Patents
Literature
1069 results about "CSF - Cerebrospinal fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
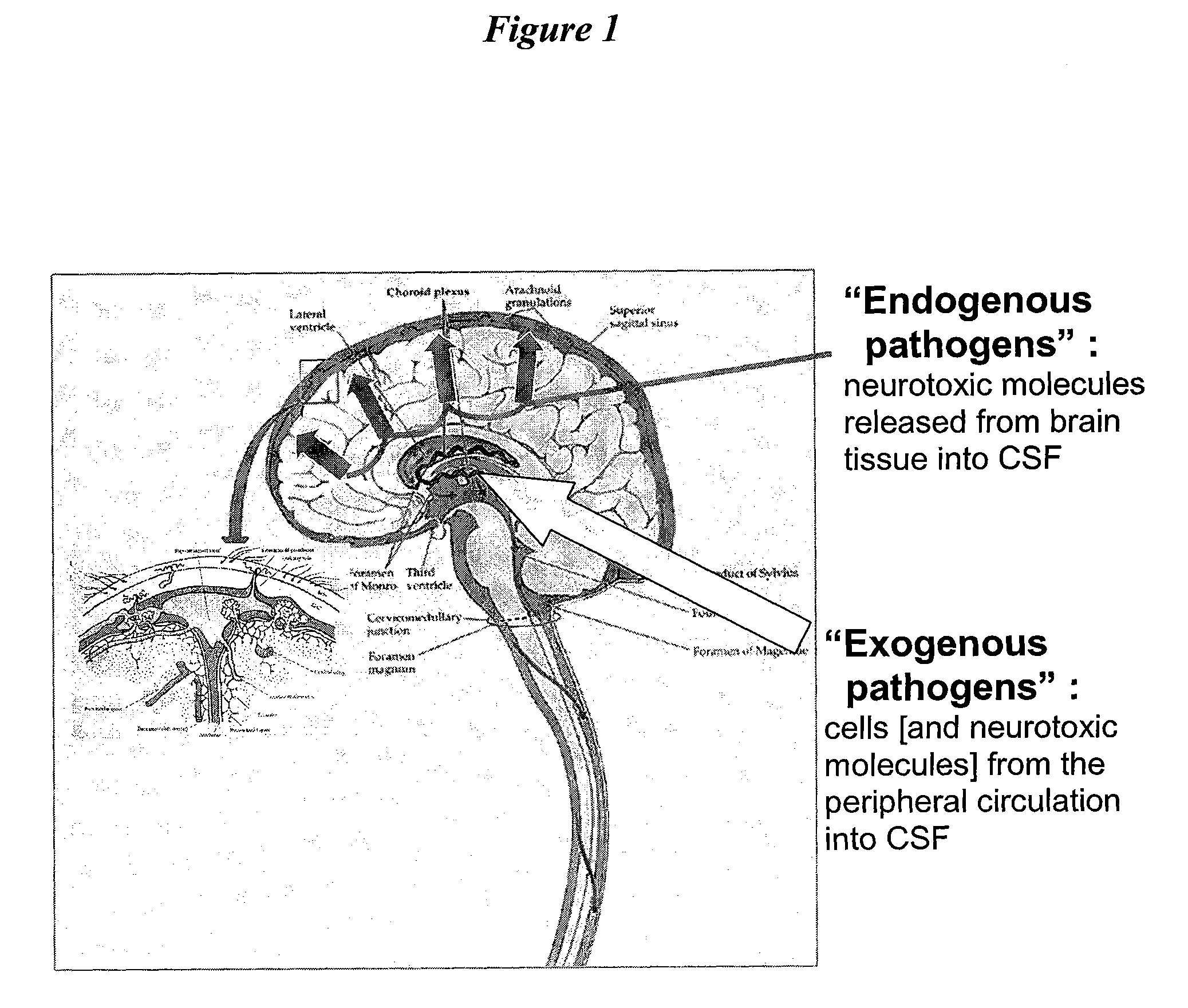
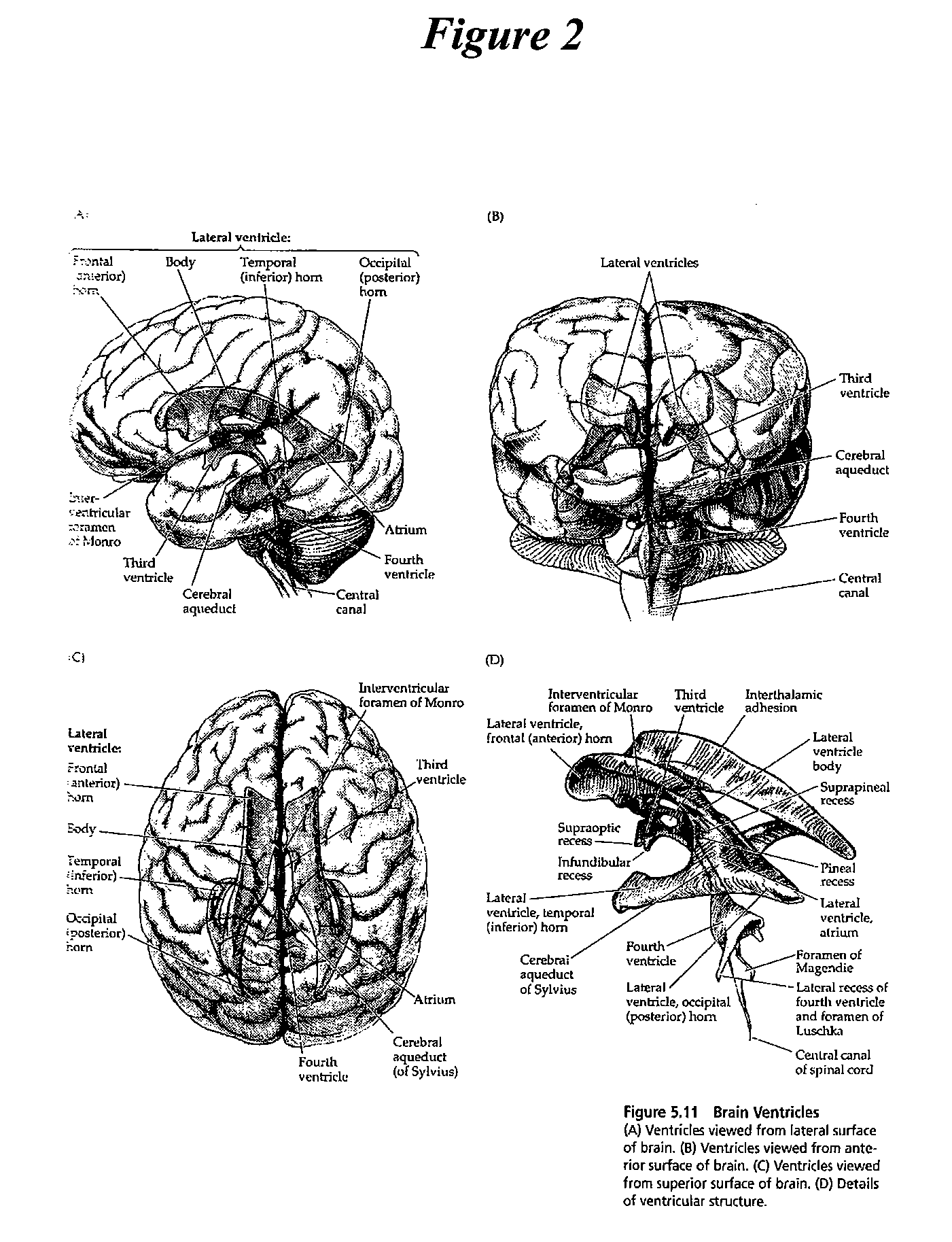
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord. It is produced by the specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations.
Process for discriminating between biological states based on hidden patterns from biological data
The invention describes a process for determining a biological state through the discovery and analysis of hidden or non-obvious, discriminatory biological data patterns. The biological data can be from health data, clinical data, or from a biological sample, (e.g., a biological sample from a human, e.g., serum, blood, saliva, plasma, nipple aspirants, synovial fluids, cerebrospinal fluids, sweat, urine, fecal matter, tears, bronchial lavage, swabbings, needle aspirantas, semen, vaginal fluids, pre-ejaculate.), etc. which is analyzed to determine the biological state of the donor. The biological state can be a pathologic diagnosis, toxicity state, efficacy of a drug, prognosis of a disease, etc. Specifically, the invention concerns processes that discover hidden discriminatory biological data patterns (e.g., patterns of protein expression in a serum sample that classify the biological state of an organ) that describe biological states.
Owner:ASPIRA WOMENS HEALTH INC +1
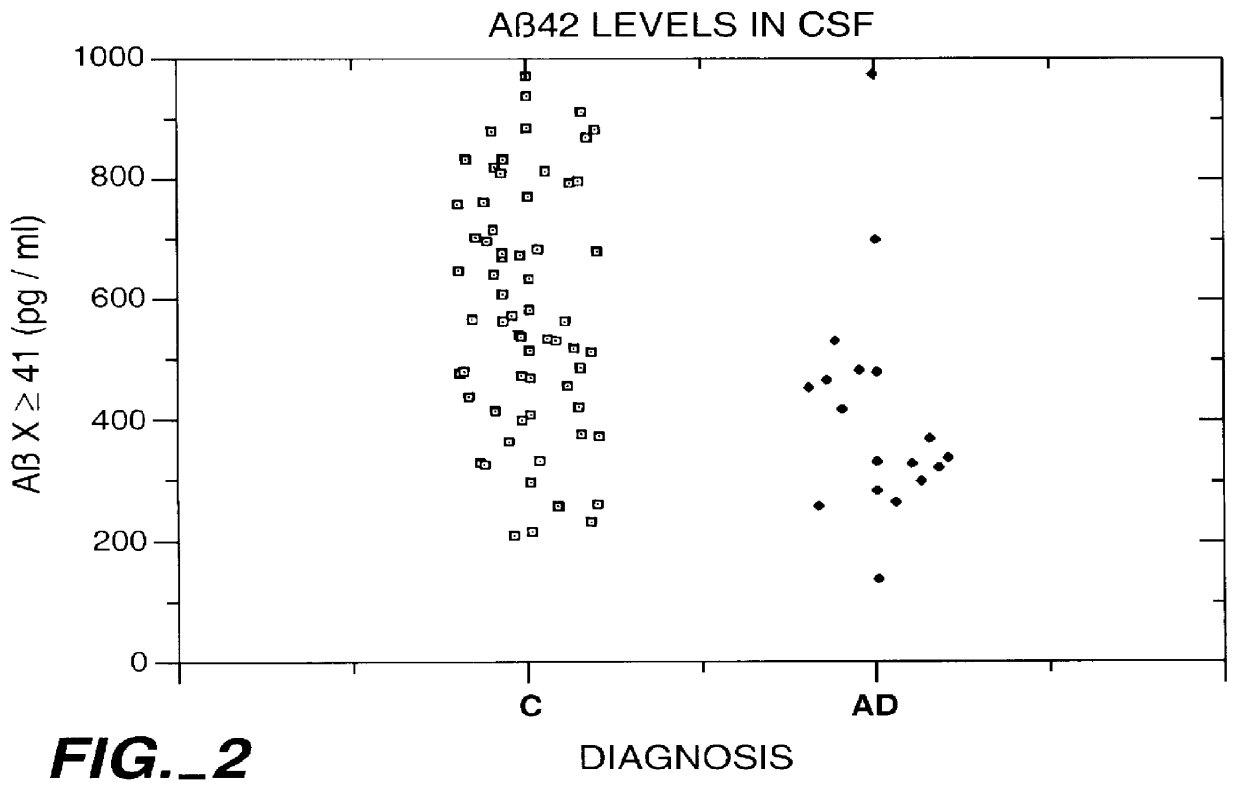
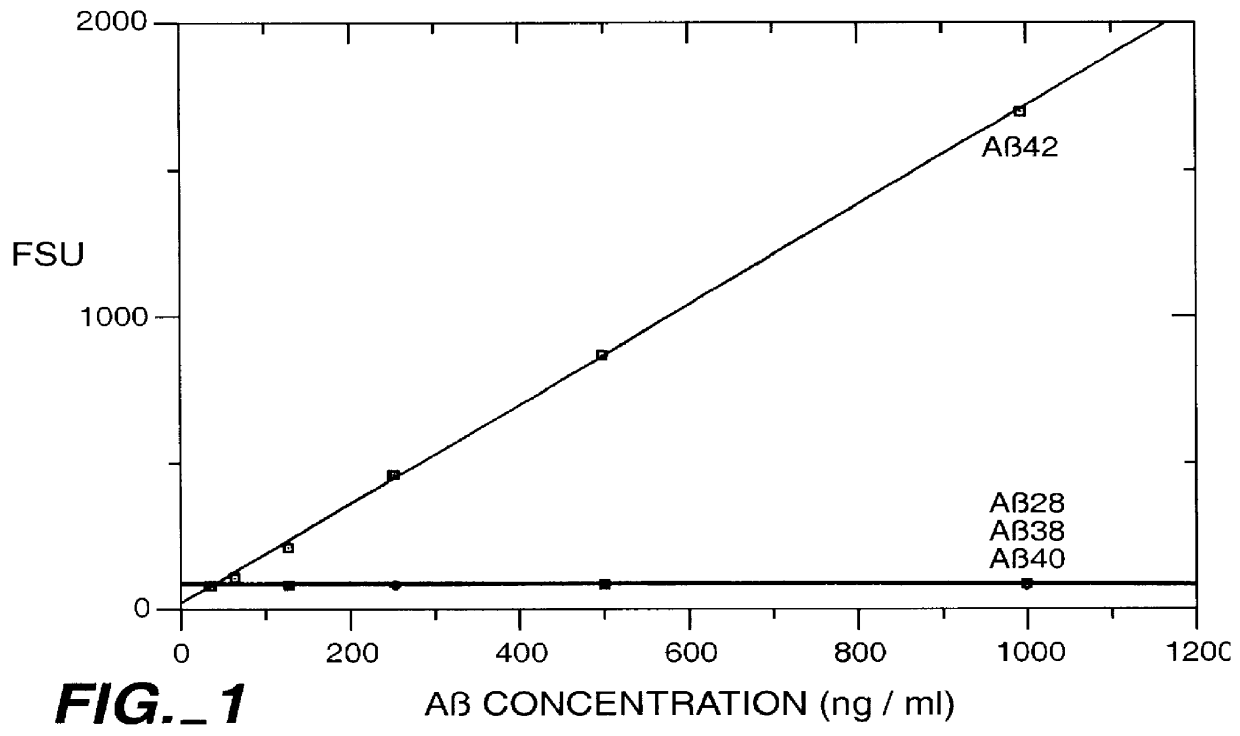
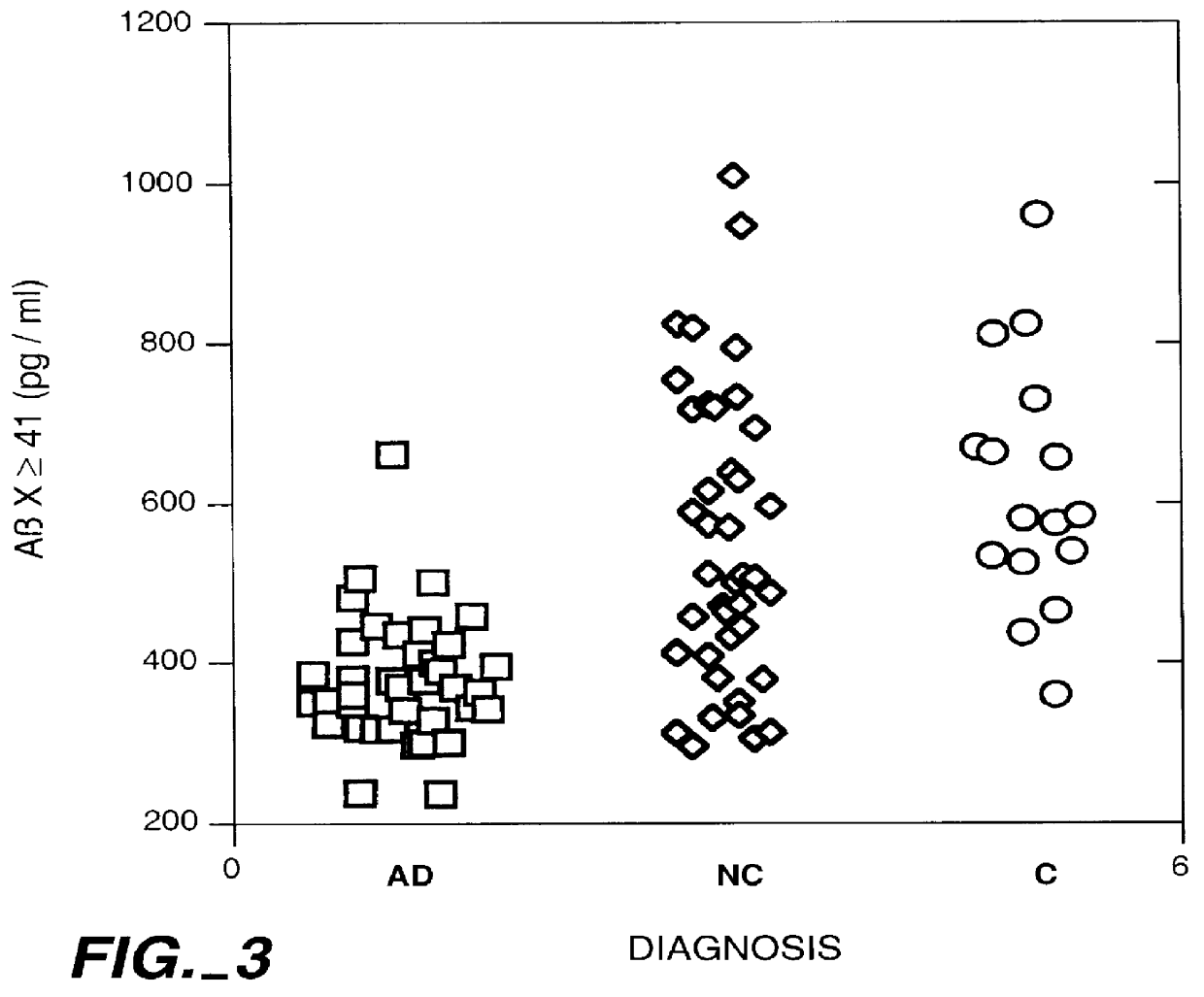
Methods for aiding in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease by measuring amyloid- beta peptide (x->/=41)
InactiveUS6114133AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisAlzheimer SyndromeDisease cause
This invention provides methods useful in aiding in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. The methods involve measuring the amount of amyloid- beta peptide (x-> / =41) in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient. High levels of the peptide generally are inconsistent with a diagnosis of Alzheimer's. Low levels of the peptide are consistent with the disease and, with other tests, can provide a positive diagnosis.
Owner:ELAN PHARM INC
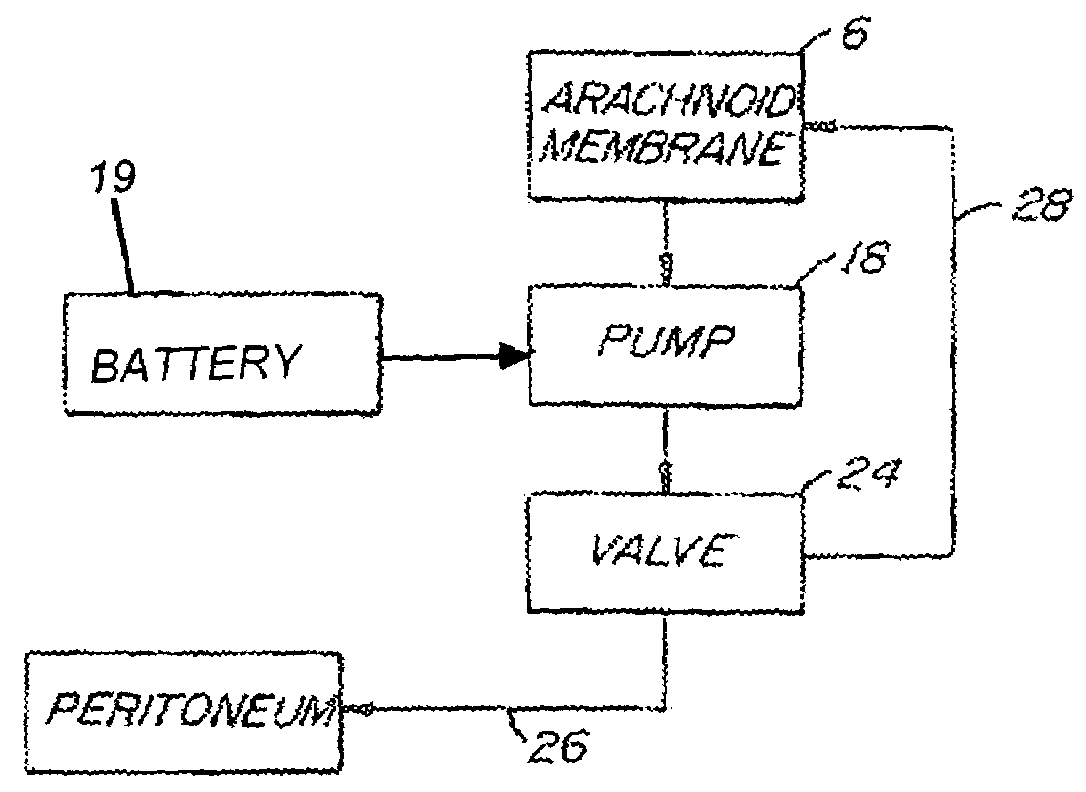
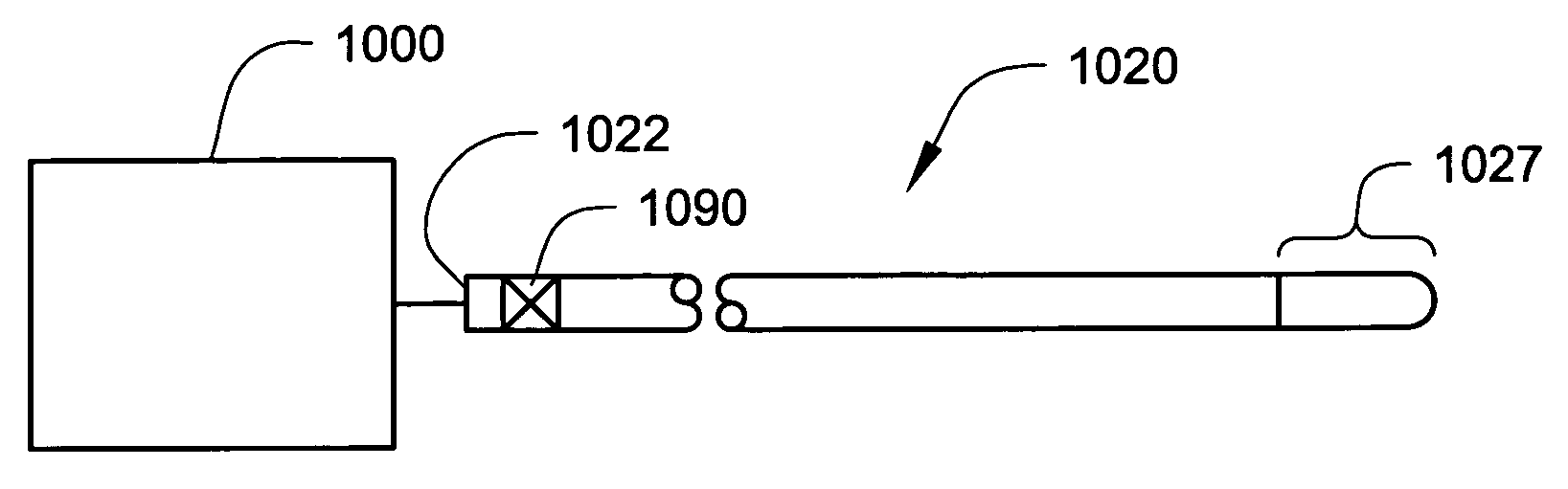
Internally powered CSF pump systems and methods
InactiveUS7025742B2Reduce eliminateEliminate progressionWound drainsIntravenous devicesSubarachnoid spaceCatheter
A method treats a patient for adult-onset dementia of the Alzheimer's type by removing a portion of the patient's cerebrospinal fluid, preferably (although not necessarily) by transporting the fluid to another portion of the patient's body. An apparatus for removing cerebrospinal fluid includes (1) a conduit with a first opening and a second opening, the first opening of the conduit being disposed in fluid communication with a space within a patient's subarachnoid space, the second opening being disposed in fluid communication with another portion of the patient's body; and (2) a flow rate control device attached to the conduit.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
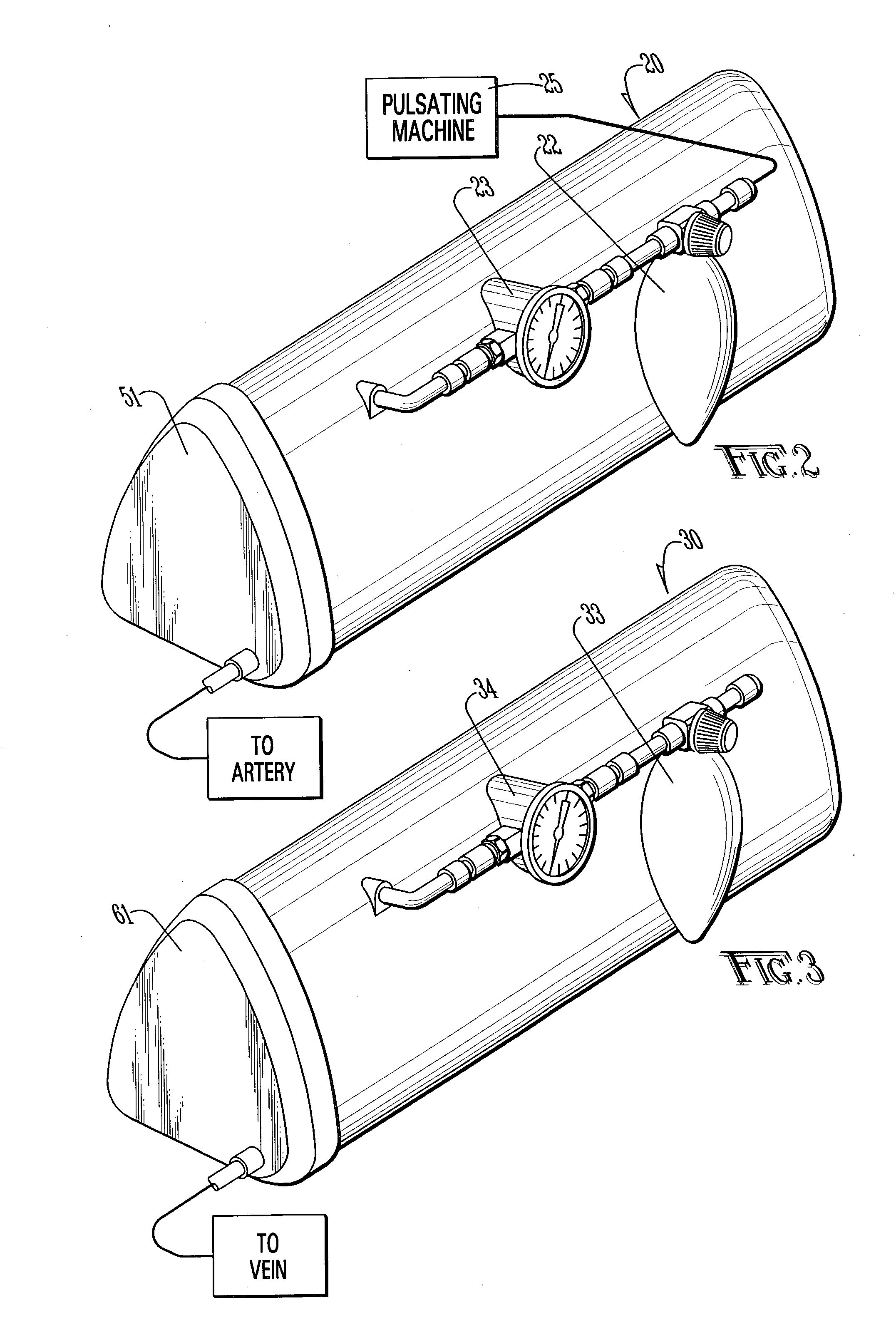
Method and apparatus for surgical training
An apparatus and method for microsurgical training using cadaveric anatomy with filling of the vascular system by fluids under pressure to simulate the appearance and function of live surgery. One or more arteries on the specimen of cadaveric anatomy are cannulated and connected to an arterial reservoir having a flexible container holding an arterial fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the arteries of the living organism from which the cadaveric anatomy is derived. Suitable static pressure simulating the arterial pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the arterial reservoir. A pulsating machine provides air pulsations to the space surrounding the flexible fluid container to simulate the normal pulsations of the arterial system. One or more veins on the specimen are also cannulated and connected to a venous reservoir having a flexible container holding a venous fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the veins of the living organism. Suitable static pressure simulating the venous pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the venous reservoir. Optionally, if the specimen includes at least a portion of spinal canal, a clear fluid reservoir can be connected to the specimen through the spinal canal to simulate cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:ABOUD GHAITH +1
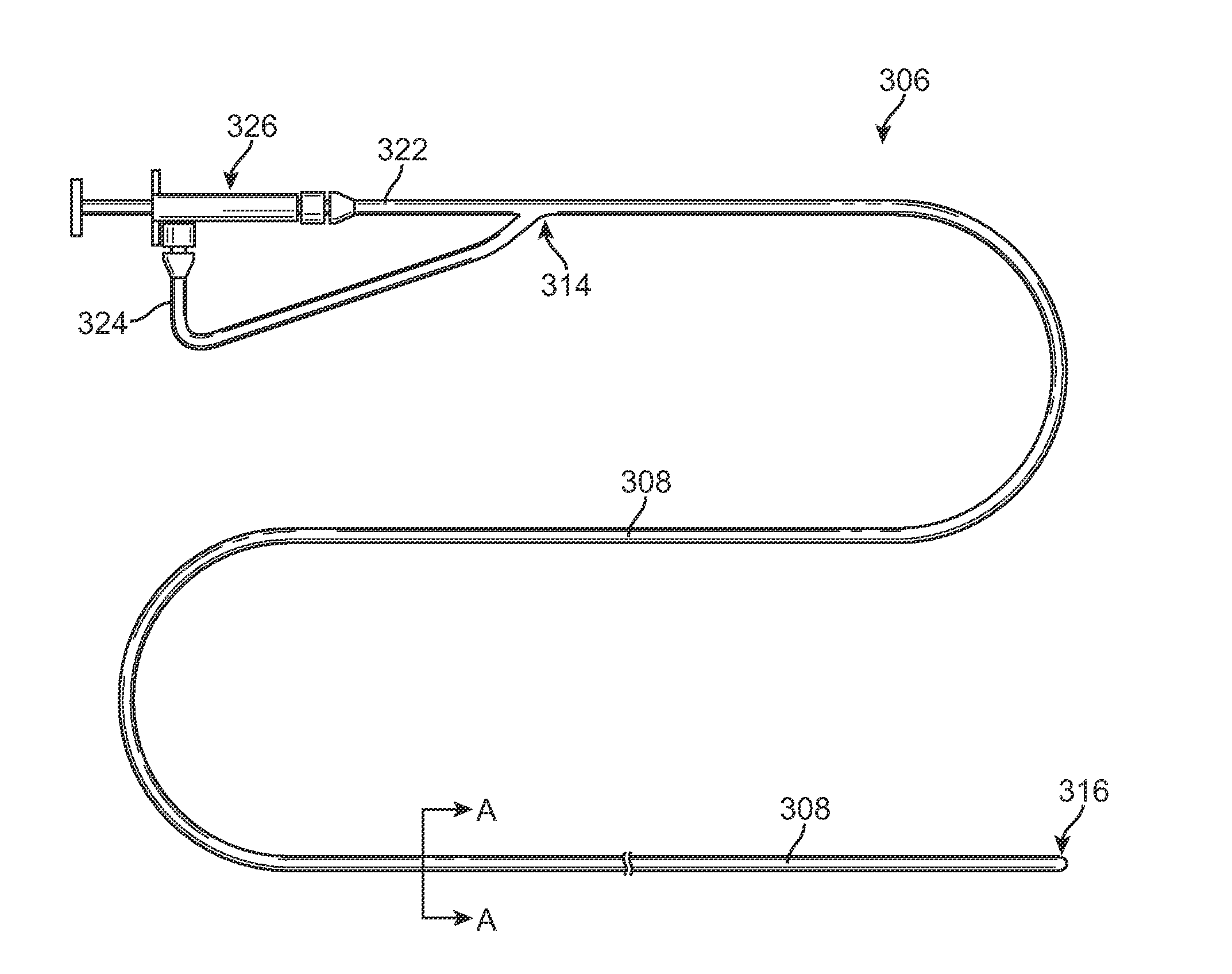
Methods for Simultaneous Injection and Aspiration of Fluids During a Medical Procedure
Methods for simultaneous injection and aspiration of fluids during a medical procedure are disclosed. Embodiments include methods for operating medical devices within the subarachnoid space of the spinal column to gain access to the ventricles of the brain, as well as the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space. A dual lumen constant volume aspiration catheter is disclosed that injects a volume of injectable fluid to break up an obstruction within the brain or cranial subarachnoid space while simultaneously aspirating a same volume of aspirated fluid from the treatment site. Methods hereof include constant volume re-circulation of cerebral spinal fluid to and from a treatment area within one of the brain and the surrounding cranial subarachnoid space, which may be desirable during a ventriculostomy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Surgically implantable hearing aid
InactiveUS20060025648A1Negligible riskAttached with easeEar treatmentDeaf-aid setsDura materAcoustic wave
The invention comprises a surgically implantable hearing aid for hearing impaired persons. The hearing aid includes a vibrational element which is vibrated by sound waves and attached to the skull of the person, and a connector which crosses the mastoid cavity and delivers the sound waves to the dura mater of the human being thereby vibrating the dura mater, the cerebrospinal fluids, and the brain to create a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to act as a tinnitus masker or used in conjunction with a cochlear implant. It can also be used in a modified form to connect directly through the skull of the human being.
Owner:ALAN J LUPIN
Multipath Stimulation Hearing Systems
A prosthetic hearing system is described that provides multi-path stimulation of the patient auditory system. A mechanical stimulation component applies mechanical stimulation signals to cerebral tissue such as the dura mater, cerebrospinal fluid, vestibular structures, etc. using multiple separate mechanical stimulation channels. And an electrical stimulation component provides electrical stimulation of auditory neural tissue of the patient user.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
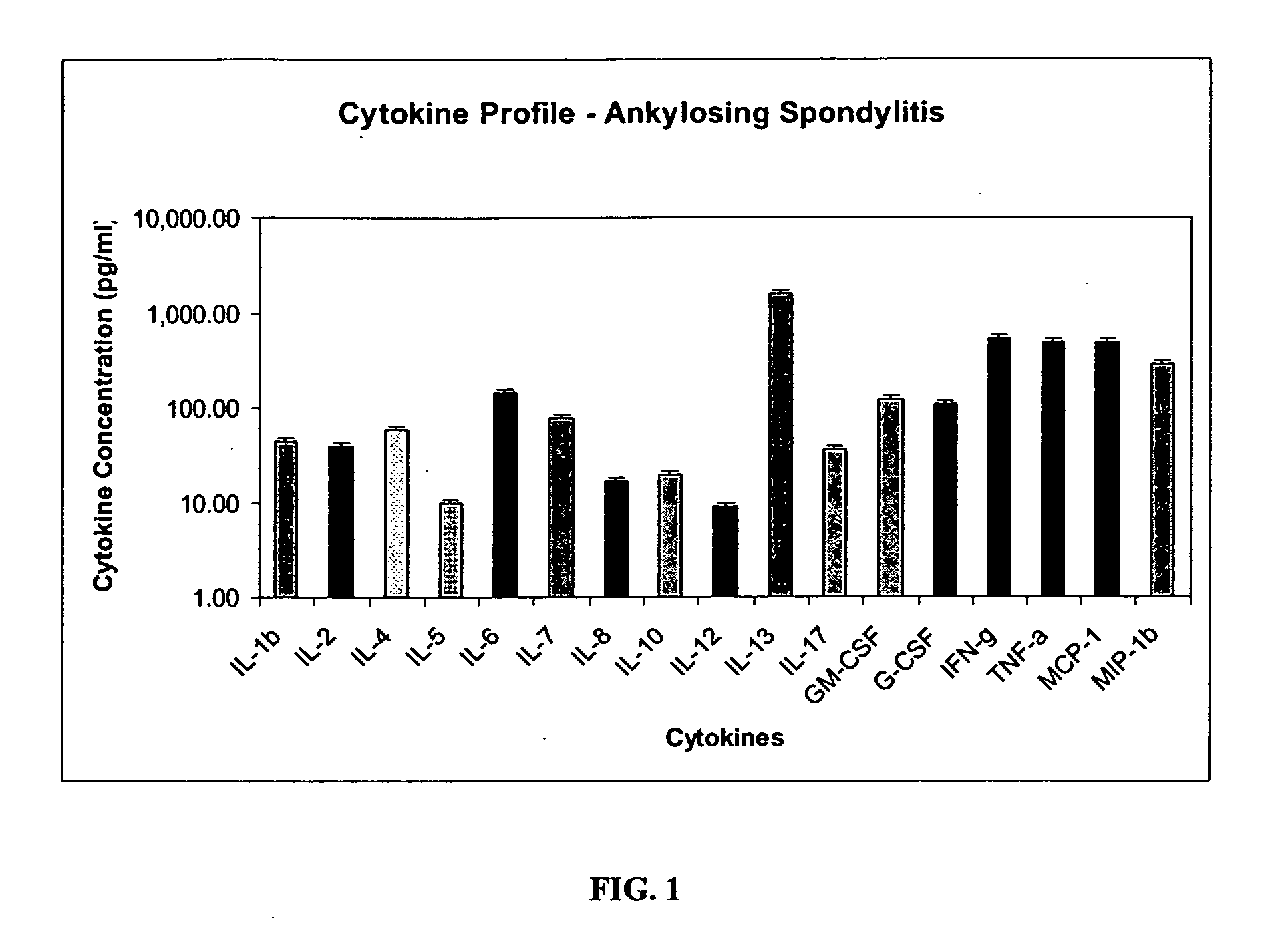
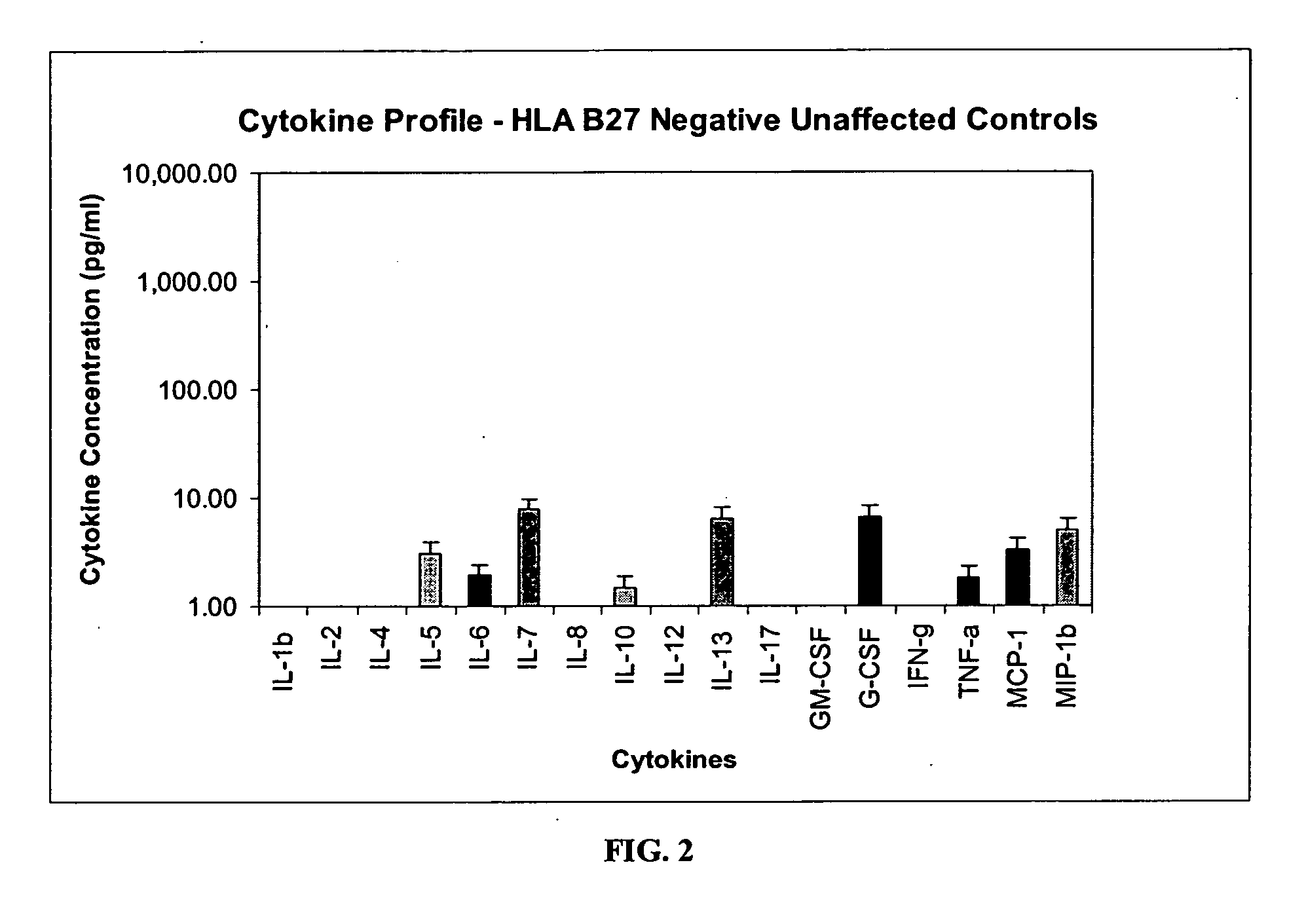
Method of using cytokine assays to diagnose treat, and evaluate inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20060094056A1Snake antigen ingredientsDisease diagnosisAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The invention provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or evaluating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases by sampling peripheral blood, serum, plasma, tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, or other bodily fluids from a human subject having a suspected diagnosis. The sample is analyzed for the presence and amount of certain cytokines, which provides the diagnosis, prognosis or evaluation of therapeutic response.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA +1
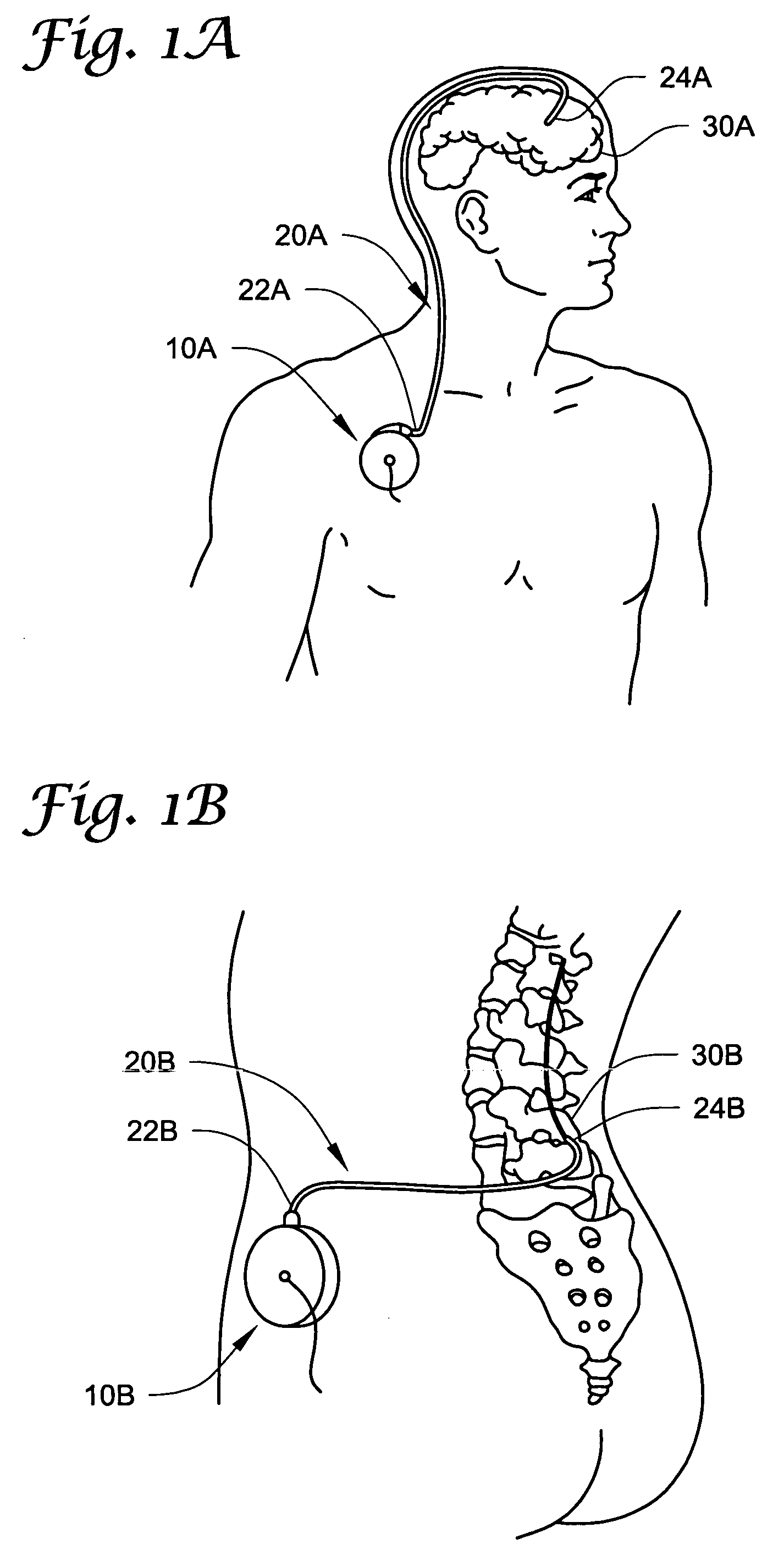
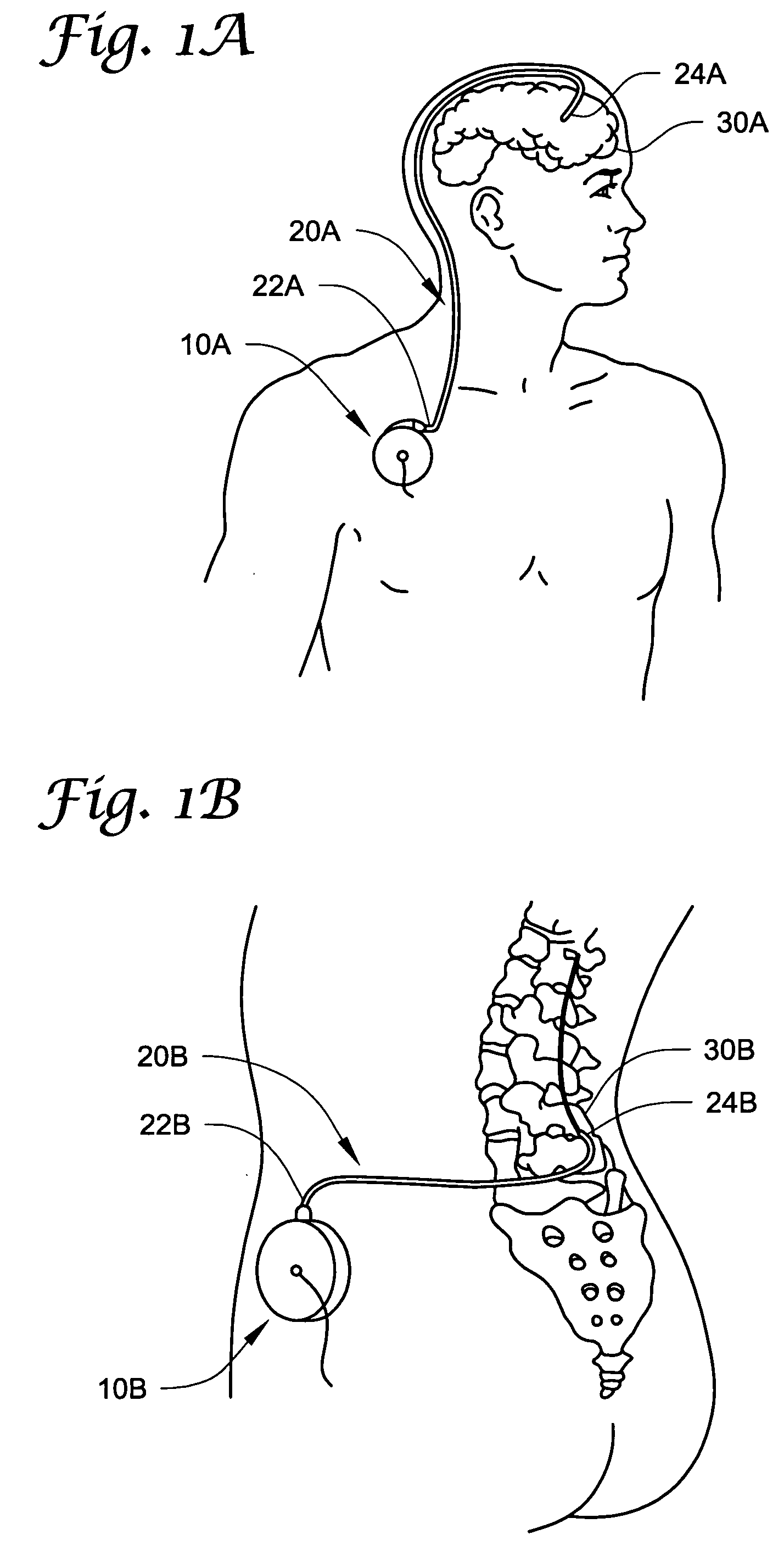
Method of delivering a TNF antagonist to the brain of a human by perispinal administration without direct intrathecal injection
InactiveUS7214658B2Improve cognitive functionReduce deliveryAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsEtanerceptTnf antagonists
The present invention provides specific methods of using and administering etanercept to improve cognitive function in a human, for both the treatment and prevention of cognitive impairment, or, alternatively, to enhance cognitive function including Alzheimer's Disease, Idiopathic Dementia, and Traumatic Brain Injury. The methods of the present invention include the perispinal administration of etanercept. For the purposes of this patent “perispinal” is to be considered as referring to “perispinal extrathecal;” therefore direct intrathecal administration is excluded. Perispinal administration leads to enhanced delivery of etanercept to the brain in a therapeutically effective amount, via the vertebral venous system and / or the cerebrospinal fluid. Delivery of etanercept to the brain utilizing the methods of the present invention includes the use of the vertebral venous system to deliver etanercept to the brain via retrograde venous flow. Physical maneuvers are used to enhance delivery of etanercept to the brain via this route.
Owner:TACT IP
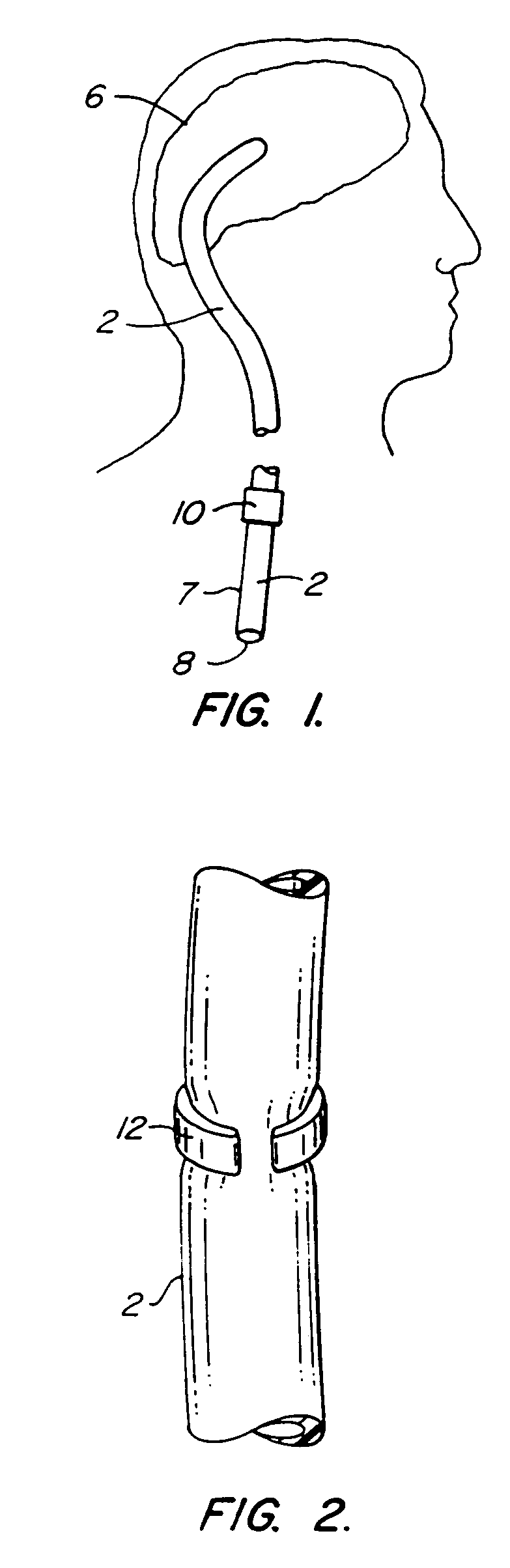
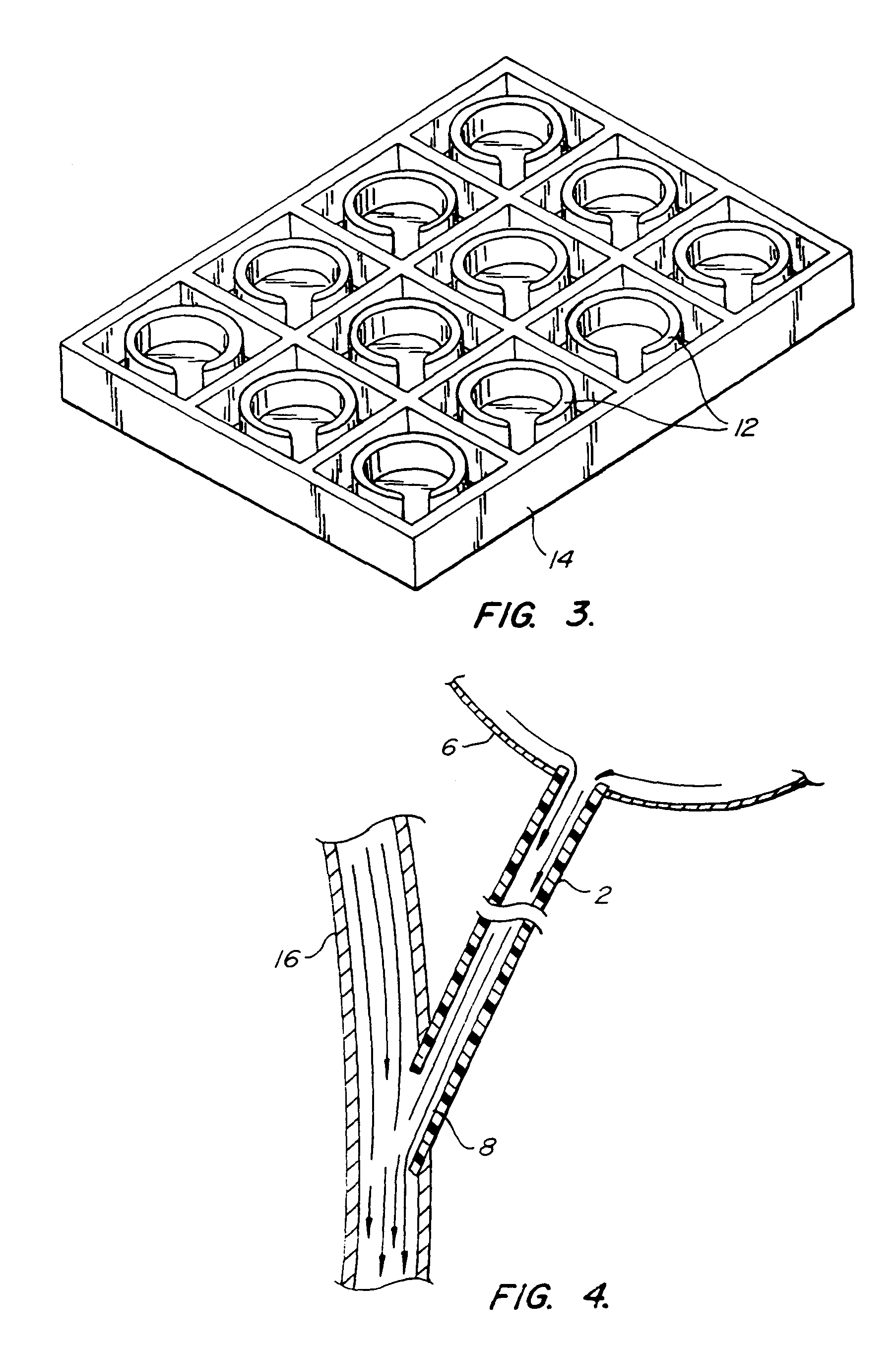
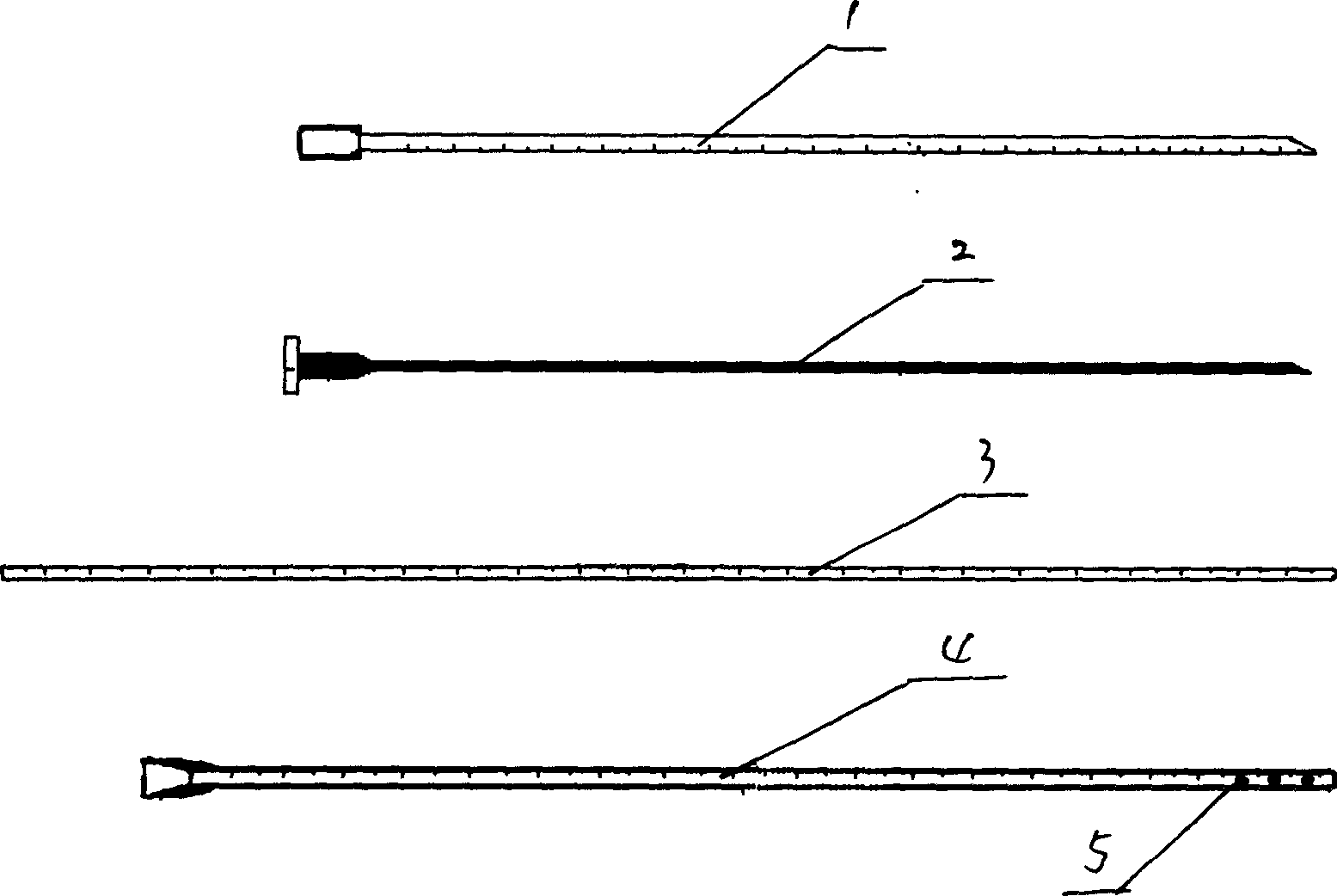
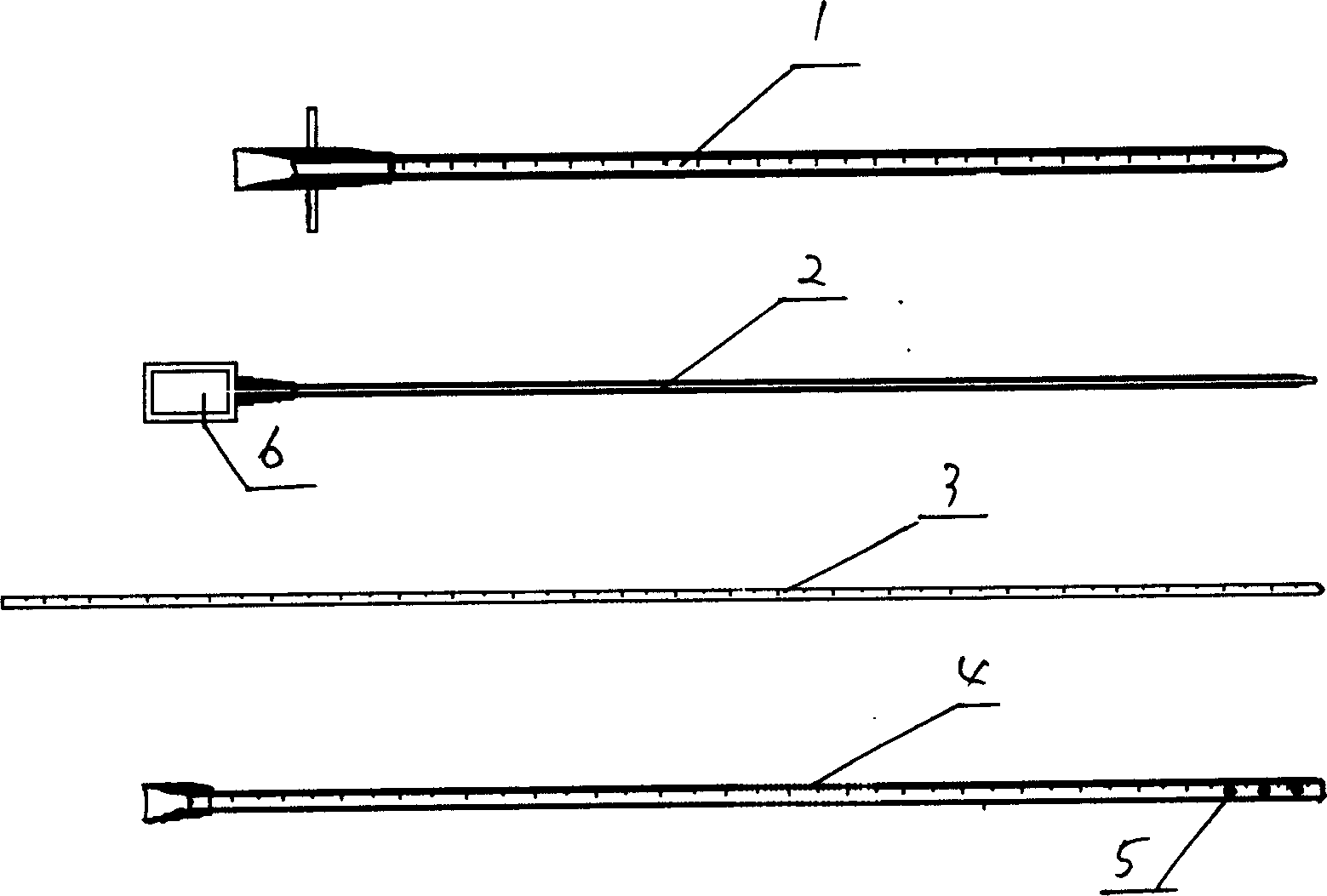
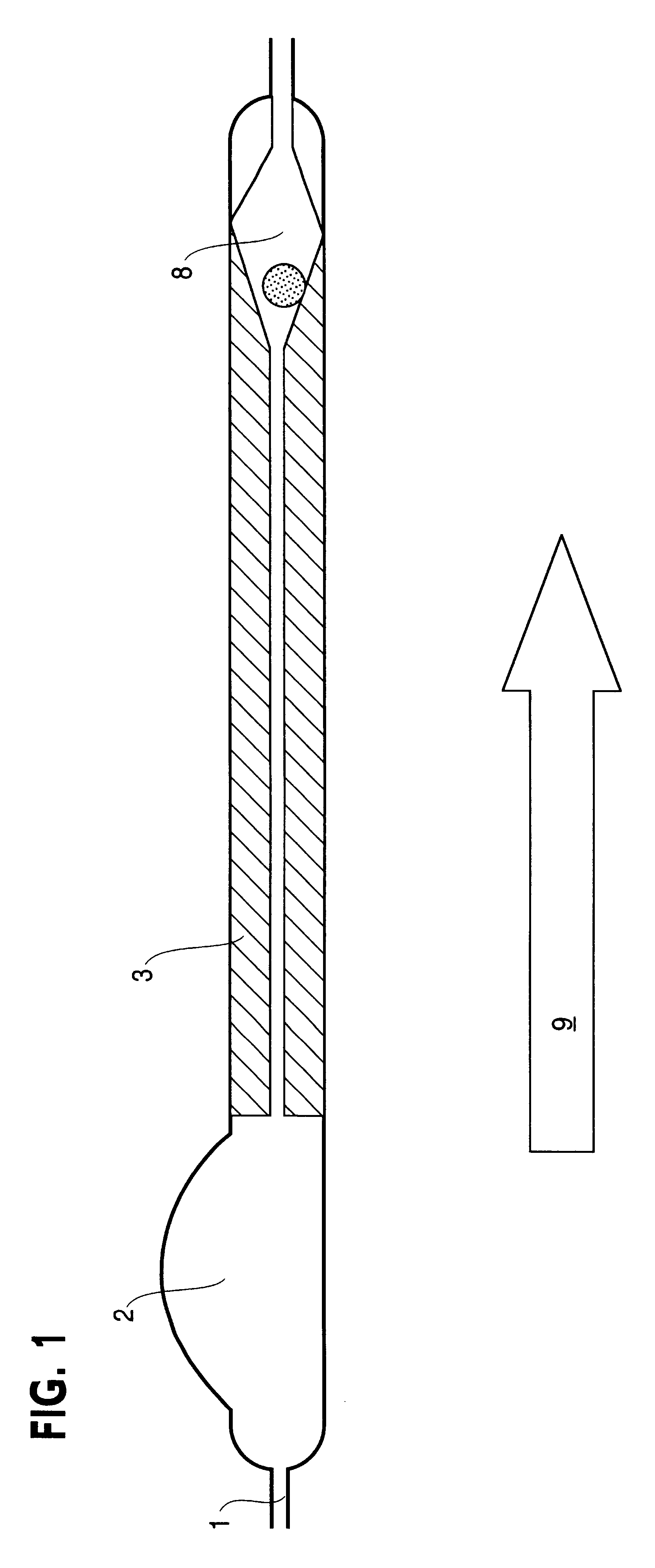
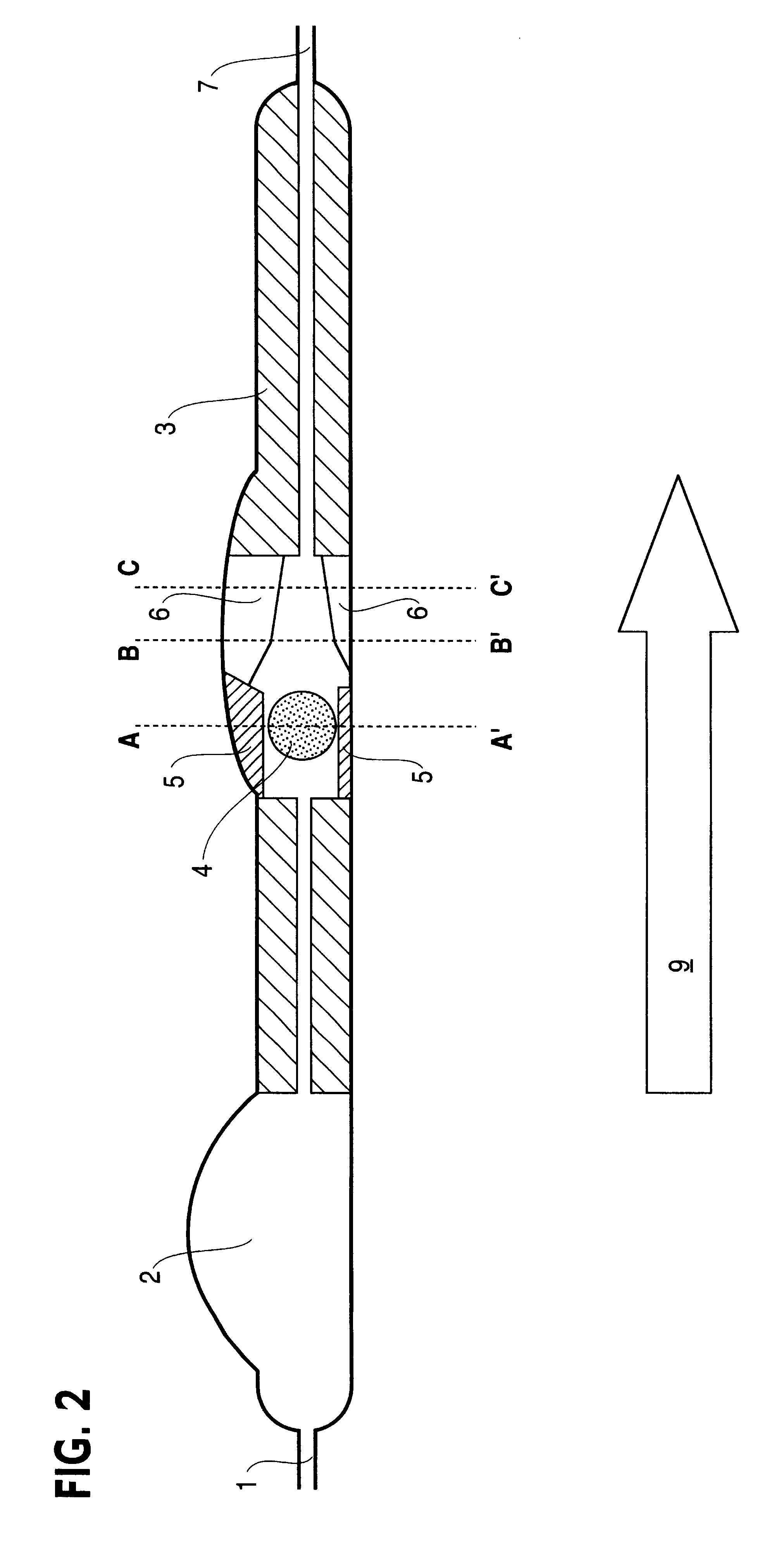
Cerebrospinal fluid puncturing drainer
The cerebrospinal fluid piercing drainer includes a piercing unit and an external draining unit. The piercing unit includes piercing needle, piercing sheath, guide wire and draining pipe. The piercing needle and the outside piercing sheath are made of stainless steel material and are used in piercing; the flexible guide wire of plastic-steel material with shape memory function is used in replacing the piercing needle; the draining pipe of soft silicone gel is used in replacing the piercing sheath and draining. During piercing, the piercing needle and the outside piercing sheath are first pierced into proper position, the piercing needle is then withdrawn and the guide wire is penetrated through the piercing sheath, and the piercing sheath is finally withdrawn and the draining pipe is fed along the guide wire to the cavity to be drained or fed to cerebral side room or even farther position under the monitoring with DSA. The draining pipe has external end connected to the draining unit.
Owner:何明利
Surgically implantable hearing aid
InactiveUS7033313B2Negligible riskSurgery is simpleEar treatmentDeaf-aid setsDura materCochlear implantation
The invention comprises a surgically implantable hearing aid for hearing impaired persons. The hearing aid includes a vibrational element which is vibrated by sound waves and attached to the skull of the person, and a connector which crosses the mastoid cavity and delivers the sound waves to the dura mater of the patient thereby vibrating the dura mater, the cerebrospinal fluids, and the brain to create a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to act as a tinnitus masker or used in conjunction with a cochlear implant. It can also be used in a modified form to connect directly through the skull of the person.
Owner:ALAN J LUPIN
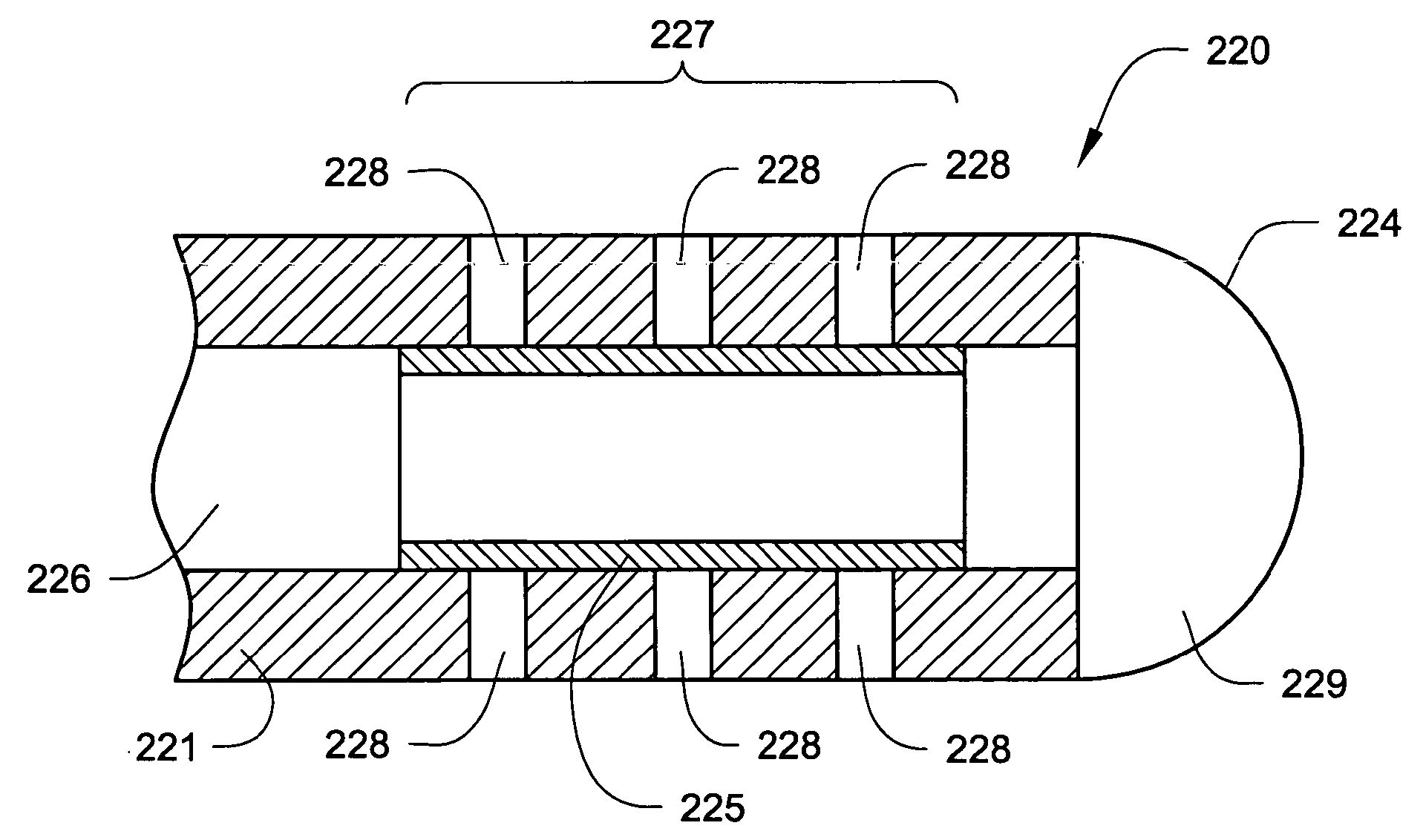
Permeable membrane catheters, systems, and methods
InactiveUS20050137579A1Improve efficacyReduce the amount requiredMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringMembrane configuration
Devices, systems and methods for delivering one or more drugs to one or more internal body locations (such as the cerebrospinal fluid) are disclosed. In various aspects, the systems and methods may involve catheters having infusion sections with permeable membranes and one or more valves that control flow to the infusion sections.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for removing harmful proteins from a mammalian's ventricular cerebrospinal fluid
A method and apparatus for removing harmful organic anions and proteins from a mammalian's ventricular cerebrospinal fluid in the treatment of brain disorders. One embodiment comprises using an implanted pump and filter system in conjunction with a drug or enzyme to clean and filter a patient's cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:GEIGER MARK
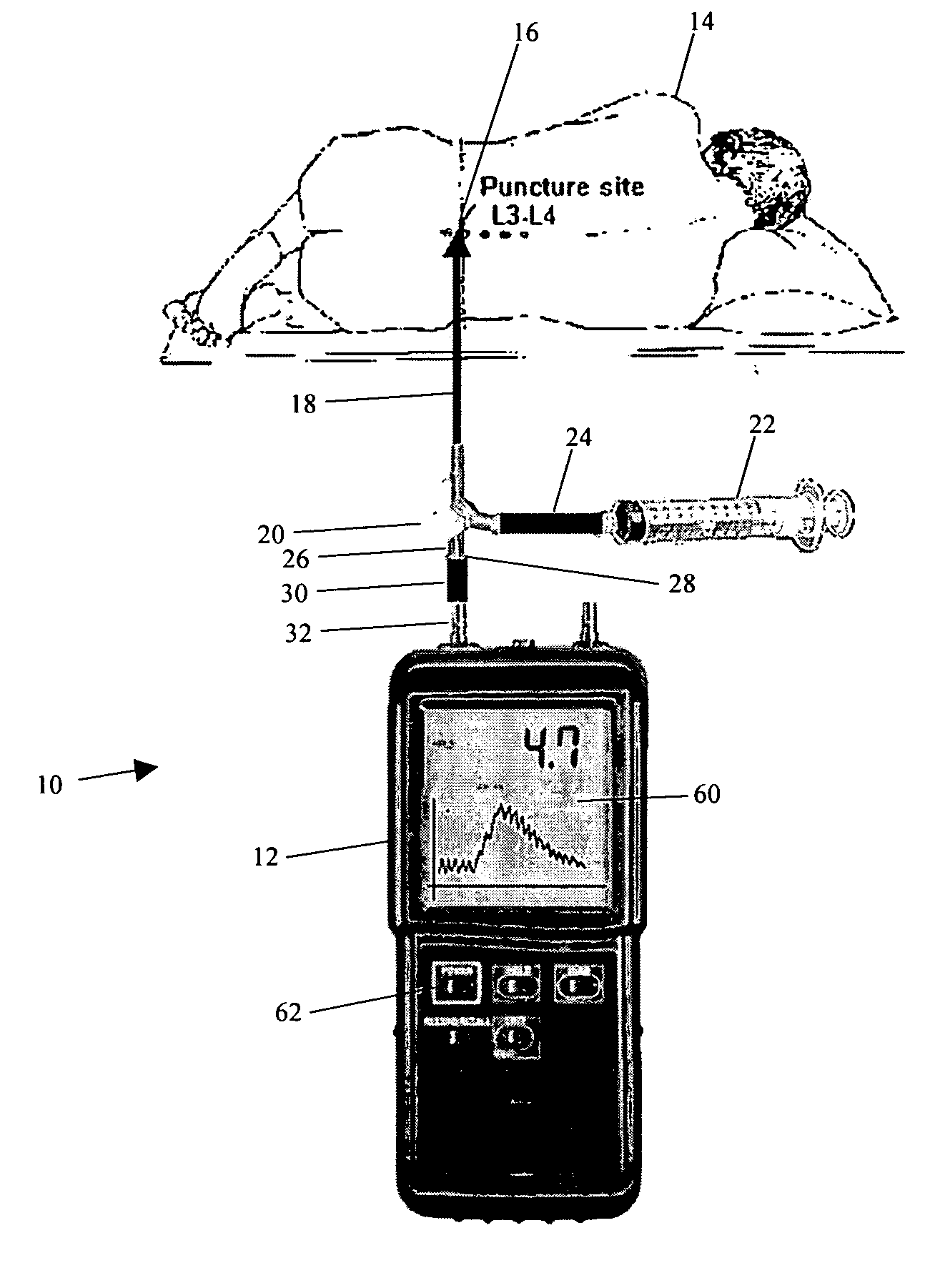
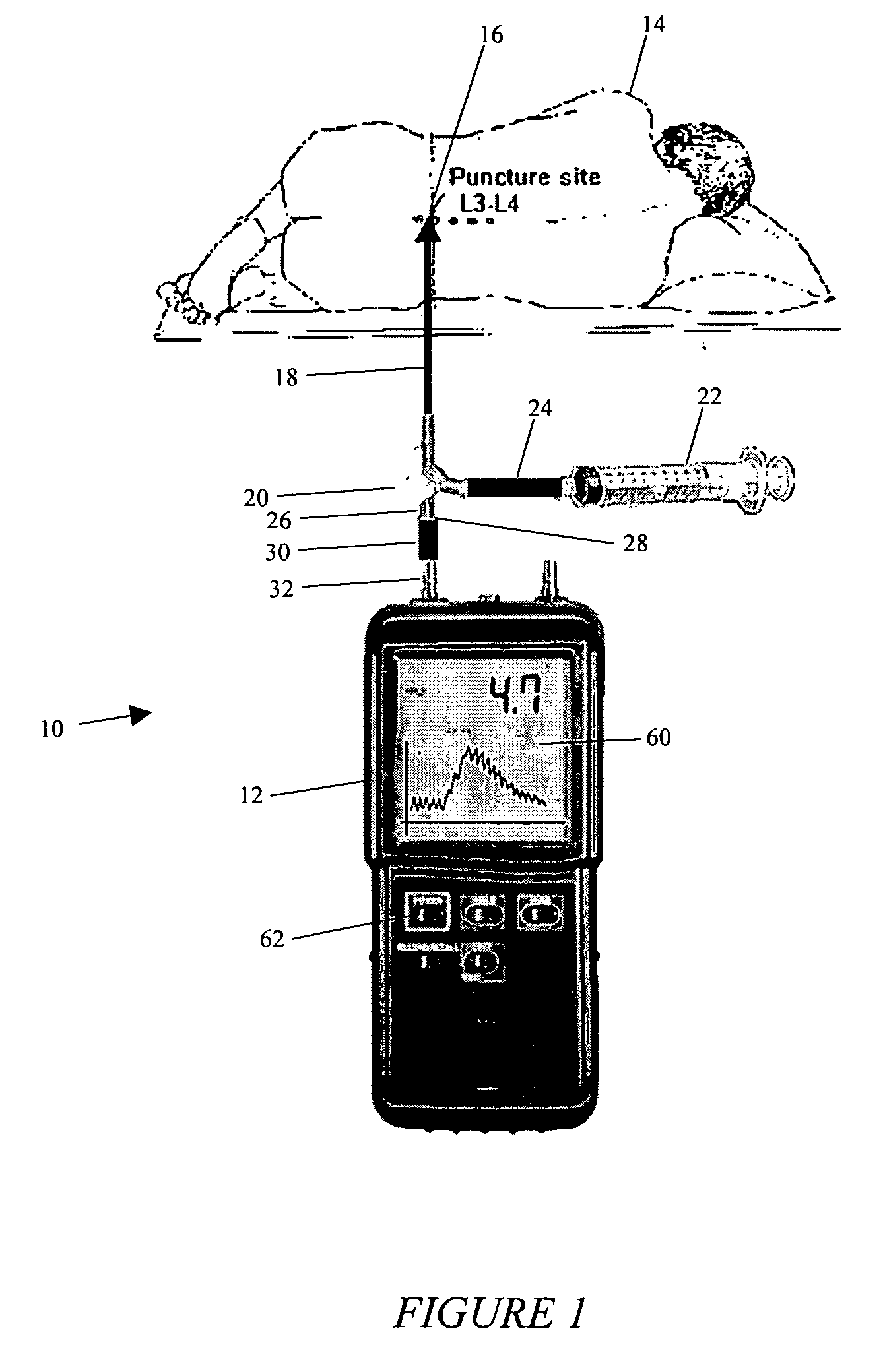
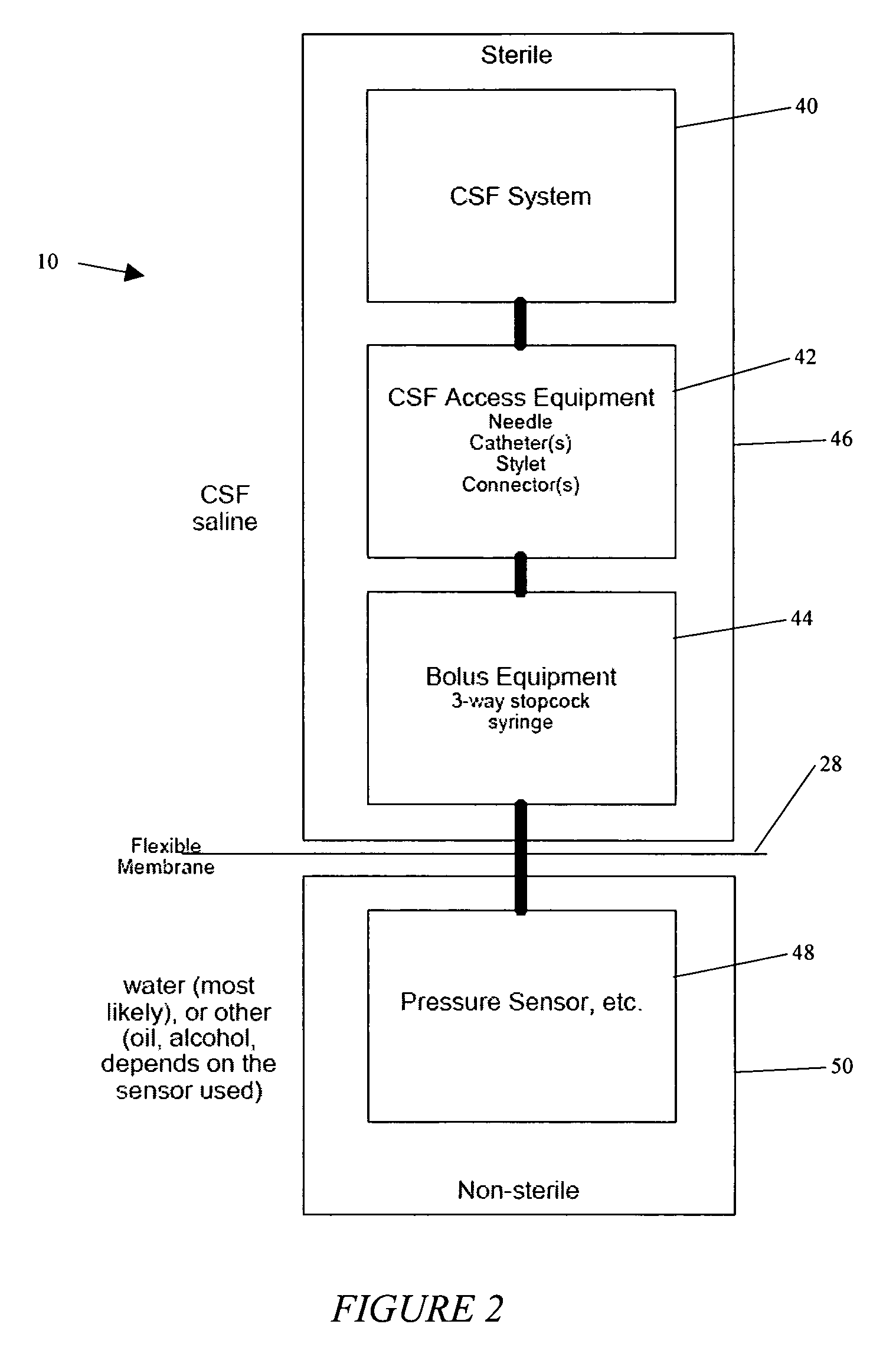
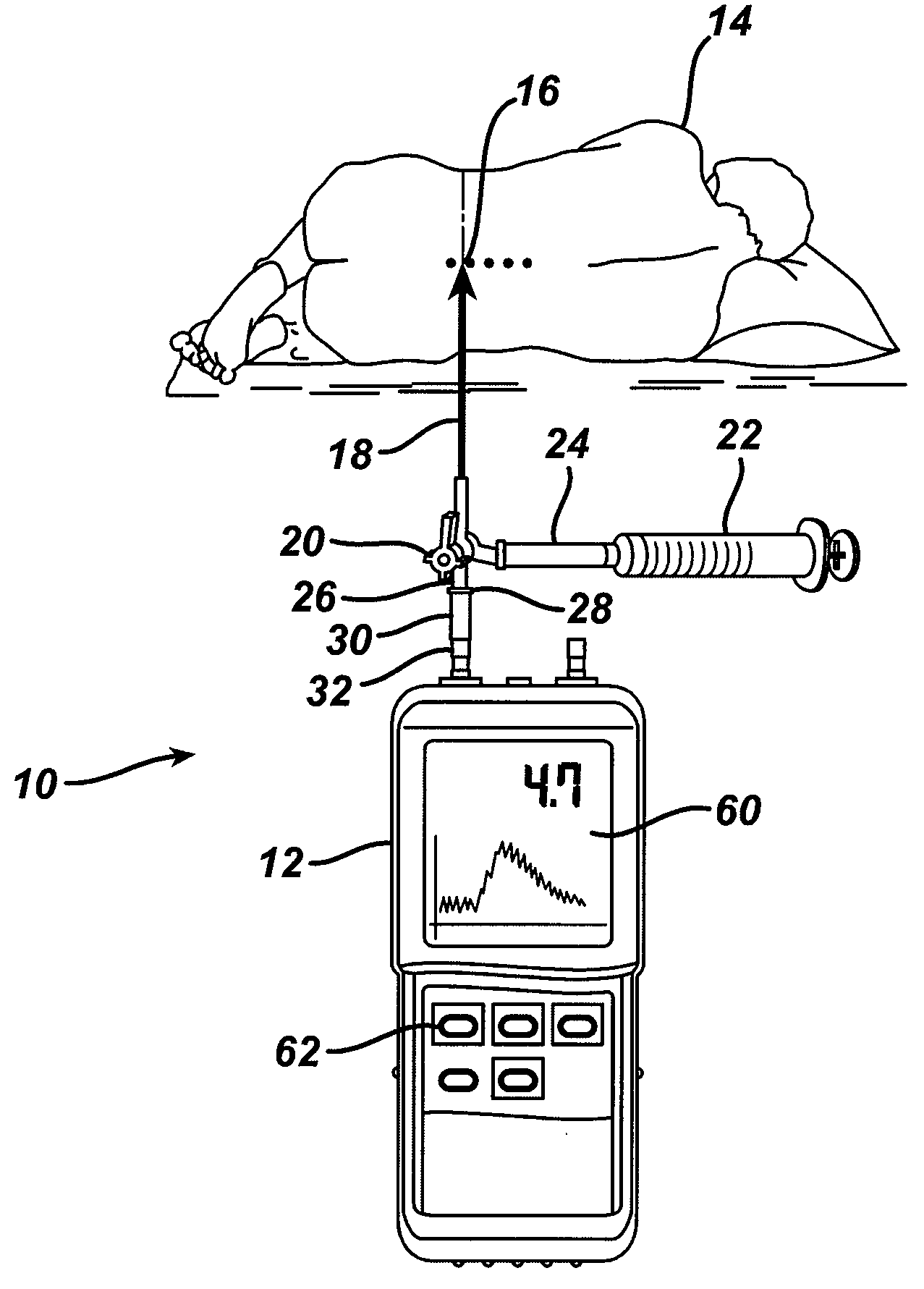
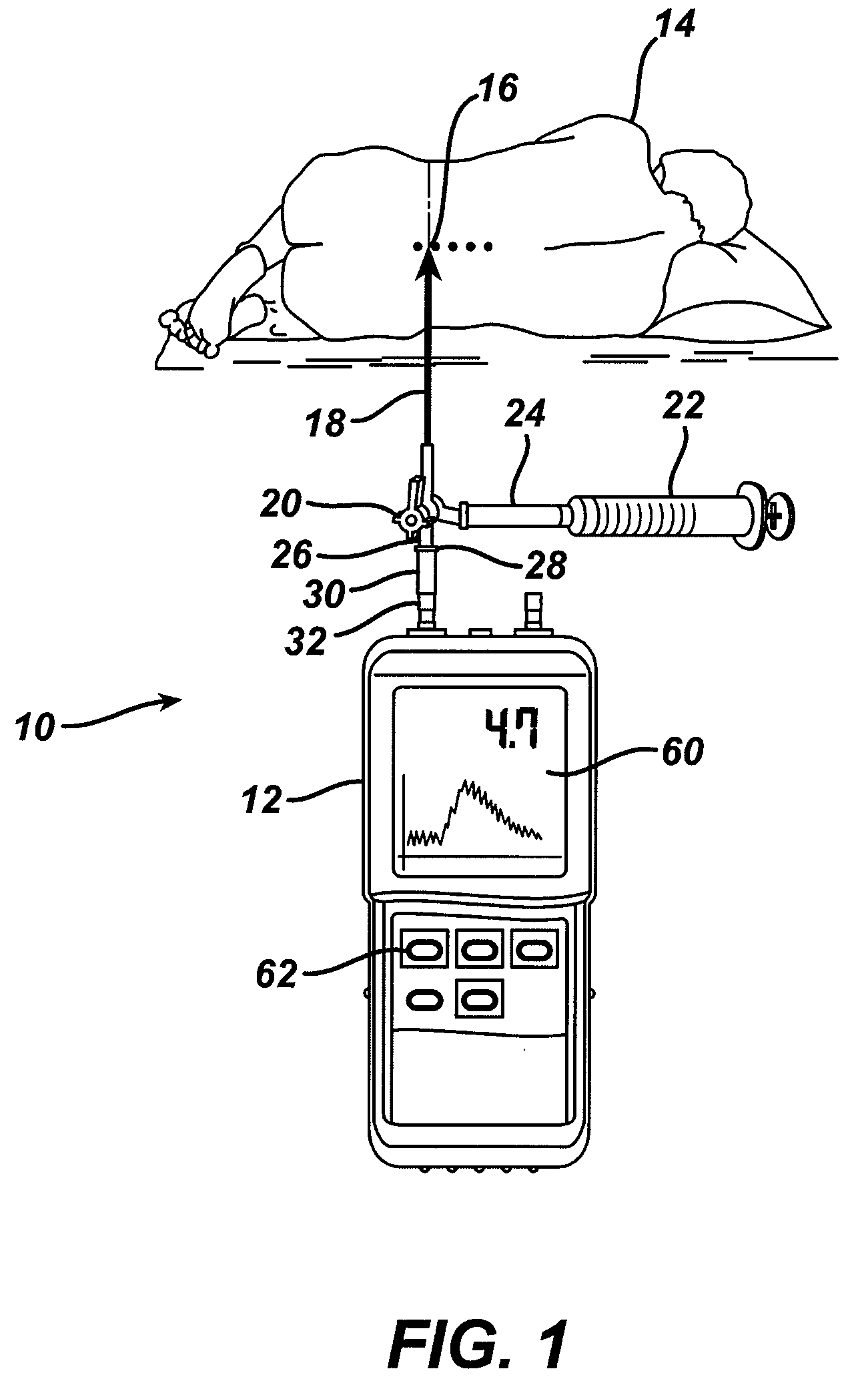
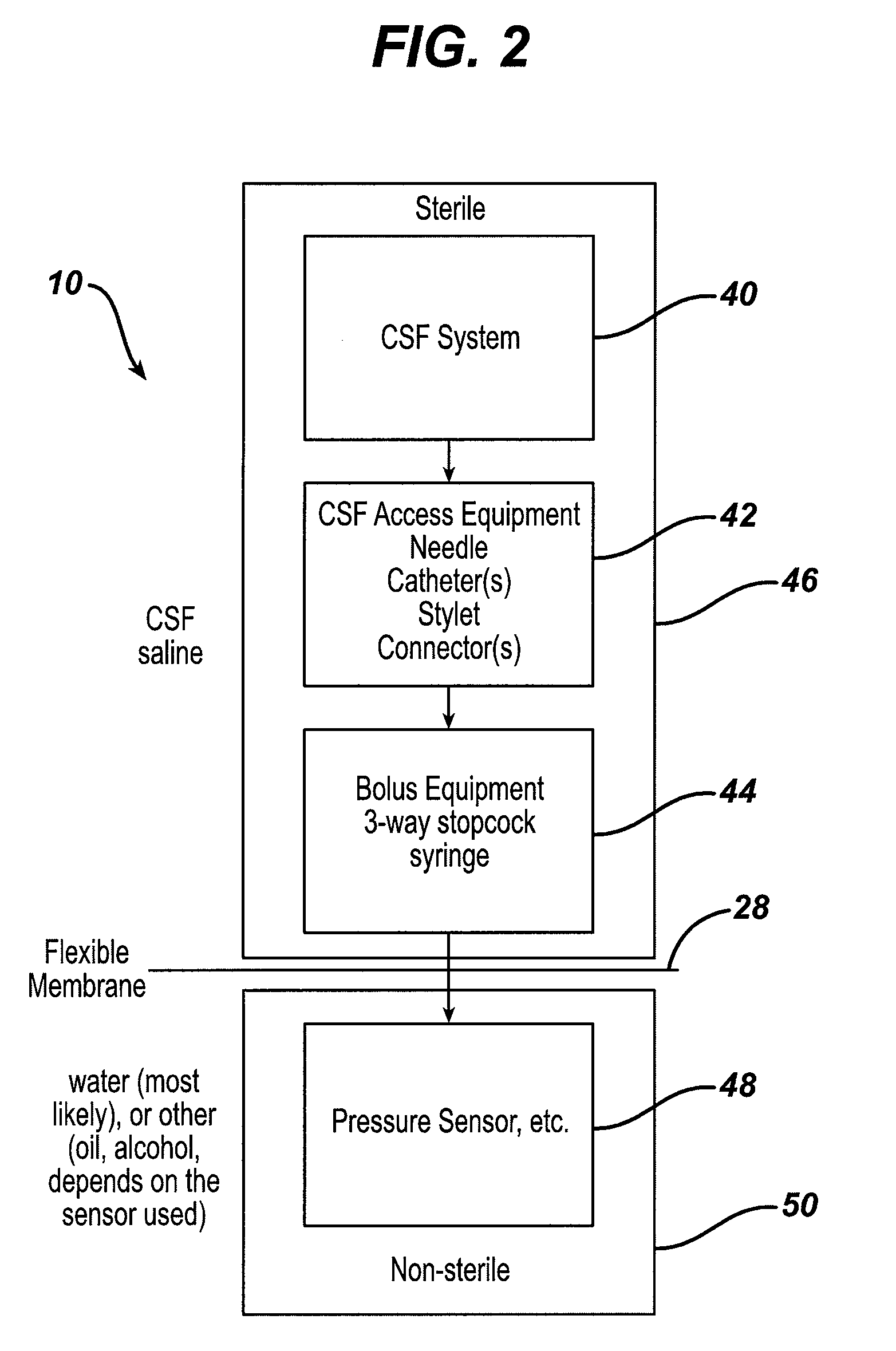
System and method for measuring the pressure of a fluid system within a patient
A pressure sensing apparatus has a pressure sensor component that includes a pressure sensing port, a pressure sensor for sensing a pressure of a fluid in the pressure sensing port, and a digital processor communicating with the pressure sensor for performing calculations involving fluid pressures sensed. The pressure sensing apparatus further includes a first chamber in fluid contact with the pressure sensing port, a second chamber fluidically connectable with a patient's cerebrospinal fluid system, and a membrane located between the first and second chambers so as to transmit fluid pressure from the second chamber to the first chamber.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
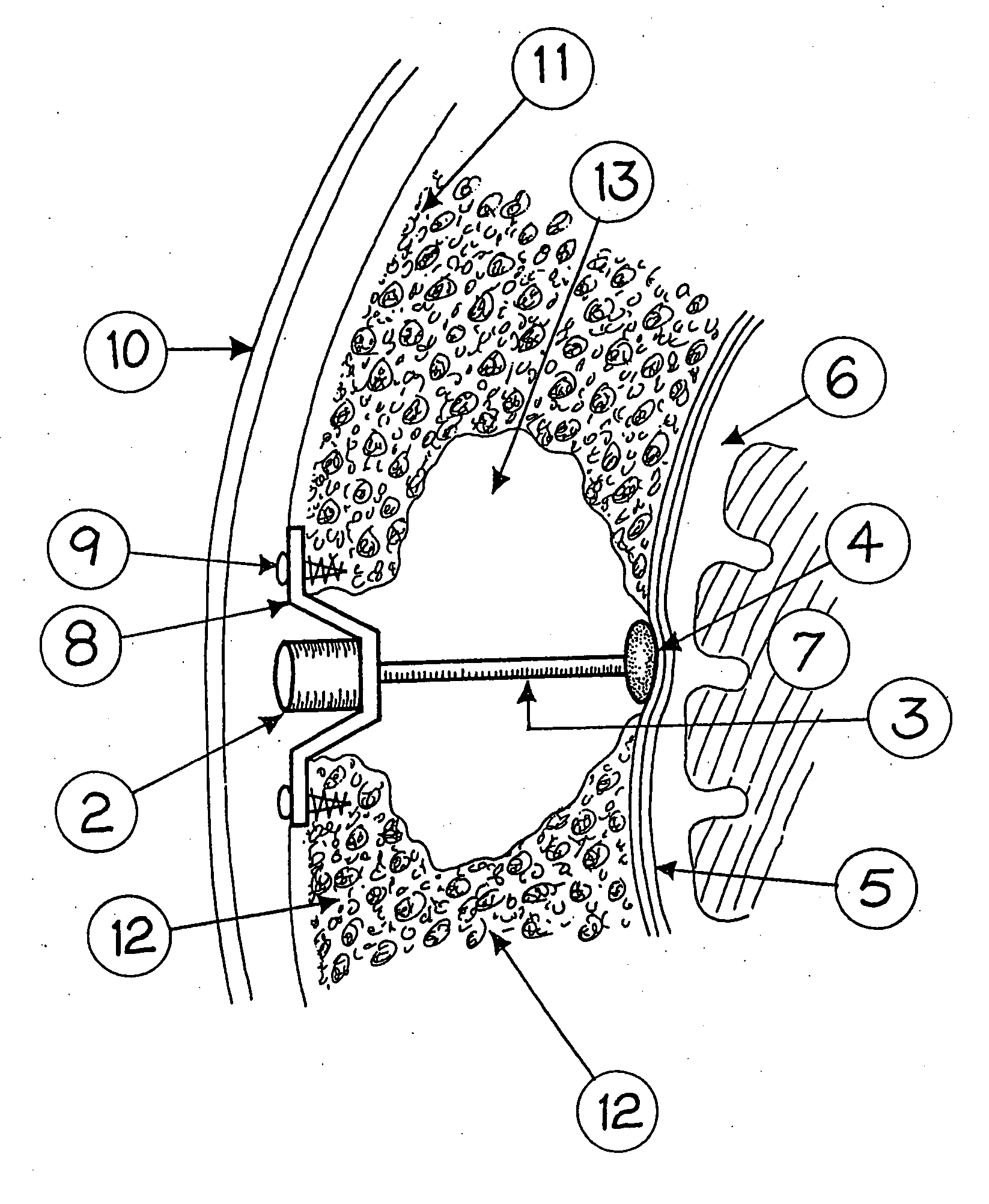
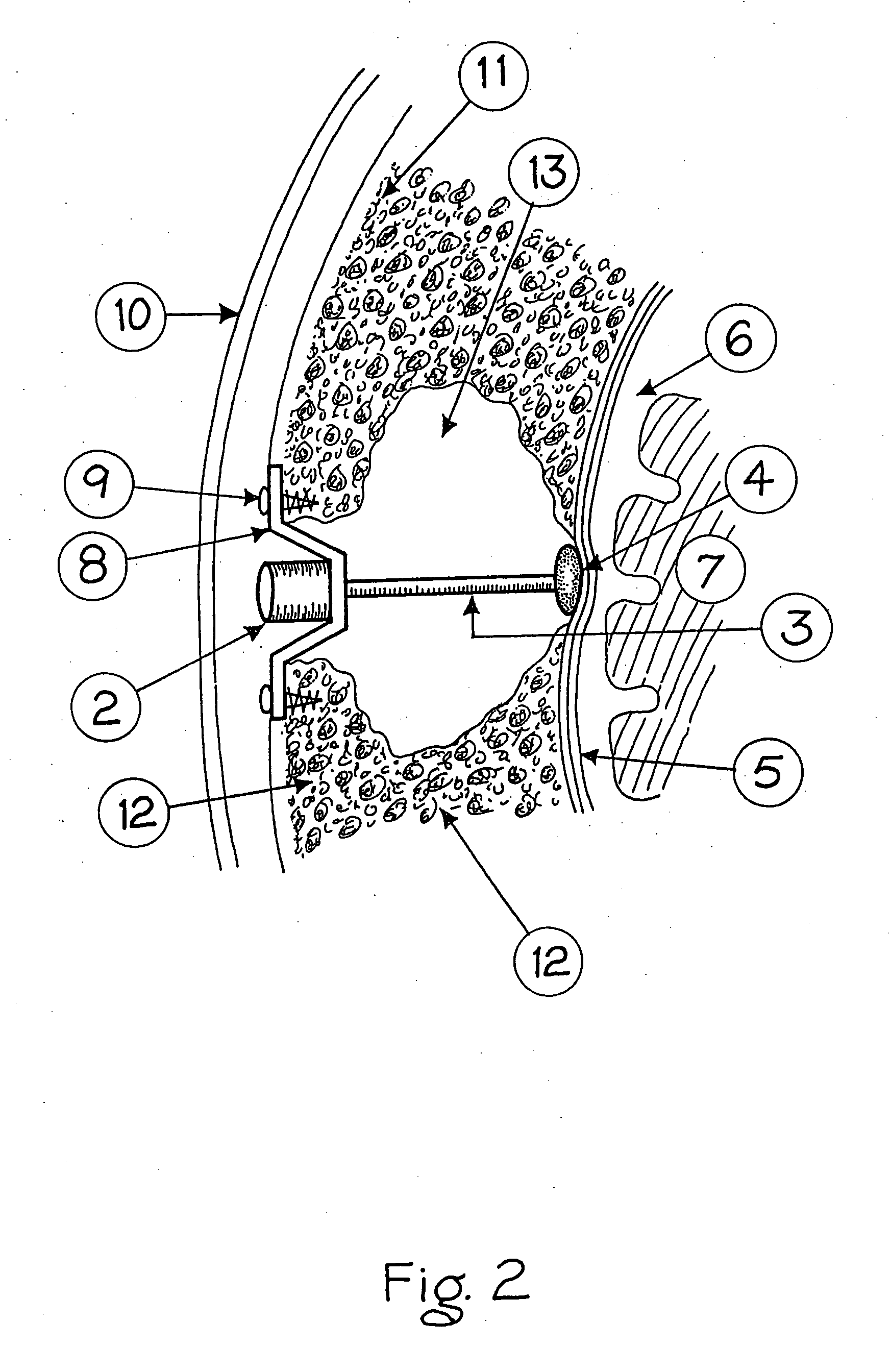
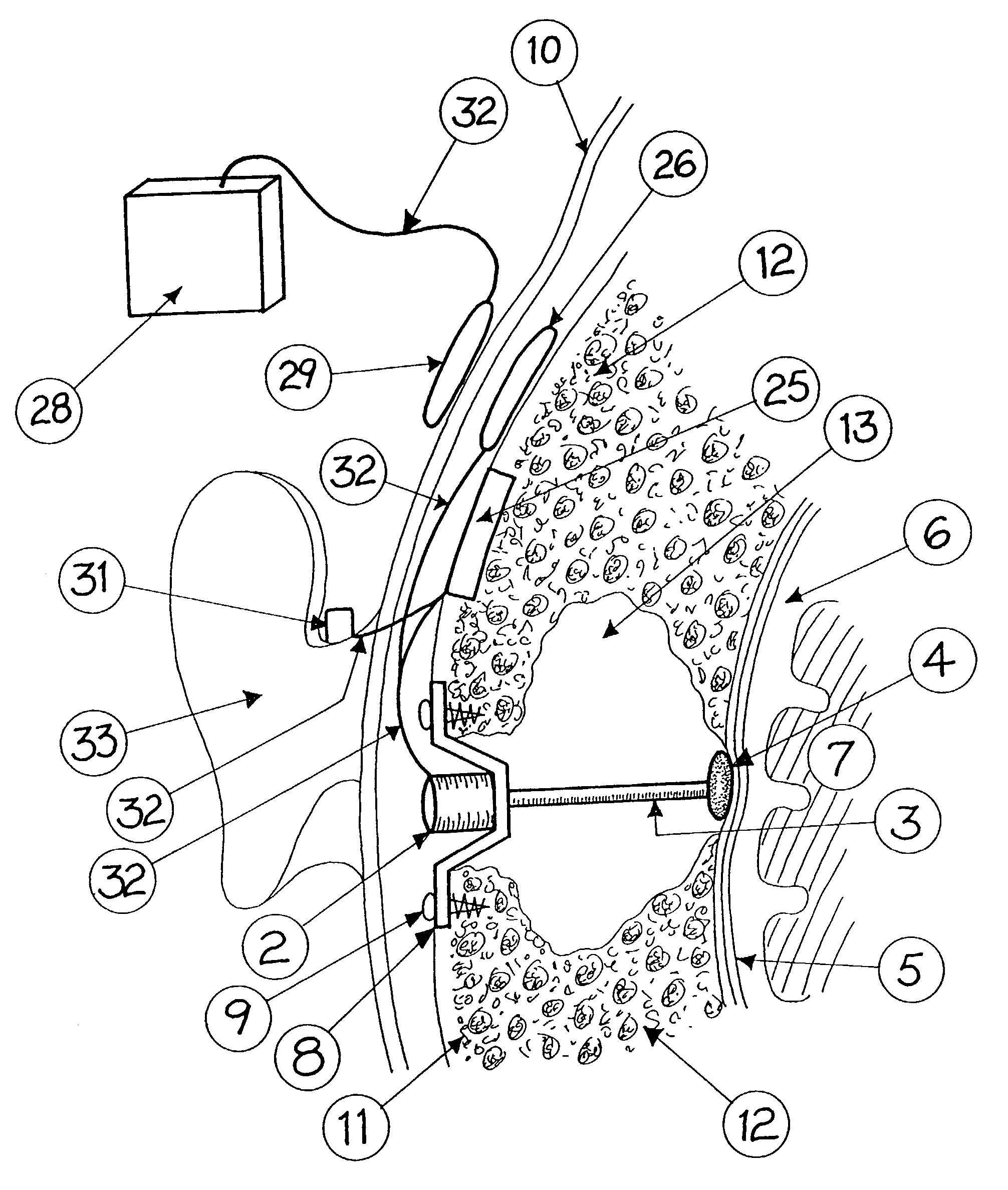
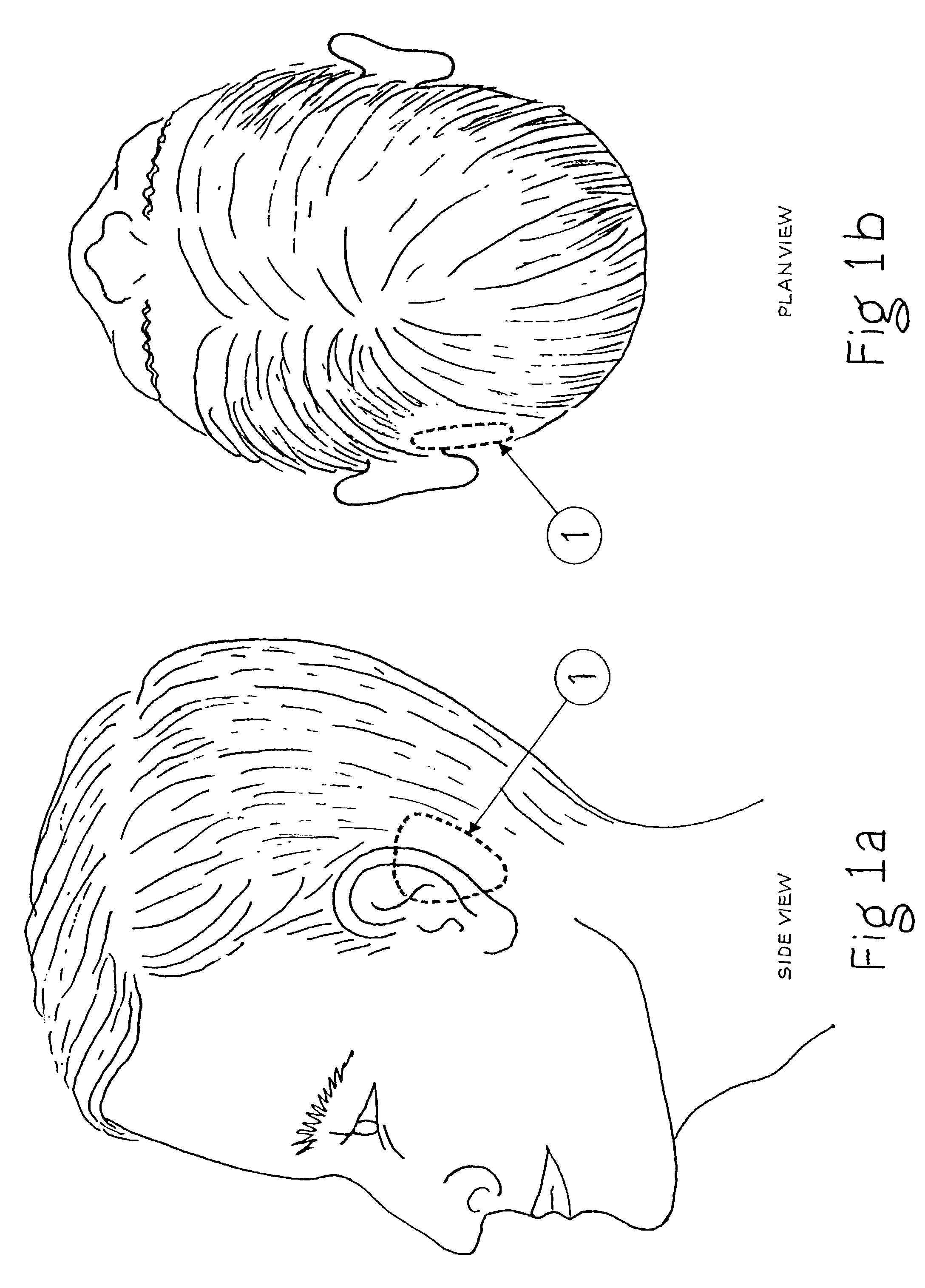
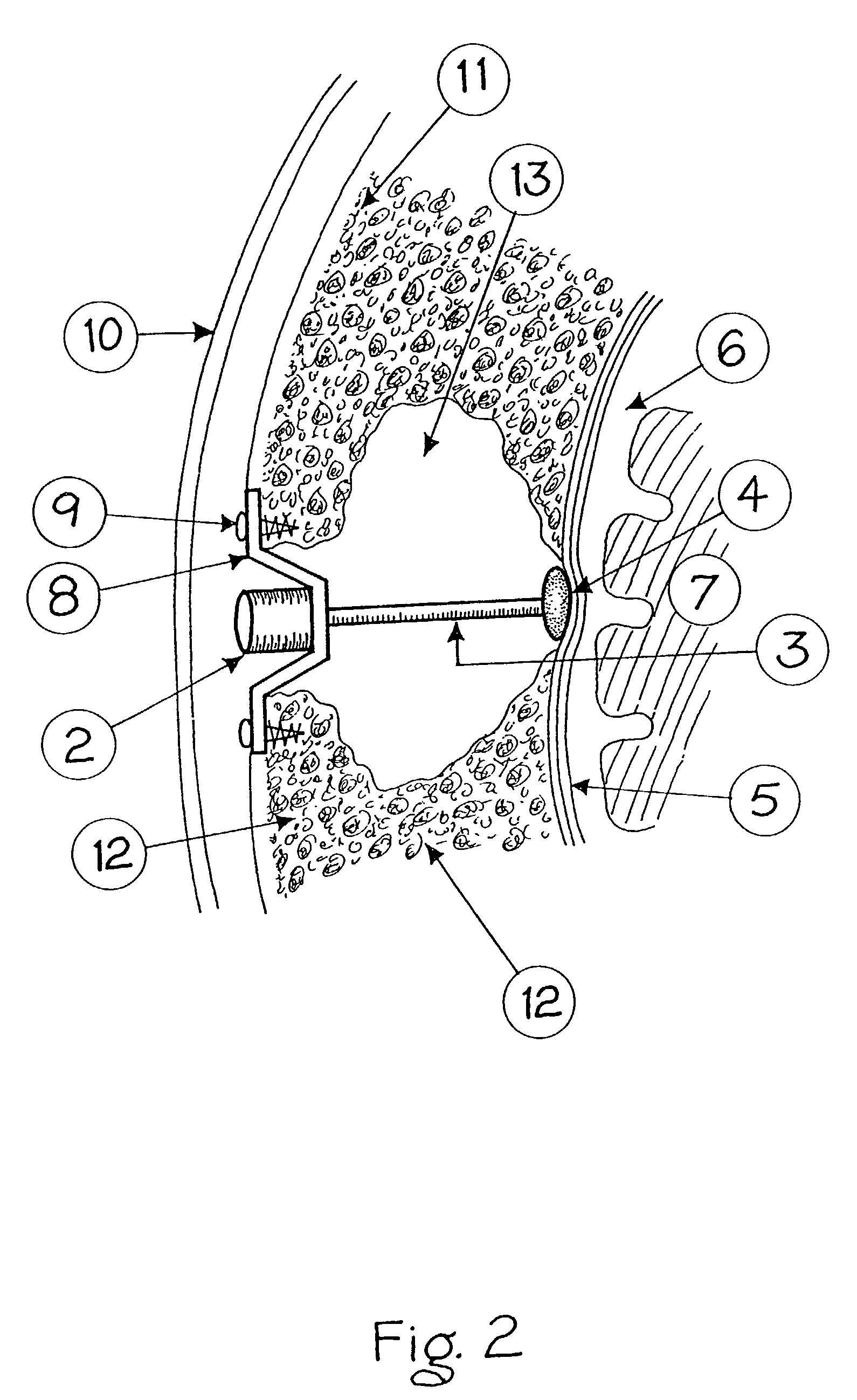
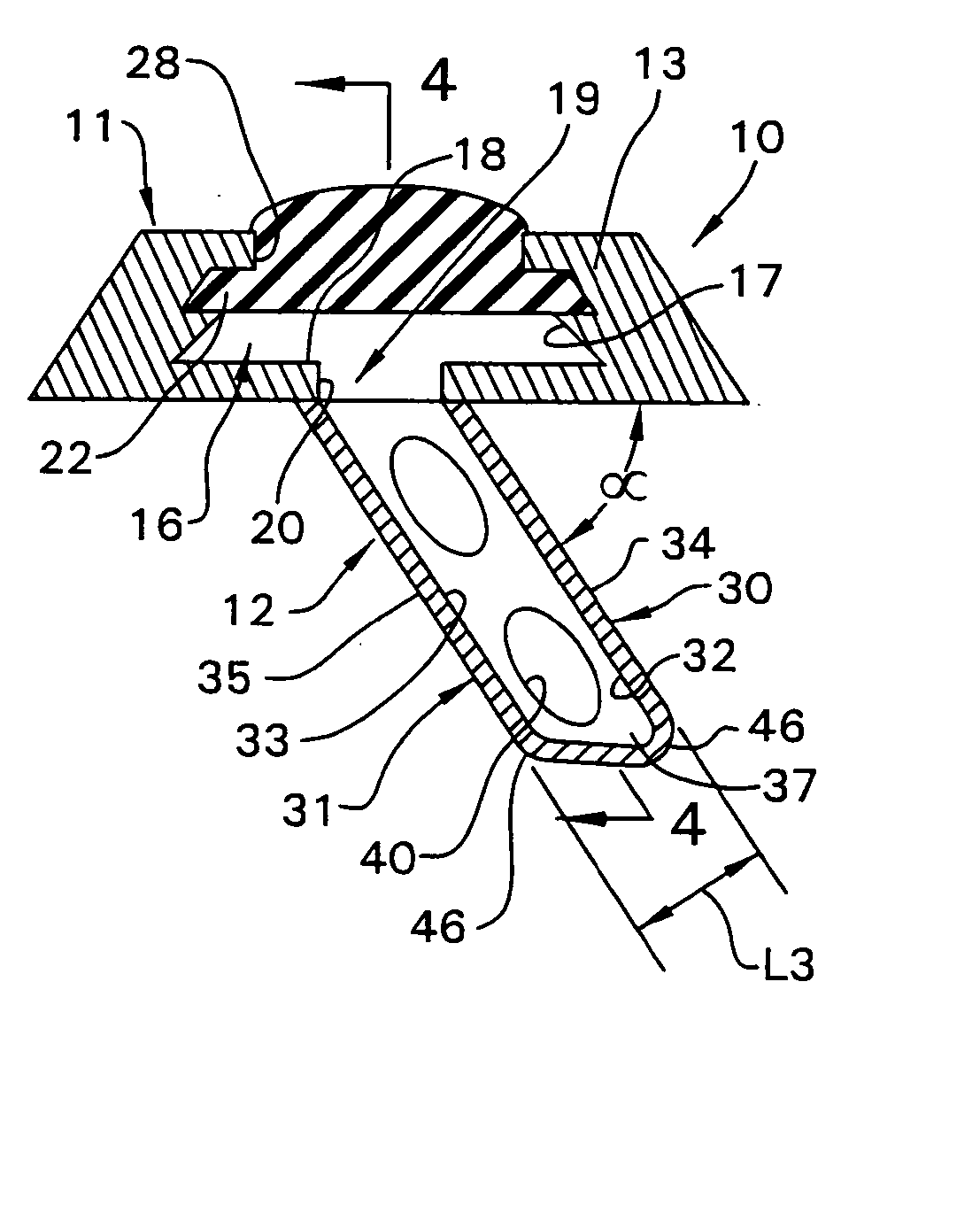
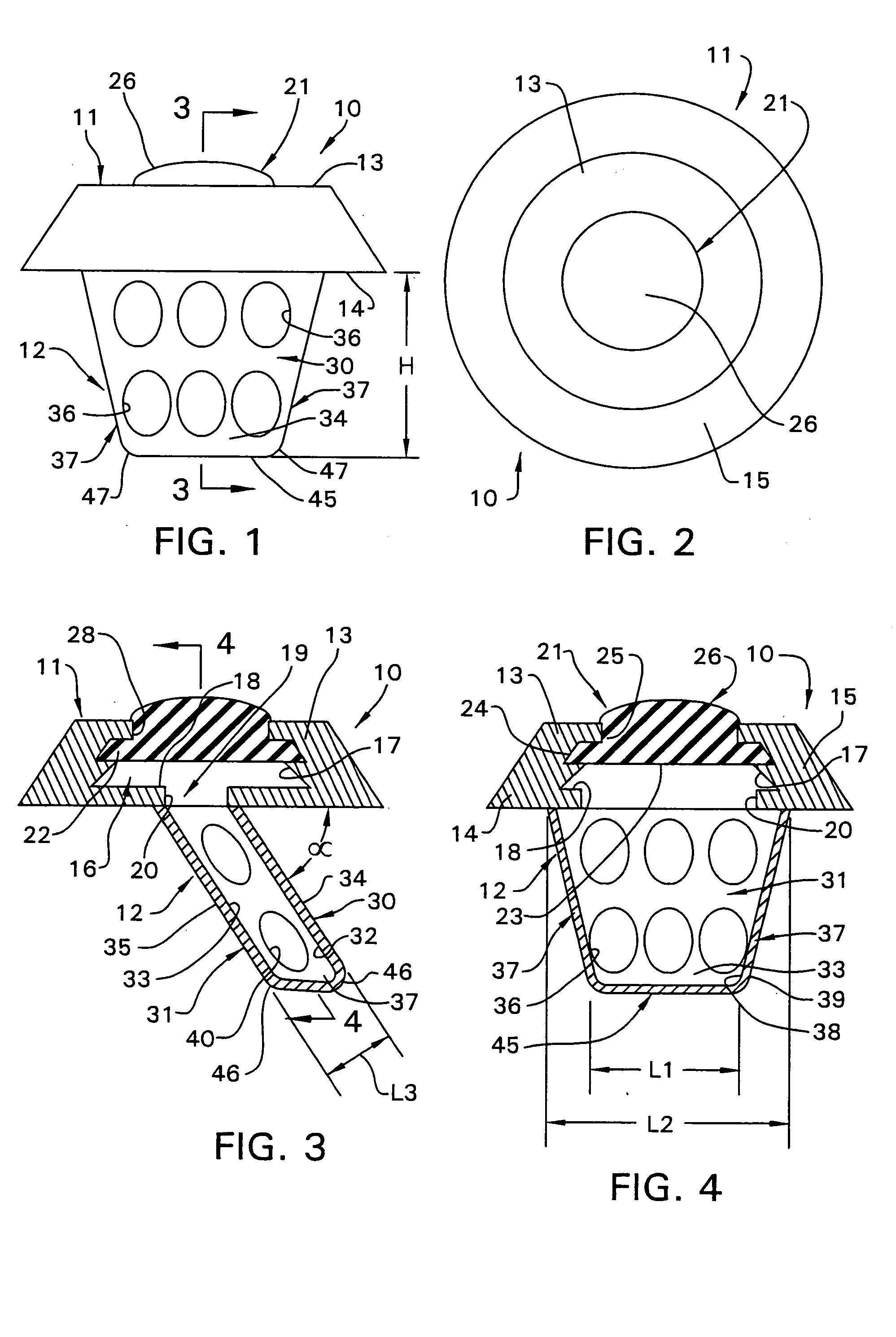
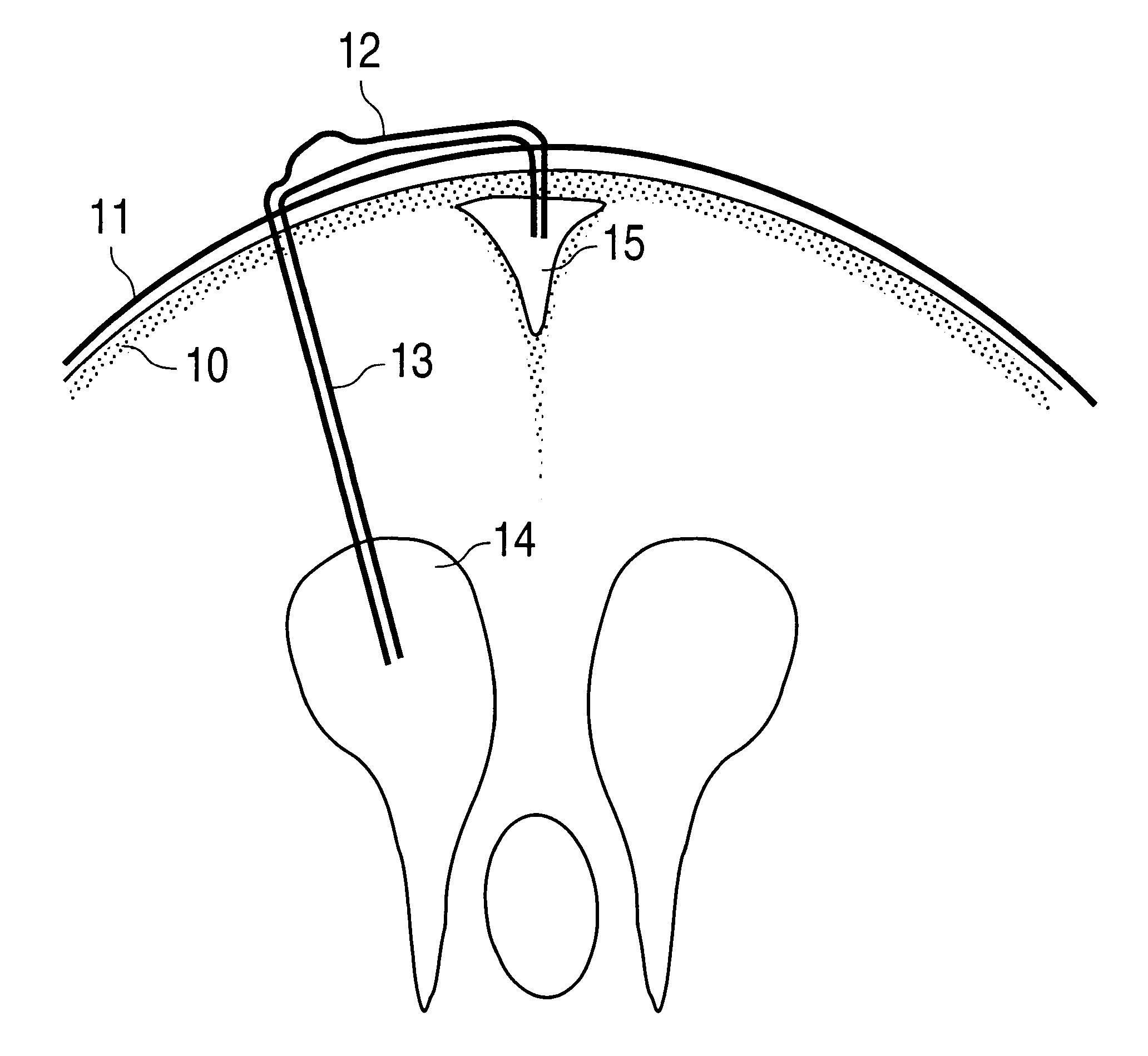
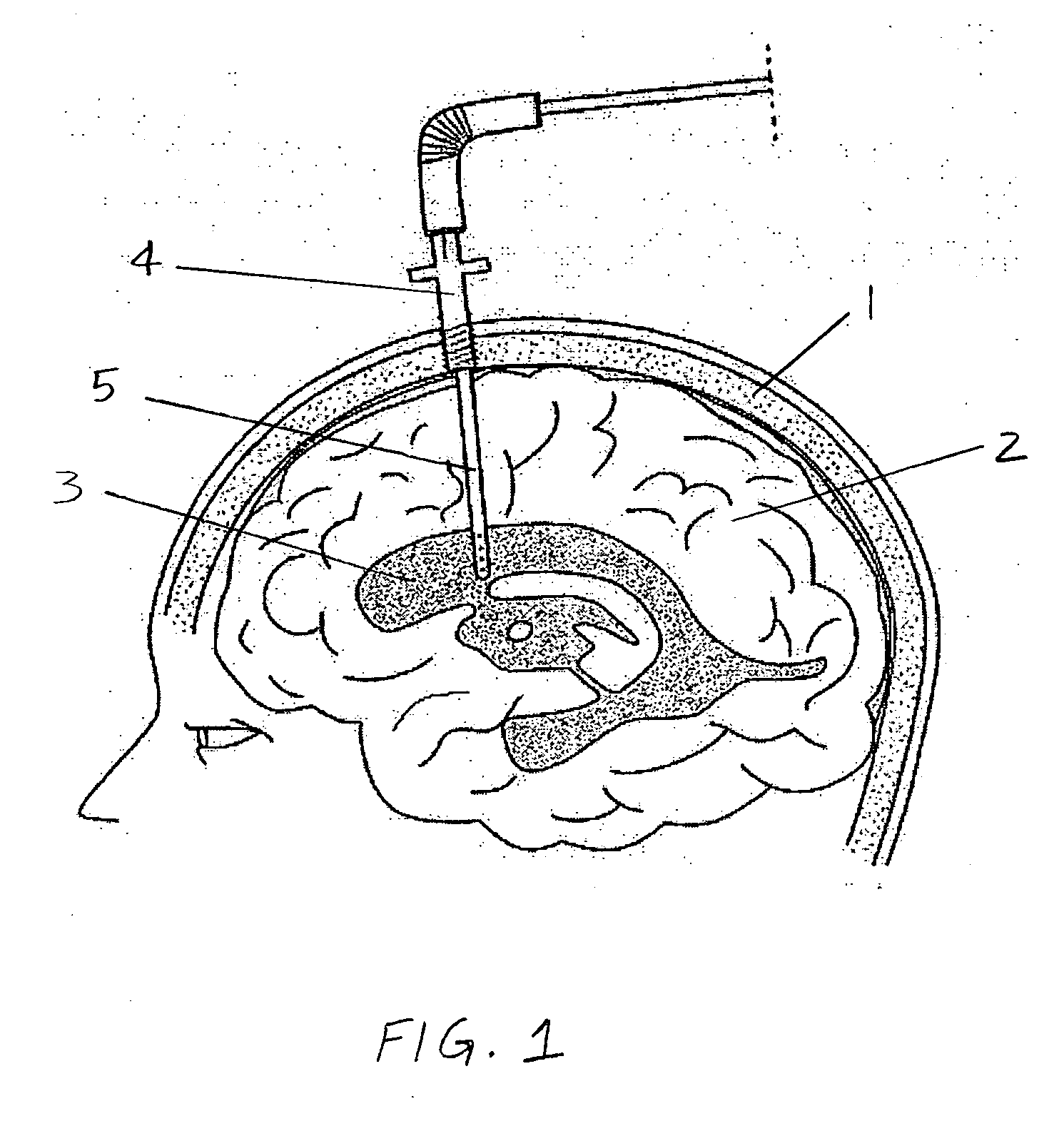
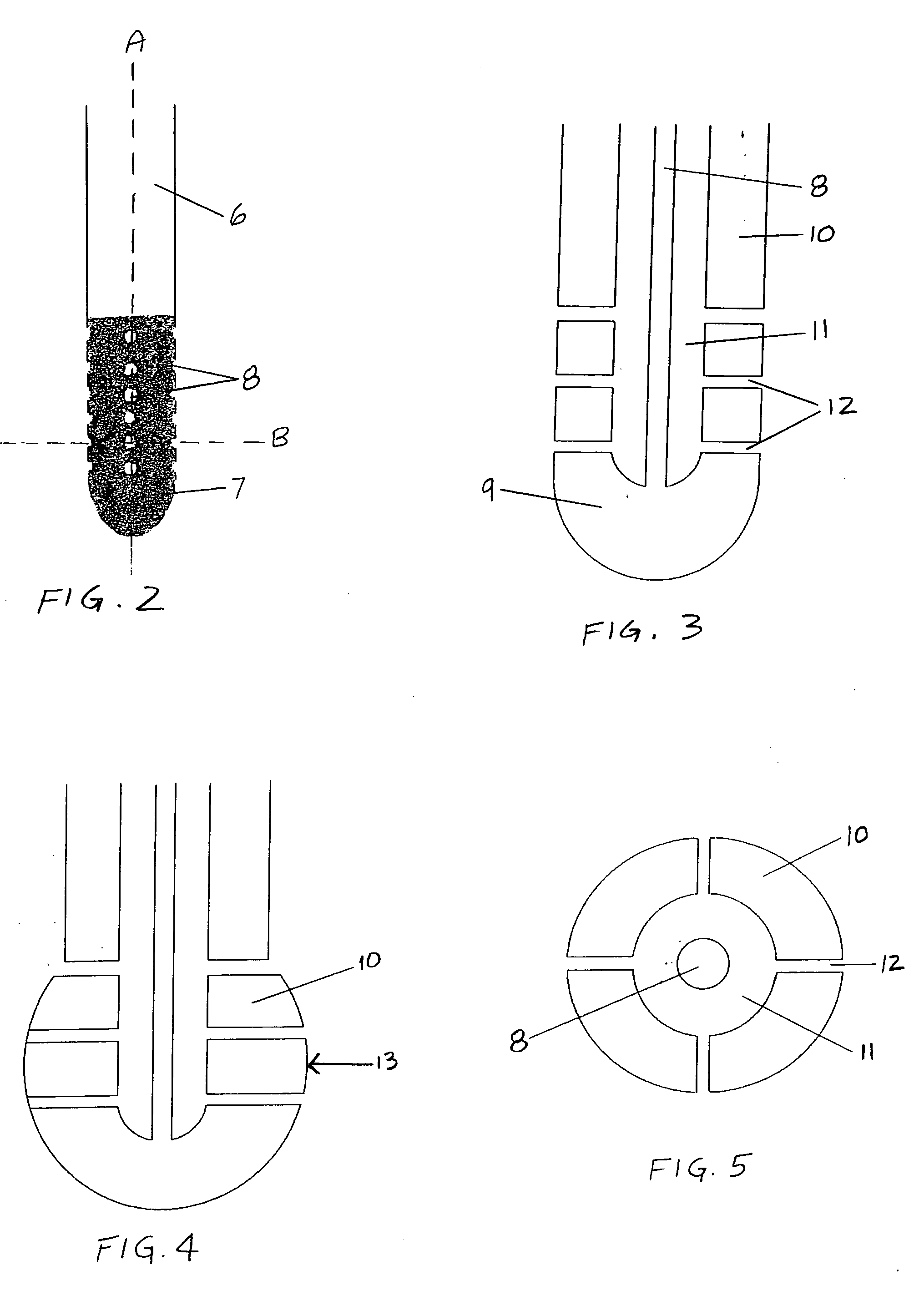
Surgical implant and method of accessing cerebrospinal fluid
A surgical implant and method of gaining access to cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. The implant includes an upper housing part which is positioned subcutaneously on the skull and a lower cage-like member which depends downwardly from the housing part. The housing part defines a chamber or reservoir therein which communicates with openings defined in the lower member. The implant is embedded between portions of the brain so that the lower member projects between the cerebellum and the cerebrum and holds same apart in order to access cerebrospinal fluid which pools in this area. The cerebrospinal fluid is accessed for sampling or dosing purposes through a septum provided within the upper housing part.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
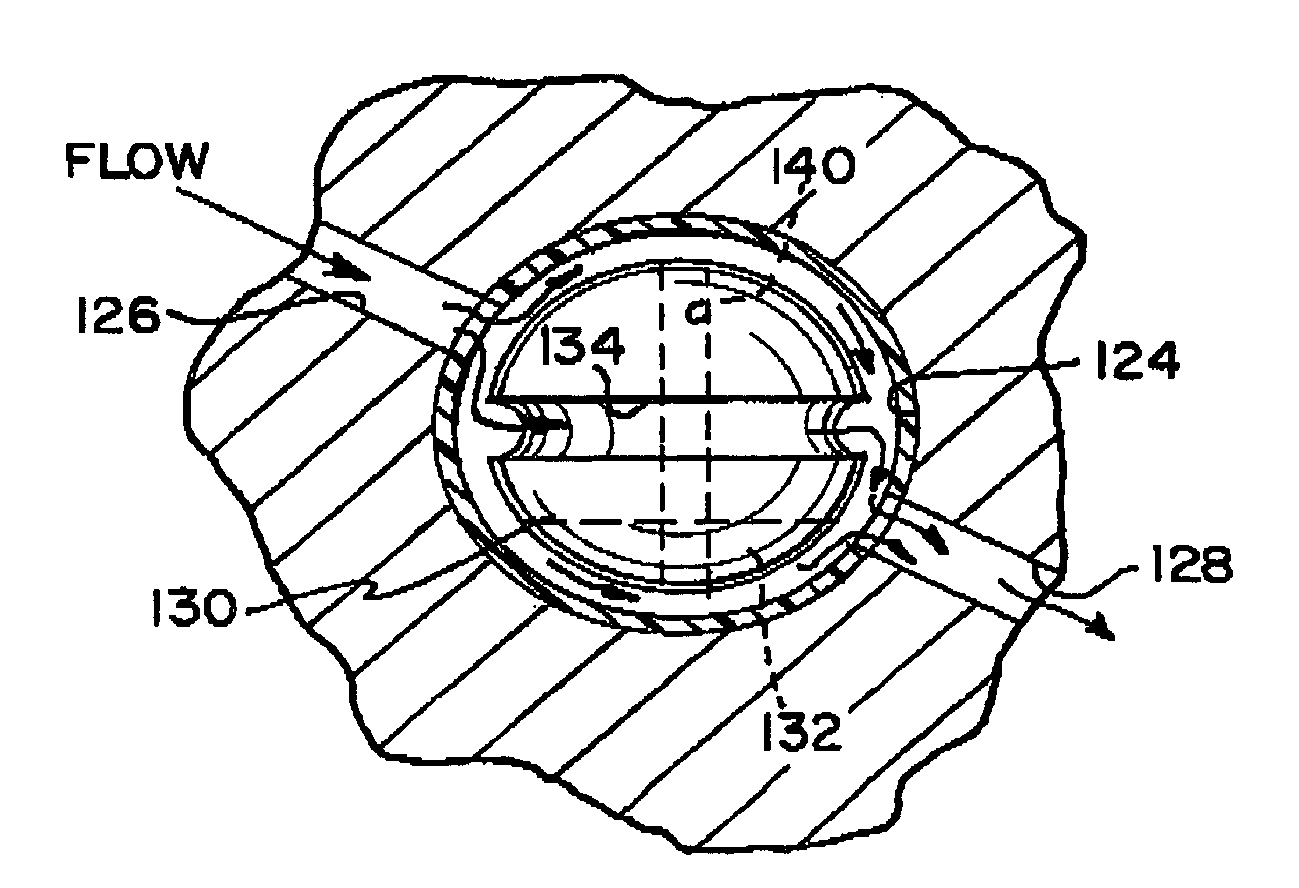
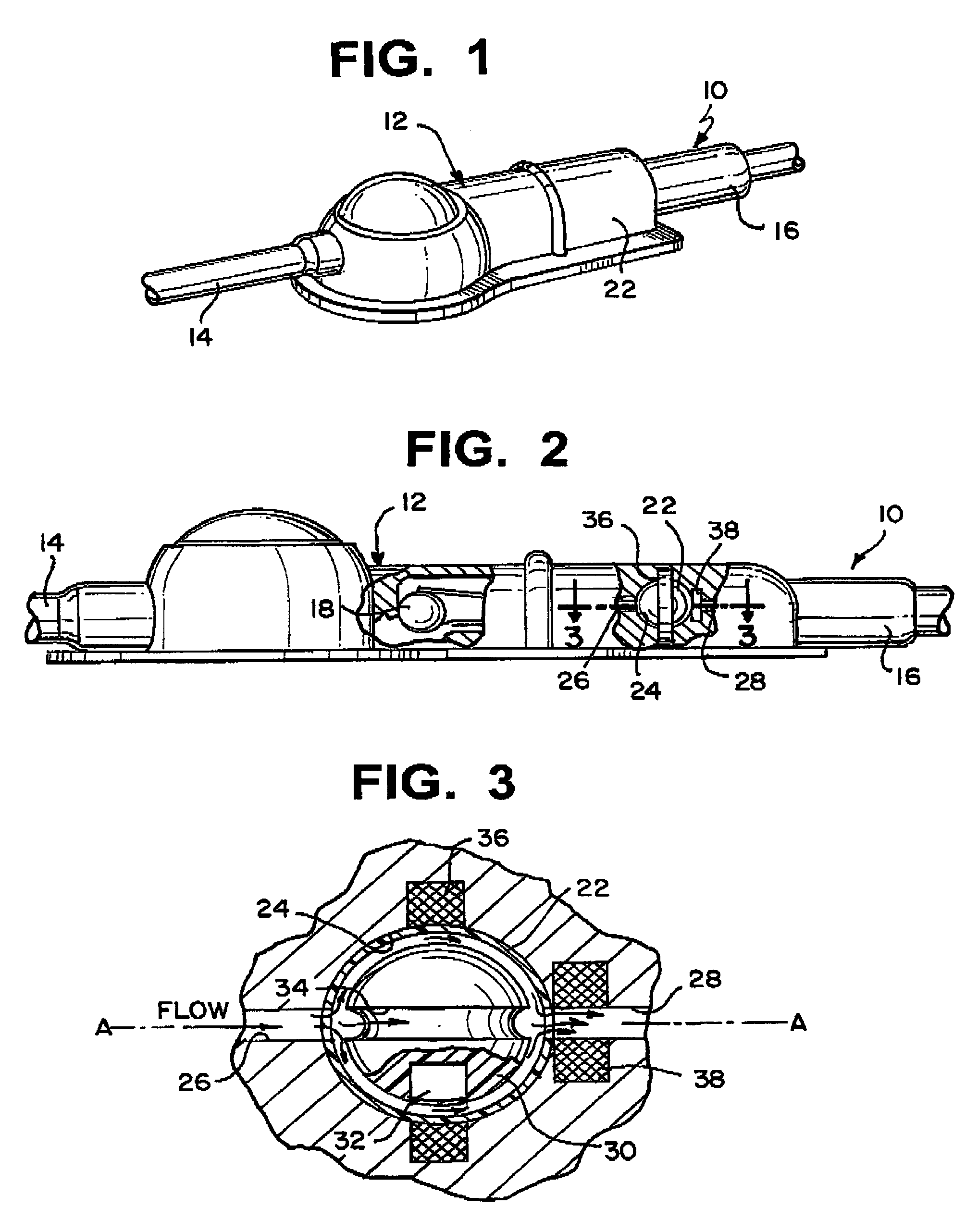
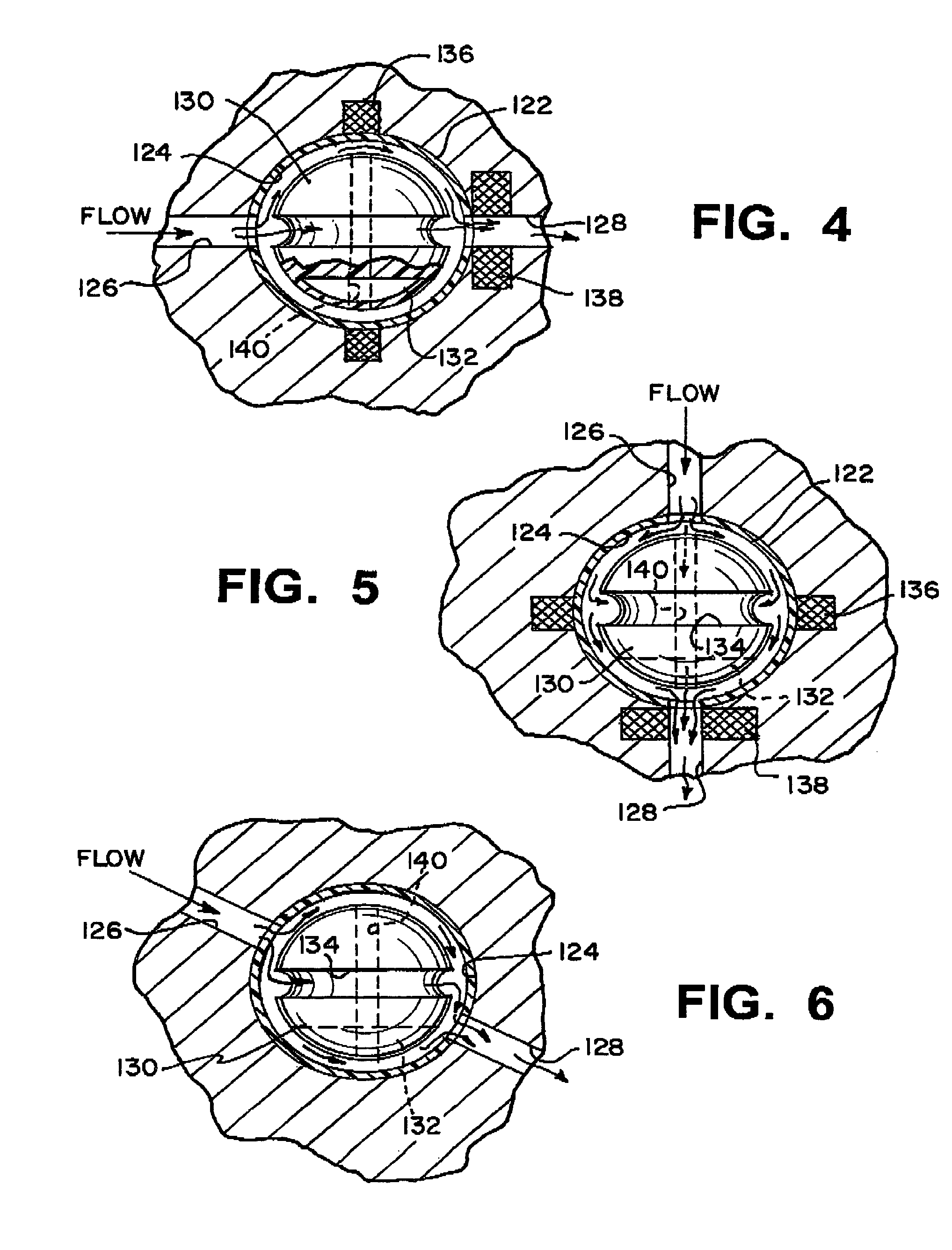
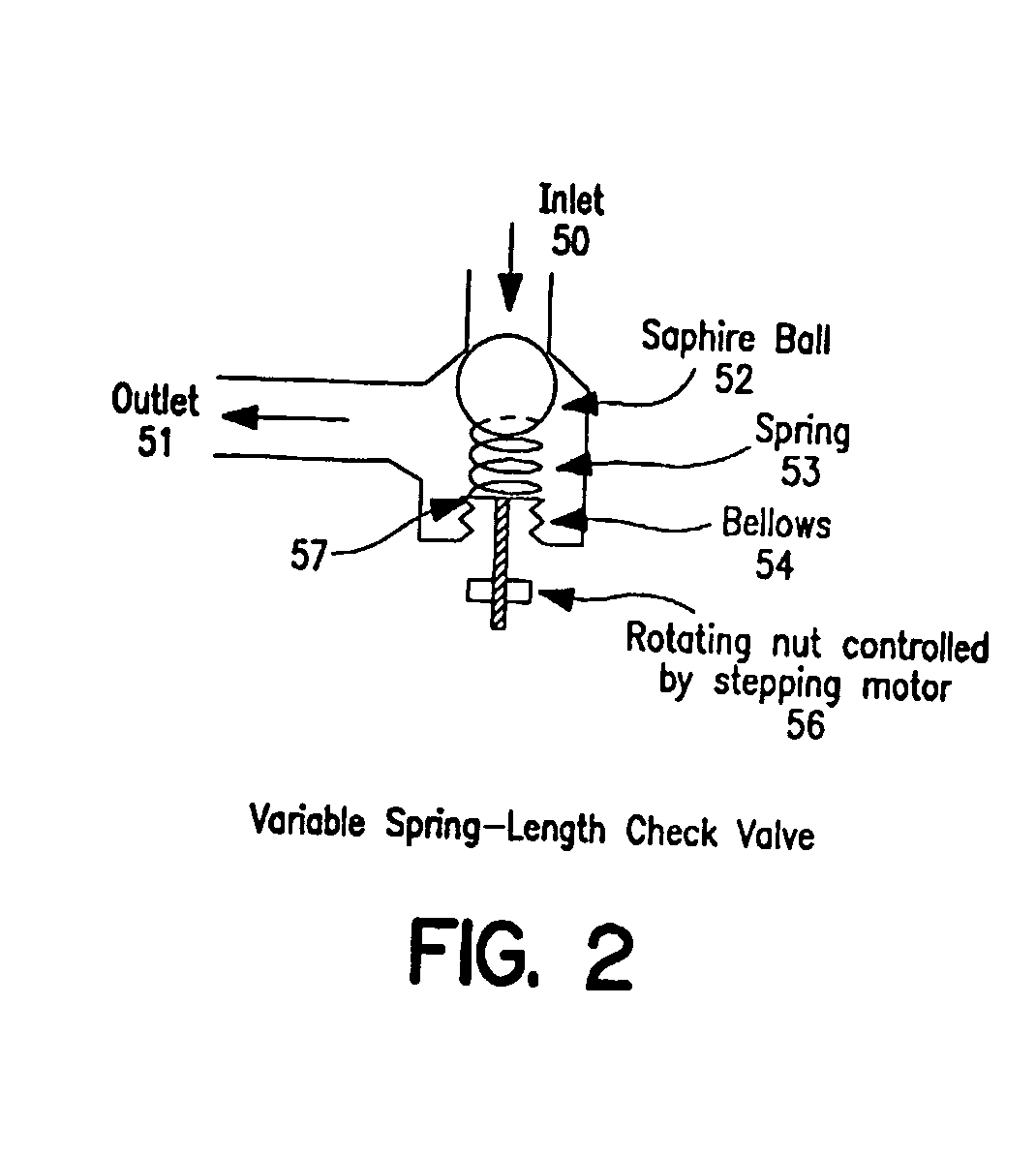
Shunt system including a flow control device for controlling the flow of cerebrospinal fluid out of a brain ventricle
ActiveUS7118549B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesWound drainsBrain VentricleBiomedical engineering
An anti-siphon device limits the flow of a fluid from a first region of a patient's body to a second region. The device includes a housing having a spherical inner surface with a predetermined inner diameter. The housing has an inlet port for receiving fluid from the first region and an outlet port for directing fluid to the second region. The inlet port and the outlet port are disposed approximately diametrically opposite from each other. A spherical ball is disposed within the housing. The spherical ball has a ferromagnetic weight disposed off center therein. The spherical ball has an outer diameter that is less than the inner diameter of the housing so that the spherical ball is free to rotate within the housing and the fluid is free to flow between the inner surface of the housing and an outer surface of said spherical ball. The spherical ball has a circumferential recess extending through its center.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Uniform selective cerebral hypothermia
InactiveUS20030130651A1Surgical instrument detailsIntravenous devicesCooling chamberTemperature difference
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for uniform selective cerebral hypothermia. The apparatus includes a brain-cooling probe, a head-cooling cap, a body-heating device and a control console. The brain-cooling probe cools the cerebrospinal fluid within one or more brain ventricles. The brain-cooling probe withdraws a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid from a ventricle into a cooling chamber located ex-vivo in close proximity to the head. After the cerebrospinal fluid is cooled it is then reintroduced back into the ventricle. This process is repeated in a cyclical or continuous manner. The head-cooling cap cools the cranium and therefore cools surface of the brain. The combination of ventricle cooling and cranium cooling provides for whole brain cooling while minimizing temperature gradients within the brain. The body-heating device replaces heat removed from the body by the brain-cooling probe and the head-cooling cap and provides for a temperature difference between the brain and the body where the brain is maintained a temperature lower than the temperature of the body.
Owner:MEDCOOL
Catheters incorporating valves and permeable membranes
ActiveUS20050137578A1Facilitate entryExtension of timeMulti-lumen catheterMedical devicesGuide tubeMembrane configuration
Devices, systems and methods for delivering one or more drugs to one or more internal body locations (such as the cerebrospinal fluid) are disclosed. In various aspects, the systems and methods may involve catheters having infusion sections with permeable membranes and one or more valves that control flow to the infusion sections.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device for the treatment of hydrocephalus
A cerebrospinal fluid shunt system comprises a brain ventricular catheter for insertion into the brain ventricle so as to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the brain ventricle. The system also comprises a sinus sagittalis catheter for insertion into the sinus sagittalis for feeding the cerebrospinal fluid into sinus sagittalis. A shunt main body is connected at one end thereof to the brain ventricle catheter and at another end thereof to the sinus sagittalis catheter. The shunt main body can provide fluidic communication between the brain ventricle catheter and the sinus sagittalis catheter. The system further comprises a tubular flow passage restricting member defined within the shunt main body. The tubular flow passage restricting member defines a resistance to flow of 8-12 mm Hg / ml / min.
Owner:SINU SHUNT
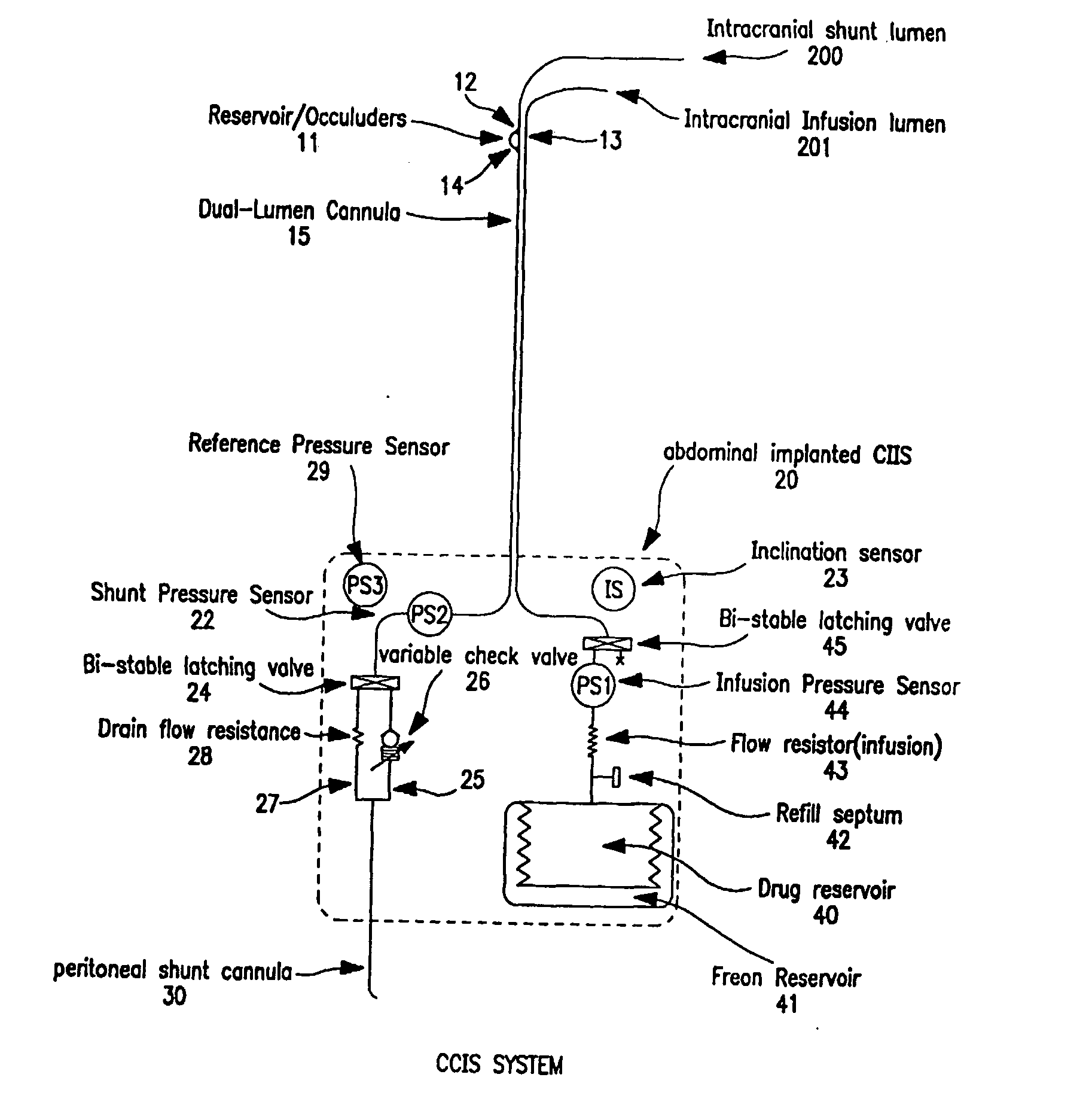
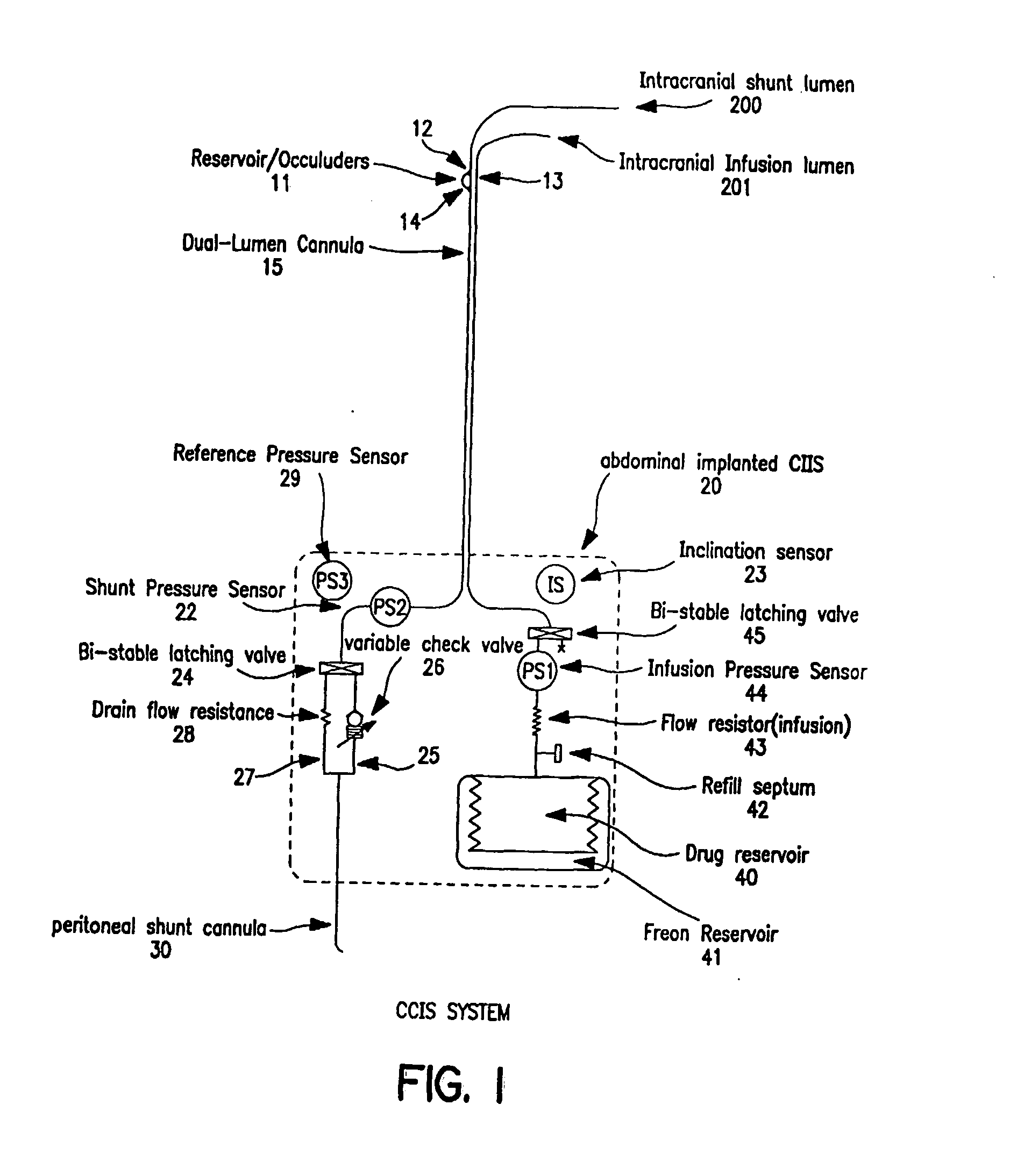
Controlled cerebrospinal infusion and shunt system
InactiveUS20050038371A1Enhance CSF turnover rateImprove turnover rateWound drainsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSupine positionCheck valve
An implantable, battery-operated controlled cerebral infusion and shunt (CCIS) system and method that is microprocessor controlled via algorithms stored in its memory. The system includes a programmable infusion system and a multi mode drainage system that contains at least two flow paths: a low resistance flow path for when the patient is in the supine or substantially supine position and a flow path containing a programmable variable check valve to prevent over-drainage when the patient is in the upright or substantially upright position. The combination of the above two functions allows modulation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) turnover rate.
Owner:KUCHTA JOHN
Method of inhibiting the formation of adhesions and scar tissue and reducing blood loss
InactiveUS20080069855A1Increased riskEasy to disassembleBiocideInternal osteosythesisWound siteBlood vessel
The present invention provides a method for inhibiting the formation of scar tissue and / or exogenous bone at a wound site in a body of a patient. The method includes administering an amount of a biologic agent to the wound site, wherein the biologic agent is synovial fluid or cerebrospinal fluid. A viscous substance applied to the wound site, advantageously incorporating the biologic agent, reduces the flow of blood from cut blood vessels, and contributes to a reduction in the formation of adhesions through action of the biologic agent, and through barrier properties introduced by the viscous substance.
Owner:P TECH
Drainage system for cerebrospinal fluid
ActiveUS20080033400A1The structure is easy to operateImprove accuracyFluid parameterWound drainsControl mannerEngineering
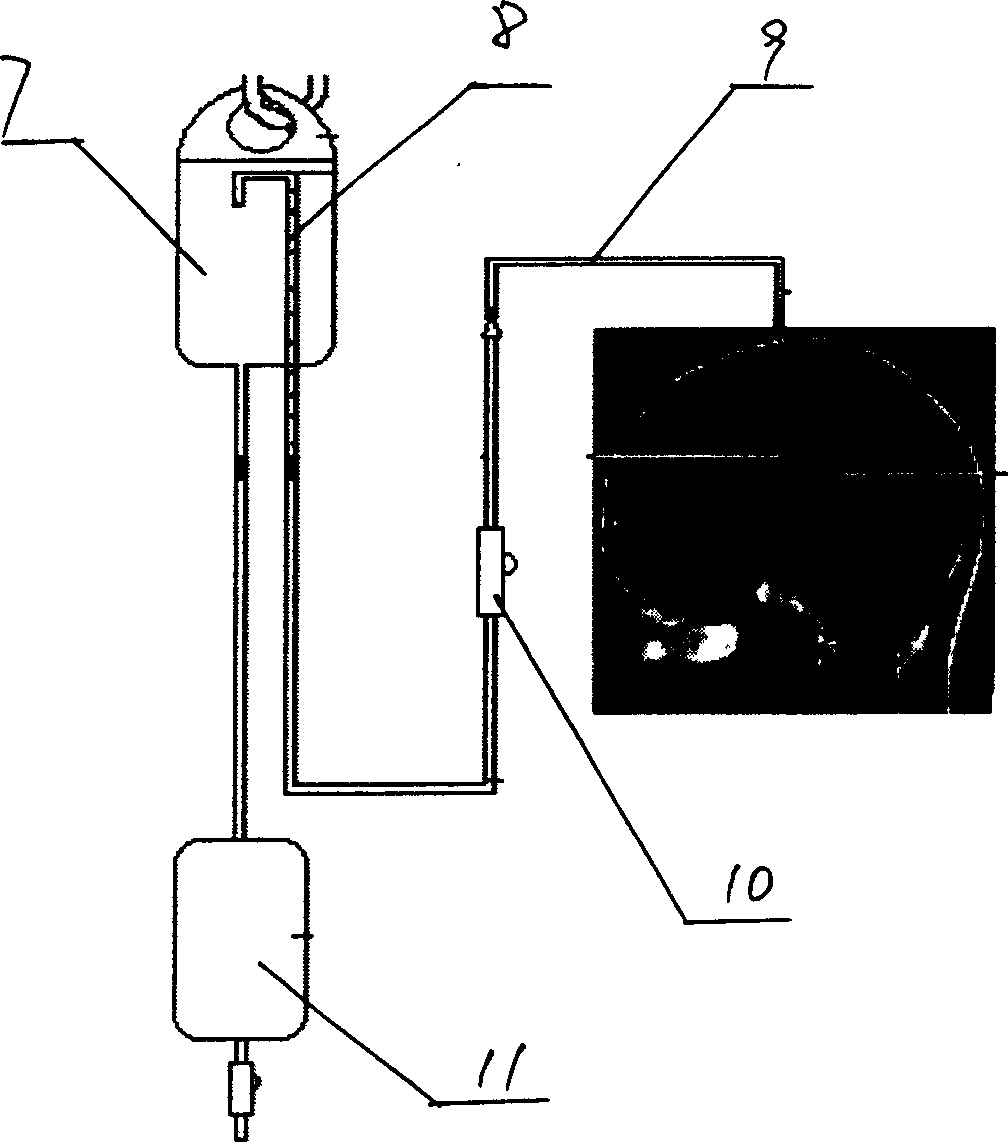
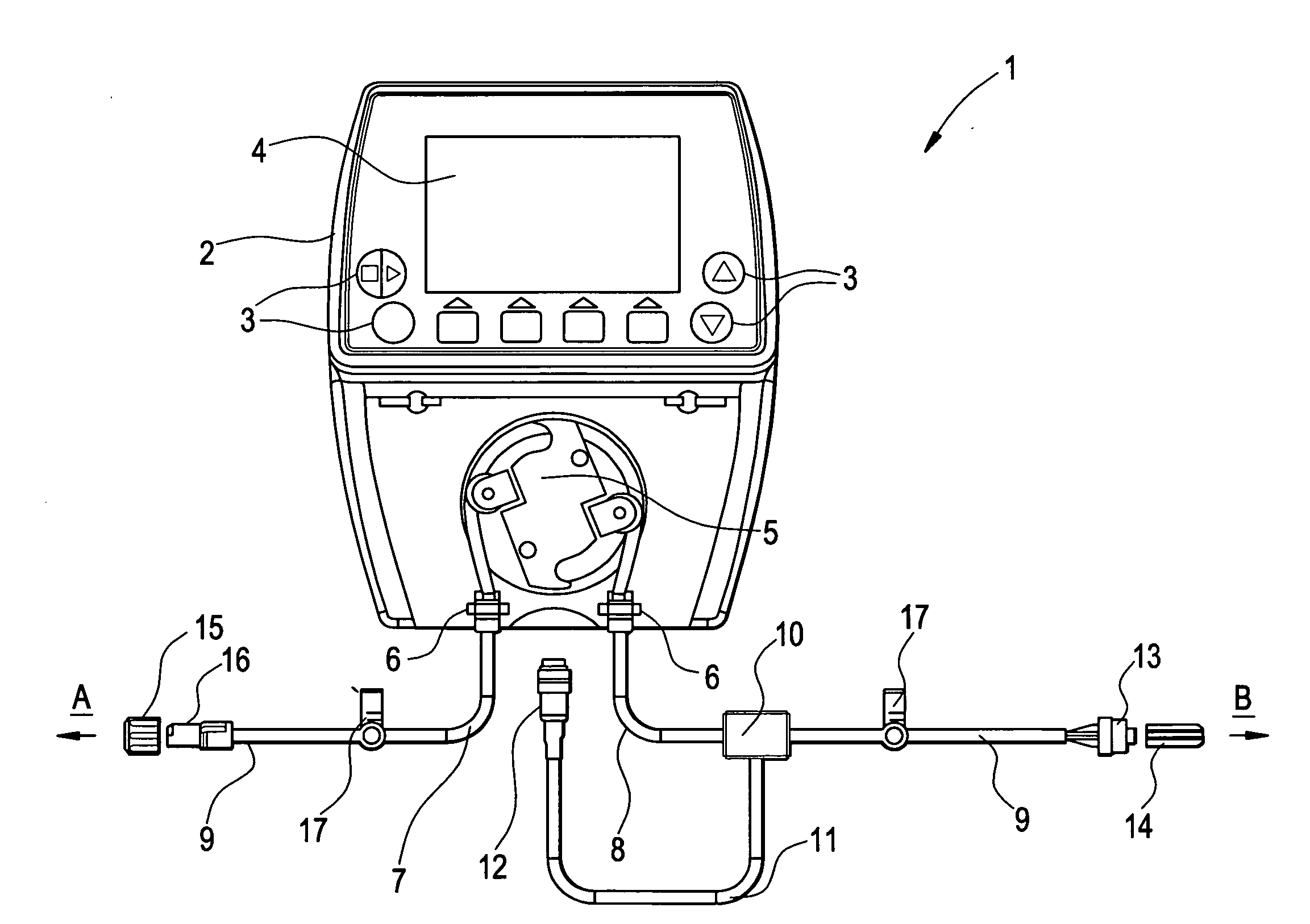
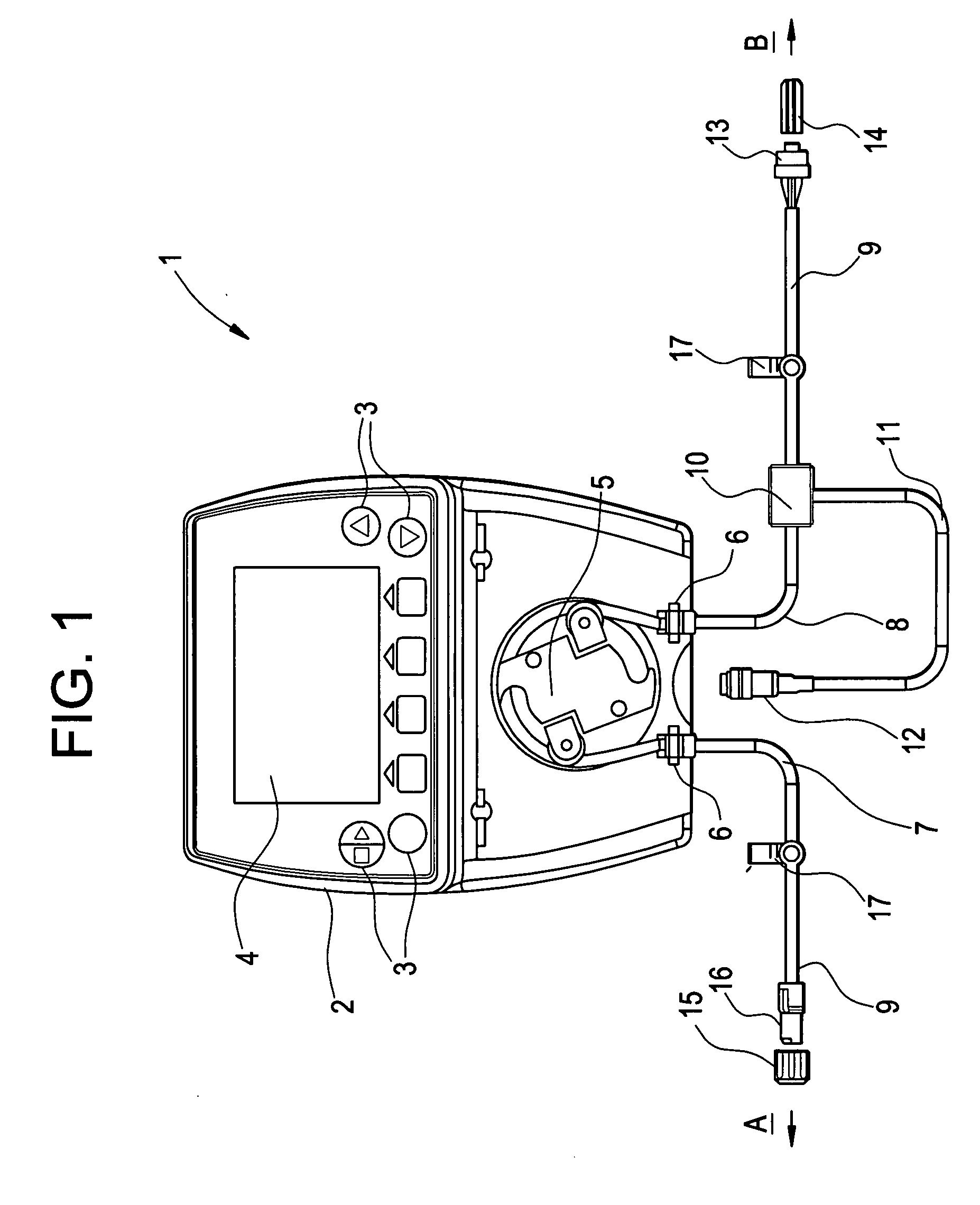
The object of providing a cerebrospinal fluid drainage system 1 which reacts precisely to changes in pressure in the cerebrospinal fluid, with ease of operation, is achieved by the present invention in that a pump 5 is used for draining the cerebrospinal fluid (liquor), wherein operating measured values supplied by sensors act as controlled variable for the operation of the pump. The pressure in the liquor line currently measured by a pressure sensor 10, the liquor pressure in the intracranial cavity being treated, measured intracorporeally by a pressure sensor, and / or the volume of liquor already pumped out, as operating measured value, can, for example, serve as the basis for operational control of the pump of the liquor drainage system. The liquor drainage system according to the invention has the advantage that the liquor is drained not only simply on the basis of the excess pressure in the intracranial cavity being treated, but is actively pumped out of the intracranial cavity in a controlled manner, in particular with constant measurement of the liquor pressure. In this way the pumping capacity can be regulated depending on requirement and the drainage pressure or the liquor pressure kept reliably within a specific pressure range.
Owner:MOLLER MEDICAL
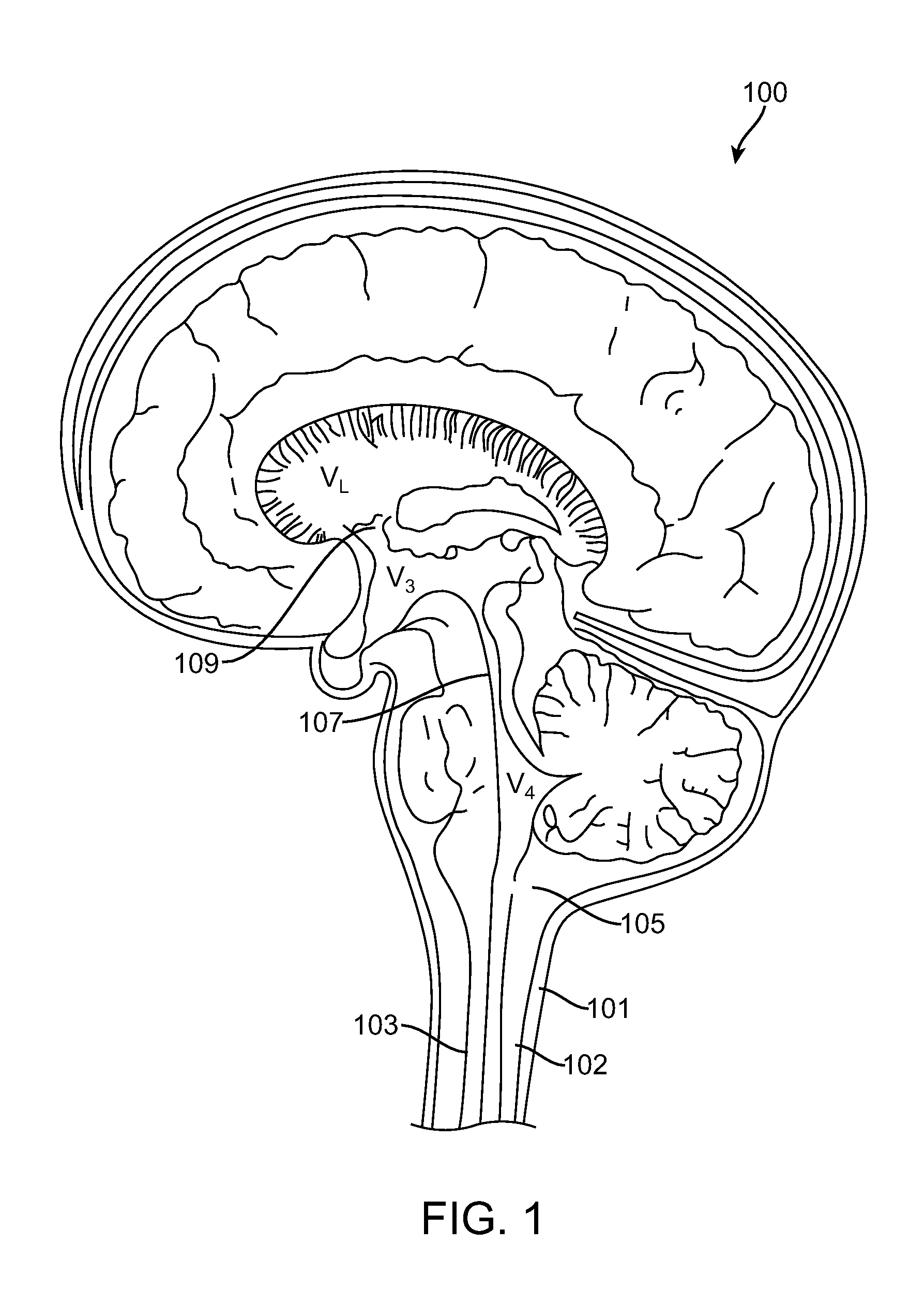
Cerebrospinal Fluid Purification System
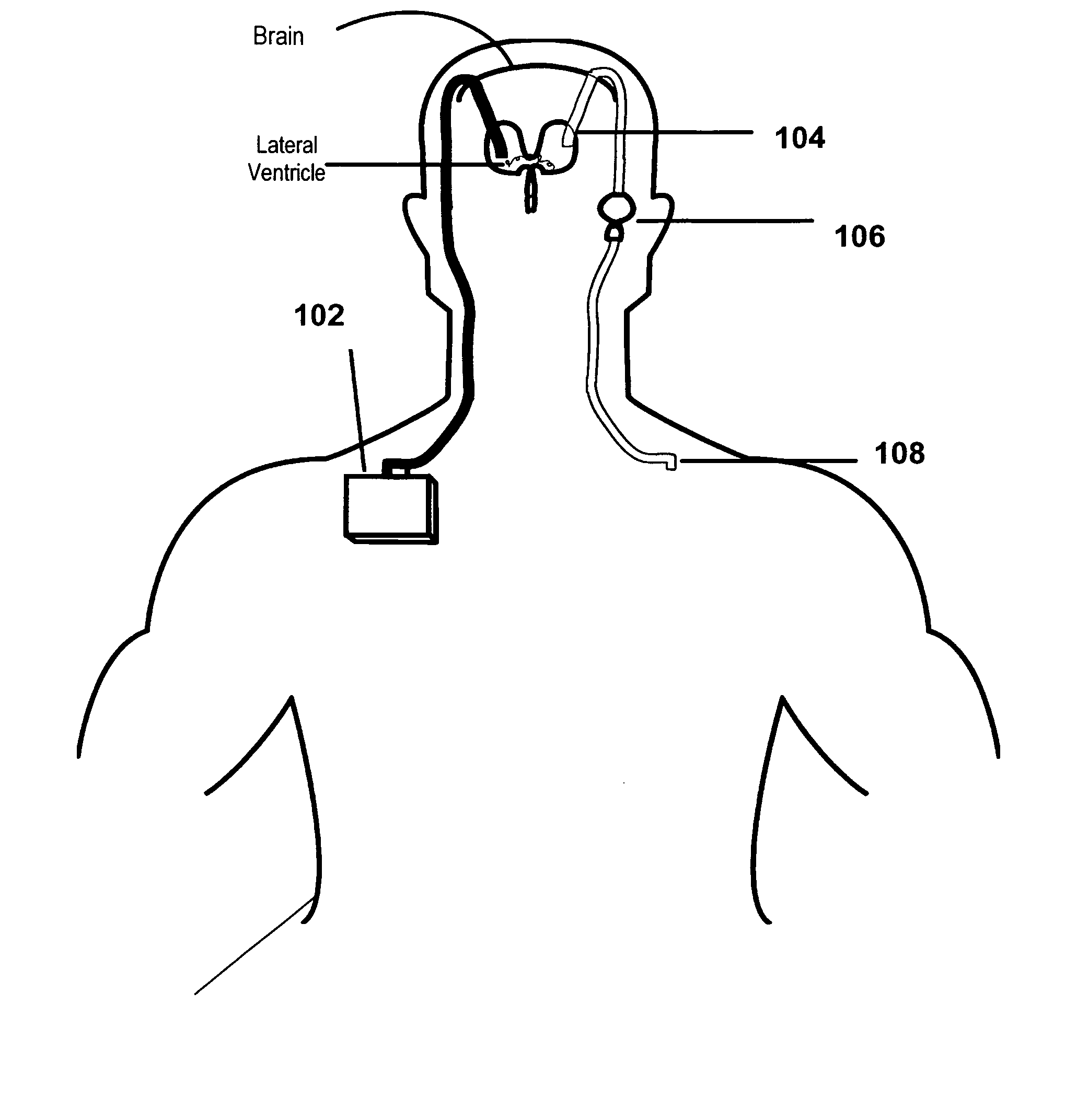
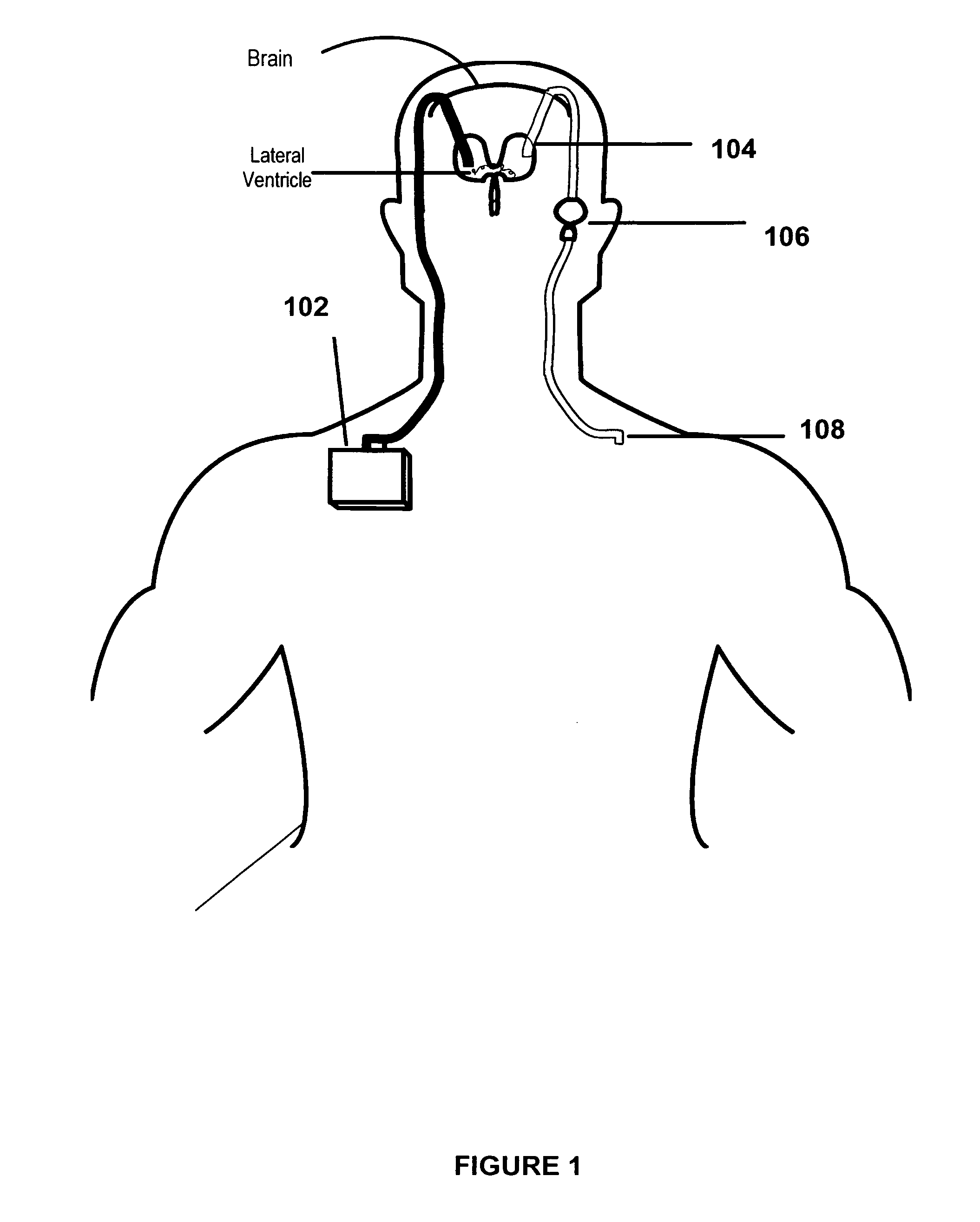
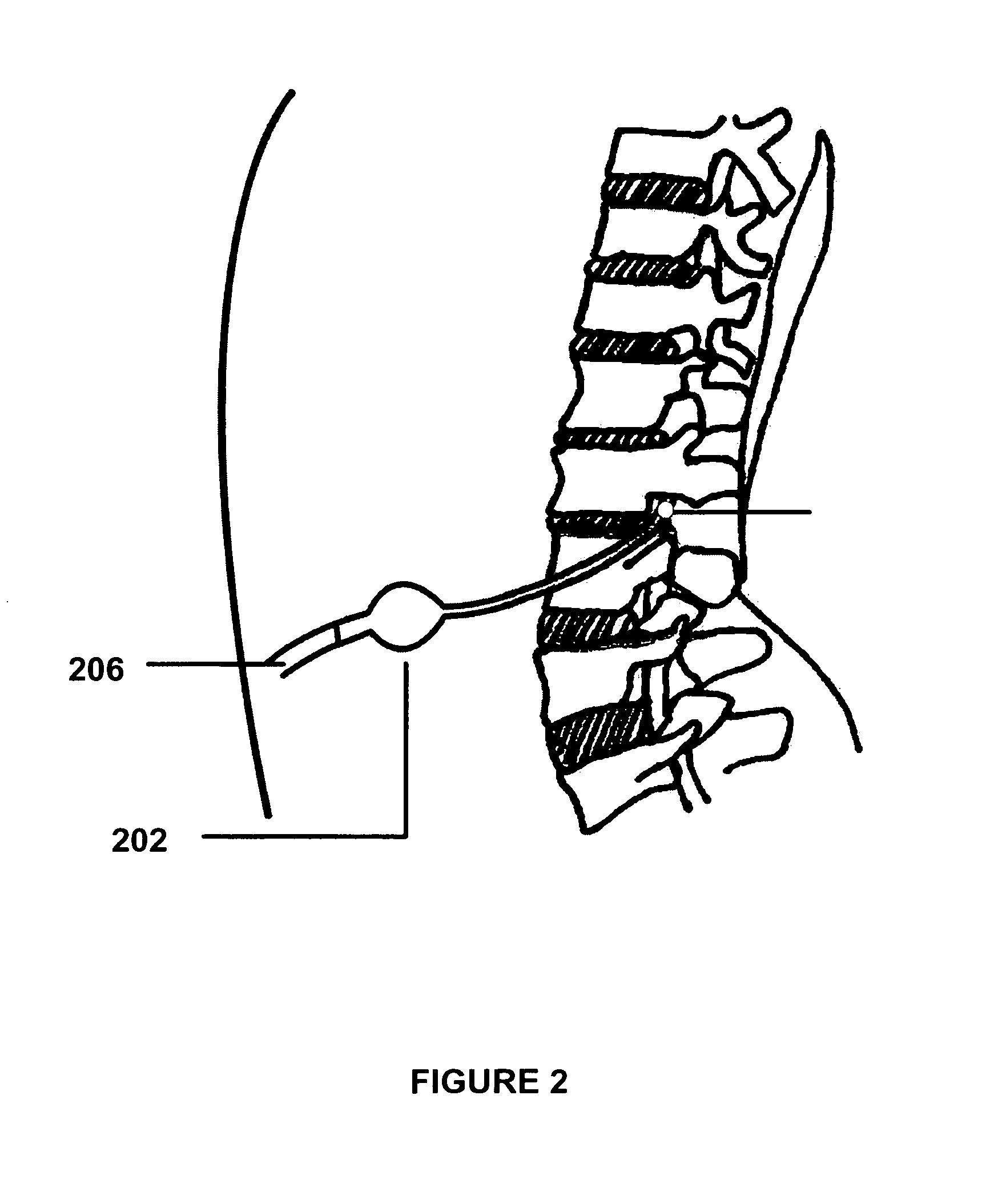
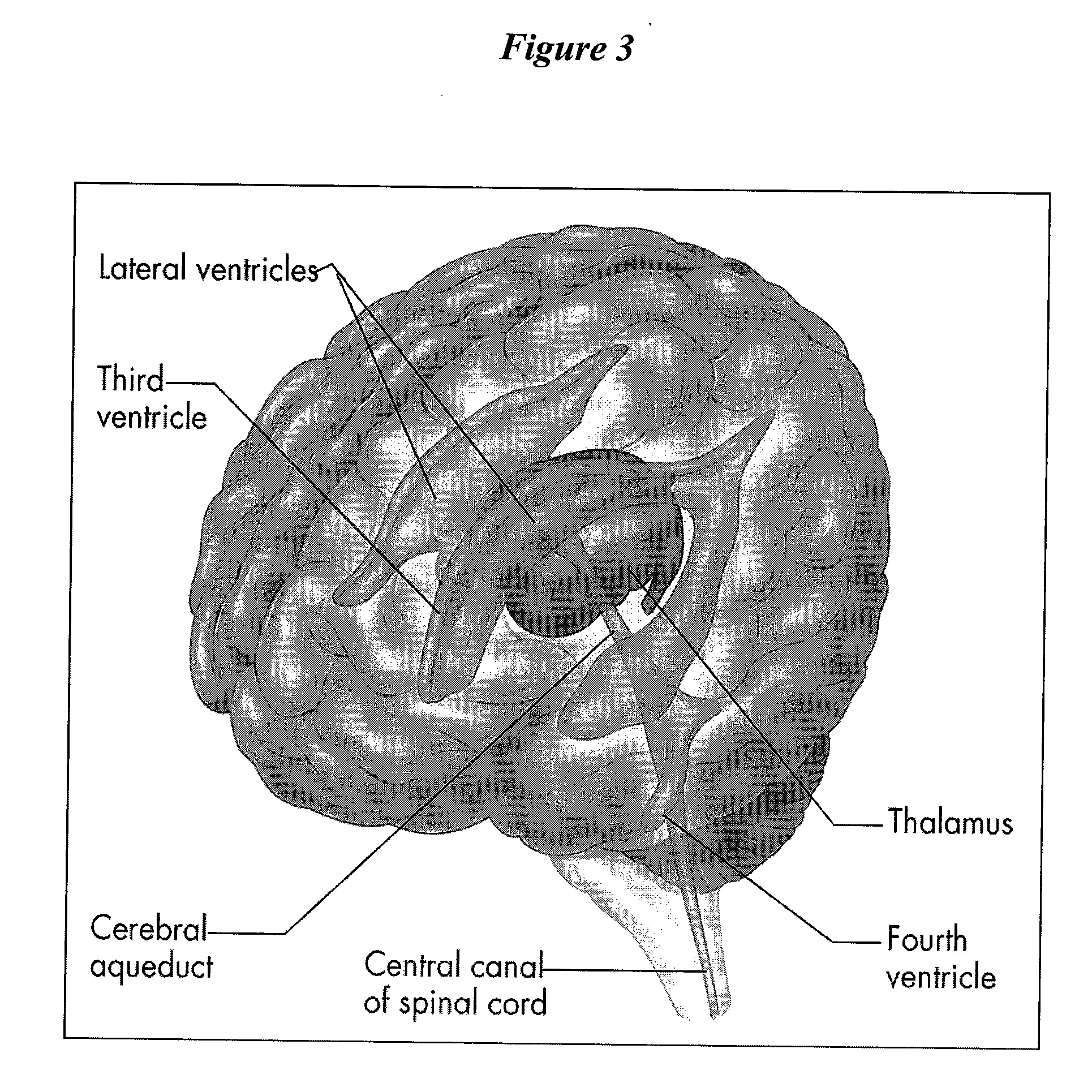
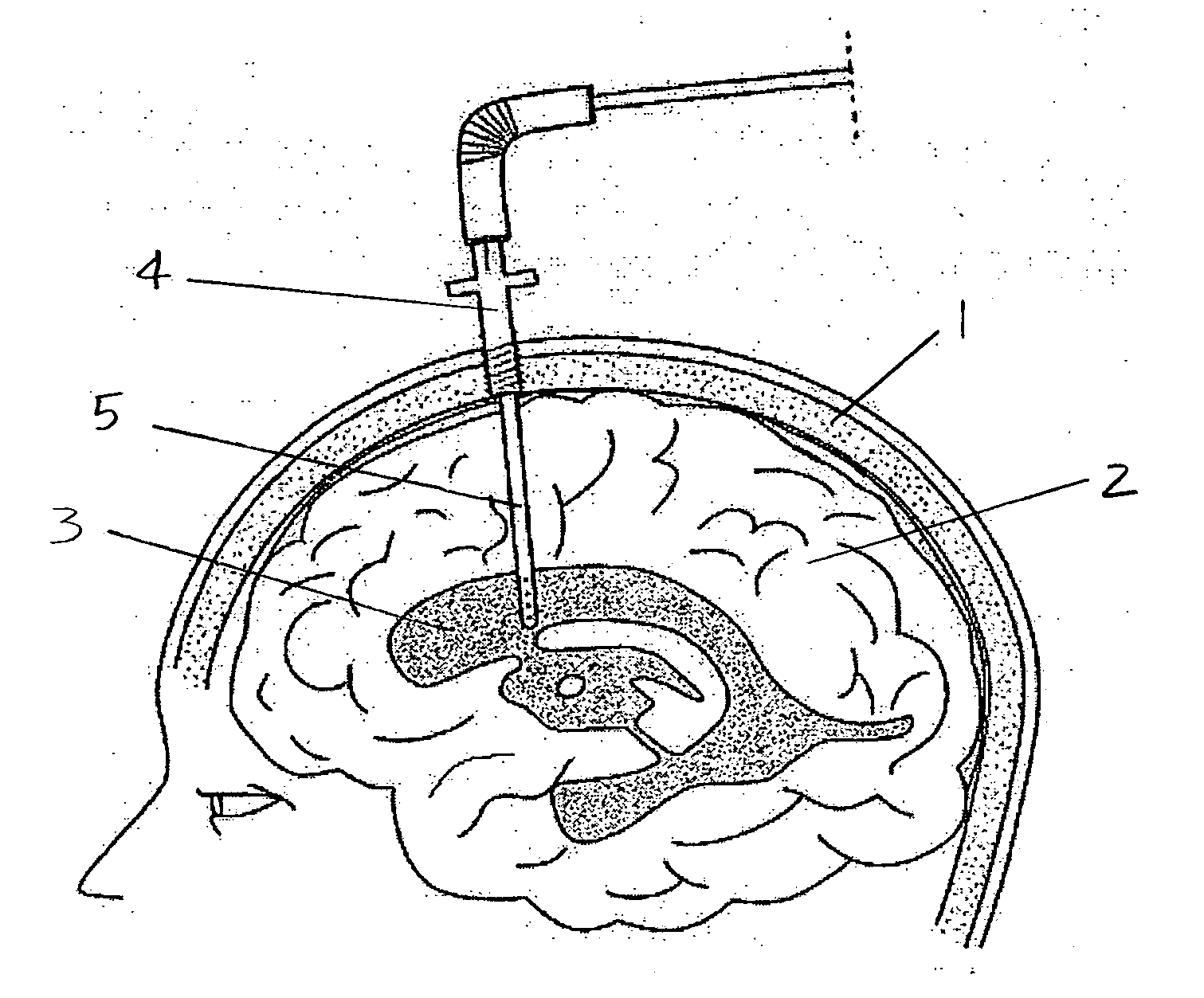
The present invention provides methods and systems for conditioning cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The methods provide for efficiently removing target compounds from CSF. The systems provide for a multilumen flow path and exchange of a majority volume portion of CSF in the CSF space. The removal and / or delivery of specific compounds can be tailored to the pathology of the specific disease. The removal is targeted and specific, for example, through the use of specific size-exclusion thresholds, antibodies against specific toxins, and other chromatographic techniques, as well as delivery and / or removal of targeted therapeutic agents. The invention finds use as a diagnostic, therapeutic and drug delivery platform for a variety of diseases affecting the CNS by accessing the CSF space. Exemplified disease conditions treatable by the present CSF processing systems and methods include, but are not limited to: Cerebral Vasospasm, Guillain Bane Syndrome, illustrating multi-lumen lumbar approach Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's, Multiple Sclerosis, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Traumatic Brain Injury, Stroke, Cancer affecting the brain or spinal cord, Prion disease, Encephalitis from various causes, Meningitis from various causes, diseases secondary to enzymatic or metabolic imbalances, Biological Warfare, etc. For the first time, the present invention offers patients a disease-modifying, disruptive technology treatment platform that addresses the known disease pathogenesis of a number of neurologic conditions to which there are presently limited and ineffective treatment options.
Owner:NEUROFLUIDICS
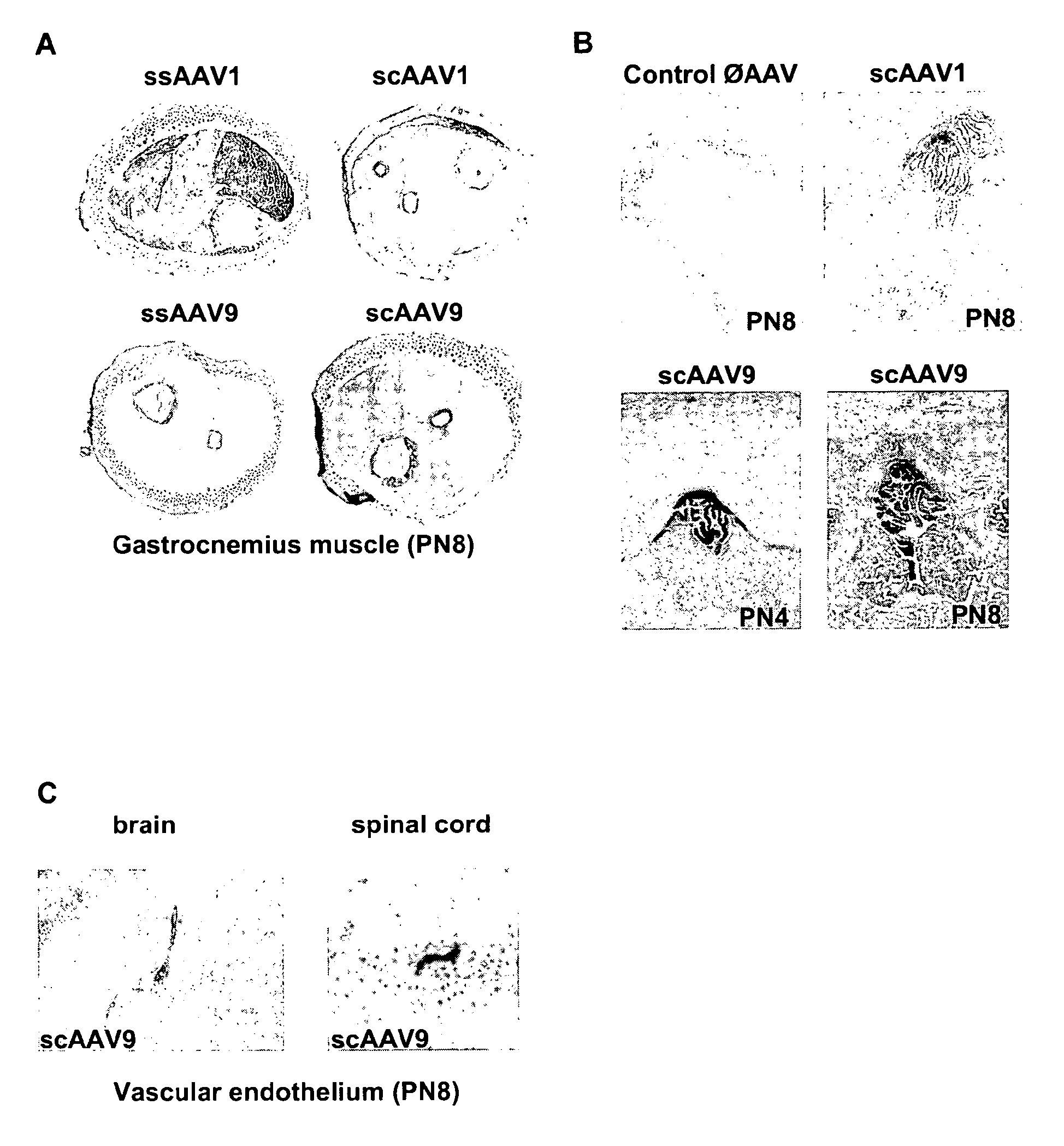
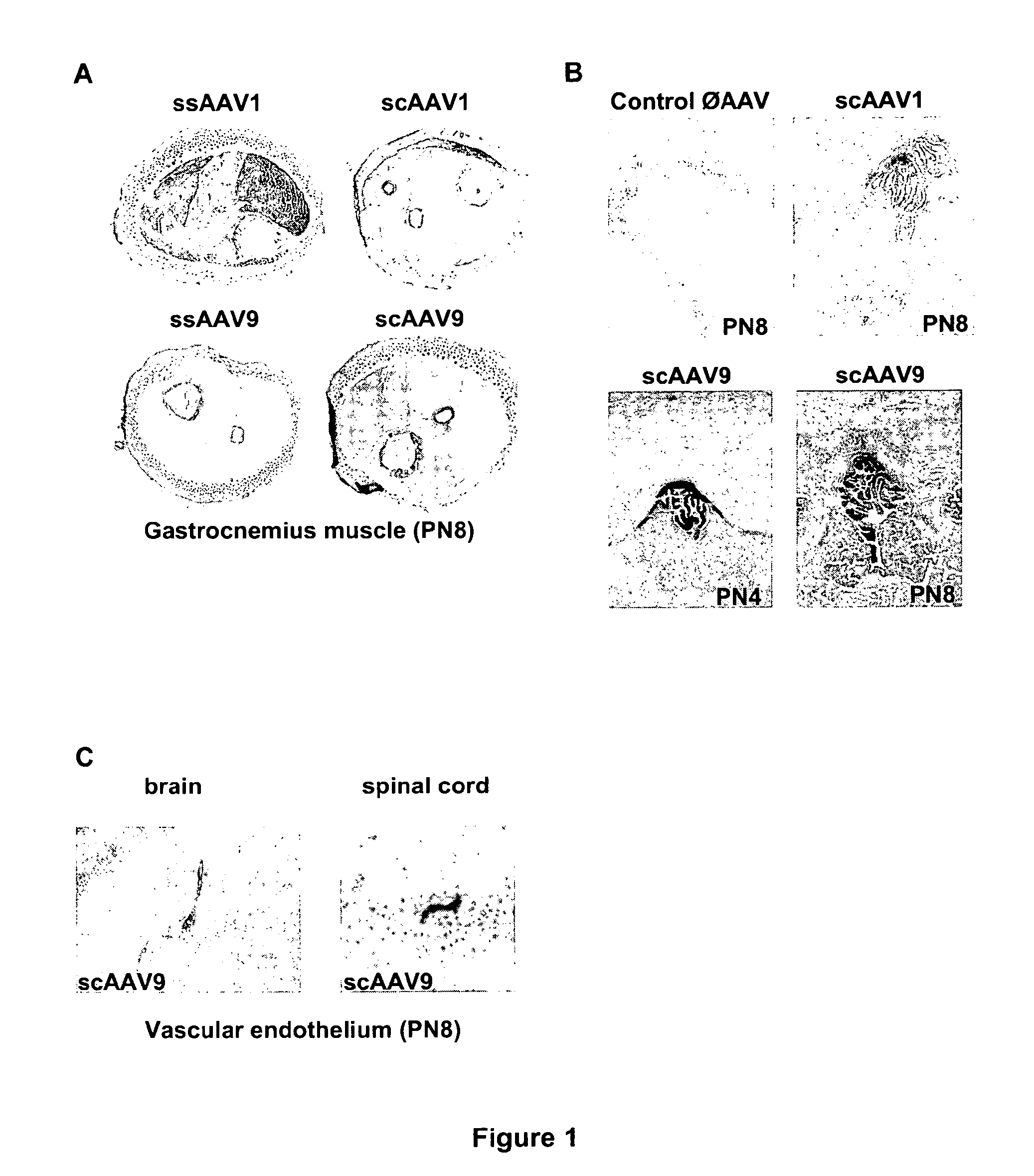
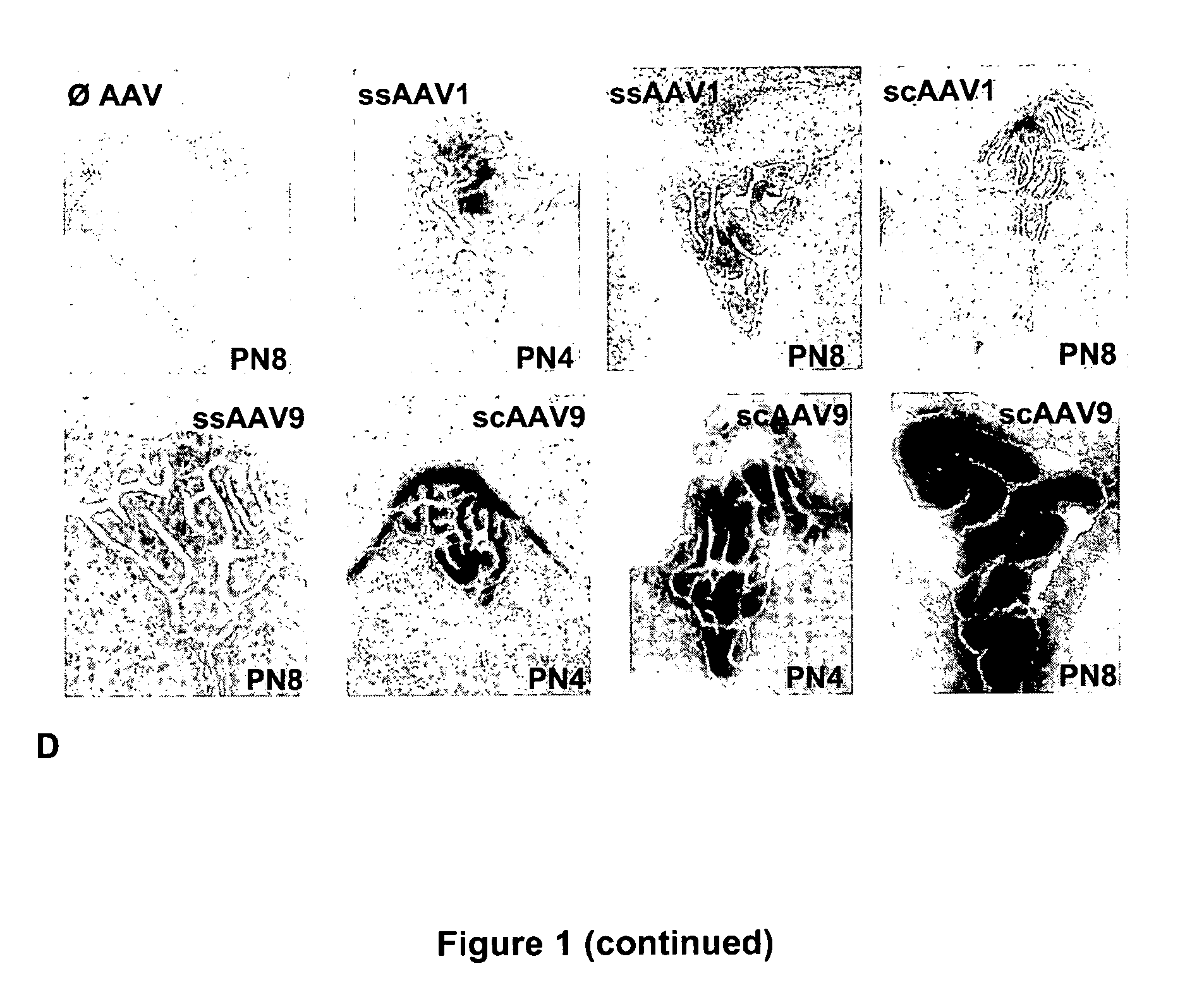
CNS gene delivery using peripheral administration of aav vectors
ActiveUS20100130594A1Safe and convenientSuitable as therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGene deliveryTherapeutic protein
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the delivery of therapeutic proteins to the CNS using recombinant AAV vectors. More specifically, the invention relates to compositions and methods for delivering proteins into the cerebrospinal fluid of mammalian subjects through peripheral administration of AAV vectors. The invention may be used to treat various disorders of the central nervous system, including degenerative diseases and motor neuron diseases.
Owner:GENETHON +1
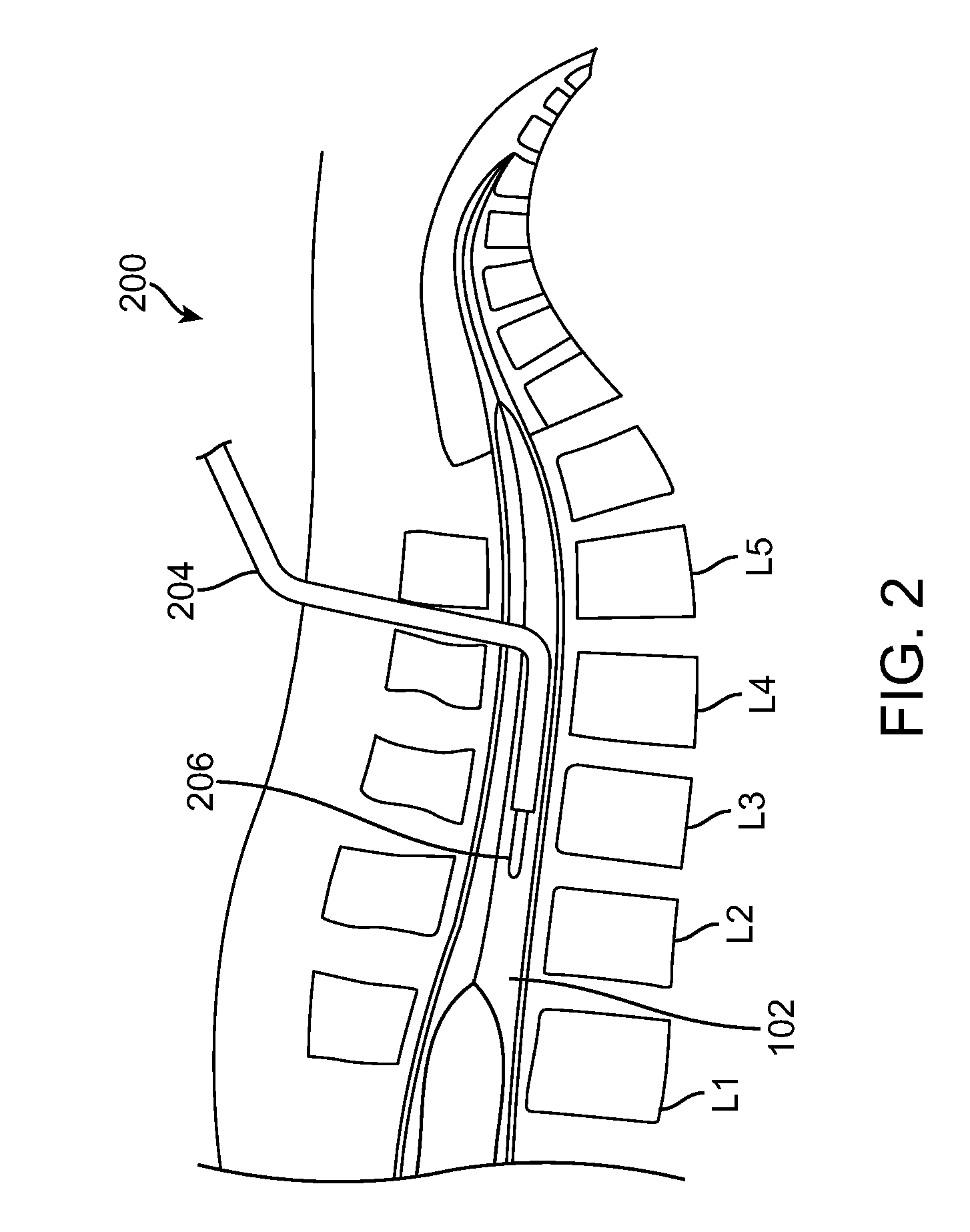
Methods and devices for draining fluids and lowering intraocular pressure
ActiveUS7354416B2Prevent and deter cloggingPrevent unwanted backflow of fluidEye implantsEye surgerySubarachnoid spaceOptic nerve
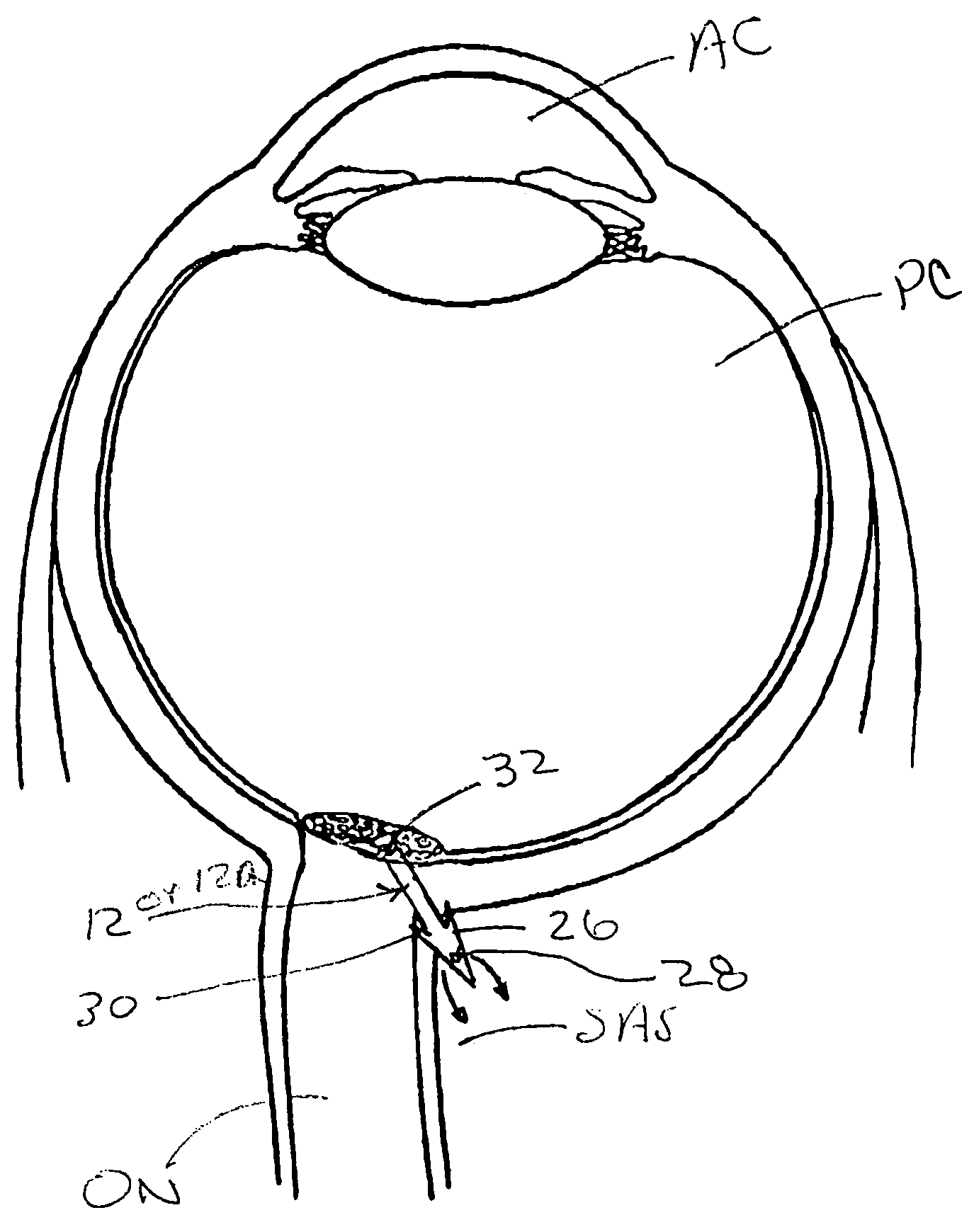
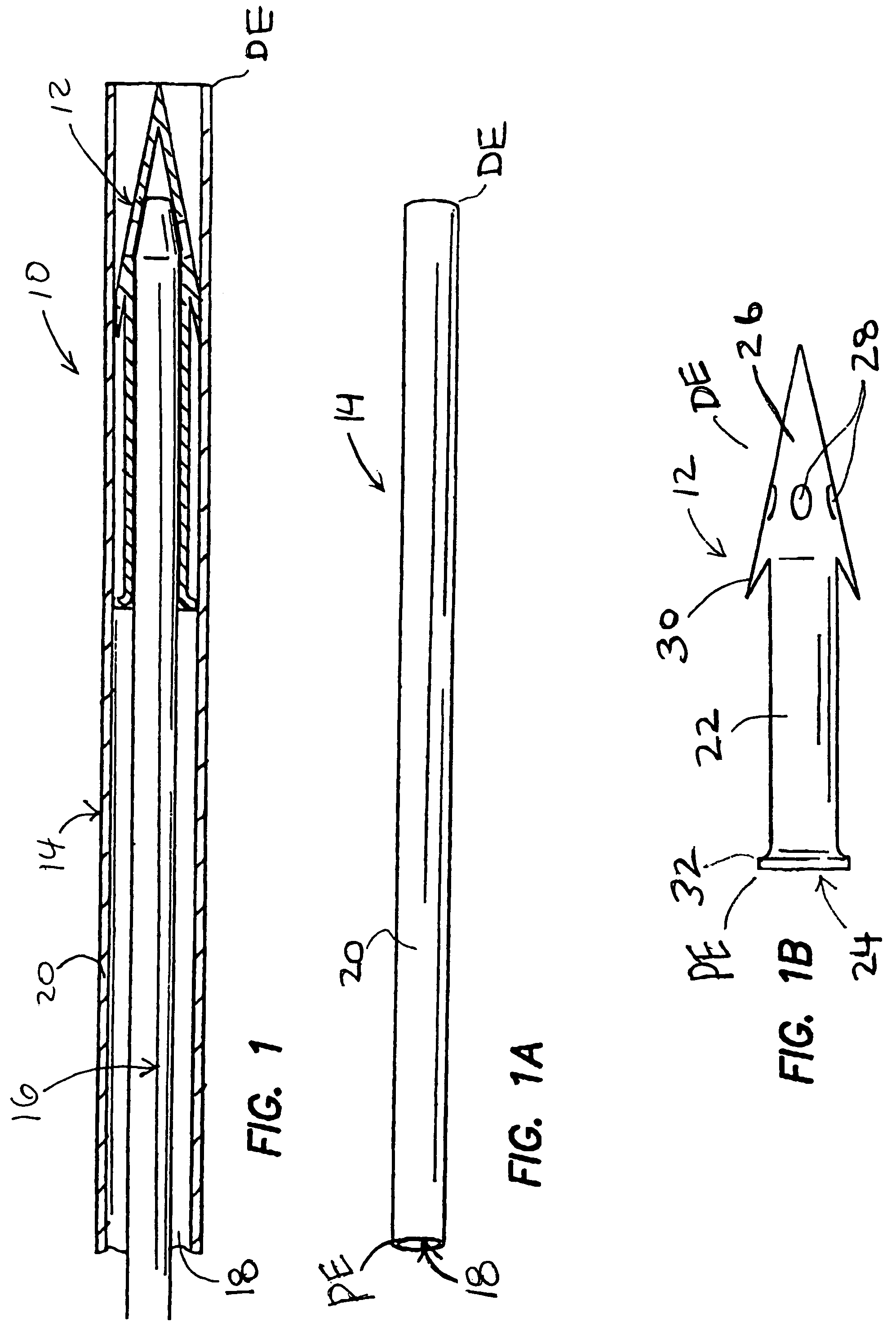
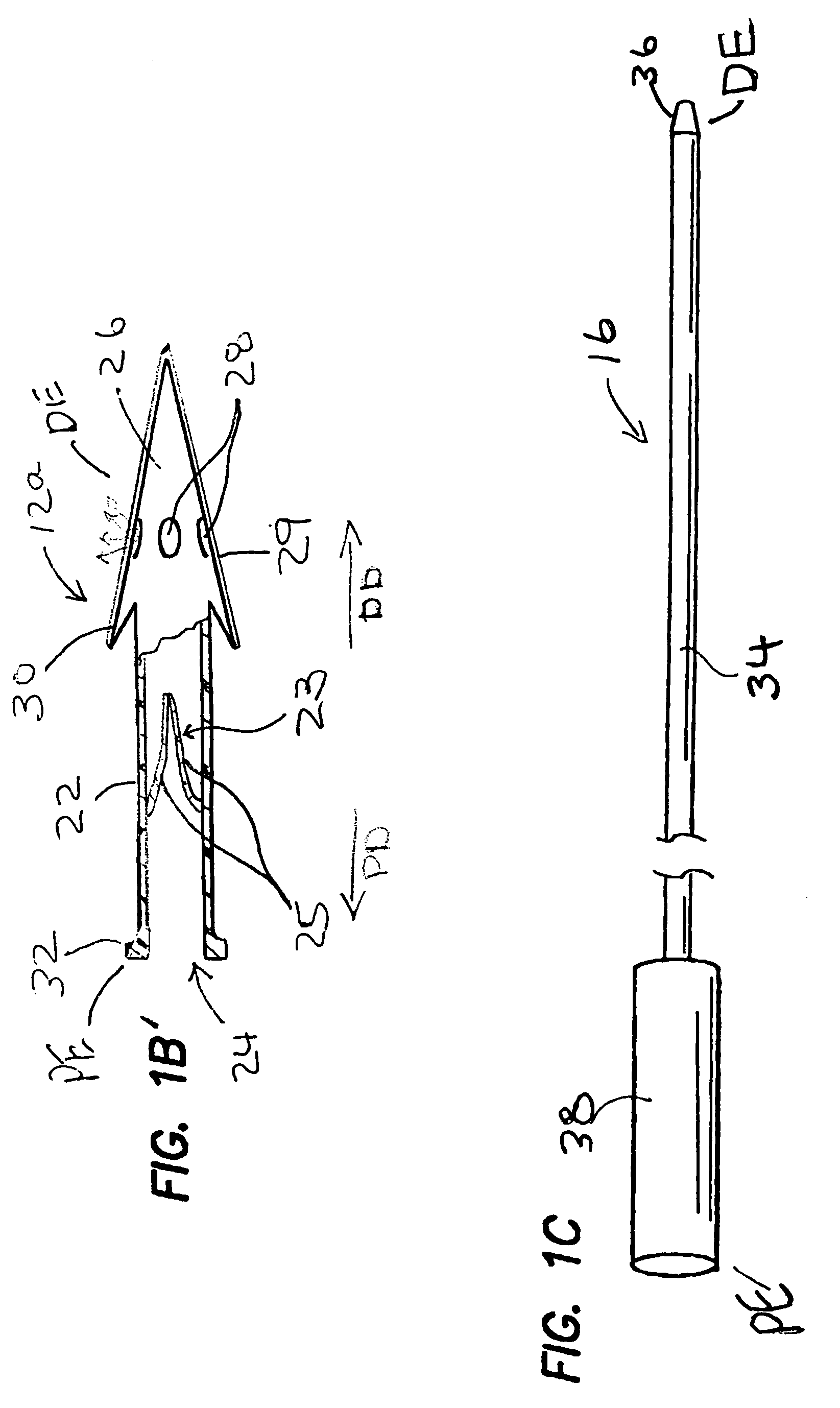
Methods, devices and systems for draining fluid from the eye and / or for reducing intraocular pressure. A passageway (e.g., an opening, puncture or incision) is formed in the lamina cribosa or elsewhere to facilitate flow of fluid from the posterior chamber of the eye to either a) a subdural location within the optic nerve or b) a location within the subarachnoid space adjacent to the optic nerve. Fluid from the posterior chamber then drains into the optic nerve or directly into the subarachnoid space, where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid. In some cases, a tubular member (e.g., a shunt or stent) may be implanted in the passageway. A particular shunt device and shunt-introducer system is provided for such purpose. A vitrectomy or vitreous liquefaction procedure may be performed to remove some or all of the vitreous body, thereby facilitating creation of the passageway and / or placement of the tubular member as well as establishing a route for subsequent drainage of aqueous humor from the anterior chamber, though the posterior chamber and outwardly though the passageway where it becomes mixed with cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:QUIROZ MERCADO HUGO +1
Central nervous system cooling catheter
ActiveUS20070005121A1Reduce riskHigh riskSurgical instrument detailsTherapeutic coolingHemolysisWhole body
The invention provides a method and apparatus for performing selective hypothermia to the brain and spinal cord for injury protection without the need for systemic cooling. A flexible catheter is inserted into the cerebral lateral ventricle or spinal subdural space. The catheter has lumens with a heat transfer element. The lumens of the catheter circulate a coolant and communicate at the distal heat transfer element for transfer of heat from the cerebrospinal fluid. Furthermore a method of maintaining catheter patency and providing blood clot hemolysis and drainage is also provided through the use of ultrasonic and / or laser energy delivered through the catheter.
Owner:KHANNA ROHIT
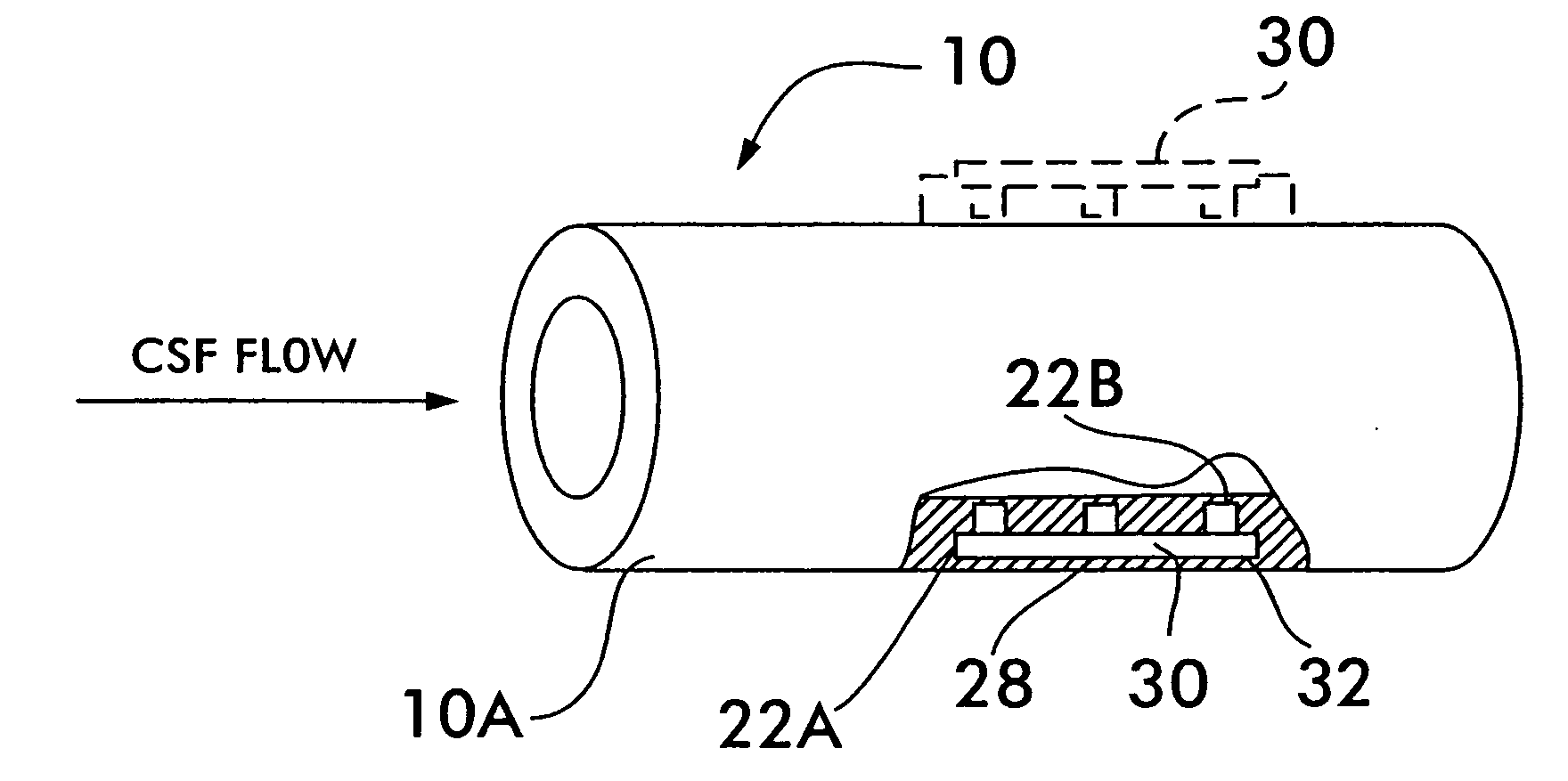
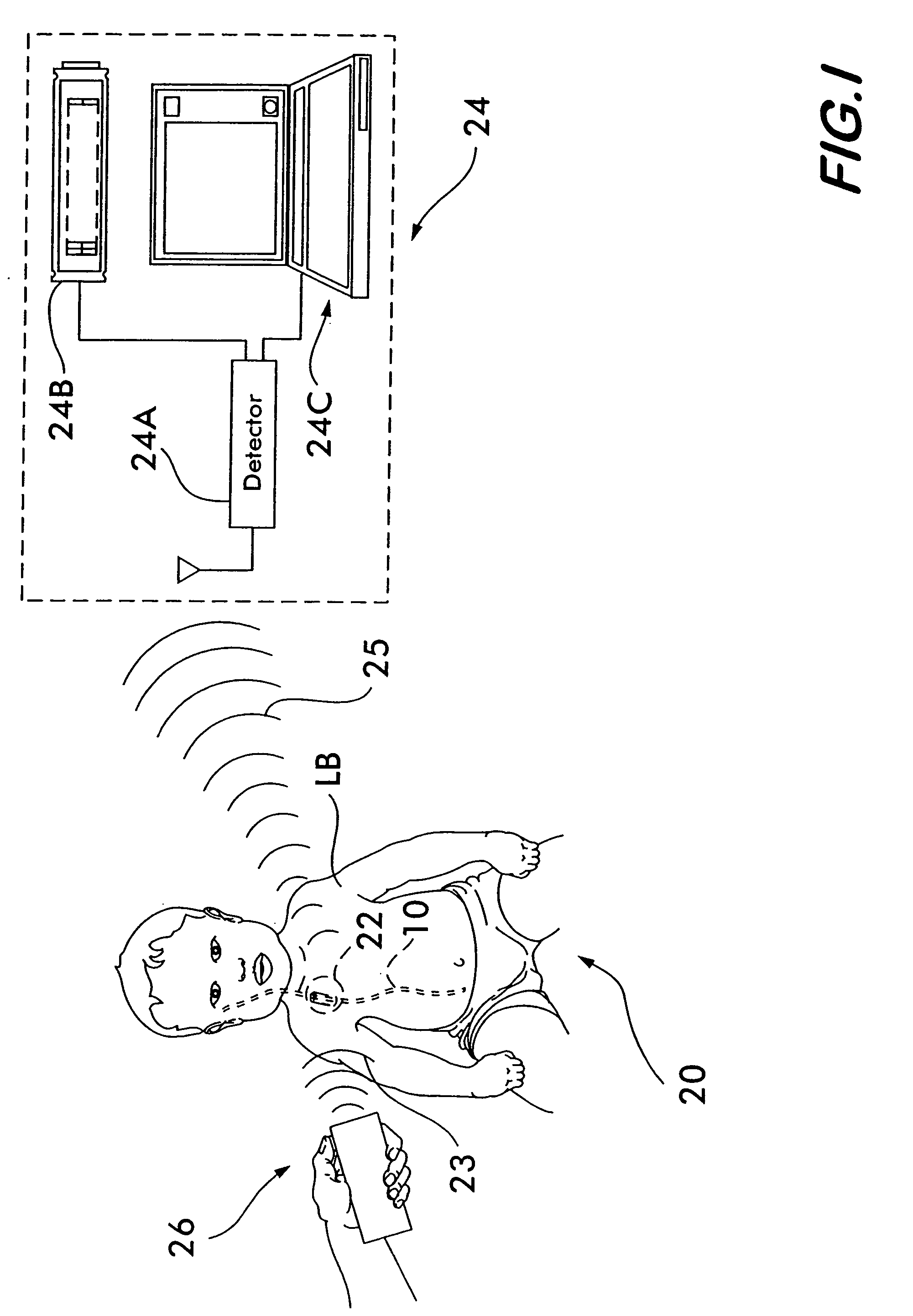
System and method for measuring flow in implanted cerebrospinal fluid shunts
InactiveUS20050204811A1Volume/mass flow by thermal effectsWound drainsFlow diverterCerebrospinal fluid shunt
A system and method for a thermal convection flow detection in a cerebrospinal fluid shunt that uses very little power for extended operation and for providing flow data to a remotely-located device.
Owner:NEFF INDIVIDUAL JANINE +1
Method for treating severe tinnitus
A method for treating severe tinnitus is disclosed. The method of the present invention comprises implanting a catheter into a patient and administering a drug formulation or fluid comprising a therapeutic agent intrathecally into the patient's cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for Measuring the Pressure of a Fluid System Within a Patient
A pressure sensing apparatus has a pressure sensor component that includes a pressure sensing port, a pressure sensor for sensing a pressure of a fluid in the pressure sensing port, and a digital processor communicating with the pressure sensor for performing calculations involving fluid pressures sensed. The pressure sensing apparatus further includes a first chamber in fluid contact with the pressure sensing port, a second chamber fluidically connectable with a patient's cerebrospinal fluid system, and a membrane located between the first and second chambers so as to transmit fluid pressure from the second chamber to the first chamber.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Compositions and methods for affecting movement of contaminants, bodily fluids or other entities, and/or affecting other physiological conditions
Compositions which self-assemble under physiological conditions are formulated for application to wounds. The formulations include a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or are provided as part of a medical device or coating. The formulations may also include other therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic agents. The formulation can be administered as appropriate for treatment of one or more disorders or conditions. For example, the formulation may be applied to repair an injury or during surgery of the lung, eye or dura, or following an epidural or spinal tap, to stop leakage of blood, interstitial fluid, or cerebrospinal fluid. The formulation may be administered to a burn or ulcer. The formulation may be dispersed in a suture or adhesive for administration at the time of or as released following suturing or gluing of a wound, thereby limiting bleeding, loss of tissue fluids, or other fluids such as those produced by parenchymal tissues such as the liver, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract. The formulation may be applied to any site of bleeding, in a bandage, gauze, sponge, or other material, for immediate control of bleeding, or released later to control bleeding if the initial treatment such as suturing or pressure is insufficient. In one embodiment, the formulation is provided as a dry or lyophilized powder. In another embodiment, the material is provided in water. In another embodiment, the material is provided in combination with an oil and forms a laminate. In another embodiment, the formulation is provided as a coating on a device, for example a stent or a catheter. The material is also useful to isolate tissue, for preservation of tissue for subsequent transplantation or reattachment, and as a bulking, stabilizing or hydrating agent.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com