Patents
Literature
325 results about "Cerebral ventricle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
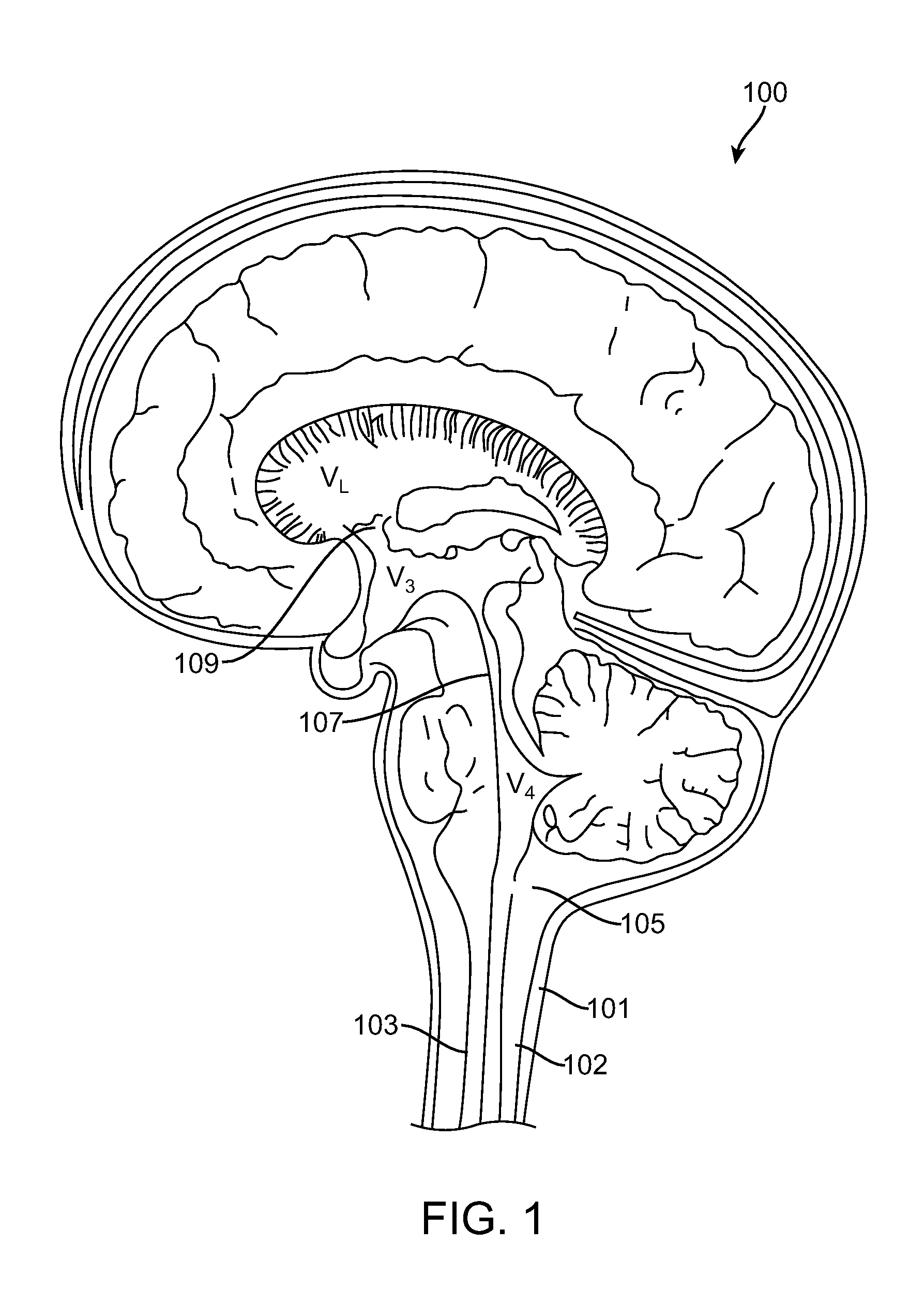
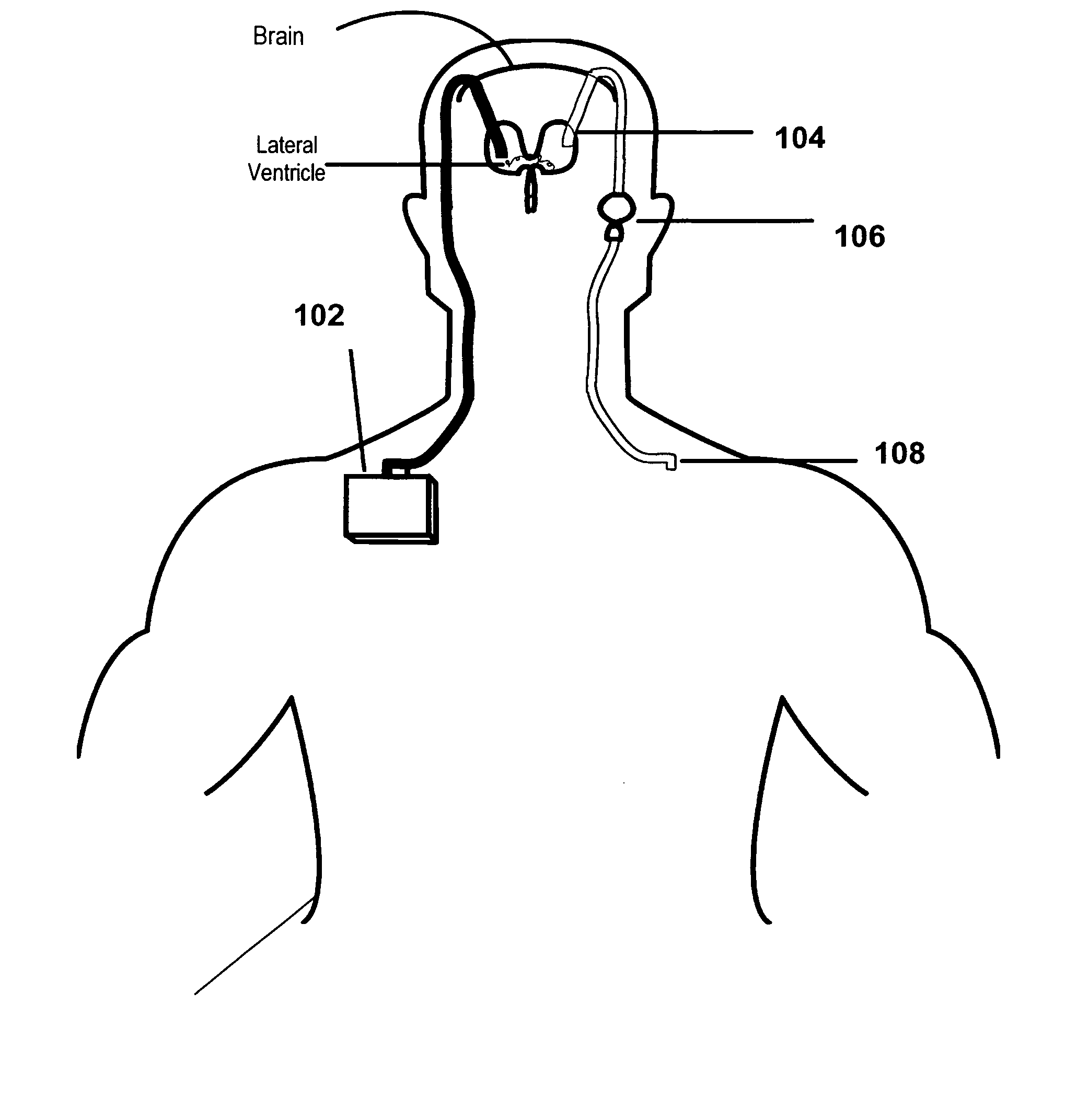
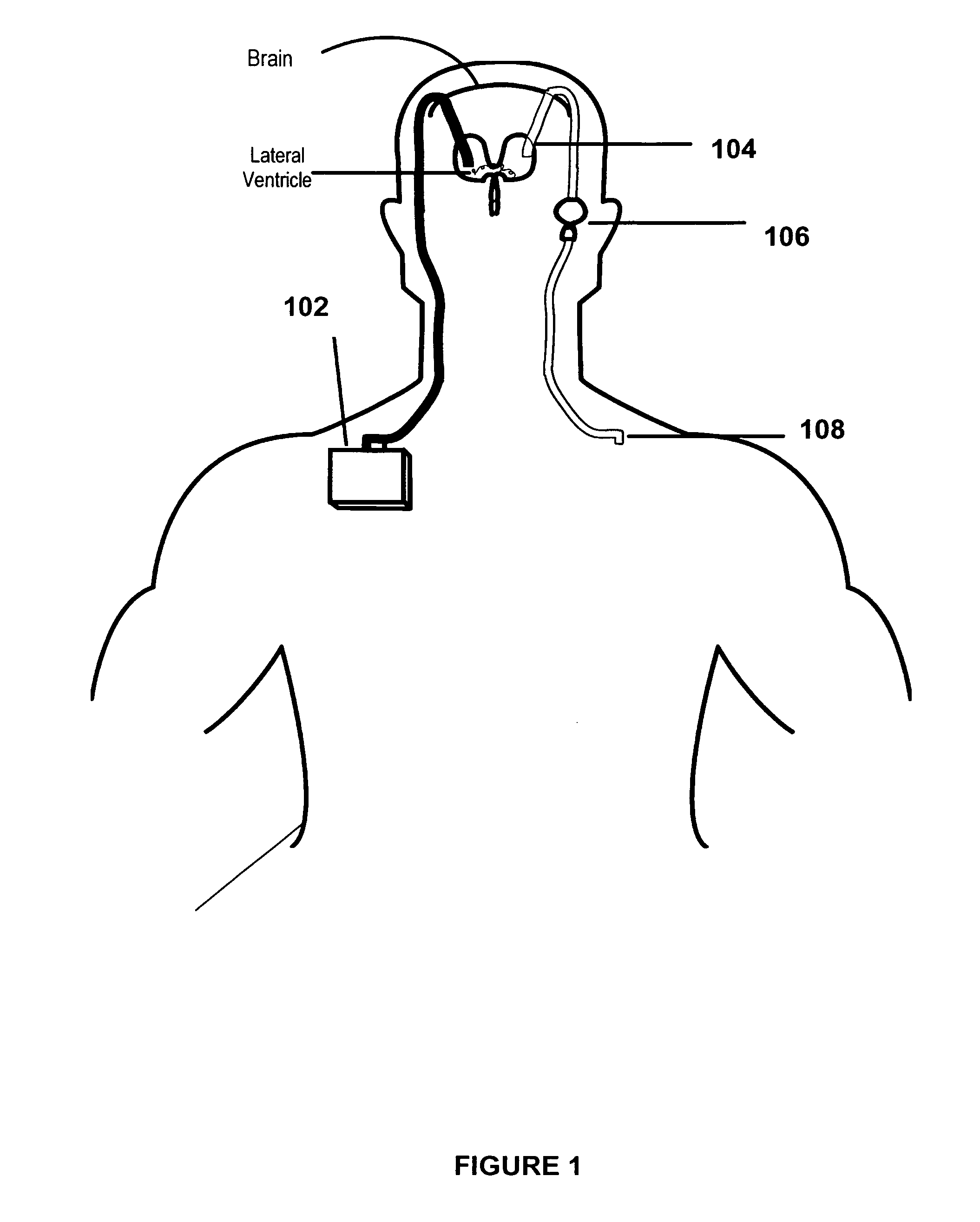
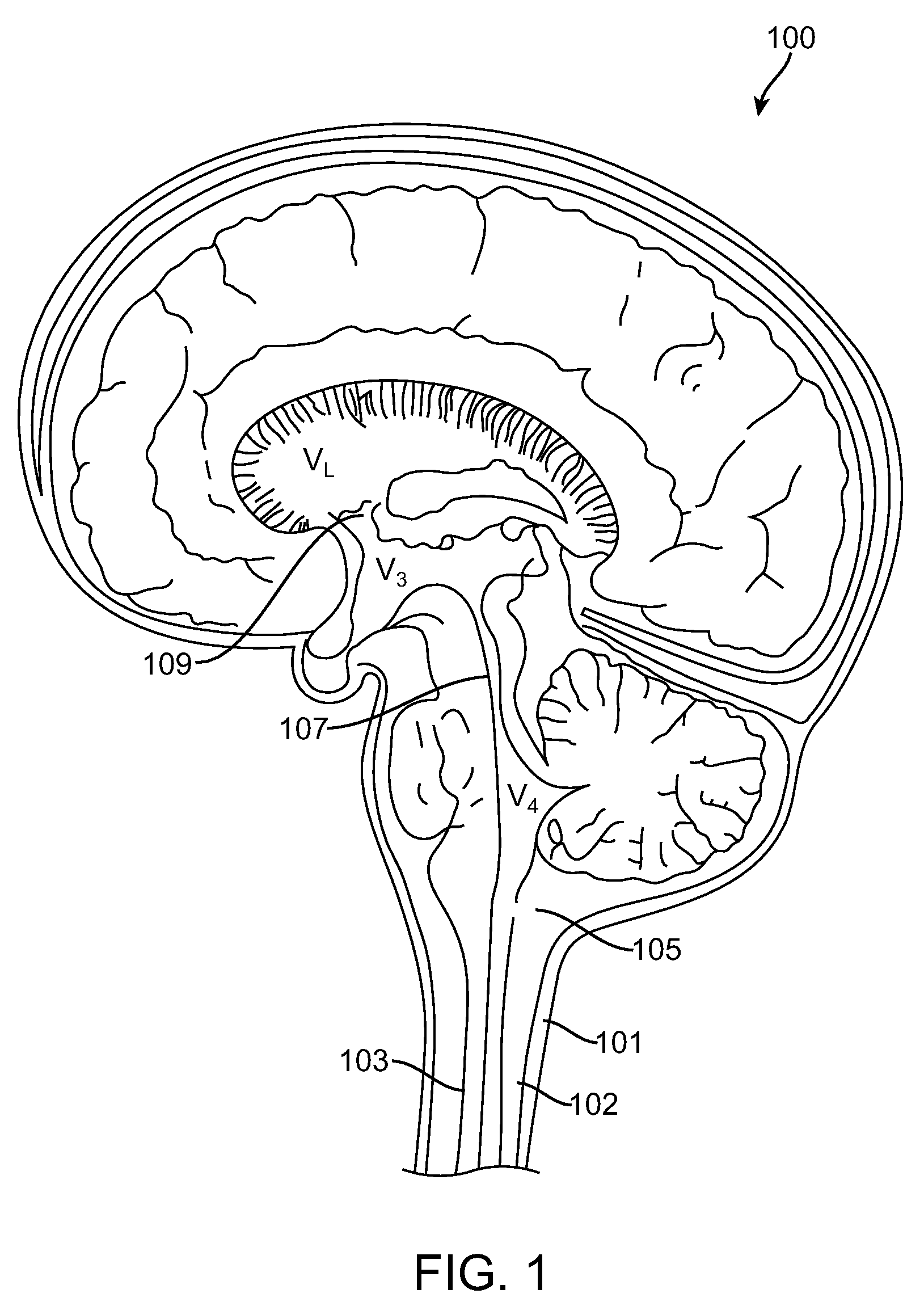
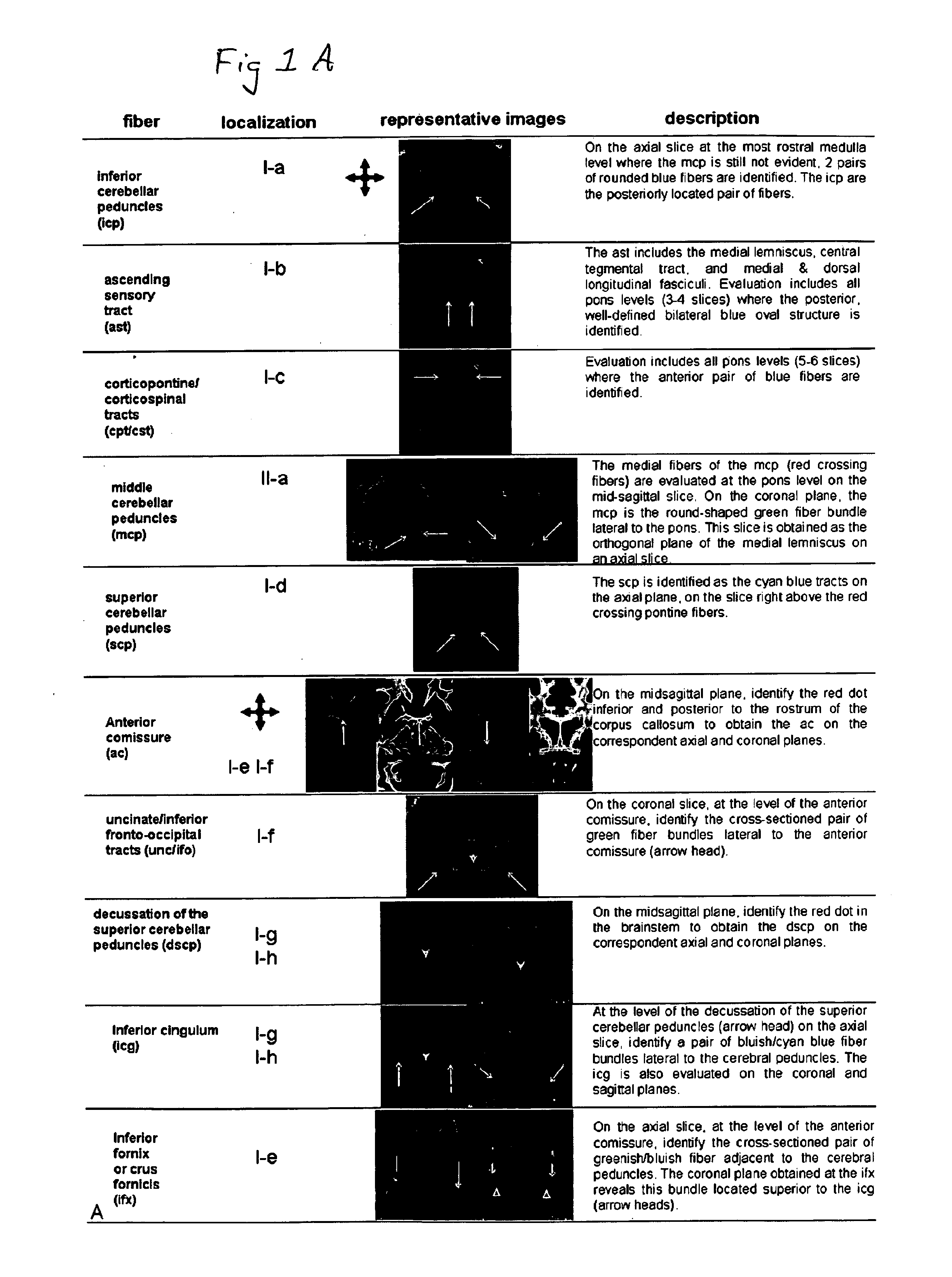
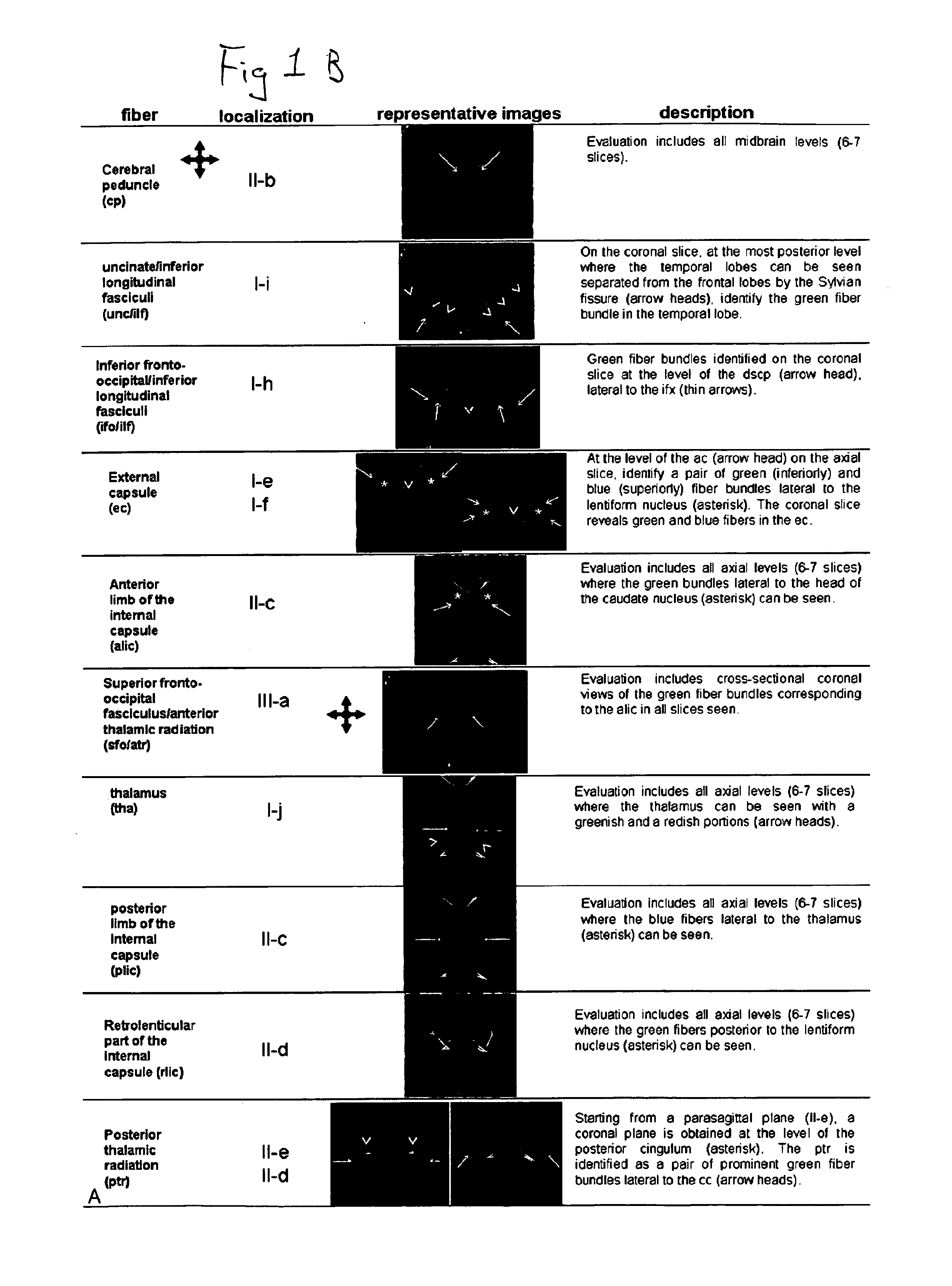
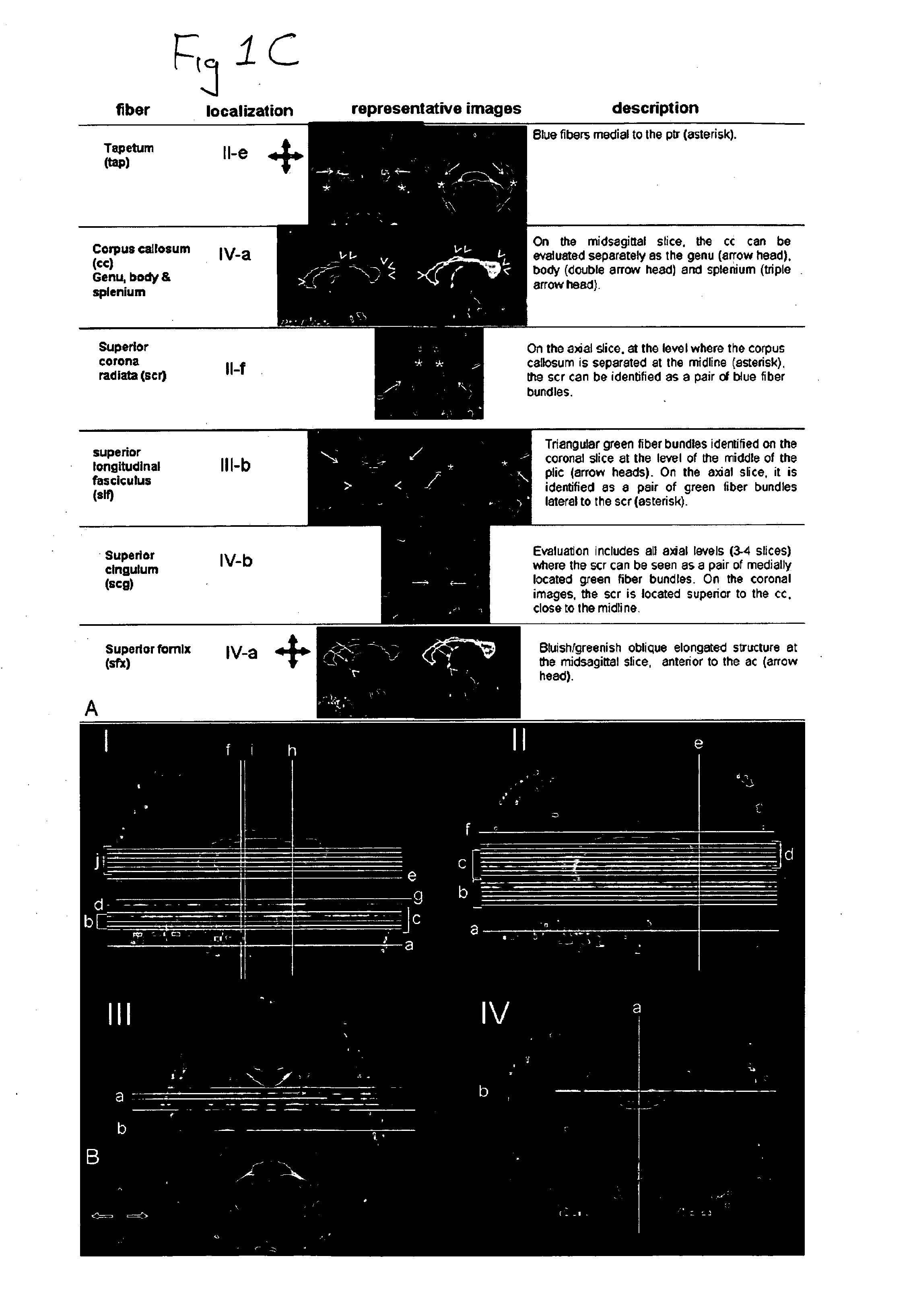
Cerebral ventricles The cerebral ventricles are a series of interconnected chambers deep inside the brain, filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
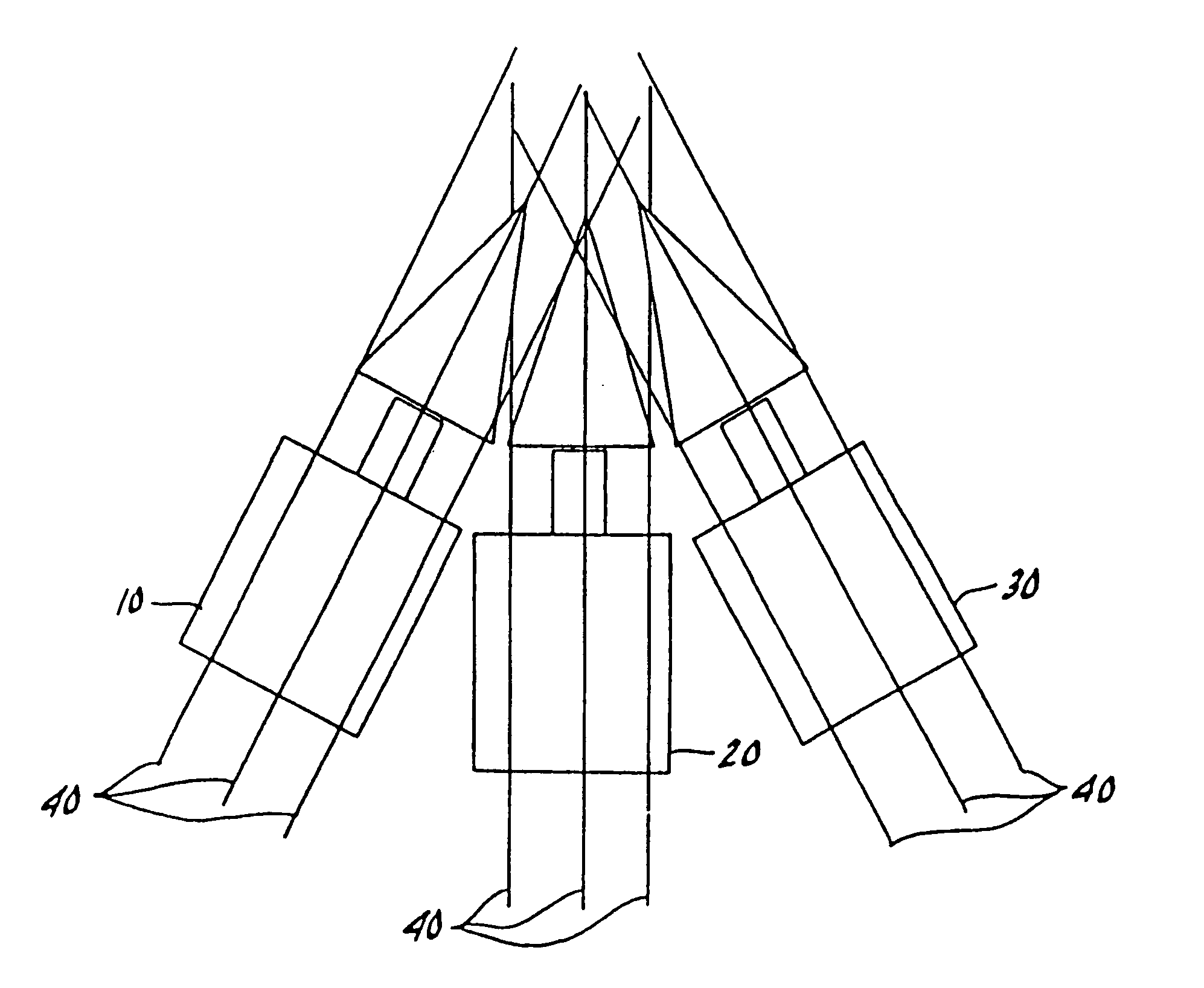
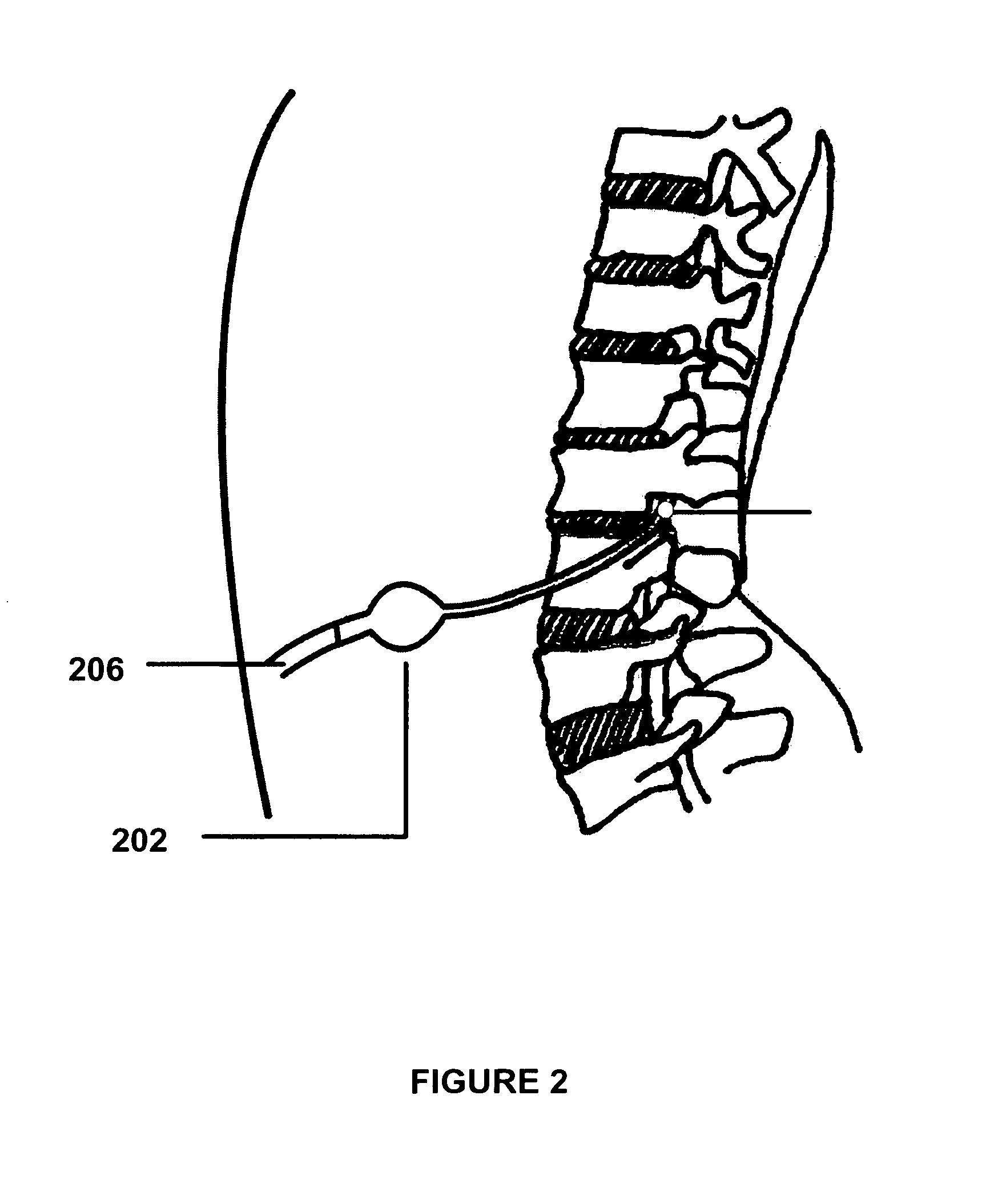
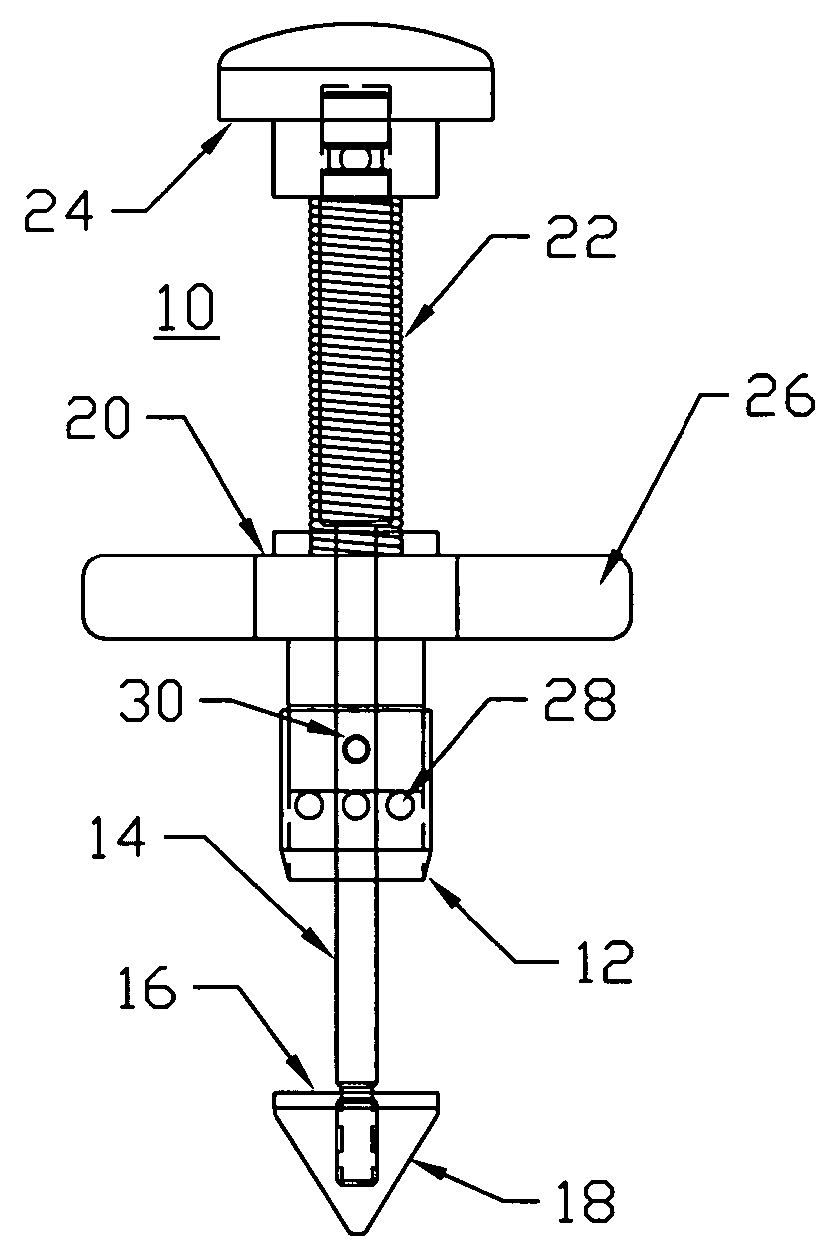
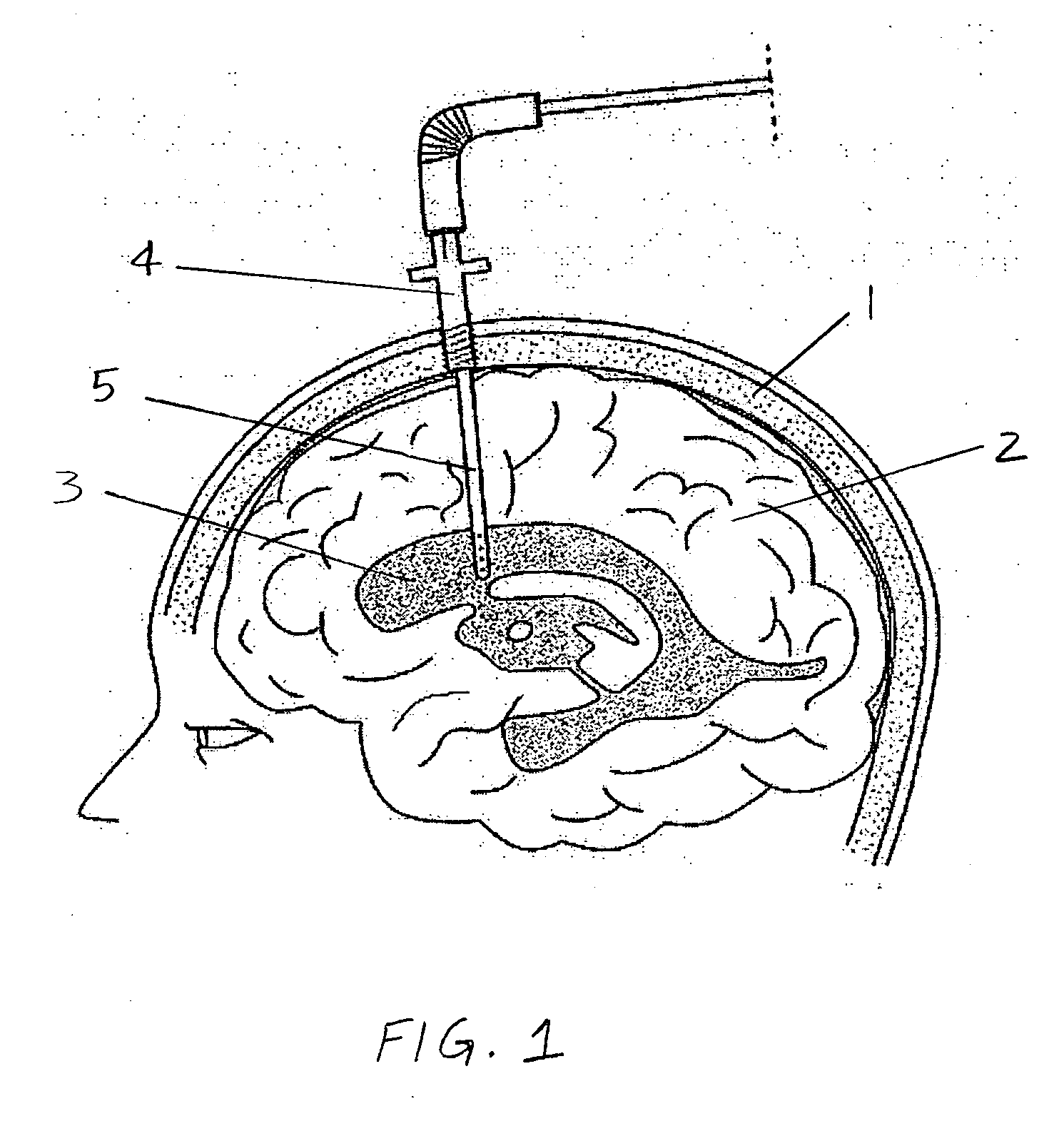
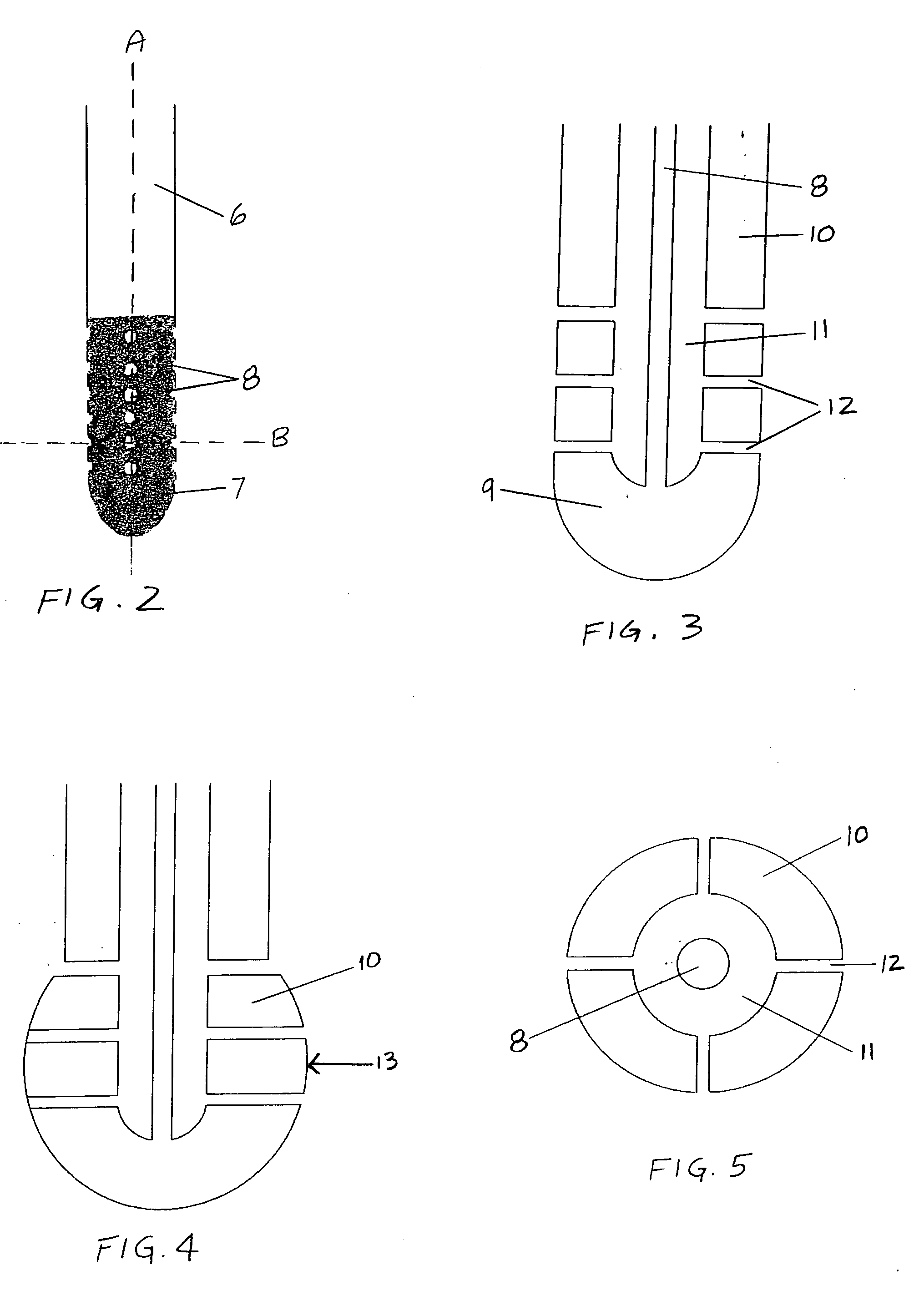
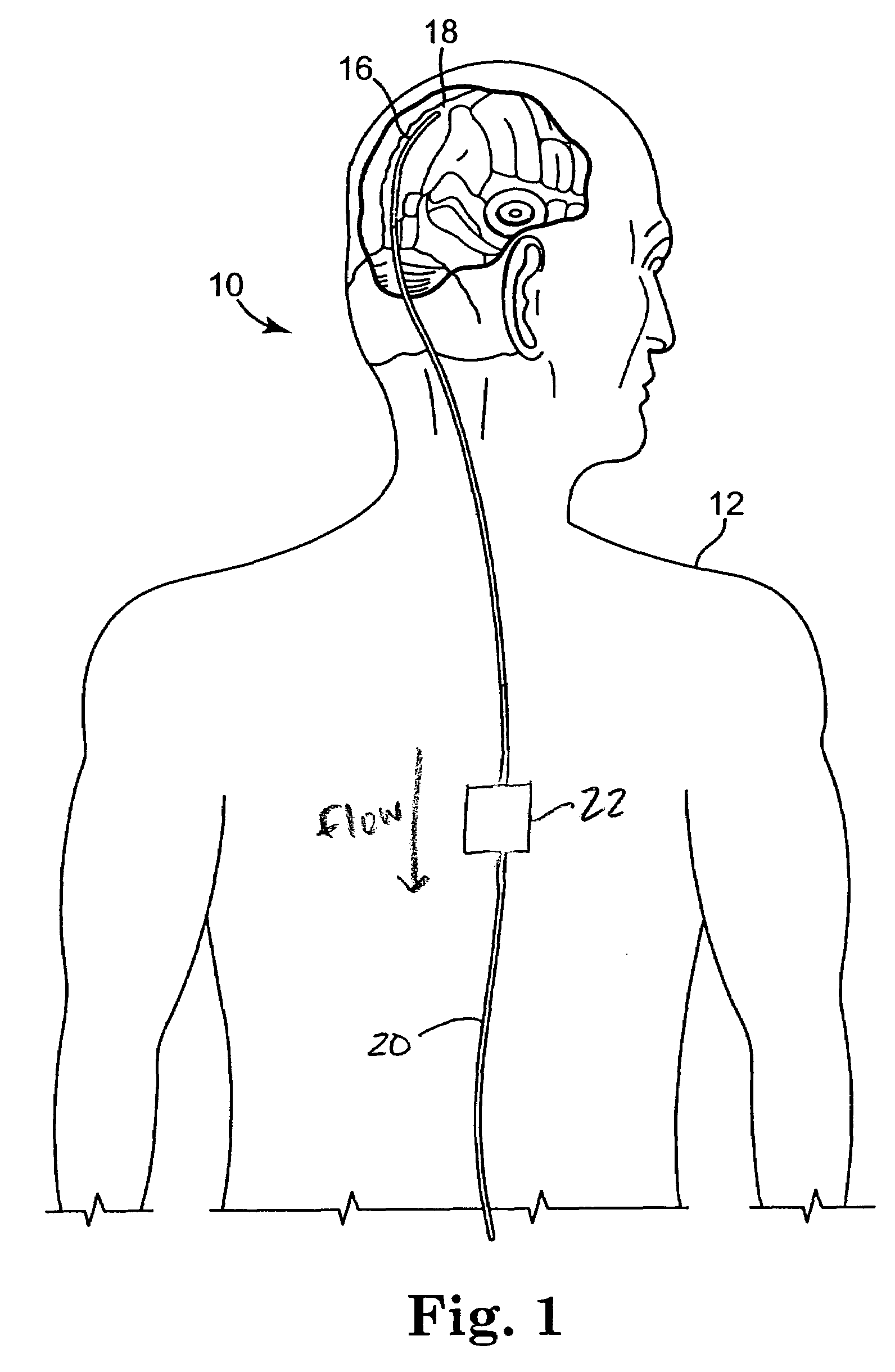
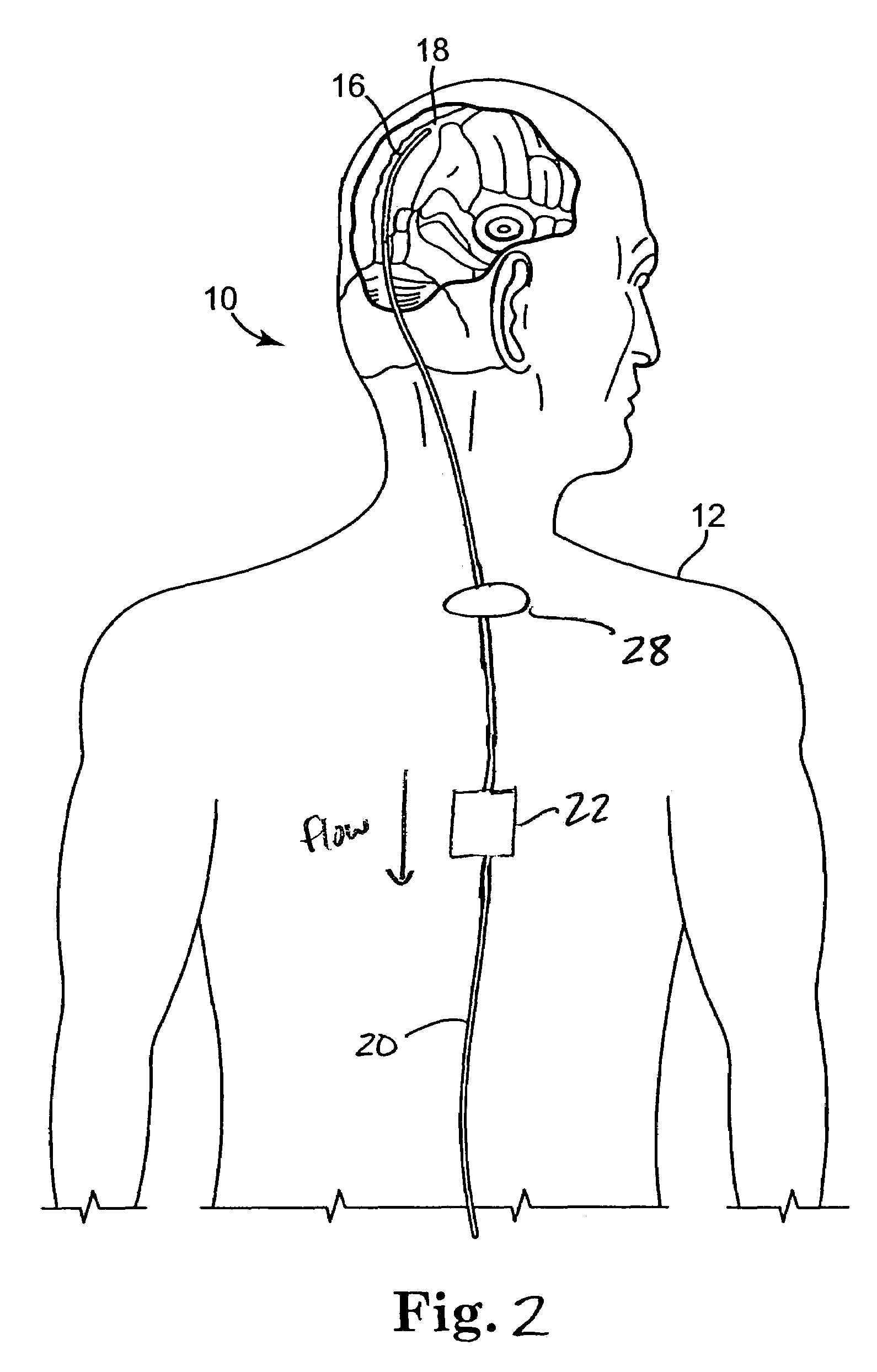
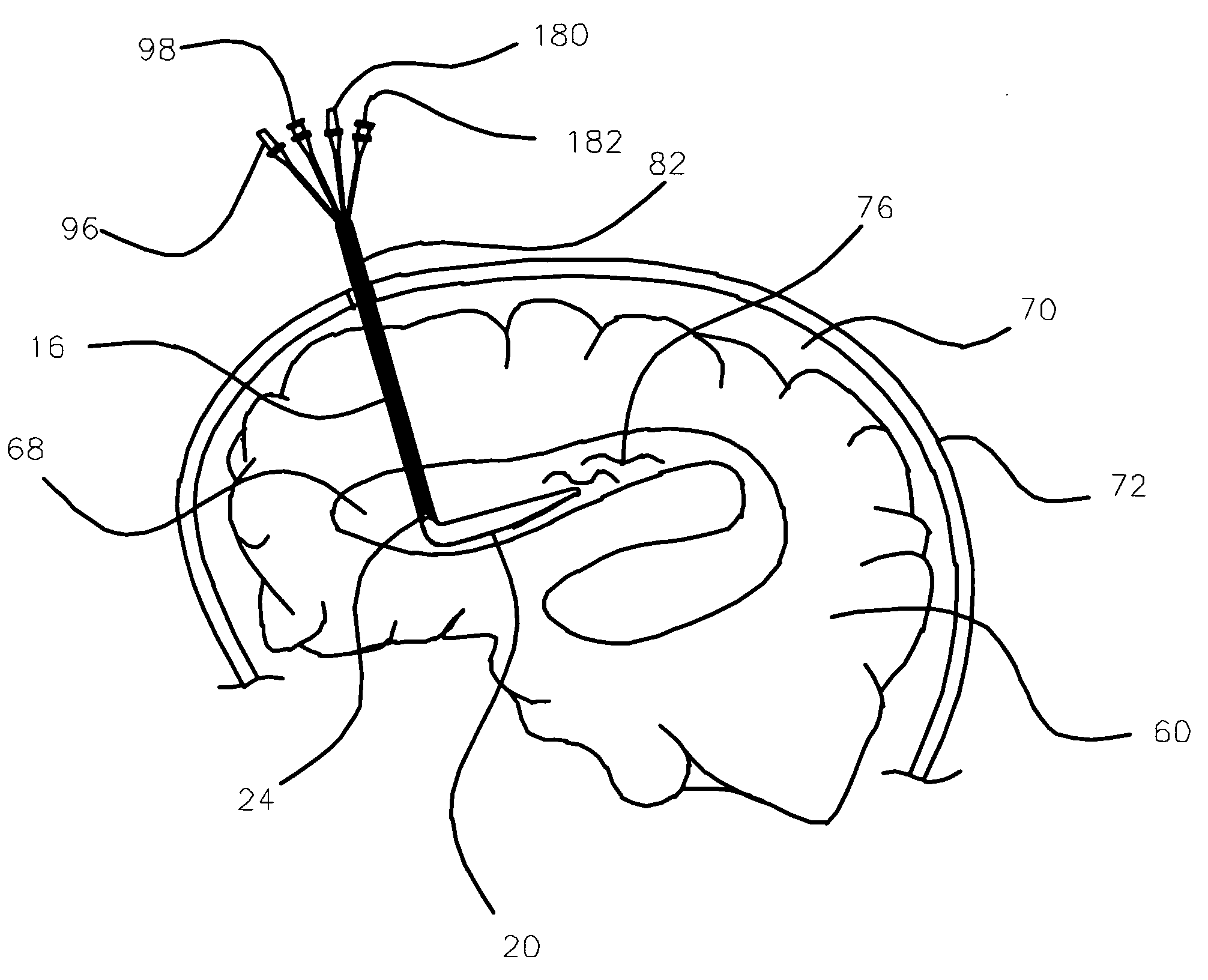
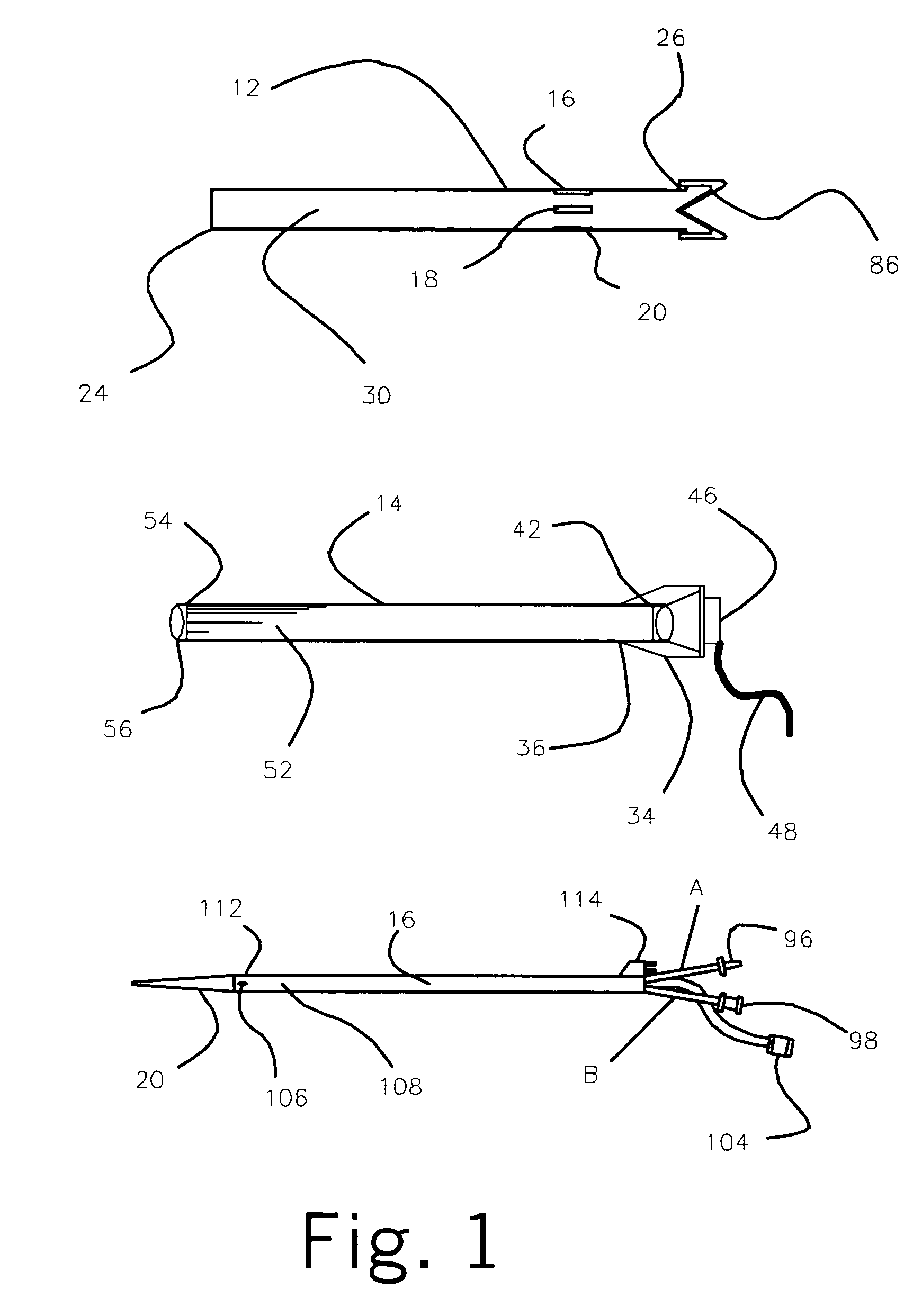
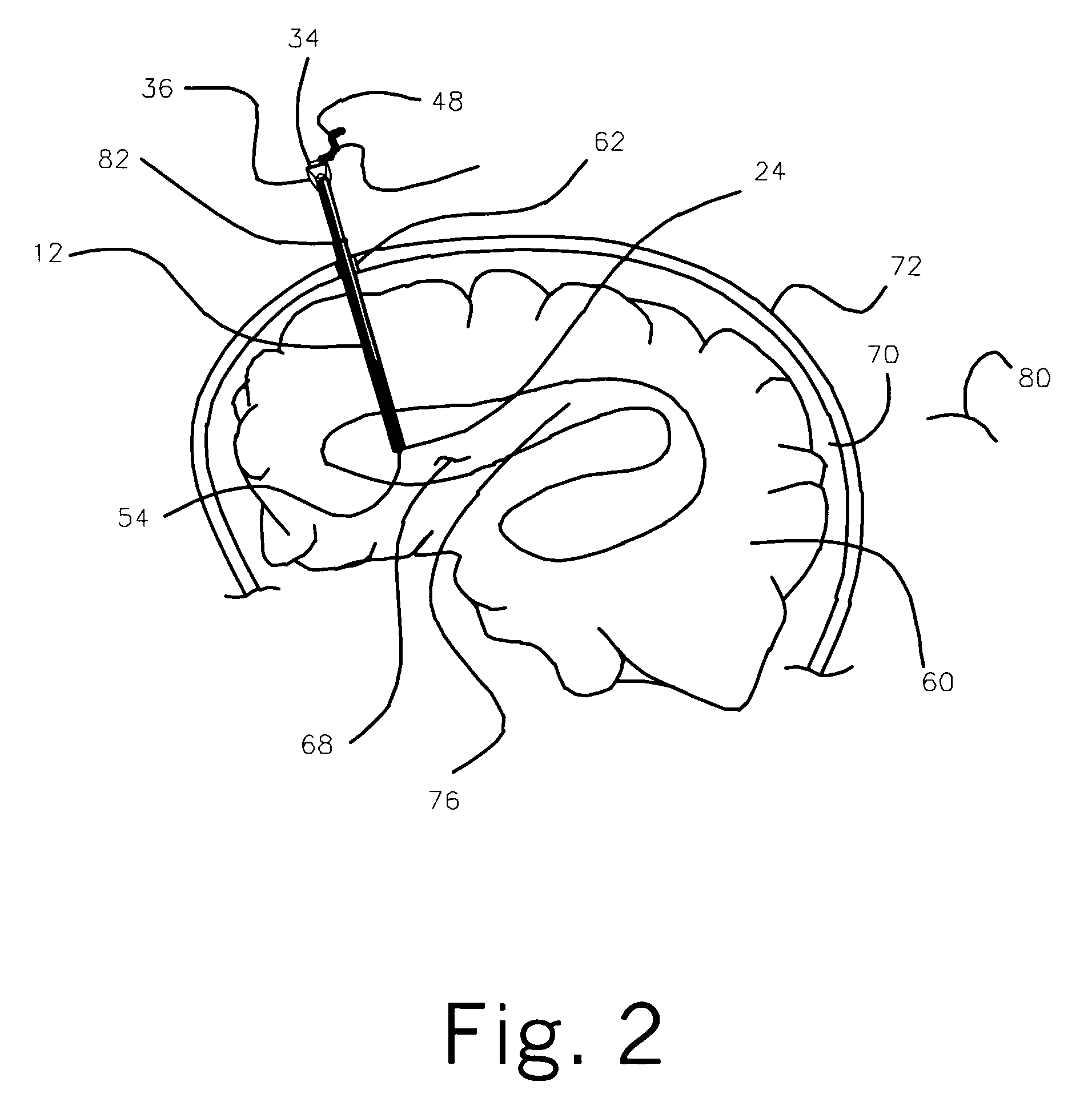
Surgical navigation systems including reference and localization frames
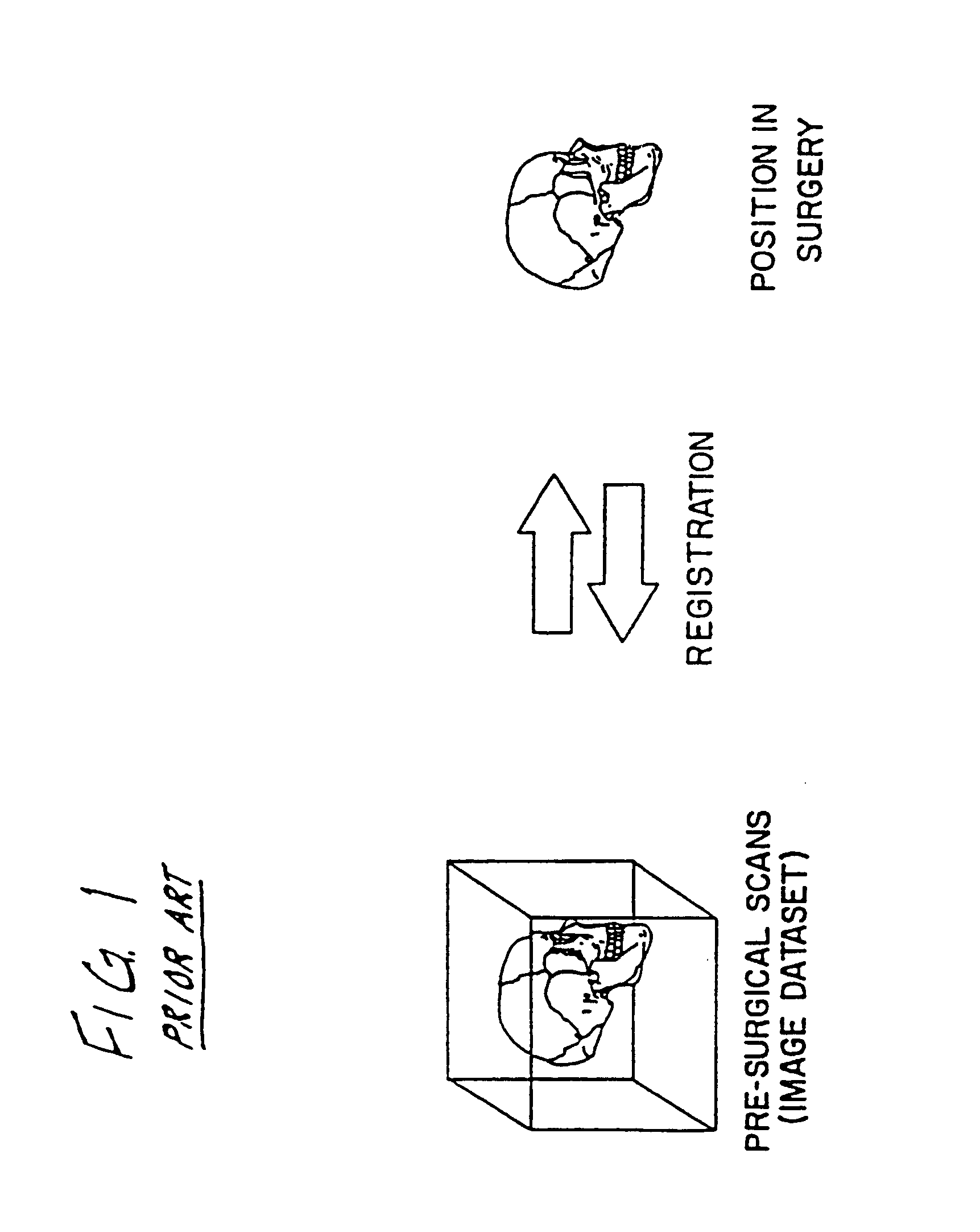
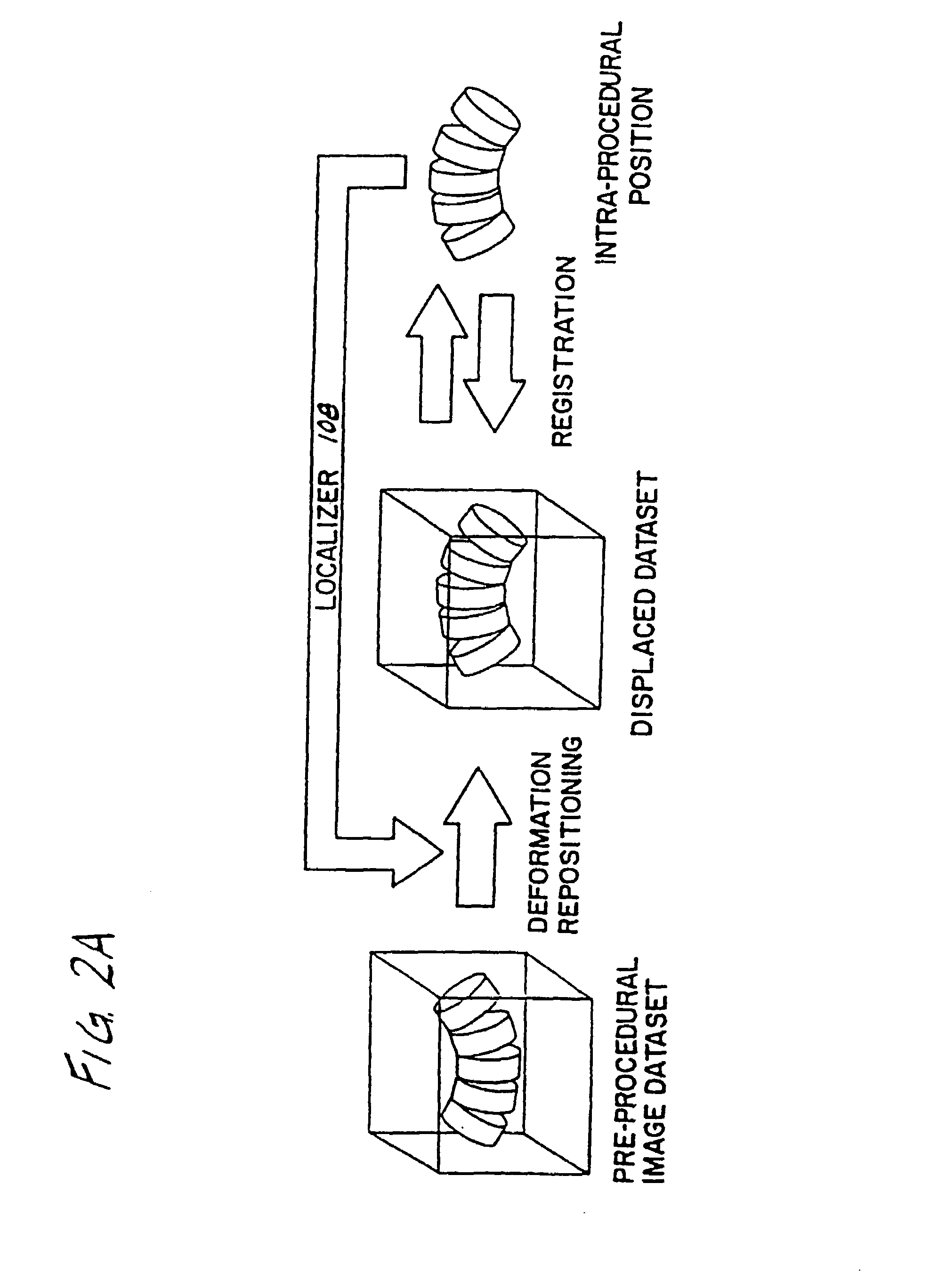
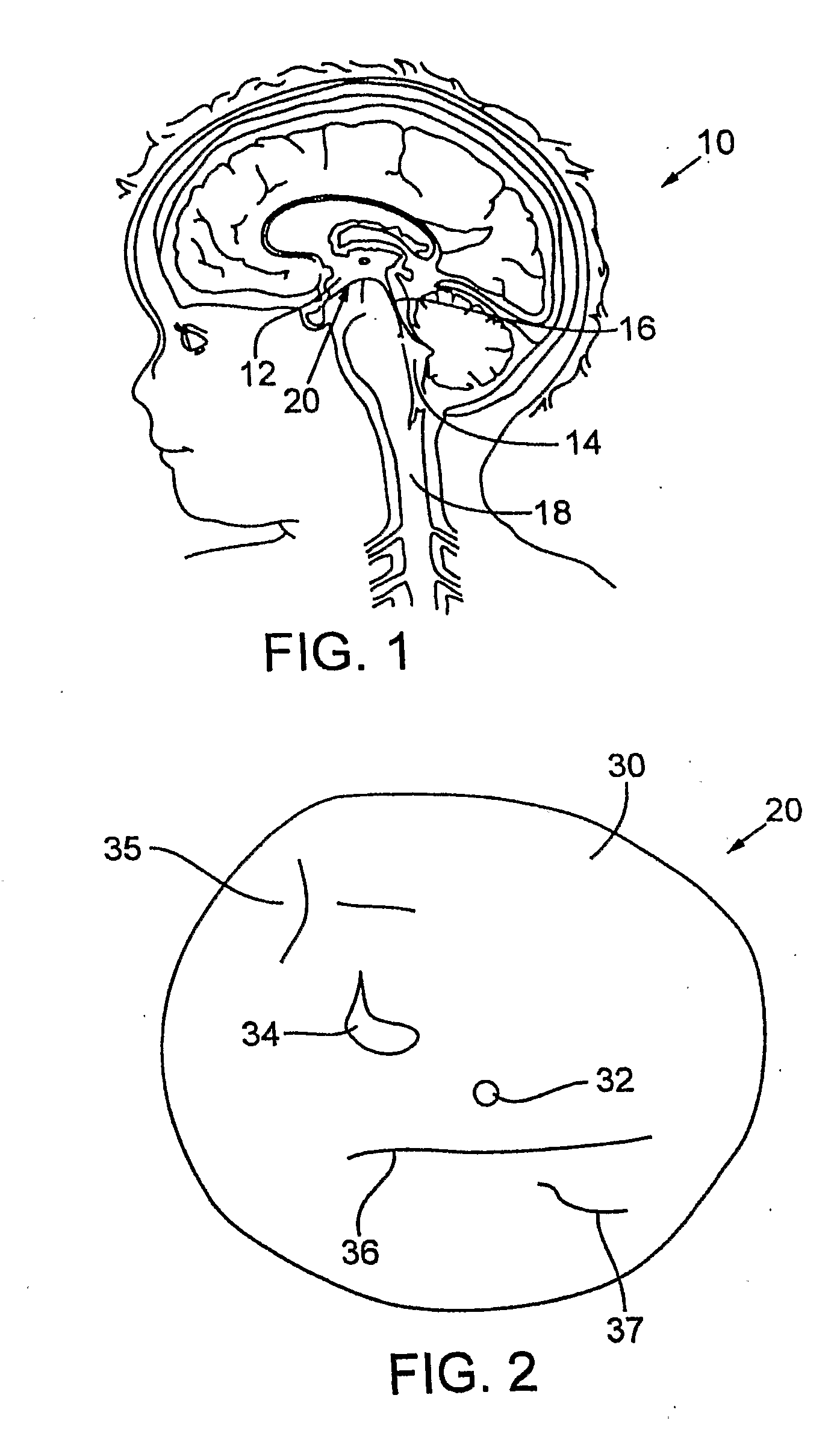
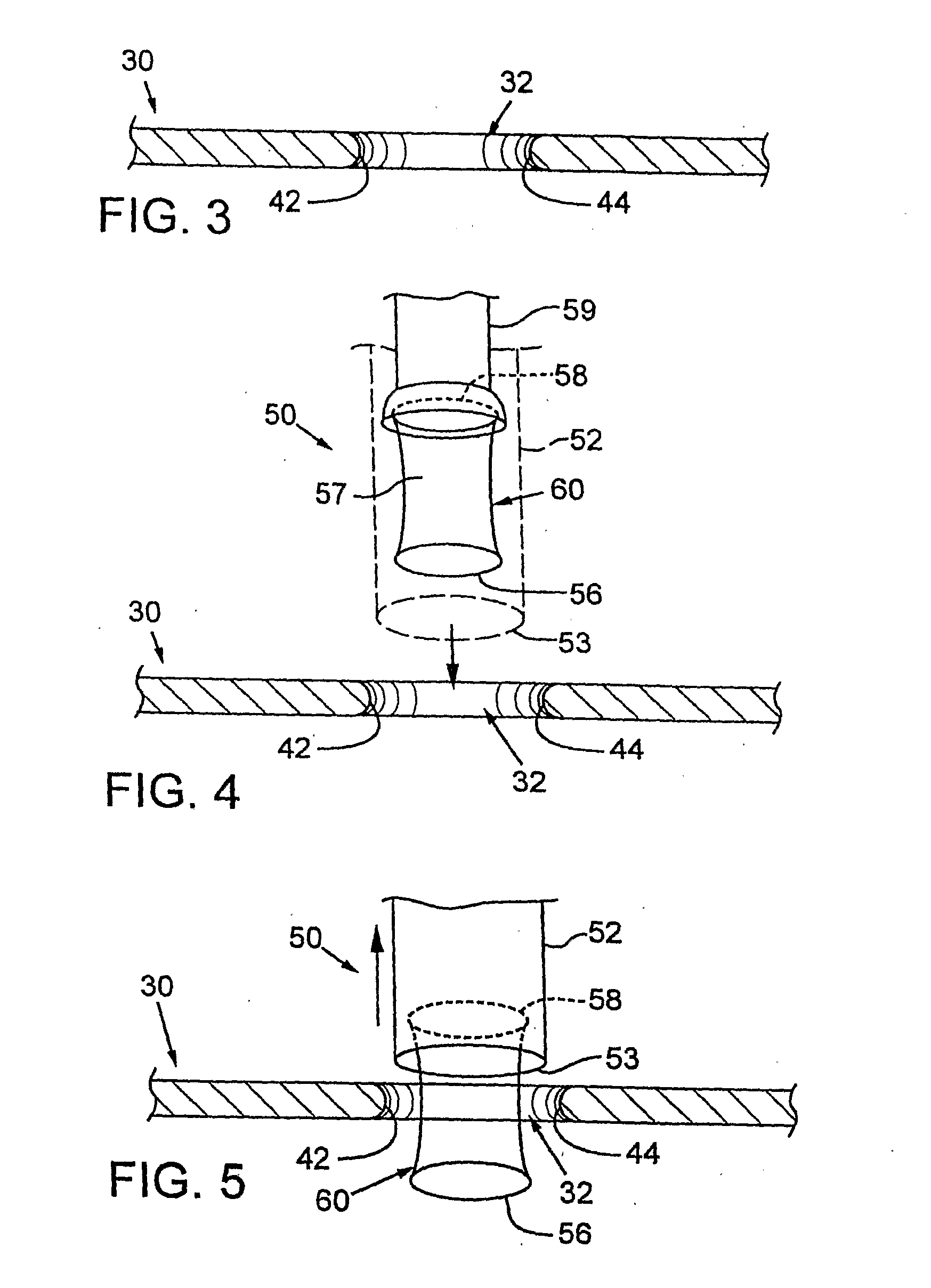
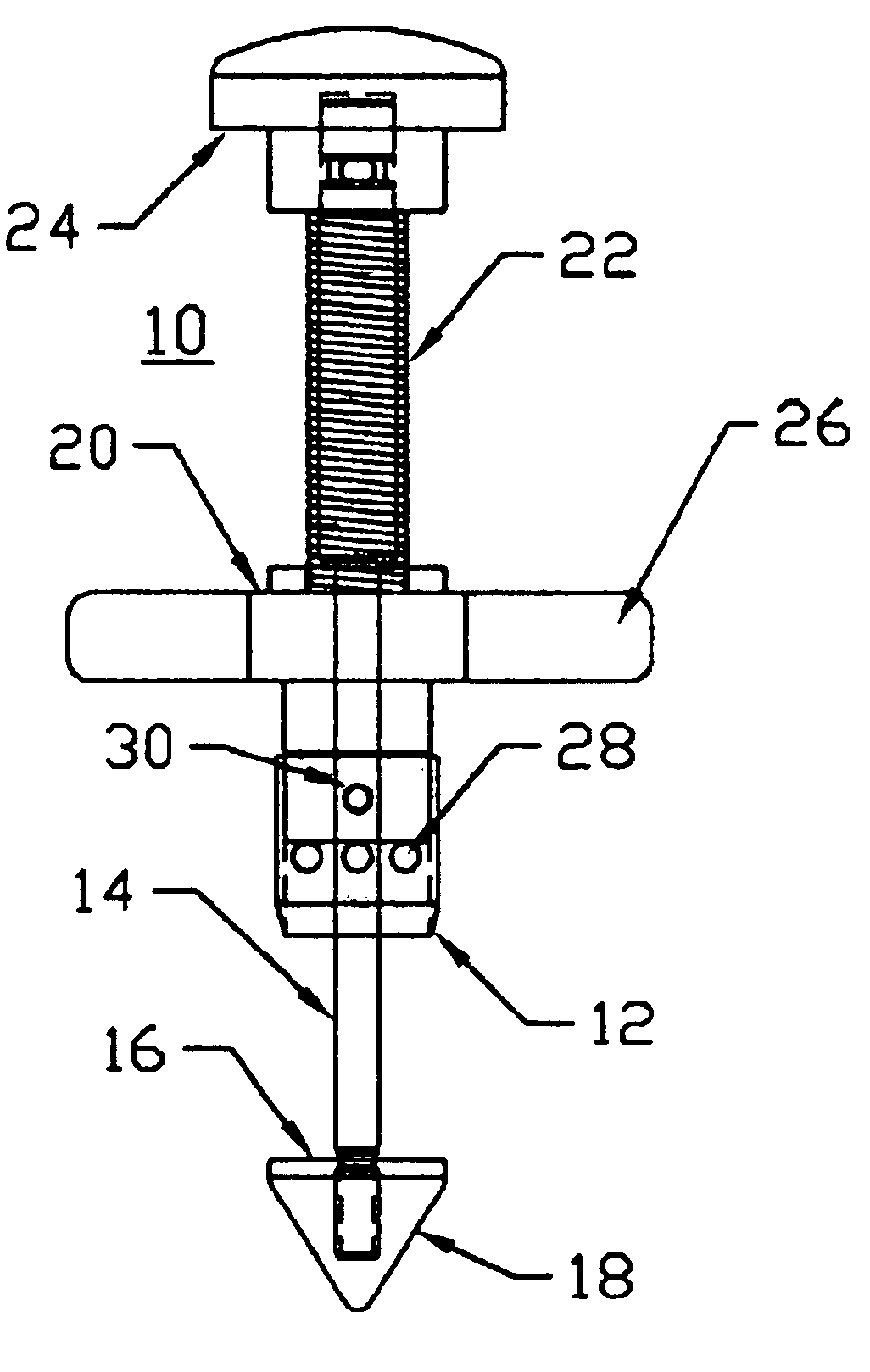
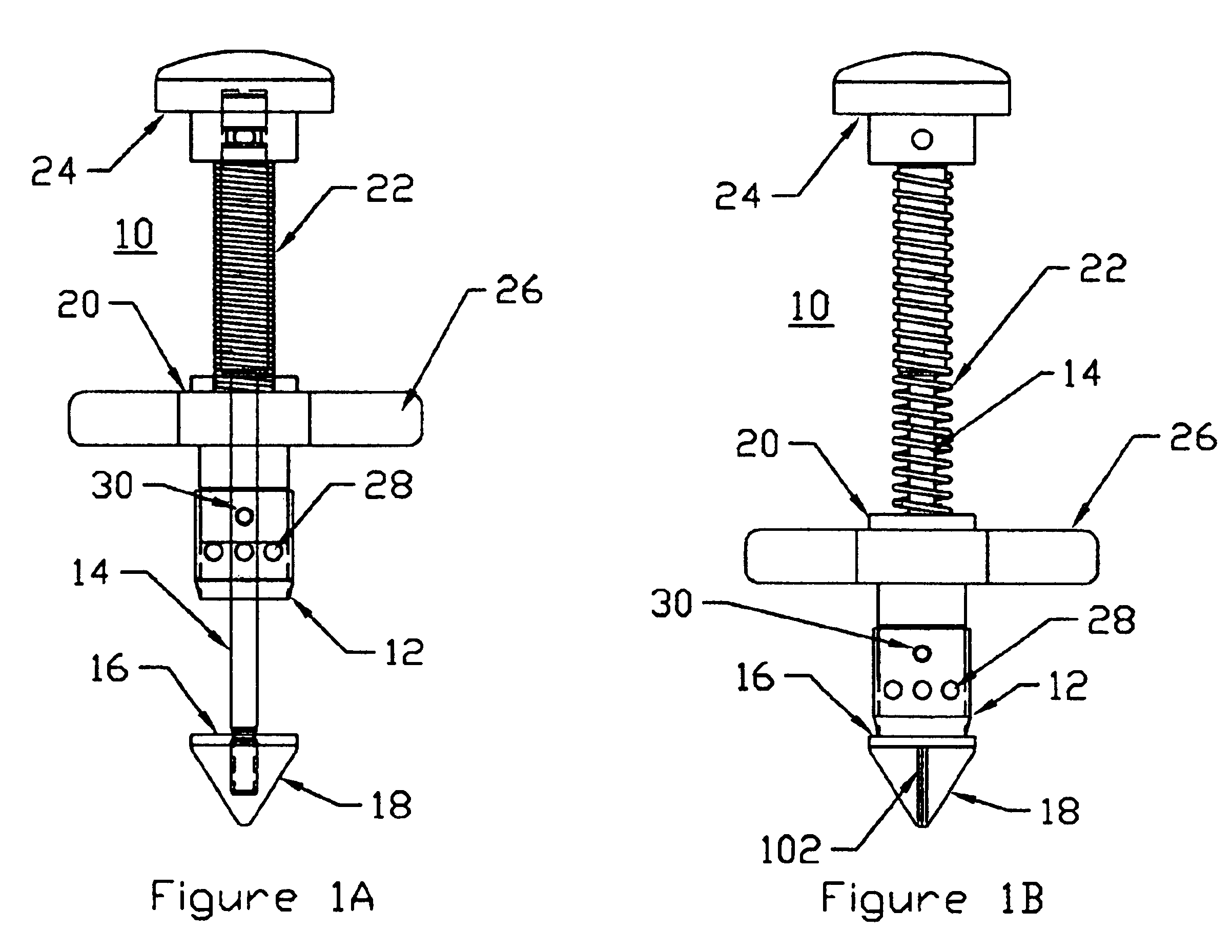
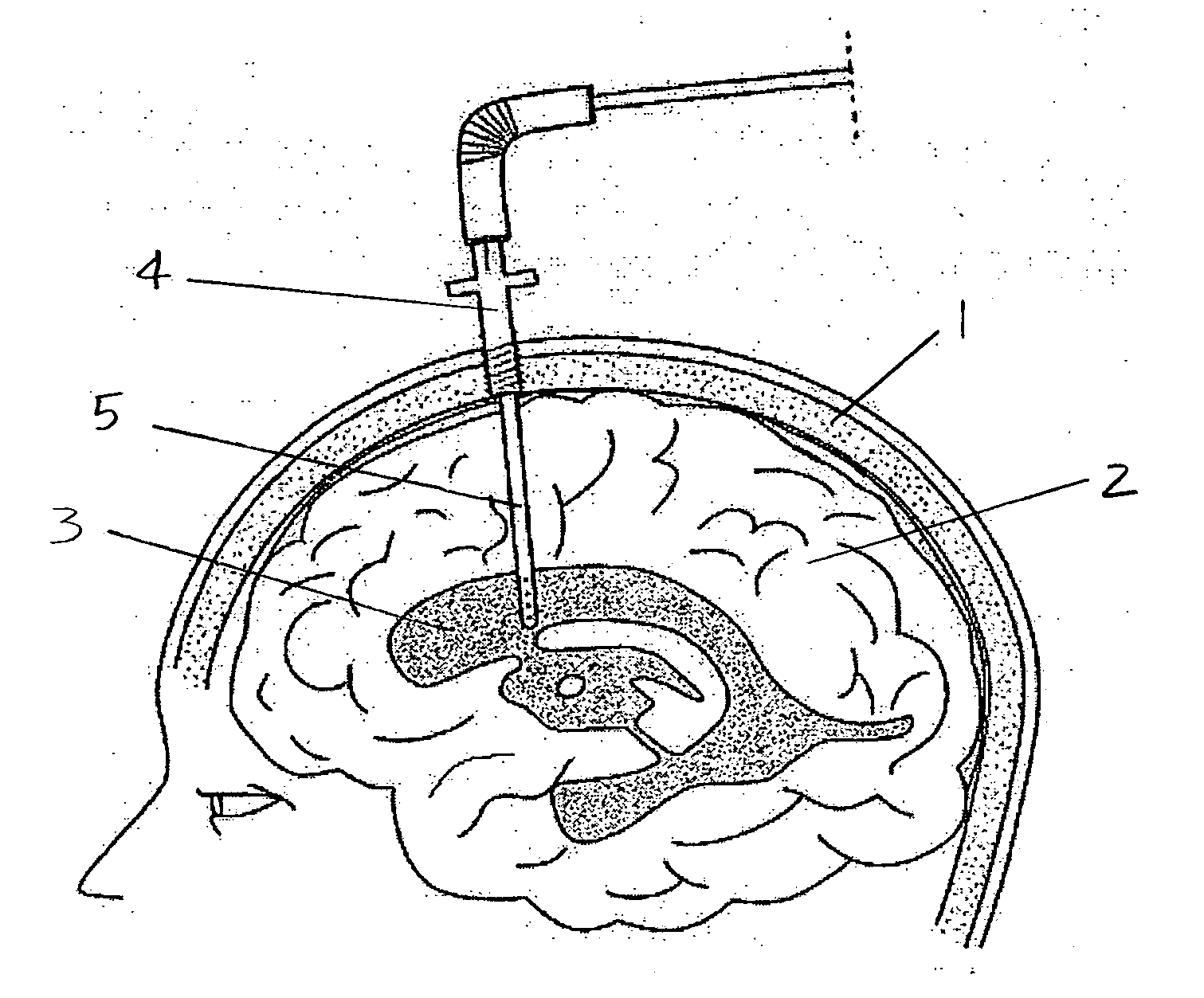
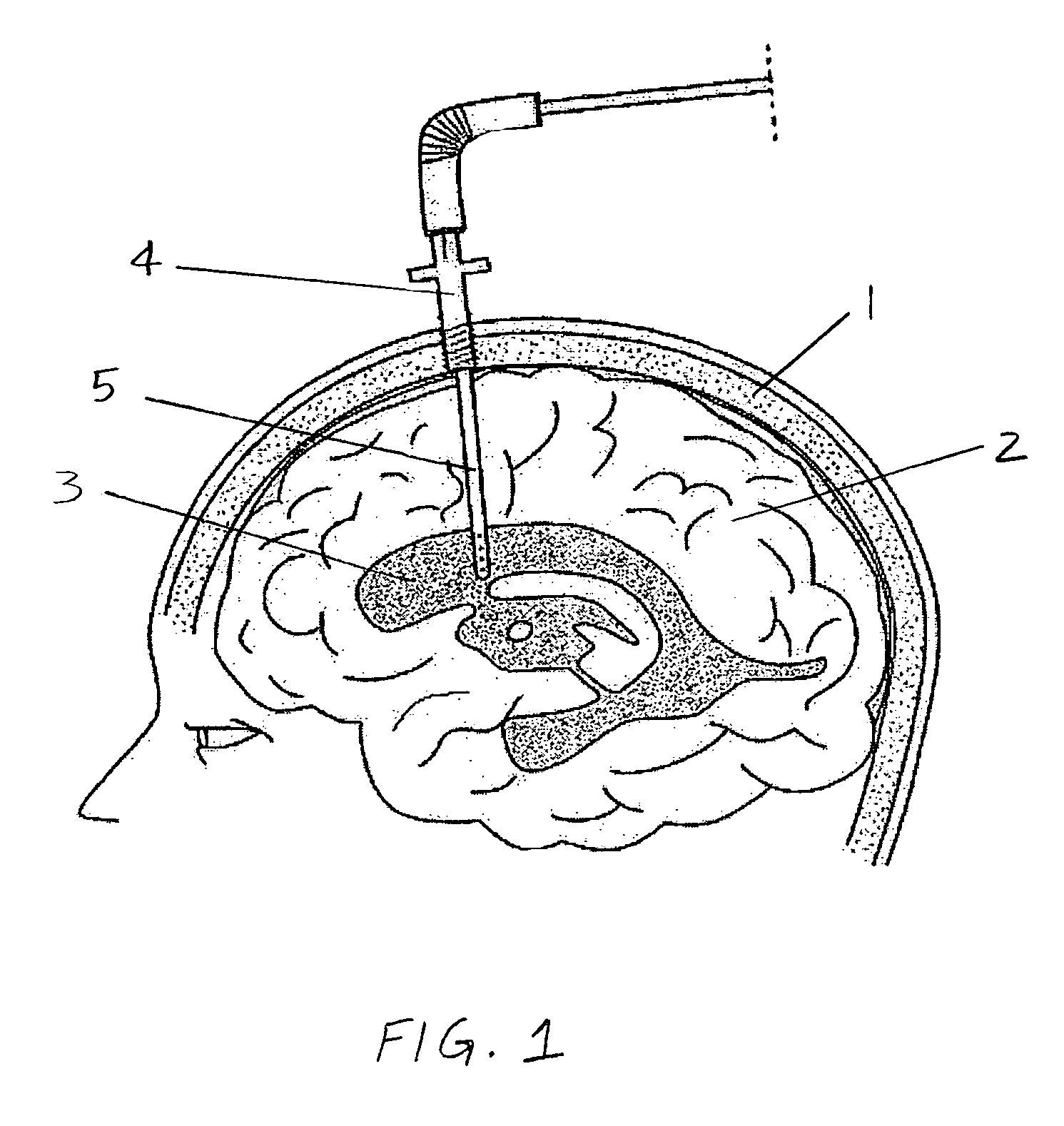
A system for use during a medical or surgical procedure on a body. The system generates an image representing the position of one or more body elements during the procedure using scans generated by a scanner prior or during the procedure. The image data set has reference points for each of the body elements, the reference points of a particular body element having a fixed spatial relation to the particular body element. The system includes an apparatus for identifying, during the procedure, the relative position of each of the reference points of each of the body elements to be displayed. The system also includes a processor for modifying the image data set according to the identified relative position of each of the reference points during the procedure, as identified by the identifying apparatus, said processor generating a displaced image data set representing the position of the body elements during the procedure. The system also includes a display utilizing the displaced image data set generated by the processor, illustrating the relative position of the body elements during the procedure. Methods relating to the system are also disclosed. Also disclosed are devices for use with a surgical navigation system having a sensor array which is in communication with the device to identify its position. The device may be a reference frame for attachment of a body part of the patient, such as a cranial reference arc frame for attachment to the head or a spine reference arc frame for attachment to the spine. The device may also be a localization frame for positioning an instrument relative to a body part, such as a localization biopsy guide frame for positioning a biopsy needle, a localization drill guide assembly for positioning a drill bit, a localization drill yoke assembly for positioning a drill, or a ventriculostomy probe for positioning a catheter.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH +1
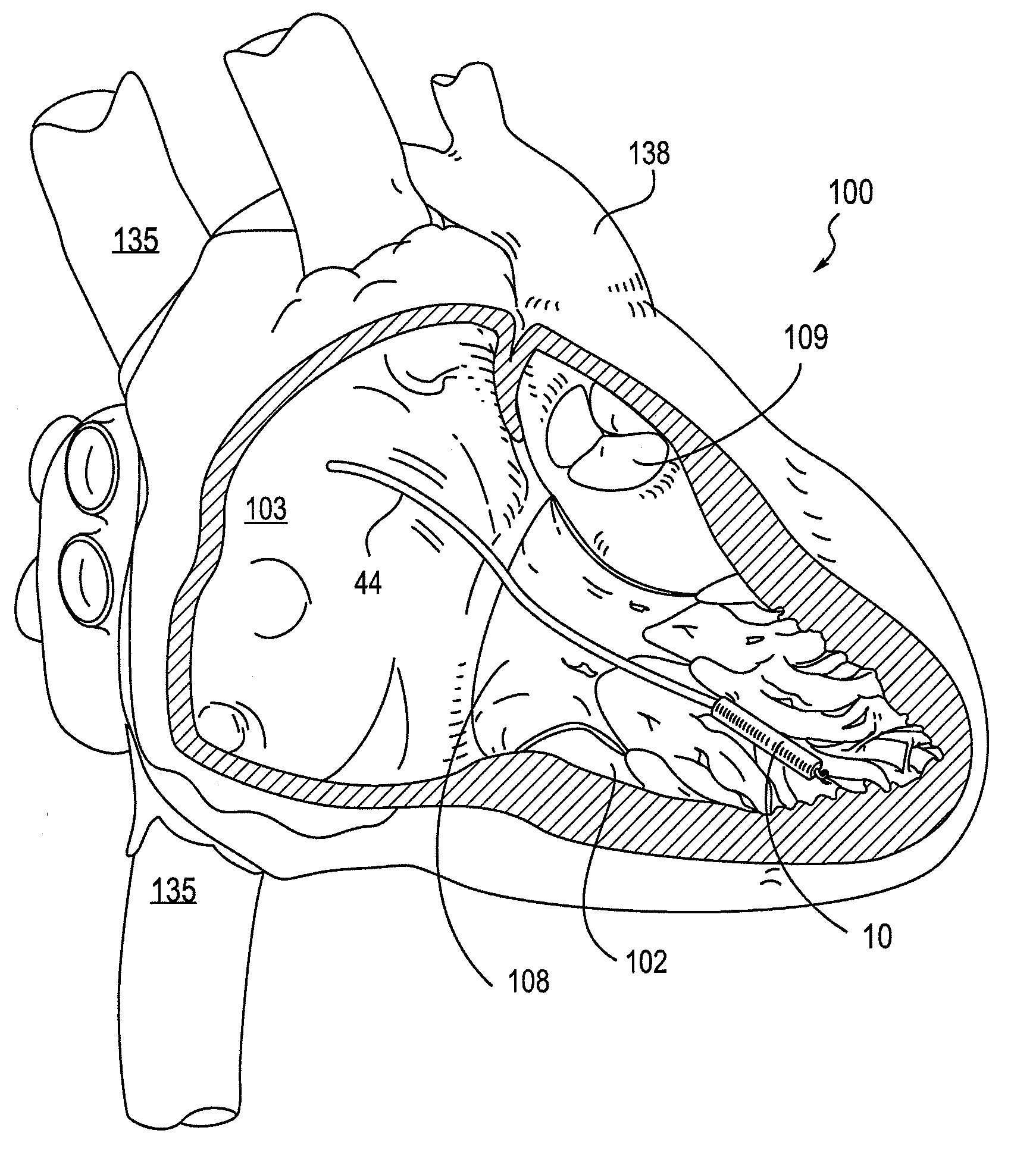
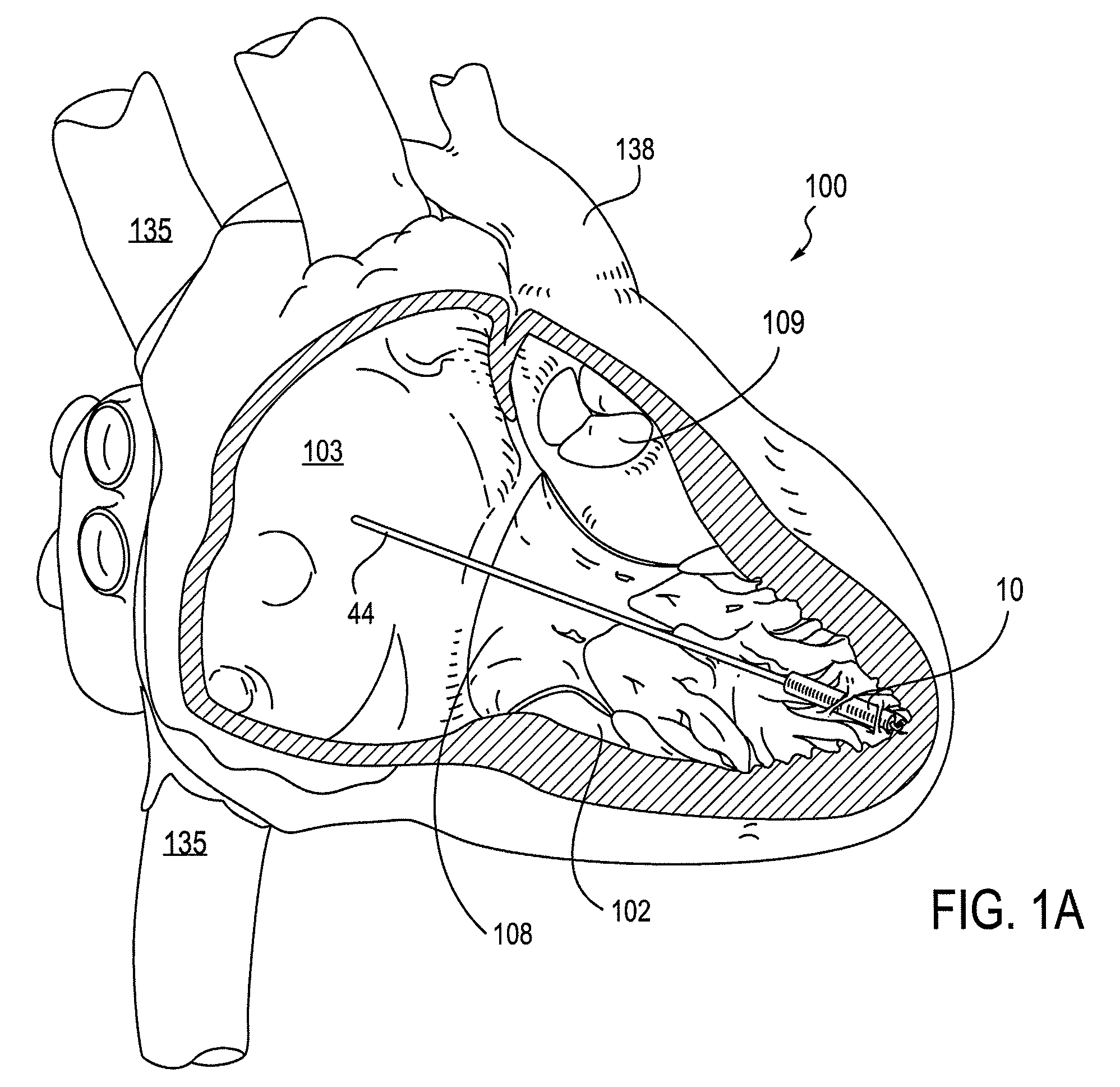
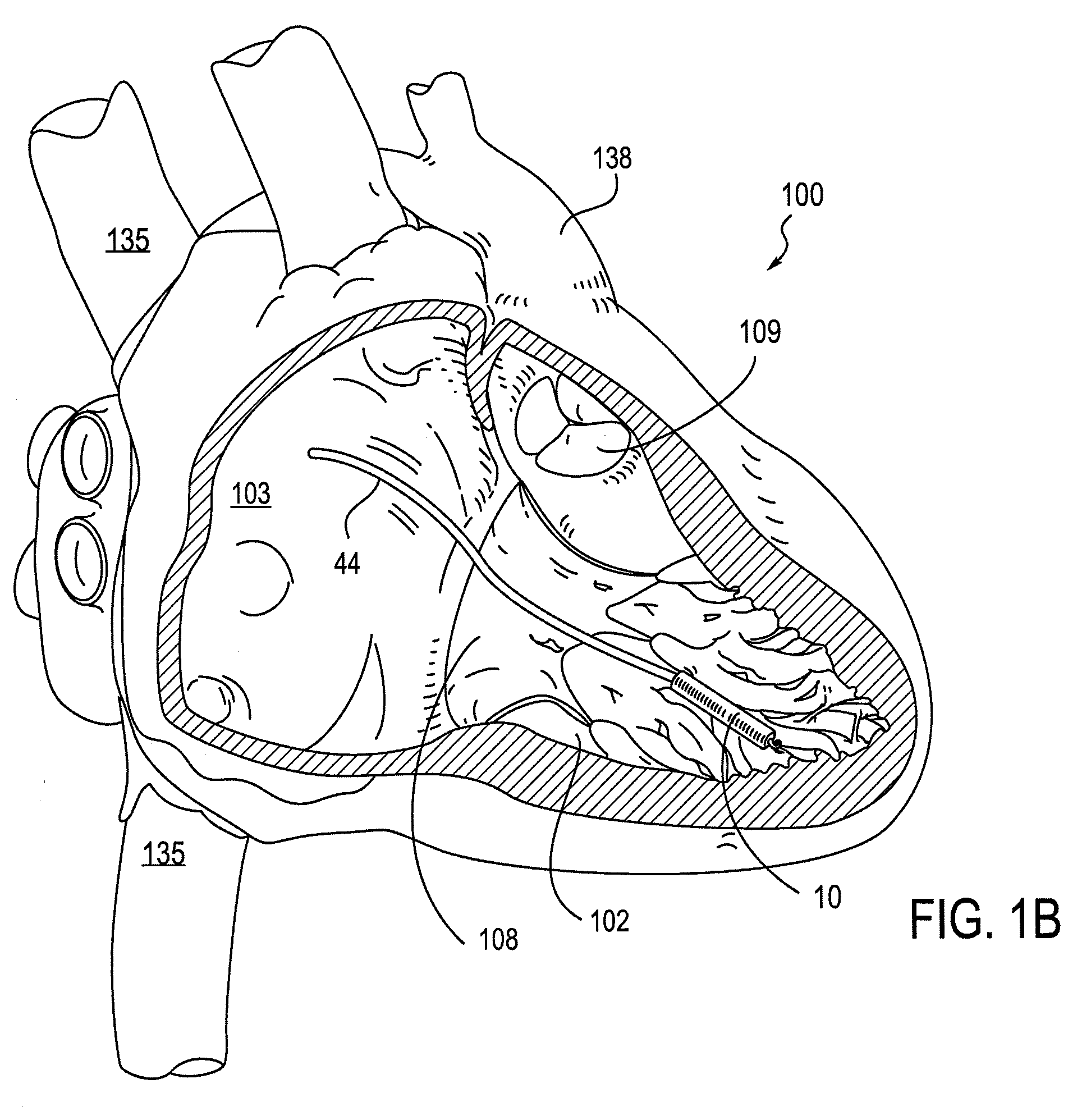
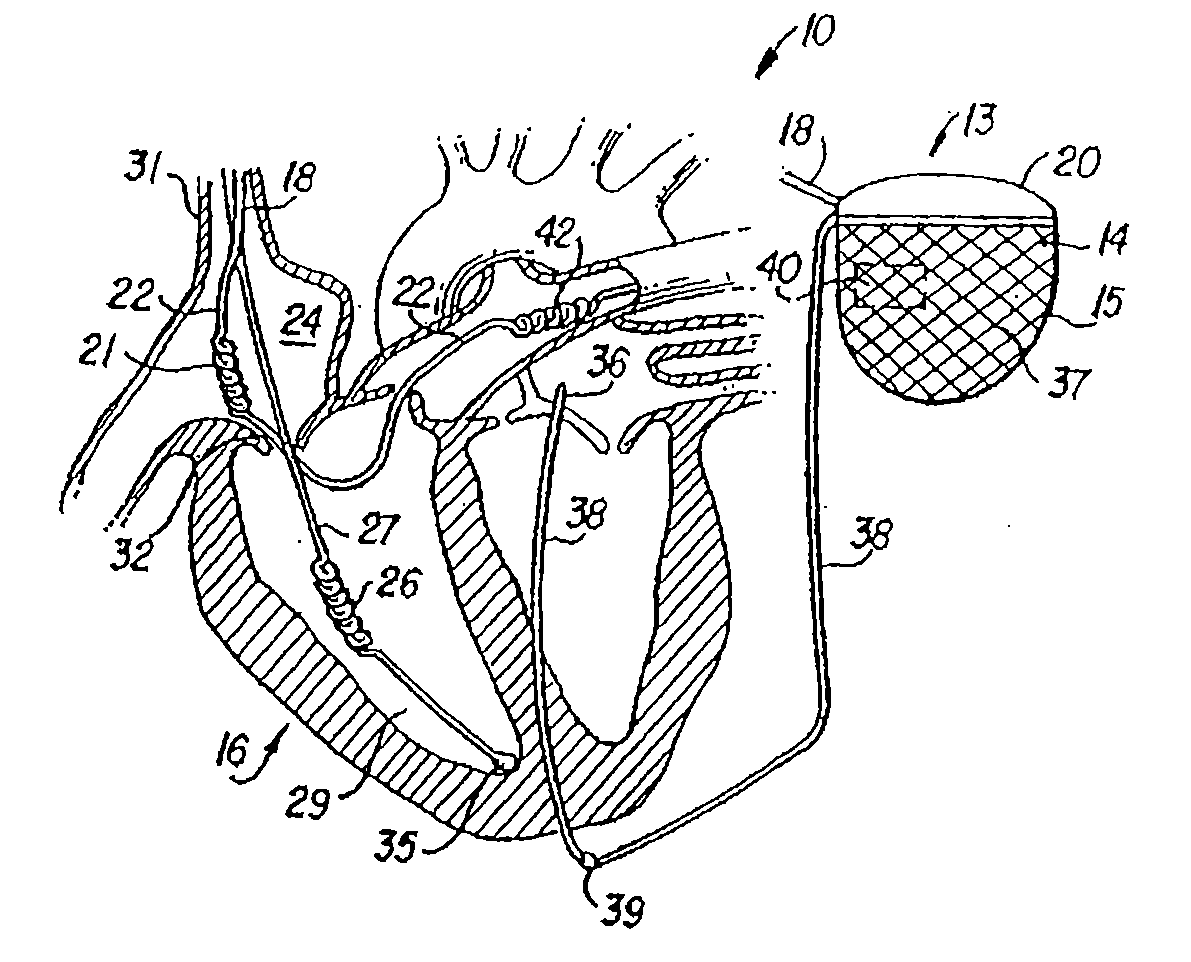
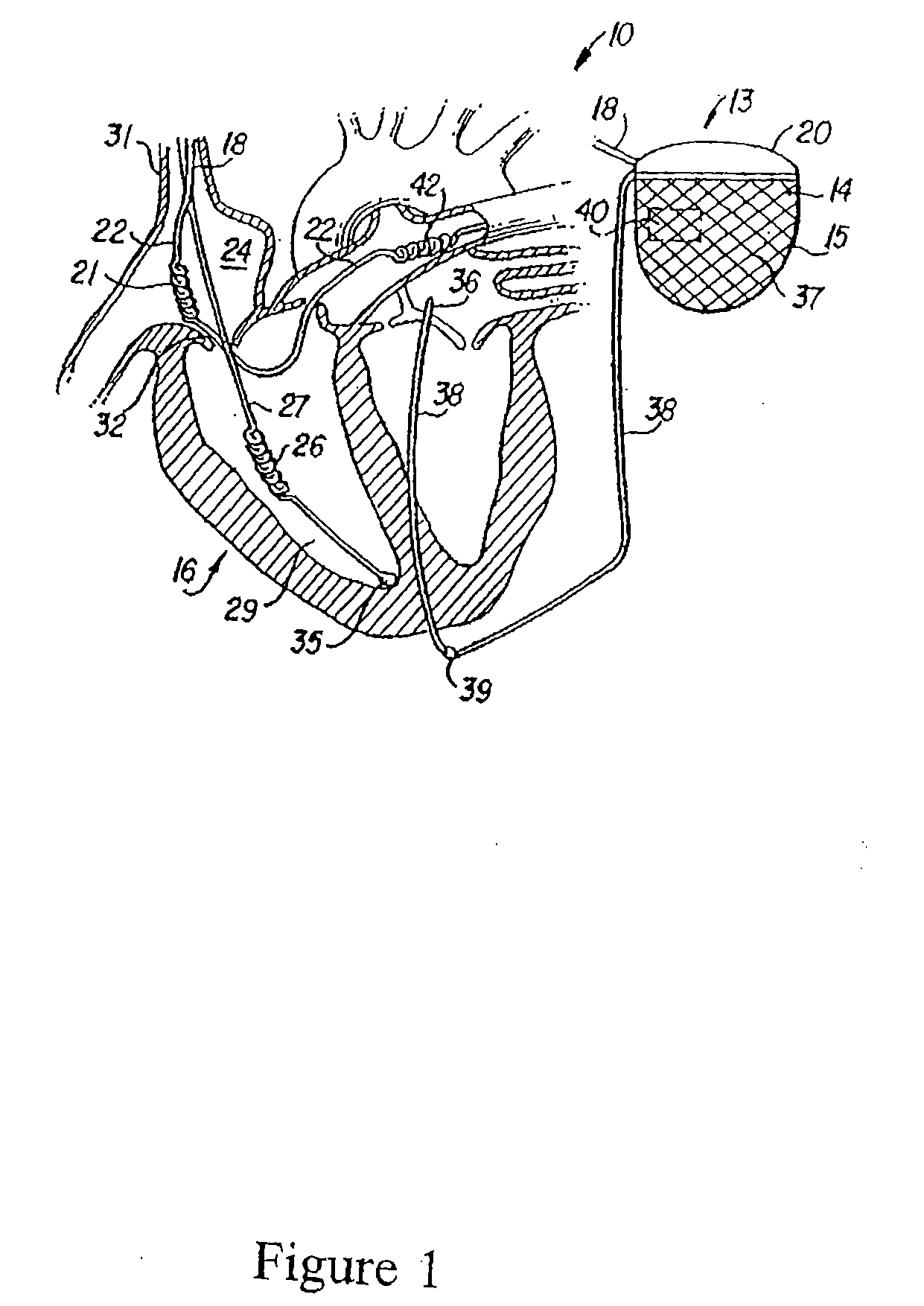
Leadless cardiac pacemaker with secondary fixation capability
ActiveUS8527068B2Discourage attachment and colonization of surfaceImprove capture abilityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationTrabeculae carneaeCardiac pacemaker electrode
The invention relates to leadless cardiac pacemakers (LBS), and elements and methods by which they affix to the heart. The invention relates particularly to a secondary fixation of leadless pacemakers which also include a primary fixation. Secondary fixation elements for LBS's may passively engage structures within the heart. Some passive secondary fixation elements entangle or engage within intraventricular structure such as trabeculae carneae. Other passive secondary fixation elements may engage or snag heart structures at sites upstream from the chamber where the LBS is primarily affixed. Still other embodiments of passive secondary fixation elements may include expandable structures.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
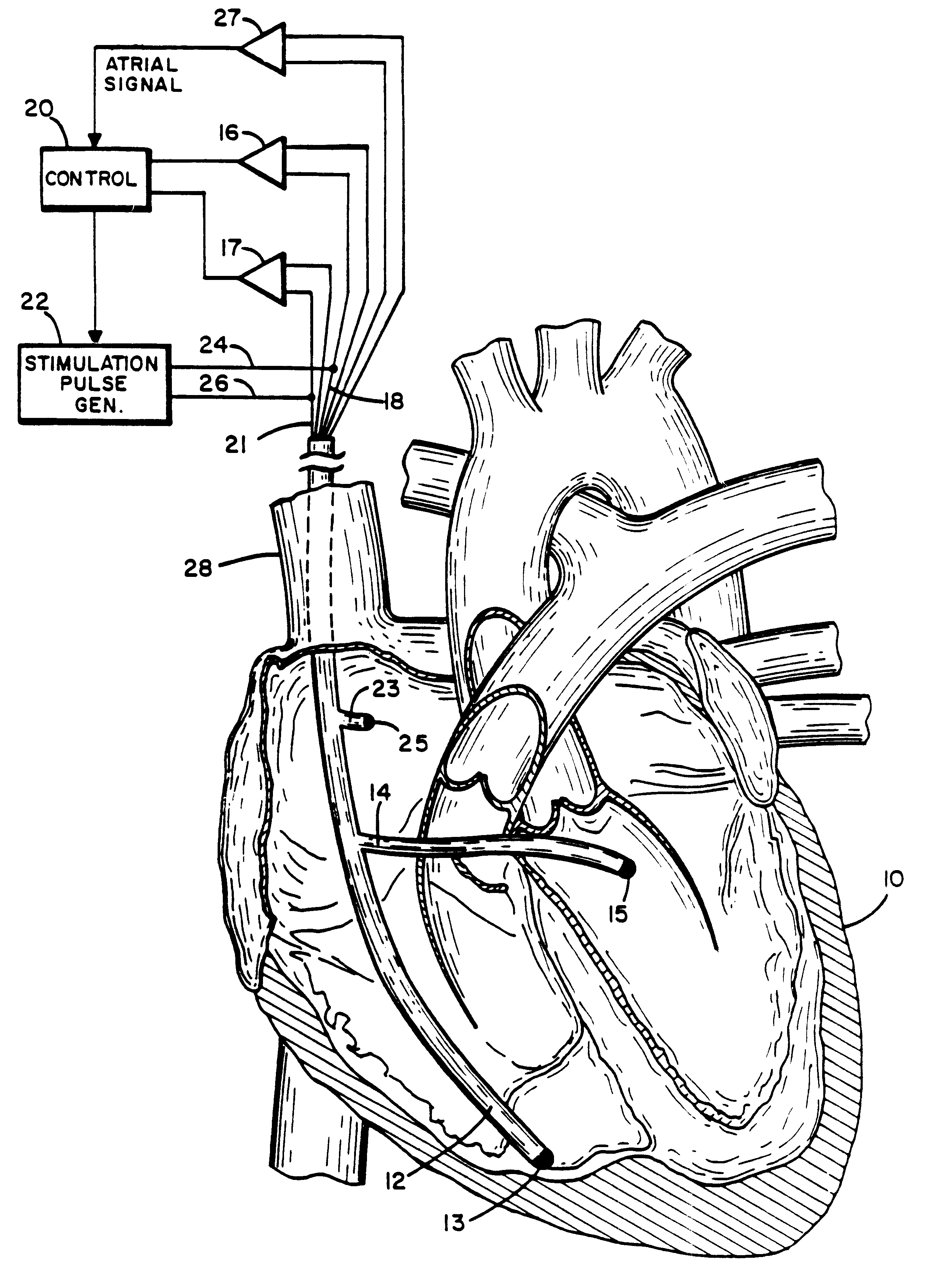
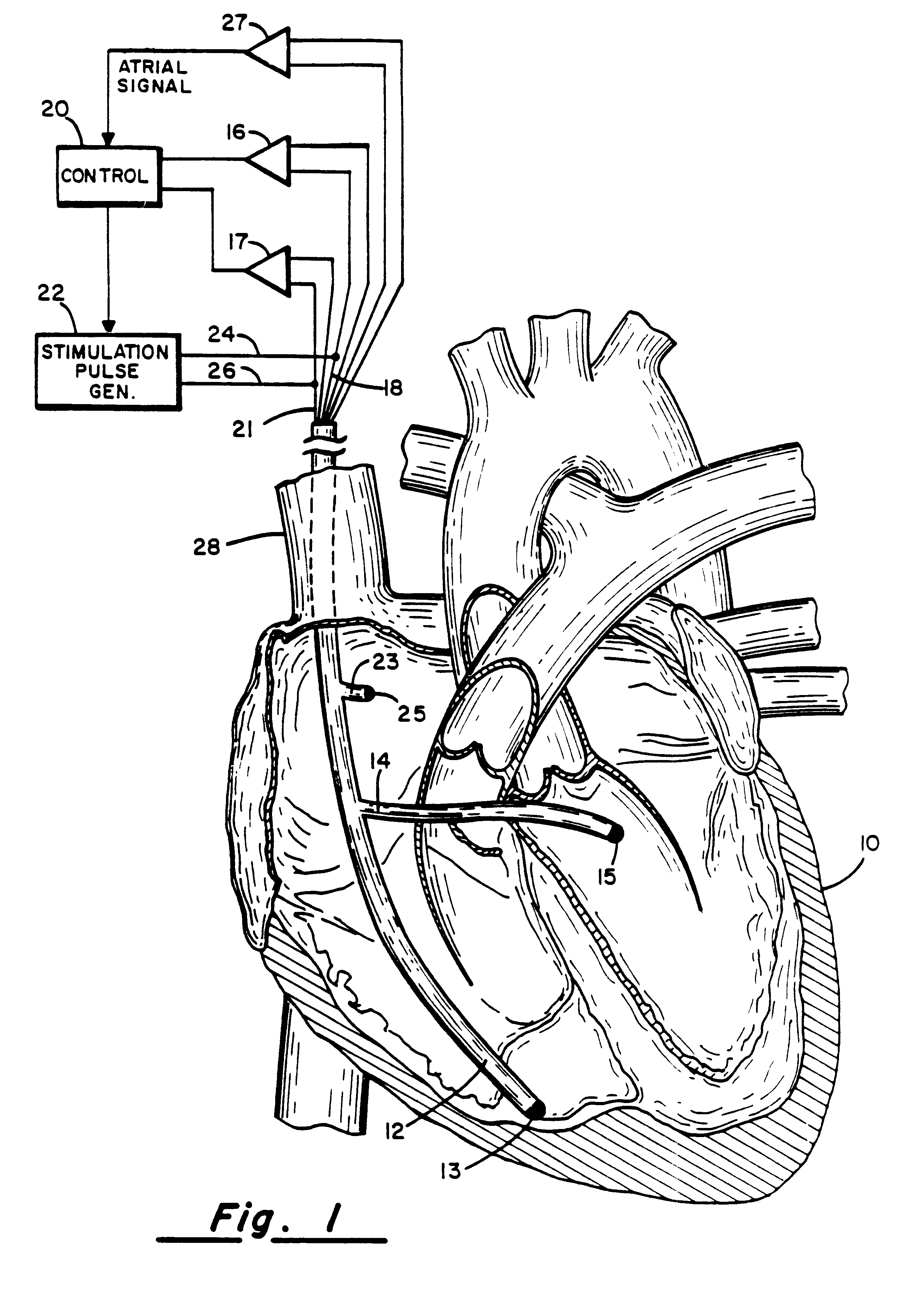
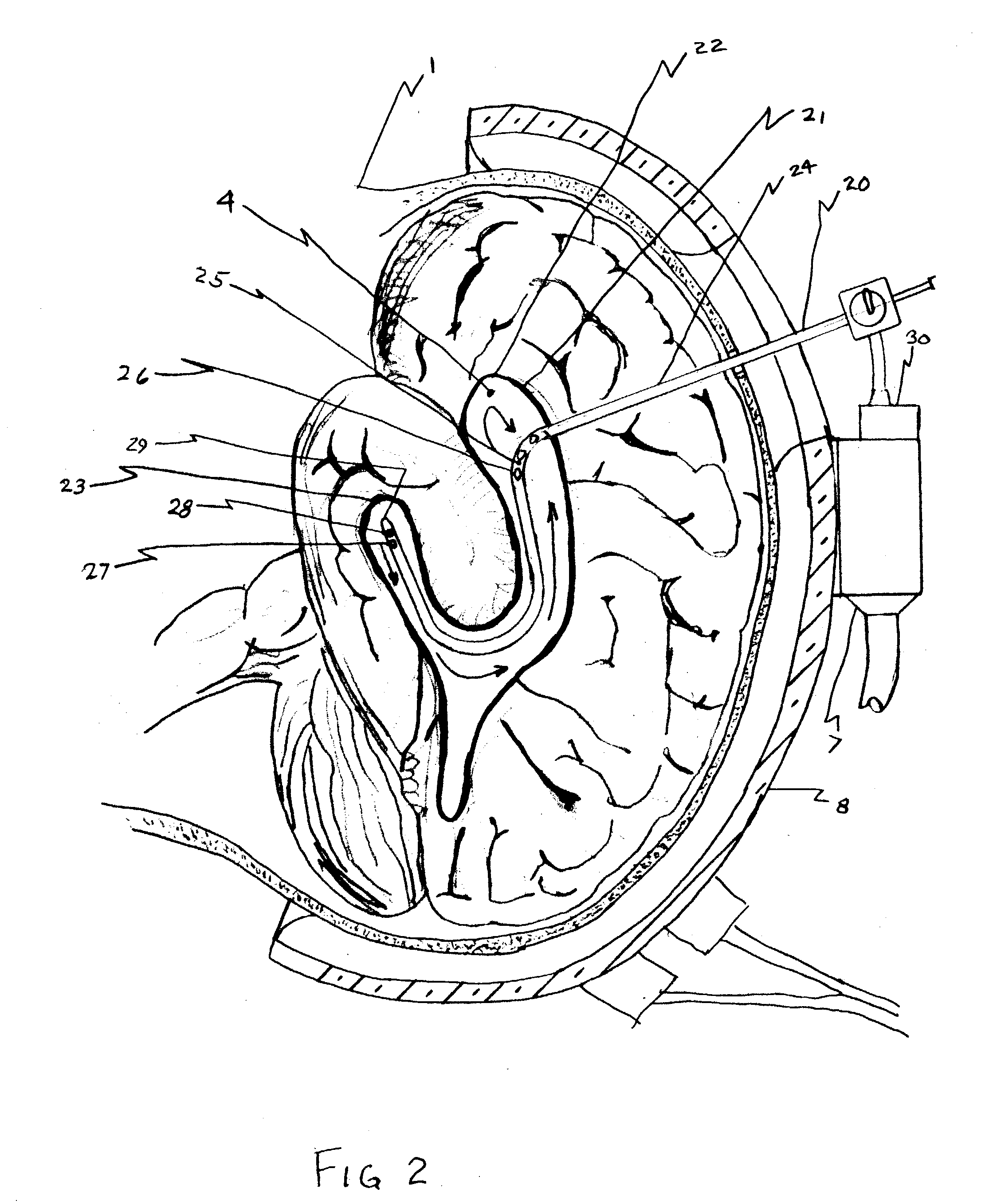
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
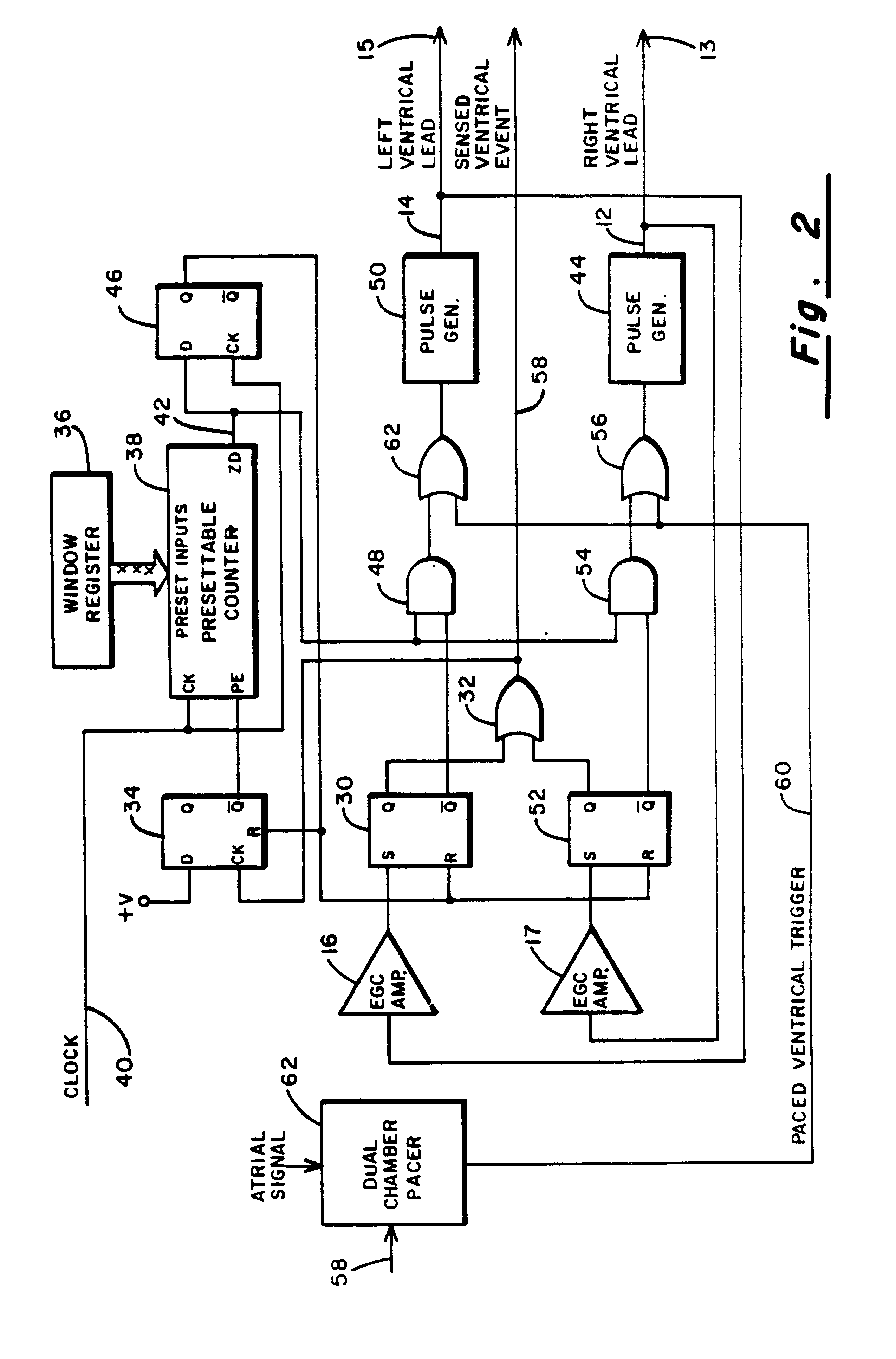
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, is placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
Methods for Simultaneous Injection and Aspiration of Fluids During a Medical Procedure
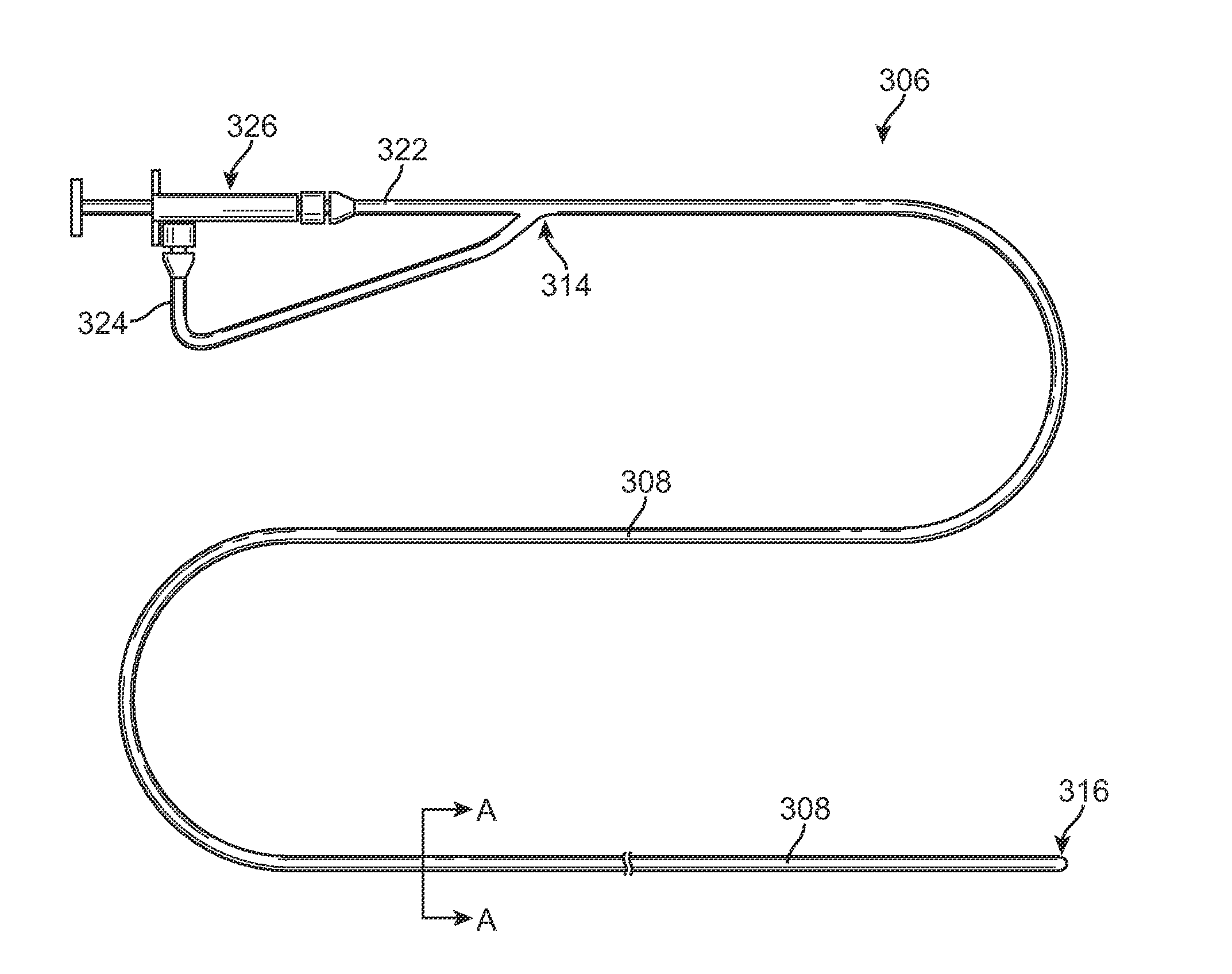
Methods for simultaneous injection and aspiration of fluids during a medical procedure are disclosed. Embodiments include methods for operating medical devices within the subarachnoid space of the spinal column to gain access to the ventricles of the brain, as well as the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space. A dual lumen constant volume aspiration catheter is disclosed that injects a volume of injectable fluid to break up an obstruction within the brain or cranial subarachnoid space while simultaneously aspirating a same volume of aspirated fluid from the treatment site. Methods hereof include constant volume re-circulation of cerebral spinal fluid to and from a treatment area within one of the brain and the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space, which may be desirable during a ventriculostomy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
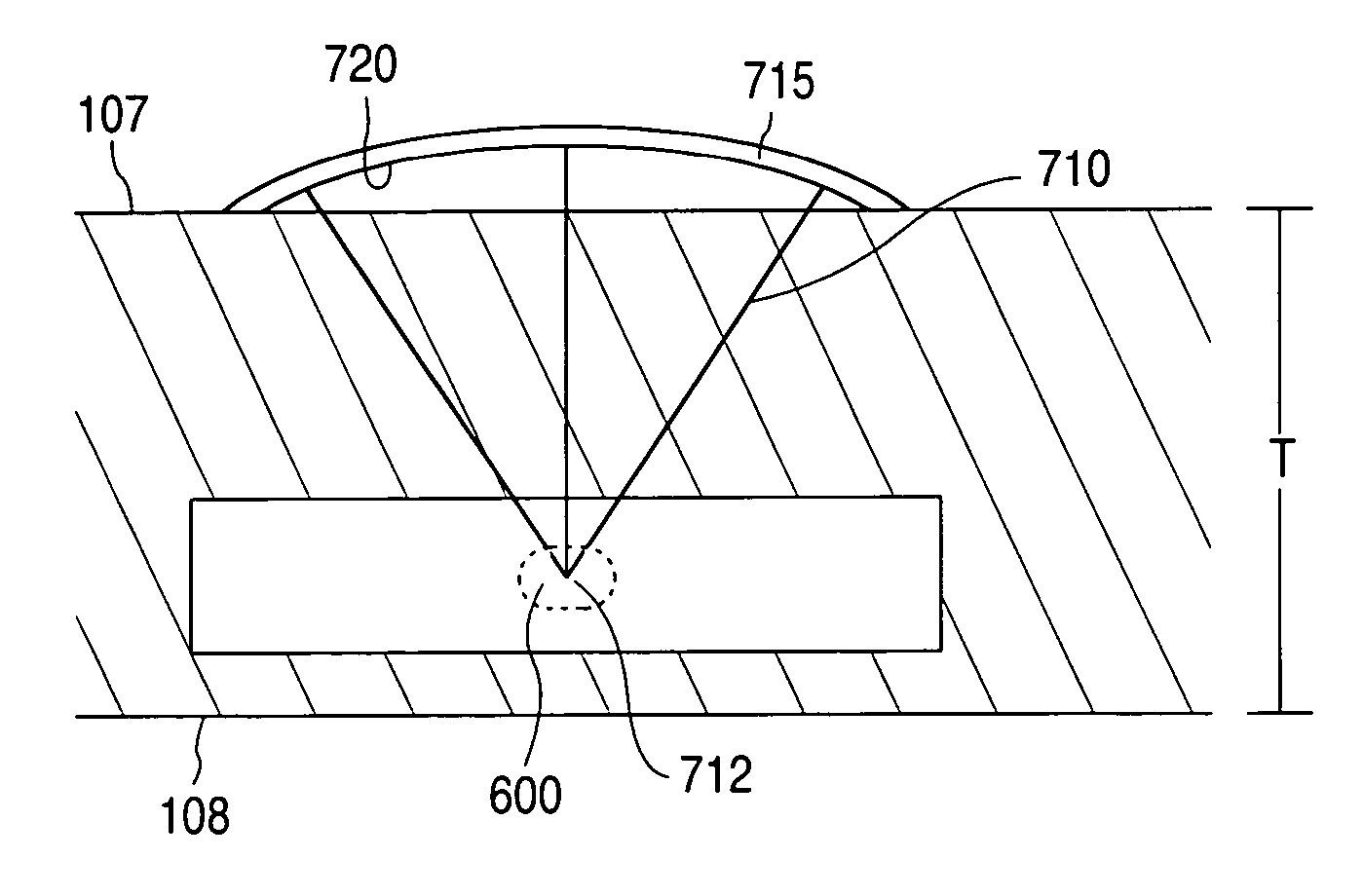
Ultrasound energy driven intraventricular catheter to treat ischemia
InactiveUS7901359B2Minimizes injuryMinimizes to riskUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCurve shapeCardiac muscle
A method and apparatus for improving blood flow to an ischemic region (e.g., myocardial ischemia) a patient is provided. An ultrasonic transducer is positioned proximate to the ischemic region. Ultrasonic energy is applied at a frequency at or above 1 MHz to create one or more thermal lesions in the ischemic region of the myocardium. The thermal lesions can have a gradient of sizes. The ultrasound transducer can have a curved shape so that ultrasound energy emitted by the transducer converges to a site within the myocardium, to create a thermal lesion without injuring the epicardium or endocardium.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Interfacial stent and method of maintaining patency of surgical fenestrations
InactiveUS20070179426A1Keep openImprovement endStentsHeart valvesThird ventriculostomyInsertion stent
A method according to one embodiment for maintaining patency of an opening inside the human body comprises introducing a radially self-expanding hollow stent into the opening through an endoscope that radially compresses the stent, wherein the stent has enlarged ends and a reduced intermediate portion. The stent is introduced into the opening such that its intermediate portion extends through the opening and the enlarged ends are positioned outside of the opening. Once deployed, the stent expands such that the enlarged ends of the stent abut against opposing faces of the opening to resist dislodgement of the stent from the opening after expansion. The stent is preferably biodegradable, such that it is eliminated from the surgical site over a period of weeks to months, by which time the patency of the opening is more assured. The method can be used in combination with, for example, an endoscopic surgical method such as endoscopic third ventriculostomy for treating hydrocephalus of a brain.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
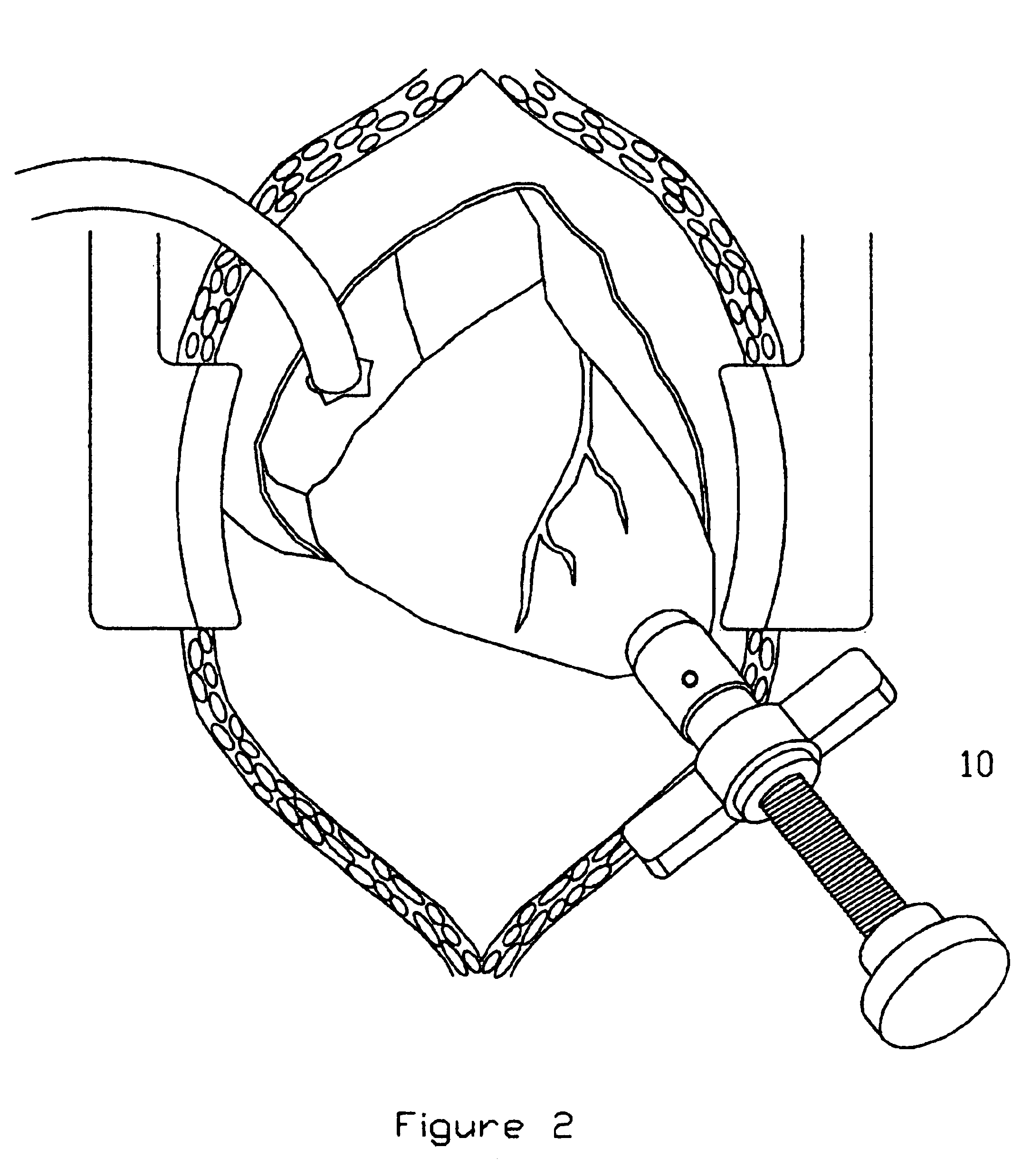
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS6863677B2Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
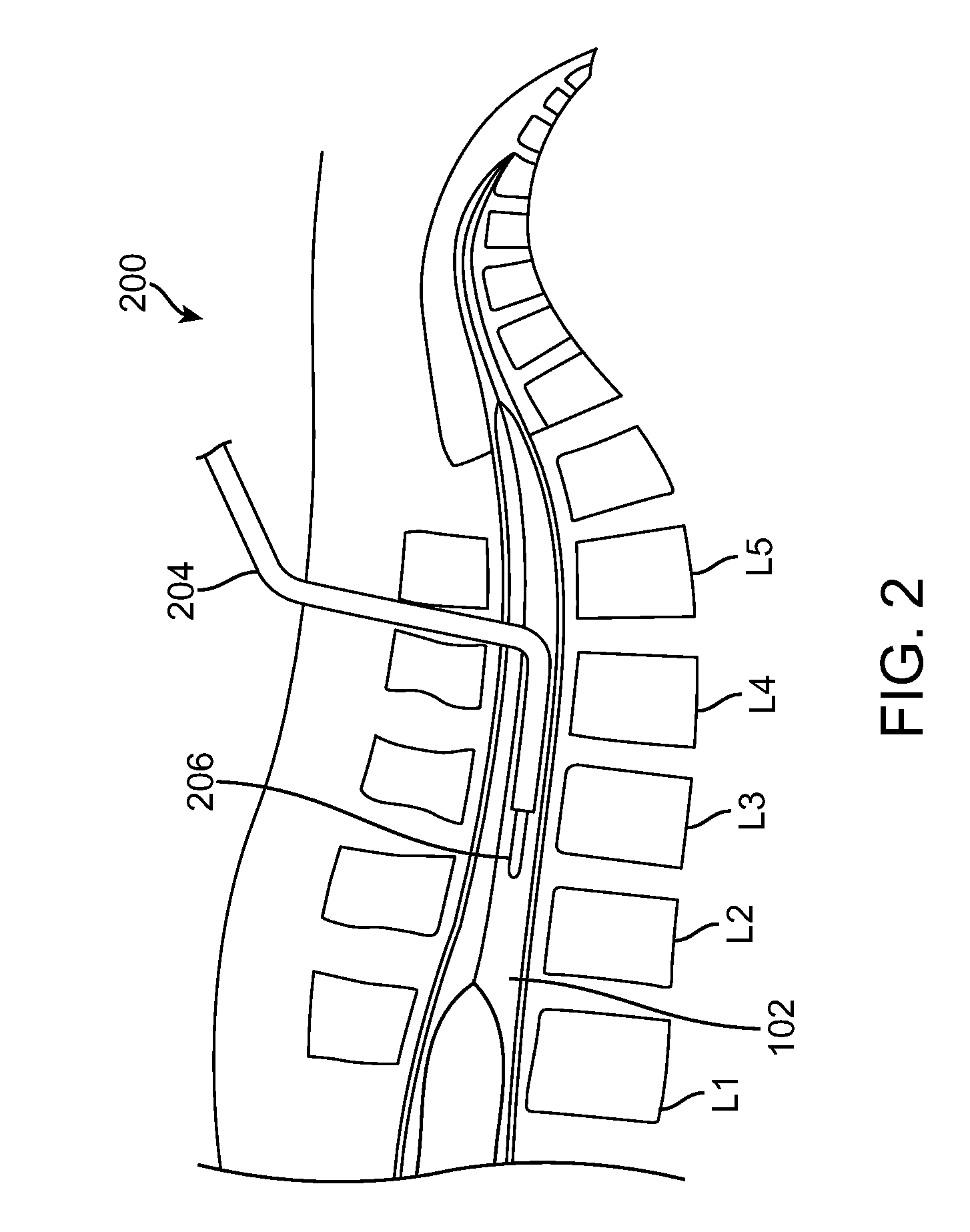
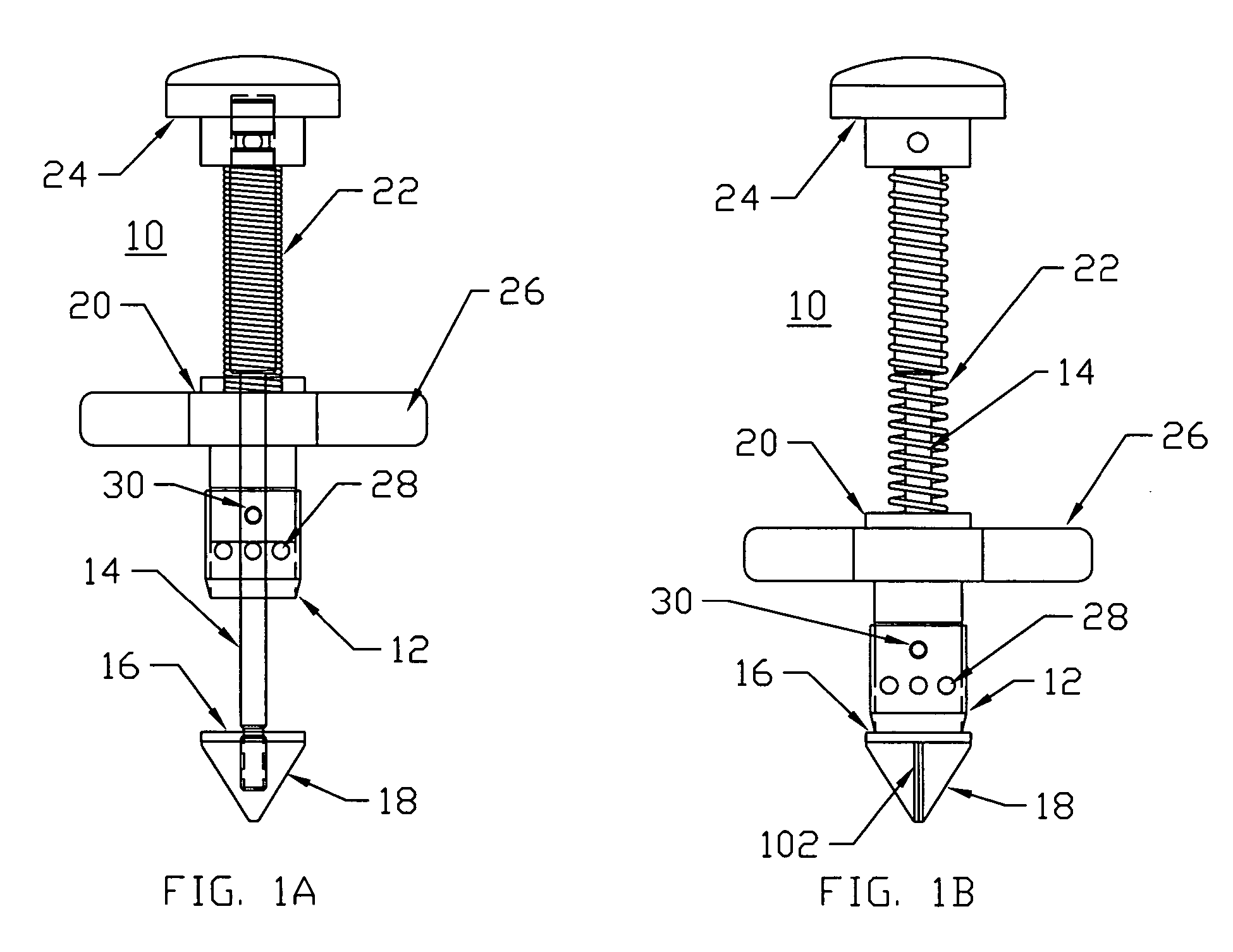
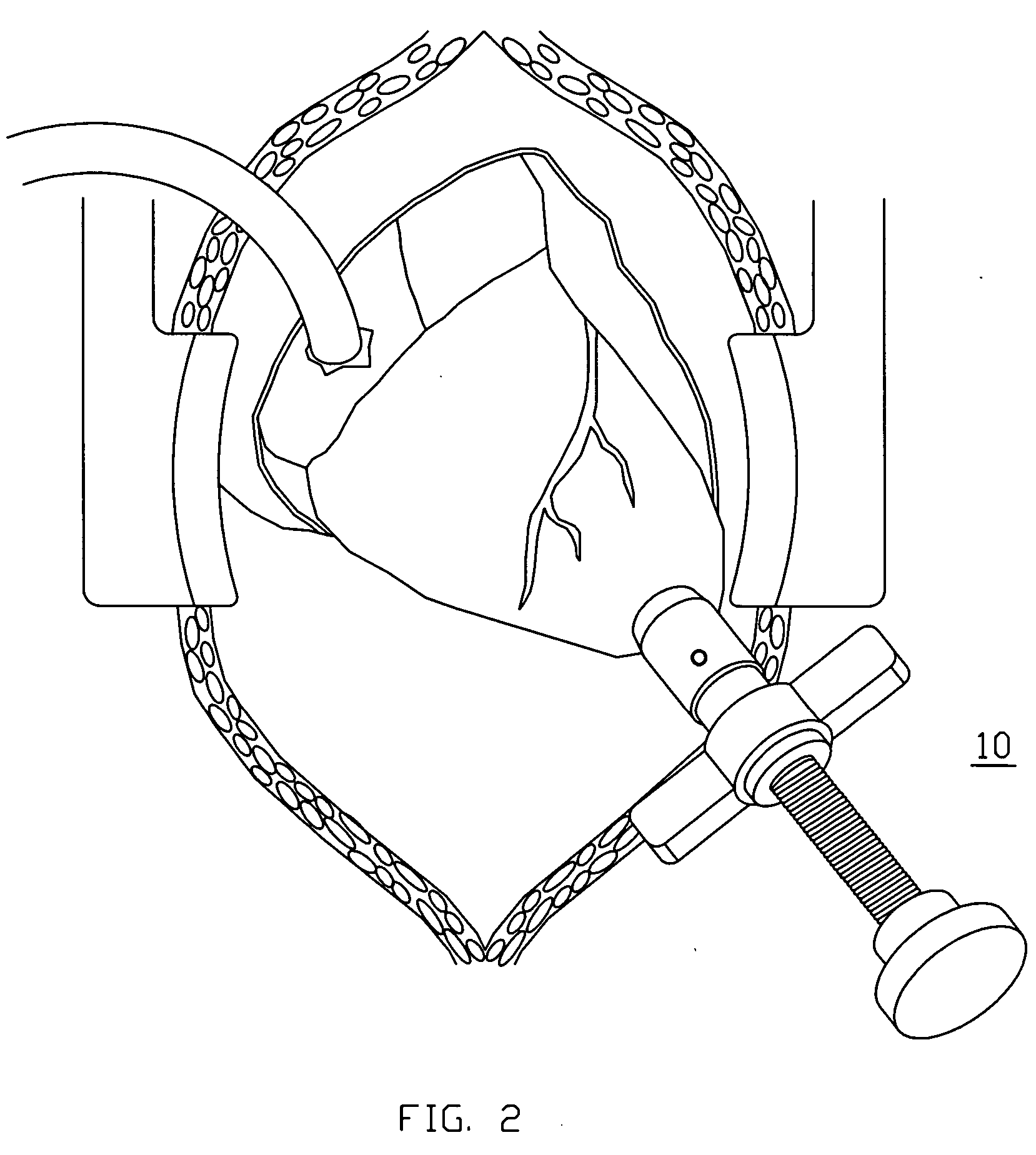
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:INDIAN WELLS MEDICAL
Cerebrospinal fluid puncturing drainer
The cerebrospinal fluid piercing drainer includes a piercing unit and an external draining unit. The piercing unit includes piercing needle, piercing sheath, guide wire and draining pipe. The piercing needle and the outside piercing sheath are made of stainless steel material and are used in piercing; the flexible guide wire of plastic-steel material with shape memory function is used in replacing the piercing needle; the draining pipe of soft silicone gel is used in replacing the piercing sheath and draining. During piercing, the piercing needle and the outside piercing sheath are first pierced into proper position, the piercing needle is then withdrawn and the guide wire is penetrated through the piercing sheath, and the piercing sheath is finally withdrawn and the draining pipe is fed along the guide wire to the cavity to be drained or fed to cerebral side room or even farther position under the monitoring with DSA. The draining pipe has external end connected to the draining unit.
Owner:何明利
Method and apparatus for removing harmful proteins from a mammalian's ventricular cerebrospinal fluid
A method and apparatus for removing harmful organic anions and proteins from a mammalian's ventricular cerebrospinal fluid in the treatment of brain disorders. One embodiment comprises using an implanted pump and filter system in conjunction with a drug or enzyme to clean and filter a patient's cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:GEIGER MARK
Method and apparatus for trephinating body vessels and hollow organ walls
InactiveUS20050154411A1Improve permeabilityReduce cleaningSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsPapillary muscleBone trephine
A system is disclosed for creating a hole in a body vessel or hollow organ. Such holes are useful in surgically preparing the hollow organ or body vessel for connection with another hollow organ, body vessel or prosthetic conduit. For example, an assist device is generally connected to the left ventricle through a ventriculotomy created at the apex of the left ventricle. This ventriculotomy is most easily created with a punch or trephine. Control over such a procedure must be precise so as not to damage the ventricular wall or intracardiac structures such as papillary muscles, chordae tendinae, etc. The punch of the current invention allows for precise location and alignment of the cutting segment. The punch of the current invention also allows for precise advance of the cutting blade and a very clean cut of the tissue. Such clean cuts improve the healing when the hole in the body vessel or hollow organ is closed or attached to a connection, either prosthetic or natural.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
Uniform selective cerebral hypothermia
InactiveUS20030130651A1Surgical instrument detailsIntravenous devicesCooling chamberTemperature difference
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for uniform selective cerebral hypothermia. The apparatus includes a brain-cooling probe, a head-cooling cap, a body-heating device and a control console. The brain-cooling probe cools the cerebrospinal fluid within one or more brain ventricles. The brain-cooling probe withdraws a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from a ventricle into a cooling chamber located ex-vivo in close proximity to the head. After the cerebrospinal fluid is cooled it is then reintroduced back into the ventricle. This process is repeated in a cyclical or continuous manner. The head-cooling cap cools the cranium and therefore cools surface of the brain. The combination of ventricle cooling and cranium cooling provides for whole brain cooling while minimizing temperature gradients within the brain. The body-heating device replaces heat removed from the body by the brain-cooling probe and the head-cooling cap and provides for a temperature difference between the brain and the body where the brain is maintained a temperature lower than the temperature of the body.
Owner:MEDCOOL
Autologous coatings for implants
ActiveUS7217425B2Avoid it happening againInhibit inflammationPeptide/protein ingredientsMedical devicesVentricular catheterMedical device
A hydrocephalus shunt having an anti-inflammatory coating applied to at least the outside surface of the ventricular catheter. Such coatings are also applicable to other medical devices or implants.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Methods and systems for treatment of neurological diseases of the central nervous system
InactiveUS20050208090A1Reduce degradationAdequate transportNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSystems designActive enzyme
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for the treatment of inborn genetic errors or other defects that cause deficiencies of active enzymes or proteins within the cells of the central nervous system. Such methods and systems generally comprise an implantable catheter system designed for the chronic delivery of specially formulated proteins to intrathecal, intracerebroventricular, and / or intraparenchymal regions of the central nervous system. The invention has application in the neuropathic aspects of the broad category of lysosomal storage diseases. These genetic based diseases are the result of insufficient enzyme activity to catabolize specific substances, which thereby accumulate in the cellular lysosomes.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
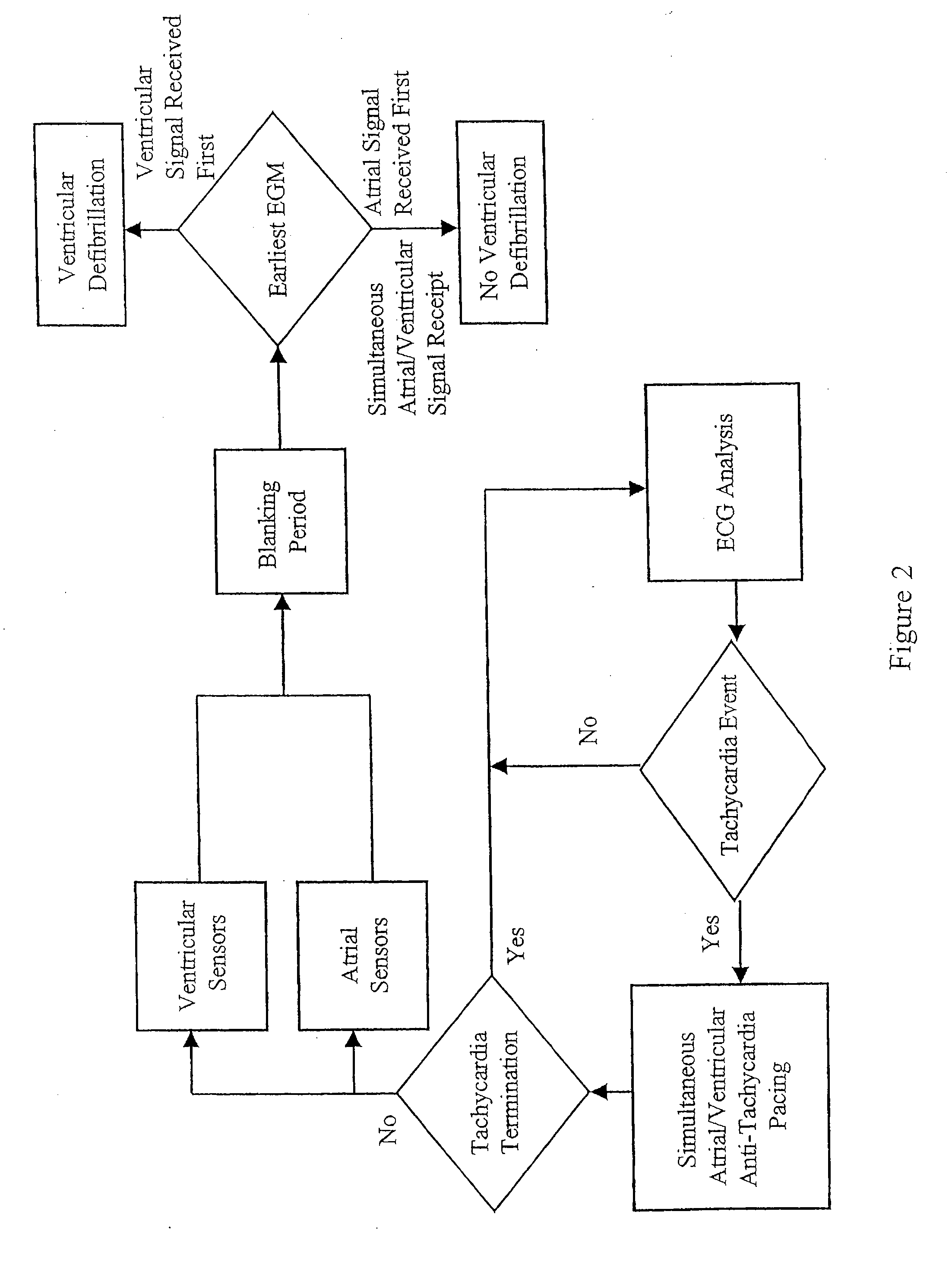
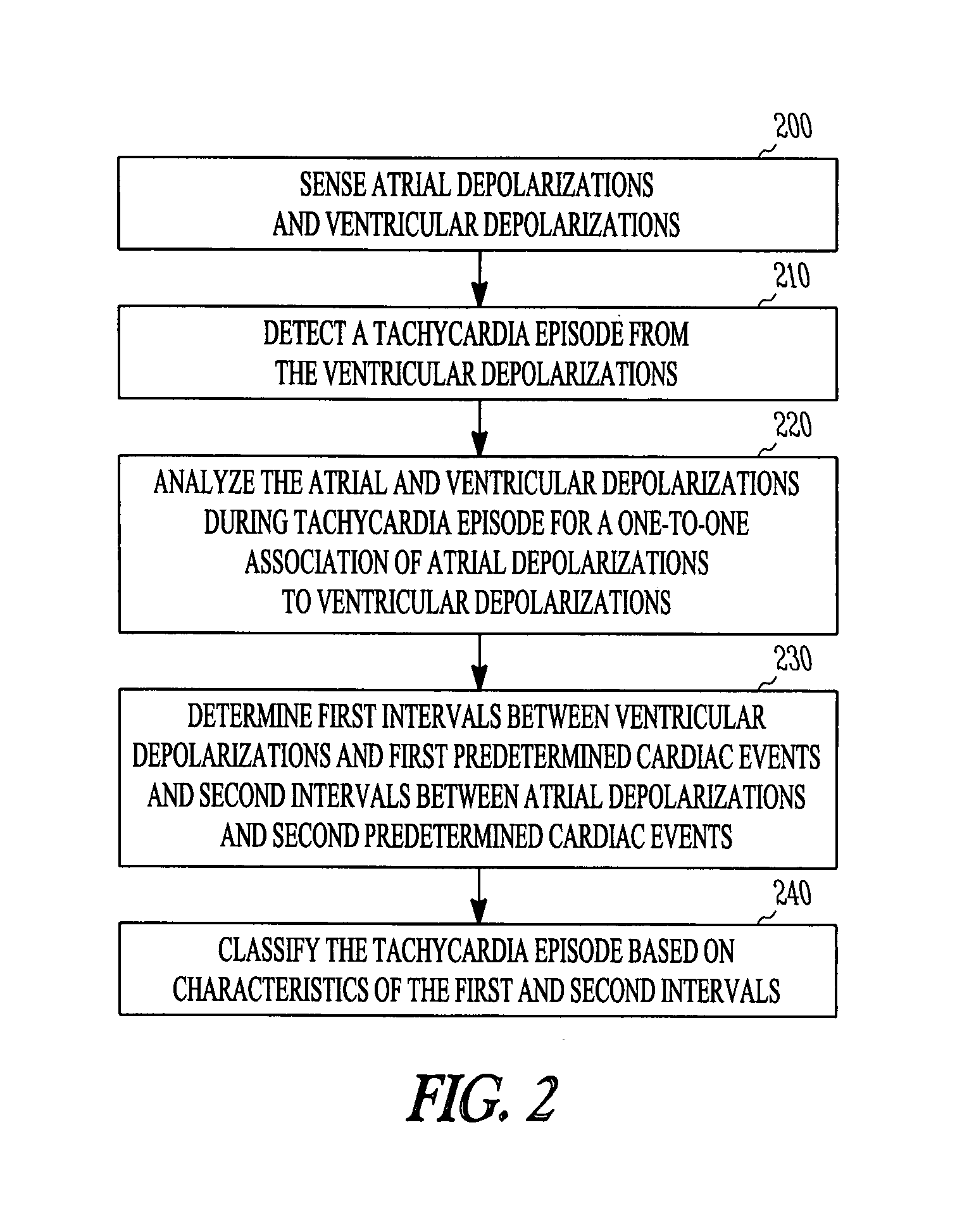
Automated Assessment Of Atrioventricular And Ventriculoatrial Conduction
ActiveUS20090143832A1Restore normal sinus rhythmHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInappropriate shock
A method discriminates between ventricular arrhythmia and supraventricular arrhythmia by determining the direction of an electrical signal conducted through the atrioventricular node. An implantable cardiac defibrillator provides atrioventricular and ventriculoatrial pacing bursts to determine if an arrhythmia with a 1:1 atrial to ventricular relationship is due to ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia. This discrimination capability reduces the incidence of inappropriate shocks from dual-chamber implantable cardiac defibrillators to near zero and provides a method to differentially diagnose supraventricular tachycardia from ventricular tachycardia.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Intraventricular Shunt and Methods of Use Therefor
Methods and apparatus for treating hydrocephalus caused by obstructions in the ventricular system and subarachnoid space of the brain. Embodiments include medical devices and methods for use within the subarachnoid space of the central nervous system to gain access to and treat an obstruction within the ventricles of the brain or a subarachnoid hemorrhage. The obstruction may be aspirated by an aspiration catheter for use in the subarachnoid space. A subarachnoid delivery catheter may then be used to deliver an intraventricular shunt to the opening in the obstruction via the subarachnoid space. A distal end of the delivery catheter is navigated across the obstruction to deploy the intraventricular shunt therein. The intraventricular shunt so positioned reopens the pathway between the ventricles and permits the return of normal cerebrospinal fluid flow there through.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Method and apparatus for treatment of intracranial hemorrhages
An ultrasound catheter with a lumen for fluid delivery and fluid evacuation, and an ultrasound source is used for the treatment of intracerebral or intraventricular hemorrhages. After the catheter is inserted into a blood clot, a lytic drug can be delivered to the blood clot via the lumen while applying ultrasonic energy to the treatment site. As the blood clot is dissolved, the liquefied blood clot can be removed by evacuation through the lumen.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
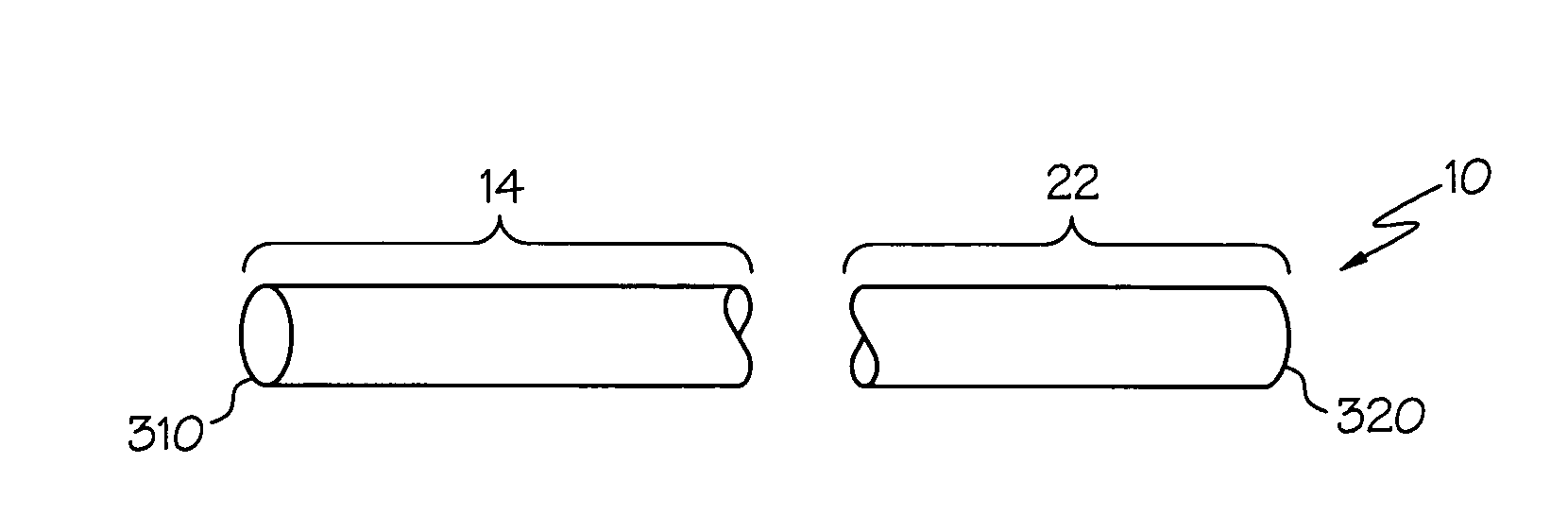
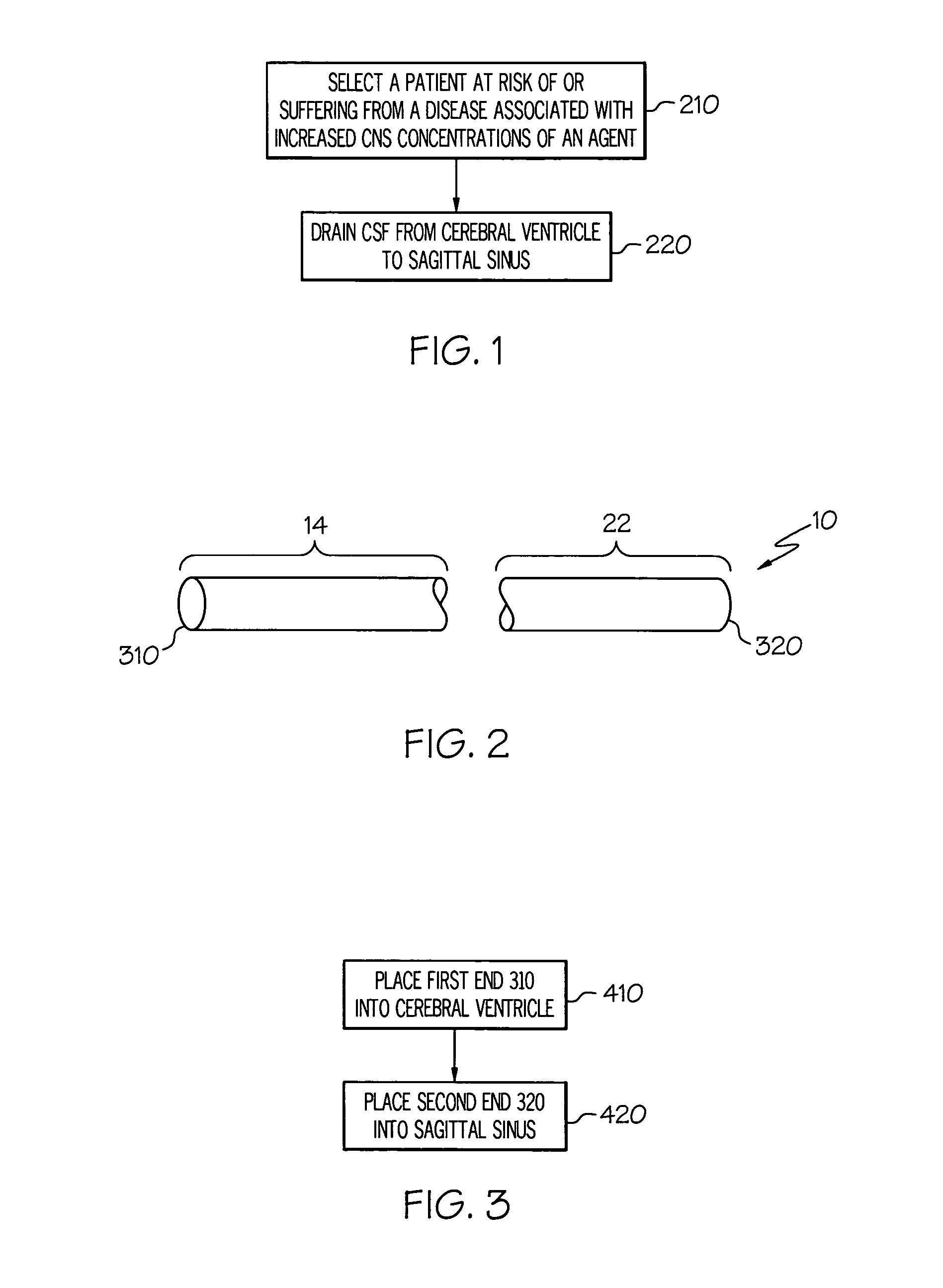
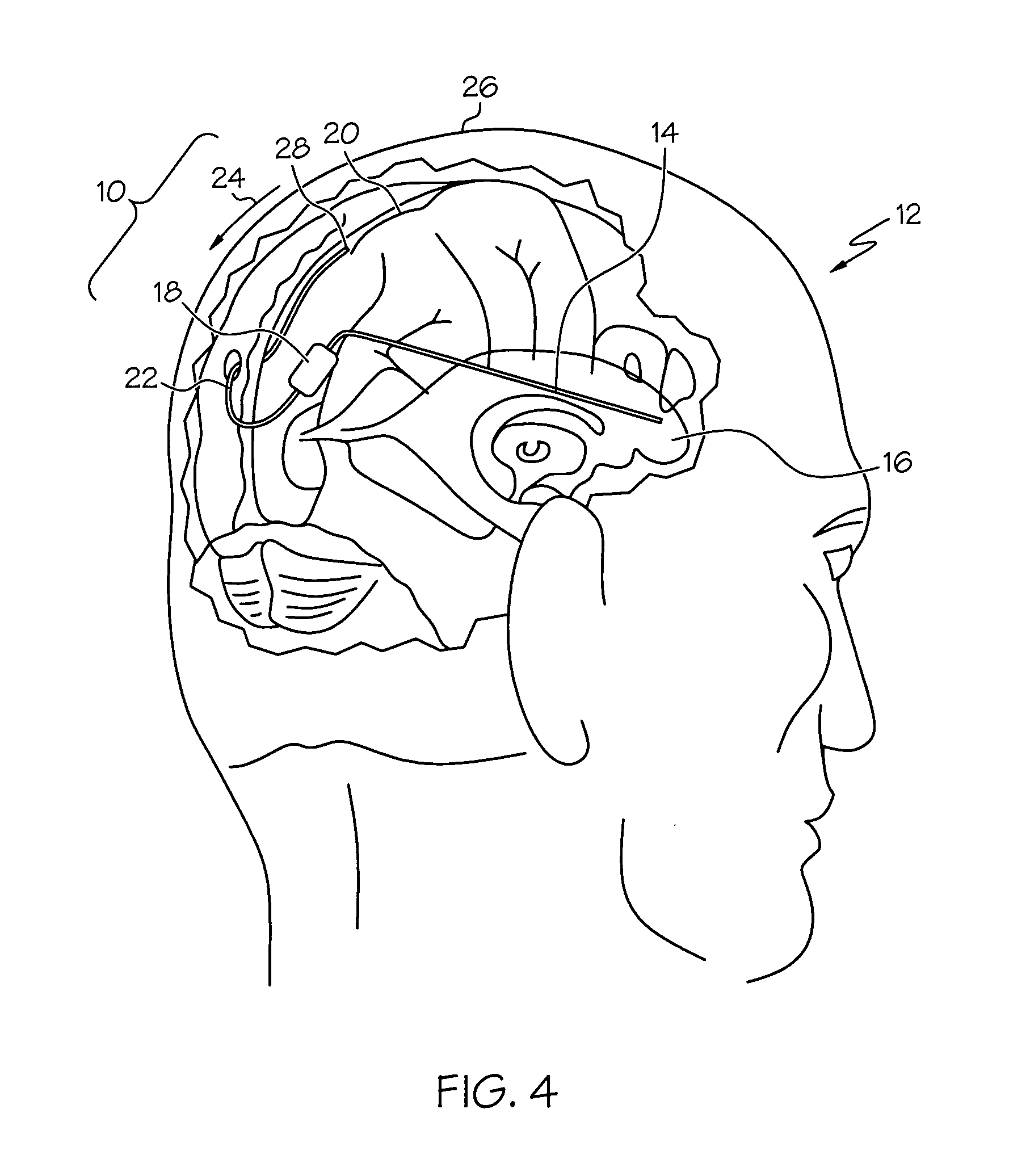
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricular catheter for insertion into the brain ventricle so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle. The system also comprises a sinus sagittalis catheter for insertion into the sinus sagittalis for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into sinus sagittalis. A shunt main body is connected at one end thereof to the brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to the sinus sagittalis catheter. The shunt main body can provide fluidic communication between the brain ventricle catheter and the sinus sagittalis catheter. The system further comprises a tubular flow passage restricting member defined within the shunt main body. The tubular flow passage restricting member defines a resistance to flow of 8-12 mm Hg / ml / min.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
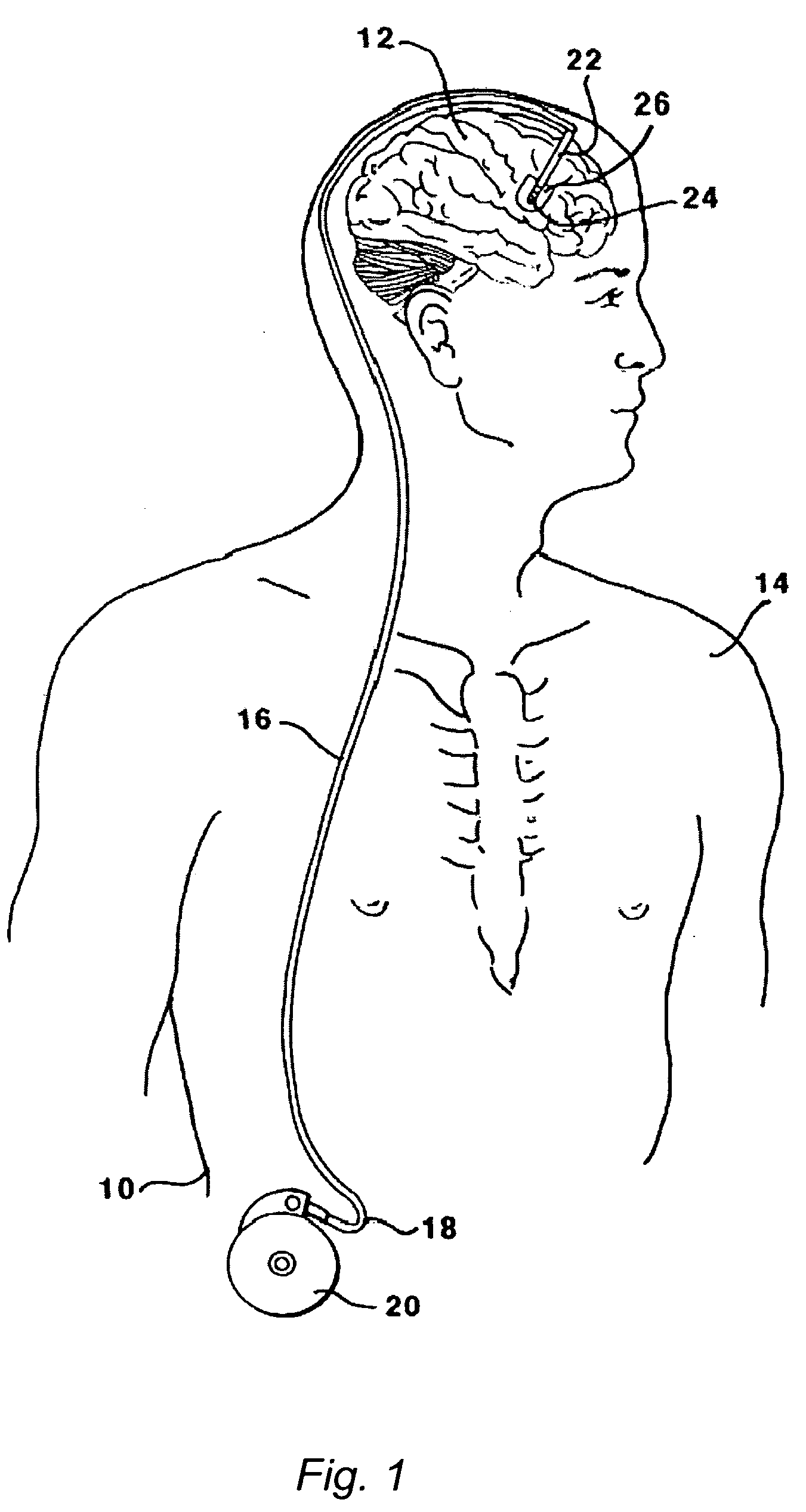
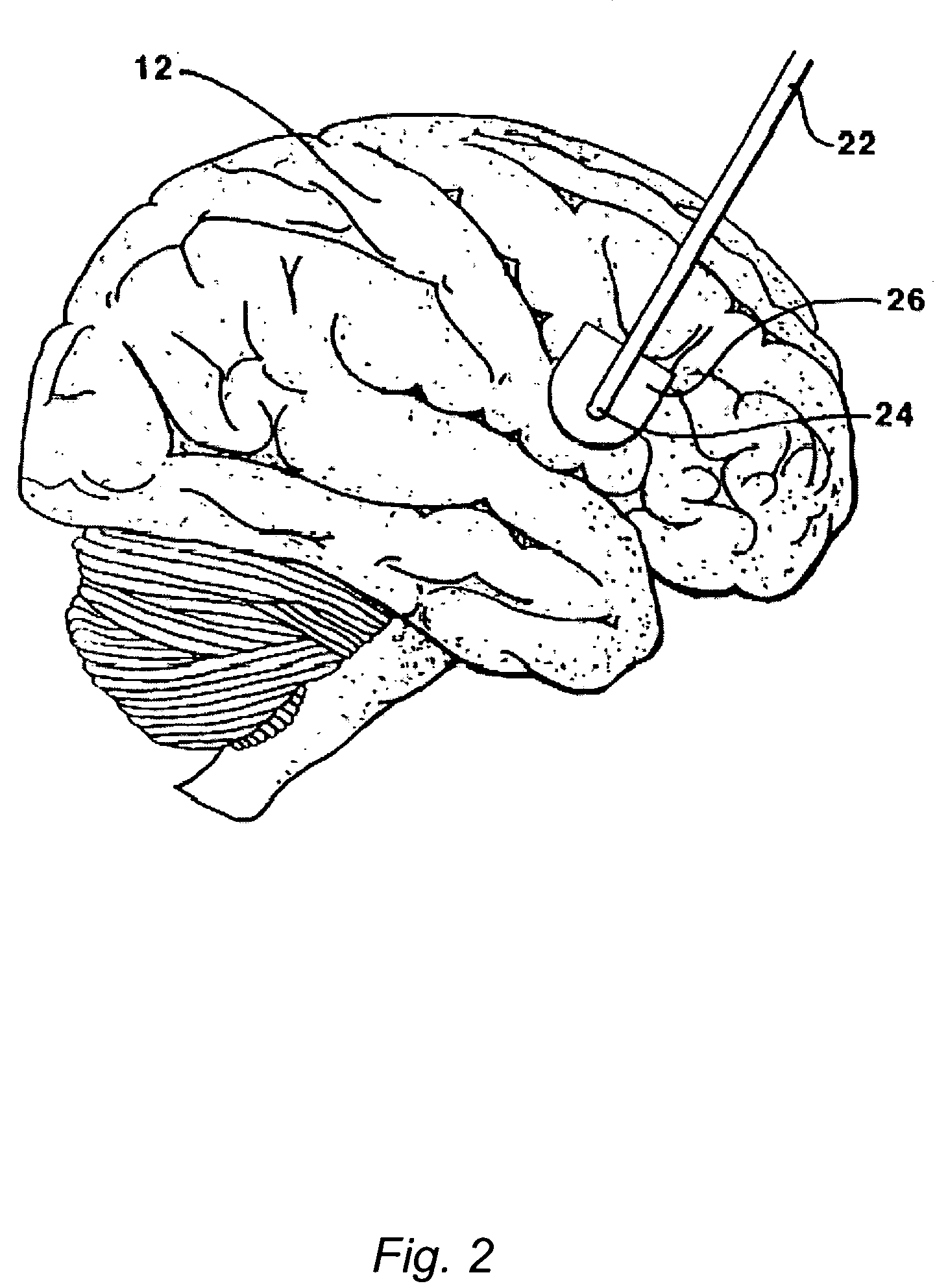
Focal noninvasive stimulation of the sensory cortex of a subject with cerebral palsy
InactiveUS20110270345A1Restore levelRegain healthInternal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsCerebral paralysisNon invasive
Disclosed are methods and related devices for use with subjects with cerebral palsy or periventricular leukomalacia. In preferred embodiments, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is used to identify neural areas and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is used to stimulate neural pathways.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
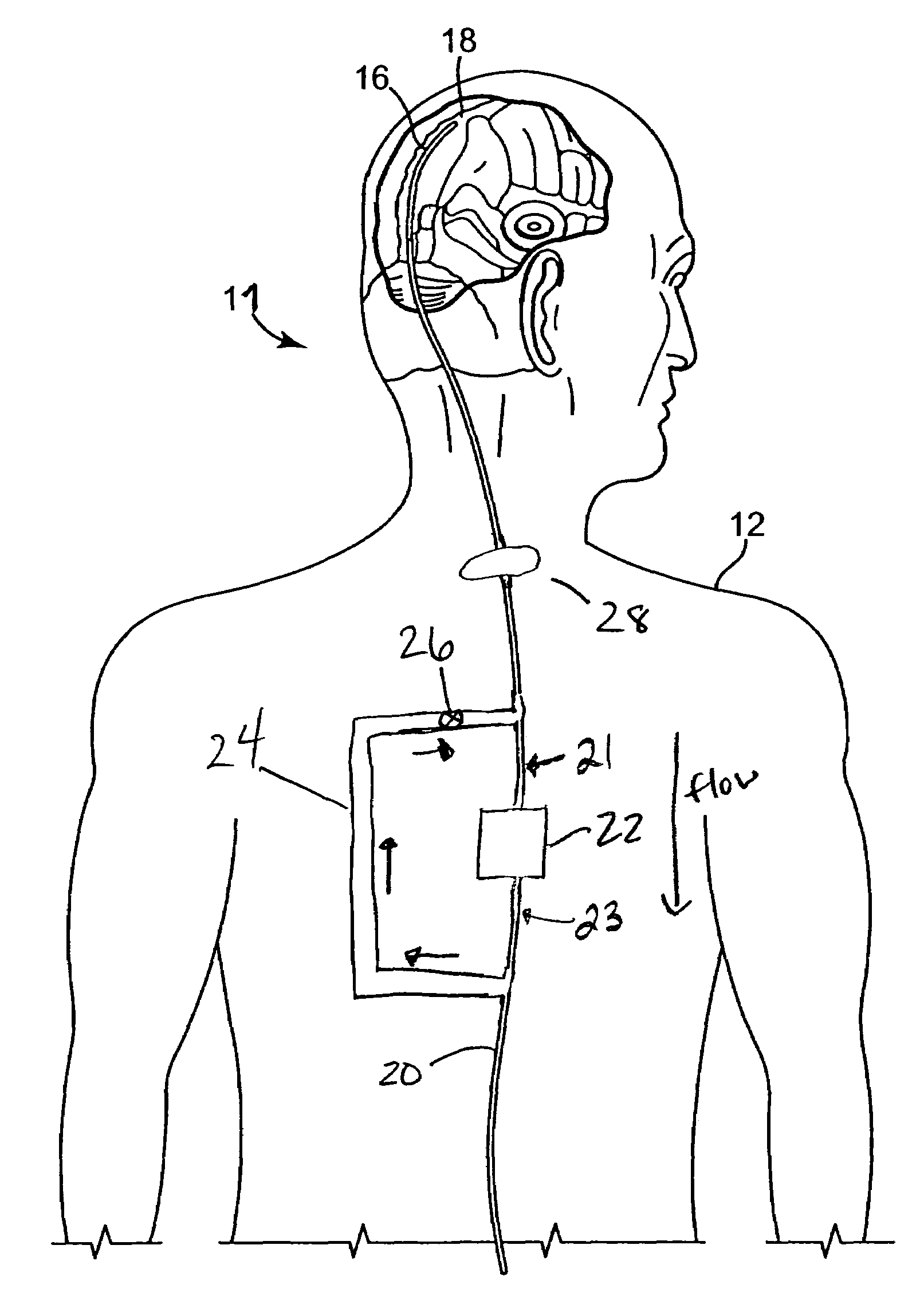
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS20070005121A1Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
Intraventricular enzyme delivery for lysosomal storage diseases
ActiveUS20090130079A1Reduction in substrate accumulated in the brain, lungs, spleen, kidney, and/or liver may be dramaticNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLysosomal enzyme defectVisceral organ
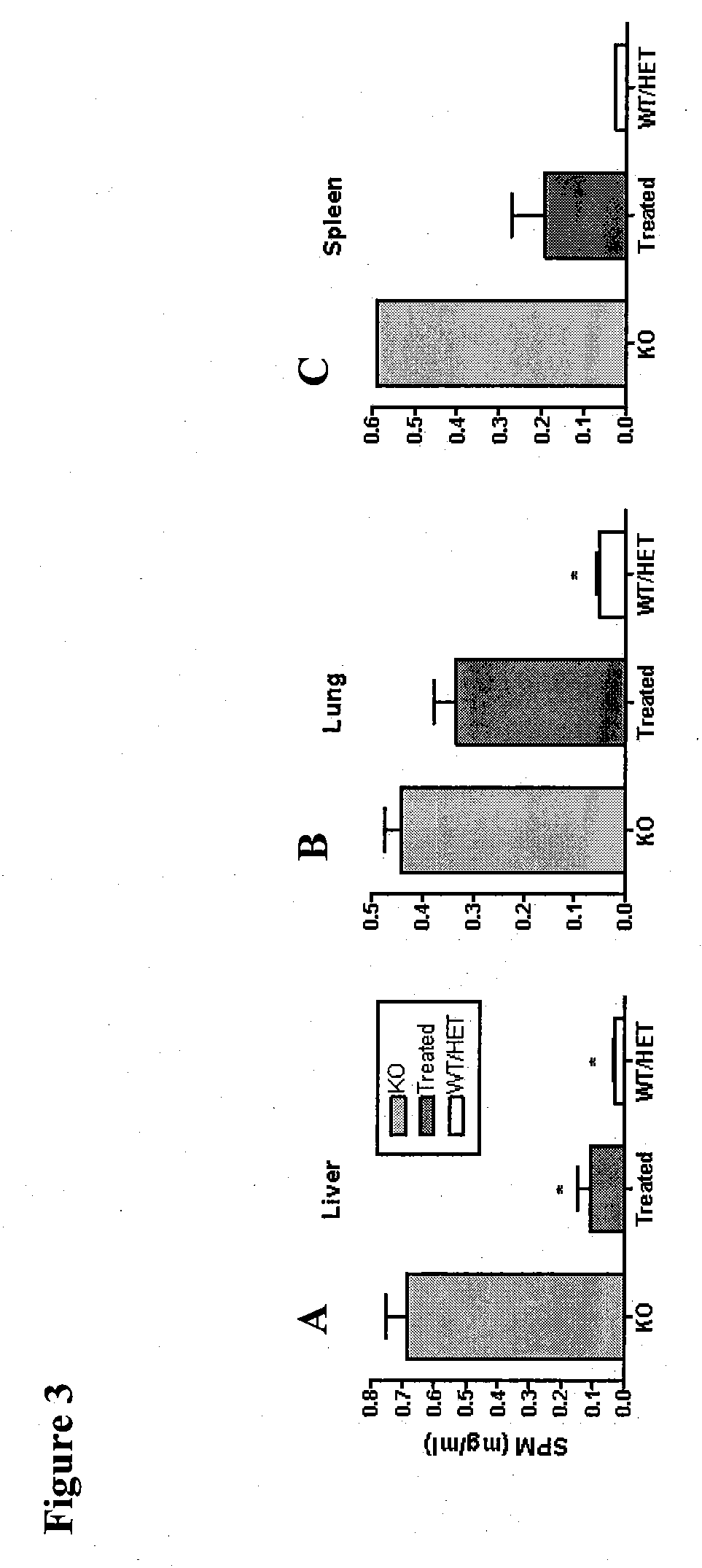
Lysosomal storage diseases can be successfully treated using intraventricular delivery of the enzyme which is etiologically deficient in the disease. The administration can be performed slowly to achieve maximum effect. Surprisingly, effects are seen on both sides of the blood-brain barrier, making this an ideal delivery means for lysosomal storage diseases which affect both brain and visceral organs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS8123789B2Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
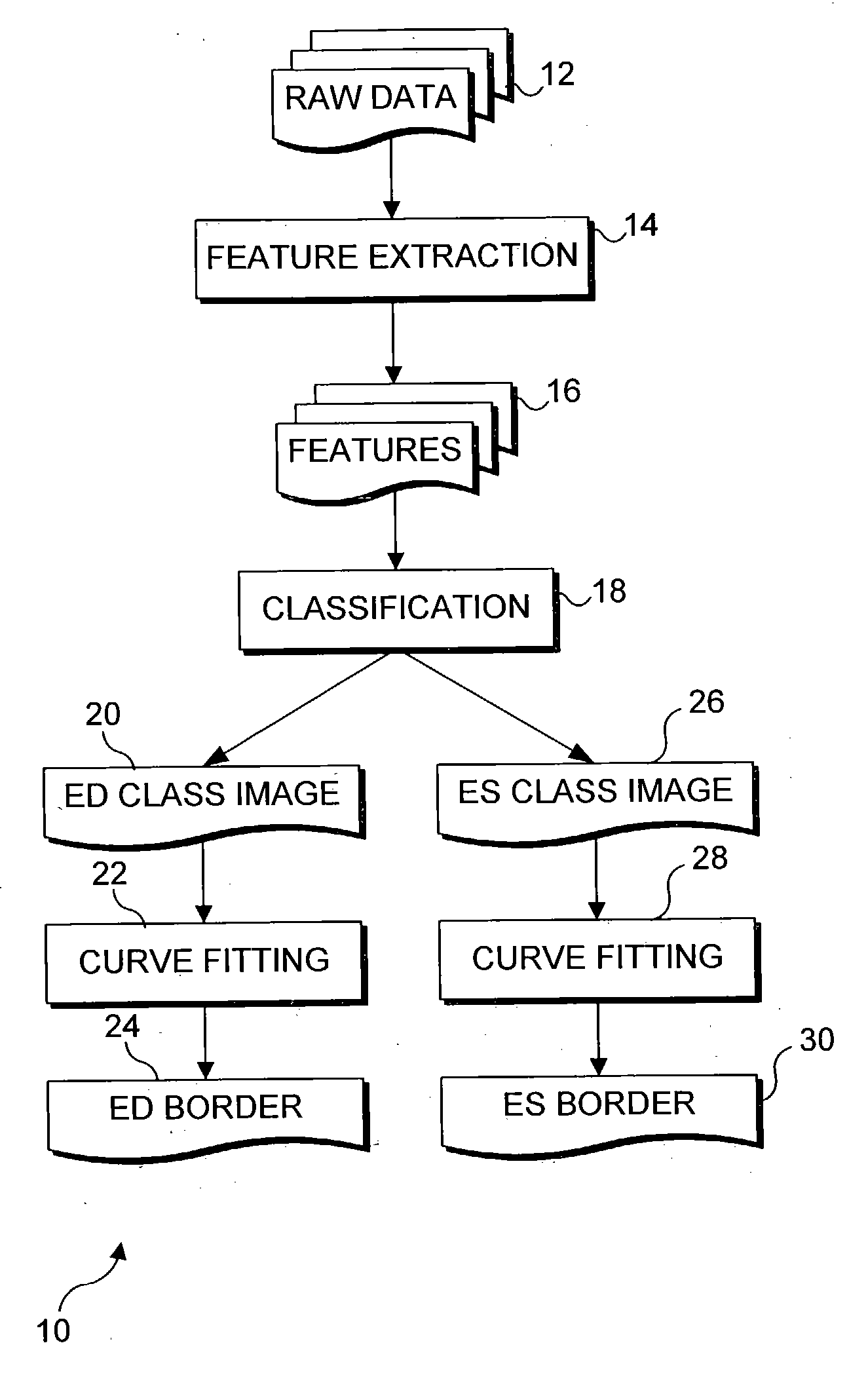
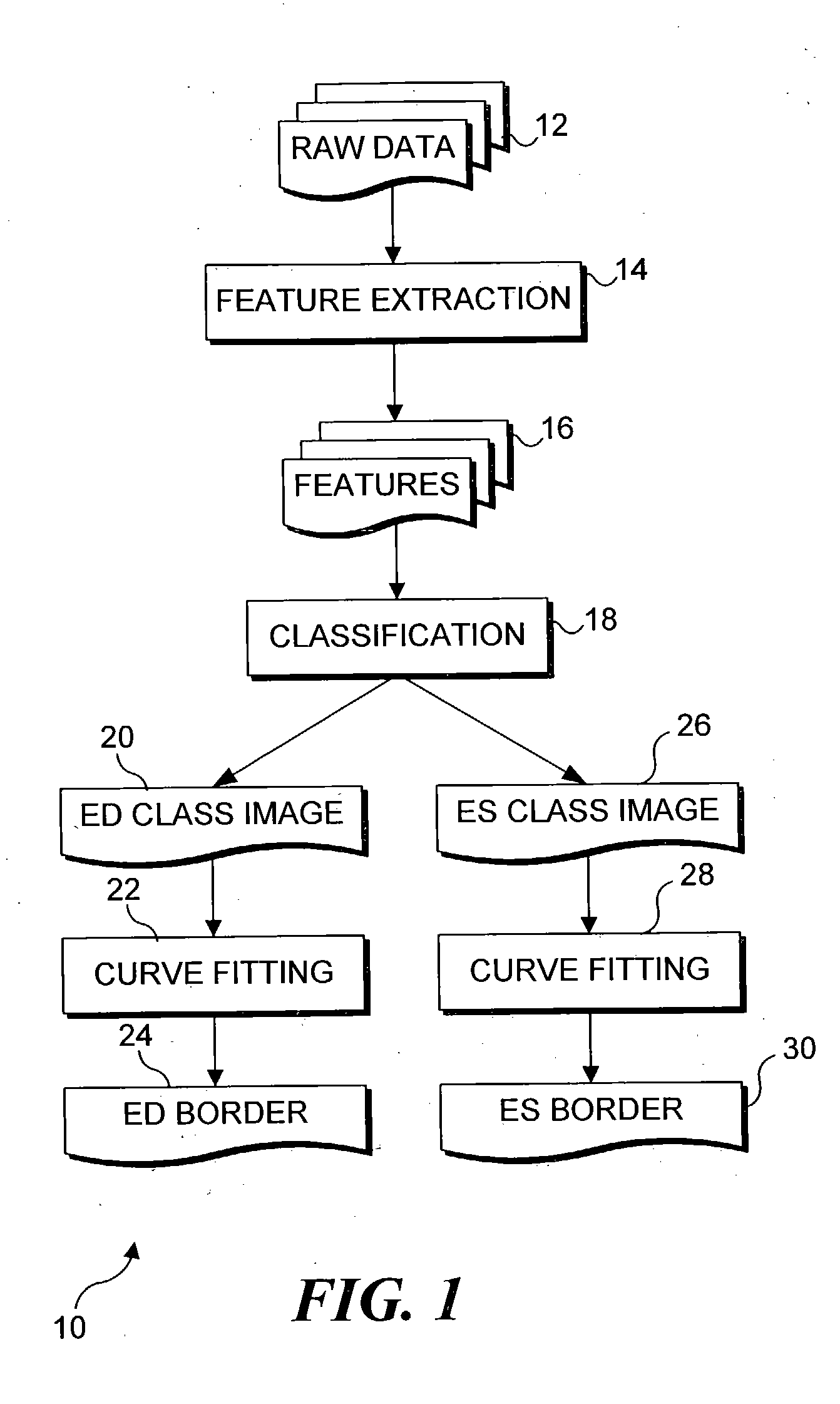
Segmentation of left ventriculograms using boosted decision trees
An automated method for determining the location of the left ventricle at user-selected end diastole (ED) and end systole (ES) frames in a contrast-enhanced left ventriculogram. Locations of a small number of anatomic landmarks are specified in the ED and ES frames. A set of feature images is computed from the raw ventriculogram gray-level images and the anatomic landmarks. Variations in image intensity caused by the imaging device used to produce the images are eliminated by de-flickering the image frames of interest. Boosted decision-tree classifiers, trained on manually segmented ventriculograms, are used to determine the pixels that are inside the ventricle in the ED and ES frames. Border pixels are then determined by applying dilation and erosion to the classifier output. Smooth curves are fit to the border pixels. Display of the resulting contours of each image frame enables a physician to more readily diagnose physiological defects of the heart.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
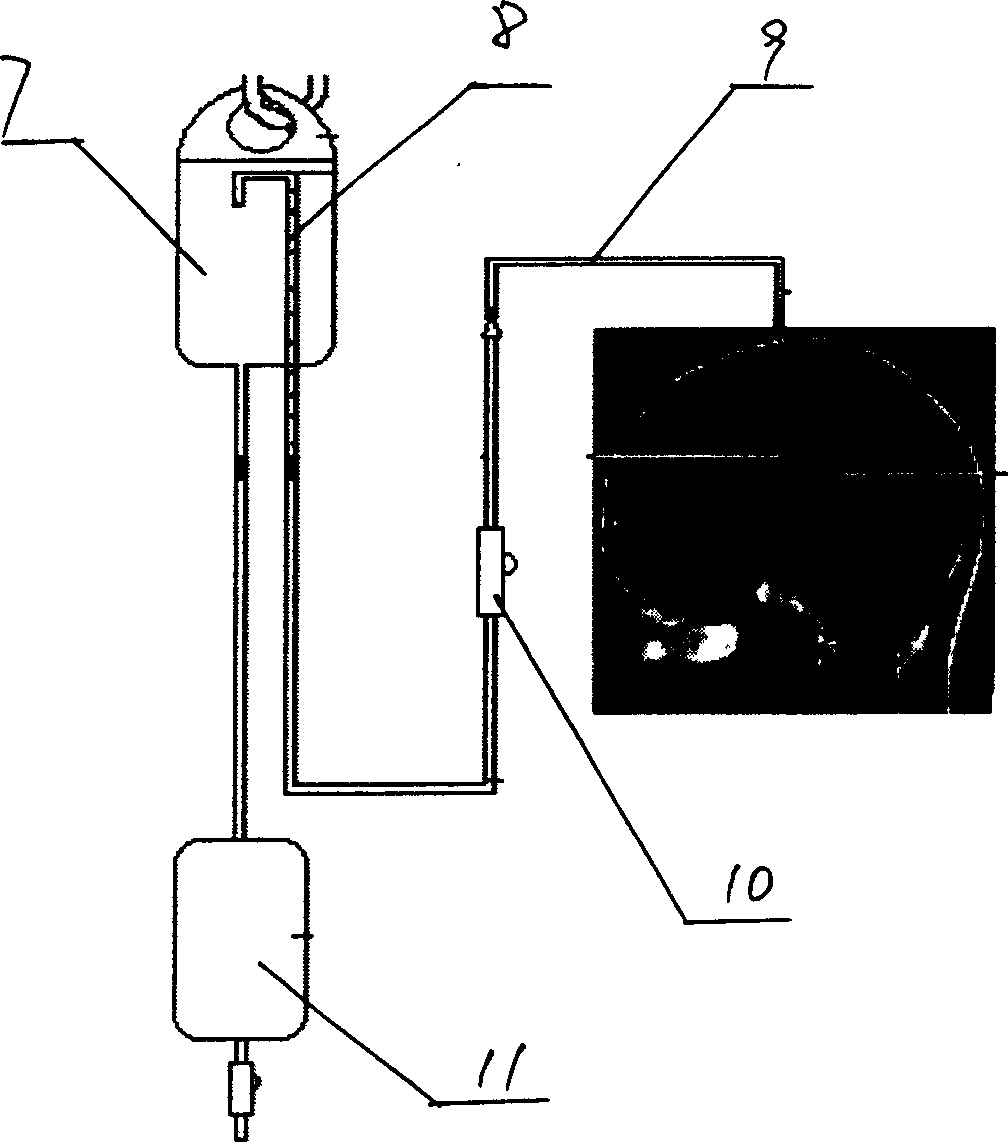
Implantable cerebral spinal fluid drainage device and method of draining cerebral spinal fluid
The invention provides a drainage system that includes a ventricular catheter, a drainage catheter, and a positive displacement pump that can function to actively drain CSF from the ventricles of the brain of a patient. Methods of using a drainage system in accordance with the invention are also provided, as well as kits.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical device and method for temperature control and treatment of the brain and spinal cord
ActiveUS7004961B2Rapid and accurate insertionFast transferUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSubarachnoid space
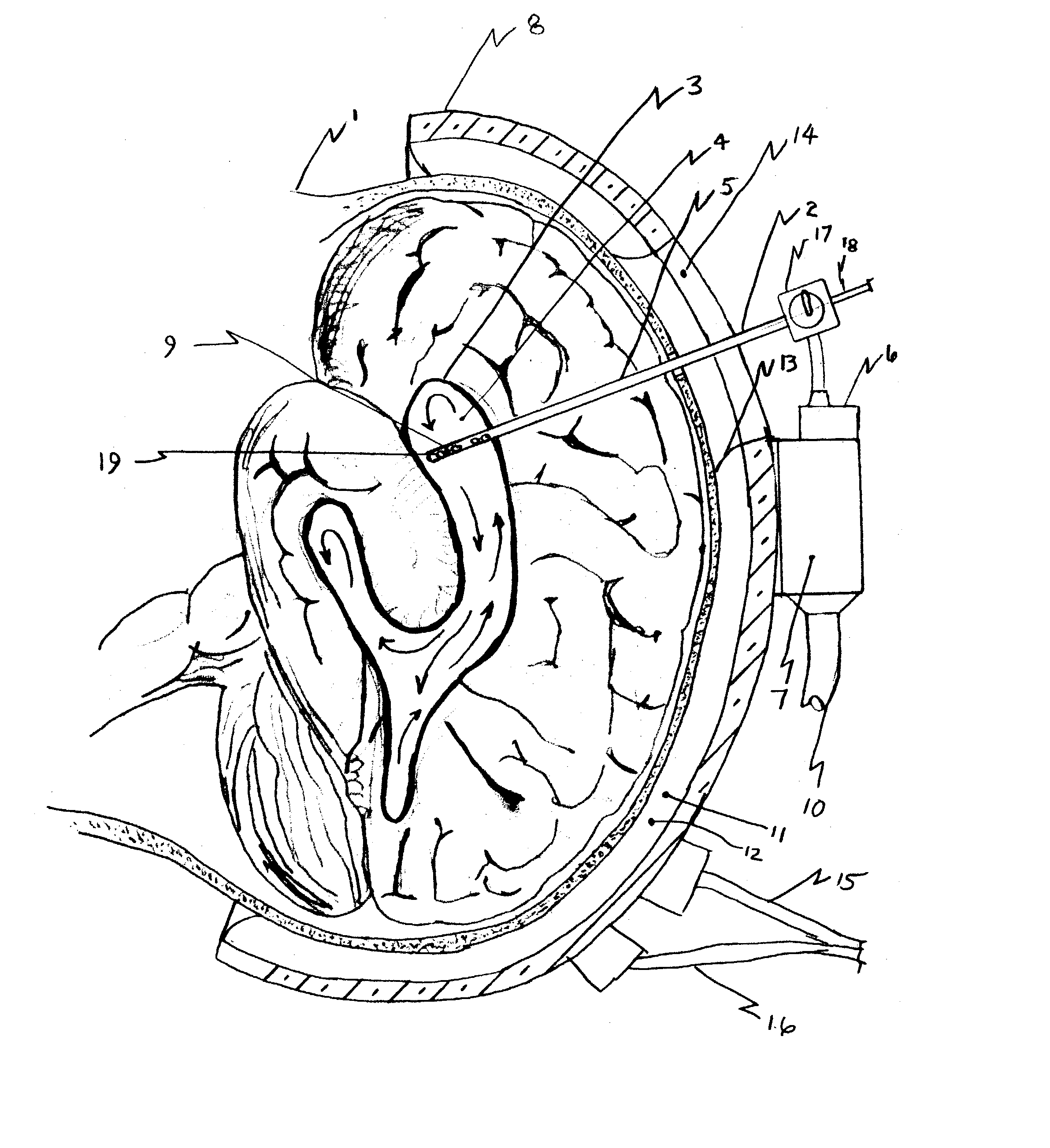
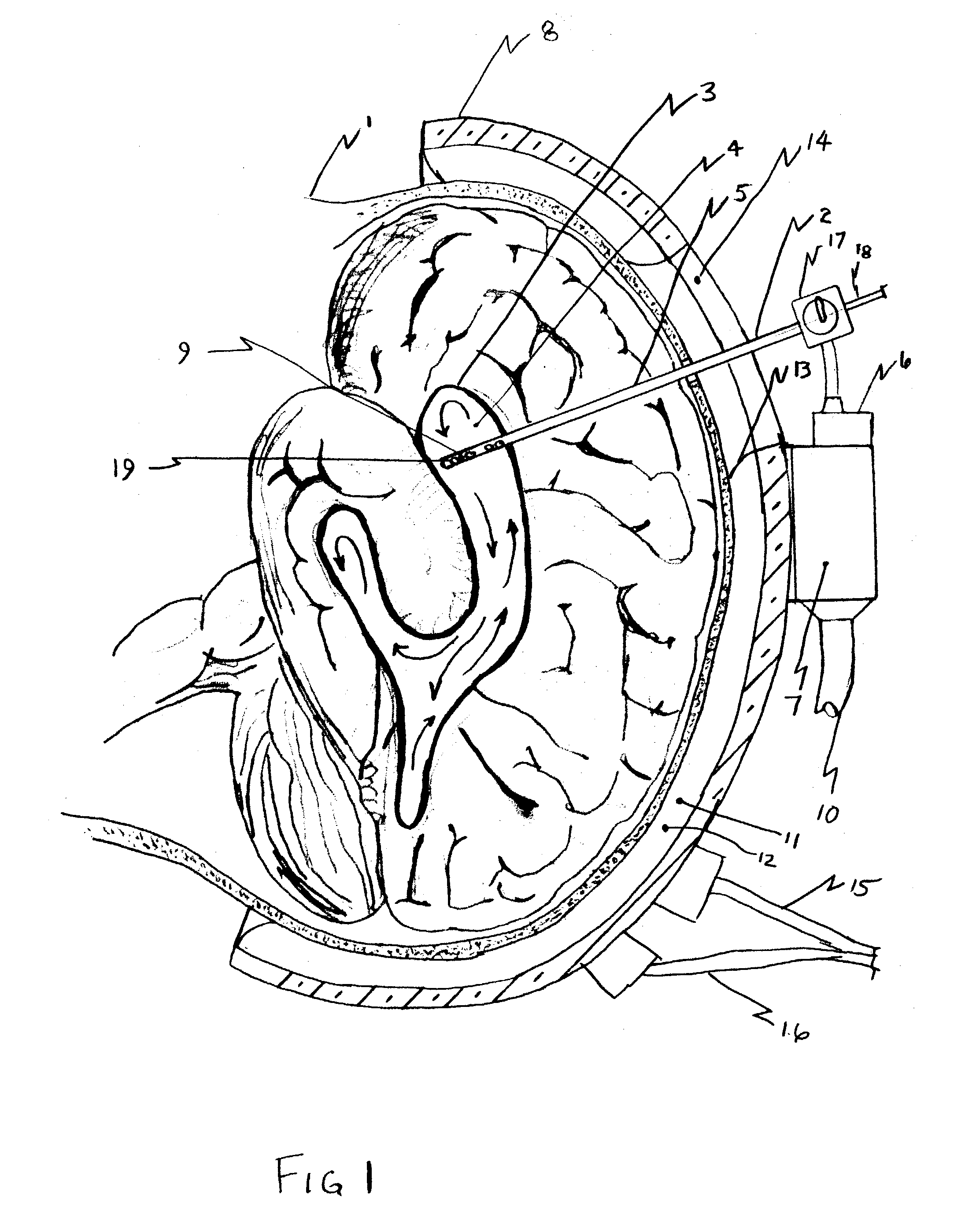
The invention provides a medical device having a thermister for temperature measurement, irrigation / aspiration ports for fluid exchange and application of therapeutic modalities, a pressure manometer for pressure measurement, and an external system for control of temperature, pressure, and flow rate. When applied to the central nervous system (CNS), this device can be used in hypothermia or hyperthermia applications, the exchange of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), the application of treatment modalities, and the insertion of a ventriculostomy or ventriculostomy-like unit. When applied to spinal cord applications, this device can provide temperature control and a method for application of treatment modalities by using a venting device placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord, a device with similar instrumentation to measure temperature and pressure. A device for ultrasound localization of the CNS device is described. A device for a fiber optic endoscope for visualization and localization is also described. Method of using the devices in treating patients suffering from cardiac arrest, circulatory arrest, exsanguination, head or neck trauma, strokes, tumors and other intracranial diseases are disclosed. In the case of hypothermia treatment of the brain, rapid cooling using principles of convection and conduction will be applied to the lateral ventricle and subarachnoid and / or subdural space simultaneously where the neurons are located in close proximity.
Owner:WONG EDWARD +2
System and method for classifying tachycardia arrhythmias having 1:1 atrial-to-ventricular rhythms
An implantable cardioverter / defibrillator includes a tachycardia detection system that detects one-to-one (1:1) tachycardia, which is a tachycardia with a one-to-one relationship between atrial and ventricular contractions. When the 1:1 tachycardia is detected, the system discriminates ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) based on analysis of a cardiac time interval. Examples of the cardiac time interval include an atrioventricular interval (AVI) and a ventriculoatrial interval (VAI). A template time interval is created during a known normal sinus rhythm. The system measures a tachycardia time interval after detecting the 1:1 tachycardia, and indicates a VT detection if the tachycardia time interval differs from the template time interval by at least a predetermined percentage of the template time interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Processing method of CT cerebral hemorrhage image
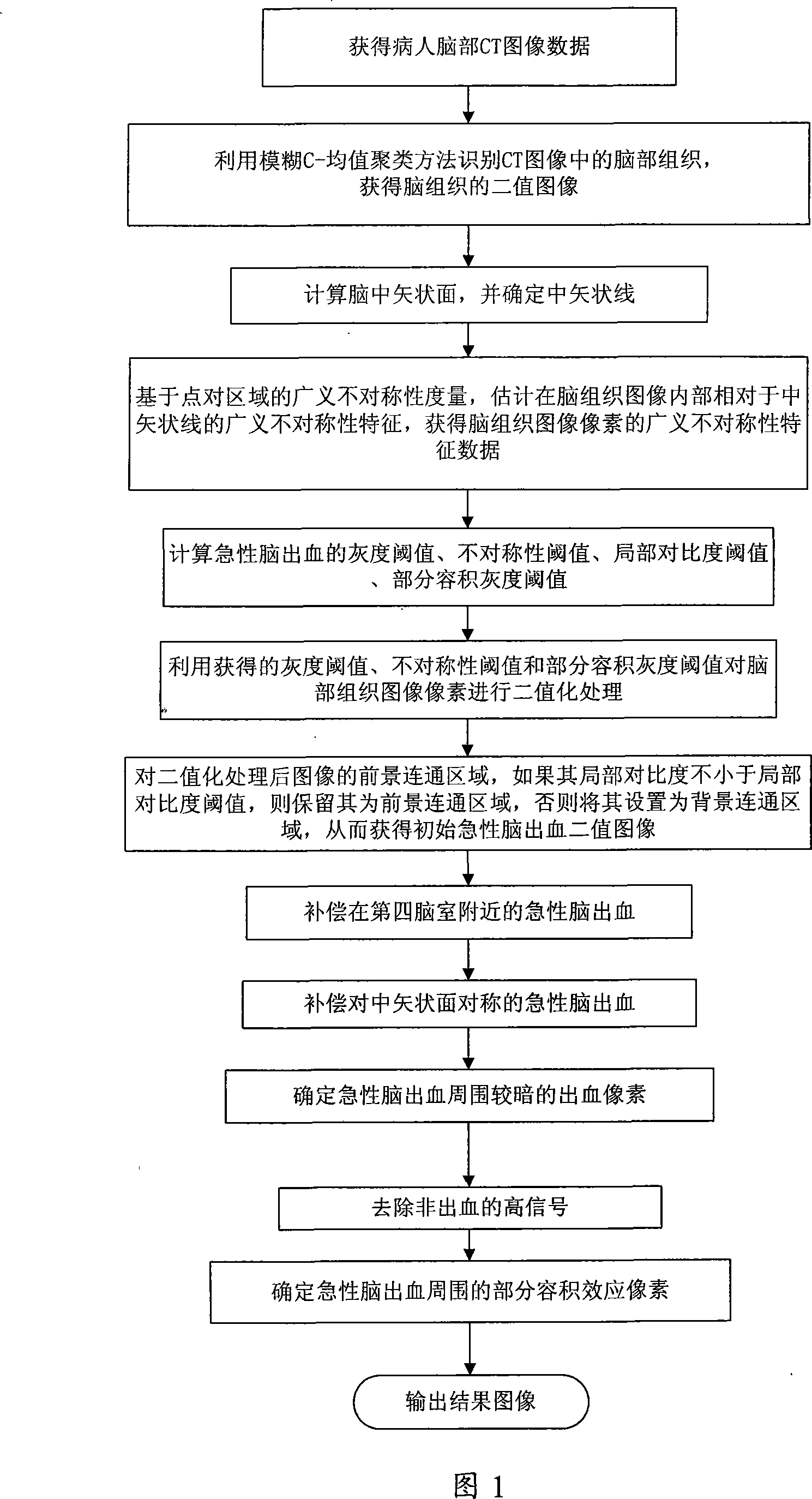
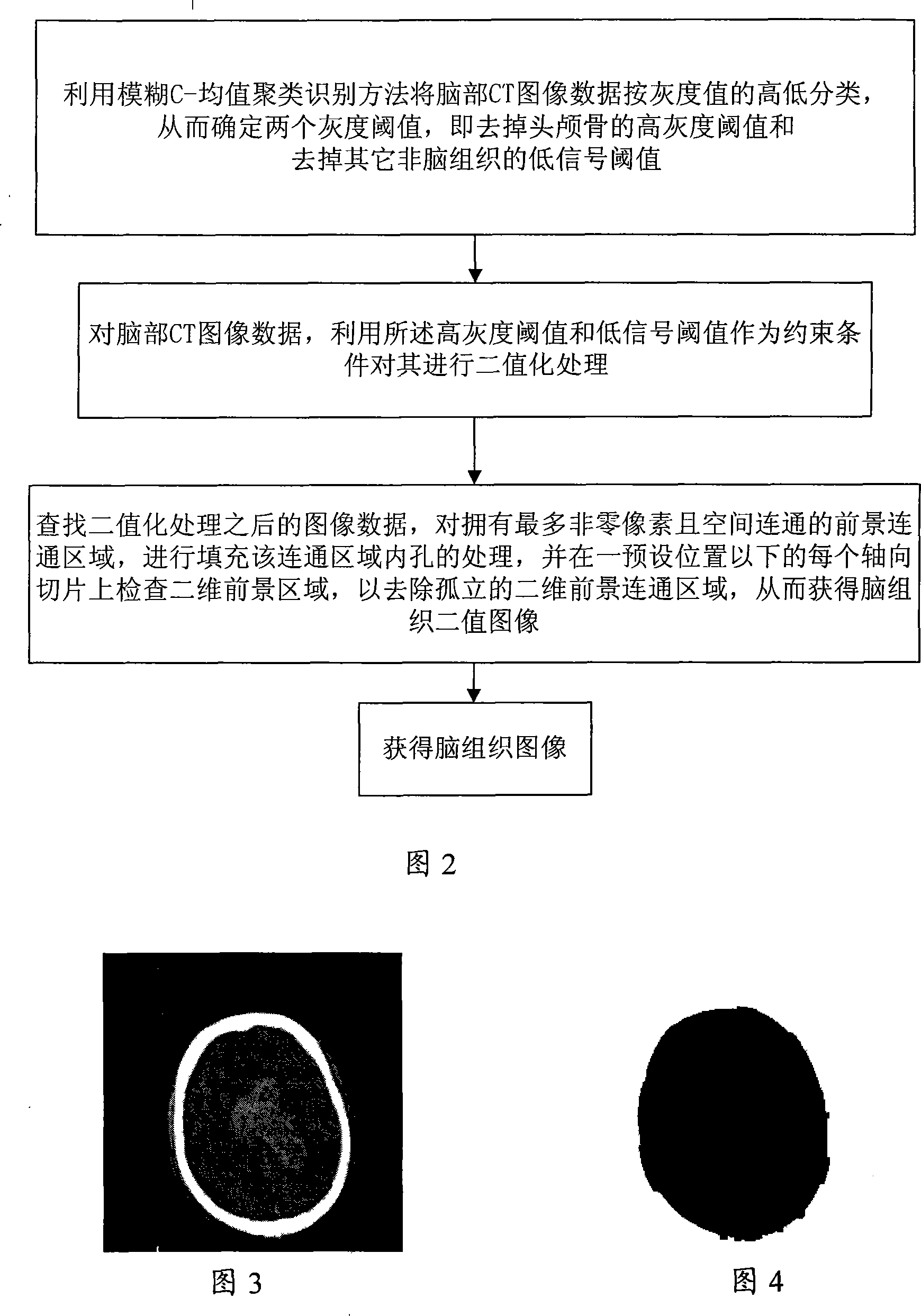
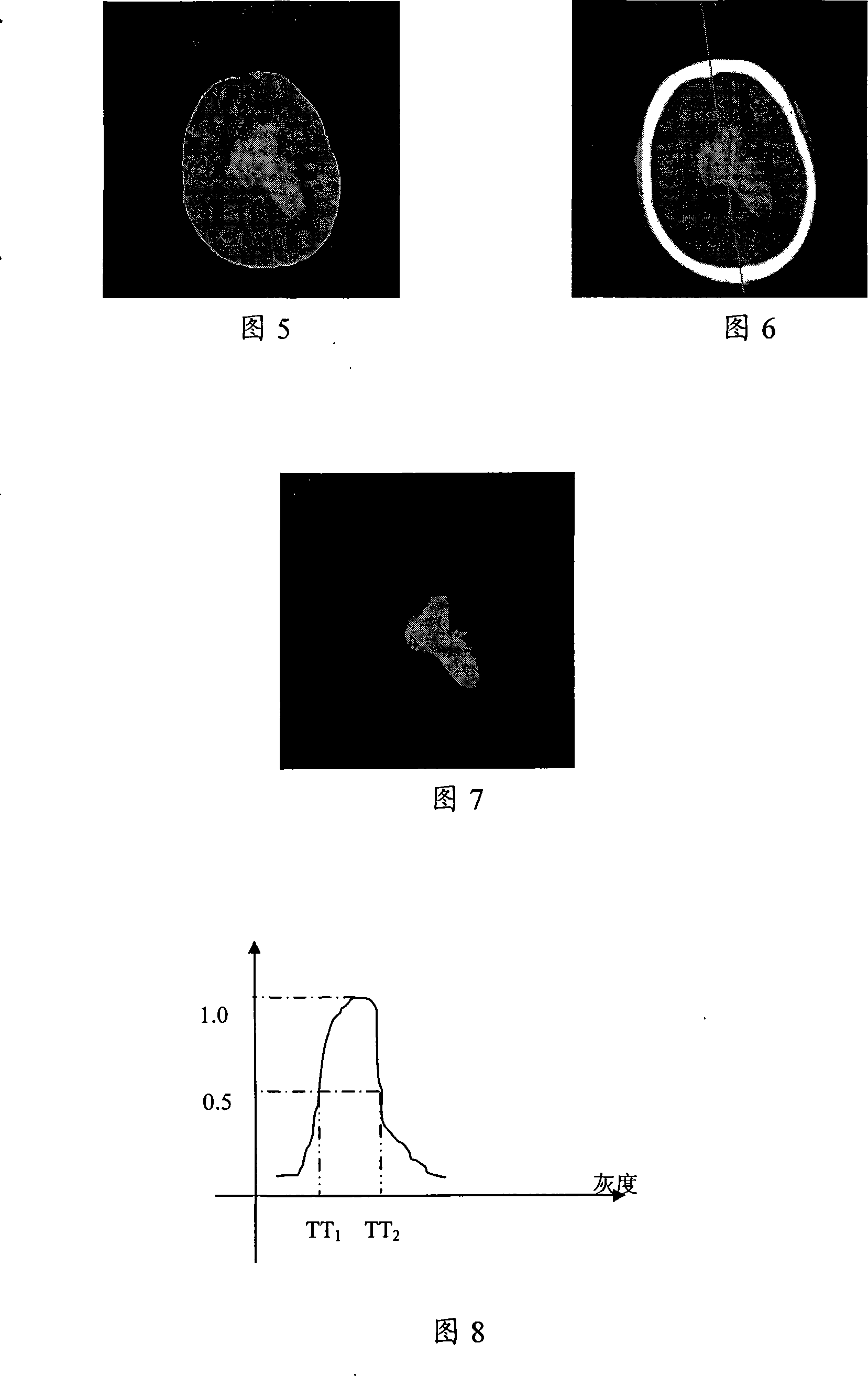
InactiveCN101238987AAccurate processingImprove local contrastImage analysisComputerised tomographsSagittal planeFourth ventricle
The invention discloses a treating method of CT cerebral hemorrhage image, comprising: automatically selecting gray level image, binary image of brain tissue or binary image of head of raw data based on nonsingular number and winkling the brain median sagittal plane based on singular number; robustly depicting the asymmetry of instant cerebral hemorrhage to the median sagittal plane based on general asymmetry of dotted pairs area; adaptively figuring out gray threshold of instant cerebral hemorrhage, threshold of general asymmetry, local contrast threshold and partial bulk effect threshold; determining threshold of instant cerebral hemorrhage near the fourth ventricle by searching the axial slice below the pertrous bone; obtaining instant cerebral hemorrhage symmetrical to the median sagittal plane from the obtained unsymmetric hemorrhage; determining darker instant cerebral hemorrhage from determined lighter (higher gray scale) instant cerebral hemorrhage; removing high signal of not instant cerebral hemorrhage; determining instant cerebral hemorrhage pixel due to partial bulk effect, therefore the final instant cerebral hemorrhage image is obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
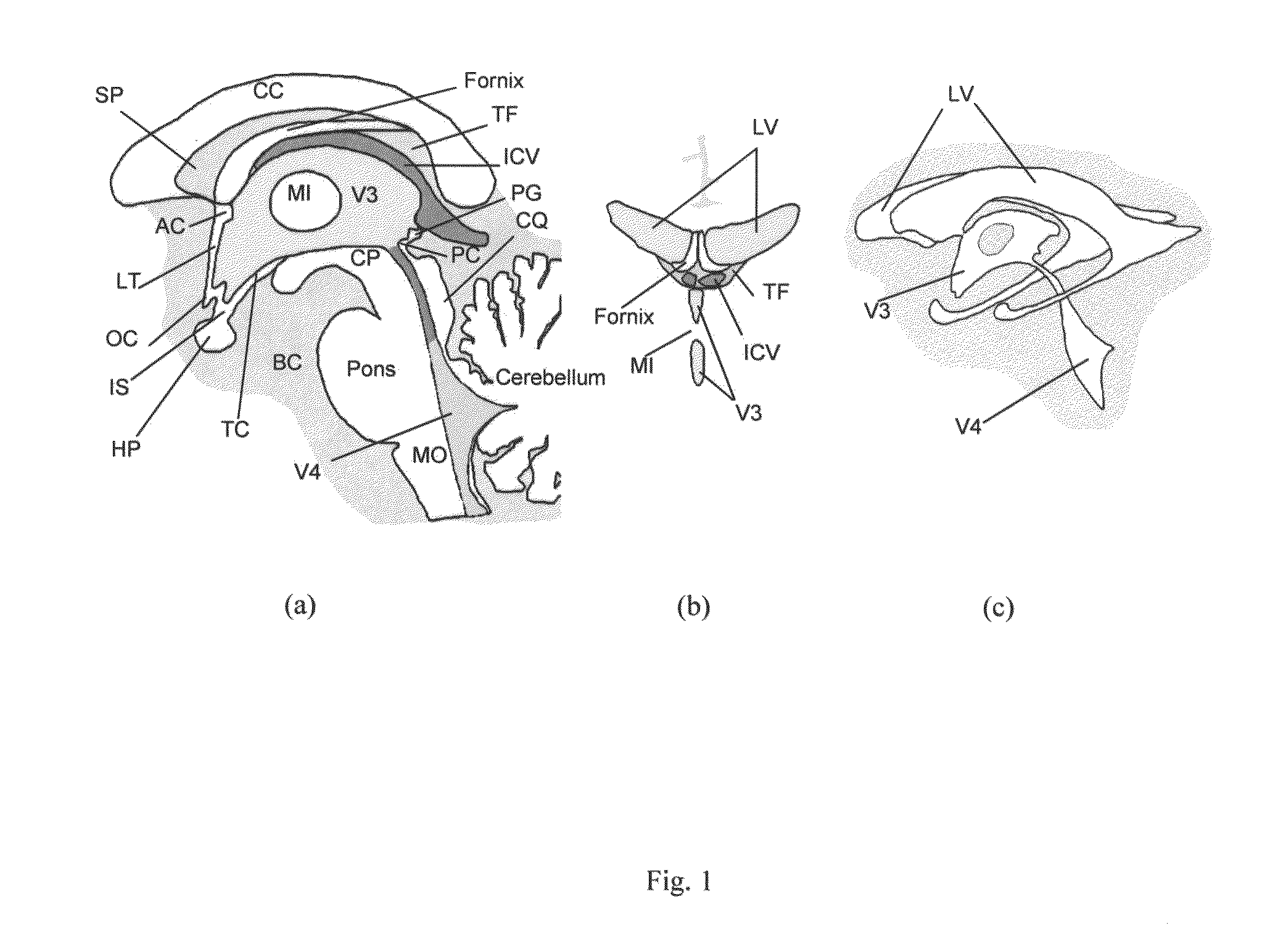
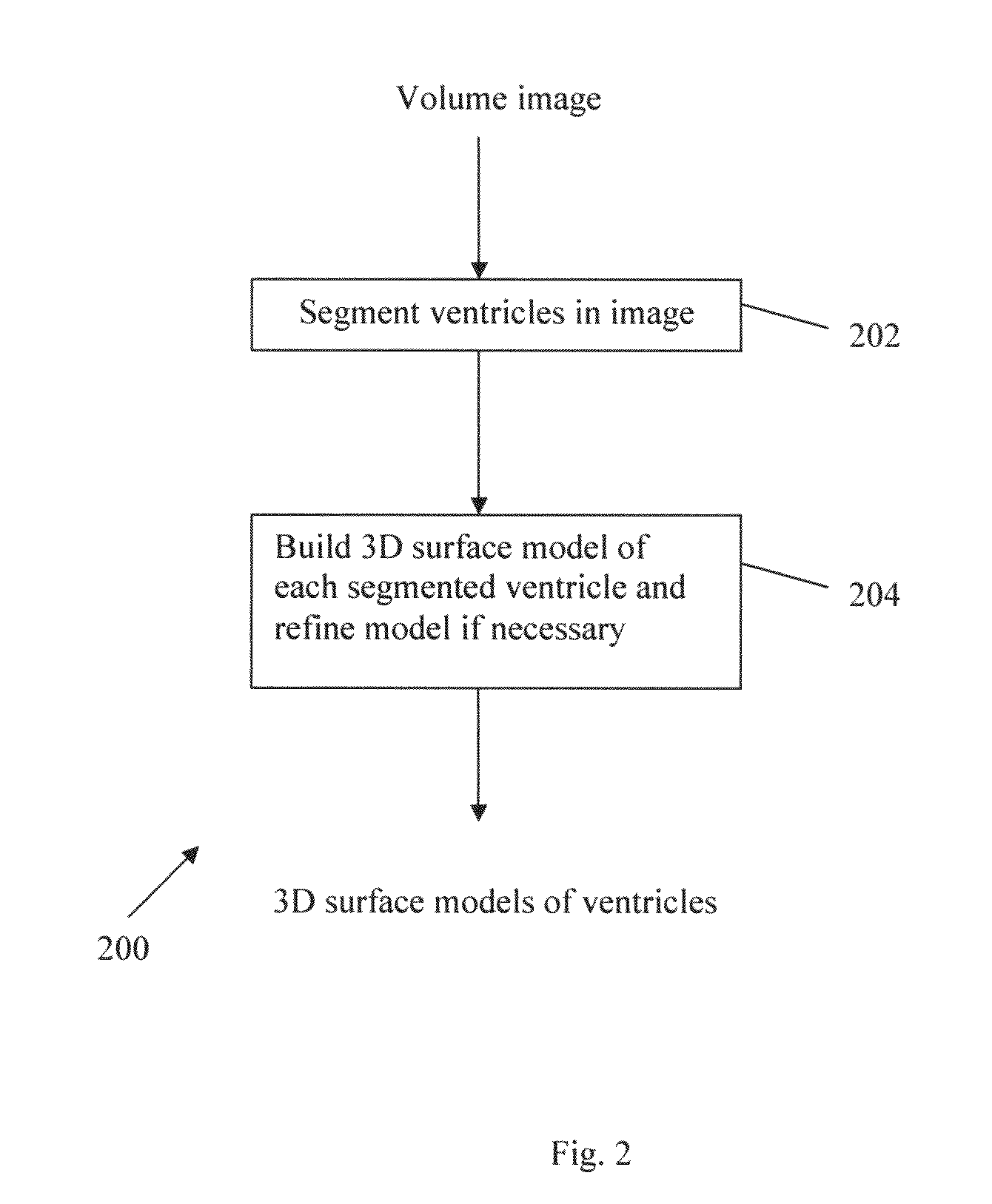
Method and system for anatomy structure segmentation and modeling in an image
A method is proposed for segmenting one or more ventricles in a three-dimensional brain scan image (e.g. MR or CT). The image is registered against a brain model, which ventricle models of each of the one or more ventricles. Respective regions of interest are defined based on the ventricle models. Object regions are first obtained by applying region growing procedure in the regions of interest, and then trimmed based on anatomical knowledge. A 3D surface model of one or more objects is constructed within a 3D space from the segmented structure. A 3D surface is edited and refined by a user selecting amendment points in the 3D space which are indicative of missing detail features. A region of the 3D surface near the selected points is then warped towards the amendment points smoothly, and the modified patch is combined with the rest of the 3D surface yields the accurate anatomy structure model.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
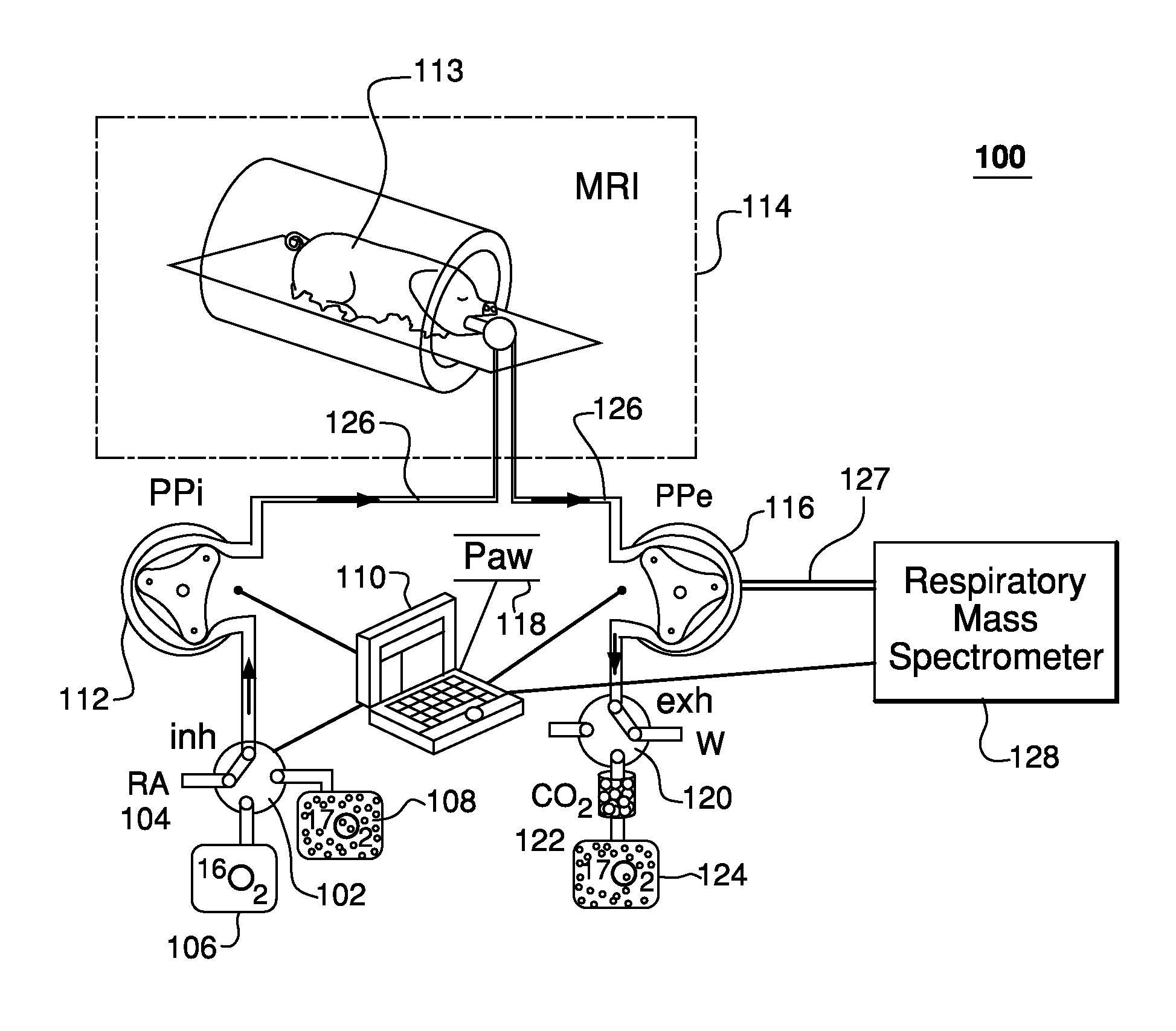
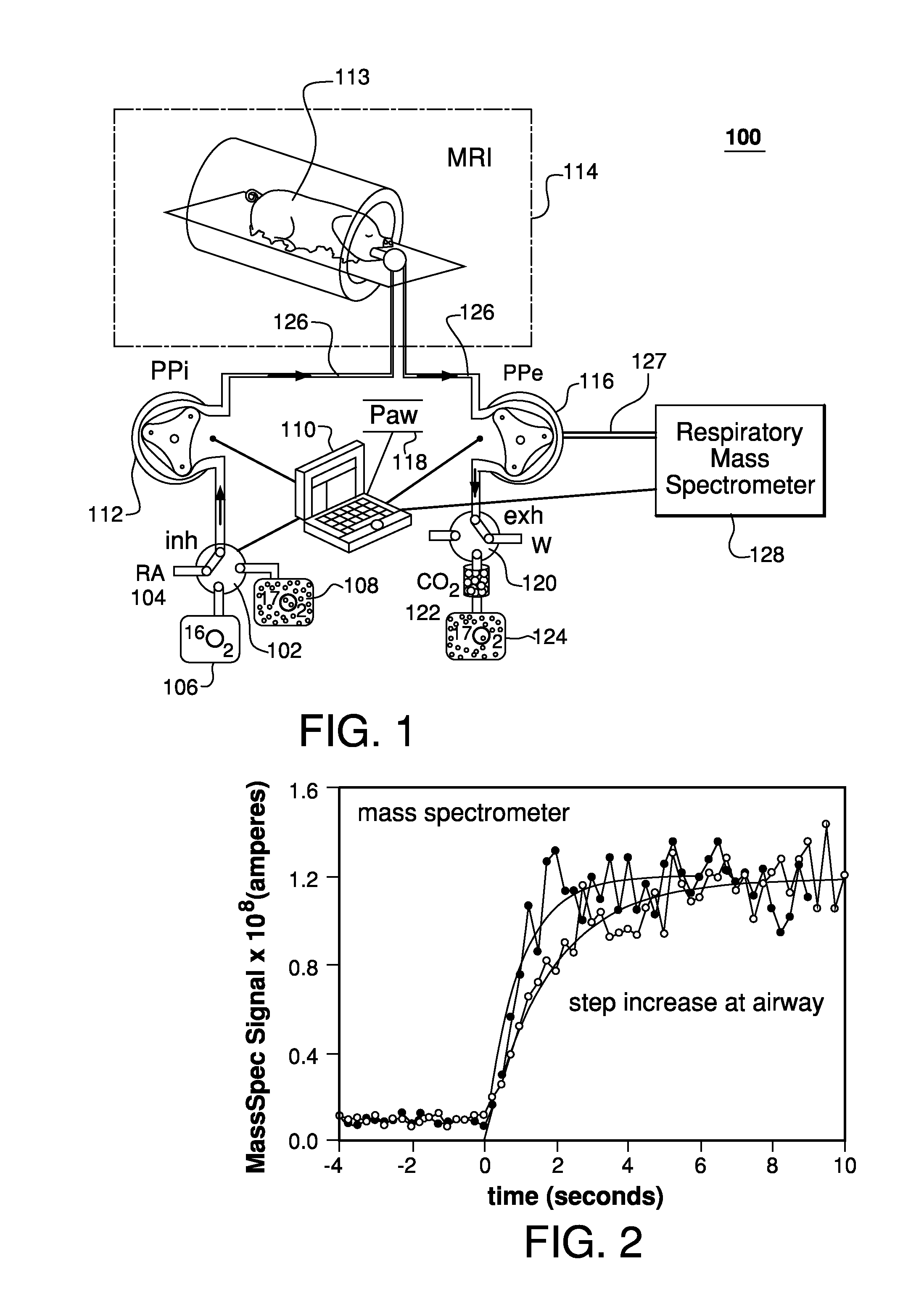
Method and apparatus for providing pulses inhalation of 17o2 for magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral metabolism
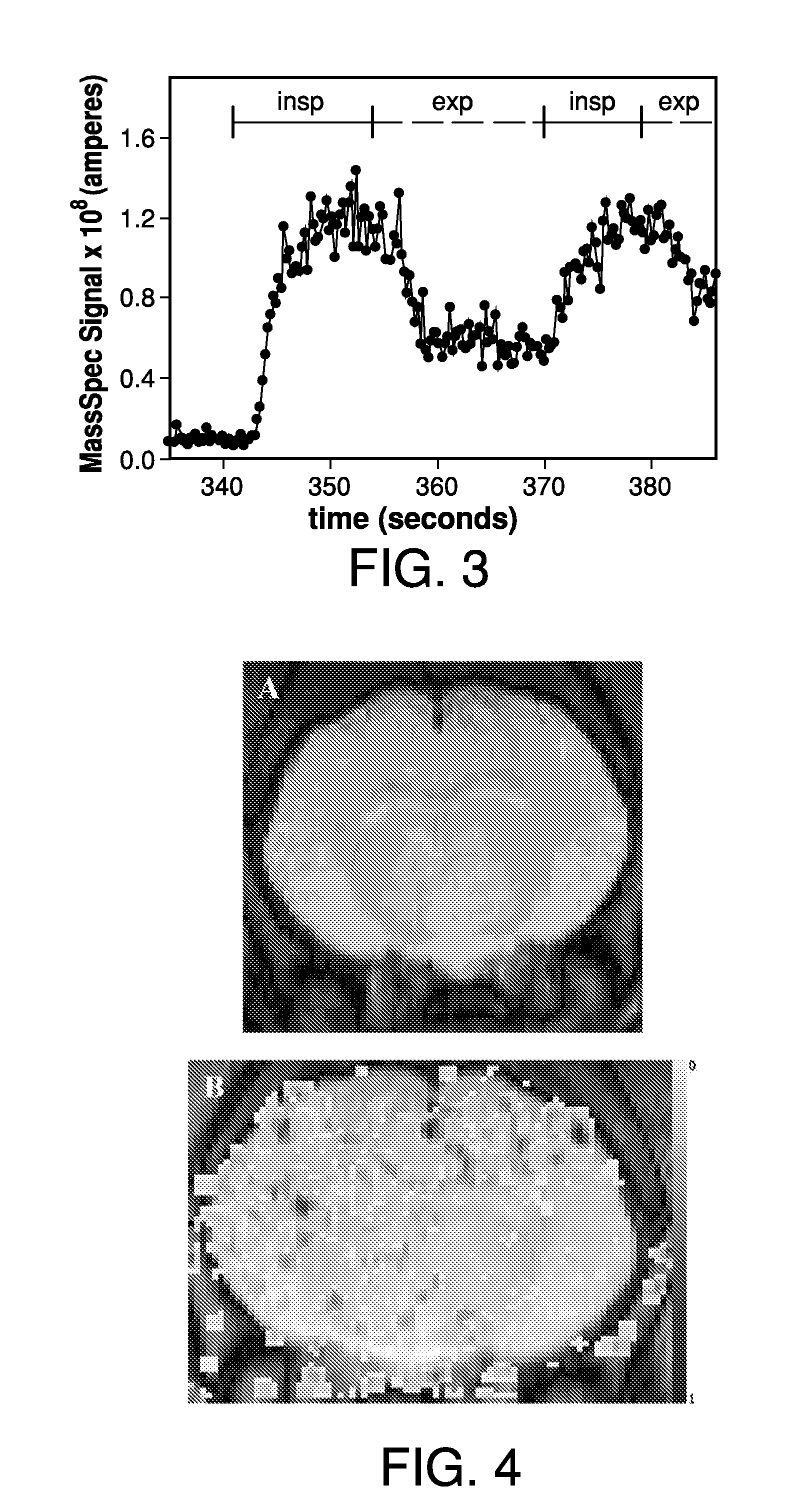
ActiveUS20100282258A1Easy to explainEliminate needRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesArterial input functionCerebral ventricle
Prior approaches have delivered O2 to a subject by inhalation, but the relationship between local signal changes and metabolism has been complicated by H217O created in non-cerebral tissues. During a brief pulse of 17O2 inhalation, this arterial input function for H217O is negligible due to convective transport delays. Additional delays in the arterial input function due to restricted diffusion of water makes pulsed inhalation of 17O2 even more effective. Accordingly, ventilator system are provided to deliver 17O2 as a brief pulse to a subject. Subsequent MR imaging demonstrates delayed appearance of H217O in the cerebral ventricles, suggesting that the arterial input function of H217O is delayed by restricted water diffusion in addition to convective transit delays. Delivery as a brief pulse therefore offers significant advantages in relating MR signal changes directly to metabolism.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Ventriculo-sinus shunting for disease treatment
InactiveUS20050256510A1Inflexible in amountImprove reliabilityWound drainsIntravenous devicesDifferential pressureHazardous substance
A method for treating a disease associated with increased concentration of an undesirable and / or deleterious agent in a central nervous system (CNS) is disclosed. A catheter having no flow restrictor member is placed is used to shunt cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from a patient's cerebral ventricle to a venous sinus within the patient's head. Physiologically based pressure differential and control mechanisms between the ventricle and the venous sinus are exploited to control ventriculo-sinus flow of CSF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and systems for intraventricular brain stimulation
ActiveUS20150011927A1Increase neural activityDecreased neural activityHead electrodesWound drainsForamenMedicine
The present application is directed to devices and methods that can treat dementia or other brain disorders via electrical stimulation. Embodiments disclosed herein utilize brain stimulation of brain areas involved in memory and cognition through an intraventricular approach. Brain stimulation is combined with CSF flow in an intraventricular electrode having one or more passageways to permit fluid to flow therethrough. For example, an intraventricular electrode shunt catheter can be safely placed in any part of the ventricular system and through any foramen or aqueduct of the ventricular system without fear of obstruction to CSF flow.
Owner:HUA SHERWIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com