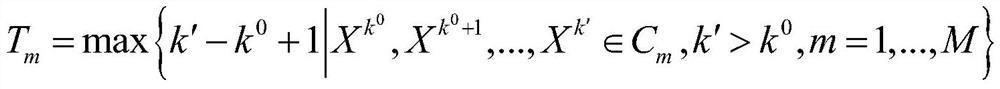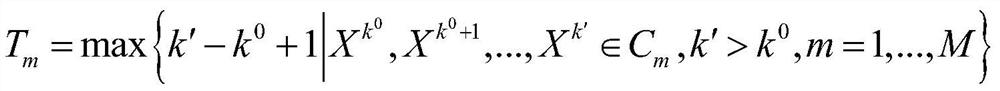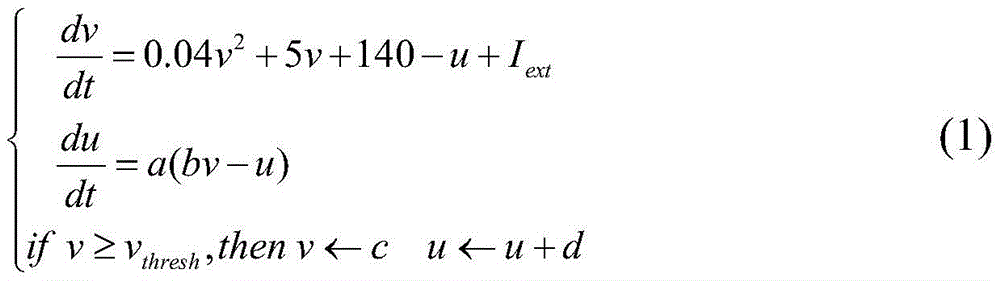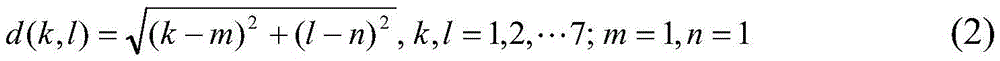Patents
Literature
32 results about "Neuronal firing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neuronal Firing. The process of normal neuronal firing takes place as a communication between neurons through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters.
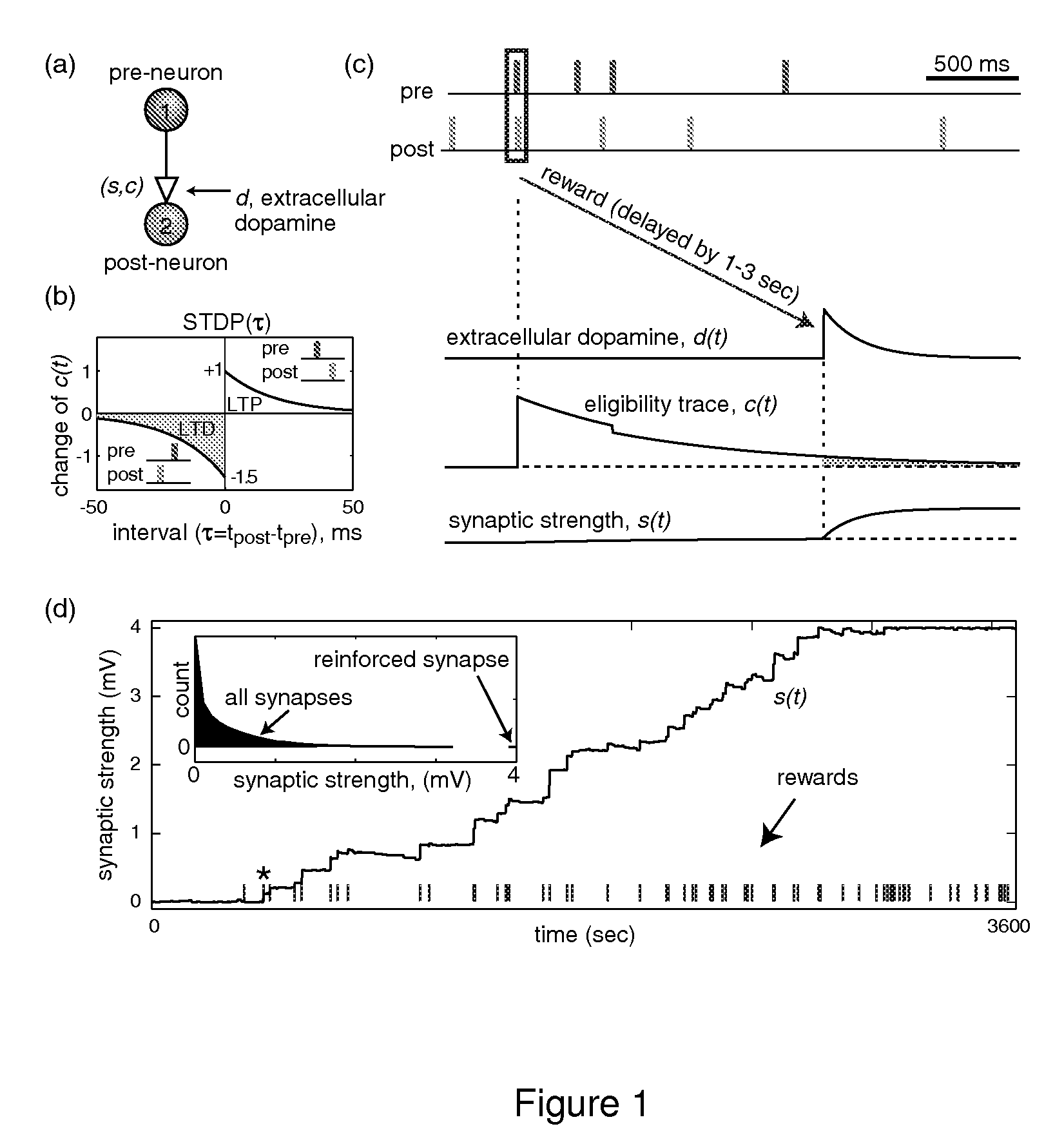
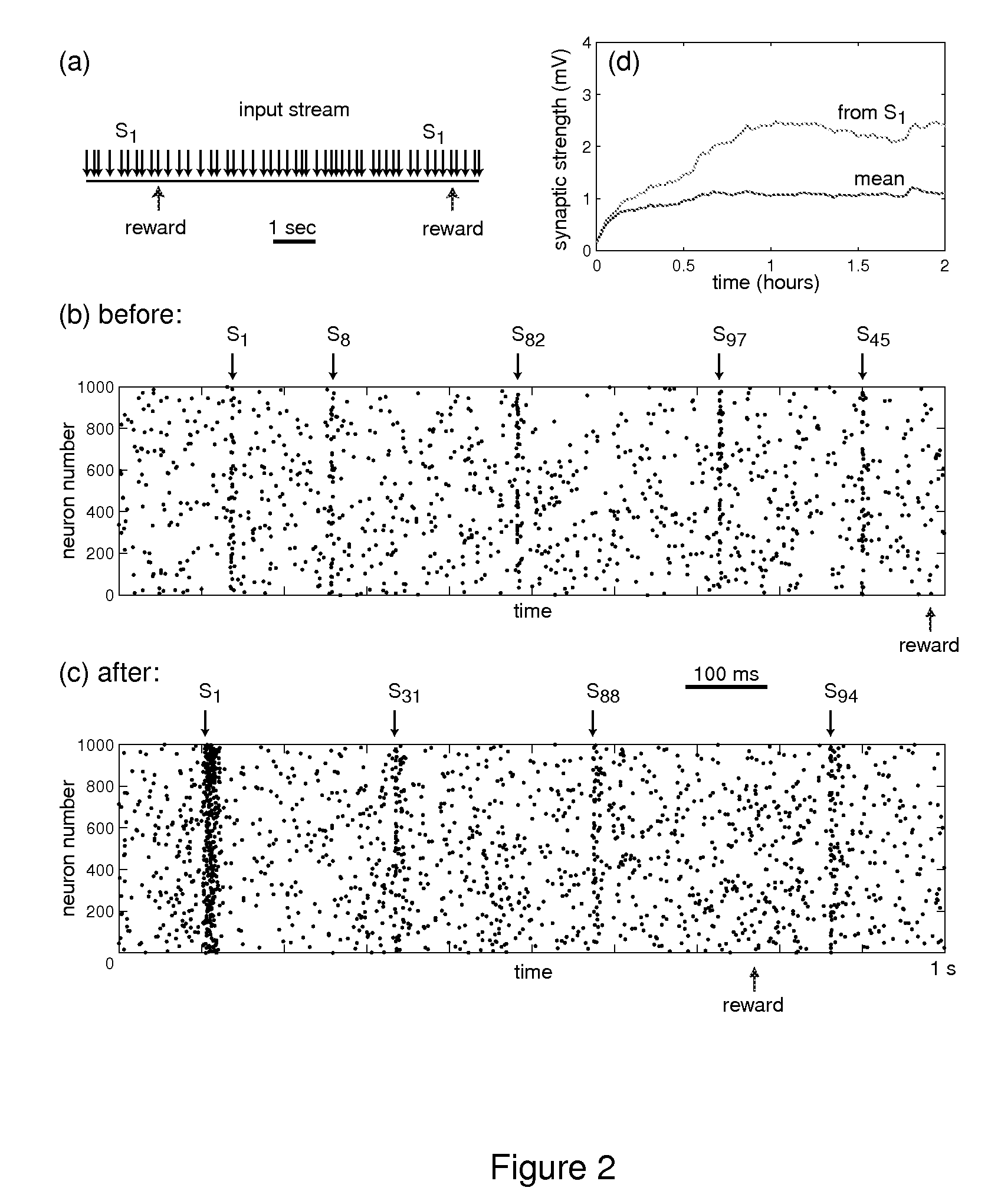
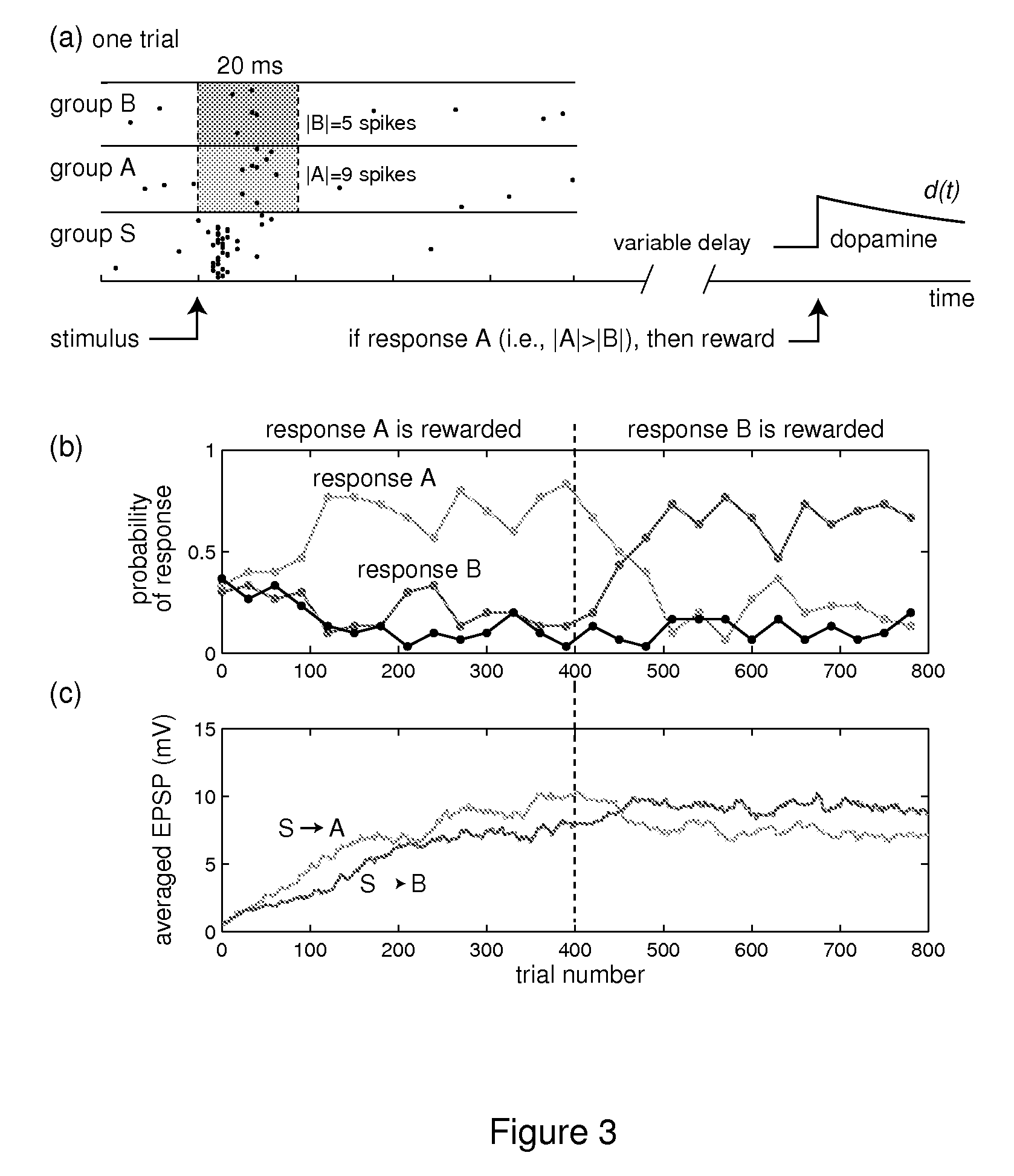
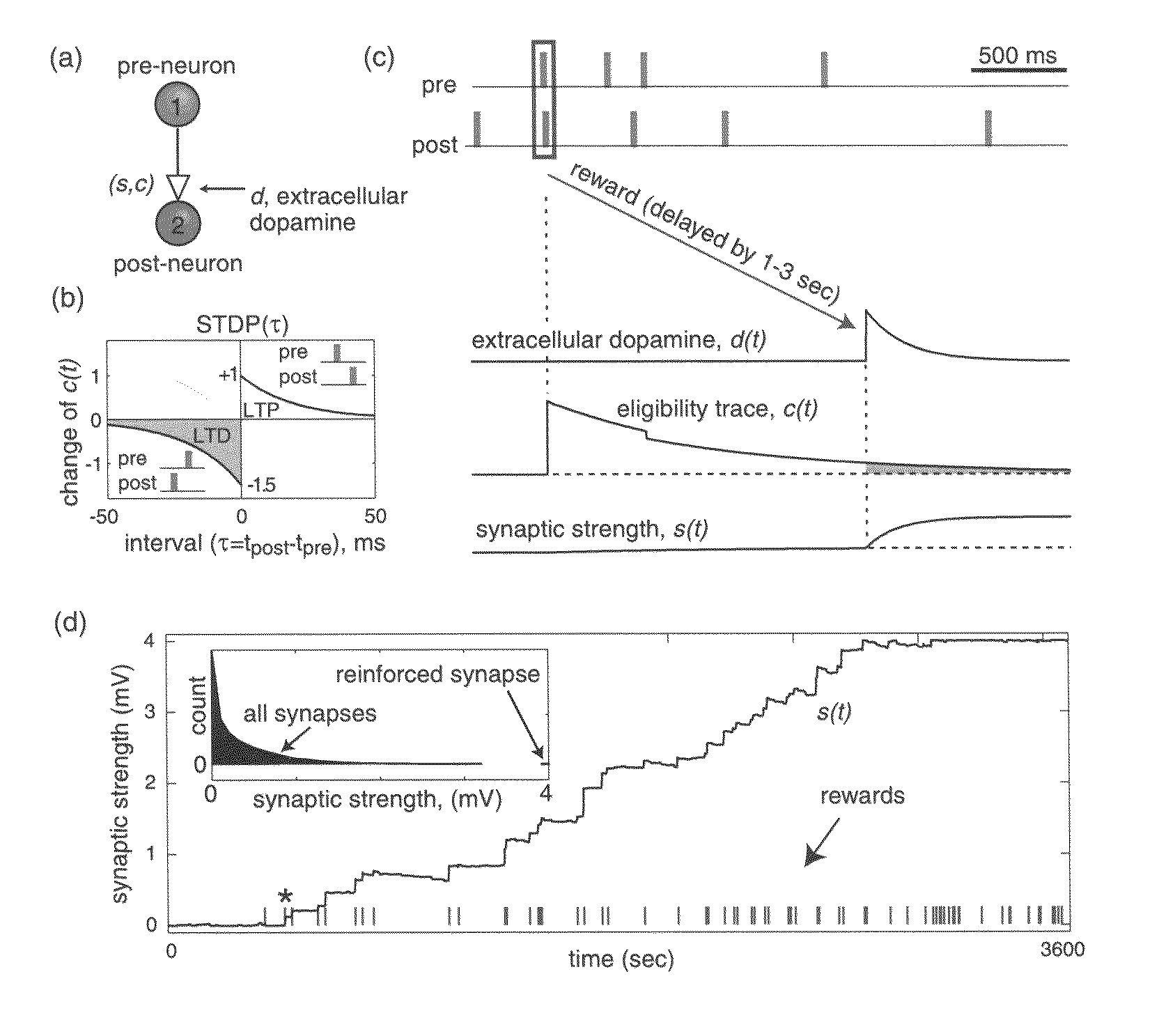
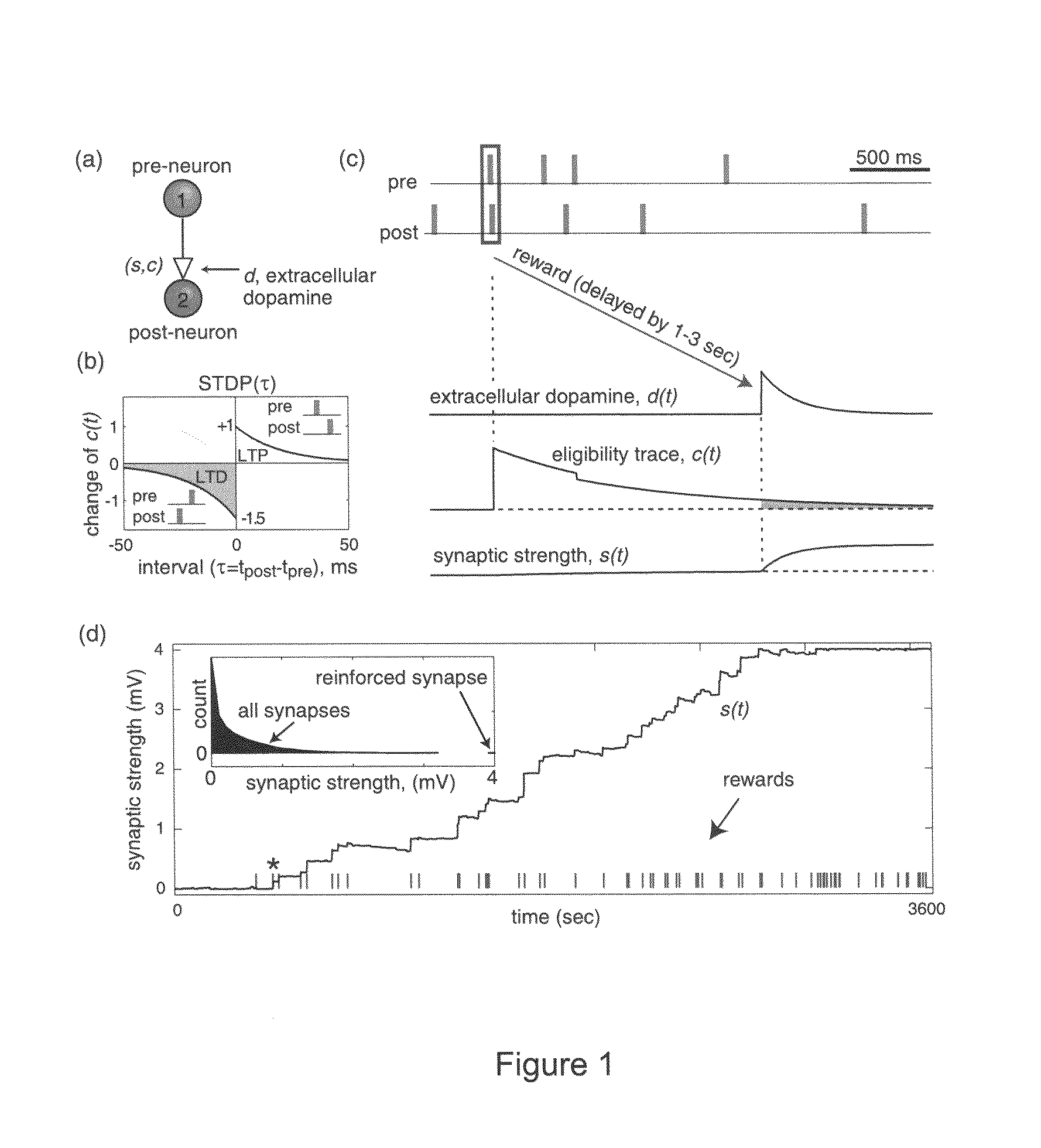
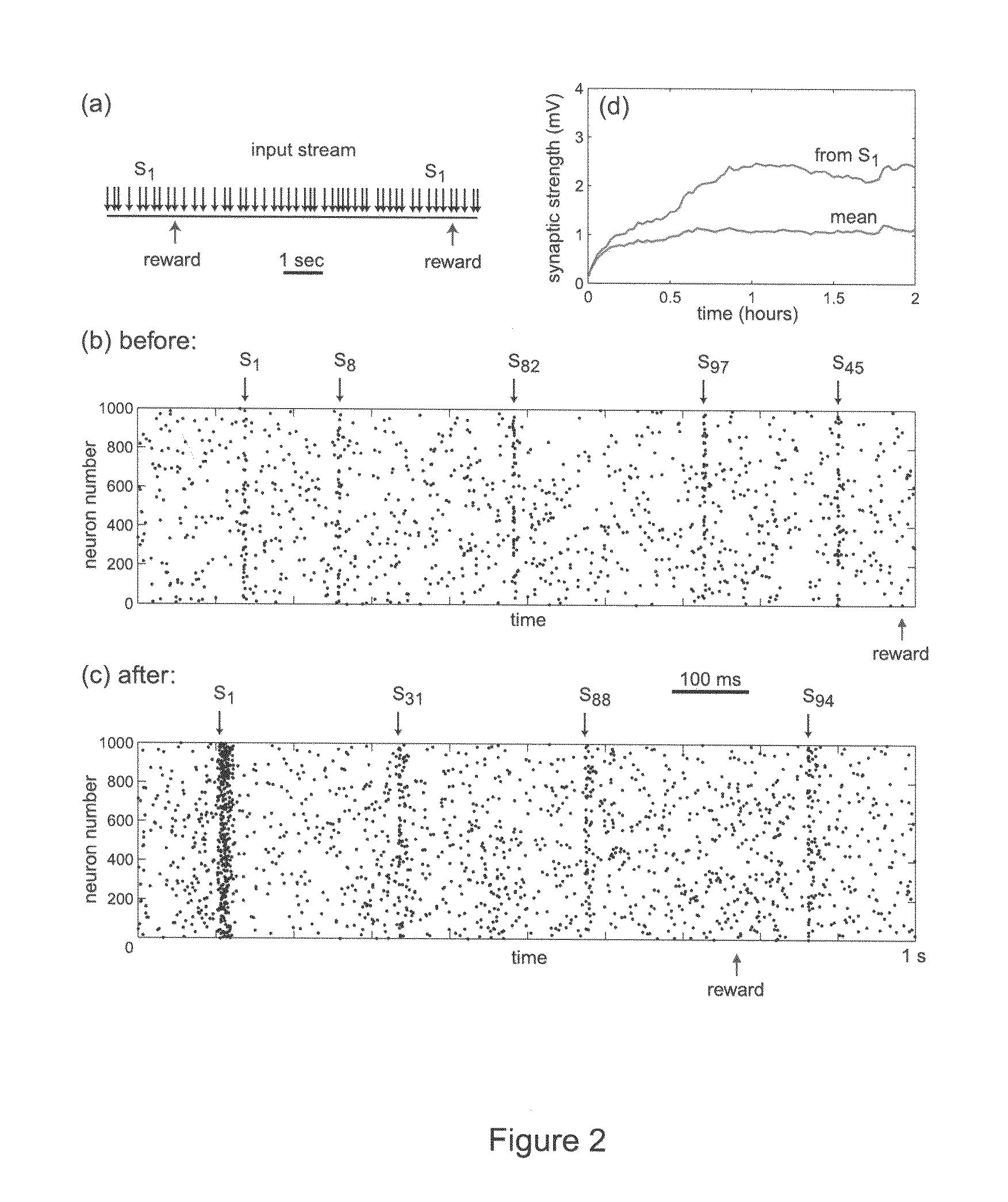
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS20080162391A1Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNerve networkCritical period
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
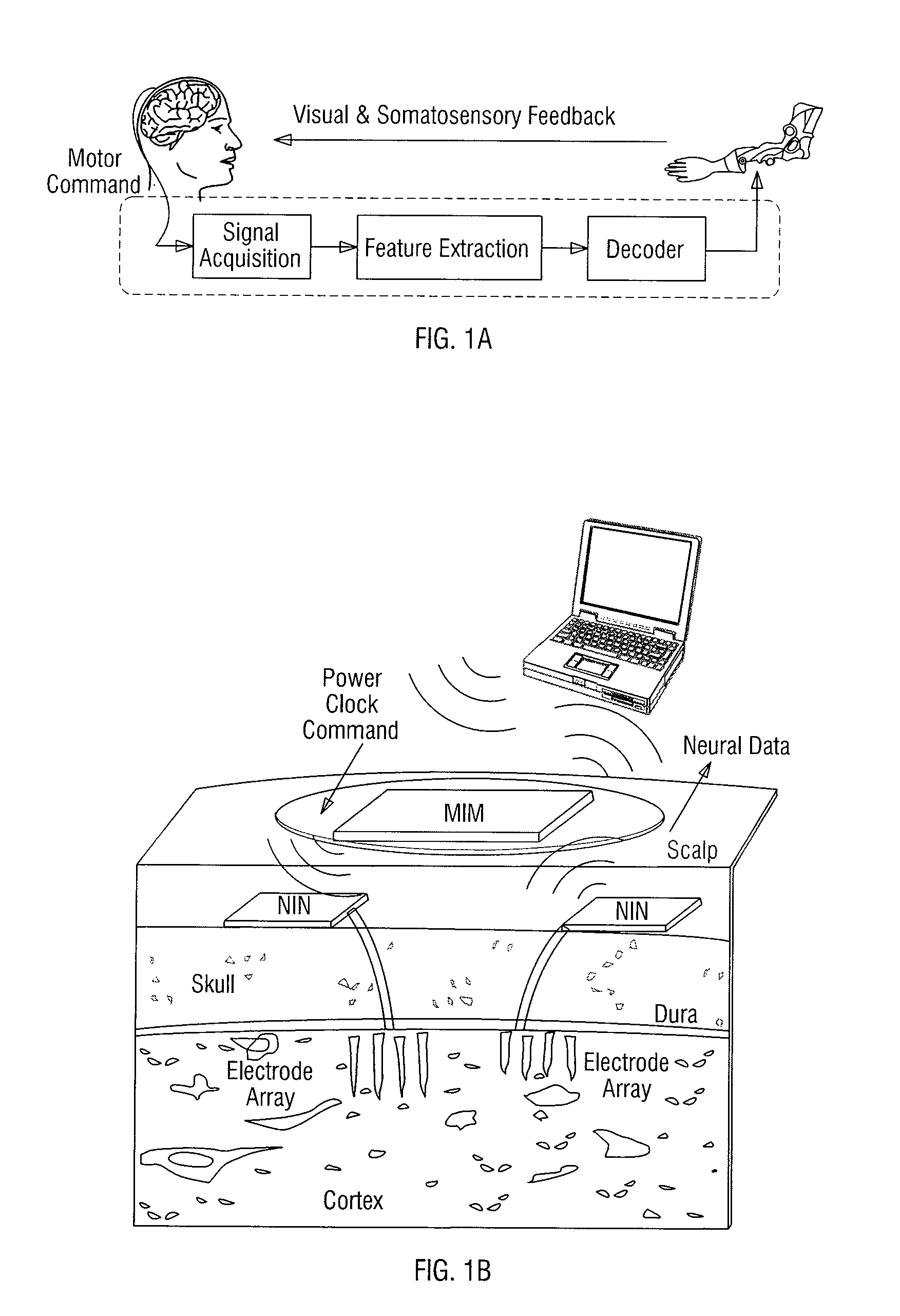
Multiscale intra-cortical neural interface system
Apparatus, systems, and methods may operate to collect neuro data from an organ, such as a brain. Spikes may be detected using raw neuro data collected from the organ. The spikes may be sorted. Underlying neuronal firing rates may be estimated using the sorted spikes. The neuronal firing rates may be transmitted outside the organ for real time decoding.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of STDP and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS8103602B2Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeCritical periodModel network
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
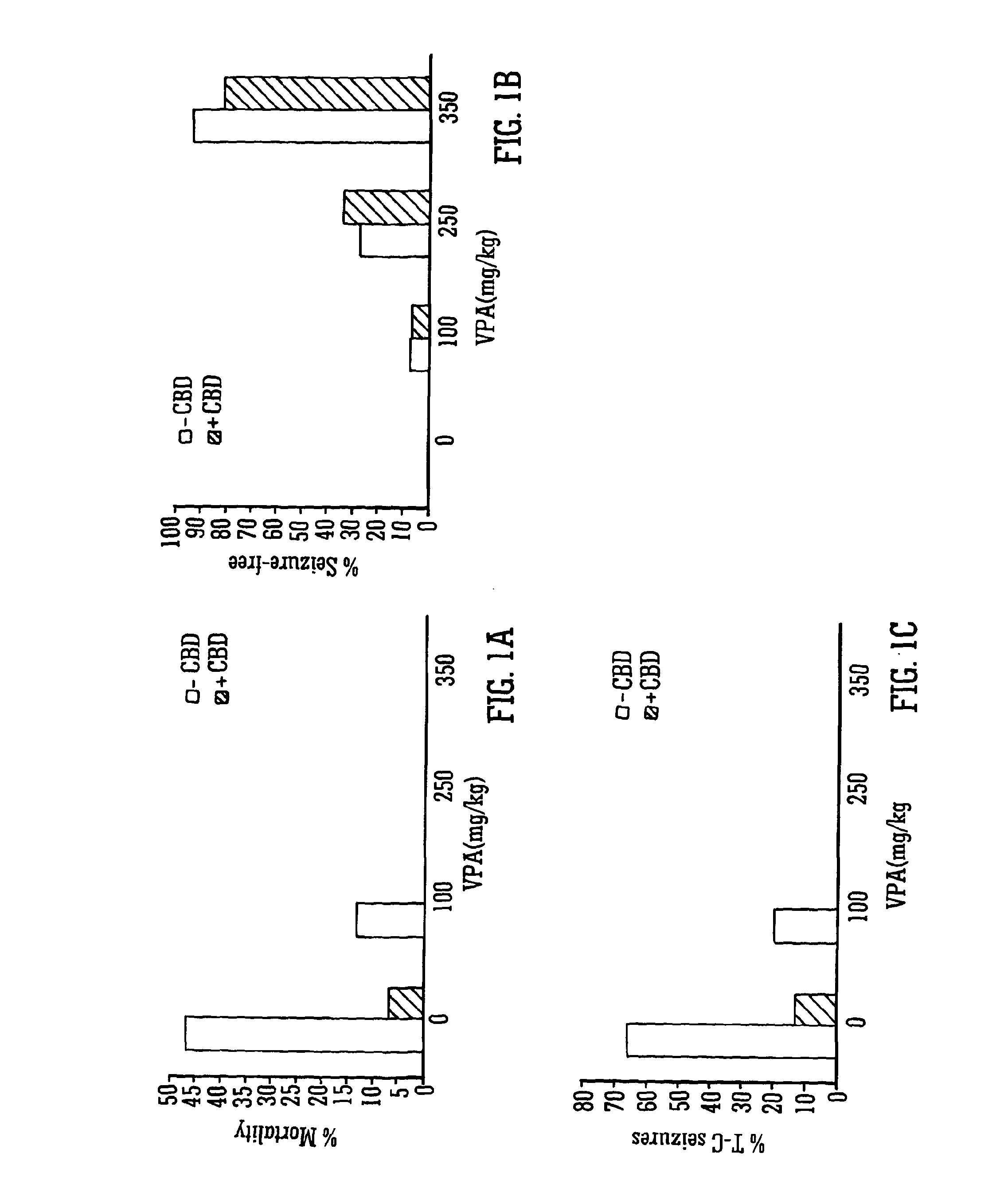
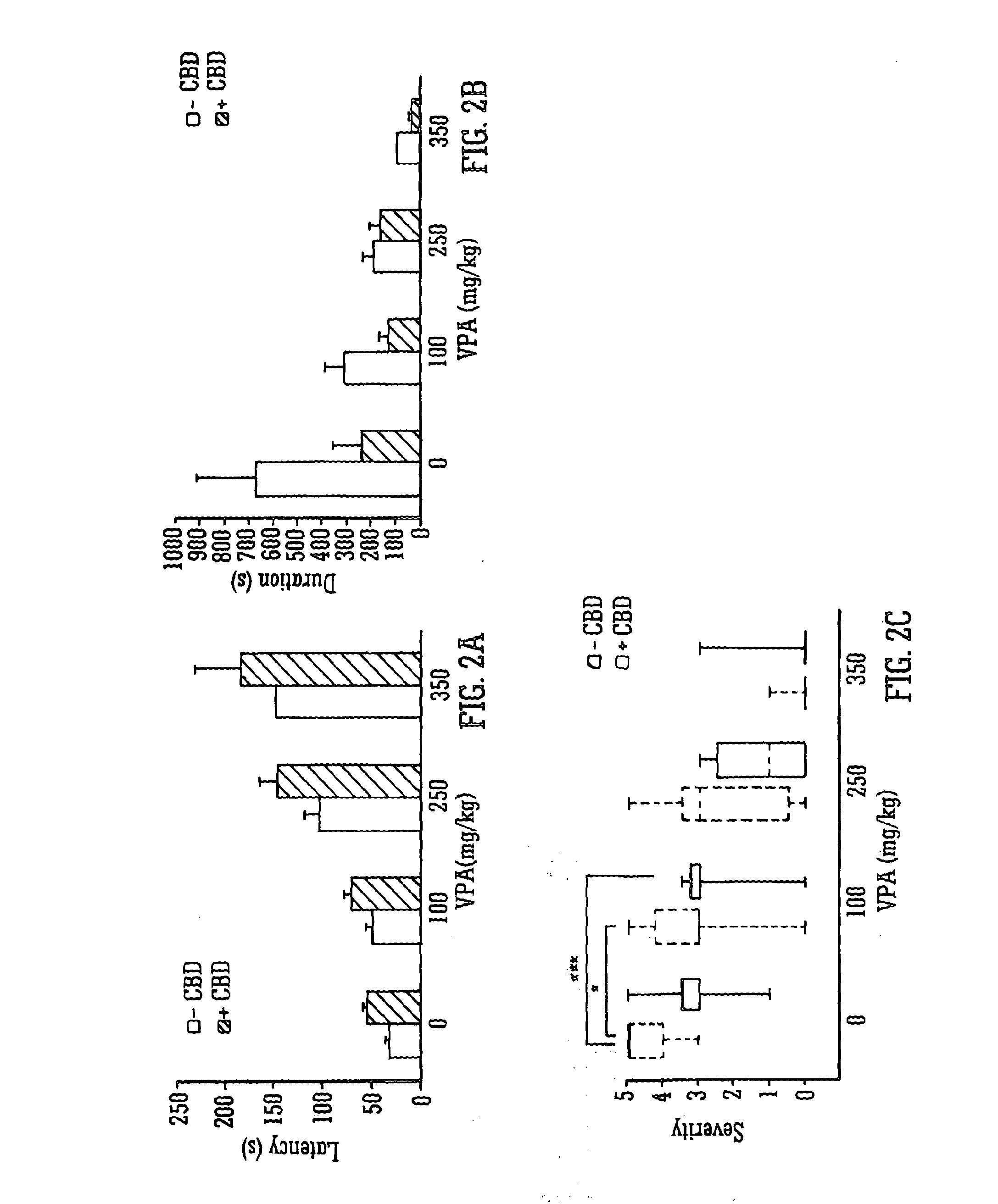
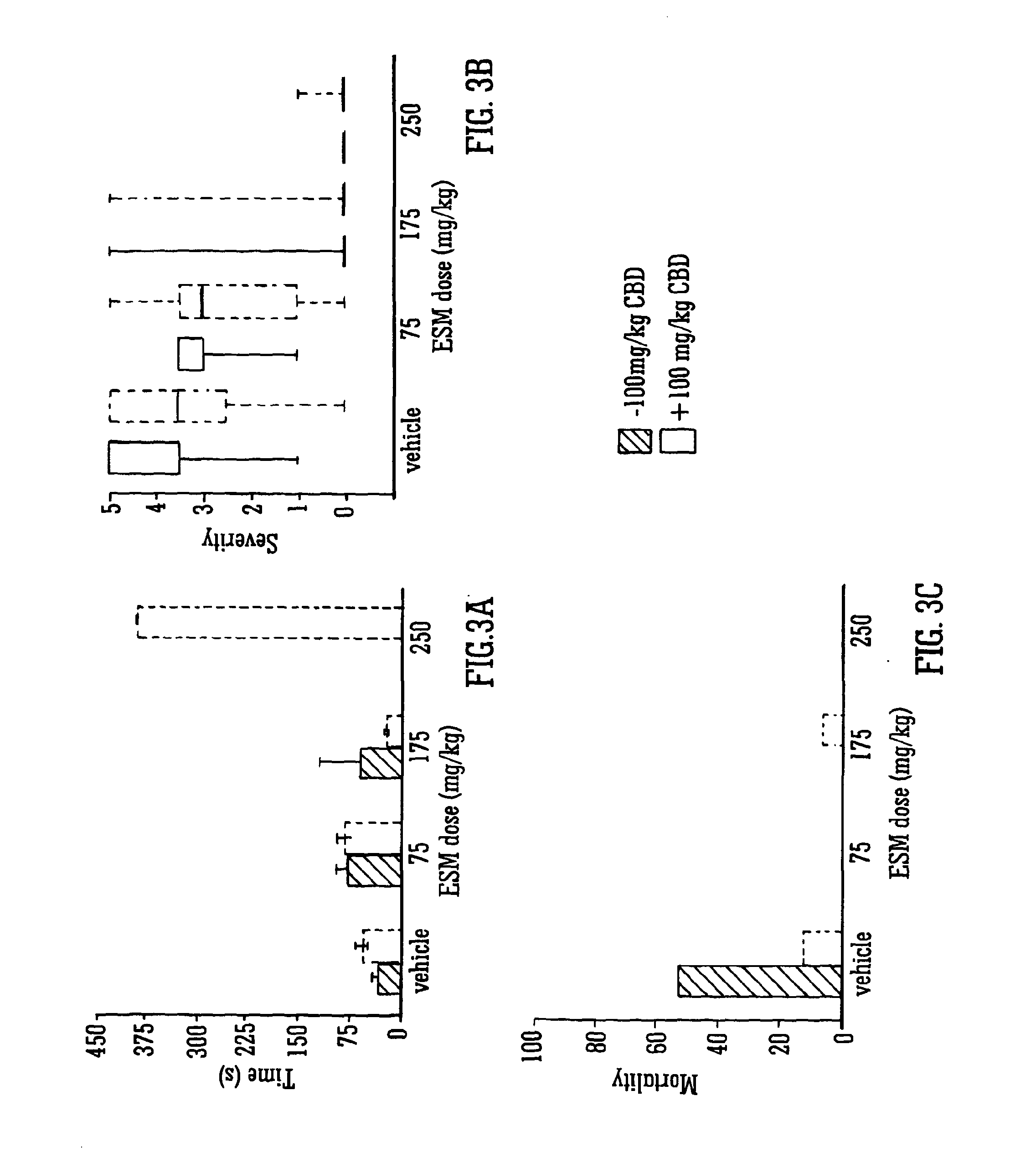
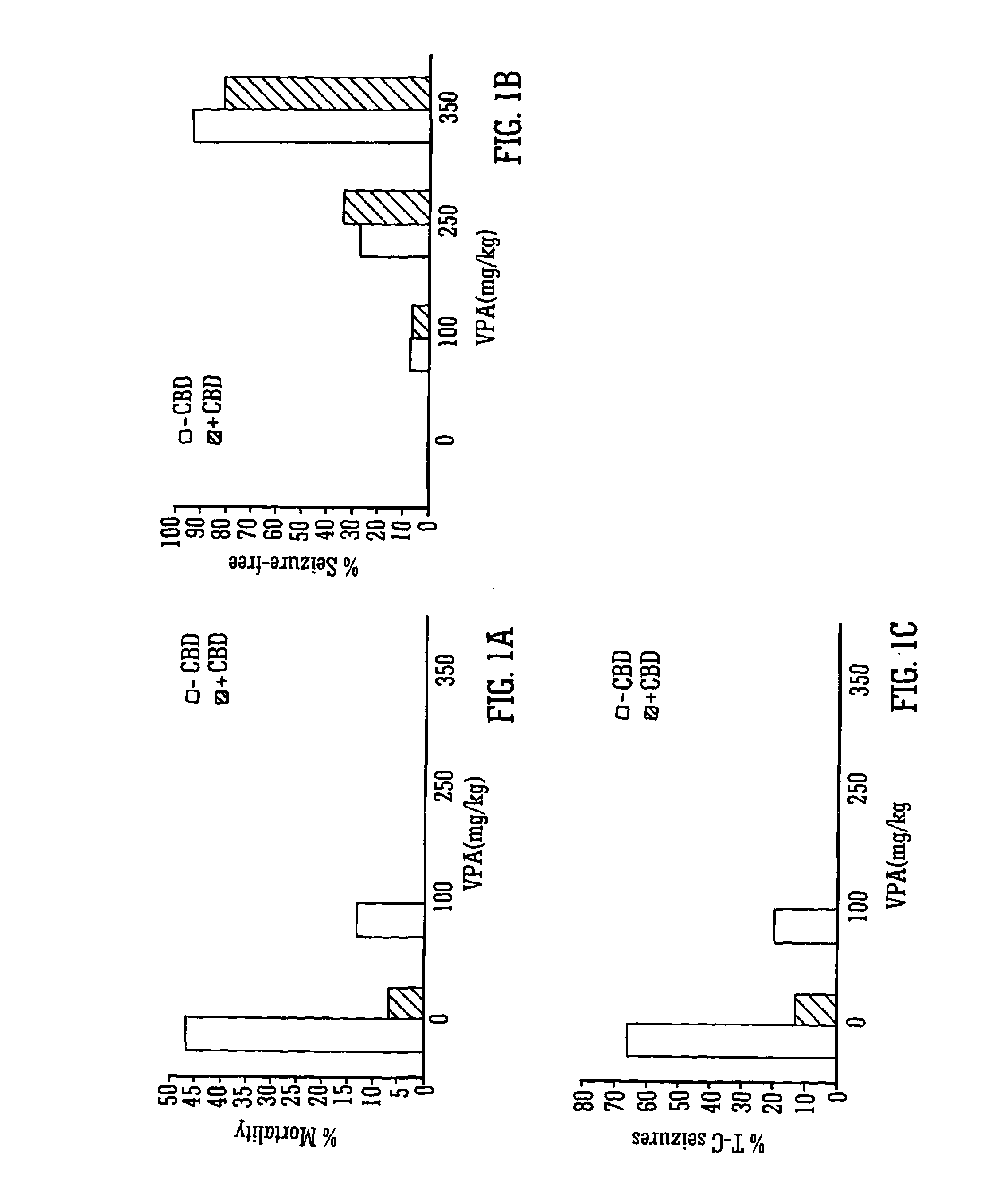
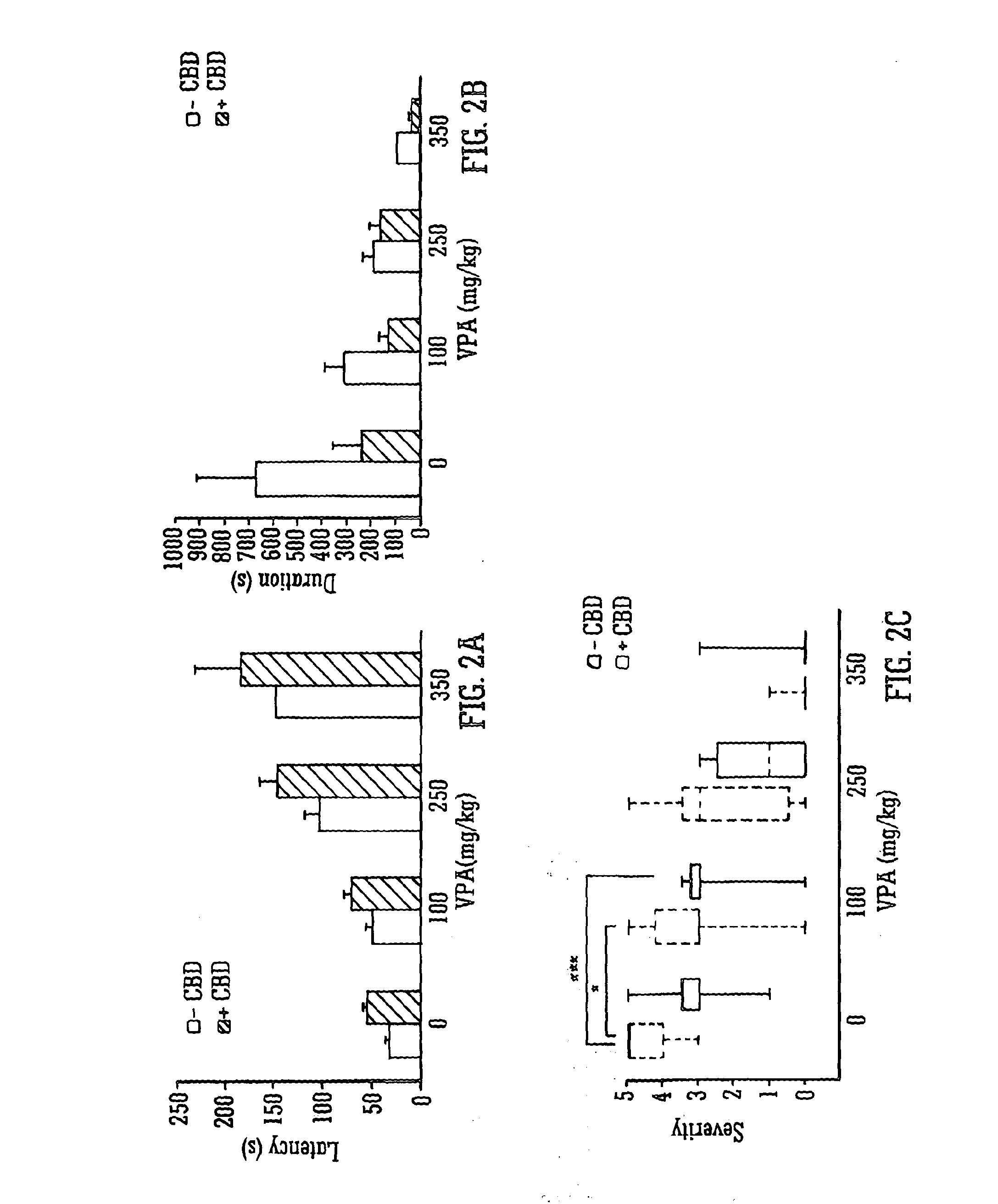
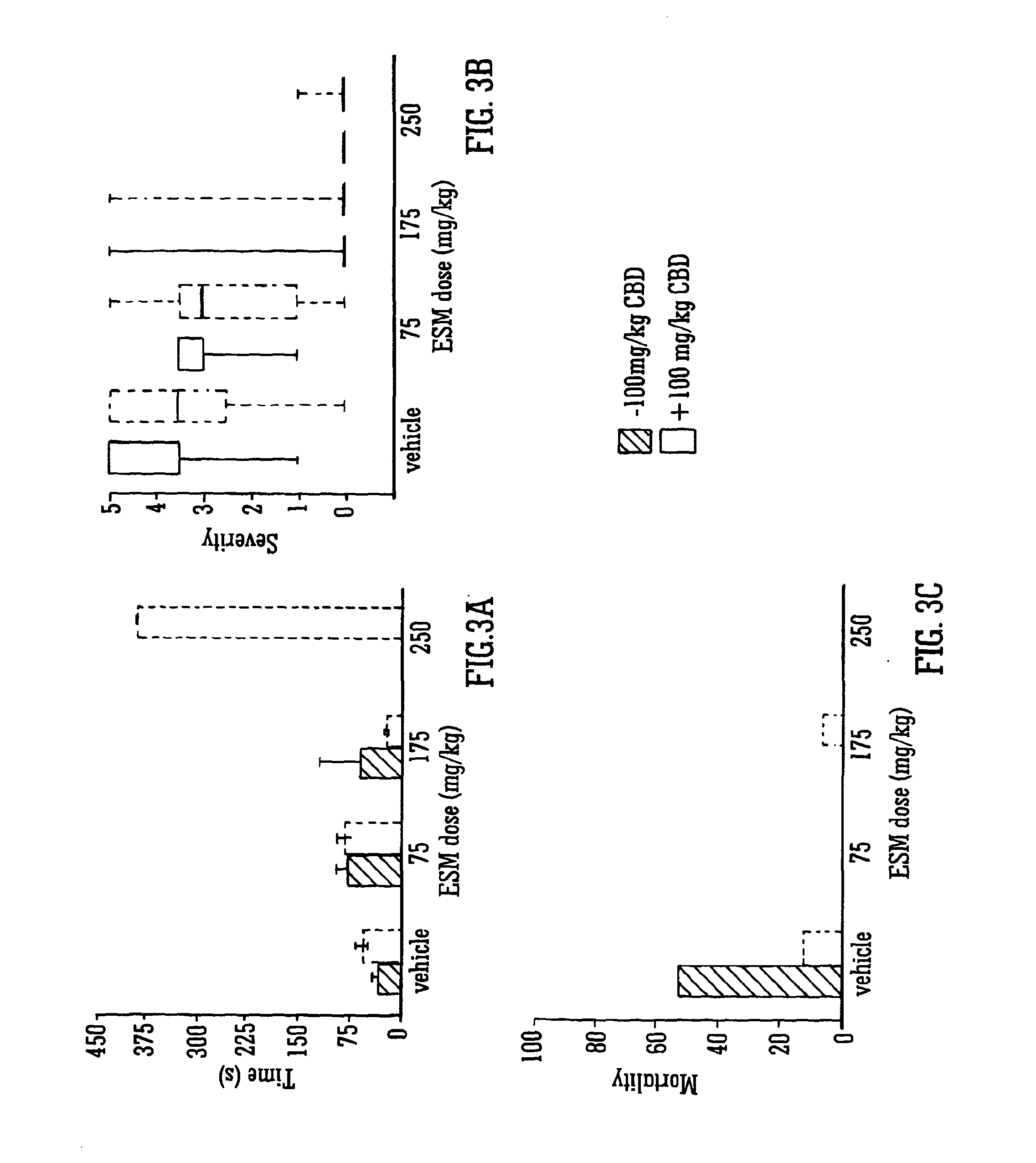
Use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) in combination with a standard Anti-epileptic drug (SAED) in the treatment of epilepsy
InactiveUS20130296398A1Reduce severityReduce mortalityBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidCannabidiol
The invention relates to the use of cannabidiol (CBD), at a dose of greater than 300 mg / day, in combination with a standard anti-epileptic drug (SAED) which acts via sodium or calcium channels, for use in the treatment of epilepsy. The SAED is preferably one which•modifies low-threshold or transient neuronal calcium currents,or•reduces high-frequency neuronal firing and sodium-dependent action potentials and enhances GABA effects. Preferred SAEDs are ethosuximide and valproate.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD +1
Use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) in combination with a standard Anti-epileptic drug (SAED) in the treatment of epilepsy
InactiveUS20140155456A9Reduces high-frequency neuronal firingGood effectBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidCannabidiol
The invention relates to the use of cannabidiol (CBD), at a dose of greater than 300 mg / day, in combination with a standard anti-epileptic drug (SAED) which acts via sodium or calcium channels, for use in the treatment of epilepsy. The SAED is preferably one which•modifies low-threshold or transient neuronal calcium currents,or•reduces high-frequency neuronal firing and sodium-dependent action potentials and enhances GABA effects. Preferred SAEDs are ethosuximide and valproate.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD +1
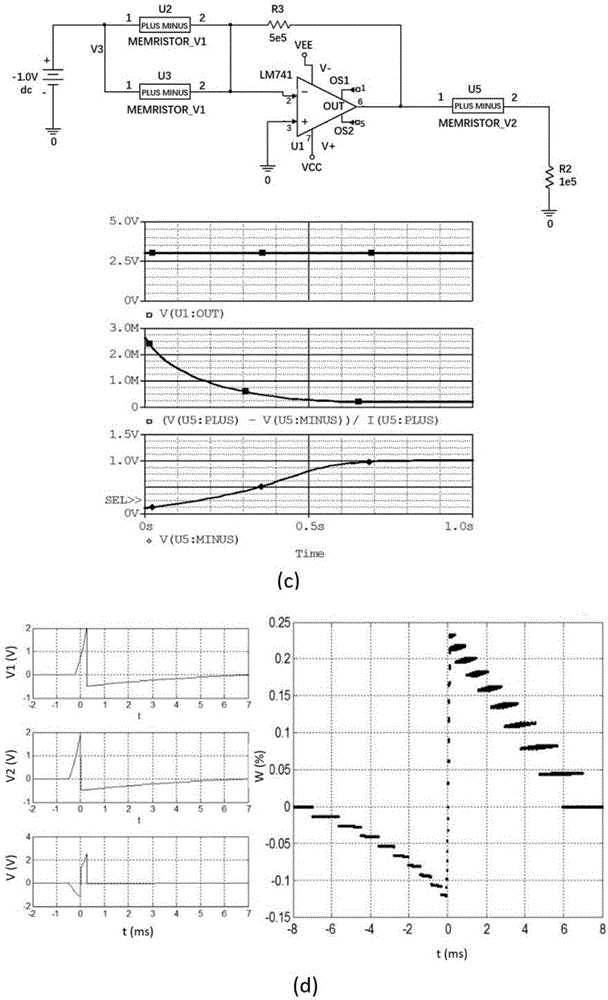
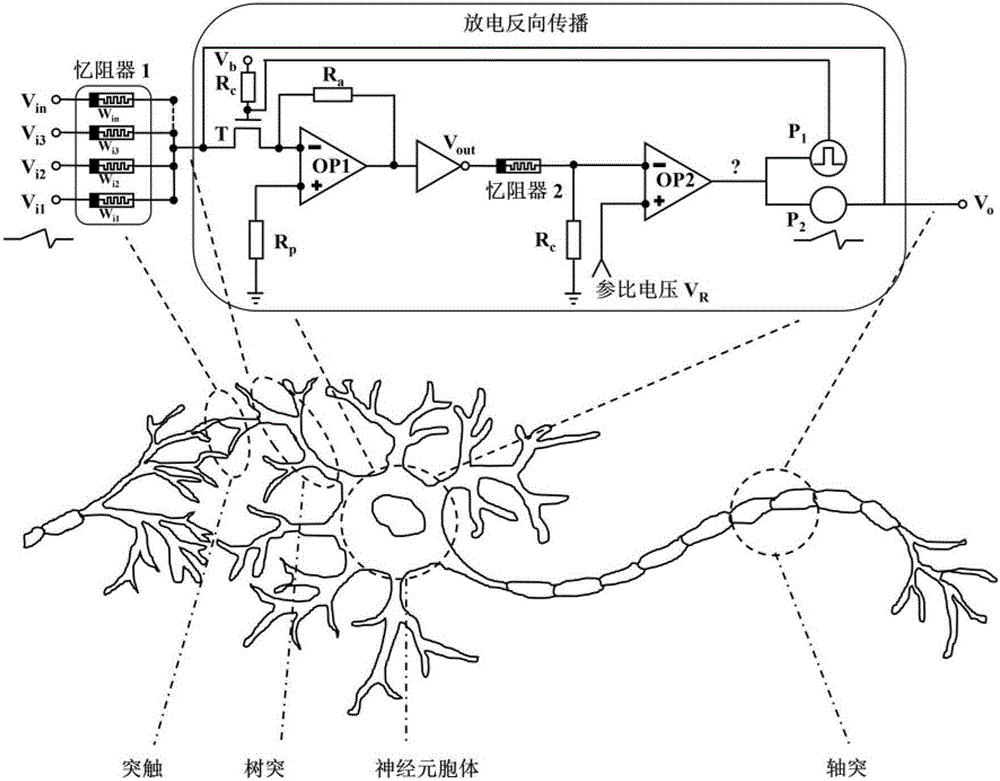
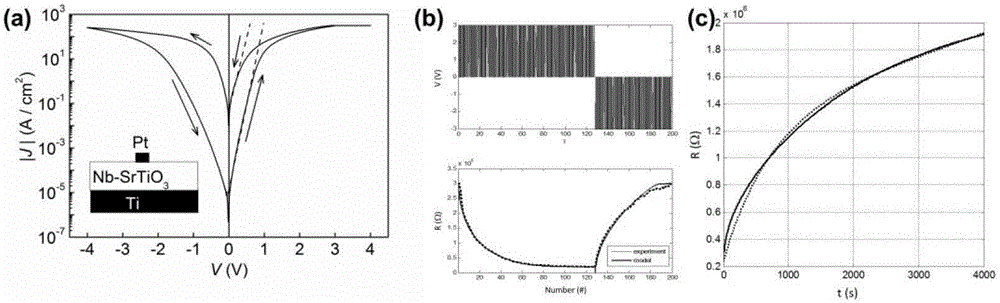
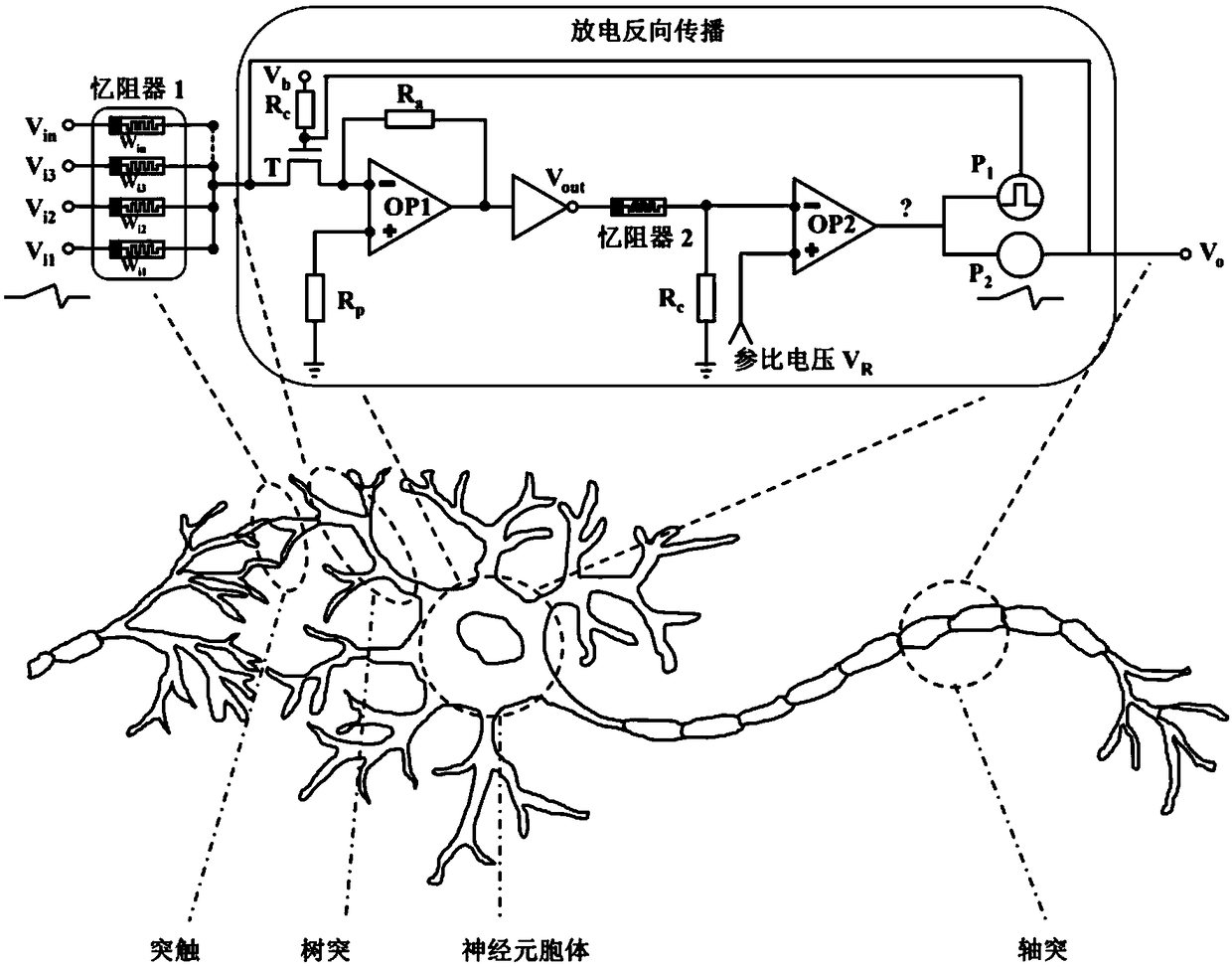
Memristor-based neuron circuit
ActiveCN106845634ARealize integrated discharge functionImplement time encodingPhysical realisationInformation processingSynapse
The invention discloses a memristor-based neuron circuit. According to the neuron circuit, partially volatile bipolar resistive transition devices are selected and used as memristors of a synapse array, and a volatile resistive transition device is selected and used as a memristor for expressing membrane potential of neurons, so that the neuron circuit is formed; and synapse basis units are arranged. The neuron circuit can realize an integral discharge function in biological neurons and express local graded potentials; and synapses have partial volatility, can express spike-timing-dependent plasticity, and have great similarity with biological neurons and synapses in the aspects of information storage, transmission and processing. According to the neuron circuit, the basic units can be provided for hardware to simulate a cerebral neural network structure; the technical problems of neuron discharge time delay, difficulty in realizing high-density integration and the like in the prior art are solved; and the neuron circuit can be used for constructing a brain-like information processing system, can quickly process a large amount of information in parallel, and has a greatly high application value in realizing a cerebral neurologic calculation network.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
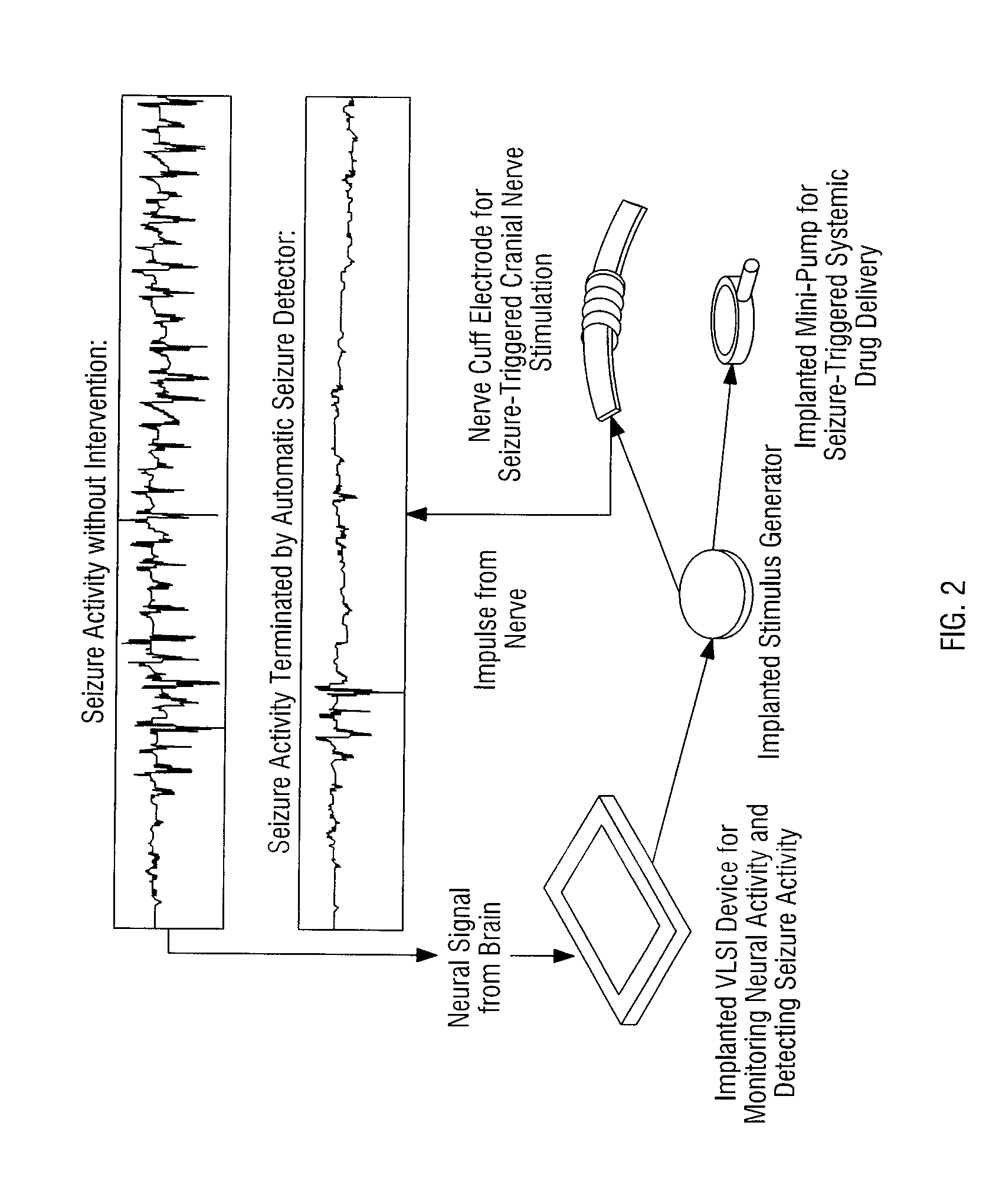
Systems and methods for improving a cognitive function
In many aspects, the invention relates to systems and methods for providing cognitive therapy through stimulation of activating and inhibiting neurons in the brain, thereby modulating neural firing rhythms. The stimulation of neurons is controlled through a feedback process whereby neuron firing rhythms are altered based on naturally occurring electrical and chemical activity in the brain. Neurons in specific regions of the brain may be targeted in order to establish neural signaling pathways and establish communication between these regions.
Owner:MEDTRODE
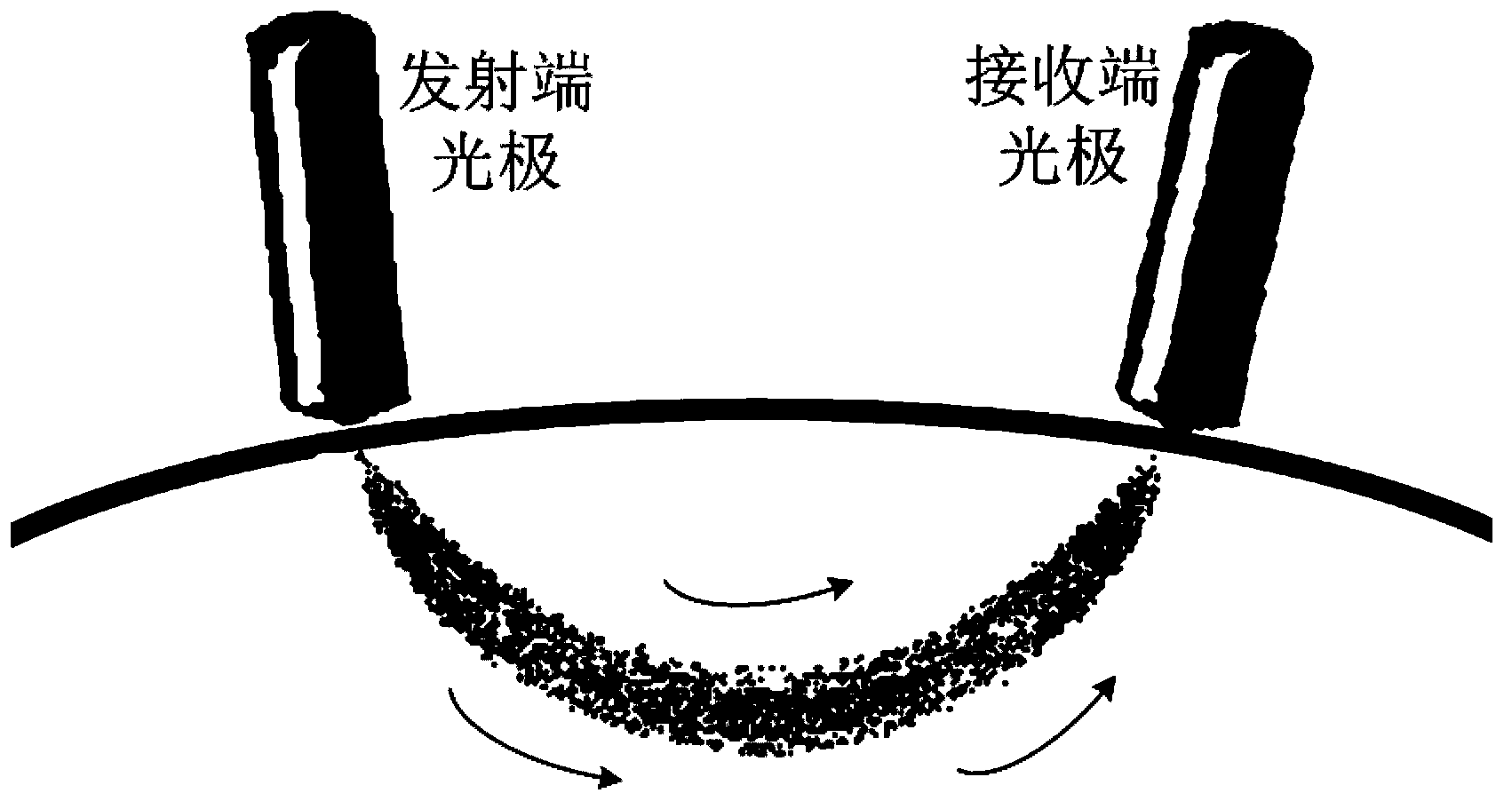
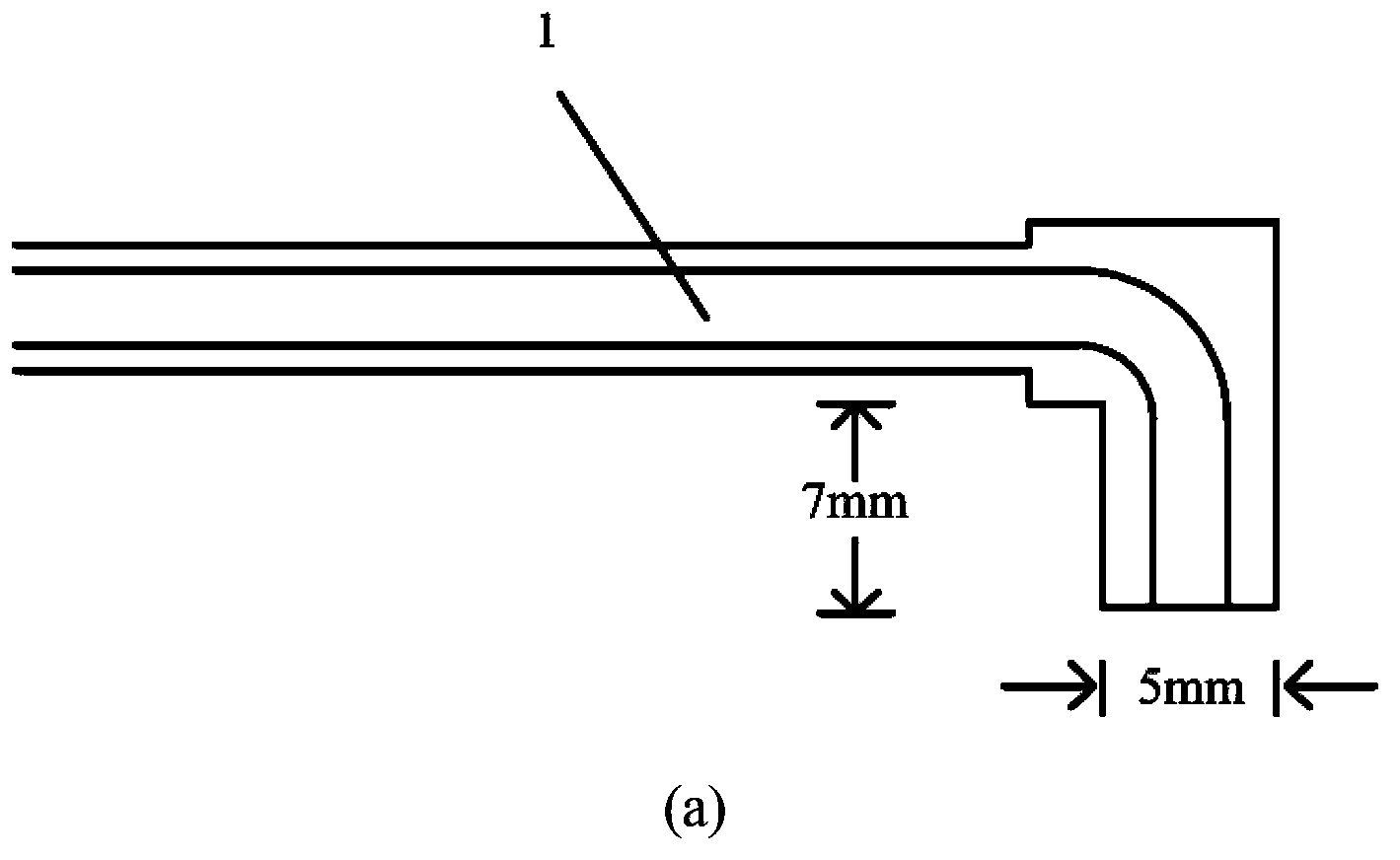
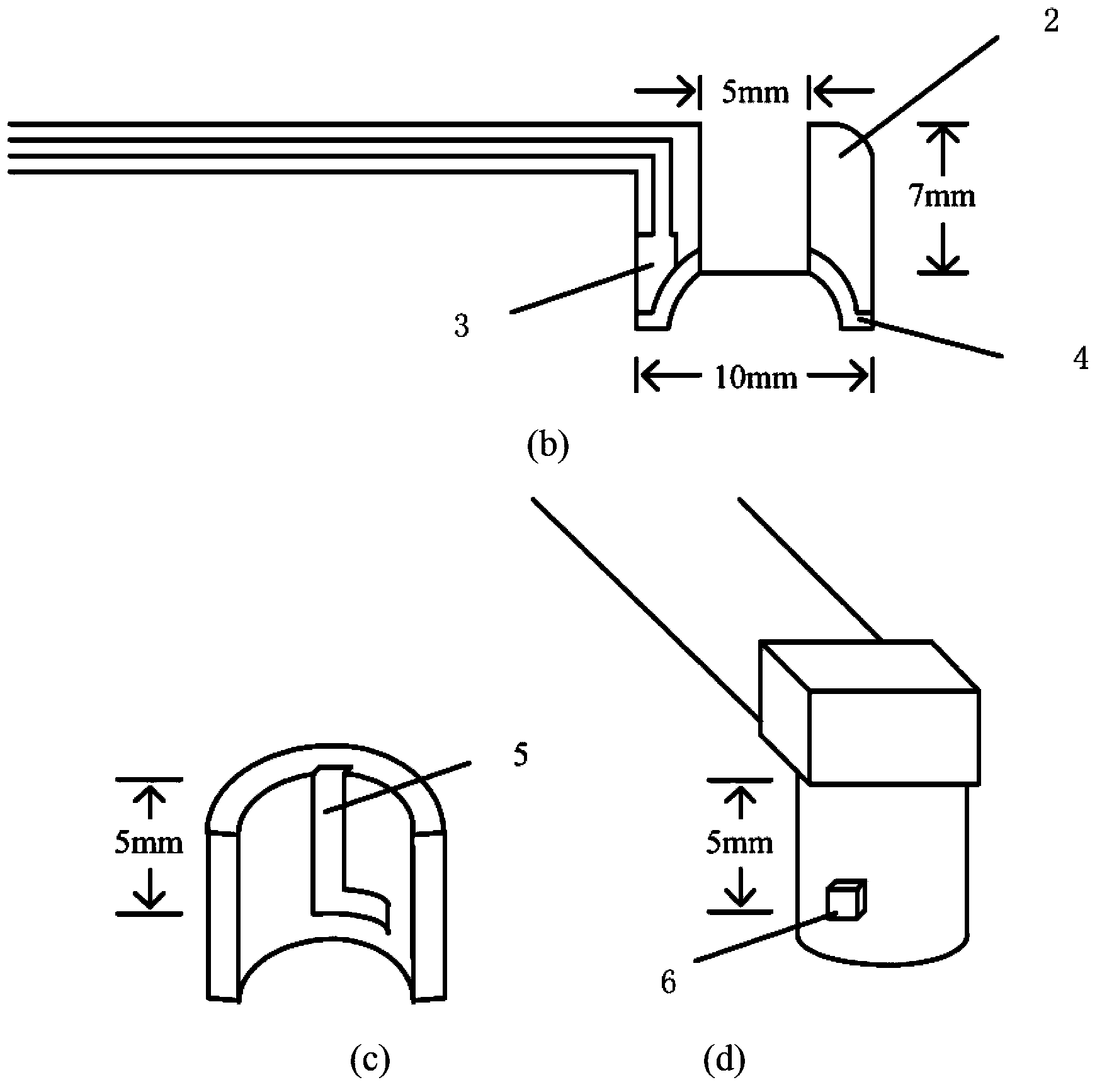
Photoelectric electrode capable of synchronously collecting EEG signals and blood oxygen signals
InactiveCN103445774ASolve the problem that the signals cannot be collected synchronously in the same areaDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineCollection system
A photoelectric electrode is capable of synchronously collecting EEG signals and blood oxygen signals. A disc electrode of an EEG collection system and a fiber probe of a near-infrared spectral cerebral function imaging system are integrated to form the photoelectric electrode. Therefore, the problem that cerebral neuronal firing activity and blood oxygen metabolic information cannot be collected synchronously is solved. The photoelectric electrode includes two separable parts, including an electrode part and a photo-electrode part. The electrode part is composed of a hollow disc electrode and a base and is used independently for collecting electroencephalograms; the photo-electrode part can be directly inserted into the base of the electrode part and is firmed through an L-shaped groove. On the basis of nationally standard 10-20 system electrode distribution, 64-channel EEG signals and 42-channel blood oxygen signals can be collected synchronously.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Modulation of bio-electrical rhythms via a novel engineering approach
ActiveUS20090291068A1Modify/improve their physiological functionReduce and eliminate sensation of painBiocideNervous disorderCardiac pacemaker electrodeTherapeutic intent
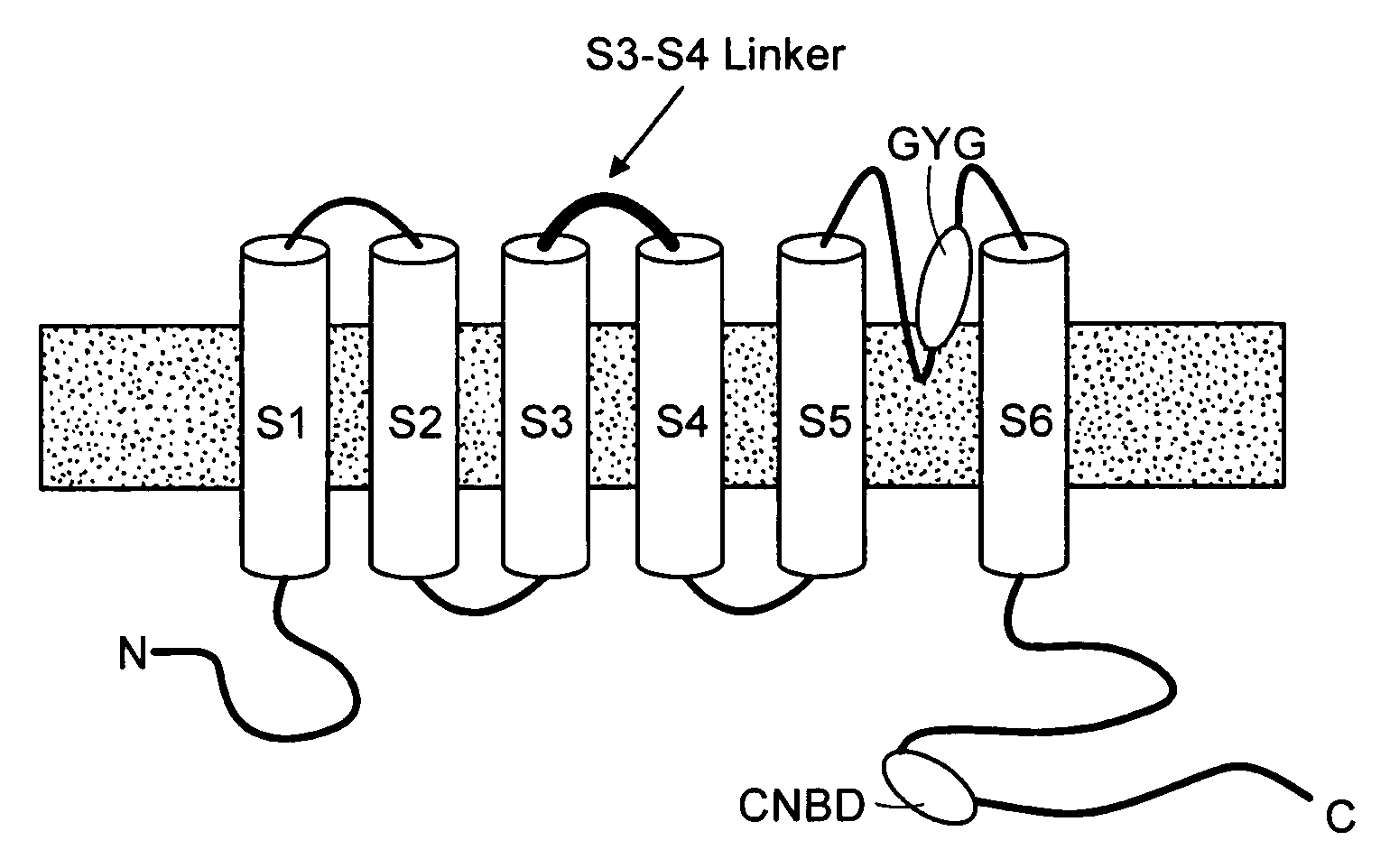
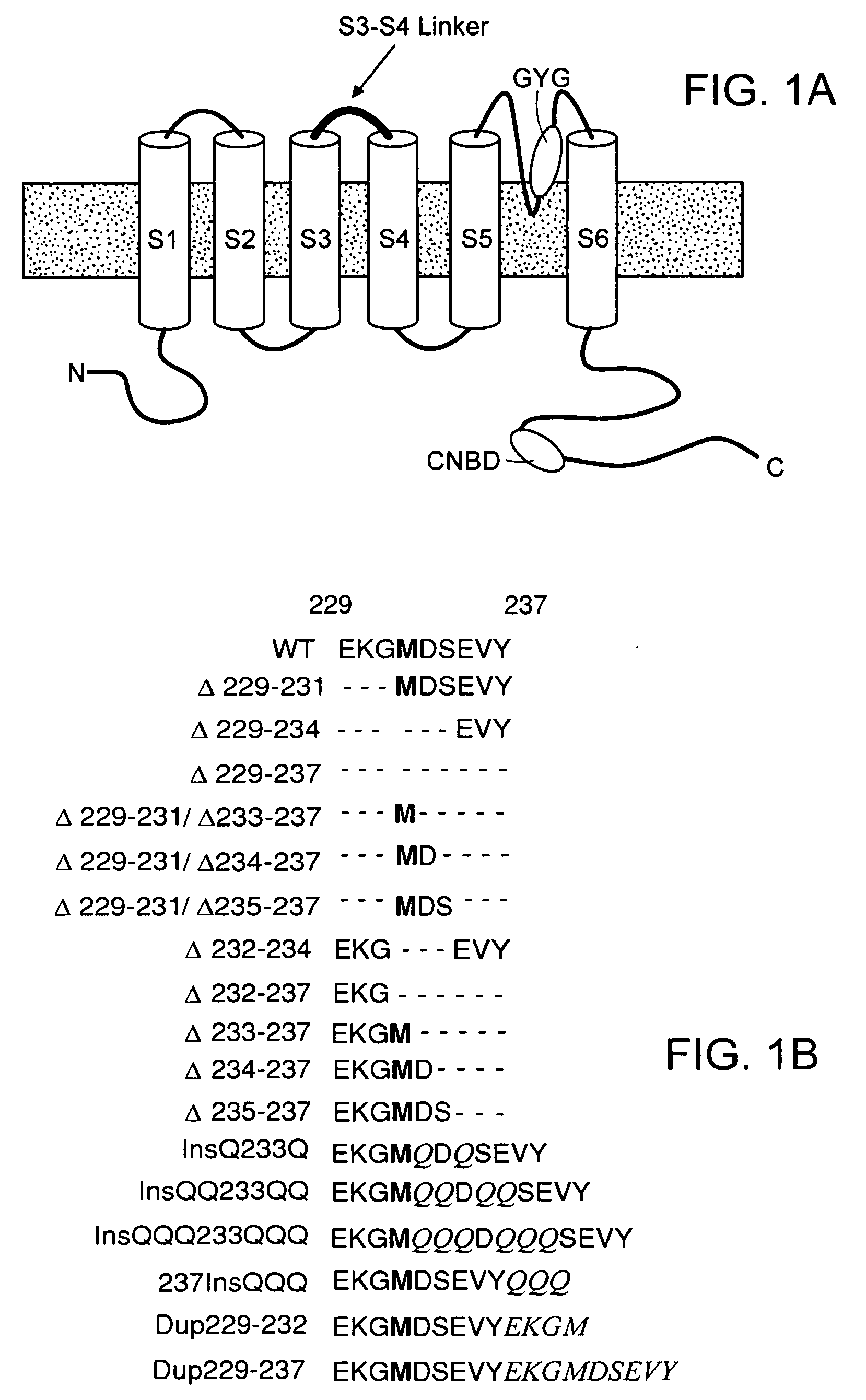
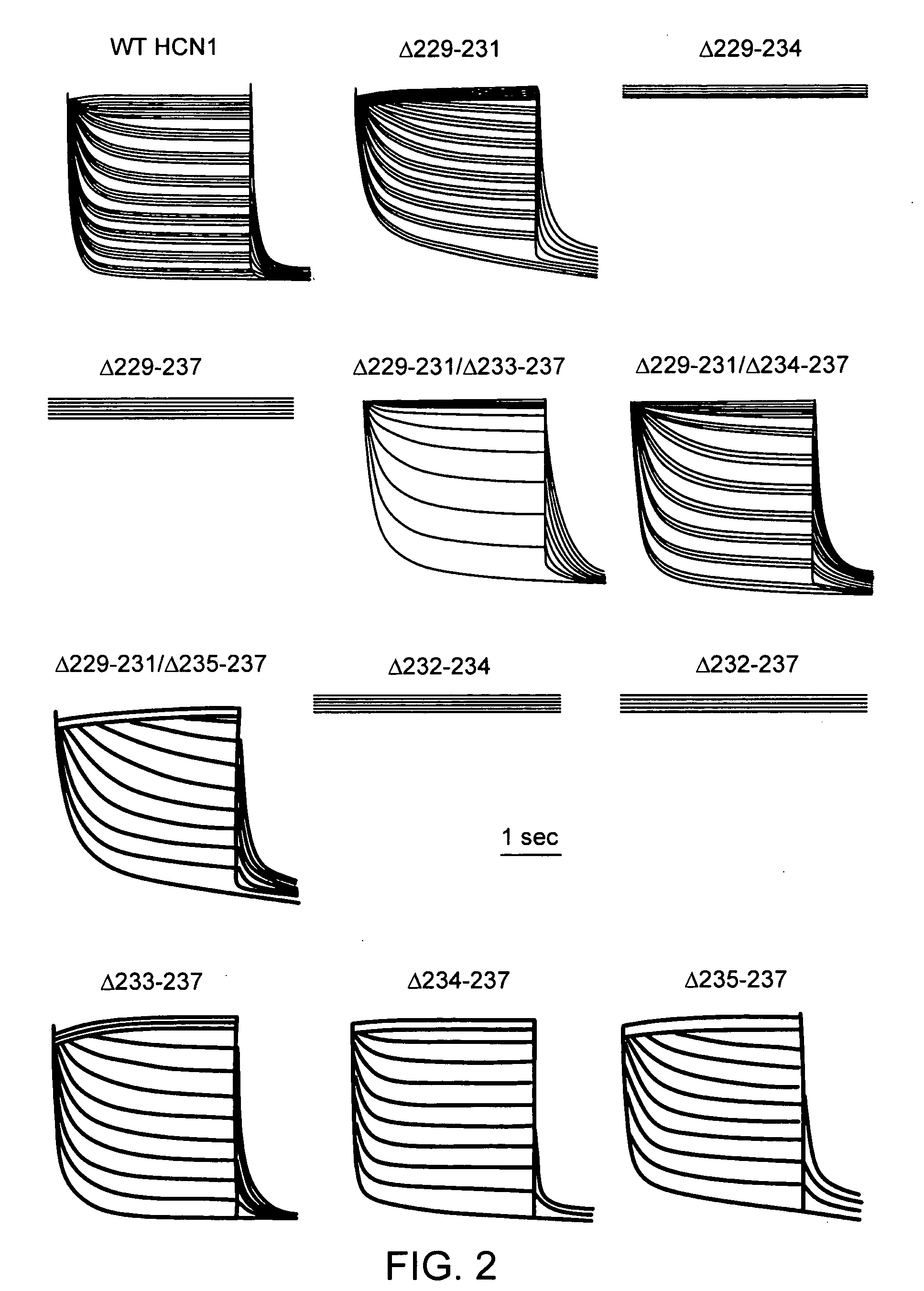
The present invention relates to novel compositions and methods to induce, and / or modulate bio-electrical rhythms (e.g. in cardiac, neuronal and pancreatic cells) by fine-tuning the activity of HCN-encoded pacemaker channels via a novel protein- and genetic-engineering approach to augment or attenuate the associated physiological responses (e.g. heart beat, neuronal firing, insulin secretion, etc) for achieving various therapeutic purposes (e.g. sick sinus syndrome, epilepsy, neuropathic pain, diabetes, etc).
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Transdermal formulations of synthetic cannabinoids and NANO colloidal silica
InactiveUS20100184848A1Eliminate side effectsPrecise positioningBiocideNervous disorderColloidal silicaNeuropathic pain
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising cannabinoids or mimics thereof. In one aspect, the invention provides transdermal formulations comprising cannabinoids or mimics thereof. In another aspect, the invention provides topical formulations comprising cannabinoids or mimics thereof. In one embodiment the formulations and compositions of the invention comprise nano colloidal silica. The formulations of the invention can be used in the therapeutic treatment of many conditions, including wherein the cannabinoids or mimics thereof are known to reduce the excessive neuronal firing characteristic of neuropathic pain. Muscle spasticity is also benefited by these formulations.
Owner:WINE WILLIAM ABRAHAM +1
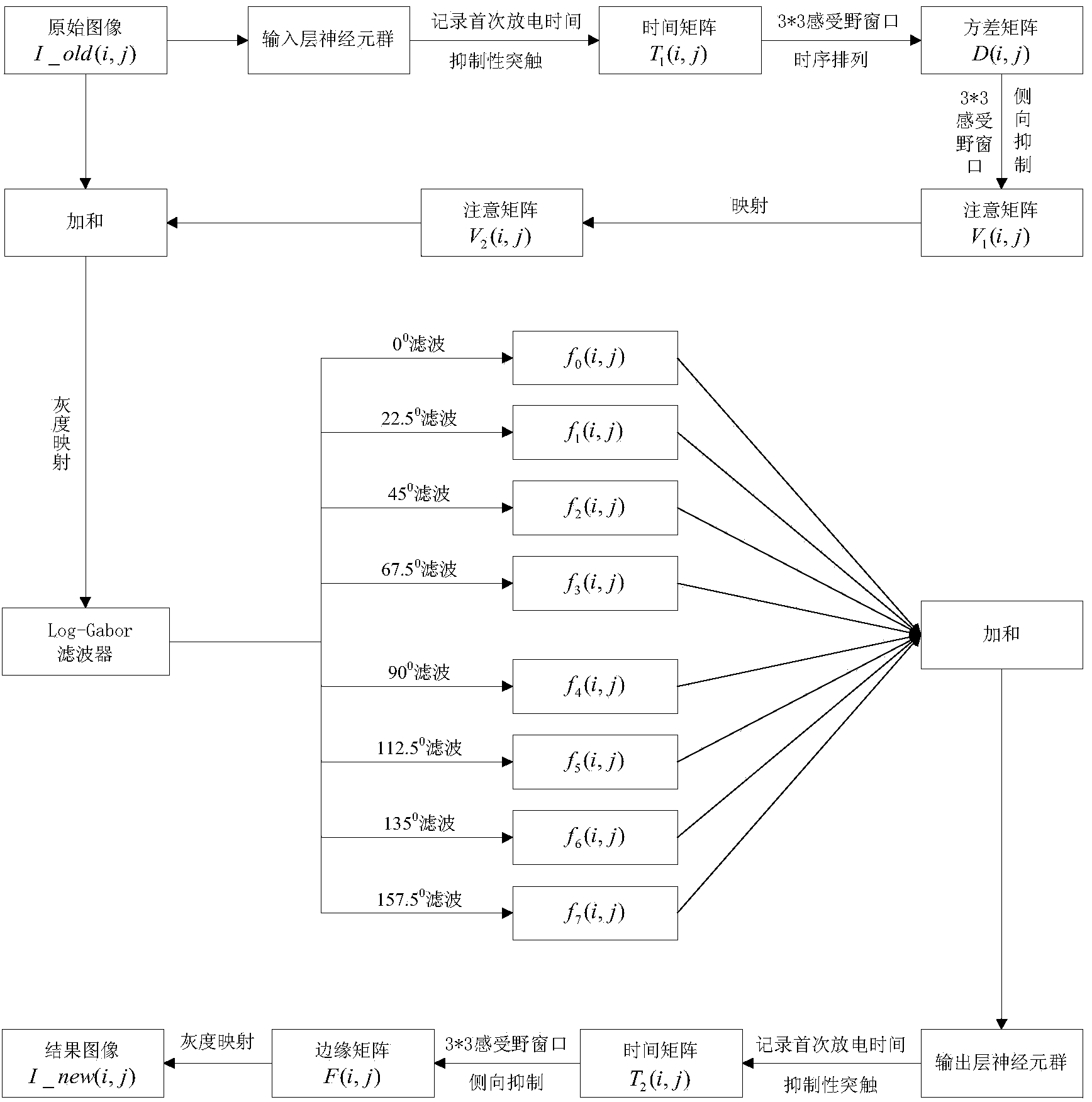
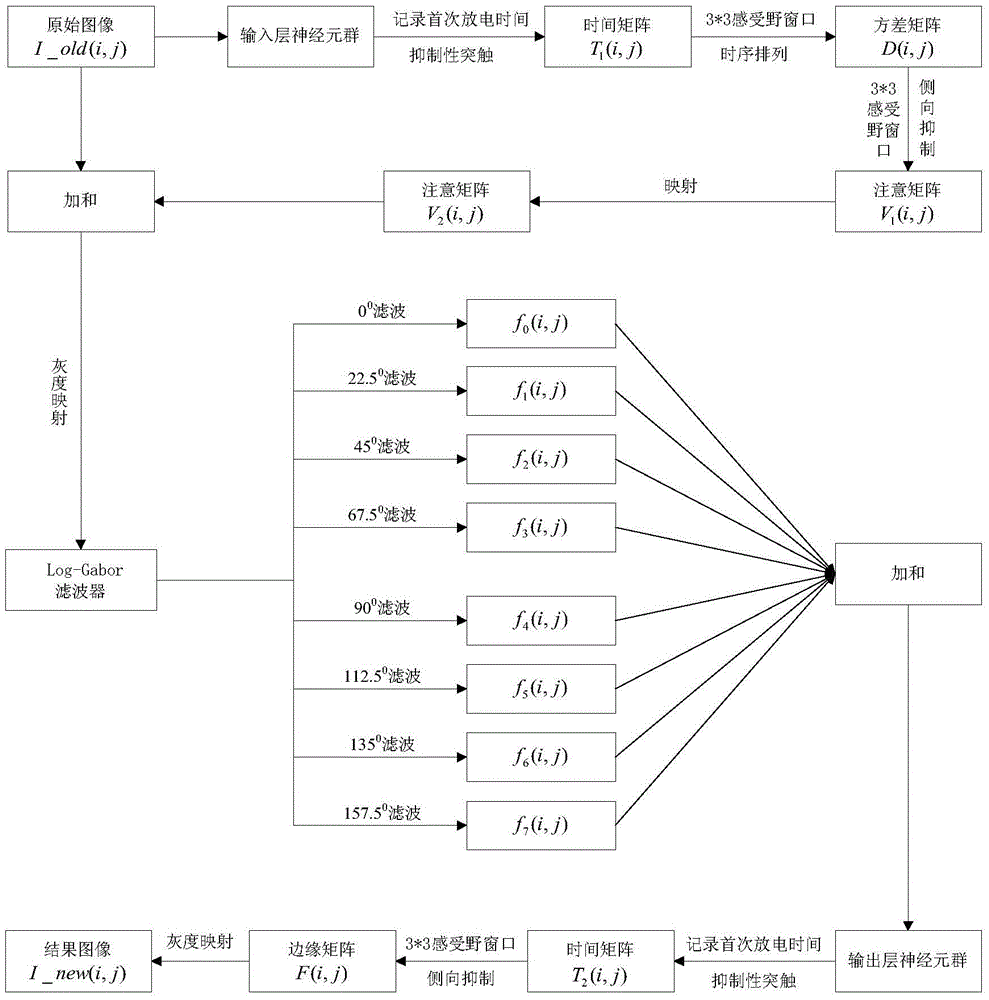
Method for detecting weak edges of images on basis of discharge information of multilayer neuron groups
The invention relates to a method for detecting weak edges of images on the basis of discharge information of multilayer neuron groups. The method includes constructing the multilayer neuron groups with interconnected inhibitory synapses, inputting digital images into input-layer neuron groups and representing image pixels by the time-space information of first discharge of various neurons; describing space details of the images by time variances by the aid of visual receptive fields and discharge time sequences of the various neurons, selecting attentive mechanisms in the consideration of lateral inhibition so as to acquire visual attention data of information of the images; implementing space variable-resolution mechanisms on the basis of a combination of selective attention procedures by the aid of Log-Gabor multi-direction filter results, acquiring reconstructed information of the edges of the images and reinforcing the information of the edges of the images by the aid of output-layer neuron groups. The method has the advantages that a synapse interconnection characteristic of the neuron groups is taken into consideration; simple visual information procedures of cortices are reflected by the aid of multi-direction filter mechanisms; the weak edges of the images can be effectively detected by the aid of the multilayer neuron groups.
Owner:盐城市凤凰园科技发展有限公司
Cells and methods utilizing same for modifying the electrophysiological function of excitable tissues
A method of treating a movement disorder in a subject is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of cells capable of modifying a neuronal discharge of the subject, thereby treating the movement disorder in the subject, wherein said administering is effected at a site selected from the group consisting of internal globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra pars reticulate.
Owner:GENEGRAFTS LTD
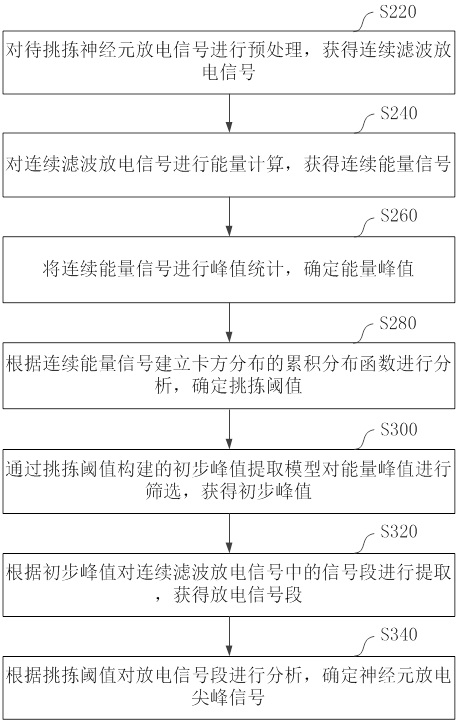
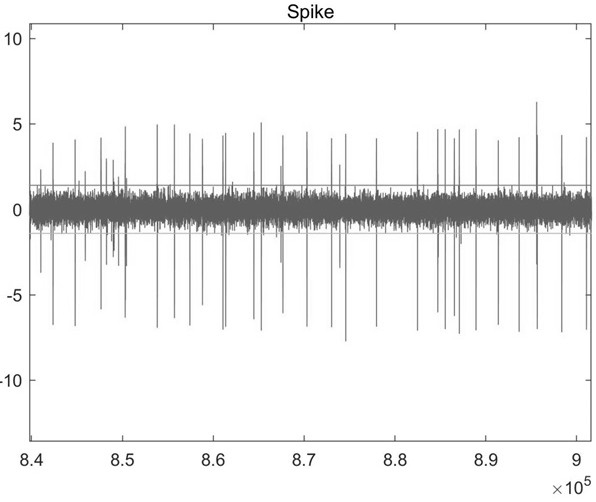
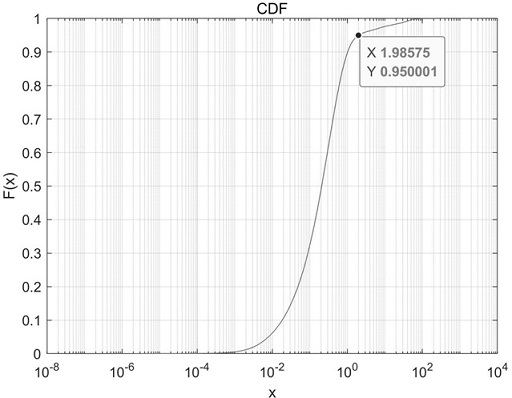
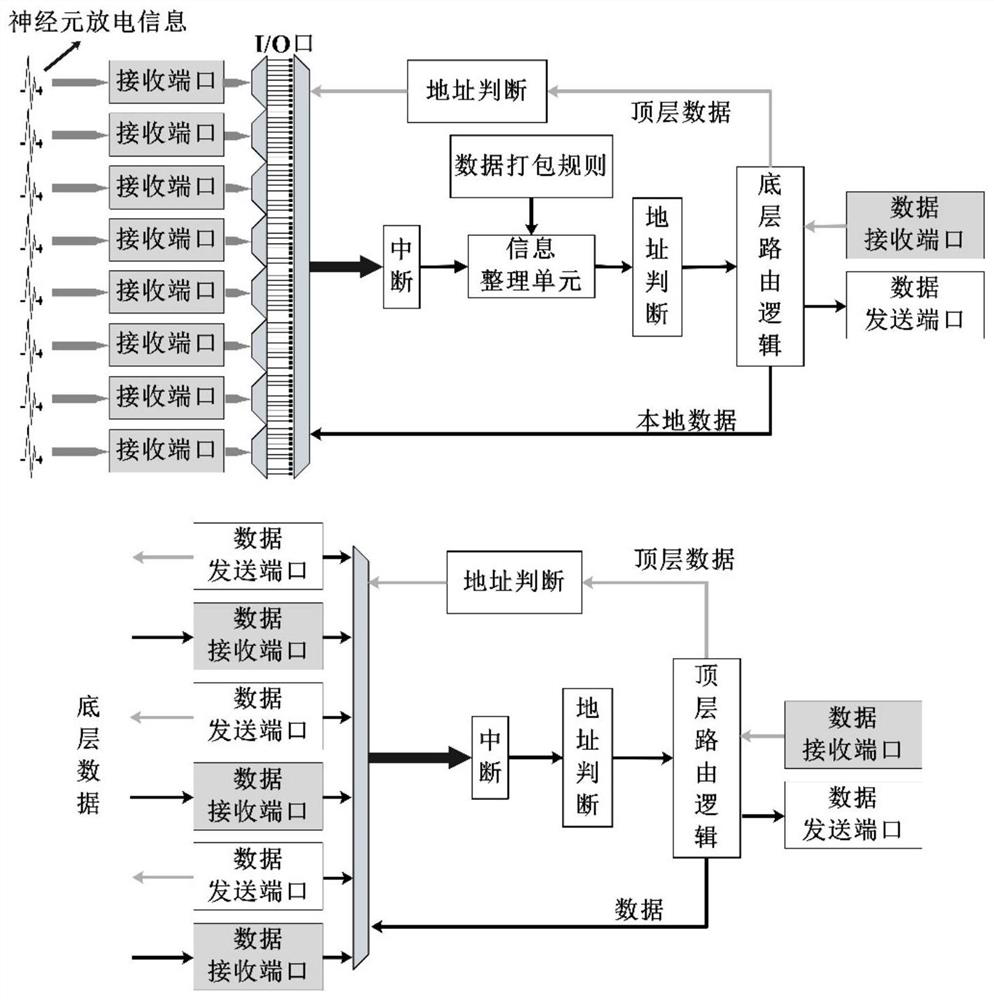
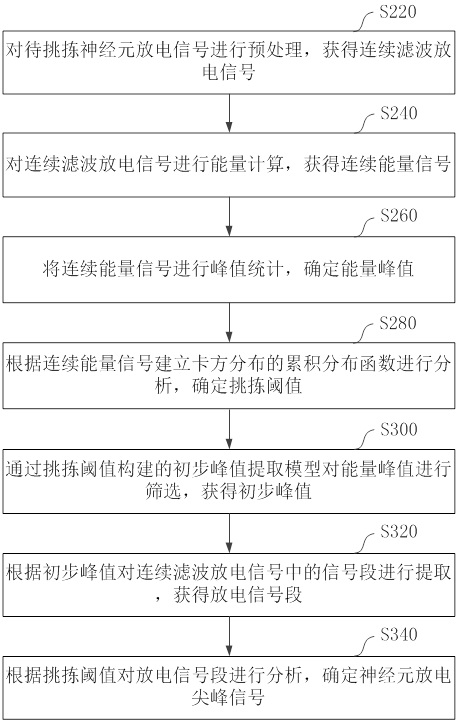
Neuron discharge spike signal picking method and device and computer equipment
ActiveCN112472108APick accuratelyImprove robustnessDiagnostic signal processingSensorsAlgorithmNeuron
The invention relates to a neuron discharge spike signal picking method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a to-be-picked neuron discharge signal to obtain a continuous filtering discharge signal; performing energy calculation on the continuous filtering discharge signal to obtain a continuous energy signal; performing peakvalue statistics on the continuous energy signal to determine an energy peak value; establishing a cumulative distribution function of chi-square distribution according to the continuous energy signals for analysis, and determining a picking threshold; screening the energy peak values through a preliminary peak value extraction model constructed by the picking threshold value to obtain a preliminary peak value; extracting a signal segment in the continuous filtering discharge signal according to the preliminary peak value to obtain a discharge signal segment; and analyzing the discharge signalsegment according to the picking threshold, and determining a neuron discharge peak signal. Through the method, the robustness of picking the neuron discharge spike signals is stronger, and the accuracy of the picking result is also improved.
Owner:南京畅享医疗科技有限公司
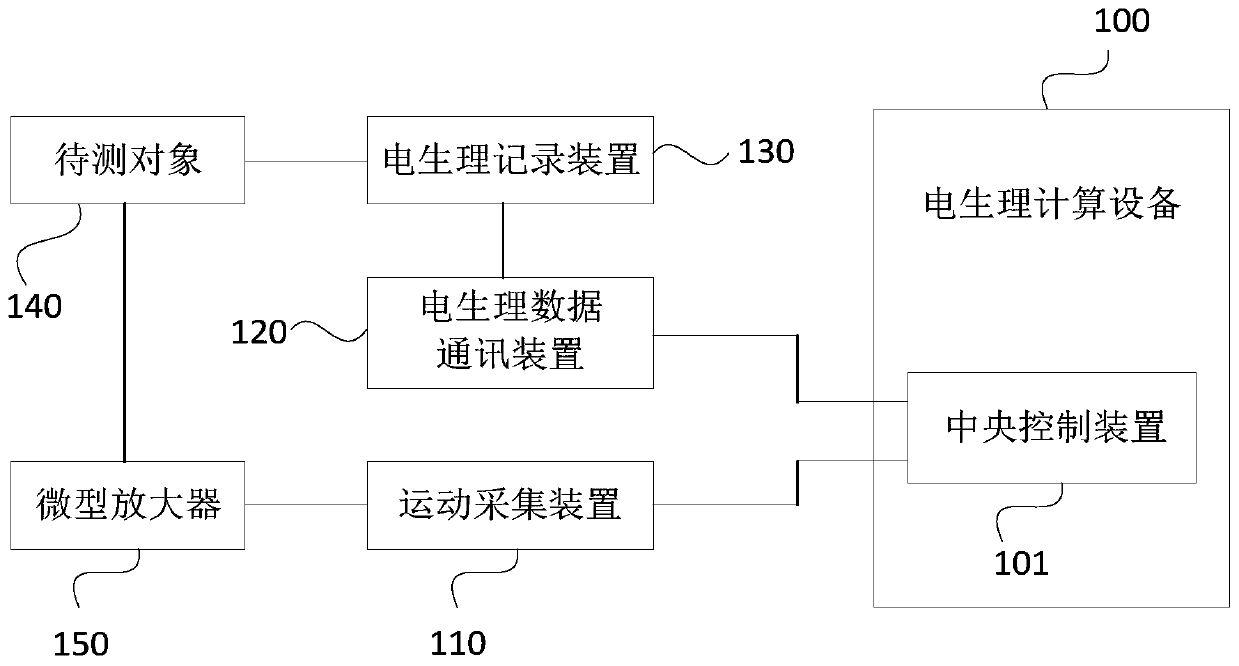
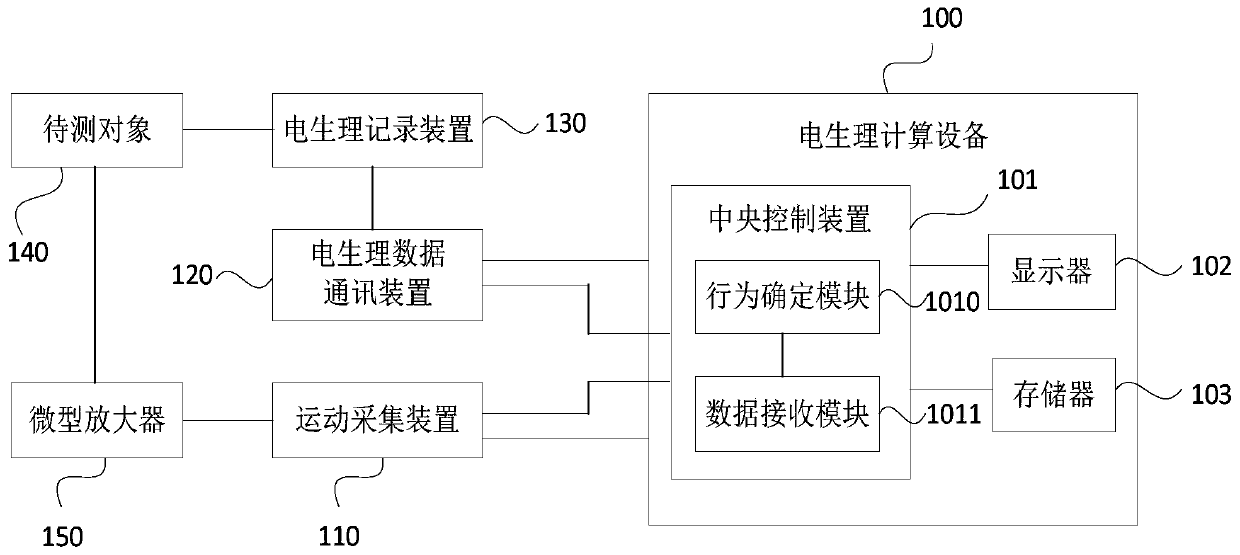
Motion monitoring system
InactiveCN111587809AImprove matchDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnimal behaviorElectro physiology
The invention discloses a motion monitoring system. The motion monitoring system comprises electrophysiological calculation equipment, a motion acquisition device, an electrophysiological data communication device and an electrophysiological recording device, wherein the electrophysiological calculation equipment comprises a central control device, and the motion acquisition device acquires 3D motion data of a to-be-monitored object and sends the 3D motion data to the central control device; the central control device generates a start instruction and an end instruction according to a triggerby a user, analyzes the 3D motion data, obtains motion state data, and records target motion state data between the start instruction and the end instruction; the electrophysiological data communication device sends generation time of the start instruction and the end instruction and the target motion state data to the electrophysiological recording device; and the electrophysiological recording device marks the received generation time in the electrophysiological data generated in neuron activities of the to-be-monitored object, and determines and records the electrophysiological data matchedwith the target motion state data. The scheme improves the matching degree of animal behaviors and neuron discharge activities in accuracy and time.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
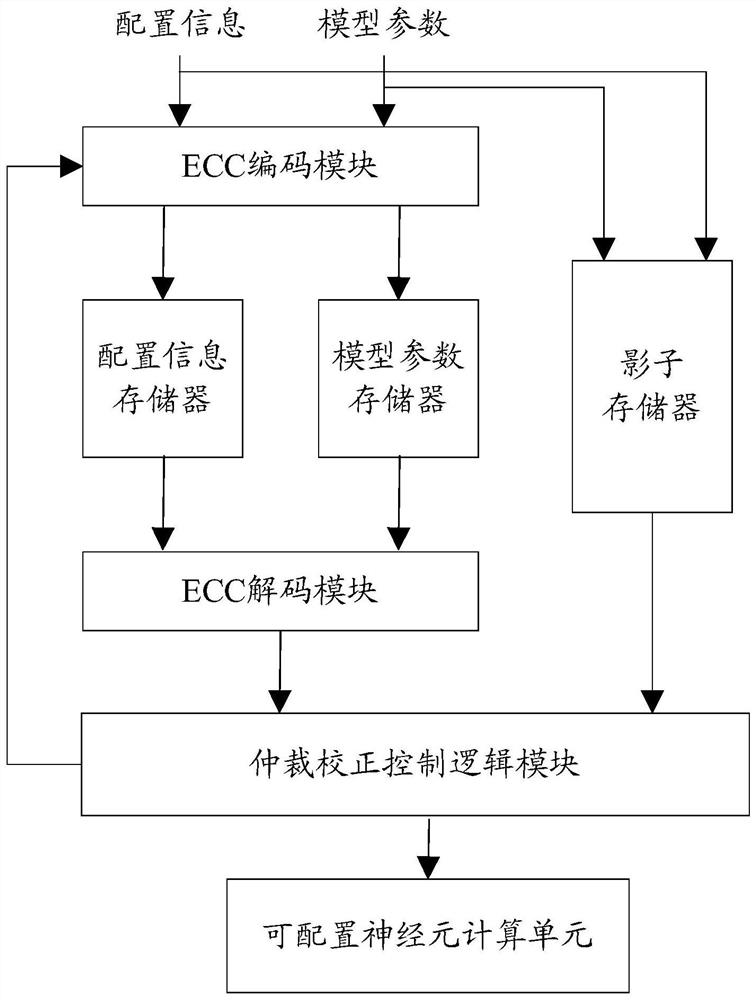
Spiking neuron reinforcing circuit and reinforcing method
PendingCN114528983AImprove reliabilityImprove adaptabilityPhysical realisationFault toleranceAlgorithm
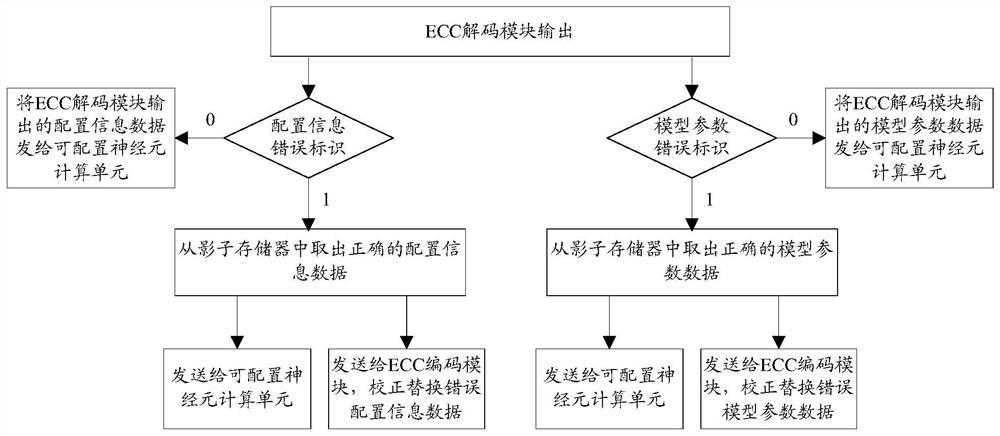
The invention relates to a spiking neuron reinforcing circuit and a spiking neuron reinforcing method, which solve the defect in the prior art that the spiking neuron is easily subjected to calculation errors due to the influence of a single event effect, and effectively improve the space environment adaptability of the spiking neuron. According to the method, spiking neurons and neuron discharge pulse signals required by the spiking neural network can be realized through configuration information and model parameters; furthermore, according to the method, error detection and fault tolerance are carried out on configuration information and model parameters through an ECC coding and decoding module; further, according to the method, backup fault tolerance is carried out on configuration information and model parameters through a shadow memory (or a register block).
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Semiconductor circuit using positive feedback field effect transistor for emulating neuron firing process
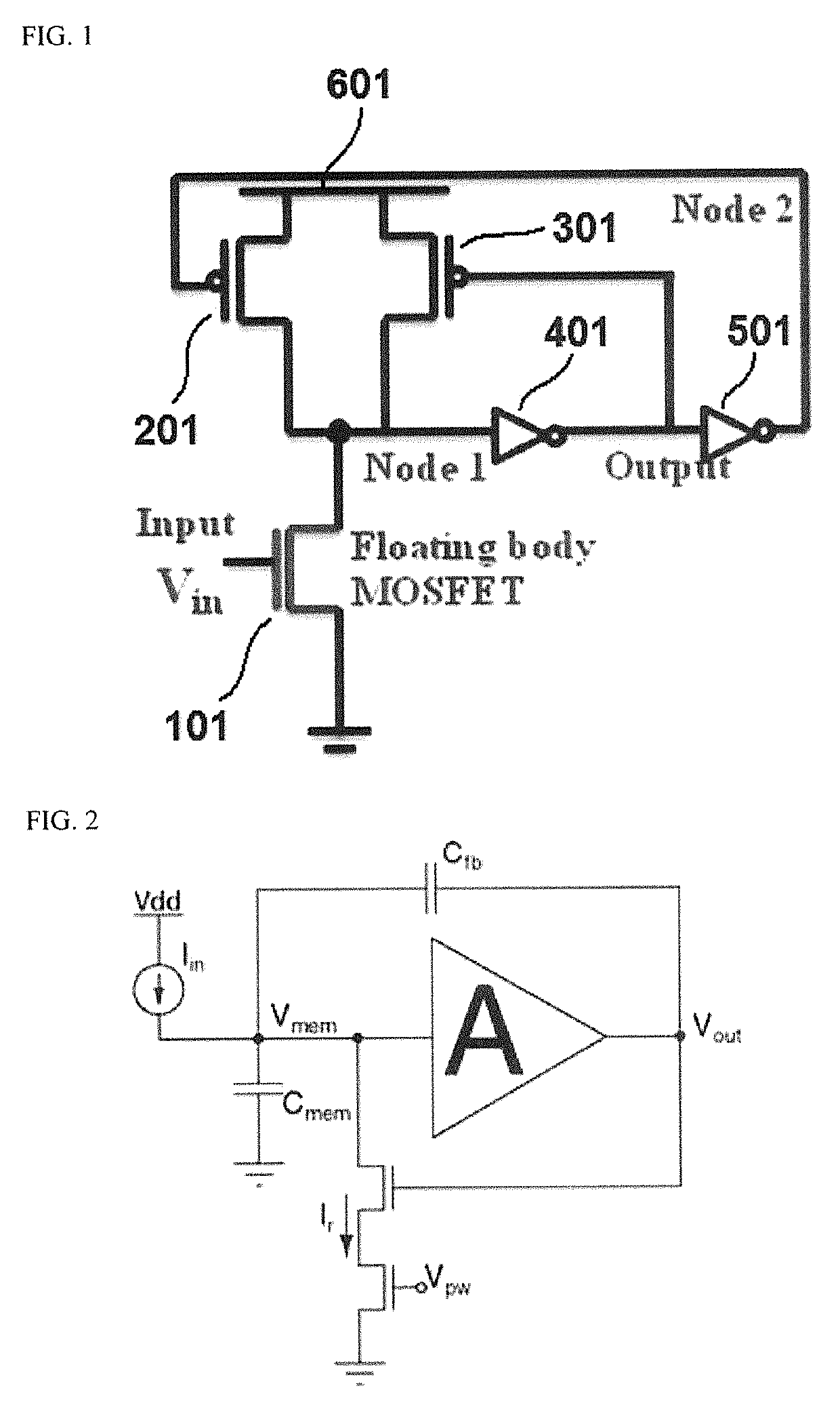
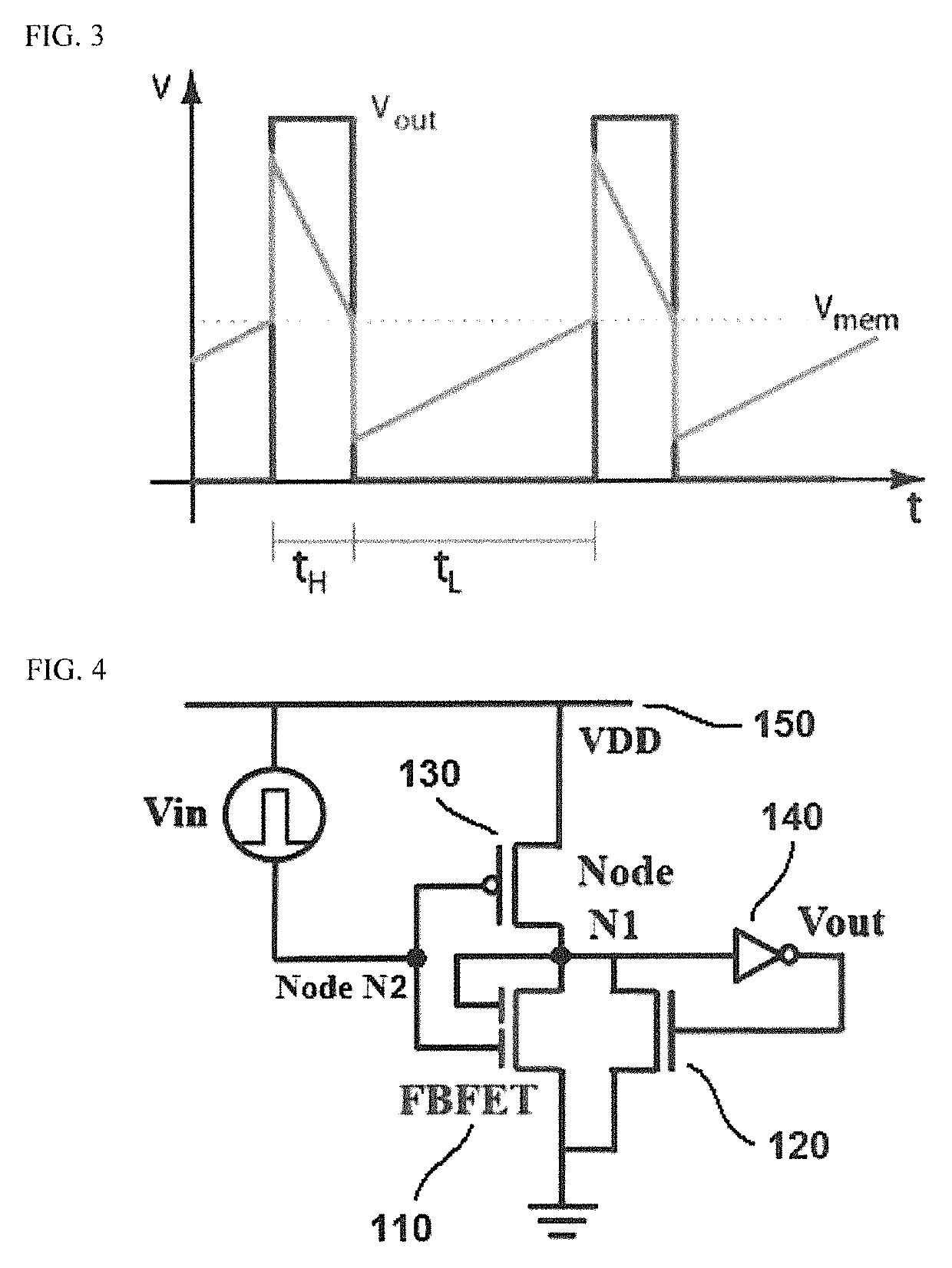
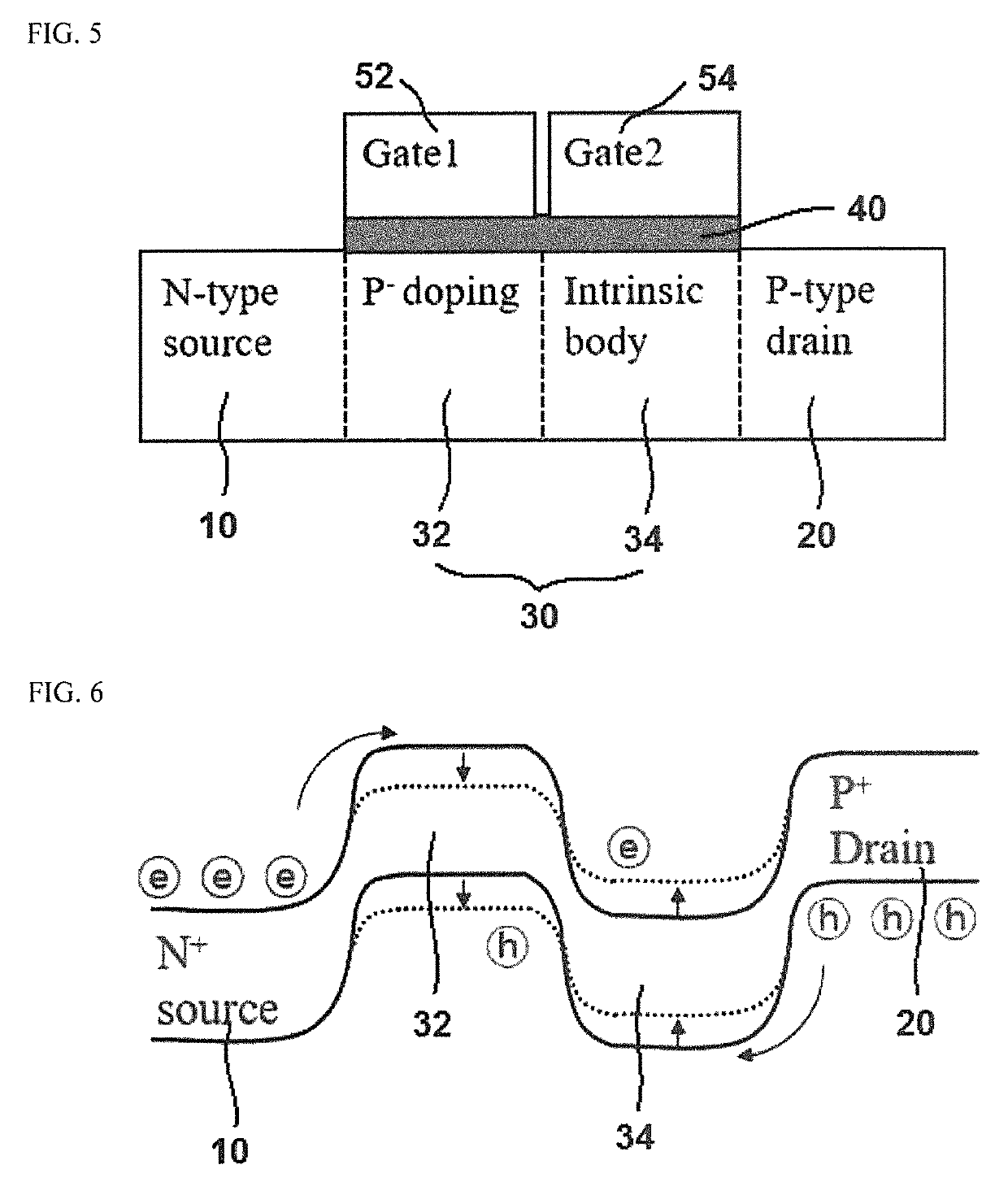
ActiveUS10522665B2Low powerMinimize power consumptionElectronic switchingLogic circuits using semiconductor devicesMOSFETEngineering
Semiconductor circuits are provided for emulating neuron firing process using a positive feedback transistor having first and second gate electrodes in the longitudinal direction of a channel region. The first gate electrode is connected to a gate electrode of a first p-channel MOSFET to be an input terminal and the second gate electrode is connected to a drain to be applied with a supply voltage. Thus electrons and holes can accumulate separately in a channel region (i.e., a body) under each of the gate electrodes by applying input signals to the input terminal and drastically reduce the wasted power consumption in the non-fired neurons because the current is turned on and off only at a moment that corresponds to a firing of the neuron. Thus, the semiconductor circuits can be driven by low power and have the same level of endurance as a general MOSFET.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
LUT based neuron membrane potential update scheme in STDP neuromorphic systems
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
A neuron circuit based on memristive devices
ActiveCN106845634BRealize integrated discharge functionImplement time encodingPhysical realisationSynapseInformation processing
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Embedded modular nerve nucleus simulation platform based on ARM (Advanced RISC Machines)
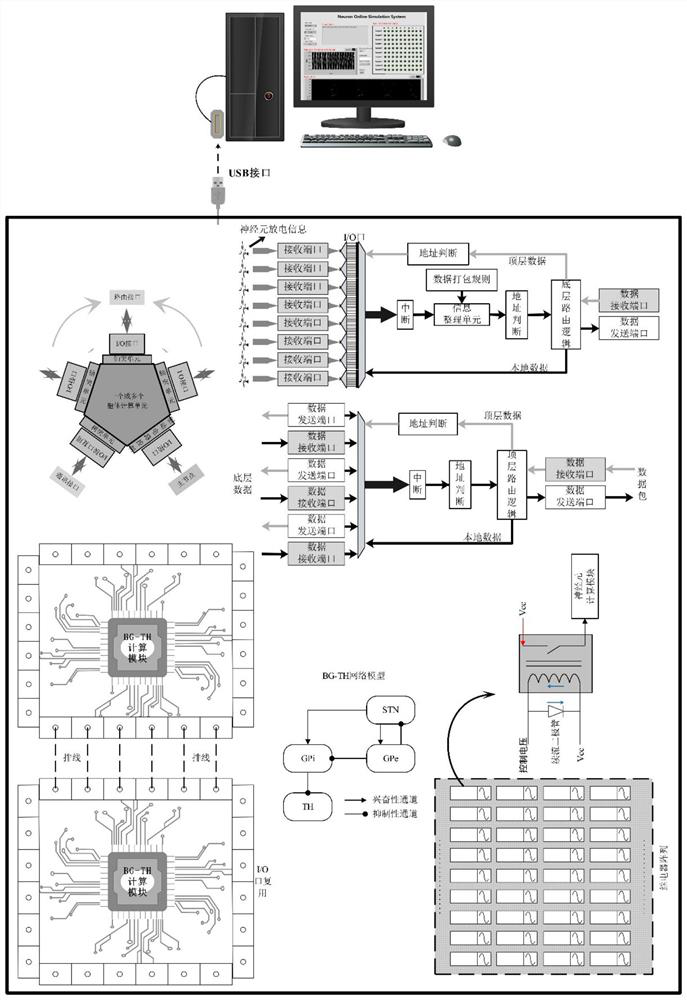
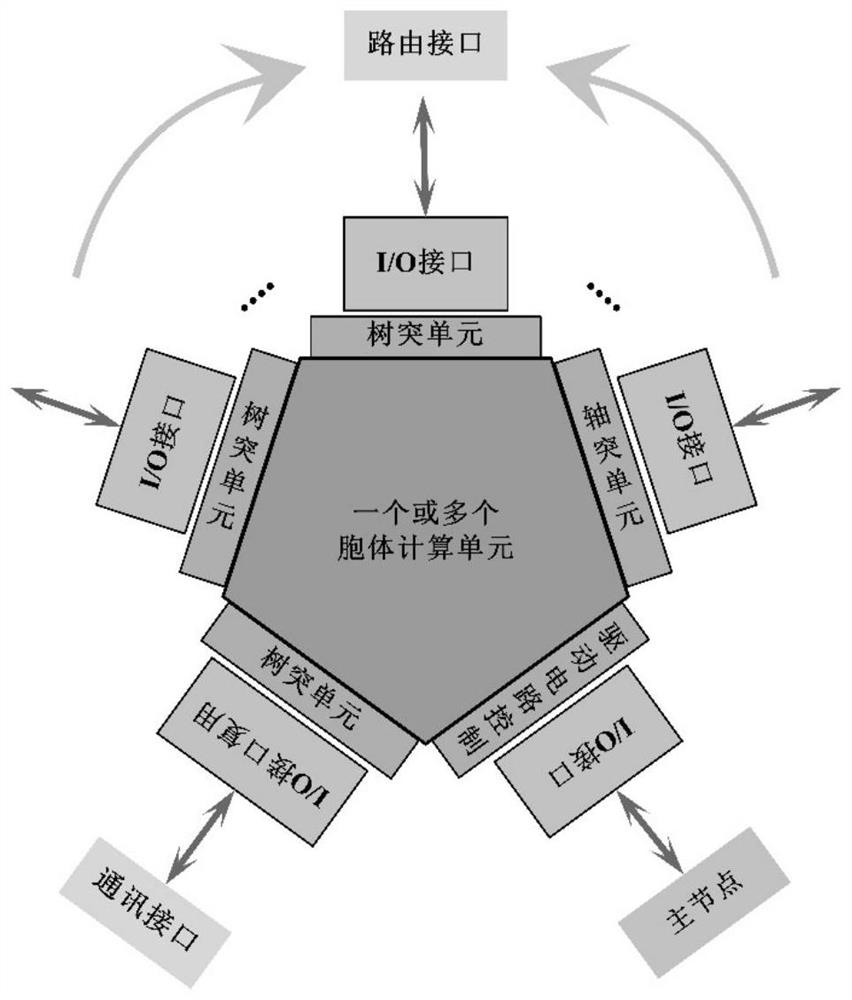
PendingCN114819123AReal-time simulationRealize data interactionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationComputer hardwareNucleus
The invention relates to an ARM-based embedded modular neural nucleus simulation platform, which can simulate a BG-TH network in real time through a neuron discharge characteristic module, a synaptic data transmission module, a miniature relay array, a modular assembly mode and upper computer debugging software, supports real-time adjustment, expansion and cutting of the network, and can simulate the BG-TH network in real time. And simulation of the BG-TH network in various intervention modes can be realized through an upper computer or by applying external stimulation. The development time of simulation of different nervous system disease states is greatly shortened, the essence of lesion and degeneration of the BG-TH network is further revealed on the level of neurons and synapses, and the BG-TH network is kept consistent with a real biological network on the time scale. The method is of great significance for exploring various nervous system diseases and related treatment schemes thereof.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Neuron firing spike signal picking method, device and computer equipment
ActiveCN112472108BPick accuratelyImprove robustnessDiagnostic signal processingSensorsAlgorithmNeuron
Owner:南京畅享医疗科技有限公司
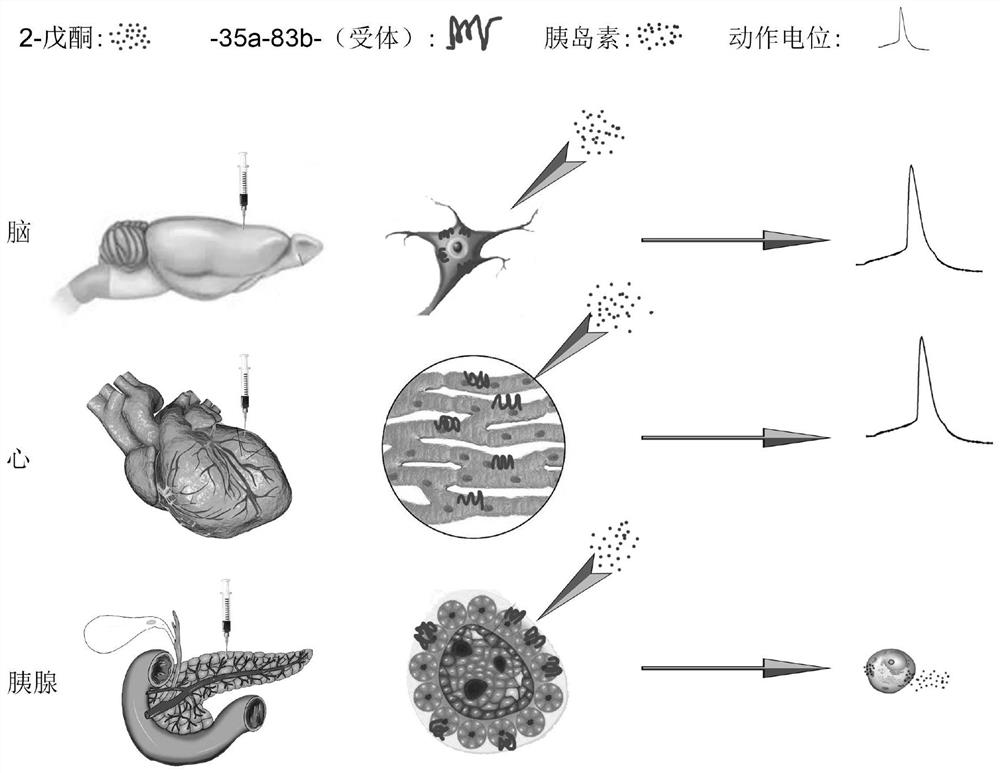
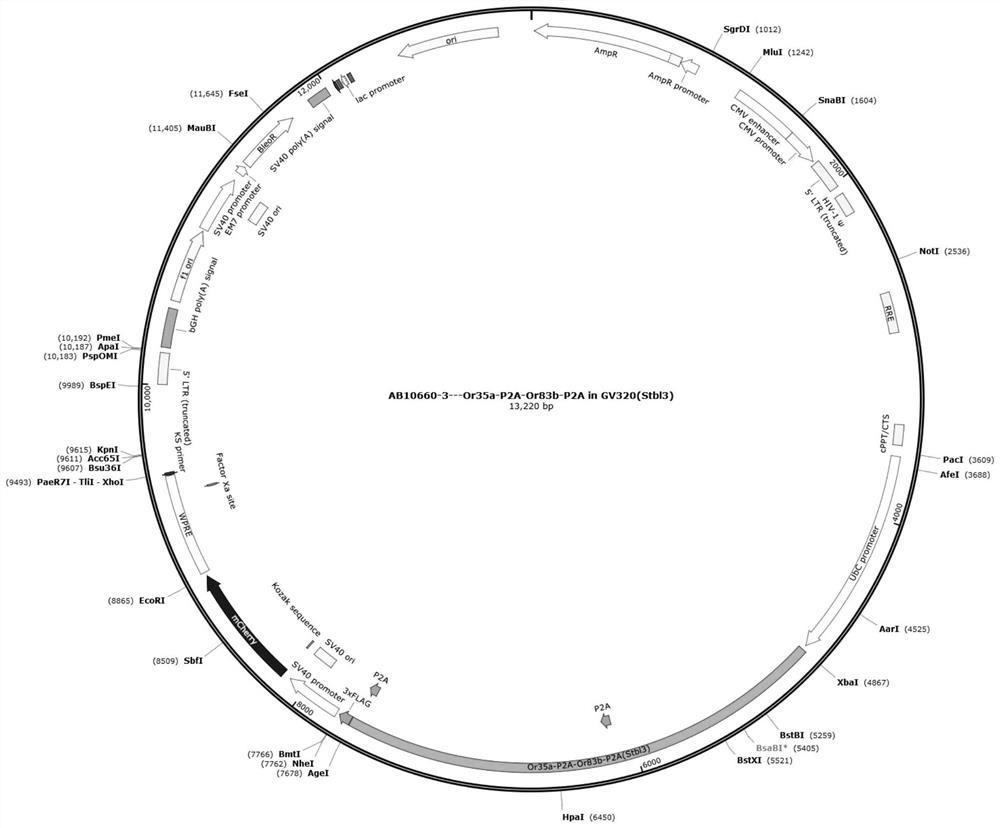
Application of 2-pentanone and specific receptor thereof in preparation of products for regulating and controlling cell functions
InactiveCN114425078ASimple test operationPromote activationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderIonic ChannelsCell membrane
The embodiment of the invention discloses application of 2-pentanone and a specific receptor thereof in the following (A1) or (A2): (A1) preparing a product for regulating and controlling cell functions; (A2) regulating and controlling cell functions; (A3) preparing a product for promoting the increase of the content of calcium in cells; and (A4) preparing a product for promoting the increase of the discharge frequency of neurons. According to the invention, a 2-pentanone specific receptor is expressed in a cultured cell or animal body, and through specific binding with 2-pentanone, a ligand gating cation channel is opened, and in the process of causing intracellular calcium ion concentration increase, cell membrane depolarization, electrical activity or endocrine generation and other activities, accurate regulation and control of tissue cell and organ functions are finally realized. After treatment, the cells can be quickly activated to generate effects, and the effects are quickly taken; after the treatment is stopped, the experiment effect can be quickly terminated, and the original state is recovered; the cells cannot be damaged after long-time treatment, and long-time treatment can be realized; the method is convenient to transform to clinical application and is used for disease treatment.
Owner:湖北优尼泰睿生物科技开发有限公司
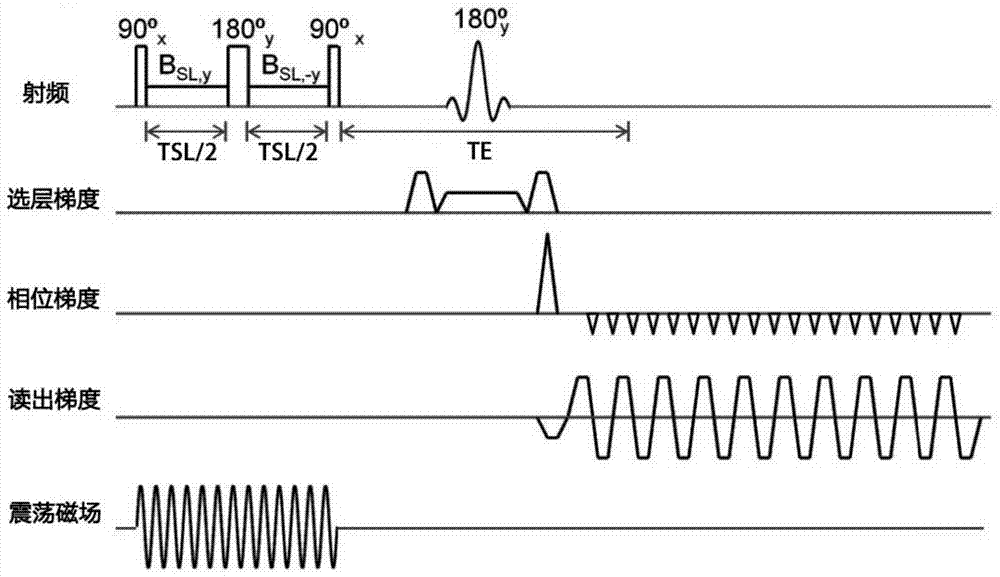
Magnetic resonance imaging method and application based on spin-locking technology to detect oscillating magnetic field
ActiveCN104914389BReduce image quality deteriorationHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetizationIn vivo
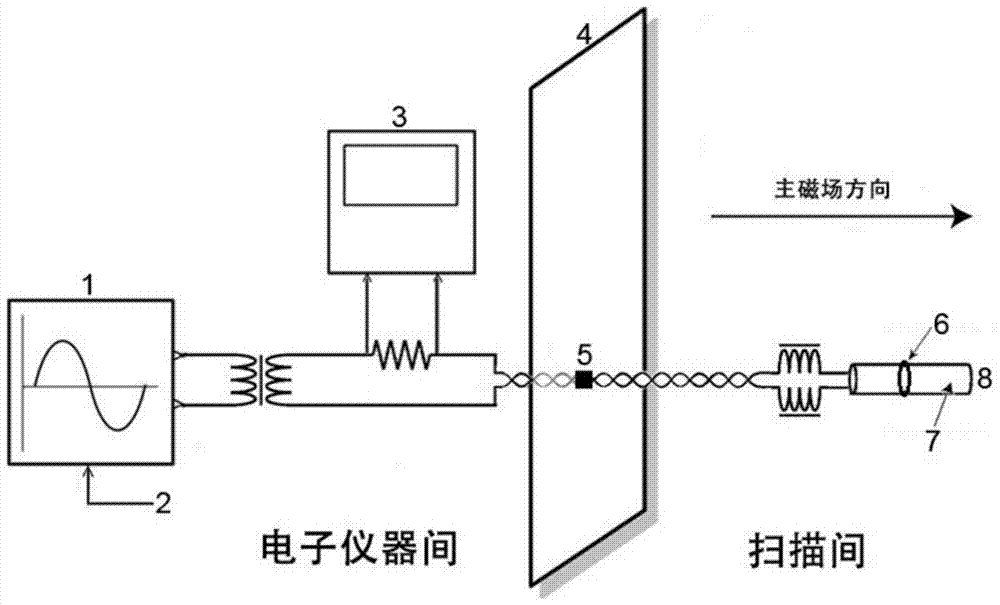
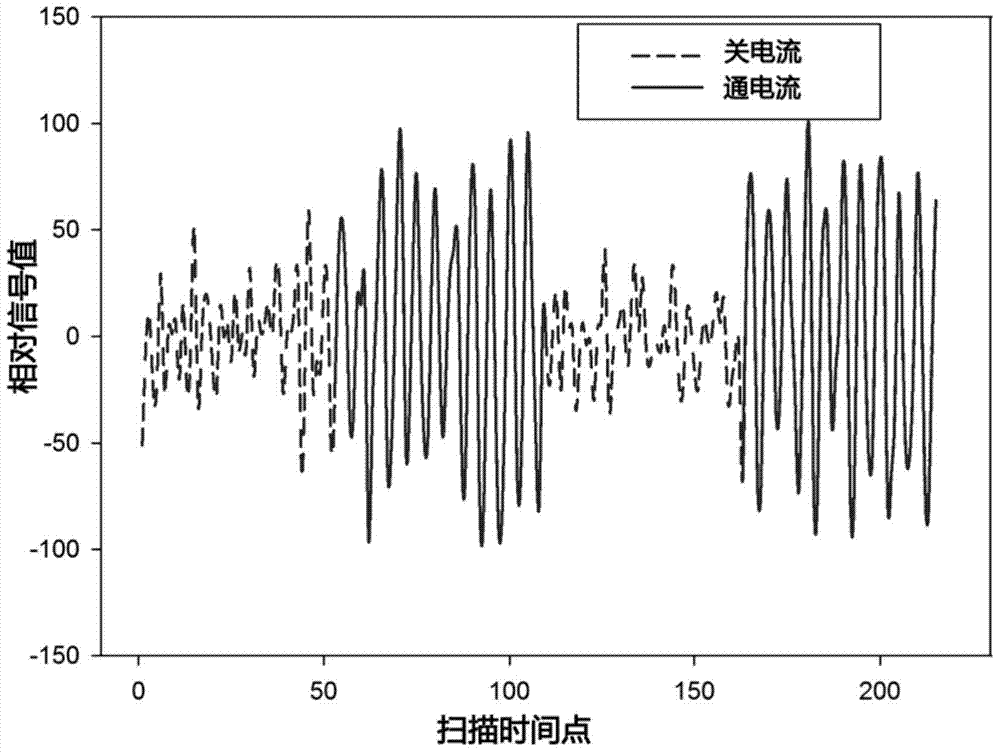
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method used for oscillatory magnetic field detection and based on a spin-locked technology and application, and names as Spin-Locked Oscillatory Excitation, SLOE. SLOE comprises a spin-locked preparation sequence insensitive to main magnetic field and radio frequency field inhomogeneity and spin planar echo acquisition. According to the method, after the spin-locked preparation sequence, any additional excitation pulse is no longer applied, and all acquired signals are magnetization vector signals deflected by oscillatory magnetic field excitation. In a data processing process, due to the fact that the initial phase of oscillatory current scanned every time is random, the fluctuation of a check signal time sequence is statistically used to detect an activation signal. According to the invention, defects of conventional neuronal discharge sequence detection are solved; the sensitivity of tiny oscillatory magnetic field detection is greatly improved; neuronal discharge can be successfully detected through magnetic resonance detection in vivo; and technological innovation in the field can be promoted.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
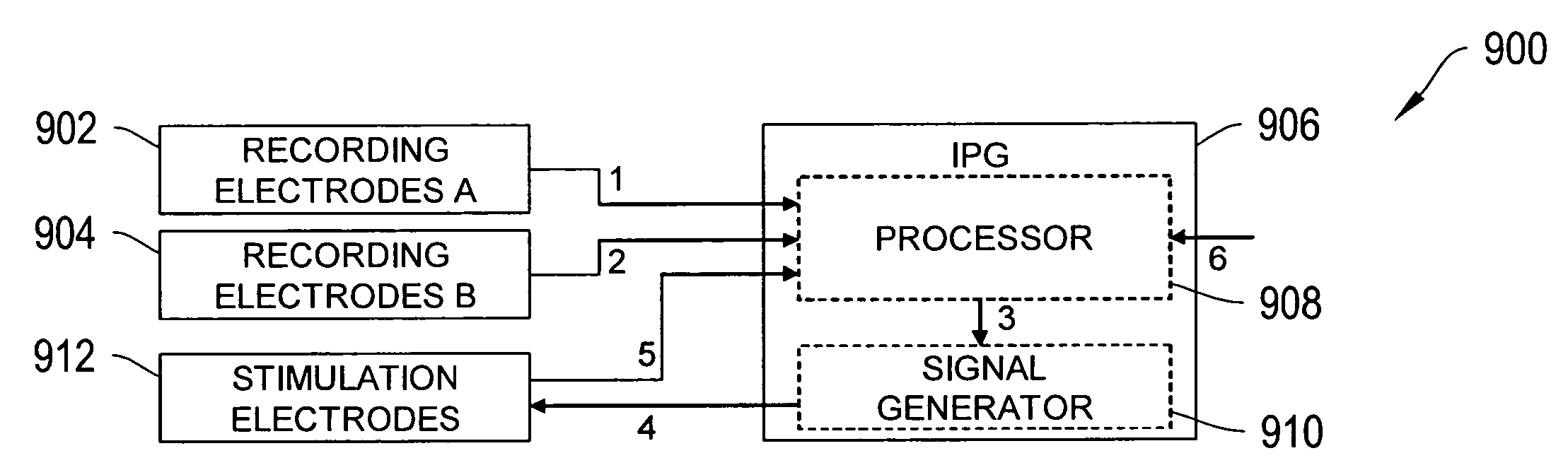
Device for treating parkinson's disease and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20110184306A1Eliminate negative effectsHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineMedical diagnosis
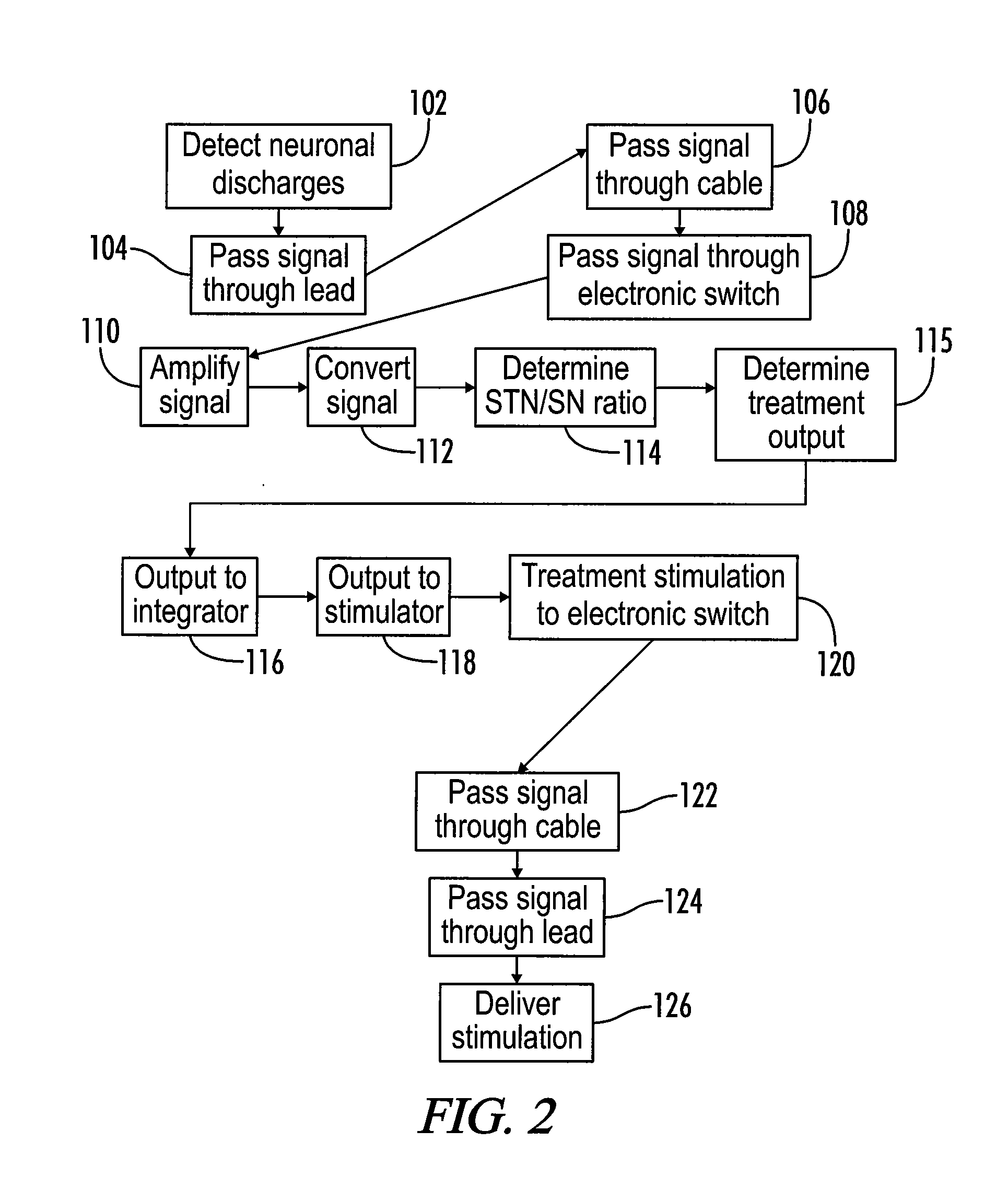
The invention includes a recordation and stimulation system for determining and delivering an electrical stimulation treatment based upon the current status of neuronal activity of a subject. The system include components for detecting neuronal activity in a subject's brain and, based upon the information received, determine an appropriate electrical stimulation treatment for the subject. The system allows immediate adjustments to the stimulation treatment as the needs of the subject change over time. The invention also includes a method for determining whether a subject has early Parkinson's Disease or advanced Parkinson's Disease. The method includes the steps of acquiring information regarding neuronal discharges in certain areas of the brain, creating a ratio based upon the neuronal activity, and determining whether a previous medical diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease is accurate.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
A Measuring System of Neuron Phase Response Characteristics Based on Firing Rate Clamping Closed Loop
InactiveCN105286848BAchieve accuracyReduce waiting timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase responseClosed loop
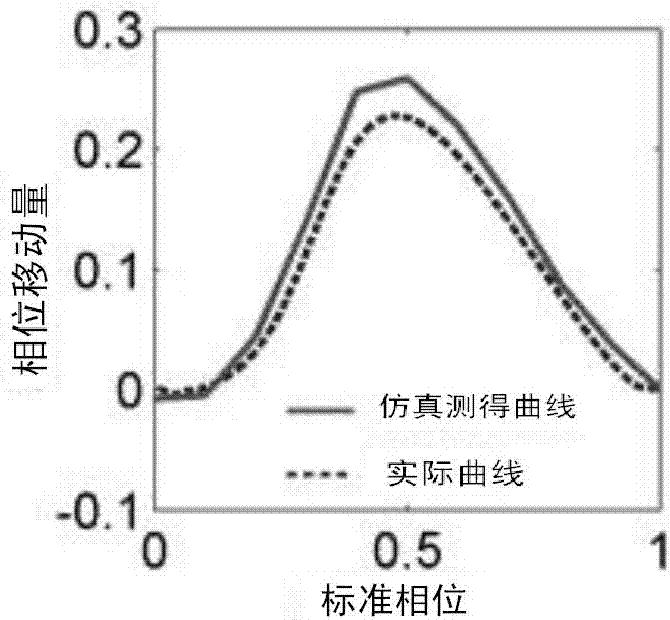
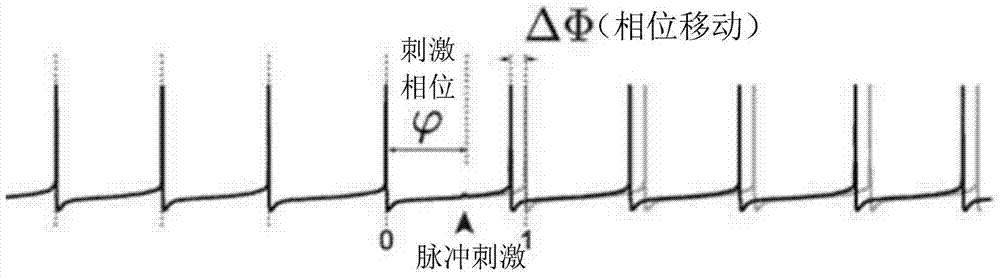
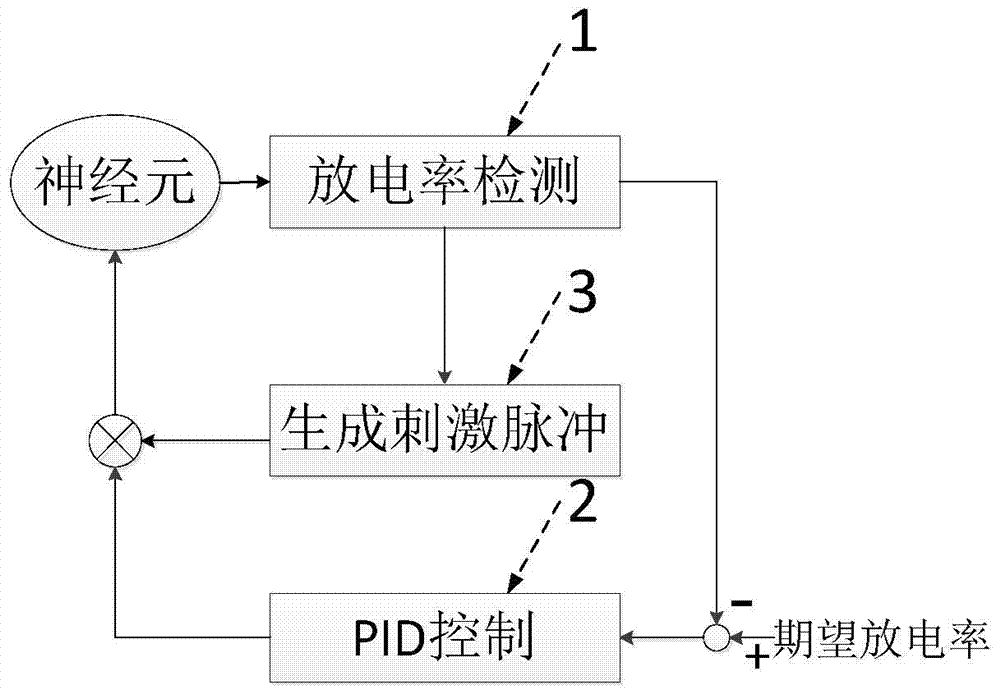
The invention provides a neuron phase response characteristic measuring system based on a discharge rate clamp closed loop. The system comprises a neuron discharge rate detection device, a PID control device and a pulse generation device which are mutually connected. The neuron phase response characteristic measuring system based on the discharge rate clamp closed loop has the advantages that according to the measuring system, by means of closed-loop control, the neuron discharge rate is maintained, the advantage of closed-loop electrophysiology is effectively utilized, measurement of multiple groups of phase response curves can be conveniently conducted by changing the discharge rate value, the accuracy of pulse stimulation time and phase positions is achieved, and important value is achieved for phase response experimental study.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
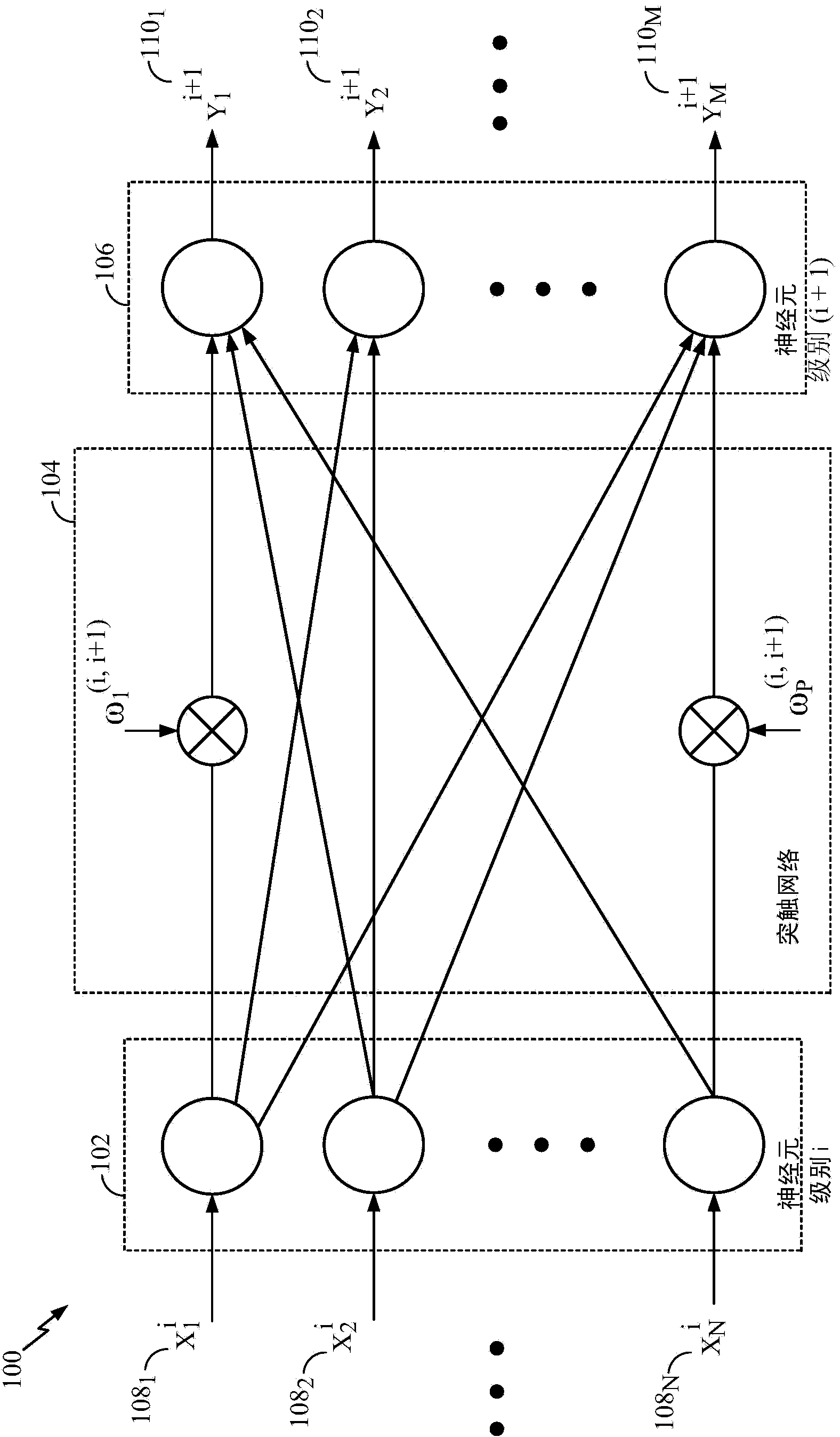
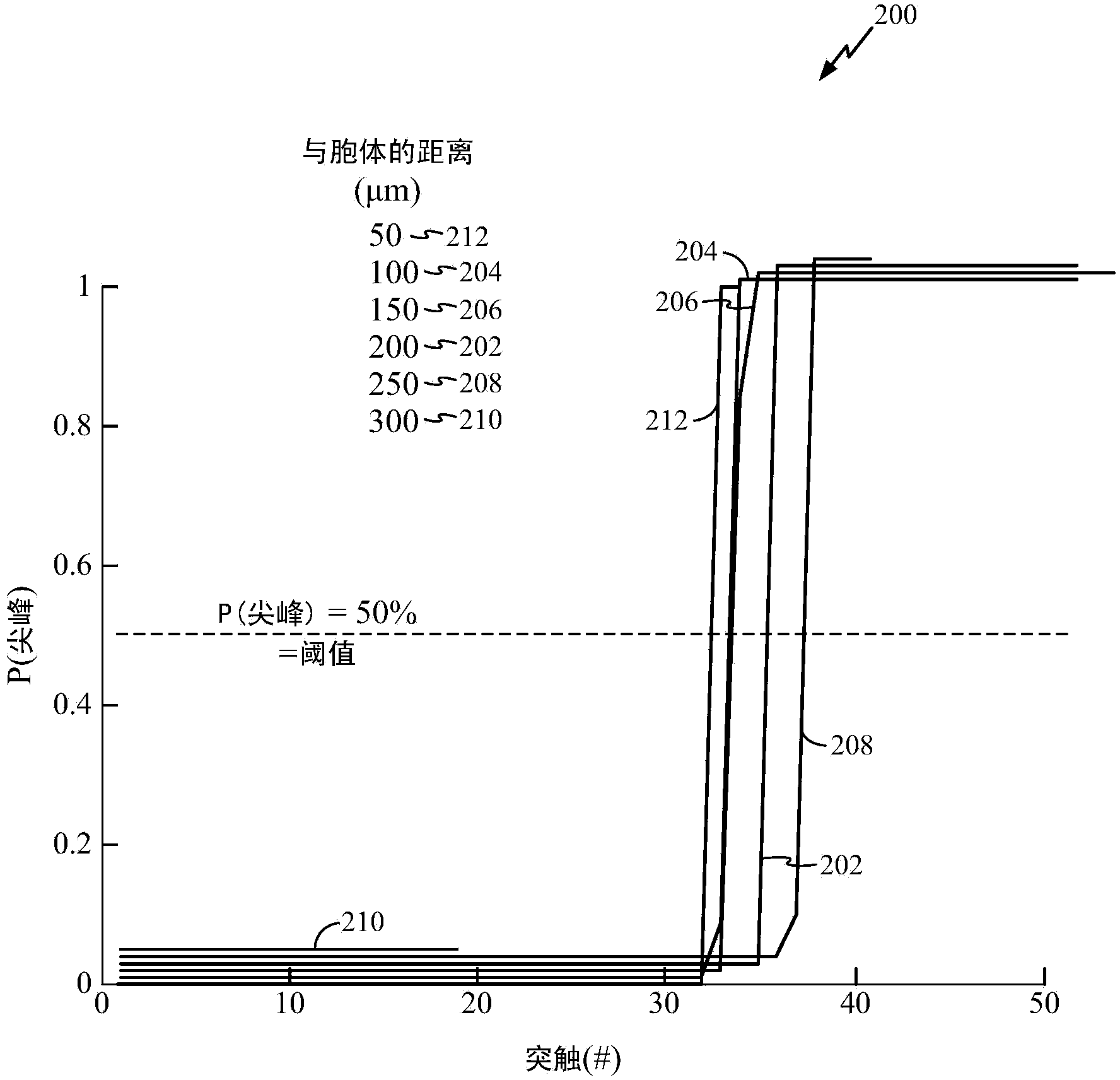
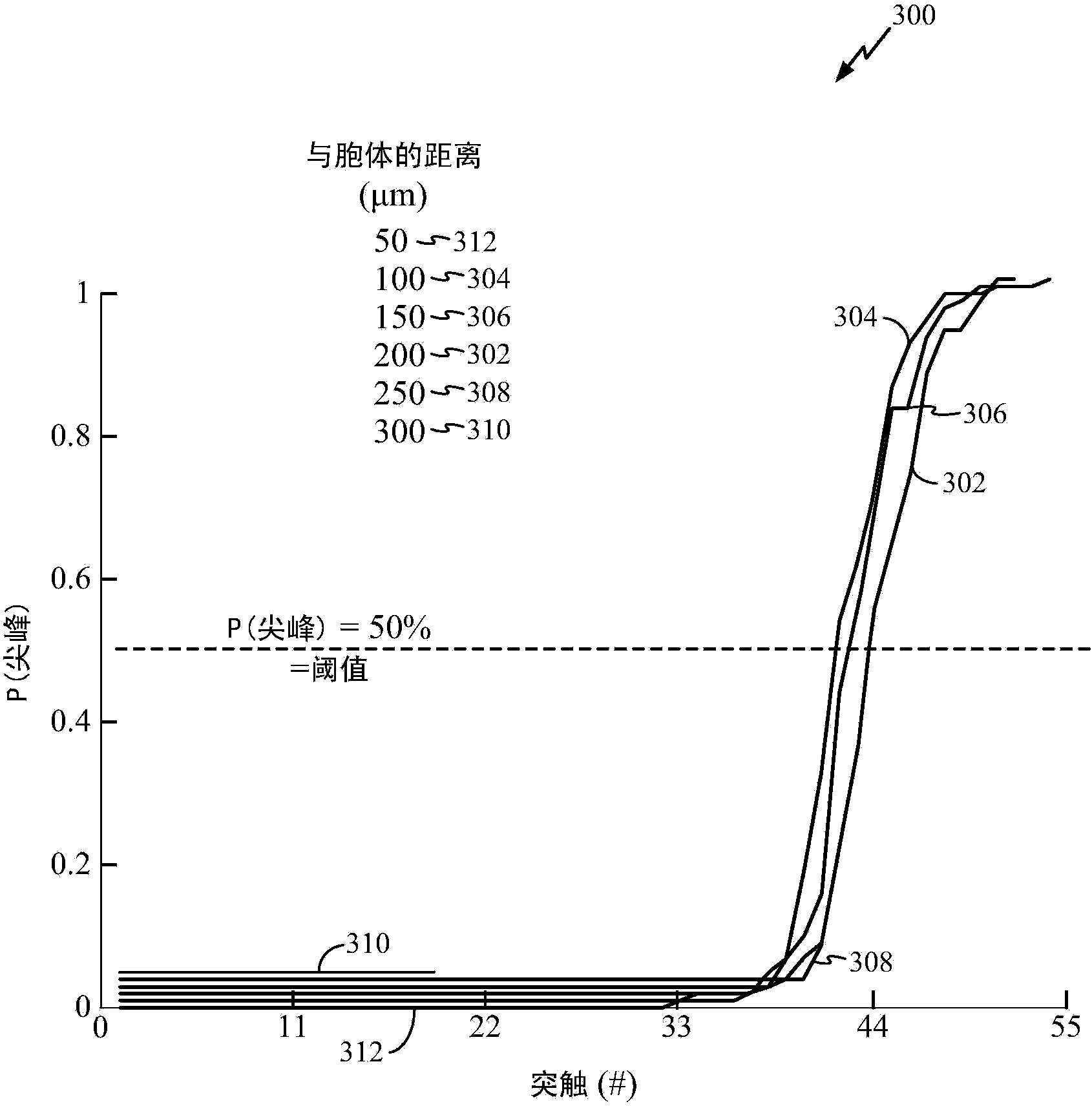
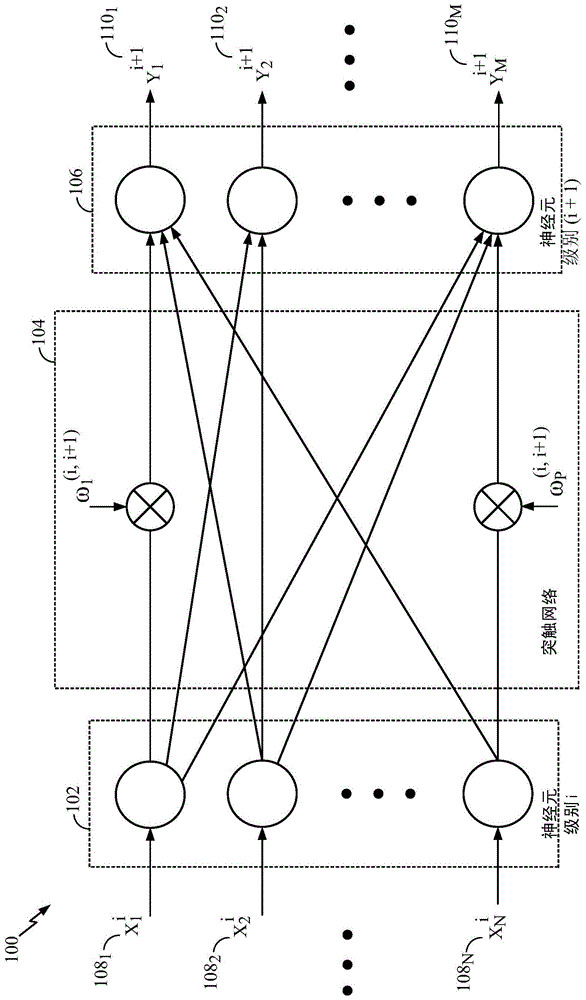
Method and apparatus of neuronal firing modulation via noise control
Certain aspects of the present disclosure support a technique for neuronal firing modulation via noise control. Response curve of a typical neuron with a threshold can transition from not firing to always firing with a very small change in the neuron's input, thus limiting the range of excitable input patterns for the neuron. By introducing local, region and global noise terms, the slope of the neuron's response curve can be reduced. This may enable a larger set of input spike patterns to be effective in causing the neuron to fire, i.e., the neuron can be responsive to a large range of input patterns instead of an inherently small set of patterns in a noiseless situation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for modulation of neuronal firing via noise control
Certain aspects of the present disclosure support techniques for modulating neuronal firing via noise control. The response curve of a typical neuron with a threshold can transition from never firing to always firing with very small changes in the neuron's input, thereby limiting the range of excitable input patterns for the neuron. The slope of the neuron response curve can be reduced by introducing local, regional and global noise terms. This may enable a larger set of input spike patterns to be effective in firing the neuron, that is, enable the neuron to respond to a large range of input patterns rather than the inherently smaller set of patterns in the absence of noise.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
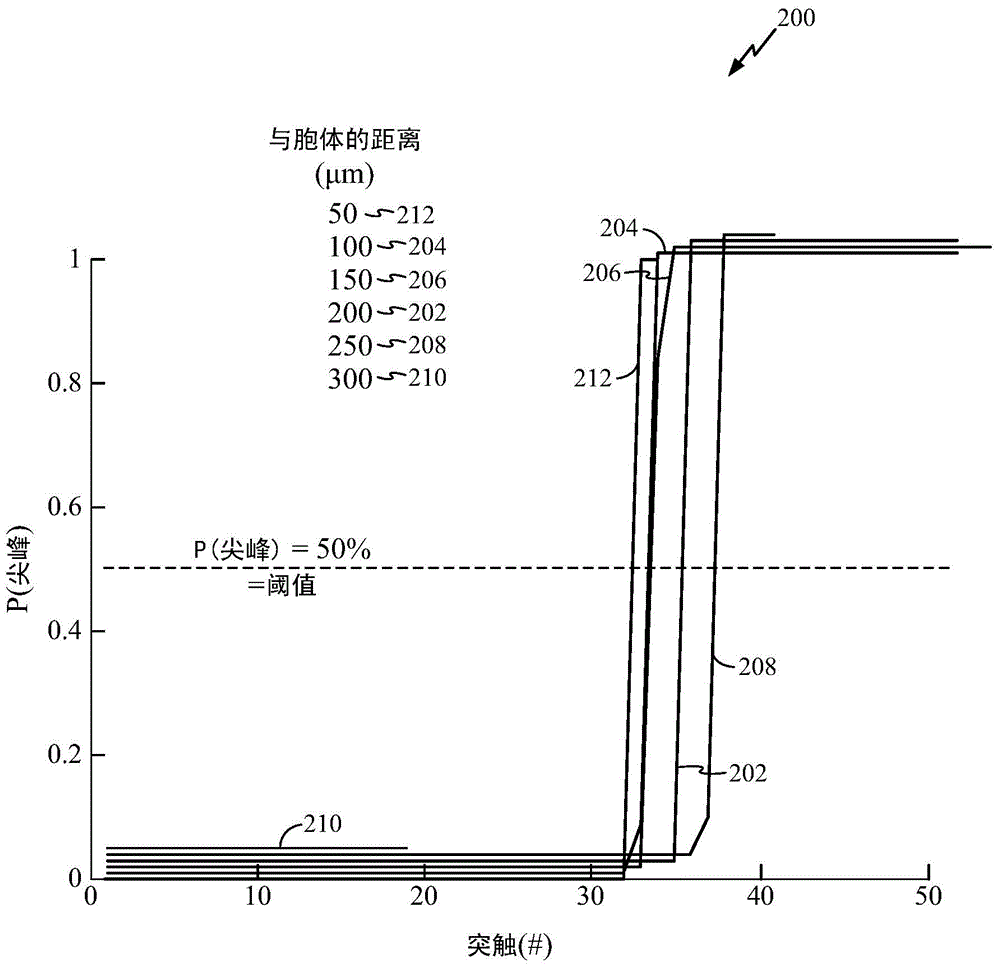
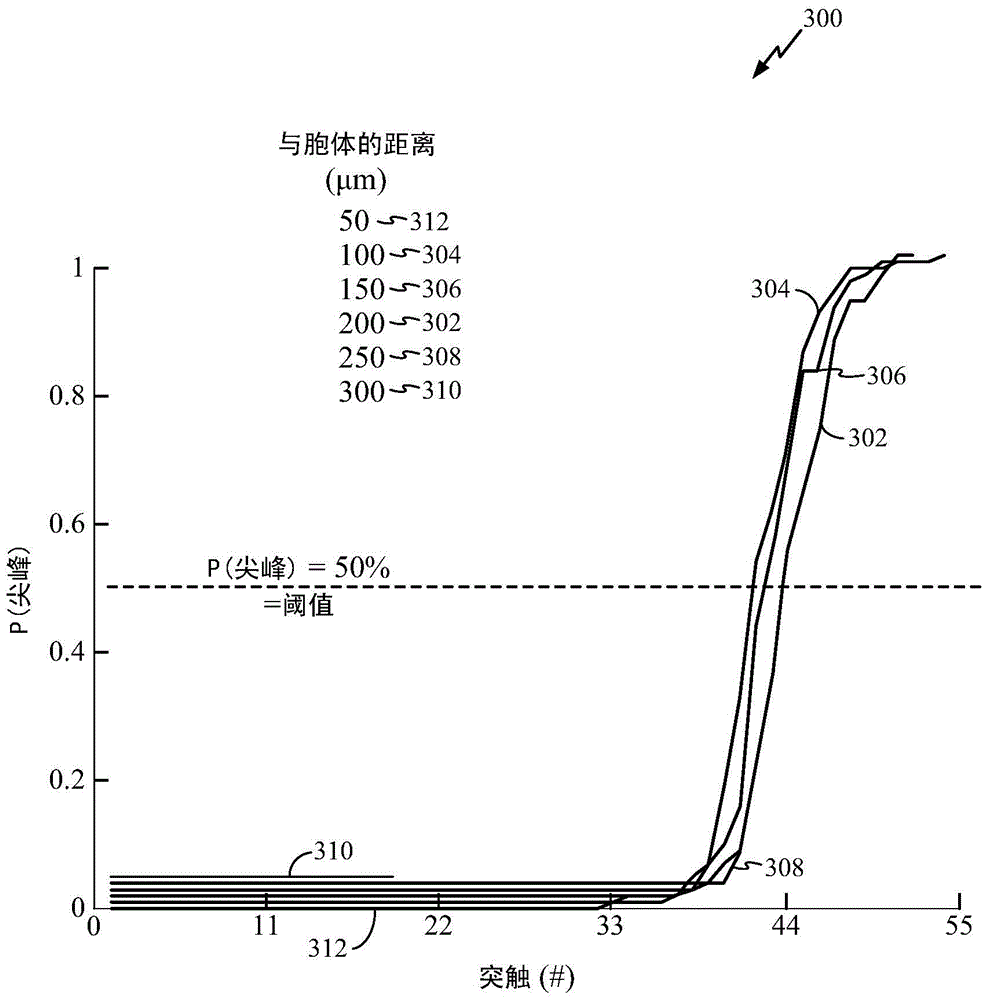
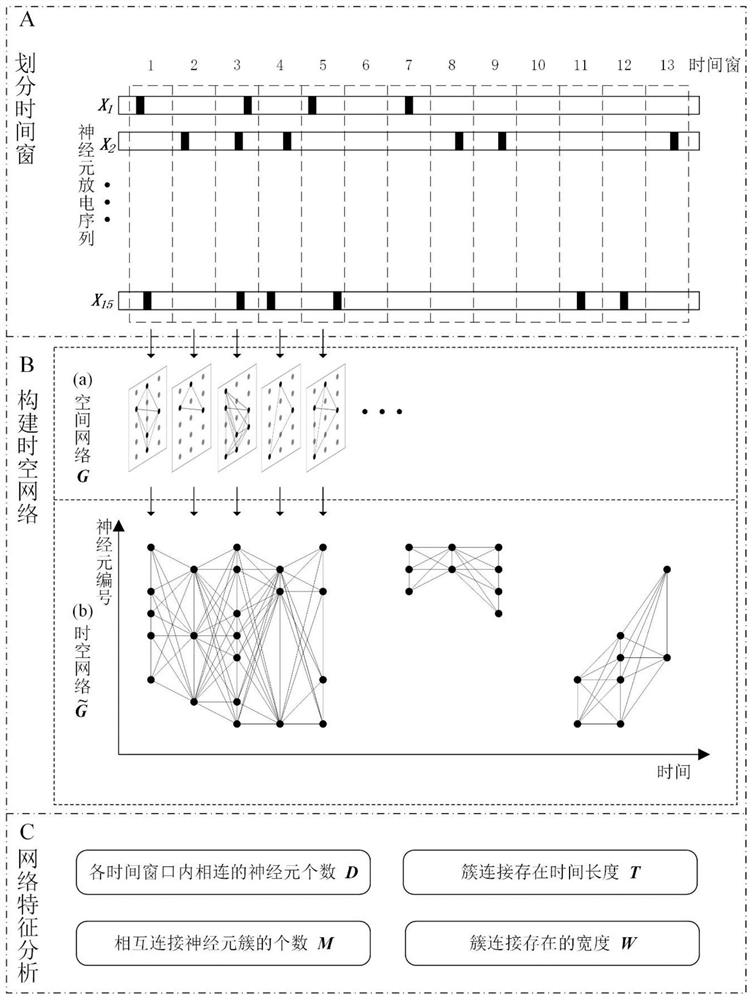
A spatio-temporal network construction method for multi-electrode array neuron firing sequences
InactiveCN109589113BReflect the characteristics of information transmissionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArtificial intelligenceNeuron
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
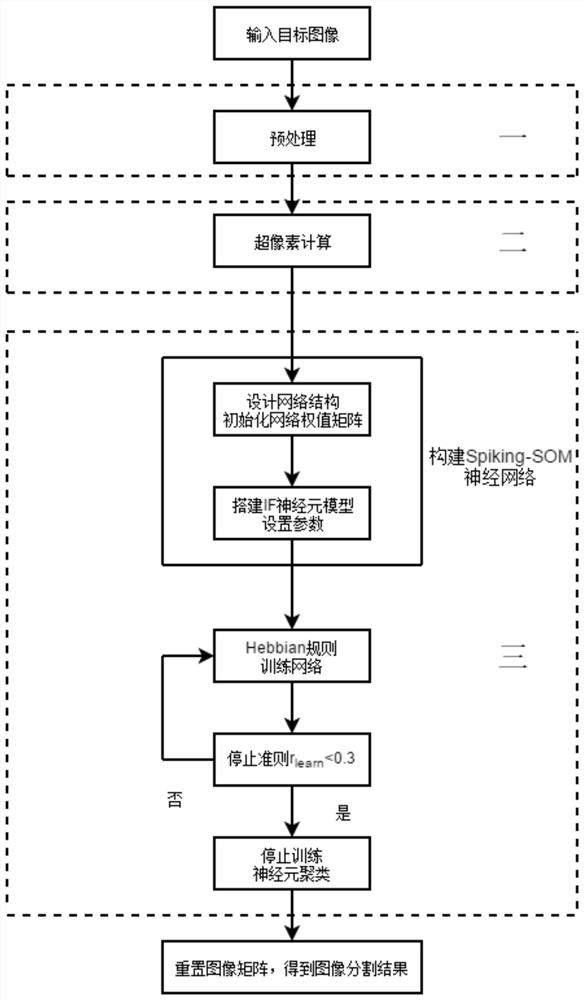
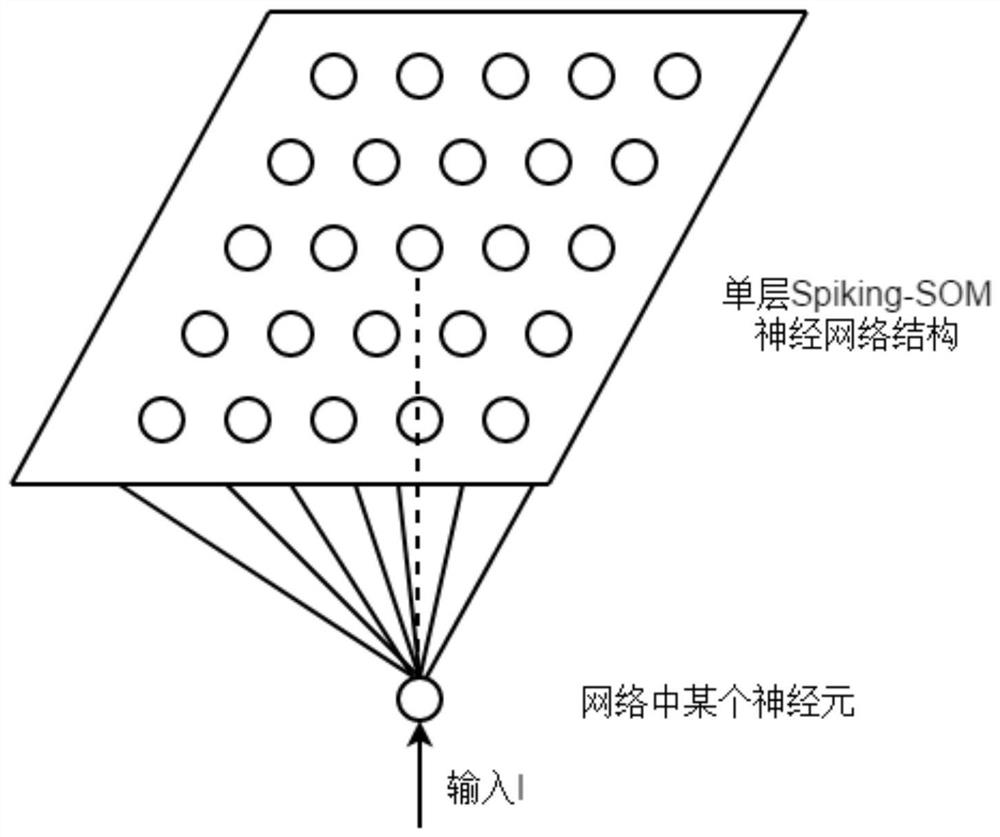
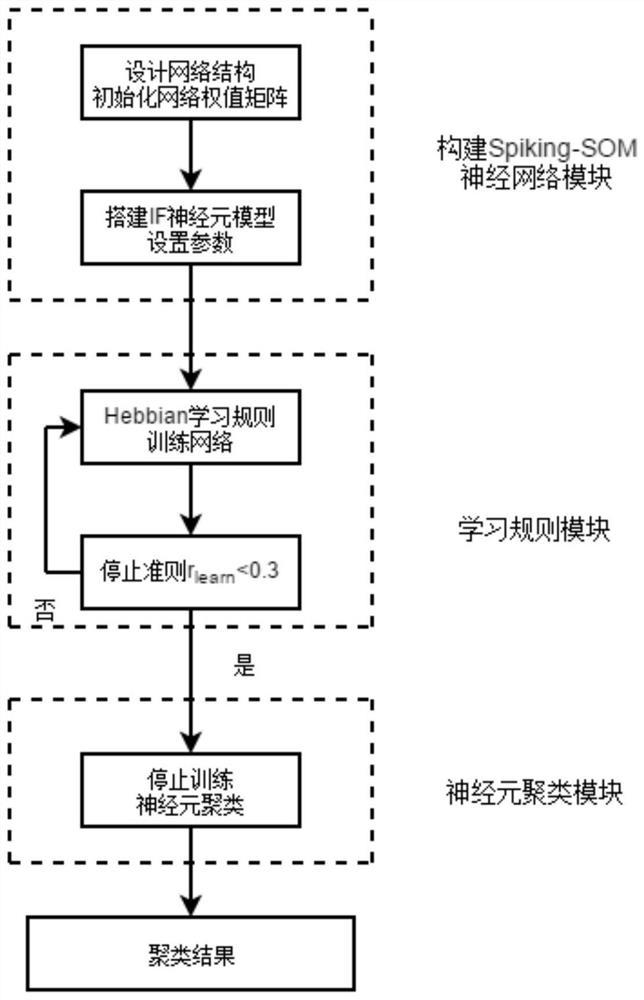
A system and method for image segmentation based on spiking-som neural network clustering
ActiveCN108876797BEffective segmentationIncrease computing speedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image
The invention discloses an image segmentation system and method based on Spiking-SOM neural network clustering. Firstly, the median filtering method is adopted to denoise the target image; Window, calculate the RGB average value of all pixels in the superpixel as the color feature of the superpixel; then select K IF neurons to construct the Spiking-SOM neural network, and construct the initial weight of the network based on the distance between the color features calculated between the superpixels Value matrix, and use the Hebbian rule to train the network. After the network training is over, clustering is performed according to the synchronization and asynchrony of neuron discharge; finally, the RGB average value of the same superpixel is calculated, and it is used to replace the original superpixel RGB value, and reset After the image matrix, the image segmentation result is obtained. The invention combines the advantages of segmentation speed and segmentation accuracy, can effectively segment color images in natural scenes, and has certain potential application value and advancement.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Image weak edge detection method based on multi-layer neuron group firing information
The invention relates to a method for detecting weak edges of images on the basis of discharge information of multilayer neuron groups. The method includes constructing the multilayer neuron groups with interconnected inhibitory synapses, inputting digital images into input-layer neuron groups and representing image pixels by the time-space information of first discharge of various neurons; describing space details of the images by time variances by the aid of visual receptive fields and discharge time sequences of the various neurons, selecting attentive mechanisms in the consideration of lateral inhibition so as to acquire visual attention data of information of the images; implementing space variable-resolution mechanisms on the basis of a combination of selective attention procedures by the aid of Log-Gabor multi-direction filter results, acquiring reconstructed information of the edges of the images and reinforcing the information of the edges of the images by the aid of output-layer neuron groups. The method has the advantages that a synapse interconnection characteristic of the neuron groups is taken into consideration; simple visual information procedures of cortices are reflected by the aid of multi-direction filter mechanisms; the weak edges of the images can be effectively detected by the aid of the multilayer neuron groups.
Owner:盐城市凤凰园科技发展有限公司
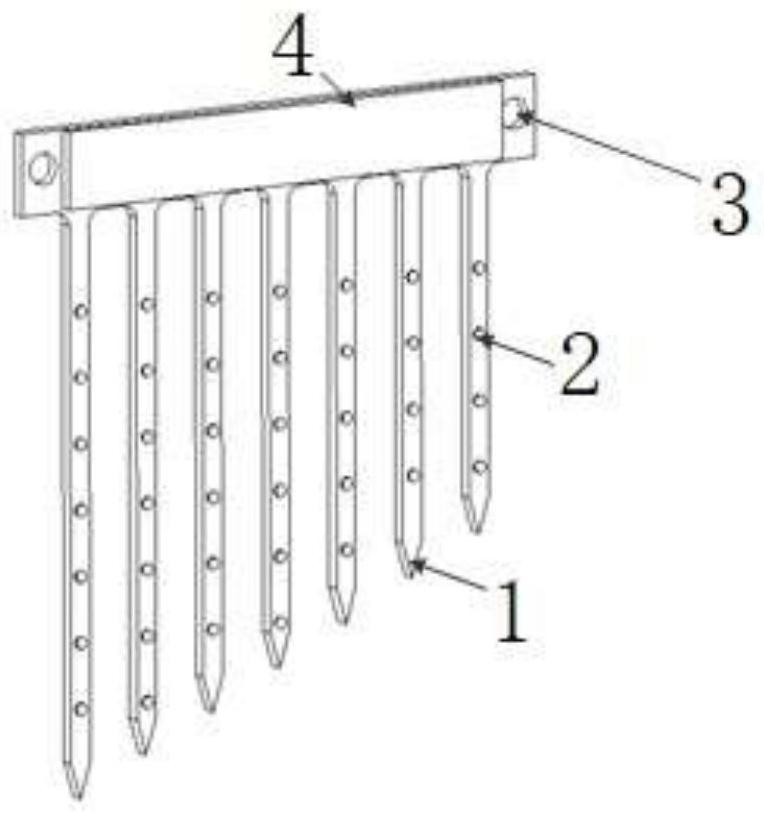
Microneedle for nerve interface
PendingCN114209333AAchieve recordRealize acquisitionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnatomyEngineering
The invention provides a microneedle for a nerve interface, which comprises at least two body electrodes, and the lengths of the at least two body electrodes are not equal. The microneedle is provided with the body electrodes with different lengths, and compared with an existing microneedle type nerve interface device, multi-electrode contact recording and nerve cell discharge information collection of different depths can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN NEURACOM TECH DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com