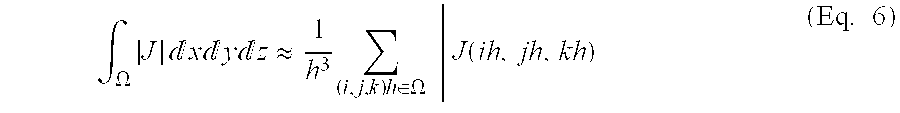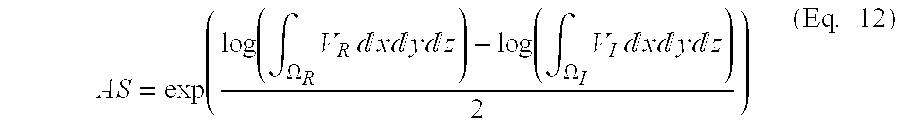Patents
Literature
34 results about "Brain Ventricle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The four connected cavities (hollow spaces) centrally located within the brain that connect posteriorly with the central canal of the spinal cord. (NCI)
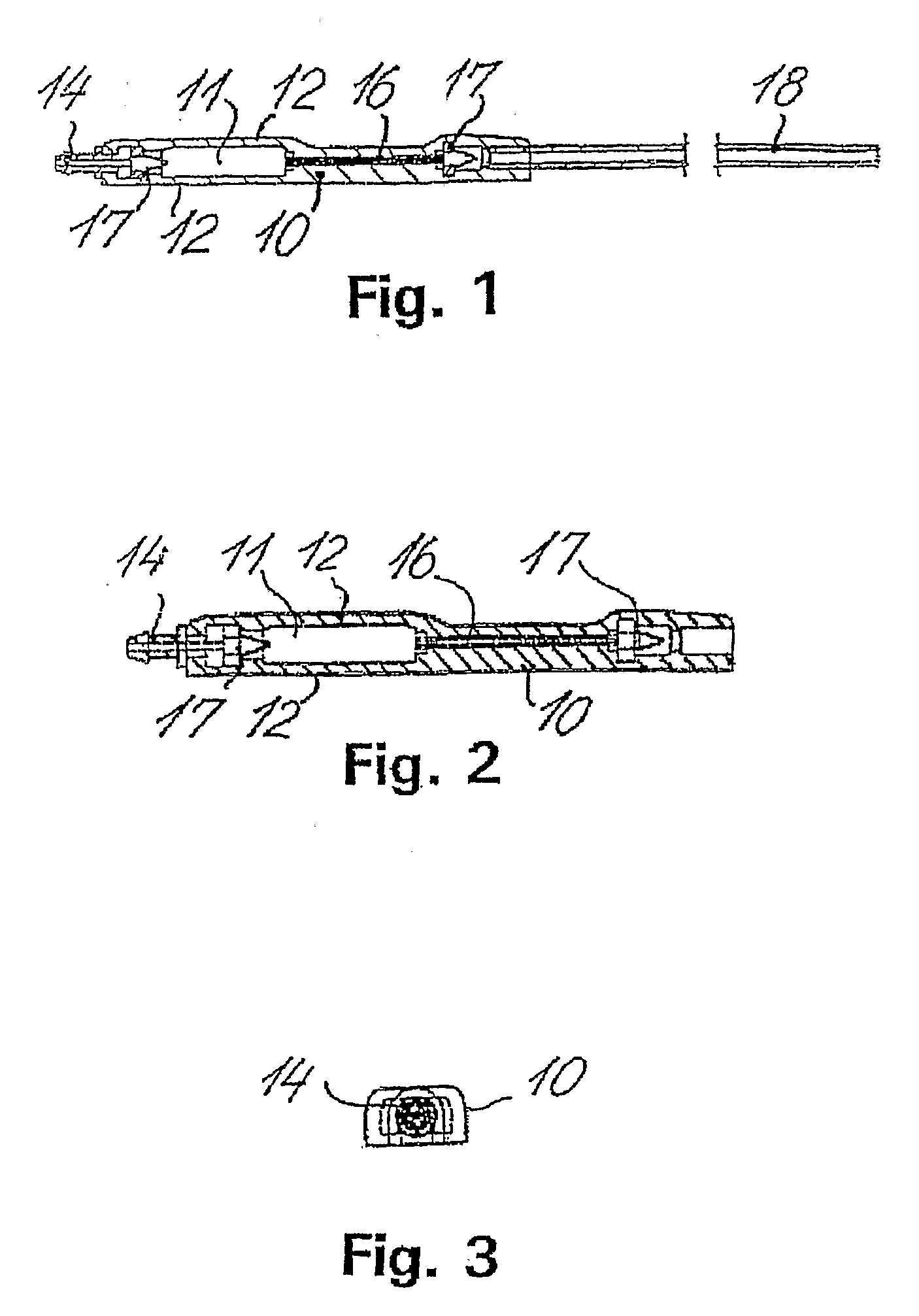
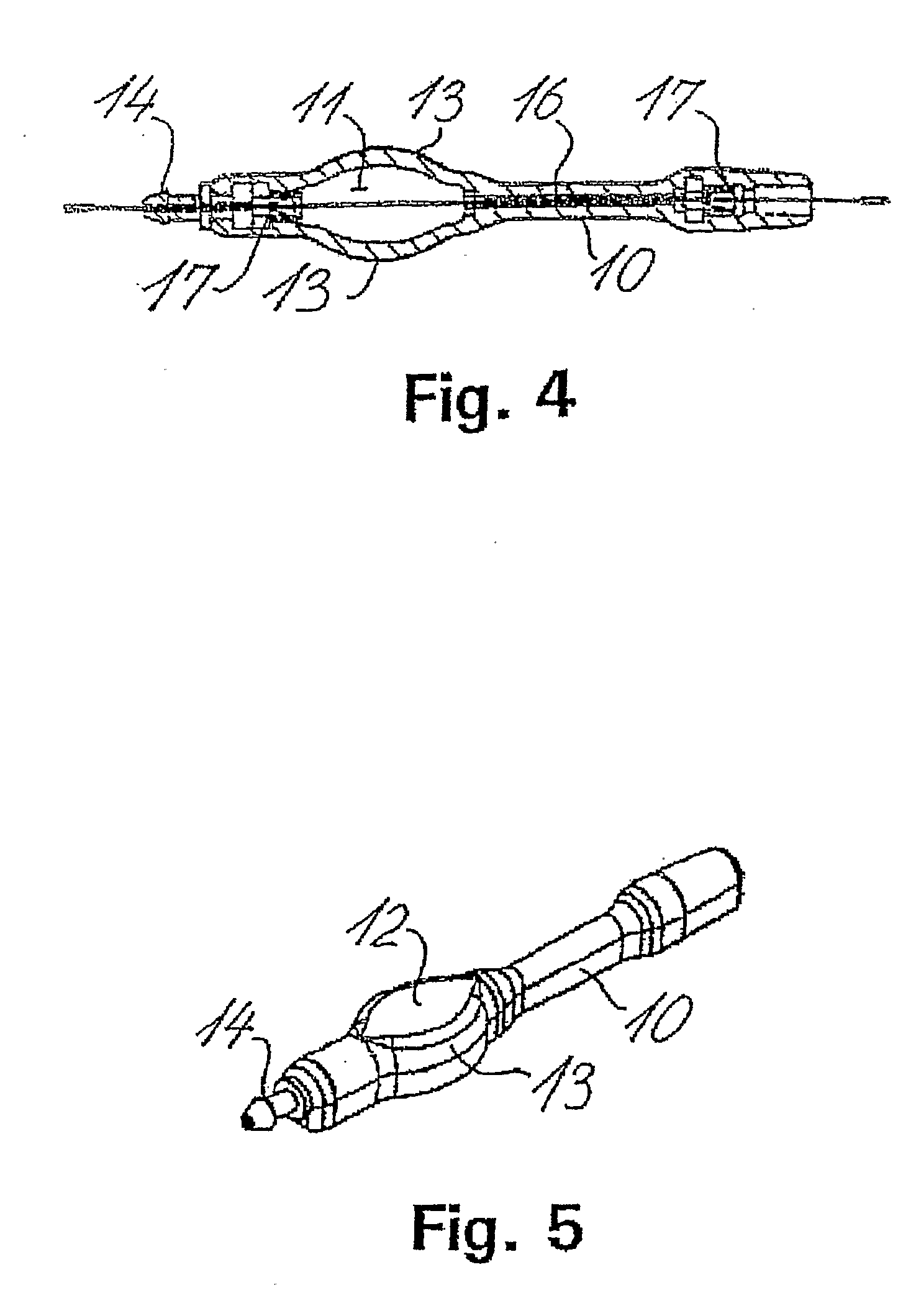
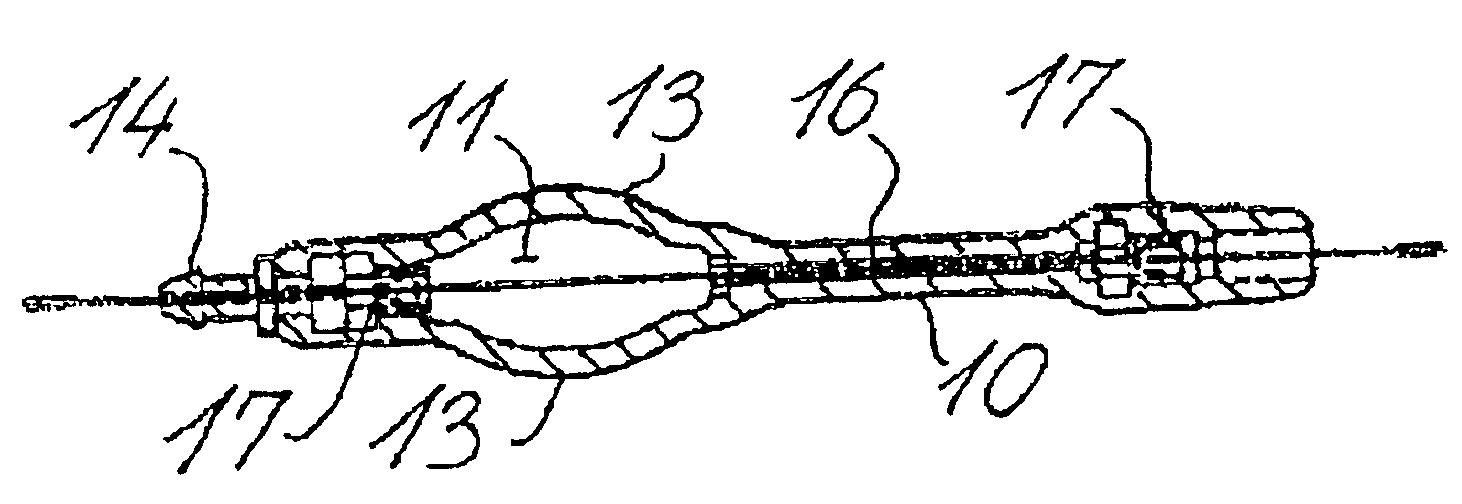
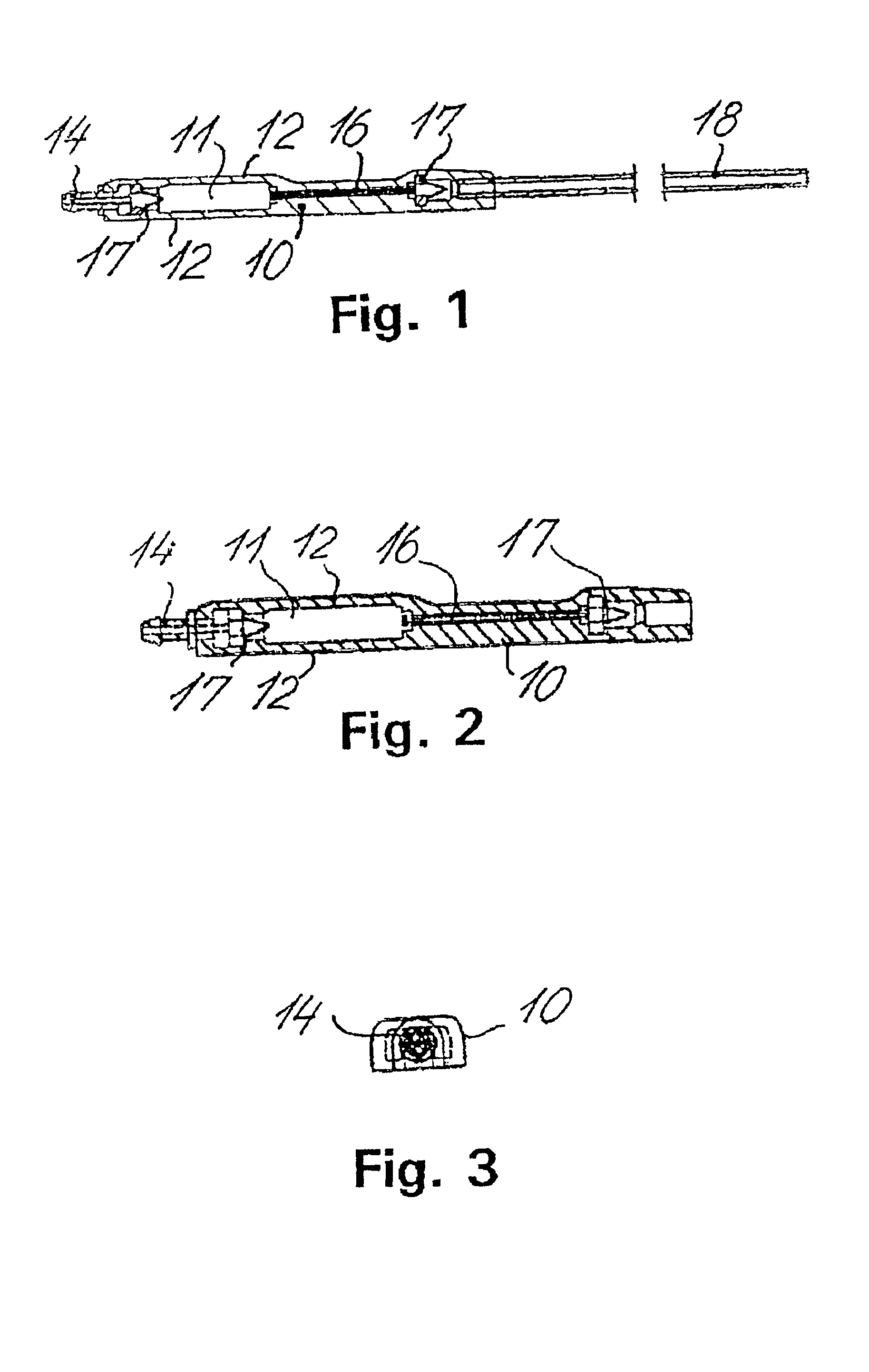
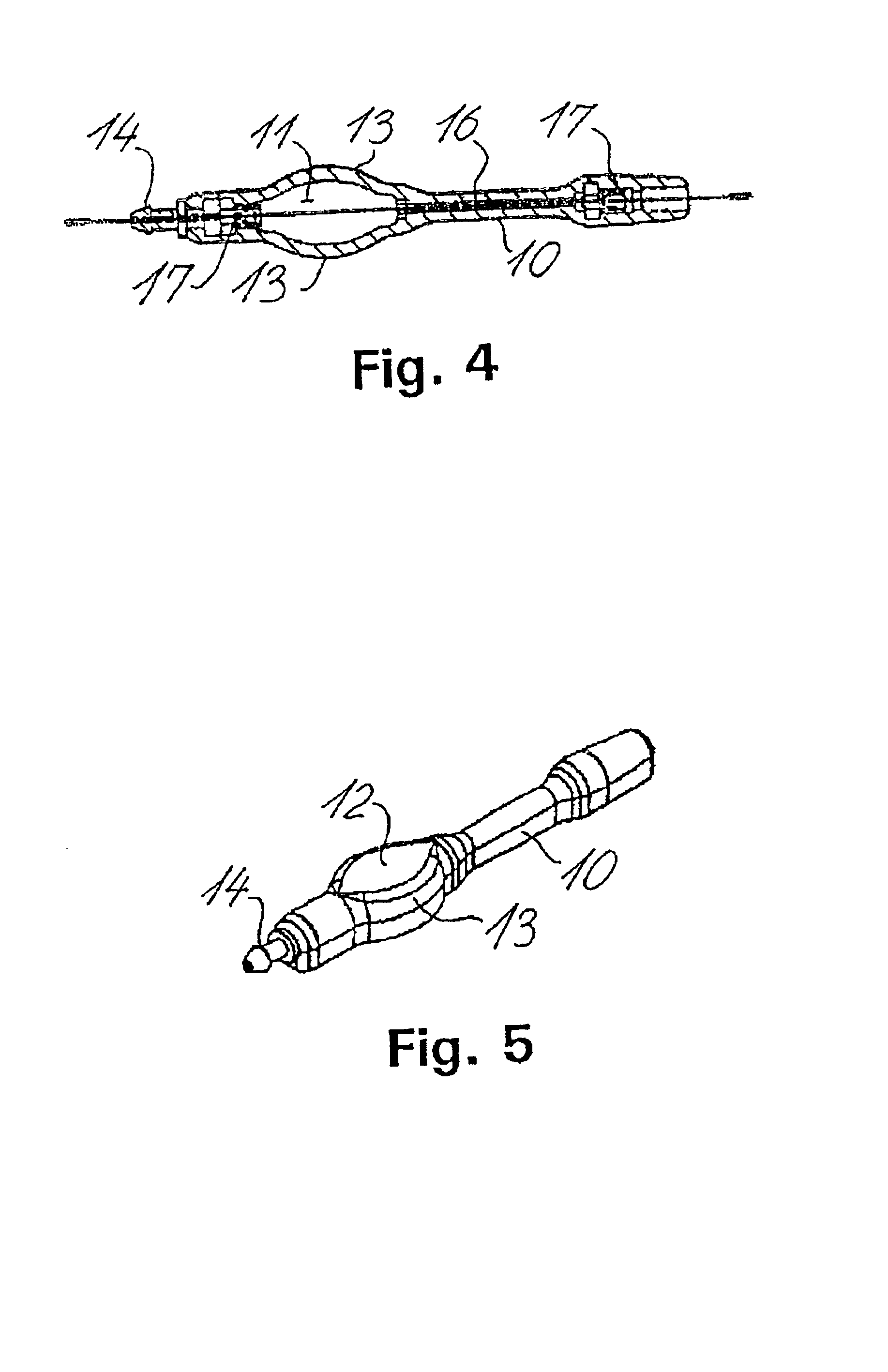
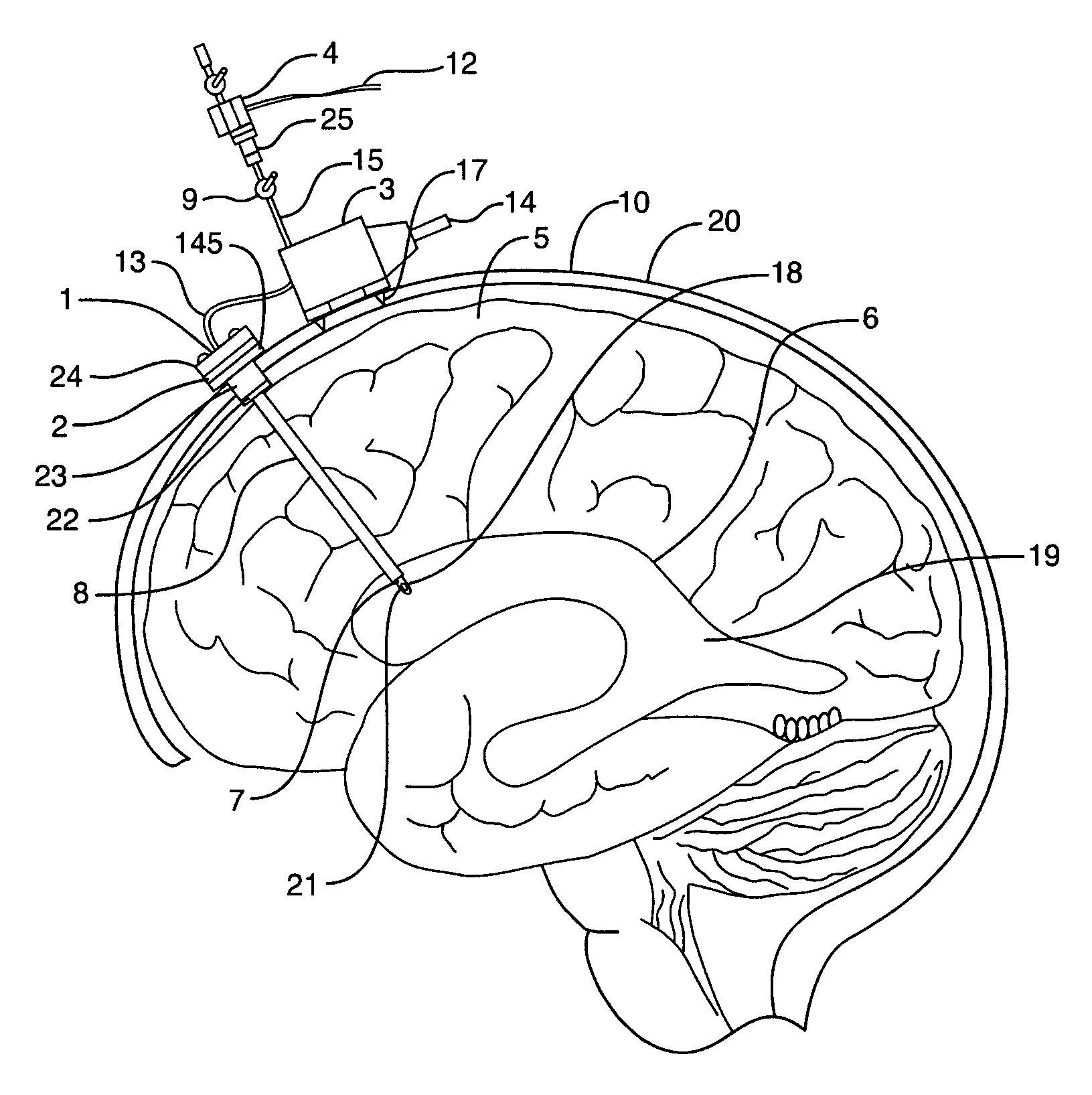
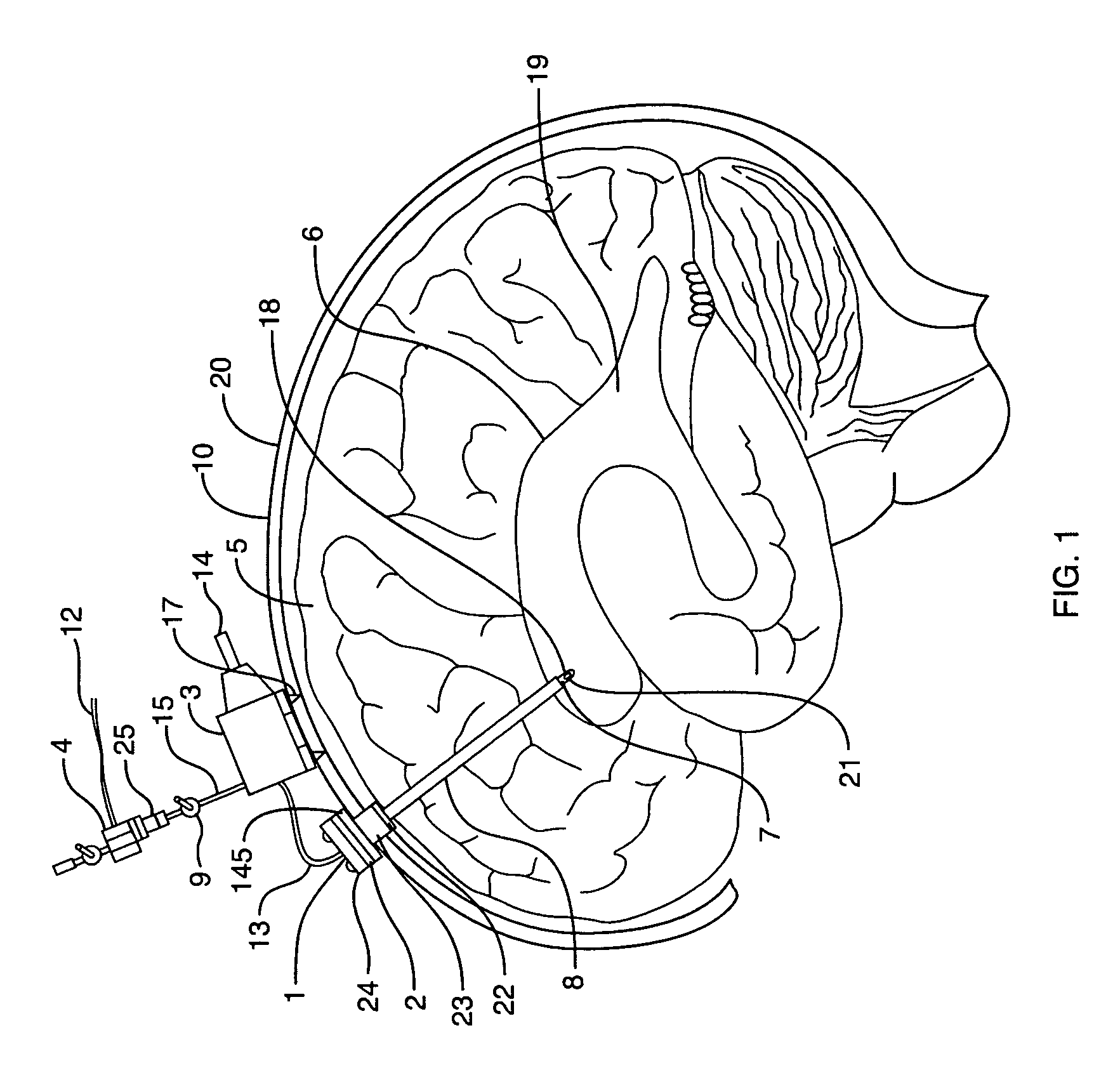
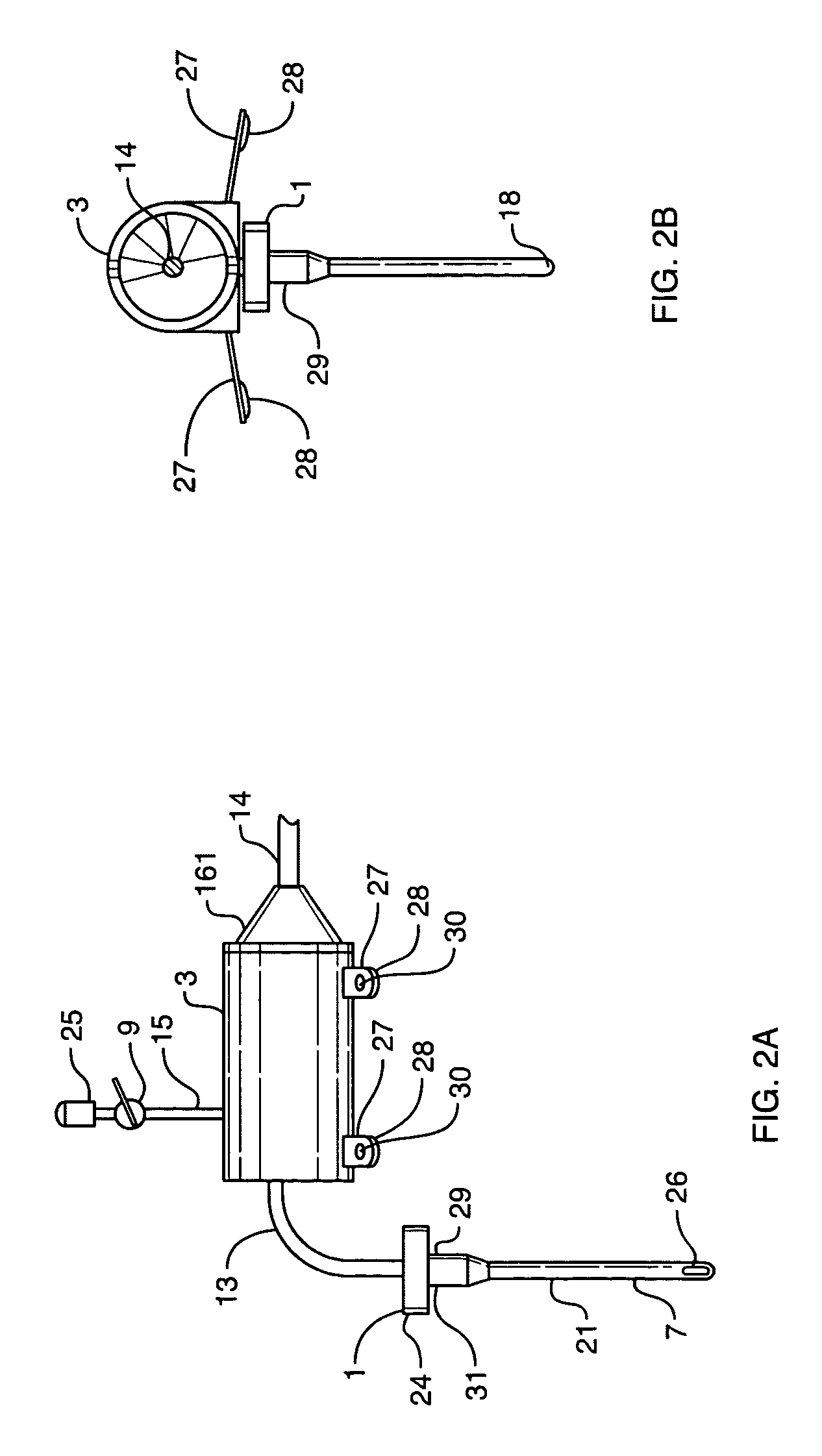
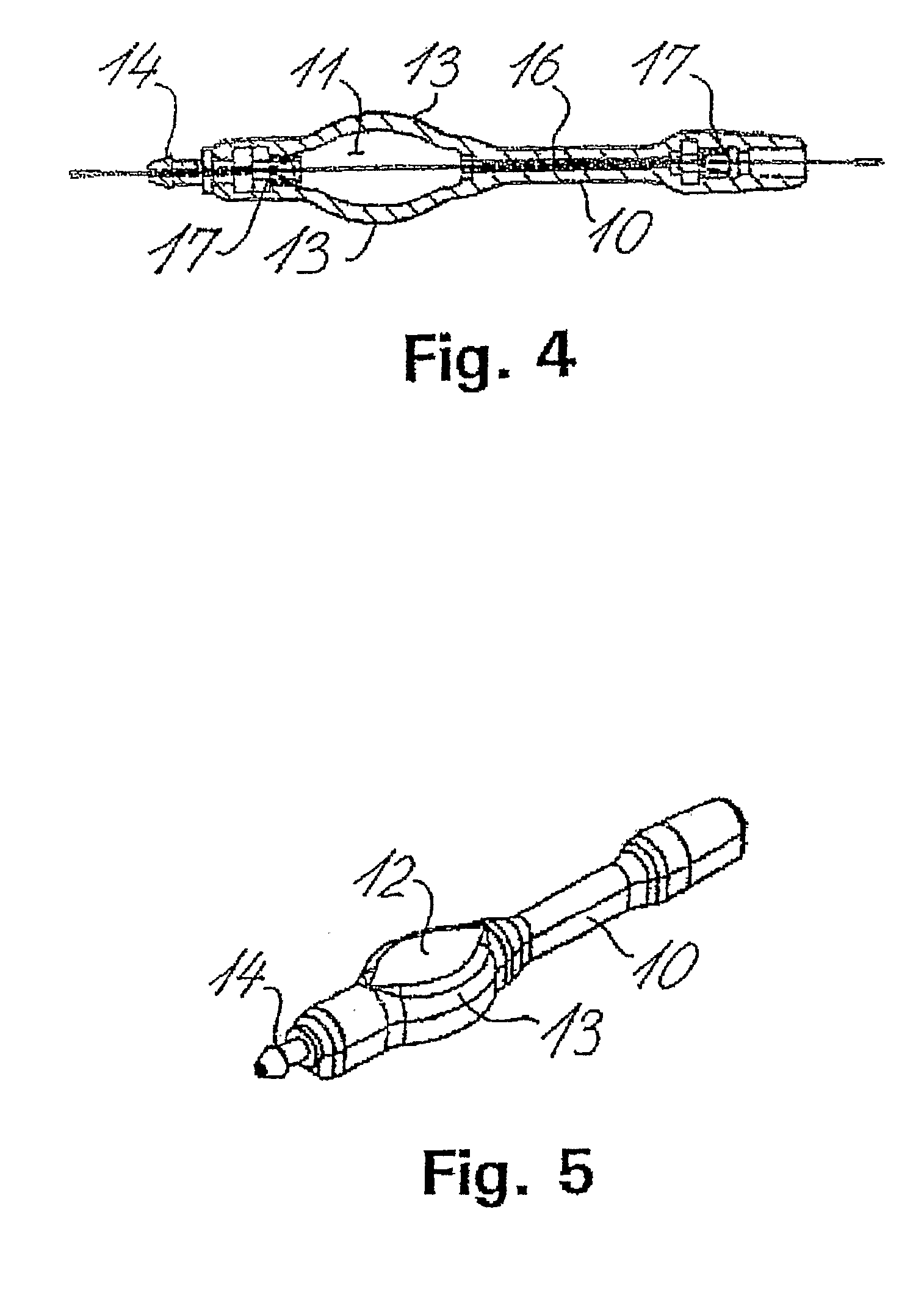
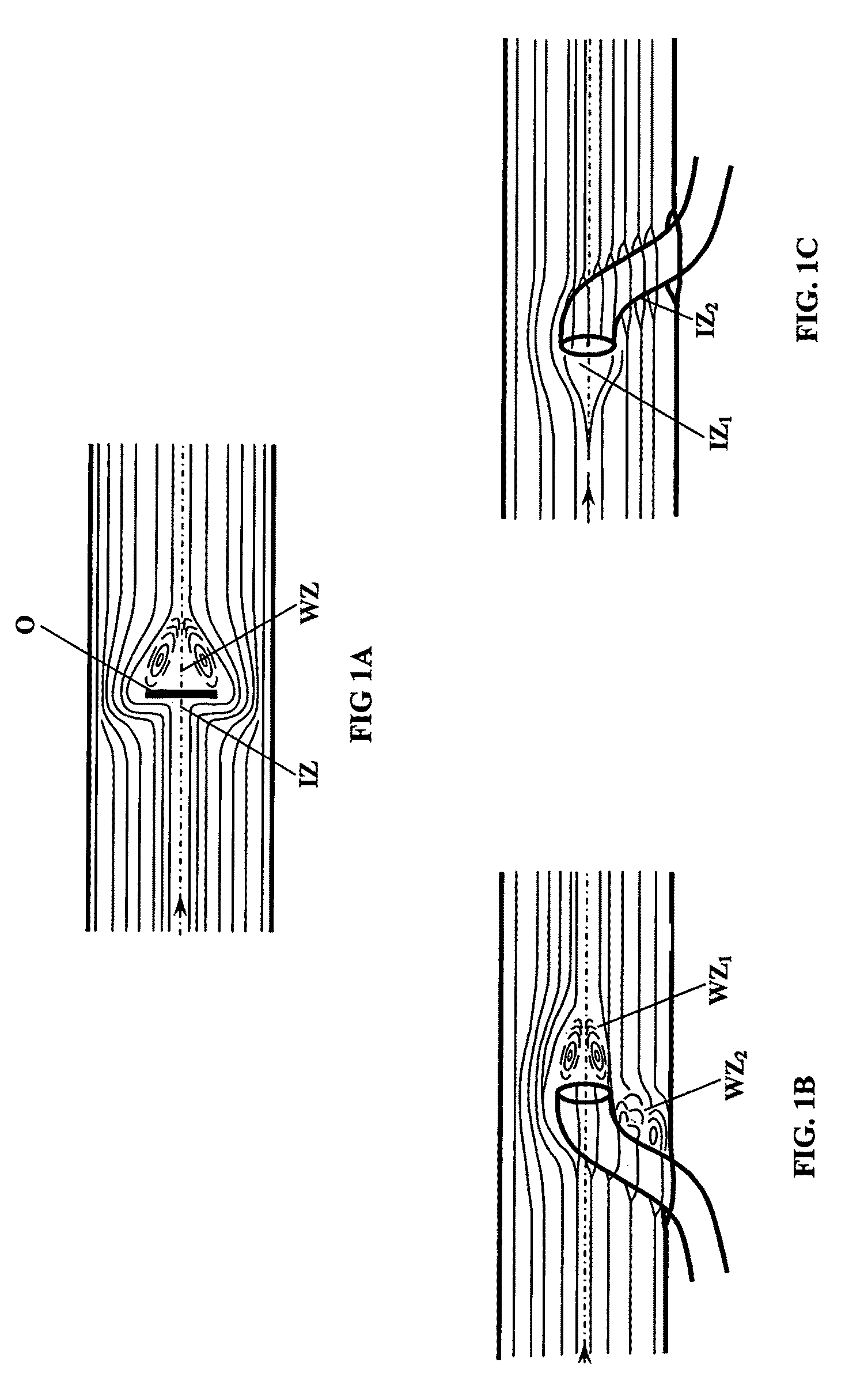
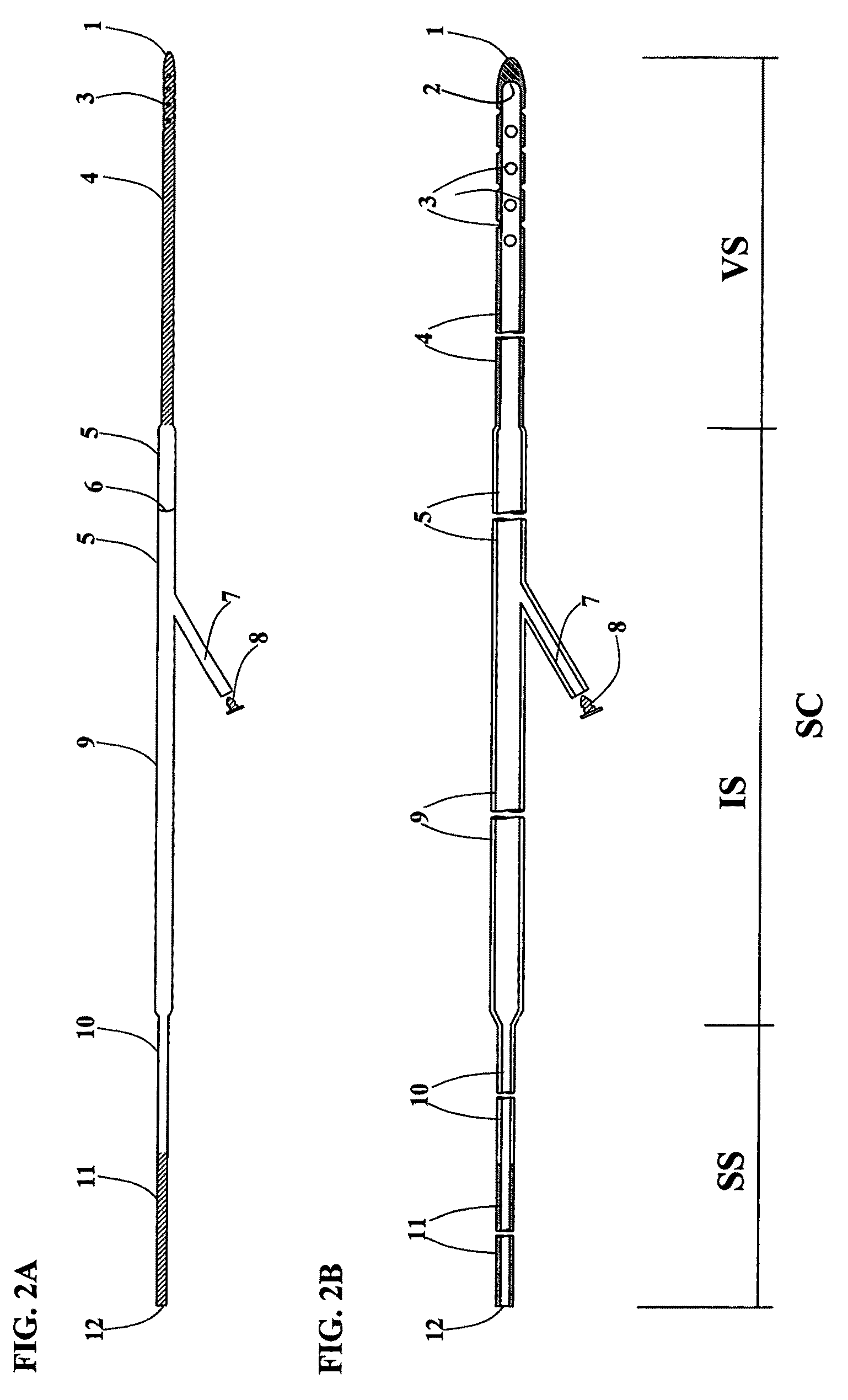
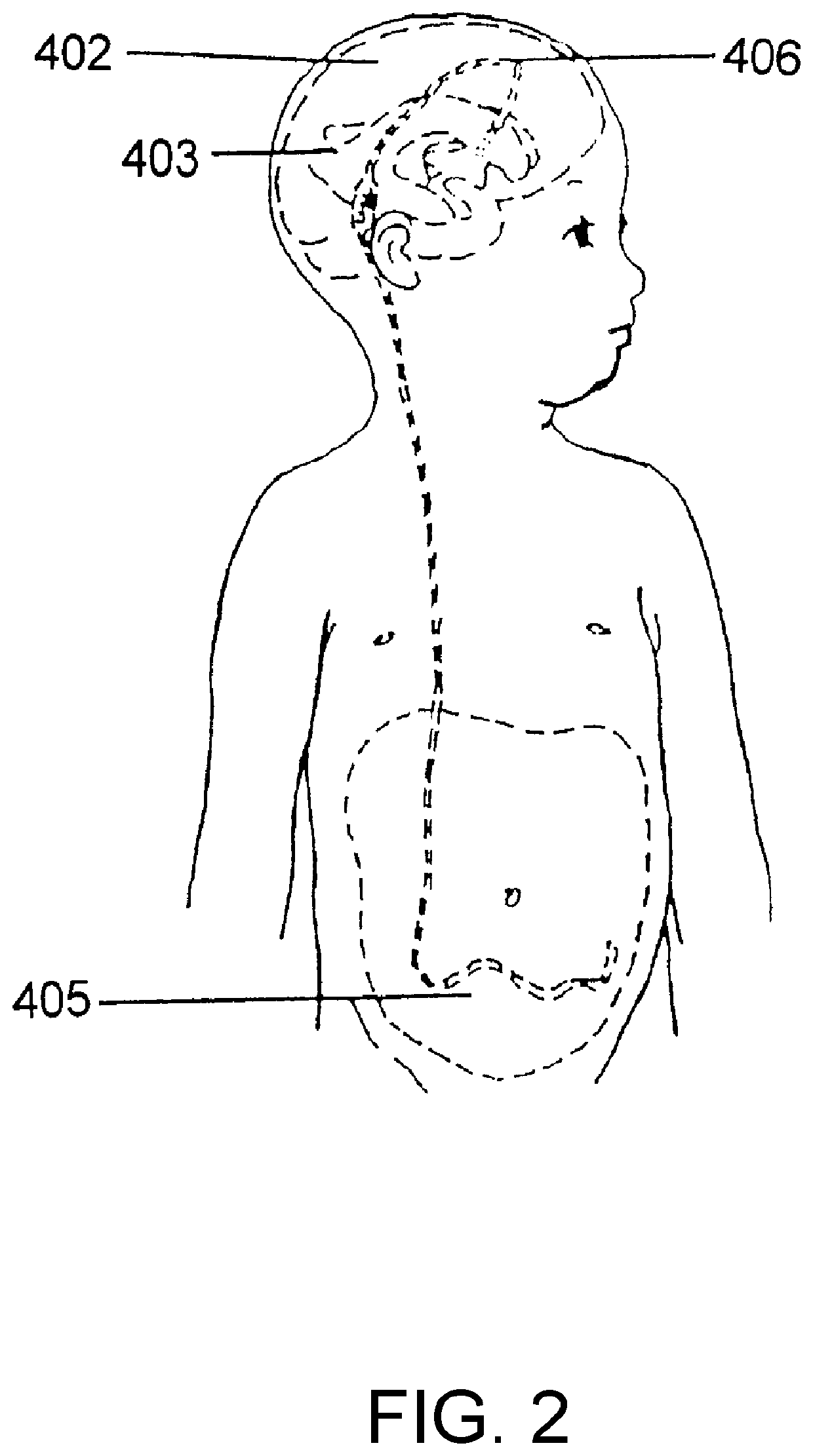
Shunt system including a flow control device for controlling the flow of cerebrospinal fluid out of a brain ventricle
ActiveUS7118549B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsBrain VentricleBiomedical engineering
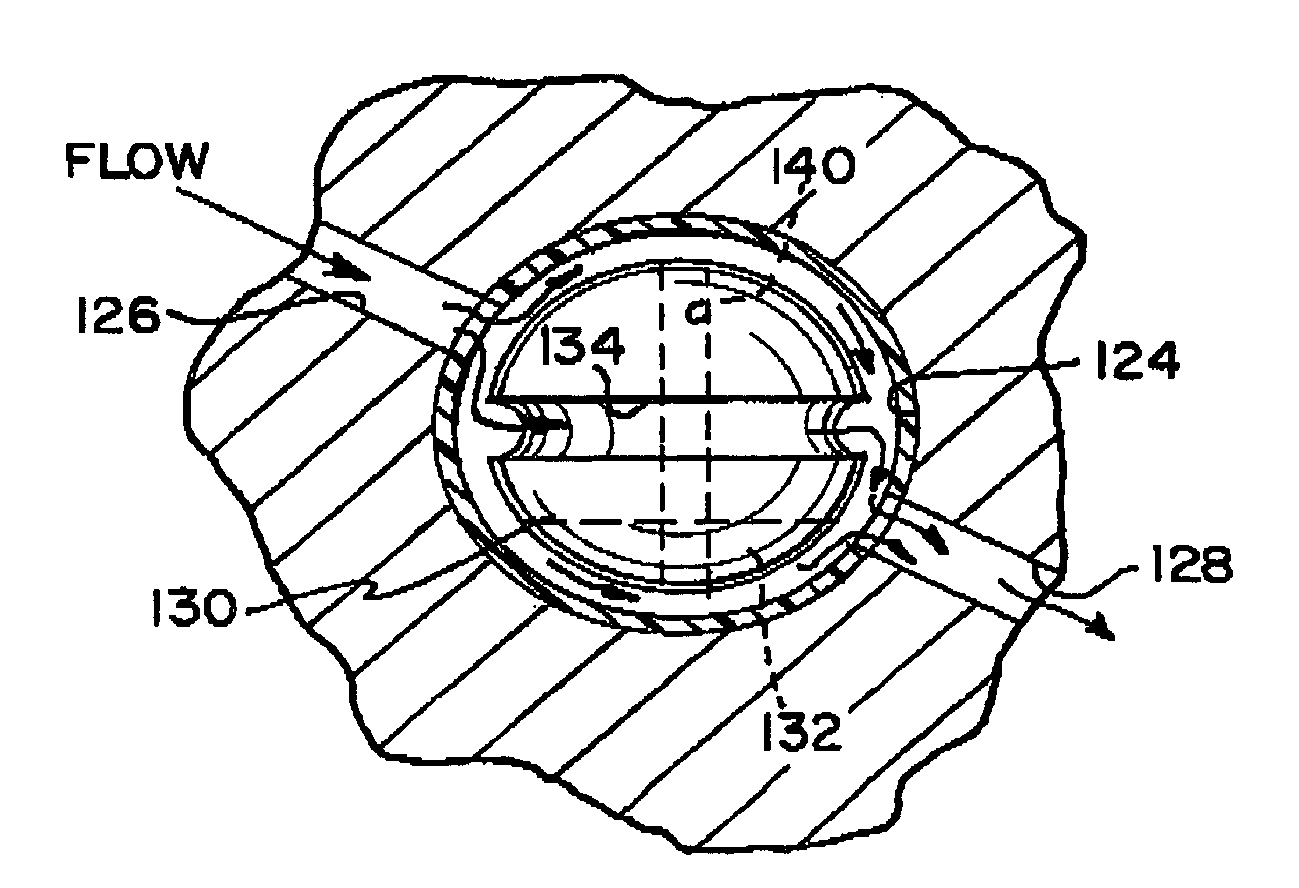
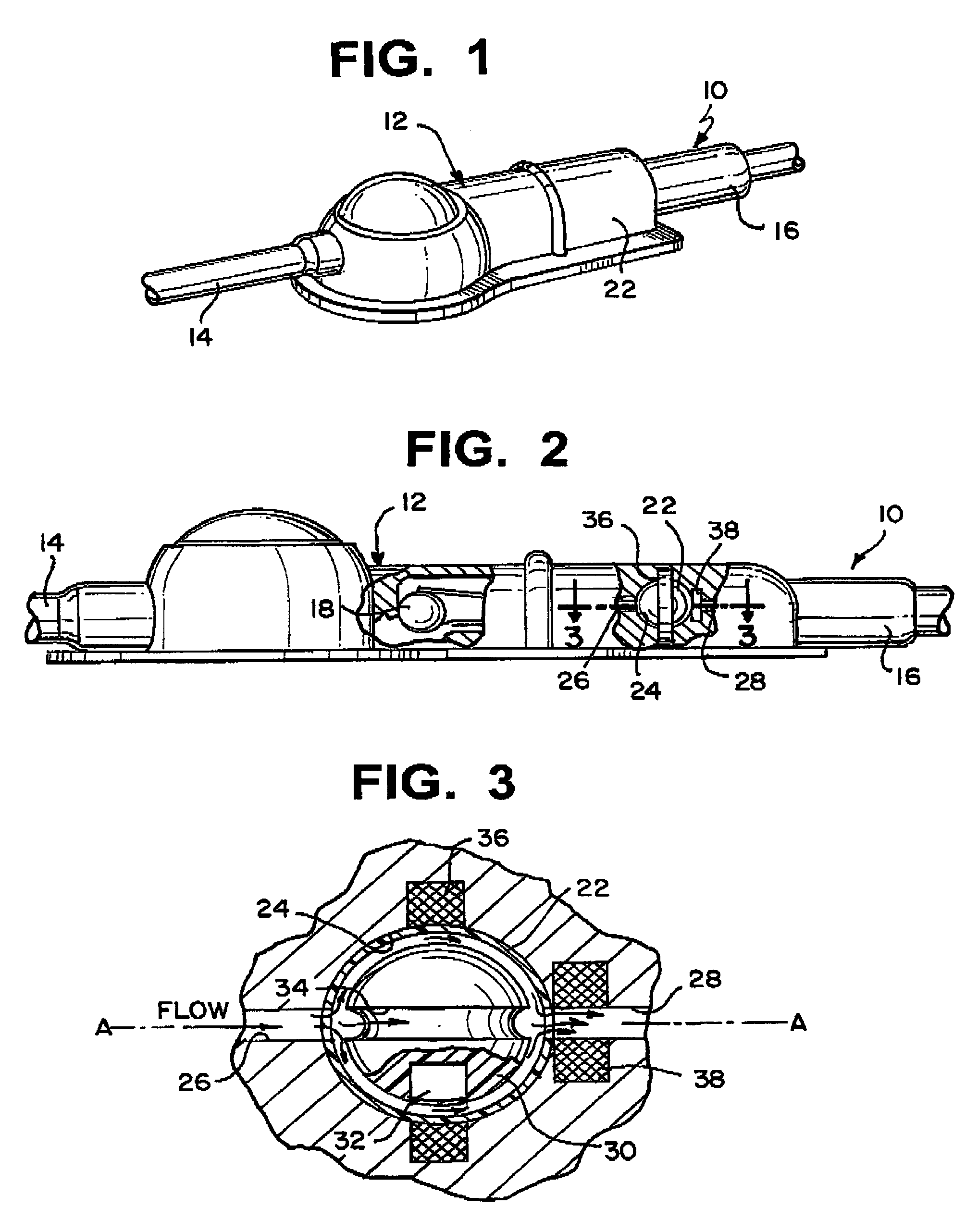
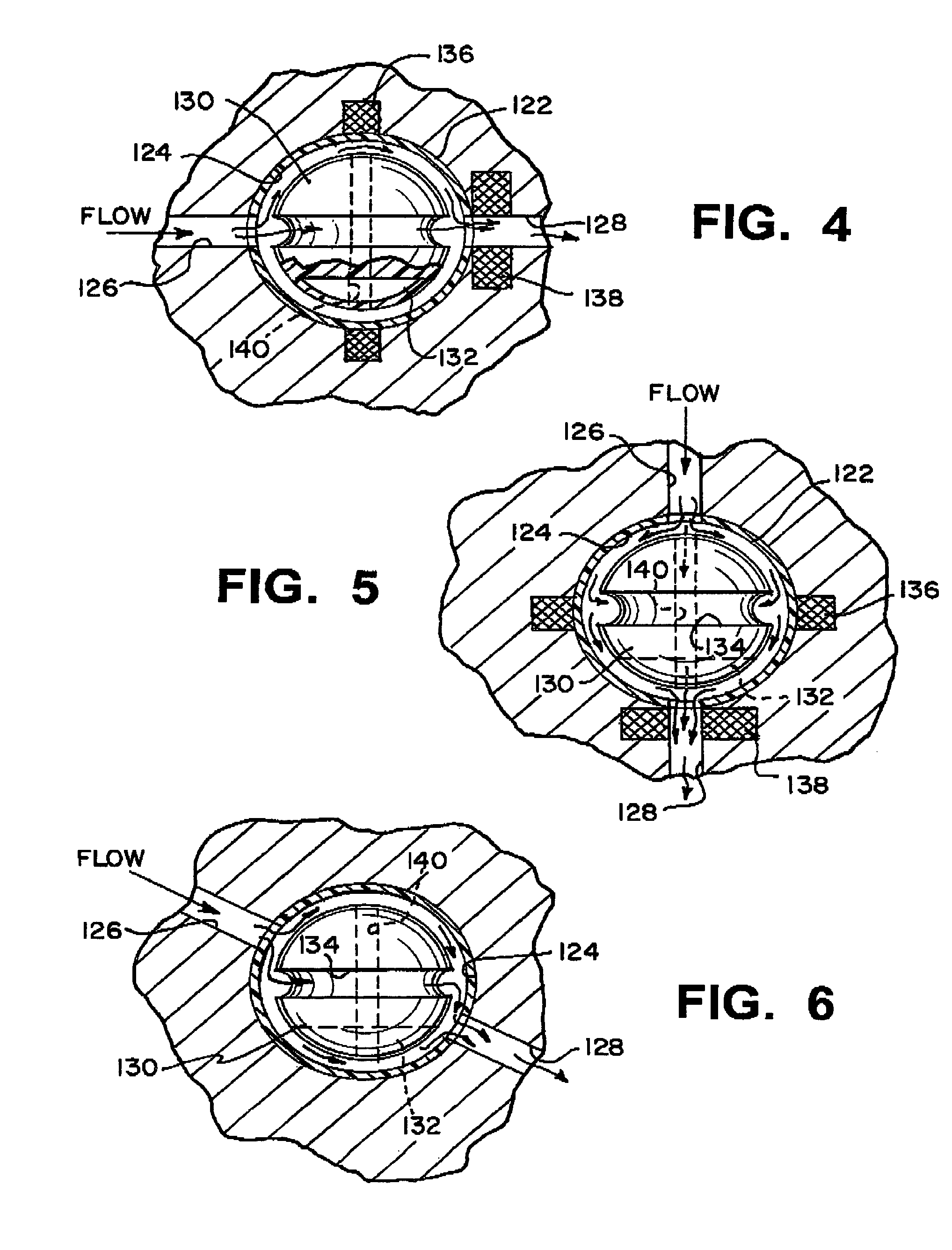
An anti-siphon device limits the flow of a fluid from a first region of a patient's body to a second region. The device includes a housing having a spherical inner surface with a predetermined inner diameter. The housing has an inlet port for receiving fluid from the first region and an outlet port for directing fluid to the second region. The inlet port and the outlet port are disposed approximately diametrically opposite from each other. A spherical ball is disposed within the housing. The spherical ball has a ferromagnetic weight disposed off center therein. The spherical ball has an outer diameter that is less than the inner diameter of the housing so that the spherical ball is free to rotate within the housing and the fluid is free to flow between the inner surface of the housing and an outer surface of said spherical ball. The spherical ball has a circumferential recess extending through its center.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Shunt system with coating and flow restricting component exerting a passive and essentially constant resistance to outflow
InactiveUS20070112291A1Reduce as muchReduce infectionWound drainsFlow monitorsCsf shuntBrain Ventricle
The present invention relates to an improved cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprising a coating covering at least part of the system and a flow restricting component exerting a passive and essentially constant resistance to flow. The present invention also relates to methods for implanting different catheters of a cerebrospinal fluid shunt system into a brain ventricle and the sinus system, respectively, of an individual. The present invention further relates to methods for shunting cerebrospinal fluid from a brain ventricle to the sinus system of an individual.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
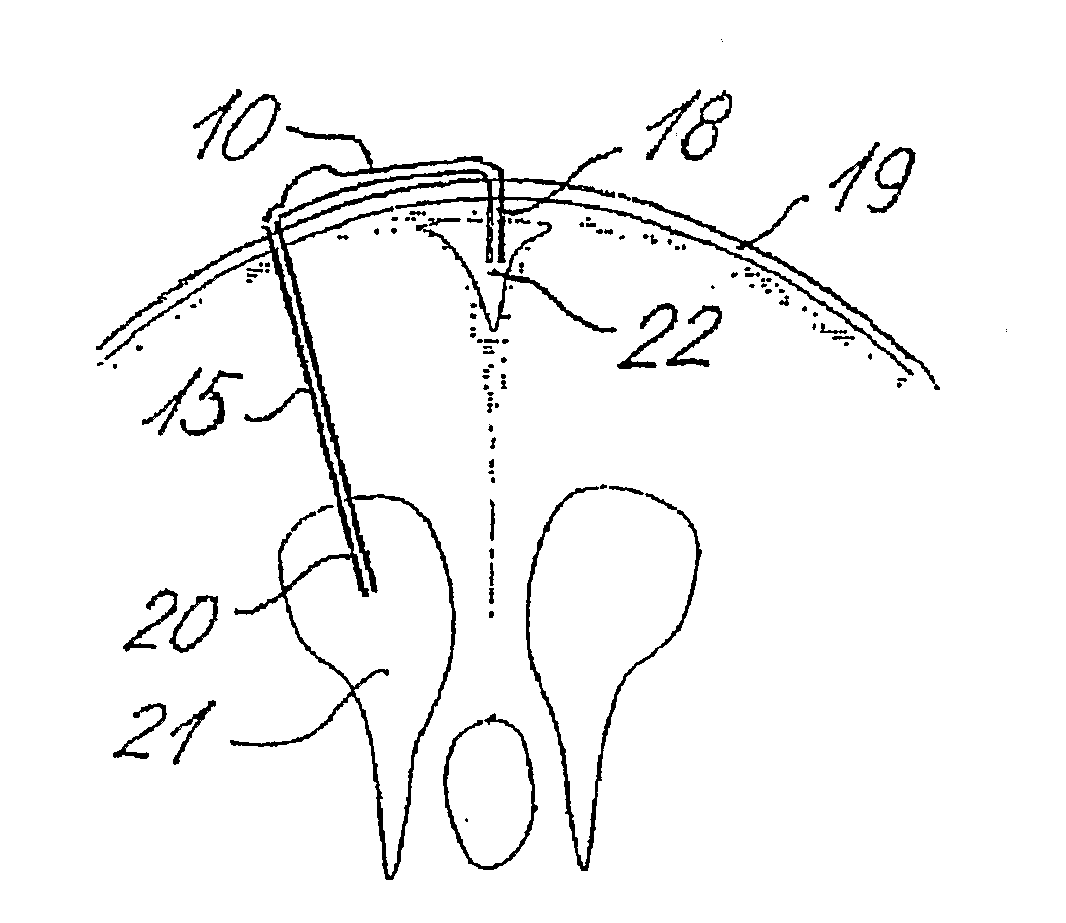
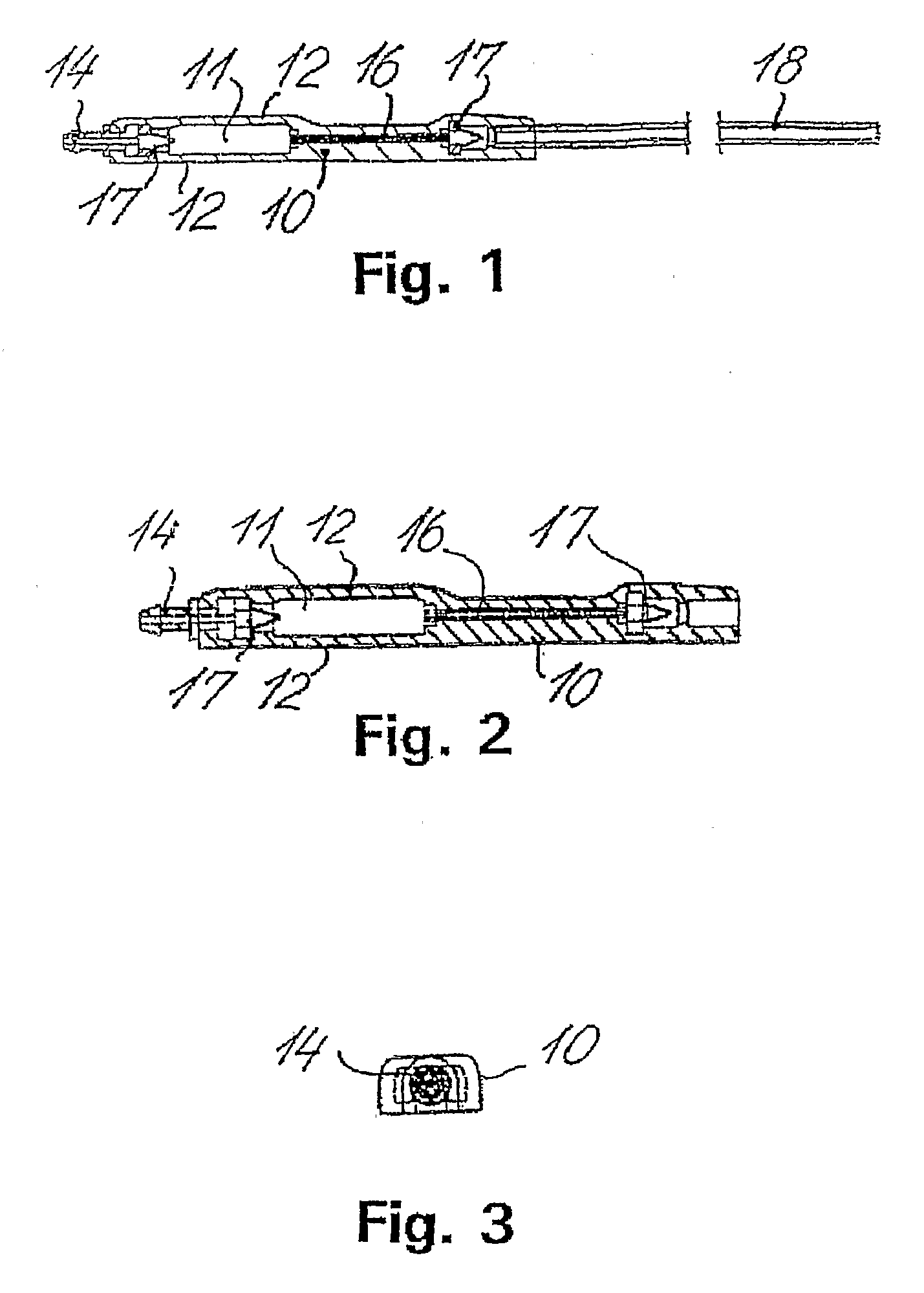
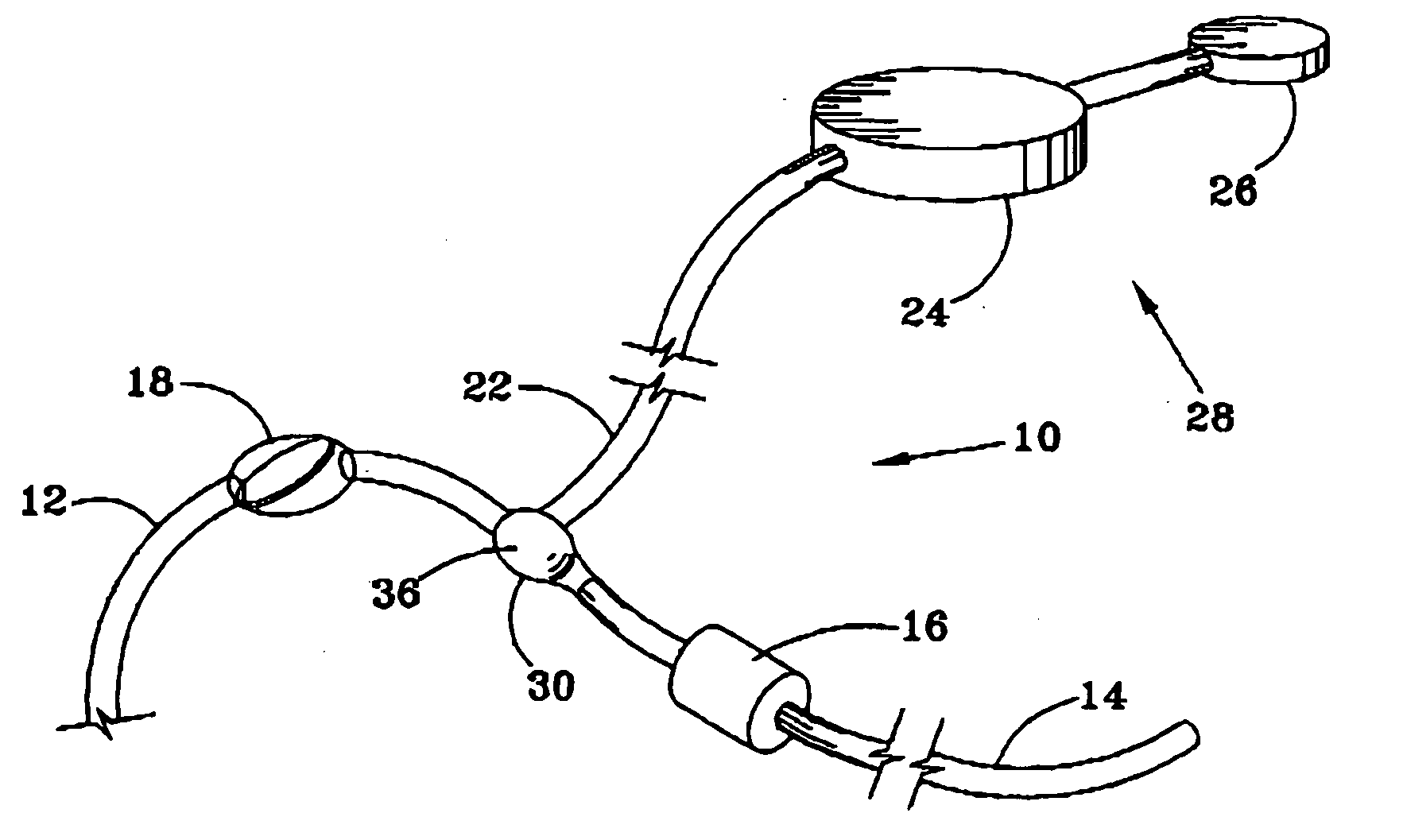
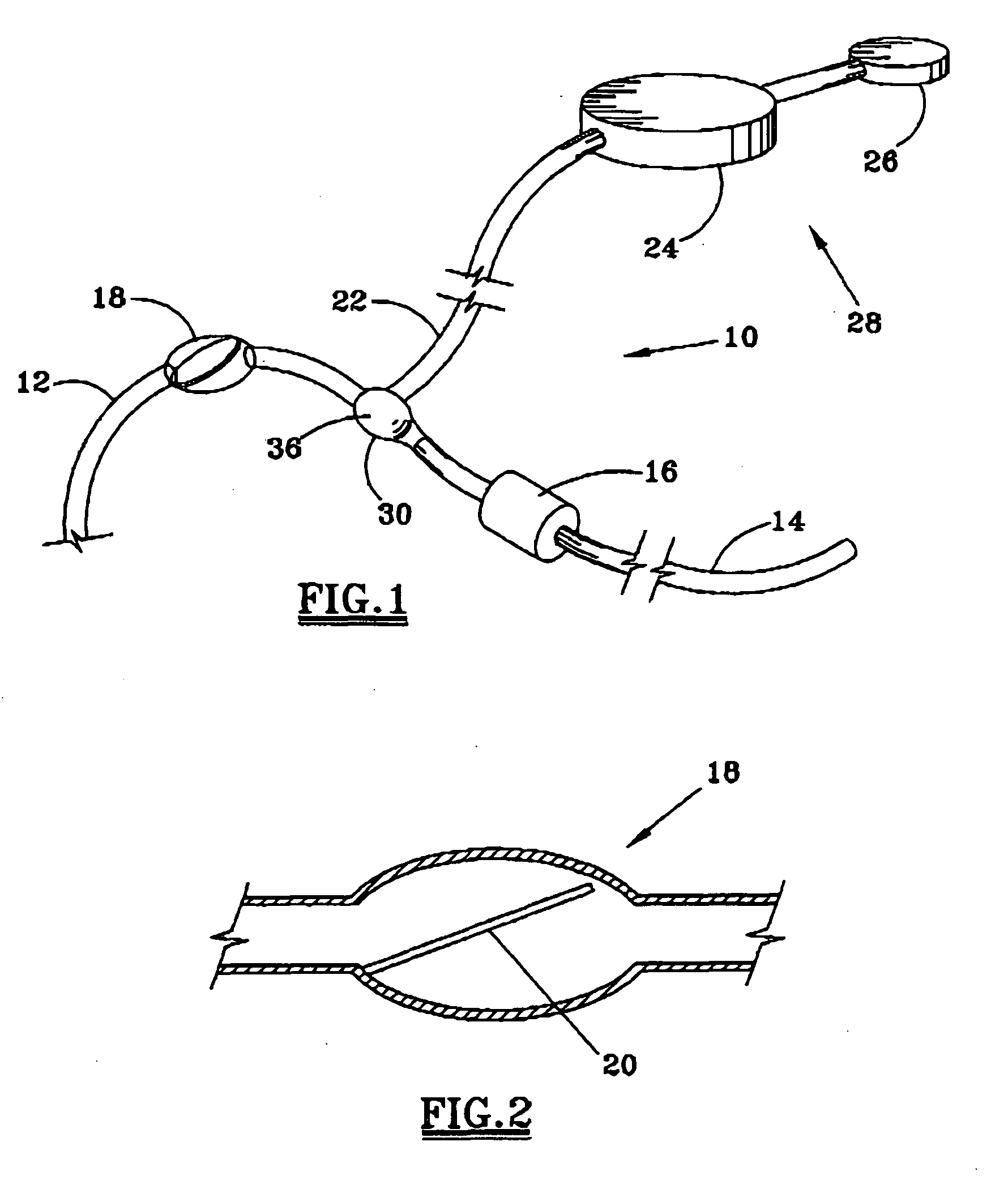
Fluid shunt system and a method for the treatment of hydrocephalus
InactiveUS6905474B2Lower resistanceInhibit posture changesWound drainsMedical devicesFlow diverterBrain Ventricle
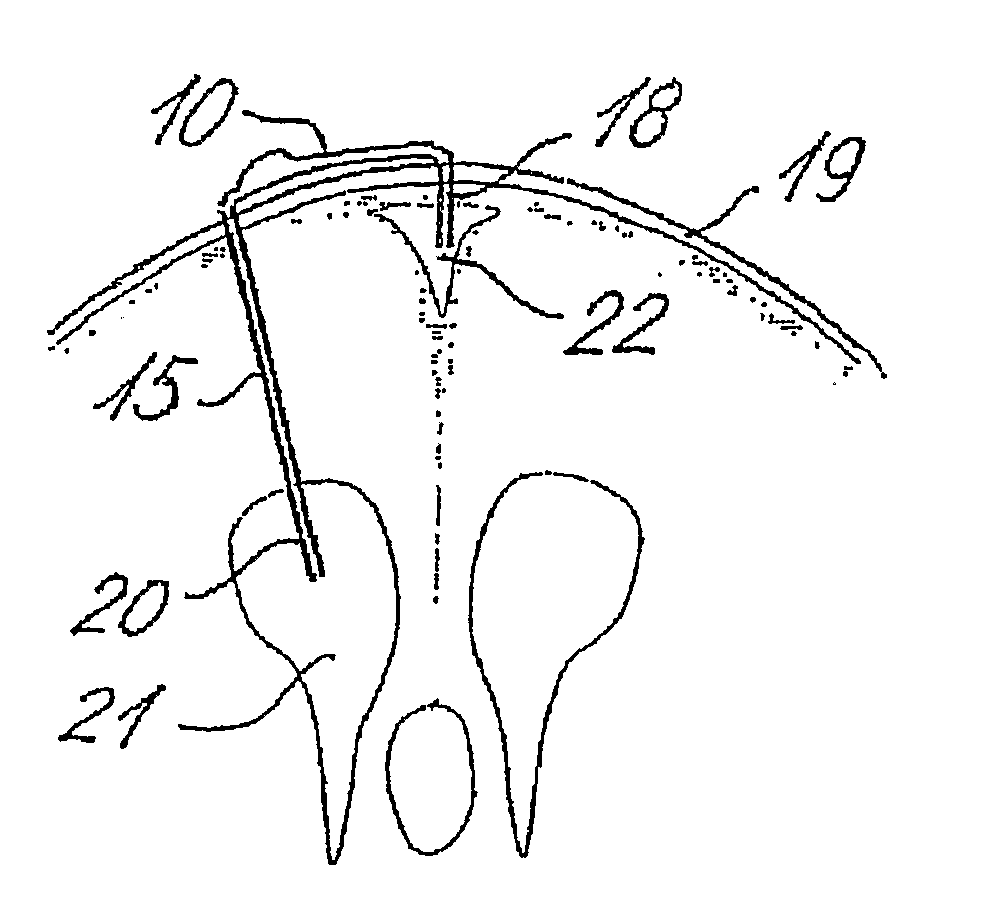
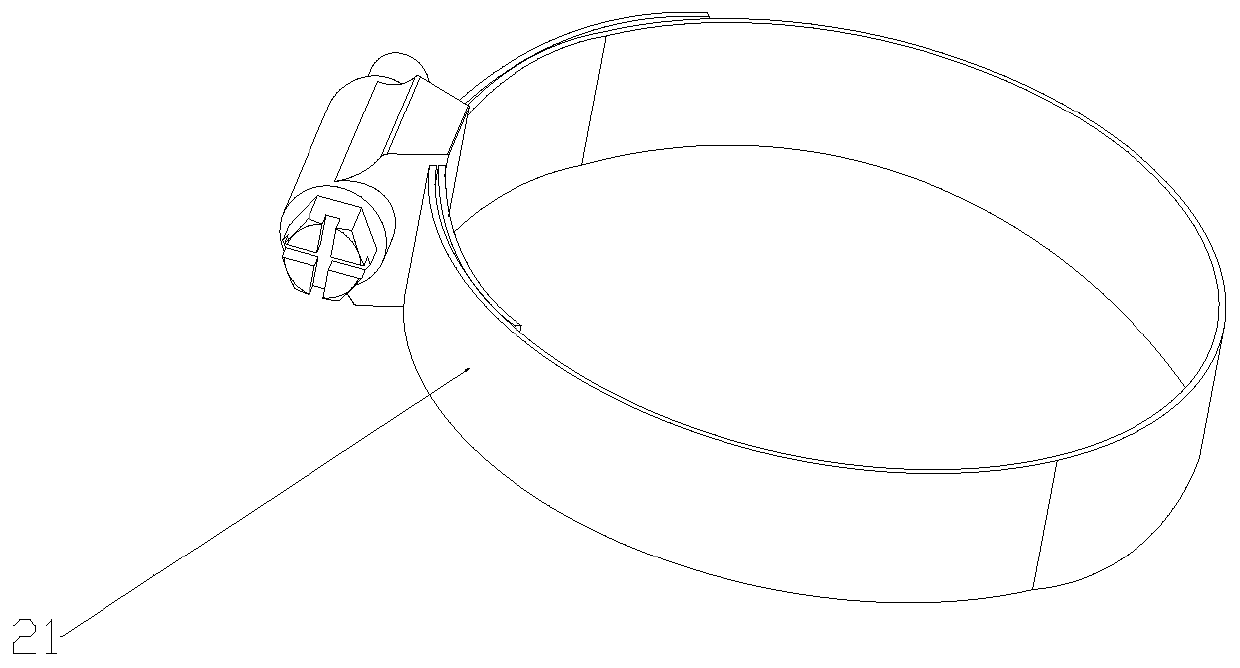
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricle catheter (15) to insert into the brain ventricle (21) so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle, a sinus catheter (18) to insert into the sinus sagittalis system (22) for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into the sinus sagittalis system, a shunt body member (10) connected at one end thereof to said brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to said sinus catheter system to provide fluidic communication between said brain ventricle catheter (15) and said sinus catheter (18), and a flow restriction (16) defined within the shunt body member (10) to maintain a resistance to fluid flow of the shunt system of less than 8 mm Hg / ml / min, such as 2-7 or 4-6 and preferably about 5 mm Hg / ml / min. When the shunt system is implanted the shunt body member (10) is placed subcutaneously on top of the calvarium of a patient, behind the coronal suture on one of side of the sagittal suture. One end of each of the catheters (15, 18) is then connected to a respective end of the shunt body member (10), and a second end of each catheter is inserted in the right ventricle (21) and in the sinus sagittalis system (22), respectively, via holes bored in the scull (19).
Owner:CSF DYNAMICS
Shunt system including a flow control device for controlling the flow of cerebrospinal fluid out of a brain ventricle
ActiveUS20050096581A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsAntisyphon deviceBrain Ventricle
An anti-siphon device limits the flow of a fluid from a first region of a patient's body to a second region. The device includes a housing having a spherical inner surface with a predetermined inner diameter. The housing has an inlet port for receiving fluid from the first region and an outlet port for directing fluid to the second region. The inlet port and the outlet port are disposed approximately diametrically opposite from each other. A spherical ball is disposed within the housing. The spherical ball has a ferromagnetic weight disposed off center therein. The spherical ball has an outer diameter that is less than the inner diameter of the housing so that the spherical ball is free to rotate within the housing and the fluid is free to flow between the inner surface of the housing and an outer surface of said spherical ball. The spherical ball has a circumferential recess extending through its center.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
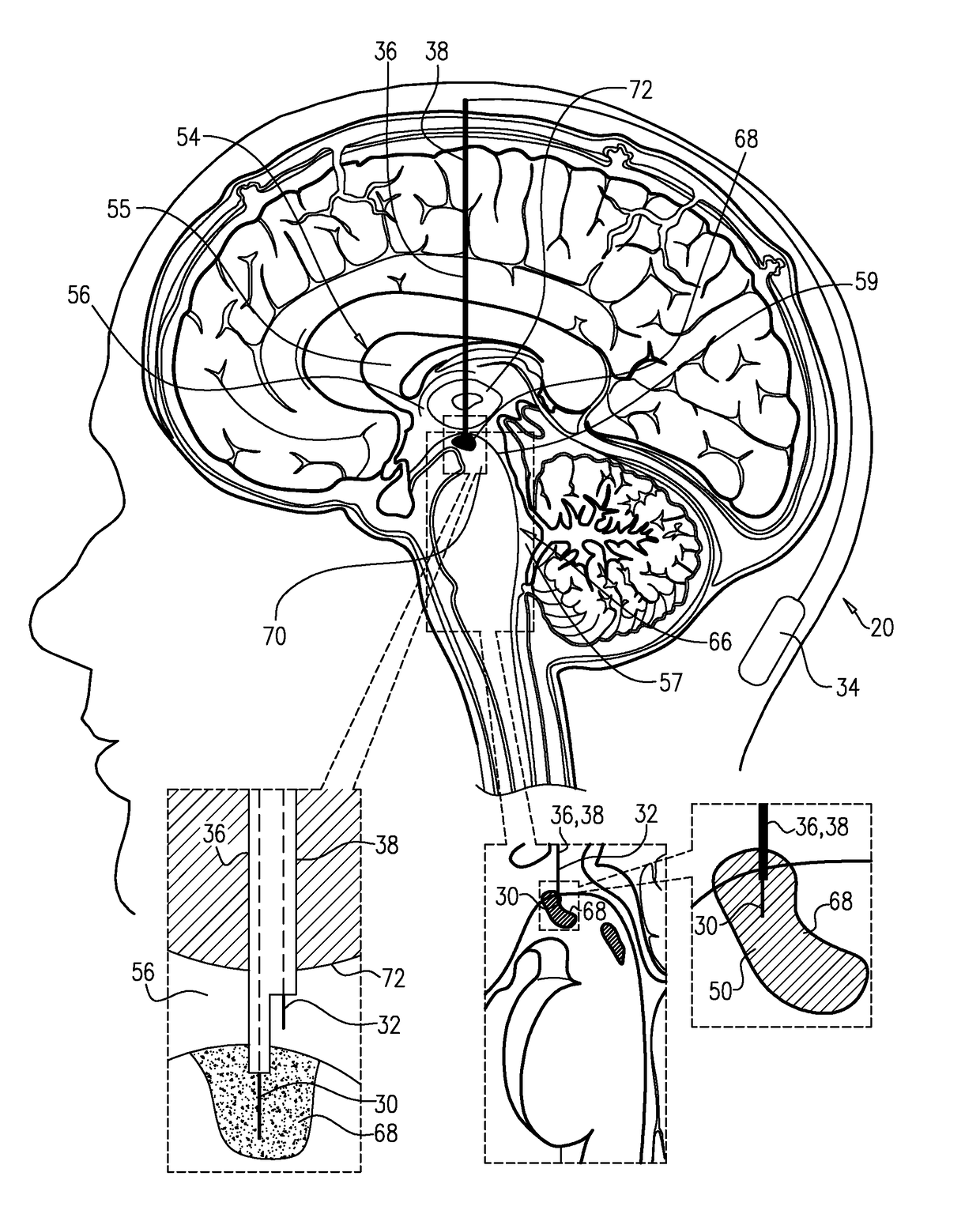
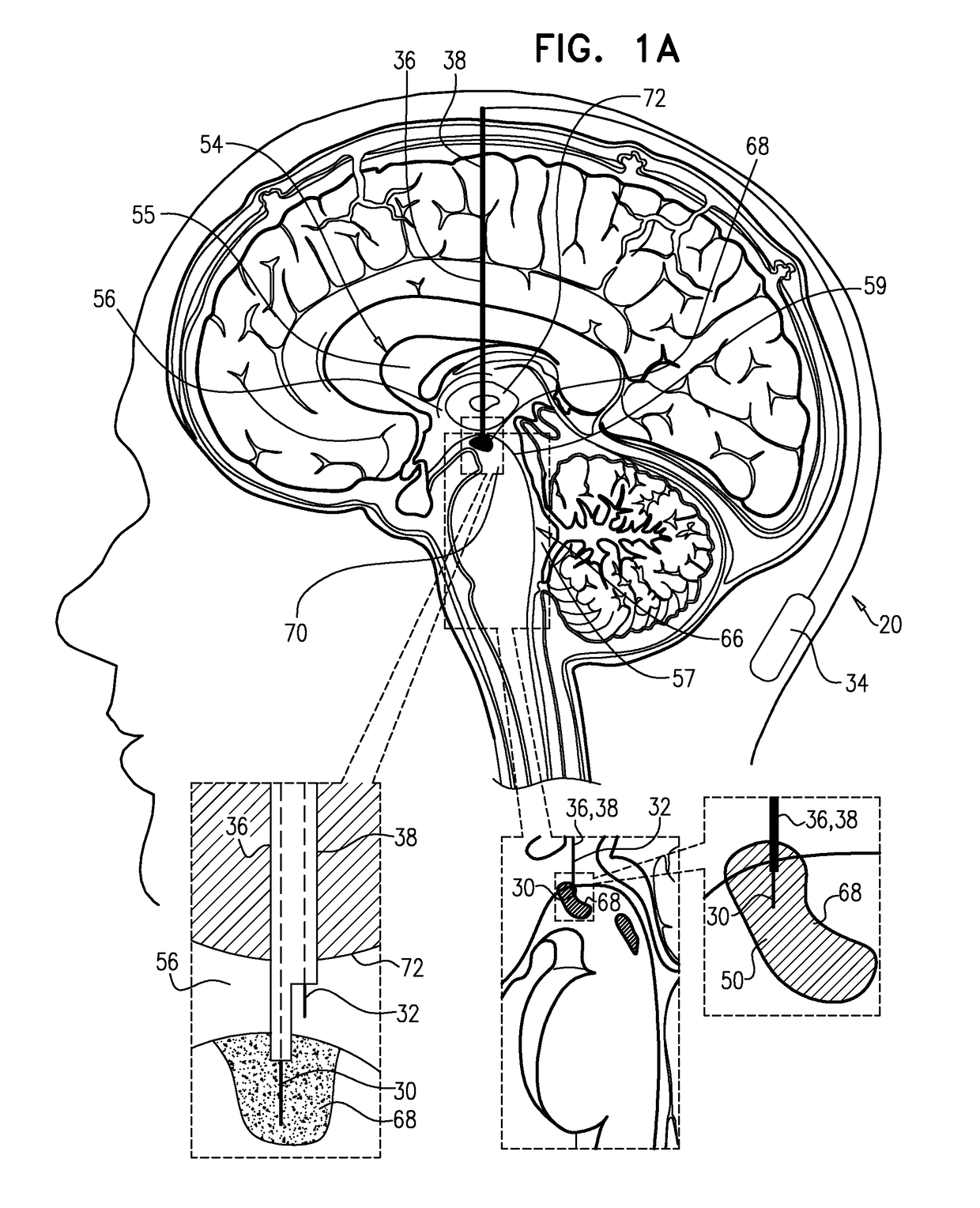
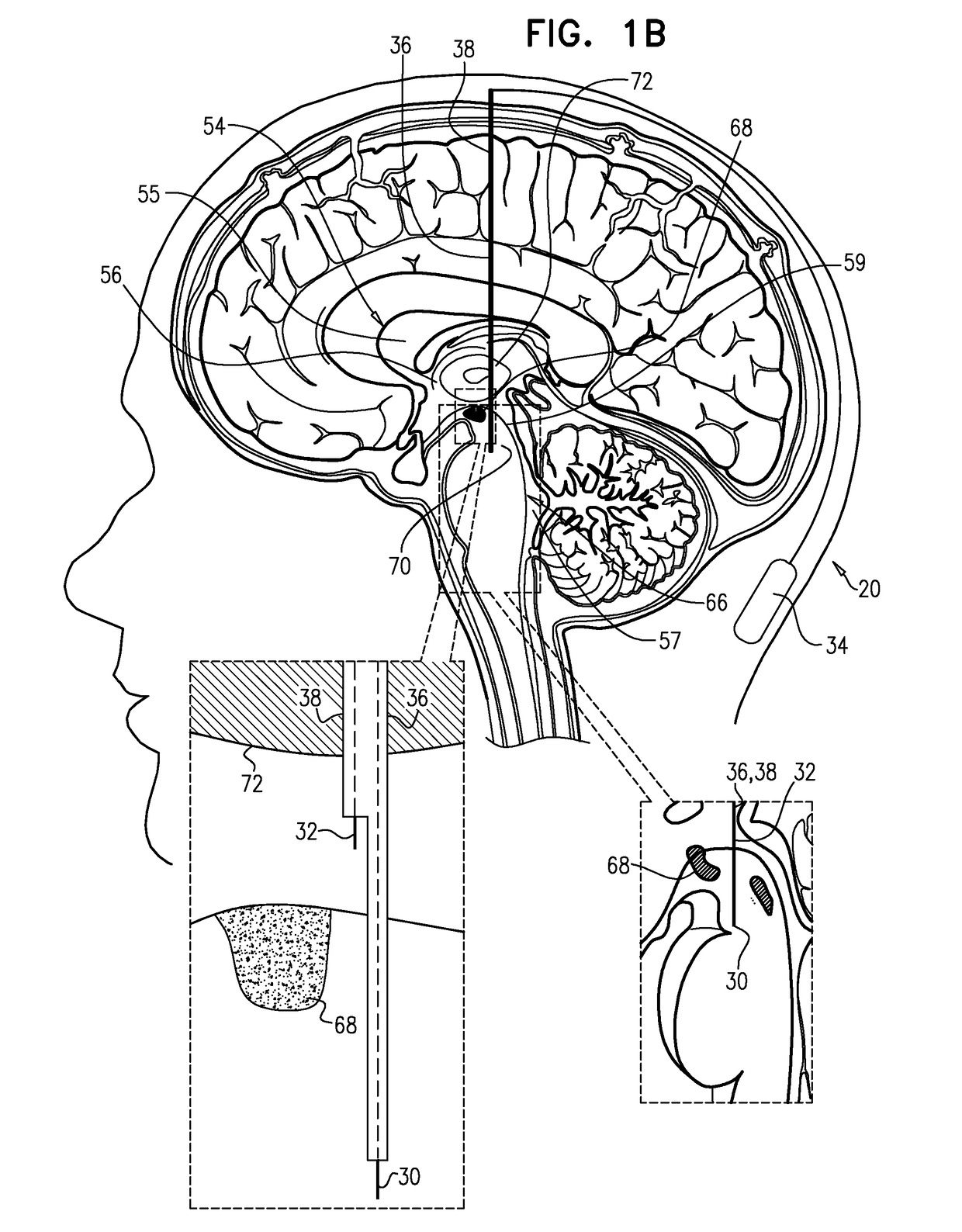
Method and device for reducing secondary brain injury
InactiveUS6929656B1Preventing secondary brain injuryTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingBrain coolingCerebral Spinal Fluid
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for reducing secondary brain injury. The apparatus includes a brain-cooling probe and a control console. The brain-cooling probe cools the brain to prevent secondary injury by cooling the cerebrospinal fluid within one or more brain ventricles. The brain-cooling probe withdraws a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from a ventricle into a cooling chamber located ex-vivo in close proximity to the head. After the cerebrospinal fluid is cooled it is then reintroduced back into the ventricle. This process is repeated in a cyclical or continuous manner in order to achieve and maintain a predetermined brain ventricle temperature lower than normal body temperature. The apparatus and method disclosed provides effective brain ventricle cooling without the need to introduce extra-corporeal fluids into the brain.
Owner:MEDCOOL
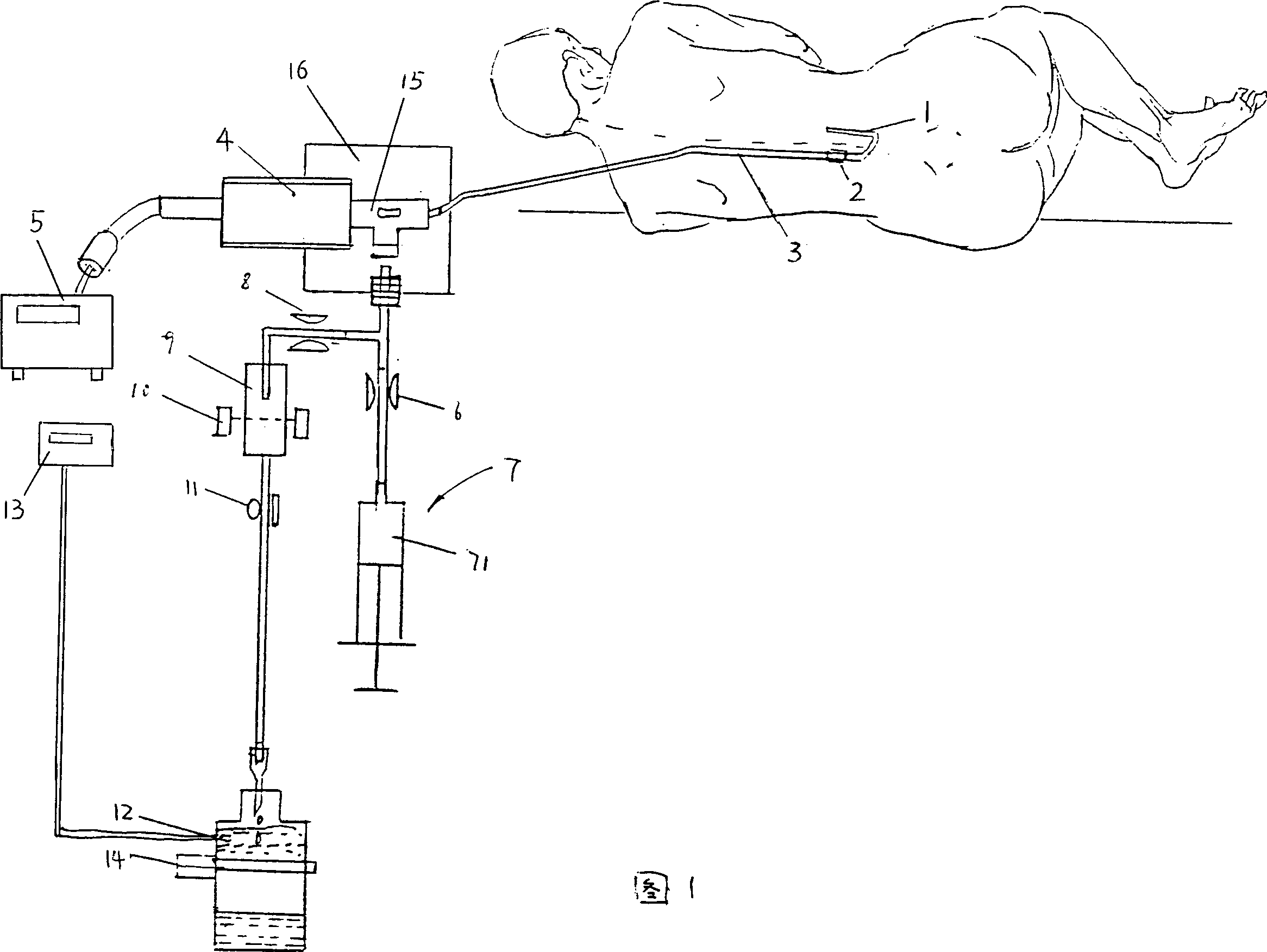
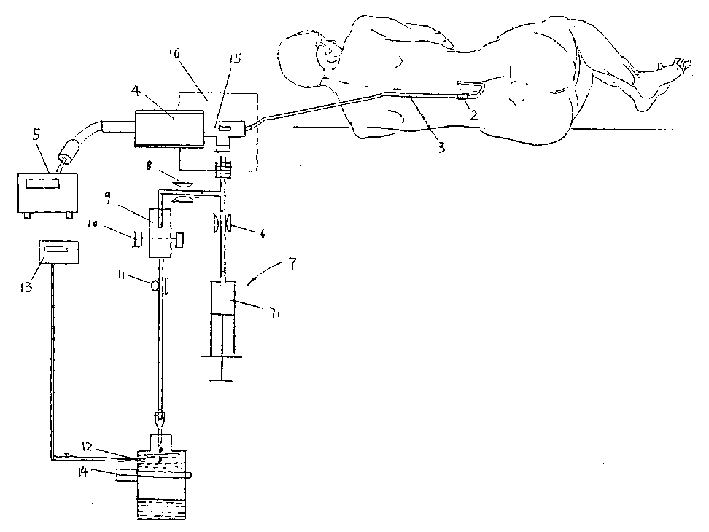
Monitoring and therapeutic apparatus for draining and displacing cerebrospinal fluid and pressurizing
InactiveCN1386552AEasy to operate, safe and reliableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseInjection pressure
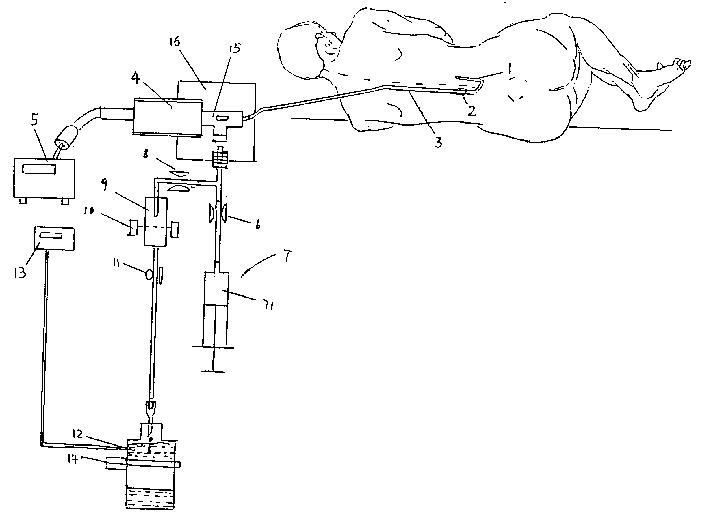
A therapeutic apparatus for treating intracranial disease by draining cerebrospinal fluid and monitoring injection pressure is composed of puncture needle, built-in tube for lower cavity of lumbar subarachnoid space or brain ventricle, pressure-measuring tube, pressure sensor, controller (YJR instrument), draining and lavation branches, and lavation pump. Its advantages are easy operation and high safety.
Owner:杨际芝
Method for shunting toxic substances from a brain ventricle to the sinus system
InactiveUS20070112293A1Reduce concentrationIncrease productionWound drainsIntravenous devicesGuillain-Barre syndromePolymyositis-Dermatomyositis
The present invention is directed to methods for controlled and optimized removal of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the CSF space of a patient. The methods are particularly intended for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other conditions which are caused by, or otherwise related to, the retention and / or accumulation of toxic substances in the CSF. One aspect of the present invention provides a method for shunting toxic substances present in a brain ventricle to the sinus system of an individual suffering from, or at risk of developing, a condition related to the retention and / or accumulation of toxic substances in the CSF, such as Alzheimer's disease. In addition to Alzheimer's disease, the present invention will be useful for treating other conditions resulting from the accumulation of toxic substances and resulting lesions in the patient's brain, such as Down's Syndrome, hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis of the Dutch-Type (HCHWA-D), epilepsy, narcolepsy, Parkinson's disease, polyneuropathies, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, dystrophy myotonic, other myotonic syndromes, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, brain tumors, Guillain-Barre-Syndrome, and the like.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
Electrical treatment of parkinson's disease
ActiveUS20180318575A1Increased dopamine synthesisReduction of dopamine synthesisHead electrodesExternal electrodesSubarachnoid spaceParenchyma
Apparatus is provided that includes a parenchymal electrode, configured to be implanted in brain parenchyma of a subject identified as at risk of or suffering from a synucleinopathy; and a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) electrode, configured to be implanted in a CSF-filled space of a brain of the subject, the CSF-filled space selected from the group consisting of: a ventricular system and a subarachnoid space. Control circuitry is configured to drive the parenchymal and the CSF electrodes to clear alpha-synuclein (aSyn) from the brain parenchyma into the CSF-filled space of the brain. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
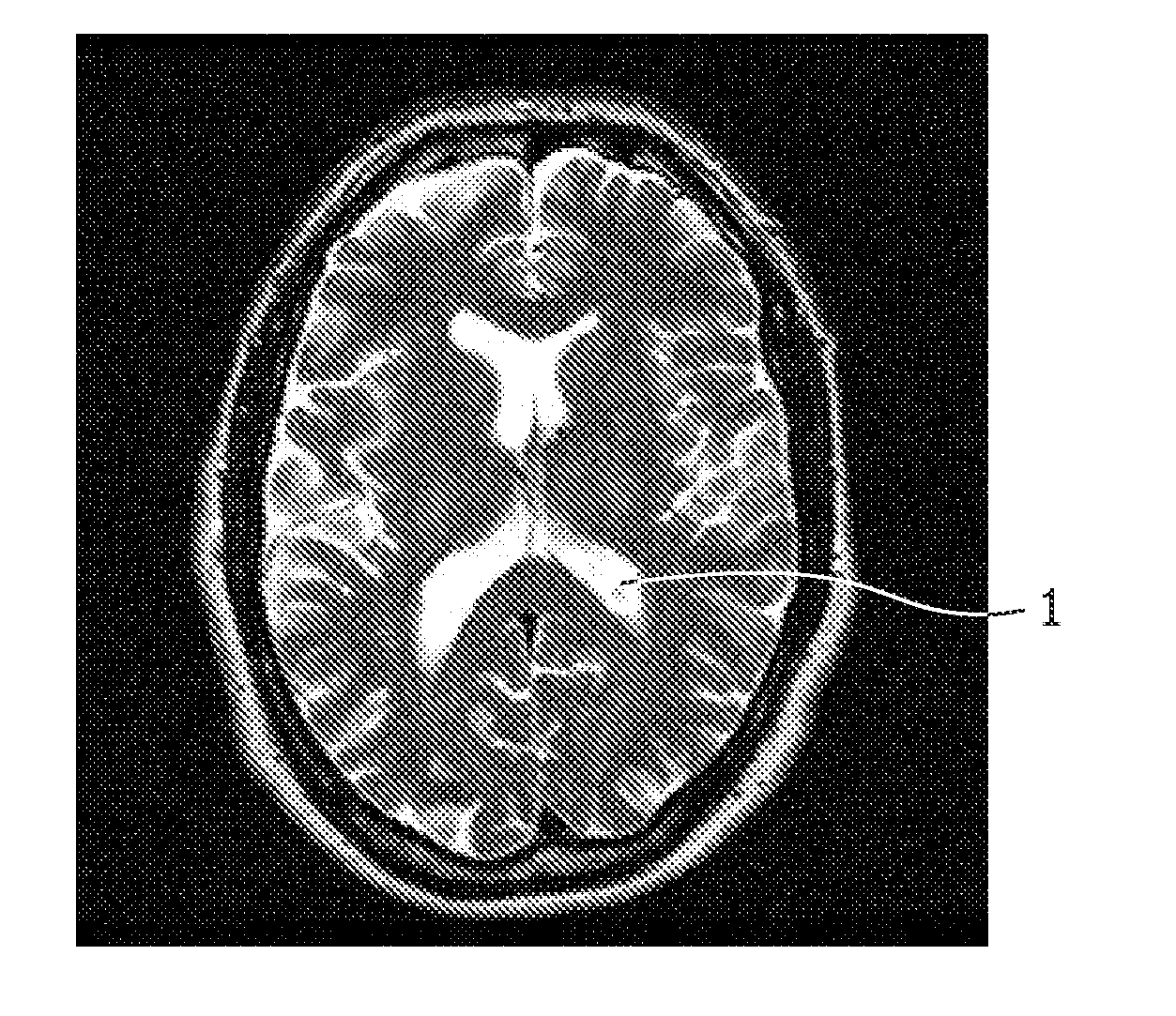
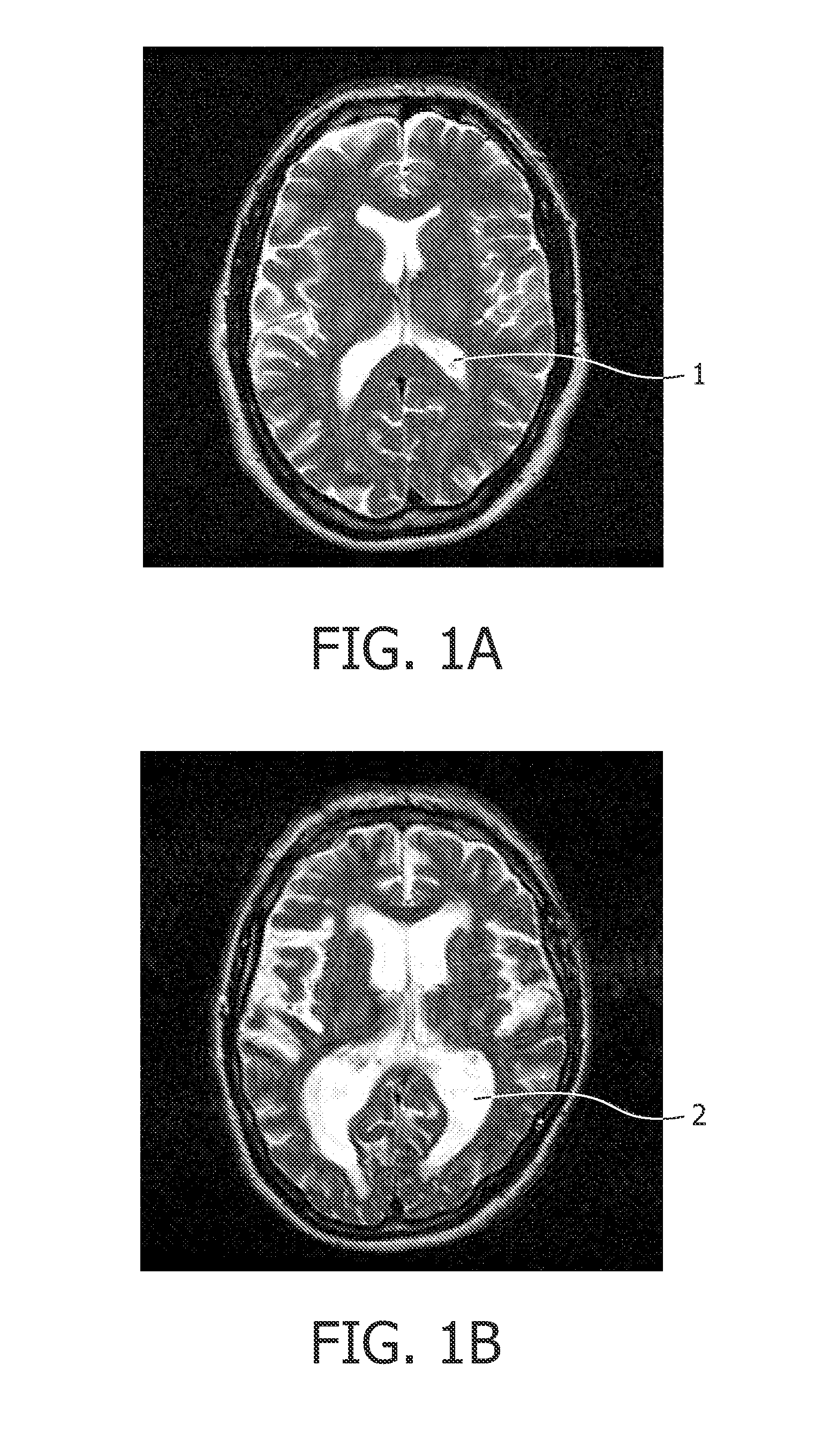
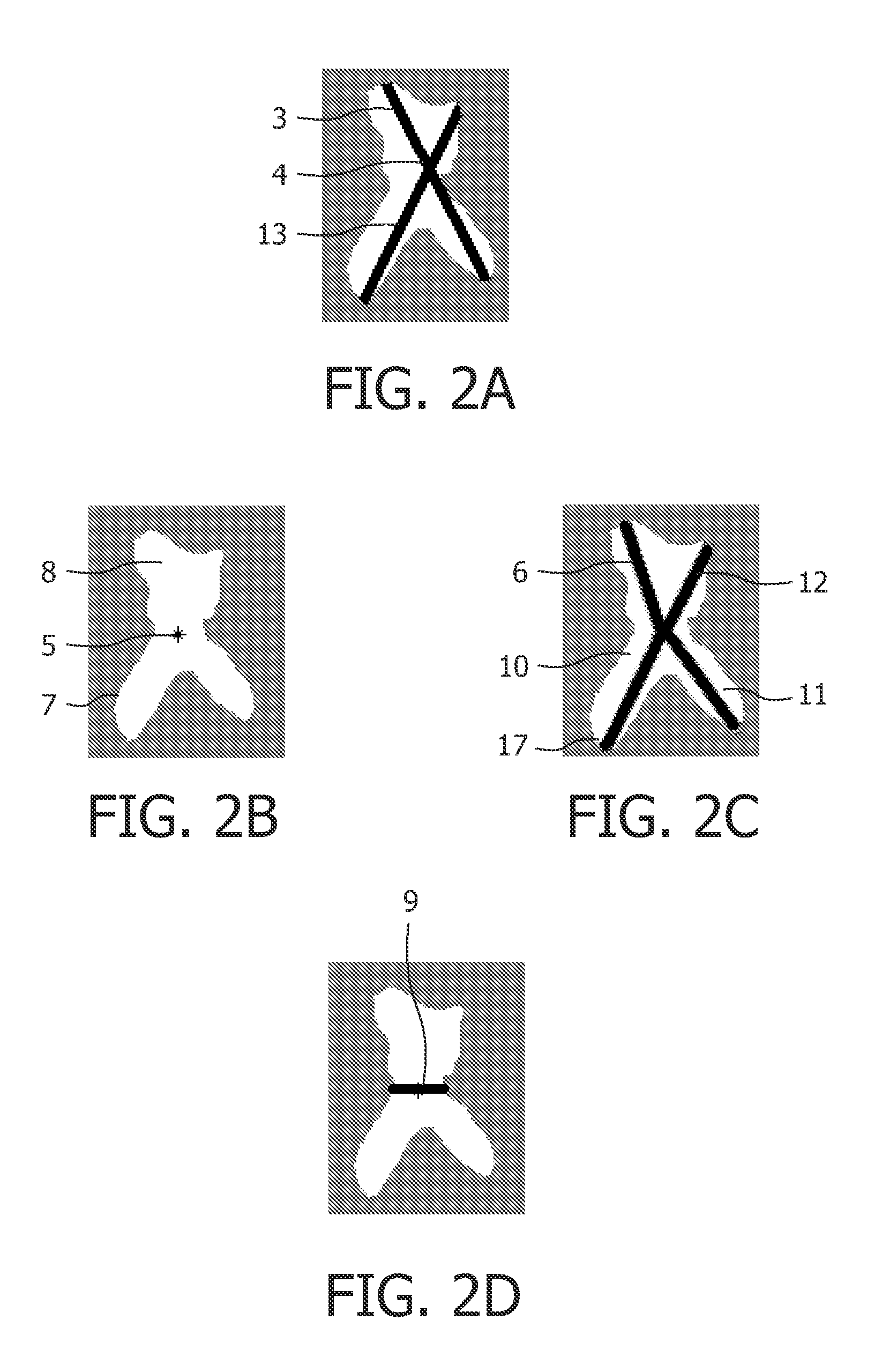
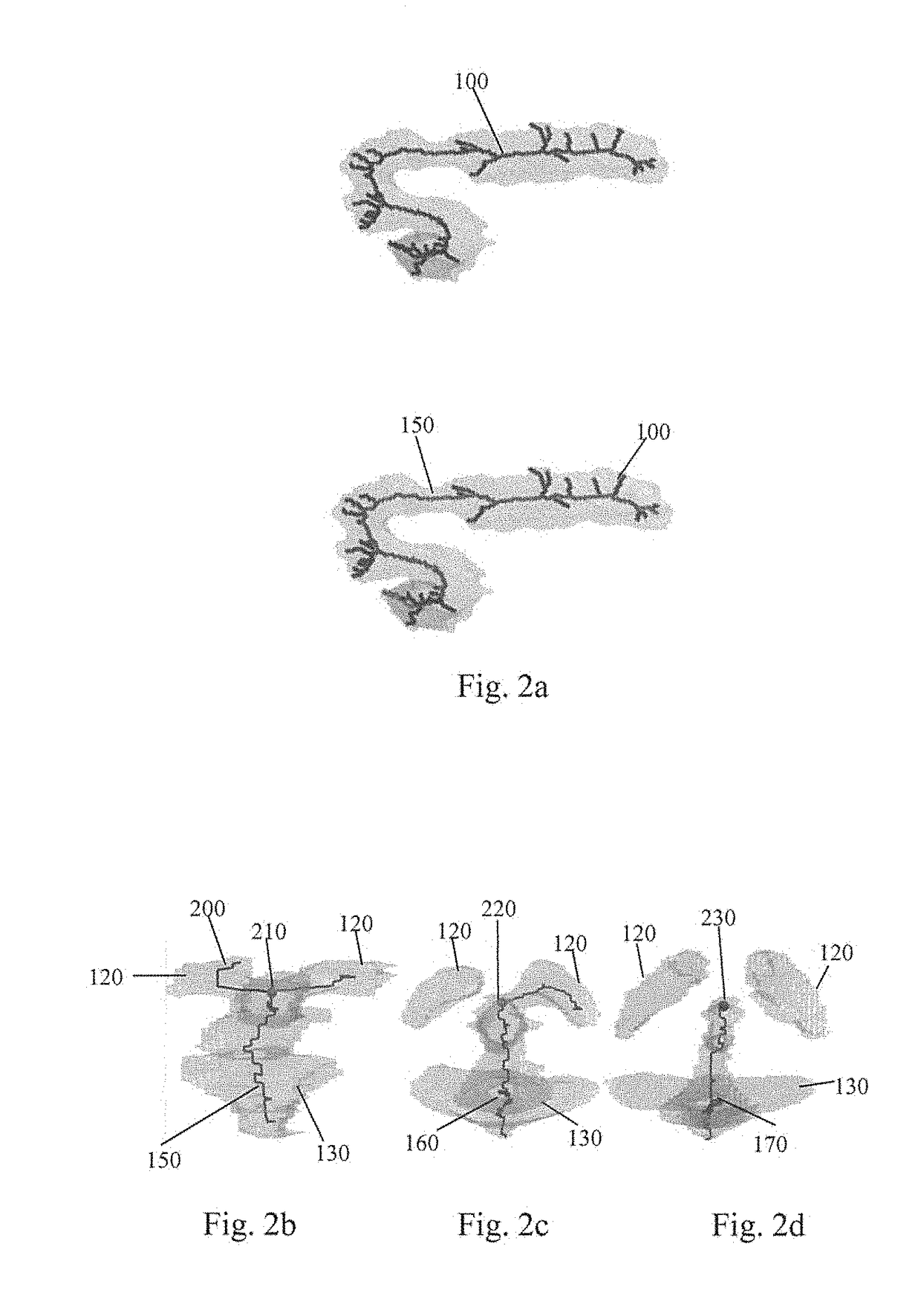
Brain ventricle analysis
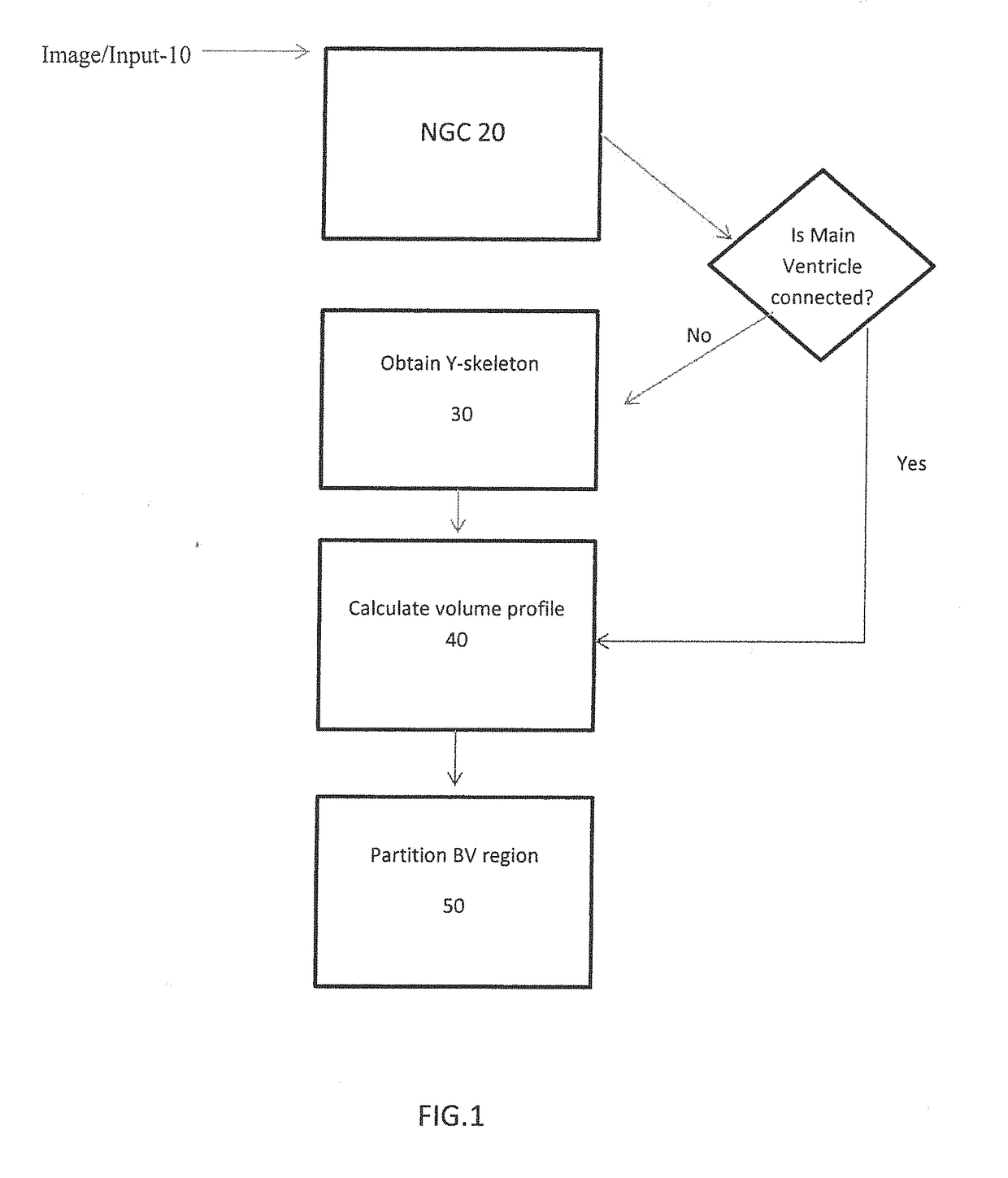
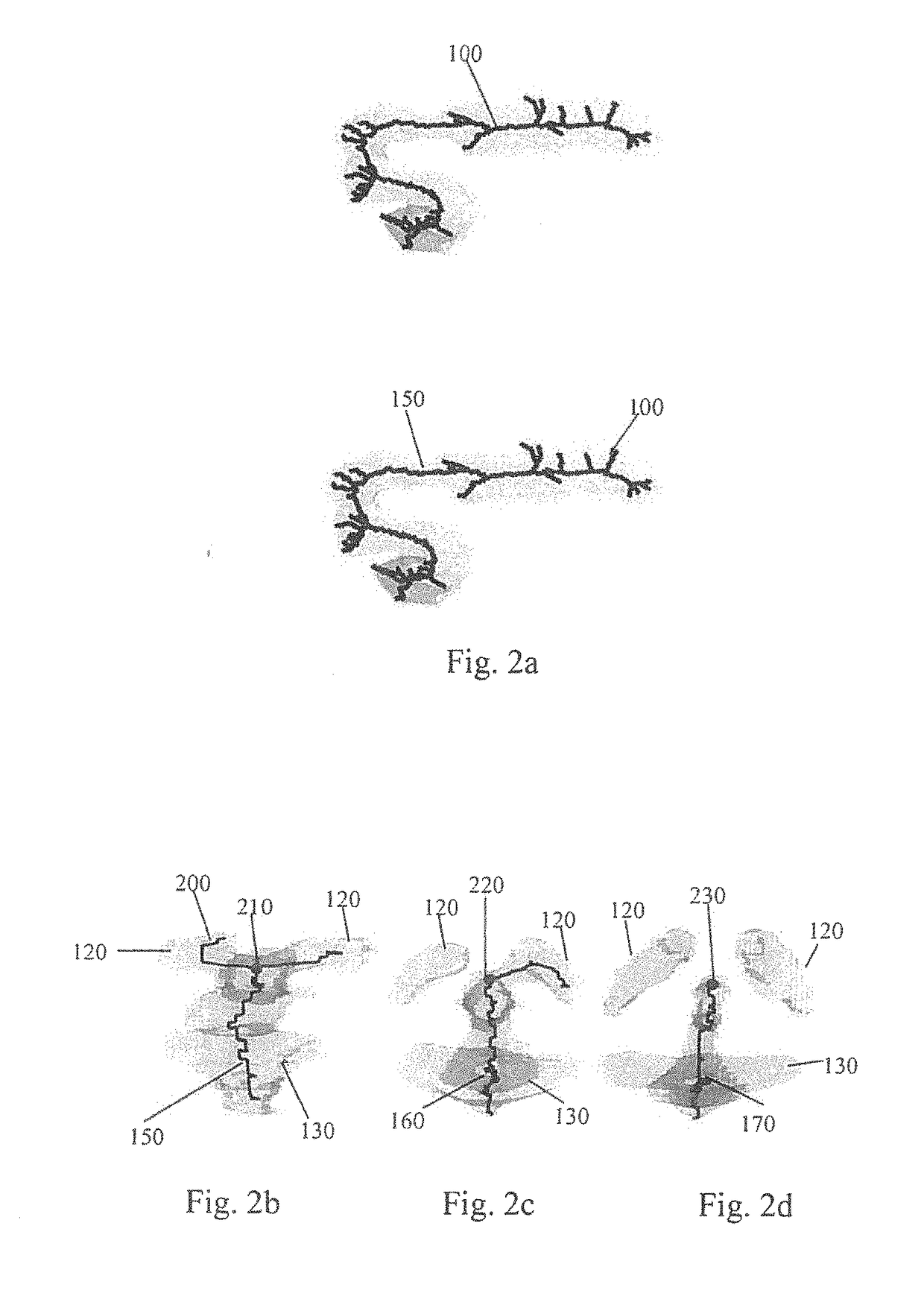
InactiveUS20110194741A1Computationally efficientRobust and accurate way of finding the length of a lobe of the ventricleImage enhancementImage analysisBrain VentricleComputer science
A system for analyzing a brain ventricle (8) is described. The system comprises an edge detector (52) for identifying an edge point (17) on an edge of the brain ventricle. Also, a length measurer (53) is provided for establishing a length measure of a path (10) starting from a central point (5) of the brain ventricle and terminating at the edge point (17). The edge detector (52) is arranged for detecting an edge point at an end of a lobe of the brain ventricle, the length measure corresponding to an extent of the lobe.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High stimulation ventricular puncture drainage training assessment standardization patient
PendingCN107871431AAdjustable pressureAdjustable drainage volumeEducational modelsPeristaltic pumpTraining assessment
The invention relates to the technical field of a medical teaching device, more exactly, relates to a high stimulation ventricular puncture drainage training assessment standardization patient, whichcomprises a high stimulation bareheaded adult upper body model, a cerebrospinal fluid circulation and pressure adjusting device, and an electronic monitoring alarm device; the high stimulation ventricular puncture drainage training assessment standardization patient is characterized in that the high stimulation bareheaded adult upper body model is provided with a high stimulation head, and eight ventricular puncture points commonly used in clinic are designed to be integrated puncture module which is closely matched with the puncture part and convenient to replace, and an annular electrode isarranged in the puncture module; sensors are closely distributed in a simulative brain; a voice chip, a loudspeaker, a reducing motor speed regulator, a peristaltic water pump, and a fluid storage bottle are arranged in the case; the case panel is provided with a cerebrospinal fluid circulation speed observing pipe, a resistance adjusting rotary button and a motor speed regulating rotary button, acerebrospinal fluid pressure testing pipe. When the ventricular puncture, the drainage training or the assessment effect are very vivid, the puncture module is convenient to replace, the automatic circulation pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid can be adjusted; when the puncture is wrong, the patient can automatically alarm by sound and light, thus the teaching quality is significantly improved.
Owner:营口市贵东医疗器械制造有限公司
Device for implantation of retrograde ventriculo-sinus shunt
InactiveUS7998103B2Prevent siphonDiscourage stagnation and clottingWound drainsCatheterVeinIntraventricular pressure
A shunt system for implantation of retrograde ventriculo-sinus shunts to establish a water tight connection that drains excess cerebrospinal fluid from hydrocephalic brain ventricles and delivers it, against the direction of blood flow, in a dural sinus comprising a valveless shunting catheter and a styforator. Retrograde ventriculo-sinus shunts mimic natural drainage of cerebrospinal fluid; they utilize natural forces to regulate the intraventricular pressure and to maintain it more than the sinus pressure, to prevent regurgitation of blood in the shunting catheter as a result of changes in posture or intra-thoracic pressure, to maintain a steady flow of cerebrospinal fluid to the venous circulation at a rate equal to and dependent upon the rate of it's formation, to discourage stagnation and clotting of blood at the venous end of the connection and to prevent siphonage in the erect posture.
Owner:EL SHAFEI ISMAIL LOTFY +1
Intravascular sub-hypothermia therapeutic instrument for intensive care unit
InactiveCN105287095AImprove securityEase of workTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingHuman bodyTriple lumen catheter
The invention provides an intravascular sub-hypothermia therapeutic instrument for an intensive care unit. The intravascular sub-hypothermia therapeutic instrument for the intensive care unit comprises a device in a human body and a device outside the human body, the device in the human body comprises a central temperature sensor probe and a central pressure sensor probe which are located on the forefoot position of the paracele of the human body and a three-cavity catheter located in a blood vessel of the human body, the device outside the human body comprises a control panel which conducts coordination treatment on the whole therapeutic instrument, a normal saline tank containing normal saline and a temperature regulating tank which contains cooling liquid and conducts regulation control on the temperature of the cooling liquid, and a complete circulation system is formed among the normal saline tank, the temperature regulating tank and the three-cavity catheter. The intravascular sub-hypothermia therapeutic instrument for the intensive care unit is simple in structure and convenient to use, the defects of an existing traditional cooling method are overcome, and the safety of a patient is improved by conducting heat exchange in the blood vessel; the temperature of a brain ventricle is measured, the temperature accuracy is guaranteed, and the safety is further improved; the temperature regulating chamber is arranged, rapid cooling and slow rewarming can be achieved, and the working difficulty of medical staff is reduced.
Owner:邹秀丽
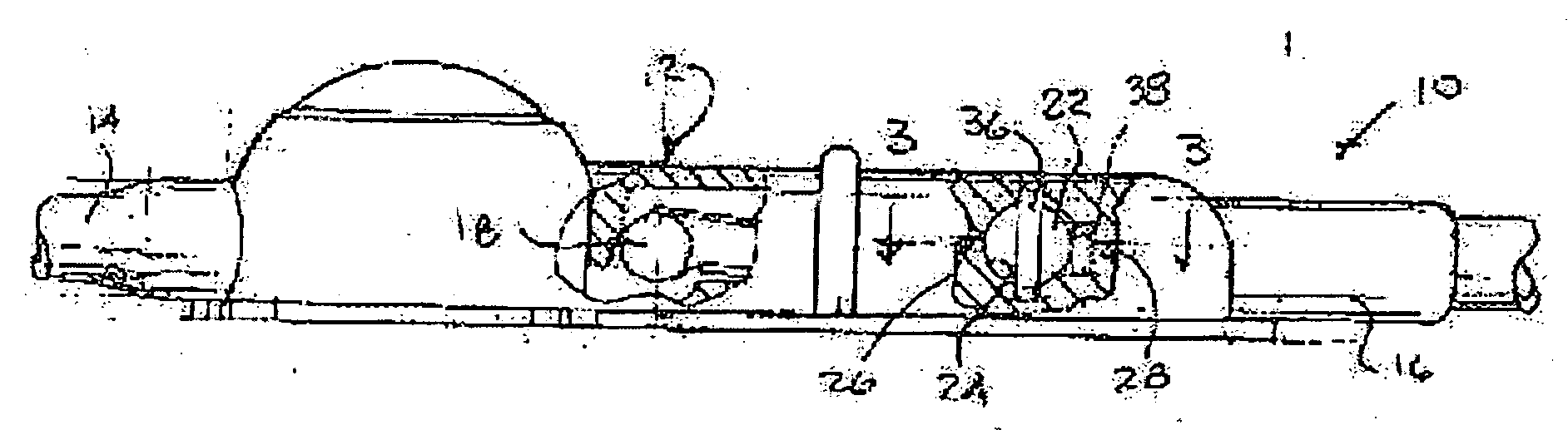
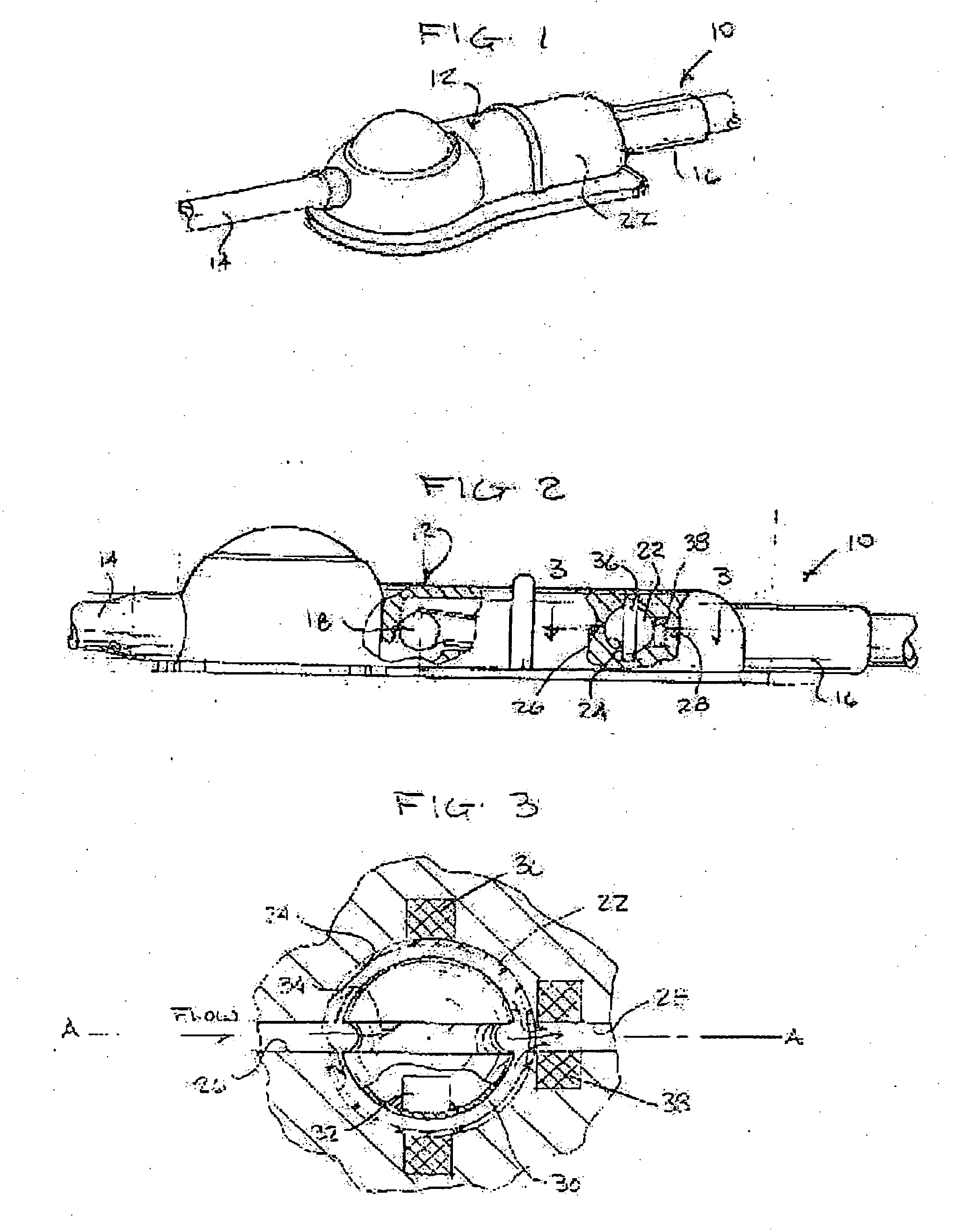
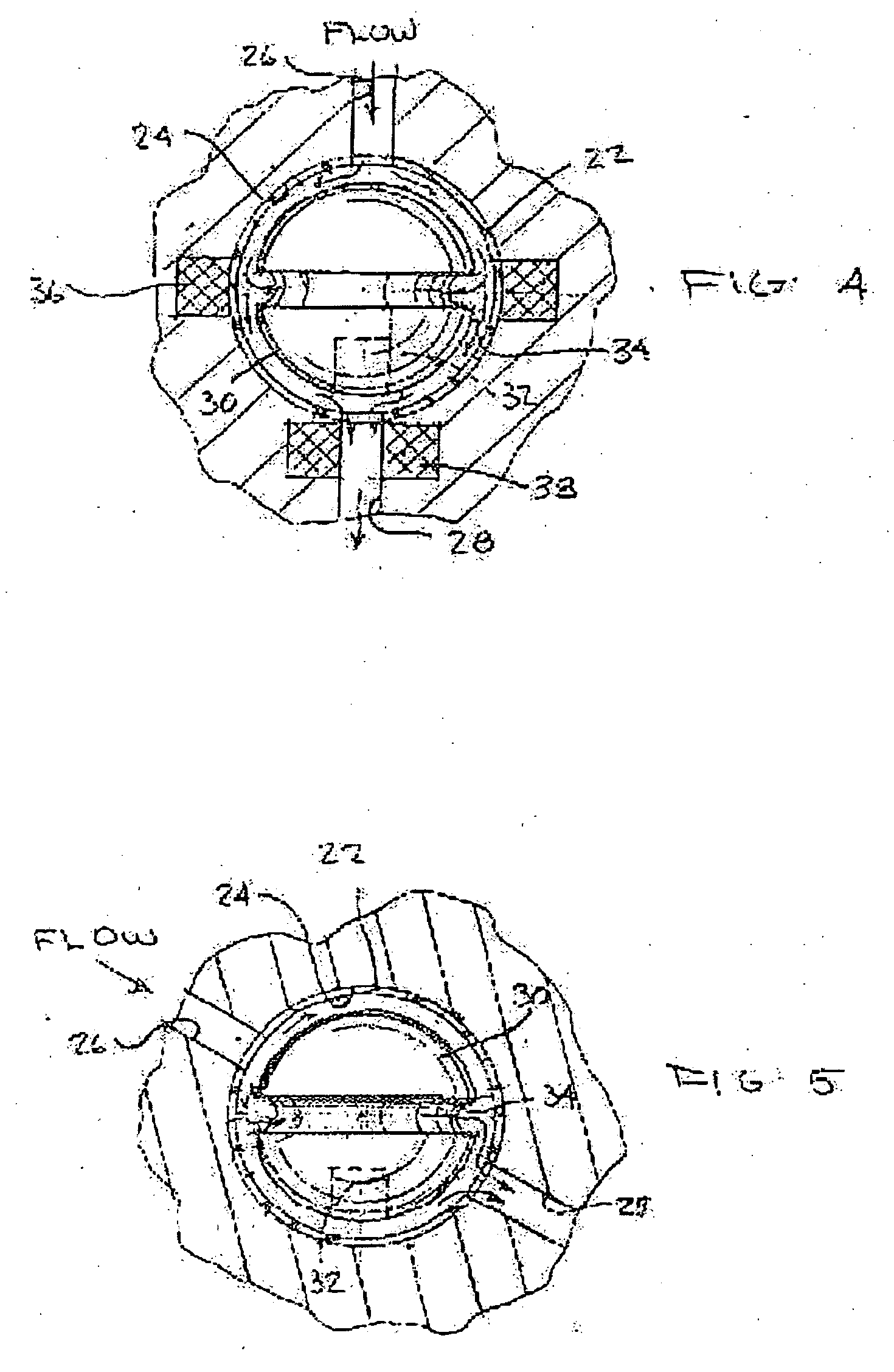
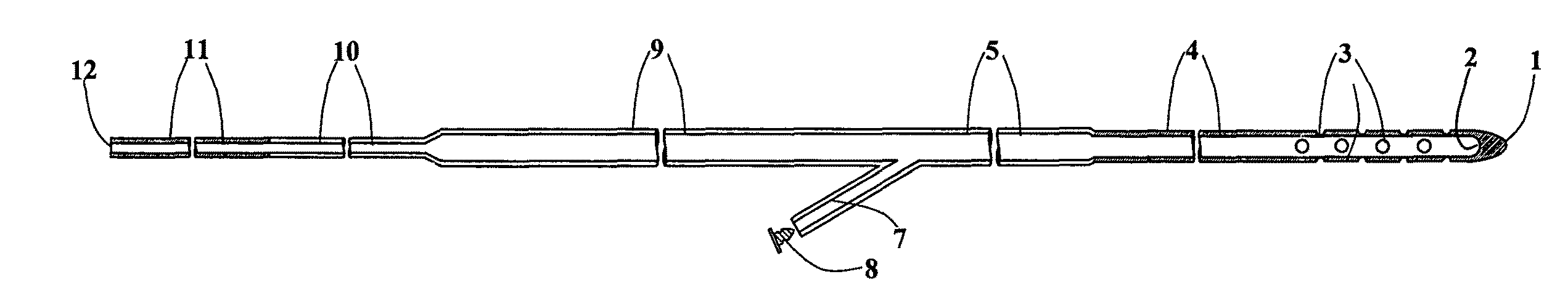
Implantable shunt system and method
InactiveUS20070055196A1Preventing high rateIncrease chanceWound drainsMedical devicesThrombusCheck valve
An implantable shunt system 10 and method include a ventricle catheter 12 for insertion into the brain ventricle, a distal catheter 14 for insertion into a selected terminus in the patient, and a regulating valve 16 for controlling flow through the distal catheter. An implantable pump 24 delivers a liquid thrombolytic solution upstream from the regulating valve, and a check valve 18 prohibits flow through the check valve in the direction toward the brain ventricle. A storage reservoir or chamber 26 is provided for containing the thrombolytic agent.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Computer Based Method for Determining the Size of an Object in an Image
InactiveUS20140357978A1Improve simplicityImage enhancementMedical imagingComputer visionBrain Ventricle
Volume changes in a brain, brain ventricle, or hippocampus are quantitatively extracted from a comparison of 3D before and after images using an algorithm that distorts a triangulated surface of the before image to produce the surface of the after image and calculates the volume change from the area change.
Owner:PAI AKSHAY +4
Method for gestational age estimation and embryonic mutant detection
ActiveUS20170213340A1Accurate stagingAbnormality in shapeImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareMedicine
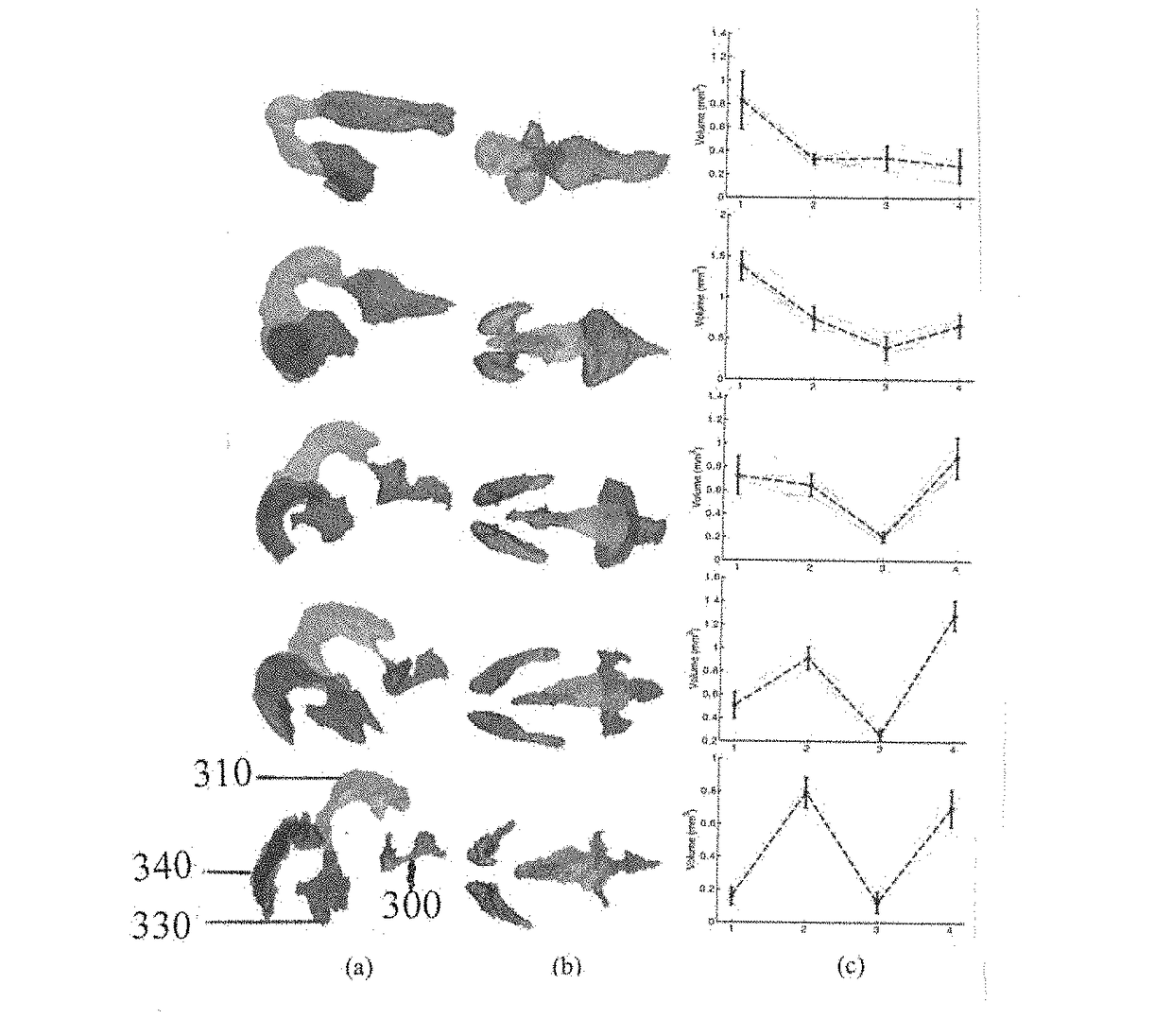
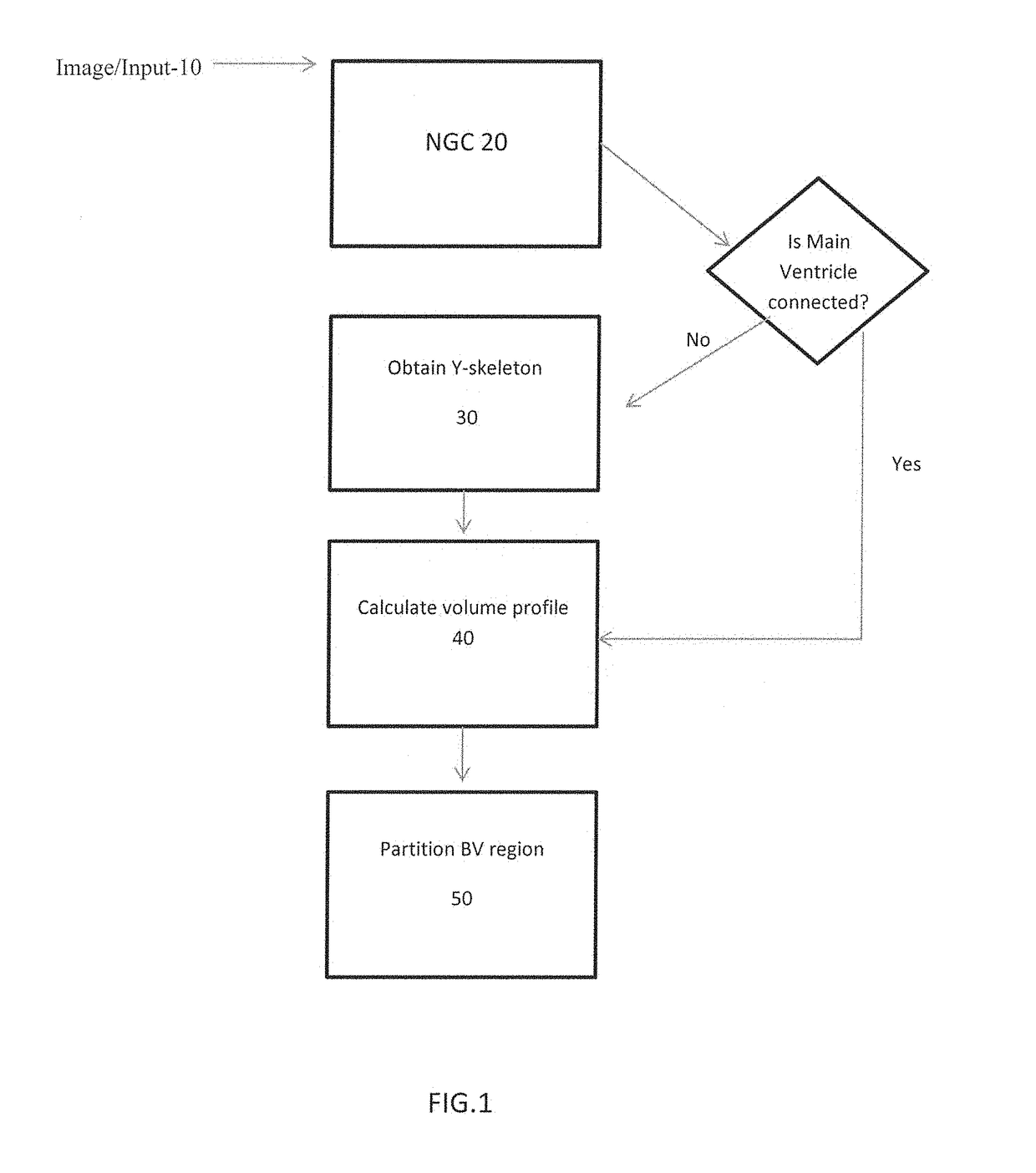
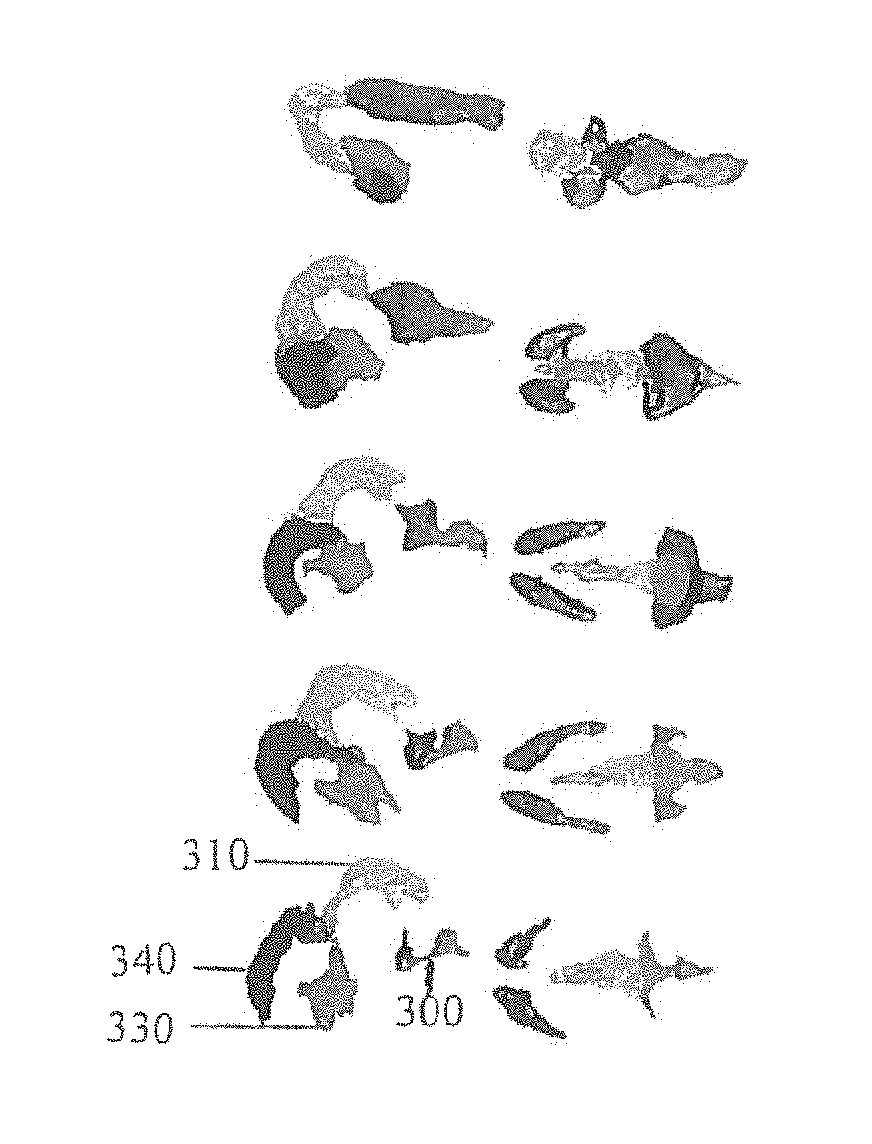
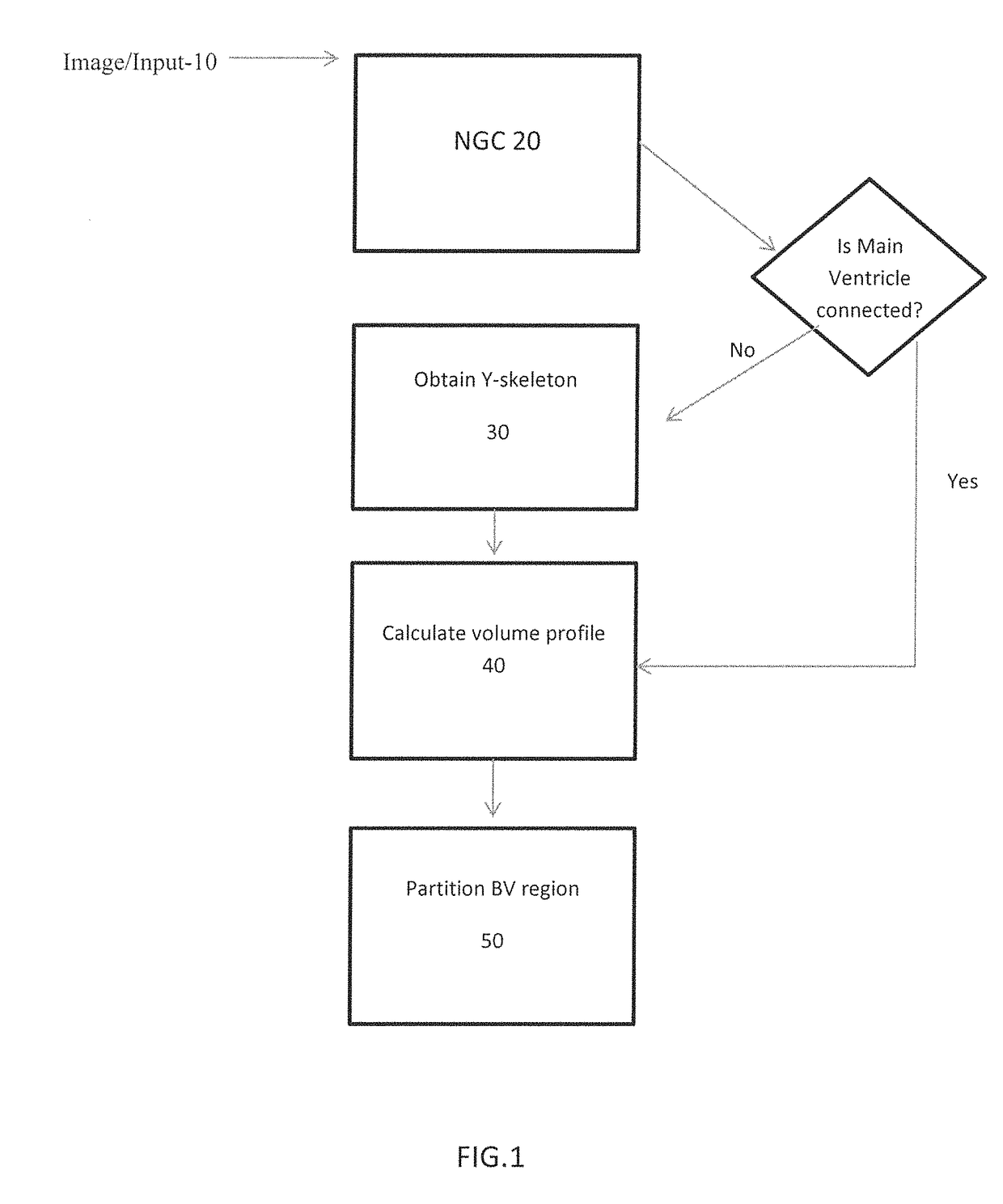
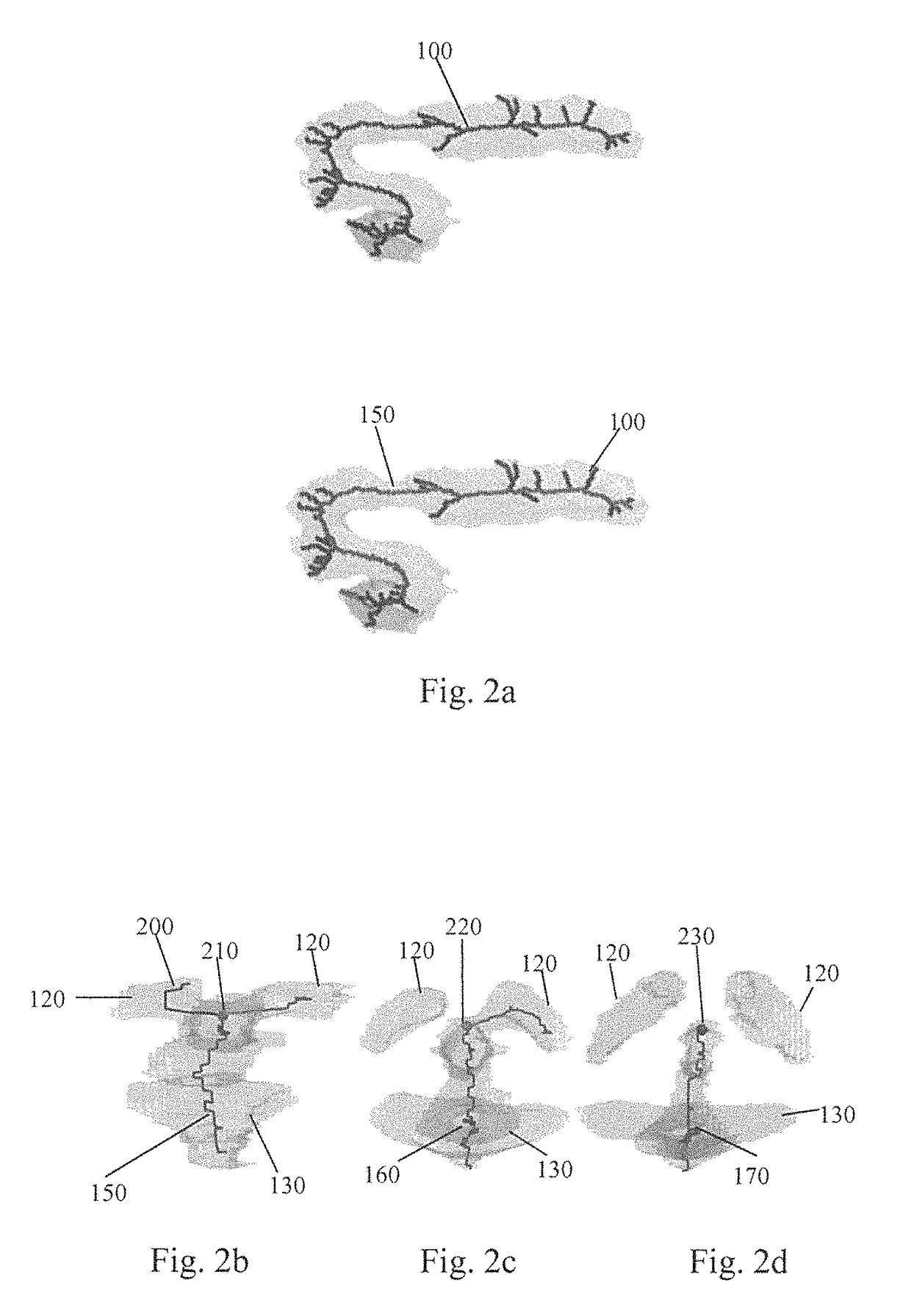
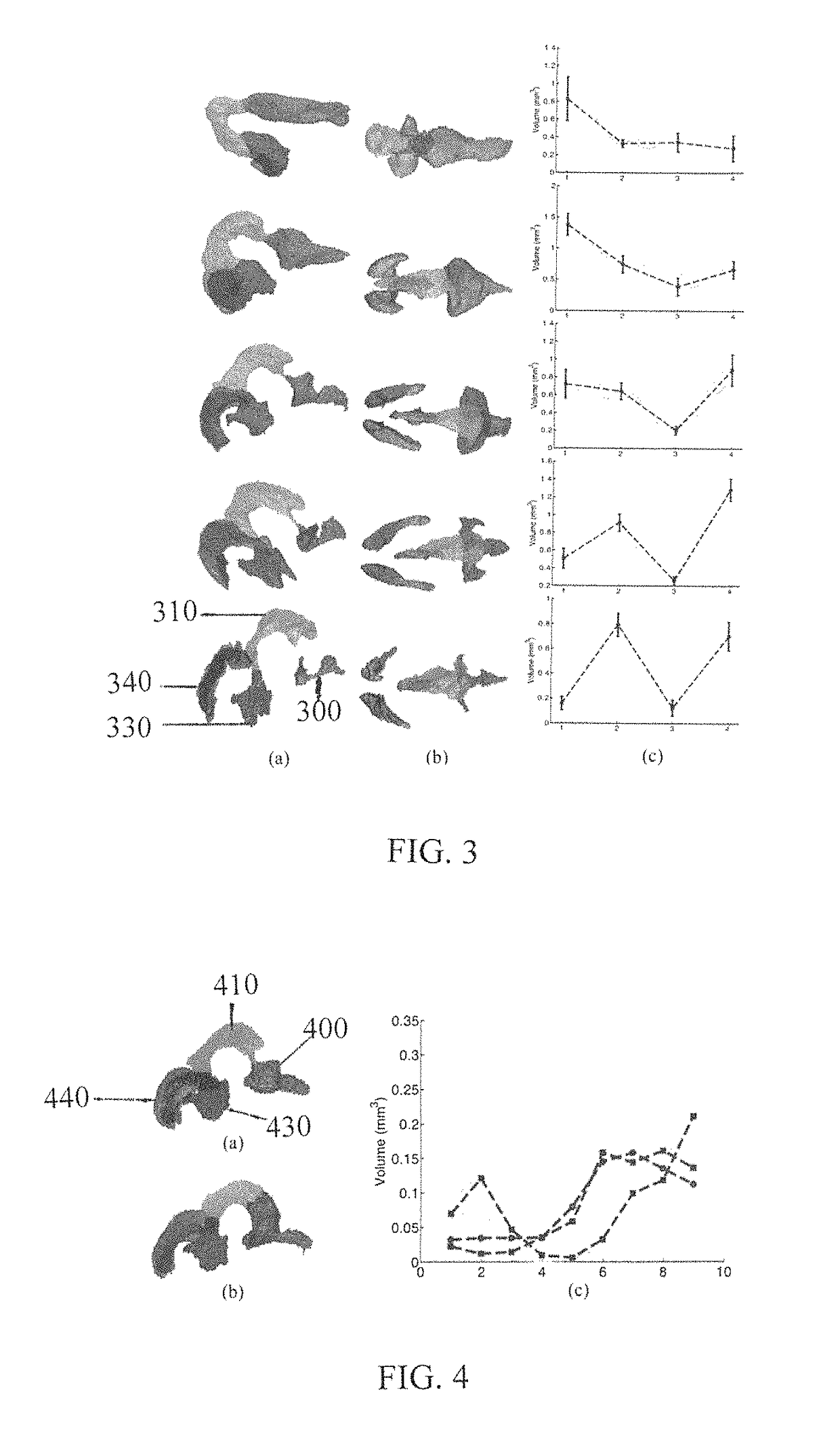
A method to characterize shape variations in brain ventricles during embryonic growth in mammals, the method including extracting a brain ventricle skeleton from one or more images, calculating a volume profile for the skeleton using the extracted images, partitioning the brain ventricle based on the volume profile along the skeleton, the brain ventricle being partitioned into two lateral ventricles and a main ventricle, the main ventricle being further partitioned into three sub regions, determining volume vectors of the two lateral ventricles and the three sub regions, computing a means square error between the determined computed volume vectors and a pretrained mean volume vector of embryos during different gestational stages, and classifying the embryo to the gestational stage having the lowest mean square error. A method to characterize mutant detection in mammals, the method including acquiring one or more images, computing a volume profile directly along a path of the detected skeleton from the one or more images, aligning the volume profile against a standard profile, and evaluating the volume profile against the standard profile to detect a mutation.
Owner:RIVERSIDE RES INST +1
Therapy for frontotemporal dementia
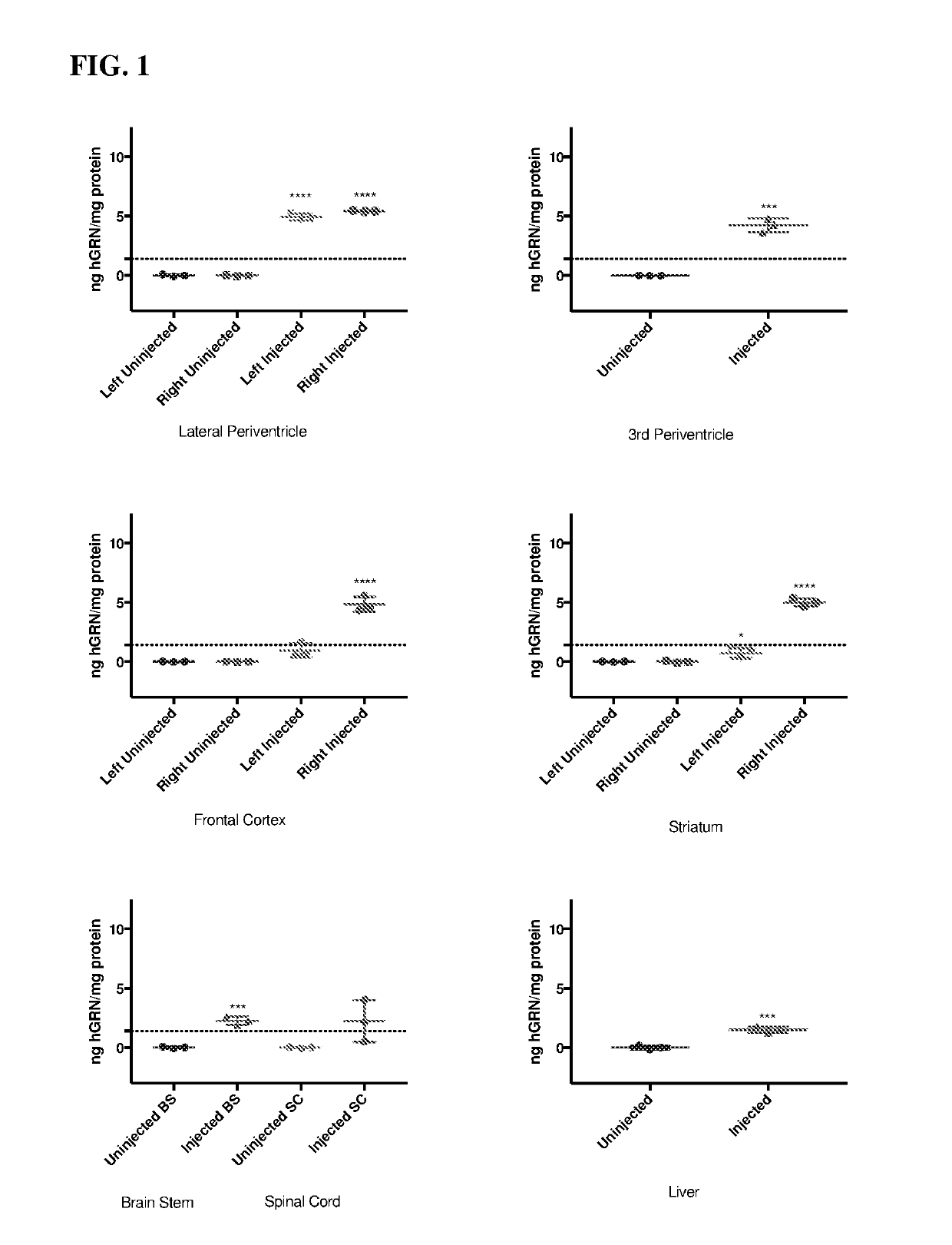
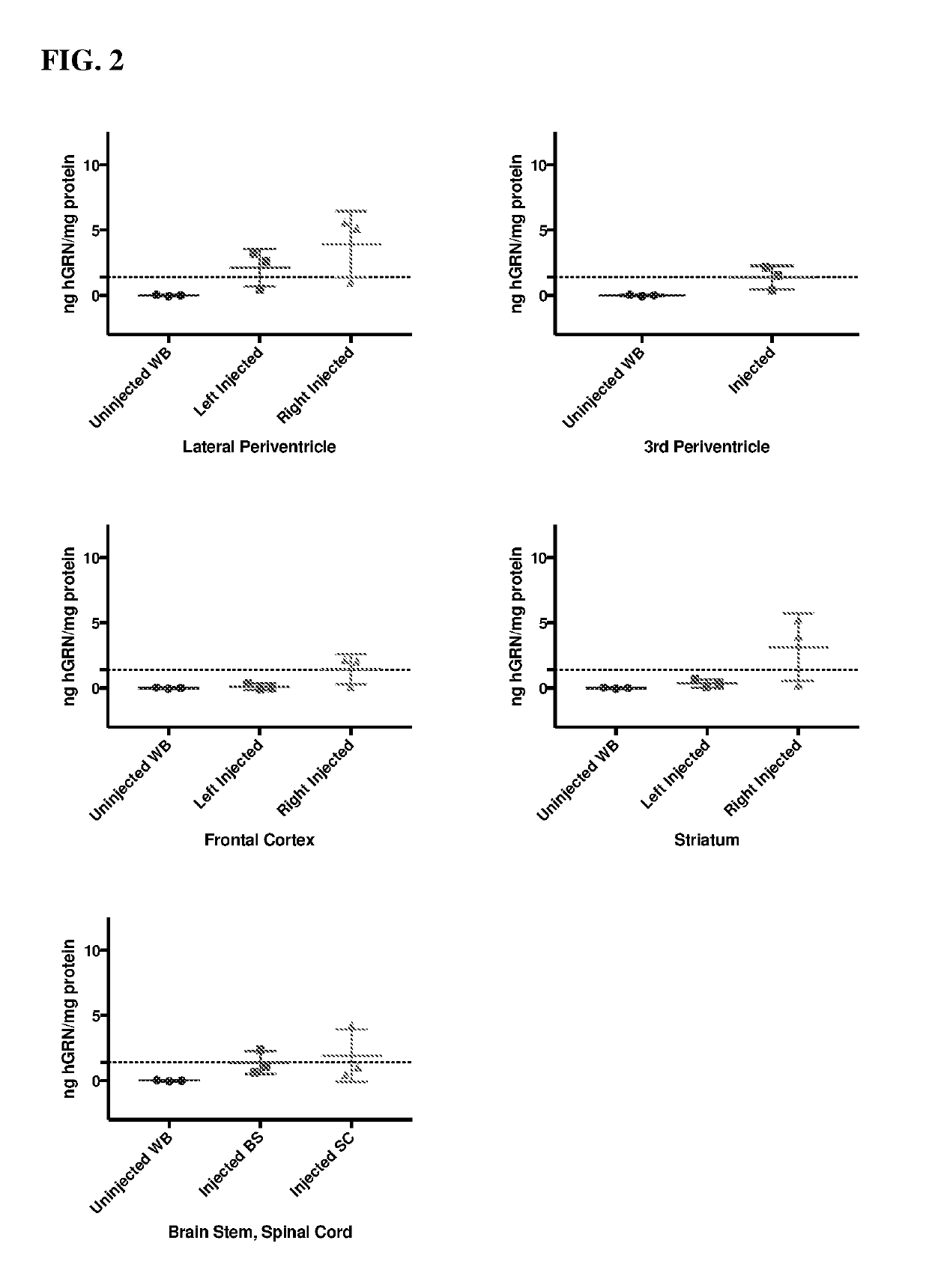
PendingUS20190328906A1Prevent degradationInhibits and decrease and prevents neuron degeneration and deathNervous disorderPeptidesBrain VentricleMammalian expression
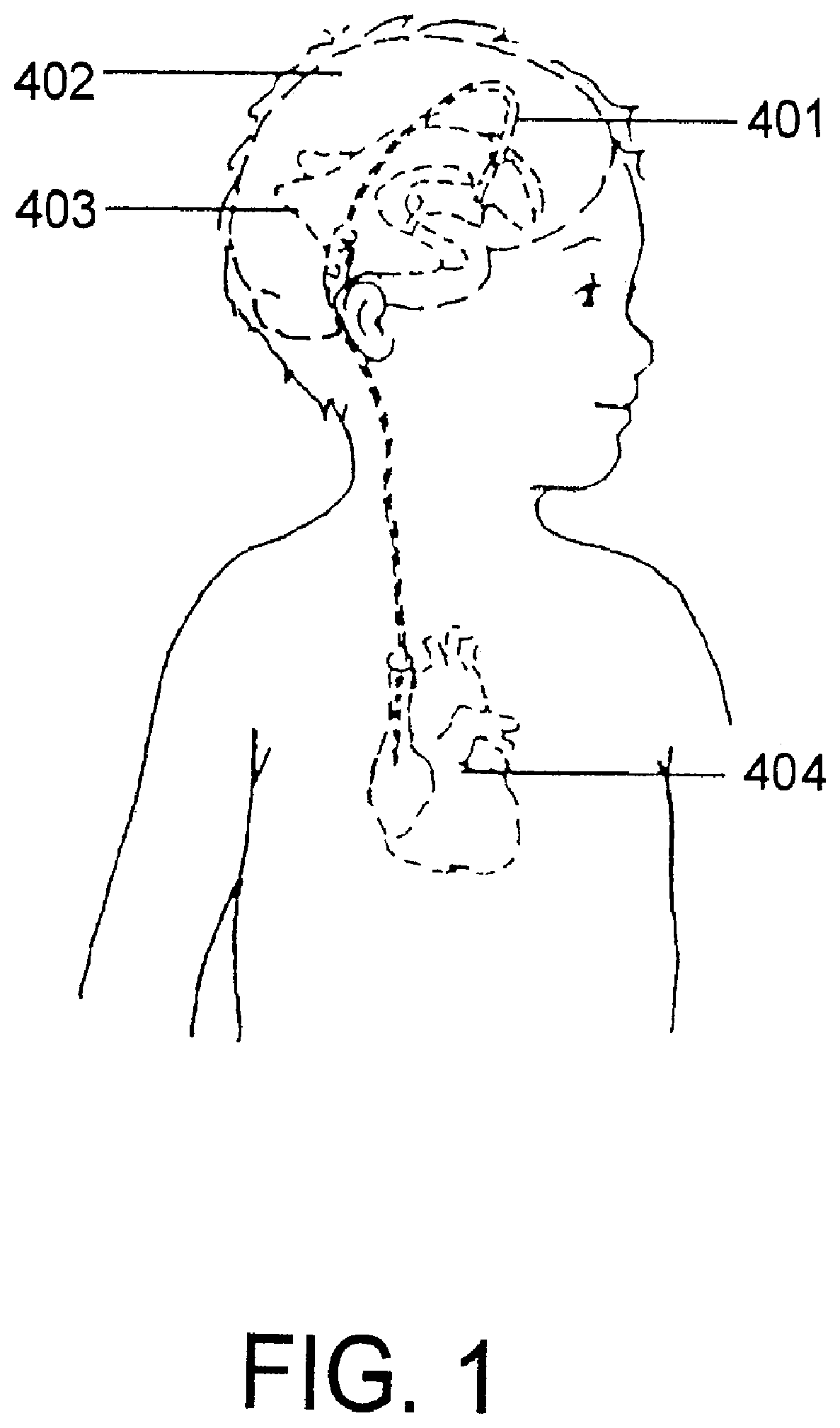
The invention provides methods and uses for delivering progranulin to the central nervous system (CNS) of a mammal. Methods and uses include, for example, administering to a mammal a vector comprising a nucleic acid encoding progranulin, variant, derivative or functional fragment thereof to the mammal's brain ventricle to transduce CNS cells and / or cells that contact the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the mammal such that the cells express the progranulin, variant, derivative or functional fragment thereof.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
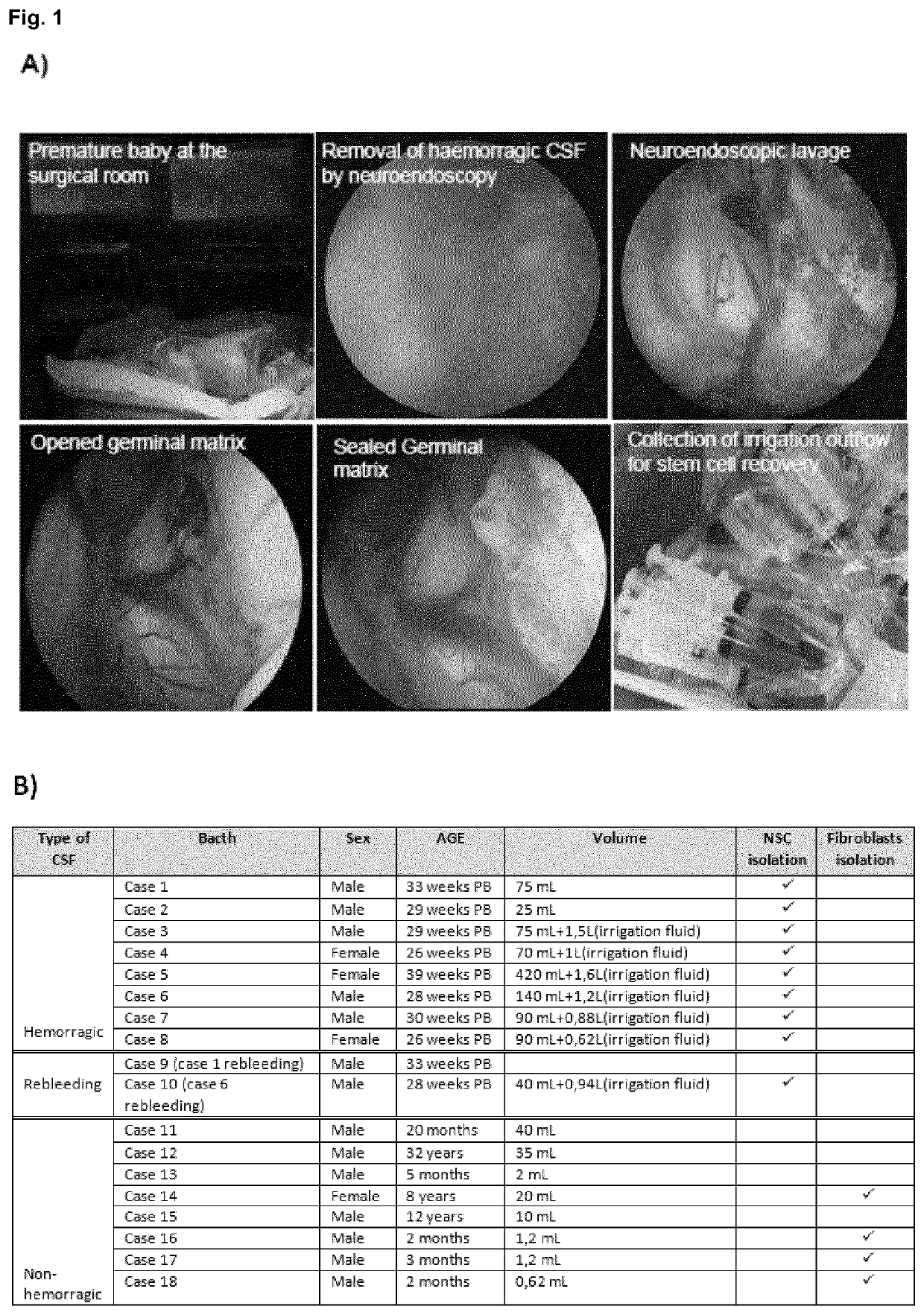
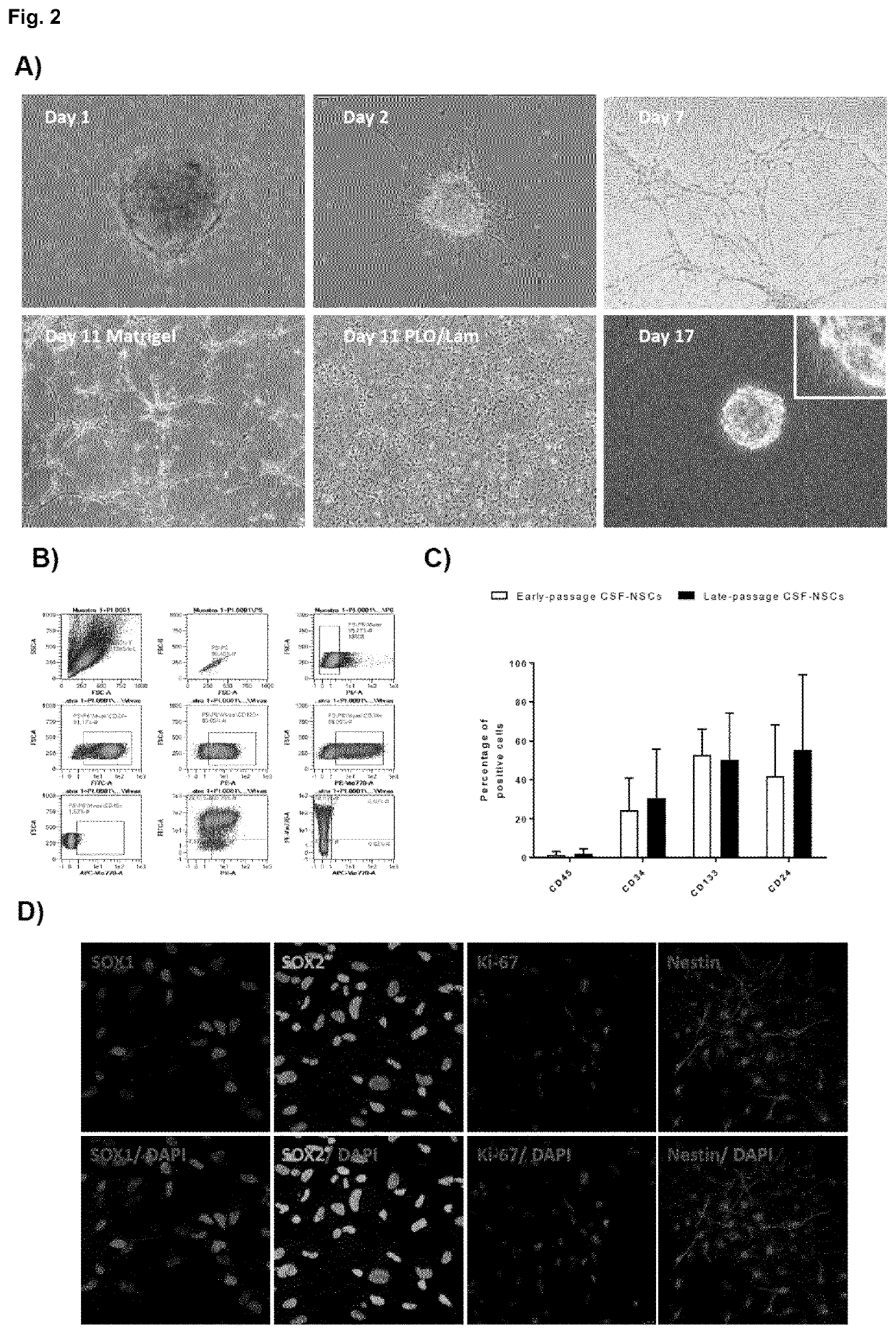
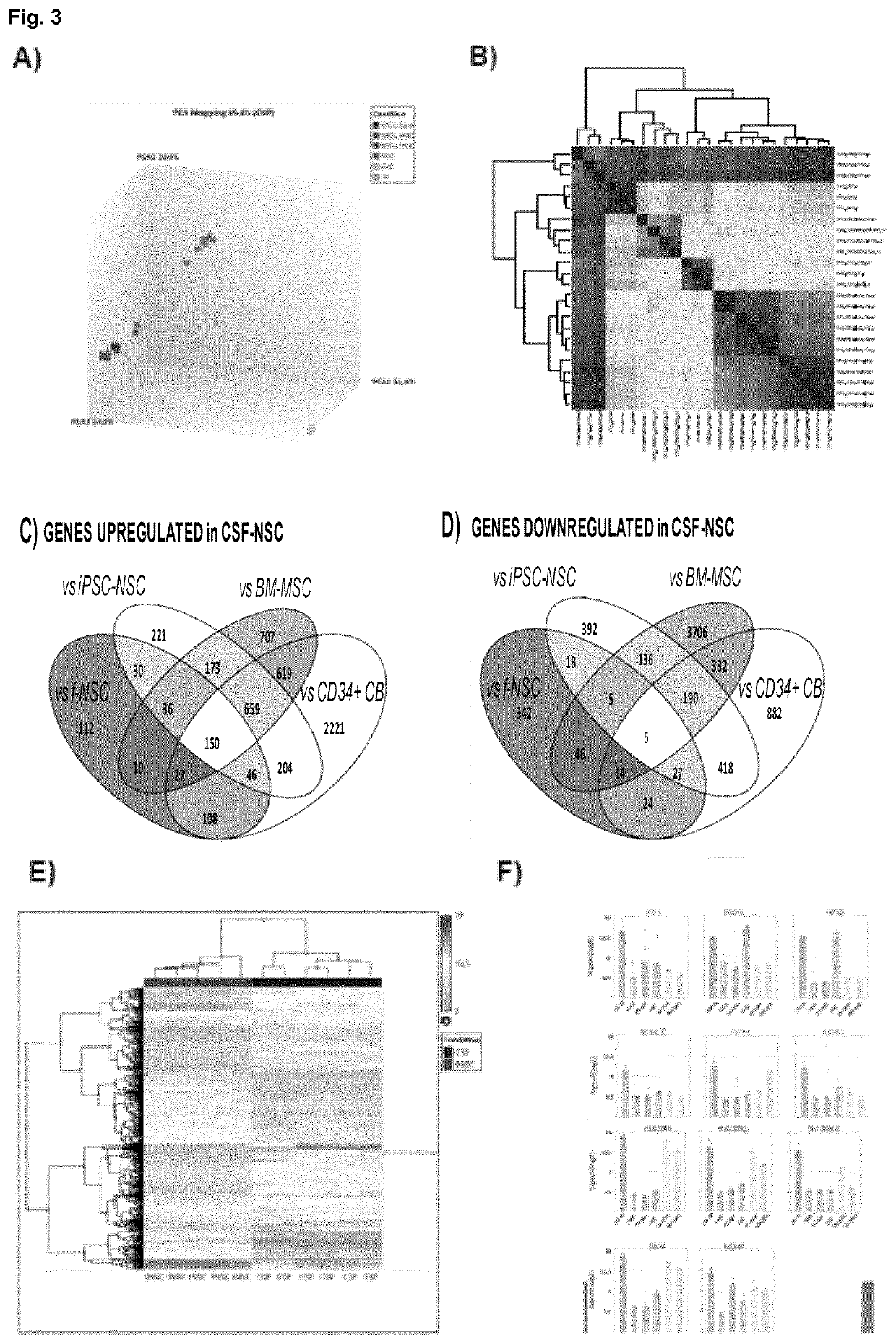
Hemorrhagic cerebrospinal fluid neural stem cells
PendingUS20210207089A1Easily and robustly isolatedHigh expressionNervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseFibroblast
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure neural stem cells (NSCs) from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of premature babies with Intraventricular haemorrhage, which produces a population enriched in NSC-CSF cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of CSF-NSC cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including Intraventricular haemorrhage and post-hemorrhage hydrocephalus / developmental deficits.
Owner:FUNDACION PUBLICA ANDALUZA PROGRESO & SALUD +2
Monitoring and therapeutic apparatus for draining and displacing cerebrospinal fluid and pressurizing
InactiveCN1186102CEasy to operate, safe and reliableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseInjection pressure
A therapeutic apparatus for treating intracranial disease by draining cerebrospinal fluid and monitoring injection pressure is composed of puncture needle, built-in tube for lower cavity of lumbar subarachnoid space or brain ventricle, pressure-measuring tube, pressure sensor, controller (YJR instrument), draining and lavation branches, and lavation pump. Its advantages are easy operation and high safety.
Owner:杨际芝
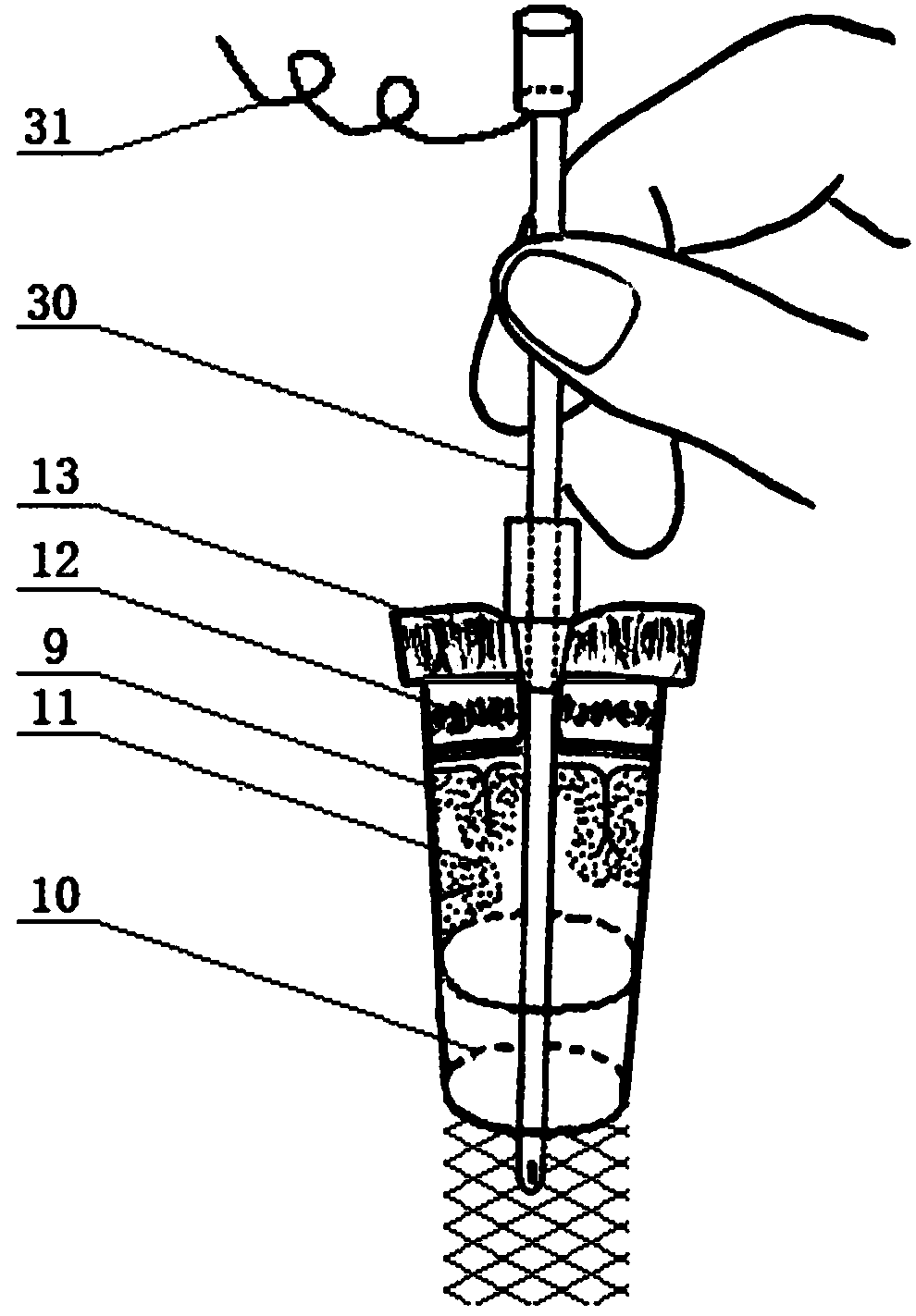
Intracranial ommaya capsule puncture drainage needle
PendingCN107496013AAdjustable speedGuaranteed unobstructedSurgical needlesCatheterHematoceleDynamic monitoring
An intracranial ommaya capsule puncture drainage needle comprises a puncture needle, a pressure sensor, a flow sensor and a drainage connecting tube, the puncture needle is connected with the drainage tube, two tube cavity channels are formed in the puncture needle, one tube cavity is a connecting channel of a pressure probe and the pressure sensor through a conduction line channel, and the other tube cavity is a liquid drainage channel; the flow sensor is arranged on the drainage tube and provided with an adjusting rotary knob; the puncture needle is divided into an intracranial section and an extracranial section which are connected through an arc corner; needle tip side holes are formed at the needle tip part of the intracranial section, and two-needle-wing structure is arranged on the extracranial section, a needle tube of the extracranial section is connected with the drainage tube, and the pressure sensor, the flow sensor and a medical T-branch tube are installed on the drainage tube. By means of the intracranial ommaya capsule puncture drainage needle, the intracranial ommaya capsule can efficiently puncture, the drainage speed of ventricular hematocele or cerebrospinal fluid is adjusted, the intracranial pressure is monitored, it is ensured that the tube is not blocked, dynamic monitoring is provided for patients suffering from ventricular hematocele or hydrocephalus, and the prognosis and treatment of the patients are facilitated.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
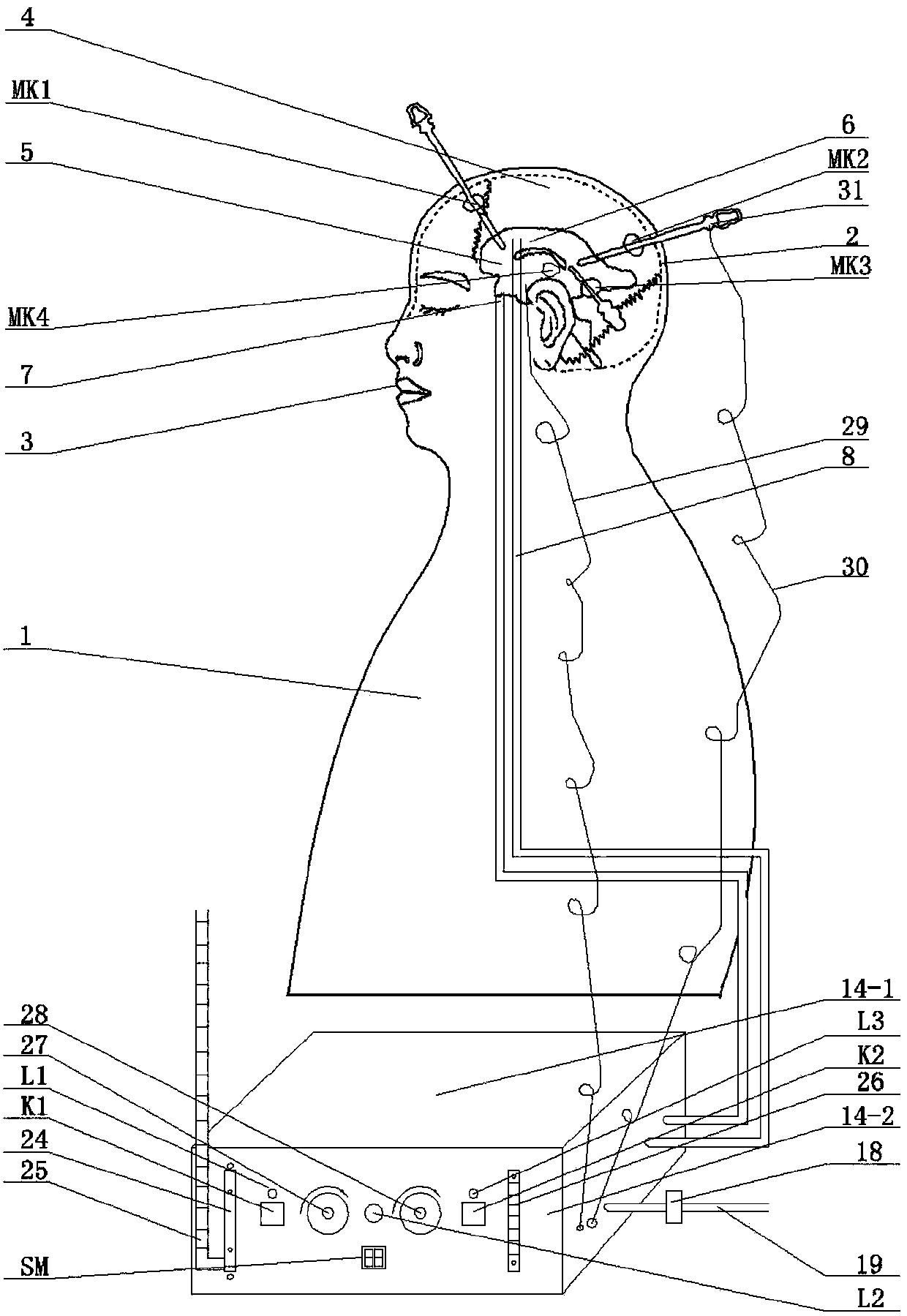
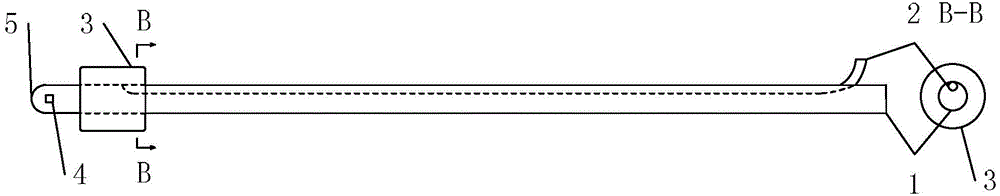
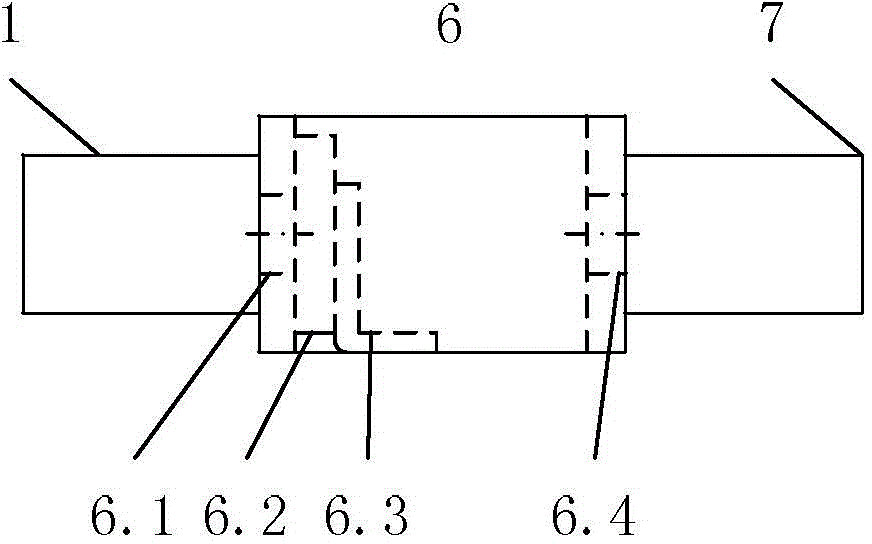
Drainage tube
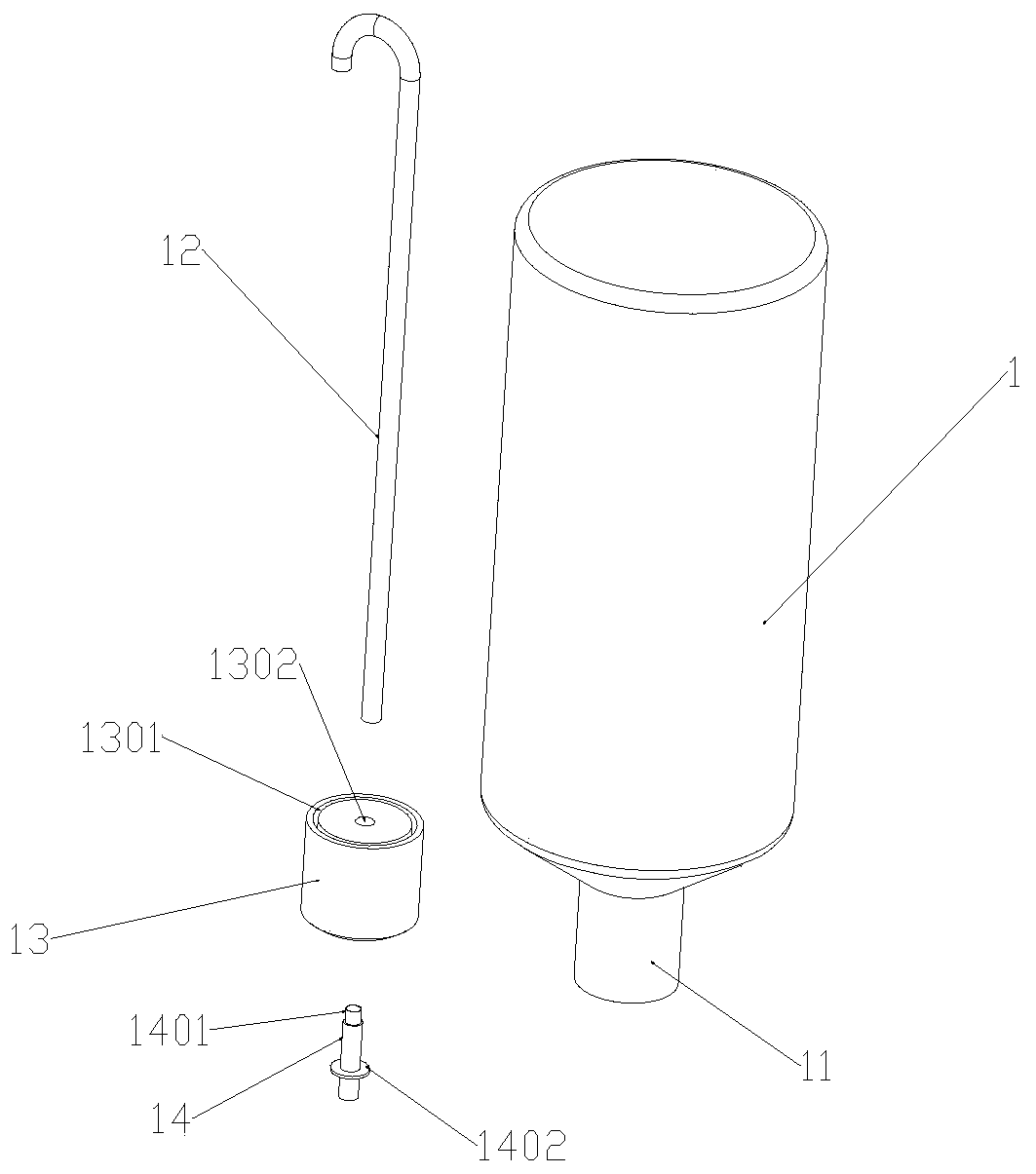
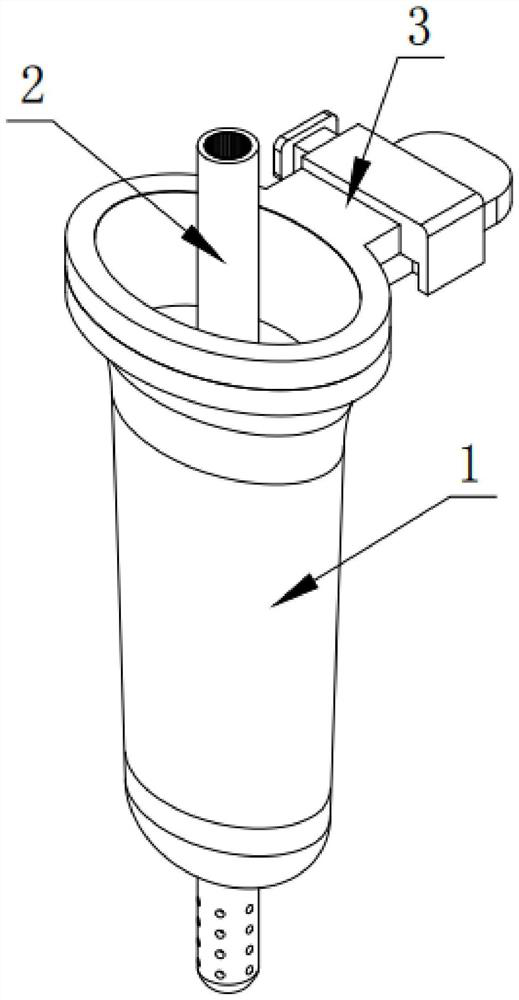
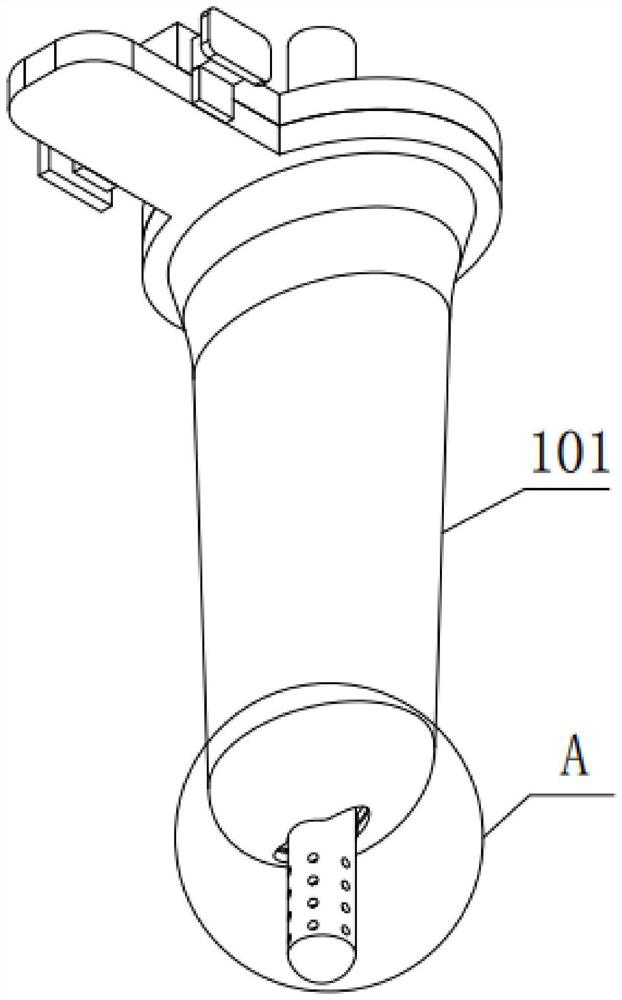
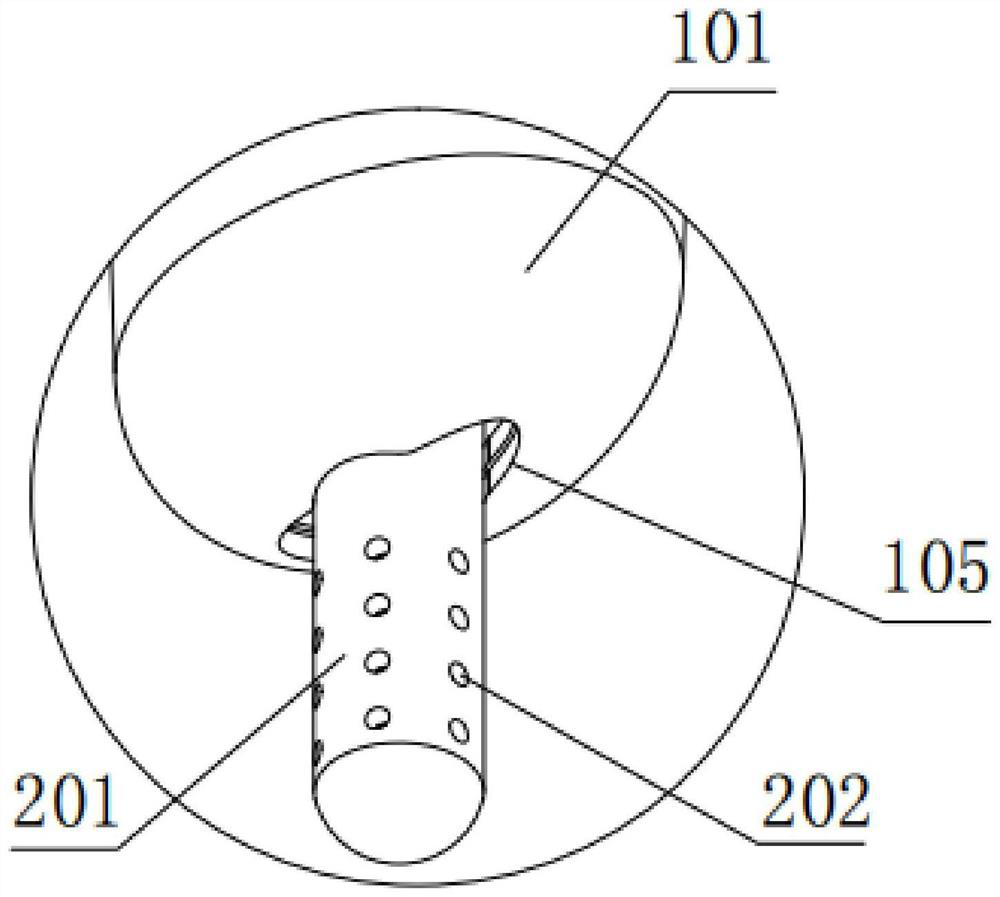
The invention relates to a drainage tube. The drainage tube is used for solving the problem that drainage tubes are prone to falling off from a brain ventricle. The drainage tube comprises an expandable elastic bladder (3), a catheter (2) and a drainage tube body (1). The elastic bladder (3) is provided with a hollow cavity; the ventricle end (5) of the drainage tube body is a closed end, and a drainage port (4) is formed close to the closed end; the elastic bladder (3) is arranged on the circumference of the drainage tube; the catheter (2) is communicated with the elastic bladder (3) and used for filling fluid into the cavity to expand the elastic bladder (3); the elastic bladder is not communicated with the drainage tube body. According to the drainage tube, the expandable elastic bladder formed in the drainage tube can limit the drainage tube inside the brain ventricle to prevent the drainage tube from falling off from the ventricle, thereby effectively avoiding accidents during a drainage process.
Owner:徐增良
Brain ventricle analysis
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for gestational age estimation and embryonic mutant detection
ActiveUS20180336681A1Accurate stagingAbnormality in shapeImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareMammal
A method to characterize shape variations in brain ventricles during embryonic growth in mammals, the method including extracting a brain ventricle skeleton from one or more images, calculating a volume profile for the skeleton using the extracted images, partitioning the brain ventricle based on the volume profile along the skeleton, the brain ventricle being partitioned into two lateral ventricles and a main ventricle, the main ventricle being further partitioned into three sub regions, determining volume vectors of the two lateral ventricles and the three sub regions, computing a means square error between the determined computed volume vectors and a pretrained mean volume vector of embryos during different gestational stages, and classifying the embryo to the gestational stage having the lowest mean square error. A method to characterize mutant detection in mammals, the method including acquiring one or more images, computing a volume profile directly along a path of the detected skeleton from the one or more images, aligning the volume profile against a standard profile, and evaluating the volume profile against the standard profile to detect a mutation.
Owner:RIVERSIDE RES INST +1
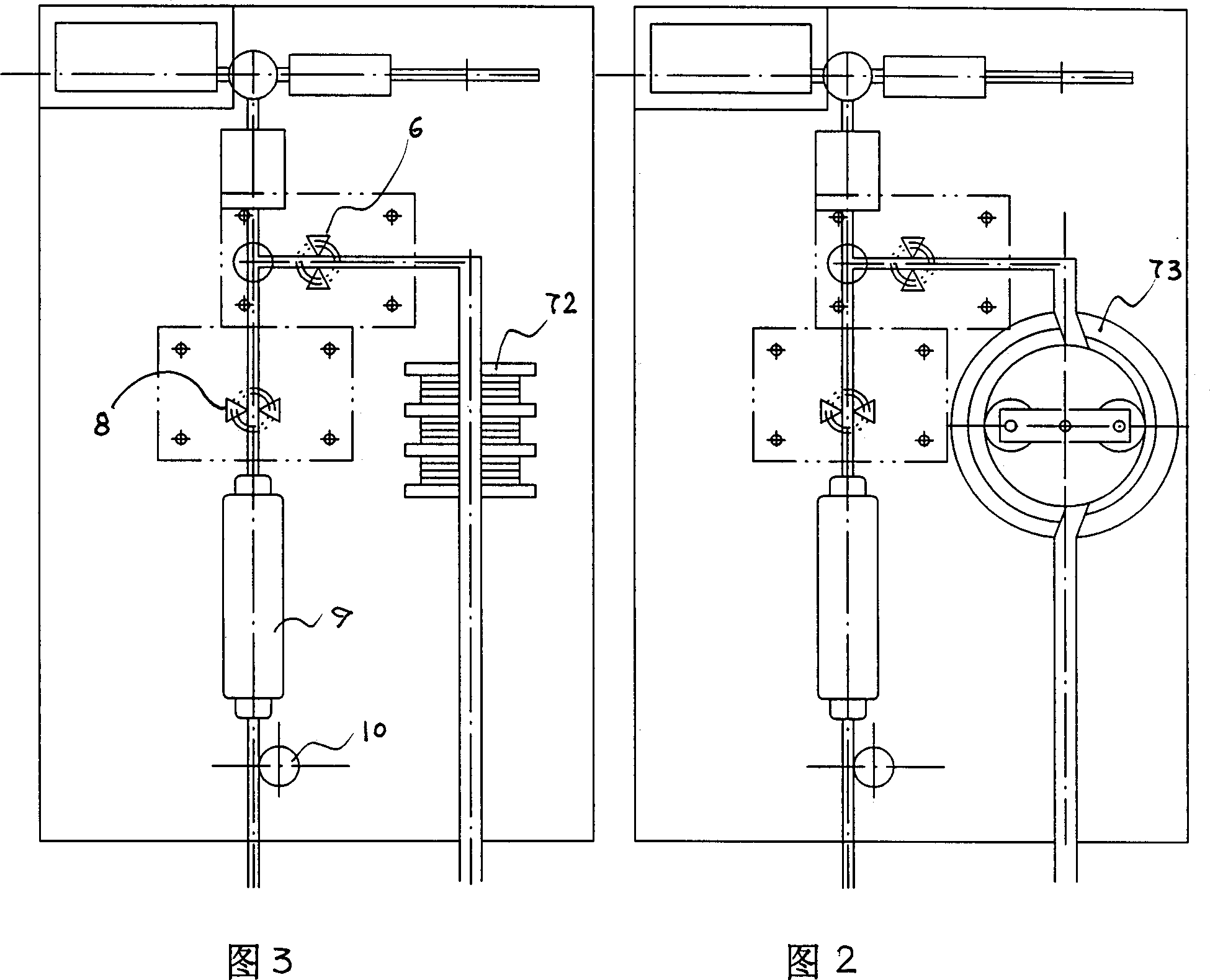
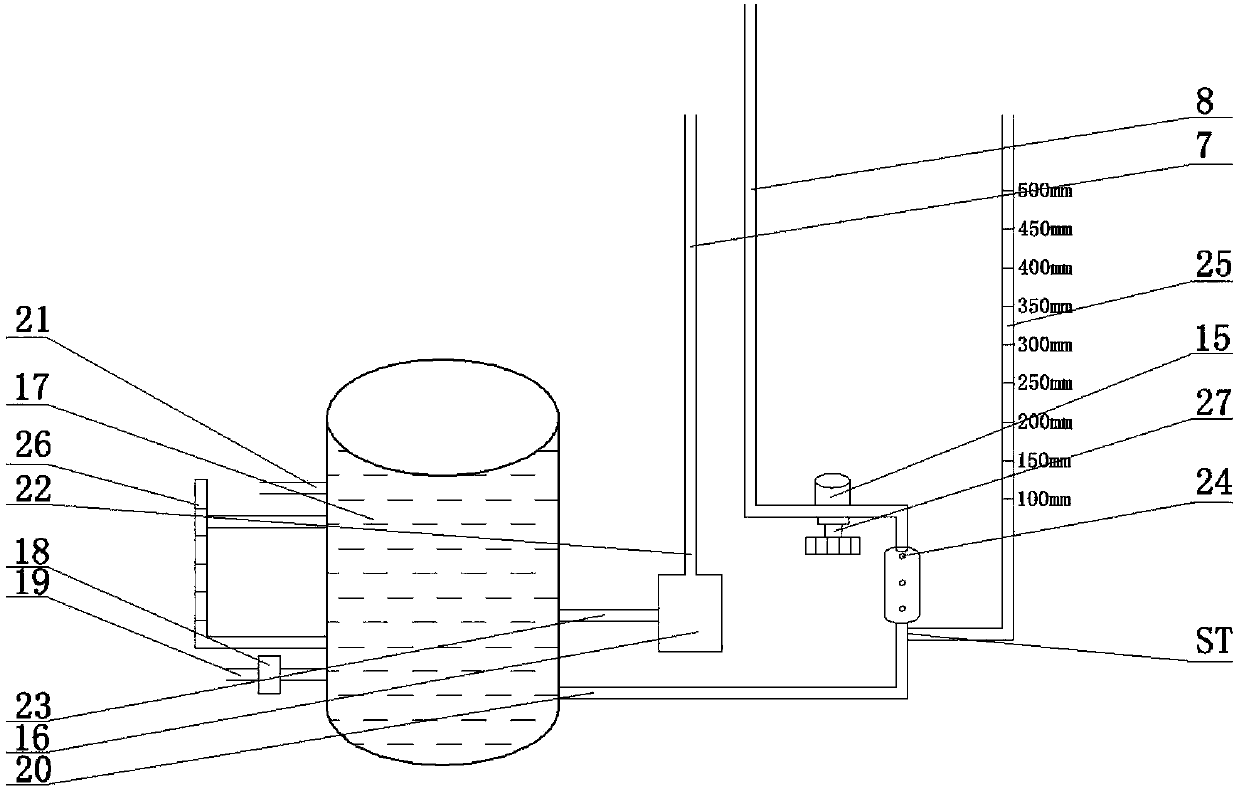
Cerebrospinal fluid quantitative shunt system and shunt method
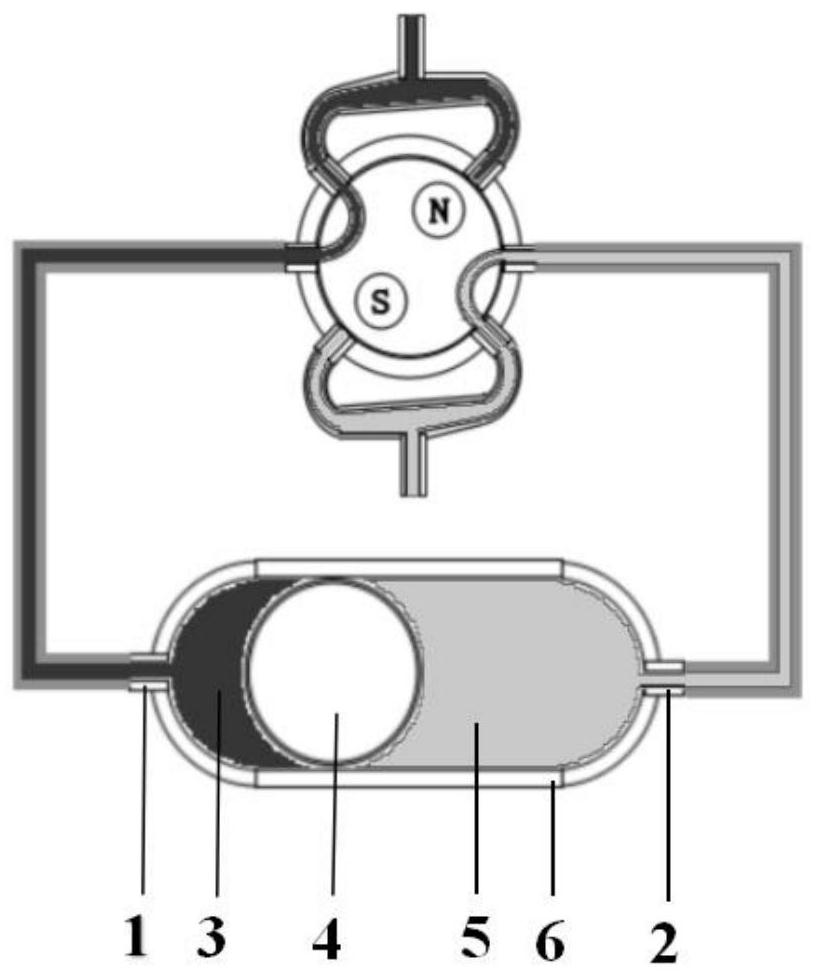
ActiveCN111760175BPrevent backflowPrevent siphonOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNon-electrical signal transmission systemsAbdominal cavityCerebrospinal fluid shunt valve
The invention discloses a cerebrospinal fluid quantitative shunt system and a shunt method. The system comprises a cerebrospinal fluid shunt valve, a liquid inlet pipe from the brain ventricle or the lumbar cistern to the cerebrospinal fluid shunt valve, a liquid outlet pipe from the cerebrospinal fluid shunt valve to the abdominal cavity, and a body surface control The device; the cerebrospinal fluid shunt valve includes a cavity and a magnetic induction valve, the cavity is divided into two chambers by a piston, and the two sides of the cavity are connected with the liquid inlet pipe and the liquid outlet pipe through the magnetic induction valve; the piston moves horizontally in the cavity under the hydraulic pressure difference ; The electromagnetic field controls the rotation angle of the magnetic induction valve in different phases, and then switches the connection between the liquid inlet pipe and the liquid outlet pipe. The external induction control card obtains the time from the opening time point to the filling time point of the chamber connected to the liquid inlet pipe, calculates the time required for a quantitative shunt, and obtains the shunt speed, thereby calibrating the upstream and downstream hydraulic pressure difference of the chamber. The invention judges whether the pressure of the ventricular system of the patient is in the normal range by calculating the pressure value of the patient's ventricular system, and avoids the occurrence of siphon, excessive shunt and cerebrospinal fluid backflow.
Owner:兴化市人民医院 +2
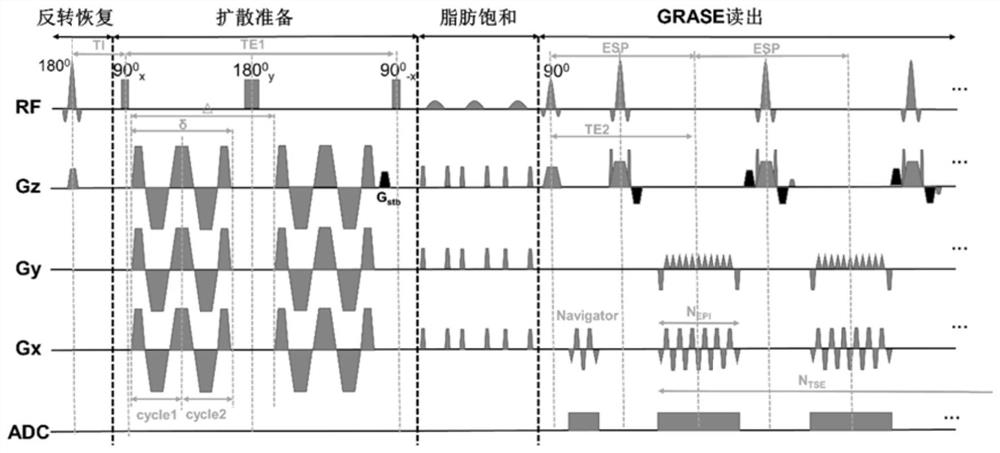
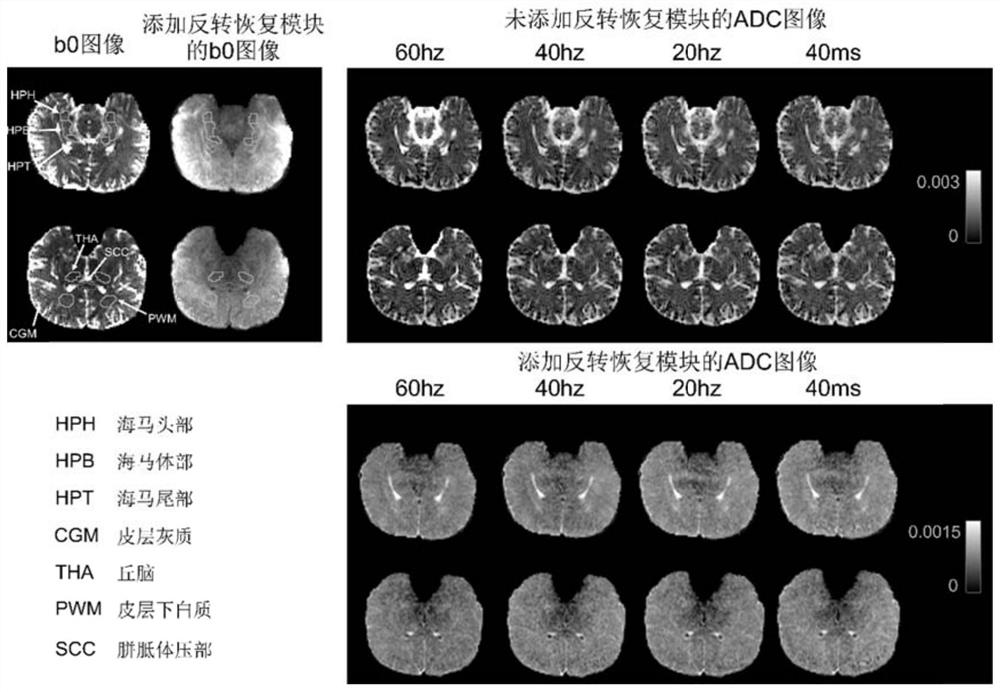
3D gradient spin echo diffusion imaging method for inversion recovery preparation, medium and equipment
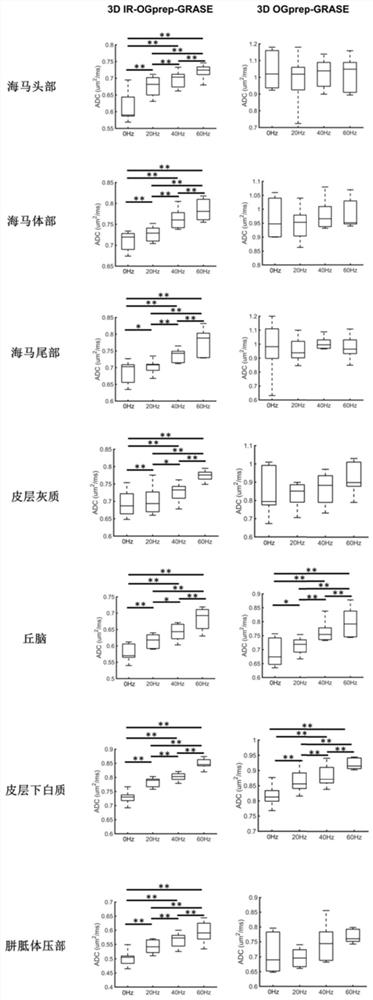
PendingCN113476031AInhibit ADC valueReduce scan timeMedical imagingDiagnostic signal processingInversion recoveryNoise (radio)
The invention discloses a 3D gradient spin echo diffusion imaging method for inversion recovery preparation, a medium and equipment. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, in an inversion recovery preparation module, applying 180-degree inversion radio frequency pulse, and setting corresponding inversion recovery time to inhibit cerebrospinal fluid and free water signals; secondly, embedding a pair of trapezoidal cosine oscillation gradients or pulse gradients into 90-degree x-180-degree y-90-degree-x radio frequency pulses through a diffusion coding module, and separating diffusion coding from signal acquisition; then, inhibiting a fat signal by using a fat saturation module; and finally, collecting signals by adopting a 3D gradient spin echo reading mode. The time and the signal-to-noise ratio of magnetic resonance diffusion imaging are improved, accurate measurement of brain tissue diffusion magnetic resonance signal time dependence is facilitated, the effect is especially obvious for a brain area which is near a ventricle and is influenced by the cerebrospinal fluid due to a partial volume effect, and the clinical transformation of a time-dependent diffusion magnetic resonance technology is effectively promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
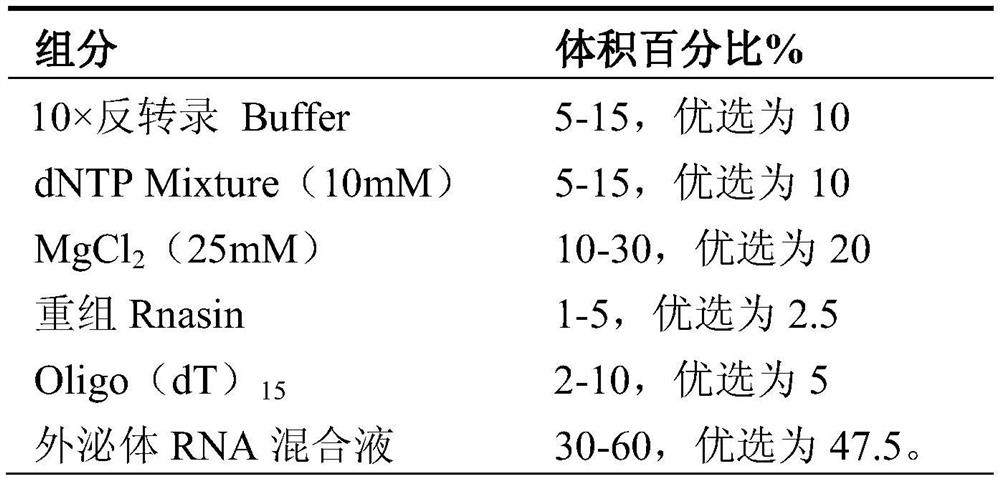
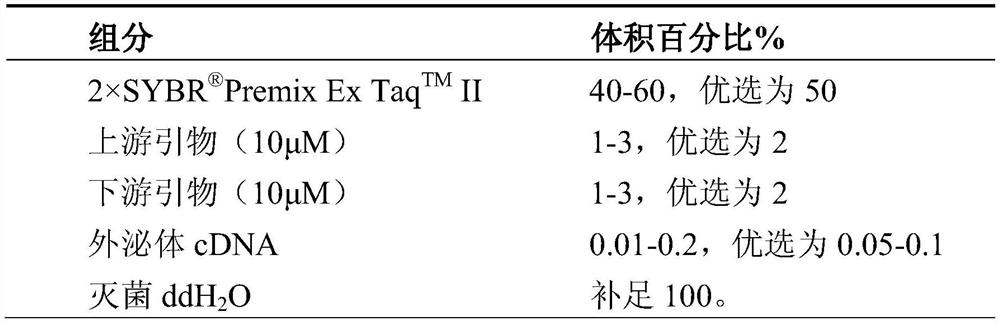
Combination of biomarkers for predicting or diagnosing postoperative recurrence of brain malignant glioma, its application and kit
ActiveCN108753984BPredict riskSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExosomeBiologic marker
Owner:BEIJING NEUROSURGICAL INST
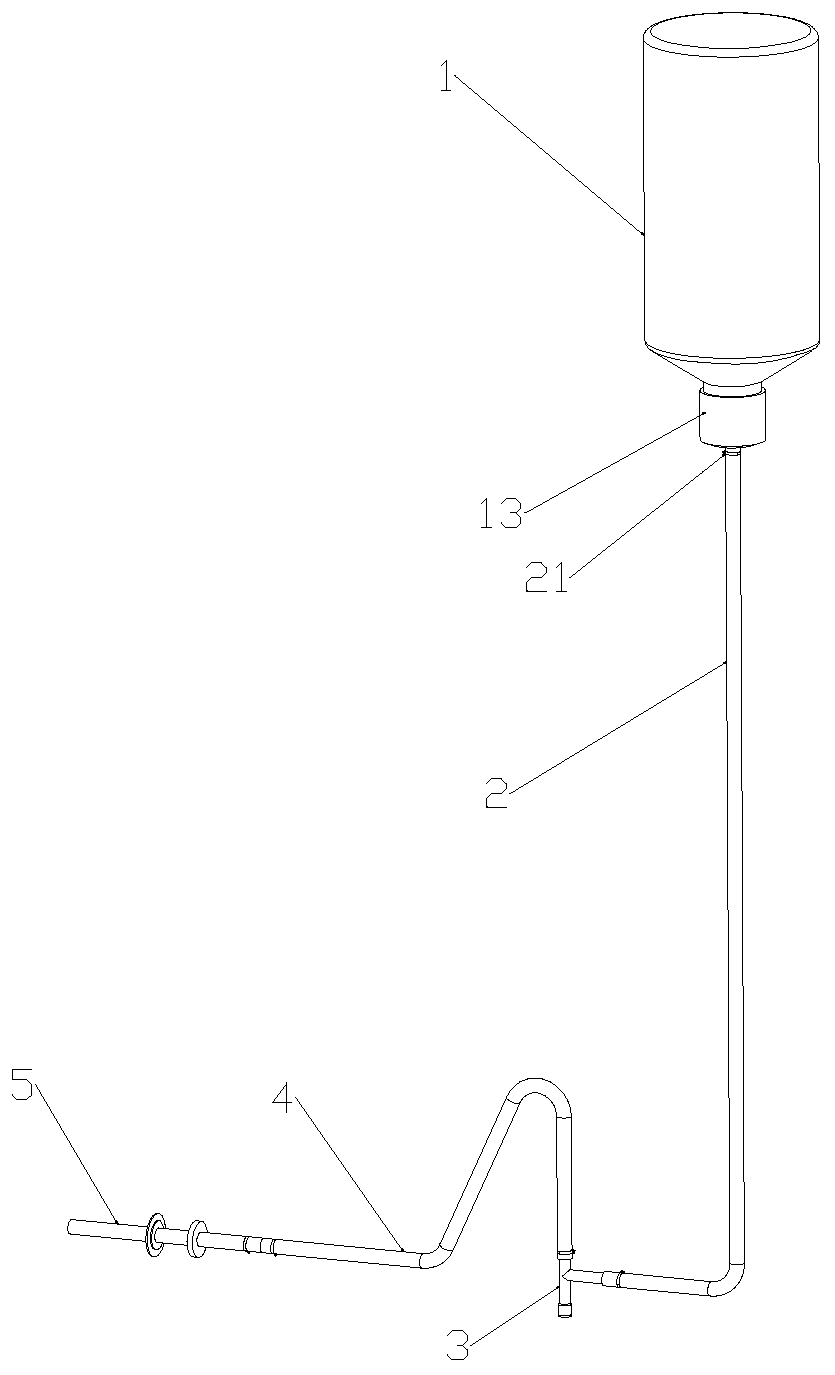
Device capable of effectively preventing infection of ventricular drainage patients
PendingCN110507868AImprove sealingActs as a double sealIntravenous devicesSuction devicesEngineeringScalp
The invention discloses a device capable of effectively preventing infection of ventricular drainage patients. The device comprises a glass bottle, wherein a first rubber plug is arranged at the bottom of the bottleneck of the glass bottle, a first rubber hose is arranged at the bottom end of the glass bottle, a tree-way part is arranged on one side of the bottom end of the first rubber hose, anda second rubber hose is arranged at the side end of the three-way part. A silicone hose is arranged at the side end of the second rubber hose, a double-layer rubber pad is connected onto the siliconehose, and a screw fastener is arranged at the side end of the double-layer rubber pad. A connecting pipe is arranged at the bottom end of the three-way part, a second rubber plug in sealing fit with the inner wall of the three-way part is arranged in the connecting pipe, a wooden plug in sealing fit with the connecting pipe is arranged below the second rubber plug, and the three-way part is effectively sealed to prevent infection; and meanwhile, the double-layer rubber pad is closely attached to scalp of a patient by tightening the screw fastener, then, the double-layer rubber pad is adhered to the scalp of the patient by adhesive tapes, the sealing performance is increased, cerebrospinal fluid leakage is prevented, and infection is prevented.
Owner:HEFEI NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Accurate positioning brain retractor
PendingCN114469206AAvoid damageEasy to operateSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsInjury brainHematocele
The invention relates to the technical field of medical apparatus and instruments, and discloses a precise positioning brain retraction device which comprises a brain retraction mechanism and a precise positioning guide mechanism, and the brain retraction mechanism is used for blocking soft tissues around a surgical field; and the precise positioning guide mechanism is used for assisting the brain retraction mechanism in precisely entering a surgical target position. According to the invention, the hard catheter can be sleeved on the navigation pen of the IGS (the navigation is influenced by neurosurgery), the hard catheter is accurately inserted into the required operation position through the D mode planning of the IGS, the whole operation process is relatively convenient, the action of repeatedly sucking effusion is not needed, the insertion accuracy is high, and the operation is convenient. After the navigation pen is pulled out and the brain retraction mechanism is inserted in place, when the pressure in the ventricle or brain tissue rises, cerebrospinal fluid or hematocele can flow out of the hard catheter, so that the brain injury caused by high pressure to the brain of a patient is avoided, and the brain retraction mechanism can be directly and successfully inserted into the ventricle or hematoma cavity at a time along the hard catheter. And contusion to surrounding brain tissues in a repeated attempt process is avoided.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
cranial catheter device
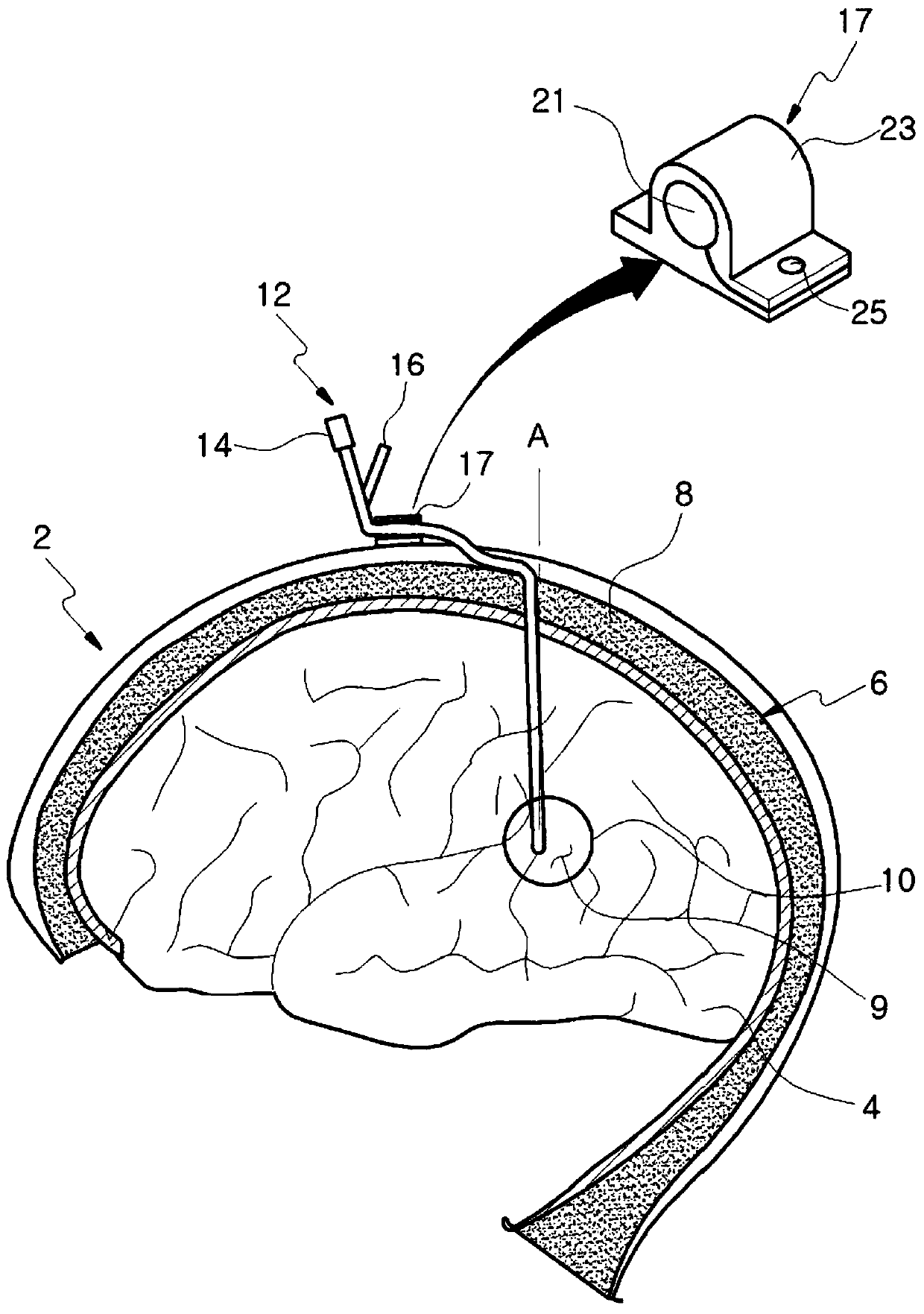
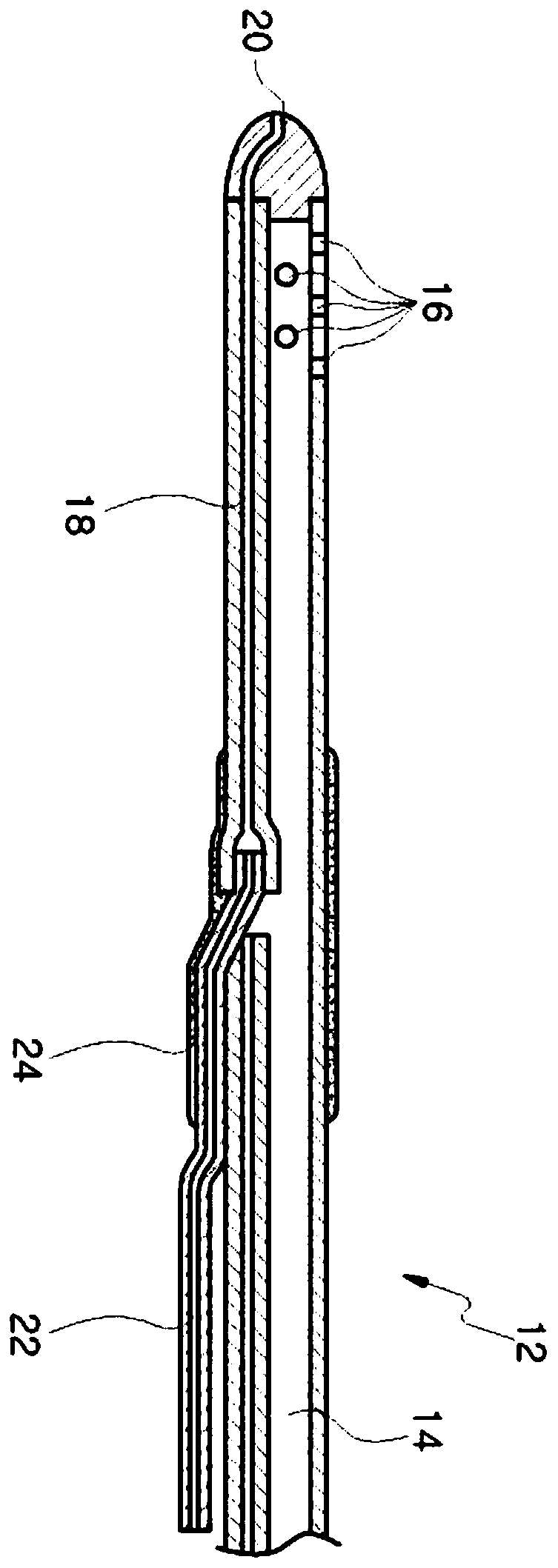
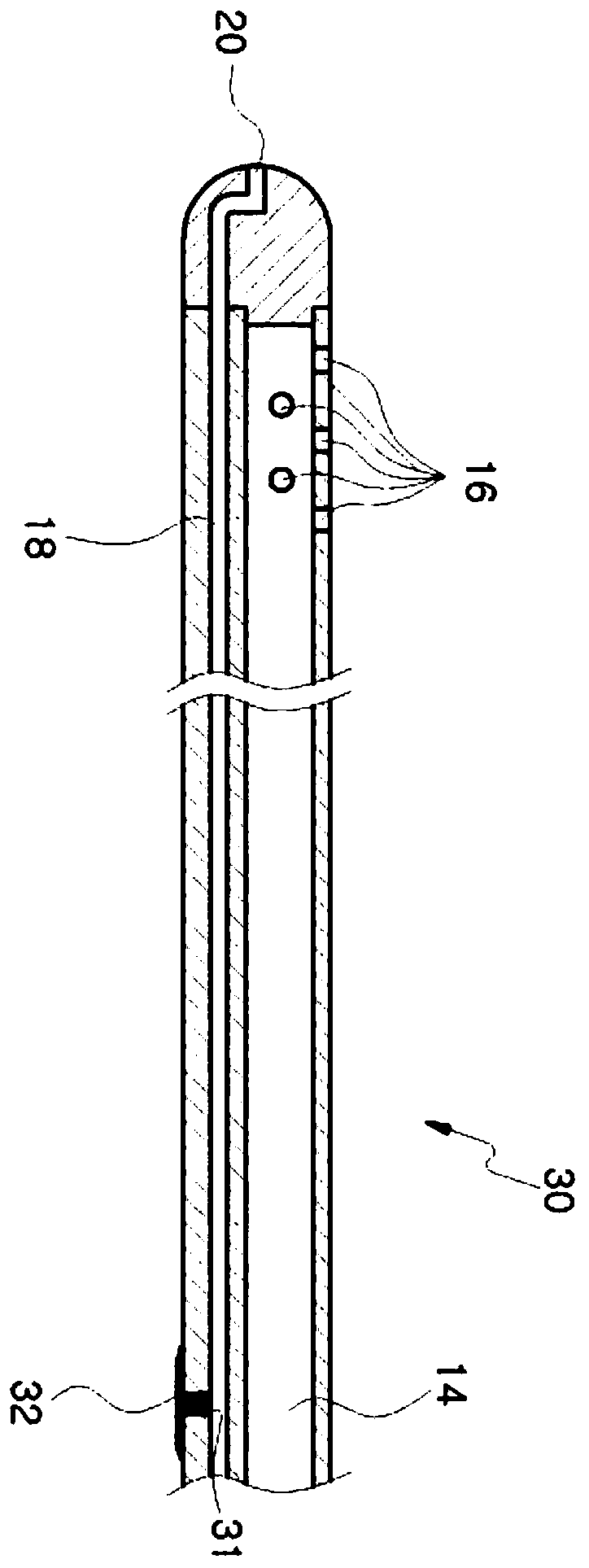
The present invention relates to a catheter device for a cranial cavity. Advantages of a conventional catheter structure for transferring a drug and a bodily liquid through different pathways are maintained, and the outer diameter of a catheter is regularly formed, so a brain positioning device which is useful in accurately positioning a catheter end in a brain ventricle can be easily used. A catheter rear side can be easily tunneled in a round space between a skull and skin, so an operation can be conveniently and easily performed and operation safety is remarkably improved. According to the present invention, the outer diameter of a catheter does not have a protruding part, so a catheter end can be accurately and easily disposed in a brain ventricle of an affected area by using a brain poisoning device. Also, a catheter can be easily induced to be bent through a round space between the top of a skull and skin, and a catheter rear end part can be easily discharged to the outside of a cranial cavity through a punching unit.
Owner:李济范
Method for gestational age estimation and embryonic mutant detection
ActiveUS10140708B2Accurate stagingAbnormality in shapeImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareMedicine
A method to characterize shape variations in brain ventricles during embryonic growth in mammals, the method including extracting a brain ventricle skeleton from one or more images, calculating a volume profile for the skeleton using the extracted images, partitioning the brain ventricle based on the volume profile along the skeleton, the brain ventricle being partitioned into two lateral ventricles and a main ventricle, the main ventricle being further partitioned into three sub regions, determining volume vectors of the two lateral ventricles and the three sub regions, computing a means square error between the determined computed volume vectors and a pretrained mean volume vector of embryos during different gestational stages, and classifying the embryo to the gestational stage having the lowest mean square error. A method to characterize mutant detection in mammals, the method including acquiring one or more images, computing a volume profile directly along a path of the detected skeleton from the one or more images, aligning the volume profile against a standard profile, and evaluating the volume profile against the standard profile to detect a mutation.
Owner:RIVERSIDE RES INST +1
Hydrocephalus shunt arrangement and components thereof for draining cerebrospinal fluid in a patient having hydrocephalus
ActiveUS10675451B2Easy to transformReliable and drift-free measurementWound drainsMedical devicesVentricular cathetersAbdominal cavity
A hydrocephalus shunt arrangement for draining cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in a patient includes a ventricle catheter, a first drainage line, a control valve, a second drainage line, and an intracranial device. The ventricle catheter is inserted into a ventricle space of the brain of a patient. The first drainage line is connected to the ventricle catheter. The control valve is connected to the first drainage line and controls the drainage of CSF from the cranium of the patient through the second drainage line into a drainage area inside an abdominal cavity of the patient. The intracranial device is implanted under the skin of the patient in or at the cranium and connected to the ventricle catheter or the control valve. The intracranial device includes a corrugated metal membrane covering a chamber disposed within a rigid housing. The control valve produces a desired, controlled, drainage of excess CSF.
Owner:CHRISTOPH MIETHKE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com