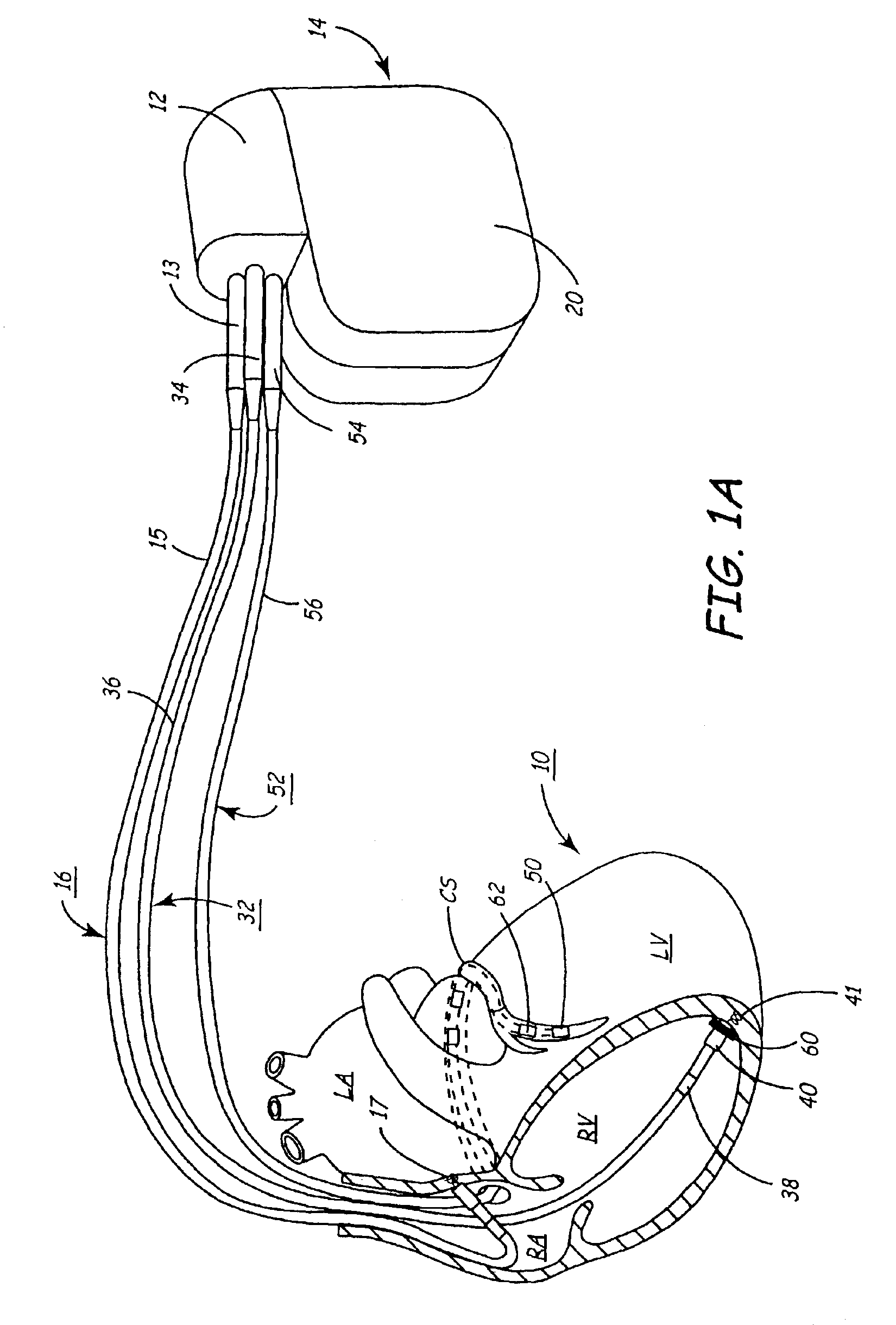
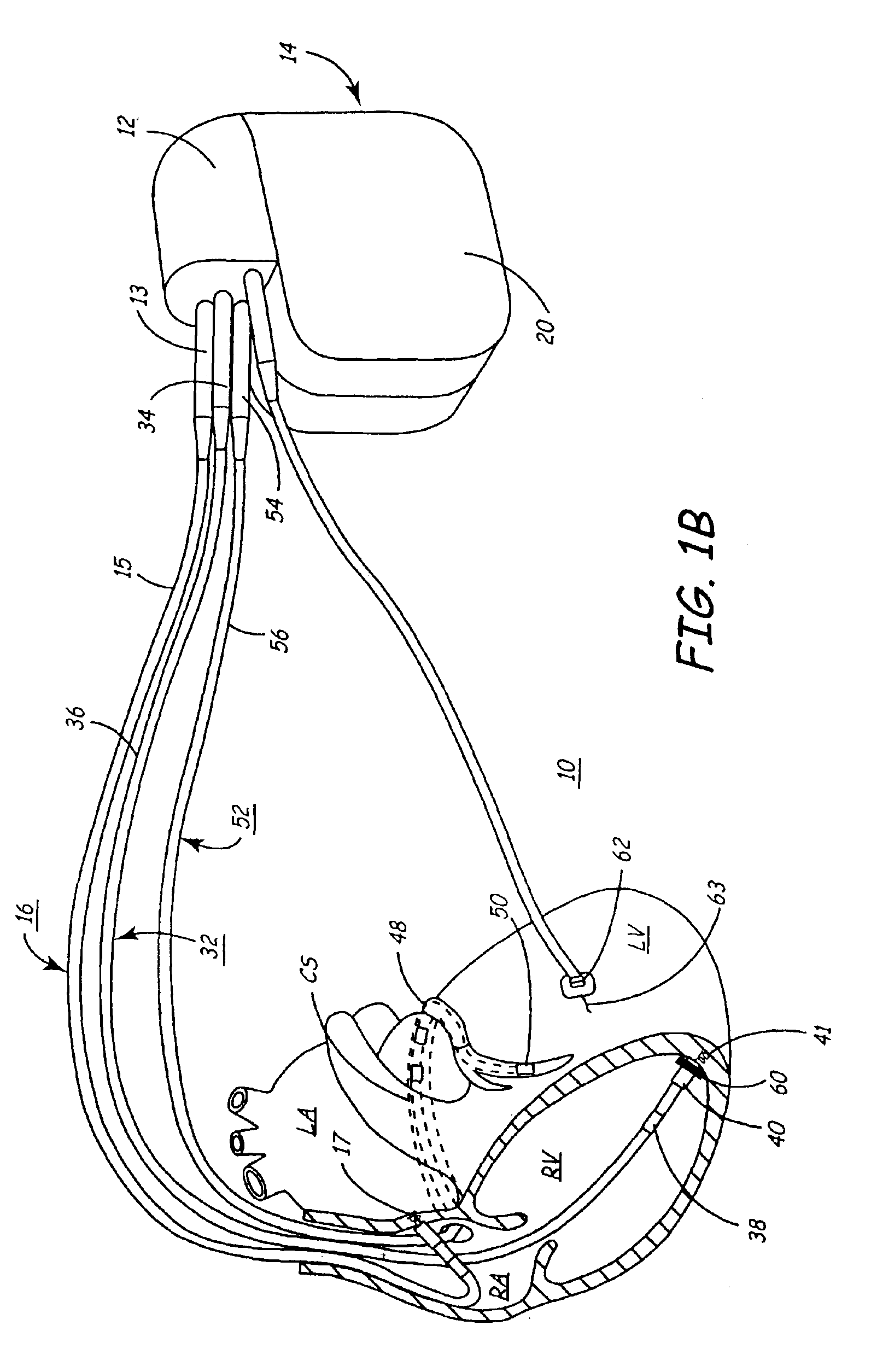
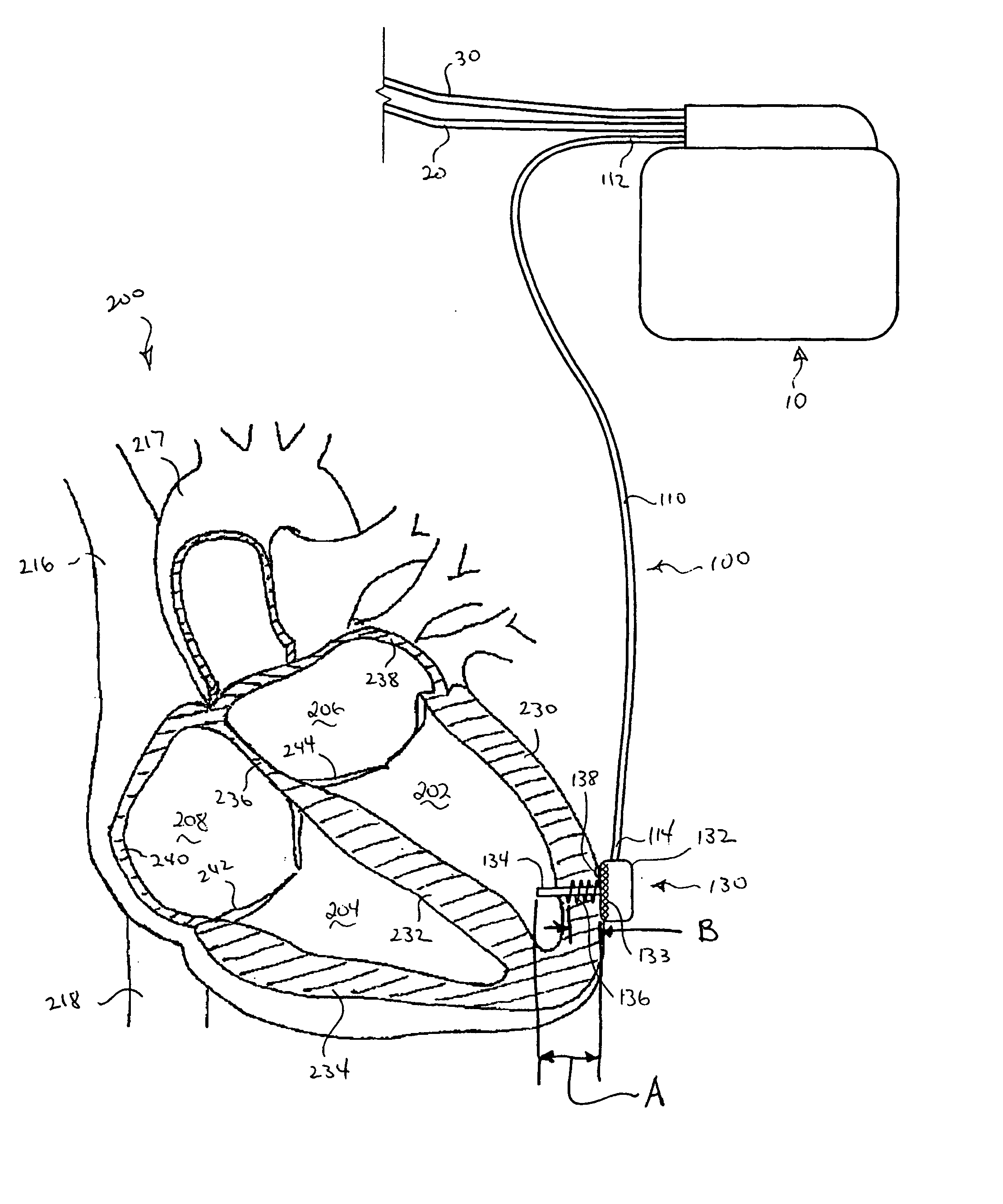
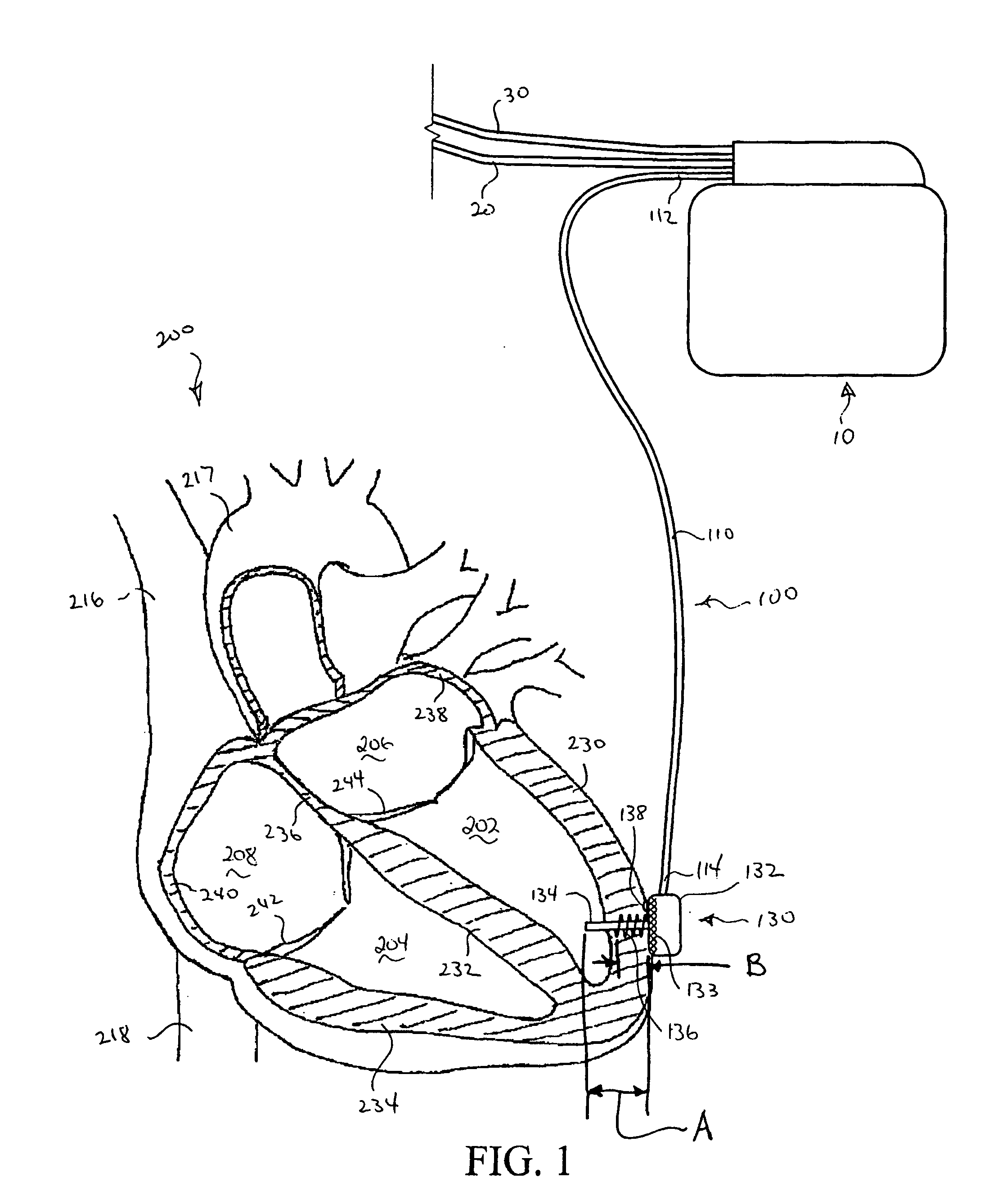
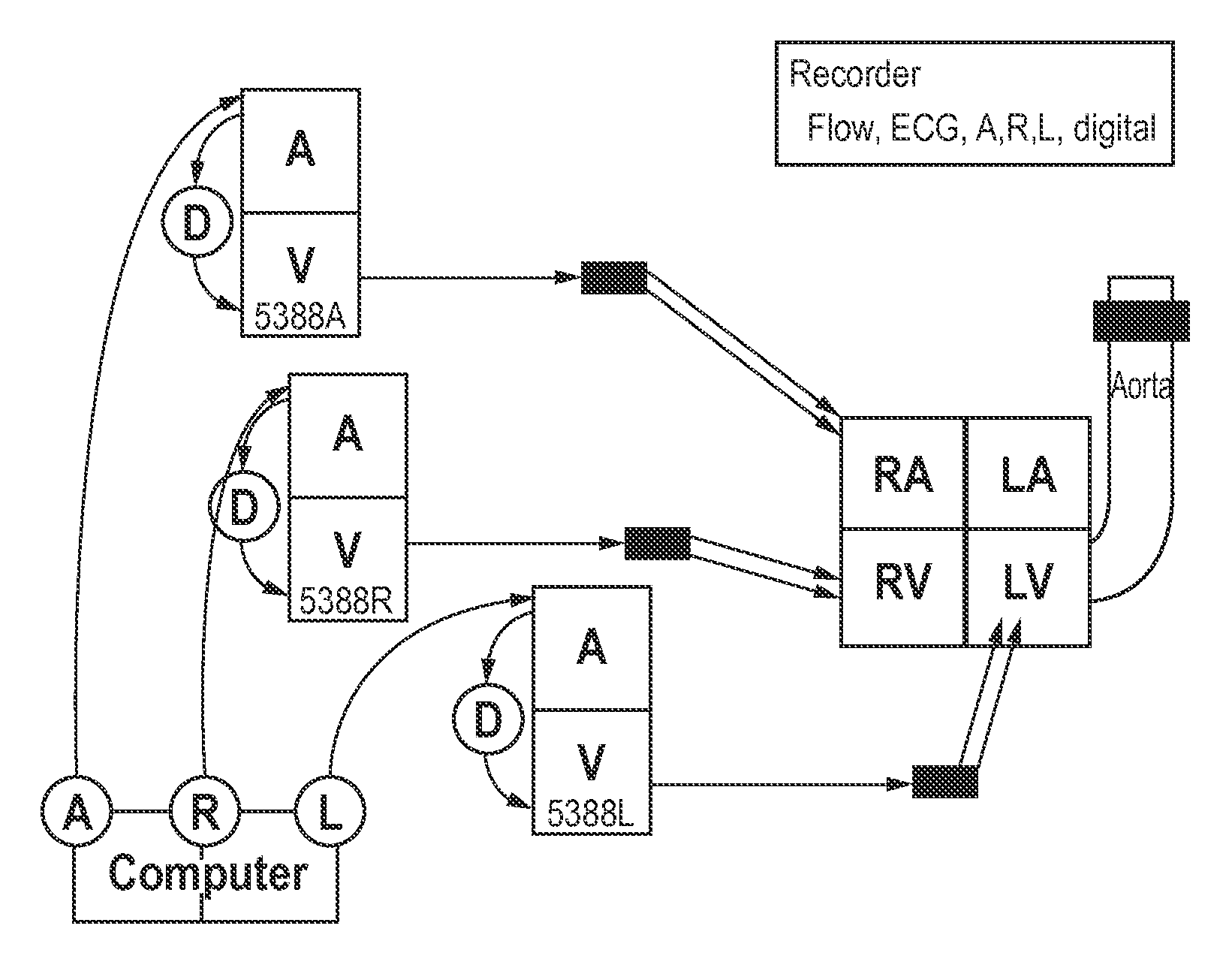
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Left cardiac chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
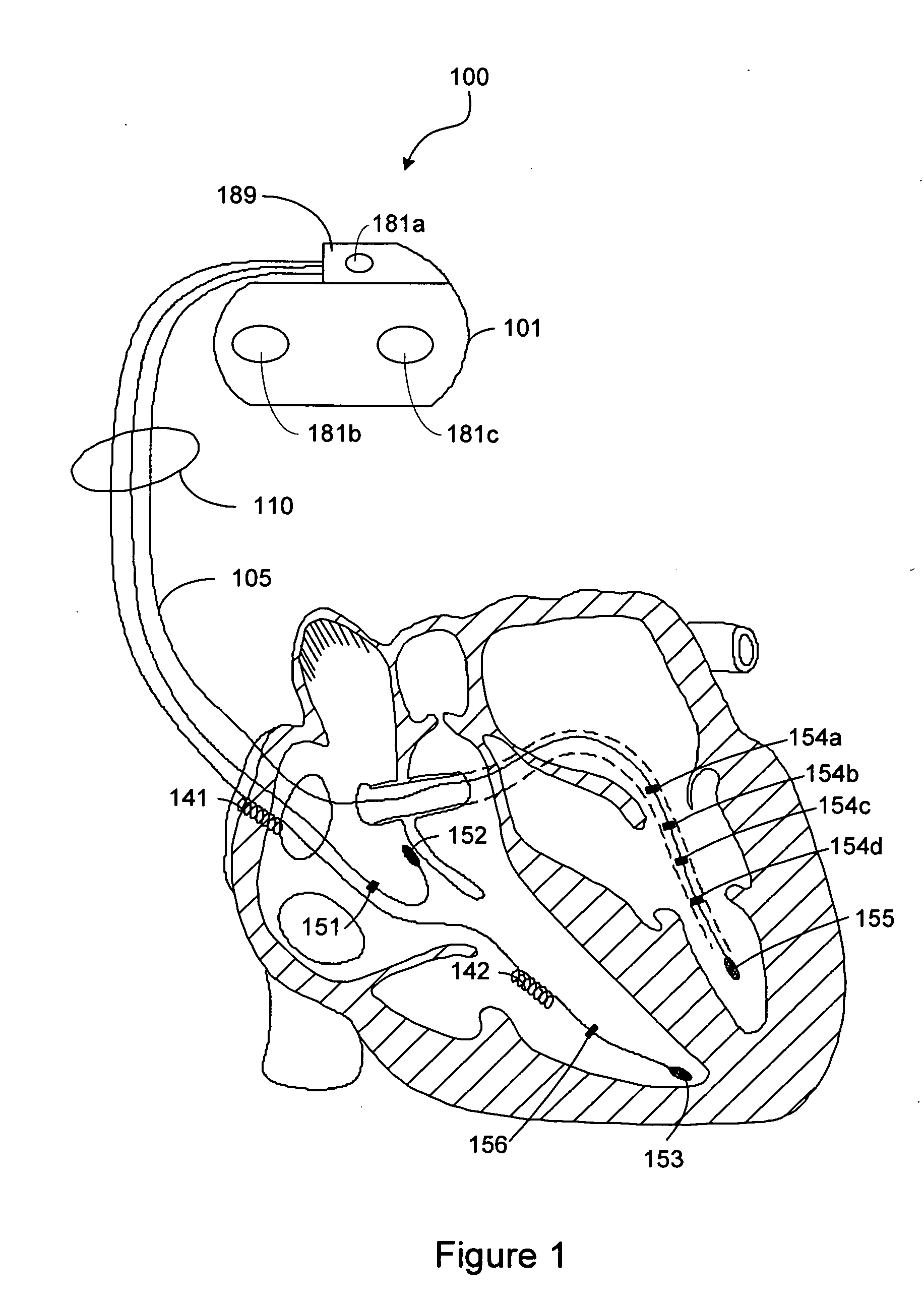
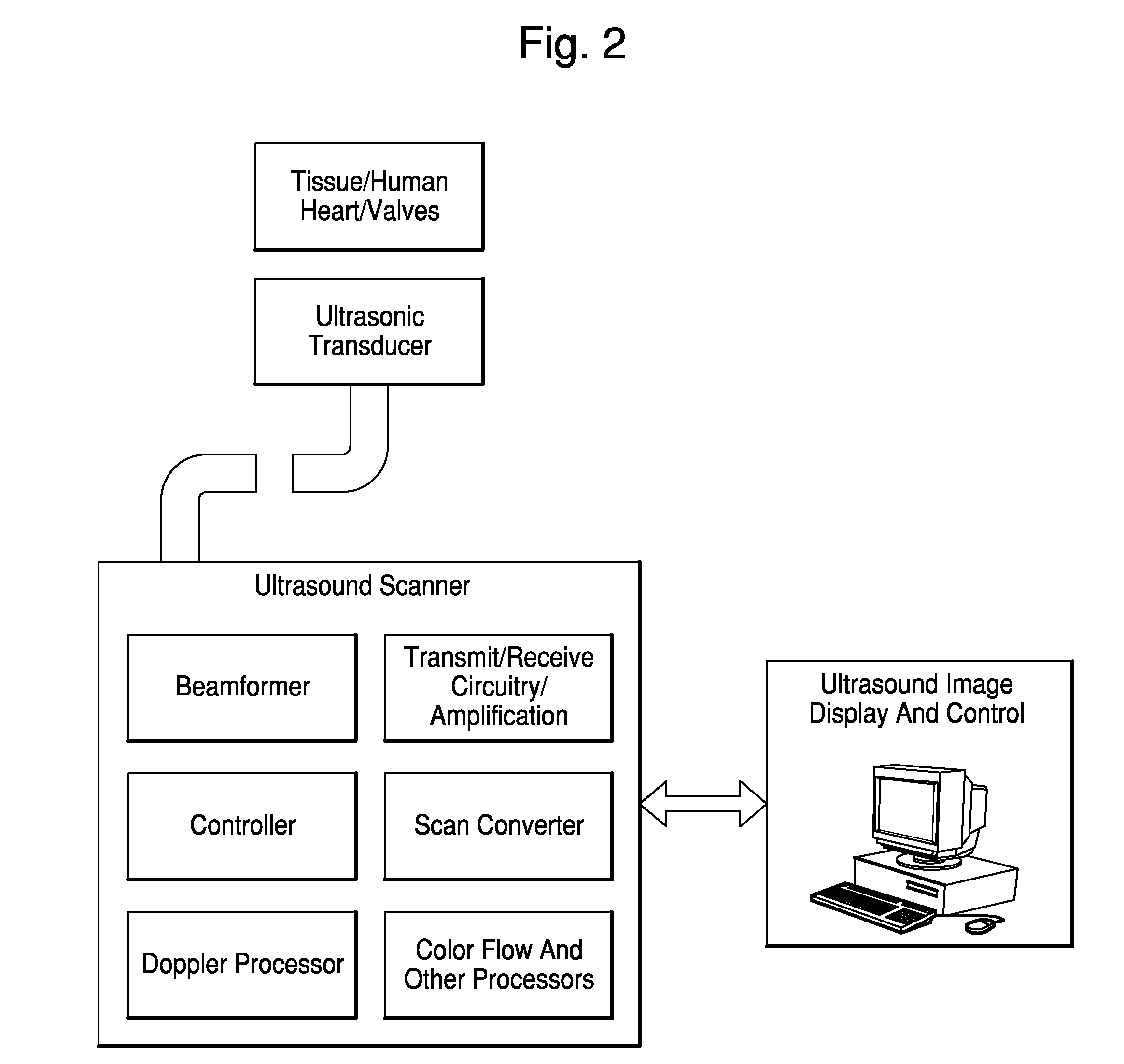
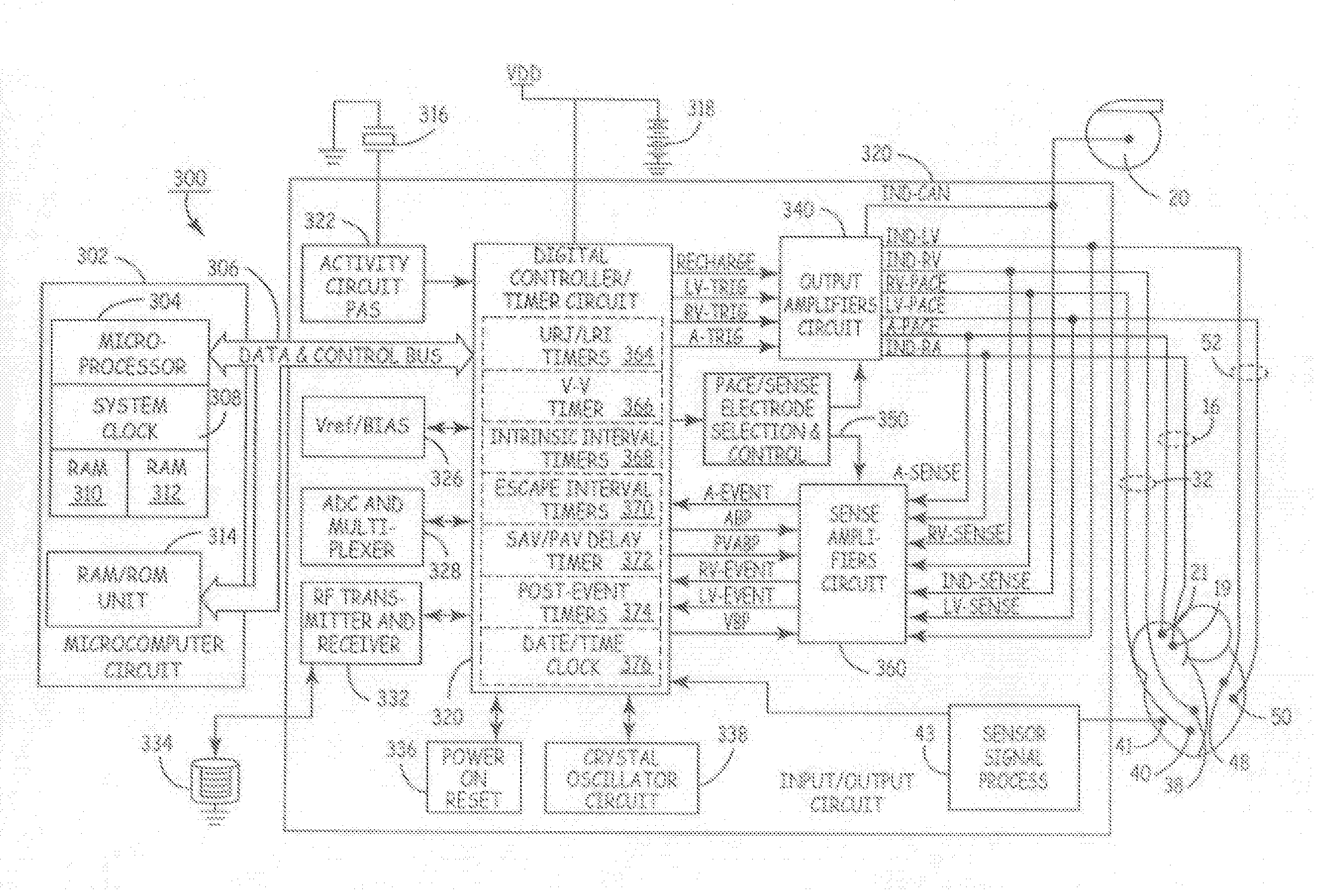
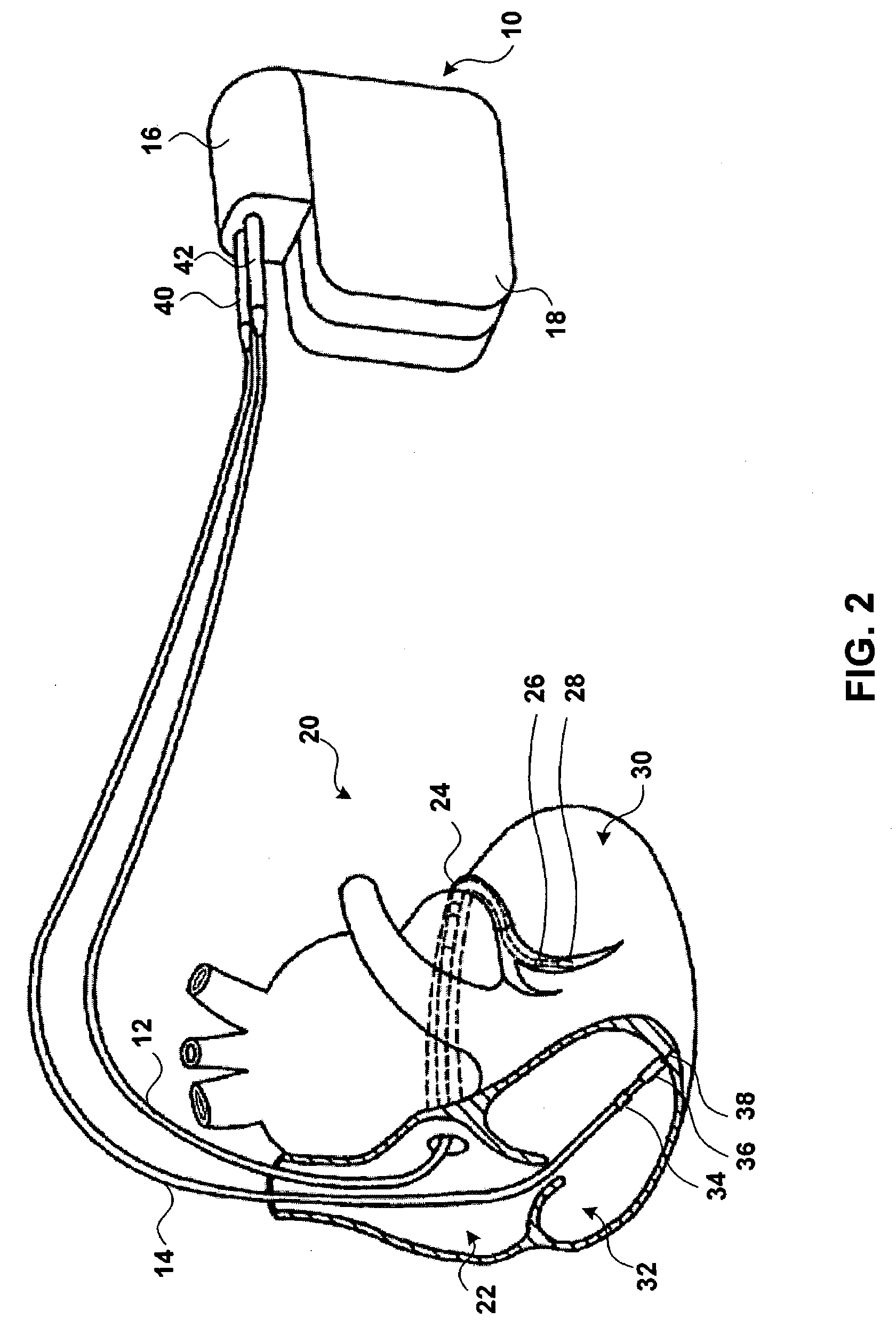
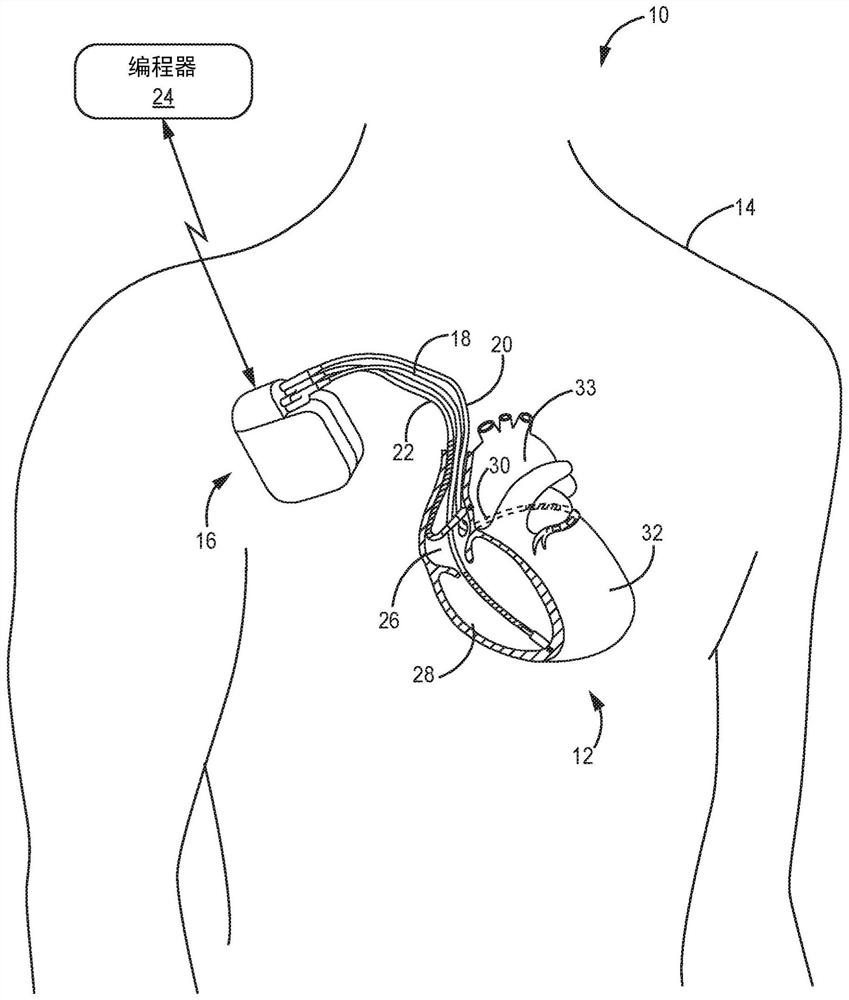
Heart pacemaker
InactiveUS6144879ASimple procedureDepolarizationEpicardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsDielectricLeft cardiac chamber
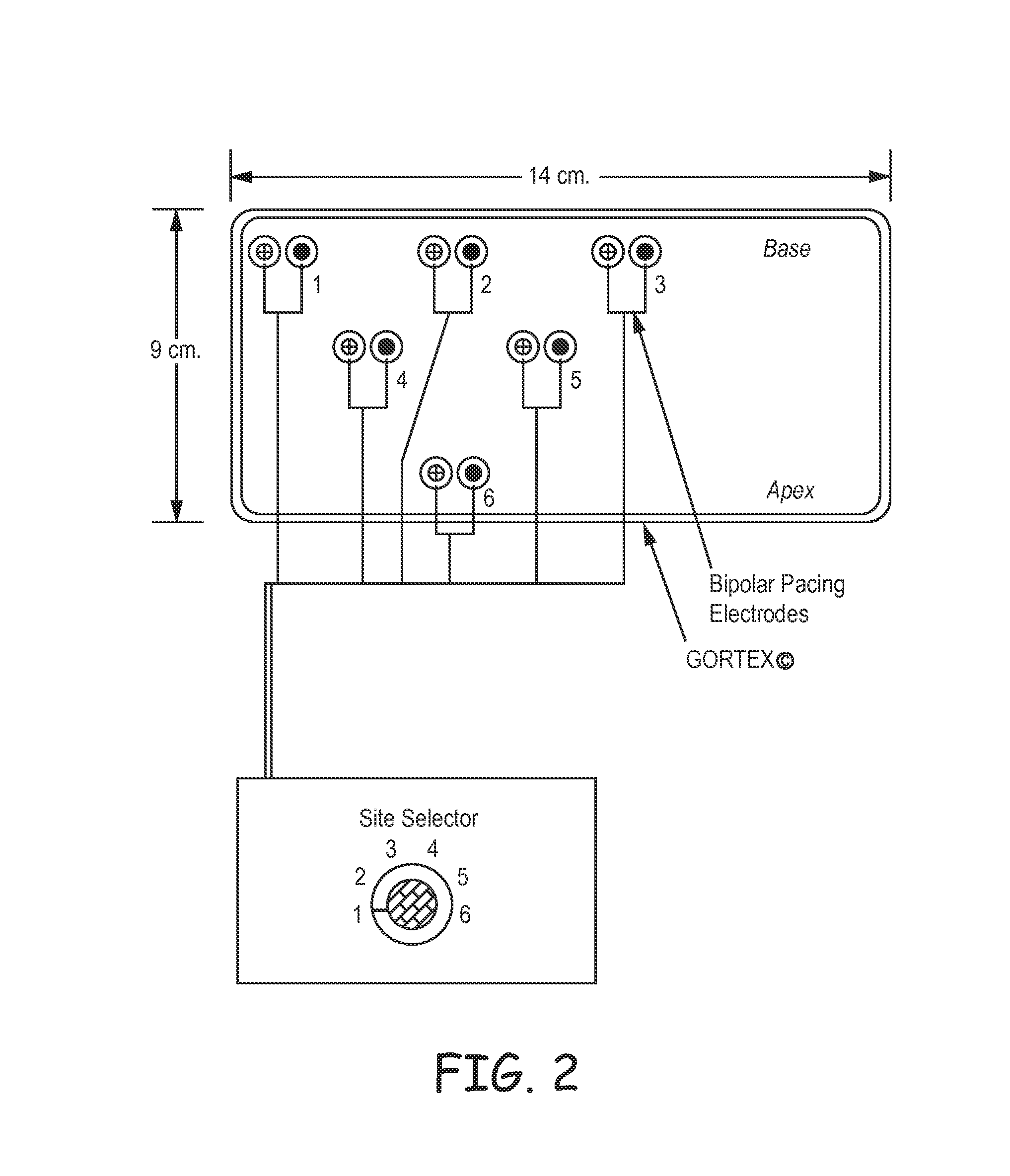
A heart pacemaker which is arranged to stimulate the apical area of the heart. Stimulation of this area provides synchronous mechanical contraction of the left and right ventricles and overcomes the problem of pacemaker induced left bundle branch block type conduction disturbance. The pacemaker has a base surface which conforms to the apical area of the heart and mounts a plurality of epicardial stimulating electrodes. Selection of electrodes can be made to provide the most clinically appropriate stimulation. An opposite side of the pacemaker is arranged to contact the diaphragm and is provided with sensing electrodes to sense activity of the diaphragm and adjust pacing of the heart in accordance with changes in physical activity of the patient. The electrodes used are preferably of capacitive construction, having first and second capacitive plates either side of a dielectric formed by the body of the pacemaker.
Owner:GRAEMED PTY
Method and apparatus for optimizing cardiac resynchronization therapy based on left ventricular acceleration
InactiveUS6885889B2Good effectExtension of timeHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
A system and method for monitoring left ventricular cardiac contractility and for optimizing a cardiac therapy based on left ventricular lateral wall acceleration (LVA) are provided. The system includes an implantable or external cardiac stimulation device in association with a set of leads including a left ventricular epicardial or coronary sinus lead equipped with an acceleration sensor. The device receives and processes acceleration sensor signals to determine a signal characteristic indicative of LVA during isovolumic contraction. A therapy optimization method evaluates the LVA during varying therapy settings and selects the setting(s) that correspond to a maximum LVA during isovolumic contraction. In one embodiment, the optimal inter-ventricular pacing interval for use in cardiac resynchronization therapy is determined as the interval corresponding to the highest amplitude of the first LVA peak during isovolumic contraction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
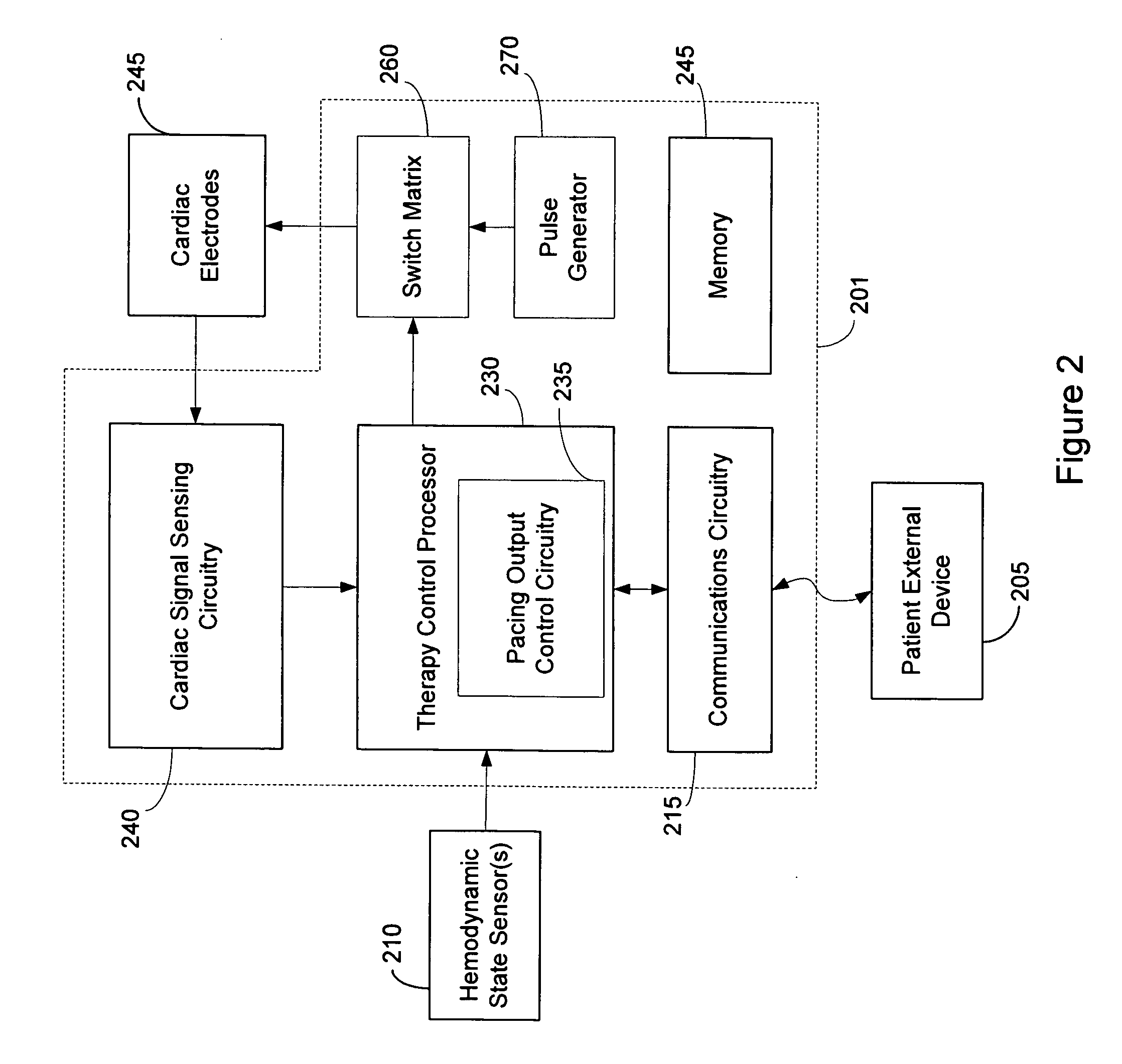
Implantable pressure sensor with pacing capability
Devices and methods for left ventricular or biventricular pacing plus left ventricular pressure measurement. For example, a pacing lead having a combined electrode and pressure sensor assembly may be used for left ventricular (LV) pacing and pressure measurement. The assembly may include one or more electrodes, a pressure sensor, and a pressure transmission catheter. Such a pacing lead is particularly suitable for biventricular pacing and may be incorporated into a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) system, for example.
Owner:TRANSOMA MEDICAL
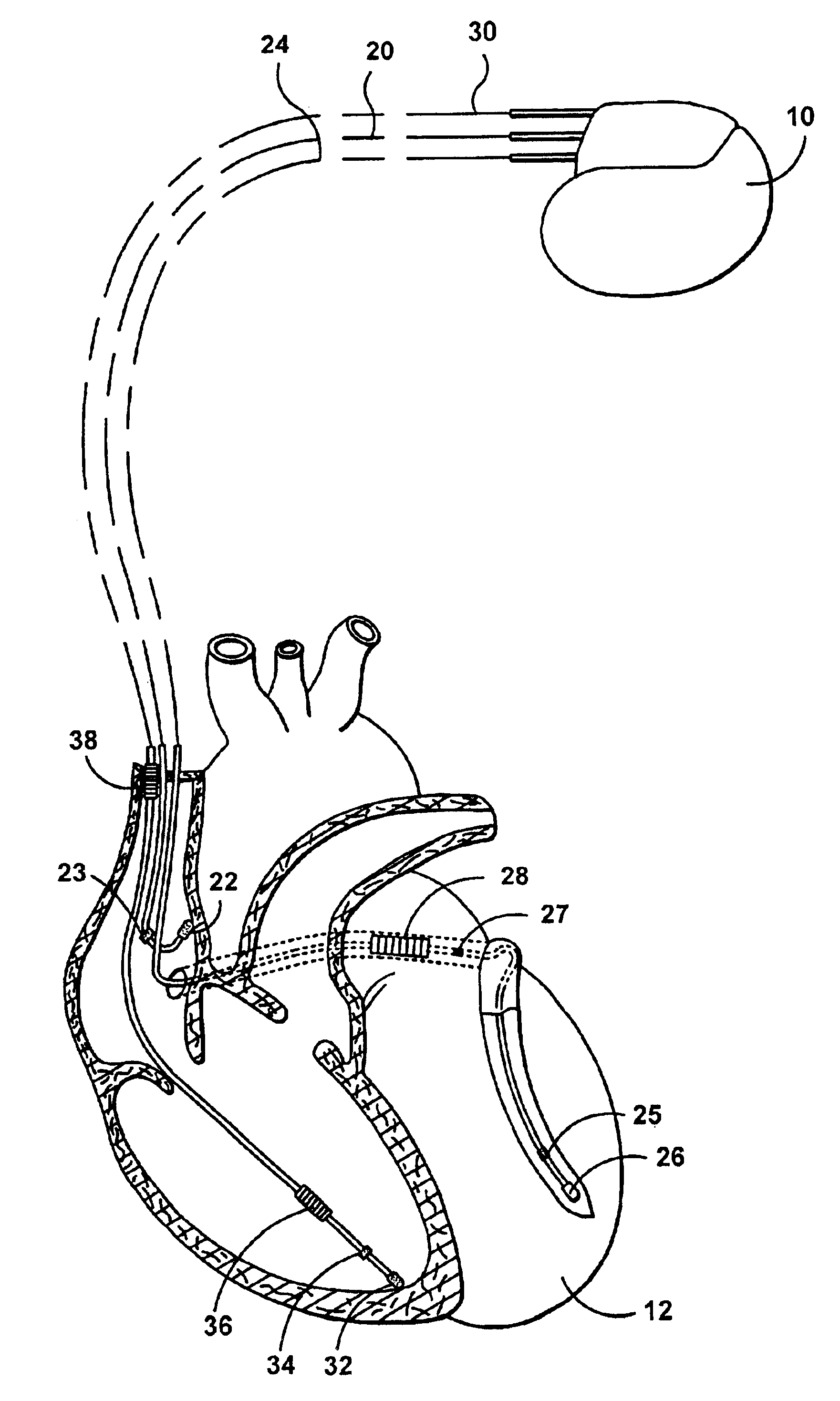
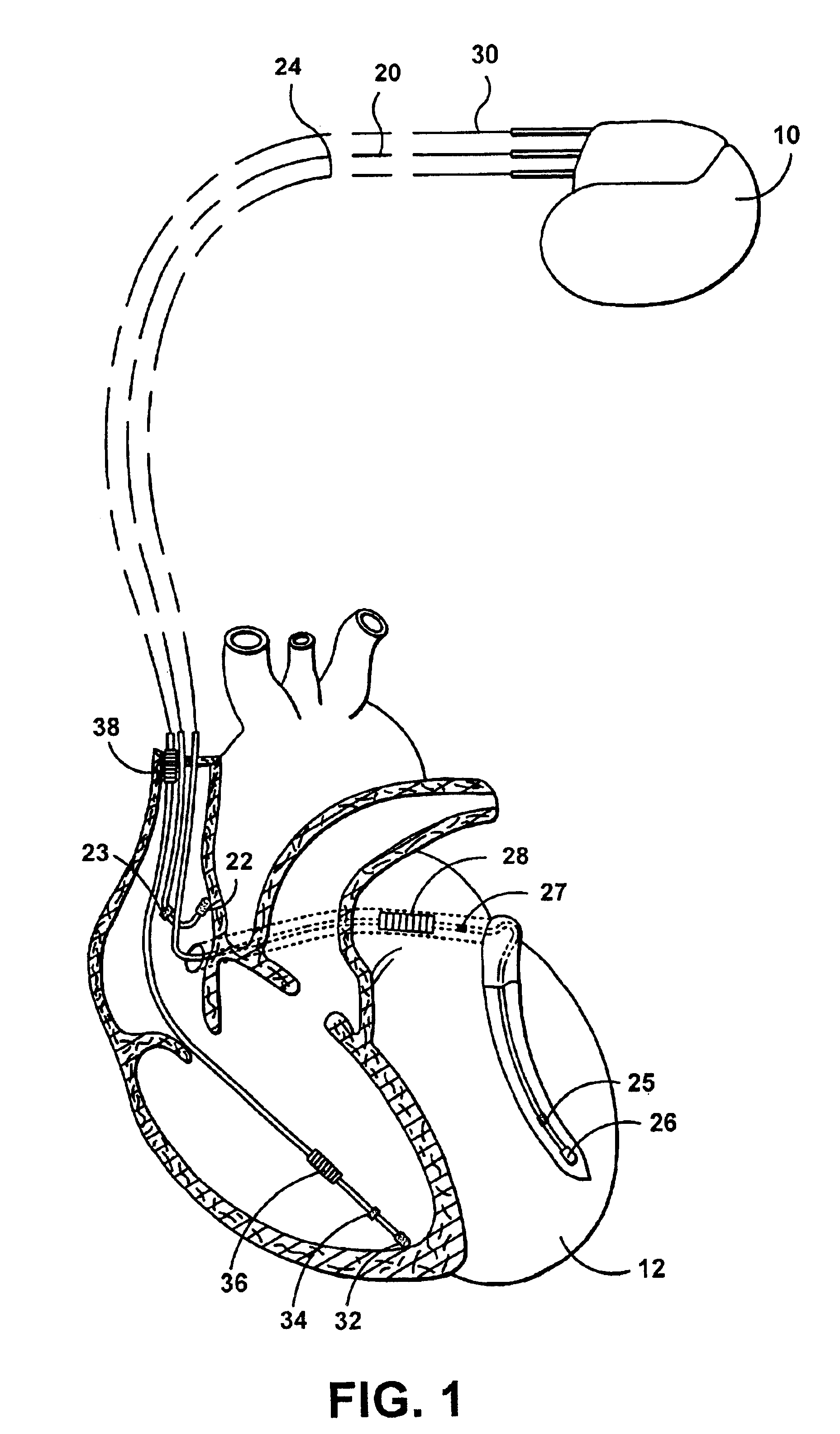
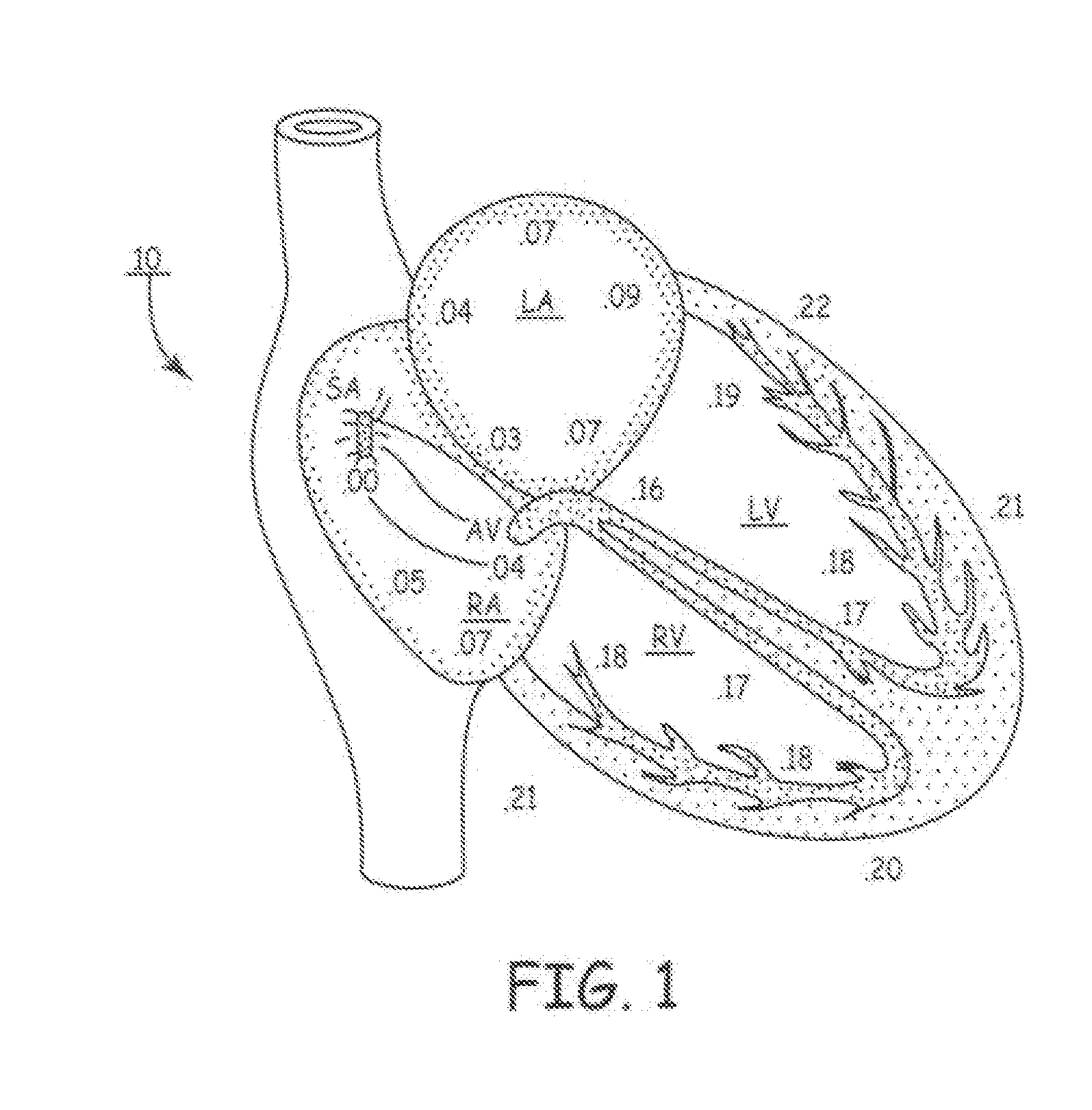
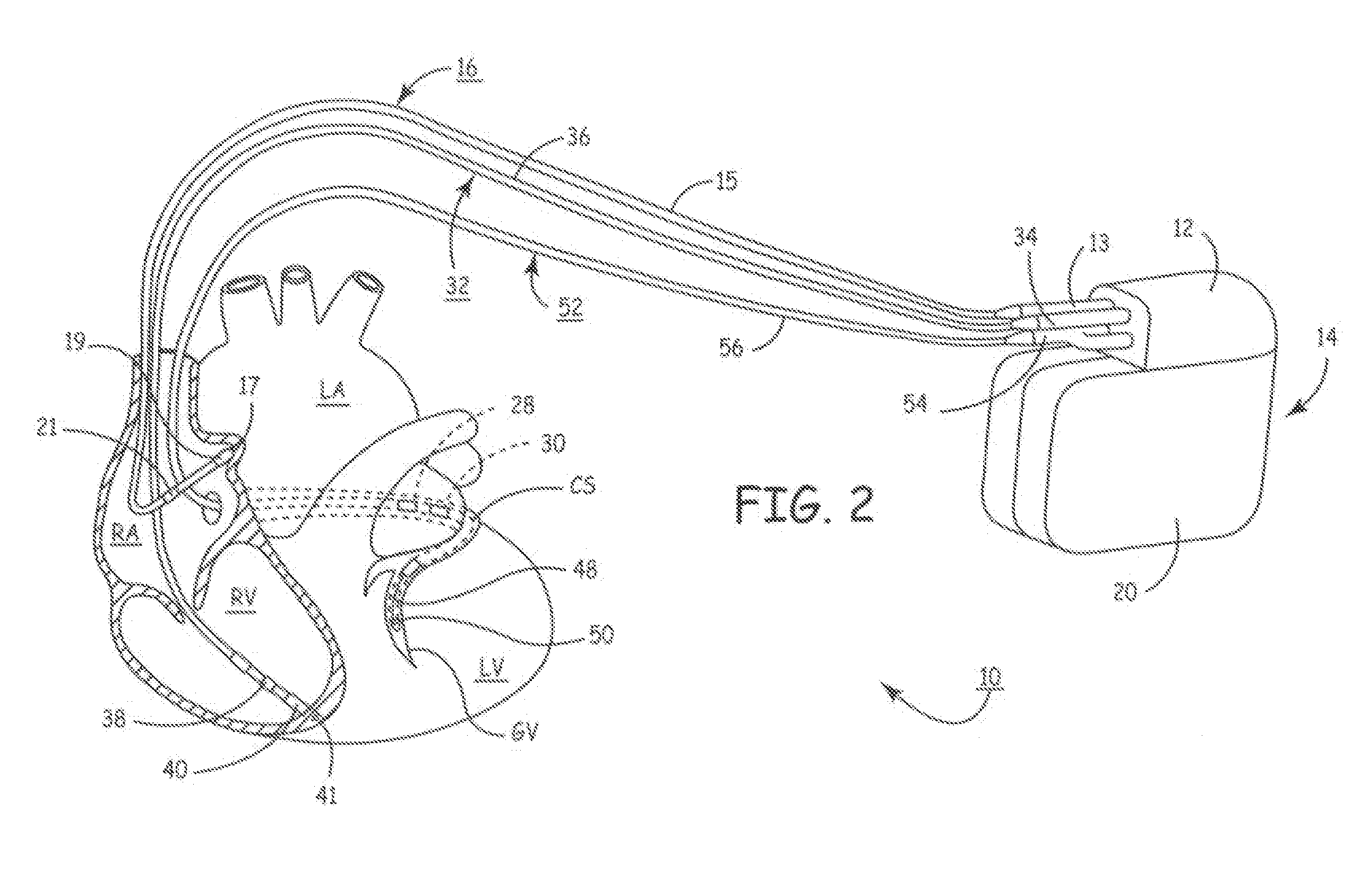
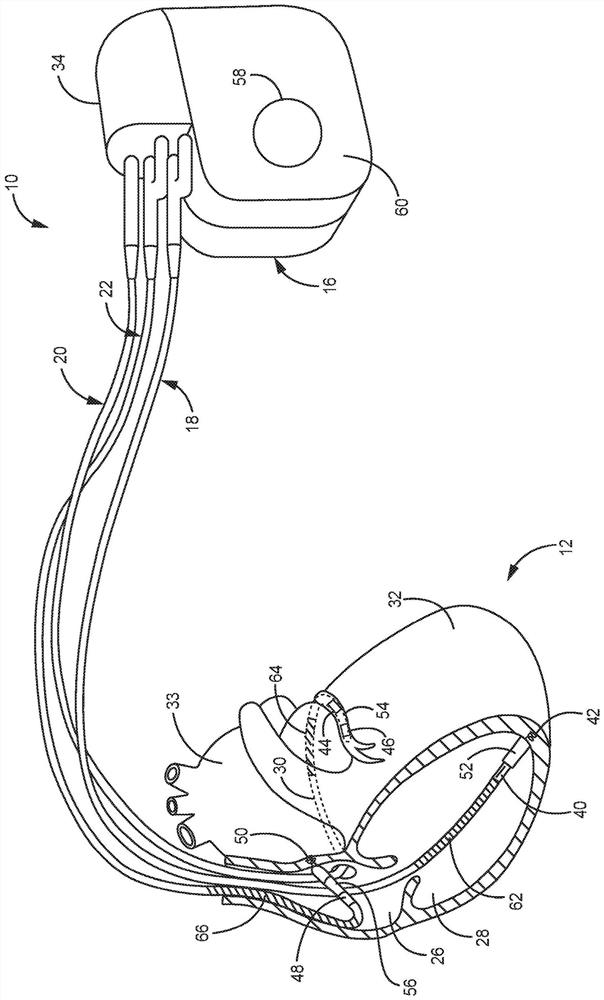
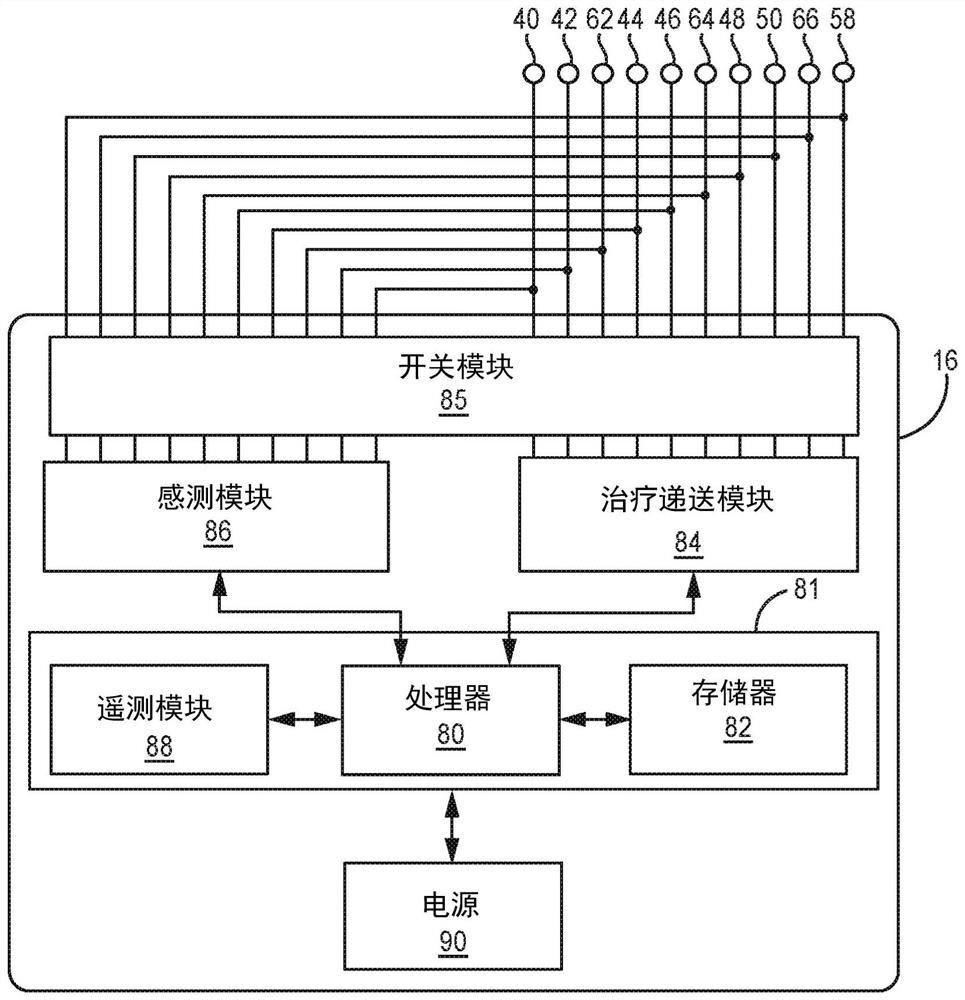
System for providing electrical stimulation to a left chamber of a heart
A medical electrical lead is disclosed that is adapted for placement in the coronary sinus, or a branch vein thereof. The lead includes a first and second pace / sense electrode. A selection mechanism is provided to select either the first or the second electrode for use as a cathode, with the other electrode being selected as the anode. According to another aspect of the invention, a high-voltage coil electrode may be provided between the first and second electrodes. The coil electrode may be electrically coupled to the anode to increase the shadow area of the coil electrode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
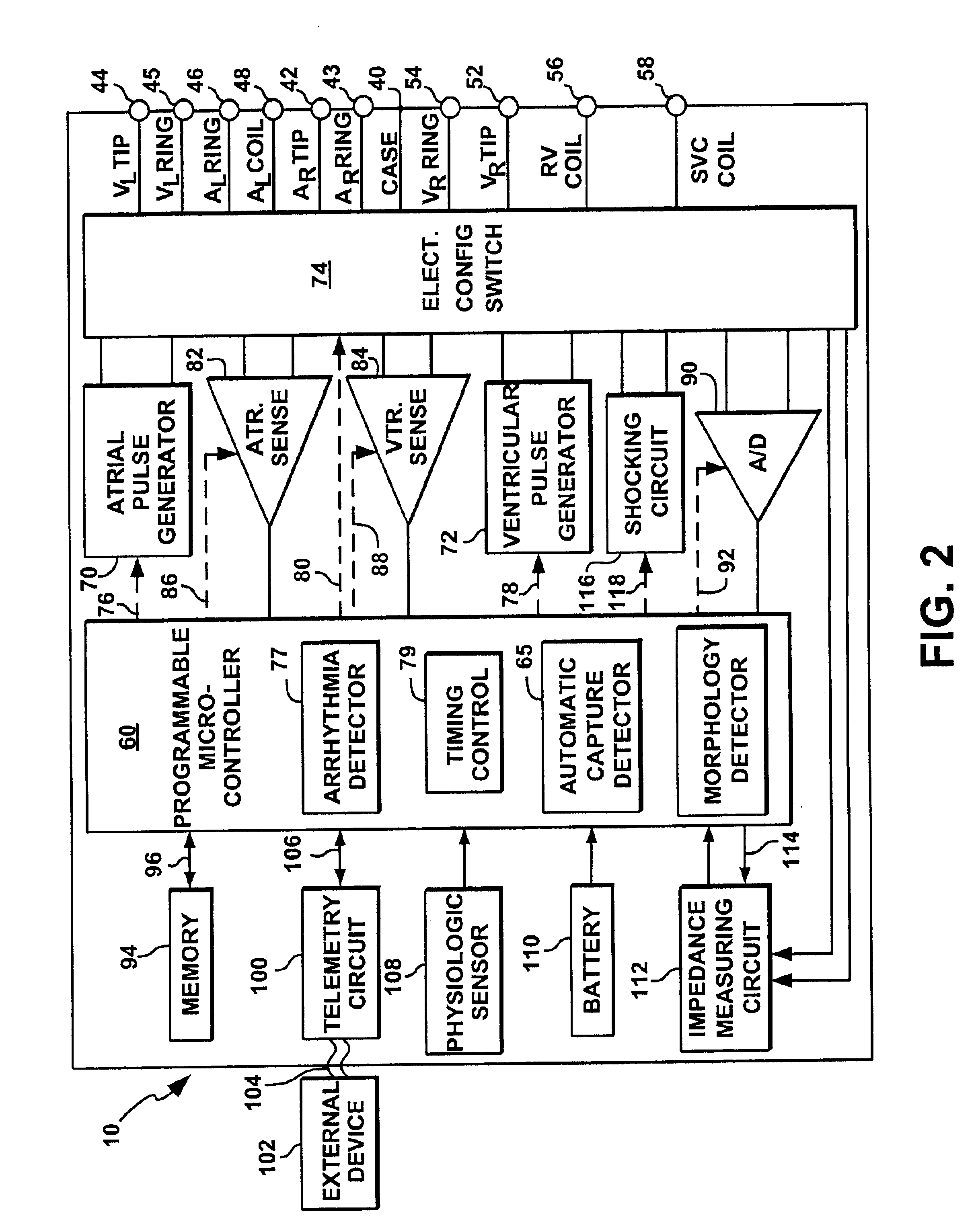
Automatic capture using independent channels in bi-chamber stimulation
InactiveUS6915164B2Extend battery lifeIncreased longevityHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberPulse energy
A cardiac stimulation device and method deliver independent stimulation pulses to right and left cardiac chambers, based on the capture thresholds of each chamber, and confirm capture in each chamber. A threshold test is performed in one chamber while stimulating the opposite chamber at increased pulse energy and adjusted interchamber delay.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Pacing output configuration selection for cardiac resynchronization therapy patients
ActiveUS20080177344A1Improve responsivenessImproved patient responsivenessHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeConfiguration selection
Cardiac therapy systems include multiple electrodes respectively positionable at multiple left ventricular electrode sites. A pulse generator is coupled to the electrodes and configured to deliver a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). A processor is configured to measure, for each left ventricular electrode site, a timing interval between first and second cardiac signal features associated with left ventricular depolarization. The timing interval is associated with a degree of responsiveness of each left ventricular electrode site to CRT. The processor is configured to determine a pacing output configuration that provides improved patient responsiveness to CRT based on the timing interval measurements and to select at least one left ventricular electrode site from the plurality of left ventricular electrode sites based on the timing interval measurements. The processor may be configured to monitor for a change in hemodynamic status of the patient based on a change in the timing interval.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for Reversing Ventricular Dyssynchrony
InactiveUS20070299479A1Rapid and systematic optimizationHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular ejection
A method for reversing ventricular dyssynchrony uses intracardiac echocardiographic measured parameters to systematically determine an optimal, individualized configuration for a cardiac resynchronization stimulator device. This method is particularly relevant for patients with congestive heart failure. The algorithm evaluates improvement in aortic flow and in left ventricular ejection fraction as atrioventricular and interventricular delay parameters of the patient's resynchronization stimulator device are varied.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
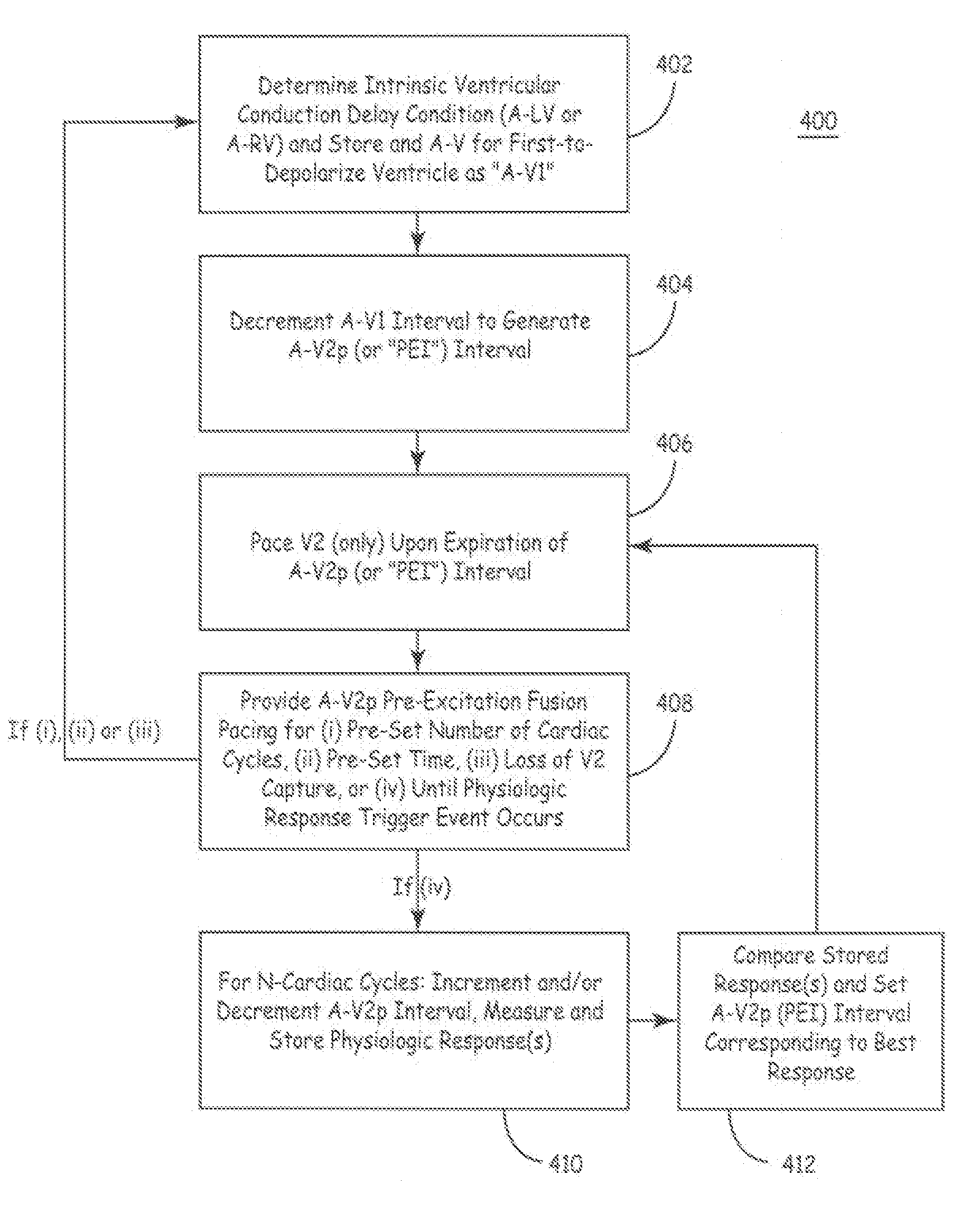
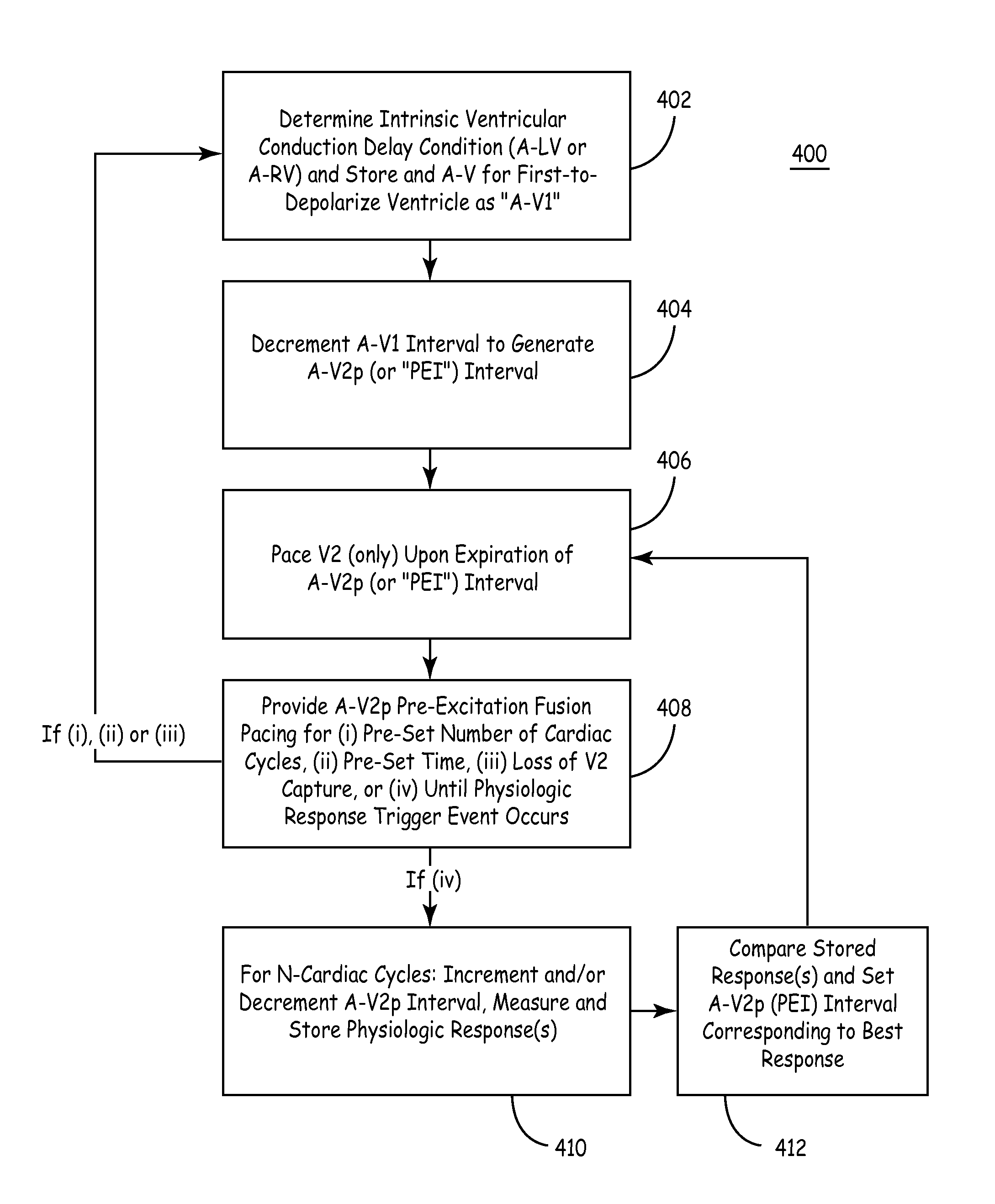
Fusion Pacing Enhancements
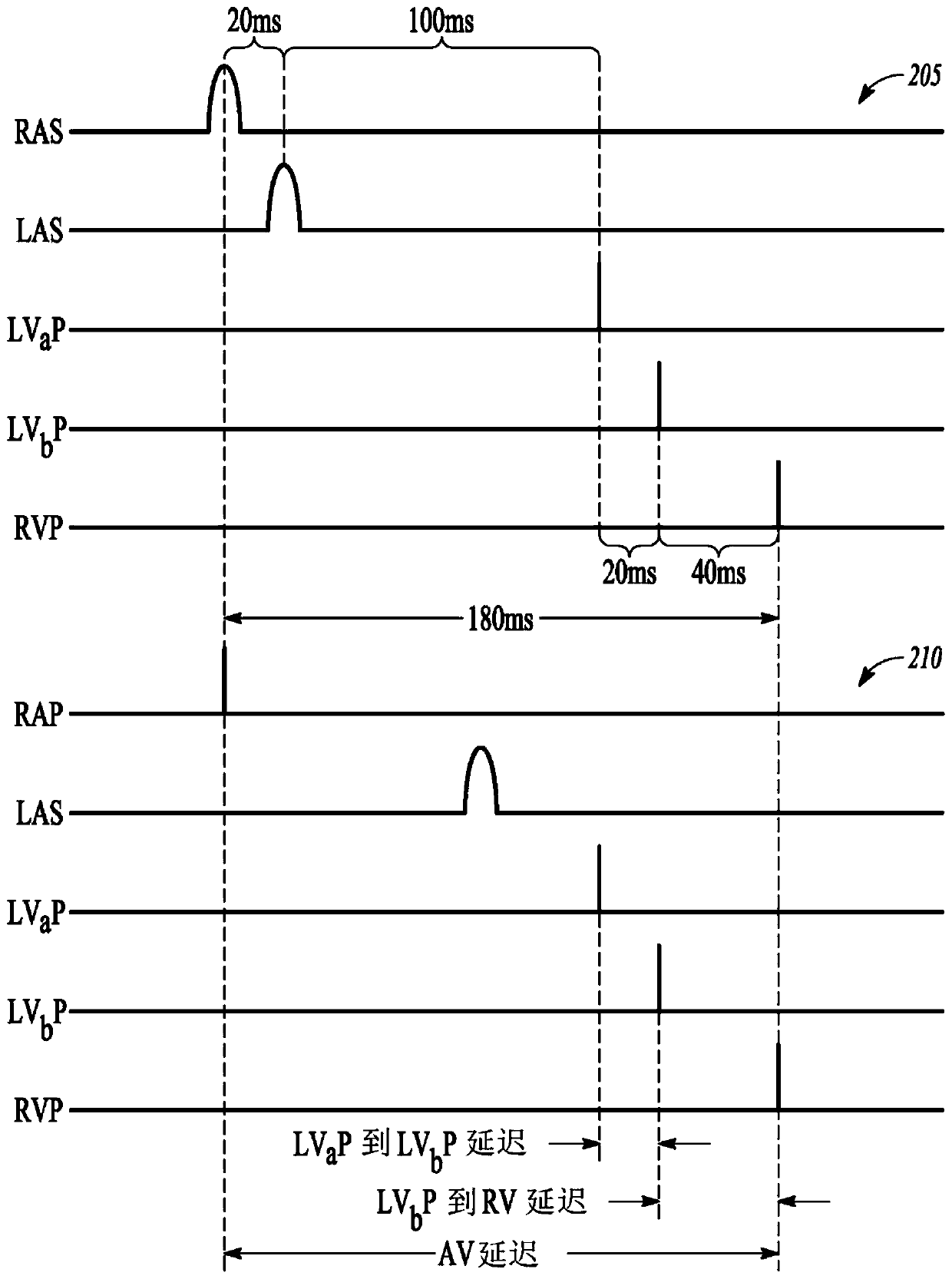
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Fusion pacing enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
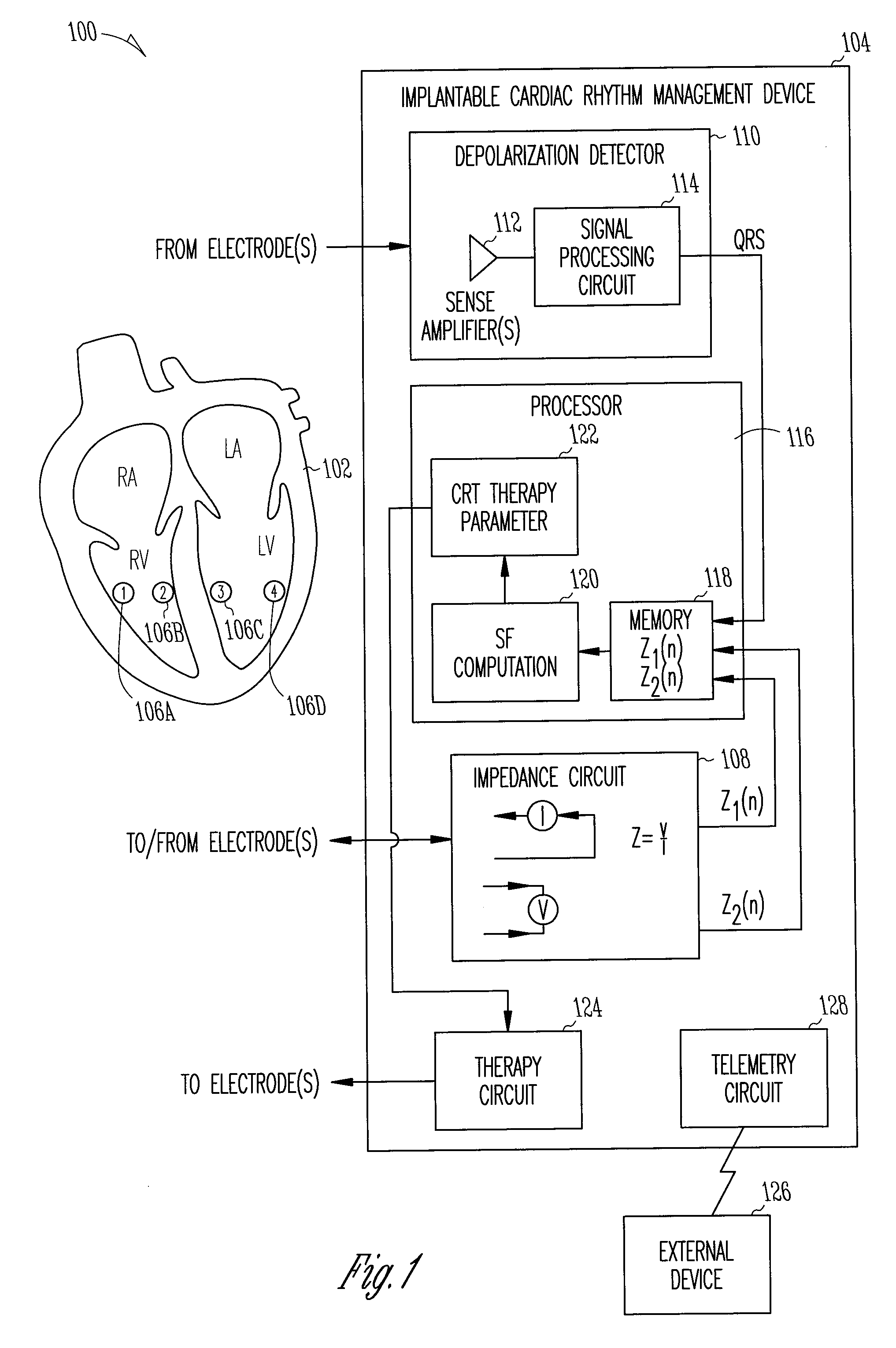
Closed loop impedance-based cardiac resynchronization therapy systems, devices, and methods
ActiveUS20080114410A1Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringLeft cardiac chamberVentricular volume
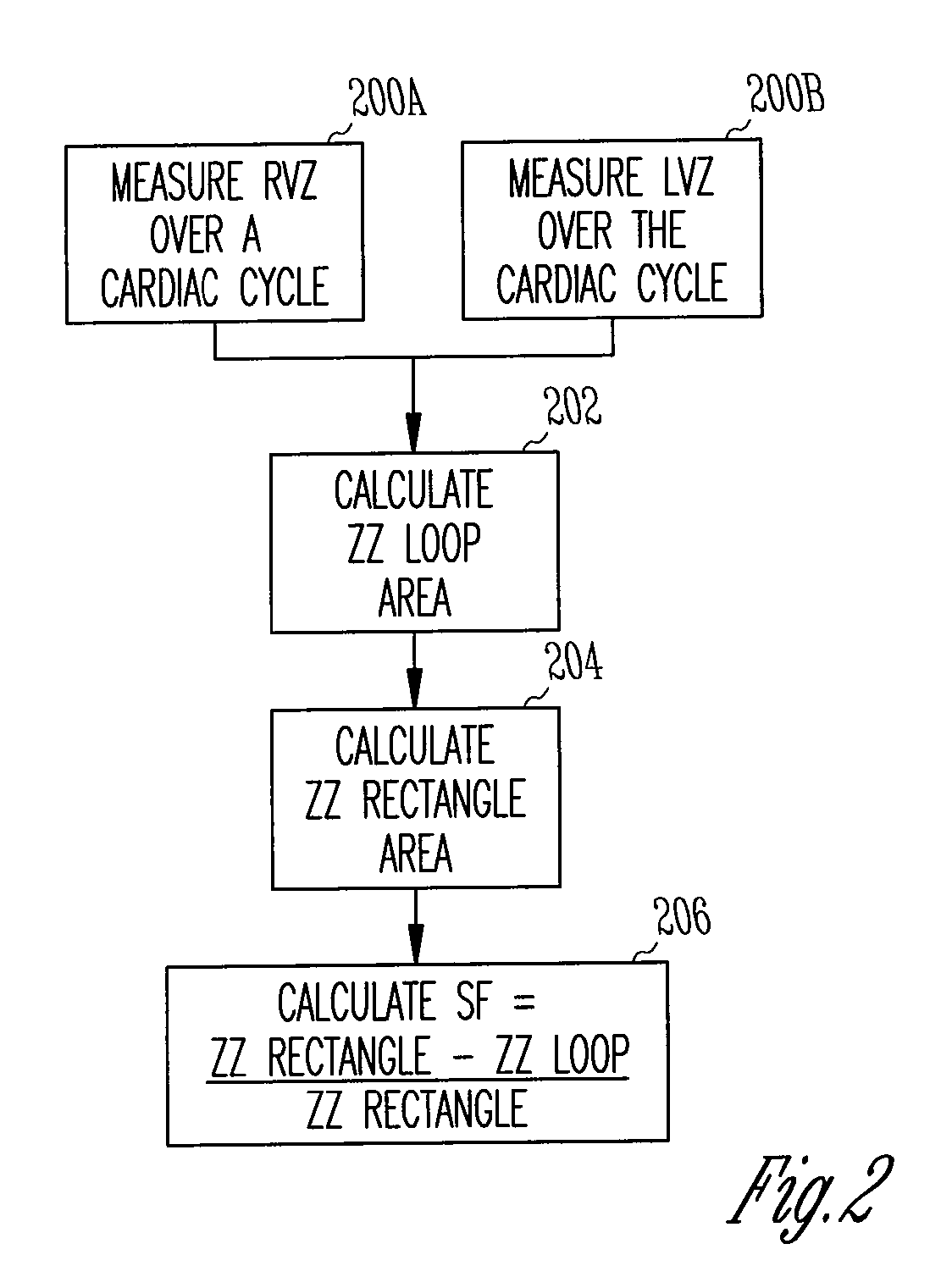
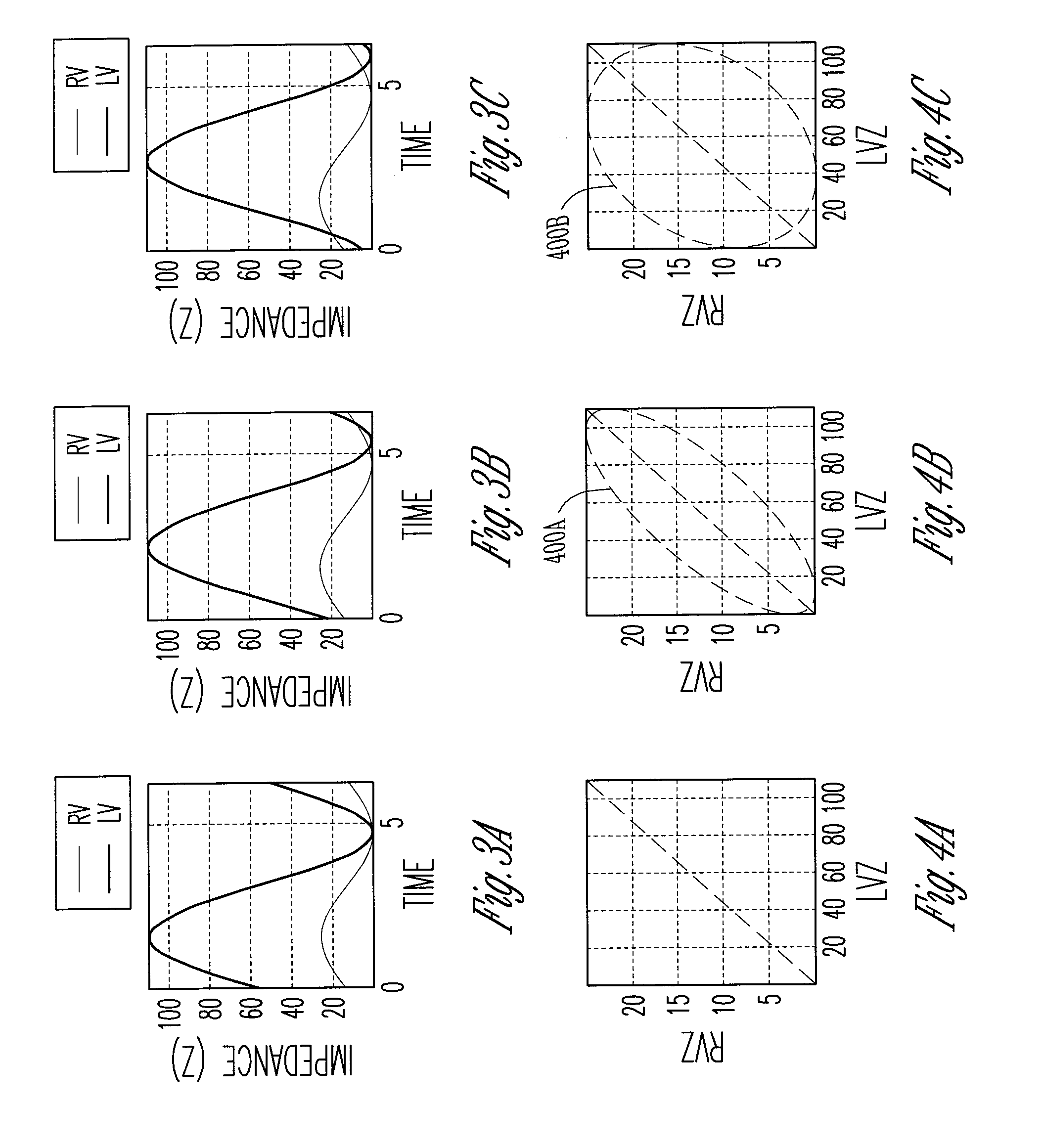
This document discusses, among other things, systems, devices, and methods measure an impedance and, in response, adjust an atrioventricular (AV) delay or other cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) parameter that synchronizes left and right ventricular contractions. A first example uses parameterizes a first ventricular volume against a second ventricular volume during a cardiac cycle, using a loop area to create a synchronization fraction (SF). The CRT parameter is adjusted in closed-loop fashion to increase the SF. A second example measures a septal-freewall phase difference (PD), and adjusts a CRT parameter to decrease the PD. A third example measures a peak-to-peak volume or maximum rate of change in ventricular volume, and adjusts a CRT parameter to increase the peak-to-peak volume or maximum rate of change in the ventricular volume.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and methods for automatic adjustment of av interval to ensure delivery of cardiac resynchronization therapy
Methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles) and delivering fusion pacing using a decremented value of the intrinsic PR interval.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medicine composition application for preparing hypertension medicine
An application of an invented medicinal composition in preparing the medicines for treating primary hypertension and protecting heart and kidney is disclosed.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Biodegradable microcapsulated ultrasonic contrast medium and its prepn process
InactiveCN1398640AIncrease contrastPlay the effect of contrast-enhanced ultrasoundNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryLeft cardiac chamberUltrasound contrast media
The biodegradable microcapsulated ultrasonic contrast medium is a hollow microcapsule with size of 1-10 microns and wall thickness of 50-6000 nm. The preparation process includes the steps of: dissolving biodegradable fatty polylactone with organic solvent to compound solution A; adding emulsifier into distilled water to compound solution B; injecting solution B into solution A via supersonic emulsifying; adding the emulsion into water solution of stabilizer via stirring; stirring for 2-10 hr to separate microcapsules particle and washing with distilled water; and freeze drying the particle to obtain powdered biodegradable microcapsule. Via intravenous injection or intravenous dripping, the present invention may be made to enter myocardial microcirculation via left cardiac chamber and coronary artery for supersonic radiographic examination.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
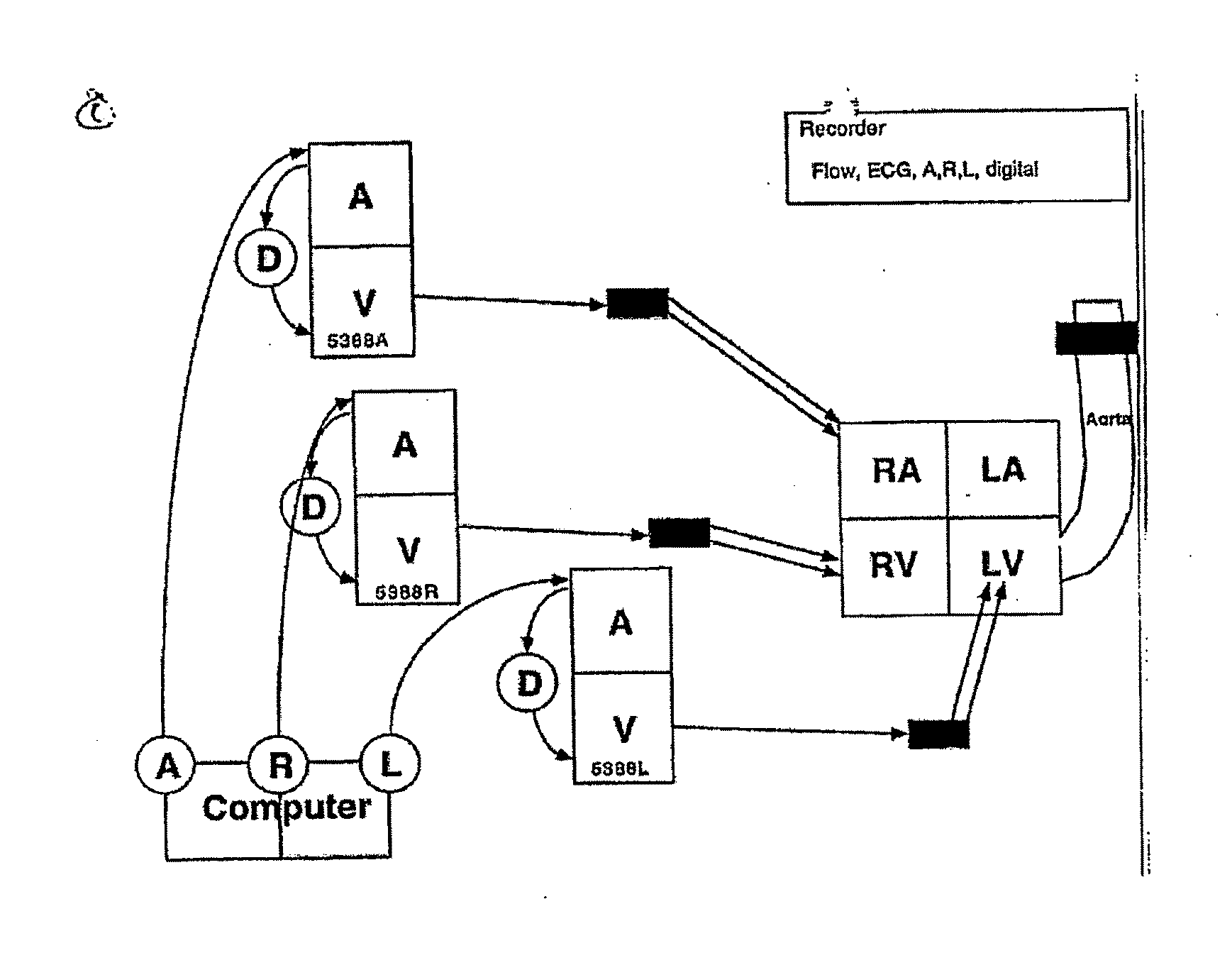
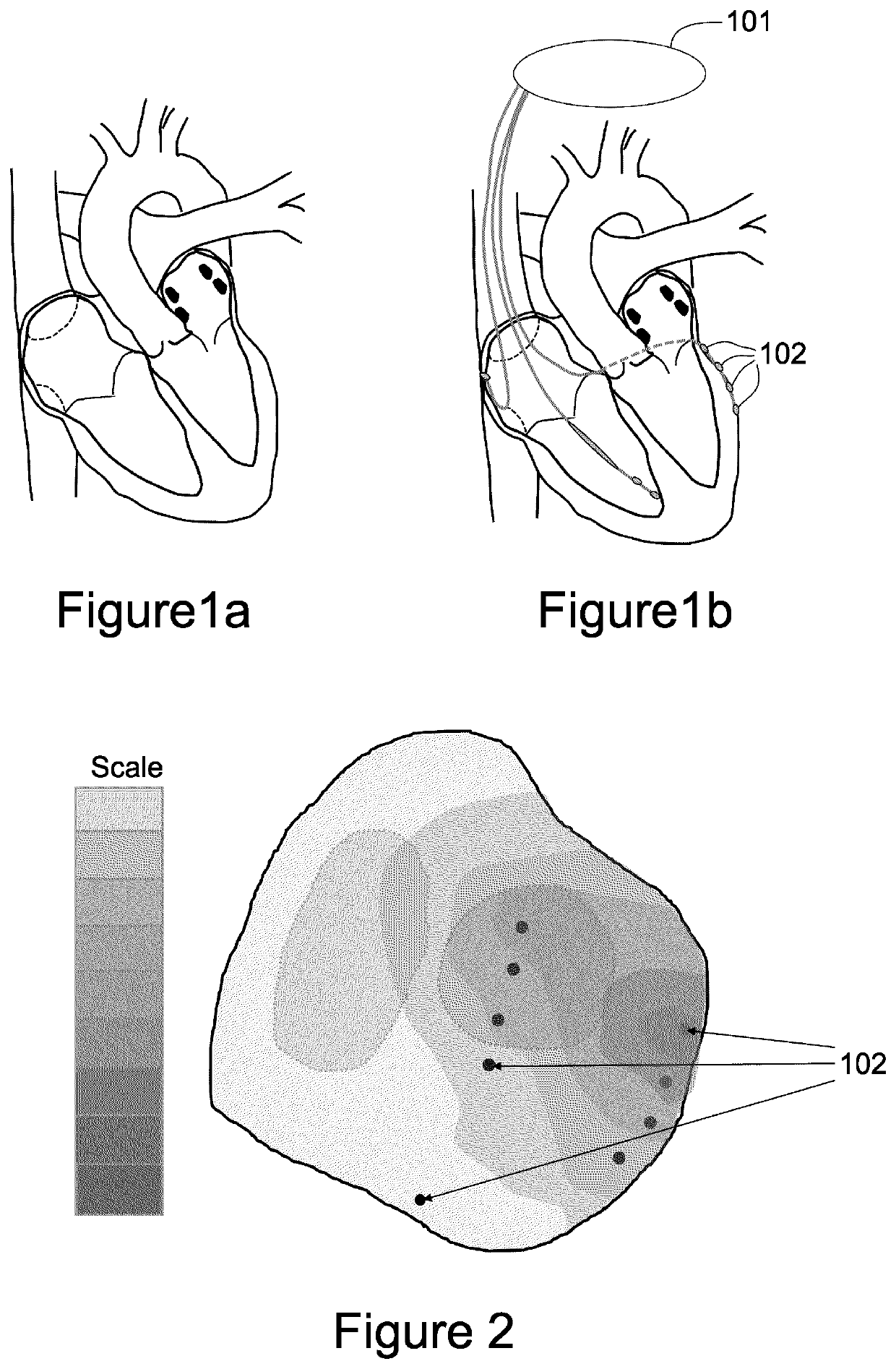
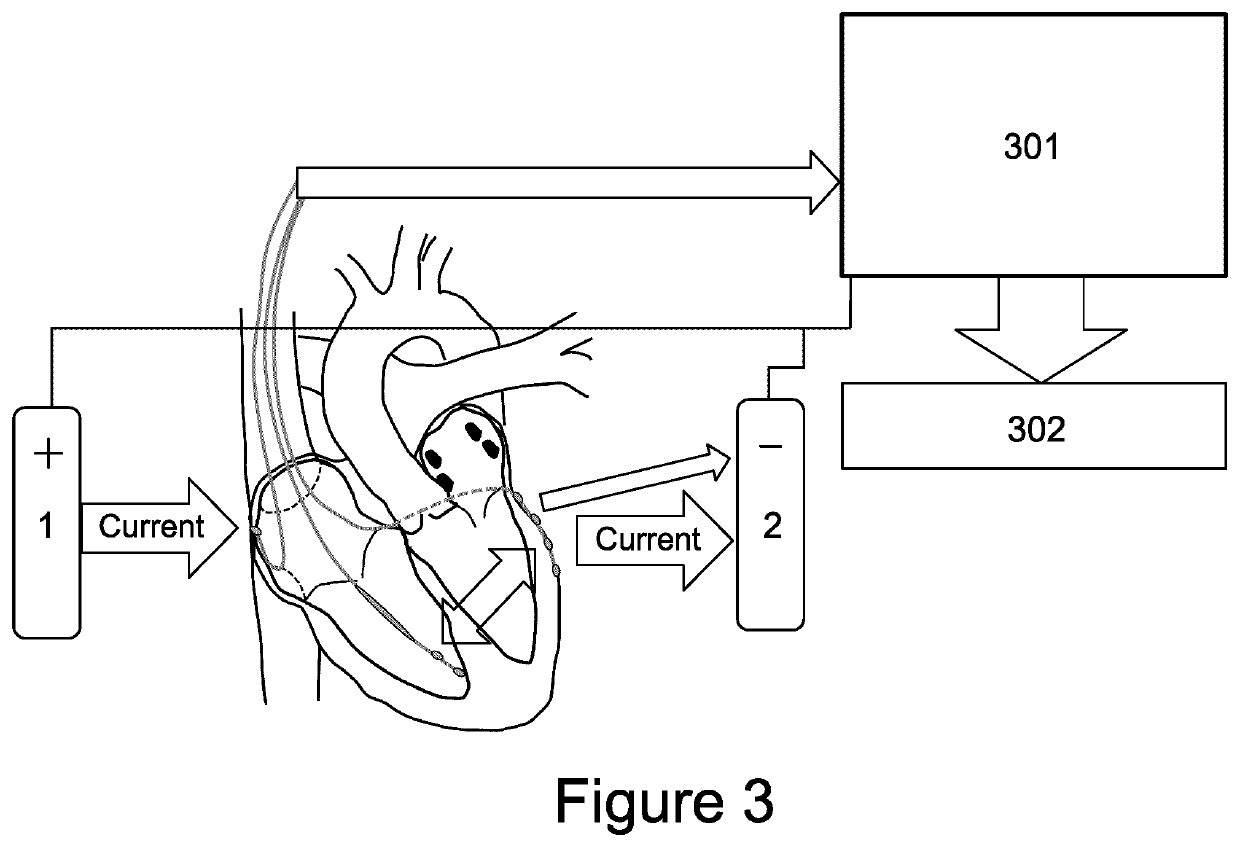
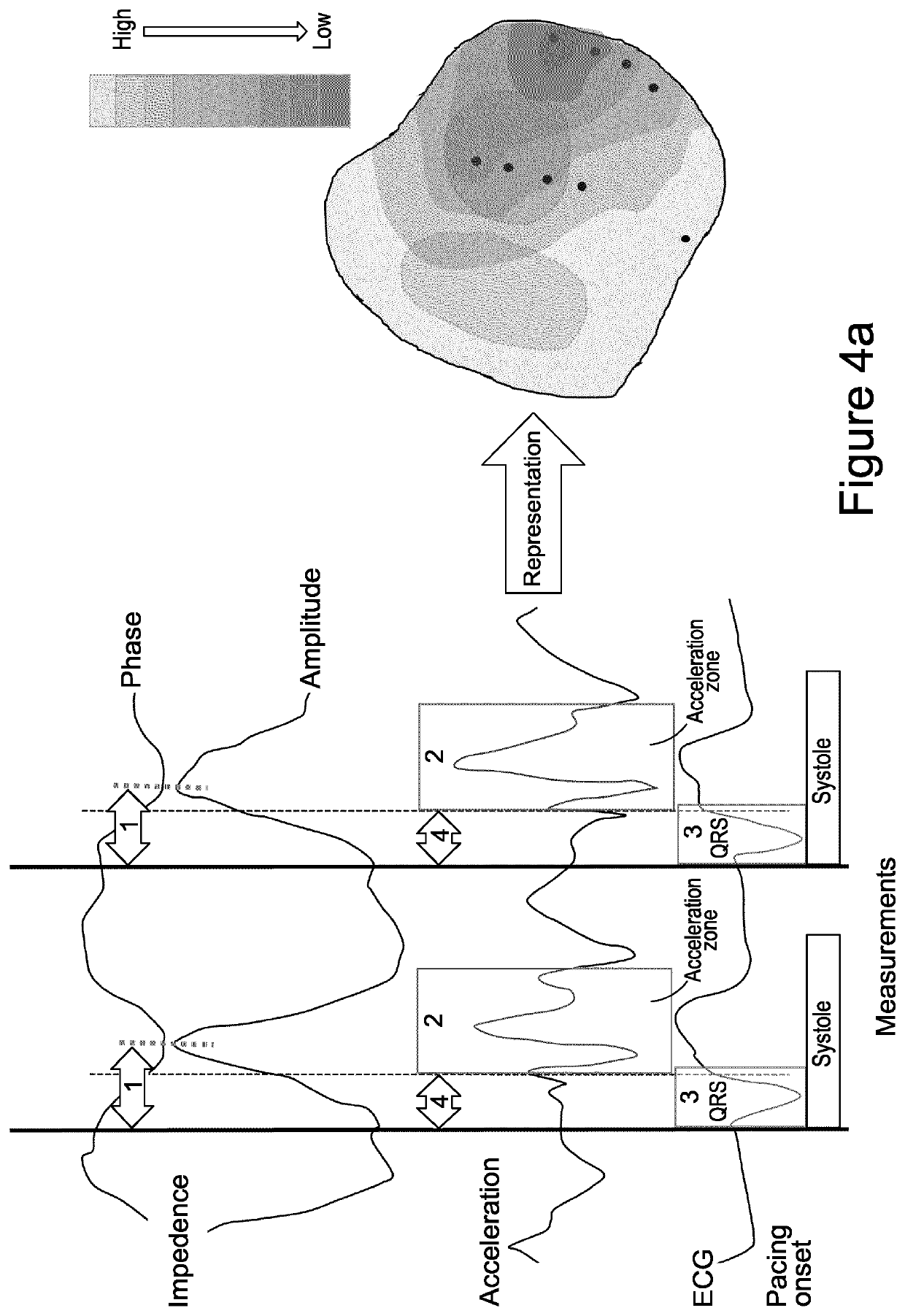
Methods for optimization of biventricular pacing devices and systems useful therefor
The invention is directed to methods and devices for optimization of biventricular pacing in subjects suffering from heart failure. The invention provides for a method for selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing, the method comprising: positioning one or more arrays of lead wires in the posterior pericardium of a subject, wherein the arrays are connected to a multiplexing switch, wherein the switch is connected to a computer processor and a biventricular pacemaker; from the computer processor, generating a randomized sequence of: (i) pacing sites (VPS), (ii) right ventricular-left ventricular delays (RLDs), (iii) heart rates (HR); (iv) atrioventricular delays (AVDs), (v) or any combination or permutation thereof; and determining cardiac output in real time, using aortic flow velocity, thereby allowing selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
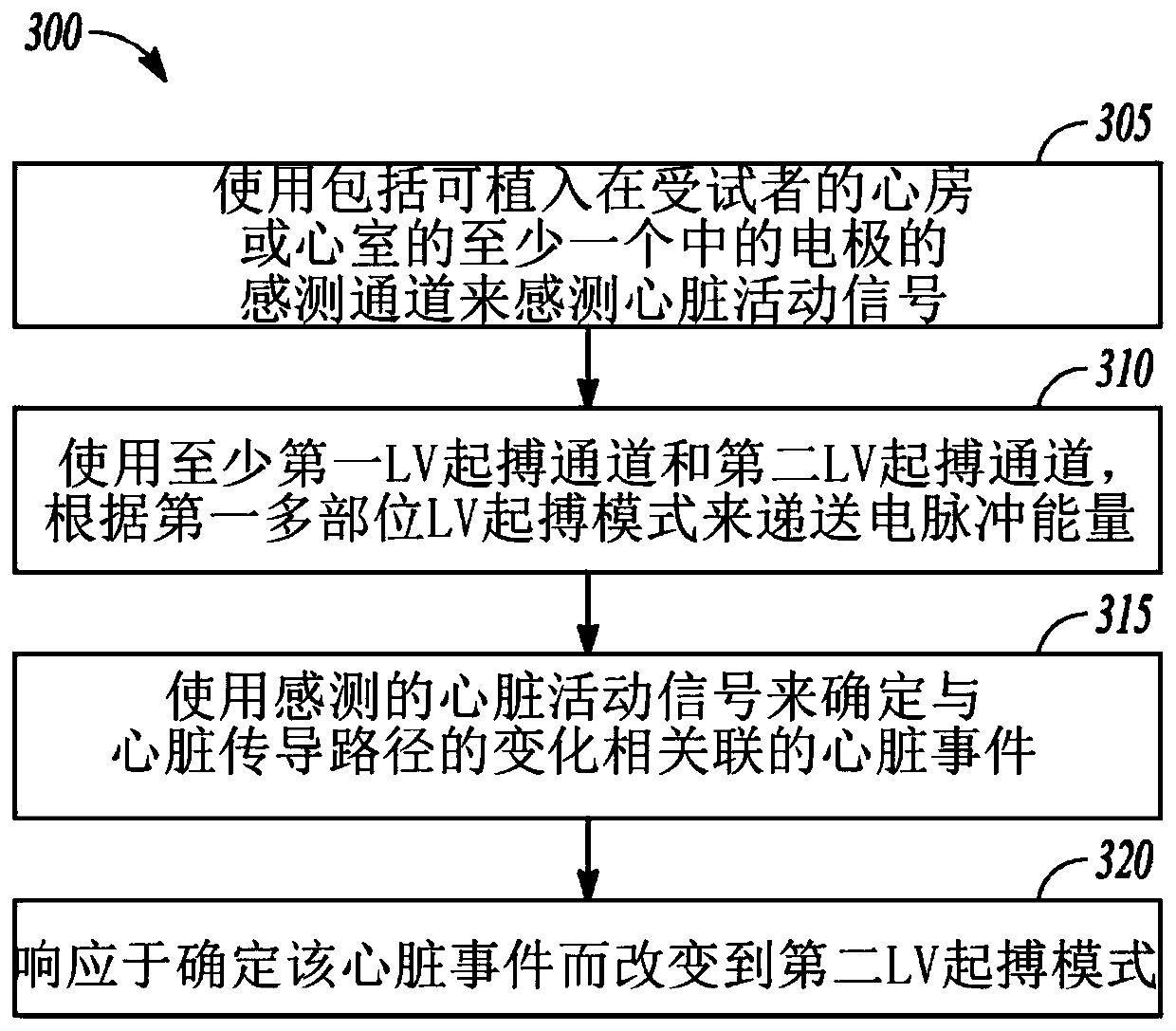
Conduction pathway driven multi-site pacing apparatus
PendingCN109952127ATransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberConduction pathway
An apparatus comprises a stimulus circuit, a cardiac signal sensing circuit, and a control circuit. The cardiac signal sensing circuit senses a cardiac activity signal using a sensing channel. The stimulus circuit provides electrical pulse energy to a first pacing channel that includes a first left ventricular (LV) electrode and a second pacing channel that includes a second LV electrode. The control circuit initiates delivery of electrical pulse energy using the first and second pacing channels according to a first multi-site LV pacing mode; determines a cardiac event associated with a changein cardiac conduction path using a sensed cardiac activity signal; and changes to a second LV pacing mode in response to determining the cardiac event. The second LV pacing mode is different from thefirst multi-site LV pacing mode in one or more of a pacing site location and inter-electrode stimulus timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
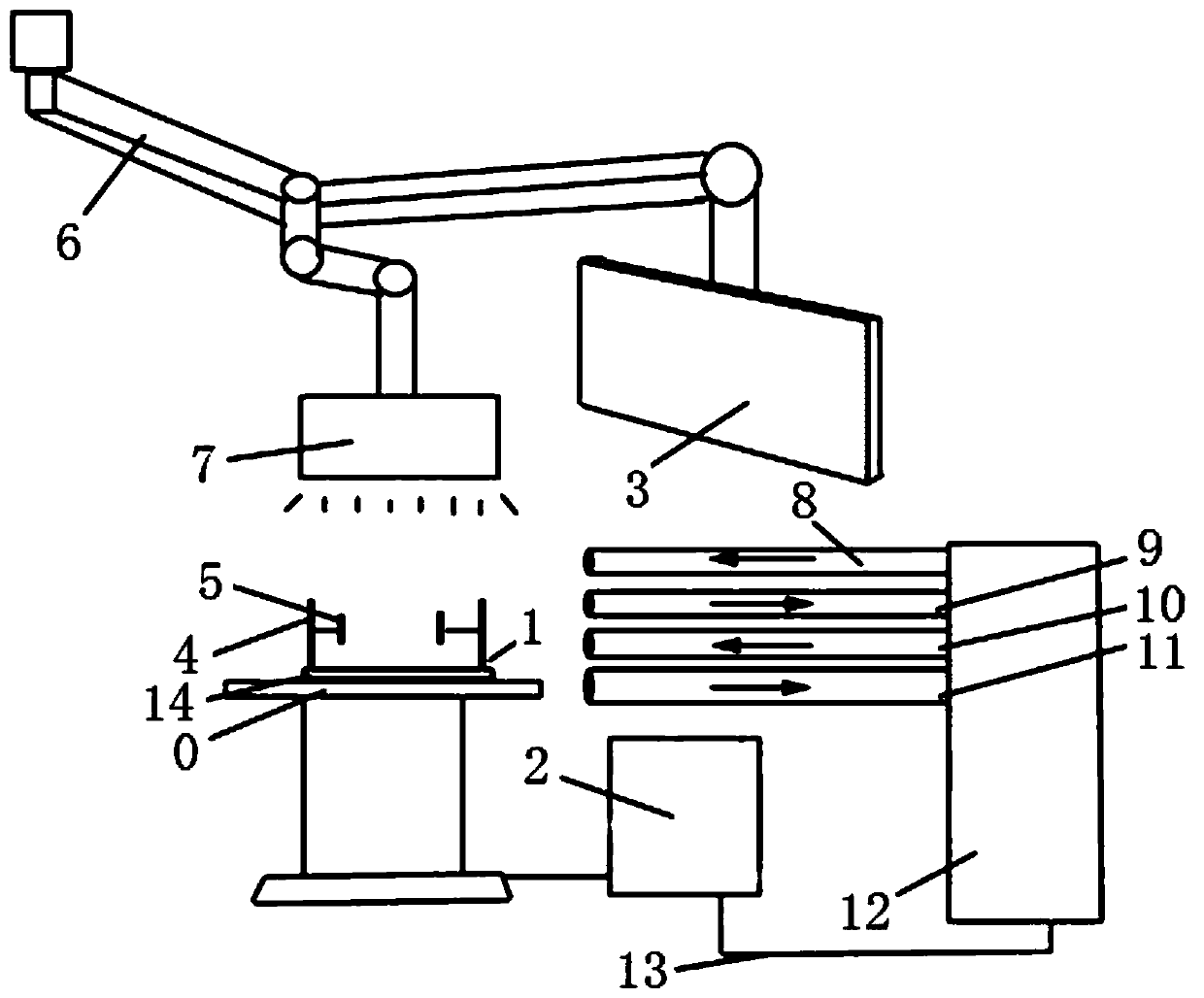
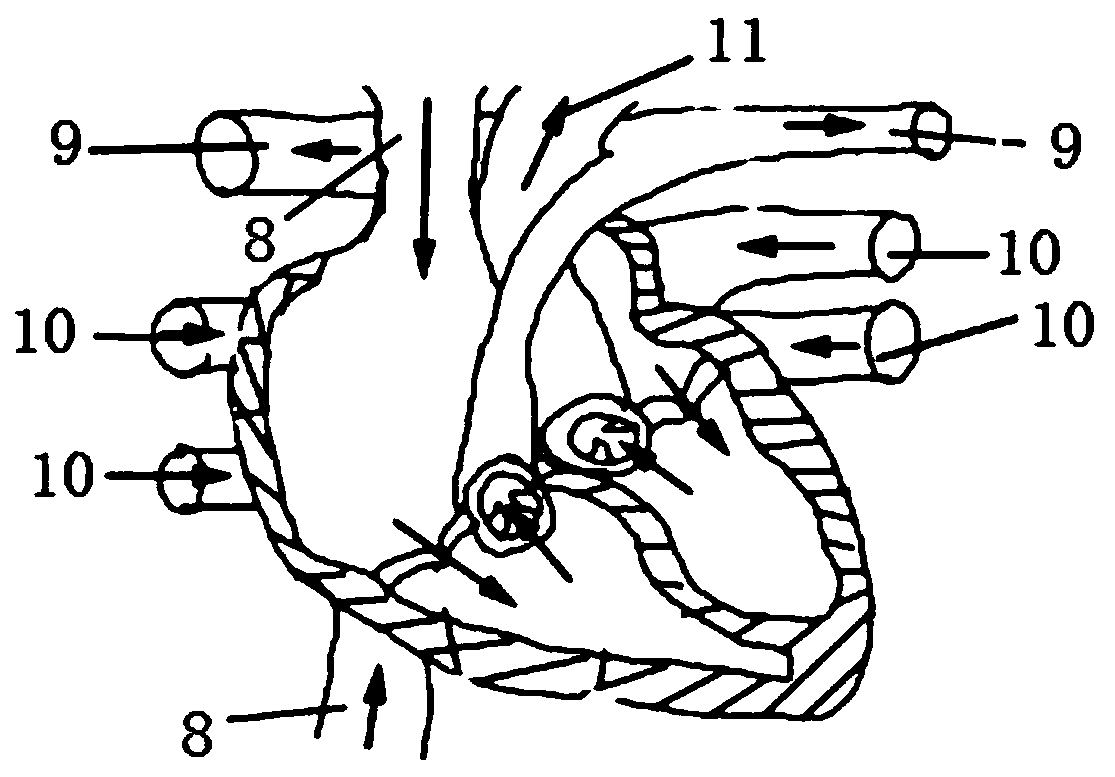
Assisted teaching device for cardiac interventional operation
InactiveCN110827642AAvoid radiation damageRealistic surgical practiceCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsExtracorporeal circulationLeft cardiac chamber
The invention discloses an assisted teaching device for a cardiac interventional operation. The device comprises a fixed device, a near infrared scanning device, an information processing device, a display device and an extracorporeal circulation device; the fixed device comprises a fixed bracket and a distance adjusting device; the near infrared scanning device comprises a tower crane, a near infrared laser emitter and a near infrared laser receiver, and a motor is arranged in the tower crane; the information processing device is used for processing and converting scanning information into aDSA image; the display device is used for displaying and simulating the DSA image; and the extracorporeal circulation device comprises an atrium dextrum catheter, a ventriculus dexter catheter, an atrium sinistrum catheter, a ventriculus sinister and a pump. By utilizing the imaging of the near infrared light, the DSA imaging can be simulated through computer software synthesis, thereby avoiding unnecessary radiation damage of an exerciser in the operation exercise process; and the human body cardiac blood flow process can be simulated by utilizing the extracorporeal circulation device, so that the operation exercise becomes more realistic, and the teaching quality and level are improved.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Methods for optimization of biventricular pacing devices and systems useful therefor
ActiveUS20110264159A1Increase cardiac outputGood effectHeart stimulatorsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
The invention is directed to methods and devices for optimization of biventricular pacing in subjects suffering from heart failure. The invention provides for a method for selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing, the method comprising: positioning one or more arrays of lead wires in the posterior pericardium of a subject, wherein the arrays are connected to a multiplexing switch, wherein the switch is connected to a computer processor and a biventricular pacemaker, from the computer processor, generating a randomized sequence of: (i) pacing sites (VPS), (ii) right ventricular-left ventricular delays (RLDs), (iii) heart rates (HR); (iv) atrioventricular delays (AVDs), (v) or any combination or permutation thereof; and determining cardiac output in real time, using aortic flow velocity, thereby allowing selection of optimal parameters for permanent pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
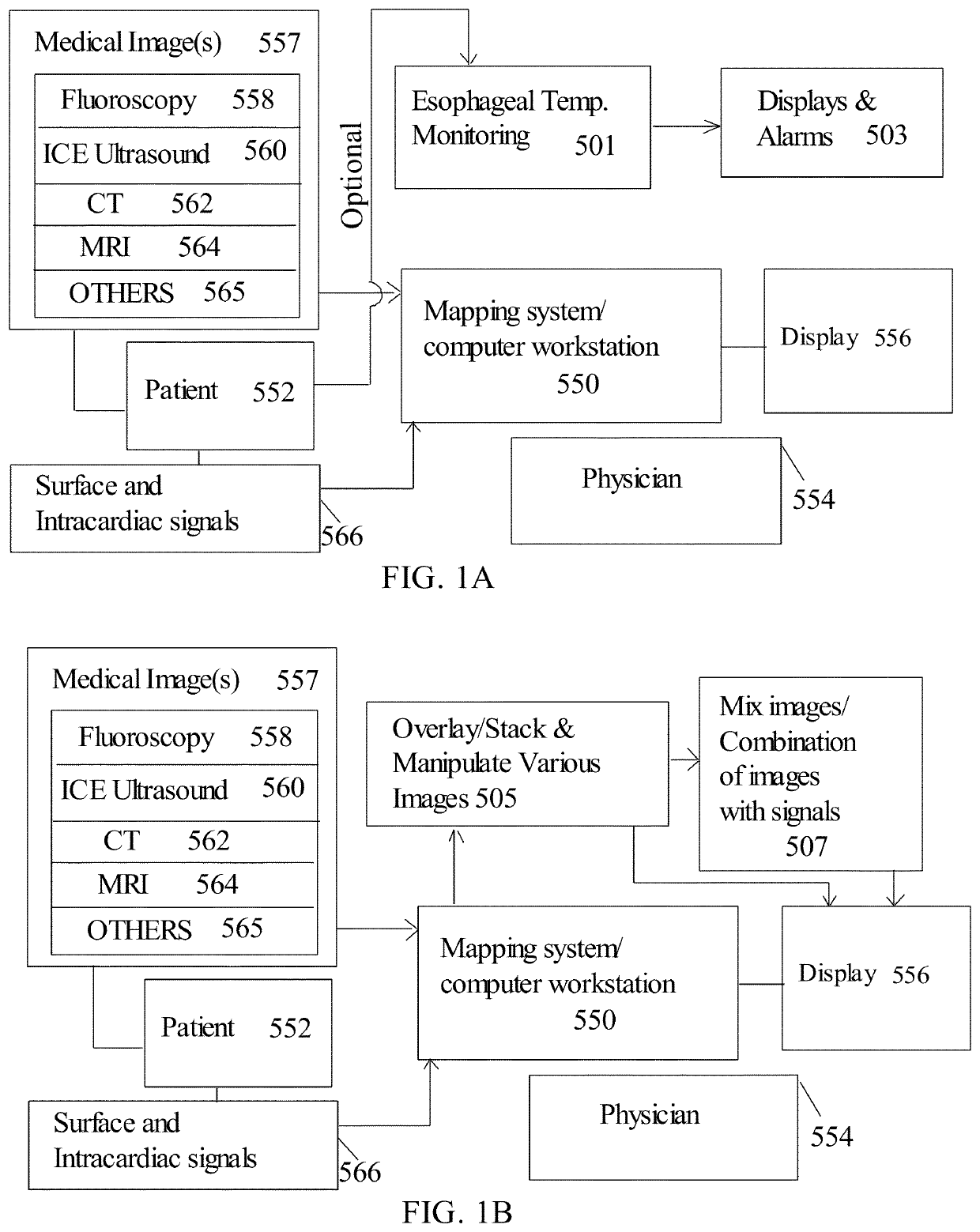
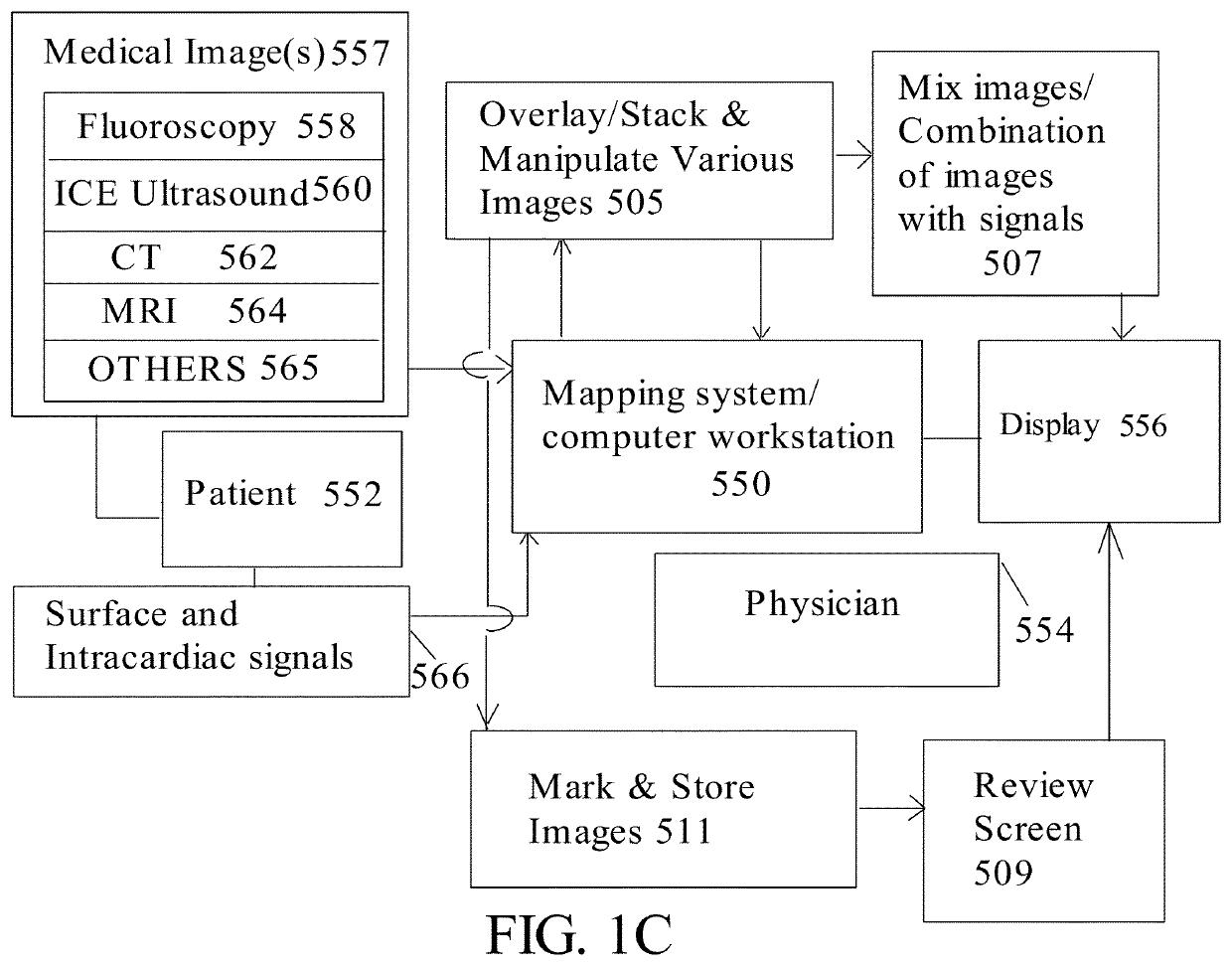
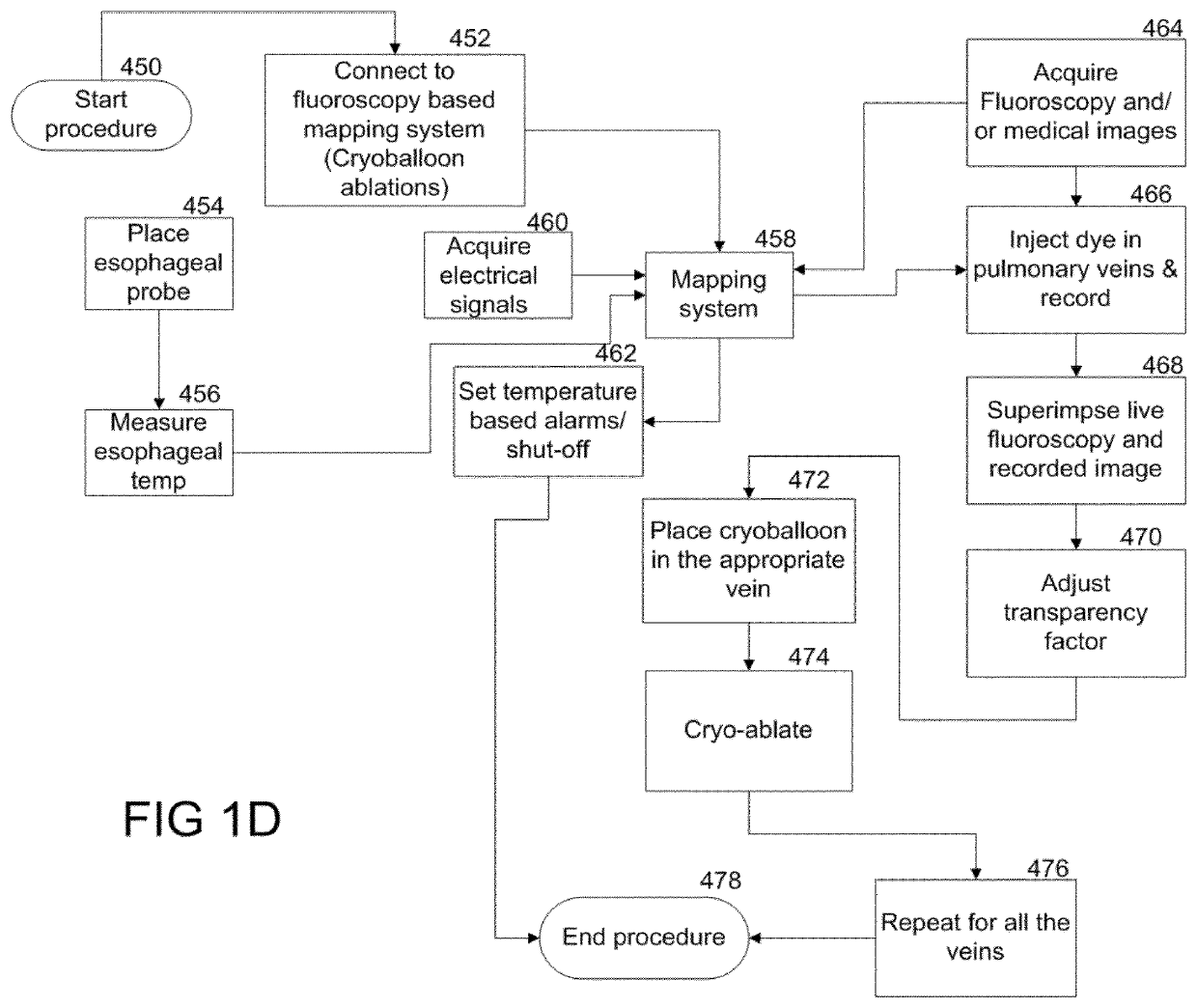
Methods and system for cardiac mapping for atrial fibrillation using balloon based catheters utilizing medical images (CT or MRI in segments) and left ventricular lead placement for cardiac re-synchronization therapy (CRT)
ActiveUS11206984B1Accurate placementImage analysisSurgical instrument detailsLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
Methods and system for atrial fibrillation mapping utilizing cardiac mapping based on medical image(s). The methods and system also adapted for any balloon based catheters including cryoballoon catheter, laser balloon catheter, or “hot balloon” catheter, as well as circular catheters. The methods and system includes overlaying of two or more images on top of each other (where the images are of various types or modalities) and aligning the images, where the transparency between the images can be adjusted for navigating and optimal placement of the balloon based catheters or circular catheters. The cardiac system also adopted for guiding optimal placement of the left ventricular (LV) lead placement for cardiac re-synchronization (CRT) therapy, and for mapping and displaying activation times from various branches of the coronary sinus for optimizing CRT therapy.
Owner:AMERICAN MEDICAL TECH LLC
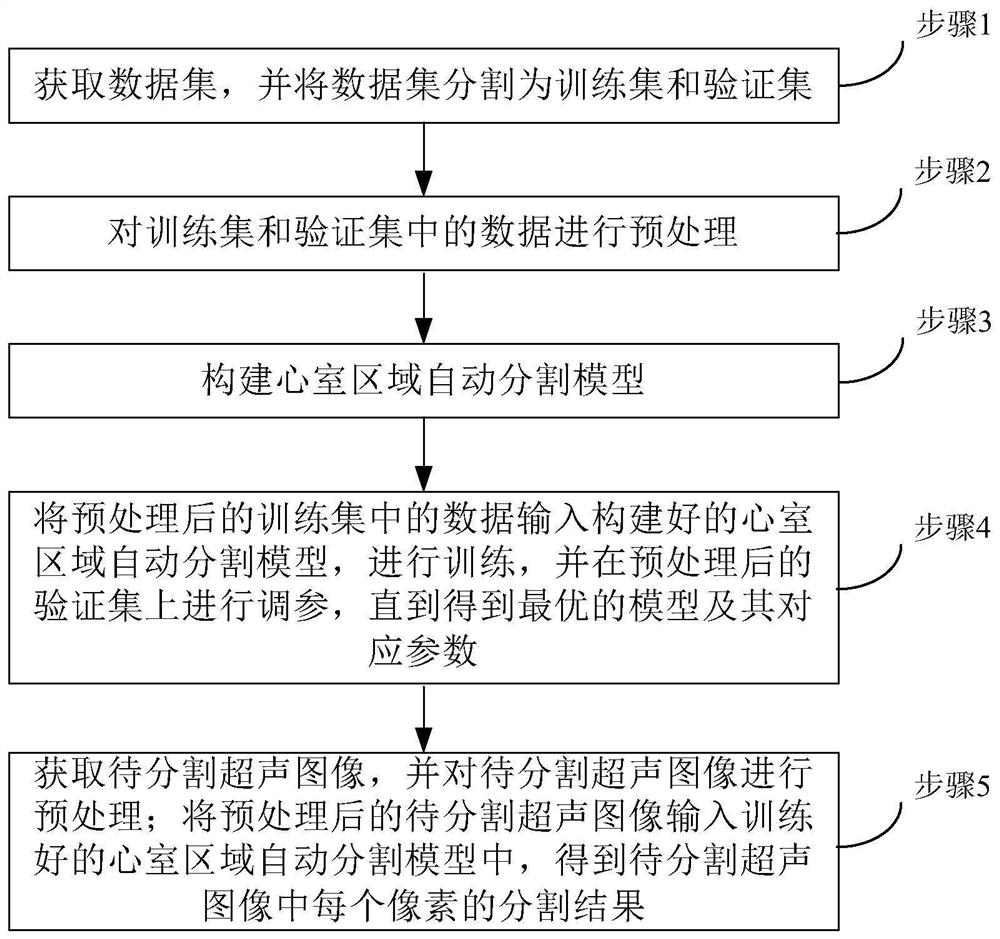
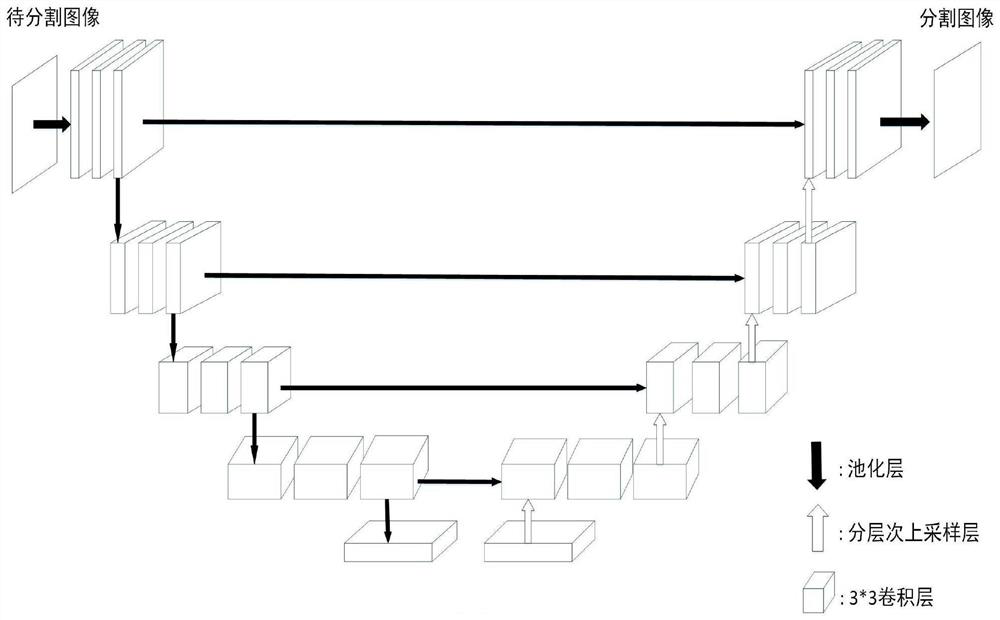
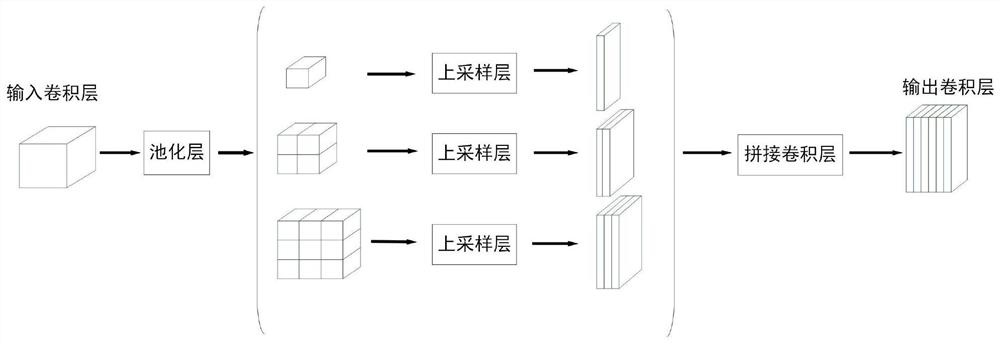
Automatic ventricular region segmentation method and device of cardiac ultrasound image and storage medium
PendingCN111915626AIncrease training speedImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
The invention provides an automatic ventricular region segmentation method and device for a cardiac ultrasound image and a storage medium, and relates to the technical field of image processing. According to the method, a ventricular region automatic segmentation model is utilized to obtain a segmentation result of each pixel in a to-be-segmented ultrasonic image. According to the ventricular region automatic segmentation model, compared with a traditional UNet method, the network structure of the model is improved, an up-sampling deconvolution layer of a decoder of the model is a multi-dimensional splicing type deconvolution up-sampling layer, the decoder can better obtain image information from multiple dimensions, and then the segmentation accuracy is improved. According to the automatic ventricular region segmentation model, the model training speed and accuracy can be effectively improved, and then the speed and accuracy of automatically segmenting the left ventricular region in the echocardiogram are improved.
Owner:东软教育科技集团有限公司
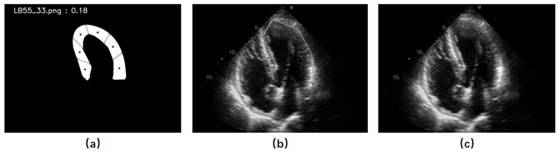
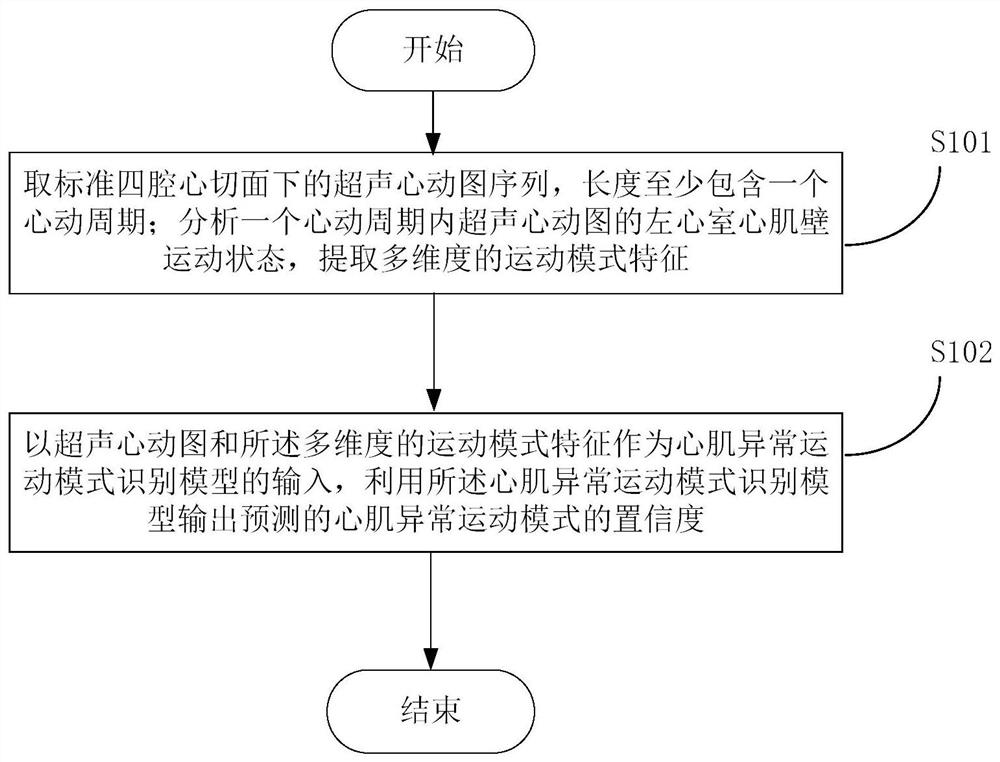
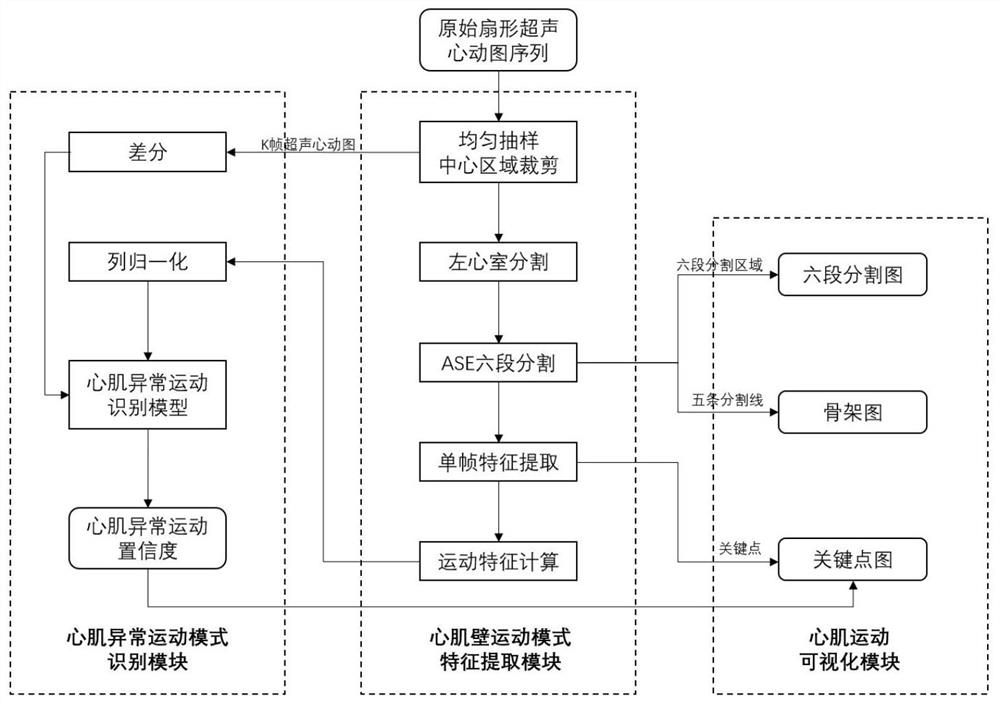
Ultrasonocardiogram myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis method and system, and storage medium
PendingCN112258476AThe recognition result is accurateFeatures fully reflectImage enhancementImage analysisLeft cardiac chamberImaging processing
The invention provides an ultrasonic cardiogram myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis method and system and a storage medium and relates to the technical field of medical image processing. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring an echocardiogram sequence under a standard four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, wherein the length at least comprises one cardiac cycle; analyzing the leftventricular myocardial wall motion state of the echocardiogram in one cardiac cycle, and extracting multi-dimensional motion mode characteristics; and taking the echocardiogram sequence and the motion mode characteristics as the input of a myocardial abnormal motion mode identification model, and outputting the predicted confidence coefficient of the myocardial abnormal motion mode by using the myocardial abnormal motion mode identification model. According to the method, by extracting the motion mode characteristics in the echocardiogram sequence in one cardiac cycle, the time sequence information and the local motion information in the echocardiogram are fully mined, so accurate myocardial abnormal motion mode analysis can be automatically carried out according to the characteristics, and the prediction result is returned.
Owner:东软教育科技集团有限公司
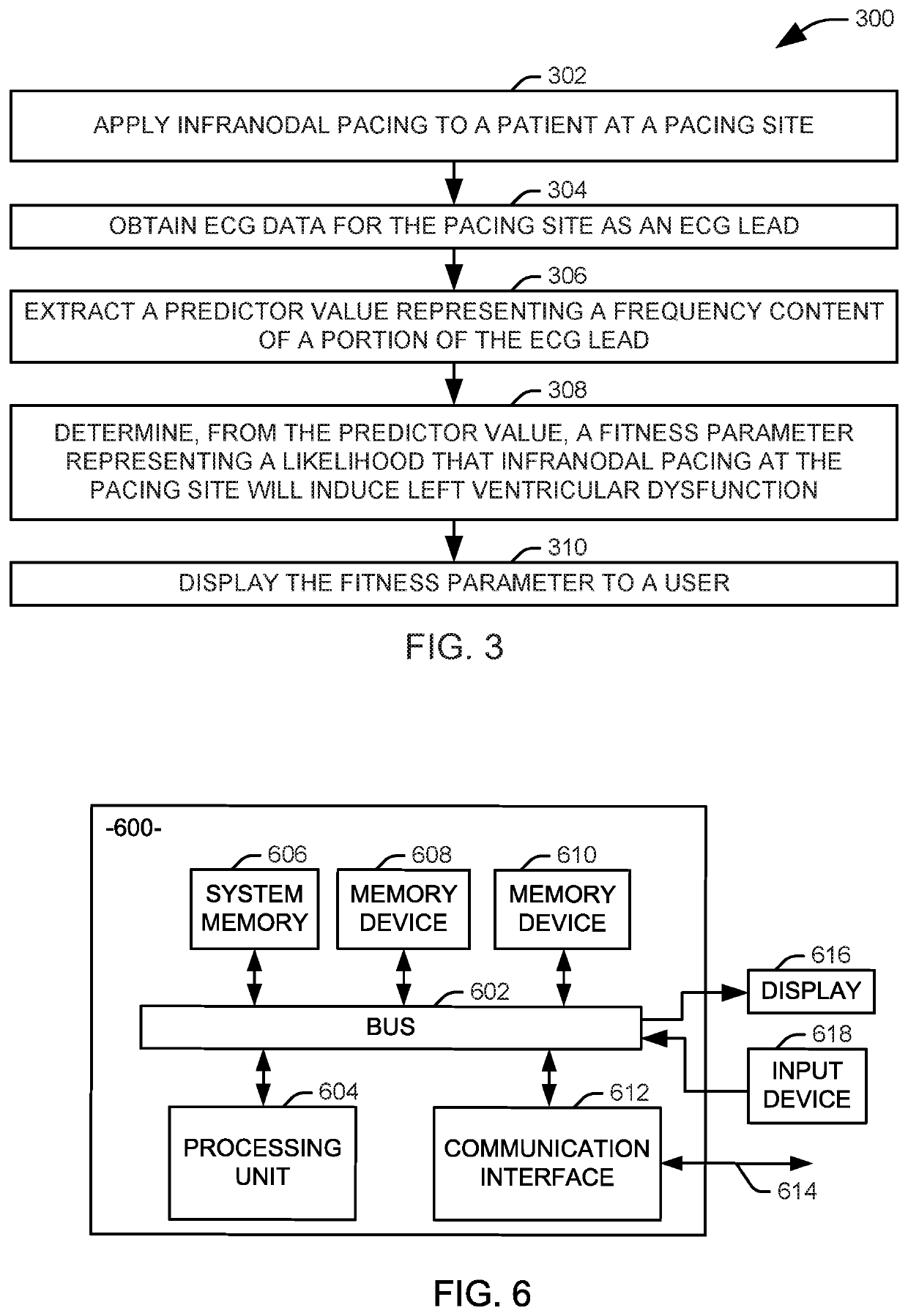
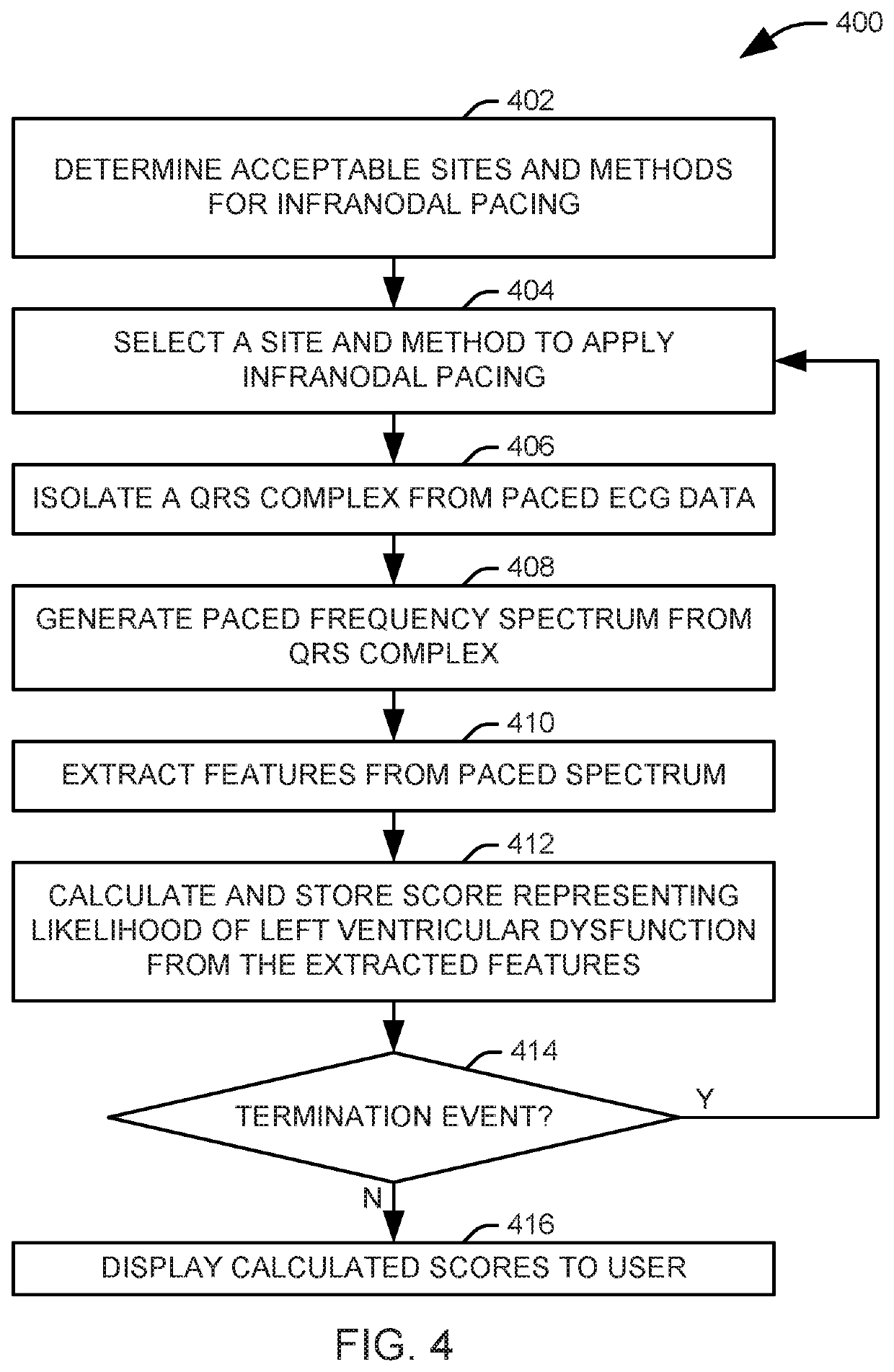
Frequency analysis for predicting left ventricular dysfunction
Systems and methods are provided for evaluating infranodal pacing is applied to a patient. Electrocardiogram (ECG) data representing the pacing is obtained from a set of electrodes as an ECG lead. A predictor value representing a frequency content a portion of the ECG lead is extracted. A fitness parameter is determined for the pacing from at least the predictor value. The fitness parameter represents a likelihood that the applied infranodal pacing will induce left ventricular dysfunction in the patient. The fitness parameter is displayed to a user at an associated display.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Systems and methods for enhanced diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis
ActiveUS11259767B2Accurate diagnosisEasy diagnosisHealth-index calculationRadioactive preparation carriersLeft cardiac chamberAnatomical structures
Systems and methods for enhanced diagnosis of transthyretin-related cardiac amyloidosis in a subject are disclosed. The systems and methods may use both SPECT imaging data as well as an anatomical imaging data, such as computed tomography (CT) data, to produce a combined image. Within the combined image, the radiotracer uptake between two volumes of interests are compared, one of which may represent the left ventricle of the subject and the other may represent the blood pool retention of the subject. Combining the anatomical imaging data with SPECT data enables better anatomical delineation and helps in avoiding areas with coronary or lymph node calcifications and overlying soft tissue and bony pathologies.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Implantable blood pumps comprising a linear bearing
ActiveUS20210275797A1Easy to driveReduce shear forceControl devicesMedical devicesLeft cardiac chamberMedicine
Systems and methods for generating blood flow with a pump incorporating linear bearing technology are provided. The pump may include an actuator assembly, a moving assembly, and a linear hydrodynamic or thin-film bearing positioned within a housing. The moving assembly may include at least one magnet and the actuator assembly may include a magnetic assembly for selectively generating a magnetic field to cause linear reciprocating movement of the moving assembly with respect to the actuator assembly. The linear hydrodynamic or thin-film bearing may include a bearing portion on the moving assembly that is in fluid communication with a bearing portion on the actuator assembly or pump housing. The system may involve an implantable pump, an extracorporeal battery and a controller coupled to the implantable pump. The implantable pump may be suitable for use as a left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
Owner:CORWAVE SA
Monitoring of his bundle pacing capture during ventricular pacing therapy
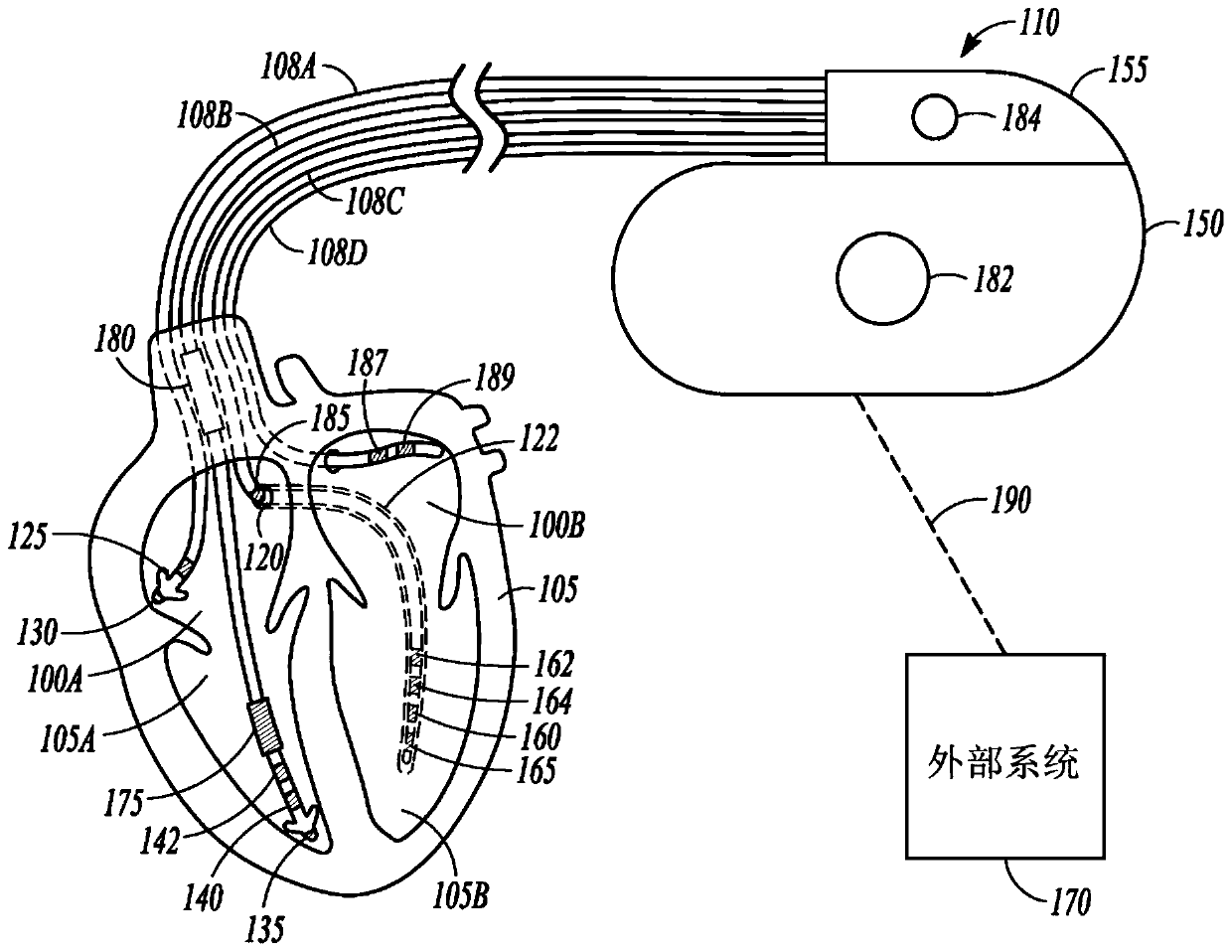
A method and system for delivering a cardiac pacing therapy that includes a cardiac signal being sensed via electrodes of an atrial lead, and an occurrence of one of an intrinsic and a paced atrial depolarization event of a current cardiac cycle being determined in response to the sensed cardiac signal. A first pacing therapy is delivered during the current cardiac cycle in response to the determined occurrence of the depolarization event, and an amplitude of the cardiac signal within the current cardiac cycle subsequent to the delivered first pacing therapy is compared to a predetermined amplitude threshold. A second pacing therapy is delivered, via a left ventricular lead, within the same cardiac cycle and subsequent to the delivered first pacing therapy in response to the amplitude notbeing more negative than the predetermined amplitude threshold and is not delivered in response to the amplitude being more negative than the predetermined amplitude threshold.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
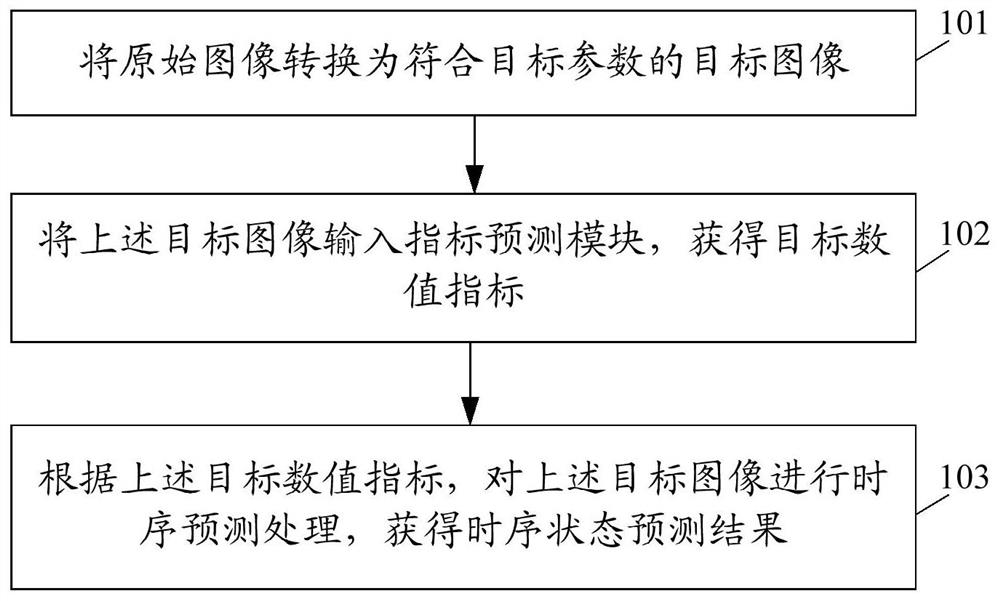
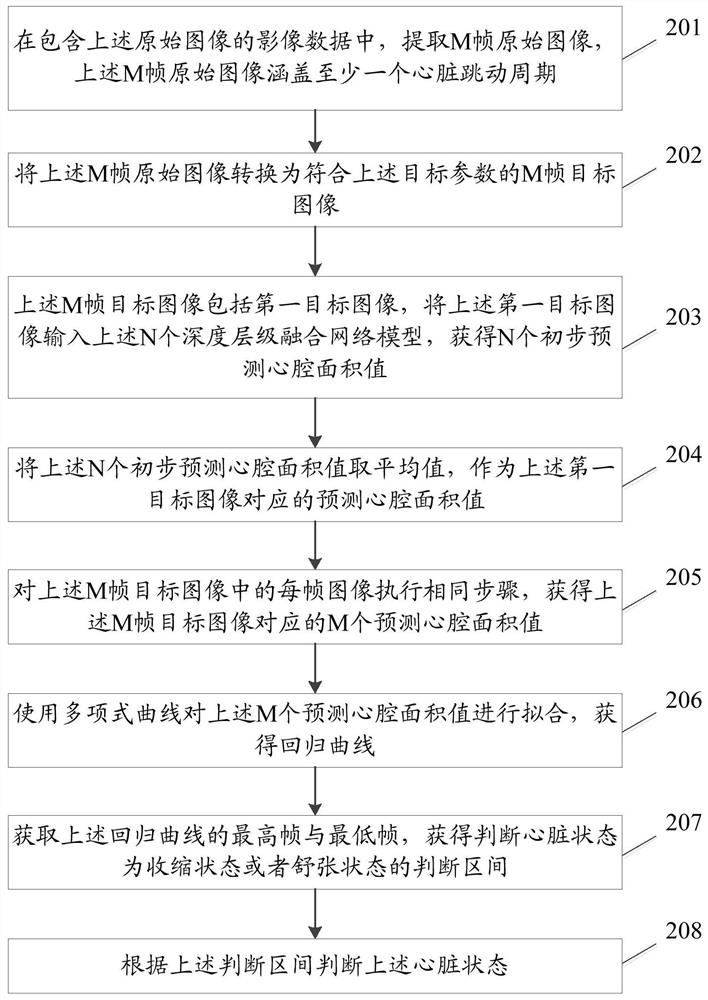
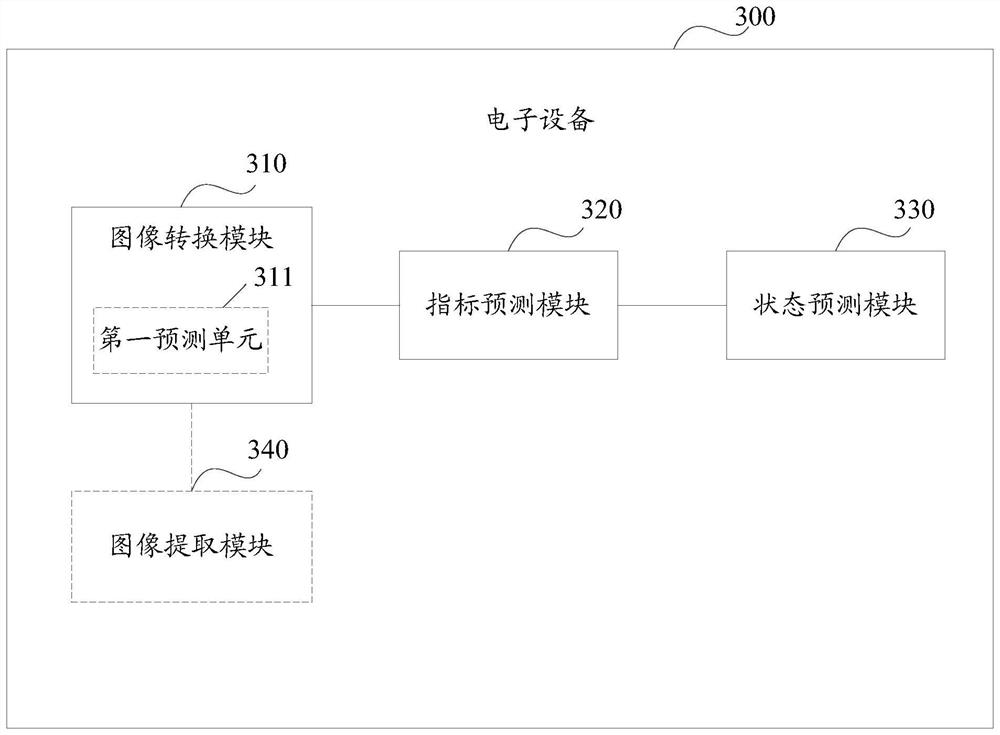
An image processing method, electronic device and storage medium
ActiveCN109003270BRealize functional quantificationImprove forecast accuracyImage enhancementMedical imagingLeft cardiac chamberImaging processing
The embodiment of the present application discloses an image processing method, electronic equipment and storage medium, wherein the method includes: converting the original image into a target image conforming to the target parameters; inputting the target image into the index prediction module to obtain the target numerical index; The target numerical index performs time-series prediction processing on the target image to obtain a time-series state prediction result, which can realize left ventricular function quantification, improve image processing efficiency, and improve the prediction accuracy of cardiac function indexes.
Owner:BEIJING SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
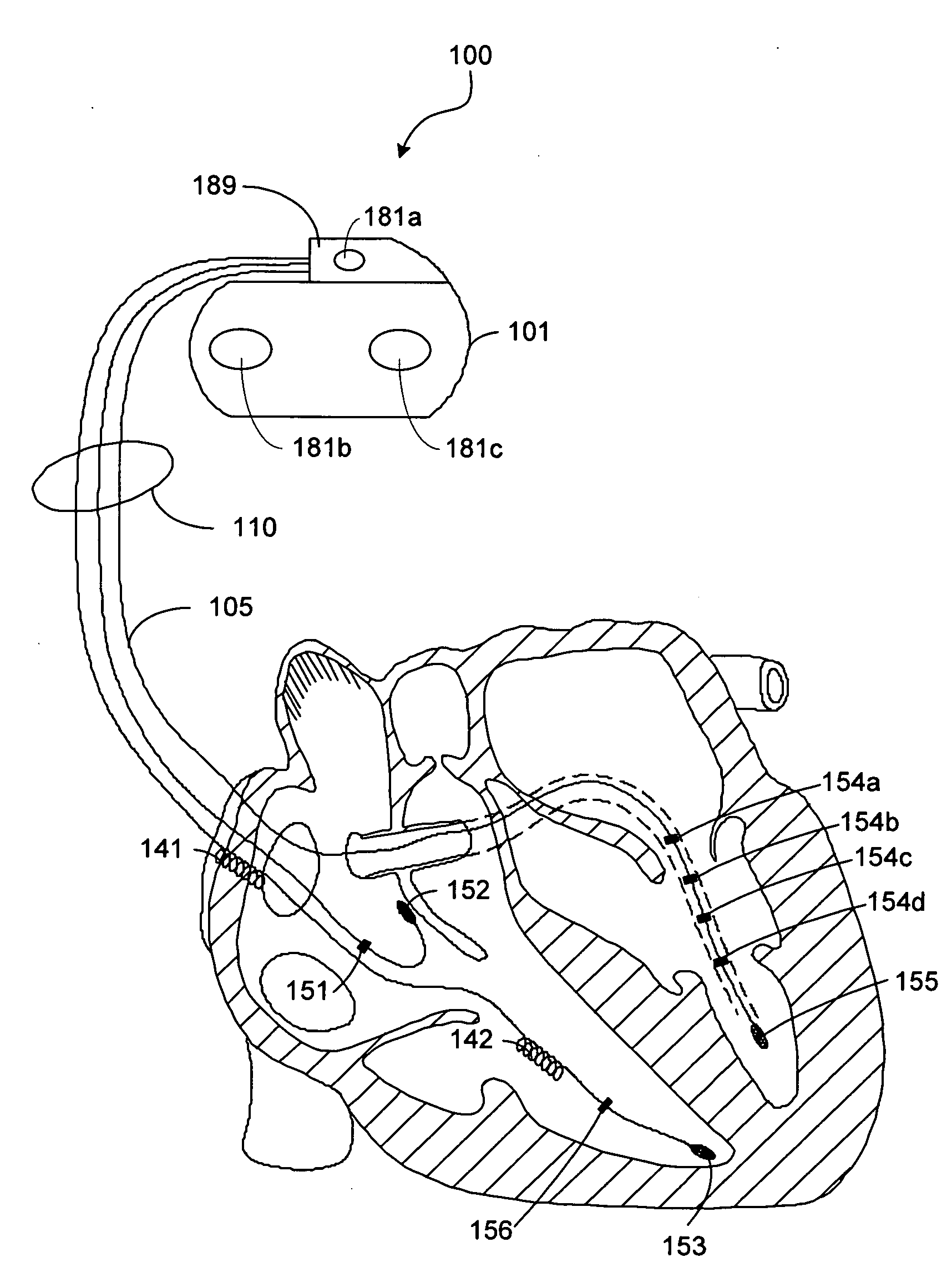
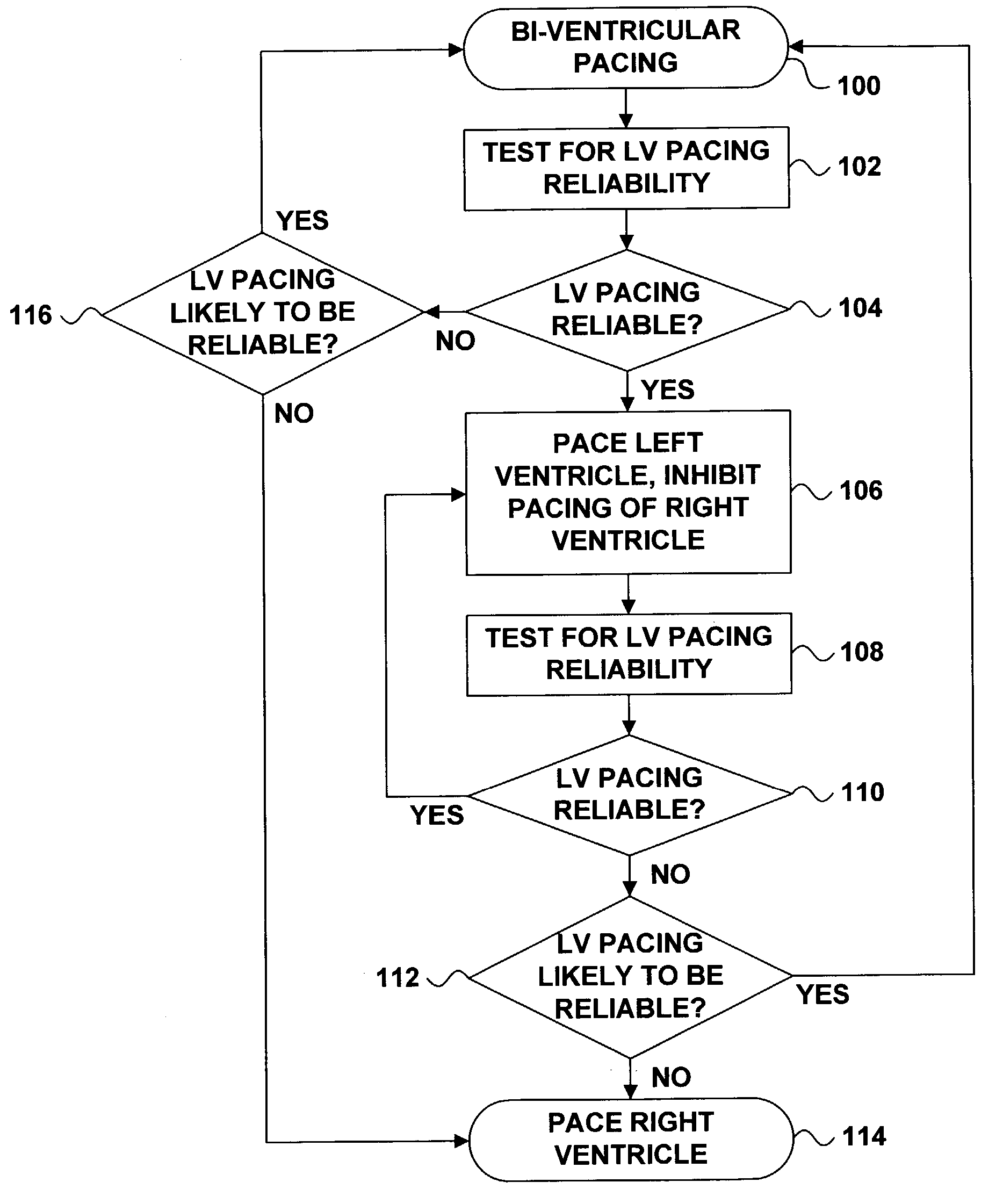
Bi-ventricular and single-ventricle pacing
The invention is directed to methods and apparatus for automatically changing from bi-ventricular pacing, in which an implantable medical device (IMD) applies pacing stimuli to both ventricles of a heart during a cardiac cycle, to single-ventricle pacing, in which the IMD paces one ventricle and inhibits pacing of the other. An IMD applying the techniques of the invention automatically changes from bi-ventricular pacing to single-ventricle pacing, or vice versa, as a function of the reliability of left ventricular pacing. Exemplary techniques for determining the reliability of left ventricular pacing include impedance measurement, capture testing, capture threshold testing, or any combination thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Measuring time to fusion as a means of determining degree of parallel activation of the heart
PendingUS20220233082A1High degreeA large amountInertial sensorsCatheterLeft cardiac chamberLeft ventricular size
A method for determining the degree of parallel activation of a heart undergoing pacing includes calculating vectorcardiogram (VCG), or electrocardiogram (ECG), or electrogram (EGM) waveforms from right ventricular pacing (RVp) and left ventricular pacing (LVp). A synthetic biventricular pacing (BIVP) waveform is generated by summing the VCG of the RVp and LVp, or by summing the ECG of the RVp and the LVp, or by summing the EGM of the RVp and the LVp. A corresponding EGM or ECG or VCG waveform from real BIVP is calculated. The method includes comparing the synthetic BIVP waveform and the real BIVP waveform and calculating time to fusion by determining the point in time in which the activation from RVp and LVp meets and the synthetic and the real BIVP curves start to deviate. A delay in time to fusion indicates a higher degree of parallel activation.
Owner:PACERTOOL AS
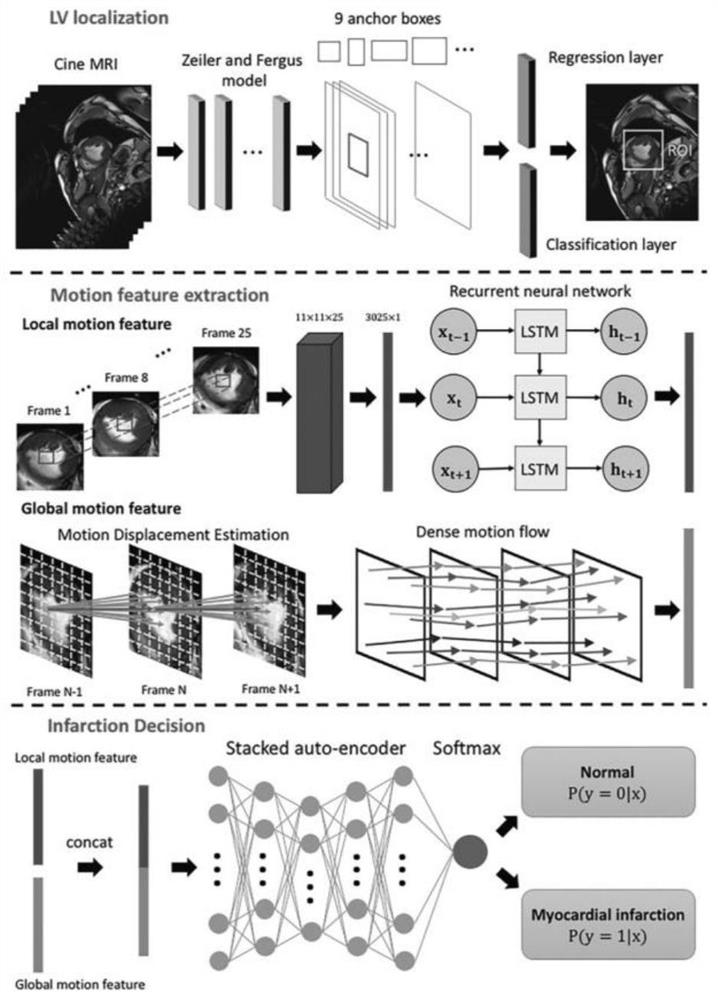
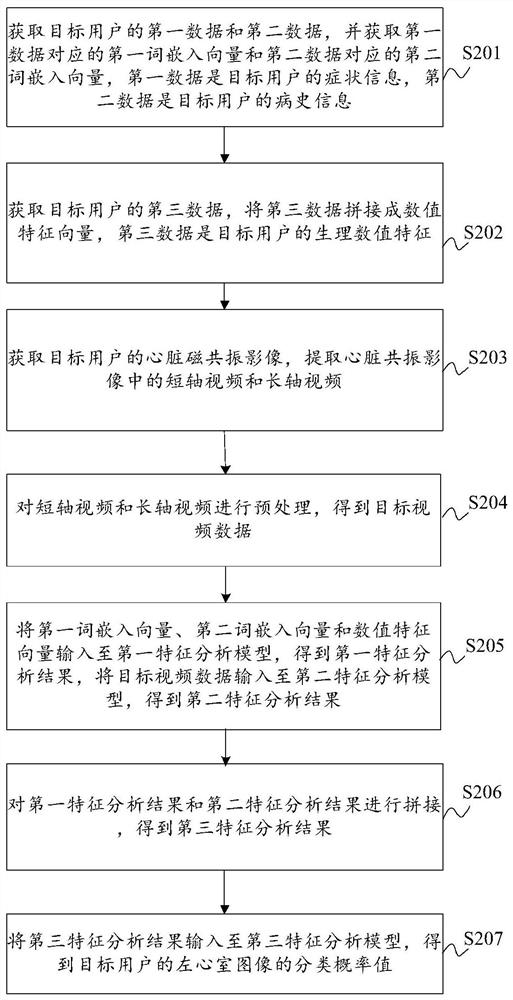
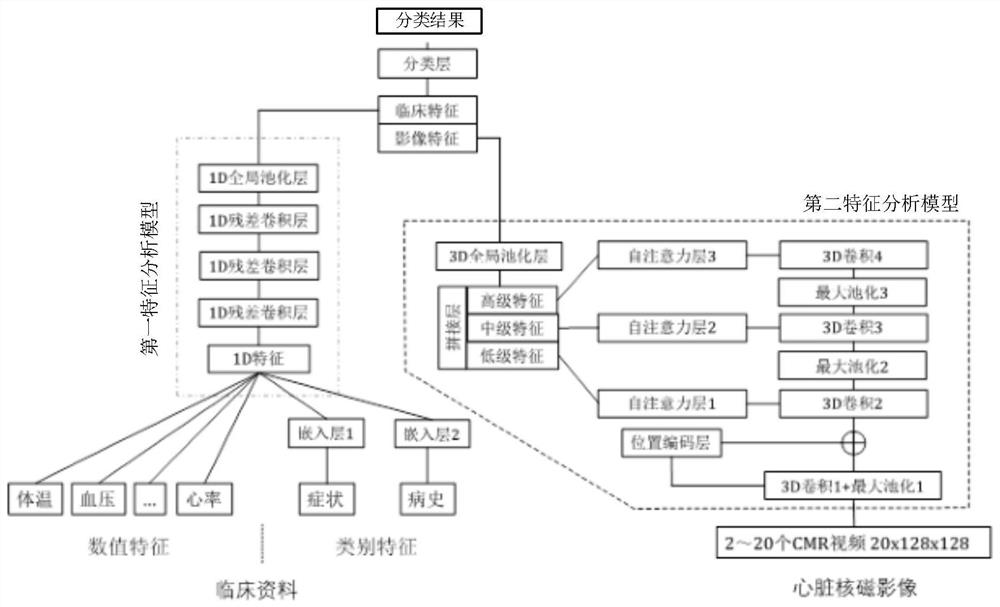
Method, device, equipment and medium for intelligent classification of left ventricular magnetic resonance images
ActiveCN112766377BThere is no cumulative errorImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisLeft cardiac chamberAnalytic model
The present application discloses a method, device, device, and medium for intelligent classification of left ventricular magnetic resonance images. The method includes: acquiring a first word embedding vector corresponding to the first data of a detection object, a second word embedding vector corresponding to the second data, The numerical feature vector formed by splicing the third data; extracting the short-axis video and long-axis video in the heart magnetic resonance image of the detection object, and preprocessing to obtain the target video data; splicing and inputting the above three vectors into the first feature analysis model to obtain the second The first feature analysis result and the target video data are input into the second feature analysis model to obtain the second feature analysis result, and the third feature analysis result is obtained, and input to the third feature analysis model to obtain the classification probability of the left ventricle image of the detection object value. The method uses multi-sequence nuclear magnetic imaging data and clinical data to make classification predictions. The results are more reliable and accurate, and it does not require complicated post-processing procedures, and there is no cumulative error, which improves the robustness.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
System for identification and adjustment of loss of effective cardiac resynchronization therapy
An implantable medical device system and method for delivering cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing that includes determining capture associated with the delivered CRT pacing is ineffectivein response to the delivered CRT pacing. A reason for capture being ineffective is determined and a safety margin is adjusted if the determined reason for capture being ineffective is loss of captureand a left ventricle (LV) pre-excitation is adjusted if the determined reason for capture being ineffective is delayed LV depolarization. Monitoring for a change in effective cardiac resynchronizationtherapy is used to confirm that the adjustment of the CRT pacing was effective in resolving the ineffective capture.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
A Registration Method of Cardiac Perfusion Magnetic Resonance Images
The invention discloses a heart perfusion magnetic resonance image registration method. The method comprises steps: a magnetic resonance image I<NT> containing a plurality of layers of slices of left ventricular are acquired, a magnetic resonance image I<1T> for the initial layer of slice in T heartbeat cycles is selected, endocardium in the magnetic resonance image I<1T> is segmented, and a reference image I<1r> and a region of interest ROI<1> are determined; magnetic resonance images I<MT> for layers from the second to the Nth of slices in the T heartbeat cycles are selected respectively, a magnetic resonance image I<MT> for the current layer of slice the T heartbeat cycles is set, with the sequence number r of the heartbeat cycle of the reference image I<(M-1)r> of the former layer of slice and the region of interest ROI<M-1> as reference, the endocardium in the magnetic resonance image I<MT> for the Mth layer of slice is segmented, and a reference image I<Mr> in the magnetic resonance image I<MT> for the Mth layer of slice is acquired; and with the reference image for each layer of slice as reference, magnetic resonance image registration for the layer of slice in the T heartbeat cycles is completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com