Patents
Literature
443 results about "Mri brain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment of epilepsy by brain stimulation
InactiveUS7003352B1Small sizeInhibition amountElectrotherapyPressure infusionMedicineElectrical stimulations
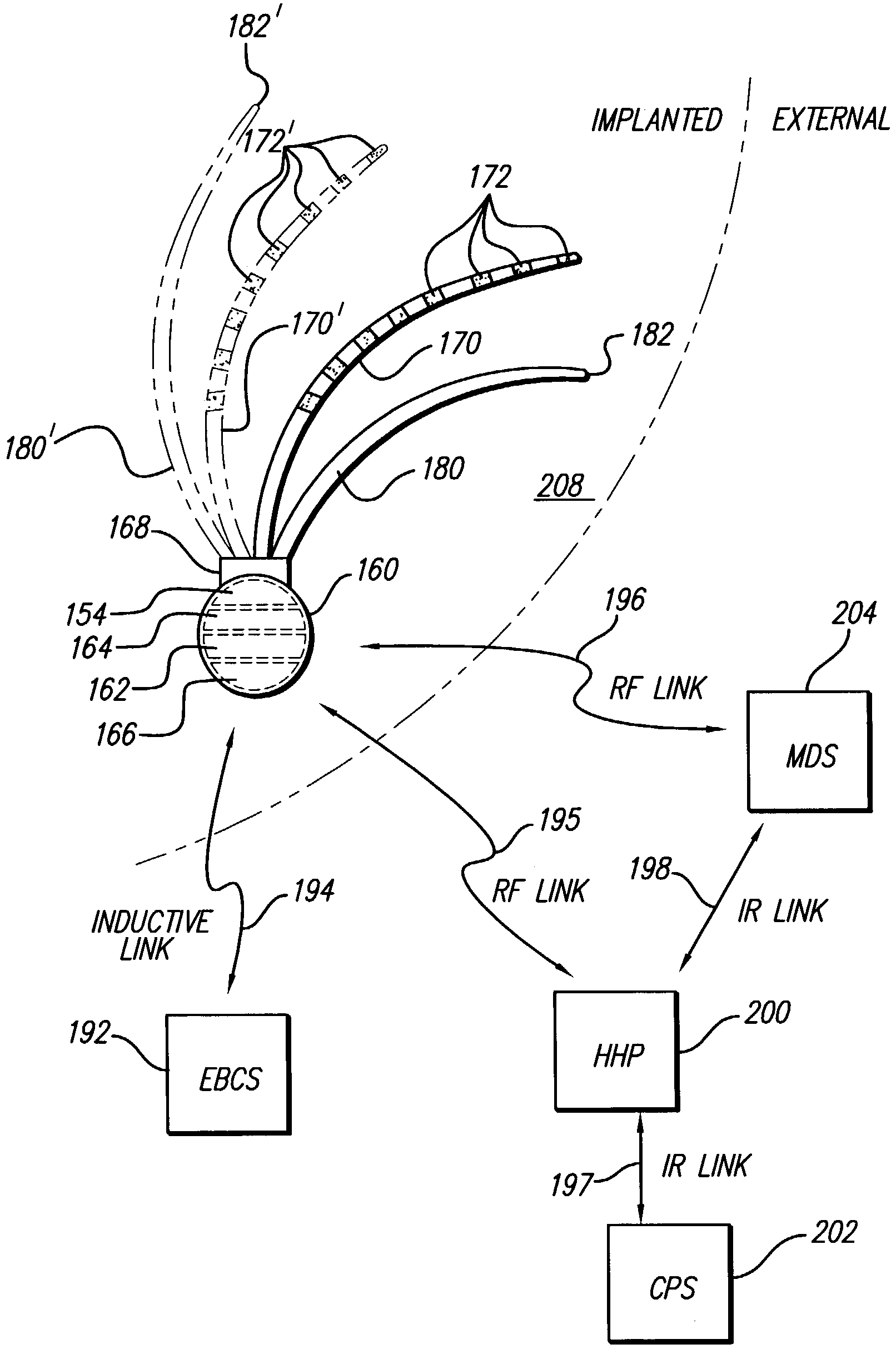
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the brain and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain is used to treat epilepsy. At least one implantable system control unit (SCU) produces electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or drug infusion pulses delivered via a catheter implanted in the brain. The stimulation is delivered to targeted brain structures to adjust the activity of those structures. The small size of the SCUs of the invention allow SCU implantation directly and entirely within the skull and / or brain. Simplicity of the preferred systems and methods and compactness of the preferred system are enabled by the modest control parameter set of these SCU, which do not require or include a sensing feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Selective brain stimulation using conditioning pulses
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
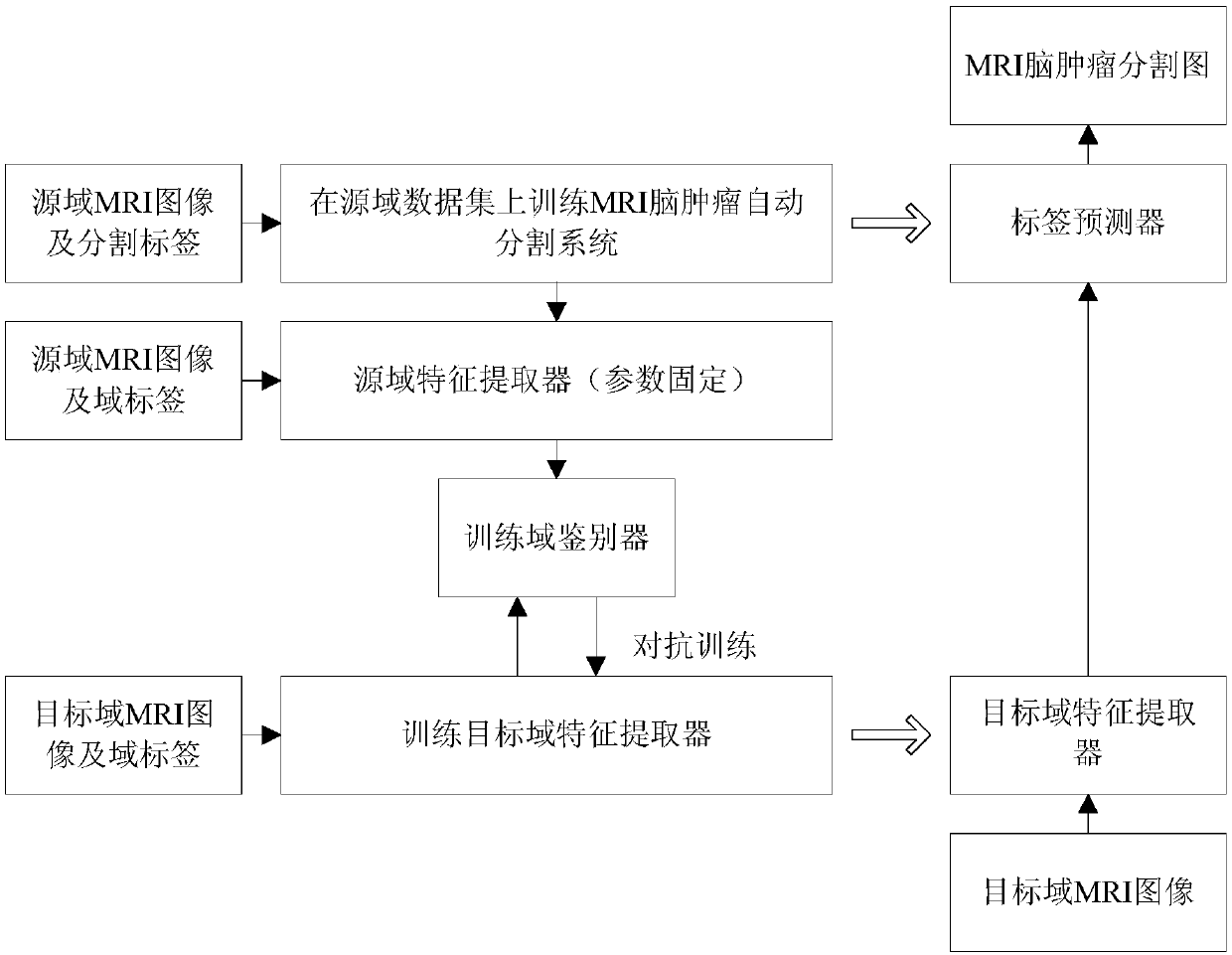
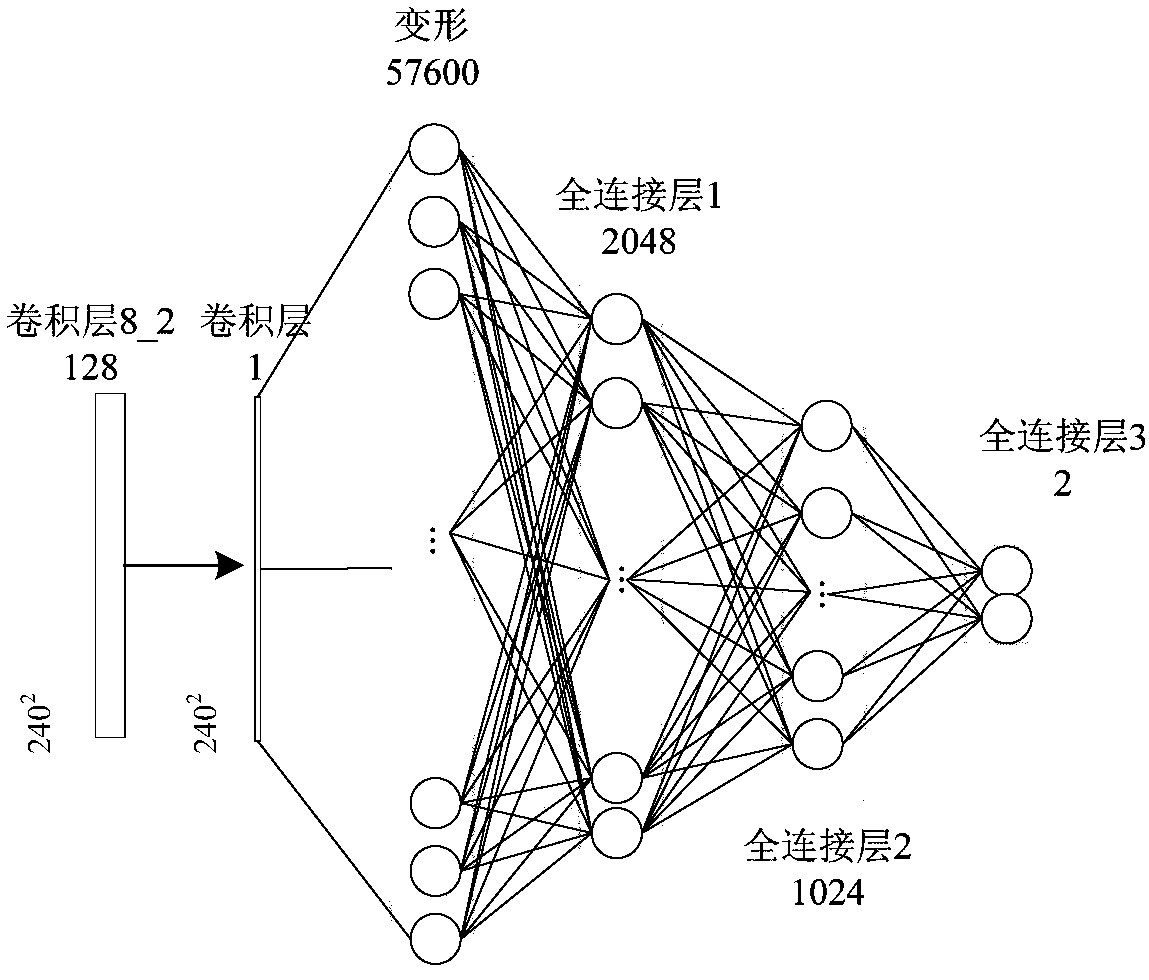
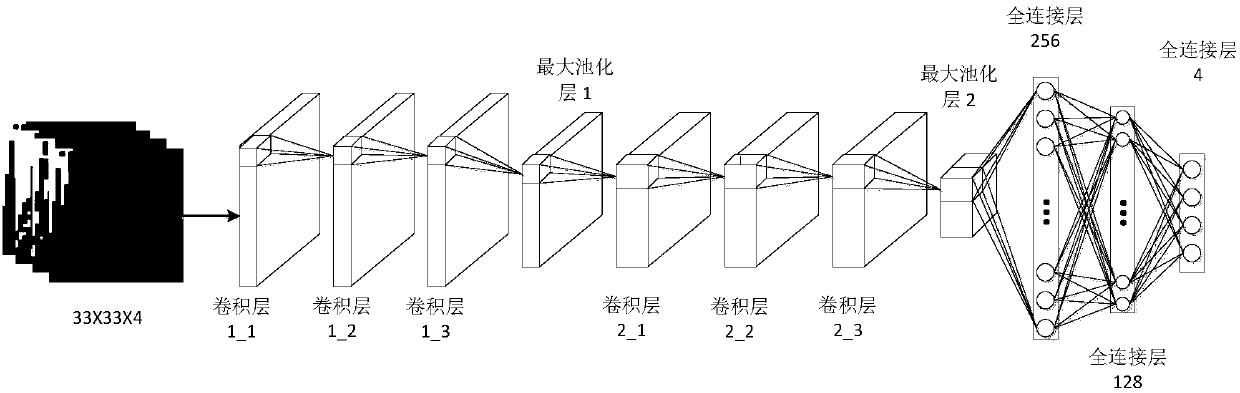
Unsupervised domain-adaptive brain tumor semantic segmentation method based on deep adversarial learning
InactiveCN108062753AAccurate predictionEasy to trainImage enhancementImage analysisDiscriminatorNetwork model
The invention provides an unsupervised domain-adaptive brain tumor semantic segmentation method based on deep adversarial learning. The method comprises the steps of deep coding-decoding full-convolution network segmentation system model setup, domain discriminator network model setup, segmentation system pre-training and parameter optimization, adversarial training and target domain feature extractor parameter optimization and target domain MRI brain tumor automatic semantic segmentation. According to the method, high-level semantic features and low-level detailed features are utilized to jointly predict pixel tags by the adoption of a deep coding-decoding full-convolution network modeling segmentation system, a domain discriminator network is adopted to guide a segmentation model to learn domain-invariable features and a strong generalization segmentation function through adversarial learning, a data distribution difference between a source domain and a target domain is minimized indirectly, and a learned segmentation system has the same segmentation precision in the target domain as in the source domain. Therefore, the cross-domain generalization performance of the MRI brain tumor full-automatic semantic segmentation method is improved, and unsupervised cross-domain adaptive MRI brain tumor precise segmentation is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
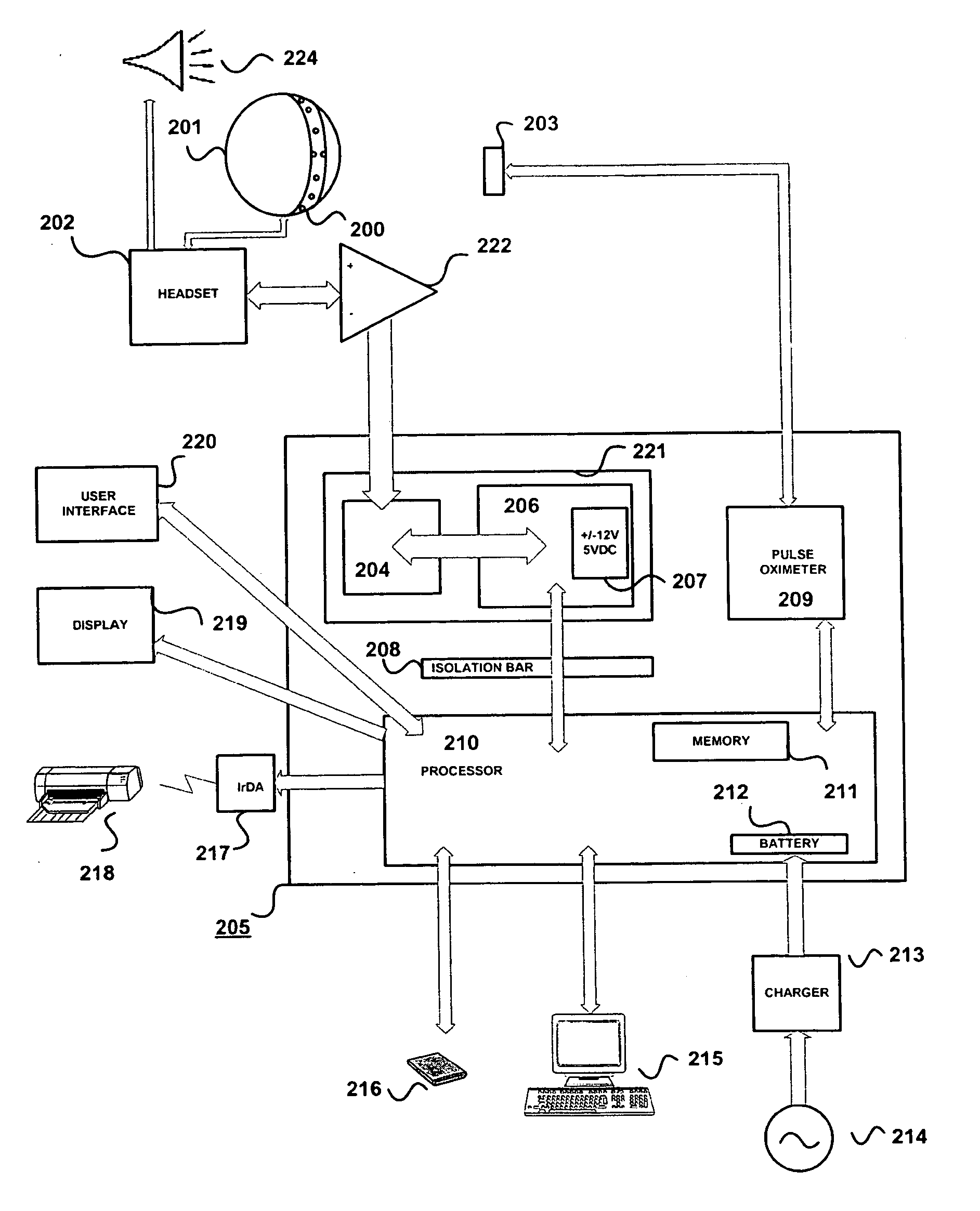
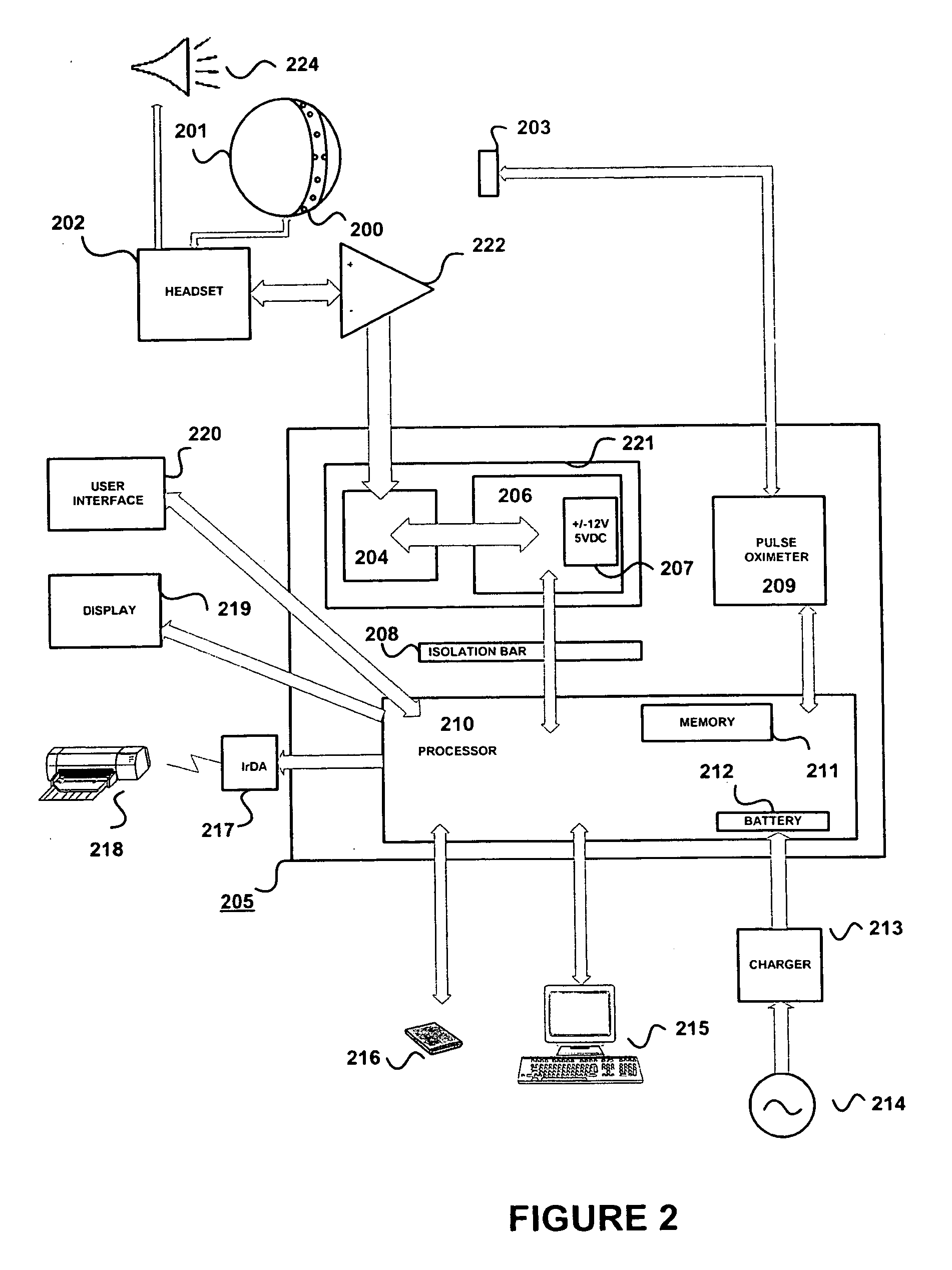
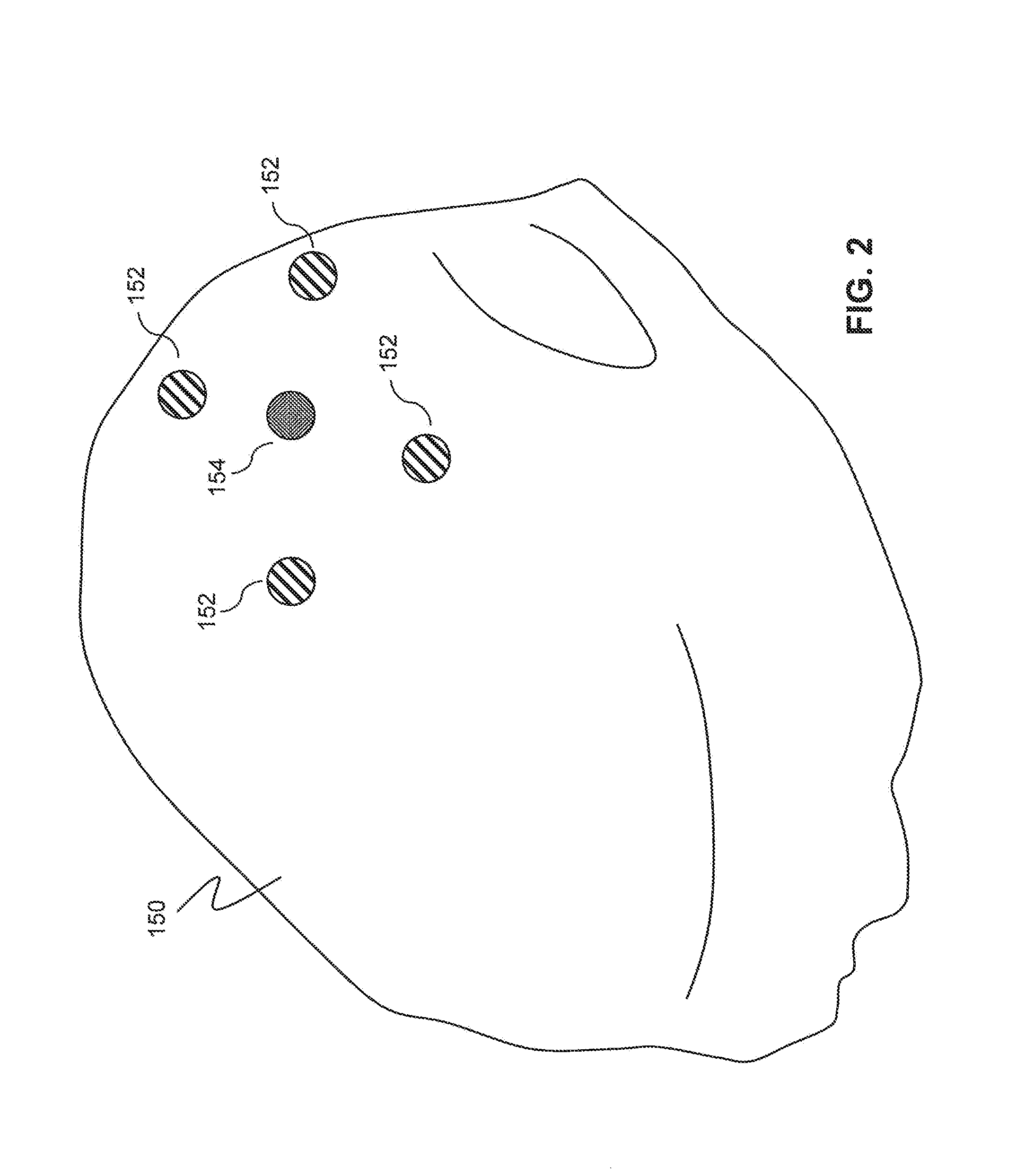
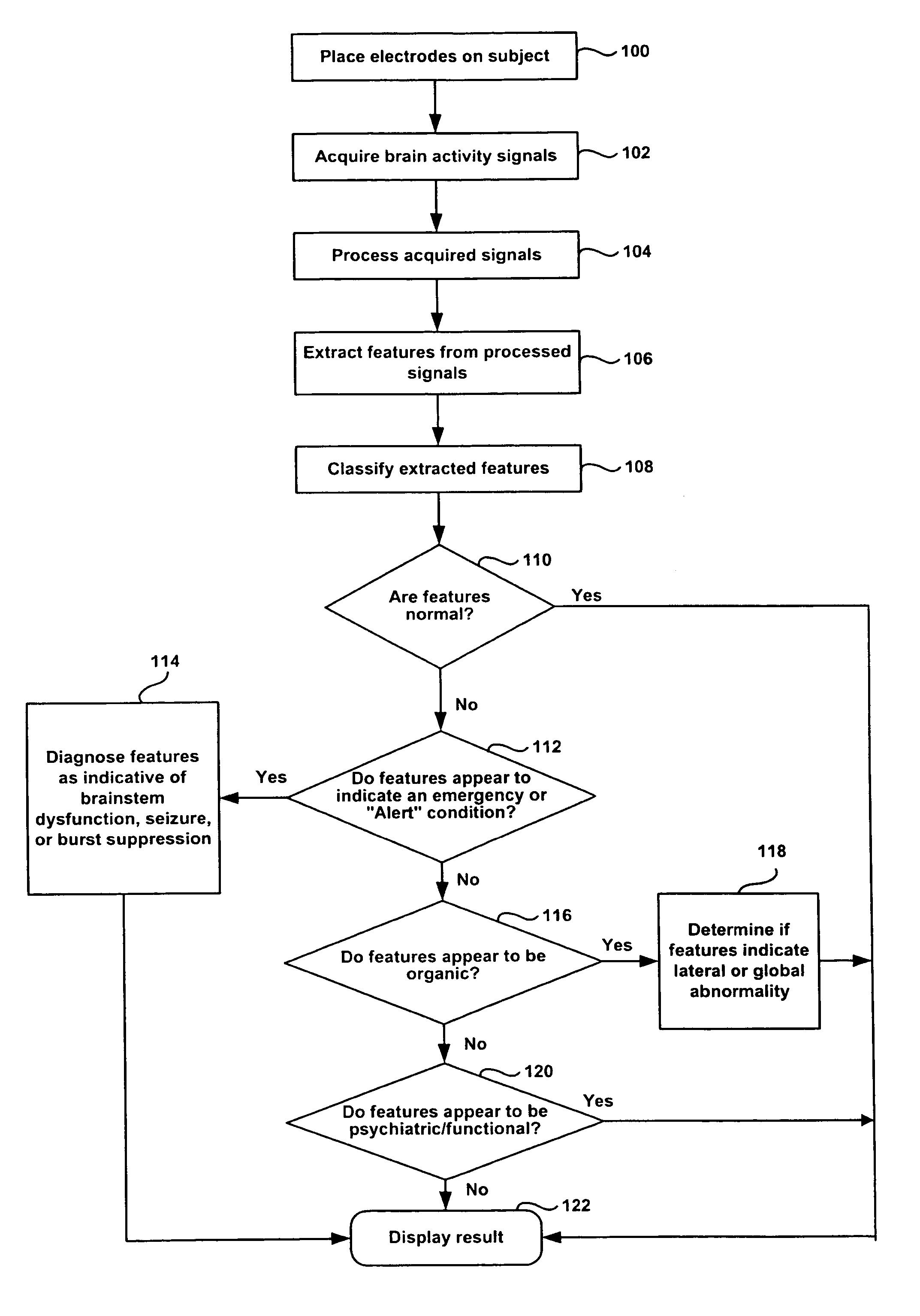
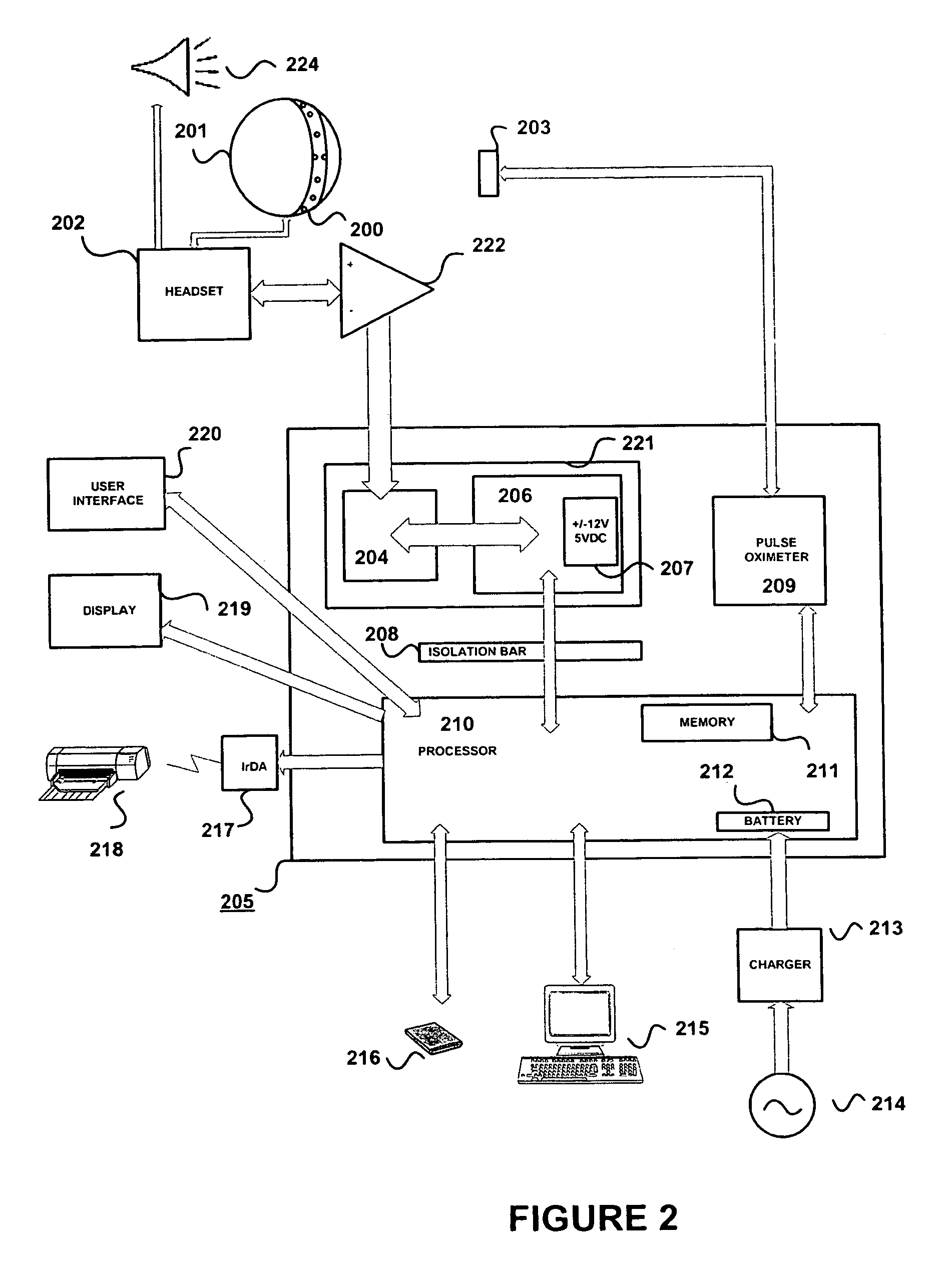
Method for assessing brain function and portable automatic brain function assessment apparatus
A method and apparatus for performing rapid brain assessment may provide emergency triage to head trauma patients by analyzing a combination of spontaneous and evoked brain potentials. The spontaneous and evoked potentials are analyzed, and the results classified, to present a real-time assessment of a patient's brain, diagnosing any potential abnormalities therein.
Owner:BS HLDG +2
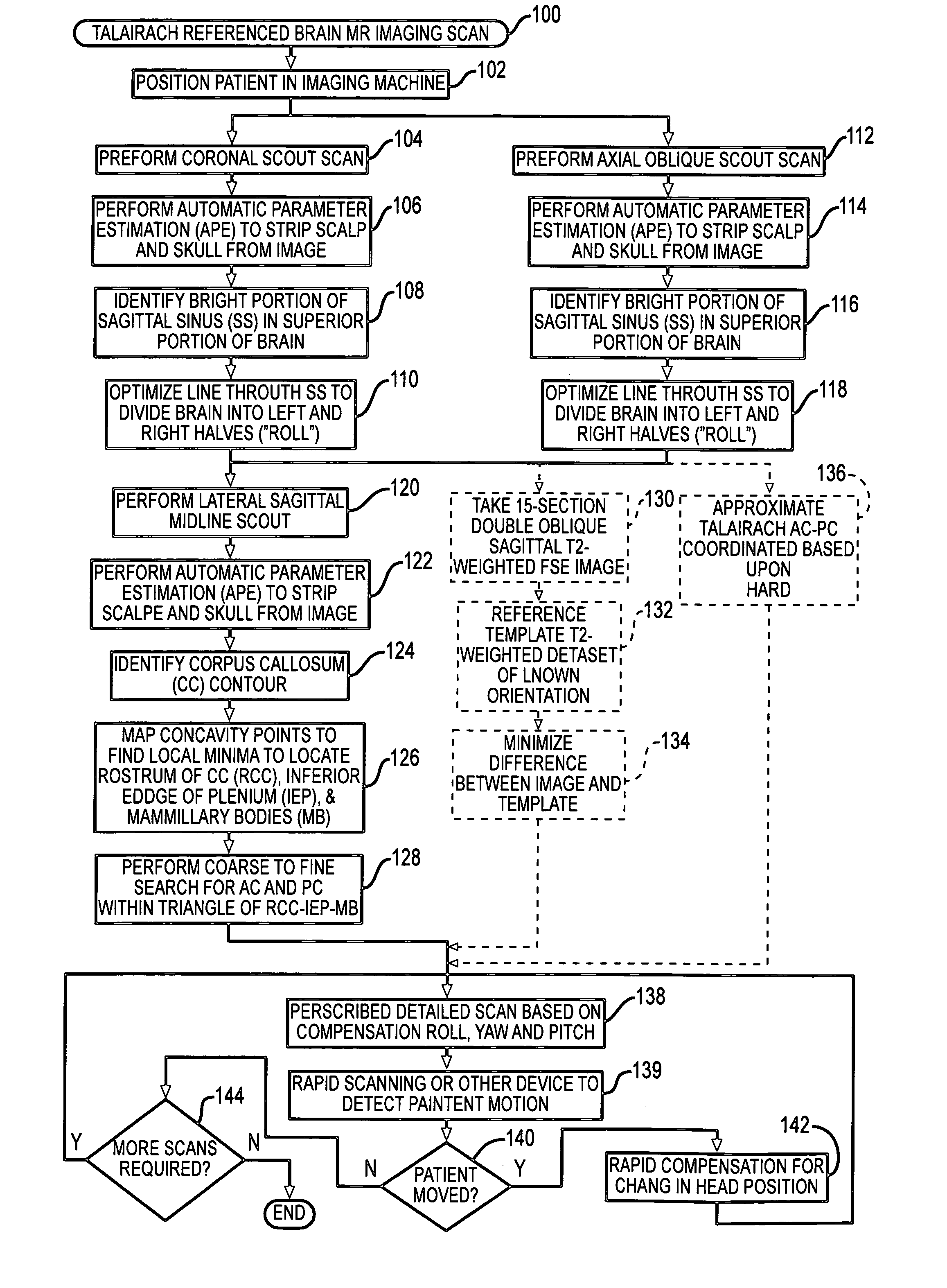
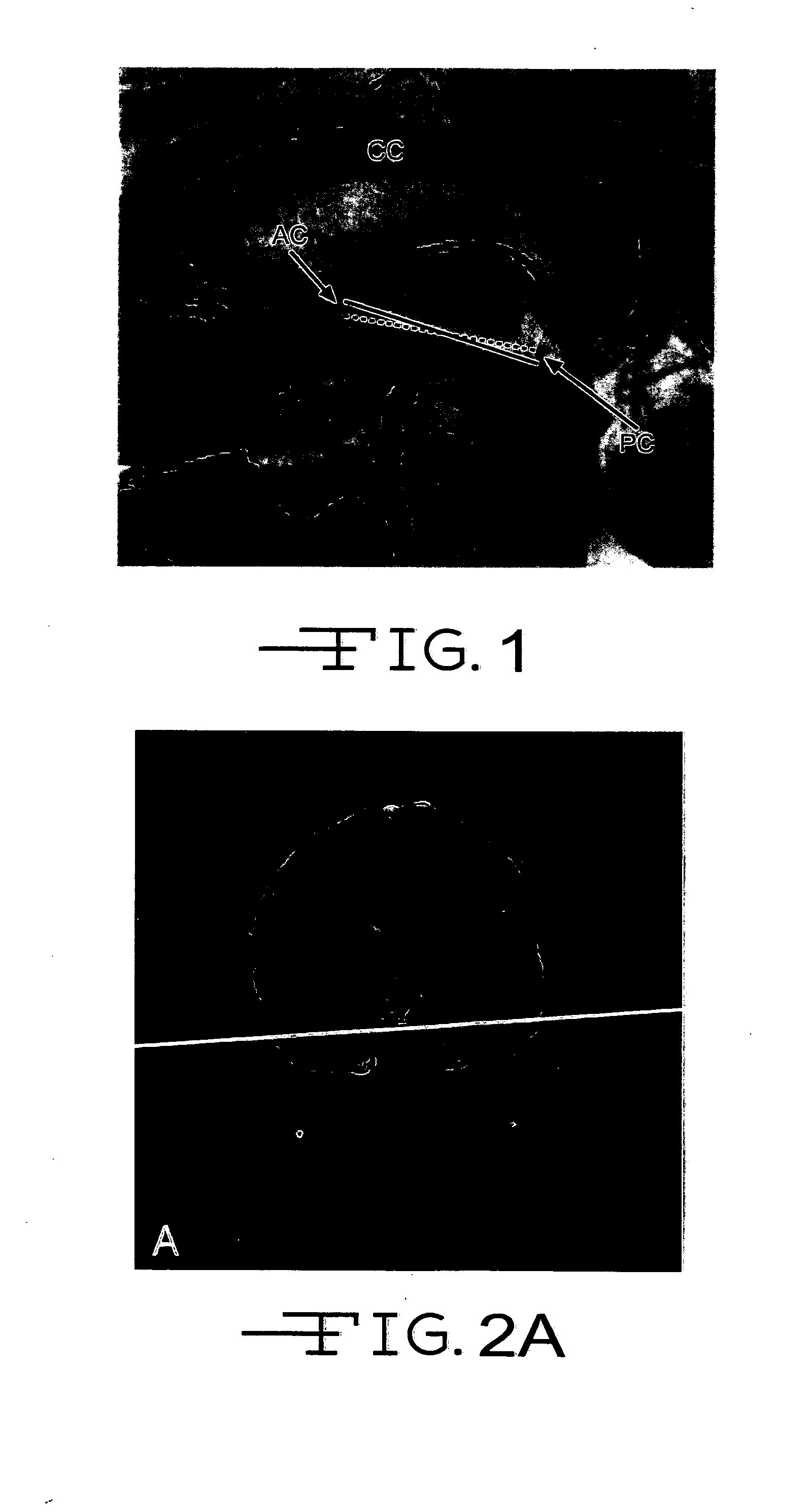
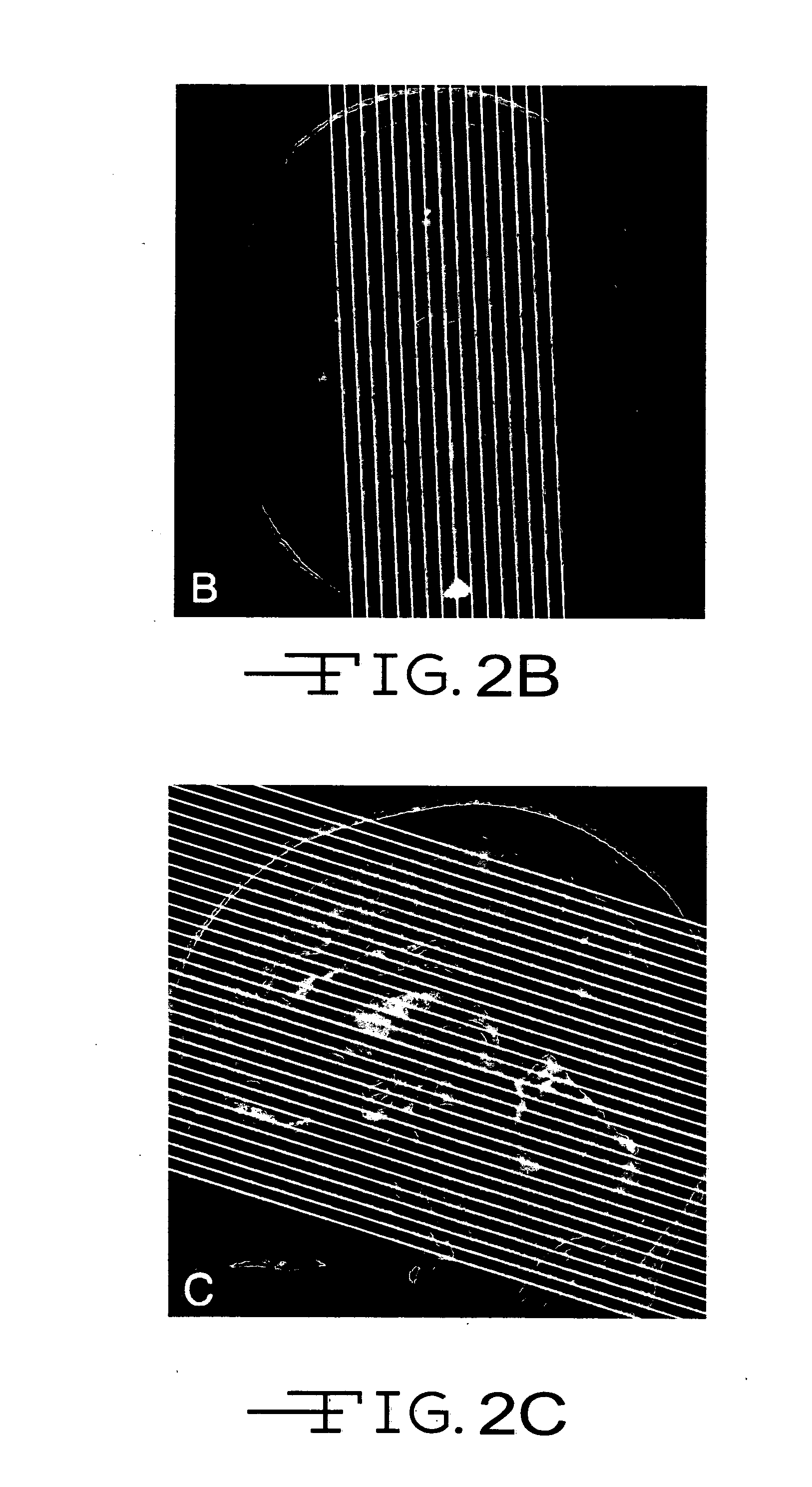
Automated brain MRI and CT prescriptions in Talairach space
InactiveUS20050165294A1Minimizes variabilitySurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic modalitiesAnterior commissure
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computerized Tomotography (CT), or other diagnostic modalities may employ a three-step procedure during initial (“scout”) cranial pre-scans that corrects for patient positioning (i.e., roll, yaw and pitch) to reduce inter- and intra-patient variation, thereby enhancing the diagnostic and comparative value of subsequent detail scans even across different diagnostic platforms. In MRI, for instance, locating the saggital sinus (SS) and optimizing a line to bisect the brain through this SS may be automated to correct for roll and yaw. By then identifying the contour of the corpus callosum in a lateral saggital scout scan, the Talairach anterior commissure (AC)—posterior commissure (PC) reference line may be found for correcting pitch. Prescription of detailed scans are improved, especially when the three-step correction is repeated periodically identifying the need to repeat a detailed scan or to adjust the coordinates of a subsequent scan.
Owner:ABSIST +1
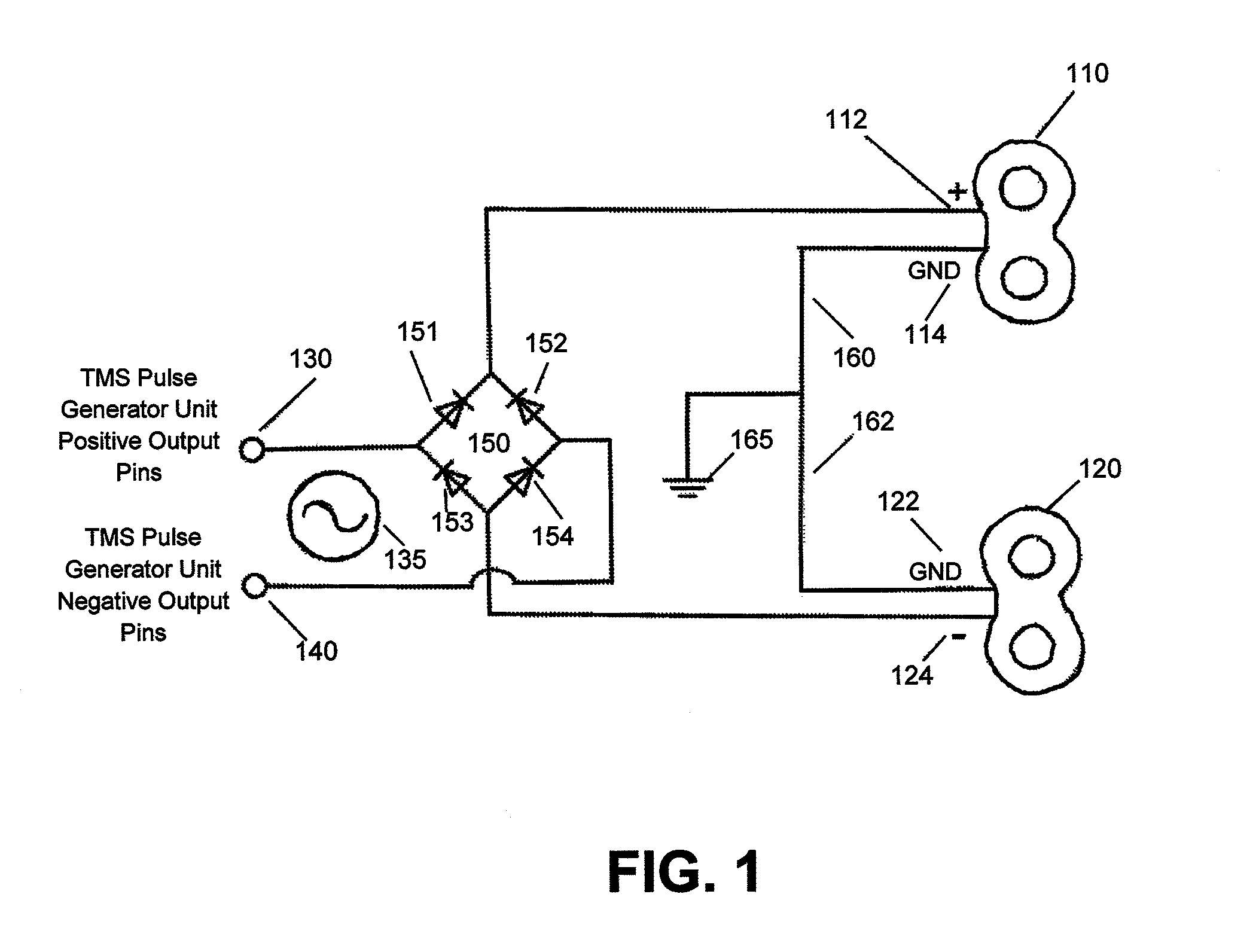
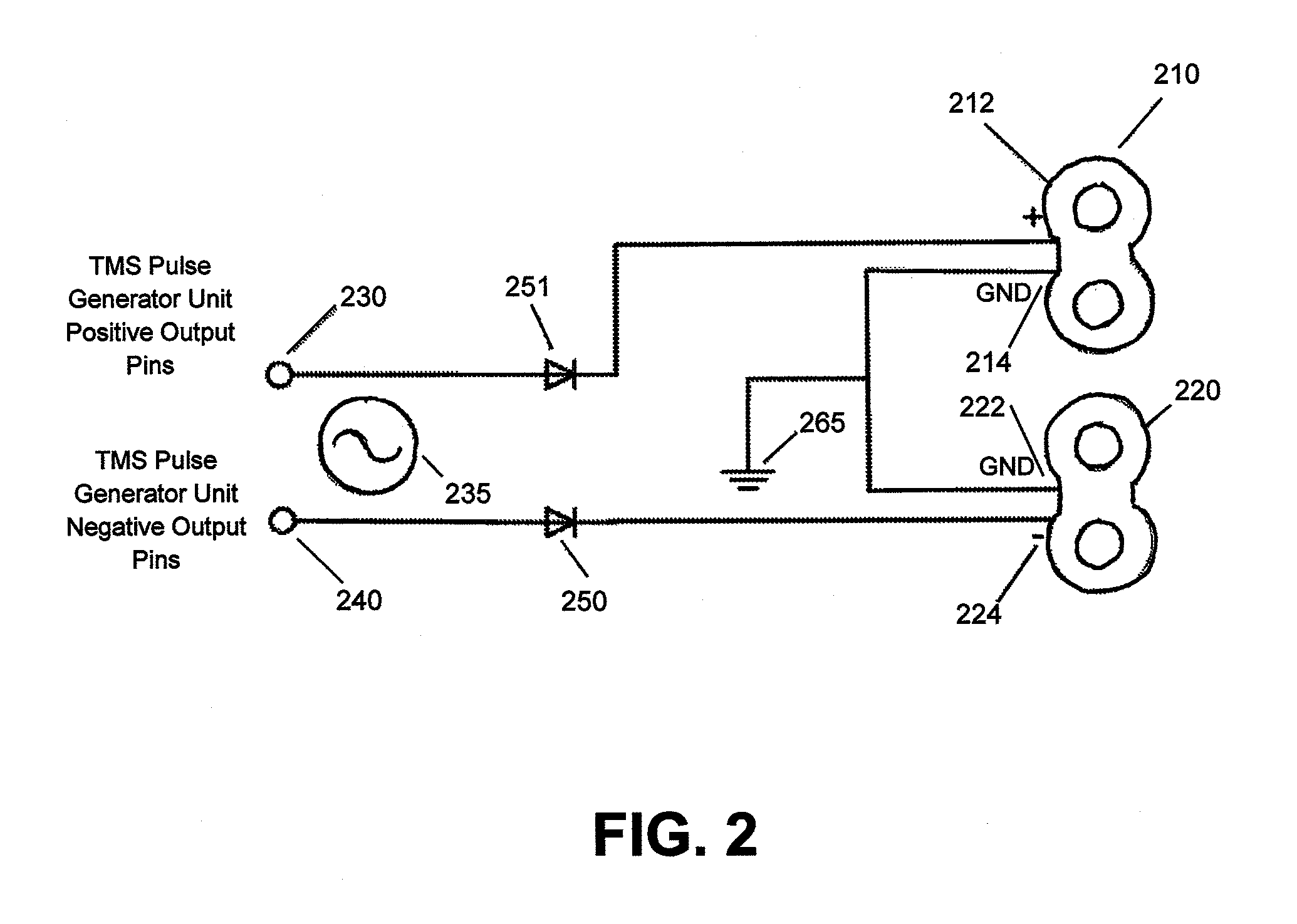
Control and coordination of transcranial magnetic stimulation electromagnets for modulation of deep brain targets
InactiveUS20100185042A1Enhance the electromagnetic field emittedDeeper, more effective Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsEngineeringMulti coil
Described herein are devices and method for control and coordination of TMS electromagnets for modulation of deep brain targets. For example, described herein are methods and devices for stimulating neural structures within the brain using multi-coil arrays. Also described herein are devices and methods that relate generally to the focusing of magnetic fields generated by electromagnets used for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Devices and methods relating generally to the focusing of magnetic fields generated by electromagnets used for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation are also described, as well as devices and methods that relate generally to moving and positioning electromagnets generating magnetic fields used for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation. Finally, also described are devices and methods that relate generally to control of moving, positioning, and activating electromagnets generating magnetic fields used for Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation.
Owner:CERVEL NEUROTECH
Accommodating intraocular lens
An Accommodating Intraocular Lens (AIOL) is disclosed herein, that is comprised of a flexible optic and a flexible haptic rim that conforms to the human eye capsule. The spherical or custom shape of the optic is engineered to be maintained during accommodation through the mechanical / optic design of the implant and the interaction between the implant and the naturally occurring position and actuating forces applied through ciliary muscle / zonules / and capsule as the brain senses the need to increase the diopter change or magnification when an object of fixation approaches the eye. The axial relocation or position of the AIOL may also be further adjusted anatomically to further improve the affect needed to achieve improved accommodation. Optionally, the accommodating intraocular lens is foldable or injectable for delivery of the lens into the eye.
Owner:STENGER DONALD C
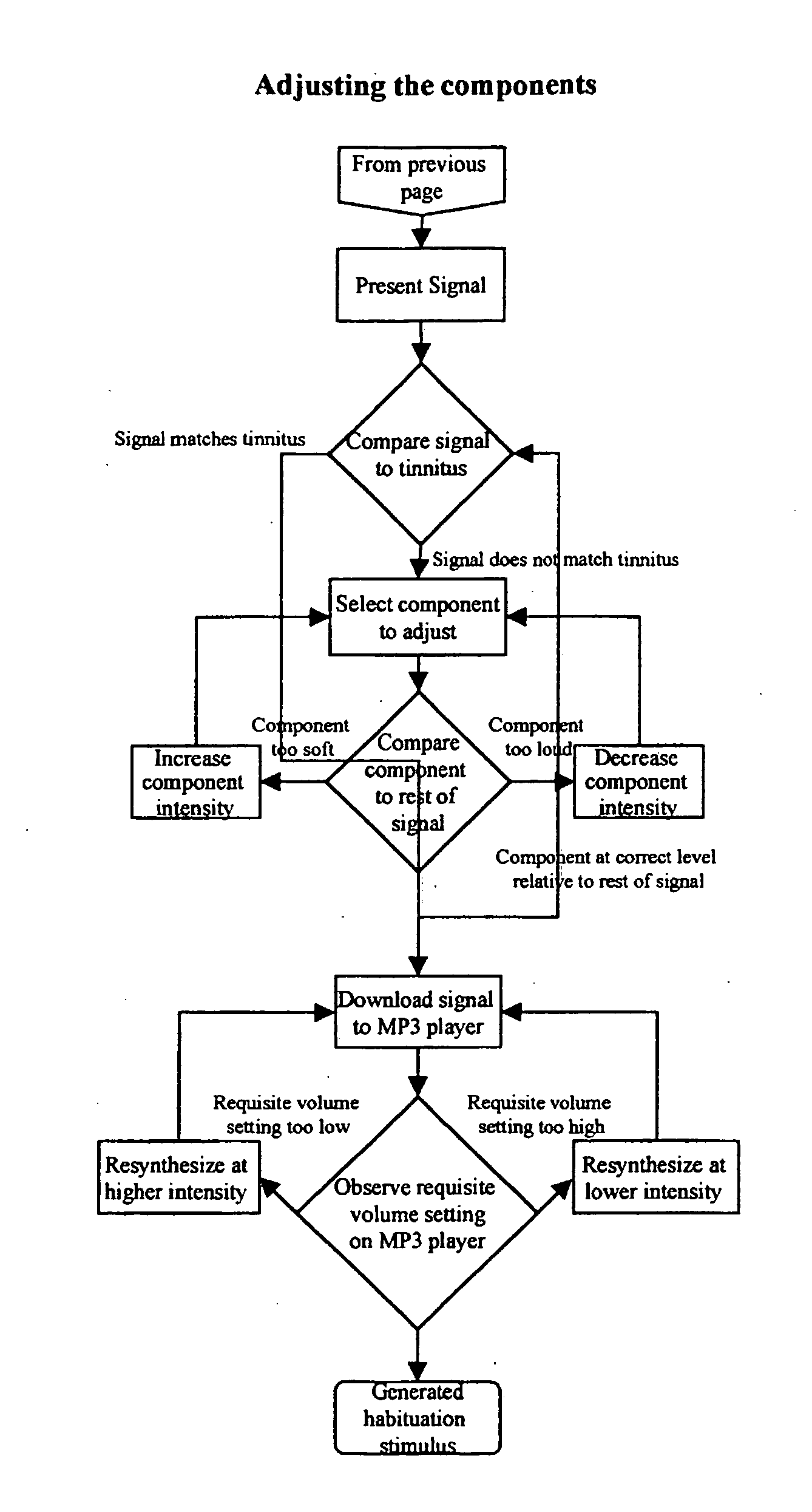
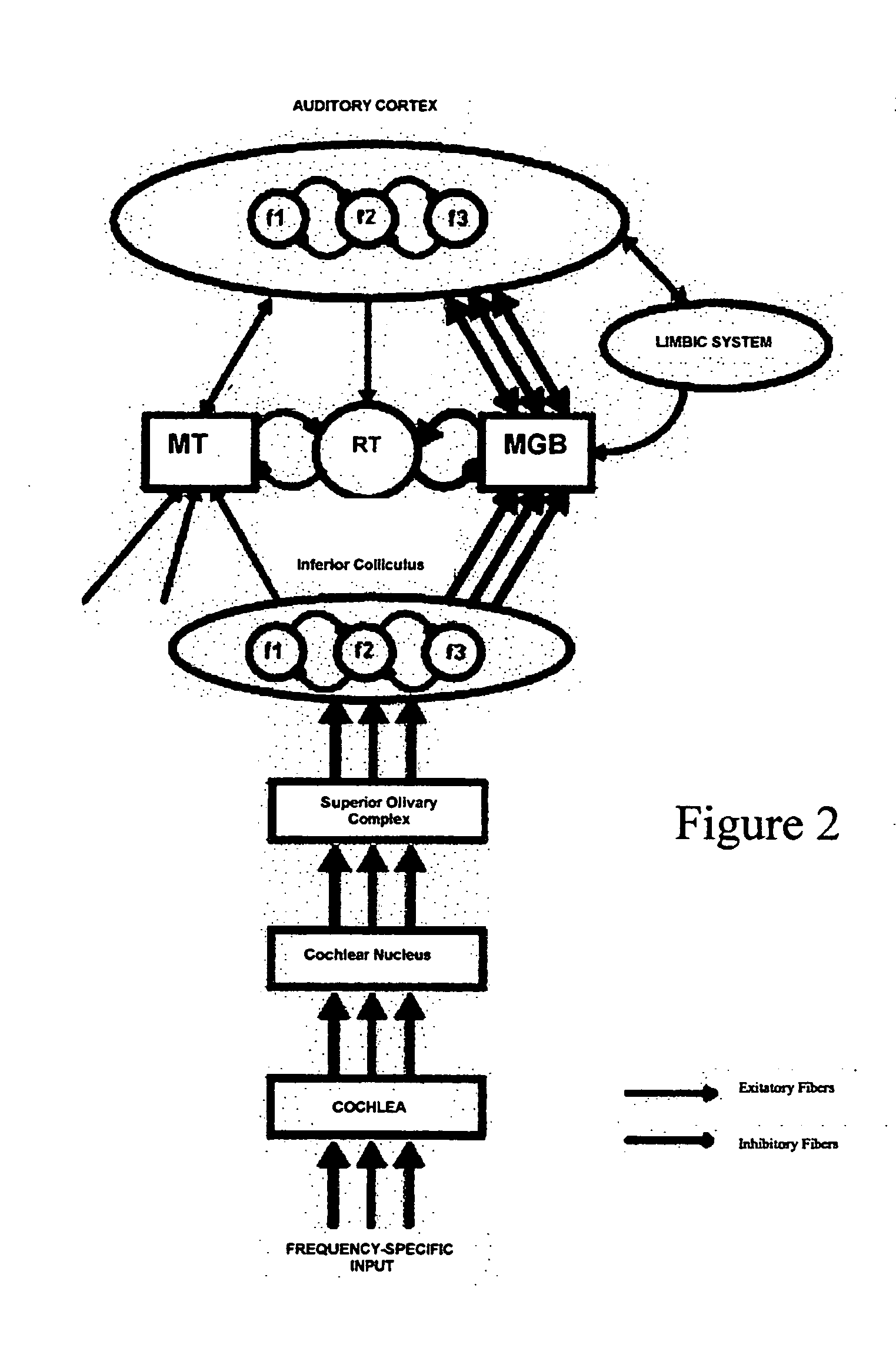
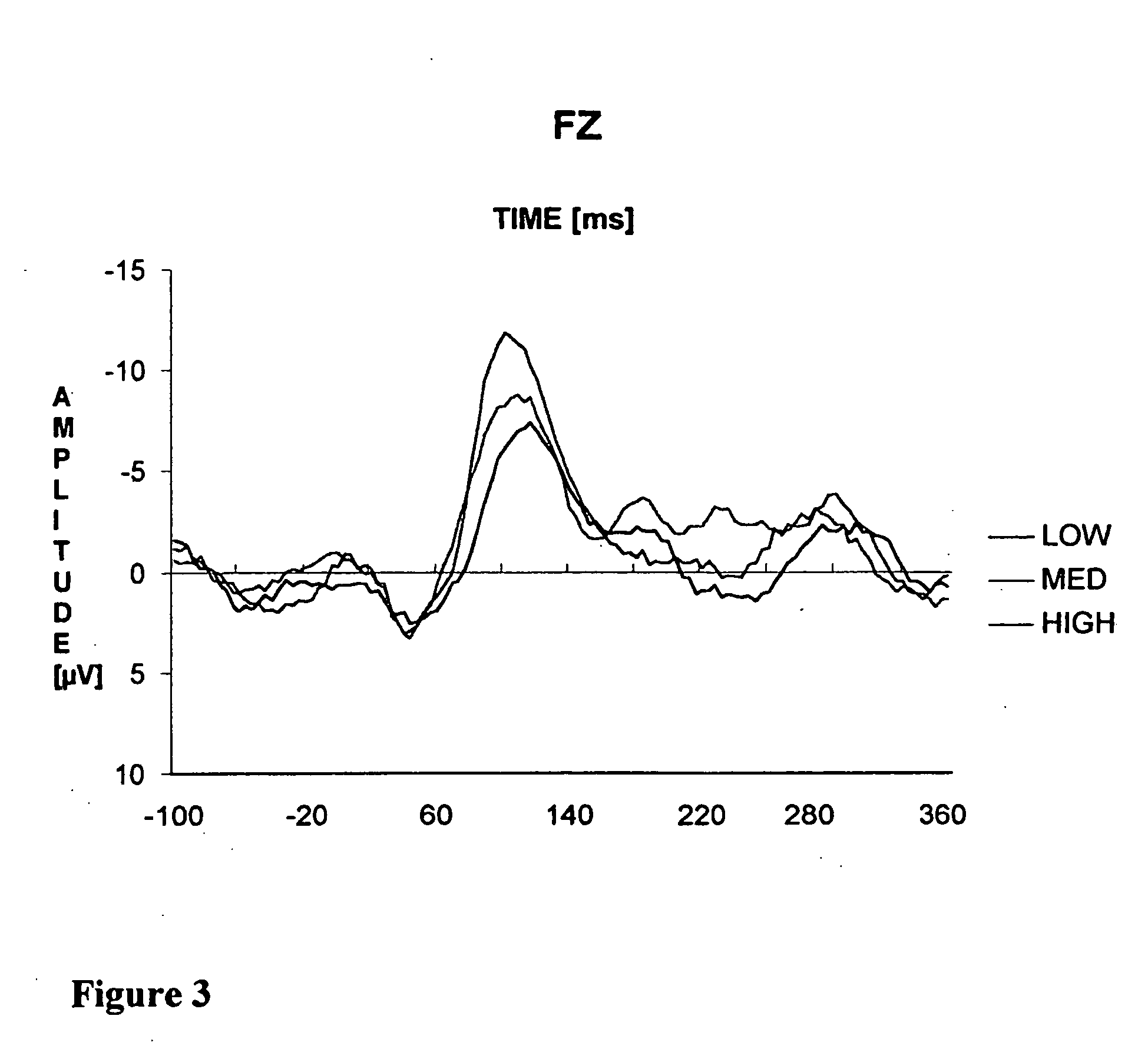
Eeg feedback controlled sound therapy for tinnitus
An automated method for treating tinnitus by habituation through use of neurological feedback, comprising the steps of connecting a subject through a set of attached headphones to an electronic sound player that is connected to a PC workstation presenting sound examples by software to the subject who can refine them by manipulating a series of controllers on the player, making an electronic recording of the sound in a digital music format, storing the recording in the computer, transferring a copy of the electronic sound file to the subject's electronic music player, generating an EEC signature of the subject's brain activity in response to the presented sound, sound using the customized sound to stimulate the auditory system while the brain activity is recorded, wherein the computer continuously monitors for the feedback signatures and drives the sound stimuli appropriately.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
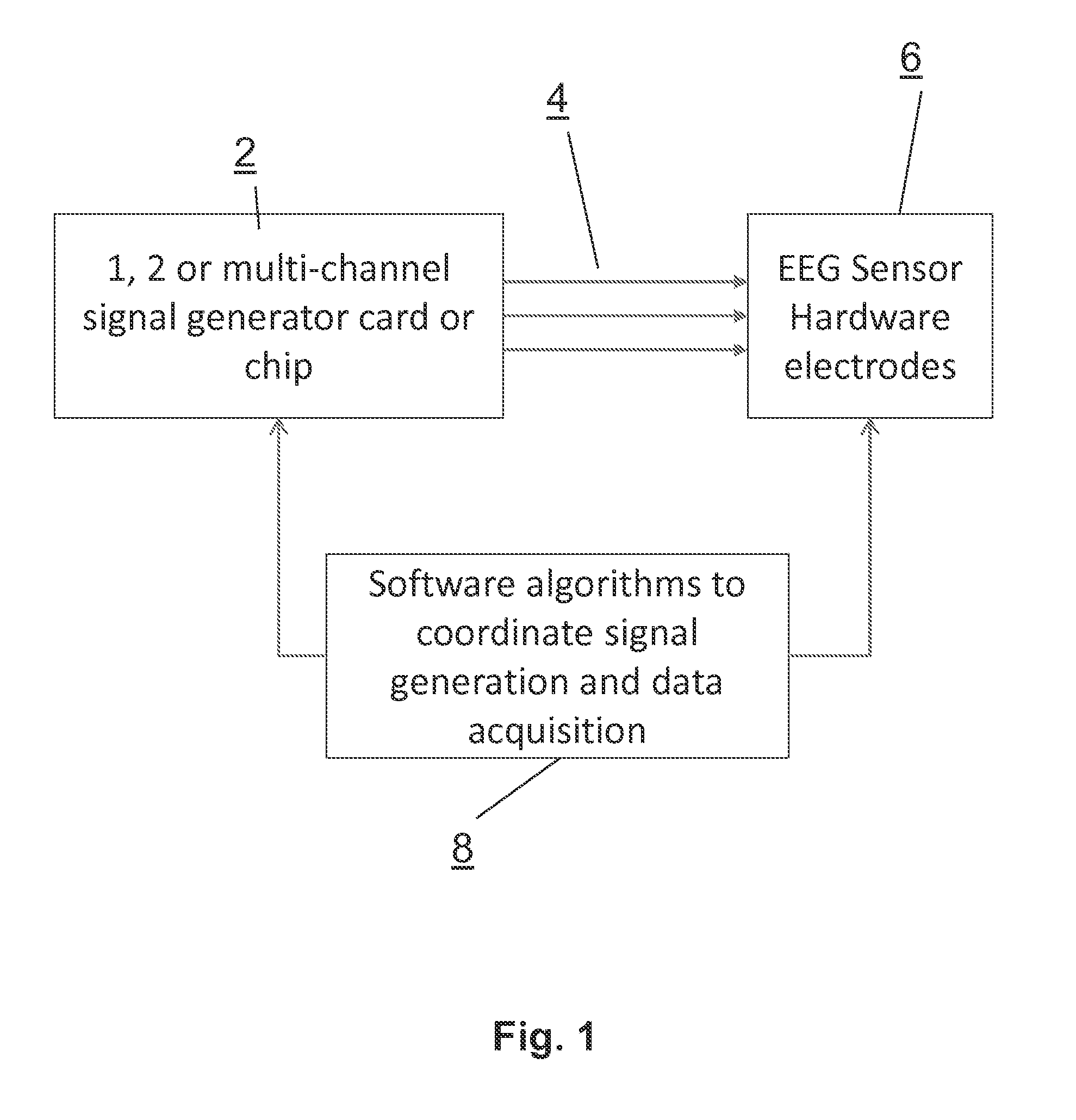
Systems and methods for the physiological assessment of brain health and the remote quality control of eeg systems
InactiveUS20150038869A1Verify performanceElectroencephalographyAutomatic recalibrationPortable EEGData acquisition
A system for calibrating and / or verifying system performance of a remote portable EEG system having at least one EEG sensor. Embodiments of the invention can provide various reference signals to calibrate and quality control the remote performance of the data acquisition EEG system. In addition a calibration cable connects a reference signal source to the EEG sensors to enable remote calibration and quality control assessment. Further, a diagnostic biomarker is included to assess the state or function of a subject's brain and enables the classification, prognosis, diagnosis, monitoring of treatment, or response to therapy applied to the brain by measuring any one of a list of candidate features extracted from a given cognitive or sensory task, and measuring changes in the EEG feature and task combination over time, among multiple states, or compared to a normative database.
Owner:CERORA
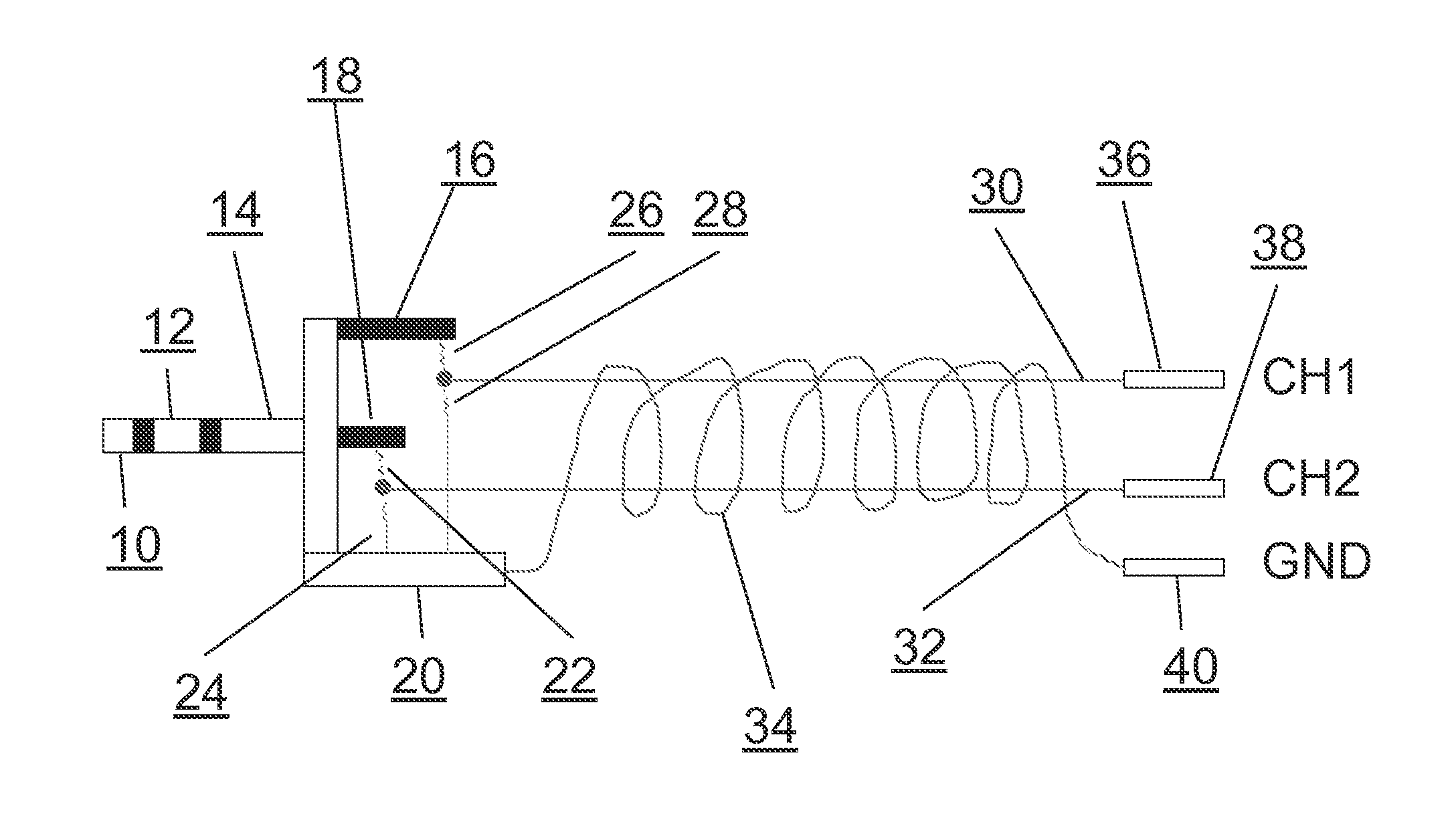
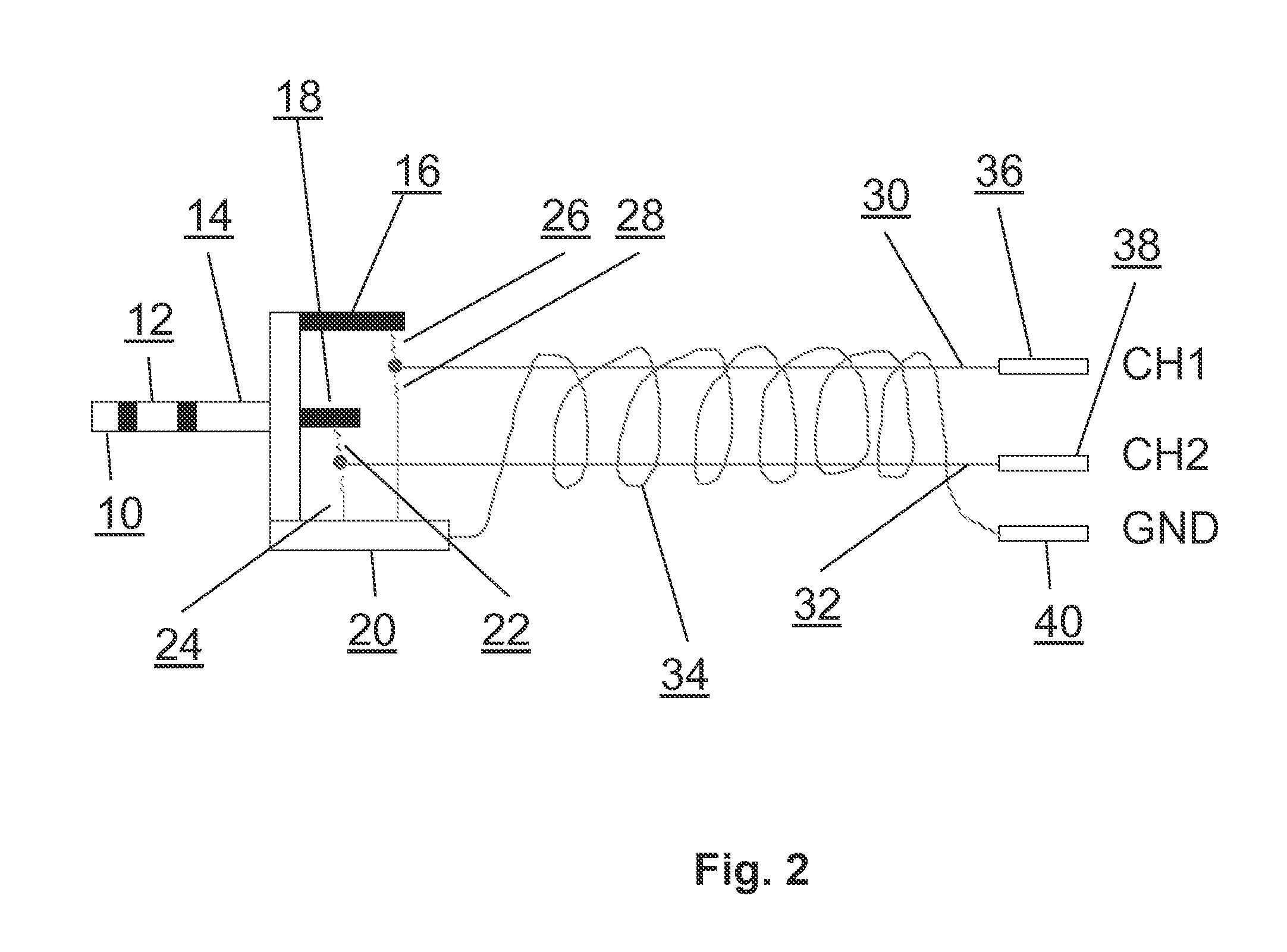
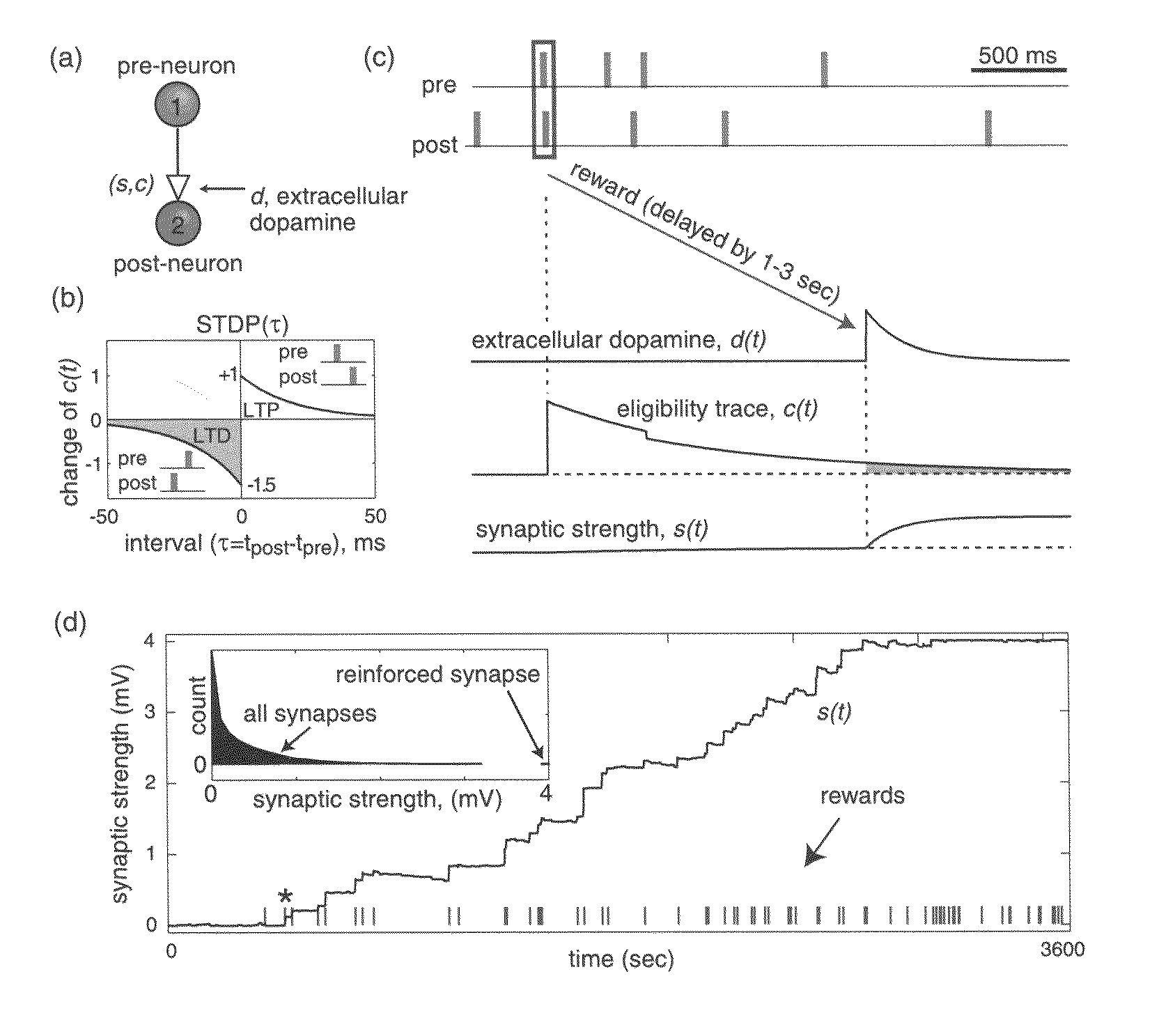
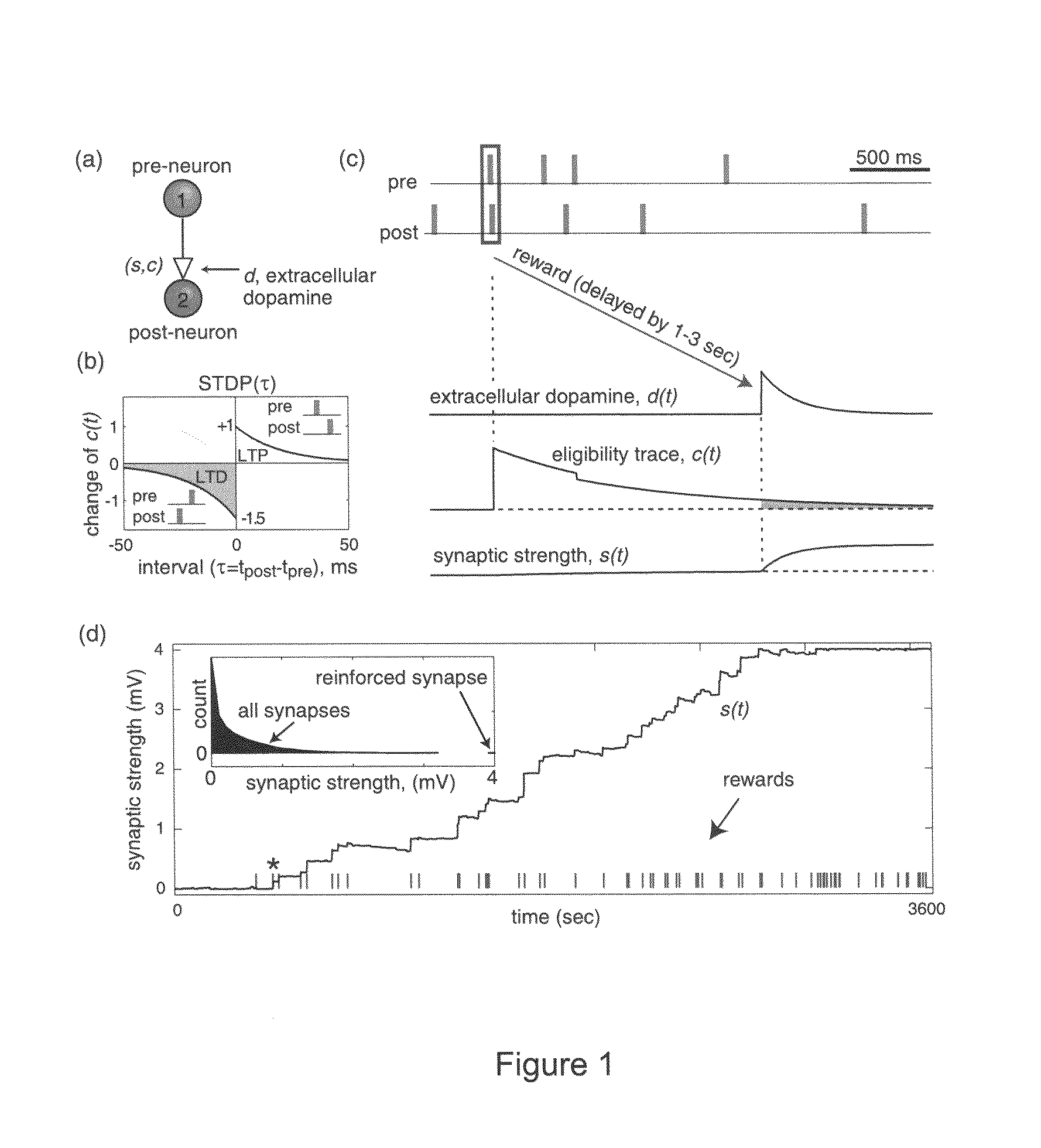
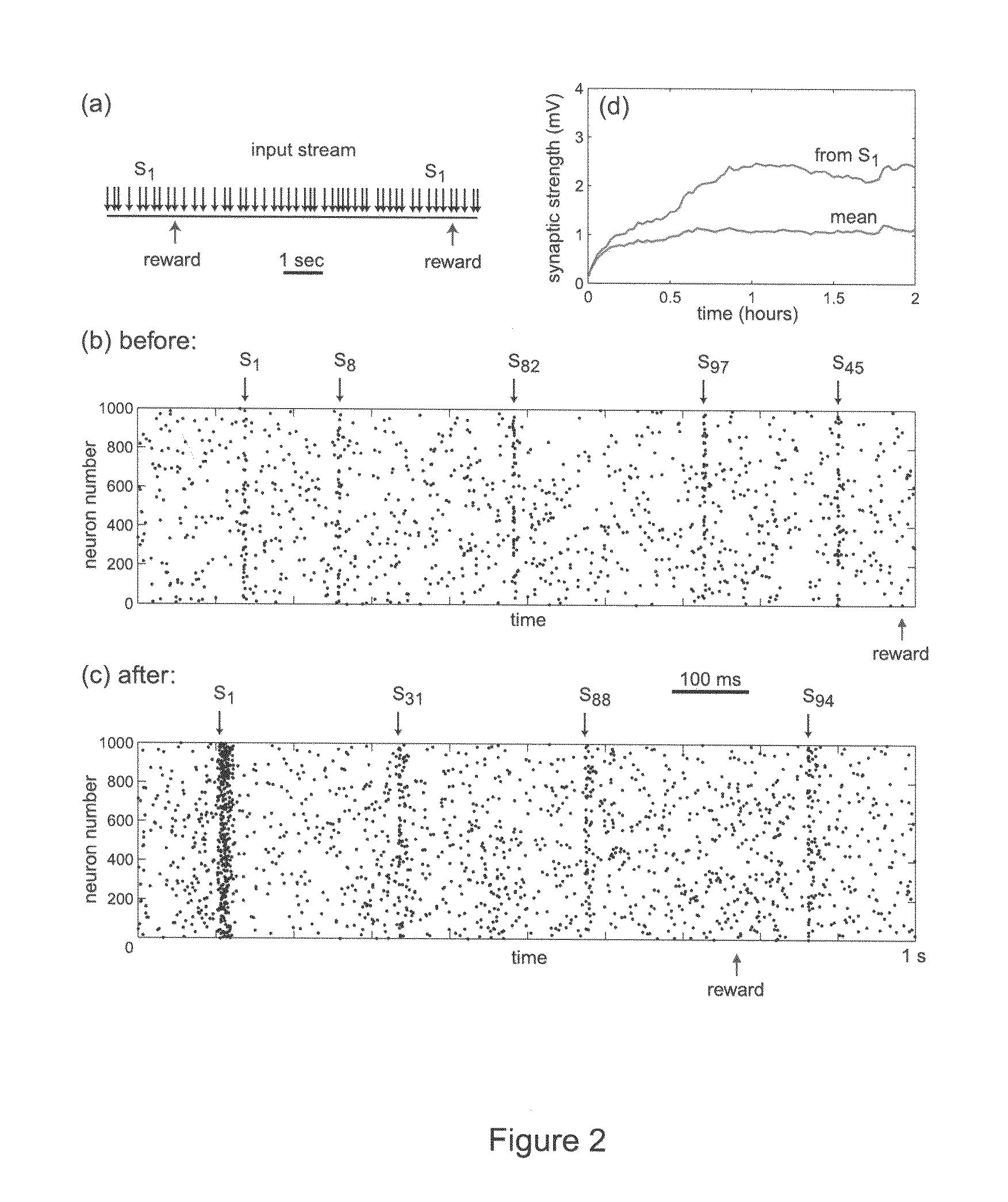
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of STDP and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS8103602B2Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeCritical periodModel network
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
Method and system for analysing sound
ActiveUS20140307878A1Improve user experienceImprove expectationsMedical simulationElectrophonic musical instrumentsSound analysisAudio frequency
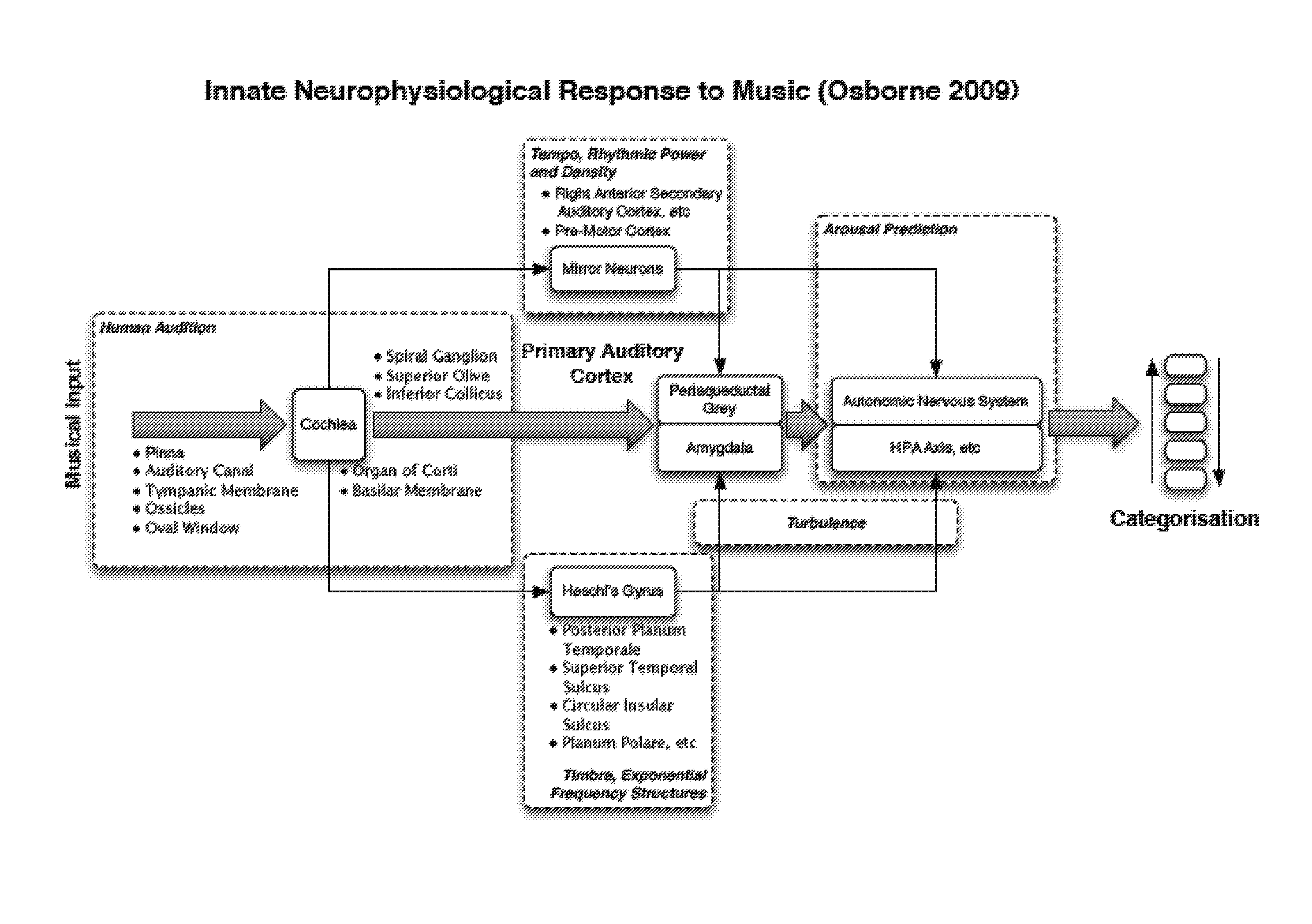
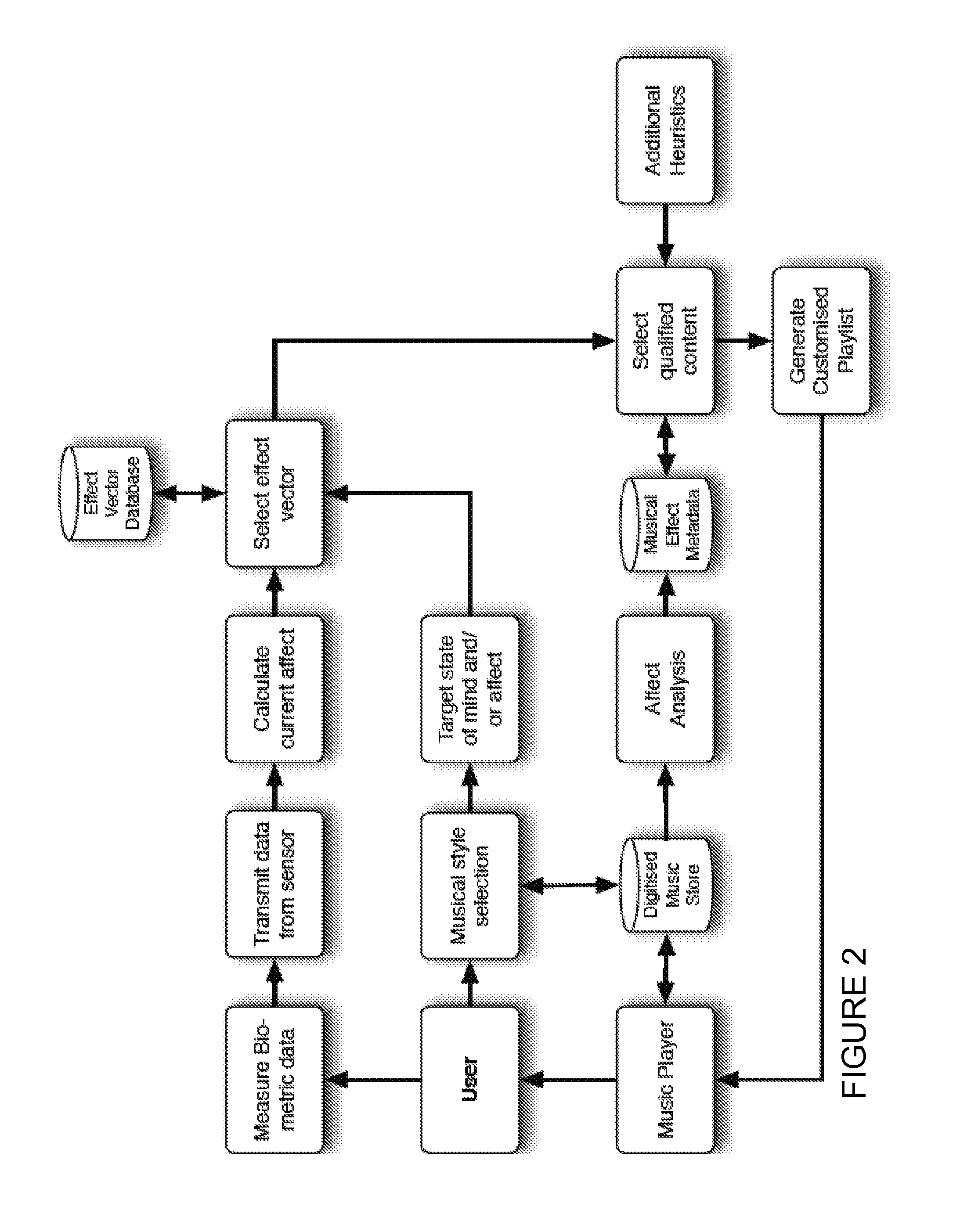
The present invention relates to a method and system for analysing audio (eg. music) tracks. A predictive model of the neuro-physiological functioning and response to sounds by one or more of the human lower cortical, limbic and subcortical regions in the brain is described. Sounds are analysed so that appropriate sounds can be selected and played to a listener in order to stimulate and / or manipulate neuro-physiological arousal in that listener. The method and system are particularly applicable to applications harnessing a biofeedback resource.
Owner:X-SYSTEMS
Method and system for identification of source of chronic pain and treatment
A method for identifying and treating a neural pathway associated with chronic pain via nerve stimulation and brain wave monitoring of a mammalian brain includes positioning a probe to stimulate a target nerve, wherein the target nerve is suspected of being a source of chronic pain; delivering a first nerve stimulation from the probe to the target nerve, wherein the first nerve stimulation is sufficient to elicit a chronic pain response in the brain; and monitoring for evoked potential activity in the brain as a result of the first nerve stimulation. The method can also include delivering second and third nerve stimulations to confirm the correct identification of the neural pathway and to treat the chronic pain, respectively. A system and apparatus for performing a procedure to identify and treat a nerve that is the source of chronic pain are also described.
Owner:AVENT INC
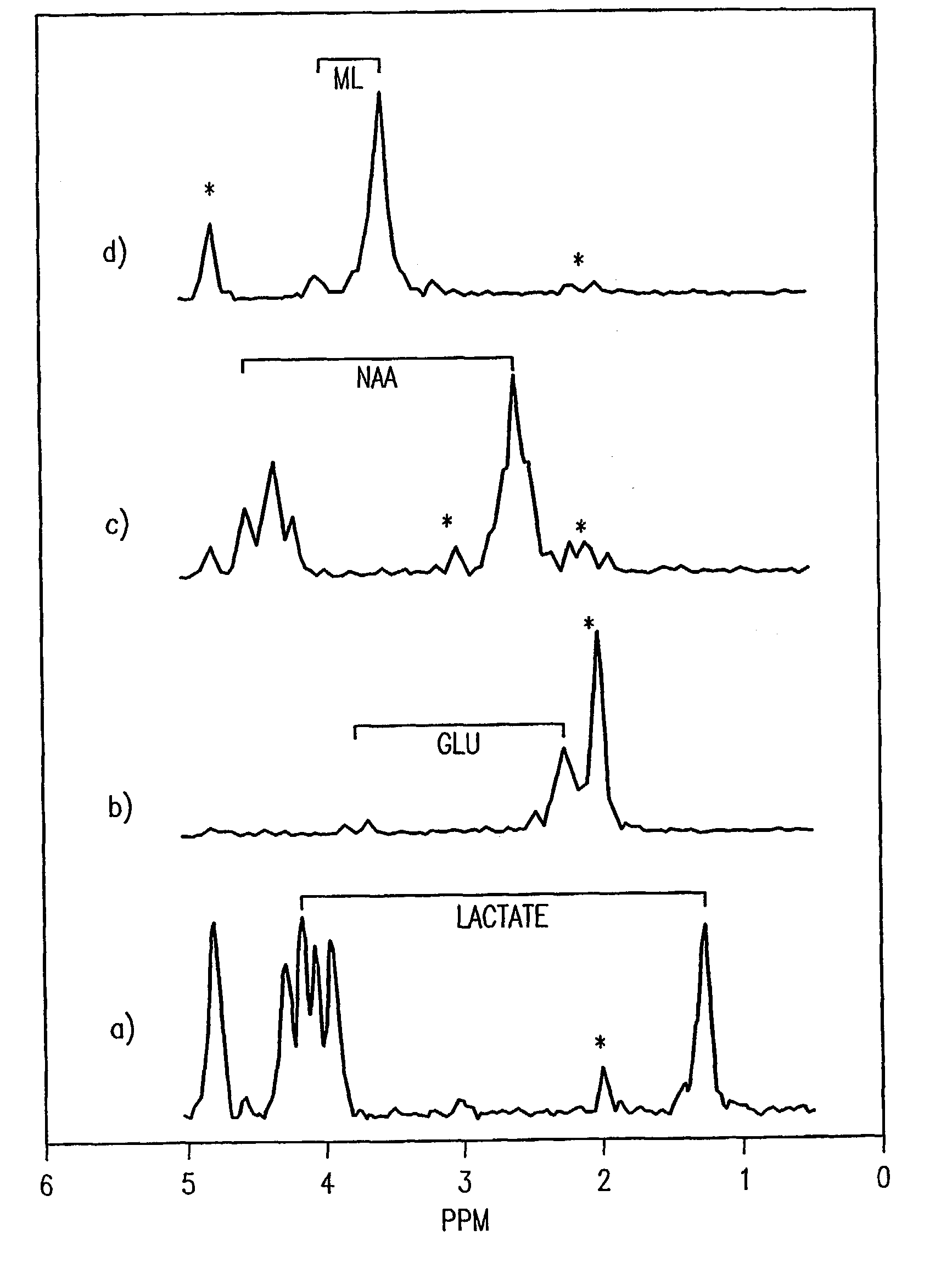
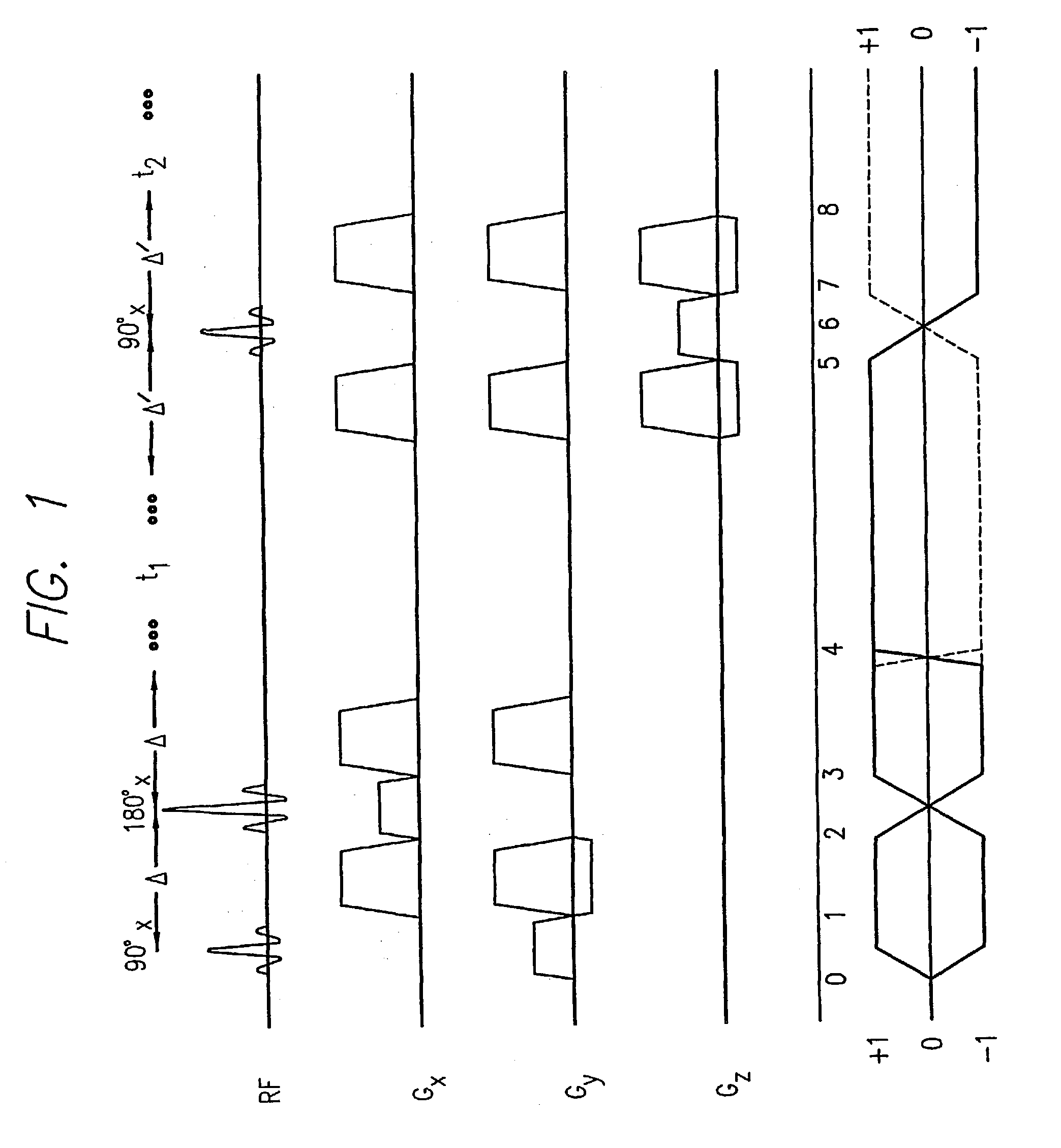
Localized two-dimensional shift correlated MR spectroscopy of human brain
InactiveUS7200430B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringWhole bodySpectroscopy
A two-dimensional (2D) chemical shift correlated MR spectroscopic (COSY) sequence integrated into a new volume localization technique (90°-180°-90°) for whole body MR Spectroscopy. Using the product operator formalism, a theoretical calculation of the volume localization as well as the coherence transfer efficiencies in 2D MRS is presented. A combination of different MRI transmit / receive rf coils is used. The cross peak intensities excited by the proposed 2D sequence are asymmetric with respect to the diagonal peaks. Localized COSY spectra of cerebral frontal and occipital gray / white matter regions in fifteen healthy controls are presented.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
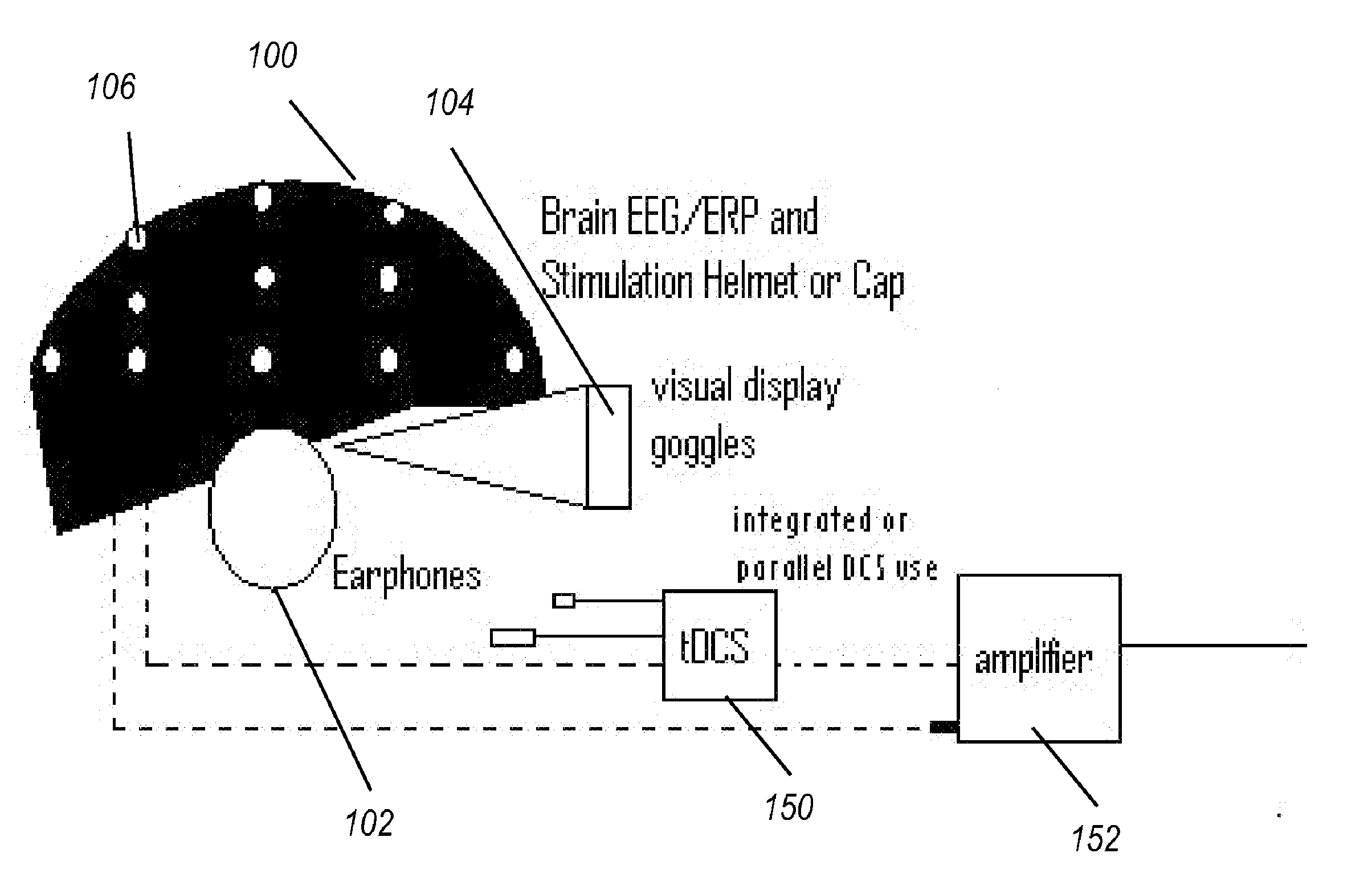
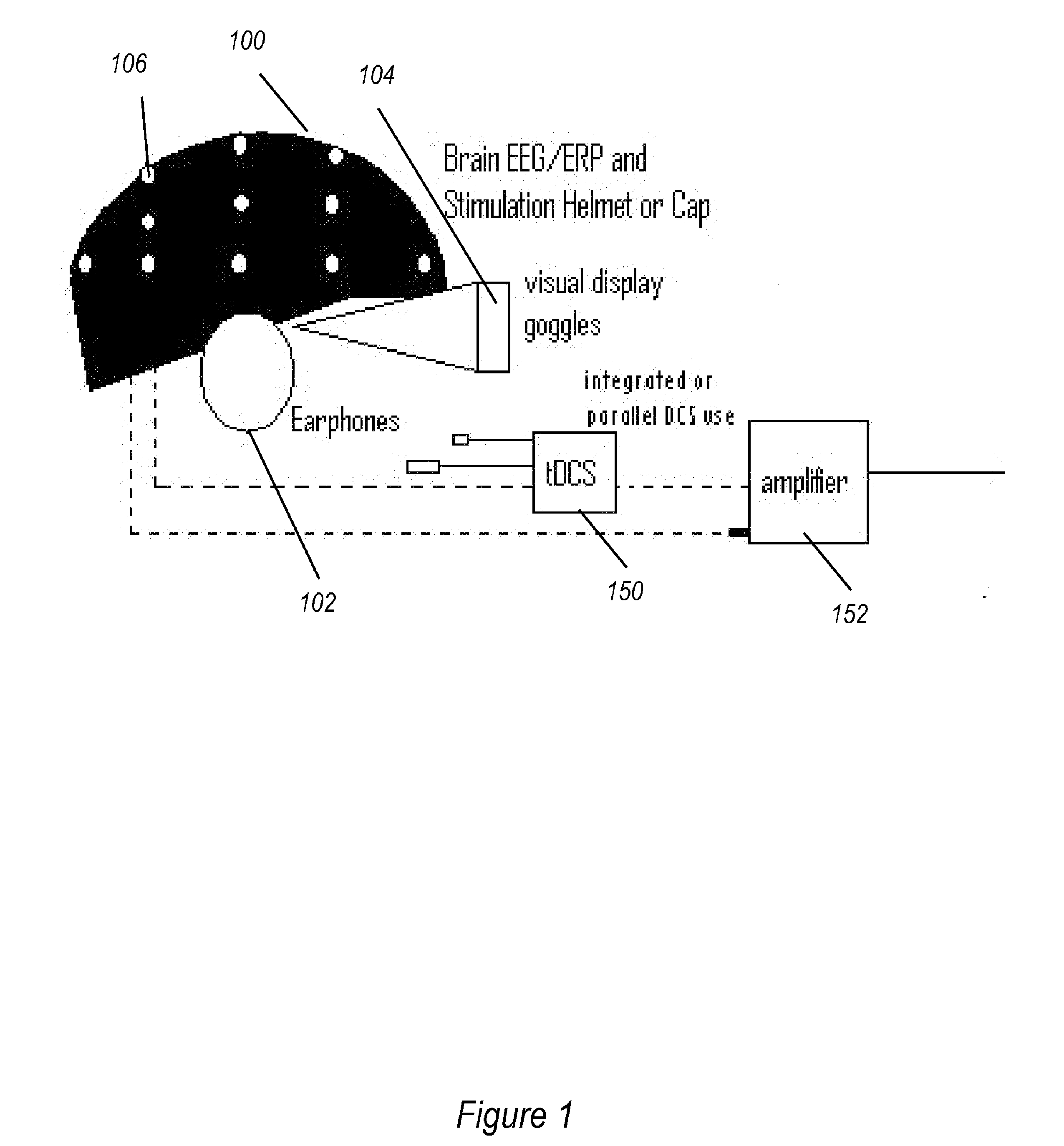
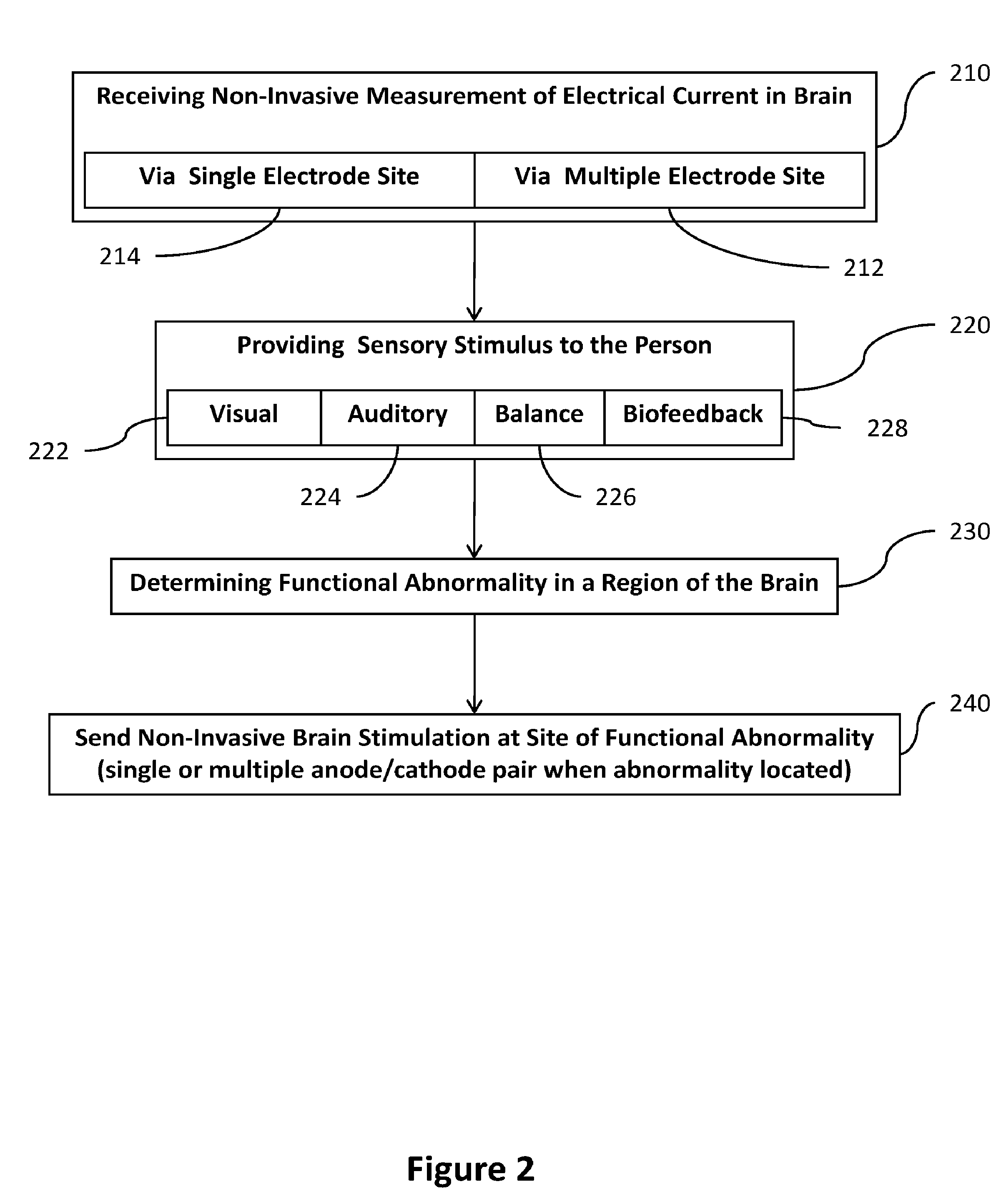
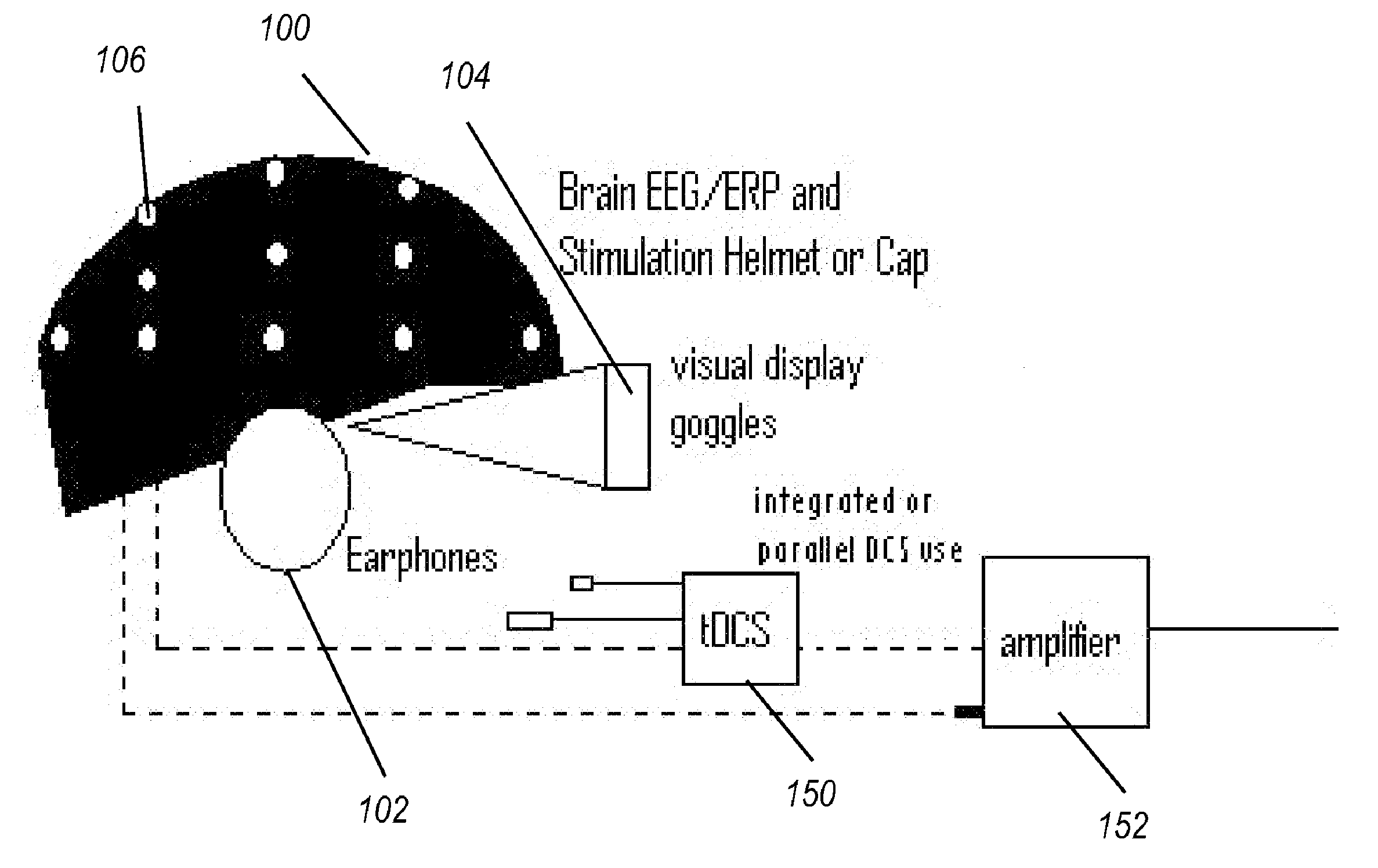
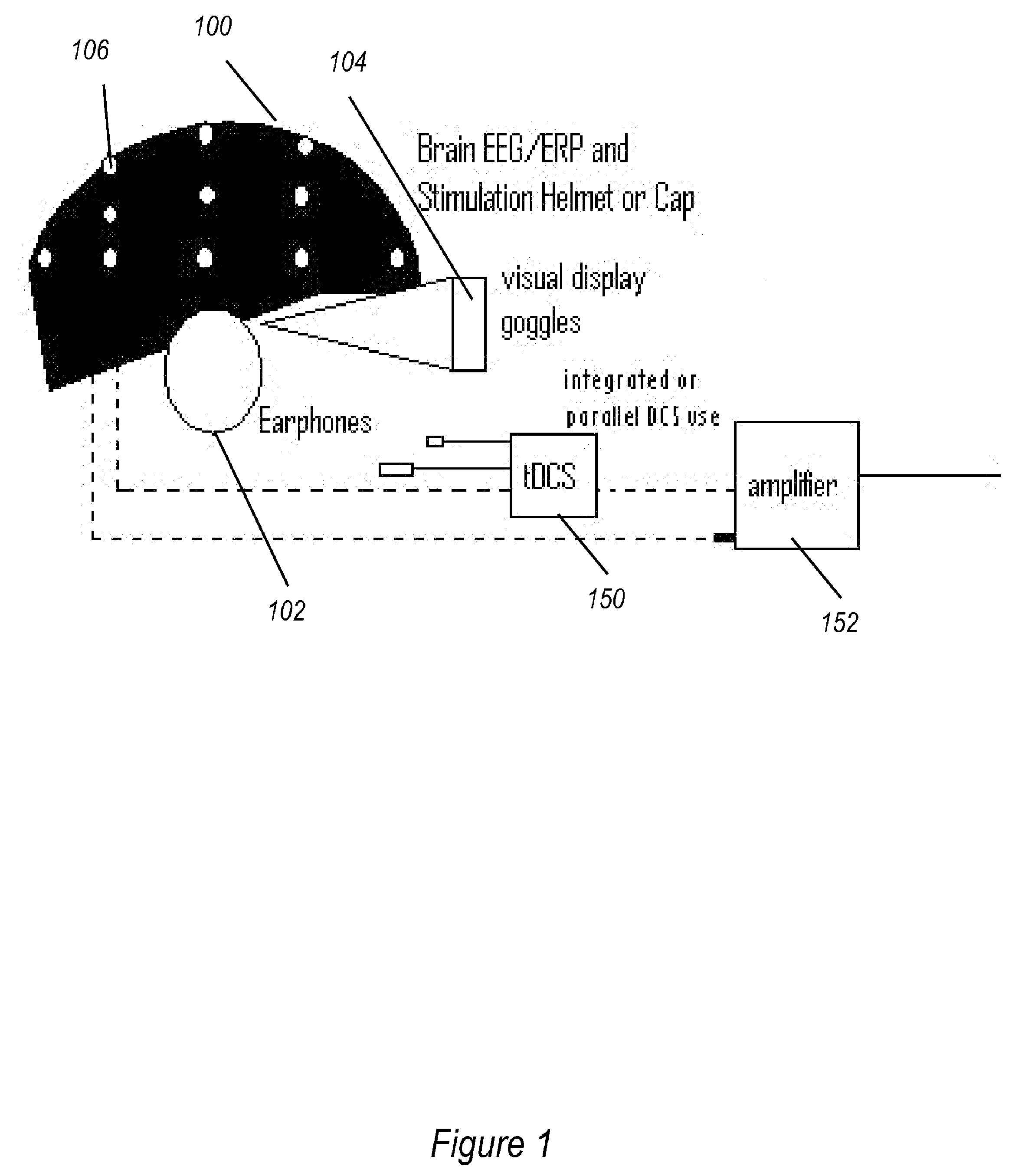
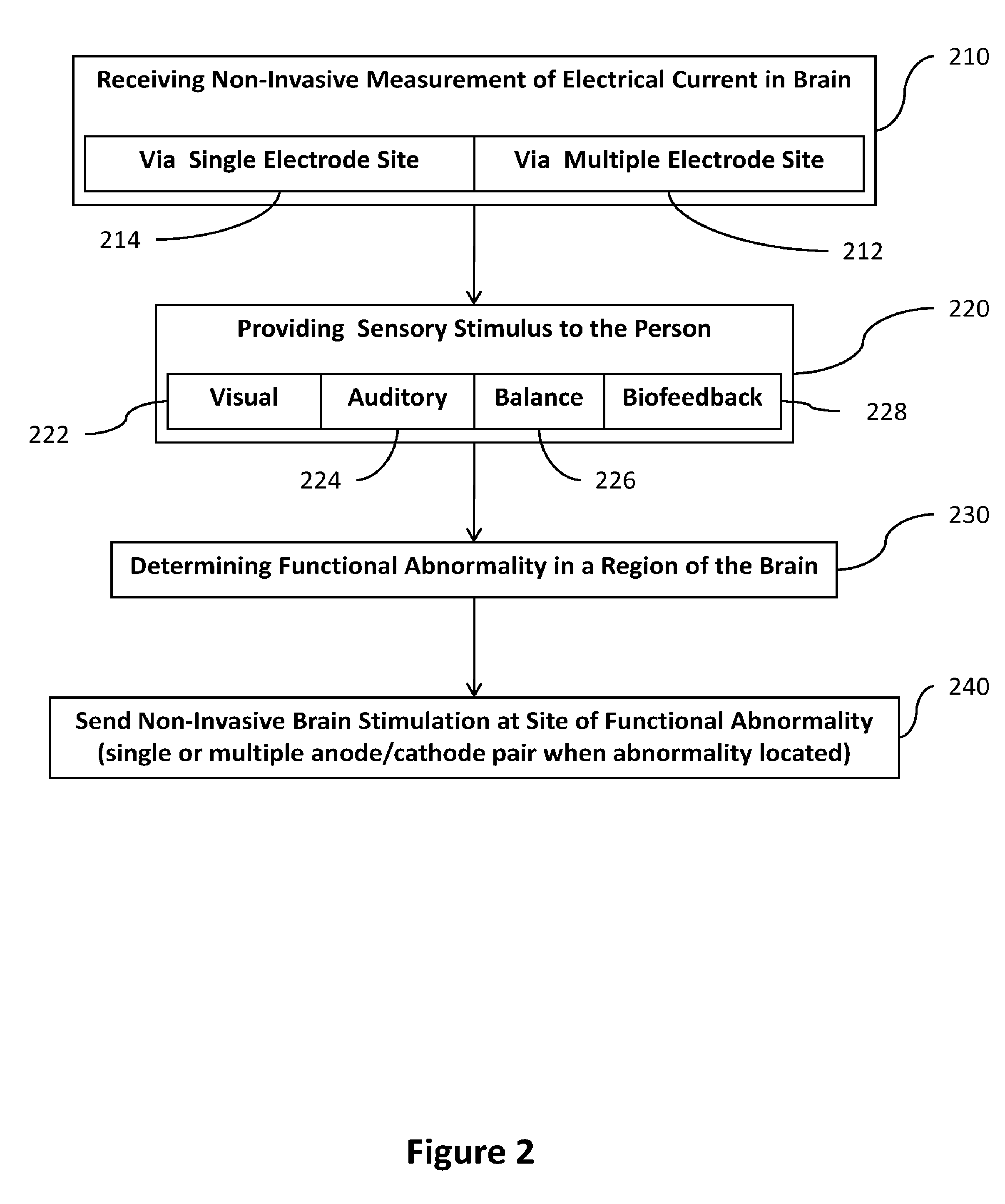
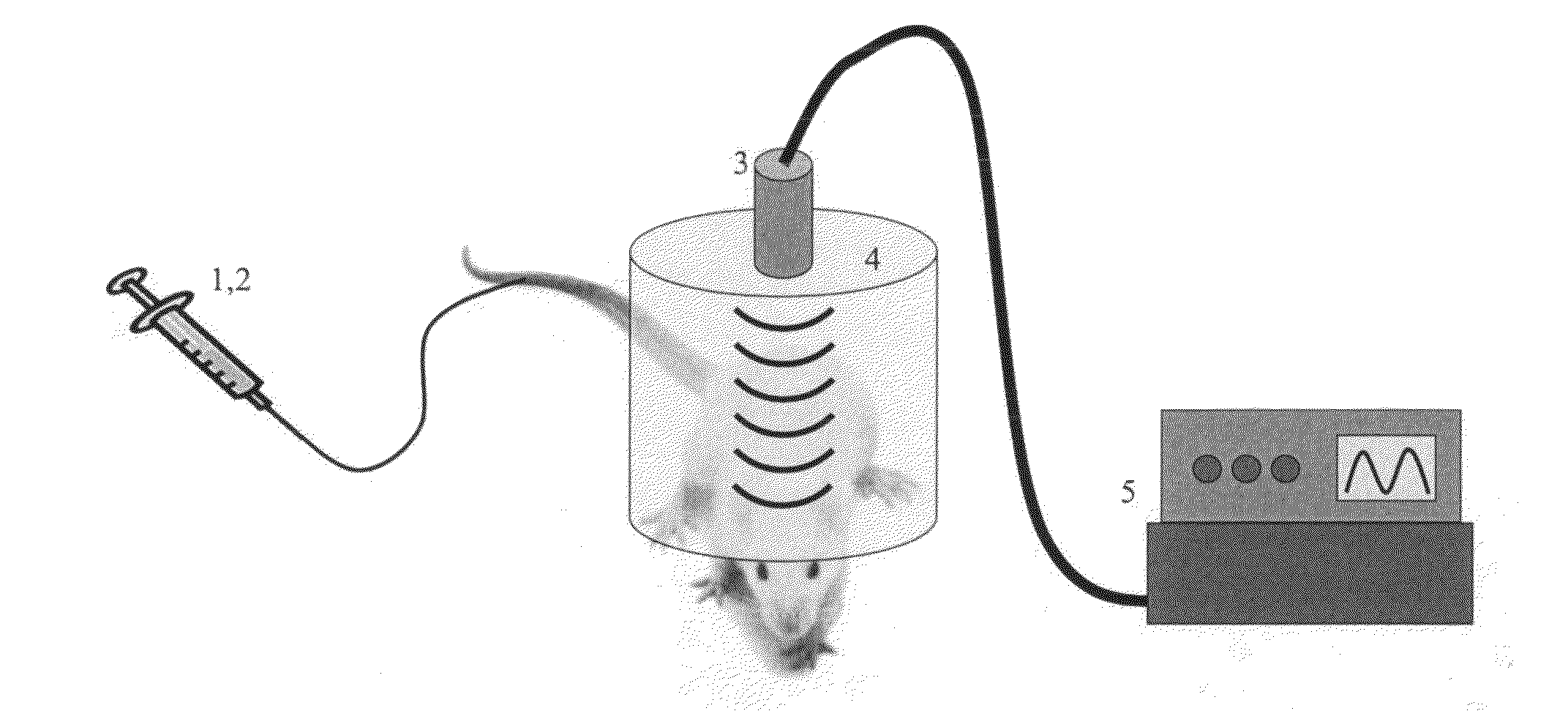
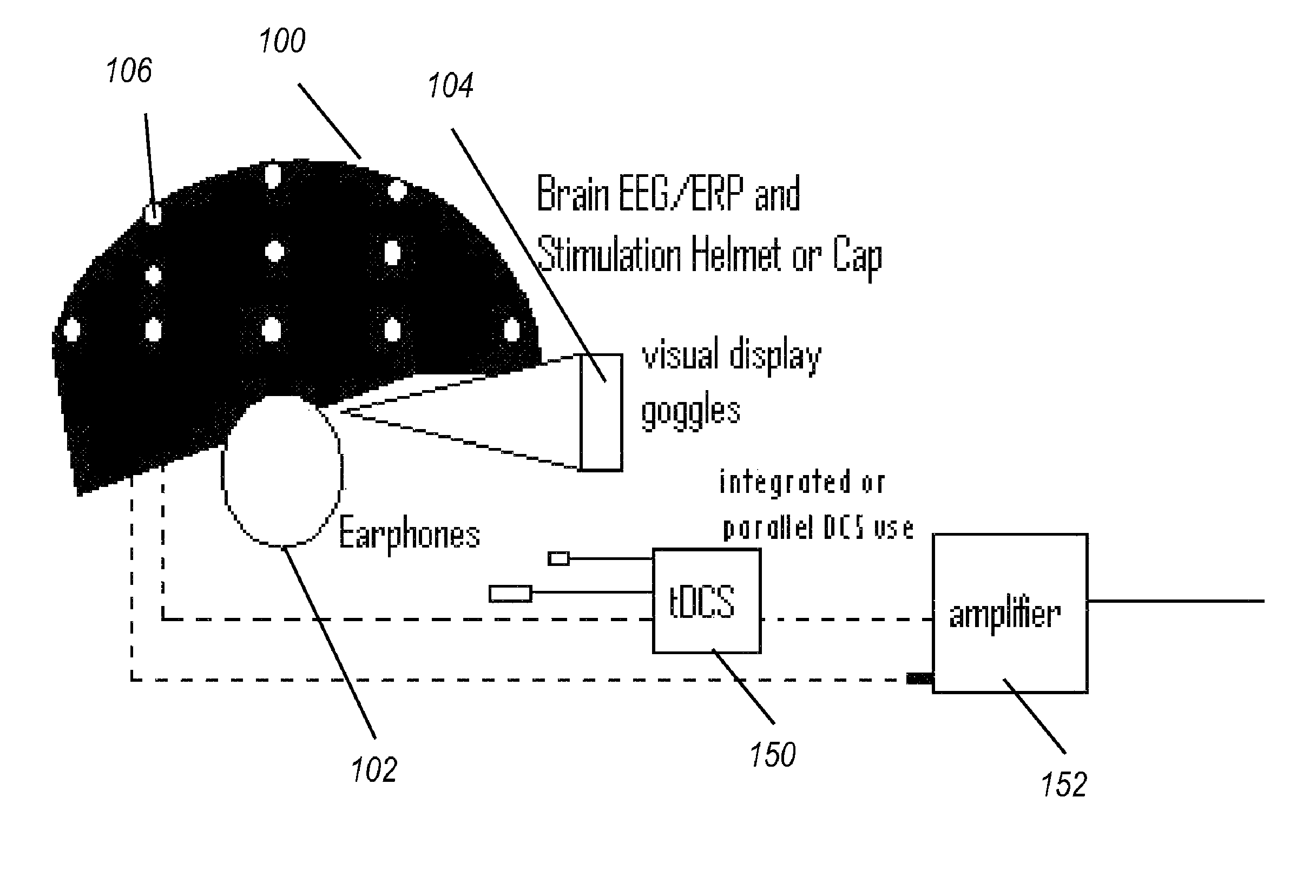
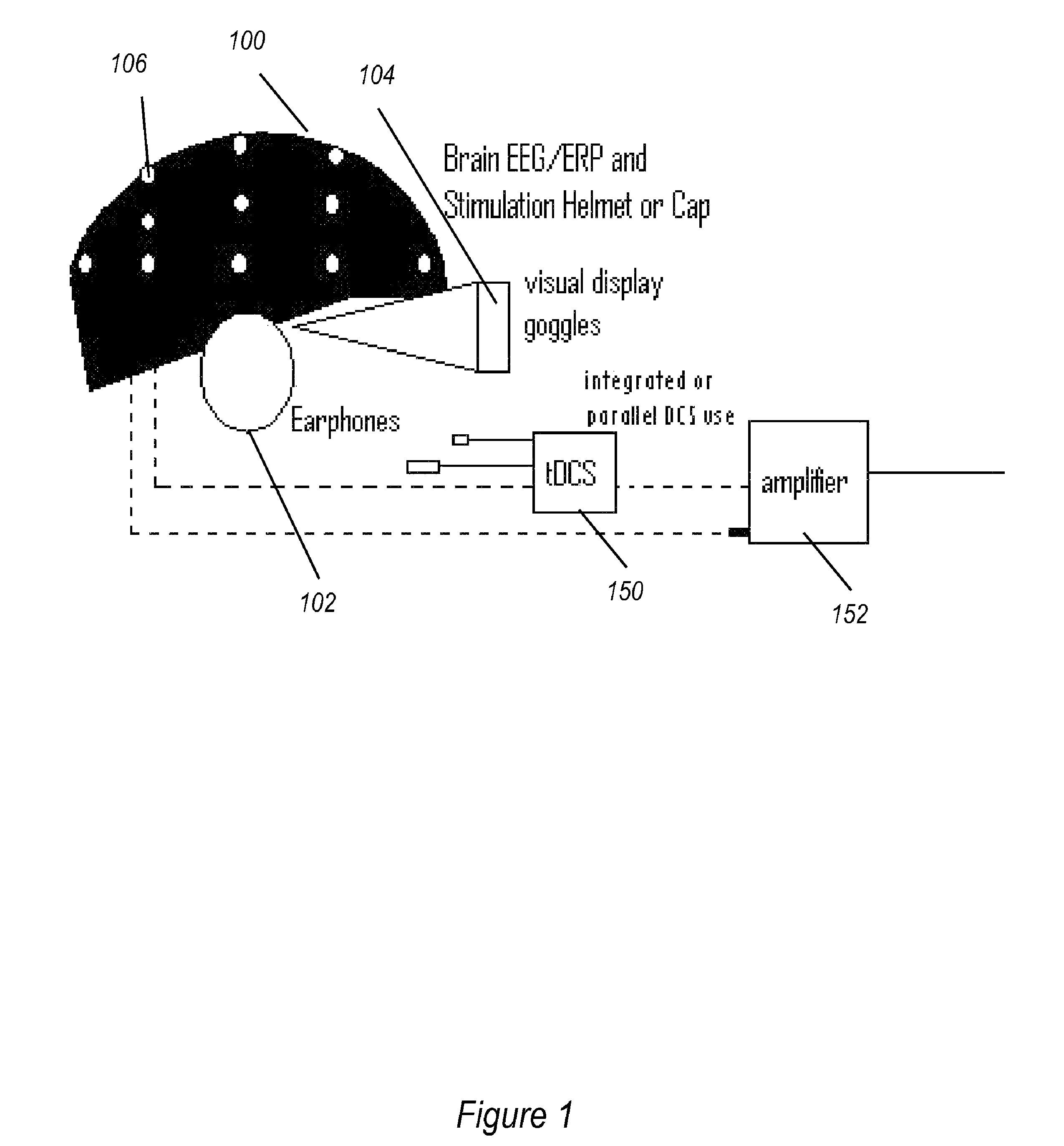
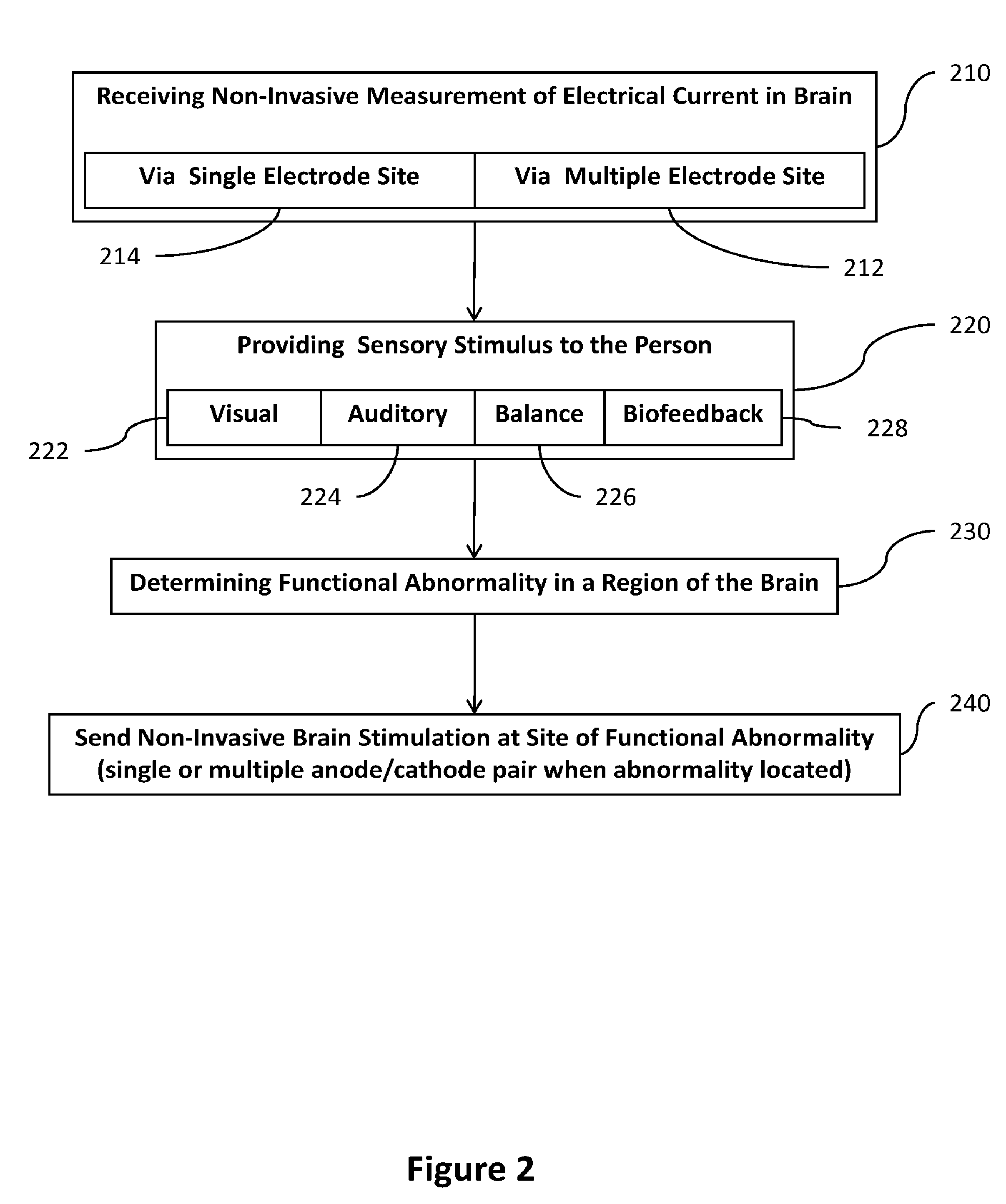
Transcranial stimulation device and method based on electrophysiological testing
Embodiments of the disclosed technology provide a combination electroencephalography and non-invasive stimulation devices. Upon measuring an electrical anomaly in a region of a brain, various non-invasive stimulation techniques are utilized to correct neural activity. Stimulation techniques include transcranial direct current stimulation, transcranial alternating current stimulation and transcranial random noise stimulation, low threshold transcranial magnetic stimulation and repetitive transcranial magnet stimulation. Devices of the disclosed technology may utilize visual, balance, auditory, and other stimuli to test the subject, analyze necessary brain stimulations, and administer stimulation to the brain.
Owner:EVOKE NEUROSCI
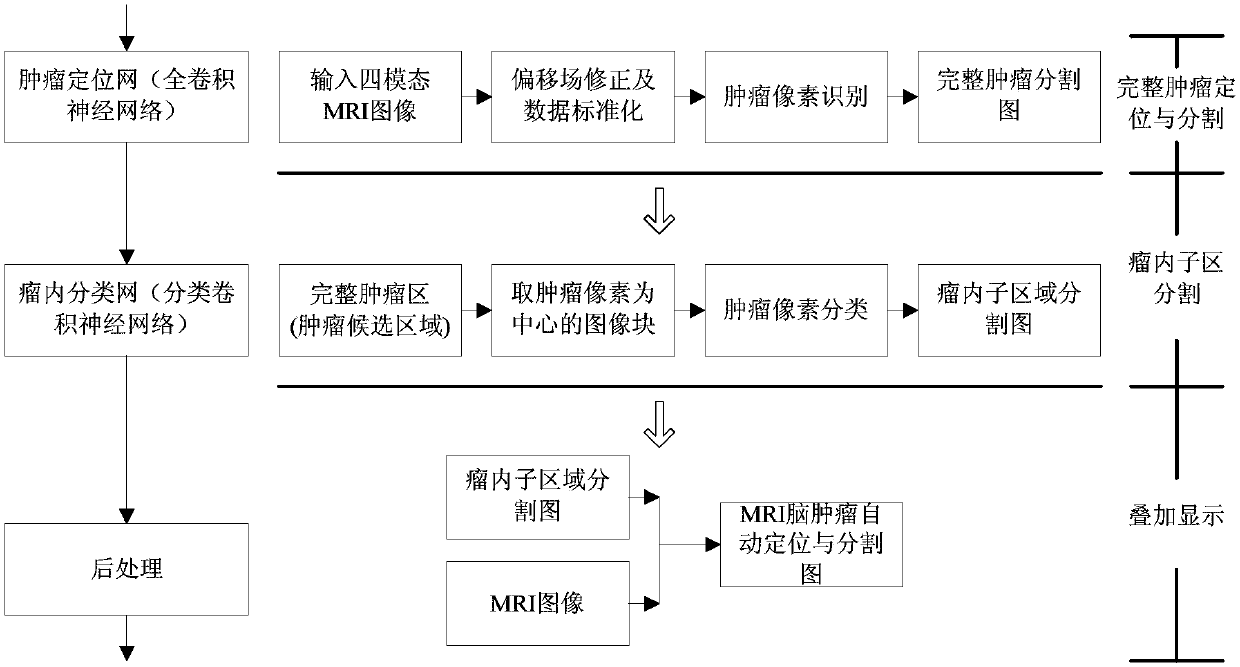
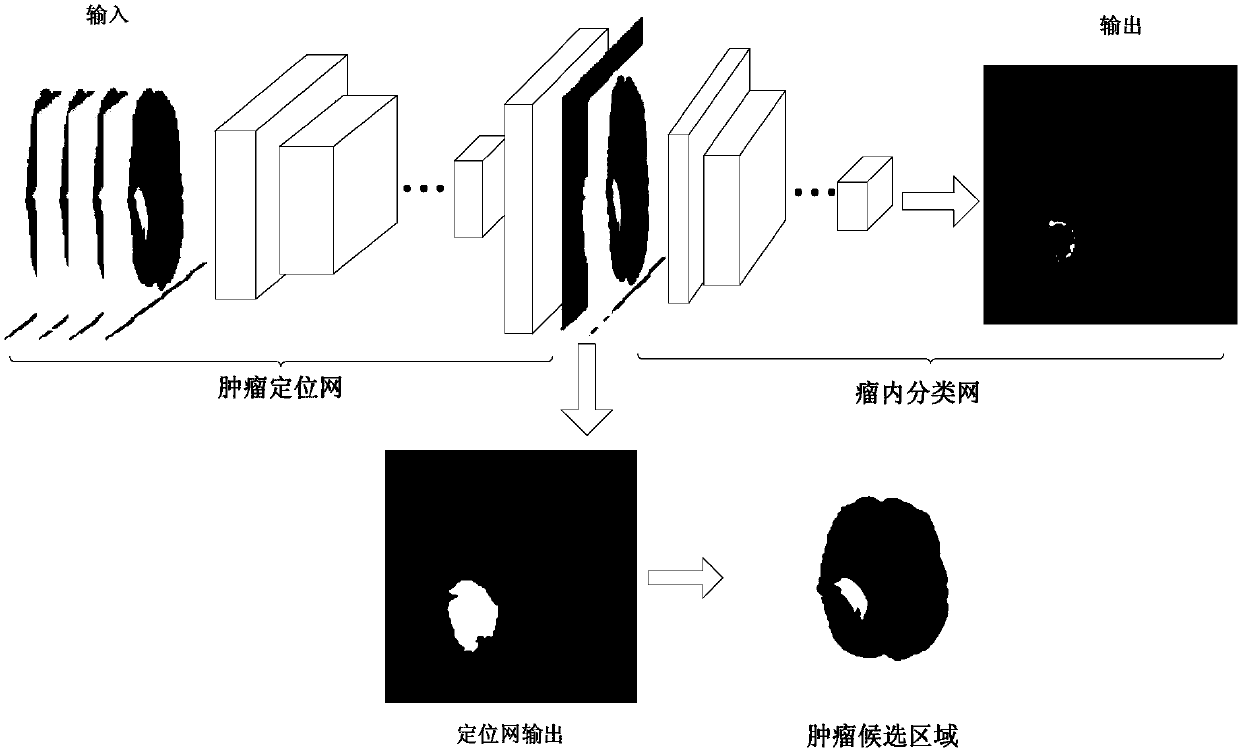
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) brain tumor localization and intratumoral segmentation method based on deep cascaded convolution network
ActiveCN108492297AAlleviate the sample imbalance problemReduce the number of categoriesImage enhancementImage analysisClassification methodsHybrid neural network
The invention provides an MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) brain tumor localization and intratumoral segmentation method based on a deep cascaded convolution network, which comprises the steps of building a deep cascaded convolution network segmentation model; performing model training and parameter optimization; and carrying out fast localization and intratumoral segmentation on a multi-modal MRIbrain tumor. According to the MRI brain tumor localization and intratumoral segmentation method provided by the invention based on the deep cascaded convolution network, a deep cascaded hybrid neuralnetwork formed by a full convolution neural network and a classified convolution neural network is constructed, the segmentation process is divided into a complete tumor region localization phase andan intratumoral sub-region localization phase, and hierarchical MRI brain tumor fast and accurate localization and intratumoral sub-region segmentation are realized. Firstly, the complete tumor region is localized from an MRI image by adopting a full convolution network method, and then the complete tumor is further divided into an edema region, a non-enhanced tumor region, an enhanced tumor region and a necrosis region by adopting an image classification method, and accurate localization for the multi-modal MRI brain tumor and fast and accurate segmentation for the intratumoral sub-regions are realized.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Systems and methods for modulating the electrical activity of a brain using neuro-eeg synchronization therapy
ActiveUS20110034822A1Expanded indicationsSymptoms improvedElectroencephalographyPhysical therapies and activitiesEeg synchronizationMedicine
Described are methods, devices, and systems for a novel, inexpensive, easy to use therapy for treatment of coma, post-traumatic stress disorder, Parkinson's disease, cognitive performance, and / or amblyopia. Described are methods and devices to treat coma, post-traumatic stress disorder, Parkinson's disease, cognitive performance, and / or amblyopia that involves no medication. Methods and devices described herein use alternating magnetic fields to gently “tune” the brain and affect symptoms of coma, post-traumatic stress disorder, Parkinson's disease, cognitive performance, and / or amblyopia.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Methods and devices for brain activity monitoring supporting mental state development and training
InactiveUS9532748B2Mitigate such drawbackElectroencephalographyMedical automated diagnosisEEG deviceEeg data
With explosive penetration of portable electronic devices (PEDs) recent focus into consumer EEG devices has been to bring advantages including localized wireless interfacing, portability, and a low-cost high-performance electronics platform to host the processing algorithms to bear. However, most development continues to focus on brain-controlled video games which are nearly identical to those created for earlier, more stationary consumer EEG devices and personal EEG is treated as of a novelty or toy. According to embodiments of the invention the inventors have established new technologies and solutions that address these limitations within the prior art and provide benefits including, but not limited to, global acquisition and storage of acquired EEG data and processed EEG data, development interfaces for expansion and re-analysis of acquired EEG data, integration to other non-EEG derived user data, and long-term user wearability.
Owner:PERSONAL NEURO DEVICES
Method and neuroprosthetic device for monitoring and suppression of pathological tremors through neurostimulation of the afferent pathways
PendingUS20140336722A1Reduce tremorReduce severityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationBiomechanicsEngineering
Method and neuroprosthetic device for monitoring and suppression of pathological tremors in a user through the neurostimulation of the afferent pathways to the brain, which comprises wearable elements placed over the parts of the body affected by tremor, wherein said wearable elements (1) have sensors selected from bioelectric sensors (3) generating a bioelectrical signal characterization of tremor, biomechanical sensors (4) generating a biomechanical signal characterization of tremor and a combination thereof, a programmable electronic device (9) comprised of a control, acquisition and processing module of the characterization signals, and a signal generator for the afferent stimulation based on the bioelectrical, biomechanical or combination of both signal characterization and stimulation electrodes (8) which transmit the neuromodulation signals to the afferent pathways projecting into the central nervous system to modulate the activity of the neural structures responsible for tremor generation.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
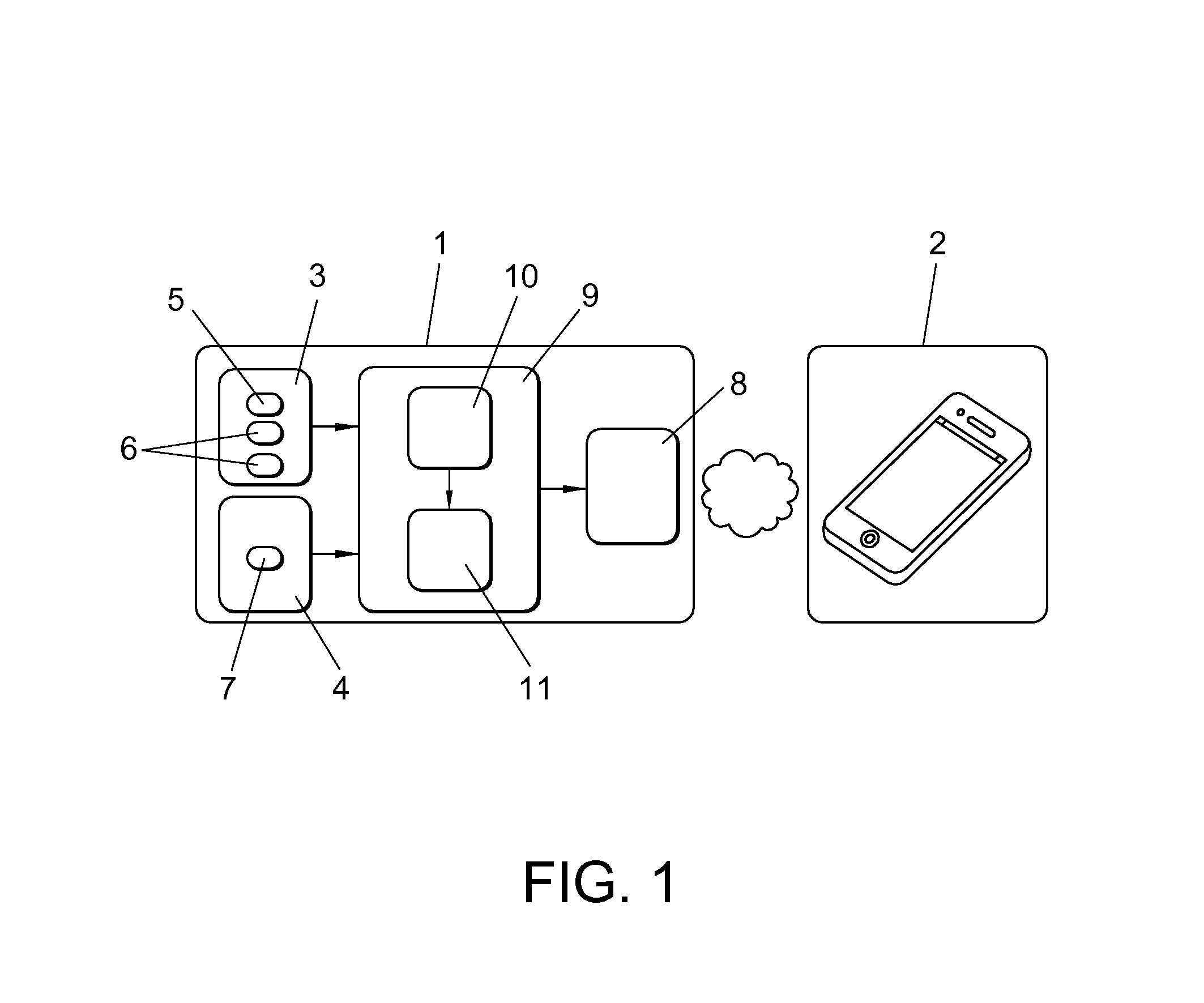
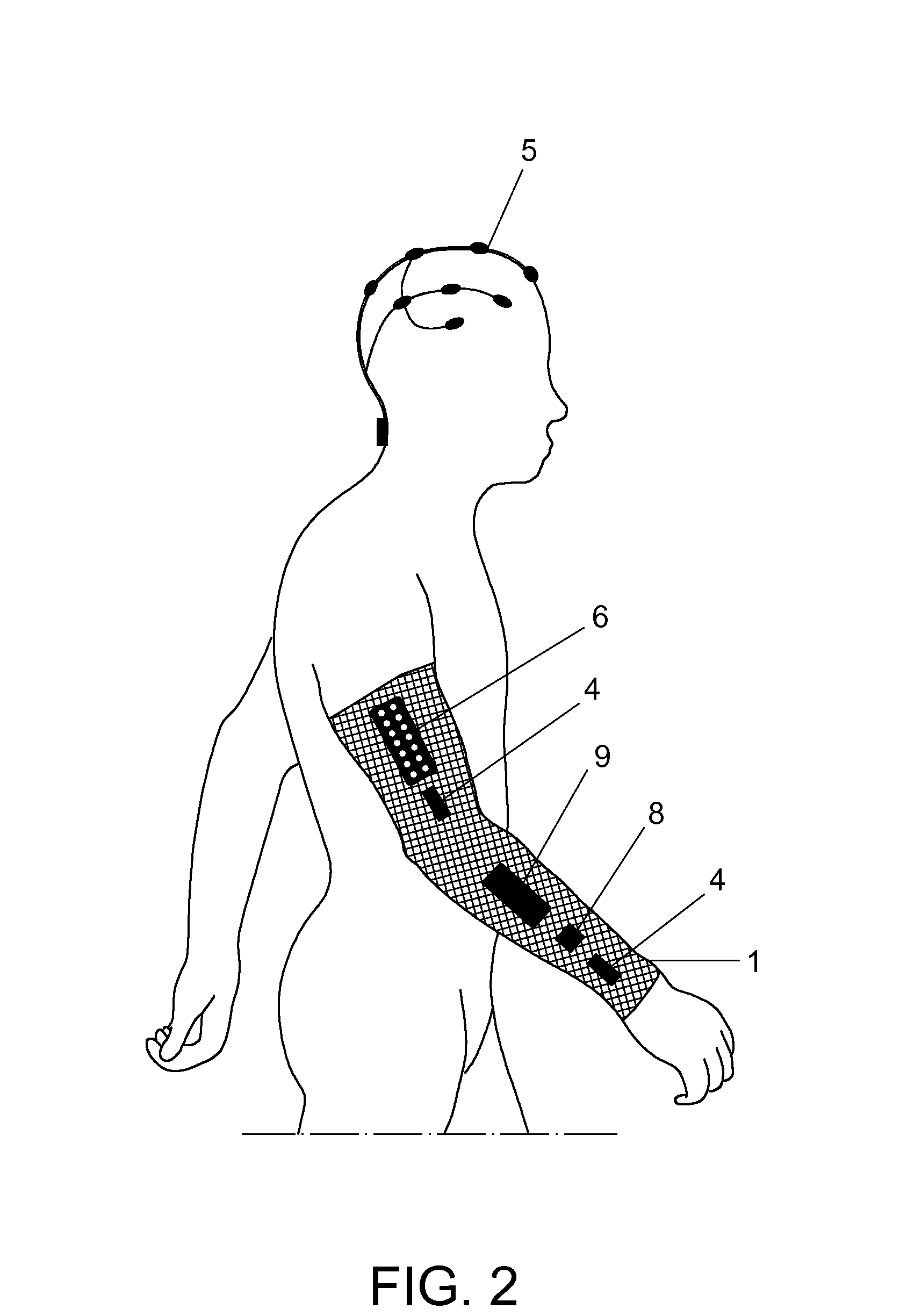
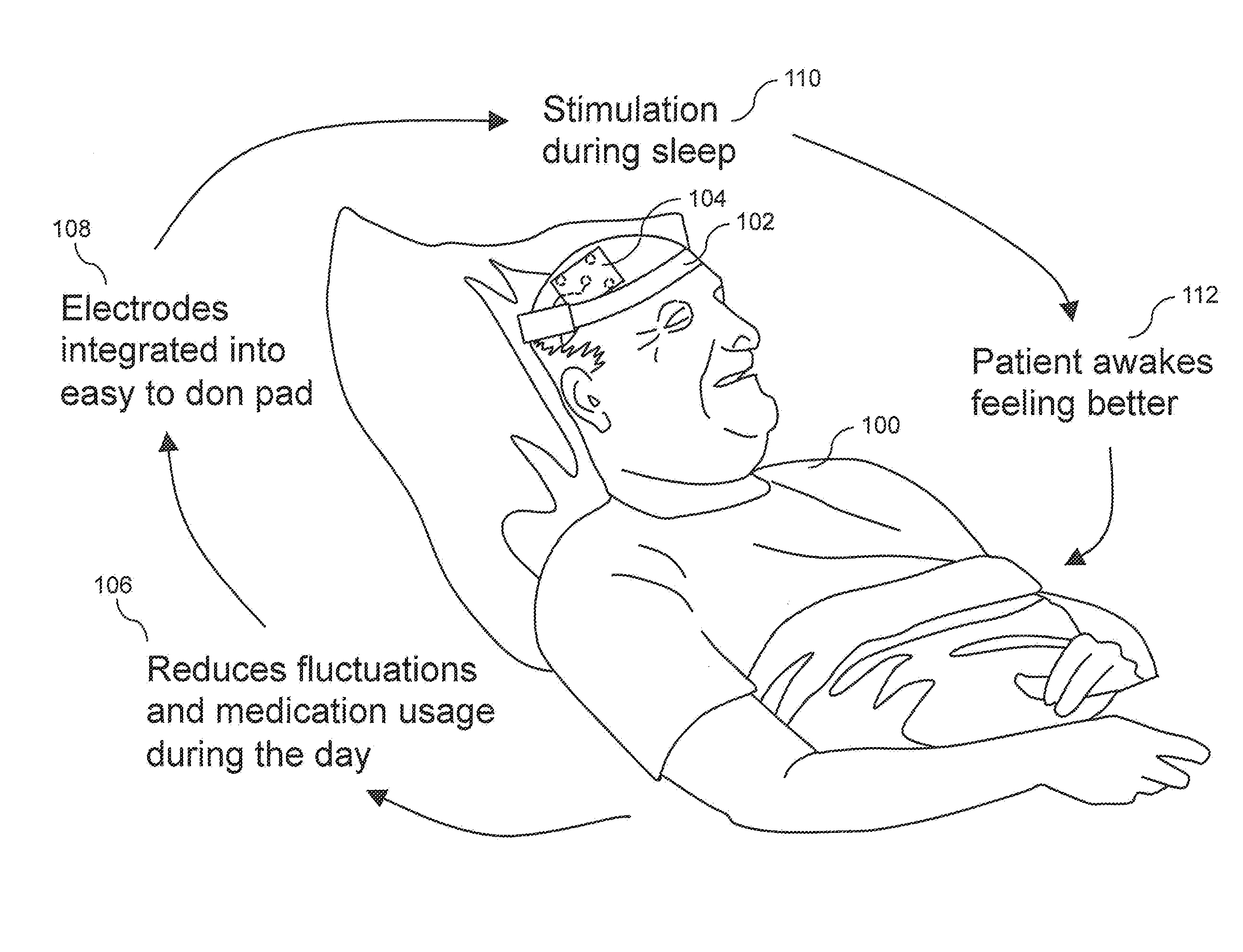
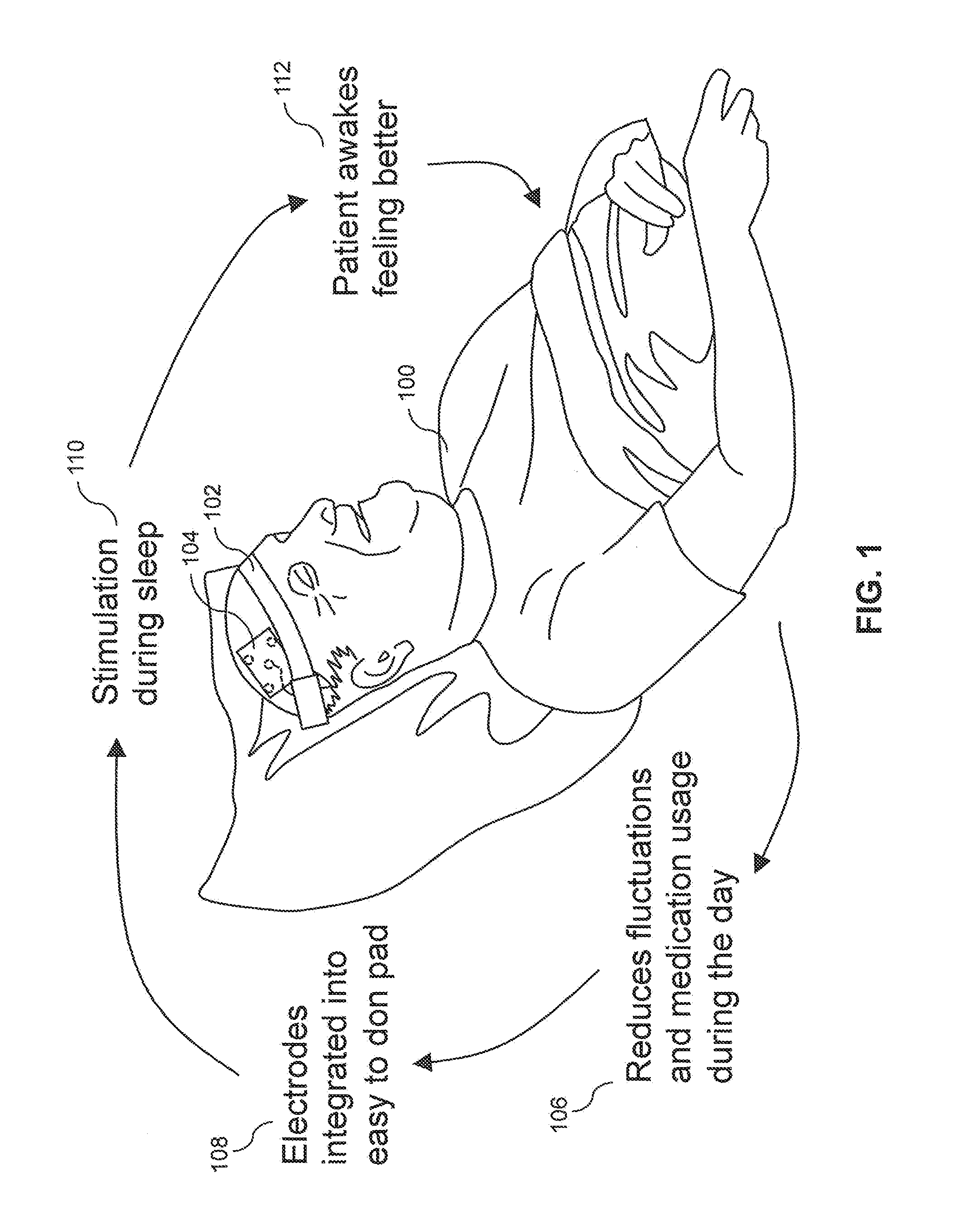
Wearable, unsupervised transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) device for movement disorder therapy, and method of using
ActiveUS8583238B1Minimize impactMinimize timeHead electrodesExternal electrodesQuality of lifeTranscranial direct-current stimulation
The present invention relates to a system and methods for noninvasively providing therapy for movement disorder symptoms. The present invention provides such a therapy system which provides trans-cranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in order to treat those symptoms and the disorders. The present invention further provides such tDCS therapy while the subject sleeps in order to minimize the time required and impact of the therapy on the subject's waking life. The system, methods, and devices of the present invention are intended to provide a low-dose electrical current, trans-cranially, to a specific area of the subject's brain while he or she sleeps in order to decrease the occurrence, severity, and duration of the symptoms of movement disorders. The present invention aims to reduce the amount of medication necessary, counteract the effects of medication wearing off during sleep, and to overall improve the quality of life of subjects suffering from movement disorders.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for assessing brain function and portable automatic brain function assessment apparatus
A method and apparatus for performing rapid brain assessment may provide emergency triage to head trauma patients by analyzing a combination of spontaneous and evoked brain potentials. The spontaneous and evoked potentials are analyzed, and the results classified, to present a real-time assessment of a patient's brain, diagnosing any potential abnormalities therein.
Owner:BS HLDG +2
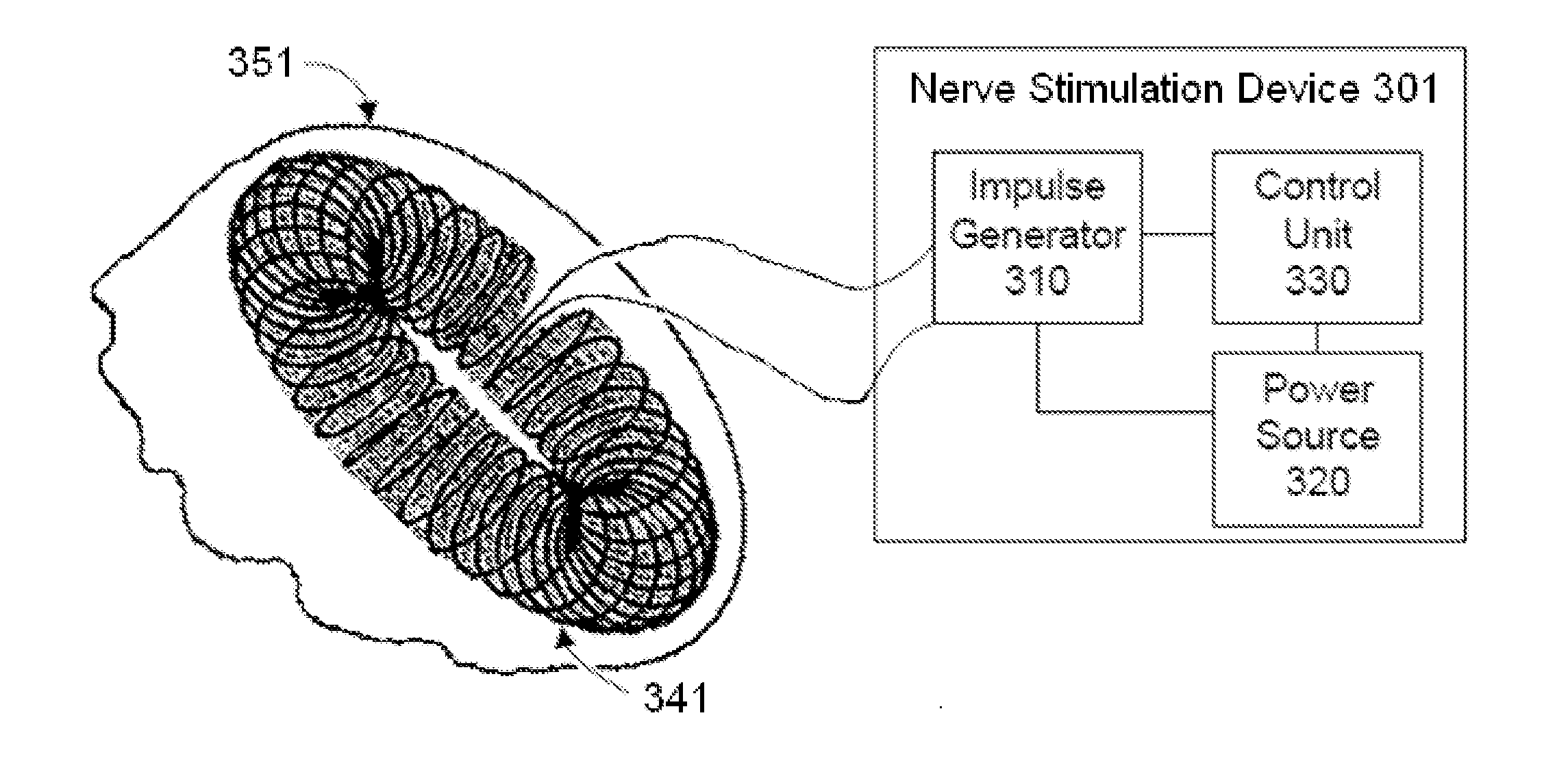
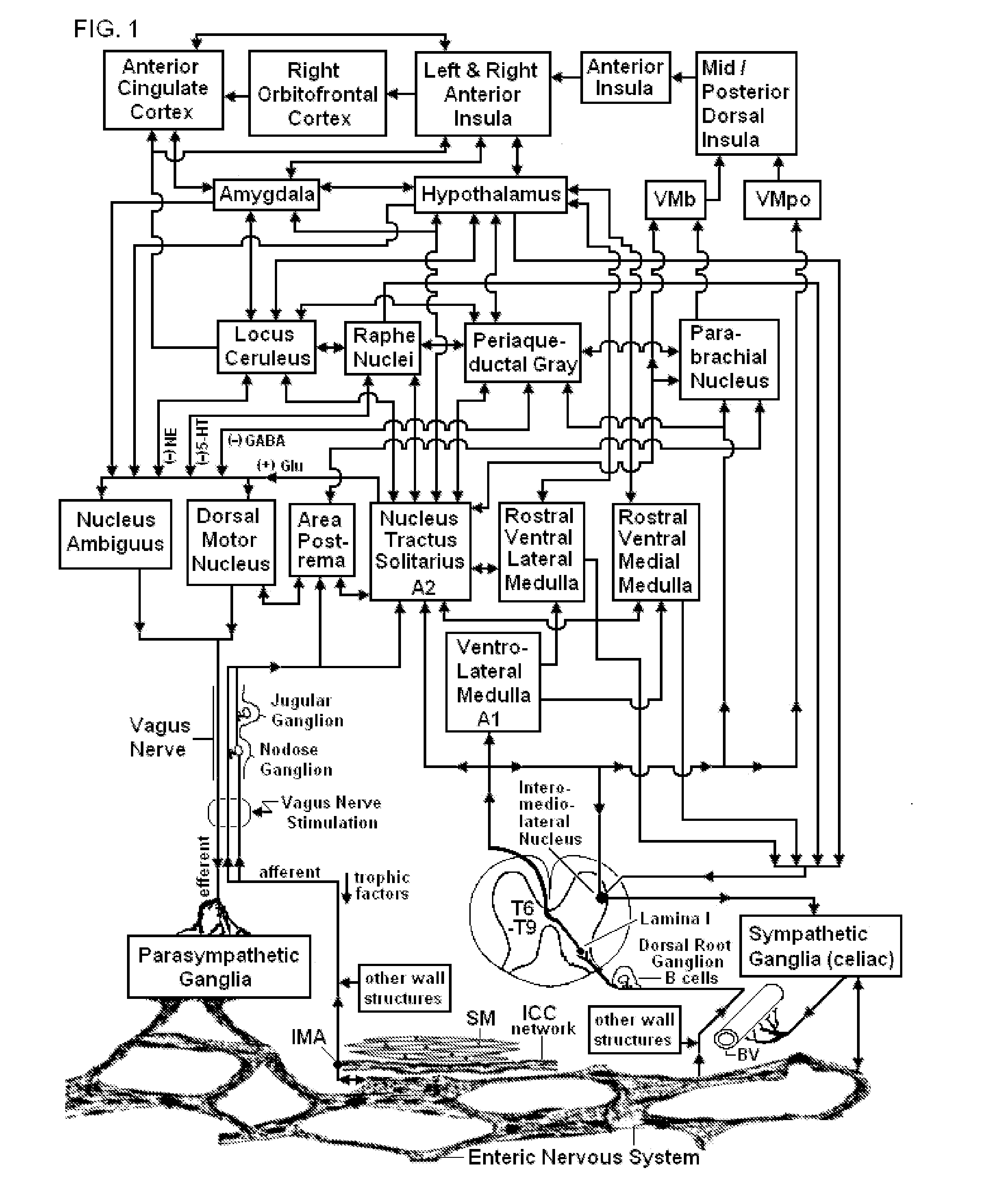
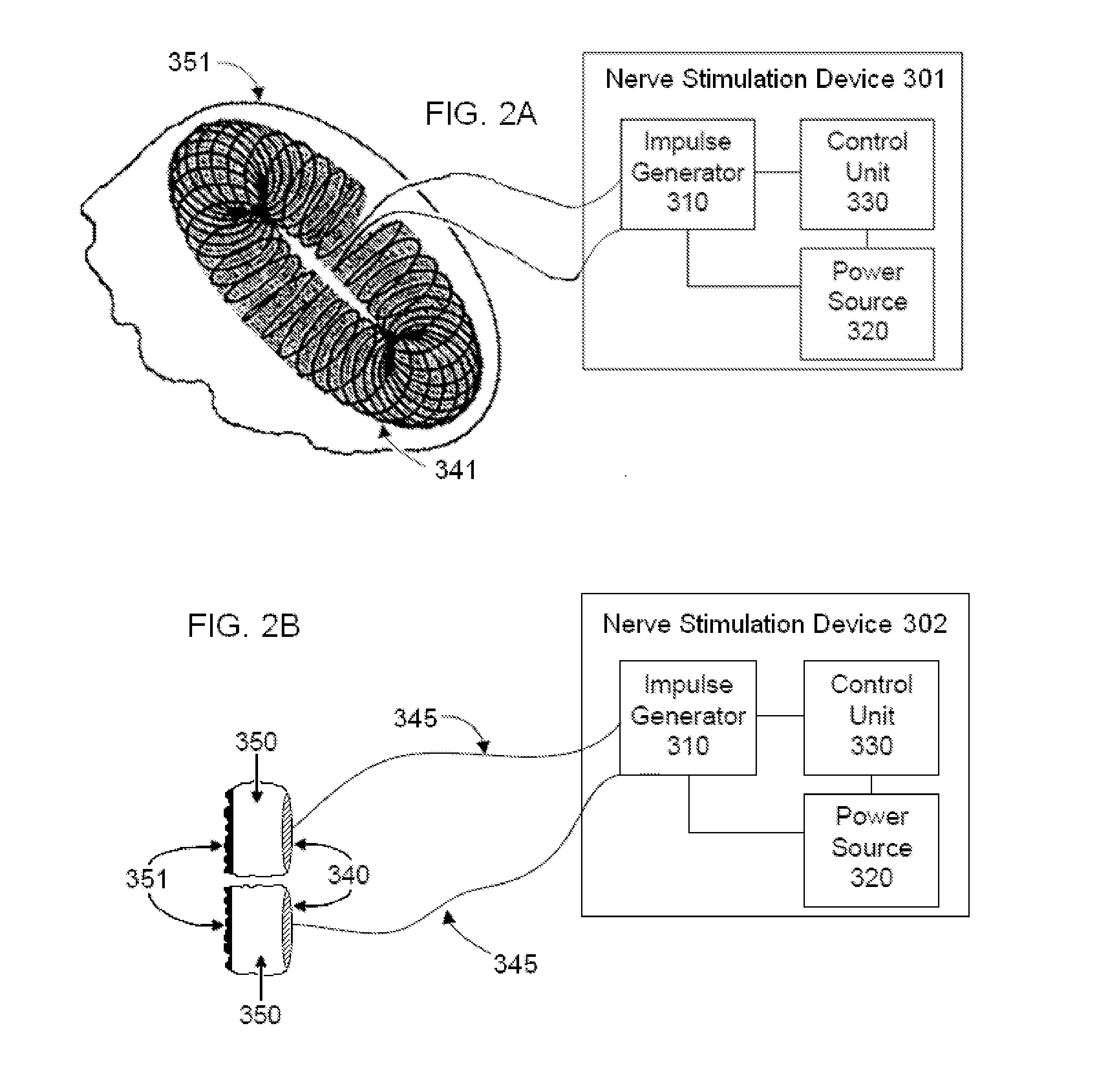
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, and other functional gastrointestinal disorders
ActiveUS20130131753A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDiseaseGastroparesis
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing gastroparesis, functional dyspepsia, and other functional gastrointestinal disorders. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. The methods provide damaged interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) with trophic factors via vagal afferent nerve fibers, thereby reversing ICC damage, and as a consequence improving gastric motility. The methods also increase levels of inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain so as to decrease neural activity within the area postrema, or they deactivate a resting state neural network containing parts of the anterior insula and anterior cingulate cortex, which will thereby reduce abnormal interoception and visceral hypersensitivity.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
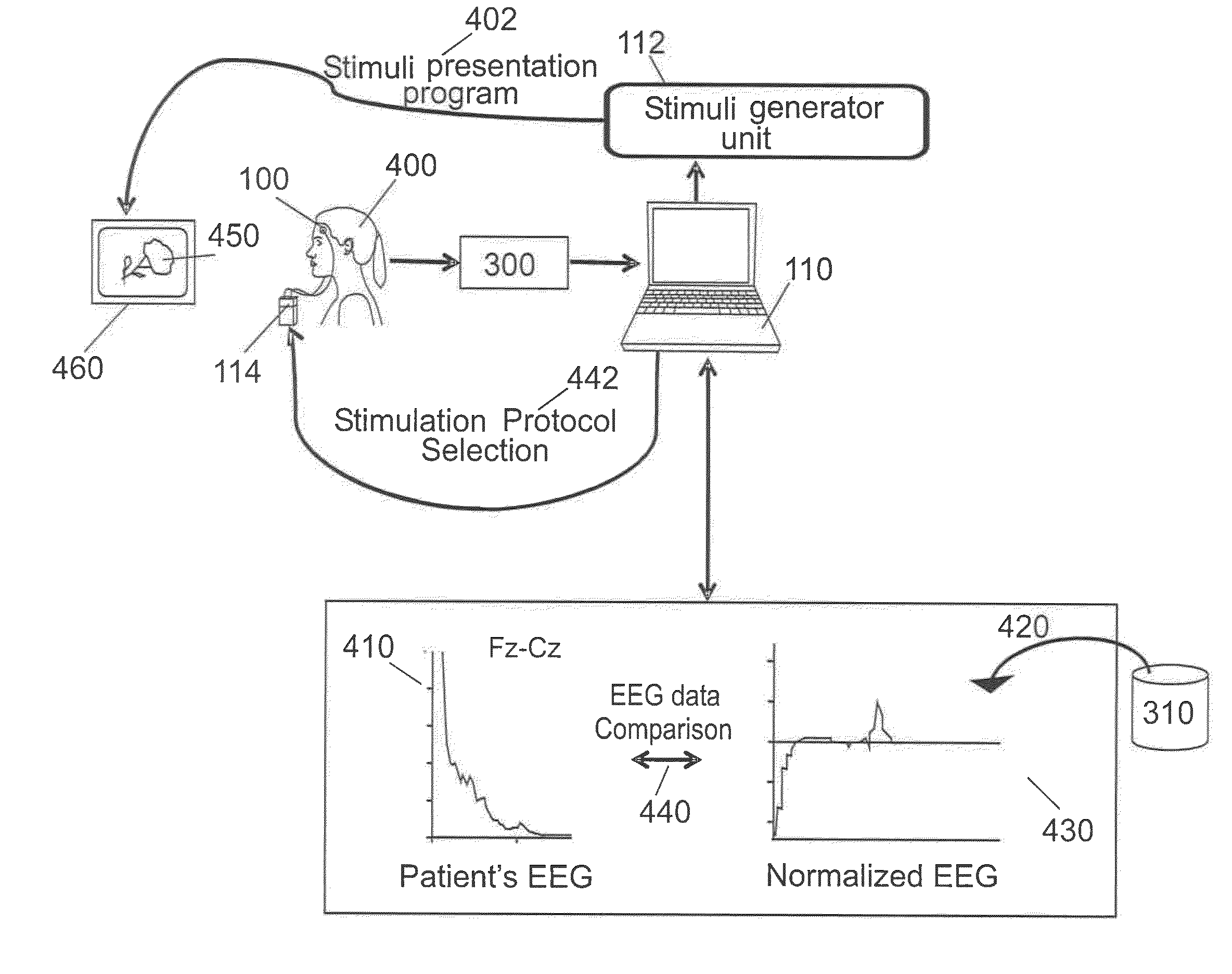
Brain therapy system and method using noninvasive brain stimulation
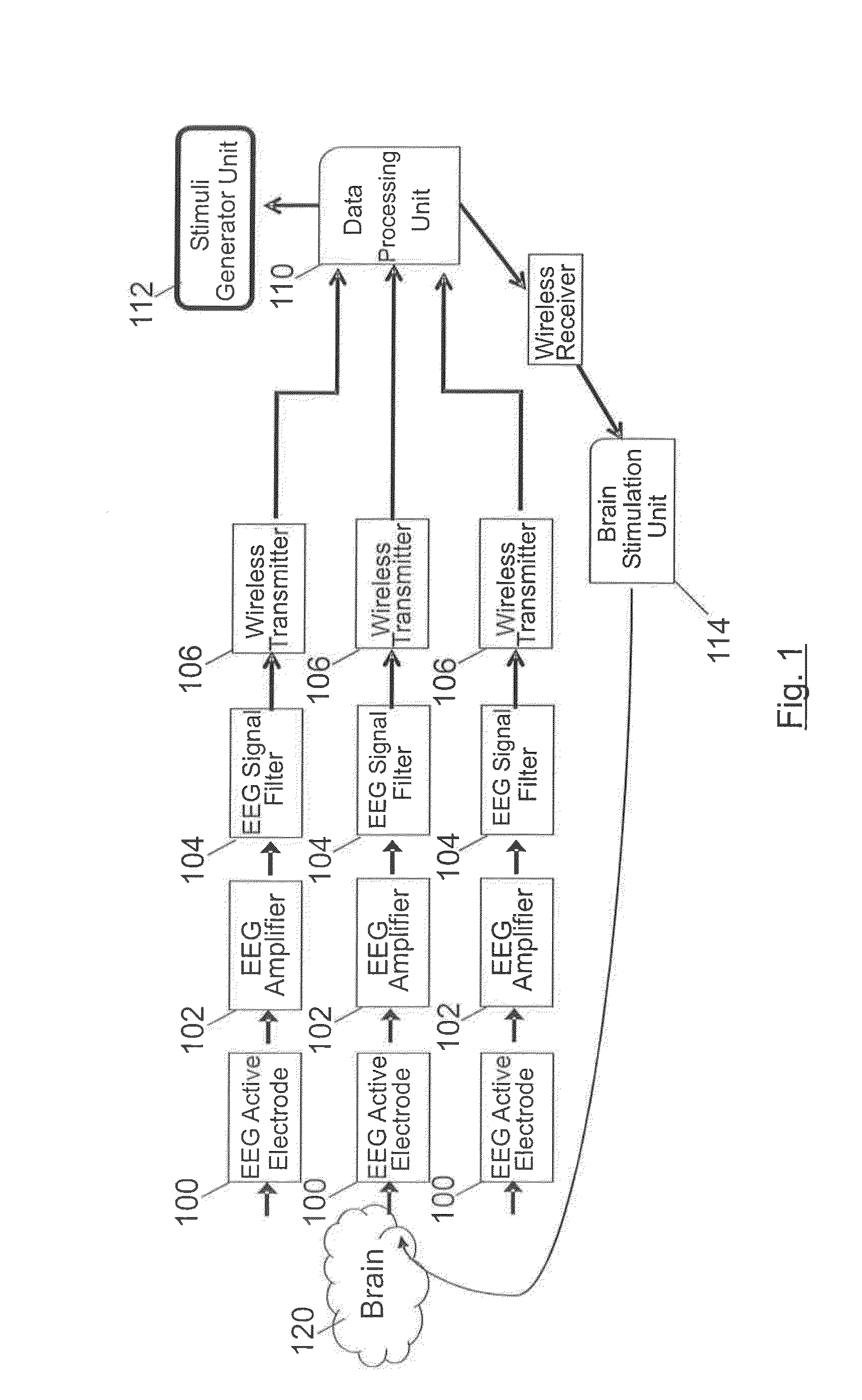
A brain therapy system and method using noninvasive brain stimulation, comprising:a stimuli generator unit for generating a stimuli presentation program;a sensor assembly comprising a plurality of active EEG electrodes for measuring the electrophysiological activity of a patient's brain subjected to said stimuli presentation program;a data acquisition unit in communication with the sensor assembly for retrieving patient EEG signals;a data processing unit in communication with the data acquisition unit for:analyzing the patient EEG signals to obtain patient EEG data, andcomparing the patient EEG data against a normalized EEG pattern retrieved from a standardized database;selecting a stimulation protocol in dependence of said comparison;a brain stimulation unit for applying the selected stimulation protocol on the active EEG electrodes.
Owner:NEUROMETRICS
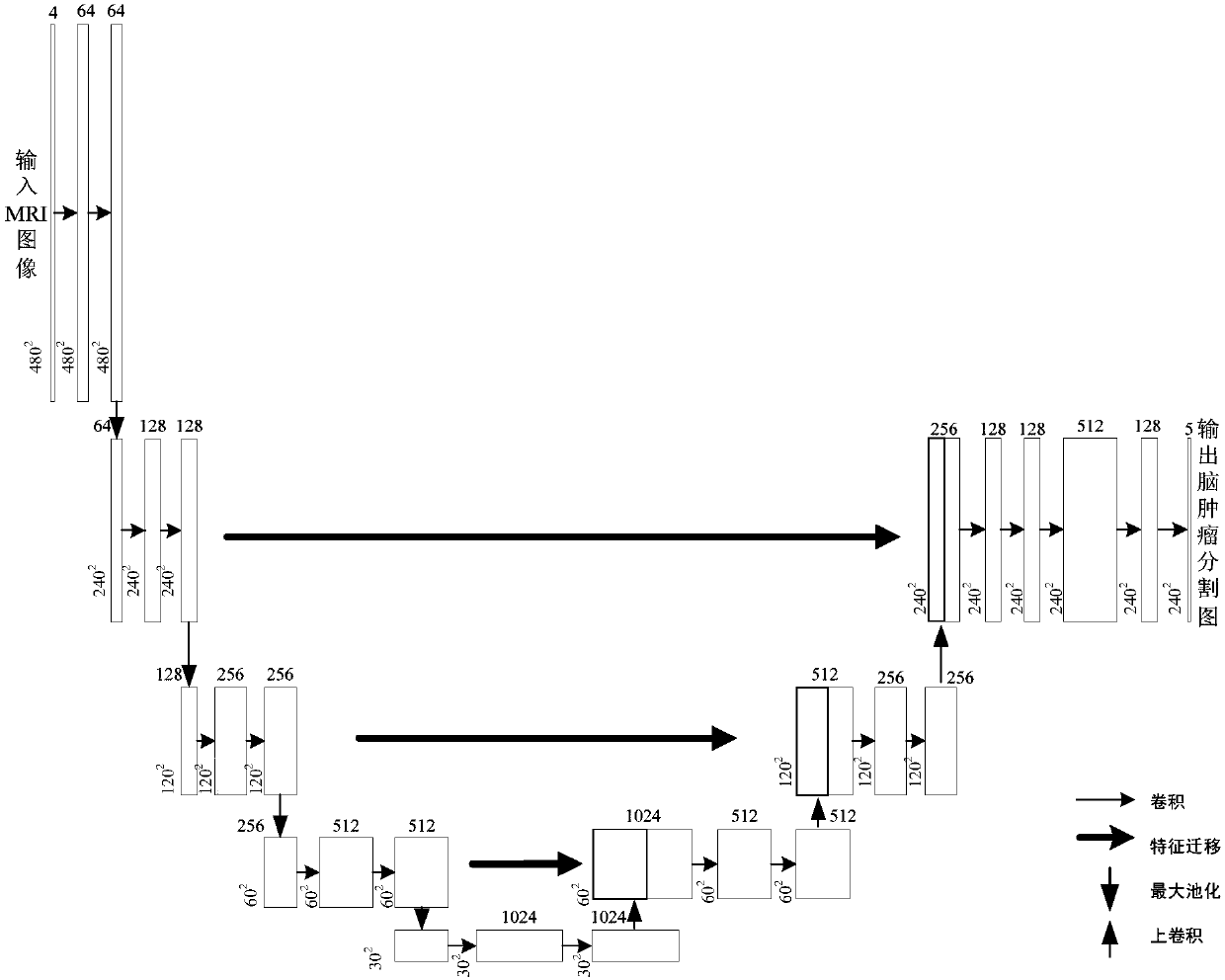
A MRI brain tumor image segmentation method based on optimized U-net network model
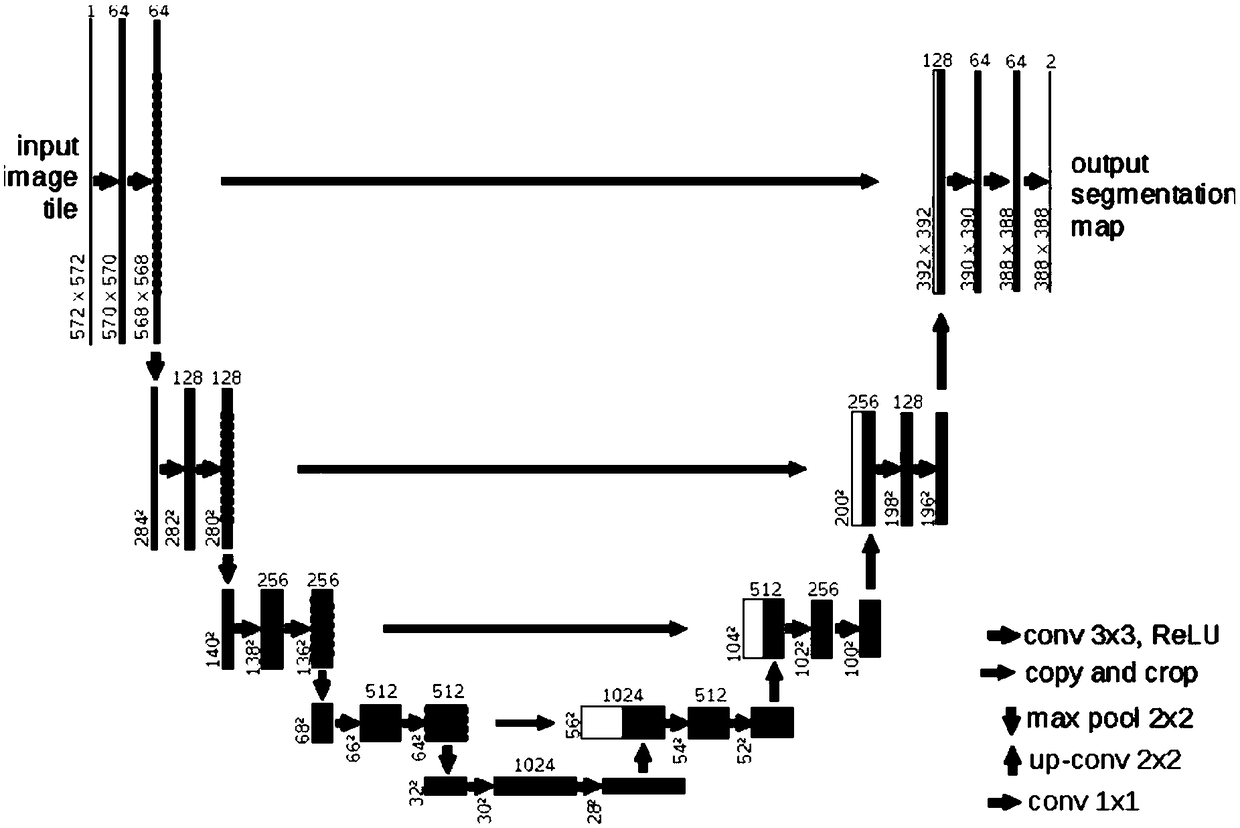
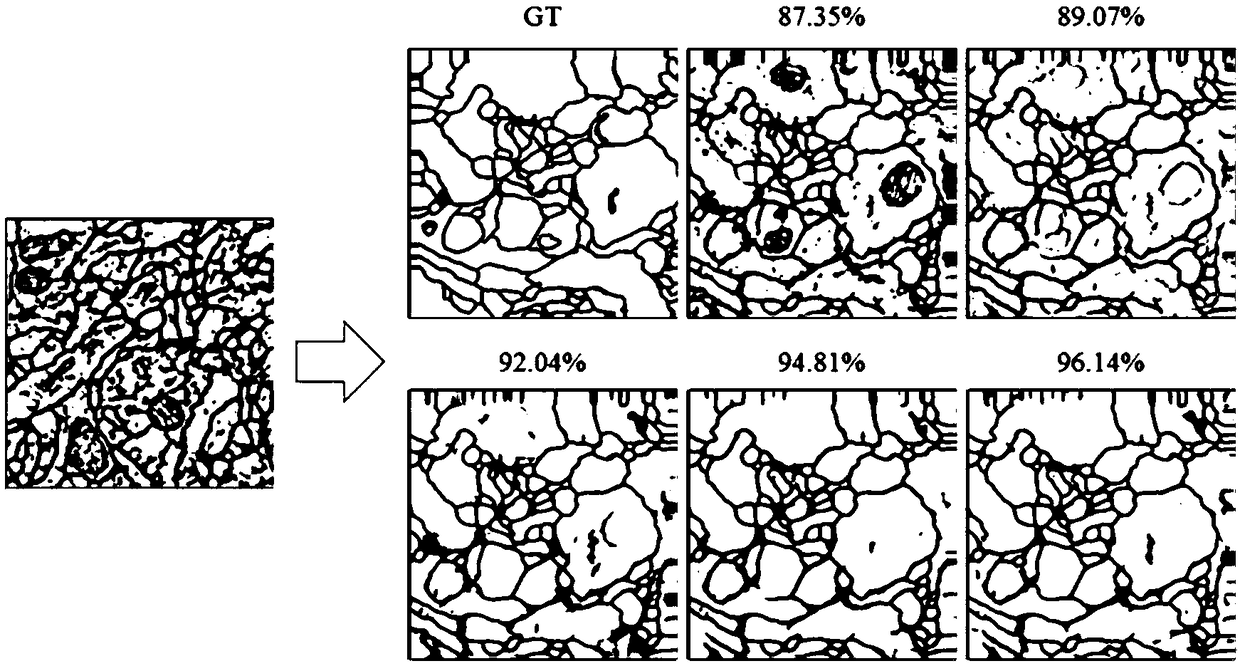
InactiveCN109087318AImprove accuracyPreserve image edge informationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationNetwork model
The invention relates to a MRI brain tumor image segmentation method based on an optimized U-net network model. The method comprises the following steps: 101, preprocessing the acquired multimodal MRIbrain tumor image data; 102, inputting the preprocessed multimodal MRI brain tumor image data into the trained U-Net network model; 103, acquiring multi-modality MRI brain tumor image segmentation data output by a U-NET network model, wherein the multimodal MRI brain tumor image segmentation data output from the U-NET network model can preserve the image edge information to generate a complete segmented image feature map. The image segmentation method provided by the invention can not only preserve the image edge information and generate a complete characteristic map, but also improve the accuracy of image segmentation.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
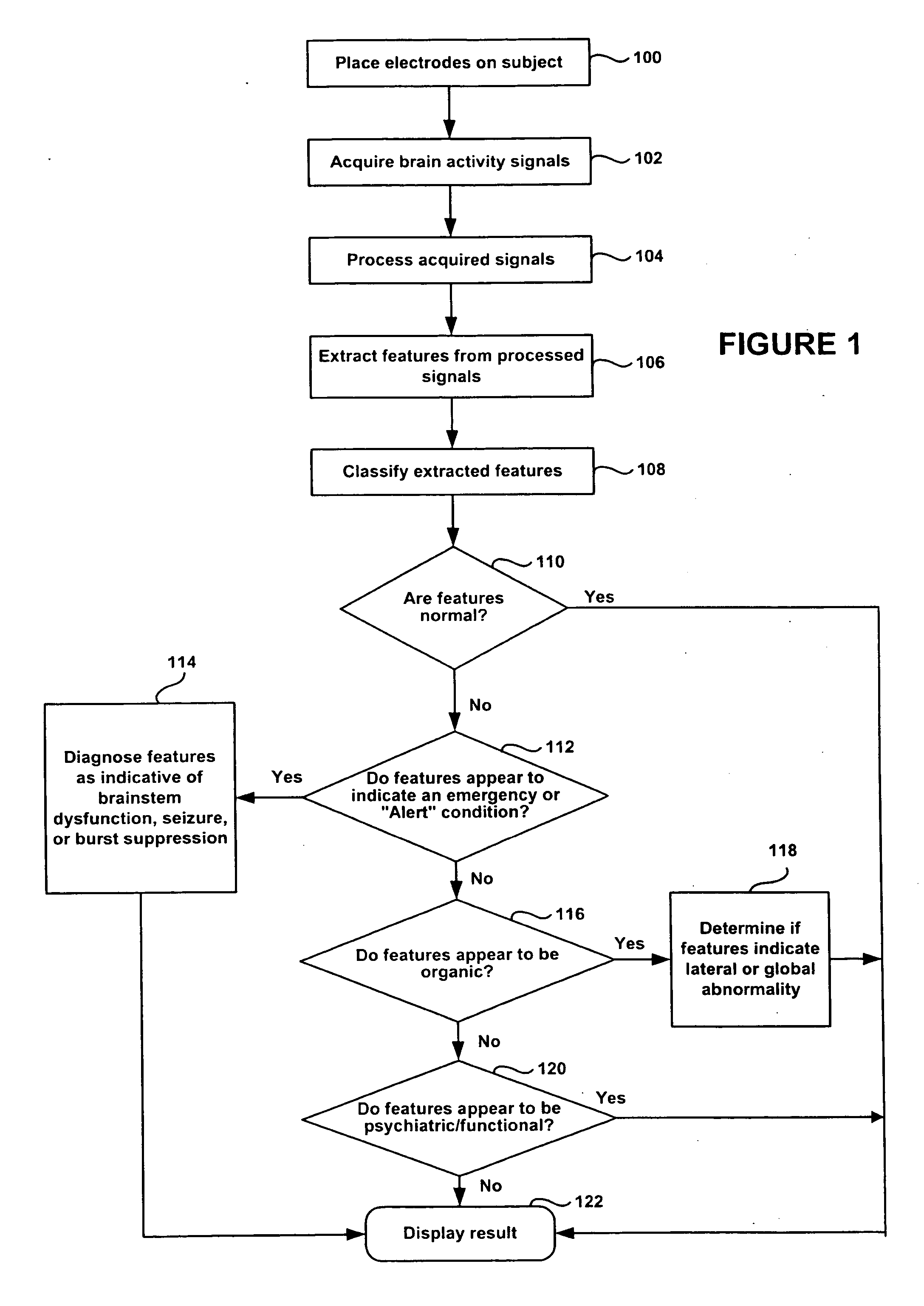
Brain Activity as a Marker of Disease
A method of monitoring brain activity is provided, wherein the method includes receiving a signal associated with neuronal activity of a mammalian brain. The method also includes processing the signal using a linear, non-linear, or combination algorithm to extract a signal feature. A neuromarker may be determined based on an association between the signal feature and a library of features, wherein the library includes a plurality of signal features correlated with a plurality of disease states.
Owner:BRAINSCOPE SPV LLC
Transcranial stimulation device and method based on electrophysiological testing
Embodiments of the disclosed technology provide a combination electroencephalography and non-invasive stimulation devices. Upon measuring an electrical anomaly in a region of a brain, various tDCS or other electrical stimulations are utilized to correct neural activity. Devices of the disclosed technology may utilize visual, balance, auditory, and other stimuli to test the subject, analyze necessary brain stimulations, and administer stimulation to the brain.
Owner:EVOKE NEUROSCI
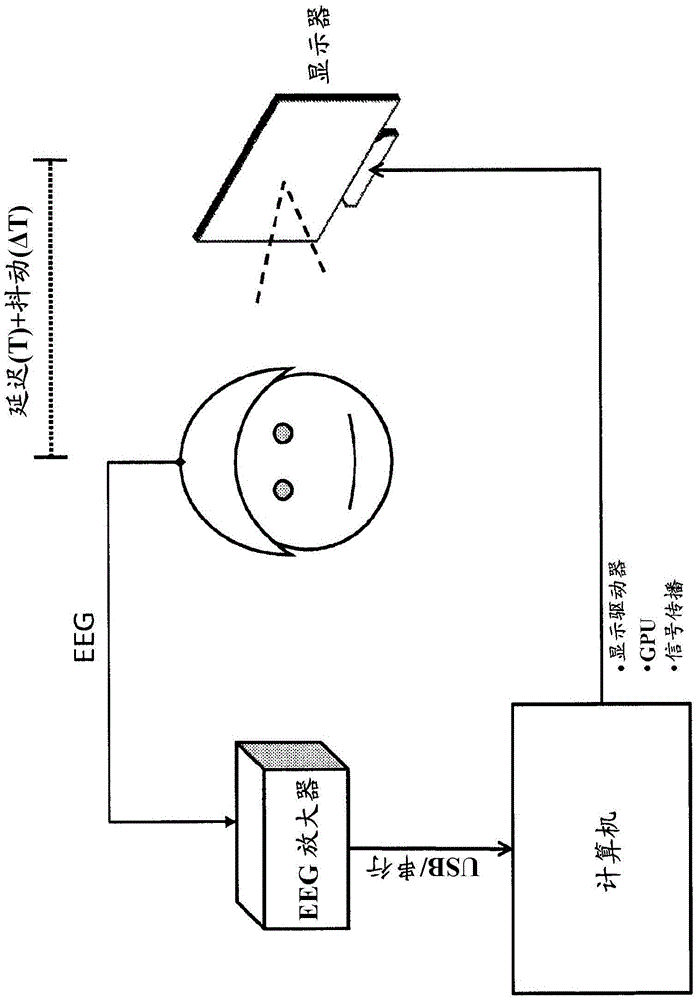
Physiological parameter measurement and feedback system
ActiveCN105578954APhysical therapies and activitiesRespiratory organ evaluationHead-up displayBrain computer interfacing
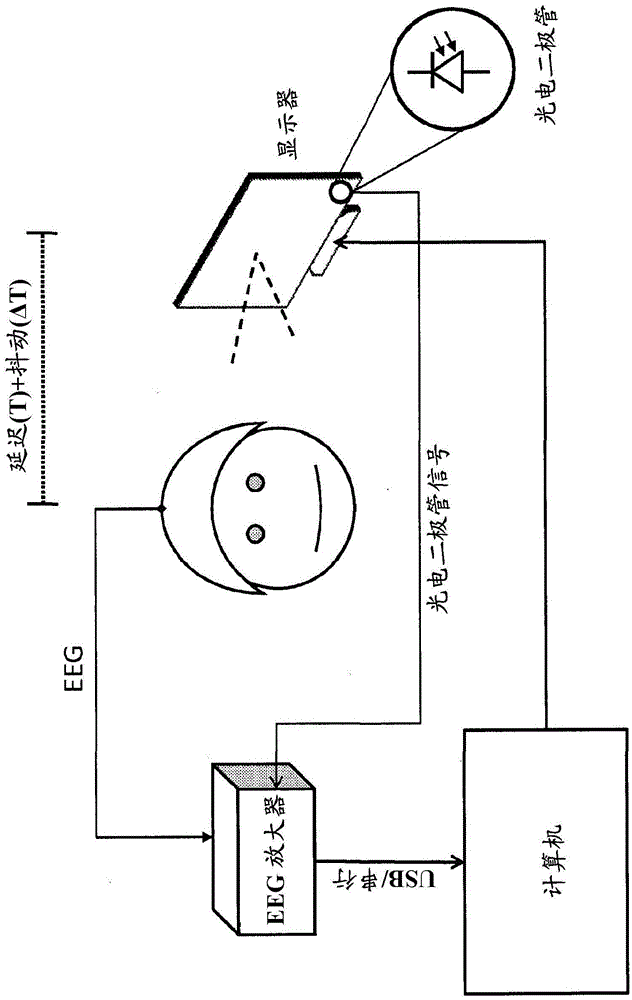
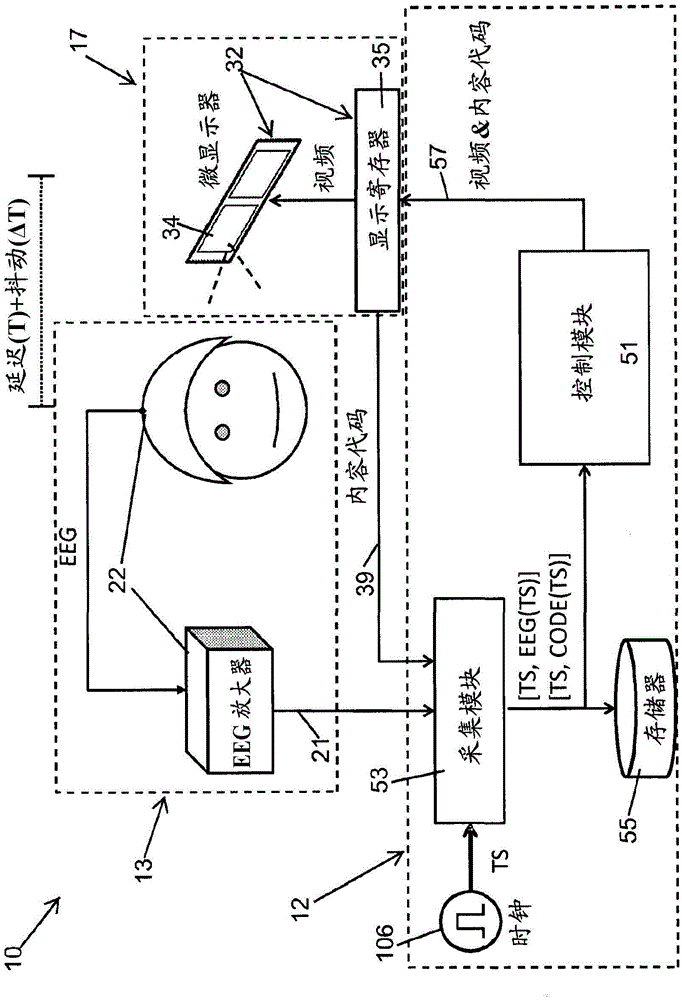
Electrical activity of the brain (EEG) and position / motion of a body part, e.g. motion of an arm, are measured. A virtual representation of either the moving body part or the intended movement as determined from the brain activity is presented as feedback to the subject on a display which can be implemented as a head-up display. A clock module is operable to time stamp information transferred from a brain electrical activity sensing system and a position / motion detection system for joint processing. This non-invasive EEG-based brain-computer-interface is particularly useful for stroke rehabilitation.
Owner:MINDMAZE HLDG SA
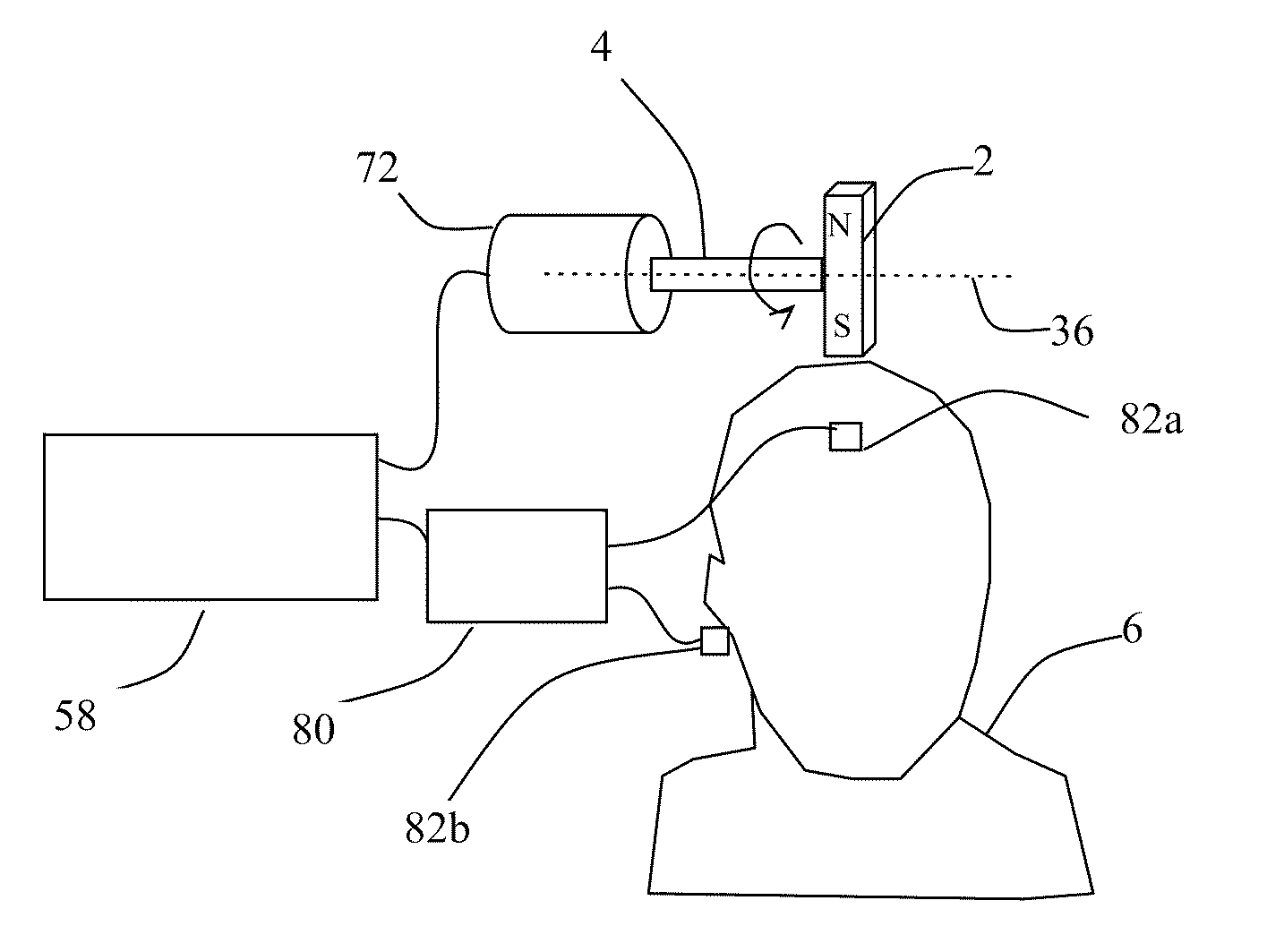
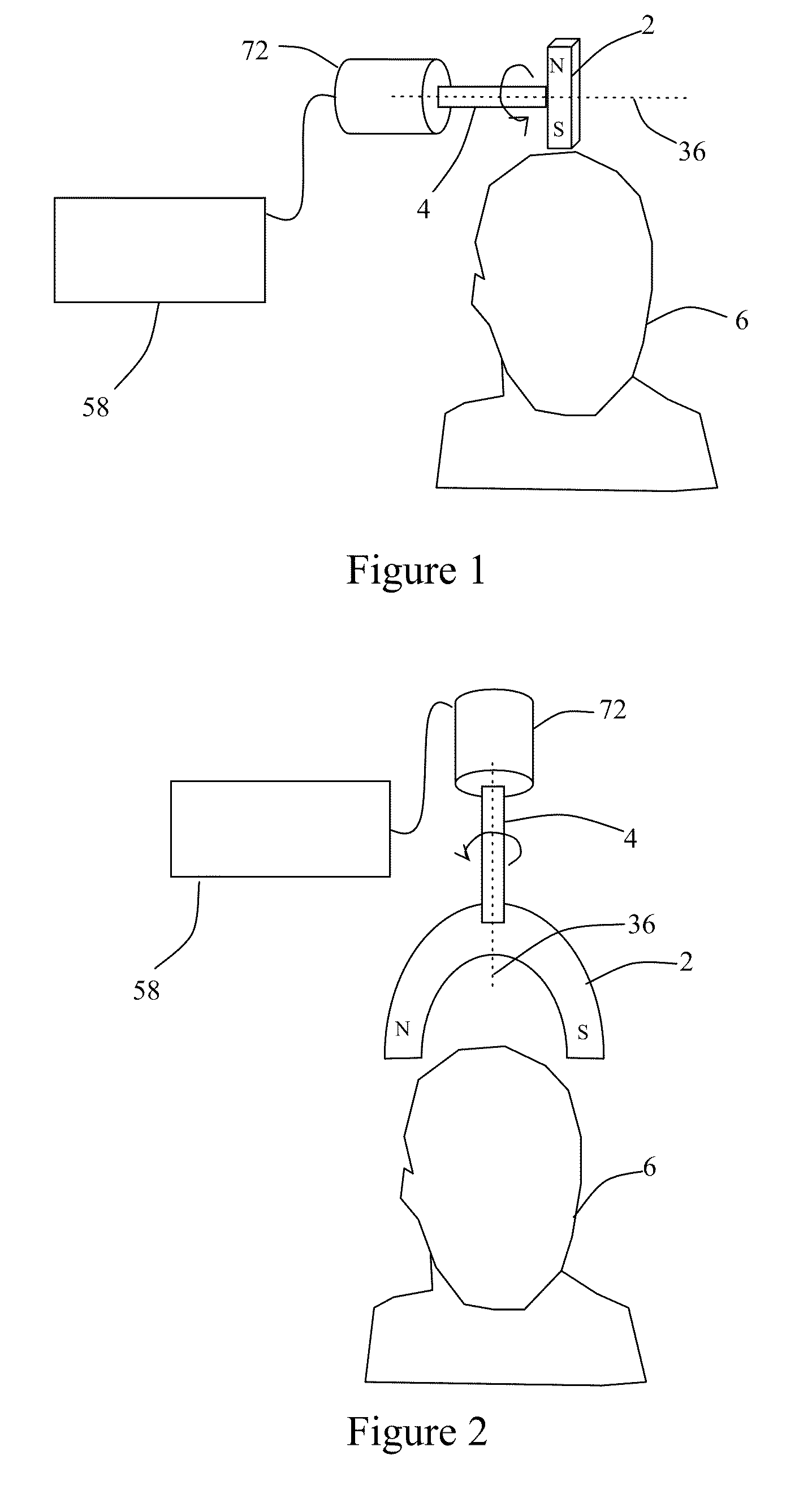
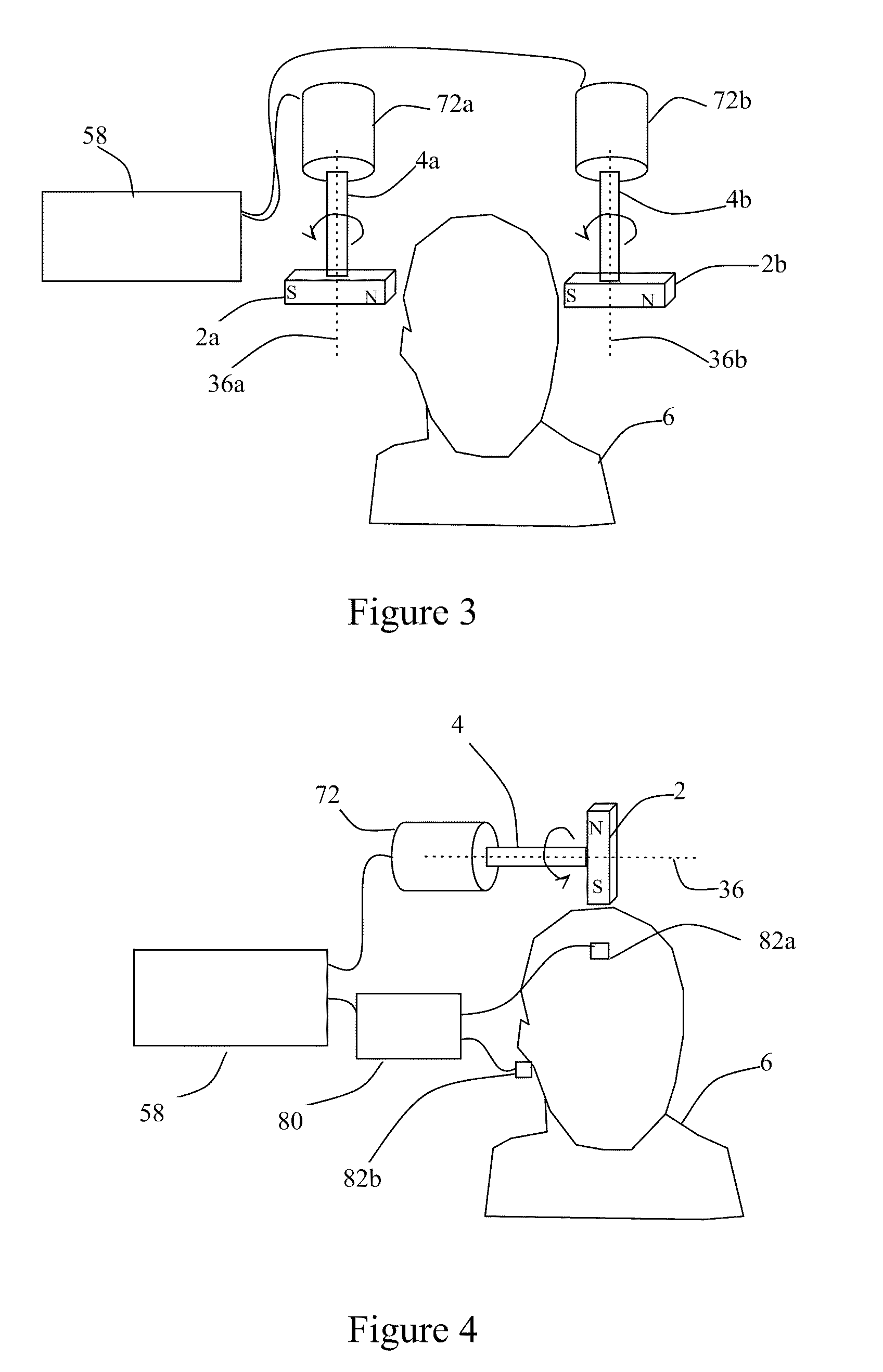
Method and System for Displaying the Electric Field Generated on the Brain by Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
ActiveUS20080161636A1Accurate representationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsDisplay deviceHead surface
A visualization surface representative of a portion of the brain at a depth below the head surface of the subject is generated by combining an actual representation of the head surface with an idealized representation of the head surface. The combining is a function of the depth and is performed to minimize in the visualization surface any irregularities existing in the actual head surface of the subject. A display shows the visualization surface overlaid on a volumetric image of the brain, the electric field induced on a region of the visualization surface by a transcranial magnetic stimulation (“TMS”) induction coil device positioned above the head surface and the TMS coil device. By viewing the display, a user of the TMS coil device can interactively position the TMS coil device in relation to the head surface and, for a target site on the brain at a selected depth, determine the position at which the TMS coil device induces a maximum E-field on a visualization surface corresponding to the selected depth.
Owner:NEXSTIM
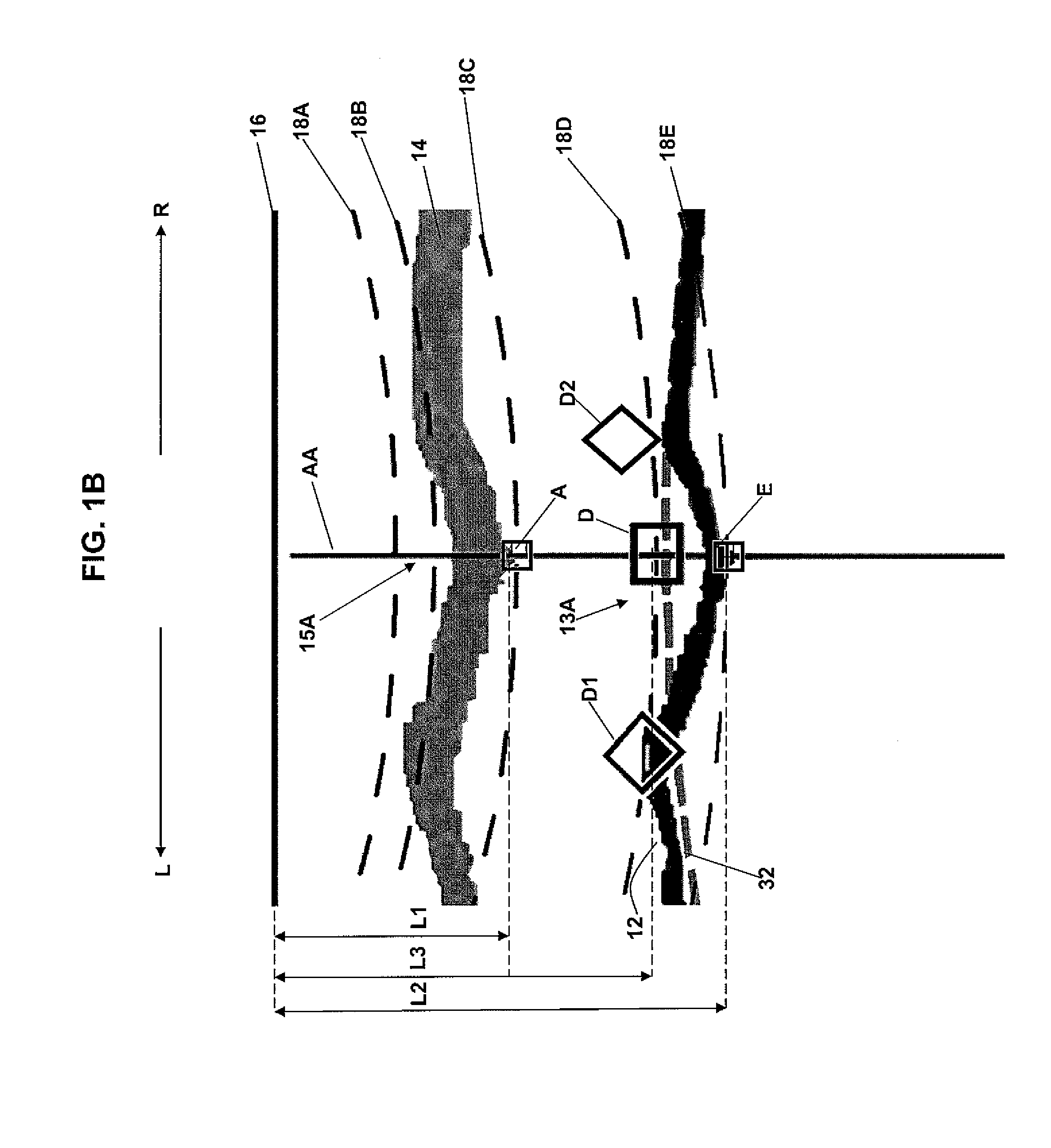
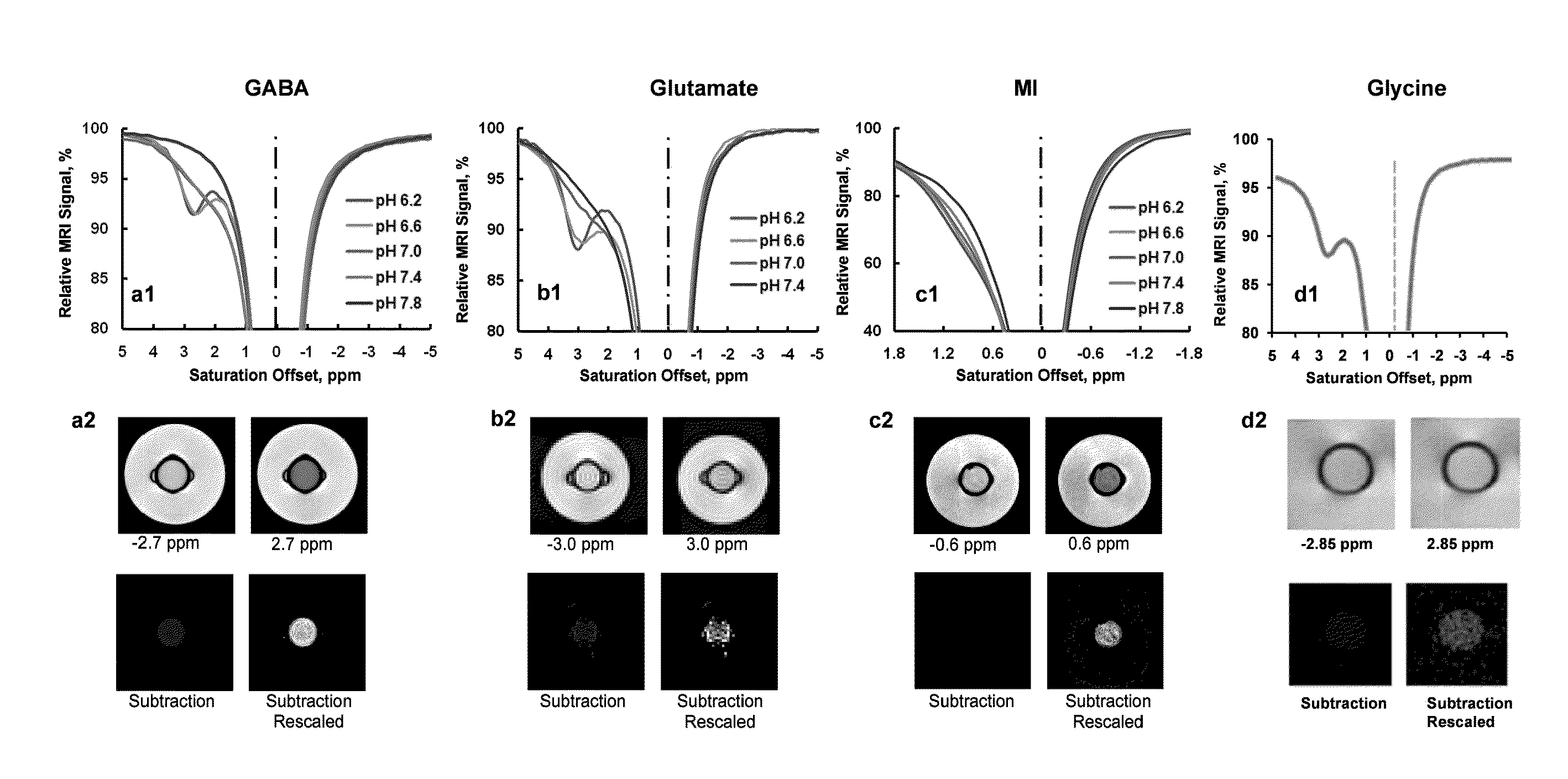
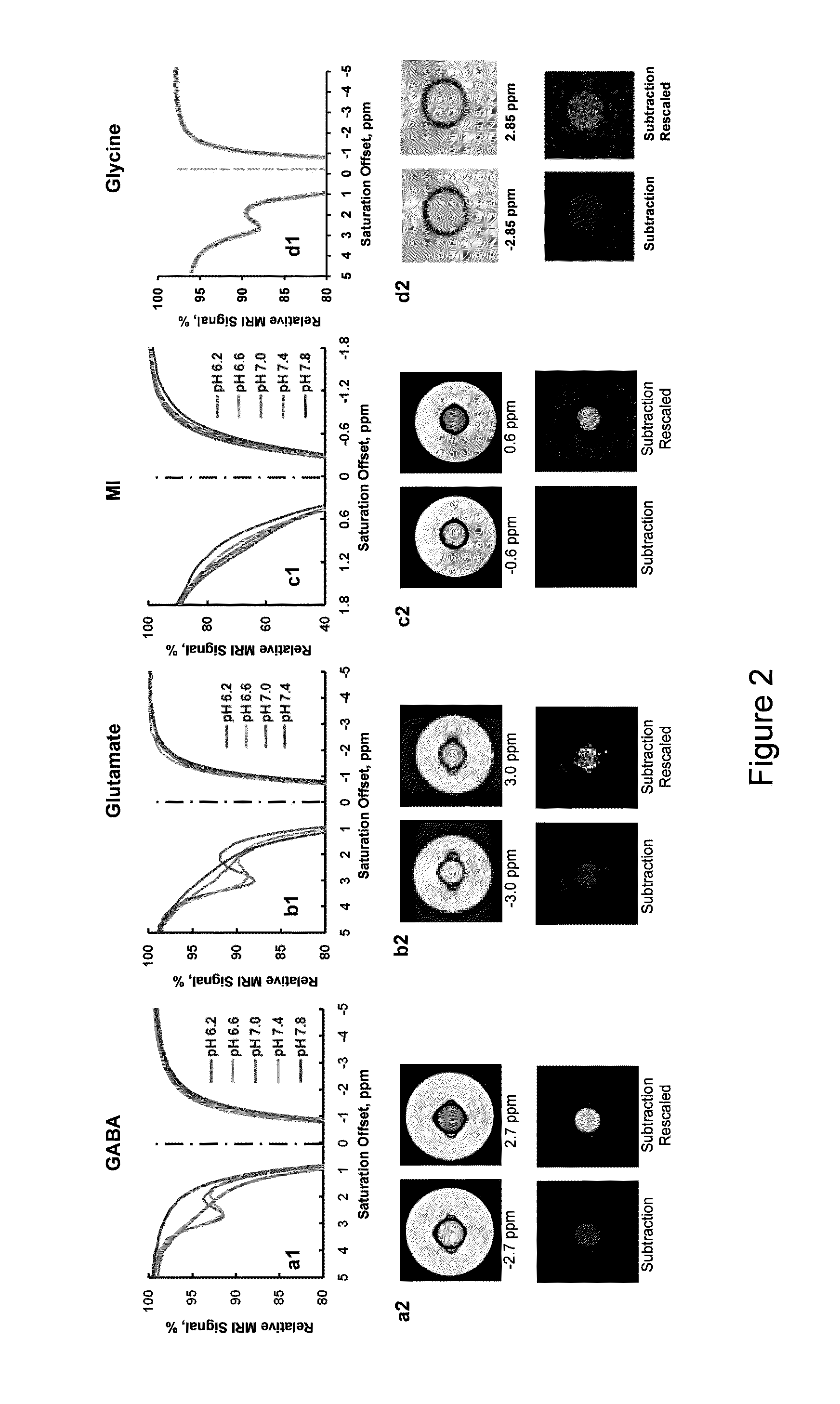
Cest MRI methods for imaging of metabolites and the use of same as biomarkers
ActiveUS20120019245A1Improve spatial resolutionEasy to detectMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionEndogenous metabolismMetabolite
The CEST effect for various neurotransmitters and energy metabolites in the brain and muscles and various endogenous metabolites in the liver, brain, and myocardium are imaged using MR imaging to illustrate a unique CEST effect that may be used to monitor the concentration of the metabolite and hence to characterize and monitor various disease states in the body correlated to the concentration of that metabolite. By adjusting the timing, amplitude, and length of the RF pulse as well as other parameters of the CEST pulse sequence to address the unique chemical shifts and exchange rates of the target, new targets with unique characteristics may be acquired using CEST MR imaging.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method and apparatus for delivery of agents across the blood brain barrier
InactiveUS20100143241A1Enhance brain imagingQuick managementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsNon destructiveSide effect
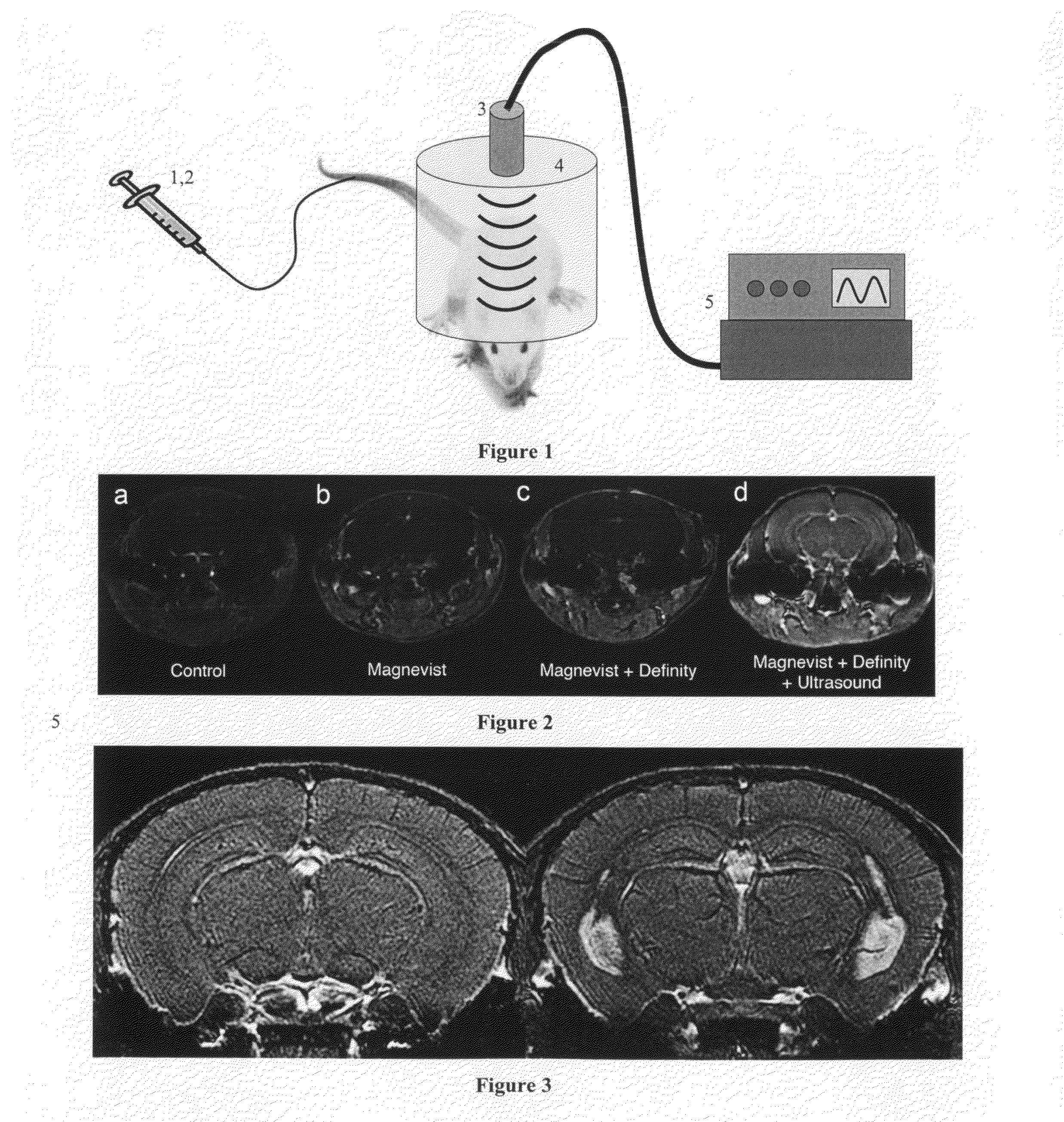
We describe a method for opening the blood-brain barrier (BBB) using ultrasound and preformed microbubbles. With this method, diagnostic or therapeutic agents may be administered to the brain. This method can open a focal region of the BBB and administer agents in a targeted fashion or the method can open large regions (or the entirety) of the brain for more global administration of agents. In one embodiment, the method can be used to administer contrast agents (e.g., agents that increase or decrease the magnetic resonance imaging signal) to the brain and thereby improve the quality or information content of imaging data. In another embodiment, a standard clinical diagnostic ultrasound scanner can be used to open specific regions of the BBB and administer diagnostic or therapeutic agents. Importantly, this invention can open the BBB in a non-destructive / non-invasive fashion, allowing the subject to be awake and suffer no detectable side effects.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Transcranial stimulation device and method based on electrophysiological testing
Embodiments of the disclosed technology provide a combination electroencephalography and non-invasive stimulation devices. Upon measuring an electrical anomaly in a region of a brain, various non-invasive stimulation techniques are utilized to correct neural activity. Stimulation techniques include transcranial direct current stimulation, transcranial alternating current stimulation and transcranial random noise stimulation, low threshold transcranial magnetic stimulation and repetitive transcranial magnet stimulation. Devices of the disclosed technology may utilize visual, balance, auditory, and other stimuli to test the subject, analyze necessary brain stimulations, and administer stimulation to the brain.
Owner:EVOKE NEUROSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com