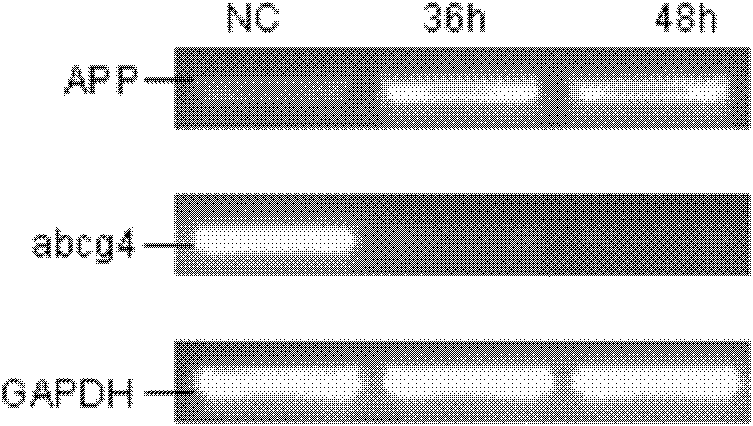Patents
Literature
83 results about "Lateral ventricles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
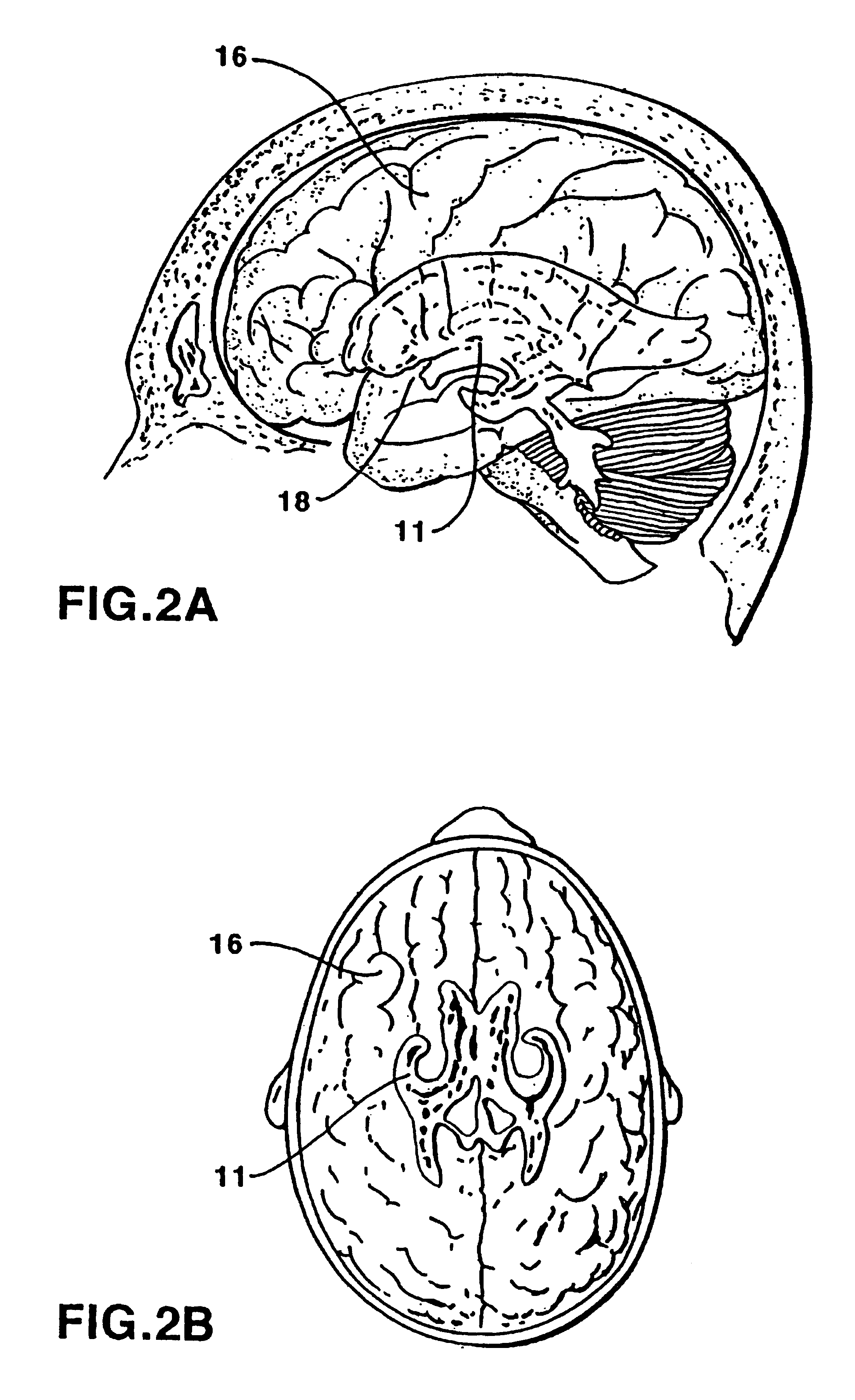
The lateral ventricles are the two largest cavities of the ventricular system of the human brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.
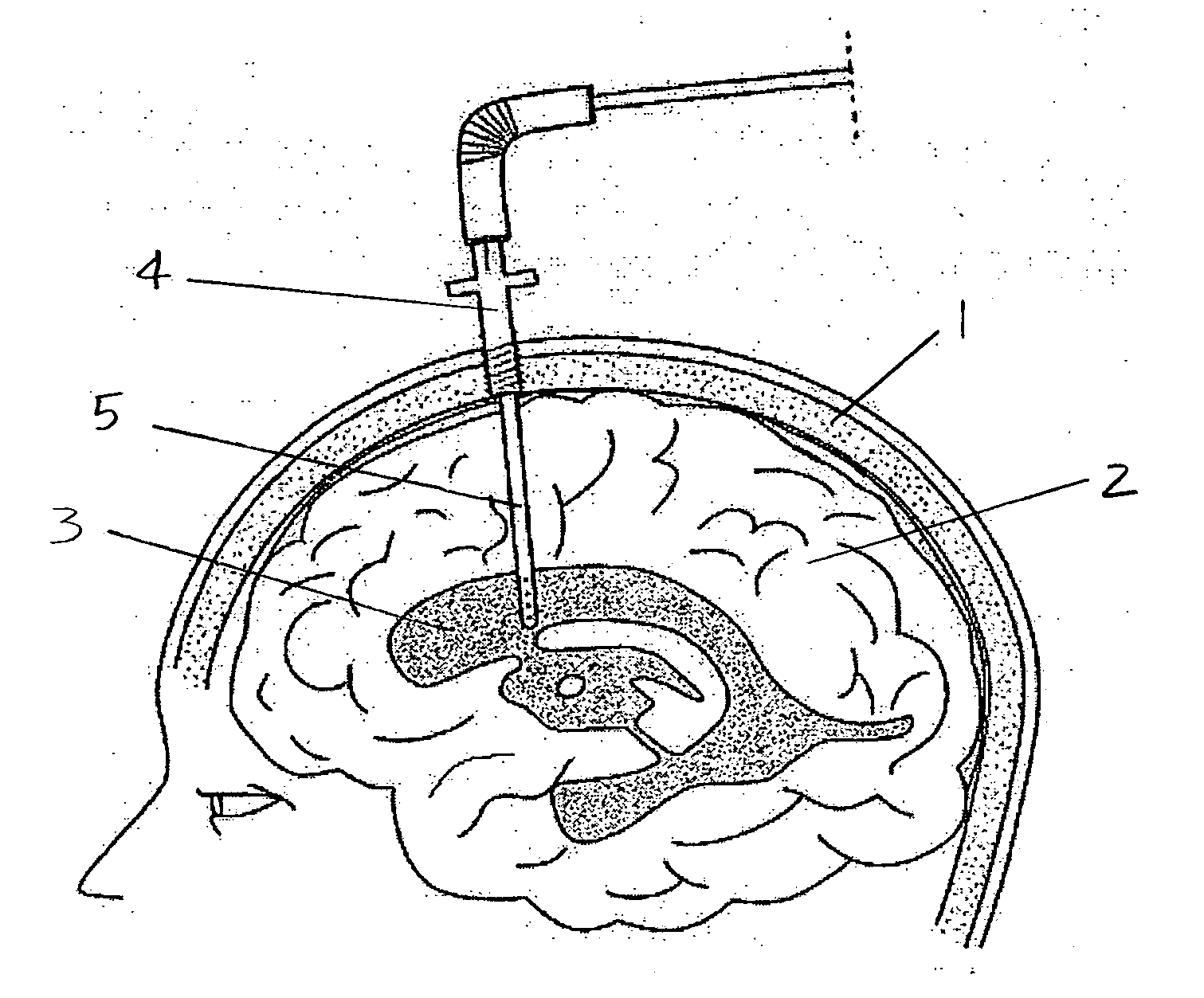
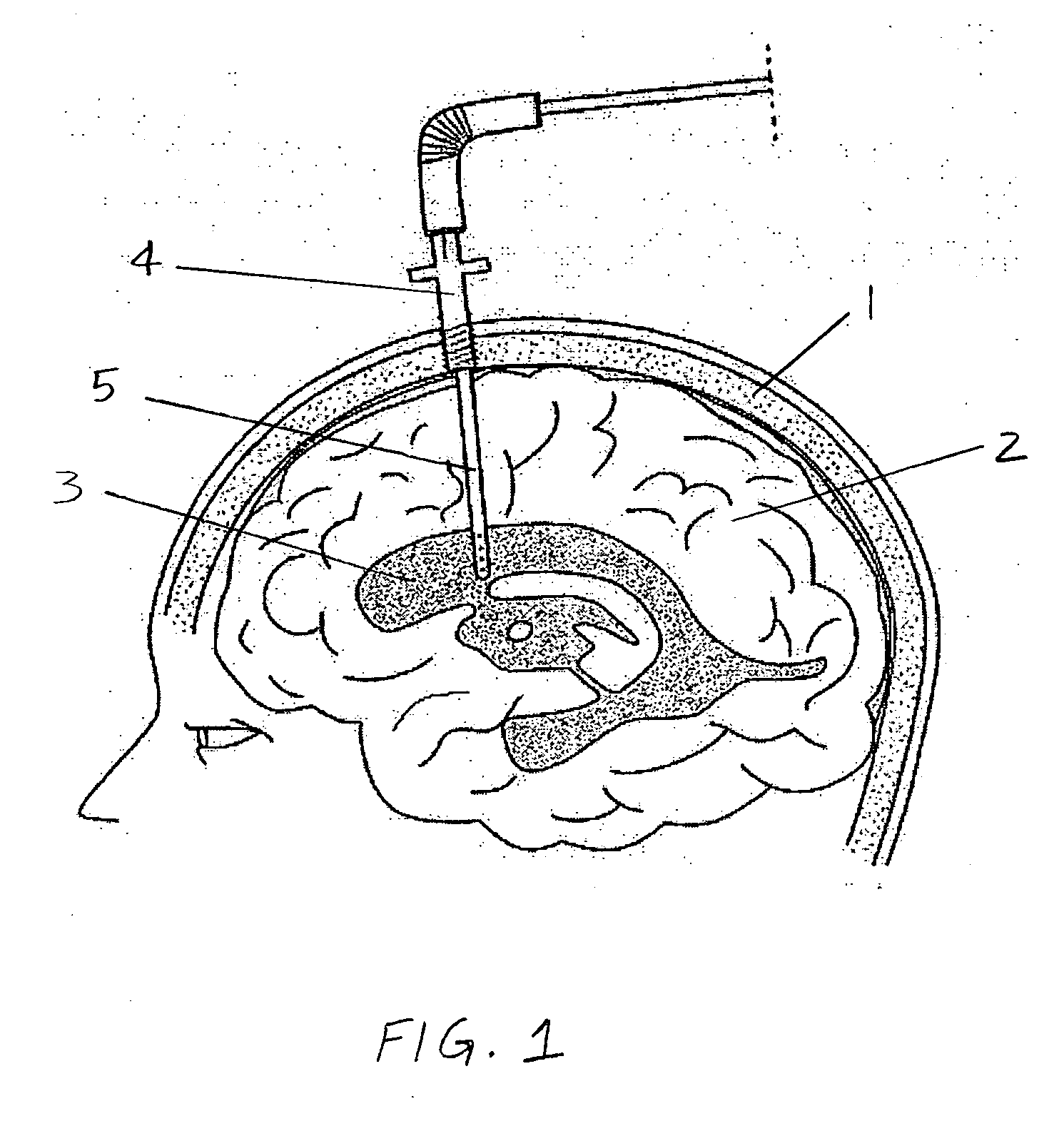
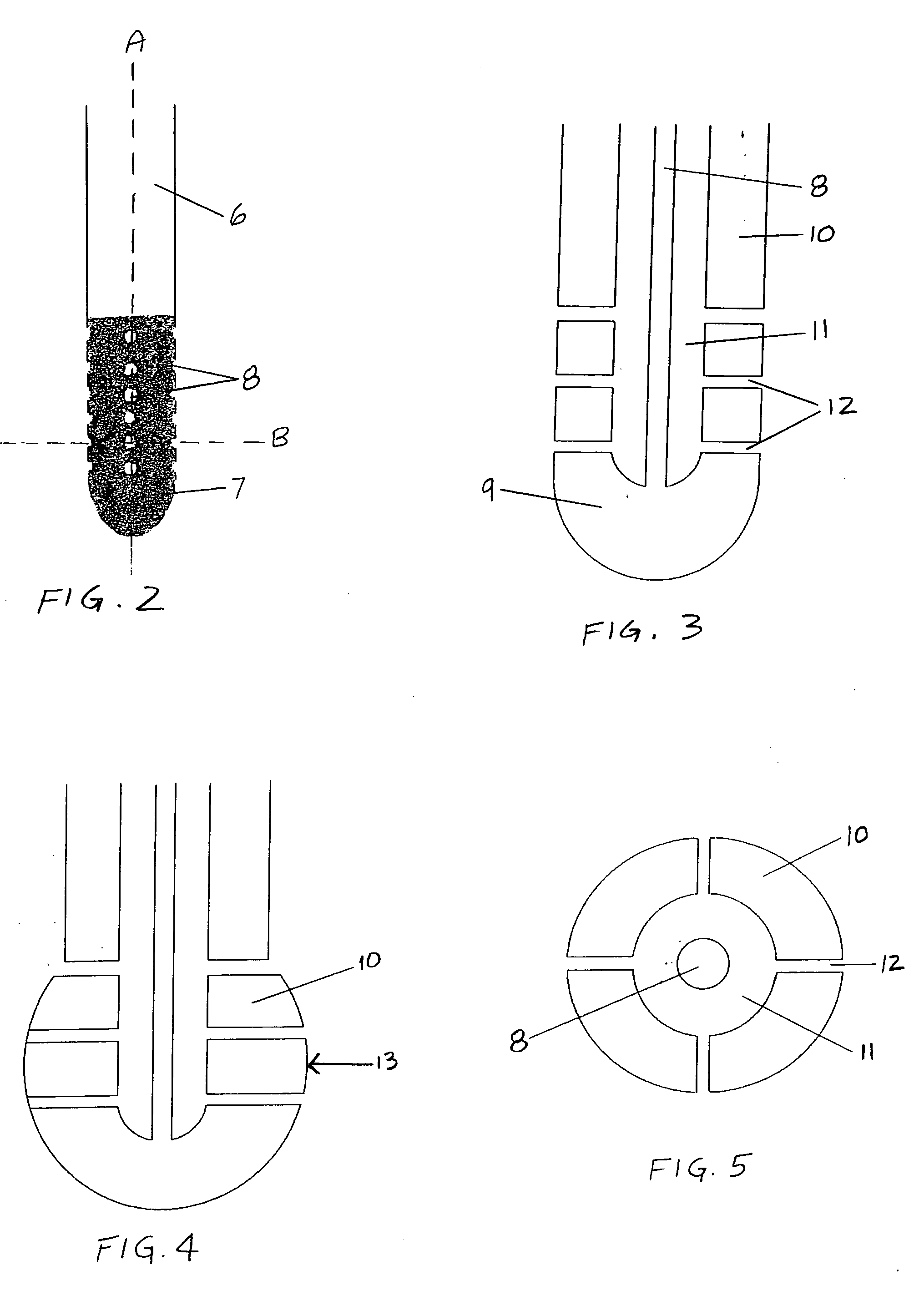
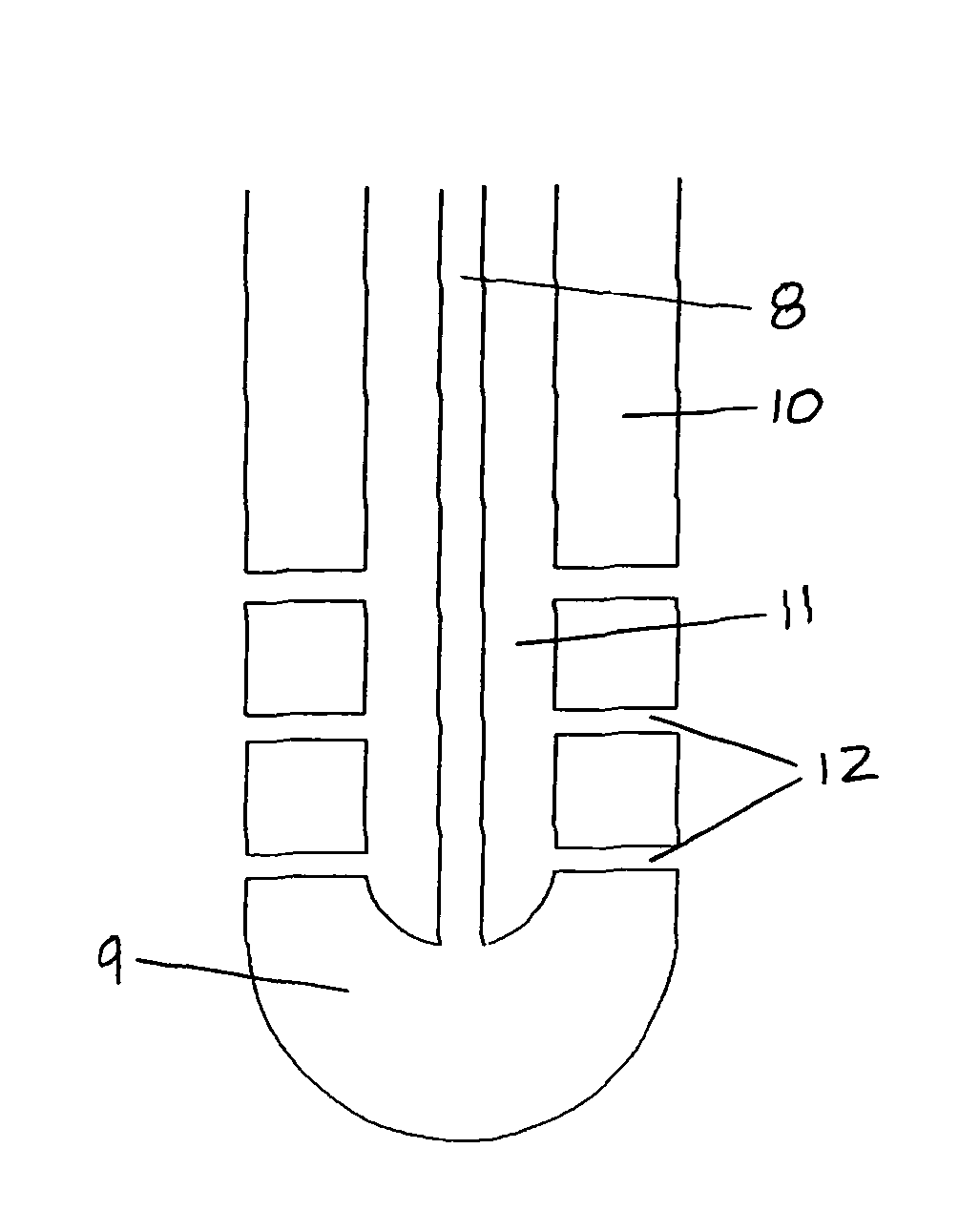
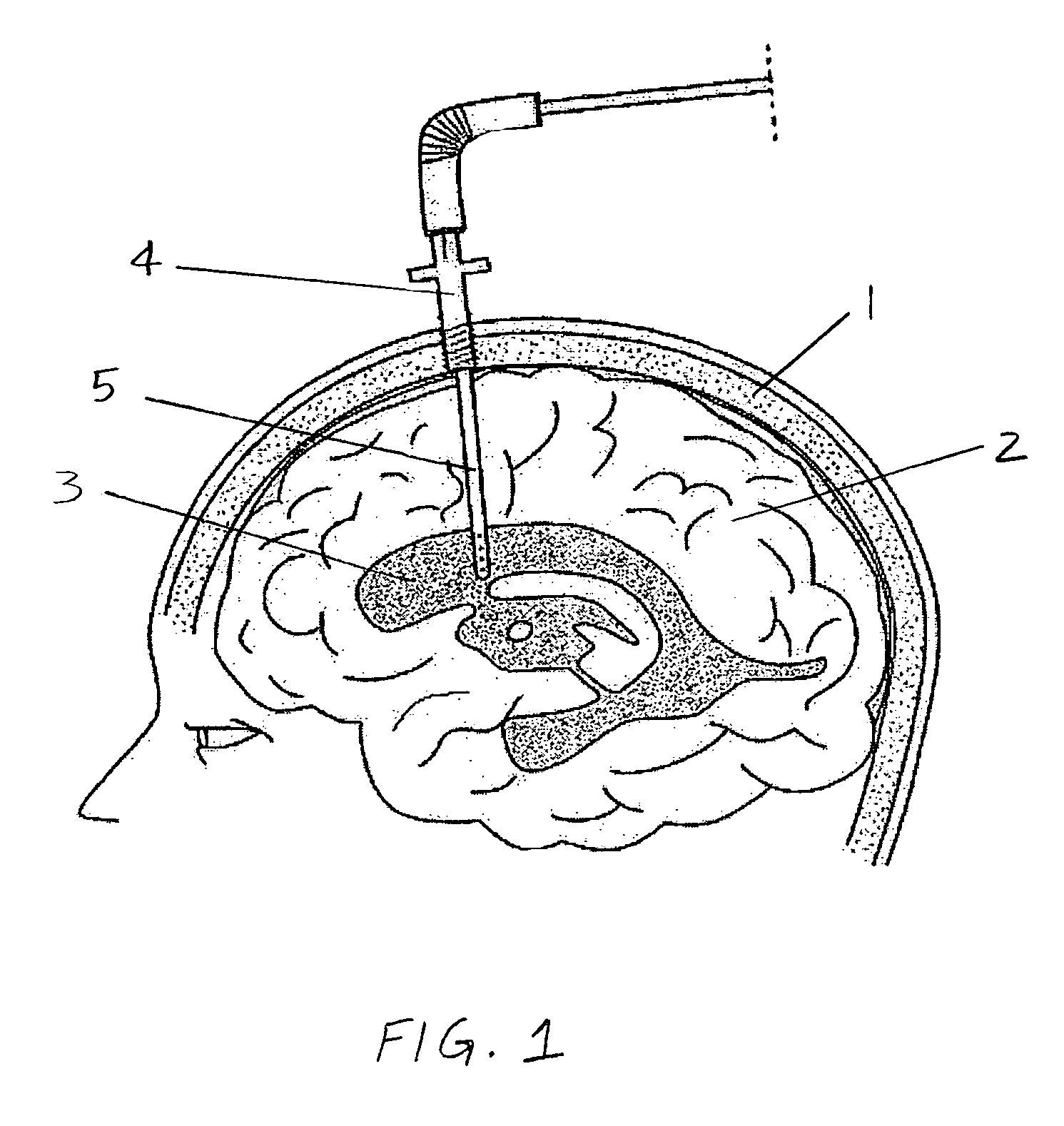
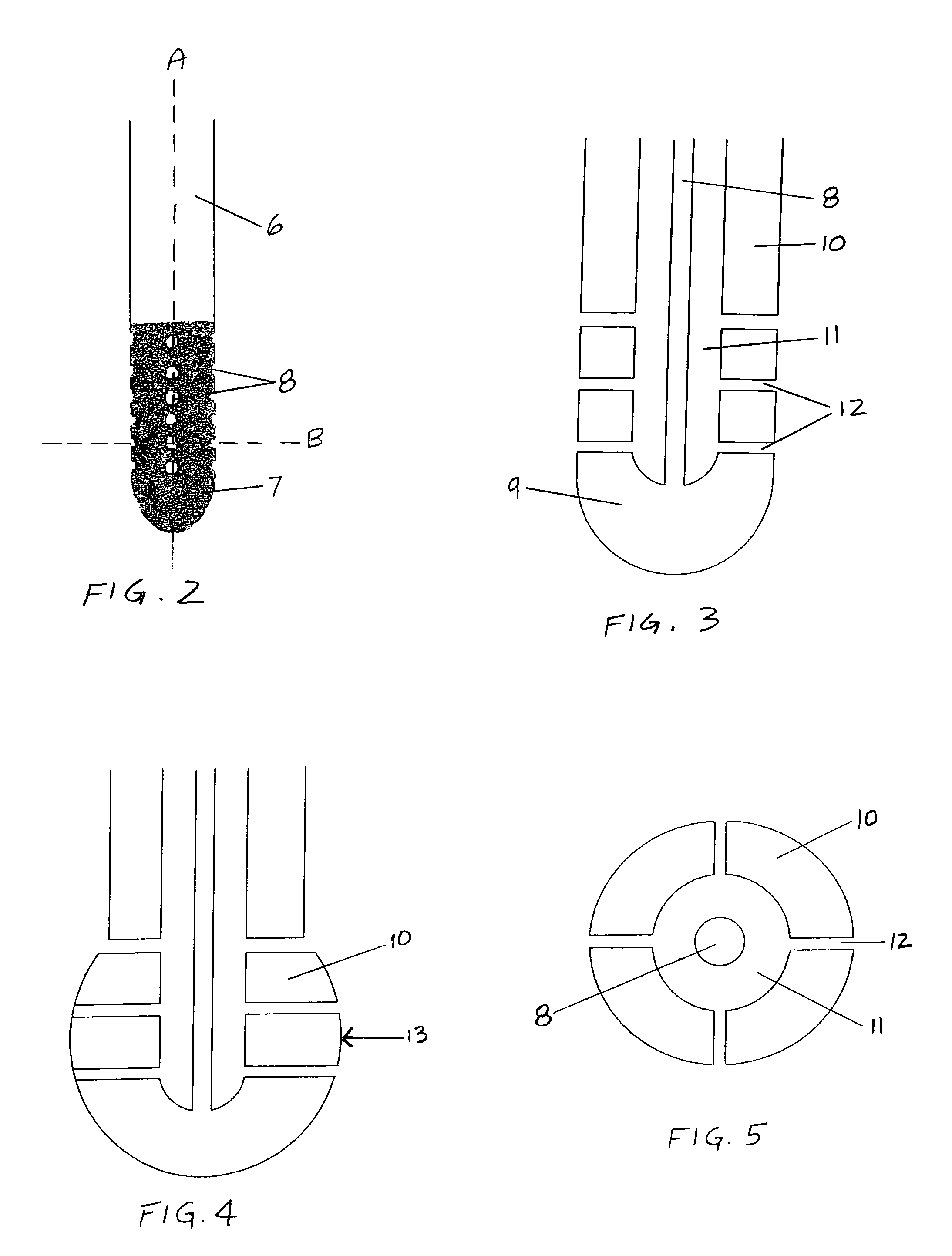
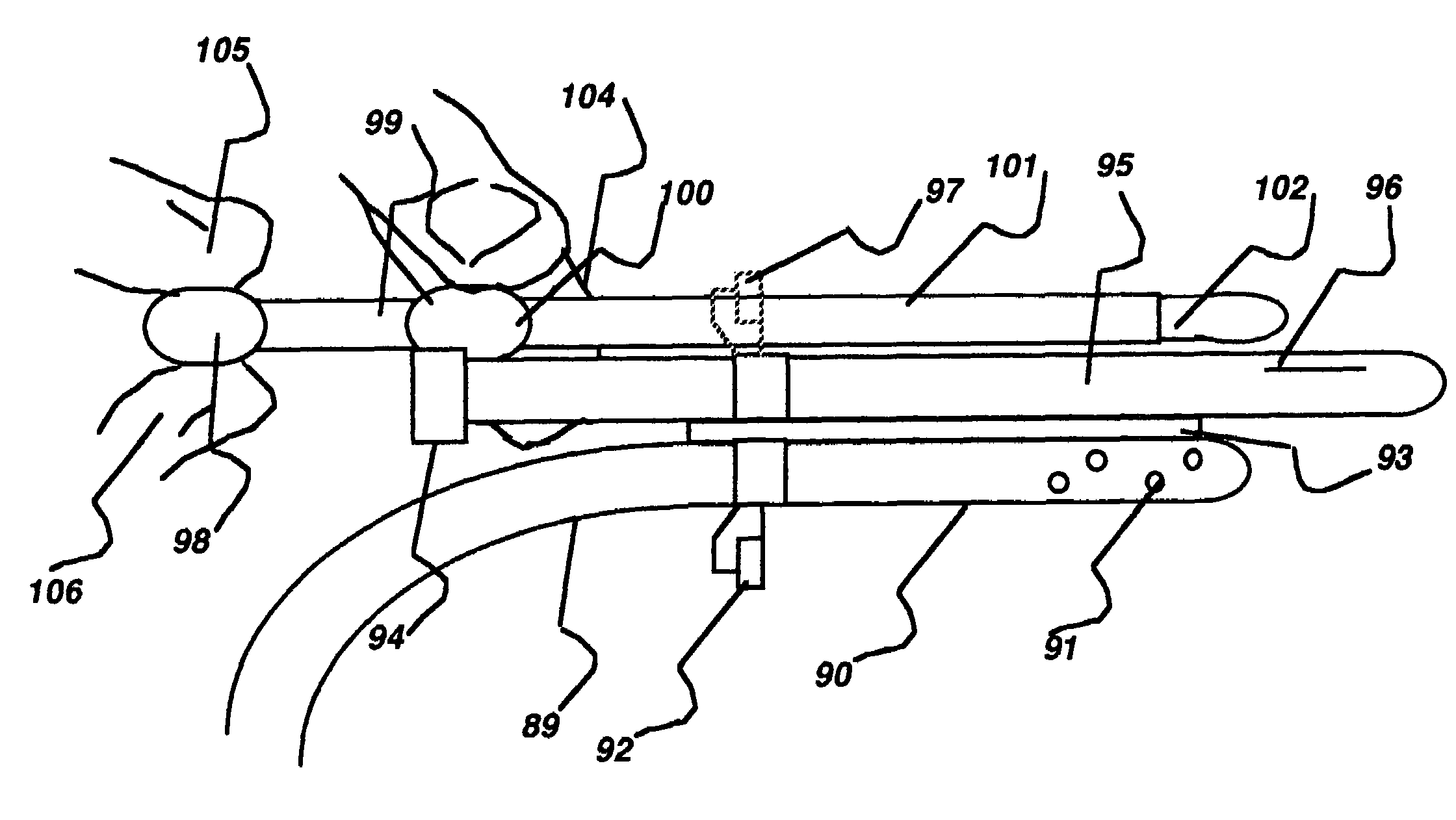
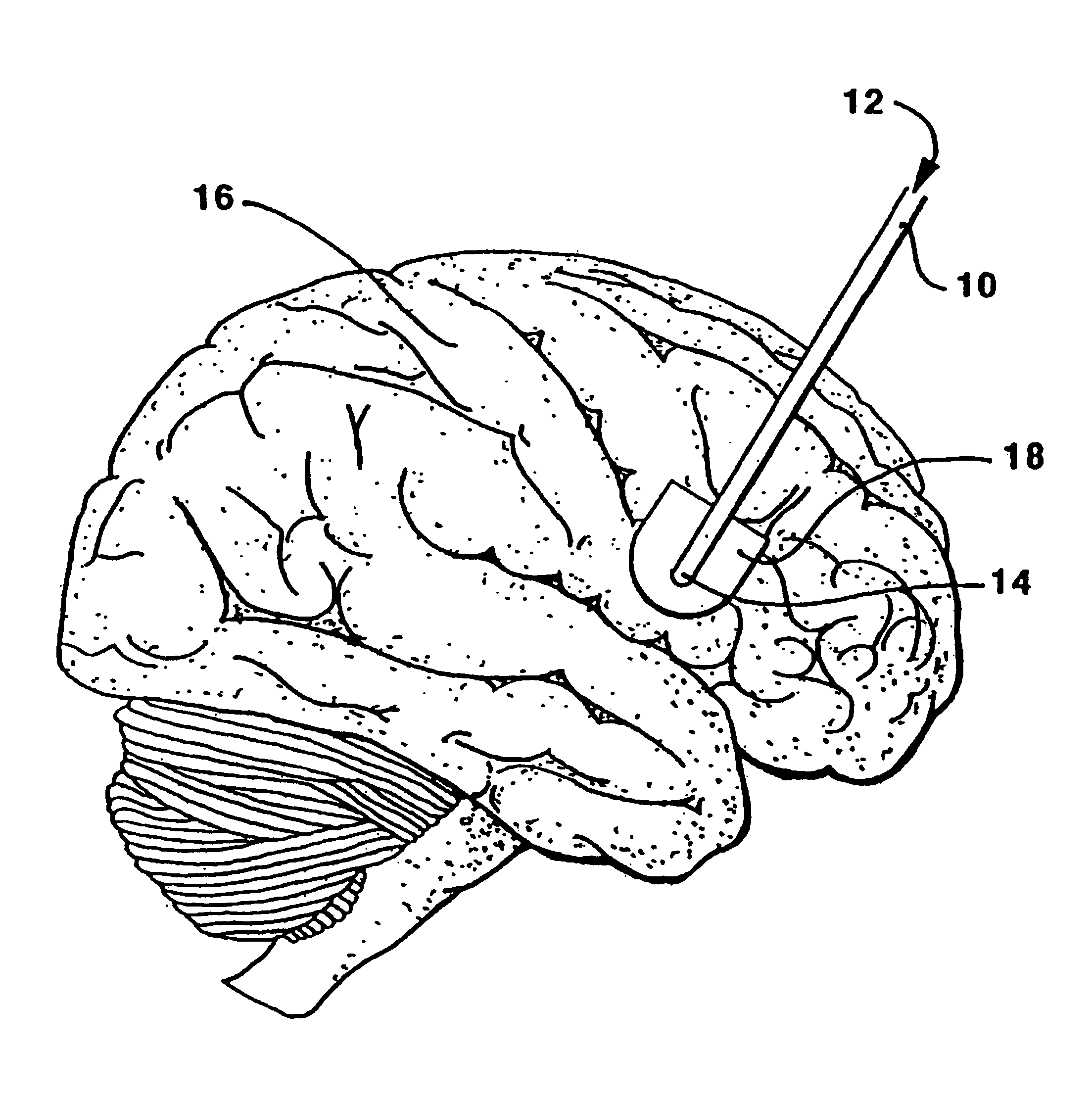
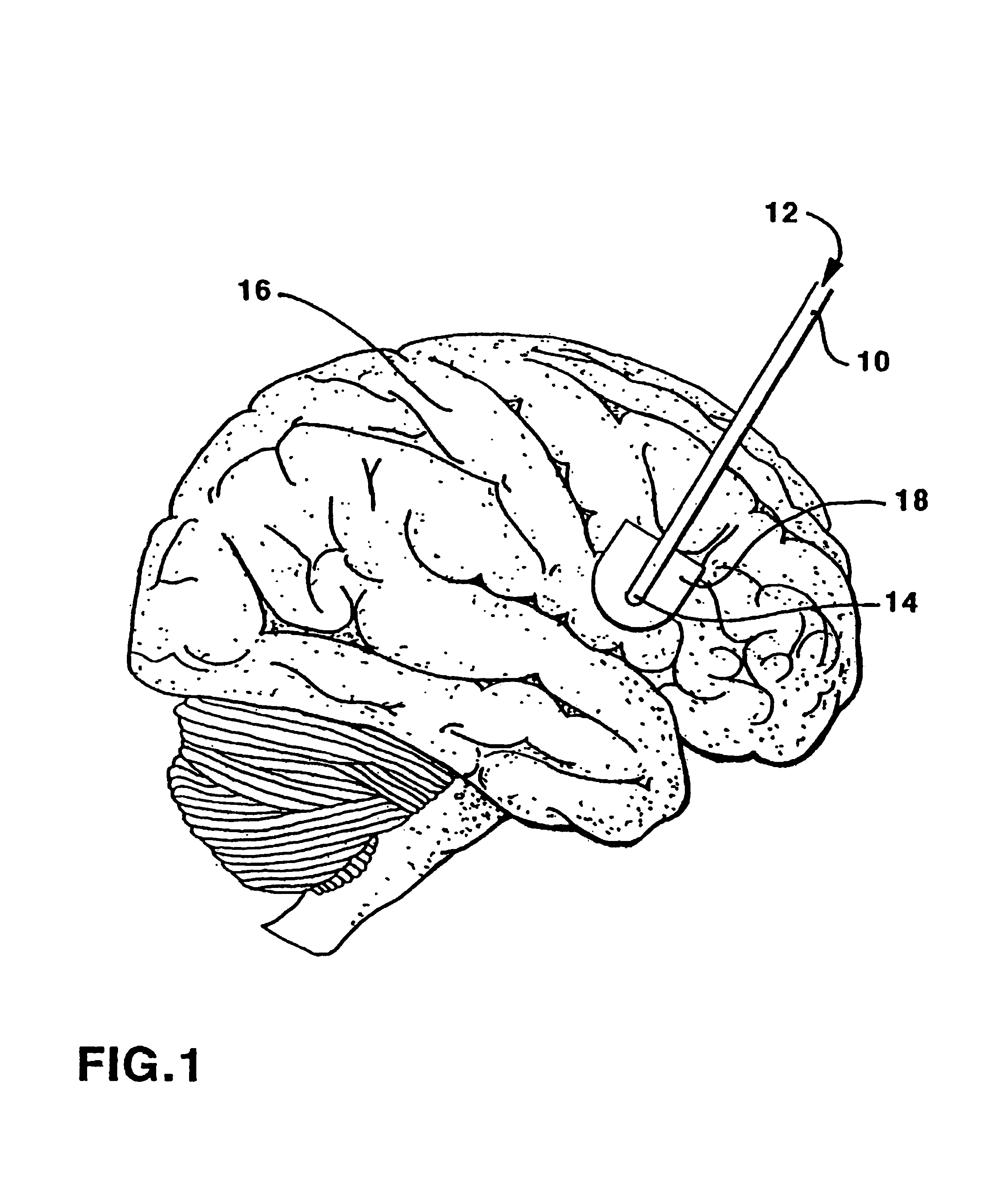
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS20070005121A1Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS8123789B2Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
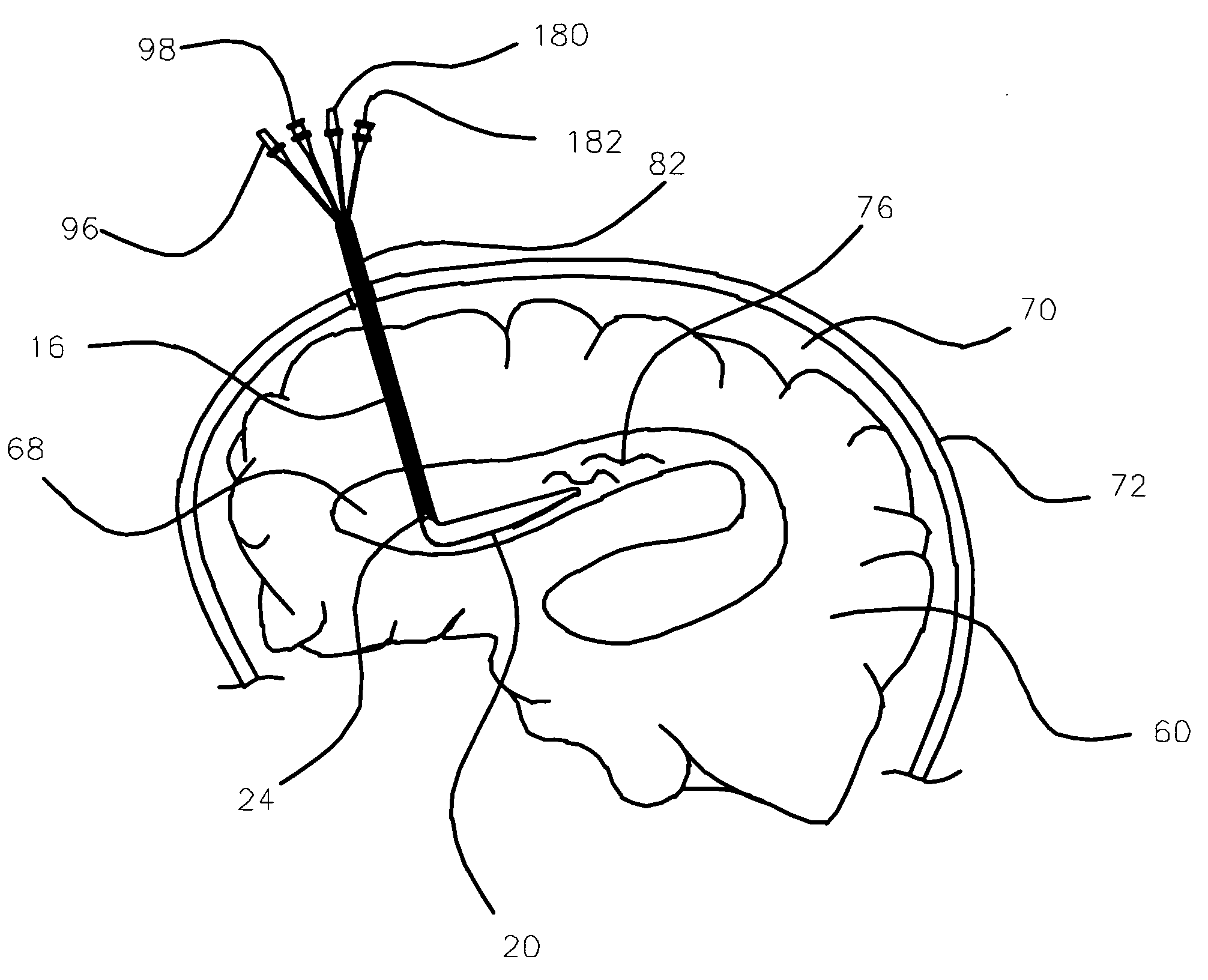
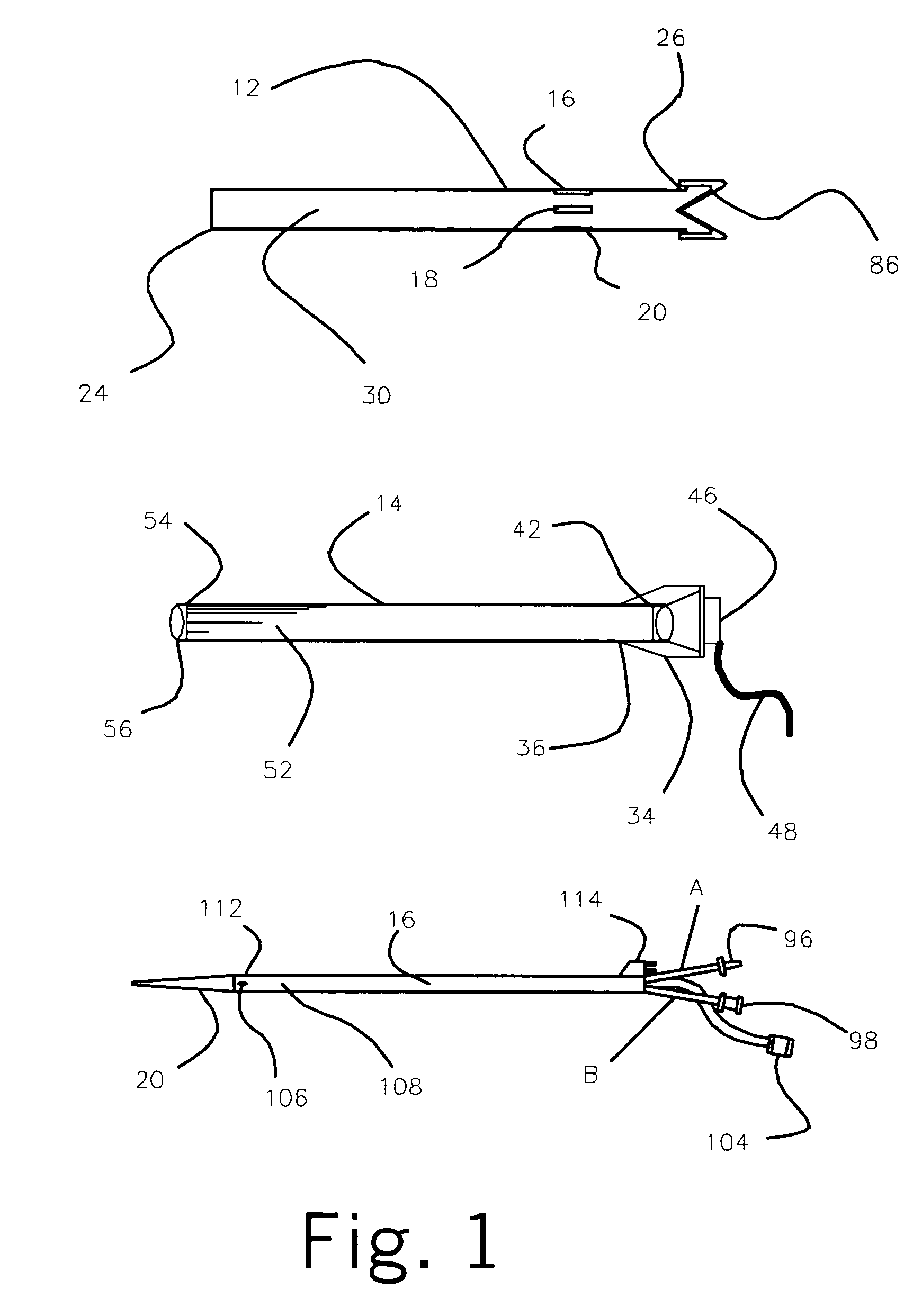
Medical device and method for temperature control and treatment of the brain and spinal cord
ActiveUS7004961B2Rapid and accurate insertionFast transferUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseSubarachnoid space
The invention provides a medical device having a thermister for temperature measurement, irrigation / aspiration ports for fluid exchange and application of therapeutic modalities, a pressure manometer for pressure measurement, and an external system for control of temperature, pressure, and flow rate. When applied to the central nervous system (CNS), this device can be used in hypothermia or hyperthermia applications, the exchange of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), the application of treatment modalities, and the insertion of a ventriculostomy or ventriculostomy-like unit. When applied to spinal cord applications, this device can provide temperature control and a method for application of treatment modalities by using a venting device placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord, a device with similar instrumentation to measure temperature and pressure. A device for ultrasound localization of the CNS device is described. A device for a fiber optic endoscope for visualization and localization is also described. Method of using the devices in treating patients suffering from cardiac arrest, circulatory arrest, exsanguination, head or neck trauma, strokes, tumors and other intracranial diseases are disclosed. In the case of hypothermia treatment of the brain, rapid cooling using principles of convection and conduction will be applied to the lateral ventricle and subarachnoid and / or subdural space simultaneously where the neurons are located in close proximity.
Owner:WONG EDWARD +2
Combined Pressure and Flow Sensor Integrated in a Shunt System
A shunt system for implantation into a patient for diverting excess fluid from the lateral ventricles of the patient's brain to a diversion site. The present shunt includes a pressure transducer for measuring ICP, a rate of flow transducer for measuring the flow rate of the CSF flowing within the shunt, and telemetry circuitry. A remote reader with an antenna is provided to selectively interrogate and provide inductive power to the implanted shunt. Upon interrogation, the pressure and rate of flow measurements are calibrated, multiplexed and transmitted on a carrier signal back to the remote reader / antenna. The reader / antenna extracts the pressure and flow rate data from the carrier wave and further separates the data by demultiplexing the signal. The reader further includes a barometer for providing local barometric pressure and uses this information together with the data from the implanted transducers to calculate and display real-time adjusted ICP, CSF flow-rate within the shunt and brain compliance.
Owner:MEDOS INT SARL
Engraftable neural progenitor and stem cells for brain tumor therapy
One of the impediments to the treatment of some human brain tumors (e.g. gliomas) has been the degree to which they expand, migrate widely, and infiltrate normal tissue. We demonstrate that a clone of multipotent neural progenitor stem cells, when implanted into an experimental glioma, will migrate along with and distribute themselves throughout the tumor in juxtaposition to widely expanding and aggressively advancing tumor cells, while continuing to express a foreign reporter gene. Furthermore, drawn somewhat by the degenerative environment created just beyond the infiltrating tumor edge, the neural progenitor cells migrate slightly beyond and surround the invading tumor border. When implanted at a distant sight from the tumor bed (e.g., into normal tissue, into the contralateral hemisphere, into the lateral ventricles) the donor neural progenitor / stem cells will migrate through normal tissue and specifically target the tumor cells. These results suggest the adjunctive use of neural progenitor / stem cells as a novel, effective delivery vehicle for helping to target therapeutic genes and vectors to invasive brain tumors that have been refractory to treatment.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +2
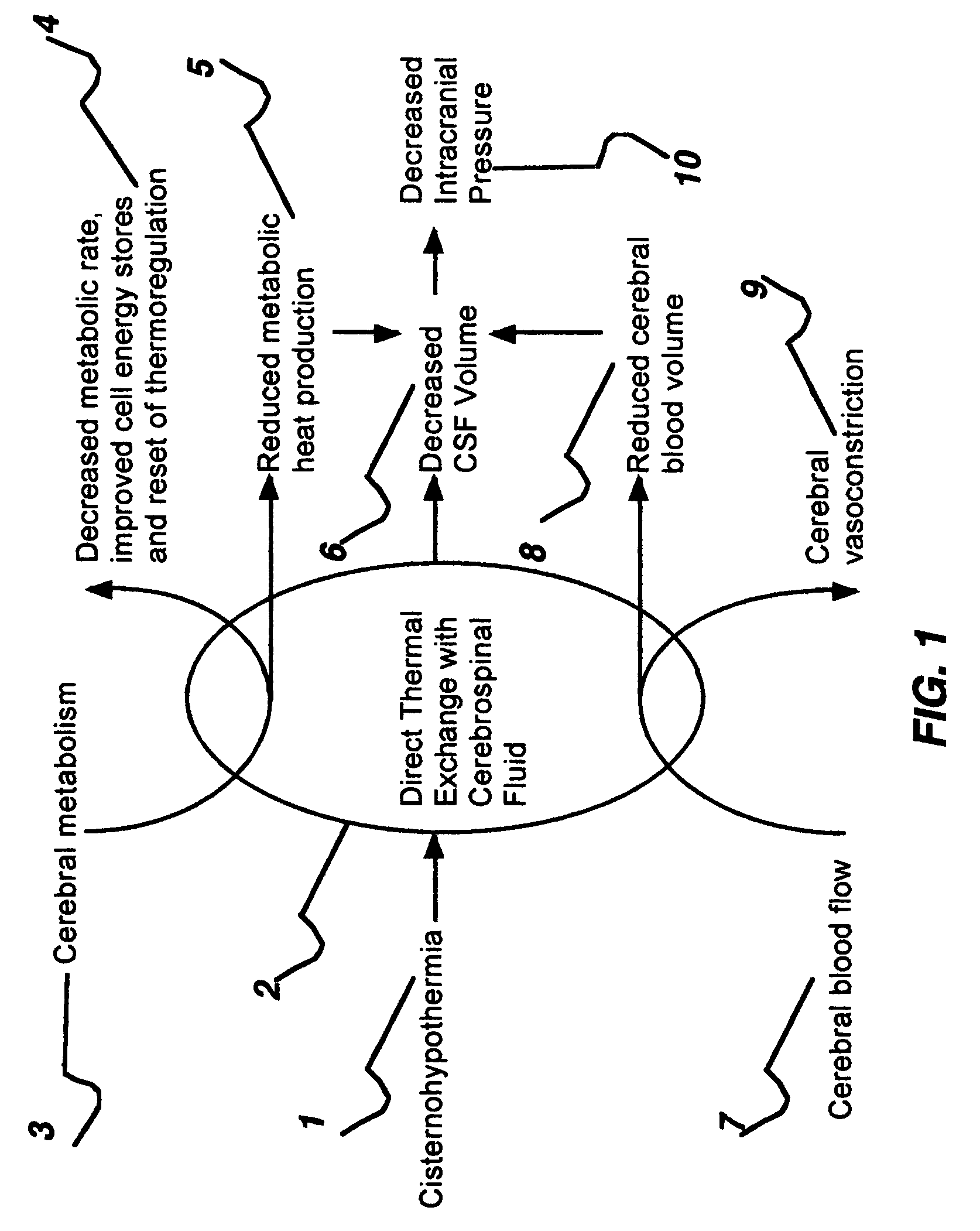
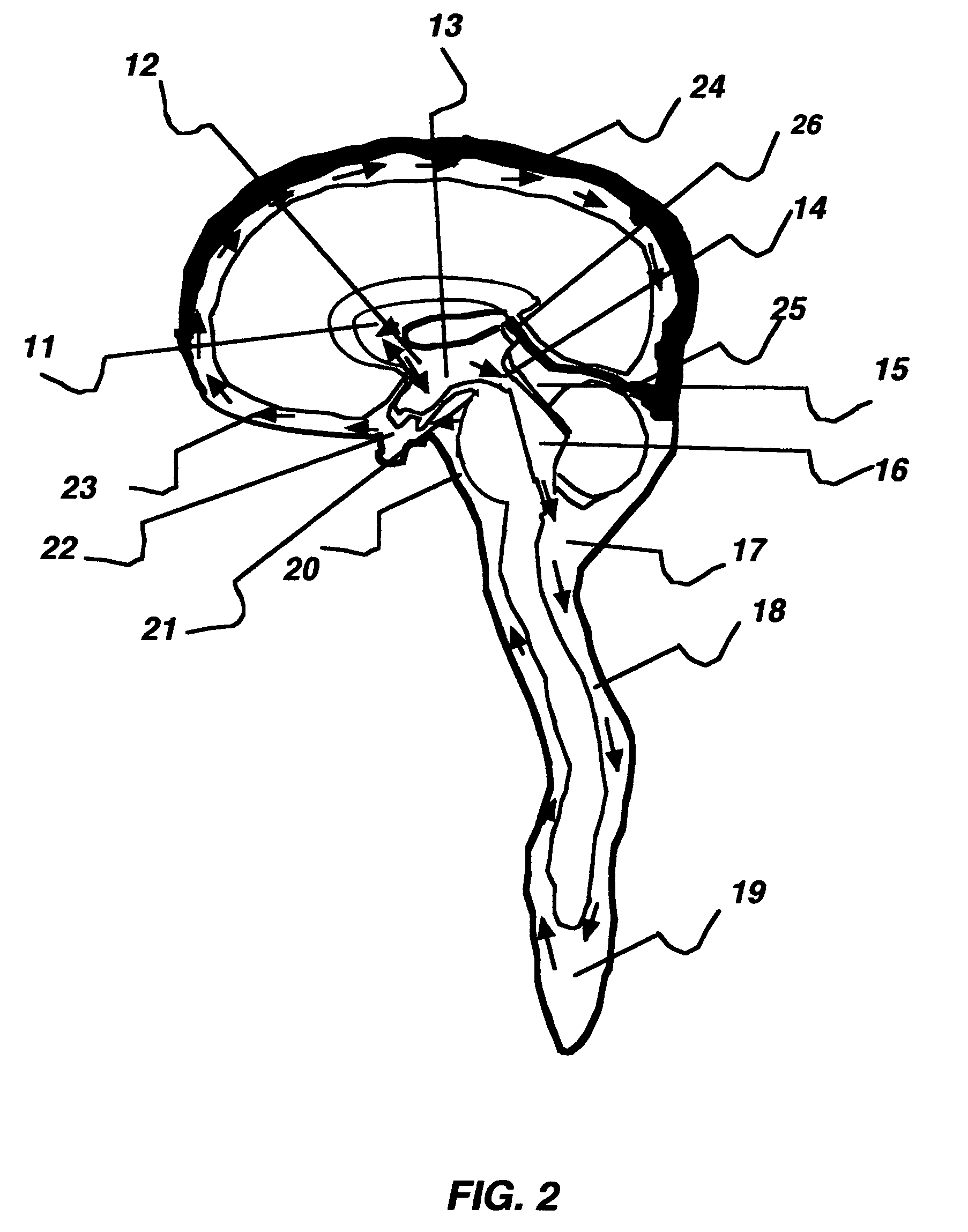
Apparatus and method for hypothermia and rewarming by altering the temperature of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
ActiveUS7318834B2Rapid cooling/rewarmingReduce riskTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingVentricular cathetersCistern
The invention relates to a method for hypothermia and rewarming of the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. In one embodiment, cooling and rewarming of the cerebrospinal fluid is accomplished by applying cooling and rewarming elements externally placed in contact with the skin overlying the cerebrospinal fluid cisterns at the back of the head and spine regions of a patient. In another embodiment, hypothermia and rewarming is accomplished using a double barrel ventricular catheter placed within the lateral ventricles with one catheter used for heat exchange and the other for drainage of excess cerebrospinal fluid. In yet another embodiment of the invention, hypothermia and rewarming is accomplished using a loop catheter with fluid running through the loop placed in the lateral ventricles.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Therapeutic method of treatment of alzheimer's disease
A method and apparatus for treating Alzheimer's disease is disclosed. The method comprises delivering indomethacin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents having cyclooxygenase inhibitor action directly to the hippocampus or the lateral ventricle through an implanted catheter. The catheter has a flexible distal end that is implanted directly in the hippocampus or lateral ventricle as the preferred embodiment. The distal end has either a porous tip or a closed end. Where the distal end is closed, or a plurality of elution holes are present indomethacin is delivered to the hippocampus or lateral ventricle through either the porous tip or the elution holes. The catheter is part of a system for delivering indomethacin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents having cyclooxygenase inhibitor action to the hippocampus or lateral ventricle that includes a pump coupled to the catheter for delivering the indomethacin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents having cyclooxygenase inhibitor action through the catheter to the hippocampus or lateral ventricle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
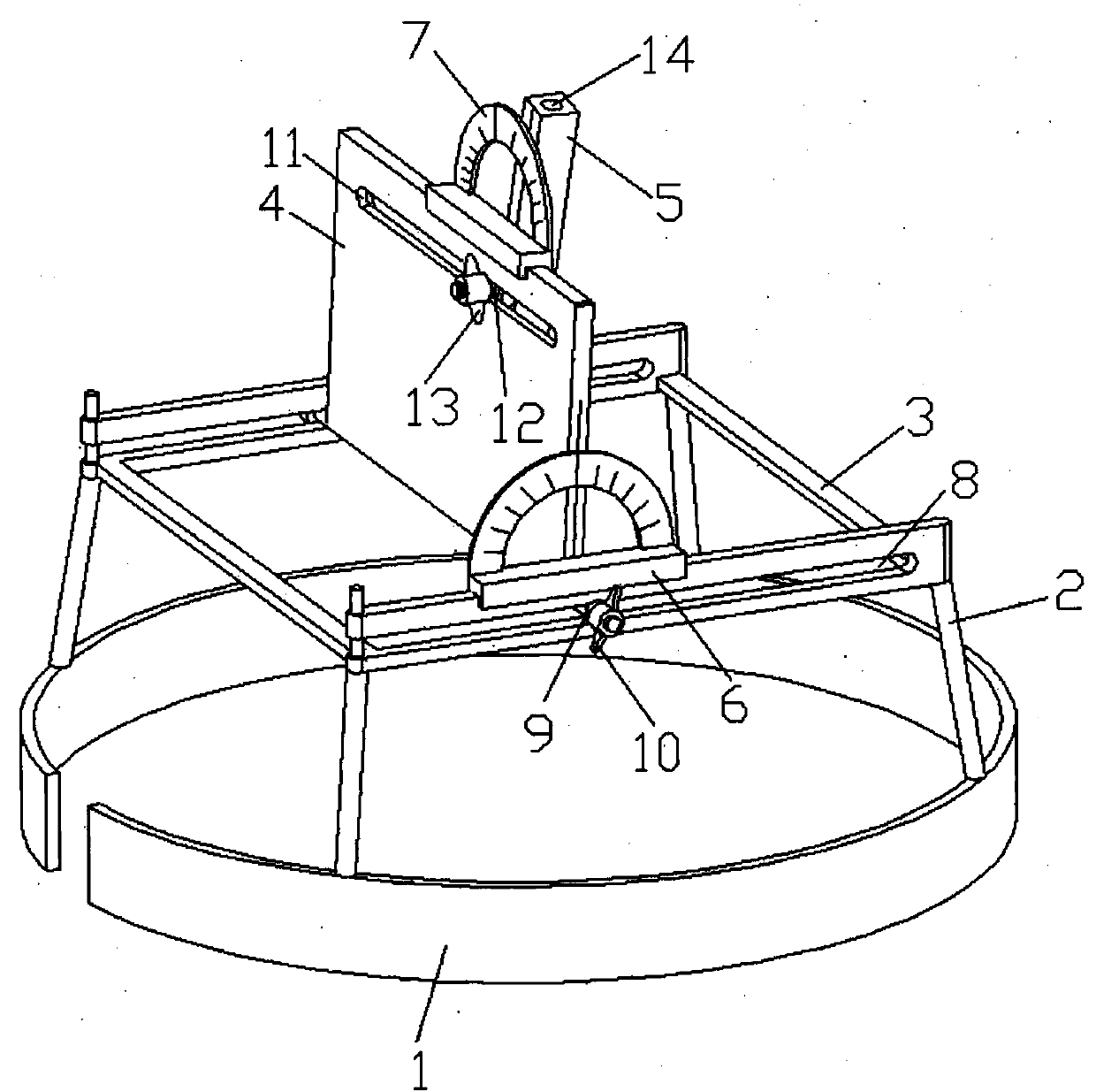
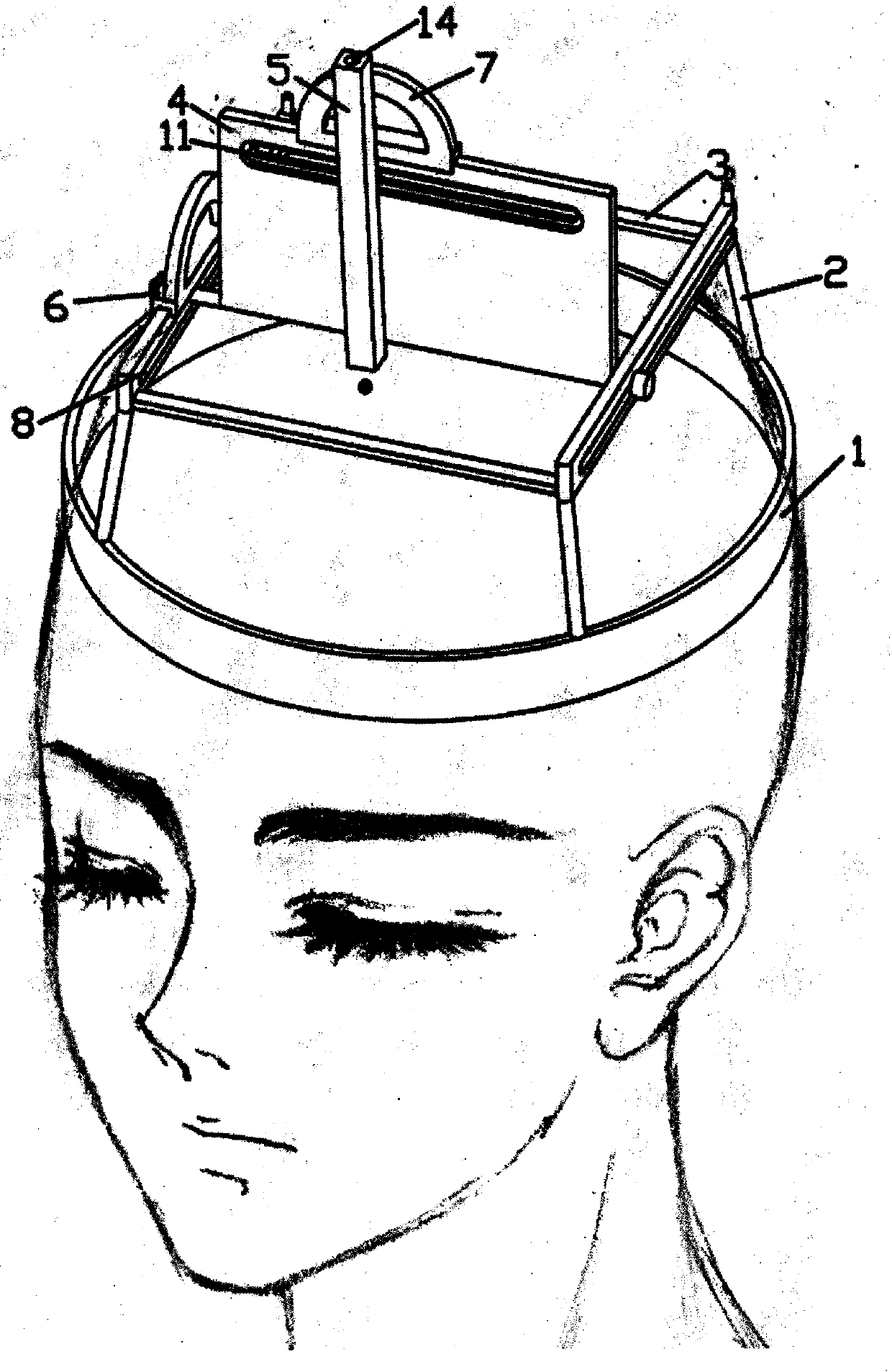
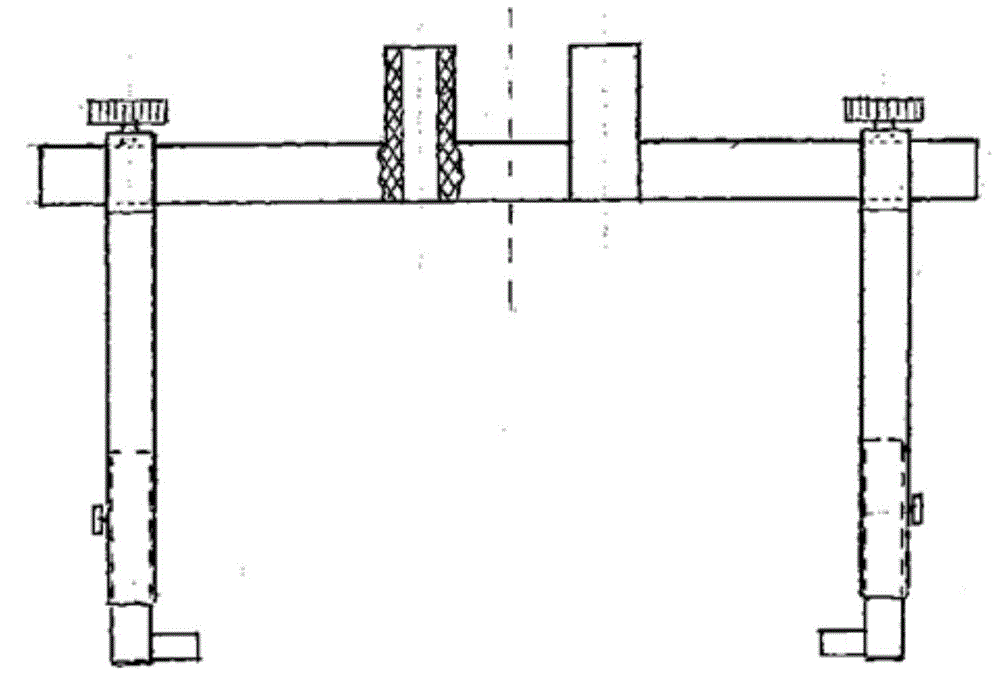
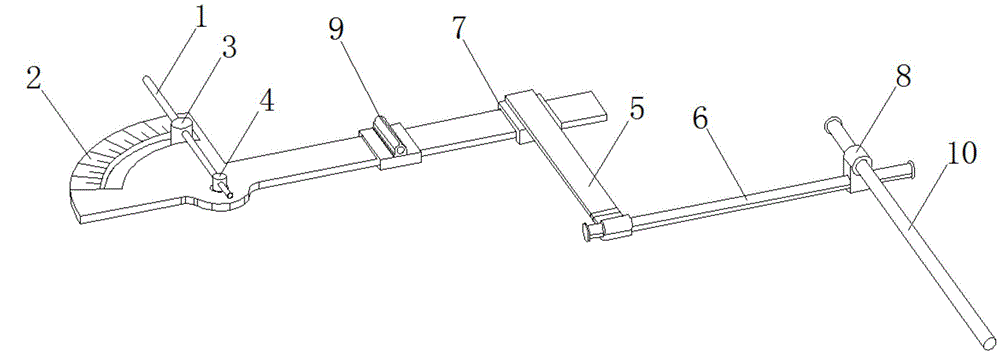
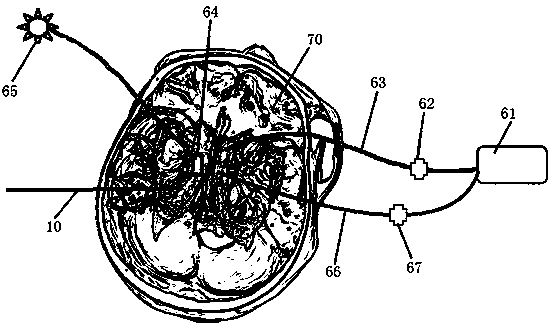
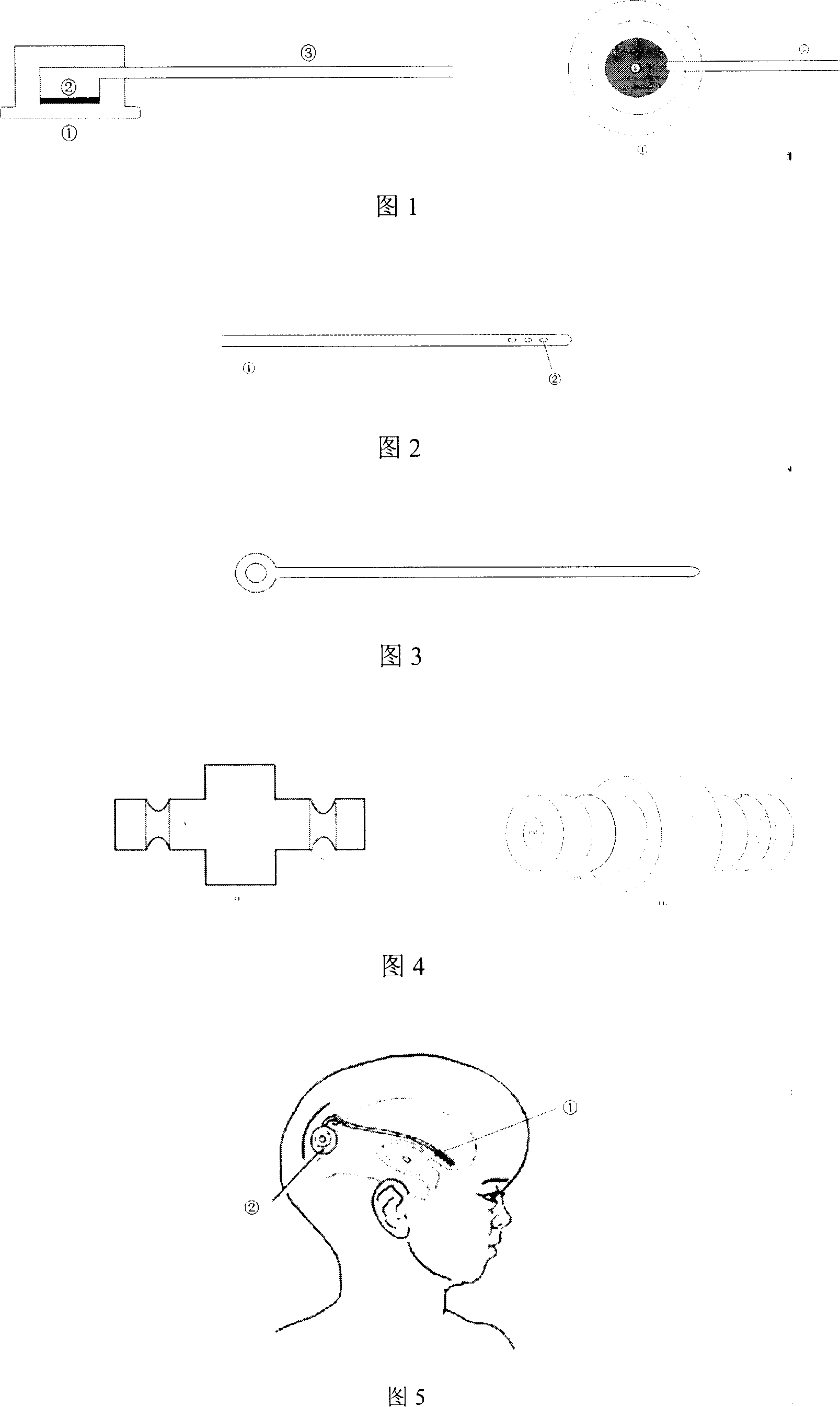
Lateral ventricle puncture location guiding device
The invention relates to a lateral ventricle puncture location guiding device. The lateral ventricle puncture location guiding device is characterized by comprising a head band, wherein the head band is used for being arranged on the head in a sleeved mode, a guide plate which can horizontally move is arranged on a support, the guide plate is vertically arranged and can swing in a front-and-back mode, the swing angle of the guide plate is set through a first protractor, a guide tube which can horizontally move is arranged on the guide plate, the moving direction of the guide tube is perpendicular to the moving direction of the guide plate, the guide tube is vertically arranged and can swing in a left-and-right mode, and when the guide tube swings to be in place, the position of the guide tube is locked through a second locking mechanism, a through hole is formed in the guide tube, and a puncture needle can be guided to penetrate into the brain through the through hole. The lateral ventricle puncture location guiding device has the advantages of being simple in structure, convenient to use, capable of providing a location guiding device for lateral ventricle puncture and capable of being used for lateral ventricle puncture operations to guide cerebrospinal fluid out.
Owner:上海中山医疗科技发展有限公司 +1
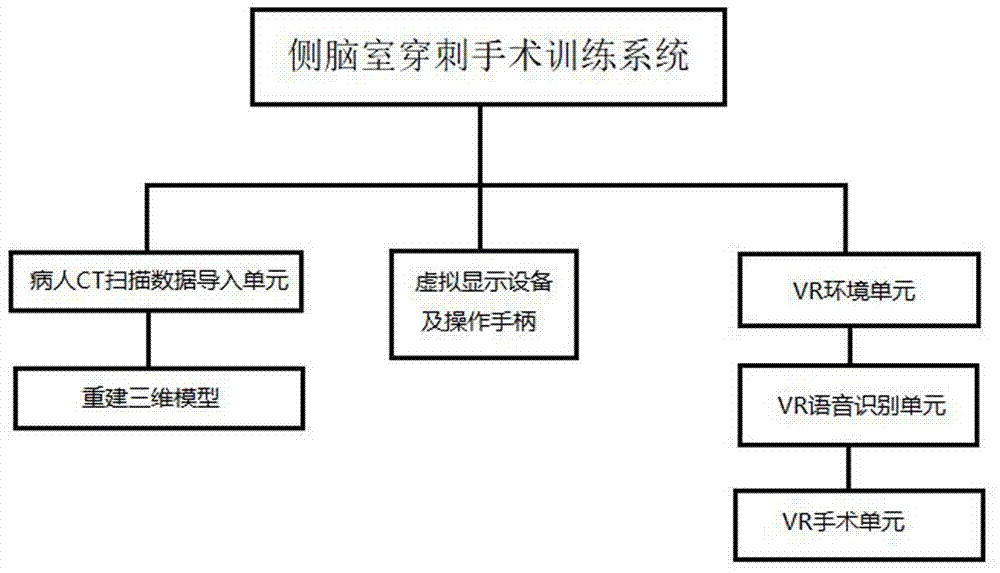
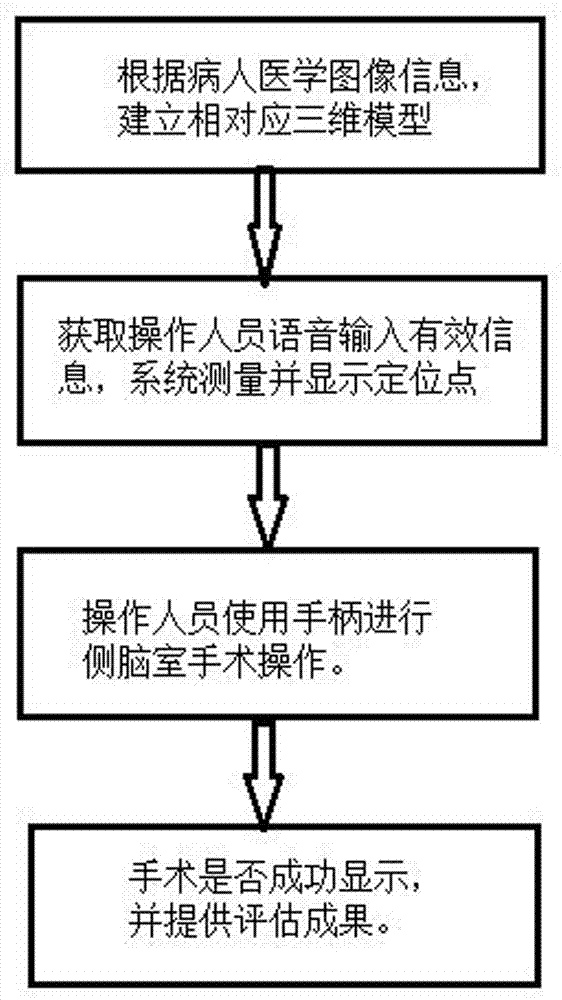
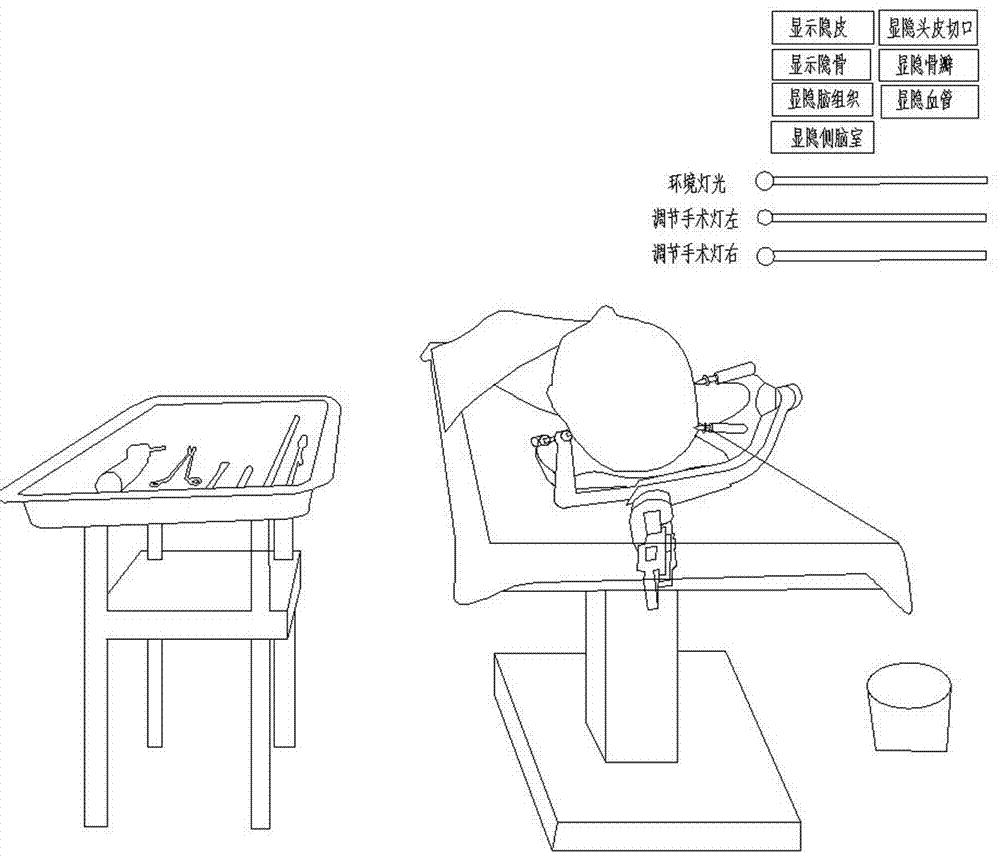
Virtual reality platform based lateral ventricle puncture training system
InactiveCN107978195AImprove realismConducive to summing up experienceInput/output for user-computer interactionCosmonautic condition simulationsSurgical operationJoystick
The invention relates to a virtual reality platform based lateral ventricle puncture training system. The system comprises a CT (computed tomography) scanning / MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) image data importing unit, a CT scanning / MRI image reconstruction unit, a virtual reality head-mounted display device, a joystick and a virtual reality processing unit. The CT scanning / MRI image data importing unit is used for providing CT scanning information of patients and patient information; the CT scanning / MRI image reconstruction unit is used for constructing a three-dimensional model, the virtualreality head-mounted display device provides virtual display environment display, and the joystick provides virtual reality environment operating information. The virtual reality processing unit comprises a VR (virtual reality) environment unit, a VR voice recognition unit and a VR surgical unit, wherein the VR environment unit is used for providing a virtual environment matched with a reality surgical environment, the VR voice recognition unit is used for operator voice recognition, and the VR surgical unit is used for executing surgical operations. The virtual reality platform based lateralventricle puncture training system has advantages that the problem of resource shortage in experiment teaching is solved, reality in doctor training is enhanced, training cost is reduced, experience summarization is facilitated for doctors, and patient-doctor disputes can be avoided.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
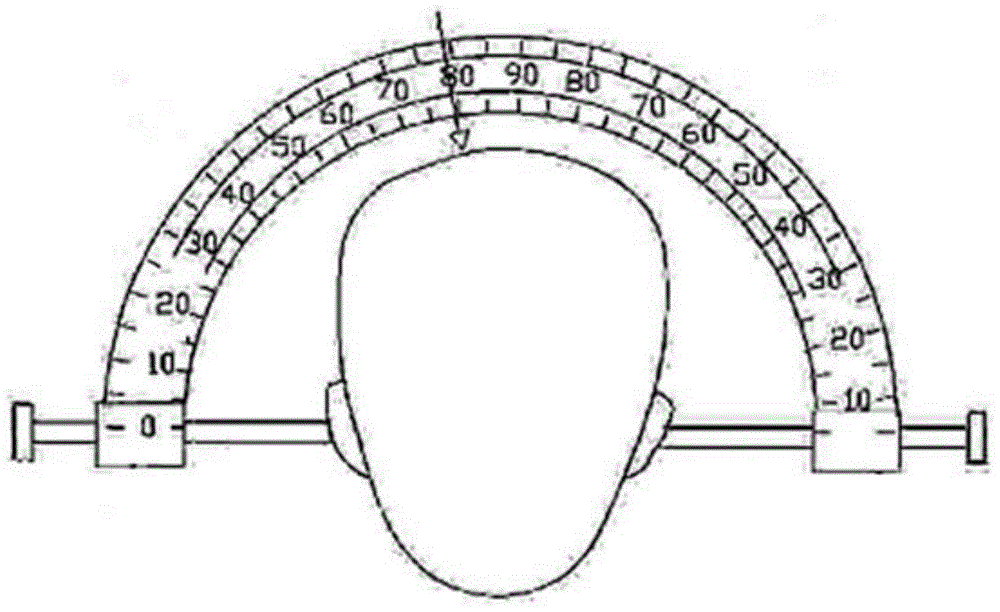
Lateral ventricle frontal angle puncture guiding device
InactiveCN104921784AImprove safety standardsReduces the chance of improper piercingSurgical needlesTrocarCatheterCerebral ventricle
The invention provides a lateral ventricle frontal angle puncture guiding device. The lateral ventricle frontal angle puncture guiding device comprises a CT machine, a fixing support, a positioning device, an angle scale and a puncture catheter. The fixing support comprises a fixing rod, the axial direction of the fixing rod is the Y direction, and the direction perpendicular to the Y direction is the X direction. The angle scale is installed on the fixing support through the positioning device, and the angle scale can horizontally move in the X direction and the Y direction and can rotate in the X direction. The puncture catheter is installed on the angle scale, and the deviation angle of the puncture catheter can be adjusted along scale marks of the angle scale. By the adoption of the lateral ventricle frontal angle puncture guiding device, the accurate position of a puncture target point of a patient is extracted through the CT machine, the puncture position, the puncture angle and the puncture depth of the puncture catheter are determined by adjusting the deviation angels of the positioning device and the puncture catheter on the angle scale, the probability of improper puncture is decreased, and the safety level of an operation is increased.
Owner:张宝国
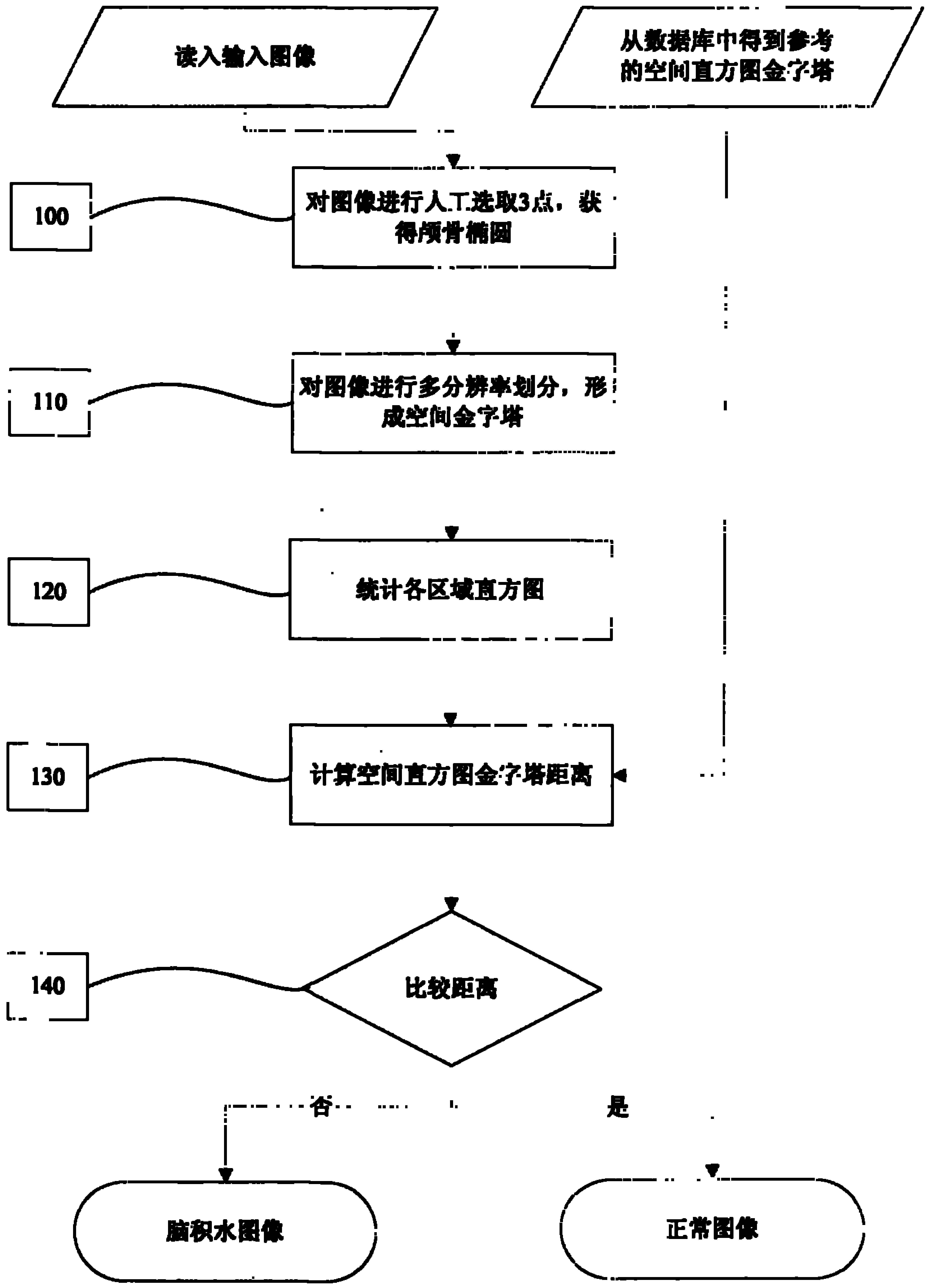
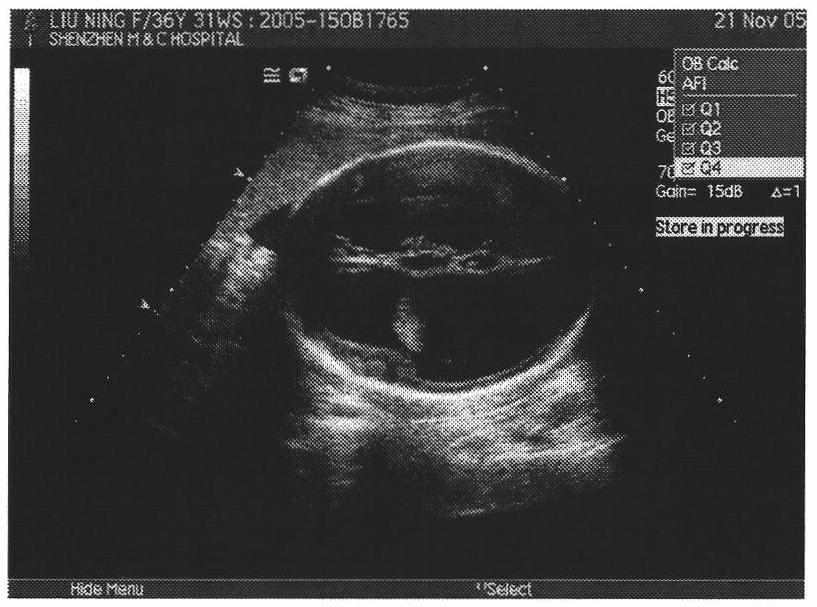
Image processing method for automatically judging fetal hydrocephalus from ultrasonic images
InactiveCN101791231ALess subjective dependenceThe method is simple and fastImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationHistogram
The invention provides an image processing method for automatically judging fetal hydrocephalus from ultrasonic images, comprising the following steps: firstly extracting skull ellipse of a new fetal brain image on the second plane, lateral ventricle horizontal plane; establishing a space histogram pyramid in the interior zone of the ellipse in the image; respectively calculating the distances among the space histogram pyramids of the given fetal ultrasonic image, the normal fetal brain images in the same gestational week and the image of hydrocephalus in the brain on the lateral ventricle horizontal plane in the same gestational week; and setting a threshold and giving the possibility of fetal hydrocephalus from judgment according to the relationship between the distances among the space histogram pyramids and the threshold.
Owner:SHENZHEN MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTHCARE HOSPITAL +1
Construction process of Alzhemer's disease rat animal model
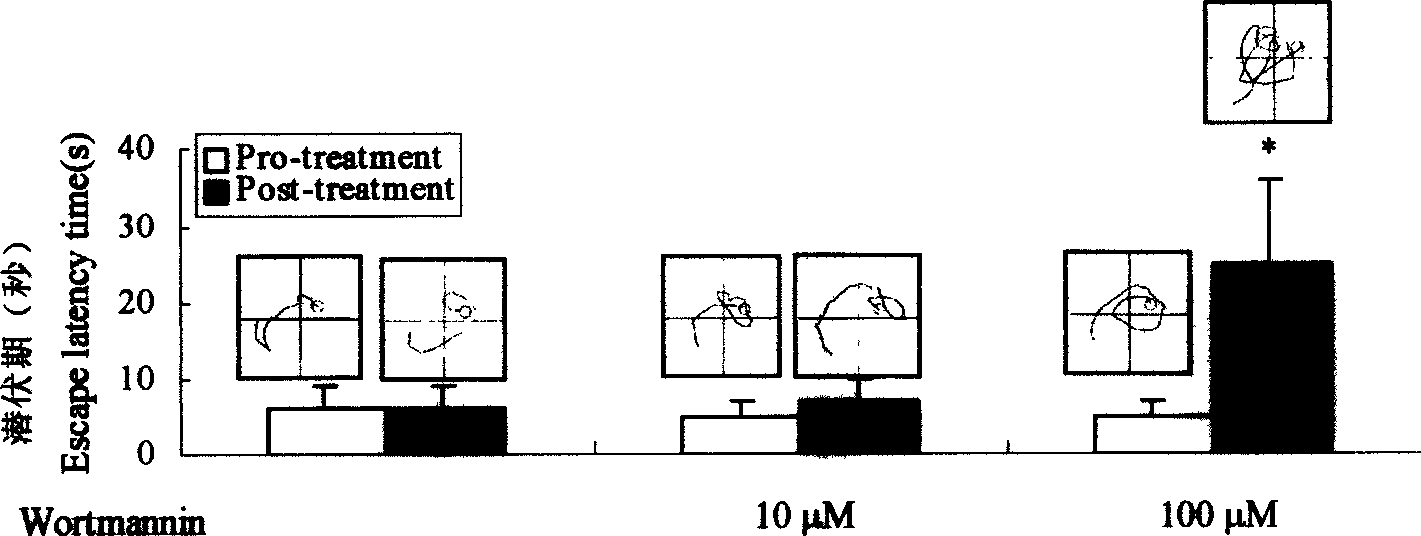
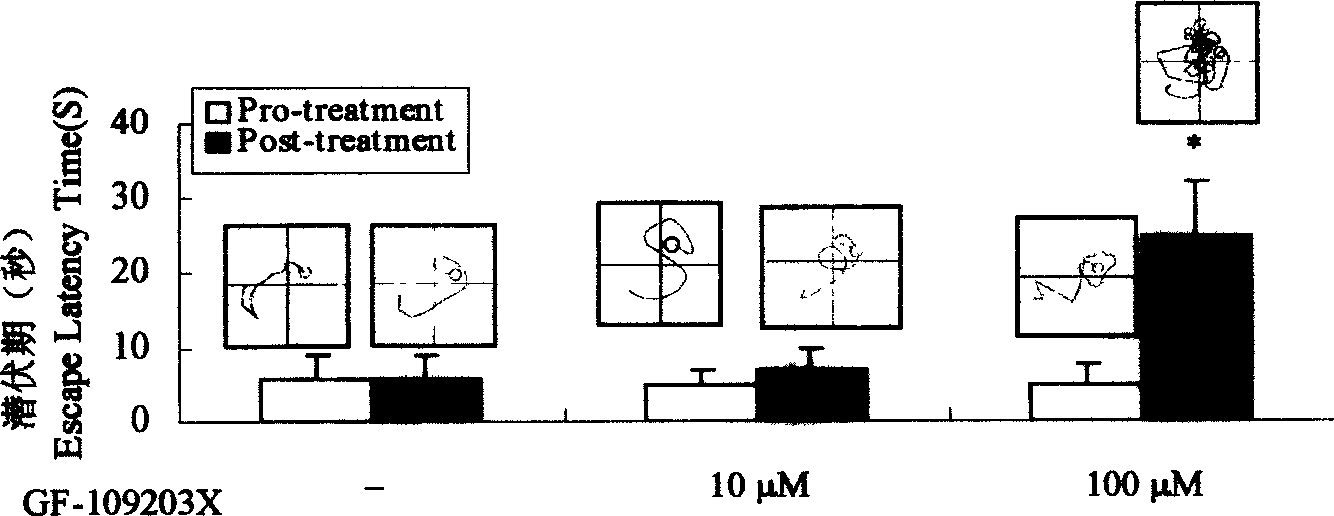
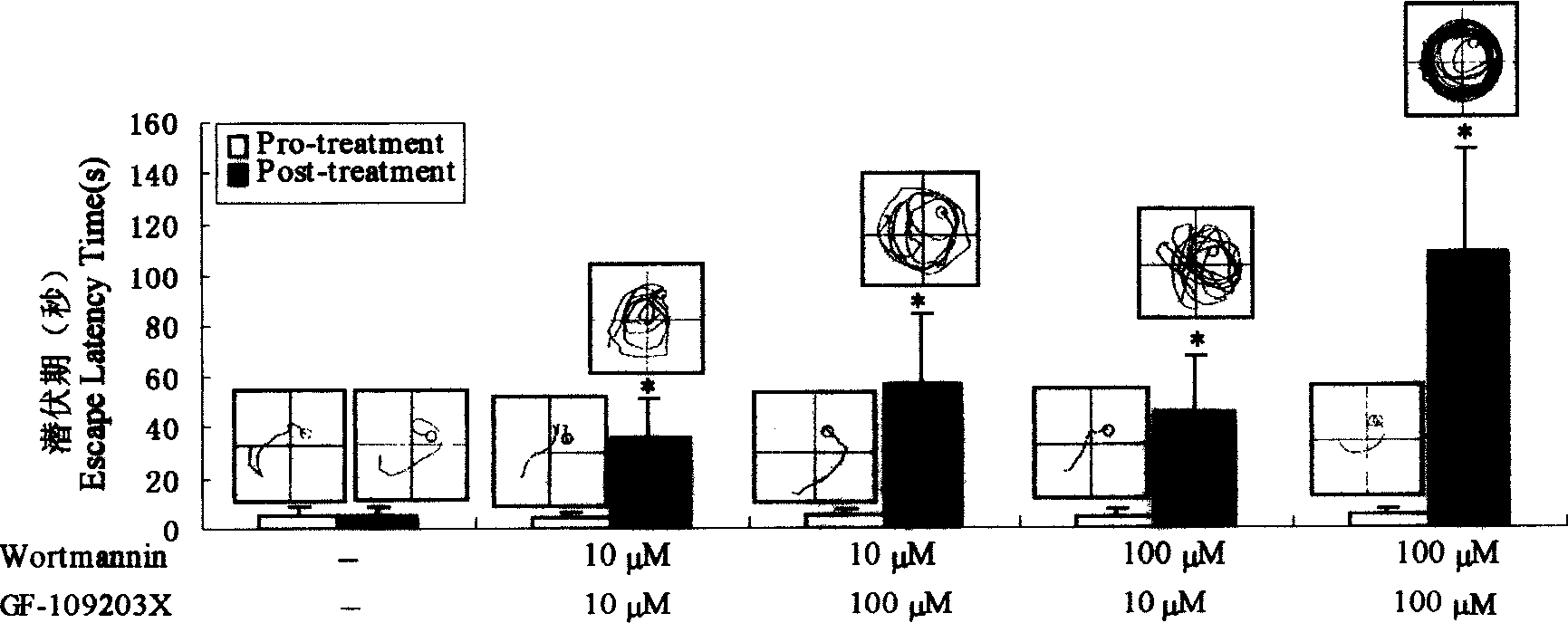
The present invention provides method of constructing Alzhemer's disease (AD) rat animal model through injecting wortmanin as phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase inhibitor and GF-109203X as protein kinase C inhibitor into rat lateral ventricle simultaneously. The method can induce AD-like abnormal excessive phosphorylation of hippocampal skelemin and neurofibrillary tangle-like pathologic changes and constitute rat animal model with co-existed learning and memory disorder. The model may be used in screening medicine for treating Alzhemer's disease and in the research of the internal relation between protein kinase and AD pathogenesis.
Owner:华中科技大学同济医学院
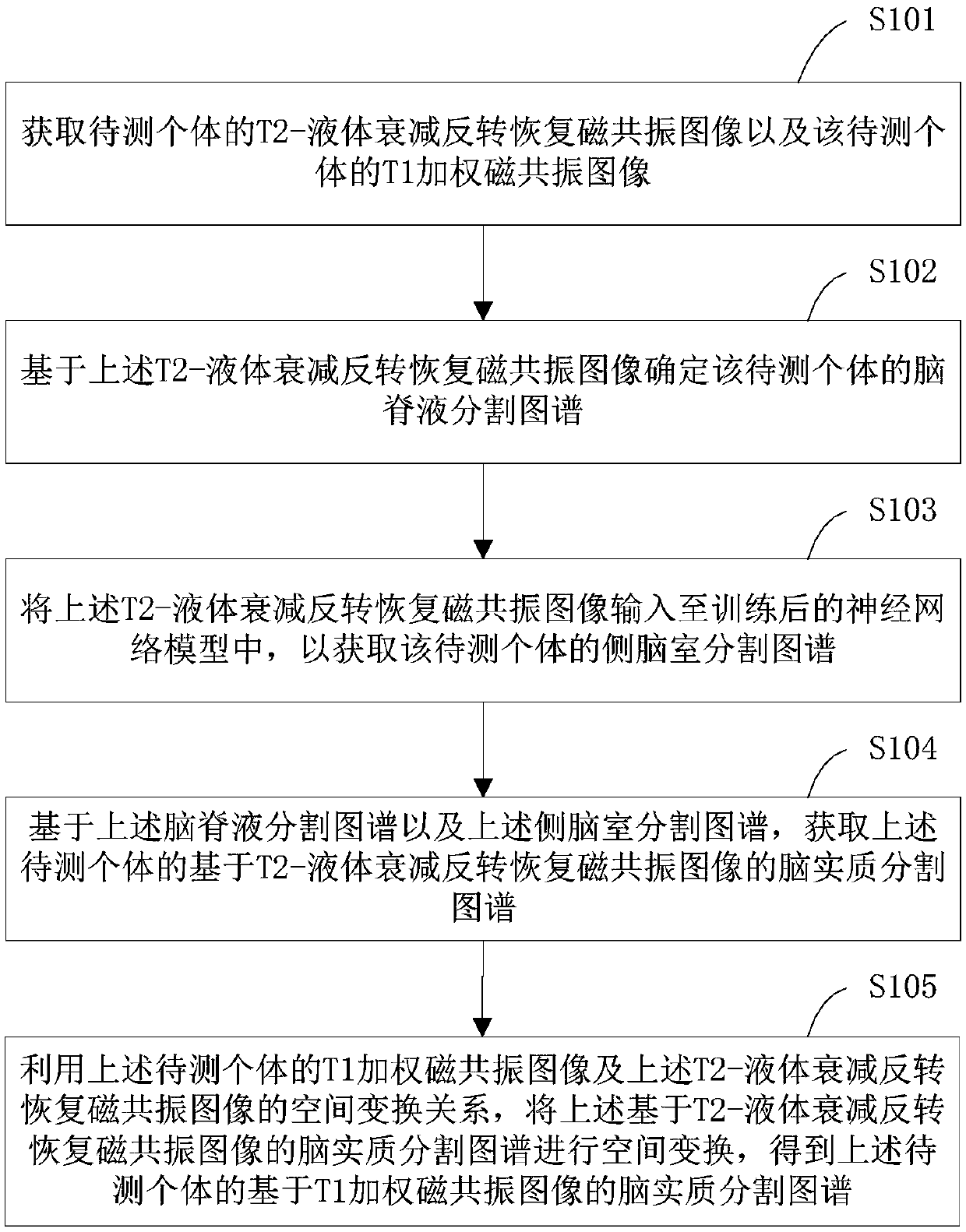
Image segmentation method, image segmentation apparatus and electronic device
ActiveCN108765447AAccurate divisionAccurately Segment AtlasesImage enhancementImage analysisParenchymaInversion recovery
The invention provides an image segmentation method, an image segmentation apparatus and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image and a T1 weighted magnetic resonance image of a to-be-tested individual; based on the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, determining a cerebrospinalfluid segmentation graph; inputting the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image to a neural network model, thereby obtaining a lateral ventricle segmentation graph; on the basis of the cerebrospinal fluid segmentation graph and the lateral ventricle segmentation graph, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based o the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image; and by utilizing a spatial conversion relationship between the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image and the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based on the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image. According to the technical scheme, a cerebrospinal fluid part and a non-cerebrospinal fluid part can be moreaccurately divided, so that the more accurate brain parenchyma segmentation graphs can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN BRAINNOW MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Use of bilobalide B in preparing medicine for promoting nerve cell regenerate
InactiveCN101396355ATo achieve the purpose of repairing nerve damageIncrease the number ofOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseBilobalides
The invention relates to the application of ginkgolide B in the preparation of drugs promoting the regeneration of nerve cell, wherein, the nerve cell is the nerve cell at the positions of brain tissue hippocampus, striaturn and lateral ventricle. The ginkgolide B can penetrate the blood-brain barrier to promote the neural stem cells at the positions of cerebral cortex, the hippocampus and the like to proliferate and be transformed into neuron, thus increasing the number of regenerative cells, so as to achieve the goal of rehabilitating neural damnification and preventing and remedying the disease of cerebral stroke.
Owner:北京鑫利恒医药科技发展有限公司 +1
Preparation method of Alzheimer's disease animal model
InactiveCN102191274AShorten the timeIncreased Alzheimer's disease symptomsMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryDiseaseAnimal brain
The invention relates to a preparation method of an Alzheimer's disease animal model. The method comprises the following preparation steps: siRNA using animal brain abcg4 as target gene is designed; through the experiment, the target sequence of the specific siRNA which can interfere the expression of abcg4 is GTGAGAAGCAAGAGGTGAA, the siRNA is dissolved with PBS; and an healthy animal is selected, 240mu g / kg (weight) of siRNA is injected in the lateral ventricle of the animal once by using a stereotaxic apparatus, and the animal model is obtained after 48 hours. By adopting the method for preparing the animal model, the time is short and the damage to the experimental animal is not serious.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
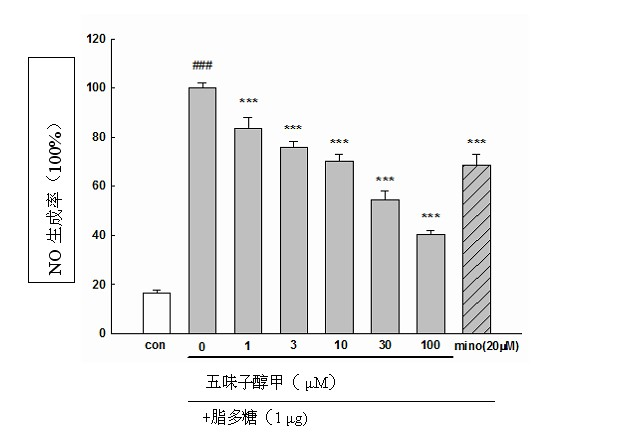
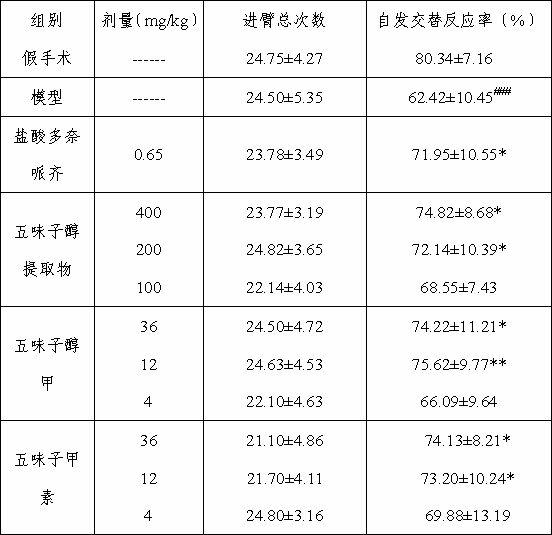
New application of schizandrol A, schizandrin and schizandrol extract to prevention and treatment of senile dementia
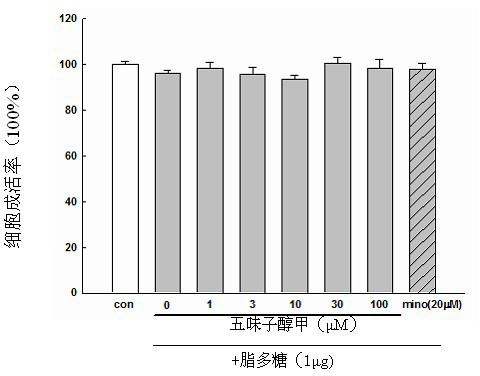
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicaments and discloses application of schizandrol A, schizandrin and a schizandrol extract to prevention and treatment of senile dementia. The invention particularly relates to the effect of the schizandrol extract, the schizandrol A and the schizandrin of improving learning memory disorder of dementia mice induced by injecting Abeta1-42 into lateral ventricle and discusses the action mechanism. The result shows that the schizandrol extract, the schizandrol A and the schizandrin can obviously improve working memory disorder and spatial discrimination learning memory disorder of the mice, can improve SOD and GSH-Px activity, reduce MDA content, can increase GSH content and can reduce GGSG content, and shows that the schizandrol extract, the schizandrol A and the schizandrin can eliminate free radicals generated by in vivo oxidation stress through various routes, can inhibit lipid peroxidation and can improve oxidation resistance of an organism so as to improve oxidative stress damage caused by Abeta1-42. The schizandrol extract, the schizandrol A and the schizandrin can be applied to preparing medicaments or health-care food for preventing and treating senile dementia.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Cerebrospinal fluid extracting device
InactiveCN104874093AShorten the timeQuick resultsSurgeryWound drainsVolumetric flaskCerebral ventricle
The invention discloses a cerebrospinal fluid extracting device which comprises a jugular vein indwelling tube device, a two-sided lateral ventricle indwelling tube device and cauda equine cone indwelling tube device. The two-sided lateral ventricle indwelling tube device comprises a two-sided lateral ventricle indwelling tube and a cerebrospinal fluid volumetric flask, the jugular vein indwelling tube device comprises a jugular vein indwelling tube and an intravenous syringe, and the cauda equine cone indwelling tube device comprises a cauda equine cone indwelling tube and a cerebrospinal fluid collector. The cerebrospinal fluid extracting device has the advantages that the cerebrospinal fluid extracting device is easy and convenient to operate, short in time and stable in operation, can become effective fast and can be used for research experiments on drugs which pass blood brain barriers, diversified nervous system diseases and nervous system disease targeted drug metabolism, intravenous administration can be facilitated, and a large quantity of cerebrospinal fluid can be continuously extracted by the aid of the cerebrospinal fluid extracting device.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for gestational age estimation and embryonic mutant detection
ActiveUS20170213340A1Accurate stagingAbnormality in shapeImage enhancementImage analysisMean squareMedicine
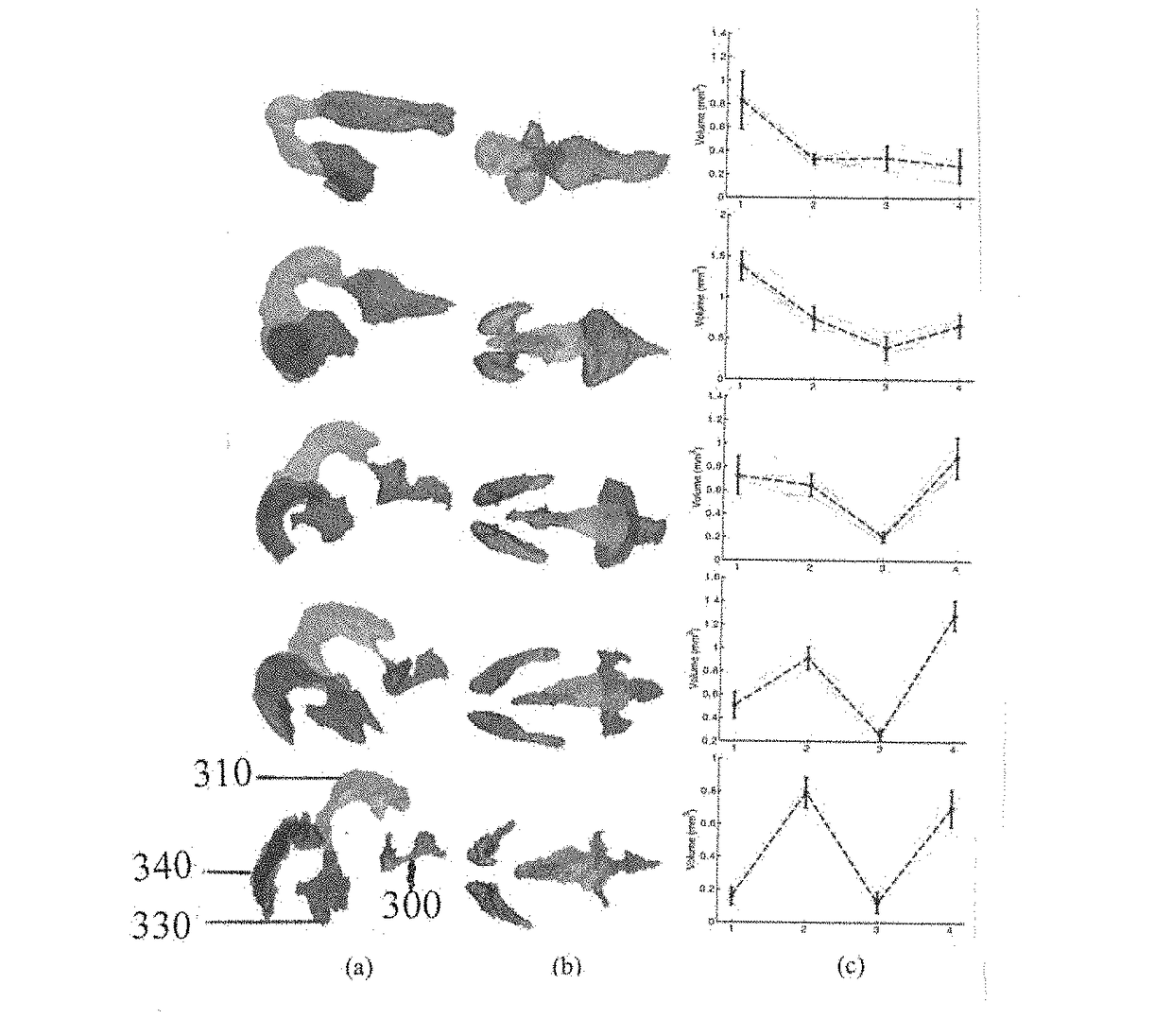
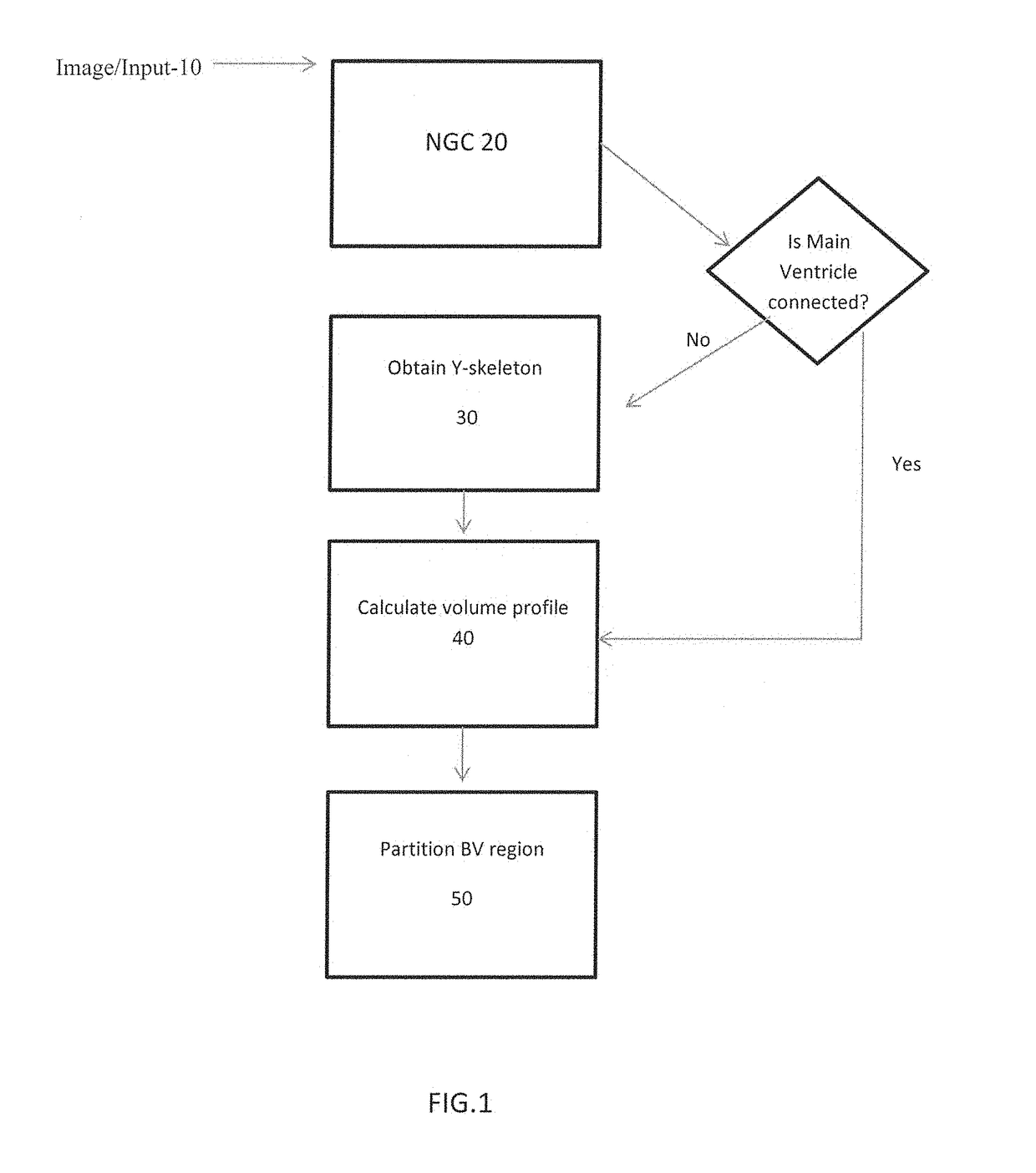
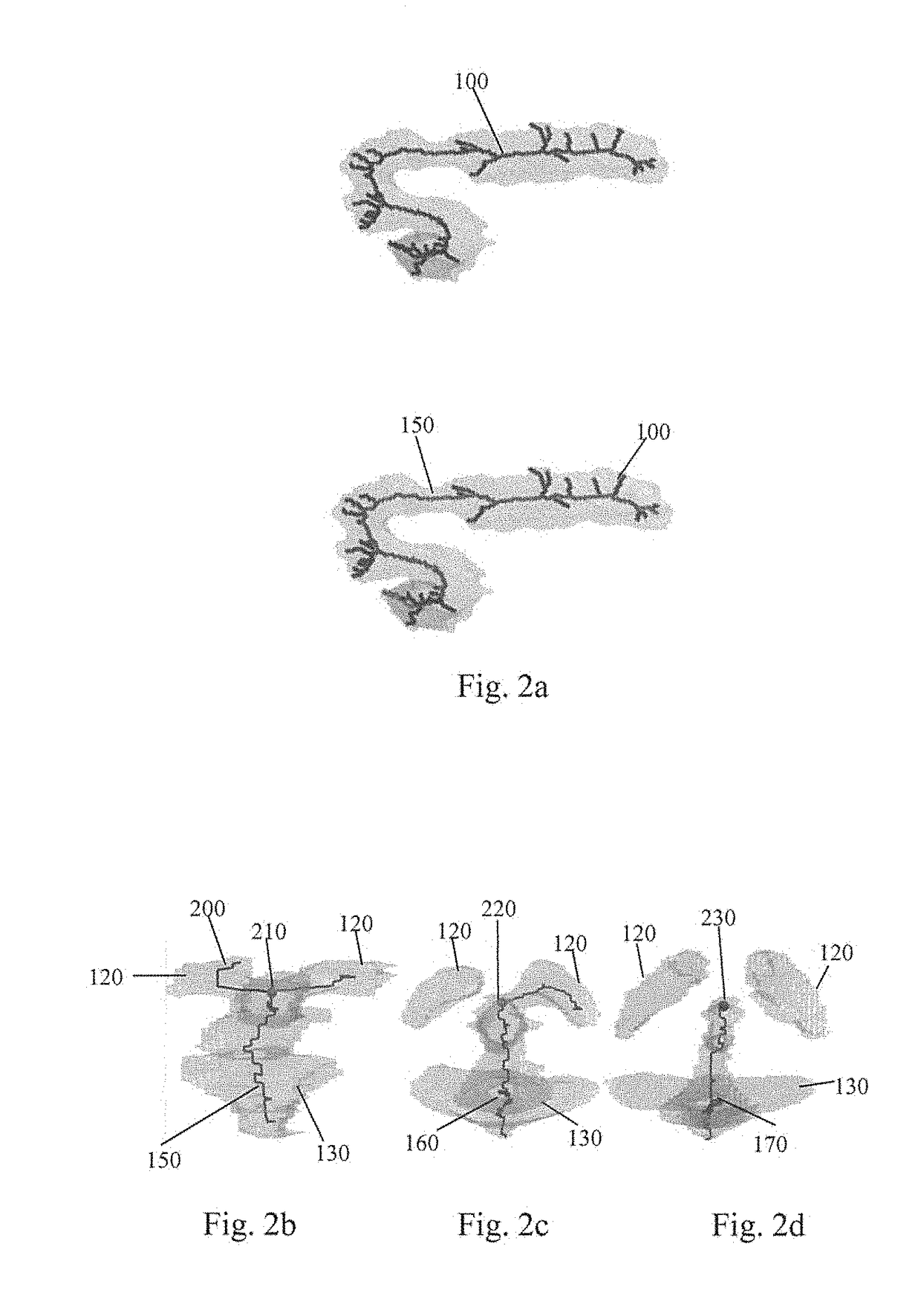
A method to characterize shape variations in brain ventricles during embryonic growth in mammals, the method including extracting a brain ventricle skeleton from one or more images, calculating a volume profile for the skeleton using the extracted images, partitioning the brain ventricle based on the volume profile along the skeleton, the brain ventricle being partitioned into two lateral ventricles and a main ventricle, the main ventricle being further partitioned into three sub regions, determining volume vectors of the two lateral ventricles and the three sub regions, computing a means square error between the determined computed volume vectors and a pretrained mean volume vector of embryos during different gestational stages, and classifying the embryo to the gestational stage having the lowest mean square error. A method to characterize mutant detection in mammals, the method including acquiring one or more images, computing a volume profile directly along a path of the detected skeleton from the one or more images, aligning the volume profile against a standard profile, and evaluating the volume profile against the standard profile to detect a mutation.
Owner:RIVERSIDE RES INST +1
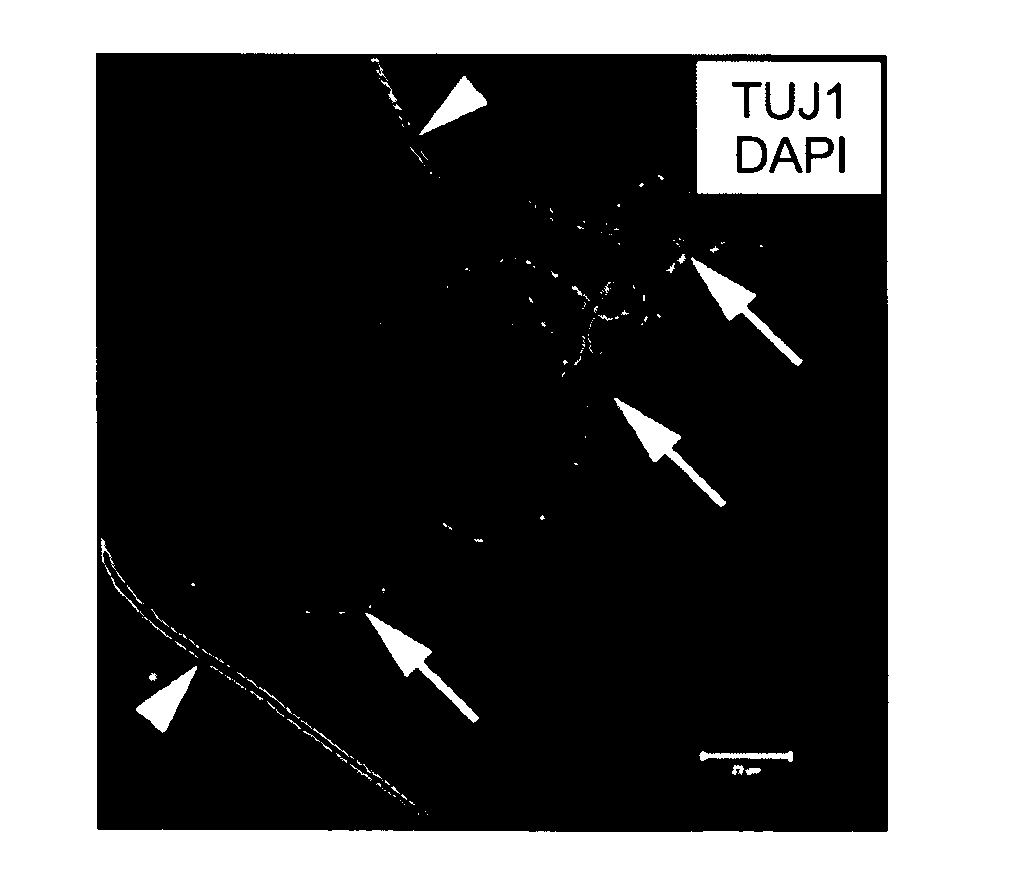
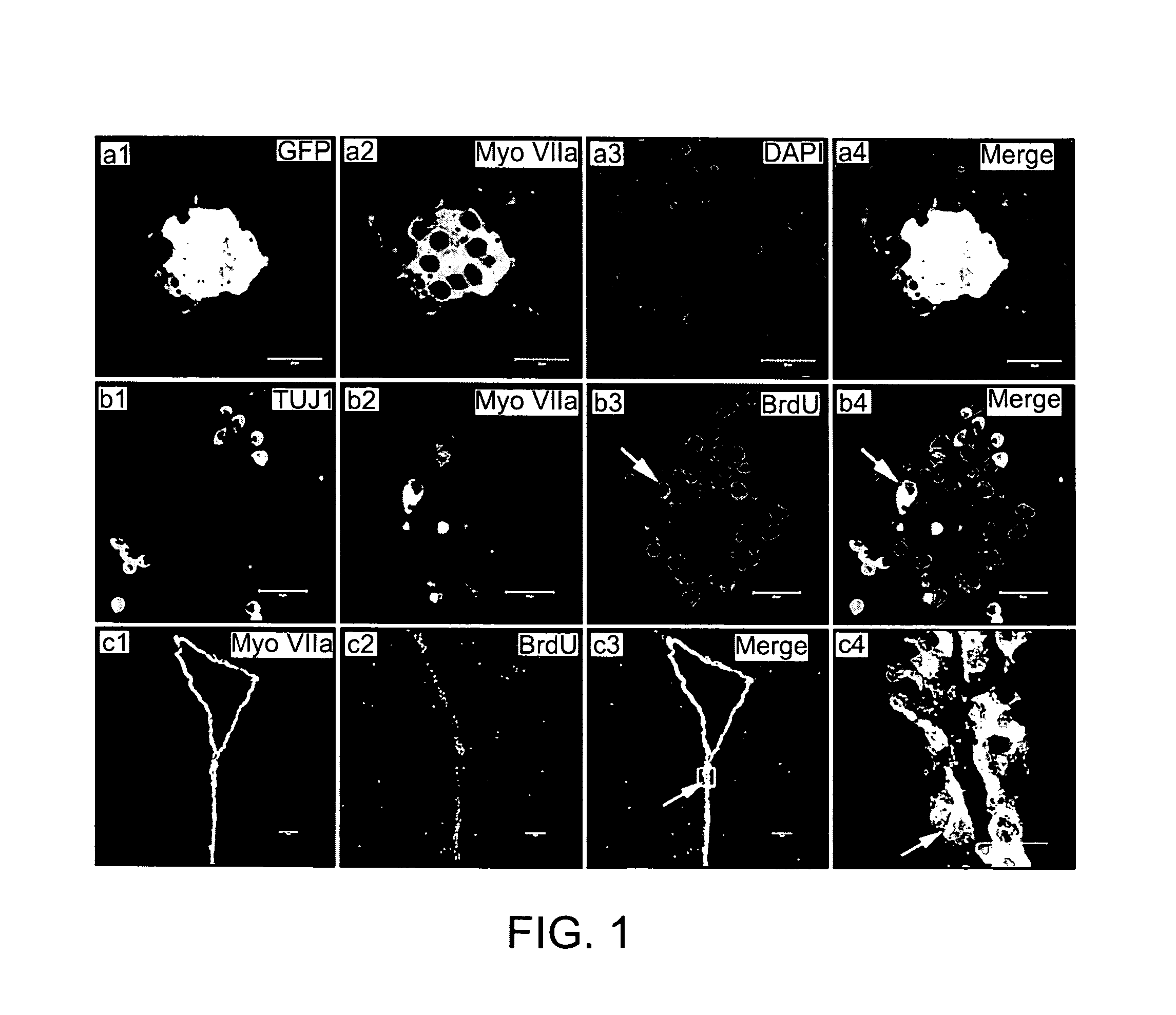
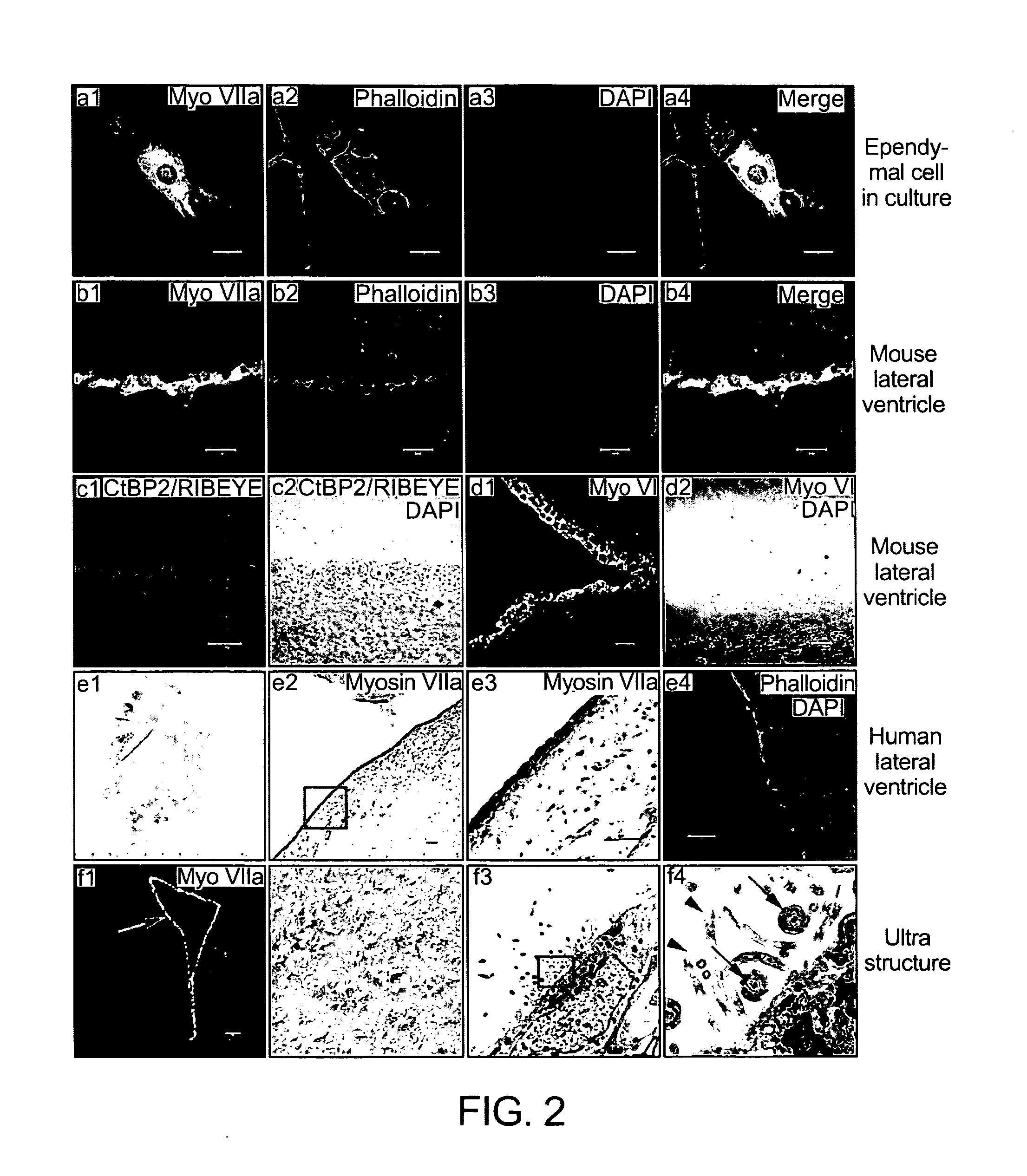
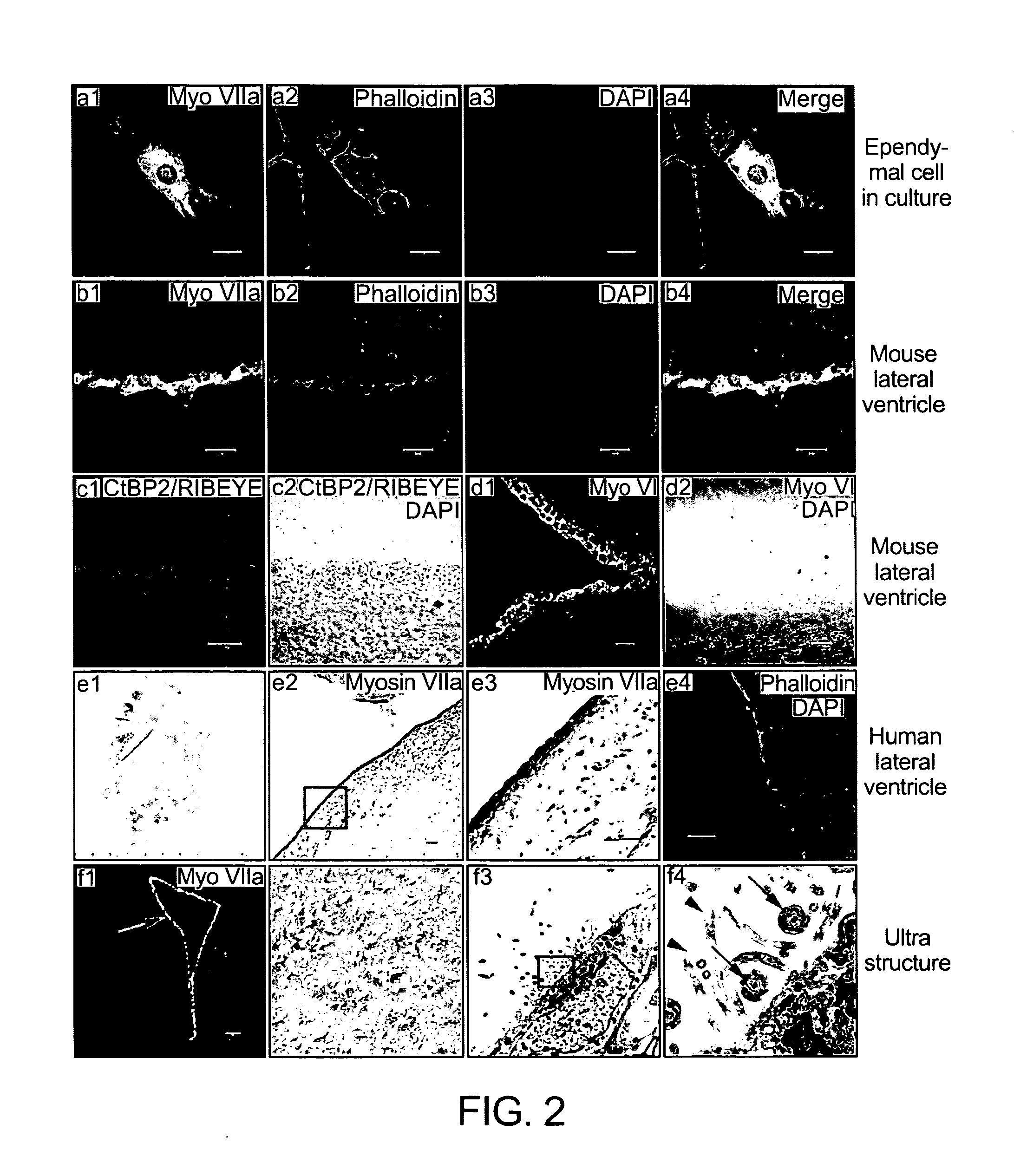
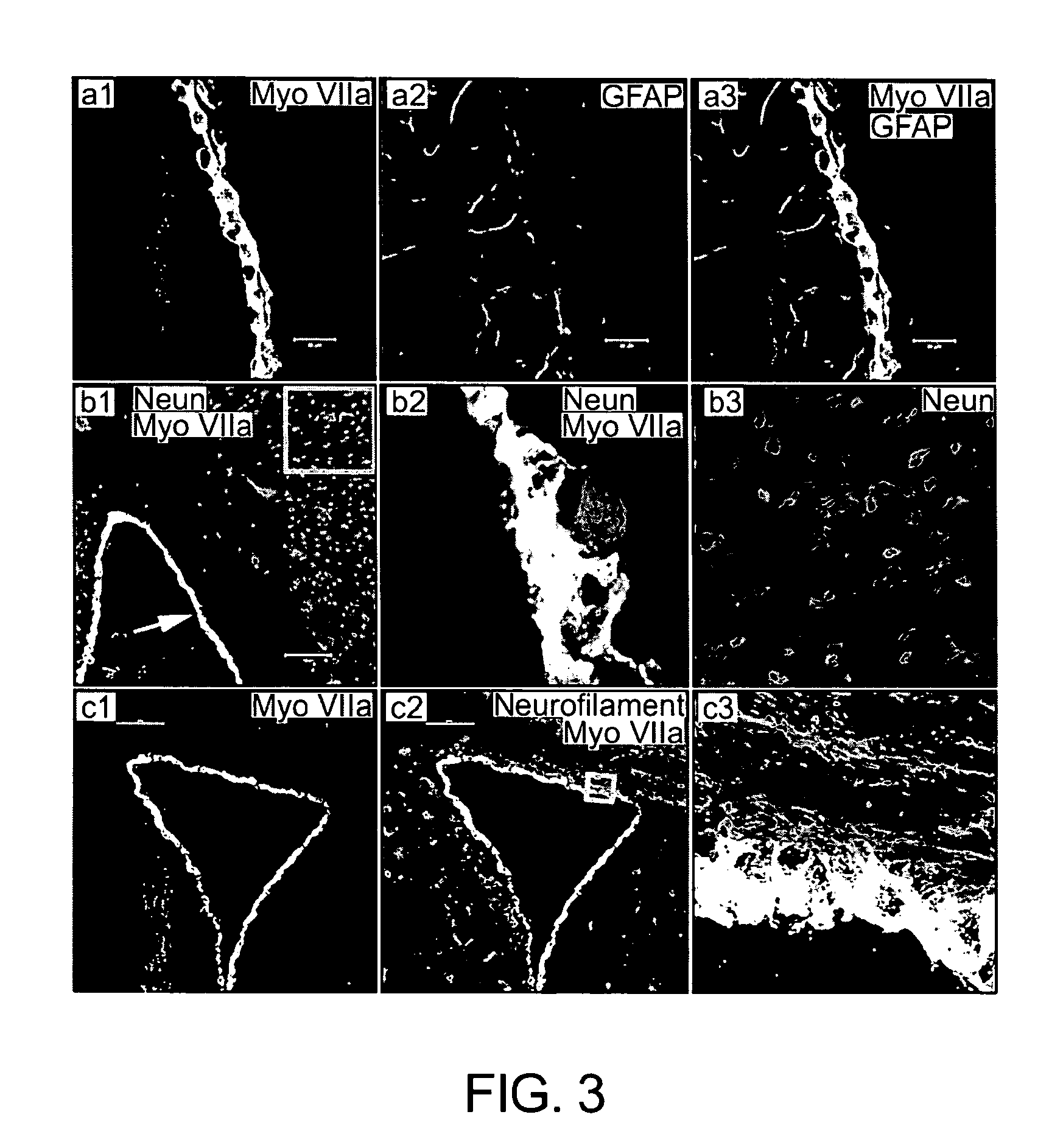
Lateral ventricle cell compositions and use for treating neural degenerative diseases
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lateral ventricle puncture training system and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN109448522AReduce surgical riskKnow the puncture situation in real timeCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsBlood vesselCerebral ventricle
The invention relates to the technical field of medical training devices and more particularly relates to a lateral ventricle puncture training system and a manufacturing method thereof. The lateral ventricle puncture training system comprises a skull model, the skull model is internally provided with a cavity simulating a lateral ventricle, a brain tissue model and a blood vessel model, a pressure sensor is arranged in the cavity and is connected to an indicating device. The cavity is connected to a pump body through a first pipe which is provided with a first valve body, wherein the pump body and the first valve body are arranged outside the skull model, the pump body injects liquid into the cavity through a first conduit, and a cerebrospinal fluid in the lateral ventricle is simulated.According to the invention, the pathological condition of a brain when the lateral ventricle puncture is simulated can be achieved, and the system is used by a doctor to perform the simulation practice of a lateral ventricle puncture operation.
Owner:MEDPRIN REGENERATIVE MEDICAL TECH
Identification and isolation of neural stem cells and neurosphere initiating cells
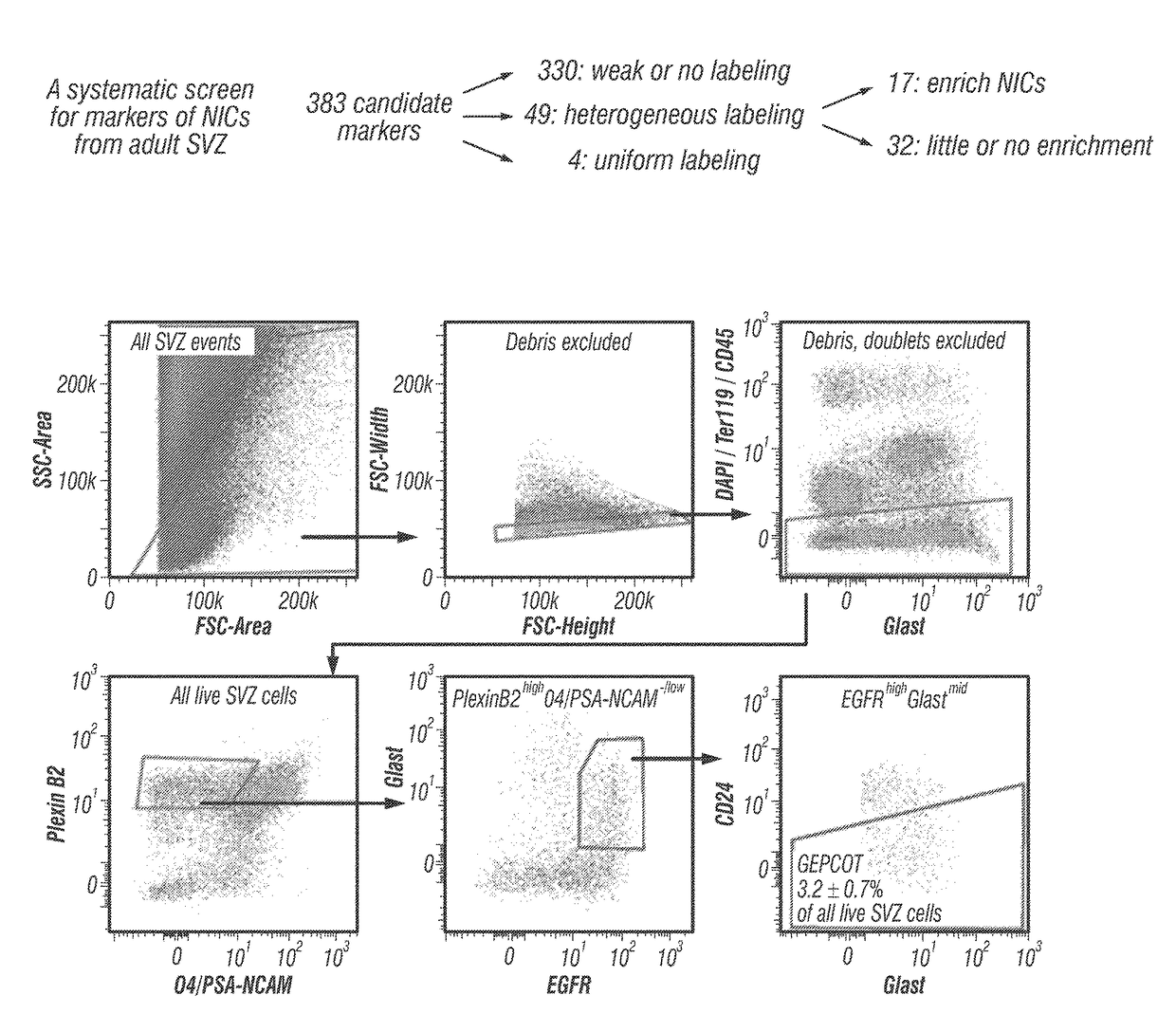
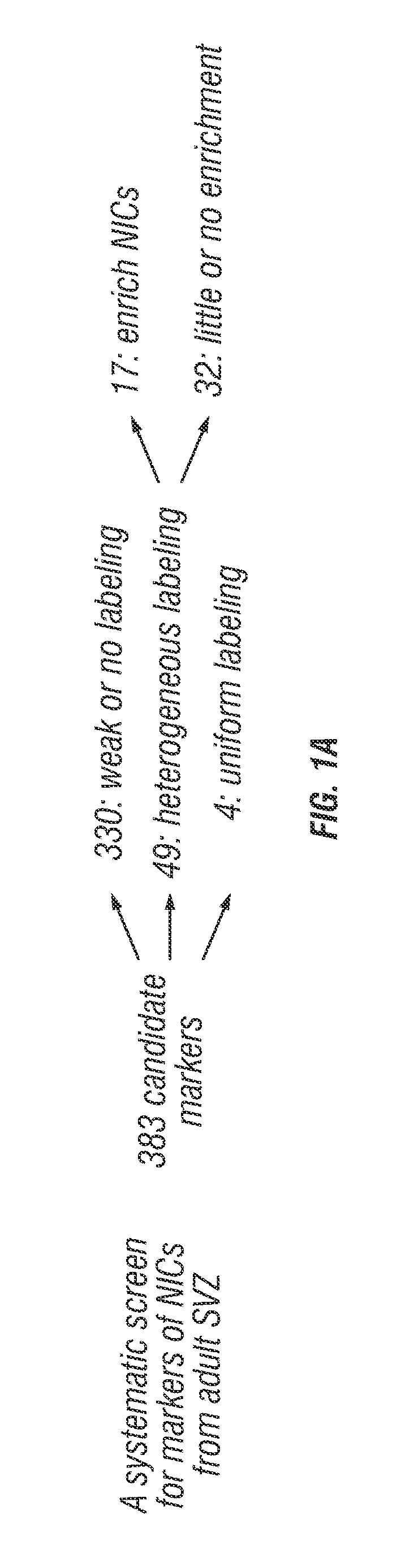
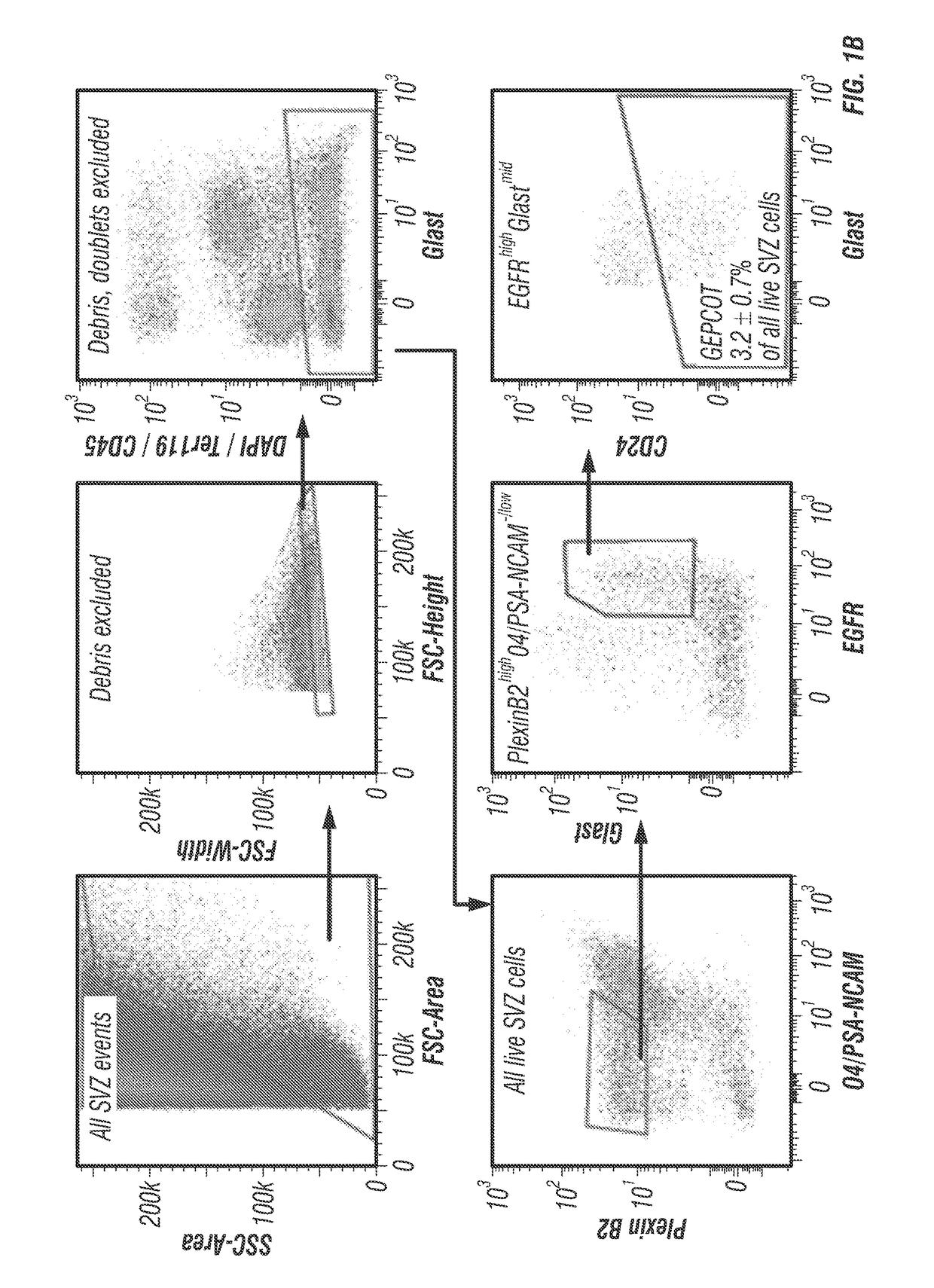
The disclosure reports on the identification and isolation of adult mouse lateral ventricle subventricular zone (SVZ) neurosphere initiating cells (NICs) by flow cytometry on the basis of GlastmidEGFRhighPlexinB2highCD24− / lowO4 / PSA-NCAM− / lowTer-119 / CD45− markers (GEPCOT cells). These cells are highly mitotic and short-lived in vivo based on fate-mapping with Ascl1CreERT2 and Dlx1CreERT2. In contrast, pre-GEPCOT cells were quiescent, expressed higher Glast, and lower EGFR and PlexinB2. Pre-GEP-COT cells could not form neurospheres but expressed the stem cell markers Glast-CreERT, GFAP-CreERT2, Sox2CreERT2, and Gli1C-reERT2 and were long-lived in vivo. While GEPCOT NICs were ablated by temozolomide, pre-GEPCOT cells survived and repopulated the SVZ. Conditional deletion of the Bmi-1 polycomb protein depleted pre-GEPCOT and GEPCOT cells, though pre-GEPCOT cells were more dependent upon Bmi-1 for p16Ink4a repression. These data distinguish quiescent NSCs from NICs and make it possible to study their properties in vivo.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Evaluation model for rat neurotoxicity of parotitis virus
ActiveCN110736654AEasy to operateLow costSsRNA viruses negative-senseImage analysisTGE VACCINEMumps virus
The invention provides an evaluation model for rat neurotoxicity of parotitis virus, concretely a device for evaluating the neurotoxicity of the parotitis virus. The model comprises(I) a virus inoculation module for performing virus inoculation of the parotitis virus to be evaluated to the lateral ventricle of a rat; (II) a processing module for carrying out vibration slicing on the fixed rat brain; (III) an imaging module for scanning and imaging an obtained mouse brain slice; and (IV) an analysis module used for calculating a neurotoxicity index through a formula I: the neurotoxicity index =S1 / S0 *100 (formula I) according to the cross sectional area S1 of a cavity formed by hydrocephalus in the longitudinal section of the rat brain and the total cross sectional area S0 of the rat brainin the obtained image. The results show that the result is stable, the stability is high, wild strains can be distinguished from vaccine strains, and compared with an existing monkey body neurotoxicity model, the animal cost and the operation difficulty are greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING CELL BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
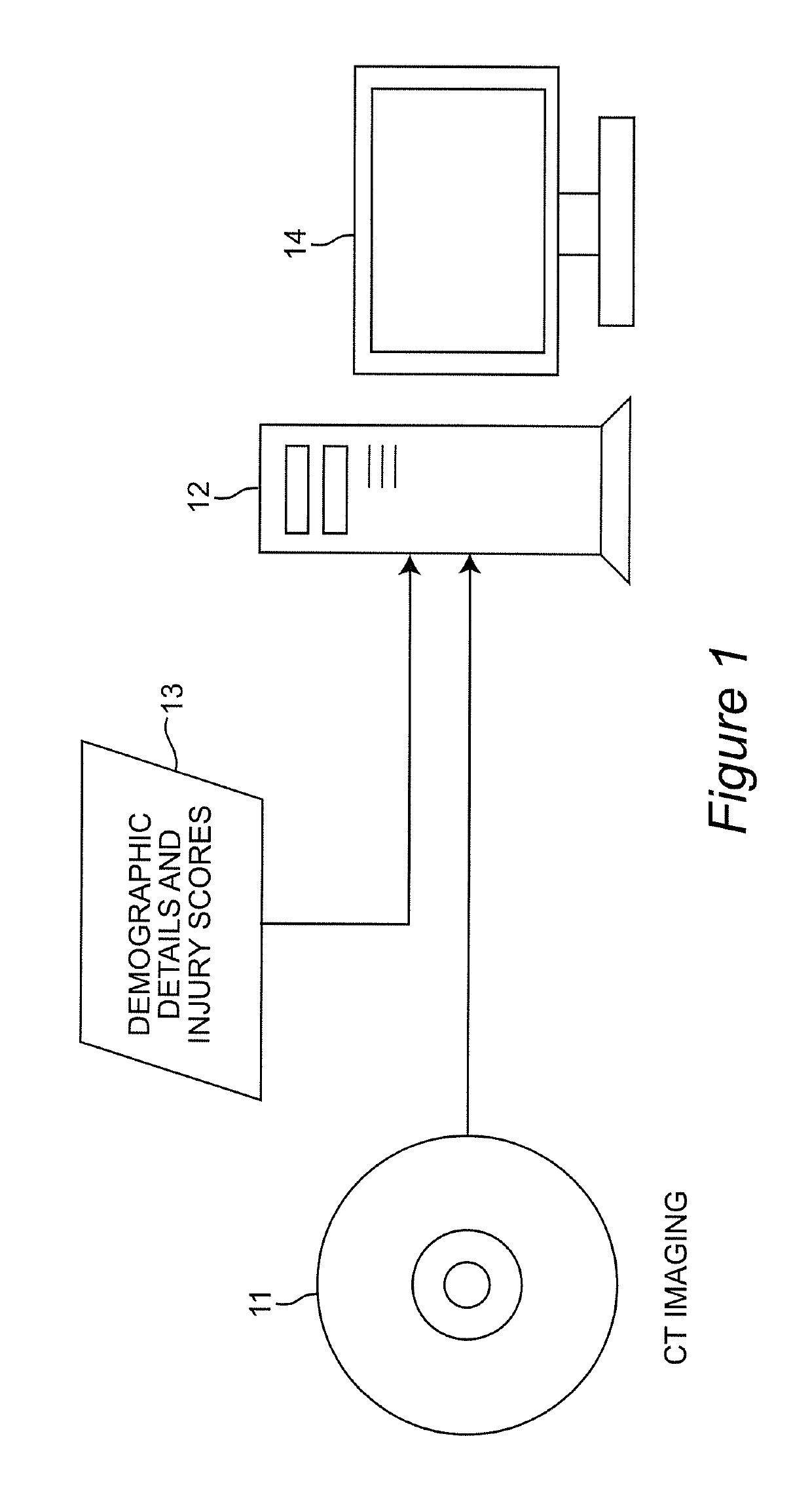
Automated measurement of brain injury indices using brain CT images, injury data, and machine learning
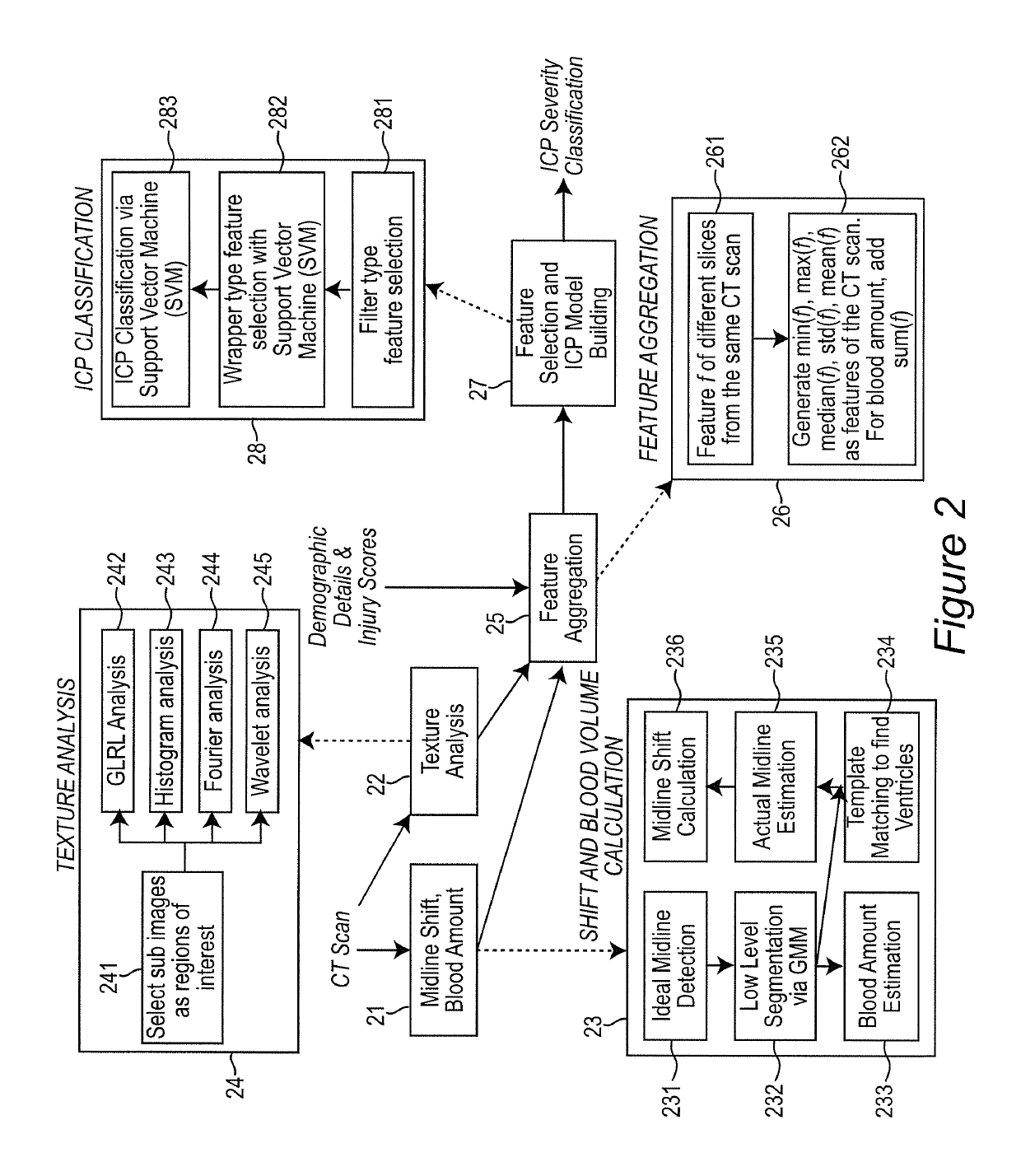
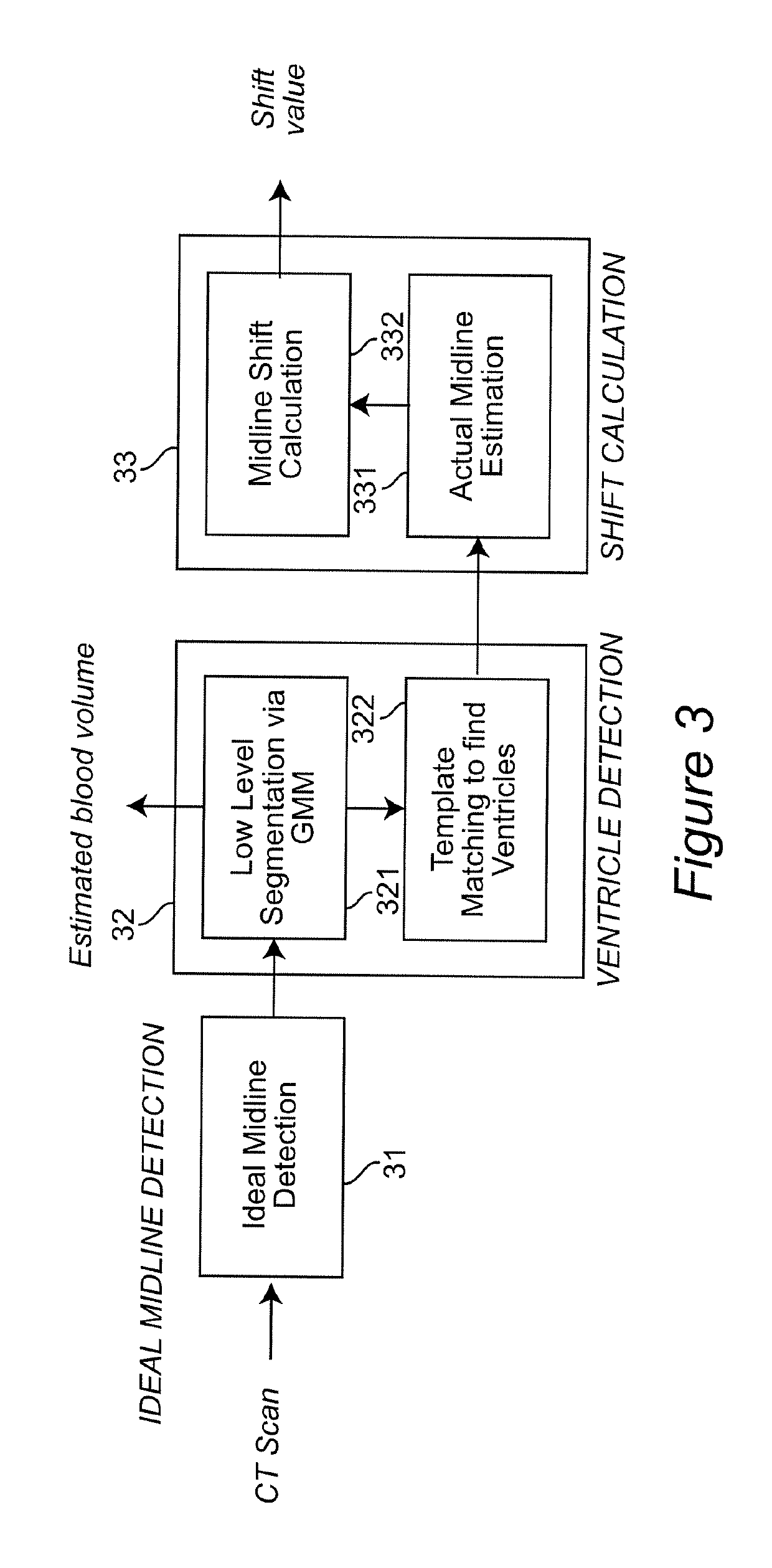
ActiveUS10303986B2Accurate detectionIncrease speedImage enhancementImage analysisInjury brainDecision taking
A decision-support system and computer implemented method automatically measures the midline shift in a patient's brain using Computed Tomography (CT) images. The decision-support system and computer implemented method applies machine learning methods to features extracted from multiple sources, including midline shift, blood amount, texture pattern and other injury data, to provide a physician an estimate of intracranial pressure (ICP) levels. A hierarchical segmentation method, based on Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), is used. In this approach, first an Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI) ventricle template, as prior knowledge, is used to estimate the region for each ventricle. Then, by matching the ventricle shape in CT images to the MRI ventricle template set, the corresponding MRI slice is selected. From the shape matching result, the feature points for midline estimation in CT slices, such as the center edge points of the lateral ventricles, are detected. The amount of shift, along with other information such as brain tissue texture features, volume of blood accumulated in the brain, patient demographics, injury information, and features extracted from physiological signals, are used to train a machine learning method to predict a variety of important clinical factors, such as intracranial pressure (ICP), likelihood of success a particular treatment, and the need and / or dosage of particular drugs.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Method for studying migration, proliferation and differentiation of brain endogenous neural stem cells
InactiveCN103940985ADisease diagnosisBiological testingGlial cell line-derived neurotrophic factorNeural cell
The invention relates to a method for studying migration, proliferation and differentiation of brain endogenous neural stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing double-labeled immunofluorescent staining on an animal brain section by 5-bromndeoxyuridine and doublecortin, 5-bromndeoxyuridine and neuronal nuclei antigen as well as 5-bromndeoxyuridine and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor, and single-labeled immunofluorescent staining by sialyl neural cell adhesion molecules; and (2) carrying out statistic analysis on data and drawing by GraphPad Prism6.0 software, and performing one-way variance analysis on single-factor multi-group data of the 5-bromndeoxyuridine positive cells, wherein the animal brain section is subjected to the following treatment: stereotactically injecting a 6-hydroxydopamine solution into a corpus striatum of the right side of the brain, injecting a PSA (prostate-specific antigen) specificity lyase stock solution into the lateral ventricle, and then injecting a 5-bromndeoxyuridine solution in the abdominal cavity. An effective method for studying migration influence of the brain endogenous neural stem cells is provided.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Method for establishing non-human primate animal model of parkinson disease by lateral ventricle administration of MPP<+>
InactiveCN103340859ATypical behavioral symptomsBasic physical condition is goodHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSide effectIodide
A method for establishing a non-human primate animal model of parkinson disease by lateral ventricle administration of MPP<+> belongs to the biomedical technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a lateral ventricle administration device; 2, according to a monkey brain atlas and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging data, acquiring a positioning coordinate of a lateral ventricle; 3, inserting a catheter into a lateral ventricle administration position through a monkey stereotaxic instrument, and beginning to administrate the drug after 5-8 days after the animal recovers; injecting a physiological saline solution containing MPP<+> into the lateral ventricle by an injector connected with the tail end of an administration pipe, with the MPP<+> concentration of 0.5-0.7 mg / mL and each administration dosage of 0.1-0.3 mL; carrying out administration one time every 48-72 hours, and after administration for 30-60 days, establishing the non-human primate animal model of the parkinson disease. The method employs a new administration mode that the MPP<+> (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium iodide) drug is directly injected into the lateral ventricle of the animal for modeling. With lateral ventricle injection, MPP<+> can perform whole brain circulation together with cerebrospinal fluid to specifically damage dopamine neurons in a brain and cause symptoms of the parkinson disease, and can furthest avoid toxic and side effects of the drug on a periphery.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Subcutaneous embedding type ventricle external drainage bursa
InactiveCN101081317AAddressing increased intracranial pressureAvoid complicationsSurgerySuction devicesShunt DeviceSilica gel
The shunt device for shunting cerebrospinal fluid from lateral ventricle to vitro includes one ventricle shunting pipe, one embedded subcutaneous shunting silica gel bag, one puncture guide needle and one shunting duct interface. It is applied in shunting cerebrospinal fluid from lateral ventricle to reduce intracranial pressure, especially for brain tumor patient with hydrocephalus and increased protein content in cerebral hydrops. The shunting bag has fluent drainage of cerebrospinal fluid, and may be applied in extracting fluid, injecting medicine, flushing. It has less transfer of bacteria and tumor cell along the shunting duct, and can make up the deficiency of ventriculo-peritoneal shunt.
Owner:傅相平 +1
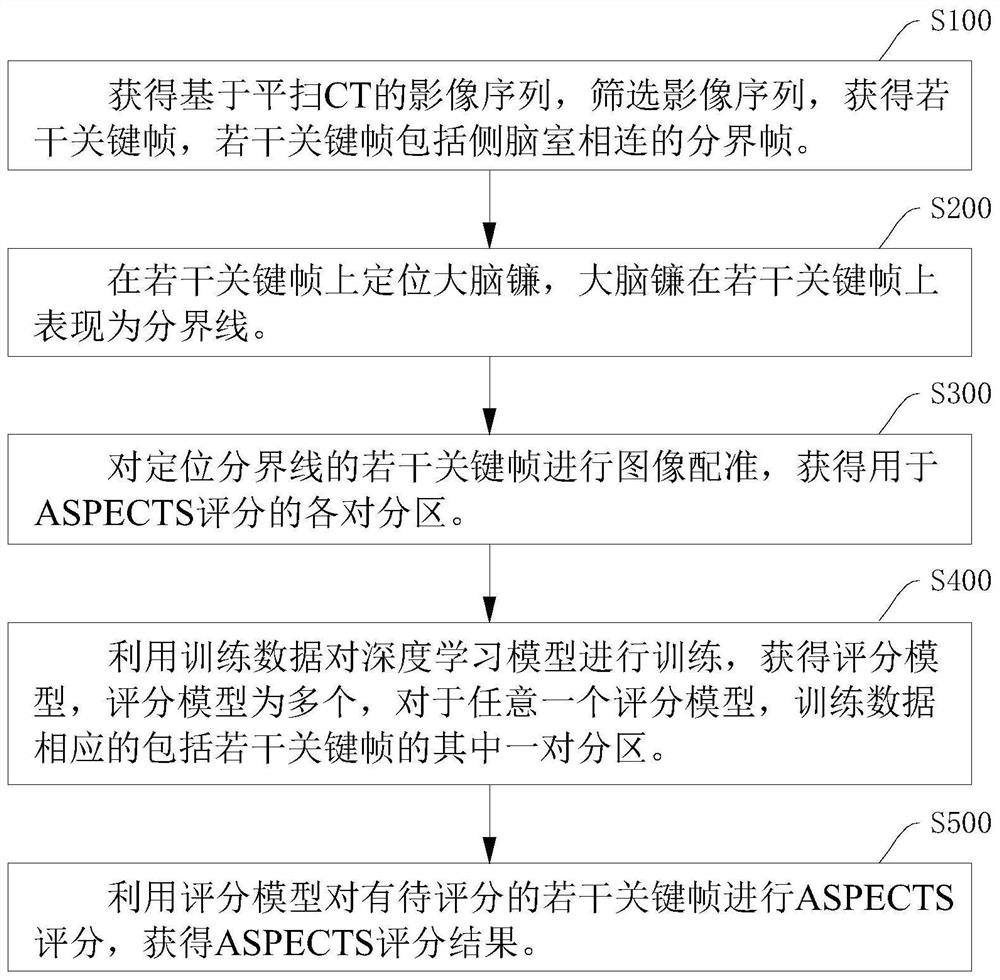
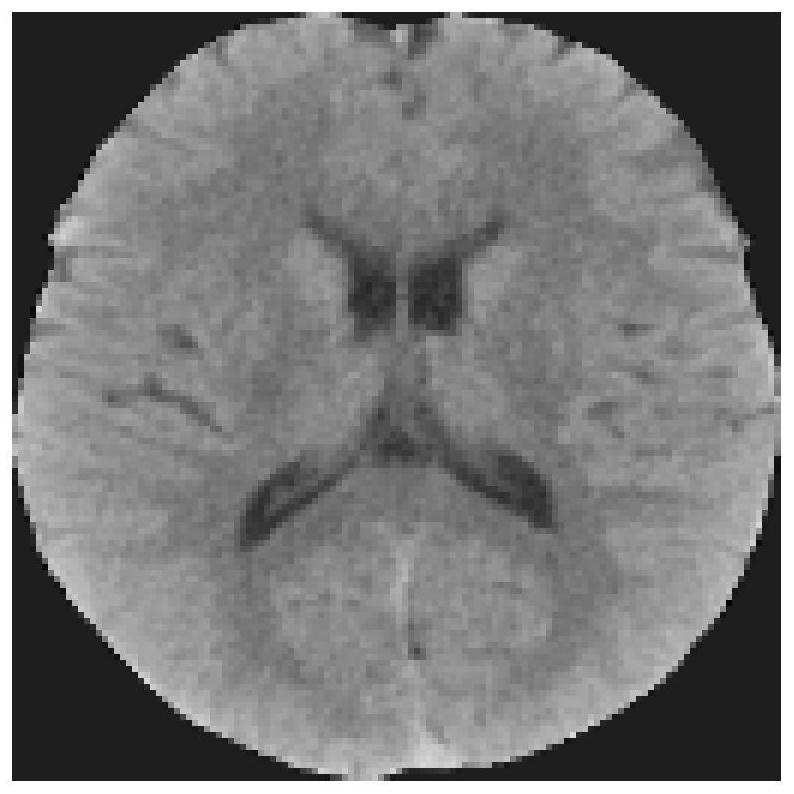
Automatic ASPECTS scoring method based on plain-scan CT, computer equipment, readable storage medium and program product
The invention relates to an automatic ASPECTS scoring method based on plain-scan CT, computer equipment, a readable storage medium and a program product, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an image sequence based on plain-scan CT, screening the image sequence, and obtaining a plurality of key frames comprising the connected boundary frames of the lateral ventricle; positioning a brain sickle on the plurality of key frames, wherein the brain sickle is represented as a boundary on the plurality of key frames; performing image registration on the plurality of key frames for positioning the boundary to obtain each pair of partitions for ASPECTS scoring; training data is utilized to train a deep learning model to obtain scoring models, the number of the scoring models is multiple, and for any scoring model, the training data correspondingly comprises one pair of partitions of the plurality of key frames; and performing ASPECTS scoring on a plurality of key frames to be scored by using the scoring model to obtain an ASPECTS scoring result. The pairs of partitions located on the two opposite sides of the boundary serve as training data of the scoring model, and the precision of the scoring model can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARTERYFLOW TECH CO LTD
Medical multifunctional height adjusting frame
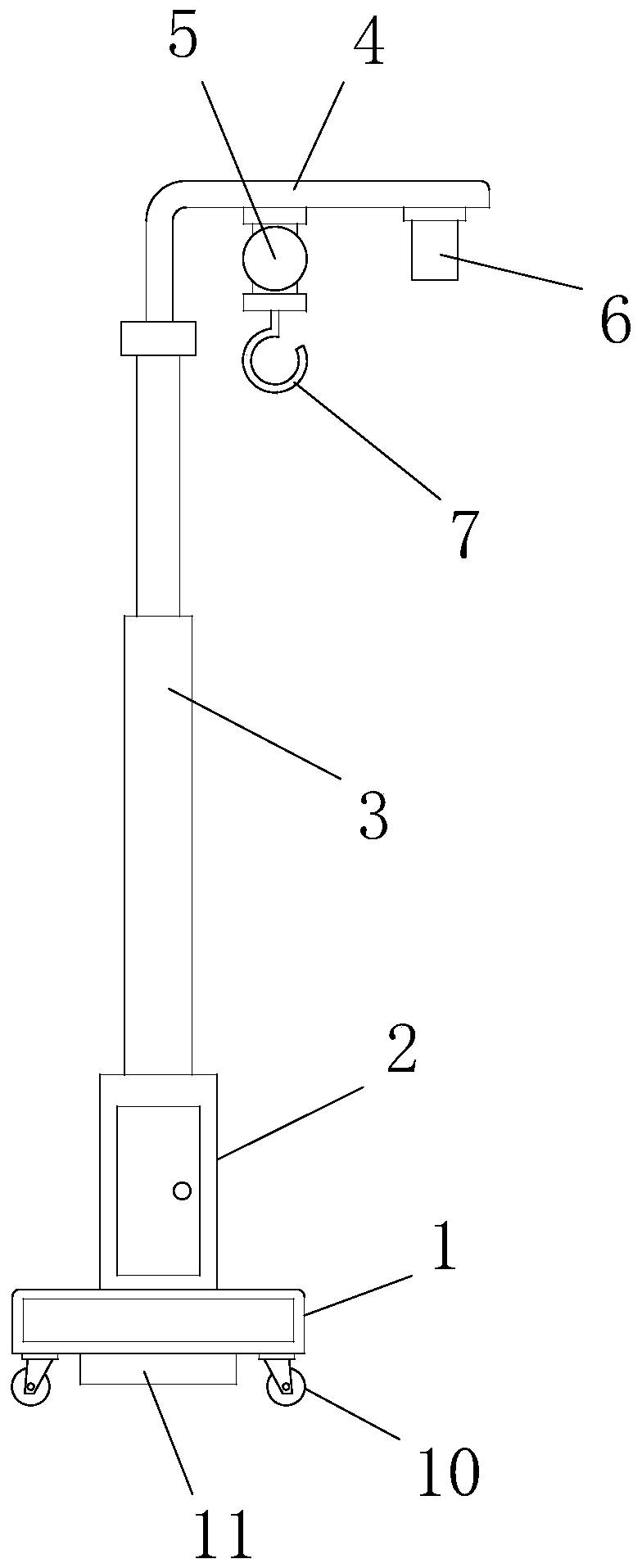
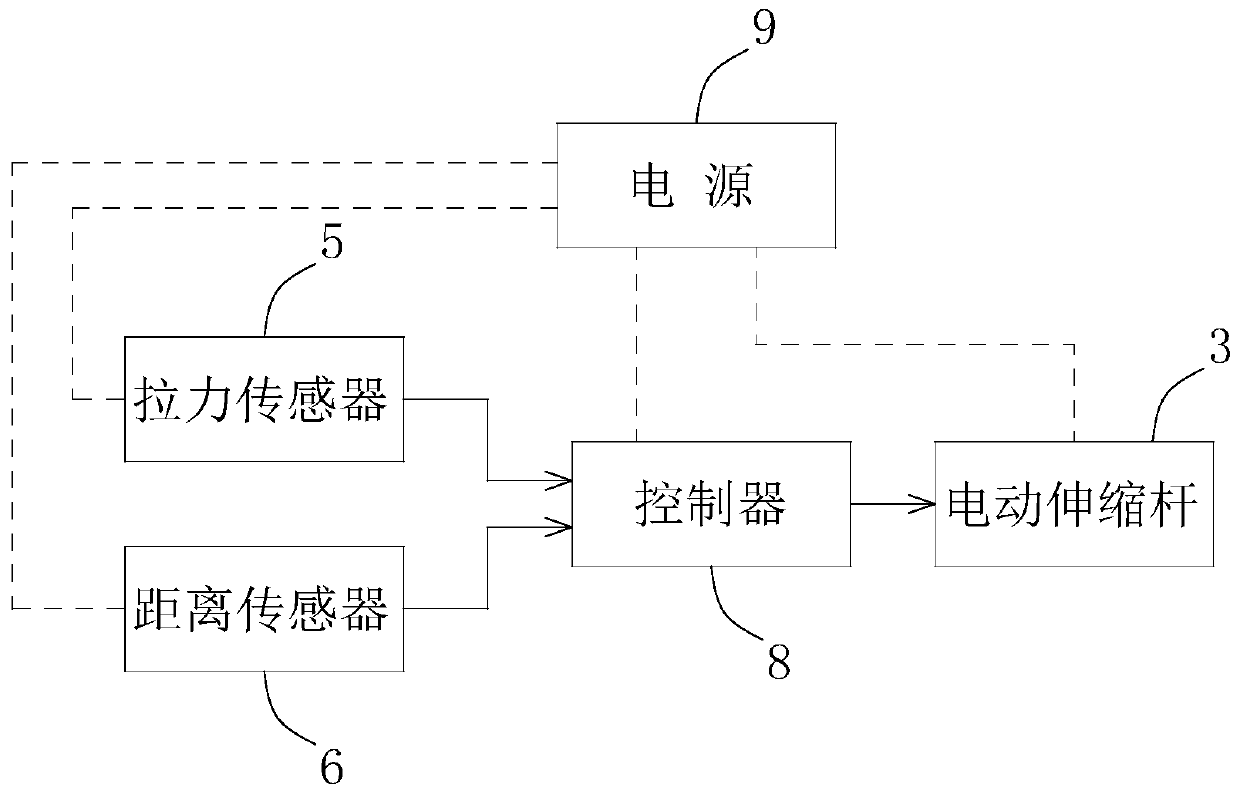
PendingCN111494730AShorten the timeImprove accuracyMedical devicesNursing bedsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention discloses a medical multifunctional height adjusting frame. The frame comprises a base, a control box is arranged on the base, an electric telescopic rod is vertically arranged at the top of the control box, a suspension frame is arranged at the top of the electric telescopic rod, a tension sensor and a distance sensor are installed on the suspension frame, a bottom end of the tension sensor is connected with a hook, the tension sensor measures the tension value of the weight of an object on the hook, and the distance sensor measures the distance value between the distance sensorand the object under the distance sensor. The medical multifunctional height adjusting frame is mainly used for hanging a ventricular drainage bag, the hanging height can be adjusted in real time according to the actual height of a sickbed and the amount of a liquid in the drainage bag, the drainage bag is made to be 10-15 cm higher than the plane of the ventricular side of a patient all the time, and adverse effects caused by over-high or over-low hanging are avoided. The adjusting frame can also be used for other operations such as drainage and enema, the adjusting process is stable, the accuracy is high, meanwhile, the time of medical staff is saved, and application and promotion are facilitated.
Owner:谷一梅 +3
Lateral ventricle cell compositions and use for treating neural degenerative diseases
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
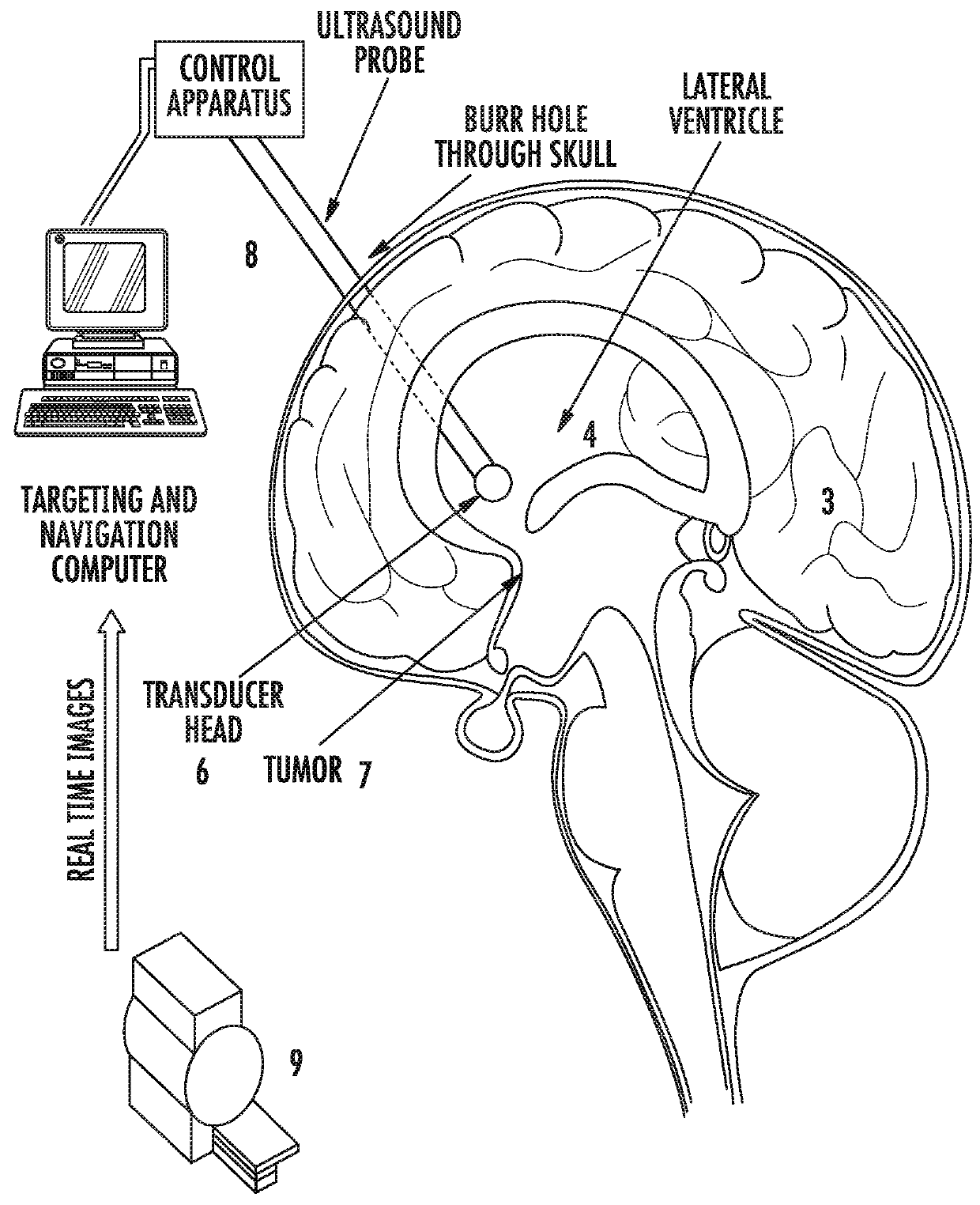
Minimally Invasive Focused Ultrasound (MIFUS) for Brain Surgery
InactiveUS20180177520A1Prevent operative infectionHigh riskUltrasound therapyCannulasFocus ultrasoundNeurosurgery
HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound) sometimes FUS or MIFUS is a highly precise medical procedure using high-intensity focused ultrasound to heat and destroy pathogenic tissue rapidly in the brain for neurosurgical purposes, by causing coagulation necrosis. Here we have described a system that uses specially designed micro-transducer heads that are placed inside the later ventricles for the purposes of MIFUS lesioning of brain targets under real time MRI, endoscopic and Doppler guidance. A minimally invasive approach using Kocher's point allows small incisions with little bleeding, recovery time, infection risk and surgical time. This approach allows insertion of the micro-ultrasound transducers into the lateral ventricles of the brain avoiding skull bone attenuation of the ultrasonic waves and unnecessary heating of brain tissues in the process.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com