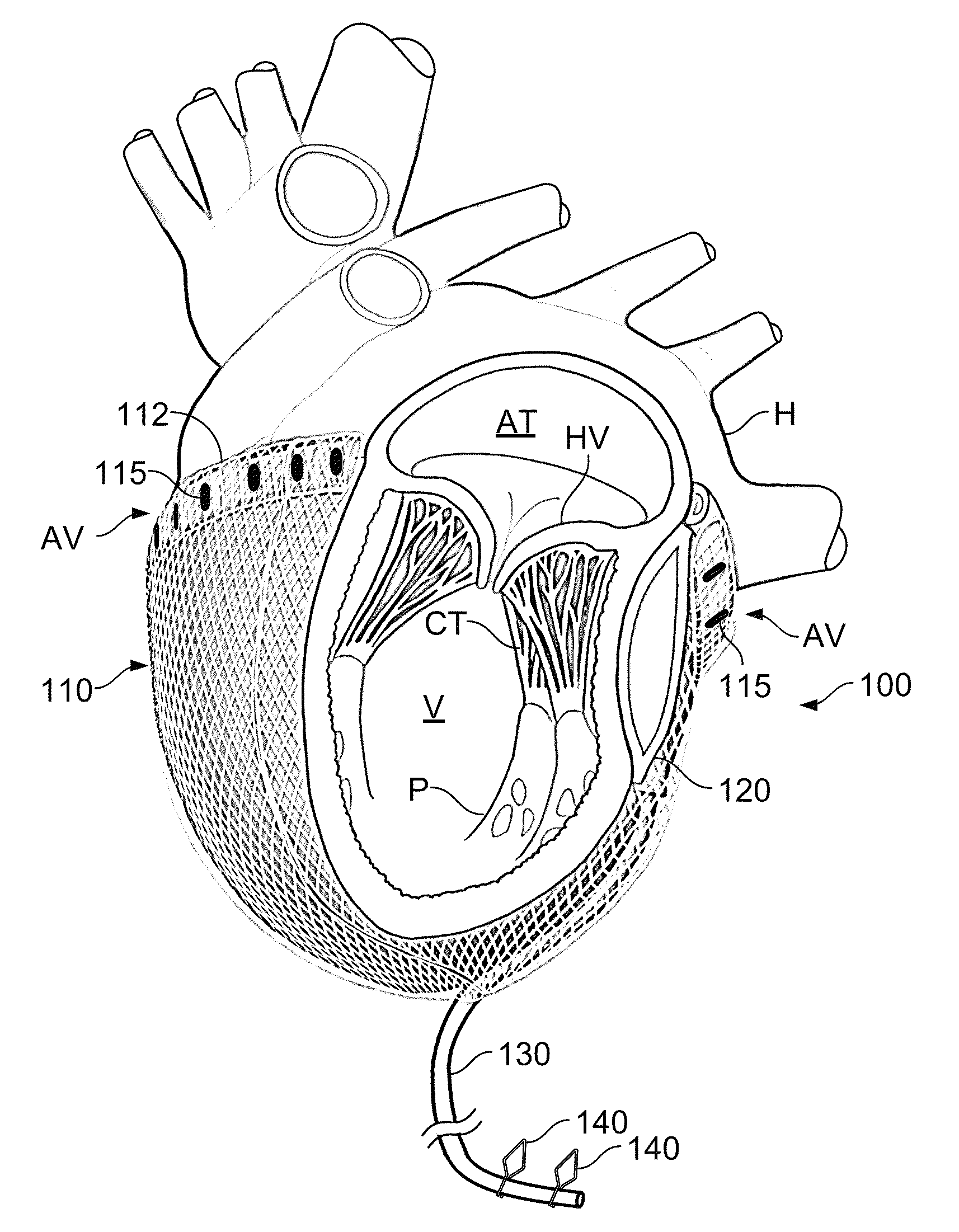
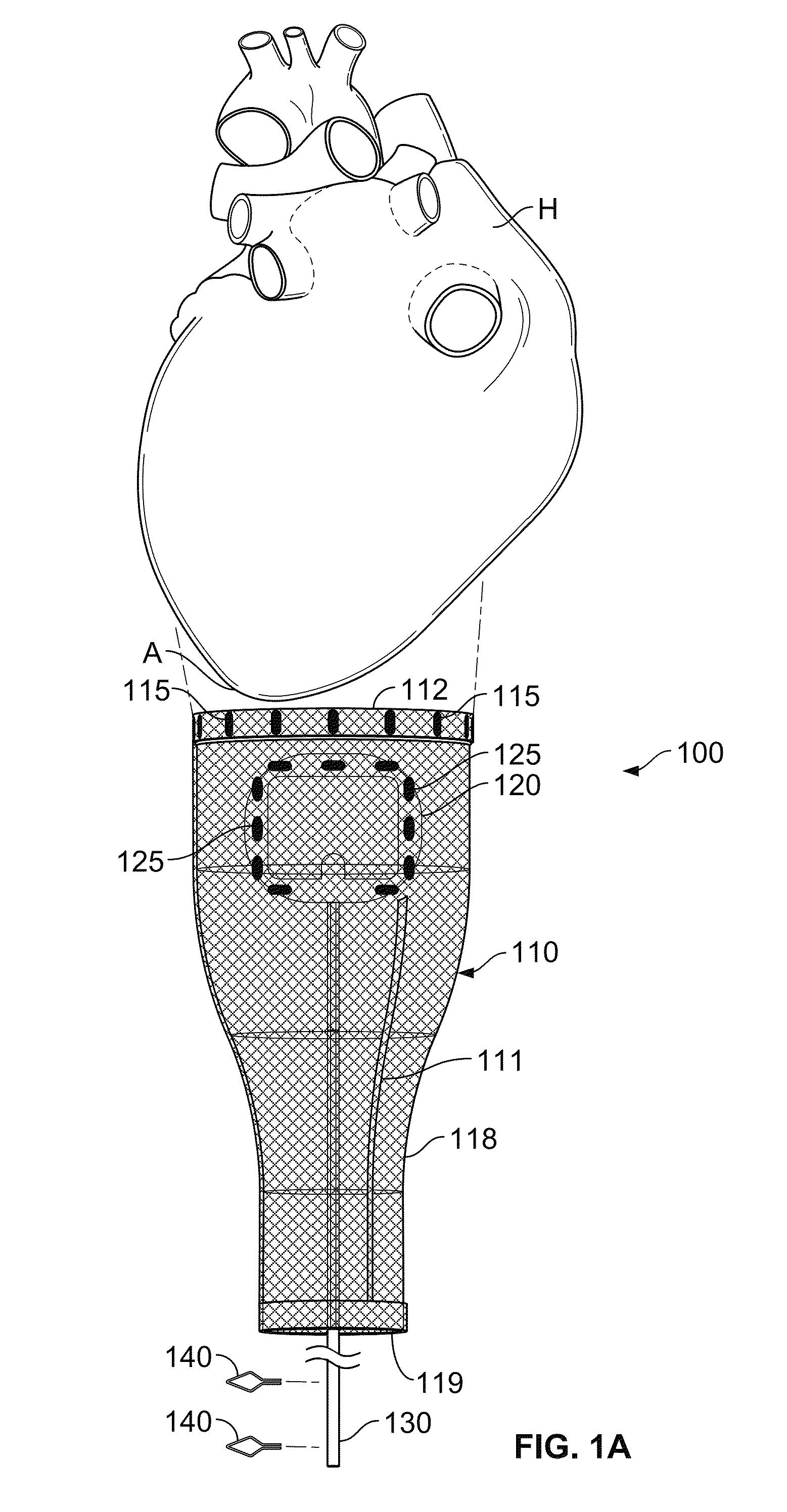
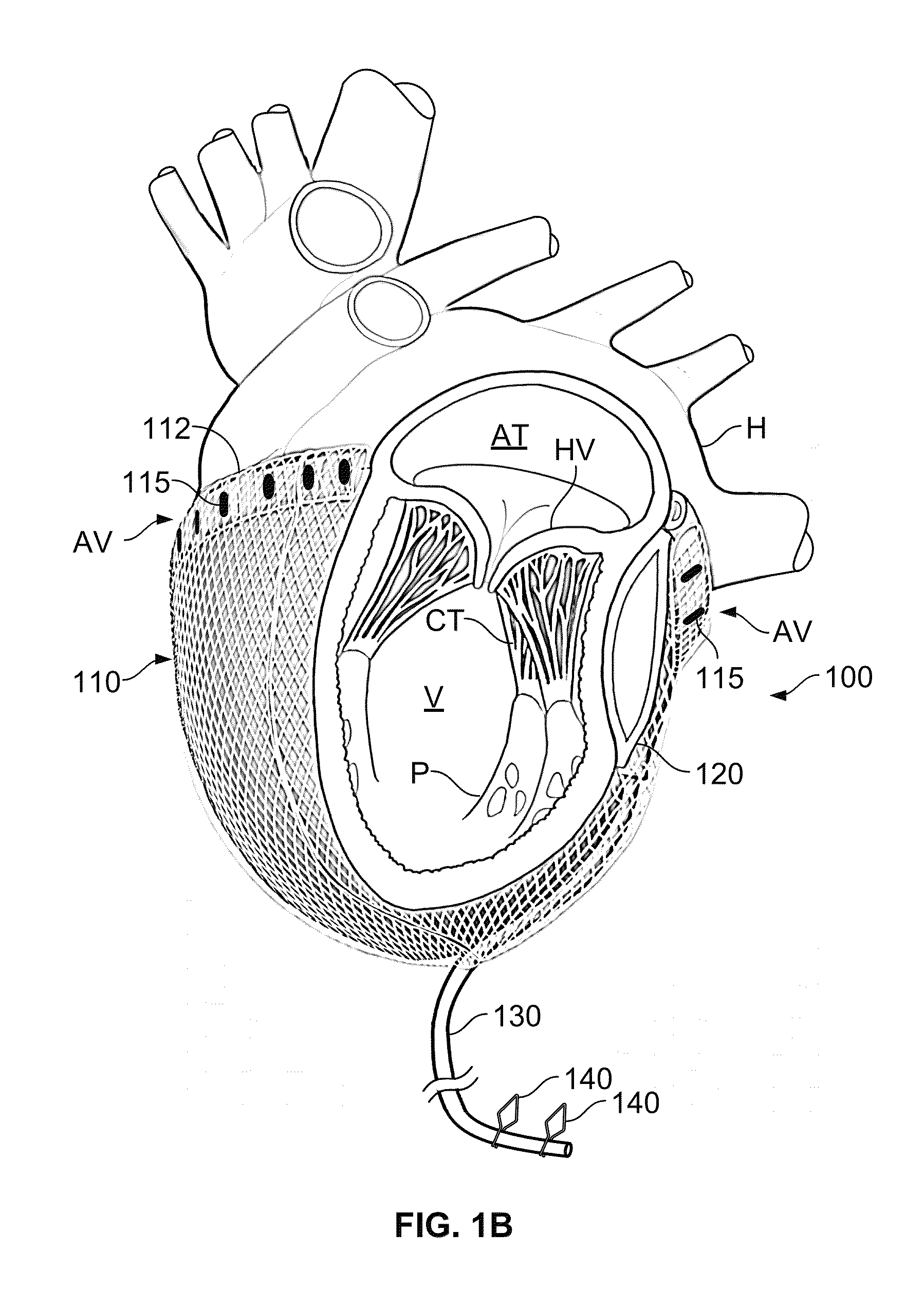
Patents
Literature
108 results about "Heart apex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
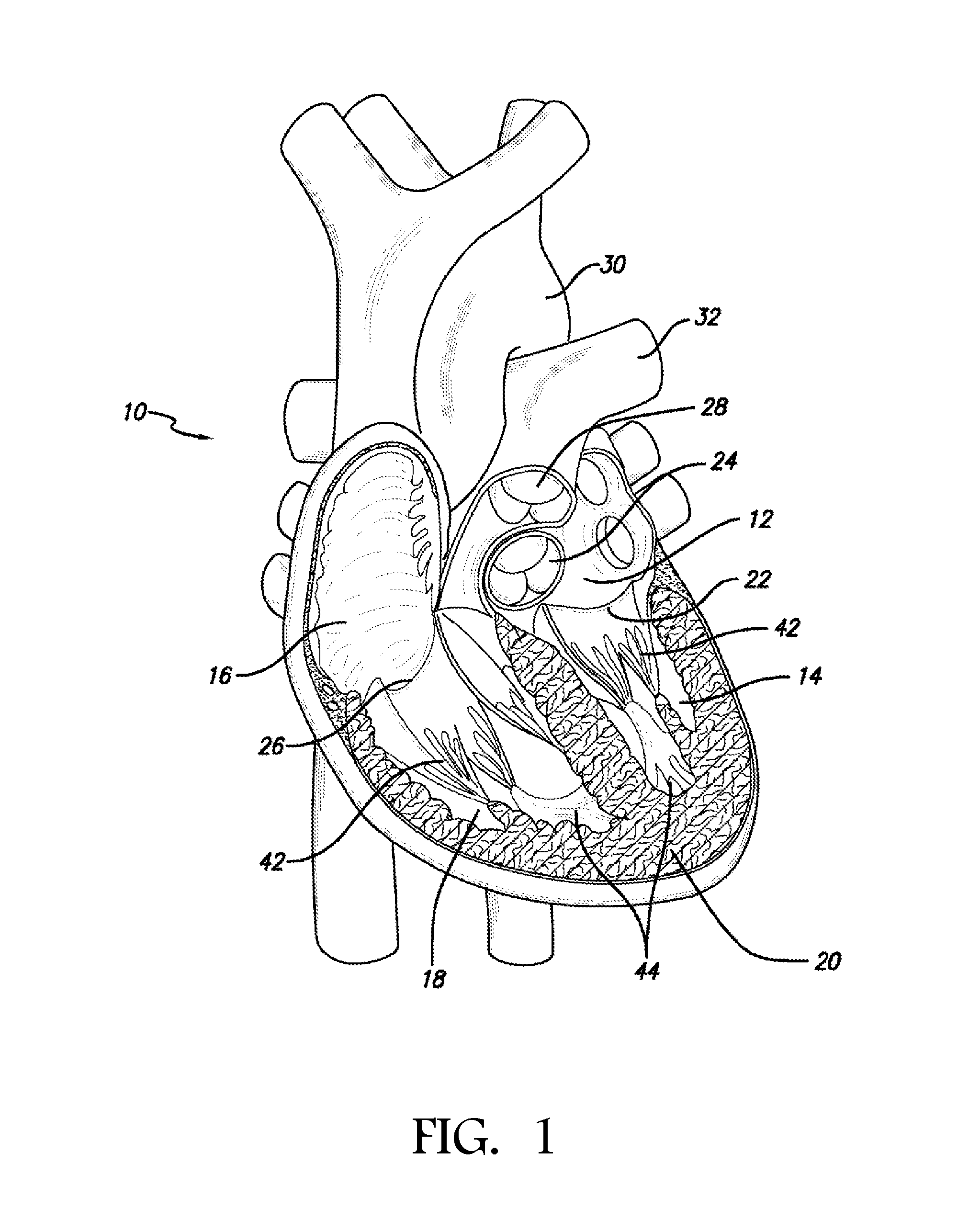
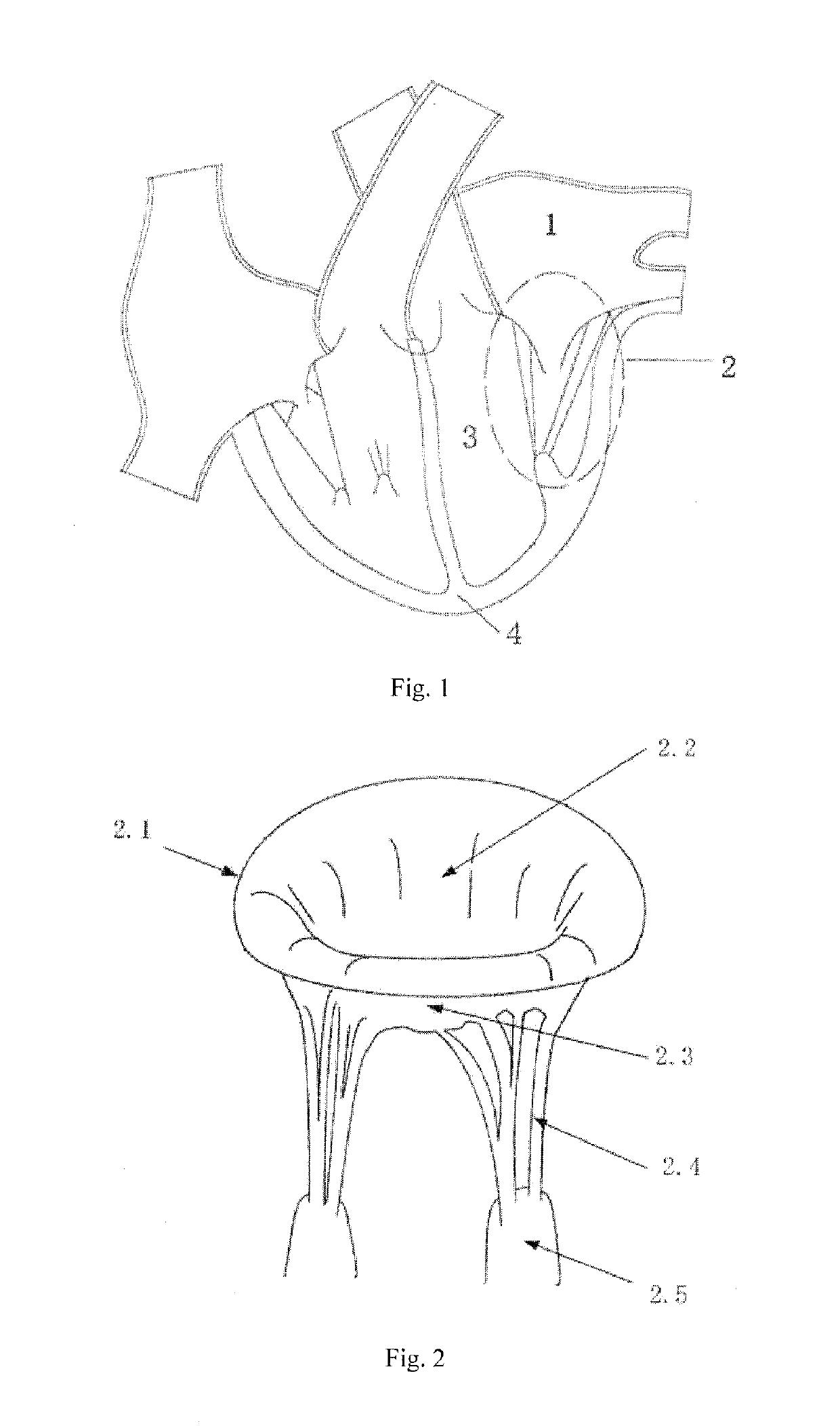
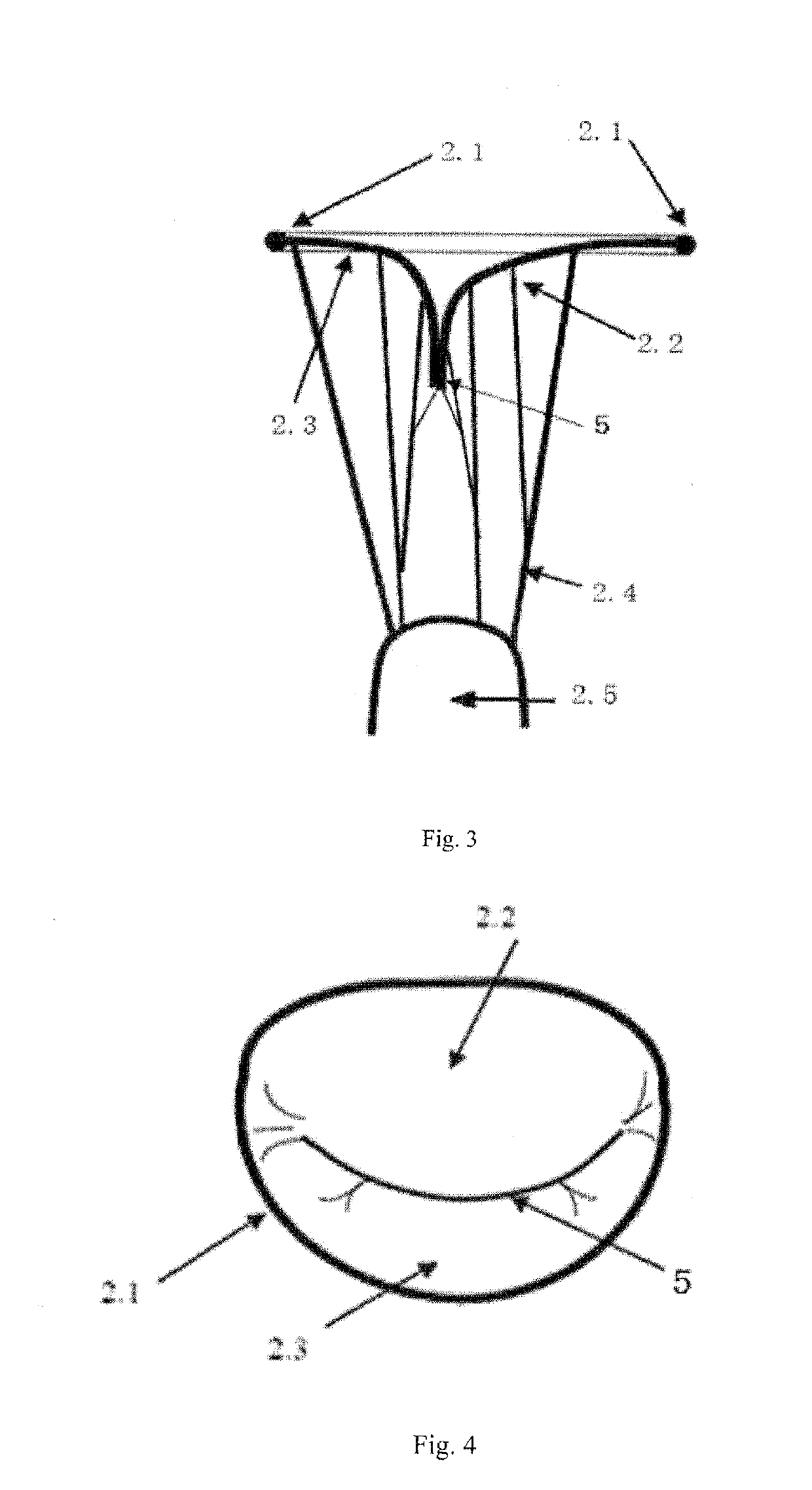
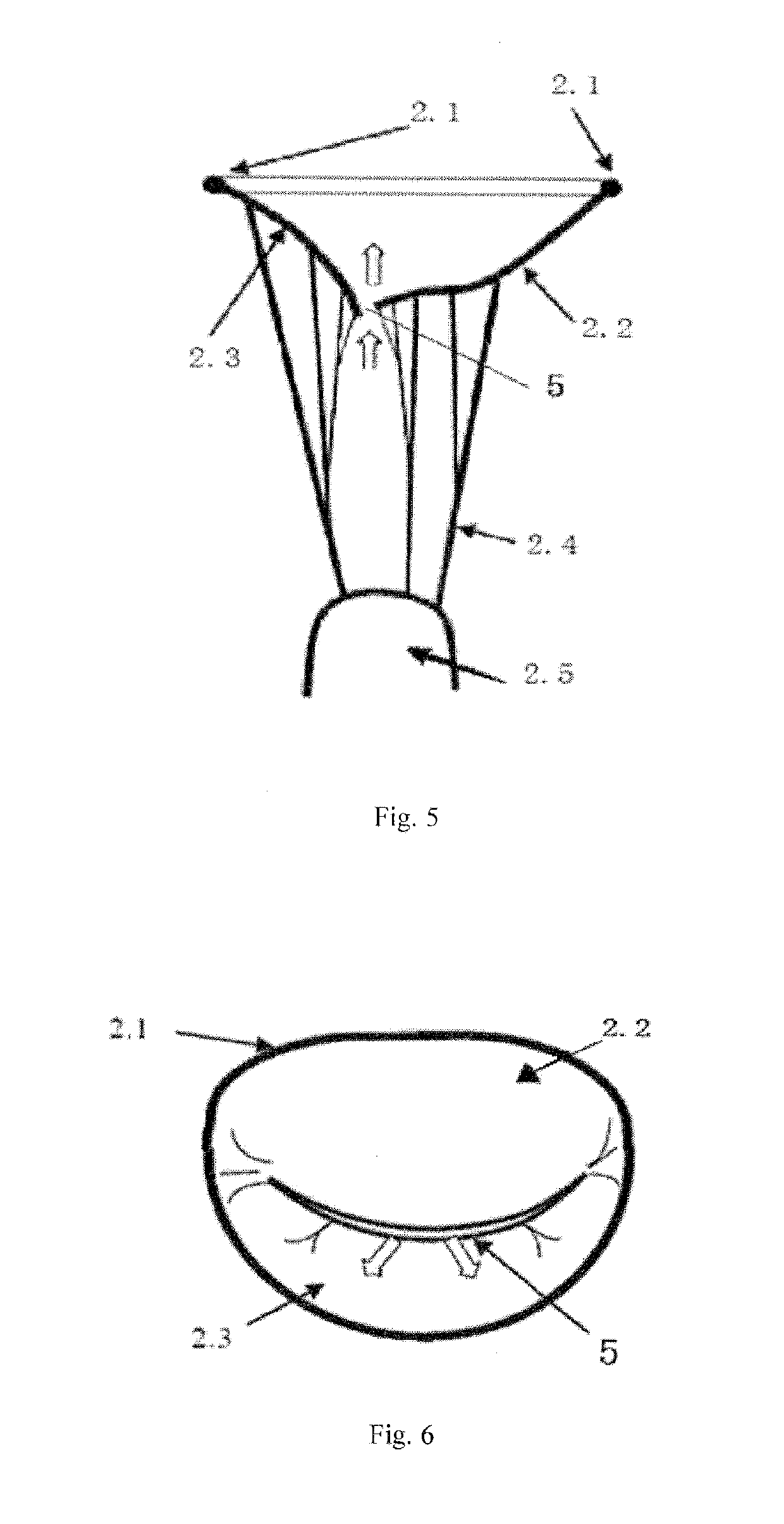
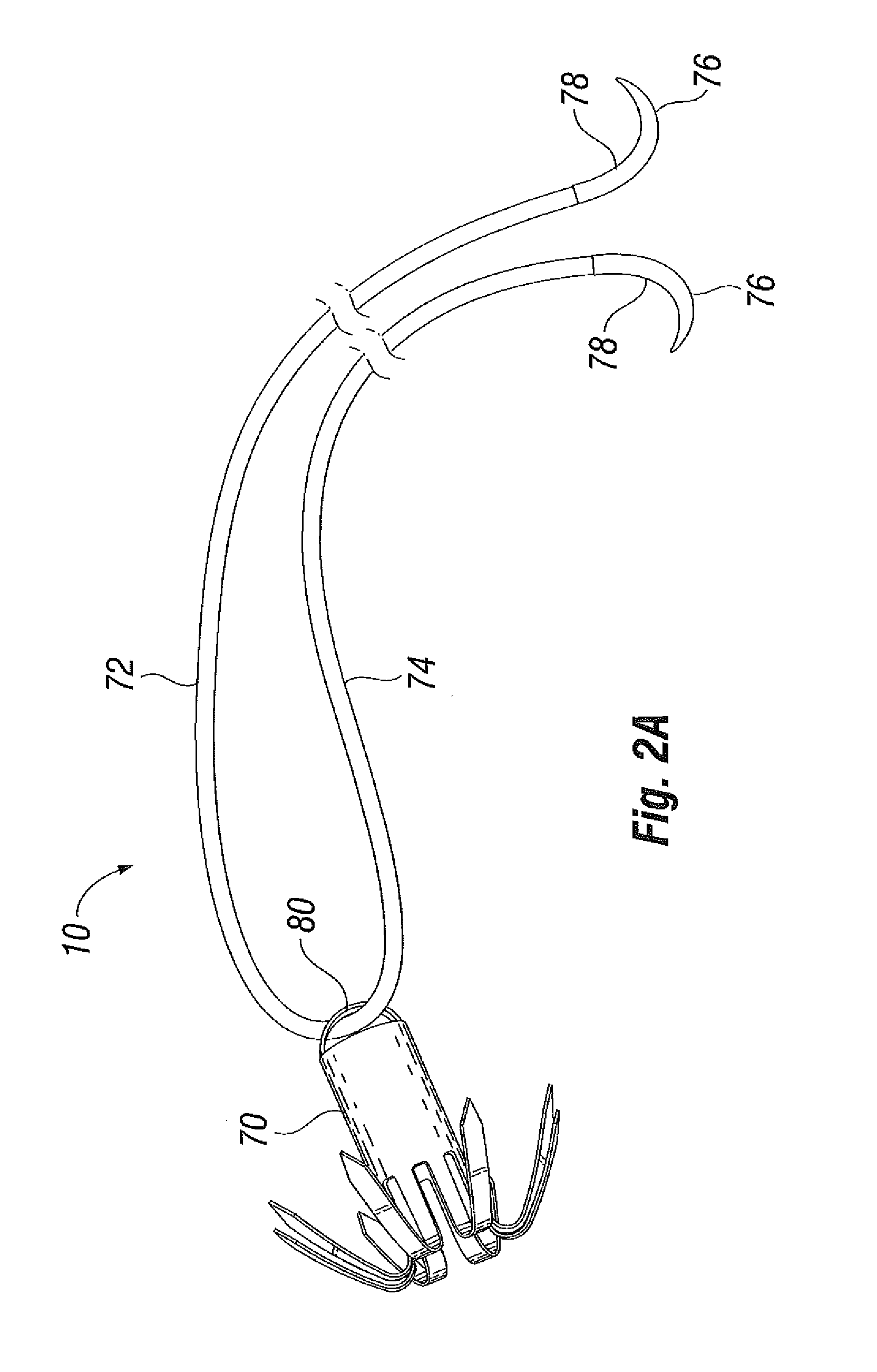
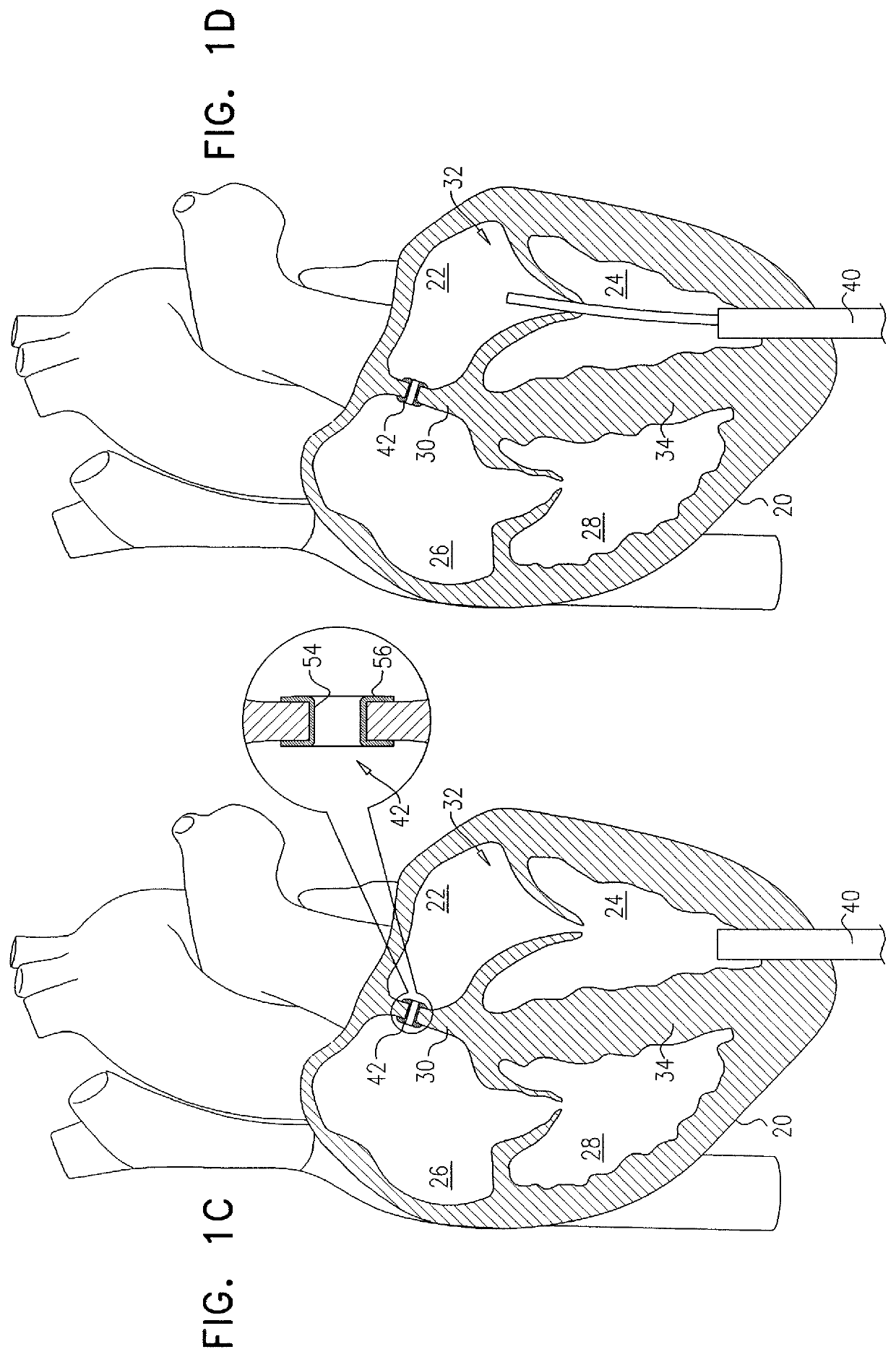
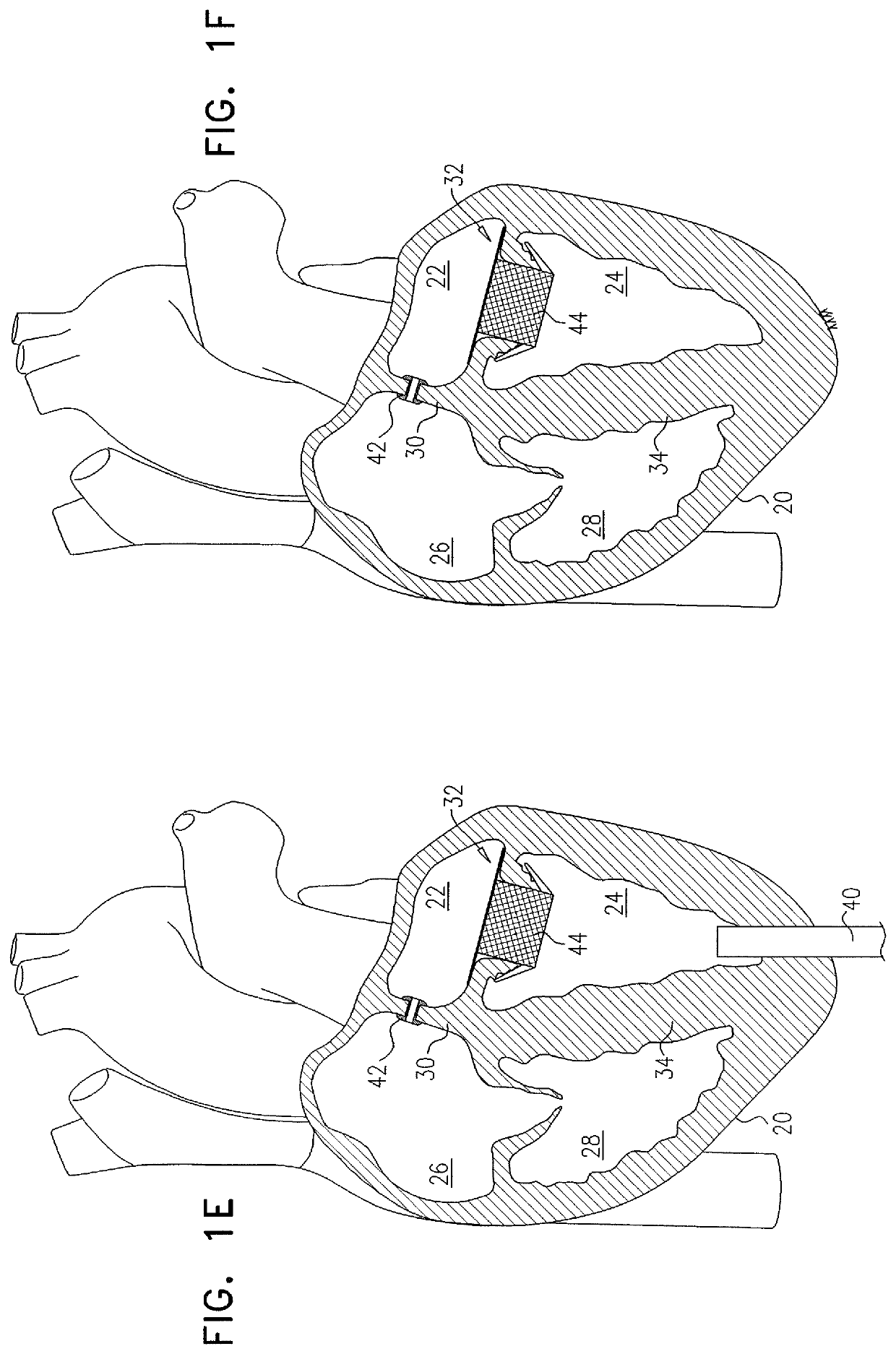
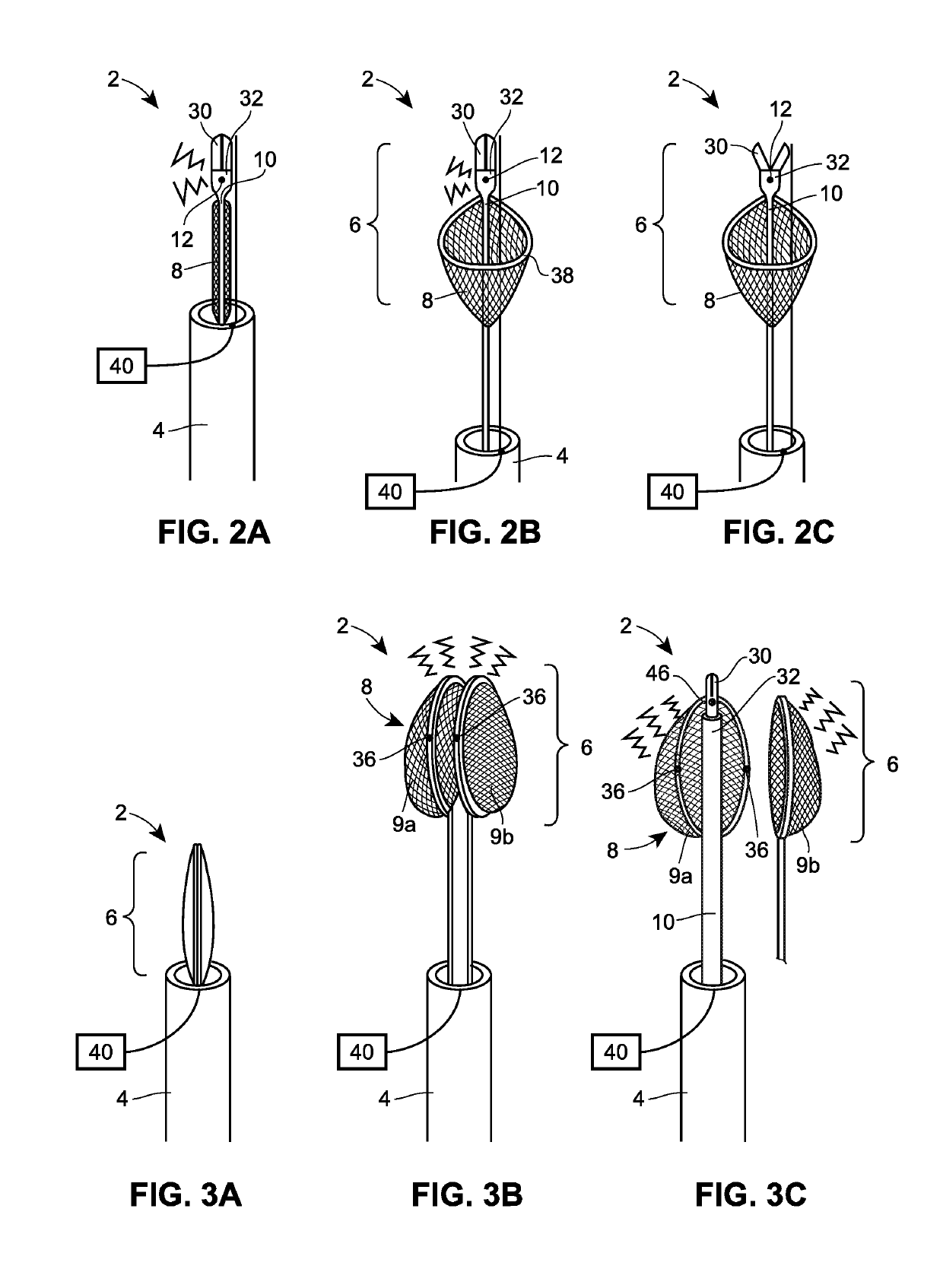
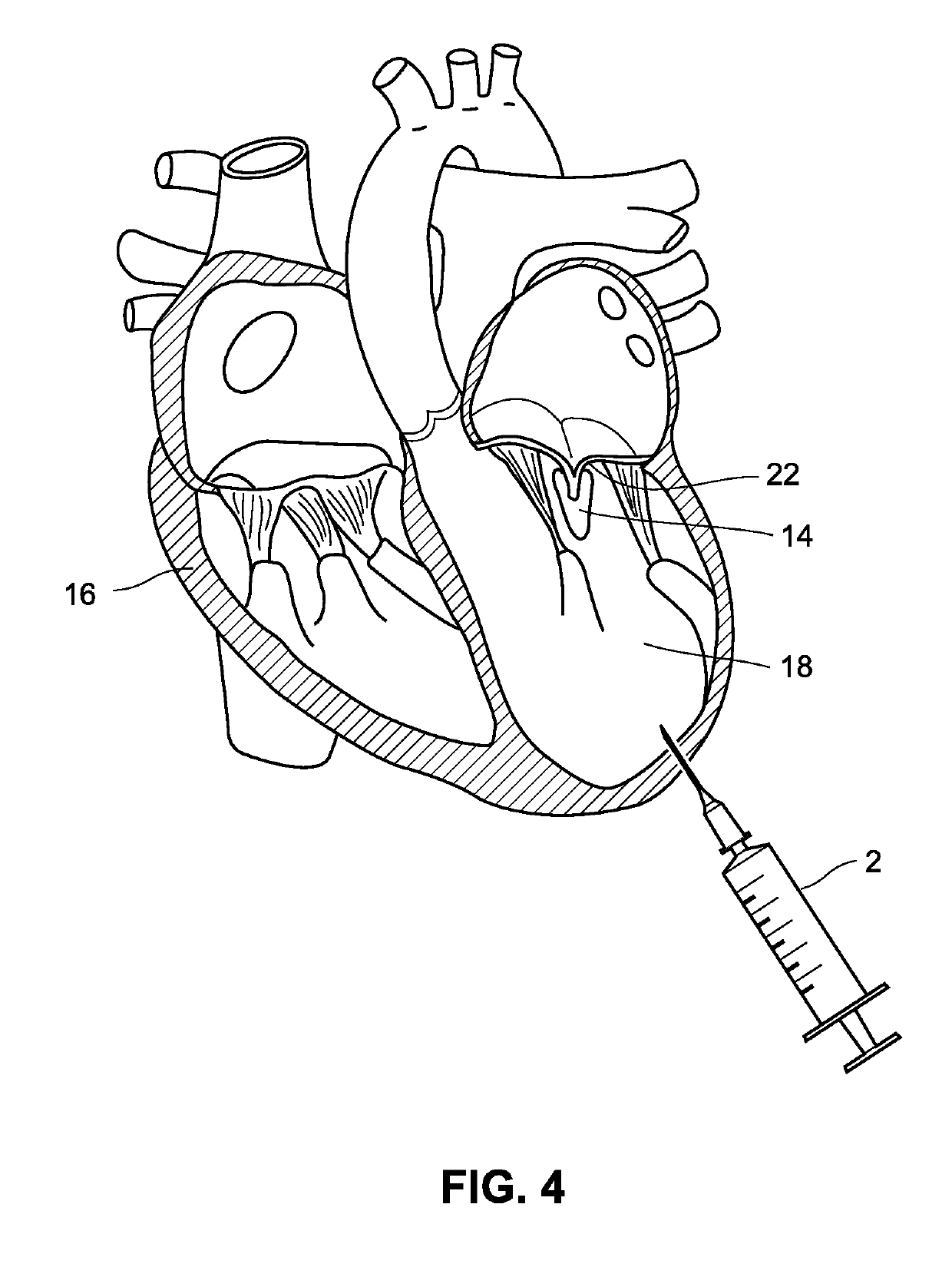
Transapical mitral valve repair device
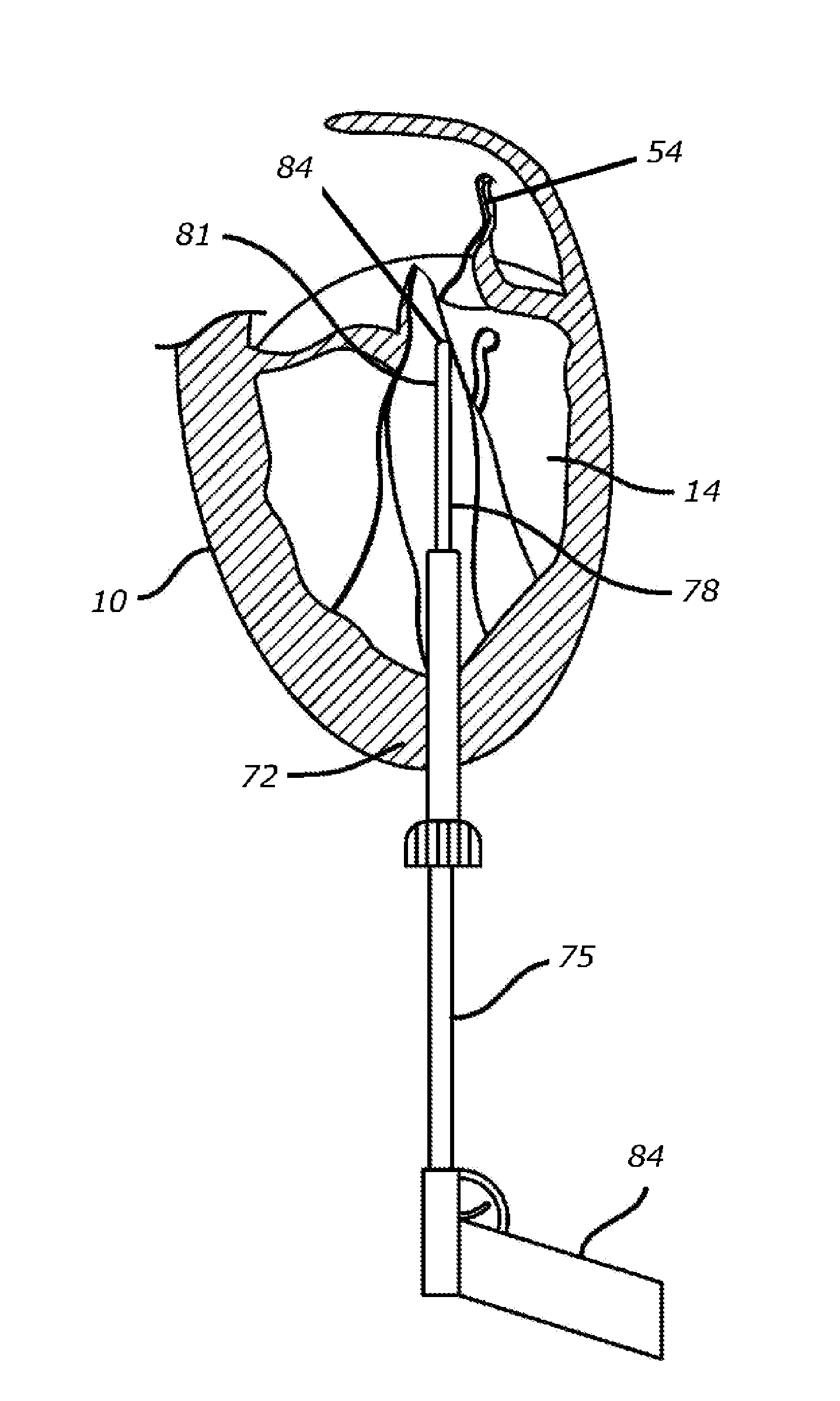
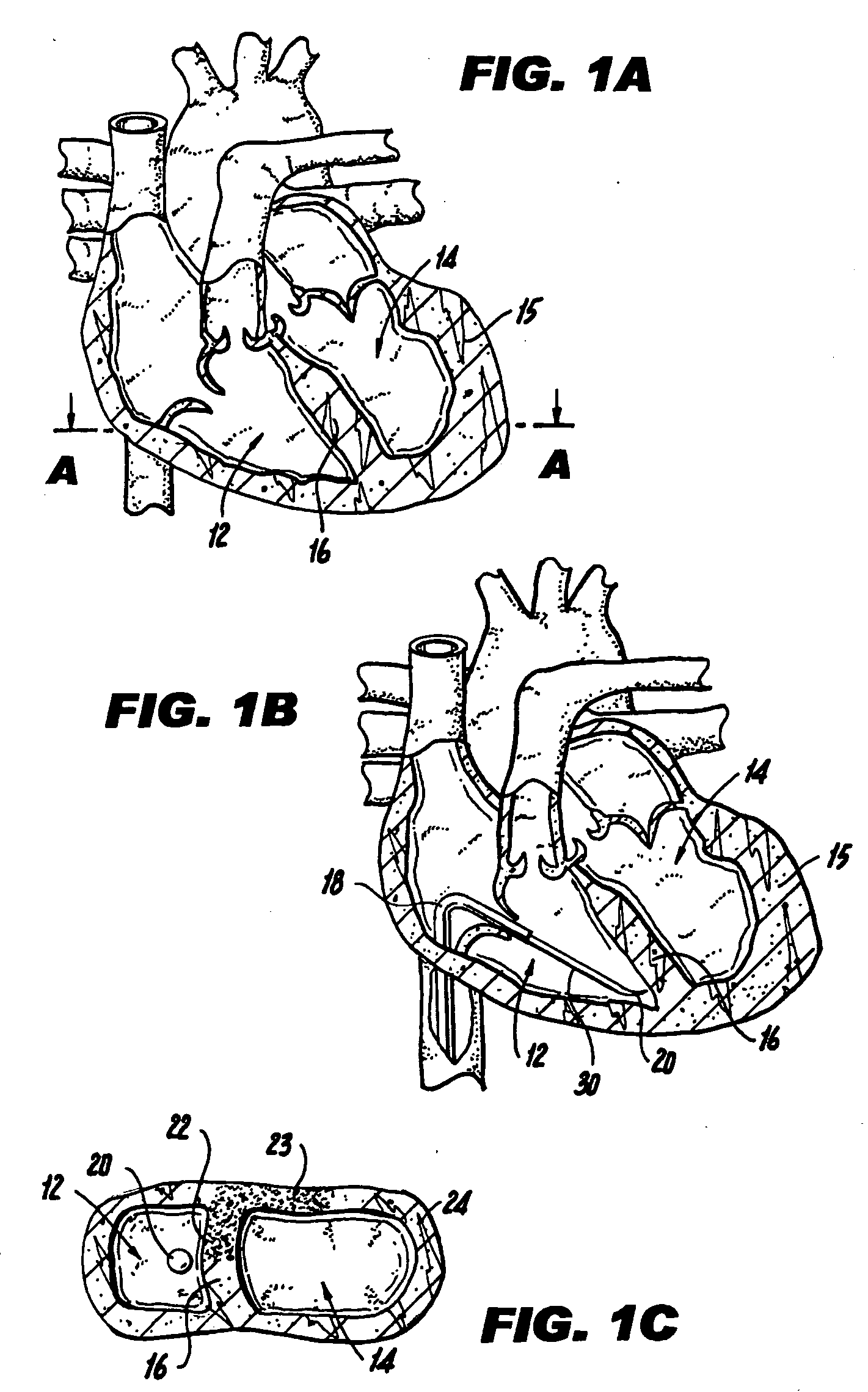
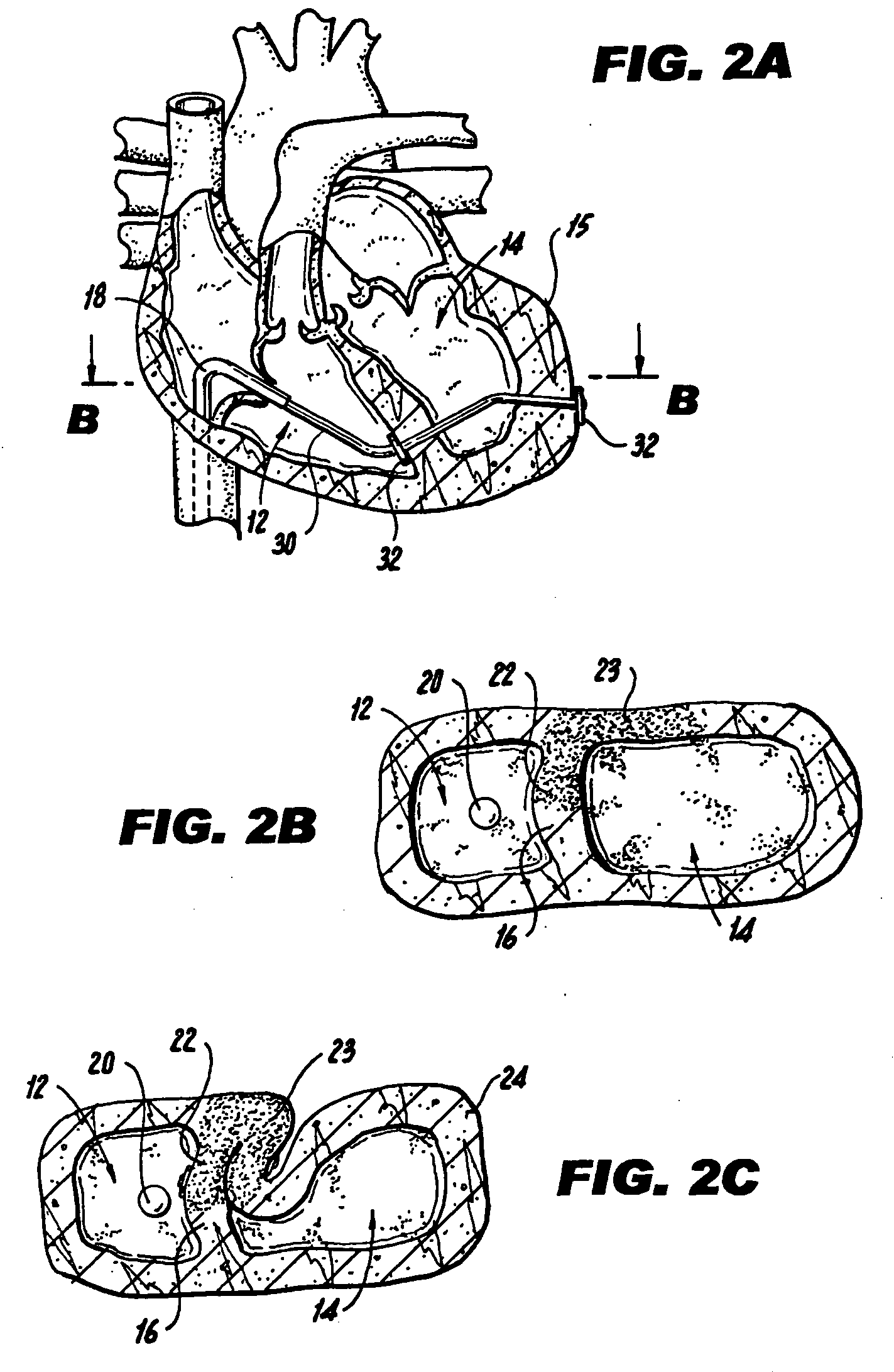
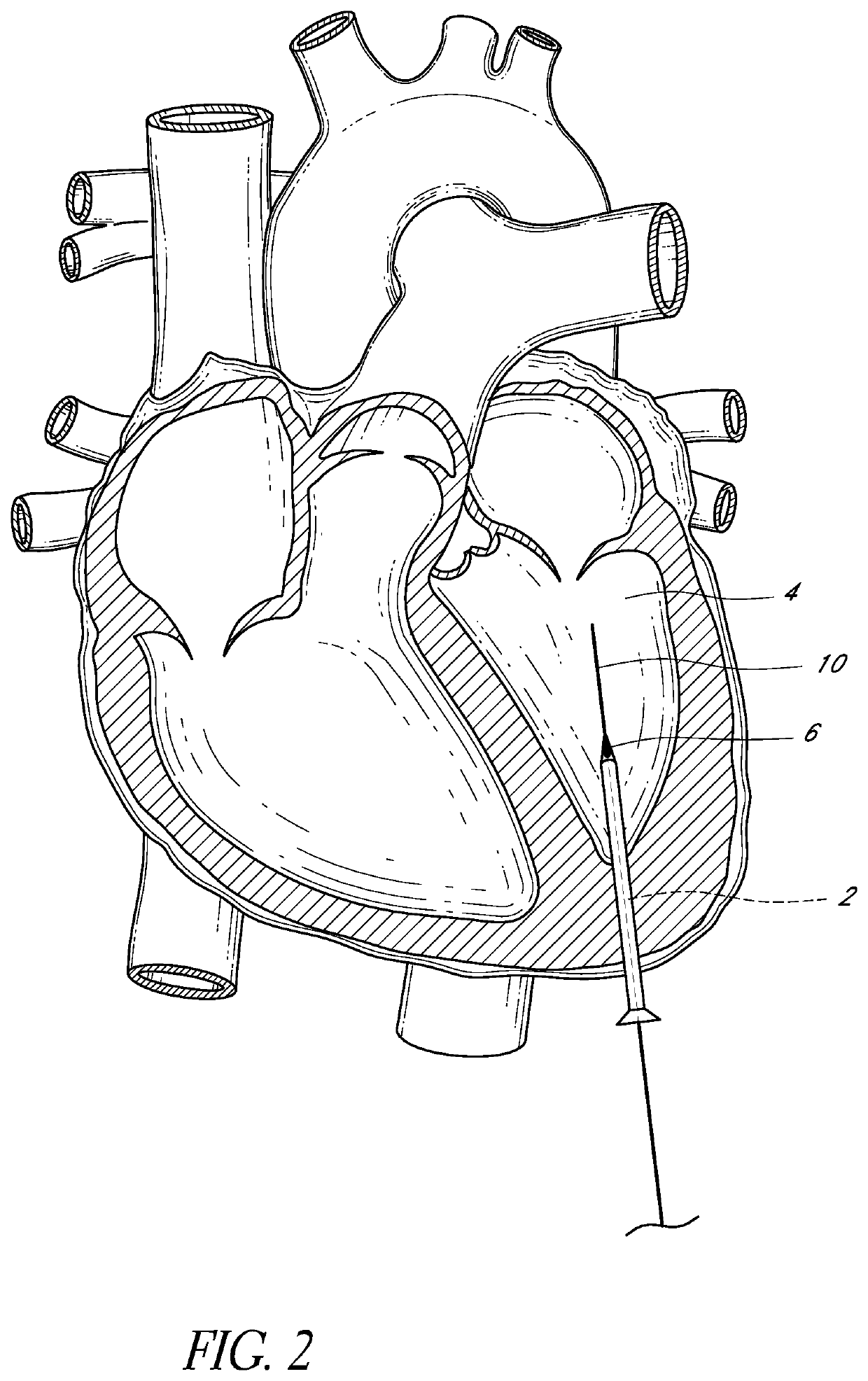
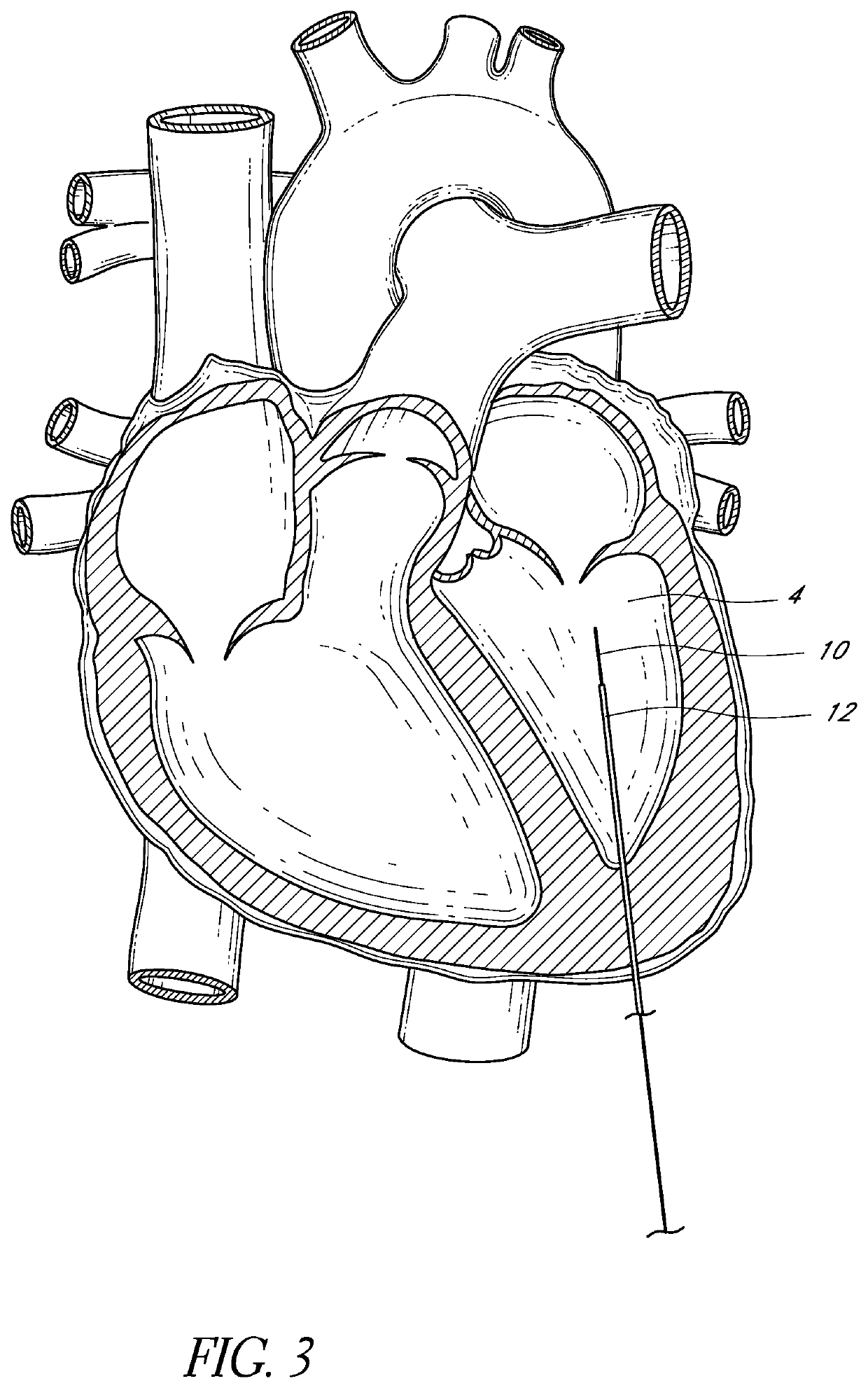
Methods and devices for repairing a cardiac valve. A minimally invasive procedure includes creating an access in the apex region of the heart through which one or more instruments may be inserted. The device can implant artificial heart valve chordae tendineae into cardiac valve leaflet tissues to restore proper leaflet function and prevent reperfusion. The device punctures the apex of the heart and travels through the ventricle. The tip of the device rests on the defective valve and punctures the valve leaflet. A suture or a suture / guide wire combination is inserted, securing the top of the leaflet to the apex of the heart. A resilient element or shock absorber mechanism adjacent to the outside of the apex of the heart minimizes the linear travel of the device in response to the beating of the heart or opening / closing of the valve.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Method for automated analysis of apical four-chamber images of the heart
InactiveUS6708055B2Maximizes long axis lengthImage enhancementImage analysisBody organsCardiac muscle
A method for quantitatively analyzing digital images of approximately elliptical body organs, and in particular, echocardiographic images is provided. In particular, methods are disclosed for obtaining short-axis apical four-chamber views of a heart, and particularly for obtaining high-quality automated images of particular regions of the heart muscle, as viewed along its long axis.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
Method and device for percutaneous left ventricular reconstruction
InactiveUS20060079736A1Reduce volumeMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsElectrocardiographyVentricular volumeChest surgery
A method for reducing left ventricular volume, which comprises identifying infarcted tissue during open chest surgery; reducing left ventricle volume while preserving the ventricular apex; and realigning the ventricular apex, such that the realigning step comprises closing the lower or apical portion of said ventricle to achieve appropriate functional contractile geometry of said ventricle in a dyskinetic ventricle of a heart.
Owner:CHF TECH A CALIFORNIA CORP
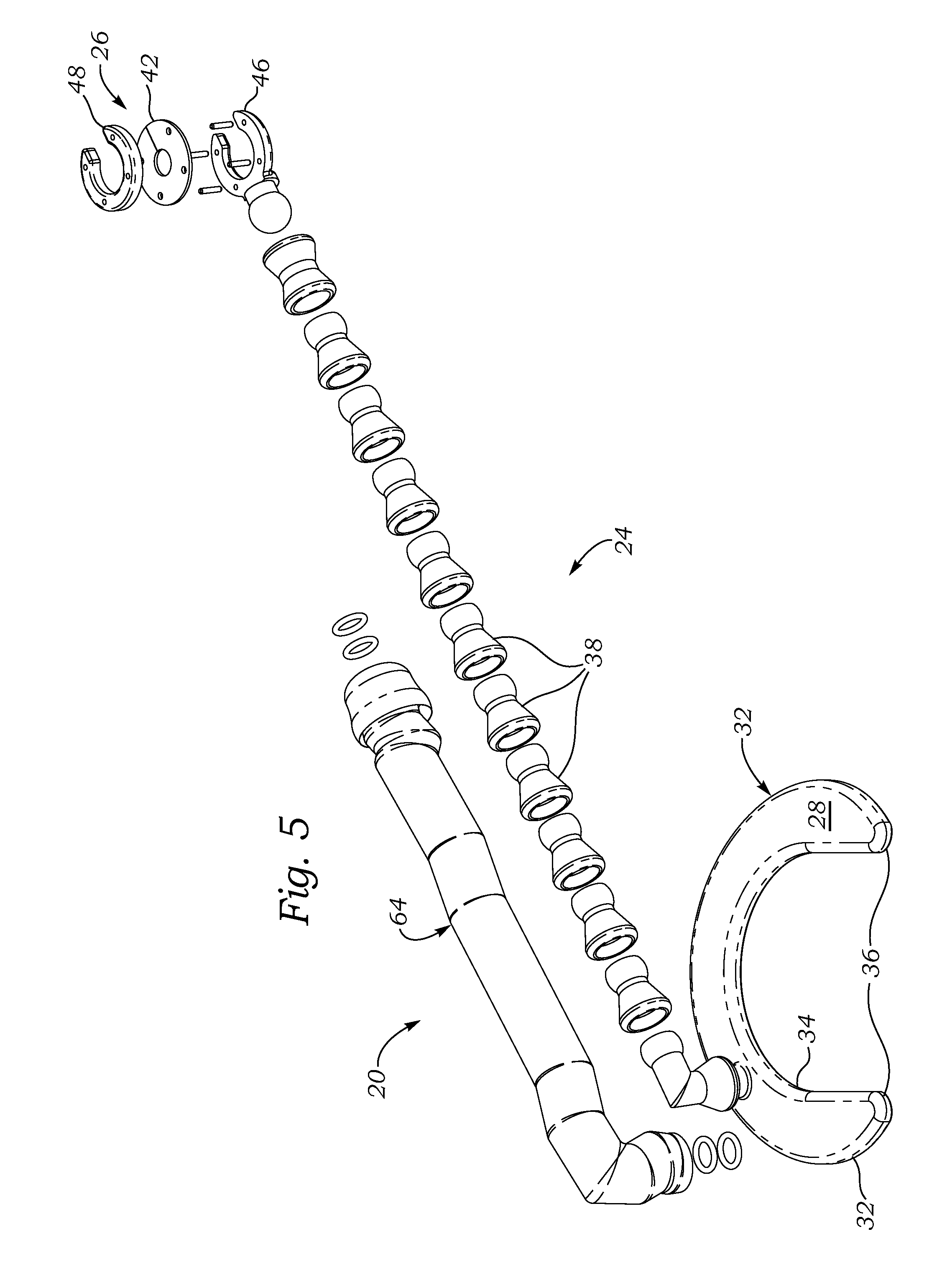
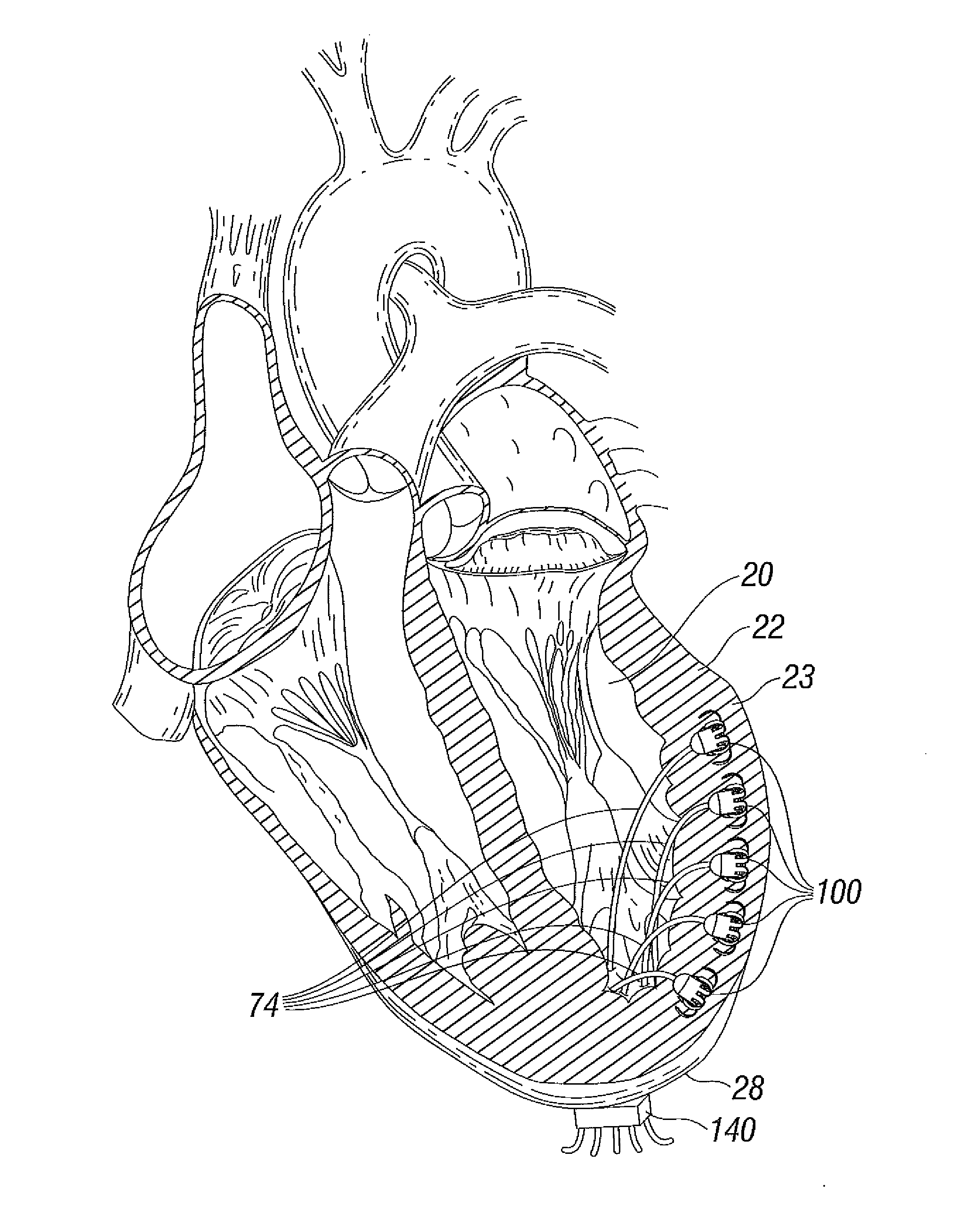
Intracardiac sheath stabilizer
A surgical stabilizer for use with a surgical site retractor has a base, a bendable arm, and a distal cuff adapted to resiliently hold a tube of an elongated port-access device. The cuff may have a body defining a partial enclosure within which is held a highly flexible gasket having a slit for resiliently receiving the tube. The surgical site retractor may have a collapsible ring and a flexible outer portion attached thereto, the ring being sized to pass through an intercostal incision and expand therein under adjacent ribs to prevent removal, and the flexible outer portion extending out of the incision and drawing over the stabilizer base to mutually secure the retractor and base. The port-access tube may be for a heart valve delivery system using an elongated port-access device for transapically delivering a prosthetic heart valve to the aortic valve annulus. A method involves partly installing the surgical site retractor, anchoring the base of the stabilizer with the flexible outer portion, deploying the port-access tube from outside the body through the incision and through a puncture in the heart wall, and resiliently capturing a tube of the port-access within the partial enclosure of the stabilizer cuff. A second bendable arm on the base having a clip may be used to hold still a proximal end of the port-access device.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
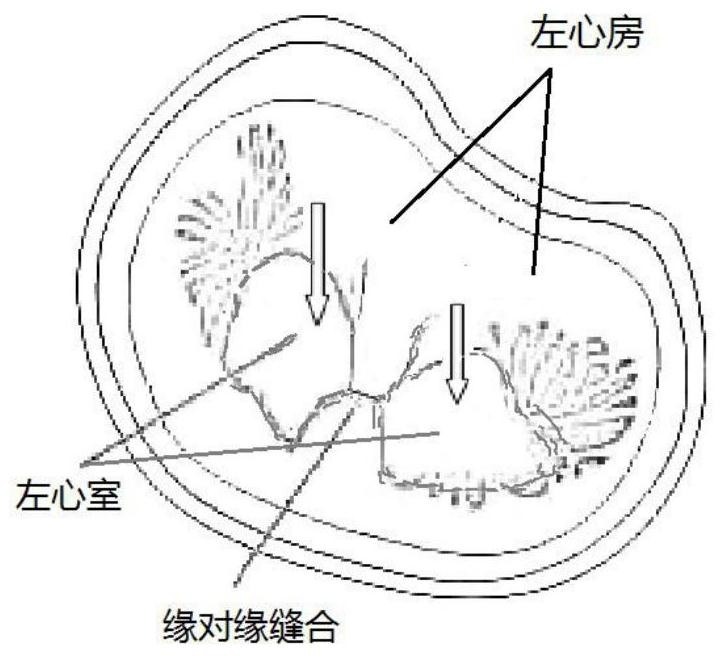
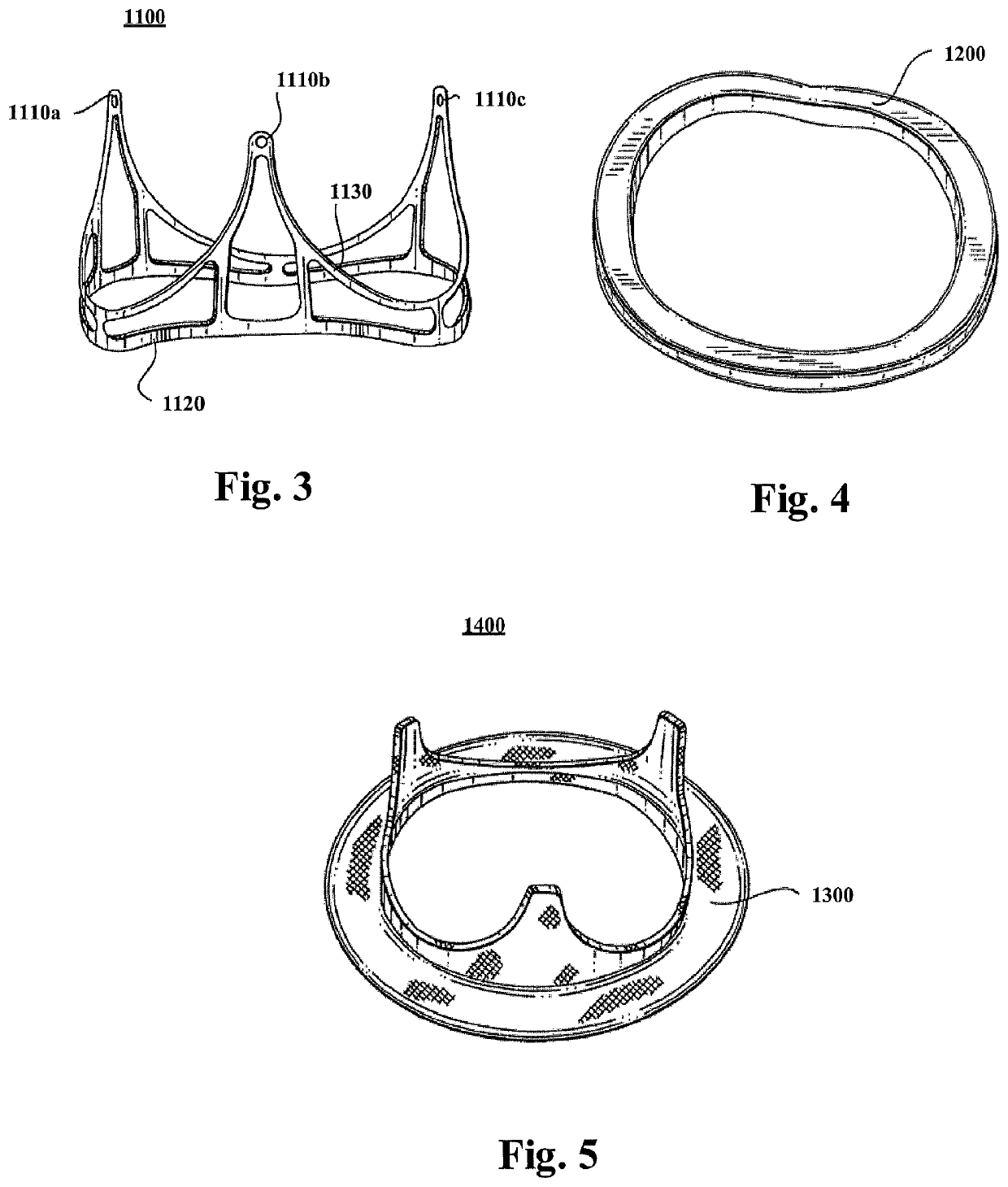
Apical implantation mitral valve balloon closure plate blocking body and implantation method
ActiveUS20190105156A1Simple structurePrevent regurgitationSuture equipmentsHeart valvesDiseaseMitral valve leaflet
An apical implantation mitral valve balloon closure plate blocking body and an implantation method, for human heart repair are disclosed. A balloon closure plate made from an elastic plastic material which may be filled with a gas or a curable liquid is implanted via a small incision on the left side of the chest, enters the left ventricle via the apex, and is placed and fixed at a backflow hole position of a front and rear leaflet closure point of the mitral valve. The present disclosure treats diseases such as functional mitral valve regurgitation, and the success rate for repairing functional mitral valve backflow is more than 90%.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
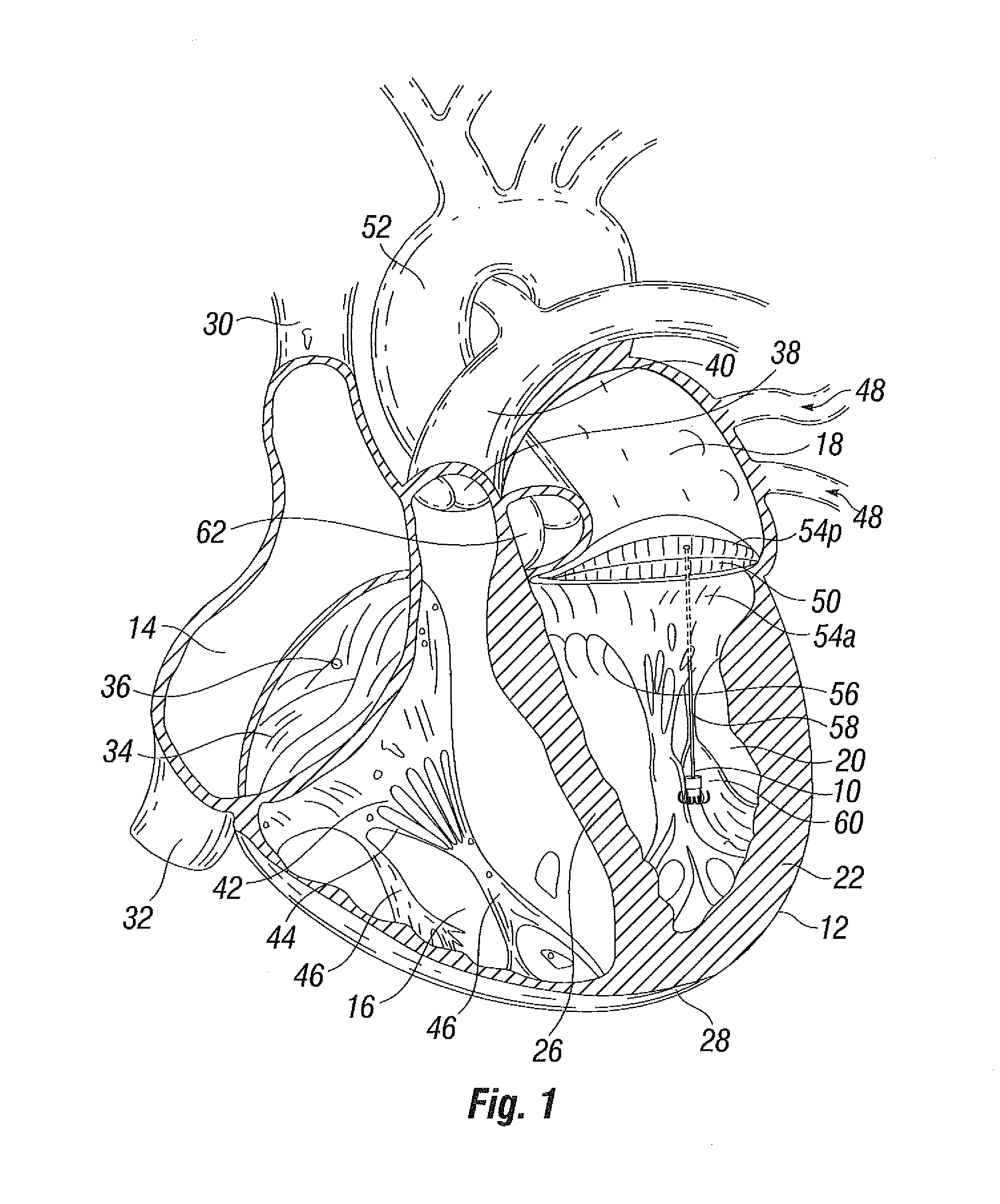
Suture and method for repairing a heart
Devices and methods for treating or repairing a heart are disclosed. The device includes at least one radially expandable tissue-engaging element, an elongate member (e.g., suture) coupled to the expandable element, and a locking mechanism (e.g., locking clip, suture knot). The expandable element may be anchored to heart tissue within the heart, such as in the left ventricle, with the elongate member extending from the expandable element and across a heart chamber to a second location such as the heart apex where the elongate member is held by the locking mechanism.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
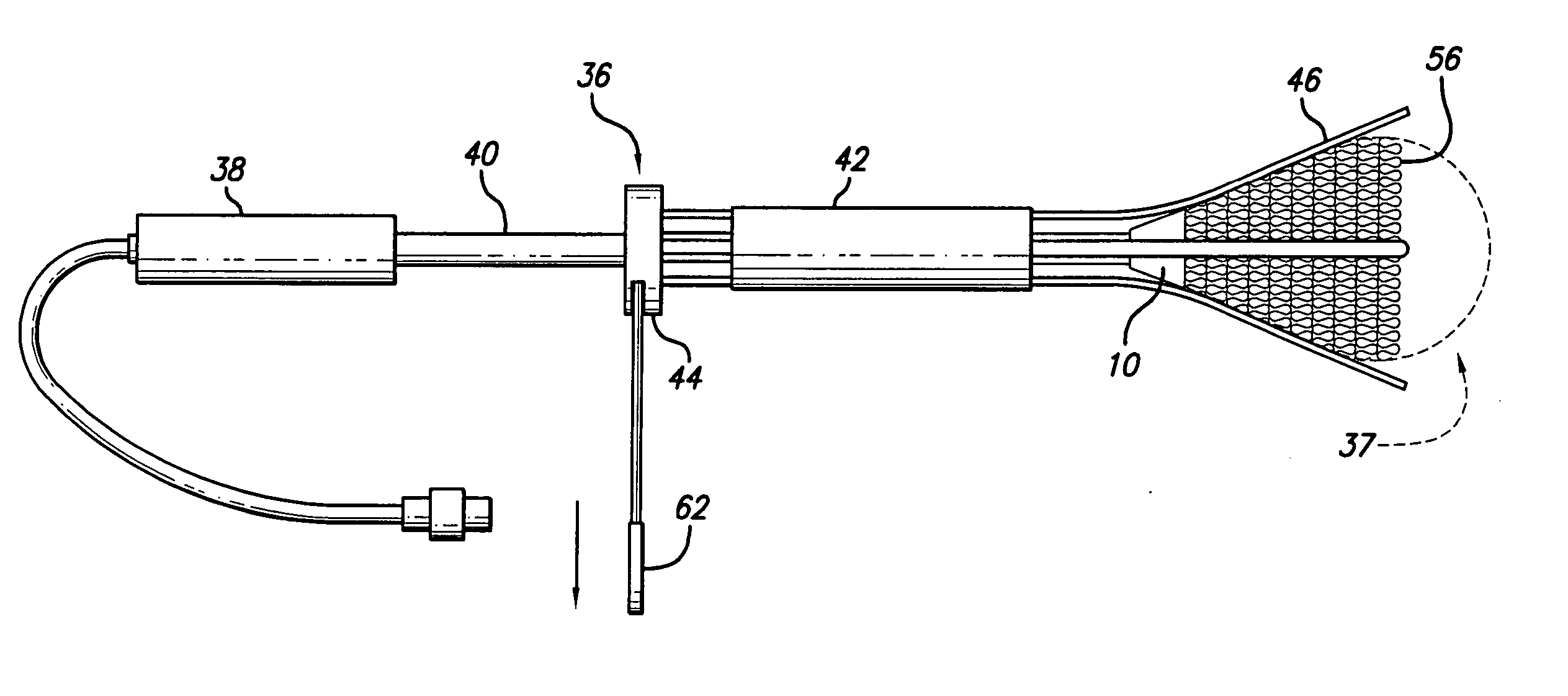
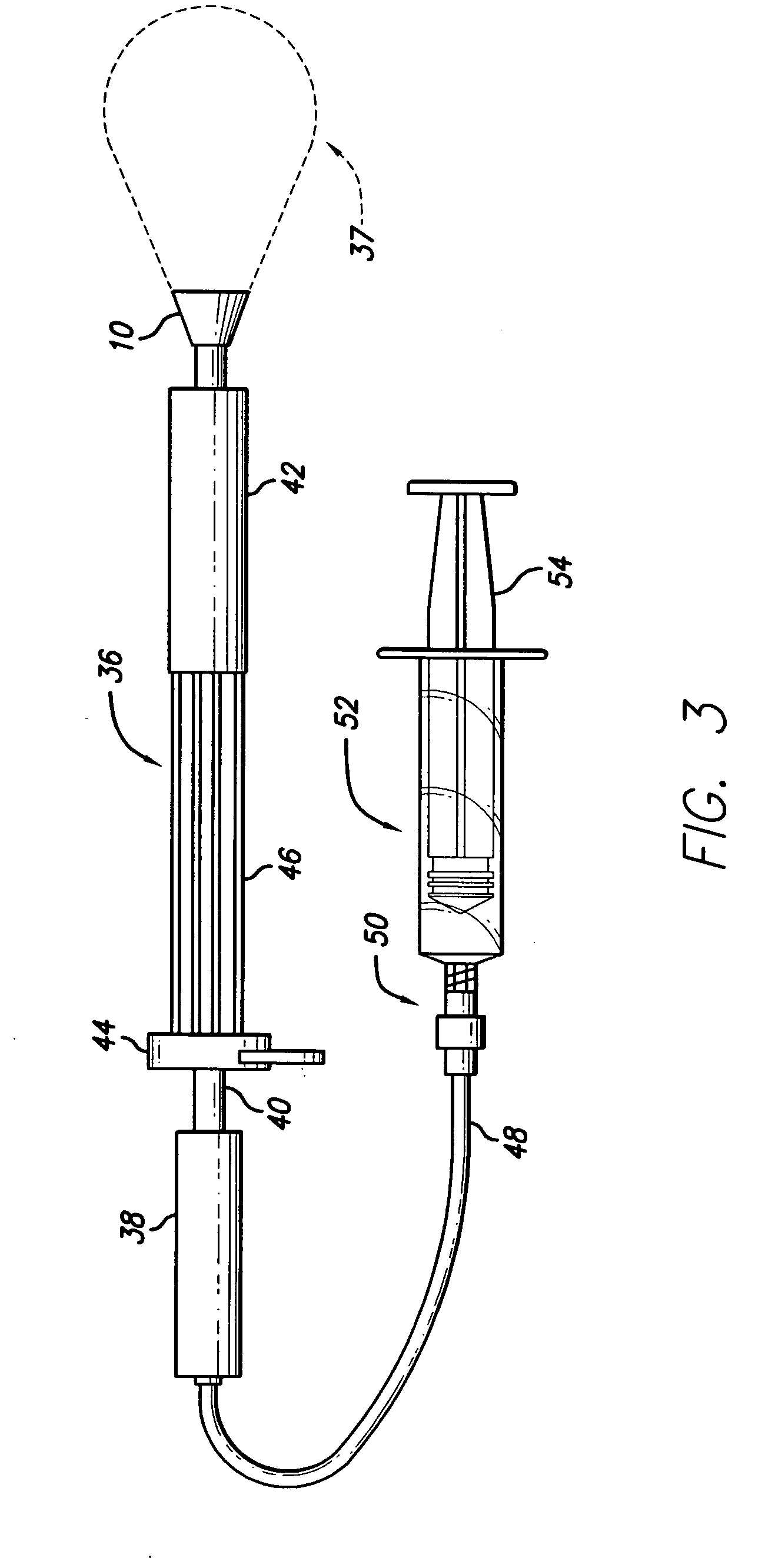
Techniques for providing a replacement valve and transseptal communication
ActiveUS20170231766A1Good blood pressureEasy to moveHeart valvesWound drainsHeart apexProsthetic valve
A method is provided, comprising: (1) making a transapical puncture into a left ventricle of the heart; (2) making a transseptal fenestration in the heart; (3) delivering a prosthetic valve via the transapical puncture and implanting the prosthetic valve at a mitral valve of the heart; and (4) subsequently to delivering the prosthetic valve and making the transseptal fenestration, closing the transapical puncture. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
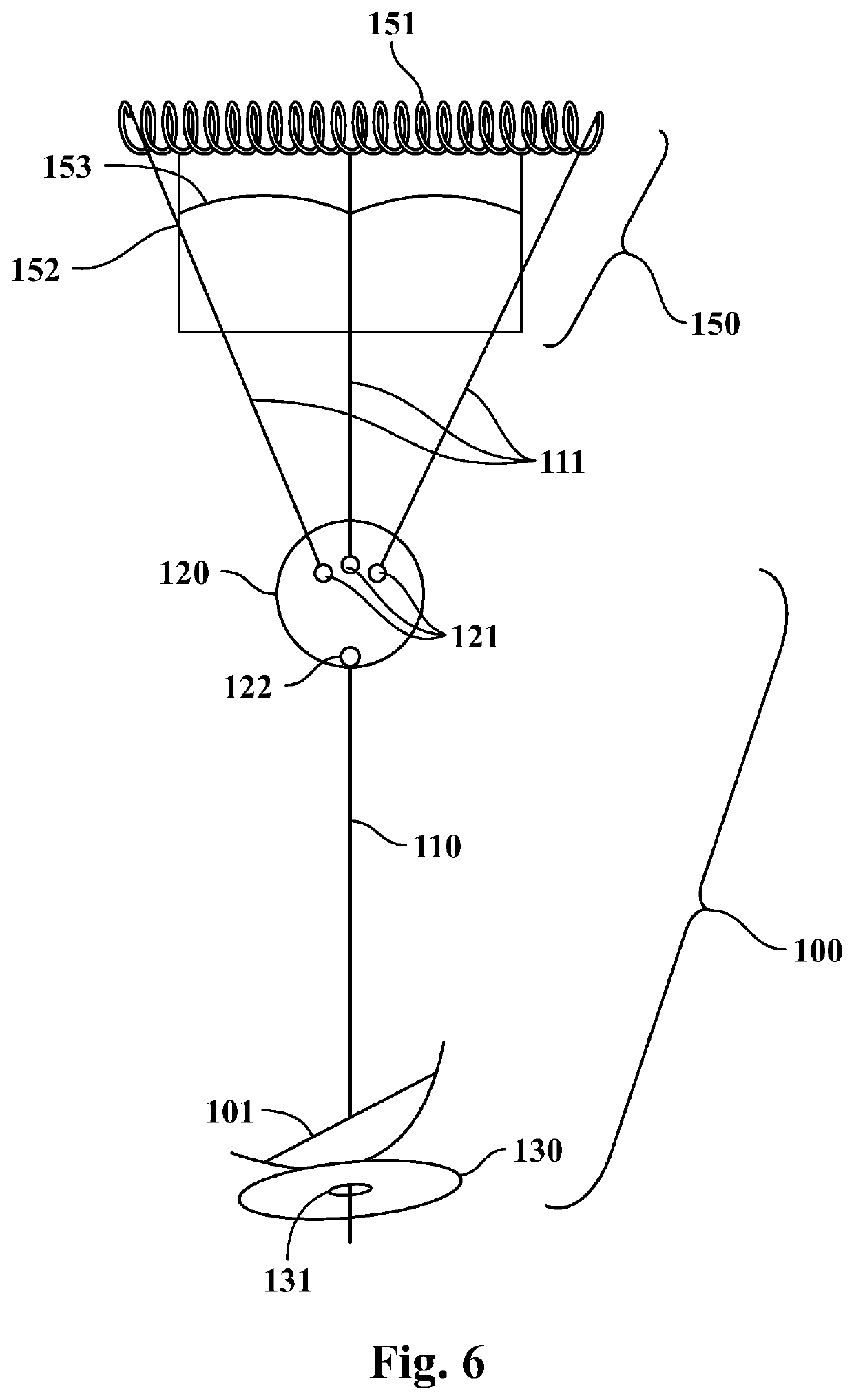
Cardiac support cannula device and method
This invention describes apical access methods and devices that enable repair, modification, removal, and / or replacement of a defective heart valve while allowing the beating heart to deliver blood flow through the defective valve annulus for an extended period of time in volumes sufficient to sustain life. The invention is comprised of a flow housing having a blood inflow opening, a blood outflow opening, and a one-way valve disposed within the flow housing between the inflow and outflow openings.
Owner:POKORNEY JAMES L
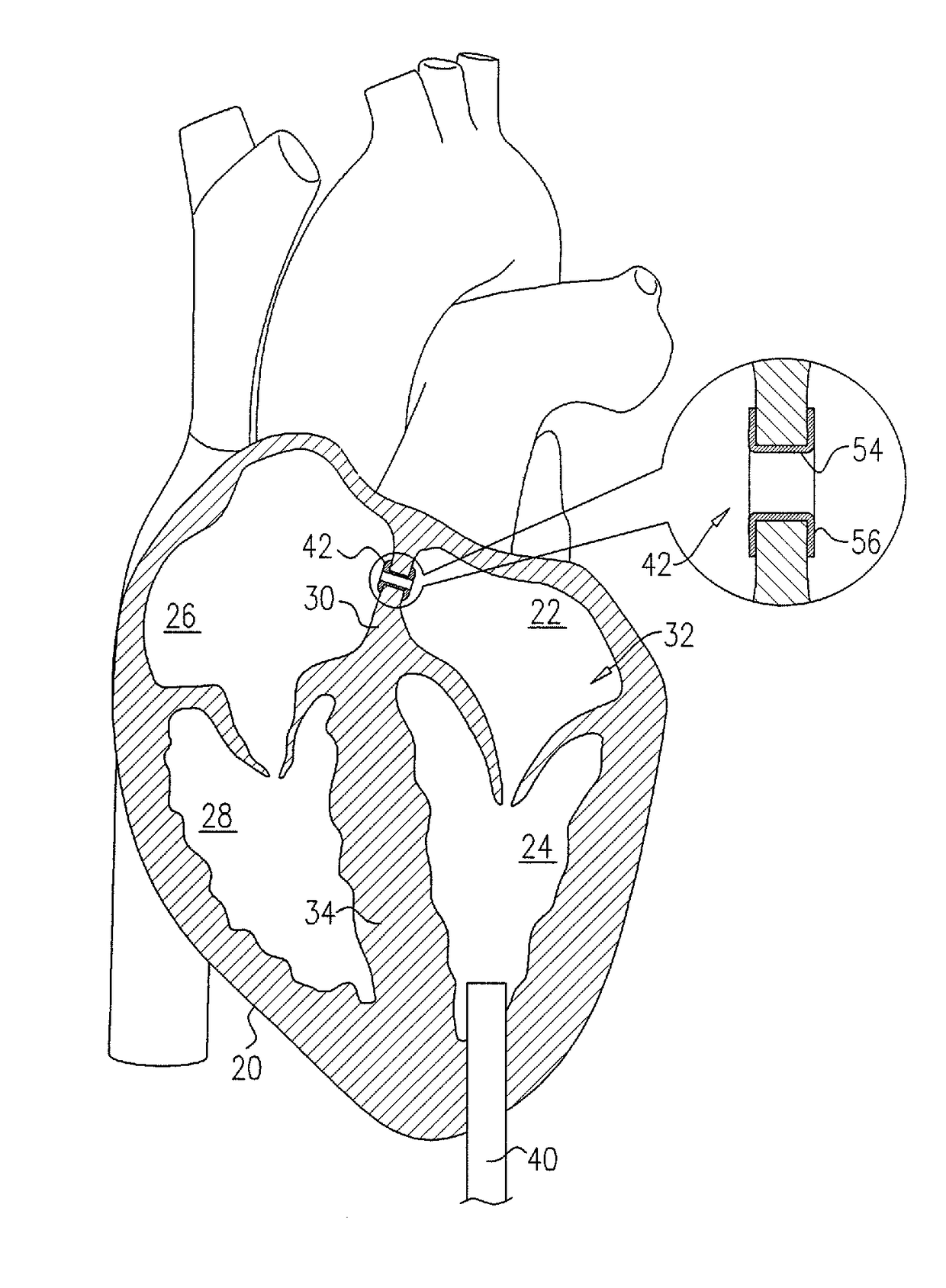
Device for connecting a cardiac biventricular assist means
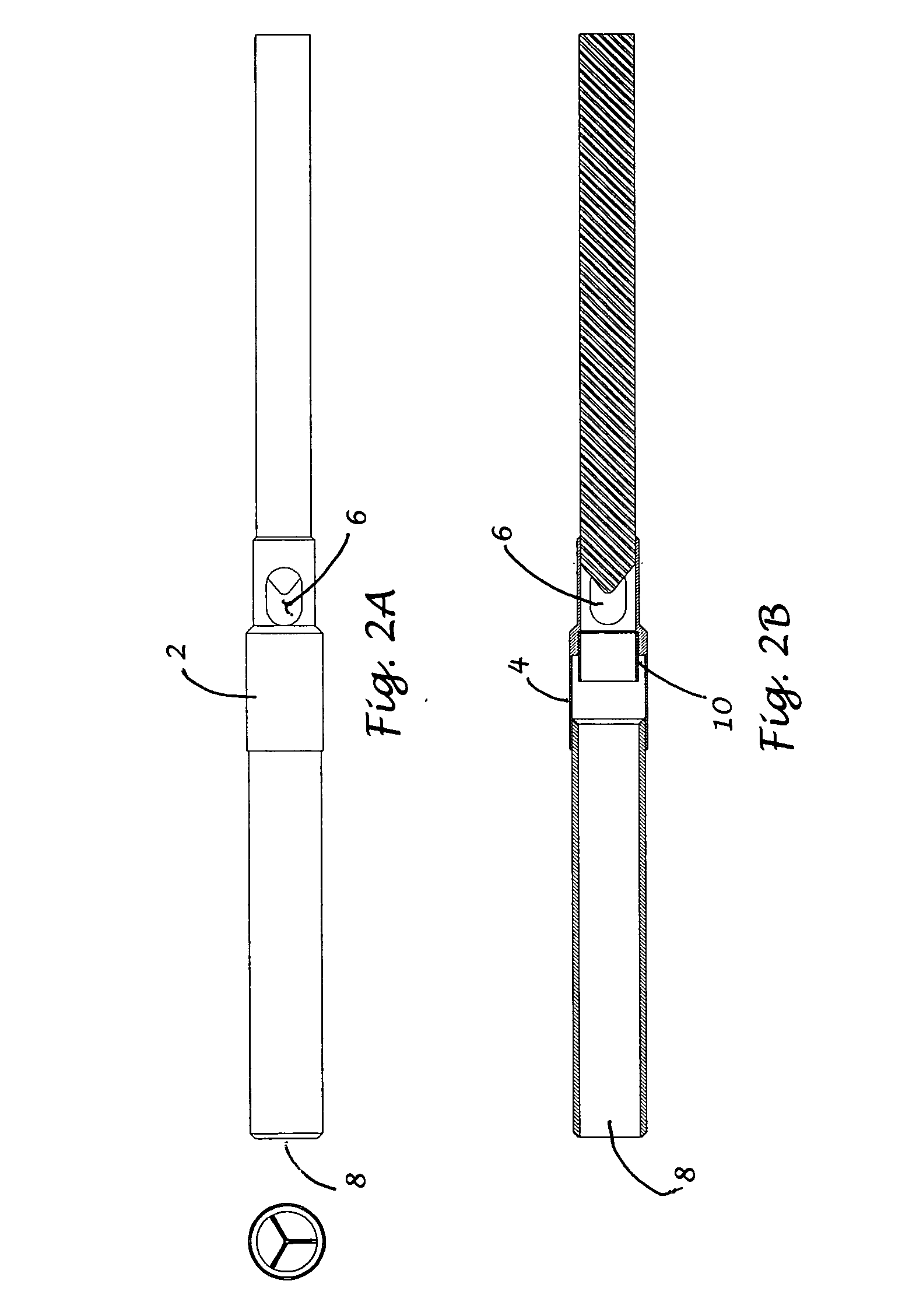
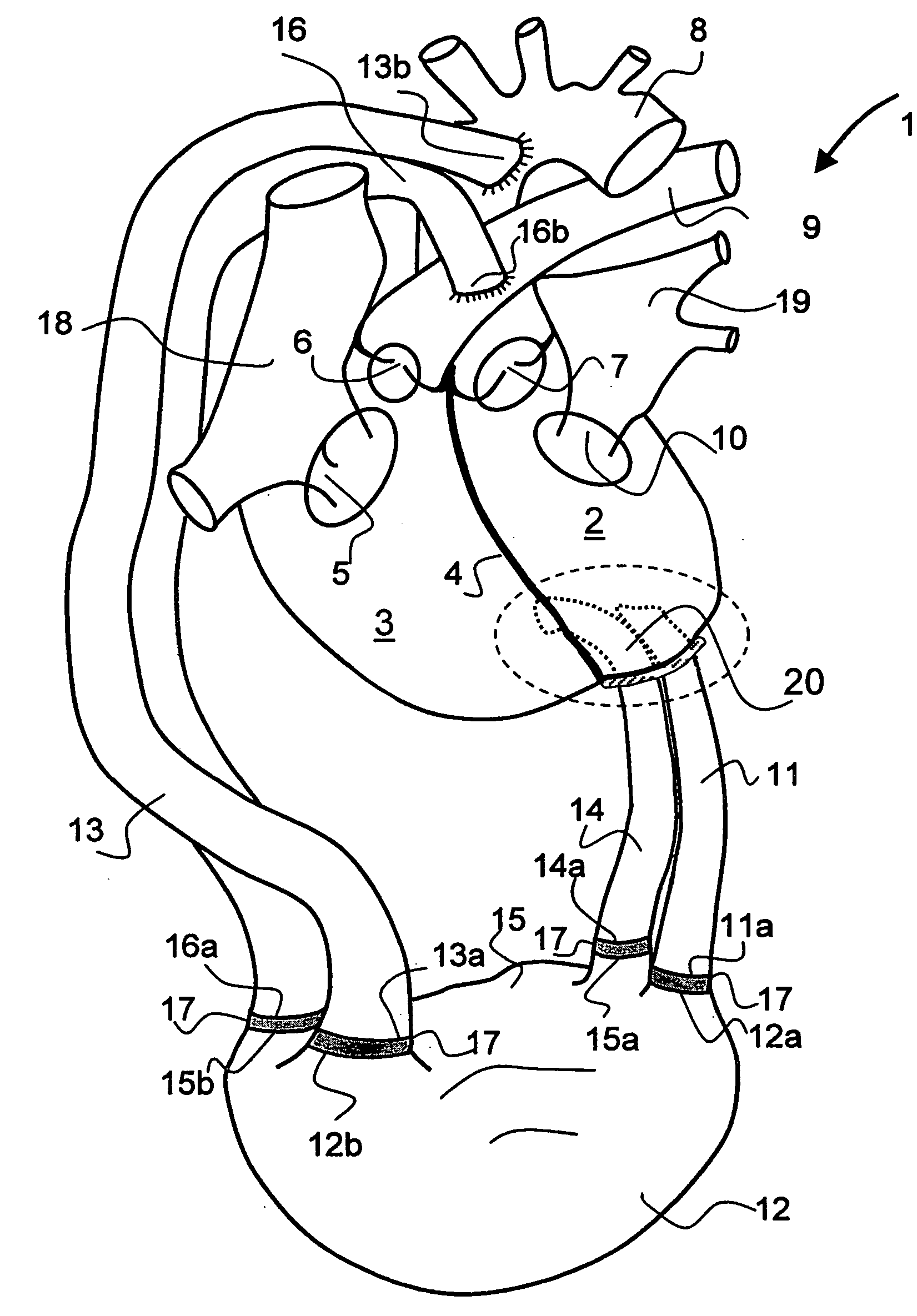
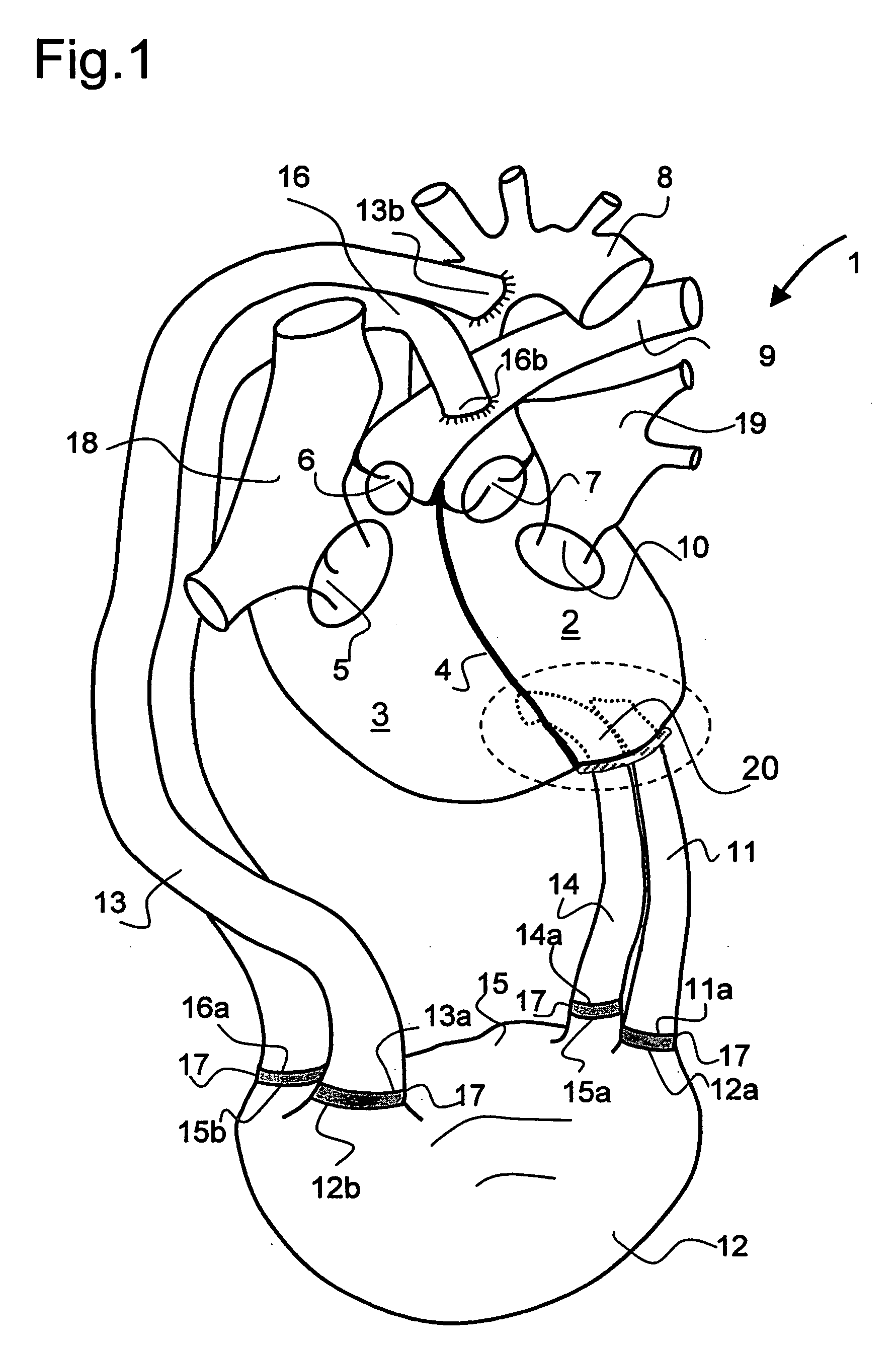
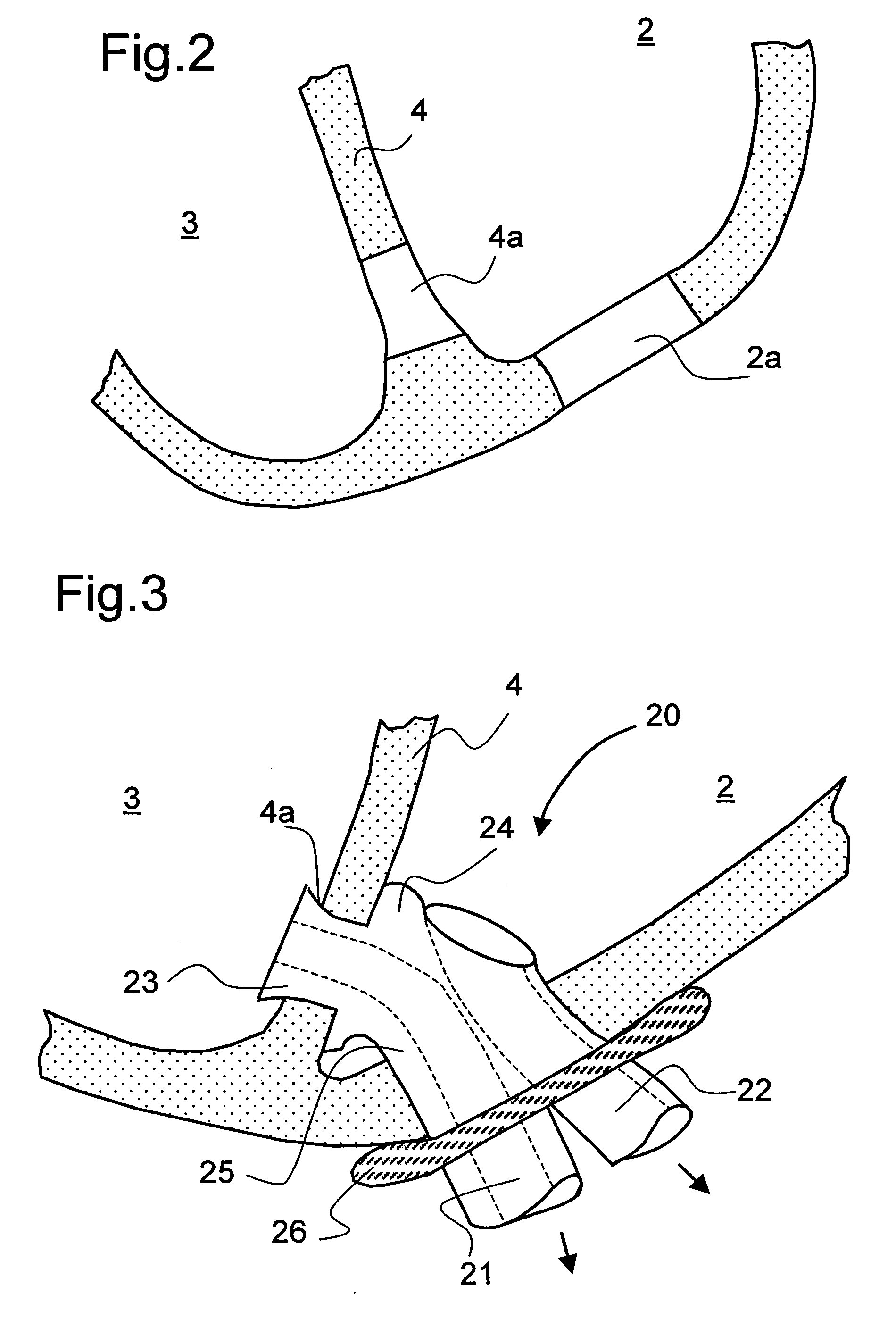
InactiveUS20050209502A1Optimal flowEasy to moveIntravenous devicesHeart stimulatorsLeft VentriclesEngineering
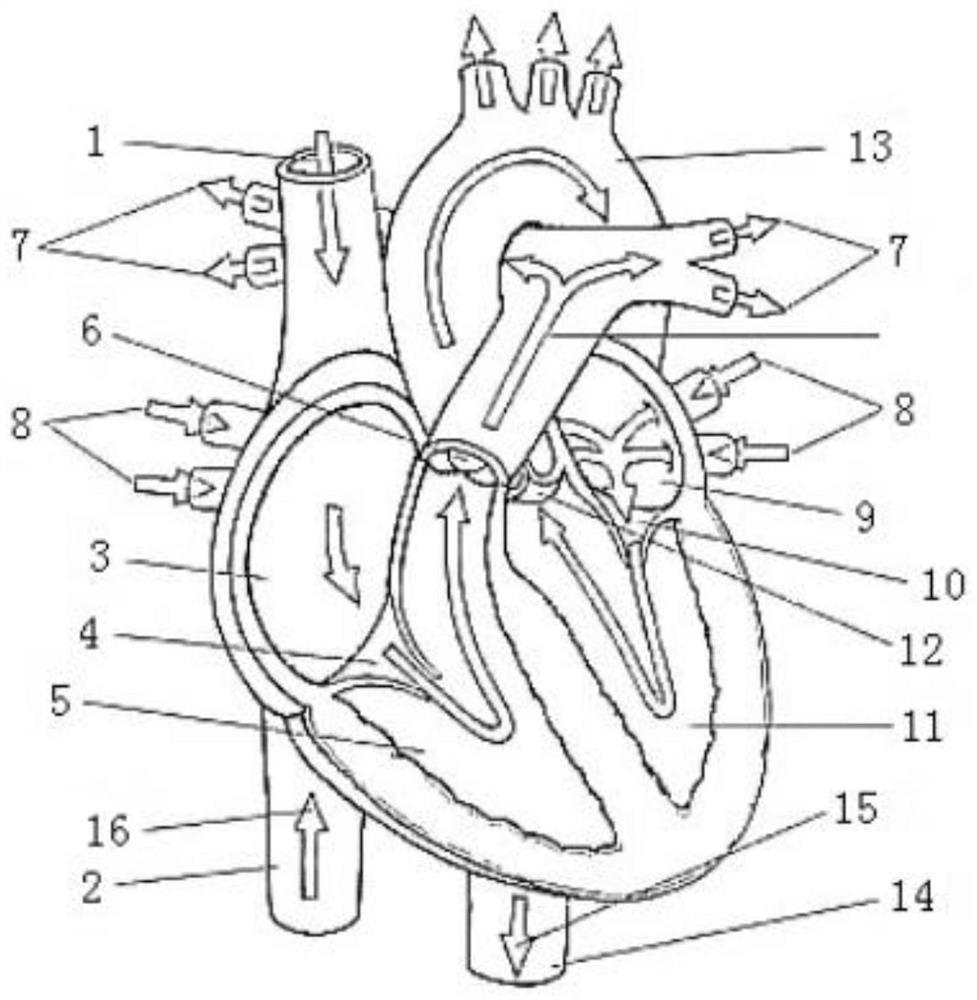
For connecting a cardiac biventricular assist means including a dual-chamber pumping device, and an electrically powered compressor means provided between the two chambers (12, 15) a partially flexible one-part or multi-part adapter (20) is provided with two through-passageways (21, 22; 34, 35) each separate from the other, said adapter being securely held, on the one hand, in a port (4a) in the apical portion of the septum (4) and, on the other, in a port (2a) in / at the apex of the left ventricle (2) so that the through-passageway (22; 35) extending into the left ventricle (2) is connected directly or by means of a first flexible tube (11) to the inlet (12a) of the one chamber (12) and the other through-passageway (21; 34) extending into said right ventricle (3) is connected directly or by means of a second flexible tube (14) to the inlet (15a) of the other chamber (15).
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Delivery of cardiac constraint jacket
Owner:MARDIL
Techniques for providing a replacement valve and transseptal communication
A method is provided, comprising: (1) making a transapical puncture into a left ventricle of the heart; (2) making a transseptal fenestration in the heart; (3) delivering a prosthetic valve via the transapical puncture and implanting the prosthetic valve at a mitral valve of the heart; and (4) subsequently to delivering the prosthetic valve and making the transseptal fenestration, closing the transapical puncture. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
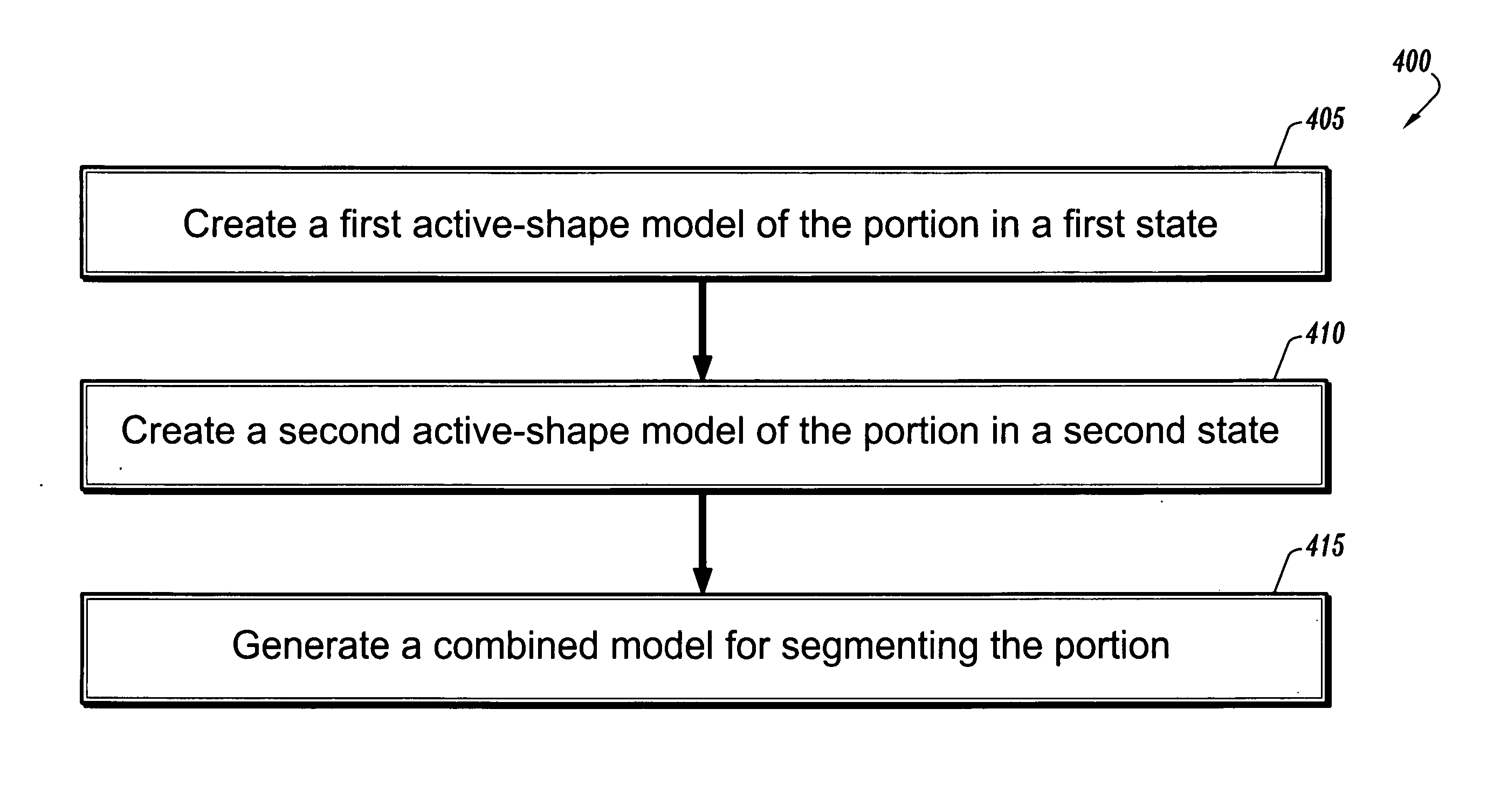
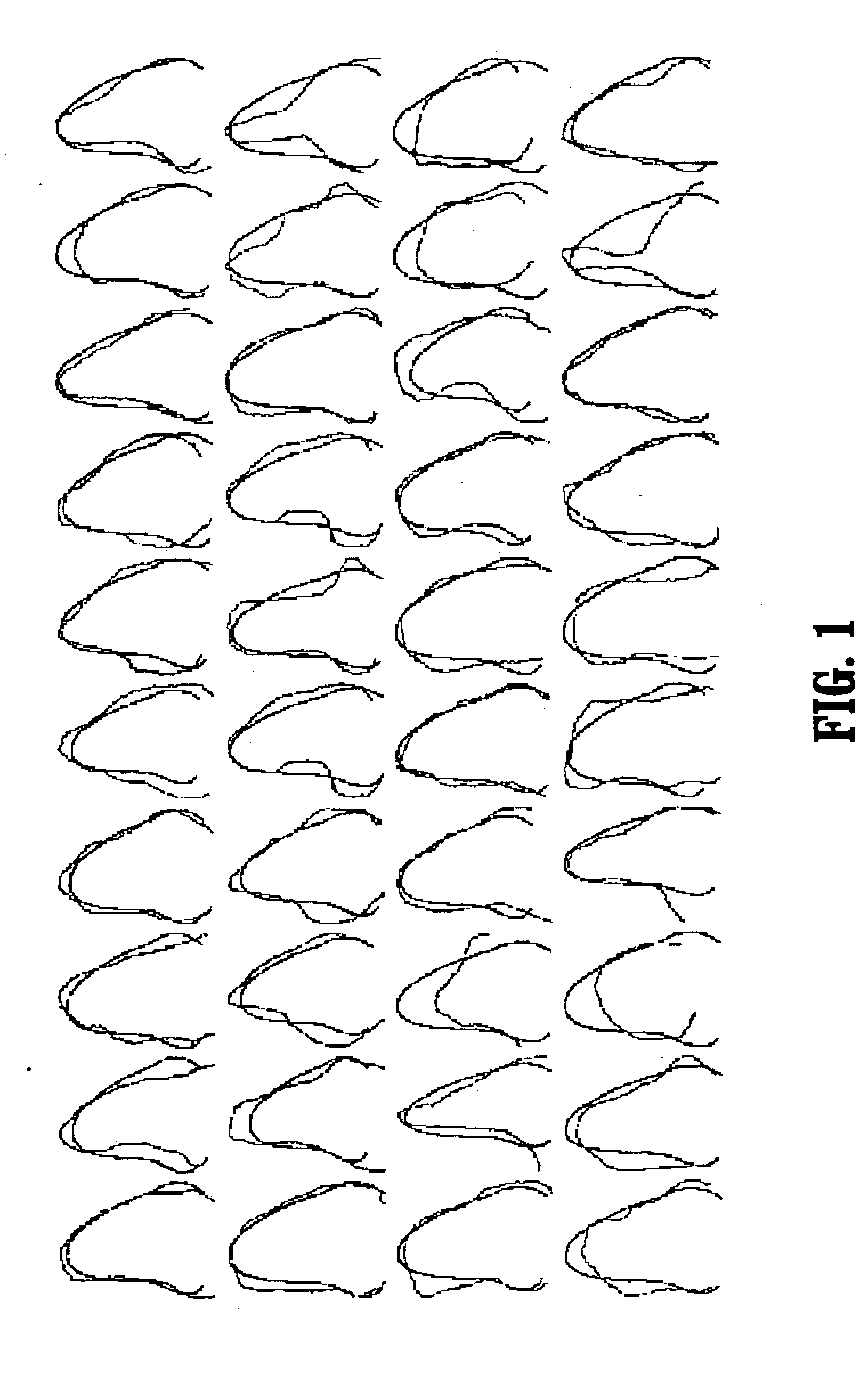
Segmentation of the left ventricle in apical echocardiographic views using a composite time-consistent active shape model
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Apparatus and method for mounting a cardiac harness on the heart
InactiveUS20060129026A1Increase flexibilityImprove sealingHeart valvesCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringSilica gel
A suction cup for use with a delivery device for delivering a cardiac harness to a heart. The suction cup includes a cup body formed of a flexible material, such as silicone, and the cup body has an upper portion and a lower portion, wherein the lower portion defines an opening leading to an inner area of the cup body. The suction cup also includes a connecting aperture formed of a rigid material that is attached to the upper portion of the cup body. The flexible material of the cup body allows the suction cup to rotate relative to the heart tissue, and to re-center itself onto the apex of the heart when the suction cup is improperly aligned with the apex, all while preserving a vacuum attachment to the heart.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL
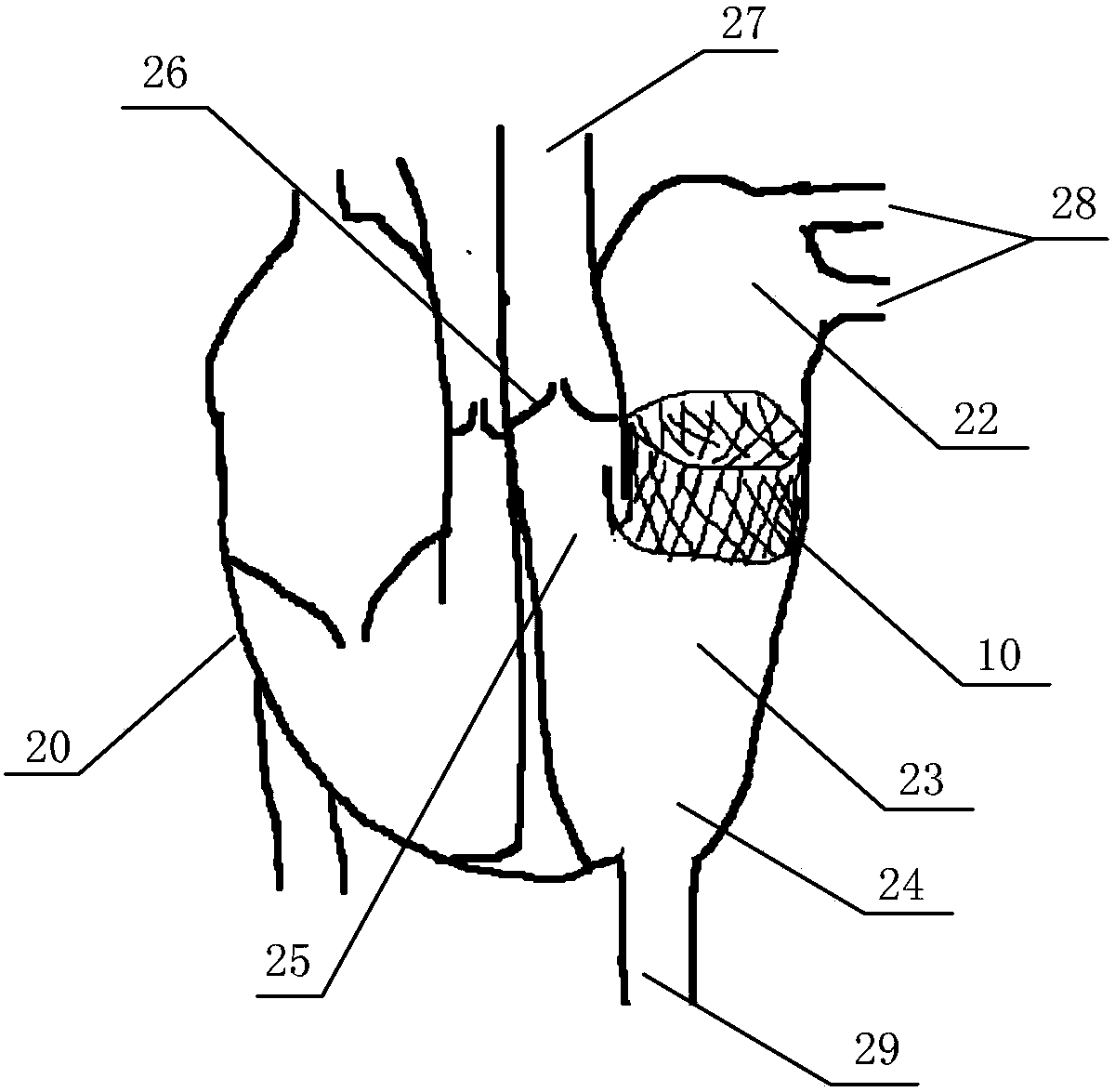
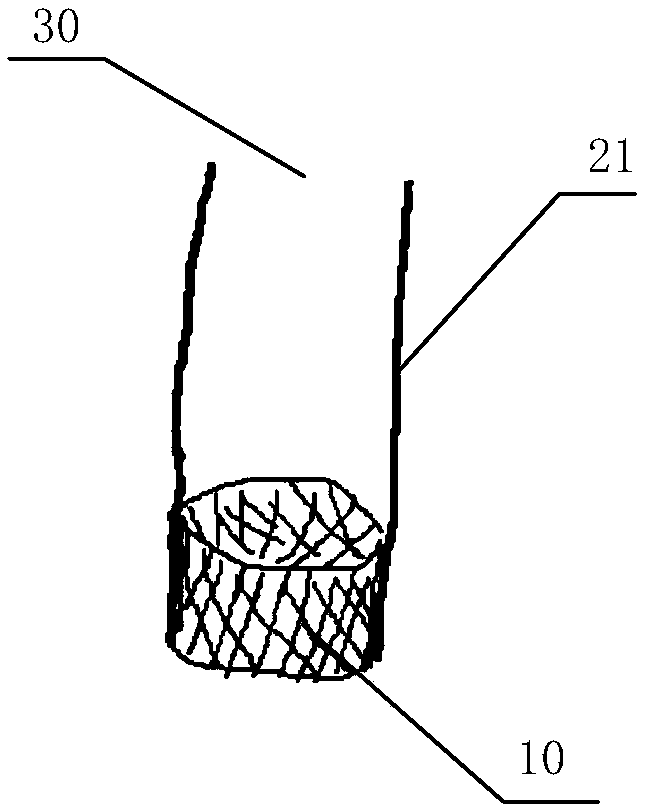
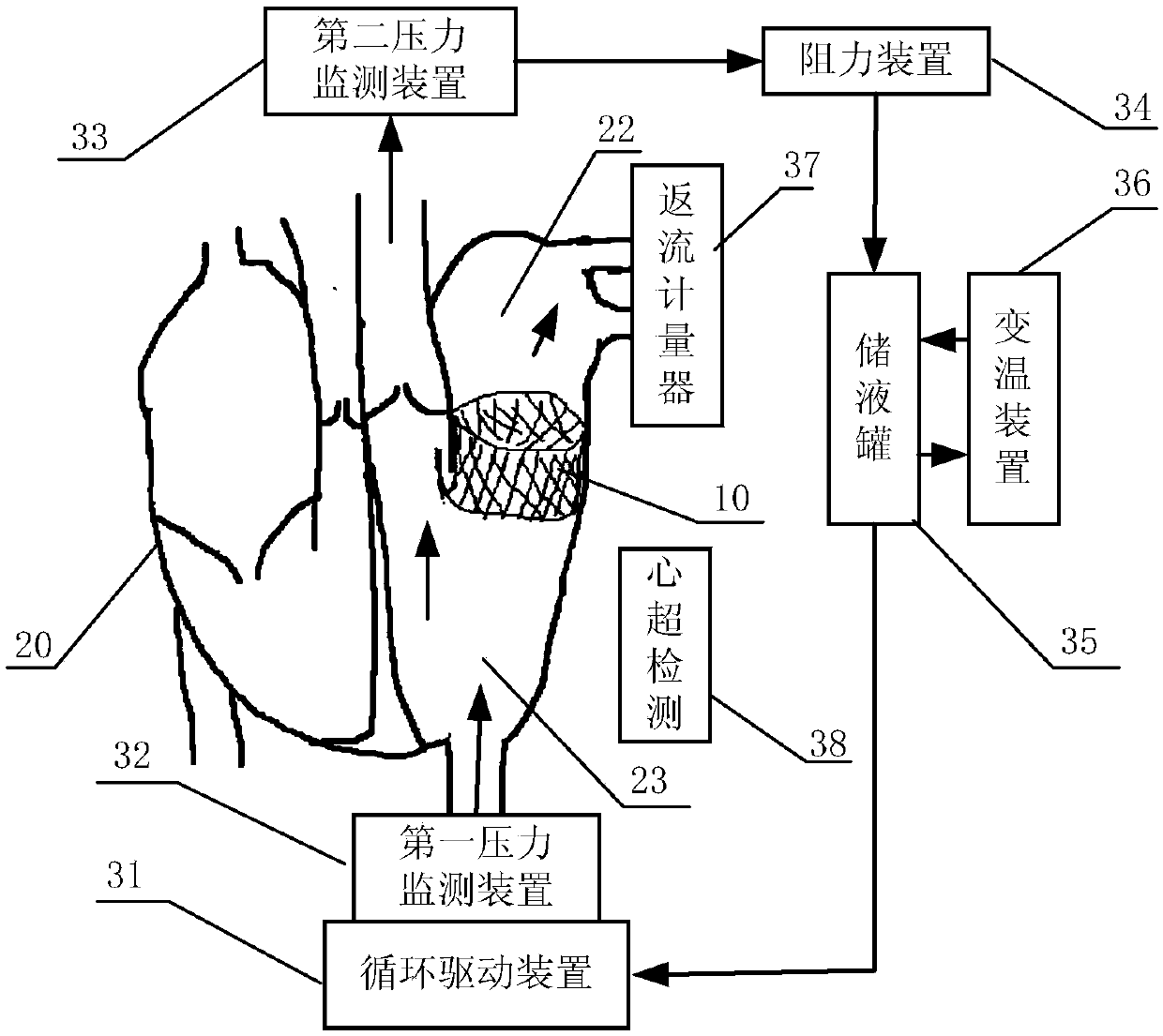
In-vitro performance testing system and testing method of transcatheter bicuspid valve valved stent
PendingCN107773328AAchieve hydrodynamic performanceEnables in vitro performance testingHeart valvesStationary stateIn vivo
The invention discloses an in-vitro performance testing system and testing method of a transcatheter bicuspid valve valved stent, and relates to prostheses capable of being implanted in vivo, in particular to a testing device and testing method applied to heart valve performance testing. The in-vitro performance testing system comprises a valve testing part which is internally provided with the bicuspid valve valved stent, a liquid circulation device and a monitoring device; a first testing part is a heart specimen of which the left ventricular apex is provided with a circulation inlet, and asecond testing part is a section of artificial blood vessel or a section of blood vessel specimen for sewing the tested bicuspid valve valved stent; the liquid testing device is connected with the first testing part to constitute a first testing circulating path for steady flow circulation and a second testing circulating path for simulating the ventricular beat of the human body; the liquid circulation device is connected with the second testing part to constitute a third testing circulating path which is connected with circulation lateral branches, in vitro tests of fluid mechanic performance, support fixing states, valve backflow, perivalvular leakage, and influences on surrounding important organization structures of the bicuspid valve valved stent can be achieved, and a durability experiment of the bicuspid valve valved stent is completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Transapical removal device
A transapical removal device that can be deployed in a catheter procedure to capture for removal or alteration a mitral valve clip or heart tissue, such as the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, and methods of use are disclosed. The removal device includes a delivery catheter configured to be deployed near a mitral valve using a guide catheter. The delivery catheter has a snare head at the distal end, which assumes a collapsed state during movement of the delivery catheter through the guide catheter and deployed state for capturing a mitral valve clip or anterior leaflet. The snare head has one or more ablation delivery catheters configured to ablate tissue surrounding the pre-positioned mitral valve clip or anterior leaflet. In some arrangements within the scope of the present disclosure, the removal device includes a deployment mechanism for deploying a new transcatheter valve into the mitral valve.
Owner:EVALVE
Mitral valve clamp capable of realizing horizontal and vertical clamp and conveyor system
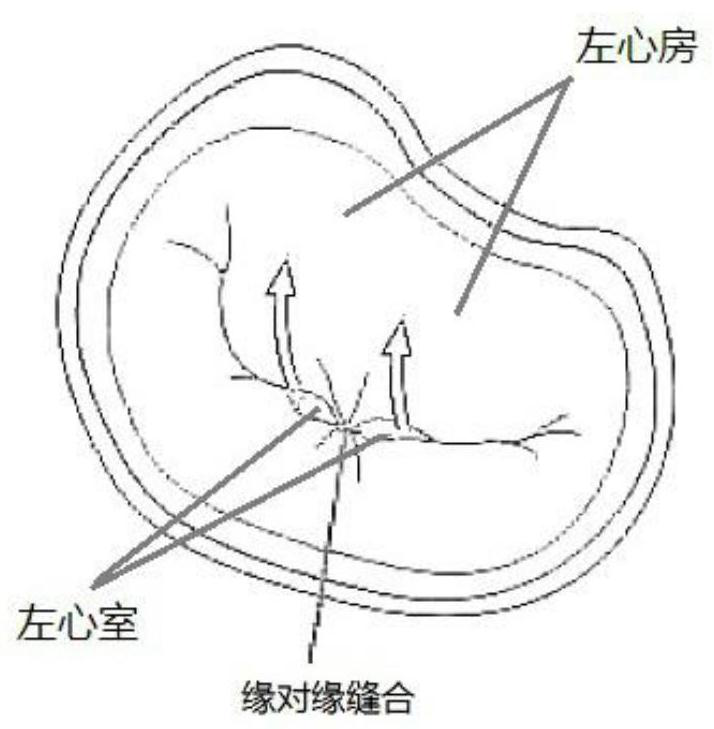
The invention discloses a mitral valve clamp capable of realizing horizontal and vertical clamp and a conveyor system. A main body of the system comprises the mitral valve clamp capable of realizing horizontal and vertical clamp and a conveyor; the mitral valve clamp is composed of an upper valve clamp member, a lower valve clamp member and a vertical arm clamp member; a clamp arm of the mitral valve clamp includes a straight neck section and an arc section, and vertical and horizontal anastomosis or clamping two clamp valve leaflets can be formed under assisted clamp of a vertical arm clamp;and the conveyor is composed of an outer push-pull tube, a vertical arm clamp push tube, a clamp tube or a screw rod and a sheath tube, the conveyor components support the mitral valve clamp and are put in the sheath tube, the conveyor realizes minimally invasive intervention from a chest and the tip of a heart, and can clamp mitral valve leaflets horizontally and vertically and effectively prevent backflow.
Owner:北京航天卡迪技术开发研究所
Epicardial ablation catheter and method of use
PendingUS20190274757A1Preventing hemodynamic collapseAvoid deathGuide needlesSurgical instruments for heatingEpicardial ablationPericardial space
An aspect of various embodiments of the present invention system and method provide, but not limited thereto, a novel means for epicardial ablation using a double-curve steerable sheath and a double-curve deflectable open irrigated-tip / suction catheter that can be guided around the apex of the heart and adjusted so as to position the distal tip optimally. The catheter can also both deliver fluid to and withdraw fluid from the pericardial space. Access to the epicardial surface of the heart is via a subxiphoid entry. The method and means presented include, but are not limited to, steering, energy delivery, bipolar mapping, placement and use of electrodes, irrigation, suction of irrigation fluid, and other details of the subject invention.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Cardiac treatment system and method
ActiveUS20140107405A1Eliminates and reduce symptomImprove blood flowHeart valvesDiagnosticsBiocompatible materialHeart disease
Devices and methods for providing localized pressure to a region of a patient's heart to improve heart functioning, including: (a) a jacket made of a flexible biocompatible material, the jacket having an open top end that is received around the heart and a bottom portion that is received around the apex of the heart; and (b) at least one inflatable bladder disposed on an interior surface of the jacket, the inflatable bladder having an inelastic outer surface positioned adjacent to the jacket and an elastic inner surface such that inflation of the bladder causes the bladder to deform substantially inwardly to exert localized pressure against a region of the heart.
Owner:DIAXAMED LLC
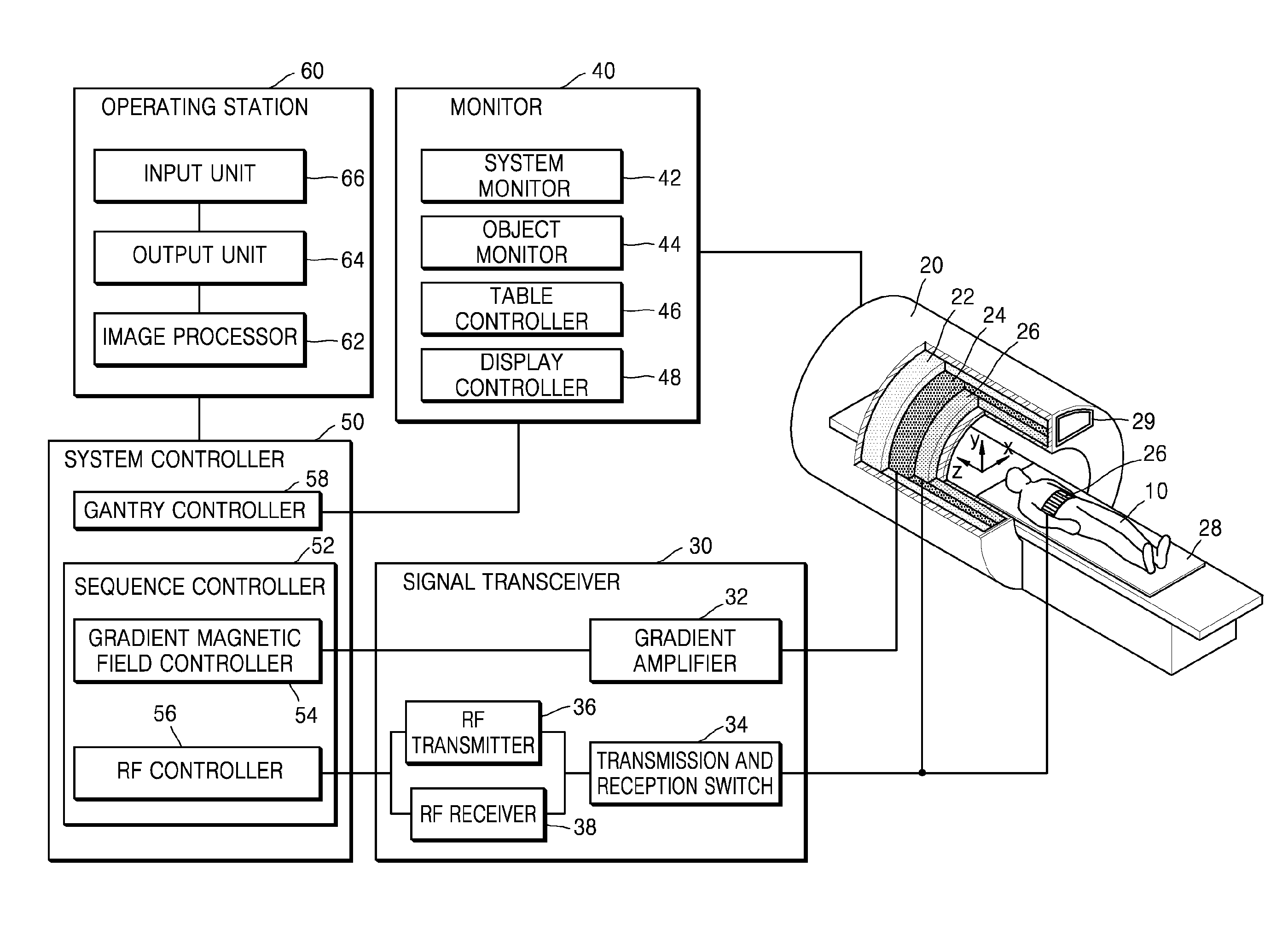
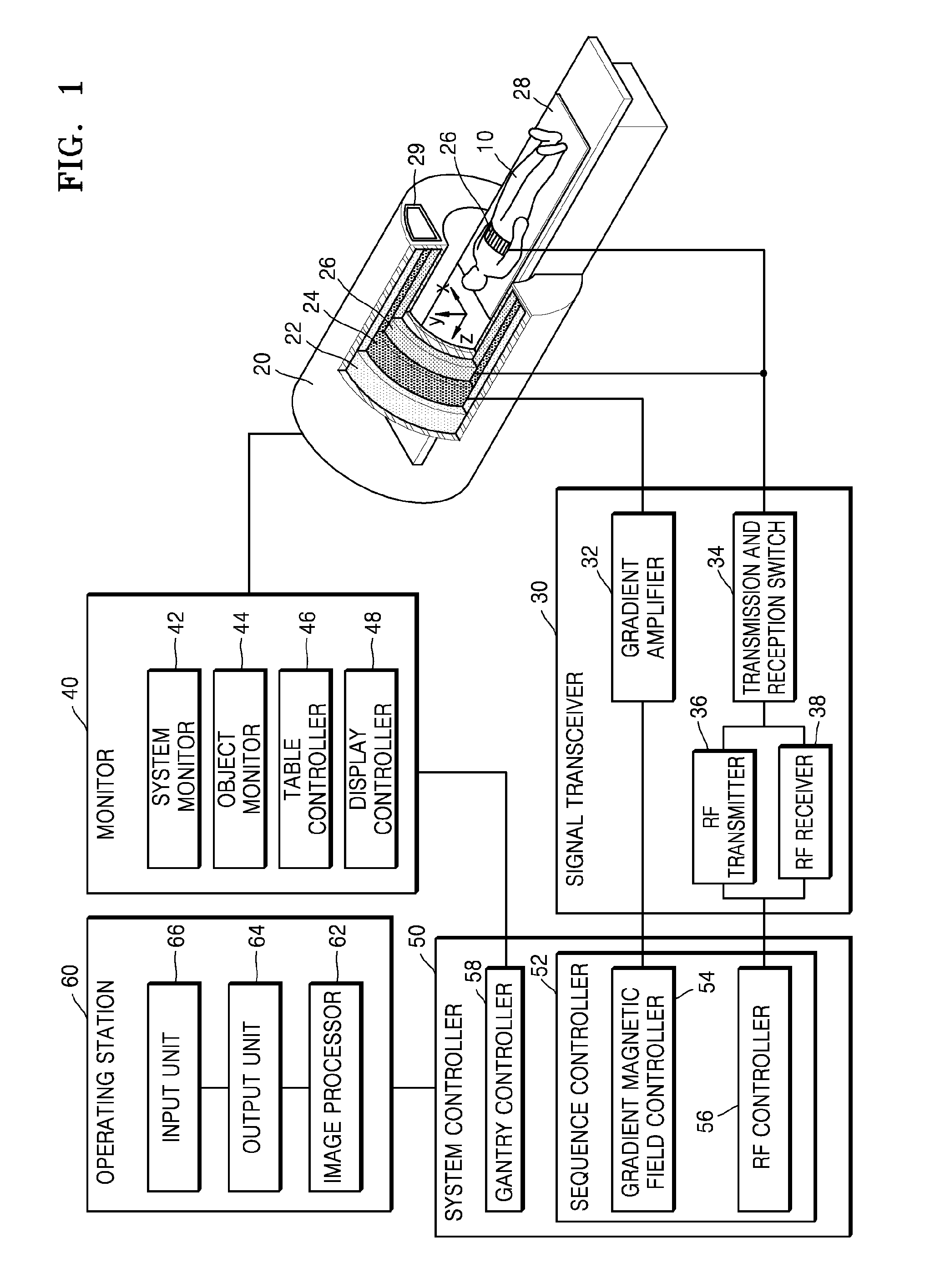
Medical imaging apparatus and method of processing medical image
A medical imaging apparatus includes: an output unit configured to display a magnetic resonance (MR) image matrix in which MR images, obtained by performing magnetic resonance imaging on a heart, are arranged in columns and rows; and an image processor configured to display at least one first indicator which indicates a column of the MR image matrix corresponding to at least one of end diastole and end systole and display at least one second indicator which indicates a row of the MR image matrix corresponding to at least one of an apex and a base of the heart, wherein the columns of the MR image matrix are arranged according to time when MR images included in the columns are captured, and the rows of the MR image matrix are arranged according to a position on a longitudinal axis of the heart corresponding to MR images included in the rows.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
left ventricular assist pump
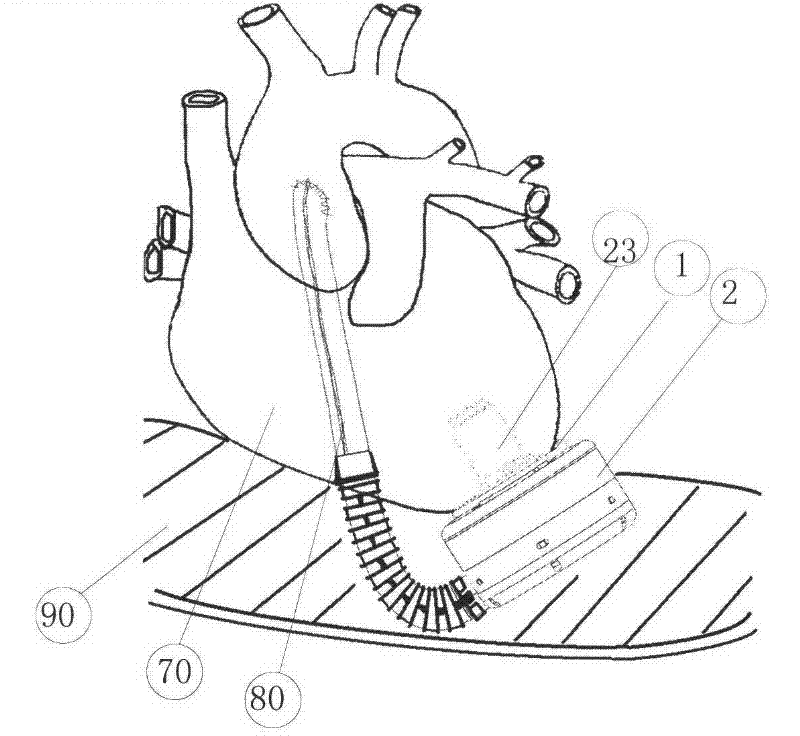
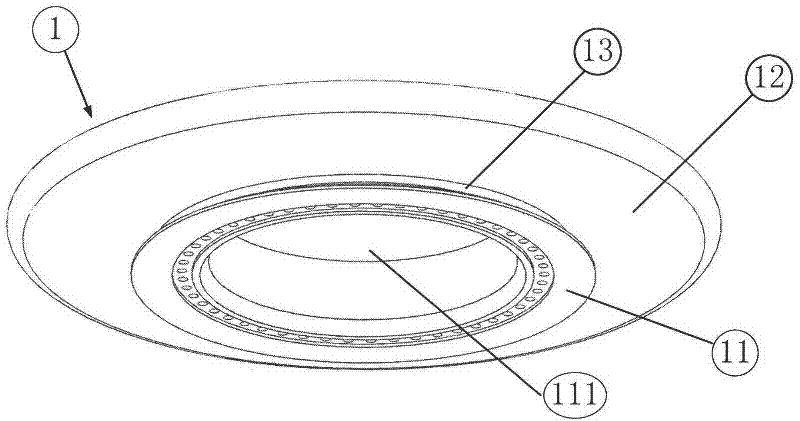
The invention discloses a left ventricle auxiliary blood pump, which comprises a cardiac apex sleevelet and a blood pump body fixedly connected with the cardiac apex sleevelet, wherein the cardiac apex sleevelet comprises a suture ring and a flexible skirt edge which is sleeved at the periphery of the suture ring; the suture ring comprises a suture ring inner hole and a convex edge which is convexly arranged in the radial direction; the blood pump body comprises an inlet pipe; the inlet pipe is convexly arranged on a rear cover of the blood pump body; a peripheral ring slot is formed between the convex edge and the flexible skirt edge; a sliding sheet which can only move in the radial direction relative to the blood pump body is arranged on the rear cover of the blood pump body and is stretched into the peripheral ring slot in a movable way; the convex edge is positioned between the sliding sheet and the bottom surface of a settling tank; and the cardiac apex sleevelet and the blood pump body are relatively axially fixed. In the invention, the sliding sheet is used for fixing the cardiac apex sleevelet and the blood pump, so that the cardiac apex sleevelet can be more conveniently and reliably connected with the blood pump; simultaneously, the axial dimension of the inlet pipe of the blood pump is reduced, so that the implantation of the left ventricle auxiliary blood pump in a pleural cavity is facilitated without damages to a diaphragm, and the success rate of a surgery is greatly improved.
Owner:苏州同心医疗科技股份有限公司
Heart auxiliary device
InactiveCN104146855AAvoid bleedingPrevent thrombosisElectrotherapyArtificial respirationHeart apexHeart right
The invention discloses a heart auxiliary device which comprises an outer shell. The outer shell is formed by bonding and fixing a non-elastic flexible rope on the outer surface of a heart model in a spiral mode, a sealed left air bag is arranged along the outer surface of a left heart chamber of the heart model and located in the outer shell, a sealed right air bag is arranged along the outer surface of a right heart chamber of the heart model and located in the outer shell, buckling rings are arranged on the upper portions of the inner walls, close to the side wall of the left air bag and the side wall of the right air bag, of the outer shell respectively, the upper end of the left air bag and the upper end of the right air bag are fixed on the buckling rings, a lower opening of the left air bag is communicated with a left air inlet pipe, a lower opening of the right air bag is communicated with a right air inlet pipe, the left air inlet pipe and the right air inlet pipe penetrate out of the heart apex at the bottom of the outer shell and extend outwards, and the extending parts of the left air inlet pipe and the right air inlet pipe are communicated with an air source control device. The heart auxiliary device is not in direct contact with blood, anticoagulation is not needed in the application process, a series of blood vessel complications like bleeding, thrombosis, hemolysis and immunoreactions are avoided, the infection rate is reduced, and the heart auxiliary device can be suitable for single-heart-chamber assistance and double-heart-chamber assistance, and is flexible in using method.
Owner:刘超
Apparatus And Methods For Minimally Invasive Transcatheter Transapical Puncture, Imaging, and Catheter Alignment Techniques
A delivery catheter system includes a guide catheter, an anchor catheter, a collapsible and expandable anchor, a balloon formed from a portion of the positioning catheter, and a needle. The anchor may be for anchoring a prosthetic heart valve in a native heart valve. The anchor may be configured to be received within the anchor catheter. The balloon may be inflated or deflated and provide mechanical support to enable the needle to pierce a ventricle wall. A metallic guide wire can simultaneously be inserted through the aorta to outline the heart when viewed through fluoroscopic imaging.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
Cardiovascular access and device delivery system
A system and method of accessing a heart of a patient is provided. A cardiac access channel is established through an apical wall of the heart to provide direct access through the apical wall to the left ventricle. A vascular access channel is established through the skin to a peripheral blood vessel. A first end of an elongate member is advanced from the outside of the apical wall through the cardiac access channel and into the left ventricle. A second end disposed opposite the first end remains outside the patient. The elongate member is drawn into and through the vascular access channel to externalize the first end of the elongate member while leaving the second end outside the apical wall of the heart.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Valve clip and clipping system thereof
PendingCN111772874AShorten the axial lengthSmall footprintAnnuloplasty ringsHeart apexSurgical operation
The invention relates to a valve clip and a clipping system thereof. The valve clip can be used for effectively treating MR (Mitral Regurgitation) and TR (Tricuspid Regurgitation) after being implanted into the human body by the clipping system. By using the valve clip, the axial operating space of the valve clip can be shortened, and the operating direction can be changed, so that the capturing and clamping operation can be performed from the other side of the valve (i.e., the atrium side) so as to reduce the injury damage on the atrium and the chordae tendineae in the surgical operation process; the length of the valve clip can be shortened, so that the implanted valve clip is shorter so as to reduce the space of the ventricle side occupied by the valve clip, reduce the injury capable ofbeing caused by the valve clip on the heart tissue, and reduce the thrombus forming risk; in addition, after the clipping system passes through the femoral vein and punctures the septum of the rightatrium and the left atrium, the right atrium and the left atrium are used as a delivery path of the clip; the intercostal incision and cardiac apex puncture are not needed; and the surgical trauma issmaller.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANYU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Mitral valve replacement system for percutaneous transcatheter
PendingCN112137764APrevention of Weekly LeakagePeripheral leakage reducedHeart valvesHeart apexBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
The invention relates to a mitral valve replacement system for a percutaneous transcatheter, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The mitral valve replacement system comprises avalve frame supporting body, an artificial valve leaflet and a ventricular septum anchoring structure. The valve frame supporting body is arranged between an atrium and a ventricle and provided with ahollow cavity with the two ends open. The artificial valve leaflet is arranged on the inner wall of the cavity of the valve frame supporting body. The ventricular septum anchoring structure is arranged between the valve frame supporting body and a ventricular septum. The invention provides the mitral valve replacement device intervened through a catheter via a femoral vein admission passage and aims to solve the problems that an existing interventional mitral valve system is generally large in valve stent, has the left ventricular outflow passage obstruction risk, has potential complicationsin transapical admission passage and anchoring and the like, and the mitral valve replacement device provided by the invention is more minimally invasive and firmer in anchoring, and the technical scheme of mitral valve replacement suffering from left ventricular outflow tract obstruction can be effectively avoided.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
Cardiac treatment system and method
ActiveUS20190076250A1Eliminates and reduces symptomIncrease blood flowHeart valvesCirculatory assistance devicesMedicineHeart disease
Devices and methods for providing localized pressure to a region of a patient's heart to improve heart functioning, including: (a) a jacket made of a flexible biocompatible material, the jacket having an open top end that is received around the heart and a bottom portion that is received around the apex of the heart; and (b) at least one inflatable bladder disposed on an interior surface of the jacket, the inflatable bladder having an inelastic outer surface positioned adjacent to the jacket and an elastic inner surface such that inflation of the bladder causes the bladder to deform substantially inwardly to exert localized pressure against a region of the heart.
Owner:DIAXAMED LLC
Tethering System For A Prosthetic Heart Valve
According to one aspect of the disclosure, a system may include a surgical prosthetic heart valve having a frame, prosthetic leaflets within the frame configured to allow blood to flow through the frame in an antegrade direction but to substantially block blood from flowing through the frame in a retrograde direction, and a cuff configured to be sutured to a native valve annulus of a heart of a patient. The system may include a valve tether having a first end configured to be coupled to the surgical prosthetic heart valve, and an anchor configured to be secured to a ventricular apex of the heart of the patient. The valve tether may include a second end opposite the first end, the second end configured to be operably coupled to the anchor.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
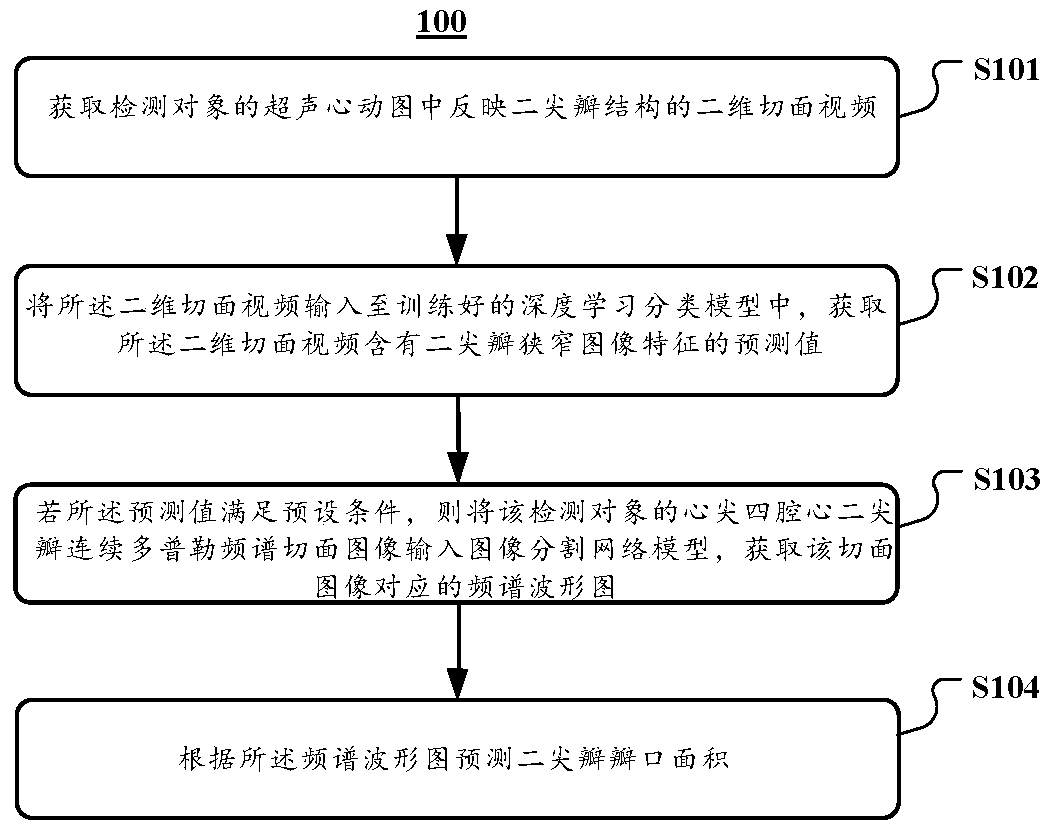
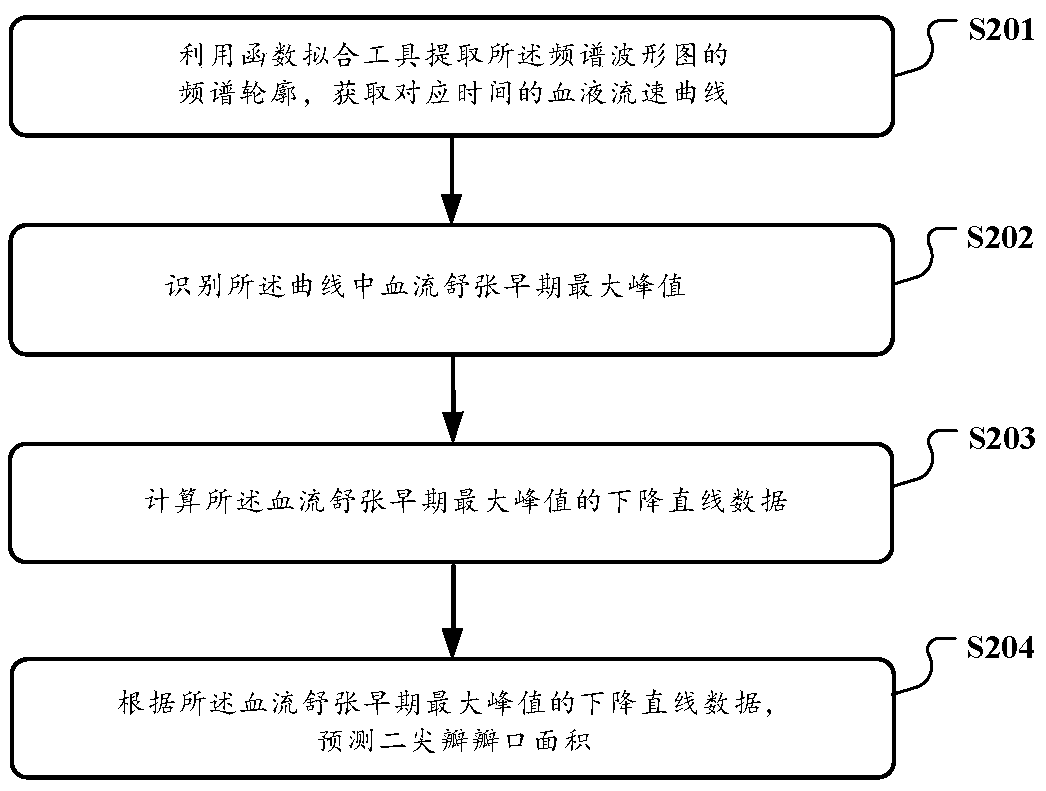
Mitral valve opening area detection method, system and device based on artificial intelligence
ActiveCN111275755AImprove accuracyImprove consistencyImage enhancementImage analysisHeart apexFrequency spectrum
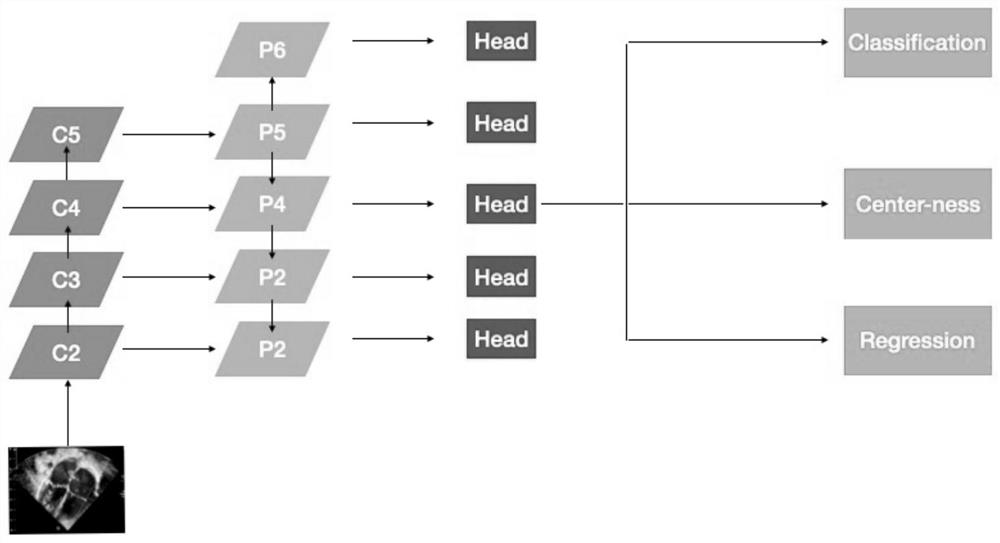
The invention discloses a mitral valve opening area detection method, system and device based on artificial intelligence. The method comprises the steps that a two-dimensional section video reflectinga mitral valve structure in an ultrasonic cardiogram of a detection object is acquired; inputting the two-dimensional section video into a trained deep learning classification model, and obtaining aprediction value of the two-dimensional section video containing mitral valve stenosis image features; if the prediction value meets a preset condition, inputting the heart tip four-cavity heart mitral valve continuous Doppler frequency spectrum section image of the detection object into an image segmentation network model, and obtaining a frequency spectrum oscillogram corresponding to the section image; and predicting the mitral valve opening area according to the frequency spectrum oscillogram. According to the method, the system and the equipment, the accuracy and the consistency of ultrasonic detection are greatly improved.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
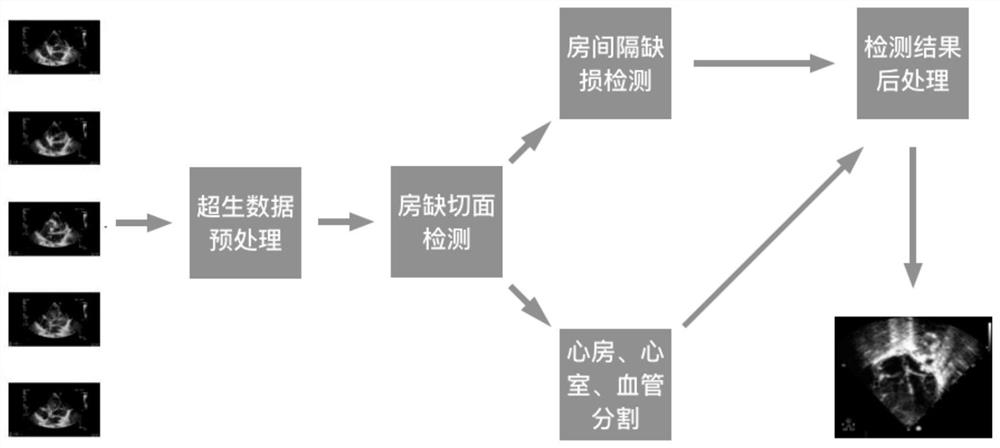
Deep learning atrial septal defect detection method and device
PendingCN111915557AAvoid detection processImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisHeart apexRight atrium
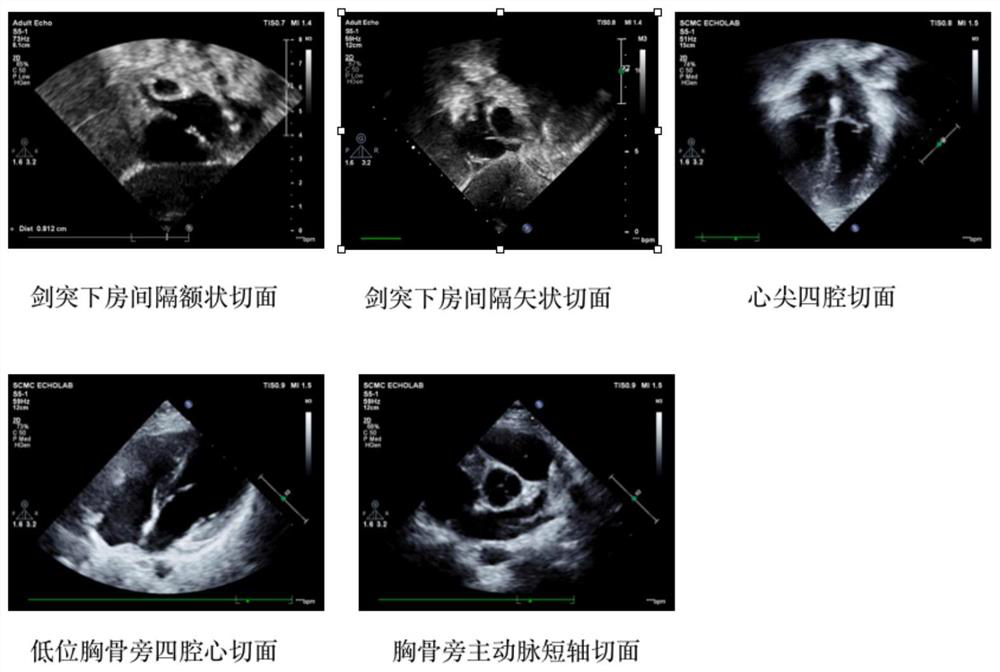
The invention provides a deep learning atrial septal defect detection method and device, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an ultrasonic cardiogram, preprocessing the ultrasonic cardiogram, and extracting a region of interest; carrying out feature extraction on the region of interest, and identifying a subsword process atrial septal frontal section, a subsword process atrial septal sagittal section, a cardiac apex four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, a low-position paracarpal four-cavity cardiac tangent plane and a paracarpal aorta short-axis tangent plane; detecting the minimum distance point of the atrial septal defect; segmenting heart structures of a subsword atrial septal frontal section, a subsword atrial septal sagittal section, a cardiac apex four-cavity cardiac tangent plane, a low paracardial four-cavity cardiac tangent plane and a paracardial aorta minor axis section to obtain segmentation results, the heart structures including a left atrium, a right atrium, a left ventricle, a right ventricle, an aorta and pulmonary arteries; and according to the segmentation results, filtering the detected minimum distance point bounding box of the atrial septal defect, andtaking the filtered result as an atrial septal defect detection result.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENRUI BOLIAN TECH CO LTD +2
Interventional transapical artificial heart valve delivery system
PendingCN112451174ATraumaShort postoperative recovery periodHeart valvesHeart apexPostoperative recovery
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to an interventional transapical artificial heart valve delivery system. The interventional transapical artificial heart valve delivery system comprises a conveying mechanism and a catheter sheath mechanism, wherein the conveying mechanism comprises an outer tube, an inner tube and a handle assembly, thehandle assembly is connected with the outer tube, one end of the inner tube is mounted on the outer tube, and the inner tube moves in the axial direction of the outer tube. An artificial heart valve is loaded on the outer tube and is clamped and matched with the inner tube. The catheter sheath mechanism is connected with the outer tube and used for conducting transapical access on the conveying mechanism so as to achieve conveying of the artificial heart valve. According to the artificial heart valve delivery system, minimally invasive interventional transcatheter artificial heart valve is adopted, the replacement operation wound is small, the postoperative recovery period is short, operation is easy and rapid, and the success rate is high.
Owner:QICHEN (SHANGHAI) MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com