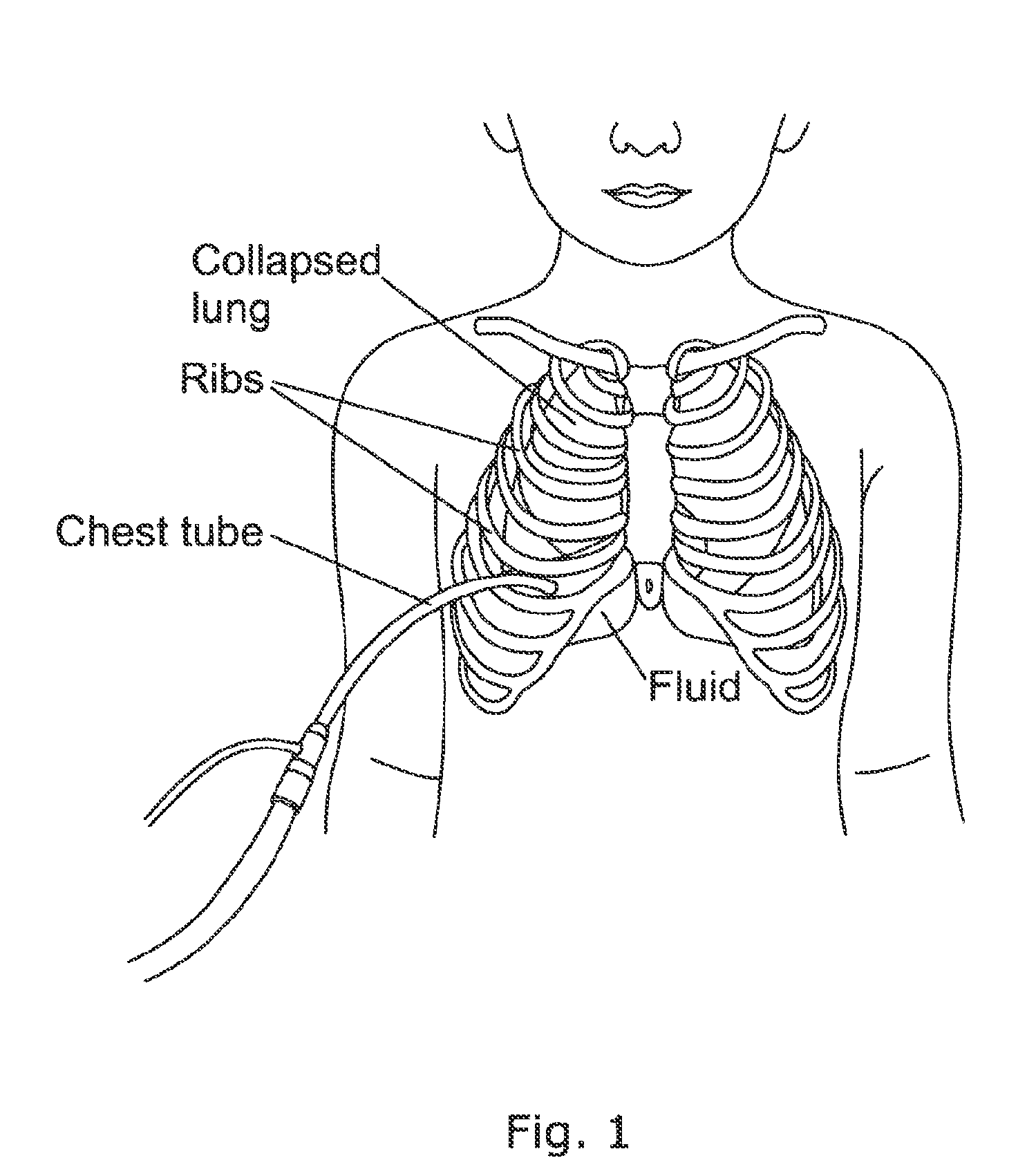
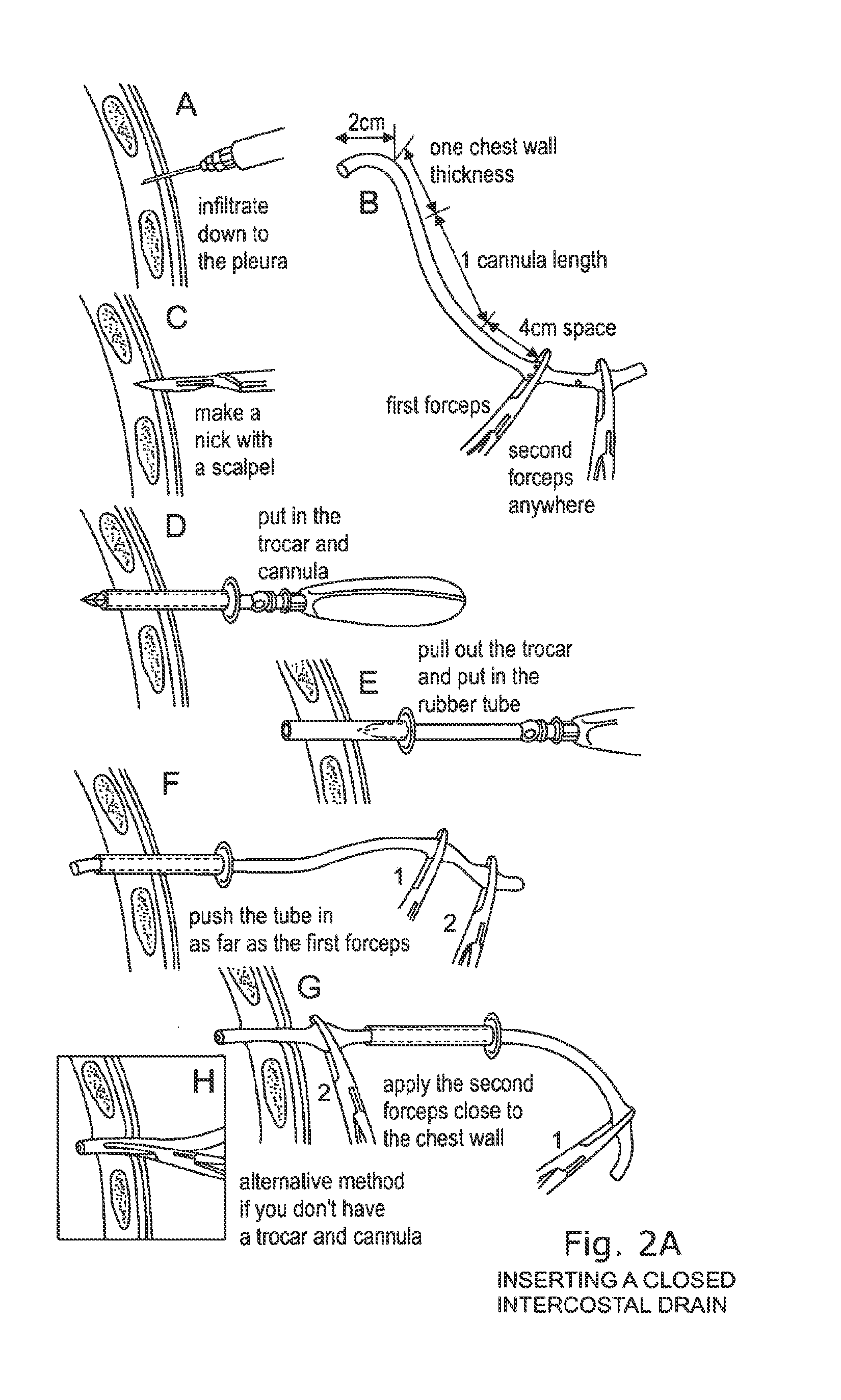
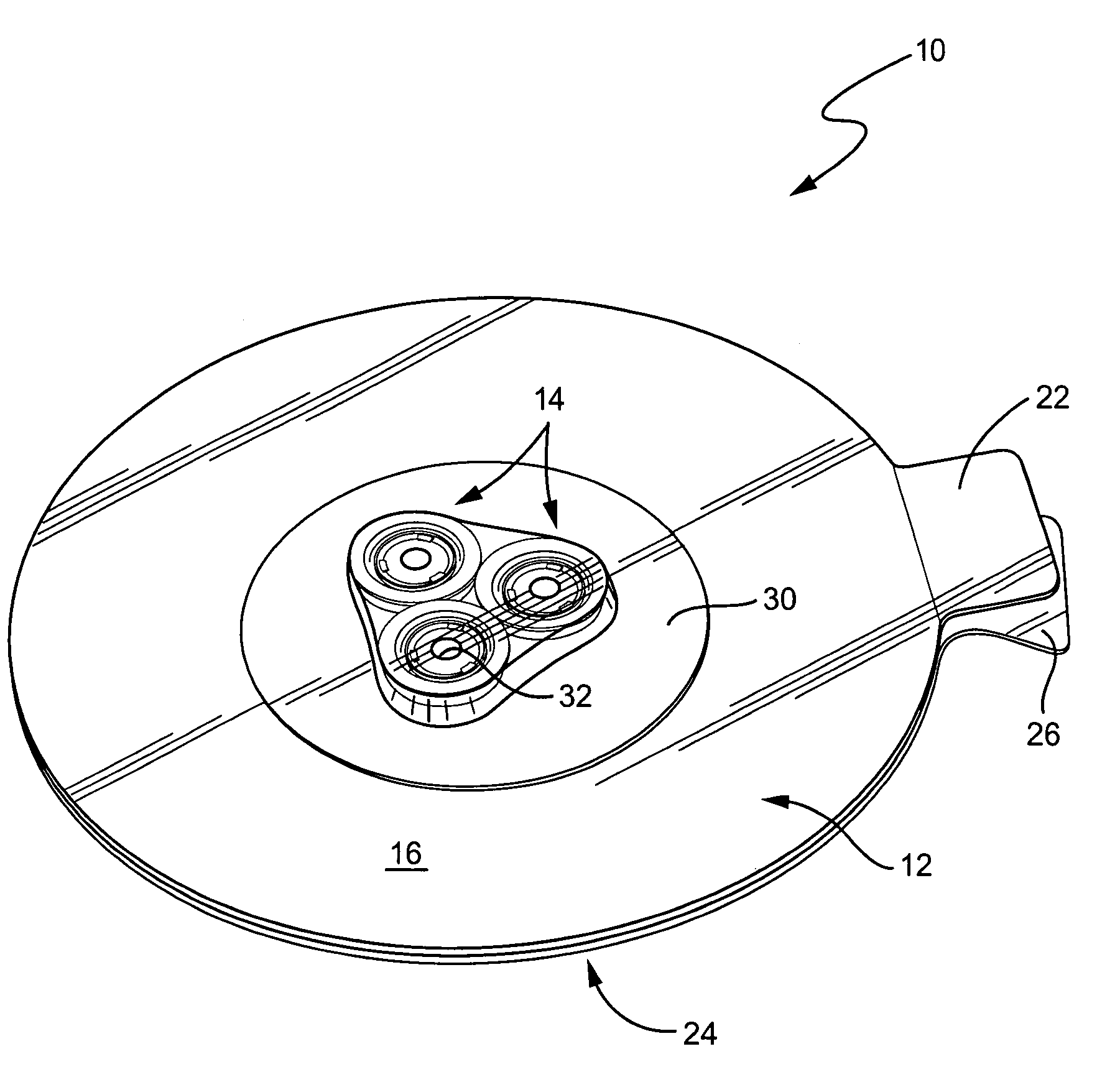
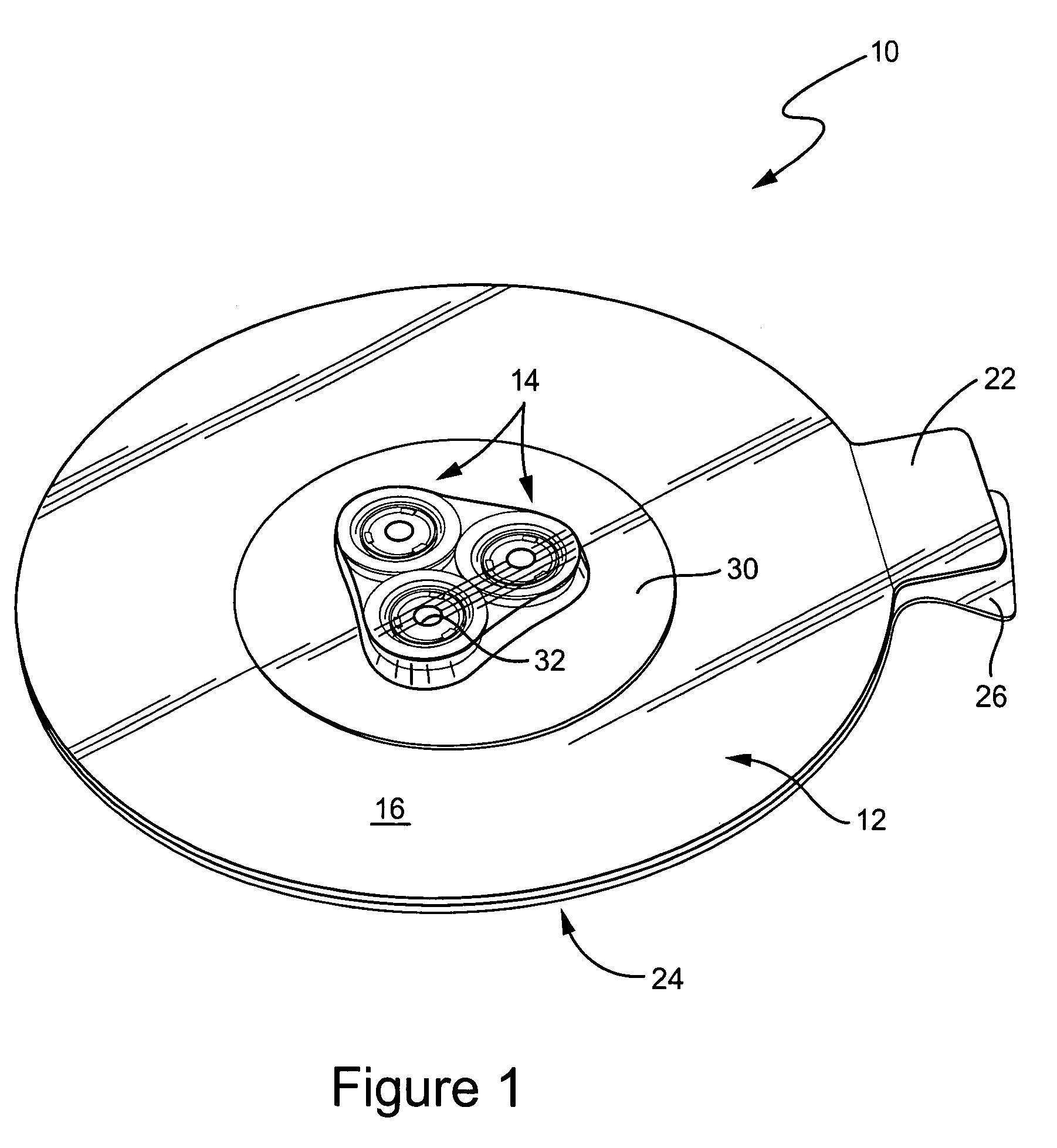
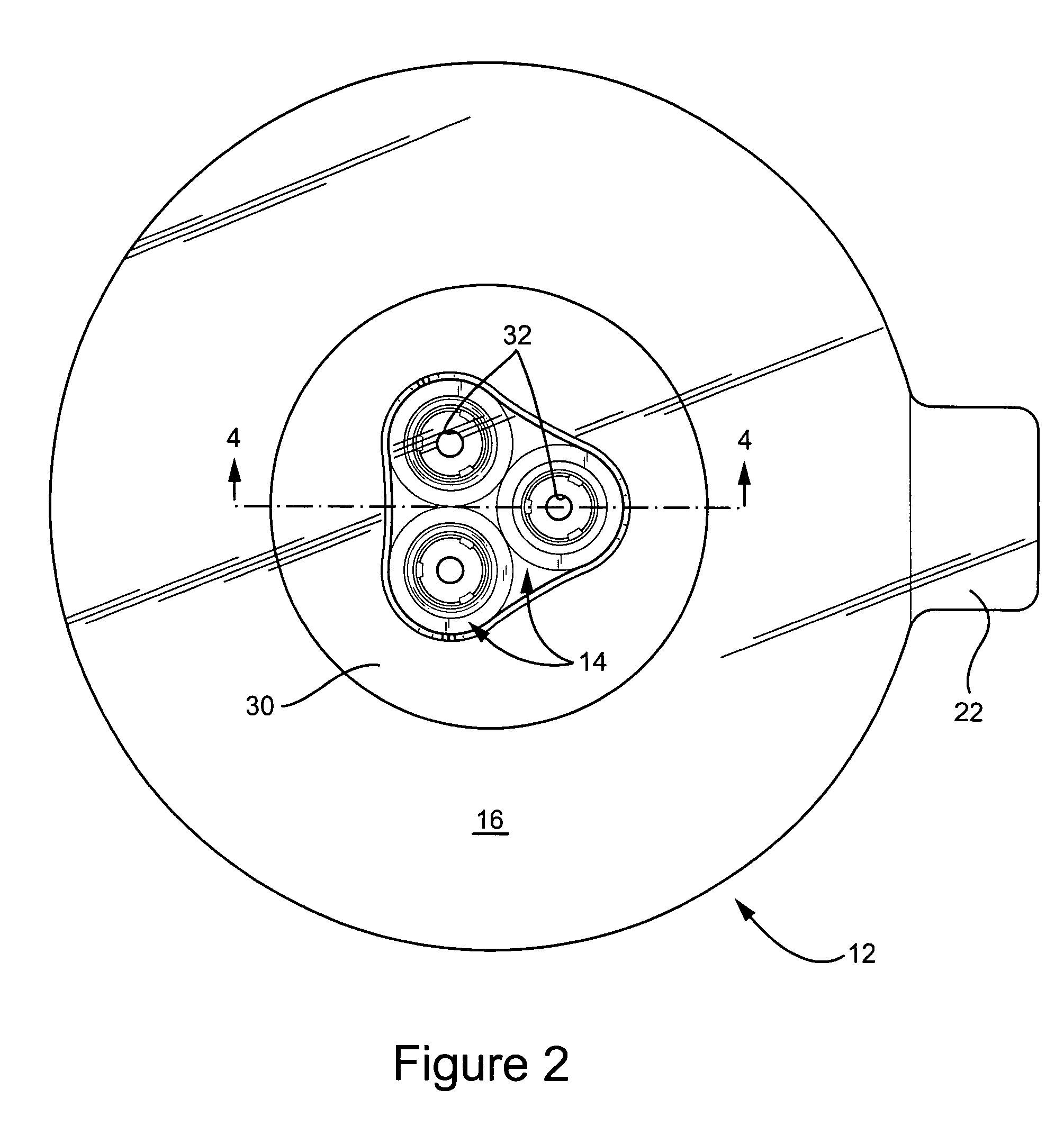
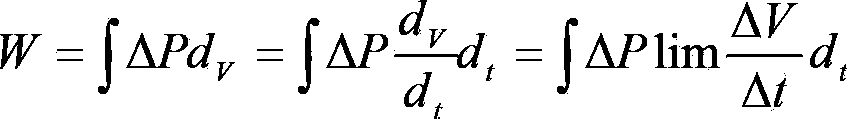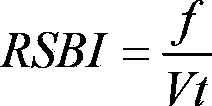Patents
Literature
109 results about "Pleural cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
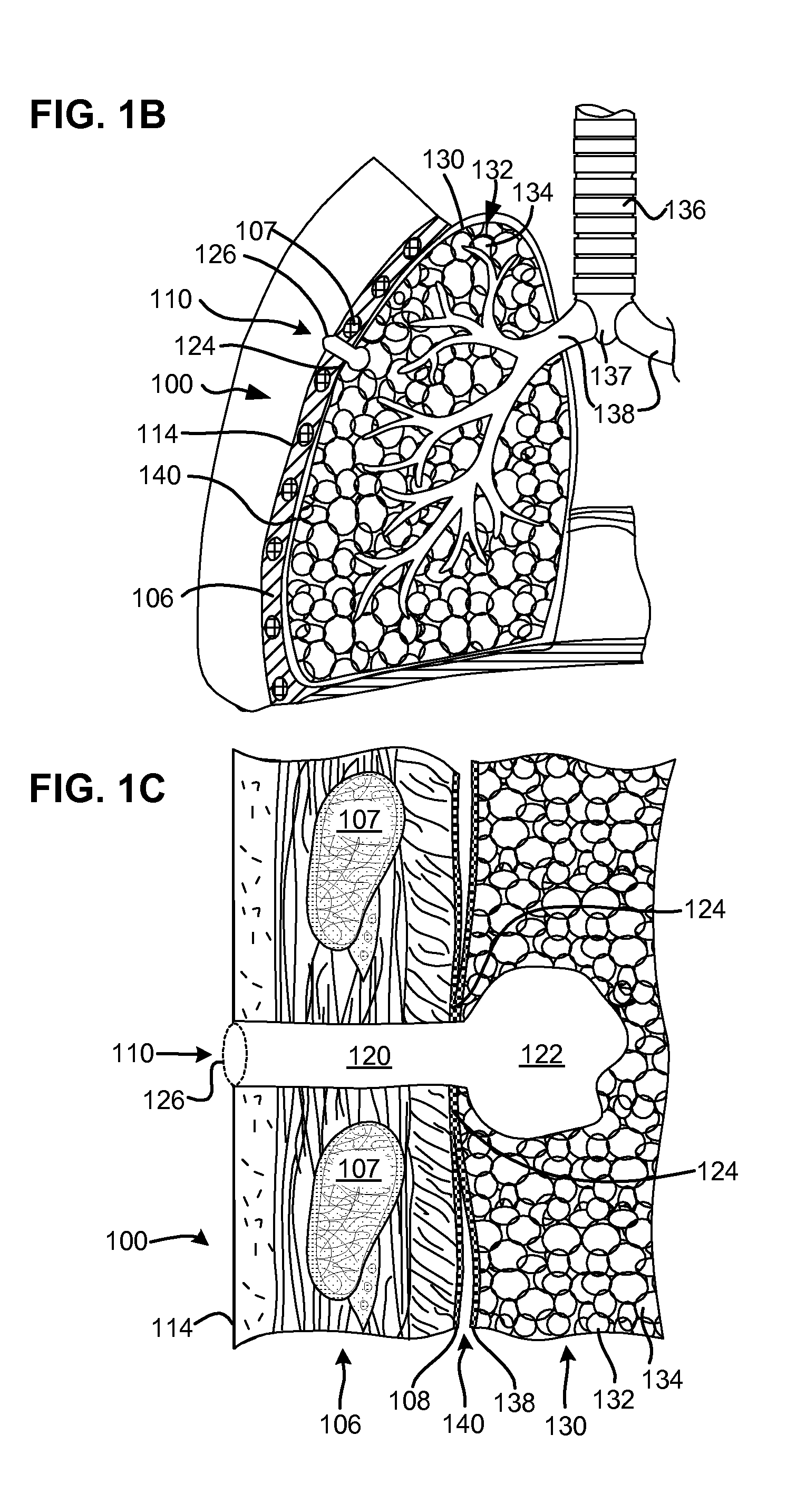
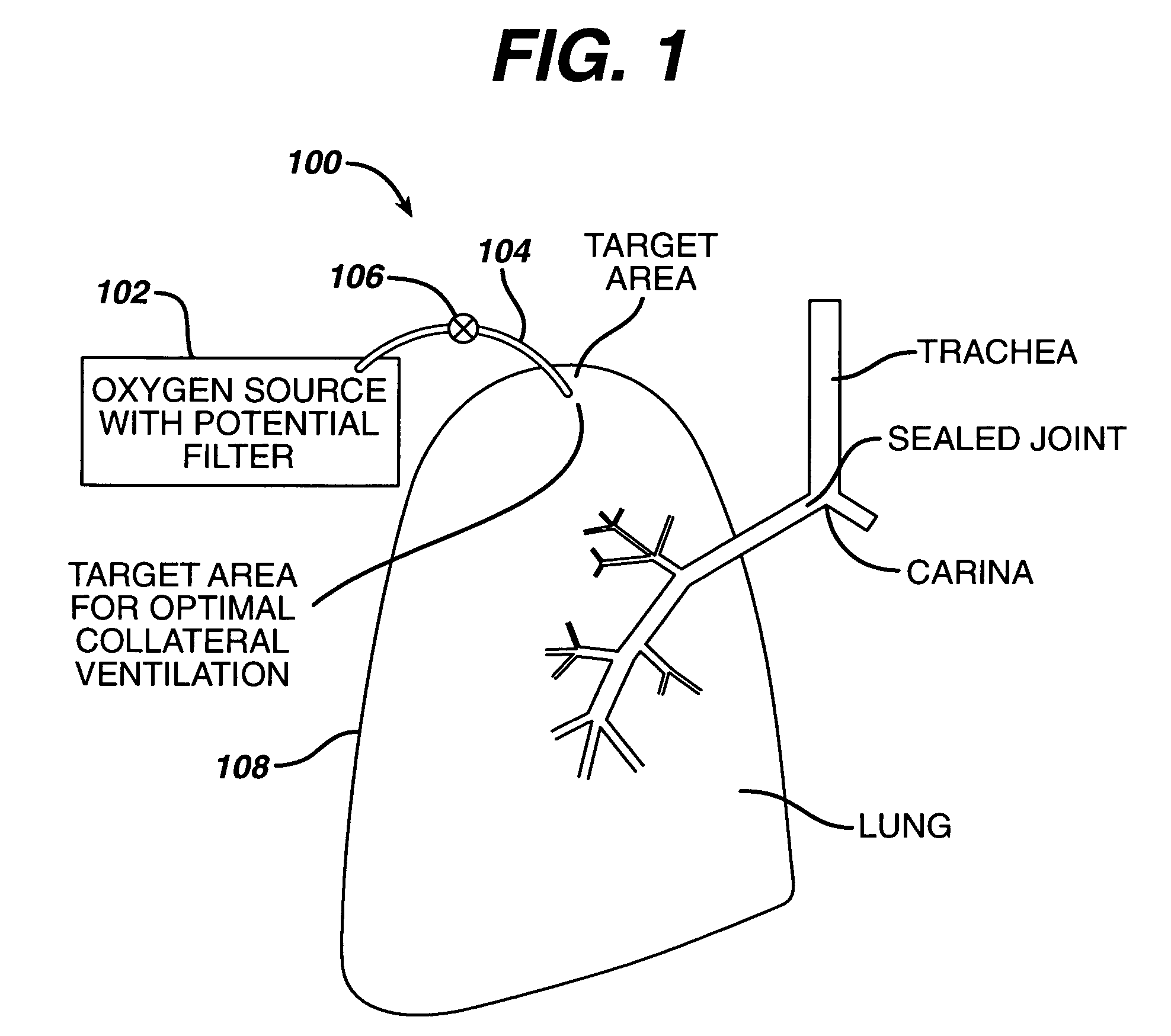
The pleural cavity also known as the pleural space, is the thin fluid-filled space between the two pulmonary pleurae (known as visceral and parietal) of each lung. A pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered membranous pleural sac. The outer pleura (parietal pleura) is attached to the chest wall, but is separated from it by the endothoracic fascia. The inner pleura (visceral pleura) covers the lungs and adjoining structures, including blood vessels, bronchi and nerves. The pleural cavity can be viewed as a potential space because the two pleurae adhere to each other (through the thin film of serous fluid) under all normal conditions. Parietal pleura projects up to 2.5 cm above the junction of the middle and medial third of the clavicle...
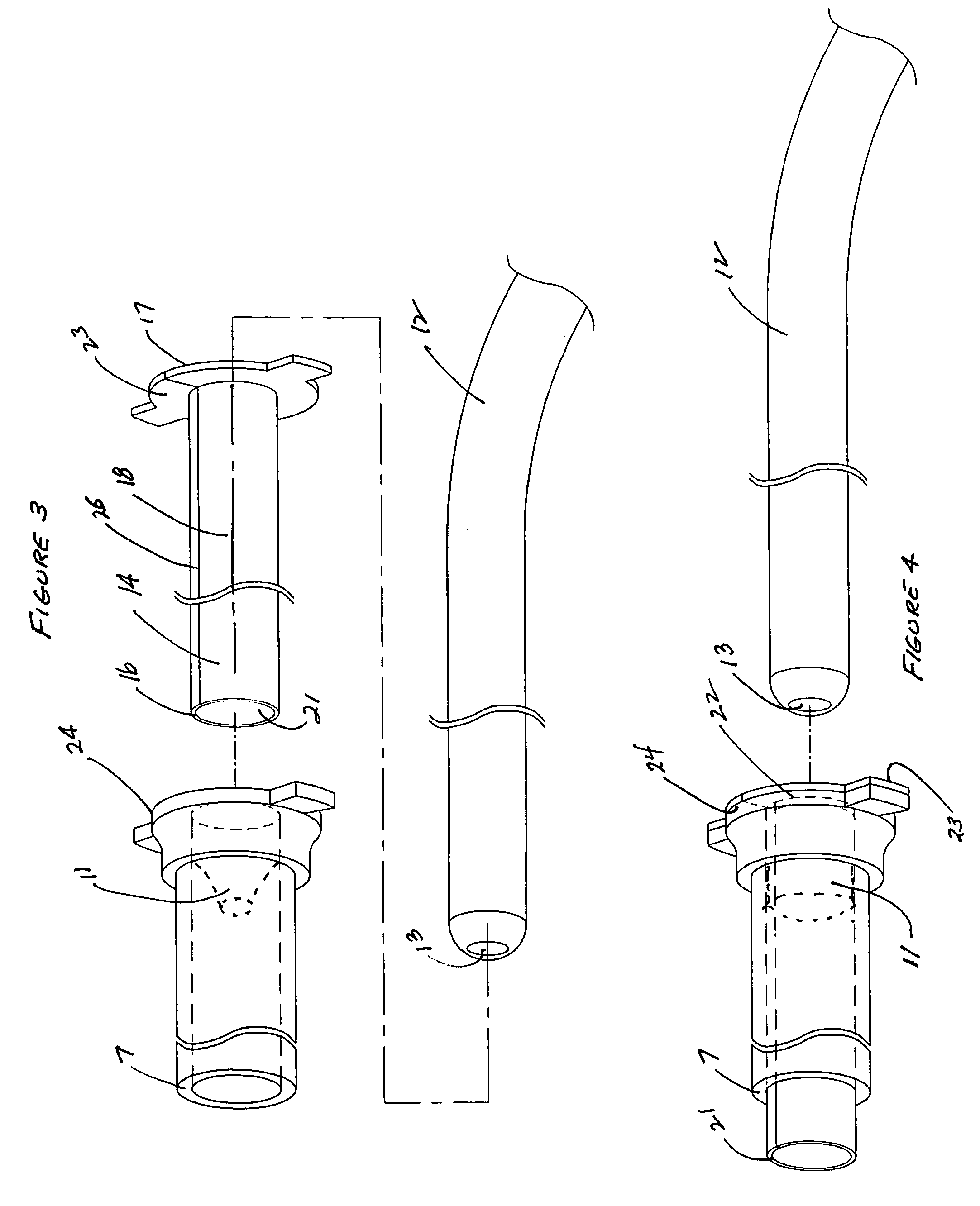
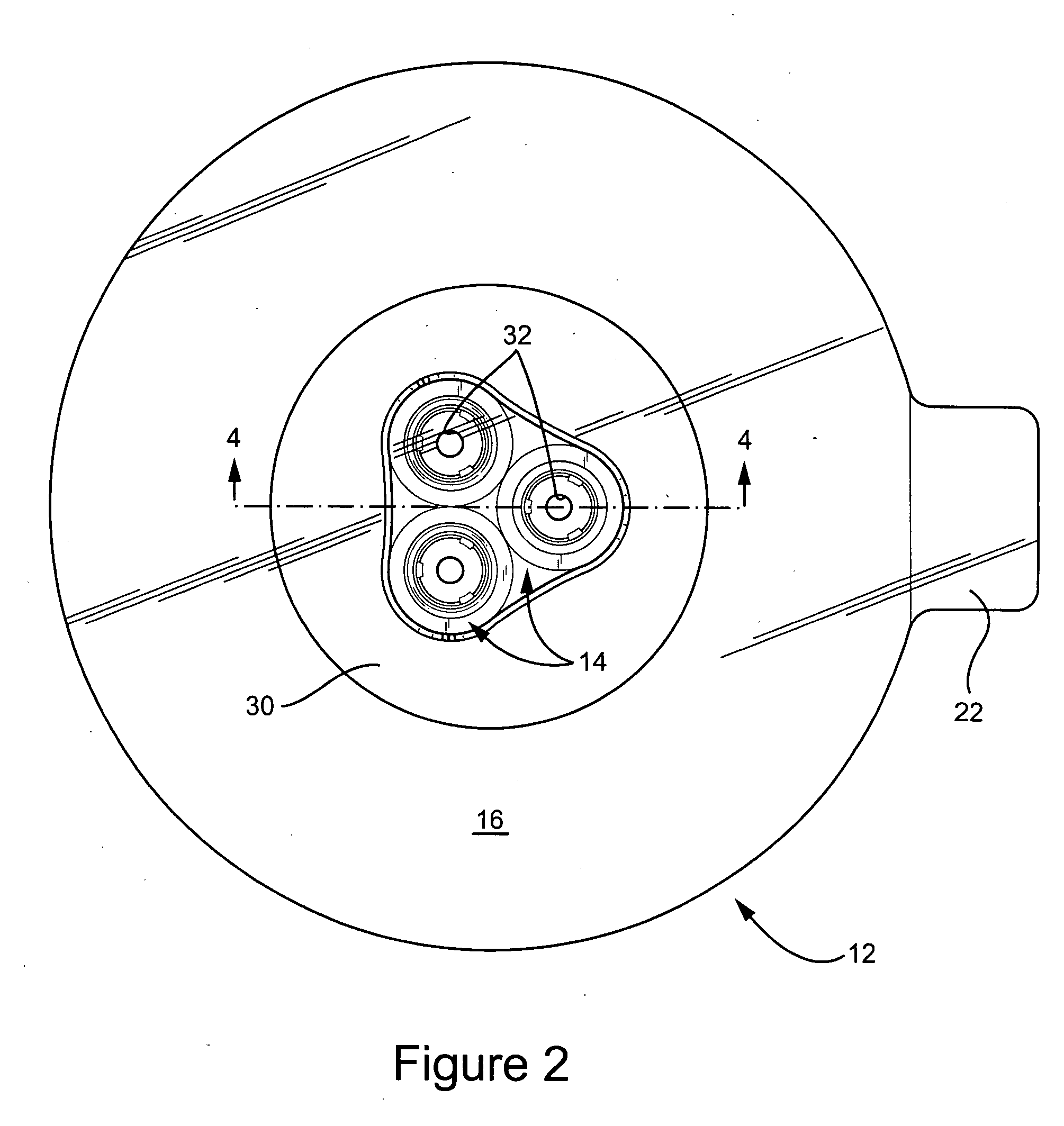
Pleural biopsy and brushing needle
InactiveUS6846292B2Accurate and effectiveEasily withdrawnSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPleural cavityPleural biopsy
A biopsy needle and method of using the same. The biopsy needle includes a pair of articulating members that can be moved between a retracted position where the articulating members are contained within the biopsy needle and an extended position where the articulating members extend outwardly from the distal end of the biopsy needle into the pleural cavity of a patient. Once extended, the articulating members have operative surfaces that contact the parietal pleura of the patient such that a biopsy sample can be obtained as the operative surfaces are moved in contact with the parietal pleura. The operative surfaces may be a brush blade or a knife blade. A passageway within the interior of the biopsy needle allows removal of fluids from the patient.
Owner:BAKRY MOHAMED
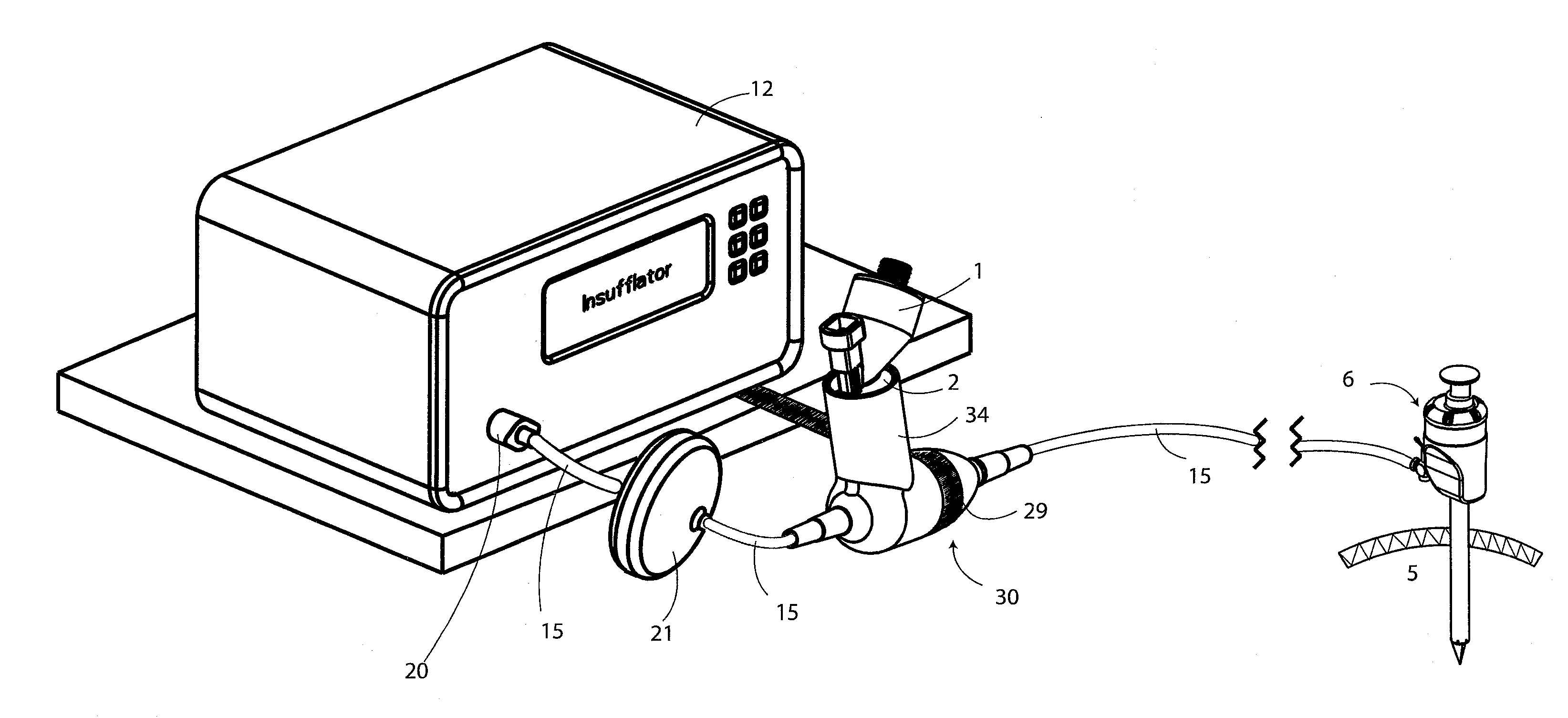
Insufflation of body cavities
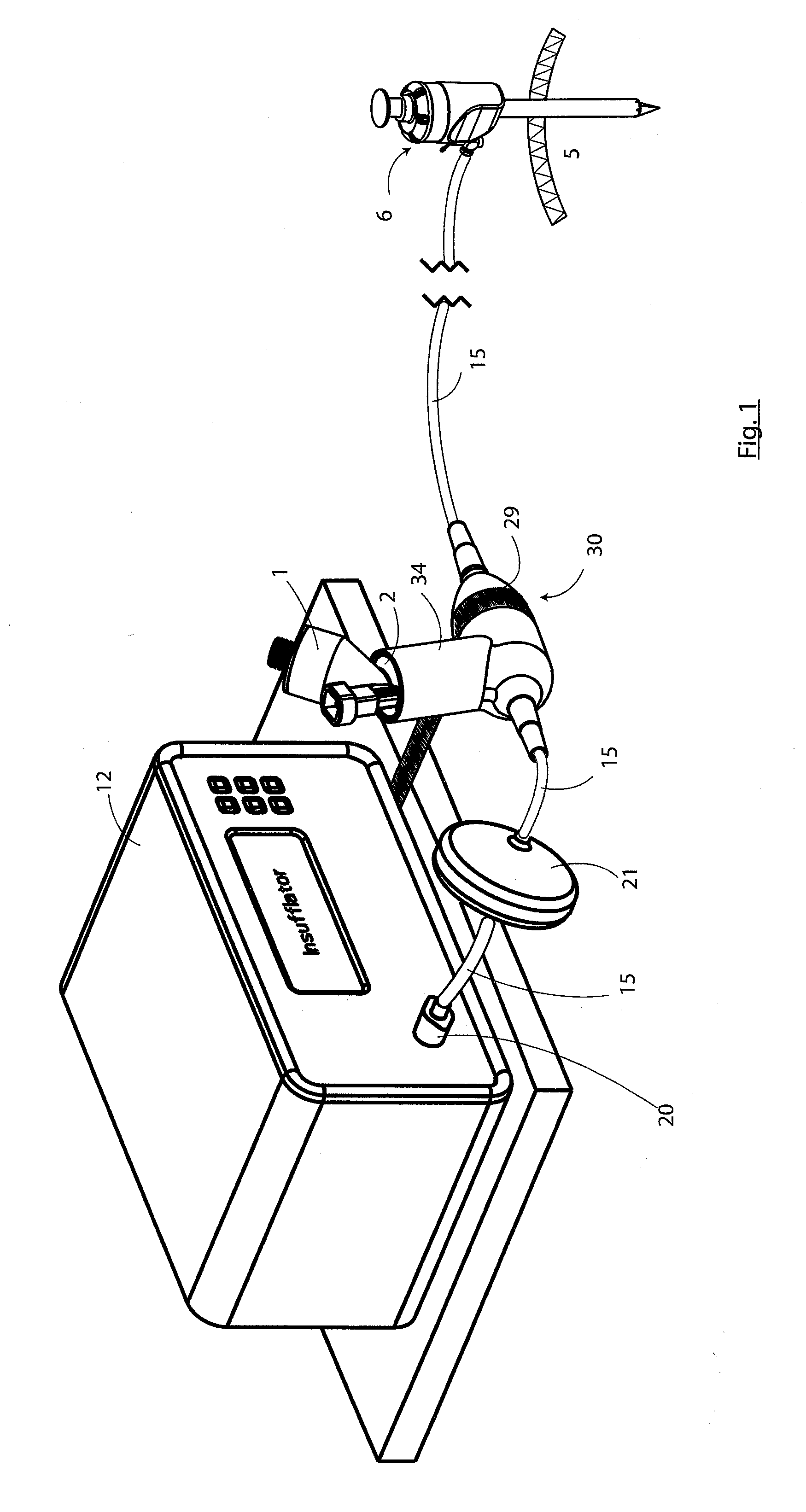
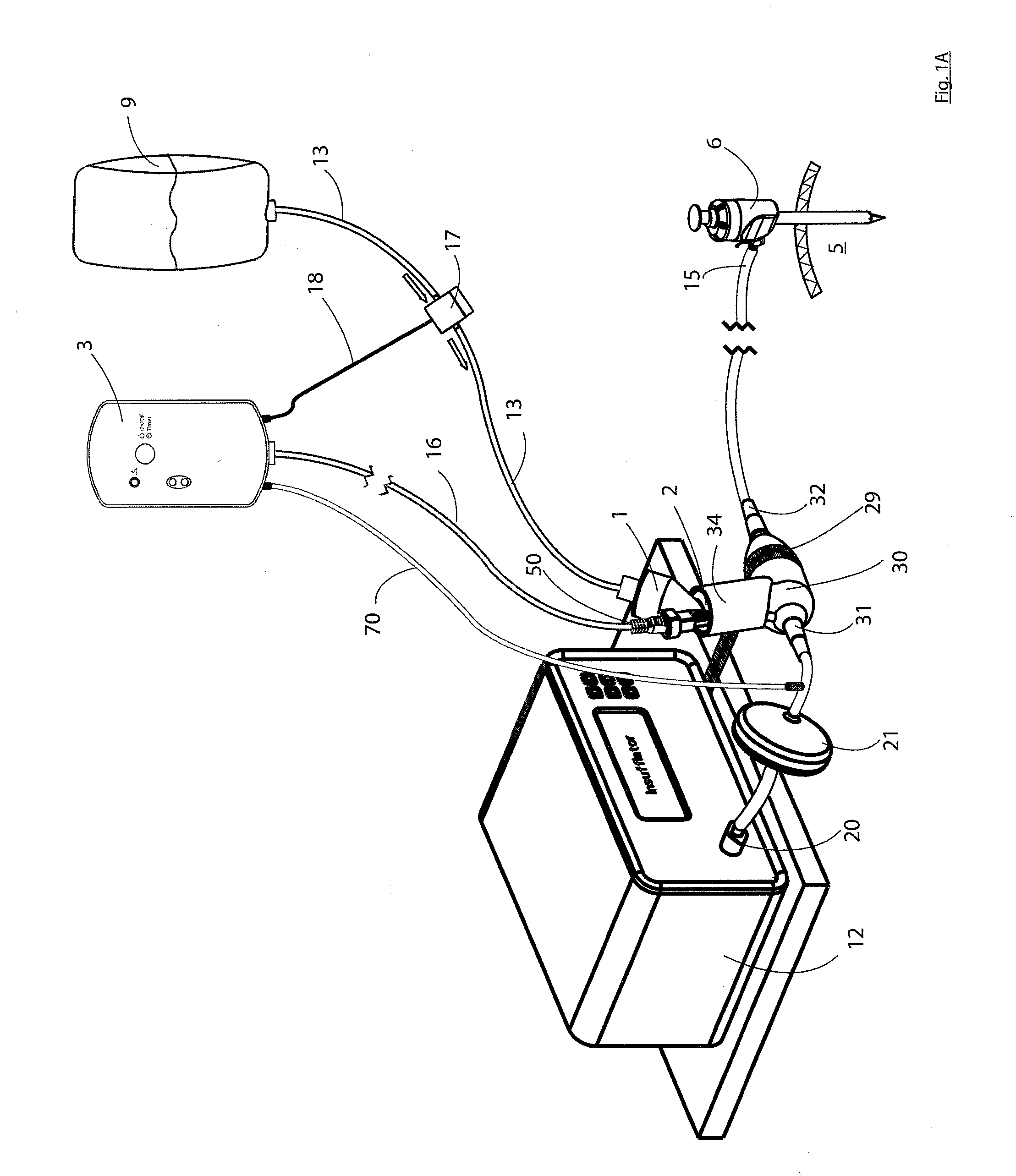
An apparatus for use in insufflation of a body cavity 5, such as through a trocar 6 is described. One such application is laparoscopic surgery. The device is also suitable for use in any situation involving insufflation of a body cavity such as in arthroscopies, pleural cavity insufflation (for example during thoracoscopy), retroperitoneal insufflations (for example retroperitoneoscopy), during hernia repair, during mediastinoscopy and any other such procedure involving insufflation. The apparatus comprises a reservoir 1 for storing an liquid solution, an aerosol generator 2 for aerosolising the solution, and a controller 3 for controlling operation of the aerosol generator 2. Aerosolised liquid solution (which main contain a pharmaceutical) is entrained with insufflation gas using a T-piece connector or housing 30 having an insufflation gas inlet 31 and an outlet 32. The connector 30 also comprises an aerosol supply conduit 34 for delivering the aerosol from the aerosol generator 2 into a mixing chamber 33 in which the aerosol is entrained with insufflation gas. The aerosol insufflation gas mixture passes out of the connector 30 through the outlet 32 and is delivered along the insufflation gas conduit 15 to the trocar 6 for delivery into a body cavity 5. The connector 30 causes a substantial sudden reduction in the velocity of the insufflation gas from the insufflation gas inlet as it enters the mixing chamber 33. The connector 30 also causes a gradual increase in the velocity of the insufflation gas with entrained aerosol between the mixing chamber 33 and the outlet 32.
Owner:AEROSURGICAL
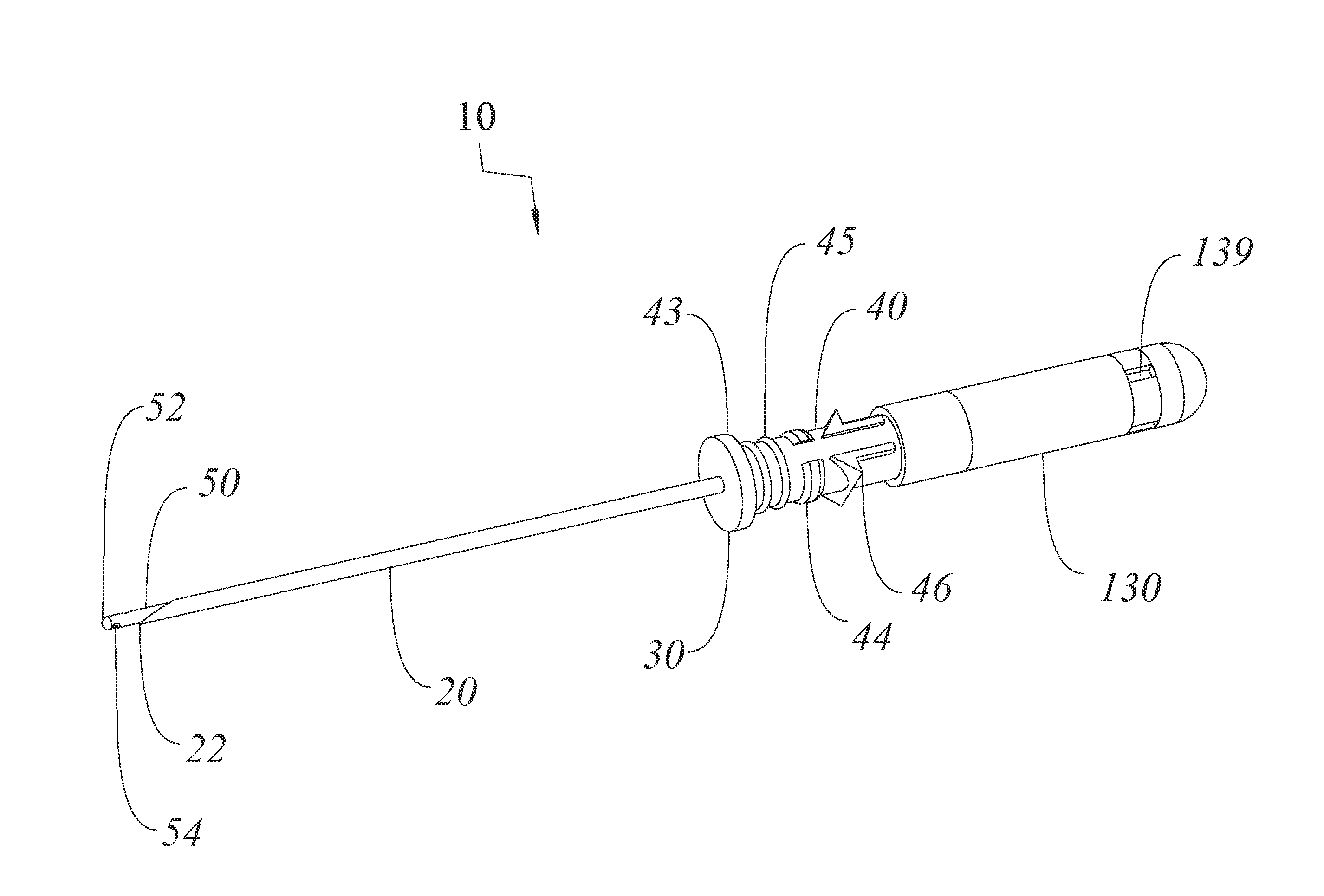
Thoracentesis catheter system with self-sealing valve
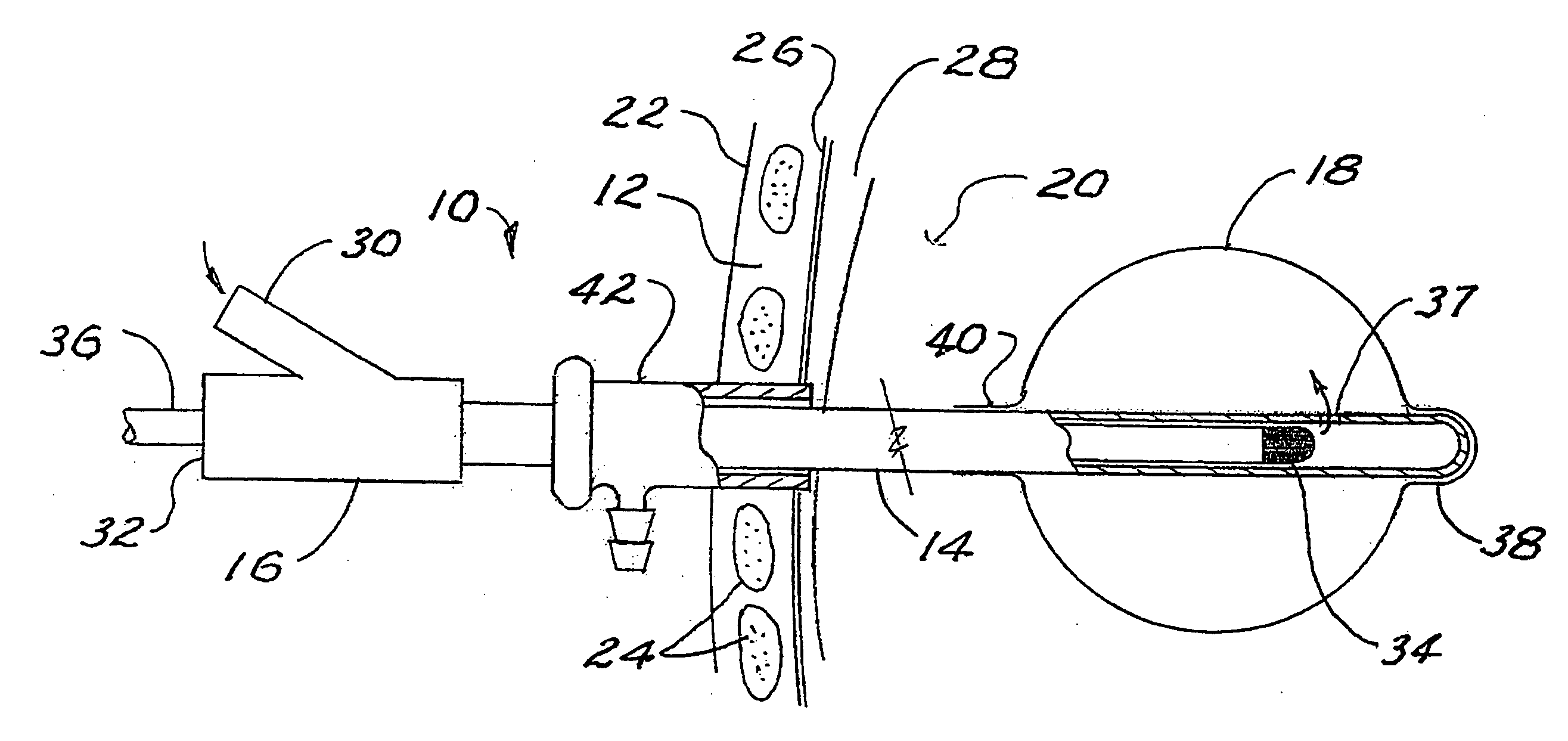
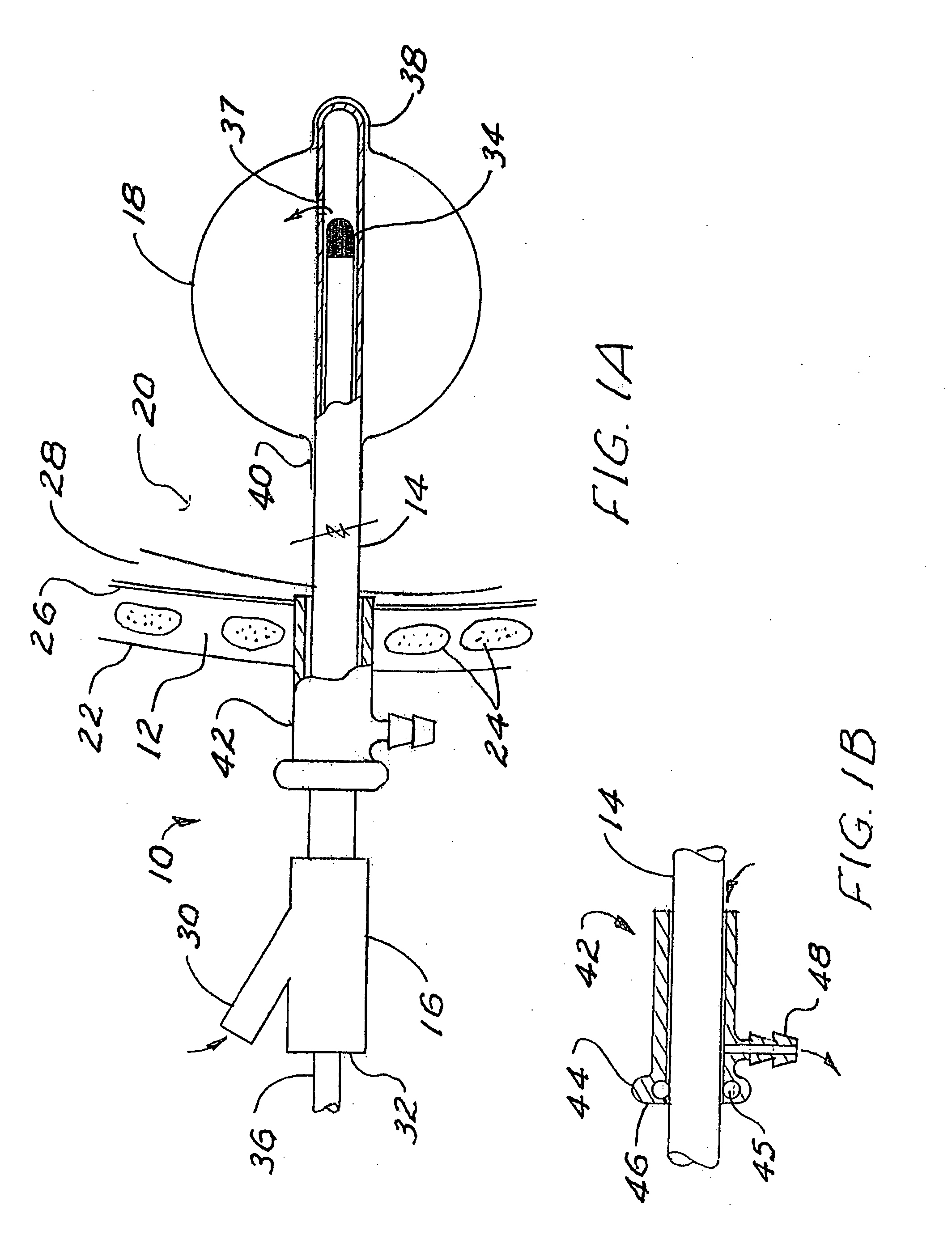
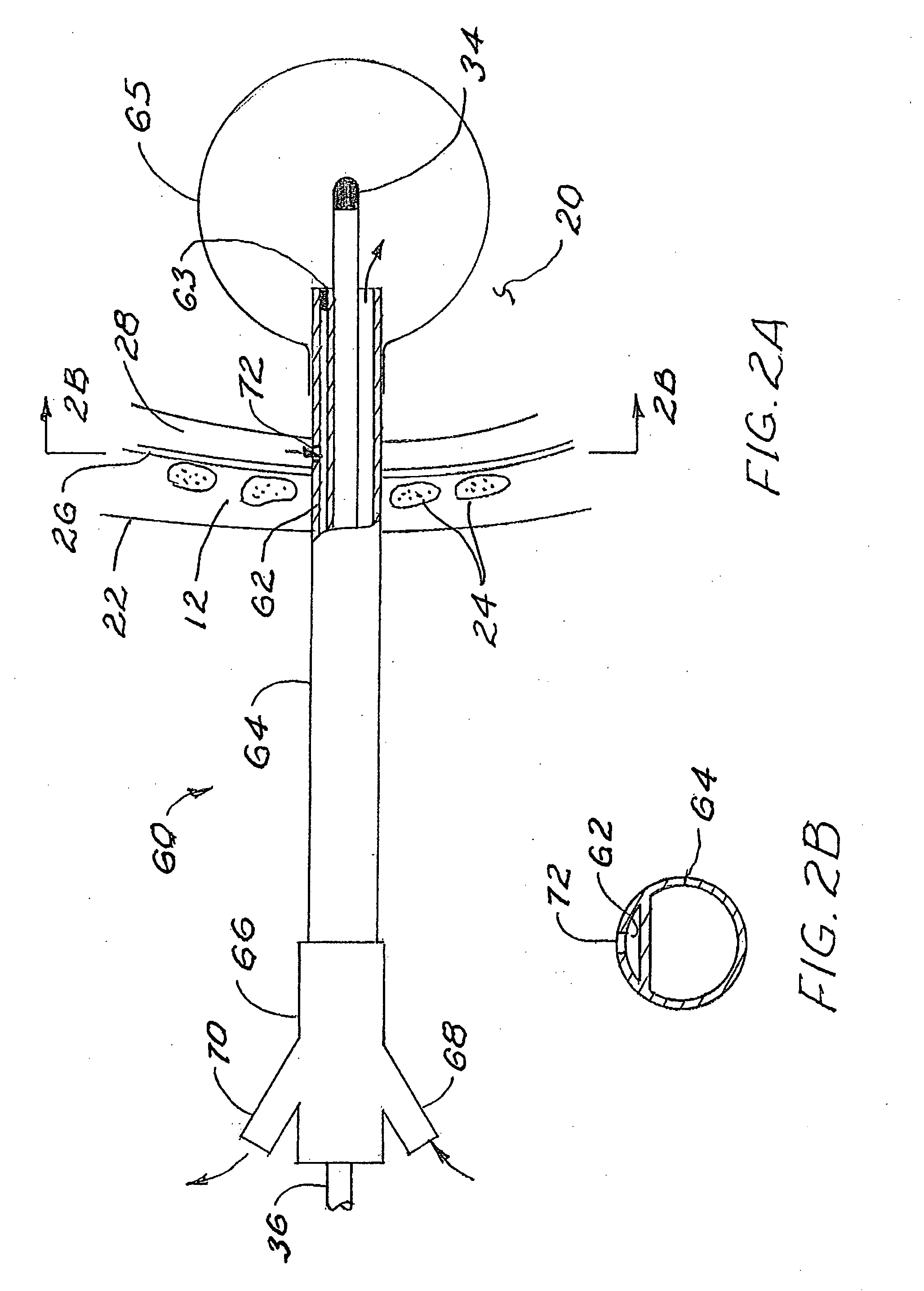
The present invention provides thoracentesis systems composed of an insertion needle, a thoracentesis catheter with self-sealing valve, and a valve opening device which are utilized in the removal of fluid or gases from a pleural cavity. The insertion needle is utilized to insert the thoracentesis catheter into the pleural cavity. The thoracentesis catheter provides automatic closure of the flow path from the pleural cavity by automatic closure of the self-sealing valve upon removal of the insertion needle from the thoracentesis catheter. The self-sealing valve prevents drainage of fluid from the pleural cavity and introduction of air into the pleural cavity when the needle is withdrawn from the thoracentesis catheter and a valve opening device is not in place. A drainage flow path from the pleural cavity is established by insertion of a valve opening device into the self-sealing valve of the thoracentesis catheter, thus opening the self-sealing valve. With the self-sealing valve opened by a valve opening device, fluid or gases can be removed from the pleural cavity.
Owner:MAYSE MARTIN L
Percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209909A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesSuture equipmentsStapling toolsPleural cavityPleural part
A percutaneous single-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. A pneumostomy instrument is introduced percutaneously through the thoracic wall, parietal membrane, visceral membrane and into the parenchymal tissue of the lung. The pneumostomy instrument crosses the pleural cavity between the parietal membrane and visceral membrane there being no pleurodesis between the membranes prior to passage of the pneumostomy instrument. A pneumoplasty device at the distal end of the pneumostomy instrument displaces and engages the parenchymal tissue of the lung and the pneumostomy instrument is used to secure the lung and visceral membrane in contact with the parietal membrane and chest wall. The pneumostomy instrument is left in place while a pneumostoma tract heals and pleurodesis occurs between the pleural membranes surrounding the pneumostomy instrument.
Owner:PORTAERO
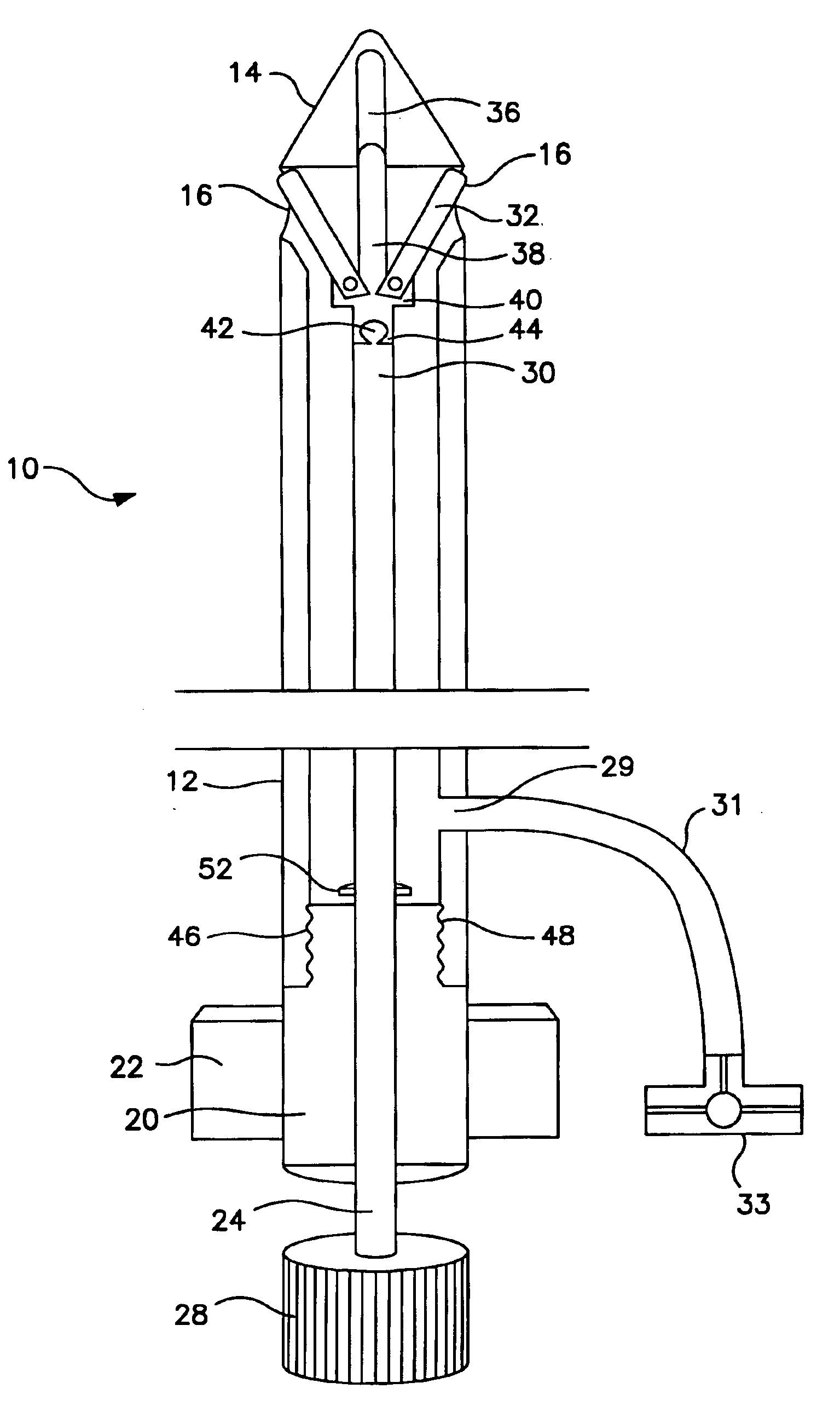
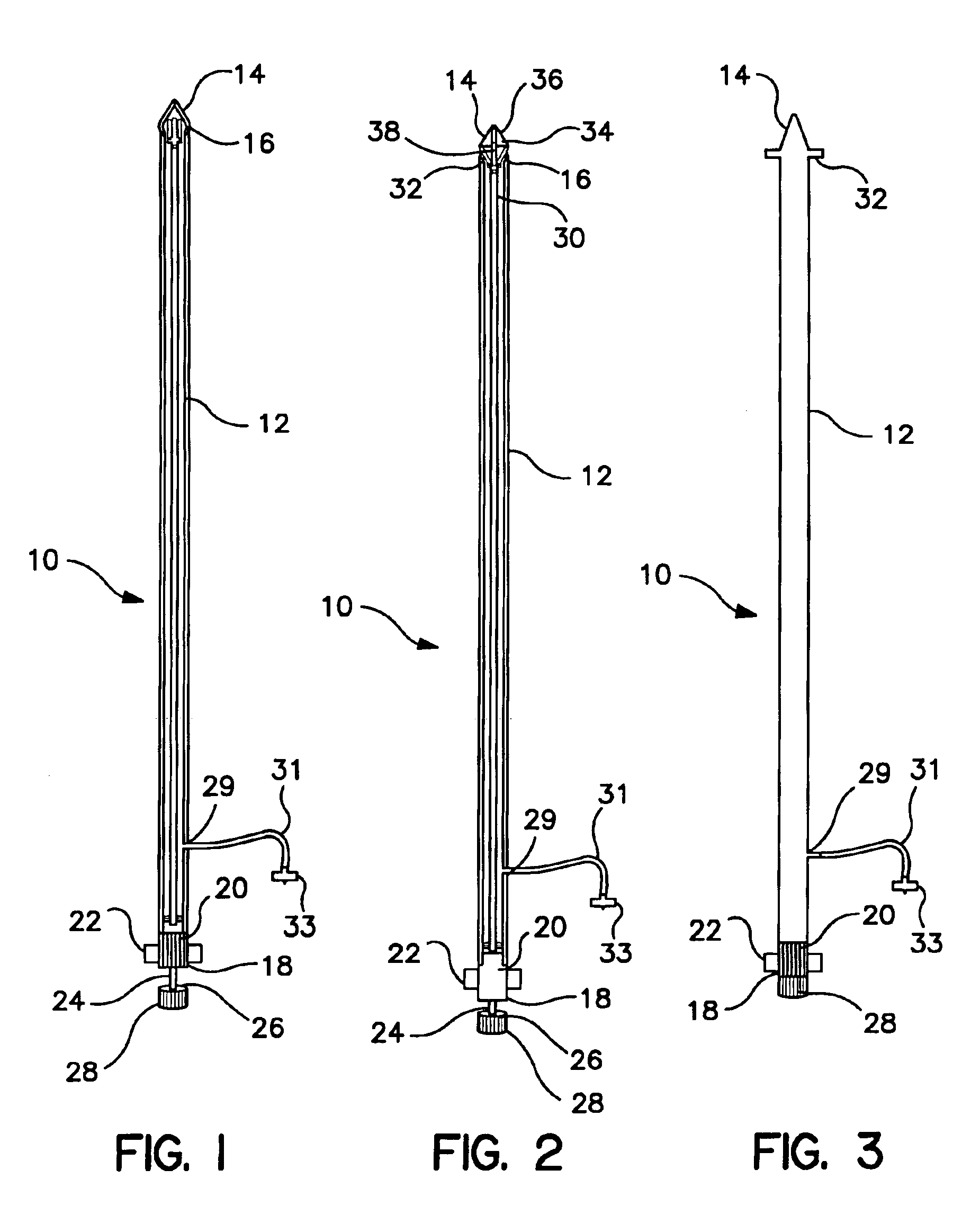
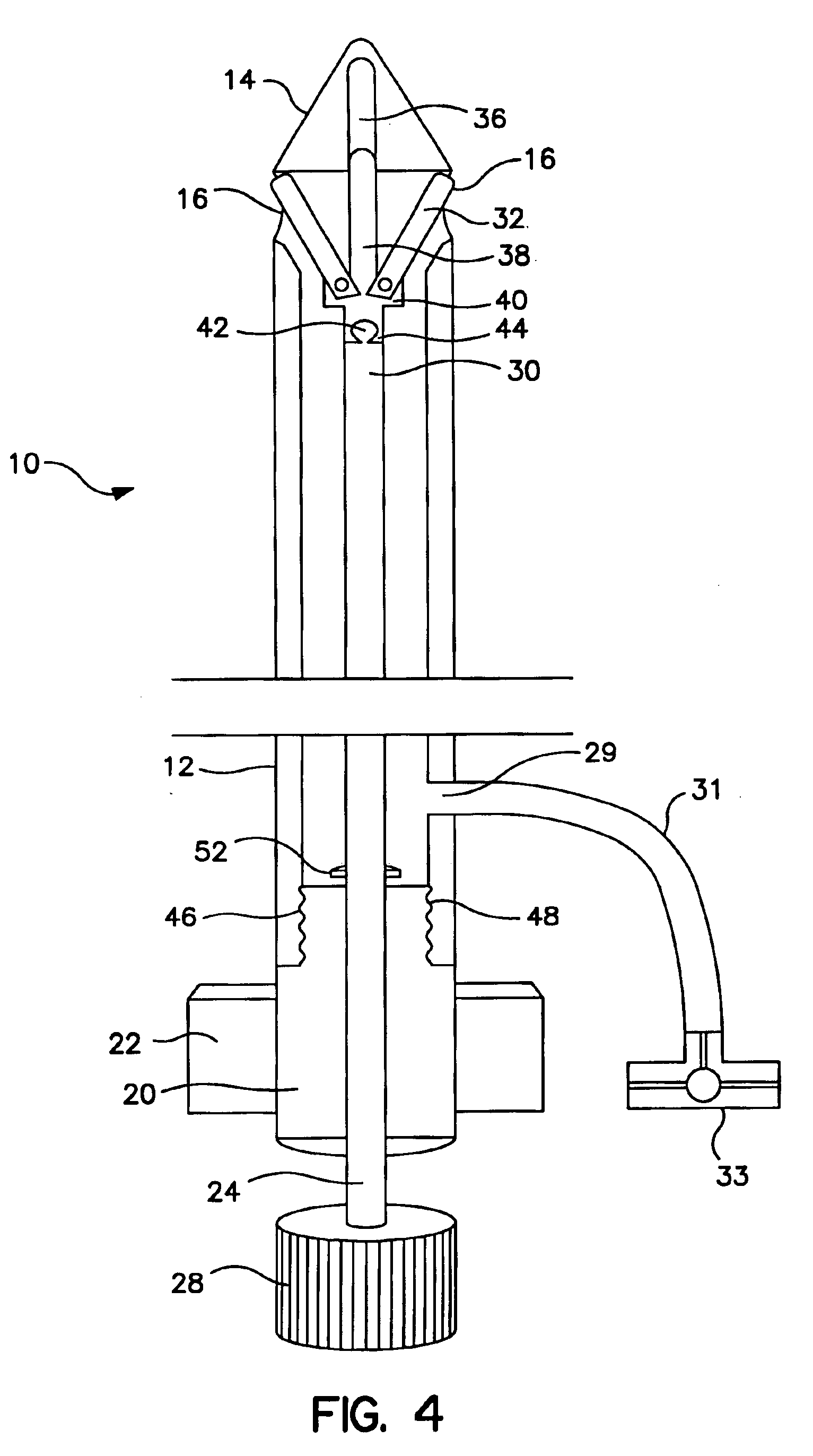
Method and device for simultaneously documenting and treating tension pneumothorax and/or hemothorax
ActiveUS20140046303A1Reduce the possibilityReduce manufacturing costDiagnosticsSurgical needlesPleural cavityAtmospheric pressure
A method and device are provided for simultaneously or near-simultaneously diagnosing and treating tension pneumothorax and / or hemothoraxA Veress-type needle portion includes a hollow needle for puncturing the chest wall over a blunt hollow probe biased by one or more springs to extend distally into the pleural cavity. Openings in the blunt hollow probe connect via a pathway to an automatic check valve, which permits the flow of air and / or fluid only in a proximal direction. Pressure from within the pleural cavity is transmitted to the interior surface of a pressure documenter. If pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is present in the pleural cavity, the pressure documenter will be automatically urged proximally to simultaneously allow air and / or fluid to escape from the pleural space through the device, thus treating the tension pneumothorax and / or hemothorax, as well as providing a stable indicator to positively document the diagnosis of increased pressure.
Owner:CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
Fluid flow indicator
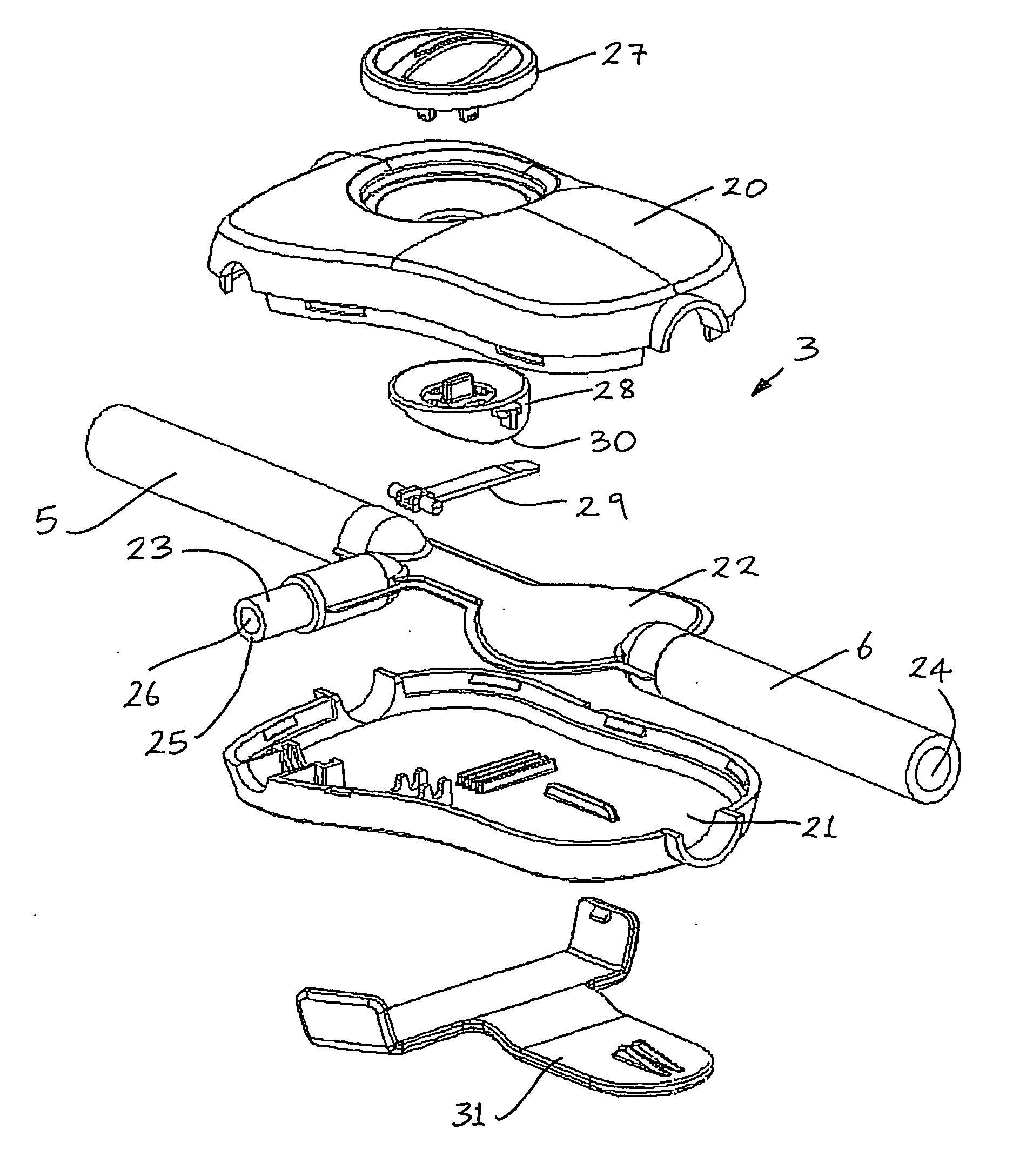
InactiveUS20070241119A1Improve sealingMinimize the possibilityCoin-freed apparatus detailsMedical devicesPleural cavityInhalation
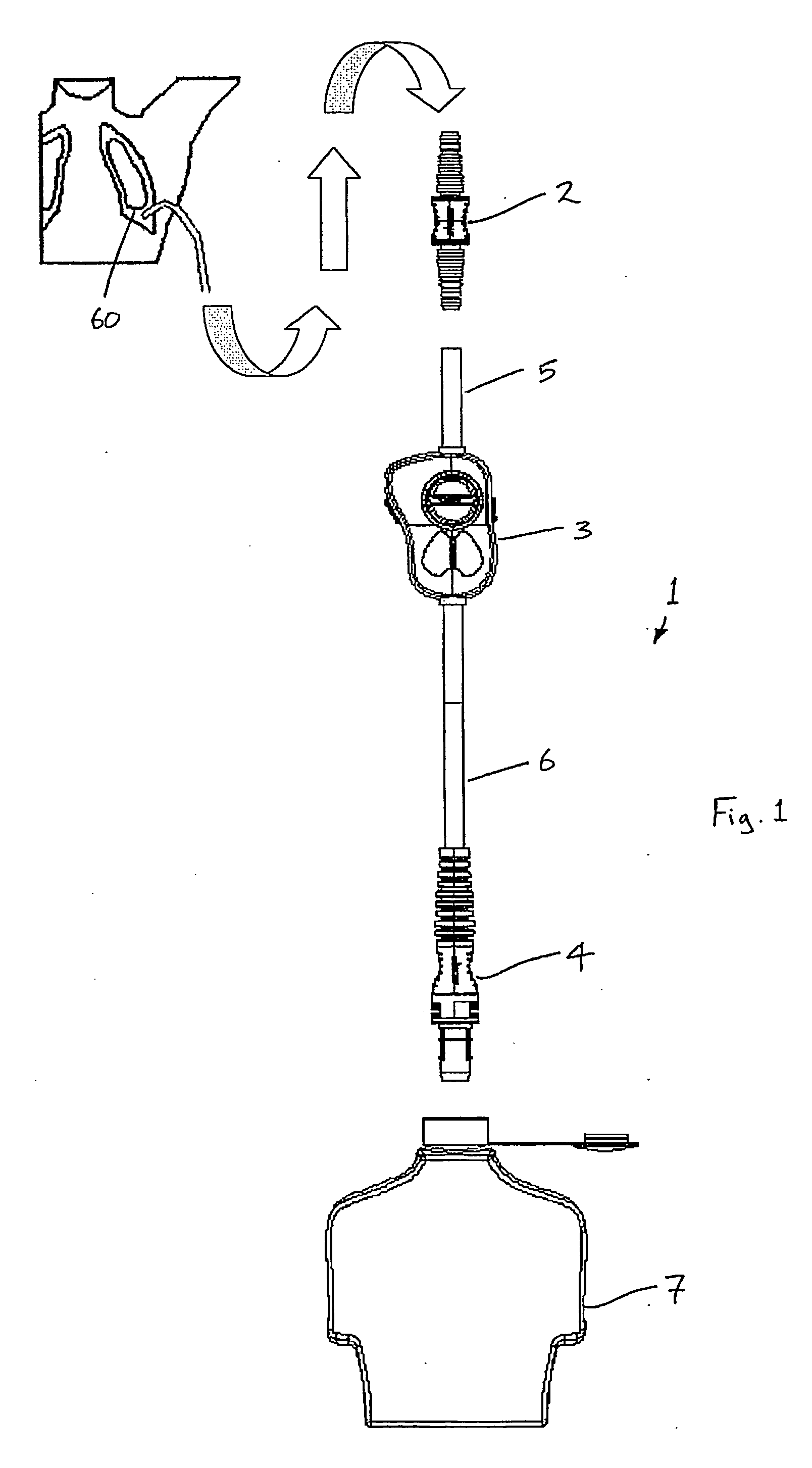
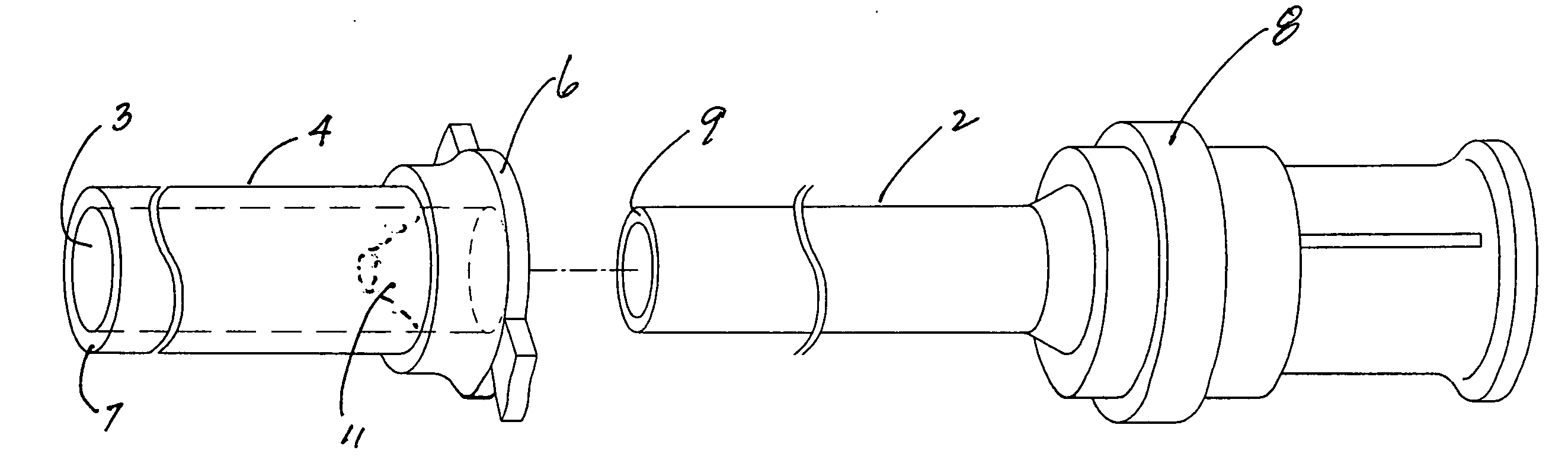
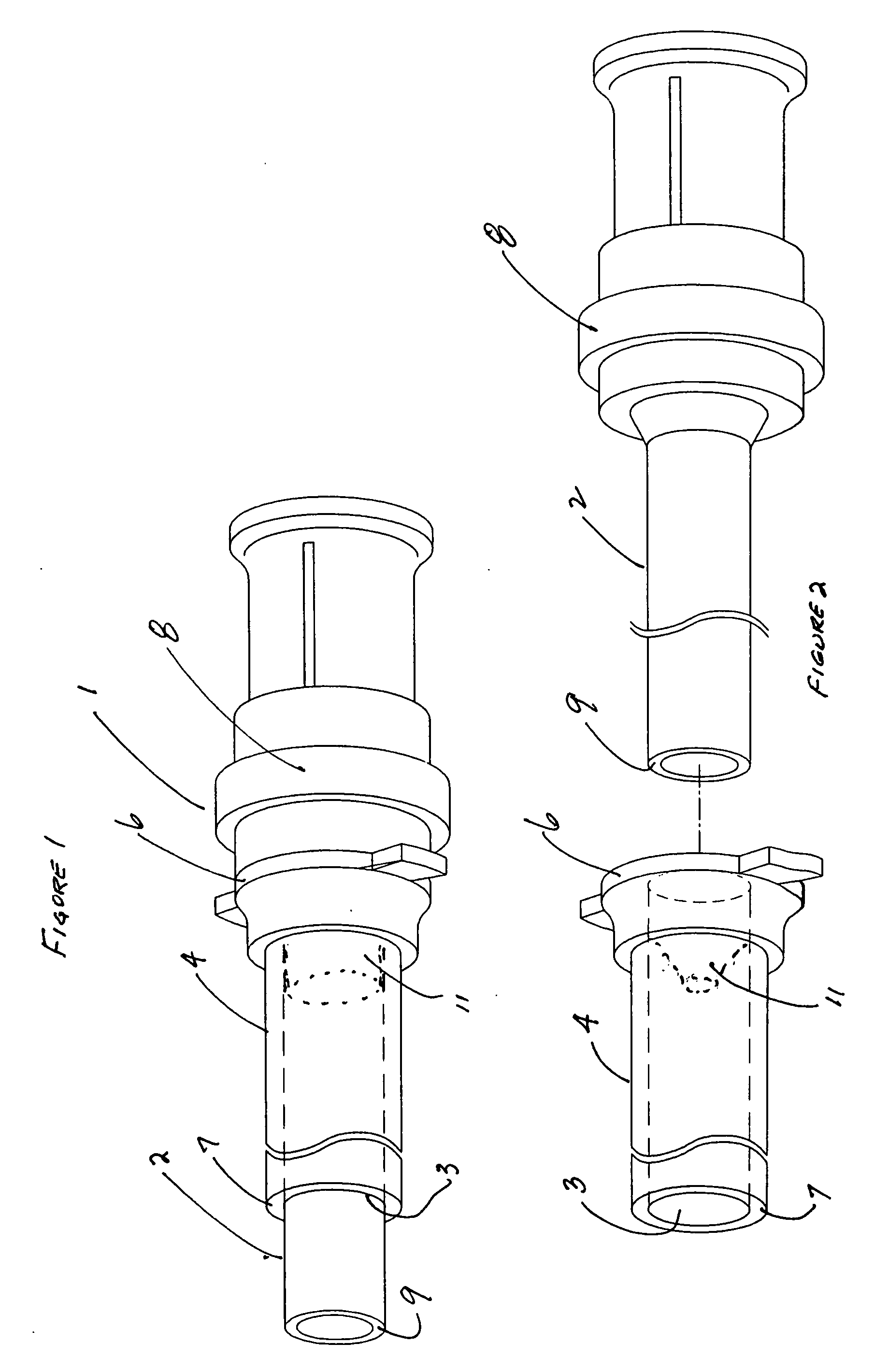
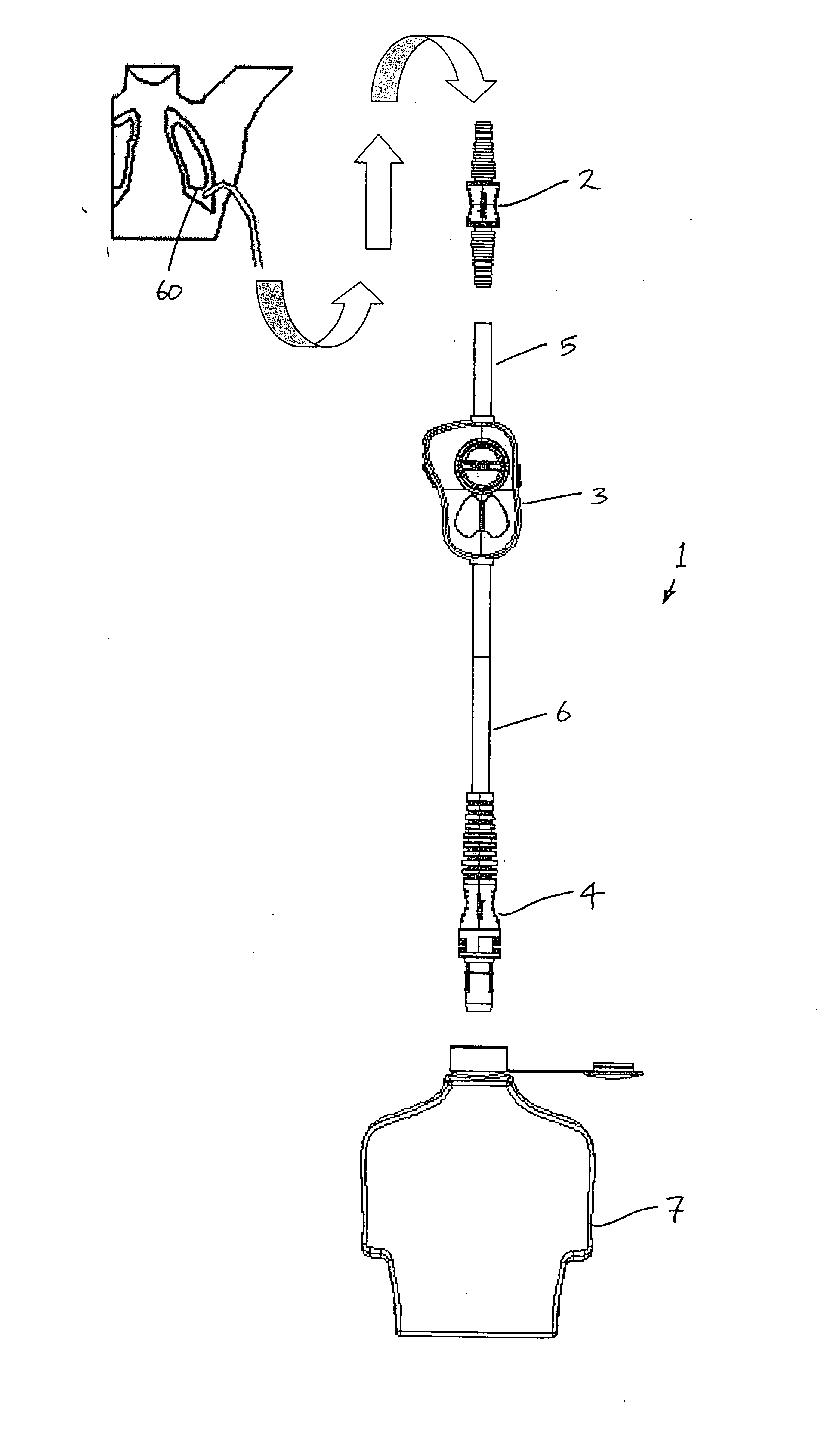
A fluid flow indicator (3) for use in a medical drainage device for draining fluid from a pleural cavity of a patient comprises an upper housing part (20), a lower housing part (21), a balloon member (22), a sampling port (23), and a control mechanism to selectively control flow of a body fluid through the balloon member (22) or through the sampling port (23). The balloon member (22) defines a lumen therethrough. Upon flow of a body fluid into the balloon member (22), for example upon inhalation of a patient, the balloon member (22) inflates from a deflated rest configuration to an inflated flow configuration. This inflation of the balloon member (22) provides a visual indication to an operator of the flow of the body fluid through the balloon member (22). When flow of the body fluid ceases, for example upon exhalation of a patient, the balloon member (22) deflates from the inflated flow configuration to the deflated rest configuration. This deflation of the balloon member (22) provides a visual indication to the operator of the cessation of the flow of the body fluid through the balloon member 22).
Owner:AVONMED HEALTHCARE
Device for shielding the lens of a flexible or rigid surgical endoscope
This invention relates to a shield member for shielding the lens of a flexible or rigid surgical endoscope from body fluid, tissue debris, and condensation deposited on a working port valve as the lens passes through the working port lumen in a posterior direction to gain access to the intra-abdominal or pleural cavity regions. The shield member has a shield lumen and is telescopically and slidably carried within the lumen. The shield member is so dimensioned and proportioned such that the distal end of the shield member may be selectively positioned posteriorly of the working port valve thereby permitting the lens to advance axially within the shield lumen and by-pass the working port valve without coming in physical contact with the working port valve.
Owner:PHILLIPS EDWARD H
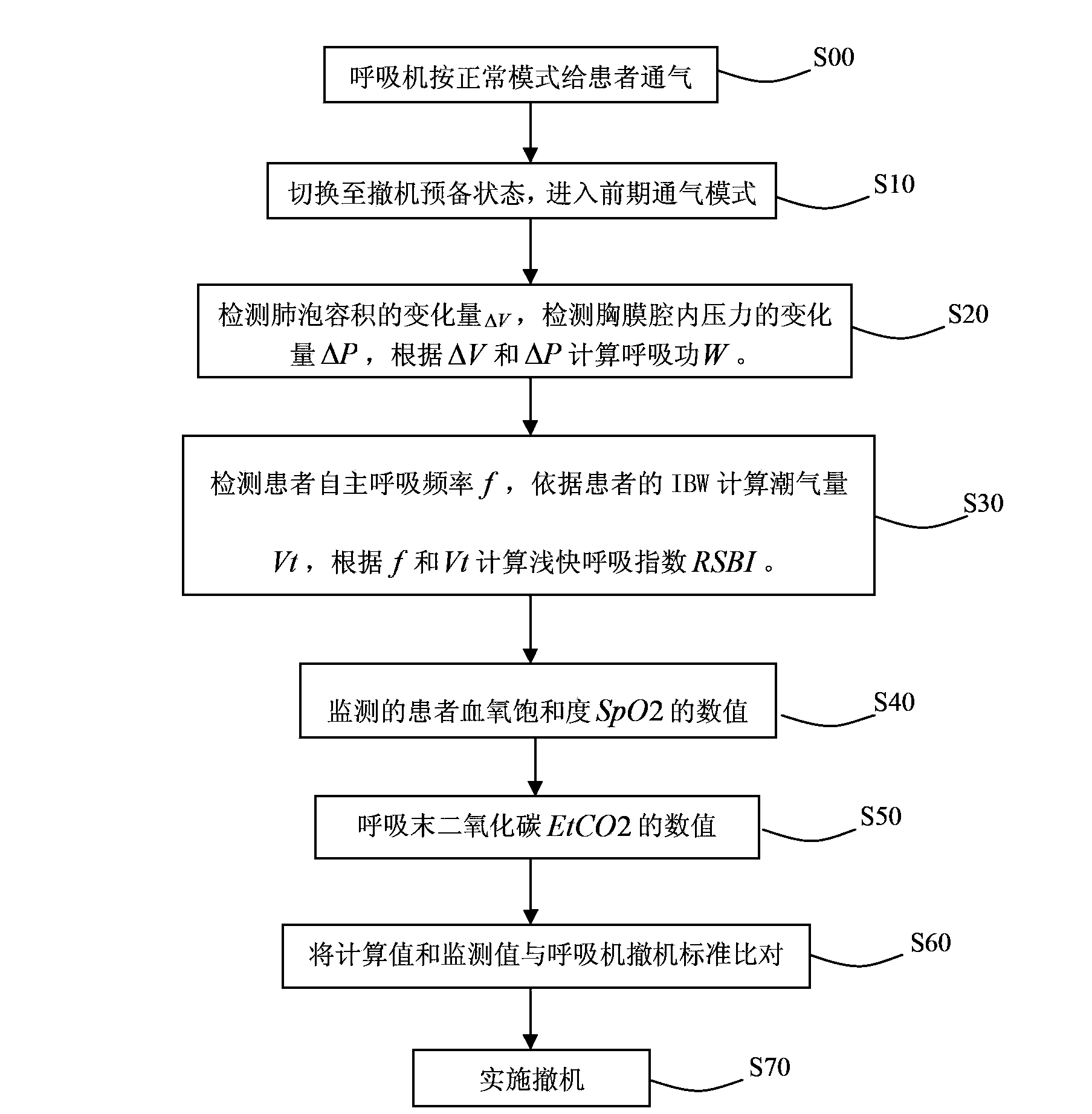
Weaning method and weaning device for intelligent breathing machine
ActiveCN103893866AHigh degree of automationImprove measurement accuracyRespiratorsWeaningInternal pressure
The invention discloses an intelligent breathing machine and a weaning method for the intelligent breathing machine. A ventilation effect can be automatically realized by the intelligent breathing machine before weaning is carried out. The weaning method includes examining variation delta V of the volumes of the pulmonary alveoli of a patient, variation delta P of the internal pressure of the pleural cavity of the patient and the spontaneous breathing frequency f of the patient at first; computing work W of breathing and a rapid-shallow-breathing index RSBI of the patient by the aid of examined values; monitoring a numerical value of the blood oxygen saturation degree SpO2 of the patient and a numerical value of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 of the patient; comparing computed values and the monitored values to weaning standards of the breathing machine; implementing weaning if the weaning standards of the breathing machine are met; implementing secondary weaning judgment if the weaning standards of the breathing machine are not met. The intelligent breathing machine, the weaning method and a weaning device have the advantages that various key indexes of vital signs of the patient are monitored automatically, so that whether weaning is implemented or not can be comprehensively judged, and the weaning judgment accuracy can be improved; a good clinical effect can be realized by the weaning method, and the weaning method and the weaning device bring convenience for medical staff to accurately implement weaning operation according to weaning information.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Device suitable for connection to a substantially tubular element
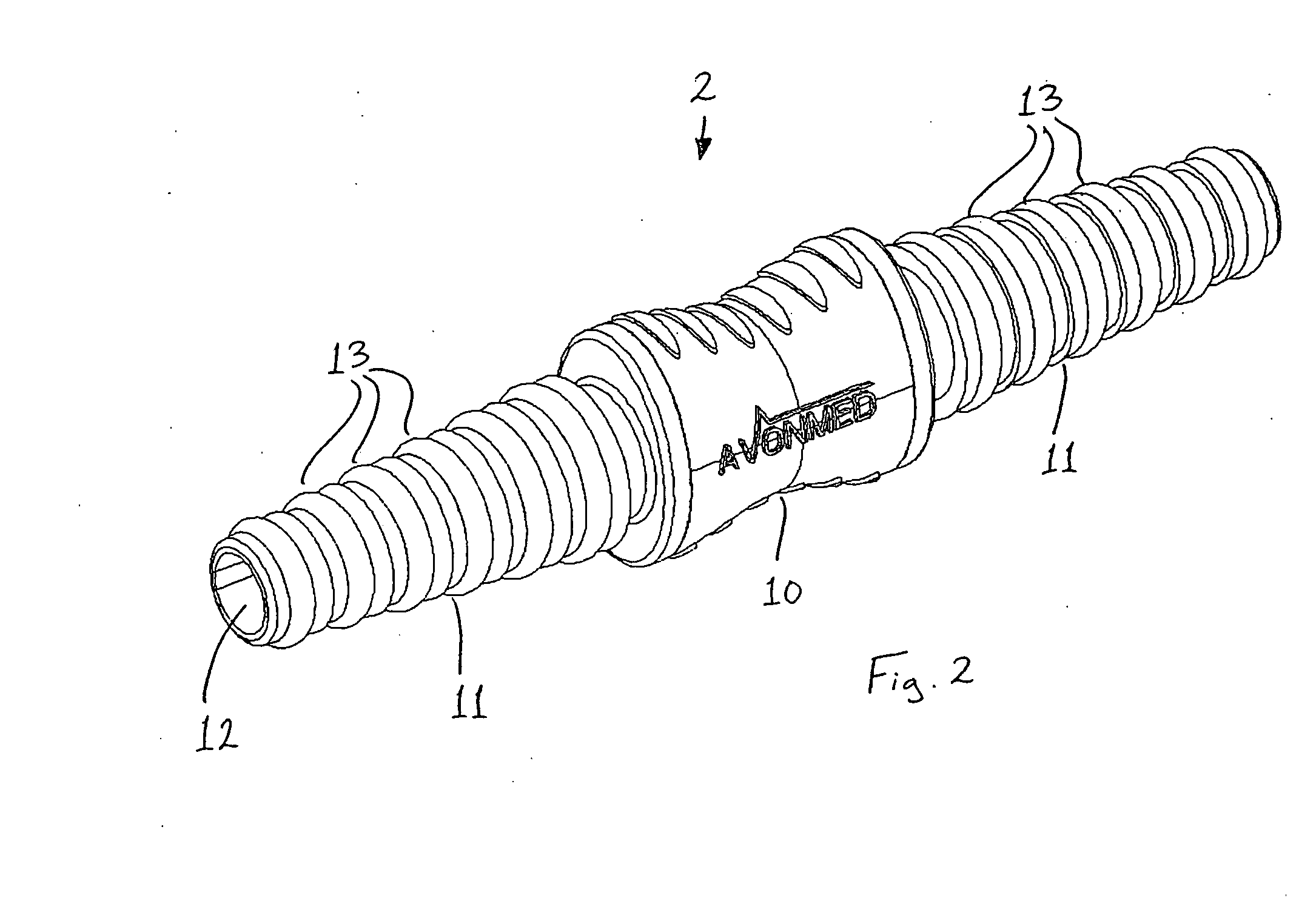
InactiveUS20080021415A1Improve sealingMinimize the possibilityMedical devicesTube connectorsPleural cavityBiomedical engineering
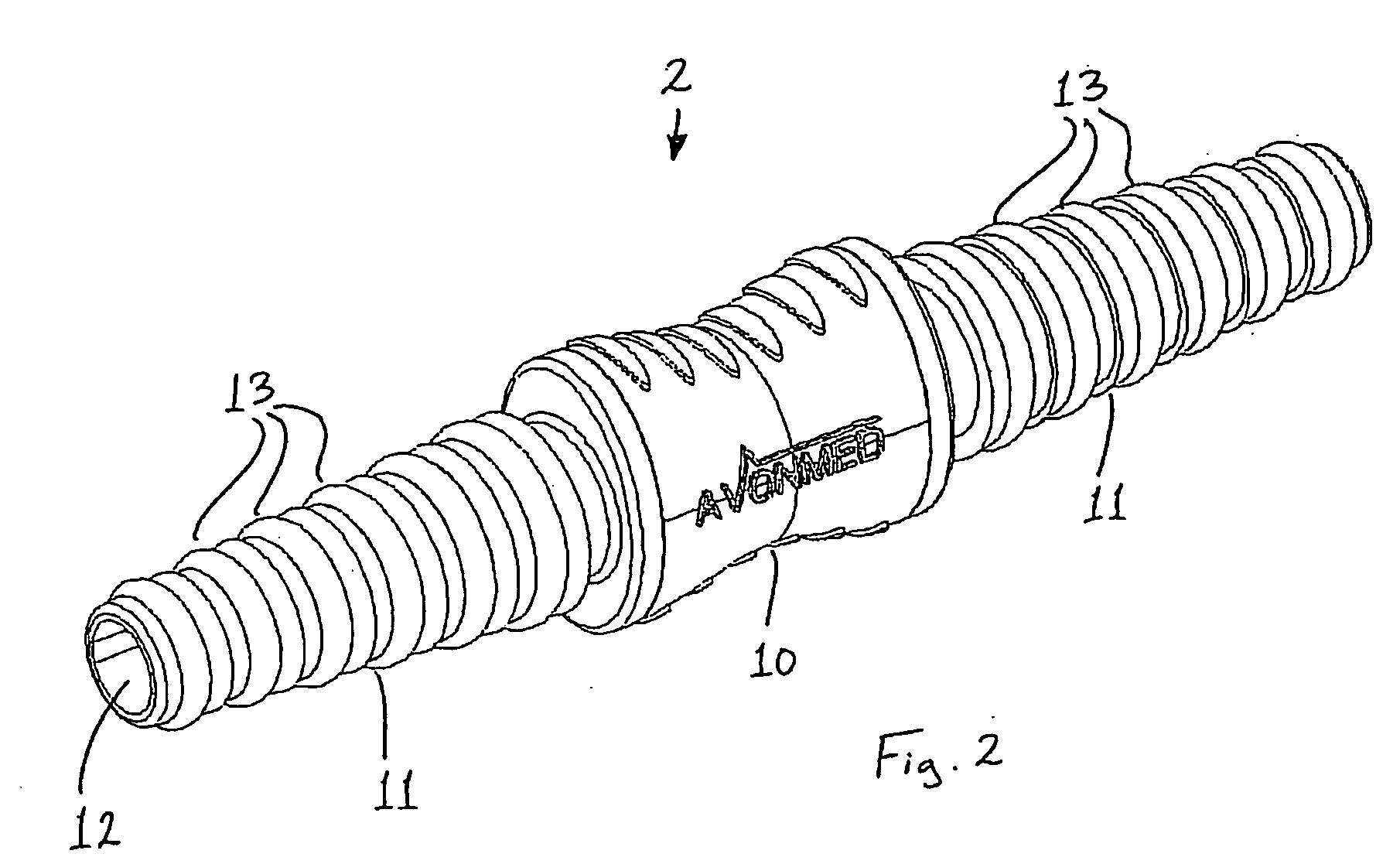
A barb connector (2) for use in a medical drainage device for draining fluid from a pleural cavity of a patient comprises a gripping portion (10), two cylindrical tubular members (11) extending outwardly from the gripping portion (10), and a plurality of annular protrusions (13) spaced-apart along the external surface of each of the tubular members (11). Each tubular member (11) comprises a plurality of recesses spaced-apart along the external surface of the tubular member (11), and the protrusions (13) are mounted in the recesses. Each protrusion (13) is of a compressible material. Upon insertion of a tubular member (11) into a lumen defined through a drain tube of the medical drainage device, the protrusions (13) engage the internal surface of the drain tube and deform to sealingly engage the internal surface.
Owner:AVONMED HEALTHCARE
Percutaneous access pathway system and method
ActiveUS20150182733A1Minimizes user errorDifferent sizeGuide needlesSurgical needlesPleural cavityImproved method
An improved method and device are provided for forming and / or maintaining a percutaneous access pathway. The device generally comprises at least one of three type of components: access pathway, insertion device, and attachment device. In one embodiment, the device is used to form and / or maintain a percutaneous access pathway into the pleural cavity (i.e. tube thoracostomy). The provided assembly substantially reduces the possibility of iatrogenic infection while accessing and / or re-accessing a body space.
Owner:CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
Low profile chest seal
ActiveUS20080234726A1Effective maintenanceLow profilePneumothorax apparatusSurgical veterinaryPleural cavityInjury mouth
A chest seal for treating an open pneumothorax that is low profile and thus unobtrusive so that the chest seal can be effectively maintained in position to seal a chest wound while allowing the pleural cavity to vent.
Owner:SAFEGUARD MEDICAL HOLDCO LLC
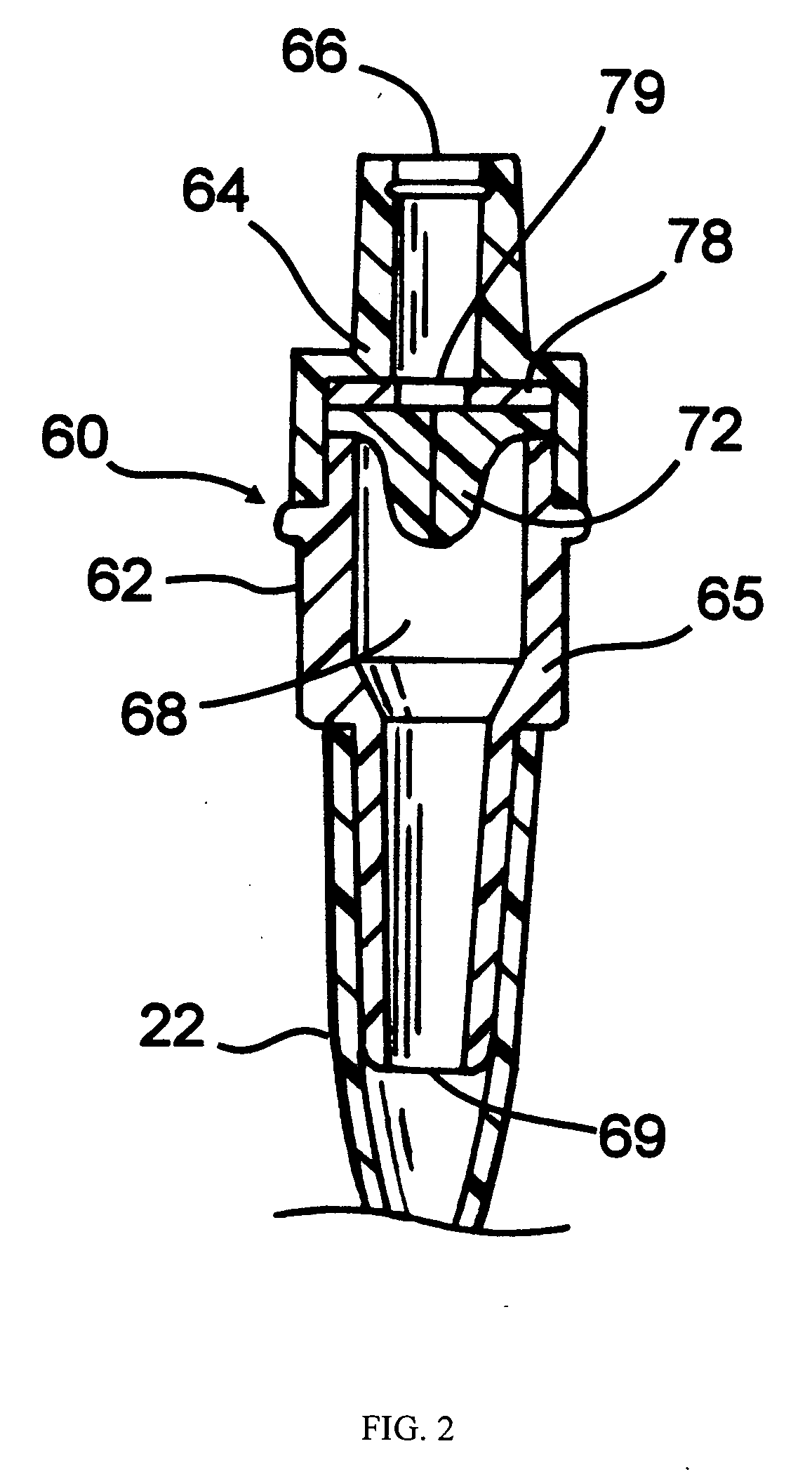
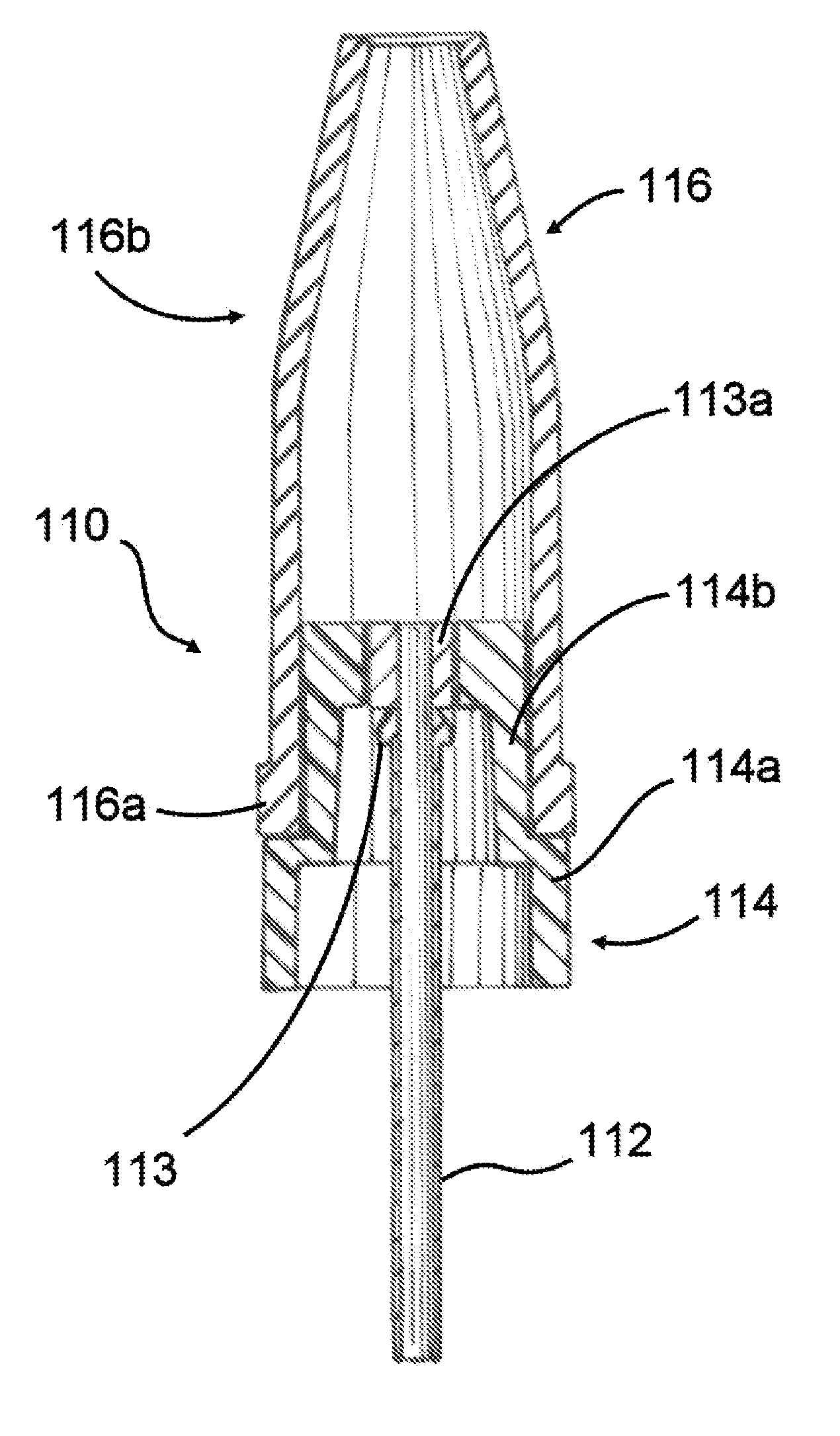
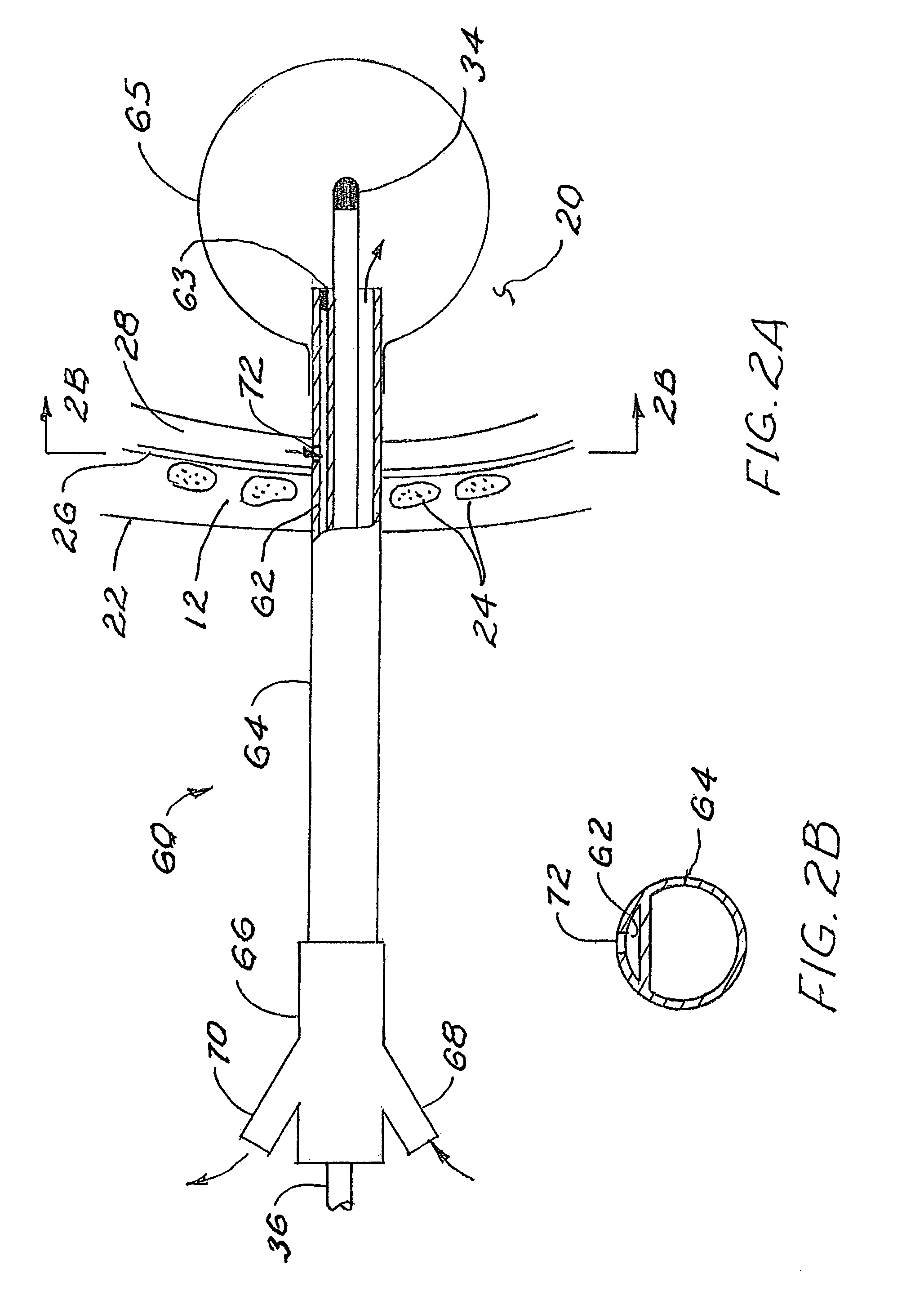
Tapered attachment for pleural catheter
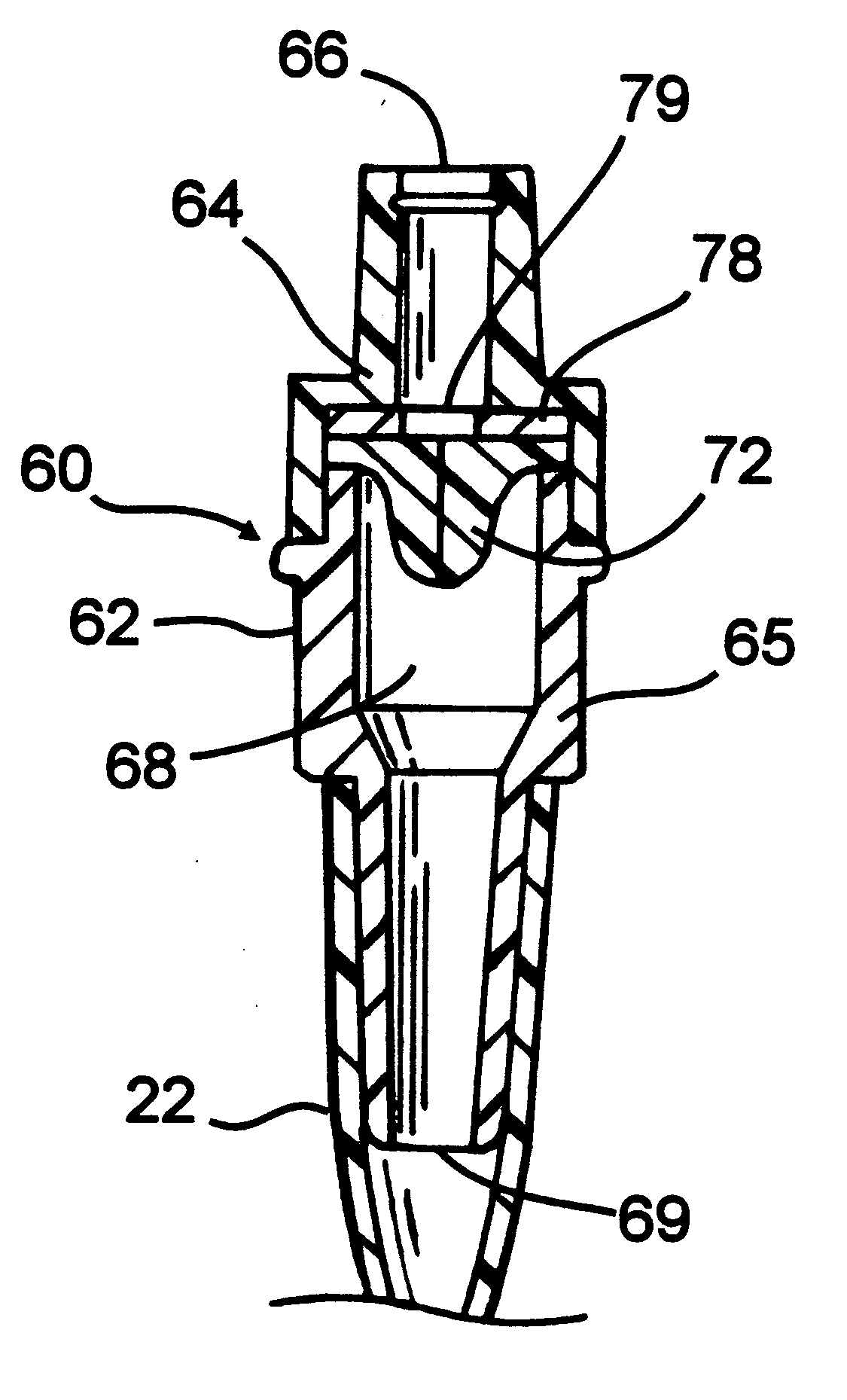
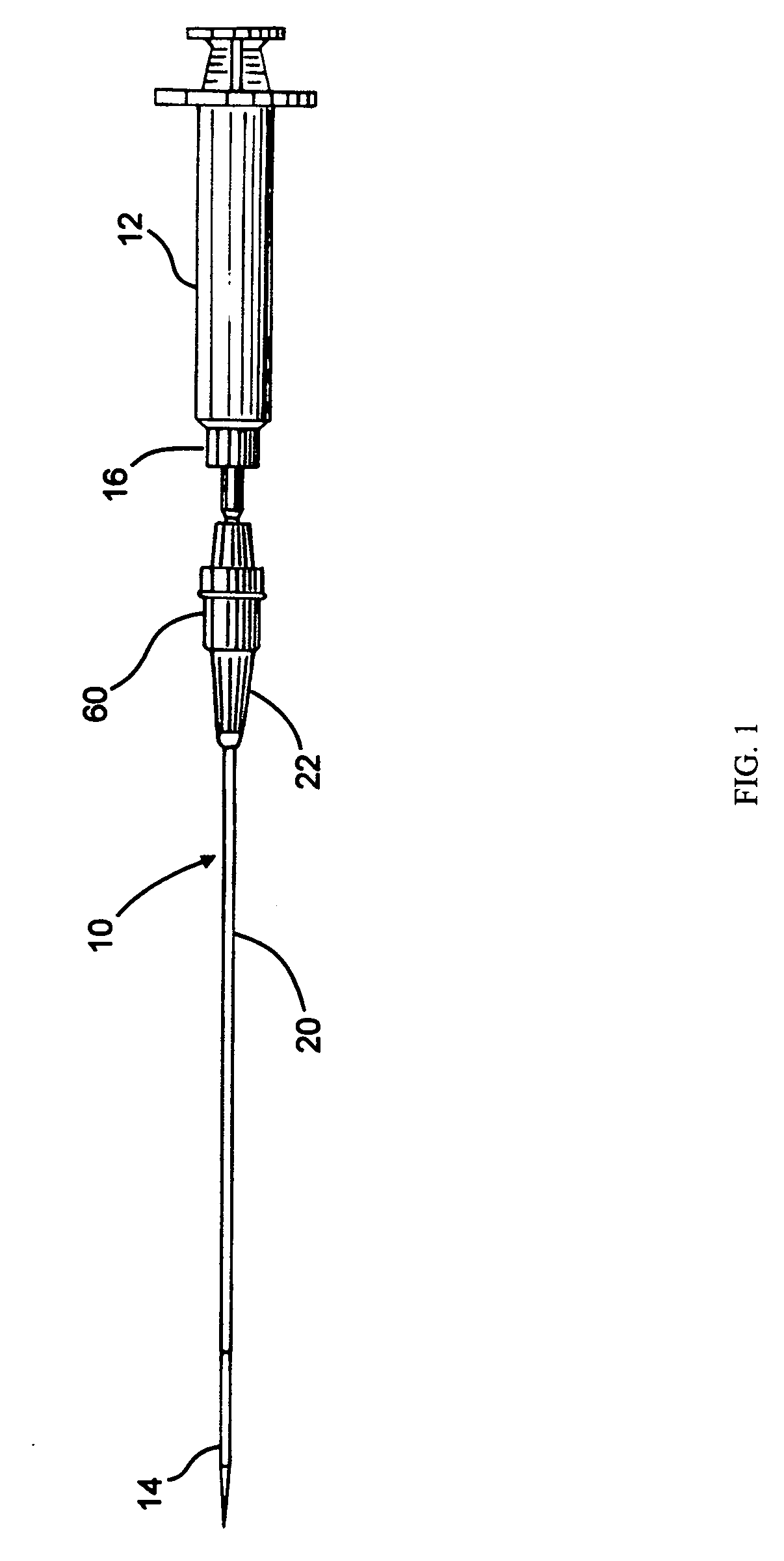
The present invention is a tapered attachment for use with a pleural catheter that connects securely to the pleural catheter and has a hollow elongated member and a tapered distal portion. When the tapered attachment connected to the prior art catheter, the hollow elongated member opens the self-sealing valve of the prior art catheter allowing communication from the interior of the pleural catheter to the interior of the tapered attachment. The distal outer taper of the invention can connect to a variety of standard drainage systems to remove fluids or gases from the pleural cavity. The invention may also have a one way valve. With the invention in place and functioning, air does not enter the pleural space. Additionally, the variations in pleural pressure that normally occur during respiration can pump fluids or gases out of the pleural cavity through the invention.
Owner:CAREFUSION 2200 INC
Methods to accelerate wound healing in thoracic anastomosis applications
InactiveUS7682332B2Speed up the flowOvercome disadvantagesRespiratorsElectrotherapyWound healingPleural cavity
Methods for creating an anastomosis between a channel through the chest wall and an opening in the visceral membrane of a lung using a medical device. The methods include creating the channel through the chest wall into the pleural cavity; forming an adhesion between the chest wall and the visceral membrane of the lung; creating an opening in the visceral membrane of the lung which communicates with the channel; and inserting the medical device into the channel. The medical device has a compression structure which spans the channel. The methods include configuring the compression structure to apply a compressive force to tissue surrounding the anastomosis and / or applying agents and materials to the tissue of the anastomosis thereby accelerating the formation and healing of the anastomosis.
Owner:PORTAERO
Implantable fluid management system having clog resistant catheters, and methods of using same
ActiveUS20180056050A1Reduce cloggingReduce potential cloggingWound drainsMedical devicesFluid managementCvd risk
A fluid management system for moving bodily fluid accumulated due to ascites, pleural effusion or pericardial effusion is provided including an implantable pump coupled to an inflow catheter, an outflow catheter, and optionally an anti-clog catheter. The fluid management system facilitates removal of fluid from a body region, such as the peritoneum, pleural cavity or pericardial sac, where drainage is desired to another body region, such as the urinary bladder or the peritoneal cavity. The system includes clog resistant mechanisms such as clog resistant catheters and / or programmed routines for cycling fluid through inlet catheters in predetermined time intervals and / or responsive to sensed conditions to minimize the risk that inlet catheters become clogged due to, for example, tissue ingrowth and / or solid objects within accumulated fluid.
Owner:SEQUANA MEDICAL NV
Method and device for simultaneously documenting and treating tension pneumothorax and/or hemothorax
ActiveUS9616203B2Improved diagnostic and treatment meanReduce riskGuide needlesDiagnosticsPressure transmissionPleural cavity
A method and device are provided for simultaneously or near-simultaneously diagnosing and treating tension pneumothorax and / or hemothoraxA Veress-type needle portion includes a hollow needle for puncturing the chest wall over a blunt hollow probe biased by one or more springs to extend distally into the pleural cavity. Openings in the blunt hollow probe connect via a pathway to an automatic check valve, which permits the flow of air and / or fluid only in a proximal direction. Pressure from within the pleural cavity is transmitted to the interior surface of a pressure documenter. If pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is present in the pleural cavity, the pressure documenter will be automatically urged proximally to simultaneously allow air and / or fluid to escape from the pleural space through the device, thus treating the tension pneumothorax and / or hemothorax, as well as providing a stable indicator to positively document the diagnosis of increased pressure.
Owner:CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
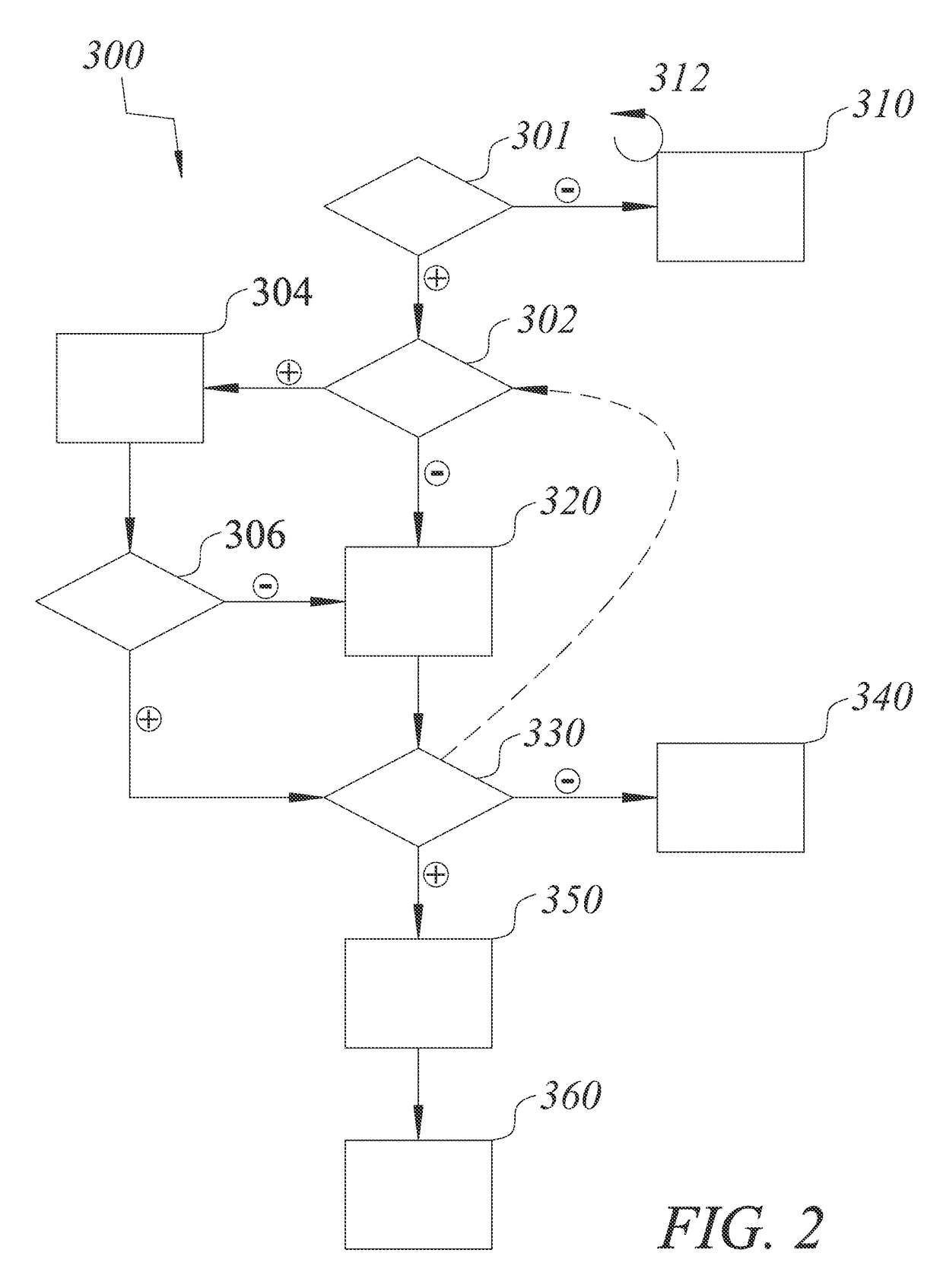
Hybrid variation bioelectrical impedance imaging method
ActiveCN106037650AOvercome errorHigh-resolutionDiagnostic signal processingSensorsSteep descentMixed finite element method
The invention provides a hybrid variation bioelectrical impedance imaging method, relating to the measurement on the conductivity of the pleural cavity of the body. According to the method, the potential spatial distribution condition is simulated by adopting a finite element method, a numerical model of the bioelectrical impedance imaging technology is established, a numerical model with large size is dispersed into small units, certain boundary conditions are applied and boundary voltage is calculated, a two-dimensional thoracic cavity numerical model and a three-dimensional thoracic cavity numerical model are respectively established, after the objective function of the hybrid variation algorithm is determined, the inverse problem solving is carried out by adopting the steepest descent method, the electrical impedance image reconstruction of the thoracic cavity is carried out, so that the resolution ratio of the reconstructed image is improved, therefore, the problems in the existing bioelectrical impedance imaging technology, the influences of noises and errors exist during the process of reestablishing the image with high resolution ratio, consequently, the excessive smooth and staircase effect are caused, and the accurate electrical impedance reconstructed image of the lung can not be obtained are solved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Medical instrument for inserting a chest drainage tube
ActiveUS20140324000A1Performed rapidly and easilyLess time-consumingSurgical needlesWound drainsSingle stagePleural cavity
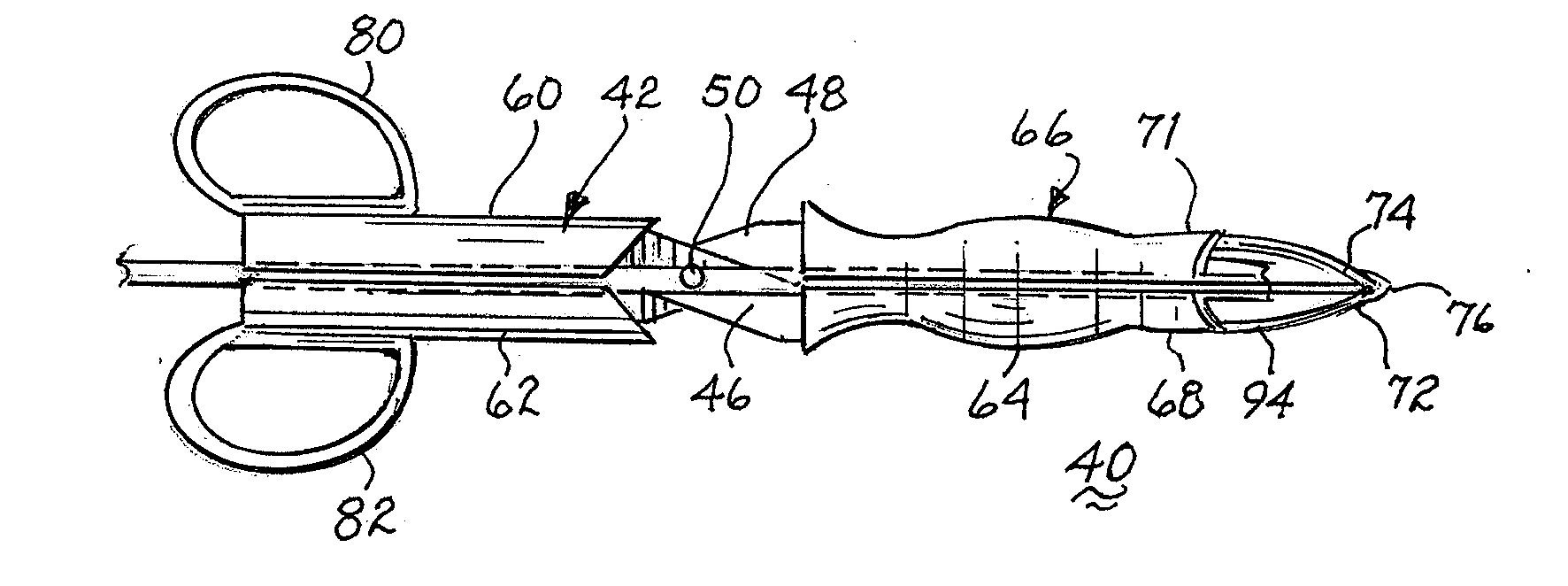
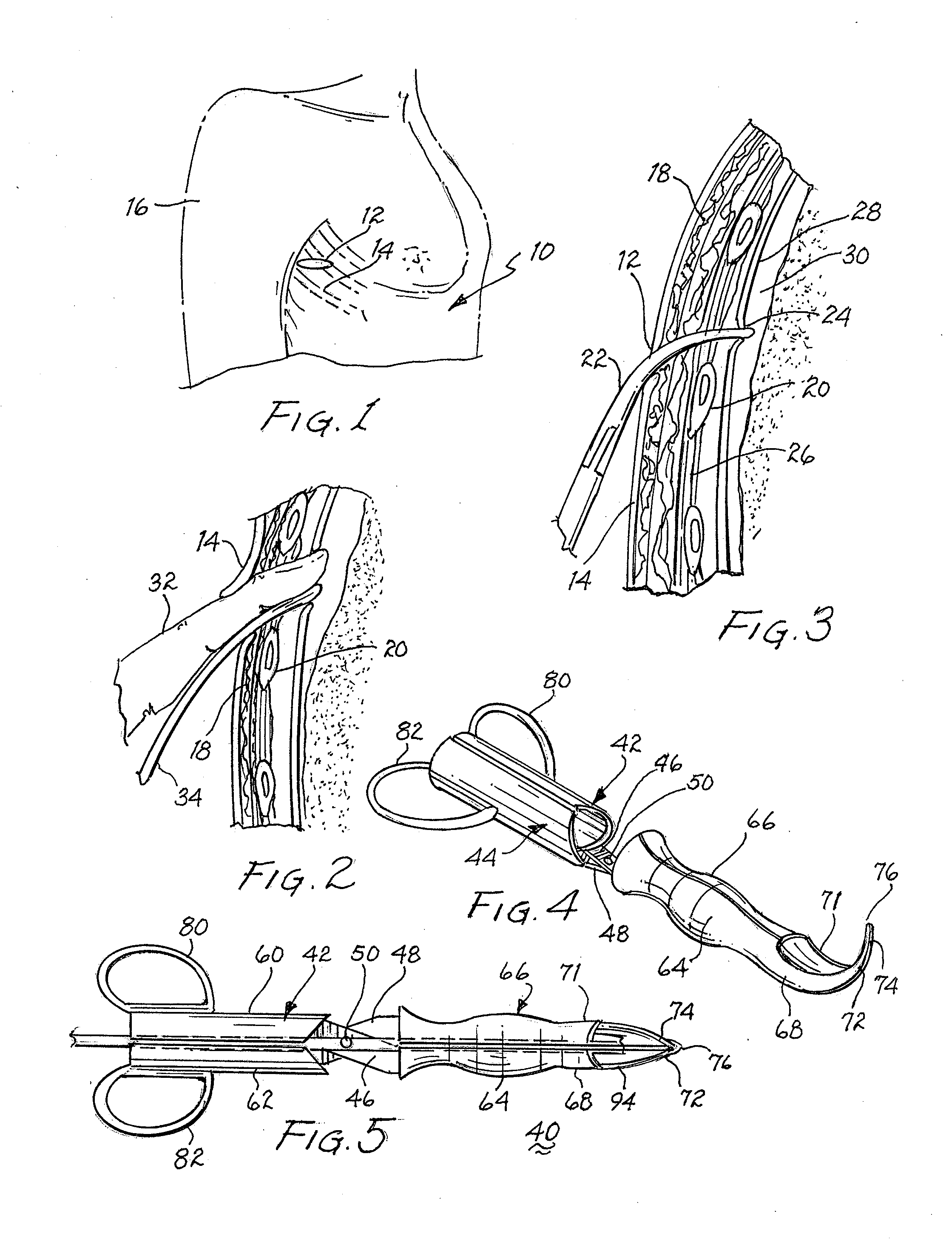
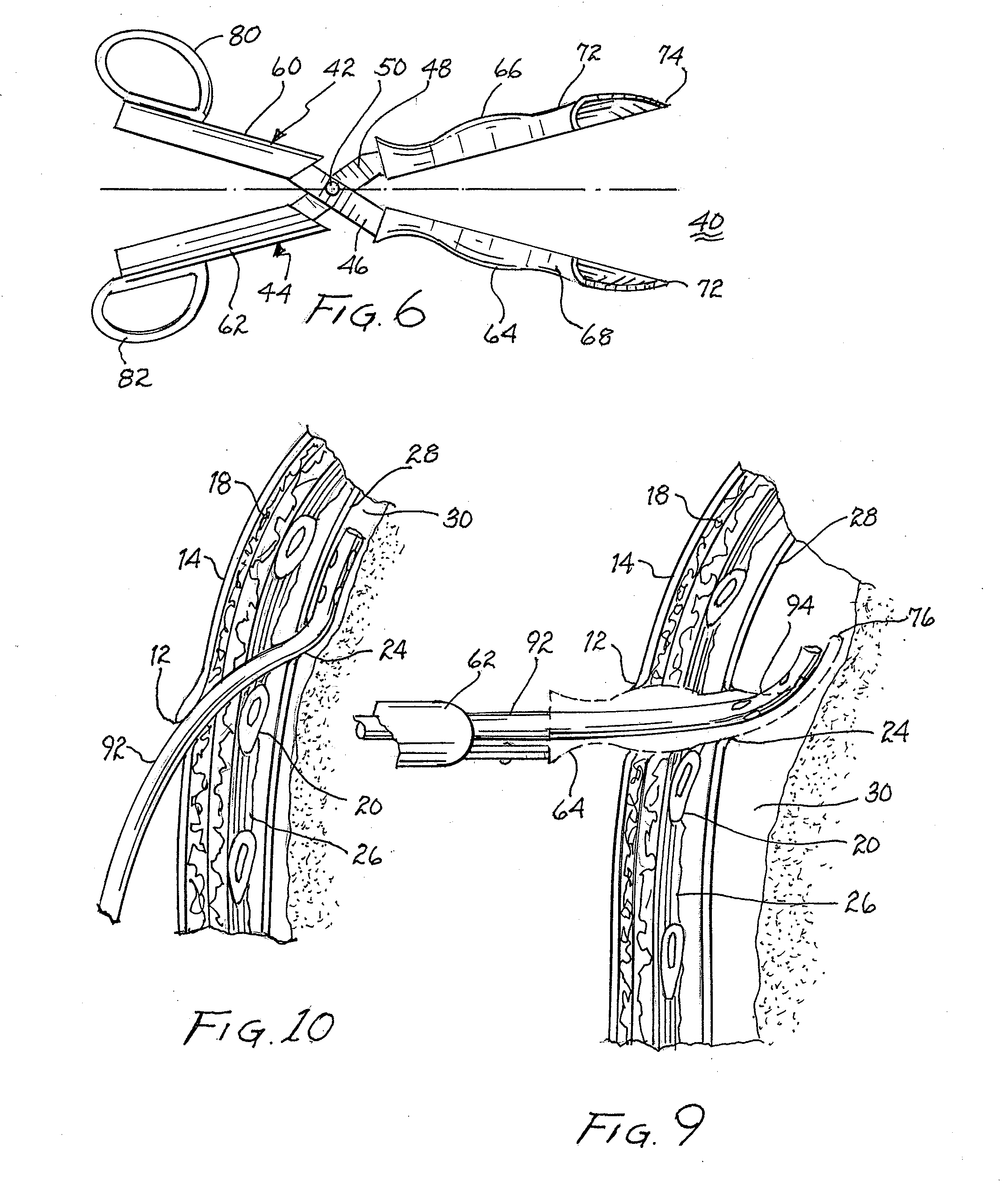
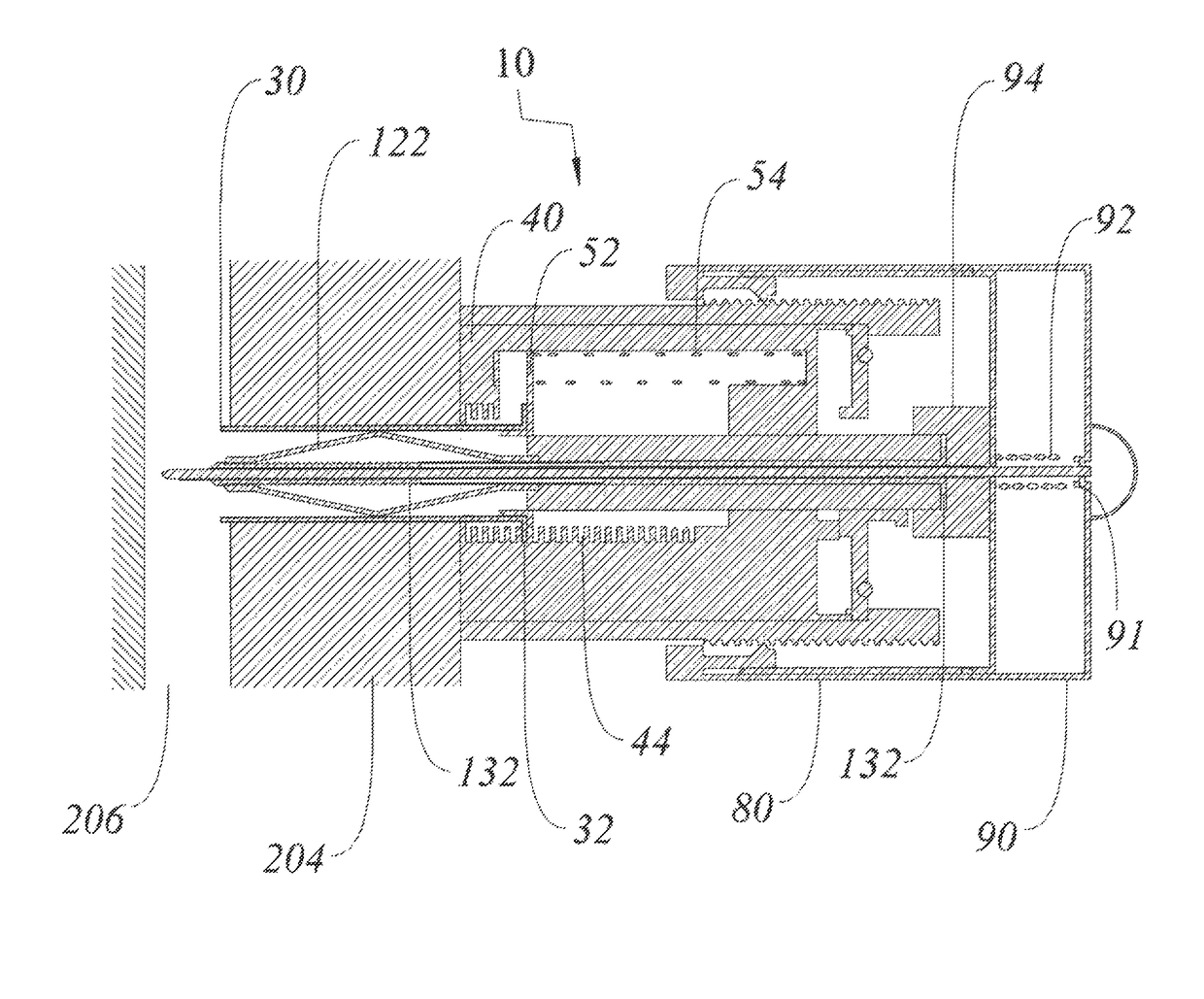
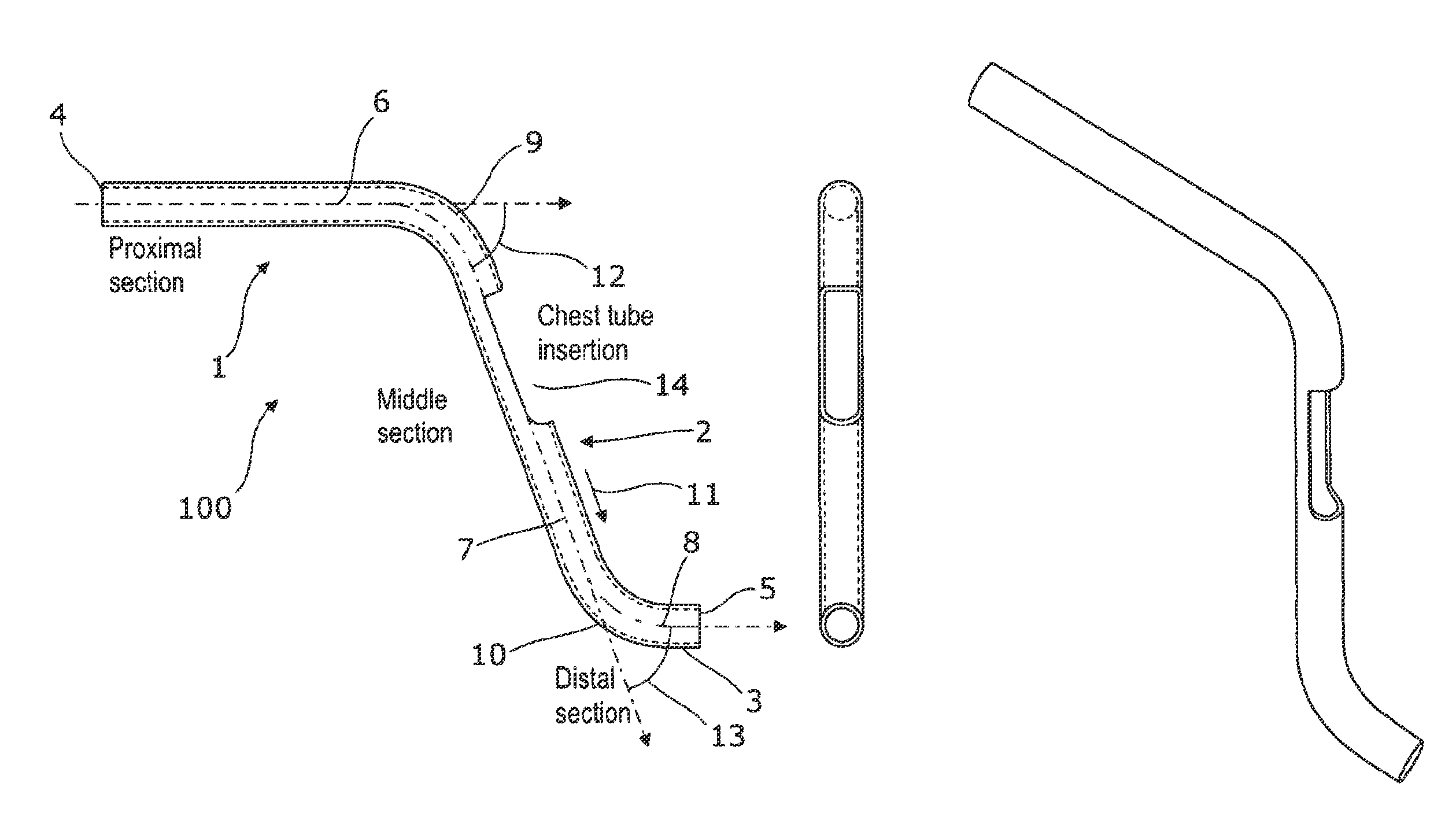
A single stage instrument is used to insert a chest drainage tube into the inter-pleural space to facilitate drainage. The instrument is scissor-like with cylinder-like channels to slidably enclose the distal section of the tube therein when closed. The tip of the instrument is curved to enter the skin incision and the offset pleural incision whereafter the instrument is rotated 180 degrees to align the curved tip with the pleural space. The curved tip facilitates sliding the chest drainage tube through the instrument to effect sufficient insertion length. Once the instrument is in place, the tube is slid along the instrument to ensure that all drainage holes in the chest drainage tube are within the pleural cavity. Thereafter, the instrument is withdrawn leaving the chest drainage tube in place. After withdrawal of the instrument, it is opened laterally for lateral disengagement with the chest drainage tube.
Owner:HILL DAVID A
Percutaneous access pathway system and method
ActiveUS10046147B2Error minimizationDifferent sizeGuide needlesSurgical needlesPleural cavityBiomedical engineering
An improved method and device are provided for forming and / or maintaining a percutaneous access pathway. The device generally comprises at least one of three type of components: access pathway, insertion device, and attachment device. In one embodiment, the device is used to form and / or maintain a percutaneous access pathway into the pleural cavity (i.e. tube thoracostomy). The provided assembly substantially reduces the possibility of iatrogenic infection while accessing and / or re-accessing a body space.
Owner:CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
Brachytherapy apparatus and method for use with minimally invasive surgeries of the lung
ActiveUS8409070B2Preventing and reducing pneumothoraxFacilitating proper lung inflationBronchoscopesEndoscopesPleural cavityBrachytherapy
Brachytherapy treatment of a patient's lung tissue following resection is effected using a balloon applicator which is inserted, normally through the same opening used for the surgery, through the chest wall and into the cavity. The lung and chest openings are closed around the applicator and generally sealed around the applicator. A suction port is provided, in a suction circuit of the applicator, to withdraw fluid from the pleural cavity, at intervals as needed, to assure that the lung can be inflated. Different embodiments of suction circuits are disclosed. A bronchial applicator and method are also disclosed.
Owner:NUCLETRON OPERATIONS +1
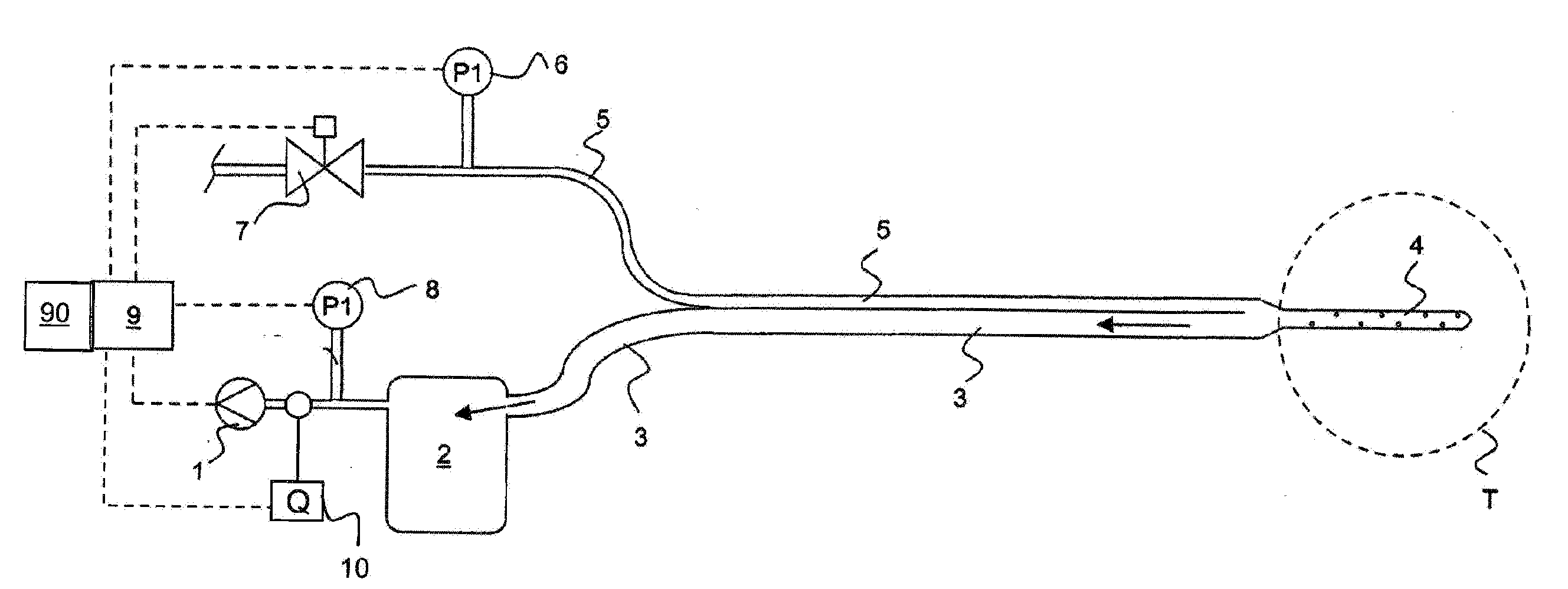
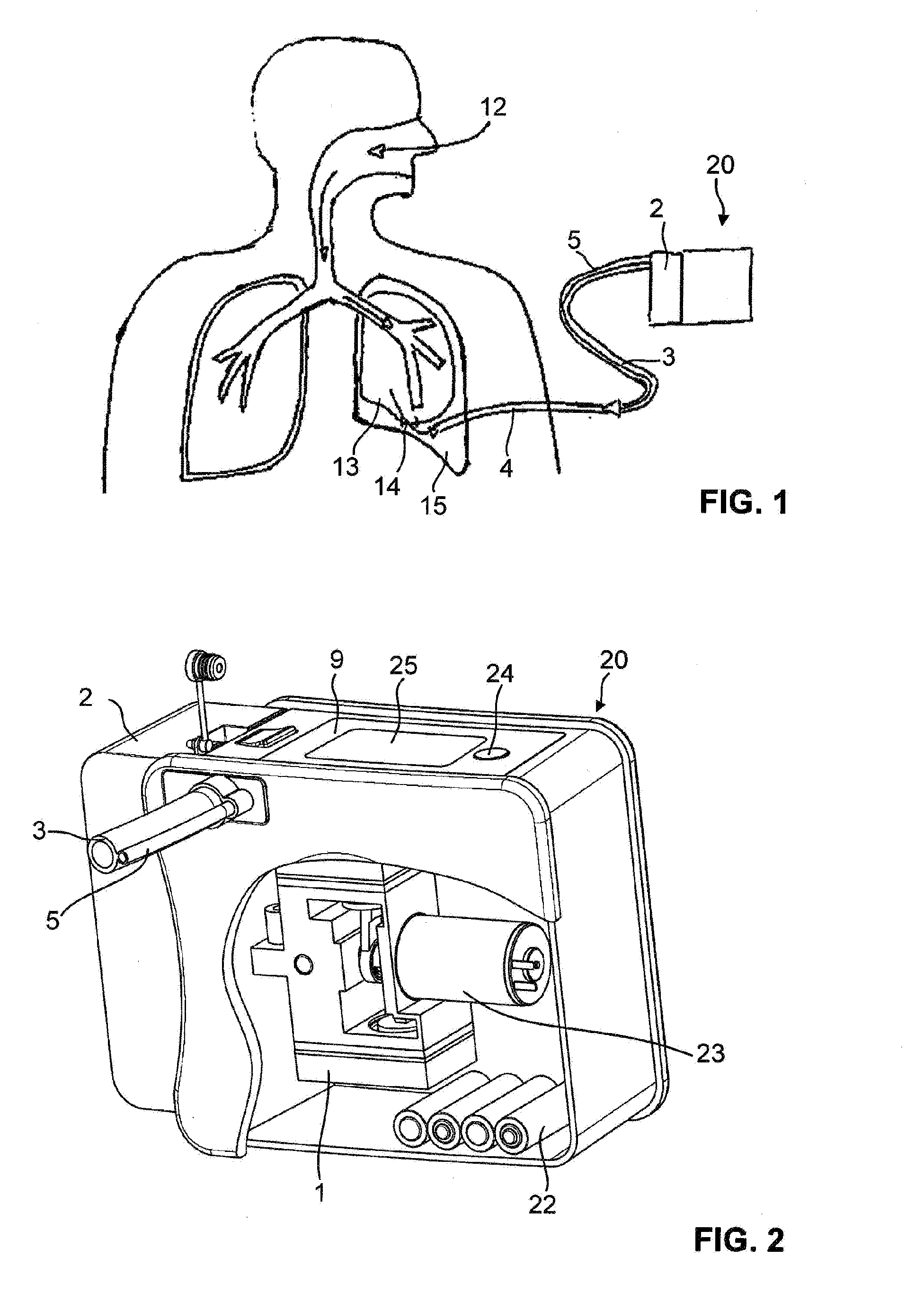
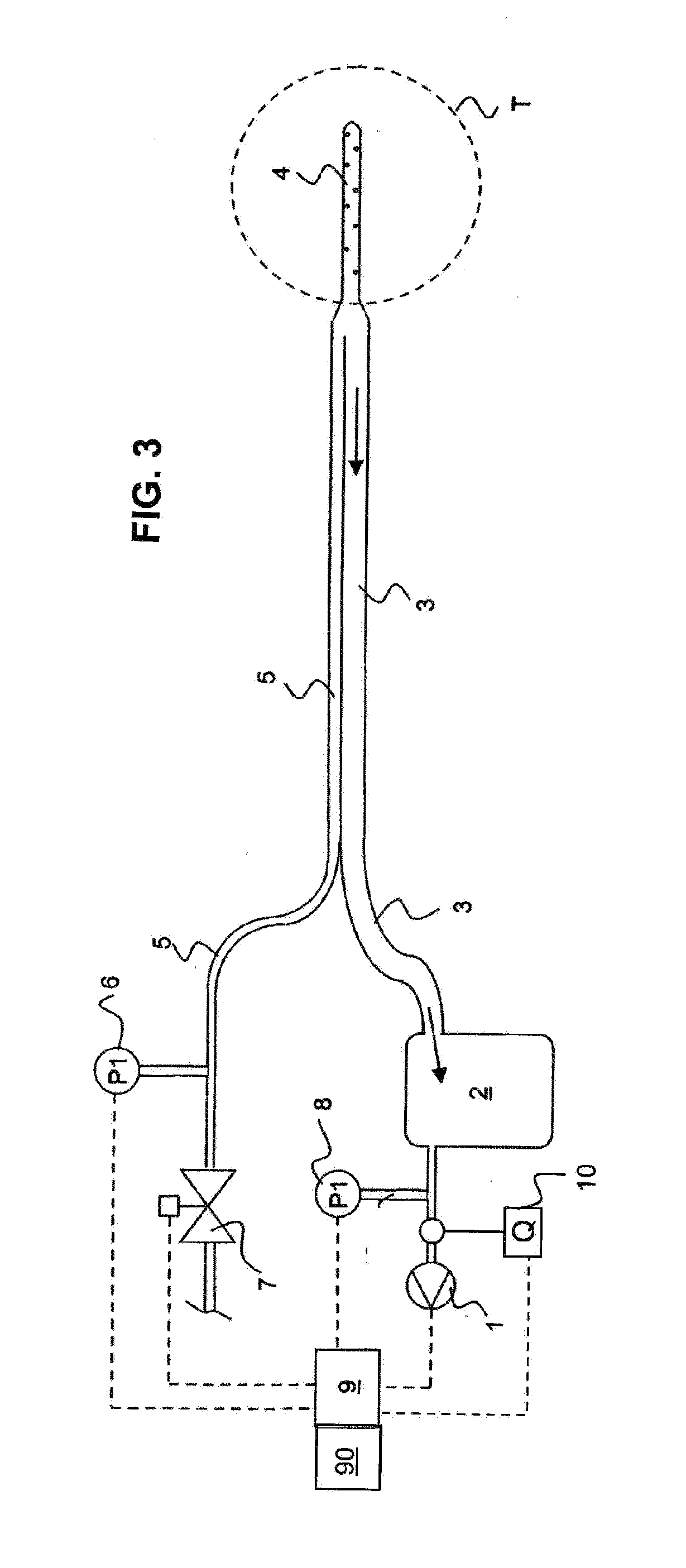
Adaptive algorithm for thoracic drainage therapy
ActiveUS20140100540A1Easy to adjustMore objectiveMedical devicesIntravenous devicesPleural cavityMedicine
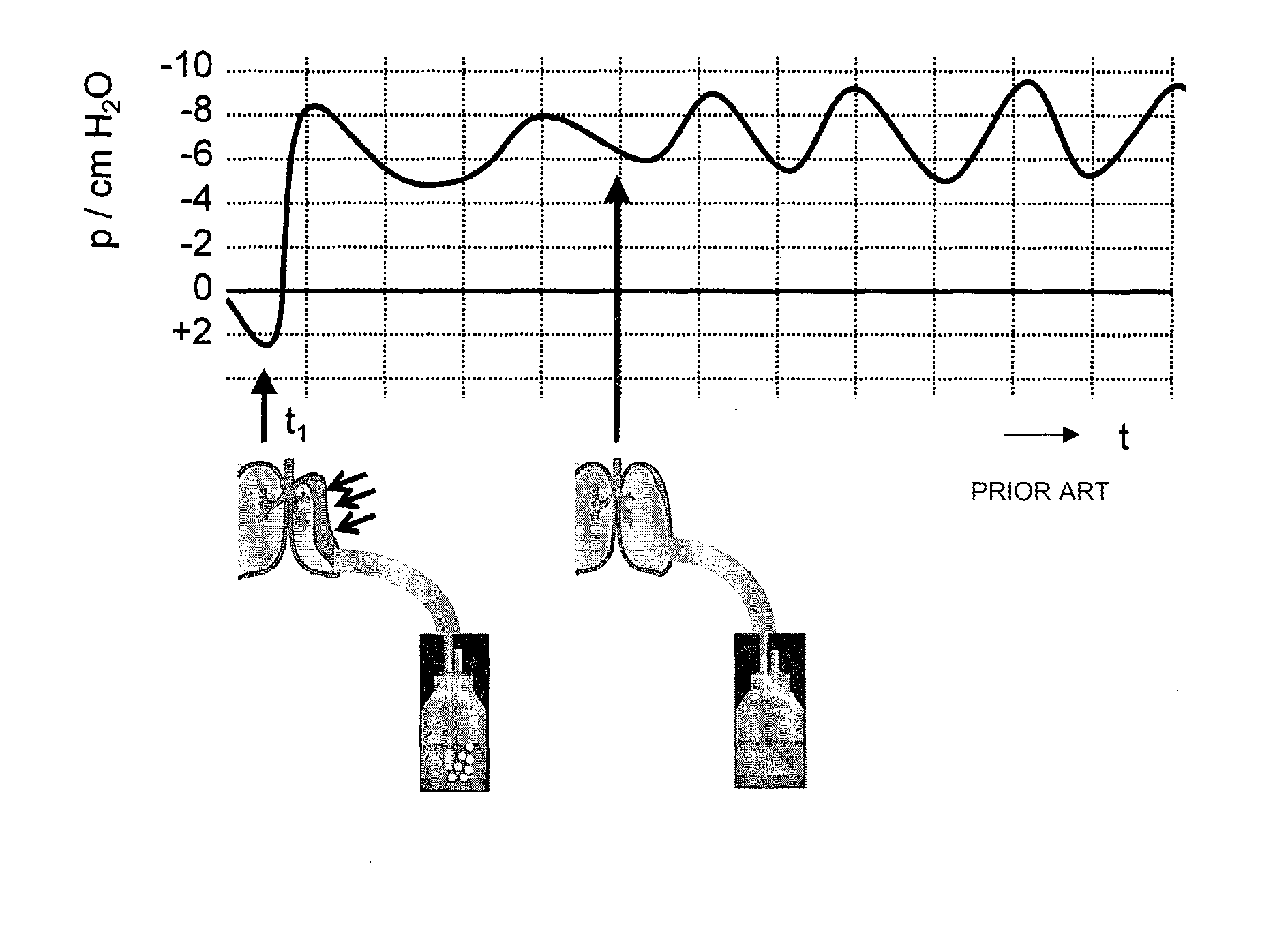
Devices and to methods for thoracic drainage for a patient having an air fistula. A vacuum is produced in the pleural cavity of the patient by means of a suction device. In order to adjust the vacuum on the basis of objective criteria, a suitable size measure for the air fistula is determined and the vacuum produced by the suction device is controlled according to said size measure. An adaptive algorithm includes: (a) determining a first value of a size measure for the air fistula; (b) changing the vacuum by a first difference value; (c) determining a second value of the size measure after a first waiting period; (d) changing the vacuum by a second difference value having the opposite sign if the second measure is greater than the first measure; (e) repeating steps (a) to (d) after a second waiting period.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Chest drainage systems and methods
ActiveUS20160193393A1Good removal effectEasy to disassembleMedical devicesIntravenous devicesPleural cavityAtmospheric pressure
A chest drainage system includes a collection device and a fluid pathway configured to extend from the collection device to a patient. A pressure source is configured to selectively provide sub-atmospheric pressure to the fluid pathway. The system is configured to introduce sub-atmospheric pressure from the pressure source at a substantially constant target pressure and at a dynamic pressure that varies from the target pressure. A method is also disclosed for draining a pleural cavity of a patient. The method involves applying dynamic pressure to the pleural cavity of a patient by changing sub-atmospheric pressure applied to the patient such that the patient's pleura moves without any or limited patient activity, thus facilitating removal of loculated fluid from the pleural cavity. The method may involve the use of the chest drain system.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
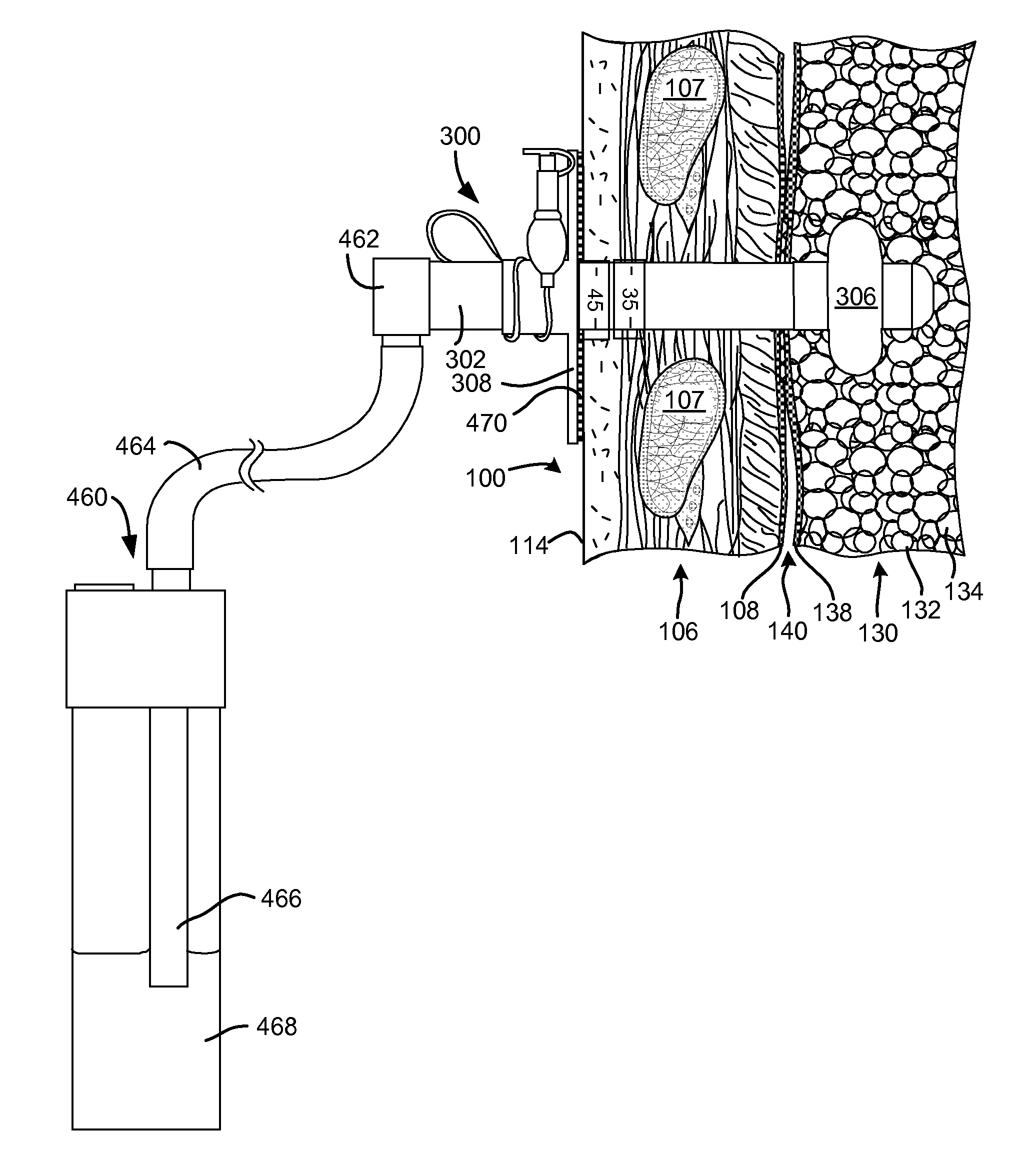
Medical device in the form of a catheter for supplying fluid to, but in particular removing fluid from body cavities, in particular the pleural cavity
InactiveCN101854974APrevent intrusionEasy to operateGuide needlesSurgical needlesPleural cavitySecretion
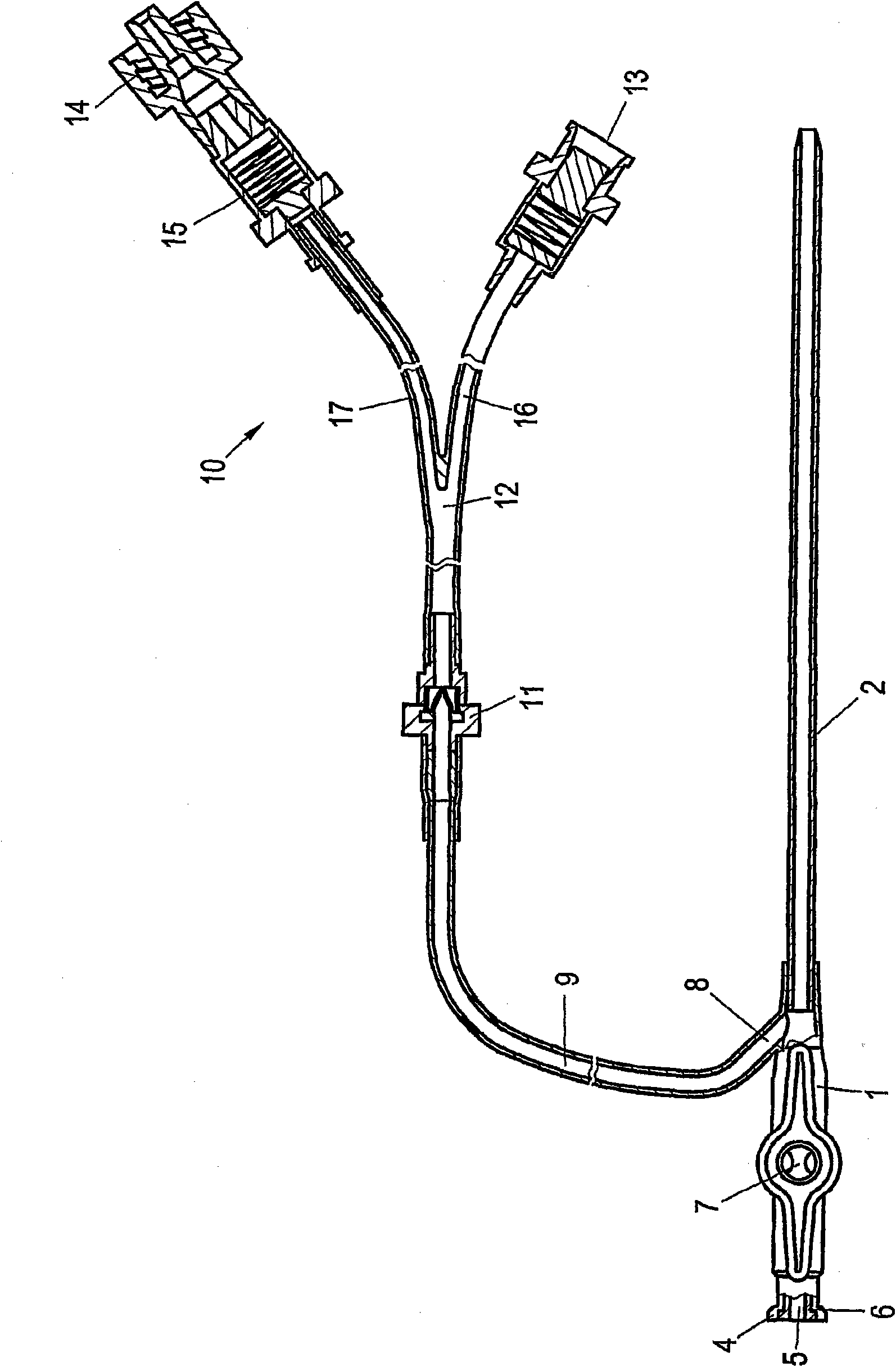
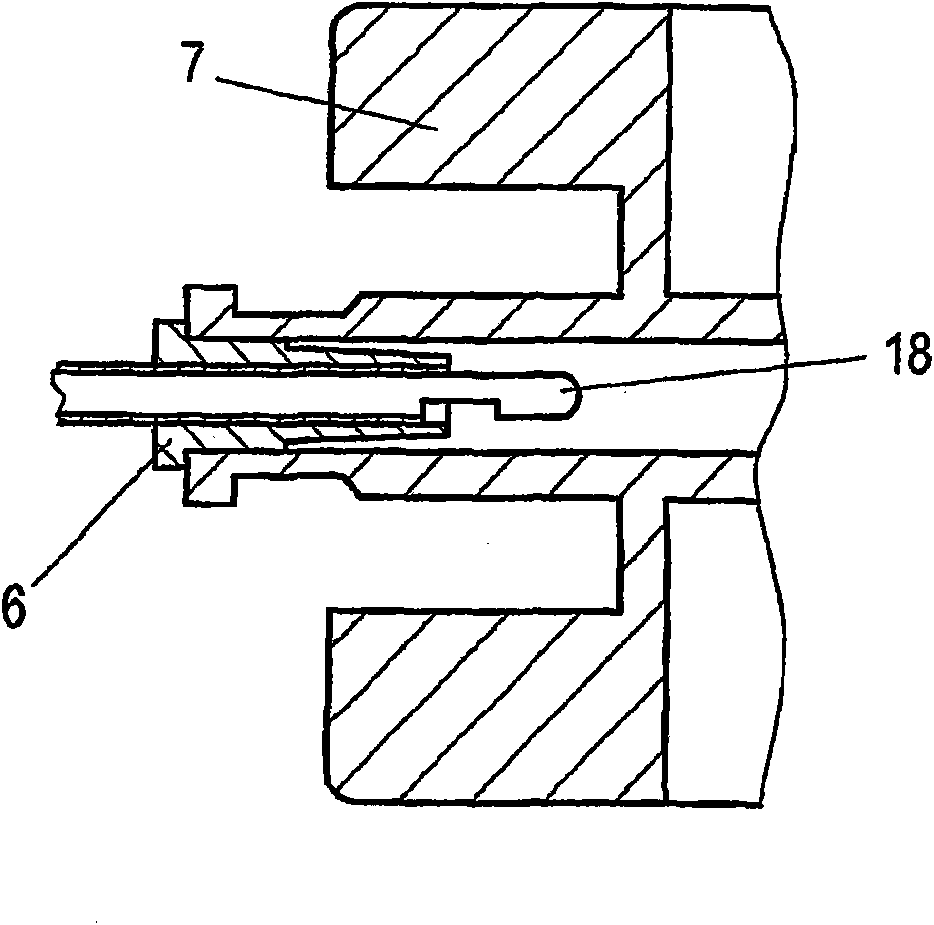
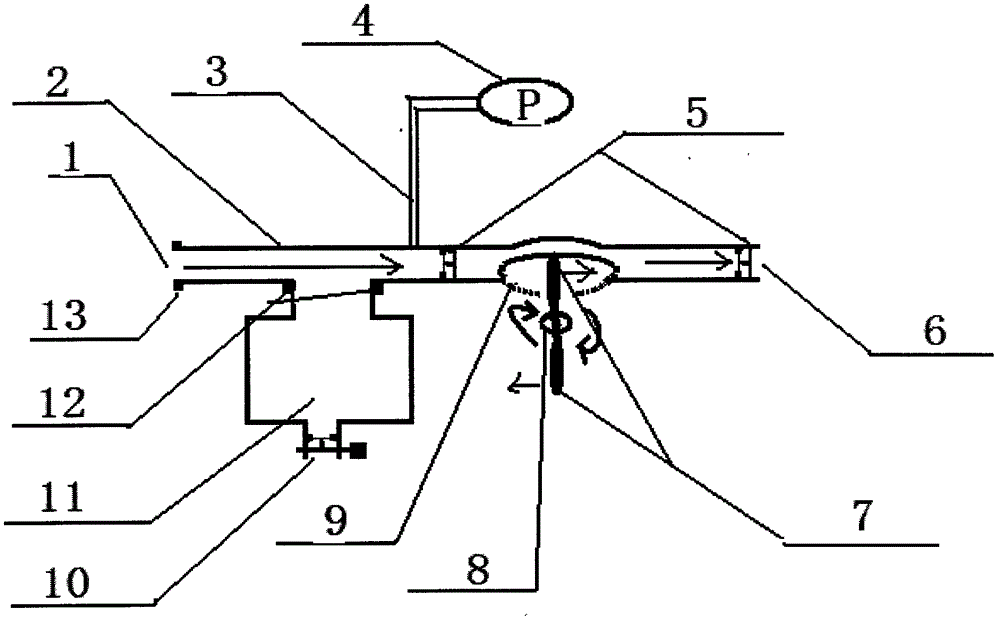
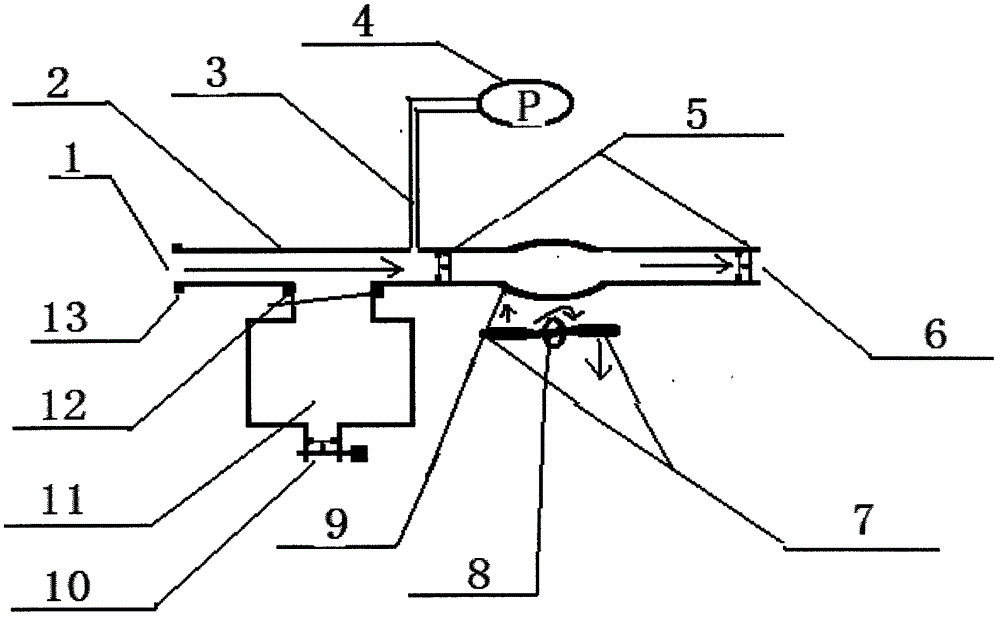
The invention relates to a medical device that is in the form of a catheter (3) for supplying fluid to but in particular removing fluid from body cavities. The catheter head (1) on the proximal end (4) comprises an inlet (5) that is provided with one or more sealing and / or blocking elements (6, 7) and that is used to introduce a hollow or Verres needle (18) into the catheter (3). In the region between the sealing or blocking element(s) and the region of the catheter shaft (2) that is introduced into the body, a branch connection (8) is arranged, said branch connection being connected to a suction pump arrangement (10) via a branch tube (9). Said branch tube (9) leads to a suction valve (11) that enables a fluid to flow in the direction of the suction device, but blocks the flow in the counter direction. The outlet of the suction valve (11) opens into a forked area (12), from which one branch (16) leads to a suction device connection, in particular an injection connection (13) that is embodied, preferably, as a Luer-lock, and the other branch thereof (17) leads to a secretion bag connection (14). A non-return valve (15) that blocks the return flow of the secretion bag is arranged between said branch (17) and the secretion bag connection (14).
Owner:ALLOMED MEDIZINTECHN
Thoracic Drainage Device Having Reduced Counter-Pressure
ActiveUS20140213992A1Easy for to force airKeep the counterpressure very lowMedical devicesEndoscopesLine tubingPleural cavity
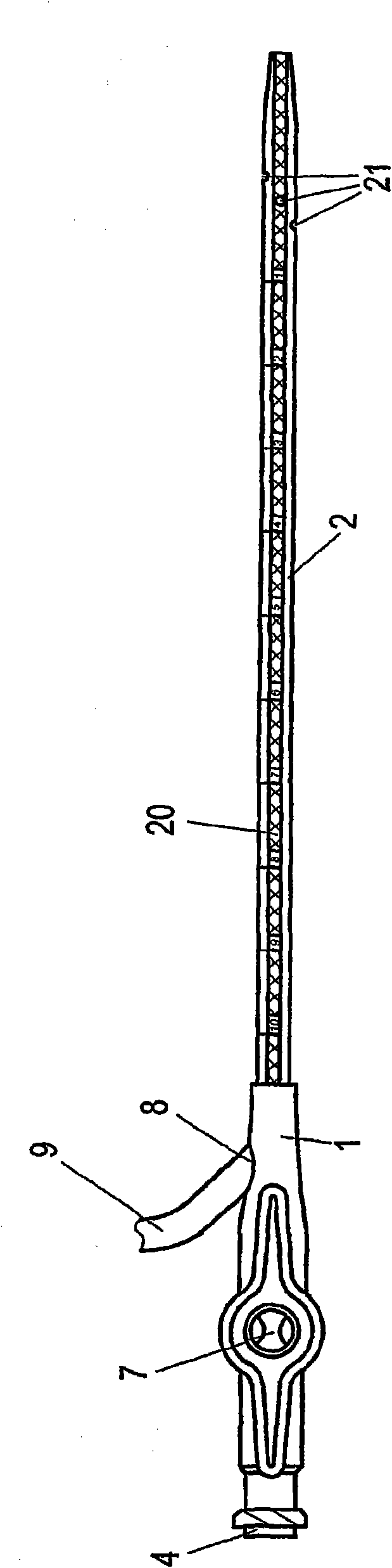
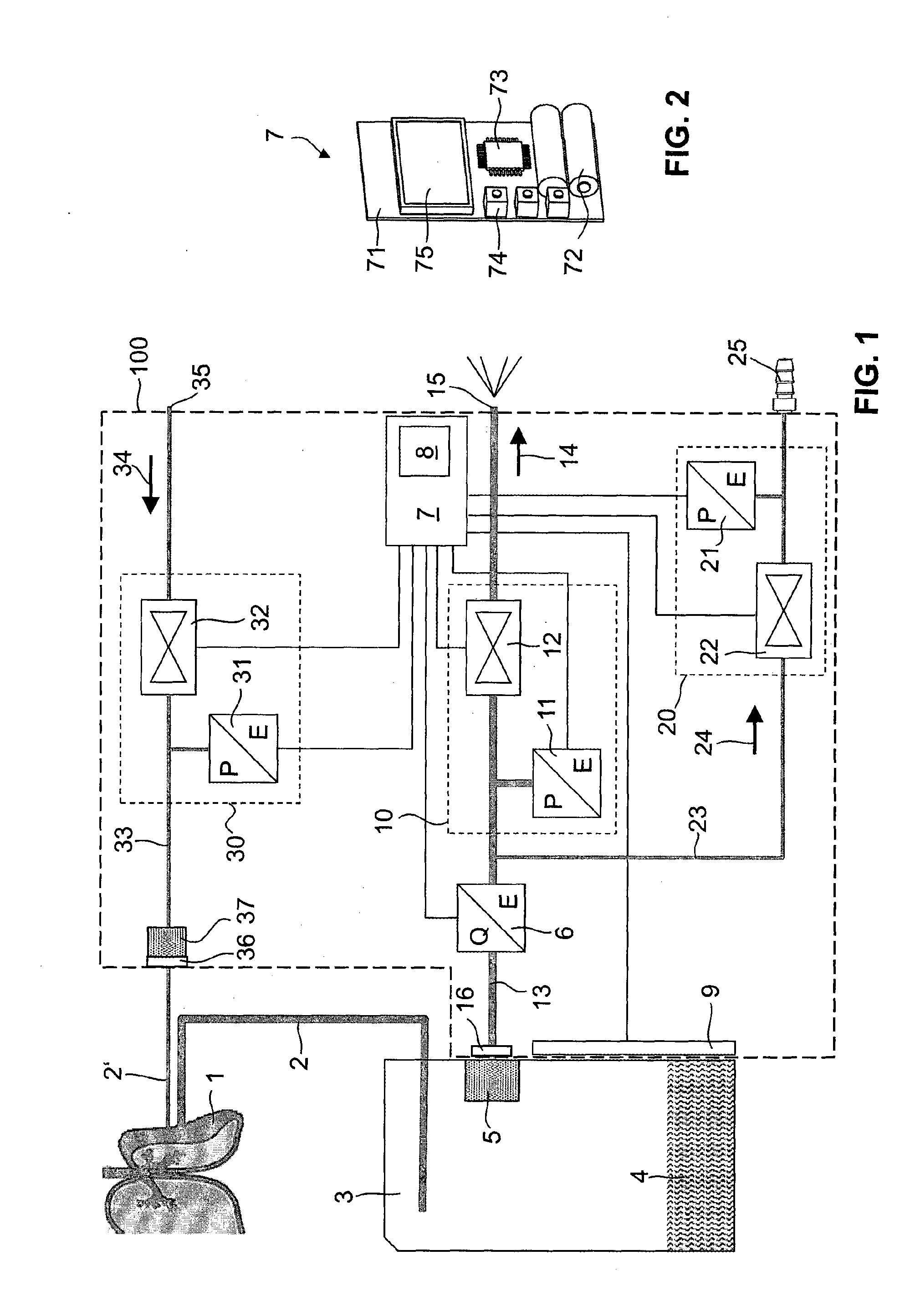
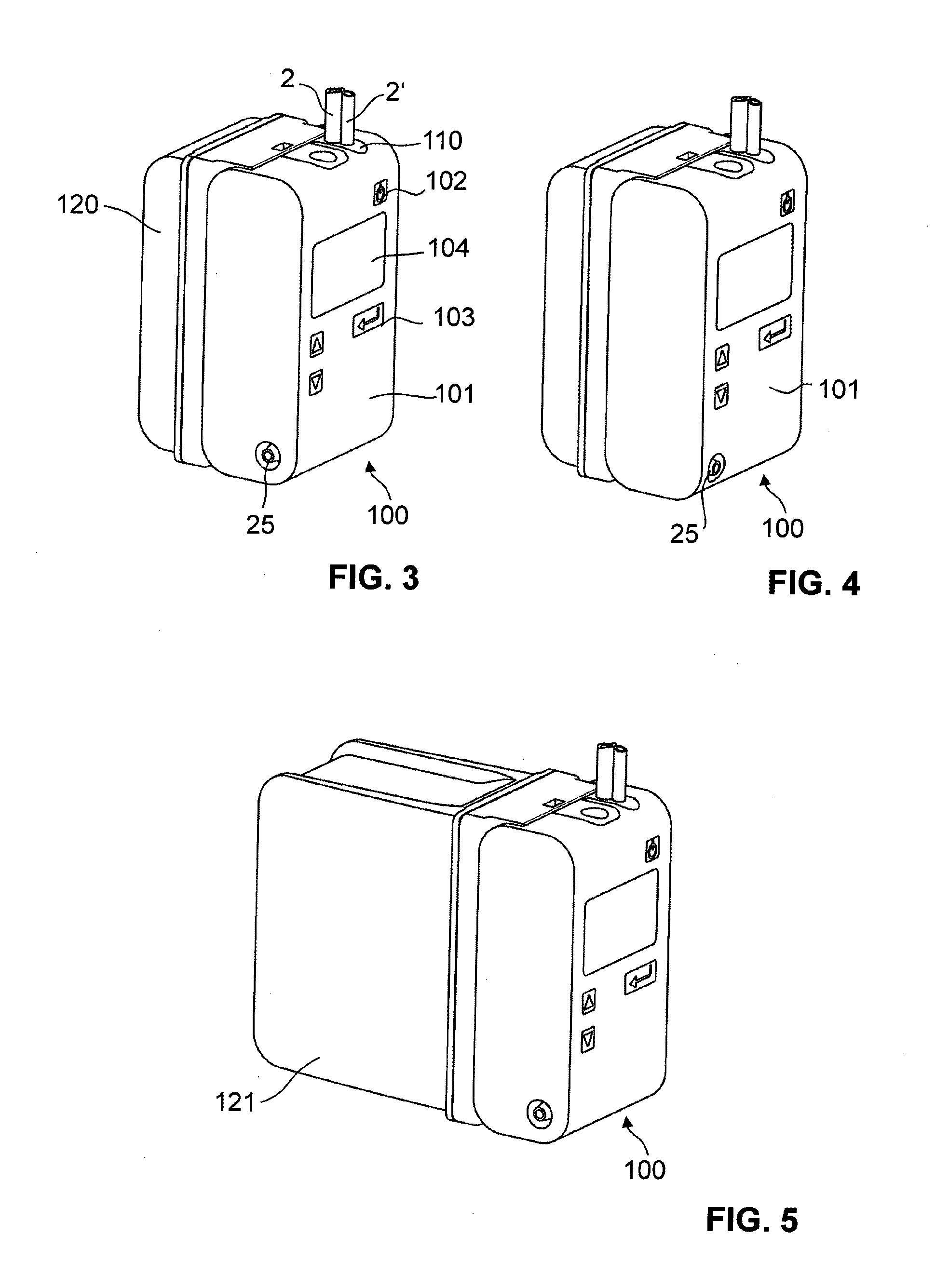
A device for thoracic drainage comprises a container connector for a secretion collection container (3), which can be connected to the pleural cavity of a patient, and a venting device (10) for releasing air from the secretion collection container in passive operation. In order to keep the counterpressure as low as possible during the air release and thus make it easier to force air out of the pleural cavity (1) of a patient, the venting device has a controllable vent valve (12). For this purpose, a control device (7) determines the pressure in the secretion collection container by reading out a pressure sensor (11) and controls the valve to release air from the secretion collection container when the determined pressure exceeds a threshold value. The device can optionally also be operated actively by way of a vacuum connector (25). An ancillary line (2′) permits monitoring of the drainage line (2).
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
Device for curing pneumothorax
The invention relates to a device for curing pneumothorax. The device ensures that a pneumothorax patient is not restricted in motion in a pleural cavity drainage period. The device is characterized by having the functions of initiative exhaust, passive exhaust, storage of liquid and pressure monitoring and alarming. The device structurally and mainly comprises a drainage connecting pipe, a pressure monitoring and alarming device, a one-way vent valve, an air driving handle, a motor, an exhaust ball bag, and a liquid storage bag. Gas of the pneumothorax patient is passively exhausted out of the body of the patient sequentially through the drainage connecting pipe, the one-way vent valve, the exhaust ball bag and the one-way vent valve. When the motor is driven by power to rotate, the air driving handle extrudes the exhaust ball bag so as to initiatively exhaust gas in the ball bag out of the body. Rotation speed of the motor can be controlled through the pressure monitoring and alarming device. The pressure monitoring and alarming device monitors air pressure value and adjusts the rotation speed of the motor. Pleural cavity liquid can be stored in the liquid storage bag, and is exhausted out through the liquid storage bag one-way vent valve.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT)
Brachytherapy apparatus and method for use with minimally invasive surgeries of the lung
ActiveUS20090112047A1Preventing and reducing pneumothoraxFacilitating proper lung inflationBronchoscopesEndoscopesPleural cavityBronchial tube
Brachytherapy treatment of a patient's lung tissue following resection is effected using a balloon applicator which is inserted, normally through the same opening used for the surgery, through the chest wall and into the cavity. The lung and chest openings are closed around the applicator and generally sealed around the applicator. A suction port is provided, in a suction circuit of the applicator, to withdraw fluid from the pleural cavity, at intervals as needed, to assure that the lung can be inflated. Different embodiments of suction circuits are disclosed. A bronchial applicator and method are also disclosed.
Owner:XOFT INC
Thorax drainage device
InactiveUS20170007749A1Risk minimizationEasy to breatheMedical devicesIntravenous devicesPleural cavityDrainage tubes
A thorax drainage device for aspirating fluids from a pleural cavity of a patient using underpressure has a fluid collection container for collecting the aspirated fluids and a drainage tube for connecting the fluid collection container to the pleural cavity of the patient. The fluid collection container is connectable to a vacuum source, in order to generate an underpressure in the fluid collection container. The thorax drainage device has an adjustable mechanism for attenuating pressure differences during the respiration of the patient, this mechanism being adjustable independently of a suction capacity of the vacuum source. This device permits a gradual expansion of the lung without risk of injury and thus prepares the lung for the completion of the drainage.
Owner:MEDELA HLDG AG
device
ActiveUS20130131549A1Accurate directionRelieve symptomsSurgical needlesWound drainsPleural cavityGuide tube
The present invention is directed to a method and a device for accurately guiding a chest tube to an intended position within a pleural cavity of an animal or human being. There is also provided a kit-of-parts comprising a catheter and a catheter guiding device according to the present invention.
Owner:PLEURATECH
left ventricular assist pump
The invention discloses a left ventricle auxiliary blood pump, which comprises a cardiac apex sleevelet and a blood pump body fixedly connected with the cardiac apex sleevelet, wherein the cardiac apex sleevelet comprises a suture ring and a flexible skirt edge which is sleeved at the periphery of the suture ring; the suture ring comprises a suture ring inner hole and a convex edge which is convexly arranged in the radial direction; the blood pump body comprises an inlet pipe; the inlet pipe is convexly arranged on a rear cover of the blood pump body; a peripheral ring slot is formed between the convex edge and the flexible skirt edge; a sliding sheet which can only move in the radial direction relative to the blood pump body is arranged on the rear cover of the blood pump body and is stretched into the peripheral ring slot in a movable way; the convex edge is positioned between the sliding sheet and the bottom surface of a settling tank; and the cardiac apex sleevelet and the blood pump body are relatively axially fixed. In the invention, the sliding sheet is used for fixing the cardiac apex sleevelet and the blood pump, so that the cardiac apex sleevelet can be more conveniently and reliably connected with the blood pump; simultaneously, the axial dimension of the inlet pipe of the blood pump is reduced, so that the implantation of the left ventricle auxiliary blood pump in a pleural cavity is facilitated without damages to a diaphragm, and the success rate of a surgery is greatly improved.
Owner:苏州同心医疗科技股份有限公司
Method and Device for Simultaneously Documenting and Treating Tension Pneumothorax and/or Hemothorax
ActiveUS20170182229A1Improved diagnostic and treatment meanReduce riskDiagnosticsSurgical needlesPleural cavityPressure transmission
A method and device are provided for simultaneously or near-simultaneously diagnosing and treating tension pneumothorax and / or hemothoraxA Veress-type needle portion includes a hollow needle for puncturing the chest wall over a blunt hollow probe biased by one or more springs to extend distally into the pleural cavity. Openings in the blunt hollow probe connect via a pathway to an automatic check valve, which permits the flow of air and / or fluid only in a proximal direction. Pressure from within the pleural cavity is transmitted to the interior surface of a pressure documenter. If pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is present in the pleural cavity, the pressure documenter will be automatically urged proximally to simultaneously allow air and / or fluid to escape from the pleural space through the device, thus treating the tension pneumothorax and / or hemothorax, as well as providing a stable indicator to positively document the diagnosis of increased pressure.
Owner:CRITICAL INNOVATIONS
Low profile chest seal
ActiveUS7834231B2Effective maintenanceLow profilePneumothorax apparatusSurgical veterinaryPleural cavityInjury mouth
A chest seal for treating an open pneumothorax that is low profile and thus unobtrusive so that the chest seal can be effectively maintained in position to seal a chest wound while allowing the pleural cavity to vent.
Owner:SAFEGUARD MEDICAL HOLDCO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com