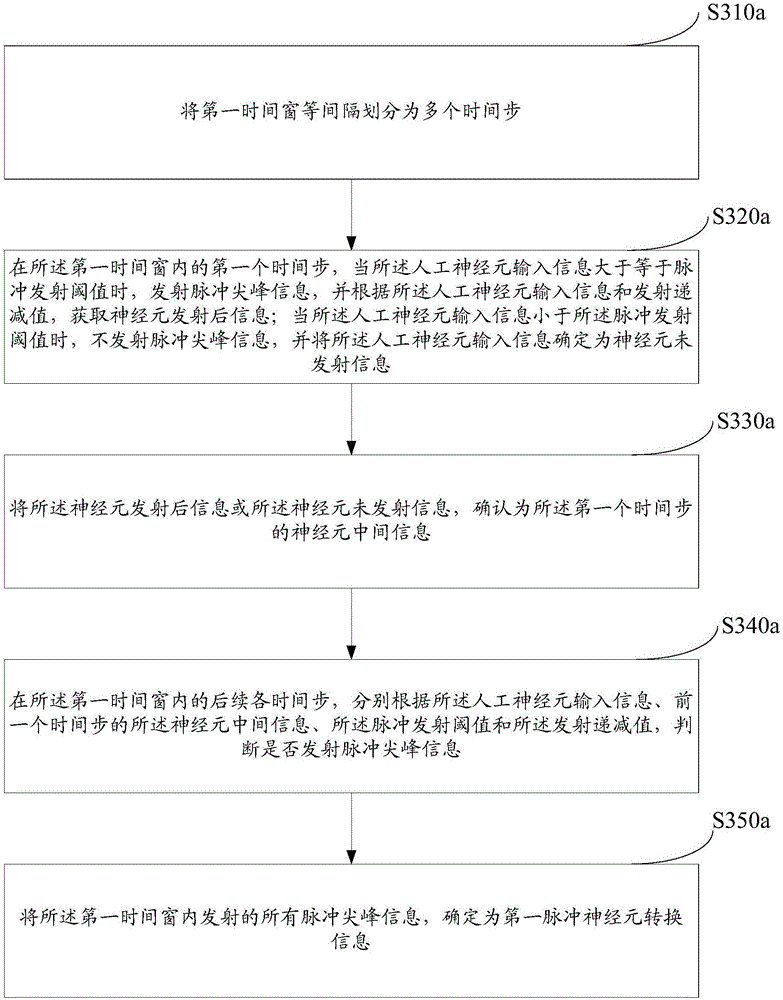
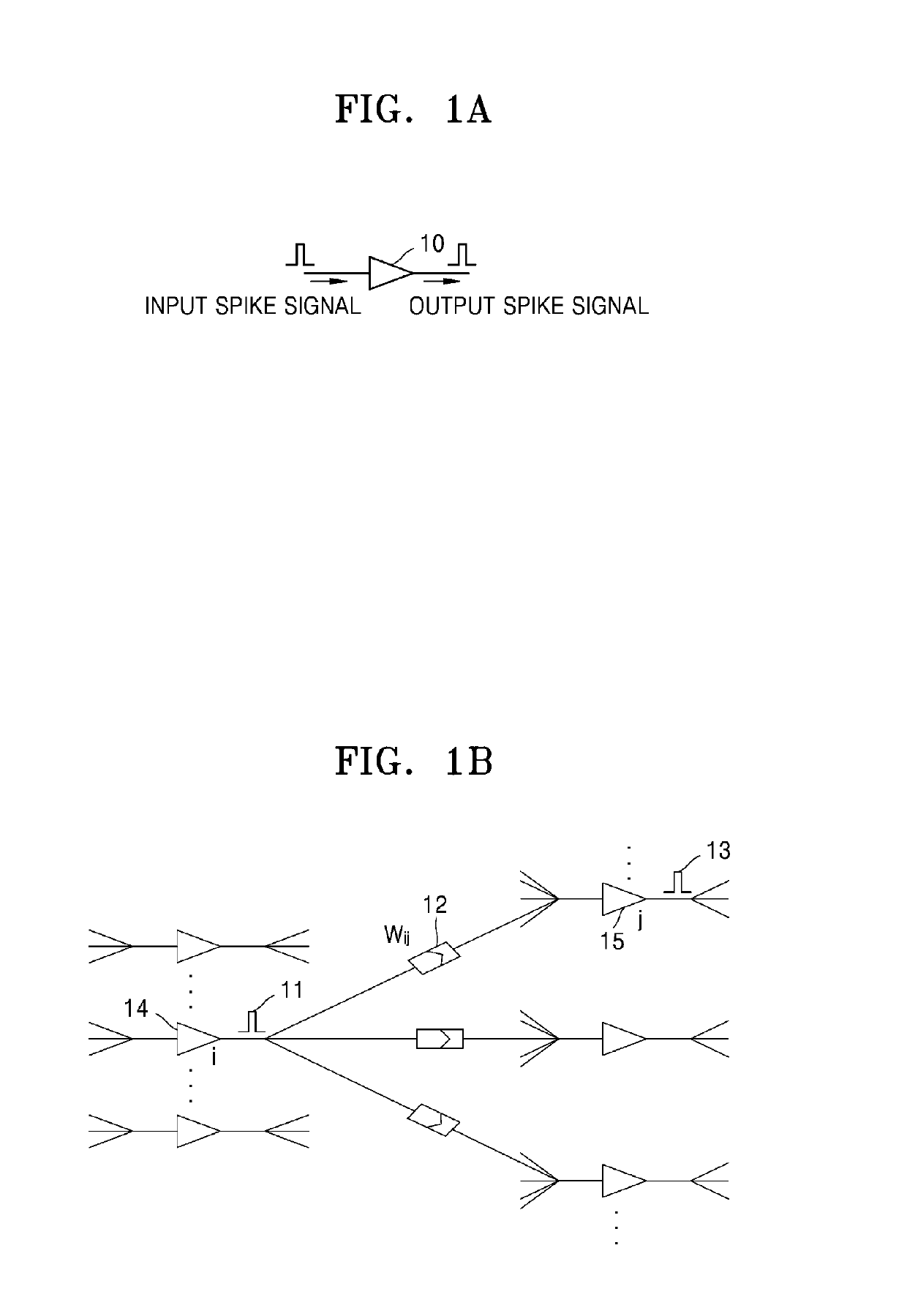
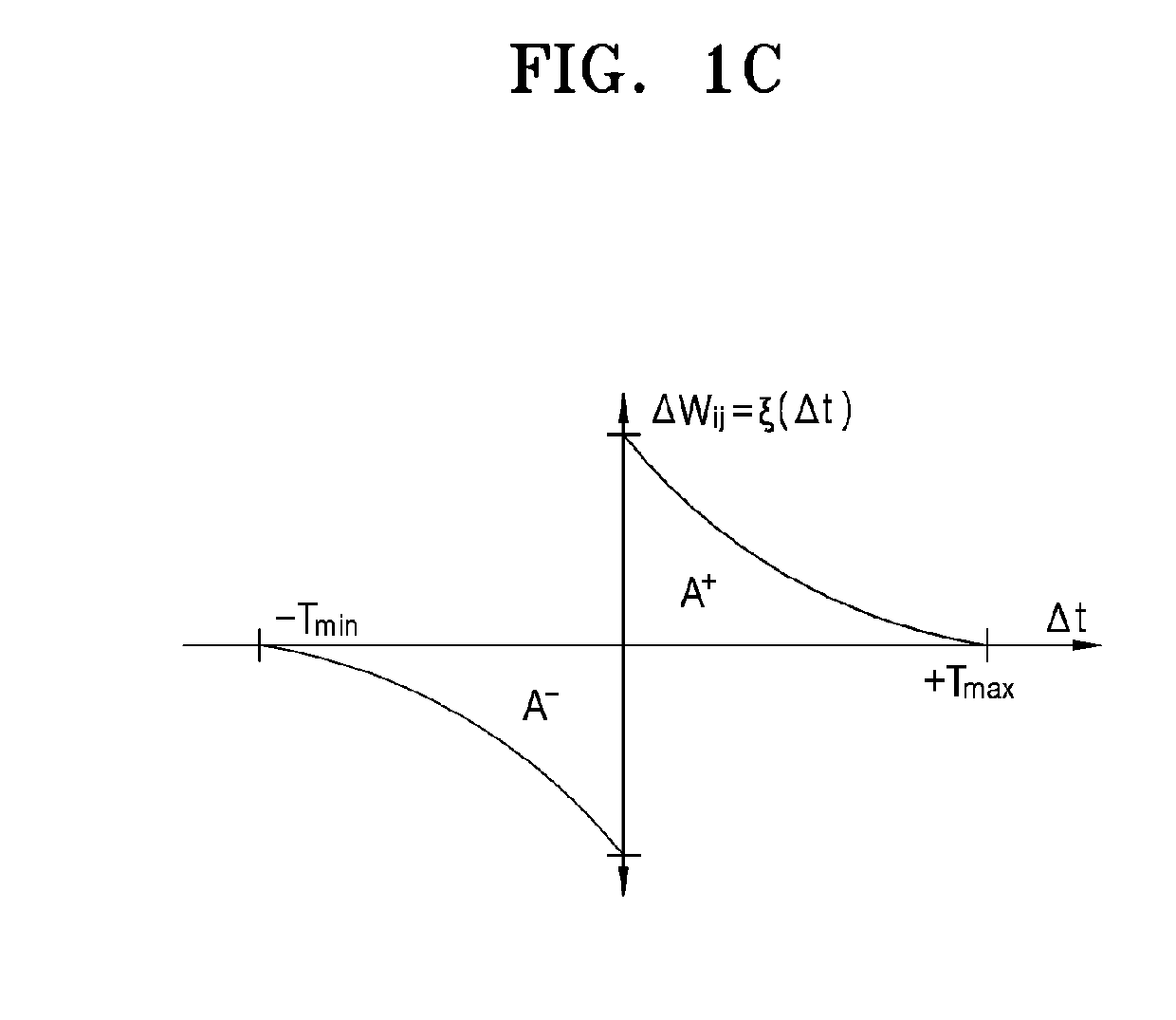
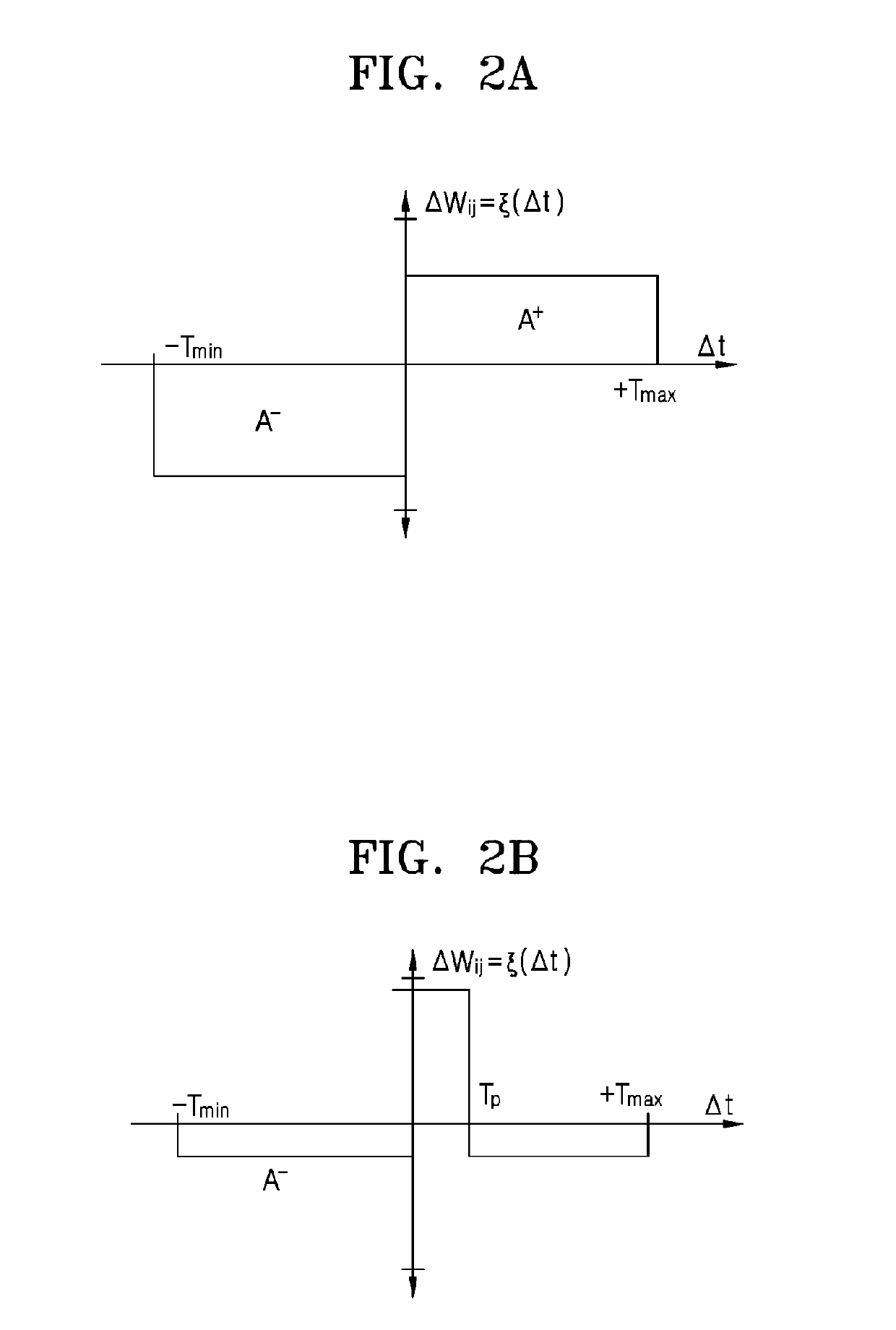
Patents
Literature
46 results about "Presynaptic neuron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
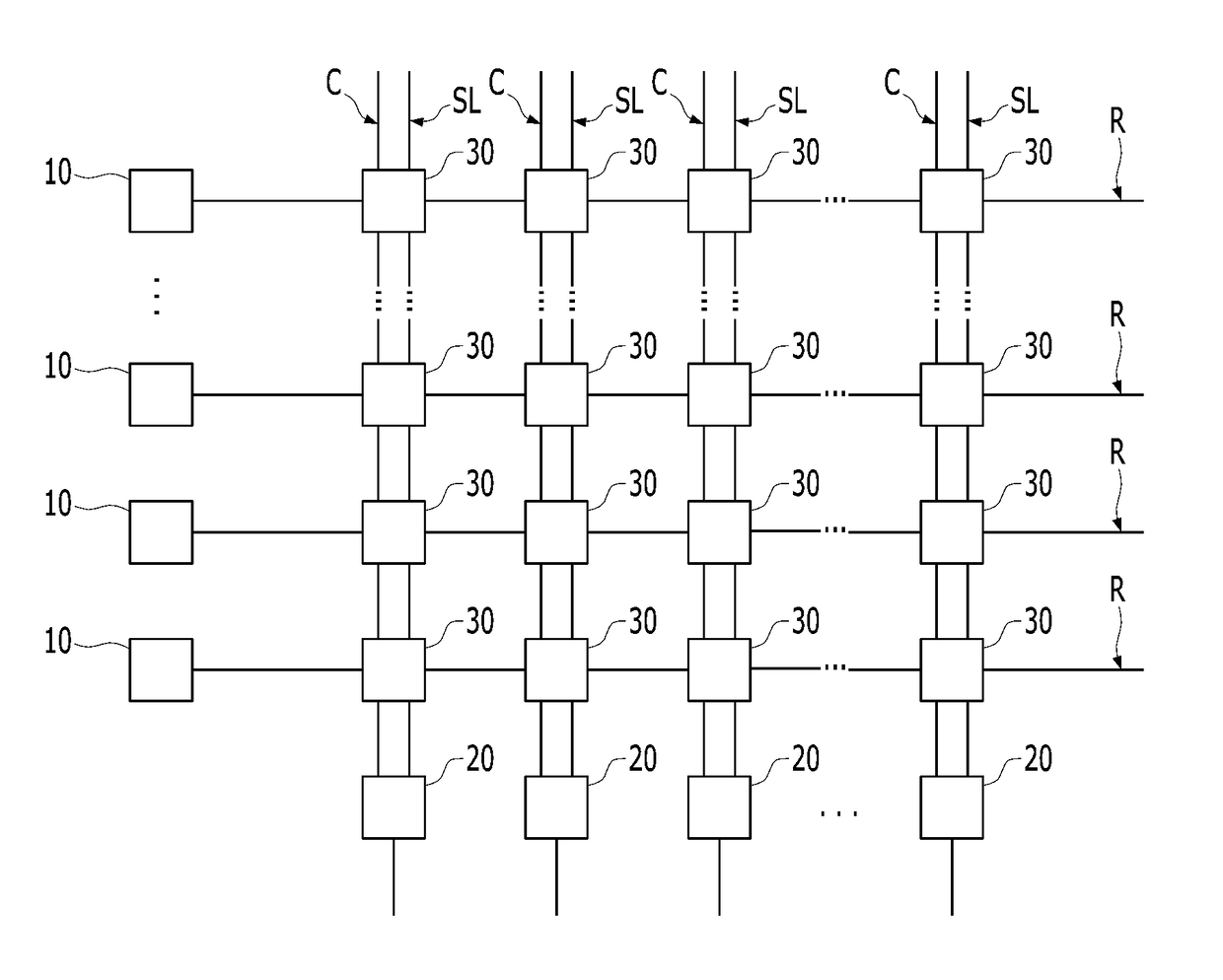
Presynaptic neuron. Type:Term. Definitions. 1. a neuron from the axon terminal of which an electrical impulse is transmitted across a synaptic cleft to the cell body or one or more dendrites of a postsynaptic neuron by the release of a chemical neurotransmitter.
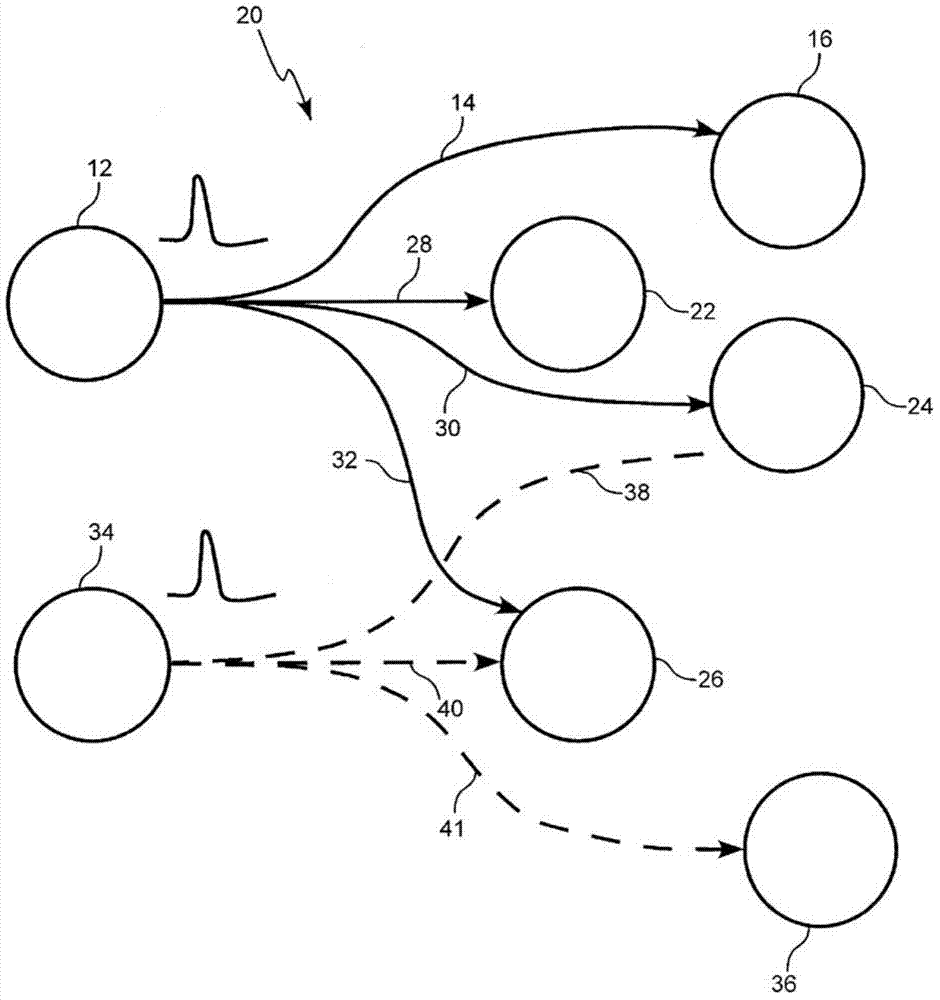
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS20080162391A1Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNerve networkCritical period
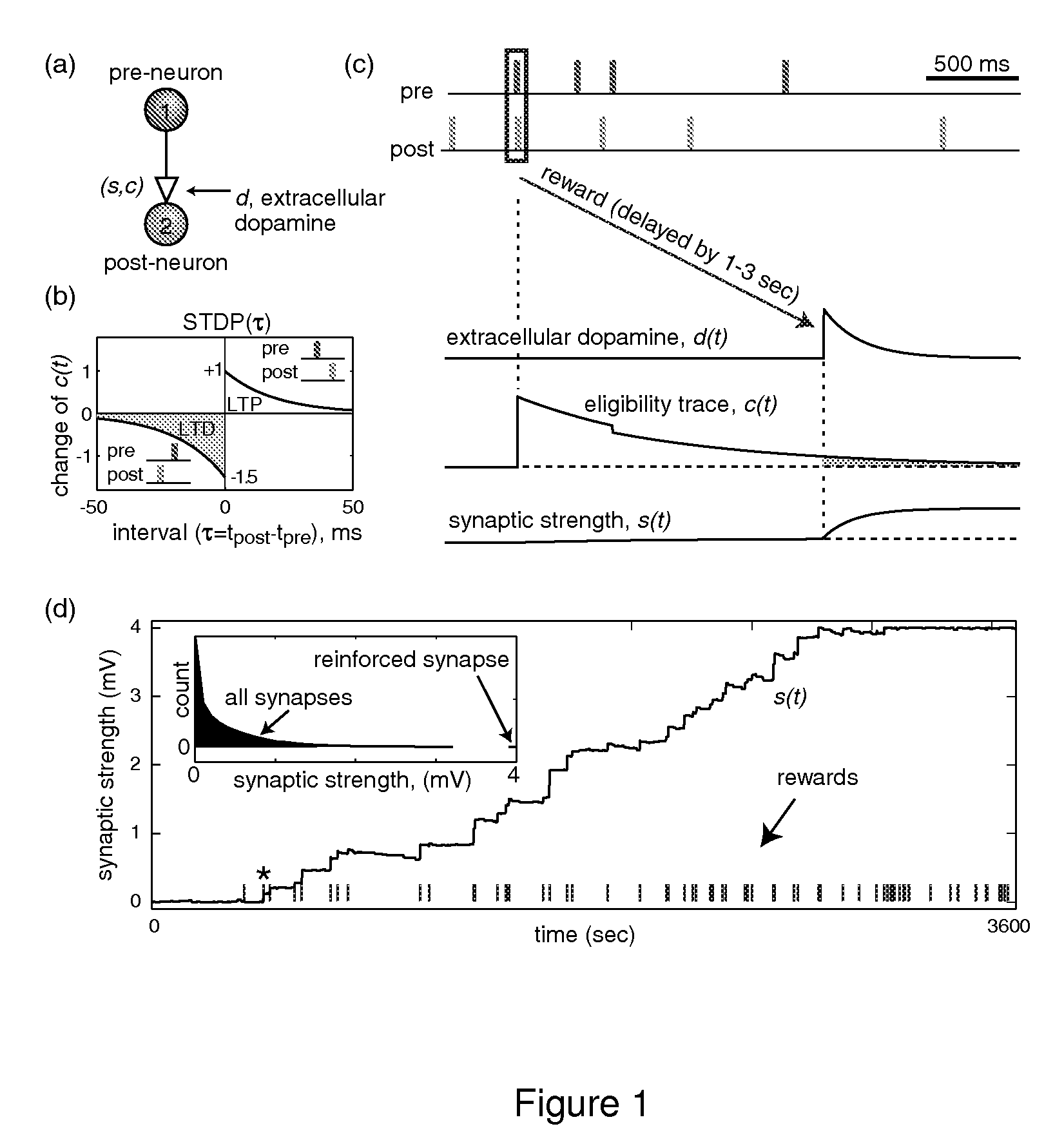
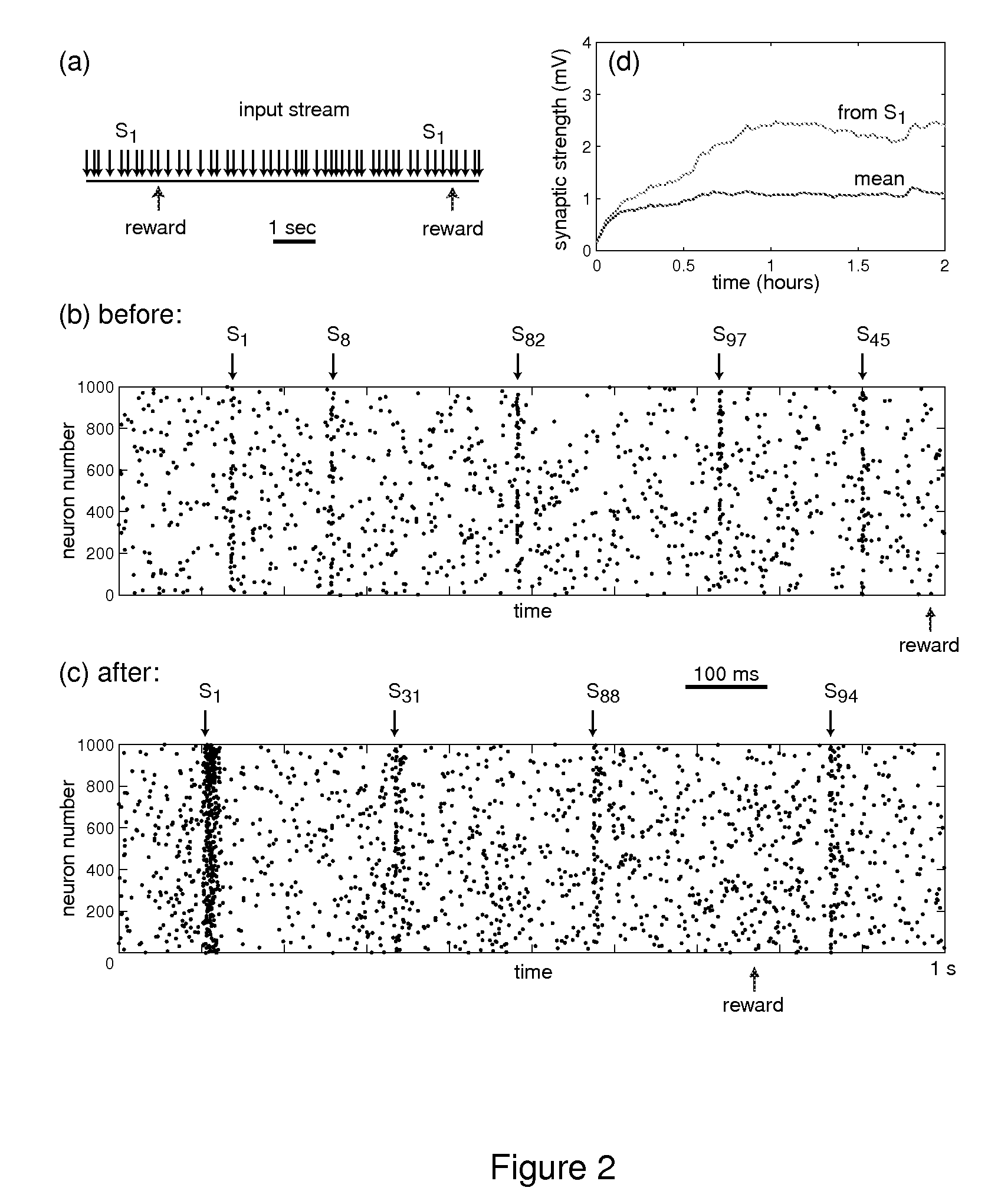
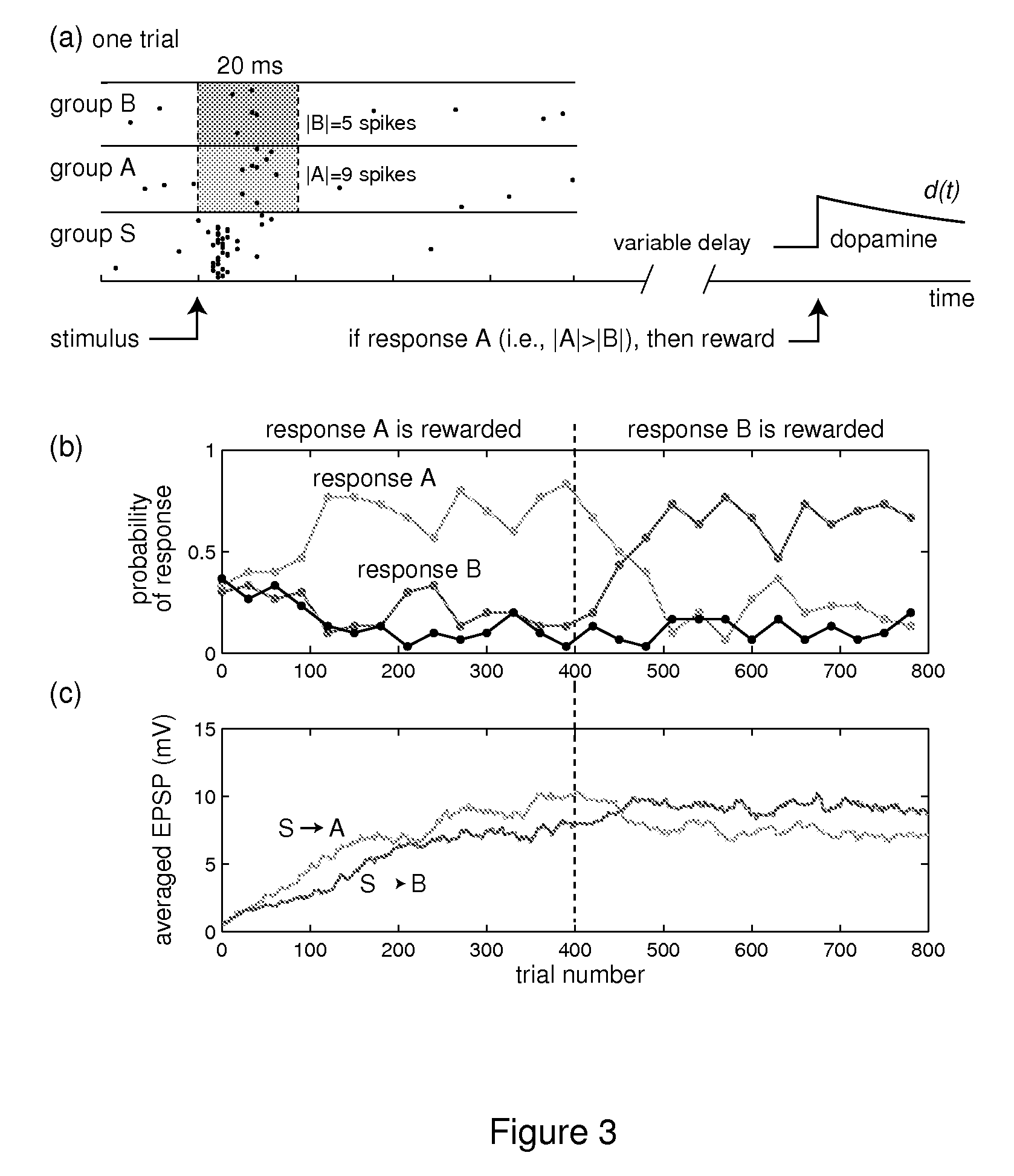
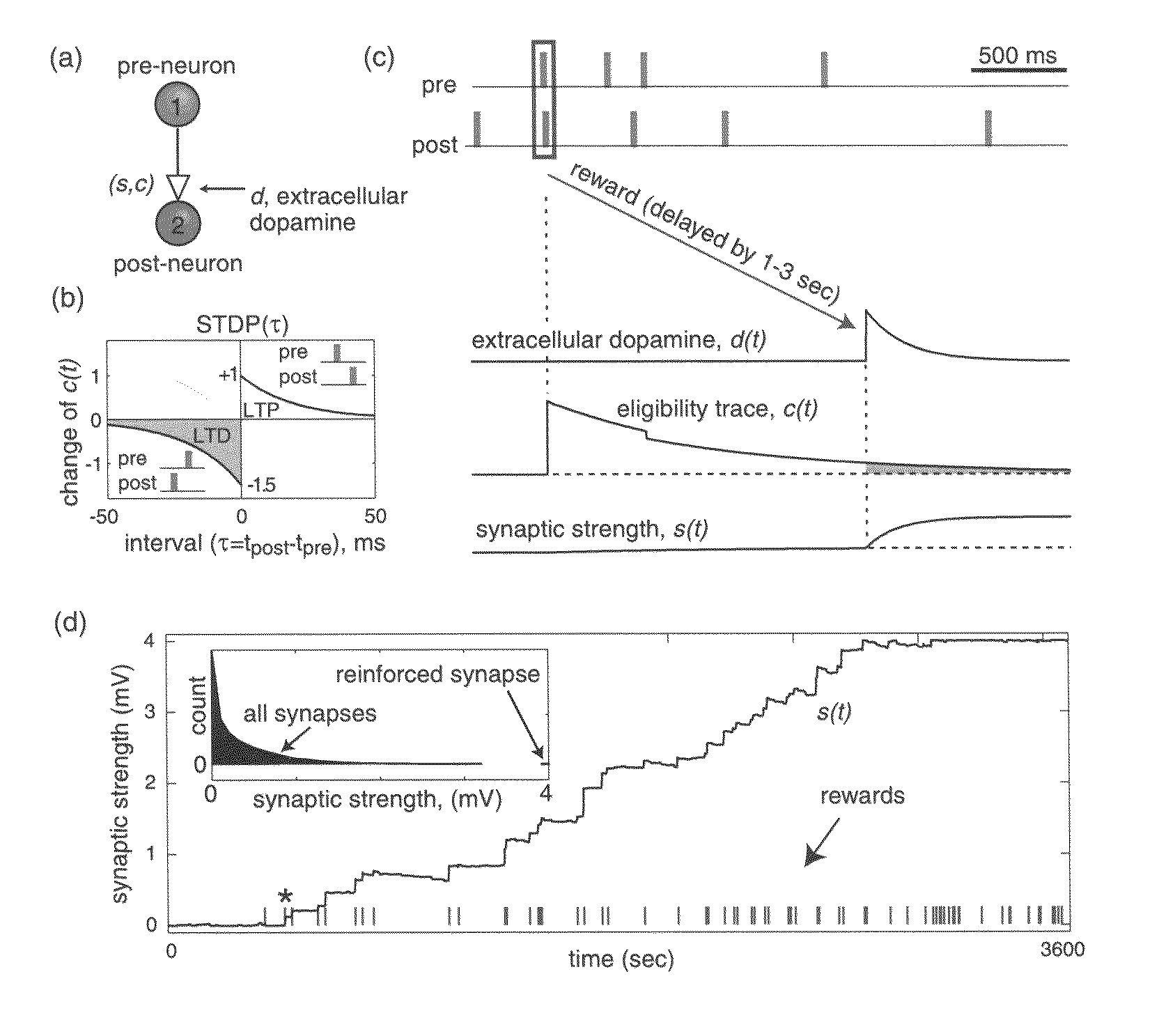
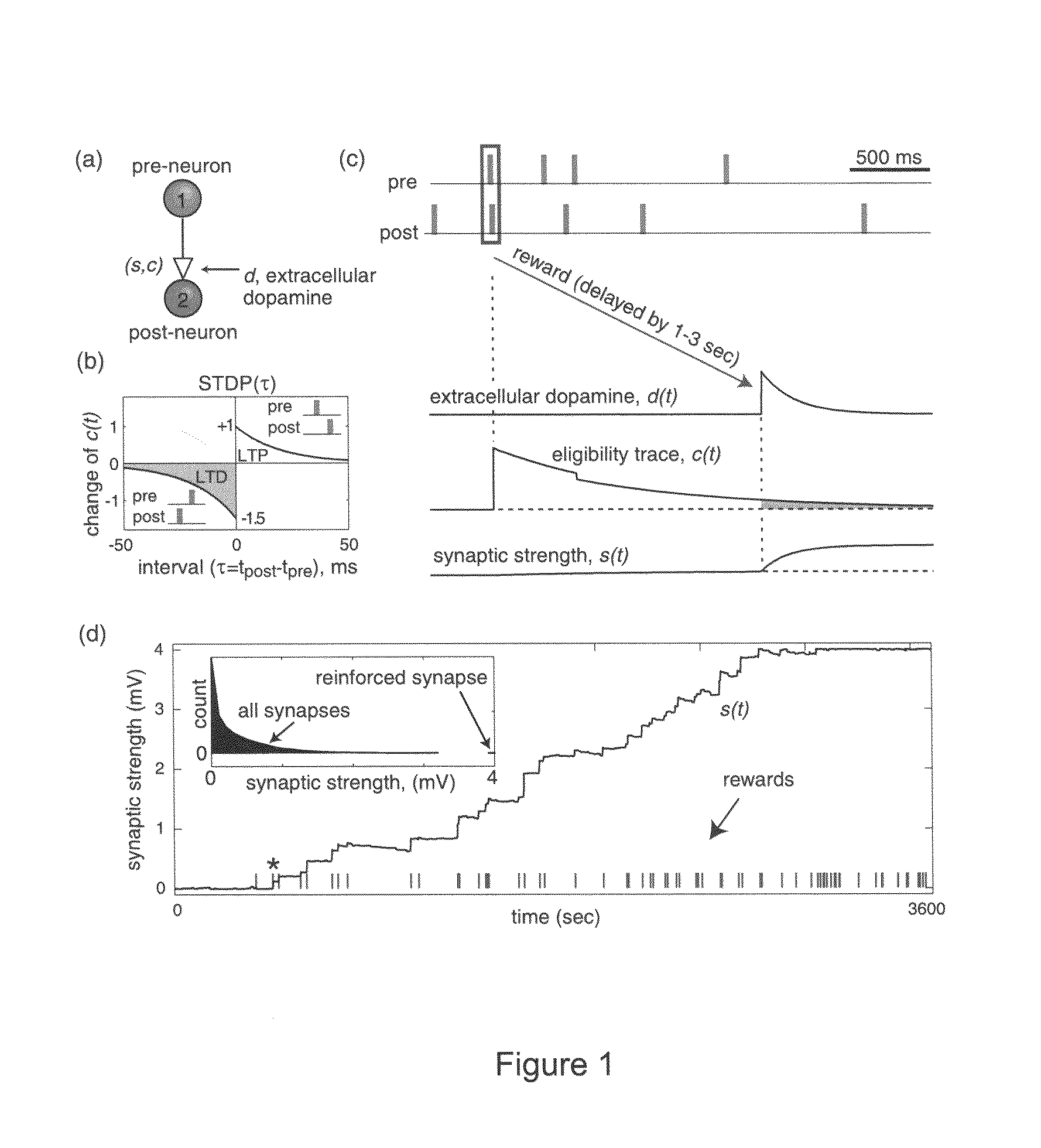
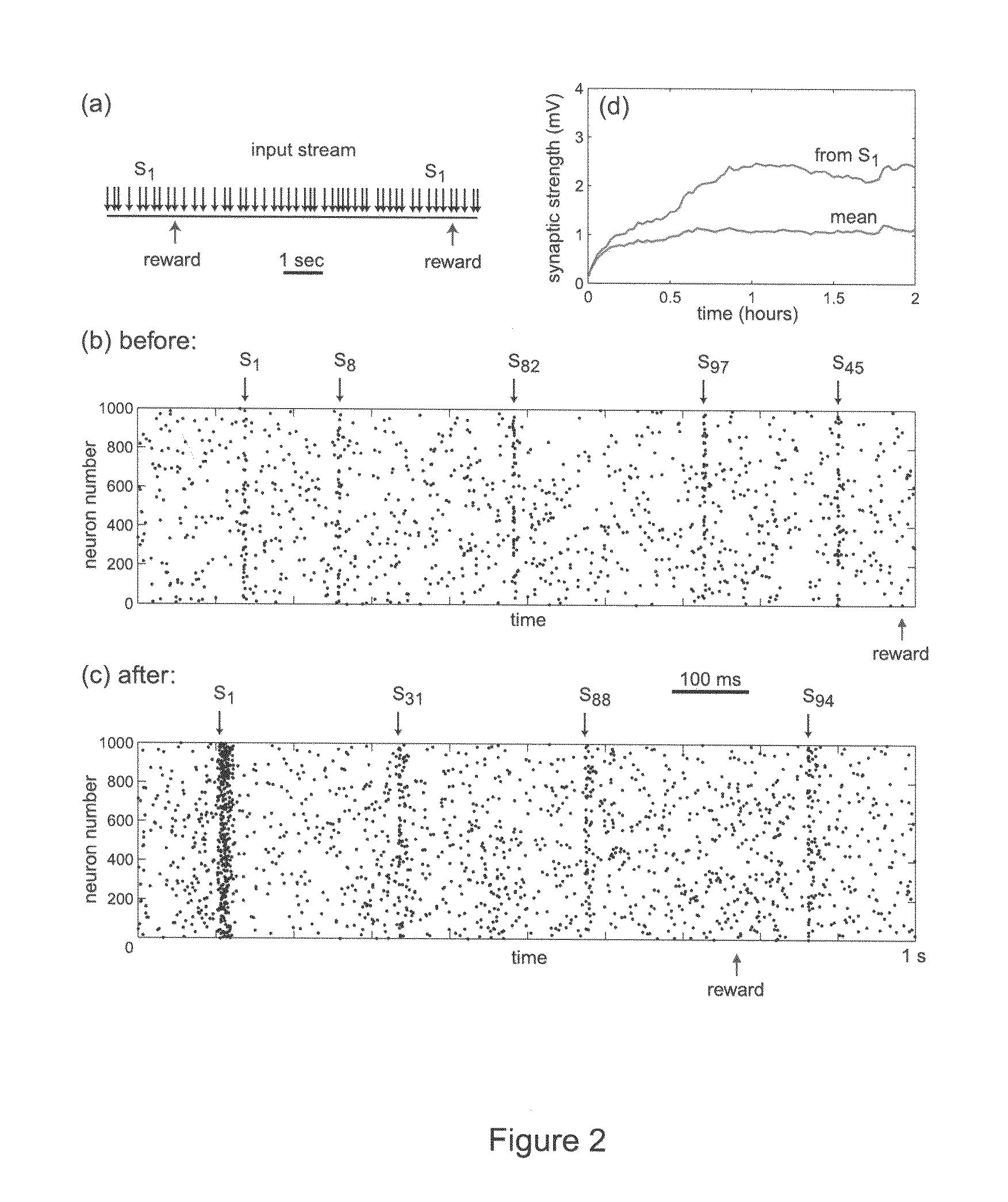
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of STDP and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS8103602B2Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeCritical periodModel network
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
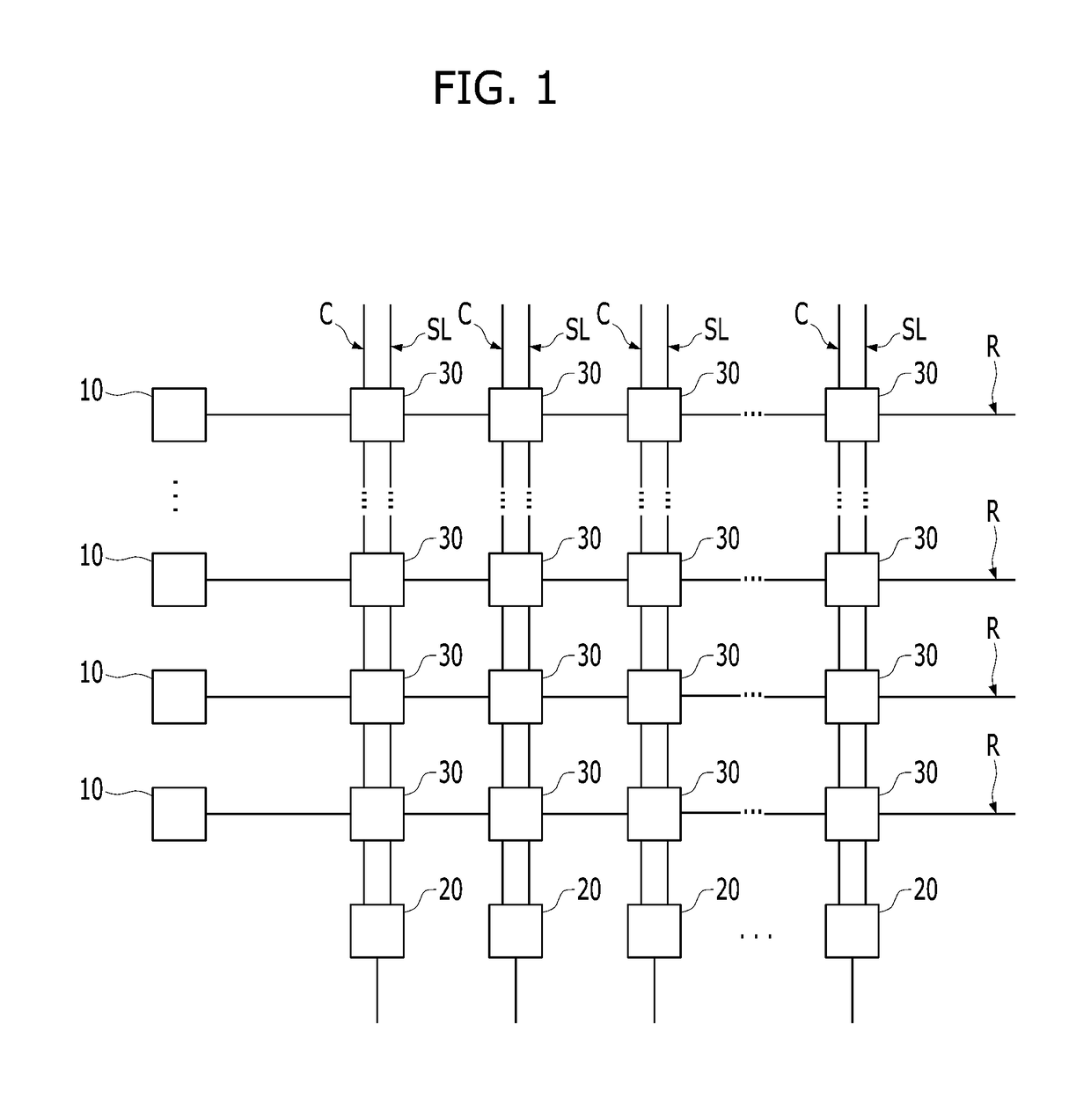
Devices, apparatus and method for providing photostimulation and imaging of structures
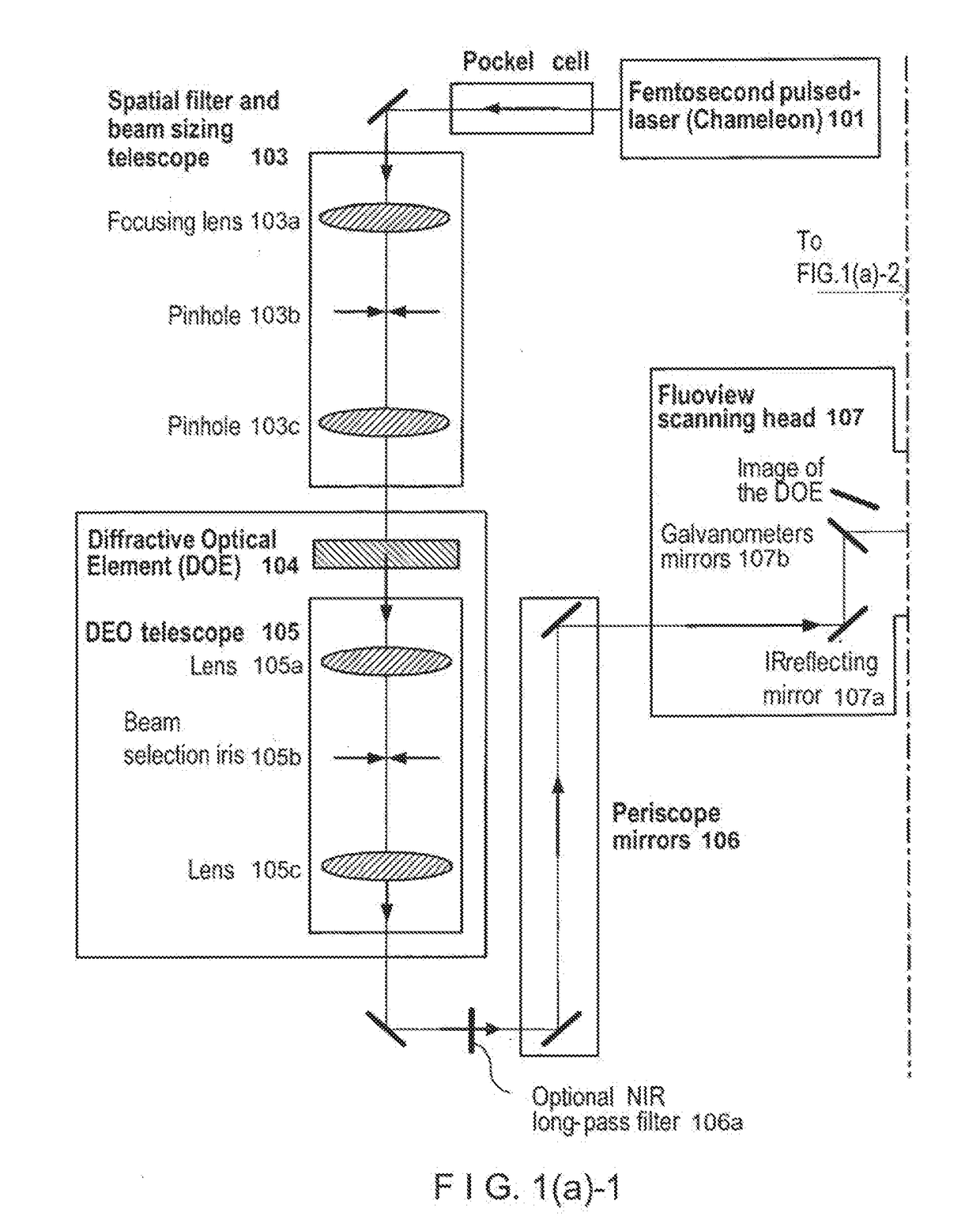
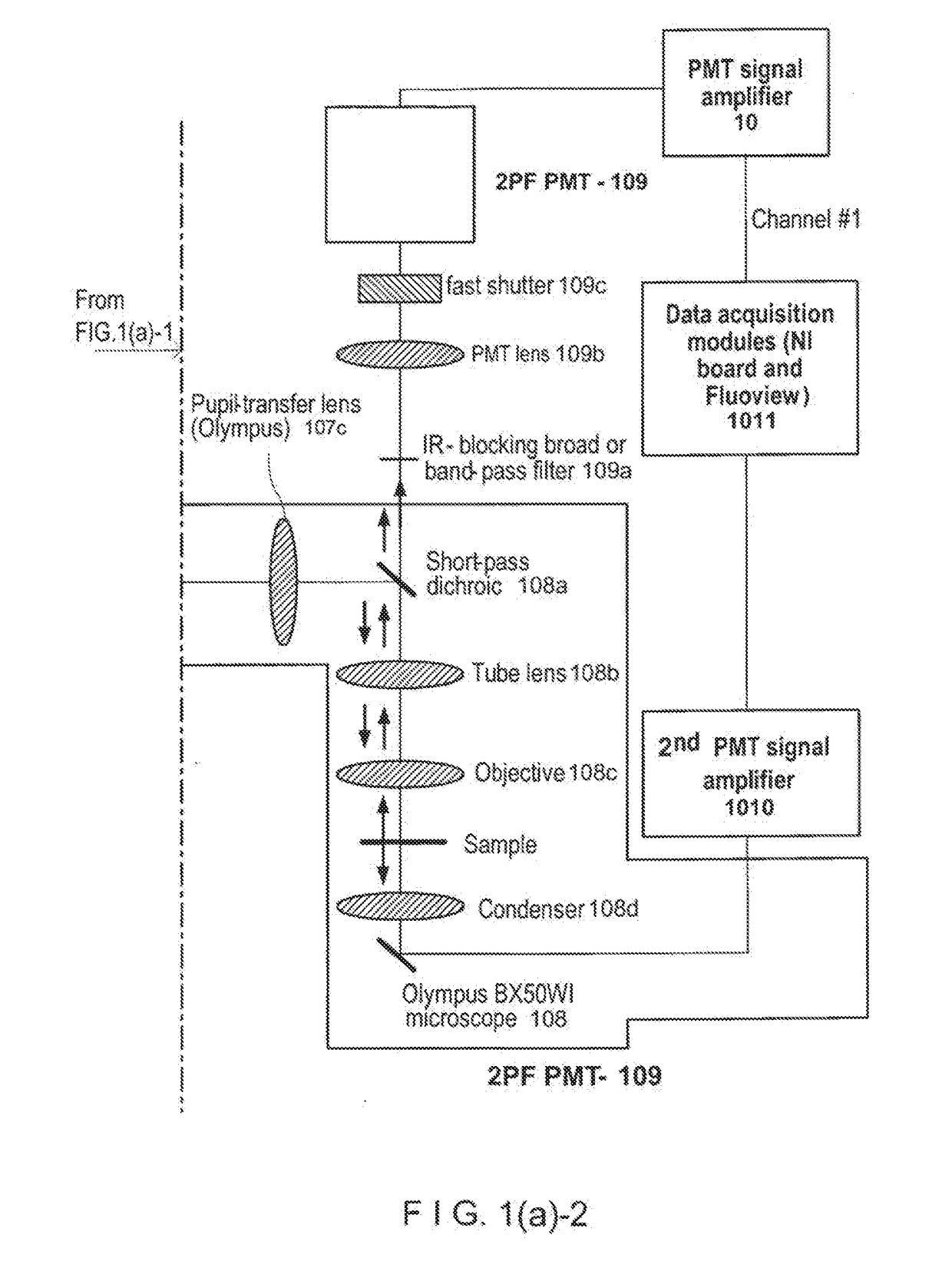
ActiveUS20110233046A1Reduce intensityEasy to detectMaterial analysis by optical meansHydrocarbonsNeuronSpatiotemporal pattern
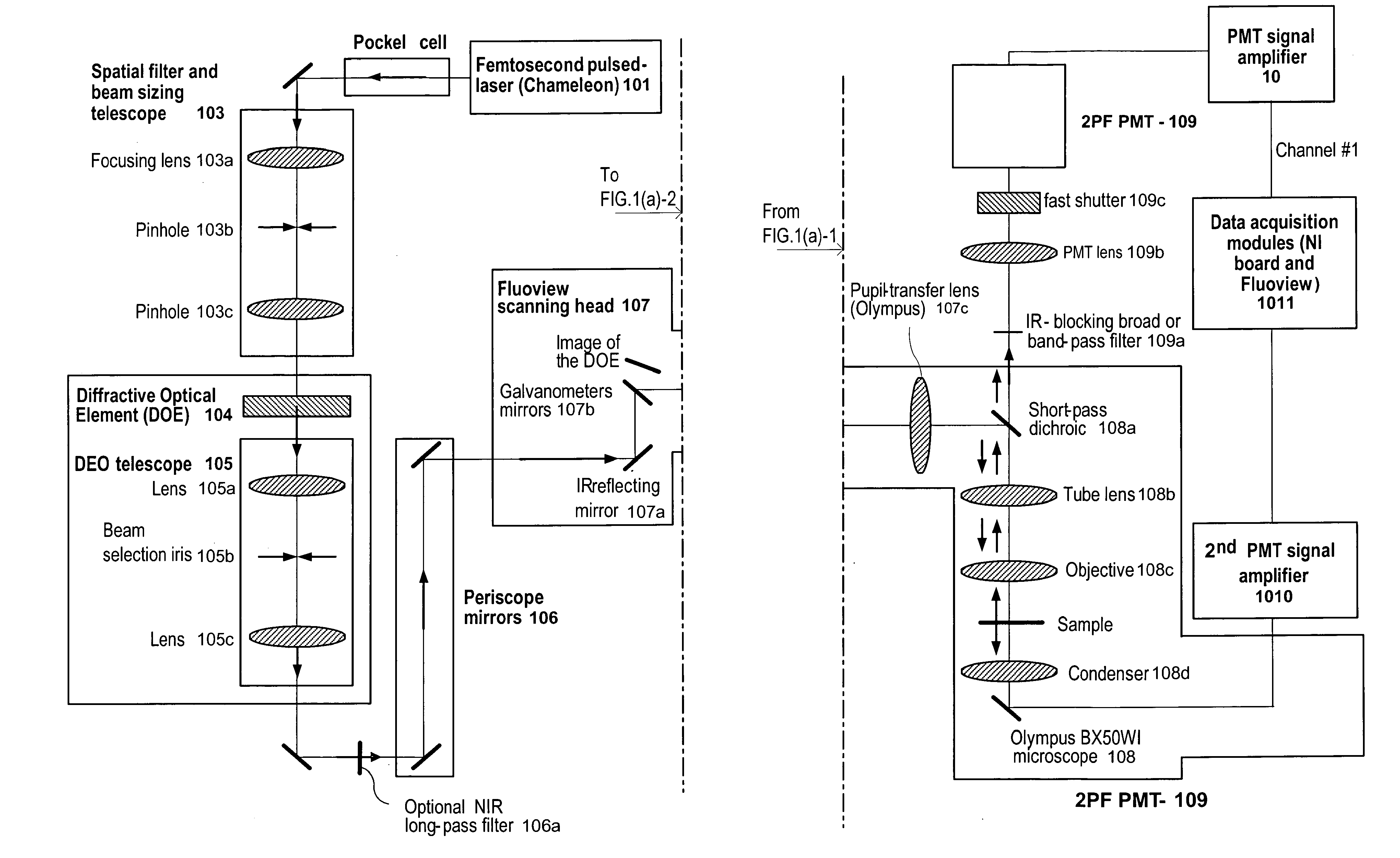
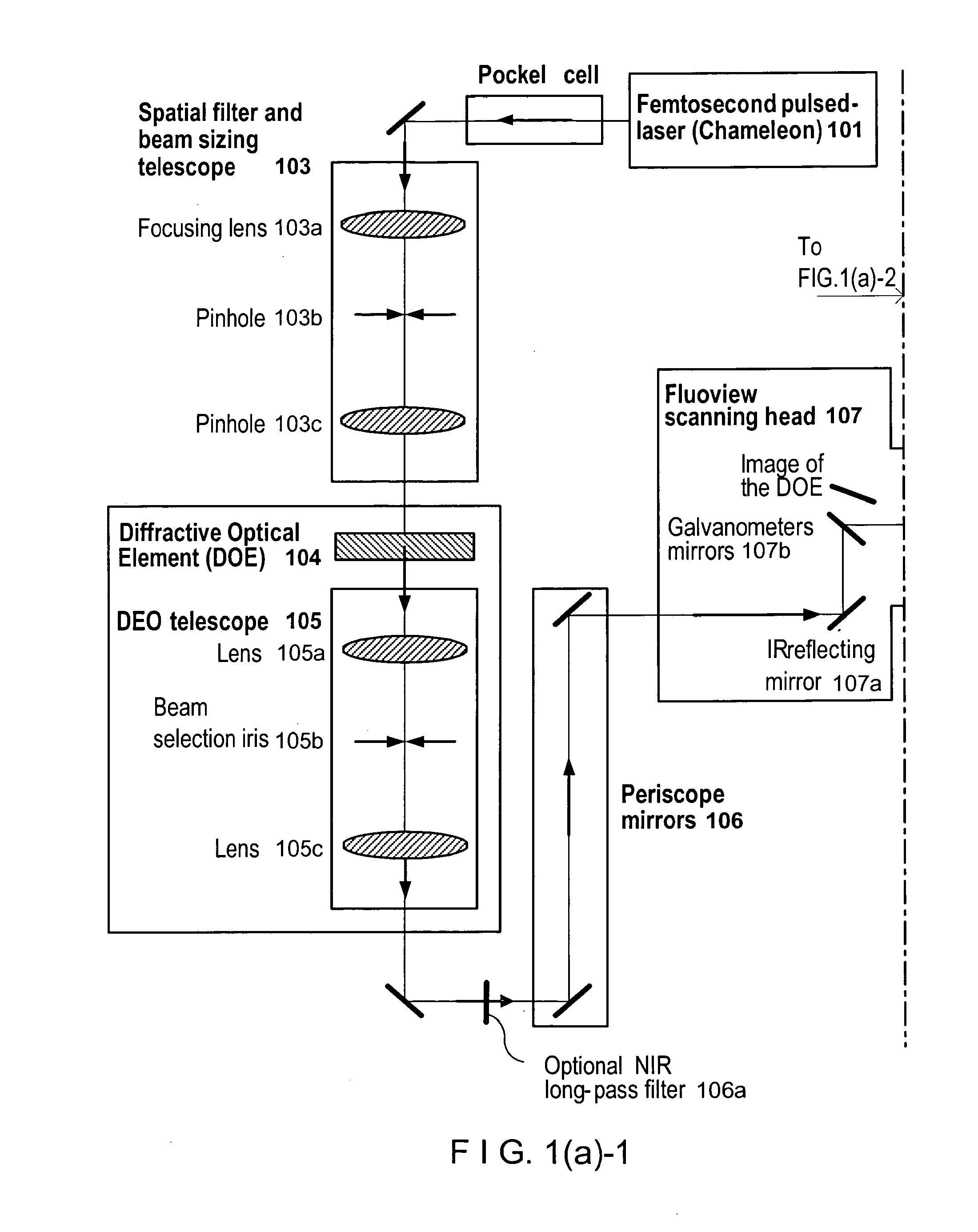
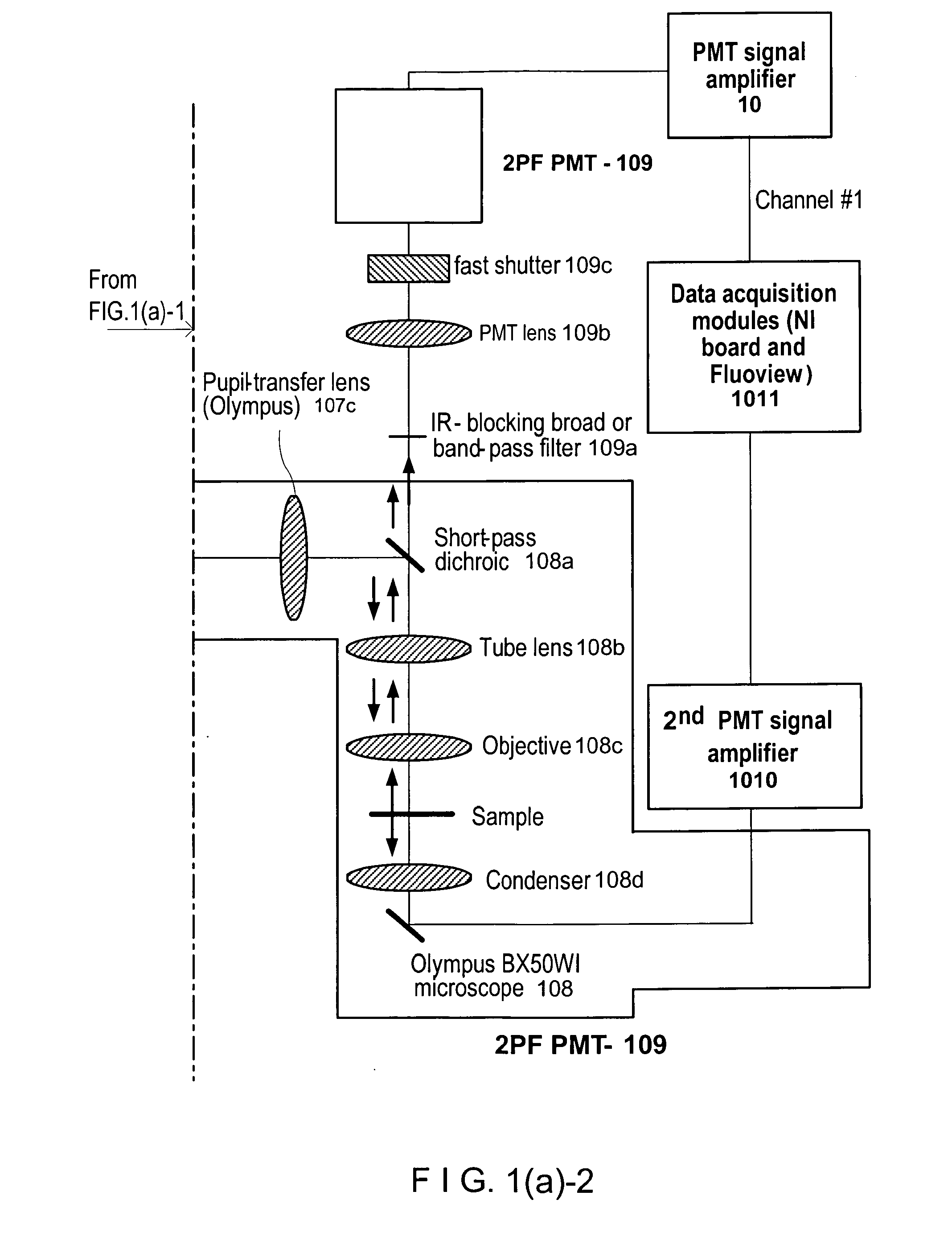
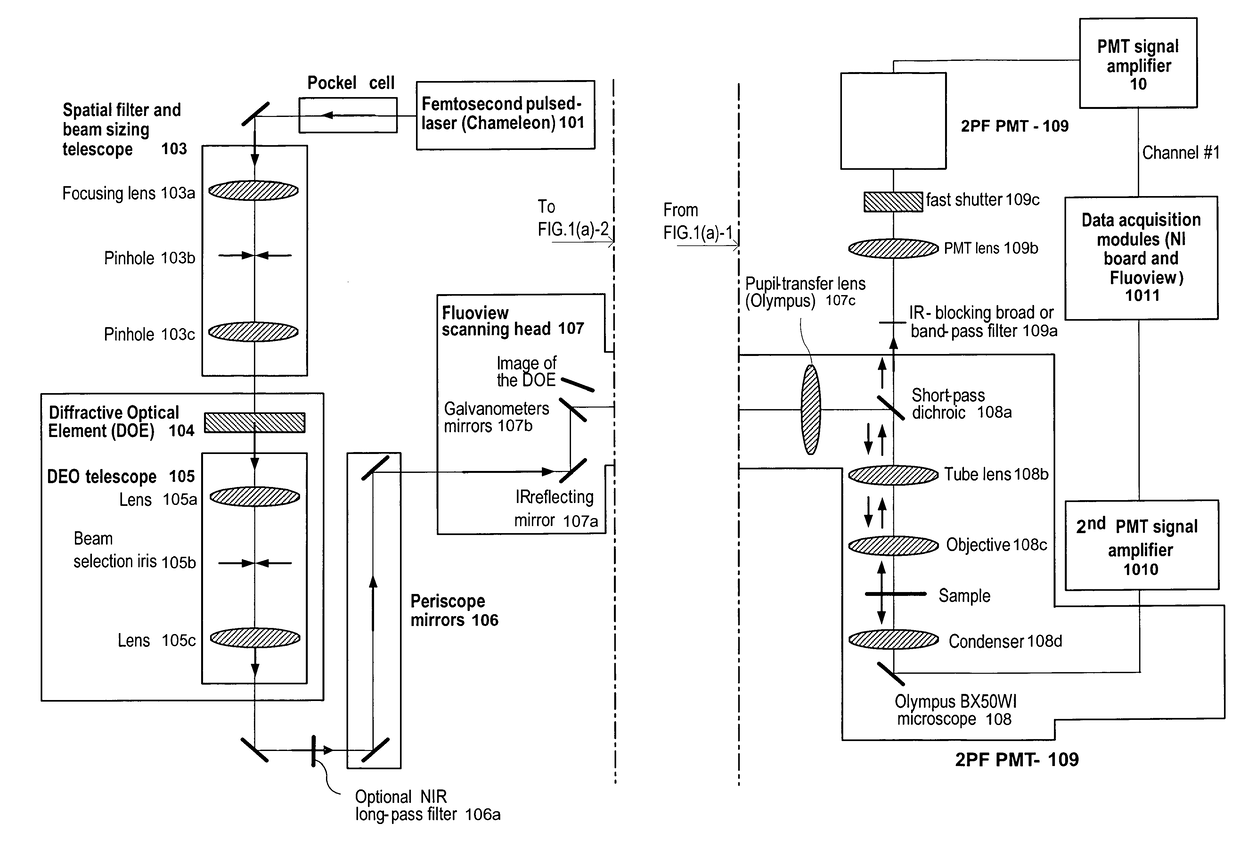
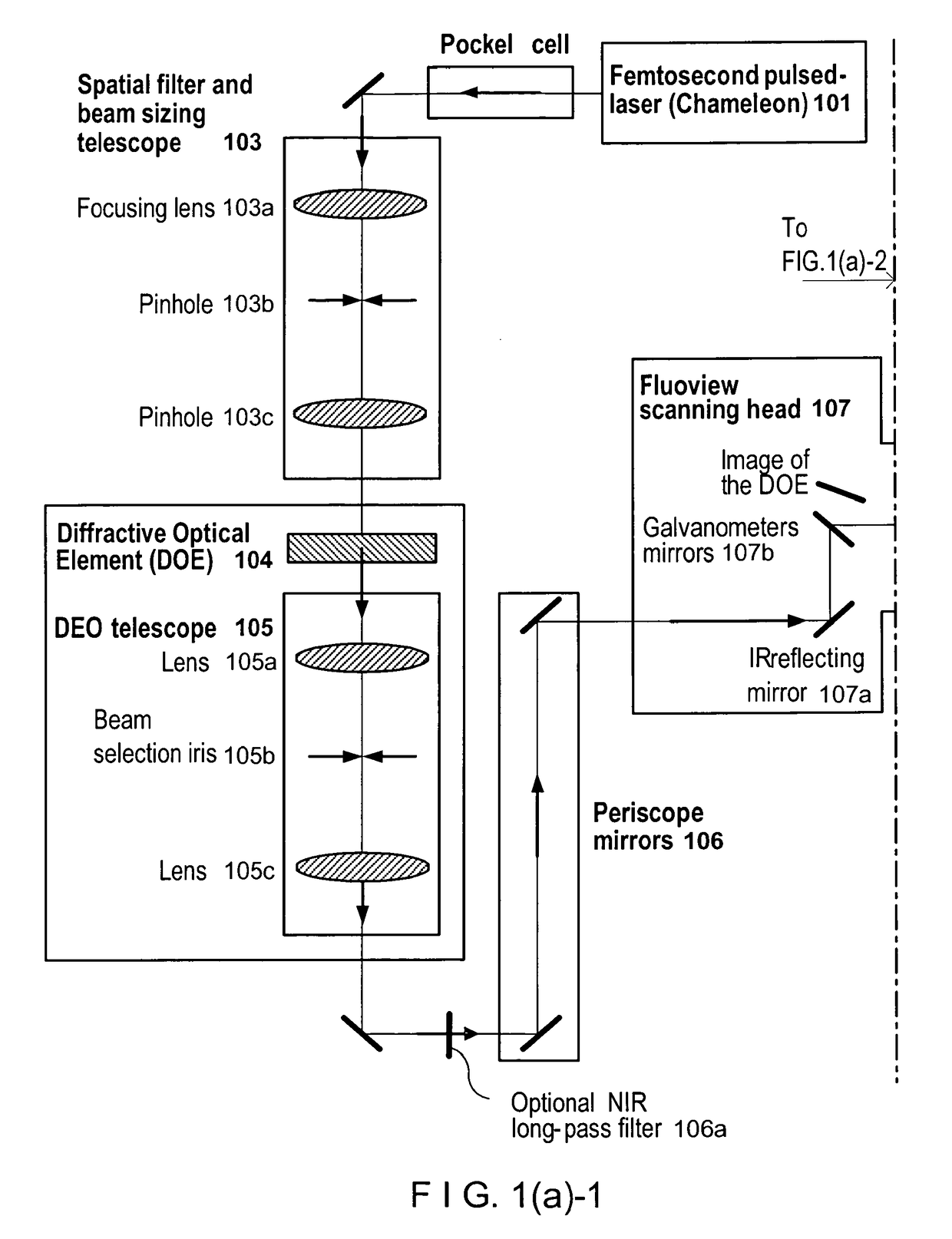
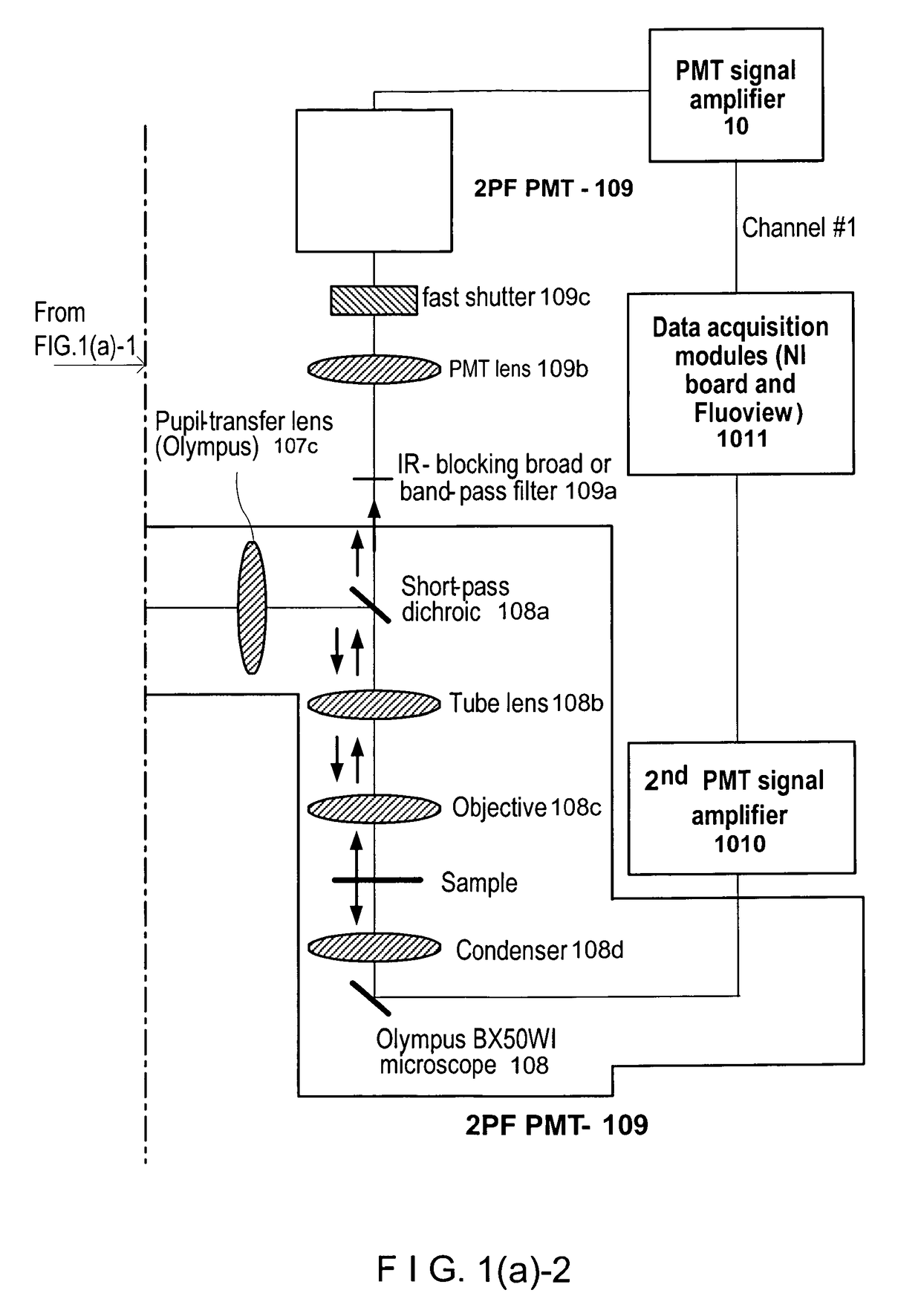
According to exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, it is possible to provide method, system, arrangement, computer-accessible medium and device to stimulate individual neurons in brain slices in any arbitrary spatio-temporal pattern, using two-photon uncaging of photo-sensitive compounds such as MNI-glutamate and / or RuBi-Glutamate with beam multiplexing. Such exemplary method and device can have single-cell and three-dimensional precision. For example, by sequentially stimulating up to a thousand potential presynaptic neurons, it is possible to generate detailed functional maps of inputs to a cell. In addition, it is possible to combine this exemplary approach with two-photon calcium imaging in an all-optical method to image and manipulate circuit activity. Further exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can include a light-weight, compact portable device providing for uses in a wide variety of applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Nerve cell synapse circuit and nerve cell circuit
ActiveCN106447033AReduce power consumptionImprove computing efficiencyPhysical realisationEnergy efficient computingCapacitanceMedicine
The invention discloses a nerve cell synapse circuit and a nerve cell circuit, wherein the nerve cell synapse circuit comprises a charging circuit, a discharging circuit and an MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) capacitor, wherein the MOS capacitor is connected with the charging circuit and the discharging circuit; the charging circuit and the discharging circuit are both formed by a plurality of MOS devices, and are connected into a pulse sequence generated by nerve cells before the synapse and a pulse sequence generated by the nerve cells after the synapse; the charging circuit is constructed to charge the MOS capacitor when the pulse sequence generated by the nerve cells before the synapse is reached earlier than the pulse sequence generated by the nerve cells after the synapse so that the simulation voltage for increasing the synapse weight is output; the discharging circuit is constructed to discharge the MOS capacitor when the pulse sequence generated by the nerve cells before the synapse is reached later than the pulse sequence generated by the nerve cells after the synapse so that the simulation voltage for decreasing the synapse weight is output. The nerve cell synapse circuit and the nerve cell circuit provided by the invention have the advantages that the circuit power consumption can be reduced; the integration degree is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neuron peripheral circuits for neuromorphic synaptic memory array based on neuron models
ActiveUS20160350647A1Neural architecturesPhysical realisationElectrical resistance and conductanceNeuronal models
A neuromorphic memory system including neuromorphic memory arrays. The neuromorphic memory system includes a presynaptic neuron circuit coupled to a postsynaptic neuron circuit by a resistive memory cell. The method includes generating a presynaptic LIF pulse on a presynaptic LIF line at time t1. An activating operation activates an access transistor coupled to the presynaptic LIF line in response to the presynaptic LIF pulse. The access transistor enables LIF current to pass through the resistive memory cell to a postsynaptic LIF line. An integrating operation integrates the LIF current at the postsynaptic LIF line over time. A comparing operation compares a LIF voltage at the postsynaptic LIF line to a threshold voltage. A generating operation generates a postsynaptic spike timing dependent plasticity (STDP) pulse on a postsynaptic STDP line if the LIF voltage is beyond the threshold voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
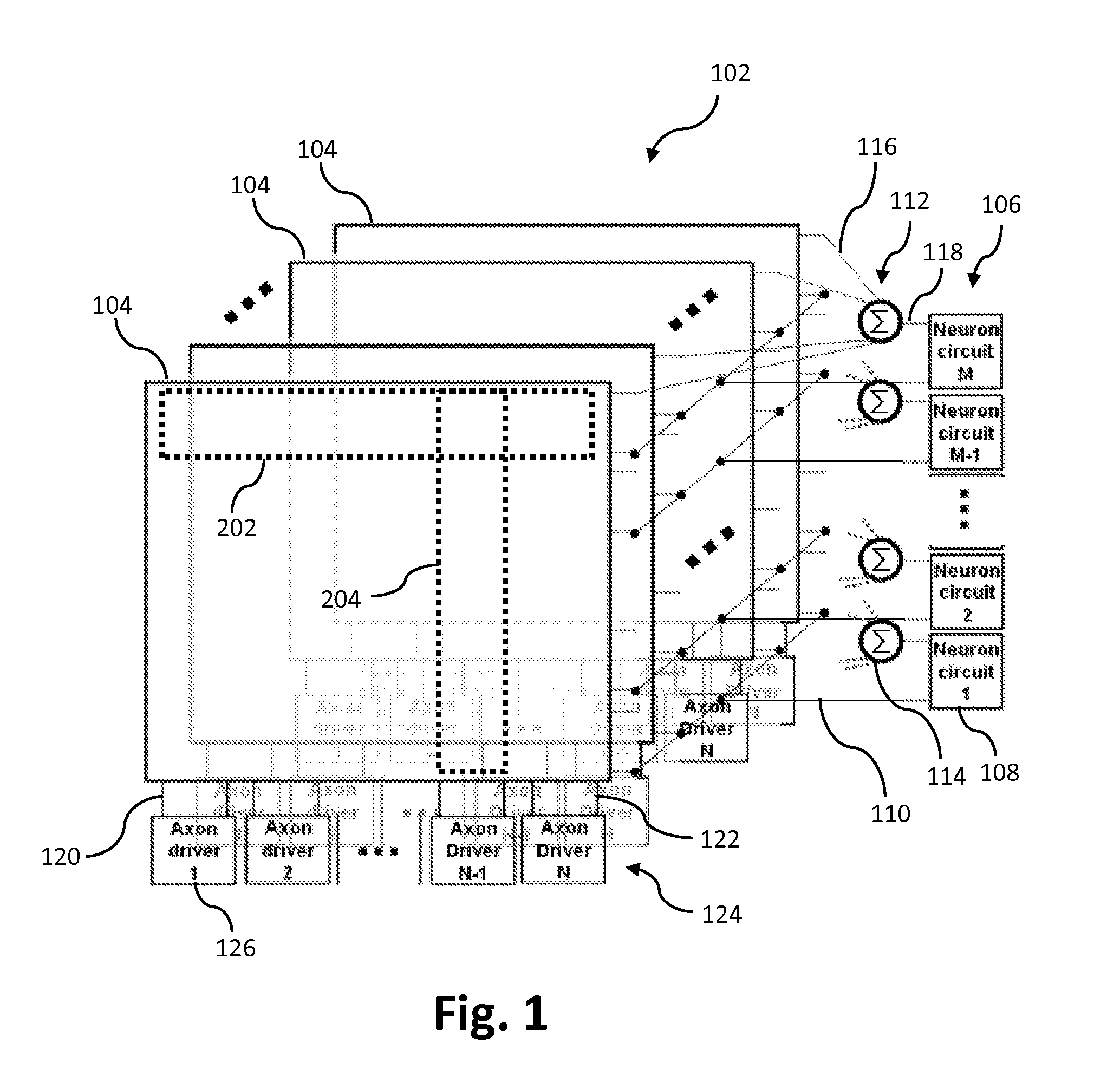
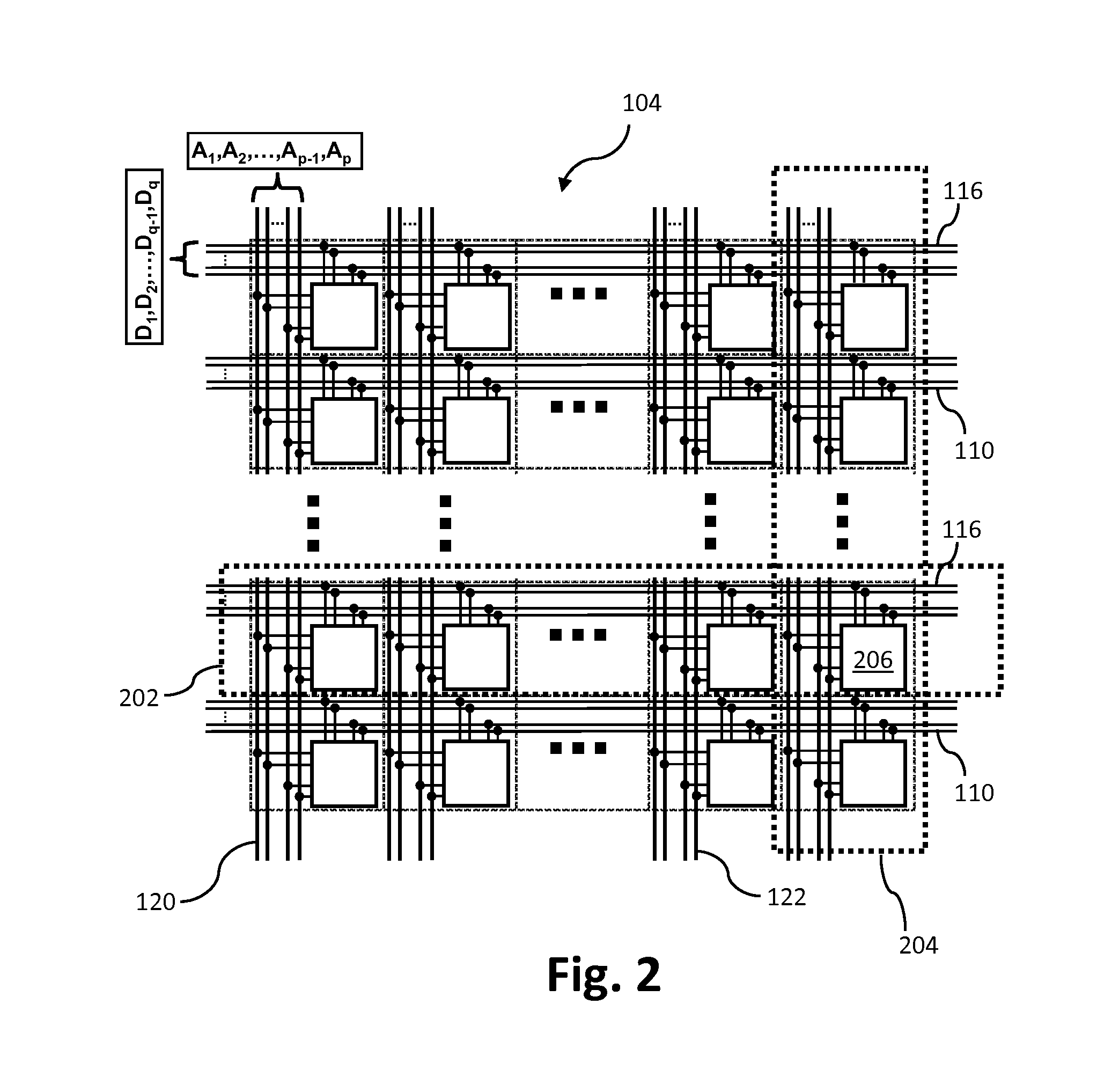
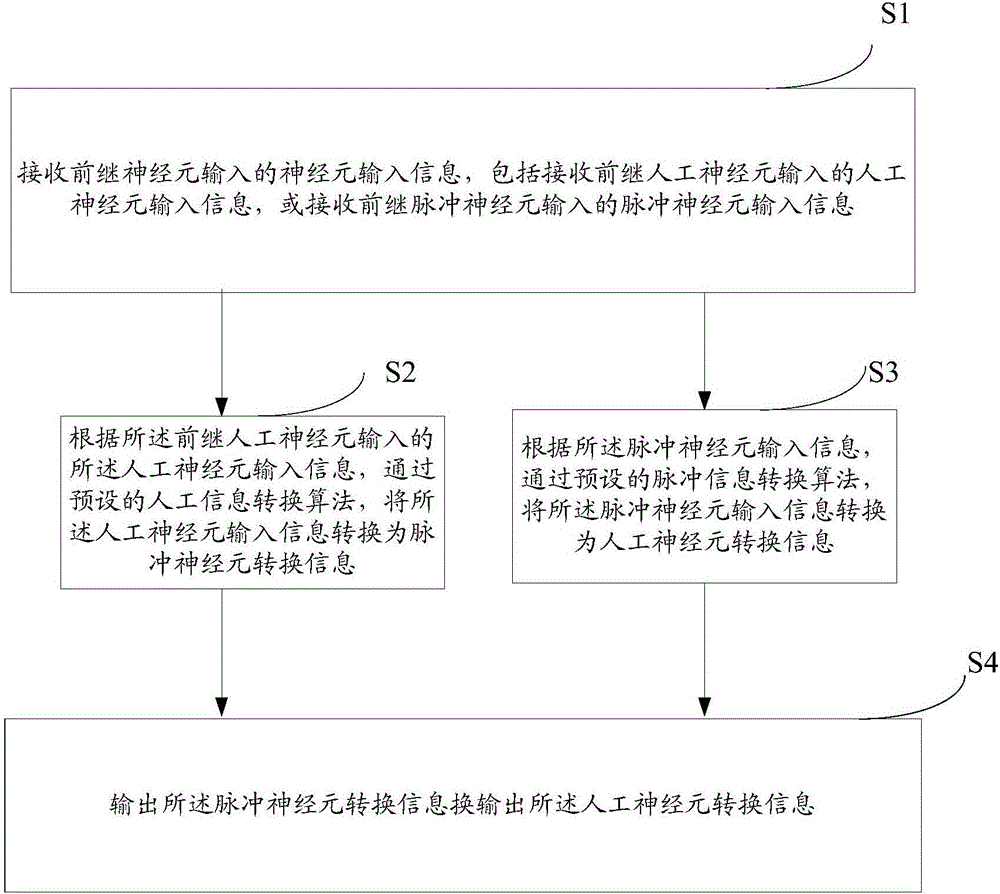
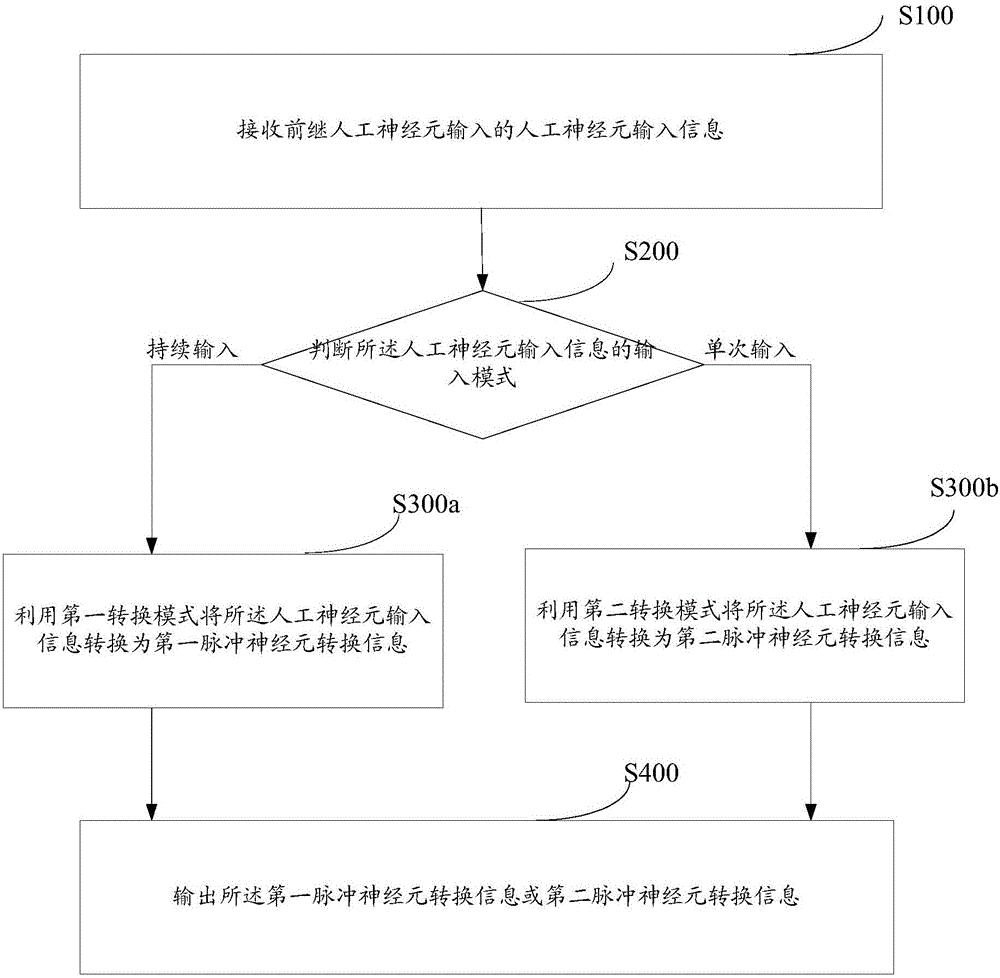
Neural network information conversion method and system
ActiveCN106845633ACalculation does not affectNeural architecturesPhysical realisationInformation processingNerve network
The invention relates to a neural network information conversion method and system. The method comprises the steps that neuron input information input by a presynaptic neuron is received, wherein artificial neuron input information input by a presynaptic artificial neuron or spiking neuron input information input by the presynaptic spiking neuron is included; according to the artificial neuron input information input by the presynaptic artificial neuron, through a preset artificial information conversion algorithm, the artificial neuron input information is converted to spiking neuron conversion information; or according to the spiking neuron input information, through a preset spiking information conversion algorithm, the spiking neuron input information is converted to artificial neuron conversion information; the spiking neuron conversion information or the artificial neuron conversion information is output. According to the neural network information conversion method and system, in one neural network, two different neuron information modes are compatible, and the information processing ability of the neural network is improved.
Owner:LYNXI TECH CO LTD
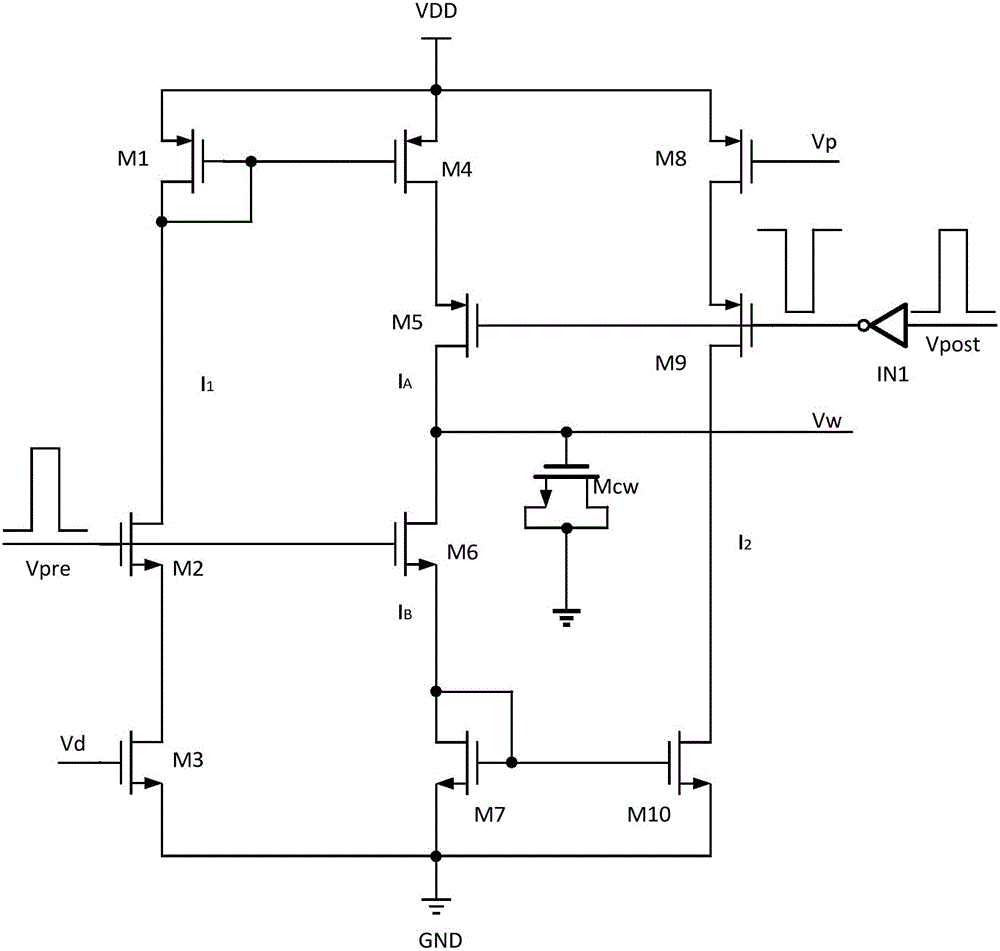
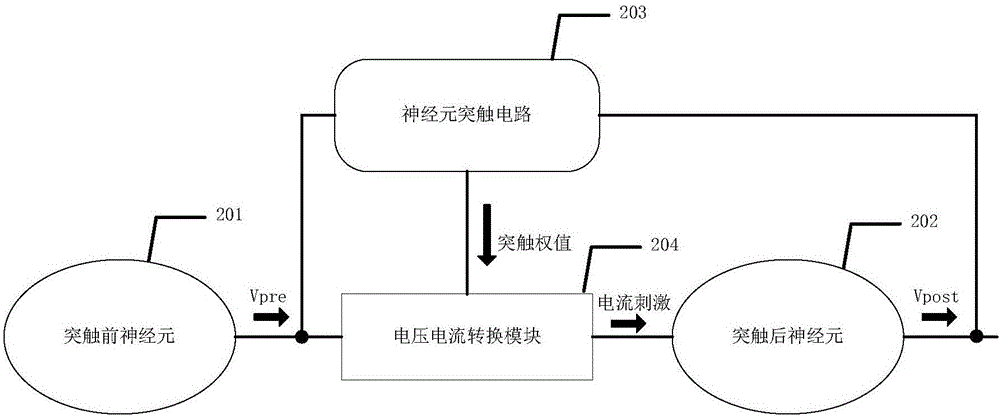
Neuron circuit, system, and method with synapse weight learning
A neuron circuit performing synapse learning on weight values includes a first sub-circuit, a second sub-circuit, and a third sub-circuit. The first sub-circuit is configured to receive an input signal from a pre-synaptic neuron circuit and determine whether the received input signal is an active signal having an active synapse value. The second sub-circuit is configured to compare a first cumulative reception counter of active input signals with a learning threshold value based on results of the determination. The third sub-circuit is configured to perform a potentiating learning process based on a first probability value to set a synaptic weight value of at least one previously received input signal to an active value, upon the first cumulative reception counter reaching the learning threshold value, and perform a depressing learning process based on a second probability value to set each of the synaptic weight values to an inactive value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
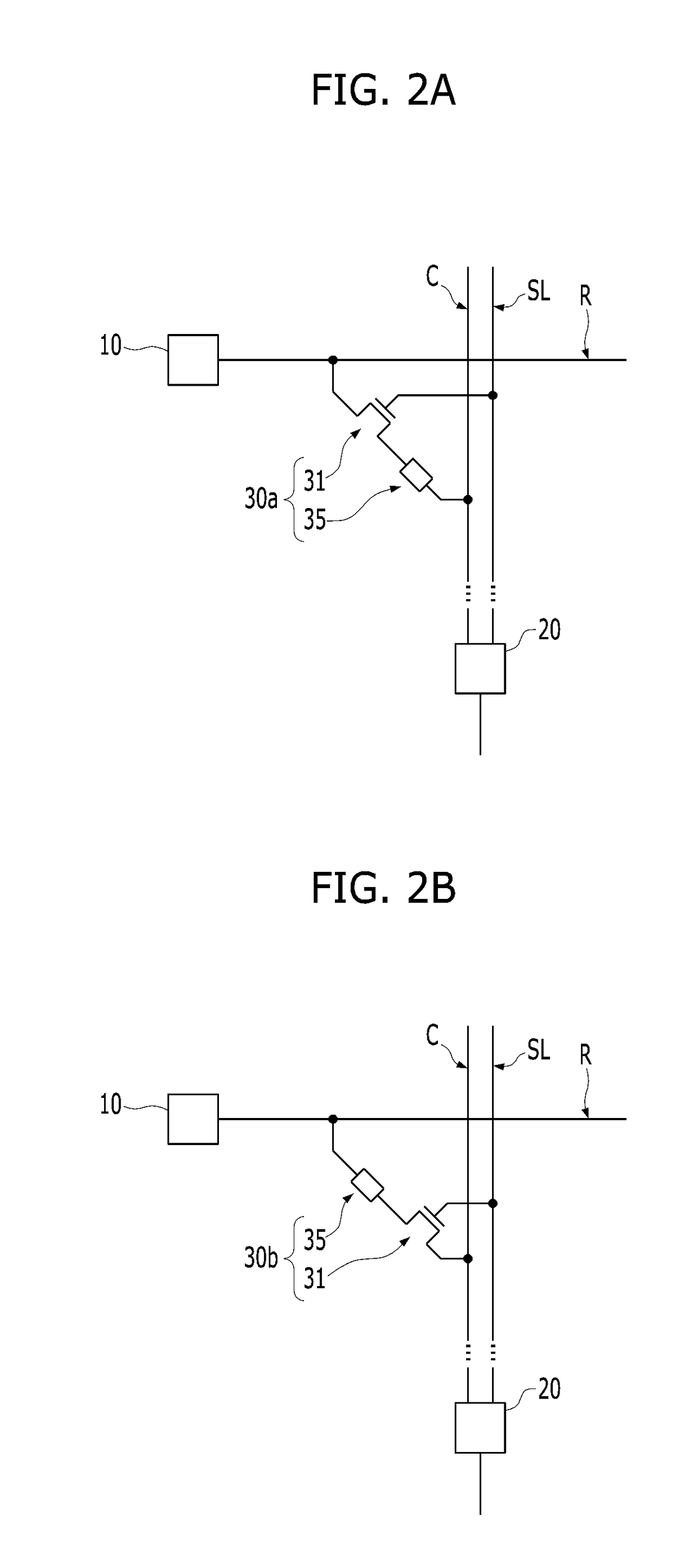
Neuromorphic device including a synapse having a variable resistor and a transistor connected in parallel with each other
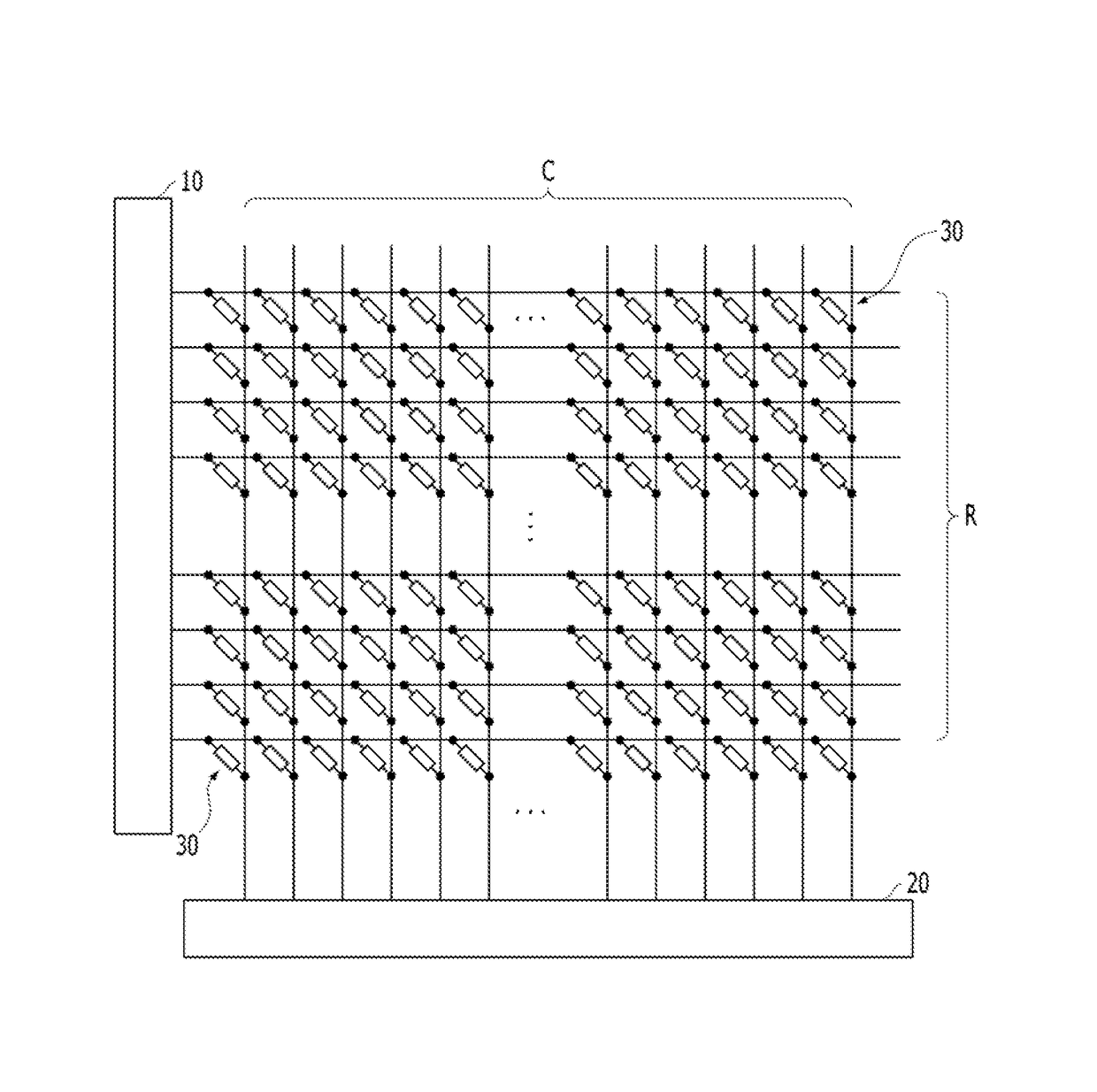
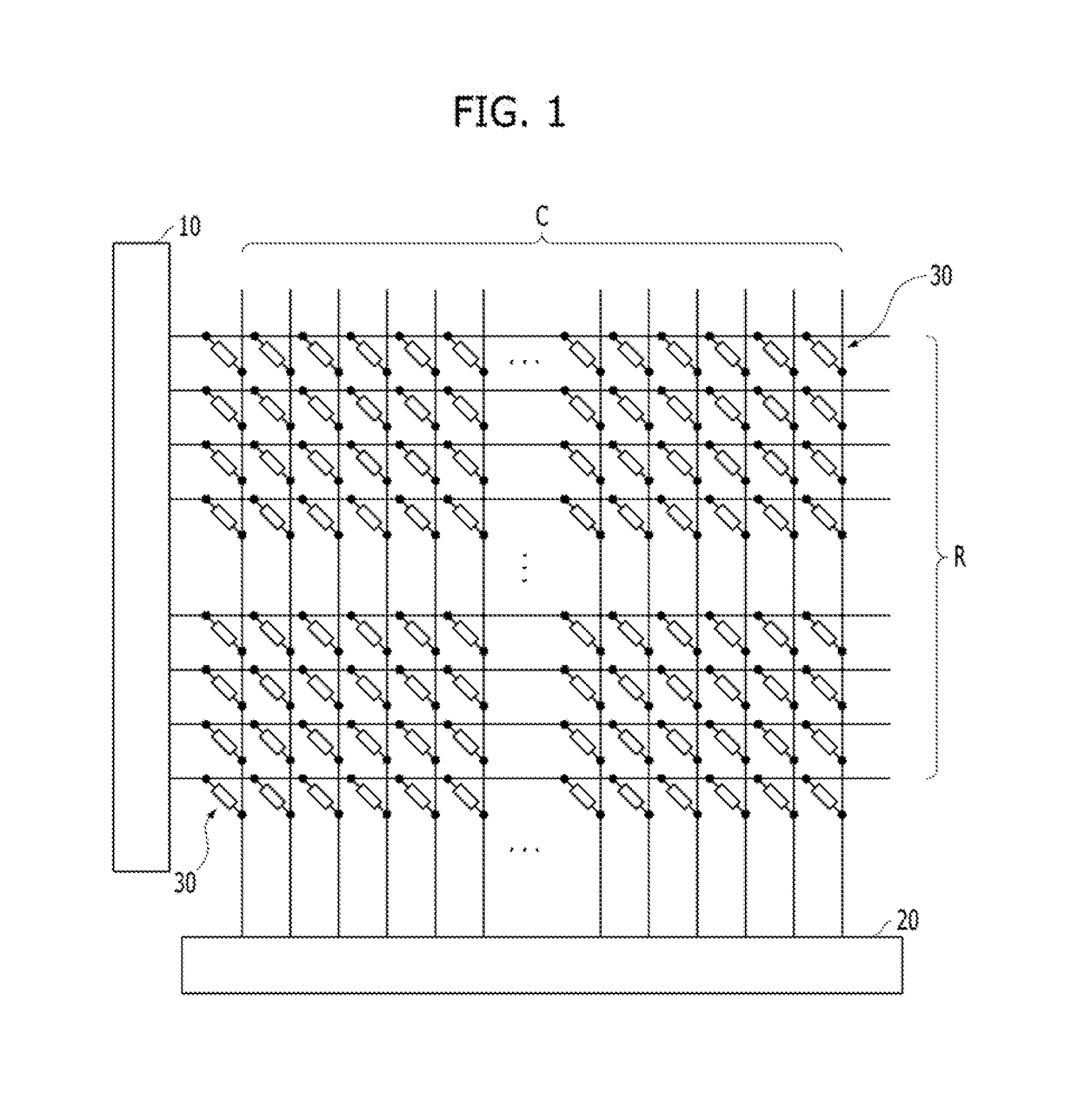
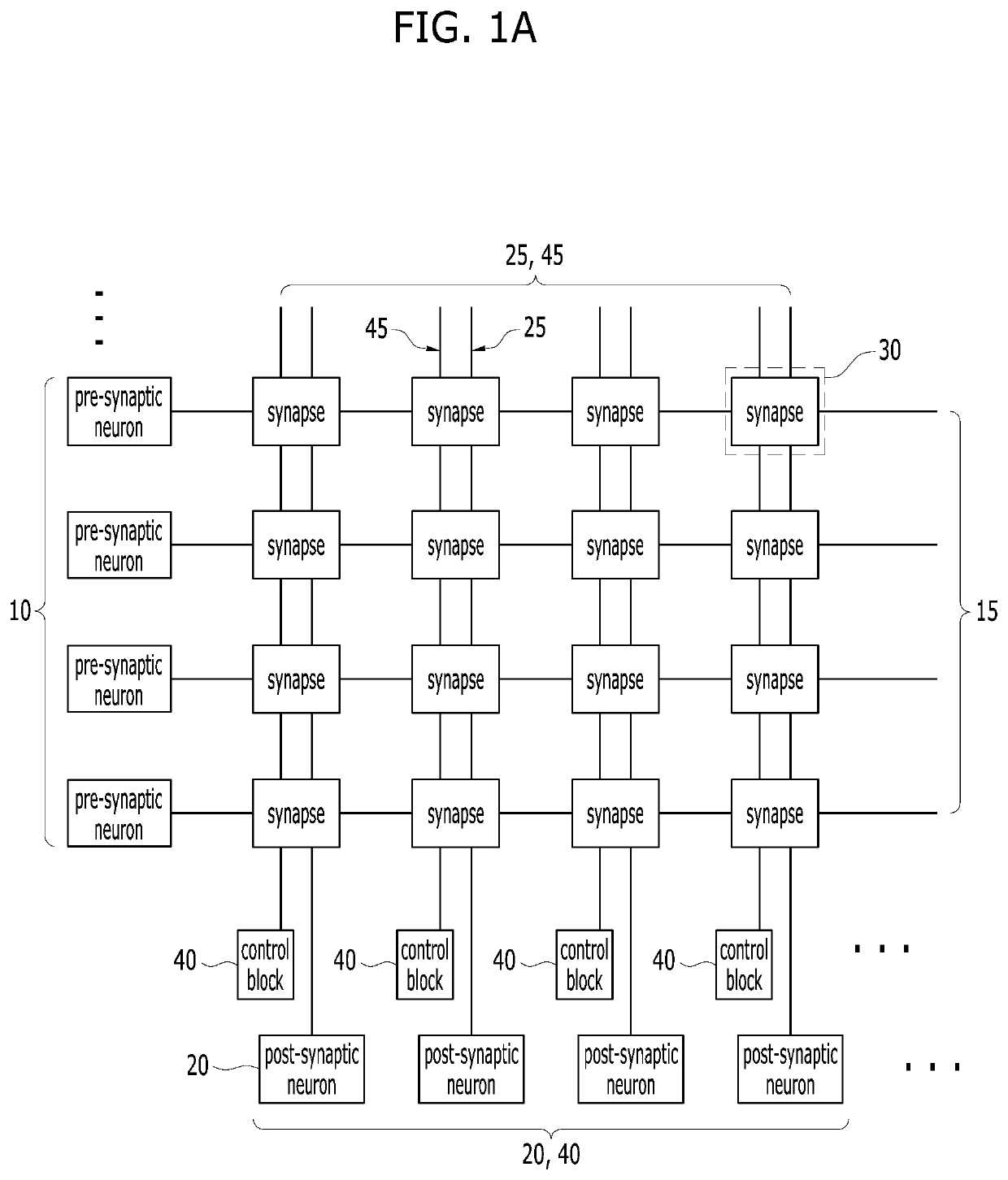
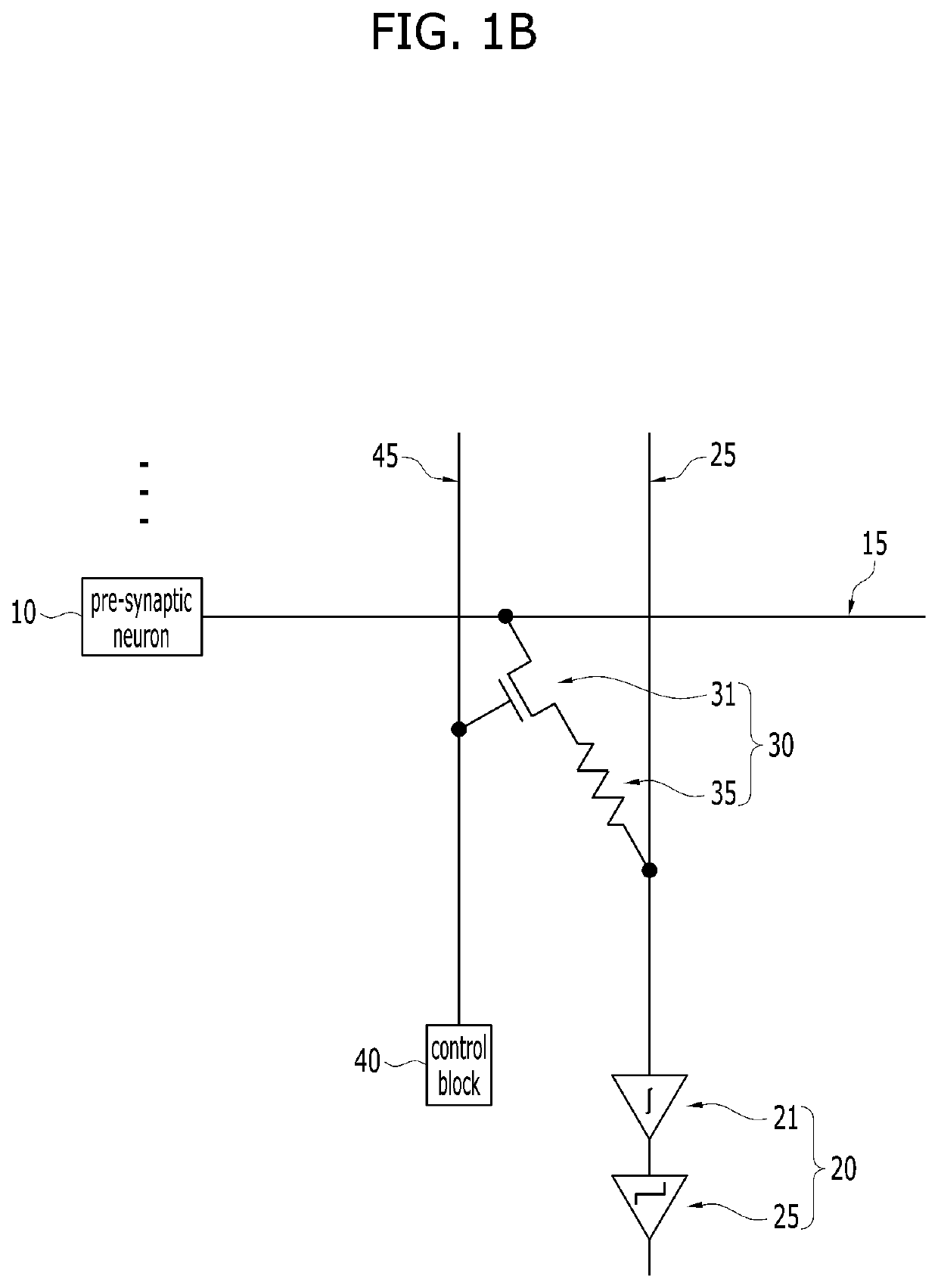
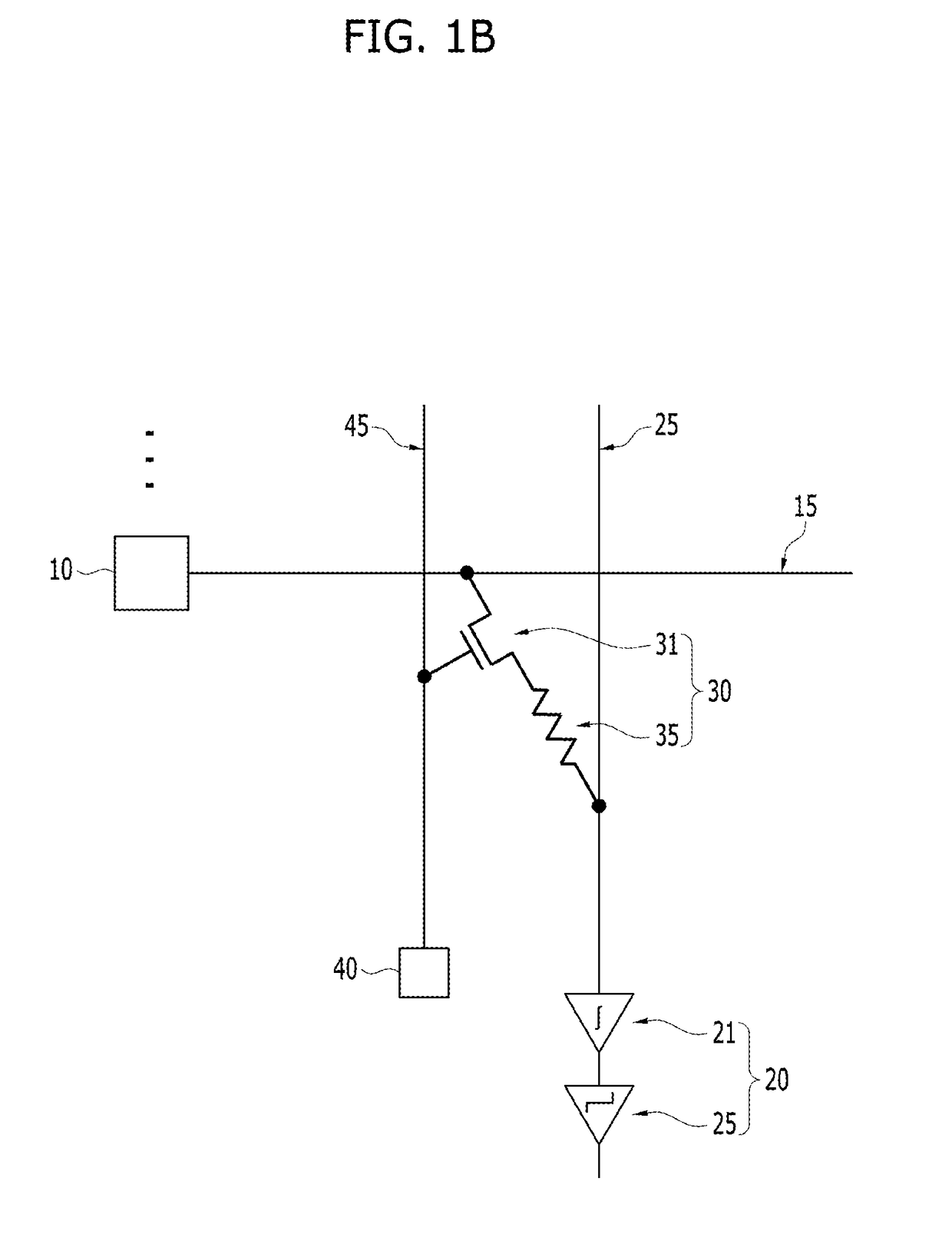
A neuromorphic device is provided. The neuromorphic device may include a pre-synaptic neuron, a row line extending from the pre-synaptic neuron in a row direction, a post-synaptic neuron, a column line extending from the post-synaptic neuron in a column direction, and a synapse at an intersection region between the row line and the column line. The synapse may include a switching device and a memristor electrically connected with each other in series. The post-synaptic neuron may include a summation circuit, a variable resistor, and a comparator.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Neuromorphic device including post-synaptic neurons having a comparator for deciding quasi-learned synapses
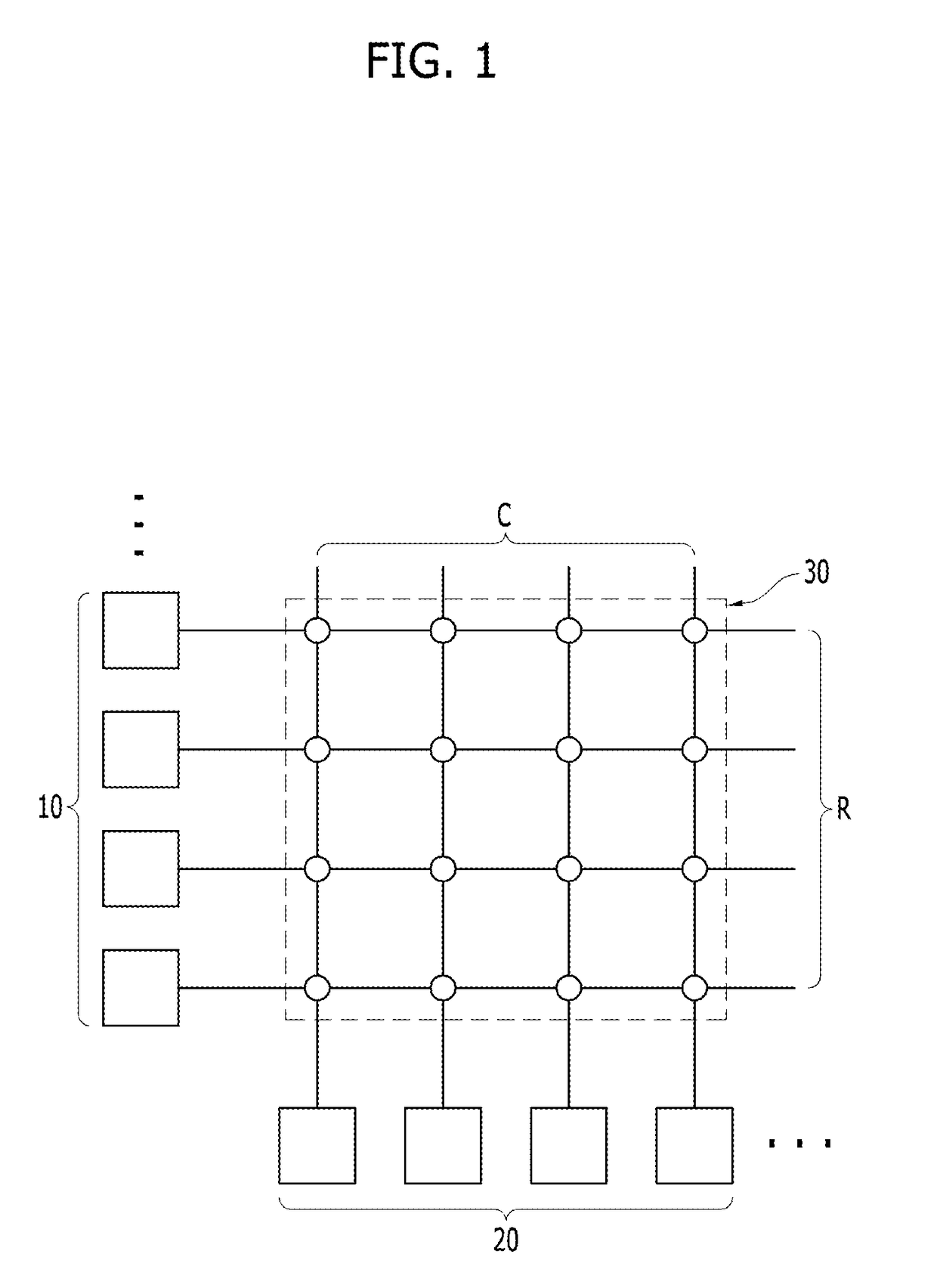
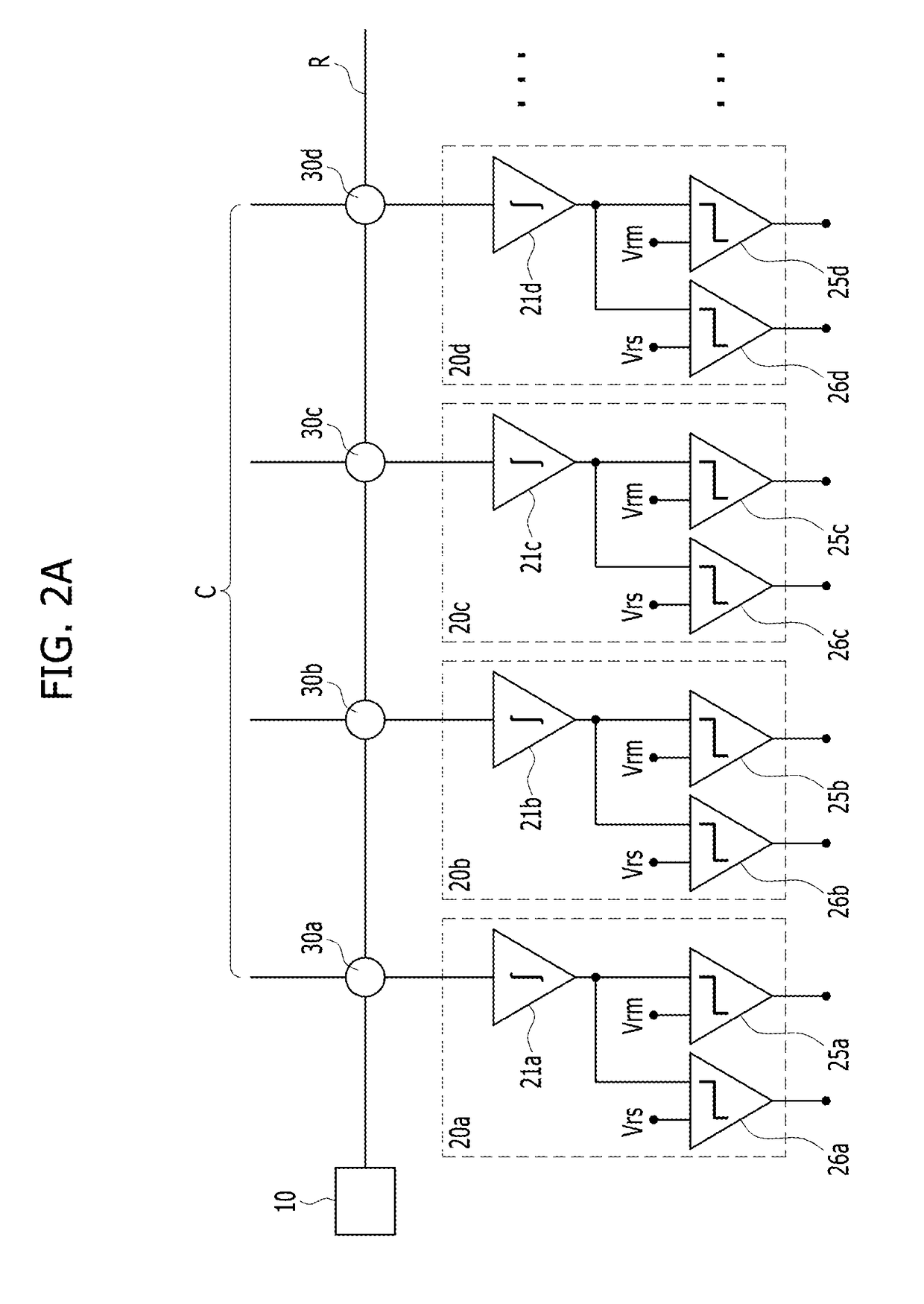
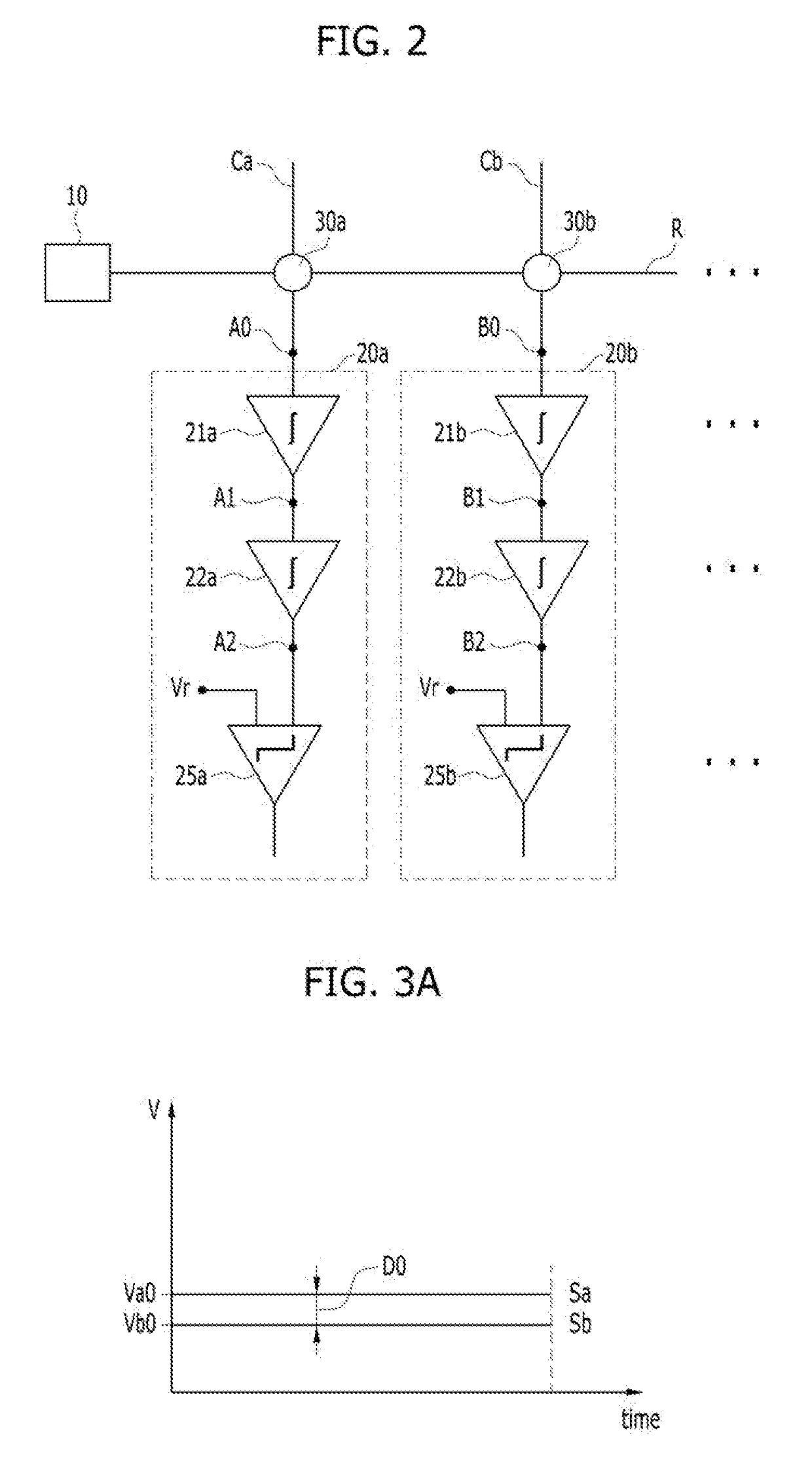
ActiveUS20170193353A1High voltage levelNeural architecturesPhysical realisationIntegratorEngineering
A neuromorphic device may include: a pre-synaptic neuron; a plurality of post-synaptic neurons; and a plurality of synapses electrically connected to the pre-synaptic neuron and electrically connected to the plurality of post-synaptic neurons. Each of the post-synaptic neurons may include: an integrator; a main comparator having a first input port connected to an output port of the integrator; and a first sub comparator having a first input port connected to the output port of the integrator.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
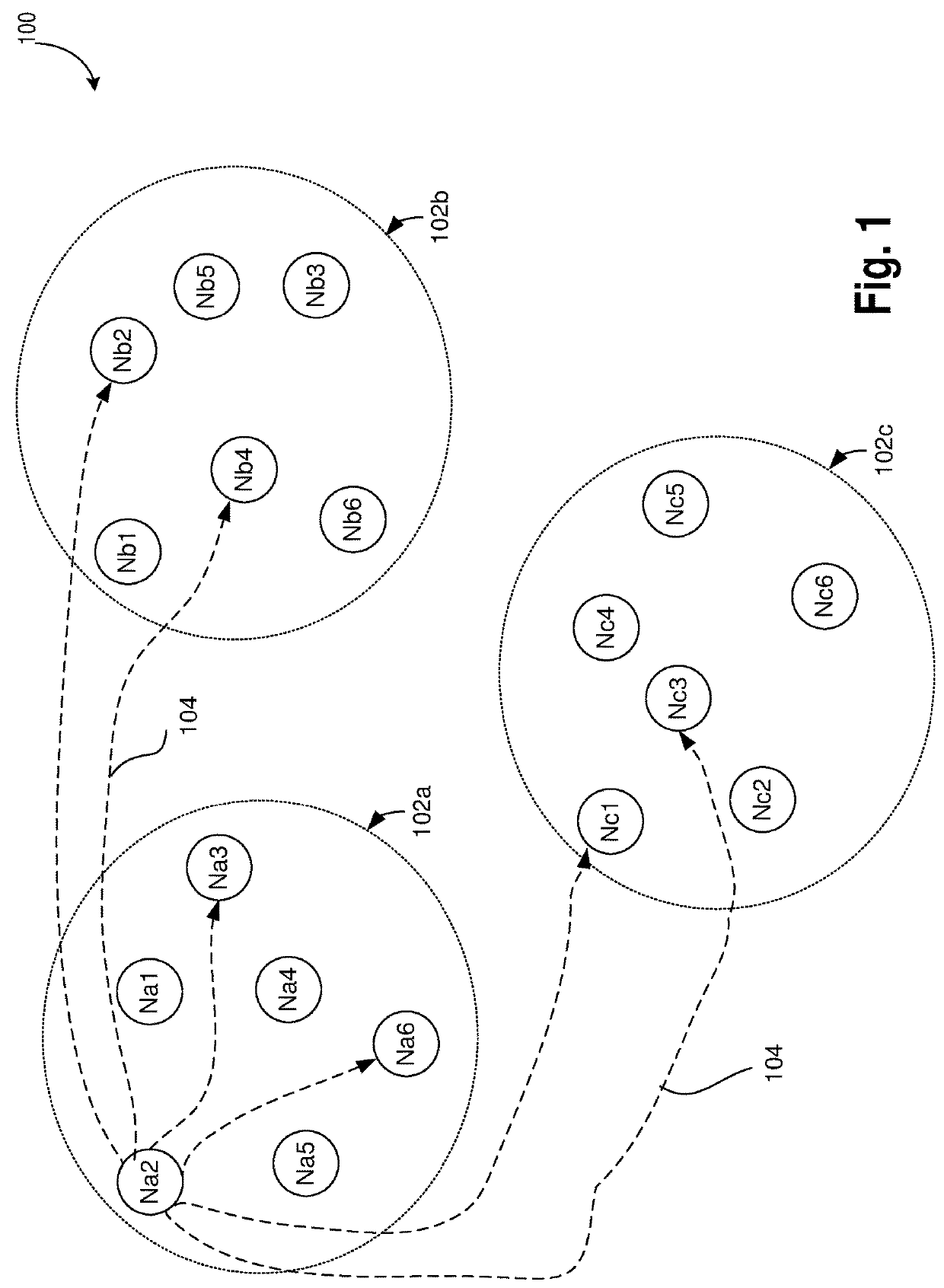
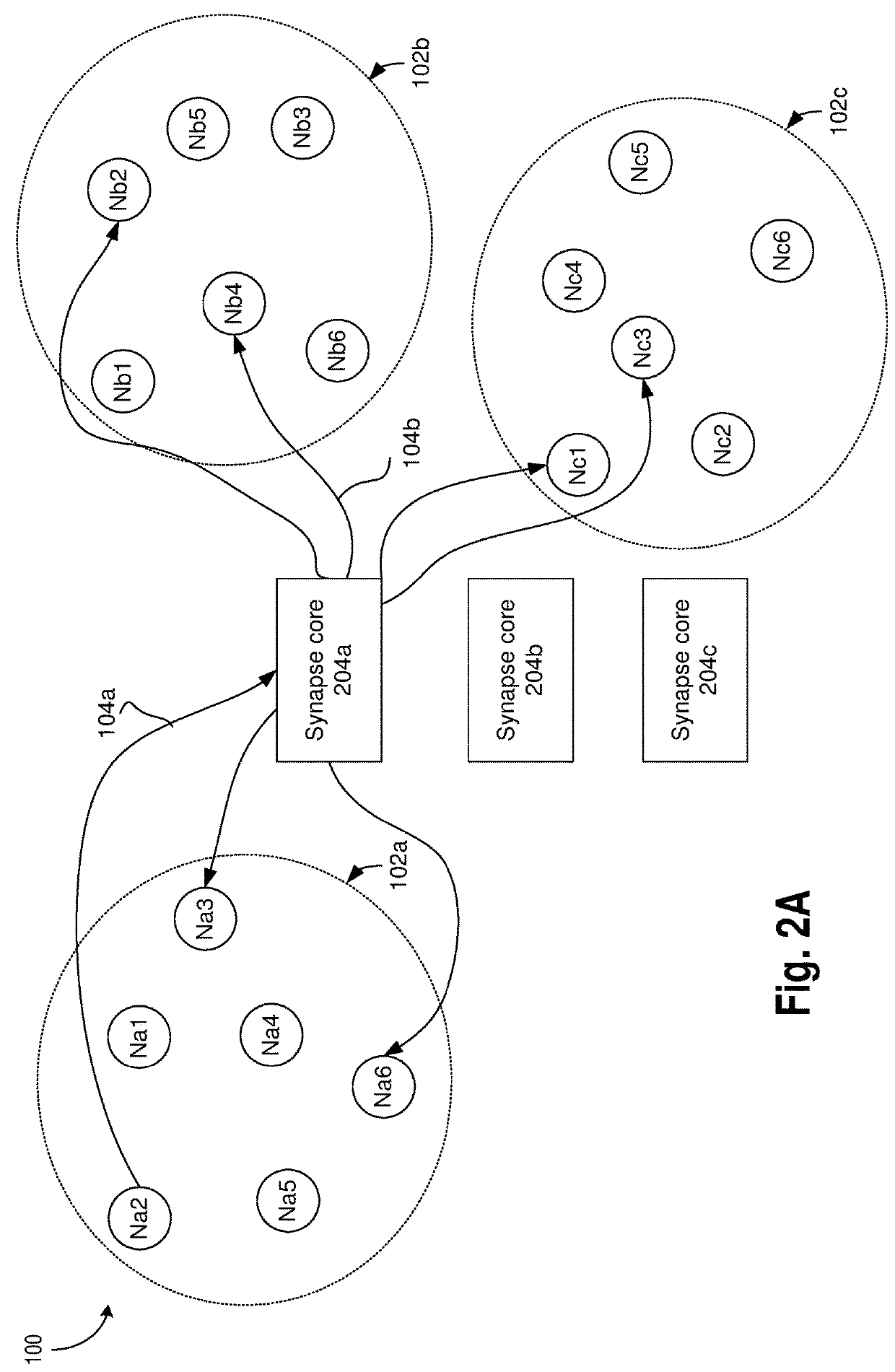
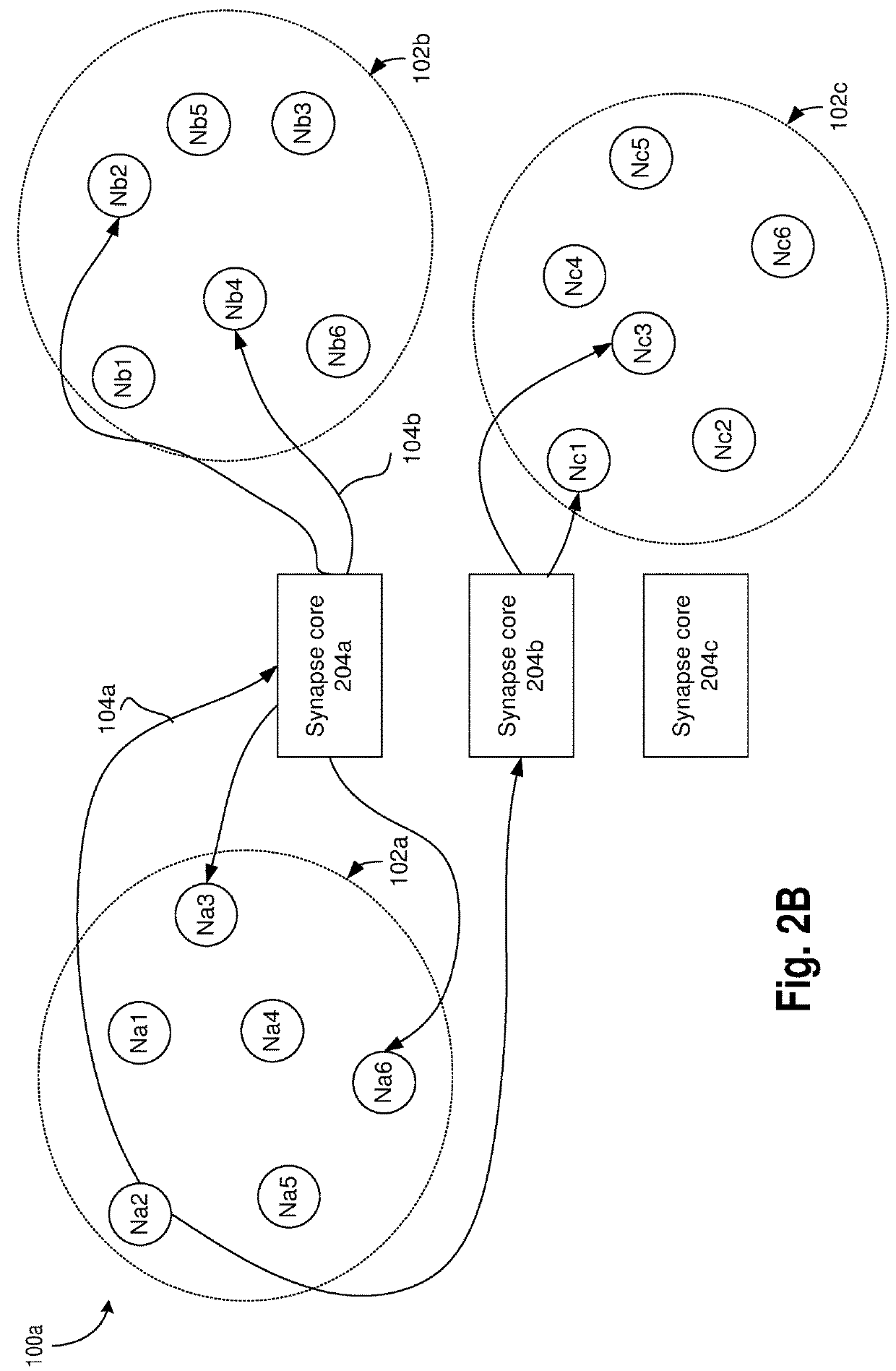
Neuromorphic circuits for storing and generating connectivity information
A neuromorphic computing system is provided which comprises: a synapse core; and a pre-synaptic neuron, a first post-synaptic neuron, and a second post-synaptic neuron coupled to the synaptic core, wherein the synapse core is to: receive a request from the pre-synaptic neuron, generate, in response to the request, a first address of the first post-synaptic neuron and a second address of the second post-synaptic neuron, wherein the first address and the second address are not stored in the synapse core prior to receiving the request.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Memristive recurrent neural network circuit
ActiveCN113469334ASimple structureIncrease flexibilityNeural architecturesPhysical realisationAlgorithmEngineering
The invention provides a memristive recurrent neural network circuit, which comprises a neuron module circuit, a reverse summation circuit and a memristive cross synaptic array circuit, wherein a pre-synaptic neuron in the memristive cross synaptic array circuit transmits a current signal to the input end of the neuron module circuit through a memristor; and the output end of the neuron module circuit transmits a current signal to the reverse summing module circuit, and the reverse summing circuit reversely propagates the current signal to the negative electrode of the memristor cross synapse array circuit. The memristive neural network is combined with associative memory, and a full connection layer of the artificial neural network is realized based on memristive, so that the network area and power consumption can be greatly reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Neuromorphic device including synapses having fixed resistance values
InactiveUS20170300806A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSynapseInterconnection
A neuromorphic device may include: pre-synaptic neurons; row lines extending in a first direction from the pre-synaptic neurons, respectively; post-synaptic neurons; column lines extending in a second direction from the post-synaptic neurons, respectively, the second direction crossing the first direction; and synapses arranged in intersection regions between the row lines and the column lines. The synapses may include resistor interconnections having various fixed resistance values. The synapses may be programmed with at least one pattern based on the various fixed resistance values.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Electronic neuromorphic system, synaptic circuit with resistive switching memory and method of performing spike-timing dependent plasticity
ActiveUS10650308B2Neural architecturesPhysical realisationSpike-timing-dependent plasticityArtificial intelligence
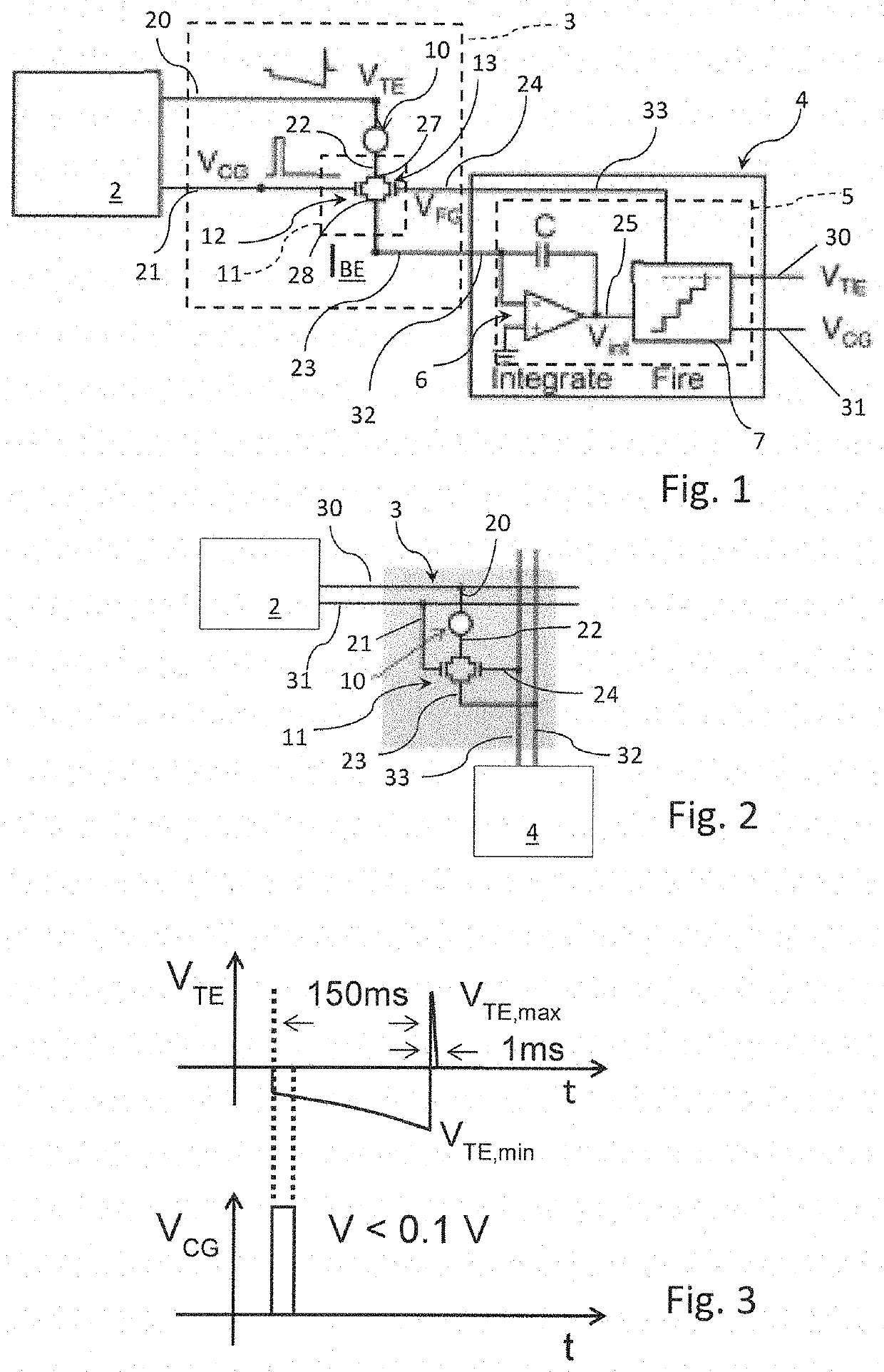
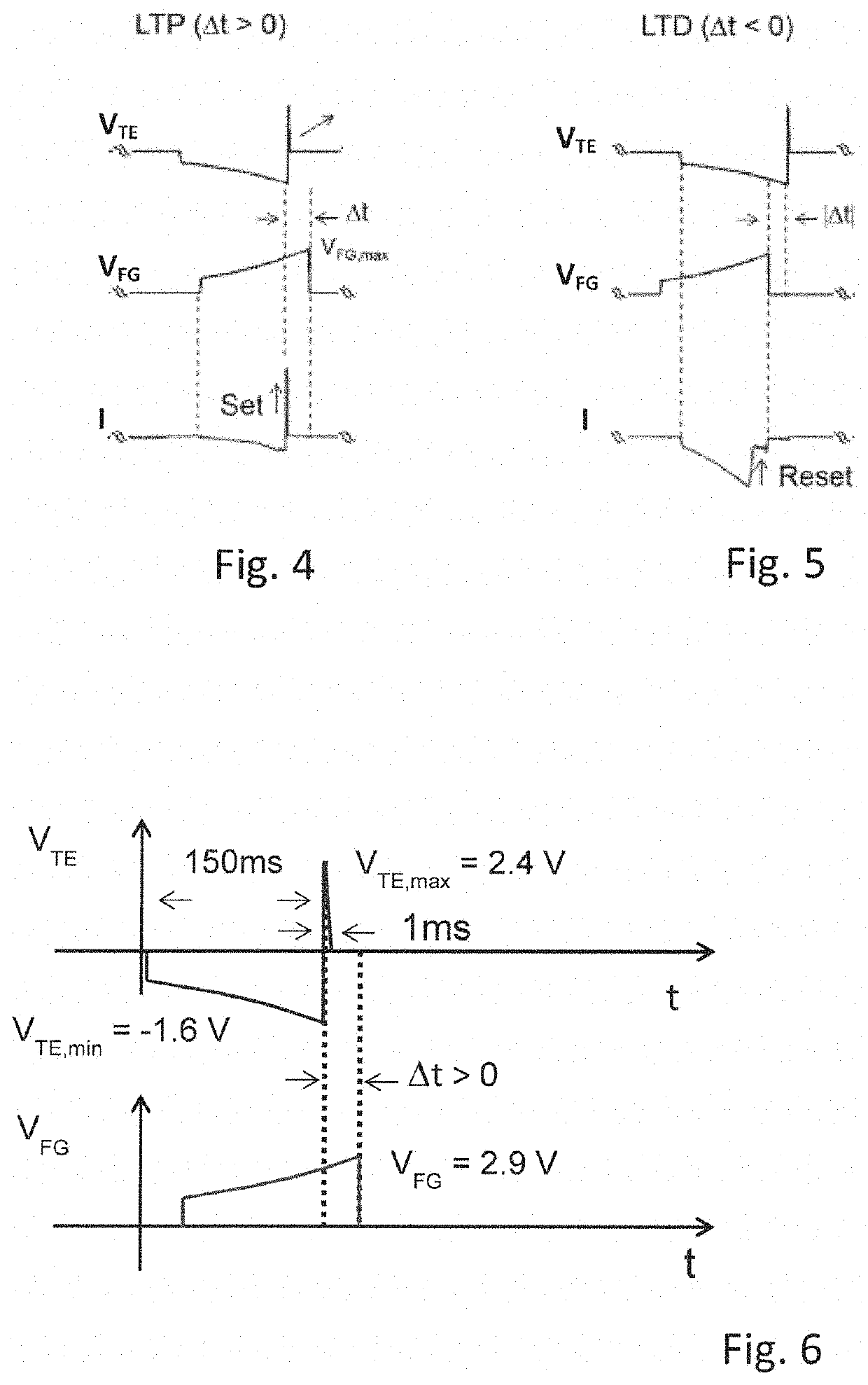
A synaptic circuit performing spike-timing dependent plasticity STDP interposed between a pre-synaptic neuron and a post-synapse neuron includes a memristor having a variable resistance value configured to receive a first signal from the pre-synaptic neuron. The circuit has an intermediate unit connected in series with the memristor for receiving a second signal from the pre-synaptic neuron and provides an output signal to the post-synaptic neuron. The intermediate unit receives a retroaction signal generated from the post-synaptic neuron and the memristor modifies the resistance value based on a delay between two at least partially overlapped input pulses, a spike event of the first signal and a pulse of the retroaction signal, in order to induct a potentiated state STP or a depressed state STD at the memristor. An electronic neuromorphic system having synaptic circuits and a method of performing spike timing dependent plasticity STDP by a synaptic circuit are also provided.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
Artificial neural circuit forming re-activatible functional link between the postsynaptic terminals of two synapses
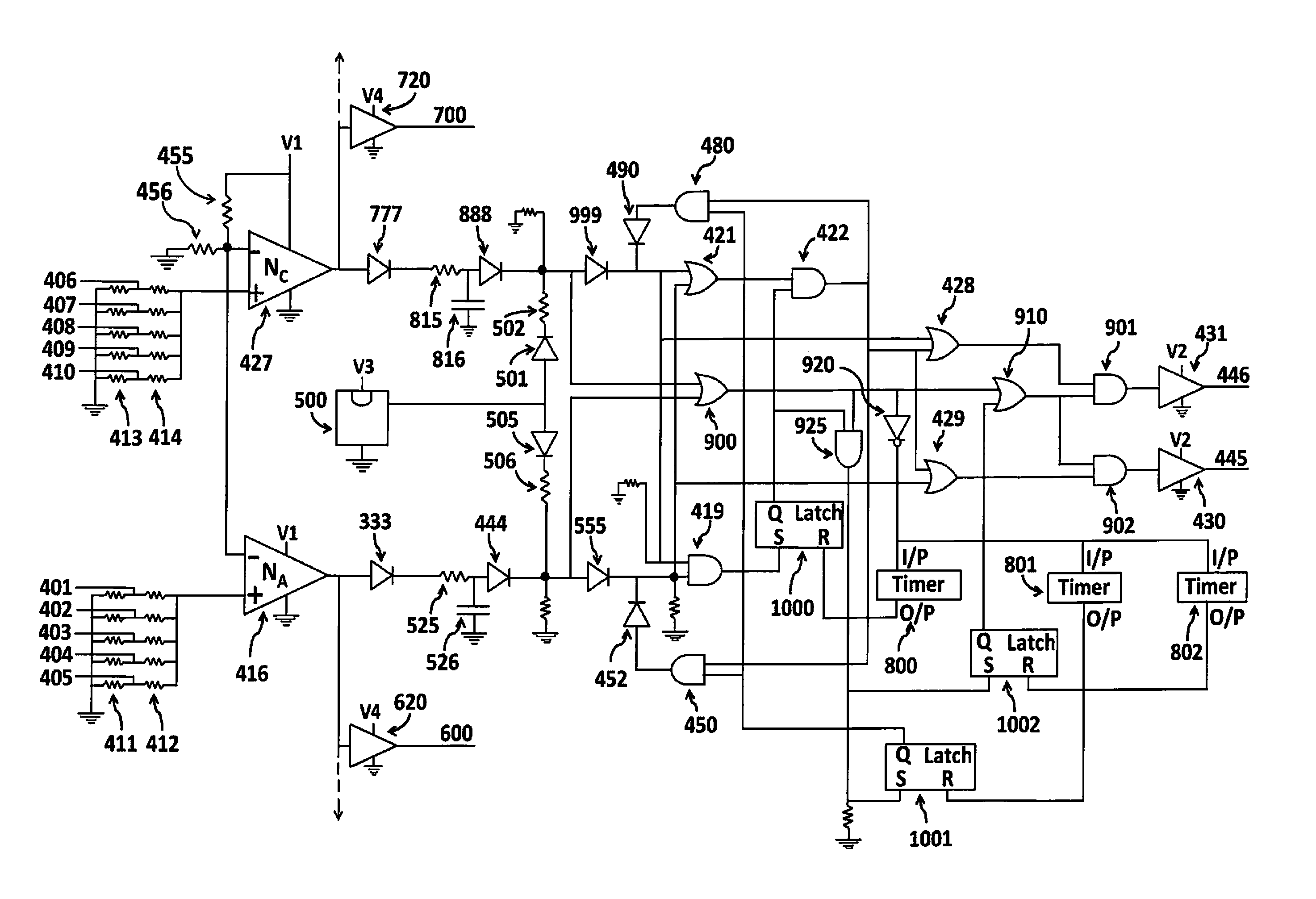
An electronic neuronal circuit system to model the interaction between the postsynaptic terminal of a first synapse between two neurons and the postsynaptic terminal of a second synapse between two neurons includes comparators to model the presynaptic neurons of the synapses, plurality of three diodes connected to the comparators to model synapses, an AND gate and latch to model the formation of functional link between the postsynaptic terminals, and timer-controlled latches for controlling the life-span of the inter-postsynaptic functional link, durations of re-activation of inter-postsynaptic functional link and flow of activity through the output postsynaptic dendritic terminals.
Owner:VADAKKAN KUNJUMON ITTIRA
Electrical activity recording method for tiny single synaptic neurons
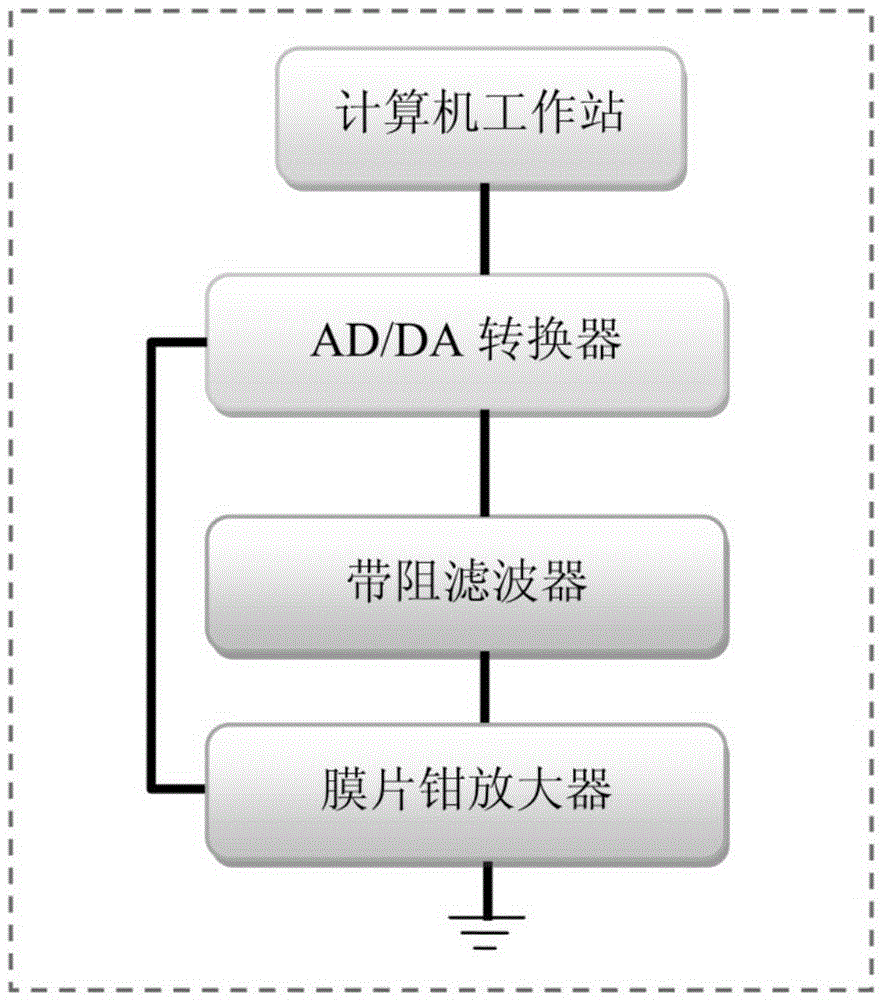
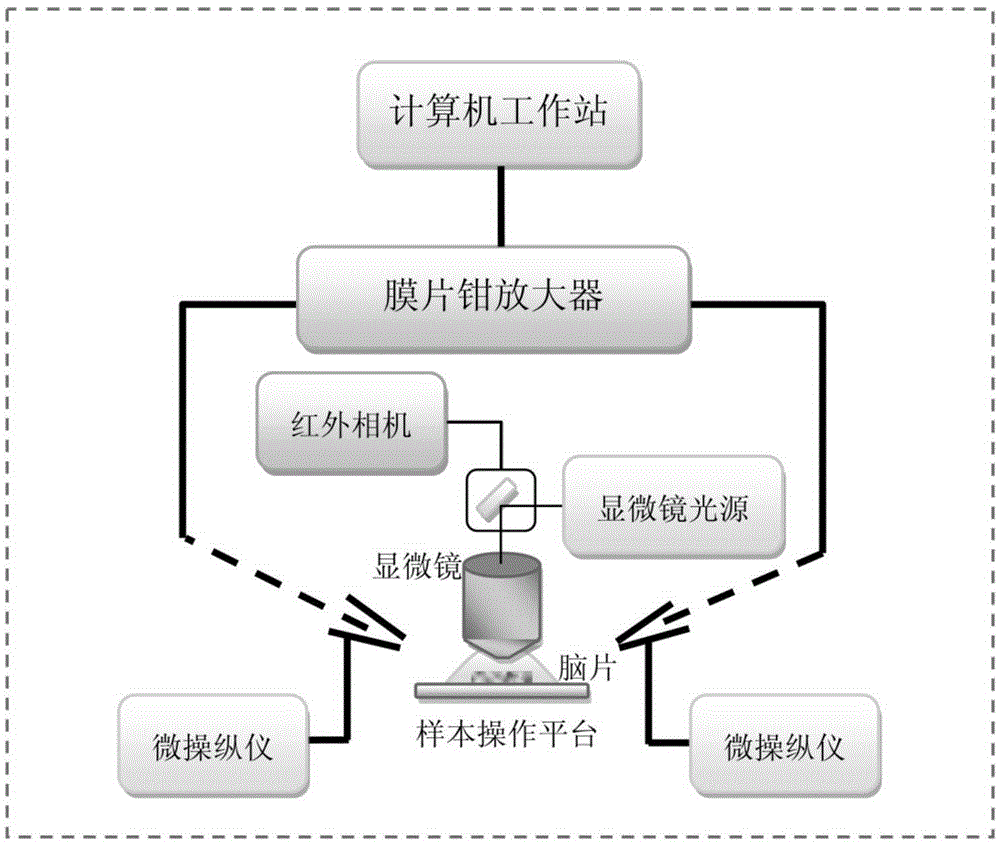
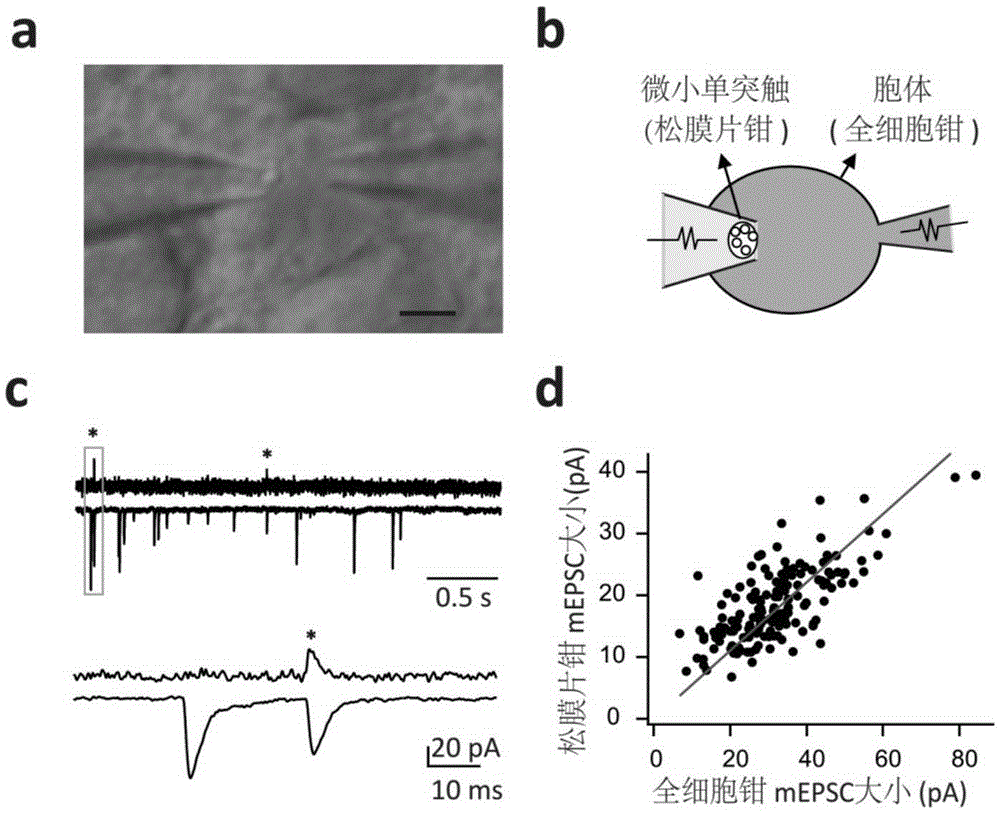
The invention discloses an electrical activity recording method for tiny single synaptic neurons and belongs to the field of neurobiology research. Based on the conventional patch clamp technique, electrical signals input through all tiny presynaptic neurons can only be recorded through postsynaptic neurons, while electrical signals input by each tiny presynaptic neuron cannot be recognized. In this way, the invention provides the above method. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the loose-patch clamp technique and the whole-cell patch clamp technique are integrated, and the electrical activity of each tiny single synapsis can be recorded simply on a brain slice in the physiological state. Therefore, based on the method, the dynamic characteristics of the vesicle spontaneous release and the vesicle induced release of the single synapsis can be detected. The method provides a direct, quantitative, real-time and high-time-resolution detection method for the dynamic characteristics of the vesicle release of the single synapsis and the synaptic plasticity.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
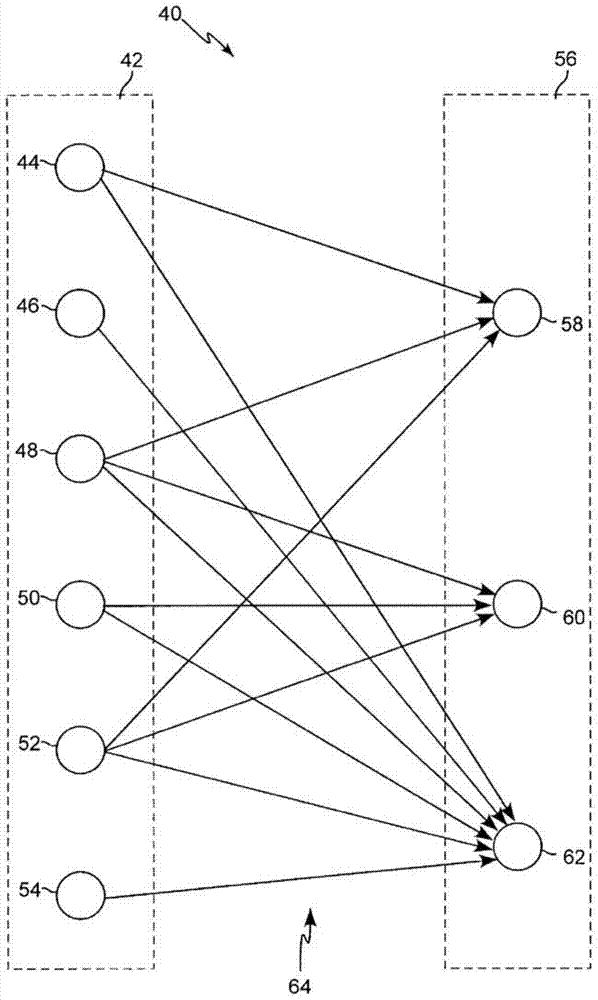
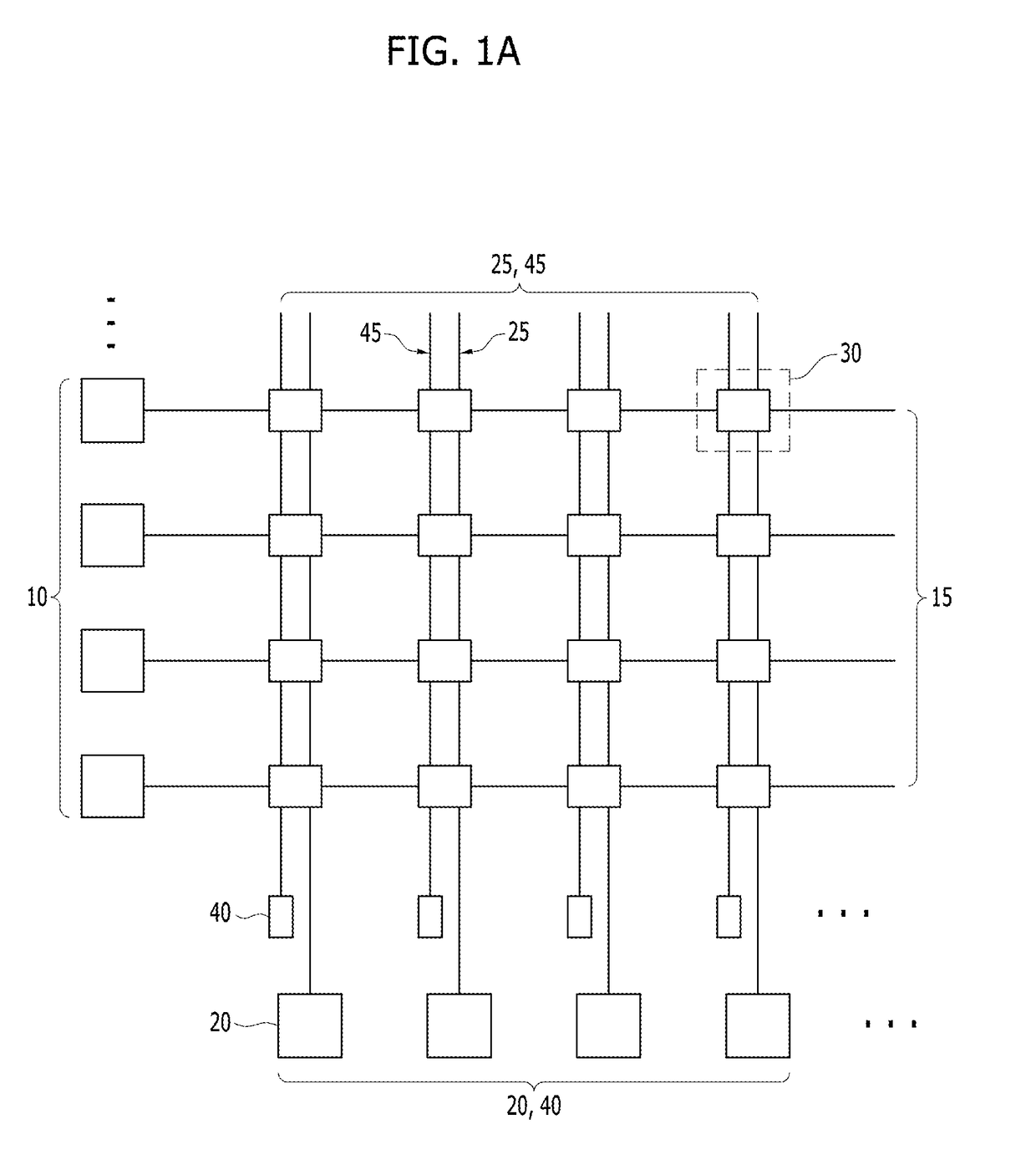
Generating messages from the firing of pre-synaptic neurons
A neural network portion comprising N pre-synaptic neurons capable each of firing an action potential, wherein the number N can be encoded in a word of n bits; the neural network portion being provided for, upon firing of a number F of pre-synaptic neurons in a predetermined period of time: if F.n<N, generating a first type message, the message comprising a unique address for each pre-synaptic neuron having fired in said predetermined period of time, each address being encoded as a word of n bits; and if F.n>N, generating a second type message, the message comprising N bits and being encoded in words of n bits, wherein each one of said N pre-synaptic neurons is represented by a unique bit, each bit having a first value if the pre-synaptic neuron represented by the bit fired in said predetermined period of time, and a second value otherwise.
Owner:HRL LAB
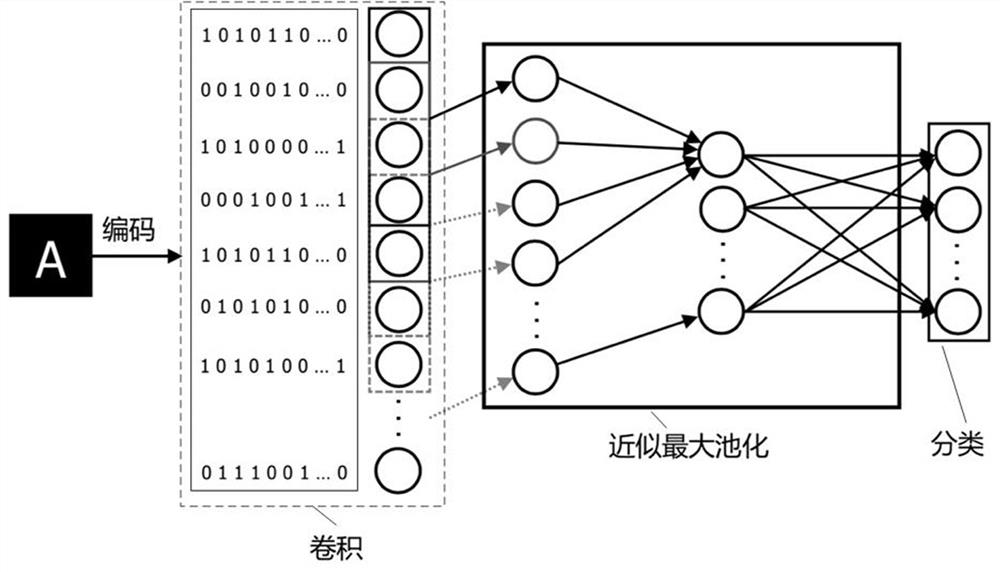
Image recognition method and system based on brain-like computing platform
ActiveCN113962371AReduce energy consumptionReduce computationNeural architecturesPhysical realisationSpiking neural networkThresholding
The invention relates to an image recognition method and system based on a brain-like computing platform. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a spiking neural network, wherein the spiking neural network comprises an approximate maximum pooling layer, the approximate maximum pooling layer comprises a pre-synaptic neuron cluster and a post-synaptic neuron cluster, the pre-synaptic neuron cluster comprises a plurality of neuron groups which are arranged in sequence, the number of pre-synaptic neurons in each neuron group is the same, the pre-synaptic neurons in the ith neuron group in the pre-synaptic neuron cluster are all connected with the ith post-synaptic neuron in the post-synaptic neuron cluster, and when spiking input by the pre-synaptic neurons in the ith neuron group exceeds a set threshold value in an accumulated manner, the ith post-synaptic neuron gives out spiking once; deploying the trained spiking neural network to a brain-like computing platform; and carrying out image recognition by adopting the spiking neural network deployed on a brain-like computing platform. According to the invention, the energy consumption of image recognition during hardware platform calculation is reduced.
Owner:中科南京智能技术研究院
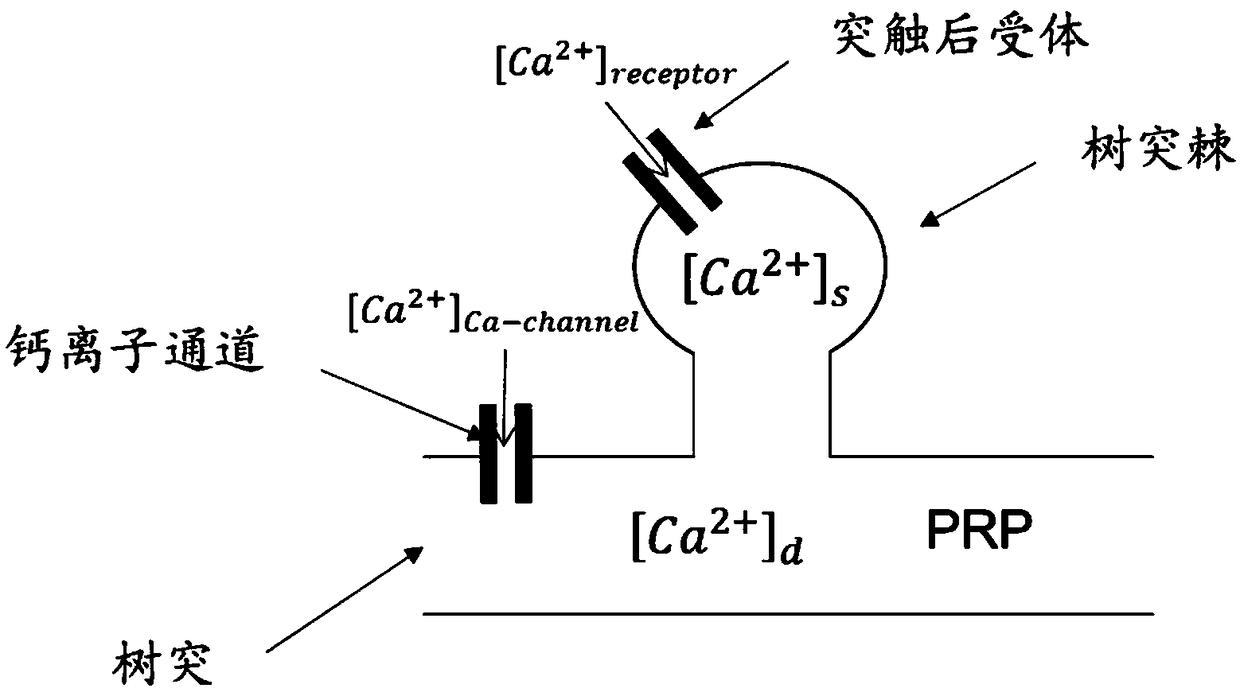
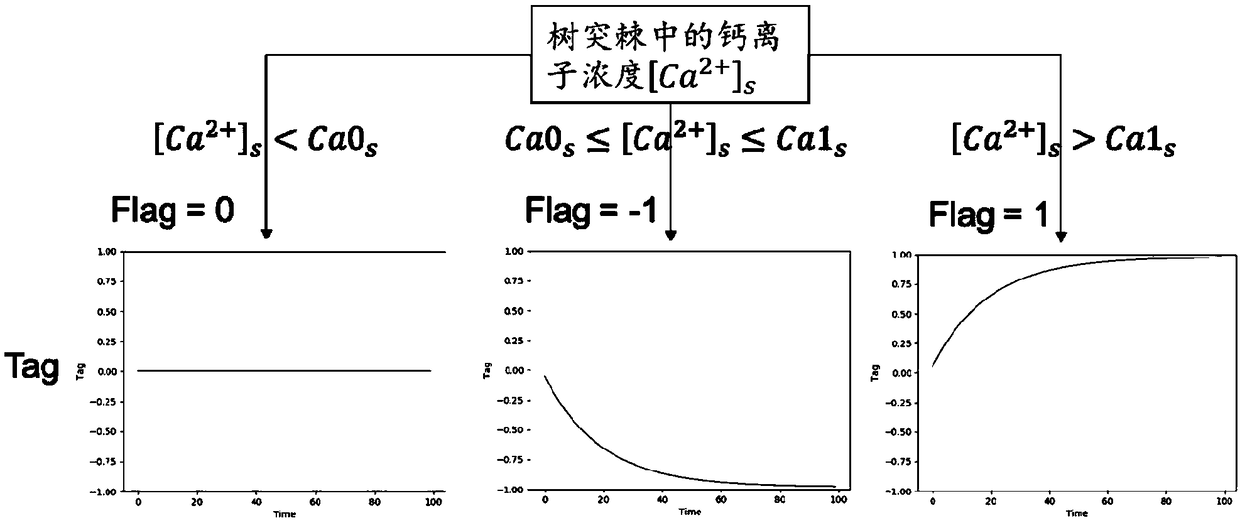
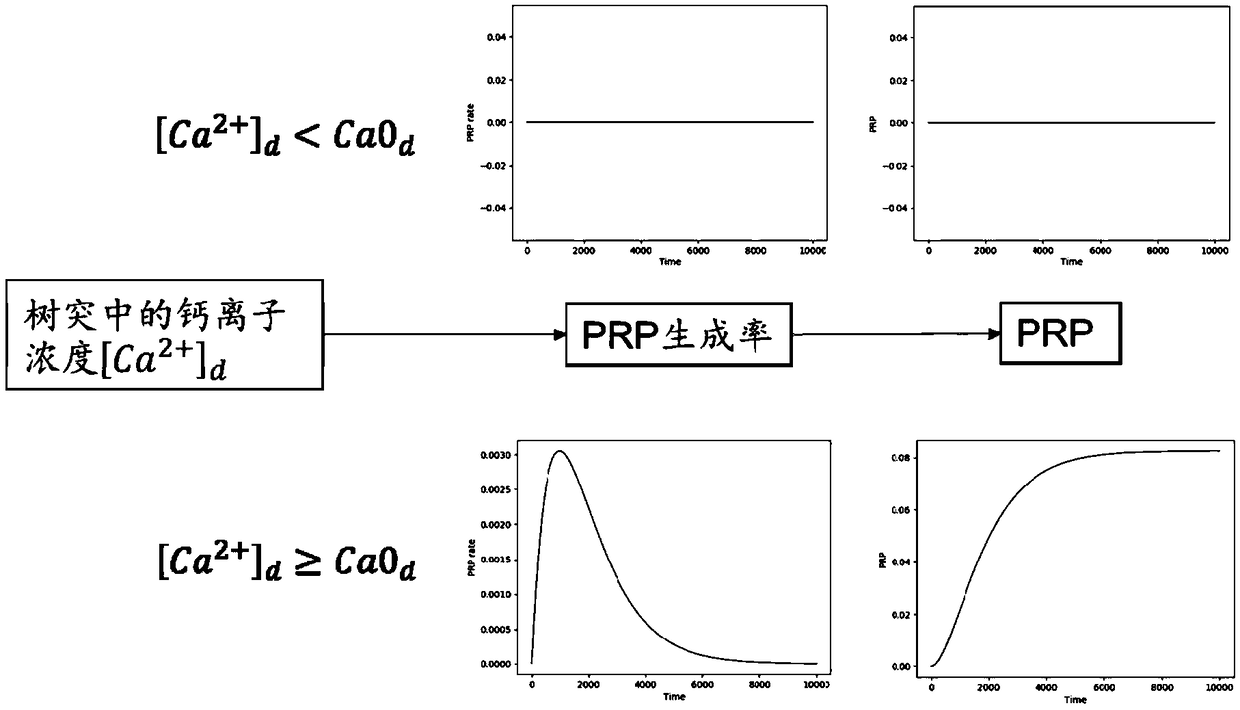
Calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration
The invention relates to a calculation method of neural synaptic plasticity based on calcium concentration, which relates to the field of brain simulation, in particular to the calculation problem ofneural synaptic plasticity of impulse neural network in brain simulation. The first is the calculation of calcium ion concentration. According to the membrane potential values of presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic neurons at the initial time t0 and the initial connecting weight w0 of synapses, the calcium ion concentrations in dendrites and spines at the next time t1 are calculated respectivelyfor the synapses that need to be calculated. Secondly, according to the calcium ion concentration in dendritic spine, the direction of weight change was obtained by comparing with the calcium ion concentration threshold Ca0s and Ca1s. According to the synaptic state tag Tag and the plasticity related protein PRP concentration, the change of synaptic weight was calculated, and the new weight at time t1 was obtained. the above procedure is repeated to calculate the strength of synaptic connections within the simulation time. The method of the invention is applied to constructing a brain-like neural network, completing the simulation of the learning and memory process required by the brain-like intelligence, realizing the universal strong artificial intelligence, and is applied to intelligentmedia, medical treatment and the like.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
Devices, apparatus and method for providing photostimulation and imaging of structures
ActiveUS9846313B2Reduce intensityEasy to detectRaman scatteringMicroscopesConfocalSpatiotemporal pattern
According to exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, it is possible to provide method, system, arrangement, computer-accessible medium and device to stimulate individual neurons in brain slices in any arbitrary spatio-temporal pattern, using two-photon uncaging of photo-sensitive compounds such as MNI-glutamate and / or RuBi-Glutamate with beam multiplexing. Such exemplary method and device can have single-cell and three-dimensional precision. For example, by sequentially stimulating up to a thousand potential presynaptic neurons, it is possible to generate detailed functional maps of inputs to a cell. In addition, it is possible to combine this exemplary approach with two-photon calcium imaging in an all-optical method to image and manipulate circuit activity. Further exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can include a light-weight, compact portable device providing for uses in a wide variety of applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Pulse neural network neuron membrane voltage calculation method
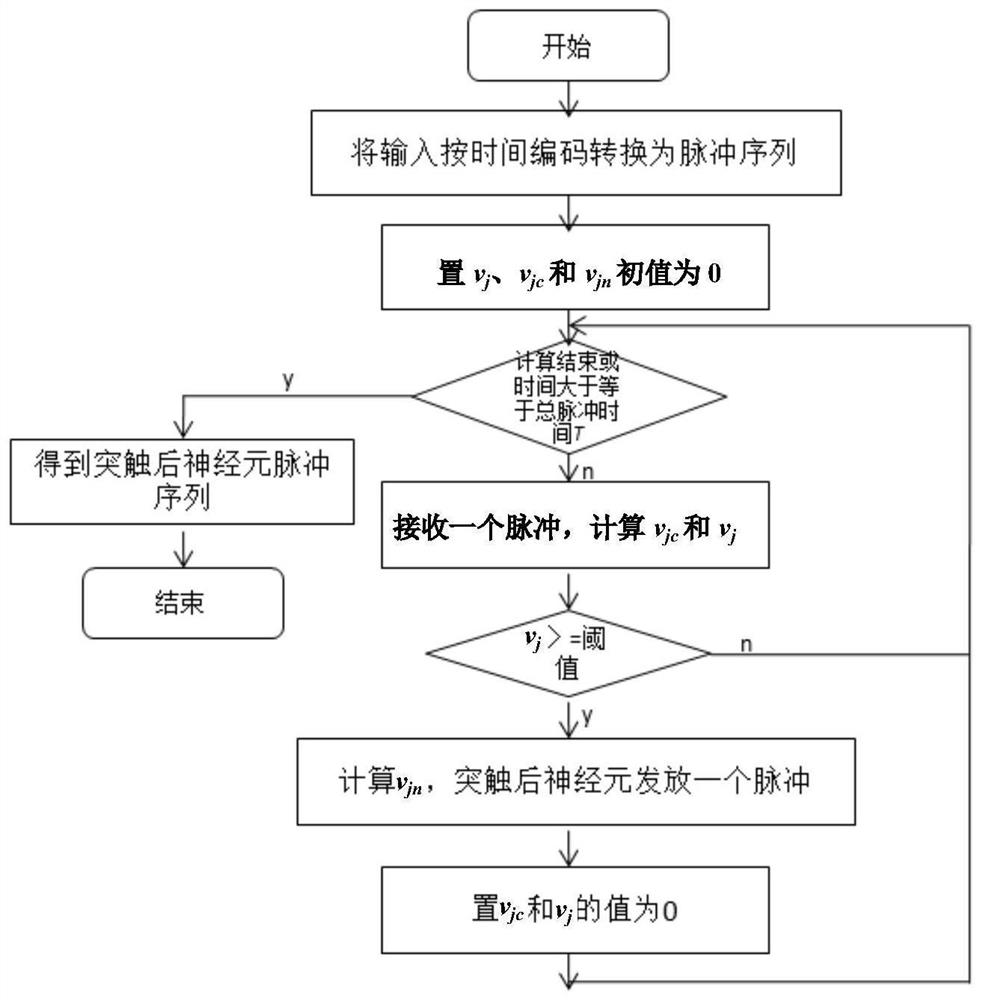
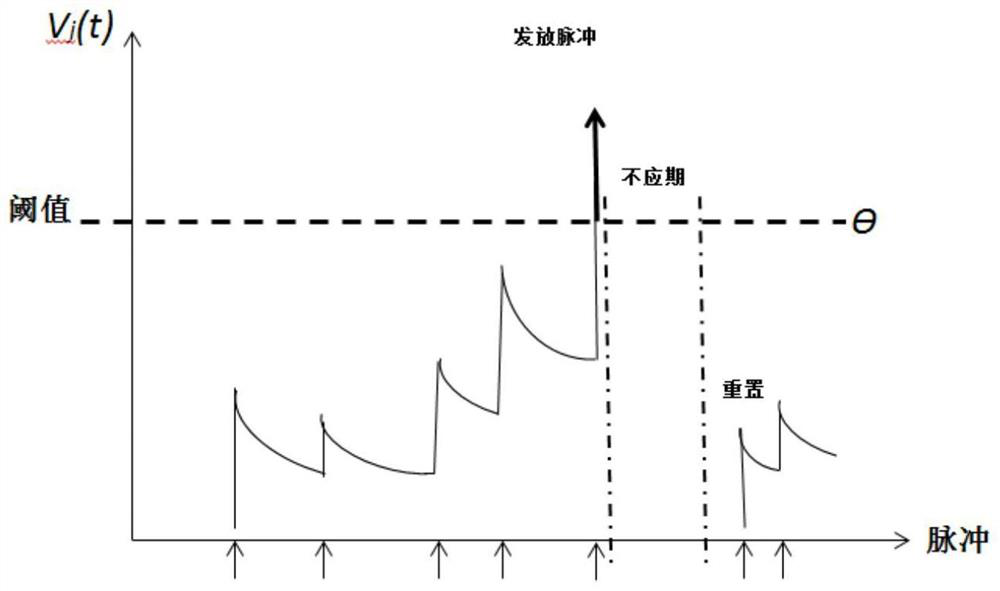
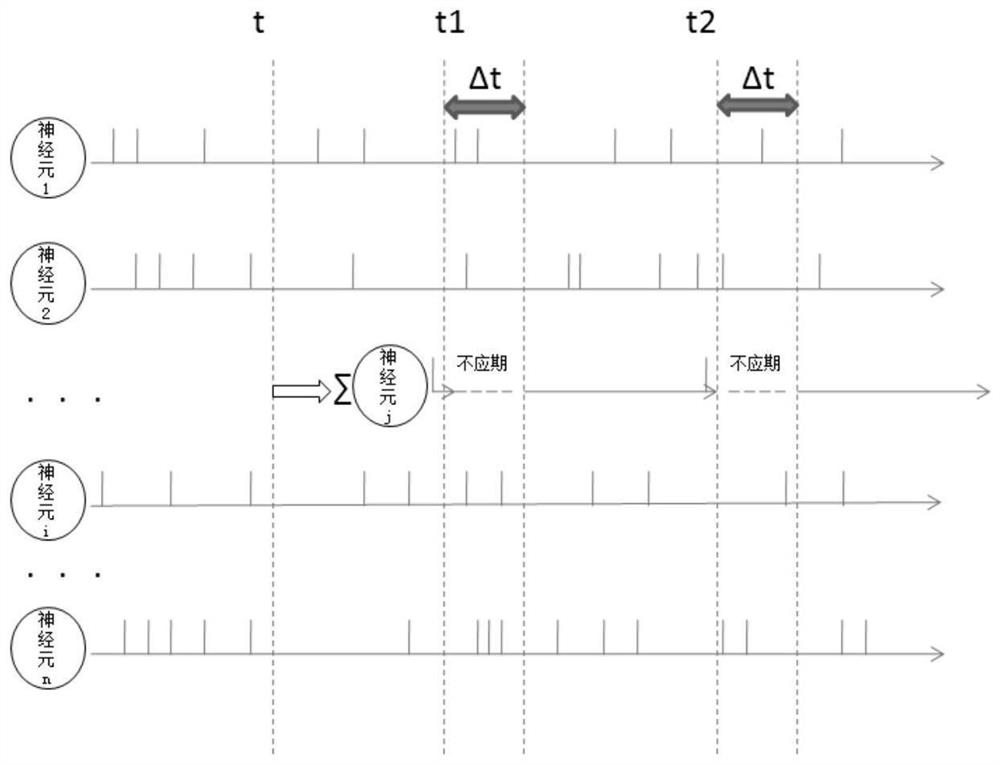
PendingCN114239405ASolve the lossMake up for the lossDesign optimisation/simulationImaging processingImage manipulation
The invention provides a method for calculating neuron membrane voltage of a spiking neural network, and relates to the technical field of spiking neural networks, and the method comprises the steps: firstly, converting an input signal into a pulse sequence through employing a time coding method, selecting a Spike Response Model neuron model as a membrane voltage calculation model of a neuron non-nonstress time period of the spiking neural network, and carrying out the calculation of the membrane voltage of the spiking neural network; then establishing a membrane voltage model generated by pulse accumulation of the pre-synaptic neurons in the post-synaptic neuron non-stress period, and finally establishing a pulse neural network neuron membrane voltage calculation model to realize calculation of the post-synaptic neuron membrane voltage; according to the method, the accumulation of neuron input pulses before the non-stress period highlights is calculated, the loss of input information is made up, the method is applied to image processing, the loss of information is reduced, and the utilization rate of the input information is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
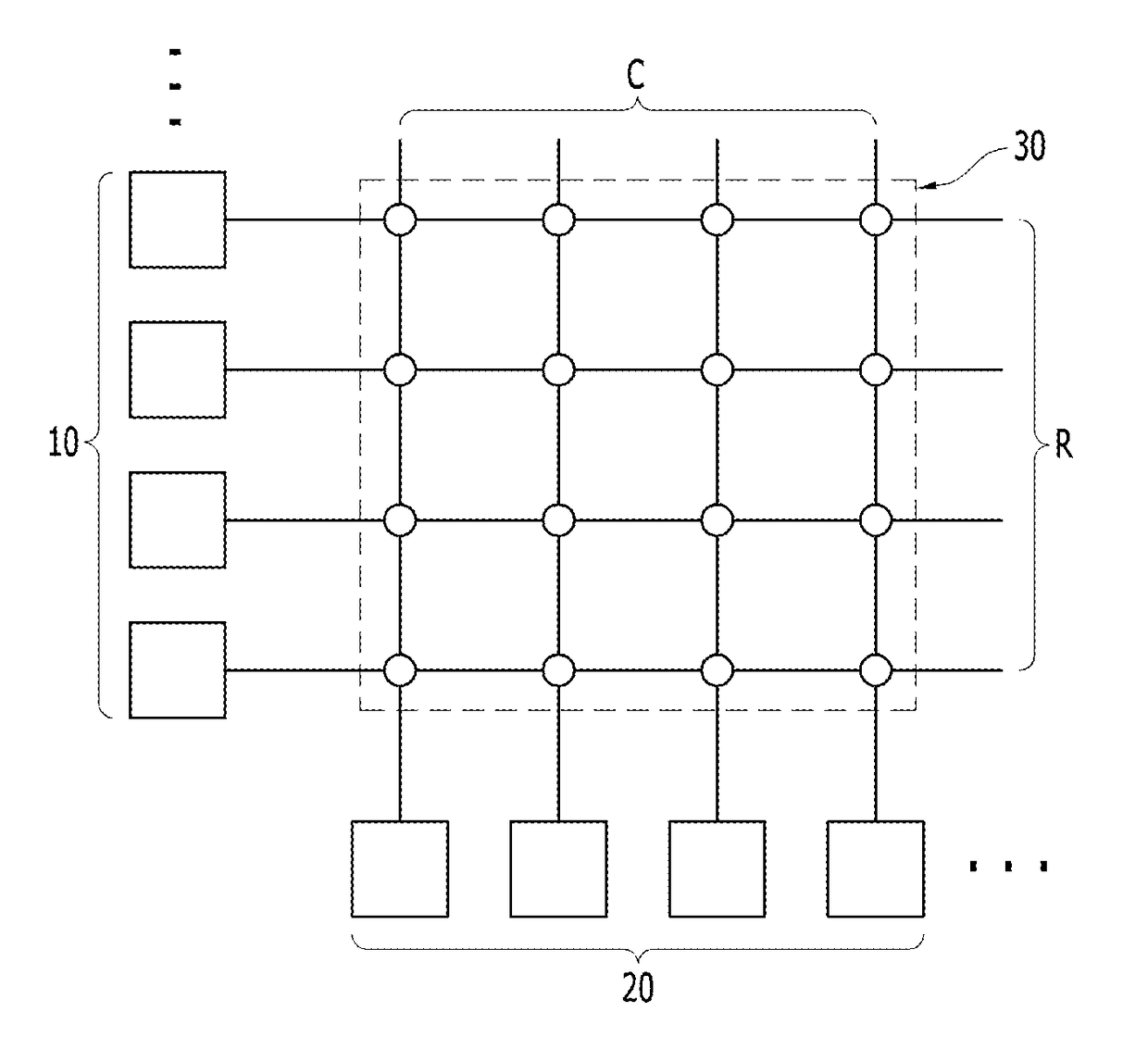
Linearly weight updatable CMOS synaptic array without cell location dependence
A neuromorphic circuit, chip, and method are provided. The neuromorphic circuit includes a crossbar synaptic array cell. The crossbar synaptic array cell includes a Complimentary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) transistor having an on-resistance controlled by a gate voltage of the CMOS transistor to update a weight of the crossbar synaptic array cell. The neuromorphic circuit further includes a set of row-lines respectively connecting the synaptic array cell in series to a plurality of pre-synaptic neurons at first ends thereof. The neuromorphic circuit also includes a set of column-lines respectively connecting the synaptic array cell in series to a plurality of post-synaptic neurons at second ends thereof. The gate voltage of the CMOS transistor is controlled by performing a charge sharing technique that updates the weight of the crossbar synaptic array cell using non-overlapping pulses on control lines that are aligned with the set of row lines and the set of column lines.
Owner:IBM CORP
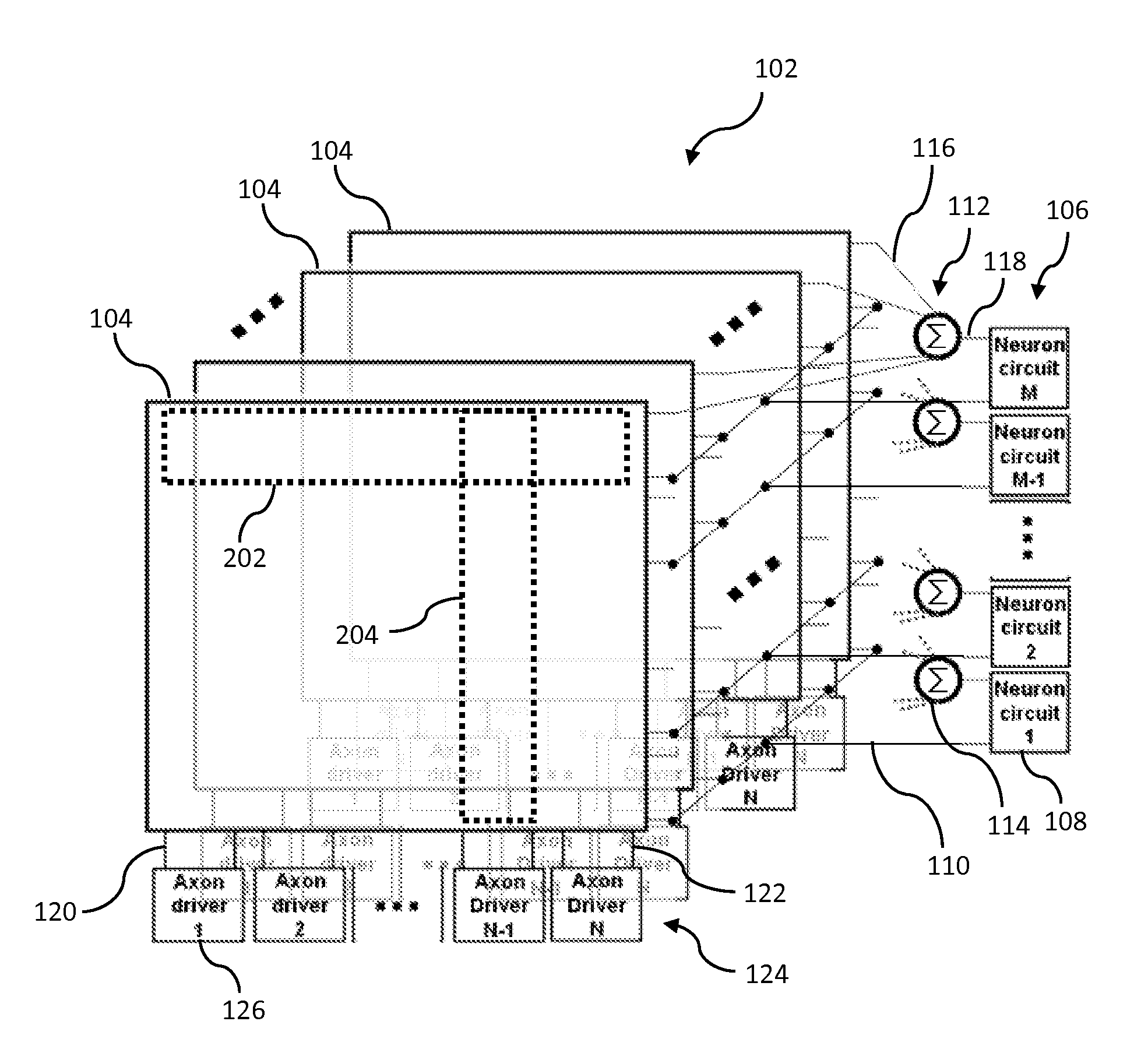
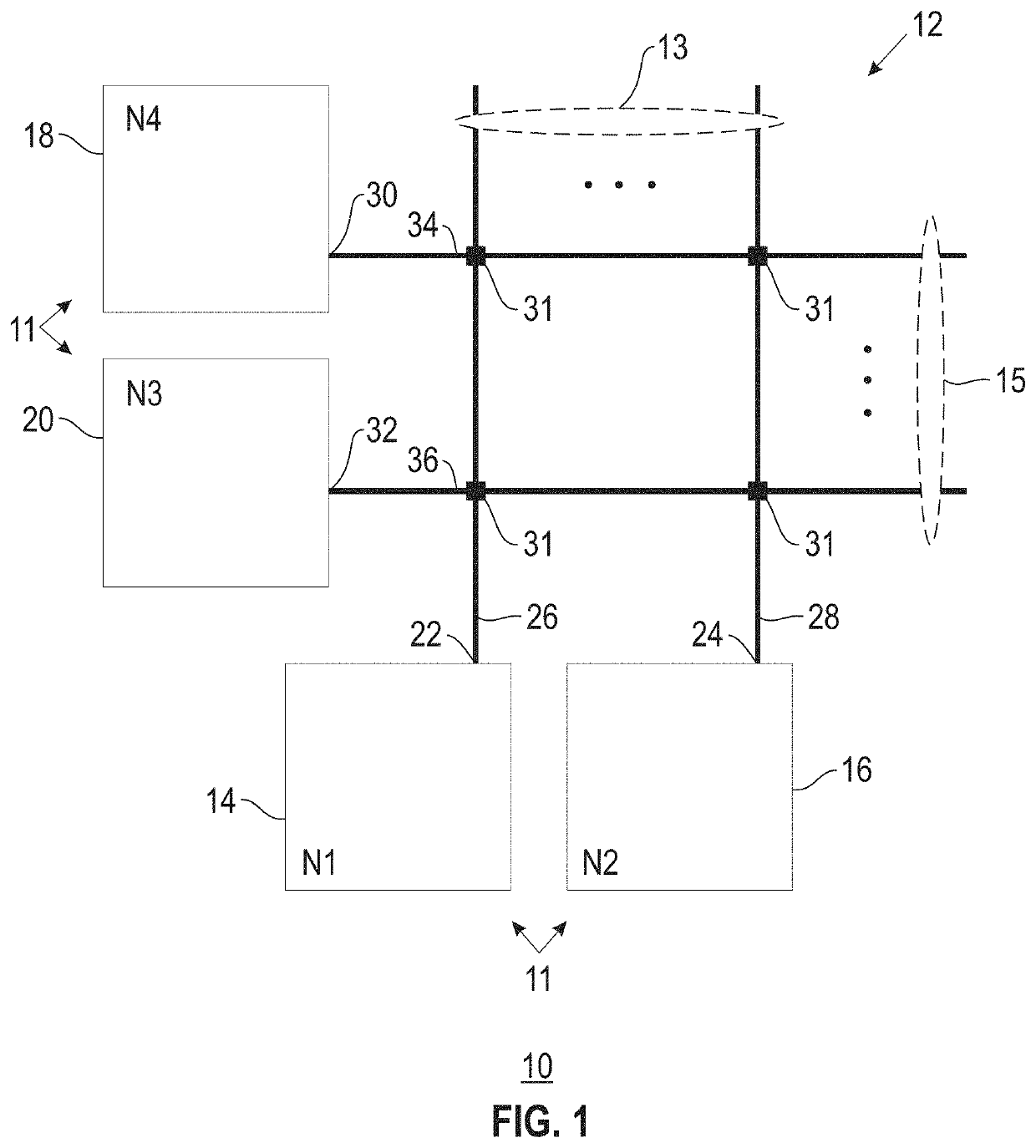
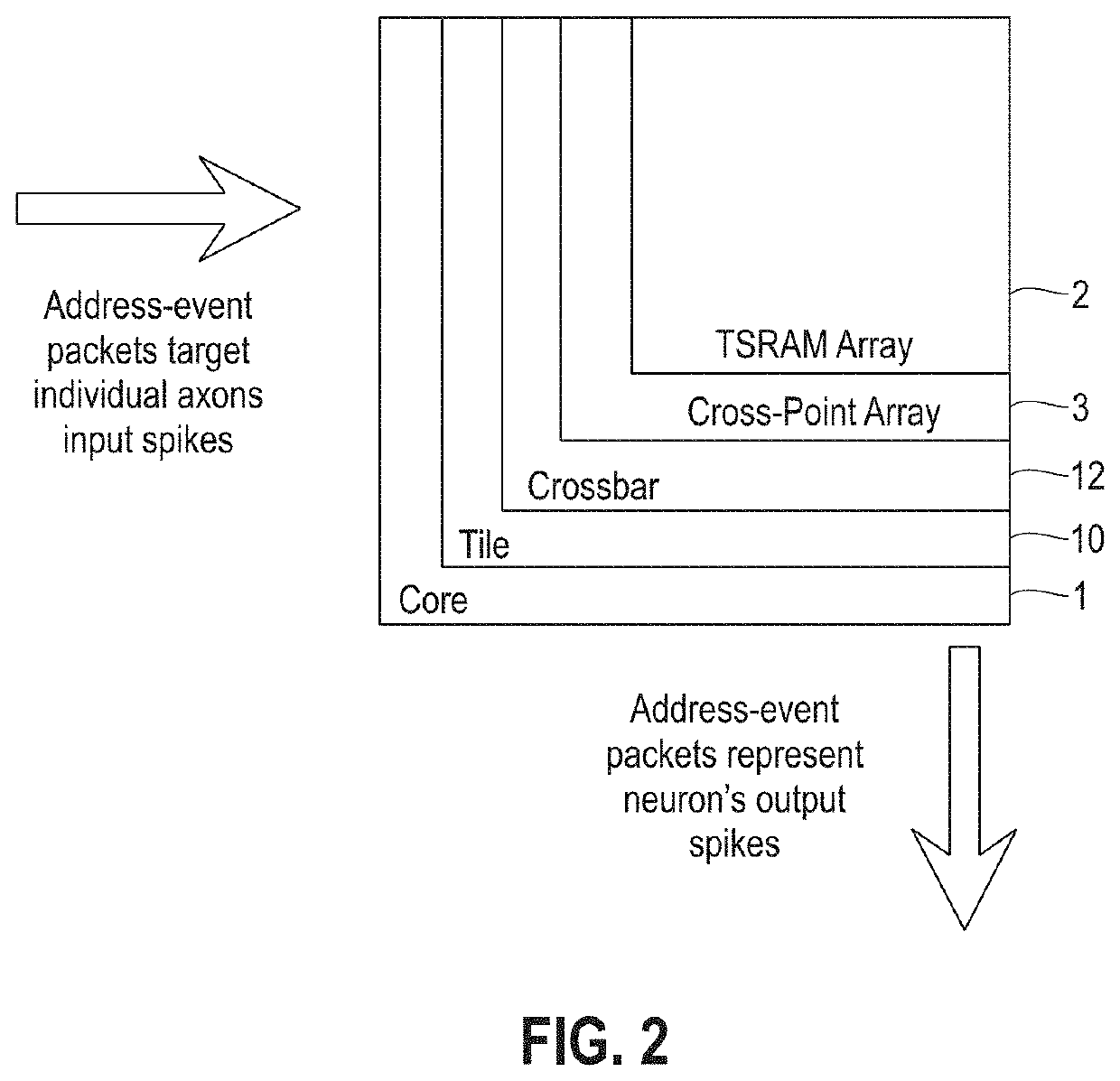
Neuromorphic event-driven neural computing architecture in a scalable neural network
An event-driven neural network includes a plurality of interconnected core circuits is provided. Each core circuit includes an electronic synapse array has multiple digital synapses interconnecting a plurality of digital electronic neurons. A synapse interconnects an axon of a pre-synaptic neuron with a dendrite of a post-synaptic neuron. A neuron integrates input spikes and generates a spike event in response to the integrated input spikes exceeding a threshold. Each core circuit also has a scheduler that receives a spike event and delivers the spike event to a selected axon in the synapse array based on a schedule for deterministic event delivery.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Associative memory circuit and method based on physical memristor
PendingCN114169511AHigh similaritySimulation results are accuratePhysical realisationSynapseMemory circuits
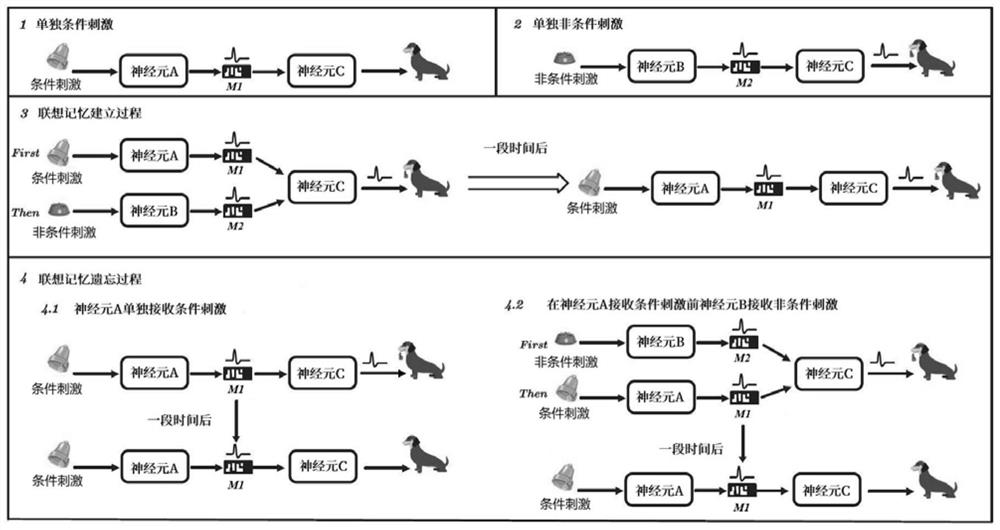
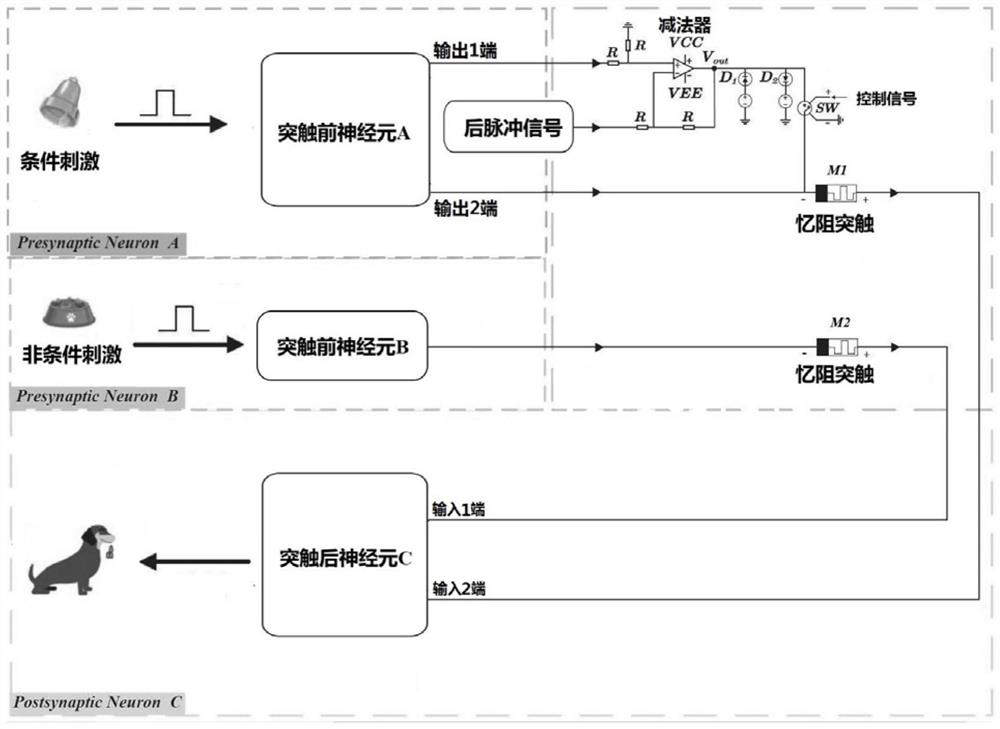
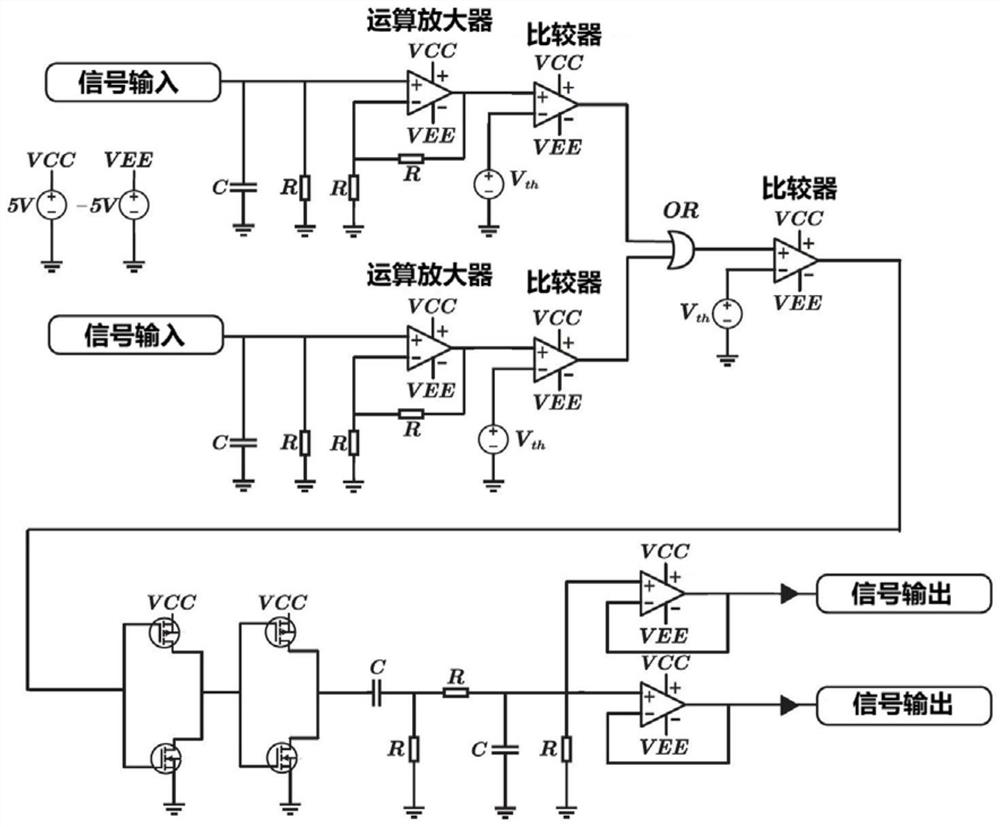
The invention provides an associative memory circuit and memory method based on a physical memristor. The circuit comprises a synaptic unit and a spiking neuron unit, the synapse unit comprises a memristive synapse M1 and a memristive synapse M2; the pulse neuron unit comprises a pre-synaptic neuron A, a pre-synaptic neuron B and a post-synaptic neuron C. The pre-synaptic neuron A and the pre-synaptic neuron B receive conditional stimulation signals and non-conditional stimulation signals respectively. The synaptic units and the spiking neuron units form a basic associative memory unit, and a plurality of basic associative memory units can form a biological neural network. The synaptic unit is based on a physical memristor, the defects that a traditional synaptic circuit is large in size and high in energy consumption are overcome, the integration level of the artificial neural network is improved, and the possibility is provided for an artificial neural network hardware circuit to simulate a large-scale biological neural network.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Artificial neural circuit forming re-activatible functional link between the postsynaptic terminals of two synapses
An electronic neuronal circuit system to model the interaction between the postsynaptic terminal of a first synapse between two neurons and the postsynaptic terminal of a second synapse between two neurons includes comparators to model the presynaptic neurons of the synapses, plurality of three diodes connected to the comparators to model synapses, an AND gate and latch to model the formation of functional link between the postsynaptic terminals, and timer-controlled latches for controlling the life-span of the inter-postsynaptic functional link, durations of re-activation of inter-postsynaptic functional link and flow of activity through the output postsynaptic dendritic terminals.
Owner:VADAKKAN KUNJUMON ITTIRA
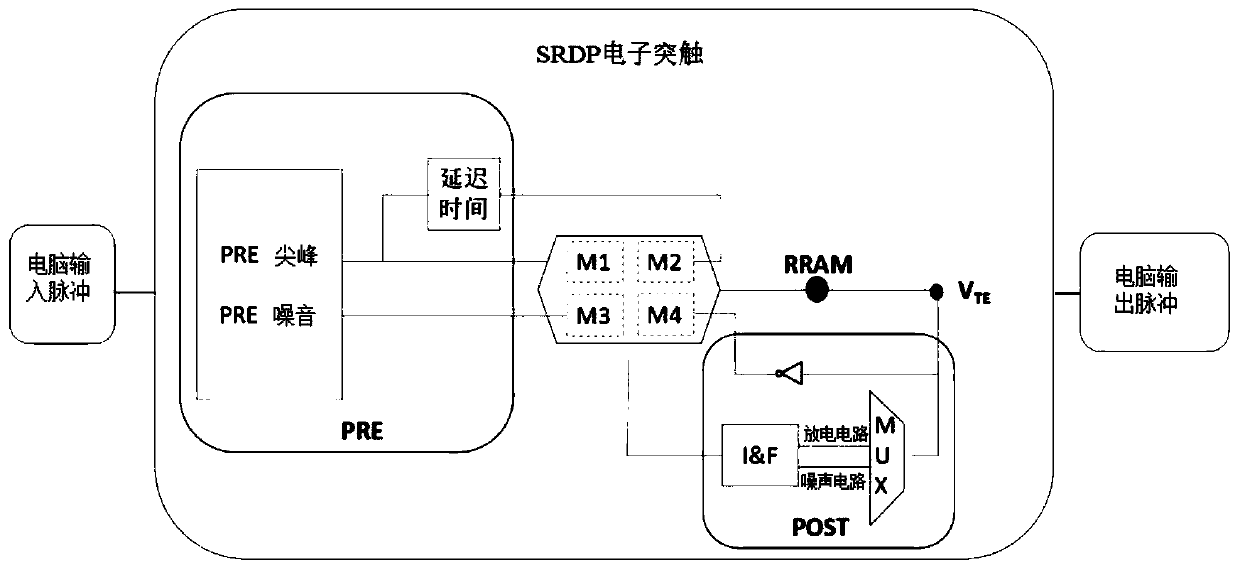
Discharge rate dependent plasticity structure and implementation method
InactiveCN110766149ASupport feasibilityImprove plasticityPhysical realisationElectronic synapseNeural network nn
The invention provides a discharge rate dependent plasticity structure and an implementation method, the discharge rate dependent plasticity structure comprises a pre-synaptic neuron PRE, a post-synaptic neuron POST and an SRDP electronic synapse, and the SRDP electronic synapse comprises four MOS transistors and a bipolar switch RRAM; wherein the four MOS transistors are respectively representedas M1, M2, M3 and M4 by using symbols, M1 and M2 form a group to form M1 / M2 branches, M3 and M4 form a group to form M3 / M4 branches, and M1 / M2 and M3 / M4 are connected in parallel; and the M1 / M2, the M3 / M4, the post-synaptic neuron POST and the bipolar switch RRAM are mutually connected in series. According to the structure and the method, plasticity of discharge time can be realized; unsupervisedlearning can be demonstrated on the neural network level, and the feasibility of a hybrid CMOS / RRAM integrated circuit supporting human brain learning ability matching is proved.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
On-chip neural network-oriented synaptic implementation architecture
ActiveCN112784972AFlexible configurationEfficient use ofArchitecture with single central processing unitPhysical realisationNeural network topologyNeuron
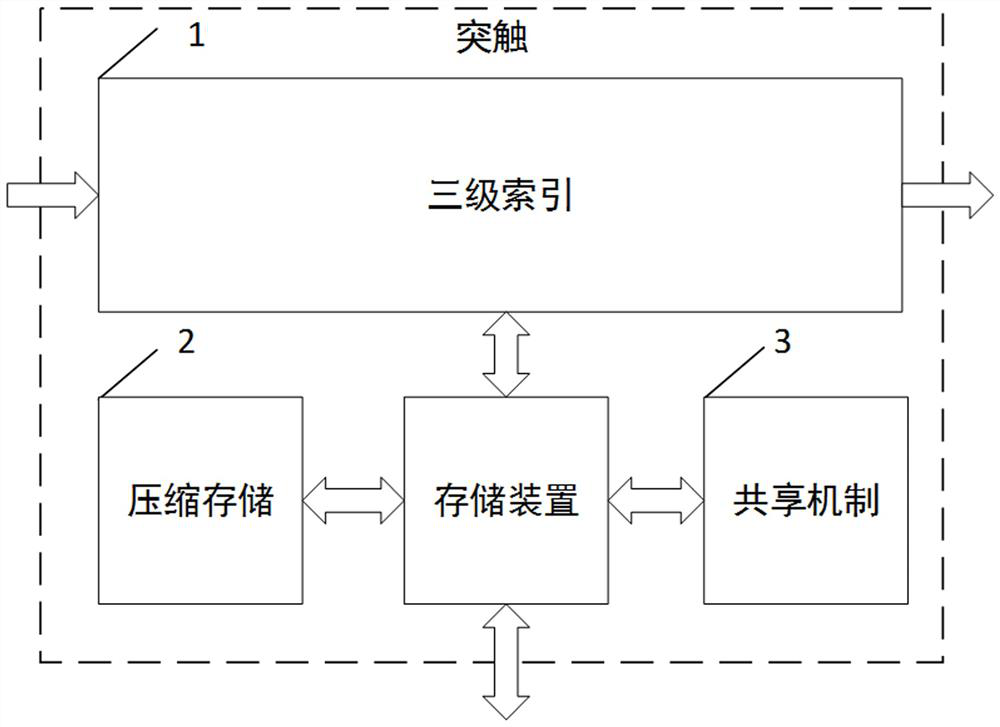
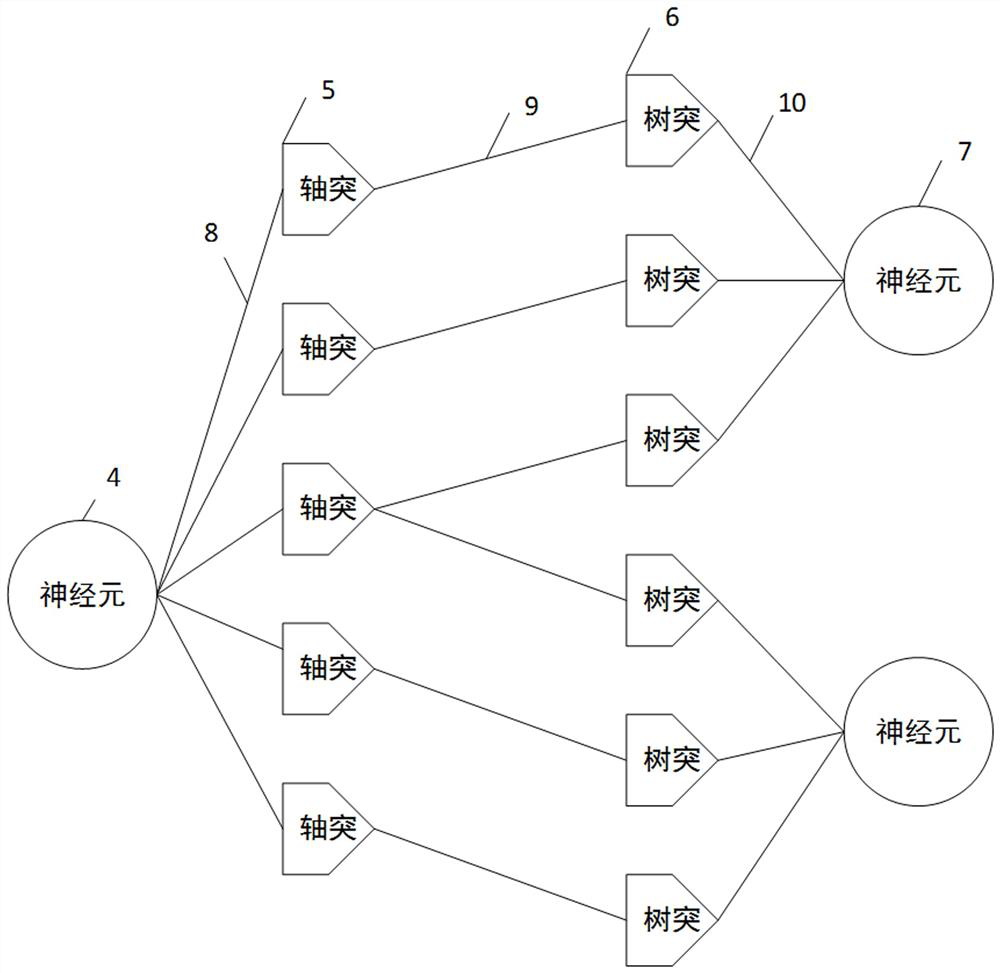
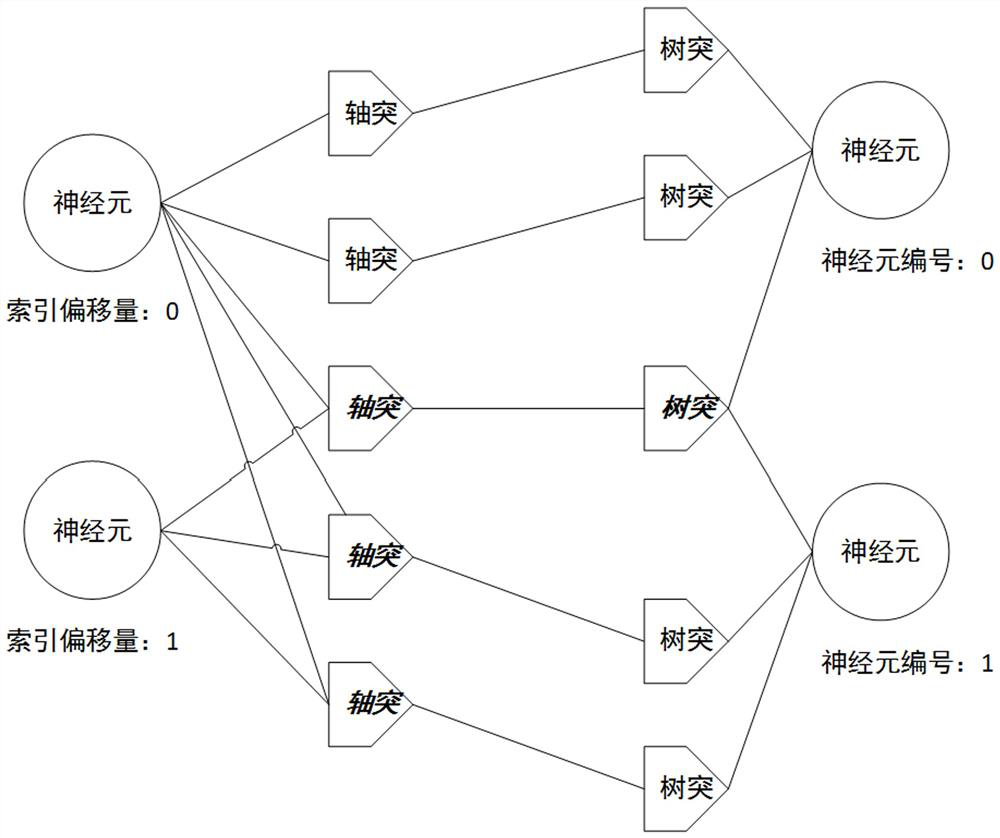
The invention belongs to the technical field of neural synapse implementation of brain-like computing chips, and relates to an on-chip neural network-oriented synapse implementation architecture based on three-level index and storage compression sharing. Synapses are connected with pre-synaptic neurons and post-synaptic neurons through a three-level index structure mode; connection information and weights in the three-level index structure mode can be stored in a synaptic storage device or distributed to pre-synaptic neurons and post-synaptic neurons, and the synaptic storage device adopts a weight sharing compression storage mode and a scene-based storage space sharing mechanism. Flexible configuration of the neural network topology structure can be supported, and the storage space of the neural network topology structure can be efficiently utilized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
Devices, apparatus and method for providing photostimulation and imaging of structures
According to exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, it is possible to provide method, system, arrangement, computer-accessible medium and device to stimulate individual neurons in brain slices in any arbitrary spatio-temporal pattern, using two-photon uncaging of photo-sensitive compounds such as MNI-glutamate and / or RuBi-Glutamate with beam multiplexing. Such exemplary method and device can have single-cell and three-dimensional precision. For example, by sequentially stimulating up to a thousand potential presynaptic neurons, it is possible to generate detailed functional maps of inputs to a cell. In addition, it is possible to combine this exemplary approach with two-photon calcium imaging in an all-optical method to image and manipulate circuit activity. Further exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure can include a light-weight, compact portable device providing for uses in a wide variety of applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Neuromorphic devices including post-synaptic neurons having at least one of integrators, amplifiers, or sampling elements
InactiveUS20170193358A1Prevent and minimize occurrenceNeural architecturesPhysical realisationSynapseNeuron
A neuromorphic device may include: a pre-synaptic neuron; a row line electrically coupled to the pre-synaptic neuron; a post-synaptic neuron; a column line electrically coupled to the post-synaptic neuron; and a synapse disposed at a cross point between the row line and the column line. The post-synaptic neuron may include: a first integrator electrically coupled to the synapse; a second integrator electrically coupled to the first integrator; and a comparator electrically coupled to the second integrator.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com