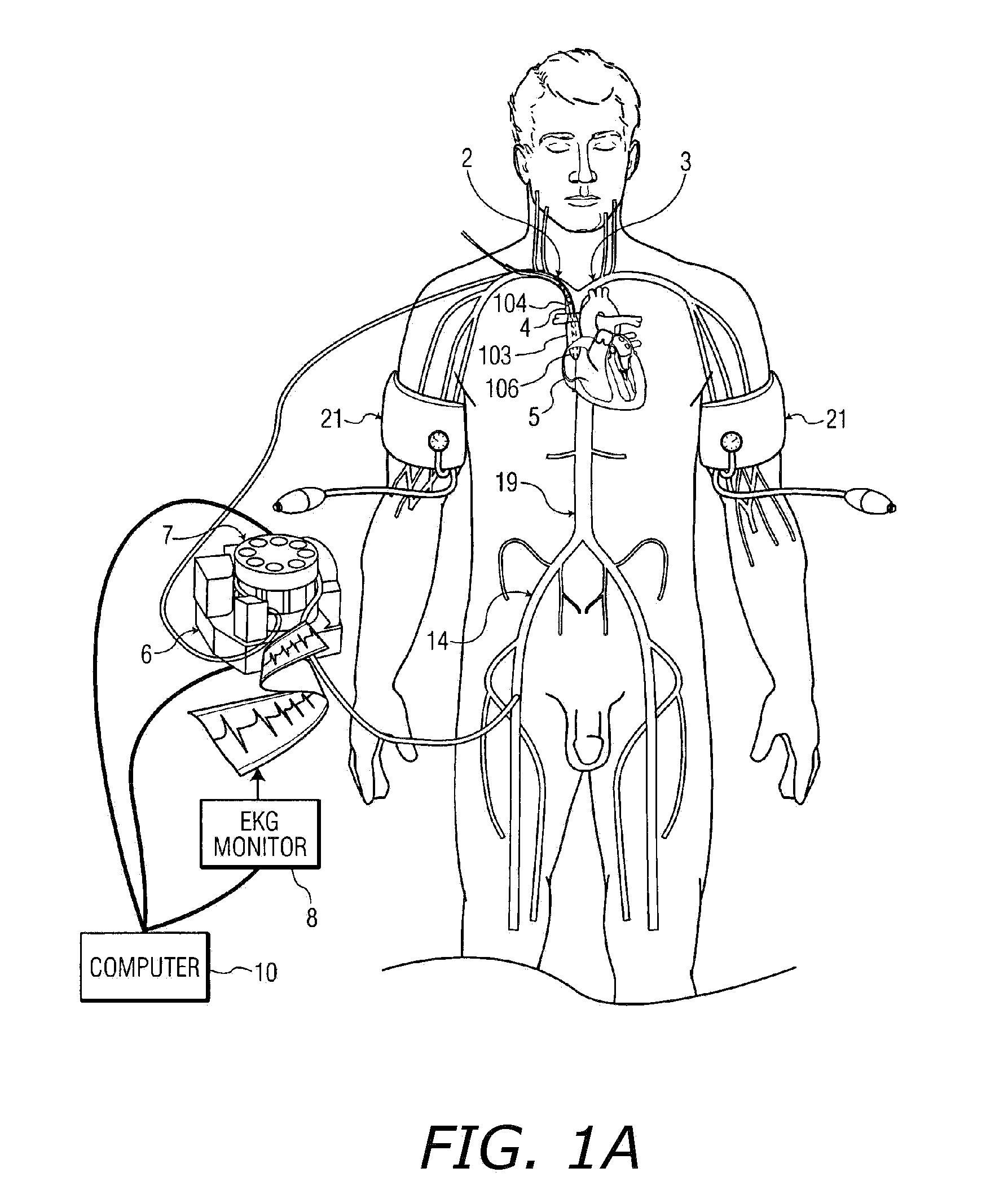
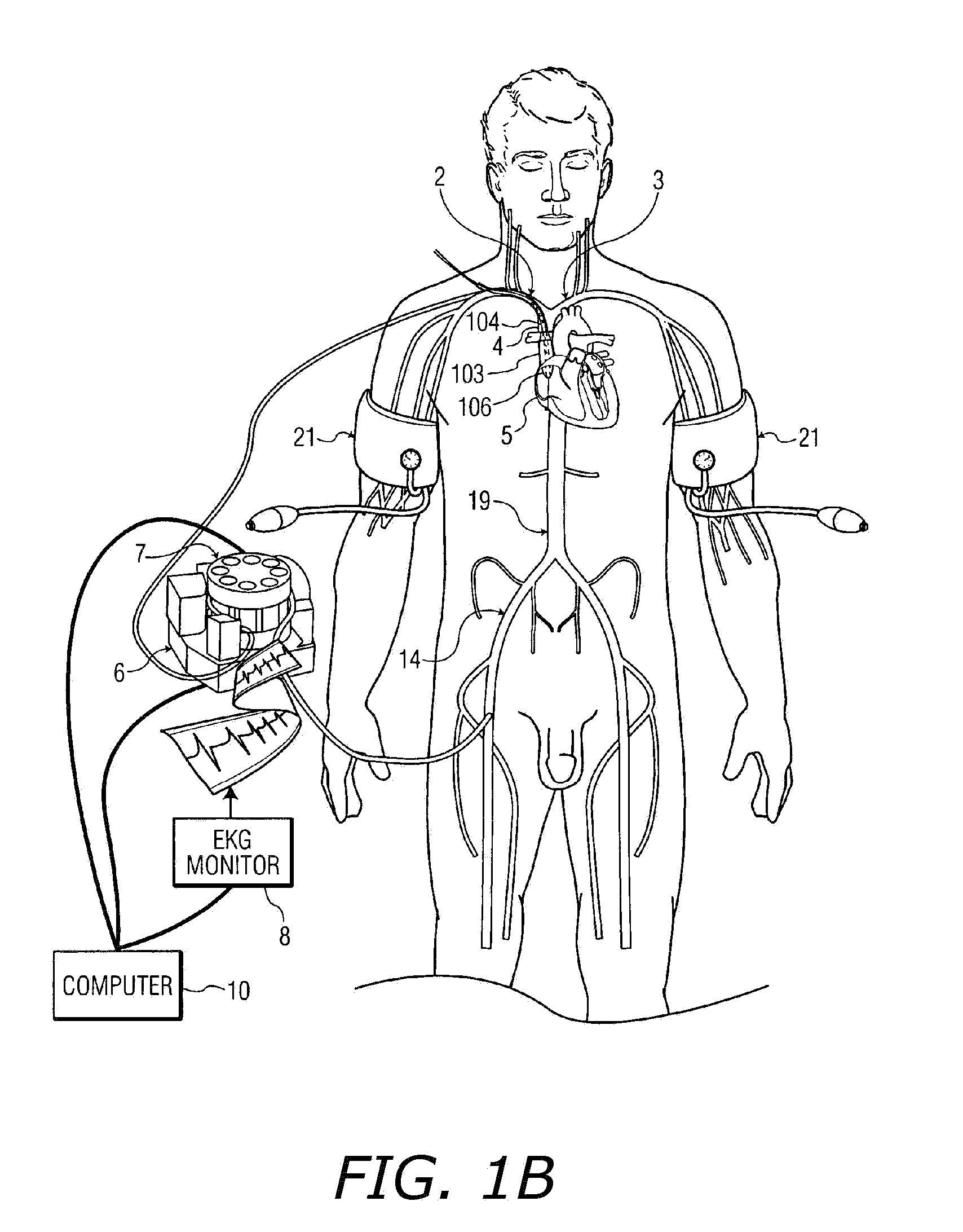
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Femoral vein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
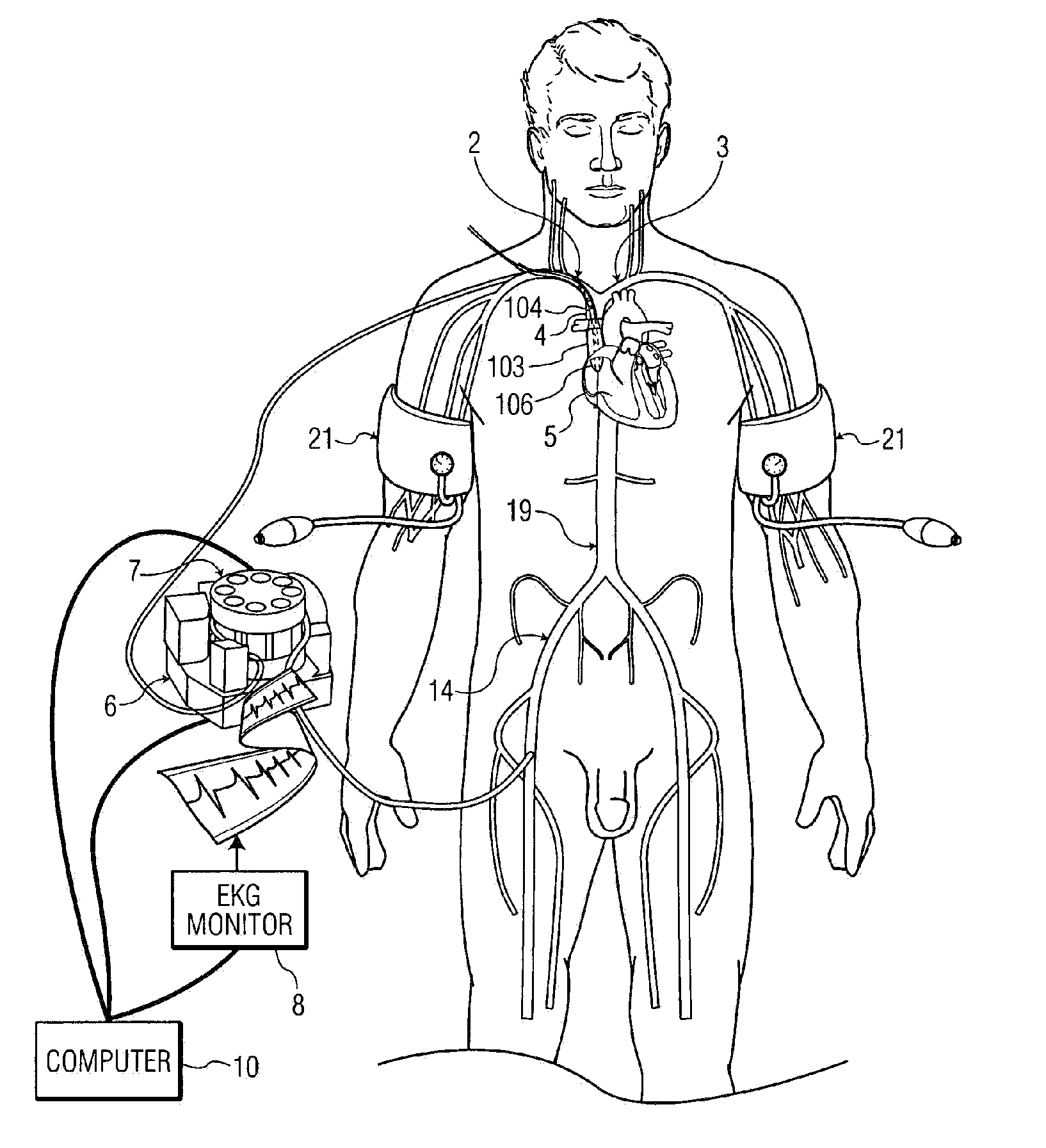
In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) and is a continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the external iliac vein. The femoral vein bears valves which are mostly bicuspid and whose number is variable between individuals and often between left and right leg.
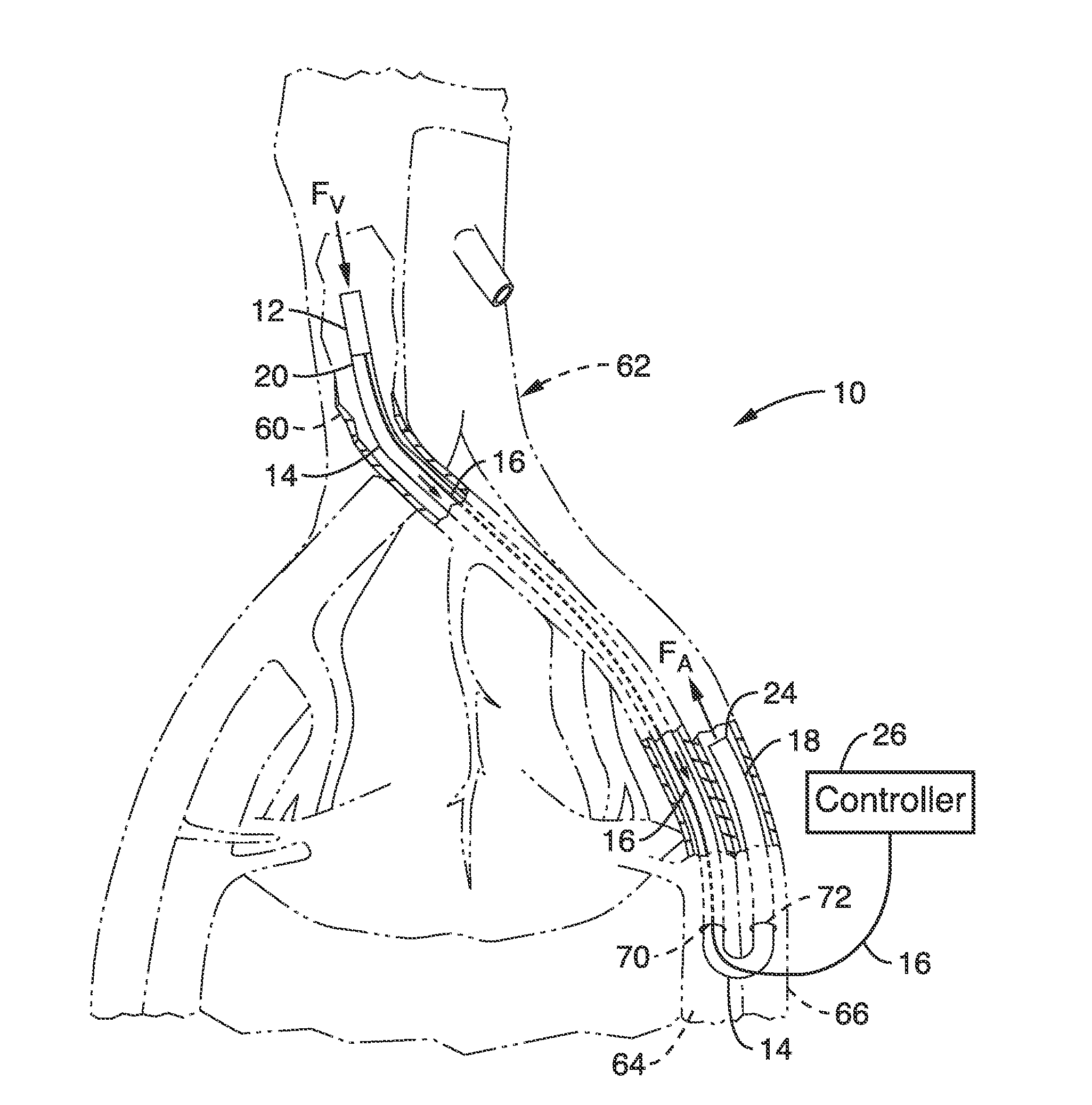
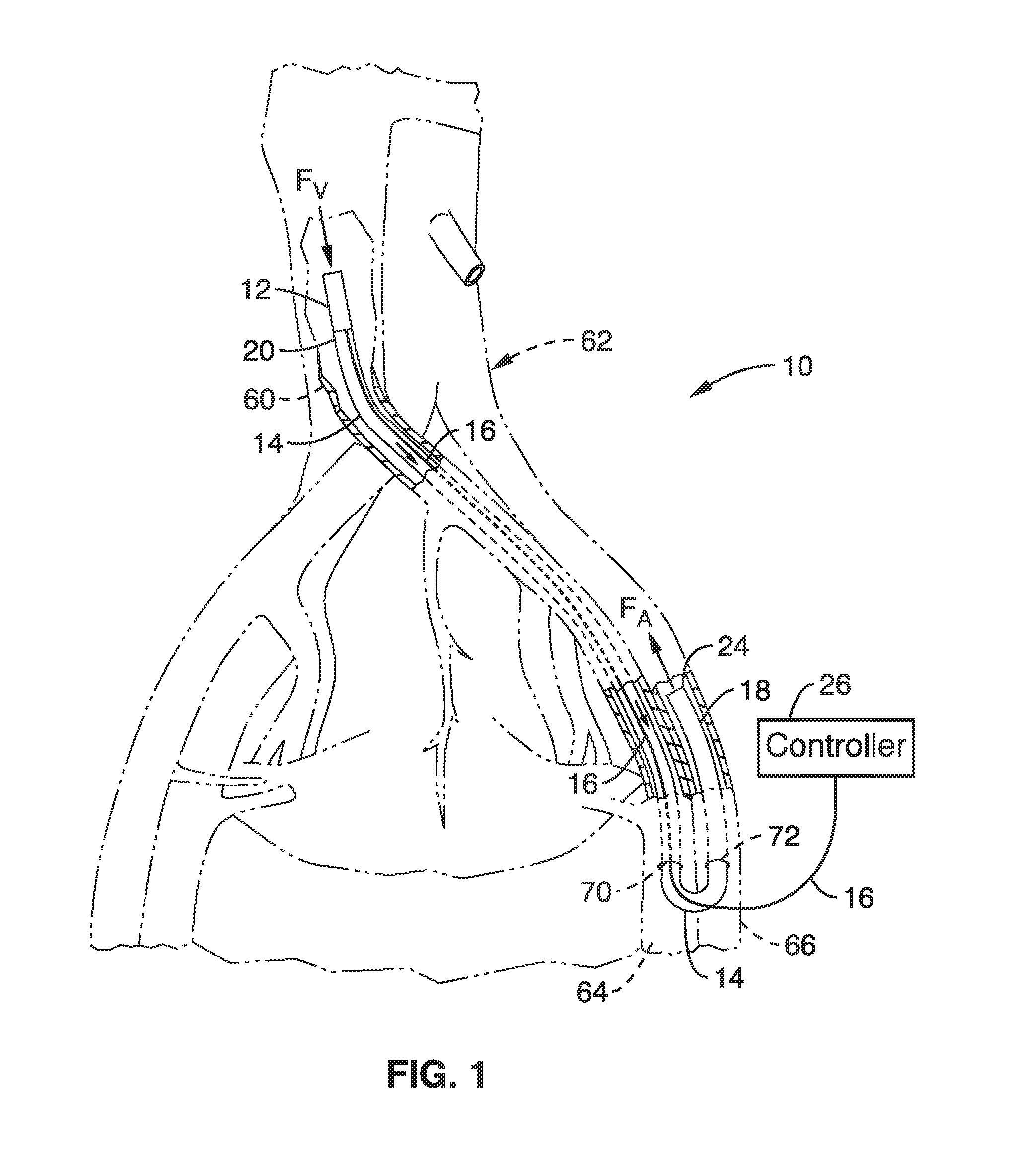
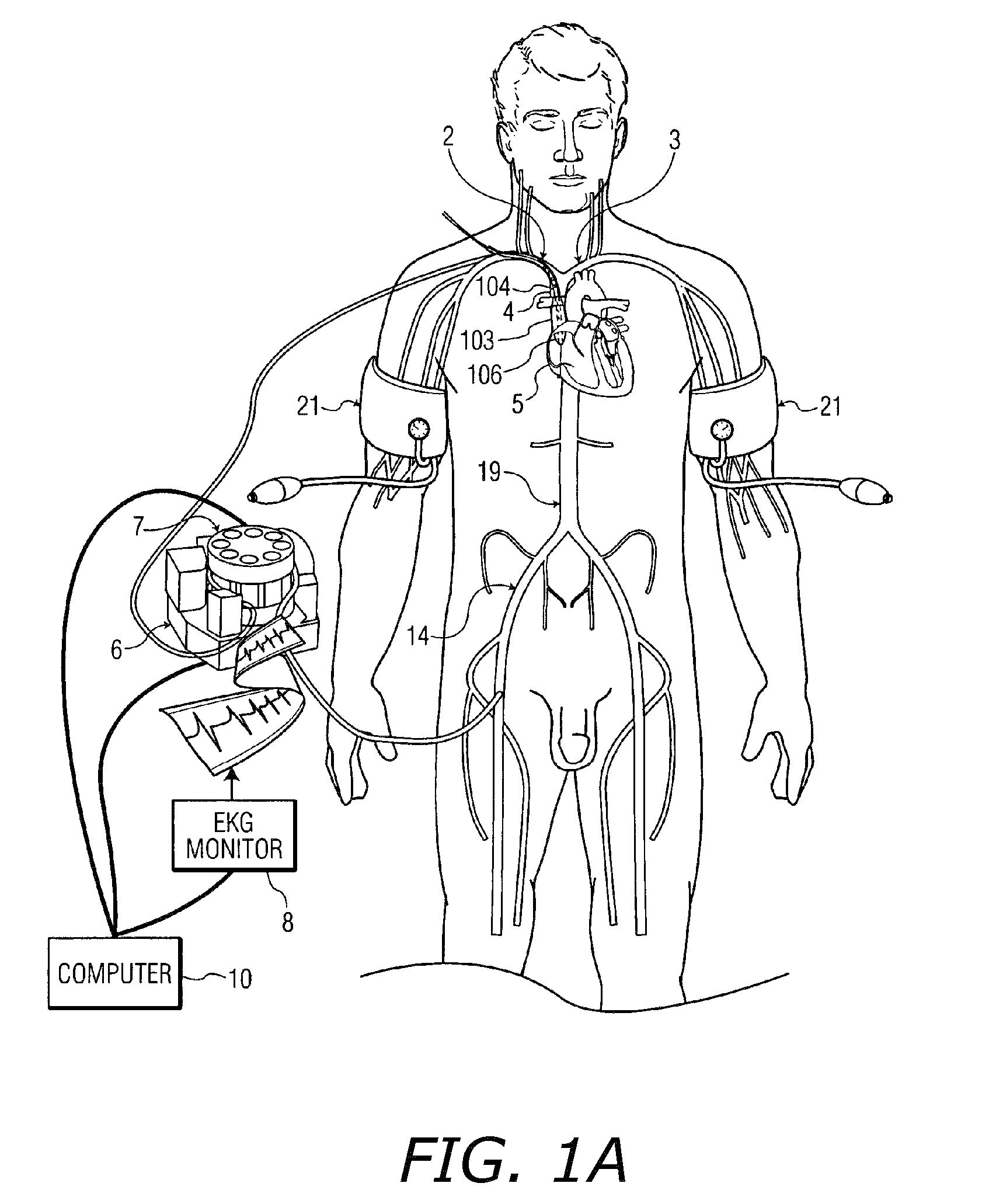
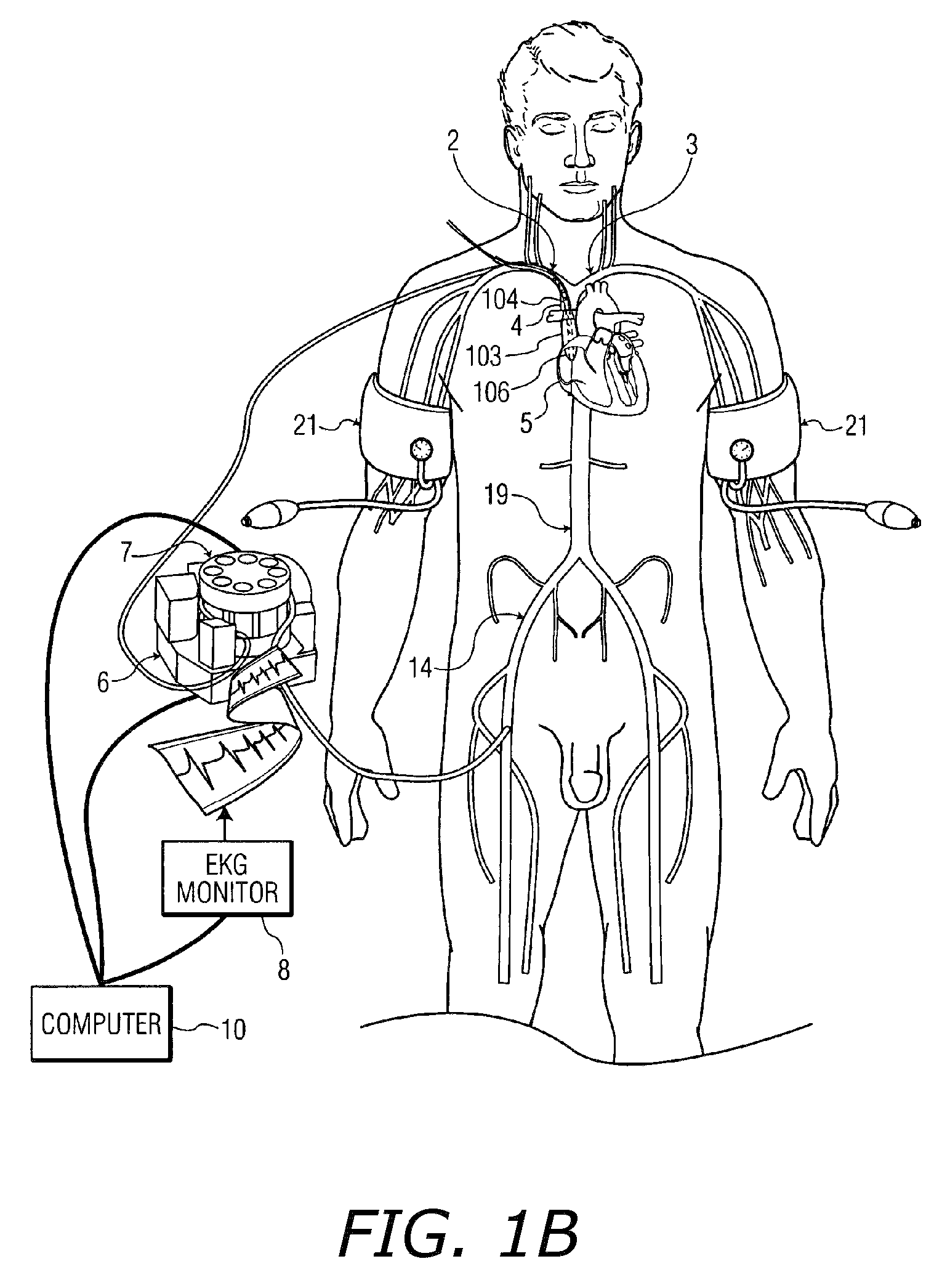
Valve implanting device
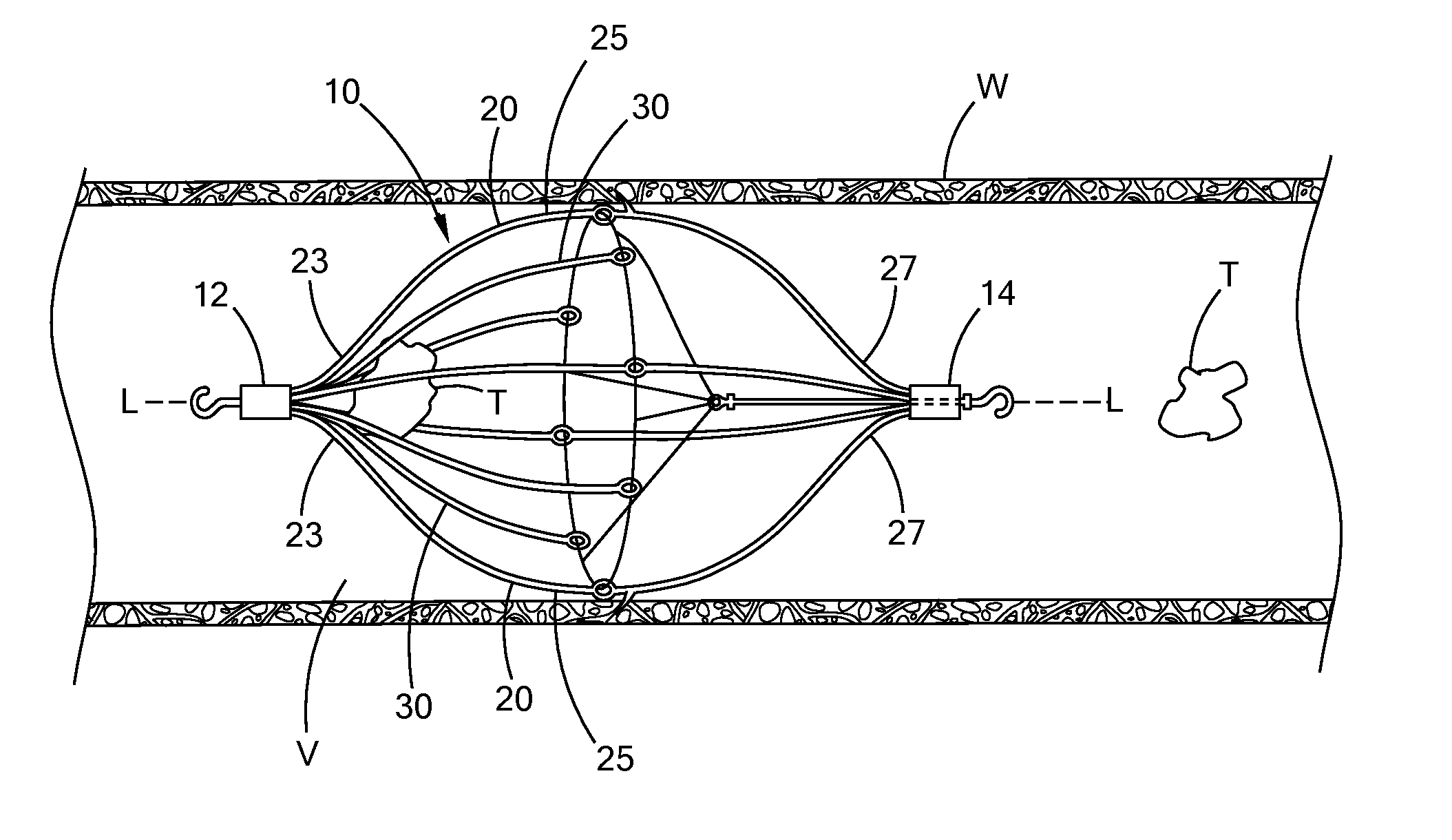
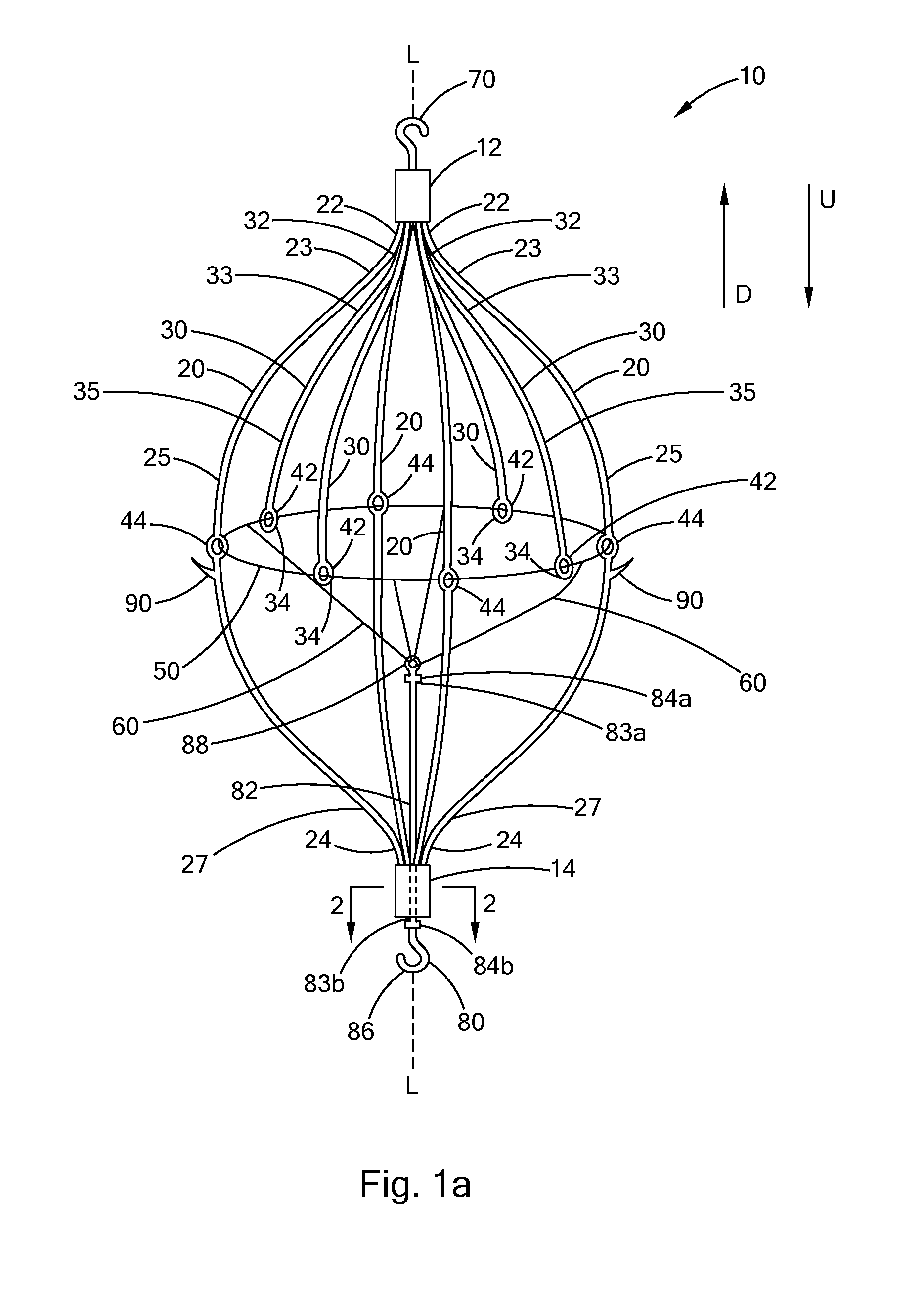
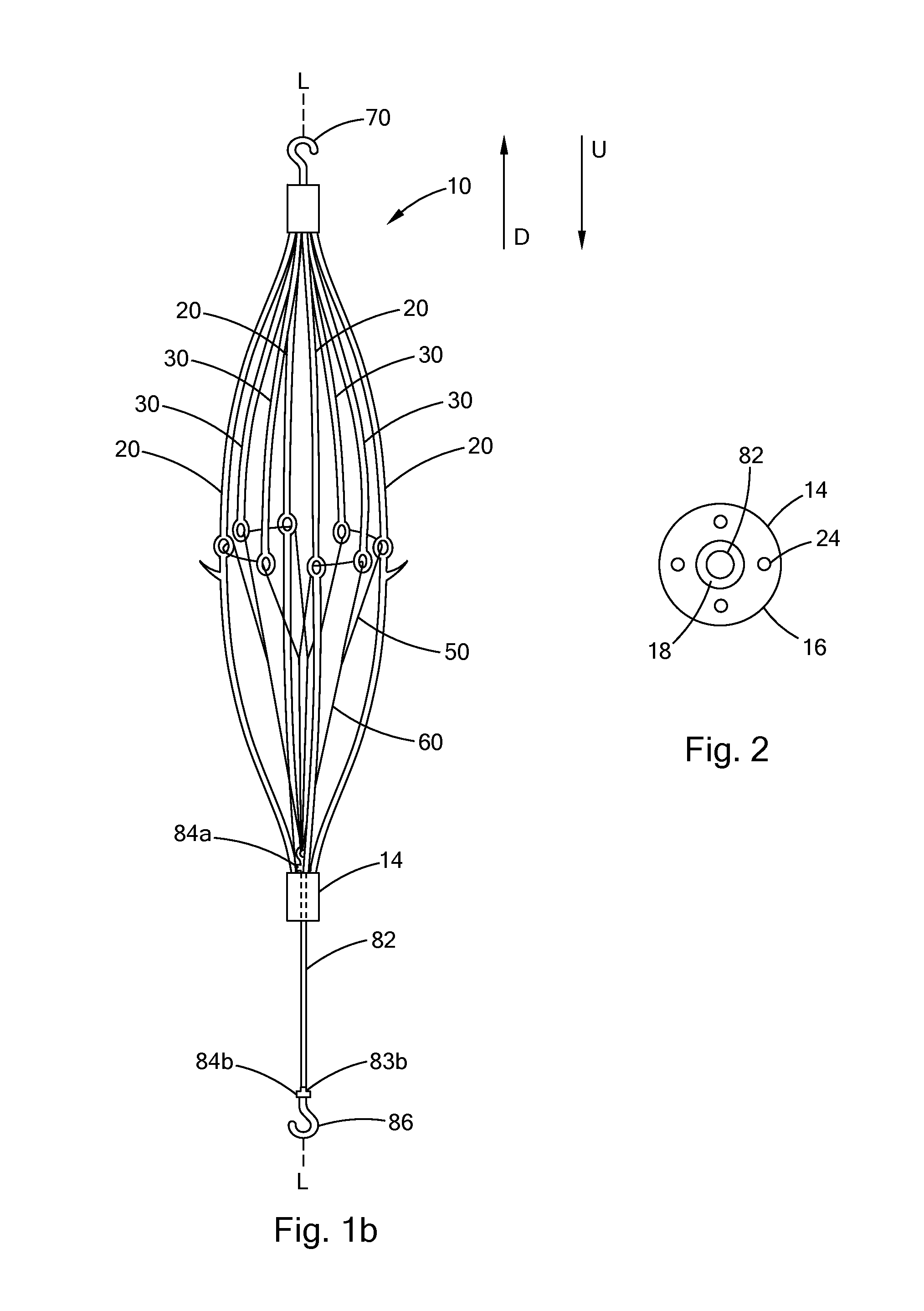
ActiveUS6951571B1Easy to replaceIncreased durabilityVenous valvesBlood vesselsImplanted deviceGuide wires
Disclosed is a valve implanting device comprising a collapsible frame, inner and outer guide wires removably connected to the collapsible frame, and a plurality of valve flaps attached to the collapsible frame. The collapsible frame is inserted into a patient's femoral vein or artery, guided to a deployment position using the guide wires, expanded using the guide wires, and stabilized using the guide wires to manipulate fixating hubs on the collapsible frame. The collapsible frame includes a central hub, a plurality of spokes, fixating hubs, gripping members, and a plurality of valve flaps.
Owner:SRIVASTAVA ROHIT
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
InactiveUS20050222532A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
This invention relates to a venous cannula for use in conjunction with cardiovascular examinations, treatments and surgery. The venous cannula is configured for two-stage drainage of oxygen-depleted venous blood from a central venous location via a peripheral venous insertion site, such as a femoral vein. The venous cannula is optimized for use in a cardiopulmonary bypass system that includes a multichannel arterial perfusion catheter. The cardiopulmonary bypass system is advantageous for use in performing standard open chest or least invasive cardiac surgical procedures.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Method of removing a vein filter
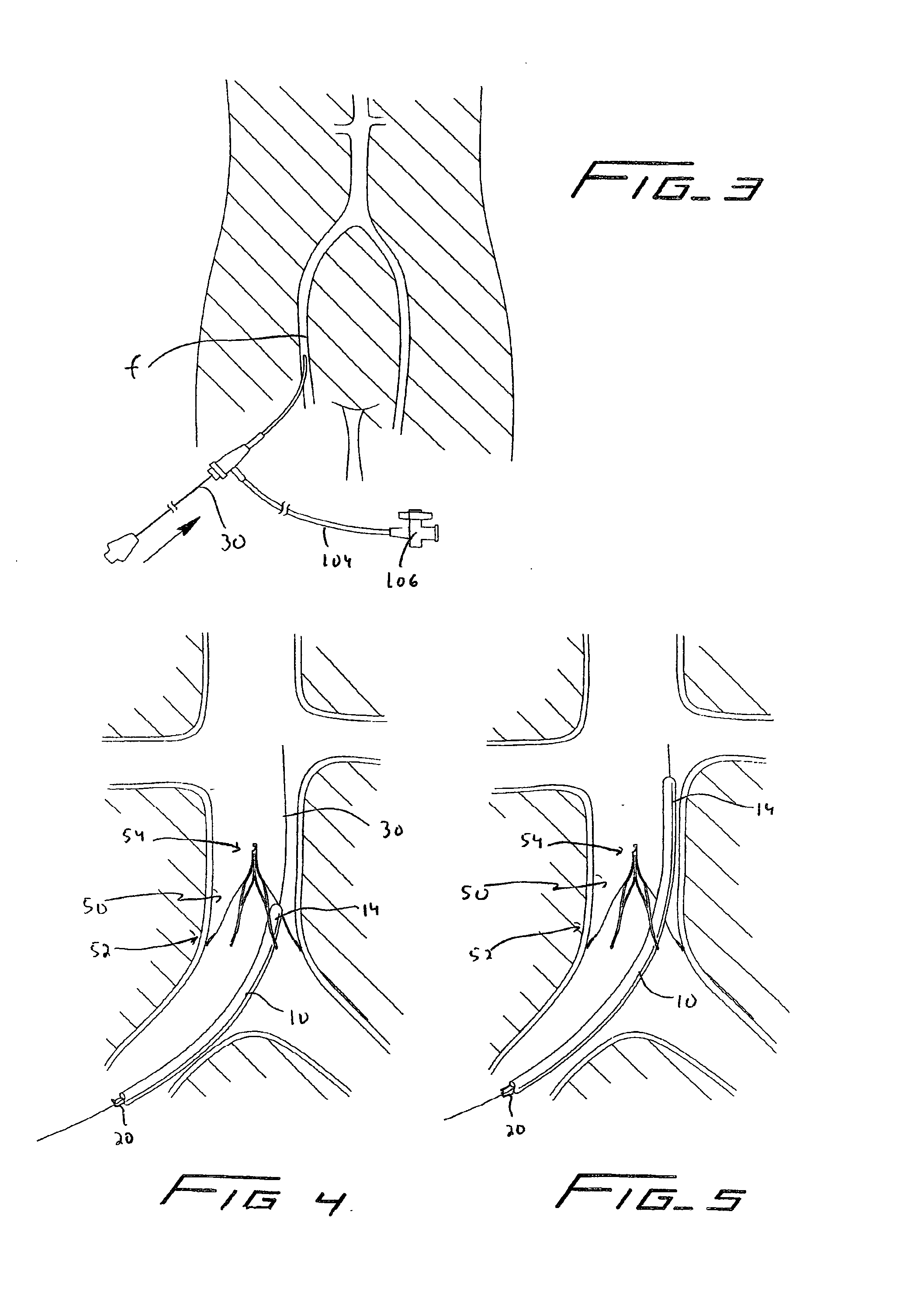
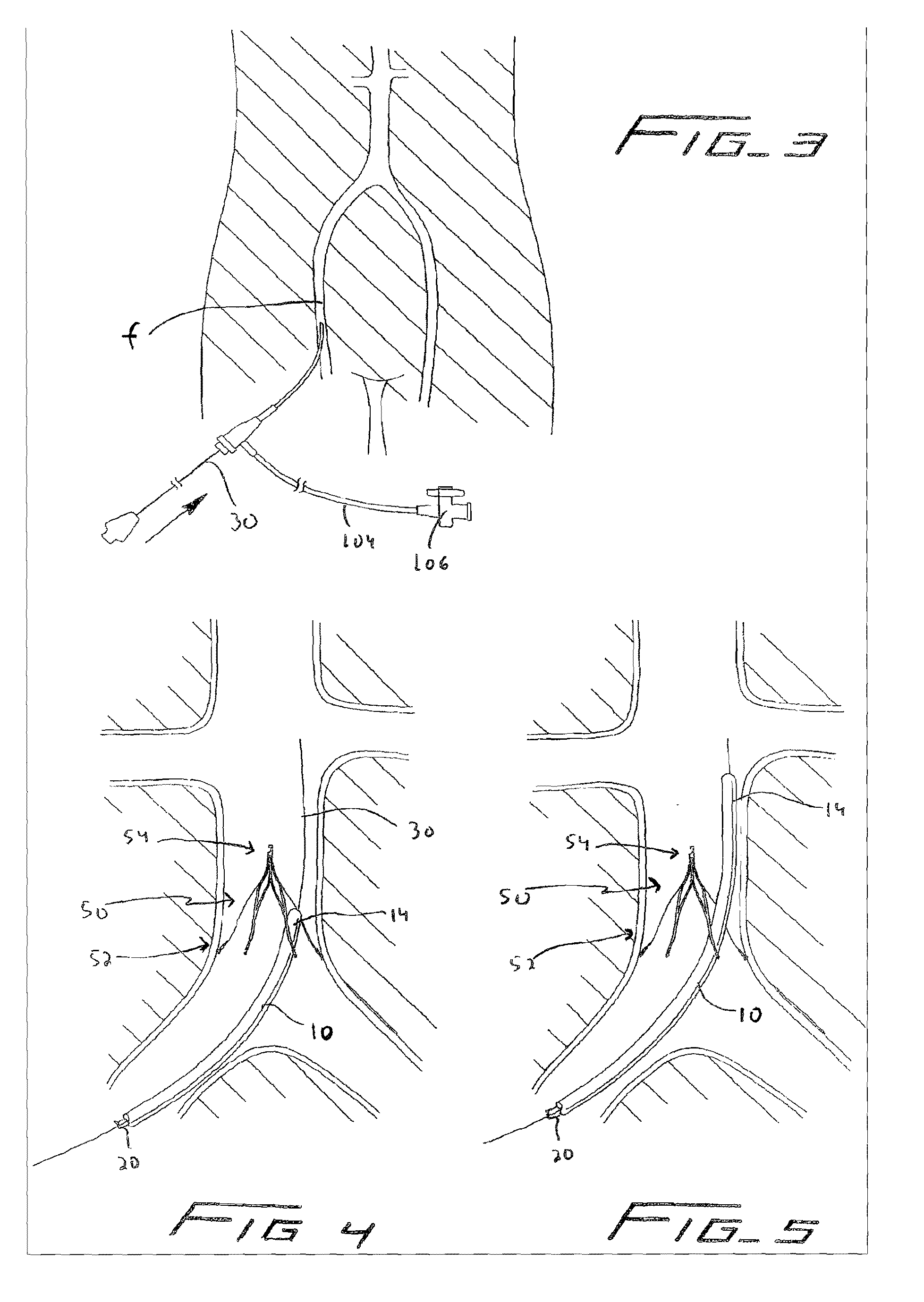
A method of removing an implanted vessel filter by a femoral approach comprising the steps of providing a catheter with a curved tip, inserting a straightening device into the catheter to move the catheter tip from a curved position to a more straightened position, advancing the catheter tip through the femoral vein and past a cranial end of the filter, withdrawing the straightening device to enable the catheter tip to return to the curved condition, and inserting a filter grasping device though the catheter and a curved catheter tip to exit a distal portion to grasp the filter.
Owner:ARGON MEDICAL DEVICES
Method of removing a vein filter
Owner:ARGON MEDICAL DEVICES
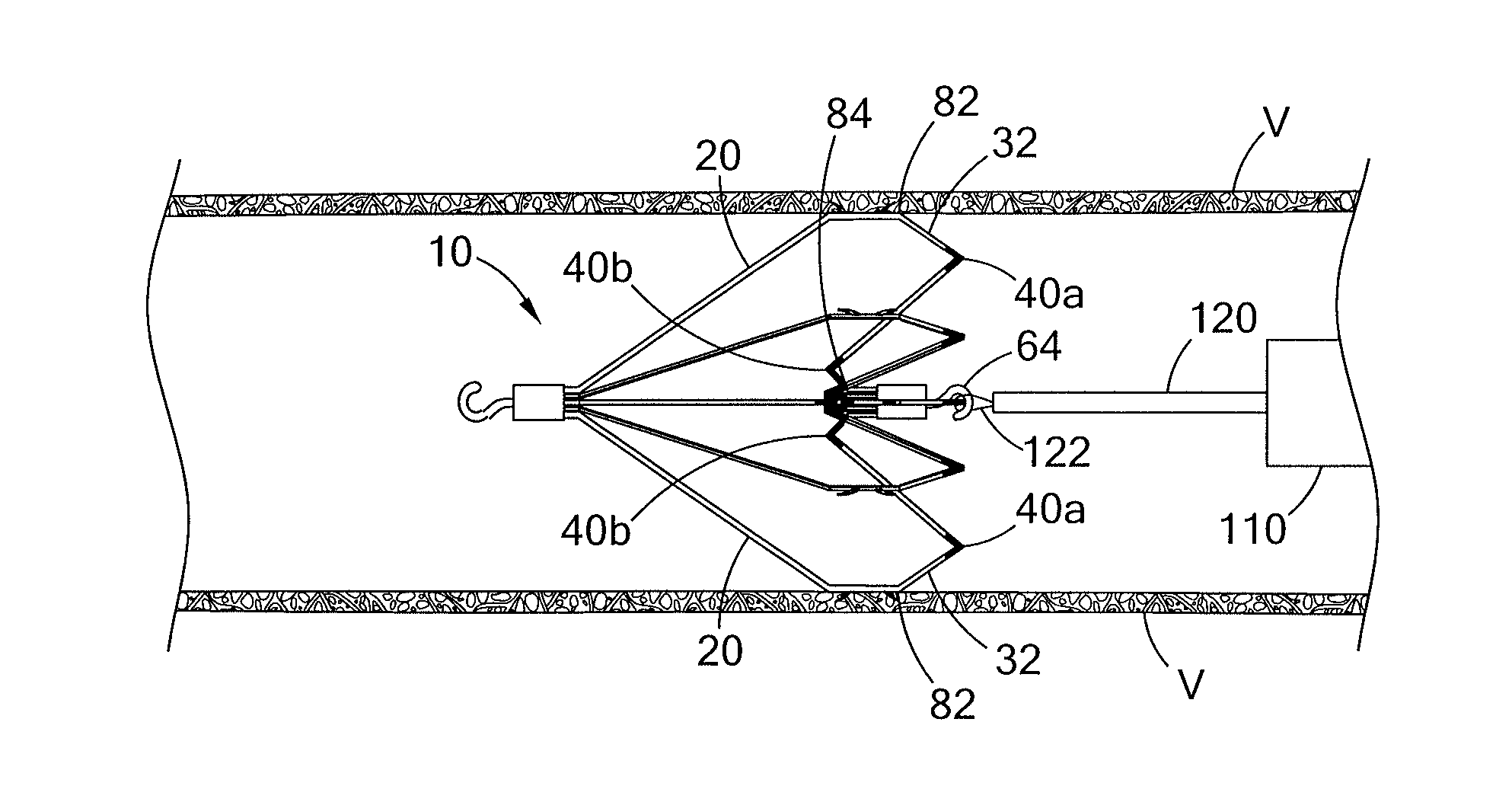
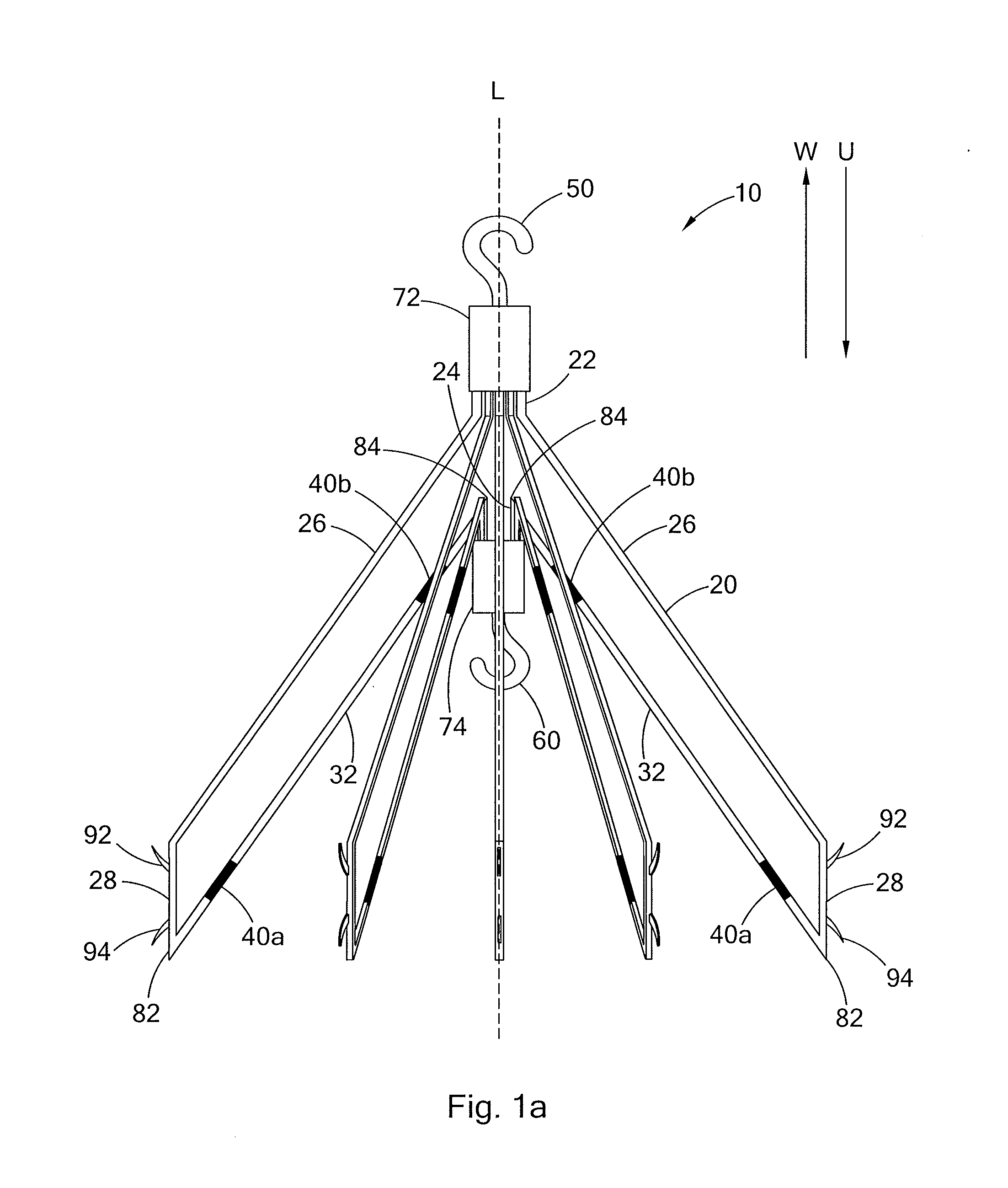
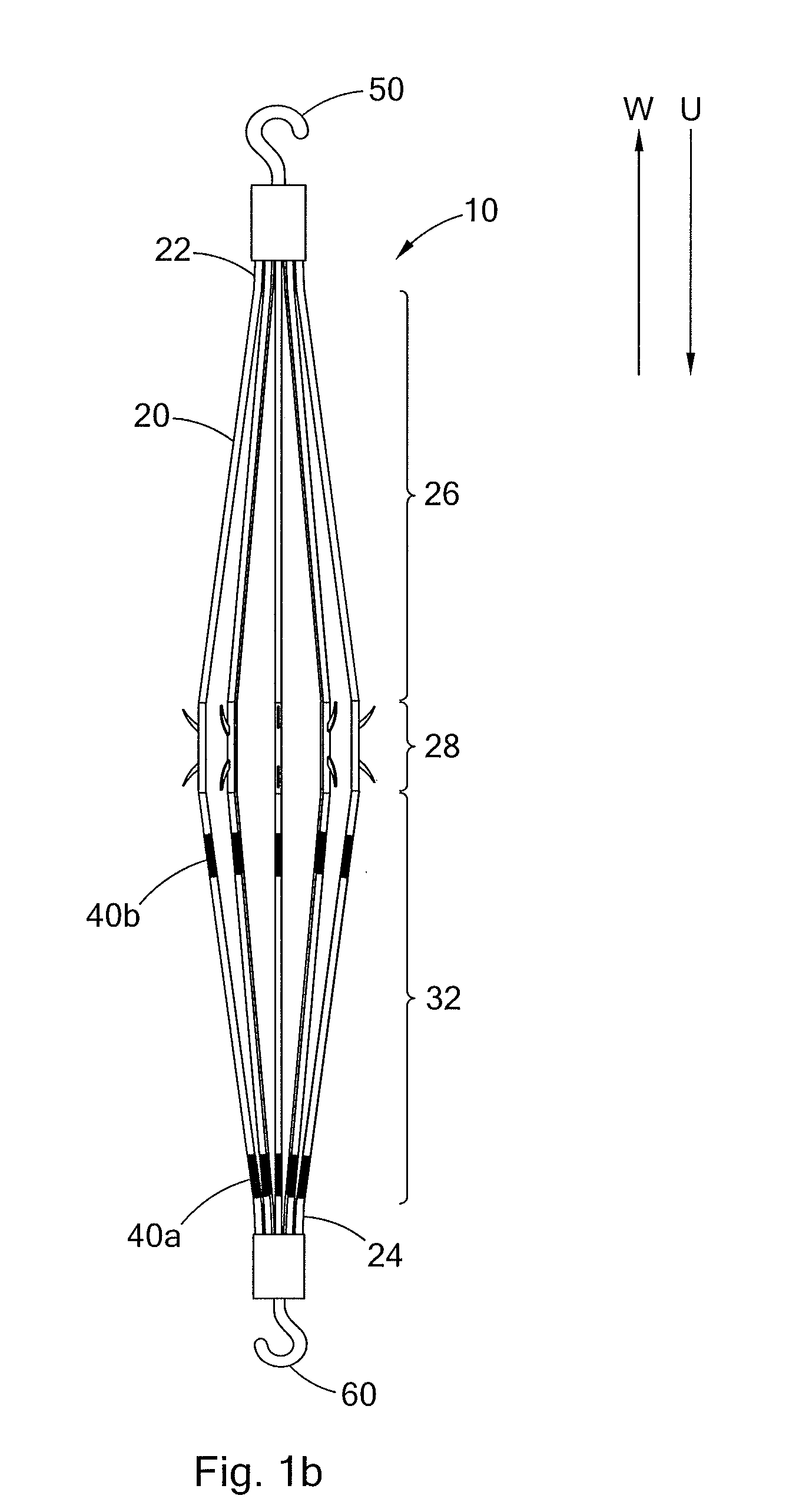
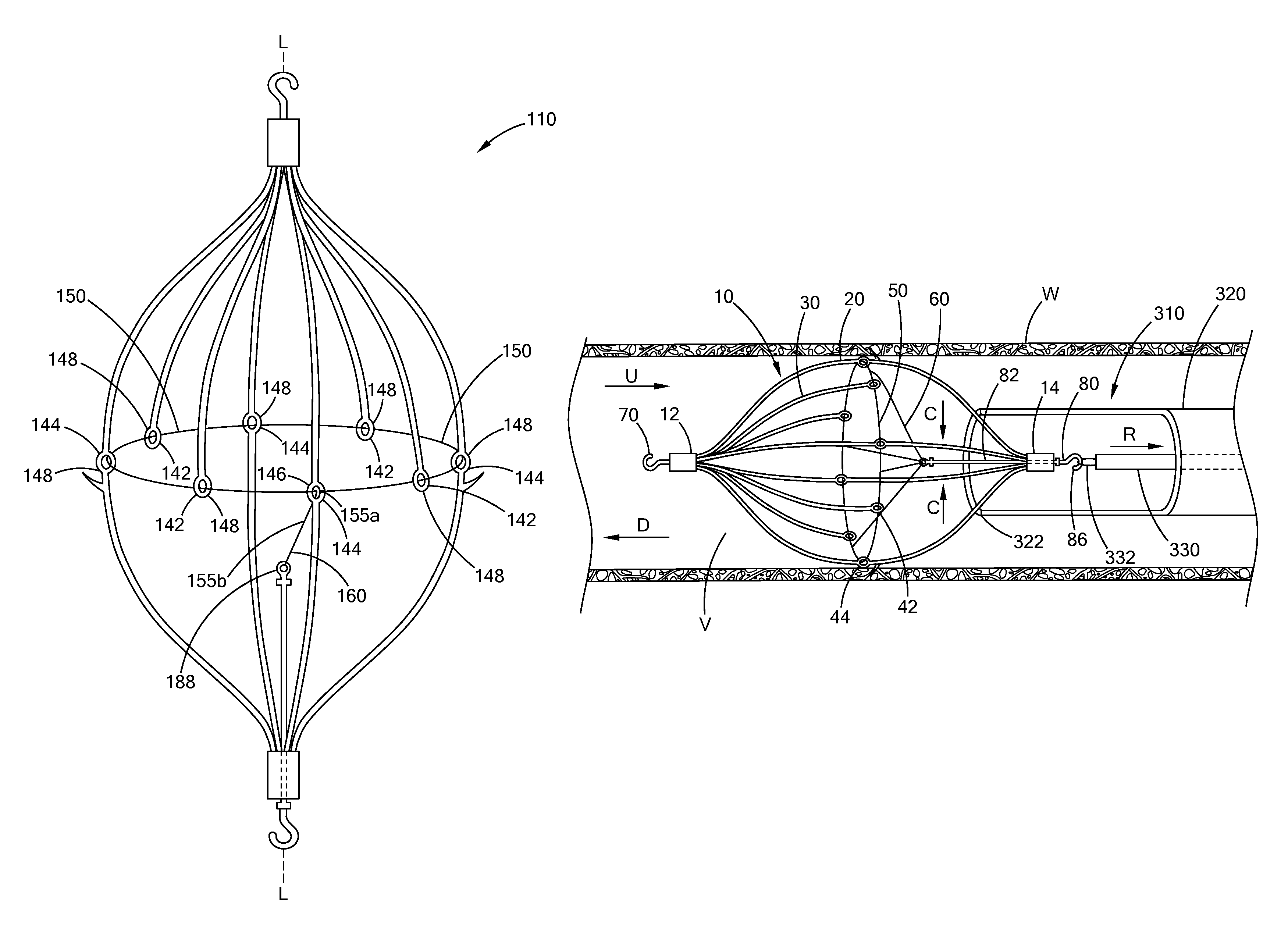
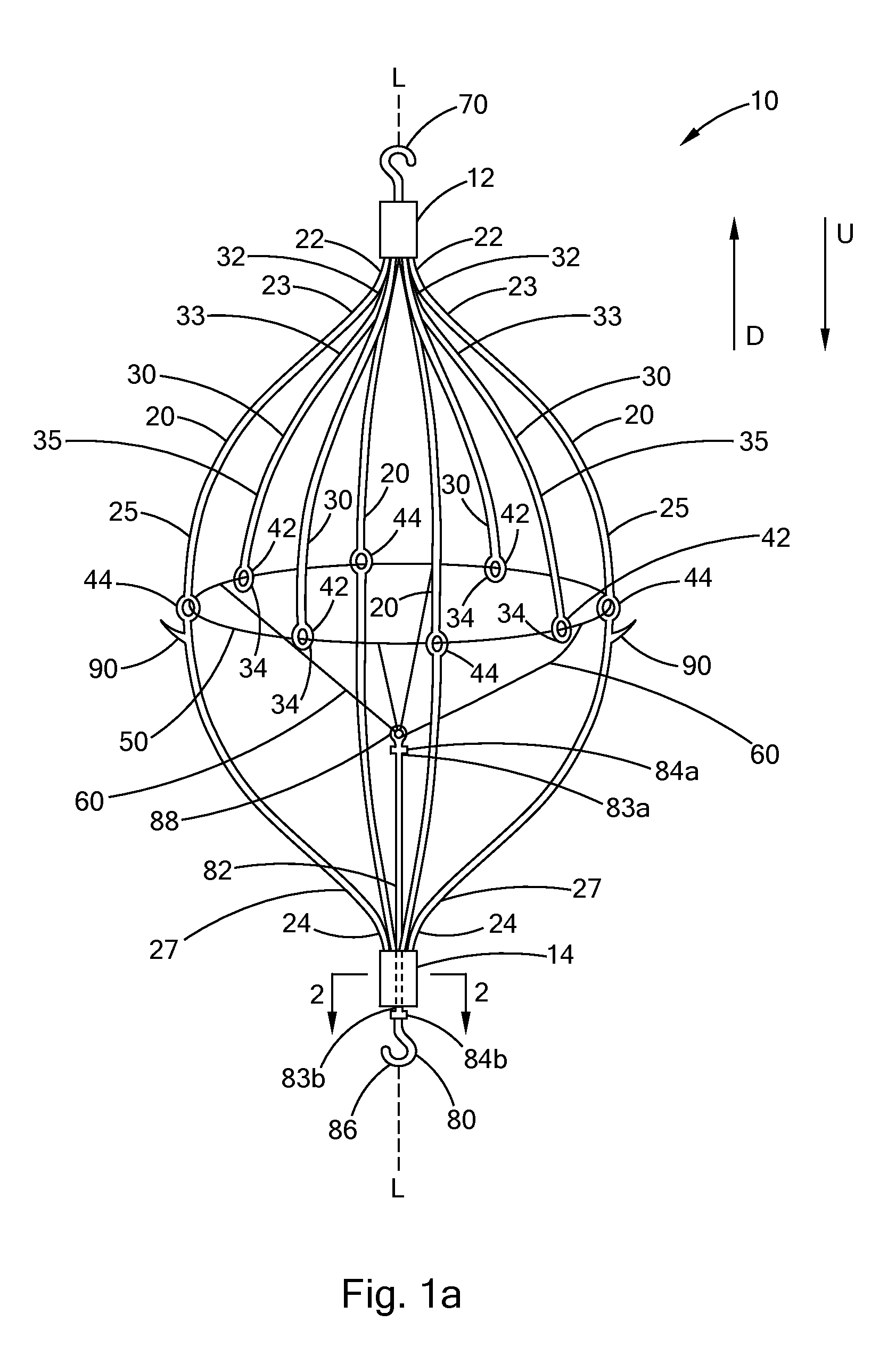
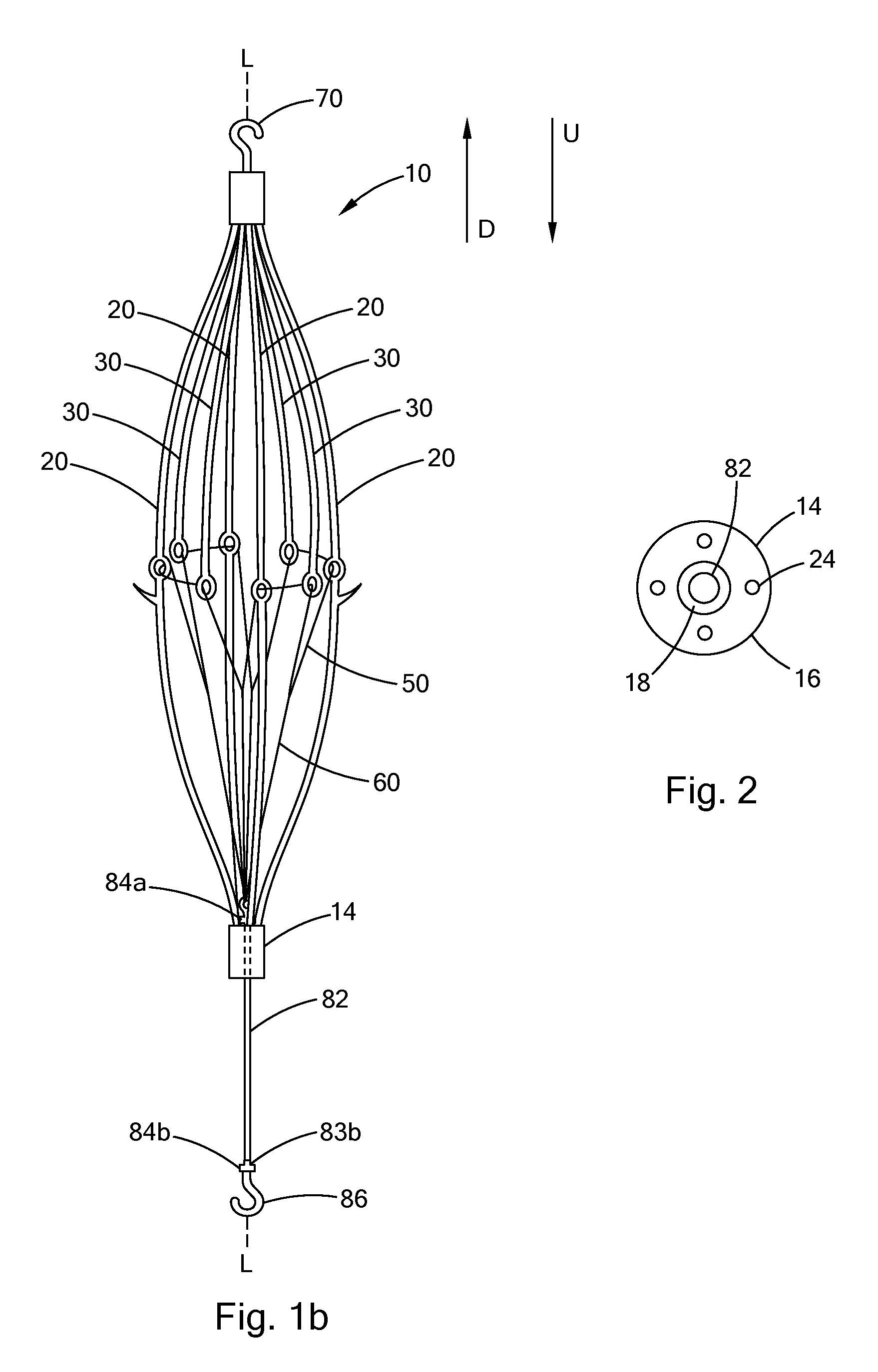
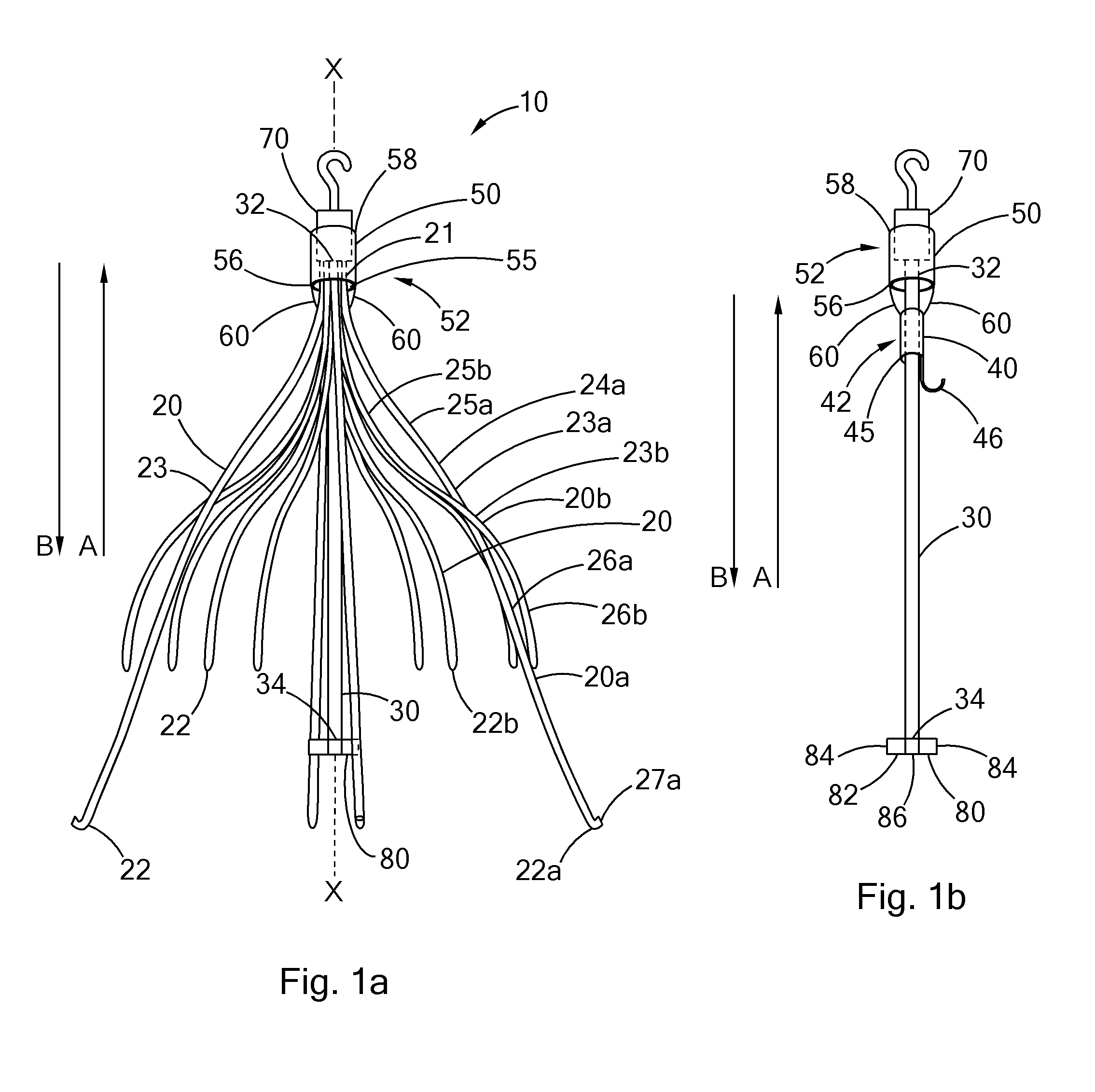
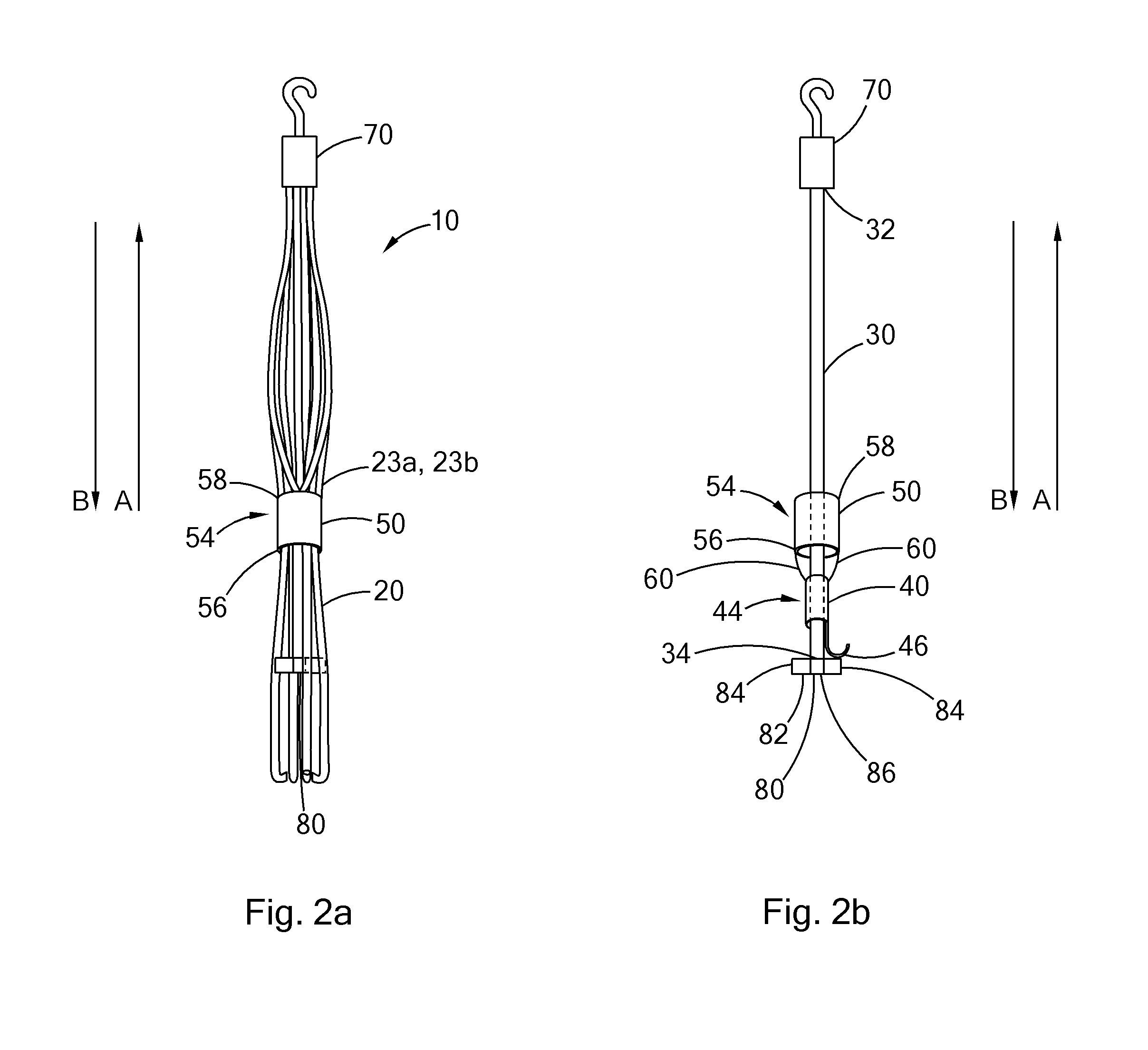
Conical vena cava filter with jugular or femoral retrieval
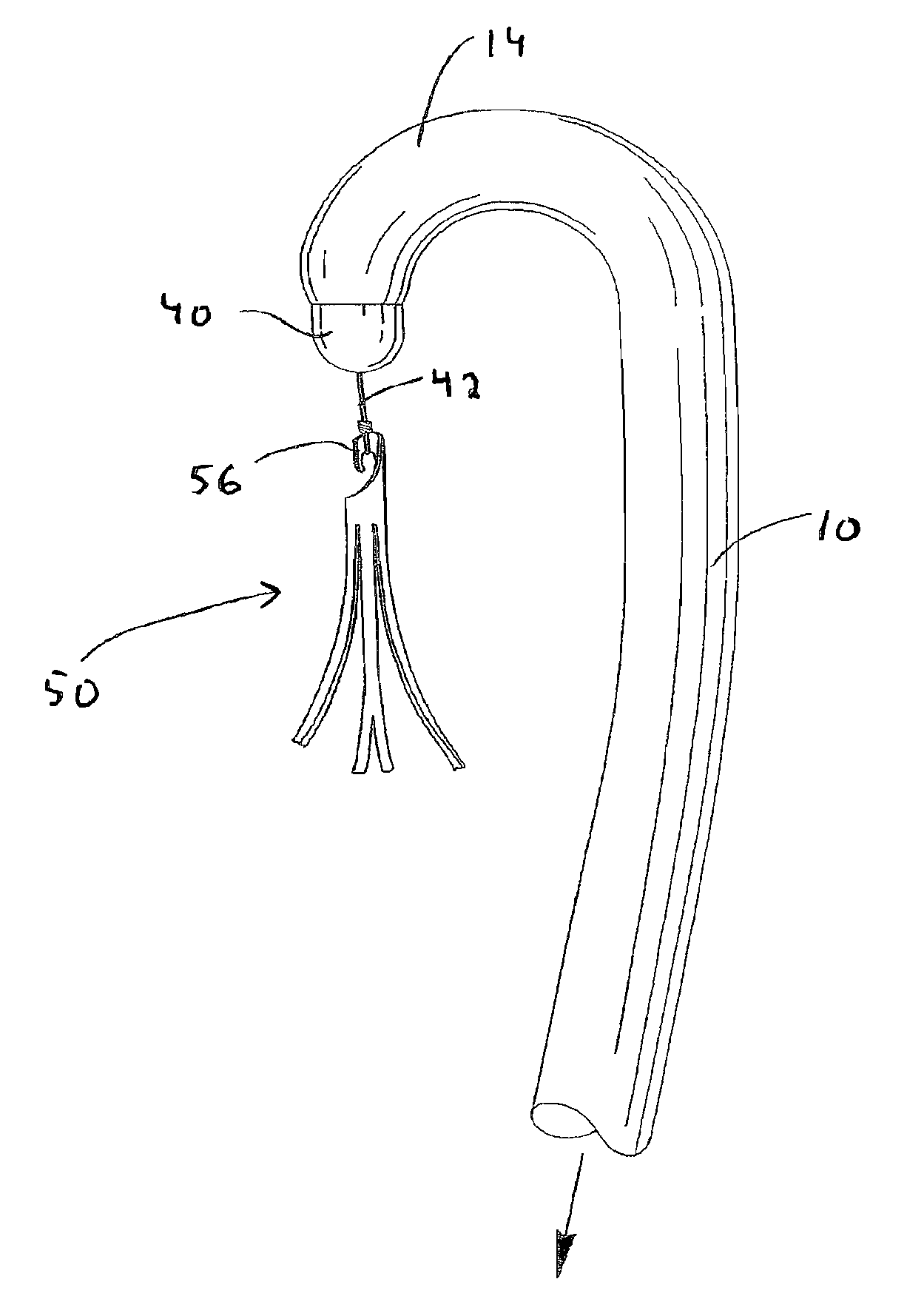
An intravascular filter configured for upstream or downstream retrieval and a method for retrieving an intravascular filter from a patient's vena cava through the patient's femoral vein. The filter includes a downstream hub, an upstream hub, a plurality of primary struts extending from the downstream hub to the upstream hub, a plurality of secondary struts extending upstream from fixed ends housed in the downstream hub to free ends, secondary strut eyelets disposed at the free ends of the secondary struts, a loop member disposed through the secondary strut eyelets, an upstream coupling element disposed with the upstream hub, and a tether extending from the loop member to the upstream coupling element.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Locally-plugged thrombus scaler
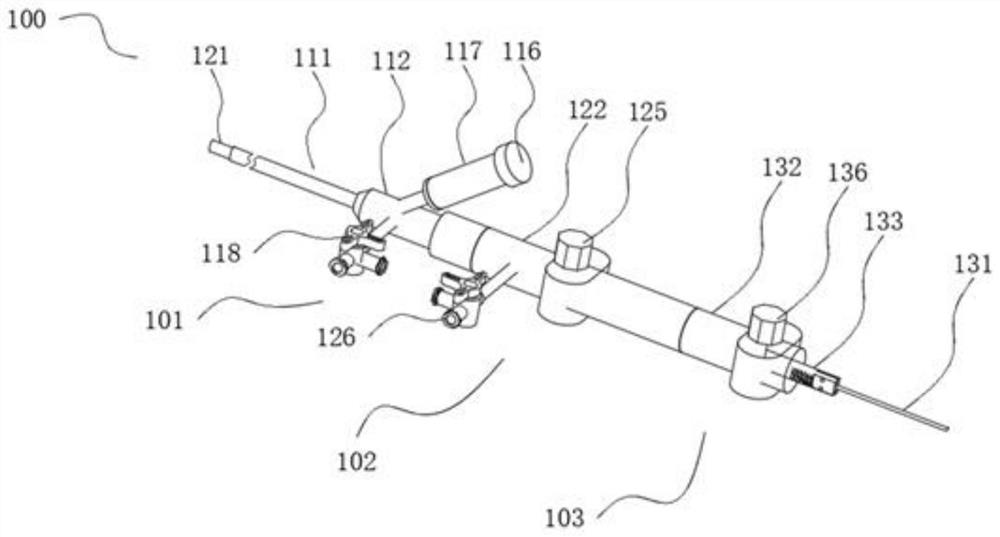
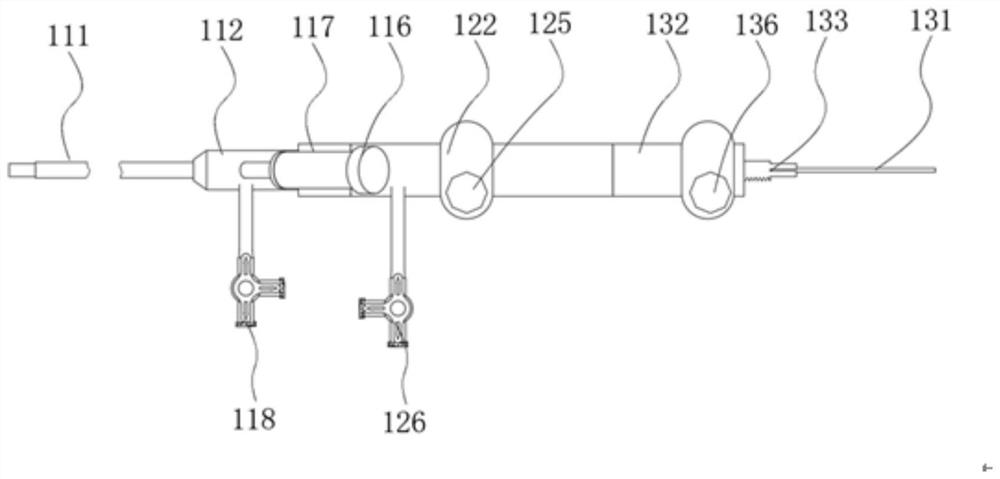
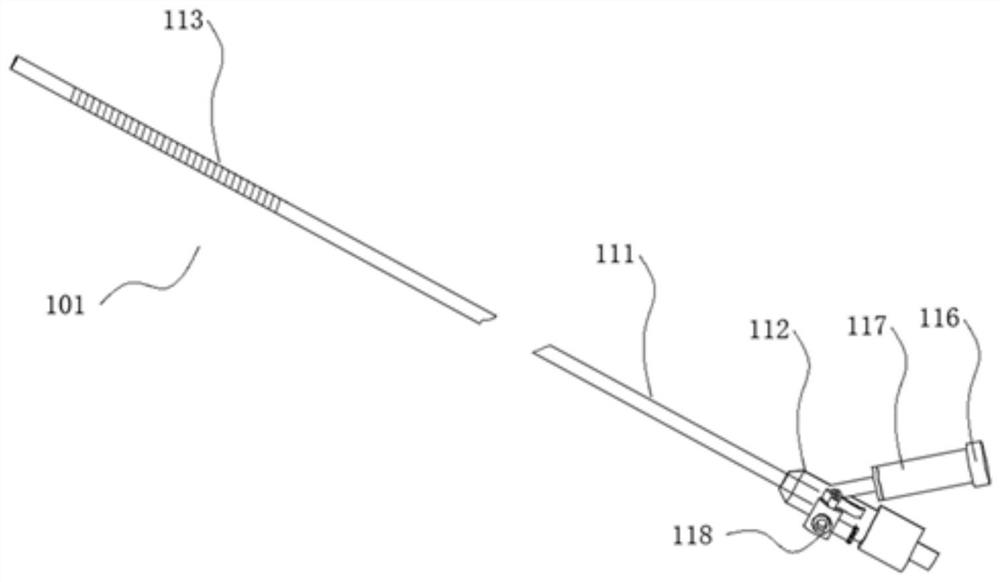
The invention provides a locally-plugged thrombus scaler, which comprises a core tube, a sleeve, a first saccule, a second saccule and a thrombus scraping skein, wherein the sleeve is sleeved outside the core tube in a movable way; the first saccule is connected to the head end of the core tube; the second saccule is sleeved outside an inner tube of the sleeve; and the thrombus scraping skein is sleeved outside the core tube in a movable way and is arranged in front of the sleeve. By the locally-plugged thrombus scaler, two saccules are expanded simultaneously to plug thrombus deposition positions on veins and form a section of closed space, and thrombus is crushed and scraped by rotating the thrombus scraping skein in the closed space. The locally-plugged thrombus scaler can scrape thrombus completely, prevent vein inner membranes from being injured, discharge the thrombus from human bodies completely and prevent crushed small thrombus blocks from remaining in the human bodies, is suitable for scraping venous thrombosis of limbs of the human bodies and is particularly suitable for scraping the thrombus at the deep positions of femoral veins of the human bodies by using a percutaneous microtrauma surgical technology.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
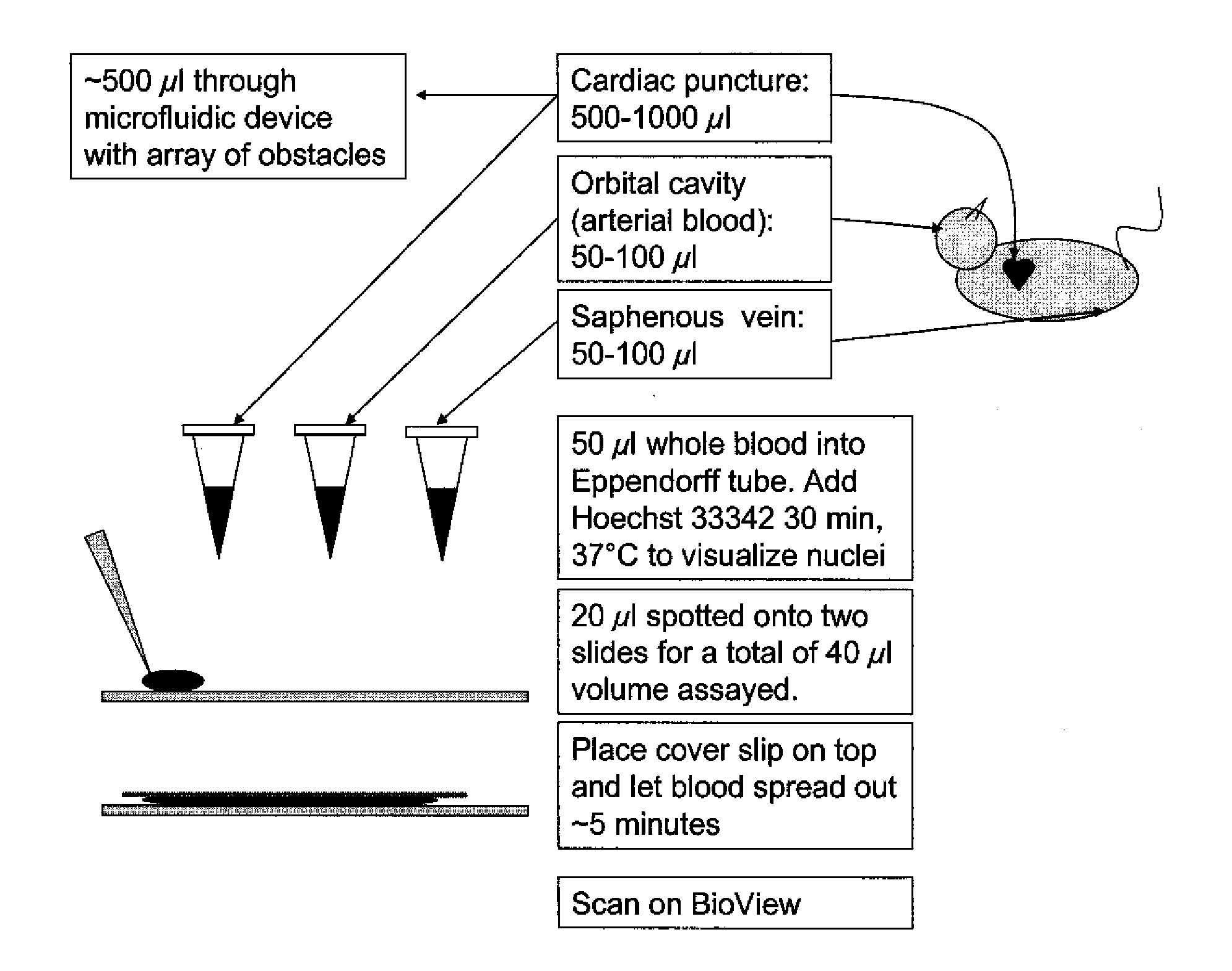
Methods for Diagnosing Cancer Using Samples Collected From A Central Vein Location or an Arterial Location
InactiveUS20090233324A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresCirculating Stem CellVein
The invention encompasses methods for selectively enriching in rare particles from blood samples harvested from the vein jugular vein the femoral vein, the subclavian vein, or an artery. These rare particles can be circulating tumor cells, circulating stem cells, or fragments thereof. Blood samples harvested from different sources can contain higher or lower concentrations of rare particles. The rare particles can be enriched by applying the blood samples to a microfluidic device with a two dimensional array of obstacles.
Owner:CELLECTIVE DX CORP
Methods and devices for treating heart failure
Systems and methods for delivering a miniaturized blood pump configured to draw partially desaturated blood via the femoral vein from the inferior or superior vena cava. A cannula connected to the pump exits the femoral vein and is connected to the femoral artery with a cannula or vascular graft. The pump receives power from a percutaneous lead which runs parallel to the flexible cannula and then exits via a percutaneous opening in the skin. The pump in the venous system removes venous blood and pumps it into the femoral artery. In so doing pressure in the aorta is increased and back pressure in the venous system is decreased.
Owner:WAMPLER RICHARD
Intrapelvic perfusion therapy with cancer therapeutic agent and apparatus for intrapelvic perfusion with cancer therapeutic agent
An intra pelvic cancer therapeutic agent perfusion apparatus and method for administering a cancer therapeutic agent to and recovering same from a cancer tissue site within the pelvis. The tip of a first sheath is percutaneously inserted into the femoral artery and the tip of a second sheath is inserted into the femoral vein. A first balloon catheter is inserted into the aorta through the femoral artery and a second balloon catheter is inserted into the vena cava through the femoral vein. The first balloon catheter is used to block the blood flow and the second balloon is inflated to form an intravenous closed region between the site of insertion in the vena cava and a lower limb side venous site. A body fluid containing a cancer therapeutic agent is administered to the intra arterial closed region through the first sheath and is removed therefrom through the second sheath.
Owner:KUMAZAKI TATSUO +1
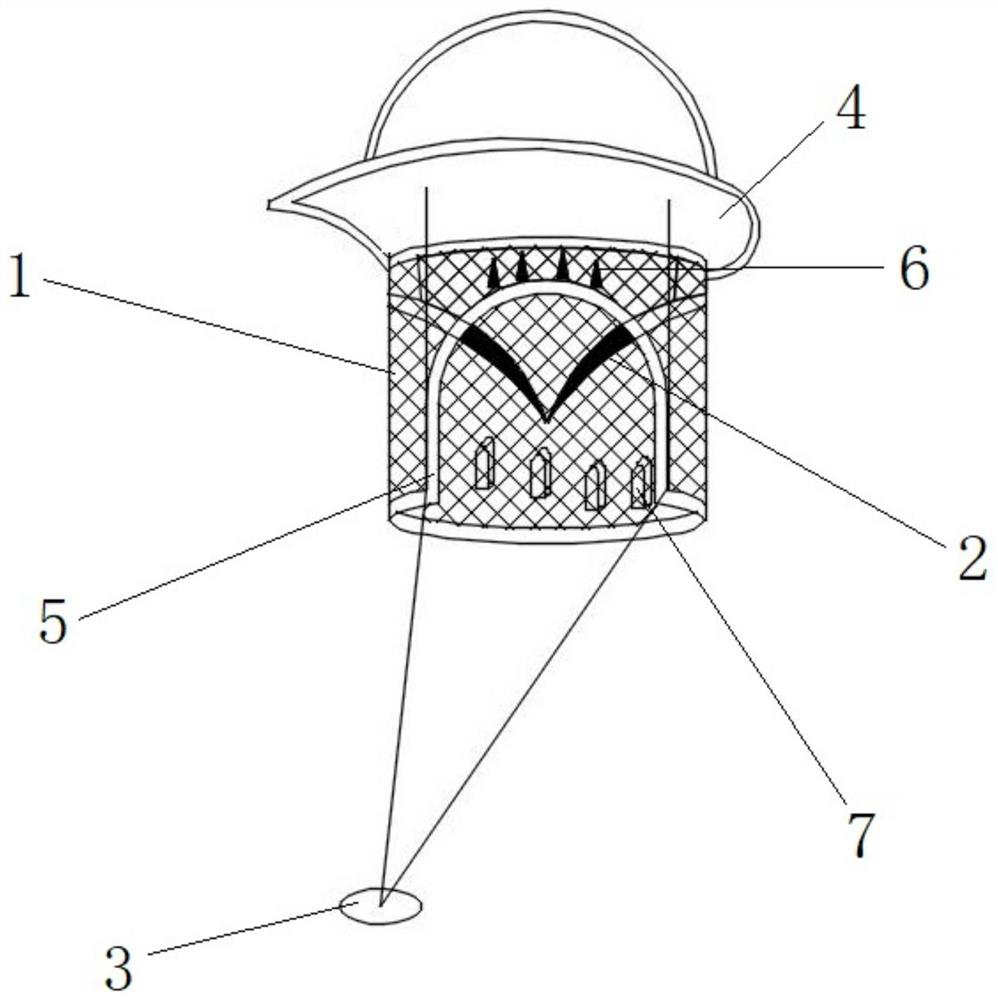
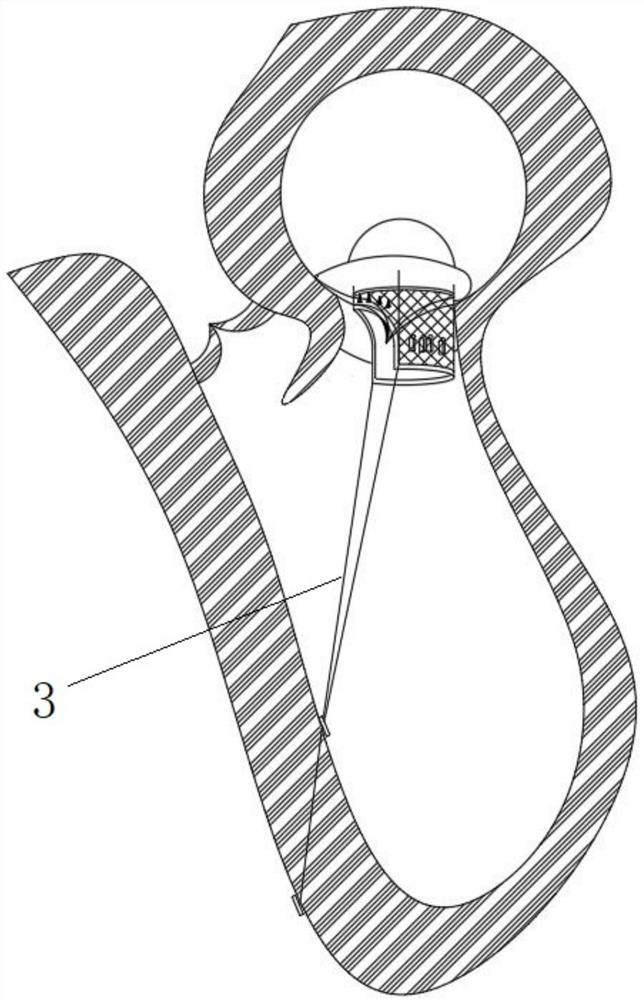
Implantable duct system connecting the intrahepatic portal vein to the femoral vein for establishing a subcutaneous porto-systemic shunt and simultaneously providing a durable access to the portal vein
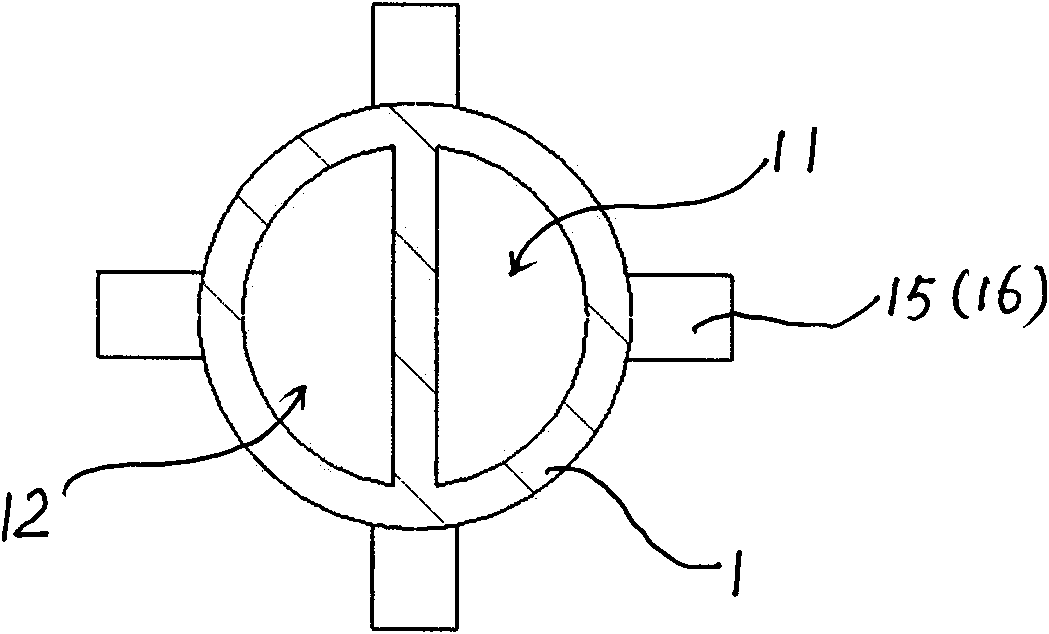
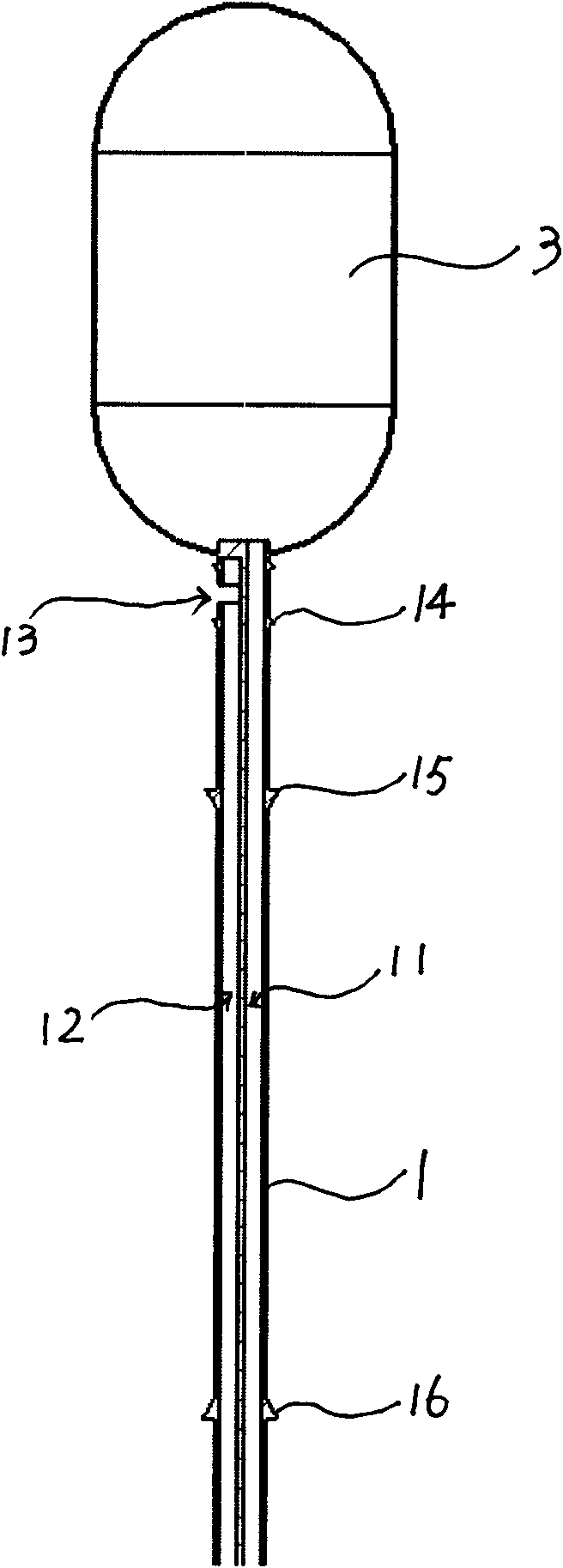
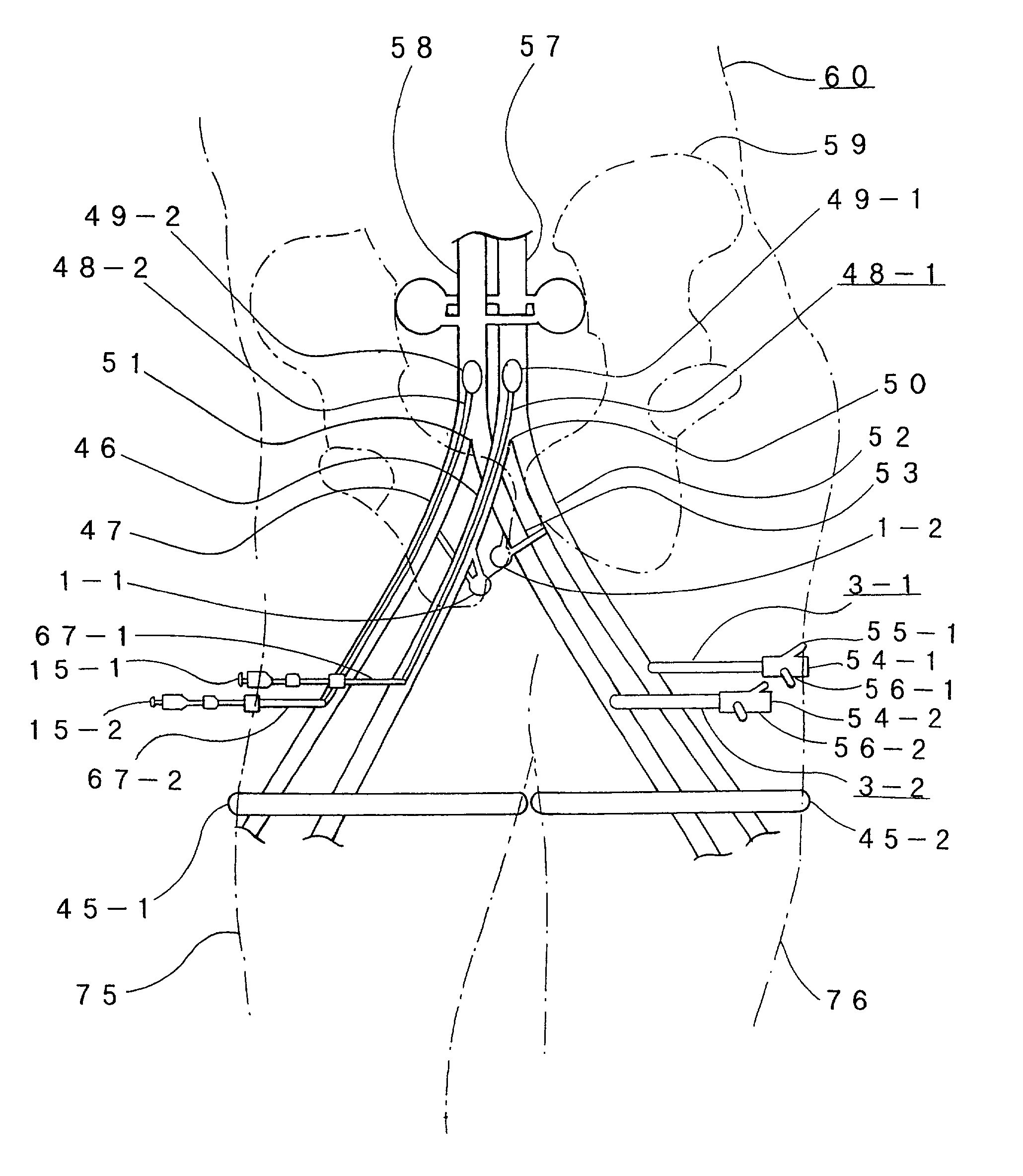
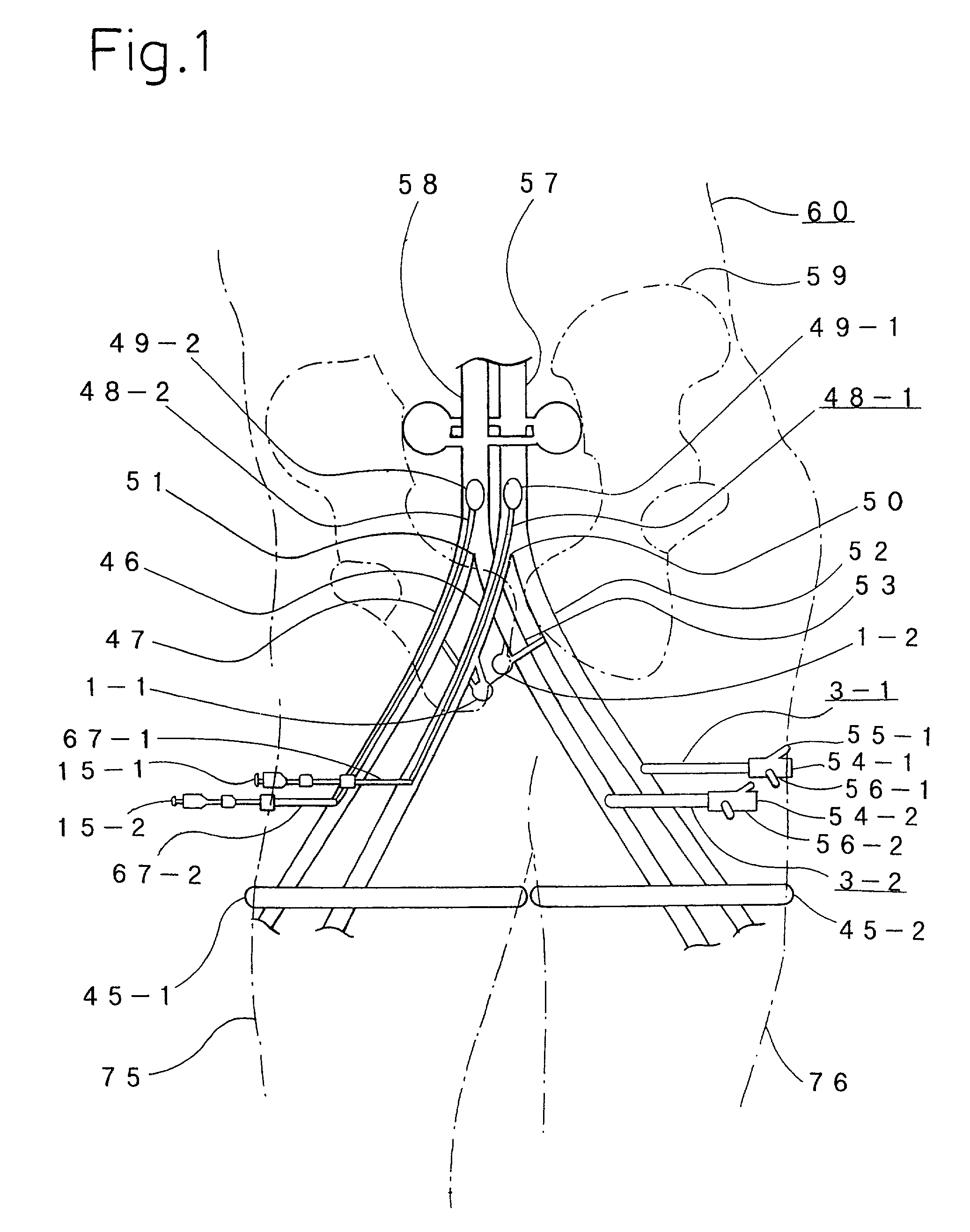
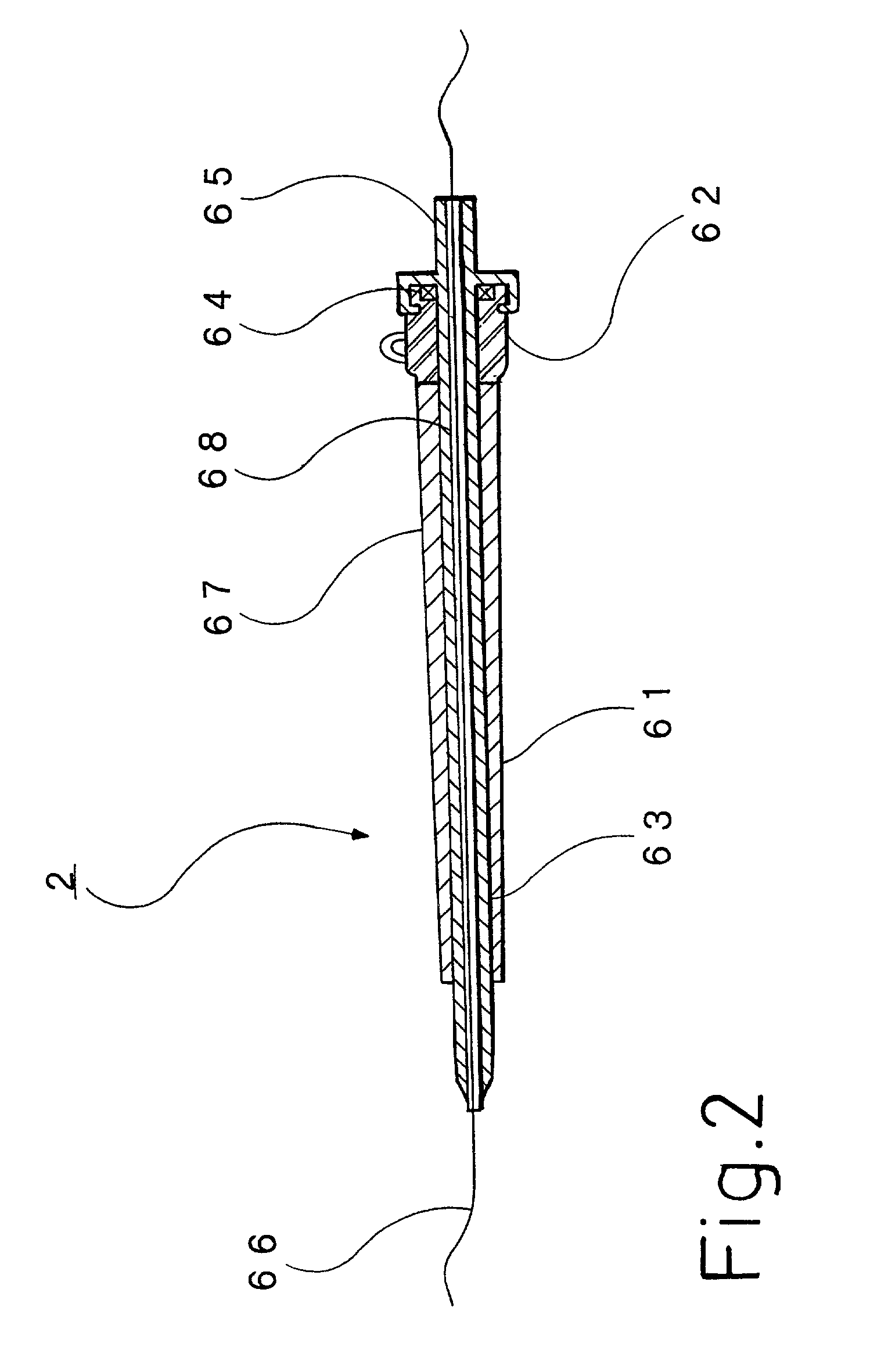
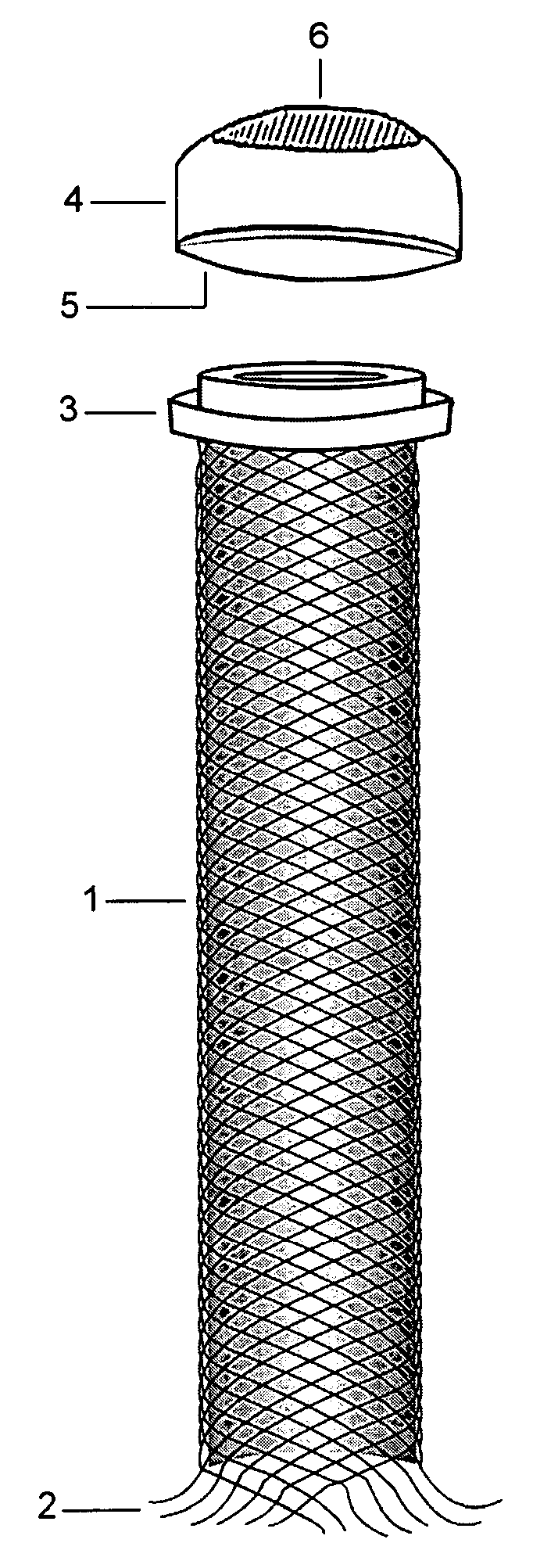
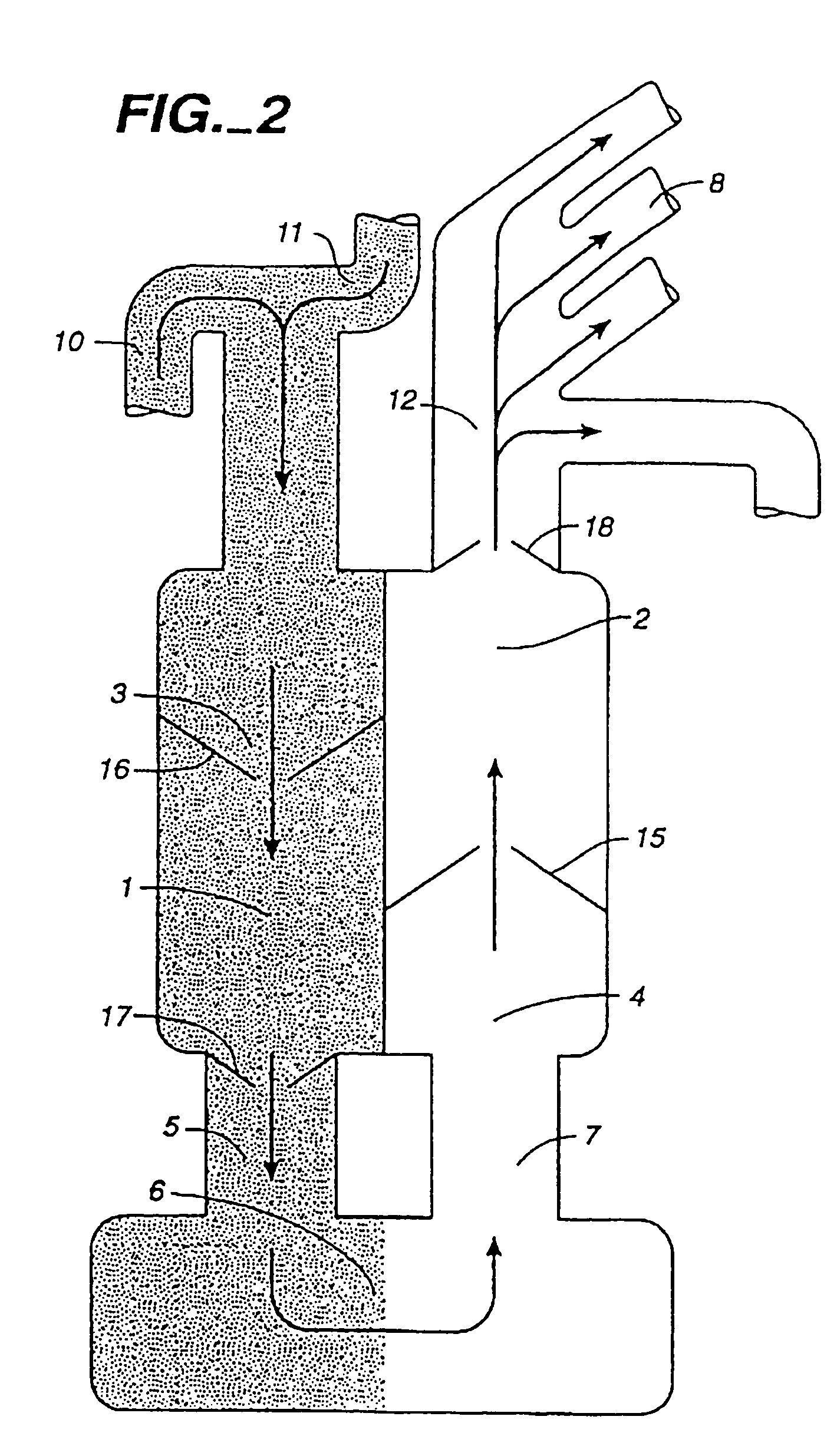
A set (FIG. 1&2) designed to provide a durable access to the portal vein and to divert portal blood to the systemic circulation in order to relieve congested portal system. The set is composed of a duct (1) and a shunt tube (7). The duct is composed of a covered flexible tubular braid with two opened ends. One end has flaring edges and forms the inner opening (2) while the other end is sealed to form a hub (3). To insert the duct into the intrahepatic portal vein through the percutaneous route the duct is mounted over a puncture needle (13) and contained in a small-constrained diameter by means of a peel-away sheath (16). After the position of the inner opening of the duct has been adjusted to the desired location the said sheath is peeled away to allow the duct to expand. The shunt tube (7) is composed of a long flexible vascular graft (8) equipped at its upper end with a head (9) while its lower end is free to be sutured with the femoral vein (21). The said head is cupped at the inner side (10) to fit in the hub (3) of the said duct (1), while back of the said head has a window covered with an elastic membrane (11). This shunt tube is applied in case both a portal access and a porto-systemic shunt are required. In case of only a durable portal access is needed, a plug (4) with a central window covered by an elastic membrane (6) is applied to the hub of the duct. This prevents bleeding from the duct and simultaneously allows entrance of needles, catheters, etc. to the duct and portal vein.
Owner:GABAL ABDELWAHAB M
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
Conical vena cava filter with jugular or femoral retrieval
A removable intravascular filter having a filtering configuration for capturing thrombi in a blood vessel and a retrieval configuration for removal from the blood vessel. The filter may be implanted in a patient's vena cava and may be removed from the vena cava through the patient's jugular or femoral vein. A method of removing an intravascular filter from a patient's vena cava through the patient's femoral vein is also provided.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Device for pneumatic treatment of an inferior limb having peripheral arteriopathy problems
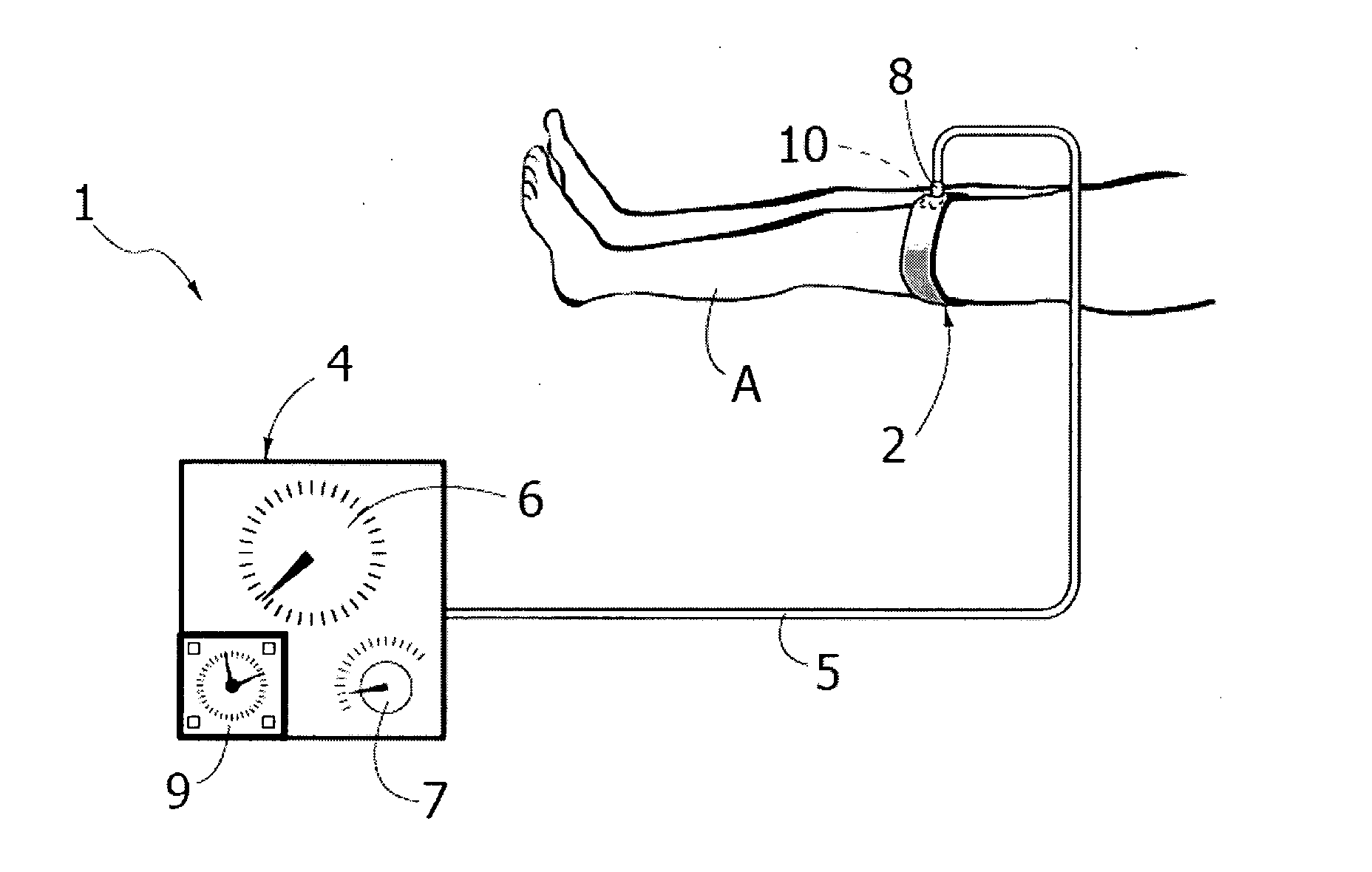
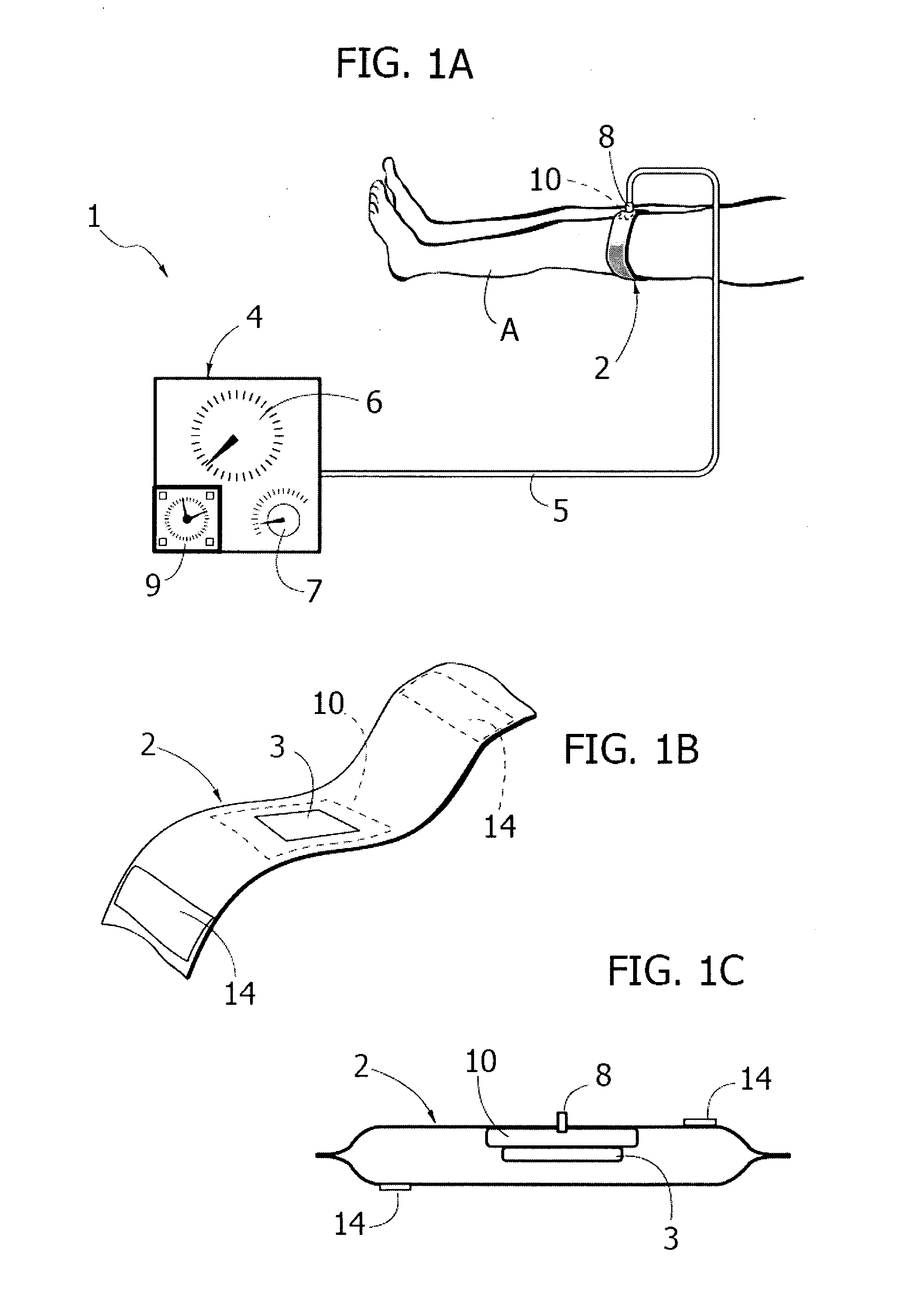
A device (1) for compression treatments of an inferior limb (A) of a subject, said device (1) comprising an inflatable element (2) apt to being placed in contact with a portion of said inferior limb (A) to exert an action of compression and decompression on said portion of inferior limb (A), wherein the inflatable element (2) includes a rigid element (3), positionable on the medial part of the thigh of the subject for compression of the internal femoral vein.
Owner:LONDON EQUITABLE & ITS CAPACITY TRUSTEE OF THE THINK TANK TRUST
Intravascular mild hypothermia therapy device
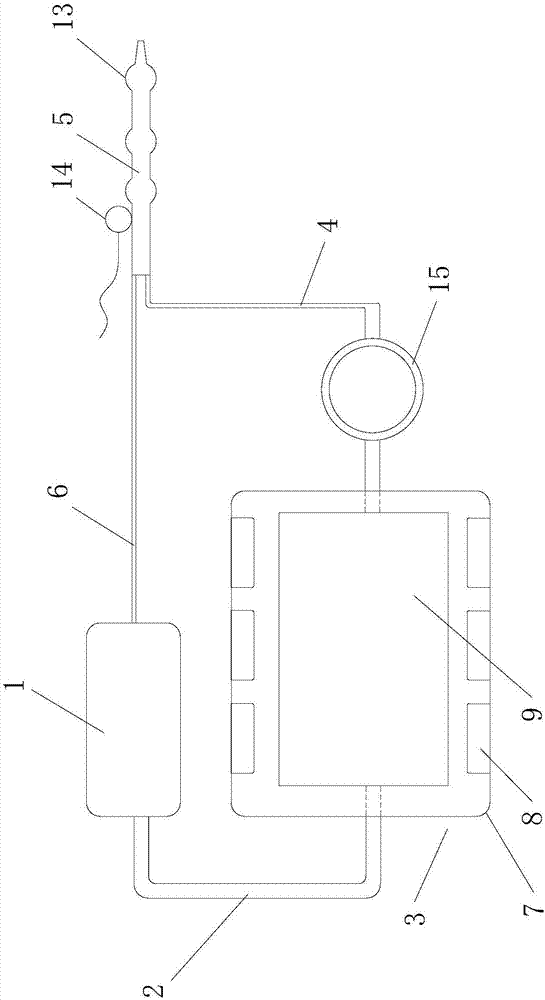
The invention relates to an intravascular mild hypothermia therapy device which comprises a normal saline storage box, a first pipeline, an electronic refrigerator, a second pipeline, a central venous catheter and a third pipeline. The normal saline storage box and the electronic refrigerator are communicated through the first pipeline. The electronic refrigerator and the central venous catheter are communicated through the second pipeline. The central venous catheter and the normal saline storage box are communicated through the third pipeline. A pushing pump is arranged on the second pipeline. The liquid inlet end of a honeycomb meshed heat exchange pipe inside the electronic refrigerator is communicated with the first pipeline, and the liquid outlet end of the honeycomb meshed heat exchange pipe is communicated with the second pipeline. Normal saline inside the normal saline storage box is conveyed by the pushing pump into the honeycomb meshed heat exchange pipe and then cooled by an electronic refrigeration sheet into low-temperature normal saline, one end of the central venous catheter enters a lower plenum central vein from a human body femoral vein puncture opening, a temperature difference between the circularly-flowing normal saline and blood inside the central venous blood vessel, and heat exchange between the surface of the central venous blood vessel and the blood in the patient blood vessel is performed.
Owner:FOSHAN BOJUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Thrombus prevention apparatus and methods
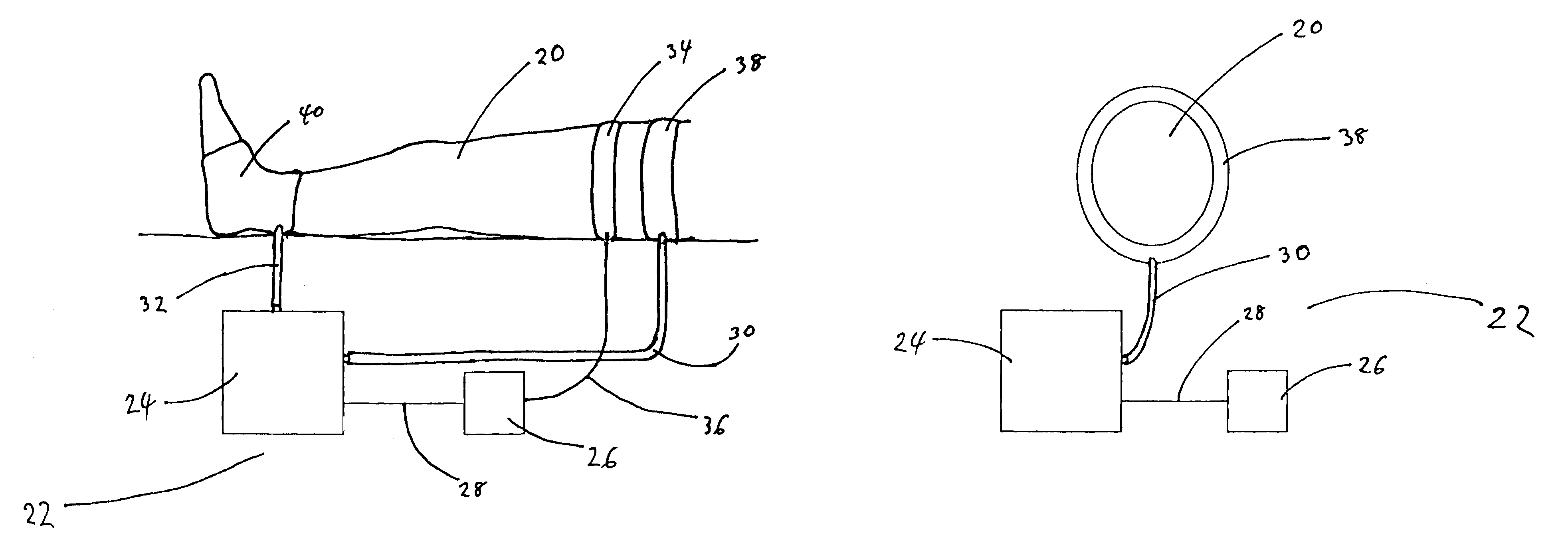
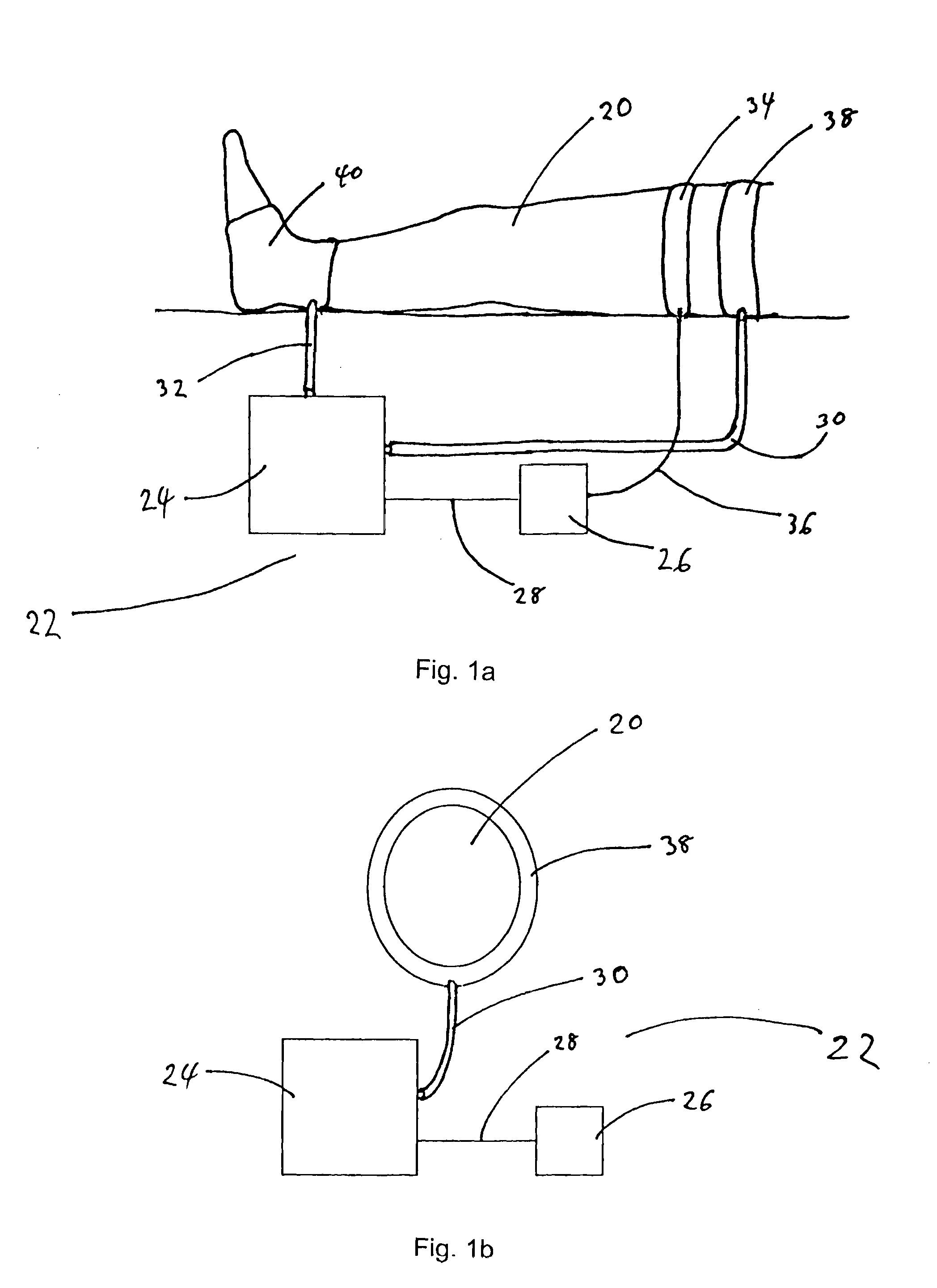
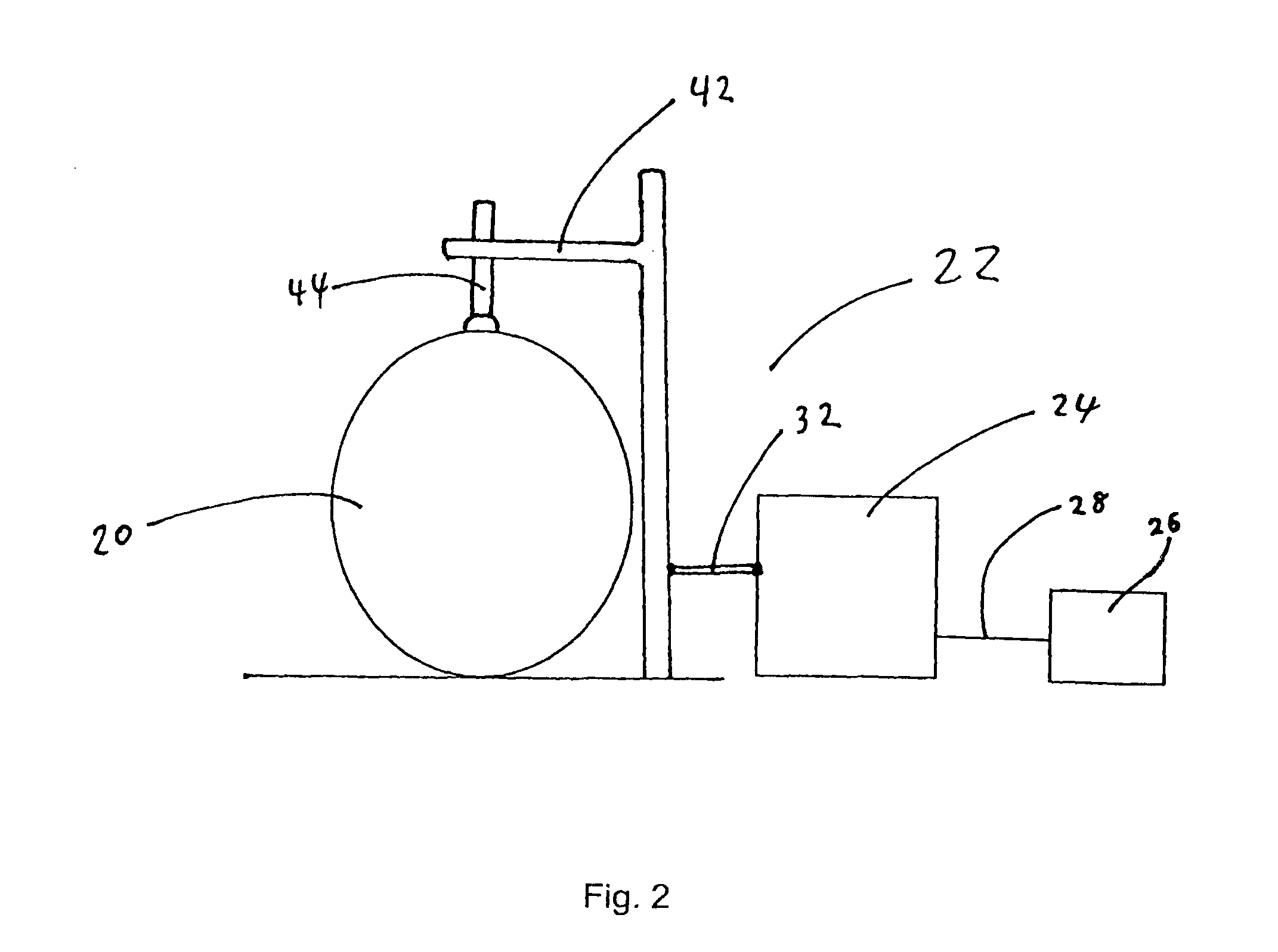
An apparatus and methods for the prevention or minimization of lower extremity venous thrombosis comprising an impedance component disposed at the proximal end of the lower extremity and a compression component disposed at the distal end of the lower extremity. The proximal impedance component is activated to impede return venous blood flow, preferably on the femoral vein, until blood volume in the lower extremity is maximized. In response to deactivation of the proximal compression component, the distal compression component is activated to assist return venous blood flow. The apparatus and methods enhance blood circulation in the lower extremity by increasing washout of stagnant blood from the lower extremity, particularly from the venous sinuses and valve cusps where thrombosis tends to form.
Owner:MEDSURG DEVICES
Conical vena cava filter with jugular or femoral retrieval
An intravascular filter configured for upstream or downstream retrieval and a method for retrieving an intravascular filter from a patient's vena cava through the patient's femoral vein. The filter includes a downstream hub, an upstream hub, a plurality of primary struts extending from the downstream hub to the upstream hub, a plurality of secondary struts extending upstream from fixed ends housed in the downstream hub to free ends, secondary strut eyelets disposed at the free ends of the secondary struts, a loop member disposed through the secondary strut eyelets, an upstream coupling element disposed with the upstream hub, and a tether extending from the loop member to the upstream coupling element.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
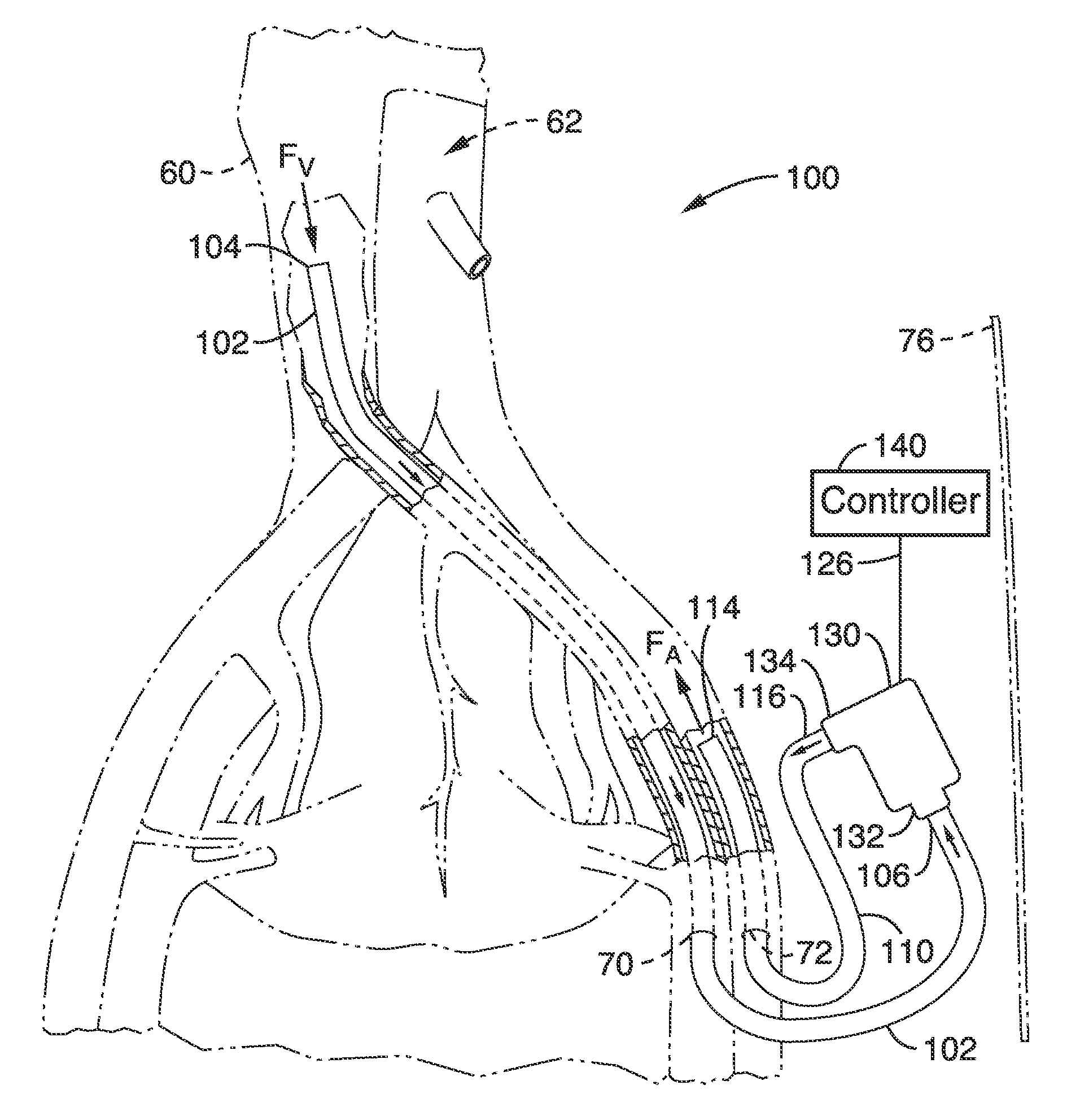
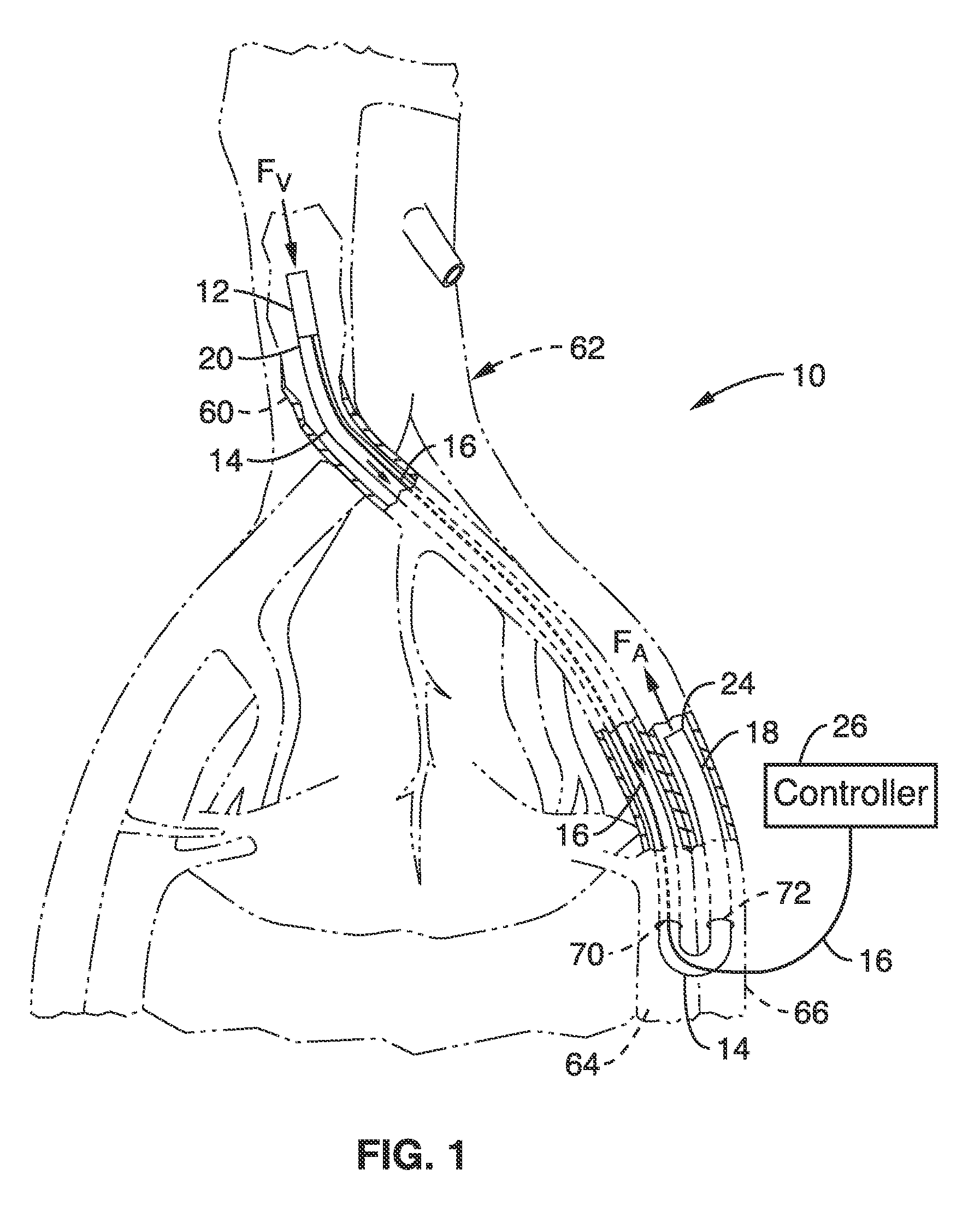
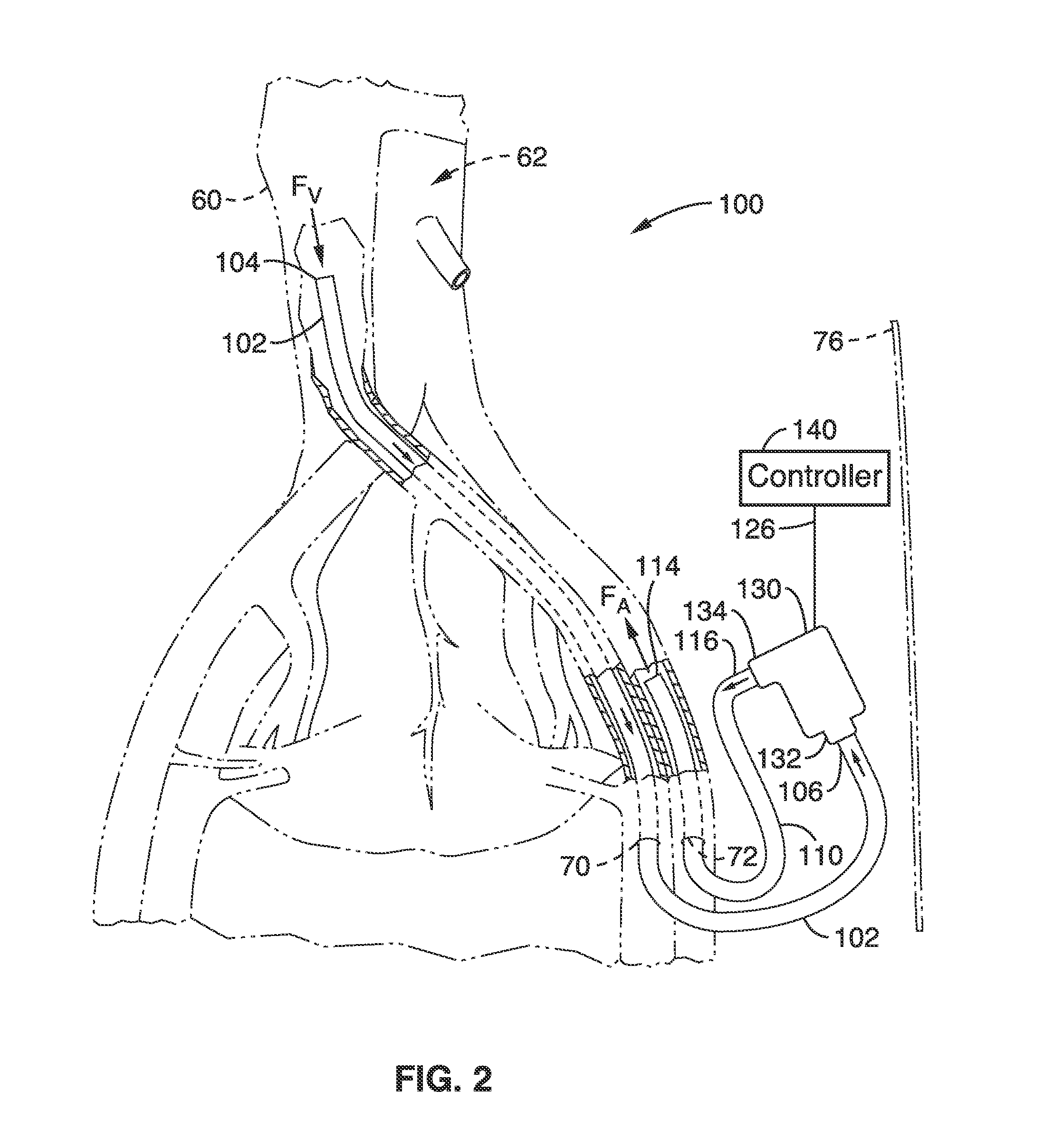
System, Methods and Apparatus for Cerebral Protection
ActiveUS20100241047A1Maintain their viabilityIncrease blood flowStentsBalloon catheterPerfusionGuide wires
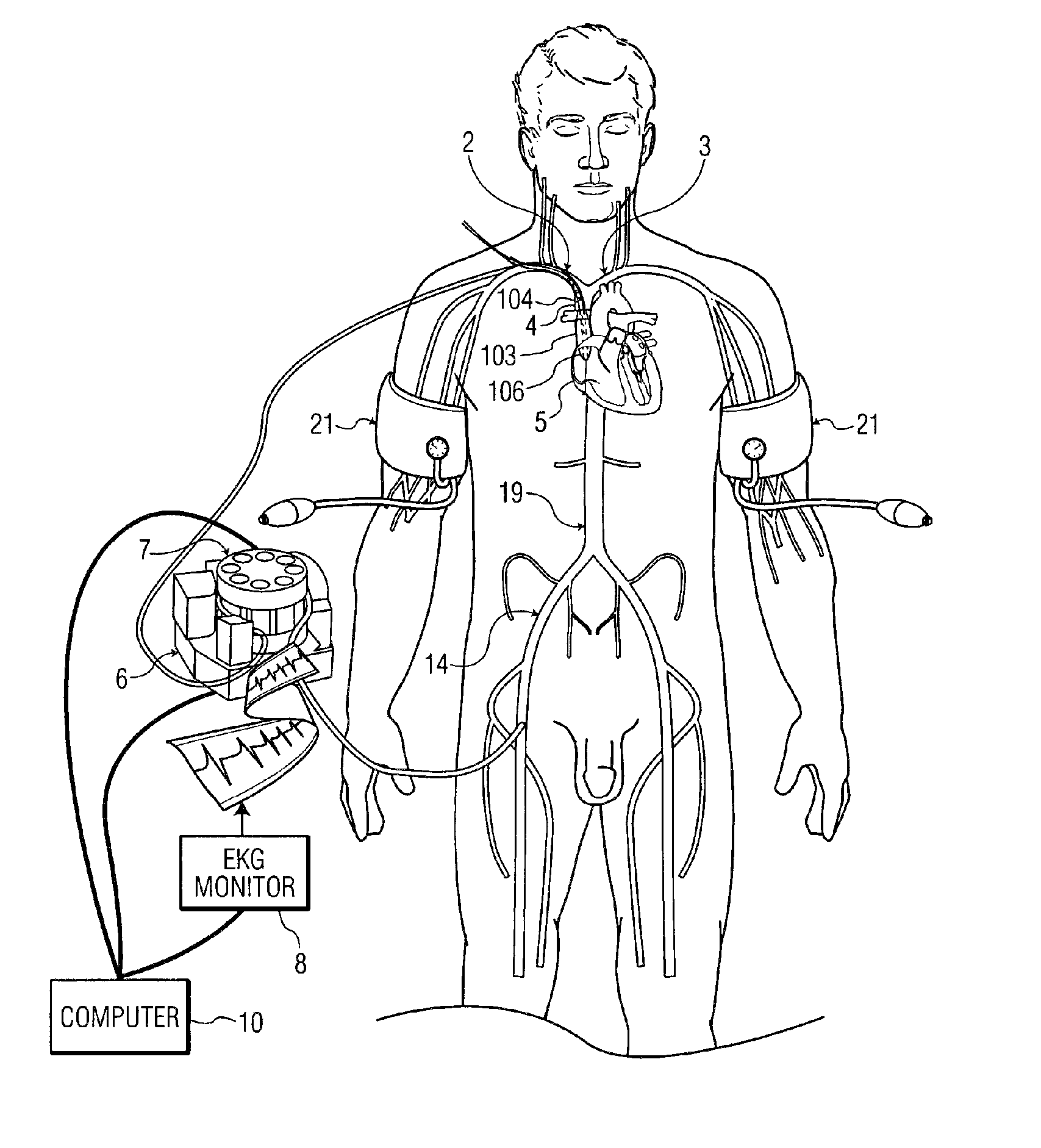
A device, system and method for perfusing an oxygenated medium in the cerebral vasculature. In the case of bihemispheric brain perfusion, it includes positioning pressure cuffs on upper extremities; providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon; inserting the catheter into a subclavian or femoral vein; advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned substantially in the superior vena cava junction substantially proximal to the take-off of the left innominate vein. During a perfusion mode, the cuffs and balloon are inflated causing an increase in cerebral blood flow, retrogradely; and oxygenated blood which may be cooled is pumped from a femoral artery into the catheter for a suitable period. During a non-perfusion mode the cuffs and balloon are deflated. The catheter has at least two regions, namely, guide wire and fluid delivery regions. Optionally, a separate balloon inflation region may be provided. In the case of unilateral (single hemisphere) brain perfusion, it includes providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon, inserting the catheter into a subclavian, jugular or femoral vein, advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned in the internal jugular vein on the side ipsilateral to the side of the brain requiring perfusion. In this unilateral scenario where the balloon is inflated in the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, no pressure cuffs are needed and only the balloon is inflated and deflated during the perfusion and non-perfusion modes respectively.
Owner:YACOUBIAN VAHE STEPHAN +1
Two-way controllable releasable vena cava filter
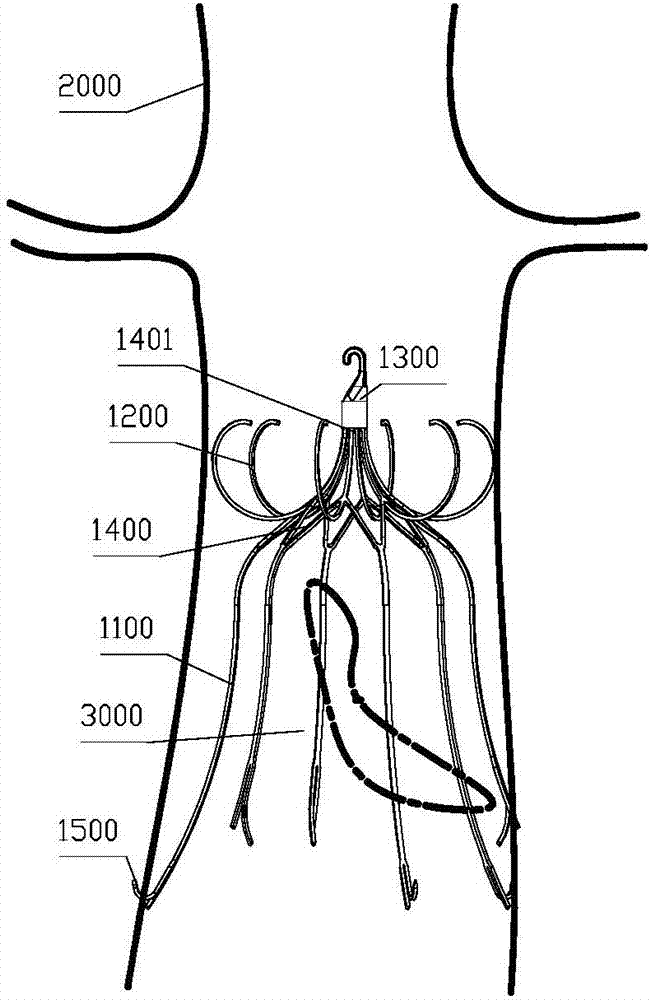
ActiveCN107307921AImprove filtering effectAchieve repeated releaseBlood vessel filtersVeinCross-link
The invention discloses a two-way controllable releasable vena cava filter. The filter comprises a filtering part and a supporting part, the filtering part is of a grid structure which is formed in the mode that a plurality of supporting rods are cross-linked with each other, and the supporting part comprises a first supporting part and a second supporting part which are arranged on two sides of the filtering part, wherein the opening of the first supporting part is opposite to that of the second supporting part; the first supporting part gradually extends from the center to the outside in the forward direction and gradually overturns and curls in the reverse direction; the second supporting part gradually extends from the center to the outside in the forward direction. According to the two-way controllable releasable vena cava filter, implantation and recycling of the filter can be conducted through the femoral vein and the jugular vein, the thrombus filtering effect is good, the filter can be recycled after being implanted for a long time, and the filter can be more easily captured and recycled.
Owner:HANGZHOU WEIQIANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Delivery system for atrial shunt
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to a delivery system for an atrial shunt. The delivery system comprises a first sheath structure, a second sheath structure and an inner core tube structure, the second sheath structure is connected with the first sheath structure and the inner core tube structure, the first sheath structure is used for puncturing and reaming an atrial septum, the second sheath structure is used for collecting the atrial shunt, and the inner core tube structure is connected with the atrial shunt, so that the atrial shunt reaches the atrial septum and is released. The delivery system for the atrial shunt can be helped to be implanted into the human body, the surgery success rate and the surgery operation convenience are improved, the atrial shunt can be implanted only by passing through the femoral vein, then passing through the heart diaphragm and then operating the delivery system, damage to a patient is small, and the service life of the patient is effectively helped to be prolonged.
Owner:QICHEN (SHANGHAI) MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Ectopic implantation valved stent system for treating tricuspid regurgitation
The invention discloses an ectopic implantation valved stent system for treating tricuspid regurgitation. The system comprises a stent, an artificial valve and a cover membrane, wherein the stent is in the shape of a cylindrical tube and provided with a grid structure, the artificial valve is sewn in the stent perpendicular to the axial direction of the stent, and the cover membrane covers at least part of the peripheral surface of the stent. The system is a valve system implanted through femoral vein. After the system is implanted in precava and / or postcava, the situation that tricuspid valve regurgitates into atrium, and then blood flows back to vena cava can be avoided, and then tricuspid regurgitation is treated. The stent system has the advantages that operation is easy, manufacturing process is simple and mature, and safety performance is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANYU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
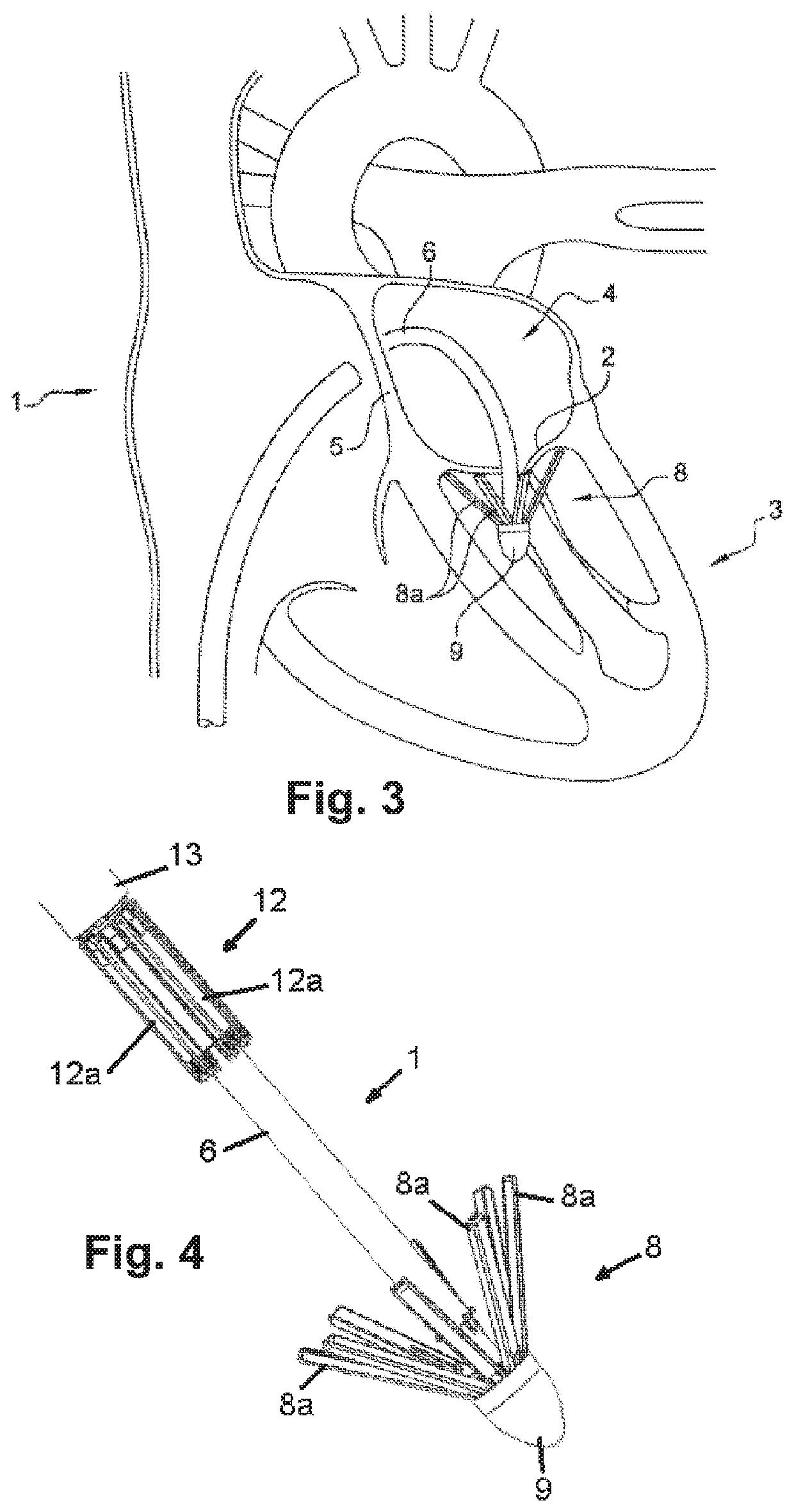
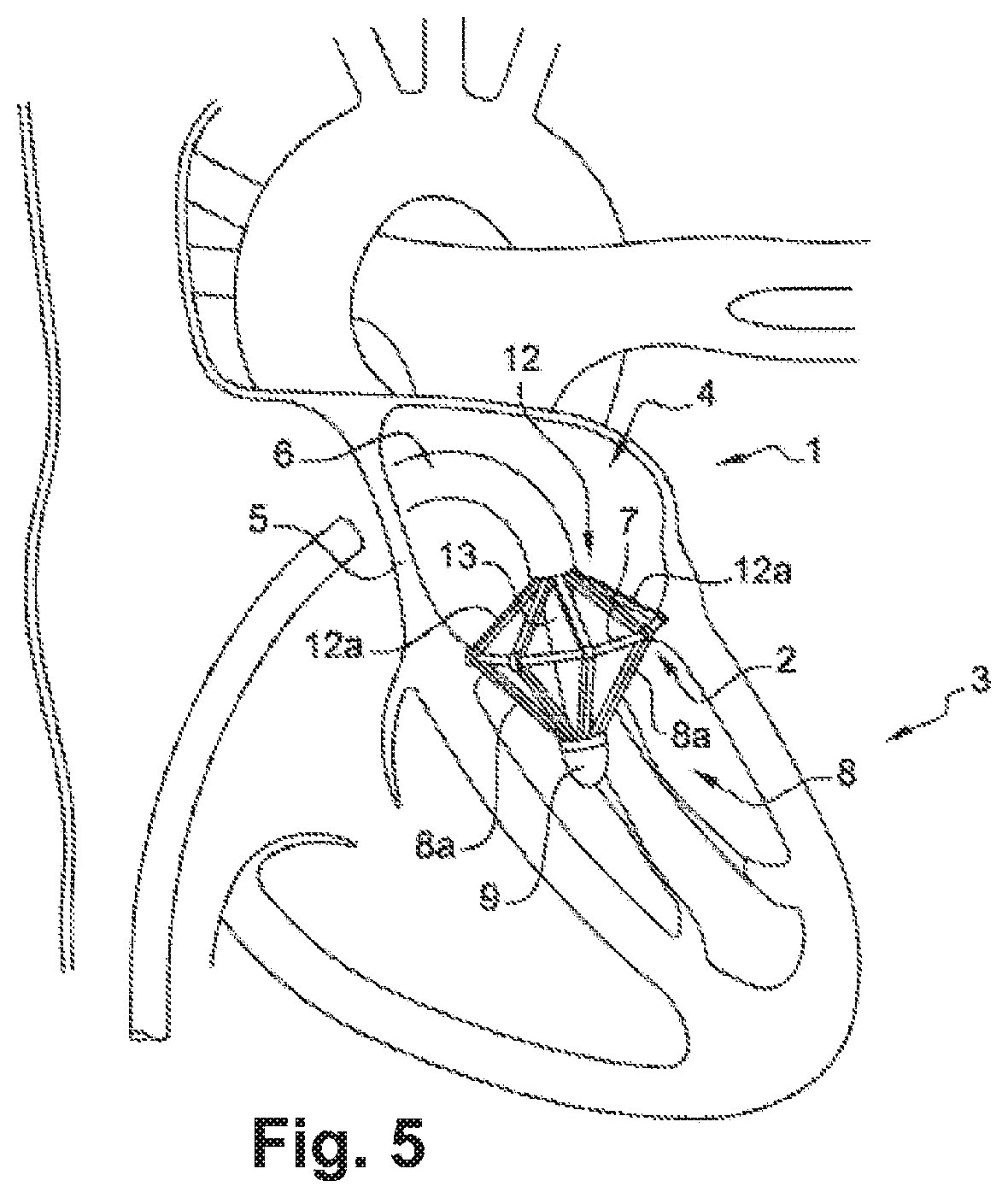
Device for performing or preparing for a mitral valve annuloplasty by a transfemoral approach
The device (1) is intended to be positioned in a sealed introducer placed in a femoral vein in order to penetrate the left atrium (4) of the heart (3) by passing through the septal wall (5) thereof. The device comprises an assembly for cooperating with a handle under the control of control means for actuation of the assembly, for placing and fixing a reinforcement ring (7) on the mitral valve (2), said assembly being arranged at the end of a manipulation rod (6) and comprising: a bearing member (8) comprising a plurality of arms (8a) connected pivotably to the end of the rod (6) so as to change, under the action of the control means, from a position folded along the rod (6) to a deployed position spaced apart from the rod (6), in order to bear under the mitral valve (2) in a manner uniformly distributed along the periphery of the mitral valve; a counter-bearing member (12) comprising a plurality of arms (12a), at the free end of which arms (12a) the reinforcement ring (7) is arranged, the arms (12a) are connected pivotably to a support (13) disposed coaxially with respect to the rod (6) in such a way as to change, under the action of the control means, from a position folded along the rod (6) to a deployed position spaced apart from the rod (6), in order to realize the counter-bearing on the mitral valve and to position the reinforcement ring (7); means for removing sutures for fixing the reinforcement ring (7) to the mitral valve.
Owner:CMINOV +1
Valve clip and clipping system thereof
PendingCN111772874AShorten the axial lengthSmall footprintAnnuloplasty ringsHeart apexSurgical operation
The invention relates to a valve clip and a clipping system thereof. The valve clip can be used for effectively treating MR (Mitral Regurgitation) and TR (Tricuspid Regurgitation) after being implanted into the human body by the clipping system. By using the valve clip, the axial operating space of the valve clip can be shortened, and the operating direction can be changed, so that the capturing and clamping operation can be performed from the other side of the valve (i.e., the atrium side) so as to reduce the injury damage on the atrium and the chordae tendineae in the surgical operation process; the length of the valve clip can be shortened, so that the implanted valve clip is shorter so as to reduce the space of the ventricle side occupied by the valve clip, reduce the injury capable ofbeing caused by the valve clip on the heart tissue, and reduce the thrombus forming risk; in addition, after the clipping system passes through the femoral vein and punctures the septum of the rightatrium and the left atrium, the right atrium and the left atrium are used as a delivery path of the clip; the intercostal incision and cardiac apex puncture are not needed; and the surgical trauma issmaller.
Owner:SHANGHAI HANYU MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Valve stent and prosthetic heart valve
PendingCN111035472APrevent slipping outReduce the thickness of the stentHeart valvesProsthetic heartLeft atrium
The invention provides a valve stent, which comprises a stent main body arranged in a grid shape, at least a grabbing lug connected with the stent main body and a flange connected with the stent mainbody. According to the invention, the outer diameter D of the flange is larger than the diameter d of the connecting position of the flange and the stent main body, so that the lower horizontal planeof the flange is tightly attached to a heart native valve ring and valve leaflets, the edge upwarping end surface is tightly attached to the inner wall of left atrium, the upper limiting and sealing effects are achieved, and the valve stent is prevented from sliding out towards the left ventricle end; when the valve stent is compressed into a sheath, the grabbing lug is embedded into the stent main body grids connected with the grabbing lugs, so that the stent thickness of the valve stent after being pressed, held and reduced is reduced, and the valve stent can intervene into a human body through a femoral vein path so as to reduce the diameter of a conveyor catheter and reduce the conveying difficulty and the damage to blood vessels; and the grabbing lug simultaneously grabs native valveleaflet and hooks chordae tendineae to form lower limiting, so that the valve stent is prevented from being disengaged towards the left atrium end due to external force such as blood flow scouring, heart extrusion and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT CARDIOFLOW MEDTECH CO LTD
Femoral removal vena cava filter
An intravascular filter configured for retrieval through a patient's femoral vein and a method for retrieving the filter through the patient's femoral vein. The filter includes a plurality of struts having connected ends attached together along a longitudinal axis, a shaft disposed along the longitudinal axis and having a first end disposed with the connected ends of the struts, a first cuff slidably disposed on the shaft, and a second cuff disposed over the struts and connected to the first cuff.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Methods and devices for treating heart failure
InactiveUS20130303832A1Reduce riskMinimally and less invasiveControl devicesBlood pumpsVenous bloodFemoral artery
Systems and methods for delivering a miniaturized blood pump configured to draw partially desaturated blood via the femoral vein from the inferior or superior vena cava. A cannula connected to the pump exits the femoral vein and is connected to the femoral artery with a cannula or vascular graft. The pump receives power from a percutaneous lead which runs parallel to the flexible cannula and then exits via a percutaneous opening in the skin. The pump in the venous system removes venous blood and pumps it into the femoral artery. In so doing pressure in the aorta is increased and back pressure in the venous system is decreased.
Owner:STAR BP INC
Mitral valve replacement system for percutaneous transcatheter
PendingCN112137764APrevention of Weekly LeakagePeripheral leakage reducedHeart valvesHeart apexBioprosthetic mitral valve replacement
The invention relates to a mitral valve replacement system for a percutaneous transcatheter, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The mitral valve replacement system comprises avalve frame supporting body, an artificial valve leaflet and a ventricular septum anchoring structure. The valve frame supporting body is arranged between an atrium and a ventricle and provided with ahollow cavity with the two ends open. The artificial valve leaflet is arranged on the inner wall of the cavity of the valve frame supporting body. The ventricular septum anchoring structure is arranged between the valve frame supporting body and a ventricular septum. The invention provides the mitral valve replacement device intervened through a catheter via a femoral vein admission passage and aims to solve the problems that an existing interventional mitral valve system is generally large in valve stent, has the left ventricular outflow passage obstruction risk, has potential complicationsin transapical admission passage and anchoring and the like, and the mitral valve replacement device provided by the invention is more minimally invasive and firmer in anchoring, and the technical scheme of mitral valve replacement suffering from left ventricular outflow tract obstruction can be effectively avoided.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
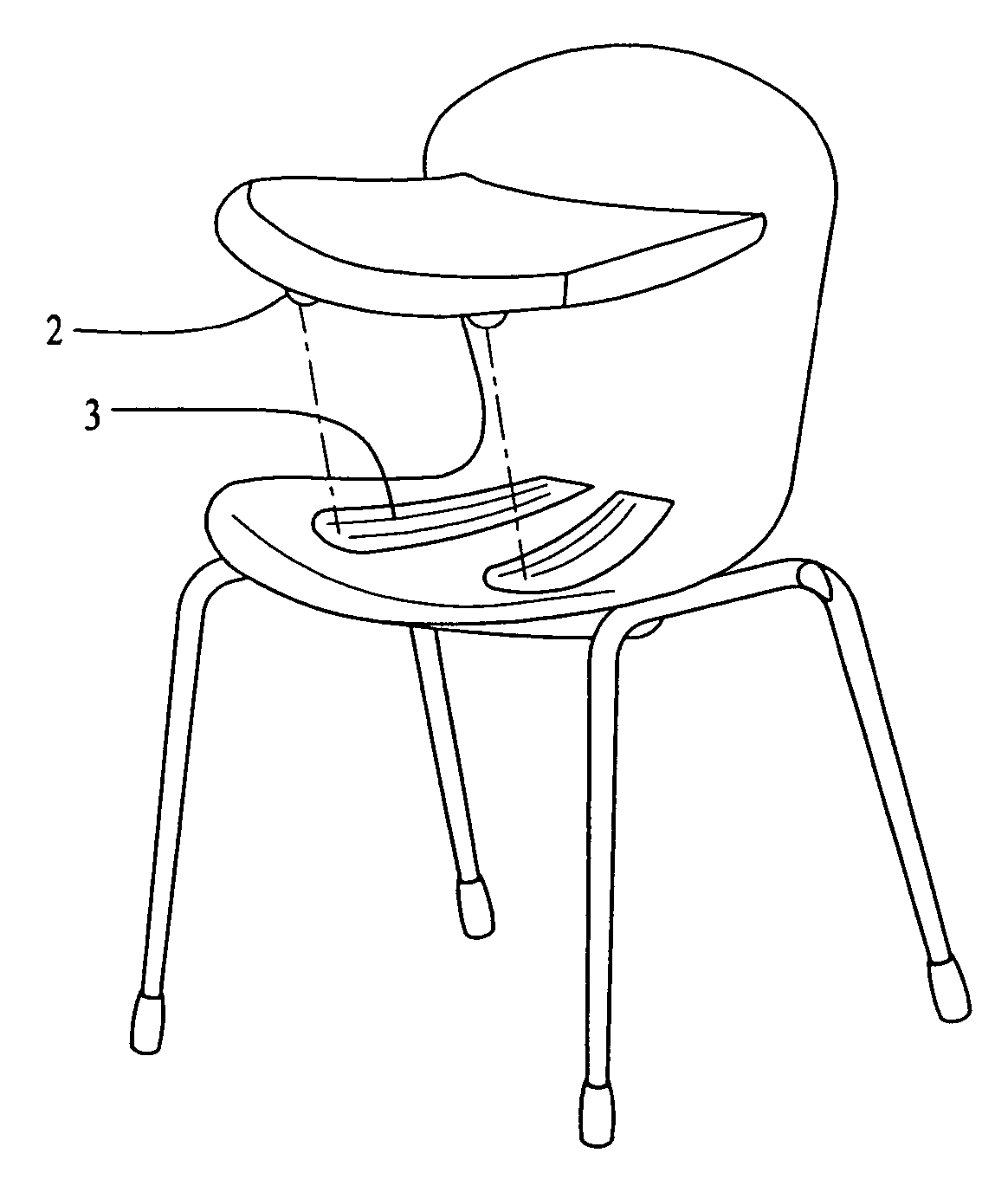
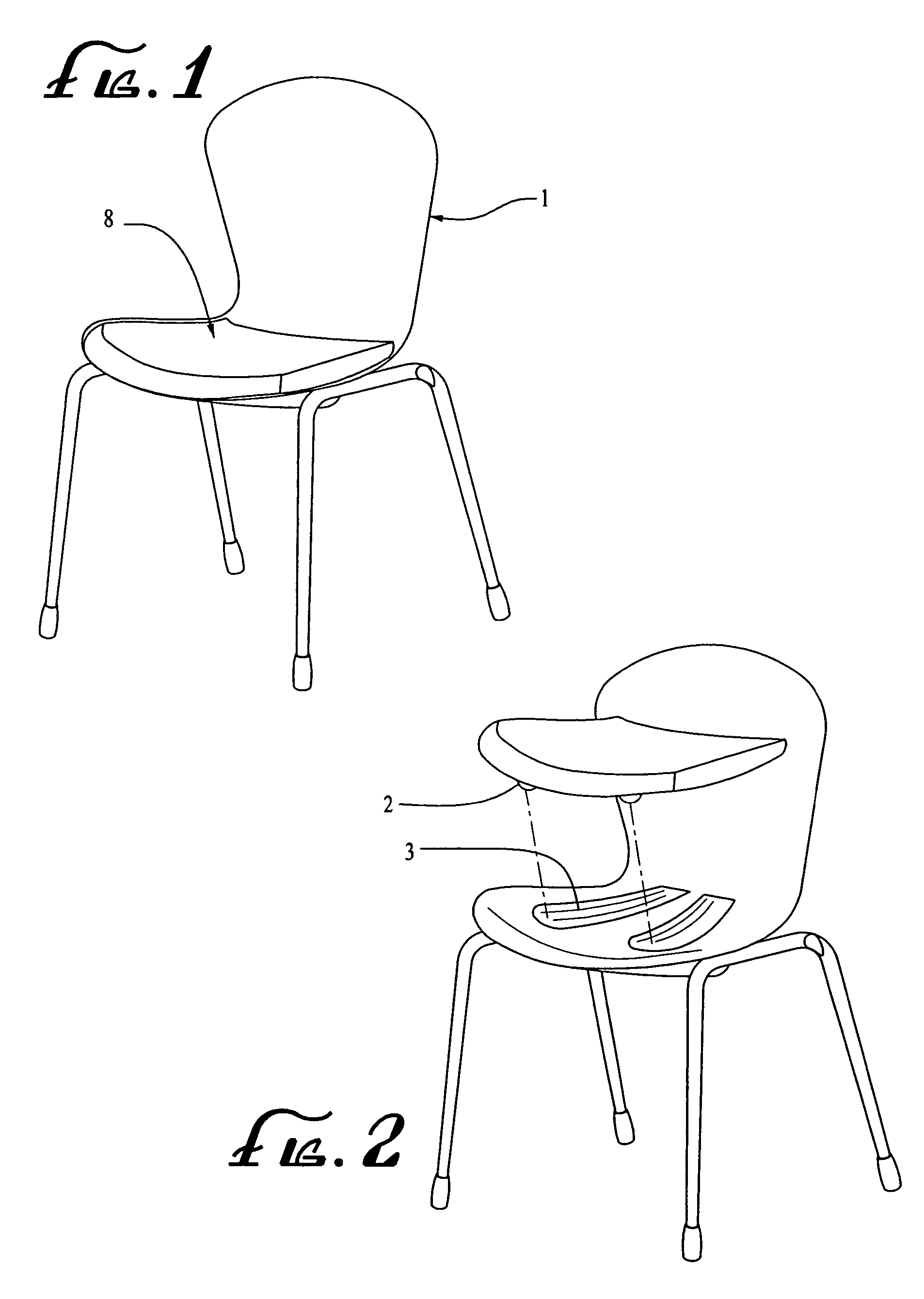
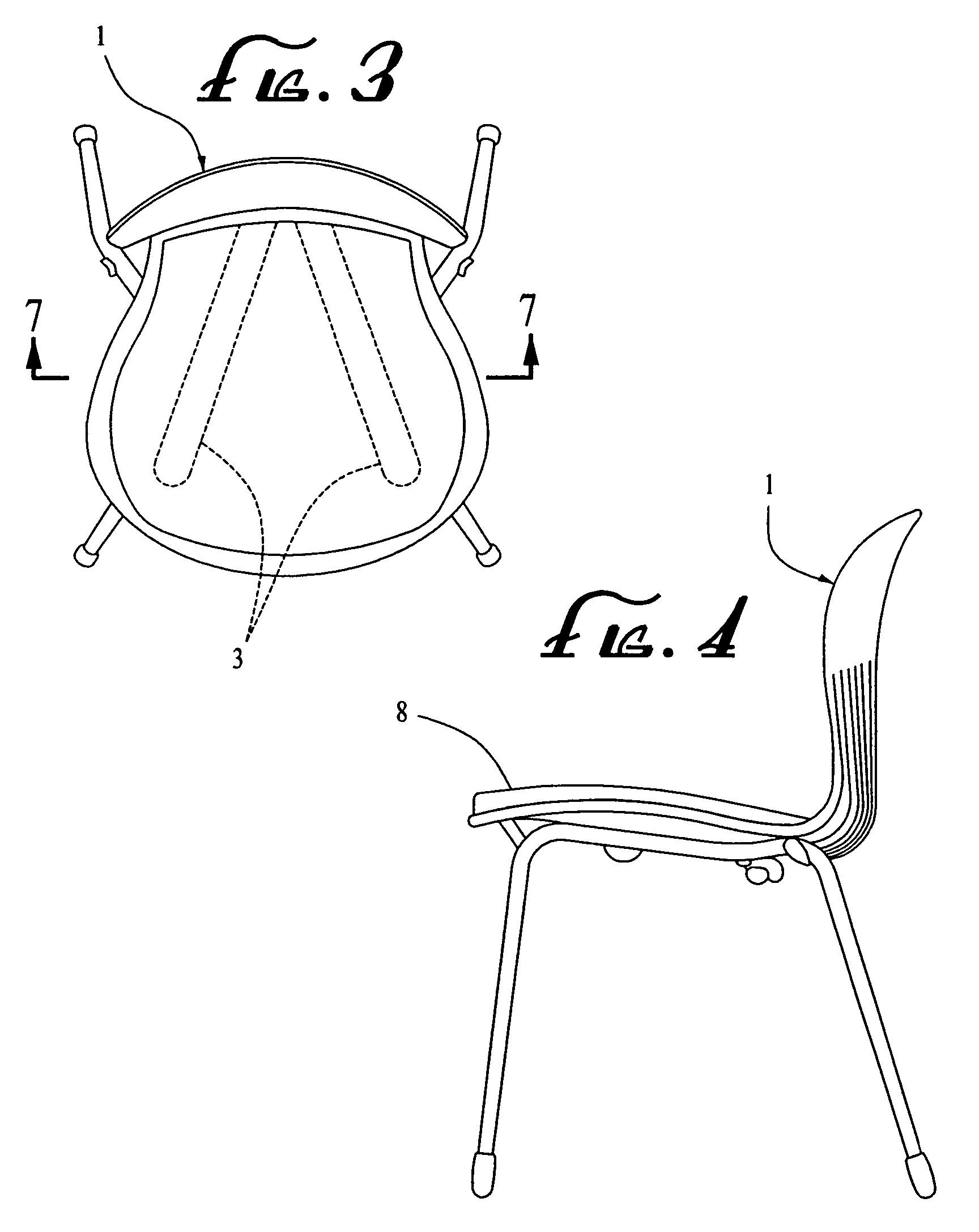
Enhanced process for making seating elements and products thereby including those specially designed for children
InactiveUS7270376B2Increases relative lordosis in the lumbar spineReduce obstructionBack restsSofasVeinIschial tuberosity
Owner:NUBAX LTD
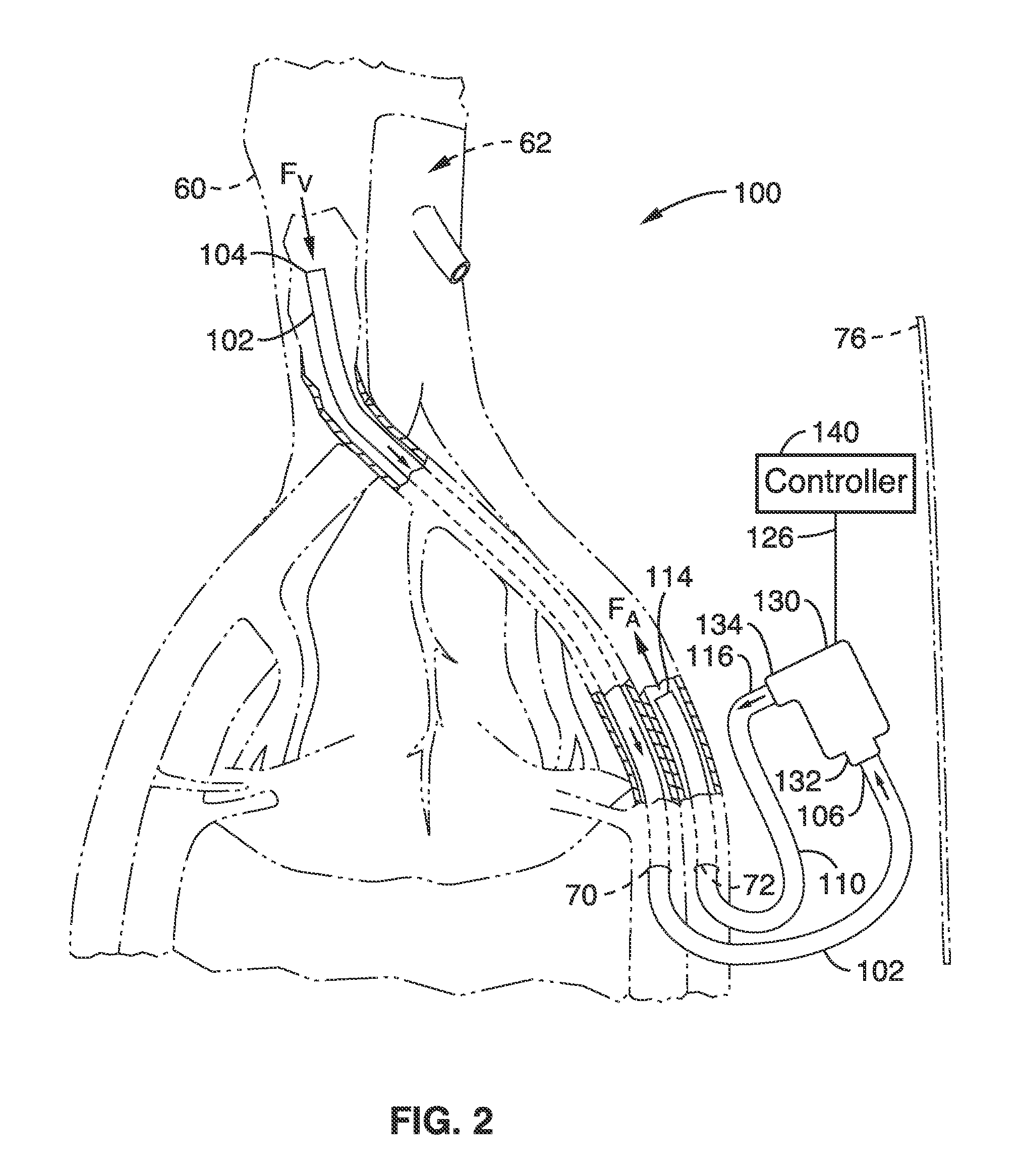
System, methods and apparatus for cerebral protection
ActiveUS8628490B2Maintain their viabilityIncrease blood flowStentsBalloon catheterPerfusionCBF - Cerebral blood flow
A device, system and method for perfusing an oxygenated medium in the cerebral vasculature. In the case of bihemispheric brain perfusion, it includes positioning pressure cuffs on upper extremities; providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon; inserting the catheter into a subclavian or femoral vein; advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned substantially in the superior vena cava junction substantially proximal to the take-off of the left innominate vein. During a perfusion mode, the cuffs and balloon are inflated causing an increase in cerebral blood flow, retrogradely; and oxygenated blood which may be cooled is pumped from a femoral artery into the catheter for a suitable period. During a non-perfusion mode the cuffs and balloon are deflated. The catheter has at least two regions, namely, guide wire and fluid delivery regions. Optionally, a separate balloon inflation region may be provided. In the case of unilateral (single hemisphere) brain perfusion, it includes providing a catheter having a multi-region configuration with a balloon, inserting the catheter into a subclavian, jugular or femoral vein, advancing the catheter such that the balloon is positioned in the internal jugular vein on the side ipsilateral to the side of the brain requiring perfusion. In this unilateral scenario where the balloon is inflated in the ipsilateral internal jugular vein, no pressure cuffs are needed and only the balloon is inflated and deflated during the perfusion and non-perfusion modes respectively.
Owner:YACOUBIAN VAHE STEPHAN +1
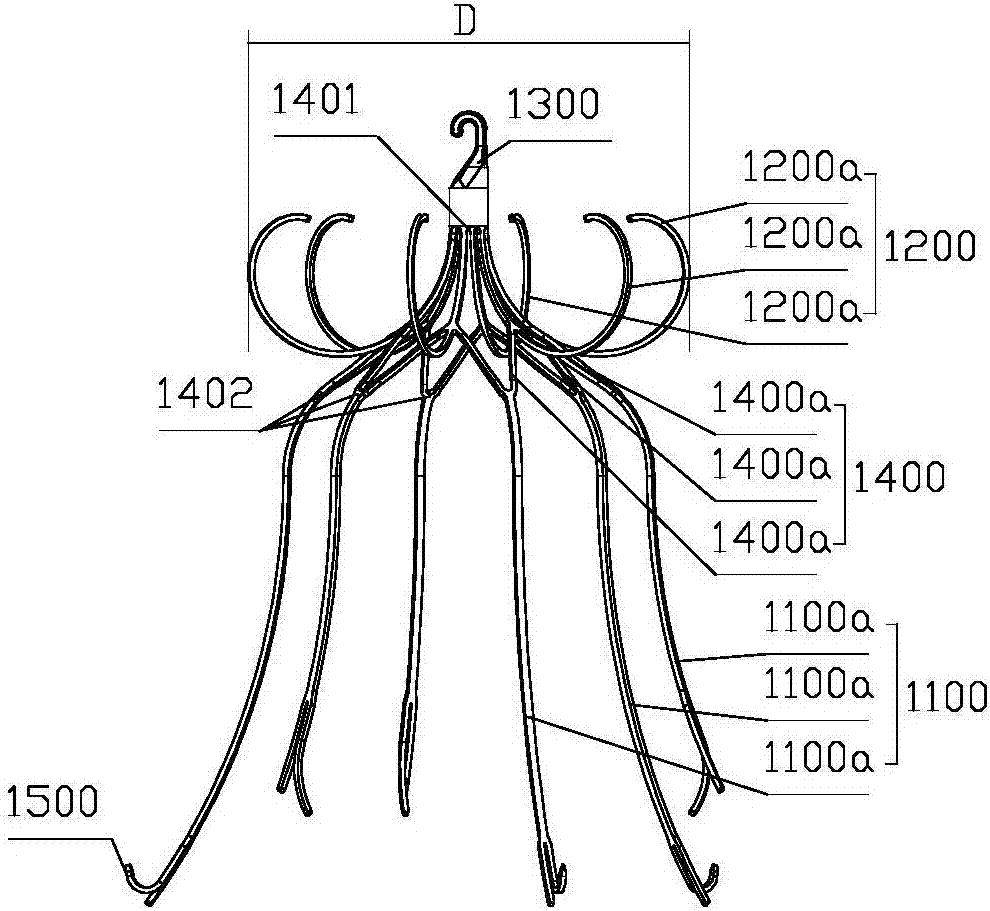
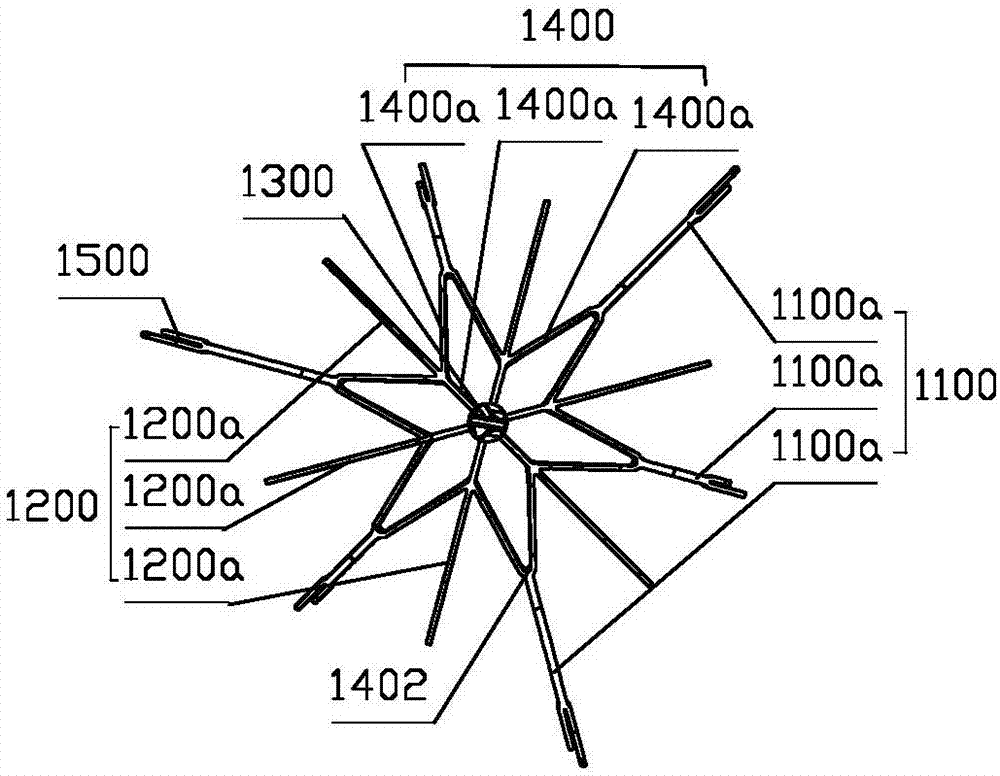
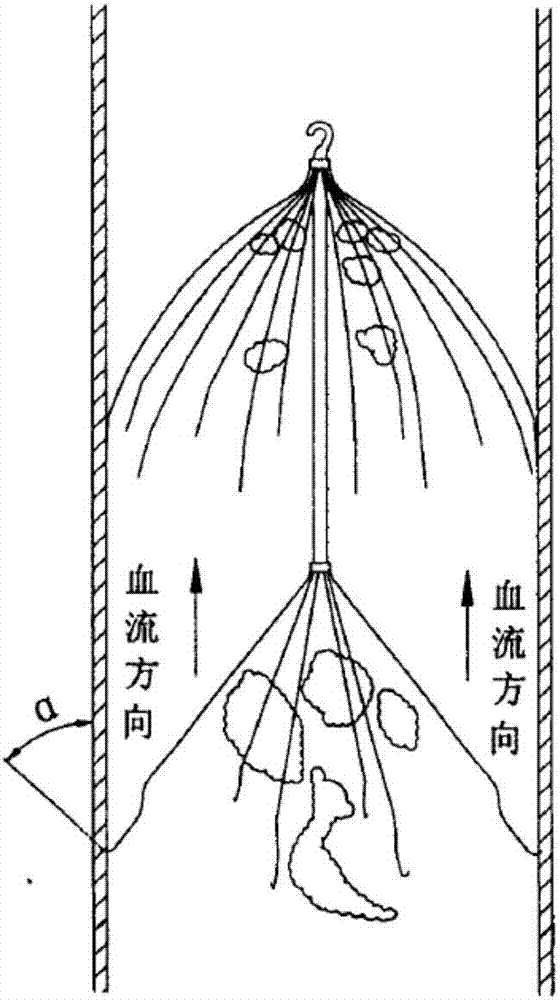
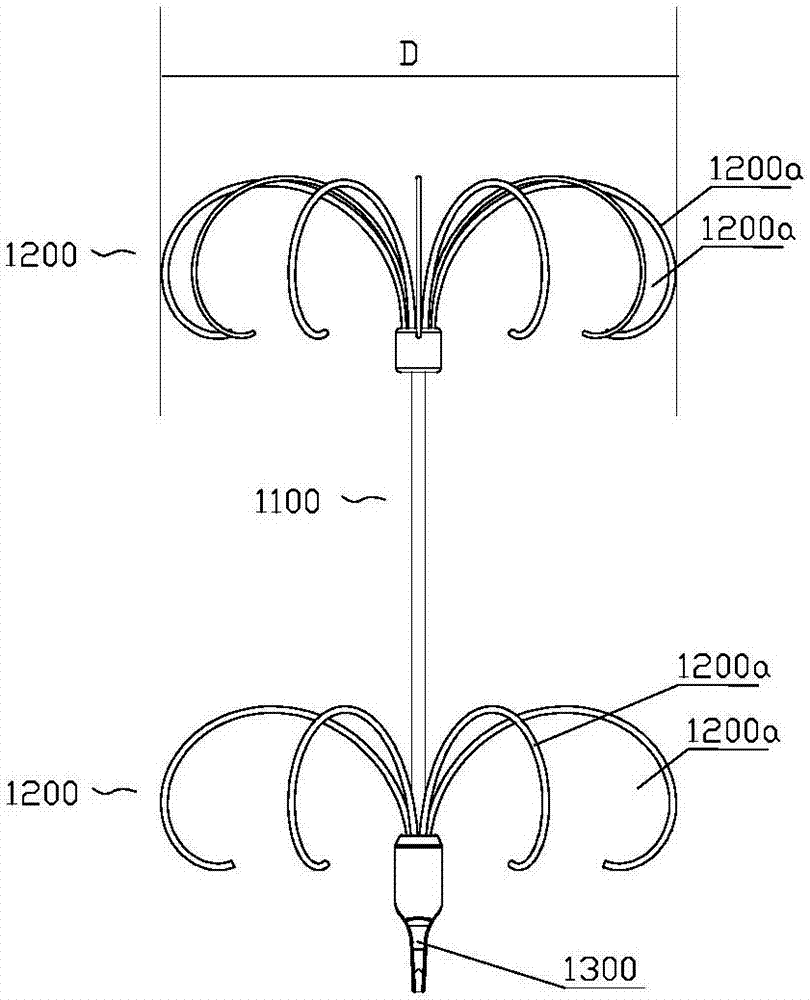
Vena cava filter of multilayer filtration
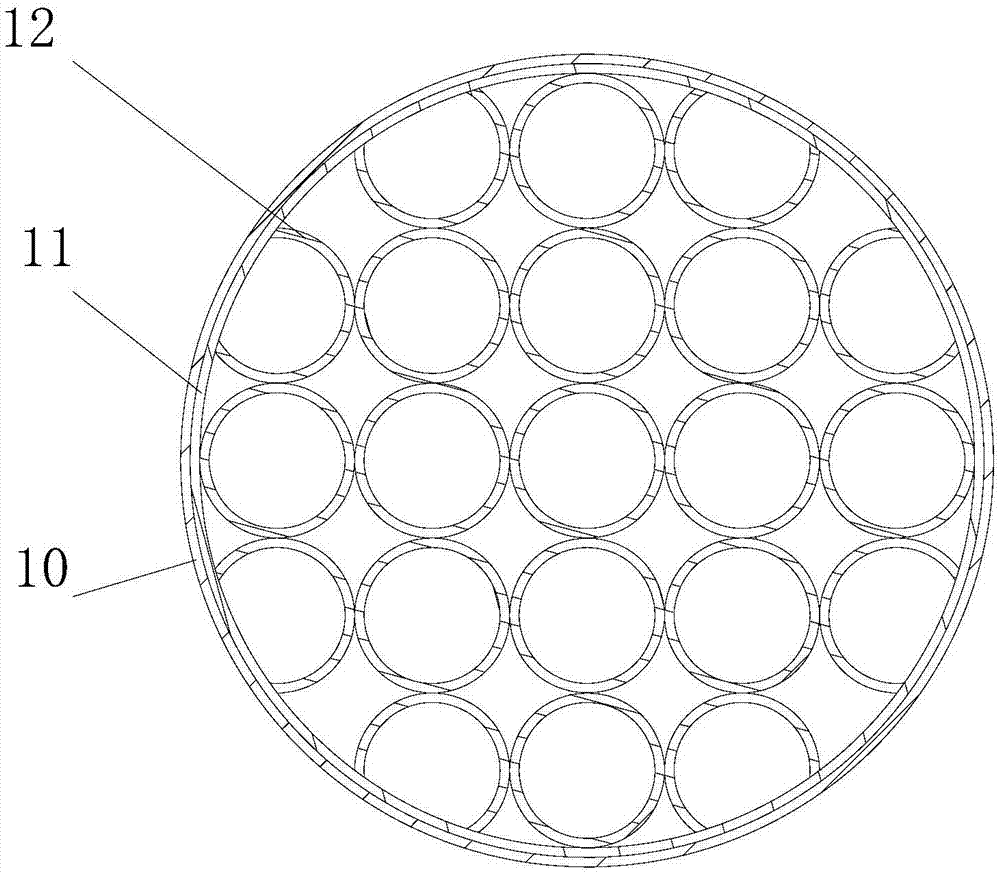
The invention discloses a vena cava filter of multilayer filtration. The vena cava filter comprises at least two filter parts arranged at intervals in the axial direction, and a connecting rod used for making the two filter parts connected is arranged between adjacent filter parts; each filter part extends from the center to the outer sides of far ends, is everted and curled in the reverse direction step by step, and supported on the inner wall of a blood vessel in a point mode respectively. Aiming at the defects that the releasing process is uncontrollable and the blood vessel wall is likely to be damaged due to the problems that, in the prior art, filters are released through a femoral vein, bounce is likely to occur and positioning is inaccurate, the vena cava filter of multilayer filtration which can be controllably released in dual directions is provided; not only can the vena cava filter of multilayer filtration be implanted and recycled through a femoral vein and a jugular vein, but the vena cava filter of multilayer filtration has better self-centrality and is easier to capture and recycle.
Owner:HANGZHOU WEIQIANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Vena cava filter with bidirectional retrieval
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com