Patents
Literature
31 results about "Neuron membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
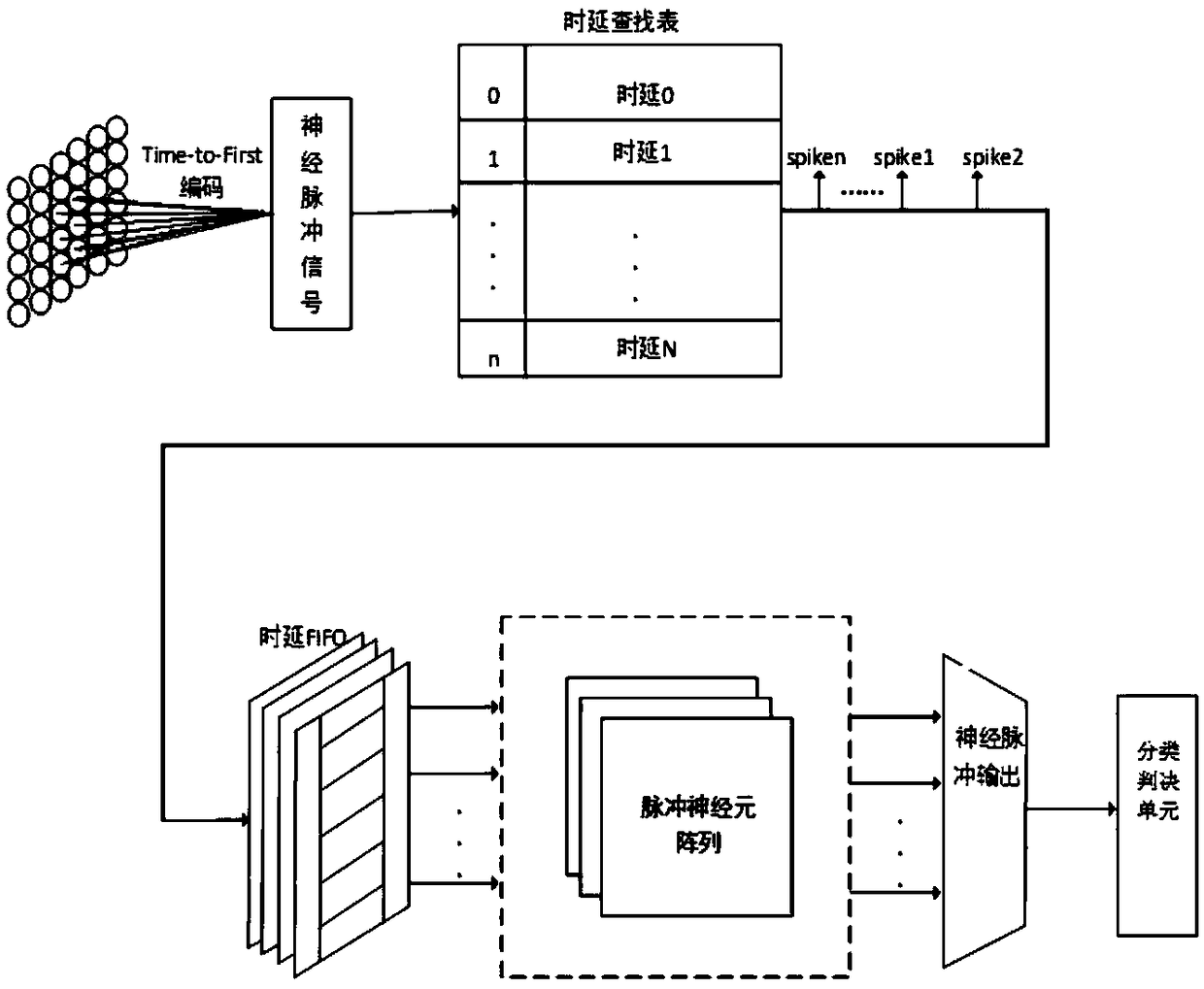
Image classification method and device based on pulse neural network
InactiveCN108846408AStrong computing powerReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesNeuronal modelsClassification methods
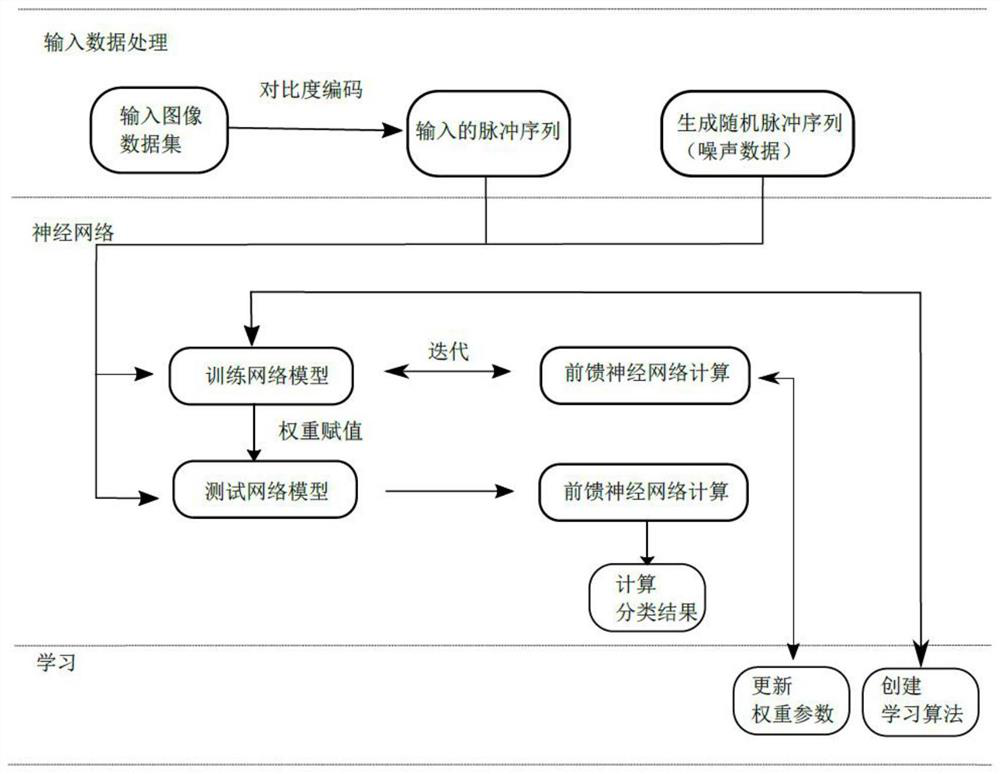
The invention discloses an image classification method based on a pulse neural network. The method comprises a step of encoding an externally input image analog quantity into a pulse time series, a step of adding time delay information to the pulse time series and storing the pulse time sequence with the added time delay information into an FIFO memory for buffering, a step of inputting the pulsetime sequence with the currently added time delay information into an IF pulse neuron model to generate a neuron membrane voltage signal, wherein a pipeline architecture is adopted by the IF pulse neuron model and a neuron model calculation method is optimized, and a step of generating a neural pulse sequence based on a Poisson distribution by comparing the membrane voltage signal and a thresholdand carrying out classification and judgment on the membrane voltage signal. According to the image classification method, the pulse neural network has powerful computing power and can simulate various neuron signals and arbitrary continuous functions, the operation efficiency is high, and so the pulse neural network has a hardware realization value.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Spiking neural network simulator for image and video processing
ActiveUS9984326B1Reduce the burden onCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAlgorithmSpiking neural network
Described is system for simulating spiking neural networks for image and video processing. The system processes an image with a spiking neural network simulator having a plurality of inter-connected modules. Each module comprises a plurality of neuron elements. Processing the image further comprises performing a neuron state update for each module, that includes aggregating input spikes and updating neuron membrane potentials, and performing spike propagation for each module, which includes transferring spikes generated in a current time step. Finally, an analysis result is output.
Owner:HRL LAB
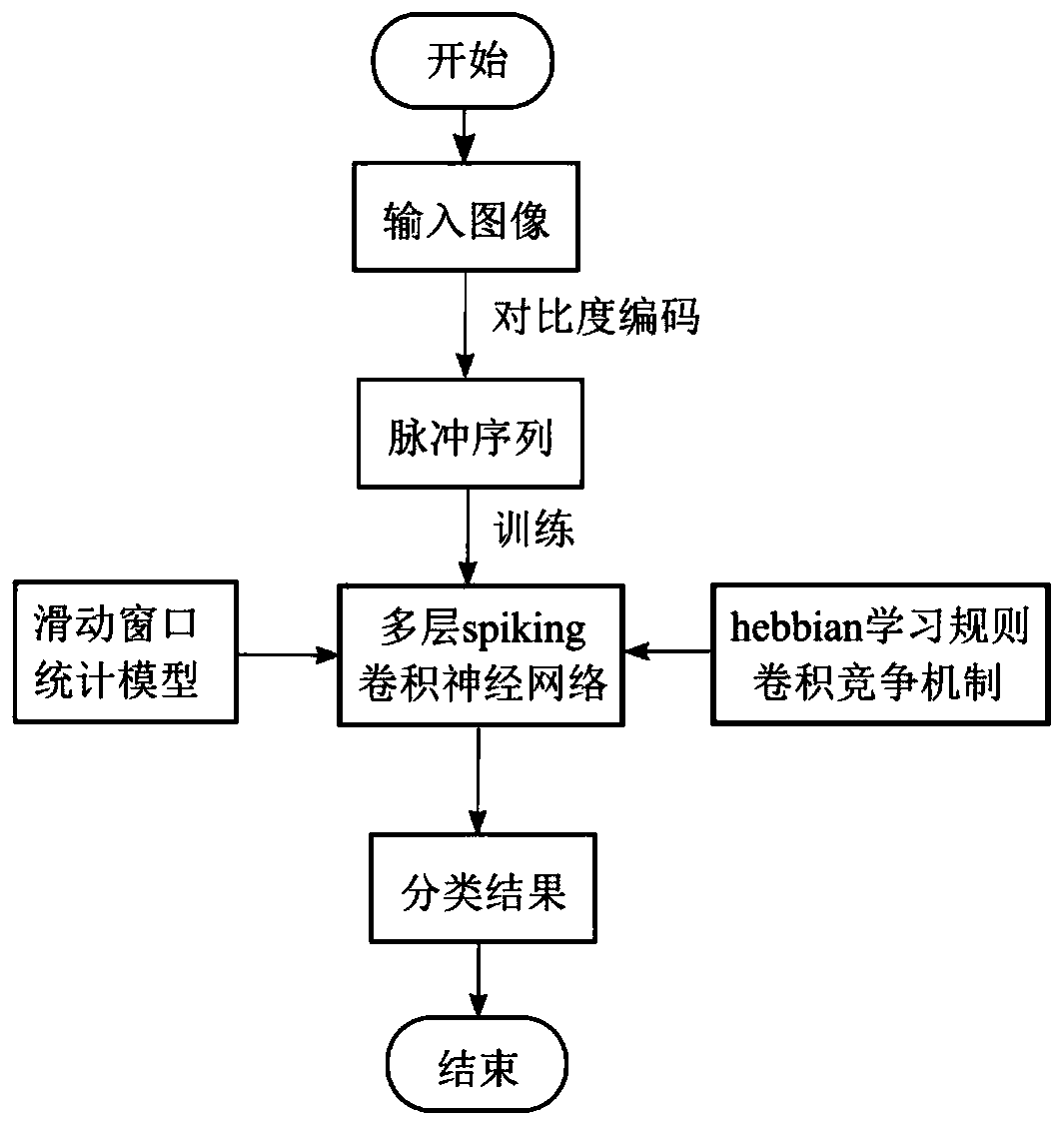
Image classification method based on multi-layer spring convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110119785AReduce the number of pulsesReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionClassification methods
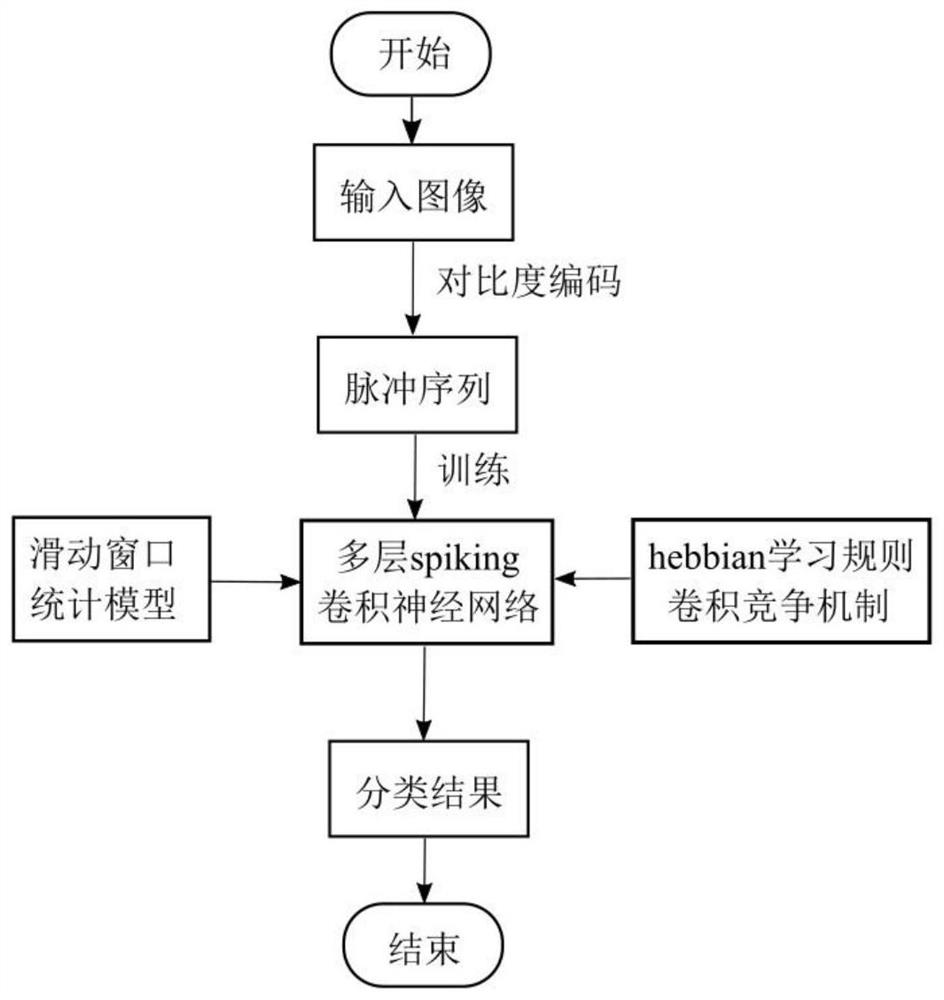
The invention discloses an image classification method based on a multilayer spring convolutional neural network, and relates to the field of image processing, and the method comprises the steps: converting images in a training set into pulse sequences; setting a spring neuron parameter, and constructing a convolutional neural network by using a spring neuron; taking the pulse sequence as input, training the convolutional neural network layer by layer, obtaining visual features of the pulse sequence, and obtaining a classification result, the training method being an unsupervised learning algorithm based on a Hebbian rule; converting the to-be-identified image into a pulse sequence, and inputting the pulse sequence into the trained convolutional neural network to obtain a classification result of the to-be-identified image. The technical problem of sparking neuron membrane voltage redundancy calculation caused by increased neuron scale is solved, and meanwhile, the technical problem oflearning non-convergence caused by the fact that an SNN activation function cannot be derived and a back-propagation calculation residual error cannot be used is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
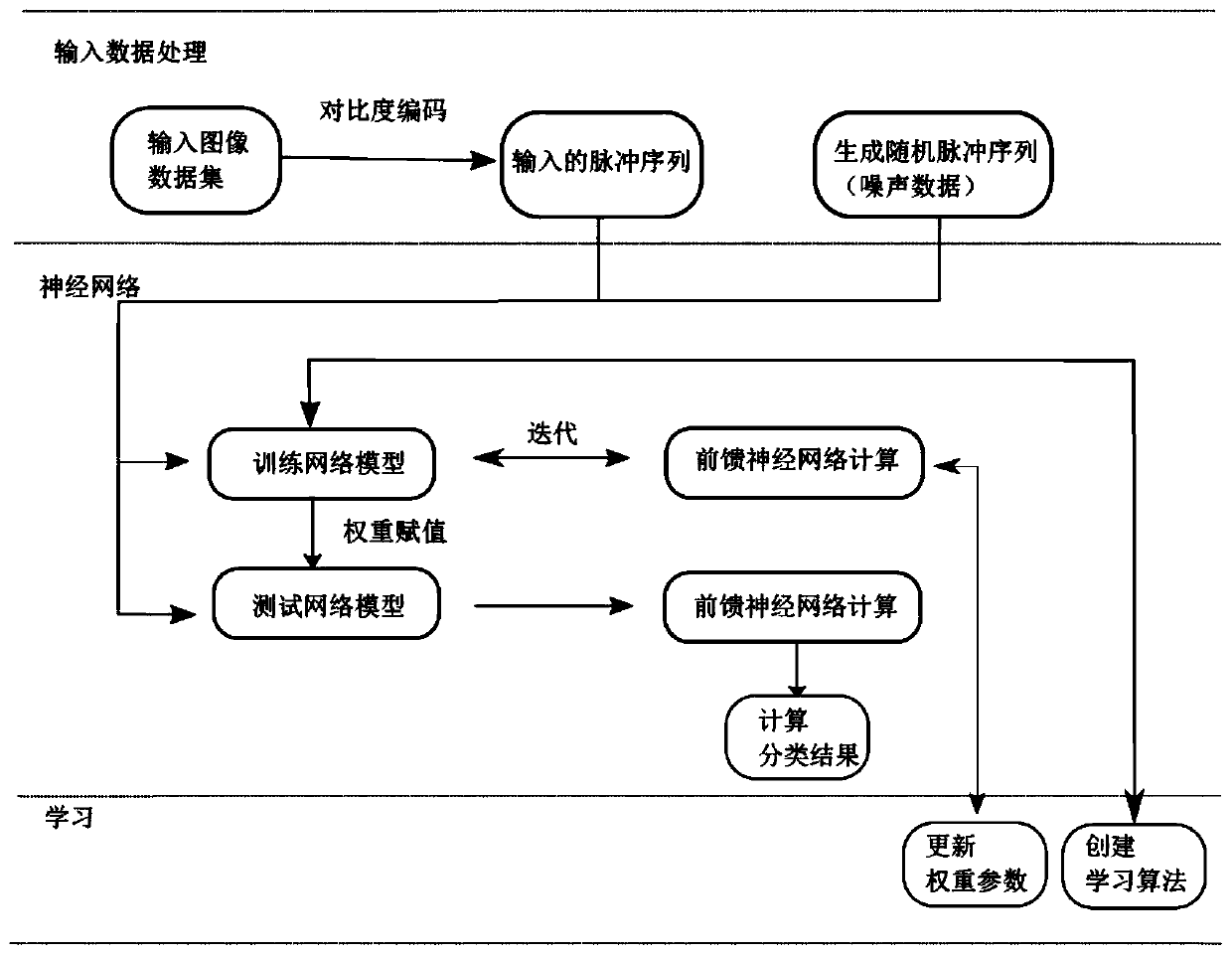
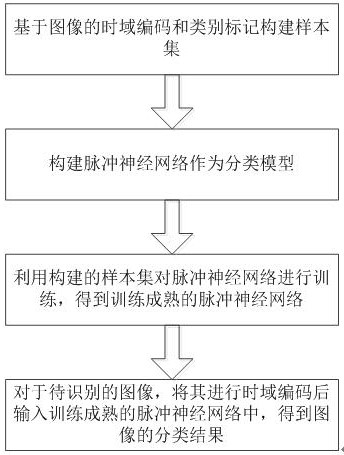
Image classification method based on time domain coding and pulse neural network
PendingCN112906828AReduce training difficultyReduce power consumptionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesTime domainClassification methods
The invention discloses an image classification method based on time domain coding and a pulse neural network. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a sample set based on time domain coding and category marking of an image; s2, constructing a pulse neural network as a classification model; s3, training the spiking neural network by using the constructed sample set to obtain a maturely trained spiking neural network; and S4, carrying out time domain coding on an image to be identified, and inputting the image to the maturely trained pulse neural network to obtain a classification result of the image. According to the invention, through a direct training framework which does not need to calculate neuron membrane potential, the training difficulty of the spiking neural network is reduced, and then real-time low-power-consumption image recognition and classification are effectively realized.
Owner:周士博
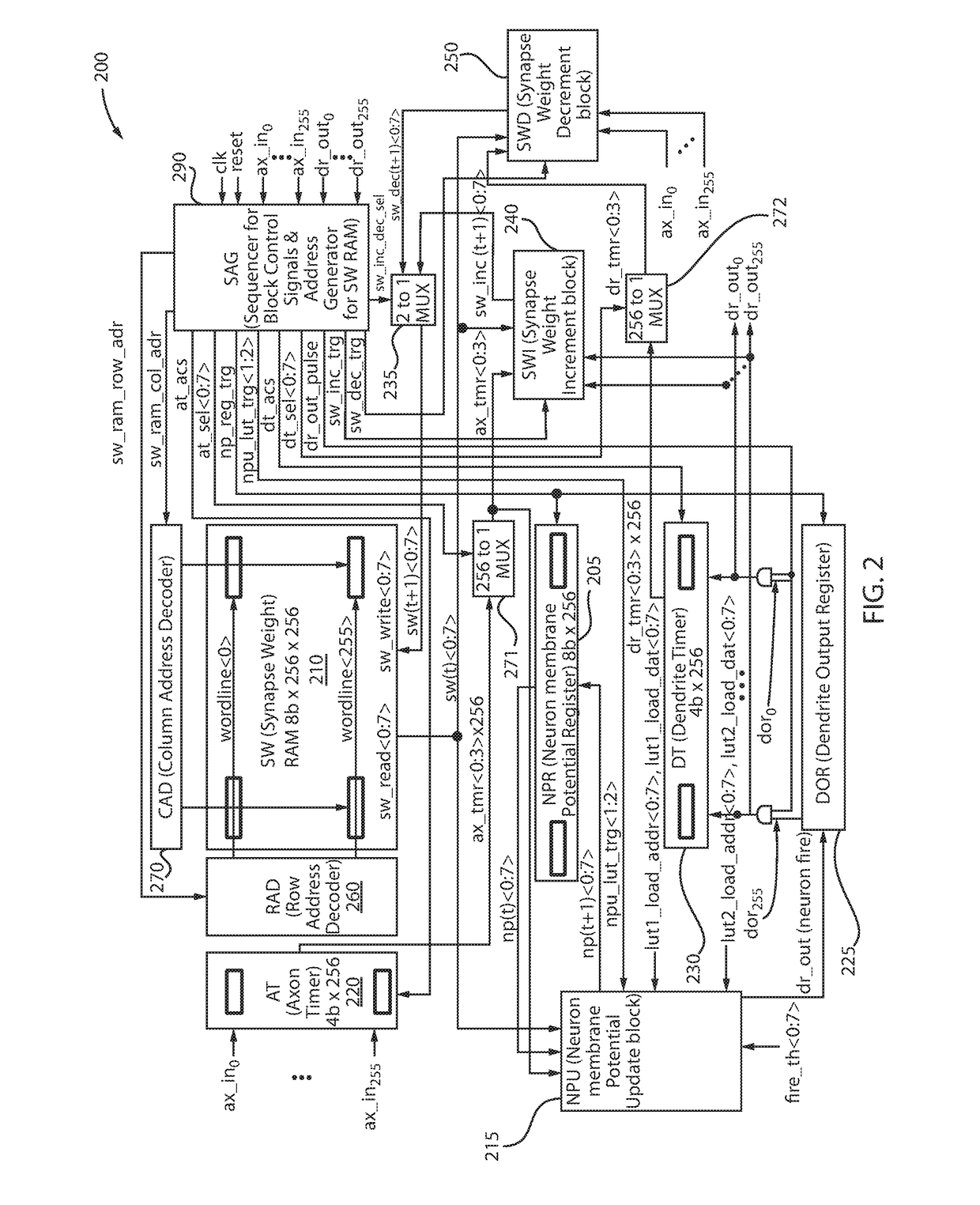
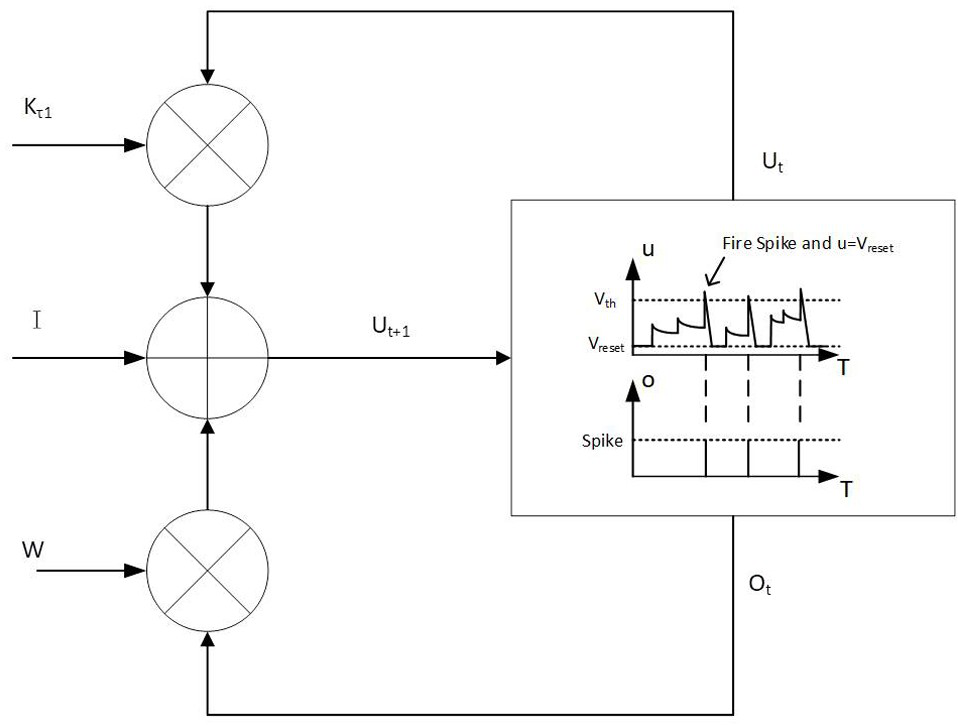
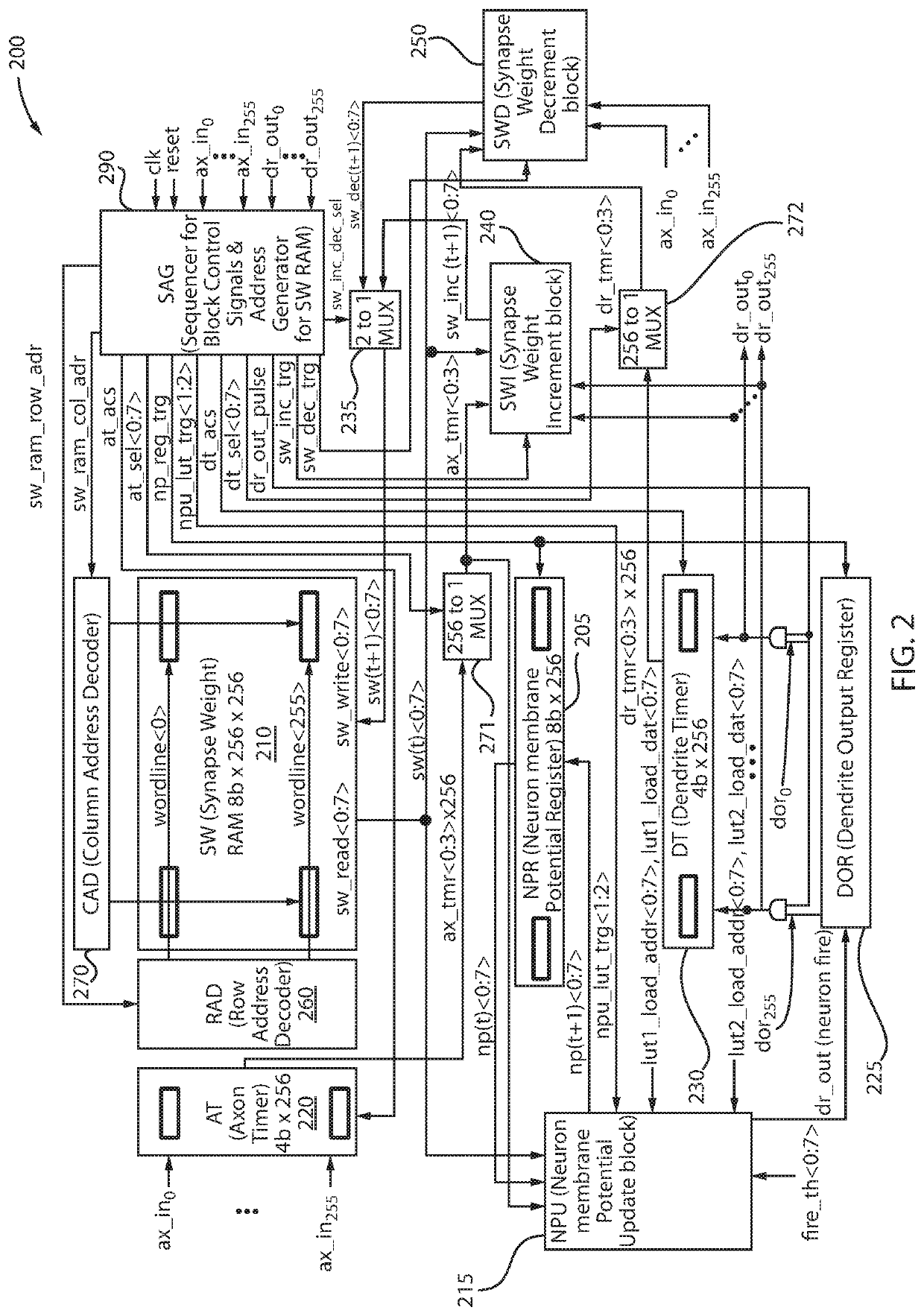
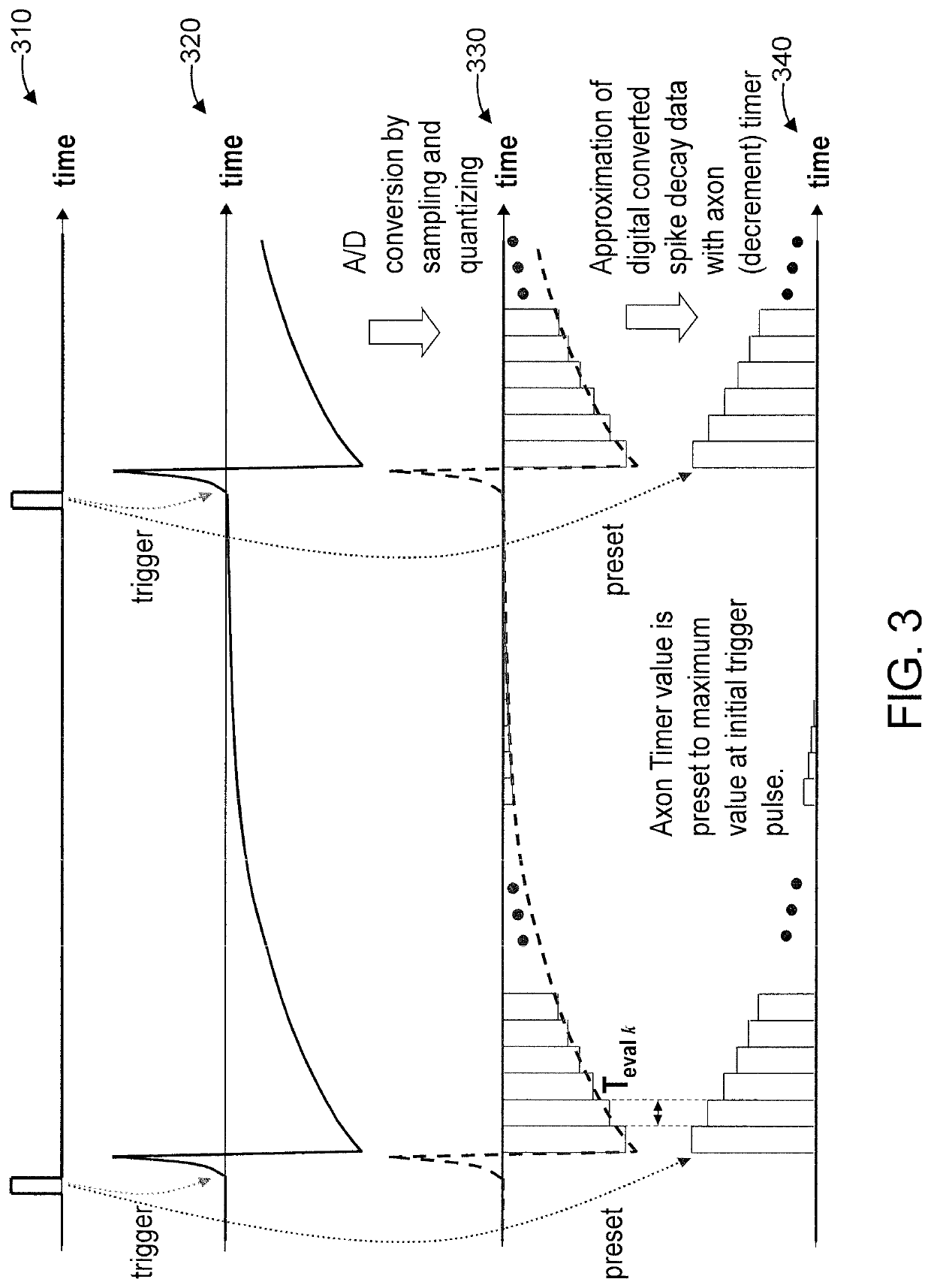
Lut based neuron membrane potential update scheme in stdp neuromorphic systems
ActiveUS20170185891A1Neural architecturesPhysical realisationSpike-timing-dependent plasticityArtificial intelligence
A method and system are provided for updating a neuron membrane potential in a spike time dependent plasticity model in a Neuromorphic system. The method includes approximating a shape of an analog spike signal from an axon input using a hardware-based digital axon timer. The method further includes generating a first intermediately updated neuron membrane potential value from a current axon timer value, a current synapse weight value and a current neuron membrane potential value using a first look-up table and an accumulator. The method also includes generating a second intermediately updated neuron membrane potential value with a leak decay effect using a second look-up table and the first intermediately updated neuron membrane potential value. The method additionally includes generating a final updated neuron membrane potential value based on a comparison of the second intermediately updated neuron membrane potential value with a neuron fire threshold level using a comparator.
Owner:IBM CORP
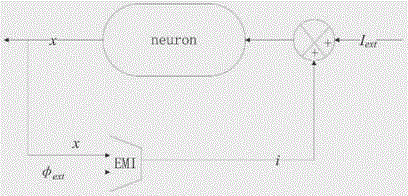
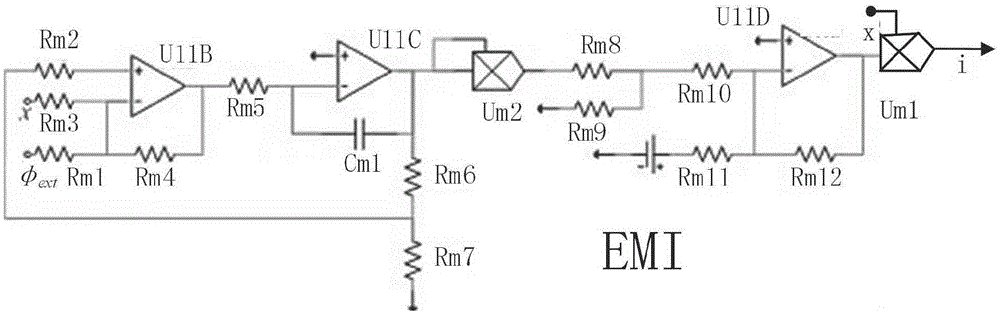
Neuron electrical activity simulator under electromagnetic radiation
InactiveCN105426957AGuarantee the regularity of electrical activityPhysical realisationMemory effectCell membrane
The invention provides a neuron electrical activity simulator under electromagnetic radiation. The neuron electrical activity simulator includes a neuron circuit, and is characterized in that the simulator also includes an electromagnetic radiation effect circuit and an adder, an input end of the electromagnetic radiation effect circuit is connected with an output end of the neuron circuit and equivalent outside magnetic flux, so as to input neuron response, i.e., membrane potential x and equivalent outside magnetic flux phi<ext>, an output end of the electromagnetic radiation effect circuit is connected with the adder, after an output electromagnetic radiation effect i of the electromagnetic radiation effect circuit to a neuron and an ionic current I<ext> that flows into a neuron cell membrane are summed through the adder, an input end of the neuron circuit is accessed, and after entering a stable operation state, the neuron electrical activity simulator outputs neuron response, i.e., membrane potential, which contains an electromagnetic memory effect. The neuron electrical activity simulator under electromagnetic radiation considers the electromagnetic memory effect of neuron membrane potential discharge, and guarantees the neuron electrical activity law.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Neuron circuit
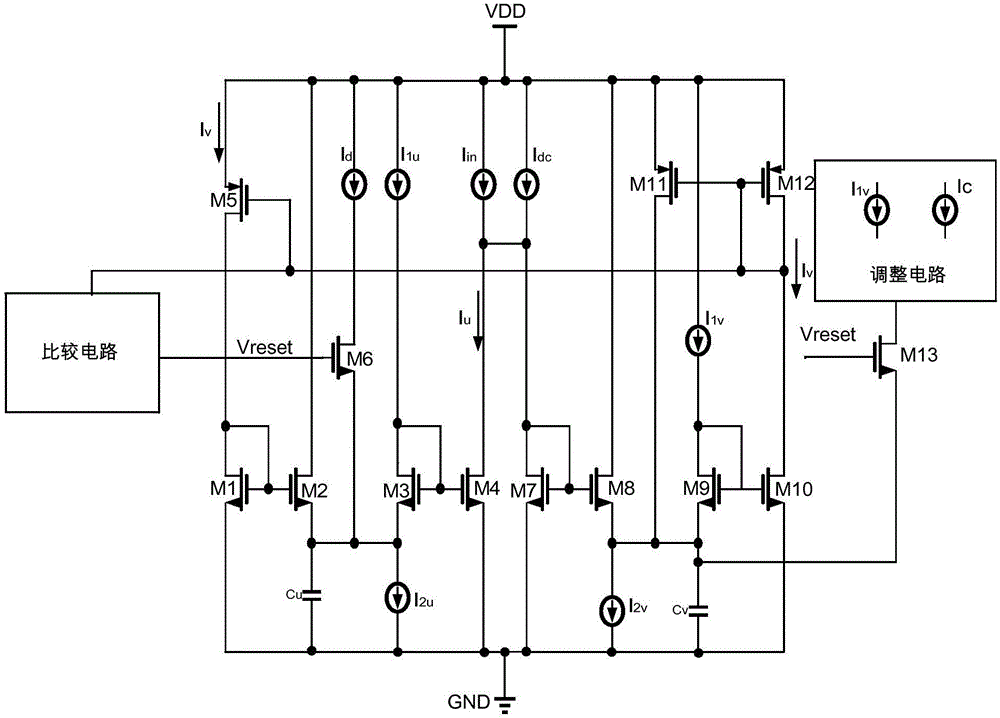
ActiveCN106250983ASimple structureReduce power consumptionPhysical realisationCapacitanceHemt circuits
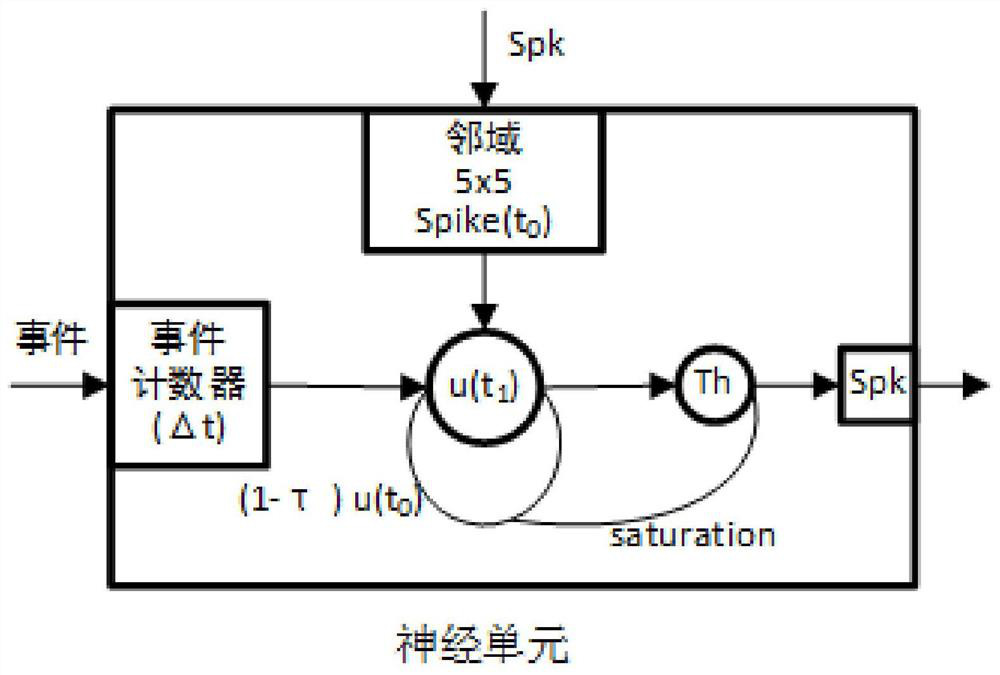
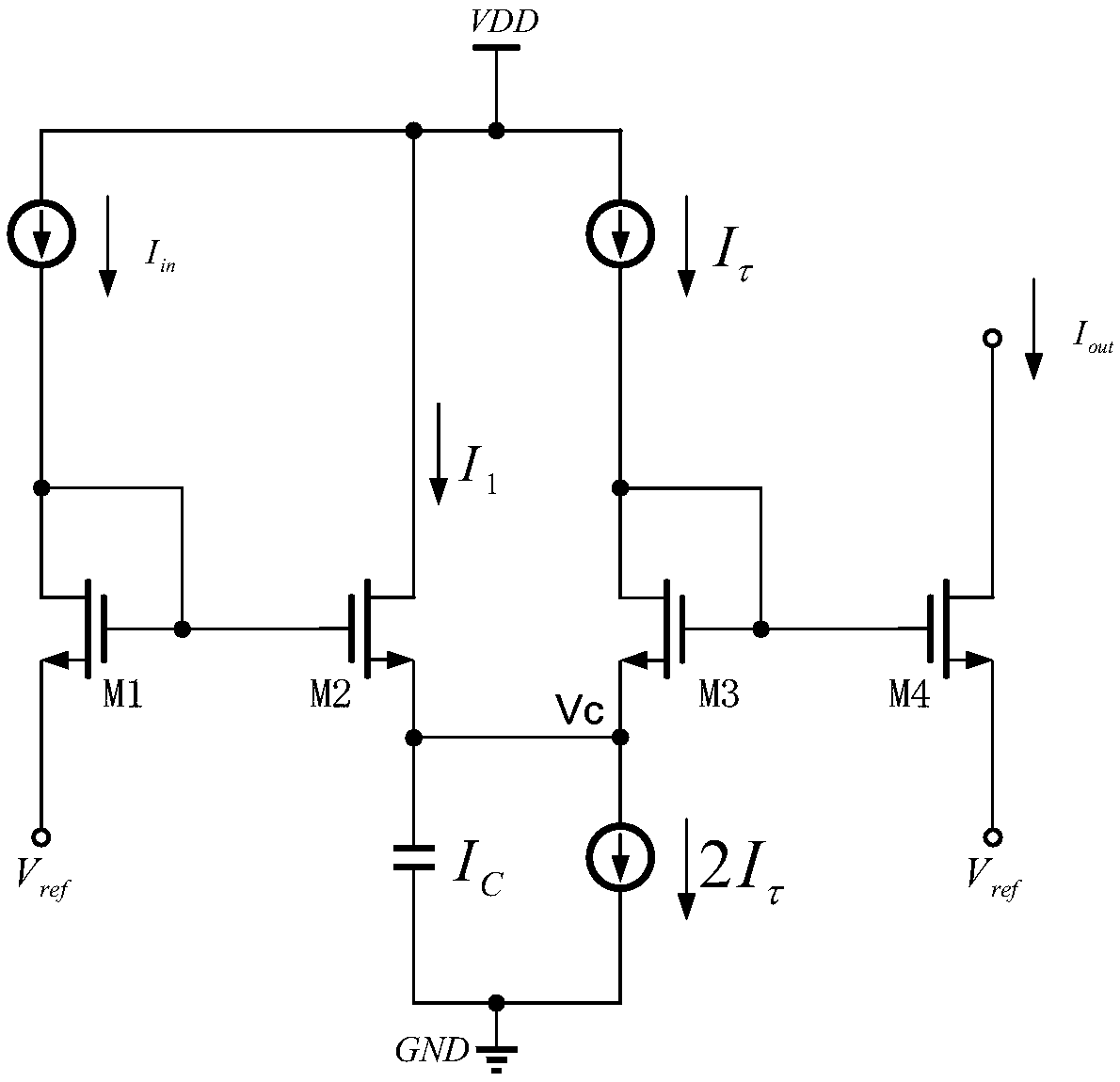
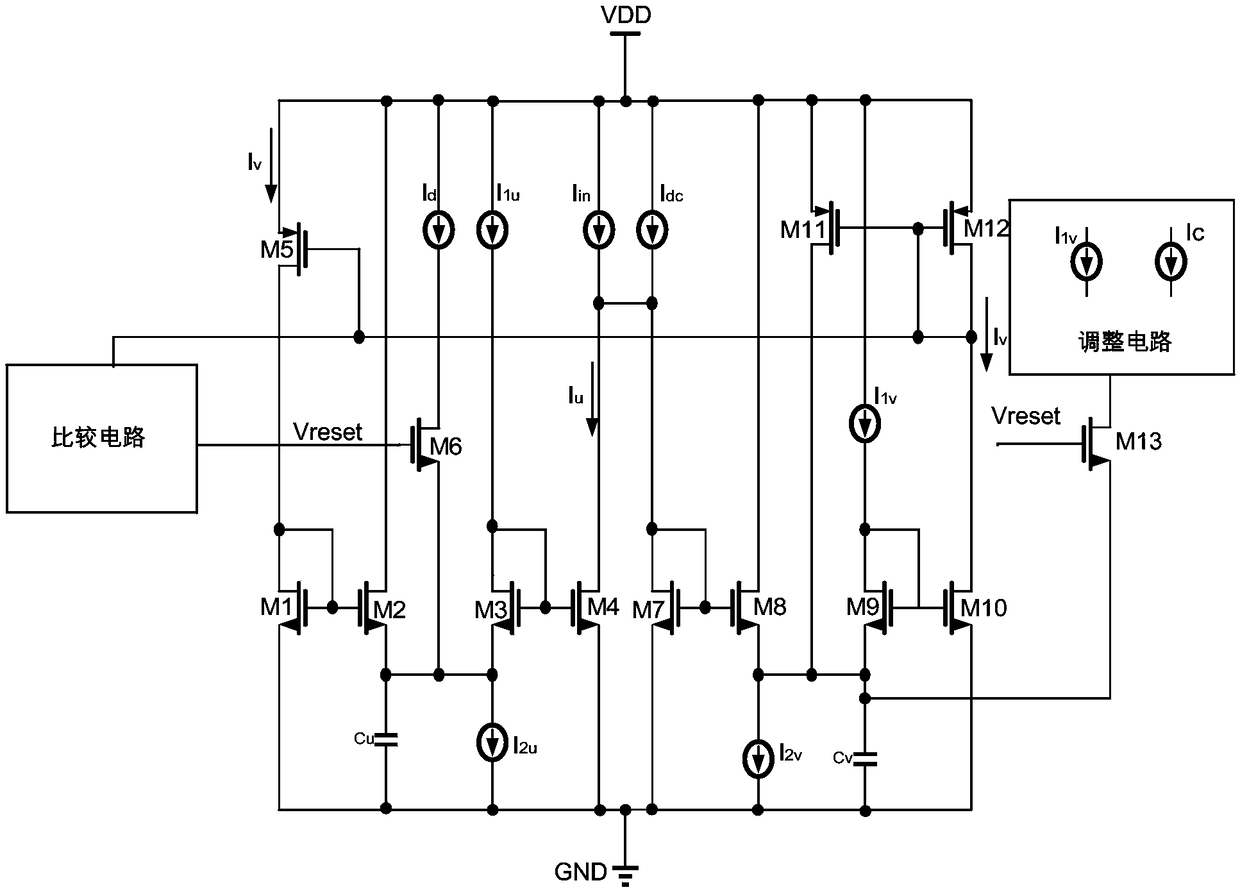
The invention discloses a neuron circuit which comprises a pulse generation circuit, an adjustment circuit, and a comparison circuit. The pulse generation circuit is configured to simulate nerve impulse oscillation through a first Tau-cell circuit structure and a second Tau-cell circuit structure, the first Tau-cell circuit structure includes a first capacitor Cv used for simulating a neuron membrane potential v, and the second Tau-cell circuit structure includes a second capacitor Cu used for simulating a neuron membrane potential adjustment variable u. The adjustment circuit is connected with the pulse generation circuit, and is used for reassigning a value to the neuron membrane potential v. The comparison circuit is connected with the pulse generation circuit, and is used for reassigning a value to the neuron membrane potential adjustment variable u. The power consumption of the neuron circuit can be lowered, and the occupied area of the neuron circuit can be reduced.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
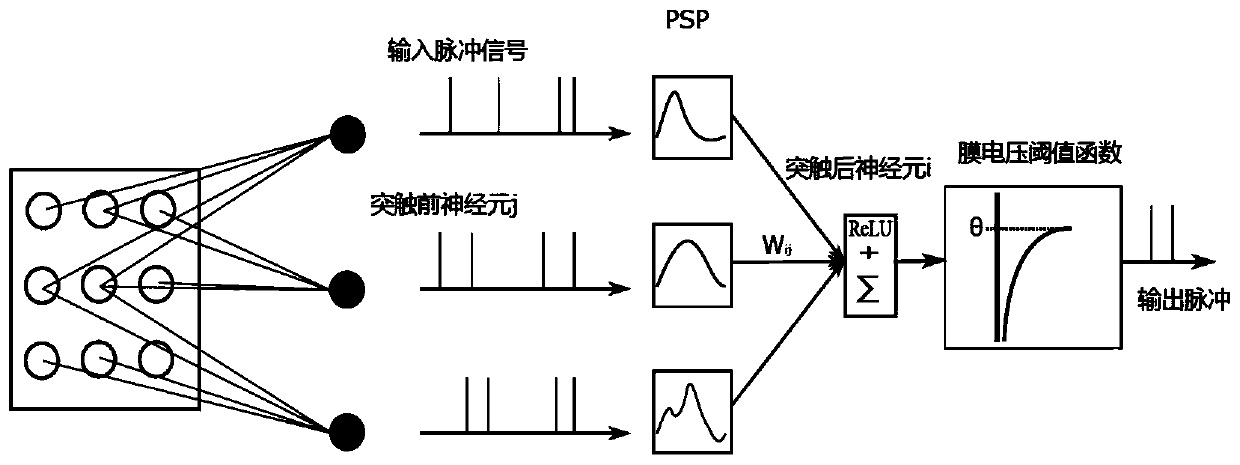
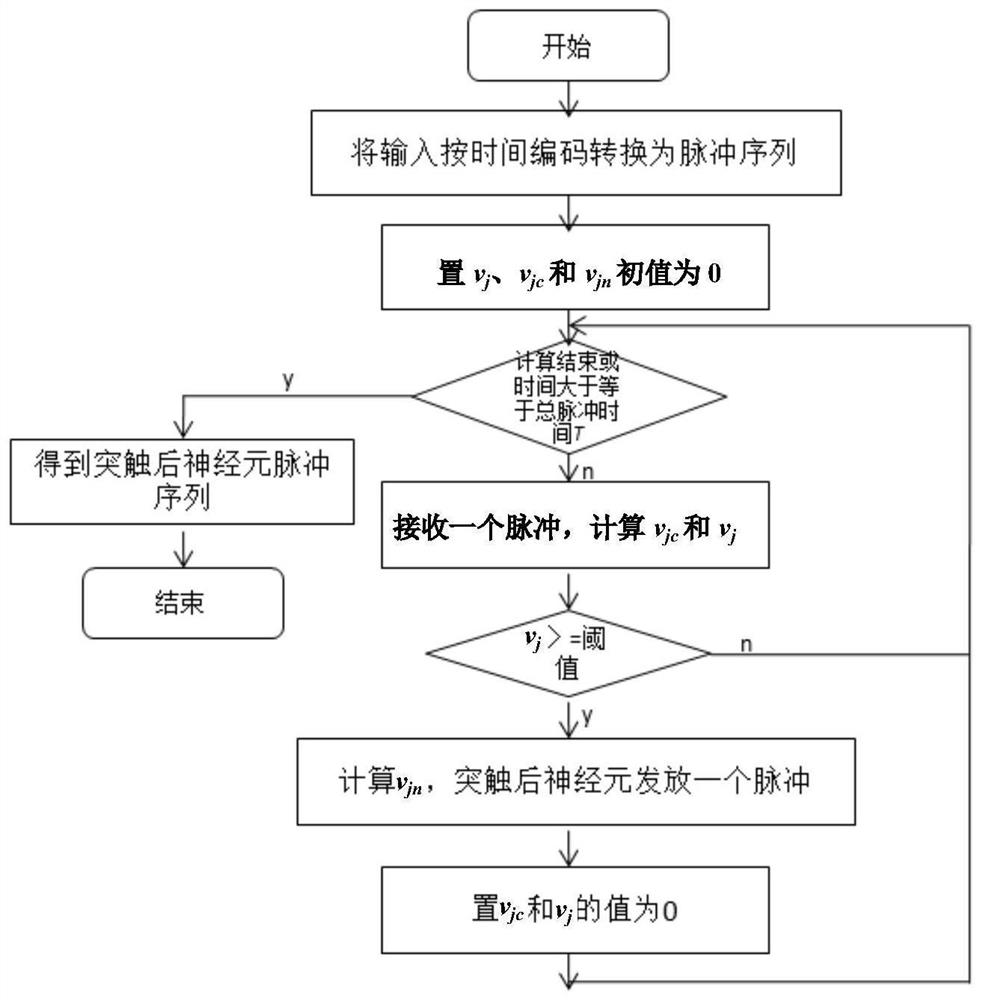
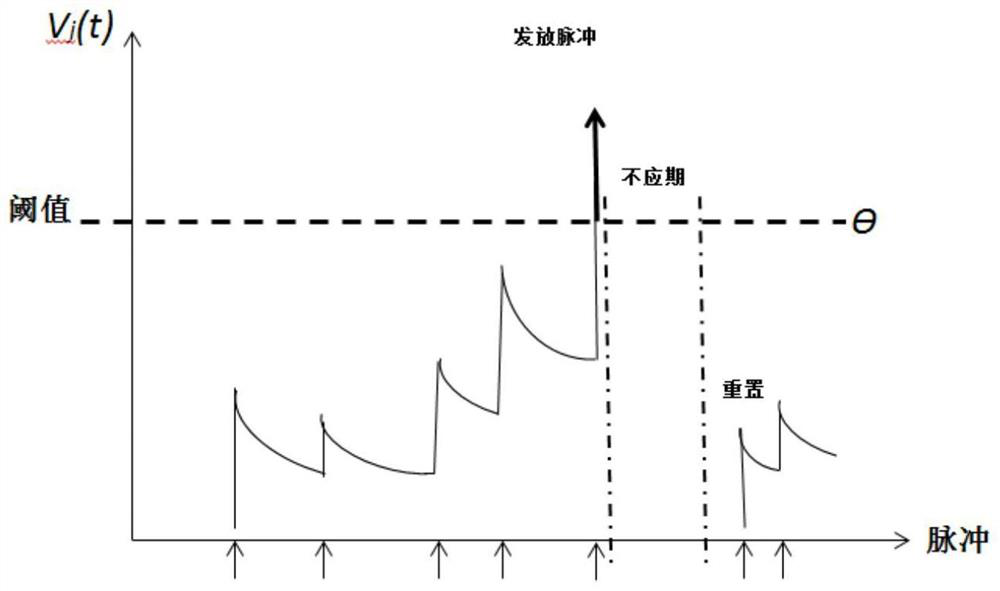
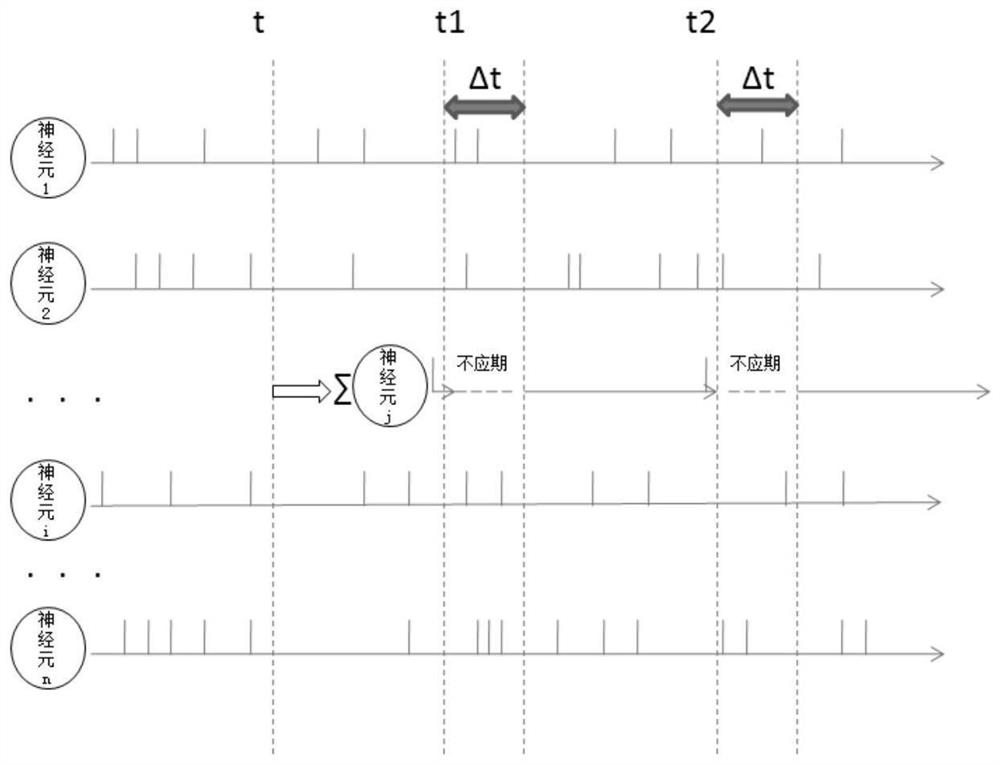
Pulse neural network neuron membrane voltage calculation method
PendingCN114239405ASolve the lossMake up for the lossDesign optimisation/simulationImaging processingImage manipulation
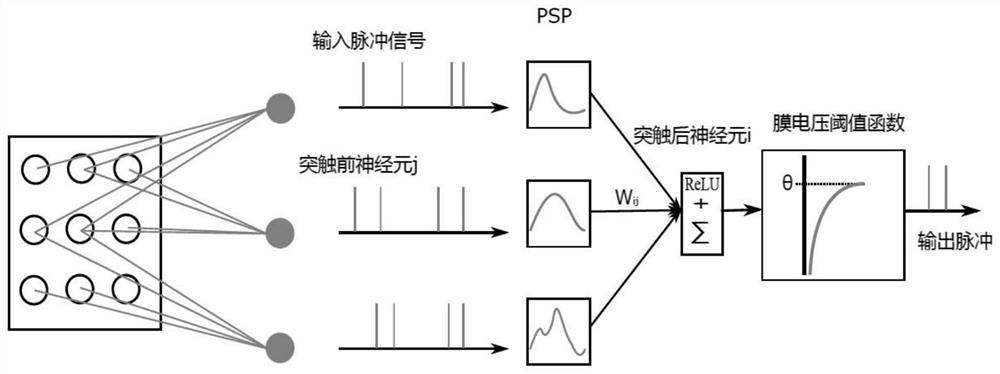
The invention provides a method for calculating neuron membrane voltage of a spiking neural network, and relates to the technical field of spiking neural networks, and the method comprises the steps: firstly, converting an input signal into a pulse sequence through employing a time coding method, selecting a Spike Response Model neuron model as a membrane voltage calculation model of a neuron non-nonstress time period of the spiking neural network, and carrying out the calculation of the membrane voltage of the spiking neural network; then establishing a membrane voltage model generated by pulse accumulation of the pre-synaptic neurons in the post-synaptic neuron non-stress period, and finally establishing a pulse neural network neuron membrane voltage calculation model to realize calculation of the post-synaptic neuron membrane voltage; according to the method, the accumulation of neuron input pulses before the non-stress period highlights is calculated, the loss of input information is made up, the method is applied to image processing, the loss of information is reduced, and the utilization rate of the input information is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
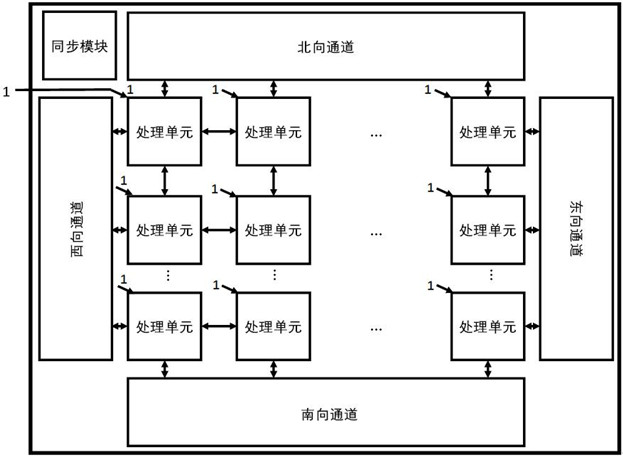
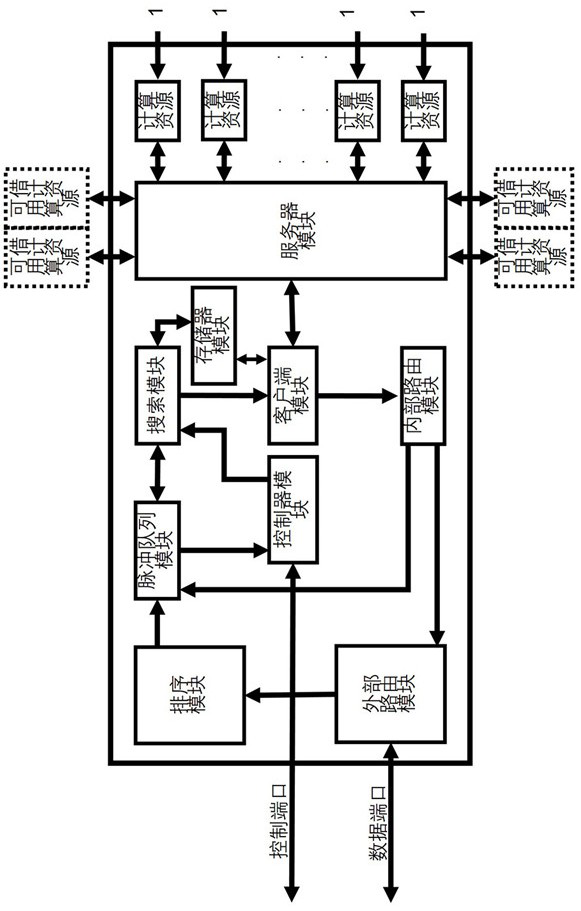
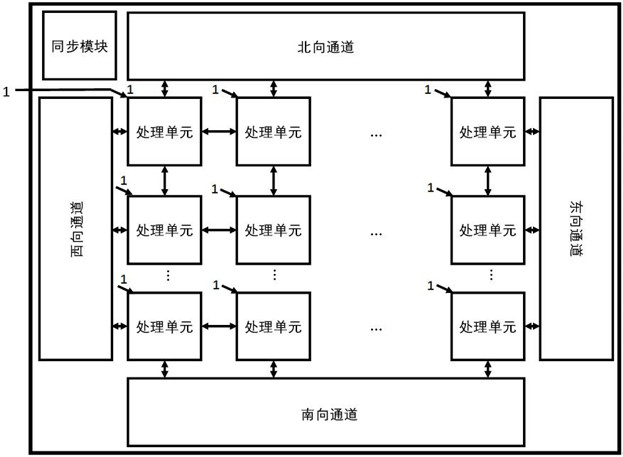
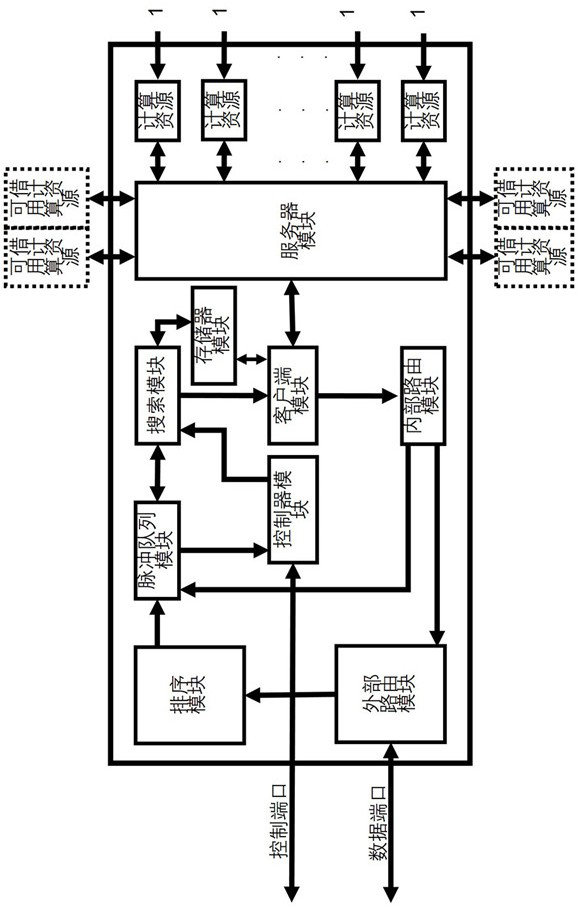
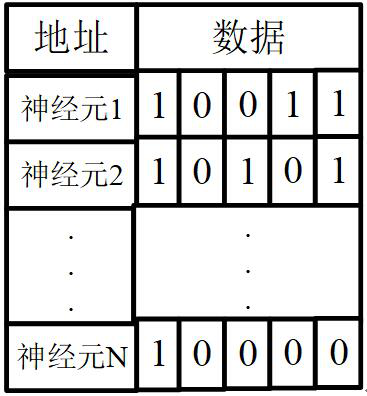
Reconfigurable autonomous learning spiking neural network processor
ActiveCN112016680ATake advantage ofHigh speedNeural architecturesPhysical realisationComputer architectureSynaptic weight
The invention provides a reconfigurable autonomous learning spiking neural network processor. The reconfigurable autonomous learning spiking neural network processor comprises a processing unit arraycomposed of a plurality of processing units and channels in the east, south, west and north directions. Each processing unit comprises an external routing module, a sequencing module, a pulse queue module, a controller module, a search module, a memory module, a client module, a server module, an internal routing module, a plurality of exclusive computing resources and a plurality of borrowable computing resources. The processor adopts a pulse packet composed of pulse generation time and a source neuron ID to transmit signals; the computing executing modes of the computing resources include aninference mode and a learning mode, and a target neuron membrane potential, a synaptic weight related variable or a synaptic weight is updated by adopting a reconfigurable circuit; the computing resources comprise a self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module, and according to the updating time interval, the computing mode that the computing unit executes updating computing is changed in a self-adaptive mode.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Digitial stdp synapse and lif neuron-based neuromorphic system
ActiveUS20190354845A1Neural architecturesPhysical realisationSynaptic weightSpike-timing-dependent plasticity
Described is a neuromorphic system implemented in hardware that implements neuron membrane potential update based on the leaky integrate and fire (LIF) model. The system further models synapse weights update based on the spike time-dependent plasticity (STDP) model. The system includes an artificial neural network in which the update scheme of neuron membrane potential and synapse weight are effectively defined and implemented.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
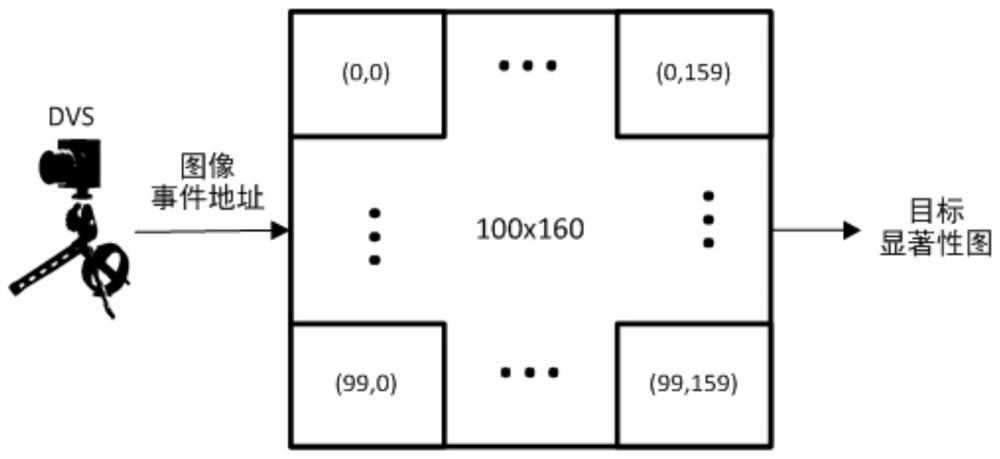
Saliency map generation system, method and device based on dynamic vision sensor
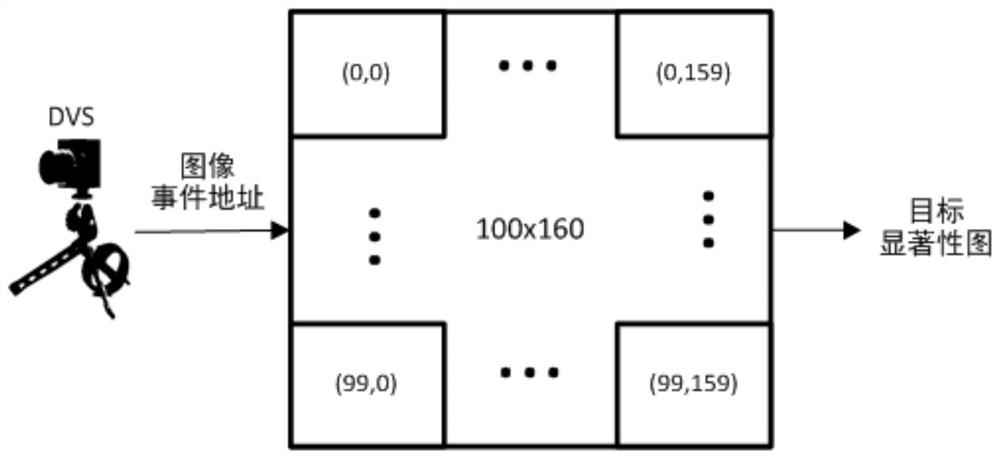
ActiveCN112215912AReduce noiseExclude background information2D-image generationNeural architecturesActivation functionSaliency map
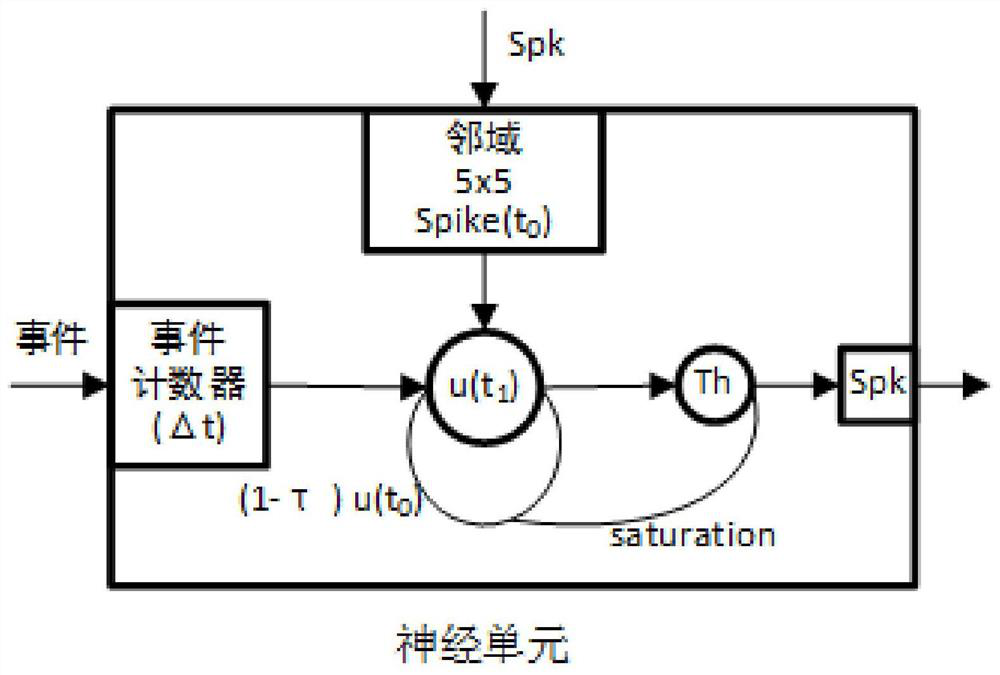
The invention belongs to the field of data processing, particularly relates to a saliency map generation system, method and device based on a dynamic vision sensor, and aims to solve the problems. Themethod comprises the following steps: acquiring event data through a dynamic vision sensor, accumulating and caching DVS event data and information acquired from mutually associated neurons through each neuron in a target detection network, acquiring a neuron membrane potential through an activation function every other preset time, and outputting a pulse signal according to the size relationshipbetween the neuron membrane potential and a preset saturation threshold; accumulating the membrane potential u (t0) at the previous moment with the currently received excitation through attenuation,and using the result for updating and judging the pulse signal and the membrane potential. According to the invention, redundant background information of the saliency map generated by the target detection network array is eliminated, the credibility and accuracy of target detection are improved, and misjudgment is avoided.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
FMRI signal noise based processing method
InactiveCN103892832AEliminate the effects ofThe result is accurateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFrequency spectrumSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses an FMRI signal noise processing method, in particular to a thermal noise processing method. The method has the advantages that a noise value of Gaussian white noise in nerve cells, affecting neuron membrane potential and energy function, is measured, and the signal-to-noise ratio of neural signals to Gaussian white noise in nerve cells is further calculated; accordingly, FMRI signals can be subjected to spectral analysis, the influence of white noise upon the FMRI signals is eliminated, and more accurate results are obtained.
Owner:XINCHANG GUANYANG TECH DEV
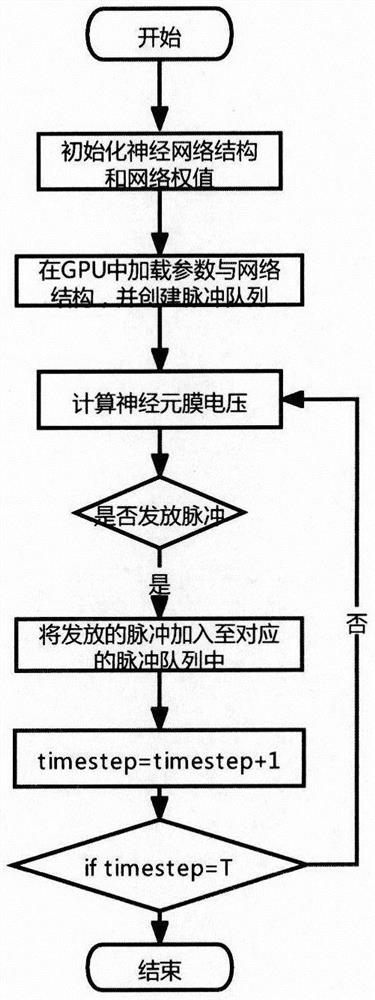
Pulse neural network simulation method based on GPU
PendingCN114186665ASave time and costPrevent invalid operationResource allocationNeural architecturesVideo memoryData set
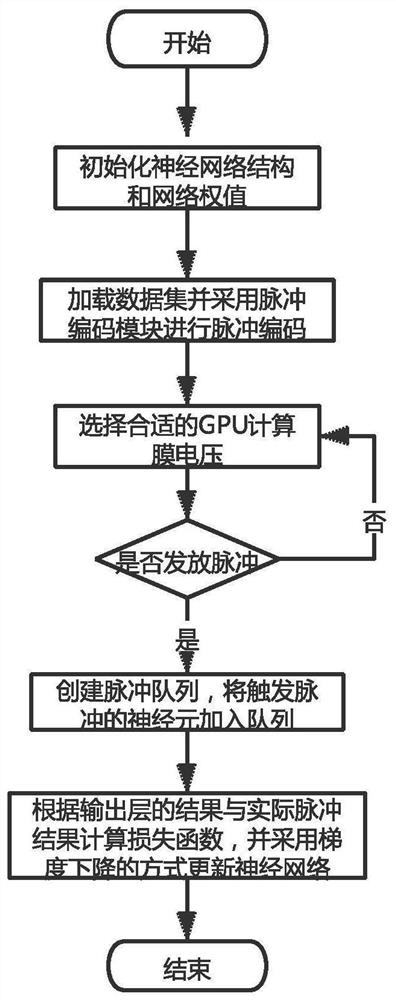
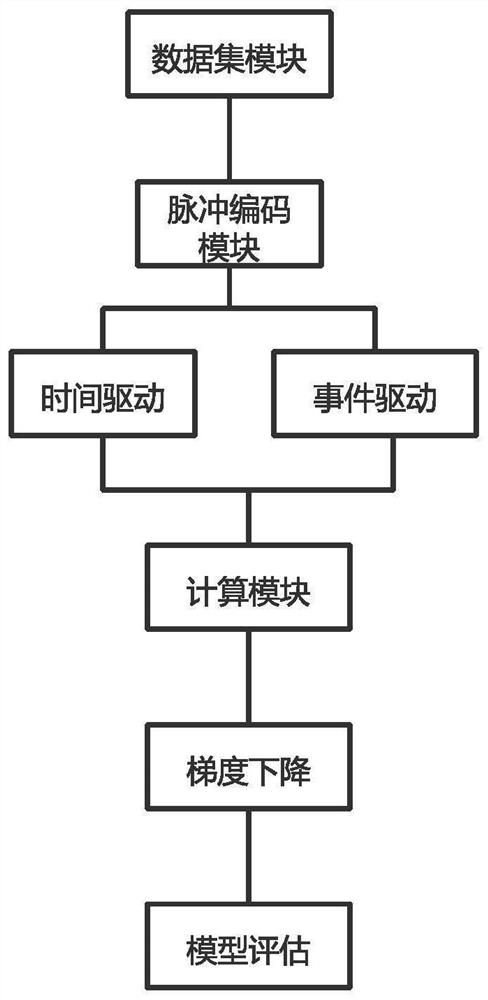
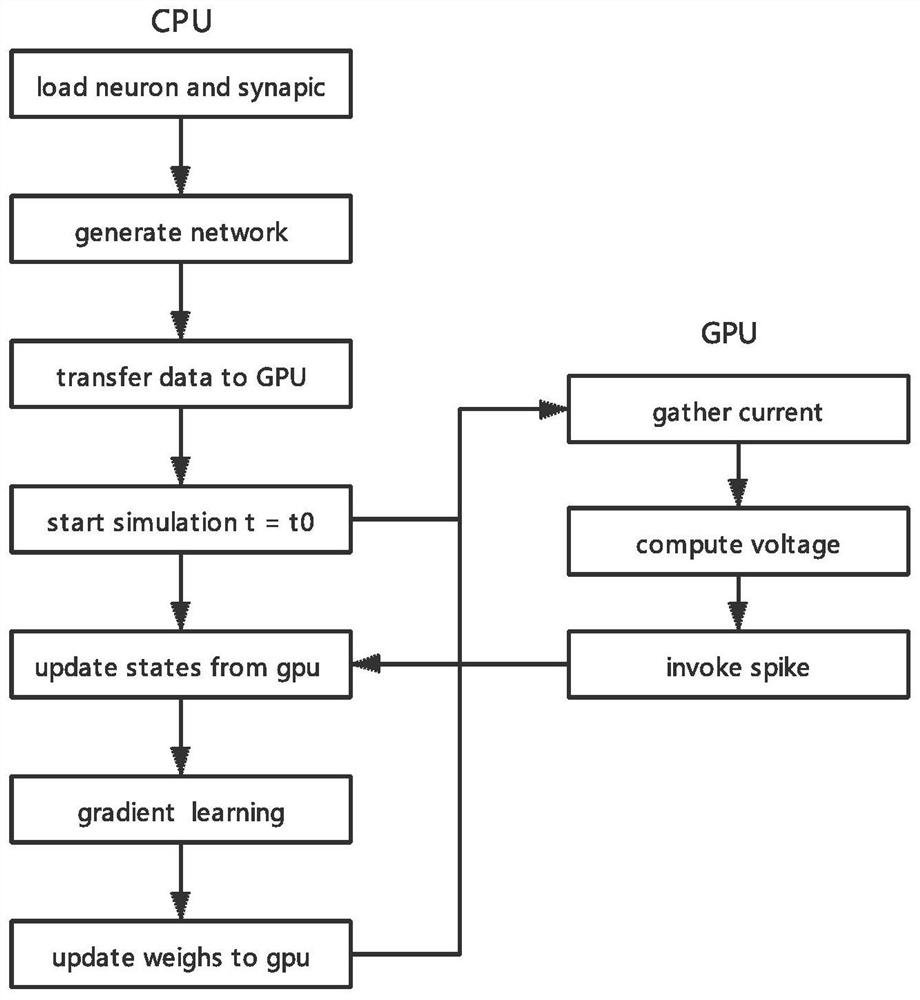
The invention discloses a GPU-based spiking neural network simulation method. The method comprises the steps of initializing a neural network structure and a network weight; loading a data set and carrying out pulse coding by adopting a pulse coding module; calling a GPU calculation module to select a proper GPU to calculate the pulse neuron membrane voltage according to the data volume, the calculation amount and the priority of the calculation task, comparing whether the pulse neuron membrane voltage exceeds a threshold value or not, and issuing a pulse; creating a pulse queue, and adding neurons of a trigger pulse into the pulse queue; if the pulse queue is not empty, finding out a post-synaptic neuron corresponding to the next layer according to the network structure, and repeating the steps S3-S5 until an output layer is reached; and calculating a loss function according to the result of the output layer and the actual pulse result, and updating the neural network by adopting a gradient descent mode until the iteration is completed. According to the invention, the training speed of the spiking neural network is accelerated, the advantages of the spiking neural network in the aspects of low power consumption and low time delay are exerted, and the conditions of overlarge data set, insufficient video memory and incapability of training are avoided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
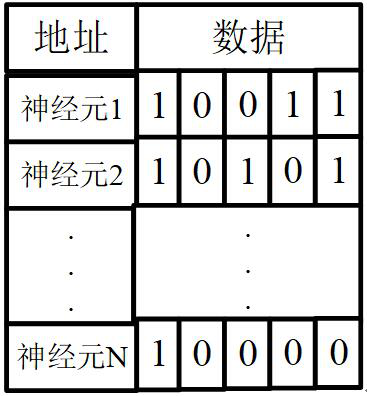
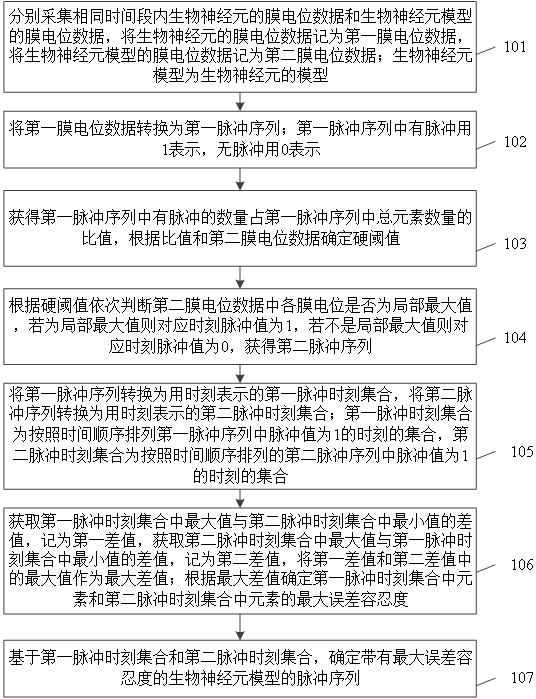
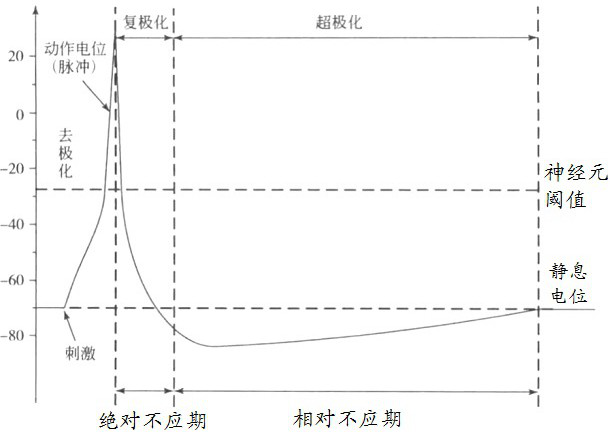
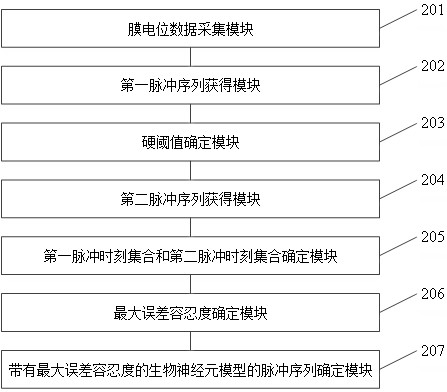
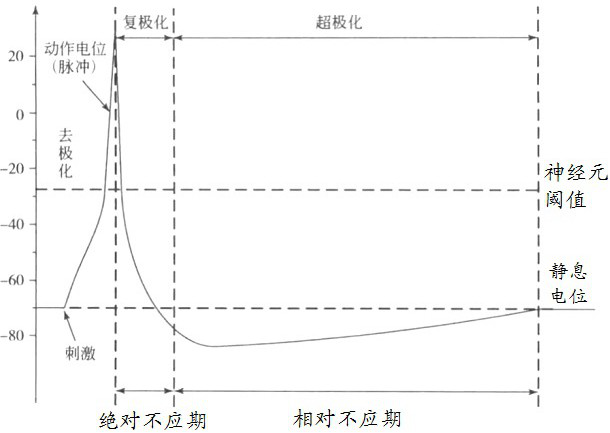
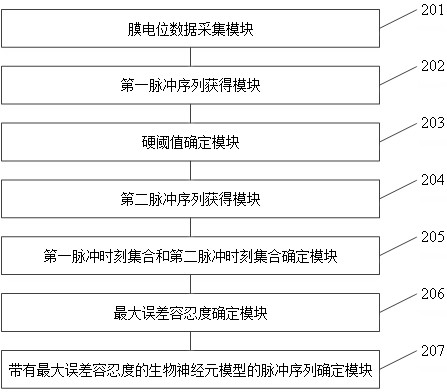
Method and system for converting neuron membrane potential into pulse sequence
ActiveCN114580622AImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNetwork controlPulse sequence
The invention relates to a neuron membrane potential-to-pulse sequence conversion method and system, and belongs to the field of neural network control, and the method comprises the steps: converting membrane potential data of a biological neuron into a pulse sequence, recording the pulse sequence as a first pulse sequence, determining a hard threshold according to the first pulse sequence and second membrane potential data, and recording the hard threshold as a second pulse sequence; converting the membrane potential data of the biological neuron model into a second pulse sequence according to a hard threshold value; converting the first pulse sequence into a first pulse moment set represented by moments, and converting the second pulse sequence into a second pulse moment set represented by moments; determining the maximum error tolerance of elements in the first pulse time set and elements in the second pulse time set according to the first pulse time set and the second pulse time set; and determining a pulse sequence of the biological neuron model with the maximum error tolerance based on the first pulse moment set and the second pulse moment set. The accuracy of converting the membrane potential of the biological neuron model into the pulse sequence is improved.
Owner:中科南京智能技术研究院
A method and system for neuron membrane potential transfer pulse sequence
ActiveCN114580622BImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNetwork controlPulse sequence
The invention relates to a method and a system for converting neuron membrane potential into a pulse sequence, belonging to the field of neural network control. The pulse sequence and the second membrane potential data determine the hard threshold, and according to the hard threshold, the membrane potential data of the biological neuron model is converted into the second pulse sequence; the first pulse sequence is converted into the first pulse moment set represented by the time, and the The second pulse sequence is converted into a second pulse time set represented by time; the maximum error tolerance of the elements in the first pulse time set and the elements in the second pulse time set is determined according to the first pulse time set and the second pulse time set; Based on the first set of pulse times and the second set of pulse times, a pulse sequence of the biological neuron model with maximum error tolerance is determined. The invention improves the accuracy of converting the membrane potential of the biological neuron model into a pulse sequence.
Owner:中科南京智能技术研究院
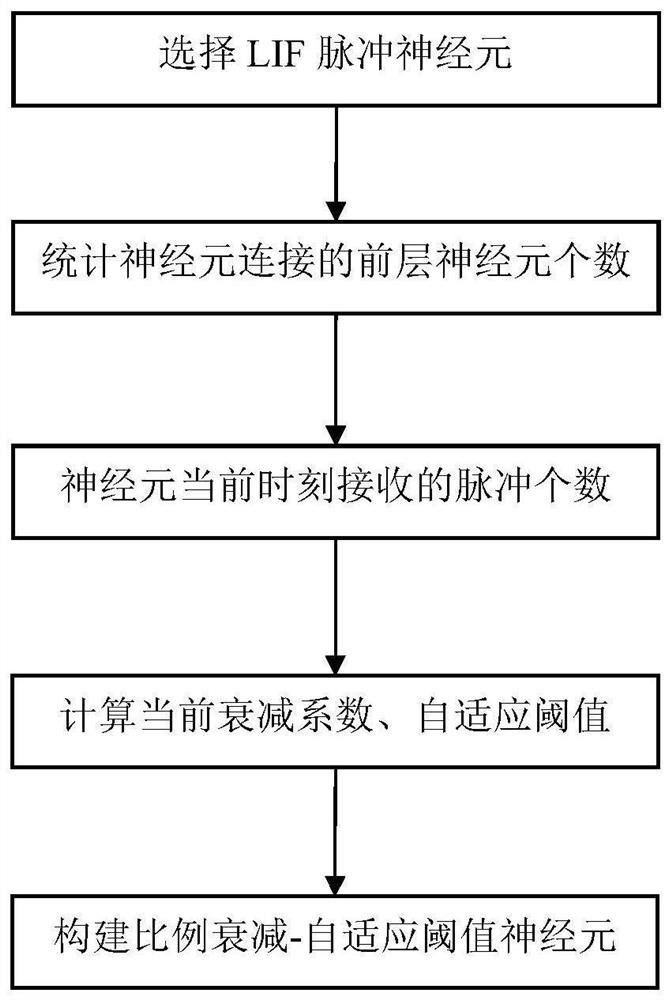
Spiking neural network target identification method
PendingCN113723594AReduce lossesSolve the problem of pulse firing underactivationNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsSpiking neural networkNeuronal models
The invention provides a spiking neural network target identification method. The loss of neuron membrane potential is effectively avoided by constructing the proportional attenuation characteristic of a spiking neuron model, the spiking emission rate of neurons is ensured, and the problem that neuron spiking emission is not activated enough is solved; the problem of neuron spiking emission rate over-activation is effectively reduced by constructing the self-adaptive threshold characteristics of the spiking neuron model.
Owner:绍兴市北大信息技术科创中心
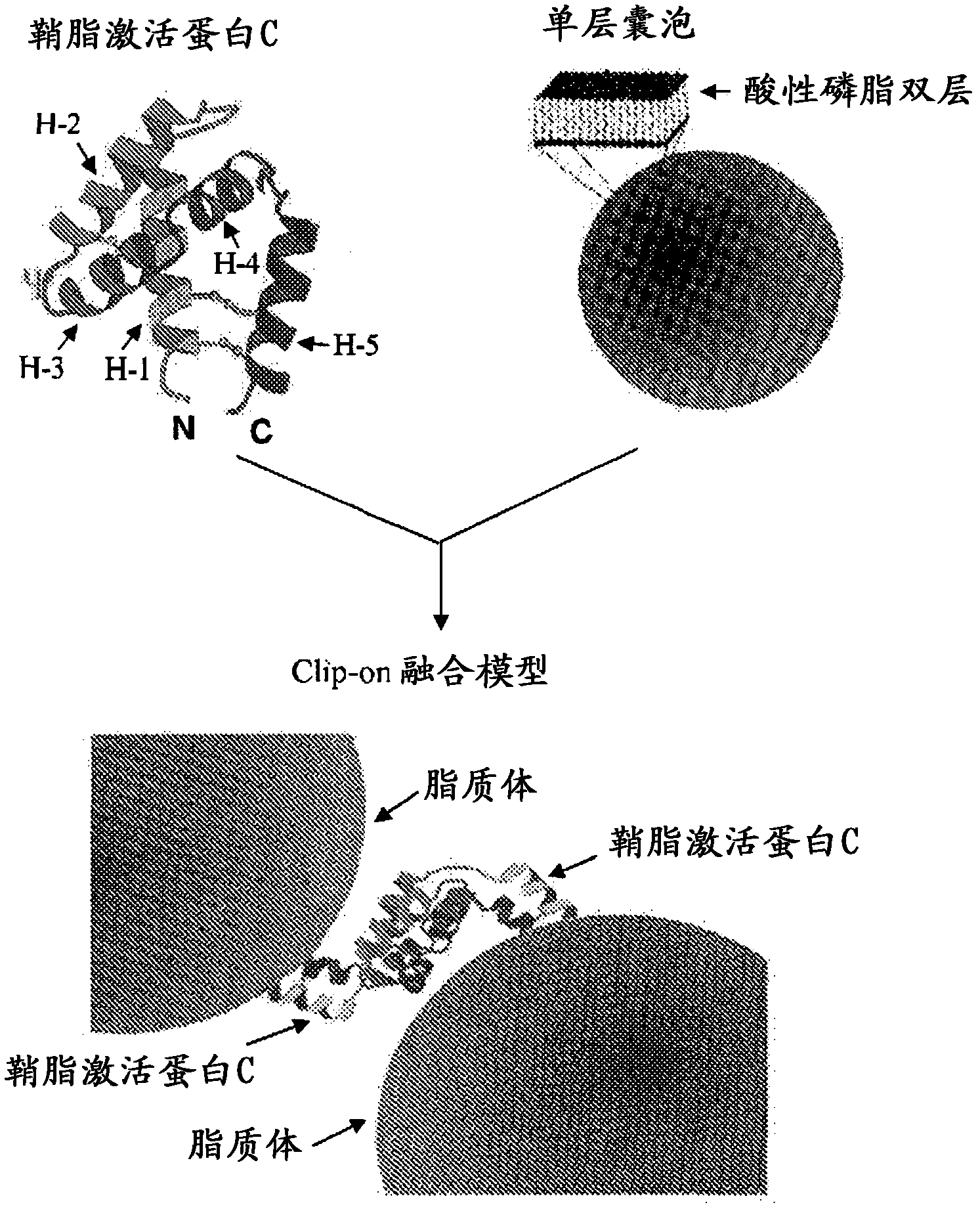
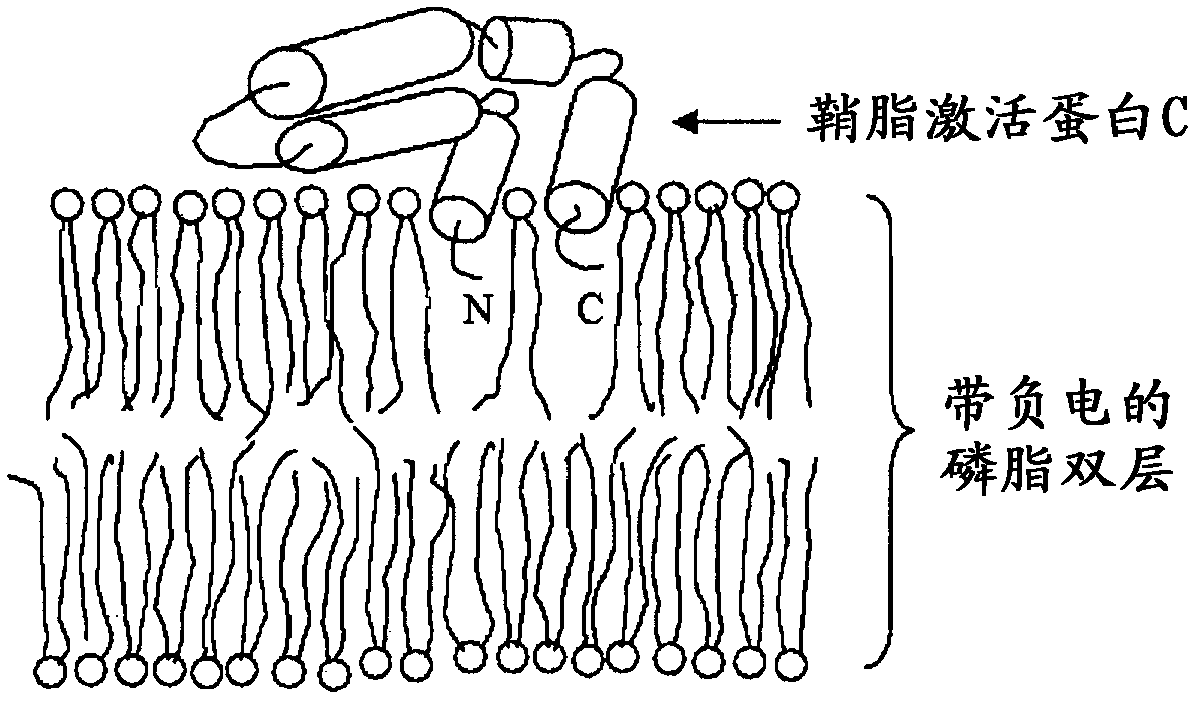
Fusogenic properties of saposin c and related proteins and peptides for transmembrane drug delivery systems
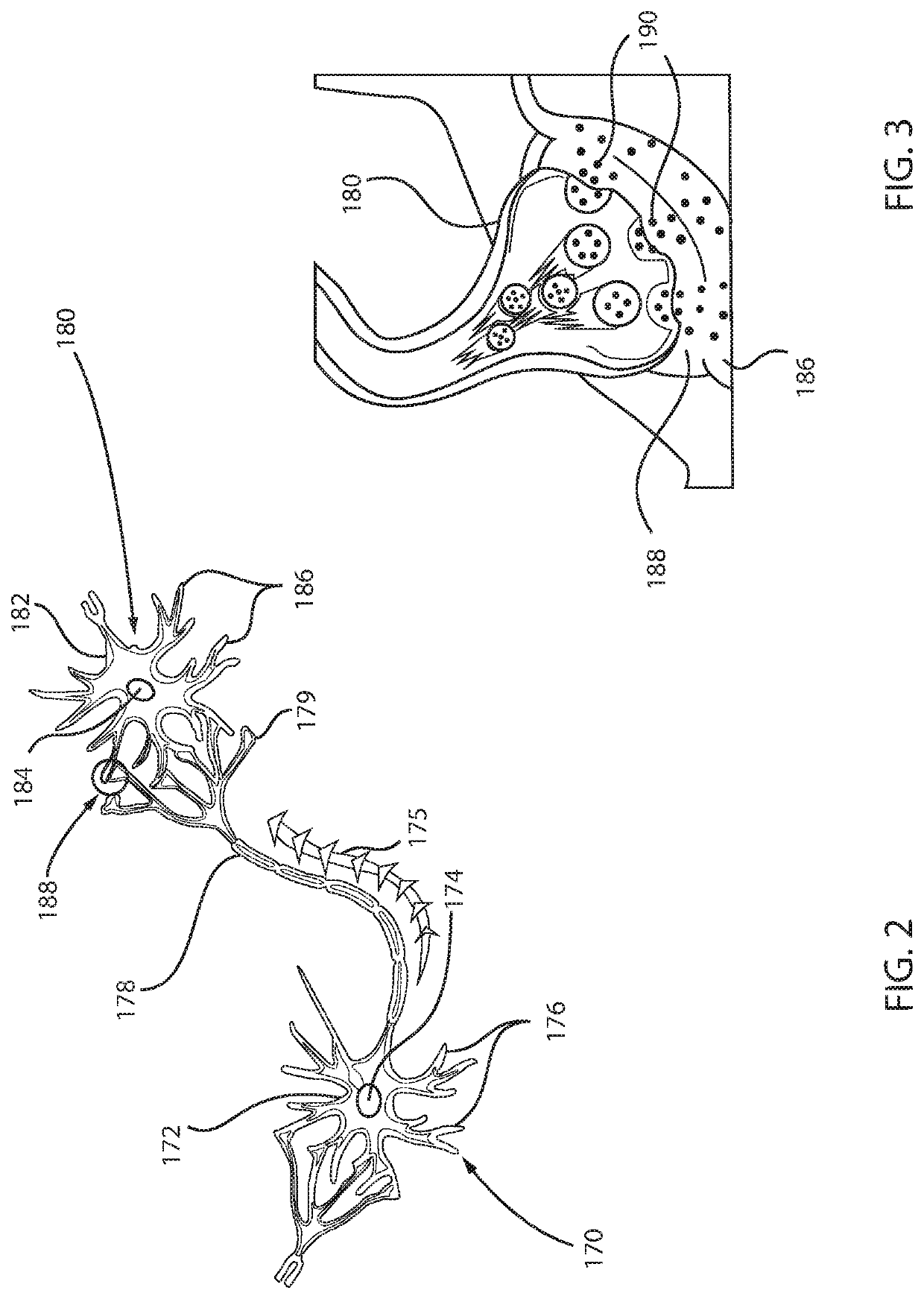
The present invention includes methods of using fusogenic proteins to deliver pharmaceutical agents and / or imaging agents into and / or through the membranes of the skin, mucous membranes, and other cells, and across the blood-brain barrier. Fusogenic proteins associate with phospholipid membranes such as liposomes. Liposomes may include dioleoylphosphatidylserine, a negatively charged long-chain lipid. Alternatively, the liposomes comprise negatively charged long-chain lipids, neutral long-chain lipids and neutral short-chain lipids. Preferred fusogenic proteins include saposin C and other proteins, polypeptides and peptide analogs derived from saposin C. Active agents contained in liposomes may include biomolecules and / or organic molecules. This technology can be used in cosmetic and medical applications where the aim is to deliver active agents into and / or under biofilms or across the blood-brain barrier and neuronal membranes.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
A reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor
ActiveCN112016680BTake advantage ofHigh speedNeural architecturesPhysical realisationSynaptic weightController (computing)
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
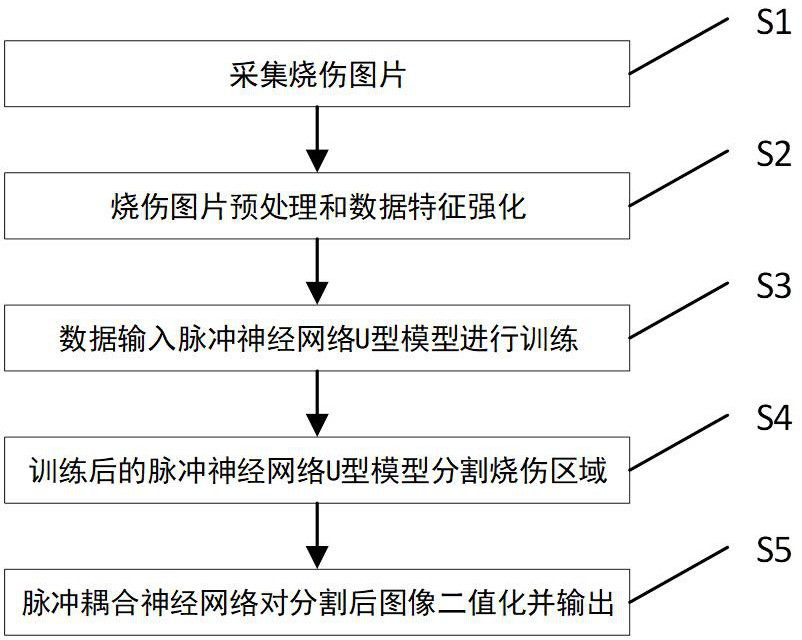
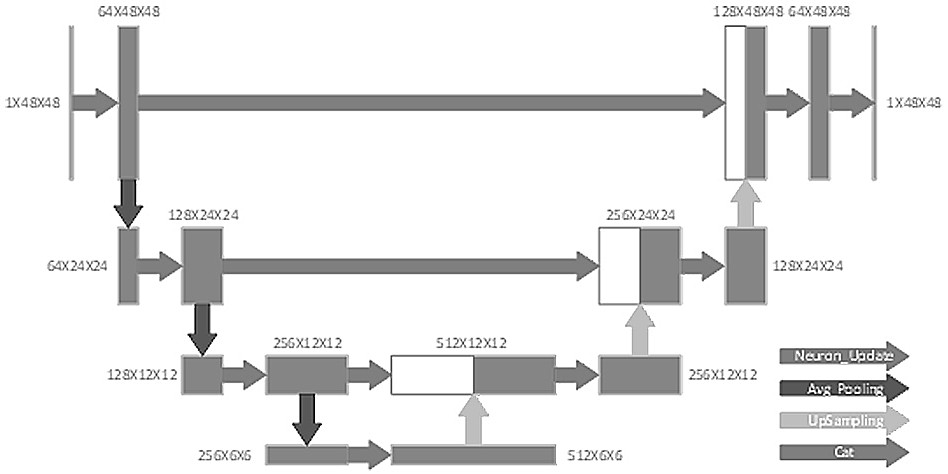
Burn area segmentation system based on pulse neural network U-shaped model
PendingCN114187306AHigh precisionLow power computingImage enhancementImage analysisThresholdingSegmentation system
The invention discloses a burn area segmentation system based on a pulse neural network U-shaped model, which comprises an image acquisition device and a neural network, and is characterized in that the image acquisition device is used for acquiring a burn image of a burn part of a patient, and the neural network comprises the pulse neural network U-shaped model and a pulse coupling neural network; the pulse neural network U-shaped model comprises a neuron membrane potential updating and pulse emitting layer, a lower sampling layer, an upper sampling layer, a feature fusion layer and a loss optimization module, training of burn area segmentation is carried out through the collected image, a burn area is segmented through the trained pulse neural network U-shaped model, and a burn area segmentation result is obtained. And the pulse coupling neural network calculates an adaptive threshold to binarize the segmentation result of the burn region to obtain a visualization result.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
LUT based neuron membrane potential update scheme in STDP neuromorphic systems
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Bionic neuron memristor and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a bionic neuron memristor and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of bionic neurons, the bionic neuron memristor comprises a substrate, parallel counter electrodes and a dielectric layer; the parallel counter electrode and the dielectric layer are arranged on the substrate; the parallel counter electrode comprises a positive electrode layer and a negative electrode layer, and the dielectric layer is arranged between the positive electrode layer and the negative electrode layer; the dielectric layer is made of a semiconductor material of which crystal lattices contain low-activation-energy ions; two kinds of low-activation-energy ions exist in crystal lattices in the dielectric layer, are regulated and controlled by an electric field under driving of the electric field, move towards the positive electrode and the negative electrode respectively and are used for simulating the membrane potential change process generated by transportation change of sodium and potassium ions inside and outside a membrane when neurons are stimulated. According to the invention, simulation of neuron membrane potential change, neuron cumulative emission phenomenon and neuron refractory behavior can be realized without building a peripheral circuit.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
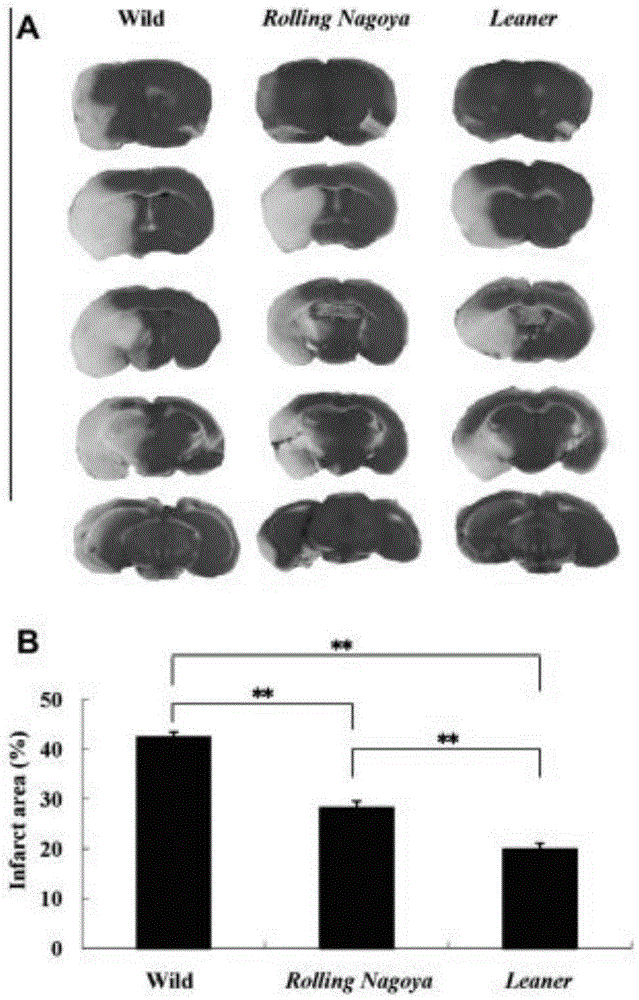
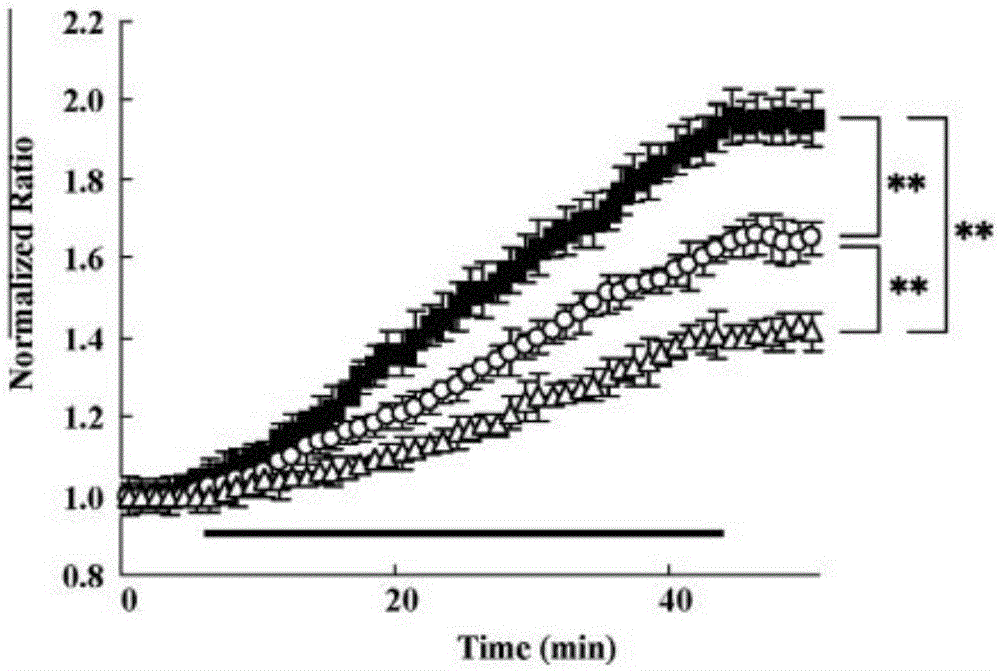
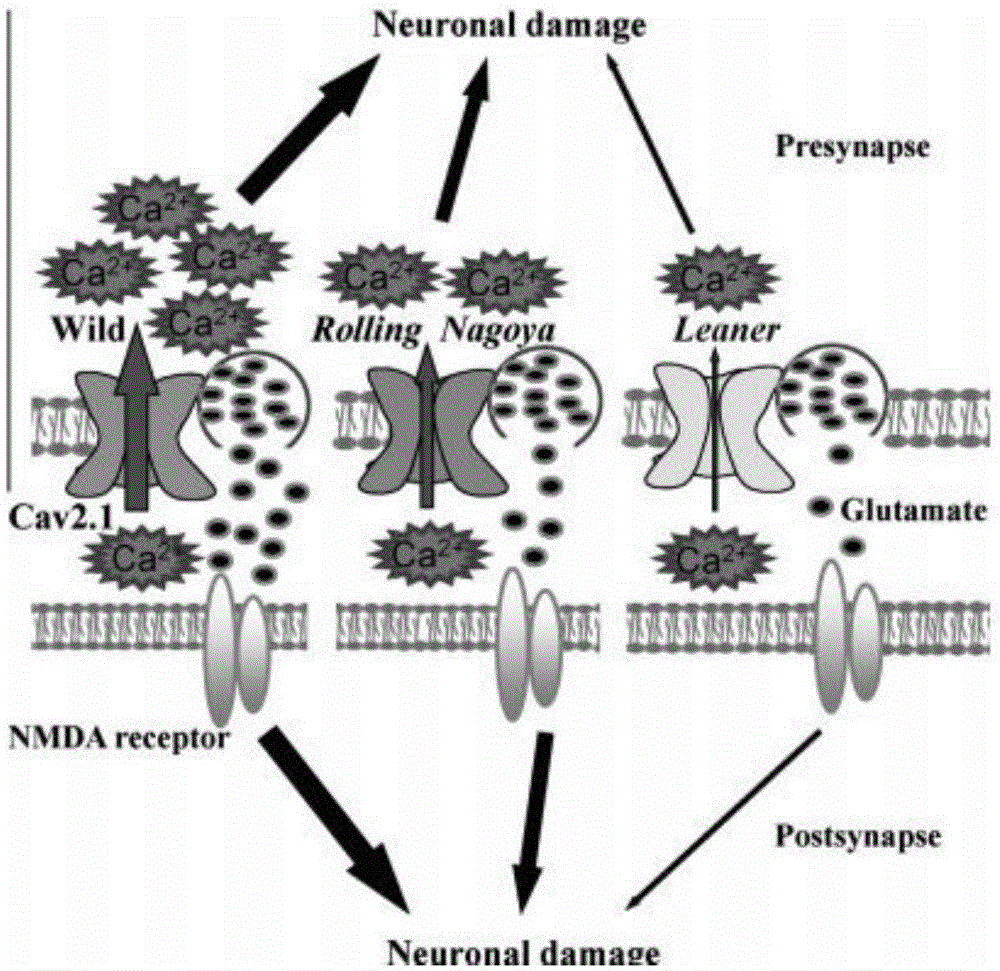
[Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model
InactiveCN106729767AMicrobiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsWild typeBiological activation
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to [Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2.1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in an in-vitro ischemia model. The primary reason of ischemia caused by cell death and cerebral injury is Ca2+ ionic regulation abnormity. Depolarization of a neuron membrane results in activation of a Ca2+ voltage gating channel and influx of Ca2+. The two Cav2.1 channel alpha 1 subunit mutation mice (rolling Nagoya and leaner mice) are used in an experiment to study a physiological effect of CaV2.1 (P-Q type) in ischemic neuron damage. A result of the ischemia experiment shows that the brain tissue embolism area of the two mutation models, namely the rolling Nagoya and Leaner mice, is obviously reduced as compared with wild mice. In an in-vitro Ca2+ imaging study, an increase rate of the Ca2+ concentration of the two Cav2.1 channel mutation mice is less than that of the wild mice. The study results show that the Cav2.1 channel plays an important role in the Ca2+ dependent ischemia model, and the blocking of the channel can exert a certain prevention and protection effect.
Owner:宁波美丽人生医药生物科技发展有限公司
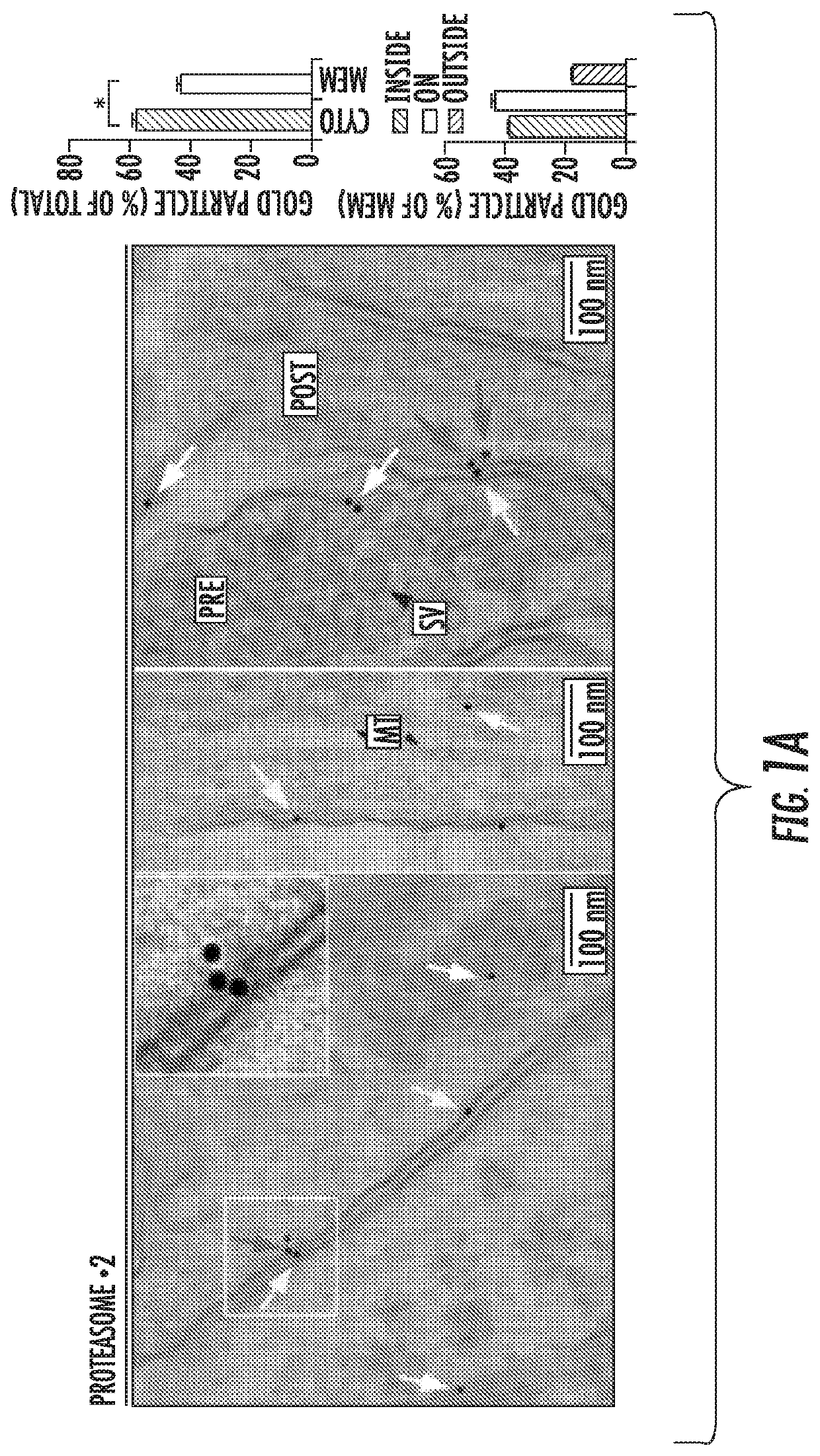
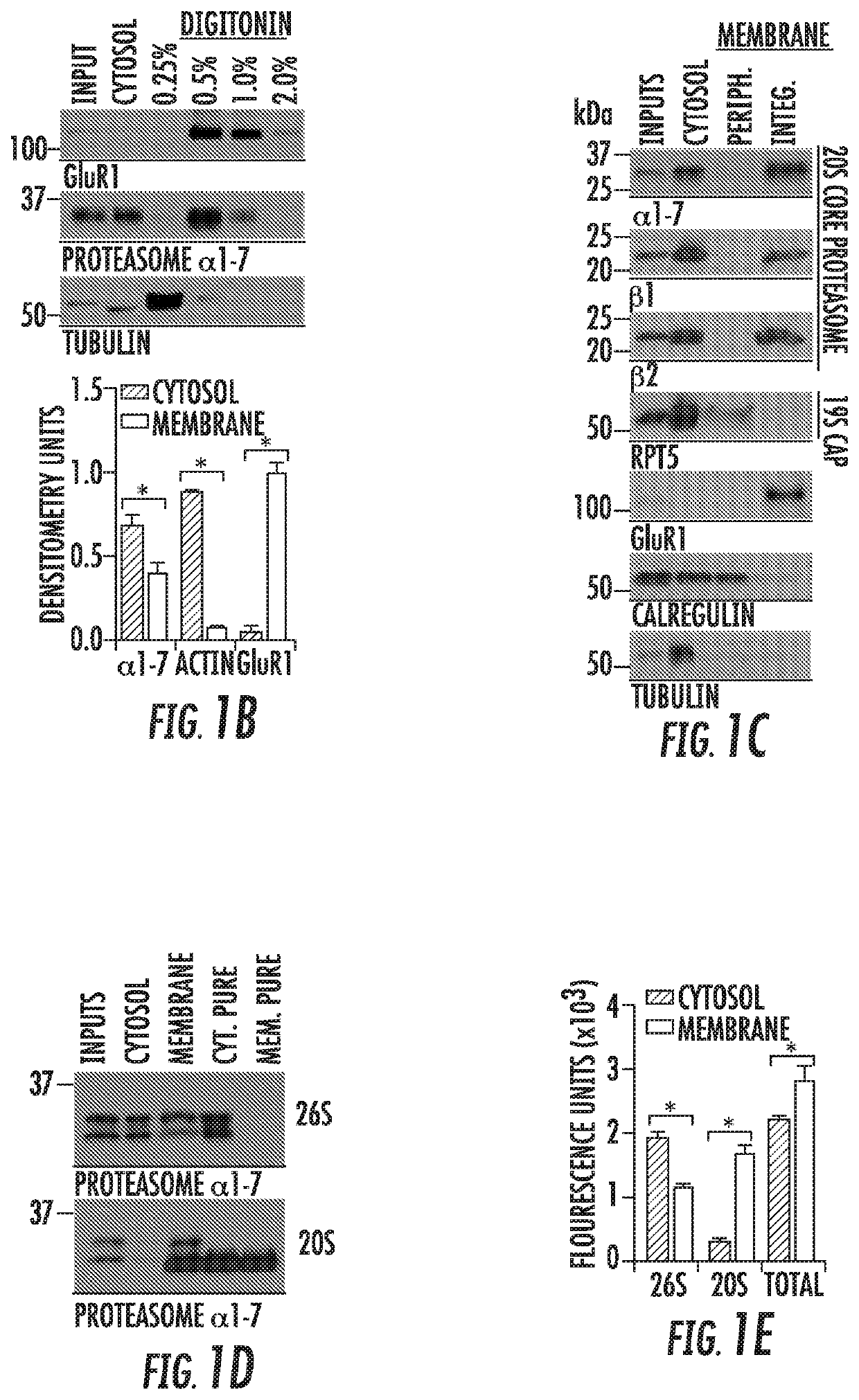
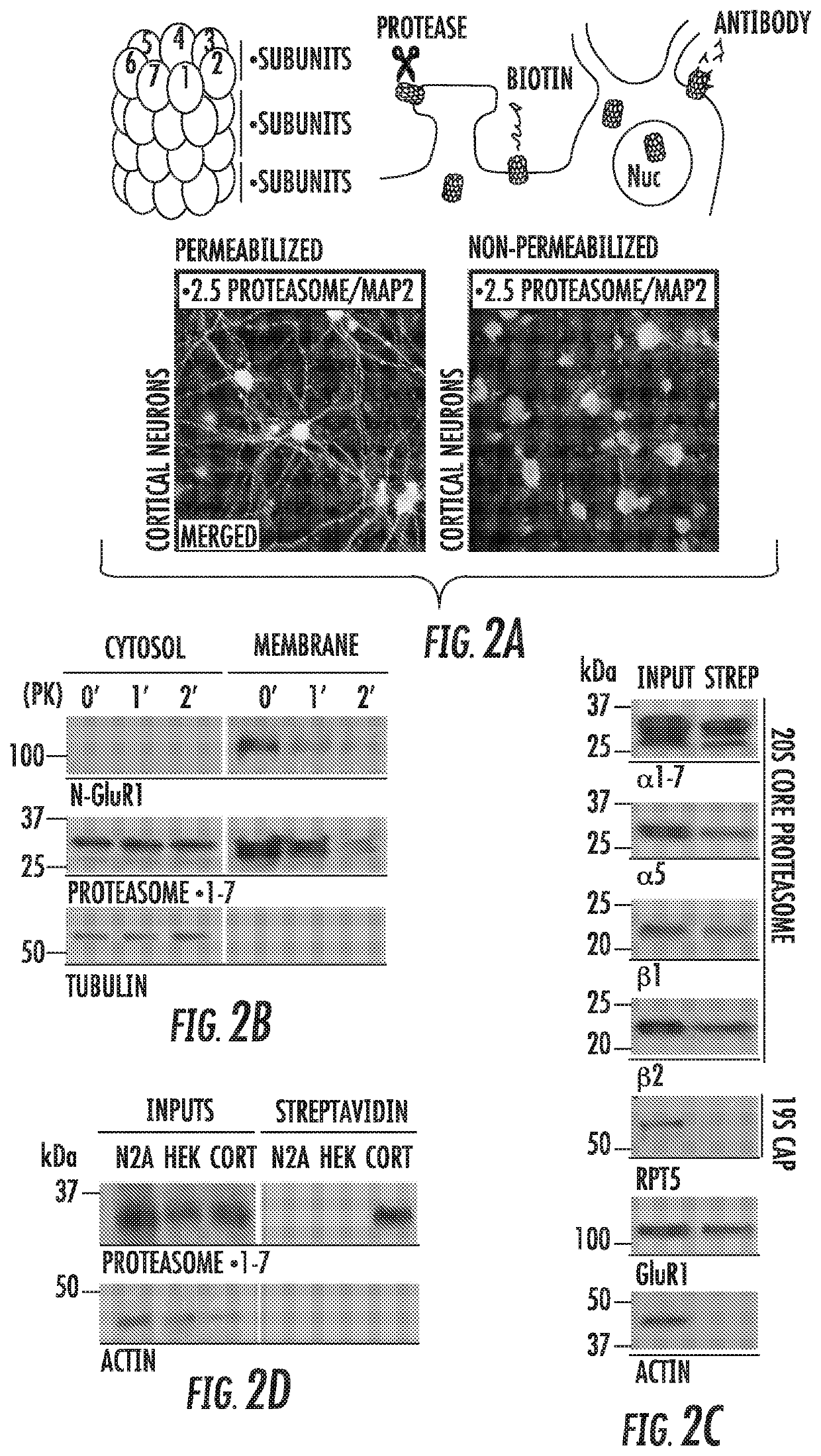
Nervous system-specific transmembrane proteasome complex that modulates neuronal signaling through extracellular signaling via brain activity peptides
ActiveUS10775391B2In-vivo radioactive preparationsDipeptide ingredientsNervous systemSignalling molecules
The inventors surprisingly found that neural stimulation caused the synthesis and degradation of proteins into peptides which were then secreted into the cell media within minutes of stimulation by a novel neural-specific and membrane bound proteasome (neuronal membrane proteasome or NMP) that is transmembrane in nature. These secreted, activity-induced, proteasomal peptides (SNAPPs) range in size from about 500 Daltons to about 3000 Daltons. Surprisingly none of the peptides appear to be those previously known to have any neuronal function. Moreover, these SNAPPs have stimulatory activity and are heretofore a new class of signaling molecules. Moreover, the NMP appears to play a highly significant role in aspects of neuronal signaling known to be critical for neuronal function. The inventors have gone on to develop all tools to study this novel mechanisms including protocols and practice for generation and purification of SNAPPs as well as a new and specific inhibitor of the NMP allowing for selective control of this process in the nervous system. The present invention provides methods of making and using these SNAPPs for both laboratory and clinical purposes, the screening for molecules which modulate NMP function in vivo and in vitro, and methods for diagnosis of NMP related diseases.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
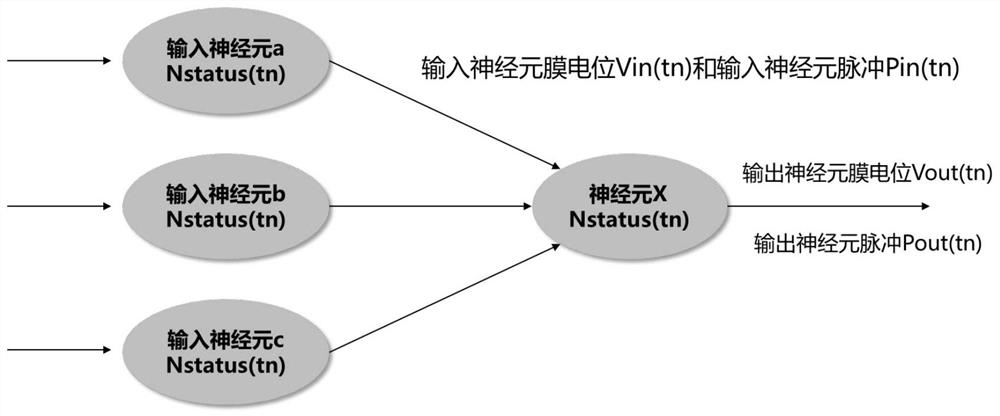
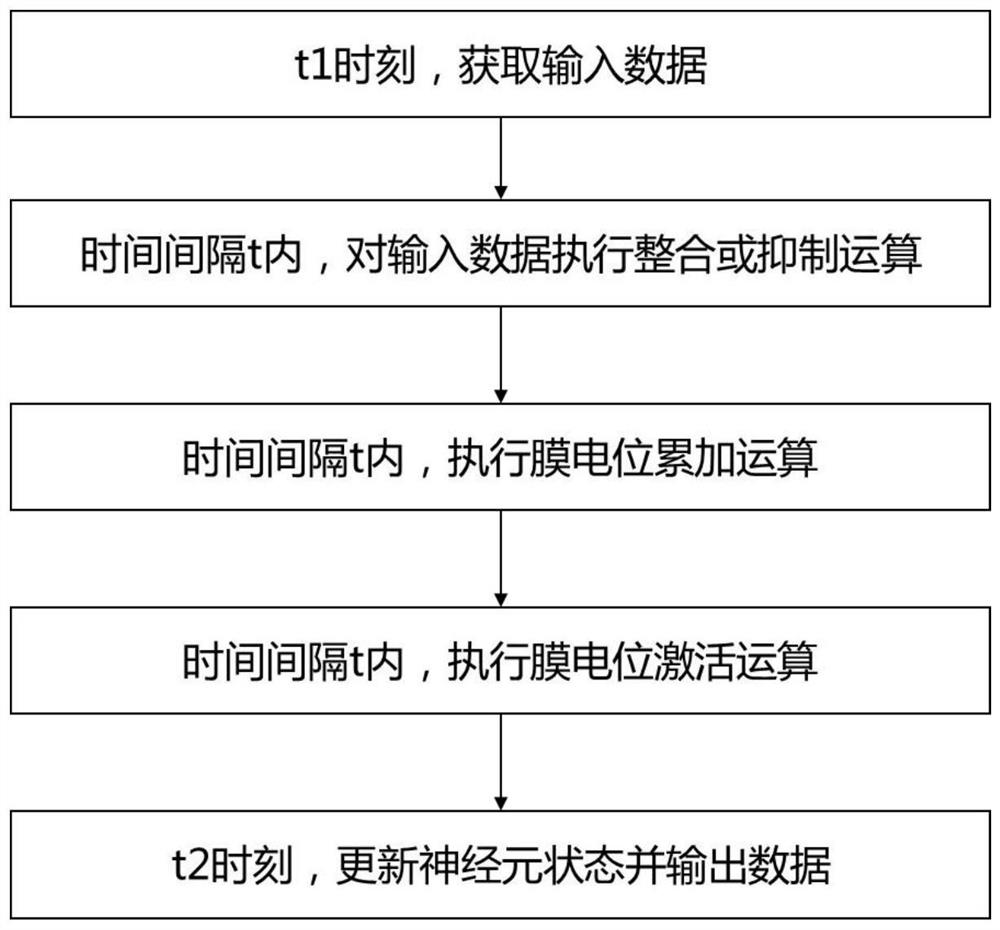
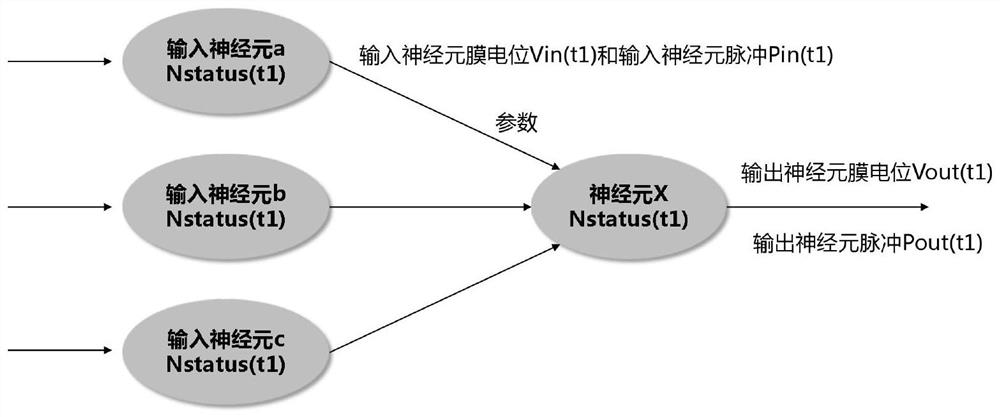
Neuron calculation method
PendingCN114819115AImprove versatilityNeural architecturesPhysical realisationArtificial intelligenceMembrane potential
The invention relates to the field of neuron calculation, in particular to a neuron calculation method. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a plurality of input neuron membrane potentials Vin (t1) and input neuron pulses Pin (t1) by neurons within a time interval t, updating the state of the neurons, and sending output neuron membrane potentials Vout (t2) and output neuron pulses Pout (t2); the unit time of the time interval t is delta t; the starting moment of the time interval is recorded as t1 = n1 * delta t, and the ending moment of the time interval is recorded as t2 = n2 * delta t; the time interval t is equal to n * delta t, and n is equal to n2-n1; comprising the following steps: acquiring input data at t1 moment; within the time interval t, performing integration or suppression operation on the input data; within the time interval t, executing membrane potential accumulation operation; within the time interval t, executing membrane potential activation operation; and at the t2 moment, updating the neuron state and outputting data. The neuron calculation method provided by the invention has better universality, so that a more universal neural network calculation system is realized.
Owner:厦门壹普智慧科技有限公司
Saliency map generation system, method and device based on dynamic visual sensor
ActiveCN112215912BReduce noiseExclude background information2D-image generationNeural architecturesPattern recognitionActivation function
The invention belongs to the field of data processing, specifically relates to a dynamic visual sensor-based saliency map generation system, method and device, and aims to solve the problem. The present invention includes: acquiring event data through a dynamic visual sensor, accumulating and caching the DVS event data and information obtained from interrelated neurons through each neuron in the target detection network, and passing the activation function at preset times Obtain the neuron membrane potential, and output a pulse signal according to the relationship between the neuron membrane potential and the preset saturation threshold, the membrane potential u(t0) at the previous moment is attenuated and accumulated with the current received excitation, and the result is used for the pulse signal and membrane potential update judgment. The invention eliminates redundant background information from the saliency map generated by the target detection network array, improves the reliability and accuracy of target detection, and avoids misjudgment.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
neuron circuit
ActiveCN106250983BSimple structureReduce power consumptionPhysical realisationNerve impulseCapacitance
The invention discloses a neuron circuit, which comprises: a pulse generating circuit configured to simulate nerve pulse oscillation through a first Tau-cell circuit structure and a second Tau-cell circuit structure; a first Tau-cell circuit structure The first capacitor Cv for simulating neuron membrane potential ν is included in the -cell circuit structure; the second capacitor Cu for simulating neuron membrane potential adjustment variable u is included in the second Tau-cell circuit structure; it is connected with the pulse generating circuit The adjustment circuit is used to reassign the neuron membrane potential ν; the comparison circuit connected with the pulse generating circuit is used to reassign the neuron membrane potential adjustment variable u. The invention can reduce the power consumption of the neuron circuit and reduce the occupation area of the neuron circuit.
Owner:ZHUHAI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
An image classification method based on multi-layer spiking convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110119785BReduce the number of pulsesReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesActivation functionImage conversion
The invention discloses an image classification method based on a multi-layer spiking convolutional neural network, relates to the field of image processing, converts images in a training set into pulse sequences; sets the parameters of spiking neurons, and uses the spiking neurons to construct a convolutional neural network ; Using the pulse sequence as input, train the convolutional neural network layer by layer, obtain the classification result after obtaining the visual features of the pulse sequence, the training method is an unsupervised learning algorithm based on hebbian rules; the image to be identified Convert it into a pulse sequence, input the trained convolutional neural network, and get the classification result of the image to be recognized; this method solves the technical problem of redundant calculation of spiking neuron membrane voltage due to the increase of neuron scale, and solves the The activation function is not derivable, and it is impossible to use backpropagation to calculate the residual, which leads to technical problems that the learning does not converge.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Optical flow-based target detection method based on compound eye vision enlightenment
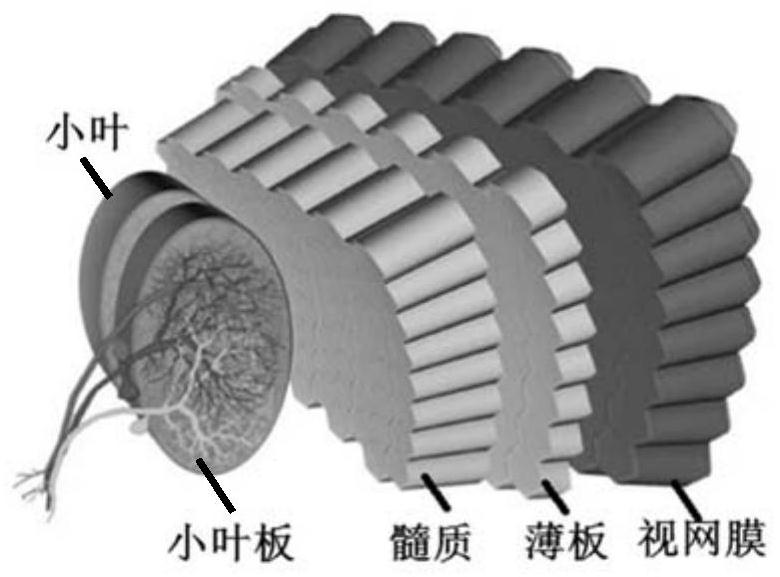
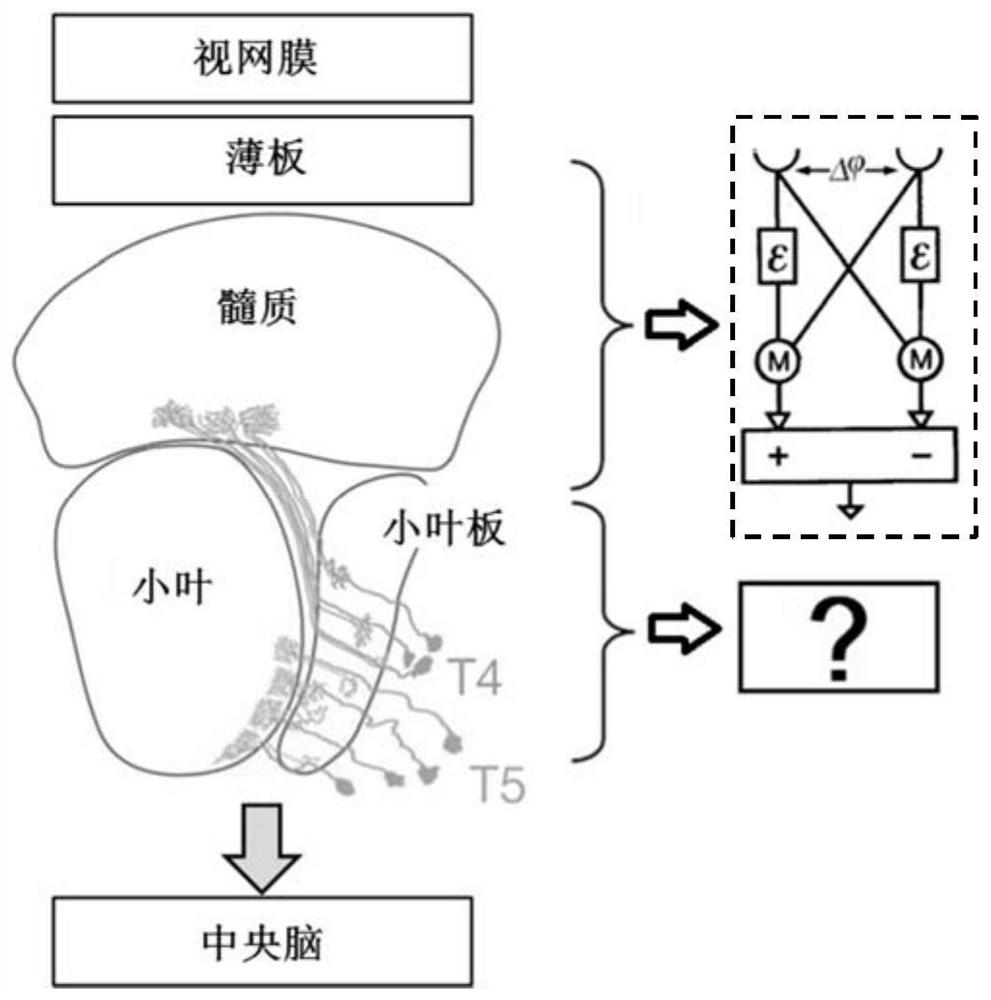
PendingCN114648558AAchieving Spatial SmoothingAchieve smoothImage enhancementImage analysisMotion detectorOptical flow
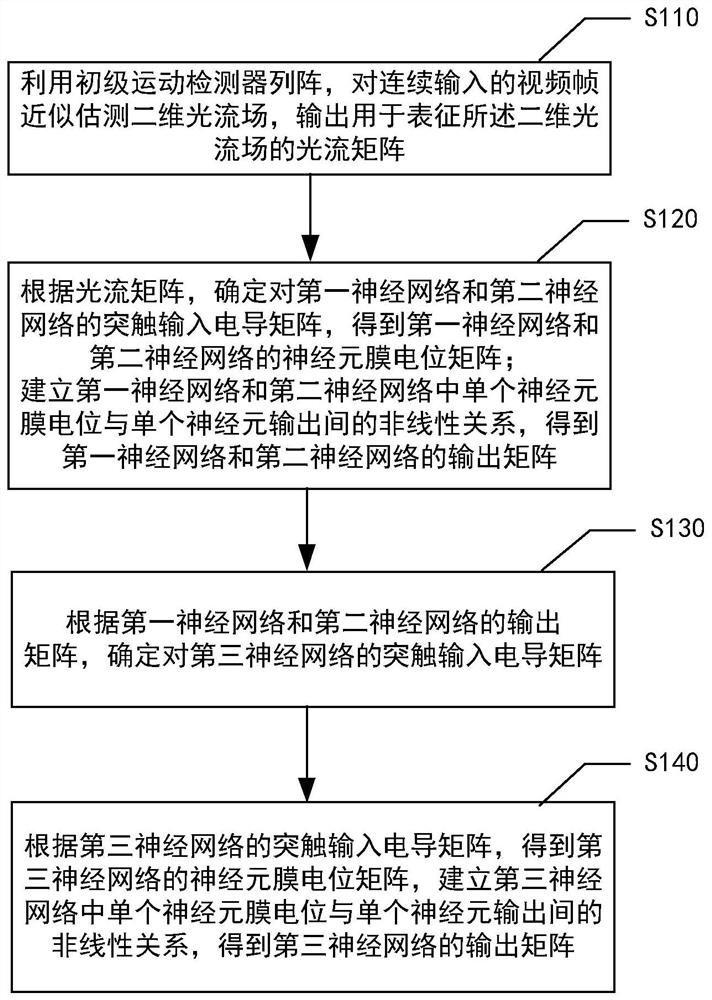
The invention provides an optical flow-based target detection method for compound eye visual inspiration, which comprises the following steps of: determining synaptic input conductance matrixes for a first neural network and a second neural network according to an optical flow matrix output by an EMD (Empirical Mode Decomposition) array; obtaining output matrixes of the first neural network and the second neural network according to the membrane potential matrixes of the first neural network and the second neural network, and further determining a synaptic input conductance matrix of a third neural network; and according to the synaptic input conductance matrix of the third neural network, obtaining a neuron membrane potential matrix of the third neural network, establishing a nonlinear relationship between a single neuron membrane potential and a single neuron output in the third neural network, and obtaining a motion detection result of the target object. According to the method, the working principle of a perfectly evolved compound eye vision system is used as a starting point for reference, and parallel point-by-point space-time smoothing and nonlinear dichotomy transformation are performed on the primary motion detector array estimation optical flow, so that motion detection and target-background separation based on a biological perception optical flow mechanism are realized.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Effect of Cav2.1 channel in Ca2+ dependent ischemia model
InactiveCN106729766ACompounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeBiological activation
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to an effect of a CaV2.1 channel in a Ca2+ dependent ischemia model. The primary reason of ischemia caused by cell death and cerebral injury is Ca2+ ionic regulation abnormity. Depolarization of a neuron membrane results in activation of a Ca2+ voltage gating channel and influx of Ca2+. Two Cav2.1 channel alpha 1 subunit mutation mice (rolling Nagoya and leaner mice) are used in an experiment to study a physiological effect of CaV2.1 (P-Q type) in ischemic neuron damage. A result of the ischemia experiment shows that the brain tissue embolism area of the two mutation models, namely the rolling Nagoya and Leaner mice, is obviously reduced as compared with wild mice. In an in-vitro Ca2+ imaging study, an increase rate of the Ca2+ concentration of the two Cav2.1 channel mutation mice is less than that of the wild mice. The study results show that the Cav2.1 channel plays an important role in the Ca2+ dependent ischemia model, and the blocking of the channel can exert a certain prevention and protection effect.
Owner:宁波美丽人生医药生物科技发展有限公司
Pulse neural network simulation strategy based on GPU
PendingCN114565083AAchieve accelerationMake up for slow speed and other problemsNeural architecturesEnergy efficient computingConcurrent computationSpiking neural network
The invention discloses a pulse neural network simulation strategy based on a GPU. The pulse neural network simulation strategy comprises the following steps: initializing a neural network structure and a network weight; loading parameters and a network structure in the GPU, and creating a pulse queue; calculating a neuron membrane voltage according to the pulse distribution condition in the pulse queue; according to the membrane voltage value of the neuron and a threshold value, whether a pulse is emitted is judged; and the process from S3 to S5 is repeated until iteration is completed. According to the method, the simulation speed of the spiking neural network is accelerated, the advantages of GPU parallel computing and the characteristics of sparsity and concurrency of the spiking neural network are brought into full play, and meanwhile simulation of a larger-scale spiking neural network model is supported.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![[Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model [Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4f7e88f4-e524-49d8-a910-b1597656350e/HDA0000857244240000011.png)
![[Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model [Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4f7e88f4-e524-49d8-a910-b1597656350e/HDA0000857244240000012.png)
![[Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model [Ca2+] i reduction of CaV2 1 alpha 1 gene mutation mice in in-vitro ischemia model](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4f7e88f4-e524-49d8-a910-b1597656350e/HDA0000857244240000021.png)