Patents
Literature
39 results about "Pleural spaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pleural space: The tiny area between the two layers of the pleura (the thin covering that protects and cushions the lungs) between the lungs and chest cavity. The pleural space is normally filled with a small amount of fluid.
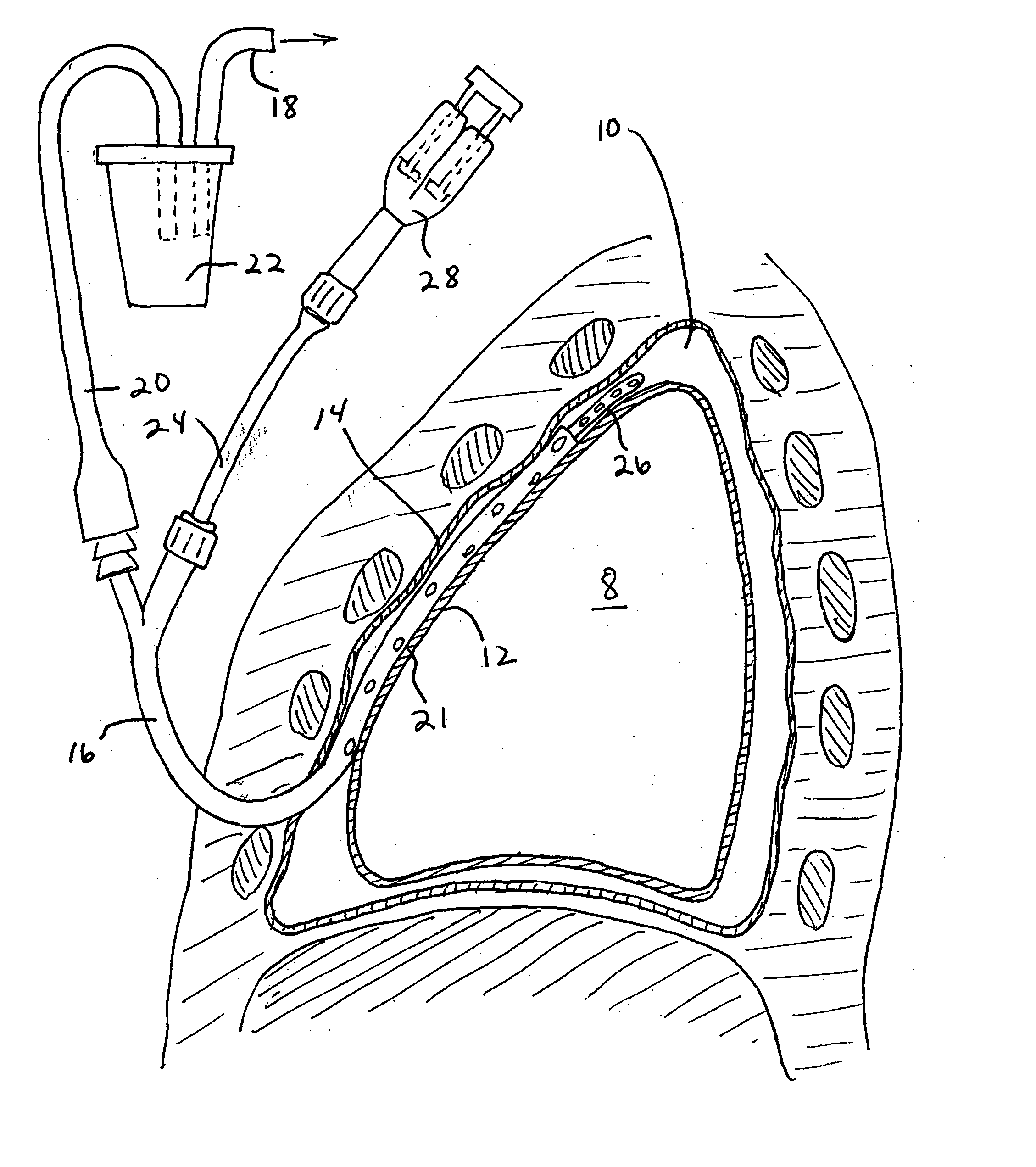
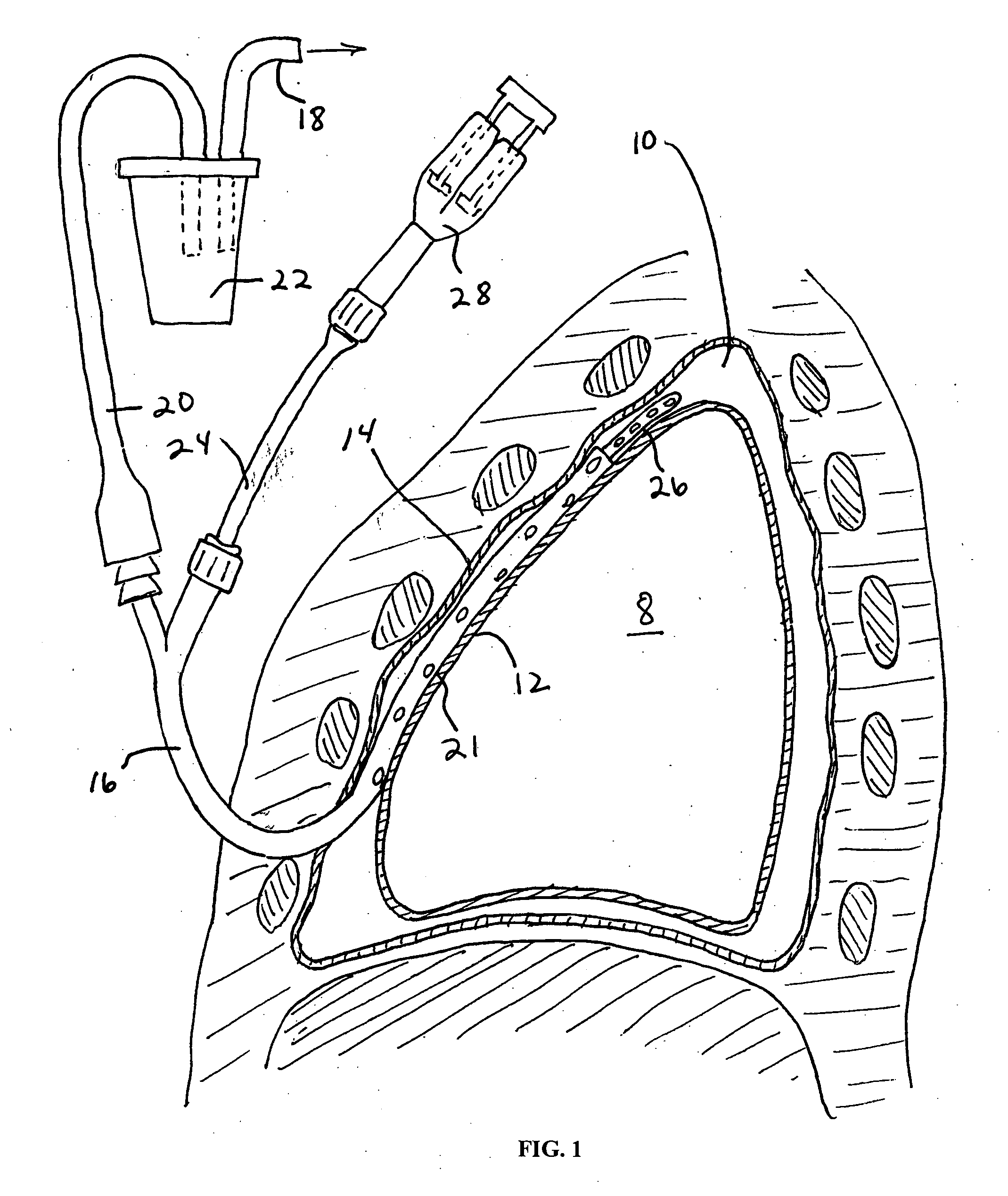
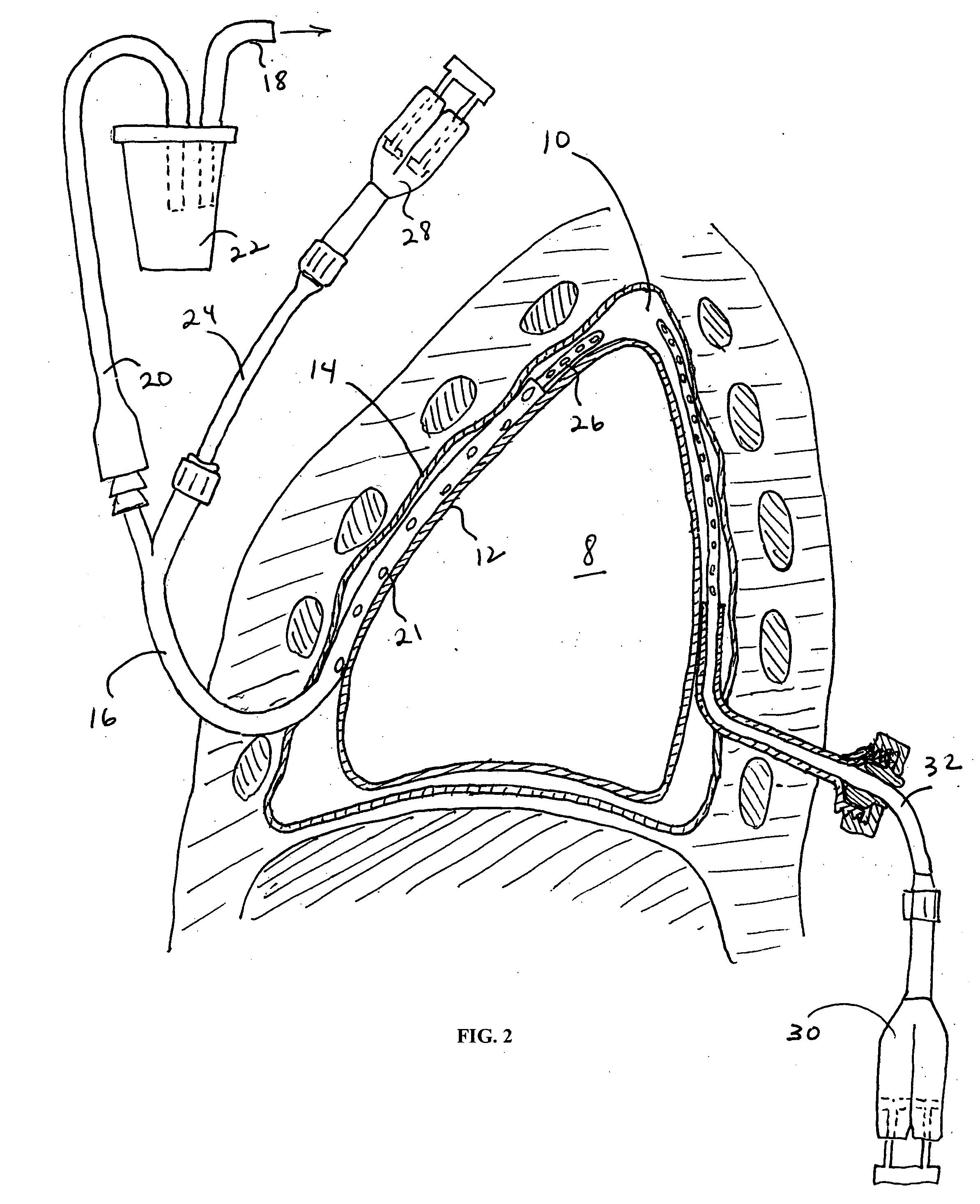
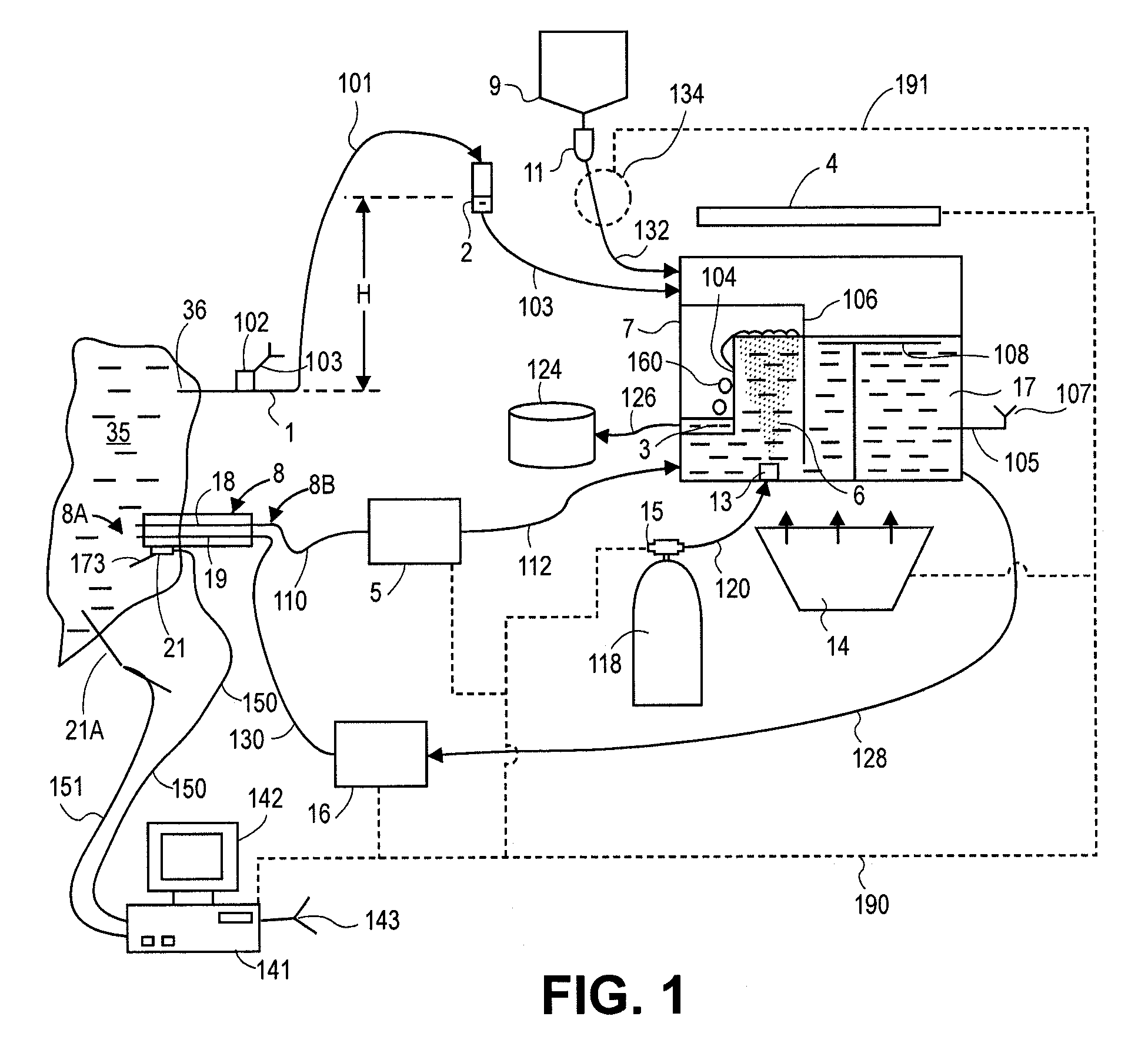
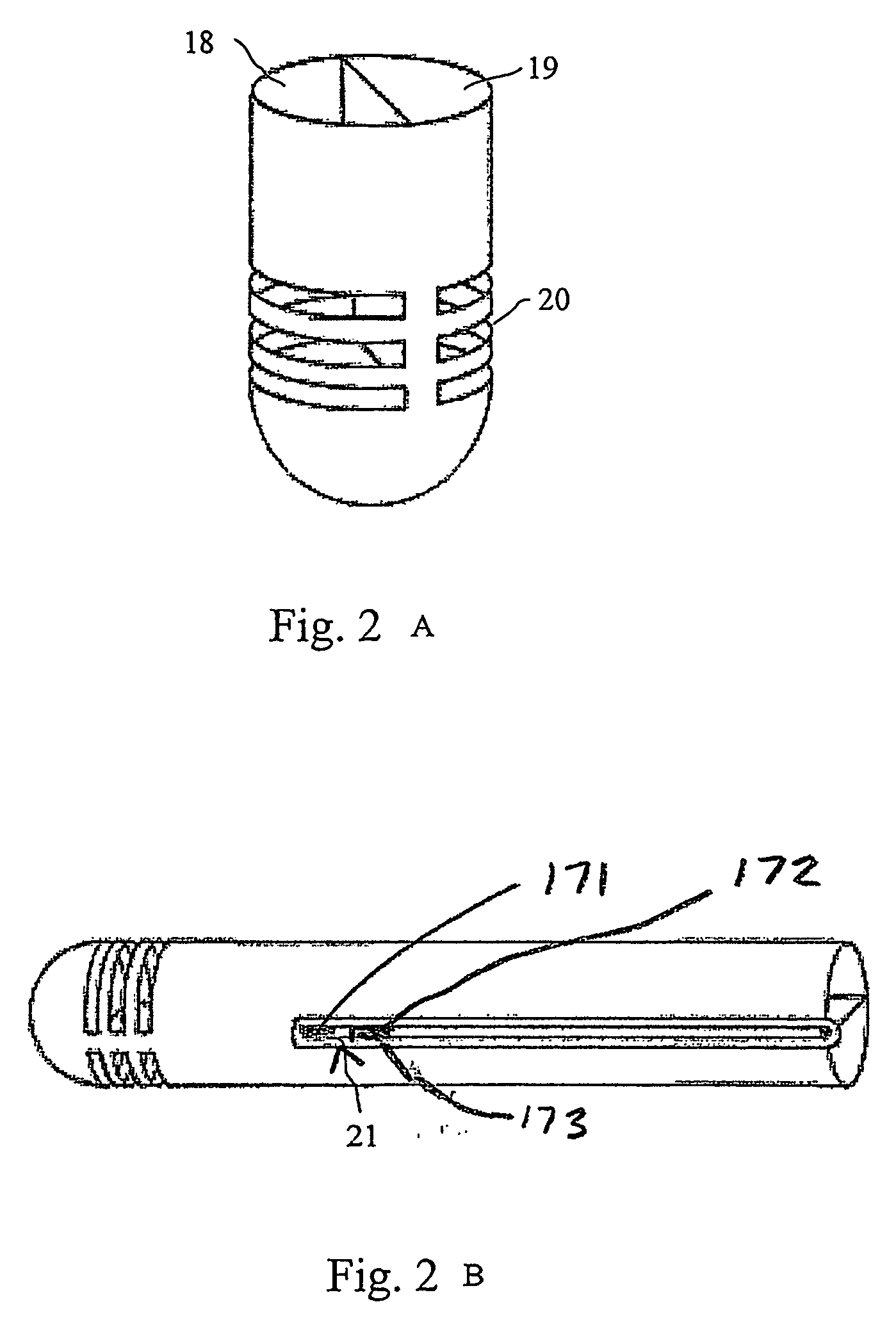
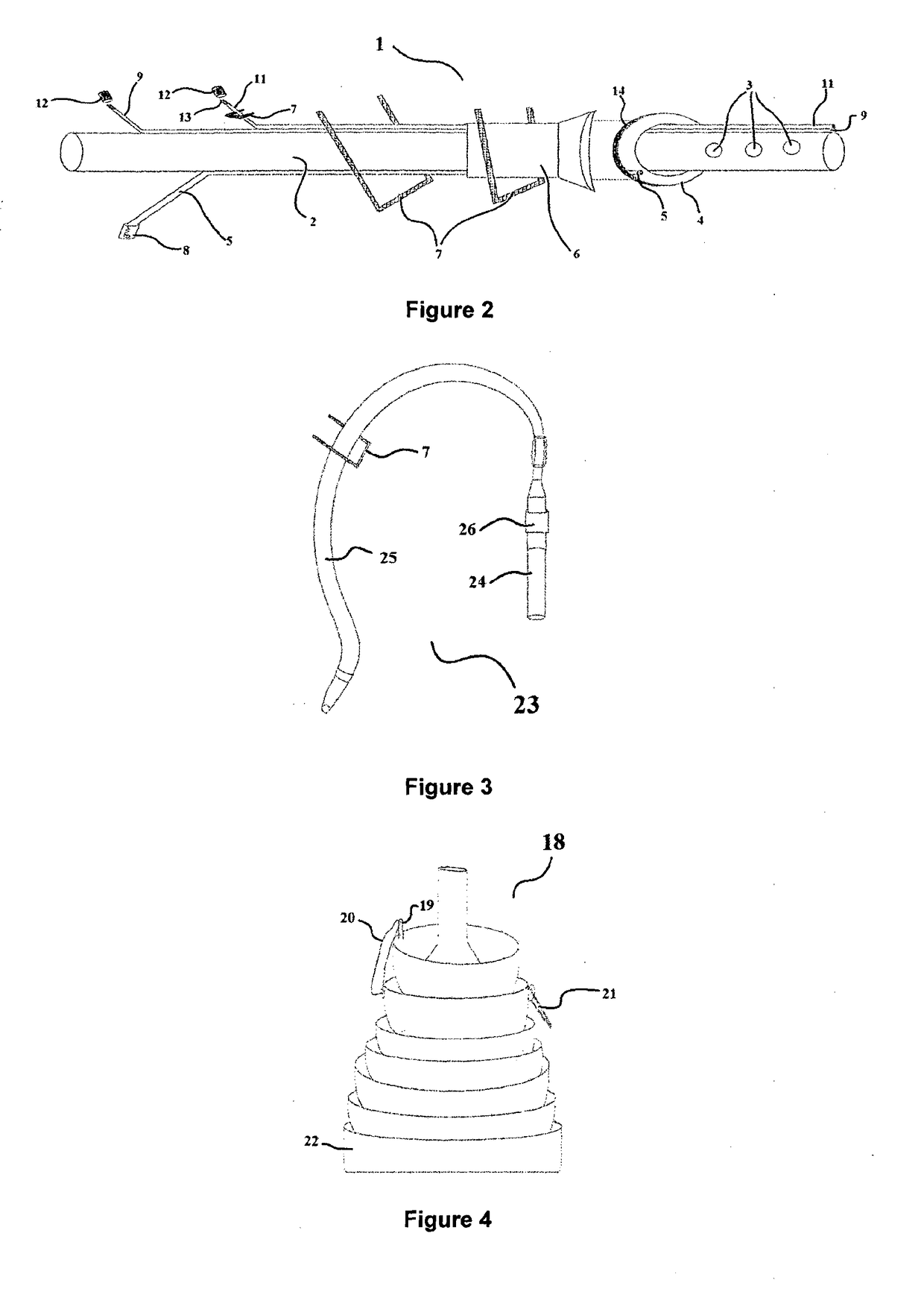
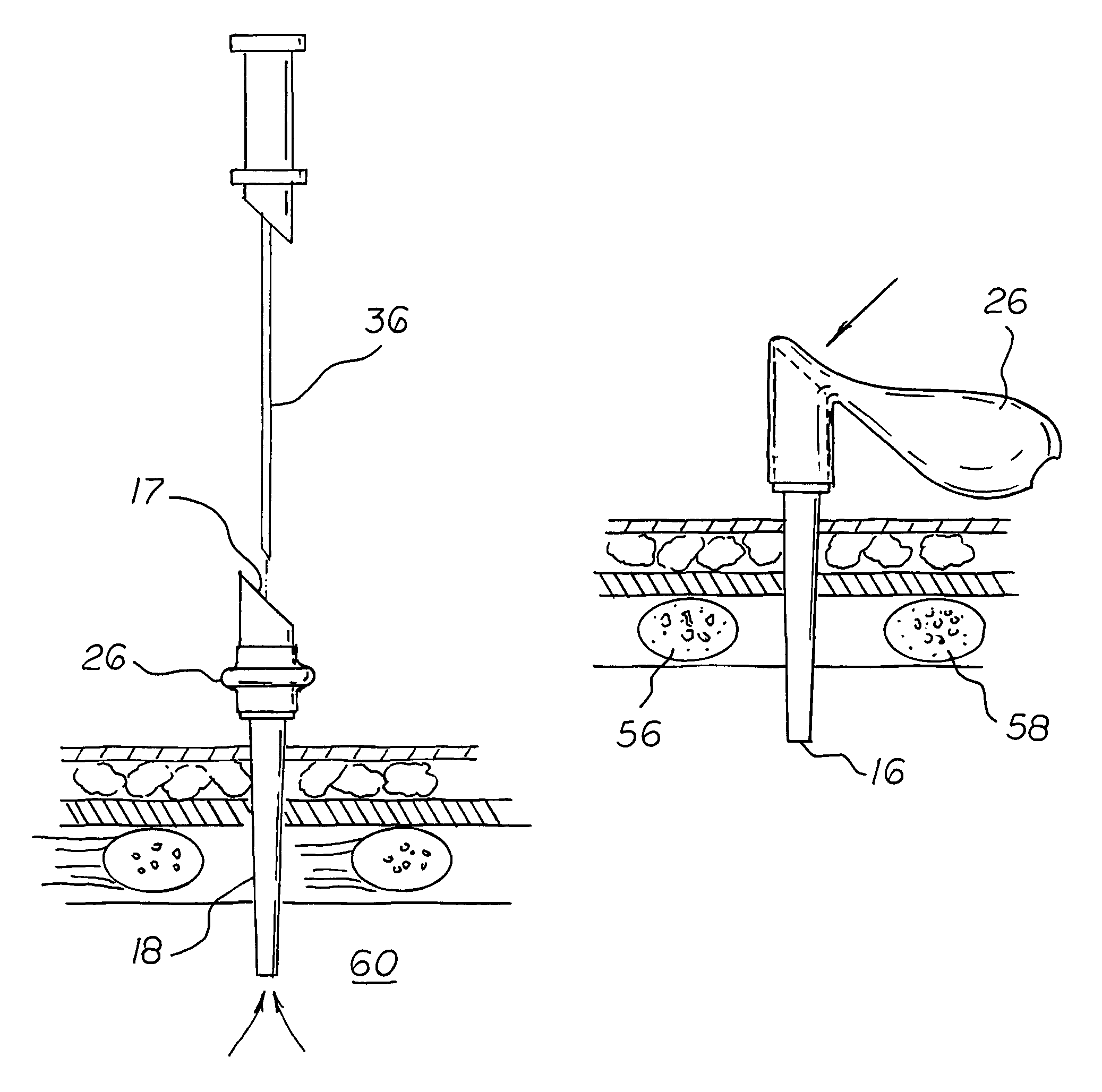
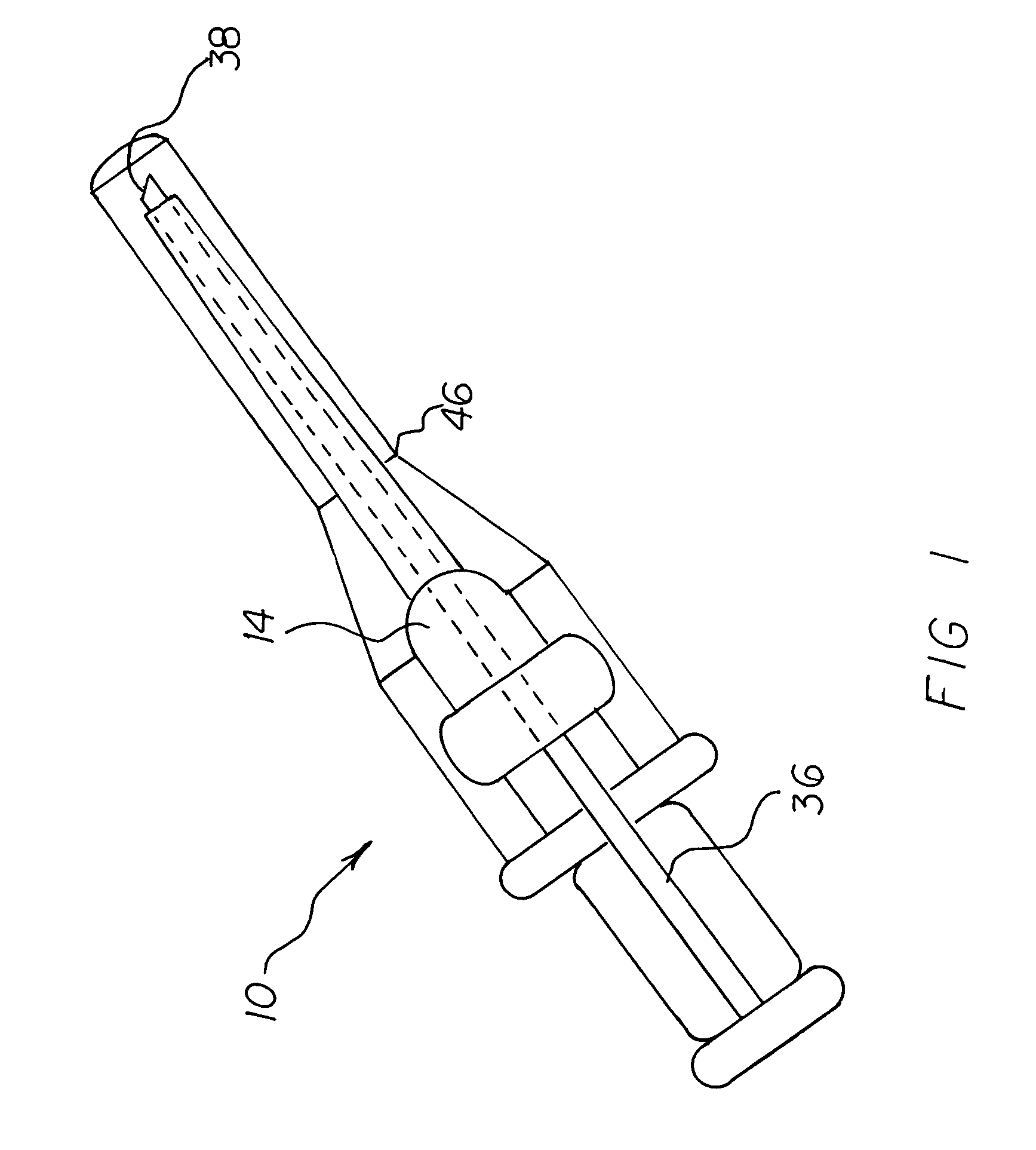
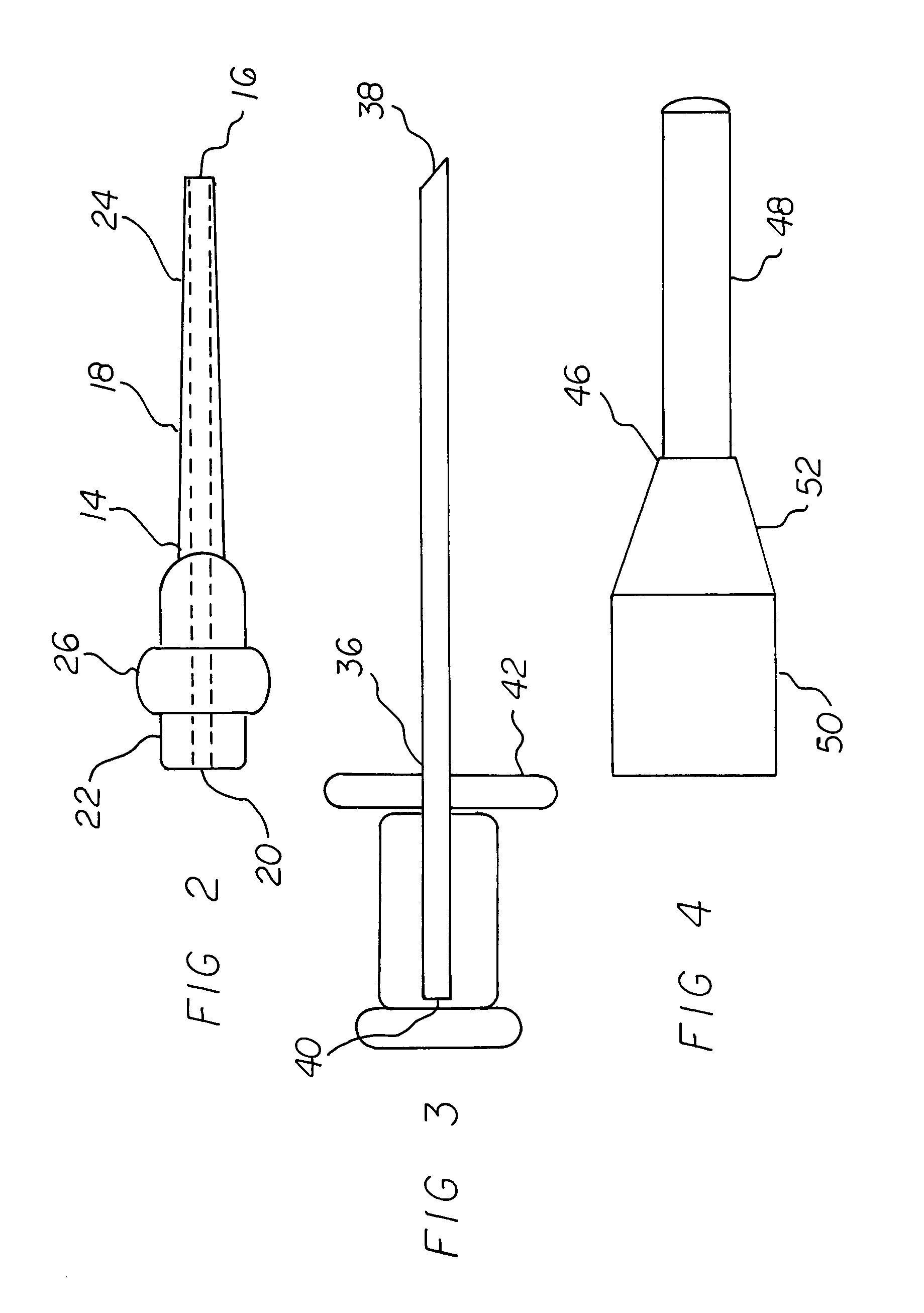
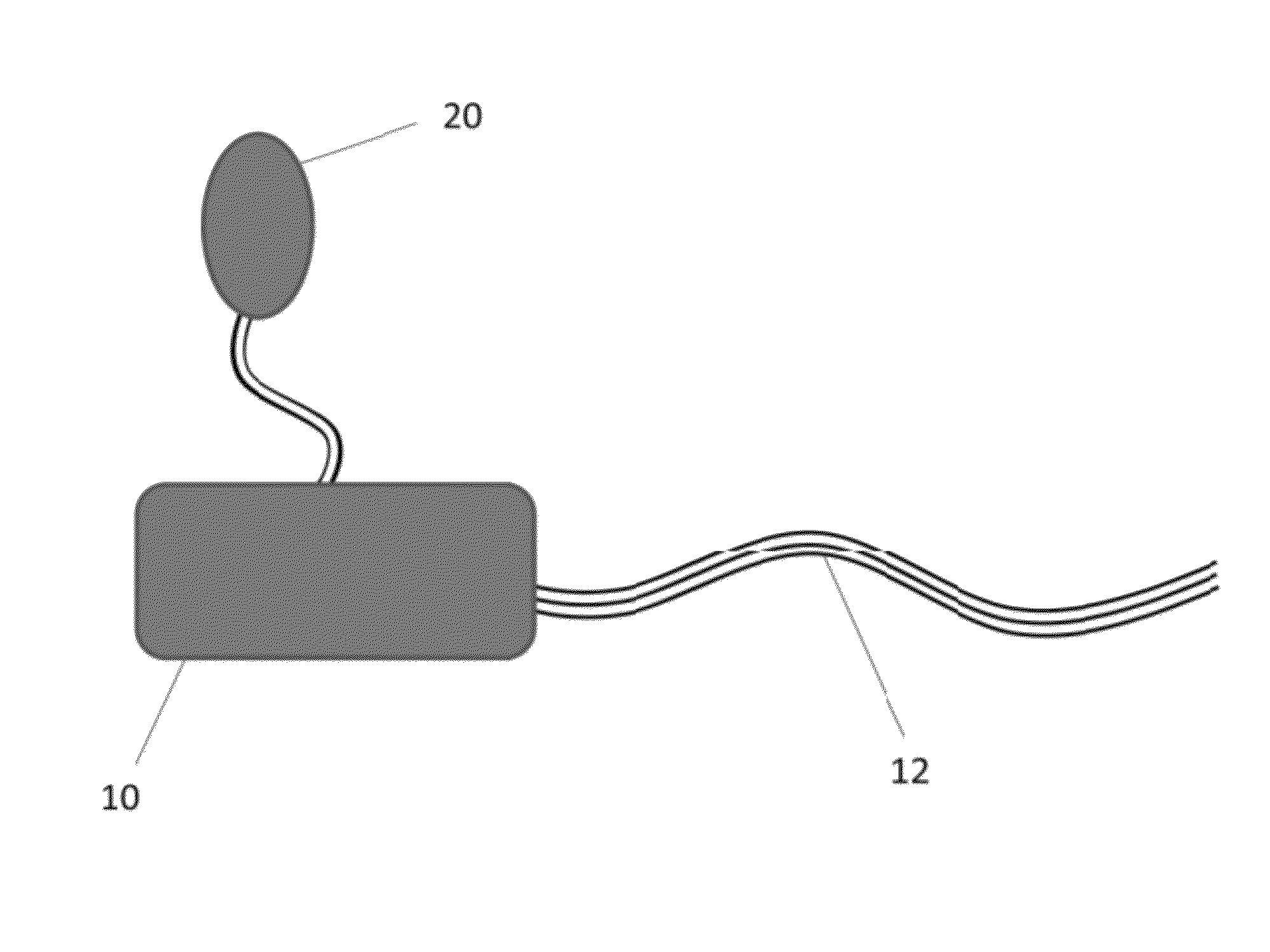
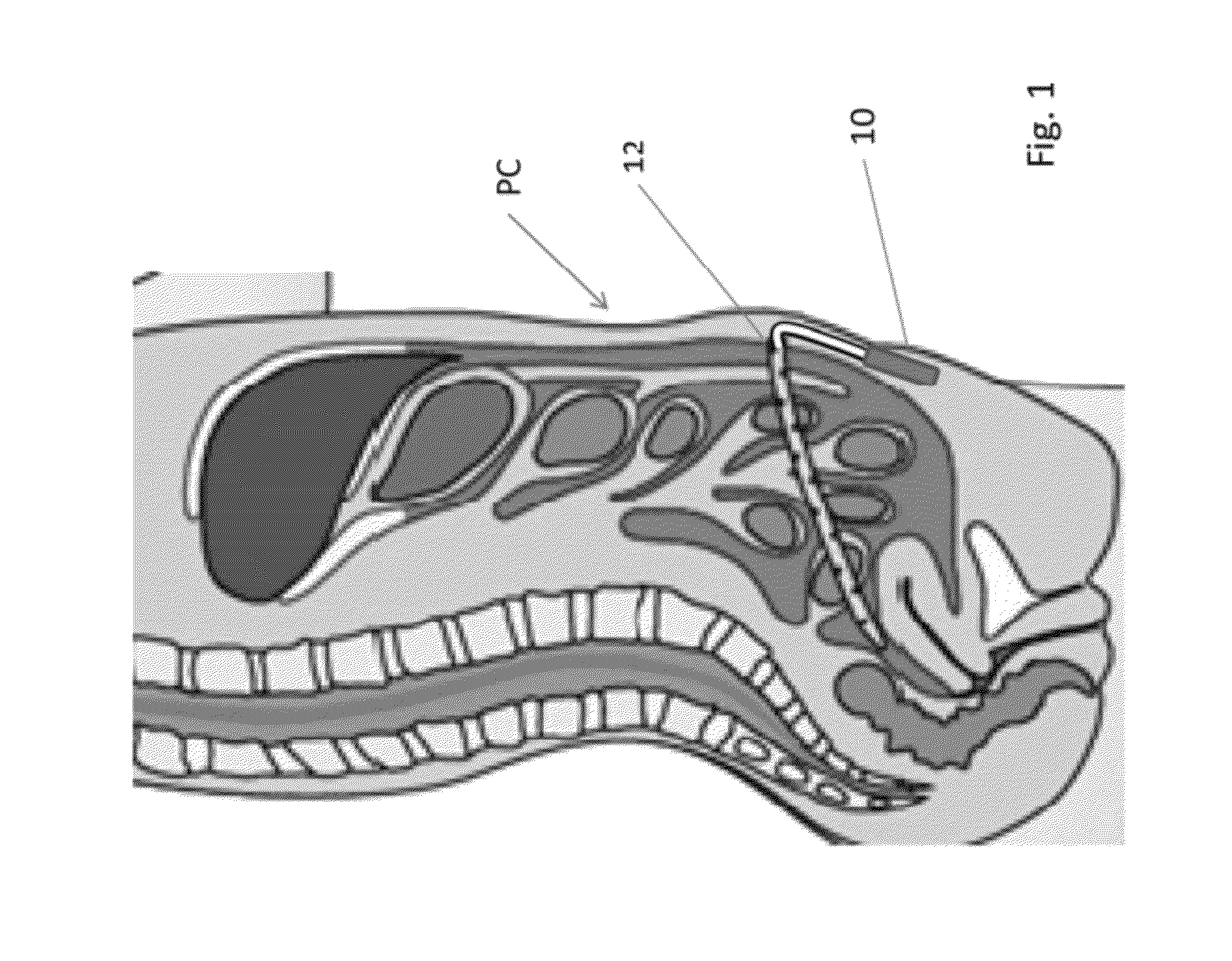
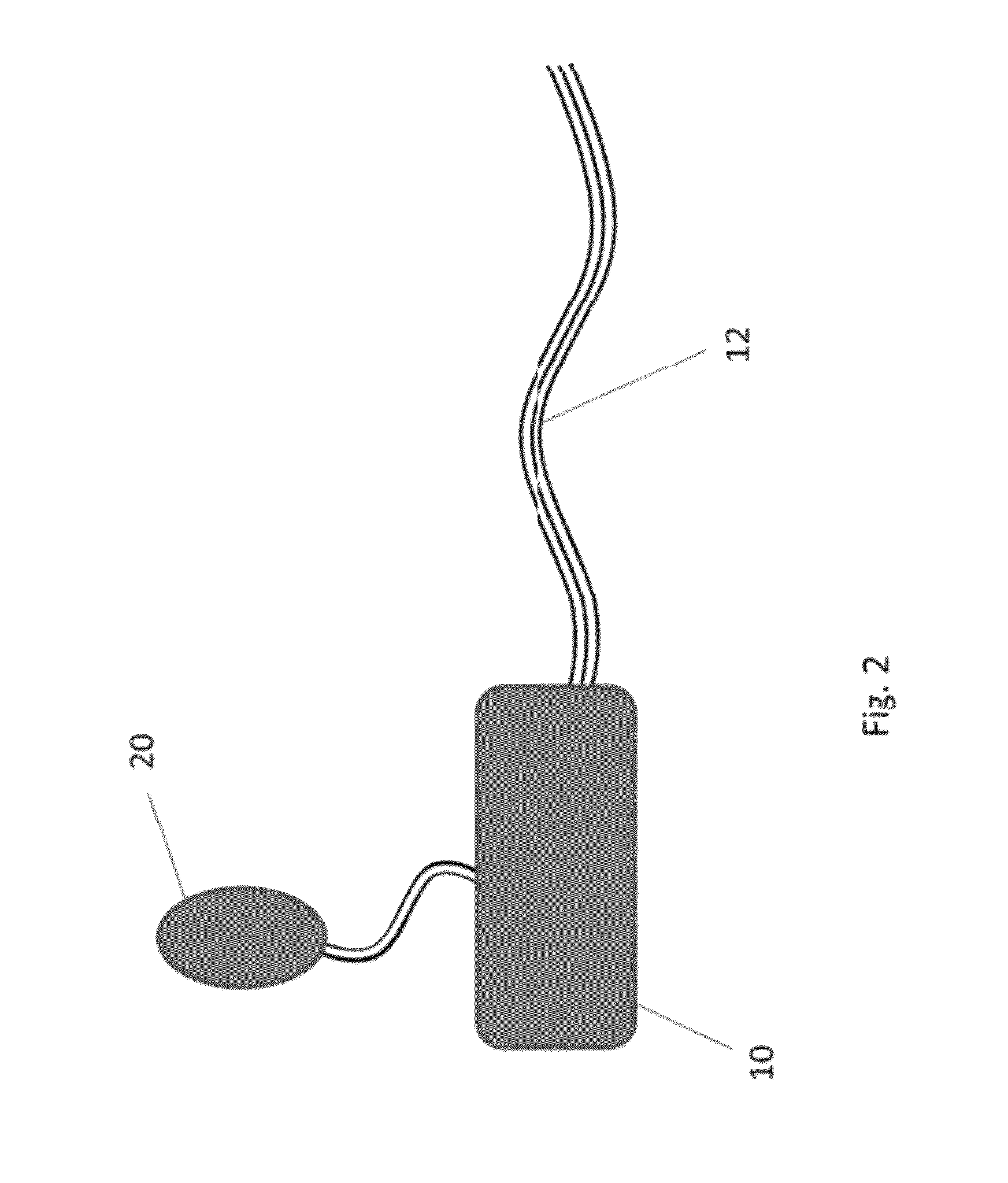
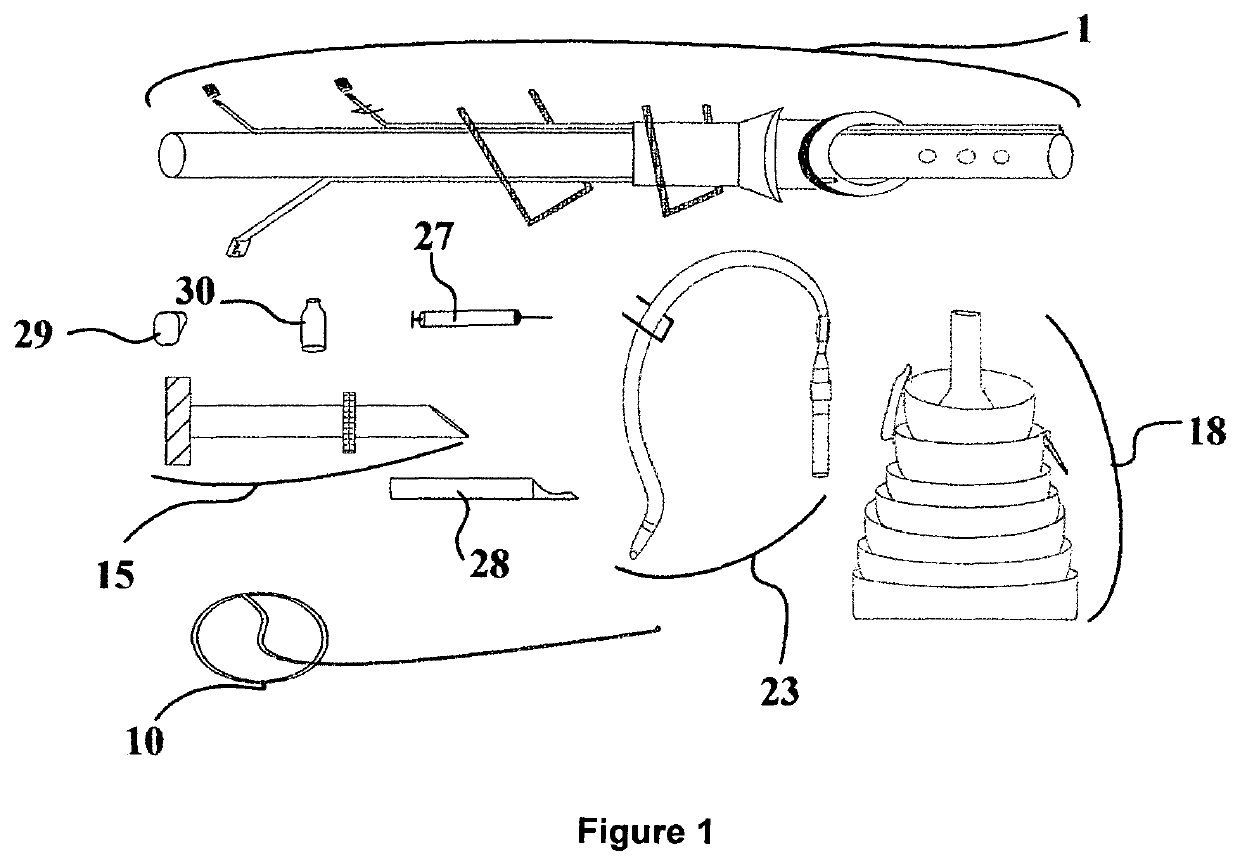
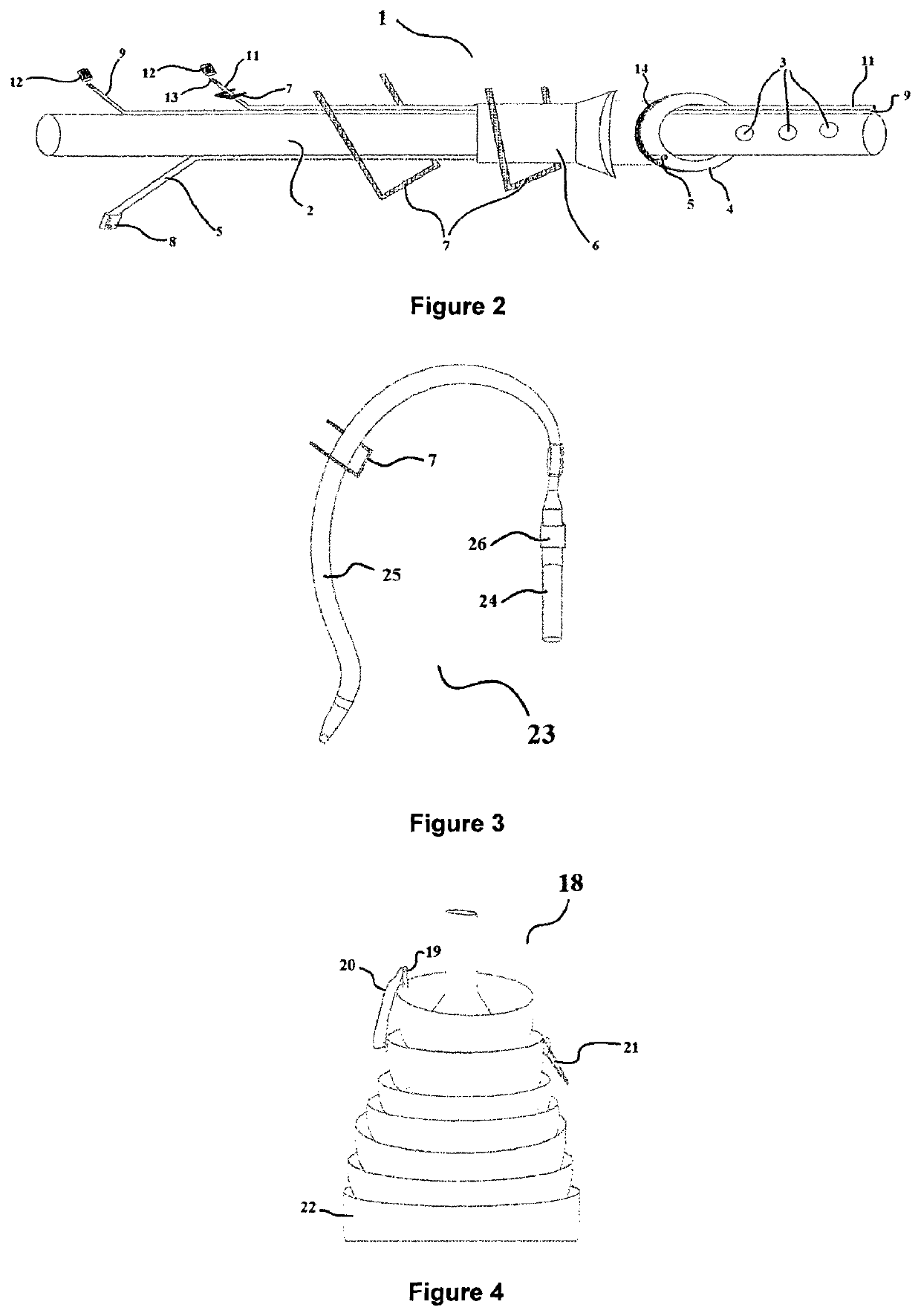
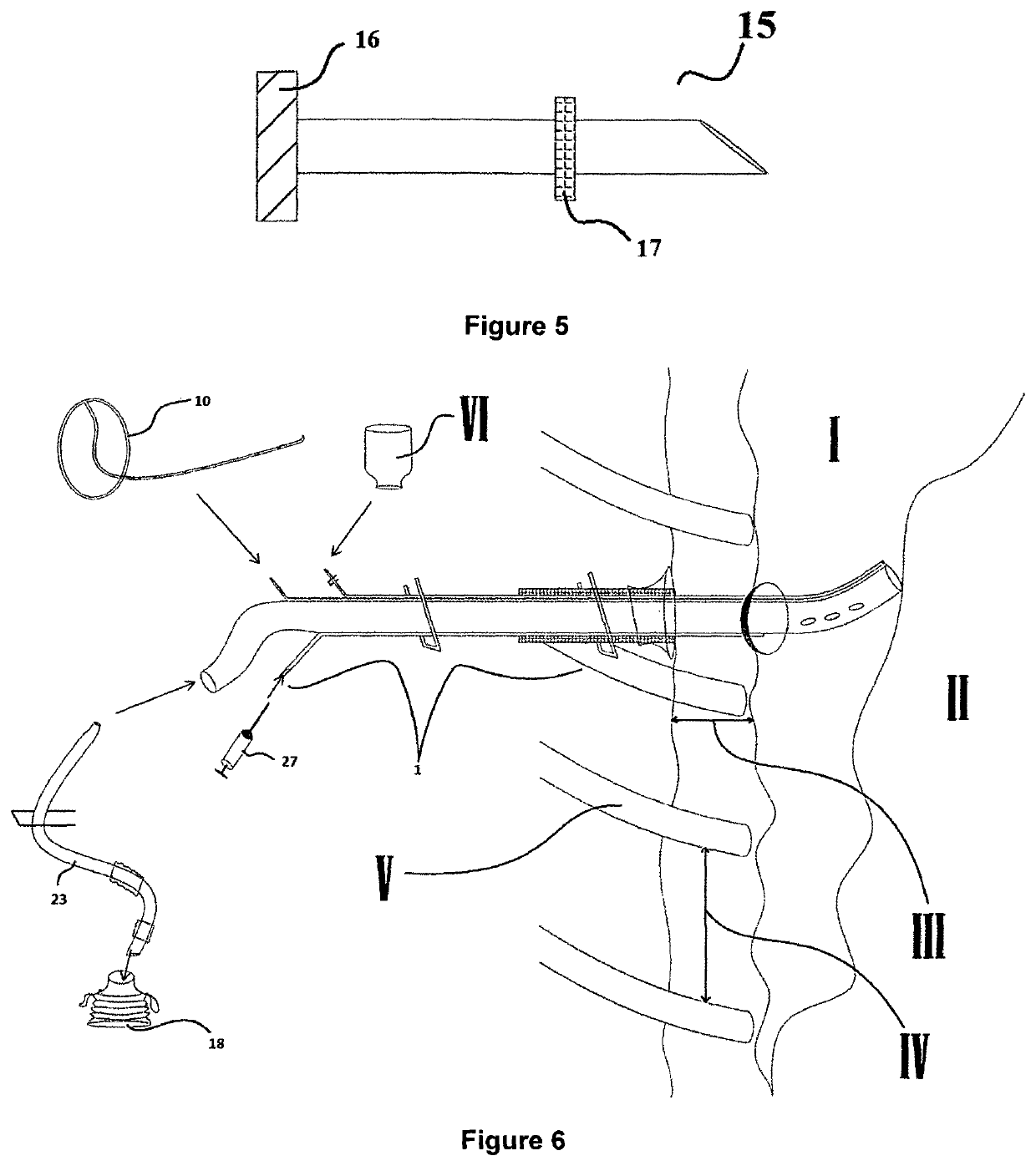
Pleural effusion treatment device, method and material
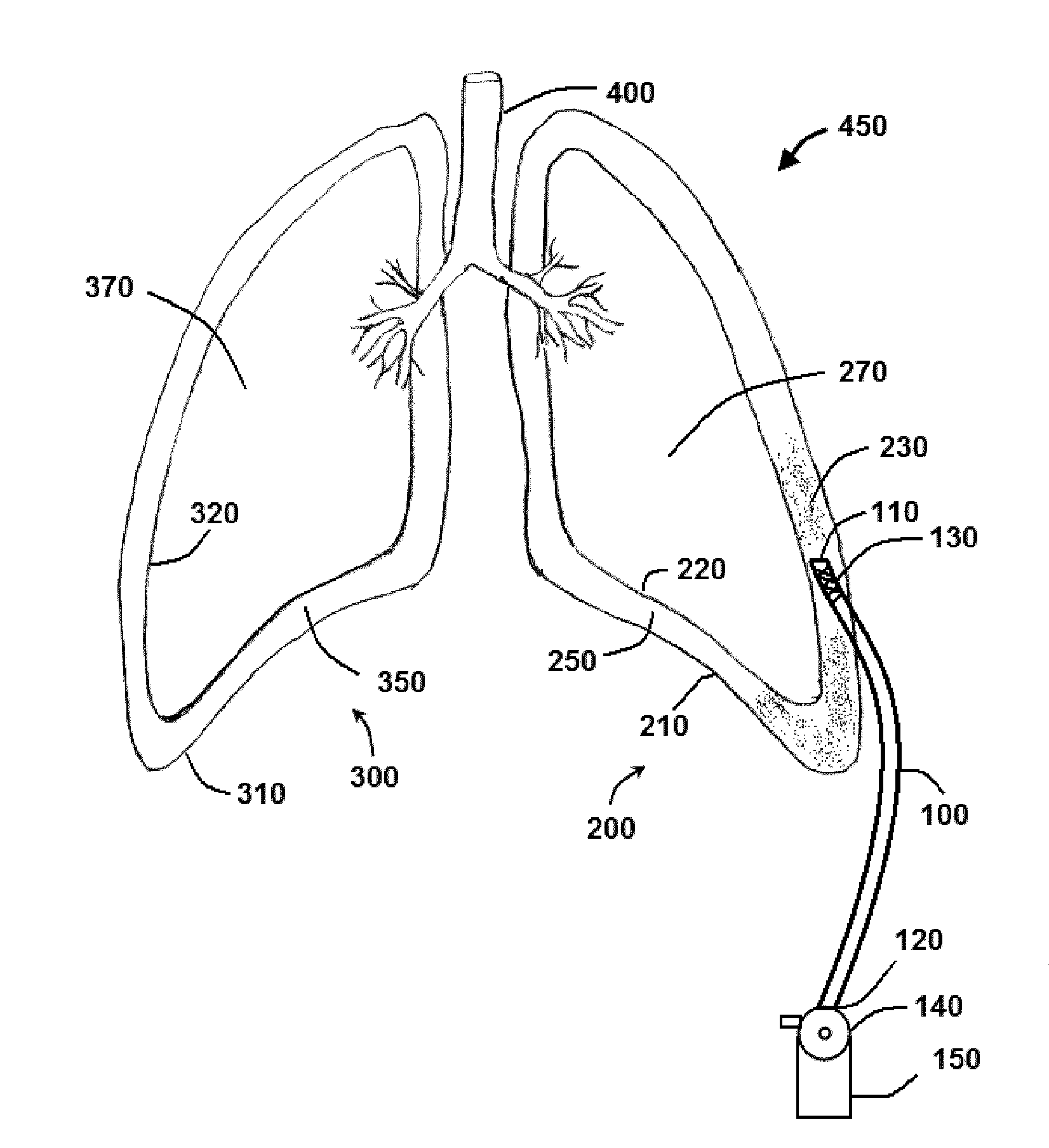
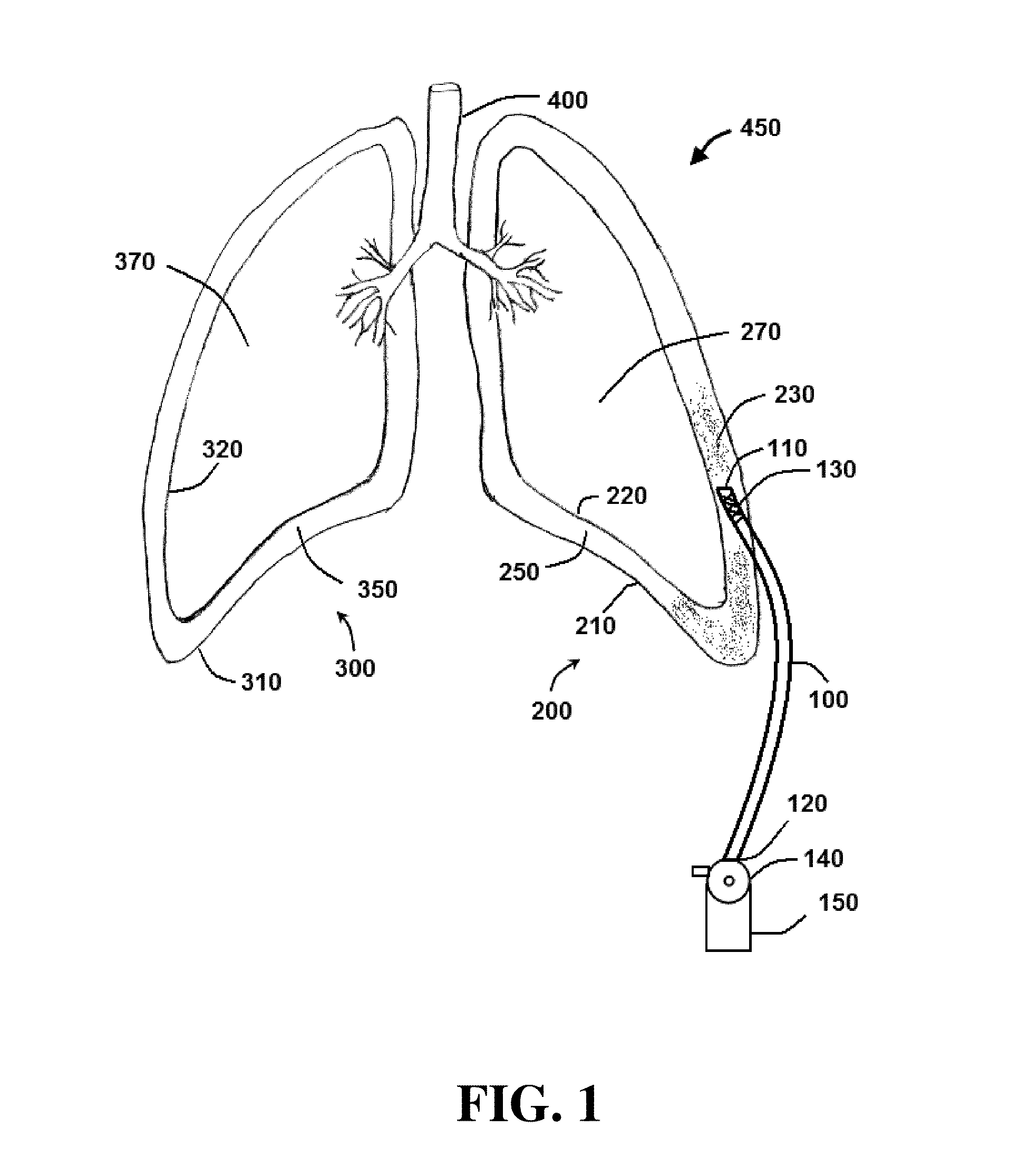
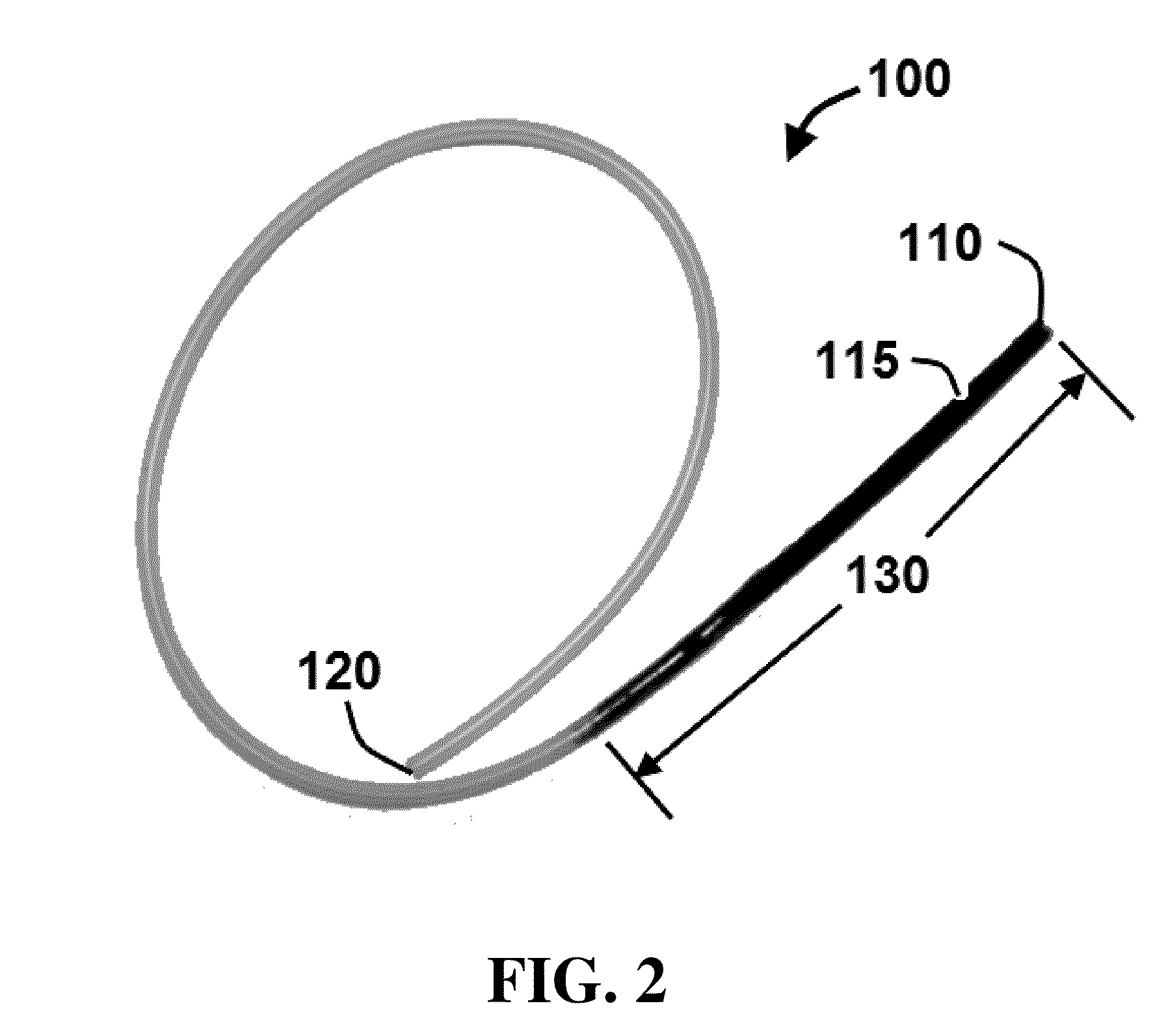
The invention discloses a method of treating a patient for pleural effusion comprising percutaneously delivering an adhesive material to a pleural space of the patient. Suitable adhesive materials for performing any of the embodiments of the methods of the invention can be selected from the group consisting of hydrogels, collagen, poly(lactic acid), poly(glycolide), cyanoacrylates, glutaraldehyde, PEG, protein, and polysaccharide and derivatives thereof. The invention also discloses a pleural effusion treatment apparatus comprising an adhesive material adapted to adhere pleural membranes defining a pleural space and a pleural space access member adapted to deliver the adhesive material to the pleural space.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS7842002B2Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Device for the extravascular recirculation of liquid in body cavities
InactiveUS20060161107A1Improves liquid distributionOptimize allocationMulti-lumen catheterOther blood circulation devicesSubarachnoid spaceDouble tube
Biocompatible liquid is pumped into a body cavity (eg. subarachnoid space, peritoneum, mediastinum, pleural space) by means of one pump and removed from it by means a second pump, preferably via a double-barreled catheter is used for insertion and removal of the liquid. An optional secondary catheter removes liquid from a distal area of the body cavity. Temperature and pressure are sensed within the cavity and can be controlled by adjusting liquid flow rates. While outside the body, the liquid can be ultraviolet-sterilized, foam fractionated to remove contaminants, oxygenated and pH balanced, cooled or warmed, and augmented with exogenous liquid that may contain drugs.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Variable parietal/visceral pleural coupling
InactiveUS20080287973A1Effective treatmentIncrease expiratory flowCannulasWound clampsCouplingCupula pleurae
Owner:PORTAERO
Continuous blood glucose monitor
A device may be implanted subcutaneously with an attached catheter inserted within, e.g., the peritoneal cavity of a subject. The catheter and / or device may also be inserted into another space, e.g., subcutaneous, vascular, peritoneal, cerebrospinal, pleural spaces, etc. The peritoneal fluid which normally collects and / or flows through the peritoneal cavity may be detected by the catheter and analyzed via the device to detect the concentration of glucose within the fluid.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Portable Pulmonary Injury diagnostic Devices And Methods
InactiveUS20090149748A1Increase chances of survivalMinimal experienceDiagnostics using vibrationsOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound attenuationMedicine
Lung injury such as pneumothorax now can be diagnosed reliably, portably and quickly. Vibro-acoustic waves are sent through the chest and the resulting wave is measured. By analyzing attenuation characteristics determined by the geometry of the chest structures, a determination can be made of whether the patient's pleural space is healthy, contains air (pneumothorax) or contains fluid (hemothorax).
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Systems, devices and methods for sensing physiologic data and draining and analyzing bodily fluids
ActiveUS20180177458A1Avoid problemsUseful in detectionMedical devicesCatheterEngineeringPleural spaces
Systems, devices and methods for sensing physiologic data and draining and analyzing bodily fluids are described which are capable of sensing physiologic data based on sensors incorporated into a catheter adapted to reside in any of a urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, rectal location, pre-peritoneal, pleural space or other body cavity. The devices aid emptying of the bladder, measure urine output and various urine parameters such as oxygen tension, urine conductance and urine specific gravity, monitor renal function, analyze urine parameters, including urine content, including the presence of infection, and track and / or control fluid administration.
Owner:POTRERO MEDICAL
Pleural effusion treatment device, method and material
Owner:EKOS CORP
Systems, devices and methods for sensing physiologic data and draining and analyzing bodily fluids
Systems, devices and methods for sensing physiologic data and draining and analyzing bodily fluids are described which are capable of sensing physiologic data based on sensors incorporated into a catheter adapted to reside in any of a urinary tract, gastrointestinal tract, rectal location, pre-peritoneal, pleural space or other body cavity. The devices aid emptying of the bladder, measure urine output and various urine parameters such as oxygen tension, urine conductance and urine specific gravity, monitor renal function, analyze urine parameters, including urine content, including the presence of infection, and track and / or control fluid administration.
Owner:POTRERO MEDICAL
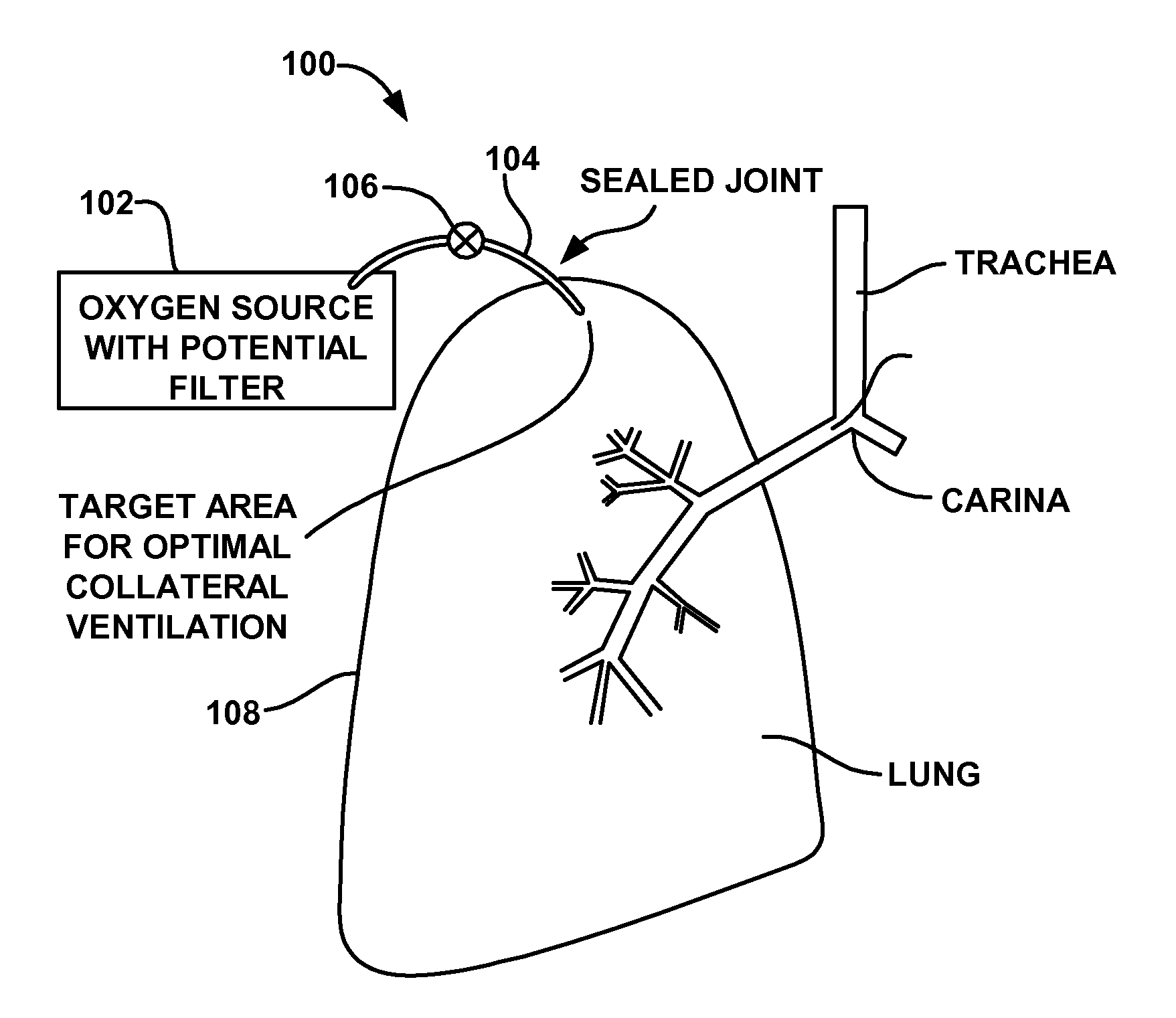
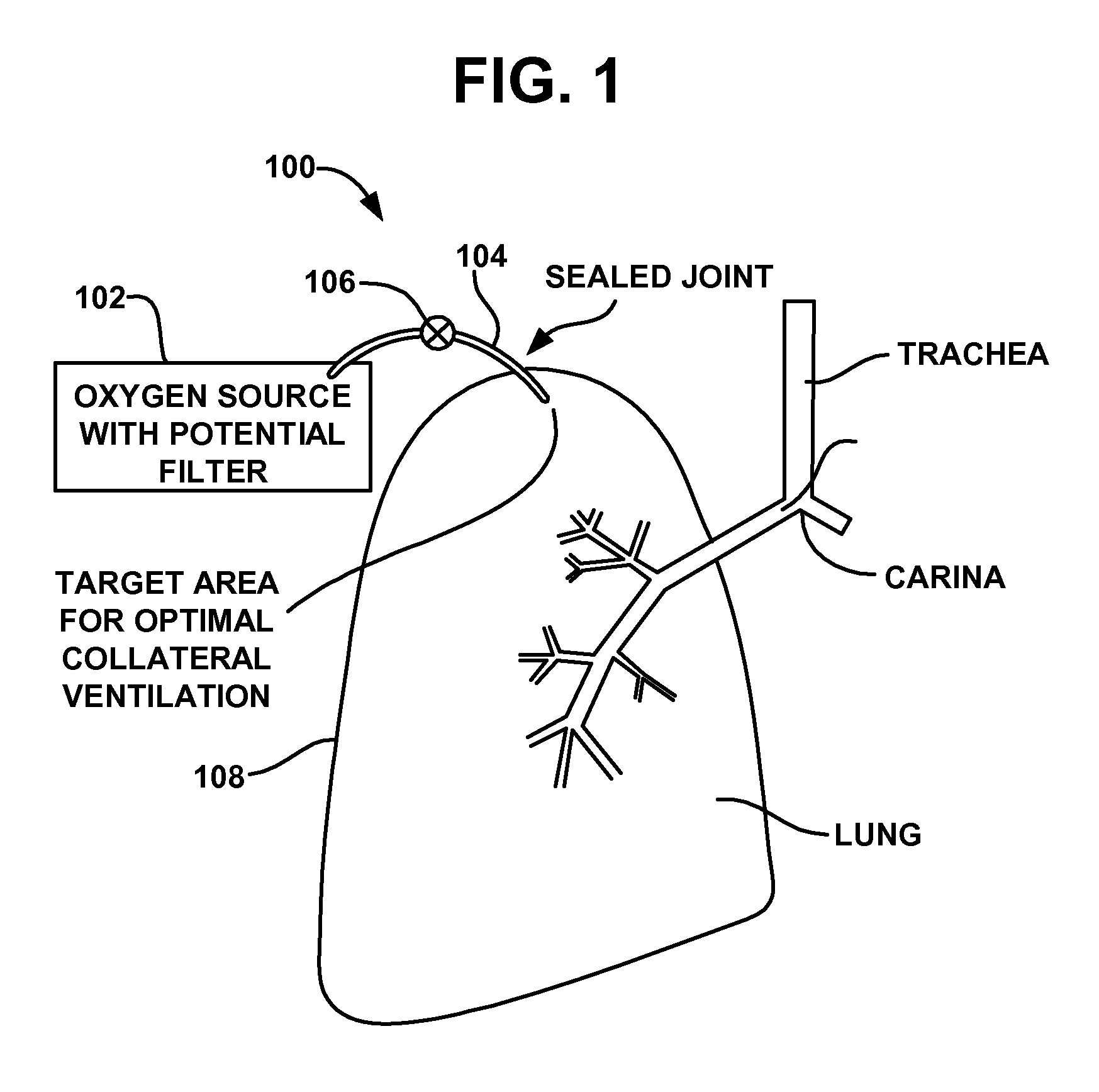
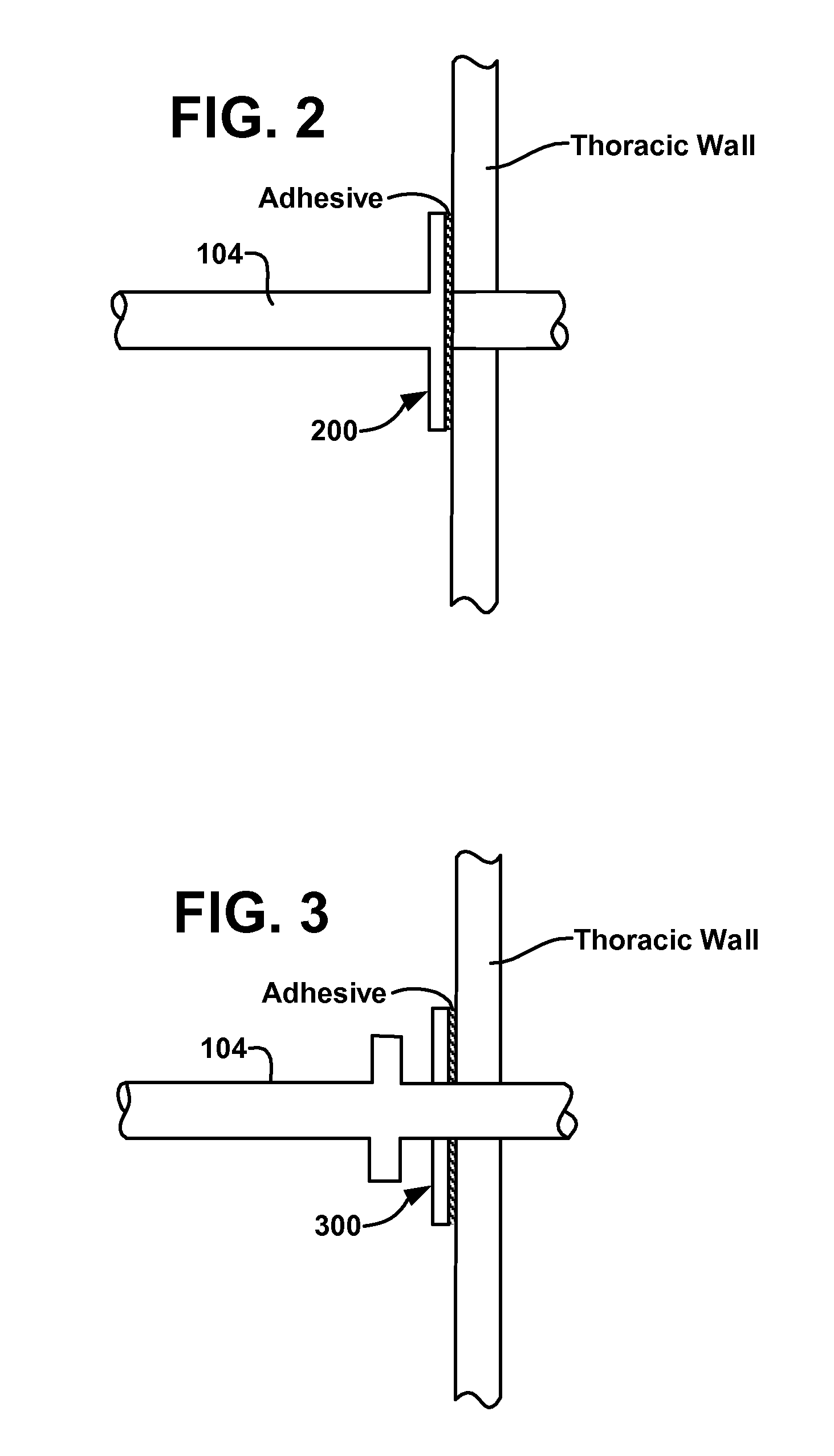
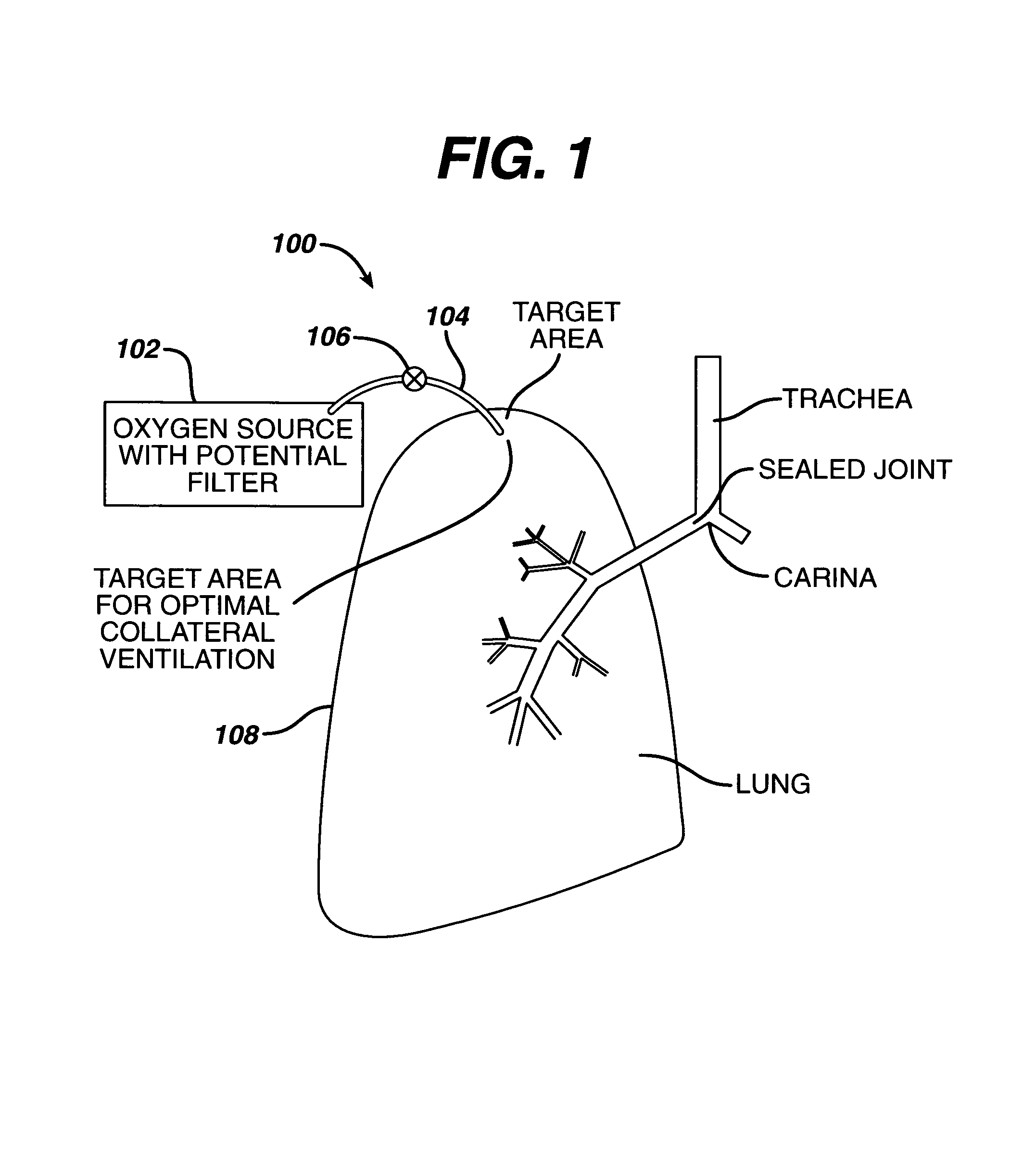
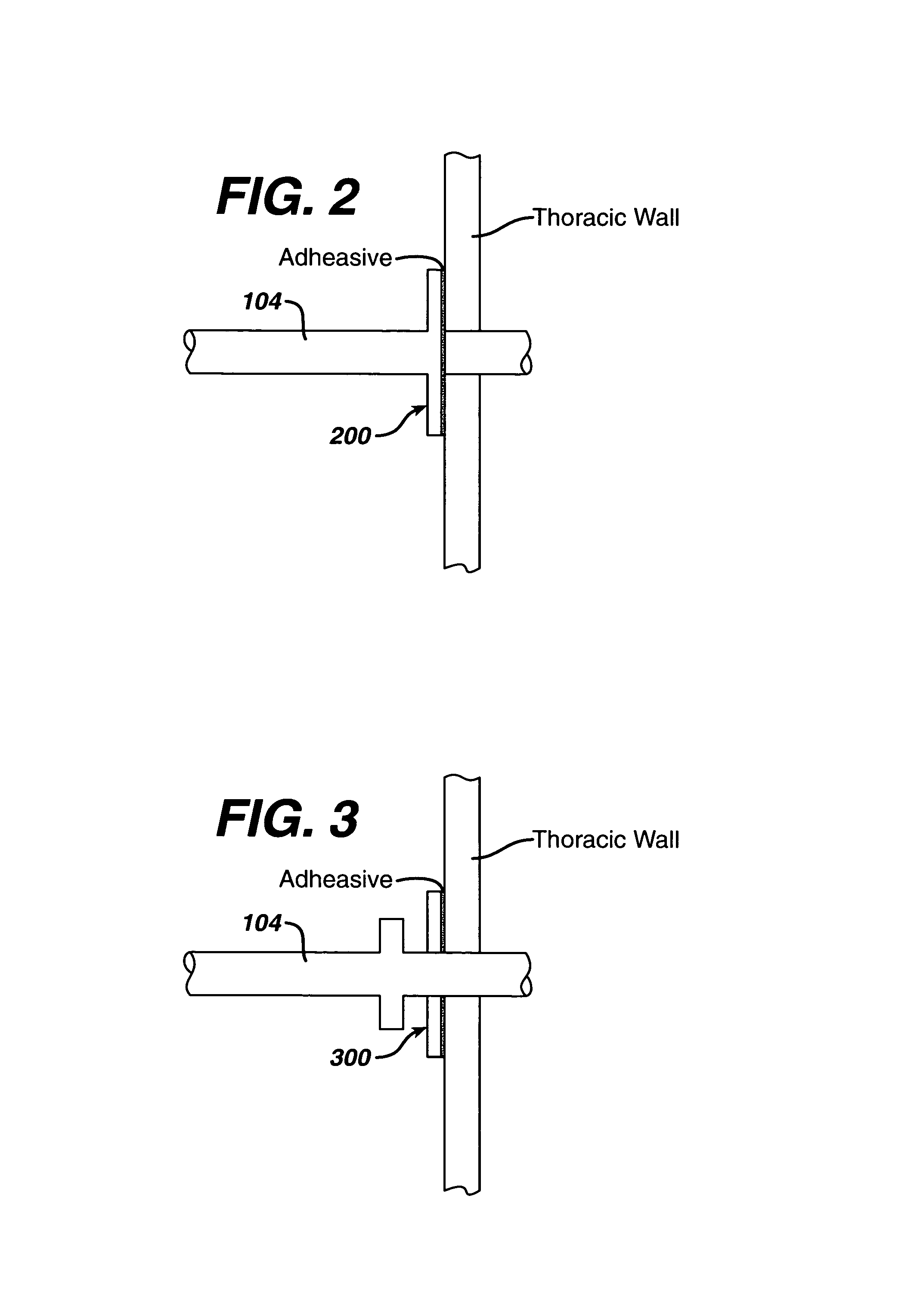
Collateral ventilation device with chest tube/evacuation features and method
InactiveUS7824366B2Speed up the flowEasy accessRespiratorsBreathing masksCollateral ventilationPleural spaces
A collateral ventilation bypass system with chest tube evacuation device may be utilized in combination to removed trapped air from the lungs. With the chest tube evacuation device, any air trapped in the pleural space may be evacuated through the bypass system to prevent a pneumothorax.
Owner:PORTAERO
Method and System for Sustained-Release of Sclerosing Agent
InactiveUS20090247983A1Minimizes problemAvoid hospitalizationMedical devicesCatheterDiseaseSCLEROSING AGENTS
Methods and systems for treating pleural disease comprising a providing a low dosage of a sclerosing agent over a period of time. Certain examples include catheter with a sclerosing agent that is inserted into the pleural space. The sclerosing agent is released in a sustained-release manner over a period of time to achieve diffuse pleurodesis of the pleural layers.
Owner:UTI LLP +1
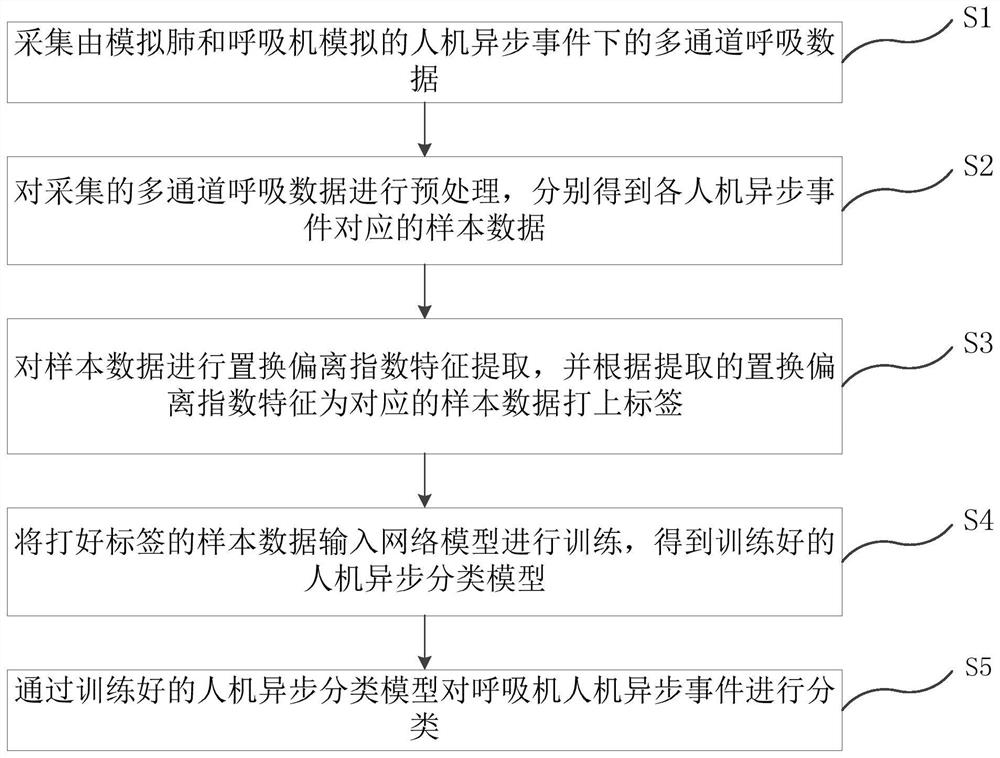
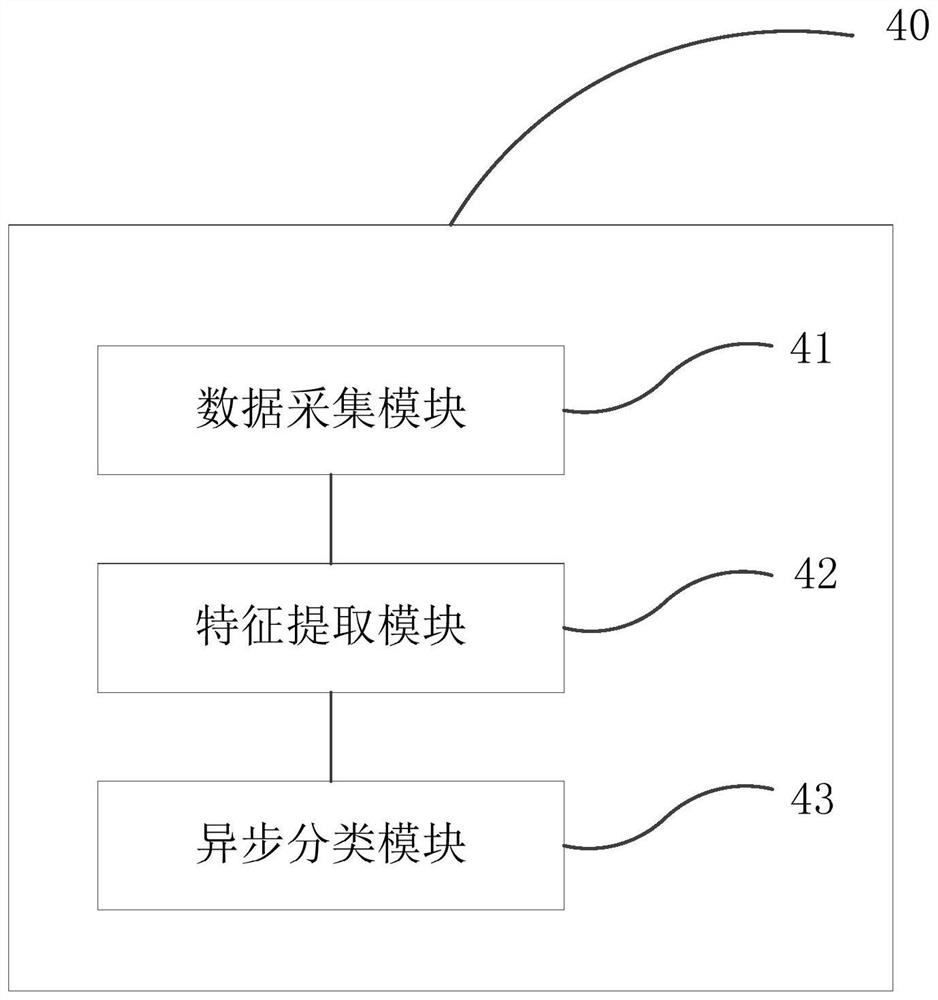
Breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method, terminal and storage medium
PendingCN113539501AEasy to collectReduce distractionsMedical simulationMedical data miningLung alveolusTidal volume
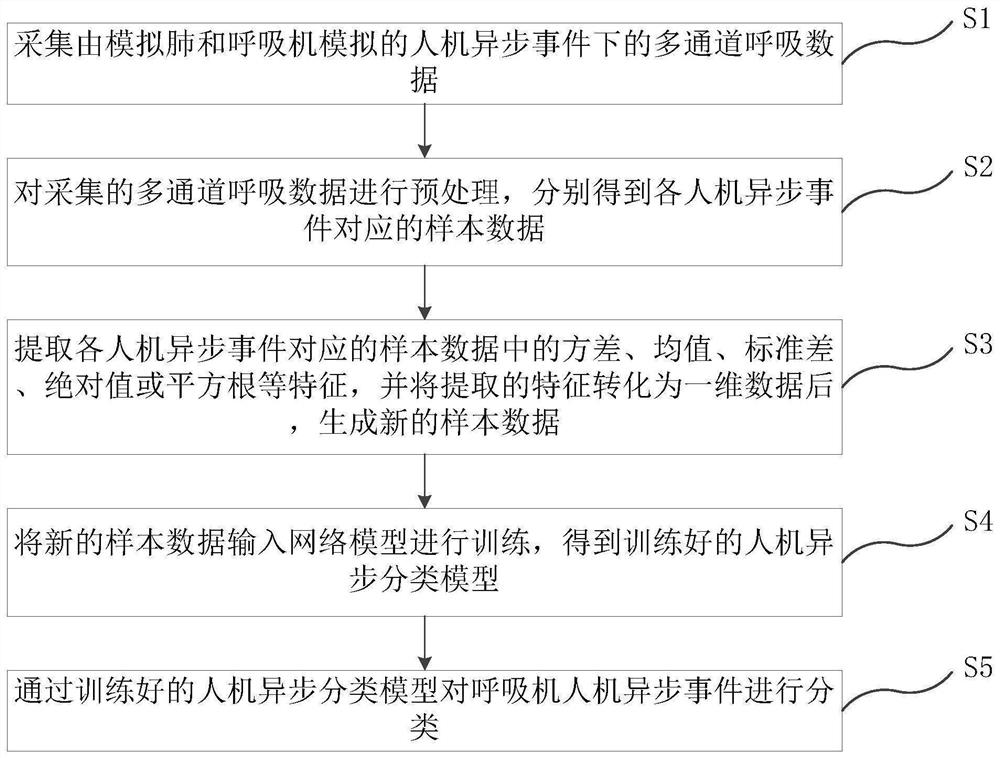
The invention relates to a breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method and system, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: collecting the multi-channel breathing data of a simulated flow channel, a tidal volume channel, airway pressure, alveolar pressure, pleural cavity internal pressure, cardiac pressure, a corrugated pipe position channel and the like under a man-machine asynchronous event simulated by a simulated lung and a breathing machine; carrying out replacement deviation index (PDI) feature extraction on the respiration data, and labeling the respiration data according to the extracted PDI features; inputting the labeled respiration data into a network model for training to obtain a trained man-machine asynchronous classification model; and classifying the breathing machine man-machine asynchronous events through the trained man-machine asynchronous classification model. According to the embodiment of the invention, the acquired respiration data is small in interference and convenient to acquire, difference analysis of the respiration data of the adjacent channels is carried out by using the PDI features, and the accuracy of man-machine asynchronous classification is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
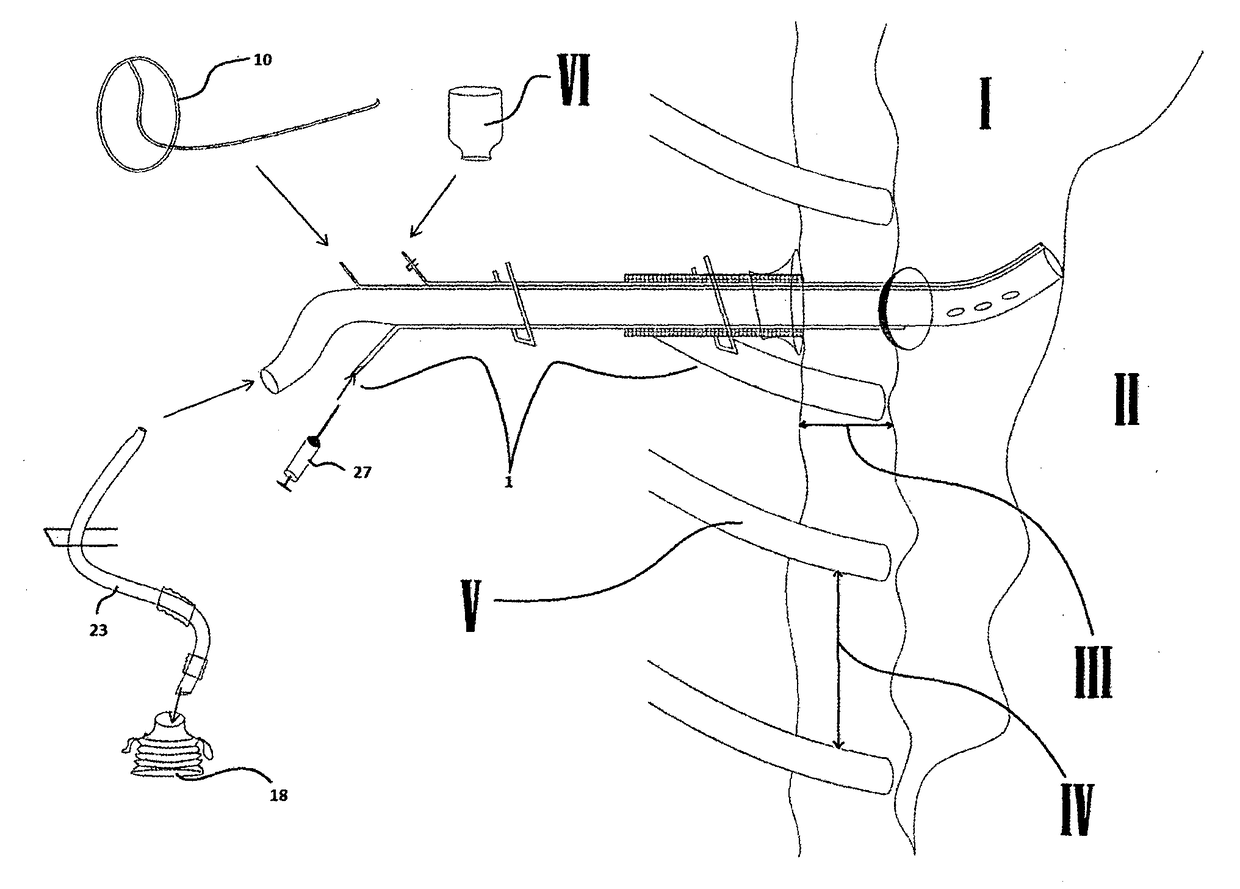
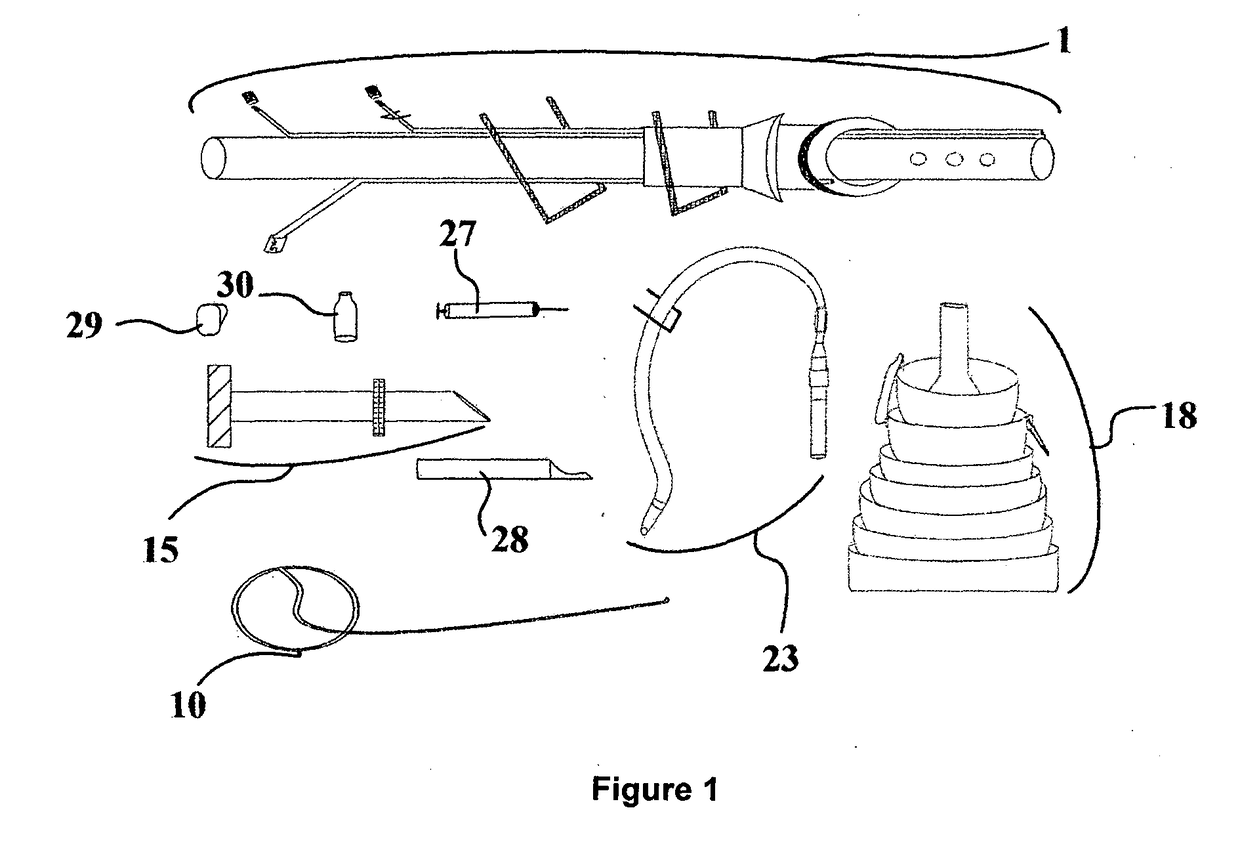
Pleural drainage set and pleural drainage method
ActiveUS20170312408A1Eliminate disadvantagesReduce riskIncision instrumentsGuide wiresPleural drainagePleural spaces
A single use pleural drainage set for medical use, which allows drainage by all physicians of air (pneumothorax), blood (hemothorax) and all other liquids (hydrothorax) accumulated abnormally in the thoracic cavity (pleural space (I)).
Owner:TOKUR MAHMUT
Method and system for sustained-release of sclerosing agent
InactiveUS8361052B2Eliminate side effectsAvoid hospitalizationMedical devicesCatheterDiseaseSCLEROSING AGENTS
Methods and systems for treating pleural disease comprising a providing a low dosage of a sclerosing agent over a period of time. Certain examples include catheter with a sclerosing agent that is inserted into the pleural space. The sclerosing agent is released in a sustained-release manner over a period of time to achieve diffuse pleurodesis of the pleural layers.
Owner:UTI LLP +1
Pneumothorax relief valve method
InactiveUS8257339B1Easy and efficient to manufactureDurable and reliable constructionMedical devicesCatheterPleural spacesGuide tube
An operative member has a cylindrical catheter, an essentially cylindrical hub, an interior passageway and a roll out, open ended flutter valve. The valve has a fixed end secured to the hub and an extendable end. A needle has a stylet distal end and a proximal end formed with a gripping handle. The needle is adapted to be removably positioned within the interior passageway of the catheter and hub. The distance between the handle and the distal end of the needle is slightly greater than the length of the catheter and the hub. After providing the components set forth above, the present invention includes the step of inserting the catheter and needle into a pleural space of a patient and then withdrawing the needle thereby creating an air passageway through the catheter and the catheter and then unrolling the flutter valve from the hub.
Owner:ROSADO MANUEL T
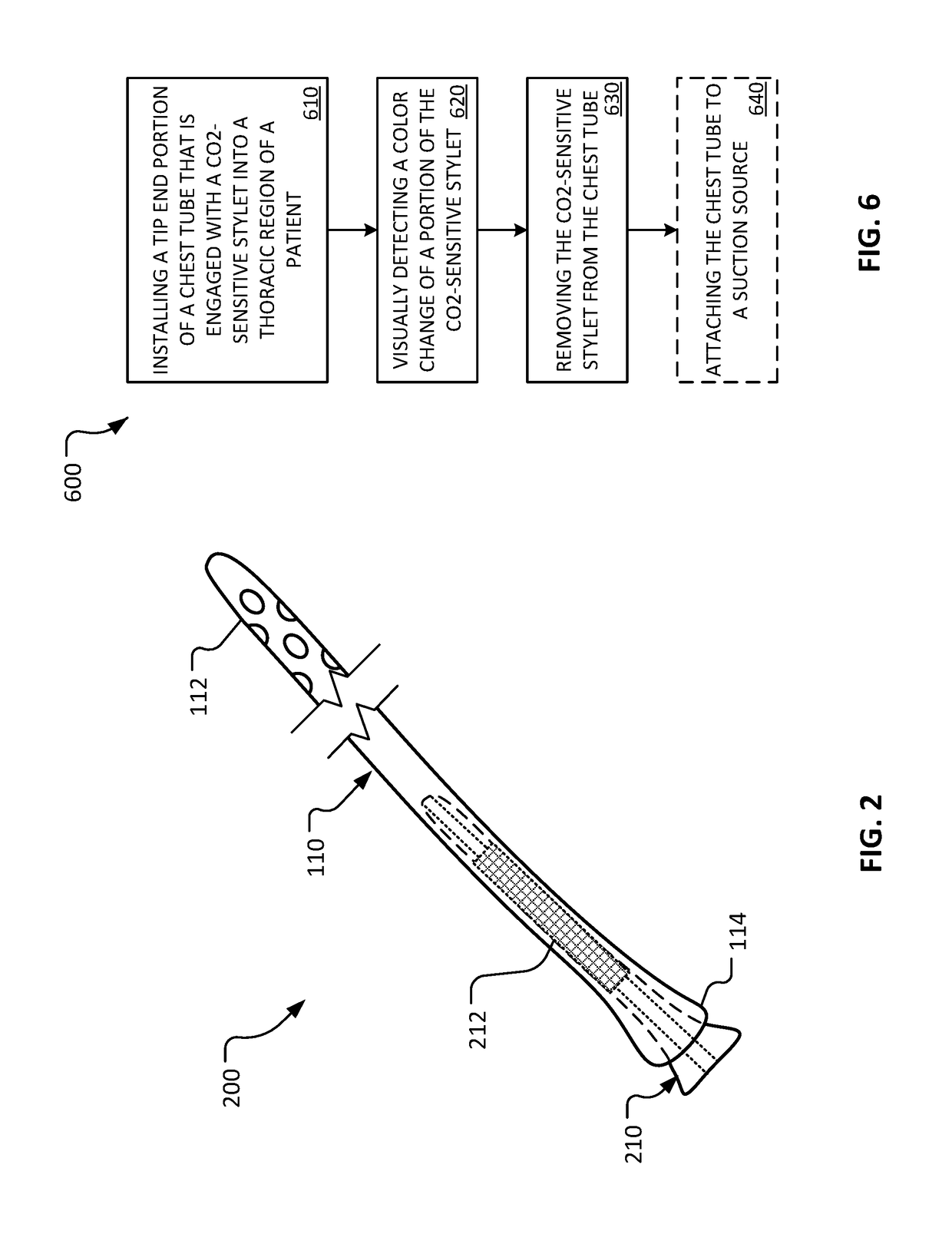
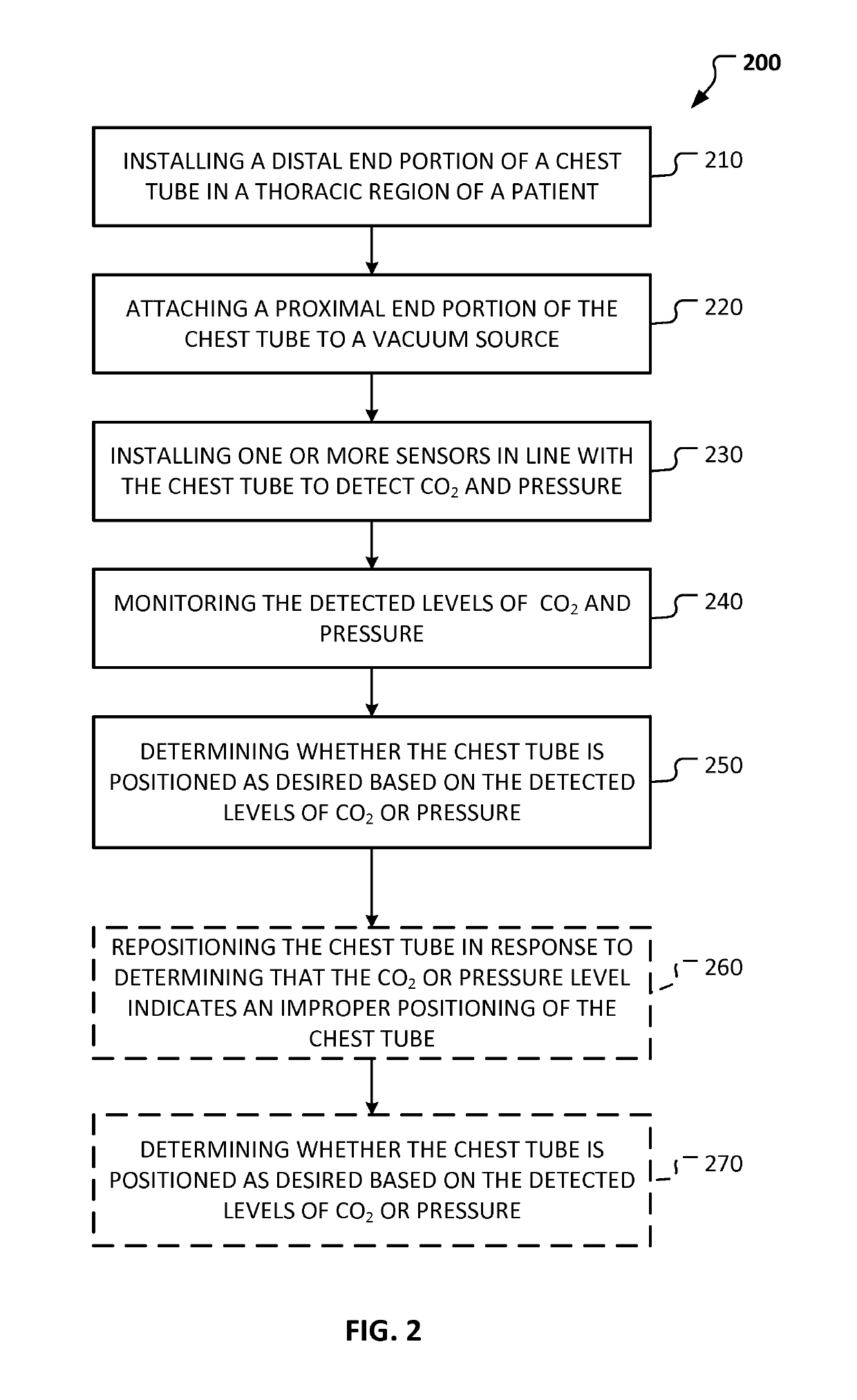
Co2-sensing chest tube and needle thoracostomy devices
ActiveUS20170368241A1Improve objectivityMedical devicesIntravenous devicesNeedle ThoracostomyPleural spaces
This document provides systems and methods that can improve the efficacy of tube and needle thoracostomy. For example, this document provides devices and methods for confirming the proper placement of a chest tube or needle within the pleural space to relieve a pneumothorax or tension pneumothoax.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
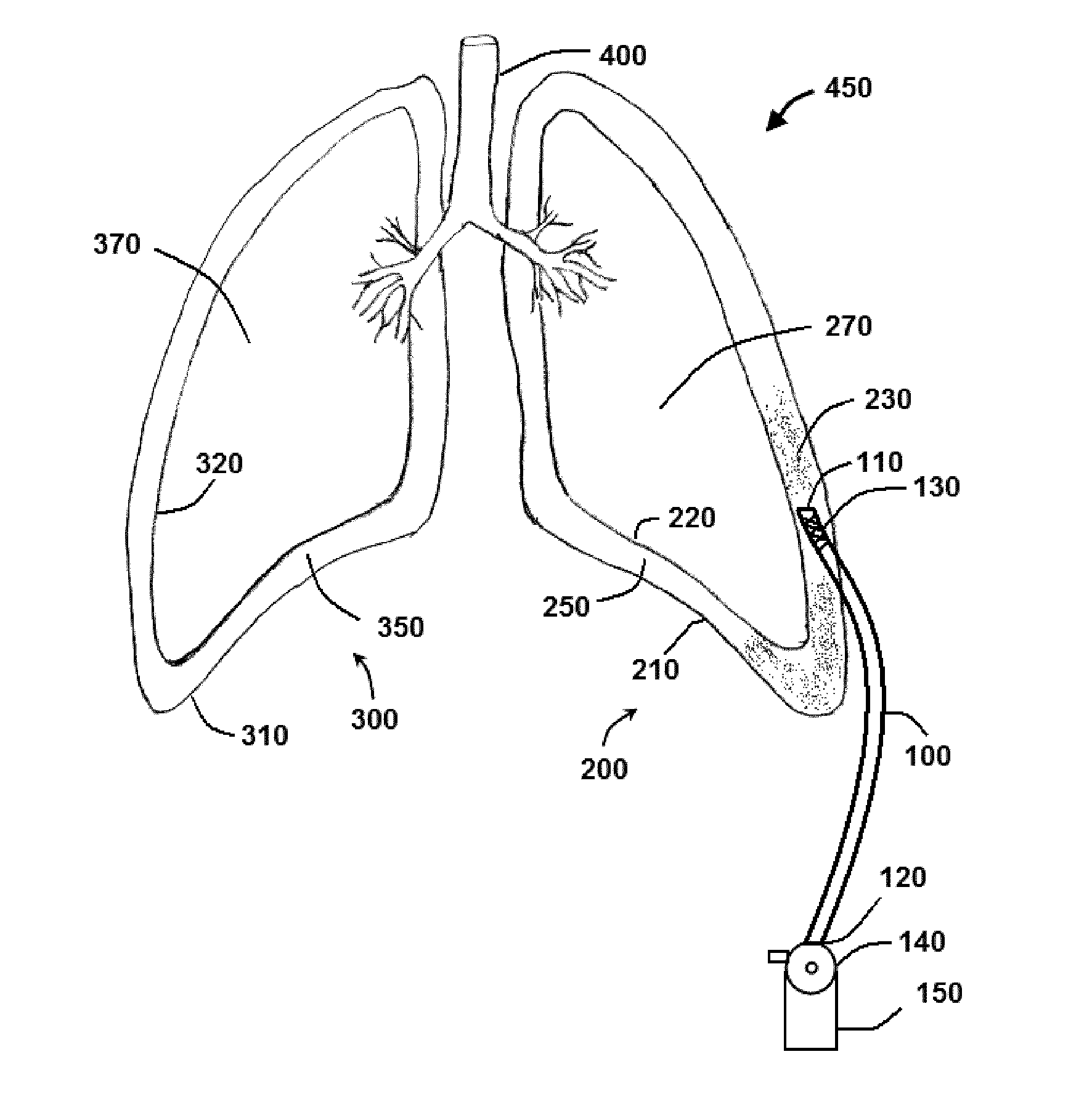
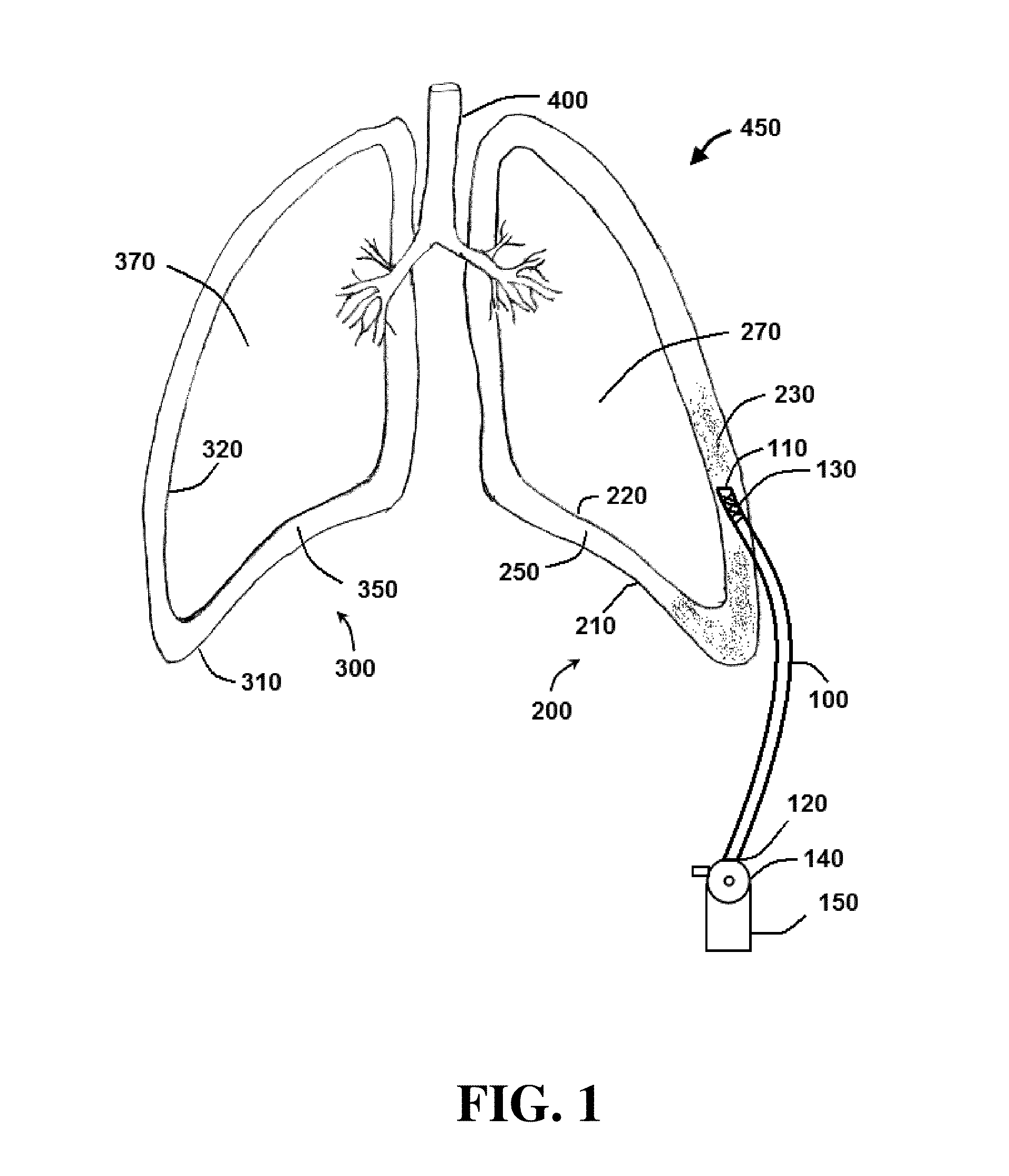
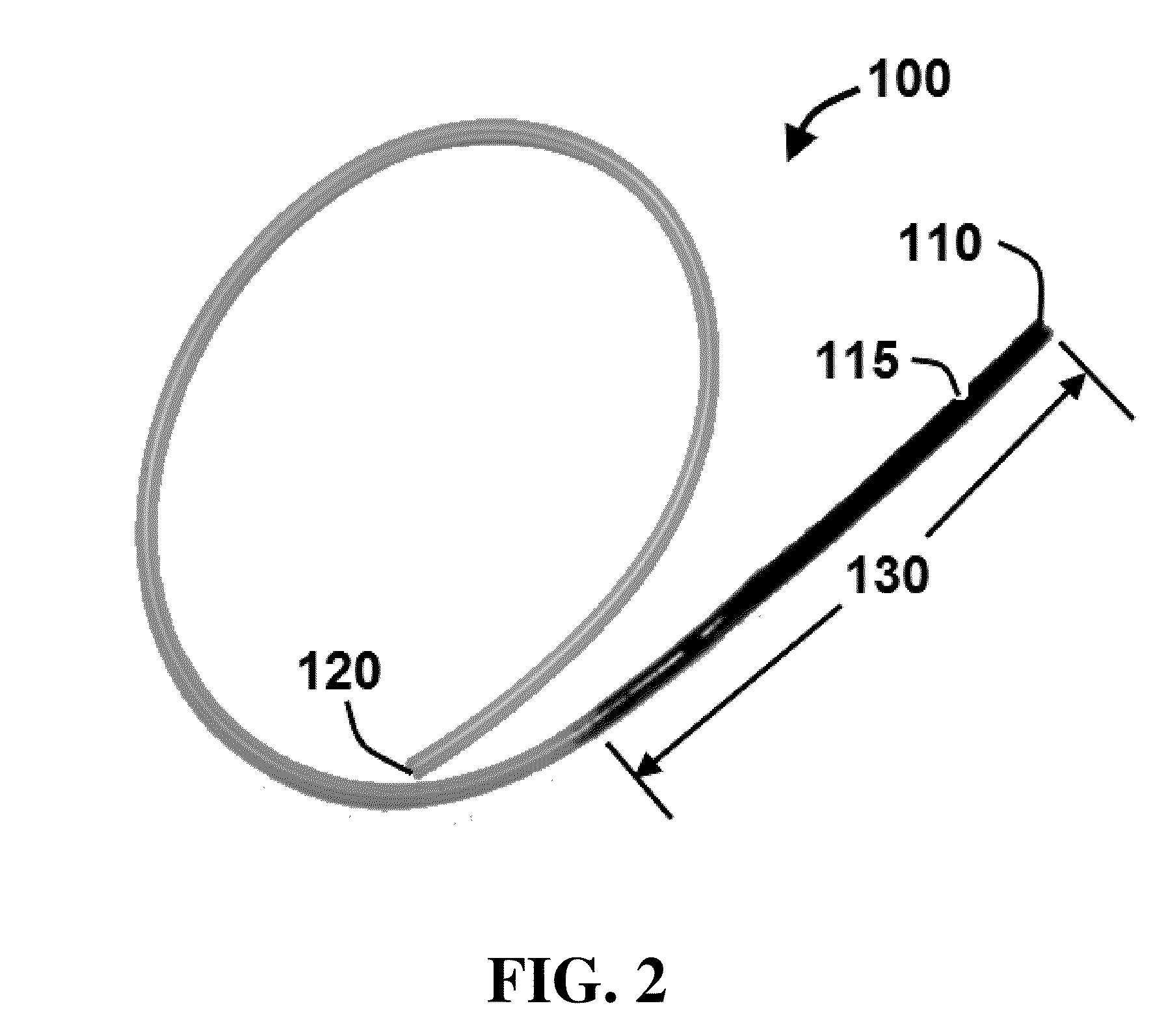
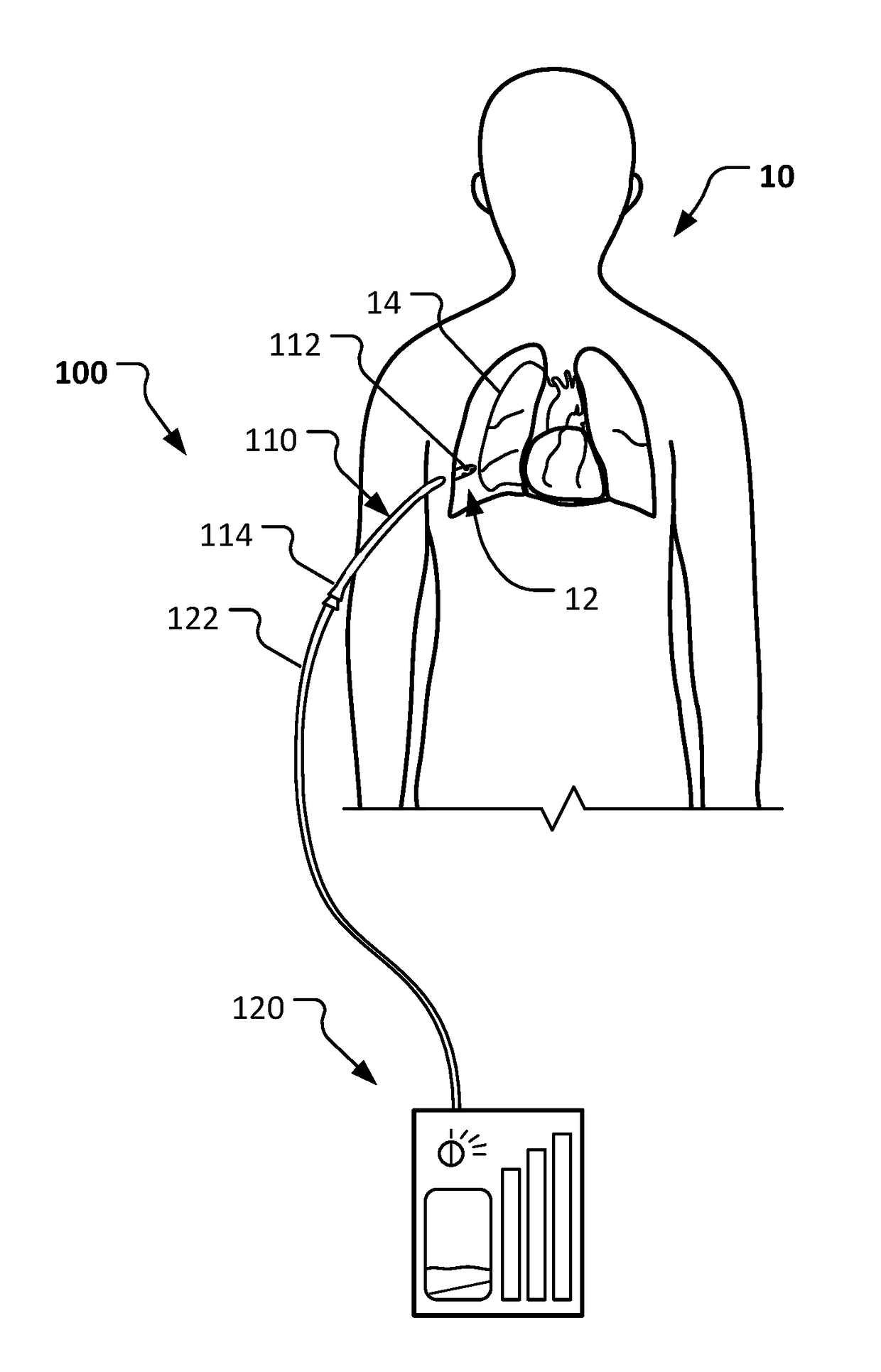
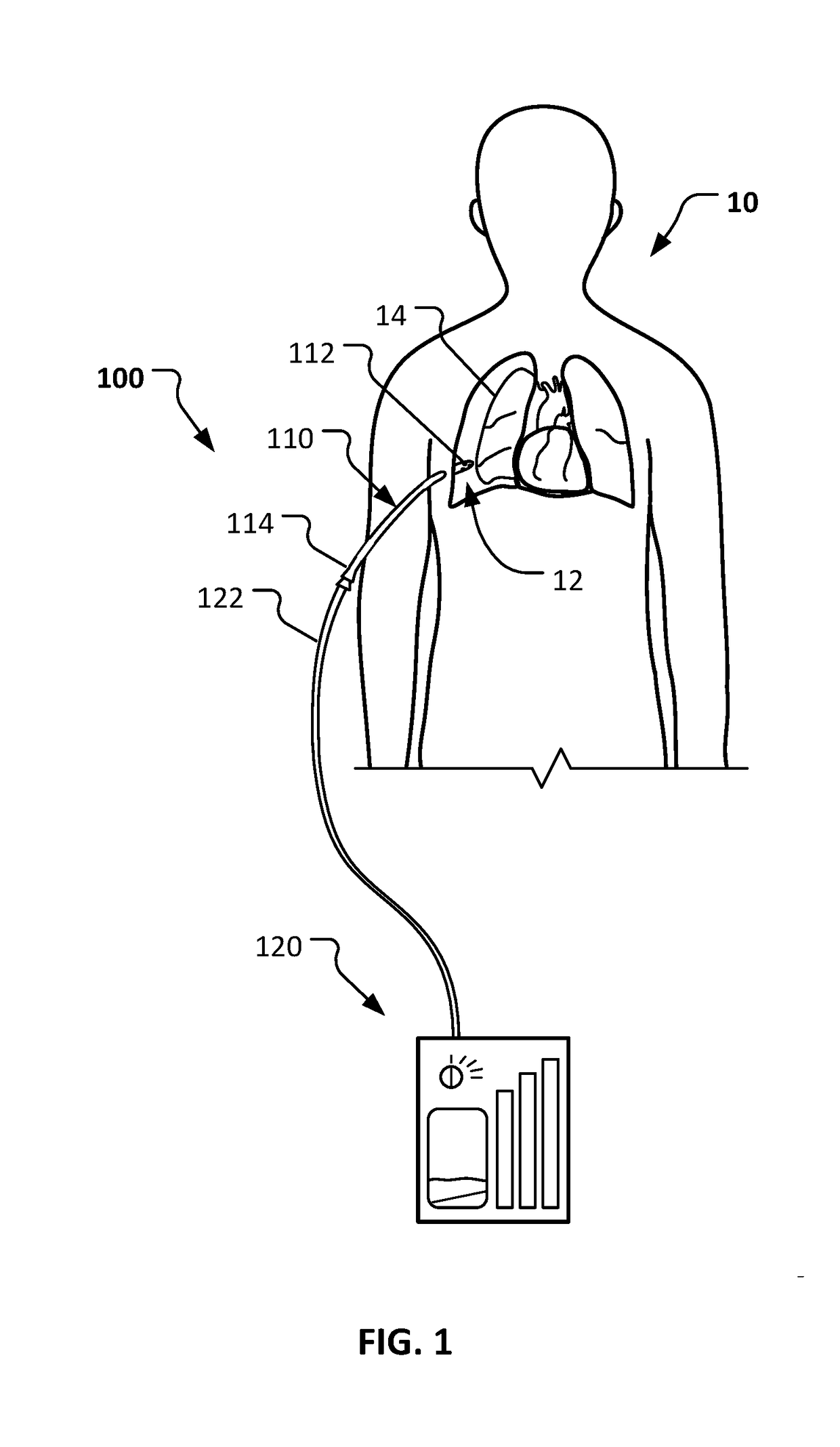
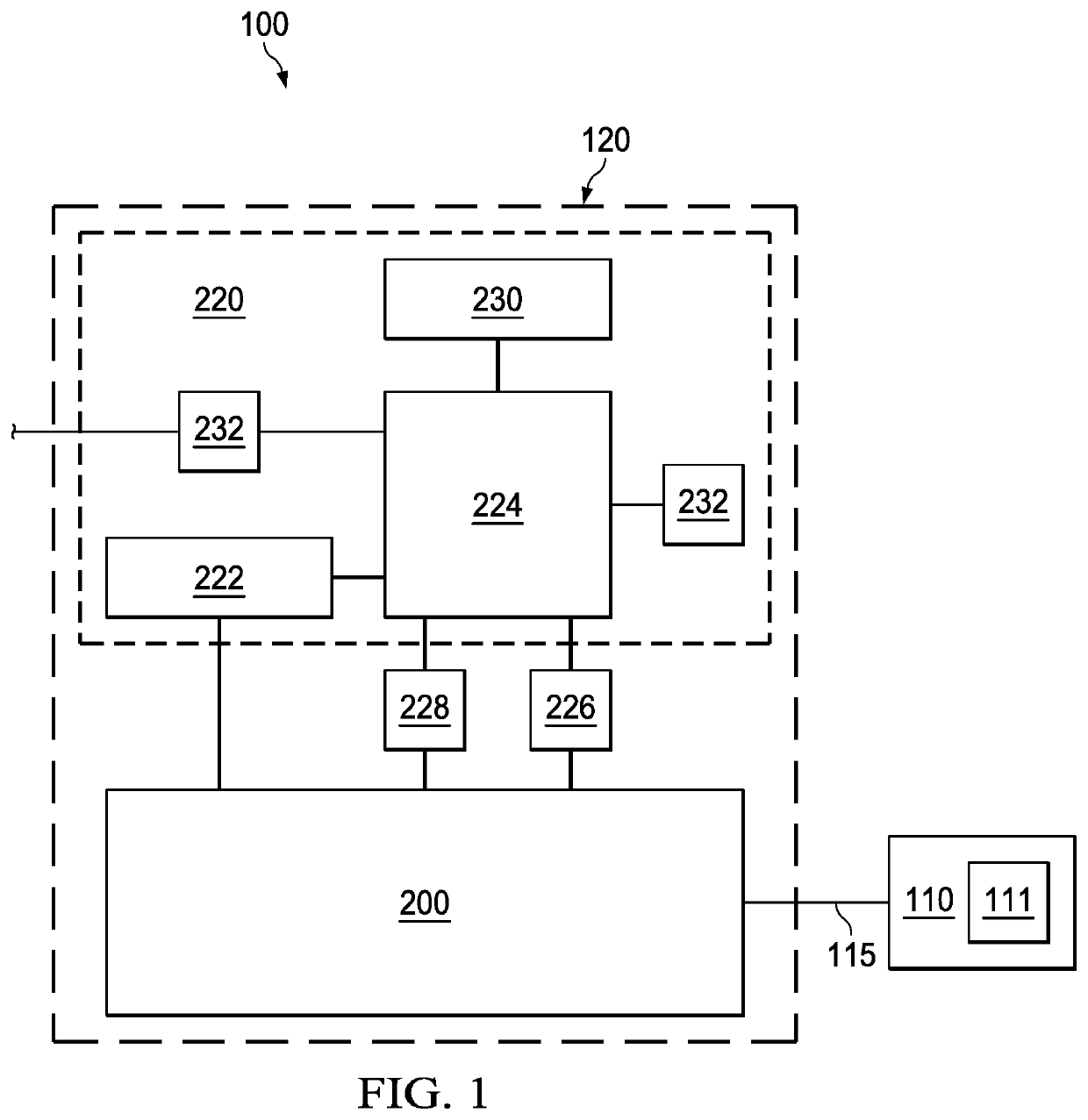
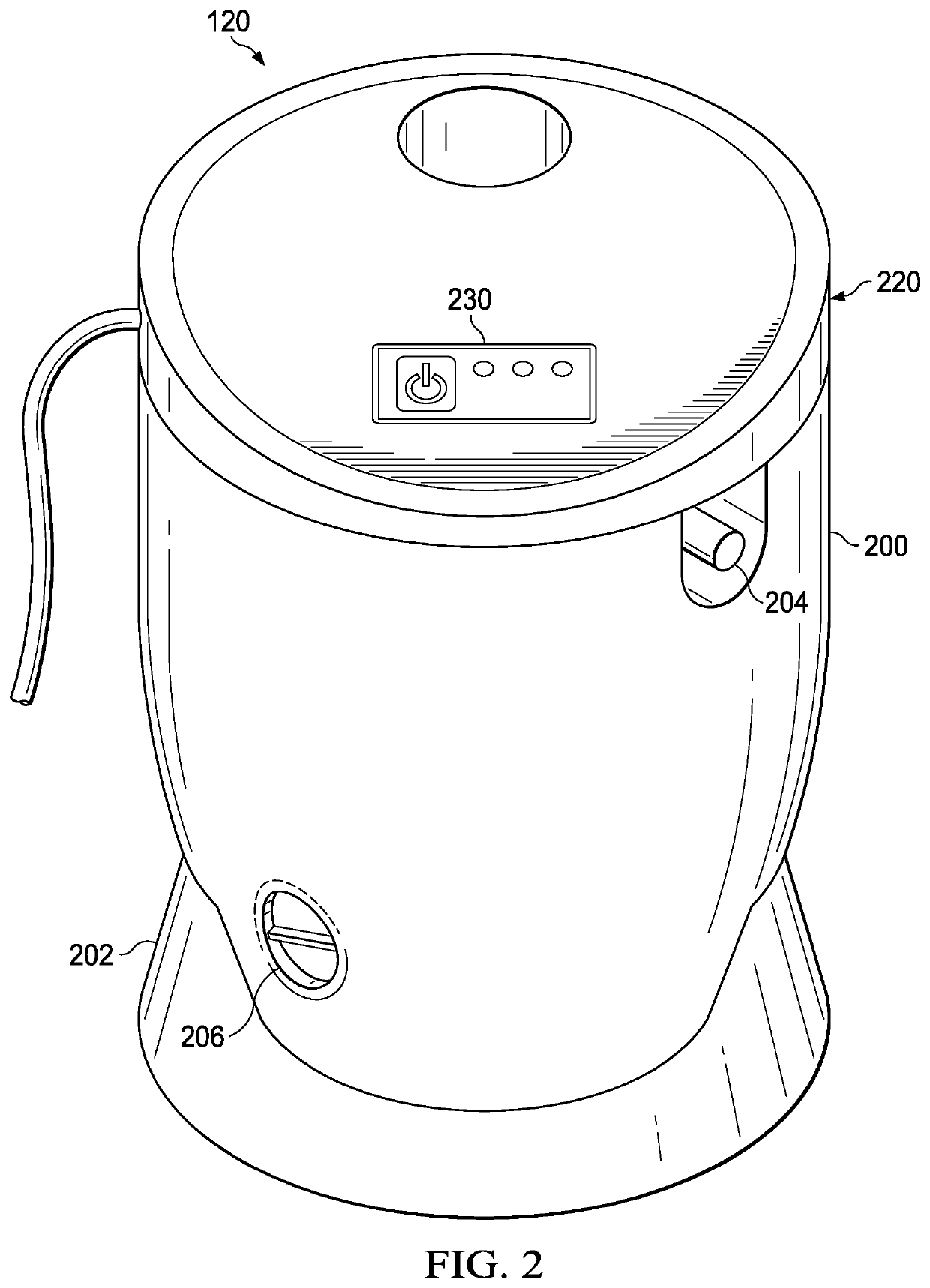
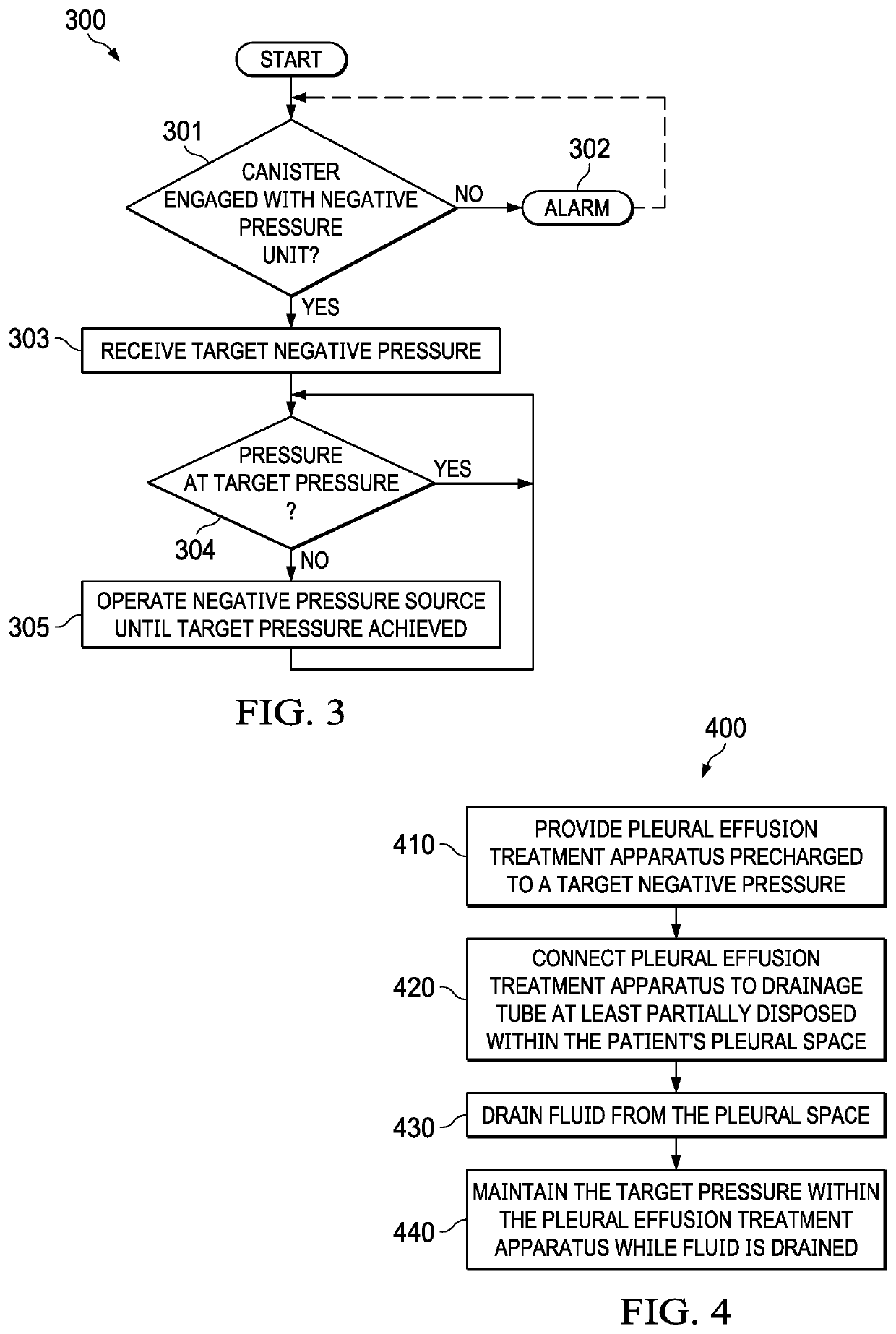
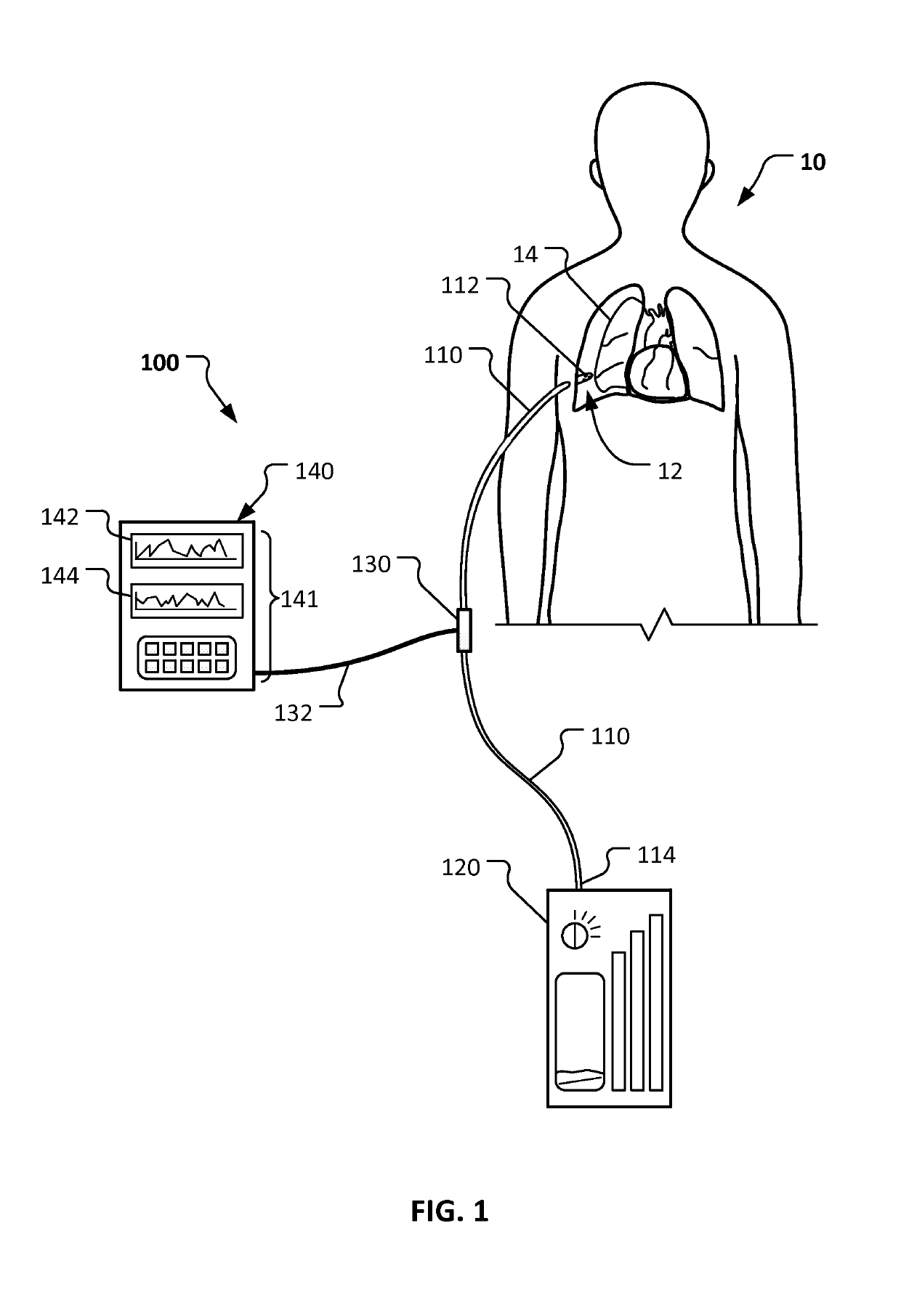
Negative pressure systems for the management of pleural effusion
Systems for the treatment of pleural effusion are disclosed herein. A first system includes a fluid conductor that provides fluid communication with a pleural space of a patient. The first system also includes a canister and a negative-pressure source in fluid communication with the canister. The negative-pressure source pre-charges the canister to a negative-pressure range and maintains the negative-pressure range within the canister while the canister and the fluid conductor are in fluid communication.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method, terminal and storage medium
PendingCN113539398AEasy to collectReduce distractionsCharacter and pattern recognitionLaboratory analysis dataAir volumeTidal volume
The invention relates to a breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method and system, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: collecting multi-channel breathing data such as a simulated flow channel, a tidal volume channel, airway pressure, alveolar pressure, pleural cavity internal pressure, cardiac pressure and a current functional residual air volume channel under a man-machine asynchronous event simulated by a simulated lung and a breathing machine; performing variance, mean value, standard deviation, absolute value or square root feature extraction on the respiration data, generating sample data according to the extracted features, and training according to the sample data to obtain a man-machine asynchronous classification model; and classifying the breathing machine man-machine asynchronous events through the trained man-machine asynchronous classification model. According to the embodiment of the invention, the acquired respiration data is small in interference and convenient to acquire, and the difference analysis of the respiration data of the adjacent channels is carried out by using the characteristics such as variance, mean value, standard deviation, absolute value or square root, so the accuracy of man-machine asynchronous classification is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
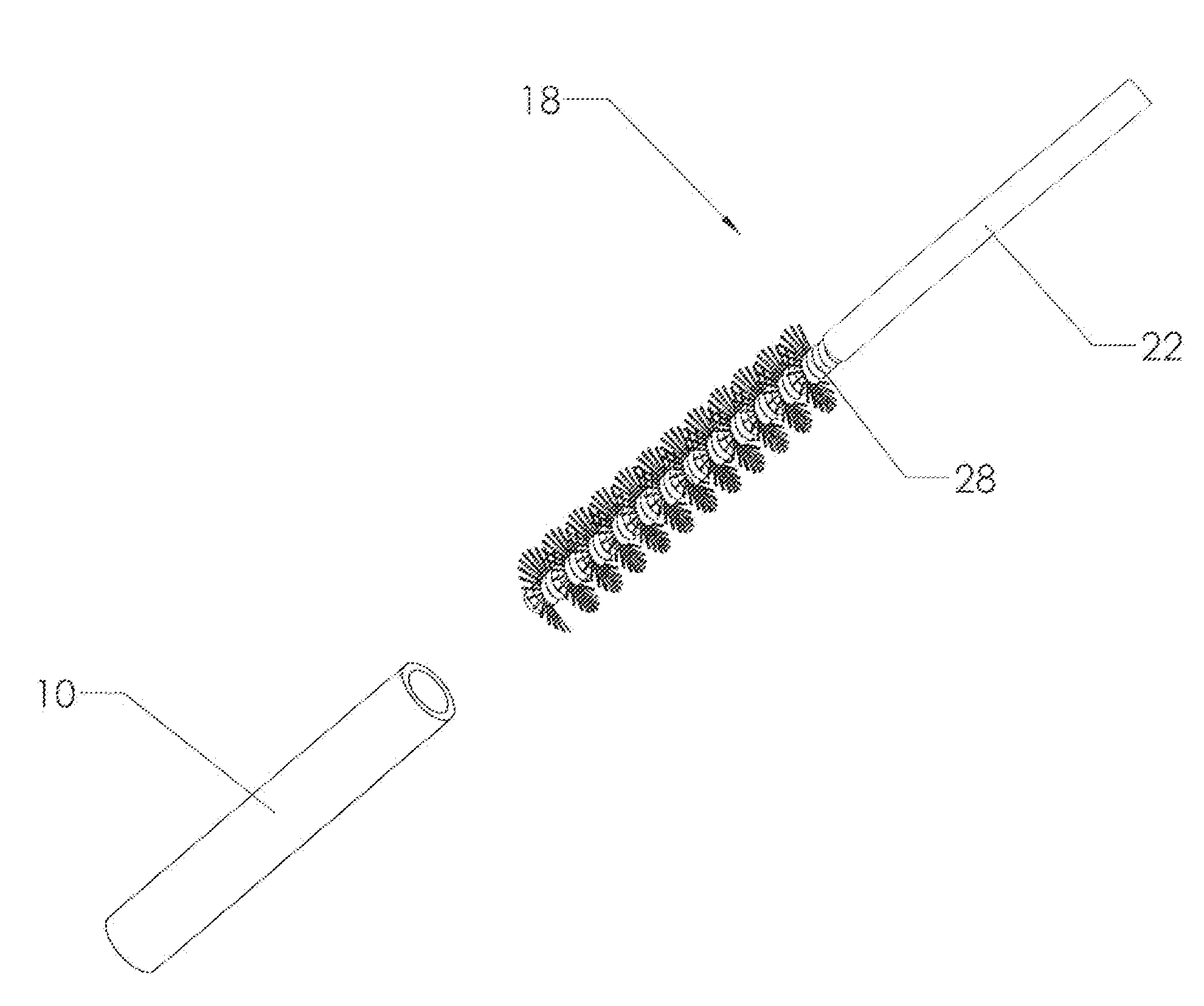
Abrading Device and Method for Creating Abrasions on a Membrane
ActiveUS20160302813A1Easy to withdrawEasily withdraw the deviceEndoscopic cutting instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersBristlePleural spaces
Owner:BUTTERFIELD KEITH
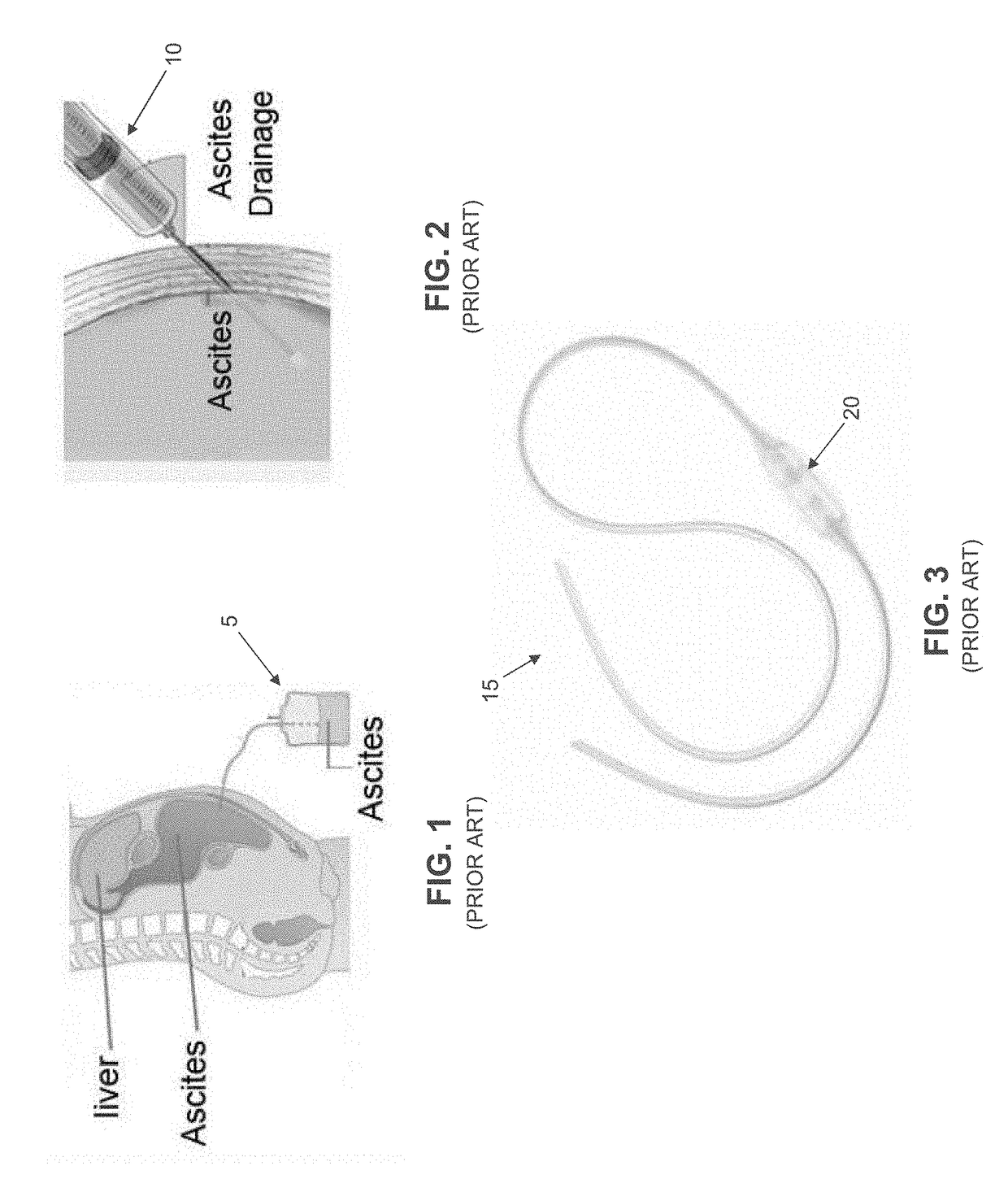
Method and apparatus for treating fluid build-up in a body cavity, including method and apparatus for treating ascites and pleural effusions
InactiveUS20180339141A1Reduce the burden onLong burdenWound drainsMedical devicesAscitic fluidPleural cavity
A method for treating pleural effusion in a patient, the method comprising: providing a valve comprising: a body having a distal end, a proximal end and a lumen extending therebetween; an inlet disposed at the proximal end of the body, the inlet being fluidically connected to the lumen; an outlet disposed at the distal end of the body, the outlet being fluidically connected to the lumen; and at least one valve element disposed in the lumen of the body, the at least one valve element being a one-way valve element configured to permit the passage of fluid in a single direction through the lumen of the body; and implanting the valve in the body of the patient such that the inlet of the valve is fluidically connected to the pleural cavity of the patient, and such that the outlet of the valve is fluidically connected to a second body cavity.
Owner:EWIMED
Automatic pleural-peritonal pump
ActiveUS20210283330A1High success rateRelieve symptomsWound drainsMedical devicesEngineeringPleural spaces
An automatic pump-based fluid management system, as described herein, comprises an intercostal pump that is, generally, a resiliently flexible bulb having an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is attached to a first tube that extends from the intercostal pump to a first area of a patient's body, for example, the patient's pleural cavity. The outlet is connected to a second tube that extends from the intercostal pump to a second area of a patient's body, for example, the patient's peritoneal cavity. In use, the intercostal pump is placed between a first rib and a second rib in a patient. The intercostal pump operates by being successively compressed and decompressed between the first and second ribs as the patient breaths.
Owner:PLEURAL DYNAMICS INC
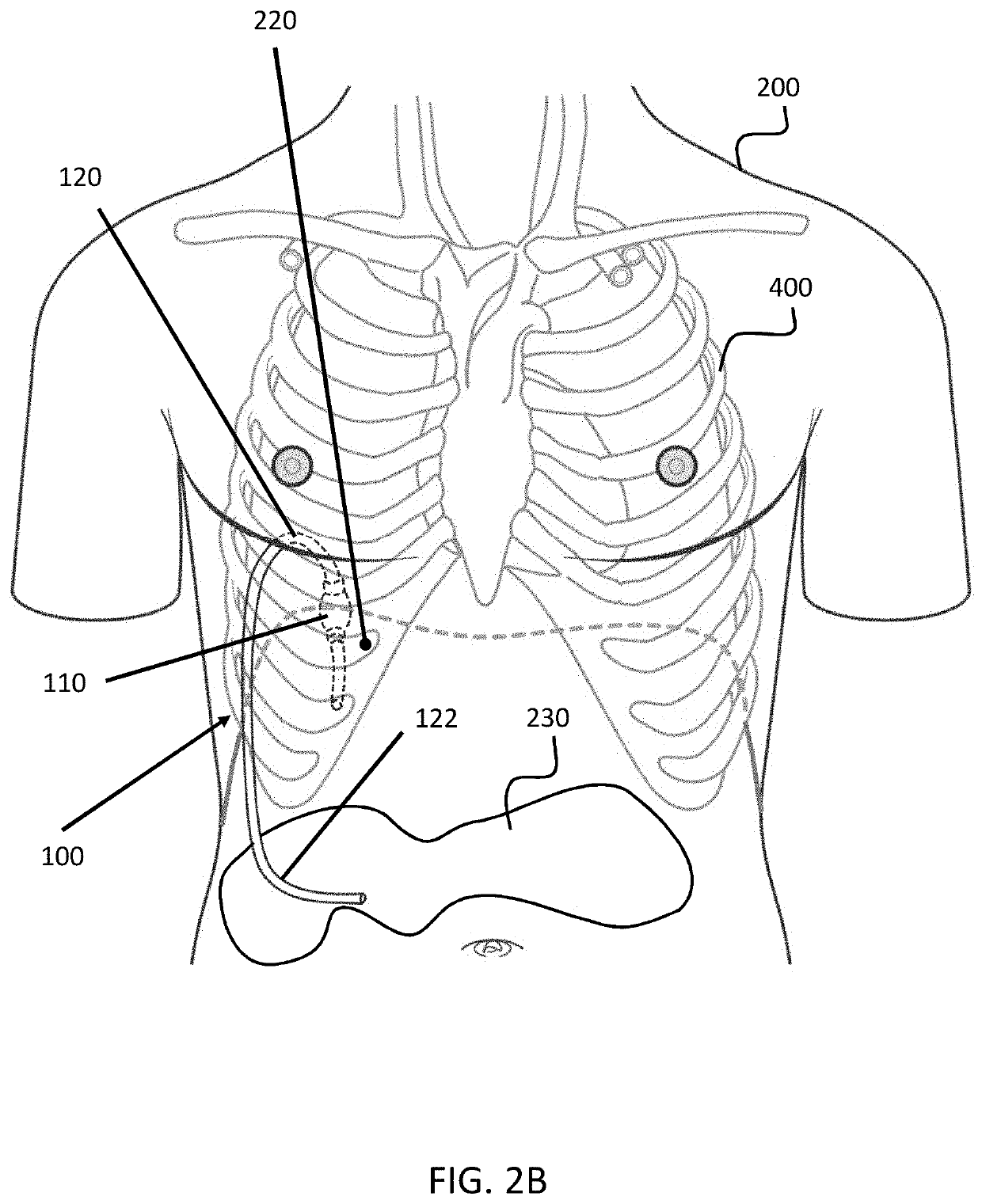
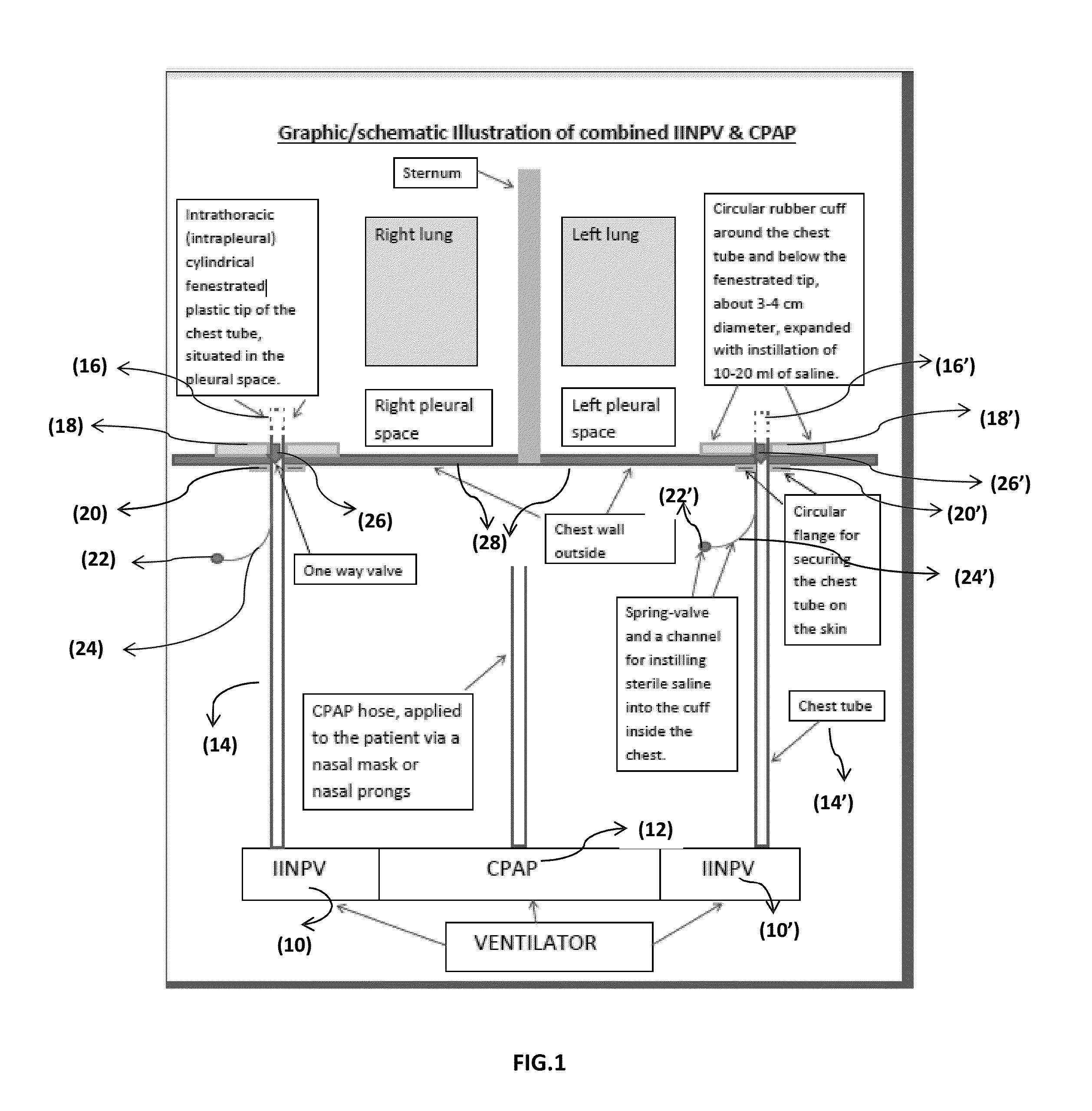
Invasive Intermittent Negative Pressure Ventilation
InactiveUS20160235623A1Prevent outward displacementImprove securityRespiratory masksInfusion devicesDiseaseDiagnostic Radiology Modality
The present invention introduces novel invasive intermittent negative pressure ventilation for treatment of adults ventilator dependent respiratory failure (VDRF) in various advanced neuromuscular disorders (NMDs). It's a combination of invasive intermittent negative pressure ventilator (IINPV) and continues positive airway pressure (CPAP) into transportable ventilator. Implementation of invasive negative pressure ventilation is via chest tubes to each pleural space, and CPAP is applied via nasal mask or nasal prongs. The IINPV's initiation of breath is patient-triggered via a flow sensor incorporated in CPAP nasal mask / nasal prongs. This novel concept of VDRF management in advanced NMDs will prove to be superior over present modalities of treatment in many aspects which include but not limited to avoidance of tracheostomies, reduction of recurrent respiratory infection, greater patient's independence and quality of life, preserved ability to speak and clear airways spontaneously, liberation from positive pressure mechanical ventilation etc.
Owner:MIRZOYAN MICHAEL
Improved method of treating pleural effusion
The present invention provides methods of treating pleural effusion in a subject, comprising removing fluid from the pleural space at an increased frequency, as compared to previous methods.
Owner:CAREFUSION 2200 INC +1
Continuous blood glucose monitor
A device may be implanted subcutaneously with an attached catheter inserted within, e.g., the peritoneal cavity of a subject. The catheter and / or device may also be inserted into another space, e.g., subcutaneous, vascular, peritoneal, cerebrospinal, pleural spaces, etc. The peritoneal fluid which normally collects and / or flows through the peritoneal cavity may be detected by the catheter and analyzed via the device to detect the concentration of glucose within the fluid.
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
Portable chest tube pressure and CO2 monitor
ActiveUS10335524B2Improve objectivityAccurate placementMedical devicesIntravenous devicesPleural spacesReady to use
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Interventional treatment system suitable for pneumology department
InactiveCN113398345AImprove absorption efficiencyEasy to moveSurgical needlesMedical devicesPleural spacesDrainage tubes
The invention provides an interventional treatment system suitable for pneumology department, which is applied to the field of medical instruments, the system mainly comprises a drainage absorption module, a puncture module, a suction module and a monitoring module, by arranging the drainage absorption module, pneumatosis and hydrops in a pleural cavity can be permeated and discharged, and meanwhile, the drainage absorption module is arranged to be a sponge, hydrops are discharged through the absorption and permeation effects of the sponge, and meanwhile, hydrops can be discharged through pores of the sponge; by arranging a traction mechanism, the cotton can be pushed out, so that the contact area between the cotton and the hydrops is increased, and the hydrops absorption efficiency is improved; by arranging the puncture module, the trachea can be opened, meanwhile, a drainage tube can be directly inserted into the pleural cavity conveniently, meanwhile, the puncture module is arranged to be of a structure convenient to disassemble, after the drainage tube is inserted, the puncture module is disassembled so that the drainage tube can be moved and operated conveniently, and meanwhile it is guaranteed that the drainage tube cannot be scratched by a puncture needle when the drainage tube is withdrawn.
Owner:王苹
Pleural drainage set and pleural drainage method
ActiveUS10828405B2Eliminate disadvantagesReduce riskIncision instrumentsGuide wiresPleural drainageThoracic structure
Owner:TOKUR MAHMUT
Connector for catheter
A connector for use with a pleural catheter that connects securely a drainage tube to a valve of the plural catheter. A system including a fluid receptacle having a negative fluid pressure, a plural catheter having an end designed for implantation into a pleural space of a subject, and an opposite second end having a valve feature, a drainage tube having an end connected to the fluid receptacle and another end having a connector that securely connects the drainage tube to the valve feature of the catheter.
Owner:CANADIAN HOSPITAL SPECIALTIES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com