Patents
Literature
172 results about "Skin incision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
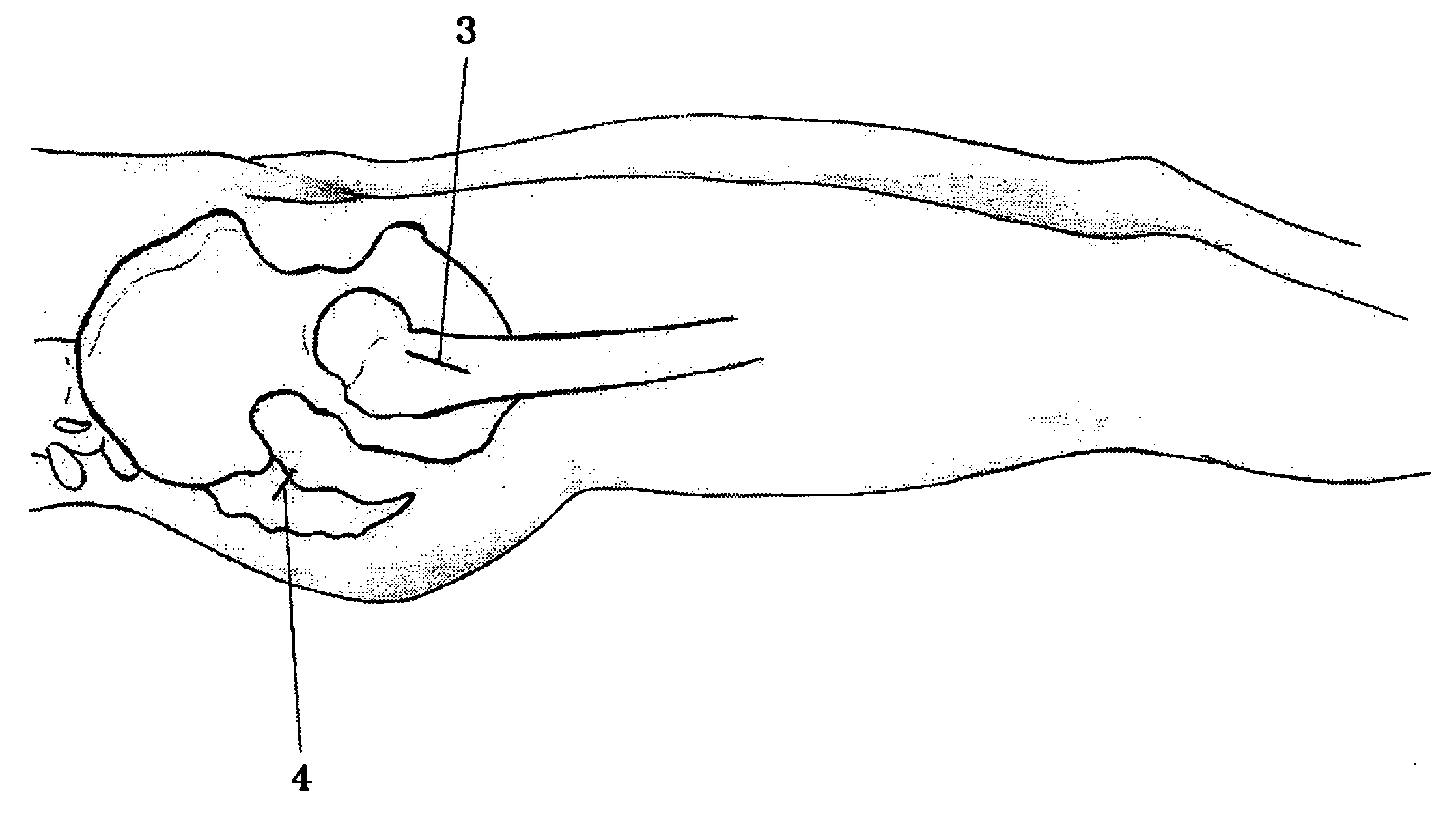
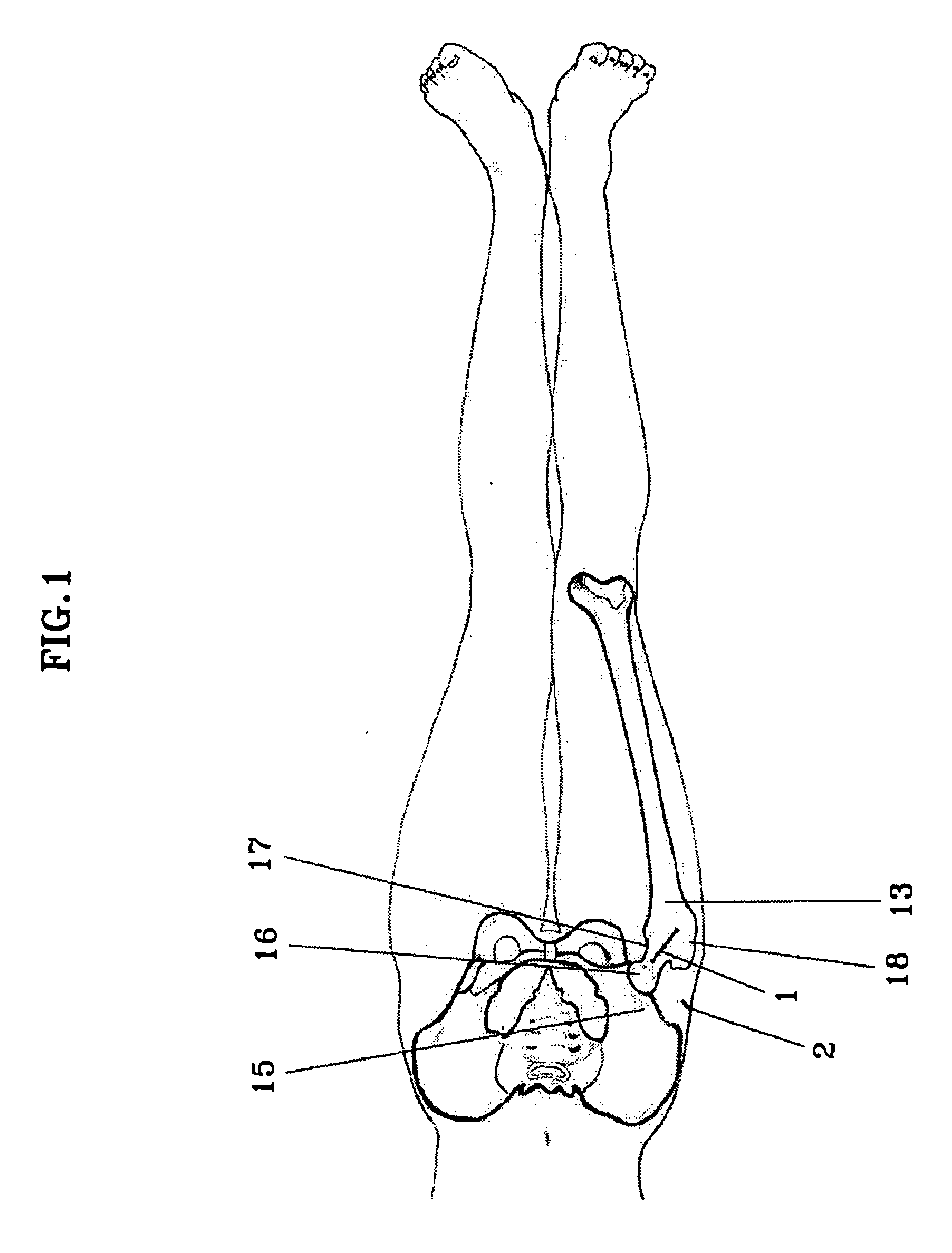
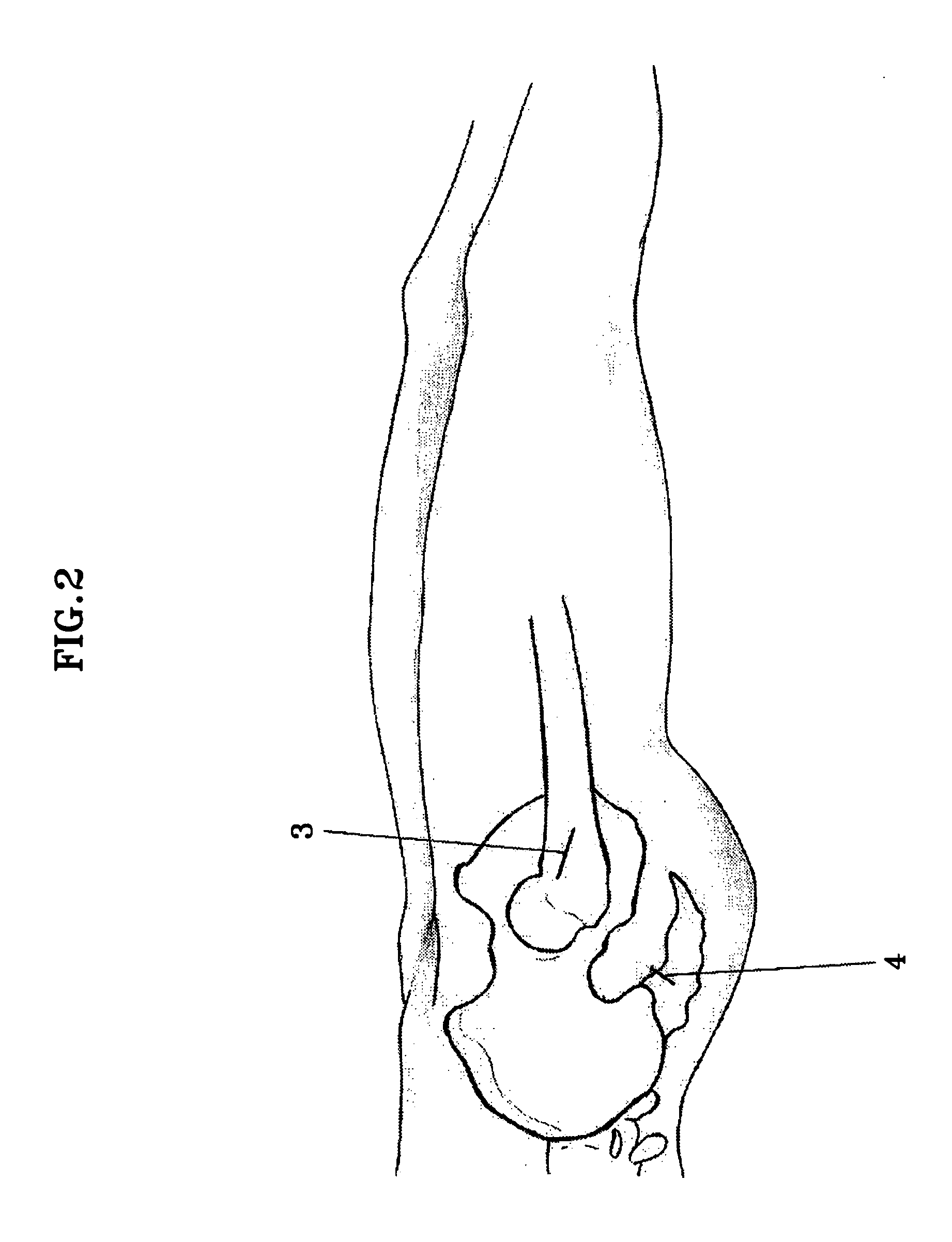
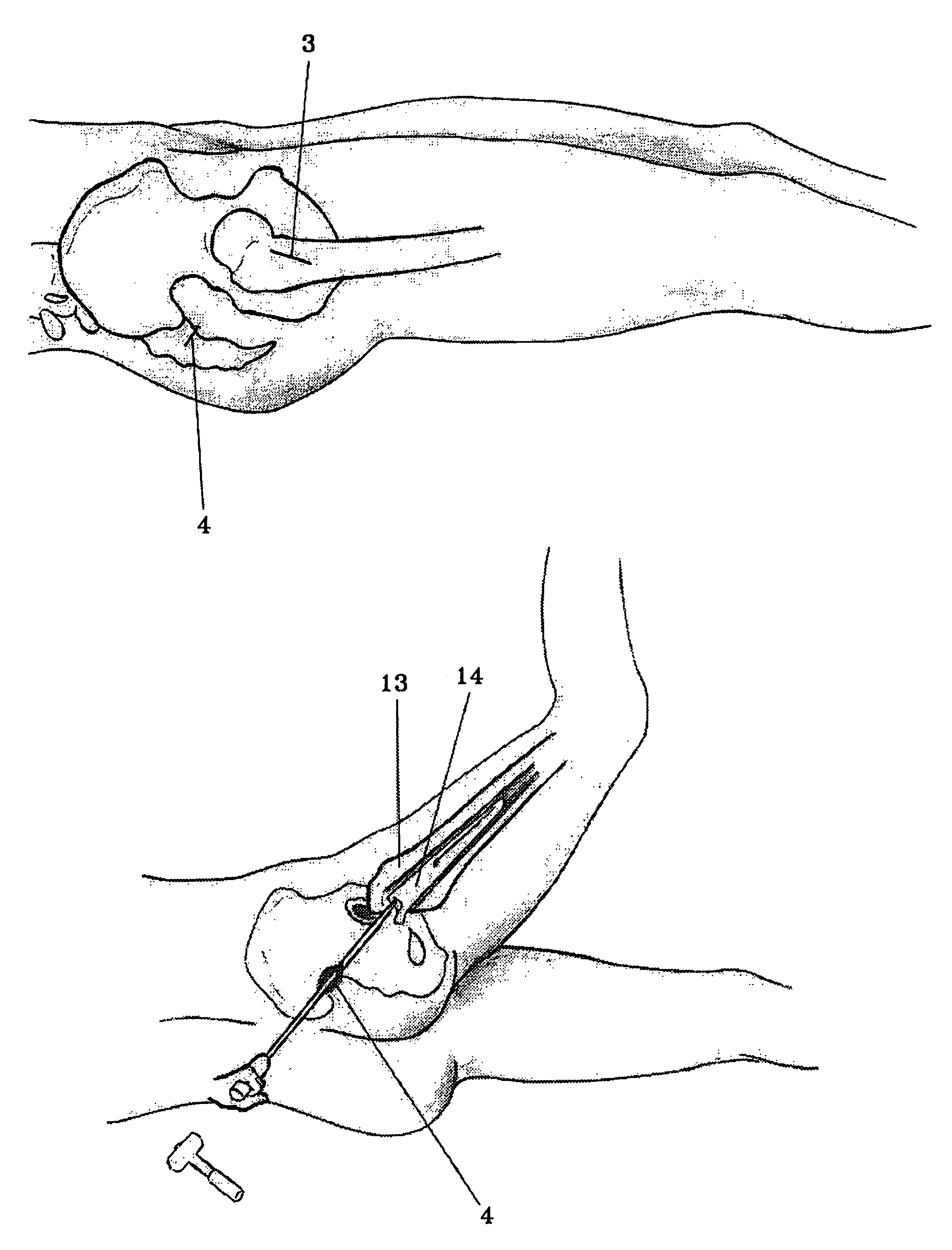
A skin incision is also referred to as a surgical wound. Stitches are commonly used to close skin incisions. Skin incisions have an elevated risk of becoming infected, so they are often covered with sterile dressings for the first few days or weeks after surgery.
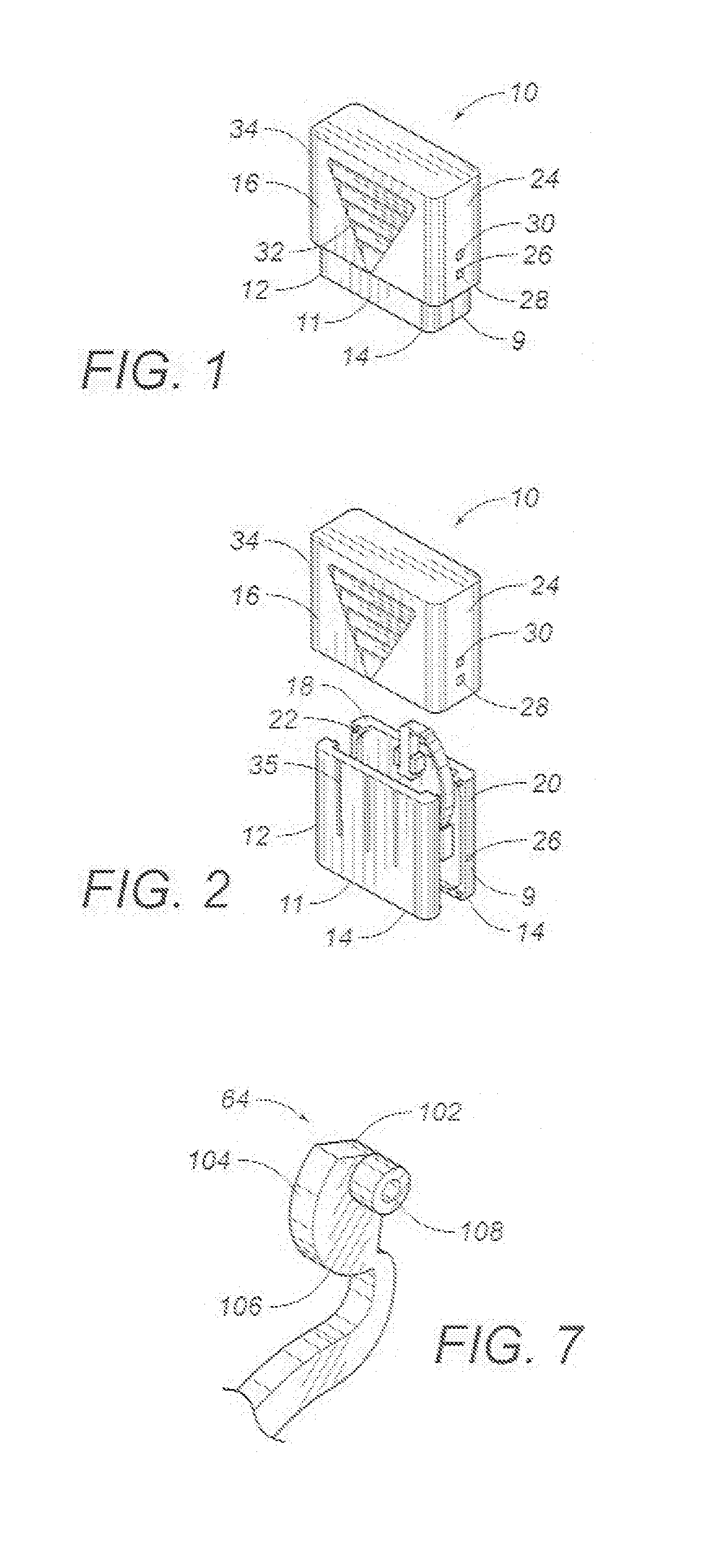
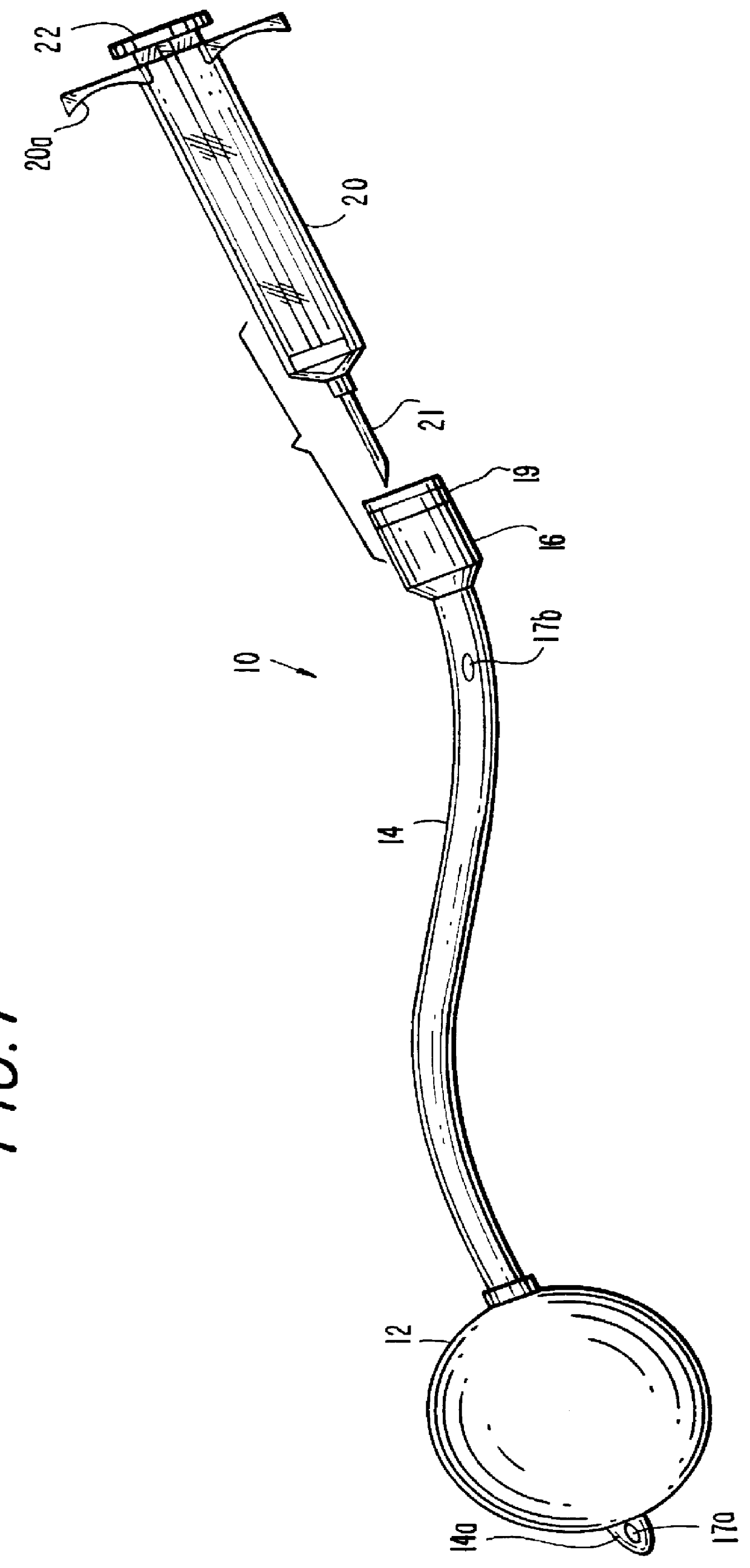
Non-rigid surgical retractor
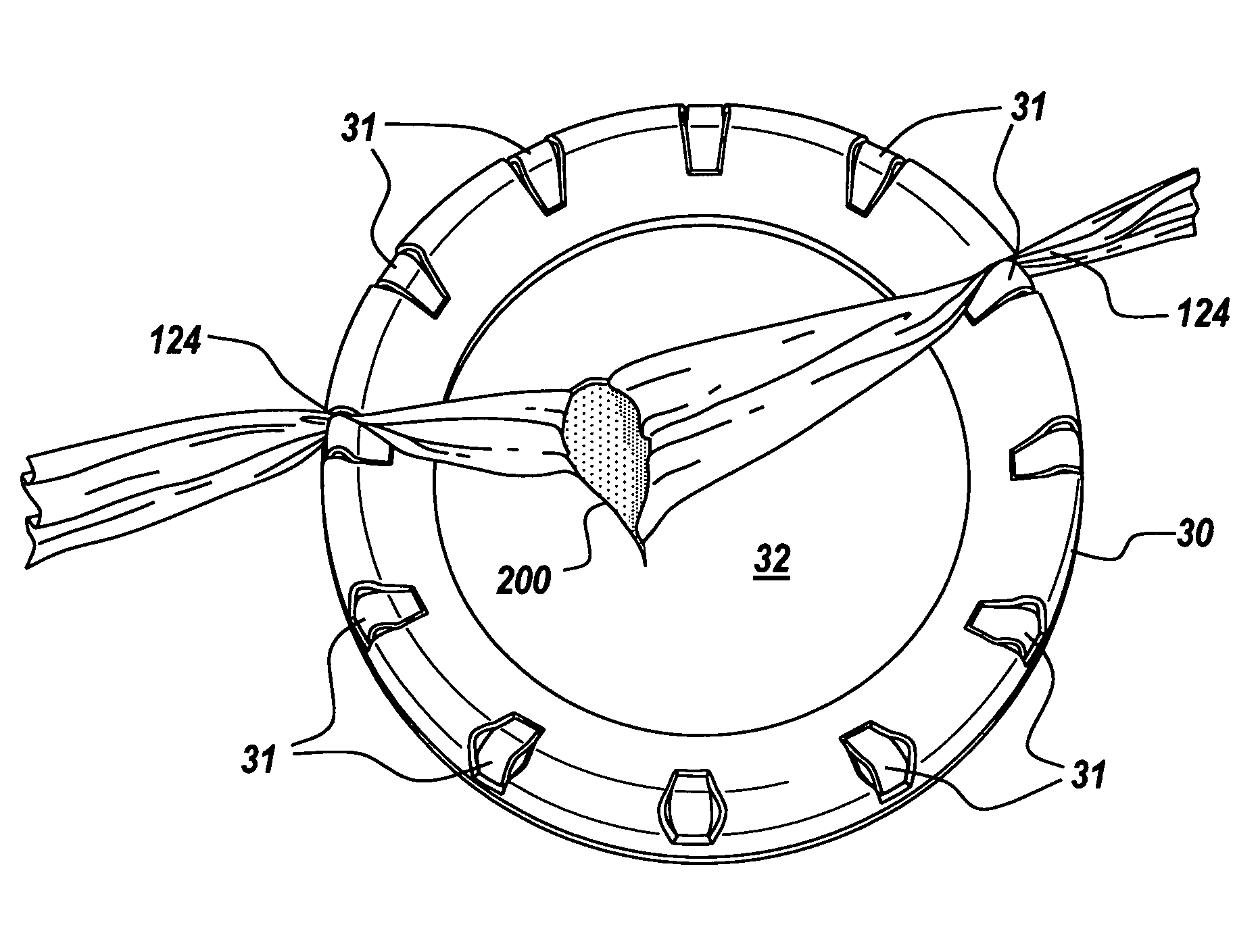
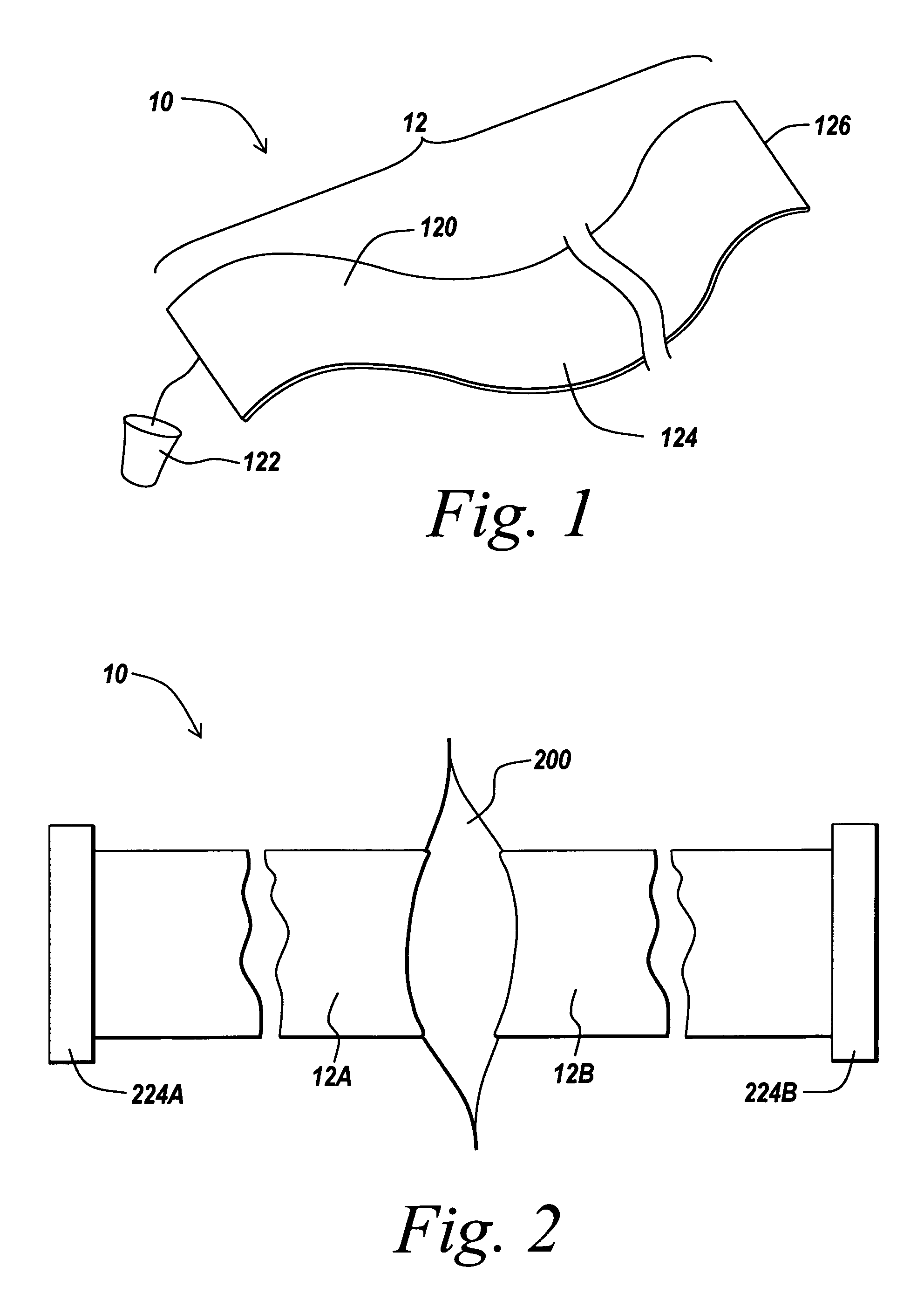
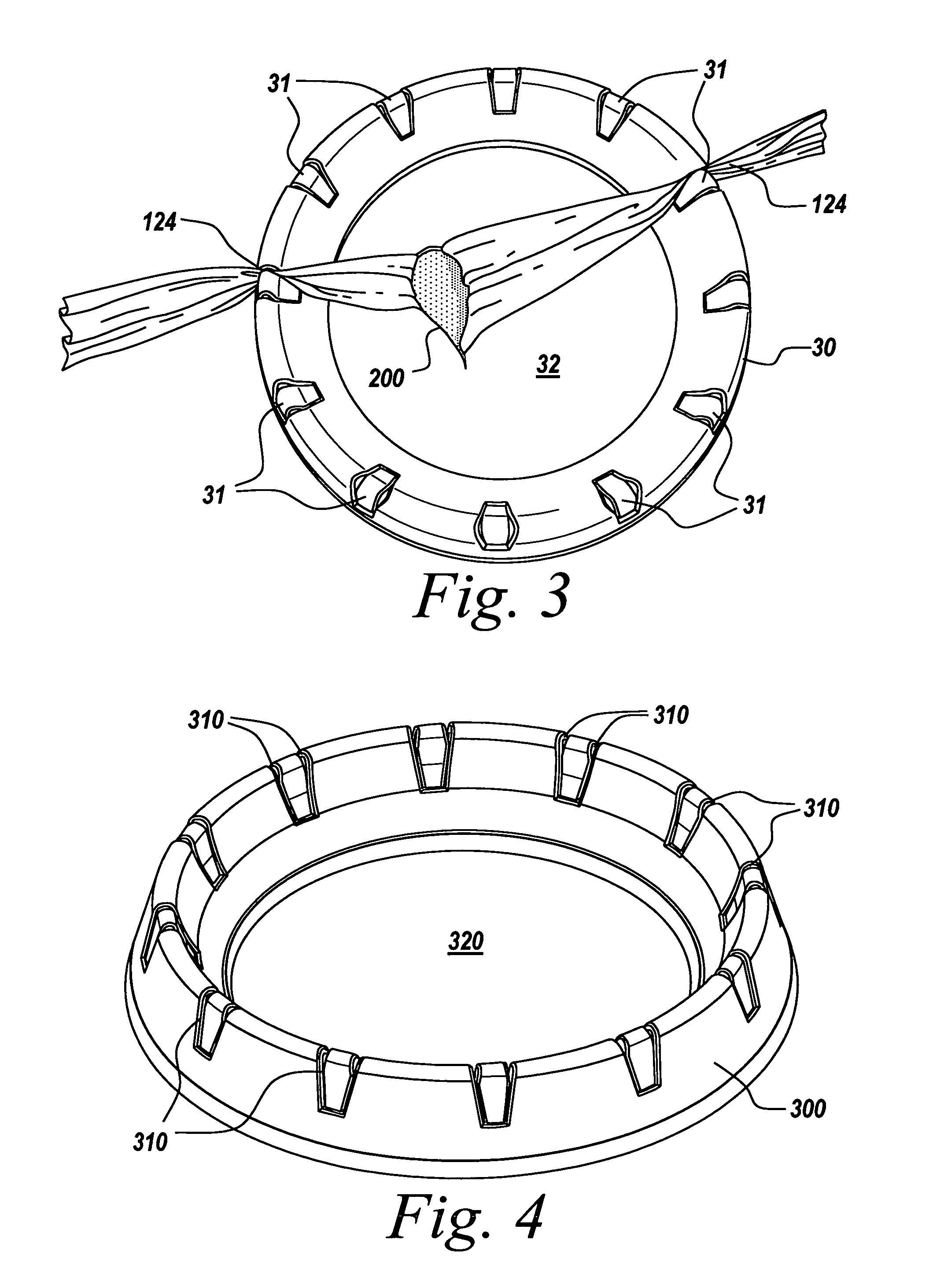
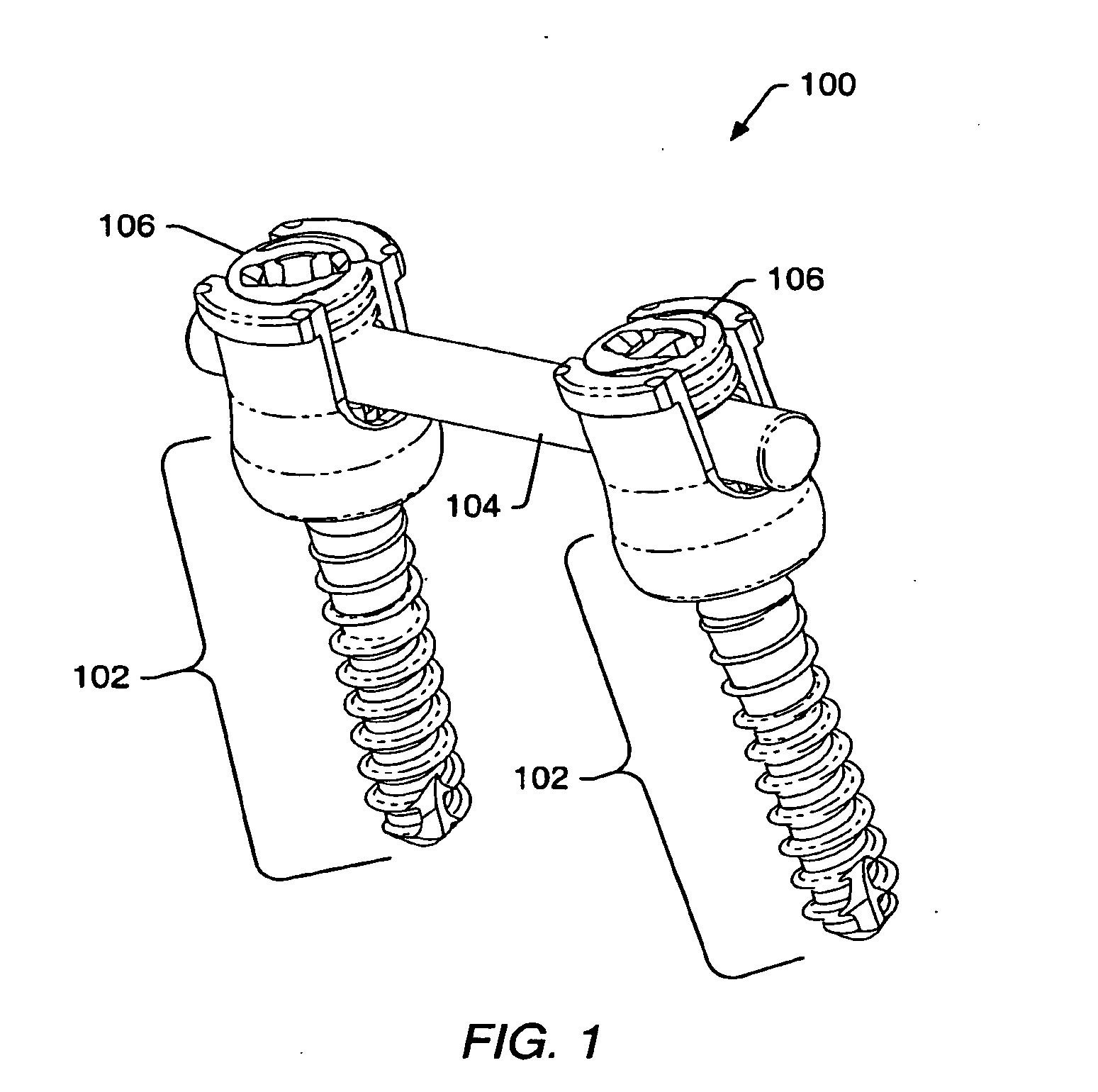
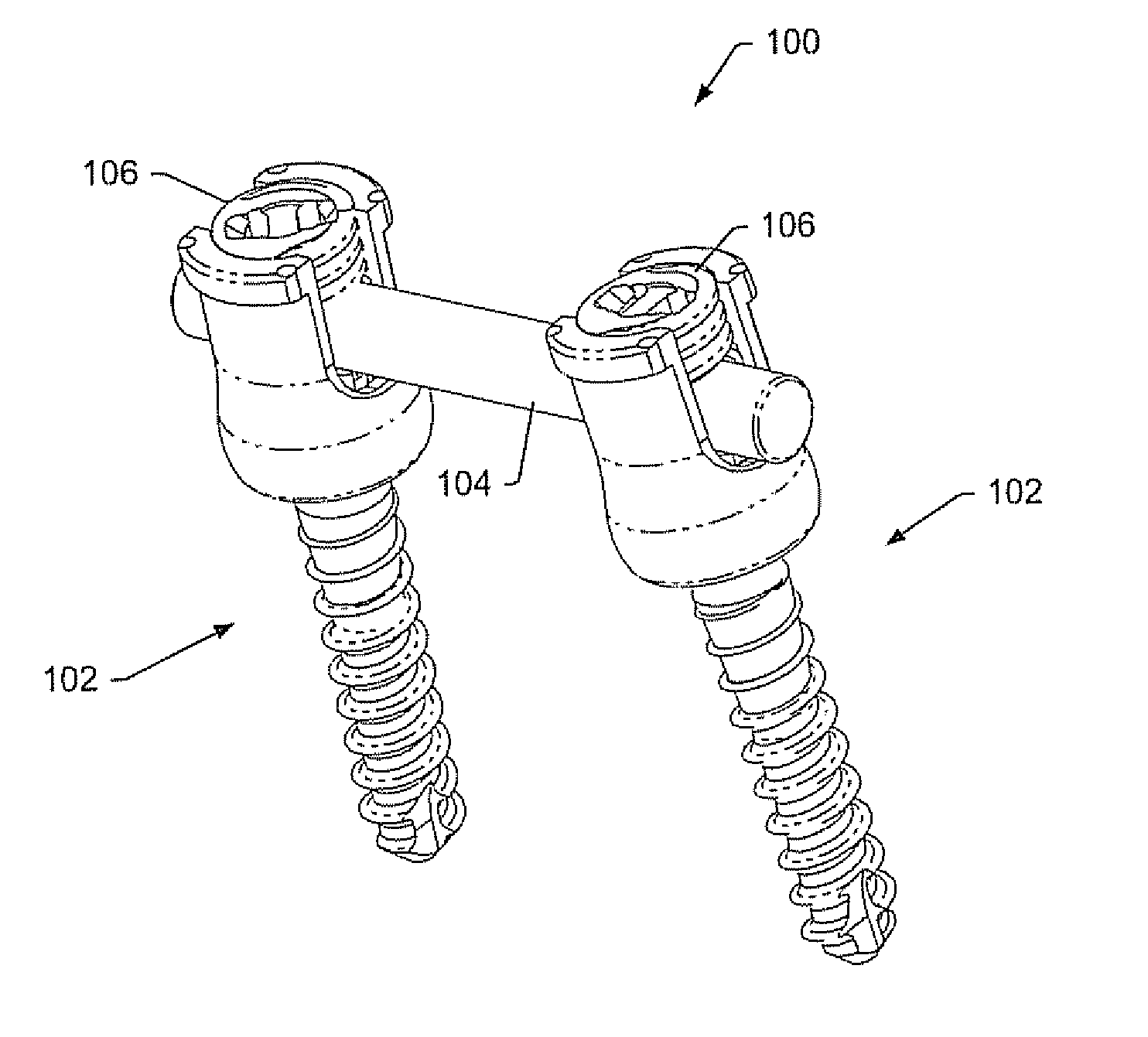
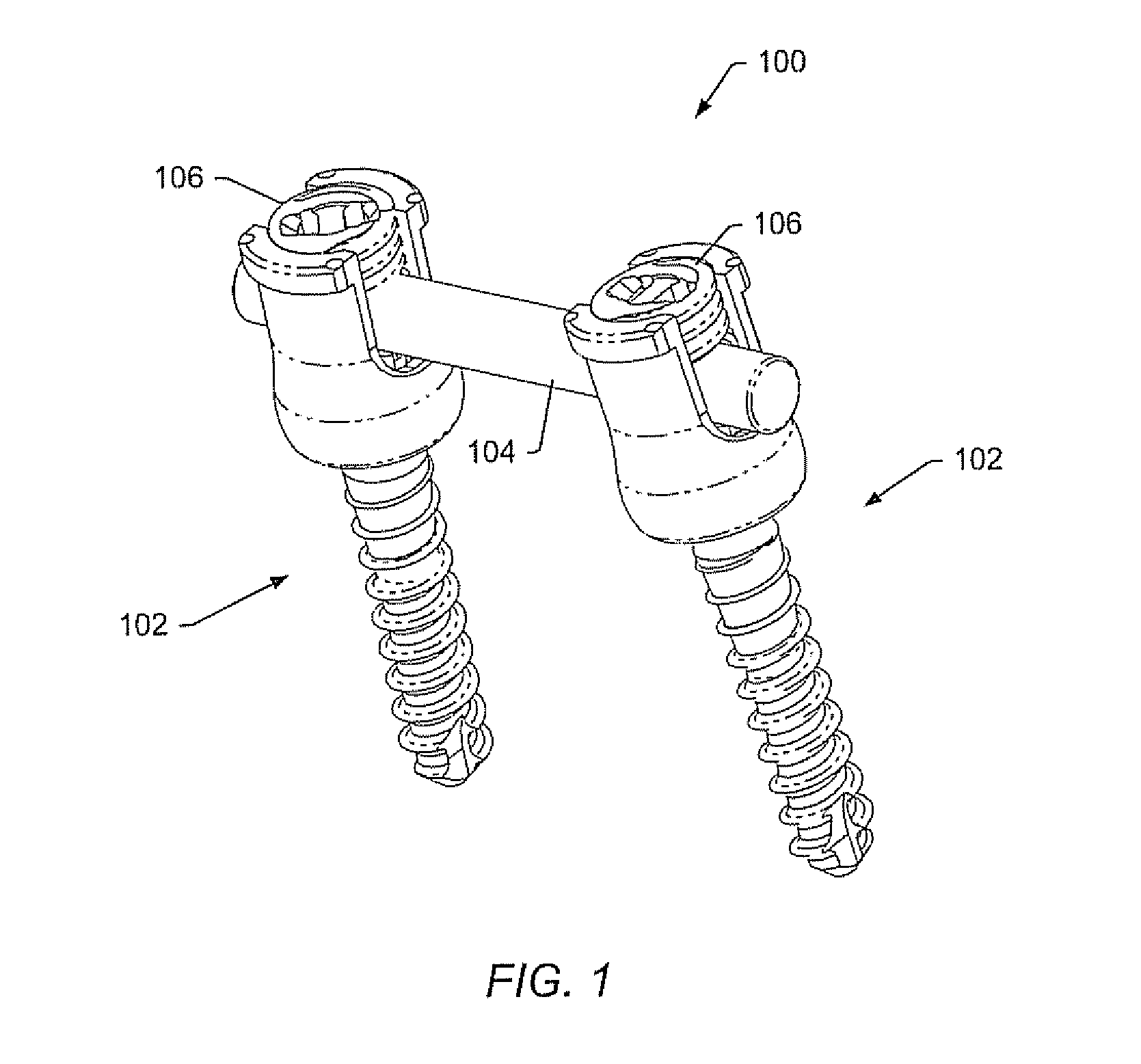
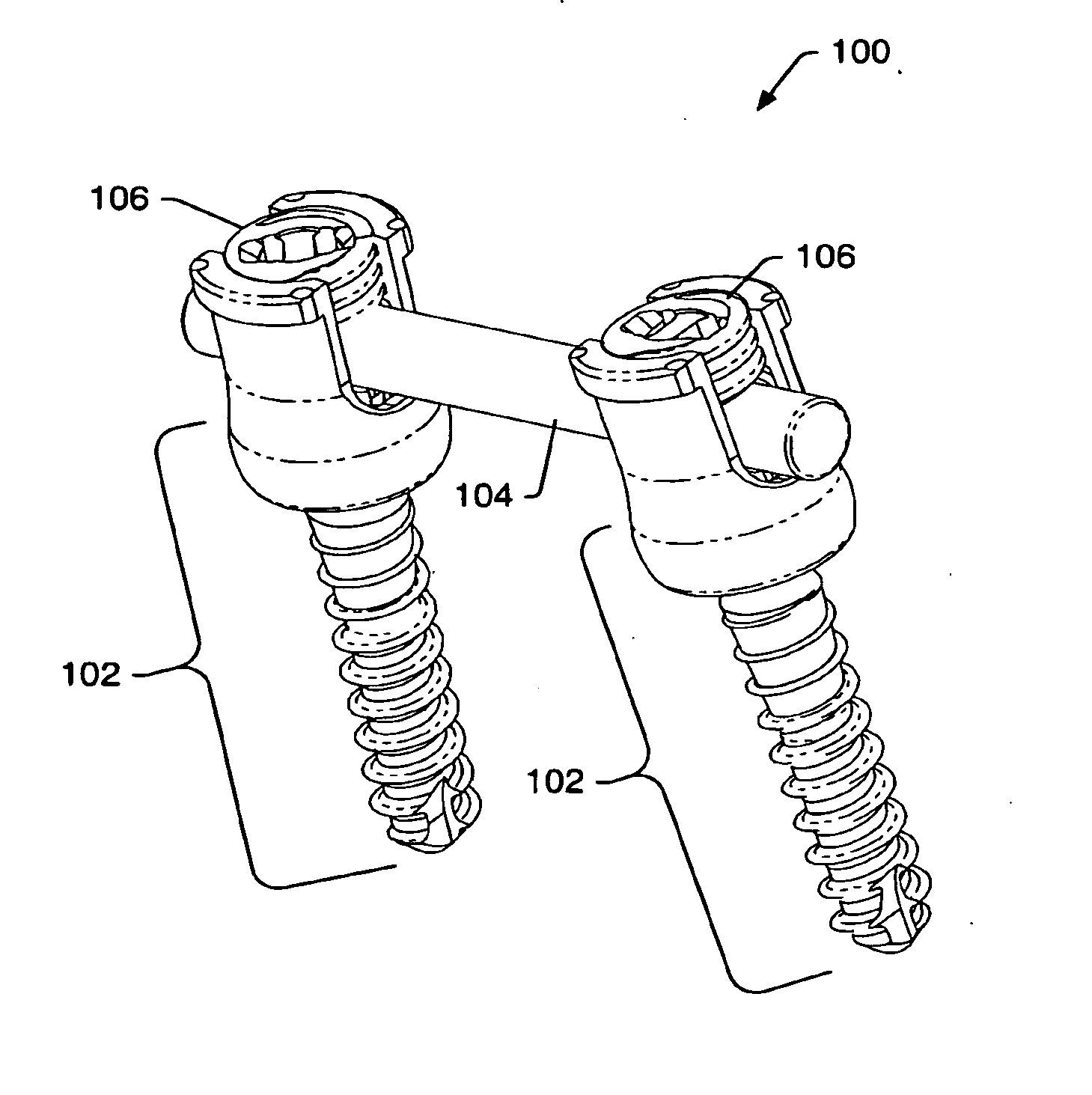
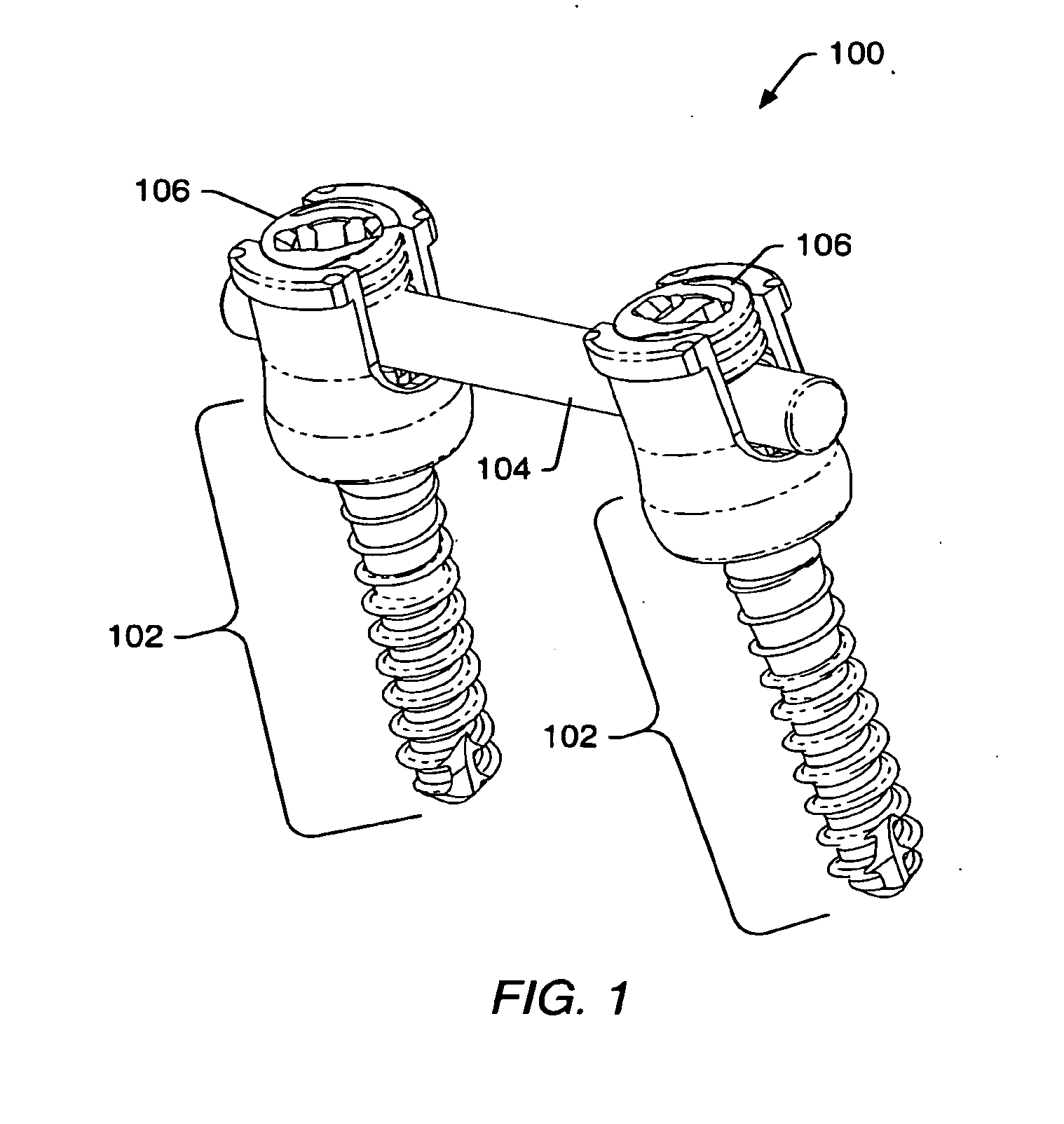
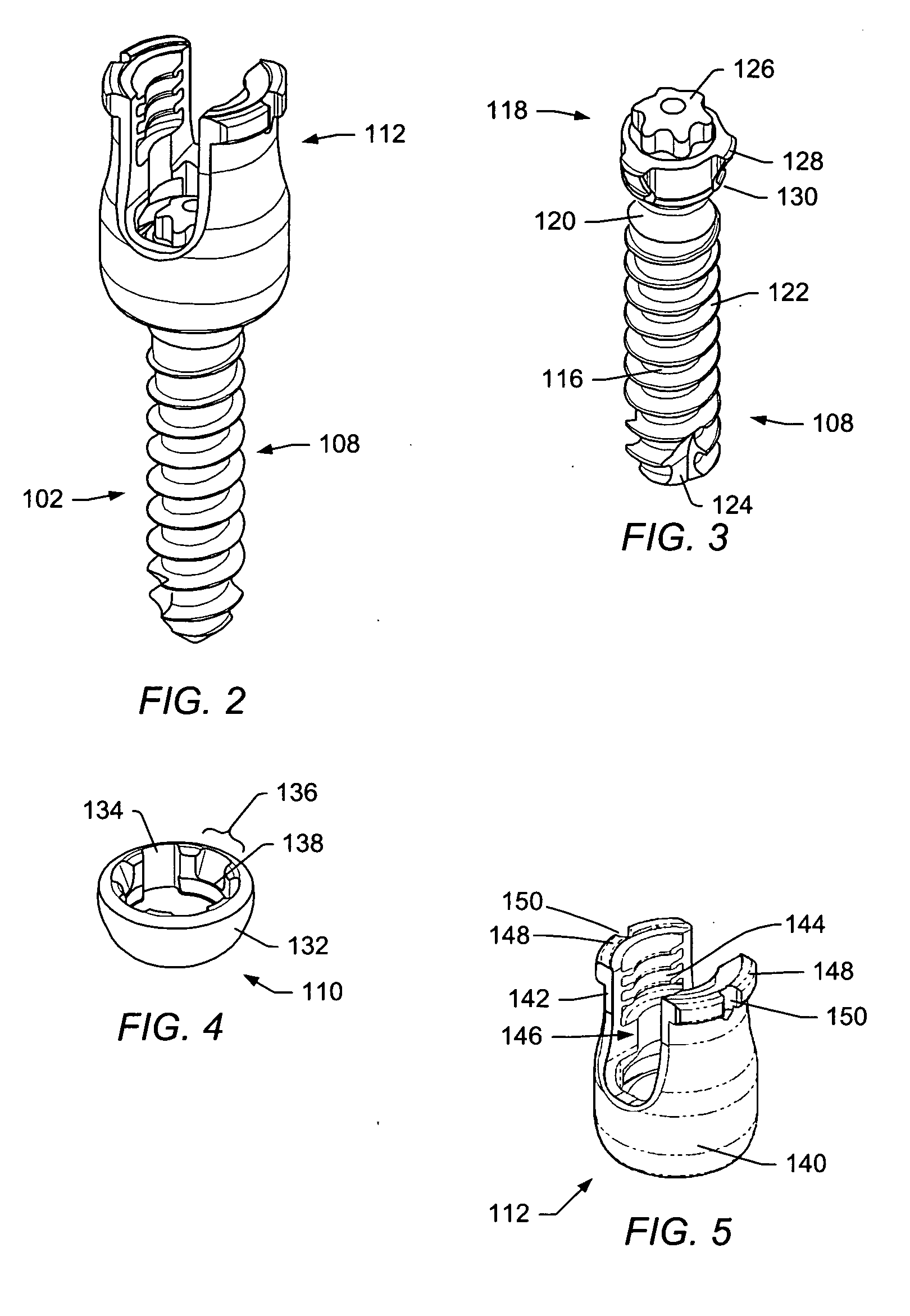
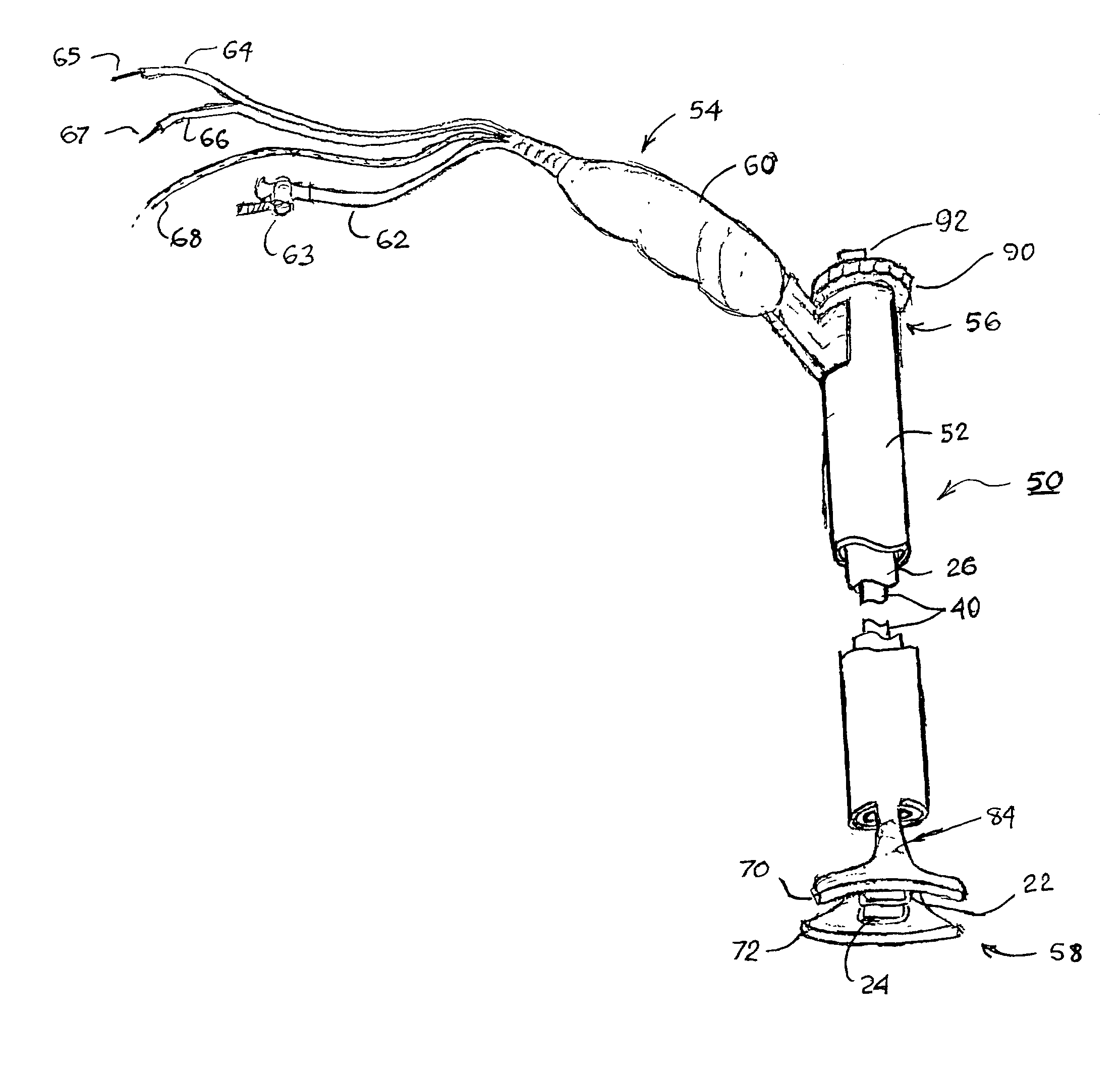
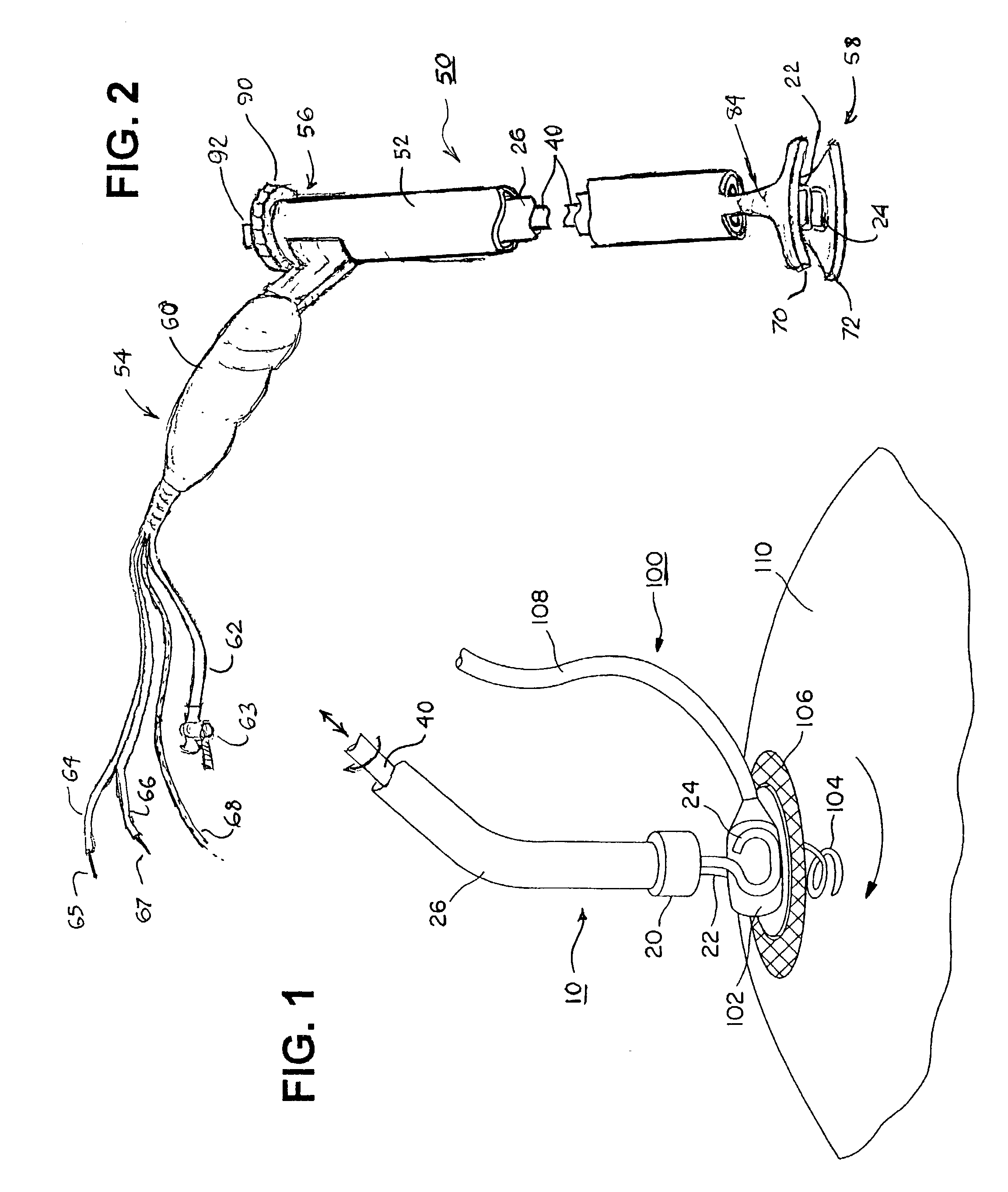
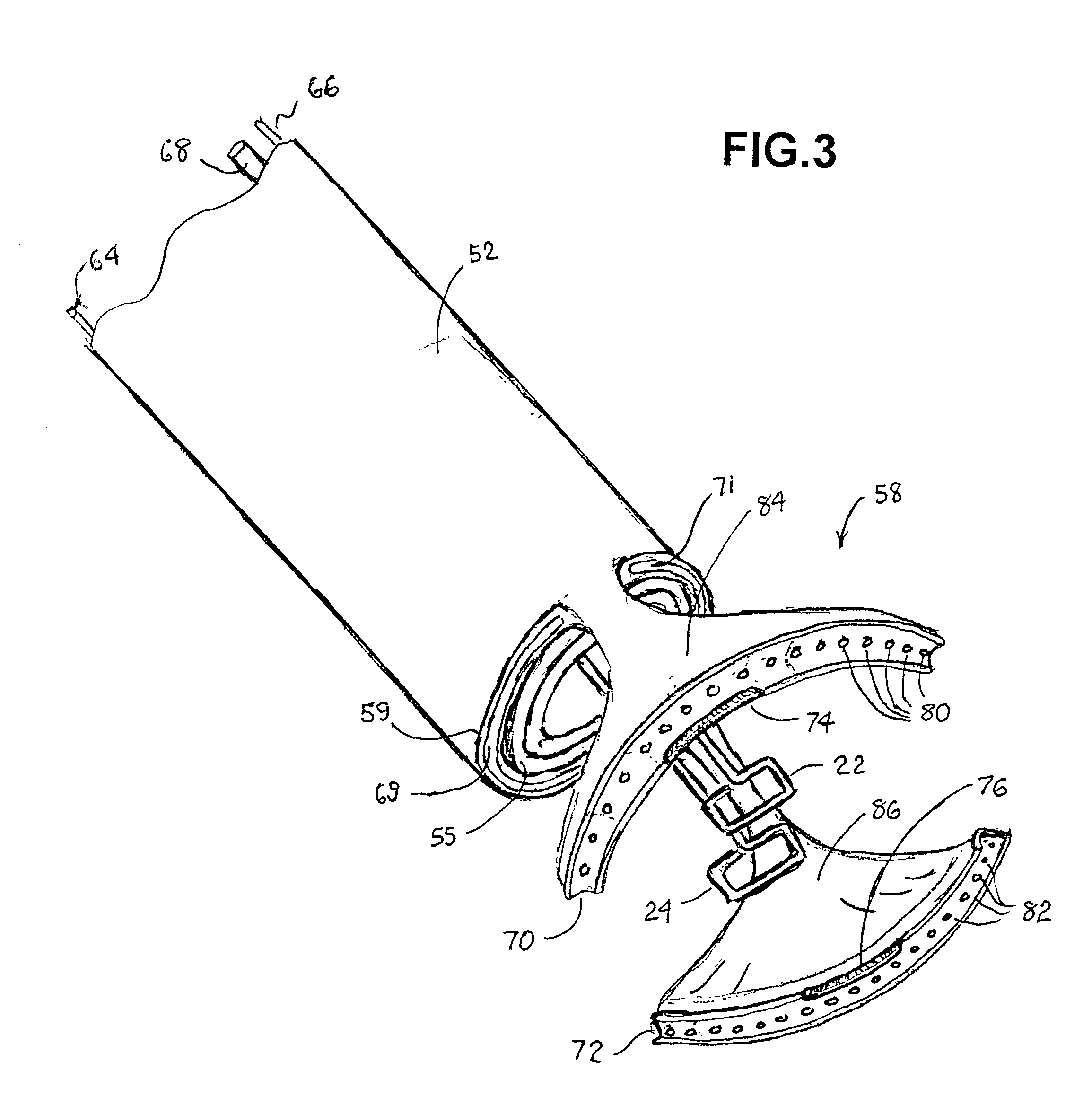
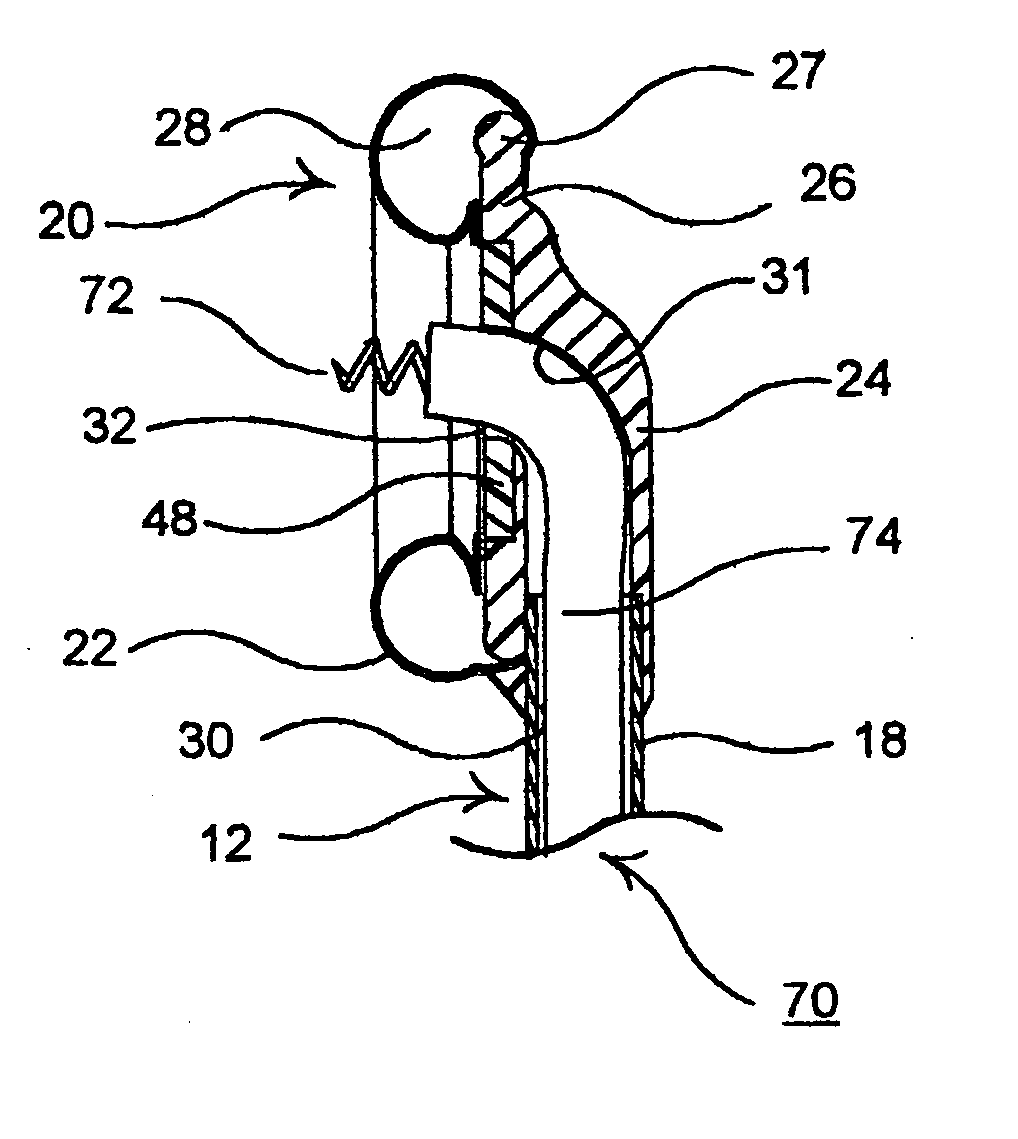
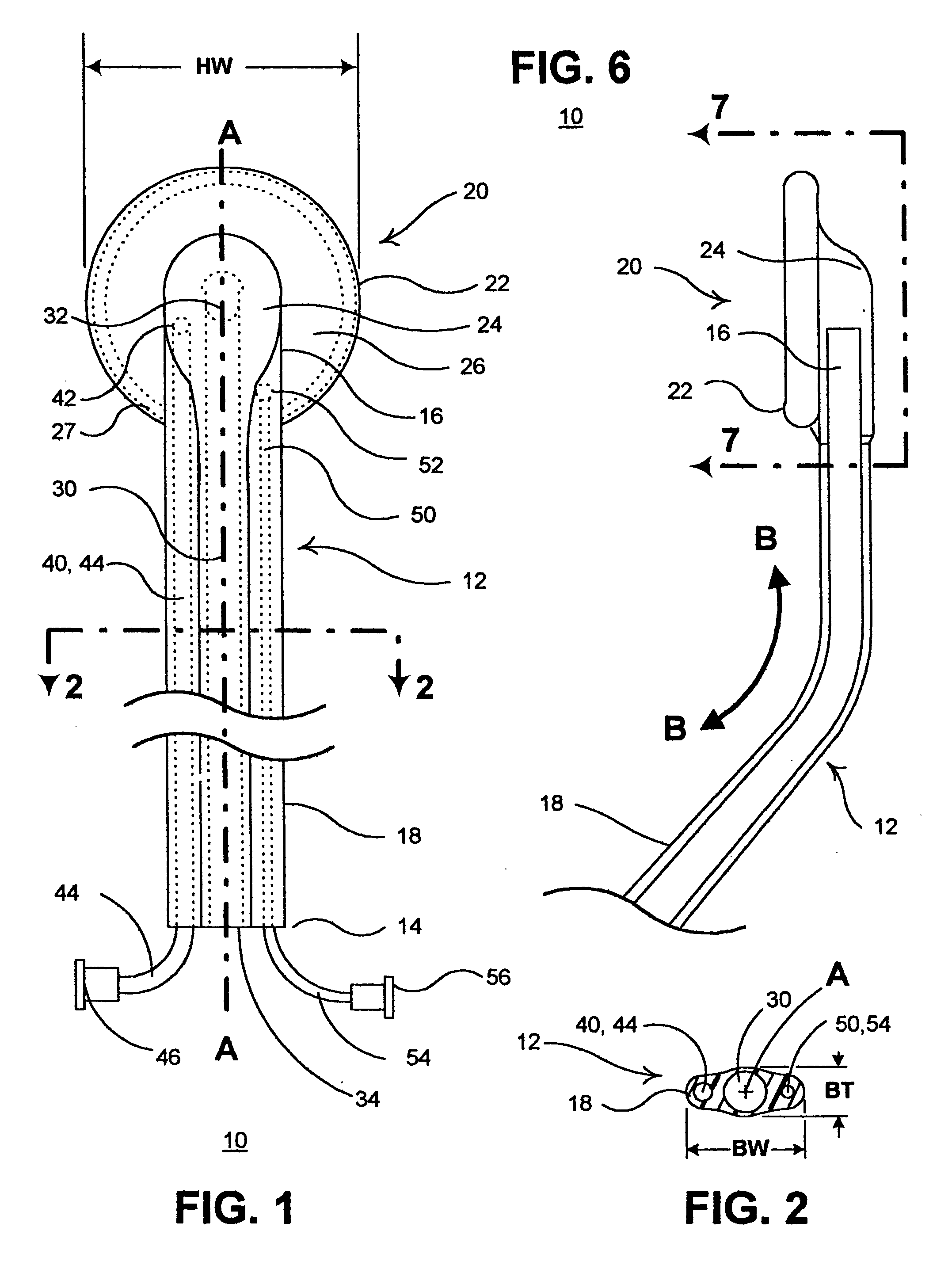
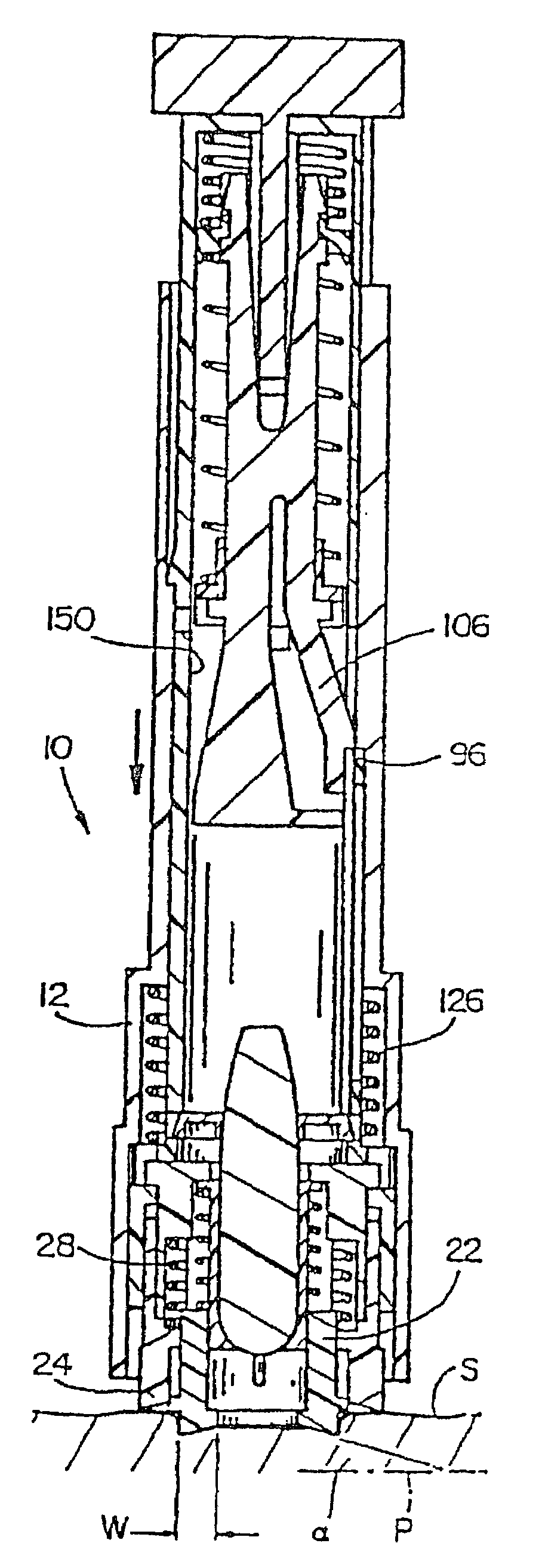
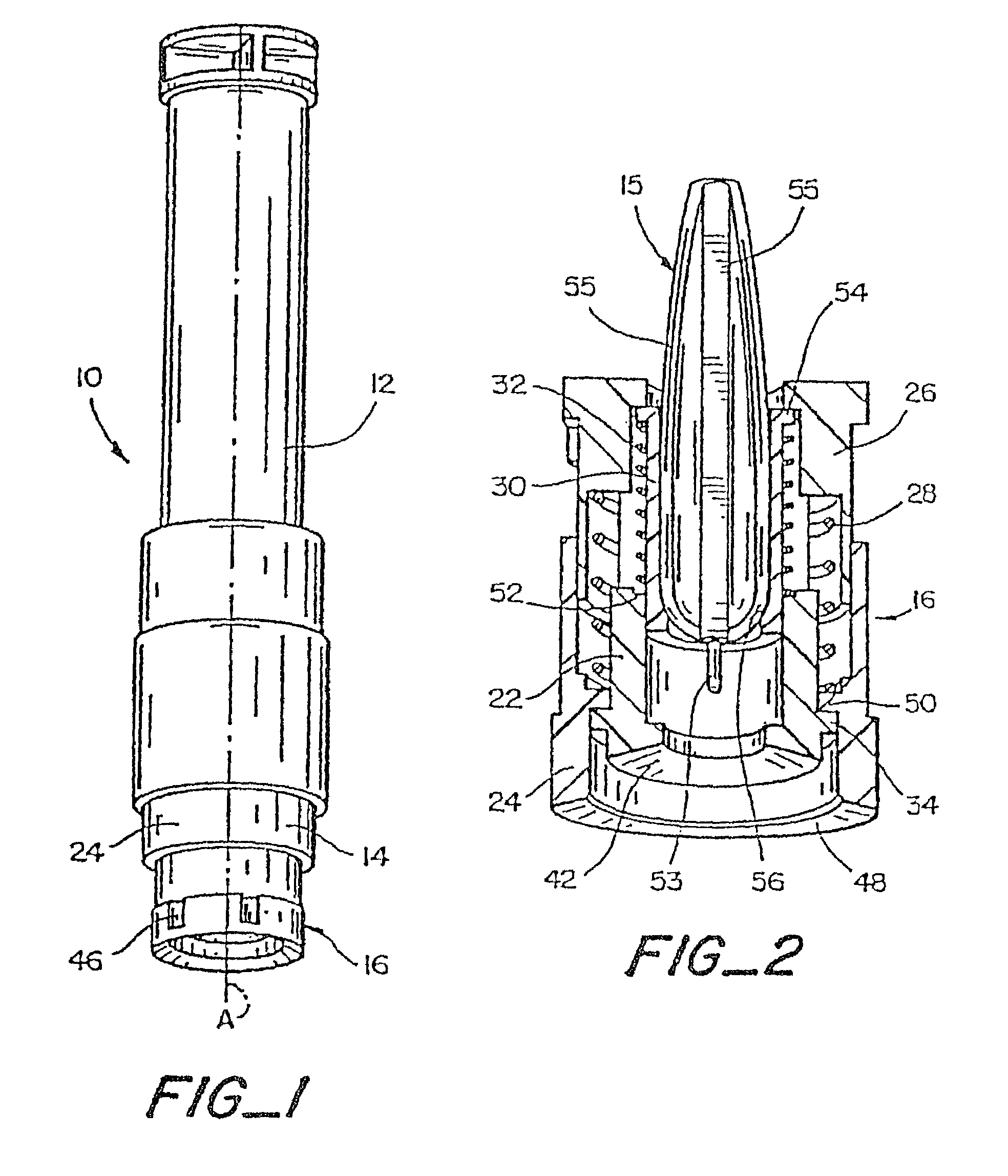
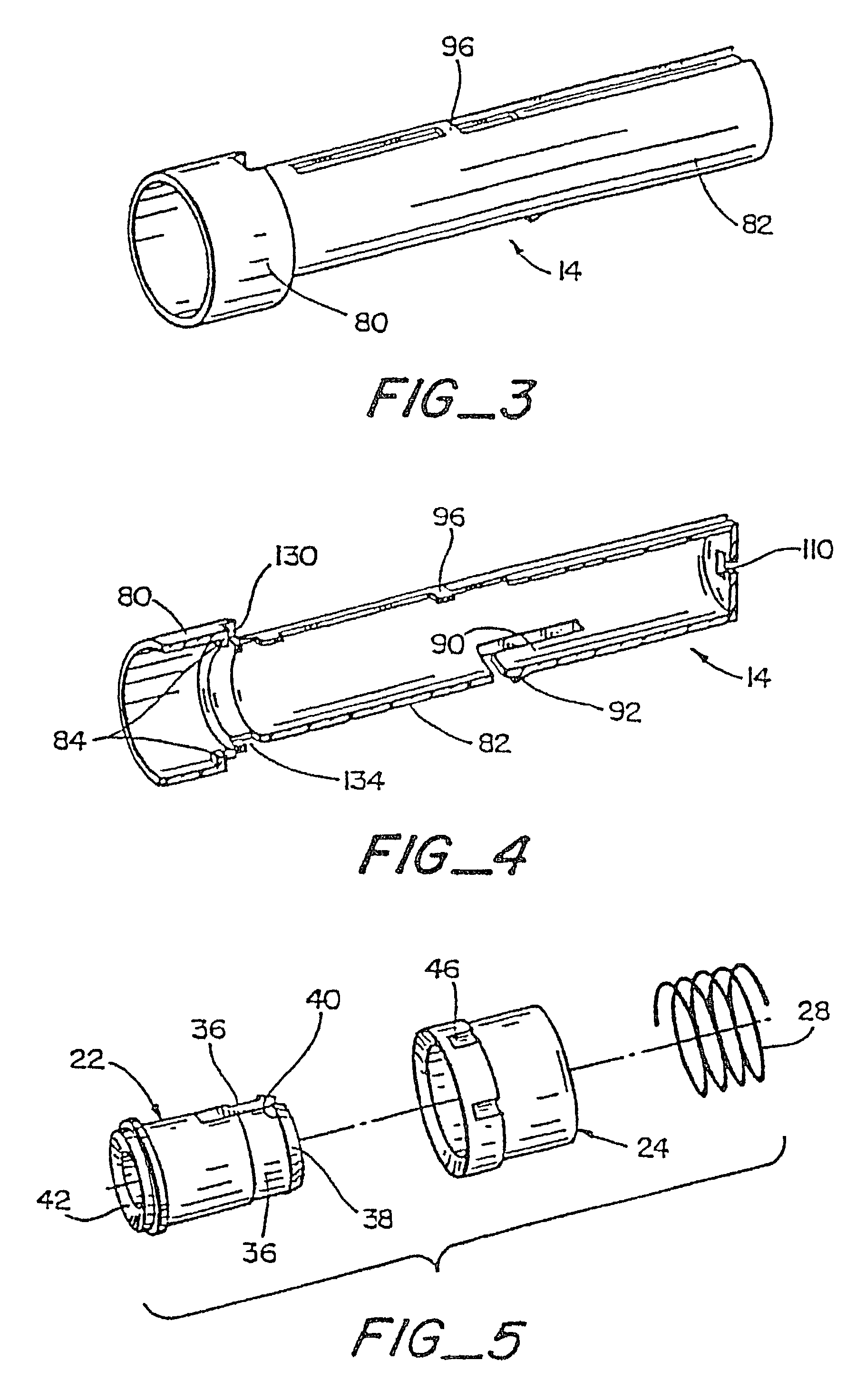
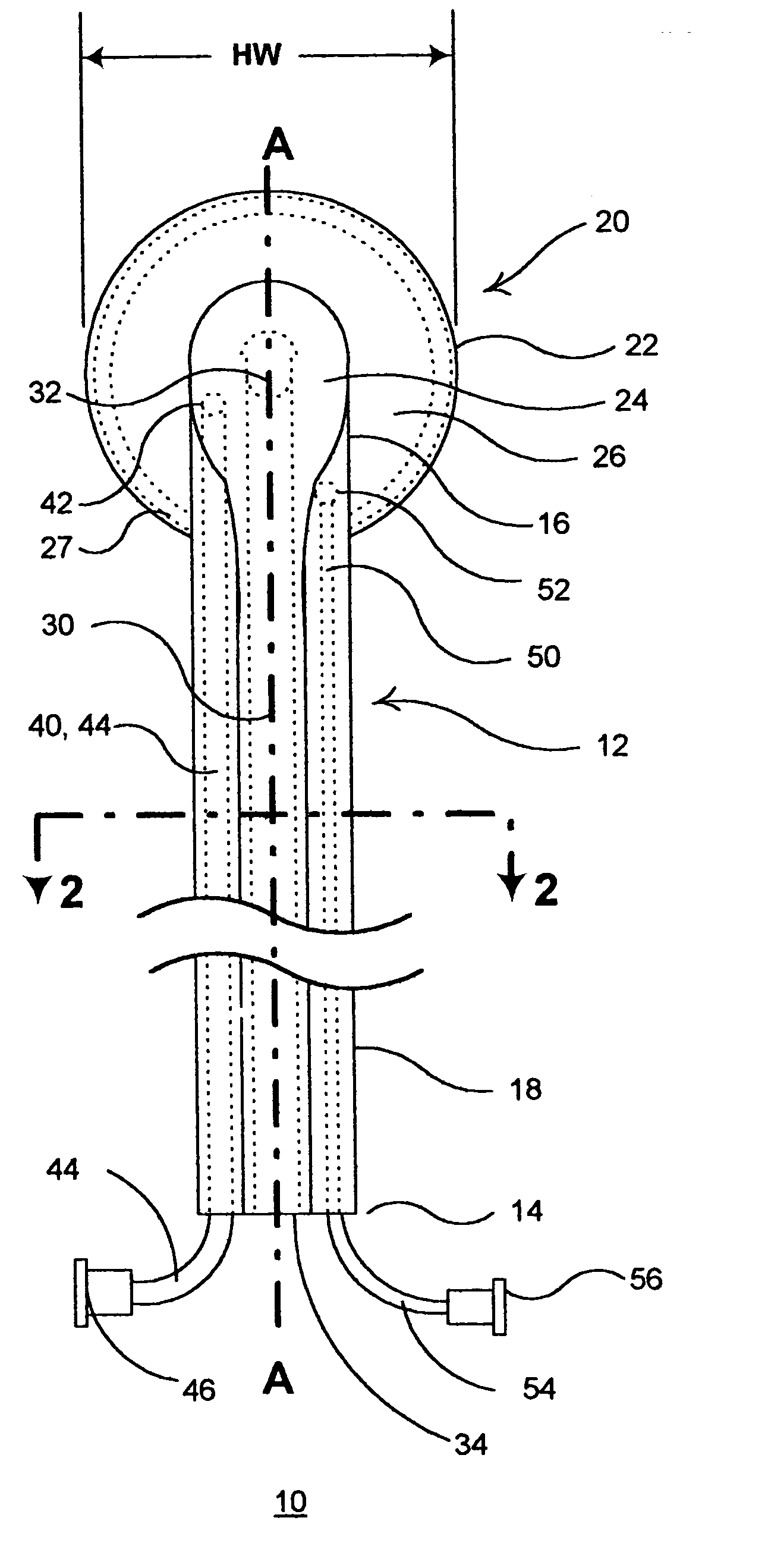
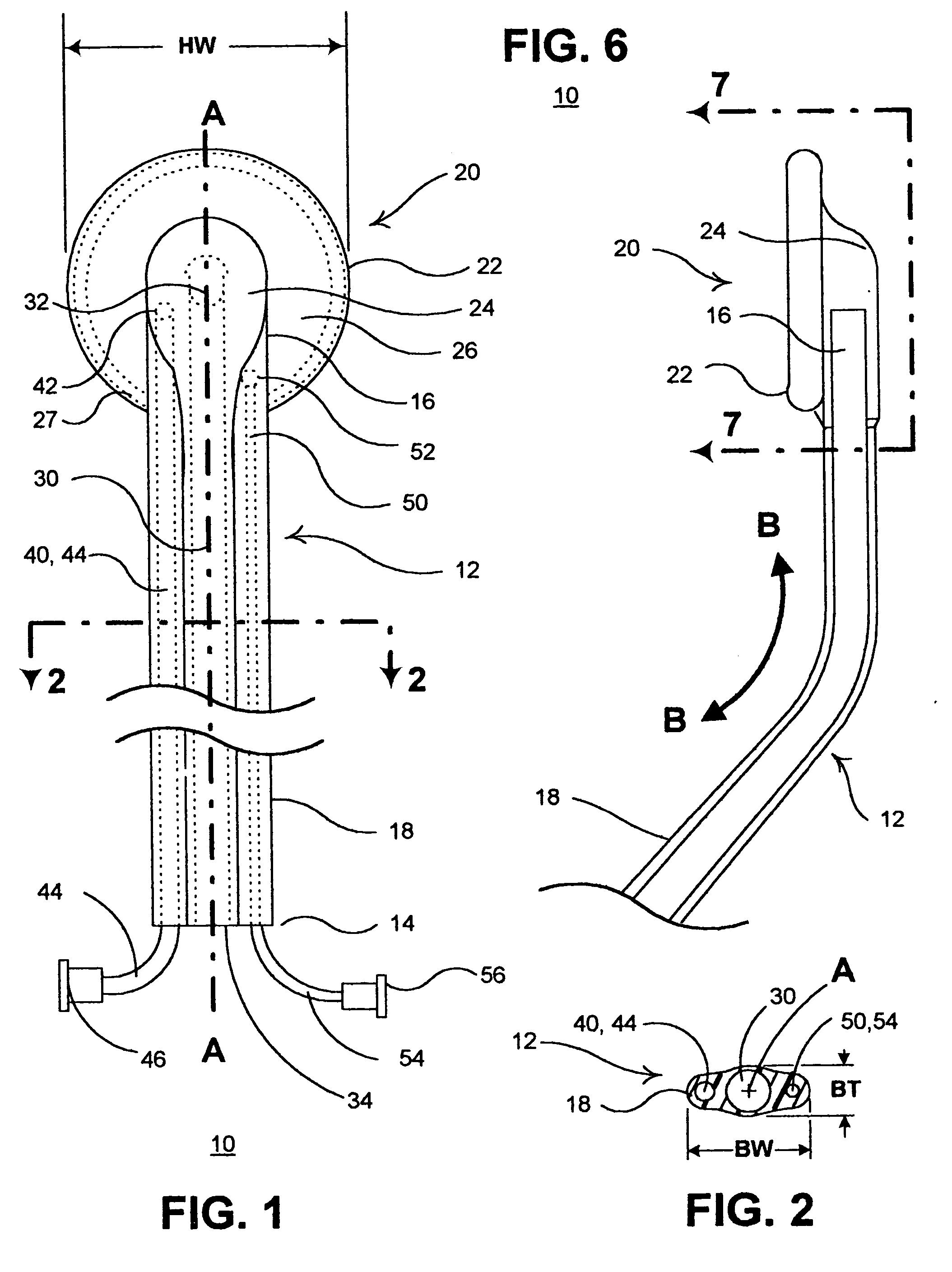
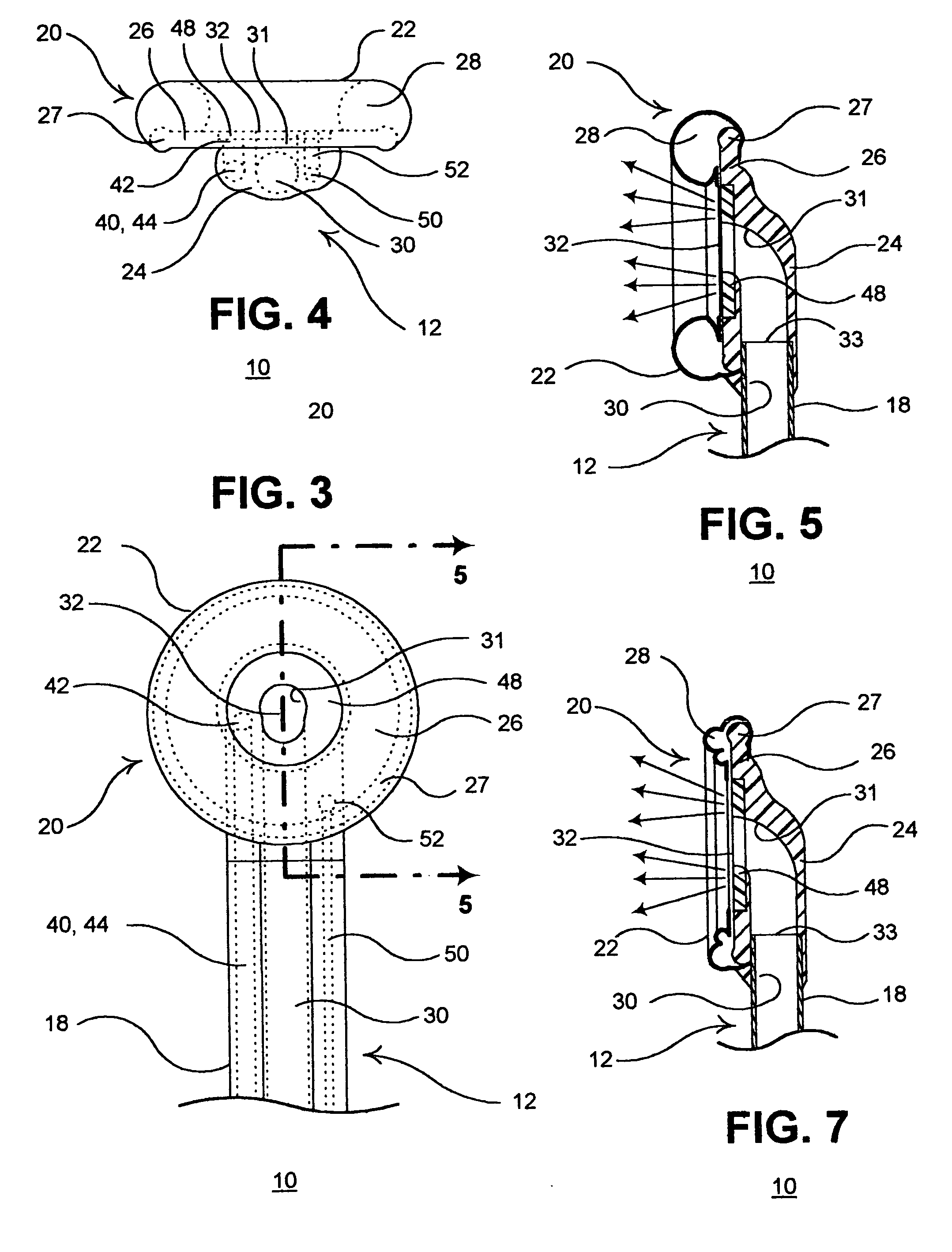
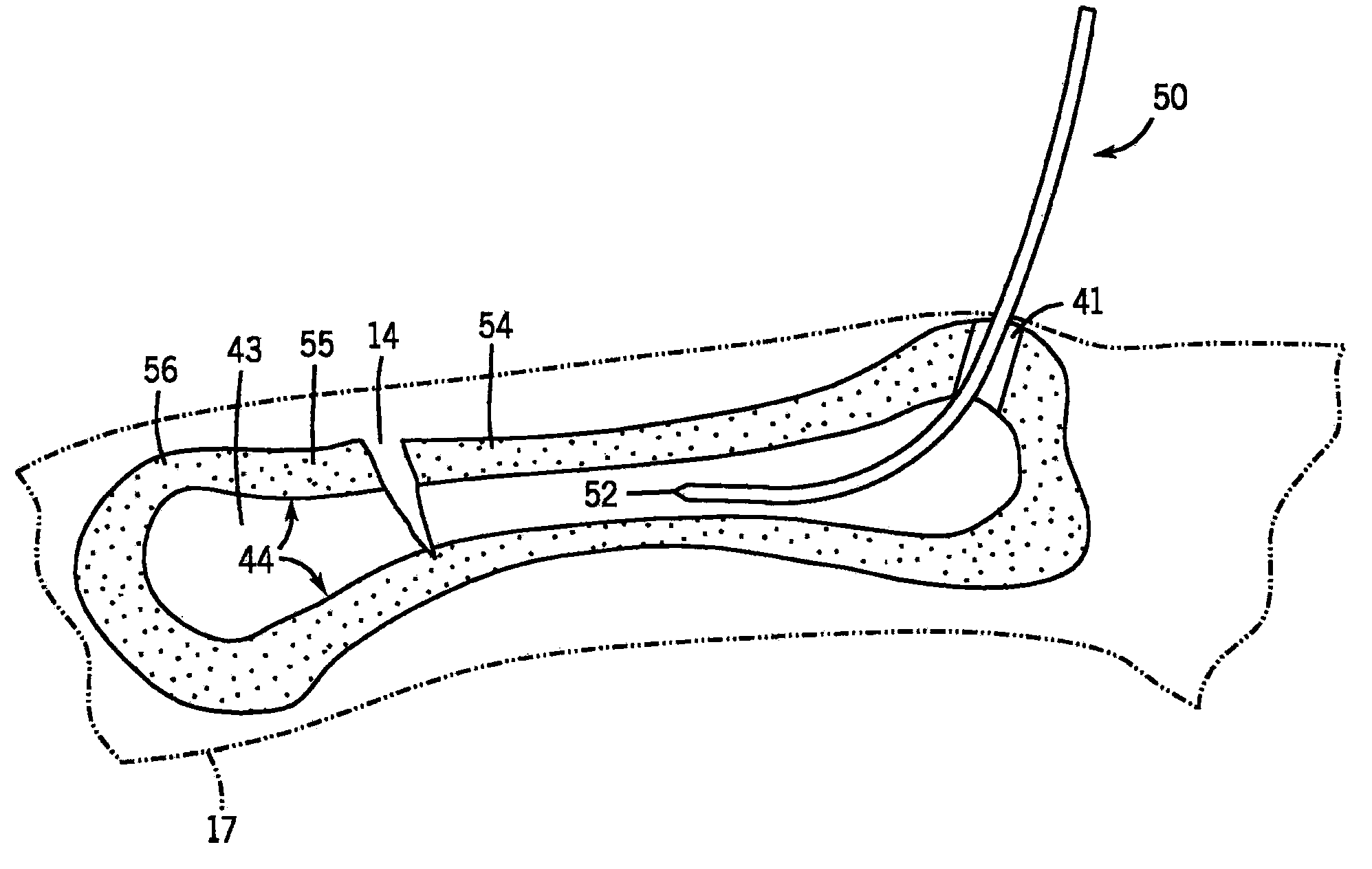
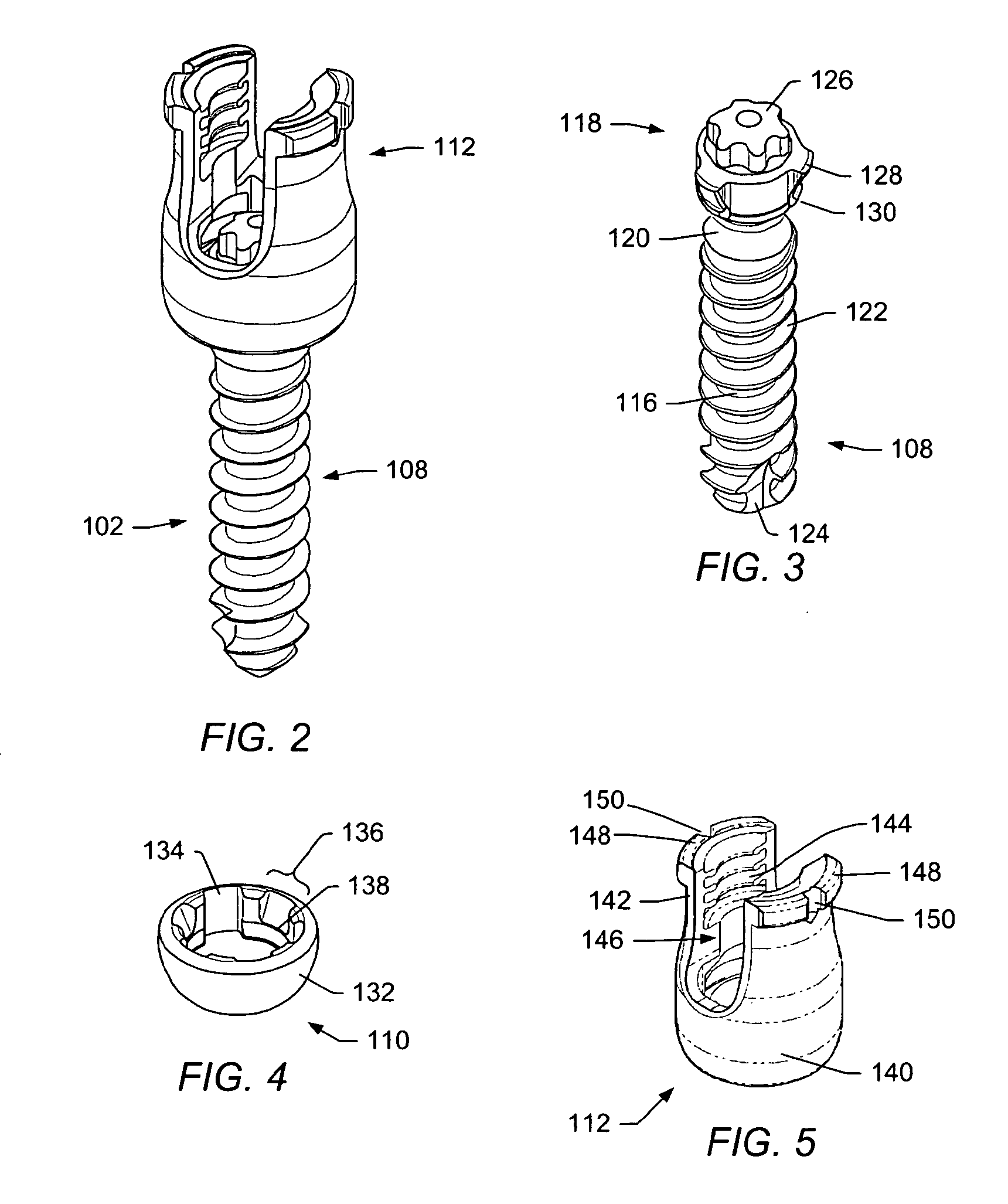
The present invention provides a non-rigid retractor for providing access to a surgical site, such as a patient's spine, during a surgical process. When used in spinal surgery, the non-rigid retractor allows a surgeon to operate on one or more spinal levels. The non-rigid retractor includes at least one flexible strap anchored at a first end to the spine or other internal body part at the surgical site. The body of the at least one flexible strap extends from a skin incision and is anchored at a second location external to the body to retract skin and muscle from the surgical site, allowing adequate visualization of the surgical site and providing access for implants and surgical instruments to pass through the retractor and into the surgical site.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
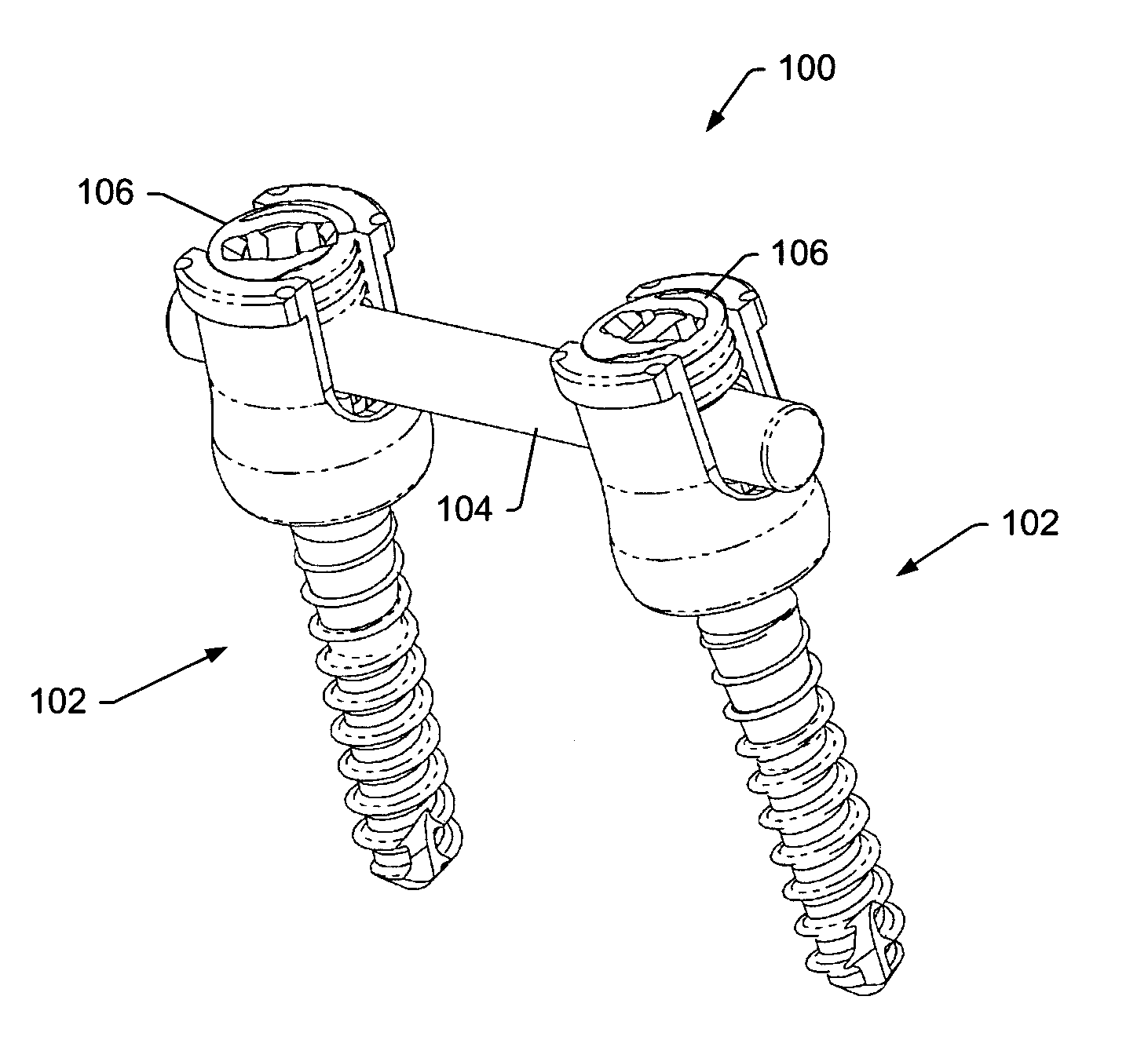
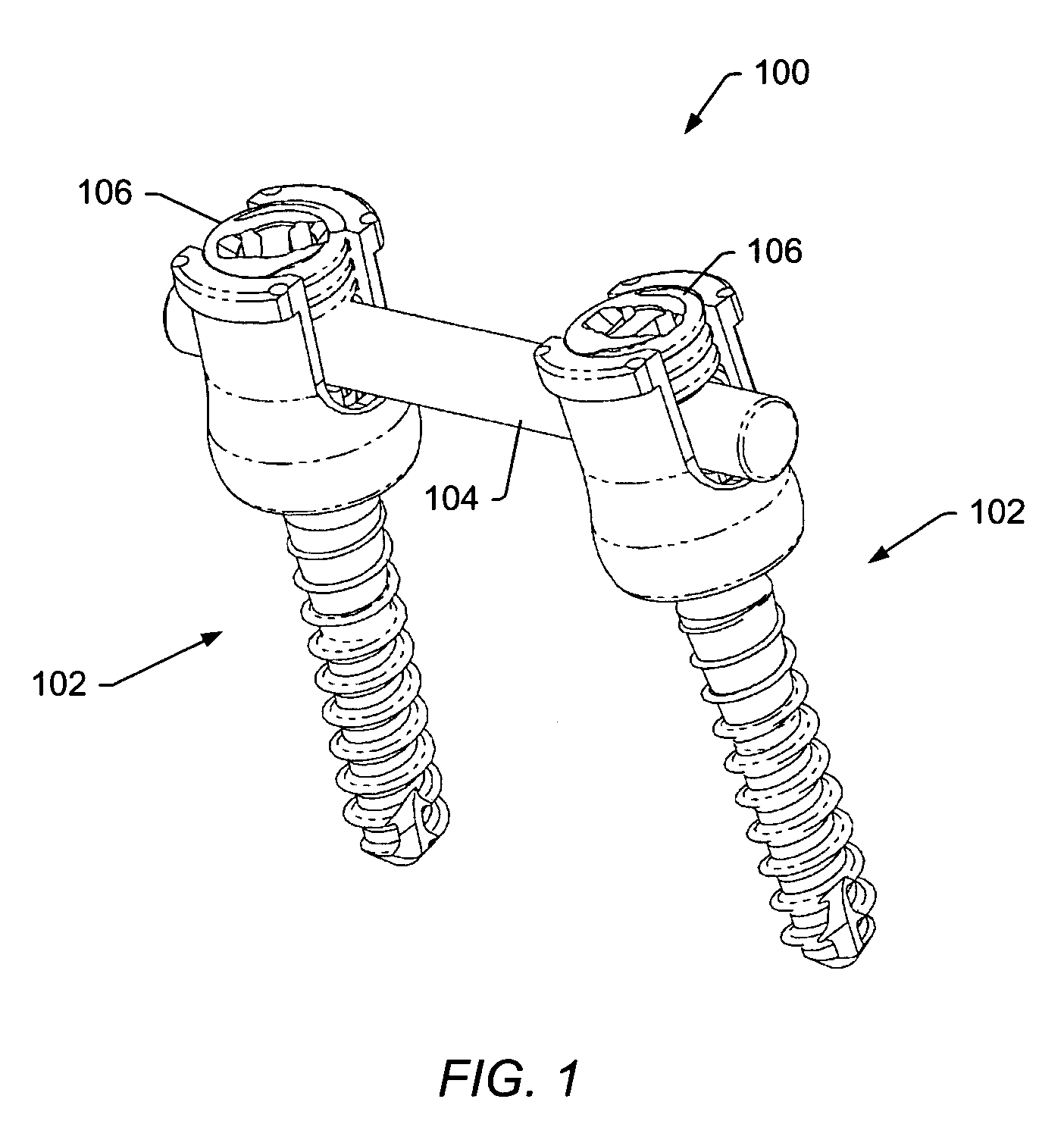
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
InactiveUS7250052B2Minimize damageProvide stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
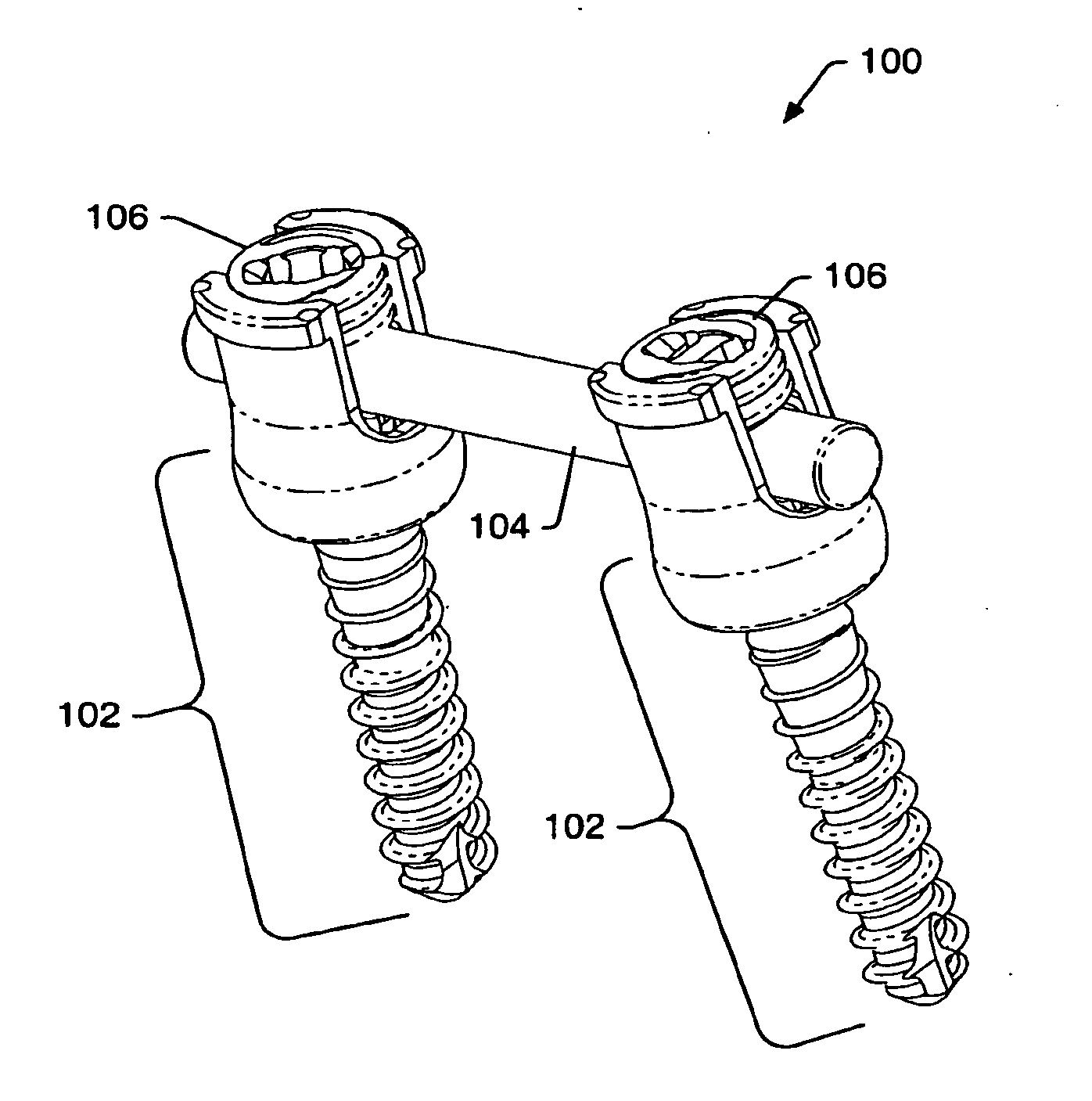
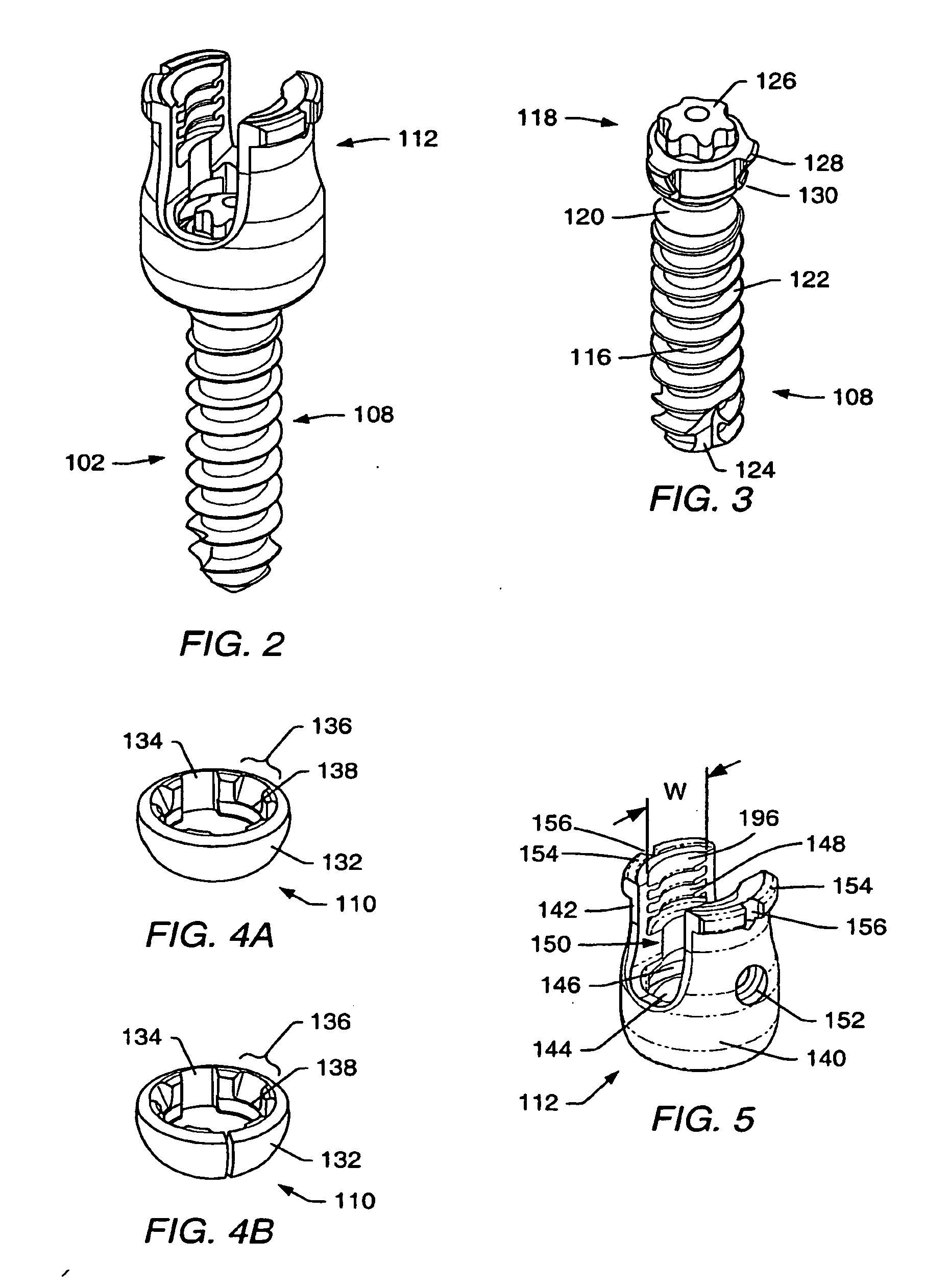
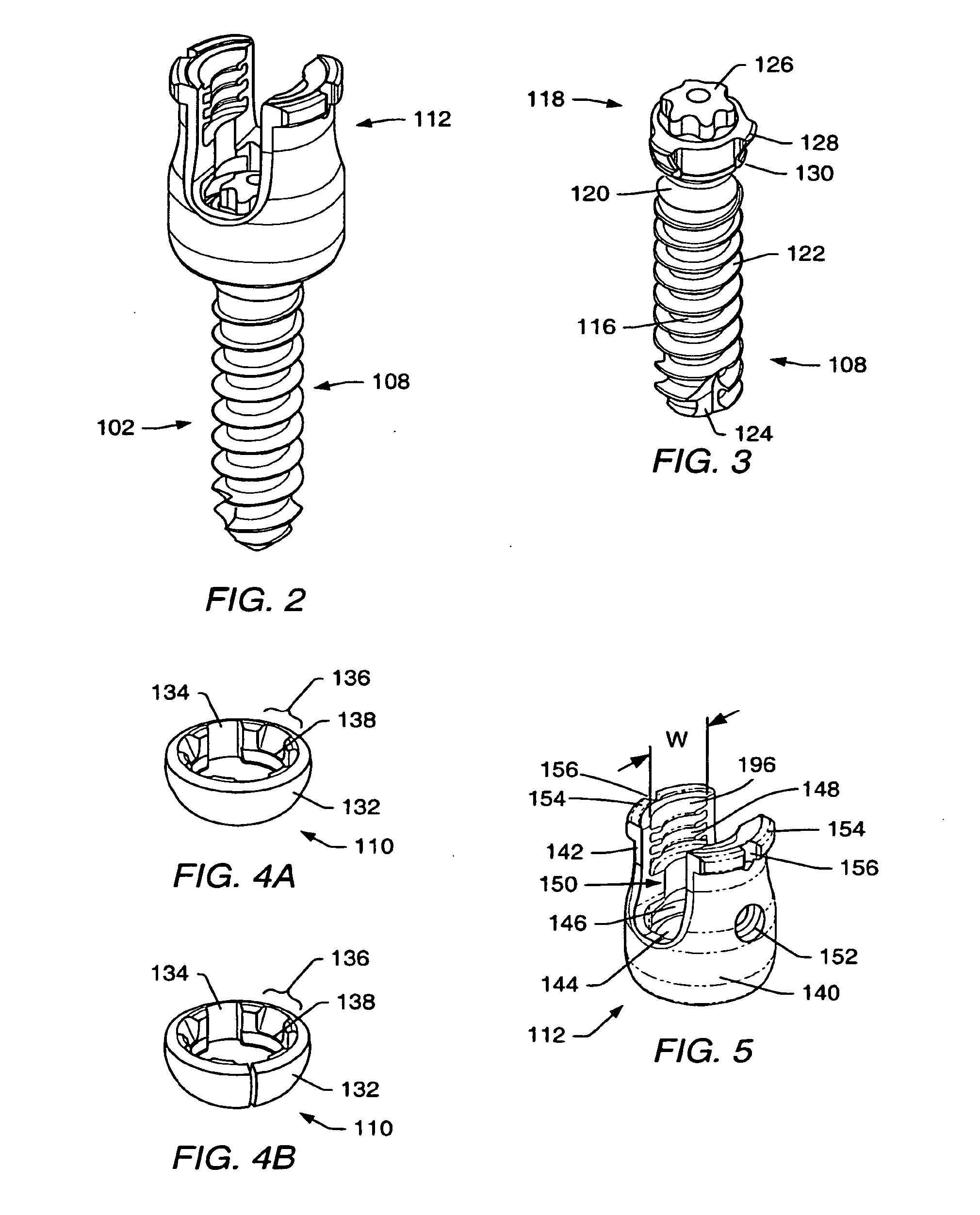
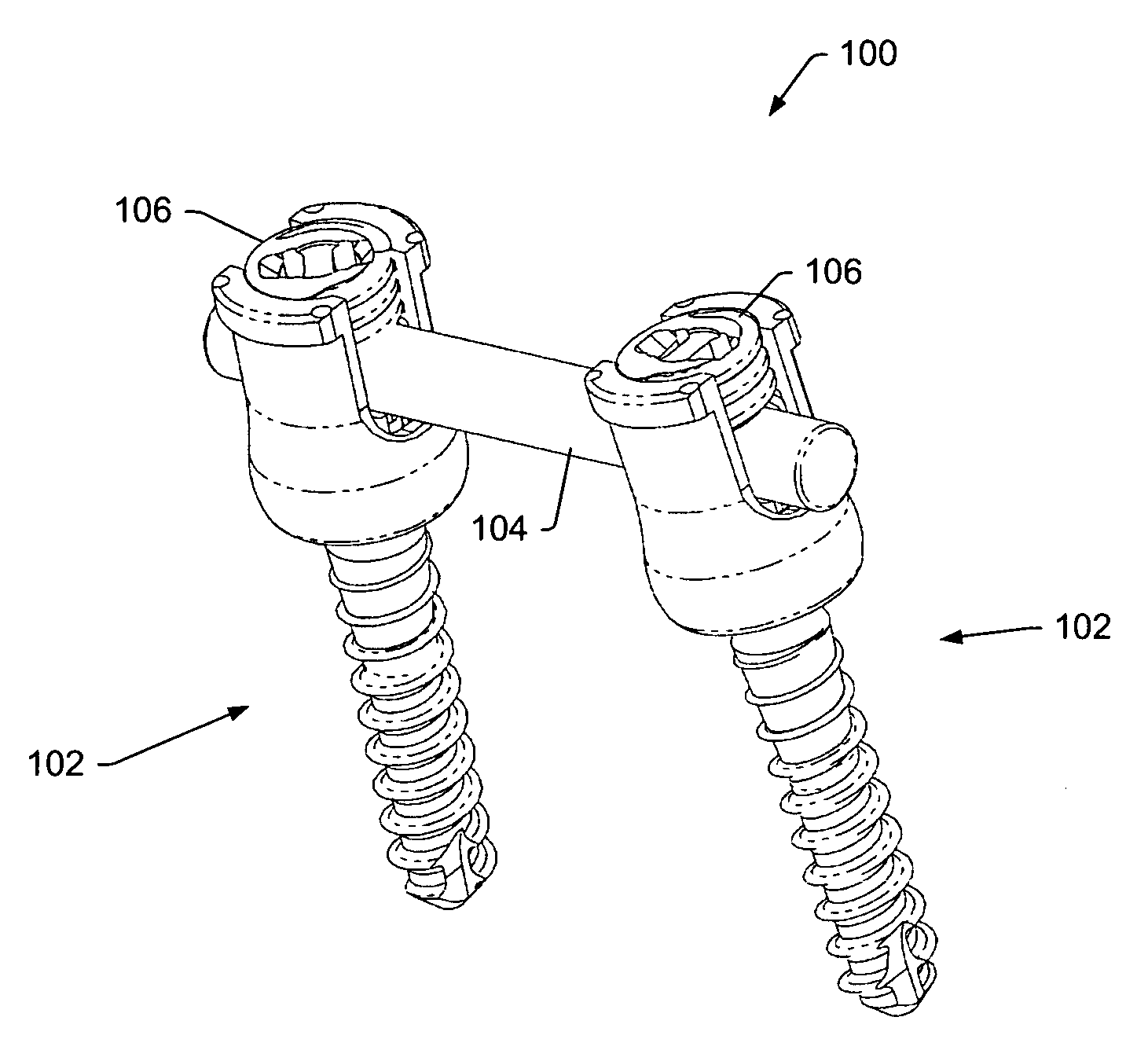
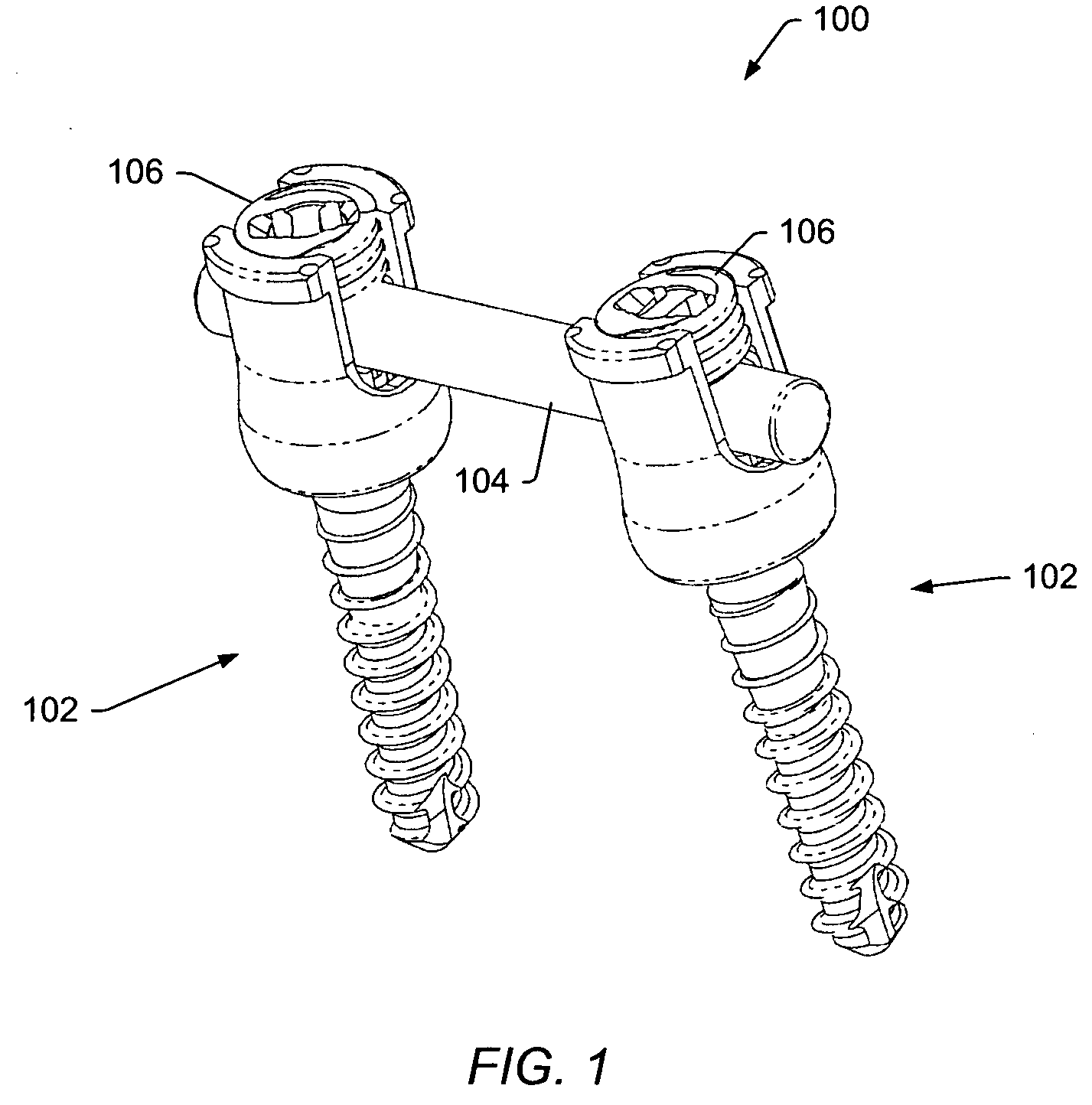
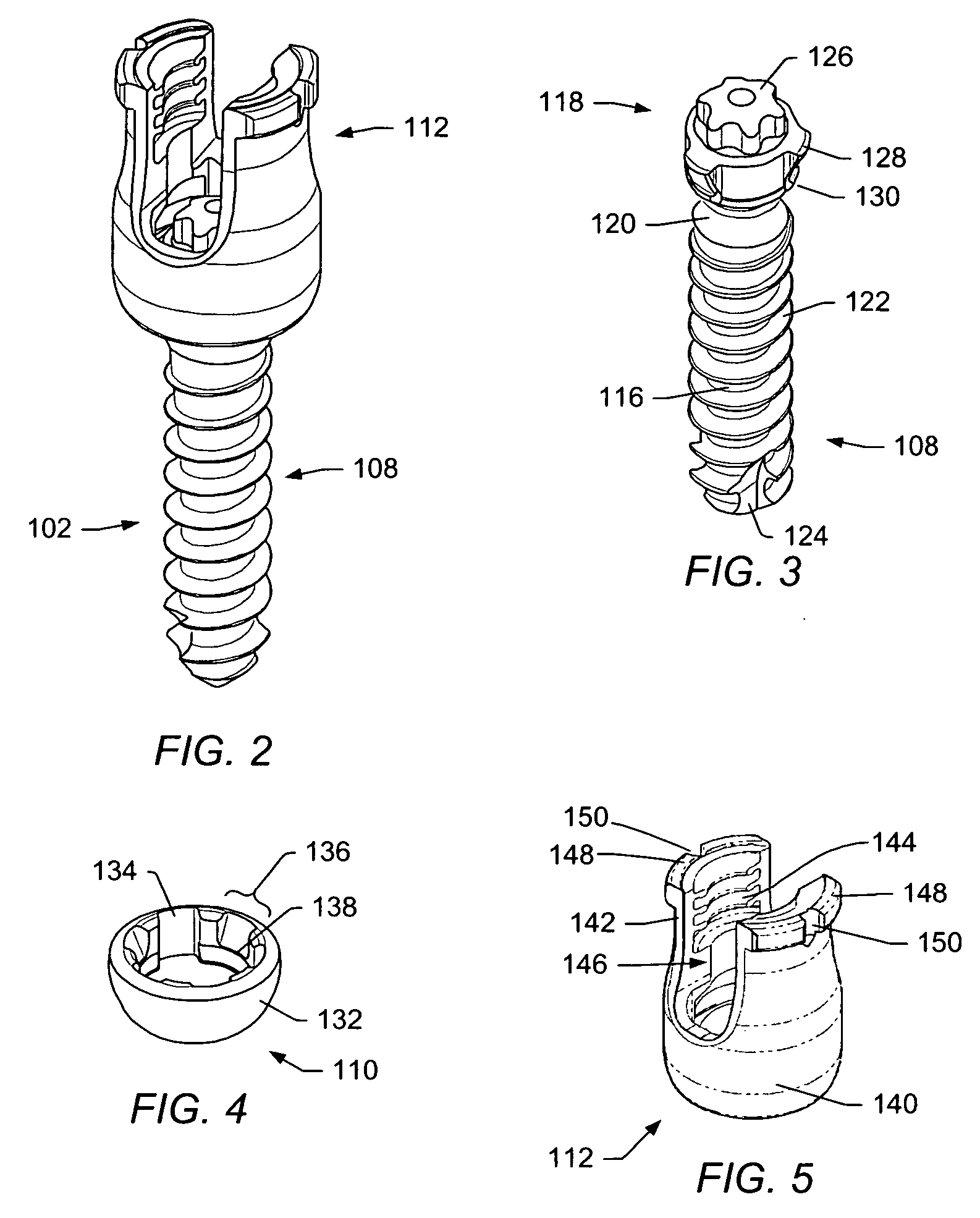
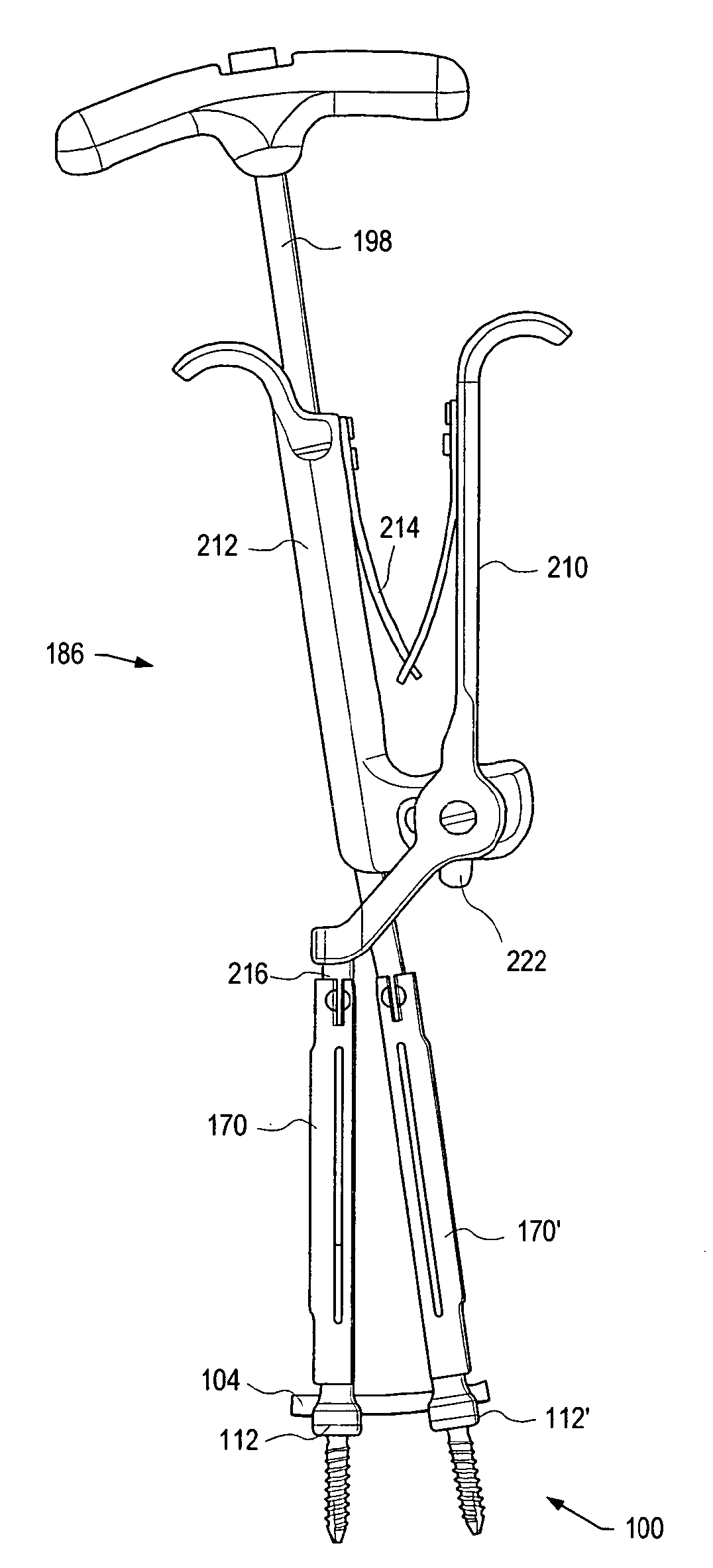
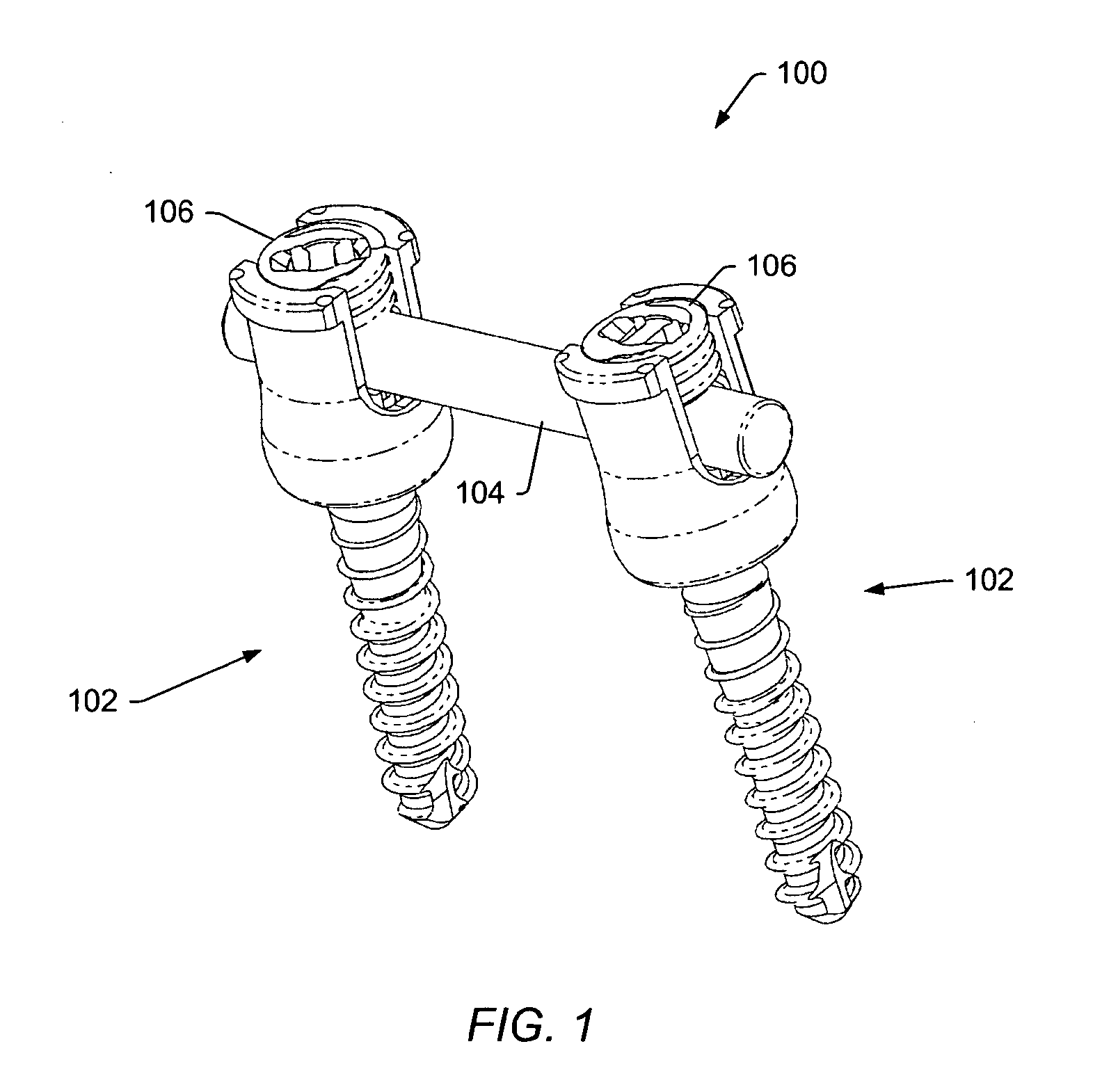
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:HIGHRIDGE MEDICAL LLC
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
ActiveUS20060142761A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Instruments and methods for reduction of vertebral bodies
ActiveUS20080009864A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsMinimally invasive proceduresReducer
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. A reducer may be used to achieve reduction of one or more vertebral bodies coupled to a spinal stabilization system.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Spinal stabilization systems and methods
ActiveUS20060084993A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMinimally invasive proceduresSkin incision
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Detachable members may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The detachable members may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
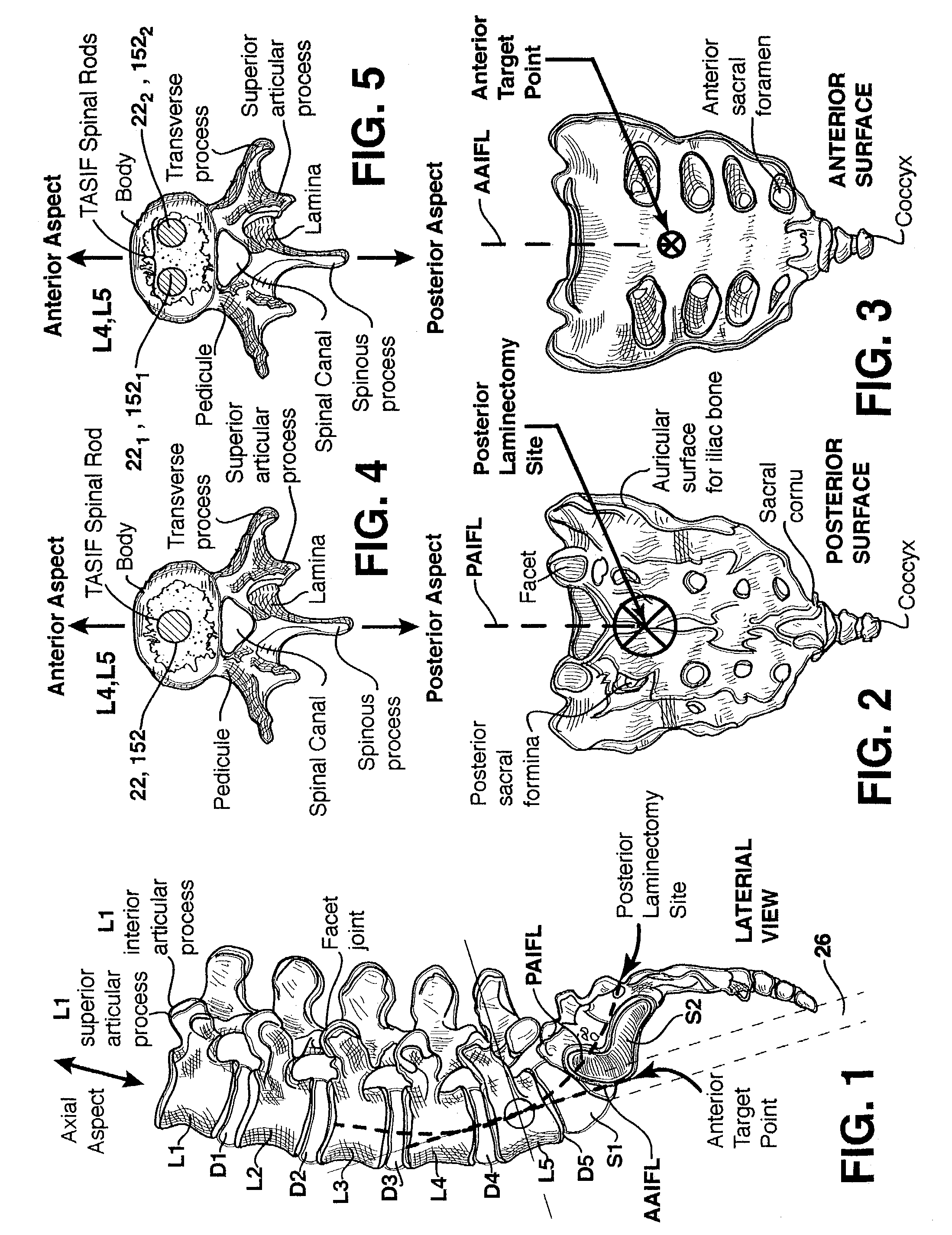
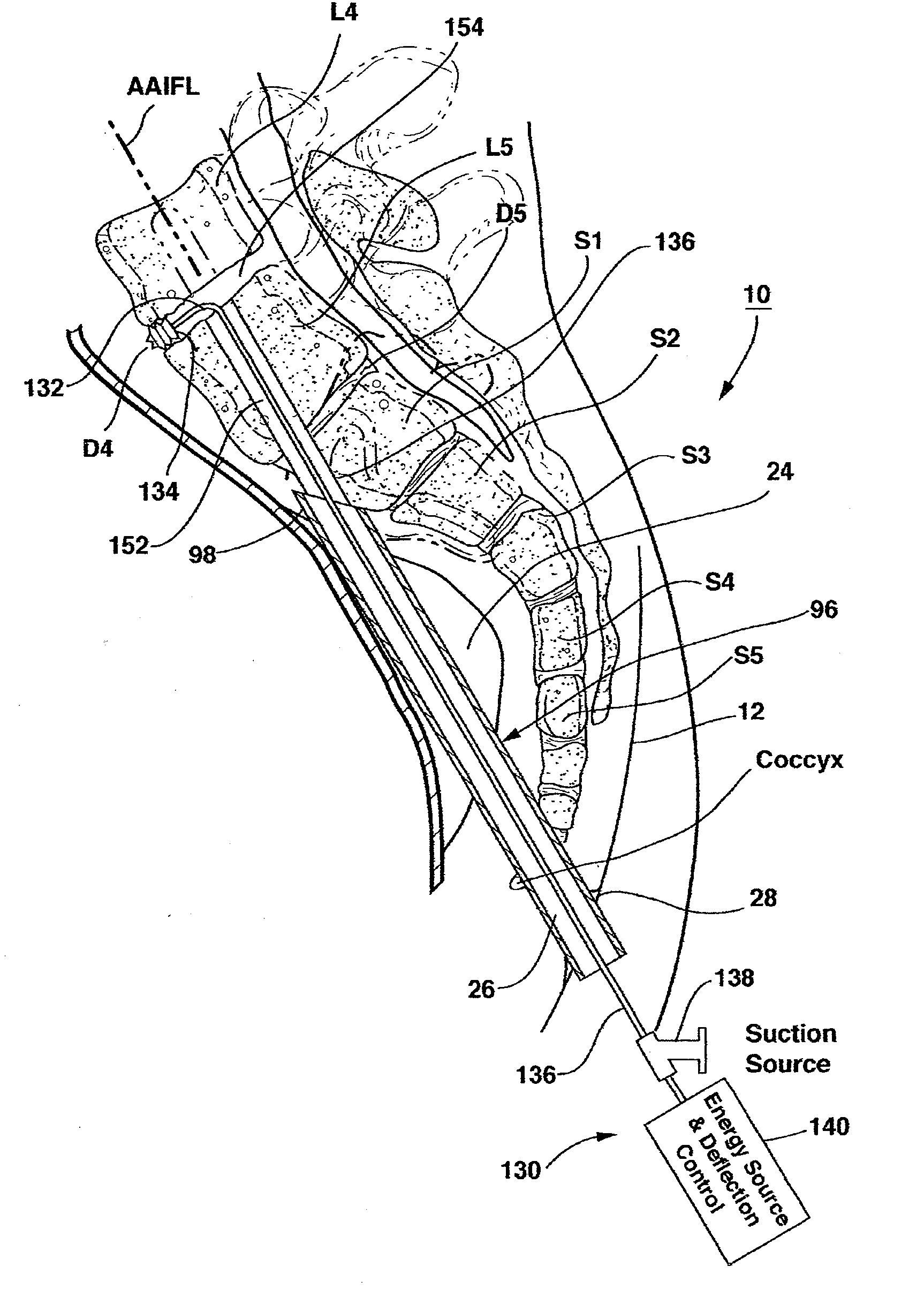
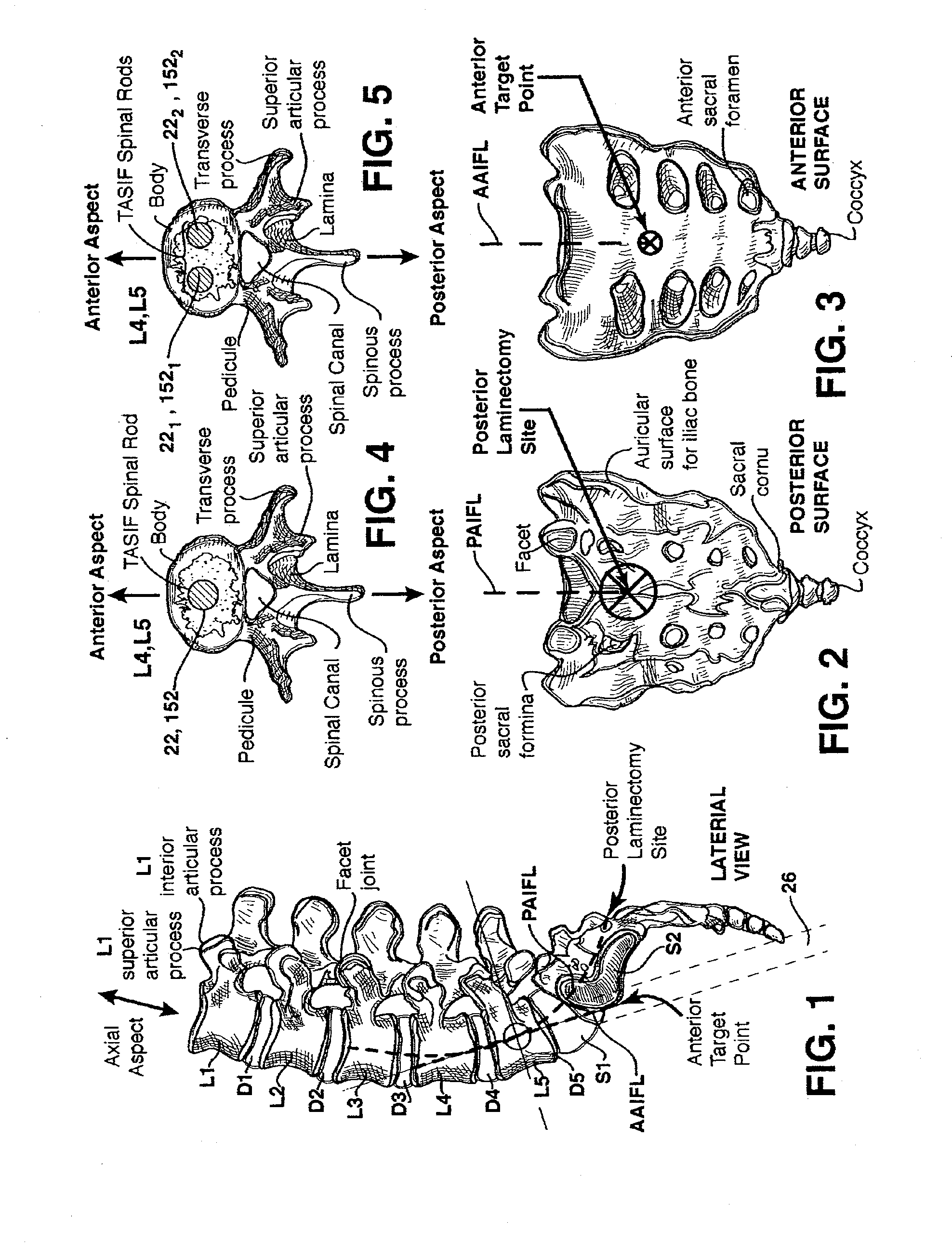
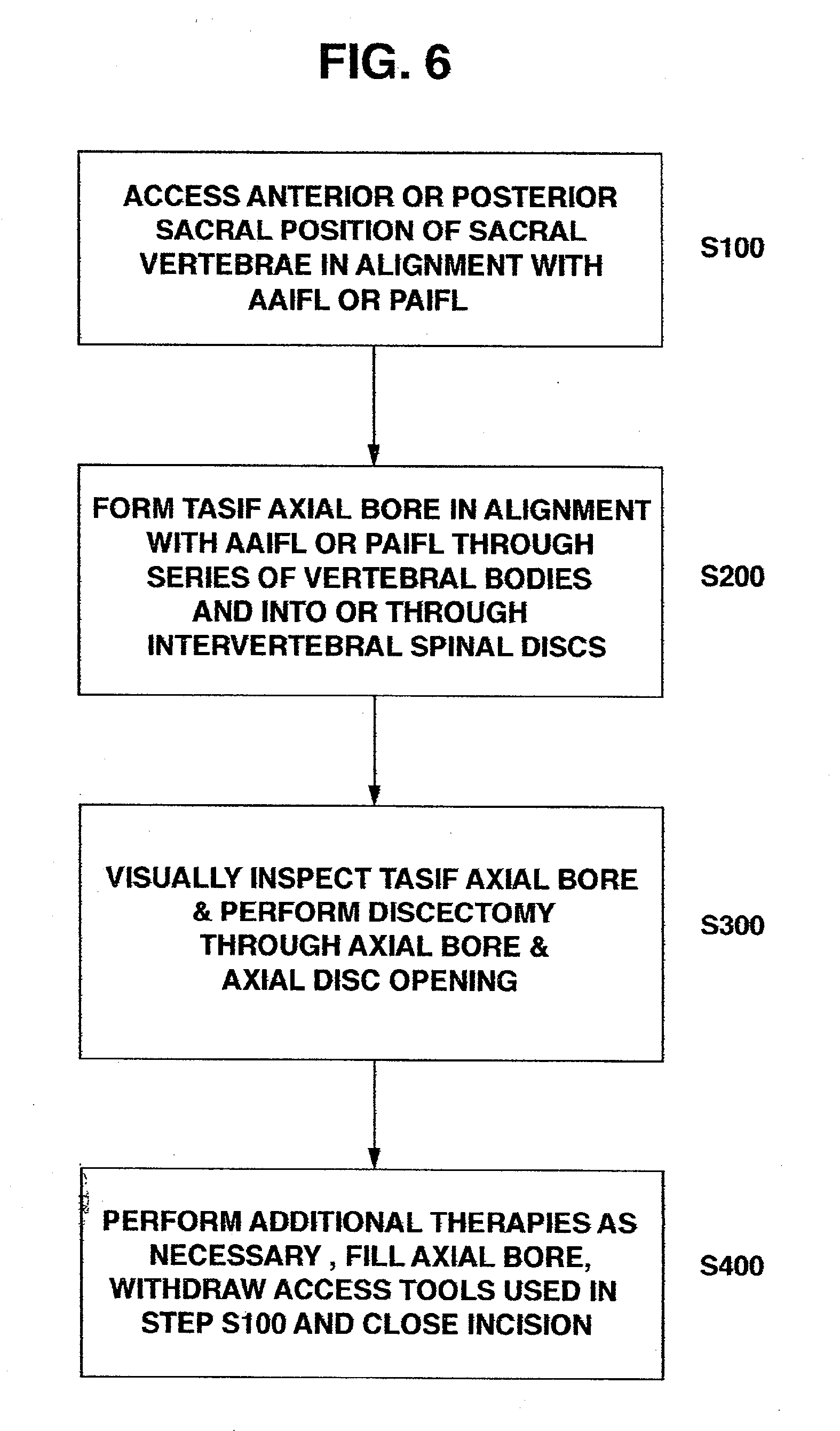
Method and apparatus for providing posterior or anterior trans-sacral access to spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS7087058B2Less discomfortMinimally invasiveInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnSacrum
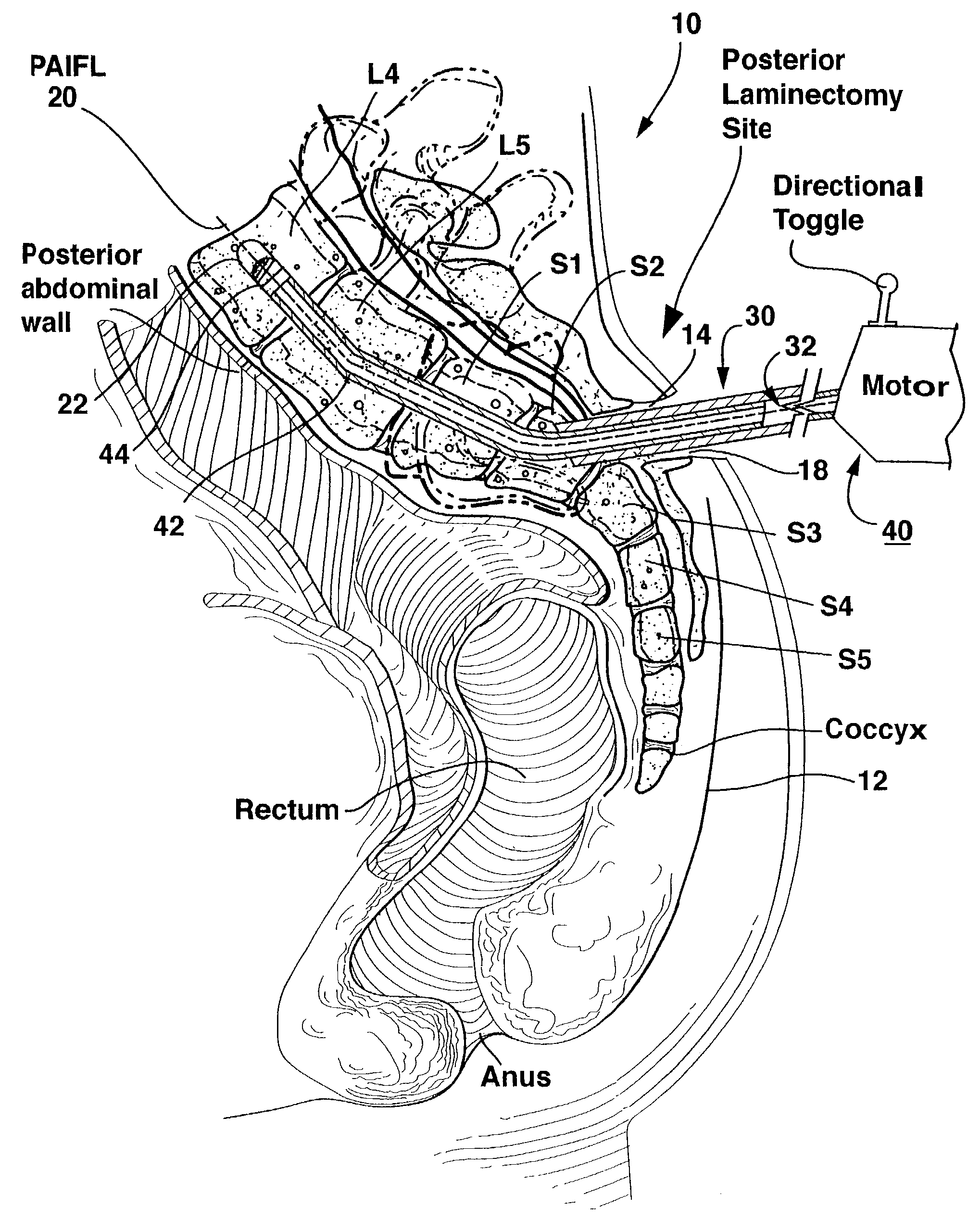
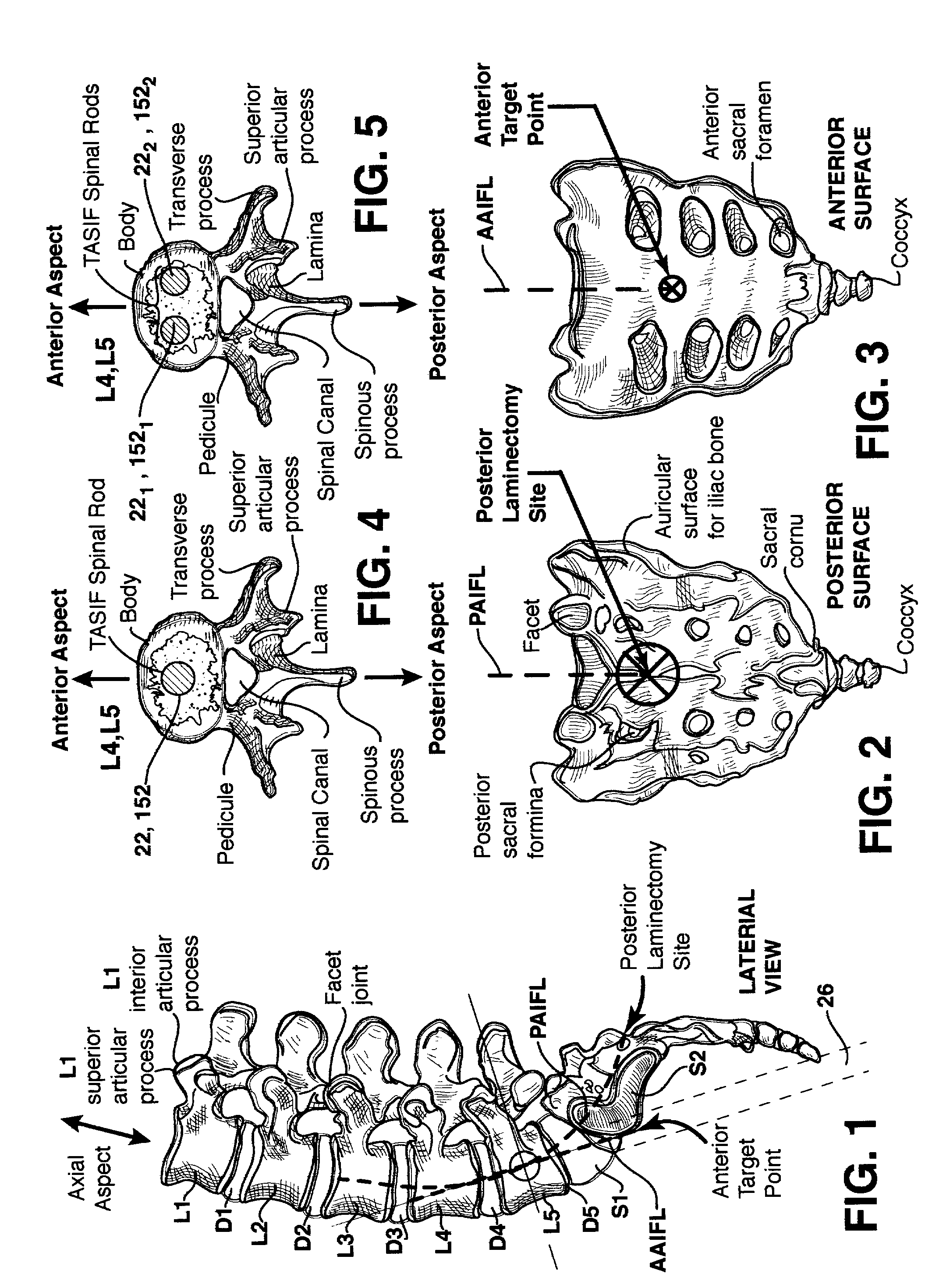
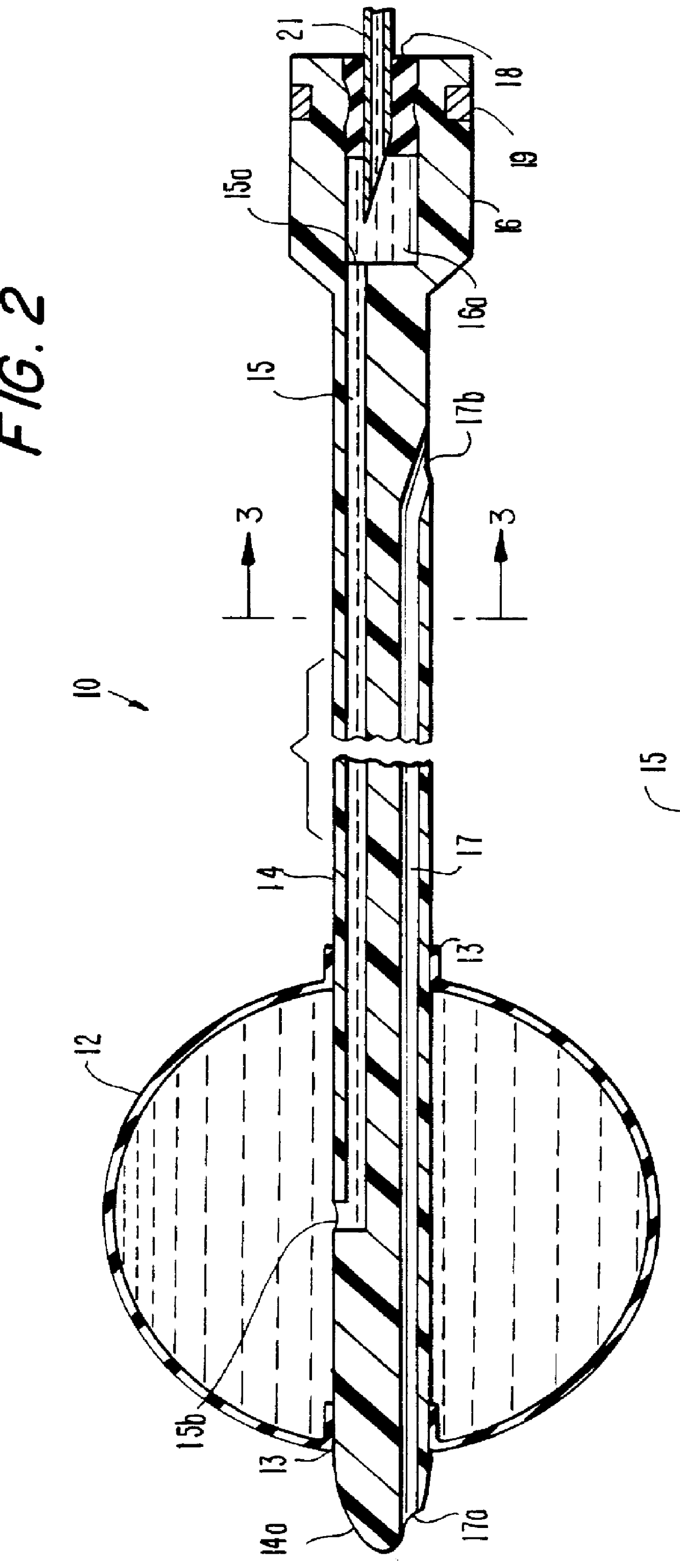
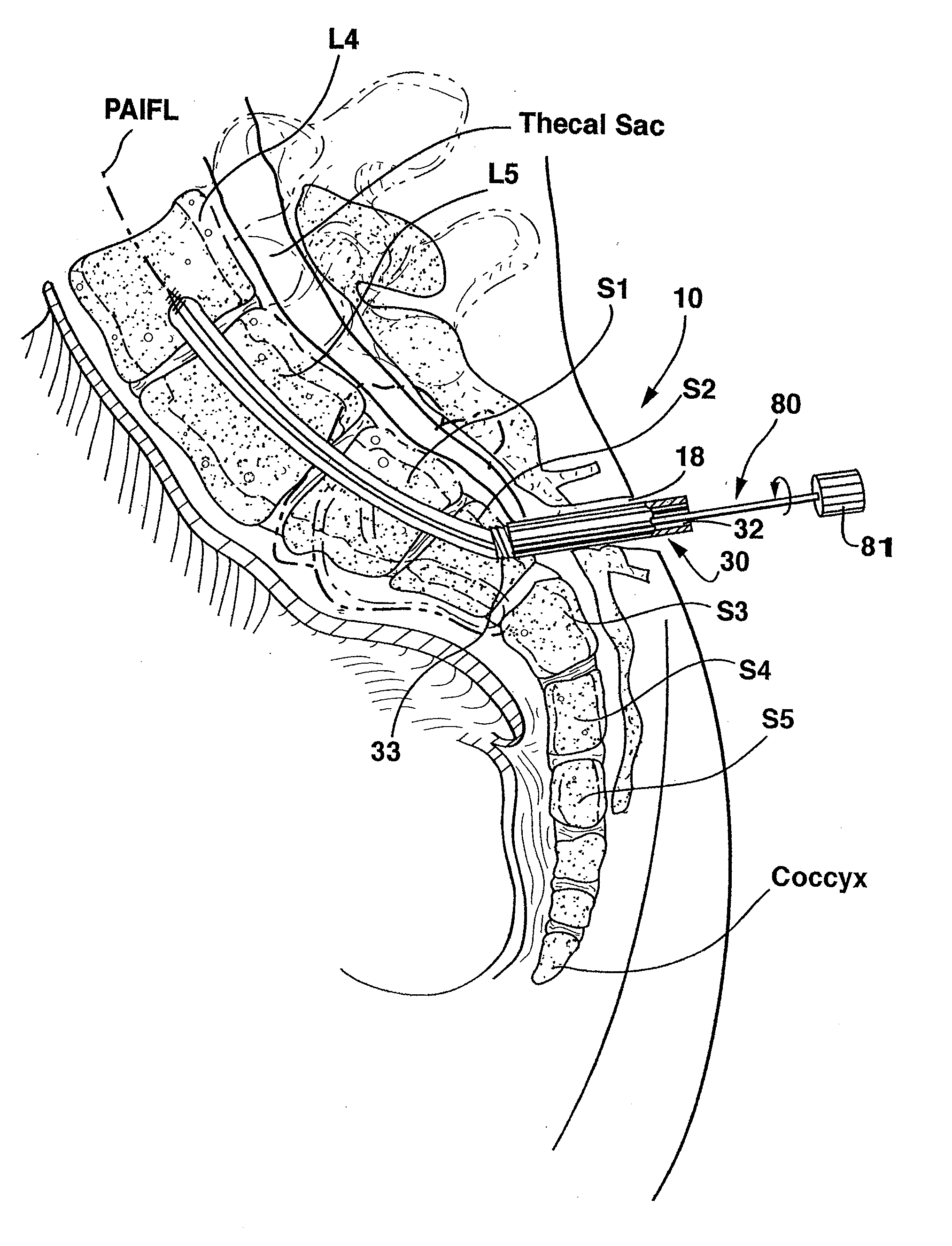
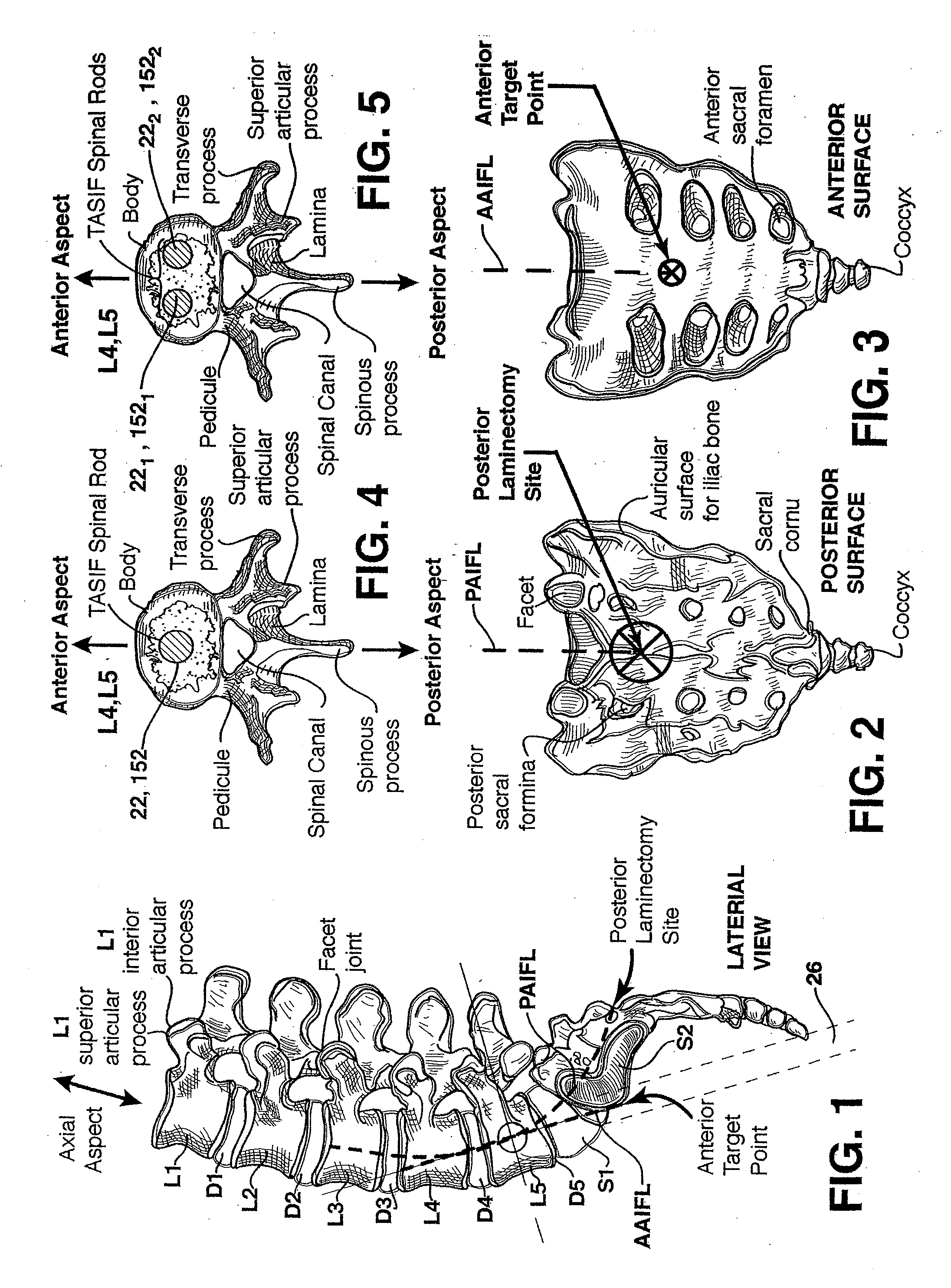
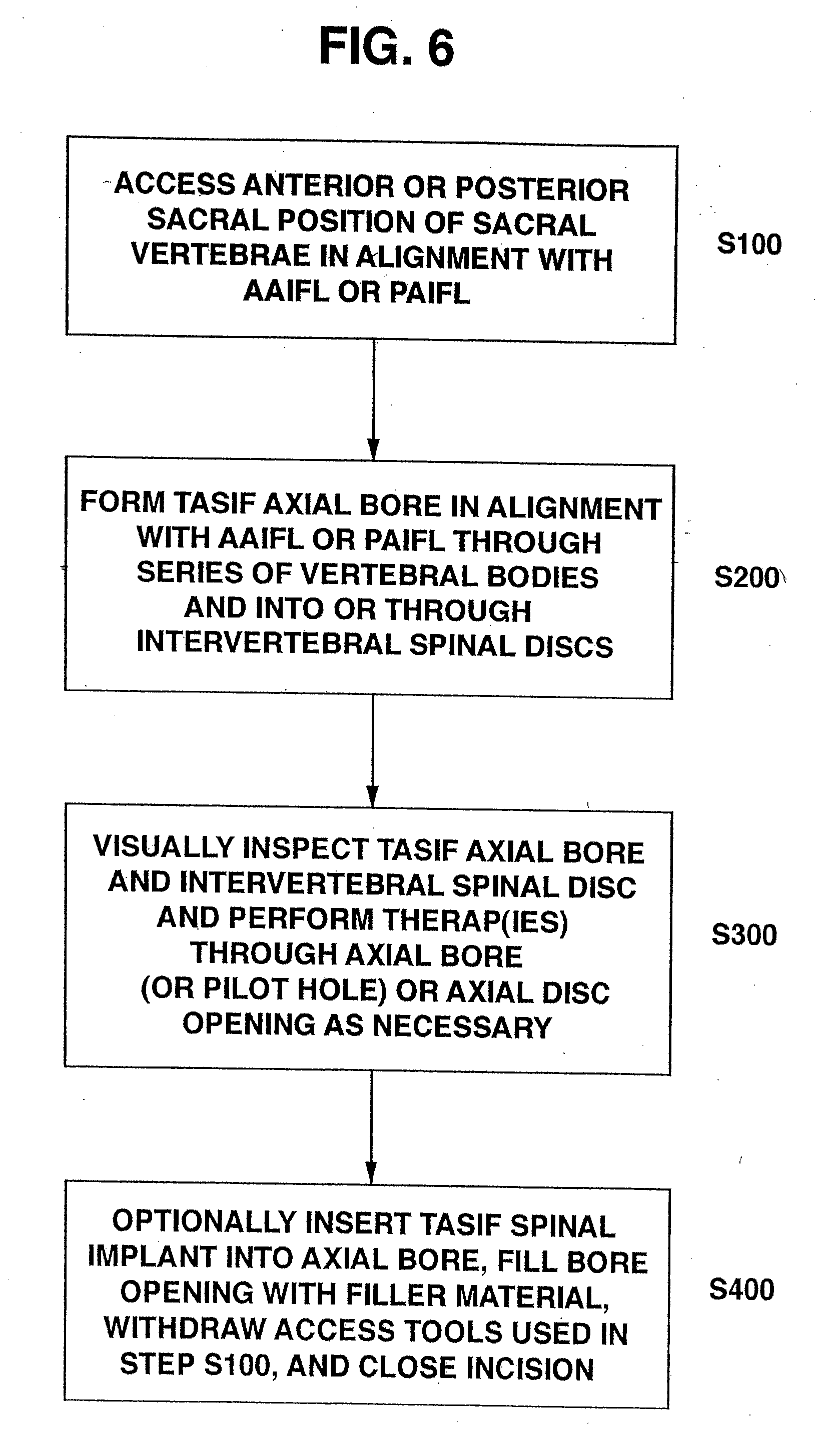
Methods and apparatus for providing percutaneous access to vertebrae in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. A number of related TASIF methods and surgical tool sets are provided by the present invention that are employed to form a percutaneous pathway from an anterior or posterior skin incision to a respective anterior or posterior target point of a sacral surface. The percutaneous pathway is generally axially aligned with an anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line extending from the respective anterior or posterior target point through at least one sacral vertebral body and one or more lumbar vertebral bodies in the cephalad direction. The provision of the percutaneous pathway described herein allows for the formation of the anterior or posterior TASIF bore(s) and / or the introduction of spinal implants and instruments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Instruments and methods for reduction of vertebral bodies
InactiveUS20060095035A1Minimize damage amountProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisFractureMinimally invasive proceduresReducer
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. The collar may be rotated and / or angulated relative to the bone fastener. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. A reducer may be used to achieve reduction of one or more vertebral bodies coupled to a spinal stabilization system.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Instruments and methods for adjusting separation distance of vertebral bodies with a minimally invasive spinal stabilization procedure
ActiveUS20060122597A1Enhanced couplingInhibition of translationInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMinimally invasive proceduresCombined use
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. An adjuster may be used in conjunction with the extenders to change a separation distance between the bone fastener assemblies.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Methods and apparatus for accessing and stabilizing an area of the heart
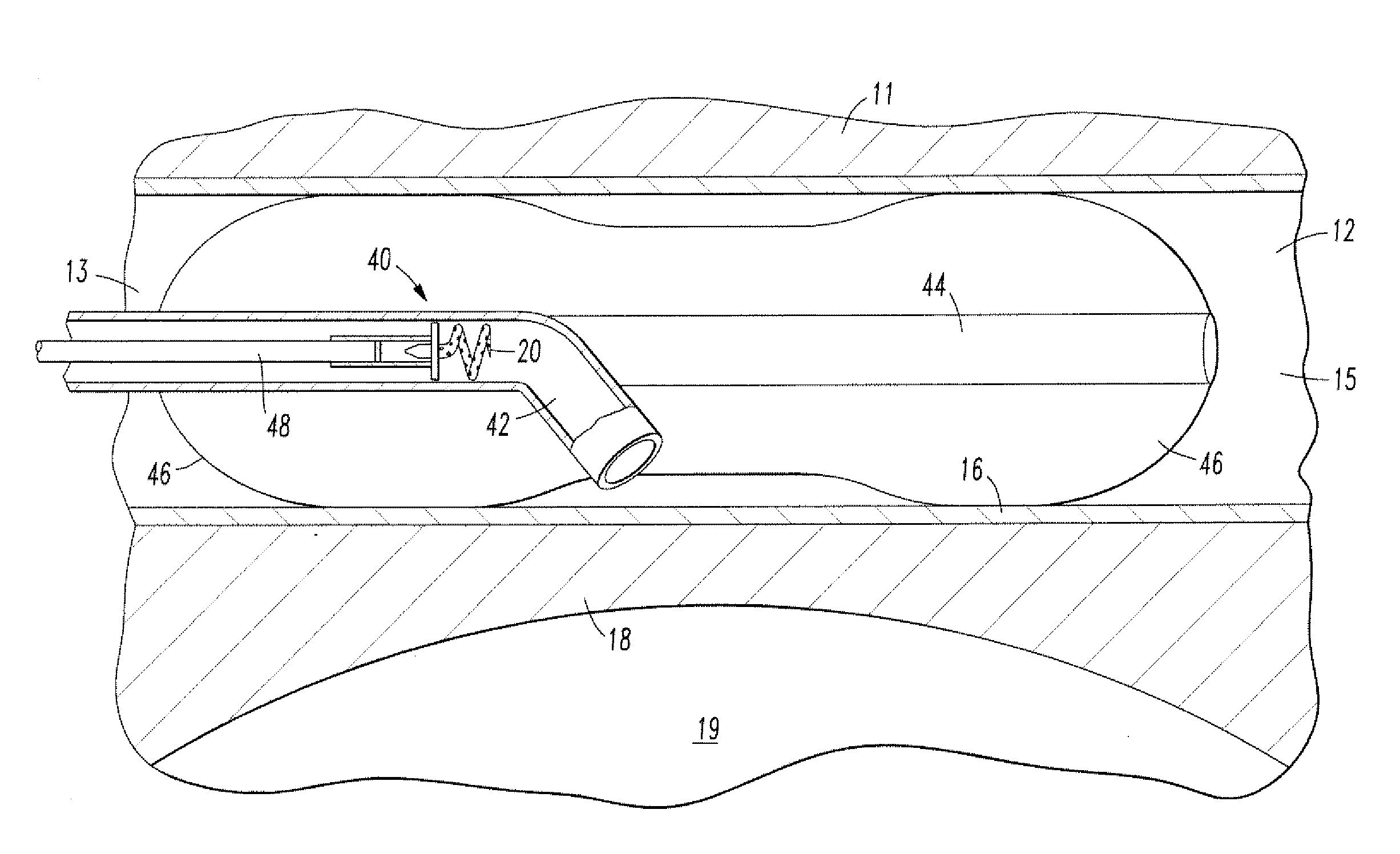
An epicardial lead installation tool having an elongated tool body extending between a tool body proximal and distal ends and encloses a tool body lumen. At least one suction pad supported by a suction pad strut extends distally to a distal end surface of the tool body distal end. A lead implantation tool extending between implantation tool proximal and distal ends is inserted through the tool body lumen to dispose the implantation tool distal end proximate to the tool body distal end. The lead implantation tool distal end is adapted to engage the distal electrode head of an epicardial lead to enable the extension of the assembly of the of the lead installation tool, the lead implantation tool and the epicardial lead through a skin incision and to apply the suction pad against the epicardium. Suction is applied through the suction pad to affix it to the epicardium while the implantation tool proximal end is manipulated to affix the distal fixation mechanism to the myocardium at the implantation site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
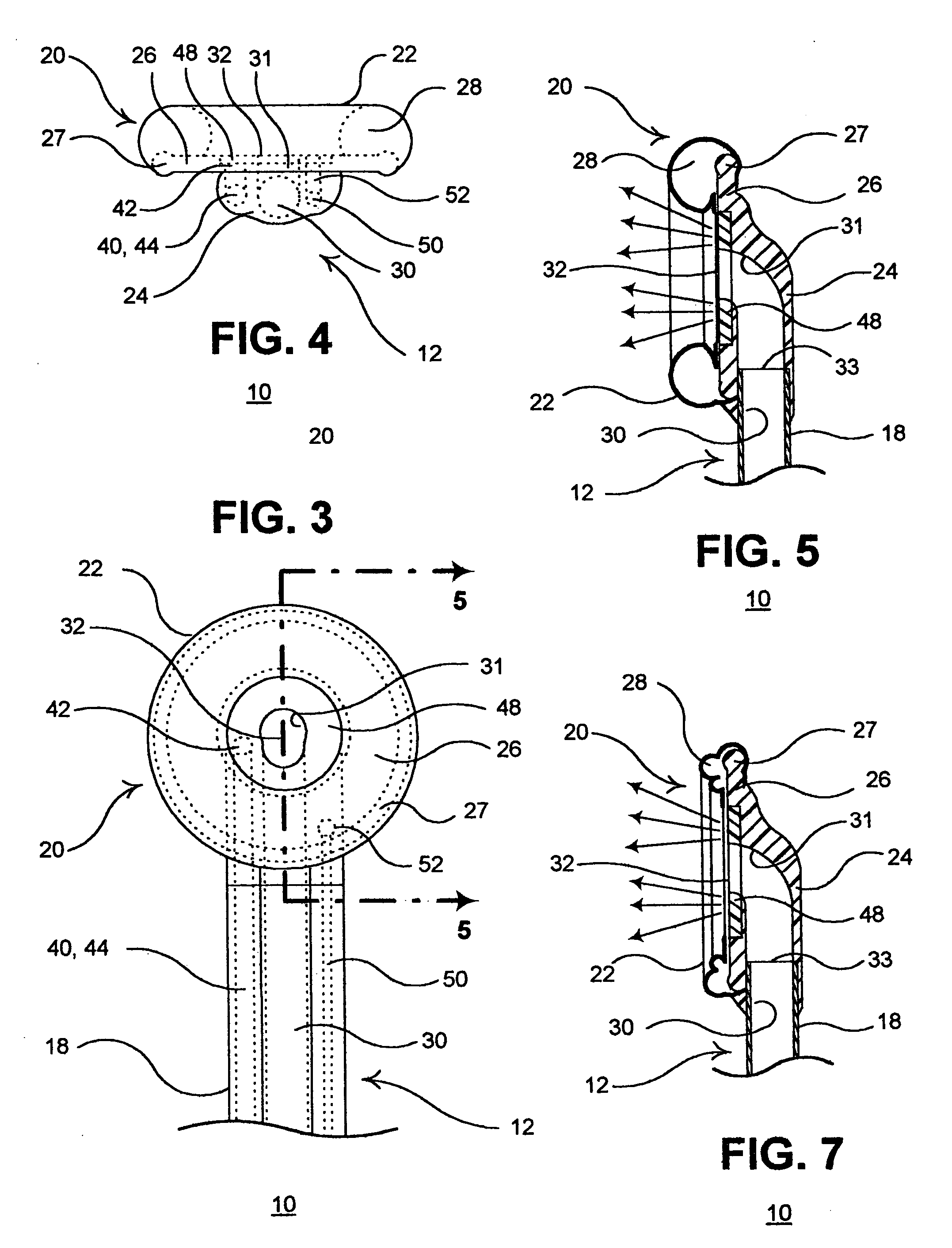
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:TRANSI
Instruments and methods for accessing an anatomic space
InactiveUS20050182465A1Convenient introductionRigid enoughStentsCannulasPericardial spaceAnatomic Site
An anatomic space of the body, particularly the pericardial space, is accessed in a minimally invasive manner from a skin incision by an access instrument to facilitate visualization and introduction of devices or drugs or other materials, performance of medical and surgical procedures, and introducing and fixating a cardiac lead electrode to the heart. An elongated access instrument body preferentially bends in one direction and resists bending in a transverse direction, whereby the access instrument body distal end can be directed through a path around body structures to the anatomic site by manipulation of the access instrument body proximal end portion. A distal header formed at the access instrument body distal end extends outward of the access instrument body in the transverse direction and supports an inflatable balloon surrounding a working lumen exit port that is directed toward an anatomic surface when the balloon is inflated by inflation media introduced through an inflation lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus for performing a discectomy through a trans-sacral axial bore within the vertebrae of the spine
Methods and apparatus for and performing a partial or complete discectomy of an intervertebral spinal disc accessed by one or more trans-sacral axial spinal instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore formed through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) line. A discectomy instrument is introduced through the axial bore, the axial disc opening, and into the nucleus to locate a discectomy instrument cutting head at the distal end of the discectomy instrument shaft within the nucleus. The cutting head is operated by operating means coupled to the instrument body proximal end for extending the cutting head laterally away from the disc opening within the nucleus of the intervertebral spinal disc and for operating the cutting head to form a disc cavity within the annulus extending laterally and away from the disc opening or a disc space wherein the disc cavity extends through at least a portion of the annulus. A discectomy sheath that is first introduced to extend from the skin incision through the axial bore and into the axial disc opening having a discectomy sheath lumen that the discectomy instrument is introduced through. The discectomy sheath is preferably employed for irrigation and aspiration of the disc cavity or just aspiration if irrigation fluids are introduced through a discectomy instrument shaft lumen. The cutting head of the discectomy tool is deflected from the sheath lumen laterally and radially toward the annulus using a deflecting catheter or pull wire.
Owner:BAXANO SURGICAL
Body fluid sampling device
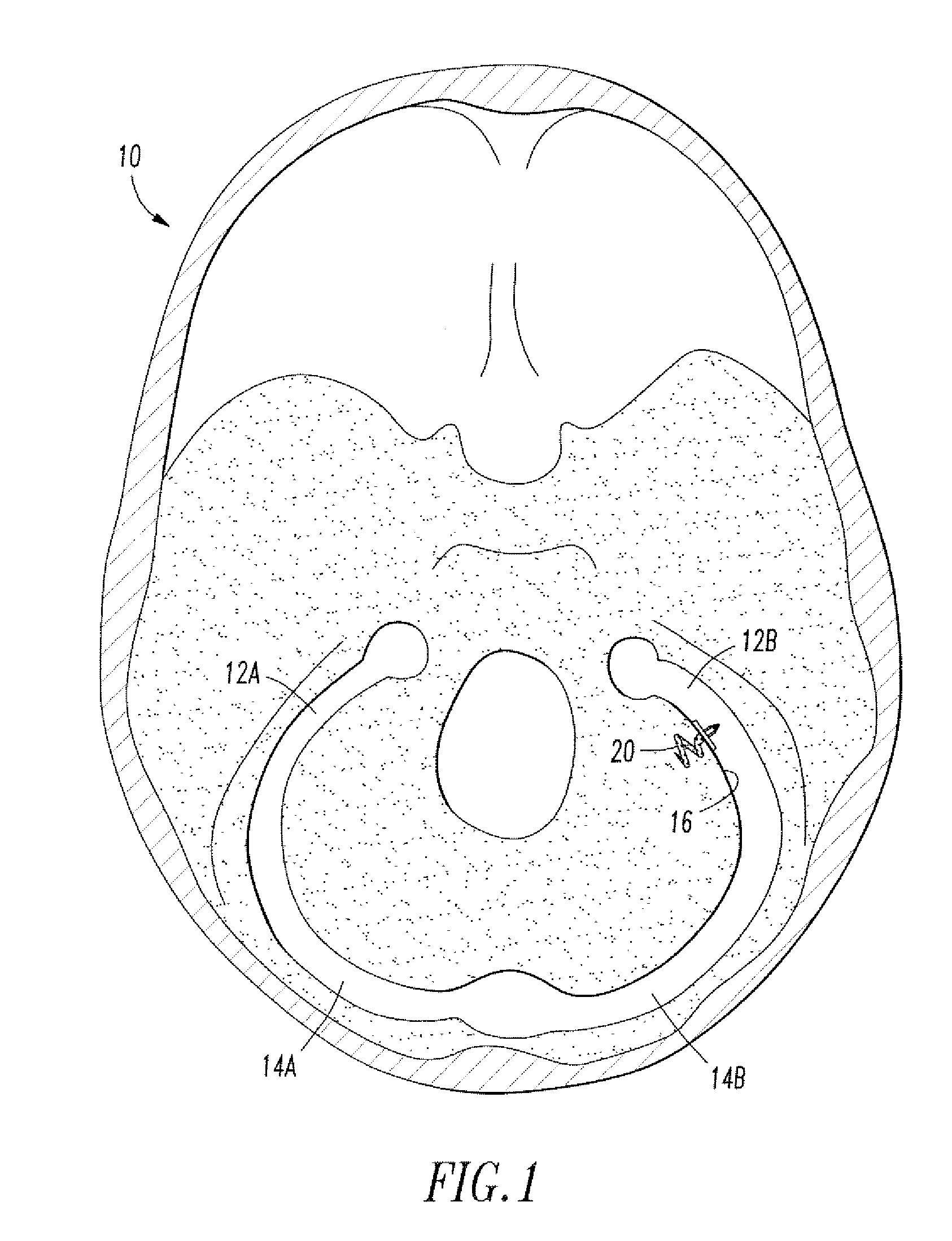
Body fluid is sampled from a skin incision by placing a ring against the skin and repeatedly applying an elastic pressing force to the ring, whereby a stimulator surface of the ring depresses a ring of skin and body tissue in surrounding relationship to the incision to force body fluid from the incision. The stimulator surface is inclined at an angle of 10 to 65 degrees; a width of the stimulator surface is from 5 mm to 20 mm, and an inner diameter of the stimulator surface is no less than 6.0 mm.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
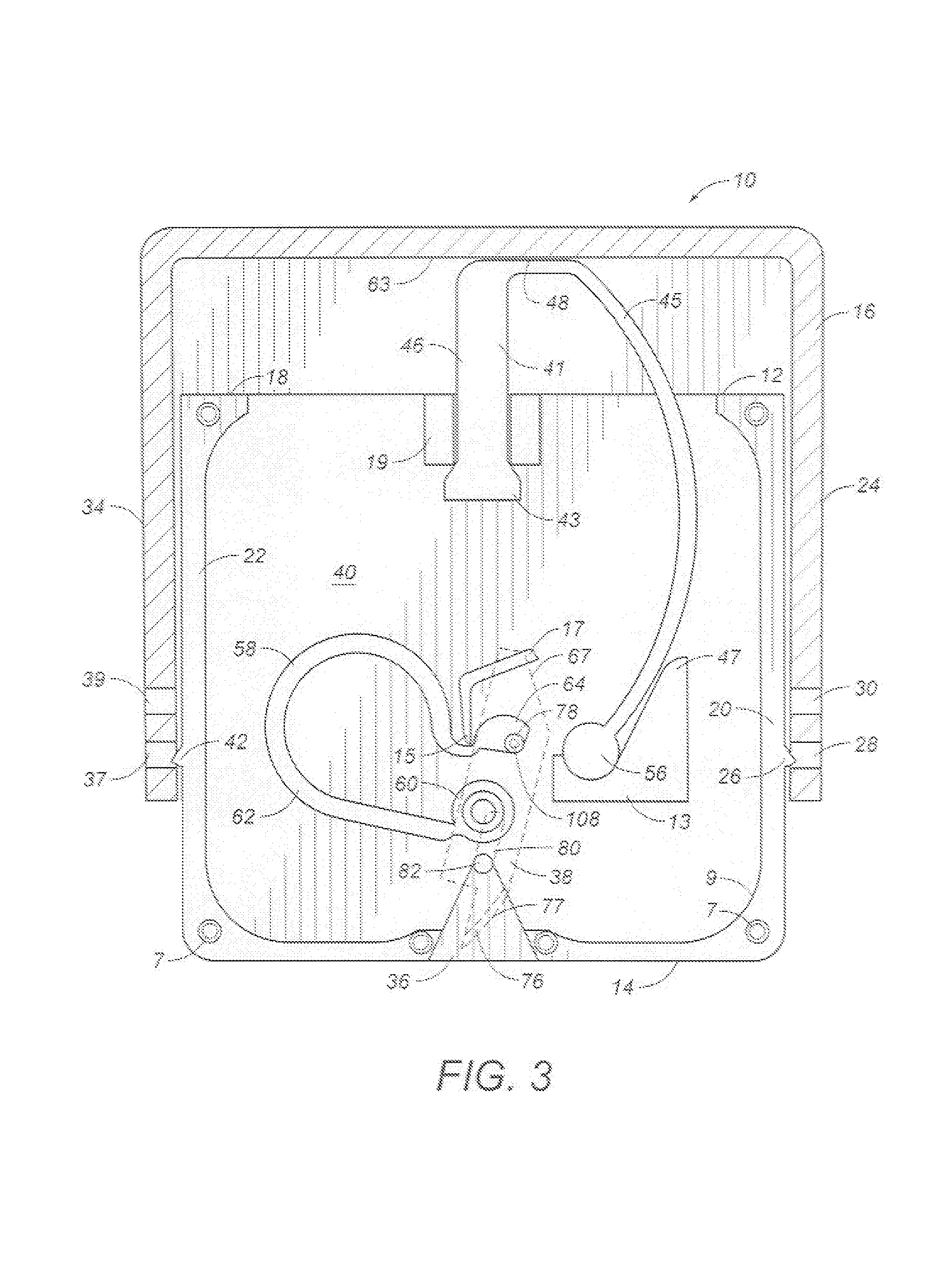
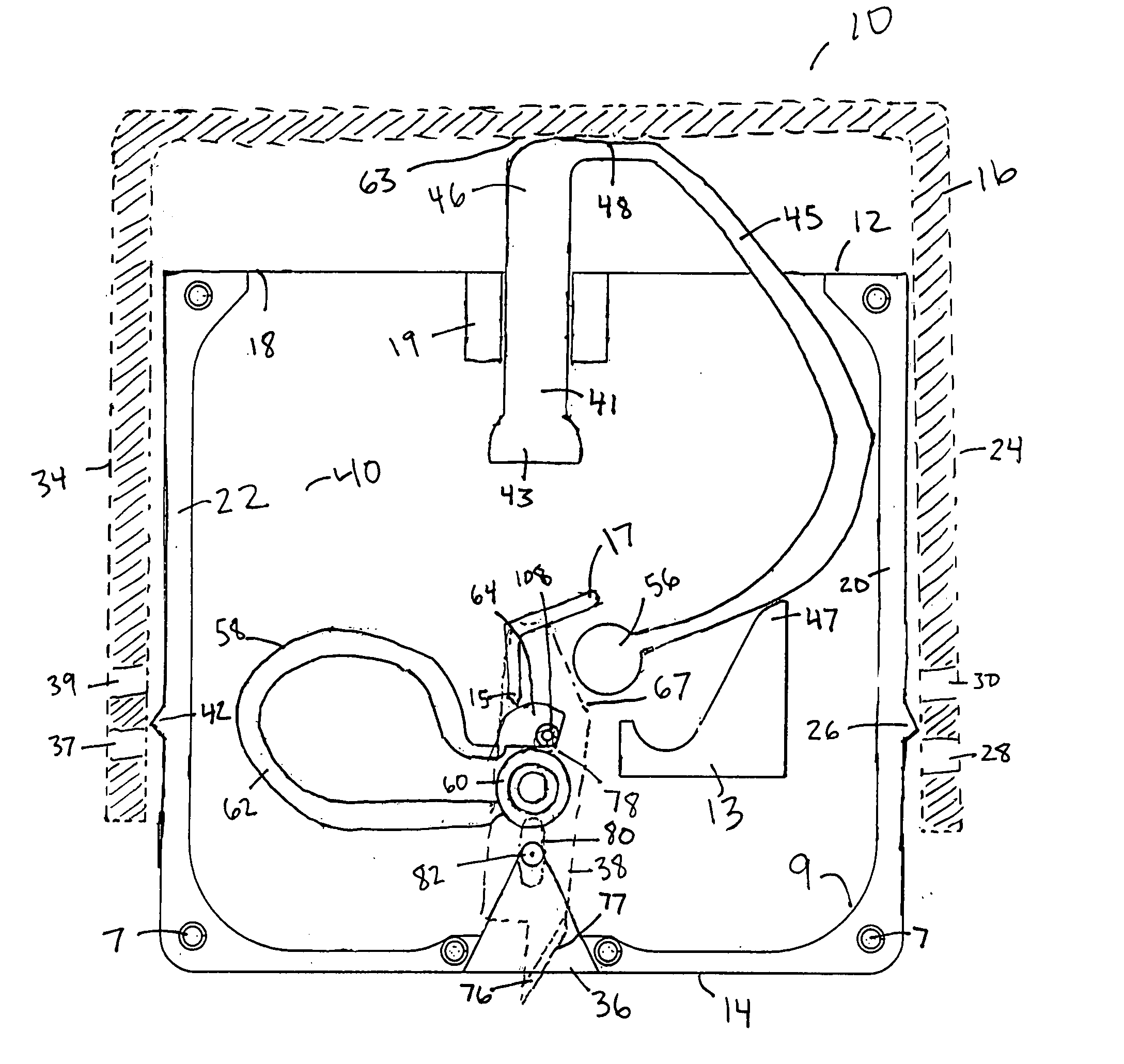
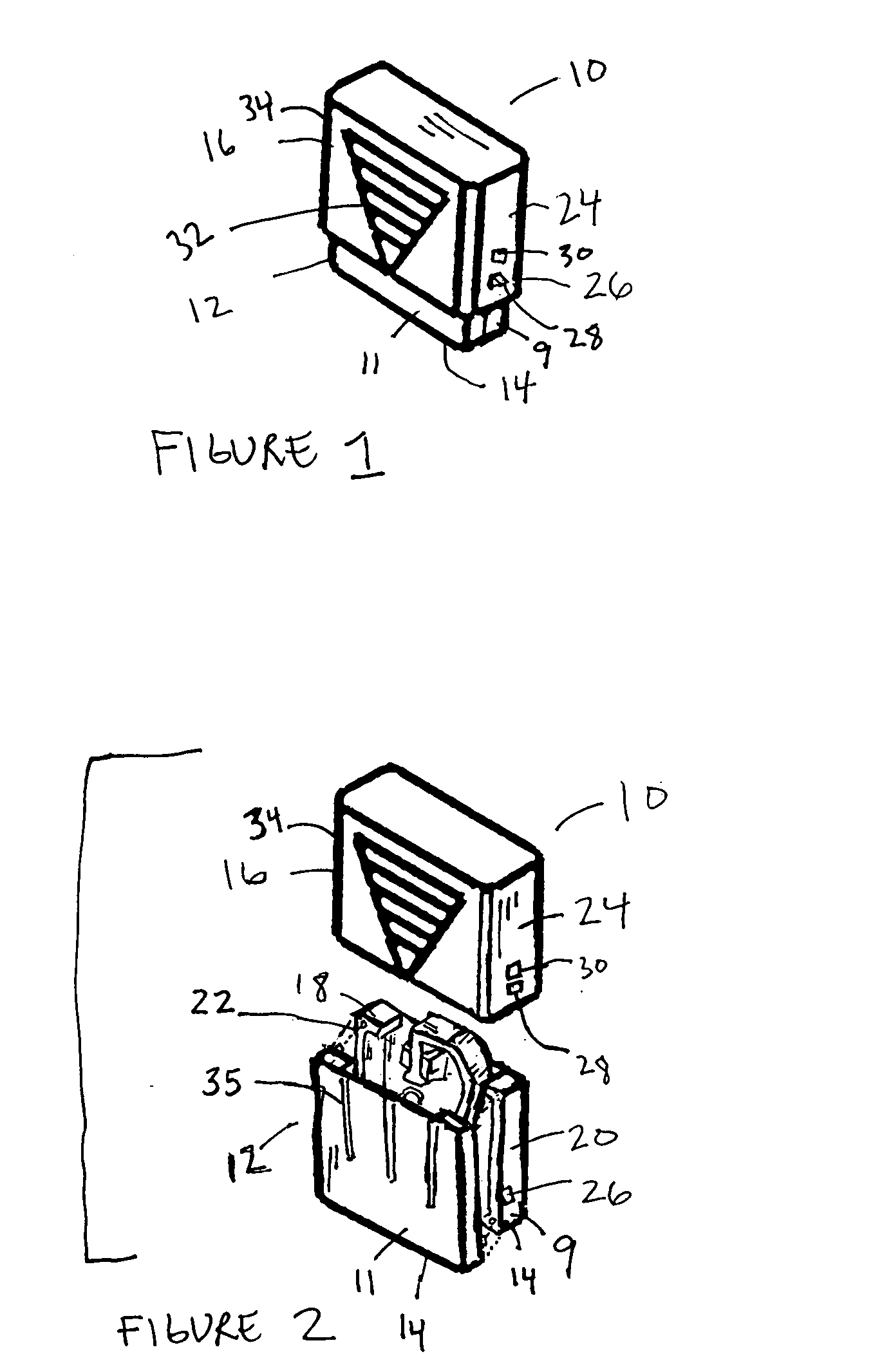
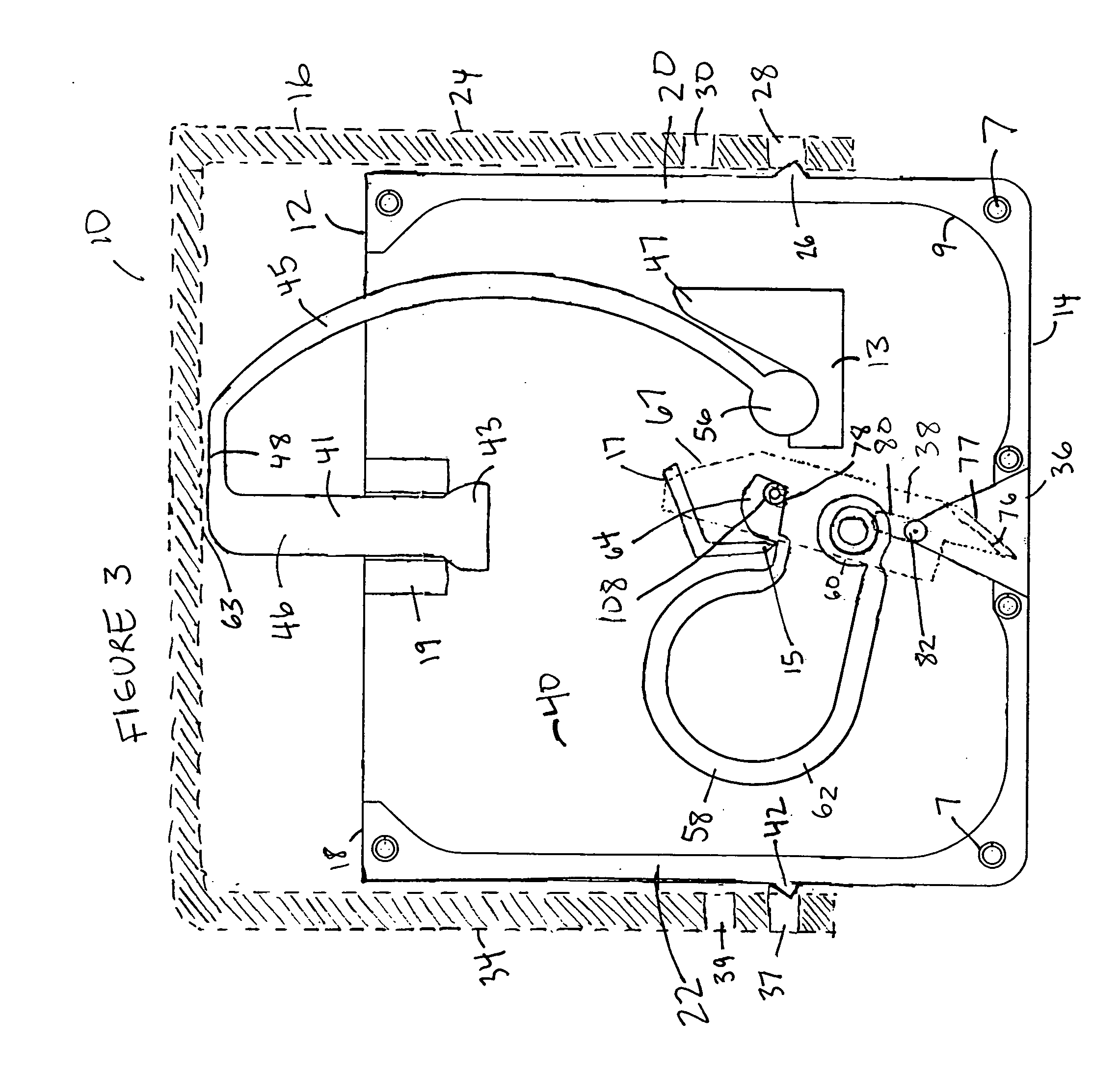
Load-controlled device for a patterned skin incision
InactiveUS7160313B2Minimize traumaReduce introductionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEngineeringSkin incision
A skin incision device has a casing having a bottom surface with a slot formed therein, a cover positioned on the casing and slidable in a direction toward the bottom surface, a blade positioned in the casing adjacent the slot, an actuator cooperatively positioned between the cover and an interior of the casing, and a carriage element. The actuator engages the blade by its horizontal displacement triggered by the slidable movement of the cover toward the bottom surface of the casing. The carriage element guides the movement of the blade between a pre-actuated position and a post-actuated position. The blade moves outwardly through the slot, cuts with a horizontal movement, and returns inwardly through the slot.
Owner:HELENA LAB
Adjustable access device for surgical procedures
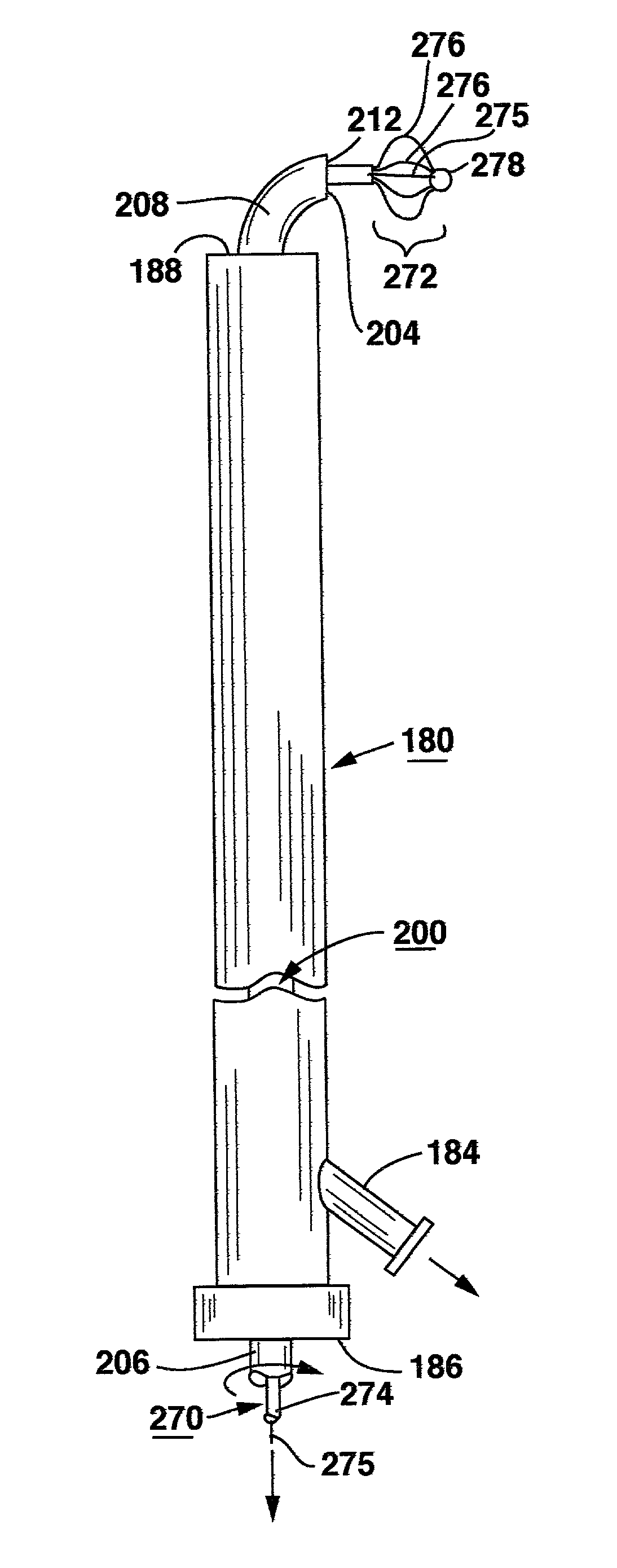
An access device for providing access from a skin incision to a surgical site is described. The access device has a first section having a proximal end and a distal end defining a first path therethrough. The access device has a second section having a proximal end and a distal end defining a second path therethrough, the second section is movable relative to the first section, and the first and second sections cooperate to form a continuous path such that movement of the second section changes the length of the path.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Non-rigid surgical retractor
The present invention provides a non-rigid retractor for providing access to a surgical site, such as a patient's spine, during a surgical process. When used in spinal surgery, the non-rigid retractor allows a surgeon to operate on one or more spinal levels. The non-rigid retractor includes at least one flexible strap anchored at a first end to the spine or other internal body part at the surgical site. The body of the at least one flexible strap extends from a skin incision and is anchored at a second location external to the body to retract skin and muscle from the surgical site, allowing adequate visualization of the surgical site and providing access for implants and surgical instruments to pass through the retractor and into the surgical site
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Load-controlled device for a patterned skin incision
InactiveUS20050125018A1Minimize traumaReduce the introductionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEngineeringActuator
A skin incision device has a casing having a bottom surface with a slot formed therein, a cover positioned on the casing and slidable in a direction toward the bottom surface, a blade positioned in the casing adjacent the slot, an actuator cooperatively positioned between the cover and an interior of the casing, and a carriage element. The actuator engages the blade by its horizontal displacement triggered by the slidable movement of the cover toward the bottom surface of the casing. The carriage element guides the movement of the blade between a pre-actuated position and a post-actuated position. The blade moves outwardly through the slot, cuts with a horizontal movement, and returns inwardly through the slot.
Owner:HELENA LAB
Method for adjustably restricting a body lumen
InactiveUS6045498AEasy to adjustSufficient longitudinal stiffnessAnti-incontinence devicesDiagnosticsUrethraImplanted device
An implantable device and method for adjustably restricting a selected body lumen such as the urethra of a patient to treat urinary incontinence. The device includes an expandable element or membrane such as a balloon attached pressure-tightly to a flexible conduit at its forward end and includes a rear port portion containing an elastic septum and flow connected to the expandable element by a first passageway. The conduit contains a second passageway which allows it to be slid along an elongated guide probe initially inserted surgically into a patient's body adjacent the body lumen which is to be adjustably restricted. A suitable flowable material is injected from a syringe source into the device rear port sufficient to expand the membrane element and restrict the body lumen to the desired degree. The syringe and guide probe are removed and the skin incision is closed over the rear port end of the implanted device. The rear port septum is located under but near the patient's skin so that if it becomes necessary to post-operatively increase or decrease the degree of body lumen restriction it may be easily accessed with the needle of the syringe.
Owner:UROMEDICA INC
Method and apparatus for providing posterior or anterior trans-sacral access to spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS20070055260A1Less discomfortMinimally invasiveSurgical needlesSpinal columnSacral vertebral body
Methods and apparatus for providing percutaneous access to vertebrae in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. A number of related TASIF methods and surgical tool sets are provided by the present invention that are employed to form a percutaneous pathway from an anterior or posterior skin incision to a respective anterior or posterior target point of a sacral surface. The percutaneous pathway is generally axially aligned with an anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line extending from the respective anterior or posterior target point through at least one sacral vertebral body and one or more lumbar vertebral bodies in the cephalad direction. The provision of the percutaneous pathway described herein allows for the formation of the anterior or posterior TASIF bore(s) and / or the introduction of spinal implants and instruments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Instruments and methods for accessing an anatomic space
InactiveUS20070010708A1Rigid enoughConvenient introductionStentsCannulasPericardial spaceAnatomic Site
An anatomic space of the body, particularly the pericardial space, is accessed in a minimally invasive manner from a skin incision by an access instrument to facilitate visualization and introduction of devices or drugs or other materials, performance of medical and surgical procedures, and introducing and fixating a cardiac lead electrode to the heart. An elongated access instrument body preferentially bends in one direction and resists bending in a transverse direction, whereby the access instrument body distal end can be directed through a path around body structures to the anatomic site by manipulation of the access instrument body proximal end portion. A distal header formed at the access instrument body distal end extends outward of the access instrument body in the transverse direction and supports an inflatable balloon surrounding a working lumen exit port that is directed toward an anatomic surface when the balloon is inflated by inflation media introduced through an inflation lumen.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Adjustable access device for surgical procedures
An access device for providing access from a skin incision to a surgical site is described. The access device has a first section having a proximal end and a distal end defining a first path therethrough. The access device has a second section having a proximal end and a distal end defining a second path therethrough, the second section is movable relative to the first section, and the first and second sections cooperate to form a continuous path such that movement of the second section changes the length of the path.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Device for adhering to the skin of a patient
The present invention relates to a device for adhering to the skin of a patient, suitable to make a skin incision there through, as well as to the use of such a device for allowing an incision or excision wound to be made through the said device, and for subsequent closing the wound. In particular, the device is suitable for adhering to the skin at the location the incision or excision is to be made, where after the incision or excision is made through the device in the skin at the envisaged location. The device comprises one or more basic layers (1, 2) that do not abut one another at the location of the wound. In contrast, an open skin area (3) is defined by the basic layer(s), which area is covered by an adhesive surface of a covering sheet (4). Further, adhesive strips (13, 23) are provided that are suitable to be adhered to the skin at both sides of the incision, therewith closing the skin in a highly controlled manner, and enabling excision wounds to be conveniently closed as well
Owner:CLOSE IT
Skin incision instrument and method for incising skin with the same
InactiveUS20100113981A1Simple definitionEfficiently formedSurgical needlesPerson identificationDilatorSkin incision
Provided are skin incision instrument to efficiently incise minimal portions and a method for incising skin with the skin incision instrument. The skin incision instrument according to the present invention comprises a holder, a needle, a needle drive unit, a skin expander, and a reader, wherein the needle and the skin expander are mounted at an end of the holder, the needle drive unit is mounted in the holder, the needle drive unit is capable of forming an incision portion in a skin caused to contact the end of the holder by moving the needle, the skin expander is capable of expanding skin at both sides of the linear incision portion away from the linear incision portion in a direction to expand the linear incision portion, and the reader determines position of the skin expander by rotating the skin expander around the needle in order to adjust an angle to 45 degrees or more and 90 degrees or less wherein the angle is a smaller angle among angles formed by the representative line connecting both ends of the linear incision portion and the direction to expand skin at both sides of the linear incision portion with the skin expander, and minimal portions are efficiently incised.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Systems and Methods for Implanting Medical Devices
InactiveUS20100318098A1Improved frictional engagementIncrease frictionDiagnosticsSurgical needlesSkin incisionMedical device
Methods and instruments forming a tissue pathway between the first and second skin incisions to draw a permanent or temporary elongated medical device or implant, e.g., a medical electrical lead, through the tissue pathway are disclosed. A tunneling instrument comprises an elongated sleeve and a needle that are mounted together to be used as the tunneling instrument to form the tissue pathway and separated so that the sleeve may be employed to engage the lead connector to pull the medical electrical lead through the tissue pathway.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
Intramedullary Fixation Device for Small Bone Fractures
InactiveUS20090275946A1Aggressive curveAdd flexiblyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFixation pointCurve shape
A fracture fixation system particularly useful for bones of the hand and foot is disclosed. The system uses curved shape-memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol) wires that have a predetermined radius of curvature to accommodate different sized bones. These shape-memory alloy wire forms can be inserted into phalanx, metacarpal or metatarsal bones via a percutaneous technique. The technique uses small skin incisions; a specialized drill guide that has holding K-wires to maintain fixation of the drill guide to the bone so that it does not lose the insertion point; a specialized drill as well as a specialized wire cutter and advancement tool to make sure that the level of the wire is below the level of the outer cortical bone. Shape-memory alloy (e.g., Nitinol) based wires with a pre-bent curve have an advantage over the typical standard K-wire in that they can spring back to their predetermined memory shape when inserted into the intramedullary canal of the bone and heated, i.e., a more aggressive curve. By increasing their bending or flexion to increase the arc of curvature, this allows fixation points for the wire, essentially locking it to bone.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
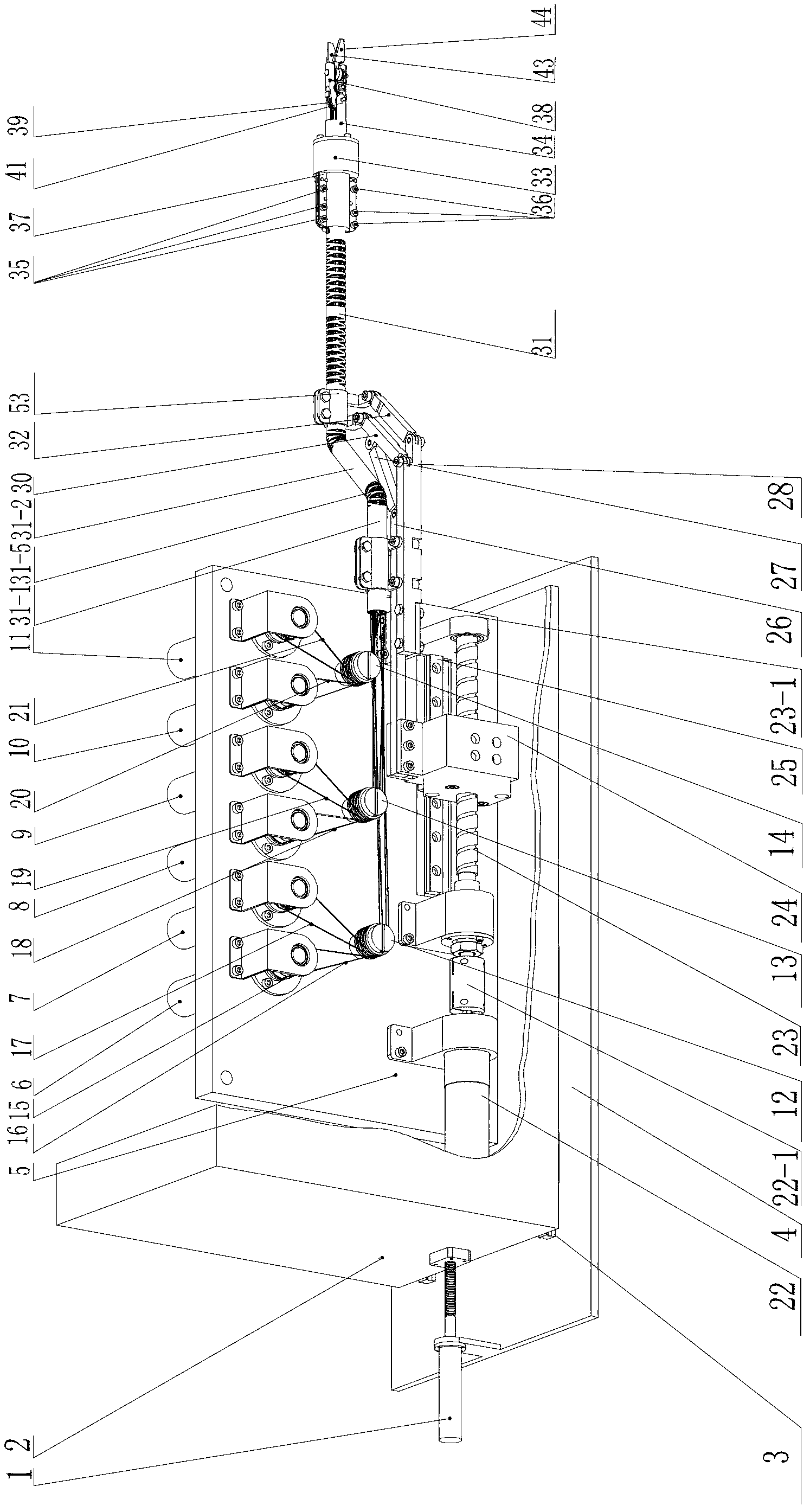
Flexible-arm robot for single-pore laparoscopic minimally-invasive operation
ActiveCN102697564APlay a supporting rolePlay an initial role in positioningDiagnosticsSurgical robotsEngineeringSecond finger
The invention relates to a flexible-arm robot for a single-pore laparoscopic minimally-invasive operation, which relates to the minimally-invasive operation robot. The robot aims at solving the problems in the traditional endoscope minimally-invasive operation that multiple skin incisions of a patient exist and the size of the operation robot is larger. A drive box is connected with a base through a first lead rail and is driven by a first motor which is fixed on the base so as to enable an entire flexible arm to deeply stretch into an abdominal cavity of the patient; a second motor drives a first finger to open and close through a first drive wire; a third motor drives a second finger to open and close through a second drive wire; a fourth motor drives a third arm of a flexible joint arm to make a pitching motion through a third drive wire; a fifth motor drives a fourth arm of the flexible joint arm to make an oscillating motion through a fourth drive wire; a sixth motor drives a drive shaft rotating joint to make a pivoting motion through a fifth drive wire; a seventh motor drives a wrist joint to make a pitching motion through a sixth drive wire; and an eighth motor drives a first connecting rod and a second connecting rod in the horizontal direction through a lead screw and a second lead rail, so that a first flexible support and a second flexible support are driven to move. The flexible-arm robot is used for the single-pore laparoscopic minimally-invasive operation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Instruments and methods for adjusting separation distance of vertebral bodies with a minimally invasive spinal stabilization procedure
ActiveUS20100069972A1Minimize damageProvide stabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnMedicine
A spinal stabilization system may be formed in a patient. In some embodiments, a minimally invasive procedure may be used to form a spinal stabilization system in a patient. Bone fastener assemblies may be coupled to vertebrae. Each bone fastener assembly may include a bone fastener and a collar. Extenders may be coupled to the collar to allow for formation of the spinal stabilization system through a small skin incision. The extenders may allow for alignment of the collars to facilitate insertion of an elongated member in the collars. An elongated member may be positioned in the collars and a closure member may be used to secure the elongated member to the collars. An adjuster may be used in conjunction with the extenders to change a separation distance between the bone fastener assemblies.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20100191168A1More physiologic drainageWound drainsMedical devicesShunt DeviceSubarachnoid space
An implantable shunt device for draining cerebrospinal fluid from a patient's subarachnoid space. The device includes a shunt having opposed first and second ends. A one-way valve is located at the first end of the shunt. A helical tip is disposed at the second end. The helical tip is constructed to penetrate a sinus wall of the patient. Upon implantation, a hollow passageway extends between the helical tip and one-way valve such that fluid can be drained through the helical tip and out through the valve. The endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt of the present invention can be placed into a patient percutaneously via a catheter inserted into the venous system of the body through a needle hole, without the need for open surgery and the skin incisions required with current shunt devices. The device also allows for more physiologic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid since the device is shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the same cerebral venous system that occurs naturally in normal people.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Two-incision minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS20050096748A1Avoid excessive injuryMore preservationDiagnosticsSurgeryRight femoral headCoxal joint
A surgical procedure for replacing a destructed hip joint with an artificial joint is disclosed. The present invention provides a two-incision minimally invasive surgery for total hip arthroplasty. This method comprises positioning of the patient on a lateral decubitus position and a series of surgical techniques including a first skin incision over the anterior side of the trochanteric area of the femur (ranging from 3 cm to 10 cm), intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus muscle (Gluteus minimus and medius) and Tensor fascia lata muscle, incision of the anterior joint capsule, osteotomy of the femoral neck, removal of the femoral head and neck, acetabular reaming and socket insertion, secondary skin incision over the Gluteus maximus muscle (ranging from 1 cm to 6 cm), dissection through the muscle fiber of the Gluteus maximus, intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus medius and Piriformis, partial incision of the joint capsule, femoral reaming, femoral stem insertion, femoral head insertion, joint capsule closure and skin closure.
Owner:YOON TAEK RIM
Two-incision minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty
InactiveUS7004972B2Avoid excessive injuryMore preservationDiagnosticsSurgeryMini invasive surgeryFemoral neck
A surgical procedure for replacing a destructed hip joint with an artificial joint is disclosed. The present invention provides a two-incision minimally invasive surgery for total hip arthroplasty. This method comprises positioning of the patient on a lateral decubitus position and a series of surgical techniques including a first skin incision over the anterior side of the trochanteric area of the femur (ranging from 3 cm to 10 cm), intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus muscle (Gluteus minimus and medius) and Tensor fascia lata muscle, incision of the anterior joint capsule, osteotomy of the femoral neck, removal of the femoral head and neck, acetabular reaming and socket insertion, secondary skin incision over the Gluteus maximus muscle (ranging from 1 cm to 6 cm), dissection through the muscle fiber of the Gluteus maximus, intermuscular dissection between the Gluteus medius and Piriformis, partial incision of the joint capsule, femoral reaming, femoral stem insertion, femoral head insertion, joint capsule closure and skin closure.
Owner:YOON TAEK RIM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com