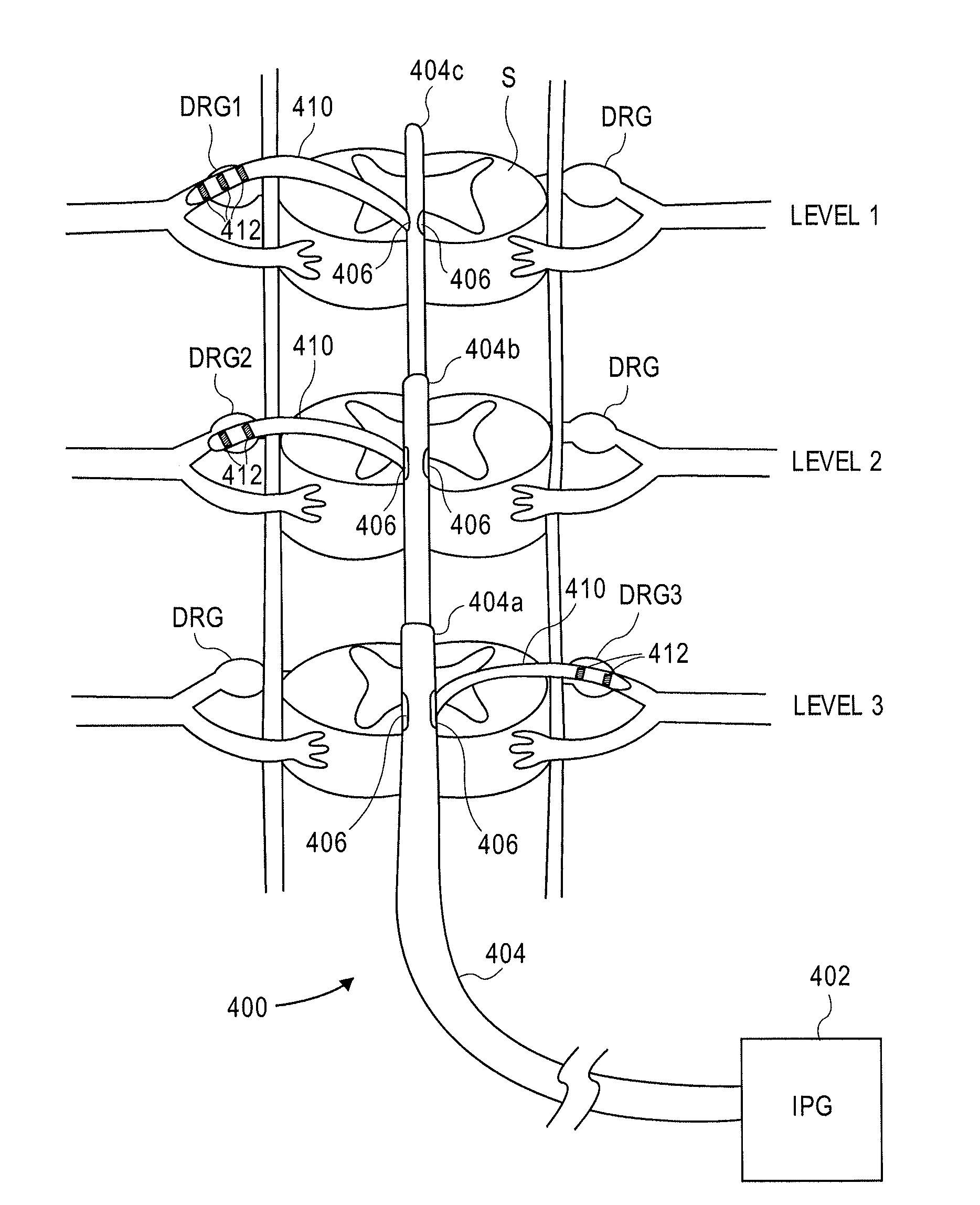
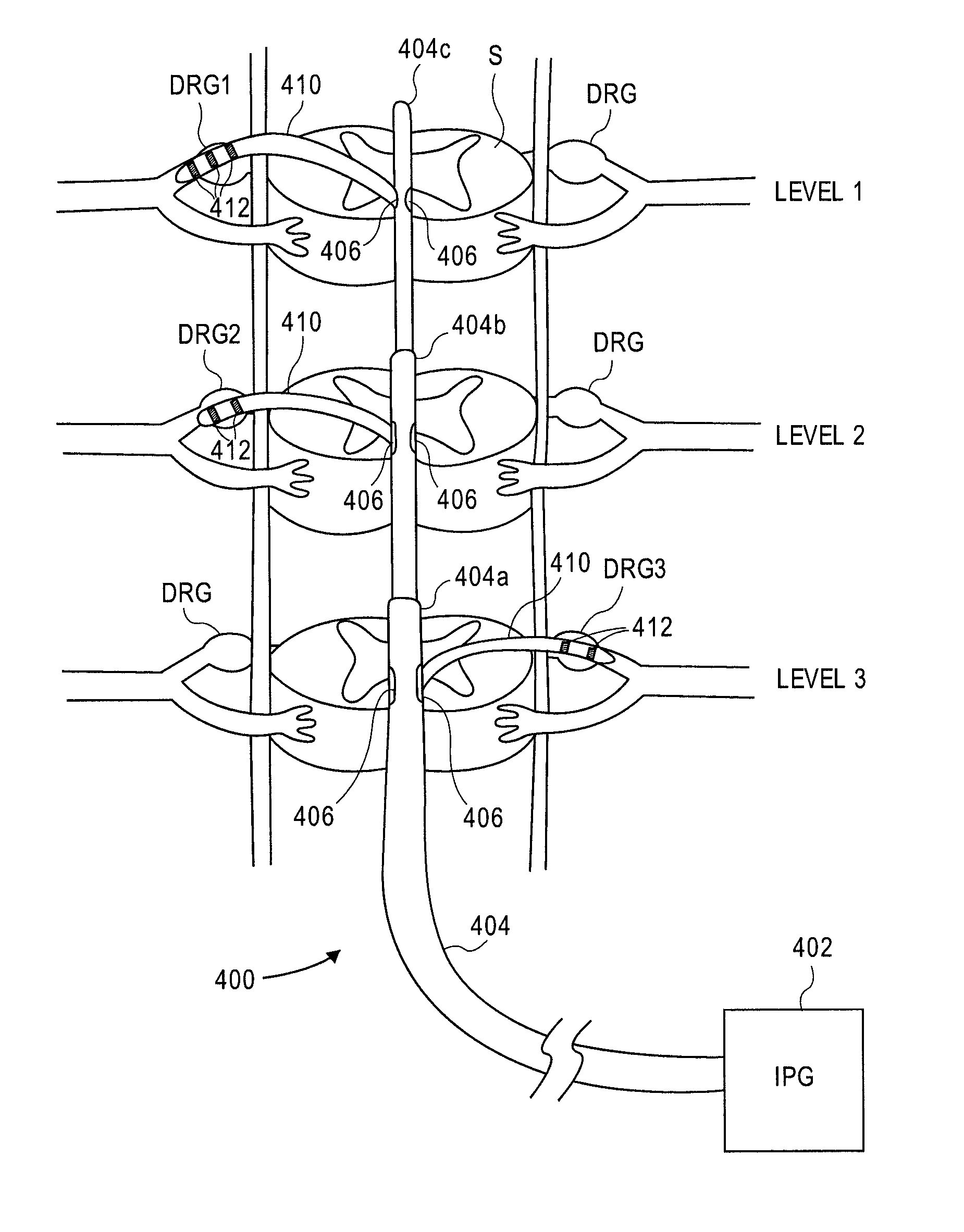
Delivery devices, systems and methods for stimulating nerve tissue on multiple spinal levels
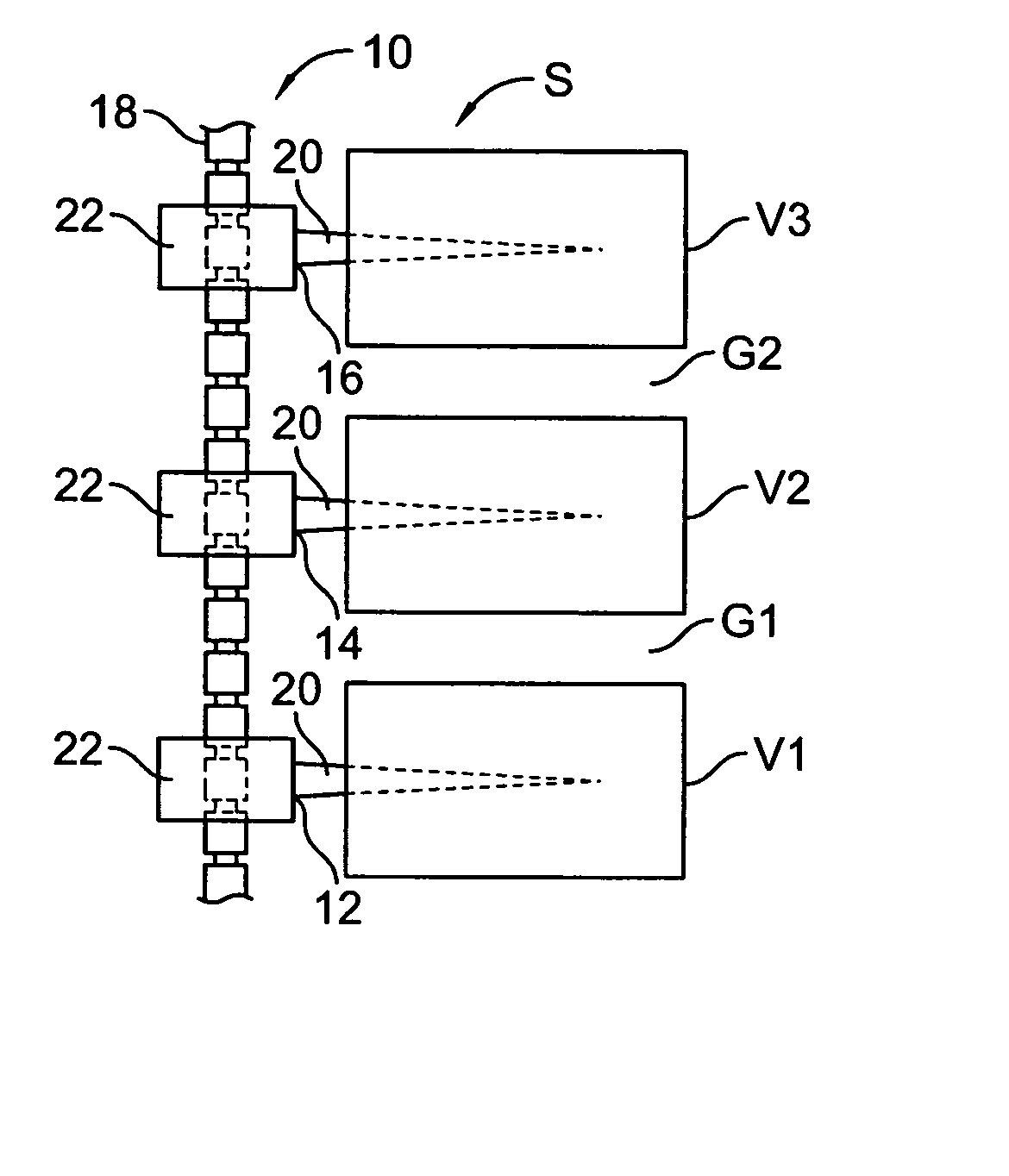
ActiveUS20080140169A1Effectively treat pain symptomReduce deleterious side effectSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsSpinal columnSpinal anatomy
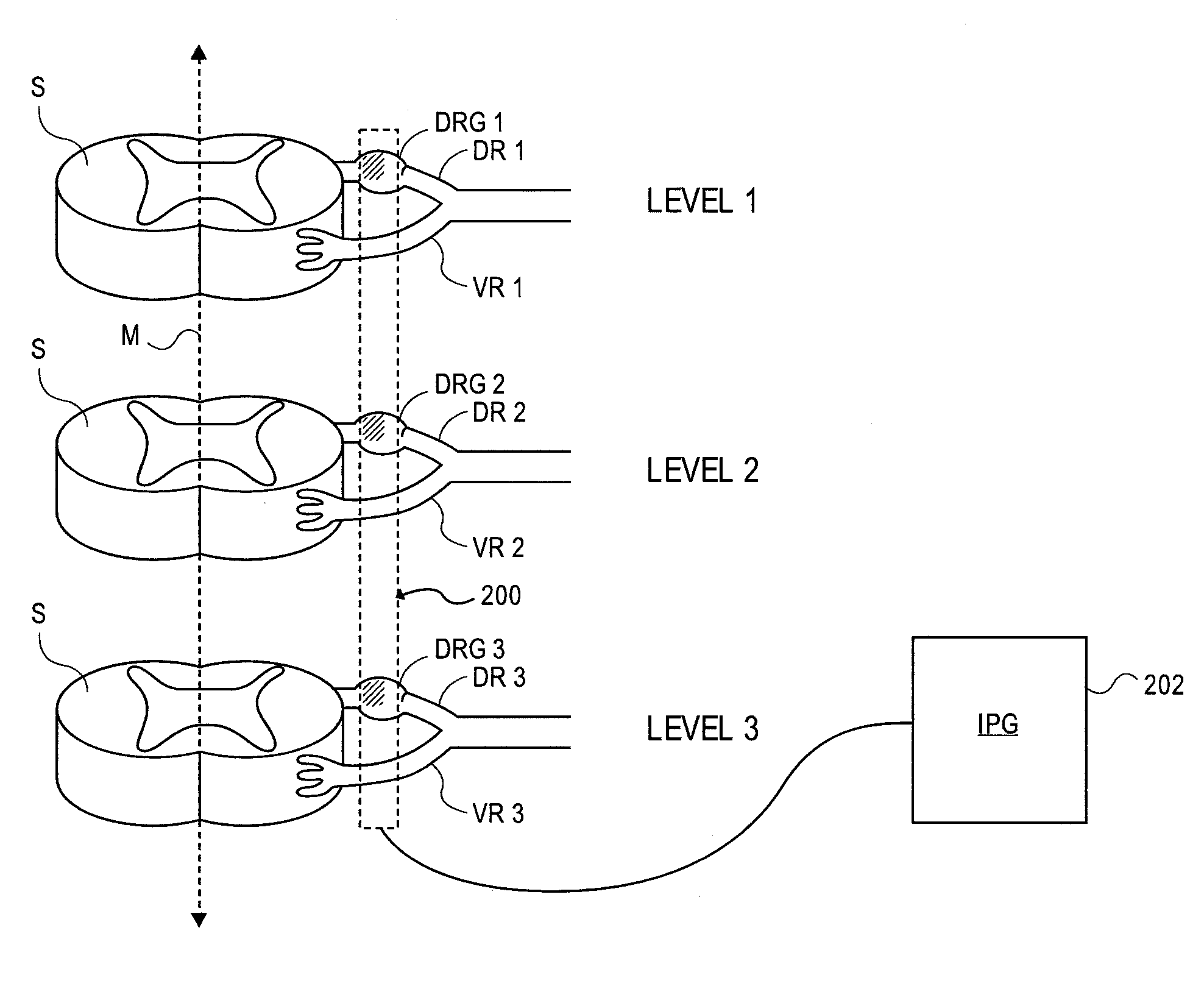
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. By stimulating multiple levels of the spinal column with the use of a single device, a single access path is created to an implantable pulse generator (IPG) rather than individual access paths for each lead at each spinal level to an IPG. By reducing the number of pathways, the procedure complexity, time and recovery are reduced. In addition, some embodiments provide additional specificity within each targeted level, such as selective stimulation of specific tissue, such as the dorsal root ganglion.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
System and method for electrical stimulation of the intervertebral disc
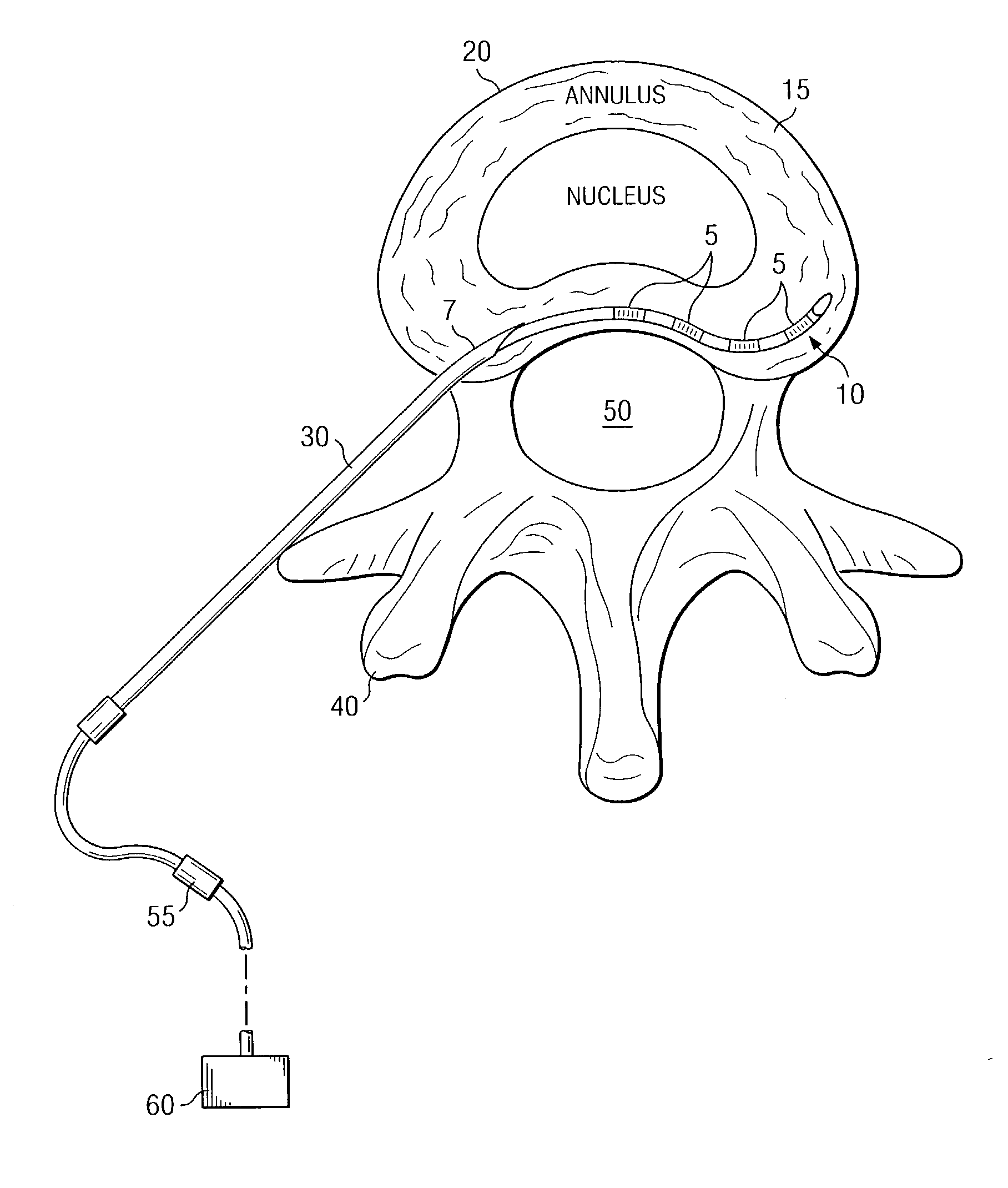
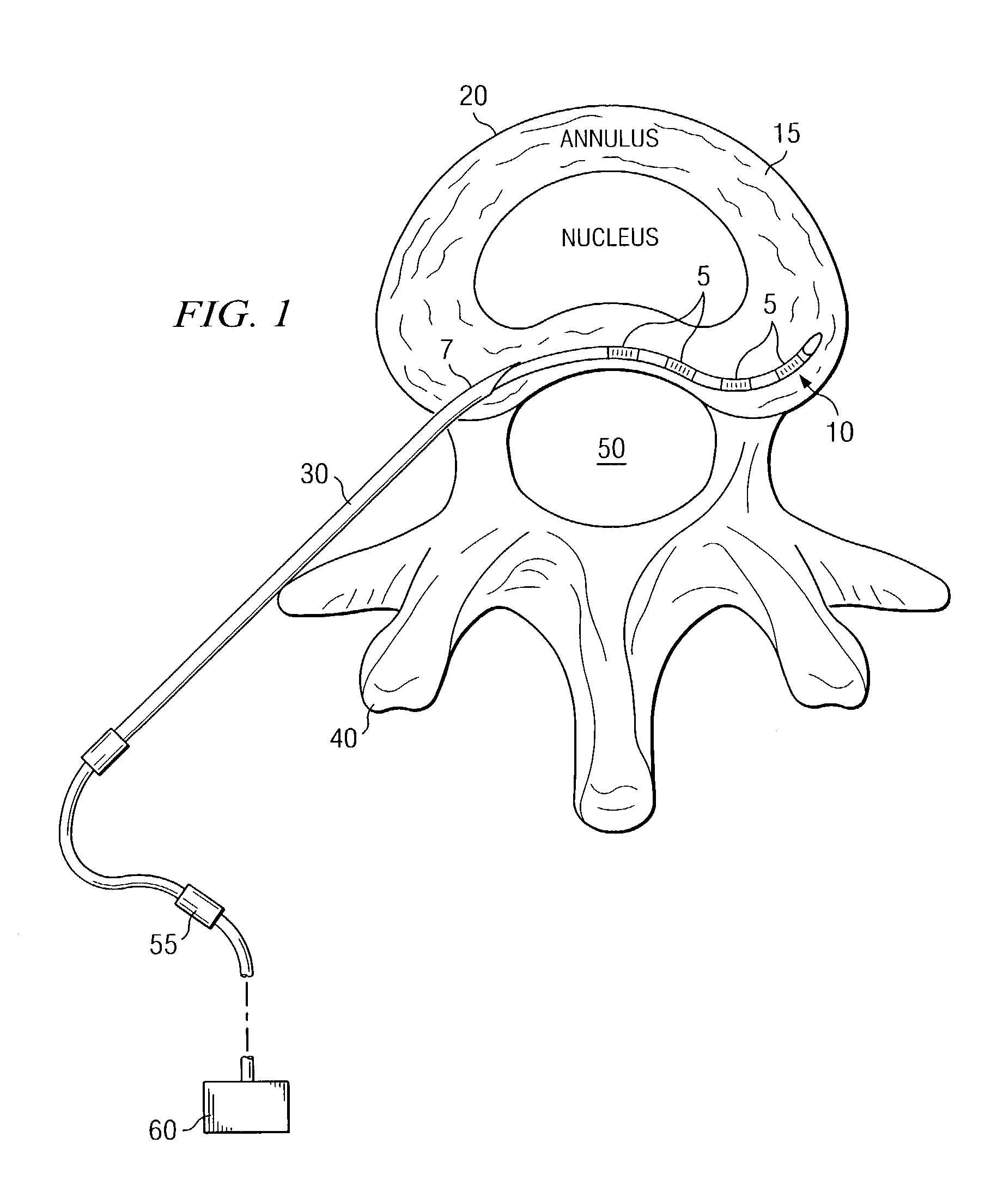
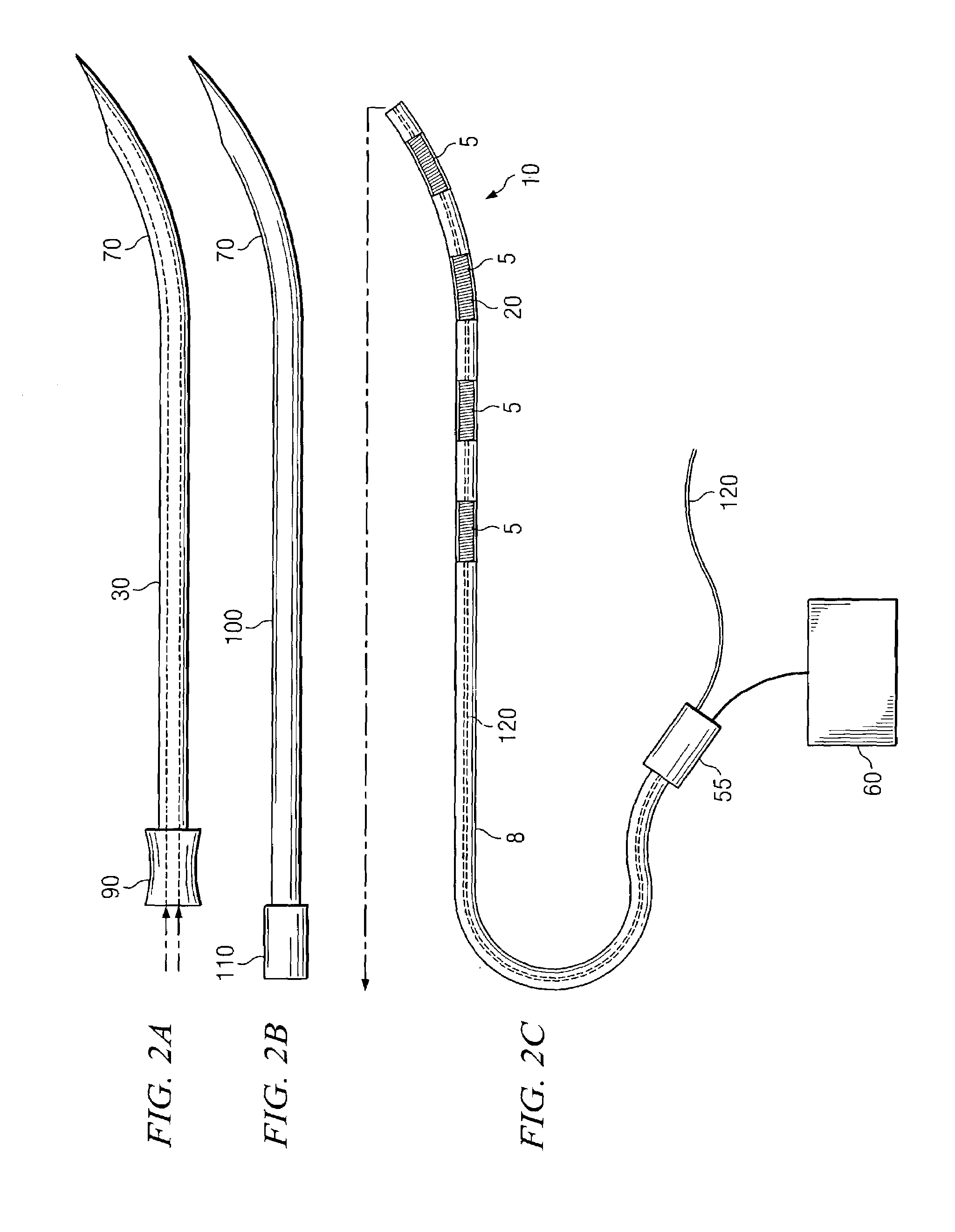
A method for electrically stimulating an area in a spinal disc is presented. The method comprises implanting a lead with one or more electrodes in a placement site in or adjacent to one or more discs at any spinal level from cervical through lumbar, connecting the lead to a signal generator, and generating electrical stimulation pulses using the generator to stimulate targeted portions of the disc. Additionally, a system for relieving pain associated with a spinal disc is presented that comprises a lead with one or more electrodes, an introducer for introducing the lead to a placement site in or adjacent to the disc, a removable stylet for guiding the lead to the placement site in the disc, and a generator connected to the lead for generating electrical pulses to the lead for stimulating the disc.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Dynamic spinal stabilizer
InactiveUS20070093813A1Substantial dimensional/diametrical stabilityRaise the possibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnLumbar vertebrae
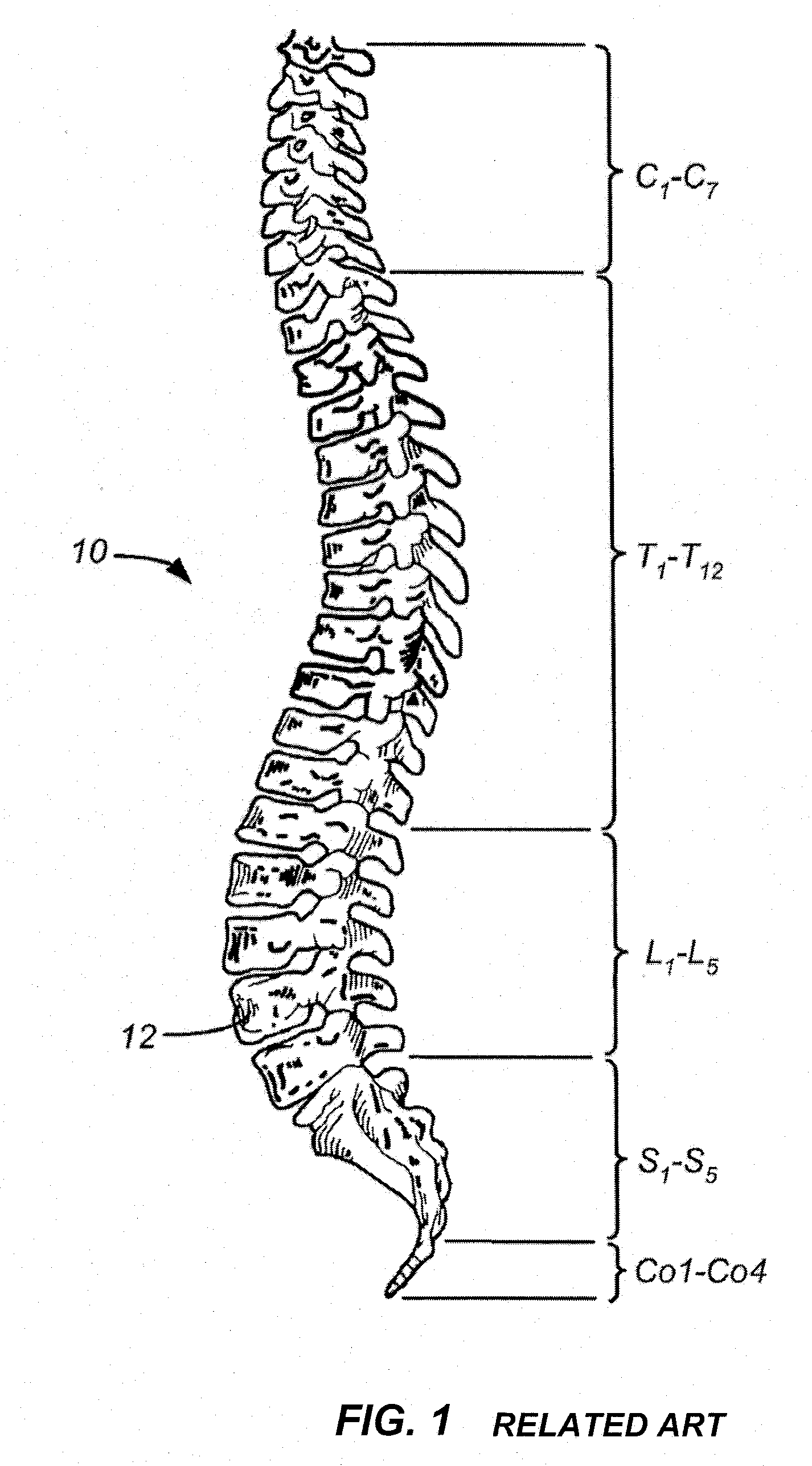
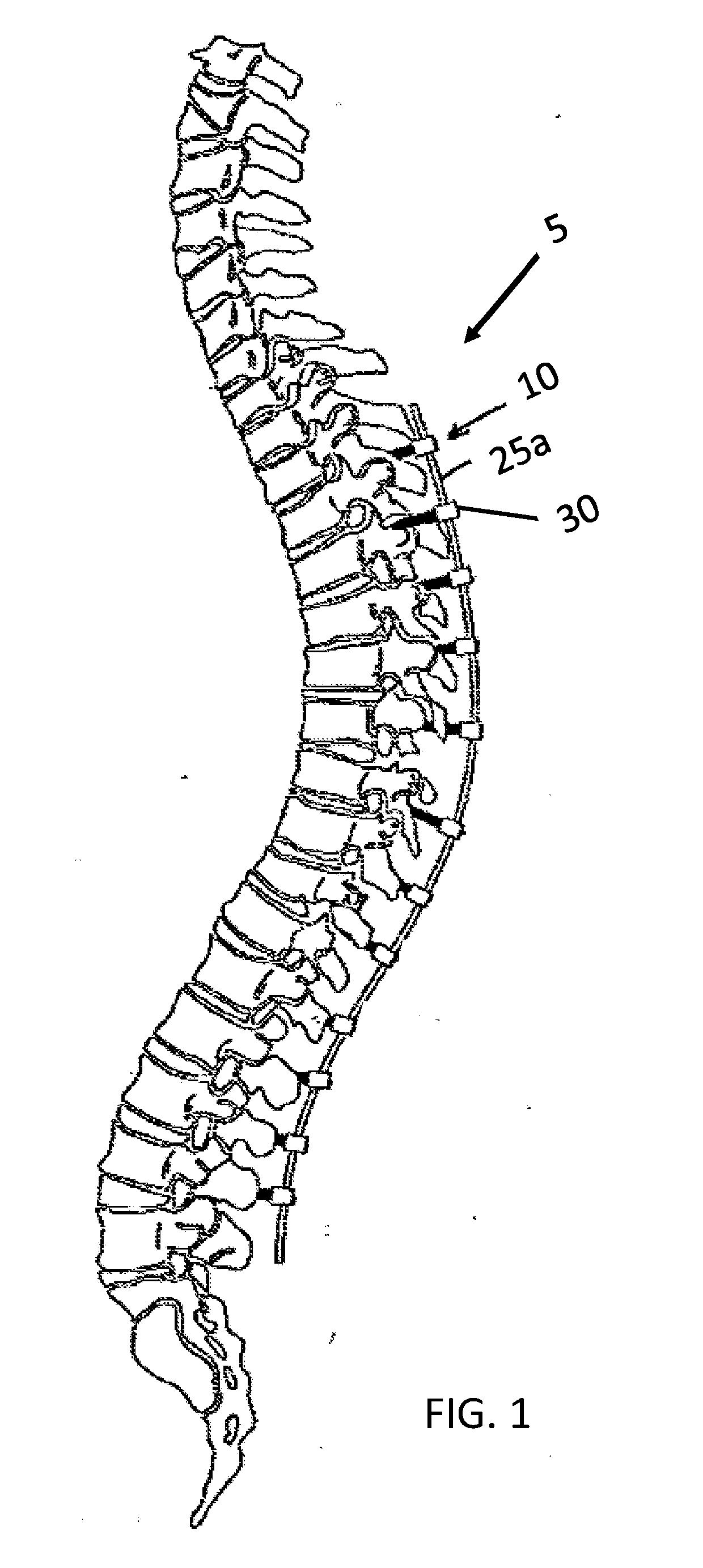
An elongated member forming a spinal support rod is implantable adjacent the spine of a patient and includes an axial span or spans for spanning respective spinal levels to promote efficacious spinal support / stabilization. The axial span has an axially articulable geometry, and manifests an angulation mechanism along one or more transverse directions of at least seven degrees across a given spinal level. The angulation mechanism may be associated with joints between structural elements assembled in serial along the axial span, or via a common connection between such structural elements and a restraining element. Rotation between such structural elements can be global. The axial span may have a rod-like profile of a diameter similar to conventional spinal support rods used for lumbar spinal fusion, and provides for use across multiple spinal levels and with multiple adjustable attachment points for associated spine attachment devices to accommodate different patient anatomies.
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Non-rigid surgical retractor
The present invention provides a non-rigid retractor for providing access to a surgical site, such as a patient's spine, during a surgical process. When used in spinal surgery, the non-rigid retractor allows a surgeon to operate on one or more spinal levels. The non-rigid retractor includes at least one flexible strap anchored at a first end to the spine or other internal body part at the surgical site. The body of the at least one flexible strap extends from a skin incision and is anchored at a second location external to the body to retract skin and muscle from the surgical site, allowing adequate visualization of the surgical site and providing access for implants and surgical instruments to pass through the retractor and into the surgical site
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Inflatable retractor
InactiveUS20080081951A1Adequate visualizationMinimizing tissue creepSurgerySurgical operationSurgical site
The present invention provides an inflatable retractor for providing access to a surgical site, such as a patient's spine, during a surgical process. When used in spinal surgery, the inflatable retractor allows a surgeon to operate on one or more spinal levels. The inflatable retractor includes an inflatable body defining a central cavity, wherein the body is flaccid in a non-inflated state and increasingly rigid in an inflated state. The inflatable retractor is inserted into an incision in a deflated, or partially inflated, state and then inflated once the retractor is in position. The inflation of the retractor retracts skin and muscle from the surgical site, allowing adequate visualization of the surgical site and forms a passage providing access for implants and surgical instruments to pass through the retractor and into the surgical site.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
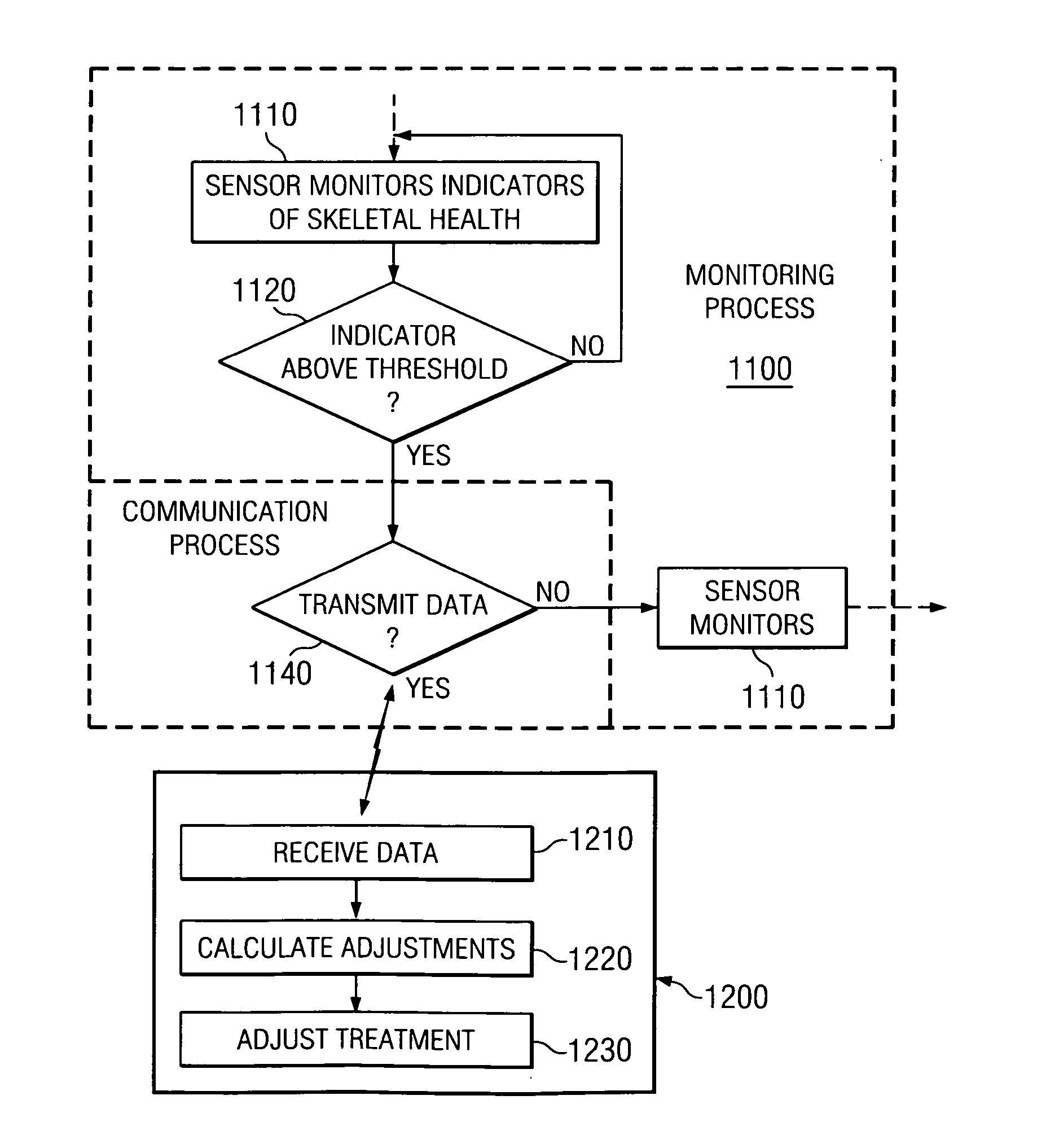
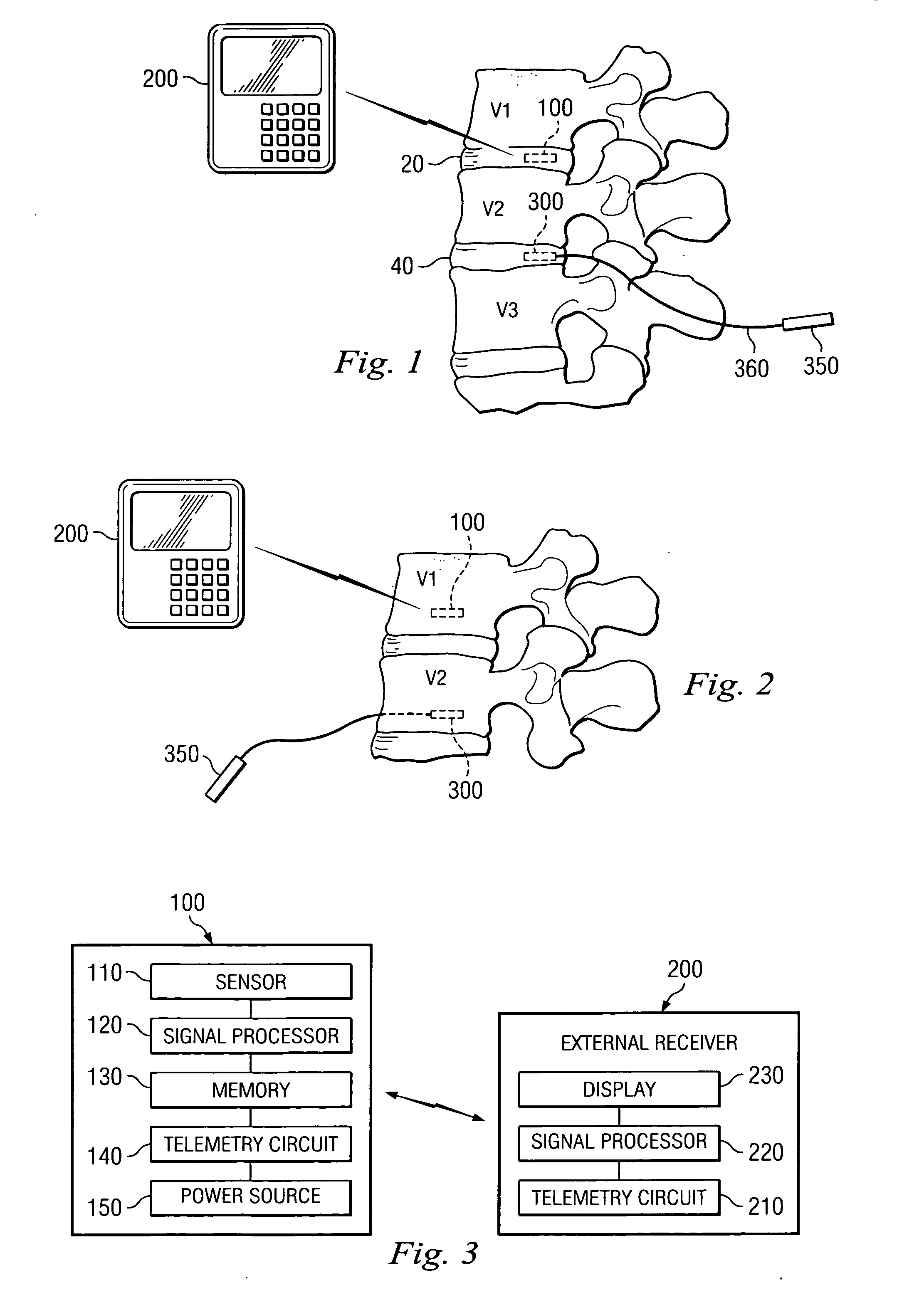
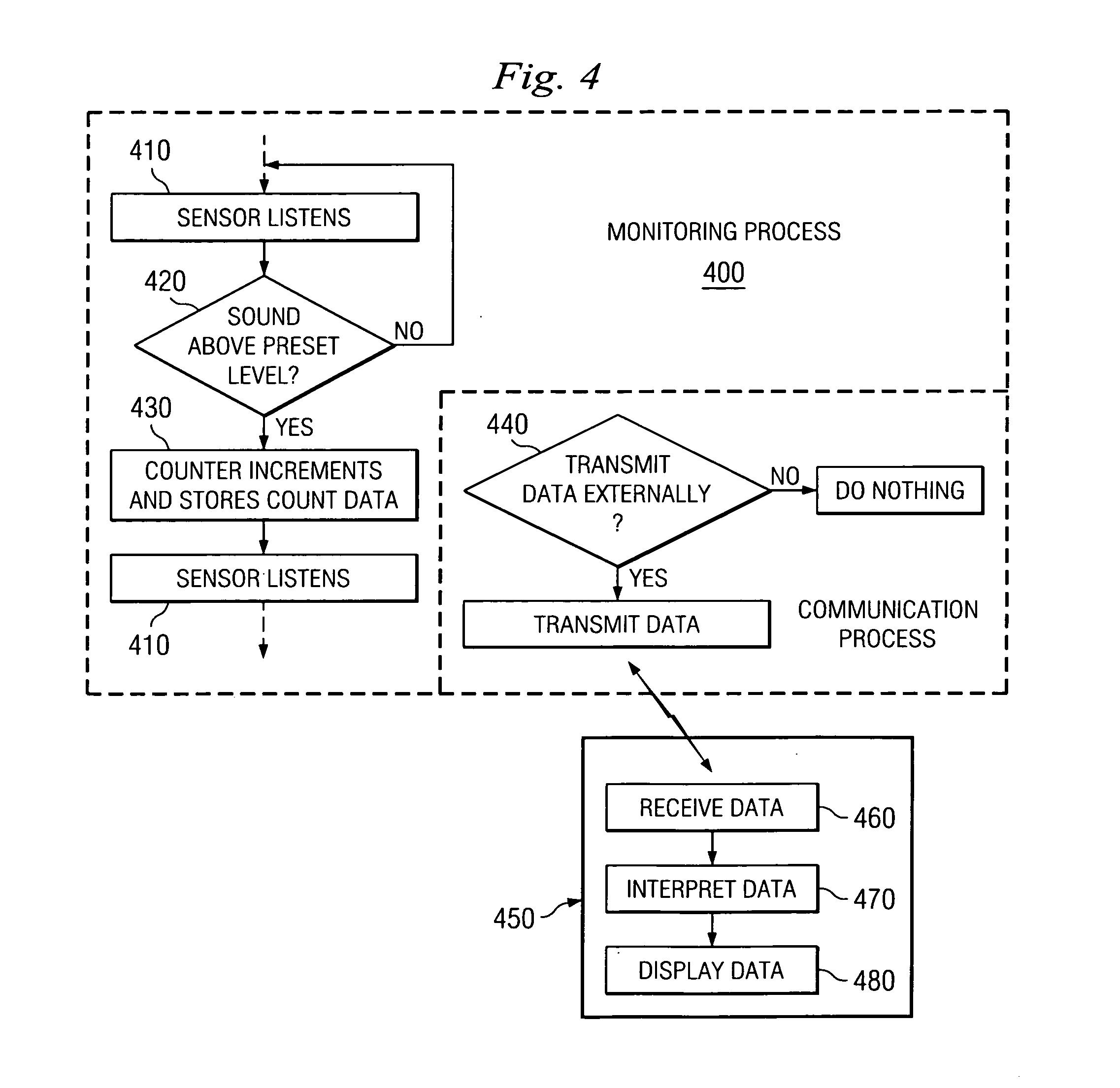
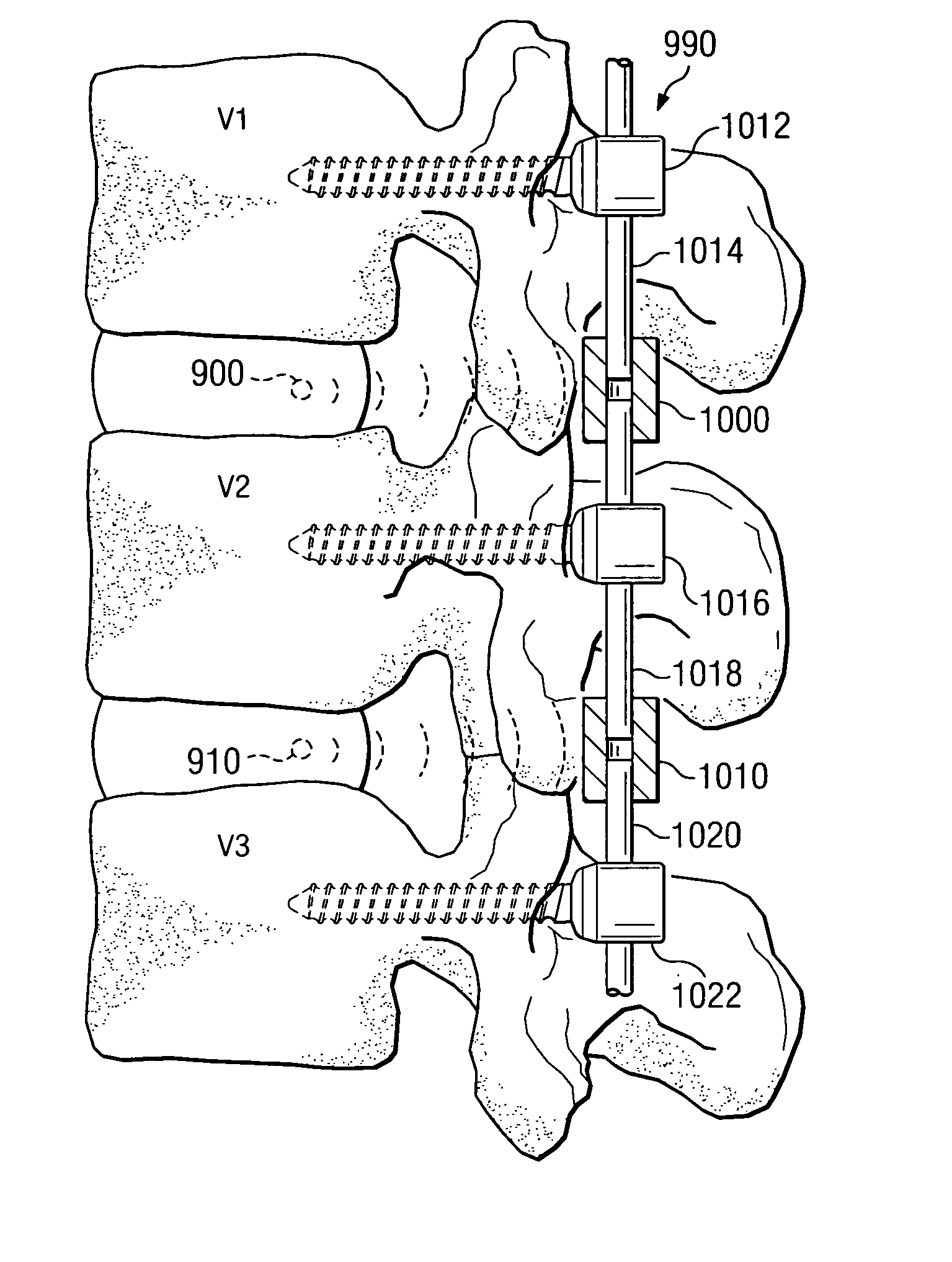
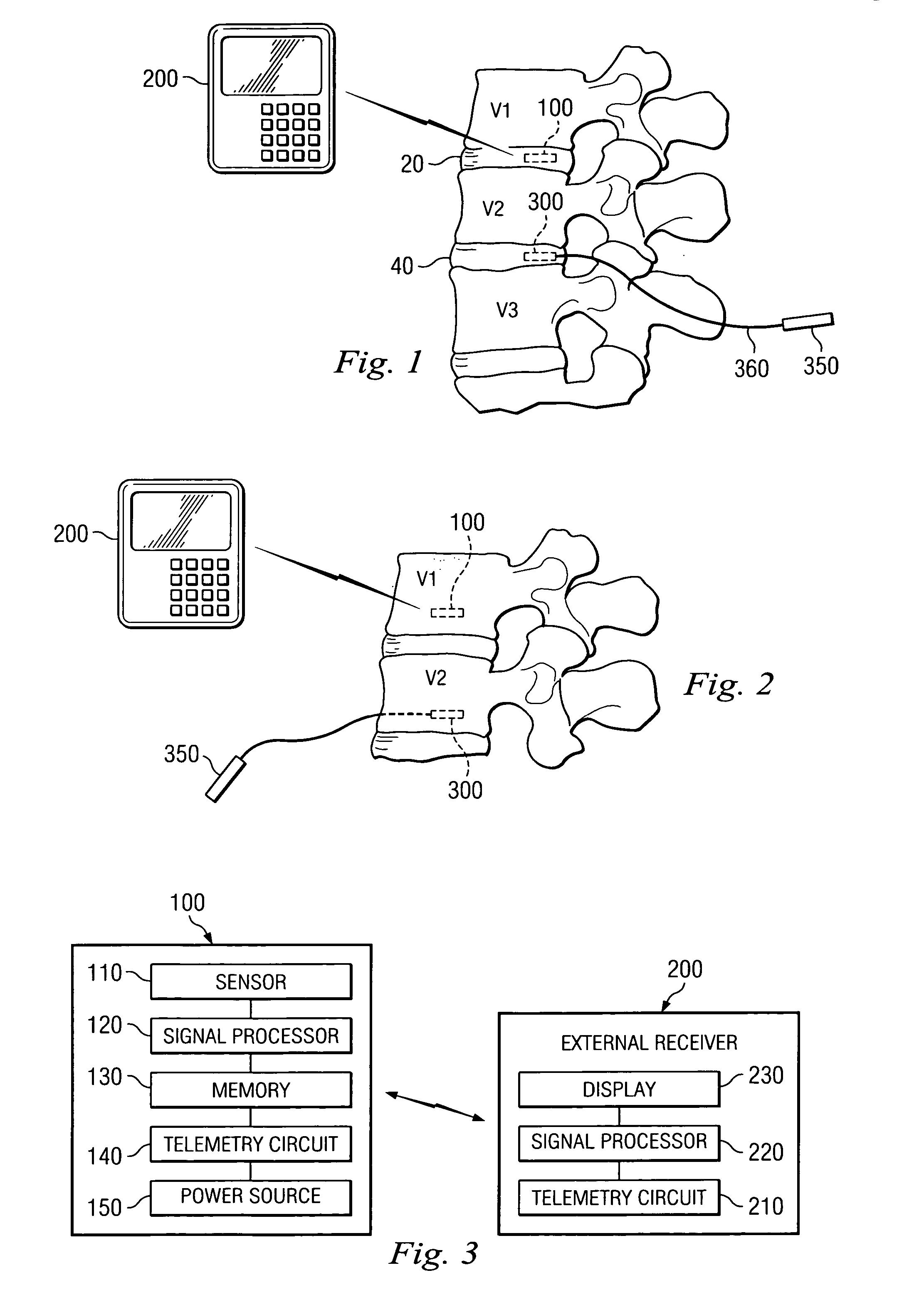
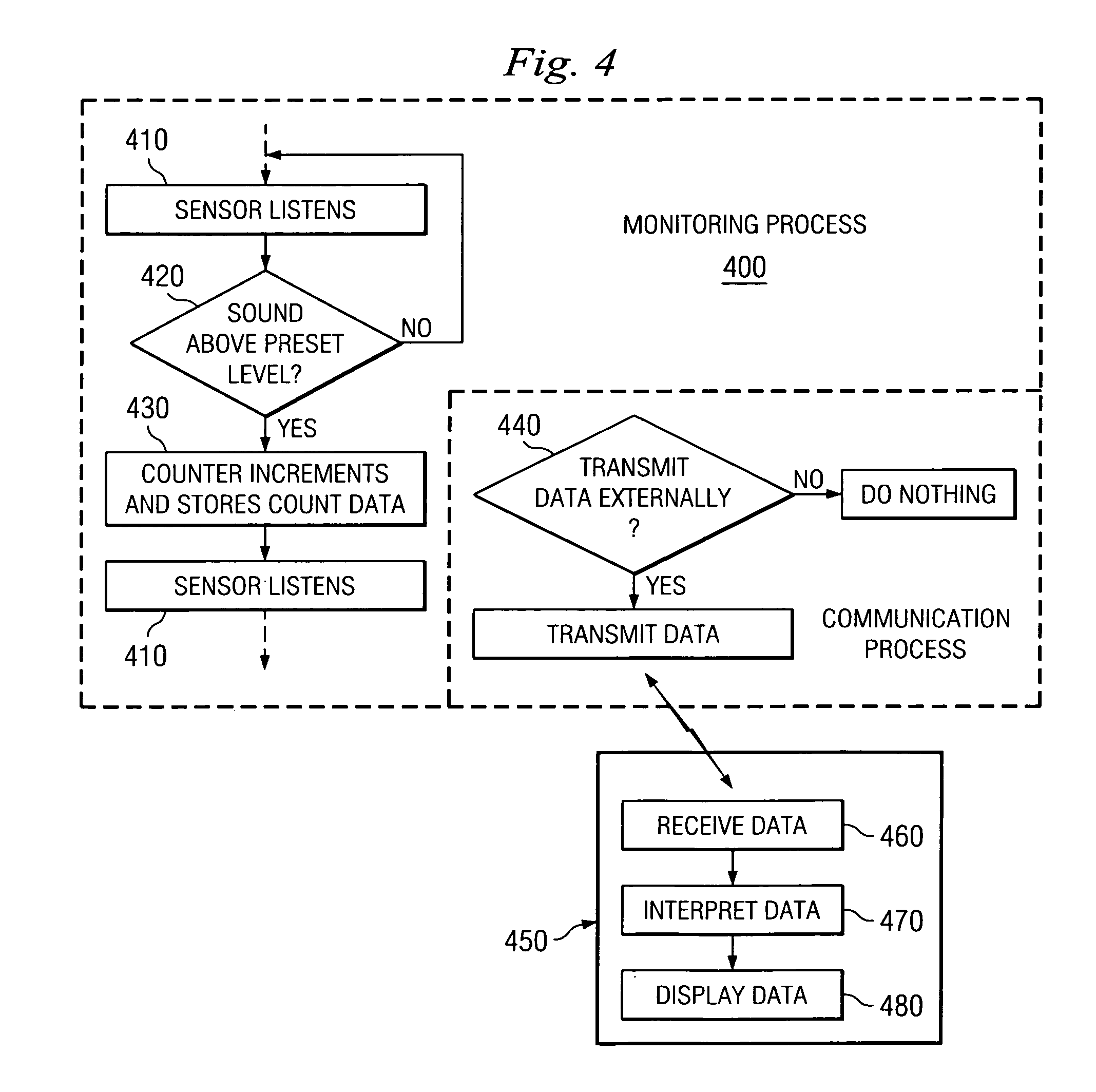
Dynamic treatment system and method of use
A system and method are provided for monitoring the condition of the skeletal system and adjusting a treatment device to provide appropriate treatment in response to the sensed signal. More particularly, in one aspect the present invention is directed to a sensor for detecting changes at a spinal level and a dynamic treatment system adjustable in response to the detected changes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Anatomic vertebral cage
ActiveUS7674297B2Precise positioningMinimize back-outBone implantJoint implantsSpinal levelEngineering
A spinal fusion system includes a cage with a fillable volume and removable locking gate, thereby enabling the fillable volume to be packed with graft, biologic or other materials prior to the gate being closed and locked. In the preferred embodiment, the locking gate is positioned anteriorally, though lateral, posterior, and combinations thereof are also possible. The cage is preferably radiolucent, being composed of a carbon fiber, but with one or more radiopaque markers to provide a certain degree of visualization. Some or all of the walls of the cage may include superior and / or inferior surface features to enhance positioning and / or minimize back-out, and the posterior wall may be indented to prevent neurocompression. The sidewalls of the cage may further include a recessed face with nipple indents and locking fasteners. According to a system aspect of the invention, multiple cages are provided, each being shaped differently for use at different spinal levels. For example, the cage may be larger and more trapezoidally-pronounced for the L5-S1 levels, or smaller and less trapezoidally pronounced for the T and L2 levels. The system may further including an implant introducer instrument geometrically matched to the cage, and the matched implant introducer instruments and cages may be color-coded to expedite the procedure.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
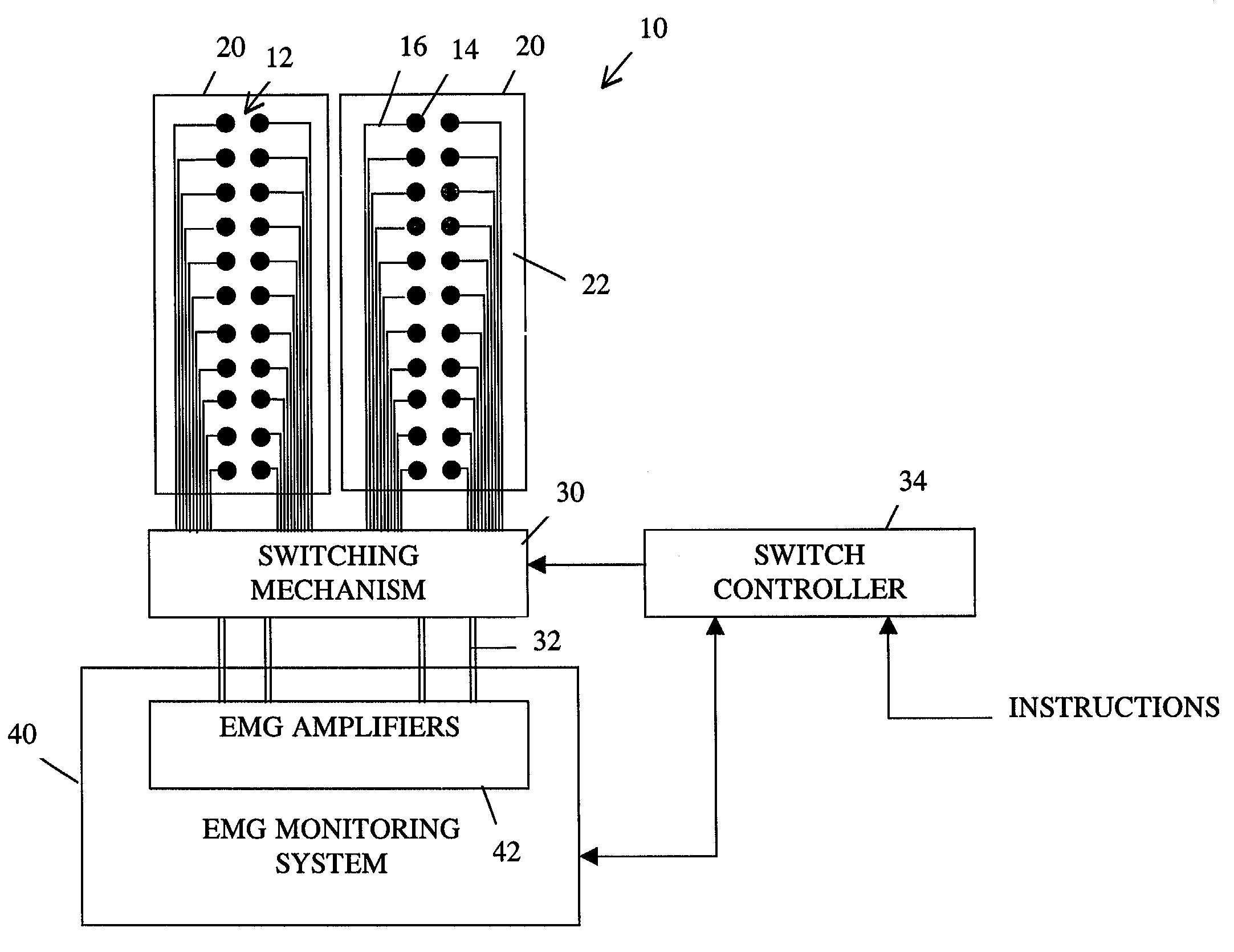
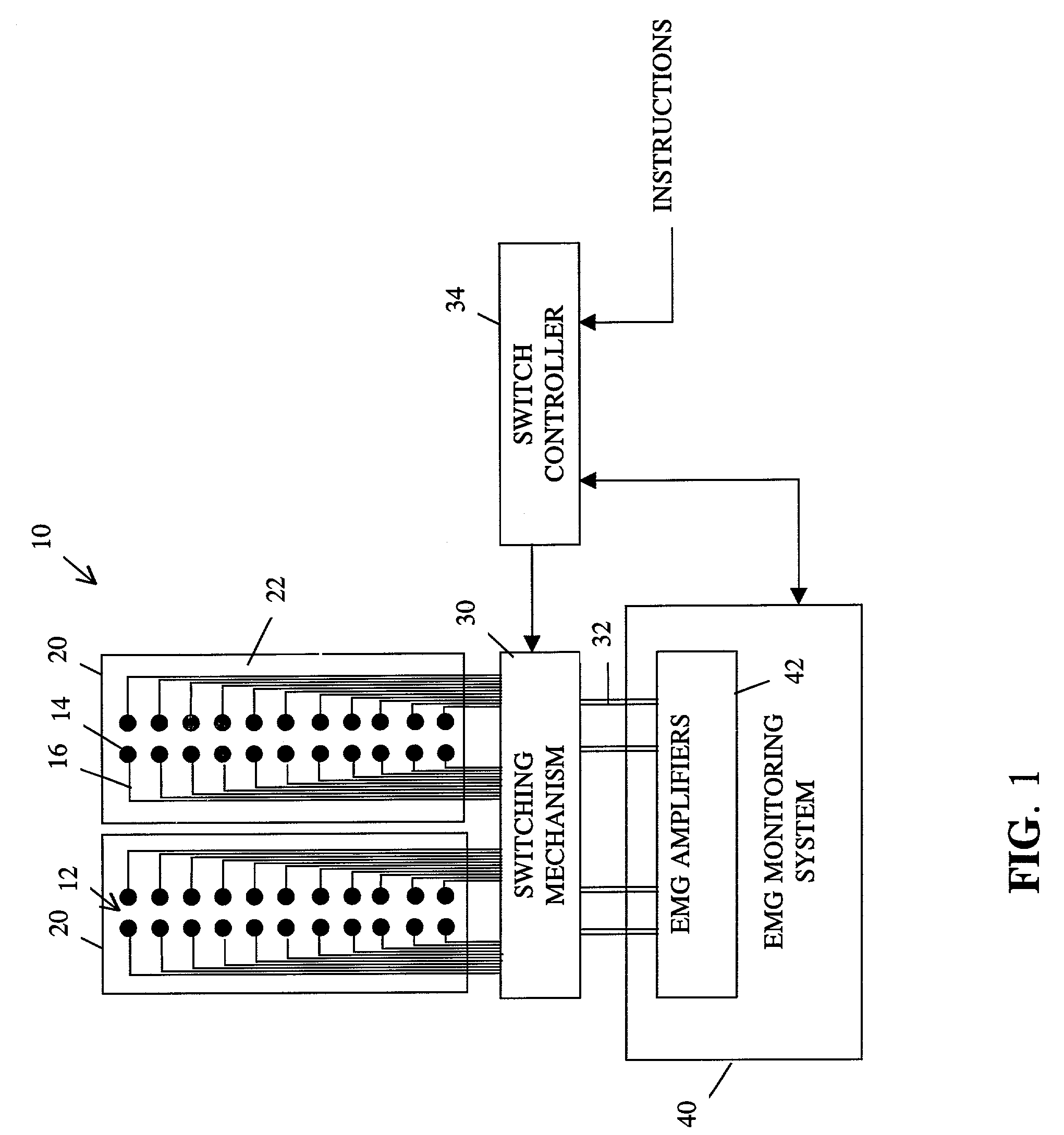
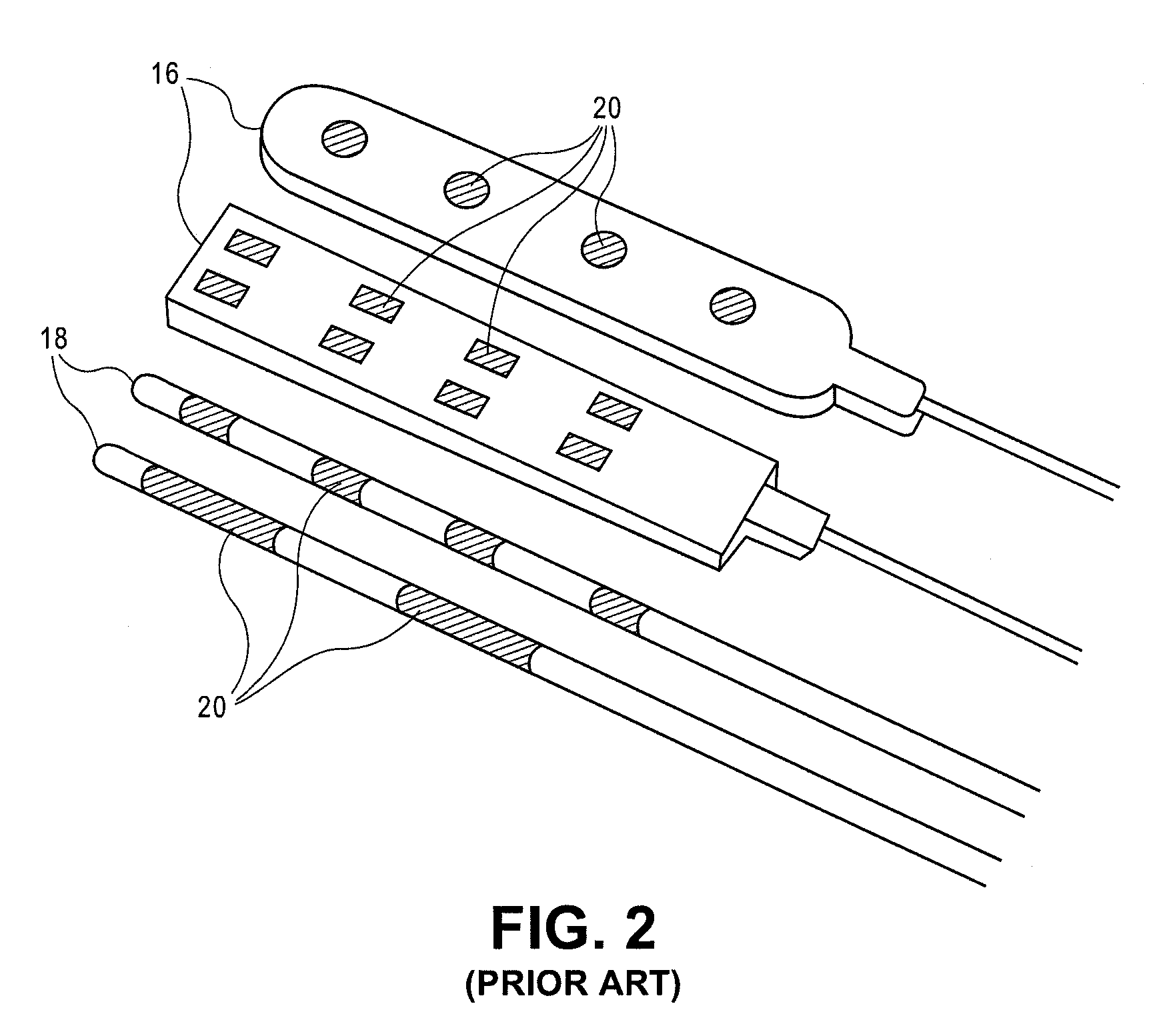
Apparatus for routing electromyography signals
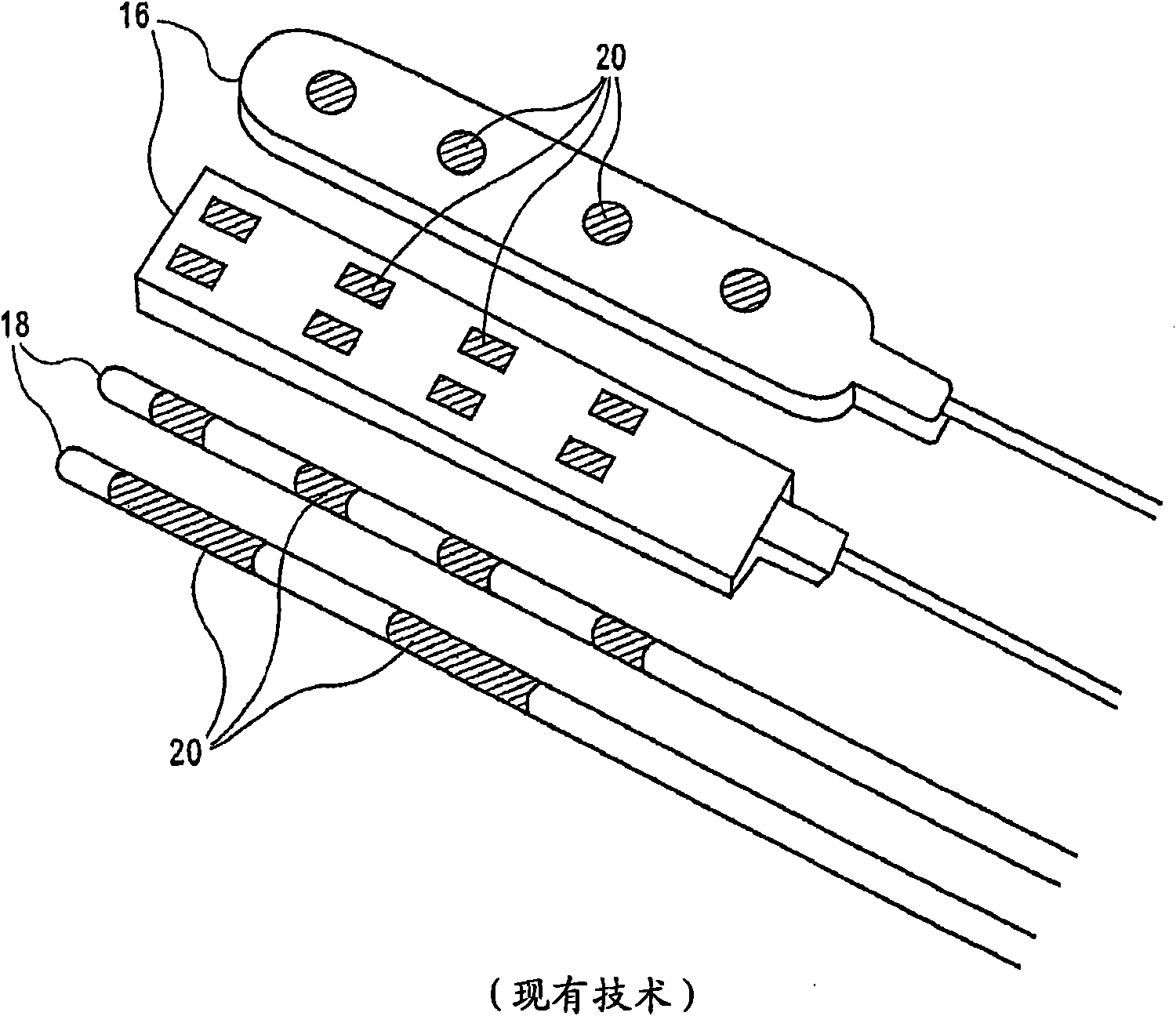
An EMG monitoring system includes a matrix of detection electrode arrays that is positioned on the patient along his or her spine. The arrays are electrically connected through a switching mechanism to EMG amplifiers that are included in conventional monitoring instrumentation. A switch controller operates the switches to provide signals to the EMG amplifiers from selected sets of detection electrode arrays. The controller controls the switches to provide signals simultaneously to each EMG amplifier. If the monitoring instrumentation includes four EMG amplifiers, the matrix of electrode arrays and the switching mechanism may be used to take simultaneous measurements at two different spinal levels. If additional EMG amplifiers are included, simultaneous measurements at additional spinal levels may also be made. The matrix may also include redundant arrays and / or electrodes, such that the clinician can select the sets of electrodes that conform to the size of the patient.
Owner:FASSTECH
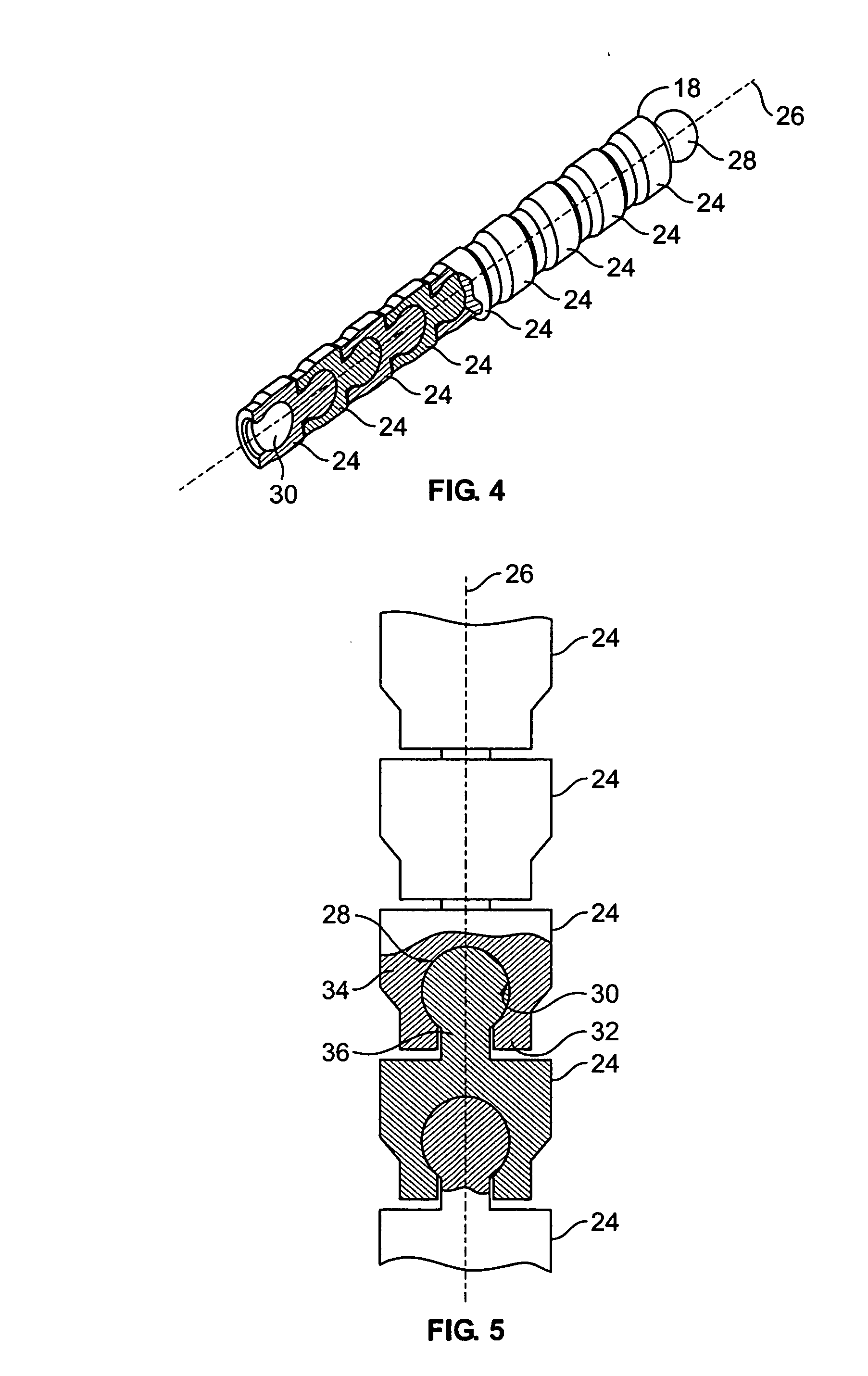
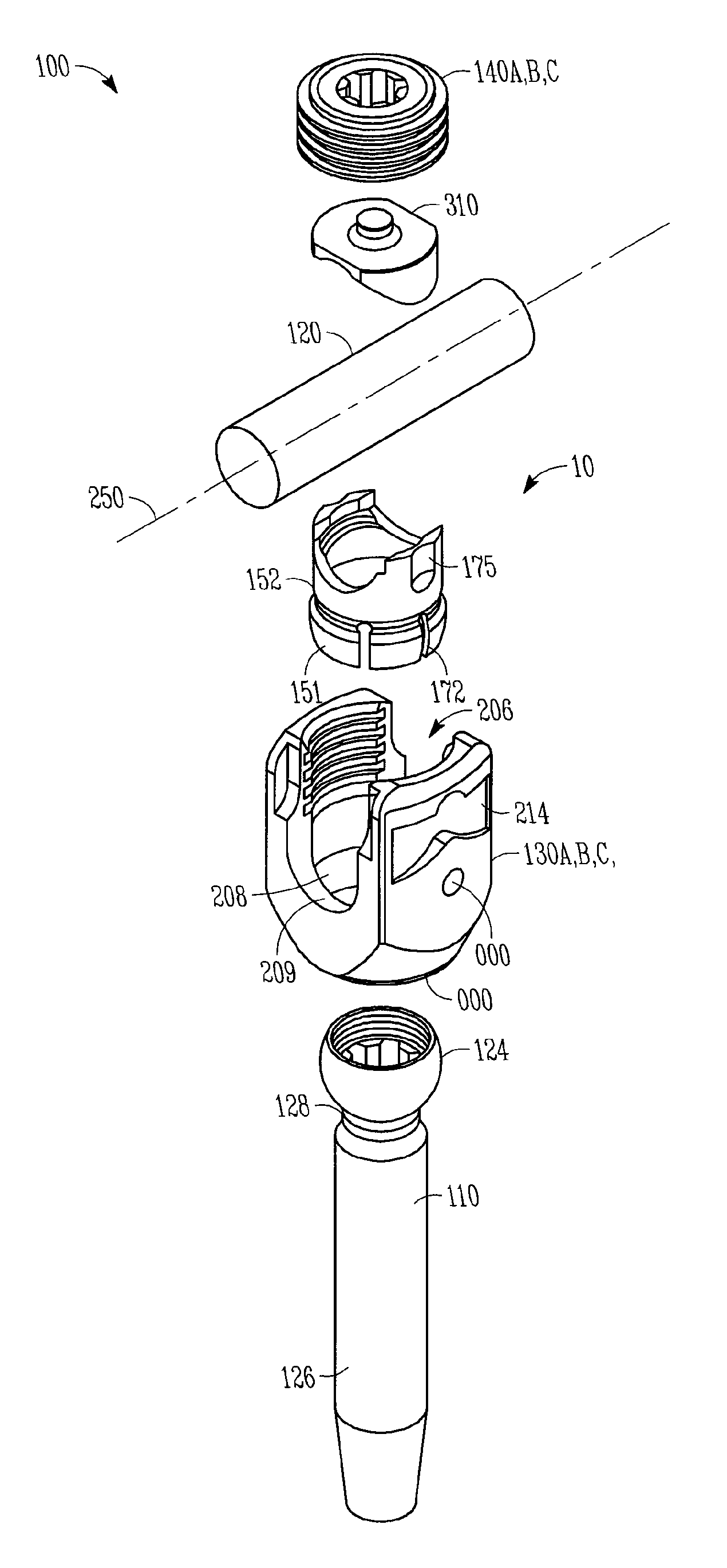
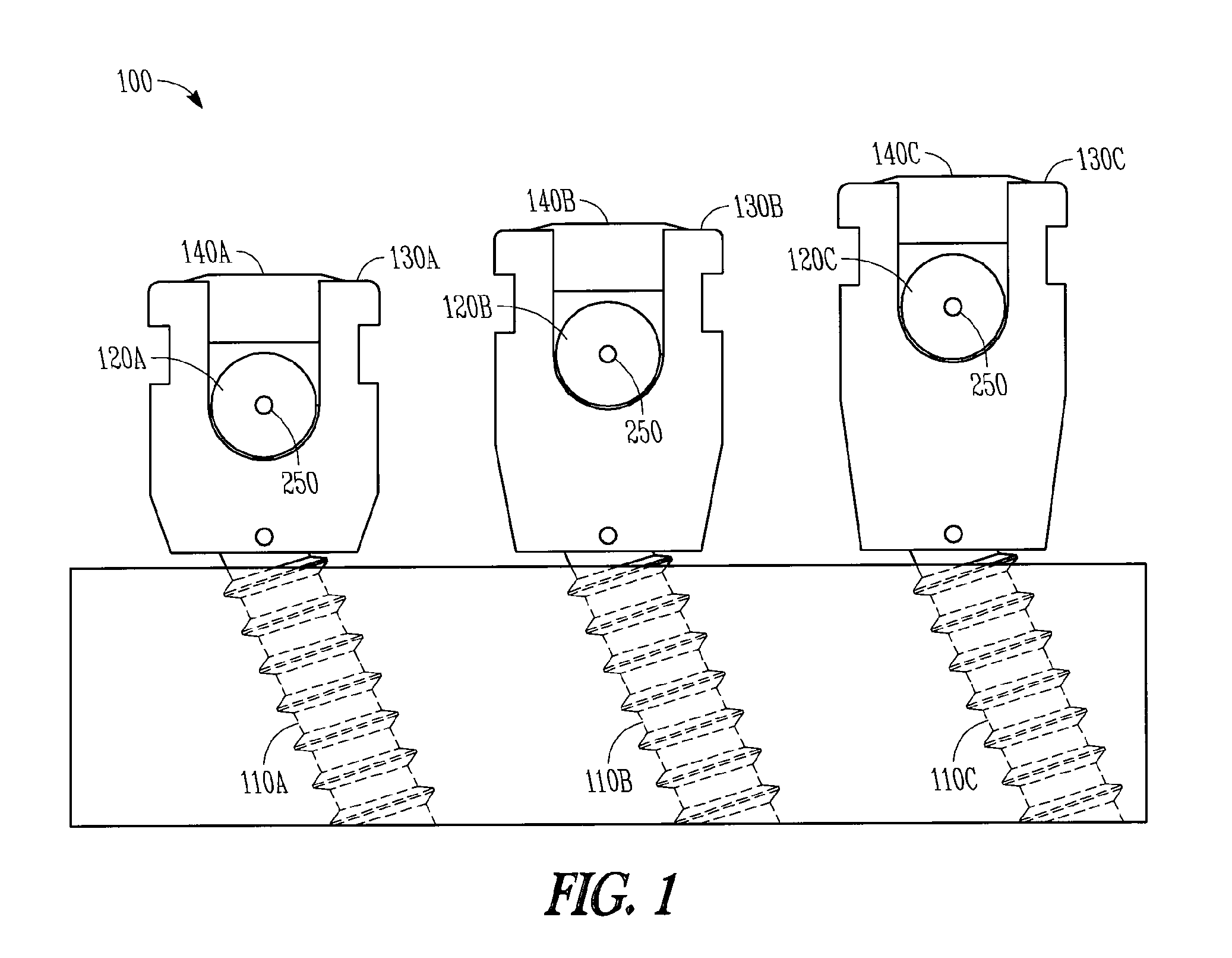
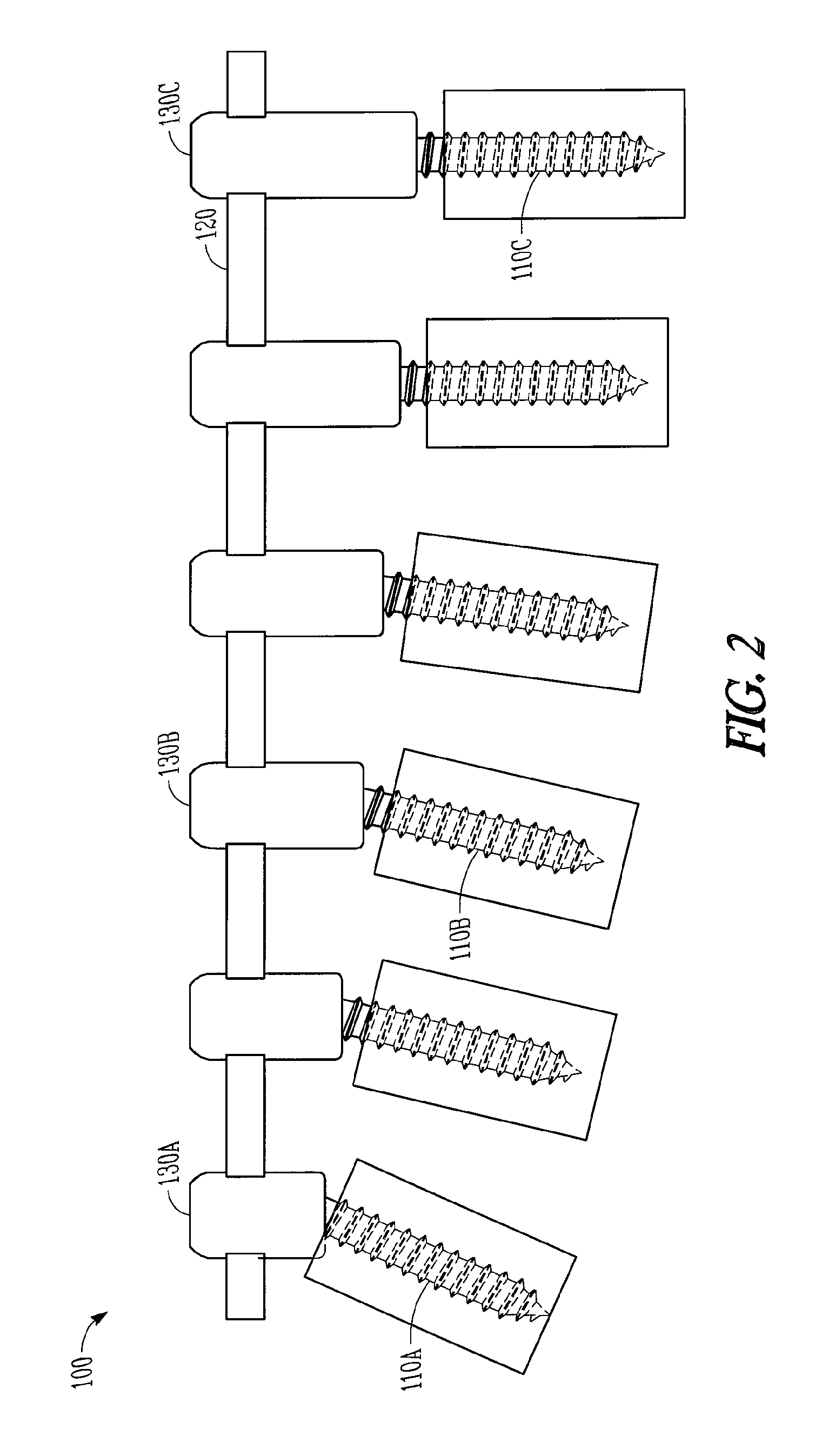
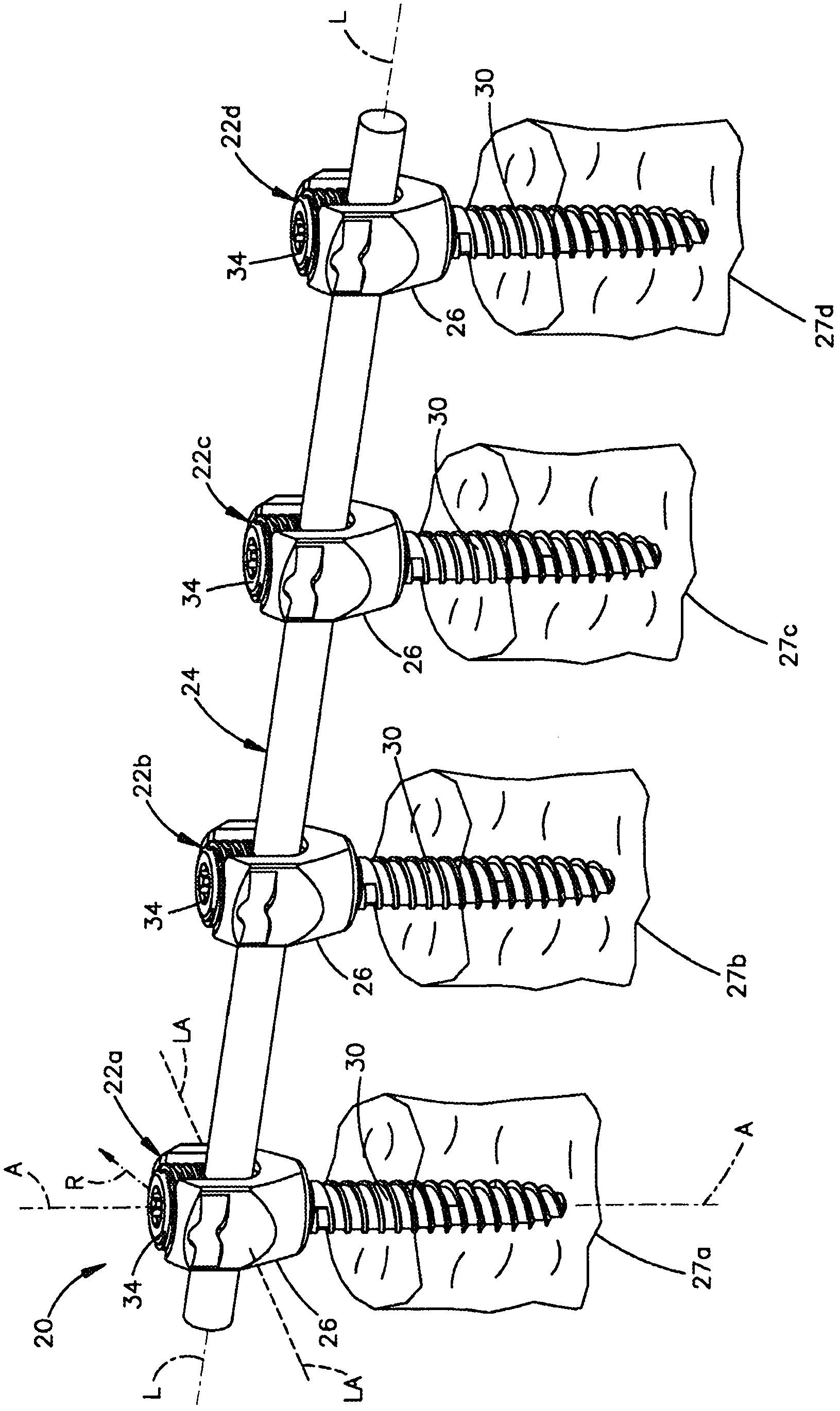
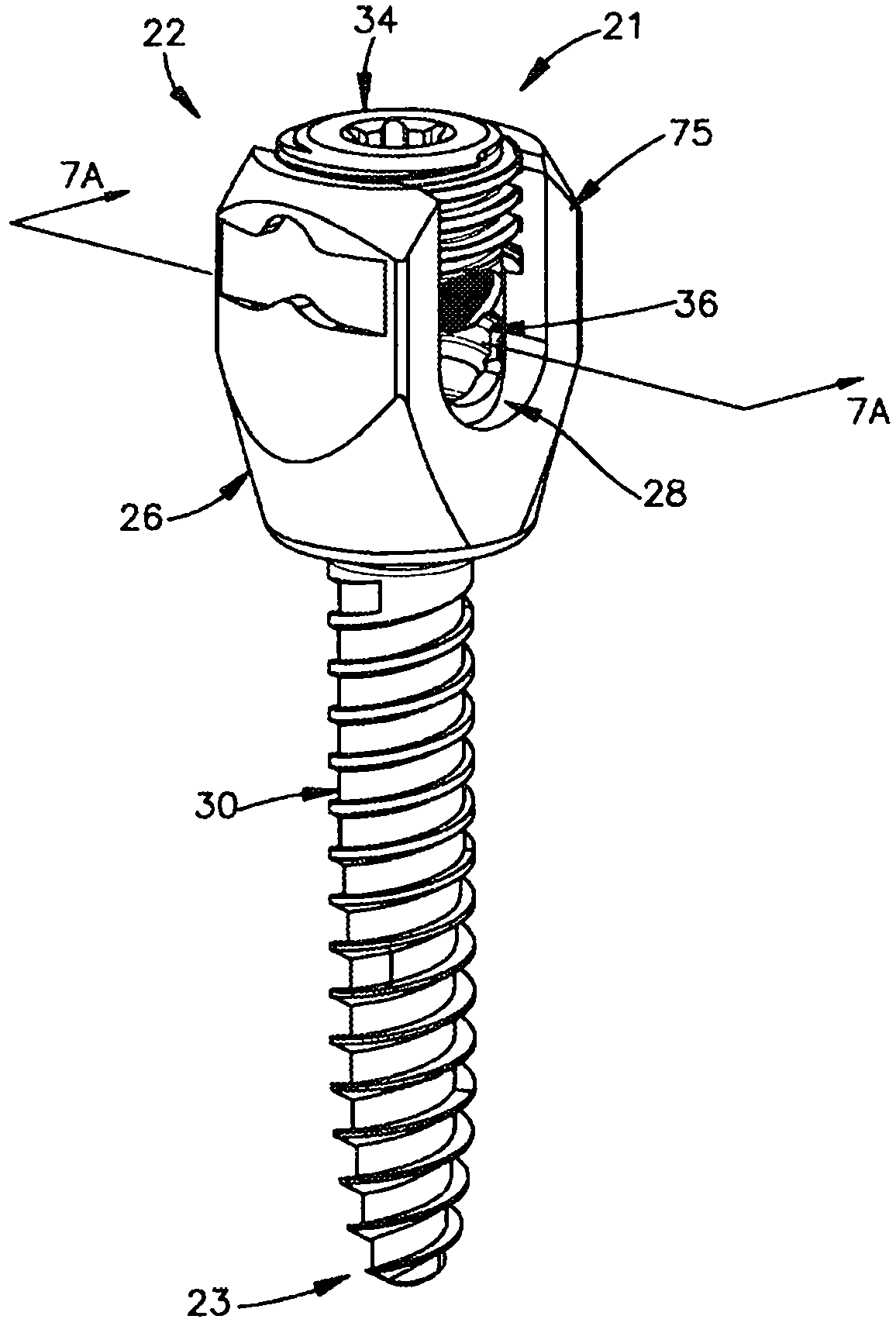
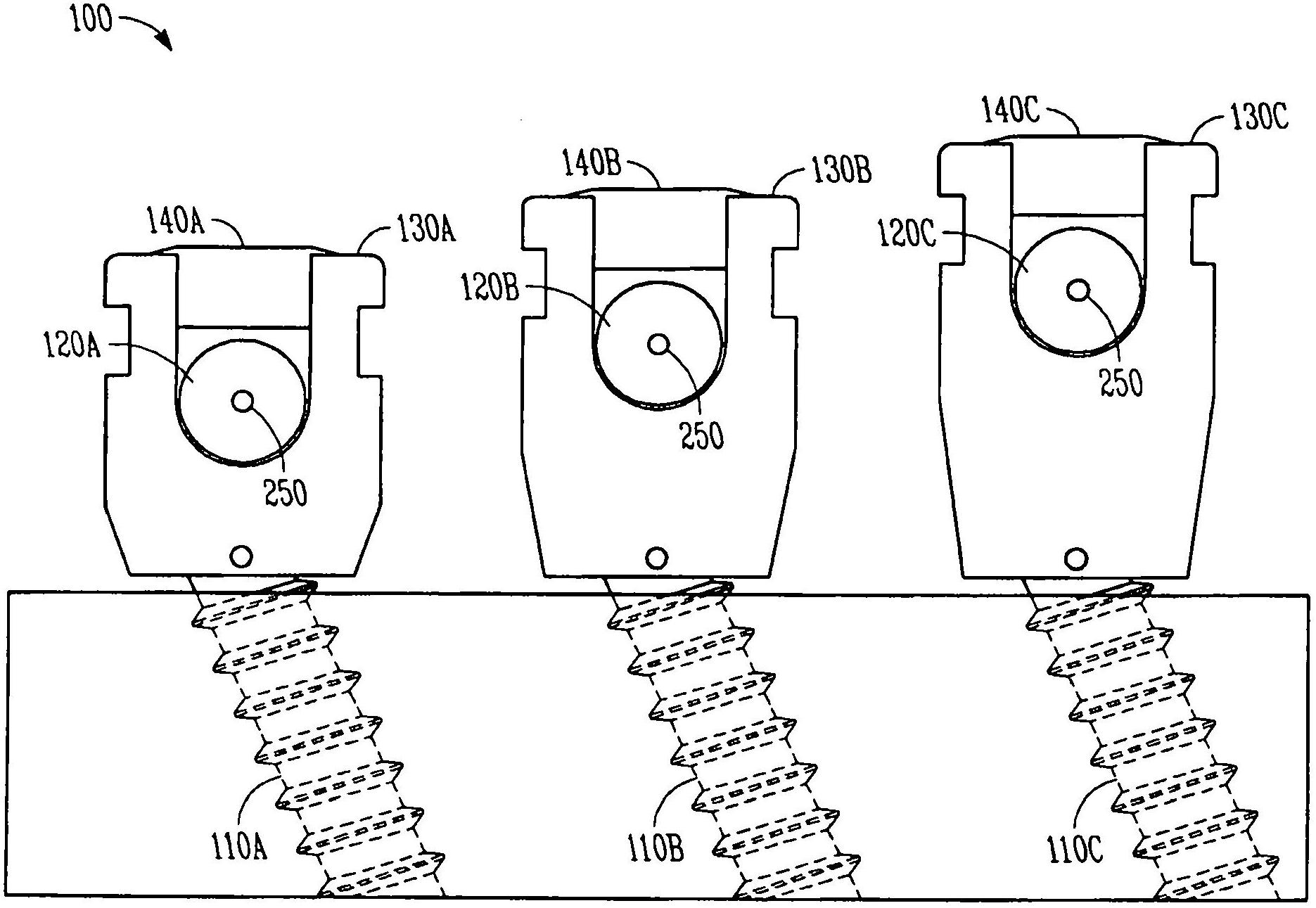
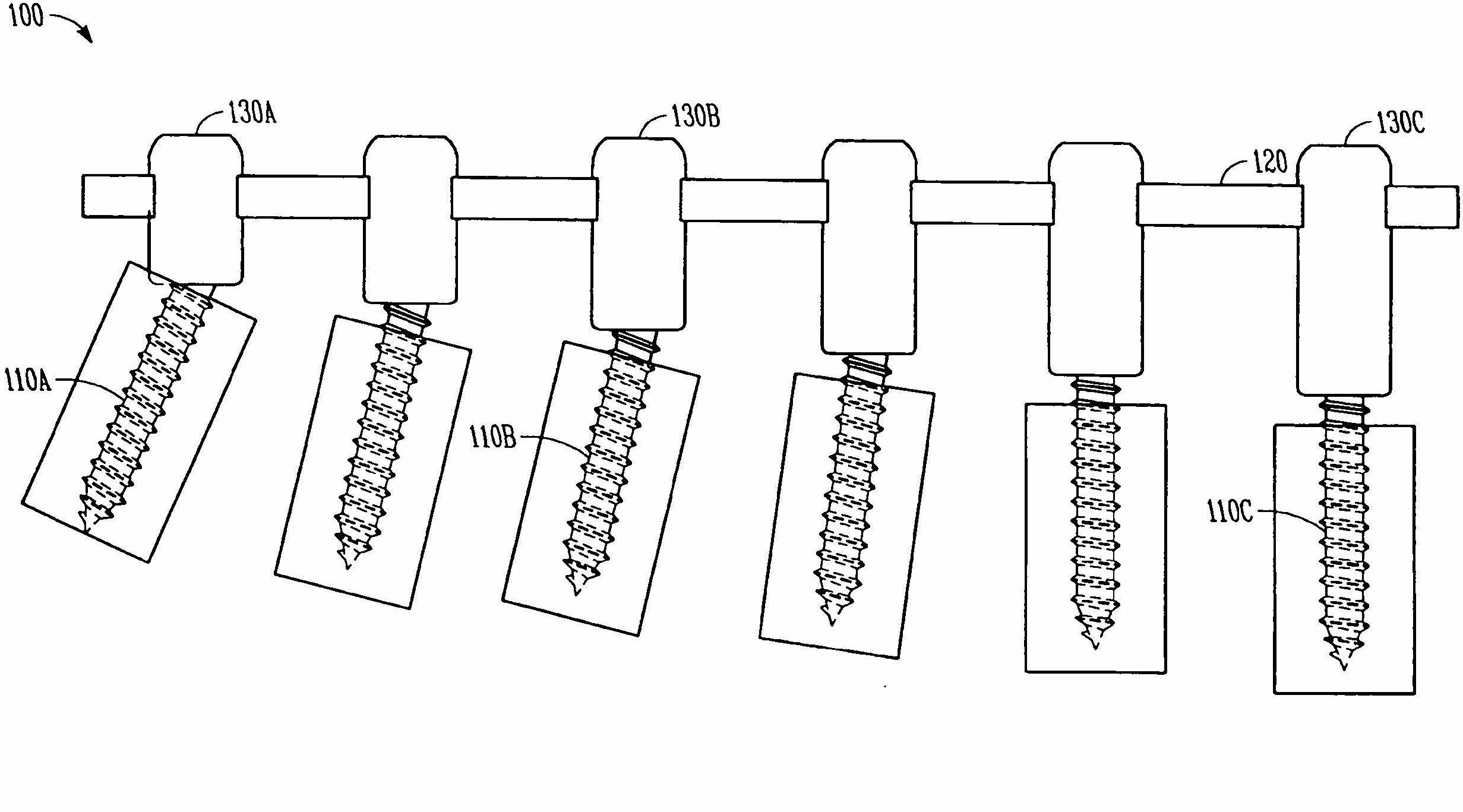
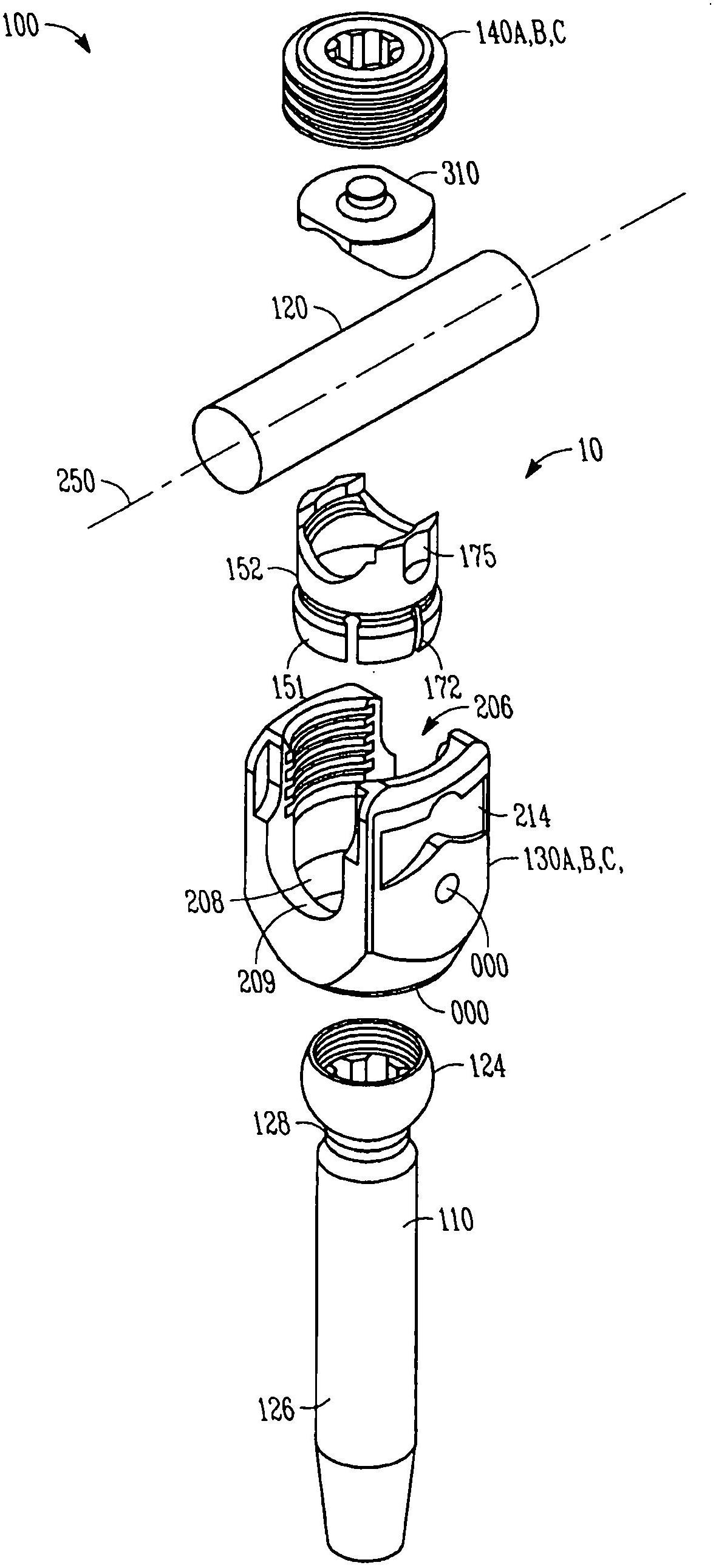
Variable offset spine fixation system and method
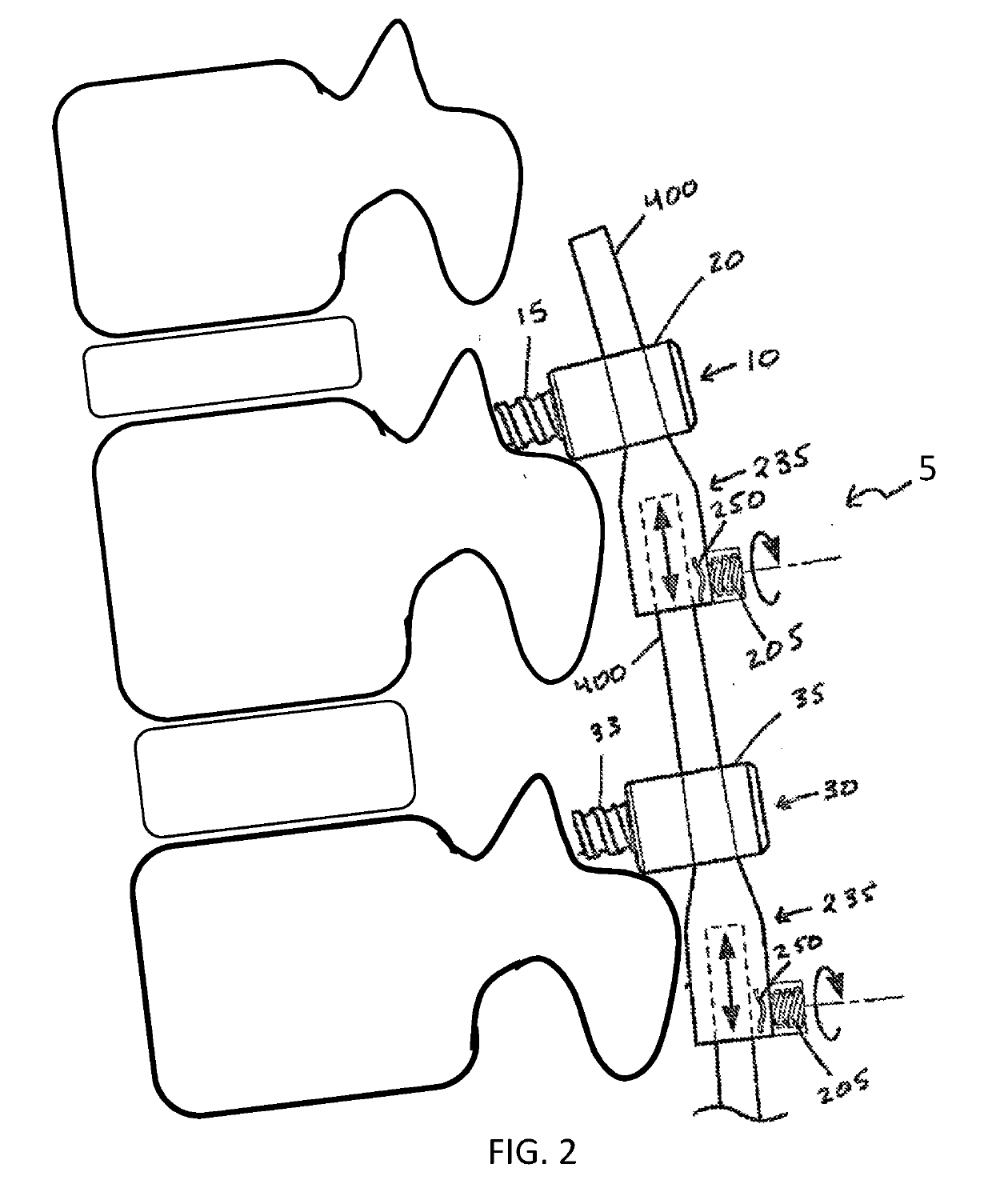
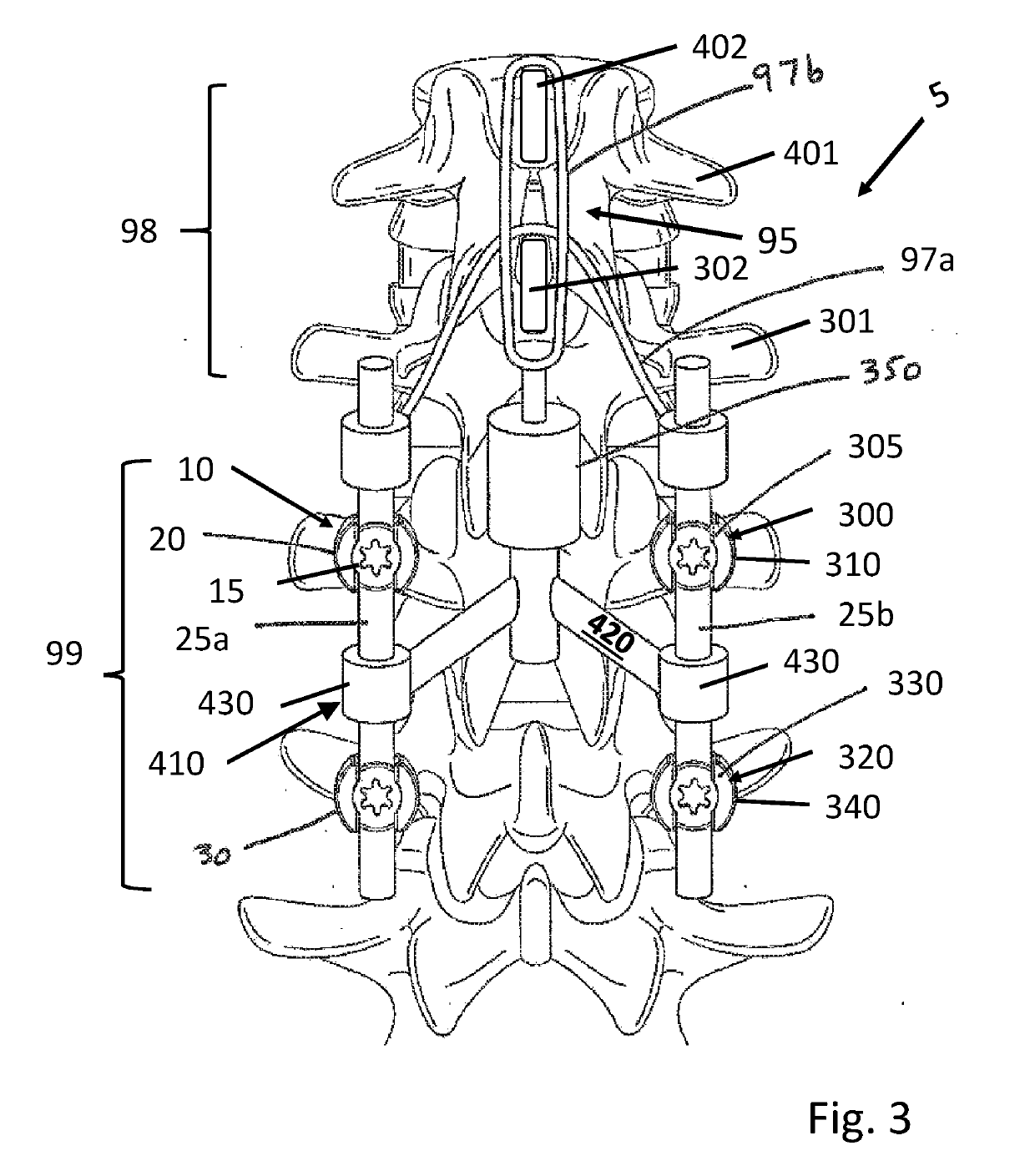
A minimally invasive system and method for coupling a spinal rod to a plurality of bone anchors implanted into a plurality of vertebral bodies. A plurality of bottom-loading polyaxial anchor seat assemblies having different vertical heights are chosen to pop over the heads of the implanted bone anchors and a spinal rod is more easily introduced and secured to the bone anchors. The variety of different heights that characterize the plurality of polyaxial anchor seat assemblies allows a surgeon to intraoperatively choose the appropriate offset for a particular spinal level during spinal corrections.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Implantable orthopedic device component selection instrument and methods
ActiveUS20080292161A1Easy to measureInternal osteosythesisCharacter and pattern recognitionSpinal levelBearing surface
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of artificial facet joints at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing an artificial cephalad facet joint including a fixation measurement element and a support arm element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of an artificial cephalad facet joint for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a measurement tool for installing a caudad facet joint including a stem element and a trial caudad bearing surface element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a caudad facet joint for implantation in a patient. Yet another aspect is a measurement tool holder including a measurement surface connected to a holder element. This tool holder assists in determining the measurements obtained with the caudad facet joint measurement tool.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Grouped leads for spinal stimulation
InactiveUS20080147156A1Effective treatment of painReduces deleterious side effectSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesAnatomical structuresSpinal column
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various target locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. In some embodiments, the devices, systems and methods stimulate the various spinal levels at specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root DR or more specifically the dorsal root ganglion DRG. Optionally, the devices, systems and methods may be used to stimulate a single DRG or other anatomies.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Measurement and trialing system and methods for orthopedic device component selection
InactiveUS20080287959A1Easy to measureParticular utilityNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal implantsBody contactProsthesis
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of artificial facet joints at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing an artificial cephalad facet joint, the tool including a trial marker having a portion configured to be placed in a hole; and a trial body comprising a bore therethrough for slidaby receiving a portion of the trial marker. In some embodiments, the trial body further comprises an arm extending generally radially outward from the bore and configured to contact an opposing spinal prosthesis component. The trial body may further comprise a lower portion configured to be placed in the hole. The trial marker and the trial body are configured to cooperate to indicate a relative positioning between them. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of an artificial cephalad facet joint for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a method of using a spinal prosthesis component selection tool comprising accessing a target anatomy, creating a hole within a portion of the target anatomy, inserting a marker rod of a component selection tool in the hole, slidably adjusting a trial stem body along the marker rod until the trial body contacts an opposing spinal prosthesis component, determining the relative position between the trial body and marker rod, and selecting a component for implantation into the target anatomy based on the determined relative position.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Facet joint prosthesis measurement and implant tools
ActiveUS20050235508A1Easy to measureInternal osteosythesisMeasurement devicesFacet joint prosthesisSpinal level
The present invention provides tools and methods designed to aid in the placement of facet joint prostheses at virtually all spinal levels. One aspect of the present invention is a measurement tool for installing a cephalad facet joint prosthesis including a fixation measurement element and a support arm element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a cephalad facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Another aspect is a measurement tool for installing a caudal facet joint prosthesis including a stem element and a trial caudal bearing surface element. This measurement tool assists in the selection and / or configuration of a caudal facet joint prosthesis for implantation in a patient. Yet another aspect is a measurement tool holder including a measurement surface connected to a holder element. This tool holder assists in determining the measurements obtained with the caudal facet joint prosthesis measurement tool.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Dynamic treatment system and method of use
A system and method are provided for monitoring the condition of the skeletal system and adjusting a treatment device to provide appropriate treatment in response to the sensed signal. More particularly, in one aspect the present invention is directed to a sensor for detecting changes at a spinal level and a dynamic treatment system adjustable in response to the detected changes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Revision connector for spinal constructs
An extender system is configured to couple a vertebral bone anchor that has been previously implanted in a vertebra, or is newly implantable in a vertebra, to an adjacent bone, which can be an additional spinal level or an occiput, for example. The extender system includes an extension member having a body and an engagement member coupled to the body. The extension member defines an aperture extending through the engagement member. A screw is configured to attach the extension member to the vertebral bone anchor. The extension member can be fastened to the adjacent bone.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Delivery devices, systems and methods for stimulating nerve tissue on multiple spinal levels
ActiveUS20150165193A1Effectively pain symptomDeleterious side effectSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsSpinal columnRadiology
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. By stimulating multiple levels of the spinal column with the use of a single device, a single access path is created to an implantable pulse generator (IPG) rather than individual access paths for each lead at each spinal level to an IPG. By reducing the number of pathways, the procedure complexity, time and recovery are reduced. In addition, some embodiments provide additional specificity within each targeted level, such as selective stimulation of specific tissue, such as the dorsal root ganglion.
Owner:TC1 LLC
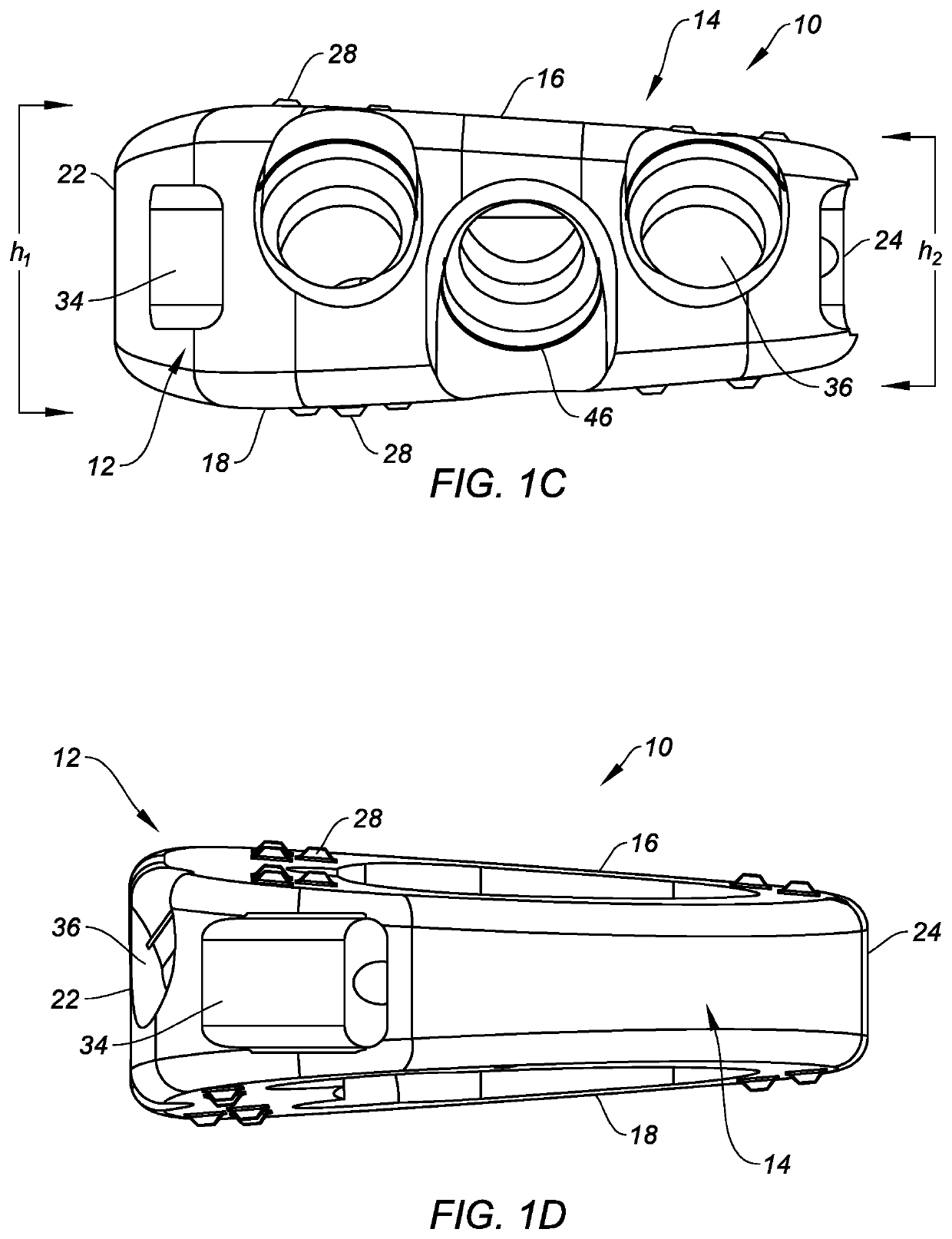
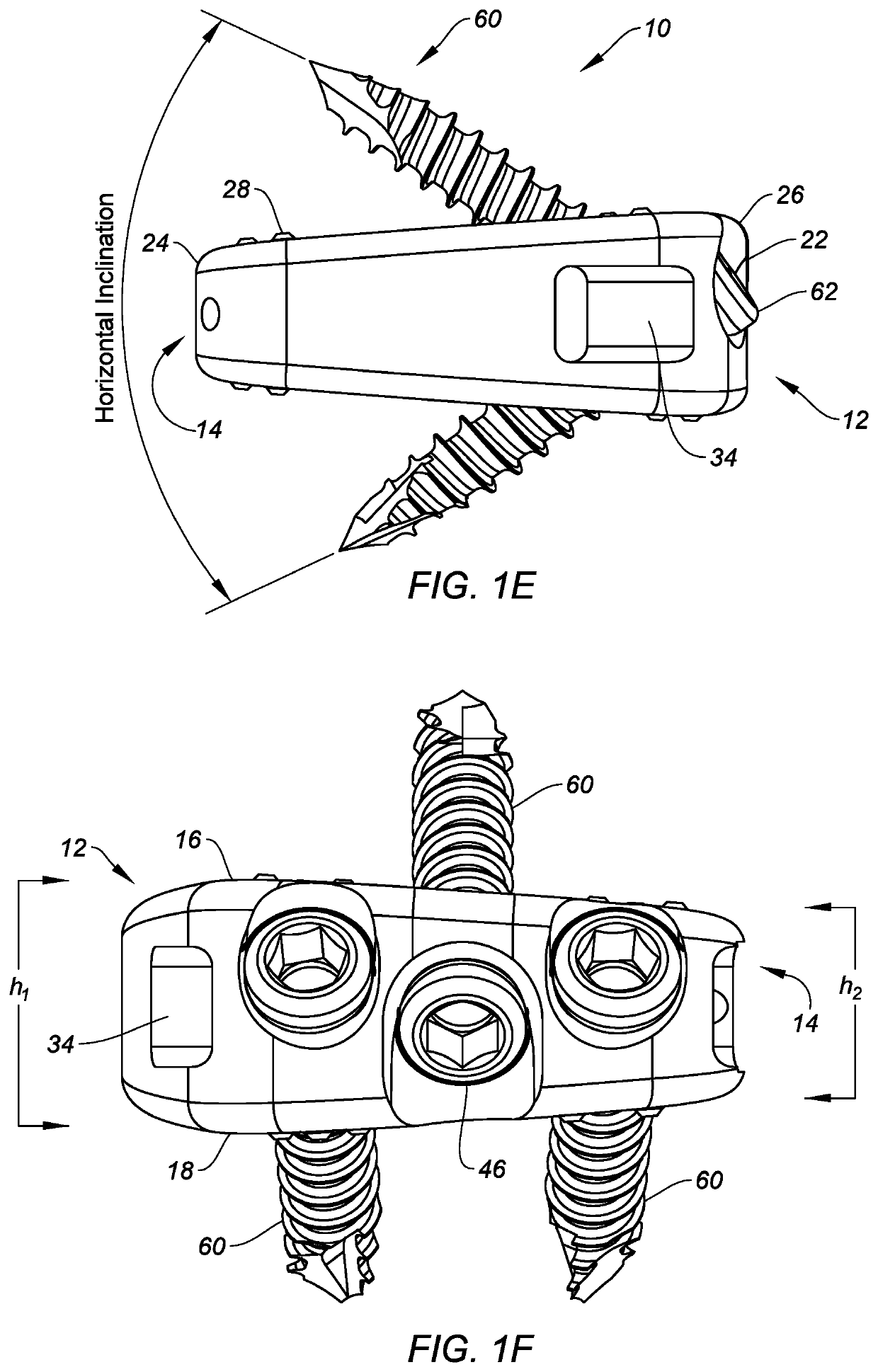
Spinal implants configured for tissue sparing angle of insertion and related methods
ActiveUS20200261242A1Easy to integrateEasy accessJoint implantsSpinal implantsSpinal columnSpinal level
Spinal implants that are configured for a minimally invasive approach to a patient's intervertebral disc space, optimized to avoid blood vessels and nervous tissue, maximizing endplate coverage and promoting sagittal balance, are provided. Insertion and fixation can be accomplished through a narrow access window, thereby allowing better access to more spinal levels while being less invasive than other approaches. The spinal implants may facilitate fusion, and include visualization features to assist in the implantation and verify proper placement and vary segmental angle of lordosis. Methods of implanting the spinal implants to treat a patient's spine are also disclosed.
Owner:SILONY SPINE CORP
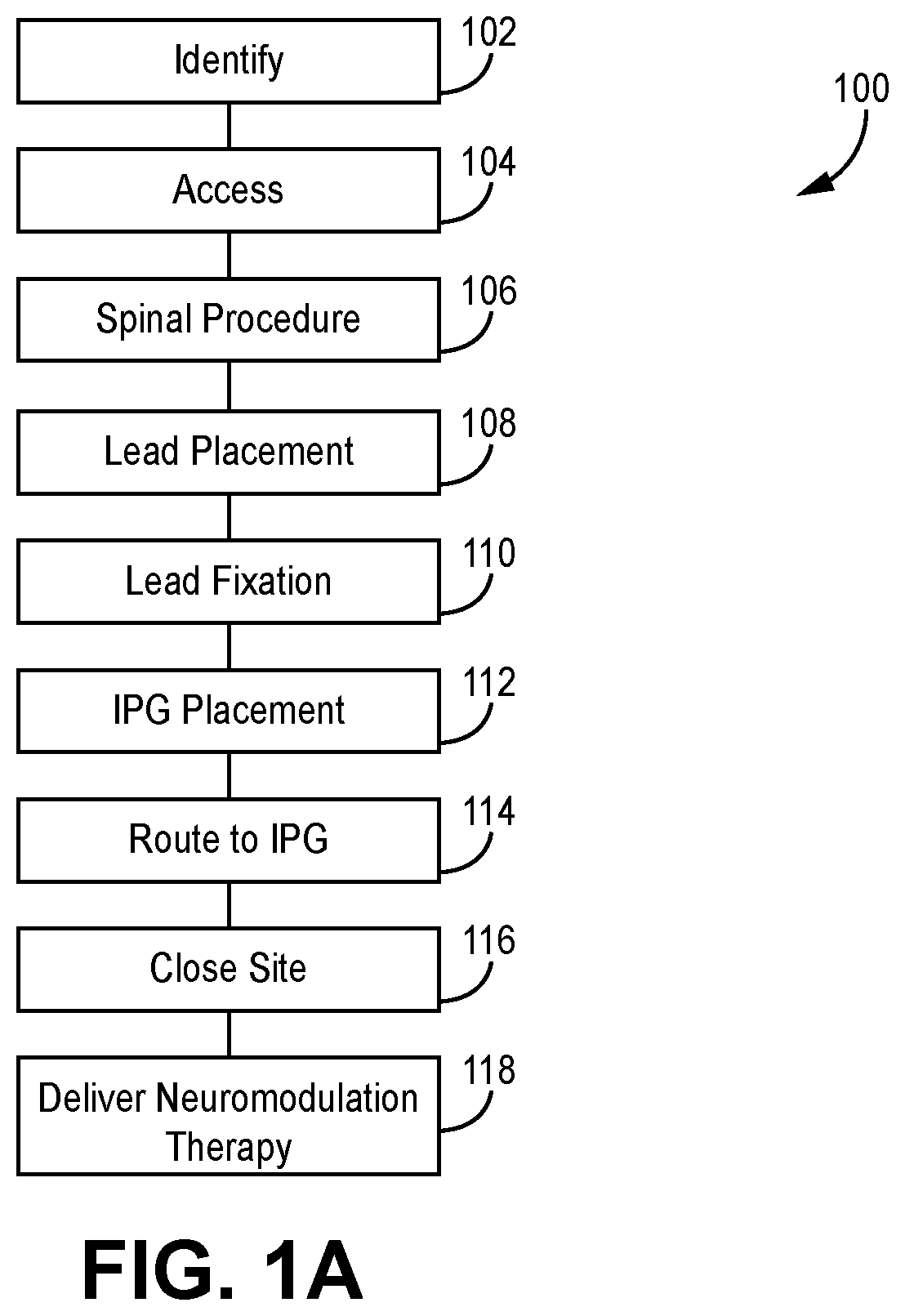
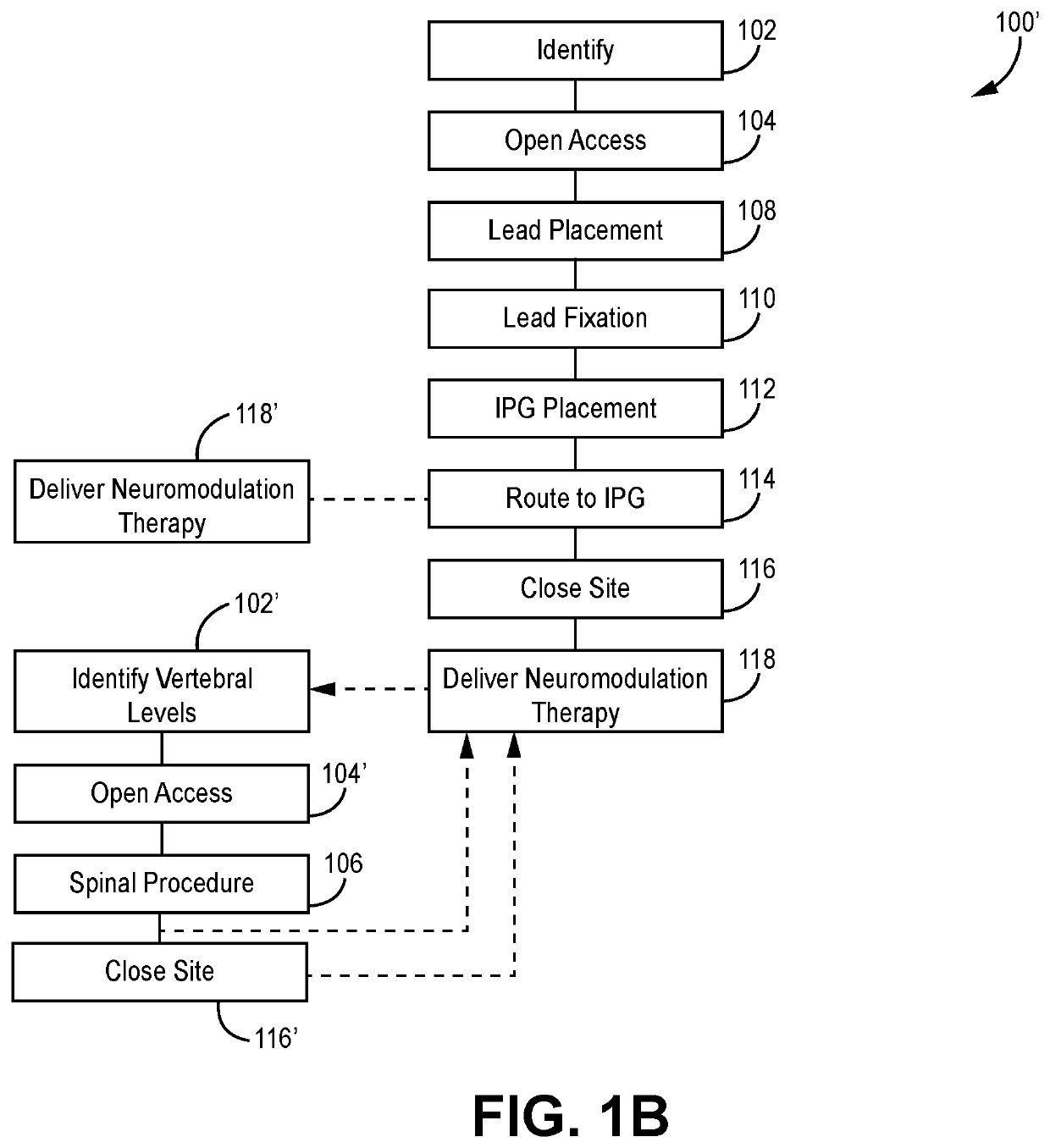
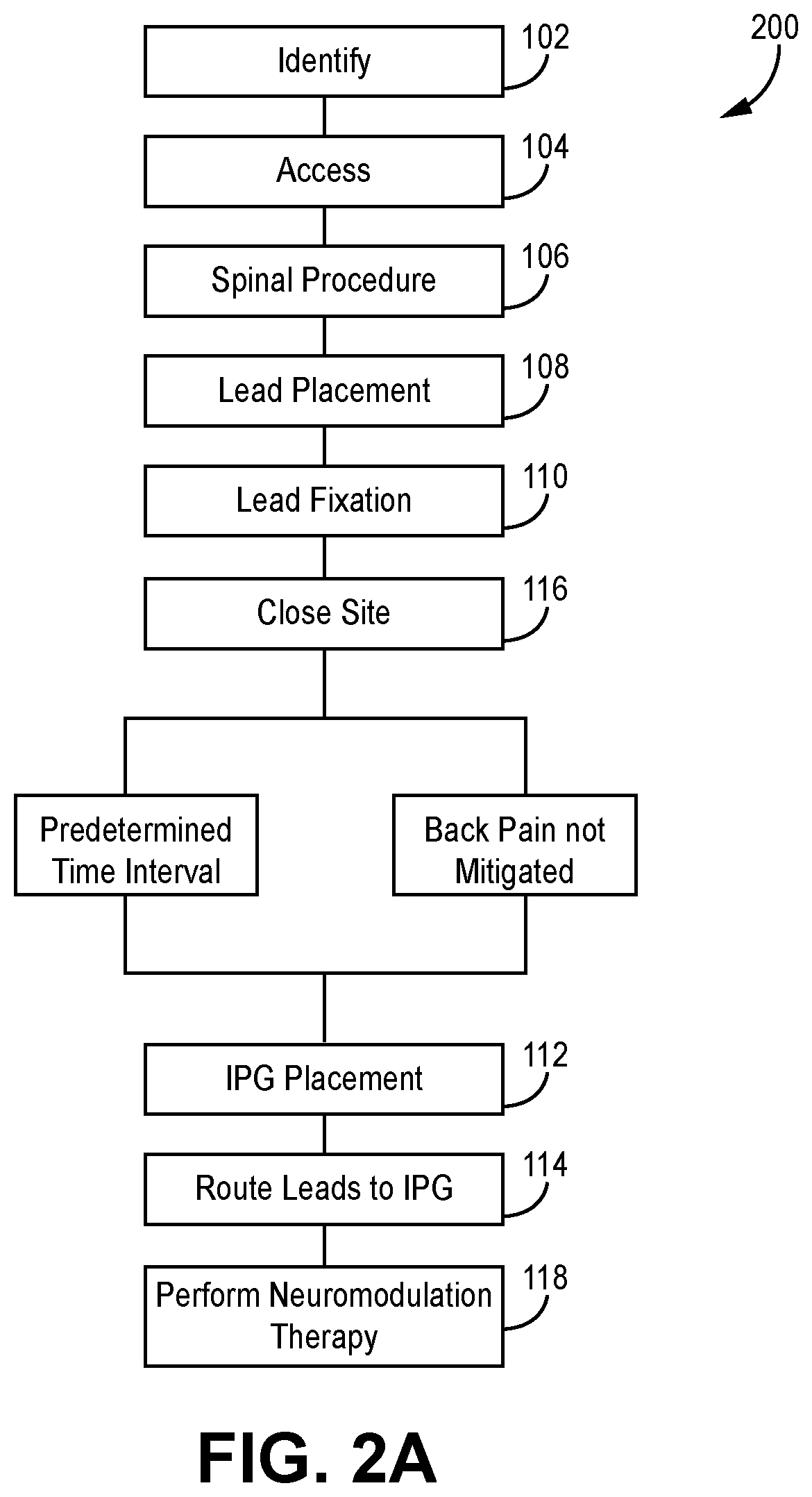
Methods and systems for implanting a neuromodulation system at a surgically open spinal treatment site
The present invention provides a single surgical method, procedure and / or system that creates open visual and physical access to an identified spinal treatment site that initially comprises spinal levels to be treated, wherein the spinal levels comprise at least one dorsal root ganglion. A spinal treatment procedure is performed generally in combination with implantation of a neuromodulation system that may comprise placement of electrical lead(s) on the at least one dorsal root ganglion, wherein each lead is in operative connection with a pulse generator that may also be implanted during the surgical method. Electrical stimulation may be generated with the pulse generator through the electrical leads to the at least one dorsal root ganglion during and / or after the closure of the identified spinal treatment site.
Owner:SYNERFUSE INC
Spinal implants configured for tissue sparing angle of insertion and related methods
ActiveUS10624757B2Easy to integrateEasy accessJoint implantsSpinal implantsSpinal columnSpinal level
Spinal implants that are configured for a minimally invasive approach to a patient's intervertebral disc space, optimized to avoid blood vessels and nervous tissue, maximizing endplate coverage and promoting sagittal balance, are provided. Insertion and fixation can be accomplished through a narrow access window, thereby allowing better access to more spinal levels while being less invasive than other approaches. The spinal implants may facilitate fusion, and include visualization features to assist in the implantation and verify proper placement and vary segmental angle of lordosis. Methods of implanting the spinal implants to treat a patient's spine are also disclosed.
Owner:CENTINEL SPINE LLC
Delivery devices, systems and methods for stimulating nerve tissue on multiple spinal levels
ActiveUS8983624B2Effectively pain symptomDeleterious side effectSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsSpinal columnRadiology
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. By stimulating multiple levels of the spinal column with the use of a single device, a single access path is created to an implantable pulse generator (IPG) rather than individual access paths for each lead at each spinal level to an IPG. By reducing the number of pathways, the procedure complexity, time and recovery are reduced. In addition, some embodiments provide additional specificity within each targeted level, such as selective stimulation of specific tissue, such as the dorsal root ganglion.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Spinal implants configured for tissue sparing angle of insertion and related methods
ActiveUS20160296343A1Easy to integrateMaximizing endplate coverageJoint implantsSpinal implantsMedicineSpinal level
Spinal implants that are configured for a minimally invasive approach to a patient's intervertebral disc space, optimized to avoid blood vessels and nervous tissue, maximizing endplate coverage and promoting sagittal balance, are provided. Insertion and fixation can be accomplished through a narrow access window, thereby allowing better access to more spinal levels while being less invasive than other approaches. The spinal implants may facilitate fusion, and include visualization features to assist in the implantation and verify proper placement and vary segmental angle of lordosis. Methods of implanting the spinal implants to treat a patient's spine are also disclosed.
Owner:CENTINEL SPINE LLC
Post-Operatively Adjustable Spinal Fixation Devices
A system for spinal fixation with a non-rigid portion at least one of the caudal or cephalad terminus. Various devices and techniques are described for transition from a rigid fixation construct to a less rigid support structure applied to a “soft zone” that helps share the stress created on the spinal levels caused by the fixed levels below. In some embodiments, the soft zone is provided by terminating the construct with one of a flexible tether or a dampening rod.
Owner:NUVASIVE
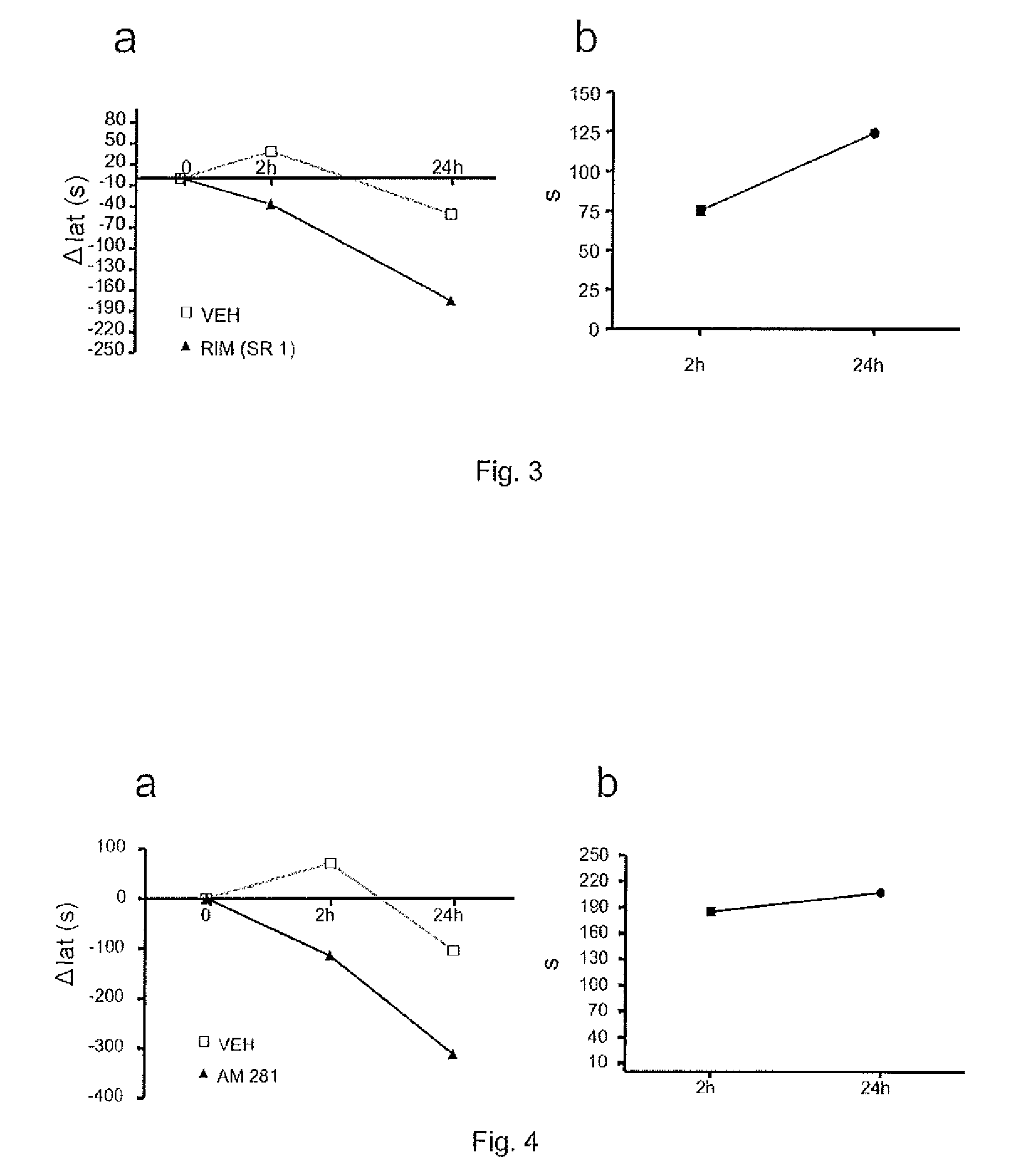
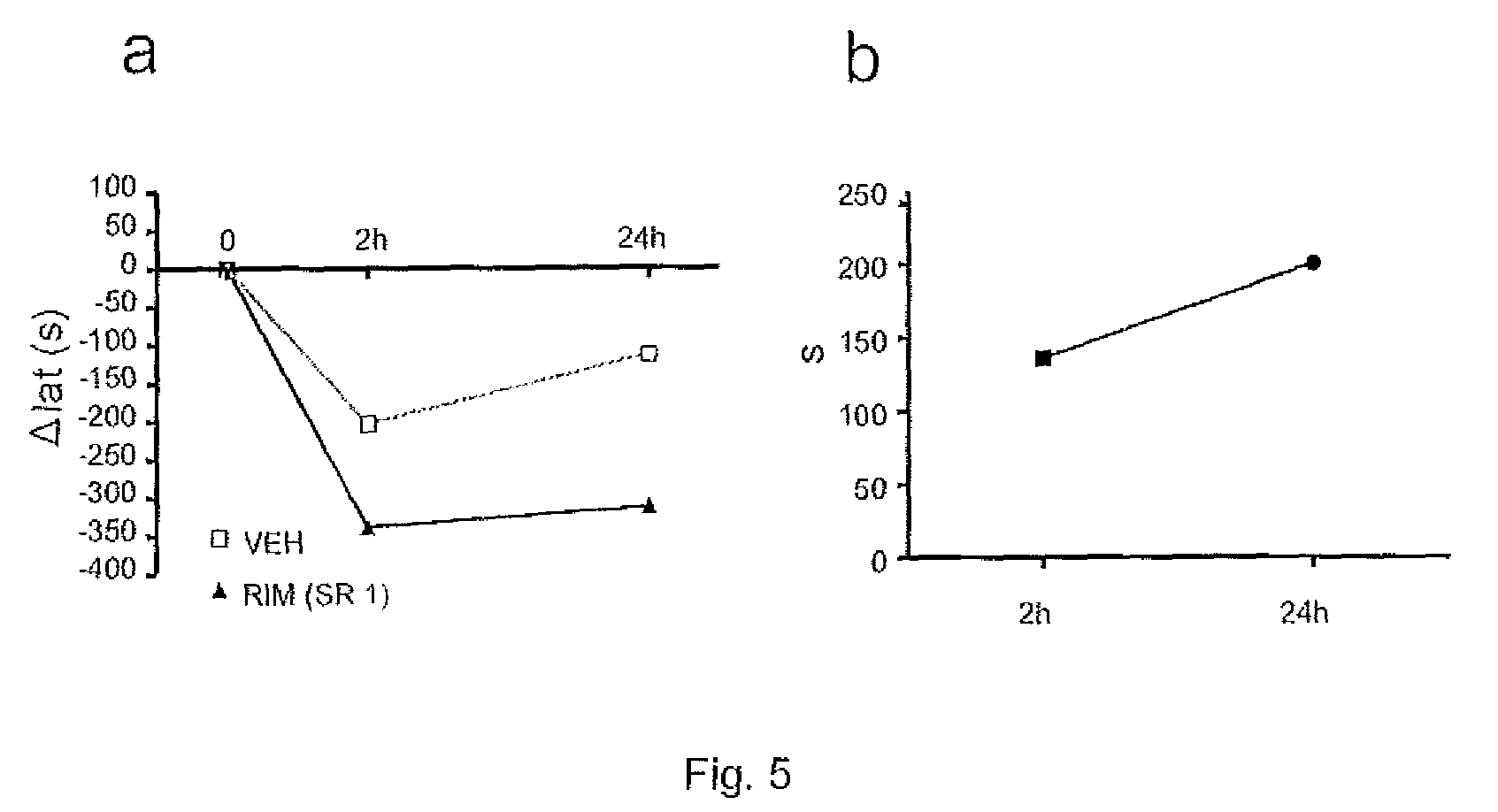
Use of CB1 antagonists and/or inverse agonists for the preparation of drugs that increase motor neuron excitability
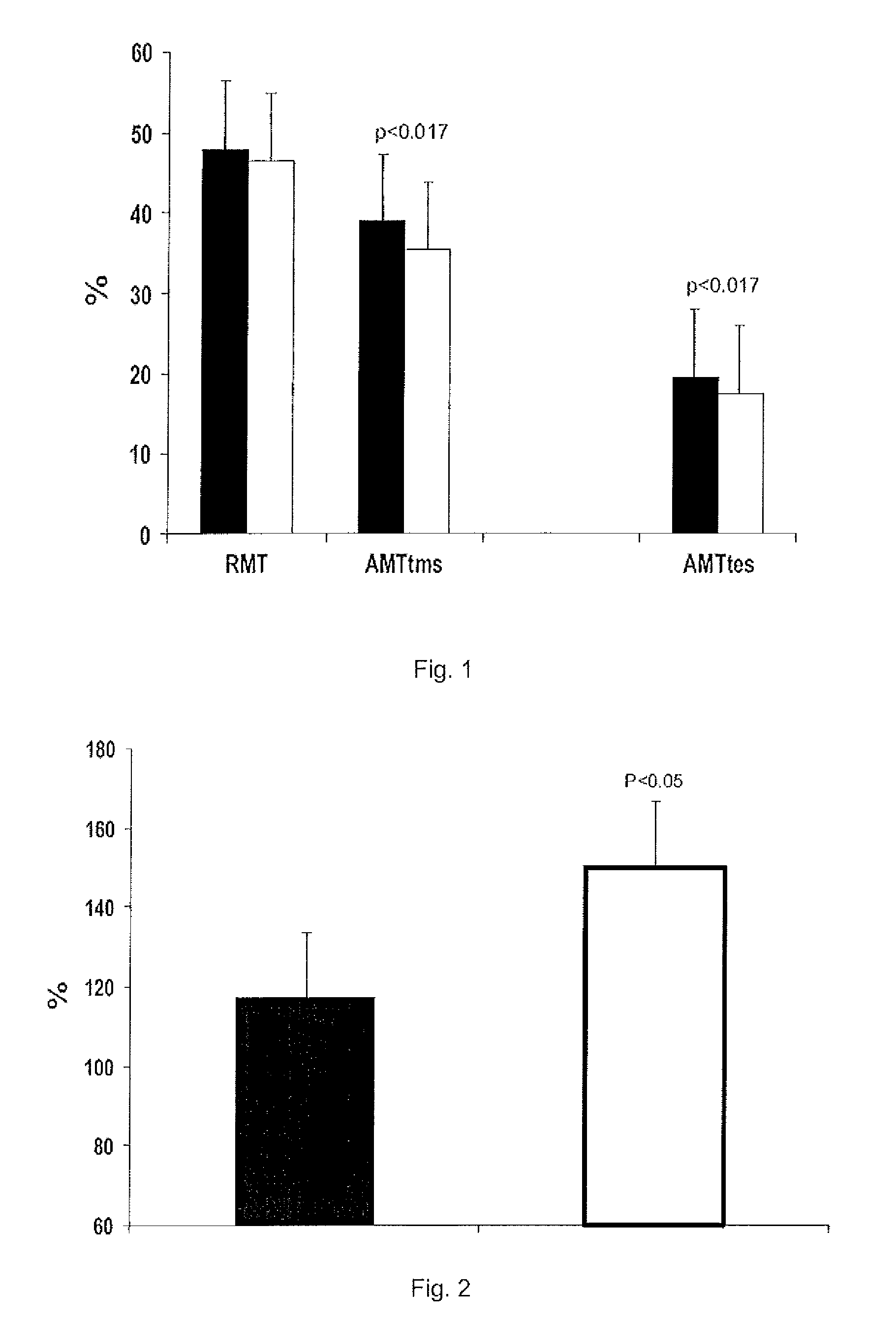
ActiveUS9238027B2Reduction of excessive daytime sleepinessReduction of bradykinesiaBiocideNervous disorderSmall brainstemSpinal level
Use of a CB1 receptor antagonist and / or inverse agonist, preferably rimonabant, for the preparation of drugs useful for increasing motor neuron excitability in the cerebral cortex and / or in the brain stem and / or at the spinal level, as well as a method for increasing motor neuron excitability through the administration of a CB1 antagonist / inverse agonist receptors, and to the use of a pharmaceutical composition which comprises a CB1 receptor antagonist and / or inverse agonist, preferably rimonabant, for increasing motor neuron excitability in the cerebral cortex and / or in the brain stem and / or at the spinal level.
Owner:FUNDACION HOSPITAL NACIONAL DE PARAPLEJICOS PARA LA INVESTIGACION & LA INTEGRACION FUHNPAIIN
Grouped leads for spinal stimulation
Devices, systems and methods are provided for simultaneously stimulating the spinal anatomy at various target locations, such as spinal levels, along the spinal cord. In some embodiments, the devices, systems and methods stimulate the various spinal levels at specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root DR or more specifically the dorsal root ganglion DRG. Optionally, the devices, systems and methods may be used to stimulate a single DRG or other anatomies.
Owner:SPINAL MODULATION INC
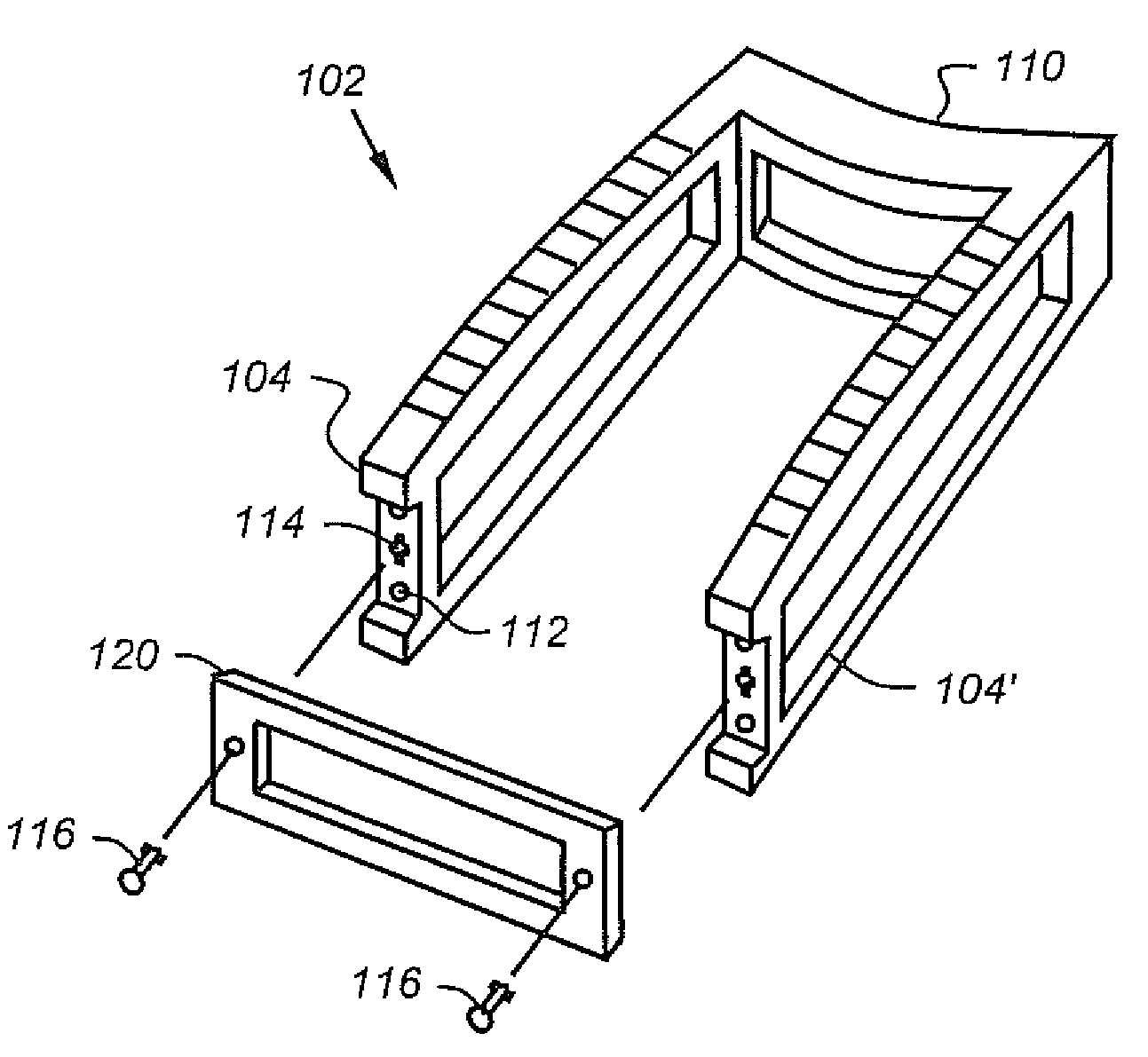
Variable offset spine fixation system and method
A minimally invasive system and method for coupling a spinal rod to a plurality of bone anchors implanted into a plurality of vertebral bodies. A plurality of bottom-loading polyaxial anchor seat assemblies (130A, 130B, 130C having different vertical heights are chosen to pop over the heads (124) of the implanted bone anchors (110A, 110B, 110C ) and a spinal rod (120) is more easily introduced and secured to the bone anchors. The variety of different heights that characterize the plurality of polyaxial anchor seat assemblies allows a surgeon to intraoperatively choose the appropriate offset for a particular spinal level during spinal corrections.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Methods for data processing for intra-operative navigation systems
ActiveUS20200085507A1Surgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingSpinal columnOrthopedic department
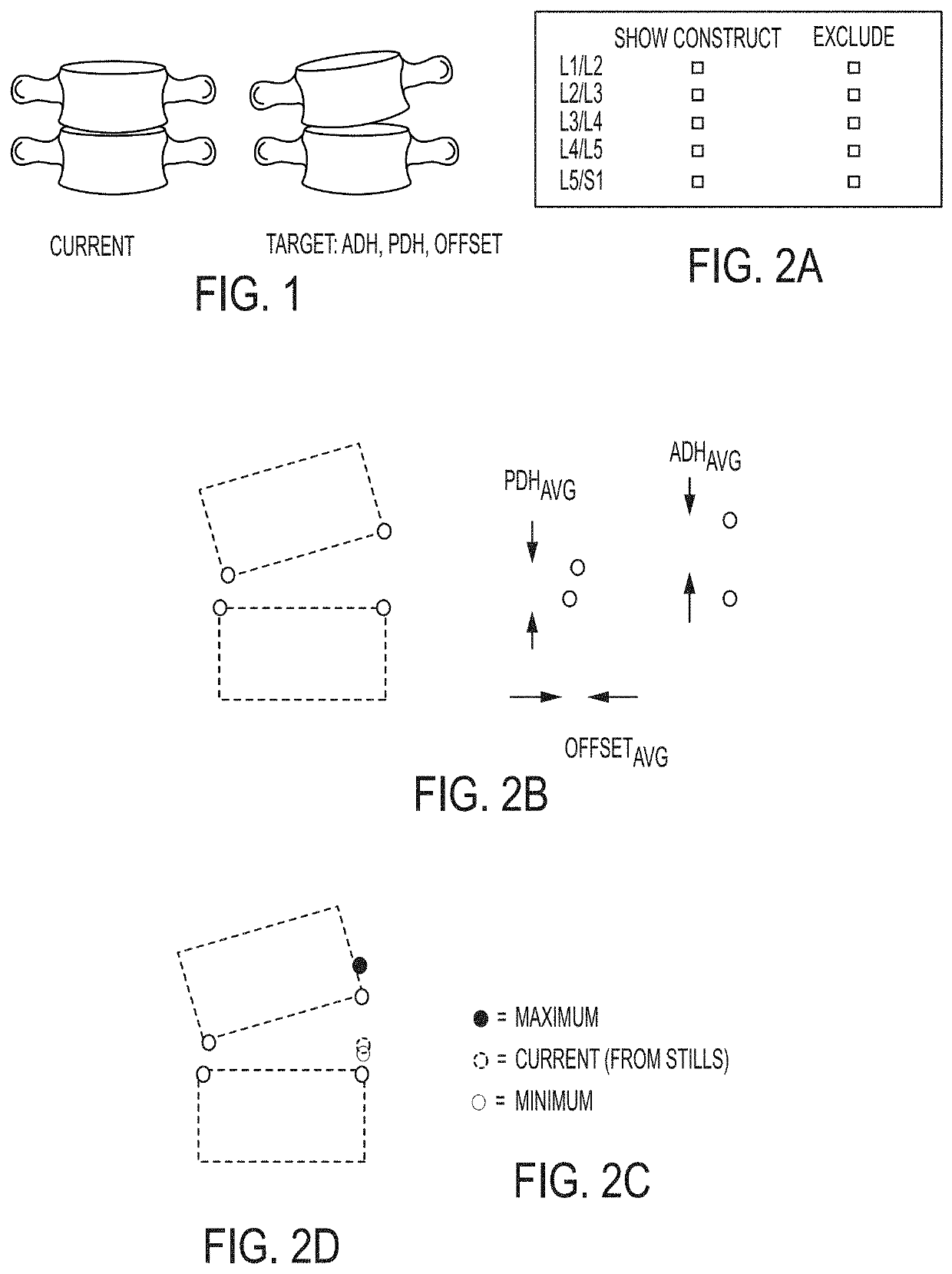
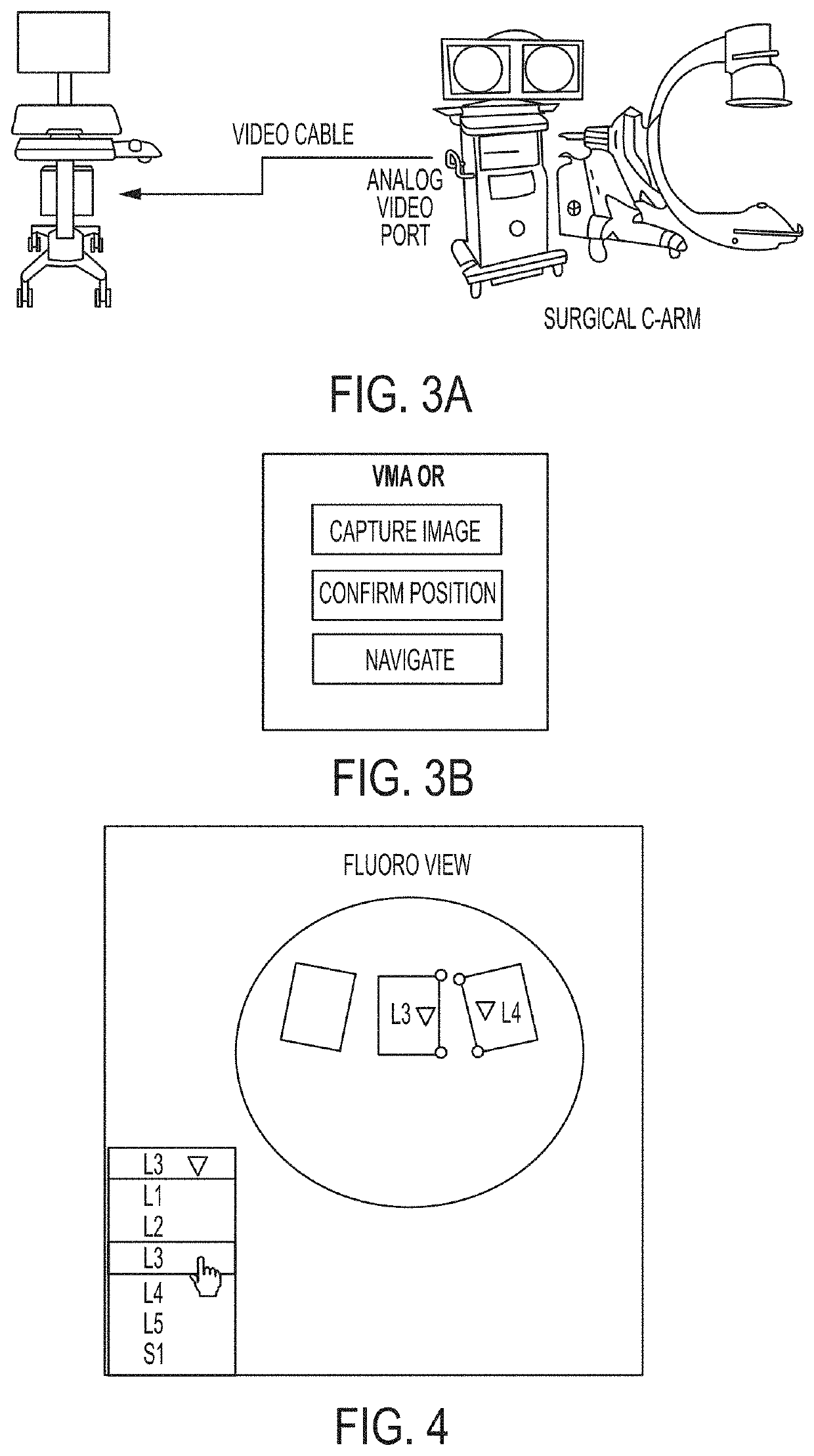
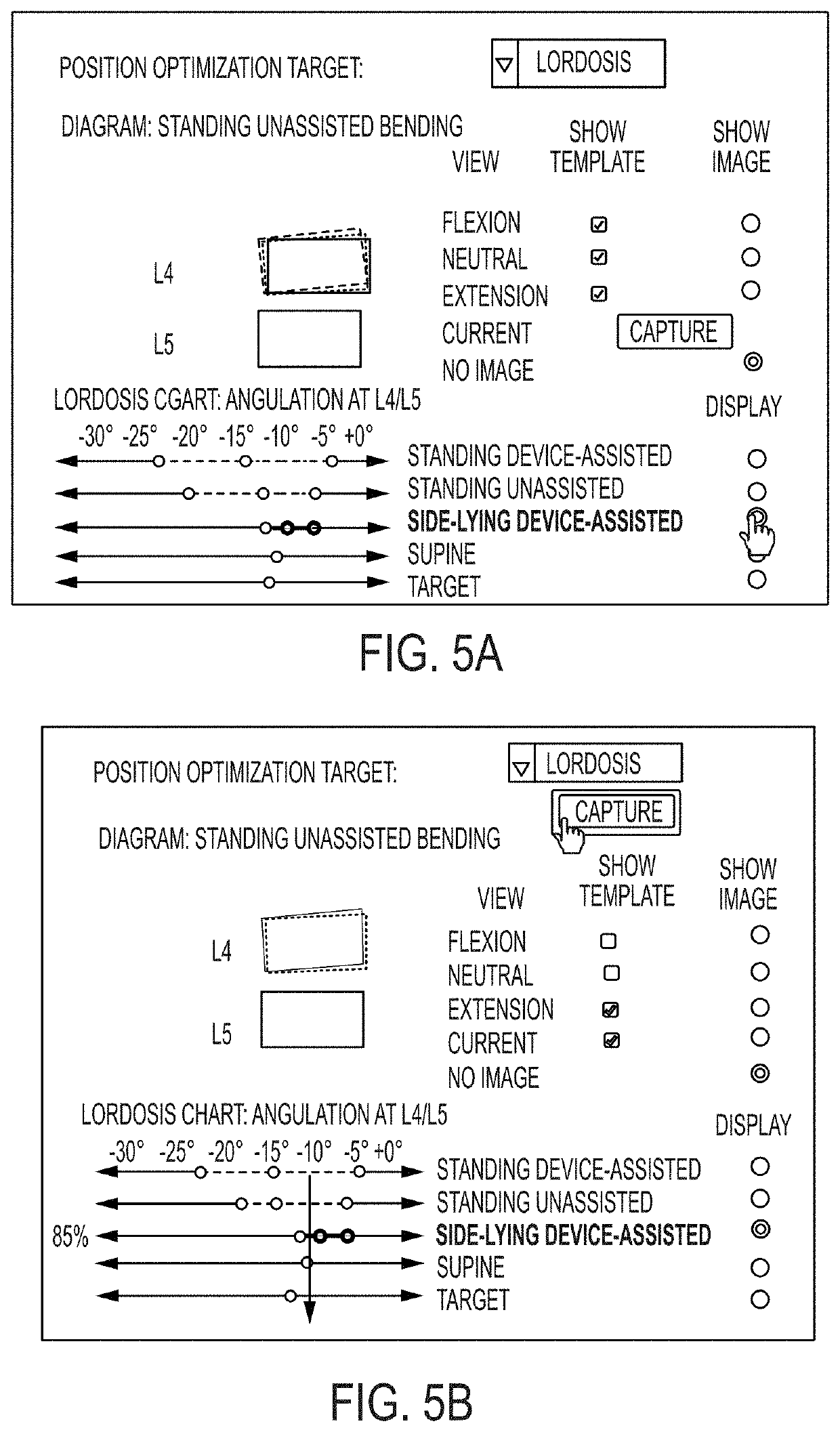
Disclosed are methods and systems used with surgical navigation systems that enable a user to generate an optimized anatomical dataset for a spine level of interest. The systems and methods allow users to determine a target geometry for a spinal level targeted for spinal surgery. Additionally, the user can project loads across the spinal orthopedic implants and determine a projected subsidence overtime.
Owner:WENZEL SPINE
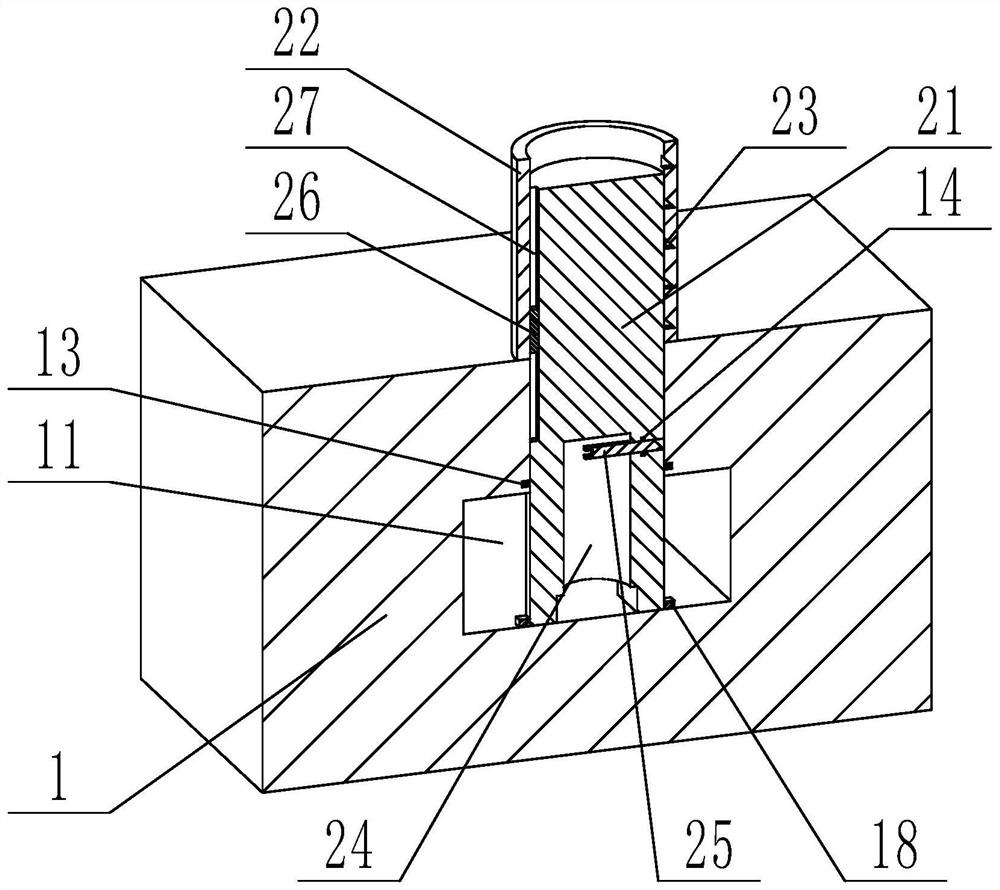
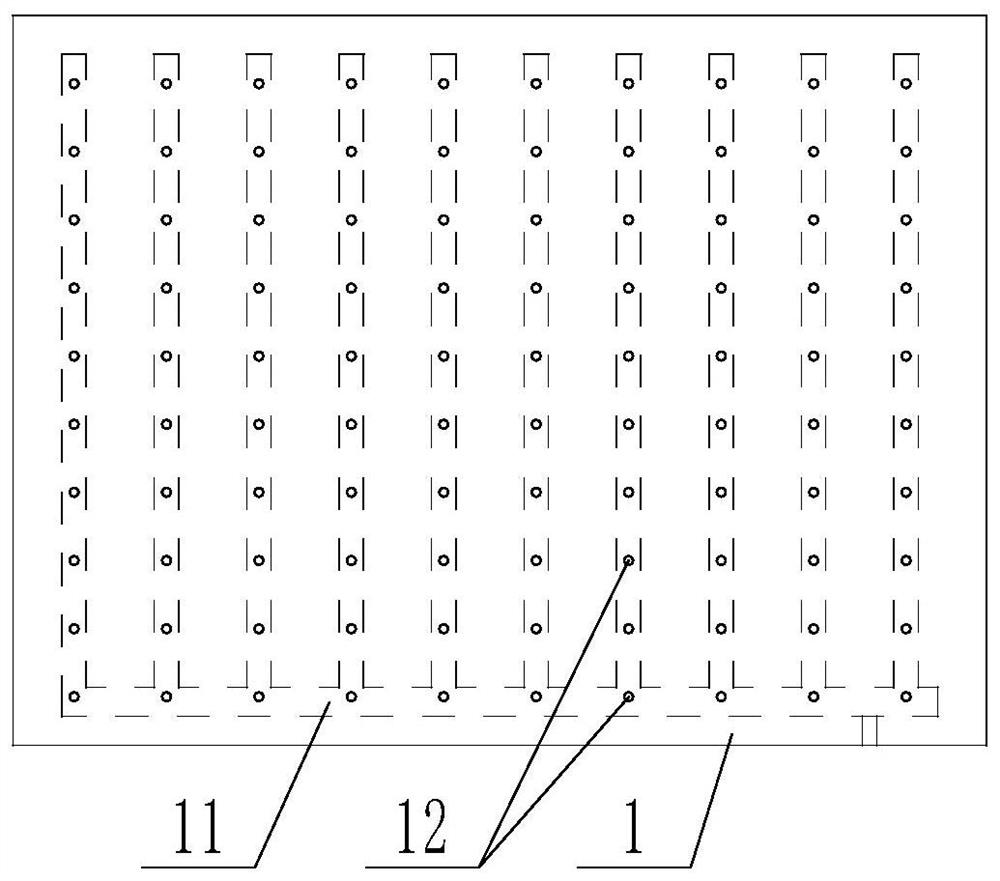
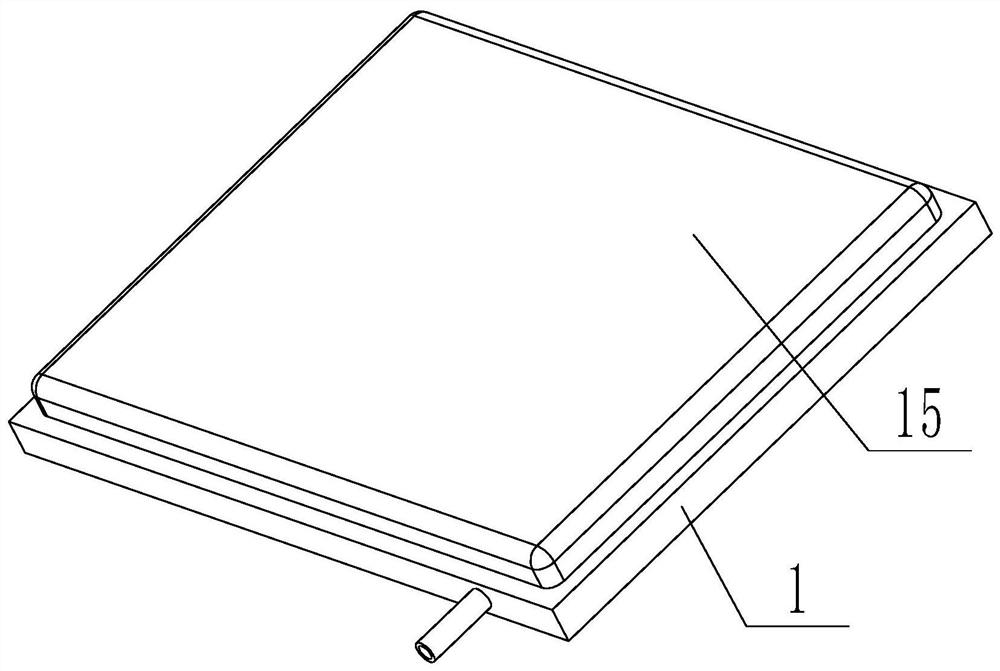
Waist puncture operation tray for neurology department
InactiveCN113907999APrevent falling backAvoid problems that affect surgeryOperating tablesSpinal columnNeurology department
The invention discloses a waist puncture operation tray for the neurology department, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The waist puncture operation tray comprises a bottom plate and a plurality of supporting devices, communicated channels are formed in the bottom plate and connected with an inflation device, and a plurality of air holes communicated with the channels are formed in the upper surface of the bottom plate; the multiple supporting devices correspond to the air holes respectively, each supporting device comprises a piston rod, and the piston rods are arranged in the air holes in a penetrating mode; and the air pump is used for providing positive pressure for the channel and supporting the waist of the patient so that the spine of the patient can be horizontal, meanwhile, in the using process, through combination of the limiting groove, the limiting rod and the air pump, the piston rod can be prevented from falling back, and the problem that the spine bends downwards and an operation is affected in the process that the patient lies on the side is solved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com