Patents
Literature
30 results about "Both ventricles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
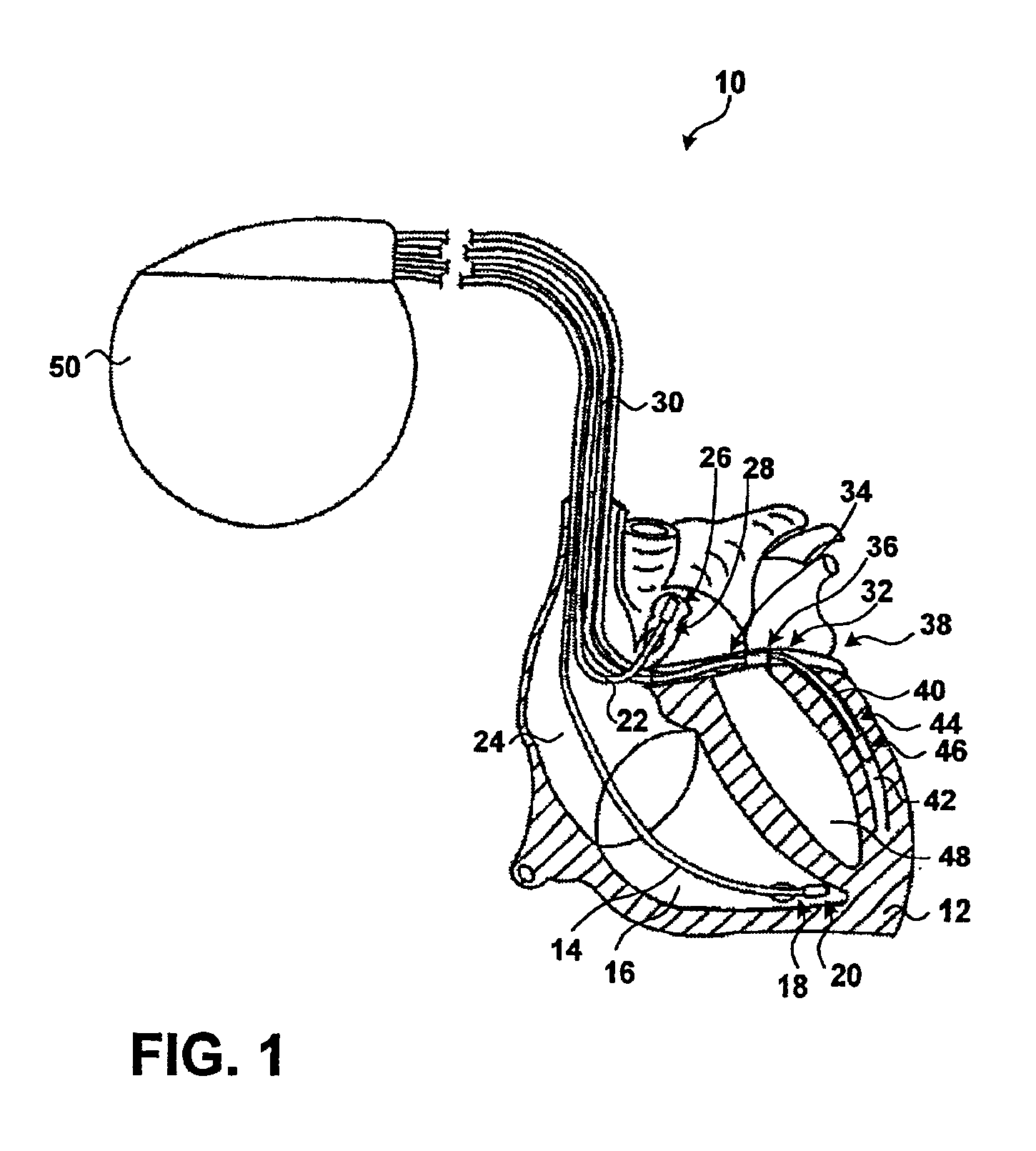
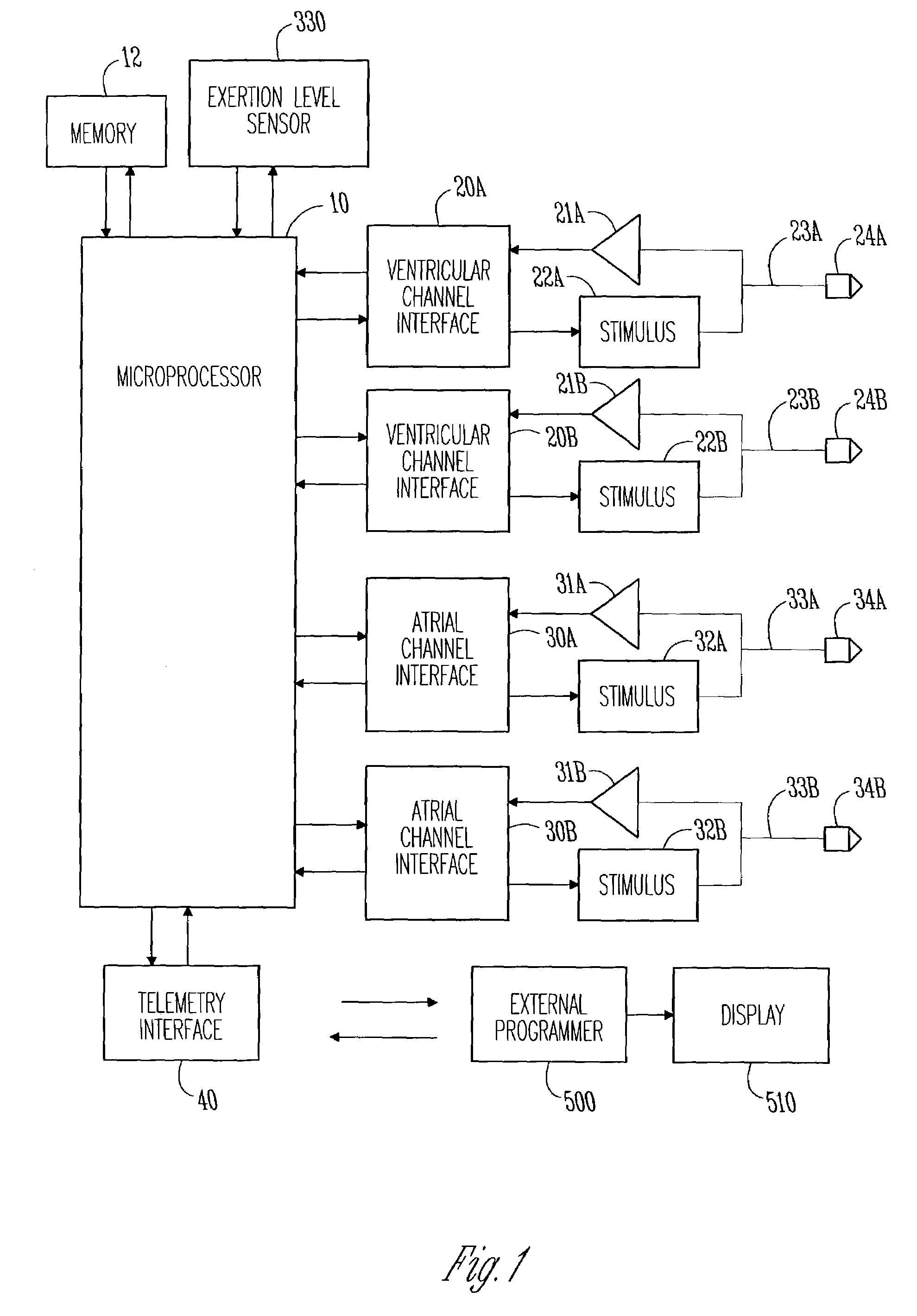
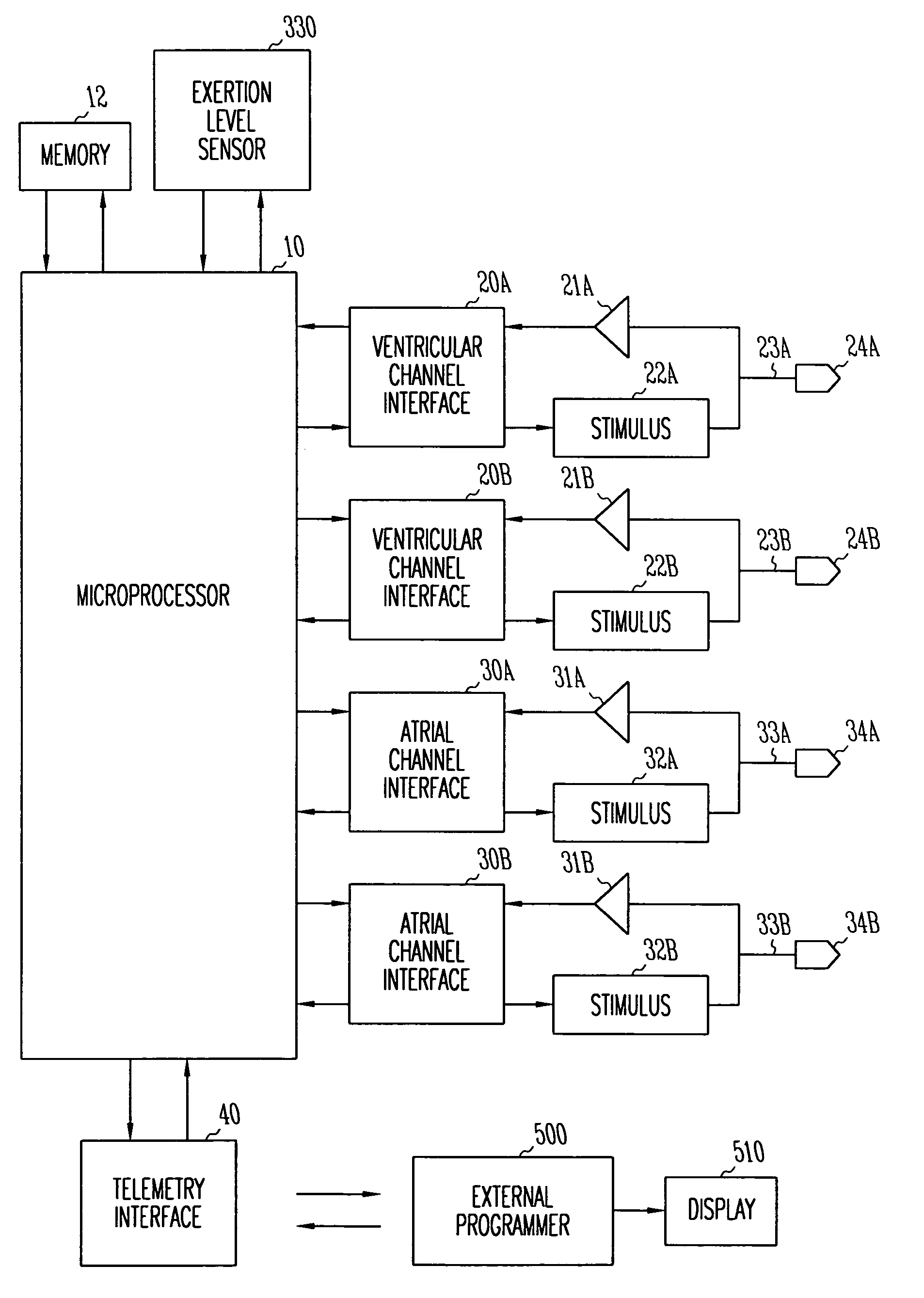
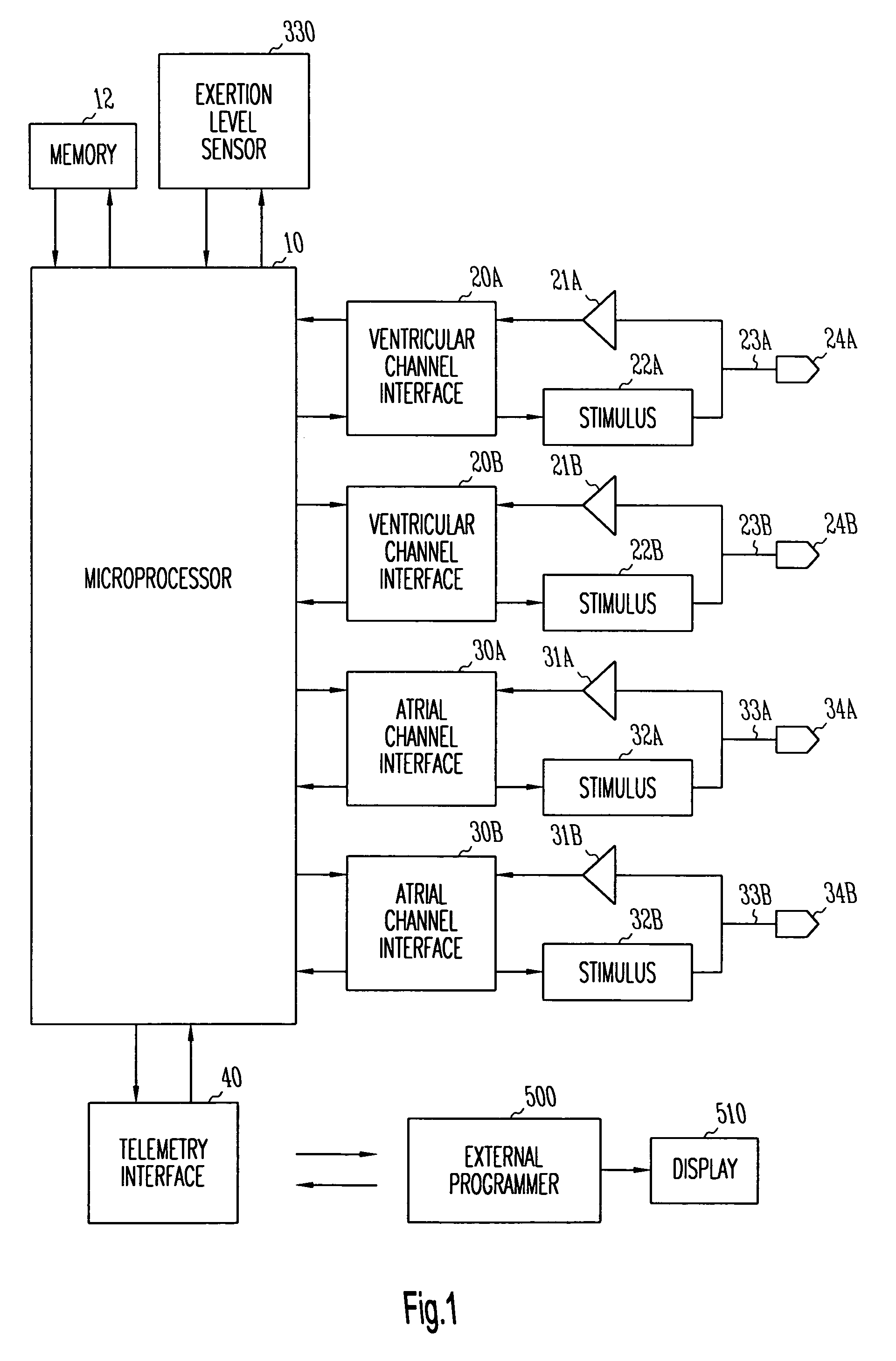
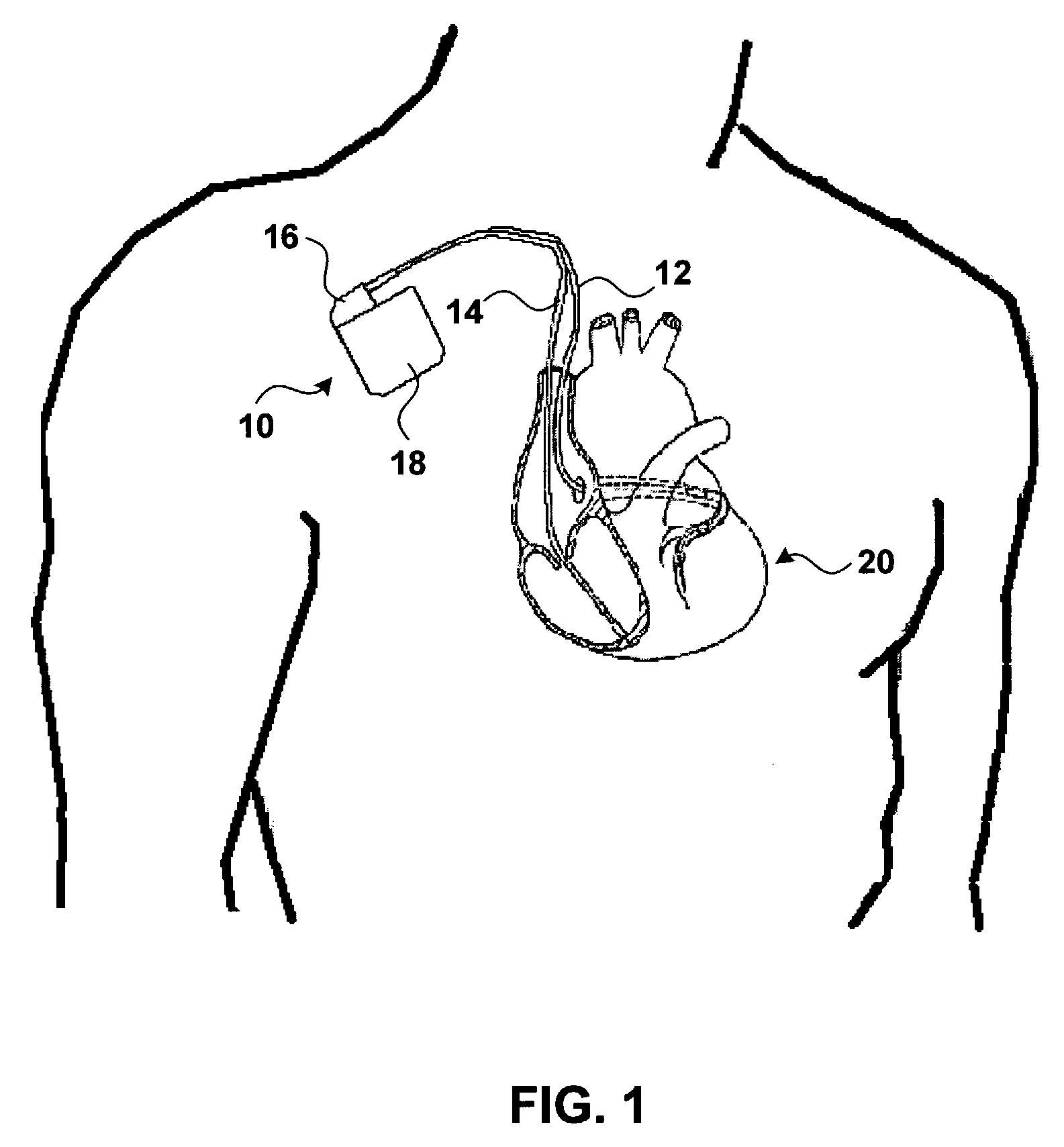
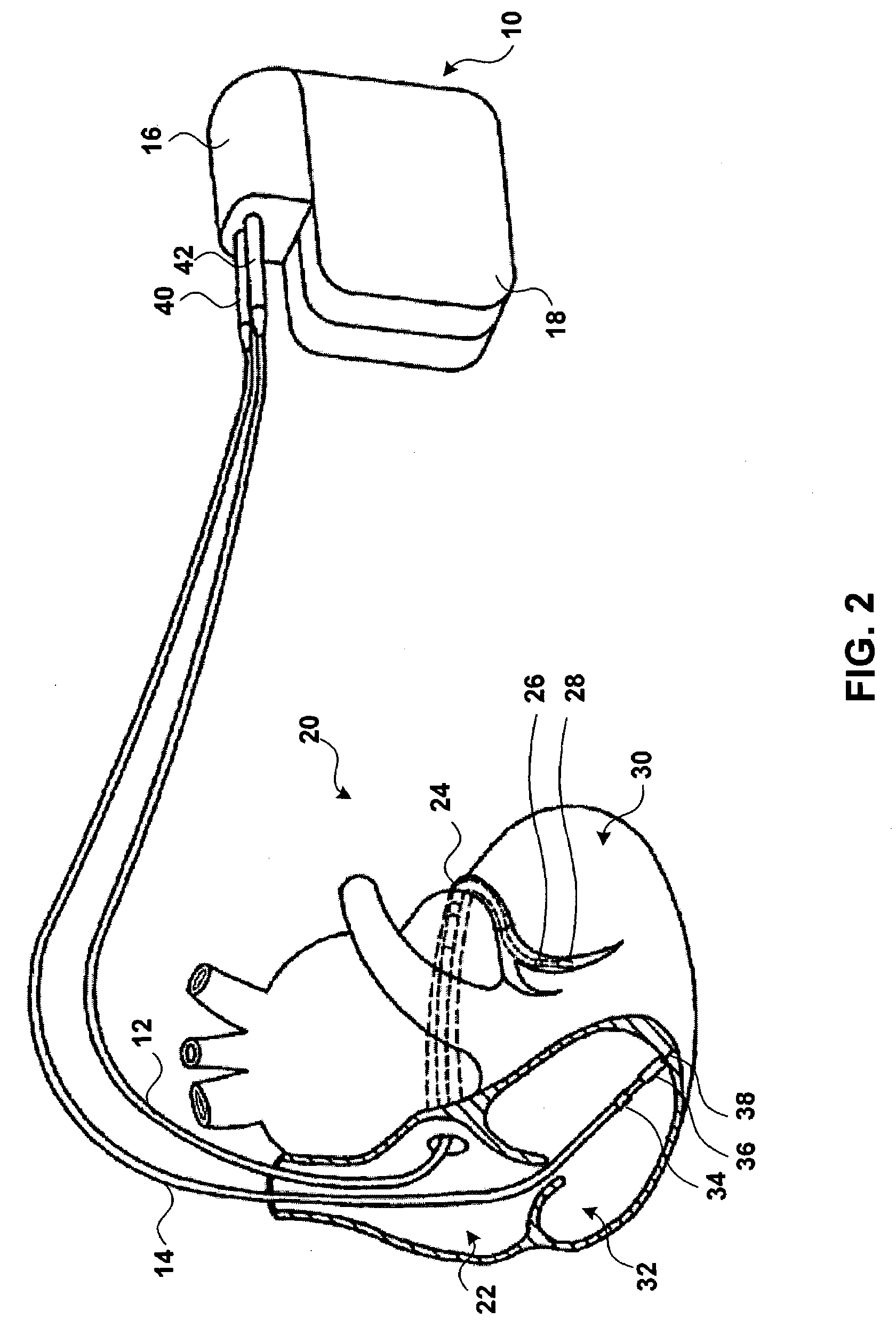
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
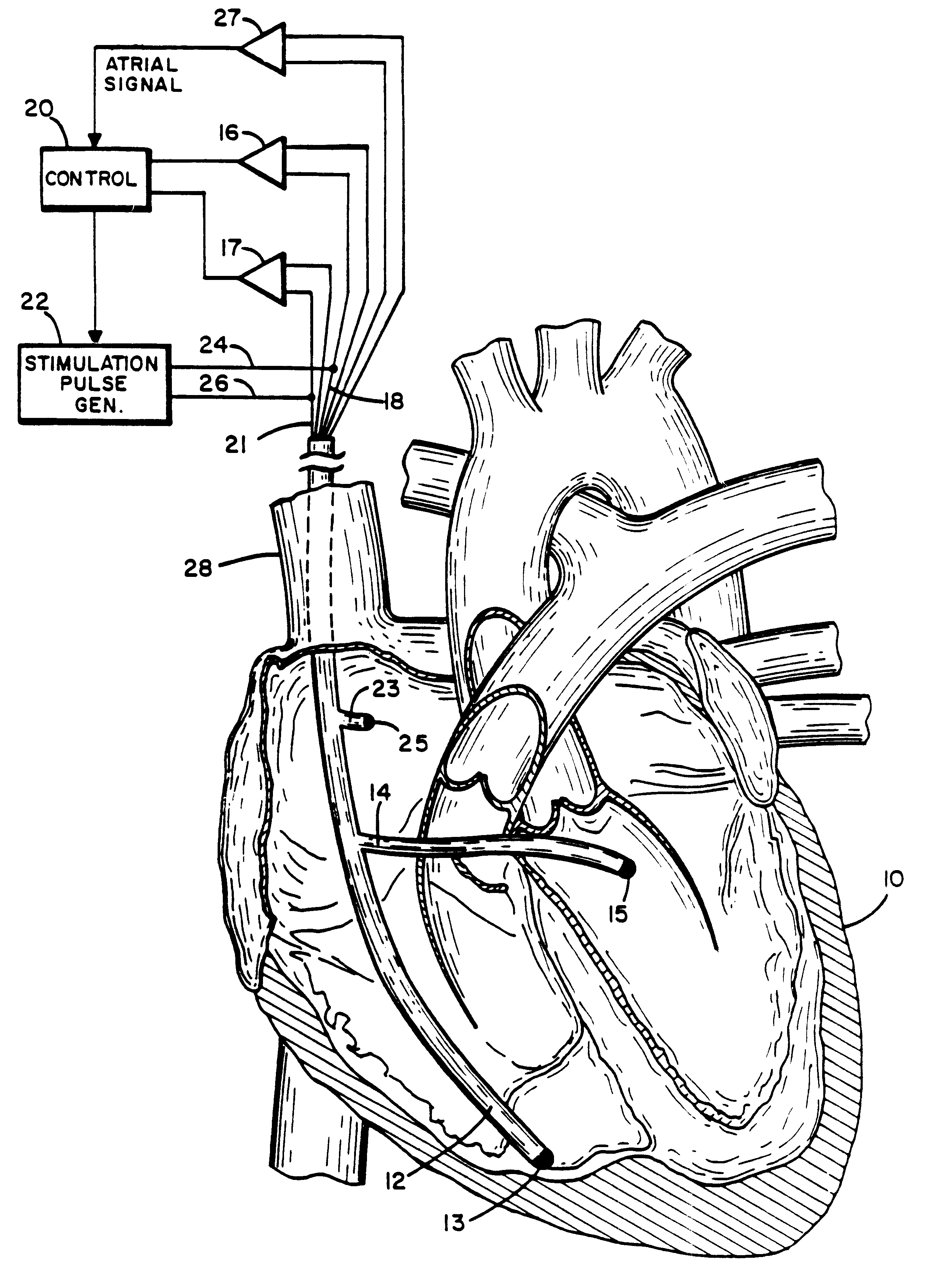
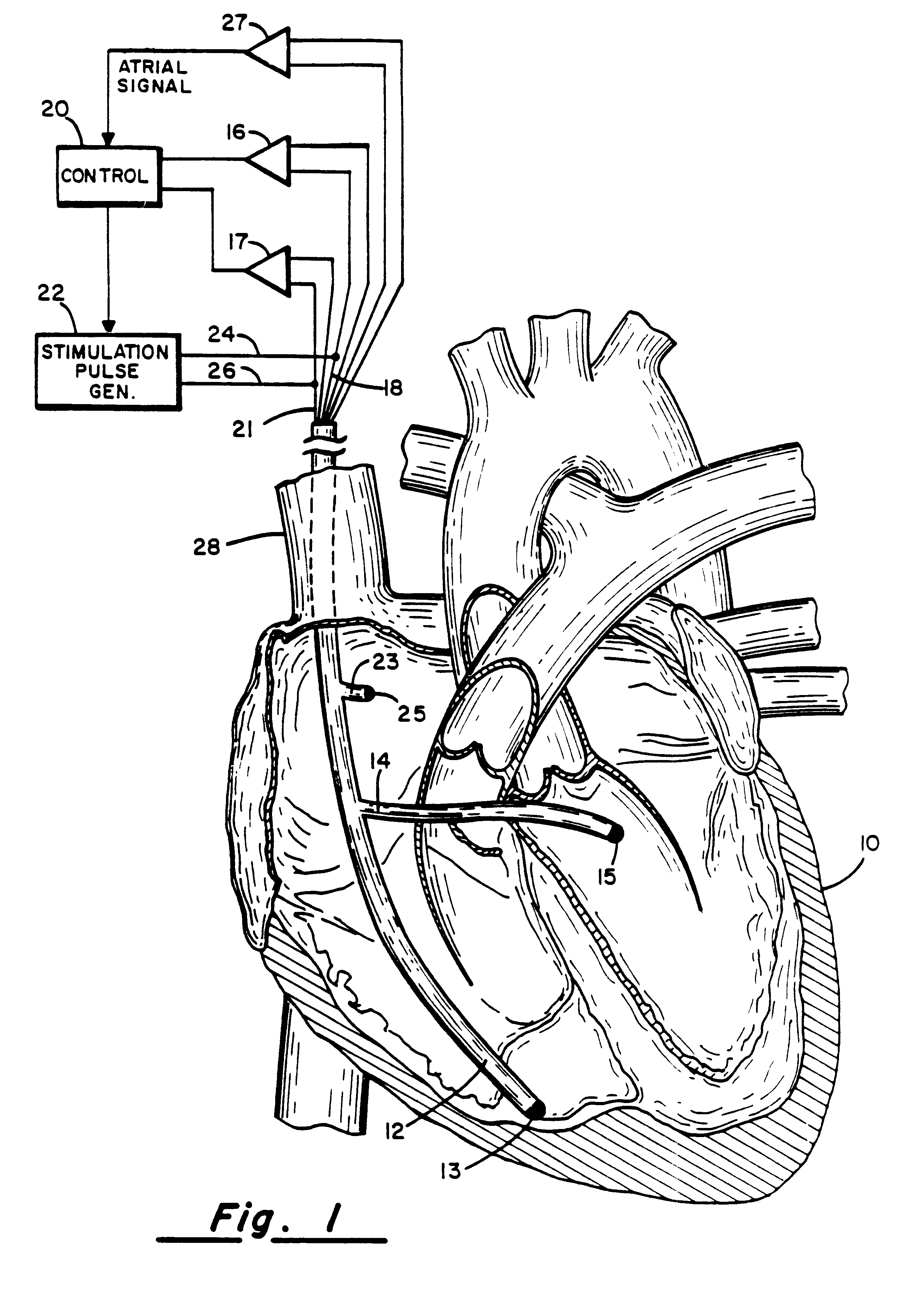
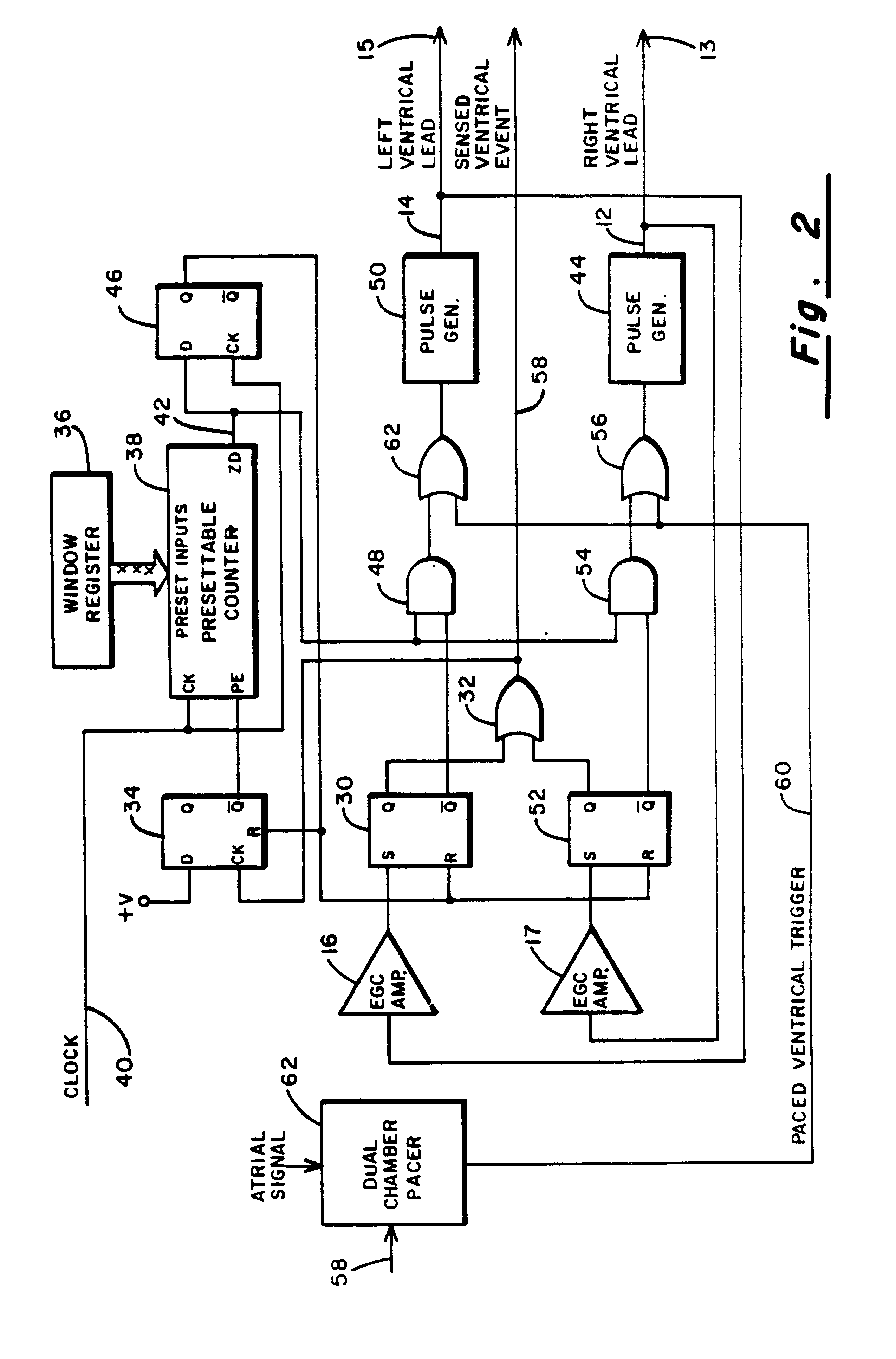
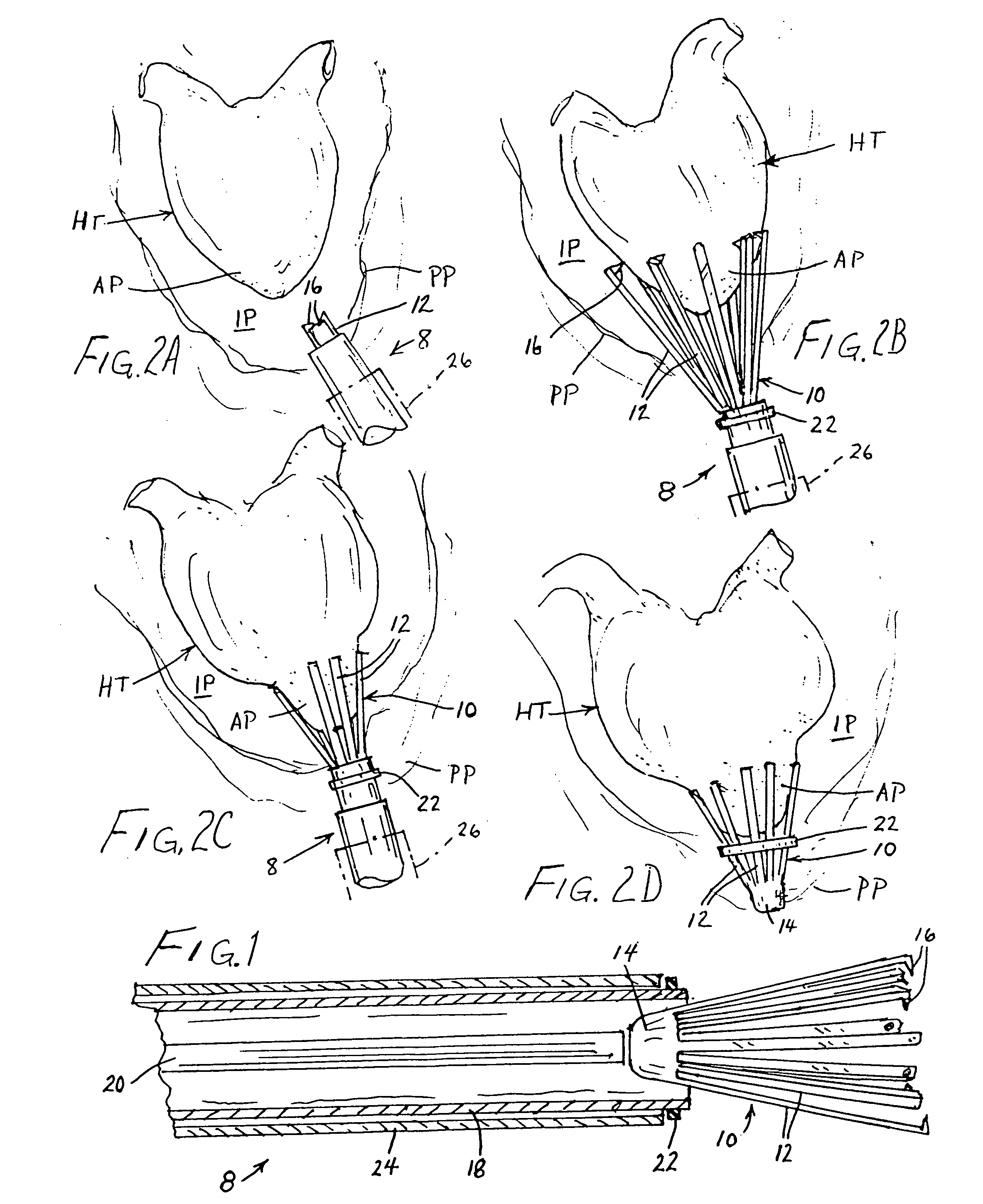
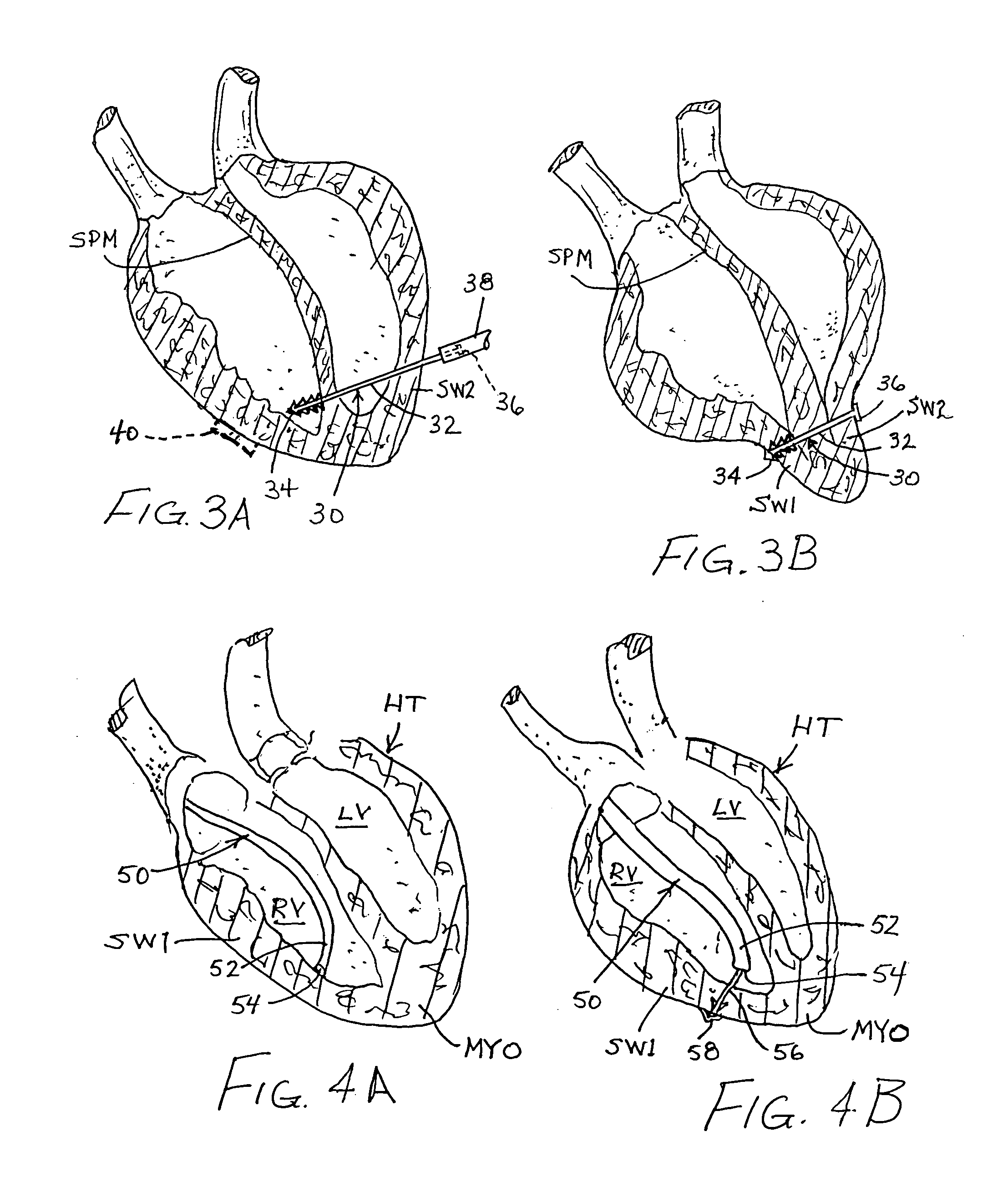
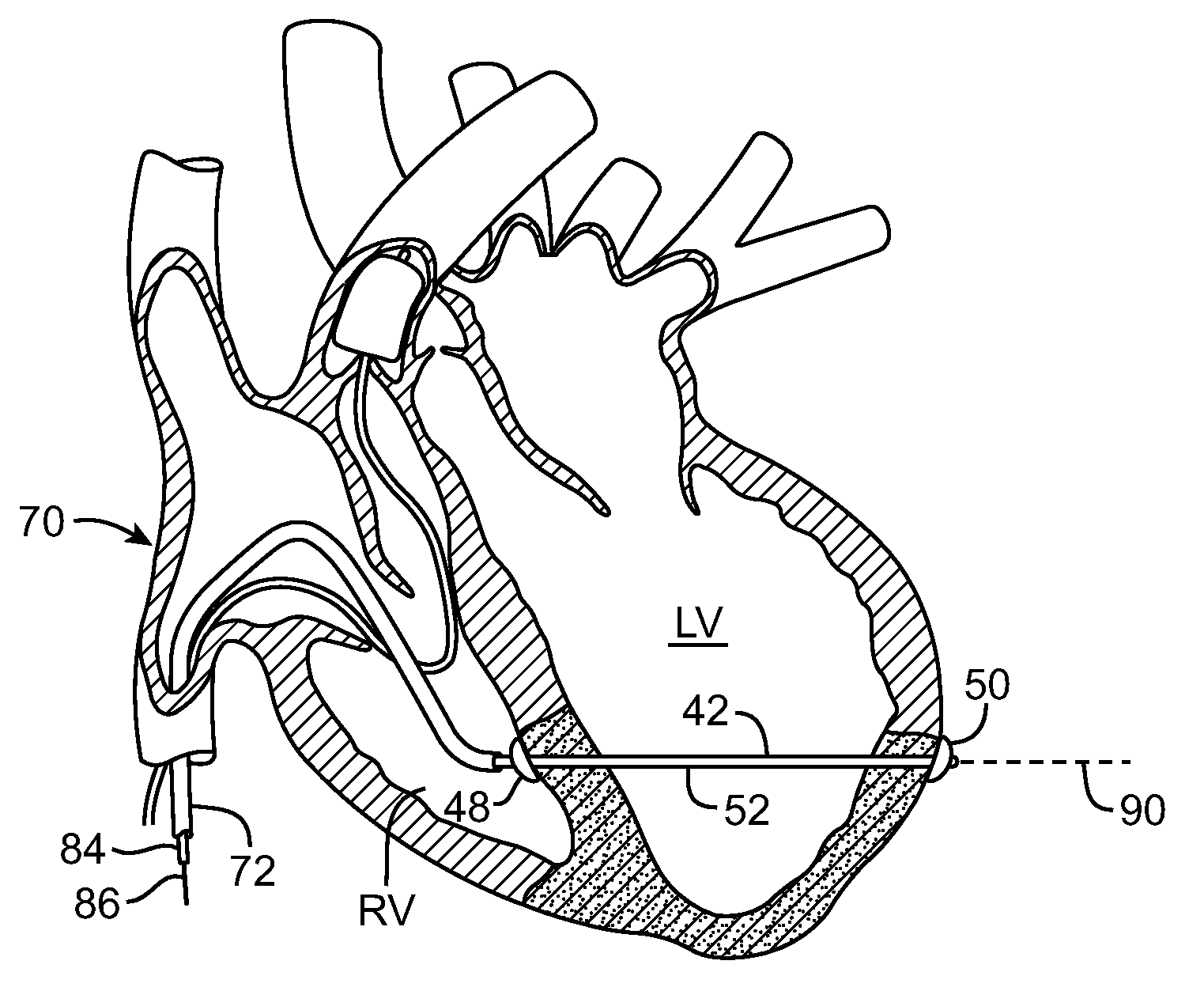
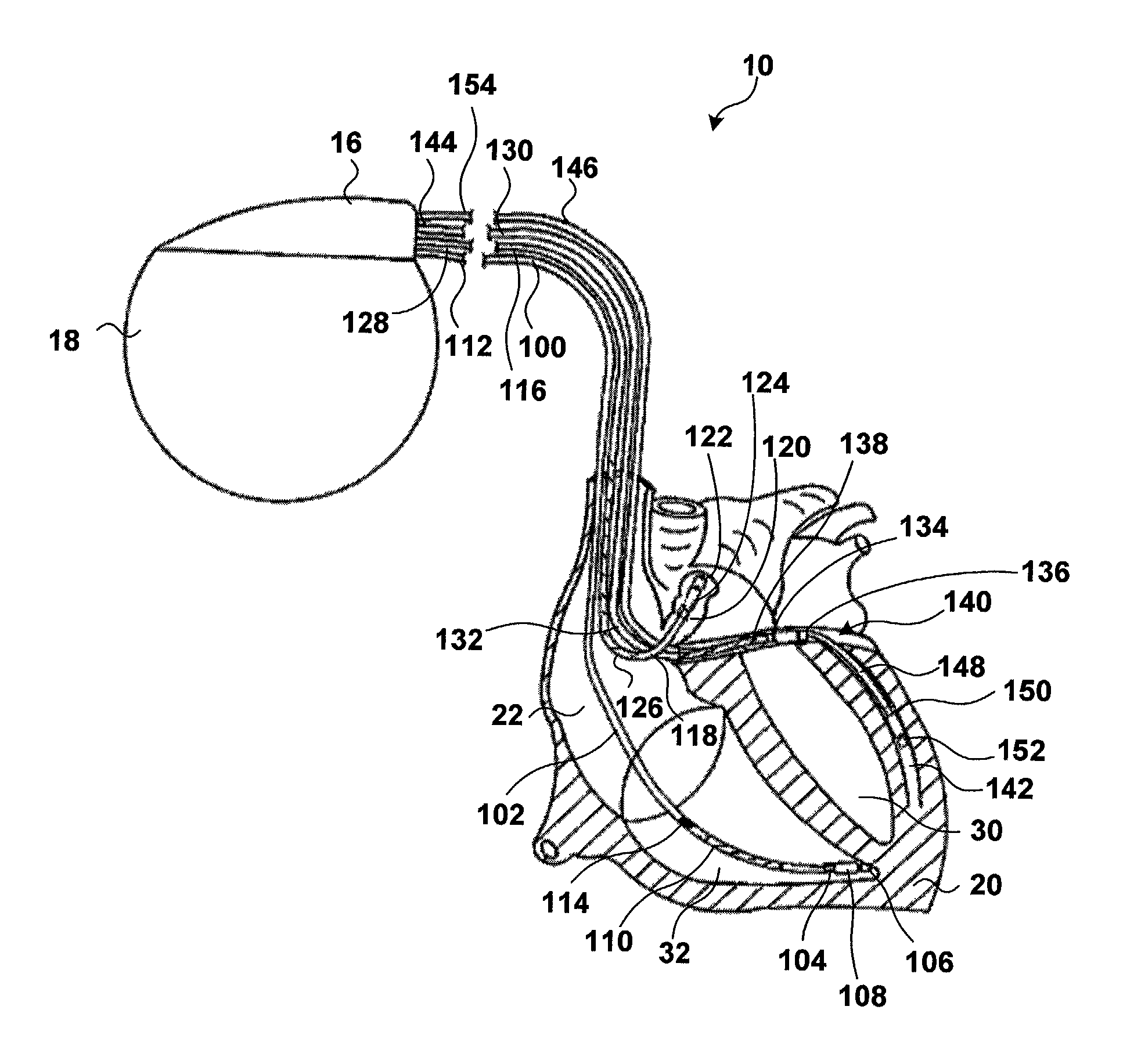
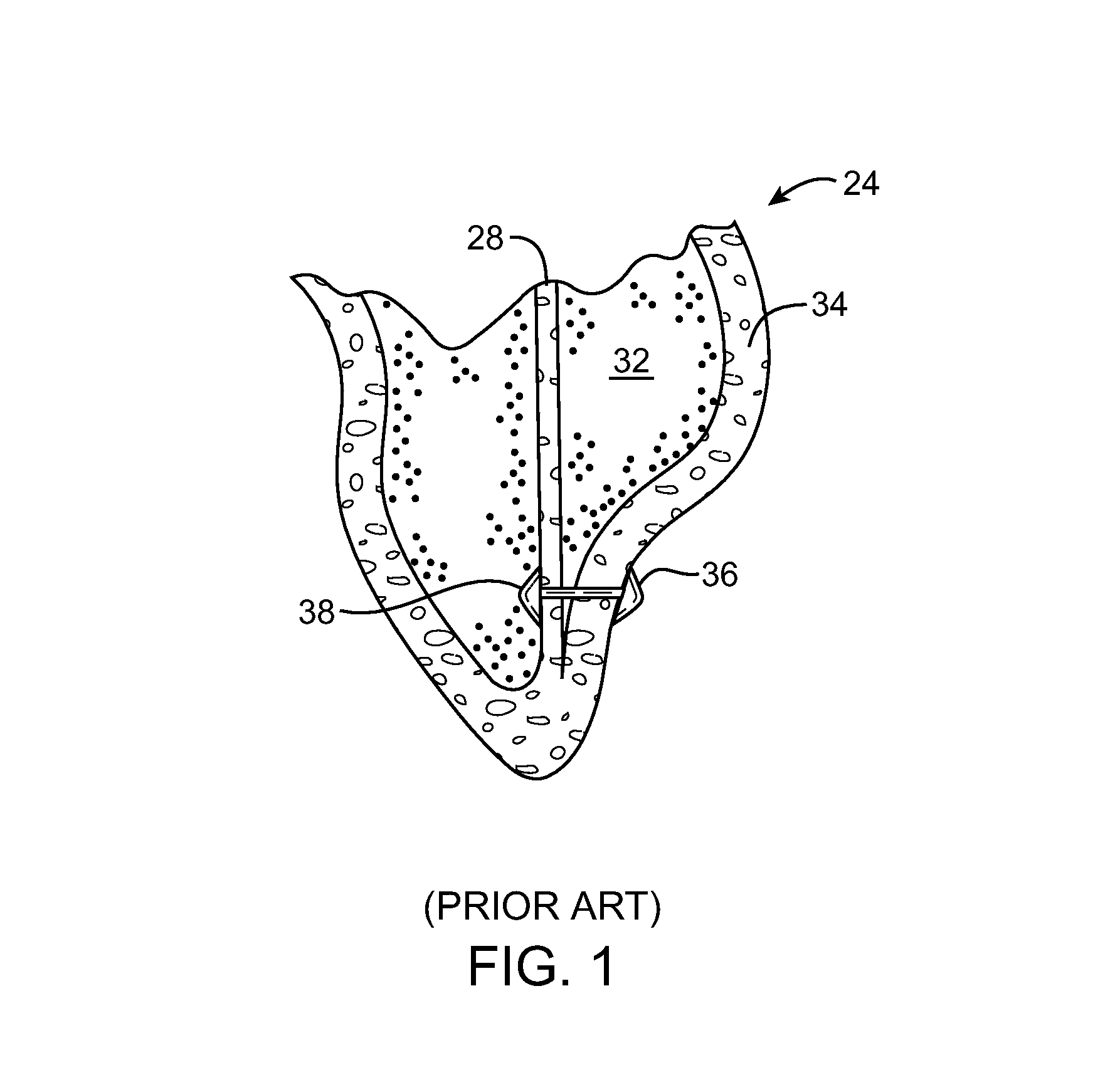
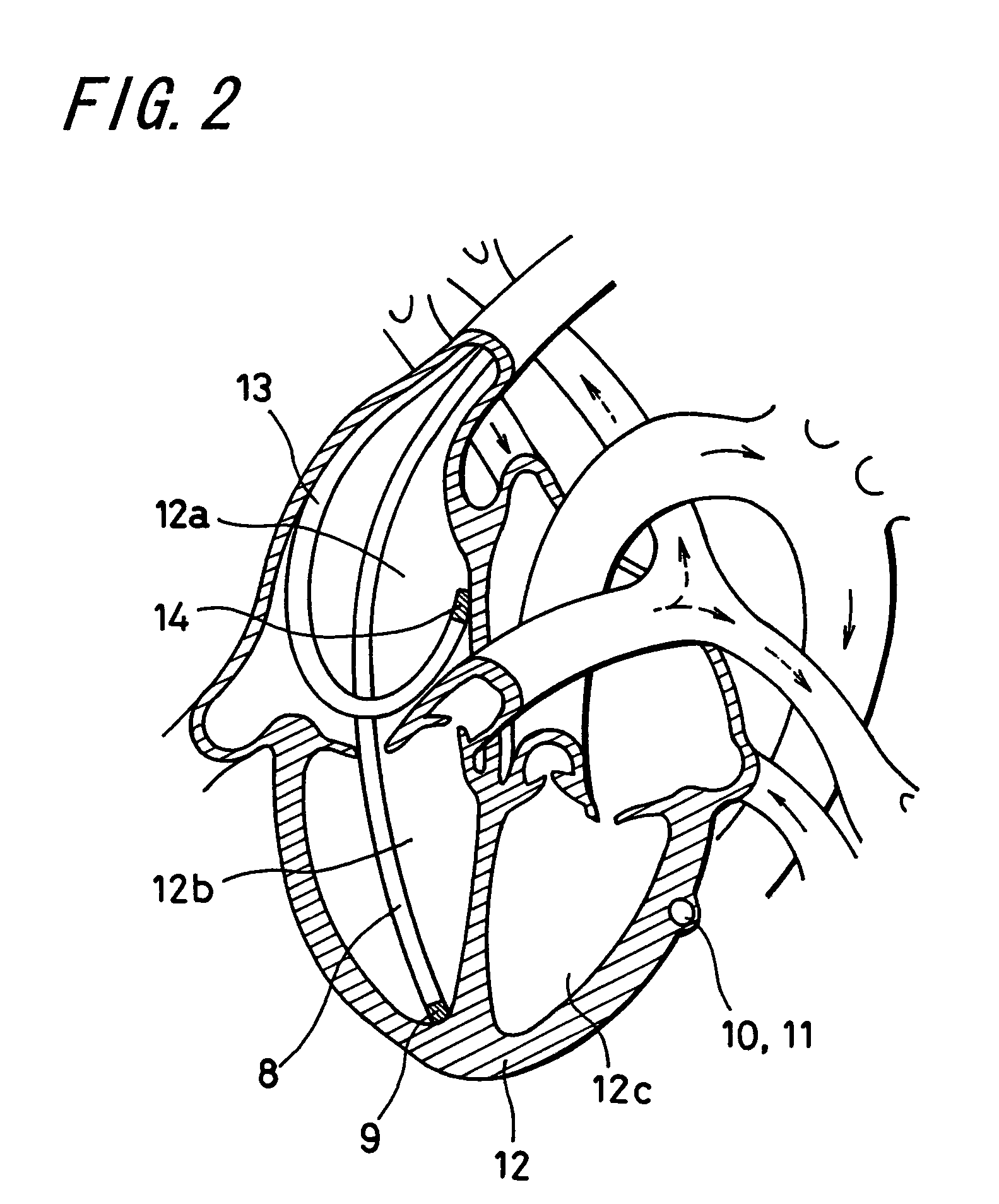
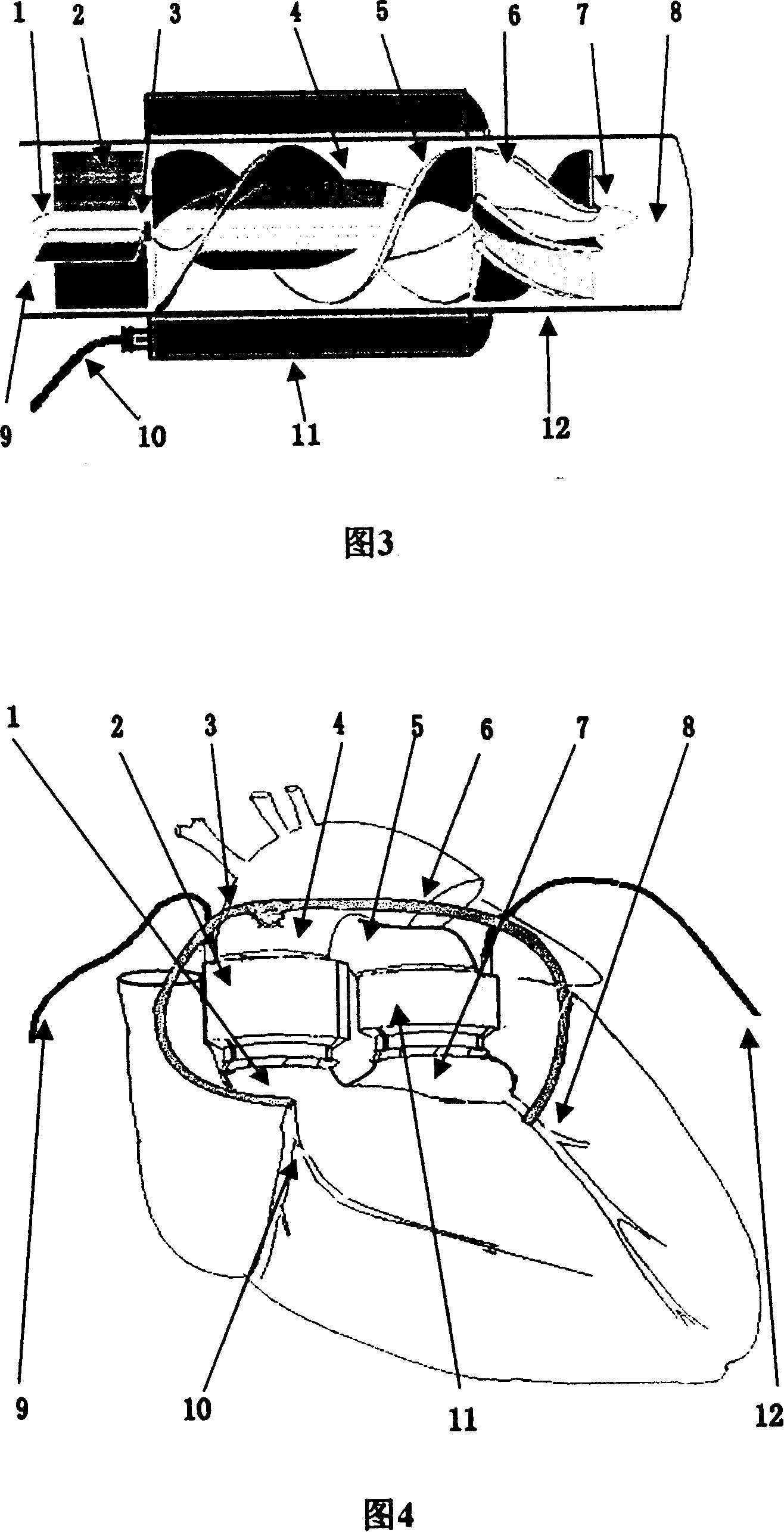
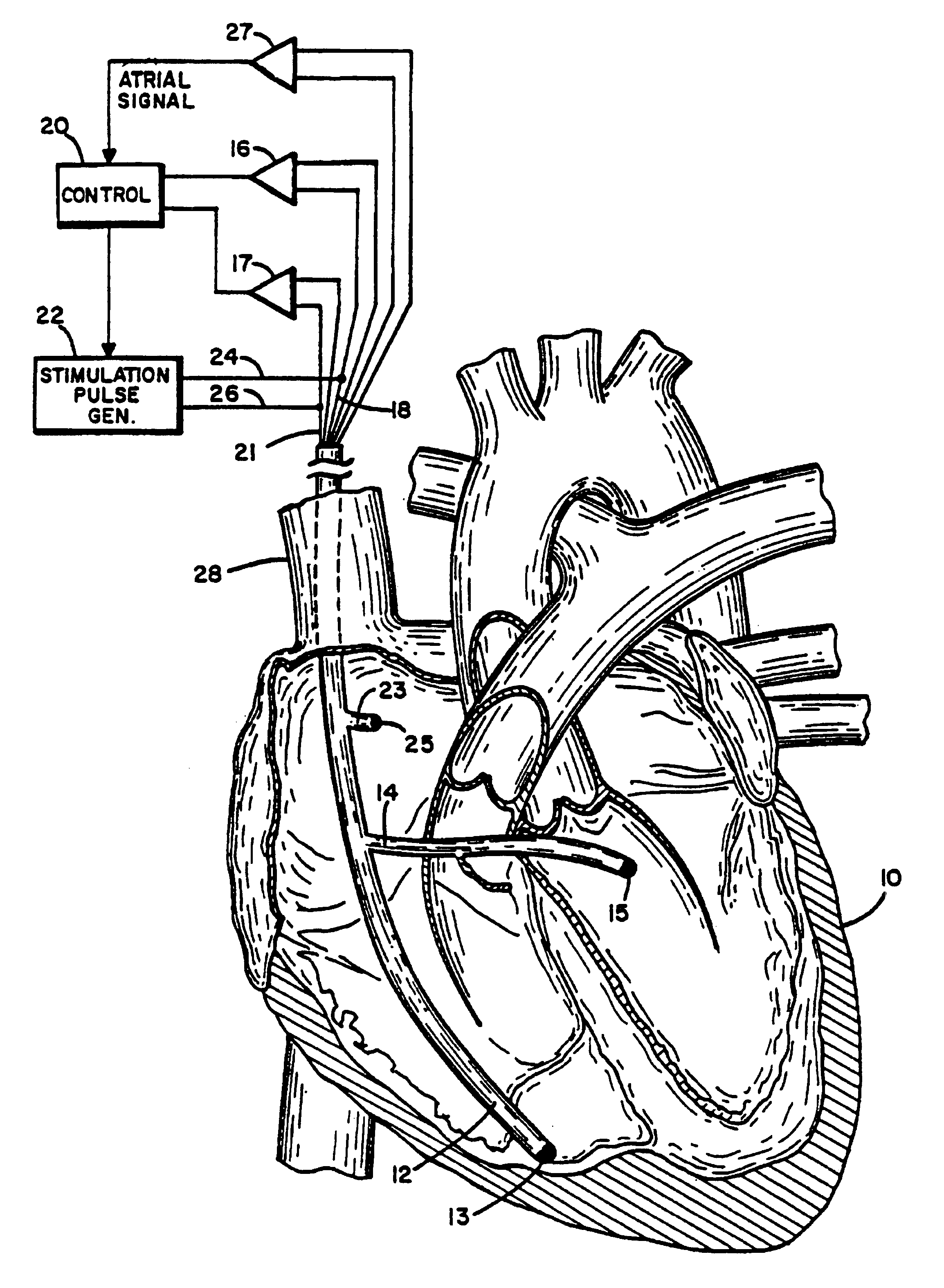
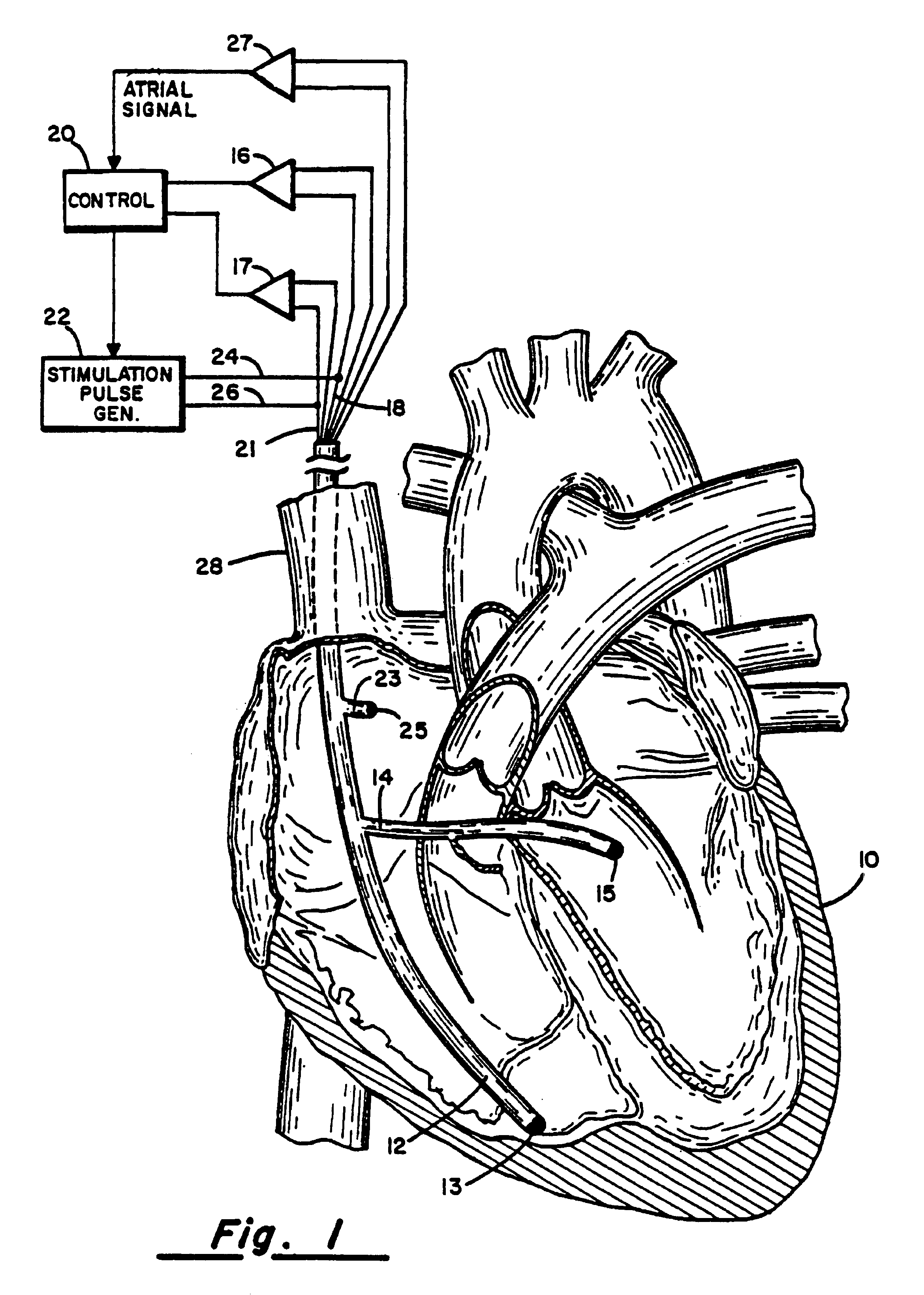
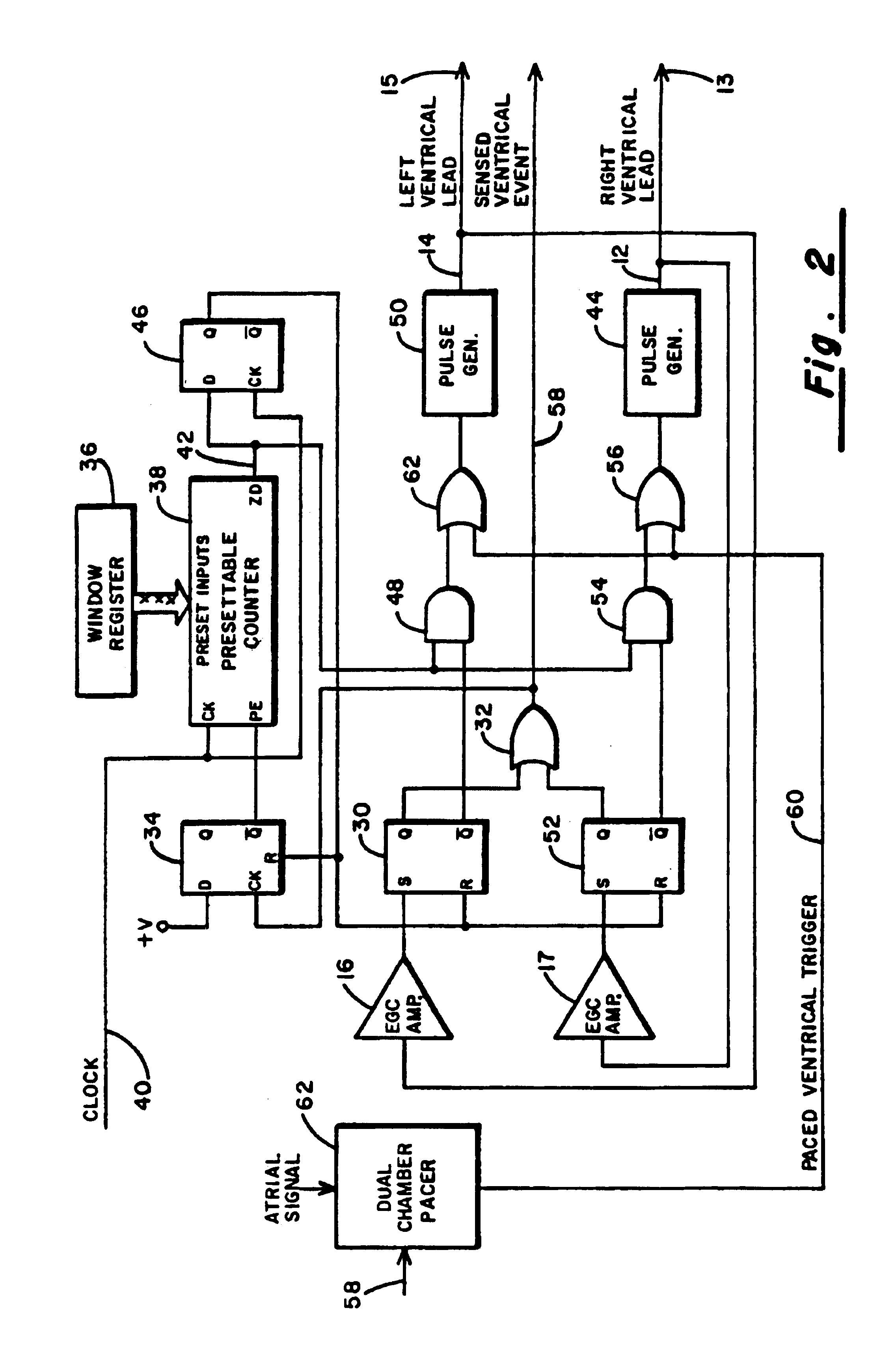
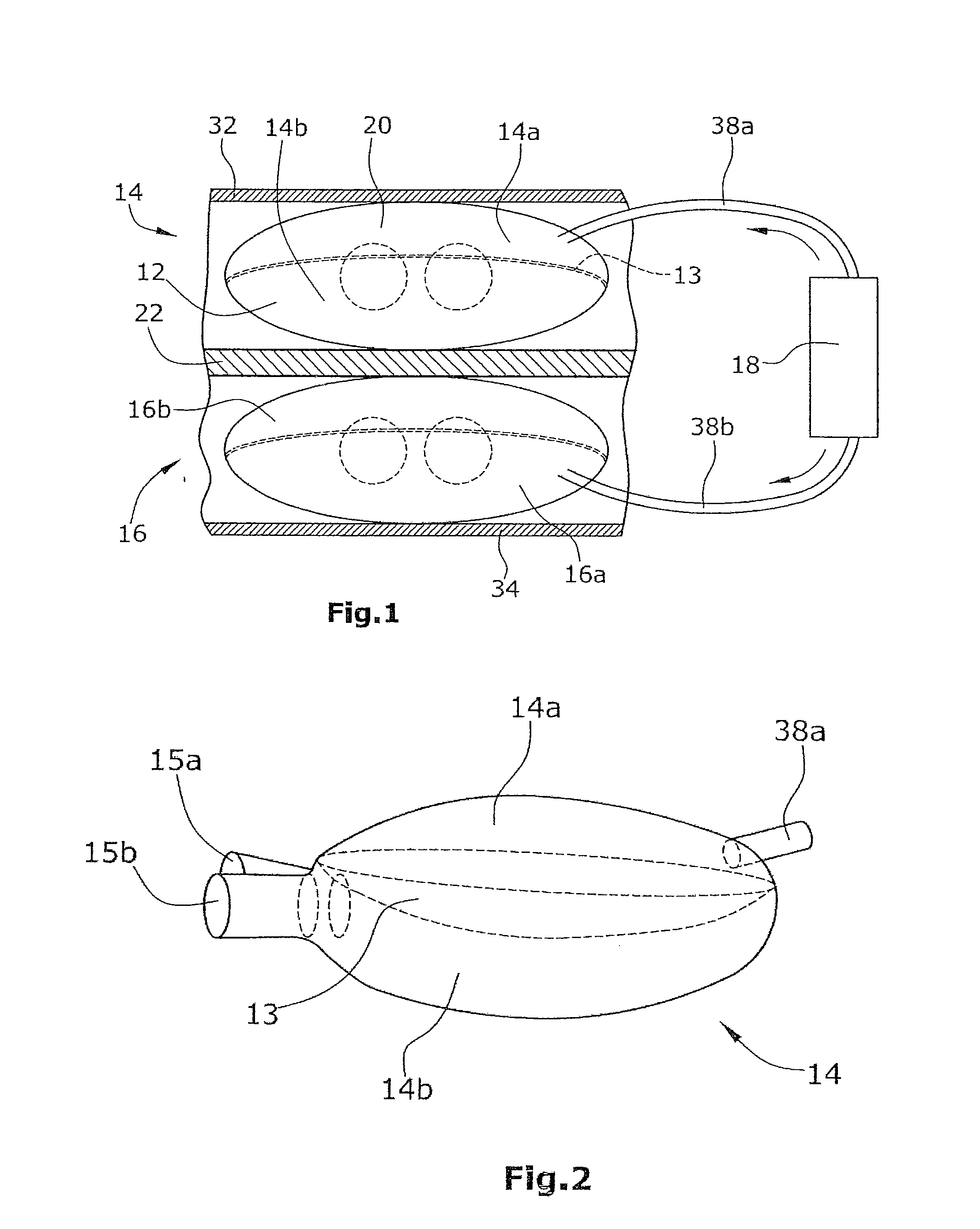
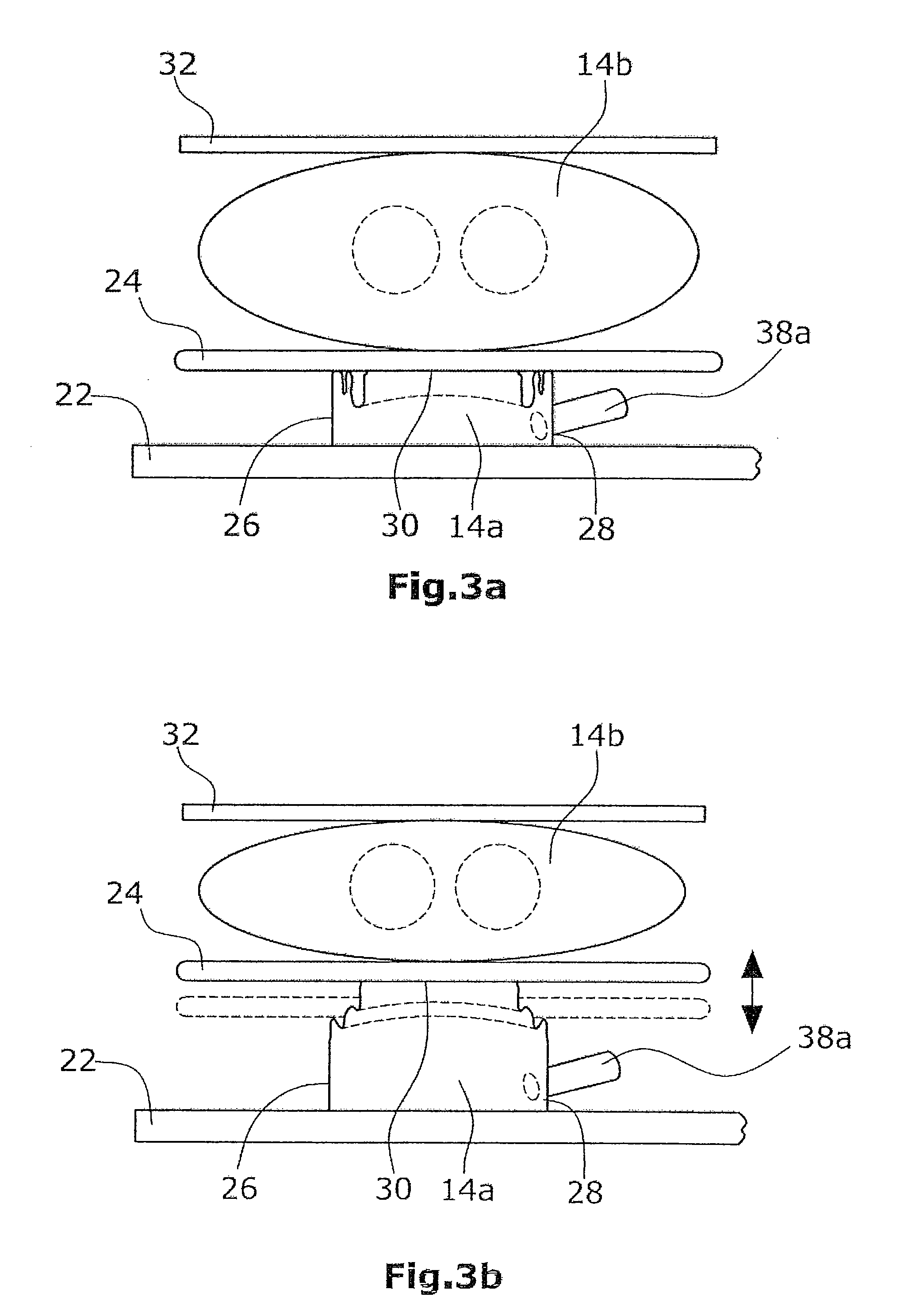
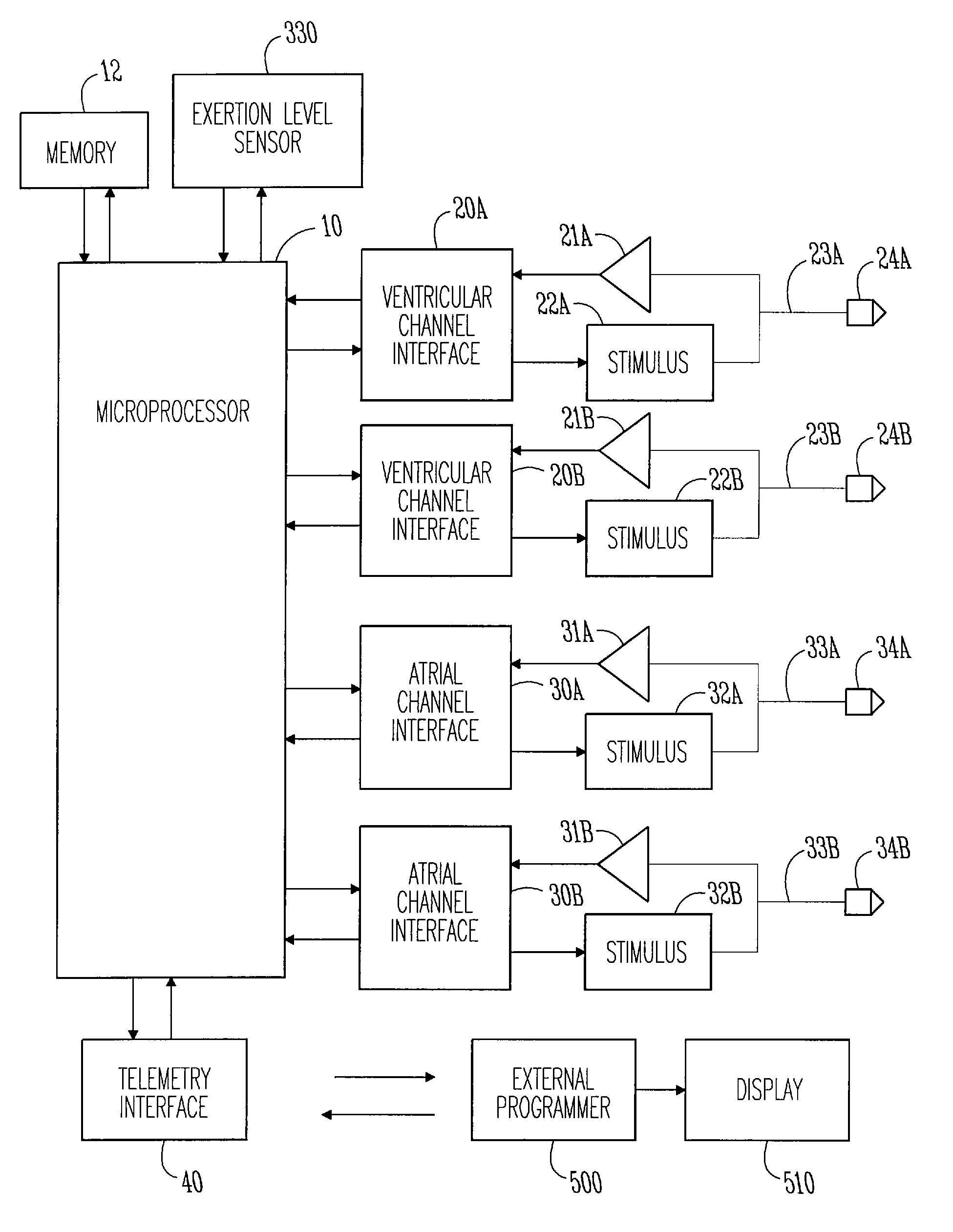
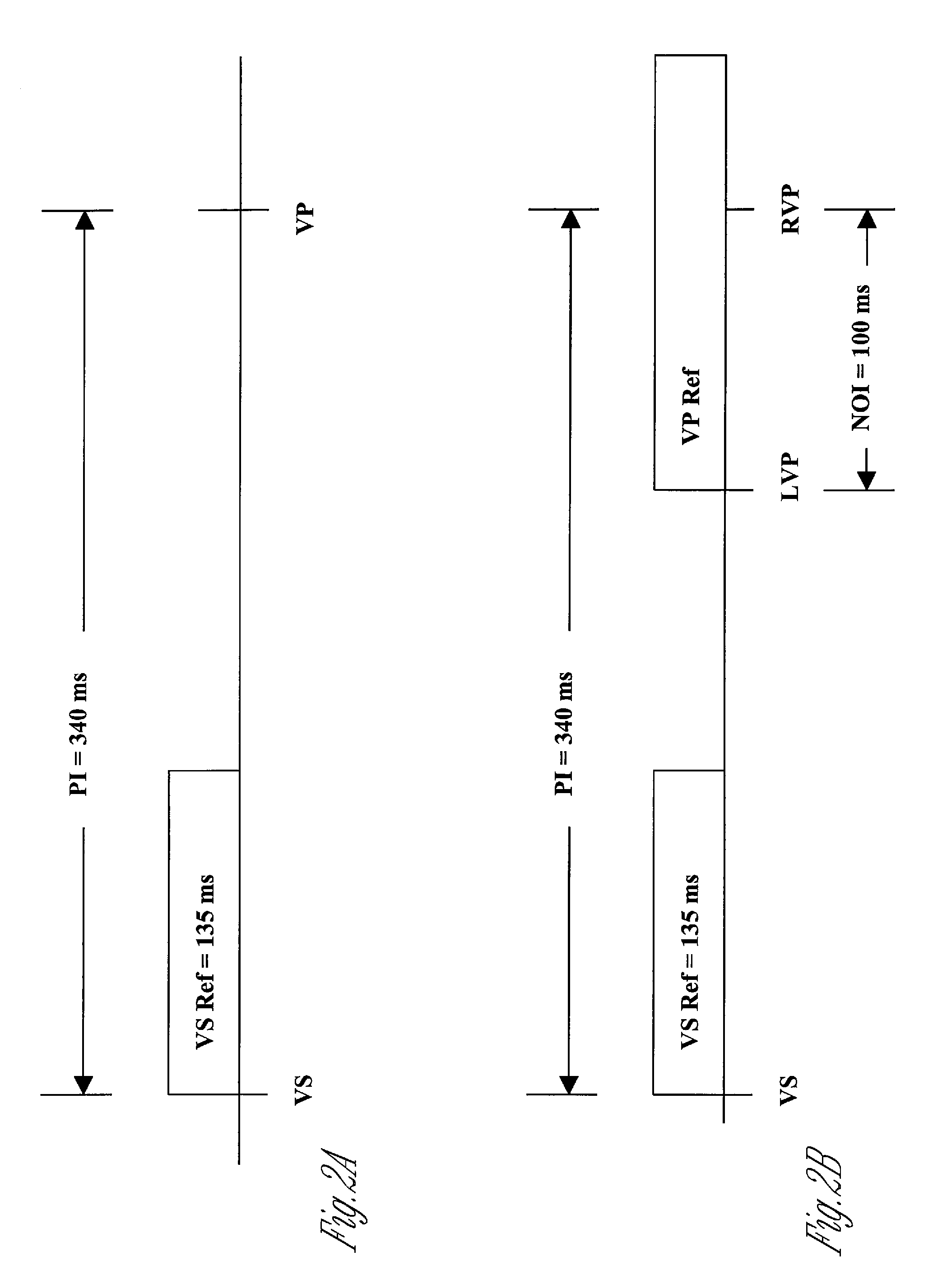
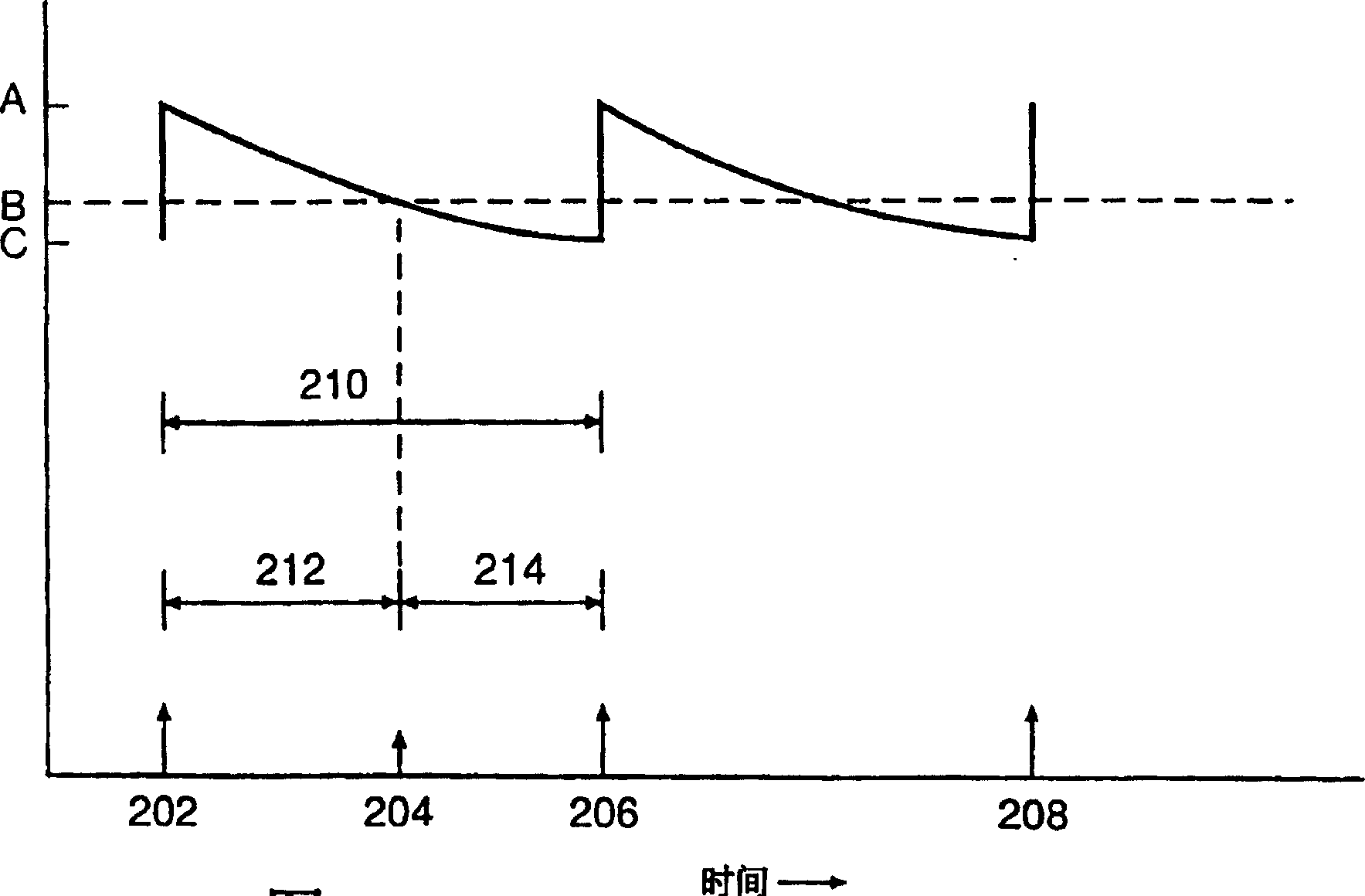
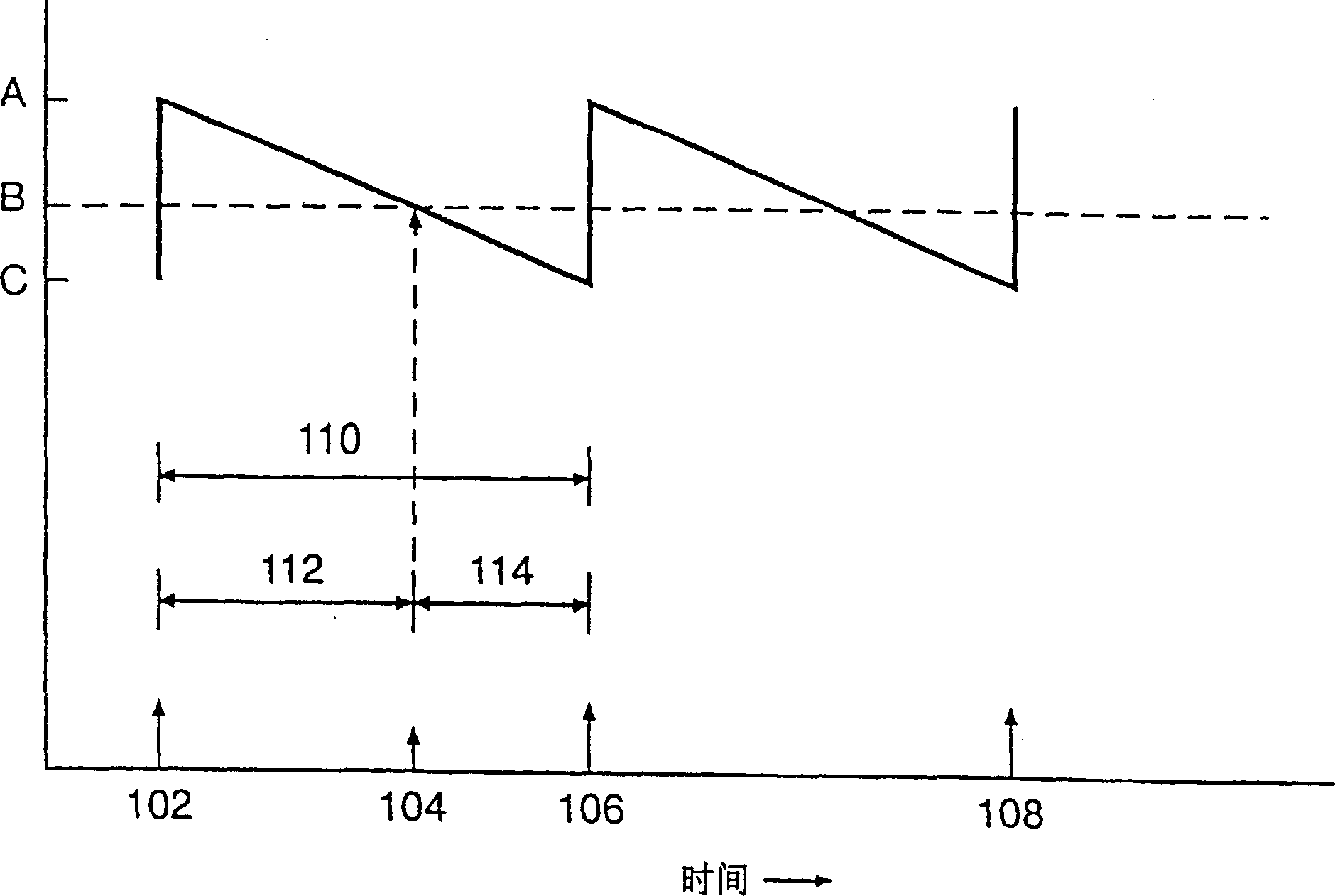
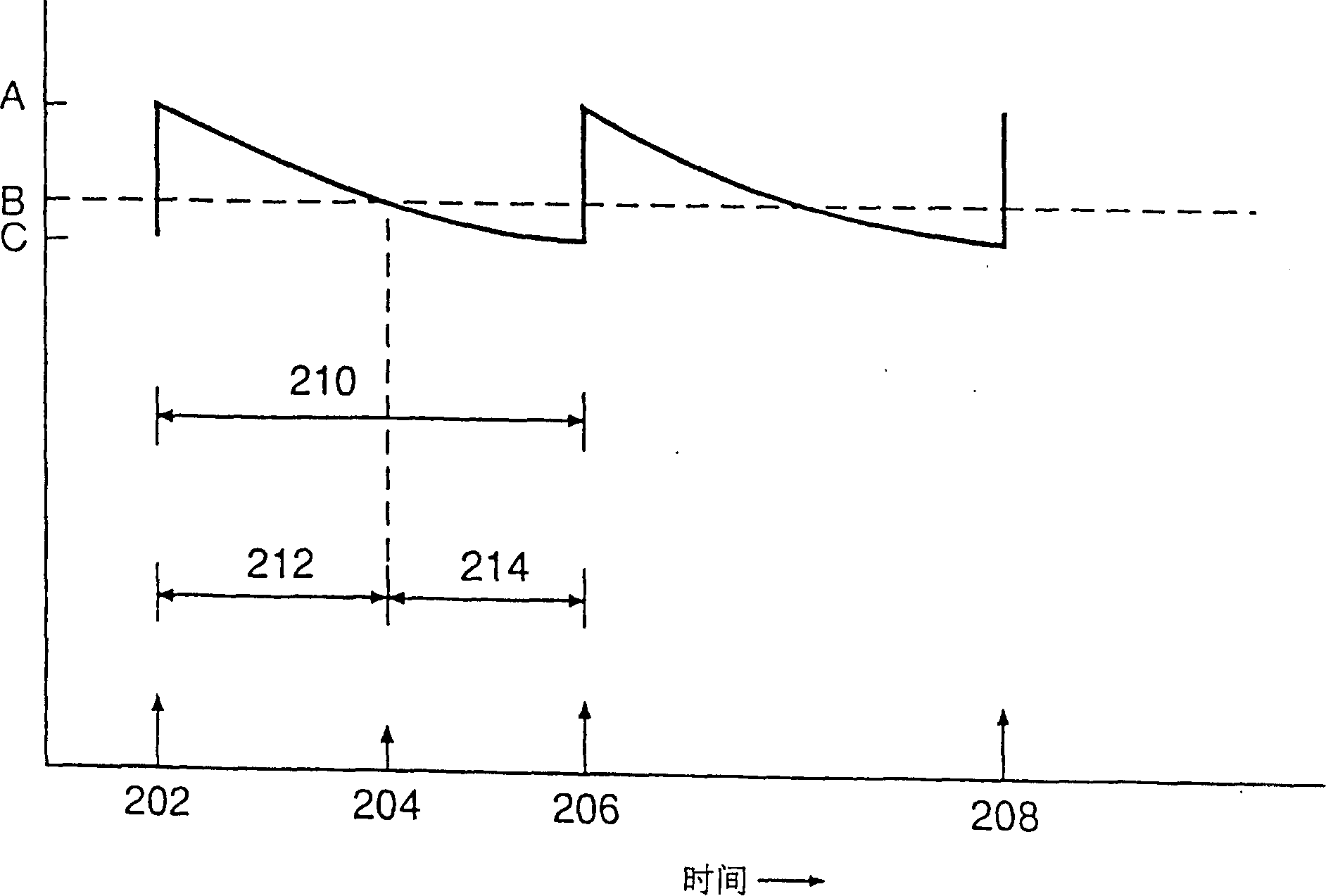
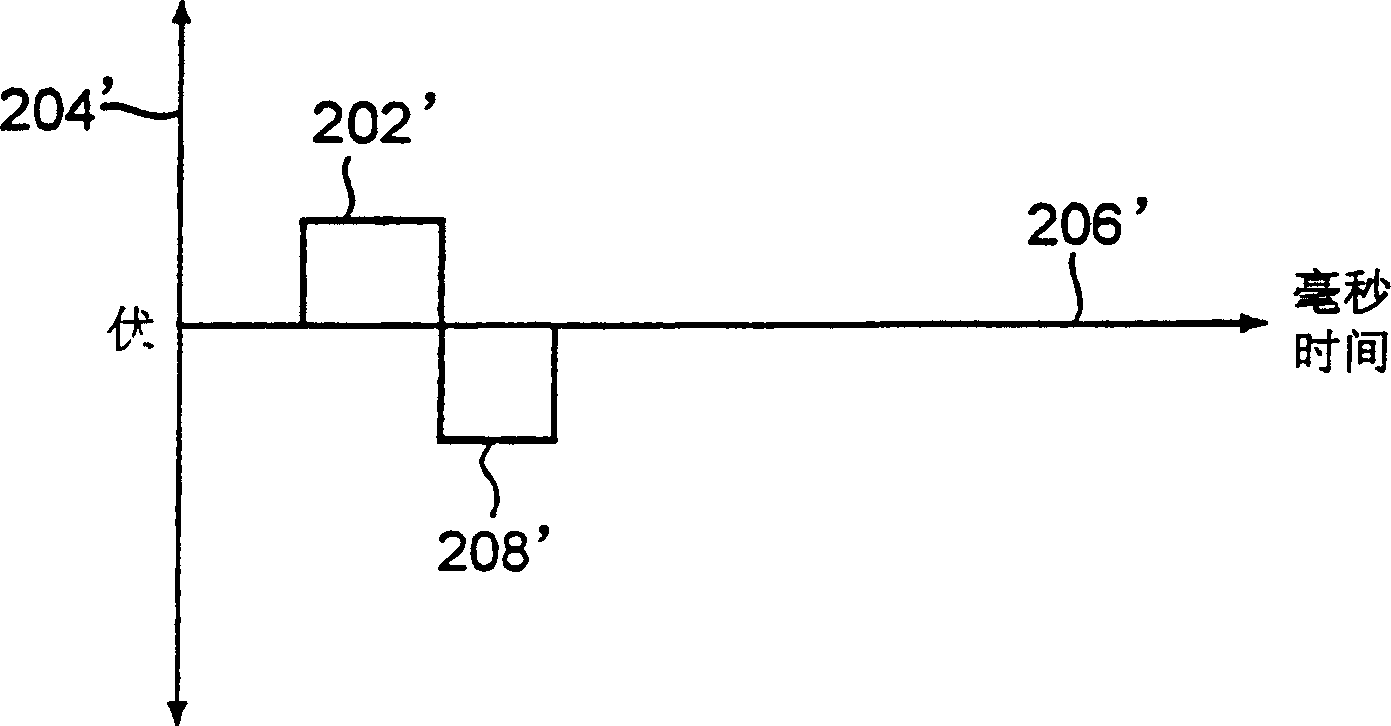
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, is placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
Method and device for improving cardiac function
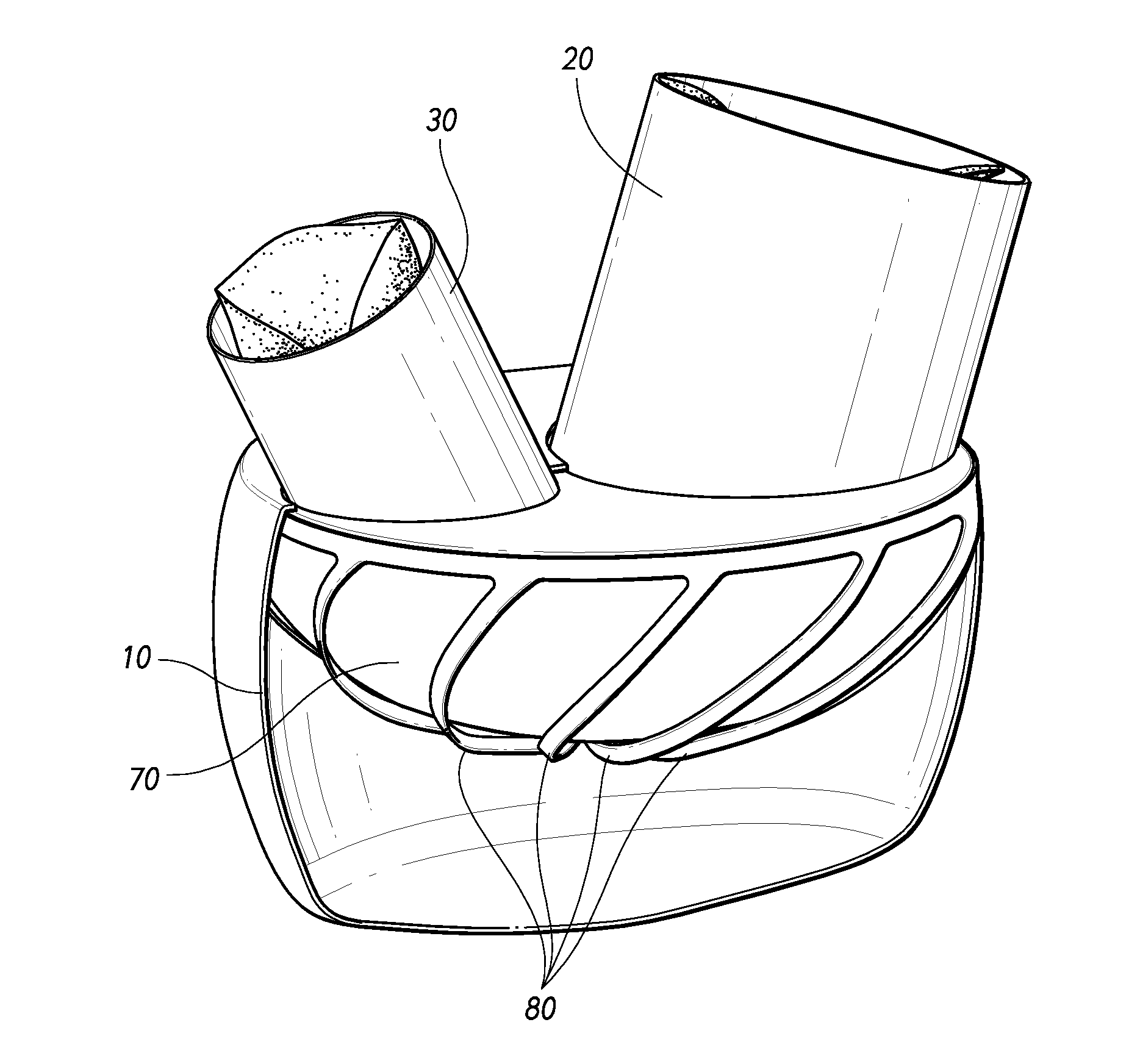
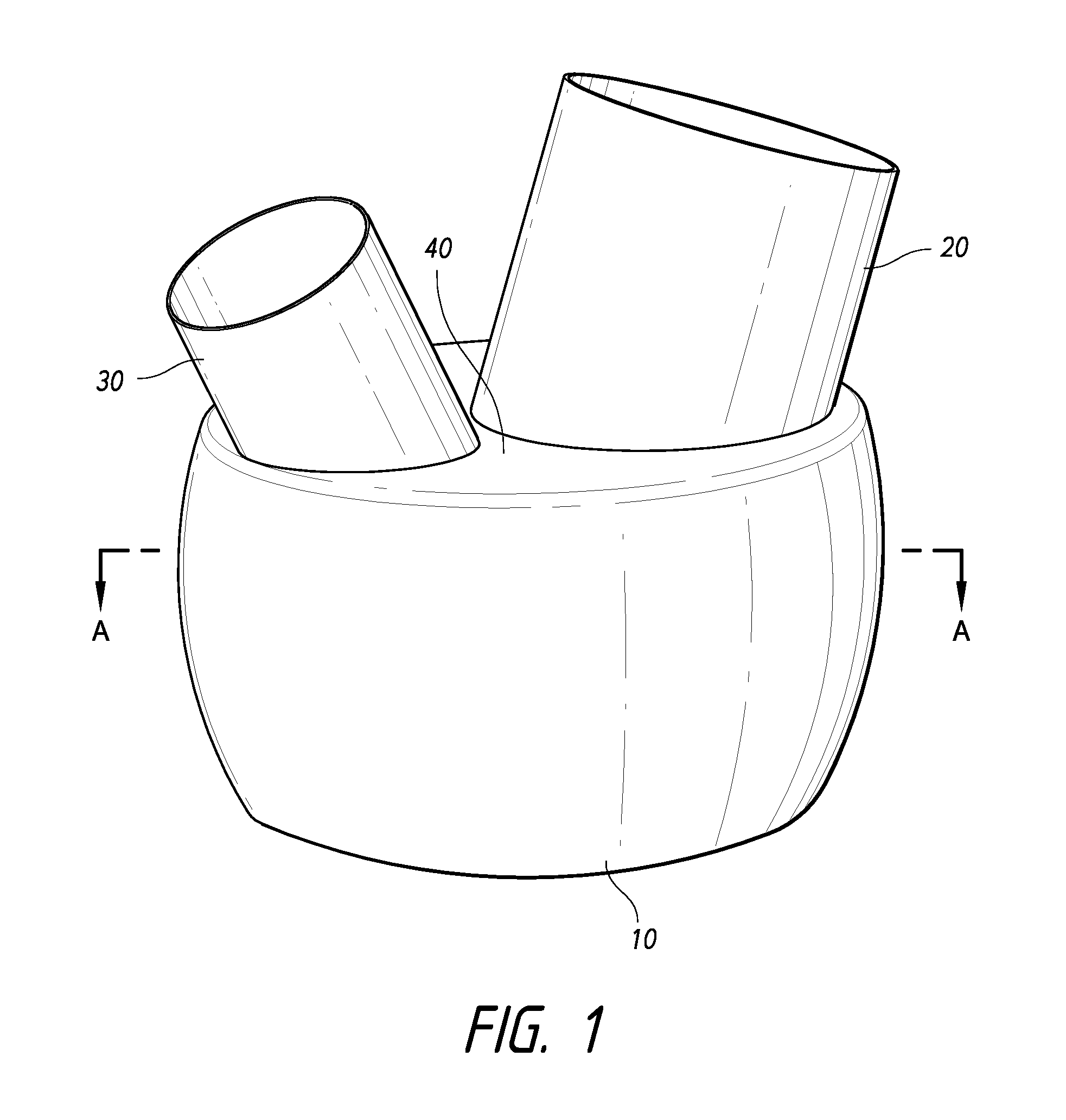
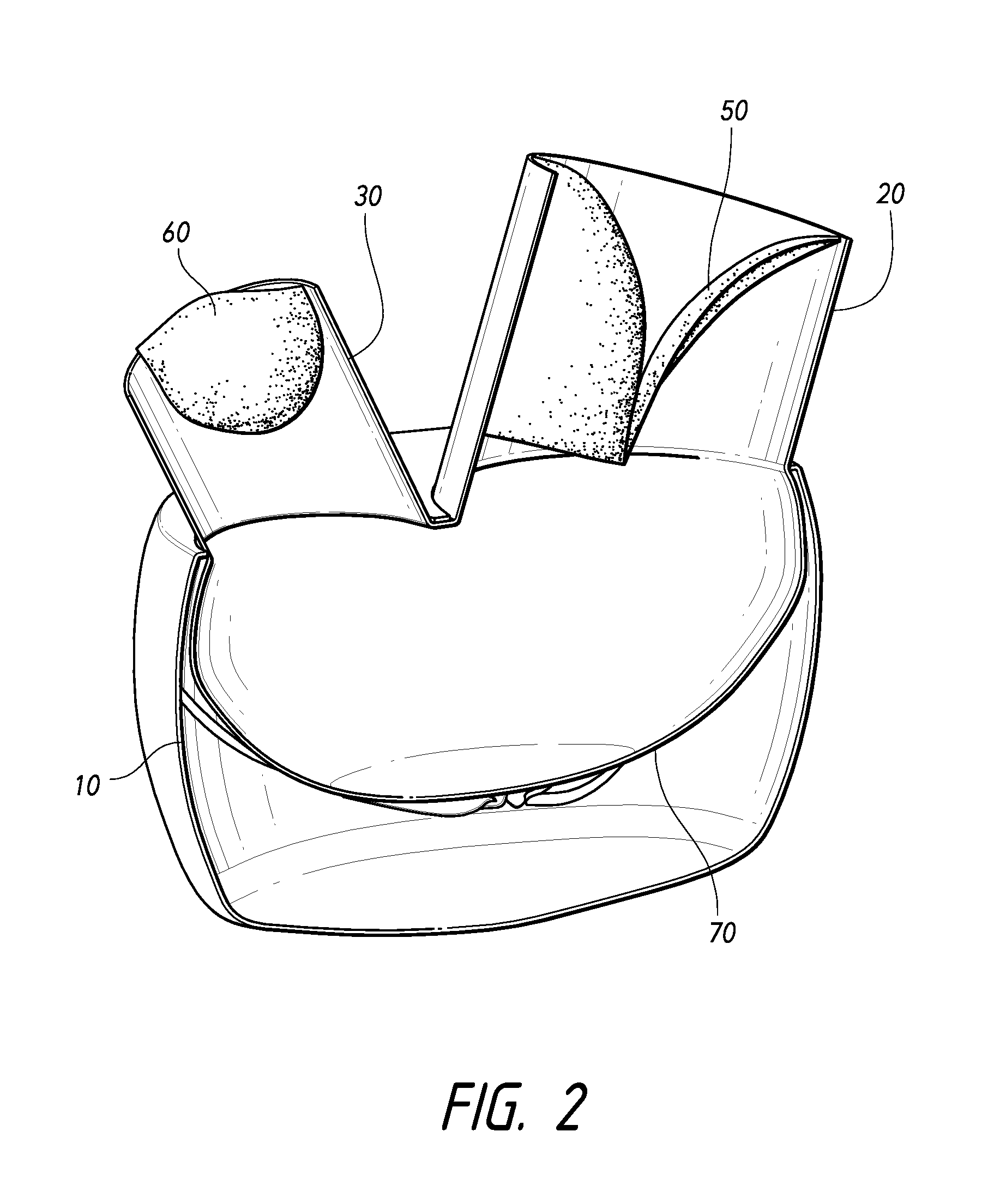
In a method for improving cardiac function, a compressive device is inserted into an intrapericardial space about a lower end portion of a heart. Thereafter the compressive device is operated to compress and close off lower portions of both ventricles of the heart.
Owner:WILK PATENT DEVMENT
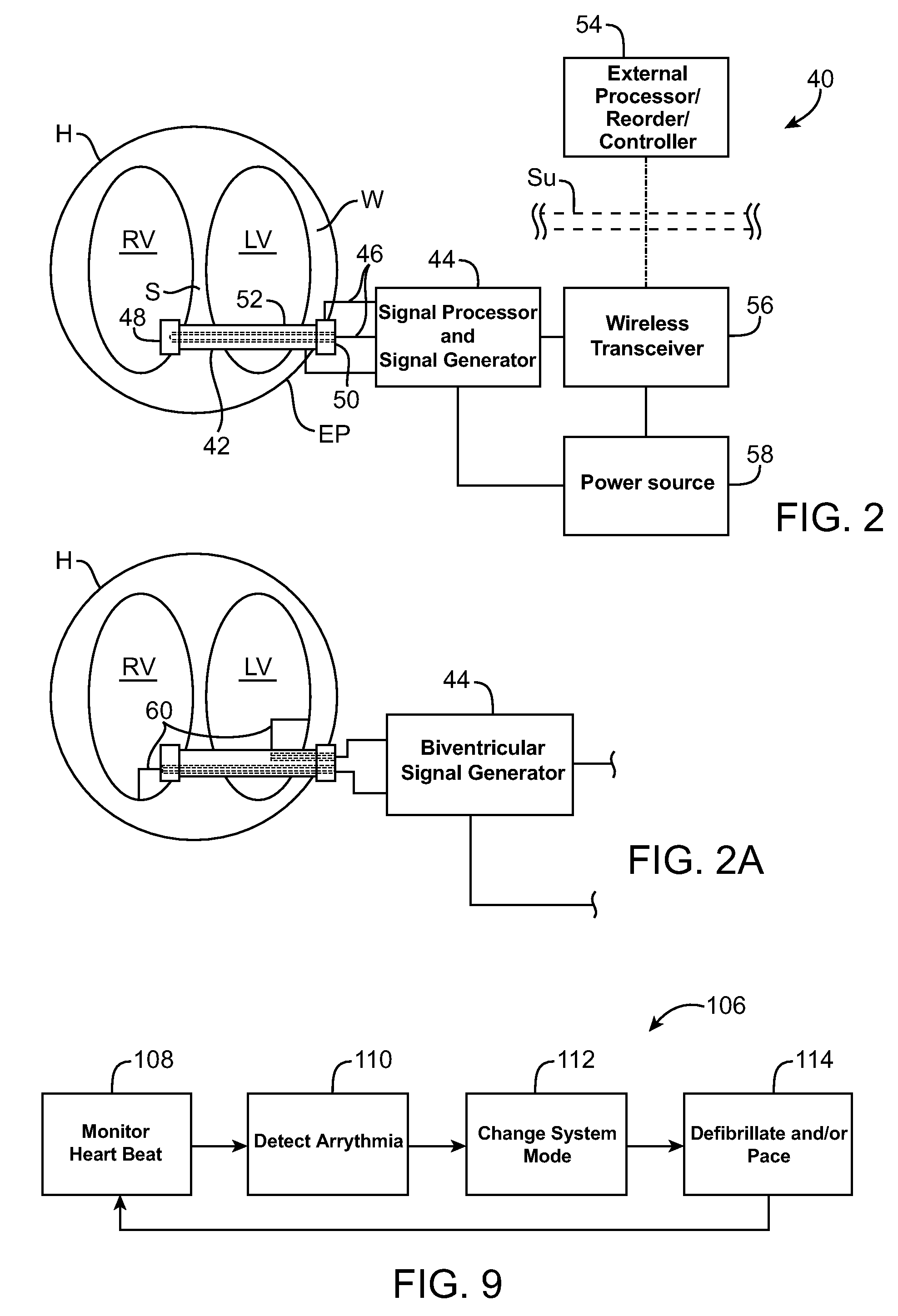
Signal Transmitting and Lesion Excluding Heart Implants for Pacing Defibrillating and/or Sensing of Heart Beat
ActiveUS20080082132A1Reducing circumferenceControl DimensionsTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart valvesControl systemCongestive heart failure chf
Devices, systems, and methods for treating a heart of a patient may make use of structures which limit a size of a chamber of the heart, such as by deploying a tensile member to bring a wall of the heart toward (optionally into contact with) a septum of the heart. The implant may include an electrode or other structure for applying pacing signals to one or both ventricles of the heart, for defibrillating the heart, for sensing beating of the heart or the like. A wireless telemetry and control system may allowing the implant to treat congestive heart failure, monitor the results of the treatment, and apply appropriate electrical stimulation.
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
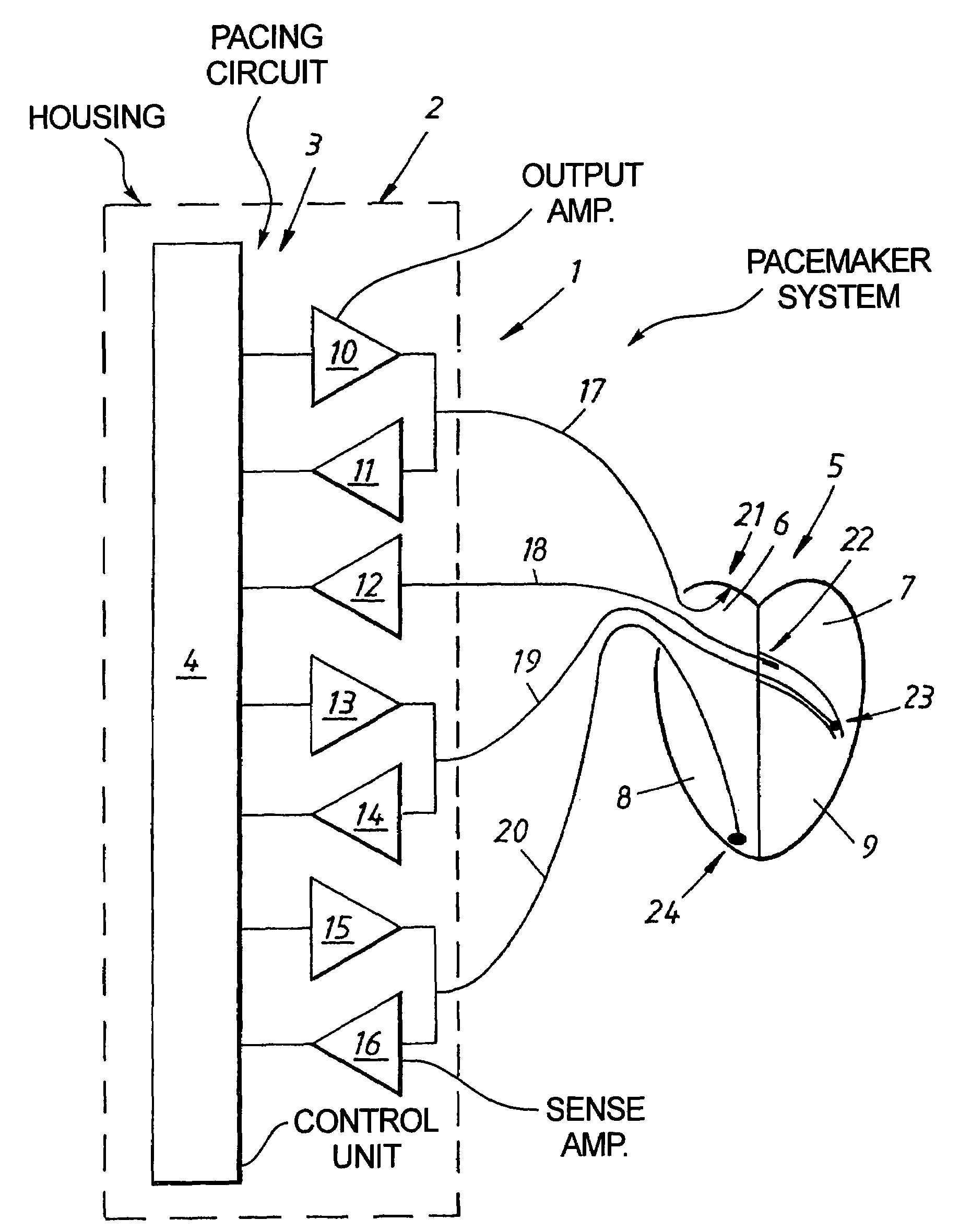
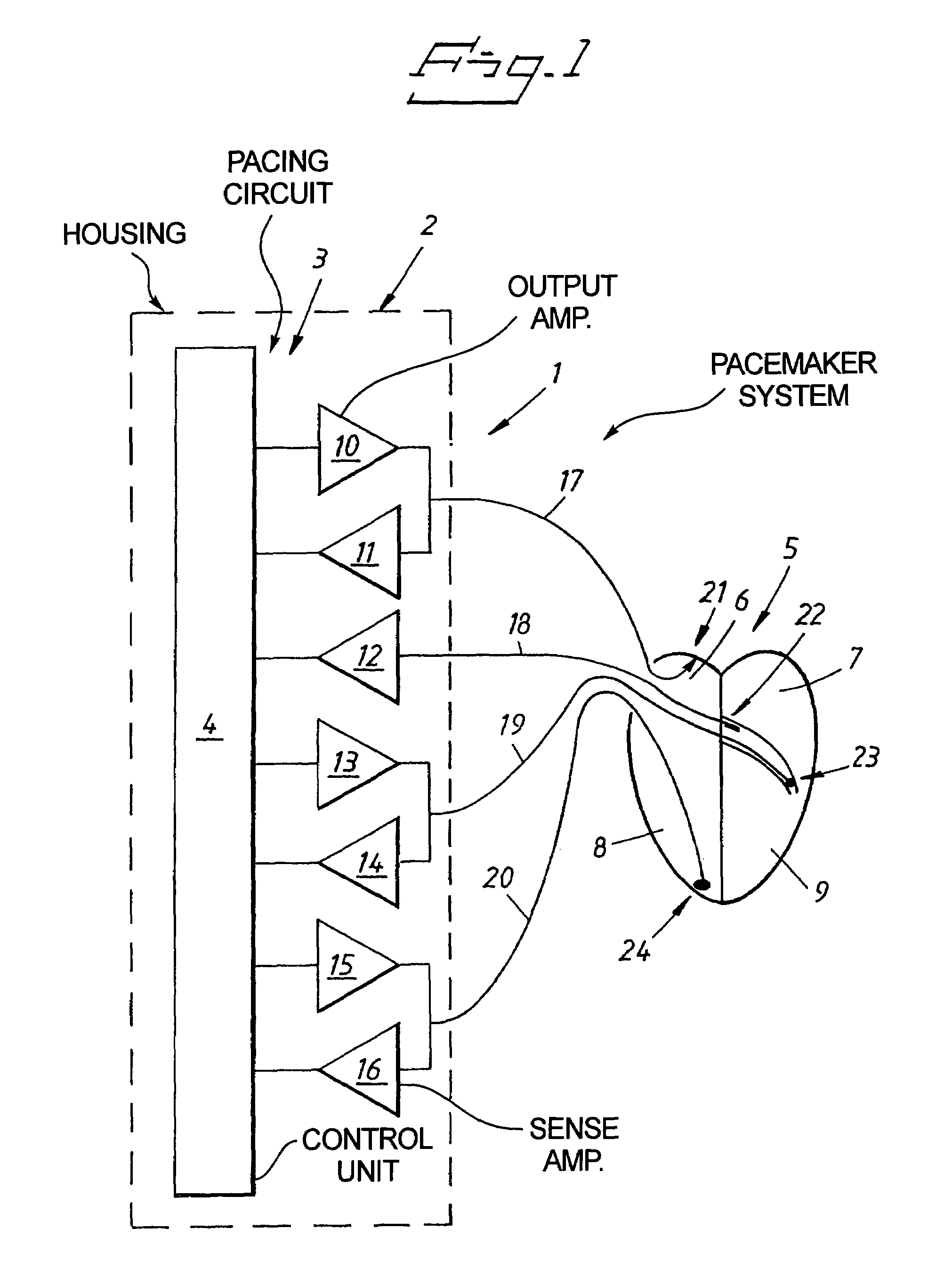
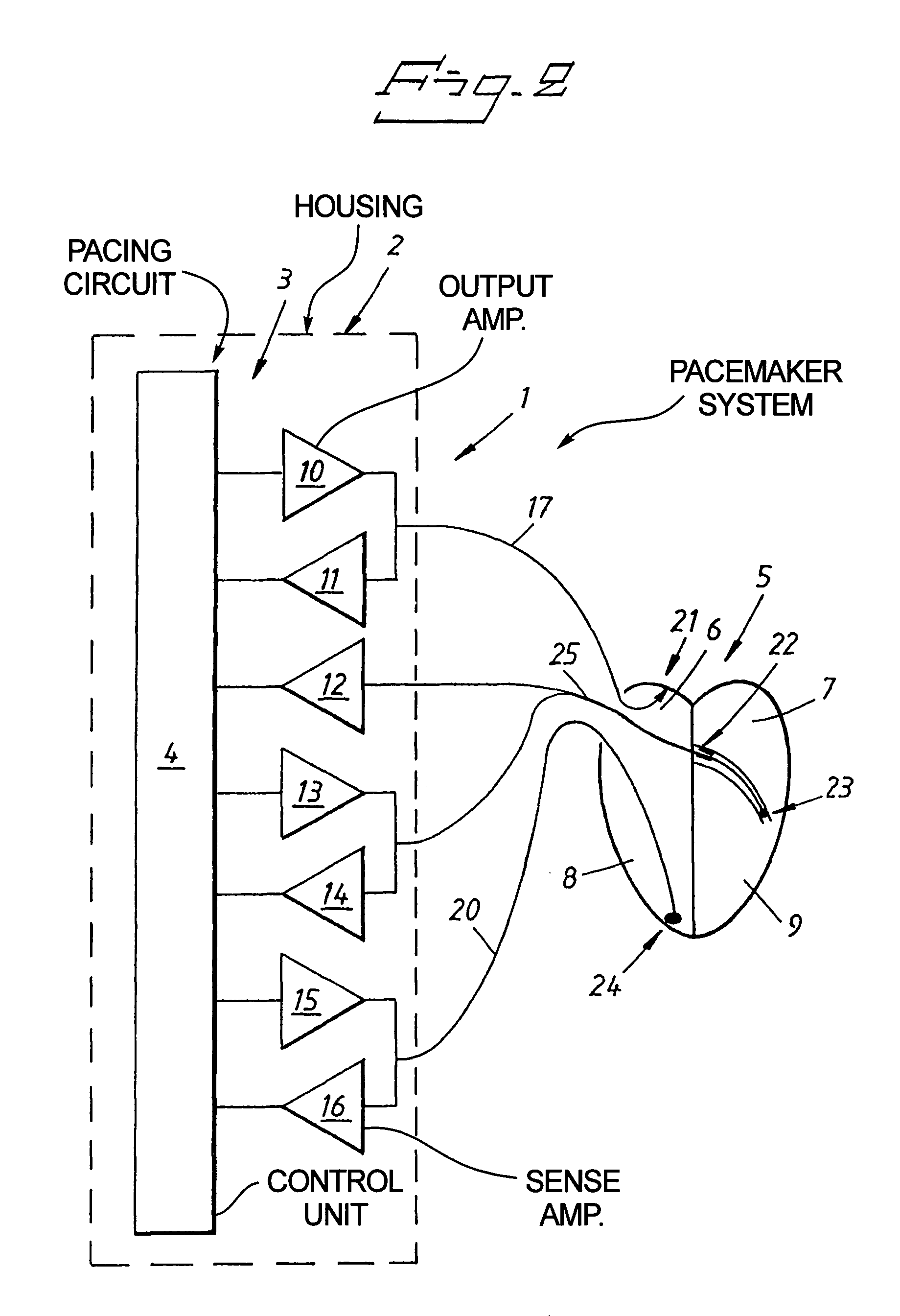
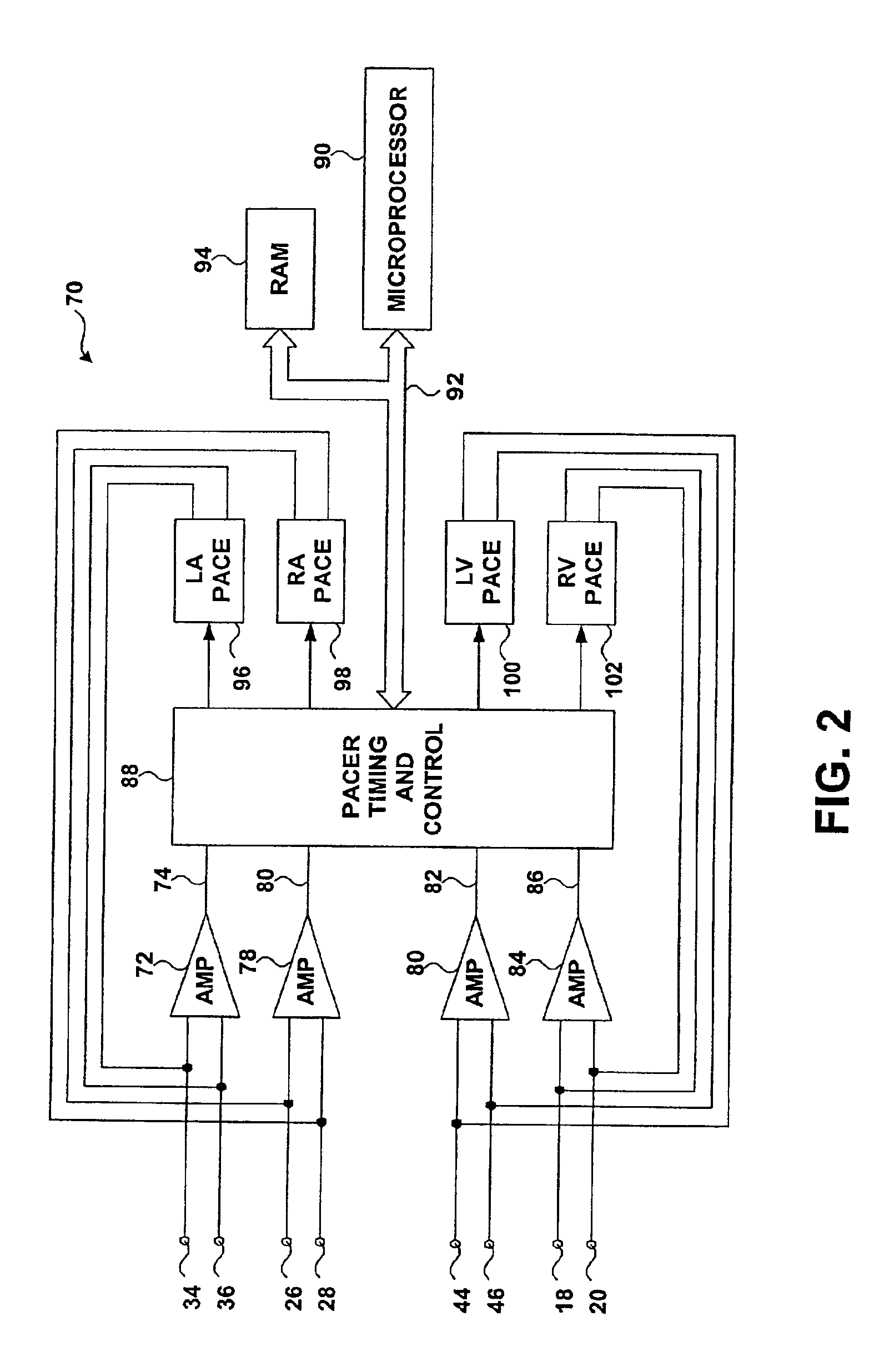
Cardiac stimulating device
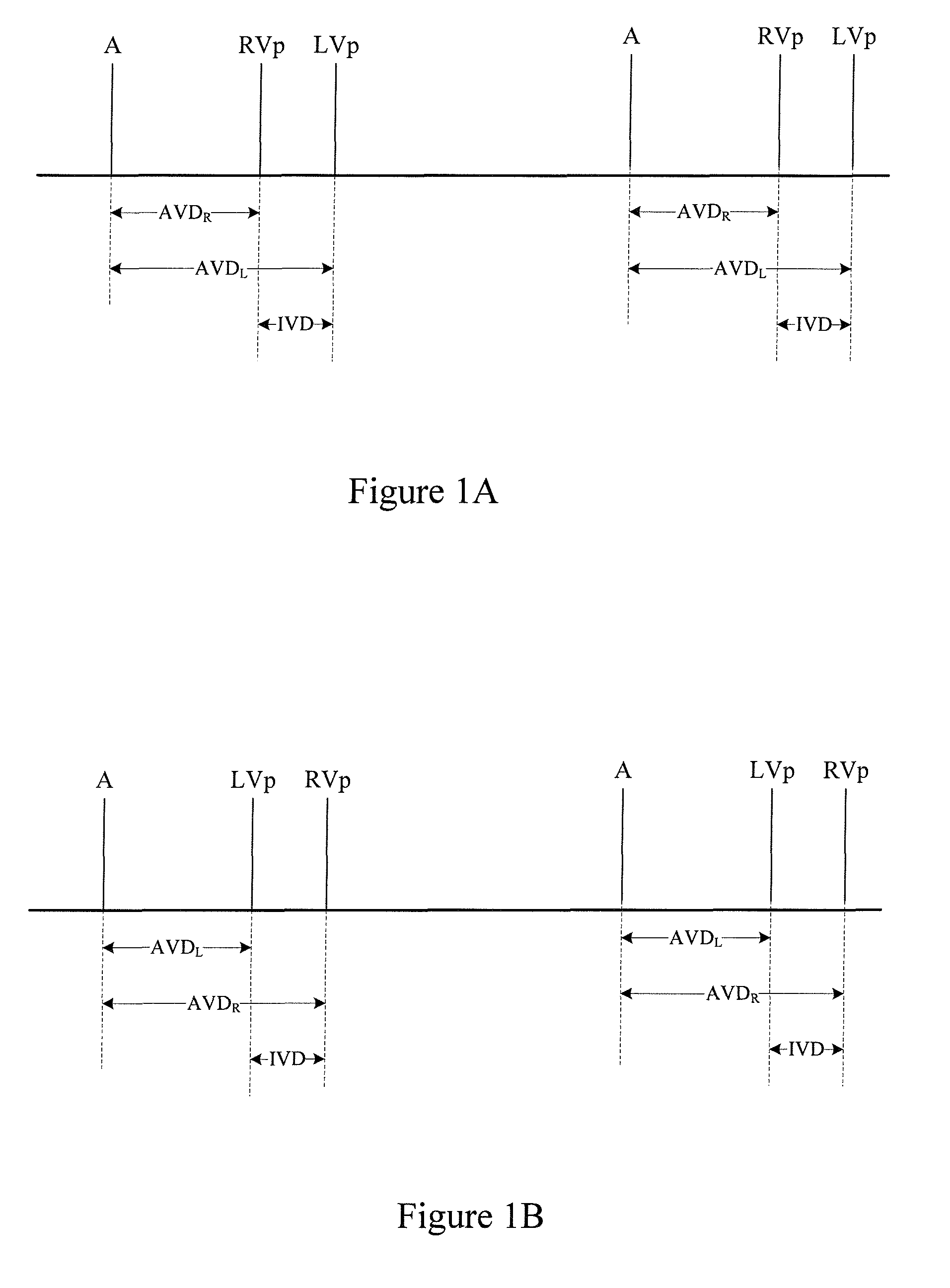
An implantable cardiac stimulating device has a pacing circuit connected via an electrode lead system to a first electrode which stimulates and detects activity in the left ventricle, a second electrode to stimulate and detect activity in the right atrium, and to a third electrode to detect activity in the left atrium. Upon the occurrence of a paced or sensed depolarization of the right atrium, a first AV-delay is started. When the subsequent left atrial depolarization is detected, a new AV-interval is started that is optimized for the left side of the heart. Either the left ventricle only, or both ventricles, is paced at the optimized left side AV-interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Cardiac output measurement using dual oxygen sensors in right and left ventricles
InactiveUS7164948B2Easy to deployAvoiding excessive formationTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterMeasurement deviceCardiac pacemaker electrode
A pacemaker provides multi-chamber pacing with a pacing interval that can be programmed and adapted in response to cardiac output measurements for a given patient. In a typical embodiment, the pacemaker may provide pacing stimuli to both ventricles of a heart. In addition, the invention may include a measurement device that incorporates first and second blood oxygen saturation sensors for deployment in the left and right ventricle. The oxygen saturation sensors provide a differential measurement that can be used to calculate cardiac output in accordance with the Fick method. The oxygen saturation sensors may be carried by a common trans-septal lead that positions one of the sensors proximate the right ventricle and the other sensor proximate the left ventricle. Alternatively, the oxygen saturation sensors may be deployed via separate leads. Whether single or dual leads are used to carry the oxygen saturation sensors, a respective lead may optionally carry electrodes for sensing, pacing, or both.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Signal transmitting and lesion excluding heart implants for pacing defibrillating and/or sensing of heart beat
ActiveUS8123668B2Reducing circumferenceControl DimensionsHeart valvesTransvascular endocardial electrodesControl systemCongestive heart failure chf
Owner:BIOVENTRIX A CHF TECH
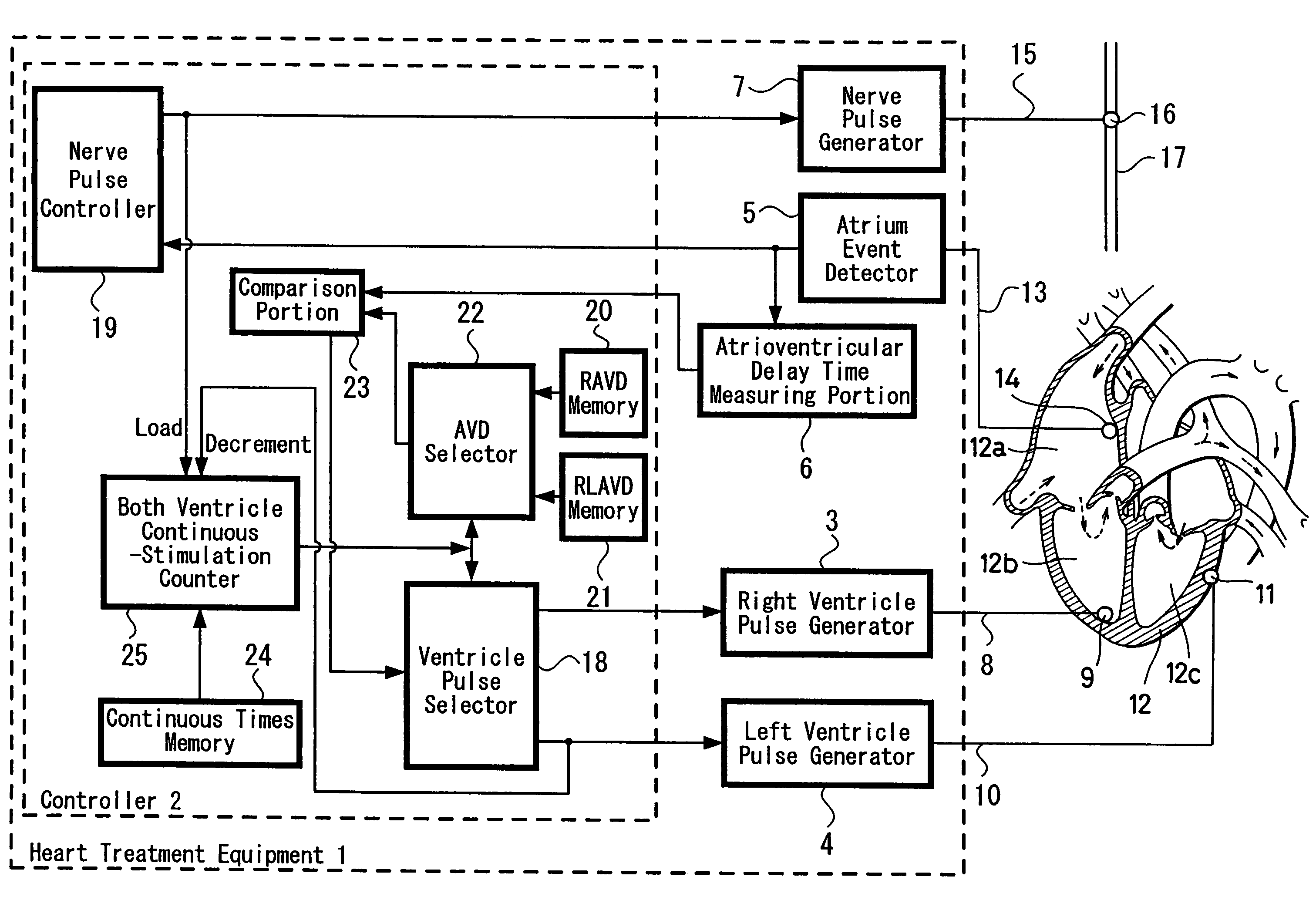
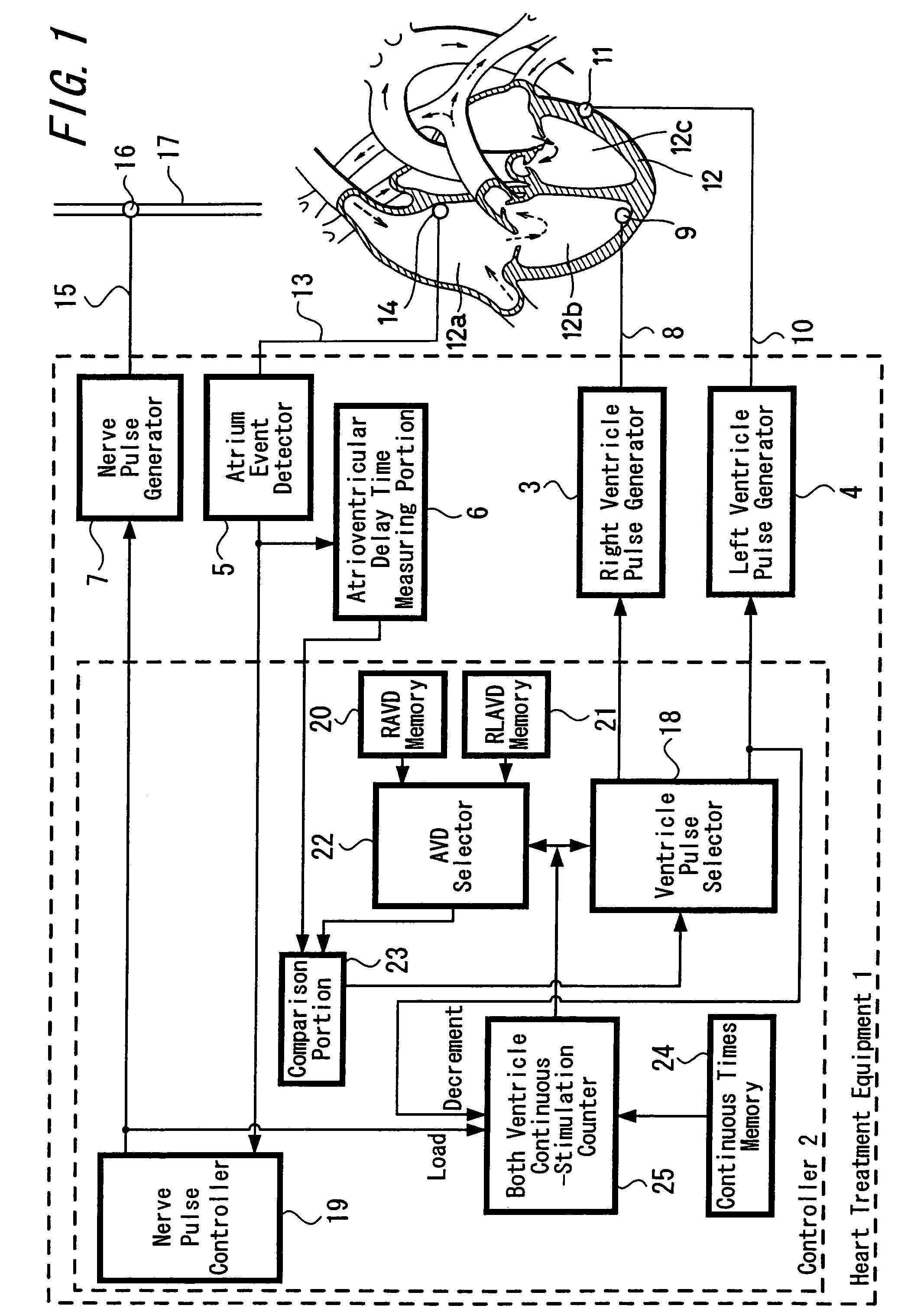
Heart treatment equipment for treating heart failure
InactiveUS7305265B2Reduce power consumptionOperation rate of stimulationHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationHeart rate deviceLeft ventricle wall
In a heart treatment equipment provided with a stimulating mechanism for both the ventricles, the both ventricle stimulation is made optimized in order to inhibit the decrease of the cardiac output when a heart rate increase or the vagus nerve stimulation is performed and the equipment comprises a right ventricle pulse generator for stimulation the right ventricle, a left ventricle pulse generator for stimulation the left ventricle, wherein the controller for selecting either one of aforesaid right ventricle pulse generator and left ventricle pulse generator or selecting both of them for the ventricle stimulation is constituted such as to select both of the right ventricle pulse generator and the left ventricle pulse generator in response to the vagus nerve stimulation or the heart rate monitor output.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Miniature, pulsatile implantable ventricular assist devices and methods of controlling ventricular assist devices
ActiveUS6969345B2Small sizeSmall and efficient and atraumatic and fully implantableControl devicesBlood pumpsSystoleEngineering
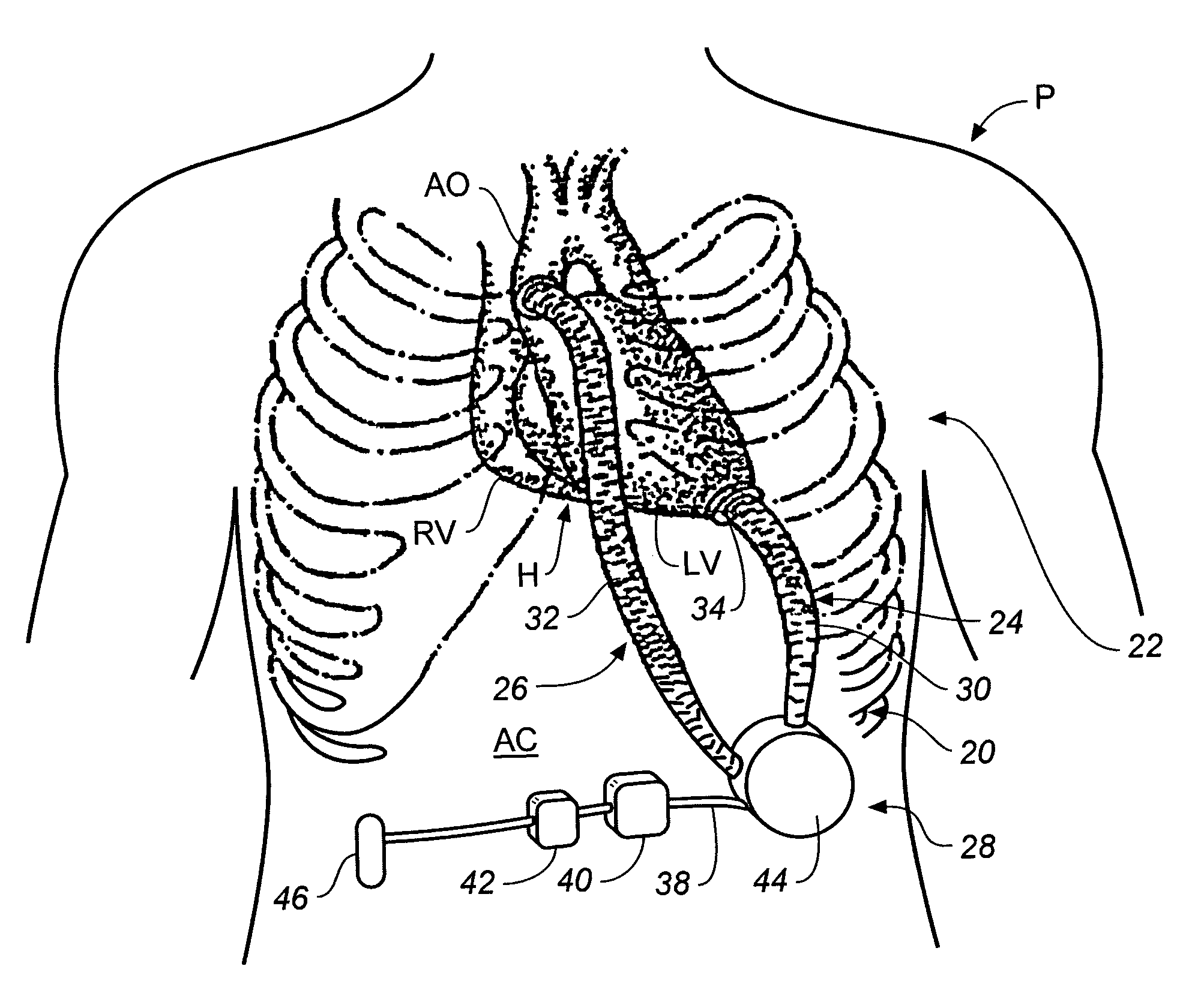
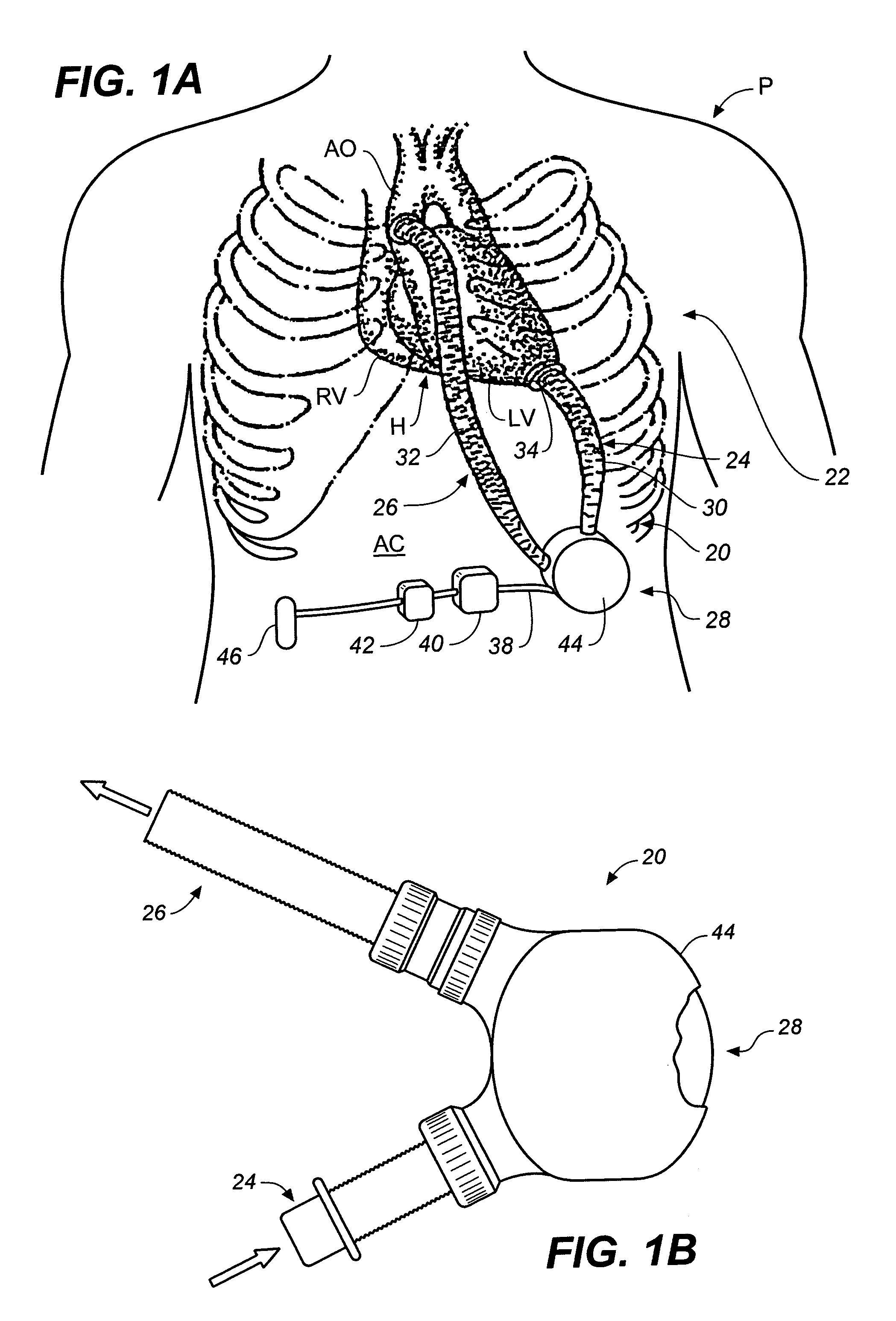
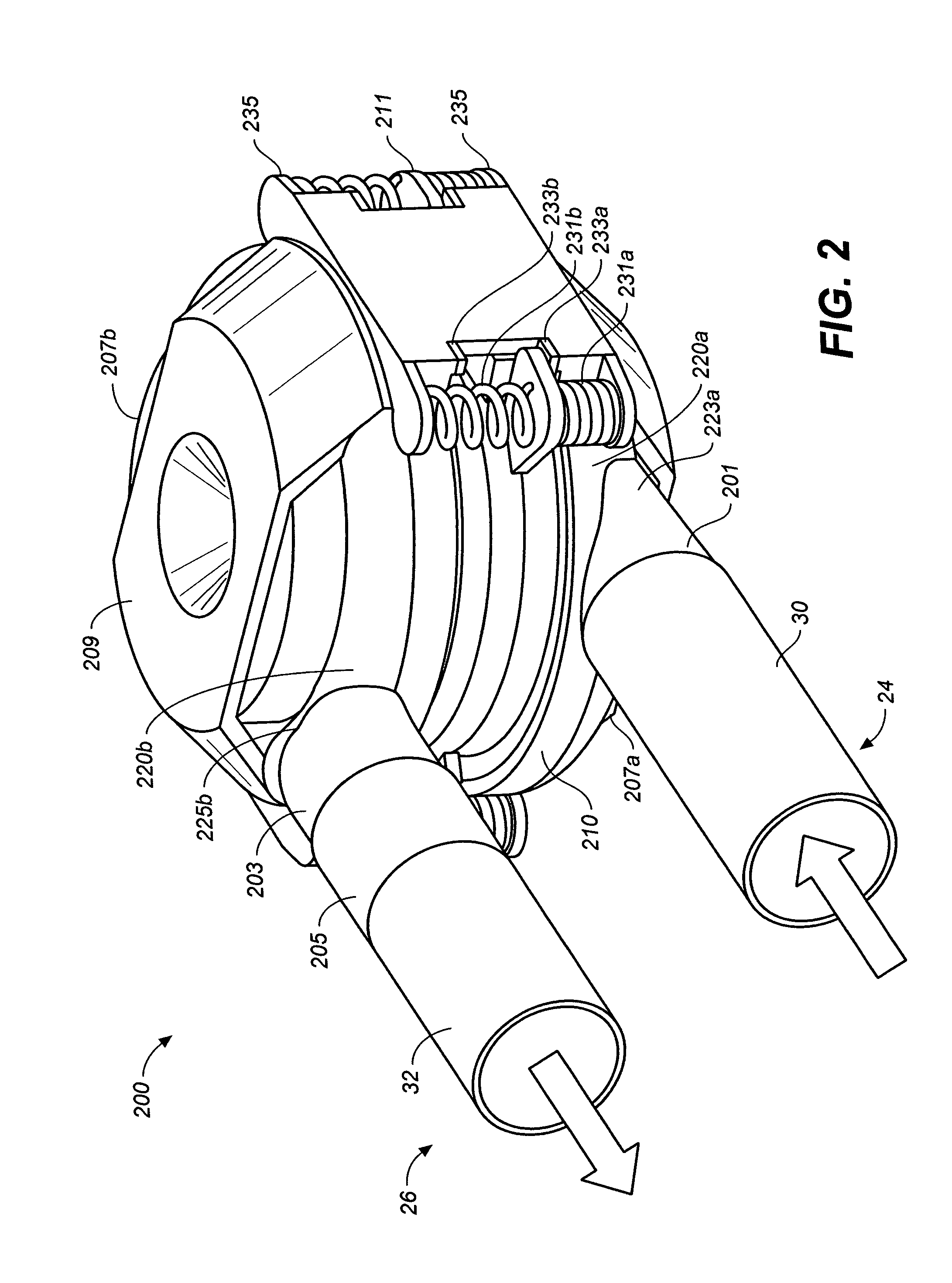
A pumping system for assisting either or both ventricles of the heart. In one embodiment, separate devices are provided for each ventricle. In another embodiment, one device provides both right and left pumping. The pumping system is small, efficient, atraumatic, and fully implantable. In addition, the pumping system can provide pulsatile flow during systole. The ventricular assist device includes an actuator plate between a pair of serially connected pumping chambers that operate in a two-stroke mode, specifically a power stroke and a transfer stroke. The ventricular assist device also includes an electromagnetic drive system that provides adjustment to the pump pressure according to the current through an electromagnet. For the pumping system, springs provide a “spring force” on the actuator plate that is towards the high-pressure pump chamber. The bias force allows the springs to store and deliver energy from the electromagnetic drive system to provide better utilization of the pump components, and to reduce the pump size and consumption of electricity.
Owner:WORLD HEART
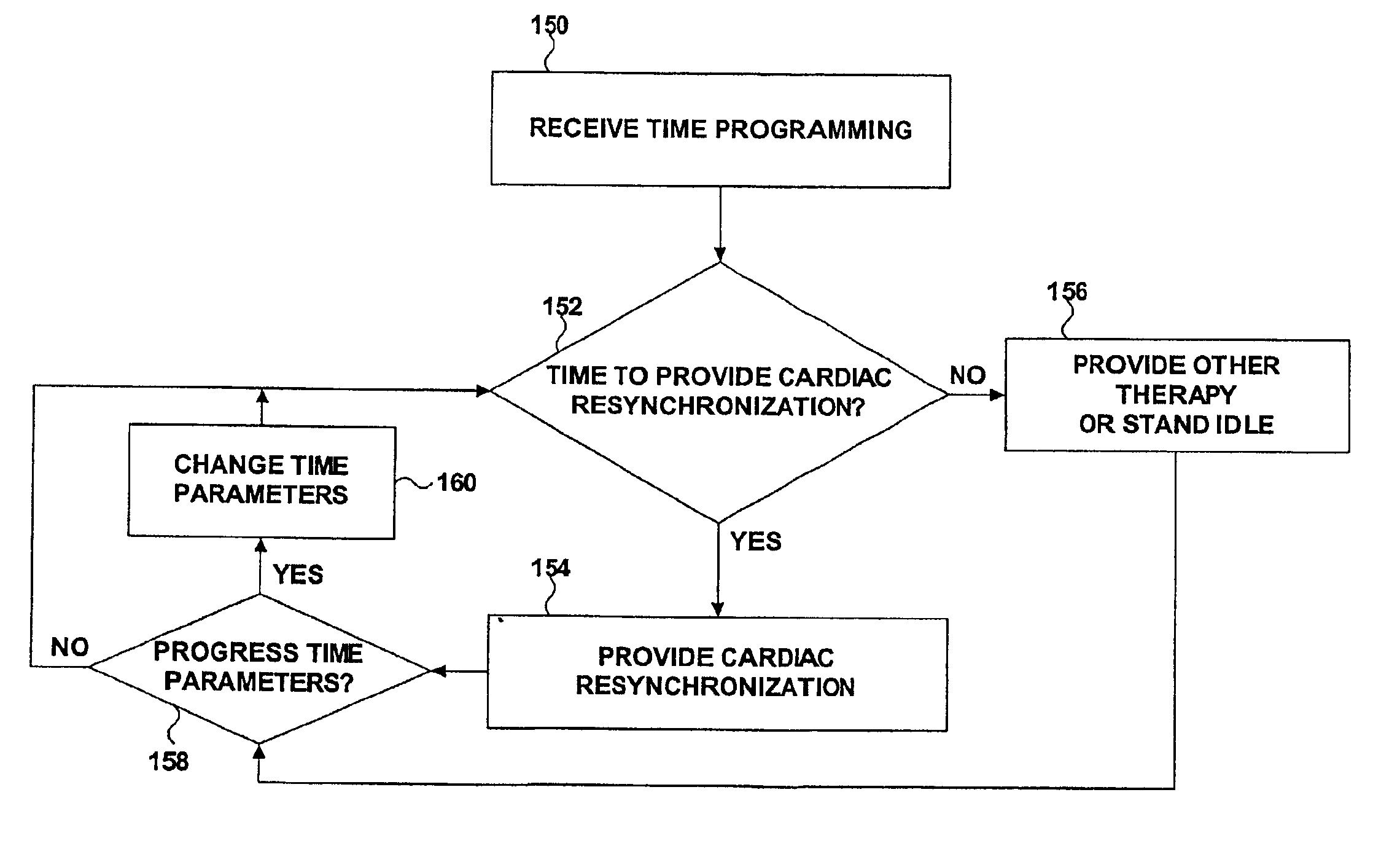
Adjustable cardiac resynchronization
InactiveUS6842642B2Decrease in paceSave battery powerHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityCardiac pacemaker electrode
Techniques are presented for providing adjustable cardiac resynchronization with an implanted medical device such as a pacemaker. For example, cardiac resynchronization may be provided during some time periods but not during other time periods, or cardiac resynchronization may be provided in response to selected sensed events. Adjustable cardiac resynchronization is applicable to therapy such as bi-ventricular pacing, in which both ventricles of the heart are paced in response to sensed atrial events.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Sleeved type permanent magnetic impeller axial flow type blood pump for assisting heart and assisting method
InactiveCN101121045AImprove efficiencyImprove accessibilitySuction devicesProsthesisThrombusIliac artery bypass
A bushing-type permanent magnetic impeller shaft bleeding pump, which is used for heart boosting and the boosting method of the bleeding pump are provided. A rotor of the bleeding pump is a whole magnetic impeller or an impeller with magnetic vanes, which greatly improves a magnetic field intensity of a bleeding pump air gap. A defending, a packing and a biochemical treatment are taken on the surface of the impeller. A tube cavity of the bleeding pump is made from a material with good blood compatibleness. A pre-diversion system structure is simplified, and a pre-diversion wimble is supported by a single cantilever, which are all in favor of preventing a thrombosis. The boosting method adopts a serial-type connection of an axial bleeding pump and ventricles of heart (left ventricle, right ventricle or double ventricles) and requests that an appearance of the bleeding pump is a geometrical shape of as ascending aorta or a main pulmonary artery which is fit for implantation, and the tube cavity and an artificial blood vessel caliber match with a natural blood vessel. In order to prevent a pumping action of the bleeding pump reduces a perfusion pressure of a coronary artery, a coronary artery and aorta bypass transplantation can be performed.
Owner:李国荣 +2
Method and apparatus for treating hemodynamic disfunction
InactiveUSRE39897E1Precise and coordinated simultaneous ventricular depolarizationImprove efficiencyHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeBundle branches
A method of treating hemodynamic disfunction by simultaneously pacing both ventricles of a heart. At least one ECG amplifier is arranged to separately detect contraction of each ventricle and a stimulator is then activated for issuing stimulating pulses to both ventricles in a manner to assure simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, thereby to assure hemodynamic efficiency. A first ventricle is stimulated simultaneously with contraction of a second ventricle when the first fails to properly contract. Further, both ventricles are stimulated after lapse of a predetermined A-V escape interval. One of a pair of electrodes, connected in series, in placed through the superior vena cava into the right ventricle and a second is placed in the coronary sinus about the left ventricle. Each electrode performs both pacing and sensing functions. The pacer is particularly suitable for treating bundle branch blocks or slow conduction in a portion of the ventricles.
Owner:MIROWSKI FAMILY VENTURES LLC
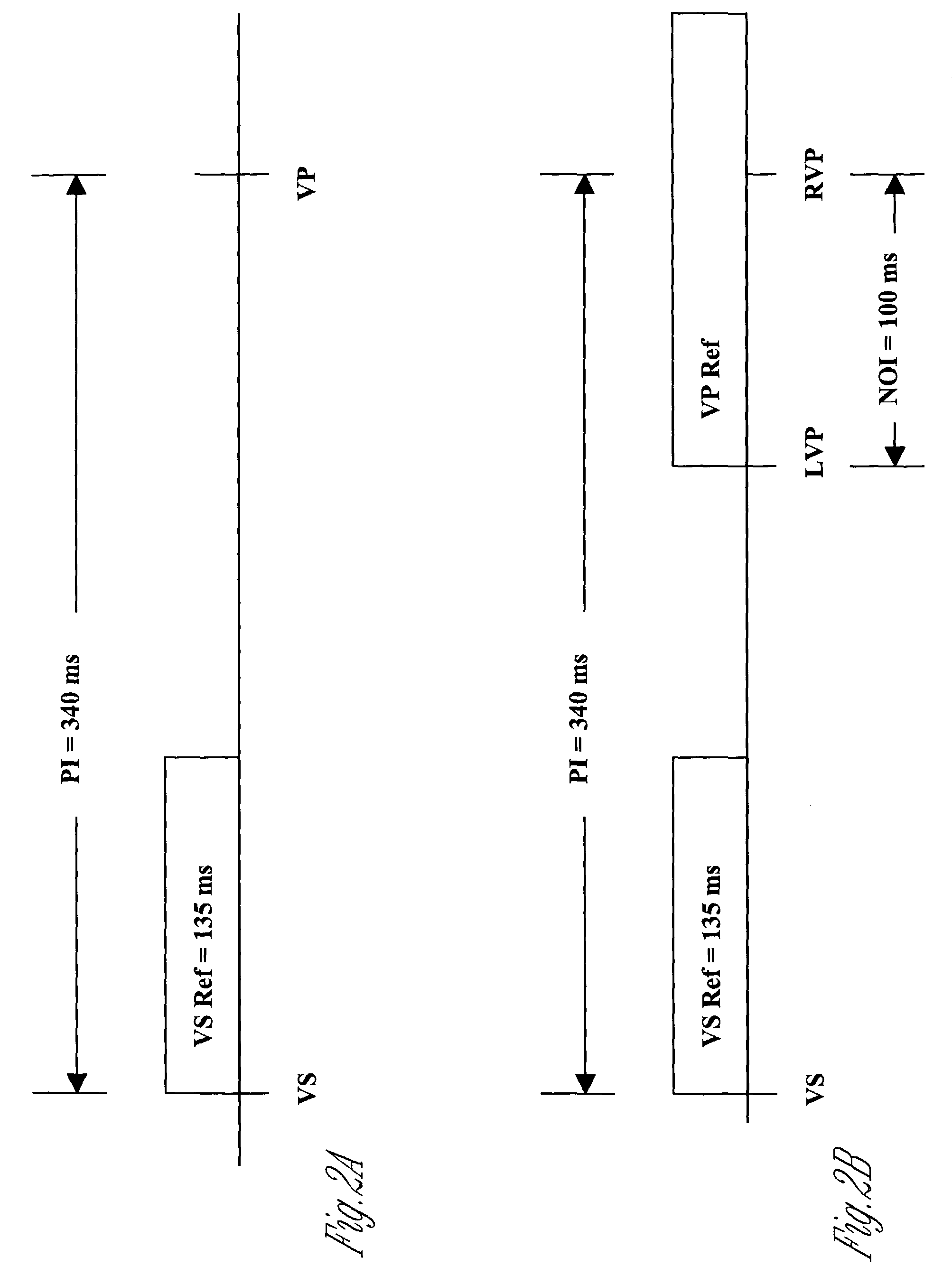
Method and apparatus to ensure consistent left ventricular pacing
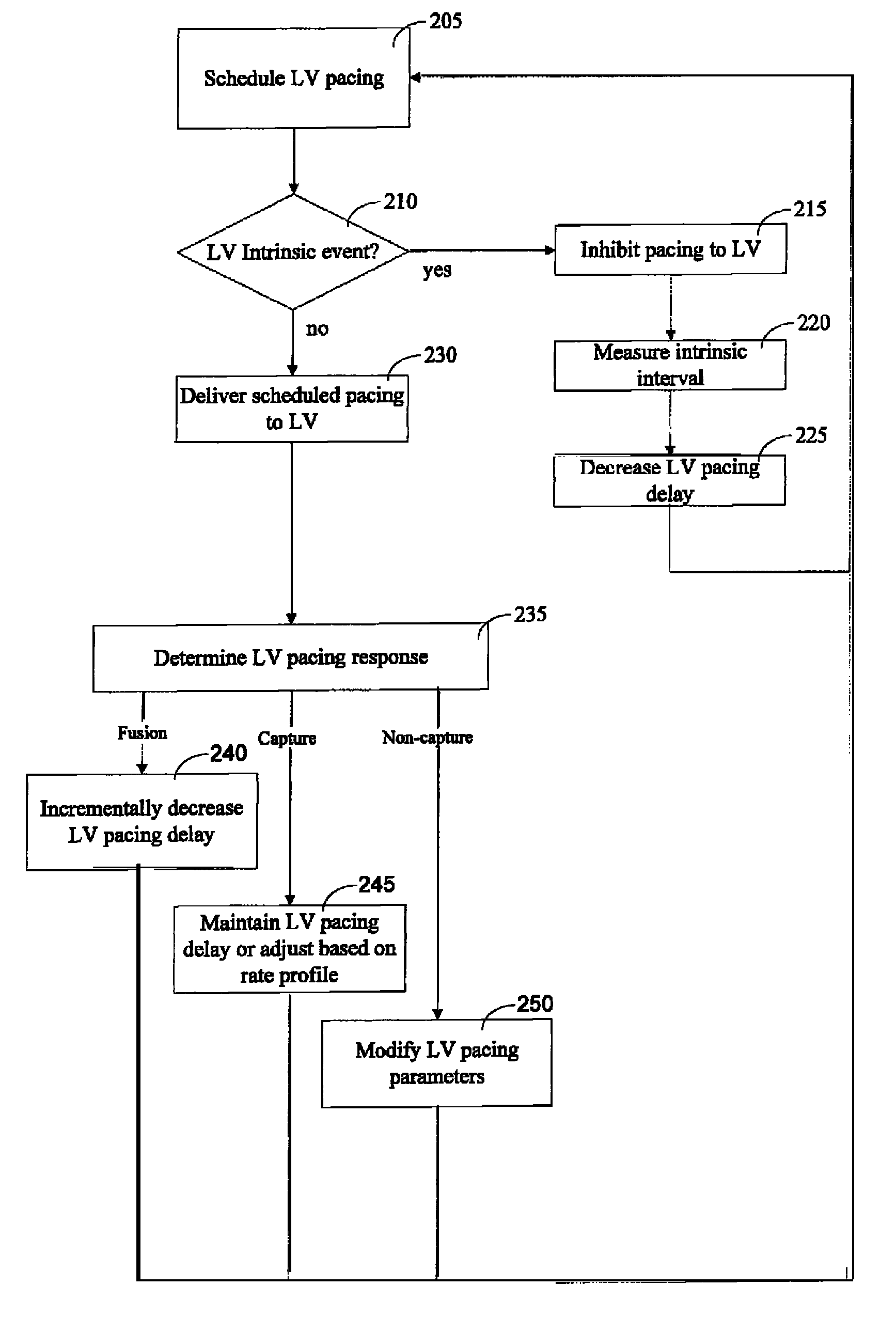
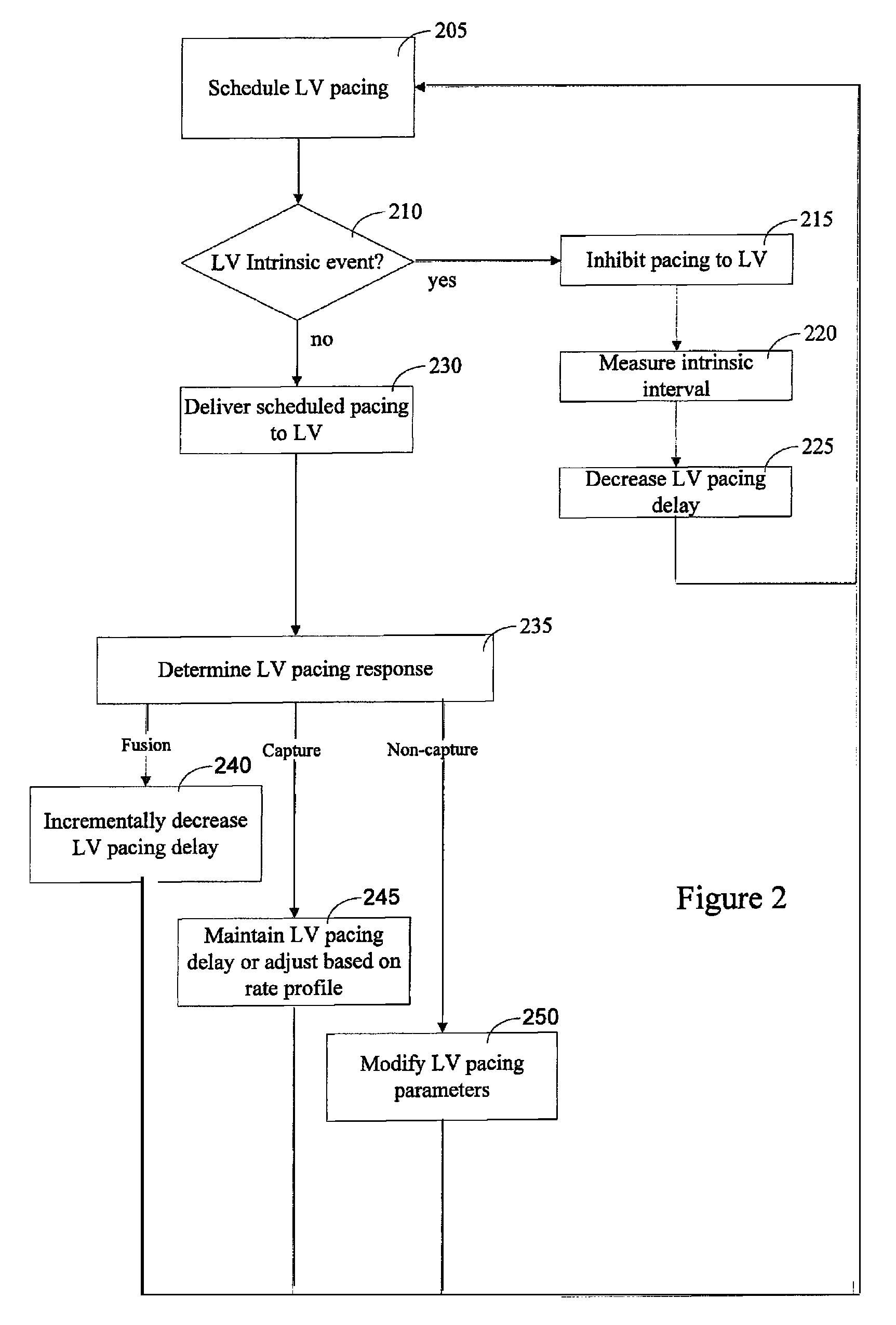
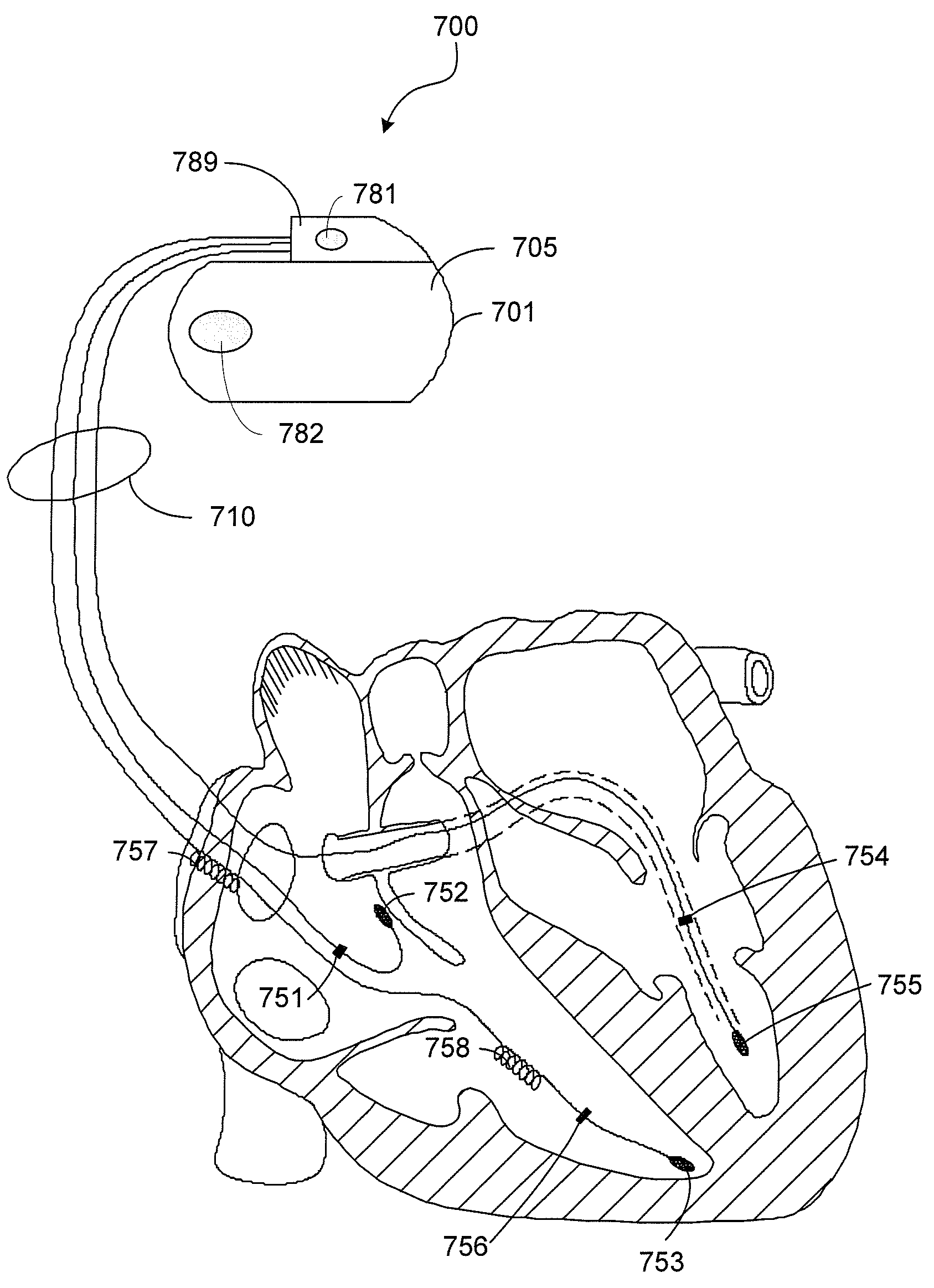
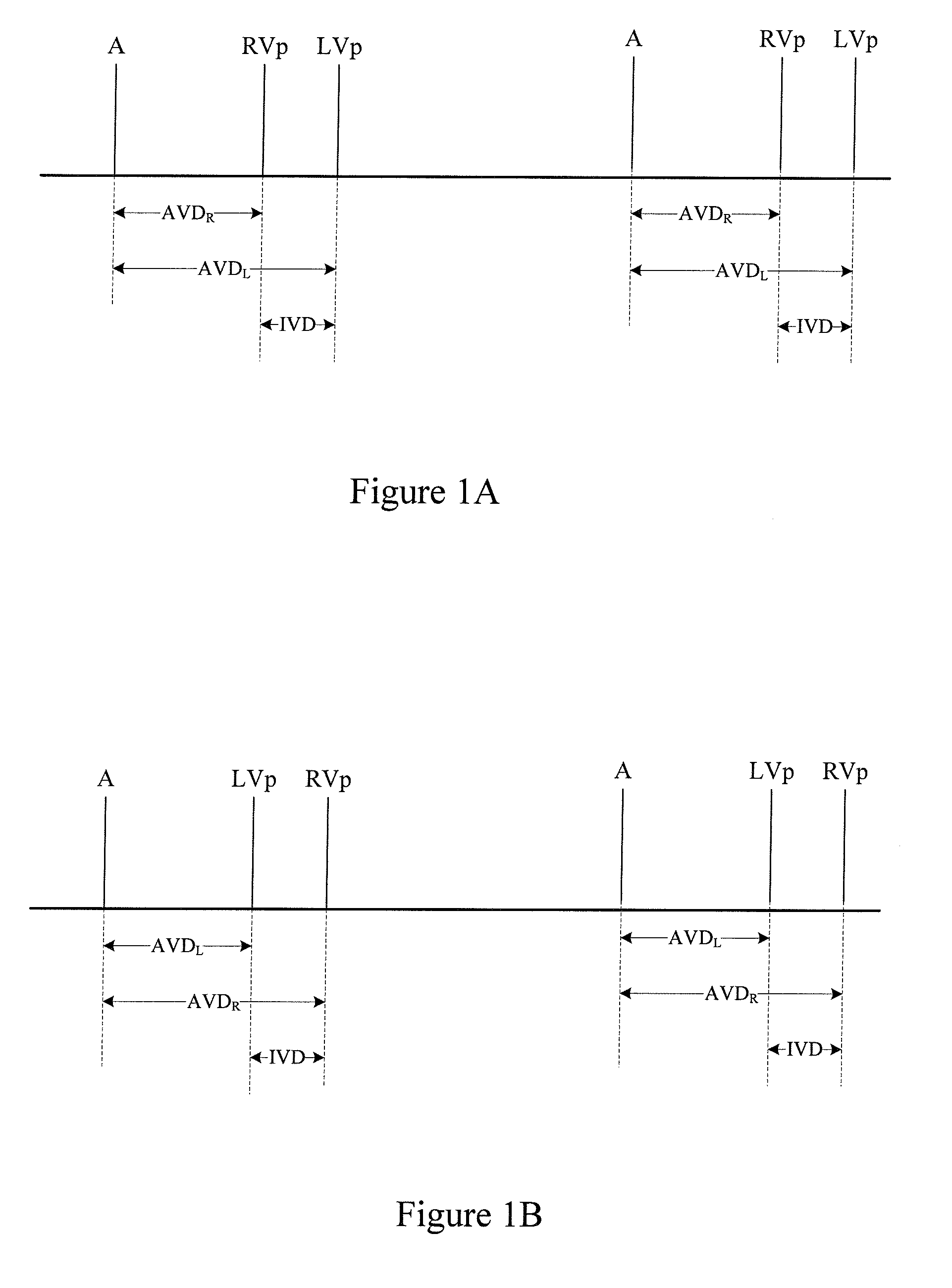
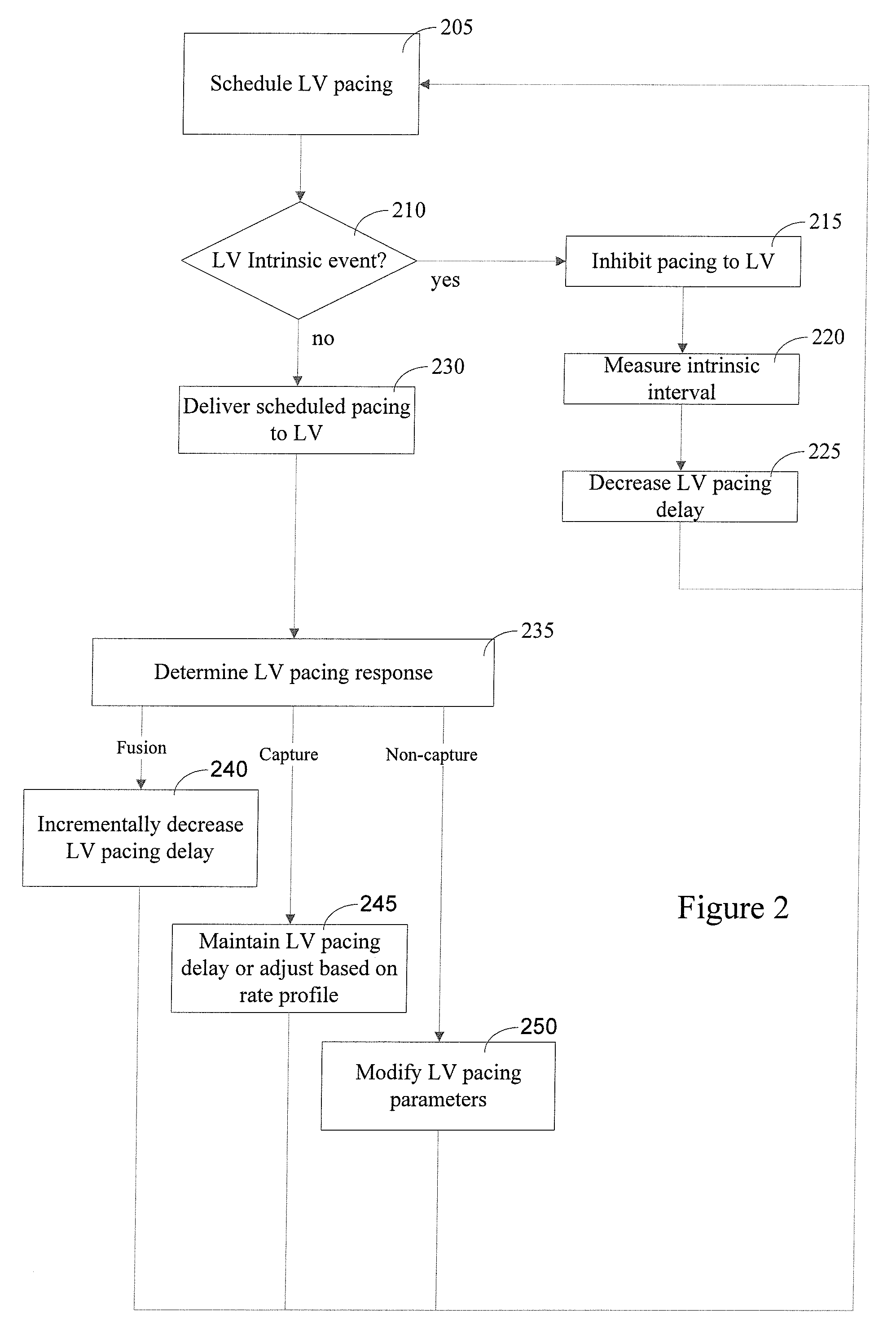
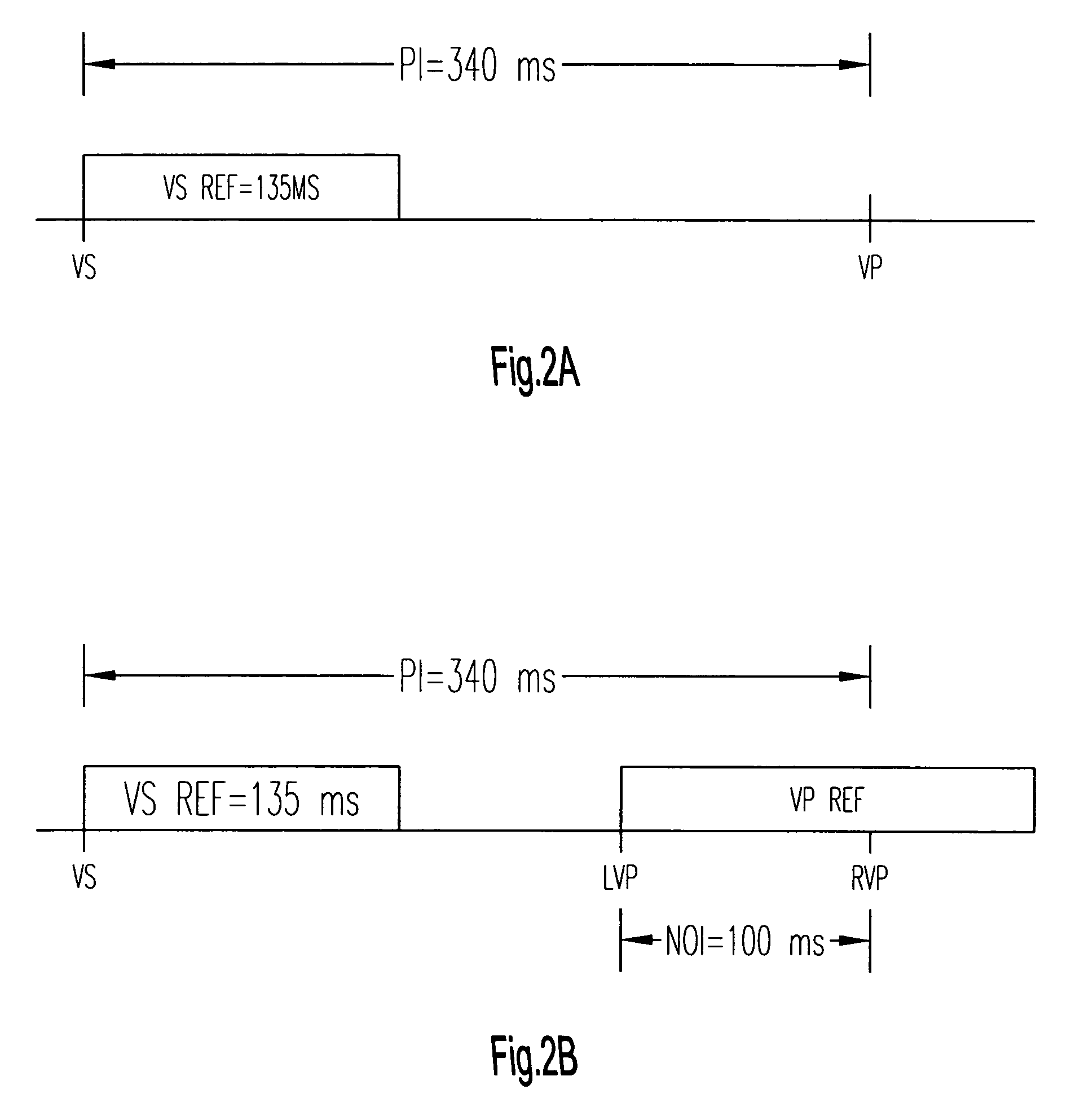
A method of operating a cardiac therapy system to deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing that includes pacing both ventricles or pacing only the left ventricle is described. Delivery of the CRT pacing to one or both ventricles is scheduled for a cardiac cycle. If an intrinsic depolarization of a ventricle is detected during a pacing delay of the ventricle, then the scheduled CRT pacing to the ventricle is inhibited for the cycle. The intrinsic interval of the ventricle, such as the intrinsic atrioventricular interval concluded by the intrinsic depolarization, is measured. During a subsequent cardiac cycle, the pacing delay of the ventricle is decreased to be less than or equal to the measured intrinsic interval. Capture of the ventricle is verified after pacing is delivered during the subsequent cardiac cycle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and Apparatus to Ensure Consistent Left Ventricular Pacing
A method of operating a cardiac therapy system to deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing that includes pacing both ventricles or pacing only the left ventricle is described. Delivery of the CRT pacing to one or both ventricles is scheduled for a cardiac cycle. If an intrinsic depolarization of a ventricle is detected during a pacing delay of the ventricle, then the scheduled CRT pacing to the ventricle is inhibited for the cycle. The intrinsic interval of the ventricle, such as the intrinsic atrioventricular interval concluded by the intrinsic depolarization, is measured. During a subsequent cardiac cycle, the pacing delay of the ventricle is decreased to be less than or equal to the measured intrinsic interval. Capture of the ventricle is verified after pacing is delivered during the subsequent cardiac cycle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
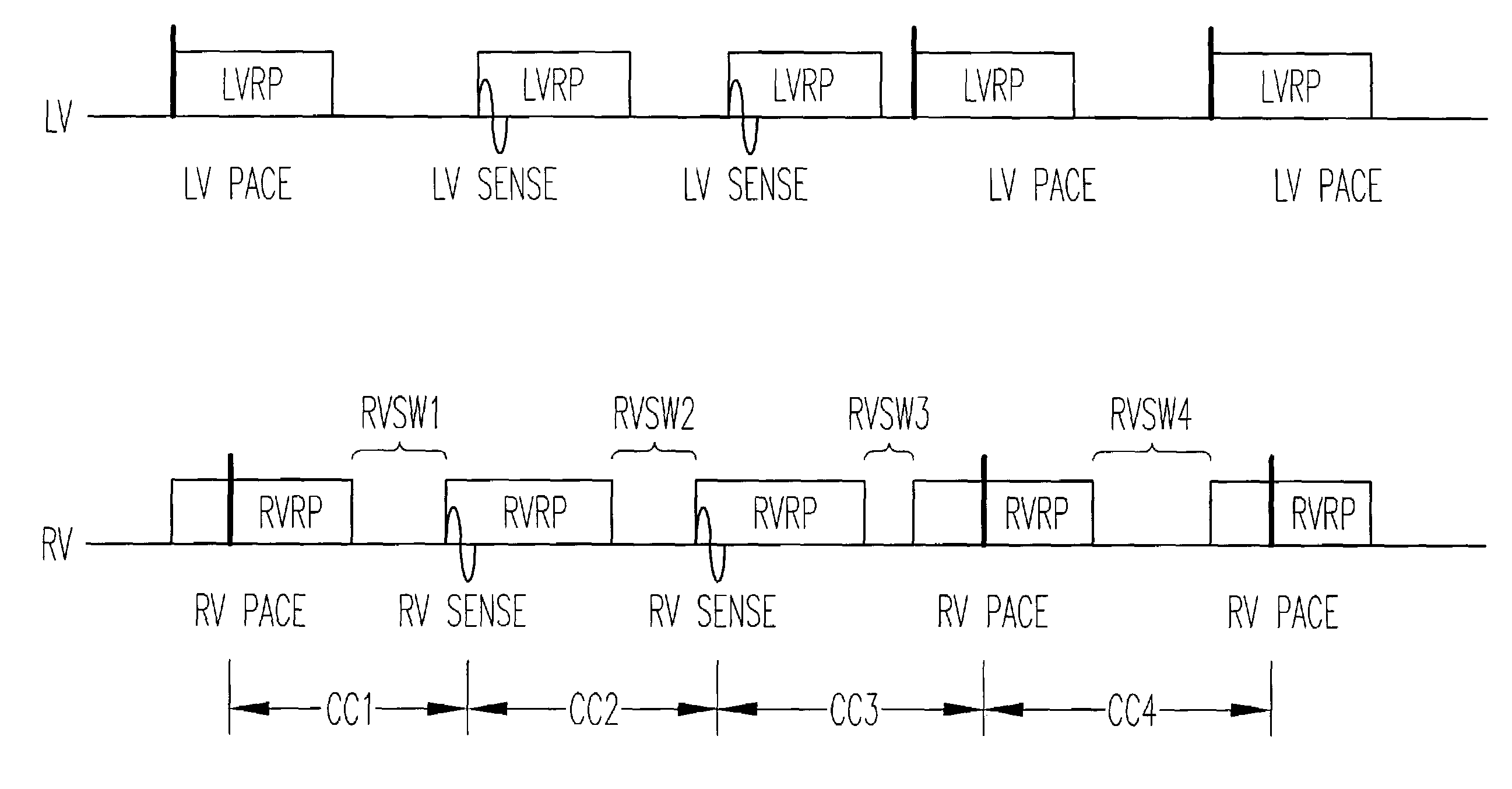
Reduction of left-ventricular offset interaction with tachyarrhythmia detection
A device and method for improving tachyarrhythmia detection when the ventricles are resynchronized by delivering paces to both ventricles separated by a specified offset interval. Timing of escape intervals and tachyarrhythmia detection is based upon senses from one of the ventricles designated as a rate ventricle. A reversion pacing mode is provided in order to prevent tachyarrhythmia detection from being compromised when the rate ventricle is paced after the other ventricle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and method for multiple site biphasic stimulation to revert ventricular arrhythmias
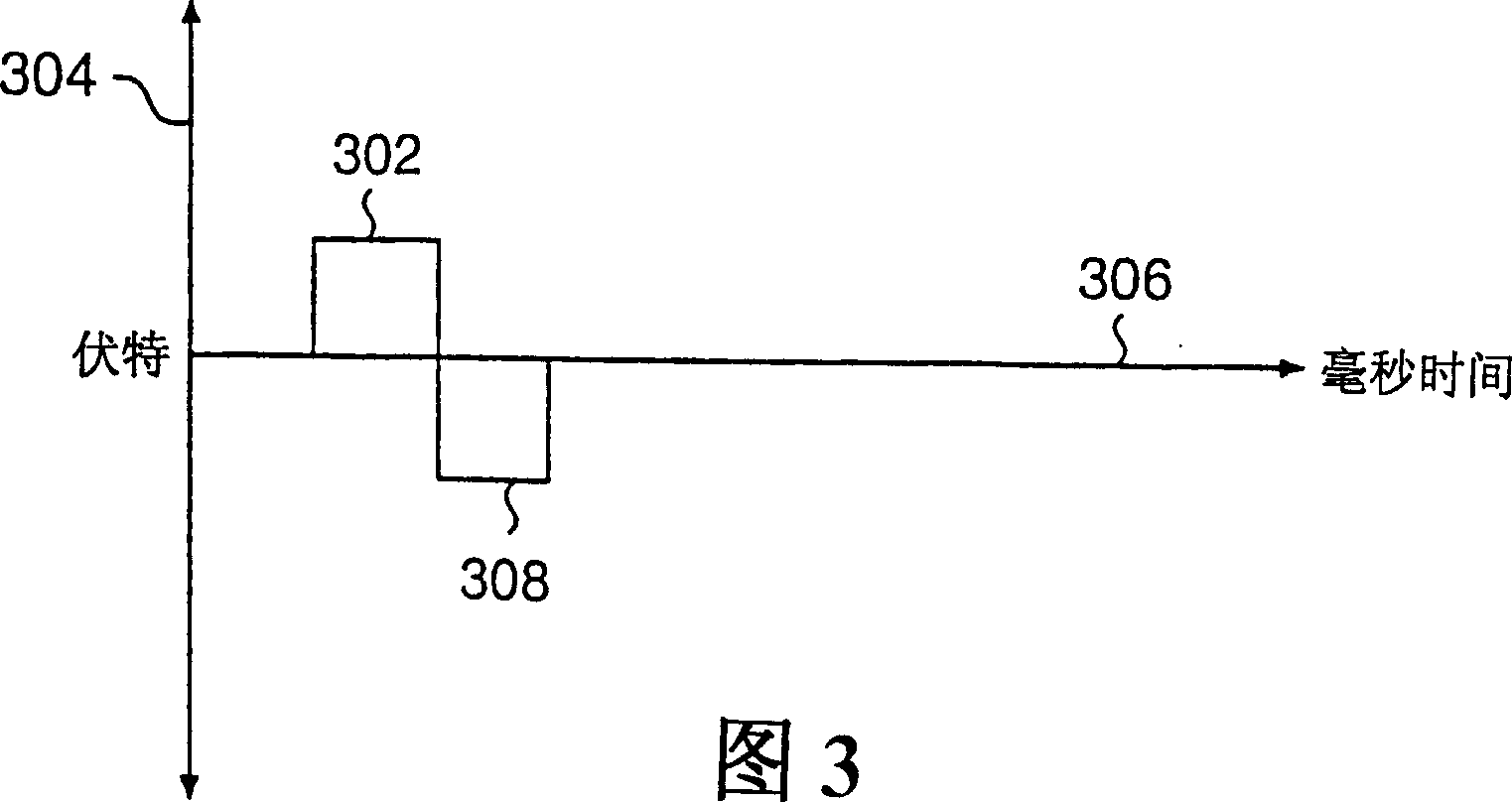
An anti-reentry apparatus and method for reverting ventricular arrhythmias. Biphasic stimulation is applied at multiple ventricular sites to revert arrhythmias caused by reentry, particularly multiple random reentry. In the preferred embodiment, the first phase of biphasic stimulation is anodal, and is at a maximum subthreshold amplitude. The anodal phase preconditions the myocardium to accept the second phase (cathodal) such that less electrical energy is required to reach the threshold amplitude to produce depolarization. The anodal phase stimulation may have a shape over time that is square wave, ramped, or a series of short square wave pulses. Multiple electrodes located at multiple ventricular sites may be stimulated simultaneously, or they may be sequentially stimulated over time in a manner mimicking the normal progress pattern of cardiac depolarization. The multiple ventricular electrodes may stimulate from internal or external surfaces. One or both ventricles may receive biphasic stimulation from multiple electrodes. The invention also may be practiced with respect to atria.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Reduction of interaction with tachyarrhythmia detection by negative offset pacing
InactiveUS7016729B2Increase ratingsIncrease the rate chamber sensing windowHeart stimulatorsMedicineArrhythmia detection
A device and method is disclosed for improving tachyarrhythmia detection when the ventricles are resynchronized by delivering paces to both ventricles separated by a specified negative offset interval. Timing of escape intervals and tachyarrhythmia detection is based upon senses from one of the ventricles designated as a rate ventricle. Techniques are presented for preventing tachyarrhythmia detection from being compromised when the rate ventricle is paced after the other ventricle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
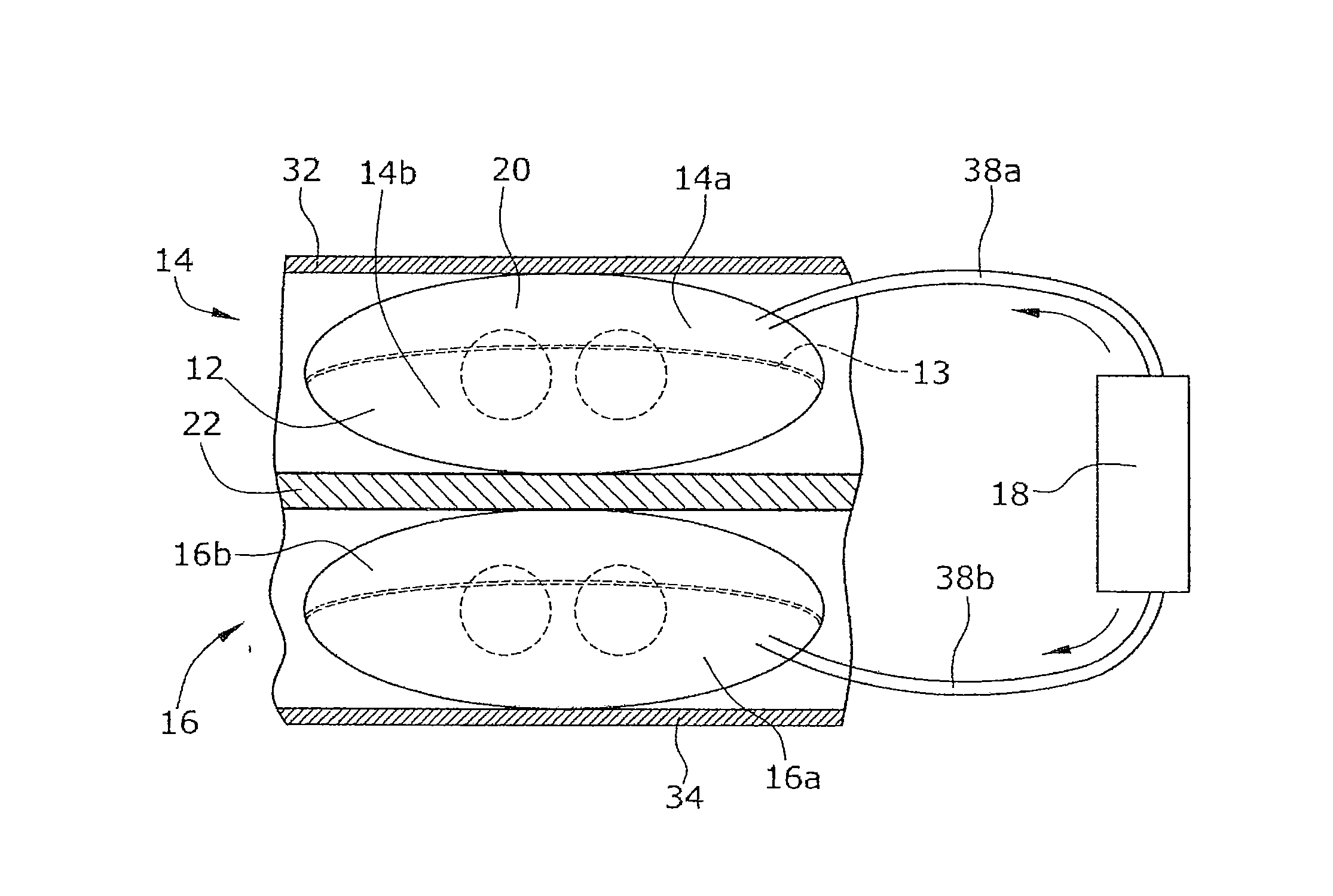
Heart support device
ActiveUS20110137107A1Lower overall heightGuaranteed uptimeIntravenous devicesBlood pumpMedicineBiomedical engineering
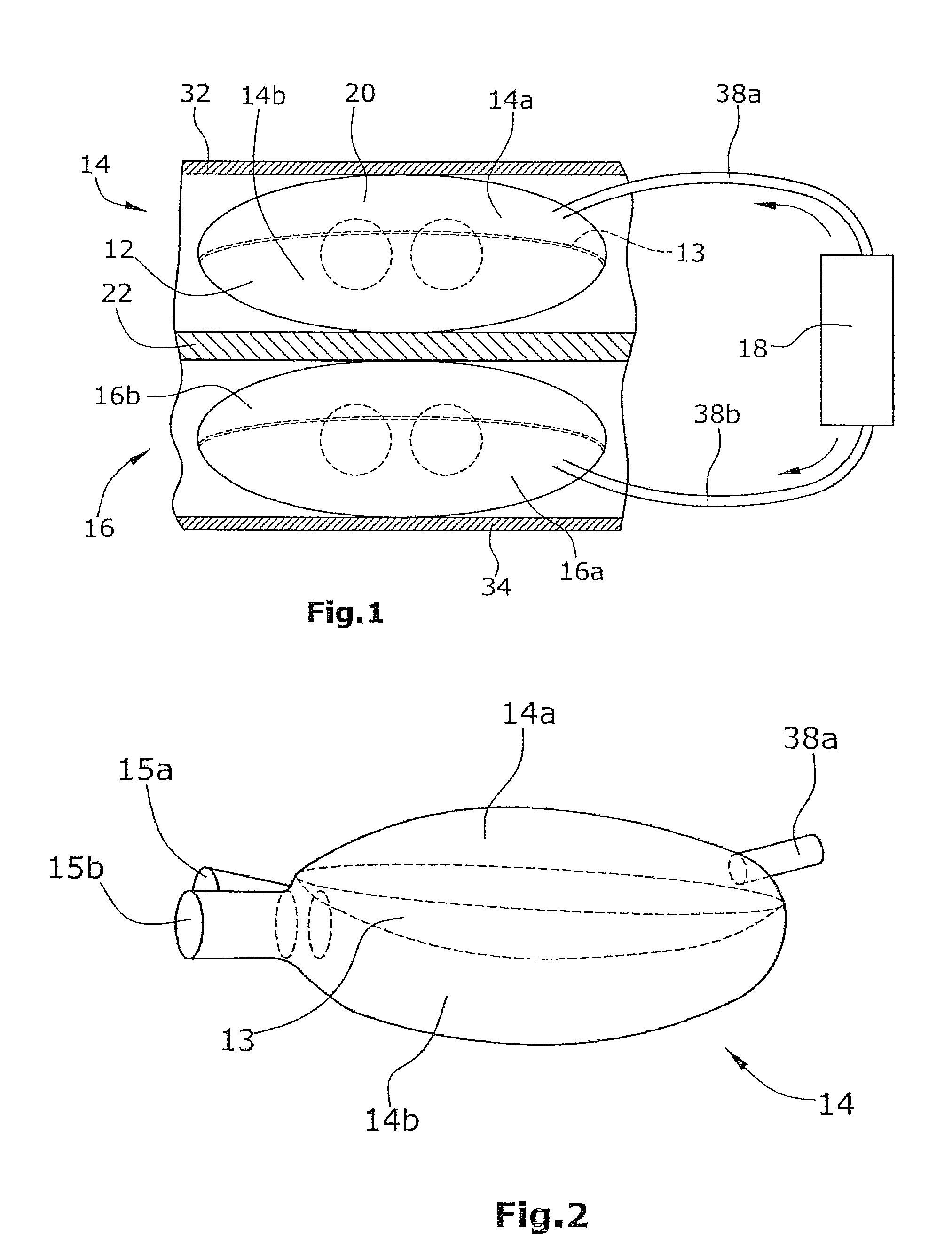
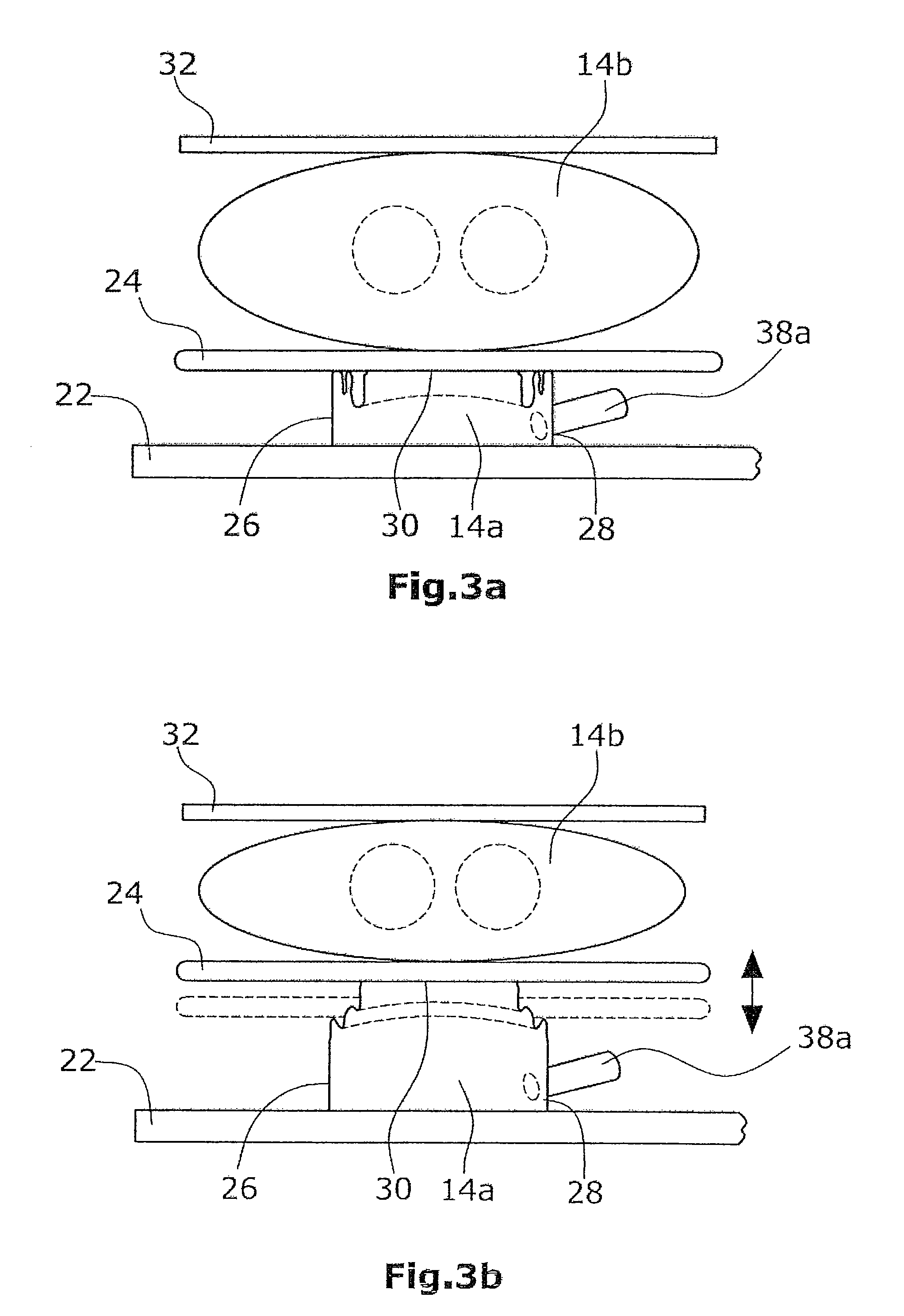
A heart support device for pulsatile delivery of blood comprising a first and a second ventricle and a pump. Both ventricles comprises a fluid chamber and a blood-conveying chamber, wherein each fluid chamber can be filled with a fluid or emptied by way of the pump in such a way that an expansion or contraction of the fluid chamber occurs. In an expansion of the fluid chamber of a ventricle, a compression of the blood-conveying chamber of the same ventricle takes place, wherein a rigid pressure plate is disposed between a fluid chamber and the respective blood-conveying chamber, said pressure plate being able to move in the direction of the respective blood-conveying chamber.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Reduction of interaction with tachyarrhythmia detection by negative offset pacing
InactiveUS20060116728A1Increase ratingsIncrease the rate chamber sensing windowHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicinePace rate
A device and method is disclosed for improving tachyarrhythmia detection when the ventricles are resynchronized by delivering paces to both ventricles separated by a specified negative offset interval. Timing of escape intervals and tachyarrhythmia detection is based upon senses from one of the ventricles designated as a rate ventricle. Techniques are presented for preventing tachyarrhythmia detection from being compromised when the rate ventricle is paced after the other ventricle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Dual-electrode combined member and stimulation system
PendingCN106994207APrevent in-depthHighly directional controllableEpicardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsDual coreHeart.interventricular septum
Owner:刘志忠 +1
Implantable artificial ventricle having low energy requirement
A pulsatile, positive-displacement mechanical circulatory support pump which can be used for assistance or replacement of one or both ventricles. The pump includes a plurality of contractile elements radiating outward from an apex of a compliance chamber, the elements being incorporated in and / or in contact with at least a portion of an outer surface of the compliance chamber. These contractile elements include an electroactive dielectric elastomer or an ion exchange membrane metallic composite. Application of electric field pulses from an implantable electrical energy source such as a pacemaker will cause the contractile elements to compress and expand the compliance chamber.
Owner:SHERIF HISHAM M F
Implanted pacemaker
InactiveCN1235651CSave energyDecreased pacing rateHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationImplant pacemakerImplanting pacemakers
Method and apparatus for cyclic ventricular pacing starting at a rate just above the intrinsic atrial firing rate (overdrive pacing), followed by relaxation to a rate just below the intrinsic atrial firing rate (ventricular escape). The method and apparatus can be applied to one or both ventricles, and can utilize one or more electrodes per ventricle. The electrode(s) can be applied to inner or outer ventricular surfaces. Relaxation protocols as a function of time can be linear, curvilinear to include exponential, or mixtures thereof. Furthermore, relaxation protocols can include one or more periods of time during which the pacing rate is held constant. Typically, the average ventricular pacing rate using this invention will be slightly greater than the intrinsic atrial firing rate, though alternate embodiments that encompass average ventricular pacing rates that are equal to or slightly less than the intrinsic atrial firing rate are also envisioned. Application of this method and apparatus to a heart in need thereof will produce a heart with an optimally minimized energy output requirement.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Implantable pacemaker
InactiveCN1803219ASave energyDecreased pacing rateHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationCardiac pacemaker electrodeBoth ventricles
Method and apparatus for cyclic ventricular pacing starting at a rate just above the intrinsic atrial firing rate (overdrive pacing), followed by relaxation to a rate just below the intrinsic atrial firing rate (ventricular escape). The method and apparatus can be applied to one or both ventricles, and can utilize one or more electrodes per ventricle. The electrode(s) can be applied to inner or outer ventricular surfaces. Relaxation protocols as a function of time can be linear, curvilinear to include exponential, or mixtures thereof. Furthermore, relaxation protocols can include one or more periods of time during which the pacing rate is held constant. Typically, the average ventricular pacing rate using this invention will be slightly greater than the intrinsic atrial firing rate, though alternate embodiments that encompass average ventricular pacing rates that are equal to or slightly less than the intrinsic atrial firing rate are also envisioned. Application of this method and apparatus to a heart in need thereof will produce a heart with an optimally minimized energy output requirement.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Implantable artificial ventricle having low energy requirement
A pulsatile, positive-displacement mechanical circulatory support pump which can be used for assistance or replacement of one or both ventricles. The pump includes a plurality of contractile elements radiating outward from an apex of a compliance chamber, the elements being incorporated in and / or in contact with at least a portion of an outer surface of the compliance chamber. These contractile elements include an electroactive dielectric elastomer or an ion exchange membrane metallic composite. Application of electric field pulses from an implantable electrical energy source such as a pacemaker will cause the contractile elements to compress and expand the compliance chamber.
Owner:SHERIF HISHAM M F
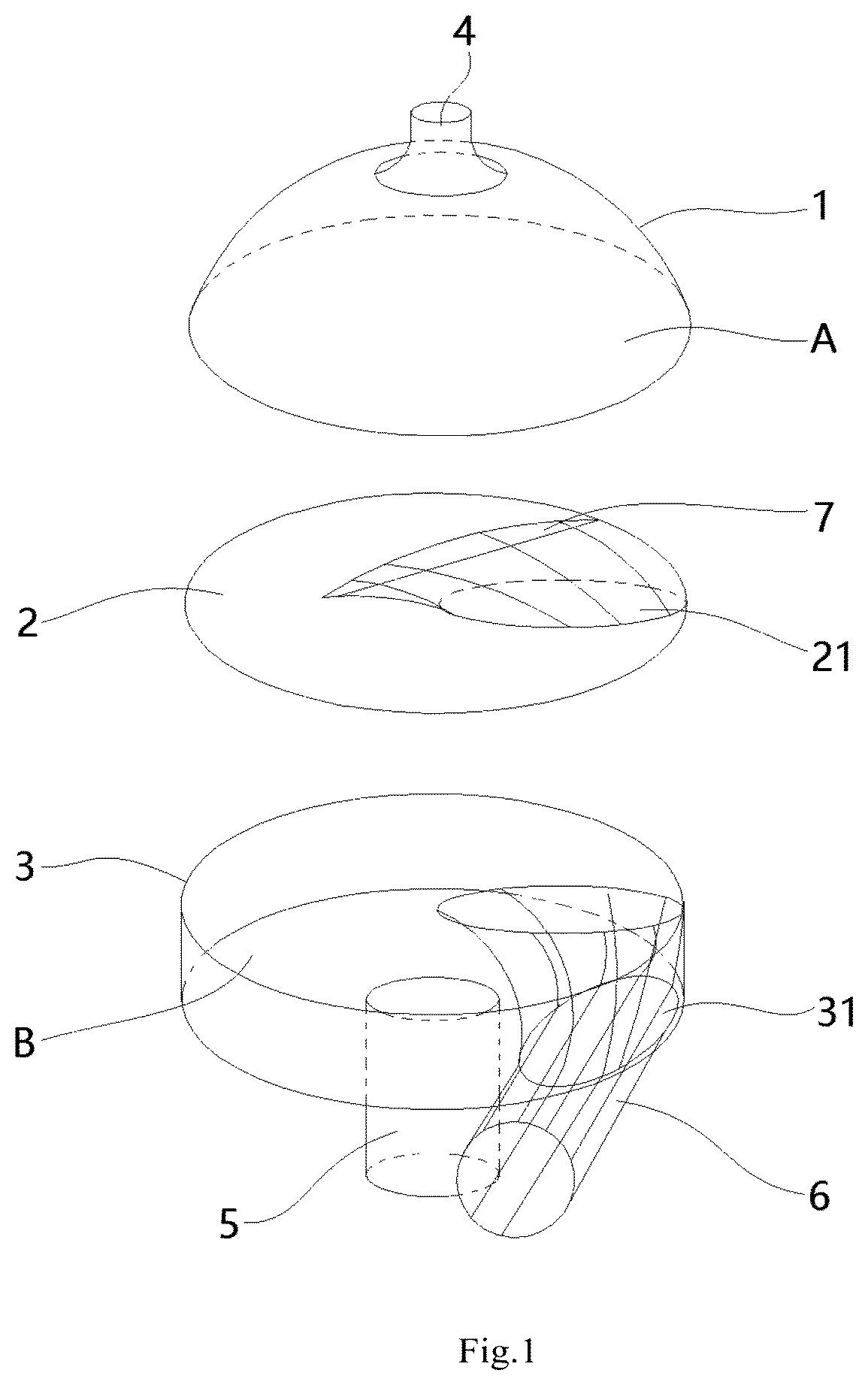
Saccular Cavopulmonary Assist Device
ActiveUS20200009305A1Restore biventricular blood flowSmall volumeControl devicesMedical devicesPulmonary vasculatureVein
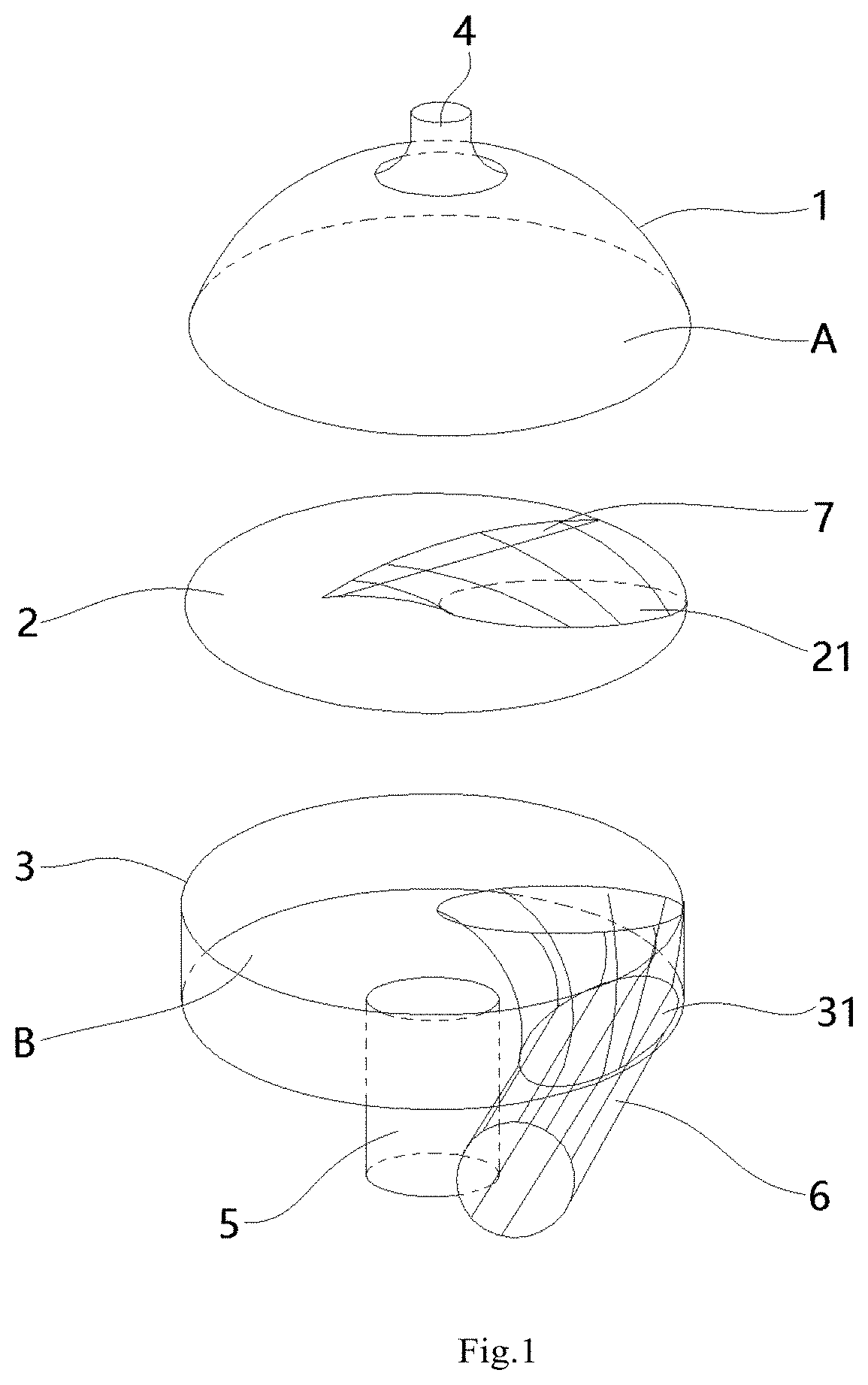
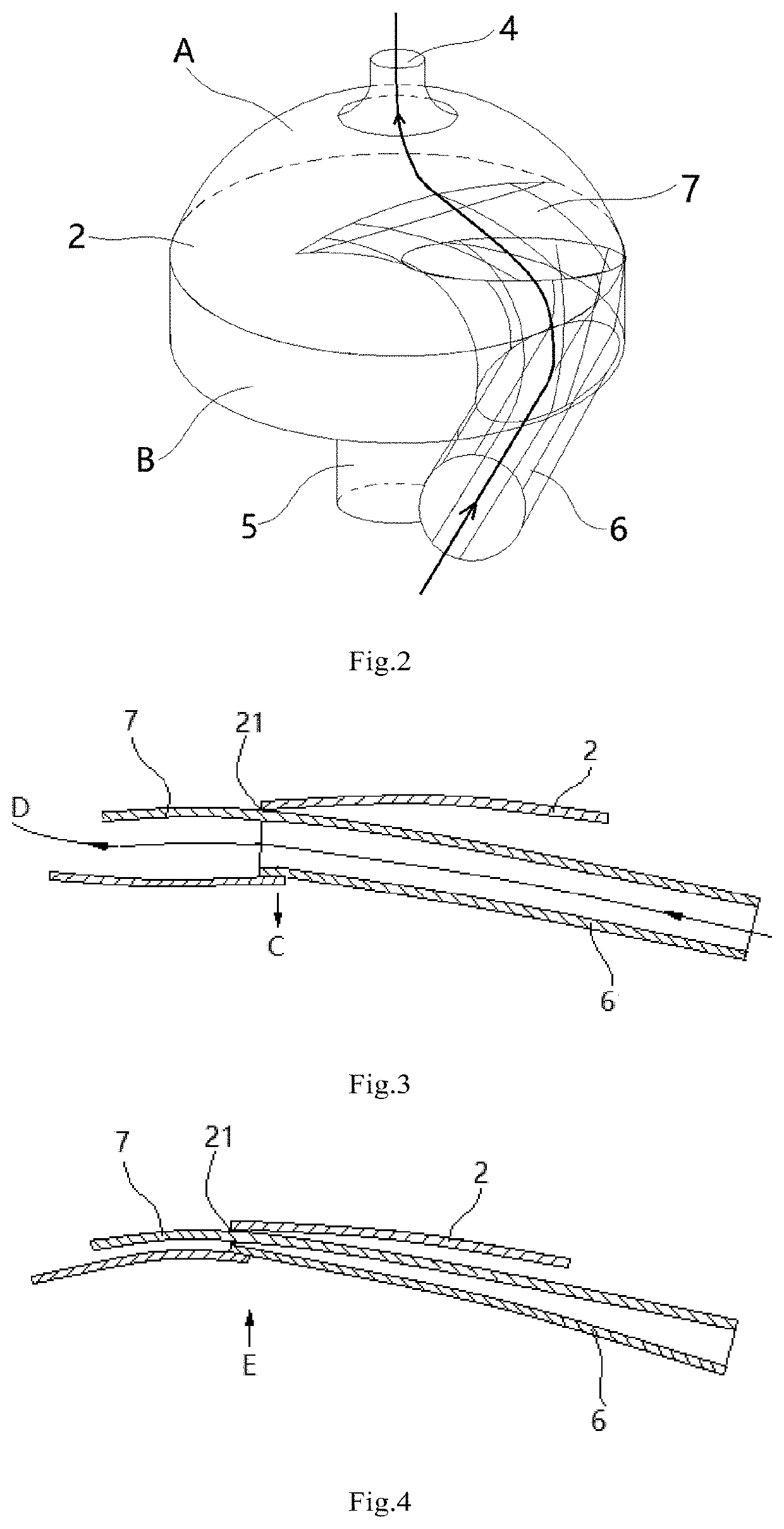
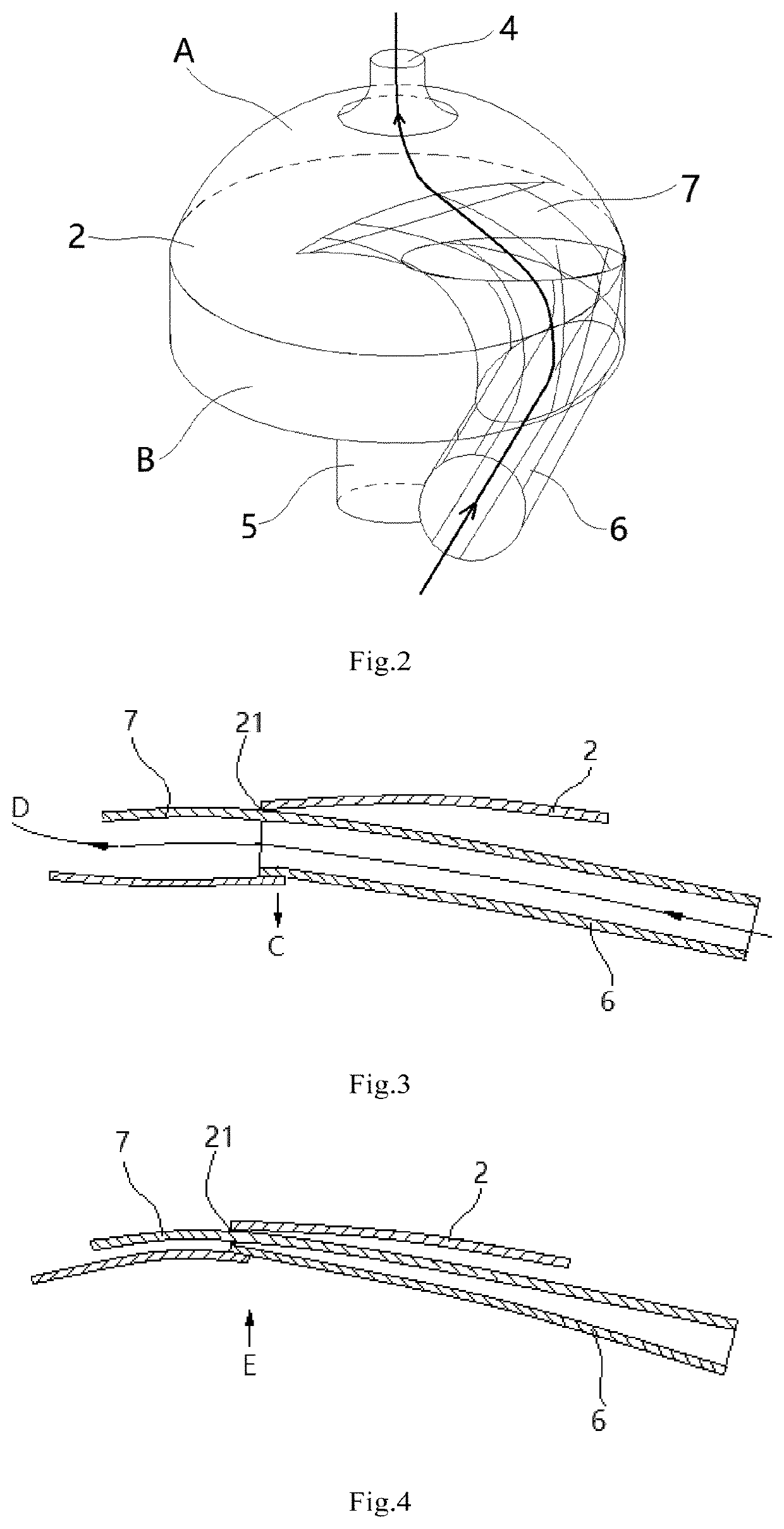
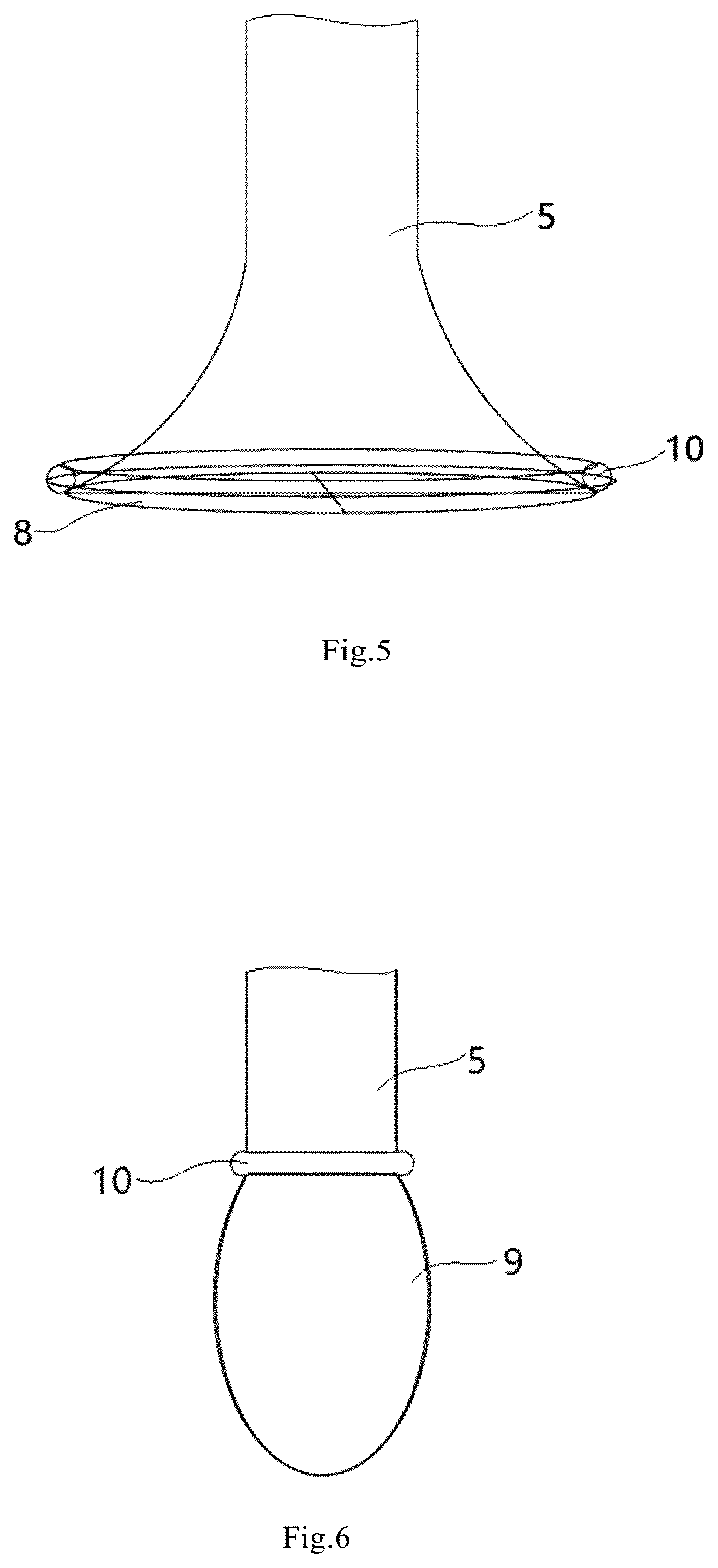
The present disclosure relates to a saccular cavopulmonary assist device, including a shell, an inflow tube (6) and an outflow tube (4), wherein a blood storage cavity (A) and a power cavity (B) are arranged in the shell, and the power cavity (B) is used for providing contraction and relaxation power for the blood storage cavity (A); the inflow tube (6) is arranged at a position corresponding to the power cavity (B) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the vena cava, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A) after passing through the power cavity (B); the outflow tube (4) is arranged at a position corresponding to the blood storage cavity (A) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the pulmonary artery, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A). This device can assist the cavopulmonary circulation of the single ventricle, realize repeated blood drawing and pumping actions, provide the required power for the pulmonary circulation of the patient, and restore the biventricular blood flow in the human body; and because the arrangement of the inflow tube in the power cavity, the internal structure of this device is more compact, the overall shape is smaller, and the energy of the power cavity can be fully utilized.
Owner:GUANGDONG CARDIOVASCULAR INSITITUTE
Heart support device
ActiveUS8834343B2Lower overall heightGuaranteed uptimeIntravenous devicesBlood pumpBiomedical engineeringBoth ventricles
A heart support device for pulsatile delivery of blood comprising a first and a second ventricle and a pump. Both ventricles comprises a fluid chamber and a blood-conveying chamber, wherein each fluid chamber can be filled with a fluid or emptied by way of the pump in such a way that an expansion or contraction of the fluid chamber occurs. In an expansion of the fluid chamber of a ventricle, a compression of the blood-conveying chamber of the same ventricle takes place, wherein a rigid pressure plate is disposed between a fluid chamber and the respective blood-conveying chamber, said pressure plate being able to move in the direction of the respective blood-conveying chamber.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
System and method for multiple site biphasic stimulation to restore ventricular arrhythmias
InactiveCN1208102CEffective and Faster StimulationQuick conversionHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleCardiac arrhythmia
A device and method for preventing relapse of ventricular arrhythmias. Biphasic stimulation acts on multiple sites in the ventricles to restore arrhythmias caused by relapses, especially multiple random relapses. In the preferred embodiment, the first phase of biphasic stimulation is anodal and is at maximum subthreshold amplitude. This anodic phase preconditions the myocardium to accept the second phase (cathode) so that less electrical energy is required to reach the threshold amplitude to produce depolarization. The waveform of anodal phase stimulation over time is a square wave, a ramp wave, or a series of short square wave pulses. Multiple electrodes located at multiple sites in the ventricles can stimulate simultaneously, or they can stimulate sequentially over time to mimic the normal progression of cardiac depolarization. Multiple ventricular electrodes can stimulate from the inner or outer surface. One or both ventricles can receive biphasic stimulation from multiple electrodes. The present invention can also be used in the atria.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Reduction of left-ventricular offset interaction with tachyarrhythmia detection
A device and method for improving tachyarrhythmia detection when the ventricles are resynchronized by delivering paces to both ventricles separated by a specified offset interval. Timing of escape intervals and tachyarrhythmia detection is based upon senses from one of the ventricles designated as a rate ventricle. A reversion pacing mode is provided in order to prevent tachyarrhythmia detection from being compromised when the rate ventricle is paced after the other ventricle.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
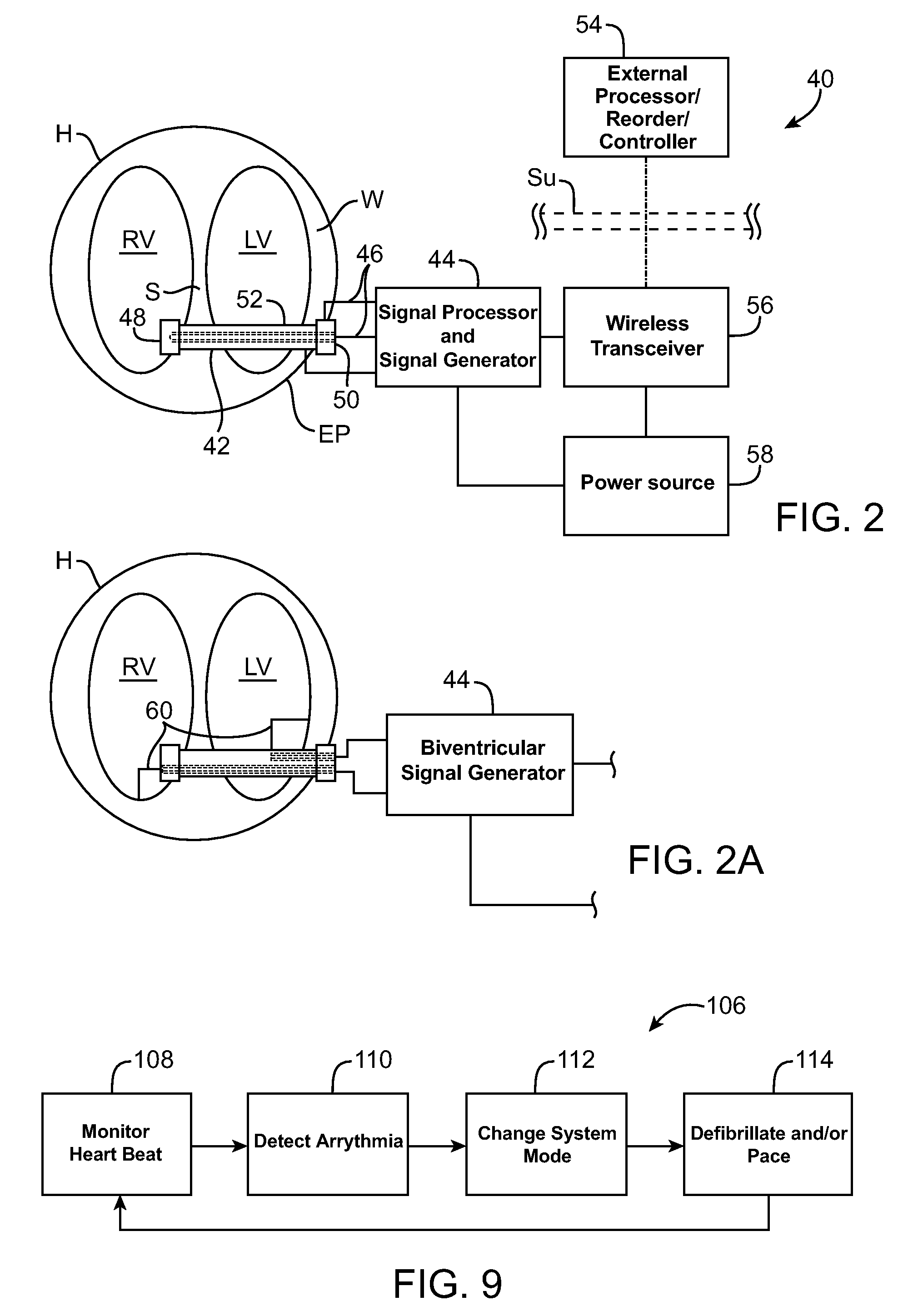
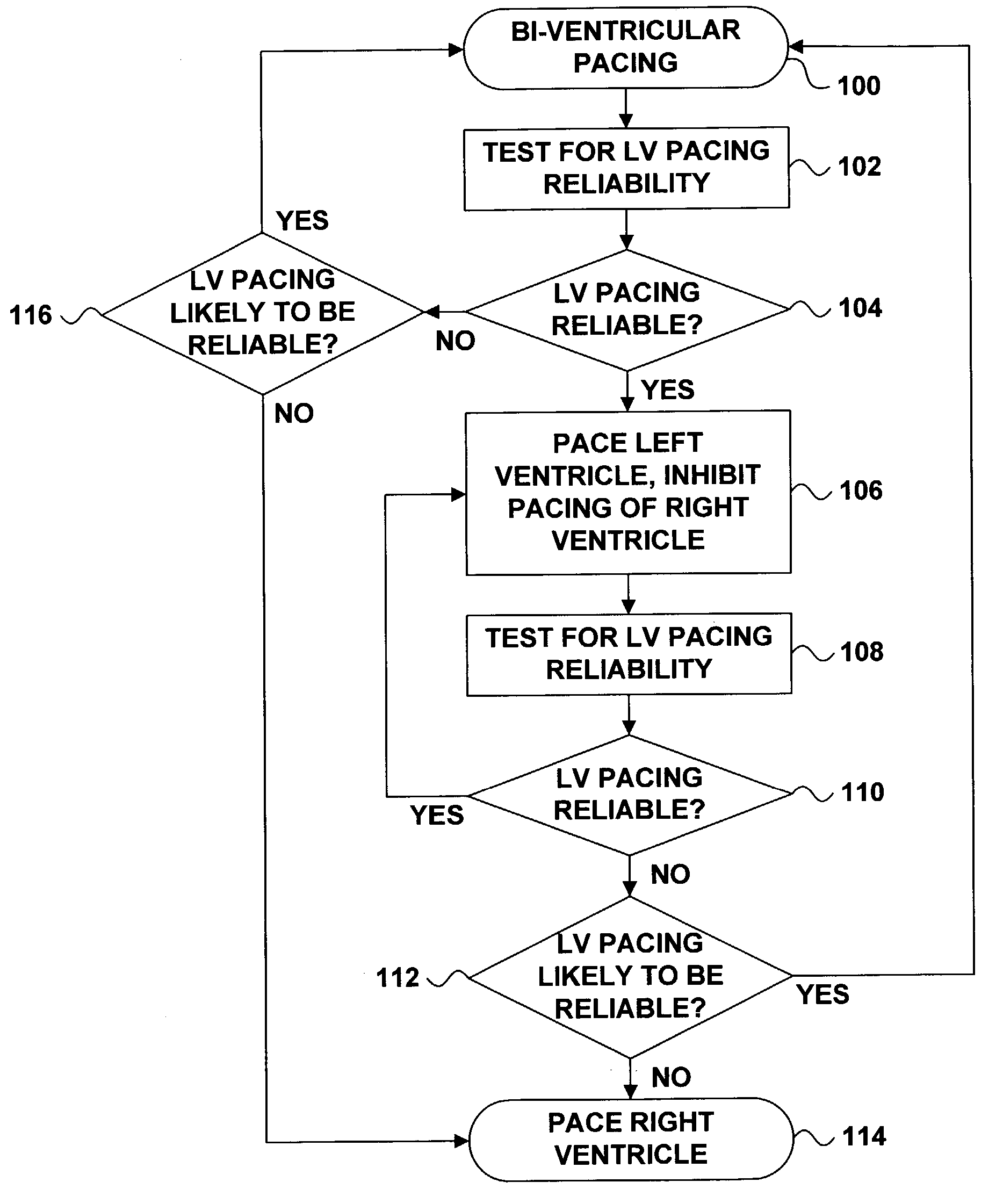
Bi-ventricular and single-ventricle pacing
The invention is directed to methods and apparatus for automatically changing from bi-ventricular pacing, in which an implantable medical device (IMD) applies pacing stimuli to both ventricles of a heart during a cardiac cycle, to single-ventricle pacing, in which the IMD paces one ventricle and inhibits pacing of the other. An IMD applying the techniques of the invention automatically changes from bi-ventricular pacing to single-ventricle pacing, or vice versa, as a function of the reliability of left ventricular pacing. Exemplary techniques for determining the reliability of left ventricular pacing include impedance measurement, capture testing, capture threshold testing, or any combination thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Saccular cavopulmonary assist device
ActiveUS11305104B2Restore biventricular blood flowSmall volumeControl devicesMedical devicesPulmonary vasculatureVein
The present disclosure relates to a saccular cavopulmonary assist device, including a shell, an inflow tube (6) and an outflow tube (4), wherein a blood storage cavity (A) and a power cavity (B) are arranged in the shell, and the power cavity (B) is used for providing contraction and relaxation power for the blood storage cavity (A); the inflow tube (6) is arranged at a position corresponding to the power cavity (B) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the vena cava, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A) after passing through the power cavity (B); the outflow tube (4) is arranged at a position corresponding to the blood storage cavity (A) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the pulmonary artery, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A). This device can assist the cavopulmonary circulation of the single ventricle, realize repeated blood drawing and pumping actions, provide the required power for the pulmonary circulation of the patient, and restore the biventricular blood flow in the human body; and because the arrangement of the inflow tube in the power cavity, the internal structure of this device is more compact, the overall shape is smaller, and the energy of the power cavity can be fully utilized.
Owner:GUANGDONG CARDIOVASCULAR INSITITUTE
Ventricular cavity simulation device and use method and application thereof
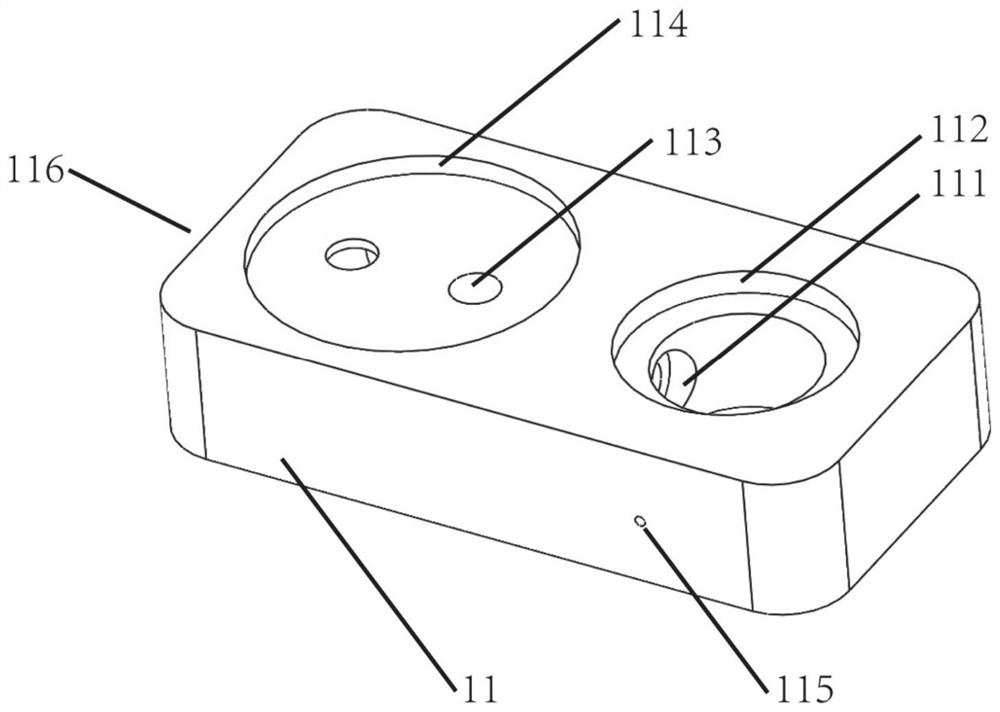
ActiveCN113990164AReal contractionTrue RotationEducational modelsReciprocating motionVentricular cavity
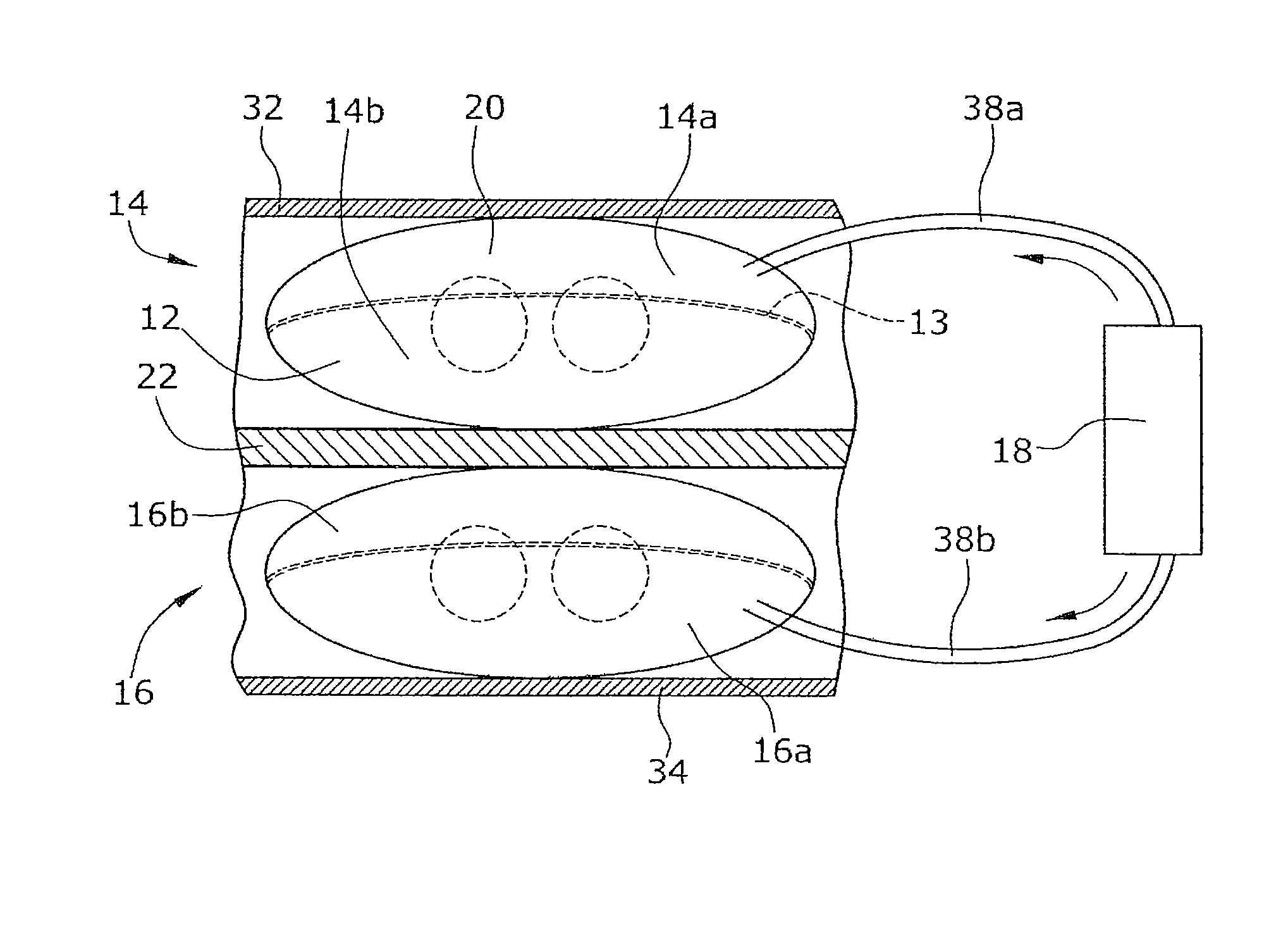
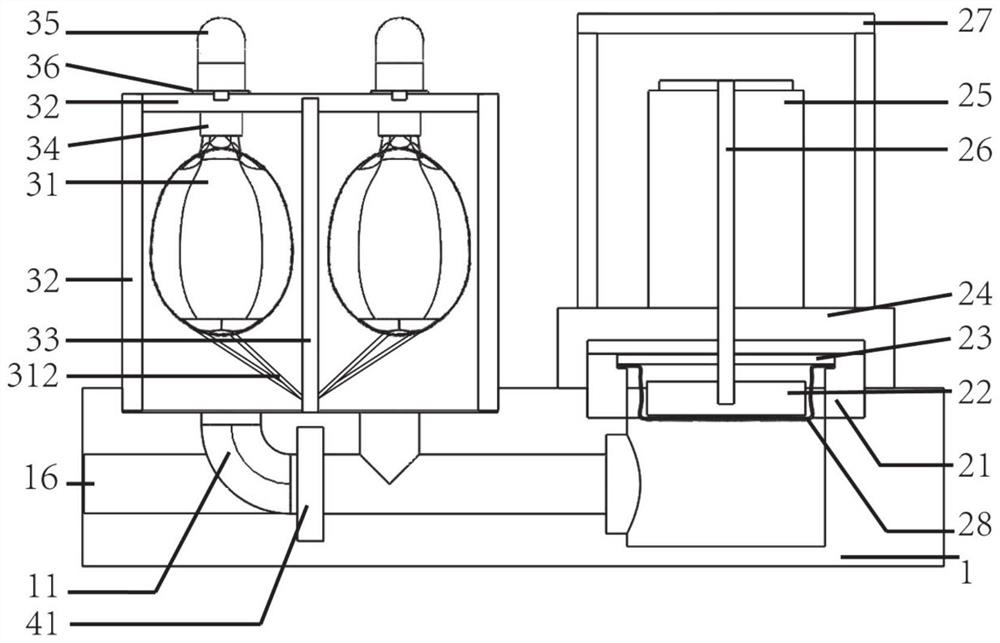
The invention belongs to the field of clinical medical treatment, and particularly relates to a ventricular cavity simulation device and a use method and application thereof. The ventricular cavity simulation device comprises a base, a bionic ventricle and a power unit, wherein the bionic ventricle and the power unit are both arranged on the base. The bionic ventricle is internally provided with flexibly sealed double ventricle sacs to simulate a left ventricle and a right ventricle; the power unit is used for providing power for enabling the double ventricular sacs to contract and simulating pulsation of a ventricular cavity; the base is used for connecting the bionic ventricle and the power unit; and a flow channel connected with the power unit and the bionic ventricle is arranged in the base, working liquid is placed in the flow channel, and the working liquid serves as a medium to enable the power unit to push the ventricular sacs to contract. According to the device, rigid reciprocating motion of the linear motor can be converted into flexible contraction motion of the ventricular sac, so that a pressure change curve in a heartbeat cycle can be better fitted, and change curves of outlet pressure and inlet pressure of the ventricular cavity in a pulsation process can be more accurately and truly simulated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com