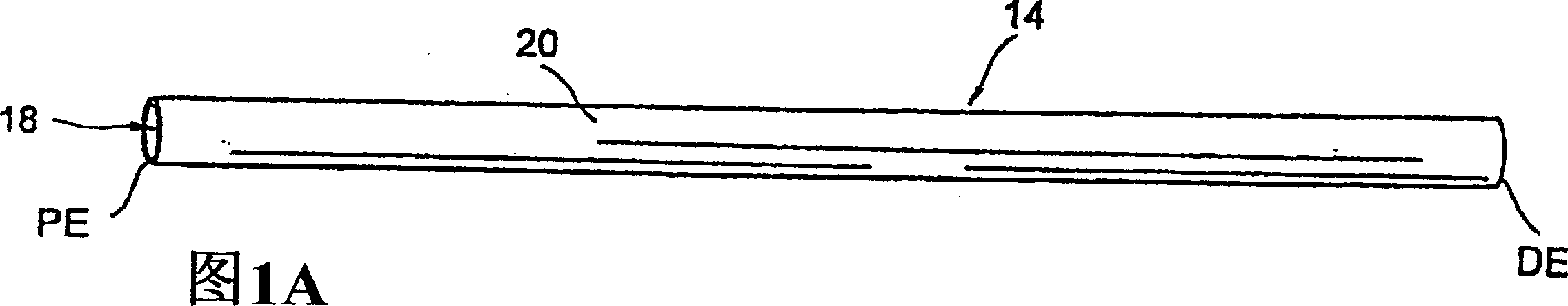Patents
Literature
115 results about "Subarachnoid space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
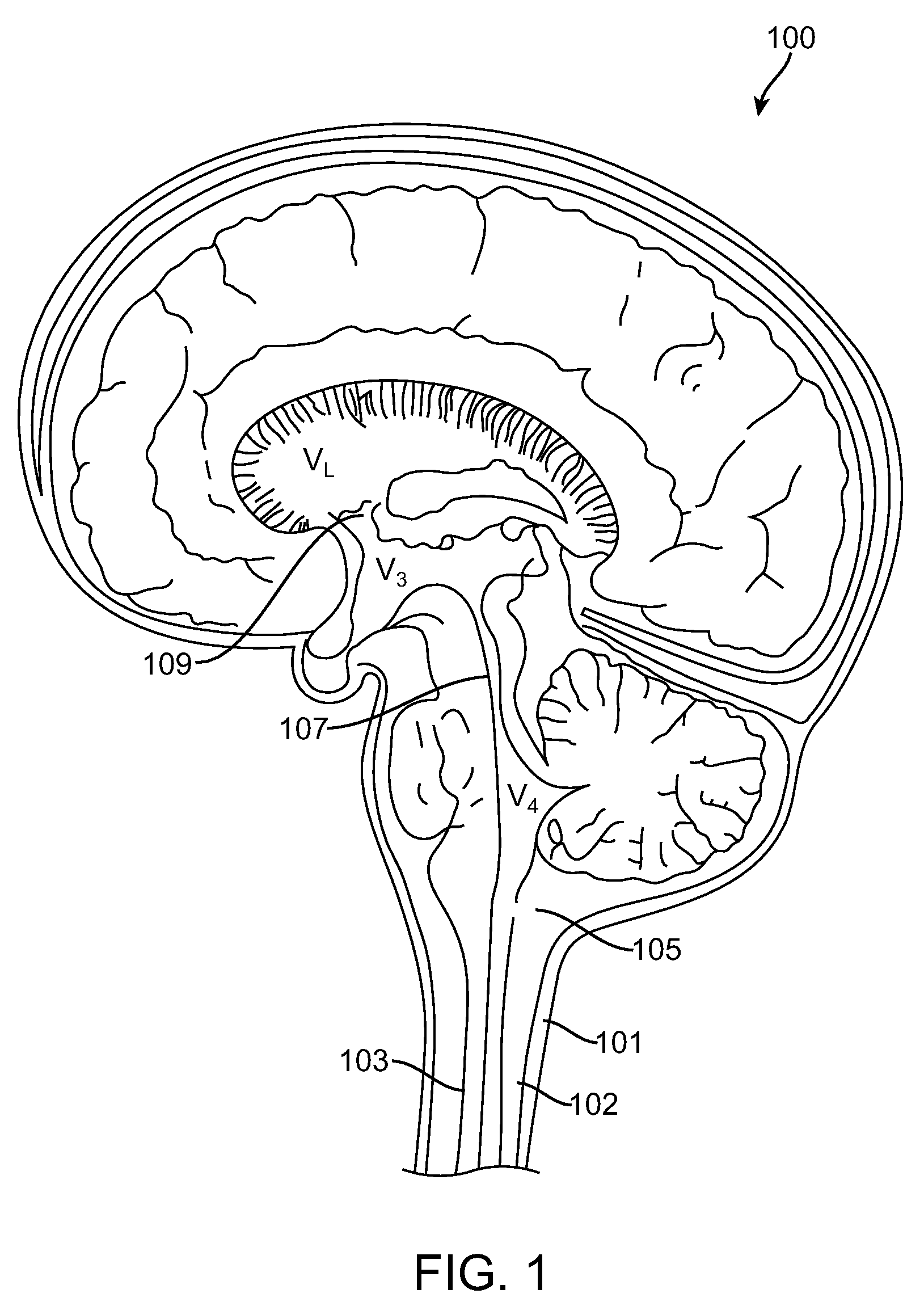
In the central nervous system, the subarachnoid cavity is the anatomic space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater. It is occupied by spongy tissue consisting of trabeculae and intercommunicating channels in which the cerebrospinal fluid is contained.
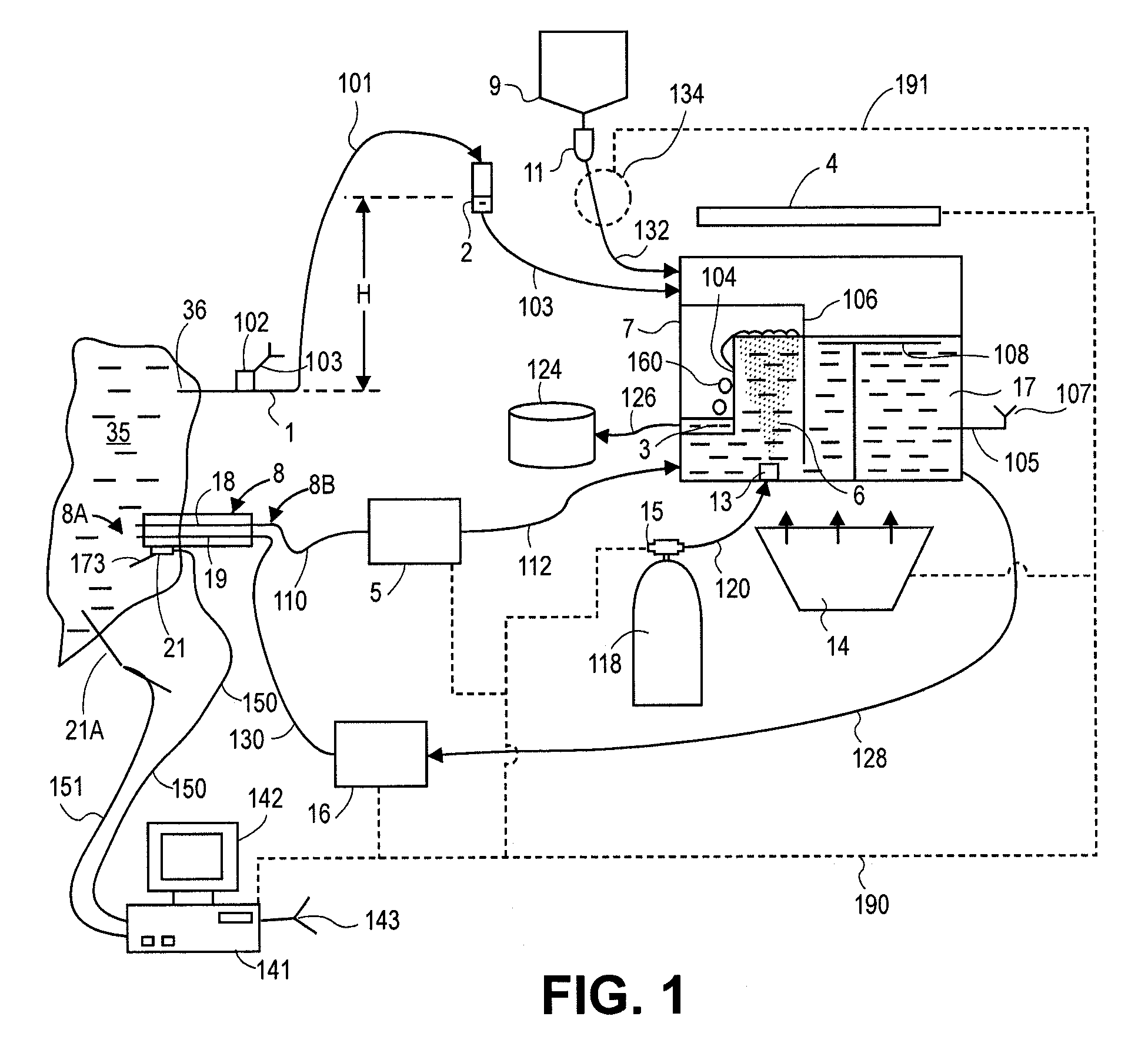
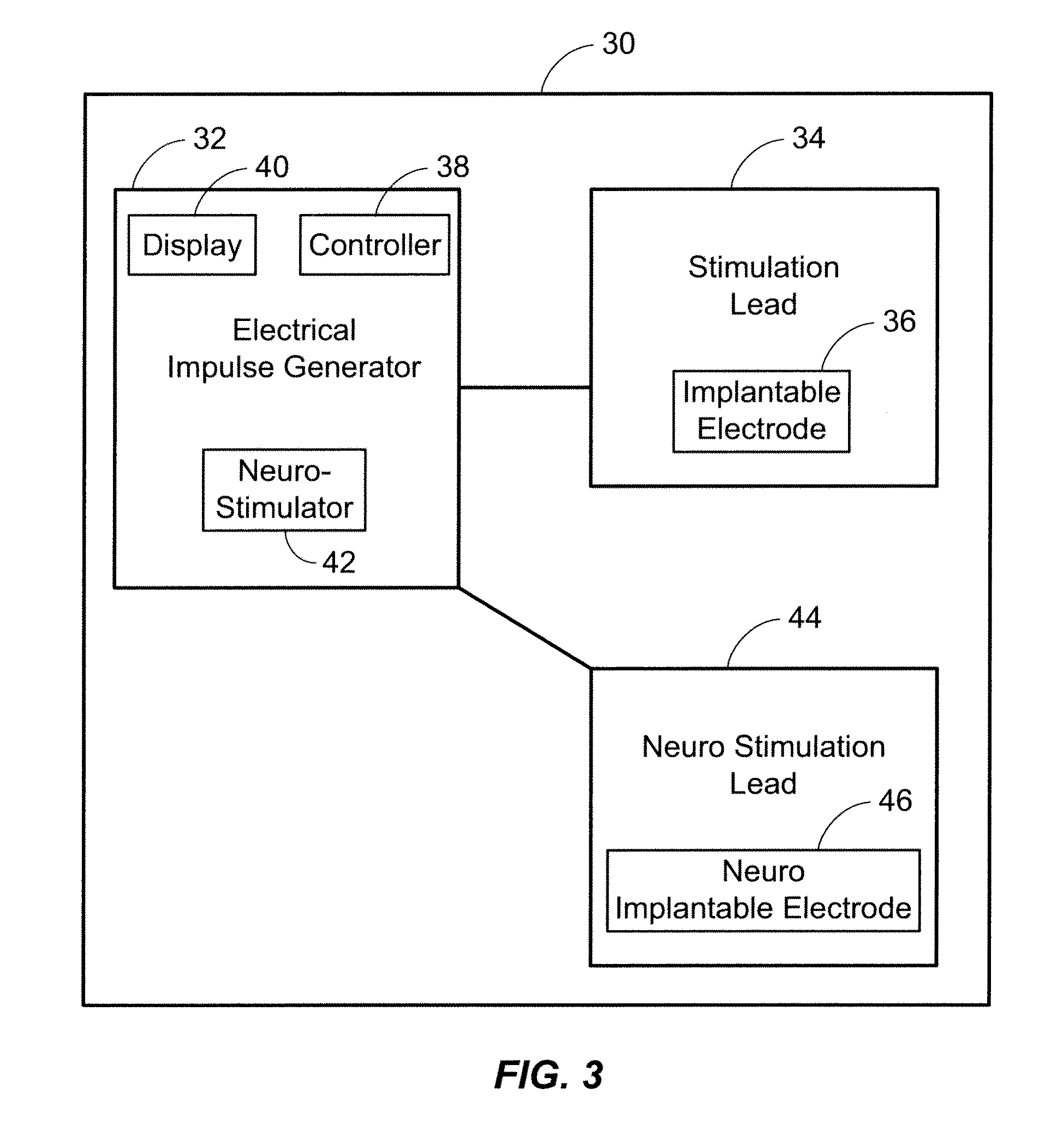
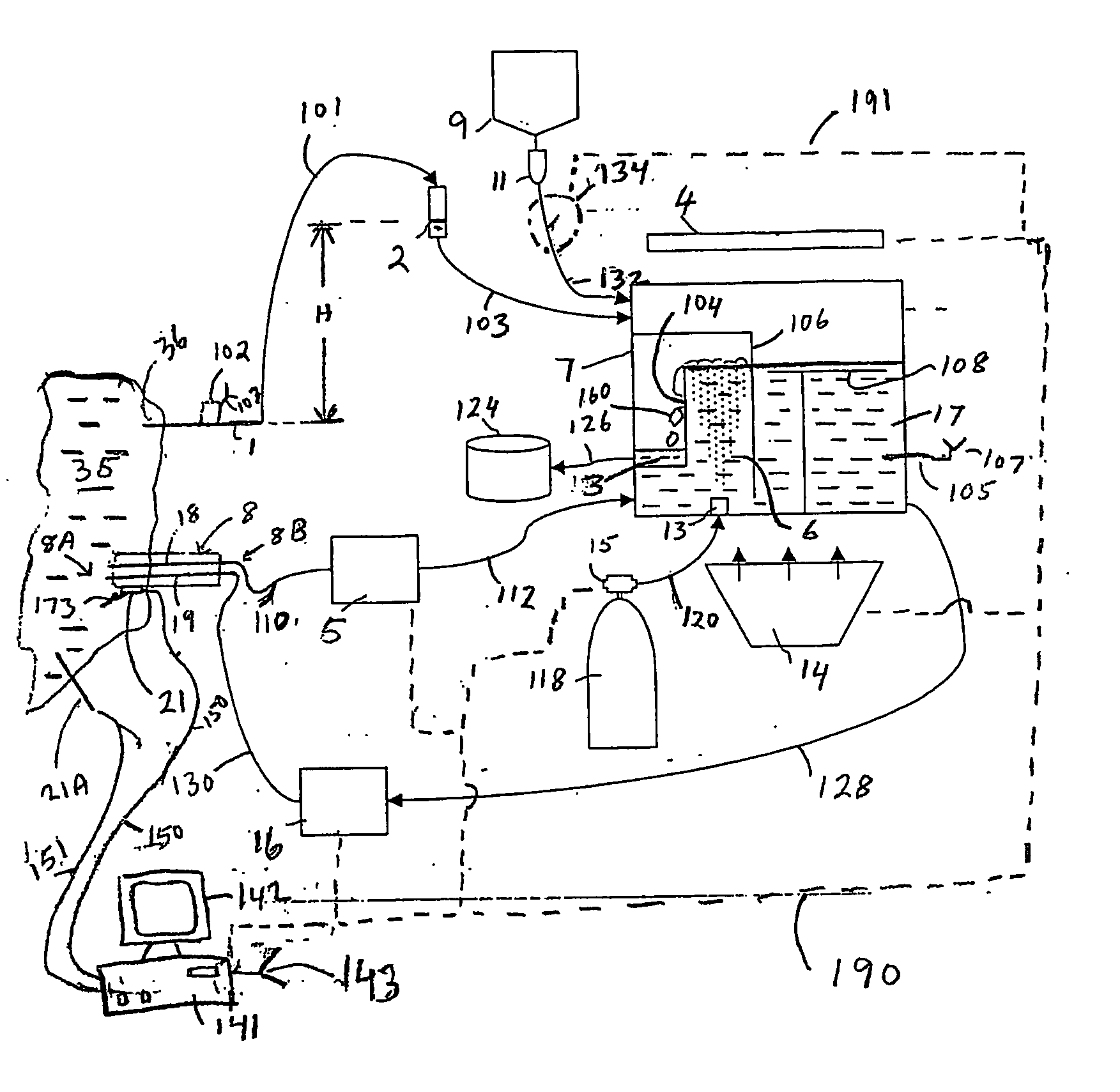
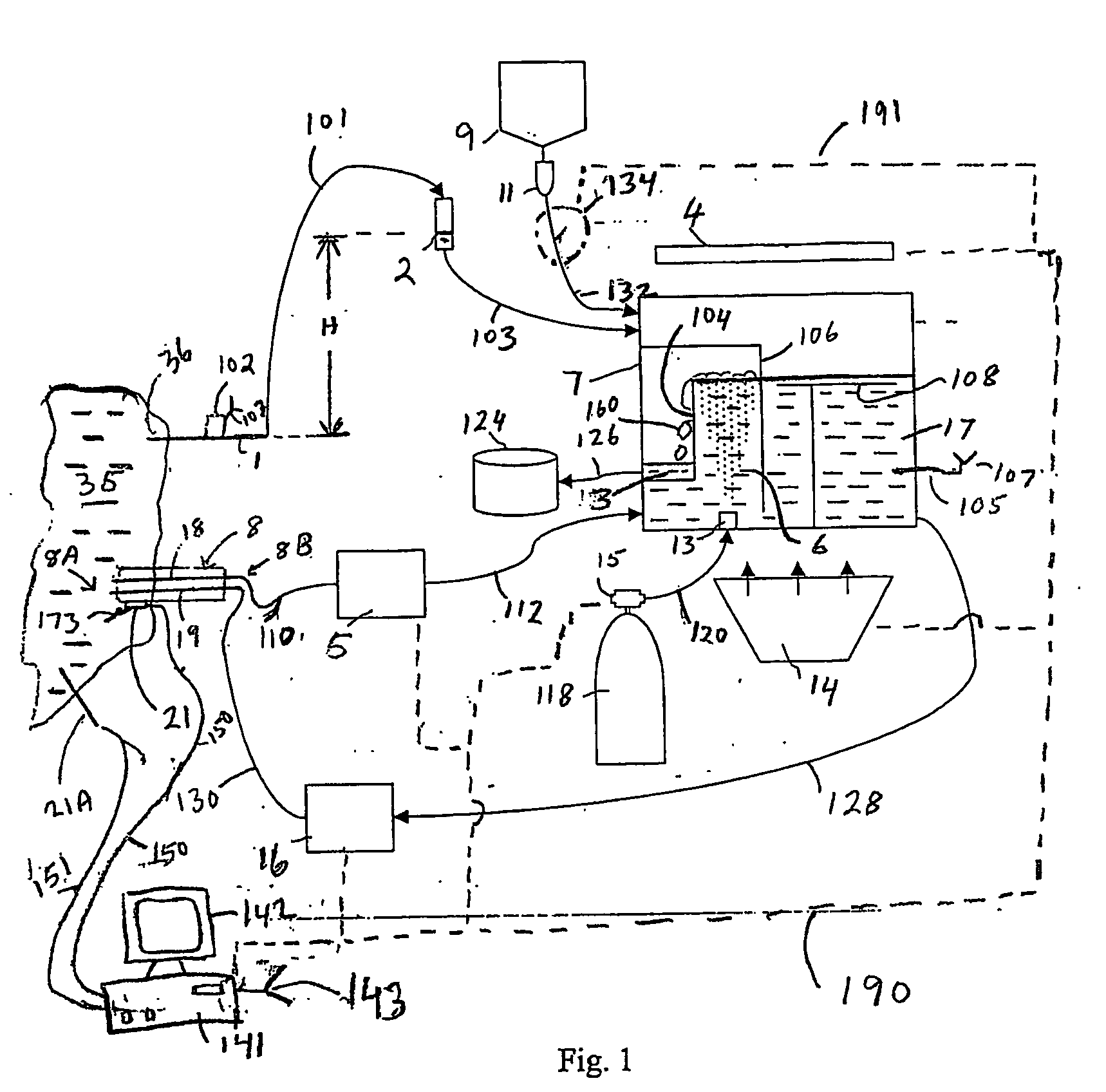
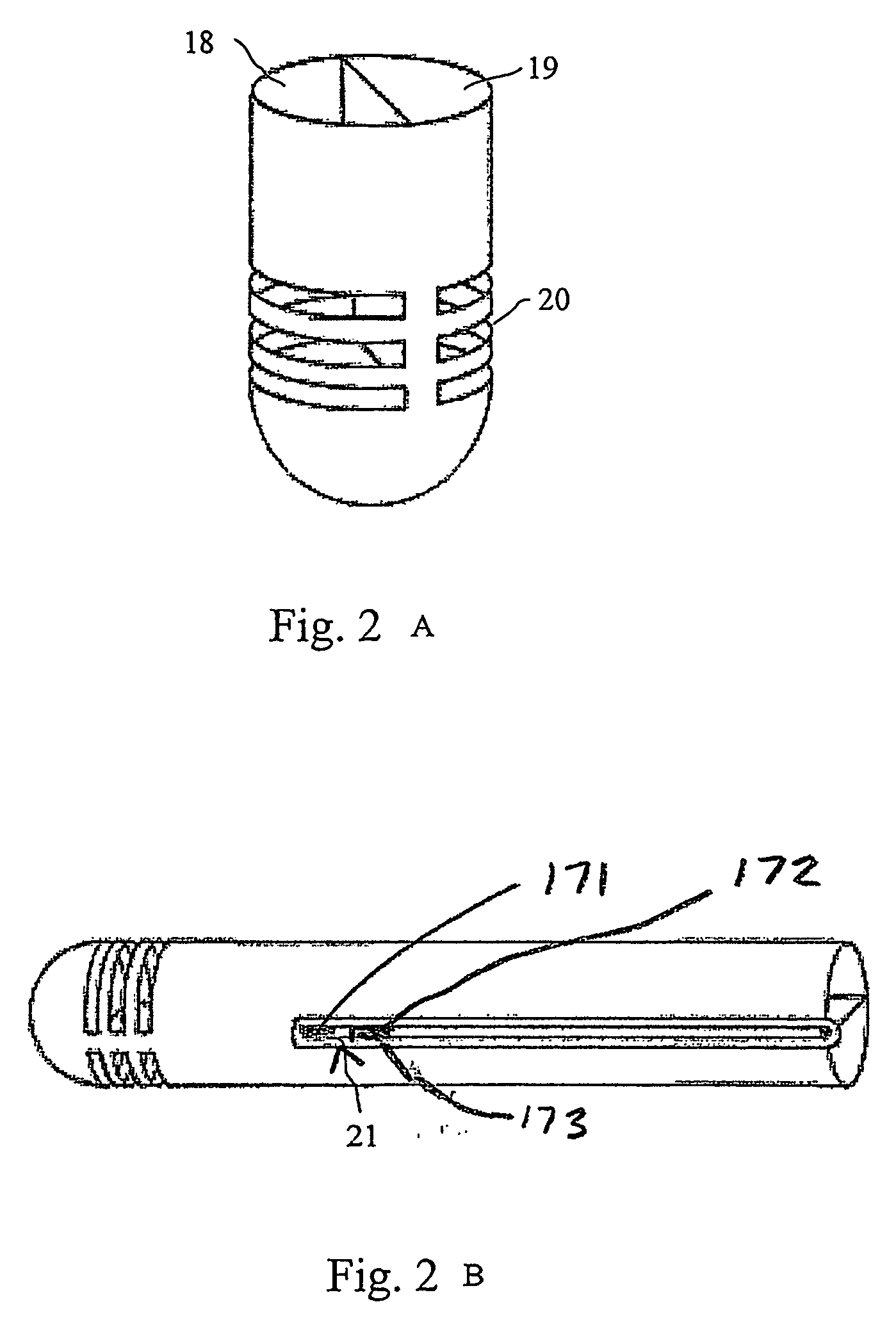
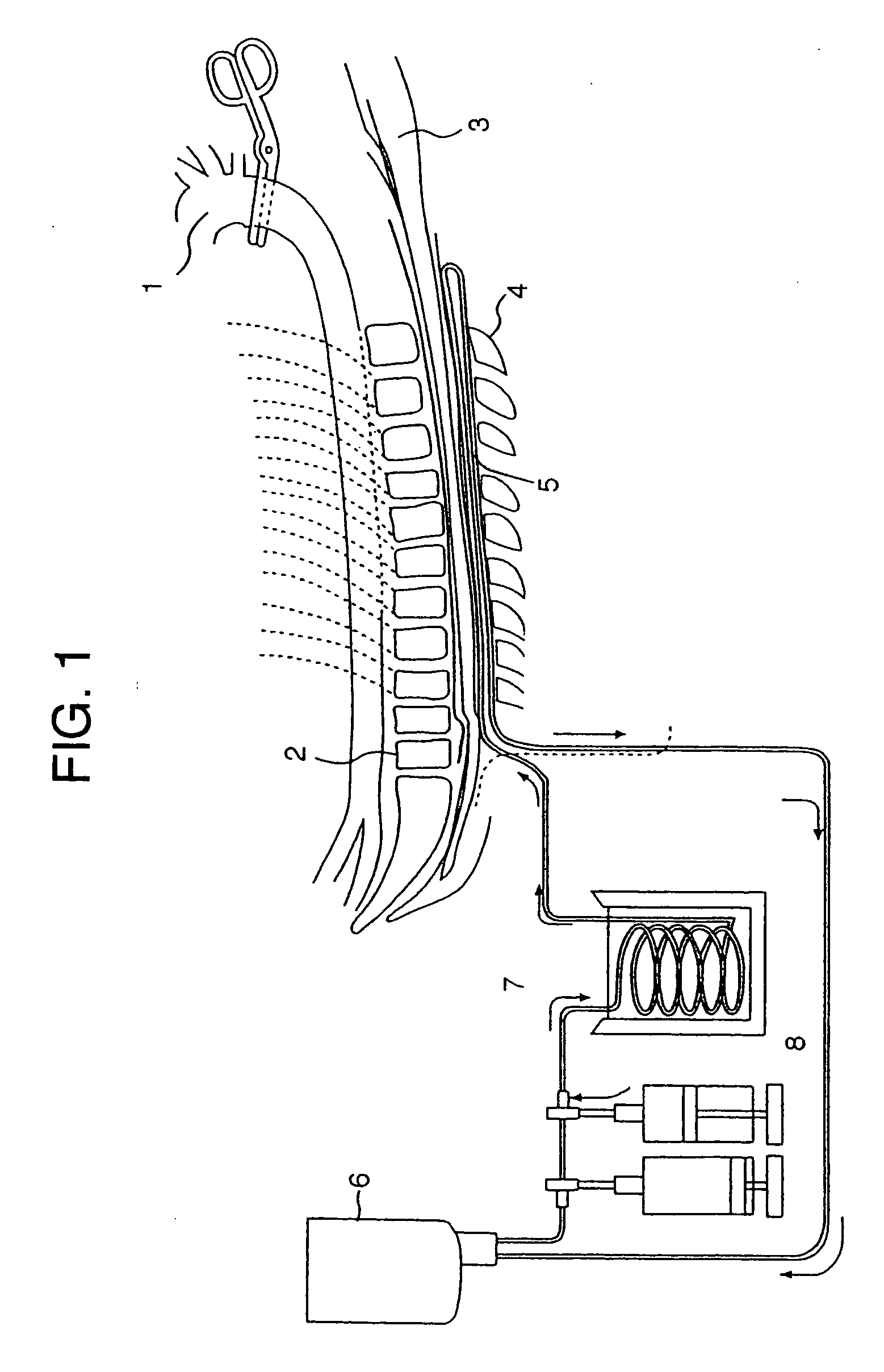
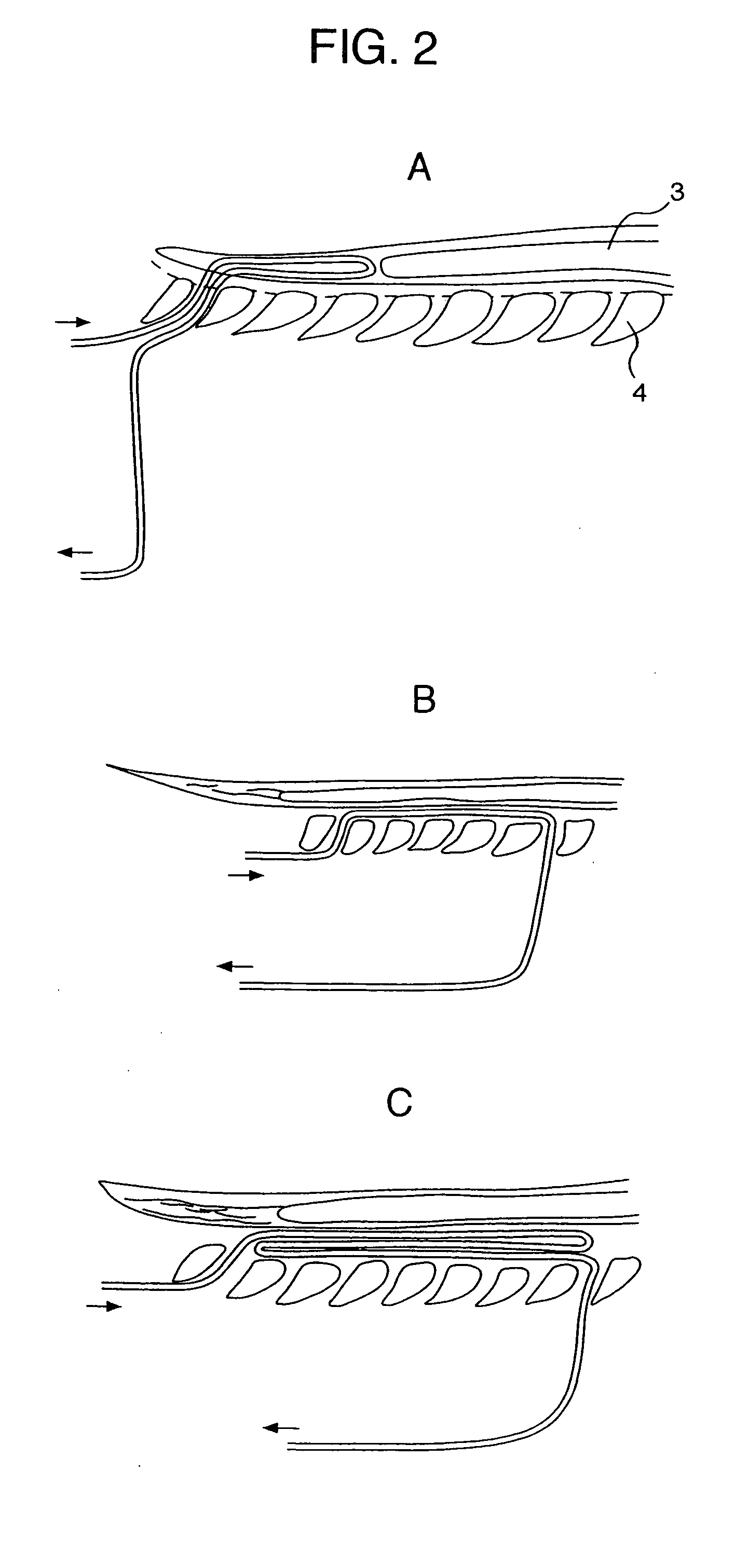
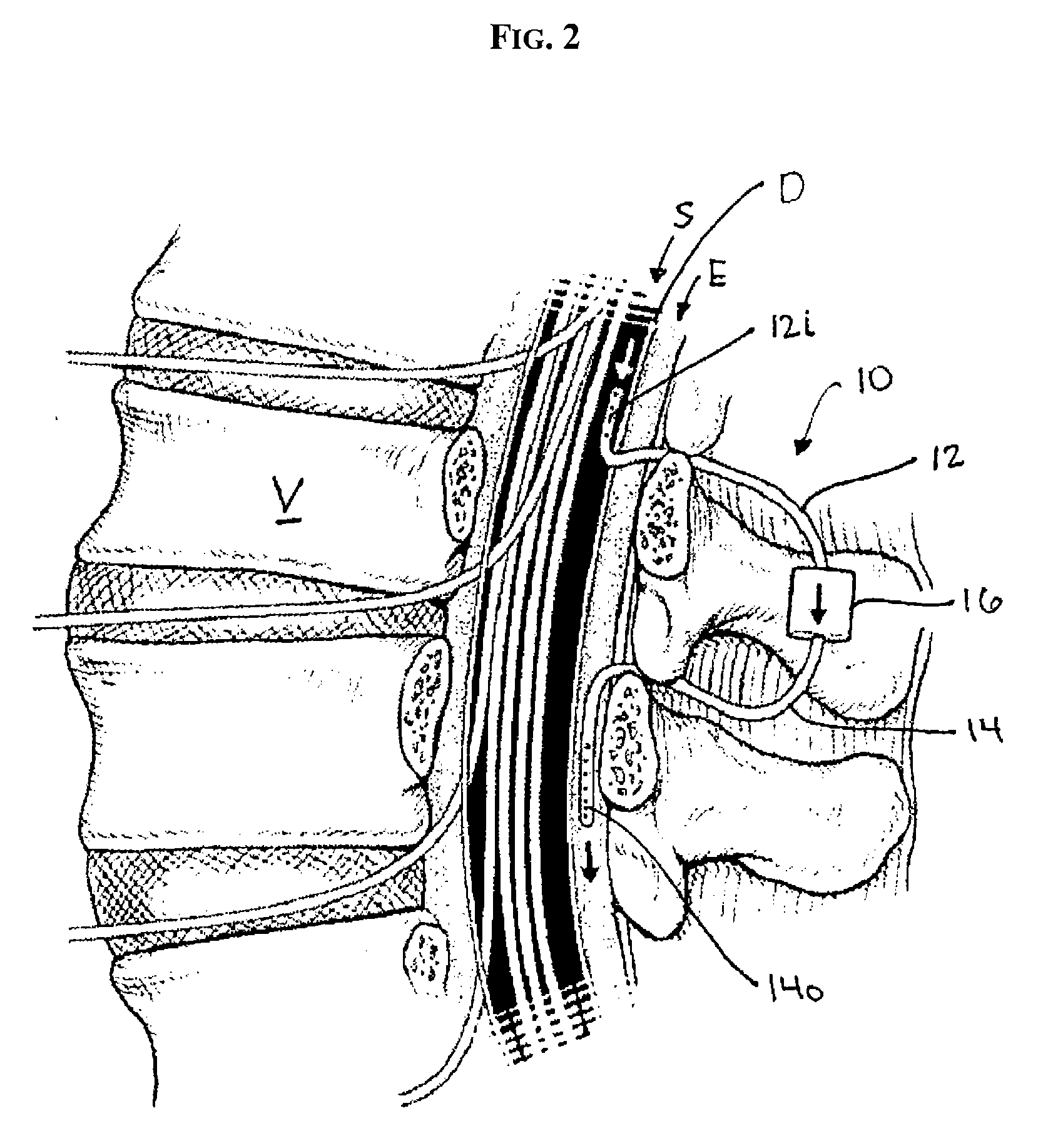
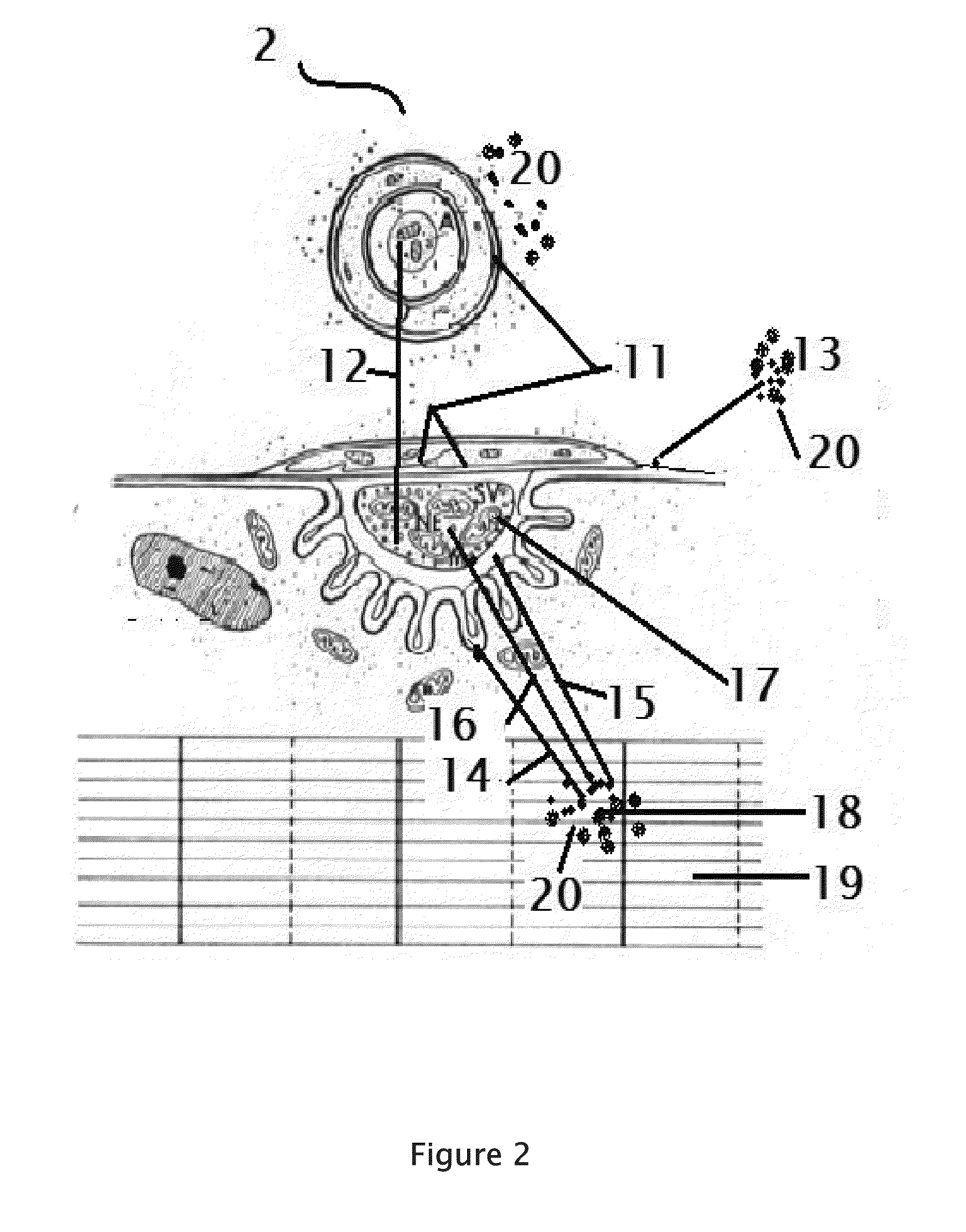
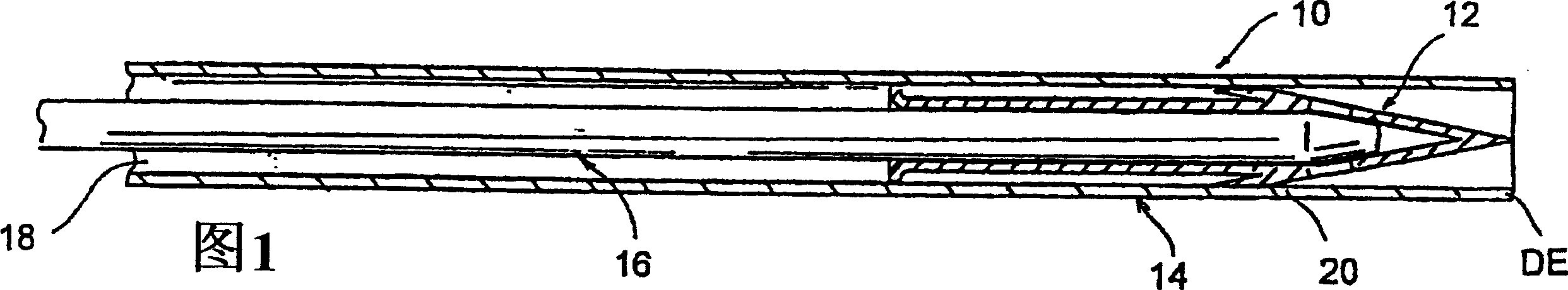
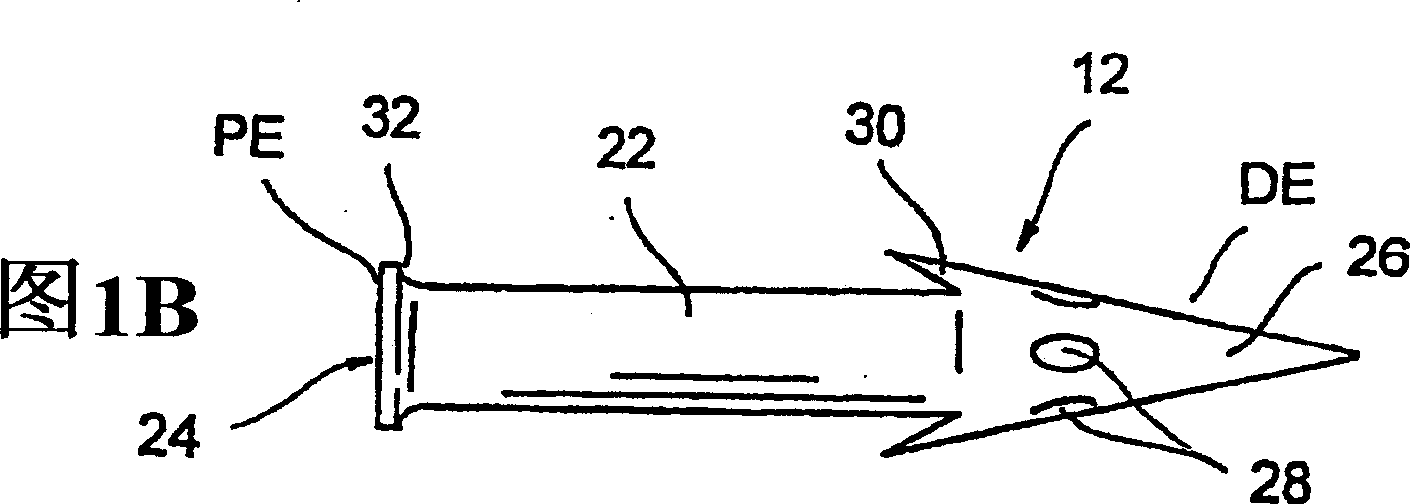
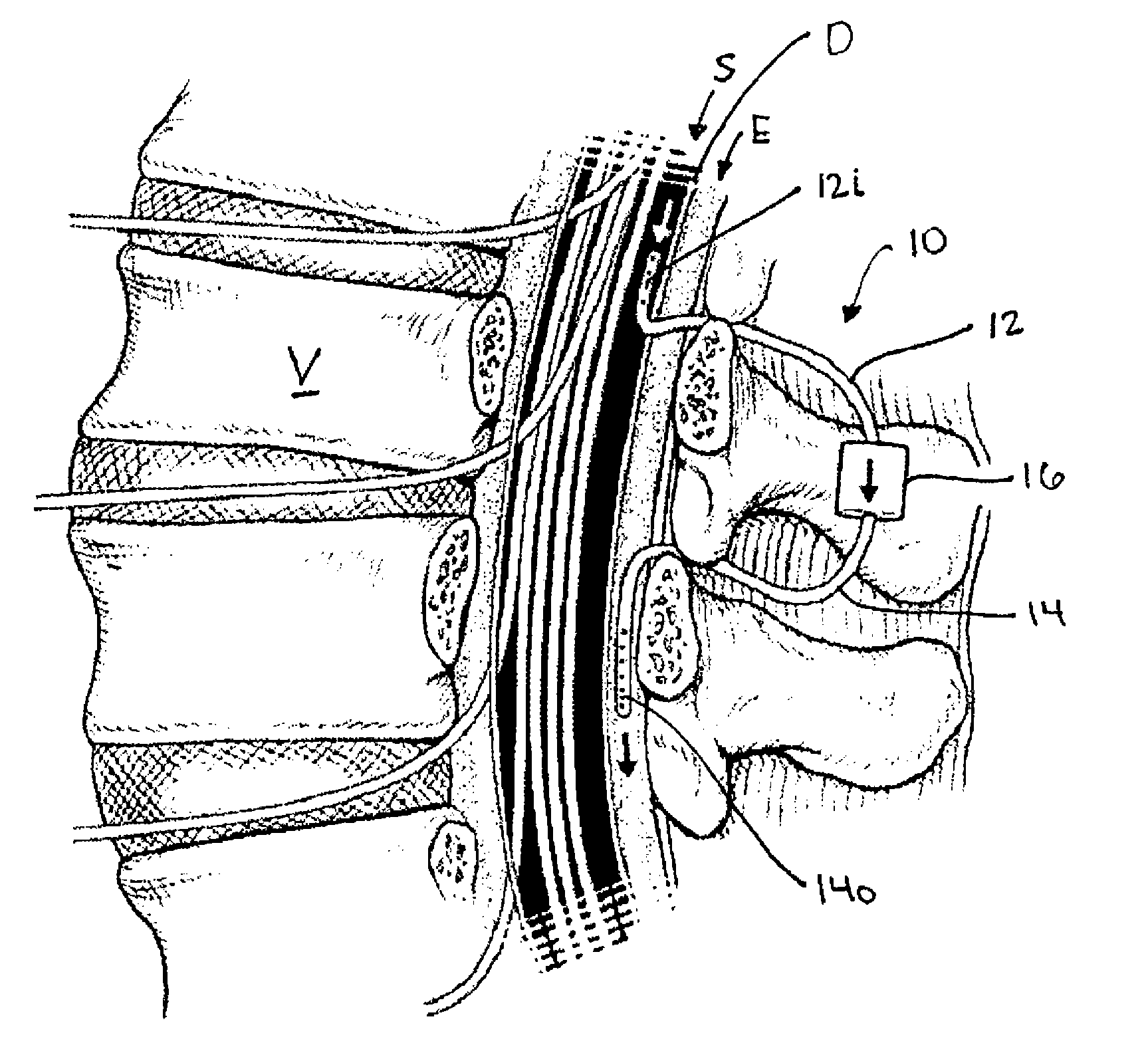
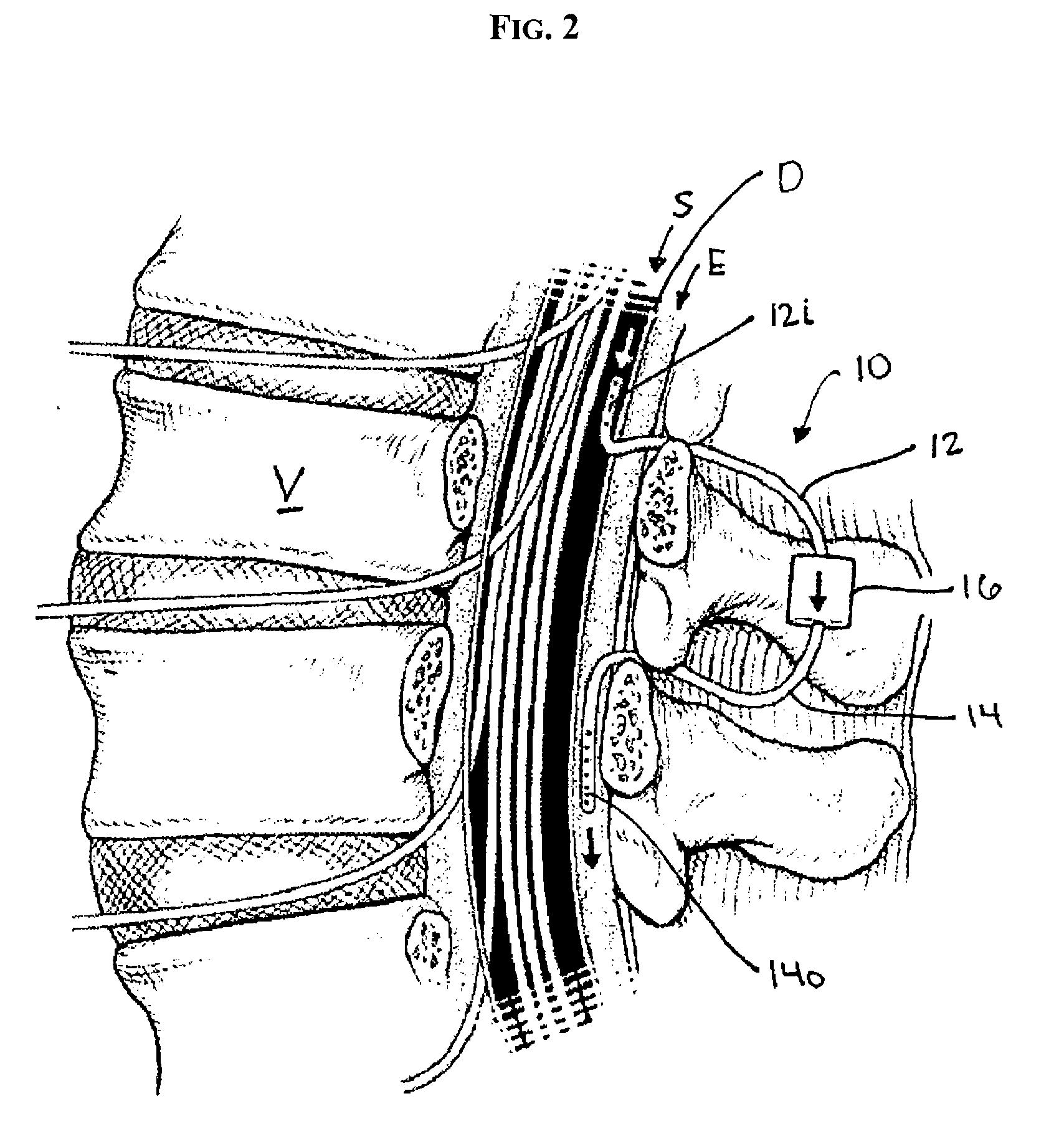
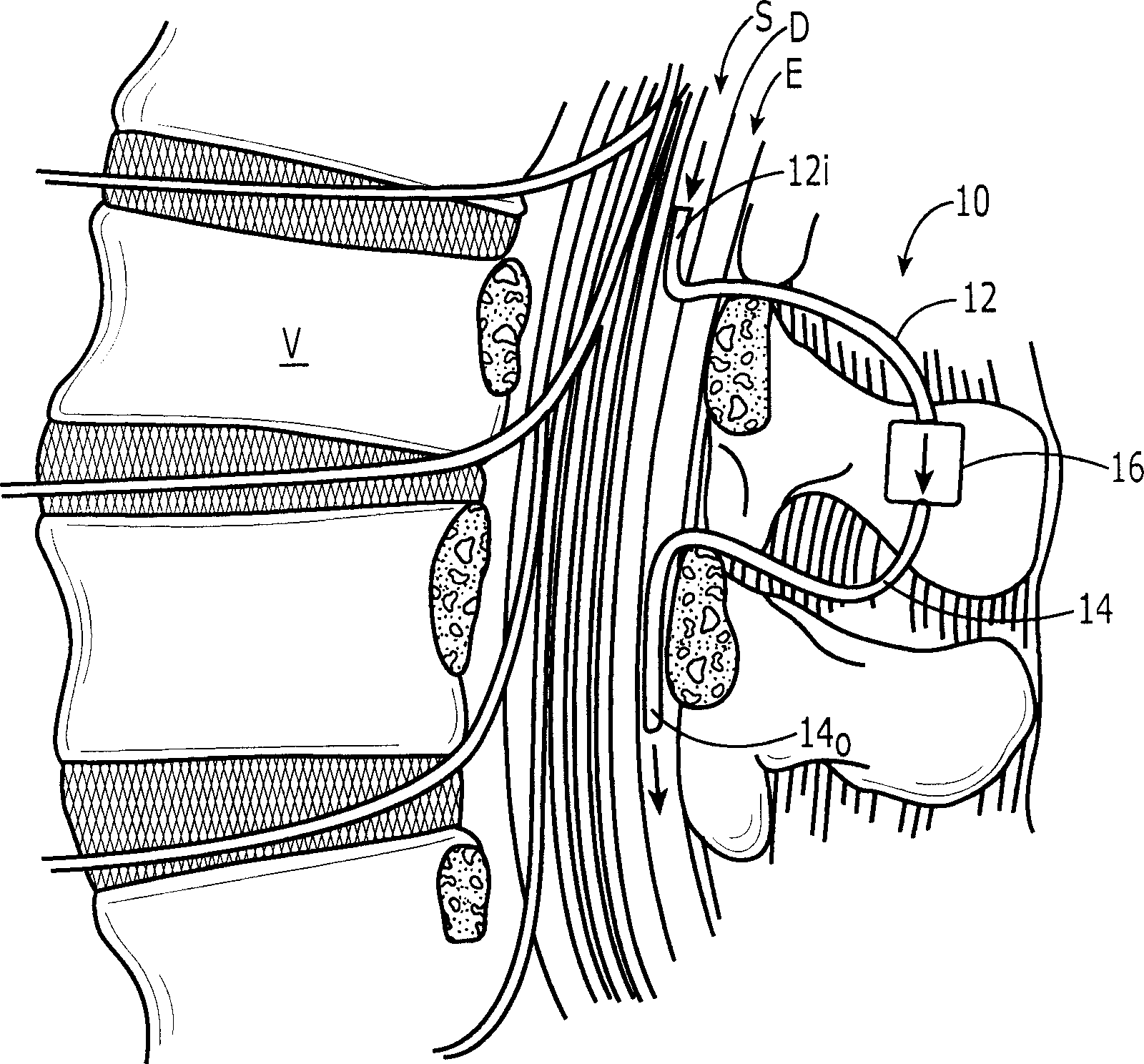
Internally powered CSF pump systems and methods
InactiveUS7025742B2Reduce eliminateEliminate progressionWound drainsIntravenous devicesSubarachnoid spaceCatheter
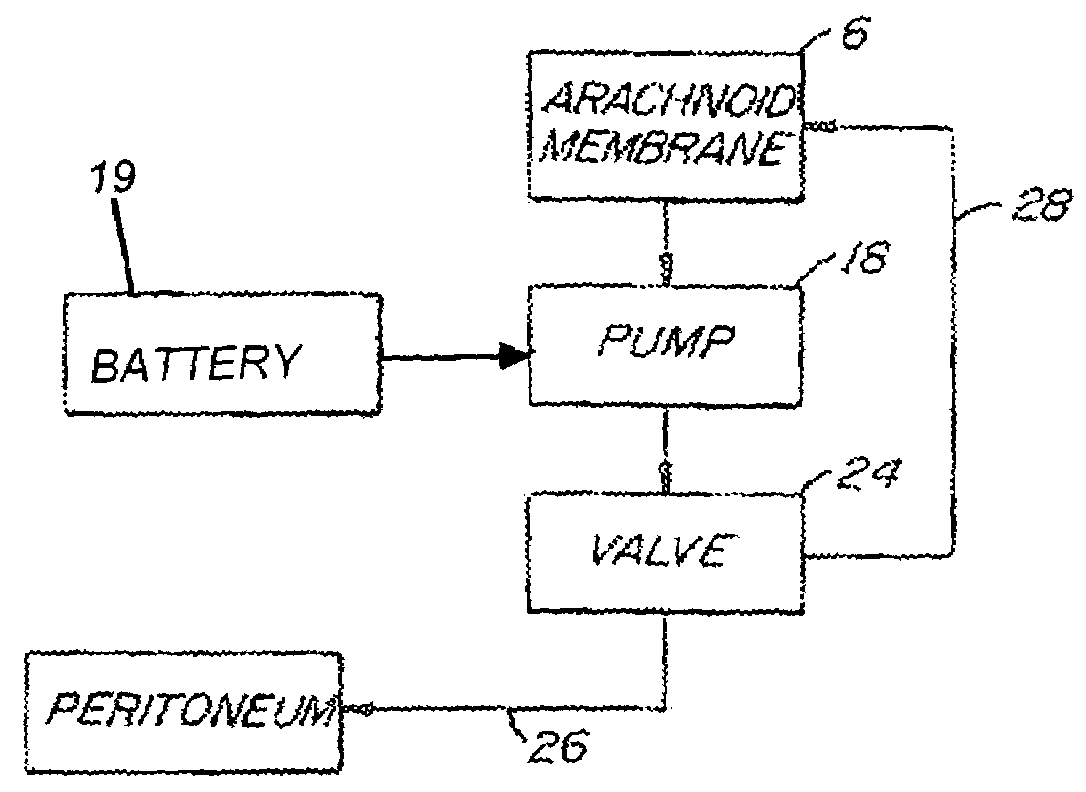
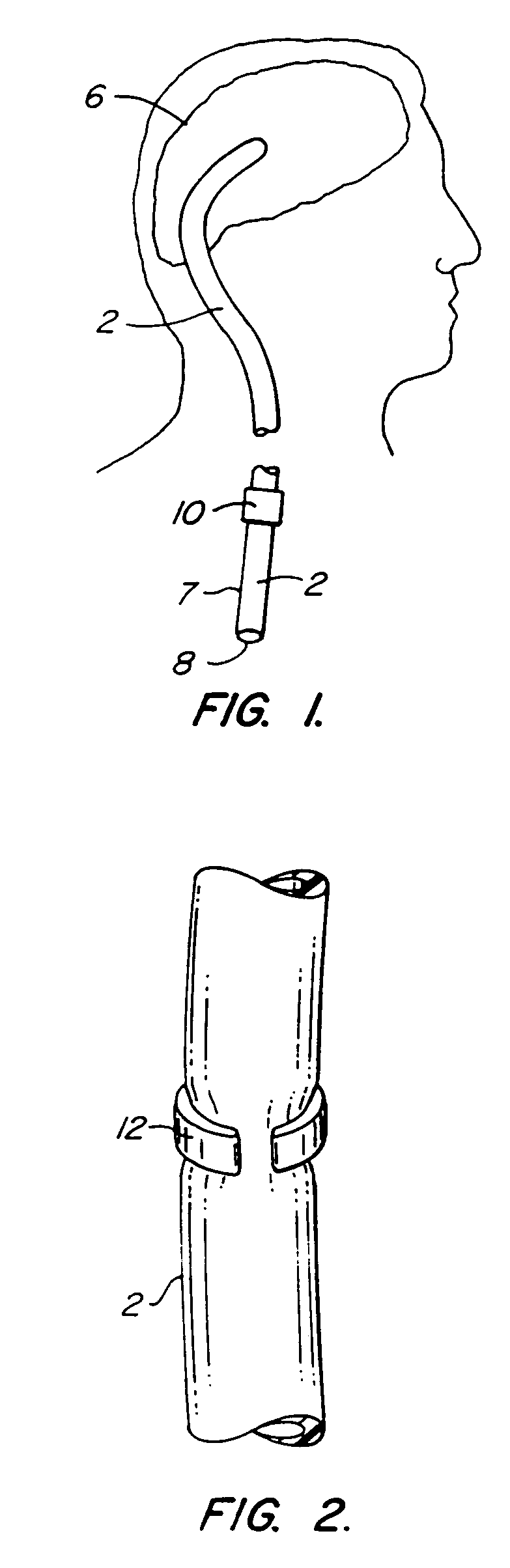
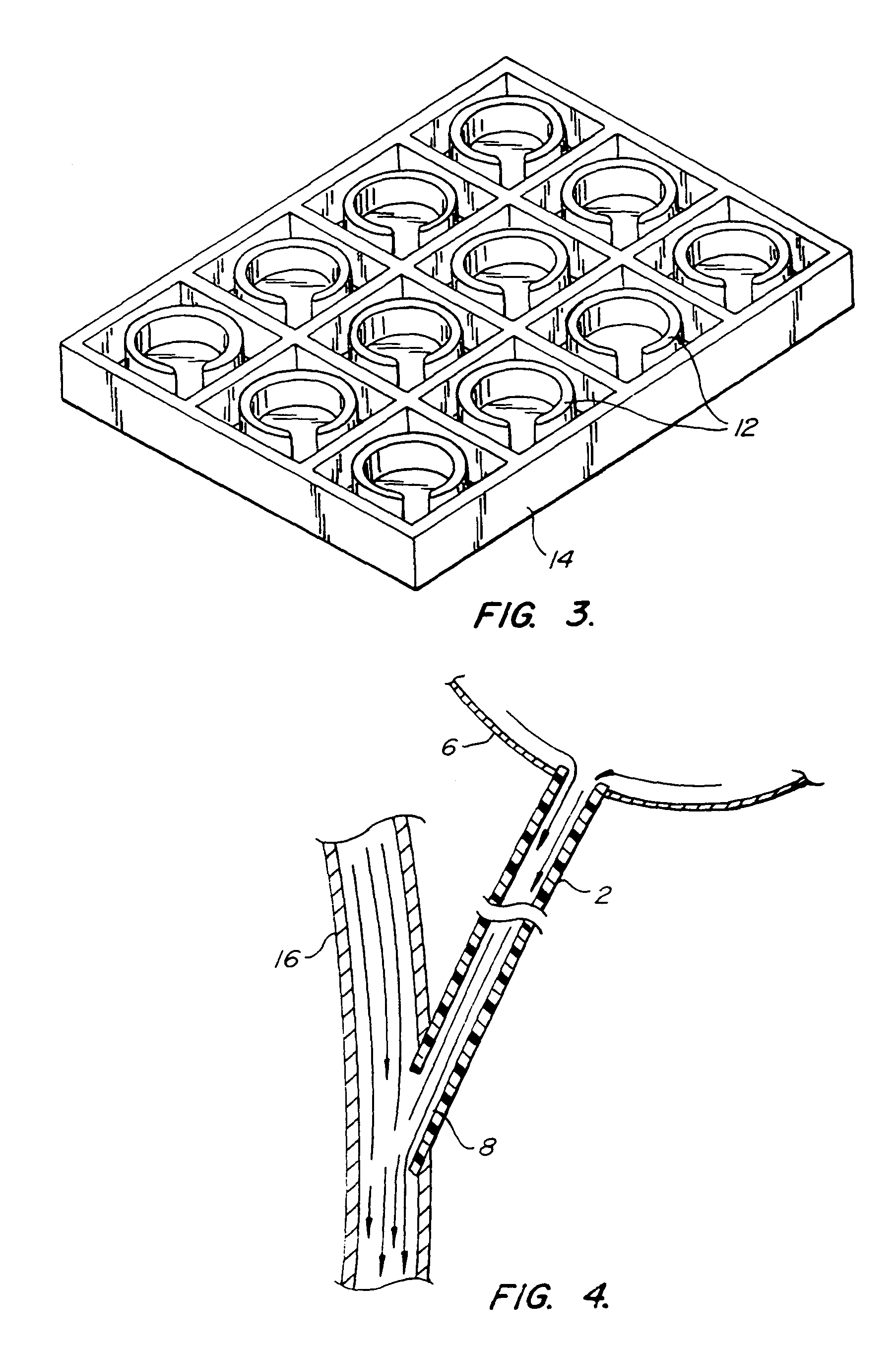
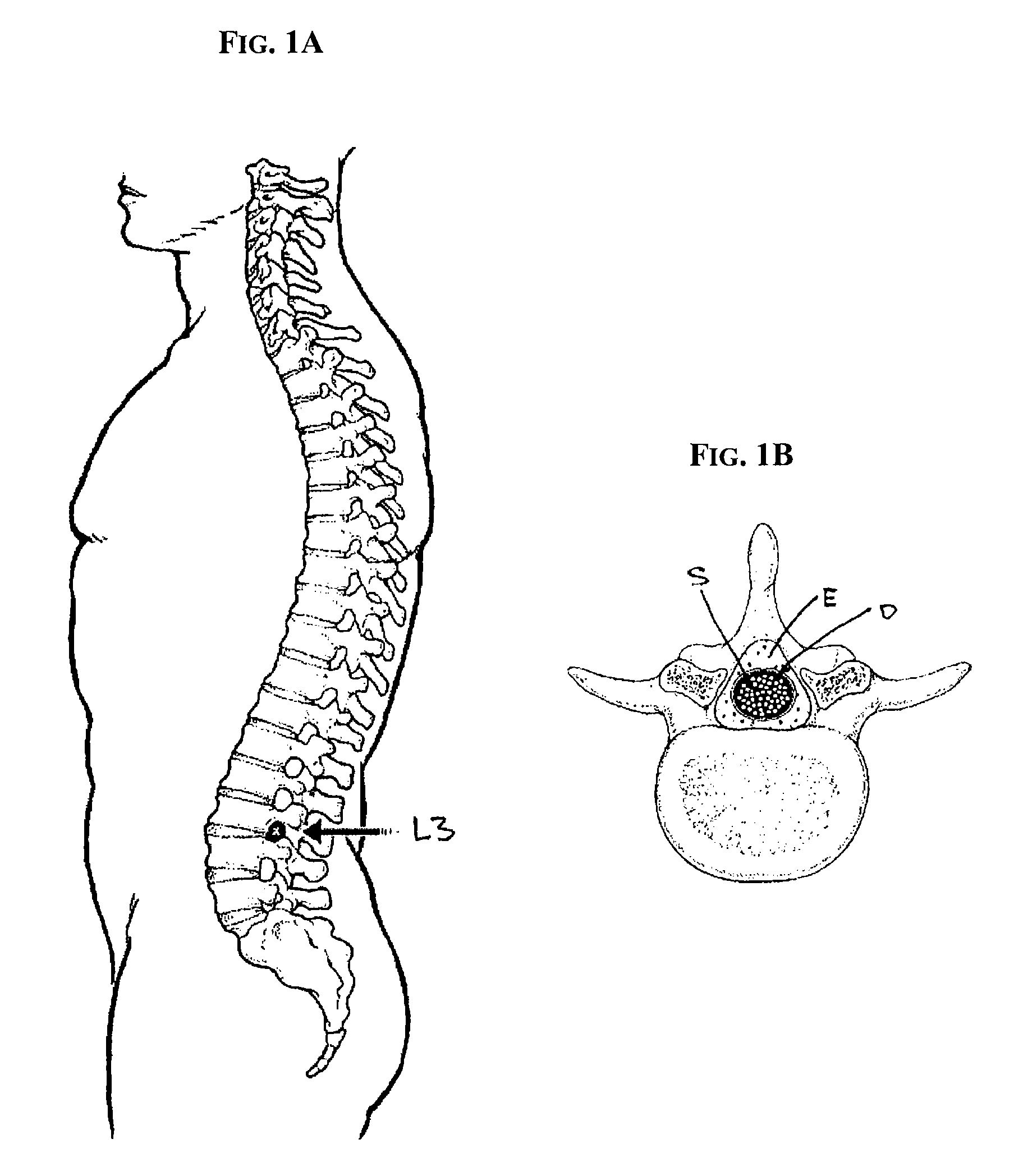
A method treats a patient for adult-onset dementia of the Alzheimer's type by removing a portion of the patient's cerebrospinal fluid, preferably (although not necessarily) by transporting the fluid to another portion of the patient's body. An apparatus for removing cerebrospinal fluid includes (1) a conduit with a first opening and a second opening, the first opening of the conduit being disposed in fluid communication with a space within a patient's subarachnoid space, the second opening being disposed in fluid communication with another portion of the patient's body; and (2) a flow rate control device attached to the conduit.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS7842002B2Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
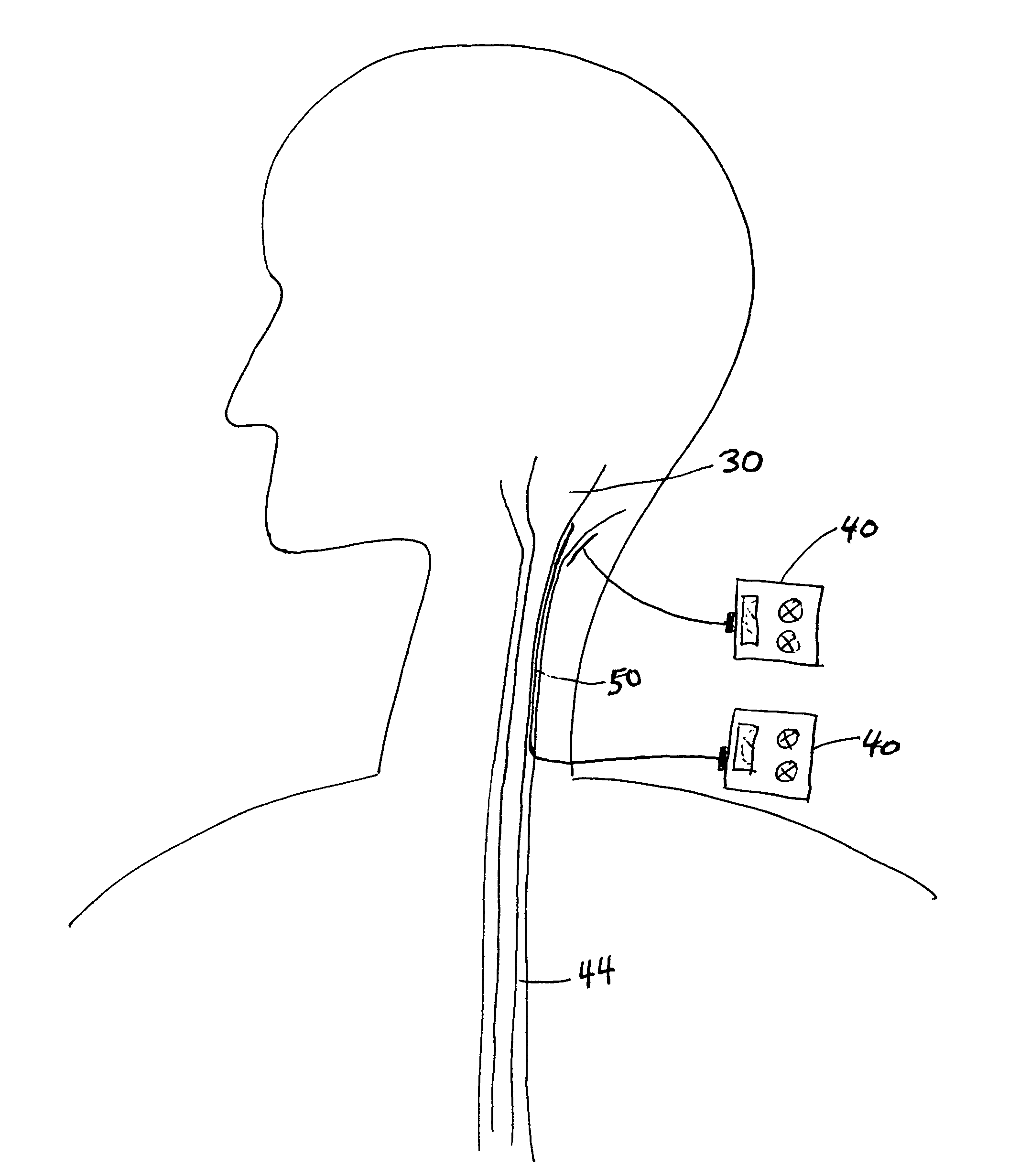
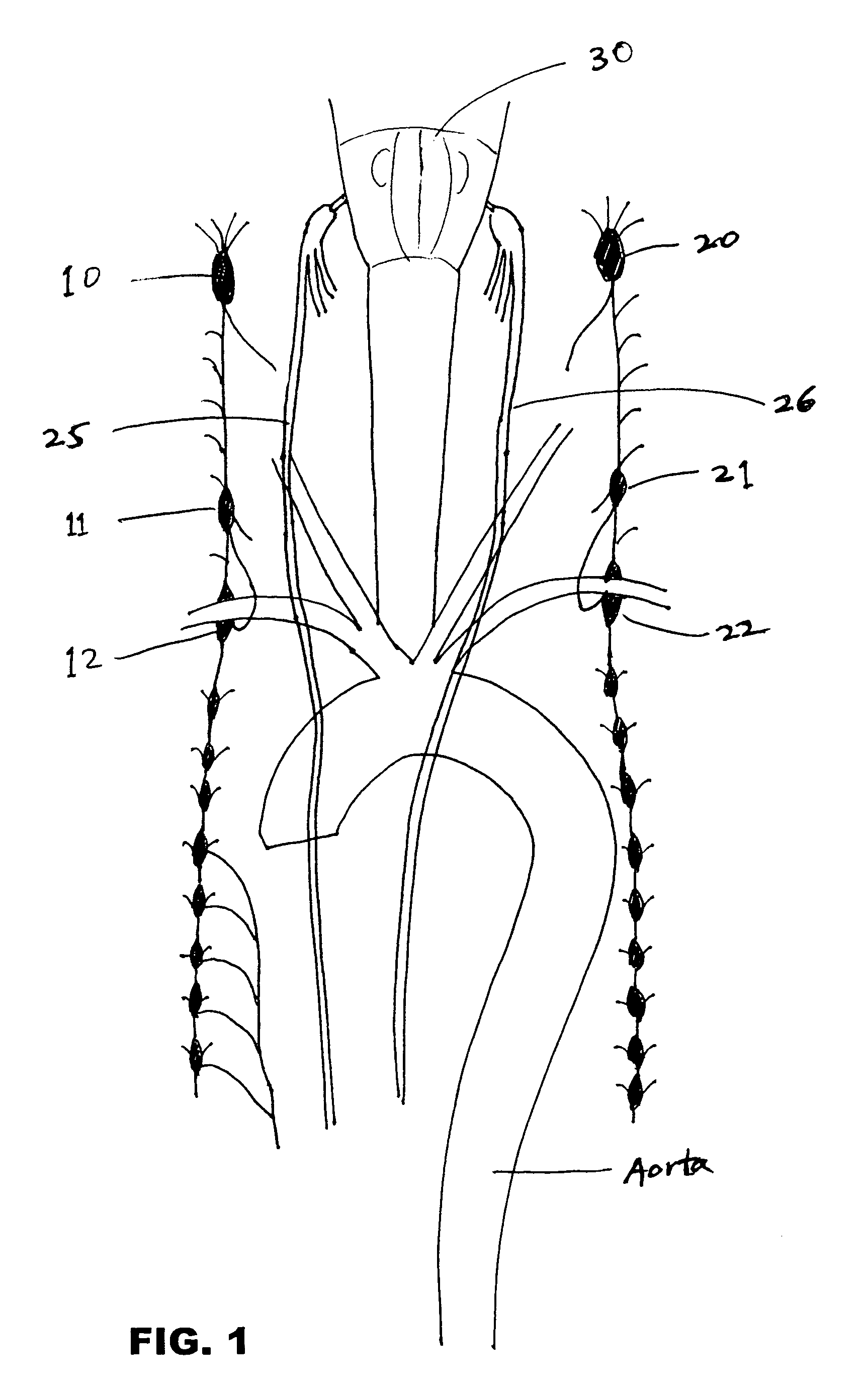
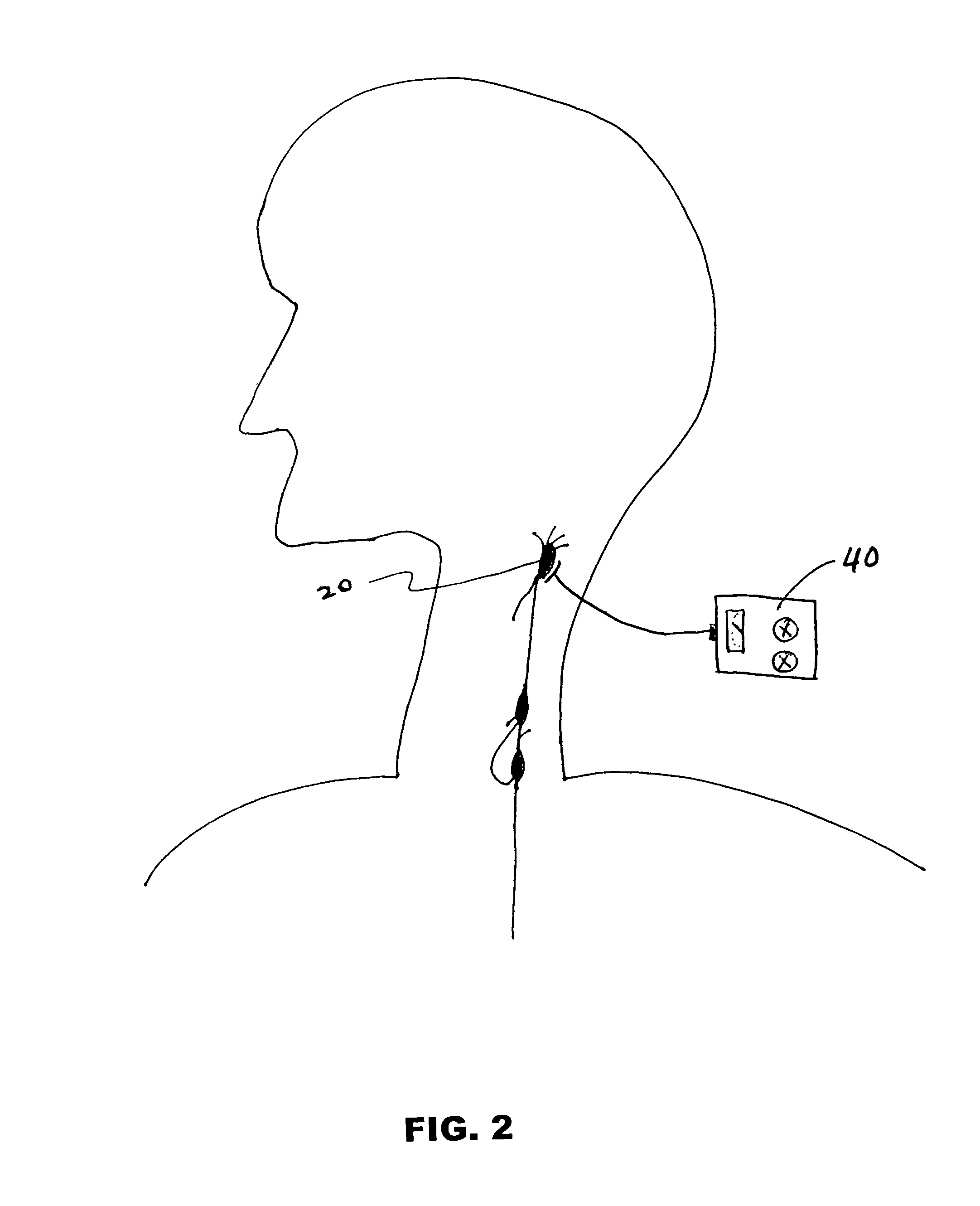
Cervical Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Treatment and Prevention of Cerebral Vasospasm
The present invention relates to a method of prevention and treatment of narrowing of cerebral blood vessels after subarachnoid hemorrhage, and in particular, to a method of applying electrical energy through electrical stimulation electrodes particularly positioned in the cervical region of a patient to affect the sympathetic tone of the blood vessels supplying the brain.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Intraventricular Shunt and Methods of Use Therefor
Methods and apparatus for treating hydrocephalus caused by obstructions in the ventricular system and subarachnoid space of the brain. Embodiments include medical devices and methods for use within the subarachnoid space of the central nervous system to gain access to and treat an obstruction within the ventricles of the brain or a subarachnoid hemorrhage. The obstruction may be aspirated by an aspiration catheter for use in the subarachnoid space. A subarachnoid delivery catheter may then be used to deliver an intraventricular shunt to the opening in the obstruction via the subarachnoid space. A distal end of the delivery catheter is navigated across the obstruction to deploy the intraventricular shunt therein. The intraventricular shunt so positioned reopens the pathway between the ventricles and permits the return of normal cerebrospinal fluid flow there through.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Methods and devices for draining fluids and lowering intraocular pressure
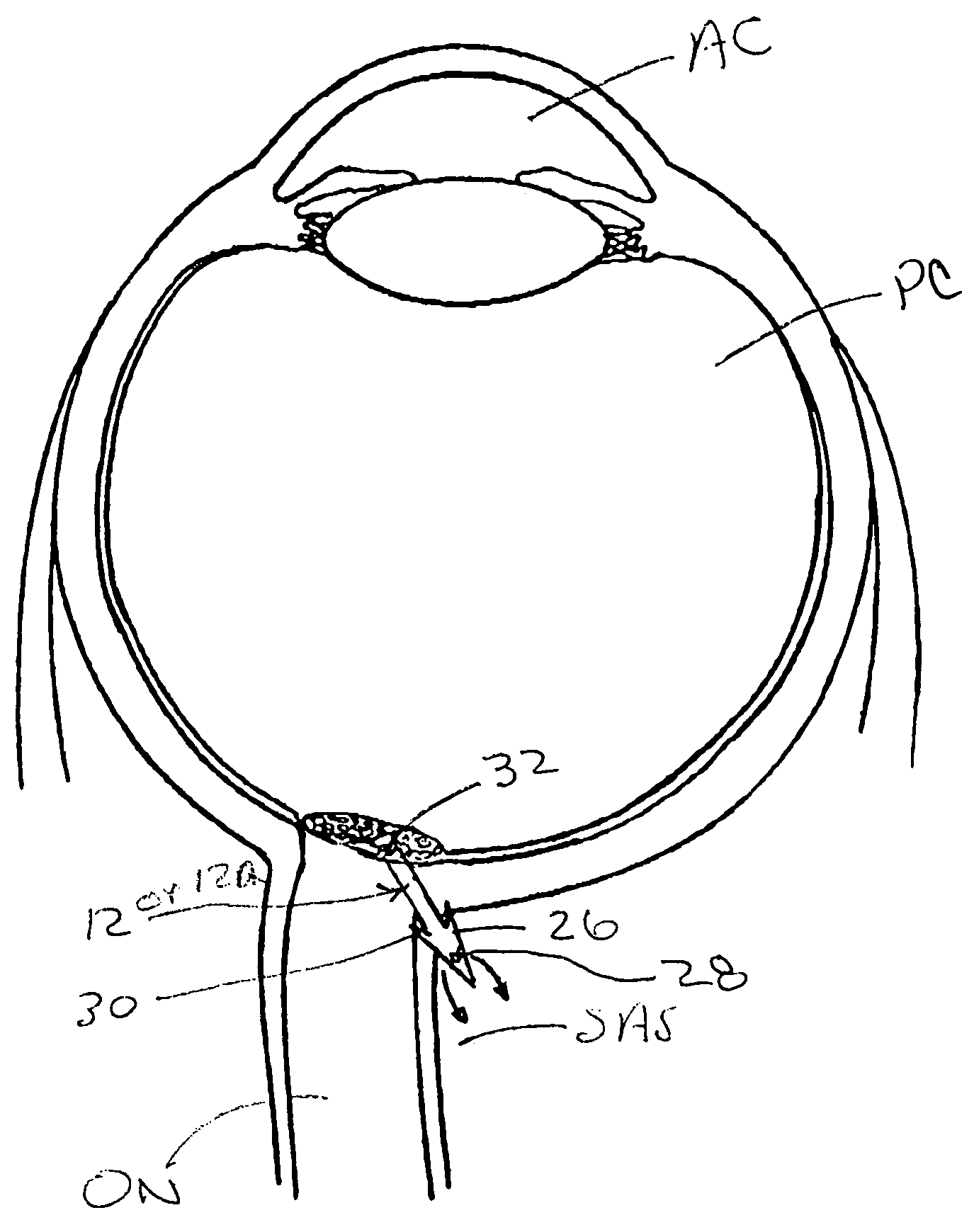
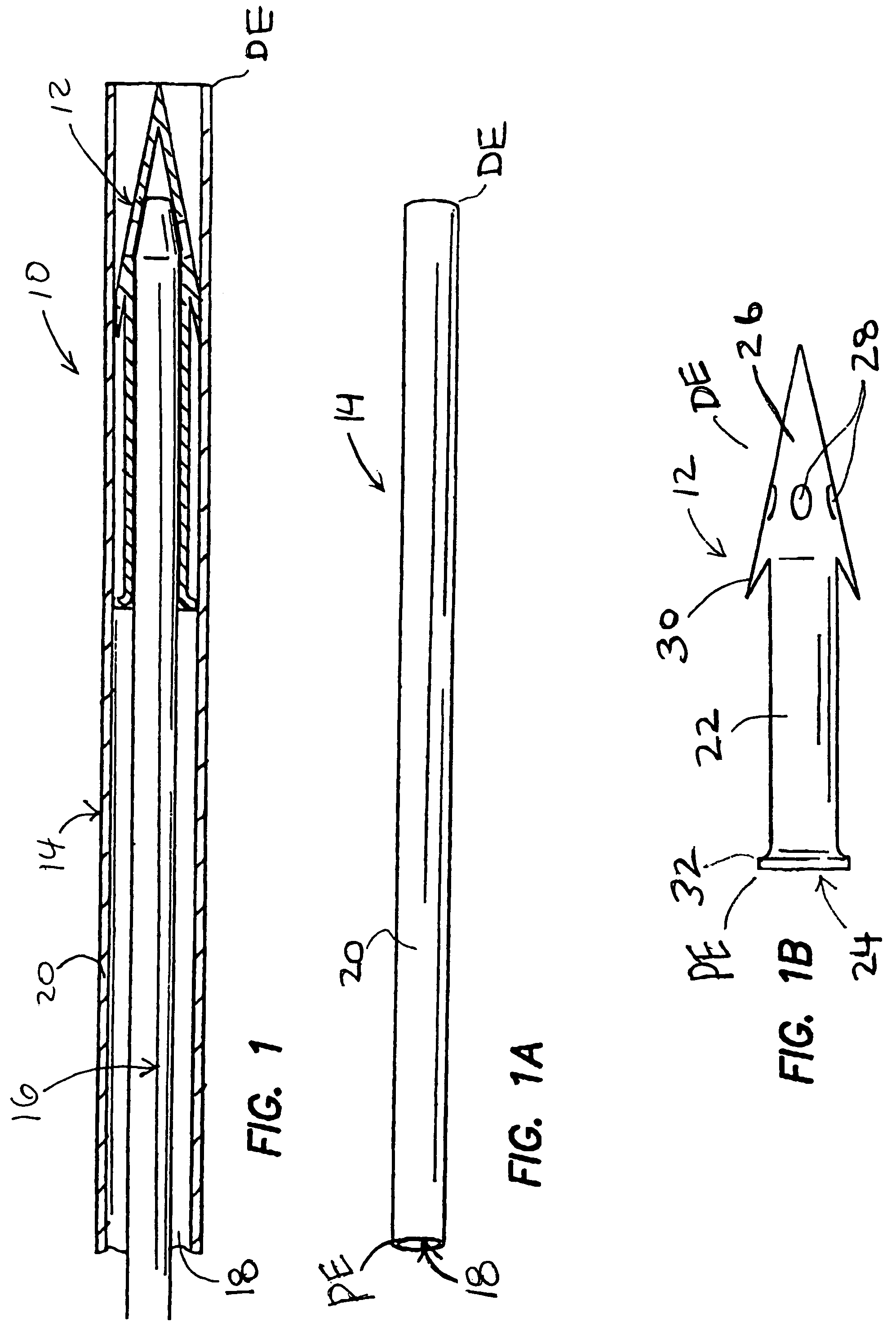
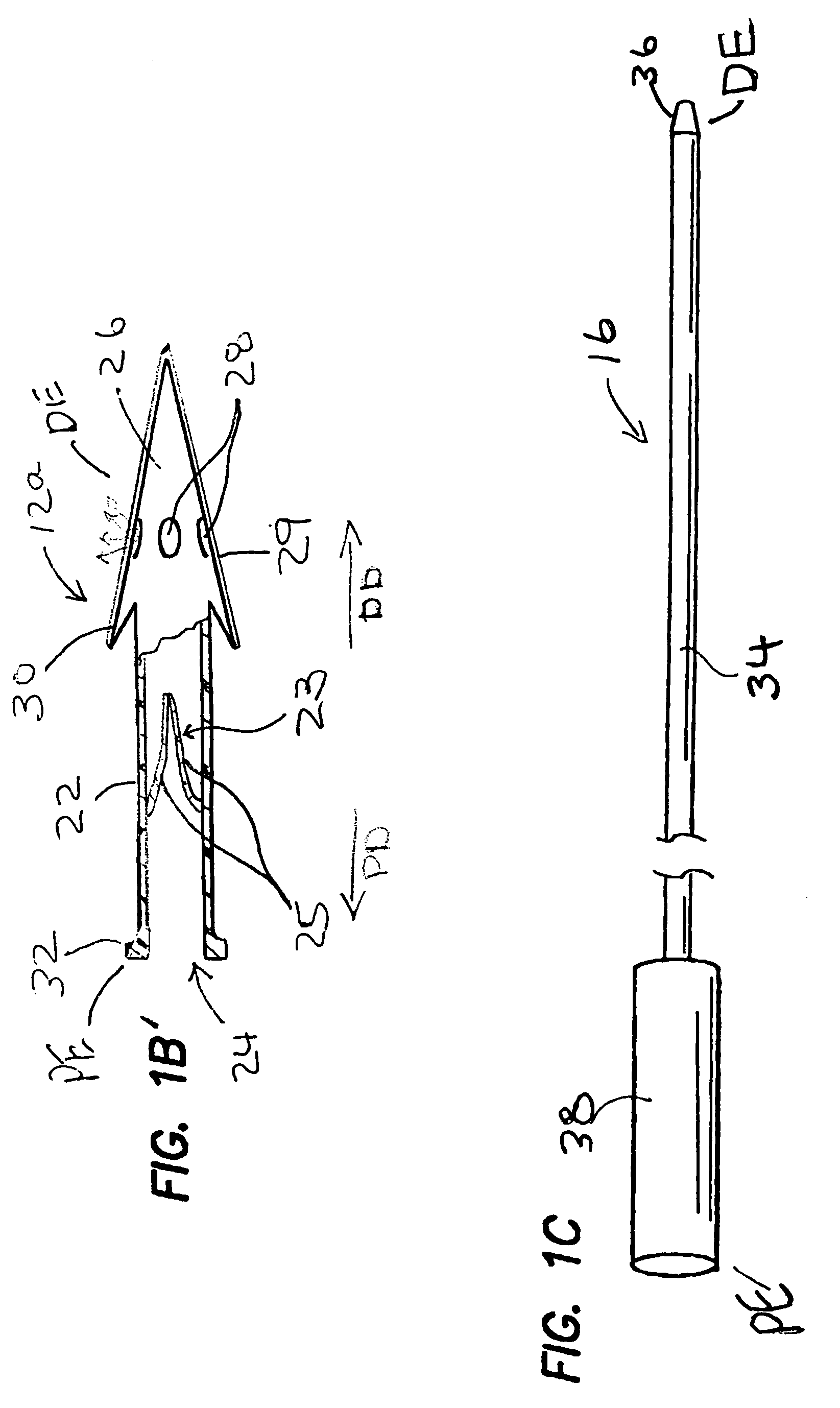
ActiveUS7354416B2Prevent and deter cloggingPrevent unwanted backflow of fluidEye implantsEye surgerySubarachnoid spaceOptic nerve
Methods, devices and systems for draining fluid from the eye and / or for reducing intraocular pressure. A passageway (e.g., an opening, puncture or incision) is formed in the lamina cribosa or elsewhere to facilitate flow of fluid from the posterior chamber of the eye to either a) a subdural location within the optic nerve or b) a location within the subarachnoid space adjacent to the optic nerve. Fluid from the posterior chamber then drains into the optic nerve or directly into the subarachnoid space, where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid. In some cases, a tubular member (e.g., a shunt or stent) may be implanted in the passageway. A particular shunt device and shunt-introducer system is provided for such purpose. A vitrectomy or vitreous liquefaction procedure may be performed to remove some or all of the vitreous body, thereby facilitating creation of the passageway and / or placement of the tubular member as well as establishing a route for subsequent drainage of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber, though the posterior chamber and outwardly though the passageway where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:QUIROZ MERCADO HUGO +1
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS20060161107A1Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
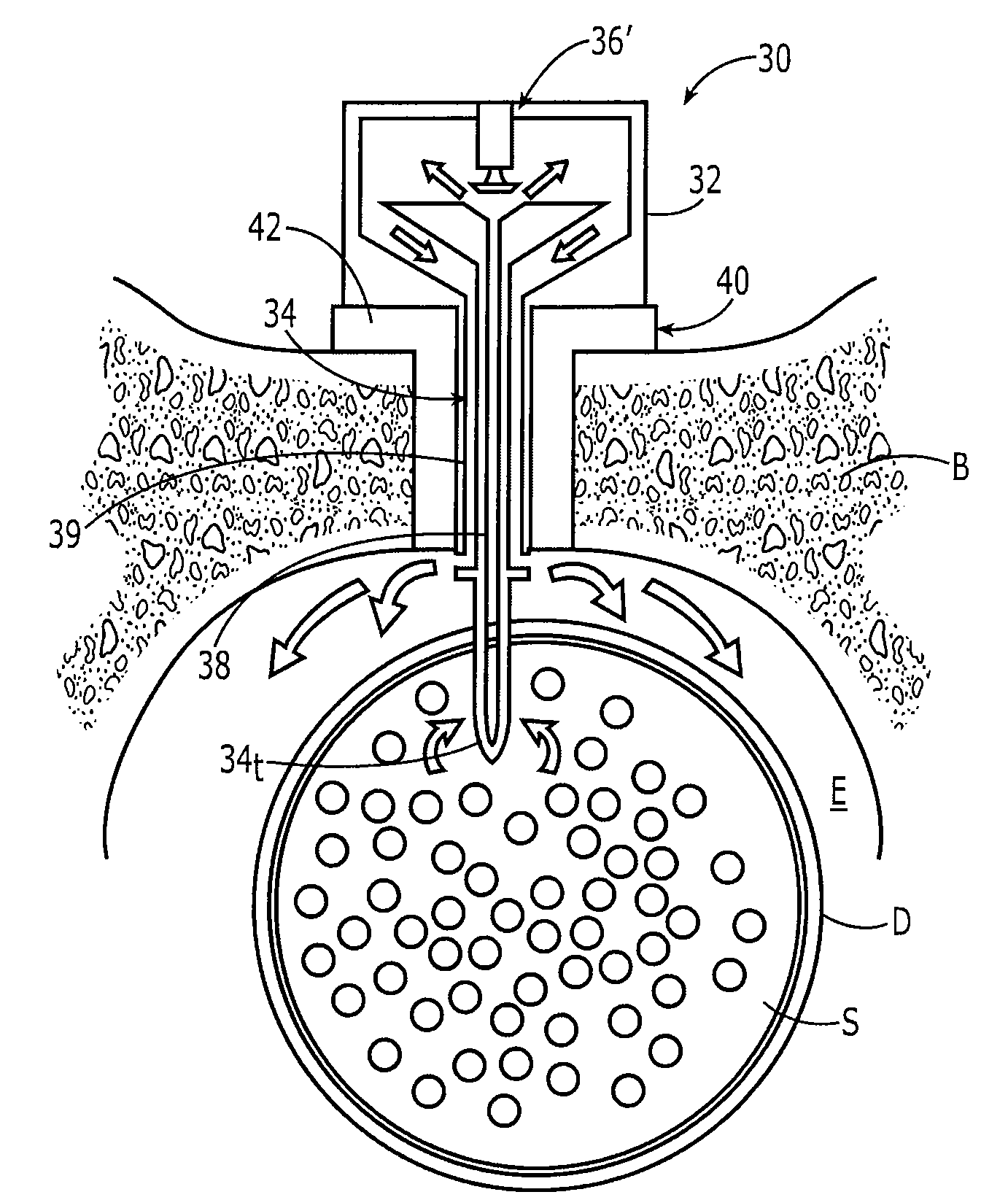
Biocompatible liquid is pumped into a body cavity (eg. subarachnoid space, peritoneum, mediastinum, pleural space) by means of one pump and removed from it by means a second pump, preferably via a double-barreled catheter is used for insertion and removal of the liquid. An optional secondary catheter removes liquid from a distal area of the body cavity. Temperature and pressure are sensed within the cavity and can be controlled by adjusting liquid flow rates. While outside the body, the liquid can be ultraviolet-sterilized, foam fractionated to remove contaminants, oxygenated and pH balanced, cooled or warmed, and augmented with exogenous liquid that may contain drugs.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
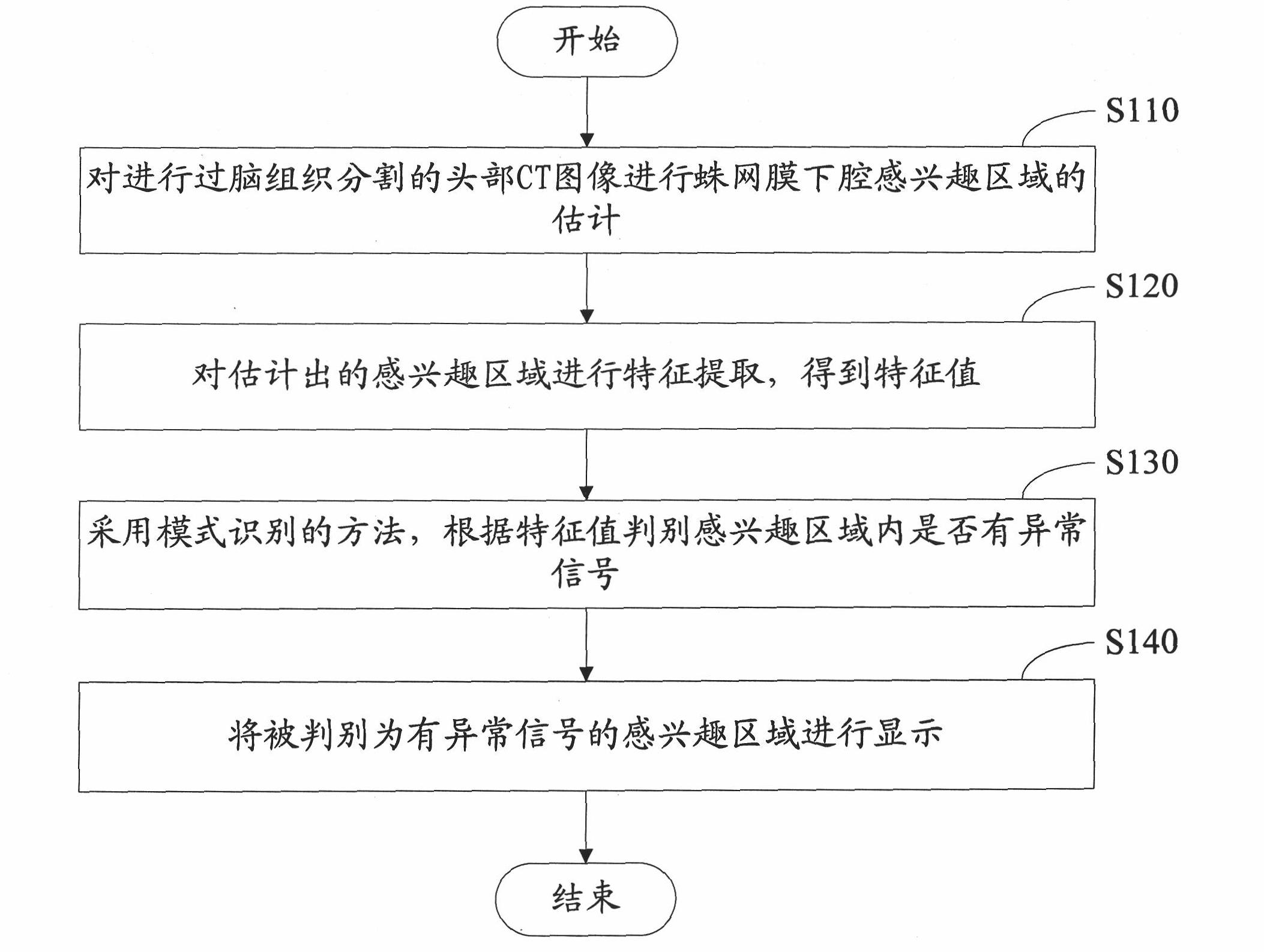
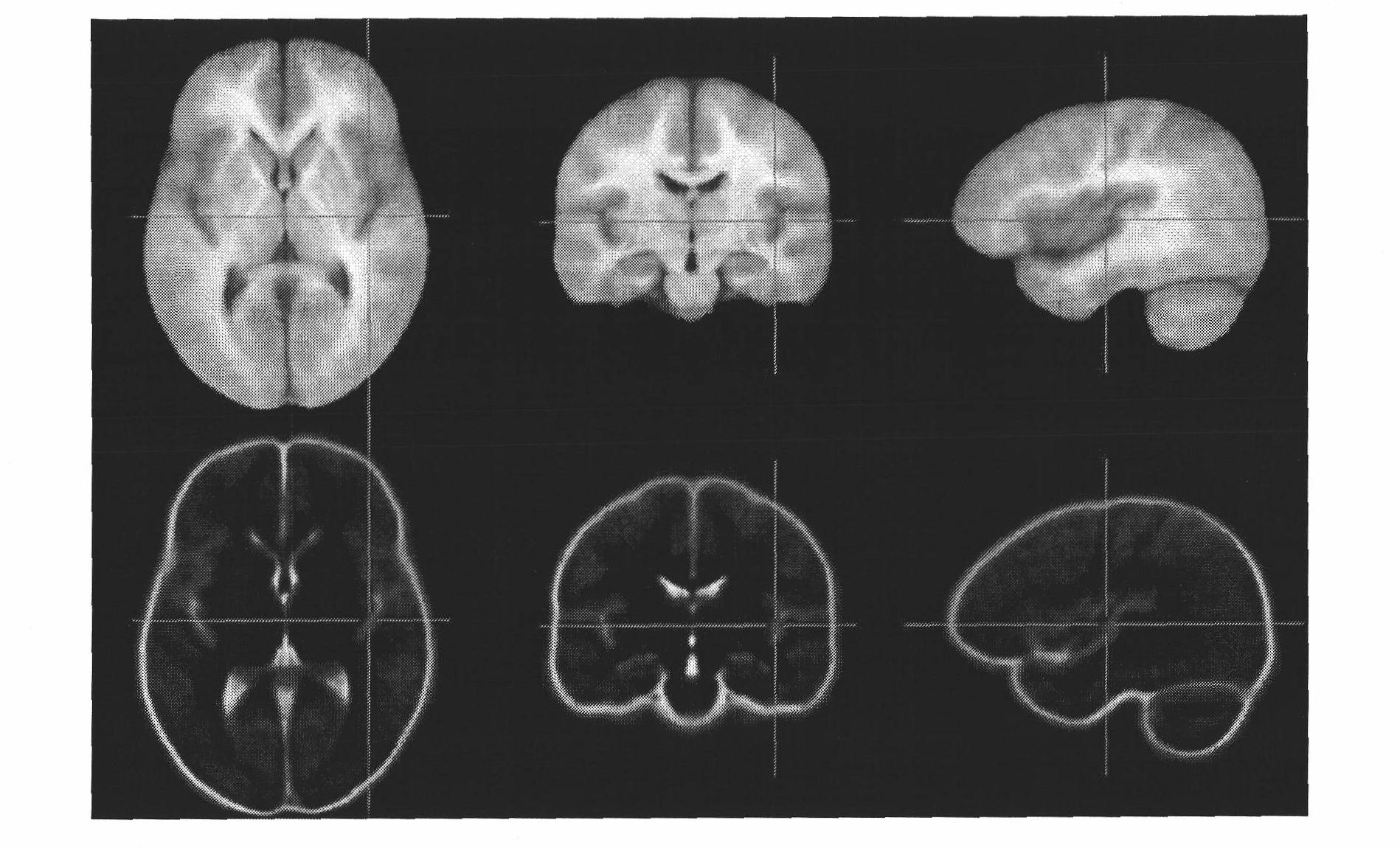
Processing method and system of CT image
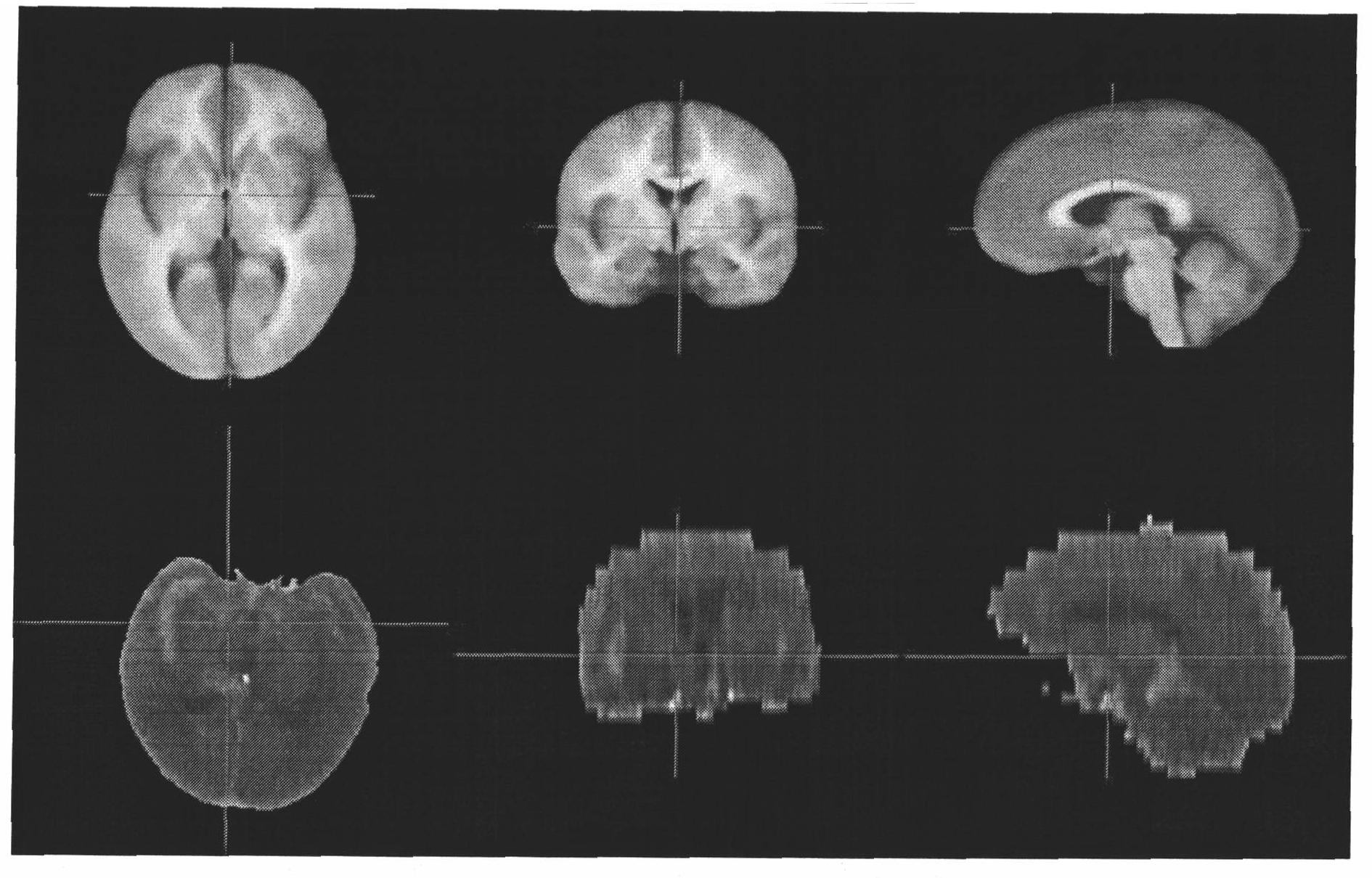
ActiveCN101916443AAccurate judgmentReduce misdiagnosis/missed diagnosis rateImage analysisComputerised tomographsSubarachnoid spaceFeature extraction
The invention relates to a processing system of a CT image, which comprises a CT image acquiring module, an interesting region estimating module, a characteristic extracting module, an abnormal signal identifying module and a displaying module. The CT image acquiring module is used for acquiring a head CT image subjected to brain tissue segmentation; the interesting region estimating module is used for estimating an interesting region of subarachnoid space to the head CT image; the characteristic extracting module is used for extracting the characteristic to the head CT image subjected to the estimation of the interesting region to acquire a characteristic value; the abnormal signal identifying module is used for identifying whether an abnormal signal is included in the interesting region according to the characteristic value by using a method of mode identification; and the displaying module is used for displaying the identified result and the interesting region in which the abnormal signal exists. The invention also relates to a processing method of the CT image. The invention can display a position in which the abnormal signal exists, which is referred by medical staffs, so as to reduce misdiagnosis / missed diagnosis rate of the subarachnoid space hemorrhage.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Enhancement of cerebral blood flow by electrical nerve stimulation
InactiveUS7340298B1Increase cerebral blood flowElectrotherapySubarachnoid spaceCerebral blood volume
A method for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient. A electrical stimulating device is provided. The electrical stimulating device is applied to the patient at a region adjacent the cervical sympathetic chain, the brain stem, the head, or the sympathetic nervous system. The electrical stimulating device is applied by any route selected from transcutaneous, subcutaneous, and subarachnoid. The electrical stimulating device is activated to stimulate or inhibit nerve impulses of the cervical sympathetic chain, thereby producing vasodilation in the cerebral vasculature, thereby increasing cerebral blood flow. Devices for increasing cerebral blood flow in a patient are also described.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
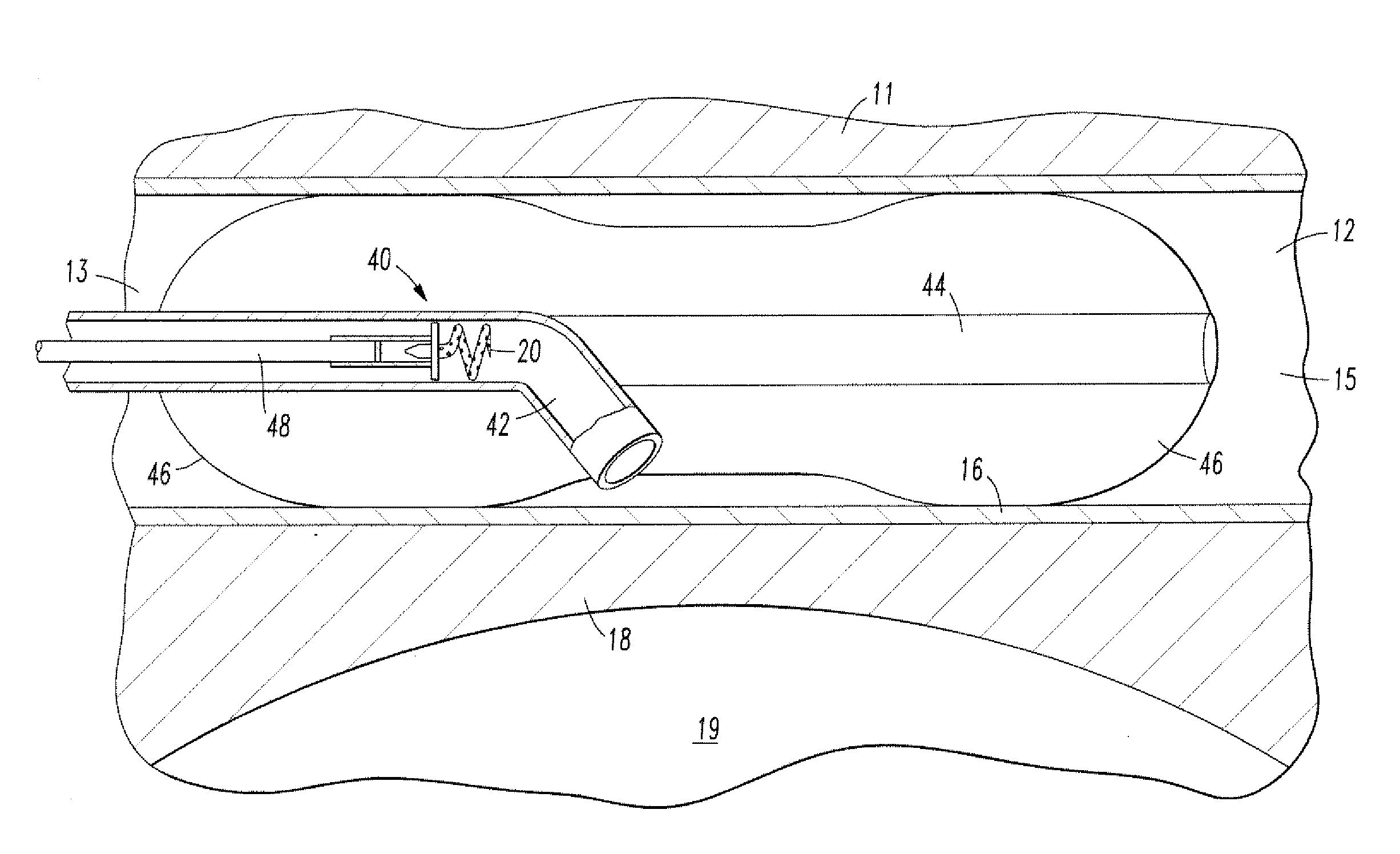
Medical device and method for temperature control and treatment of the brain and spinal cord
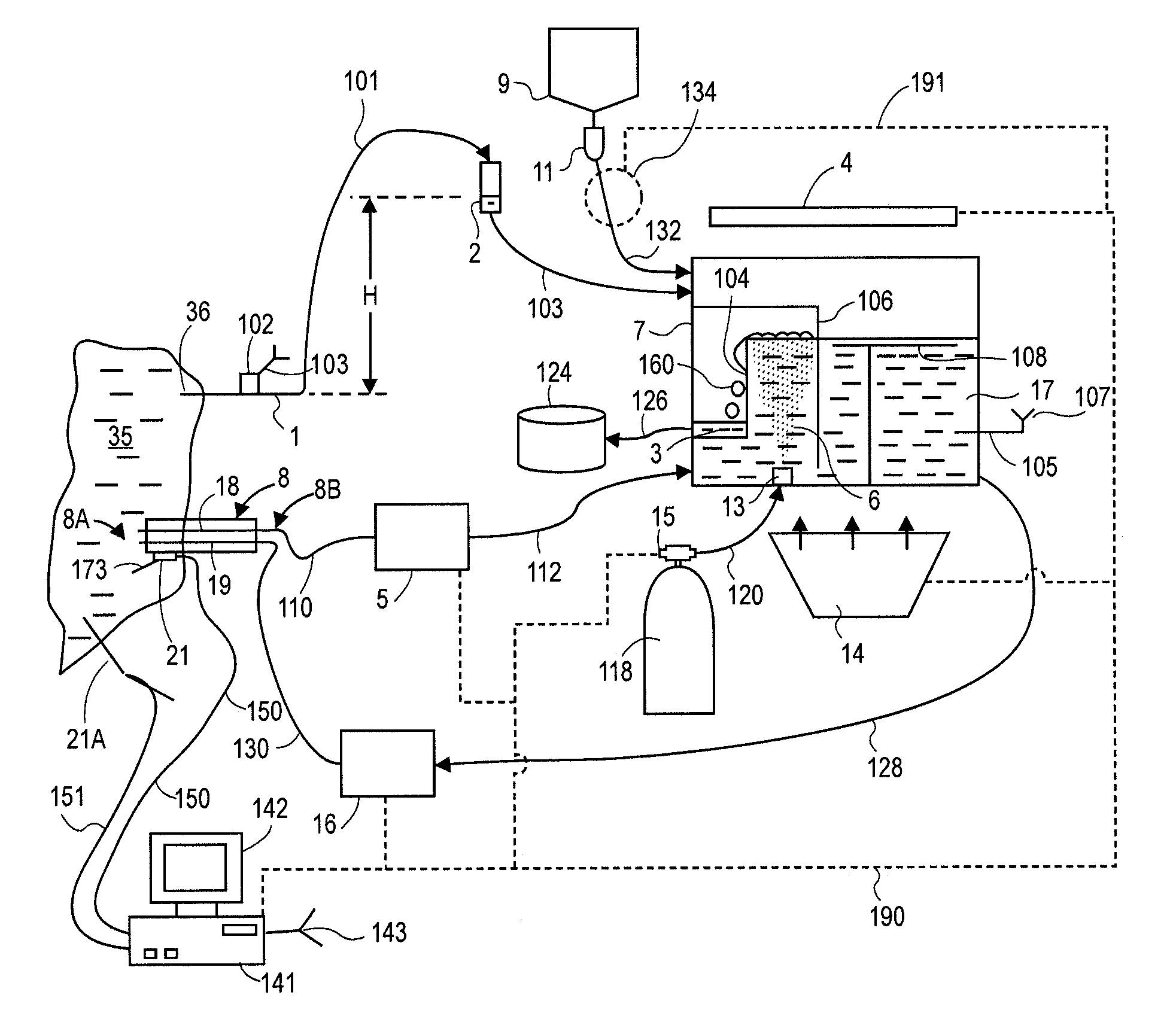
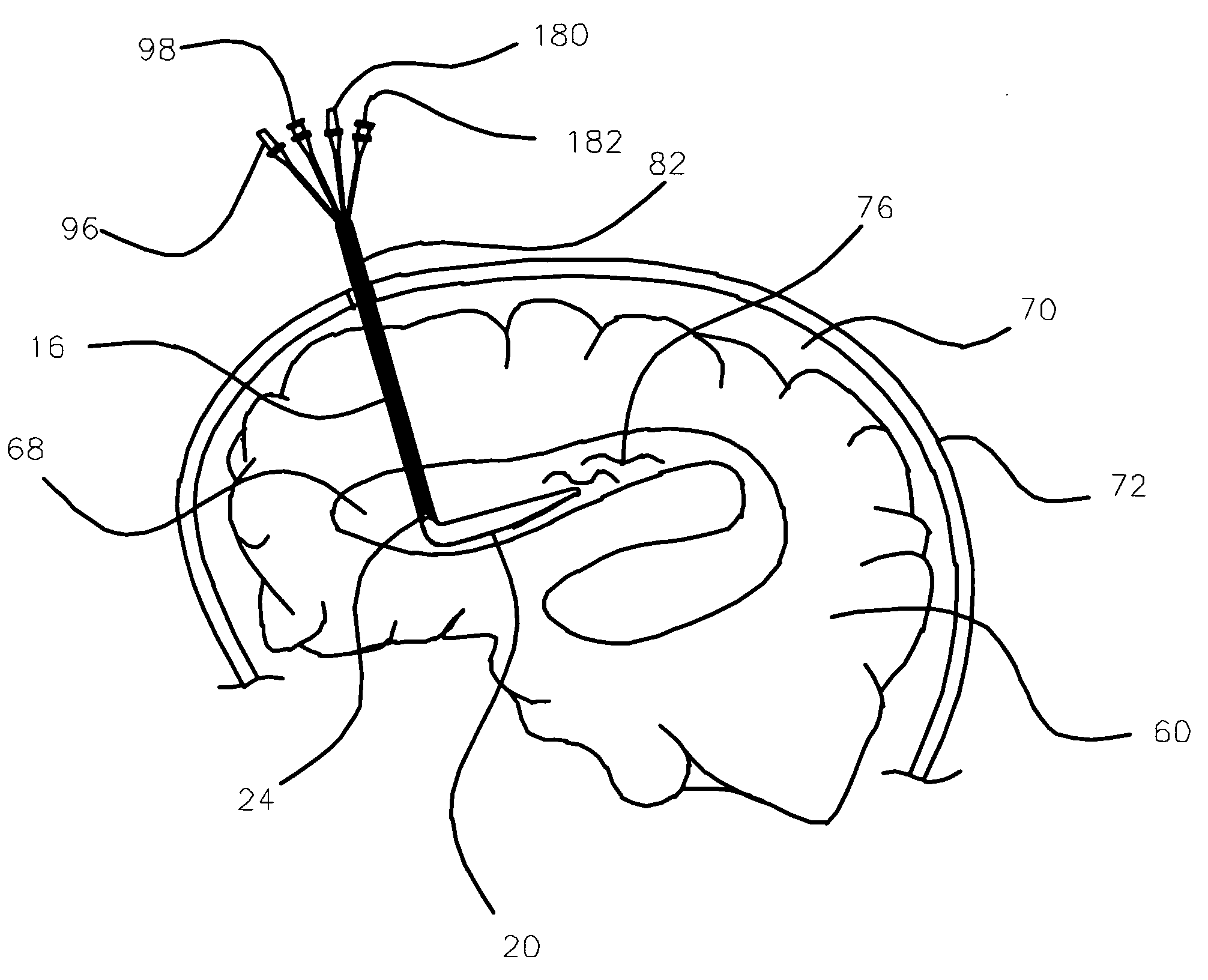
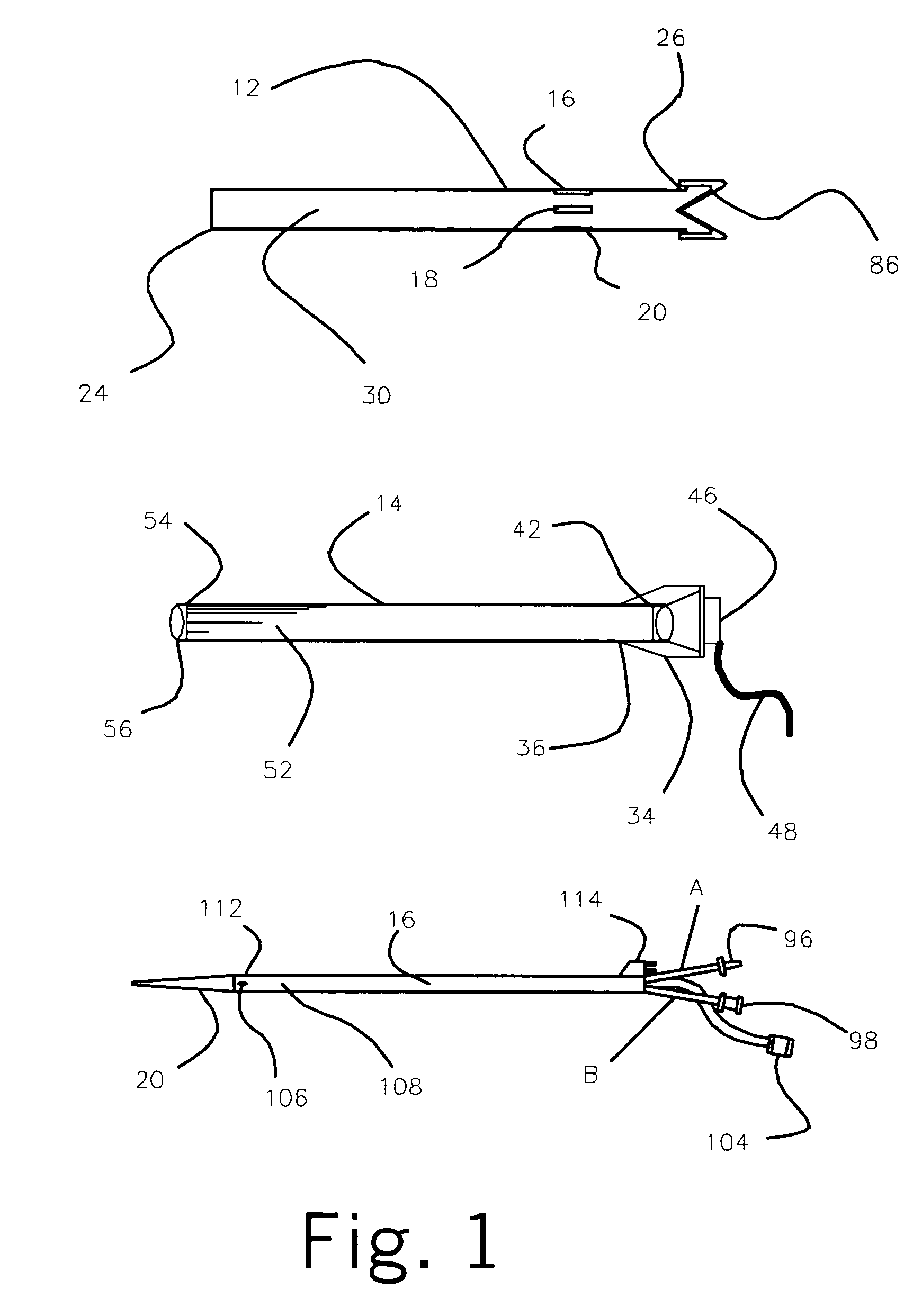
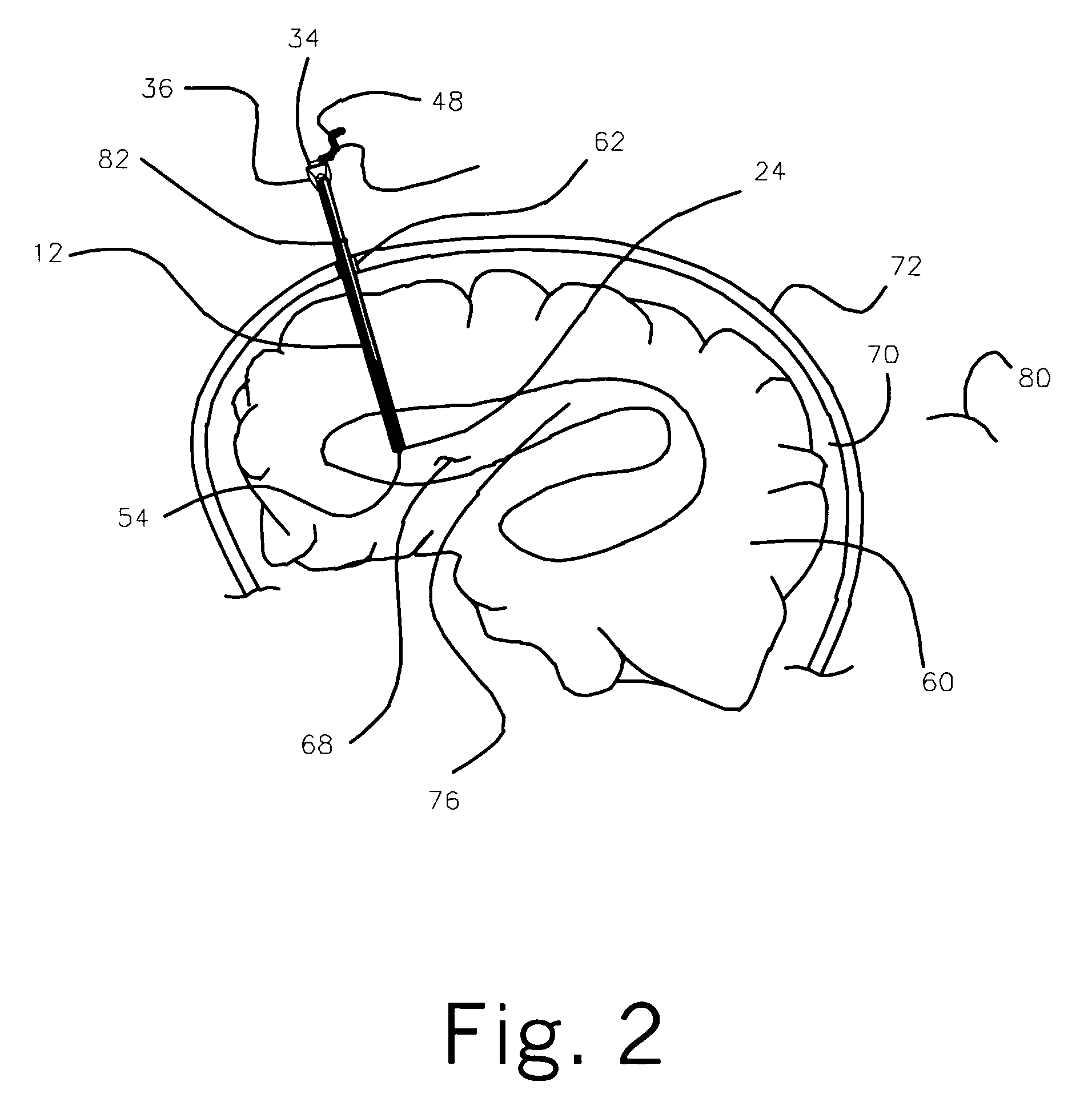
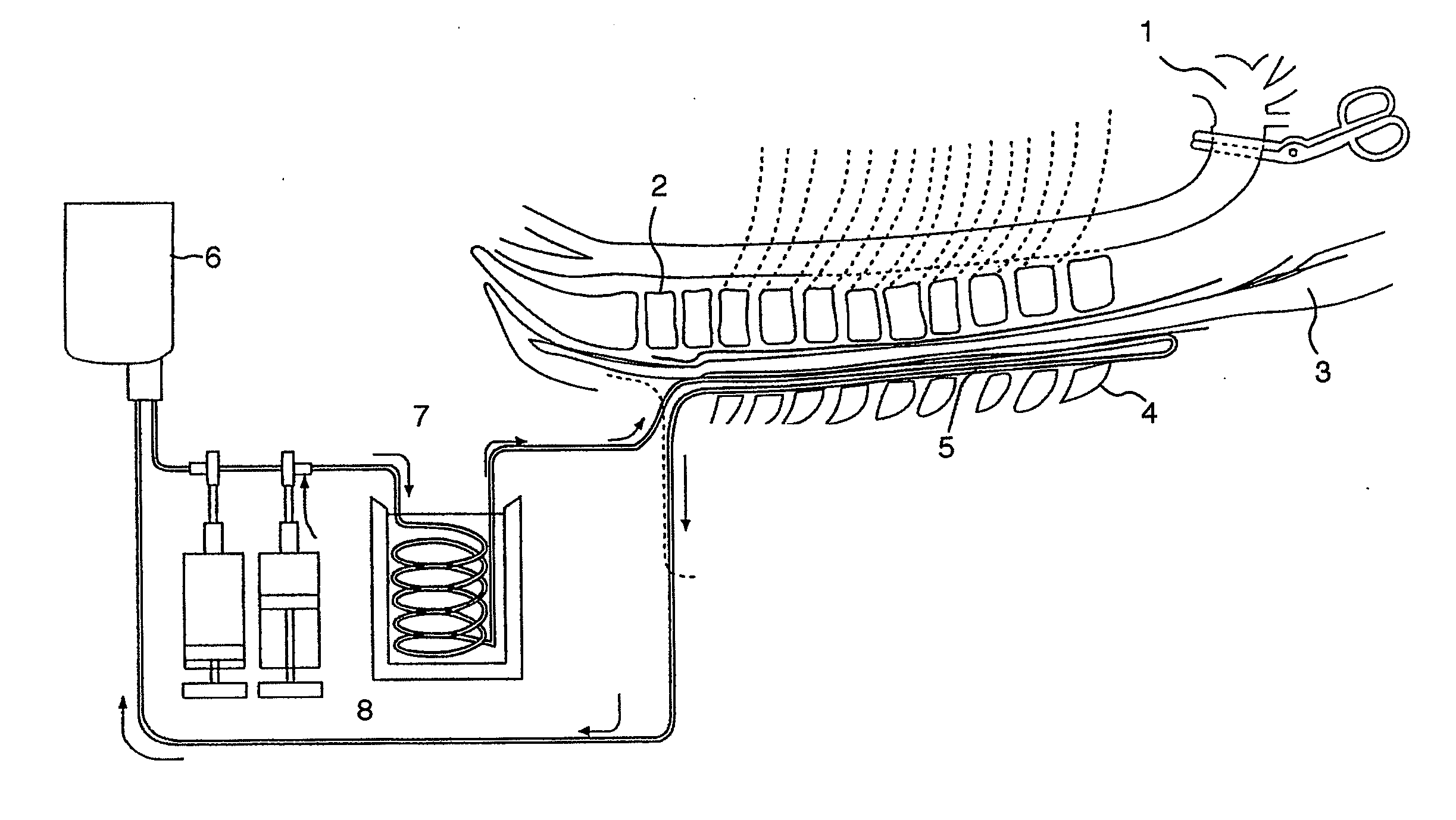
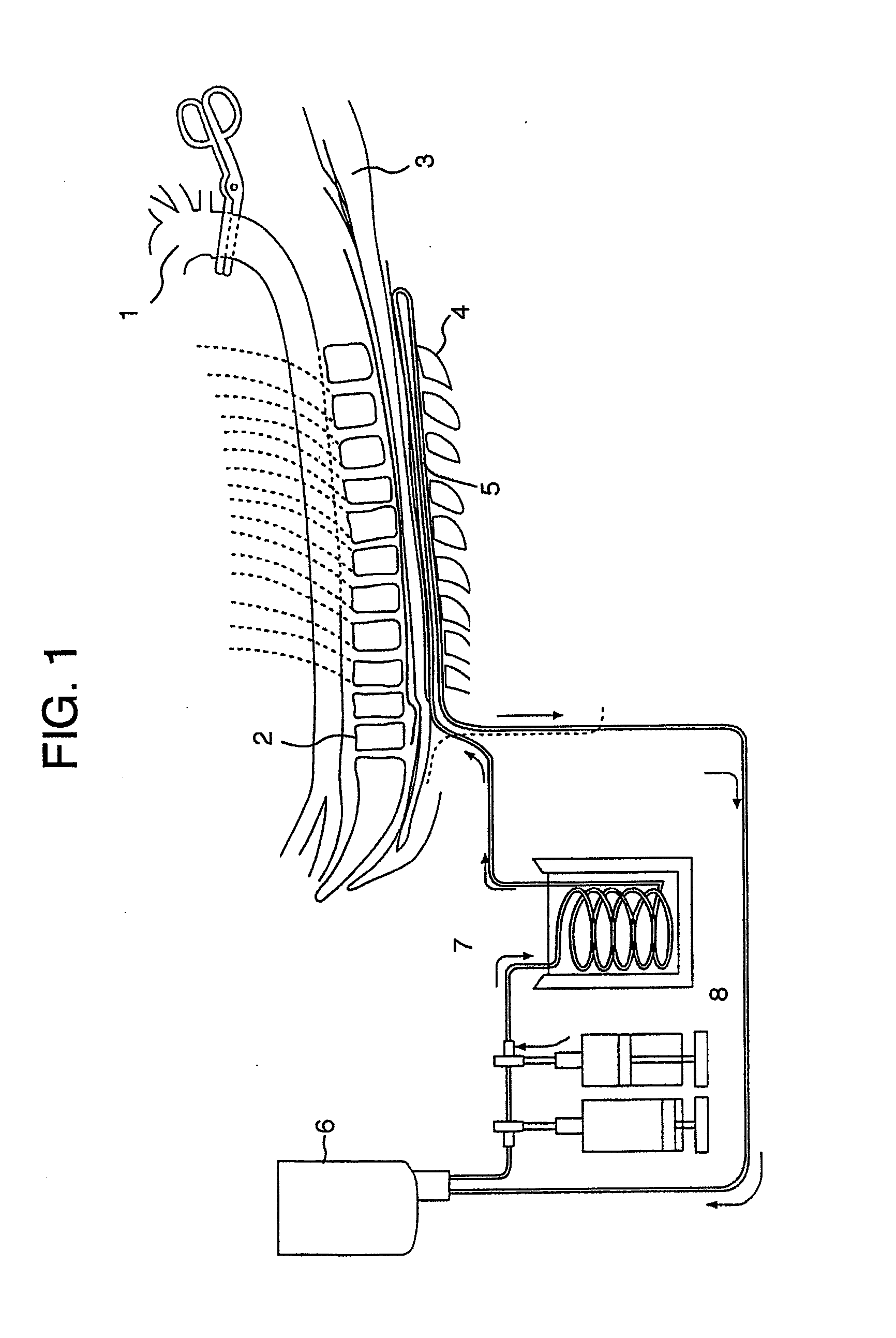
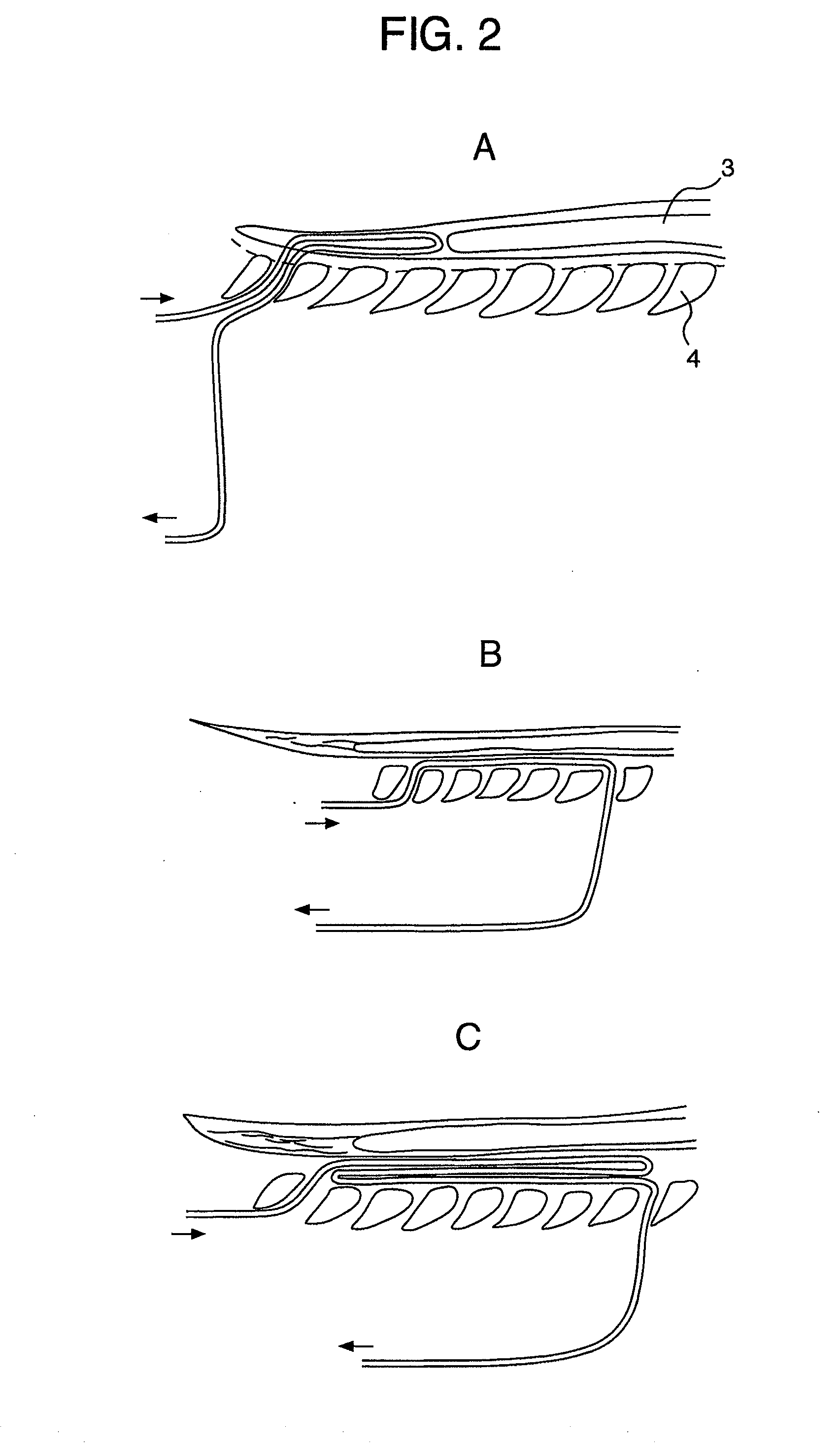
ActiveUS7004961B2Rapid and accurate insertionFast transferUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSubarachnoid space
The invention provides a medical device having a thermister for temperature measurement, irrigation / aspiration ports for fluid exchange and application of therapeutic modalities, a pressure manometer for pressure measurement, and an external system for control of temperature, pressure, and flow rate. When applied to the central nervous system (CNS), this device can be used in hypothermia or hyperthermia applications, the exchange of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), the application of treatment modalities, and the insertion of a ventriculostomy or ventriculostomy-like unit. When applied to spinal cord applications, this device can provide temperature control and a method for application of treatment modalities by using a venting device placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord, a device with similar instrumentation to measure temperature and pressure. A device for ultrasound localization of the CNS device is described. A device for a fiber optic endoscope for visualization and localization is also described. Method of using the devices in treating patients suffering from cardiac arrest, circulatory arrest, exsanguination, head or neck trauma, strokes, tumors and other intracranial diseases are disclosed. In the case of hypothermia treatment of the brain, rapid cooling using principles of convection and conduction will be applied to the lateral ventricle and subarachnoid and / or subdural space simultaneously where the neurons are located in close proximity.
Owner:WONG EDWARD +2
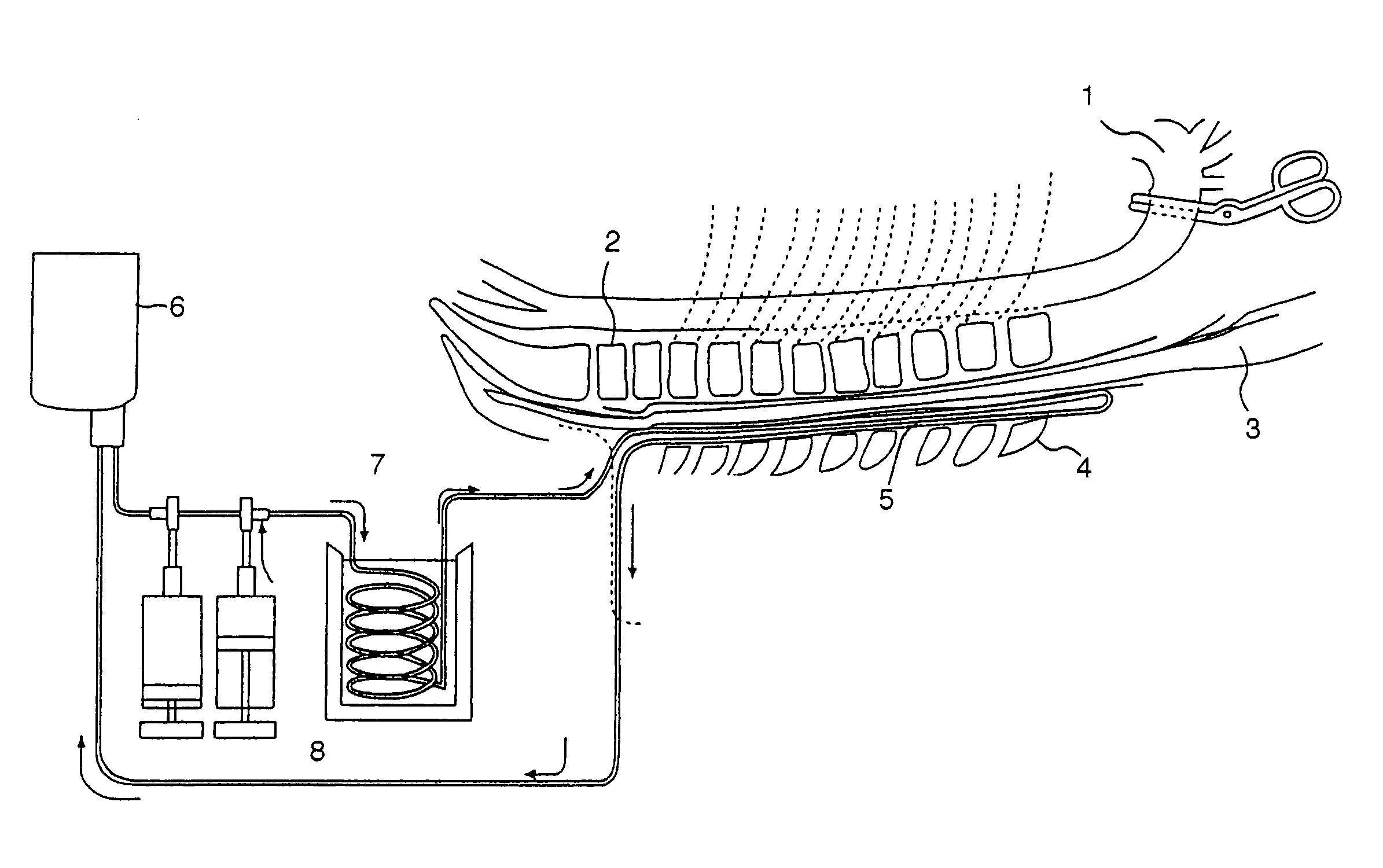
Catheter for topical cooling and topical cooling device using the same
InactiveUS20050222652A1Free from riskImprove survivalSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingSubarachnoid spaceDisease
Topical cooling of spinal cord, brain, esophagus, etc. can be selectively and continuously carried out under convenient control without causing any changes in internal pressure of spinal cord cavity, brain pressure, etc. by inserting a catheter, which has no hole connecting to the outside and in which a heat-cooling medium is circulated in its inner space to thereby cool a topical site; into the spinal cord, the epidural cavity, the subdural cavity or the subarachnoid cavity of the brain or the esophageal cavity and placing therein and then circulating the heat / cooling medium within the inner space of the catheter; or using a device composed of a heat absorption member in the form of a catheter, a heat insulation member and a heat radiation member, inserting the heat absorption member in the form of a catheter into the spinal cord, the epidural cavity, the subdural cavity or the subarachnoid cavity of the brain or the esophageal cavity and placing therein and then absorbing heat from the heat absorption member and radiating the heat from the heat radiation member via the heat insulation member, thereby contributing to the treatment of spinal diseases including prevention of paraplegia accompanying thoracic aortic aneurysm surgery and the treatment of brain injury, esophageal injury and so on.
Owner:MORI ATSUO
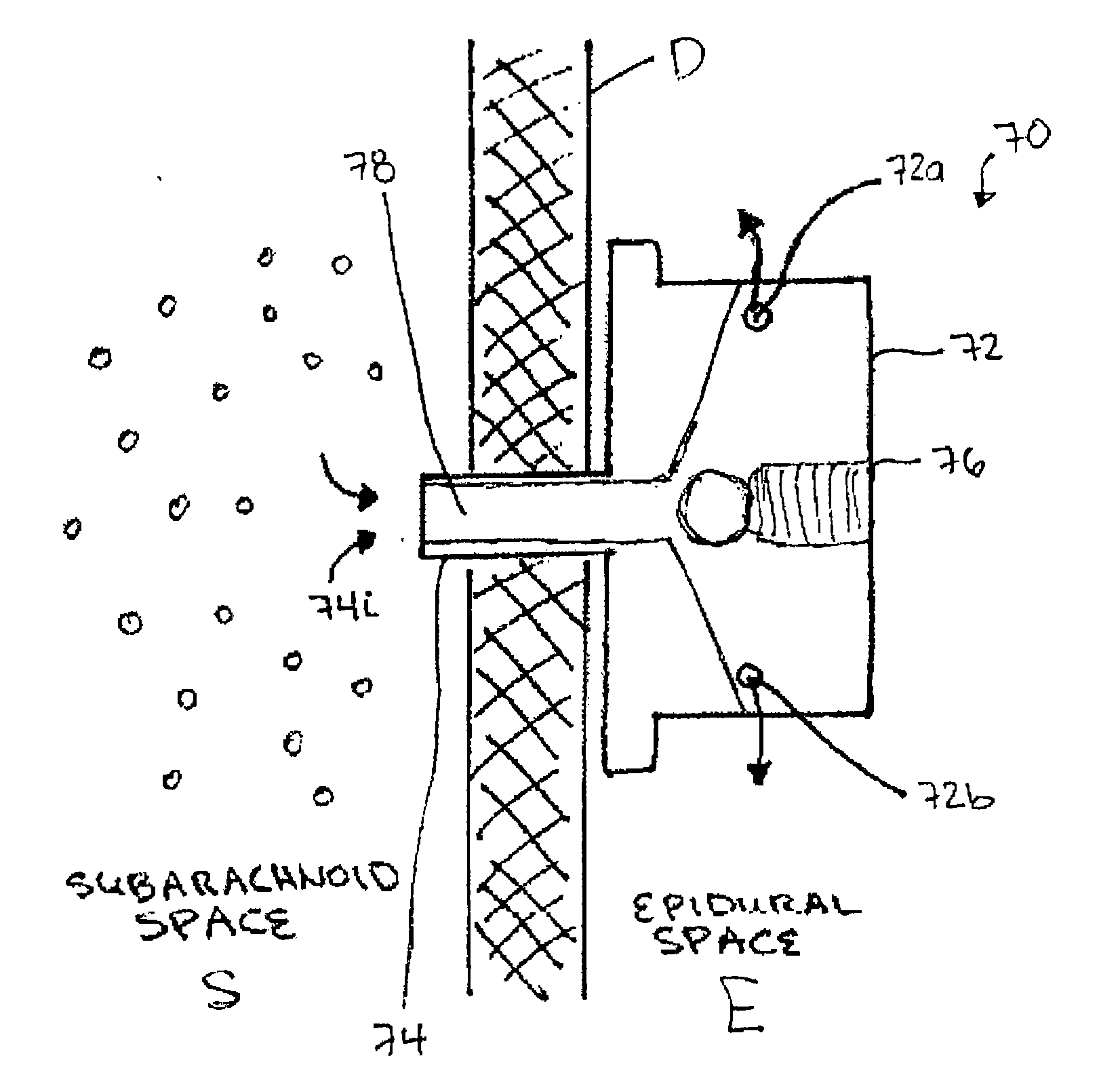
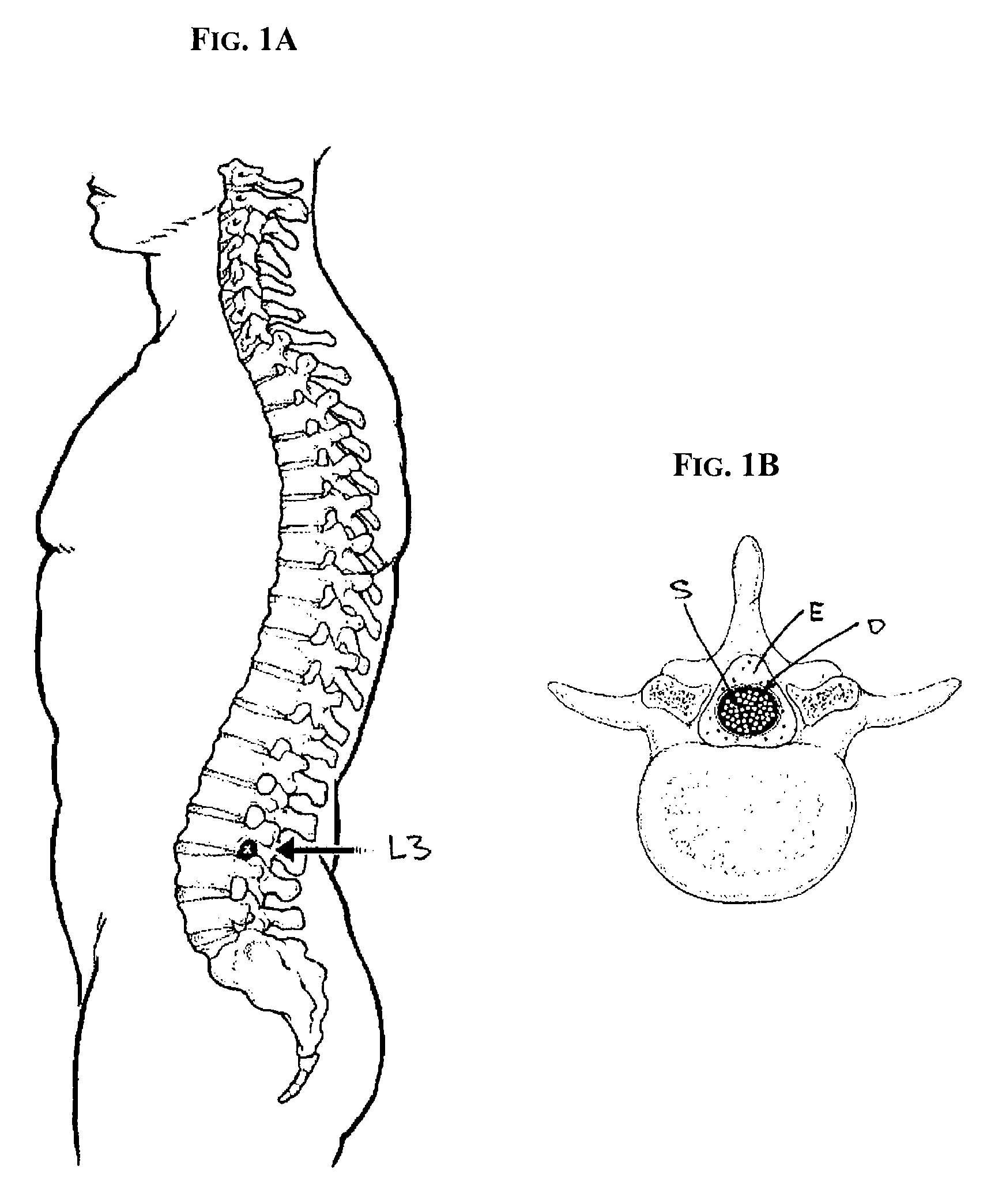
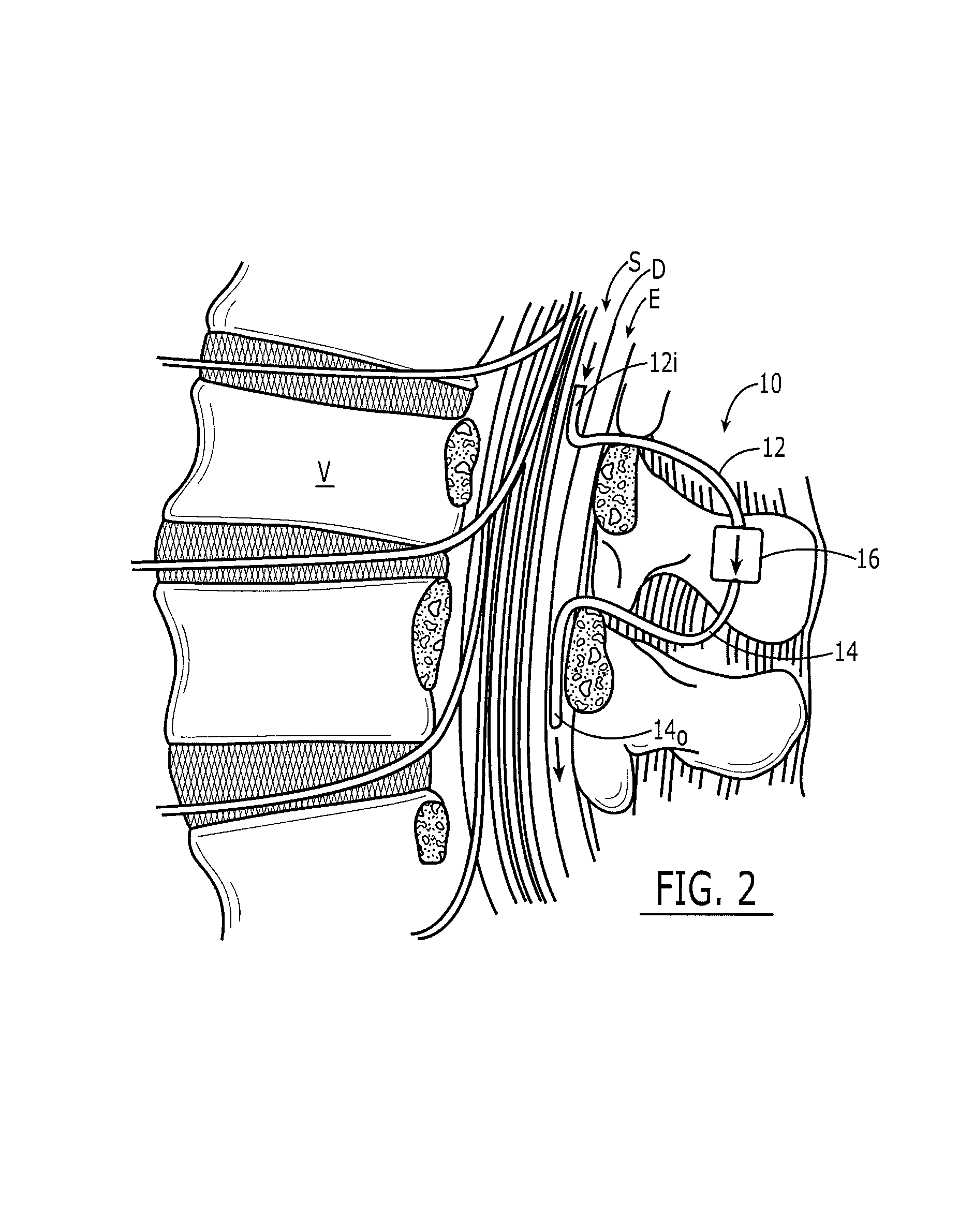
Subarachnoid epidural shunt
InactiveUS20060224101A1Promote growthEffective controlWound drainsIntravenous devicesSpinal columnSubarachnoid space
Methods and devices are provided for shunting fluid to treat hydrocephalous, and in particular for treating normal pressure hydrocephalous, or Alzheimer's, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH), or any other condition in which it is necessary to drain and / or cleanse CSF. The methods and devices utilize a shunt having an inlet port, and outlet port, and a flow control component for controlling fluid flow from the inlet port to the outlet port. The shunt can be implanted at a location along or within a patient's spinal column. In one exemplary embodiment, an inlet port of a shunt can be implanted within the subarachnoid space, and an outlet port of a shunt can be implanted at a drainage site. In certain exemplary embodiments, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the epidural space.
Owner:GLENN BRADLEY J
Endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt
InactiveUS20100191168A1More physiologic drainageWound drainsMedical devicesShunt DeviceSubarachnoid space
An implantable shunt device for draining cerebrospinal fluid from a patient's subarachnoid space. The device includes a shunt having opposed first and second ends. A one-way valve is located at the first end of the shunt. A helical tip is disposed at the second end. The helical tip is constructed to penetrate a sinus wall of the patient. Upon implantation, a hollow passageway extends between the helical tip and one-way valve such that fluid can be drained through the helical tip and out through the valve. The endovascular cerebrospinal fluid shunt of the present invention can be placed into a patient percutaneously via a catheter inserted into the venous system of the body through a needle hole, without the need for open surgery and the skin incisions required with current shunt devices. The device also allows for more physiologic drainage of cerebrospinal fluid since the device is shunting cerebrospinal fluid into the same cerebral venous system that occurs naturally in normal people.
Owner:TUFTS MEDICAL CENTER INC
Intracochlear drug delivery to the central nervous system
InactiveUS20110208161A1Improved surgical easeOrganic active ingredientsEar treatmentLipid formationSubarachnoid space
The present invention is directed to method and system for delivery of brain-targeted drugs to the cerebrospinal fluid via the perilymphatic fluid of the inner ear. The system utilizes the passage of cochlear aqueduct as a drug delivery route from the inner ear to the subarachnoid space of the brain. The delivery system includes an otological conduit which enables transfer of drugs from the auditory ear canal to the inner ear and a wearable dispenser for supplying drugs to the otological conduit. The drug composition comprises a suspension of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) which facilitate delivery through the cochlear aqueduct. Employing aspects of present invention, a method and system for treating chronic pain is described.
Owner:IVRI YEHUDA
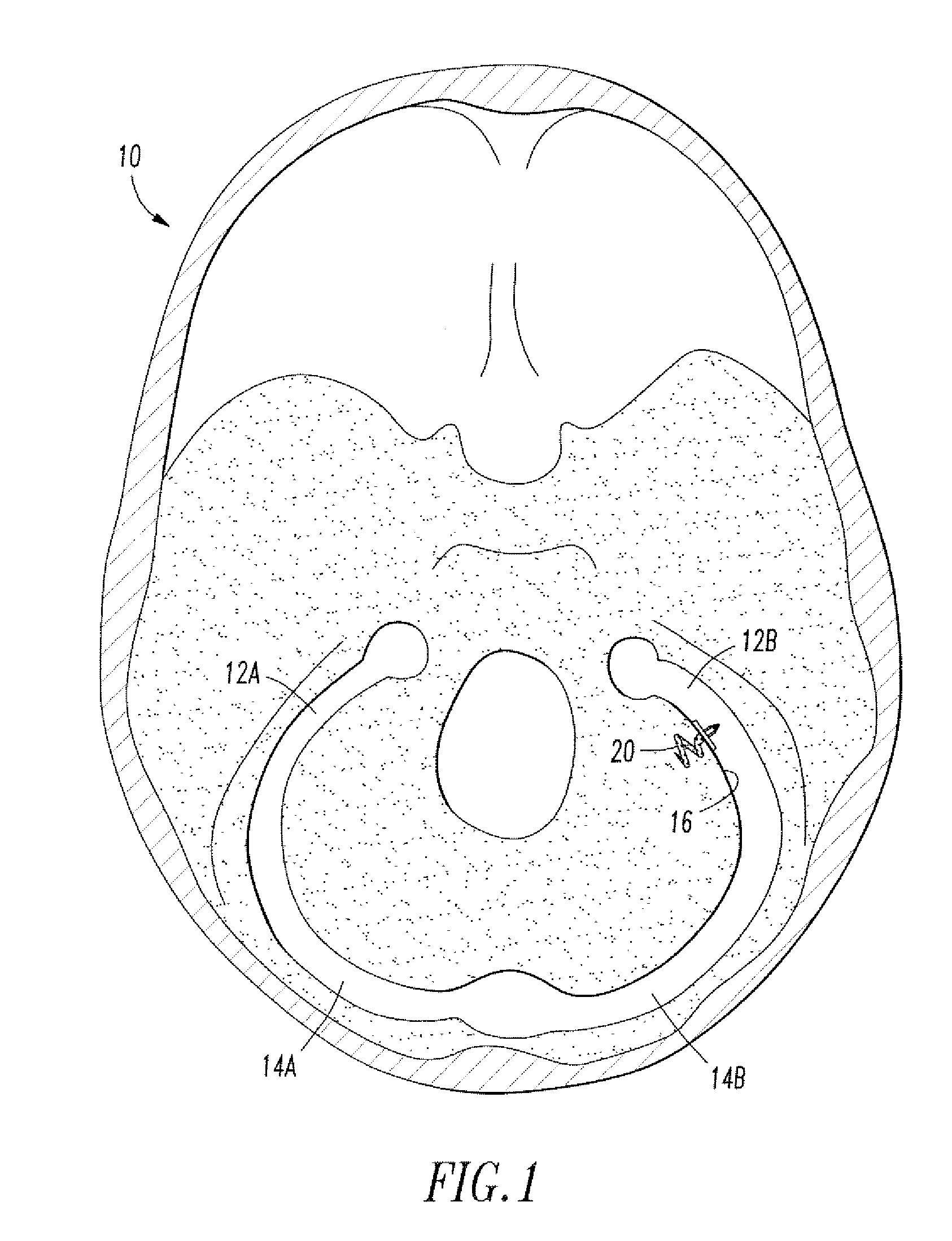
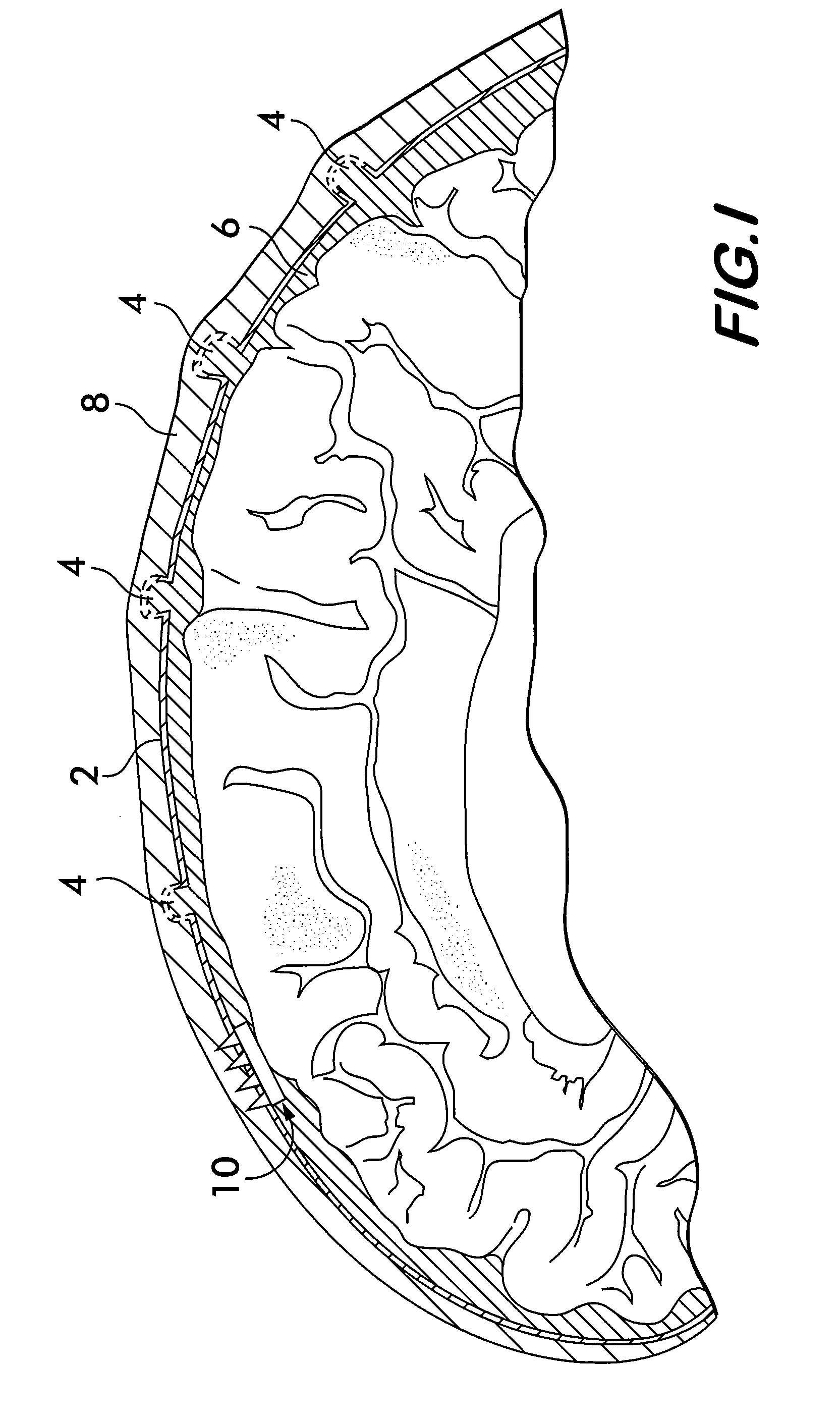
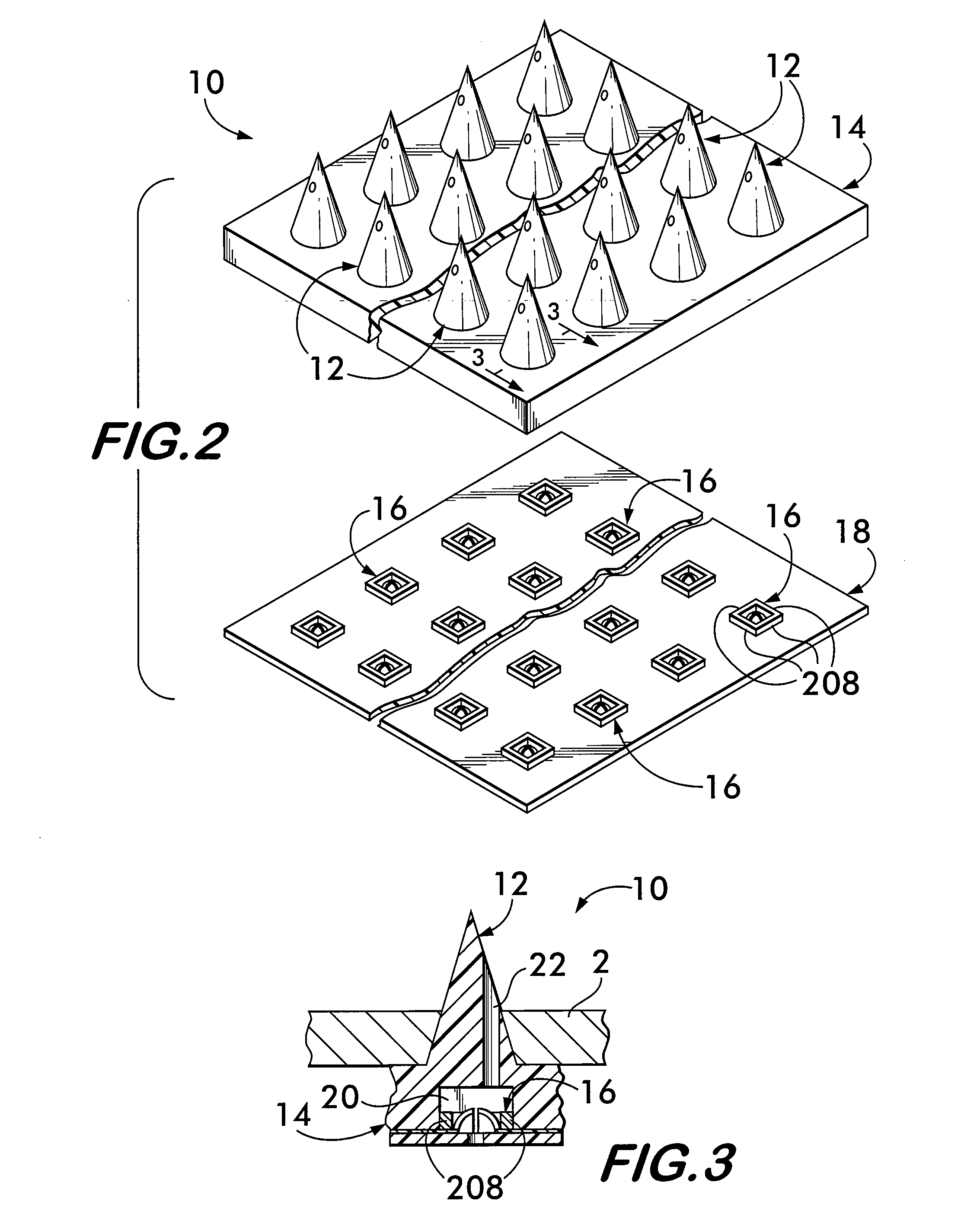
Implantable micro-system for treatment of hydrocephalus
An implantable system for the treatment of hydrocephalus includes a plurality of microneedles in a fixed array relative to each other adapted to extend from the subarachnoid space containing CSF surrounding the brain, through dura mater forming the wall of the superior sagital sinus. A microvalve is associated with a proximal end of each of the microneedles and is adapted to permit the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space through the wall of the superior sagital sinus and deposited in the venous return of the brain. The method of treating hydrocephalus with the system of this invention also constitutes a part of the invention.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Rabies cure
InactiveUS20110020279A1Inhibit rabies virus multiplicationAvoid spreadingSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsSubarachnoid spacePresent method
This invention is for a method of treatment of rabies once the patient develops signs and symptoms of rabies with the intent to save the patients from death and disability using insulin combined with various anti rabies viral therapeutic, pharmaceutical, biochemical, and biological agents or compounds with added supportive therapies administered through OM, SAS, IVB, IV, and IA routes. An embodiment provides devices for intranasal delivery of therapeutic agents to olfactory mucosal area. Another embodiment uses the technology to deliver the therapeutic, pharmaceutical, biochemical, and biological agents or compounds to the subarachnoid space and ventricular system by using continuous catheters and Ommaya reservoir at the same time. The present method incorporates breaking the blood brain barrier to allow the entry of the anti rabies therapeutic agents into the neuropile. Additionally, an embodiment incorporates cooling of the brain and inducing hibernation to preserve the brain from damage due to rabies.
Owner:SHANTHA TOTADA R
Conpositions and method to prevent and treat brain and spinal cord injuries
The cerebrospinal fluid and intracranial pressure are two major reasons why central nervous system is so vulnerable to injuries. A composition and method for treating injured central nervous tissue, or preventing injury to central nervous system tissue is provided. The composition is comprised of a combination of colloidal osmotic agents and crystal osmotic agents. The method comprise of: a). Withdrawing cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid spaces around the tissue to be treated or protected and b). Injecting the composition which is dissolved by patient's own cerebrospinal fluid into subarachnoid spaces. The treatment can be augmented with agents that suppress production of cerebrospinal fluid, or with other known neuroprotective agents.
Owner:WANG YANMING
Composition and method to prevent and treat brain and spinal cord injuries
A composition and method for treating and preventing injury to central nervous system tissue are provided. The composition is comprised of agents that can increase colloidal osmotic pressure and osmolality. The method comprise of: a). Withdrawing cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid spaces around the tissue to be treated or protected and b). Injecting the composition into subarachnoid spaces.
Owner:WANG YANMING
Subarachnoid epidural shunt
Methods and devices are provided for shunting fluid to treat hydrocephalous, and in particular for treating normal pressure hydrocephalous, or Alzheimer's, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH), or any other condition in which it is necessary to drain and / or cleanse CSF. The methods and devices utilize a shunt having an inlet port, and outlet port, and a flow control component for controlling fluid flow from the inlet port to the outlet port. The shunt can be implanted at a location along or within a patient's spinal column. In one exemplary embodiment, an inlet port of a shunt can be implanted within the subarachnoid space, and an outlet port of a shunt can be implanted at a drainage site. In certain exemplary embodiments, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the epidural space.
Owner:GLENN BRADLEY J
Catheter for Topical Cooling and Topical Cooling Device using the same
ActiveUS20080275535A1Free from riskImprove survivalSurgical instruments for coolingTherapeutic coolingSubarachnoid spaceDisease
Owner:MORI ATSUO
Gene therapy for cerebrovascular disorders
InactiveUS6936594B1Decreased blood flowInduce angiogenesisBiocideNervous disorderSubarachnoid spaceCerebrovascular disorder
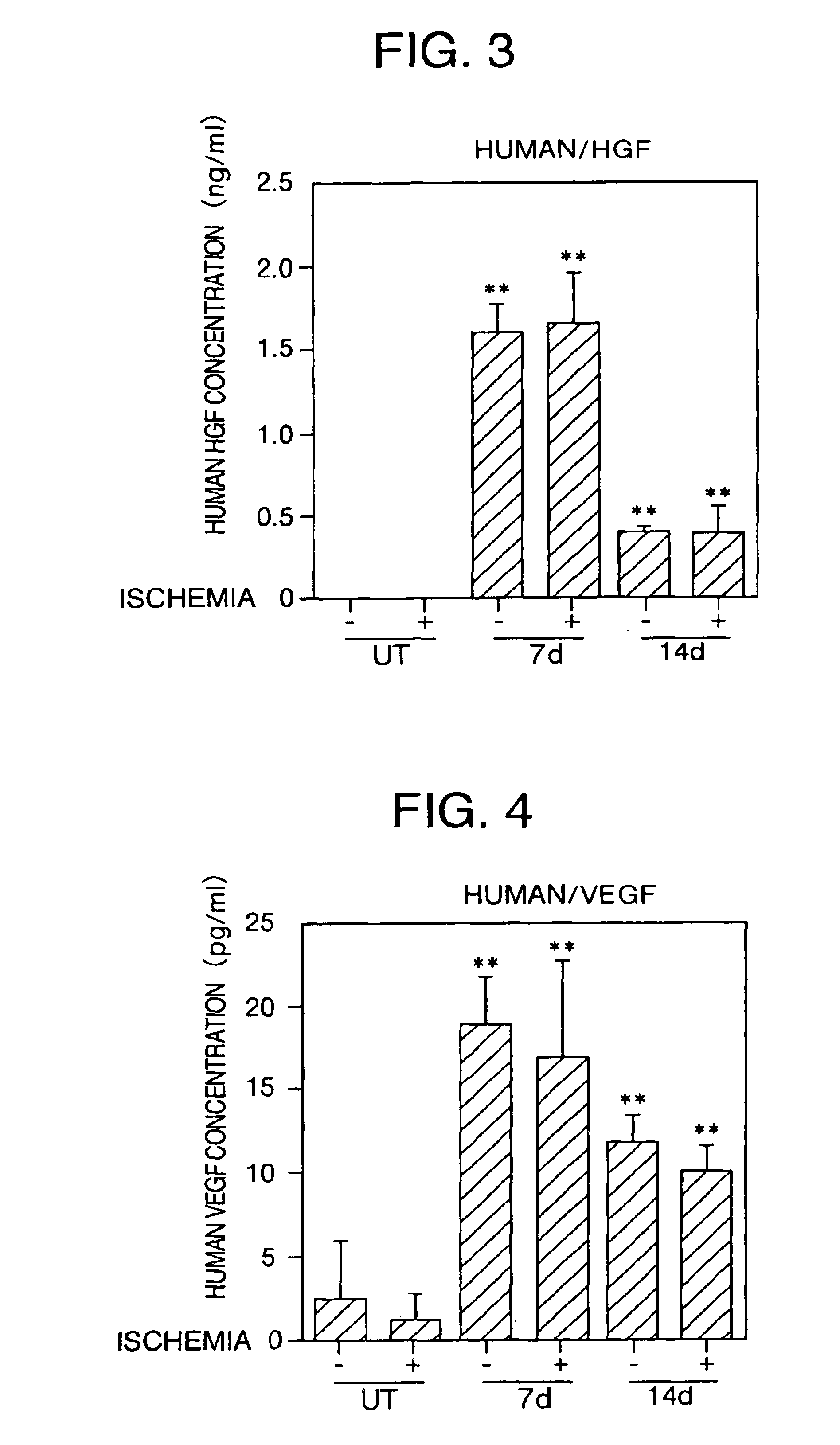
By introducing hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) gene and / or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene into the subarachnoid space in humans, cerebrovascular disorders such as cerebrovascular obstruction, cerebral infarction, cerebral thrombosis, cerebral embolism, stroke, cerebral bleeding, moyamoya disease, cerebrovascular dementia, and Alzheimer's dementia can be effectively treated or prevented.
Owner:ANGES MG INC +1
Composition and method to prevent and treat brain and spinal cord injuries
InactiveUS20060057065A1Reduce productionLow COPBiocideNervous disorderSubarachnoid spaceCerebral edema
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contains low concentration of albumin and insulin because of the blood-CSF barrier. This is the major reason for cerebral edema and the resultant blood perfusion deficit when brain or spinal cord is injured. A composition and method for treating brain and spinal cord are provided. The composition includes magnesium, colloidal osmotic agent, insulin and ATP in artificial CSF. The method includes withdrawing a volume of cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid space and infusing the invented composition.
Owner:WANG YANMING
Electroactive polymer-based flexing access port
Methods and devices are disclosed for providing access through tissue to a surgical site, such as anatomical cavities ranging in size from the abdomen to small blood vessels, such as veins and arteries, epidural, pleural and subarachnoid spaces, heart ventricles, as well as spinal and synovial cavities. In one exemplary embodiment, an access port is provided having one or more electrically expandable and contractible actuators that are adapted to change an orientation of the access port.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Methods and devices for draining fluids and lowering intraocular pressure
Methods, devices and systems for draining fluid from the eye and / or for reducing intraocular pressure. A passageway (e.g., an opening, puncture or incision) is formed in the lamina cribosa or elsewhere to facilitate flow offluid from the posterior chamber of the eye to either a) a subdural location within the optic nerve or b) a location within the subarachnoid space adjacent to the optic nerve. Fluid from the posterior chamber then drains into the optic nerve or directly into the subarachnoid space, where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid. In some cases, a tubular member (e.g., a shunt or stent) may be implanted in the passageway. A particular shunt device and shunt-introducer system is provided for such purpose. A vitrectomy or vitreous liquefaction procedure may be performed to remove some or all of the vitreous body, thereby facilitating creation of the passageway and / or placement of the tubular member as well as establishing a route for subsequent drainage of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber, though the posterior chamber and outwardly though the passageway where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:汉帕尔·卡拉乔济安 +1
Assessment and Modulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid for Head Pain
The disclosure relates to the discovery that certain cerebrovascular disorders in humans who exhibit seemingly normal intracranial pressure (ICP) and do not exhibit hydrocephalus can be alleviated or prevented by reducing ICP in the human. Disorders of this type are herein designated normotensive, nonhydrocephalus tenso-responsive cerebrovascular disorder (NNTCDs). The disclosure describes methods of relieving head pain and other symptoms of NNTCDs, for example by withdrawing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space of a human or by administering a pharmaceutical agent that modulates CSF production, uptake, or both. Methods of assessing whether a human is afflicted with one or more NNTCDs are also described. The disclosure describes numerous pharmaceutical compositions suitable for administration to humans afflicted with NNTCDs to alleviate or prevent such disorders. Such compositions can, for example, include both a CSF-reducing agent and a symptomatic (e.g., head pain) relief agent.
Owner:BHL PATENT HLDG
Subarachnoid epidural shunt
InactiveUS20060224102A1Promote growthEffective controlWound drainsIntravenous devicesSubarachnoid spaceSpinal column
Methods and devices are provided for shunting fluid to treat hydrocephalous, and in particular for treating normal pressure hydrocephalous, or Alzheimer's, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH), or any other condition in which it is necessary to drain and / or cleanse CSF. The methods and devices utilize a shunt having an inlet port, and outlet port, and a flow control component for controlling fluid flow from the inlet port to the outlet port. The shunt can be implanted at a location along or within a patient's spinal column. In one exemplary embodiment, an inlet port of a shunt can be implanted within the subarachnoid space, and an outlet port of a shunt can be implanted at a drainage site. In certain exemplary embodiments, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the epidural space.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Compositions and treatment method for brain and spinal cord injuries
InactiveUS20040142905A1Effective treatment and preventionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSubarachnoid spacePreventing injury
Owner:ONYX OPTICS
Brain-protective agent
A brain-protective agent containing an NF-κB decoy. In brain diseases, the brain can be particularly effectively protected against brain disorders (for example, cerebral vasospasm following a subrachnoidal hemorrhage and apoptosis of the nerve cells following a cerebrovasucular accident or serious head injury) caused by the undesired activation of cytokines or cell adhesion factors which are regulated by NF-κB by administering the brain-protective agent containing an NF-κB decoy, i.e., acompound antadonistic specifically to a nucleic acid to which NF-κB binds.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
A drug delivery system for the prevention of cerebral vasospasm
InactiveCN101873858AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSubarachnoid spaceCerebral arterial spasm
The present invention relates to the treatment and prevention of vasospasm. The present invention provides a system for treating a cerebral vasospasm in a human utilizing a pharmaceutical composition and administrating a therapeutically effective amount of the pharmaceutical composition to a predetermined location in close proximity to a cerebral artery within a subarachnoid space, wherein the pharmaceutical composition produces a localized pharmacologic effect thereby treating the cerebral vasospasm.
Owner:EDGE THERAPEUTICS
Subarachnoid epidural shunt
Devices are provided for shunting fluid to treat hydrocephalous, and in particular for treating normal pressure hydrocephalous, or Alzheimer's, Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH), or any other condition in which it is necessary to drain and / or cleanse CSF. The devices utilize a shunt having an inlet port, and outlet port, and a flow control component for controlling fluid flow from the inlet port to the outlet port. The shunt can be implanted at a location along or within a patient's spinal column. In one exemplary embodiment, an inlet port of a shunt can be implanted within the subarachnoid space, and an outlet port of a shunt can be implanted at a drainage site. In certain exemplary embodiments, the cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the epidural space.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Electroactive polymer-based flexing access port
Methods and devices are disclosed for providing access through tissue to a surgical site, such as anatomical cavities ranging in size from the abdomen to small blood vessels, such as veins and arteries, epidural, pleural and subarachnoid spaces, heart ventricles, as well as spinal and synovial cavities. In one exemplary embodiment, an access port is provided having one or more electrically expandable and contractible actuators that are adapted to change an orientation of the access port.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com