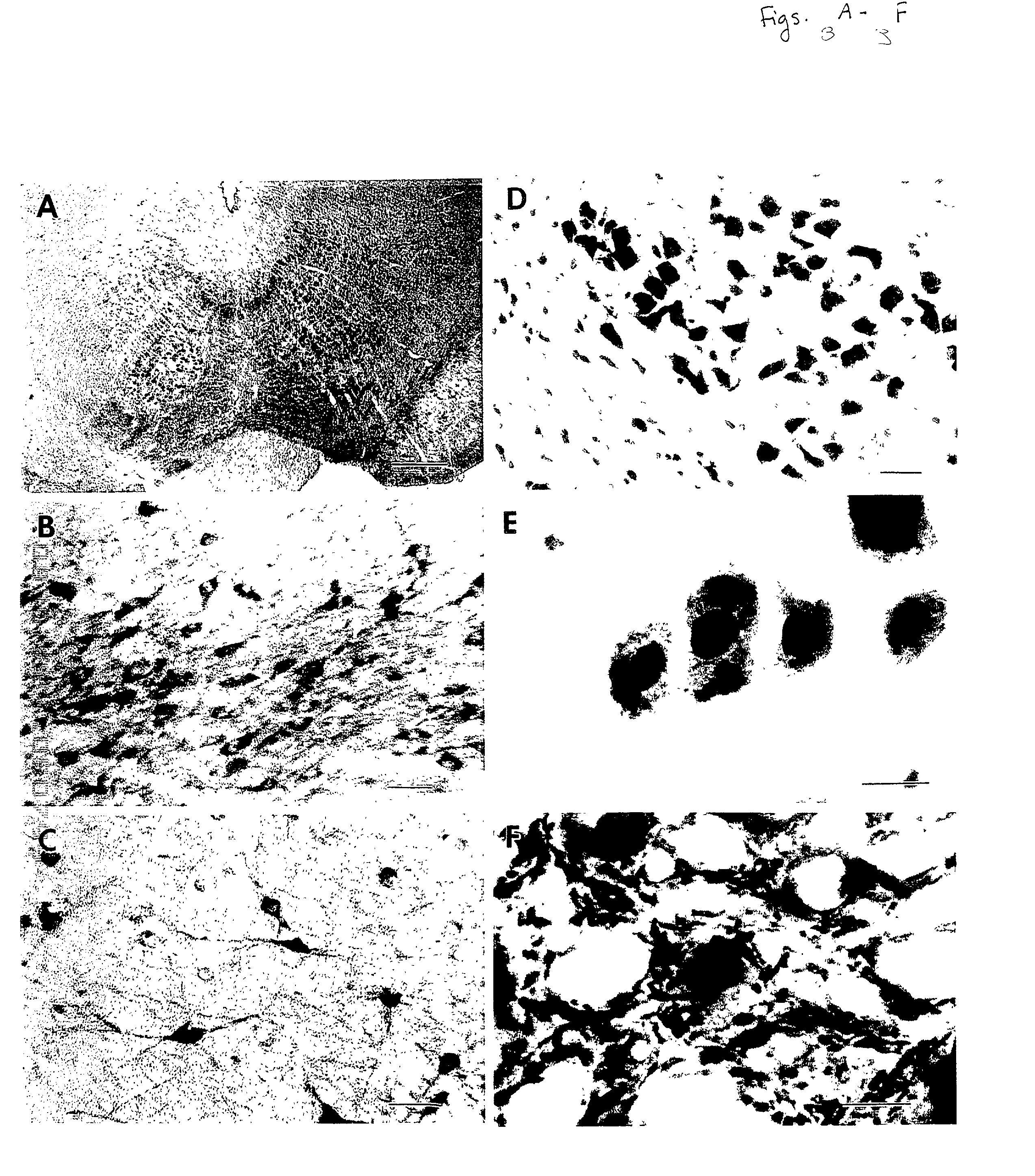
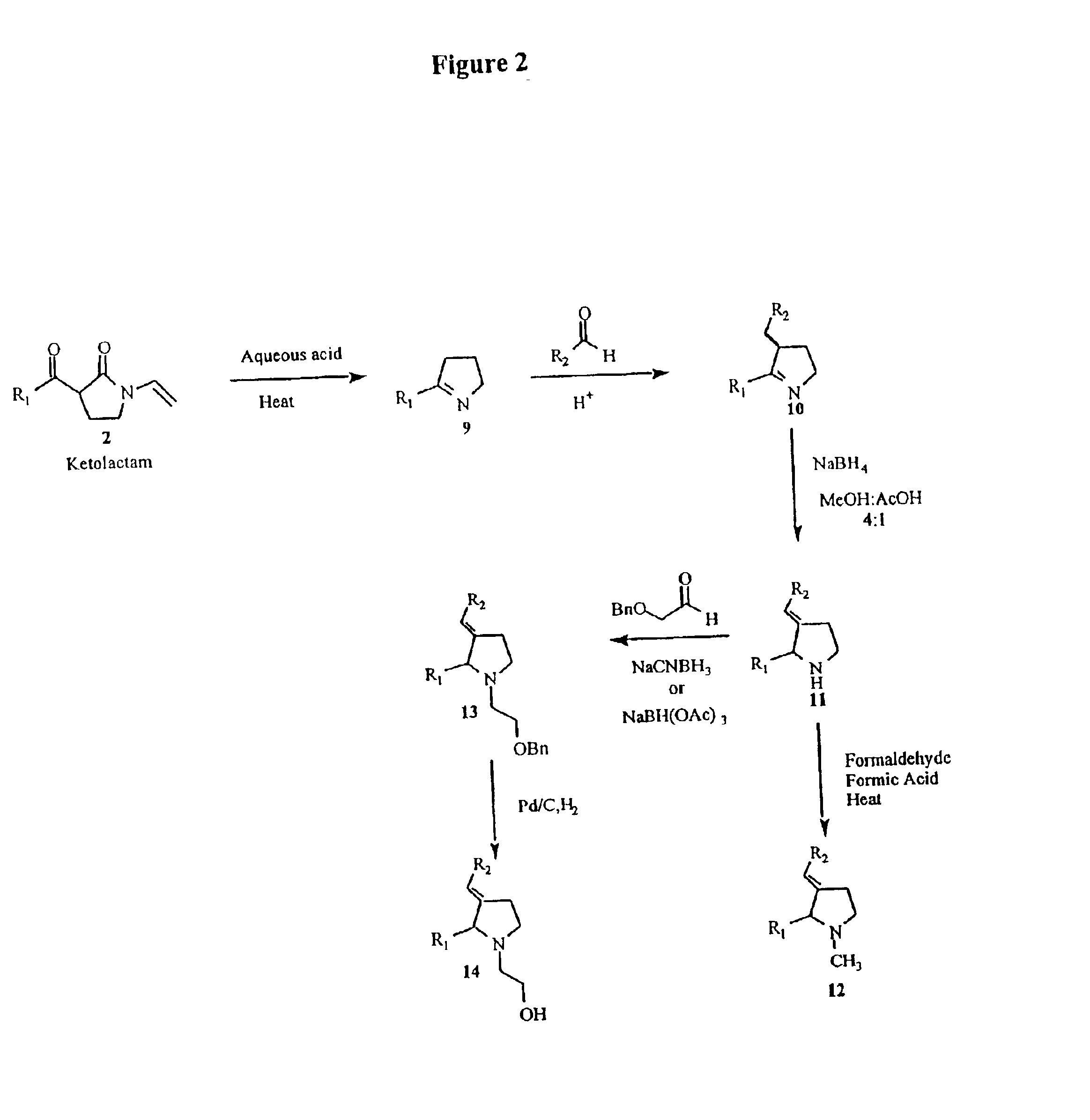
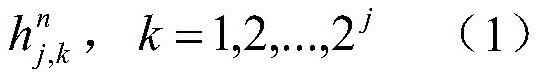Patents
Literature
137 results about "Cerebellum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans.
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Frequency Stimulation Trainer
InactiveUS20090076421A1Relief the painRelieve painMassage combsMassage beltsRe educationPerformance enhancement
A preferably non-electrical nerve communication enhancement tool that sends specific, pre-timed, controlled vibrational and / or acoustical stimulation frequencies to the body to enhance nerve communication for the purpose of assisting in proper function of skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, and facilitating rapid and improved cerebellar timing circuit and related cerebellar learning mechanism pathways such as the inferior olivary-Purkinje-Thalamus cell system and other similar neuronal pools, to improve muscle memory, coordinated functional neuron-musculo-skeletal performance improvement, enhance blood flow, increased range of motion, flexibility, strength and dexterity, neuromuscular re-education, muscle tone recovery, pain modulation, improved eye-hand coordination, gait improvement, balance and stability gains, kinetic chain integration, neurological performance enhancement, sensory dysfunction reduction, and improvement in mental and cognitive function.
Owner:STIMTRAINER
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) differentiate into neuron-like phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, engrafted into normal or denervated rat striatum. The BMSC did not remain localized to the site of the graft, but migrated throughout the brain and integrated into specific brain regions in various architectonic patterns. The most orderly integration of BMSC was in the laminar distribution of cerebellar Purkinje cells, where the BMSC-derived cells took on the Purkinje phenotype. The BMSC exhibited site-dependent differentiation and expressed several neuronal markers including neuron-specific nuclear protein, tyrosine hydroxylase and calbindin. BMSC can be used to target specific brain nuclei in strategies of neural repair and gene therapy.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
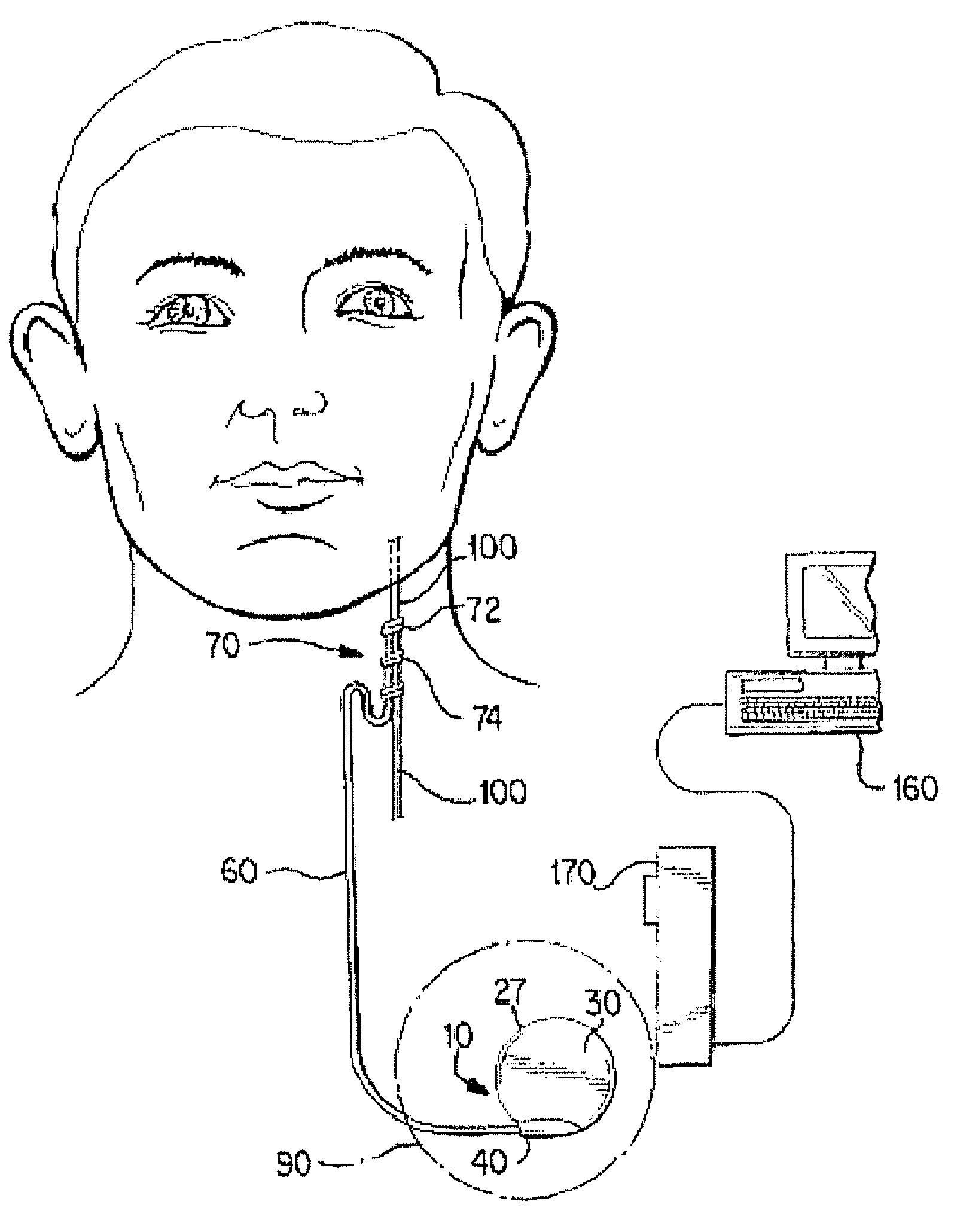
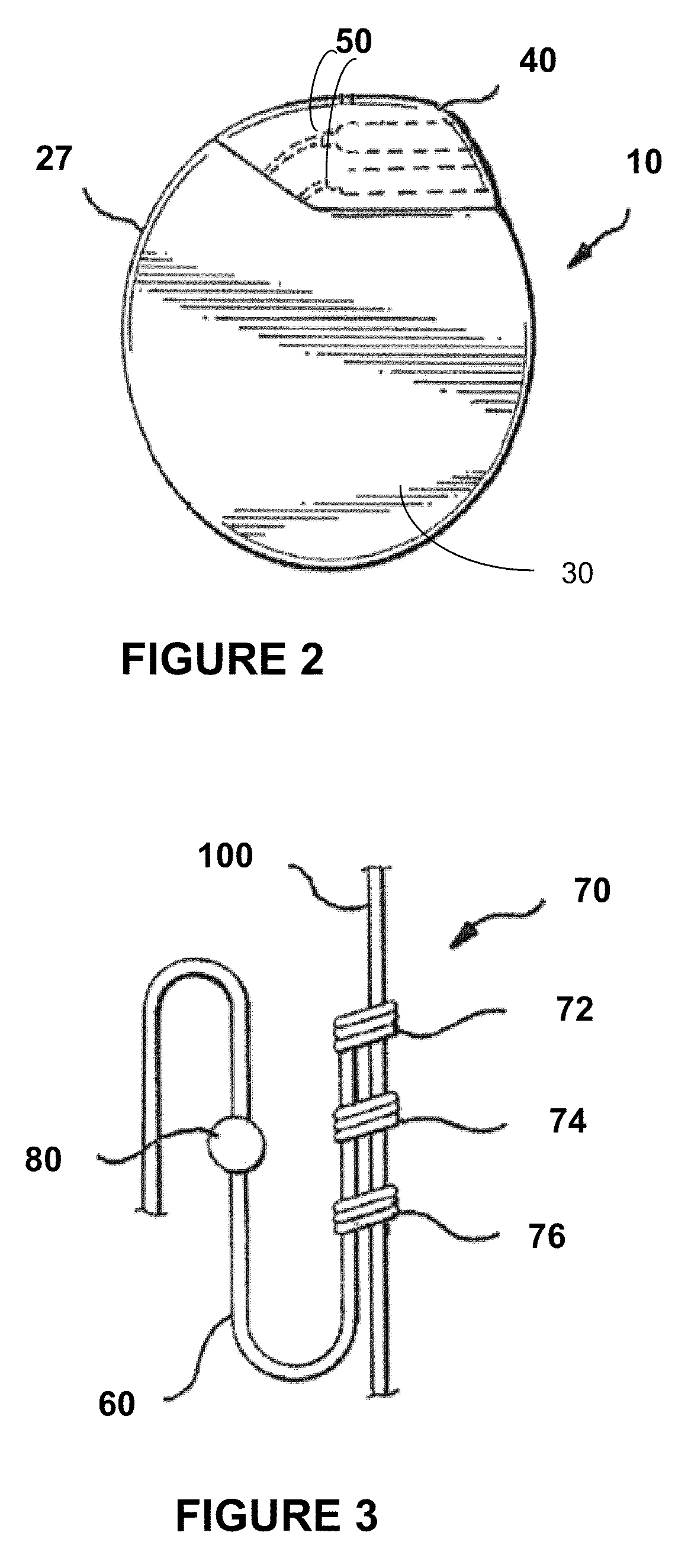
Surgical implant and method of accessing cerebrospinal fluid
A surgical implant and method of gaining access to cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. The implant includes an upper housing part which is positioned subcutaneously on the skull and a lower cage-like member which depends downwardly from the housing part. The housing part defines a chamber or reservoir therein which communicates with openings defined in the lower member. The implant is embedded between portions of the brain so that the lower member projects between the cerebellum and the cerebrum and holds same apart in order to access cerebrospinal fluid which pools in this area. The cerebrospinal fluid is accessed for sampling or dosing purposes through a septum provided within the upper housing part.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Vagus nerve stimulation by electrical signals for controlling cerebellar tremor
A neurostimulator system for alleviating cerebellar tremor associated with multiple sclerosis, for instance, comprises a programmable electrical pulse generator. The programmable electrical pulse generator is programmed to generate electrical signals with the following parameters: a current magnitude of about 1 mA or less, a stimulation signal on-time to signal off-time ratio in the range of 2:1 to 1:1.8, signal on-times and off-times in the range of about 10 seconds to about 5 minutes, a signal frequency below 15 Hz, and a pulse width within the range of 50 μs to 300 μs. Other embodiments are disclosed and claimed.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Method of Inducing the Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells Into Nerve by Serum-Free Suspension Culture
ActiveUS20080044901A1Effectively lead to differentiationEfficient inductionNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsSerum free mediaNervous system
The present invention provides a clinically applicable method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells into forebrain neurons. More specifically, the present invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, comprising culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of the embryonic stem cells into nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neurons and sensory organ cells; a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells obtained by culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium; and cells derived from a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells, particularly nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neuron, sensory organ cells such as retinal precursor cells, and the like.
Owner:RIKEN
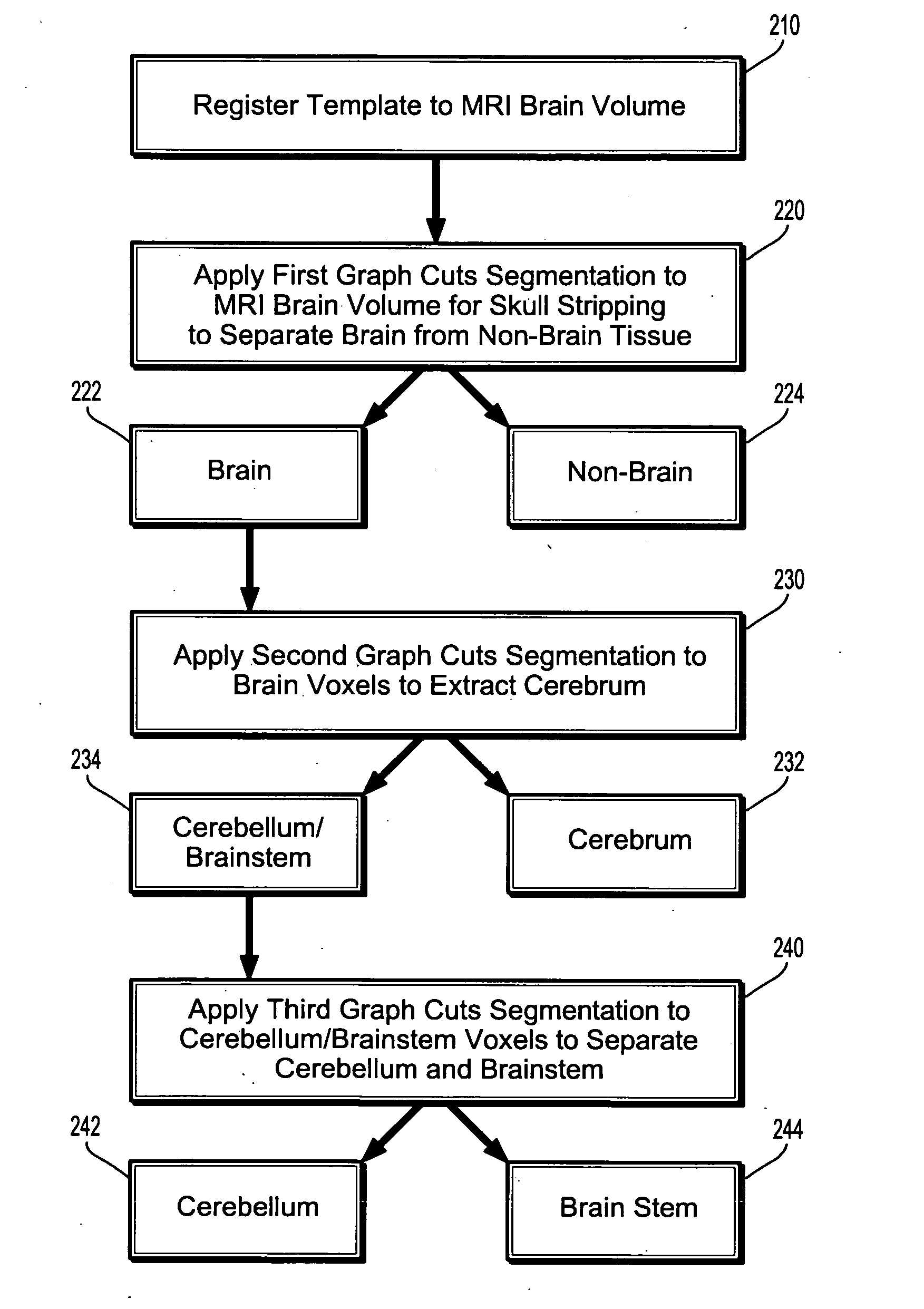
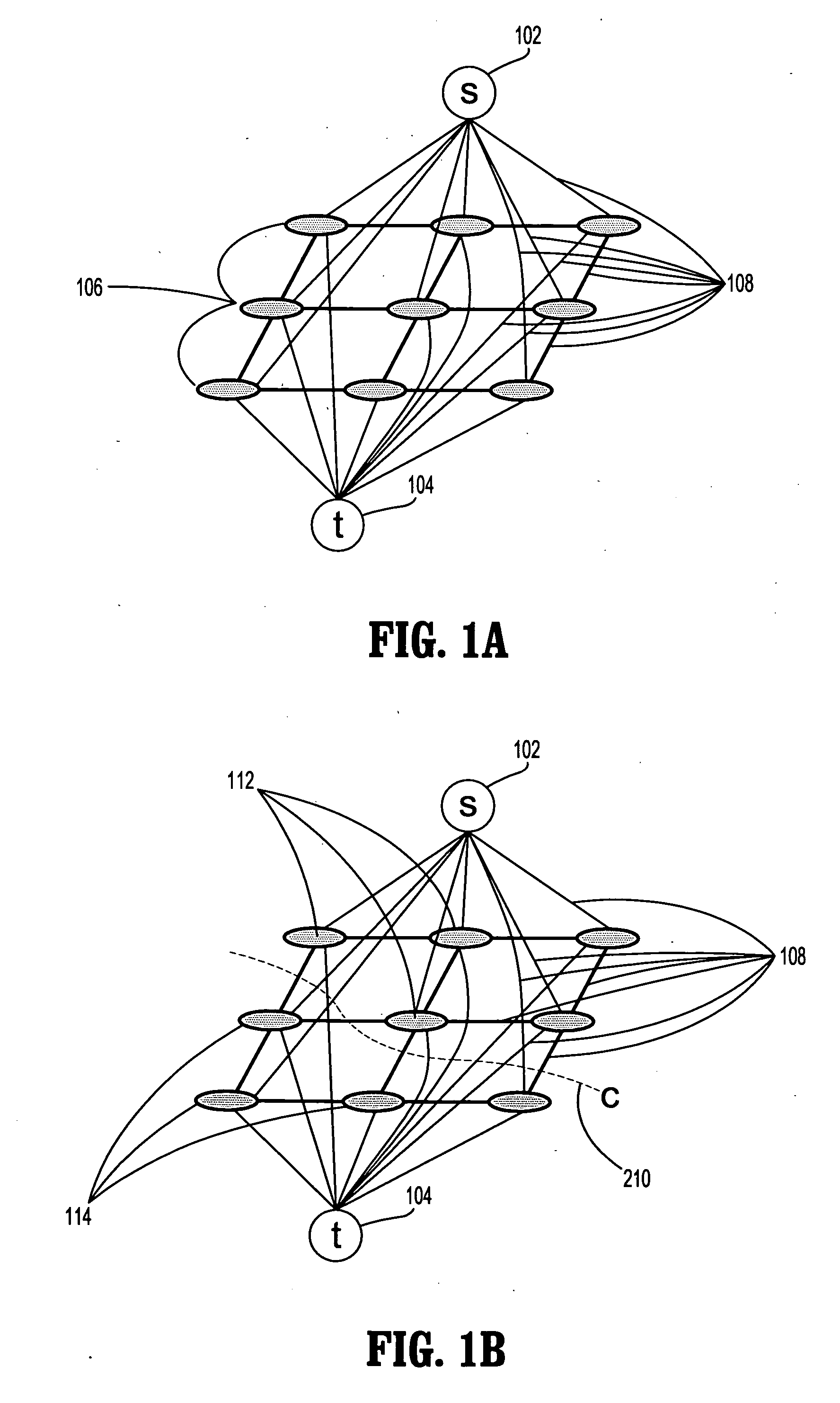
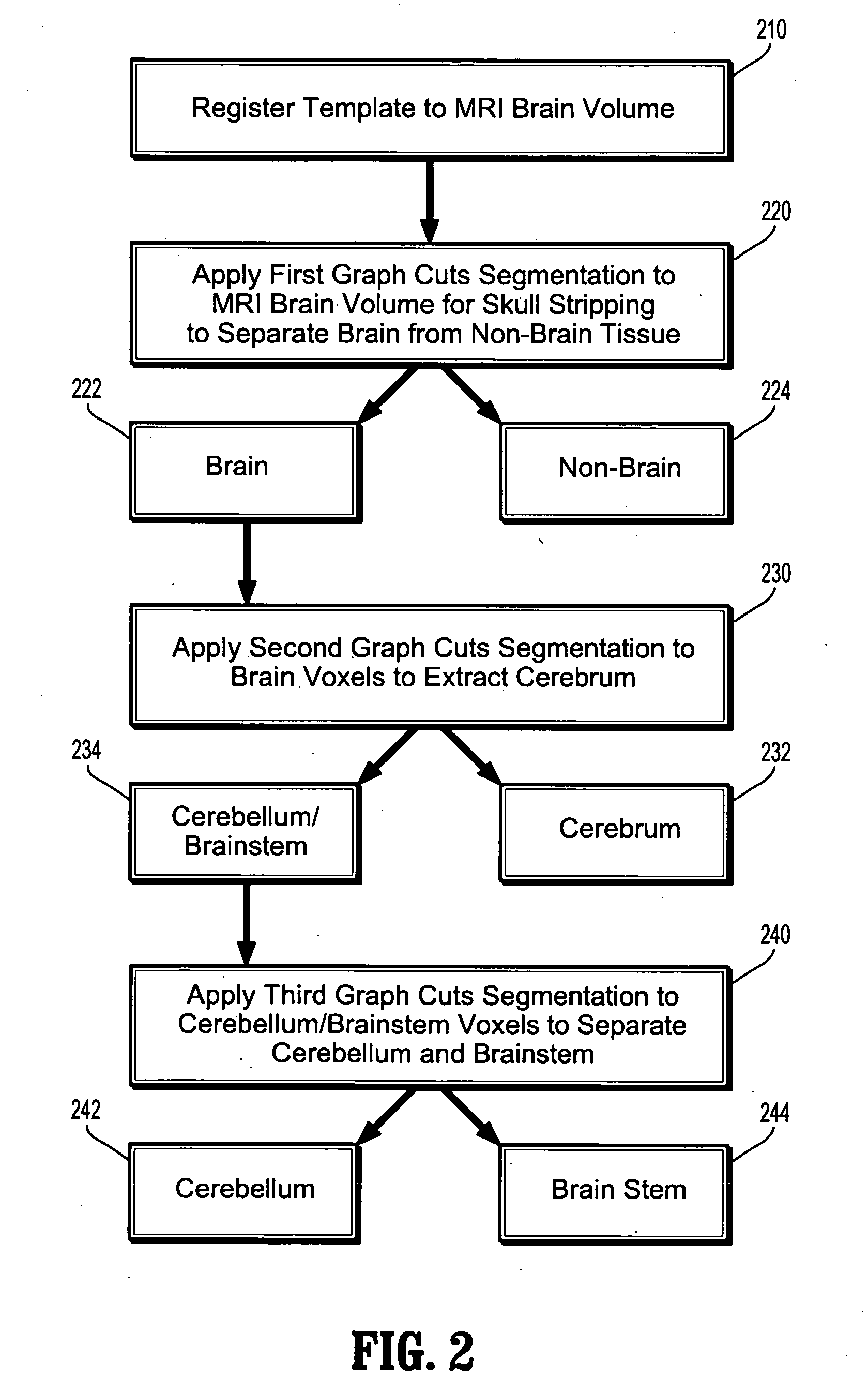
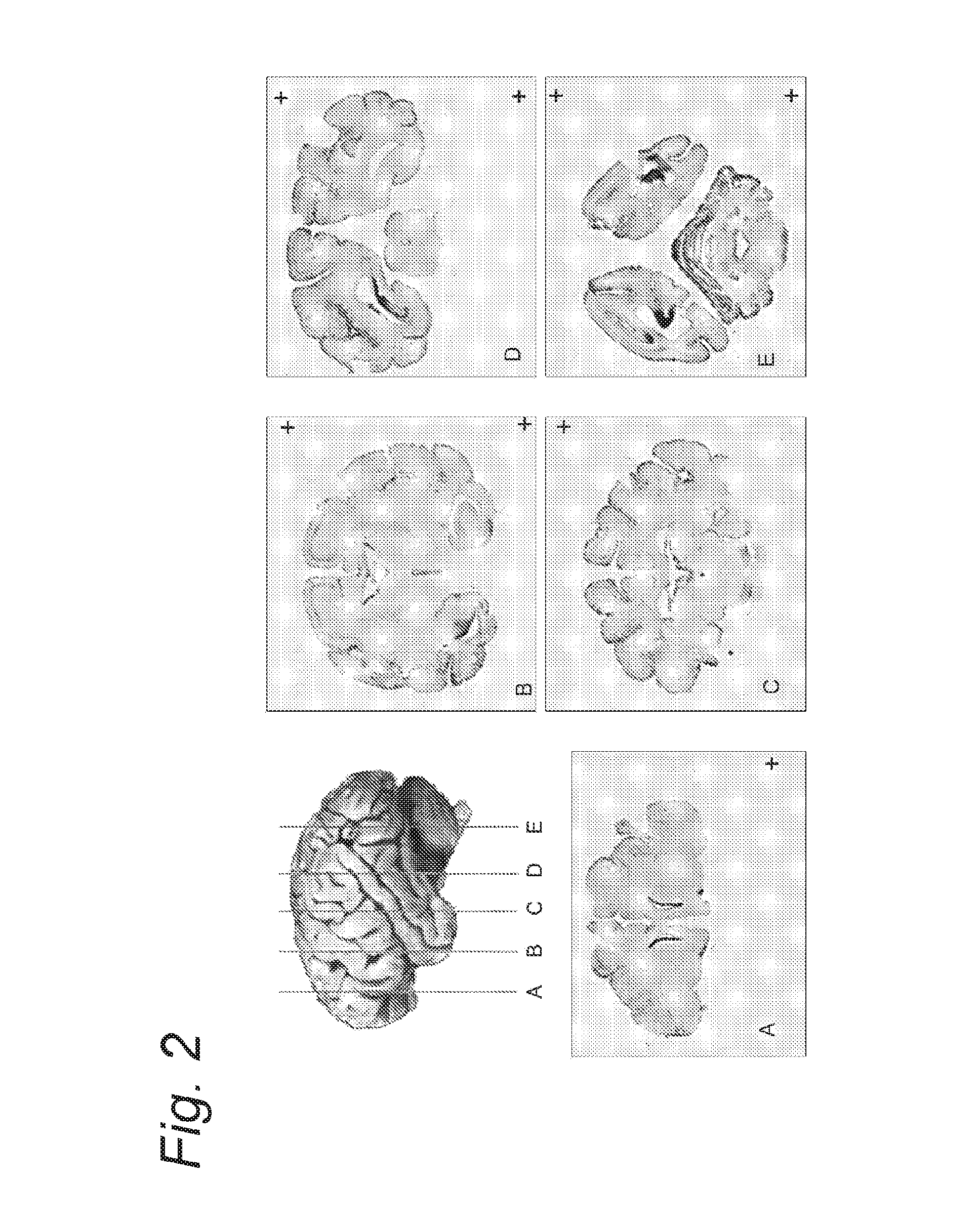
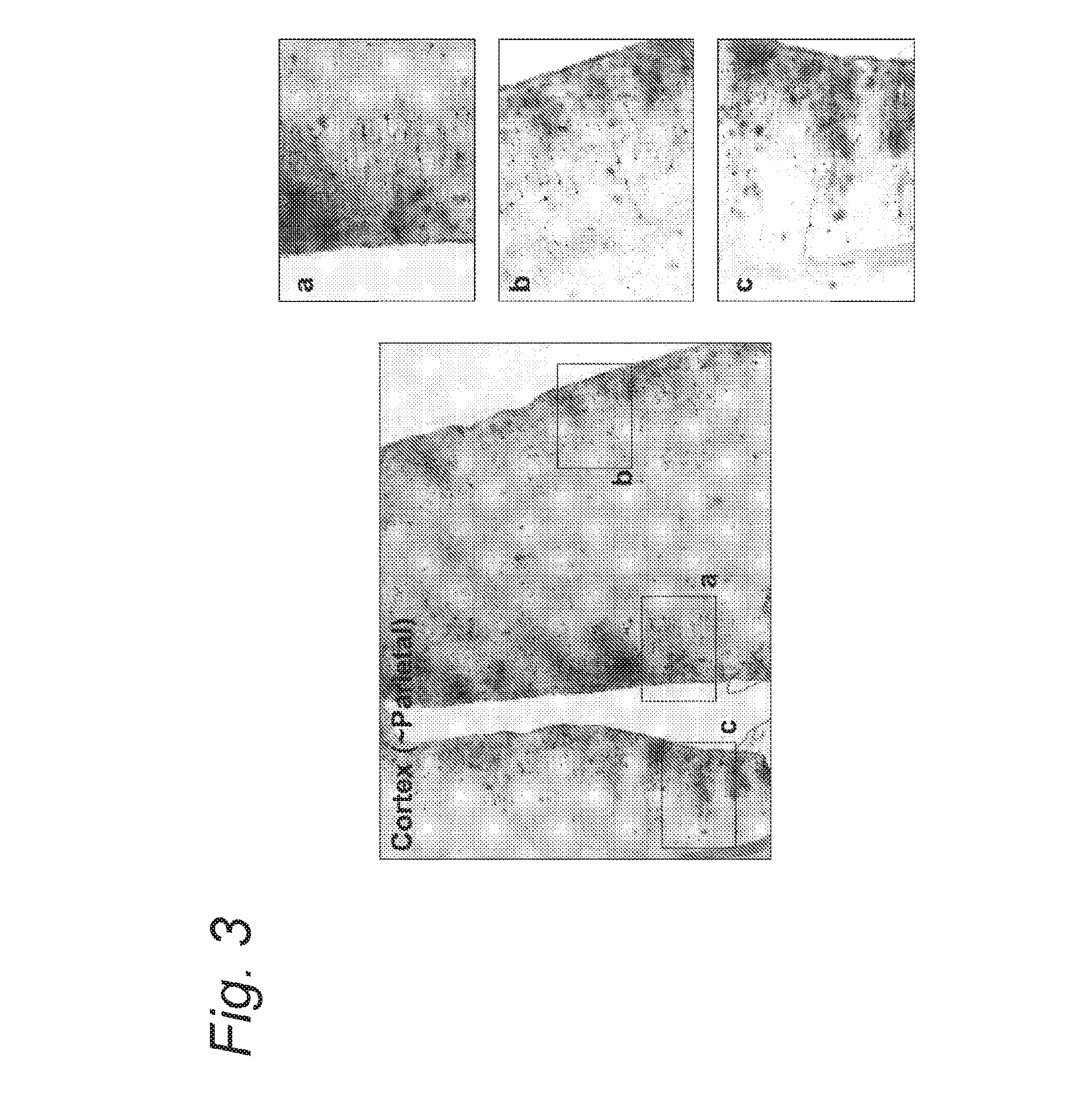
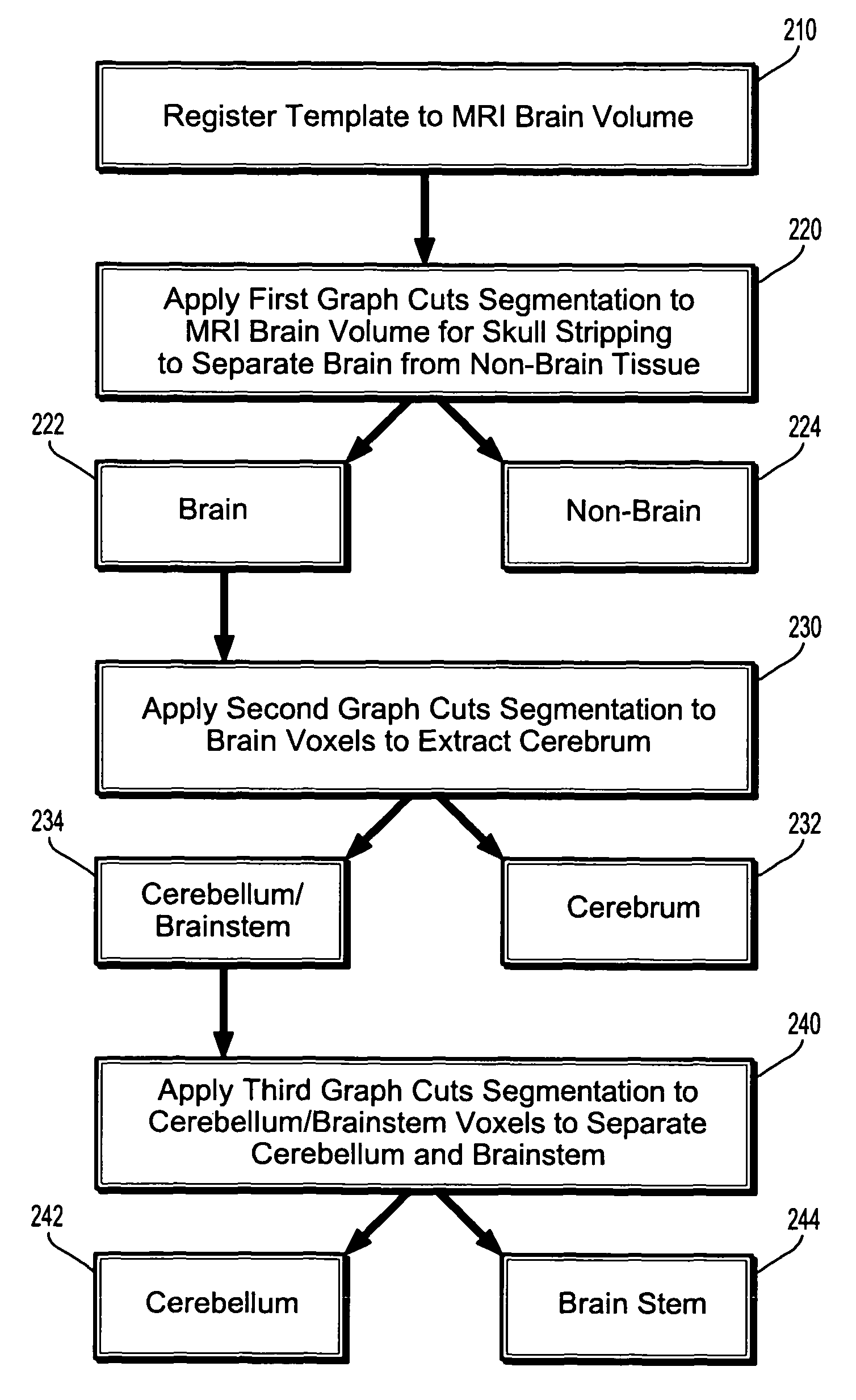
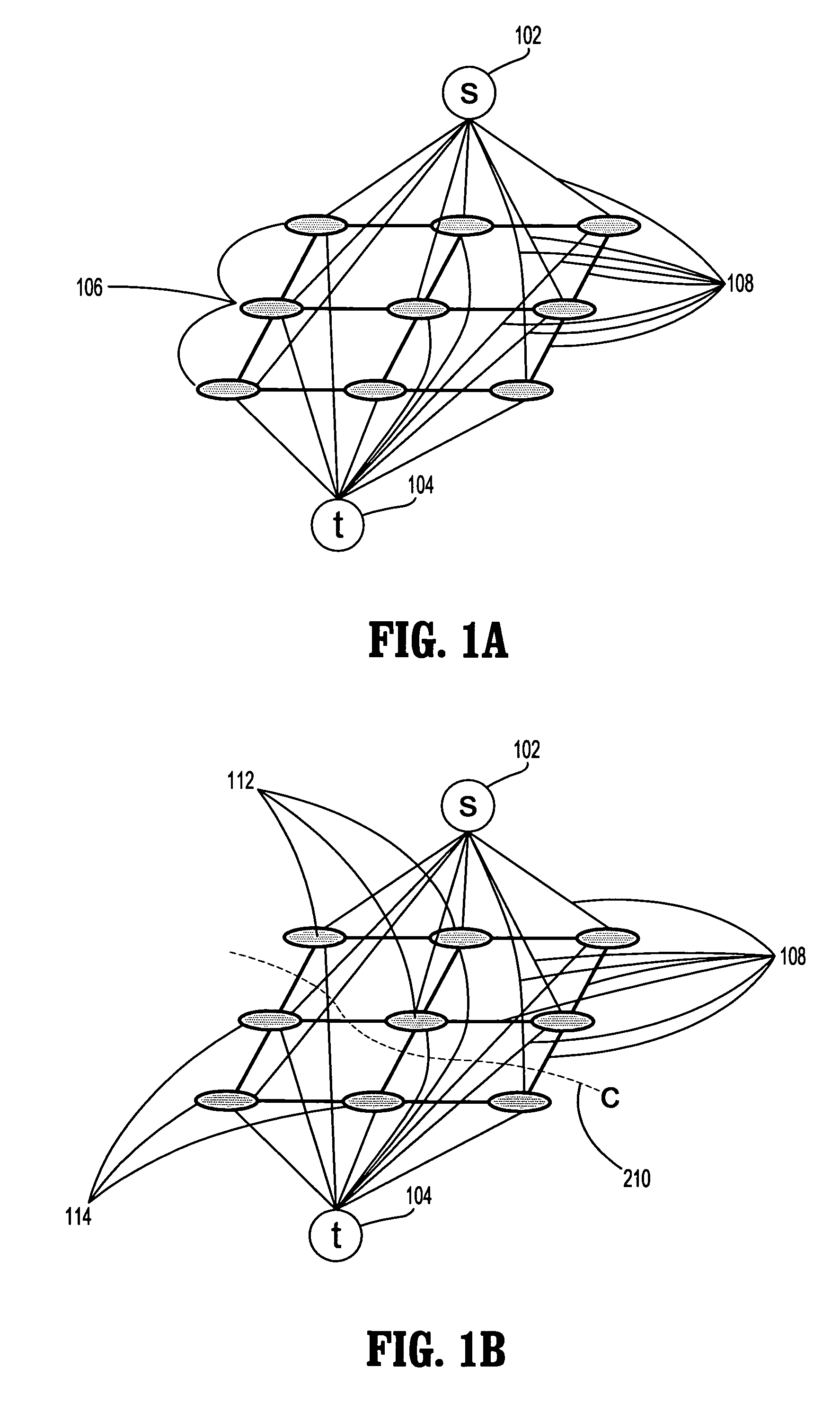
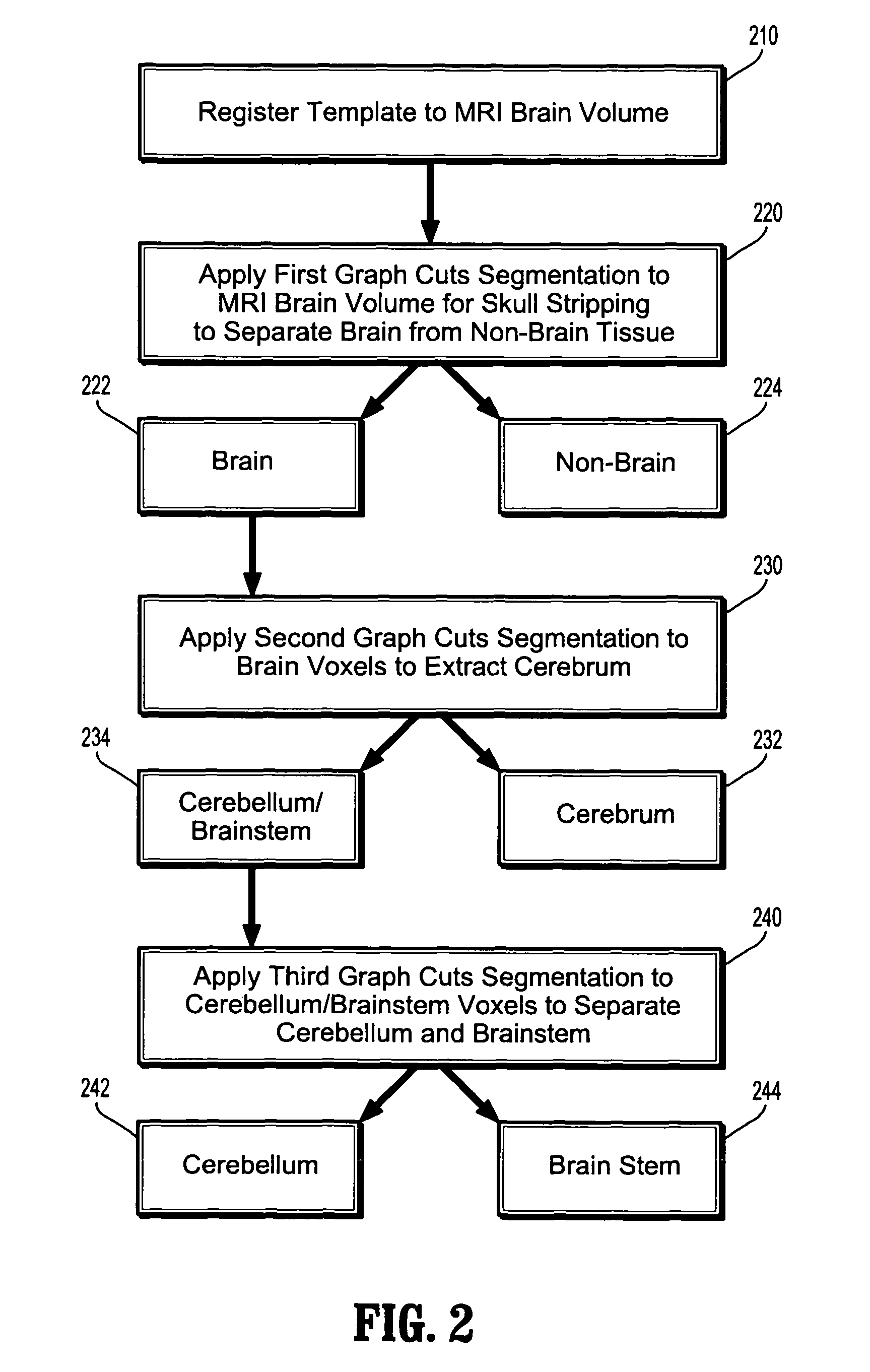
System and Method For Segmentation of Anatomical Structures In MRI Volumes Using Graph Cuts
InactiveUS20070160277A1Overcome problemsRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsAnatomical structuresGraphics
A system and method for segmentation of anatomical structures in MRI volumes using graph cuts is disclosed. In this method, a template is registered to an MRI brain volume. The template identifies seed points of anatomical brain structures, such as the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem, in the MRI brain volume. Any or all of the anatomical brain structures can be segmented using graph cuts segmentation initialized based on the seed points identified by the template. It is possible to segment each of the anatomical brain structures by performing a hierarchical three-phase segmentation process including brain / non-brain segmentation, cerebrum / cerebellum and brain stem segmentation, and cerebellum / brain stem segmentation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
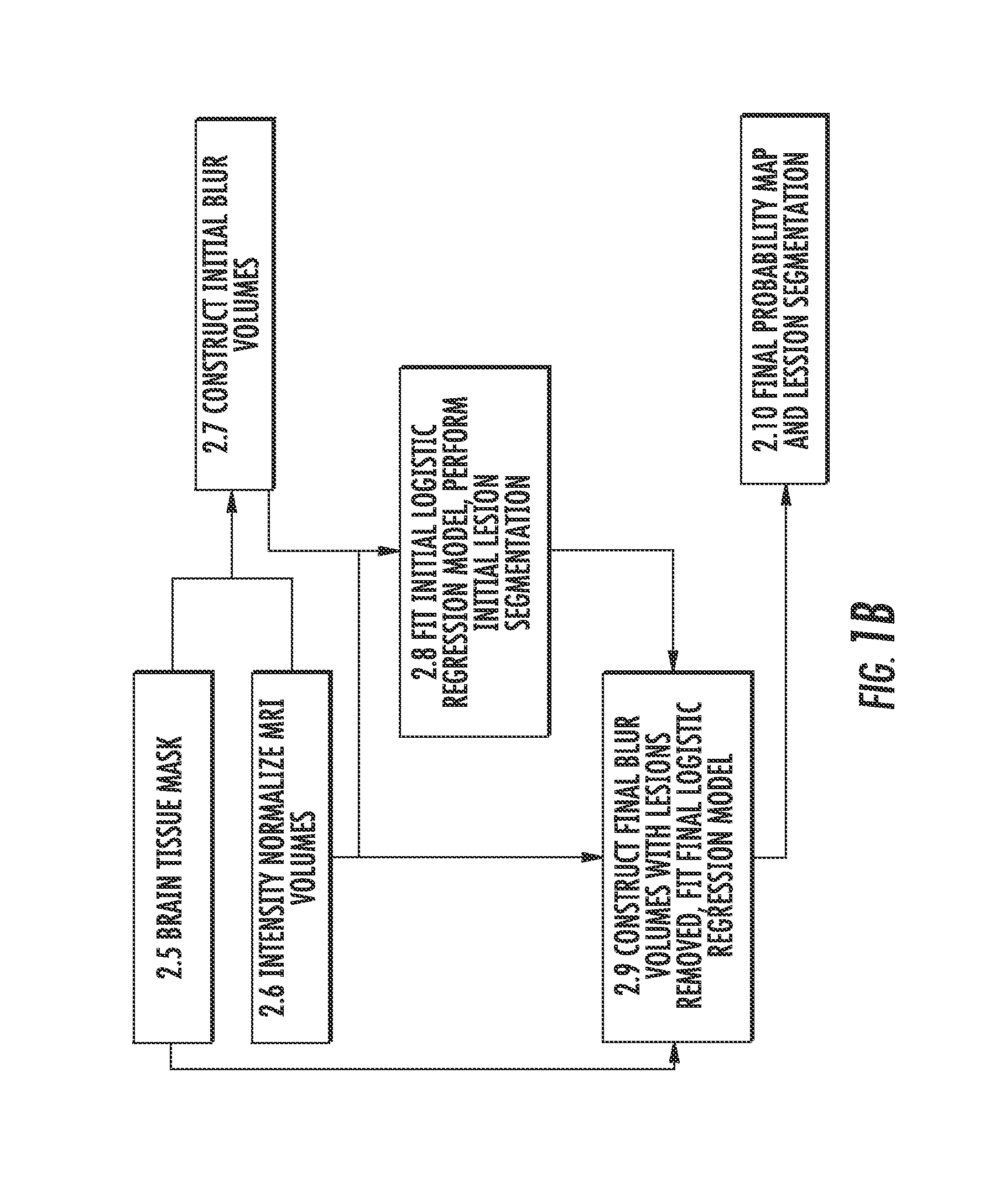
Method of analyzing multi-sequence MRI data for analysing brain abnormalities in a subject
The present invention, referred to as Oasis is Automated Statistical Inference for Segmentation (OASIS), is a fully automated and robust statistical method for cross-sectional MS lesion segmentation. Using intensity information from multiple modalities of MRI, a logistic regression model assigns voxel-level probabilities of lesion presence. The OASIS model produces interpretable results in the form of regression coefficients that can be applied to imaging studies quickly and easily. OASIS uses intensity-normalized brain MRI volumes, enabling the model to be robust to changes in scanner and acquisition sequence. OASIS also adjusts for intensity inhomogeneities that preprocessing bias field correction procedures do not remove, using BLUR volumes. This allows for more accurate segmentation of brain areas that are highly distorted by inhomogeneities, such as the cerebellum. One of the most practical properties of OASIS is that the method is fully transparent, easy to implement, and simple to modify for new data sets.
Owner:THE HENRY M JACKSON FOUND FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF MILITARY MEDICINE INC +2
Combination of atypical antipsychotics and 5HT-1B receptor antagonists
InactiveUS20050256112A1Reduce morbidityDifferent recognizableNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseHeadaches
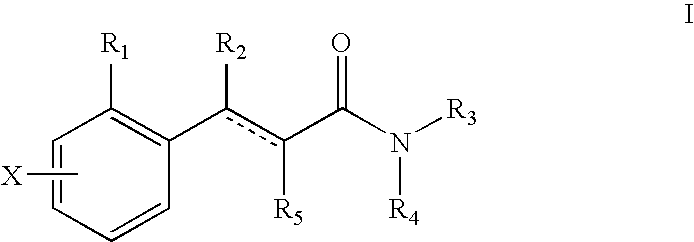
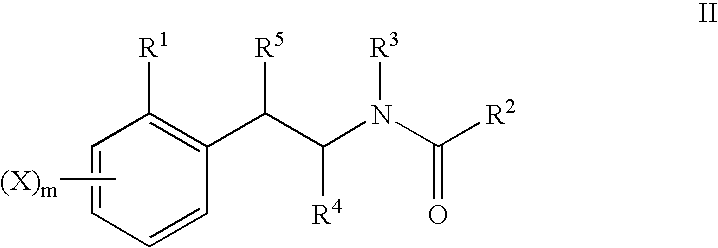
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating, for example, a disorder or condition selected from the group consisting of hypertension, depression, generalized anxiety disorder, phobias, posttraumatic stress disorder, avoidant personality disorder, sexual dysfunction, eating disorders, obesity, chemical dependencies, cluster headache, migraine, pain, Alzheimer's disease, obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, memory disorders, Parkinson's diseases, endocrine disorders, cerebellar ataxia, gastrointestinal tract disorders, negative symptoms of schizophrenia, premenstrual syndrome, Fibromyalgia Syndrome, stress incontinence, Tourette syndrome, trichotillomania, kleptomania, male impotence, cancer, chronic paroxysmal hemicrania and headache in a mammal, preferably a human, comprising (i) an atypical antipsychotic or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, (ii) a 5-HT1B receptor antagonist or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the 5-HT1B receptor antagonist is selected from the group consisting of (A) a compound of the formula I as described in the specification and (B) a compound of the formula II as described in the specification, and optionally (iii) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:PFIZER INC
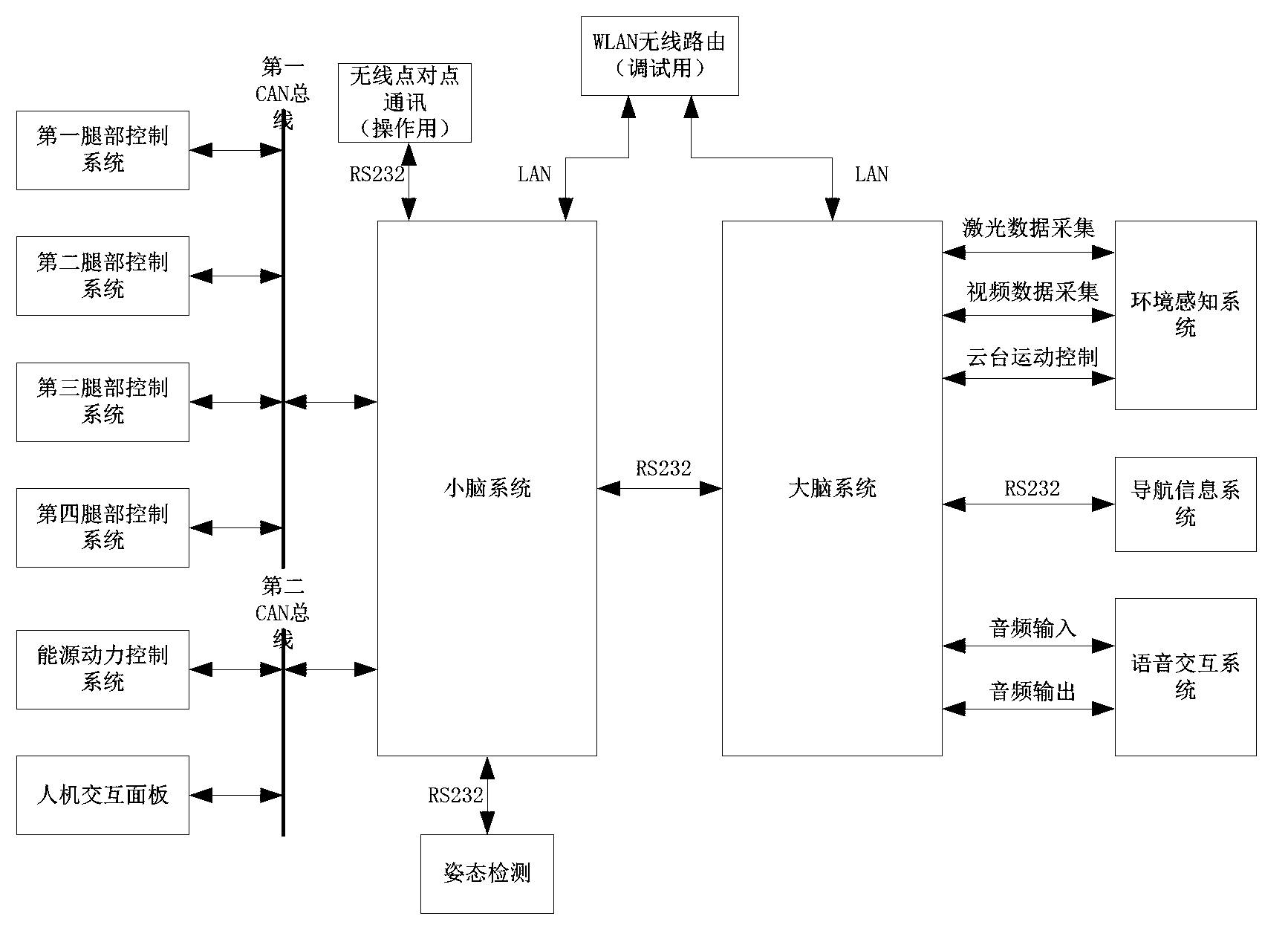
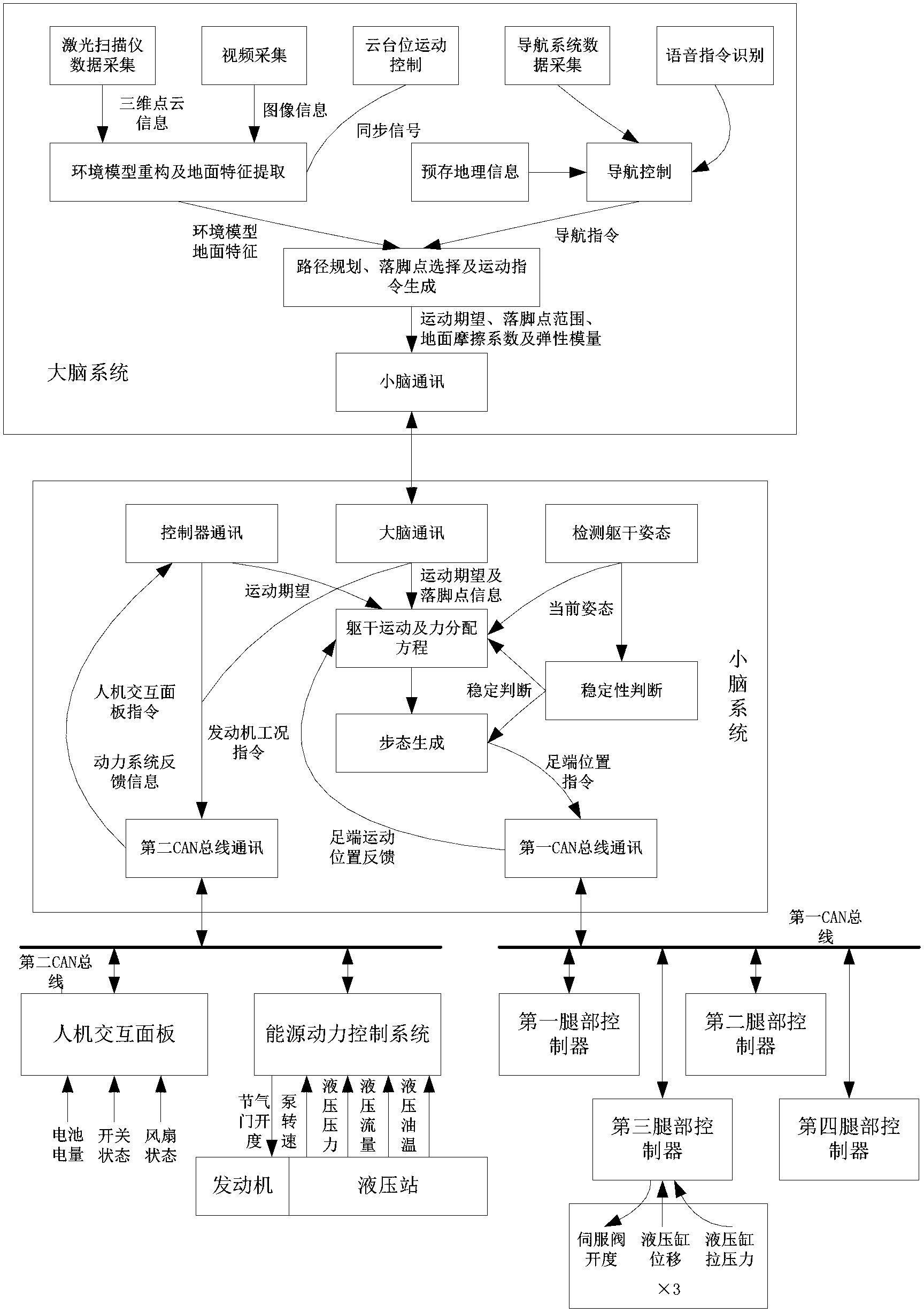
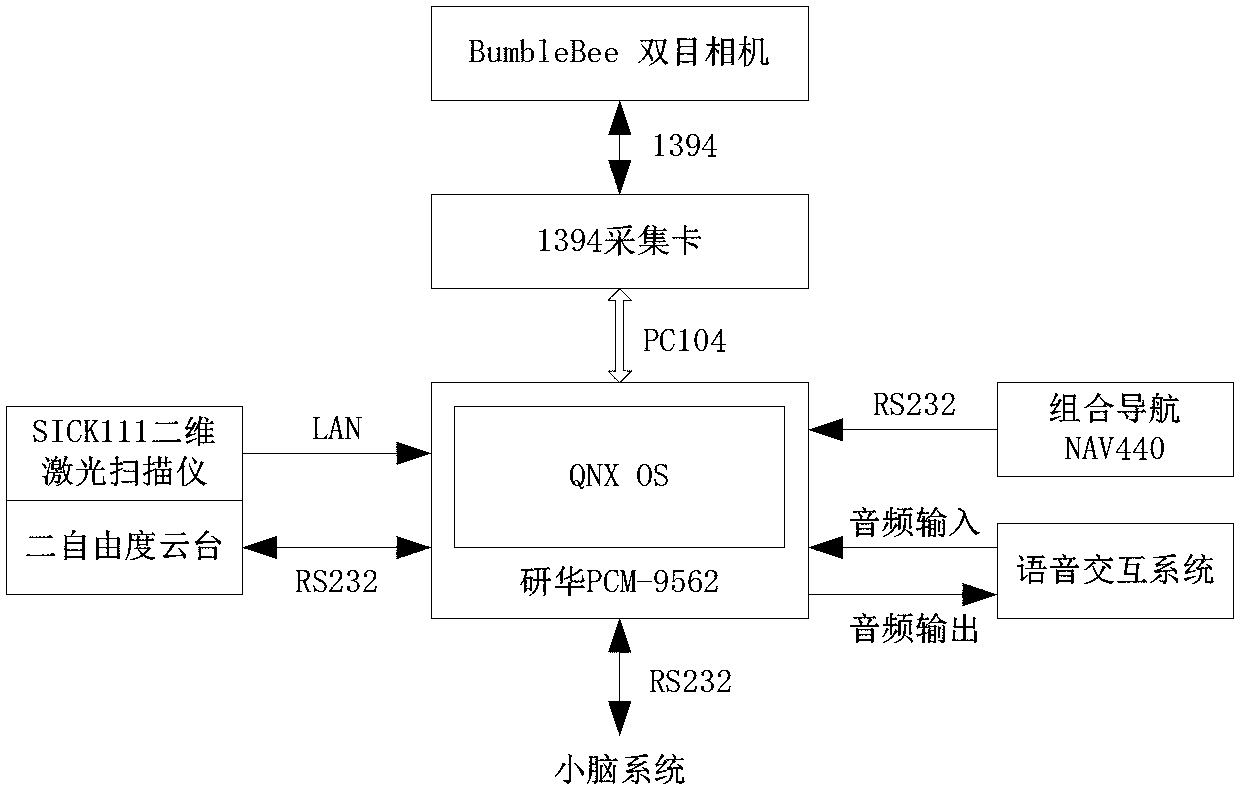
Distributed type control system of hydraulic quadruped robot and control method
ActiveCN103279113AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlInteraction systemsDistributed structure
The invention discloses a distributed type control system of a hydraulic quadruped robot and a control method. The distributed type control system of the hydraulic quadruped robot comprises a brain system, the brain system is connected with an environment sensing system, a navigation information system and a voice interaction system to obtain data, the brain system transmits the obtained data to a cerebellar system, the cerebellar system controls a leg control system through a first CAN bus, and the cerebellar system is further communicated with an energy and power control system and an interpersonal interaction panel through a second CAN bus. According to the distributed type control system of the hydraulic quadruped robot, the previous integral control idea of the quadruped robot is changed, and the control method of the quadruped robot is divided into intelligent control, body motion control and leg motion control. The control method forms an organic whole by adopting a distributed type structure, the processor of each part works under reasonable calculation, the power consumption of the system is reduced, and the real-time performance and the reliability of the control system are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating spinal muscular atrophy
ActiveUS20160074474A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSpinal muscular atrophiesSpinal column
The present provides methods for treating spinal muscular atrophy using a self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) viral particle comprising a transgene expressing SMN. In one aspect, the viral particles are administered the spinal column or cisterna magna in a human subject; for example, a pediatric human subject. Viral particles comprising AAV9 capsids are contemplated.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
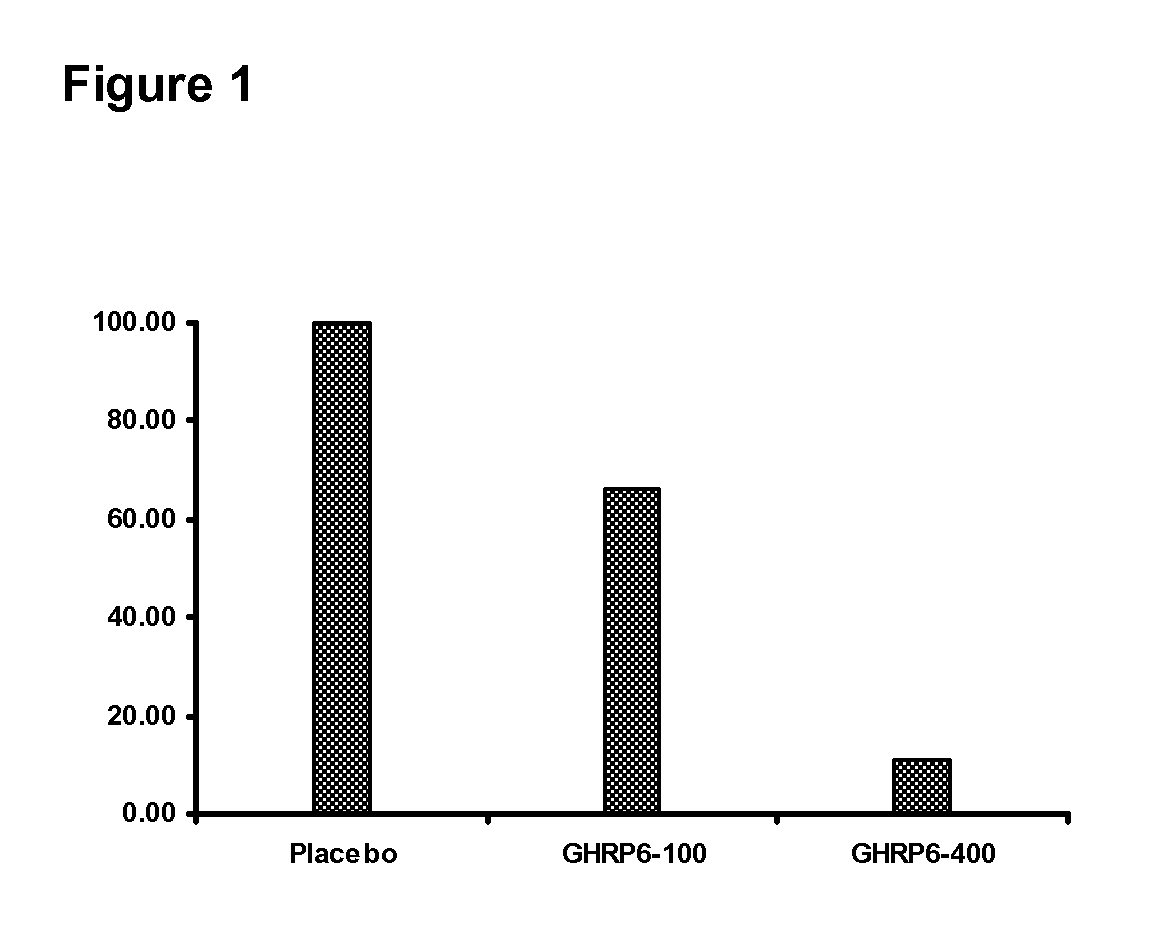
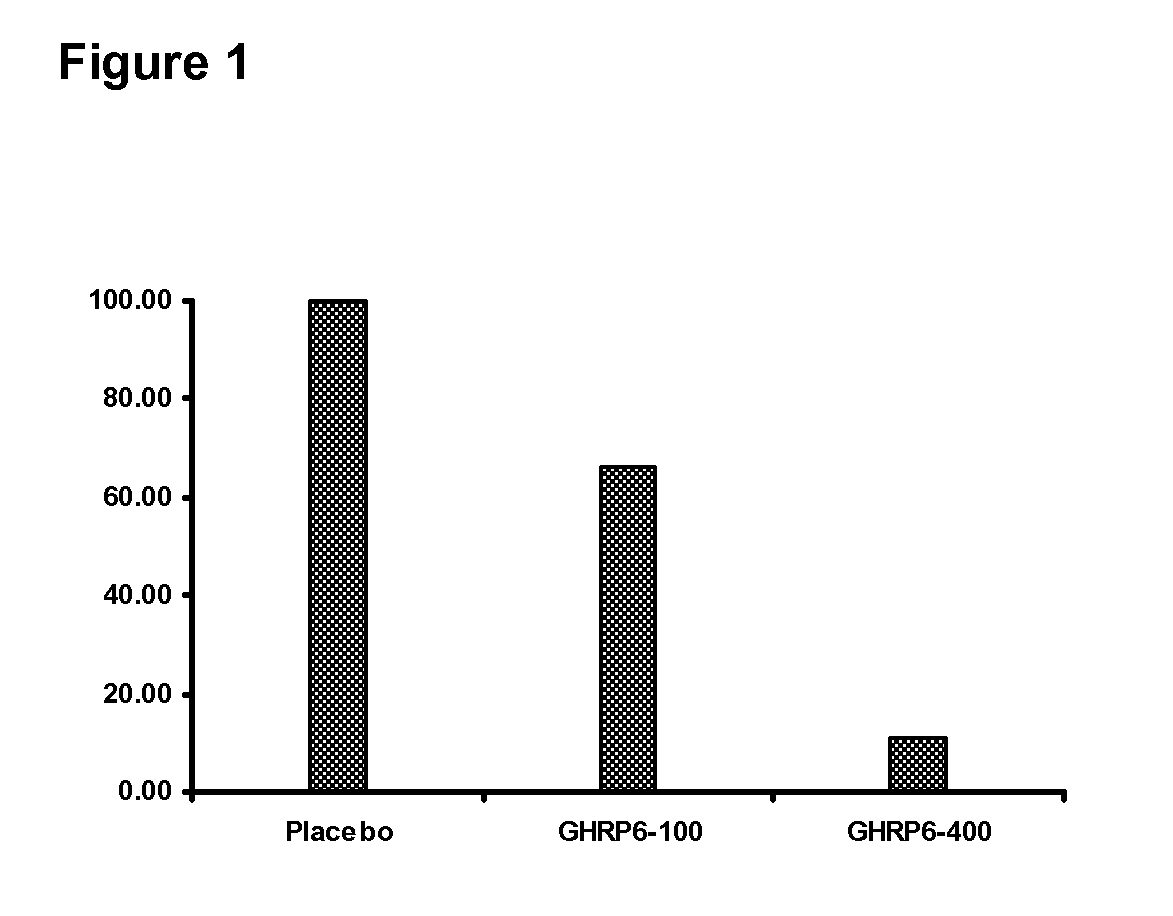
Pharmaceutical composition containing ghrp-6 to prevent and eliminate fibrosis and other pathological deposits in tissues
The present invention is related to the use of secretagogue peptides repeatedly administered as part of a pharmaceutical composition that prevent and eradicate the deposition of pathological fibrotic material in parenchymal tissues of internal organs like the liver, lungs, esophagus, small intestine, kidneys, blood vessels, joints, and other systemic forms of cutaneous fibrosis of any etiopathogenesis. Additionally, these peptides prevent and eradicate deposition of amiloid and hyaline materials in any of their correspondent chemical forms and tissue manifestations in the brain, cerebellum, blood vessels, liver, intestines, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, joints and the skin, among others. By this way, cellular, tissular and organ dysfunctions generated by these depositions are corrected. The peptides of the present invention are infiltrated or topically applied, contributing to prevent and eradicate keloids and hypertrophic scars in the skin, derived as sequelae of burns and other cutaneous trauma.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
Treatment of neurological diseases using adeno-associated virus (AAV) comprising AAV-5 capsid proteins
InactiveUS20160243260A1Improve stabilityReduced expression levelNervous disorderMuscular disorderDiseaseAdeno associate virus
The present invention relates to methods for treating disorders affecting motor function, such as motor function affected by disease, injury to the brain and / or spinal cord using an adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy vector comprising adeno-associated virus 5 (AAV5) capsid proteins and a gene product of interest flanked by AAV ITRs. In particular, the gene therapy vector of the present invention is administered via injection into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), preferably by lumbar injection and / or injection into the cisterna magna.
Owner:UNIQURE IP BV
Pharmaceutical Composition Containing GHRP-6 To Prevent And Eliminate Fibrosis And Other Pathological Deposits In Tissues
The present invention is related to the use of secretagogue peptides repeatedly administered as part of a pharmaceutical composition that prevent and eradicate the deposition of pathological fibrotic material in parenchymal tissues of internal organs like the liver, lungs, esophagus, small intestine, kidneys, blood vessels, joints, and other systemic forms of cutaneous fibrosis of any etiopathogenesis. Additionally, these peptides prevent and eradicate deposition of amiloid and hyaline materials in any of their correspondent chemical forms and tissue manifestations in the brain, cerebellum, blood vessels, liver, intestines, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, joints and the skin, among others. By this way, cellular, tissular and organ dysfunctions generated by these depositions are corrected. The peptides of the present invention are infiltrated or topically applied, contributing to prevent and eradicate keloids and hypertrophic scars in the skin, derived as sequelae of burns and other cutaneous trauma.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
System and method for segmentation of anatomical structures in MRI volumes using graph cuts
A system and method for segmentation of anatomical structures in MRI volumes using graph cuts is disclosed. In this method, a template is registered to an MRI brain volume. The template identifies seed points of anatomical brain structures, such as the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem, in the MRI brain volume. Any or all of the anatomical brain structures can be segmented using graph cuts segmentation initialized based on the seed points identified by the template. It is possible to segment each of the anatomical brain structures by performing a hierarchical three-phase segmentation process including brain / non-brain segmentation, cerebrum / cerebellum and brain stem segmentation, and cerebellum / brain stem segmentation.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Application of cerebroside compound
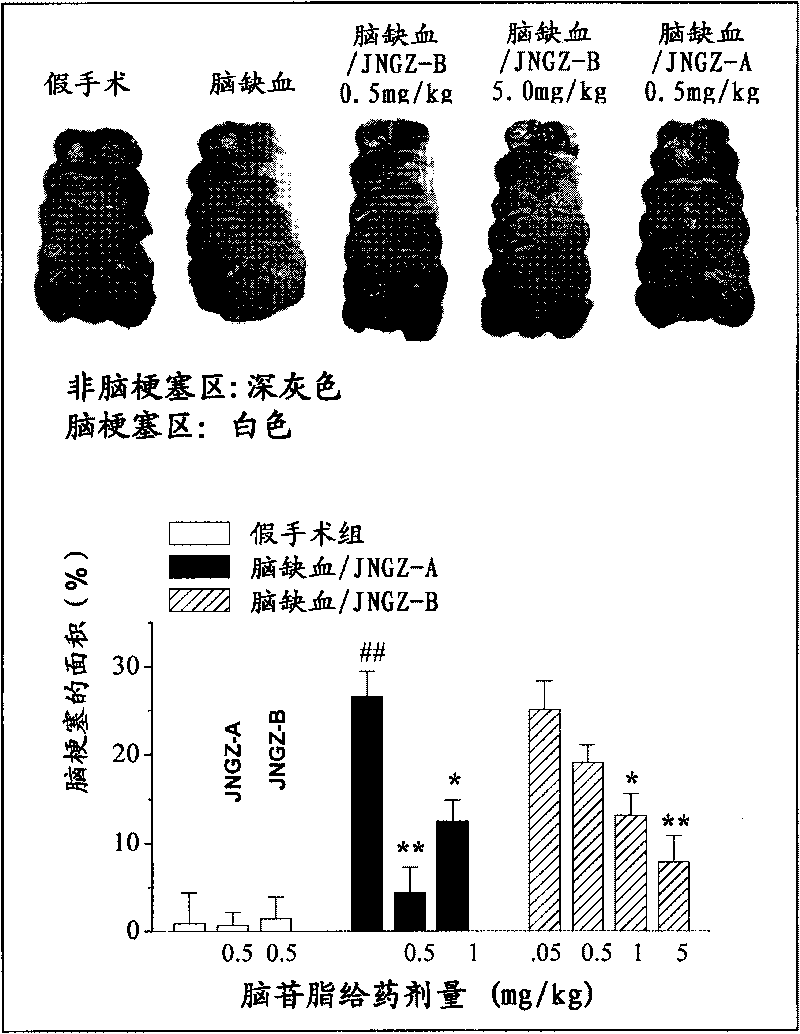
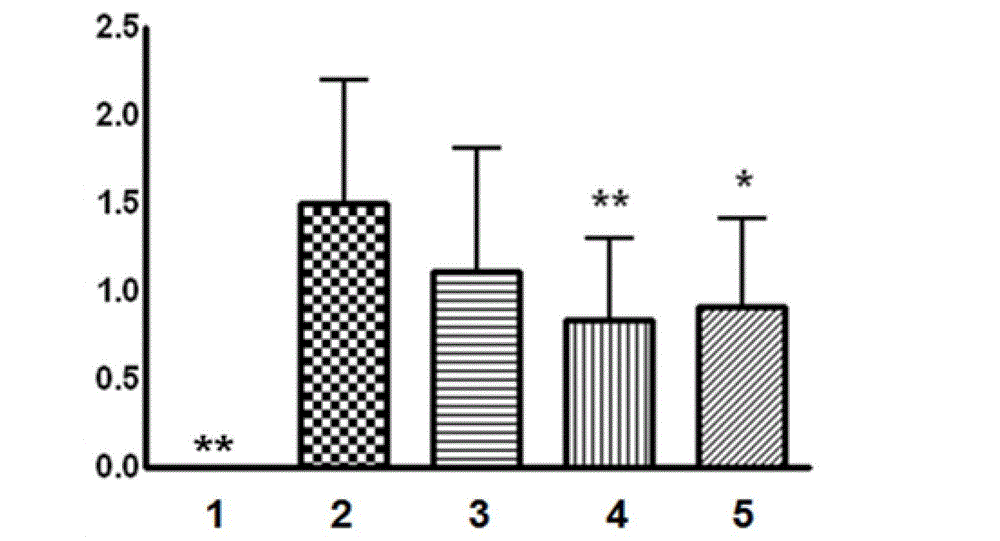
InactiveCN101703515AOvercome the difficulty of not being able to separate and purifyHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCerebellumTherapeutic effect
The invention provides application of a cerebroside compound (cerebroside A and cerebroside B) extracted and prepared from termitomyces in the preparation of medicaments for treating brain injury after cerebral ischemia. Through pharmacological experiments, the invention confirms that the cerebroside compound has significant therapeutic effect on ischemic brain injury, can permeate blood-brain barriers, reduces the area of cerebral infarction caused by cerebral ischemia, alleviates cerebral edema, reduces neuronal cell death, simultaneously promotes the recovery of motor and cognitive function after stroke, and reduces stroke mortality. The invention develops novel medicament use of the cerebroside compound, and provides a novel therapeutic medicament for treating stroke diseases.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV +2
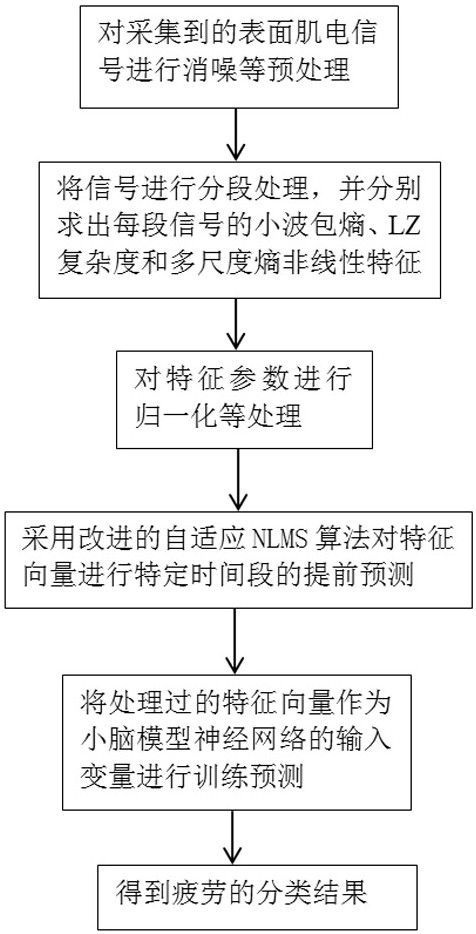
Muscle fatigue advanced prediction and classification method based on surface electromyographic signals
InactiveCN112120697ADiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsLeast mean squares filterClassification methods
The invention relates to a muscle fatigue advanced prediction and classification method based on surface electromyographic signals. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting the surface electromyographic signals of muscles related to joint movement; (2) preprocessing the acquired surface electromyographic signals, then carrying out segment handling on the signals, and extracting nonlinear characteristic parameters from each segment of signals to serve as fatigue characteristic vectors, the nonlinear characteristic parameters including a wavelet packet entropy, LZ complexity and a multi-scale entropy; (3) respectively carrying out characteristic parameter prediction on each characteristic parameter by adopting an improved adaptive normalized least mean square filter (NLMS)algorithm, and by the improved adaptive NLMS algorithm, performing advanced prediction on the characteristic parameters according to a set advanced prediction time period through utilizing the characteristic of adaptive update of an NLMS in each time step; and (4) carrying out fatigue classification identification on the predicted characteristic parameters by adopting an improved cerebellum modelneural network. The method can predict muscle fatigue in advance.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Application of total saponins of bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. in preparation of medicaments for resisting cerebral ischemia
The invention provides an application of total saponins of bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. in preparation of medicaments for resisting cerebral ischemia. The total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. mainly comprise the following dammarane type triterpenoid saponin compounds: bacopaside I, bacoside A3, bacopaside II, bacopasaponin cisomer and bacopasaponin C. The invention further provides an application of the bacopaside I in preparation of a medicament for resisting cerebral ischemia. The experimental study shows that the total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. and the bacopaside I have the effects of improving the behavioral symptoms caused by cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury, reducing the cerebral infarct volume and reducing the cerebral edema caused by cerebral ischemia of a rat. Therefore, the total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. can be used for preparing the medicaments for preventing and treating cerebral ischemia. The medicaments for preventing and treating the cerebral ischemia are prepared from the total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. or bacopaside I as the active component and medicinal accessories by adopting a conventional method. The invention further expands the function of the bacopaside I and the total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. and provides the novel medicaments for preventing and treating the cerebral ischemia. The bacopaside I and the total saponins of the bacopa monnieri (L.) wettst. have high clinical application values.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
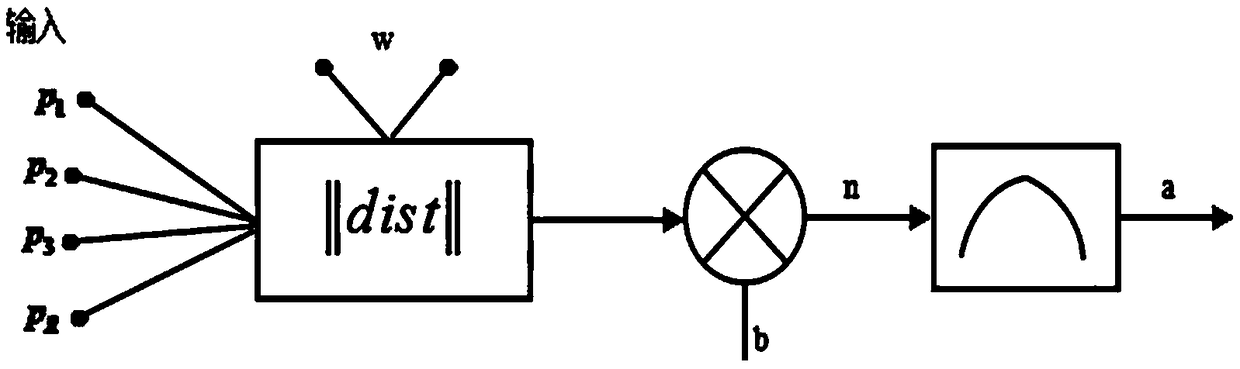
Mechanical arm control method based on RBF neural network
InactiveCN109227550AReduce workloadSelf-learning abilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMathematical modelSimulation
The invention discloses a mechanical arm control method based on an RBF neural network. The method includes the steps of firstly, providing a cognition learning model mechanism of a mechanical arm; secondly, putting forward a behavior cognition model based on cerebellum-basal ganglion and a hybrid learning algorithm; thirdly, establishing a mathematical model for the mechanical arm to autonomouslylearn through the artificial neural network and a reinforcement learning method; fourthly, establishing a mechanical arm imitation experimental model in a Matlab; fifthly, verifying the mechanical arm control method based on the RBF neural network. The method has the advantages that the method is not only suitable for the mechanical arm, but also can be applied to other mechanical fields; the method can be applied to other control fields; the method is more suitable for application, and the workloads of programmers can be greatly reduced; the mechanical arm with the autonomous learning capacity has higher competitiveness in future.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for promoting induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be nerve cells
ActiveCN105331583ASpeed up induction of differentiationGood growthNervous system cellsNeurulationSpinal cord
The invention discloses a method for promoting induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be nerve cells, which comprises steps: induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are blown and absorbed to disperse to be single cell suspension after being digested, and are separately planted in culture holes, and rock (ROCK) inhibitors are added into each culture hole; a supernate is adsorbed to discard in the first day after the iPS cells are separately planted, is added into a neural induction complete culture medium, and rapamycin needs to be added into the neural induction complete culture medium to promote autophagy; the neural induction complete culture medium is changed to add low concentration rapamycin to promote autophagy neural cells to differentiate the neural induction complete culture medium after two days, and can be induced to differentiate to be neural cells after being cultured for 12-15 days. The method for promoting the induced pluripotent stem cells to induce and differentiate to be the nerve cells can speed up neurons to induce and differentiate, and improves neuron growth states ofspinocerebellum ataxic three-type iPS.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Analogs of choline for neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement in neurodegenerative disorders
InactiveUS6881738B2Prevent further deteriorationIncrease awarenessBiocideNervous disorderParaneoplastic cerebellar degenerationDementia with Lewy bodies
The present invention relates to novel analogs of choline and methods of use or treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and / or conditions such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington disease, Alzheimer's disease and related disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedrich's ataxia, Pick's disease, Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome, Refsom's disease, retinal degeneration, Cruetzfelt-Jacob syndrome or prion disease (mad cow disease), dementia with Lewy bodies, schizophrenia, paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration and neurodegenerative conditions caused by stroke. The present compounds are effective to treat any neurological condition where acetylcholine transmission neurons and their target cells are affected. Compounds according to the present invention are effective to alleviate and / or reverse the effects of a neurodegenerative condition, prevent further deterioration and / or enhance cognition and memory in patients suffering from neurodegenerative disorders, especially Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:AUGUSTA UNIV RES INST INC +1
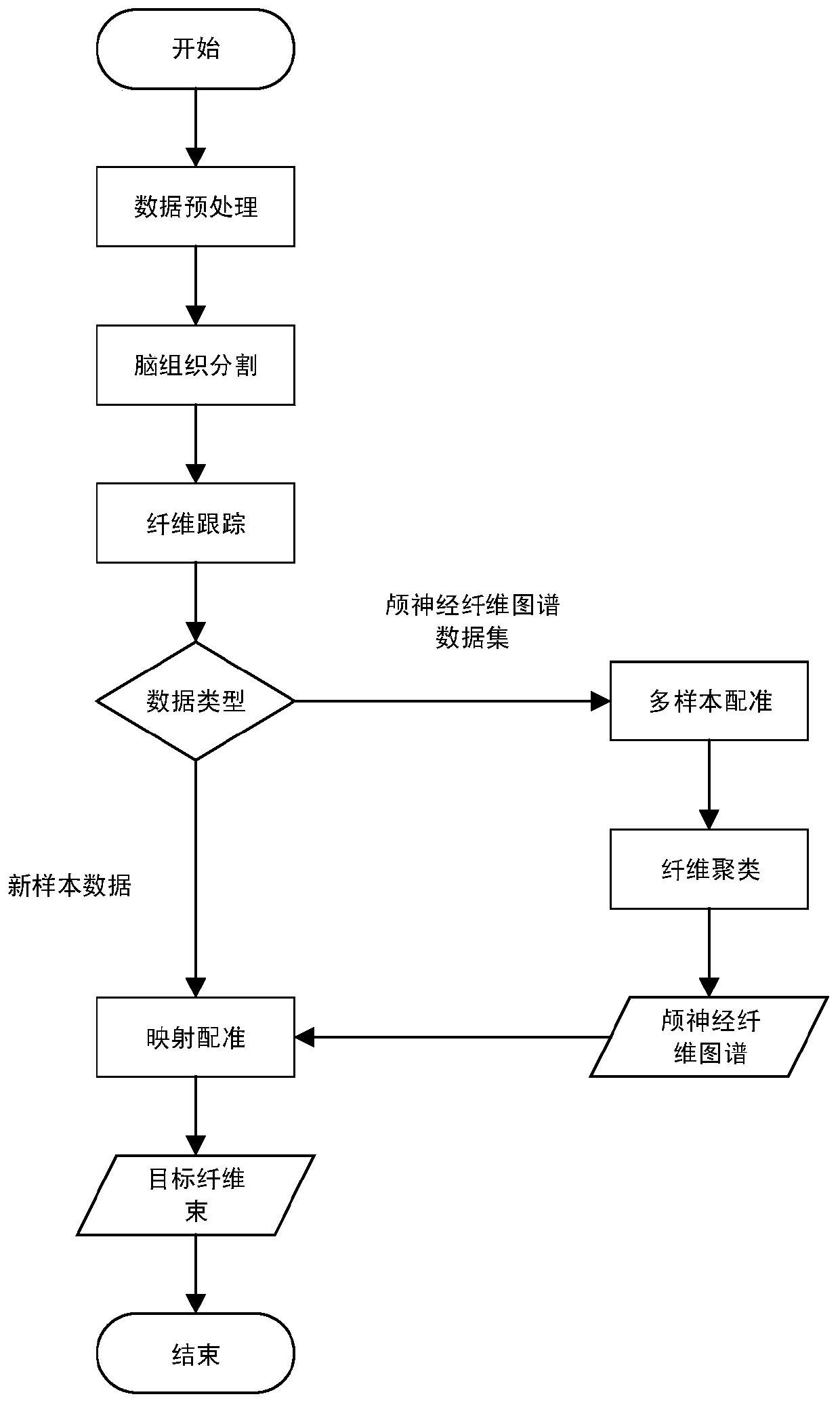
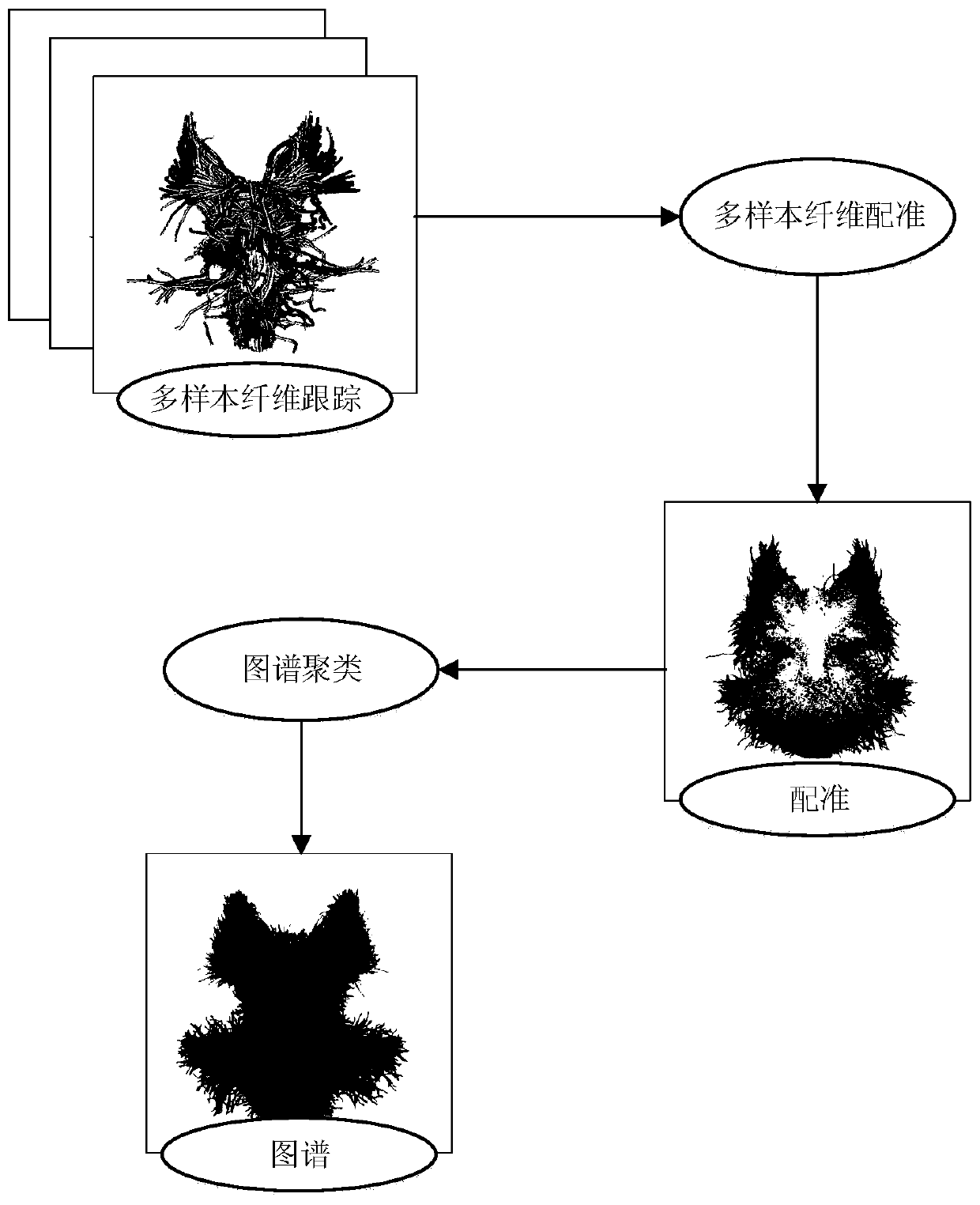
Cranial nerve automatic segmentation method based on large sample data driving
ActiveCN110533664ARealize automatic segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisCranial nervesData error
The invention discloses a cranial nerve fiber automatic segmentation method based on large sample data driving. A FreeSurfer tool is used for carrying out brain region segmentation. A deterministic tracking method based on spherical deconvolution (SD_STREAM) is applied to perform fiber tracking of brainstem and cerebellum parts on original DTI data, and on the basis of a cranial nerve fiber atlasobtained by a multi-sample registration and clustering method, sample data is mapped and registered to obtain a target cranial nerve fiber bundle. Compared with a common method for manually drawing ROI and removing wrong fibers, the method has the advantages that subjectivity introduced by manual operation is eliminated, meanwhile, the imaging determinacy of the fiber bundle is guaranteed, data errors are reduced, and an efficient, accurate, stable and repeatable method can be provided for cranial nerve fiber segmentation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Red peony root injection and its preparation method
InactiveCN1481882AImprove stabilityEasy to usePharmaceutical delivery mechanismUnknown materialsAcute hypoxiaAcute cerebral infarction
The present invention is one kind of red peony injection prepared with red peony root as material and through alcohol extraction, n-butanol extraction or macroporous resin purification, and adding proper amount of medicinal supplementary material and injection water. It is stable and may be used in intramuscular injection, intravenous injection and intravenous instillation. Pharmacodynamic experiment shows that the medicine of the present invention can improve the behavior disorder of rat with cerebral infarction obviously, reduce the area of cerebral infarction, decrease water content in infracted brain tissue, reduce the peroxidation damage of lipoid in brain tissue and raise the acute oxygen lack tolerance of mouse and thus has excellent treat effect on cerebral infarction.
Owner:秦吉兴
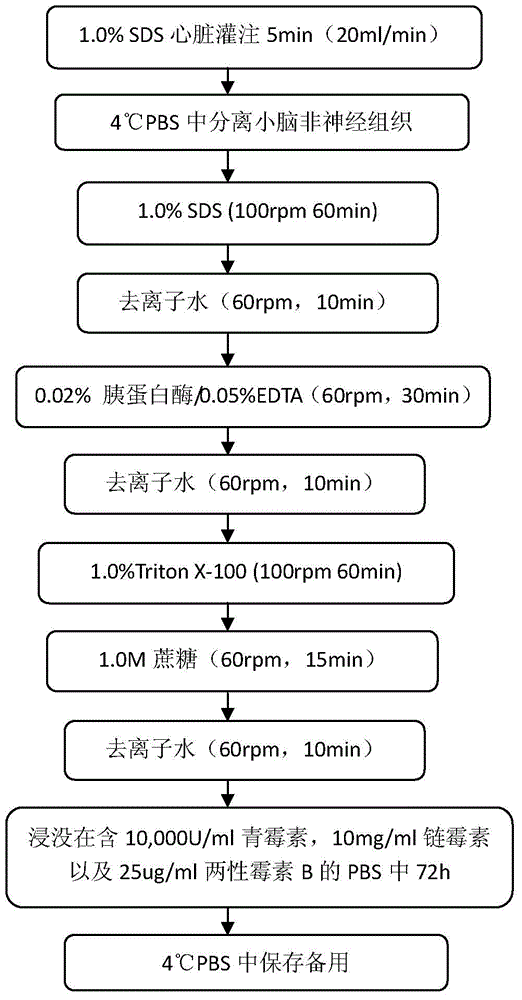
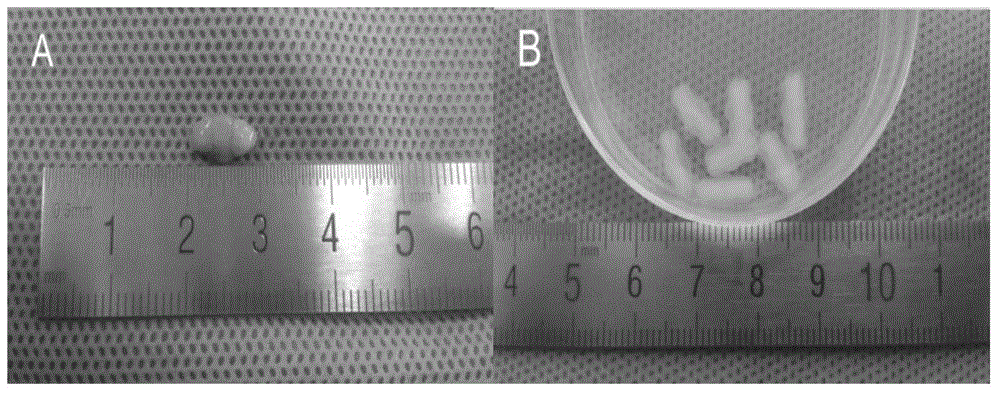
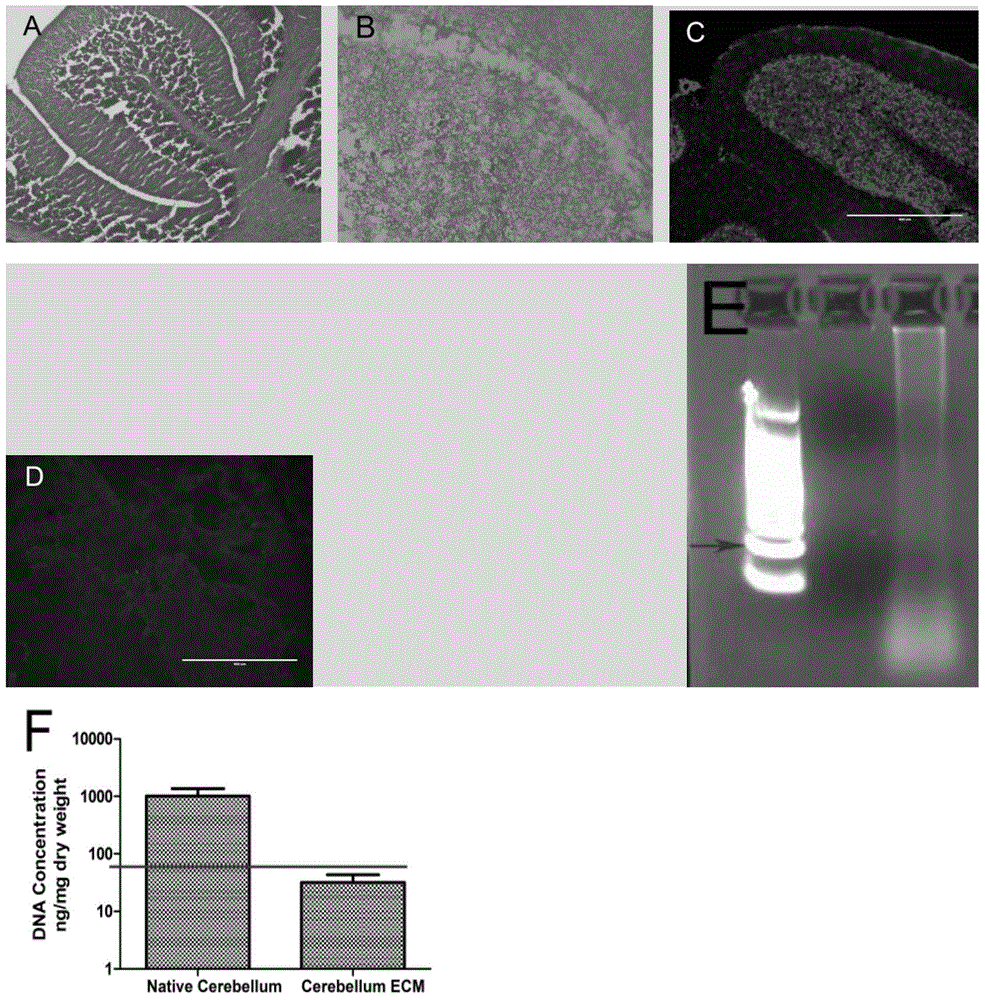
Cerebellar decellularized regeneration biological scaffold, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106693055APromotes Adhesive GrowthPromote formationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiomechanics
Belonging to the field of biological tissue engineering and medical materials, the invention relates to a decellularized cerebellar extracellular matrix regeneration biological scaffold containing multiple neurotrophic factors and a preparation method thereof. As a cerebellum regeneration scaffold material, the natural cerebellar decellularized scaffold adopted by the invention is a three-dimensional network structure, and the spatial configuration conforms to the cerebellar physiological structure spatial configuration. The regeneration biological scaffold and its biomechanical properties are similar to normal cerebellus, and can provide physiologically similar channels for reconstruction of nerve pathways so as to provide correct guidance for growth. The scaffold surface has cell-membrane receptor recognition sites and partially active factors, thus being conducive to adhesion growth of cells and functioning of physiological functions. Engineered seed cells can secrete a variety of neurotrophic / growth factors, also can promote the formation of new extracellular matrixes, and provides regeneration guidance signals. With good biocompatibility, the regeneration biological scaffold can be used for preparation of neural repair preparations for treatment of nerve injuries.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
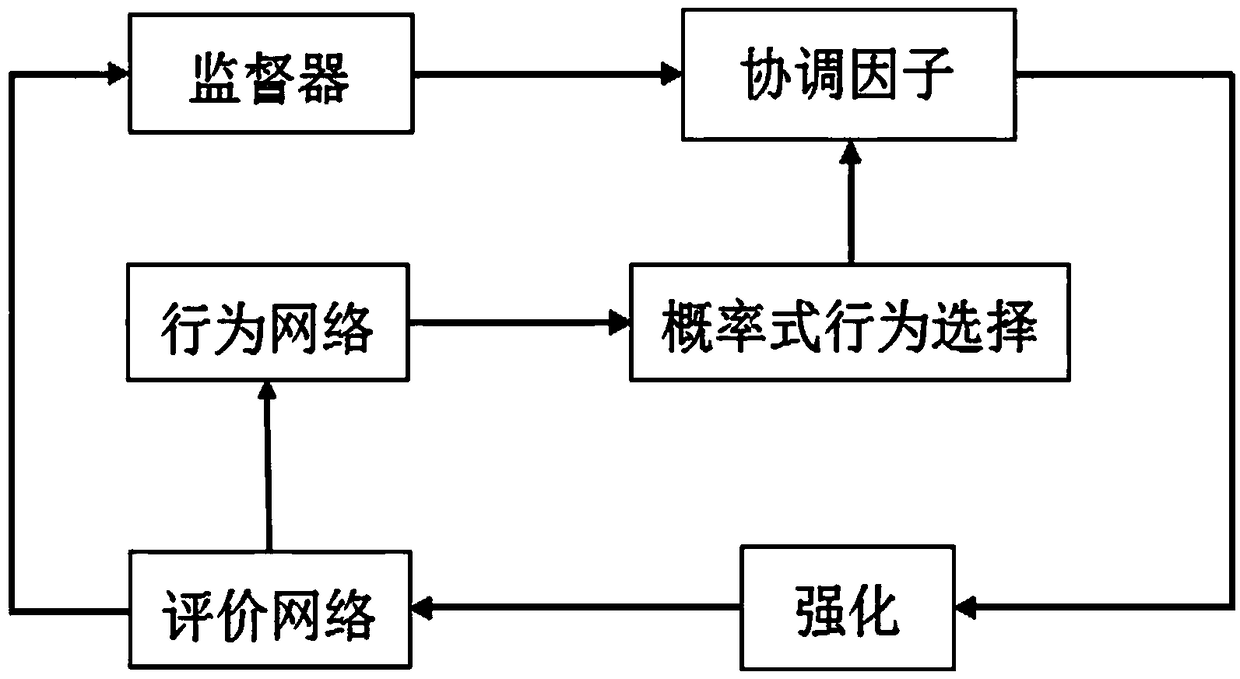
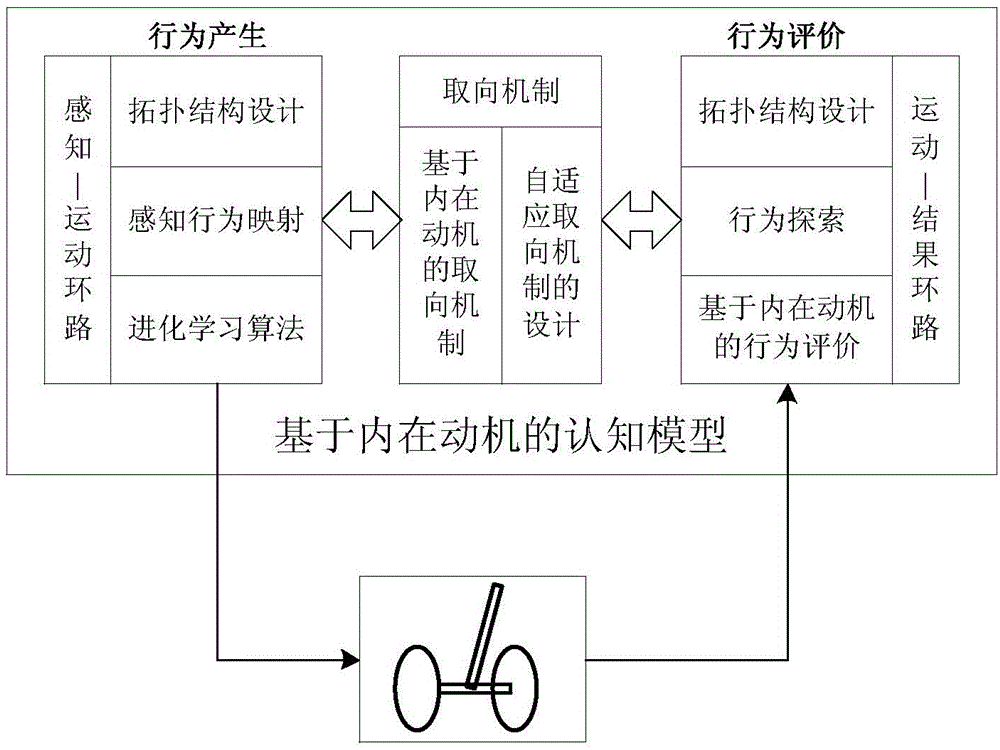
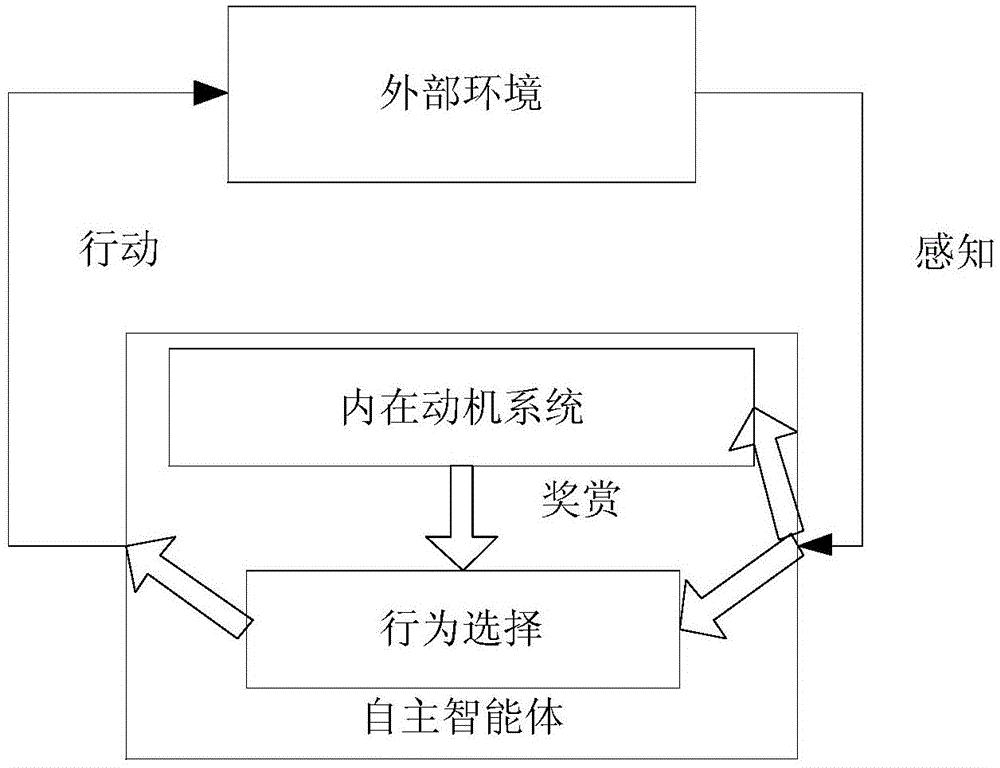
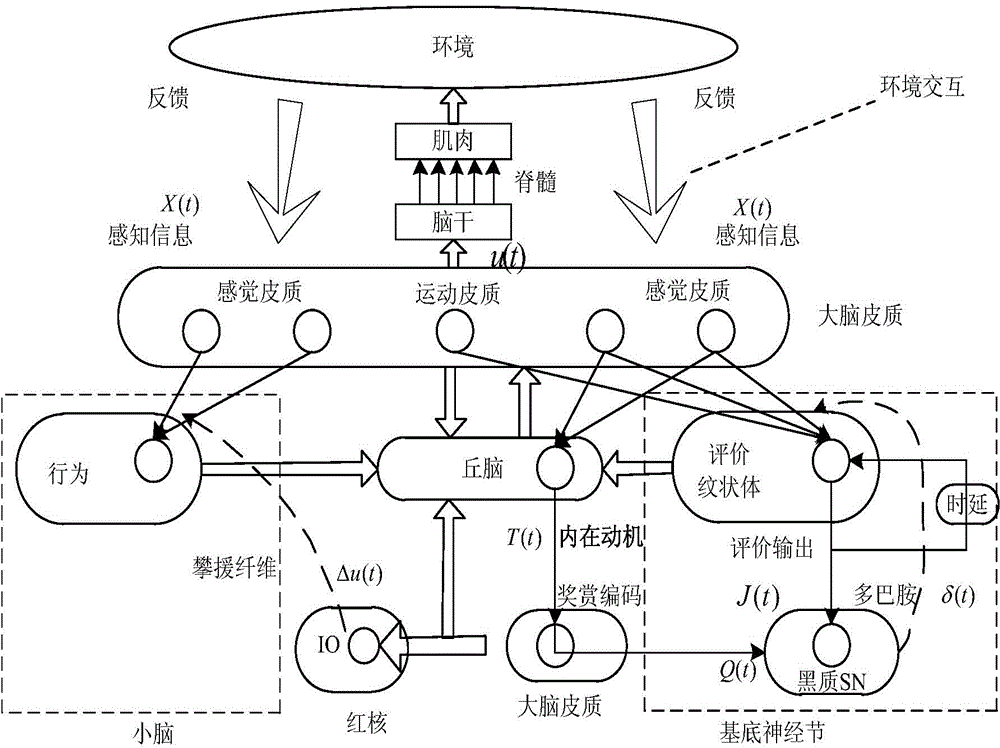
Intrinsic motivation based self-cognition system for motion balance robot and control method
InactiveCN104992059ASolve self-awareness problemsSolve the "conversion" problemSpecial data processing applicationsRoboticsIntrinsics
The invention discloses an intrinsic motivation based self-cognition system for a motion balance robot and a control method. The system comprises an intrinsic motivation based cognition model composed of behavior generation, behavior evaluation and orientation mechanism; the behavior generation is the formation of a 'perception-motion' loop; the behavior evaluation is the formation of a 'motion-result' loop; and the orientation mechanism is used for connecting the behavior generation with the behavior evaluation. The method comprises the steps that: a cortex-cerebellum system calculates action output amount according to sensory cortex information fed back by an intelligent body; a cortex-striatum system in a basal ganglion obtains an evaluation value by utilizing the sensory cortex information fed back by the intelligent body and motor cortex information calculated by cerebellum; and the cortex-striatum system and the cortex-cerebellum system are subjected to synaptic modification. According to the system and the method, neurophysiology, cognitive psychology and robotology are combined, a cognition mechanism is described and realized in a mathematic mode, and the self-cognition problem of the robot is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
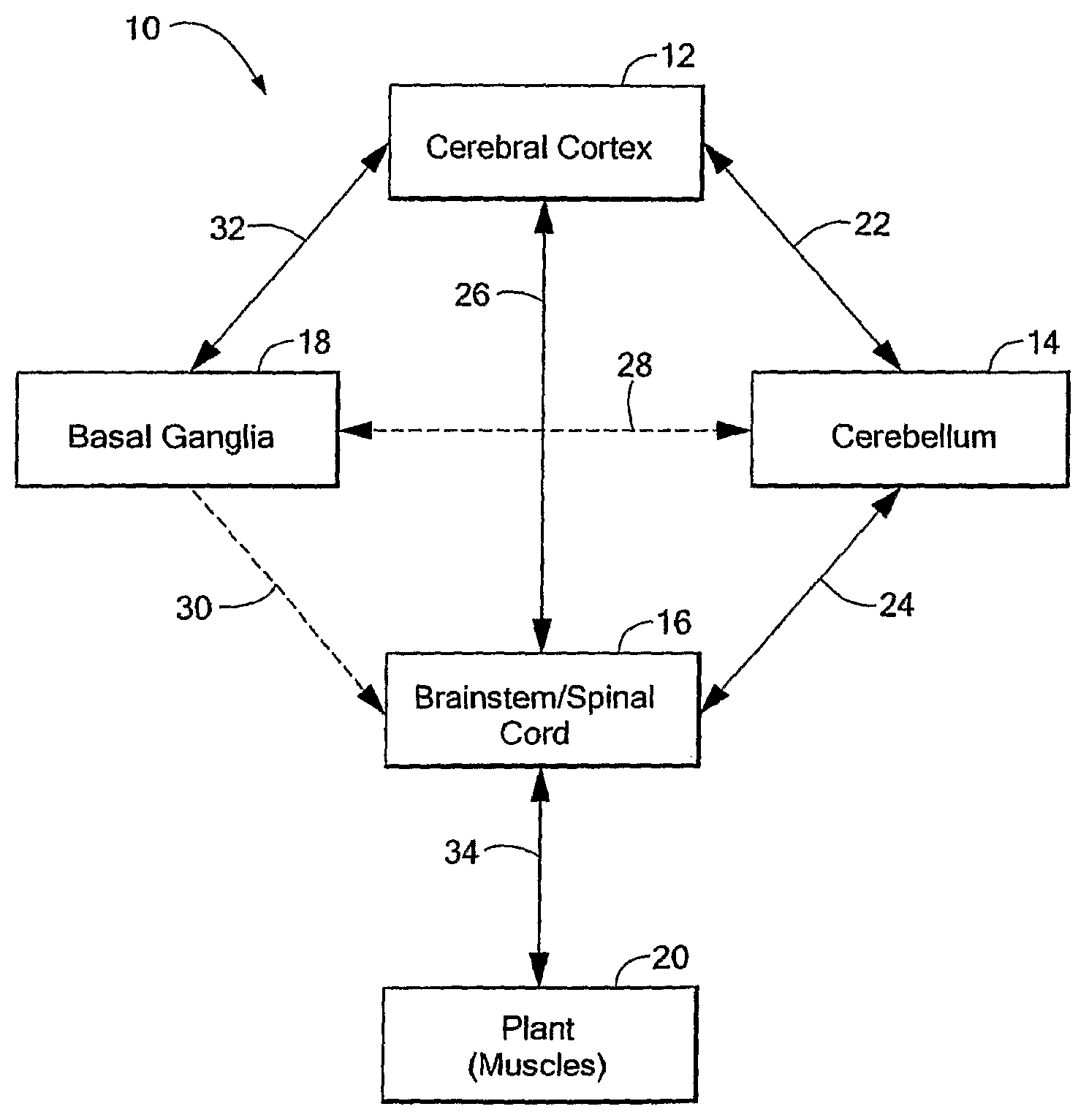
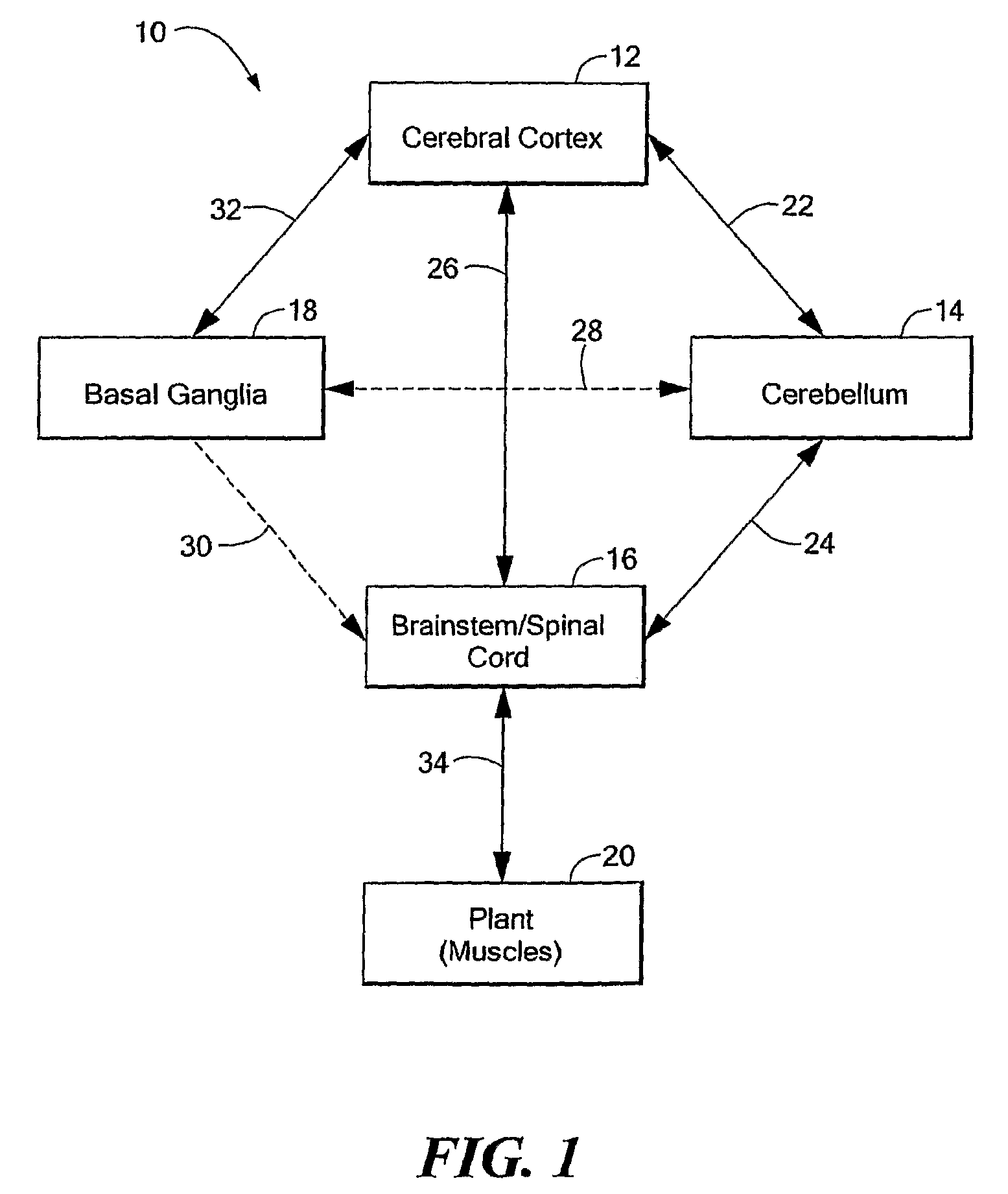
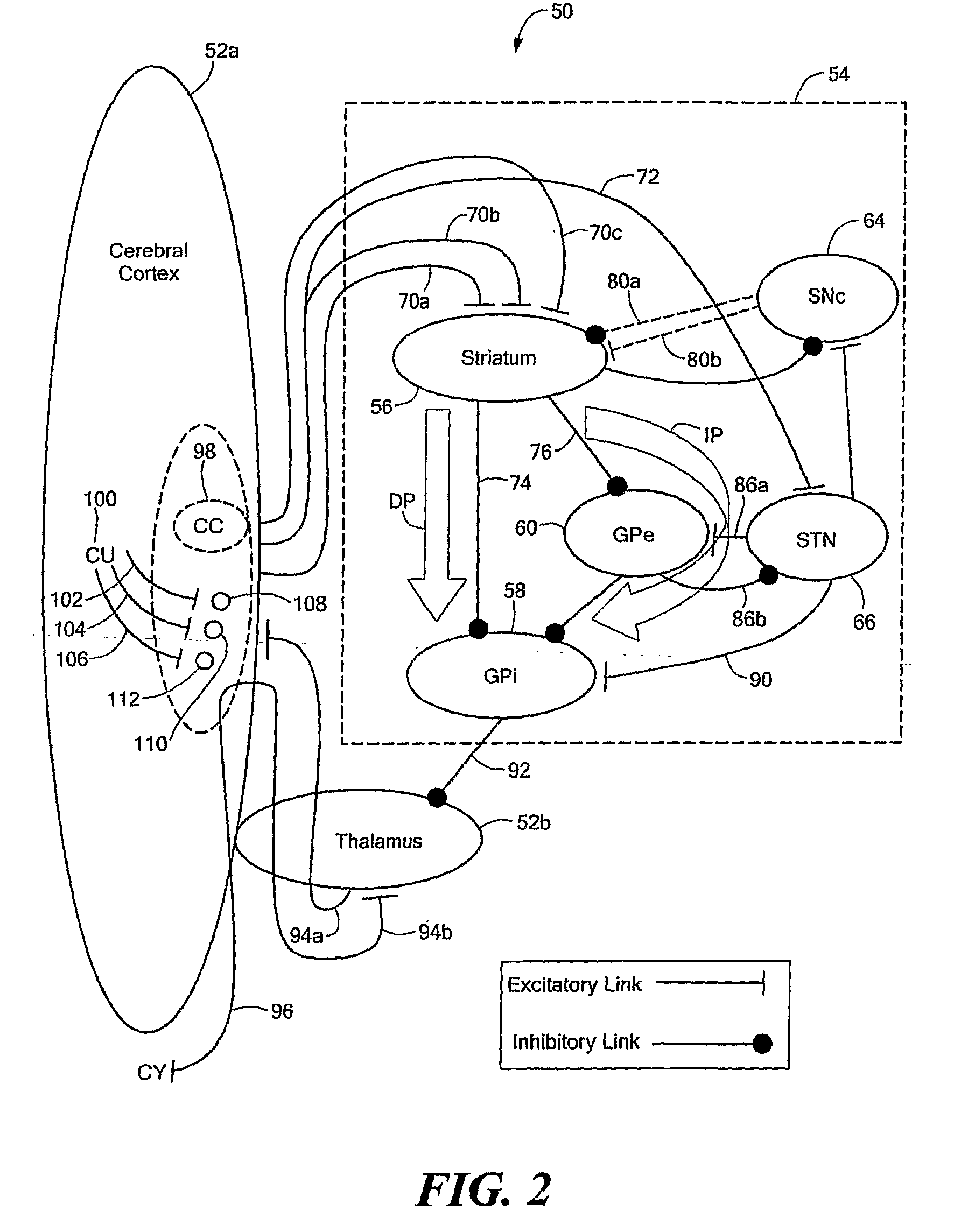
Computer-Implemented Model of the Central Nervous System
A computer-implemented model of the central nervous system includes at least one of a basal ganglia portion, a cerebral cortex portion coupled to the basal ganglia portion, or a cerebellum portion coupled to the cerebral cortex. Each one of the basal ganglia portion, the cerebral cortex portion, and the cerebellum portion is comprised of respective elements representative of real neuroanatomical structures of a central nervous system and the respective elements are adapted to perform functions representative of real neuroanatomical functions of the central nervous system. At least one of the basal ganglia portion, the cerebral cortex portion, or the cerebellum portion is adapted to control a plant.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method of inducing the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into nerve by serum-free suspension culture
ActiveUS8492147B2Effectively lead to differentiationEfficient inductionNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsSerum free mediaNervous system
The present invention provides a clinically applicable method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells into forebrain neurons. More specifically, the present invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells, comprising culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium, particularly a method of inducing differentiation of the embryonic stem cells into nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neurons and sensory organ cells; a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells obtained by culturing the embryonic stem cells as a floating aggregate in a serum-free medium; and cells derived from a floating aggregate of embryonic stem cells, particularly nervous system cells such as forebrain neurons and cerebellar neuron, sensory organ cells such as retinal precursor cells, and the like.
Owner:RIKEN
Remedies for spinocerebellar ataxia and compositions for treating spinocerebellar ataxia
InactiveUS7067545B1Reduce in quantityBiocideNervous disorderSpinocerebellar DegenerationsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Remedies for spinocerebellar degeneration or compositions for treating the same which contain as the active ingredient one or more members selected from among D-cycloserine, D-serine esters, D-serine and salts thereof. A method for treating spincerebellar degeneration which comprises administering to a patient with this disease in an efficacious dose of one or more members selected from among D-cycloserine, D-serine esters, D-serine and salts thereof.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Cytochrome p450ra1-2 and related proteins
InactiveUS20060115811A1High radioactivityMaintain standardCompound screeningBiocideDiseaseMetabolite
The present invention provides a novel all-trans-RA inducible all-trans-RA metabolizing cytochrome P450, P450RAI-2, that is predominantly expressed in the brain, cerebellum in particular. Human P450RAI-2 show 42% amino acid identity to human P450RAI-1 and when transfected into COS-1 cells causes the rapid conversion of all-trans-RA into more polar metabolites including the inactive products 4-oxo-RA, 4-OH-RA and 18-OH-RA. P450RAI-2, as with P450RAI-1, is also inducible in certain cultured cell lines exposed to all-trans-RA. Methods for and uses of the new polynucleotide, polypeptide, fragments thereof and inhibitors thereof, include the treatment of dermatological disorders and cancer.
Owner:PARTEQ INNOVATIONS
Cow brain tissue sampling method
The present invention relates to brain tissue sampling method, and is especially ox brain tissue sampling method. The technological scheme of the present invention includes the following steps: 1. locating the sampling range 1-2 cm before the midpoint of ox horn root line; 2. drilling hole through the ox skull in the location; and 3. puncturing with a biopsy needle and sampling the required giant brain, little brain or brain stem tissues. The method of the present invention is simple, convenient and accurate.
Owner:HUNAN CANWA BIOSCI DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com