Patents
Literature
49 results about "Ischial tuberosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
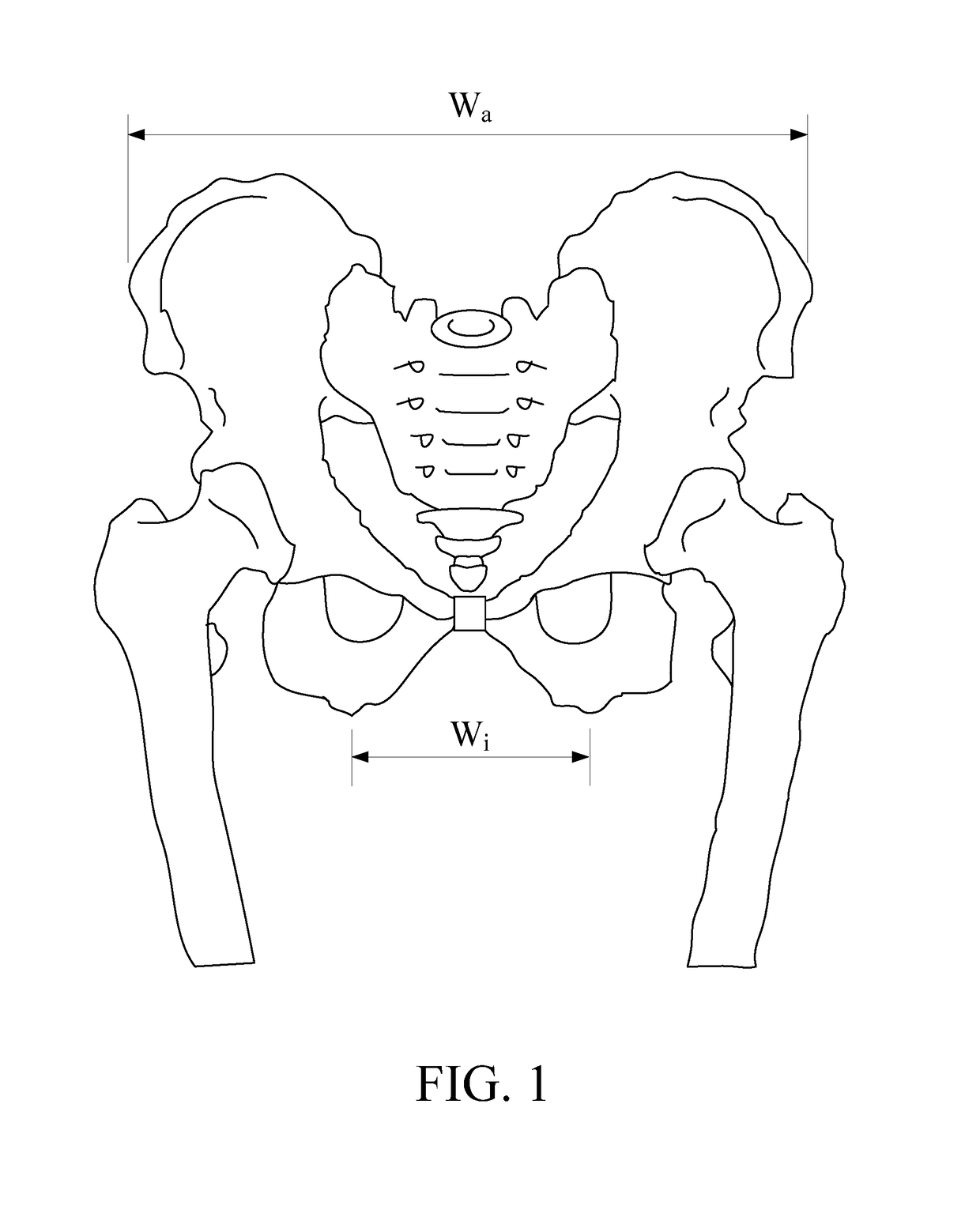
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known informally as the sit bones, or as a pair the sitting bones is a large swelling posteriorly on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks the lateral boundary of the pelvic outlet.
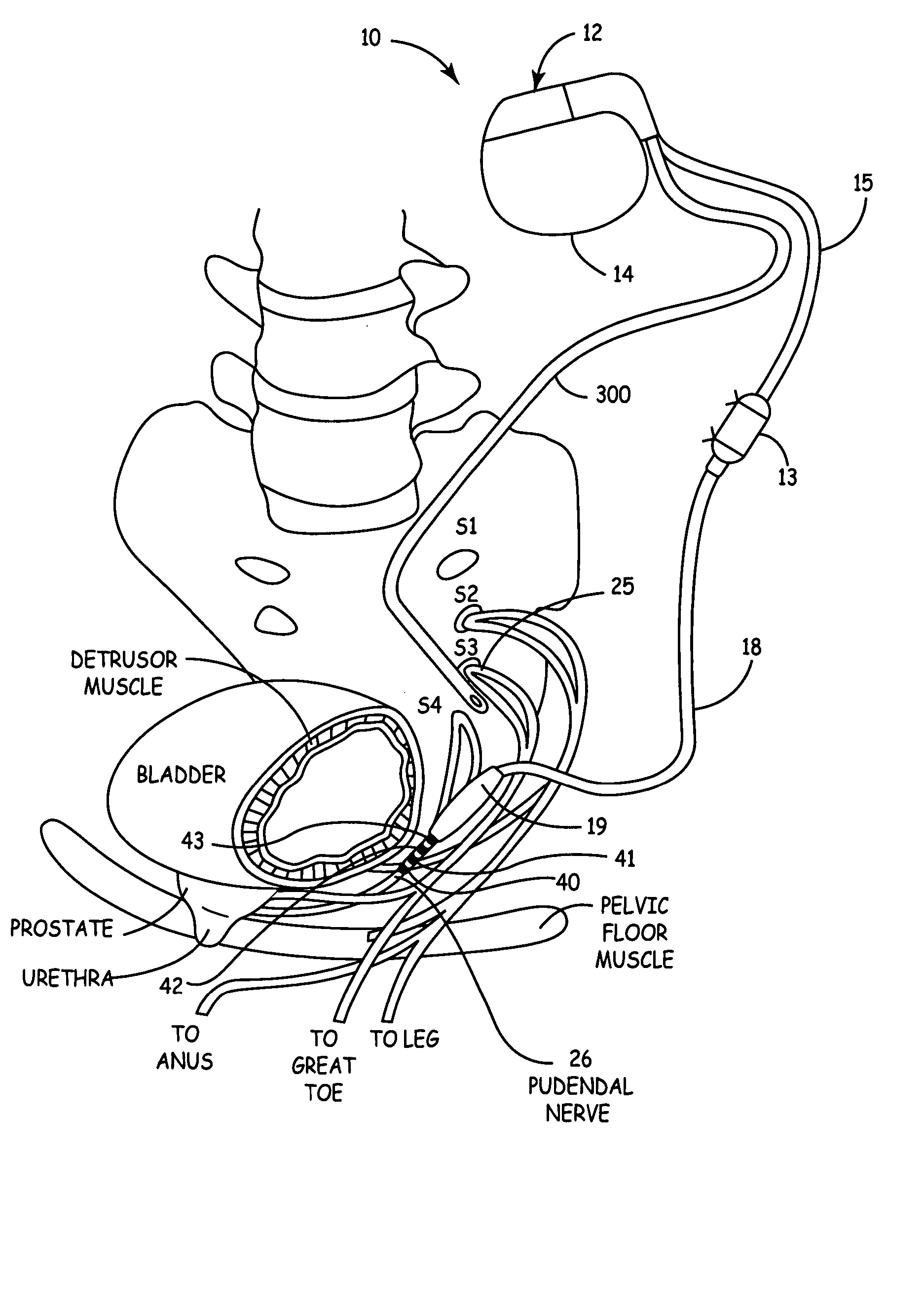
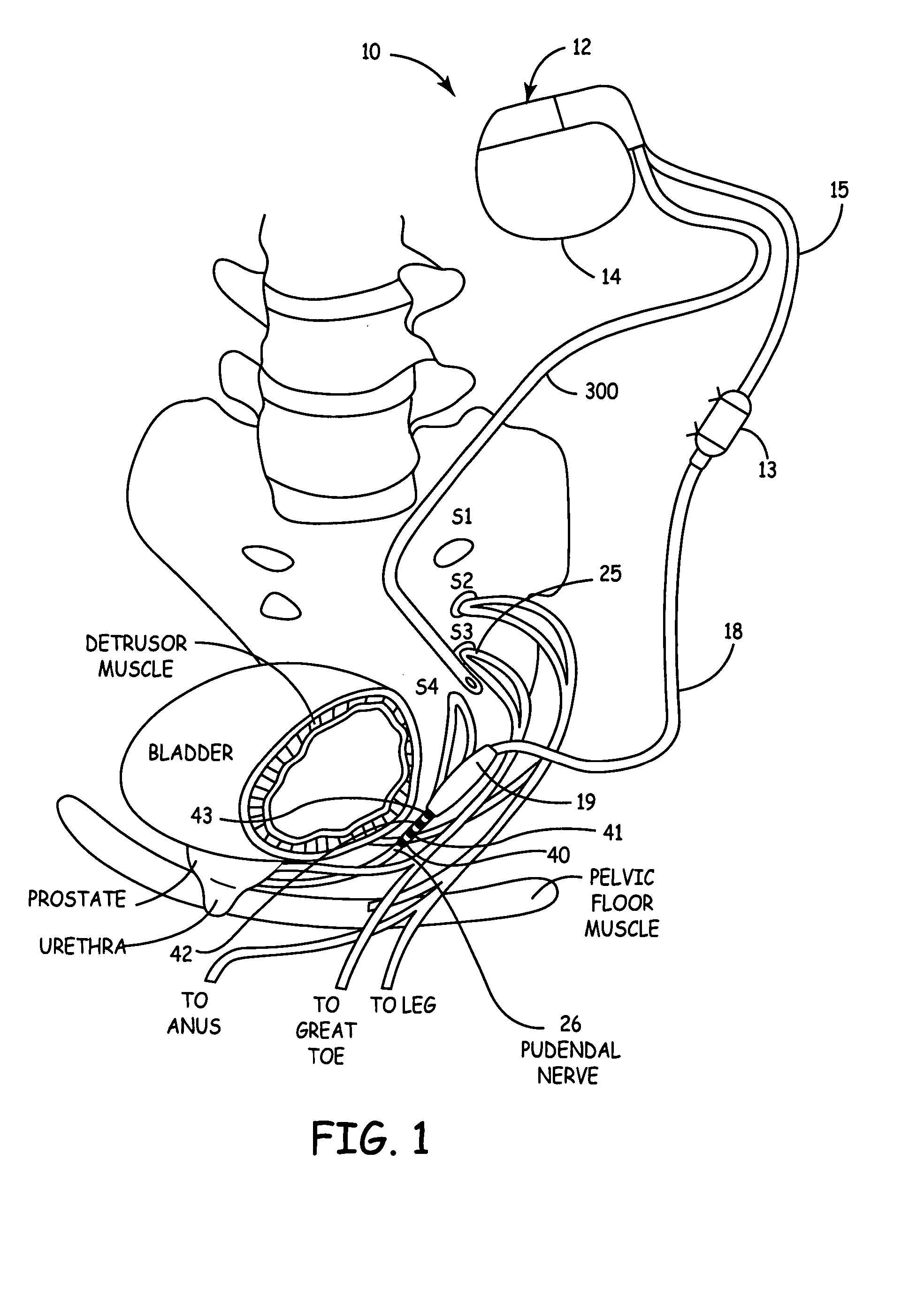
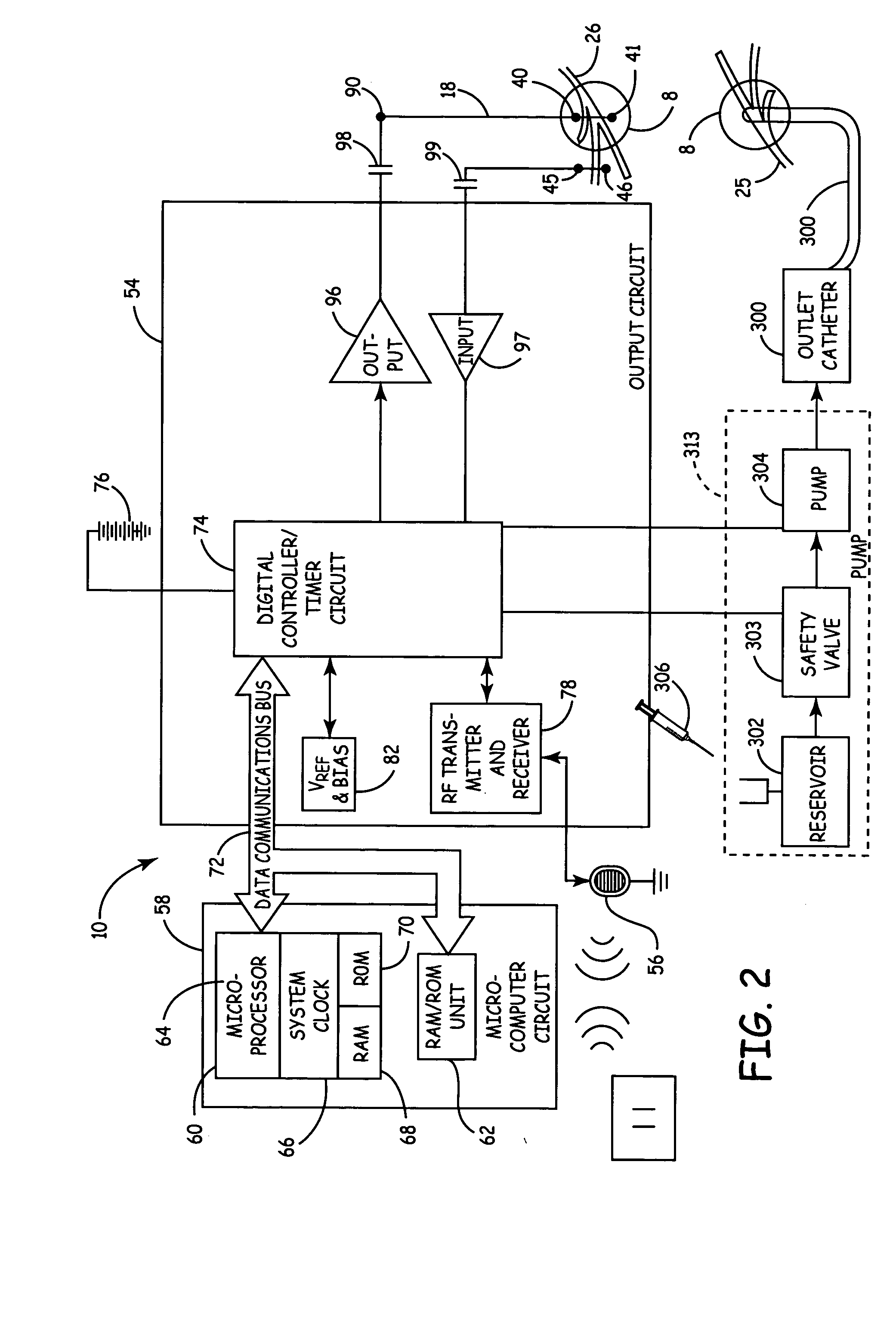
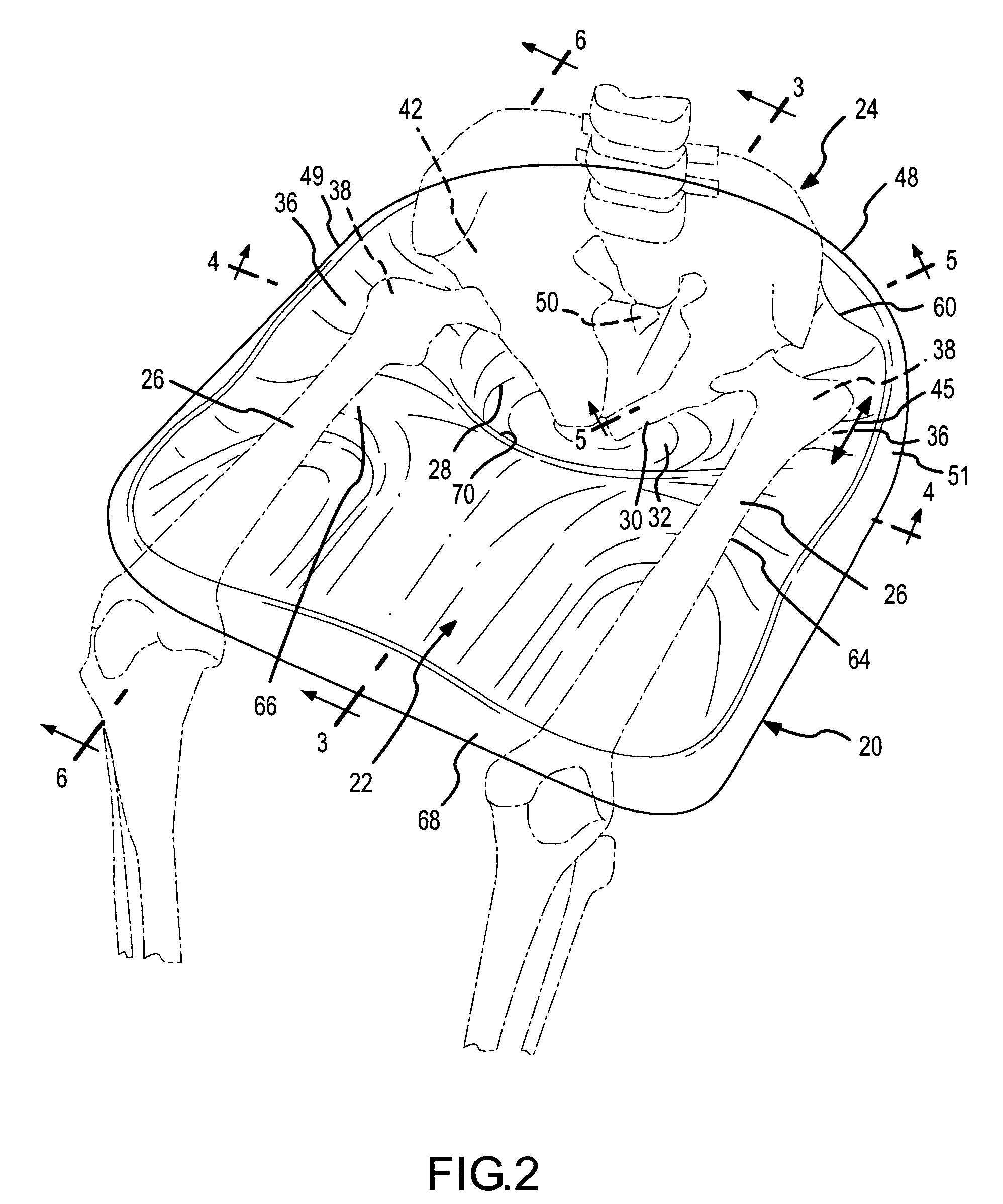
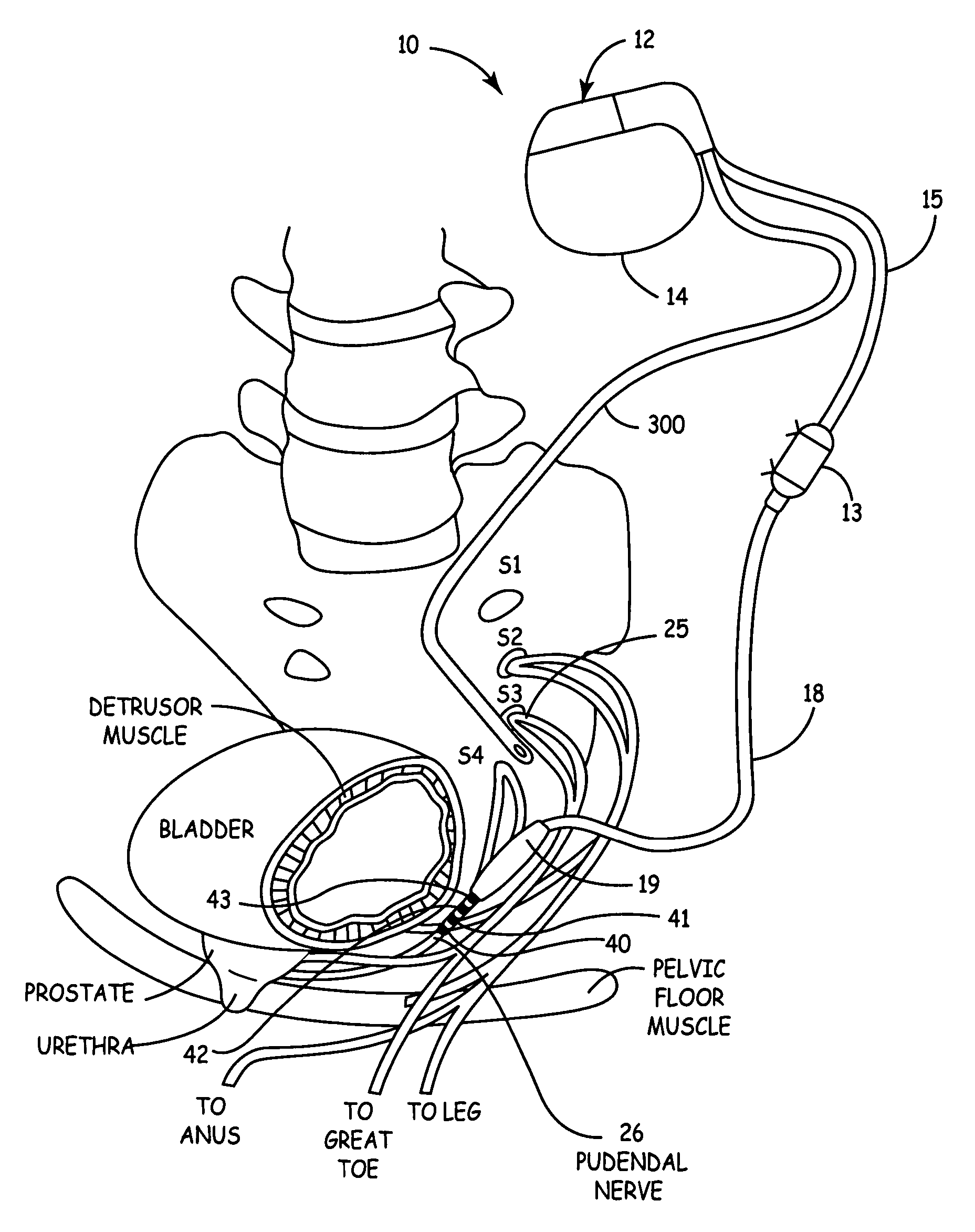
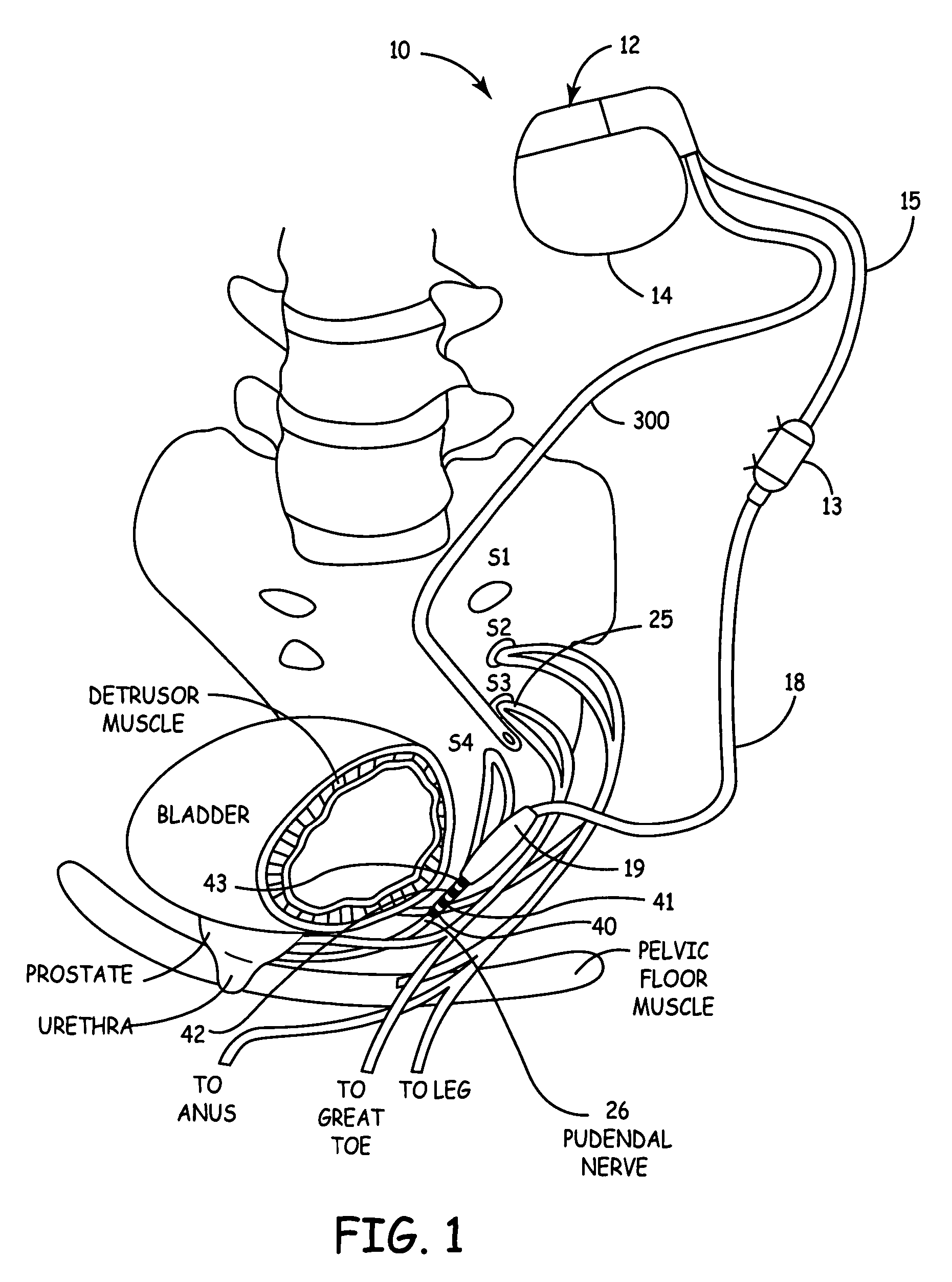
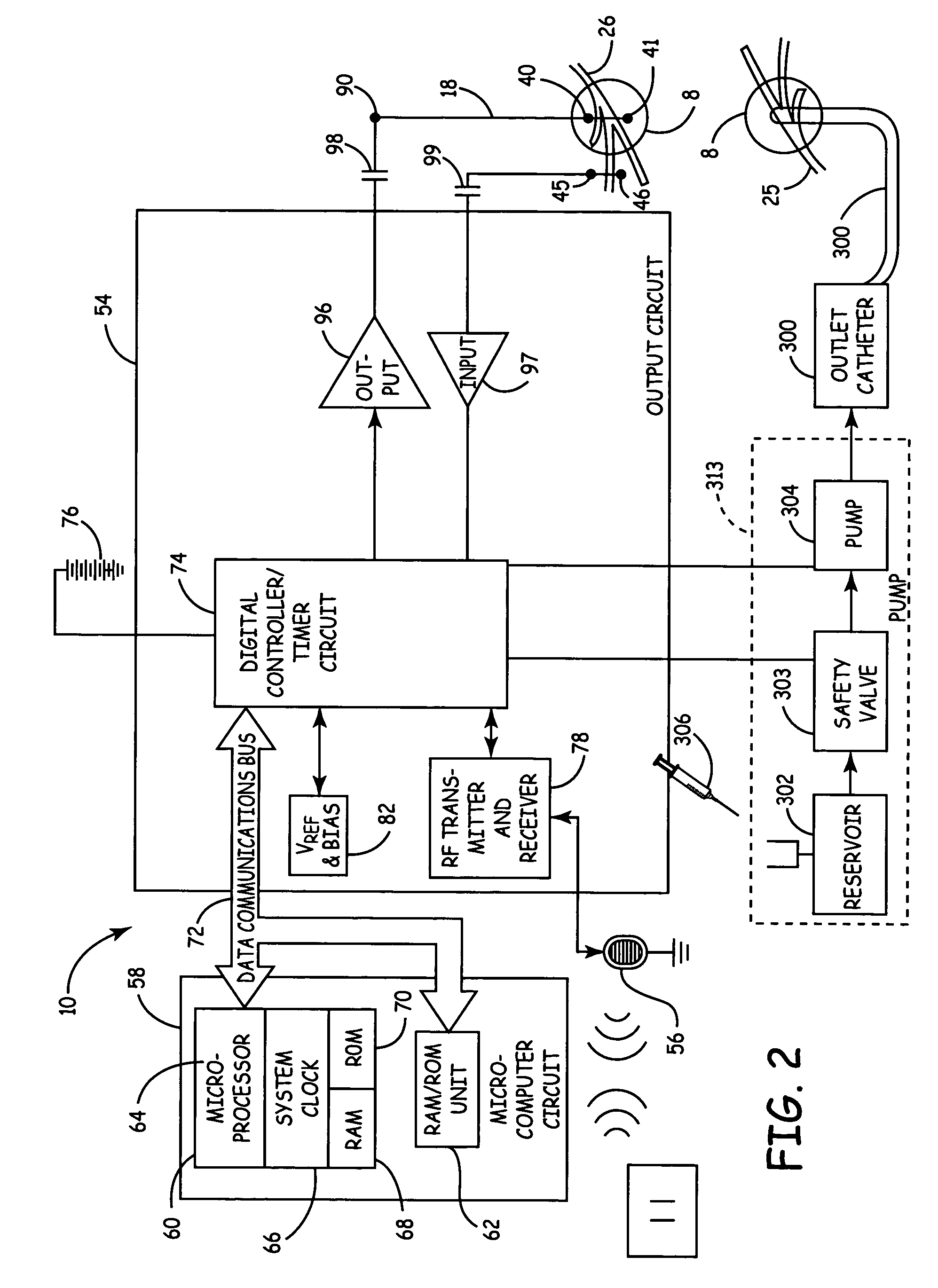
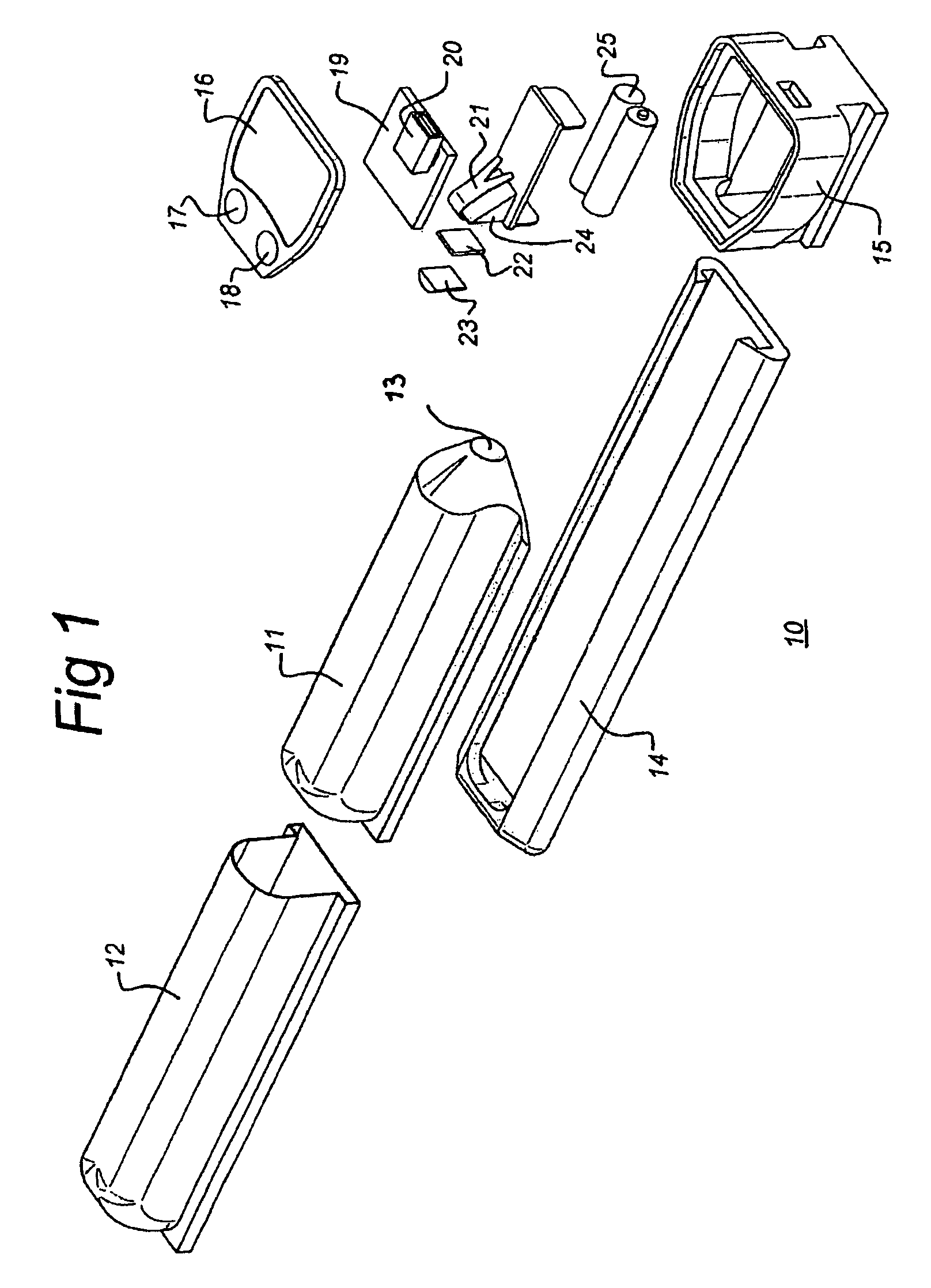
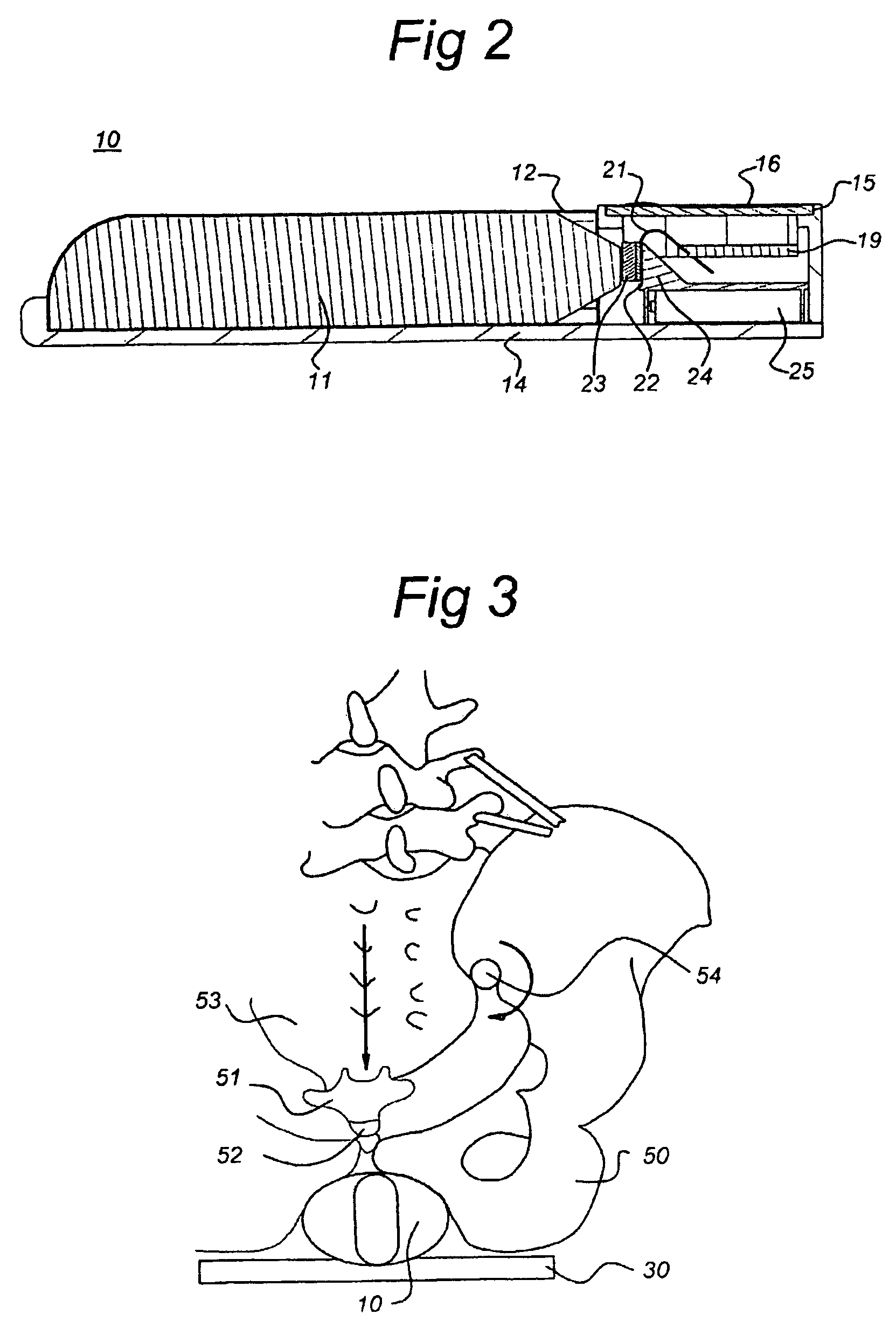
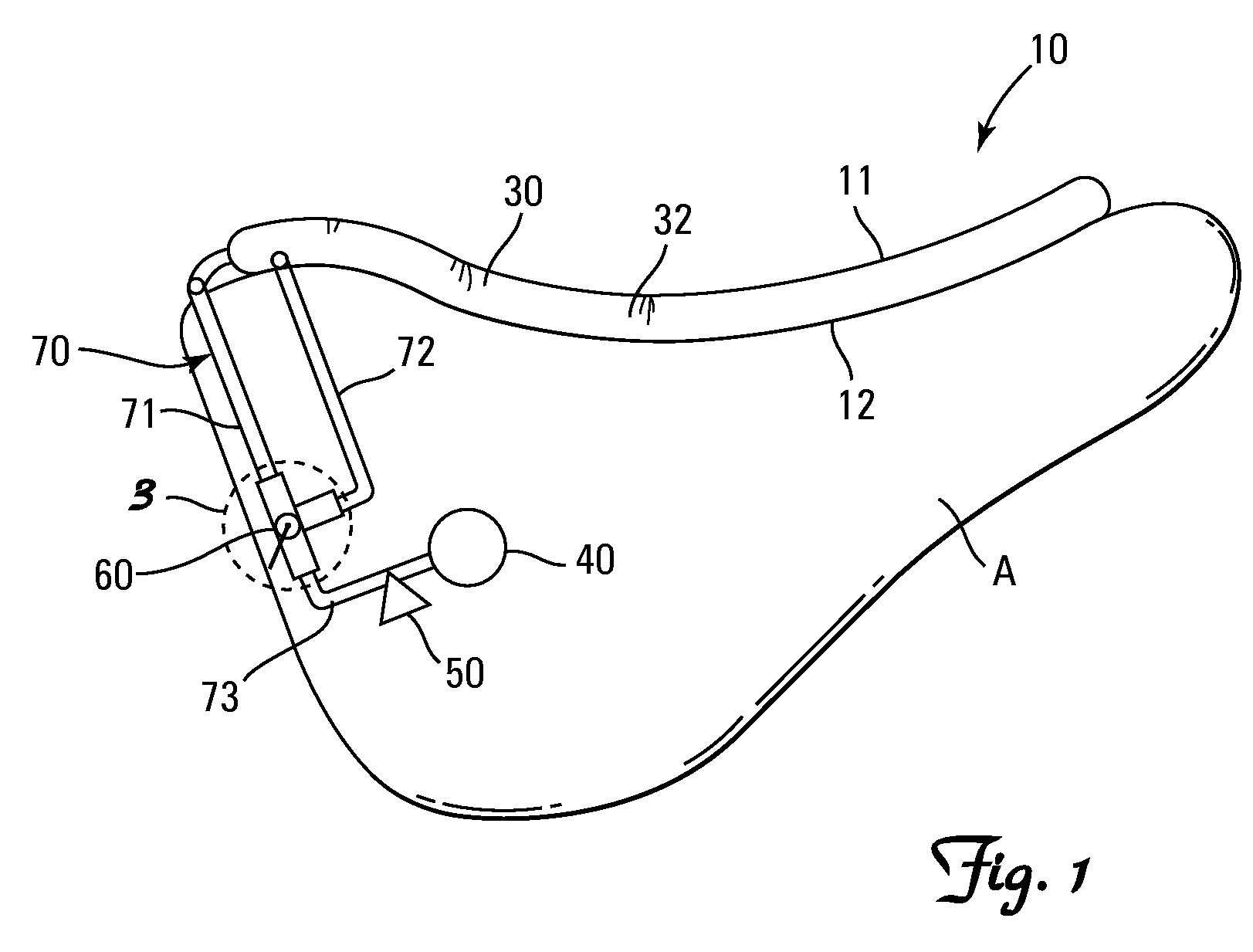
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by delivering drugs to various nerves or tissues
InactiveUS20050010259A1Strong specificityLower medical costsElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseLigament structure
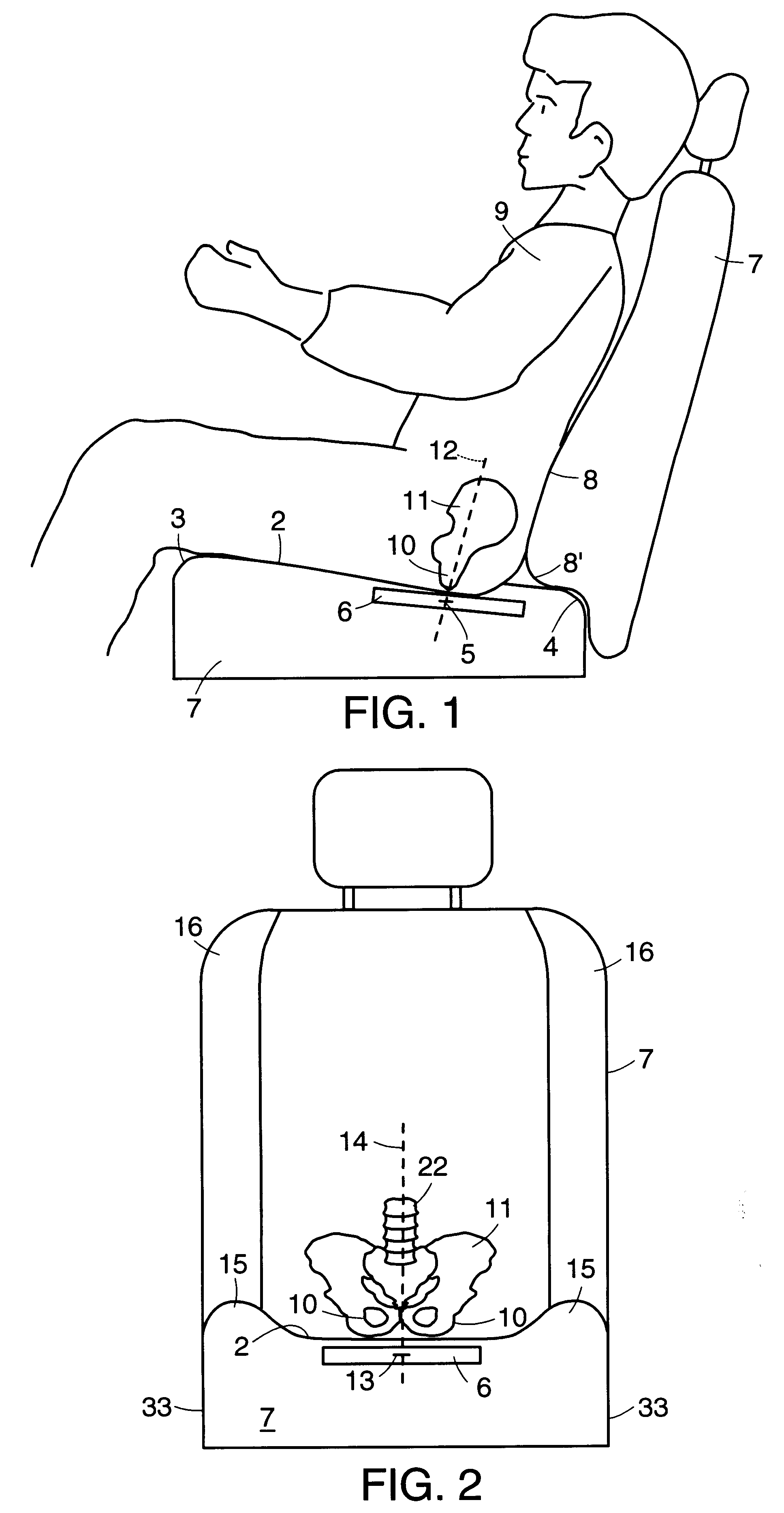
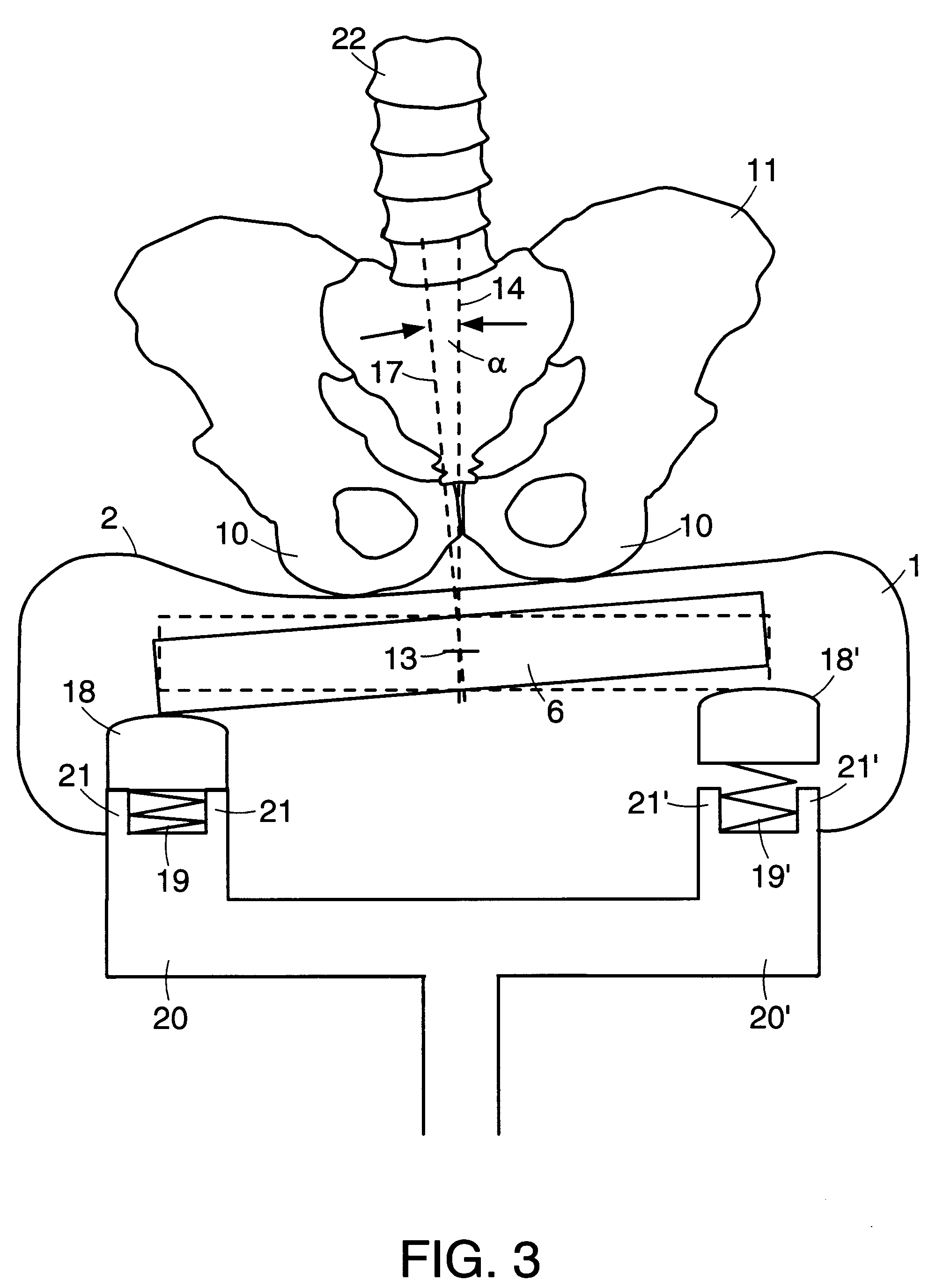
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by delivering one or more drugs to a patient's hypogastric nerve or branches or portions thereof, prostatic plexus nerve or branches or portions thereof, sacral splanchnic nerve or branches or portions thereof, pelvic splanchnic nerve or branches or portions thereof, prostate or branches or portions thereof, pelvic floor, colon or branches or portions thereof, bladder or portions thereof, vagina or portions thereof, anus or portions thereof, external anal sphincter or portions thereof, urethra or portions thereof, penile dorsal nerve or portions thereof, inferior rectal nerves or branches or portions thereof, perineal nerves or branches or portions thereof, scrotal nerves or branches or portions thereof, scrotum or portions thereof, Alcock's Canal or branches or portions thereof, sacro-tuberous ligament or branches or portions thereof, ischial tuberosity or branches or portions thereof, greater sciatic foramen or branches or portions thereof, or lesser sciatic foramen or branches or portions thereof. One, two or more drug delivery regimes are provided on a continuous, alternating, intermittent or other basis to one or more selected nerves, nerve portions or tissues in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
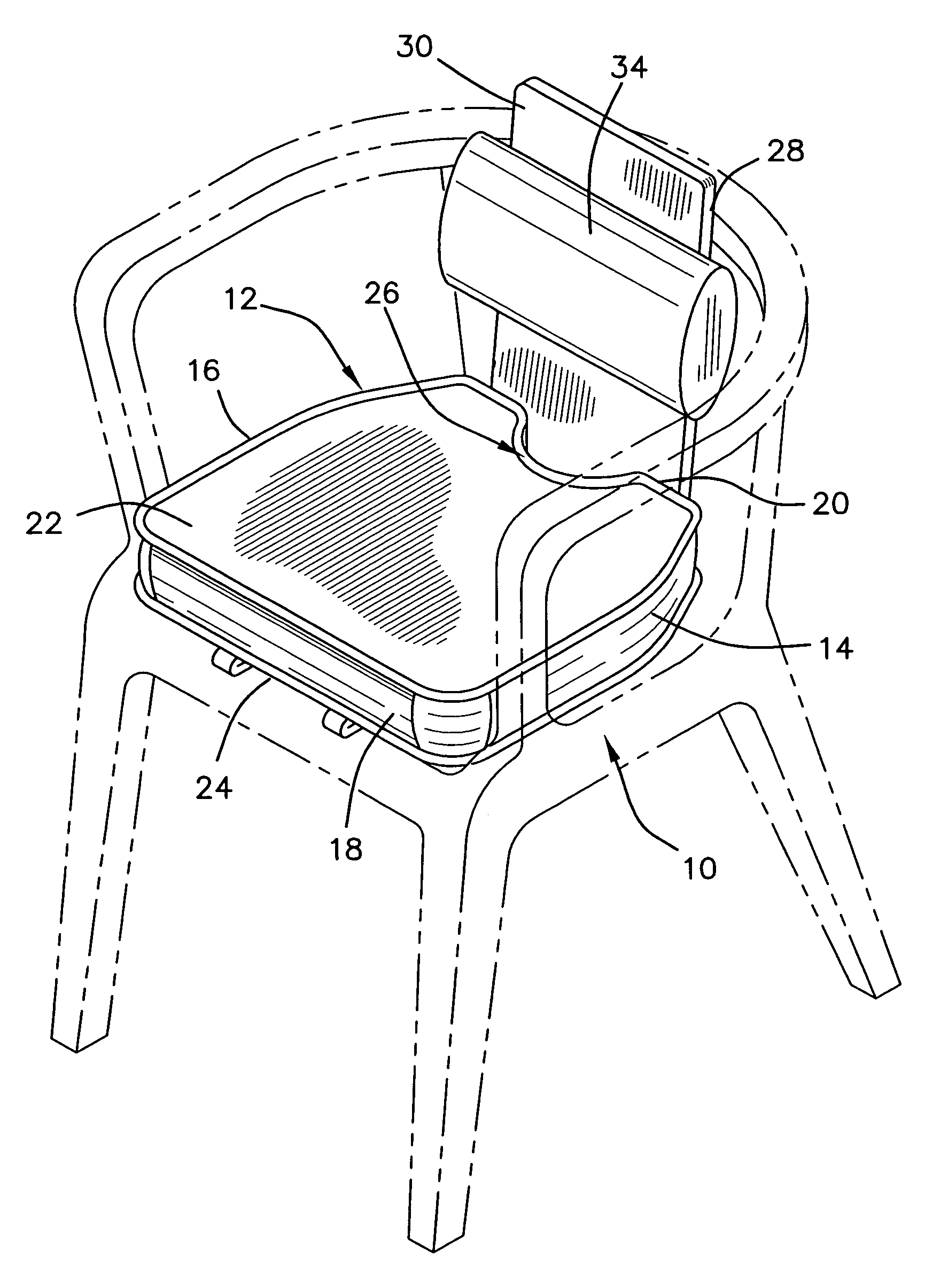
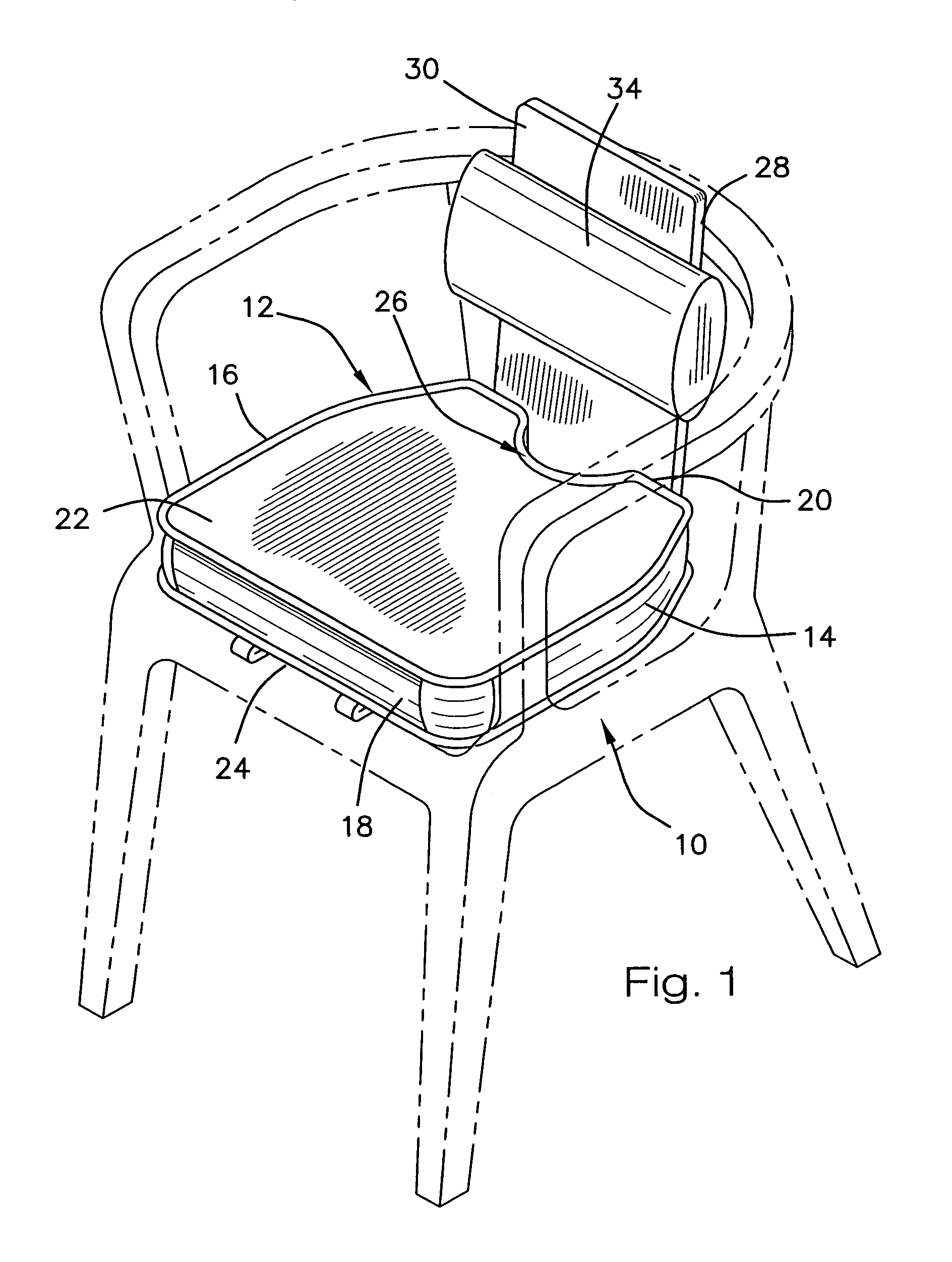
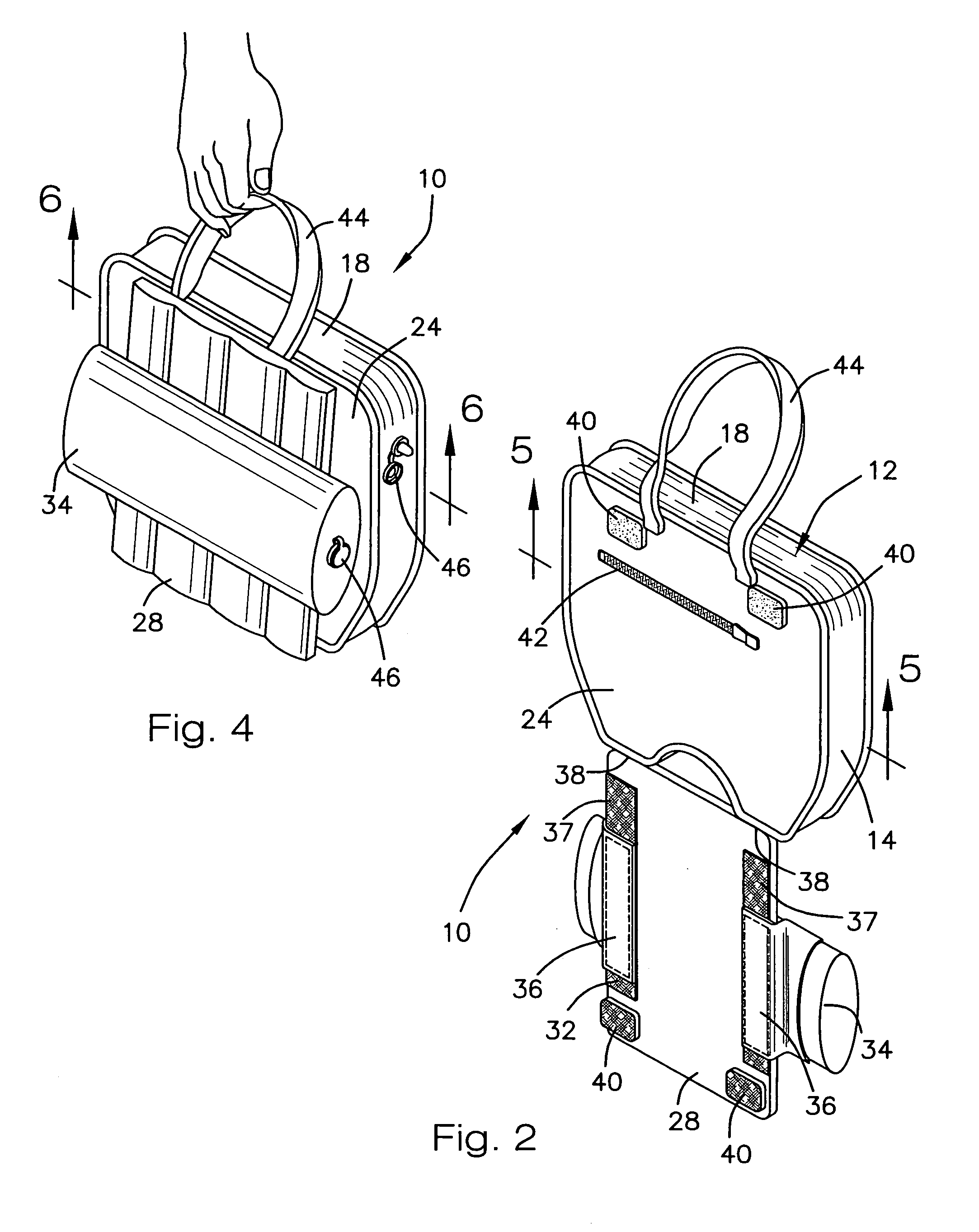
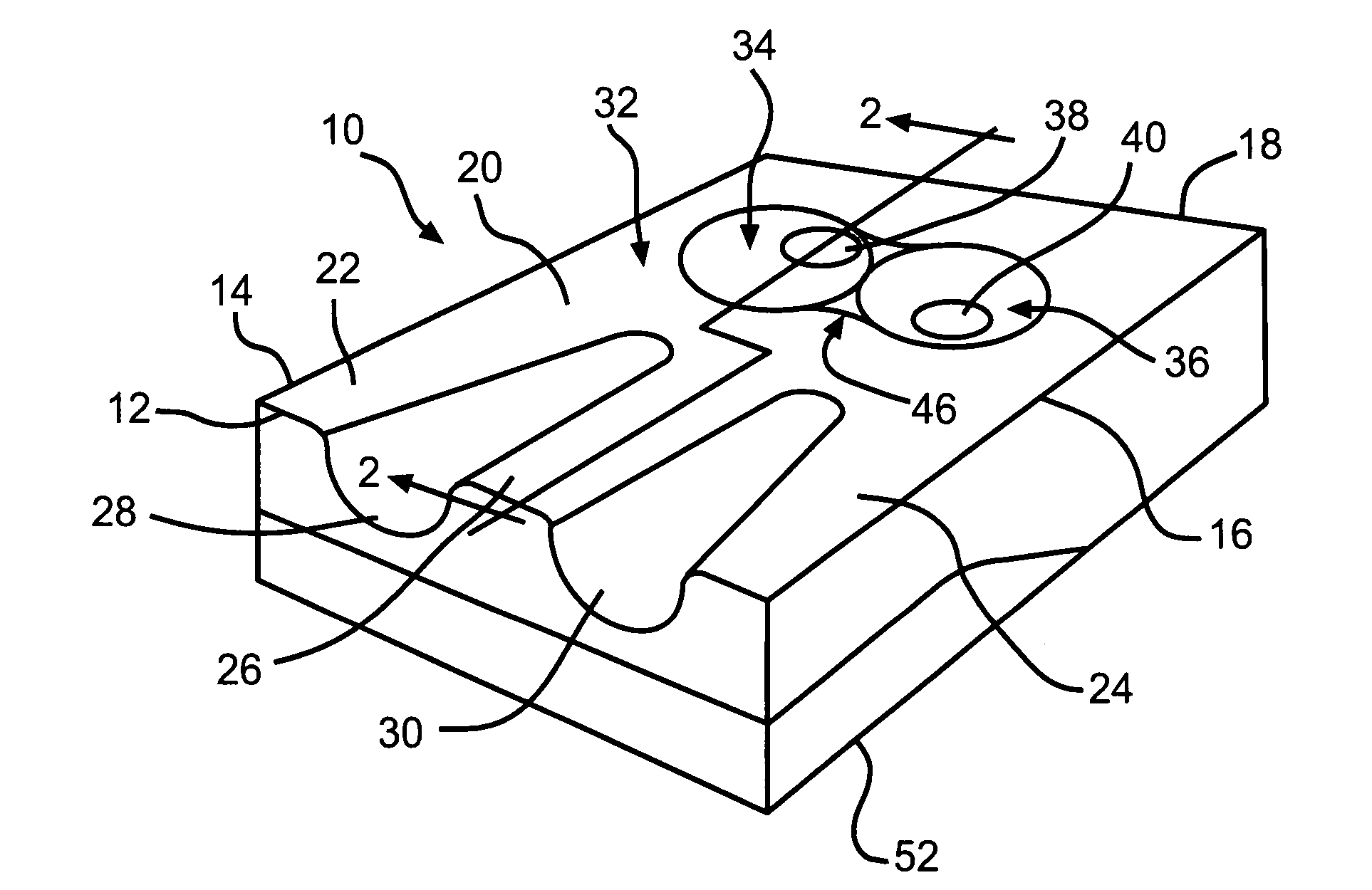
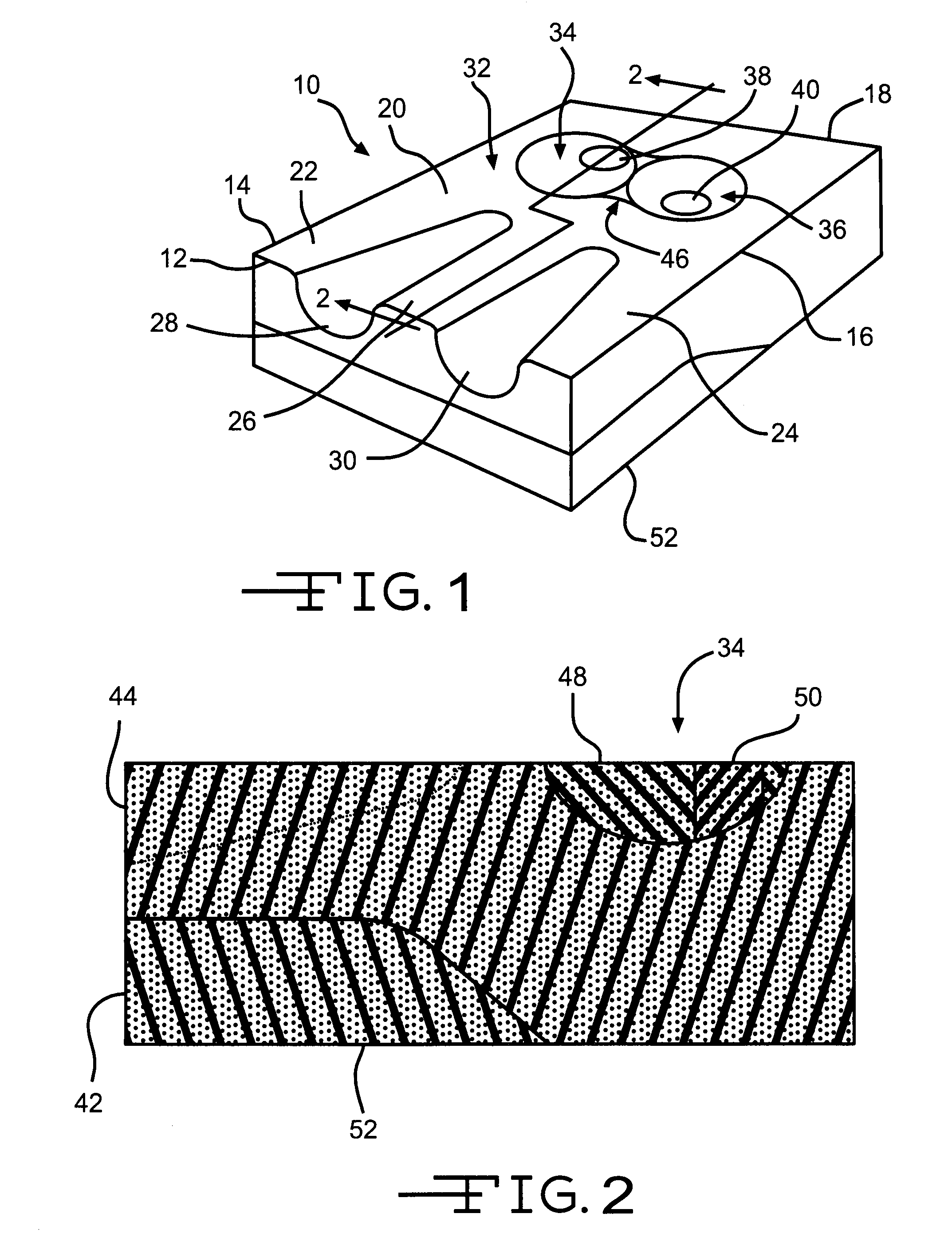
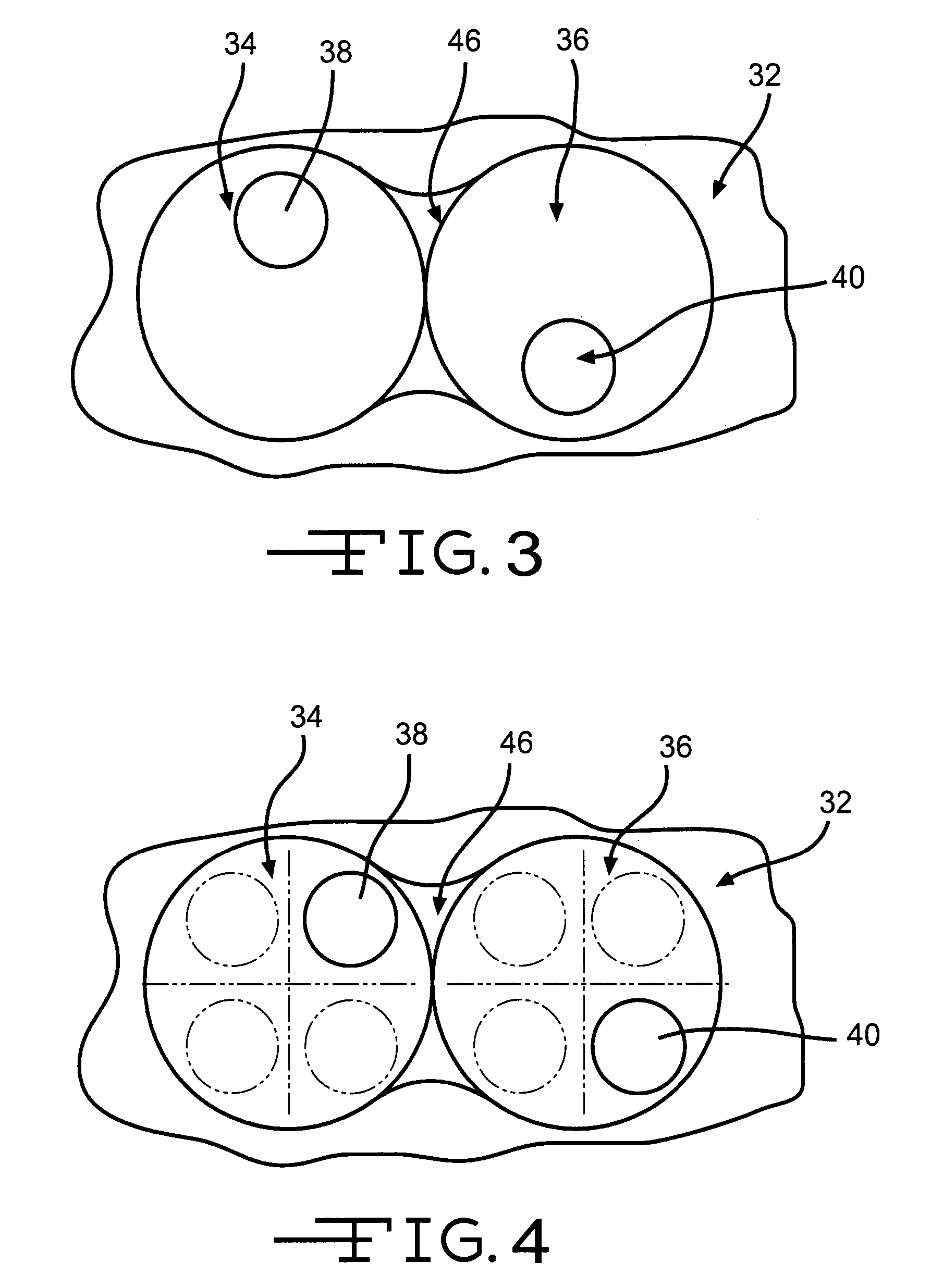
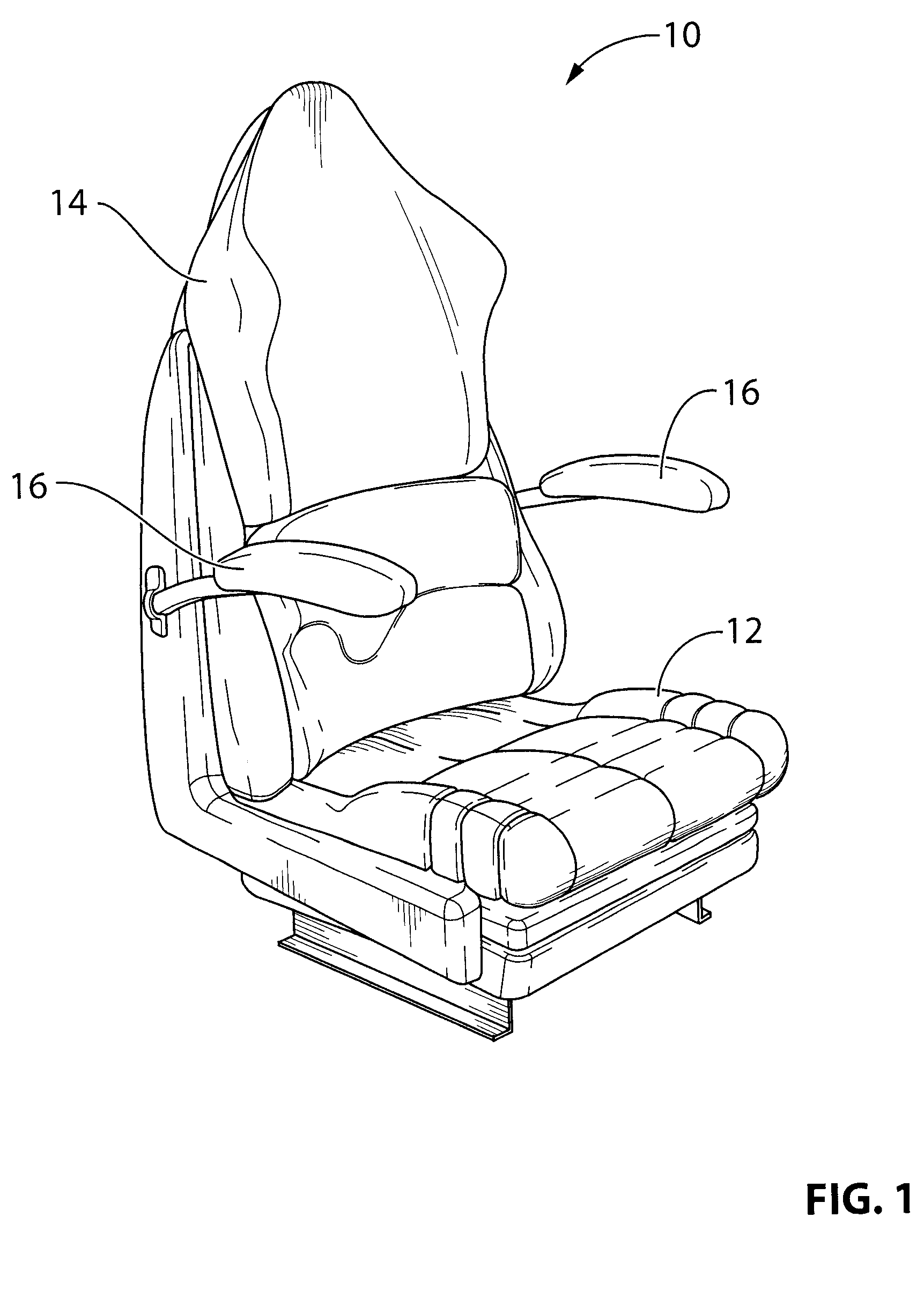
Portable ergonomic cushion
InactiveUS6929325B1Easy to installImprove application flexibilityStuffed mattressesDismountable chairsCoccyxIschial tuberosity
A new and improved portable ergonomic cushion for relieving pressure on the coccyx (tailbone) and on the ischial tuberosities, for promoting correct positioning of the sacroiliac joint and for supporting the lower back of the user is described. The portable ergonomic cushion includes a narrow ridge back support allowing the cushion to be used with numerous styles of chairs and seats, and a lumbar support cushion that is removably attached to the back support. The portable ergonomic cushion may also make use of inflatable cushions for increasing the flexibility of the sitting cushion by allowing users to adjust the cushions to their desired support by varying the amount the cushions are inflated. The portable ergonomic cushion is also foldable into a compact non-use position for easy transportation and storage, and futher does not require the use of straps for retaining the cushion while in use.
Owner:GOELO FRANCOIS
Contoured seat cushion and method for offloading pressure from skeletal bone prominences and encouraging proper postural alignment
InactiveUS7216388B2Reduce riskIncreased riskSofasWheelchairs/patient conveyanceSkin breakdownButtocks
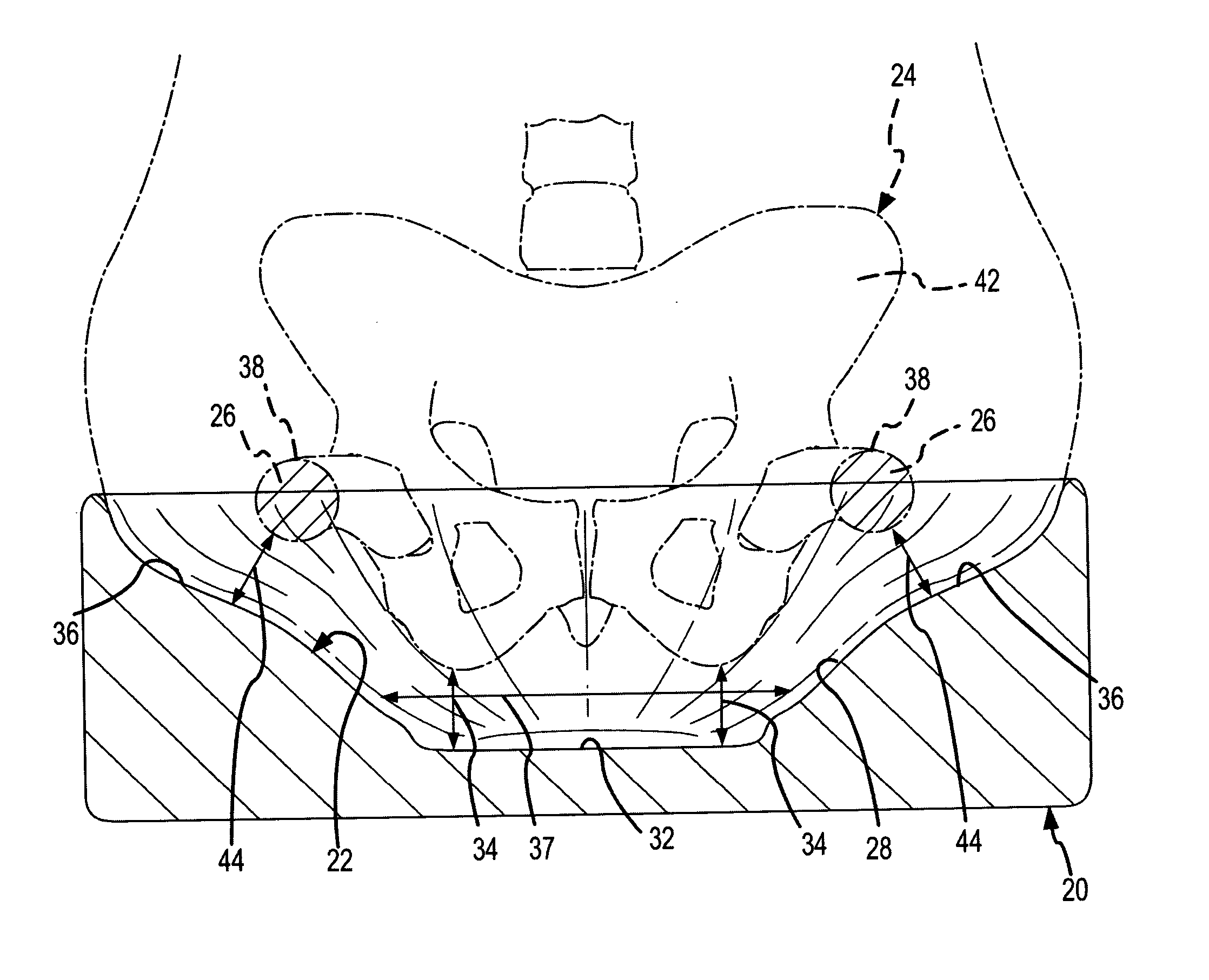
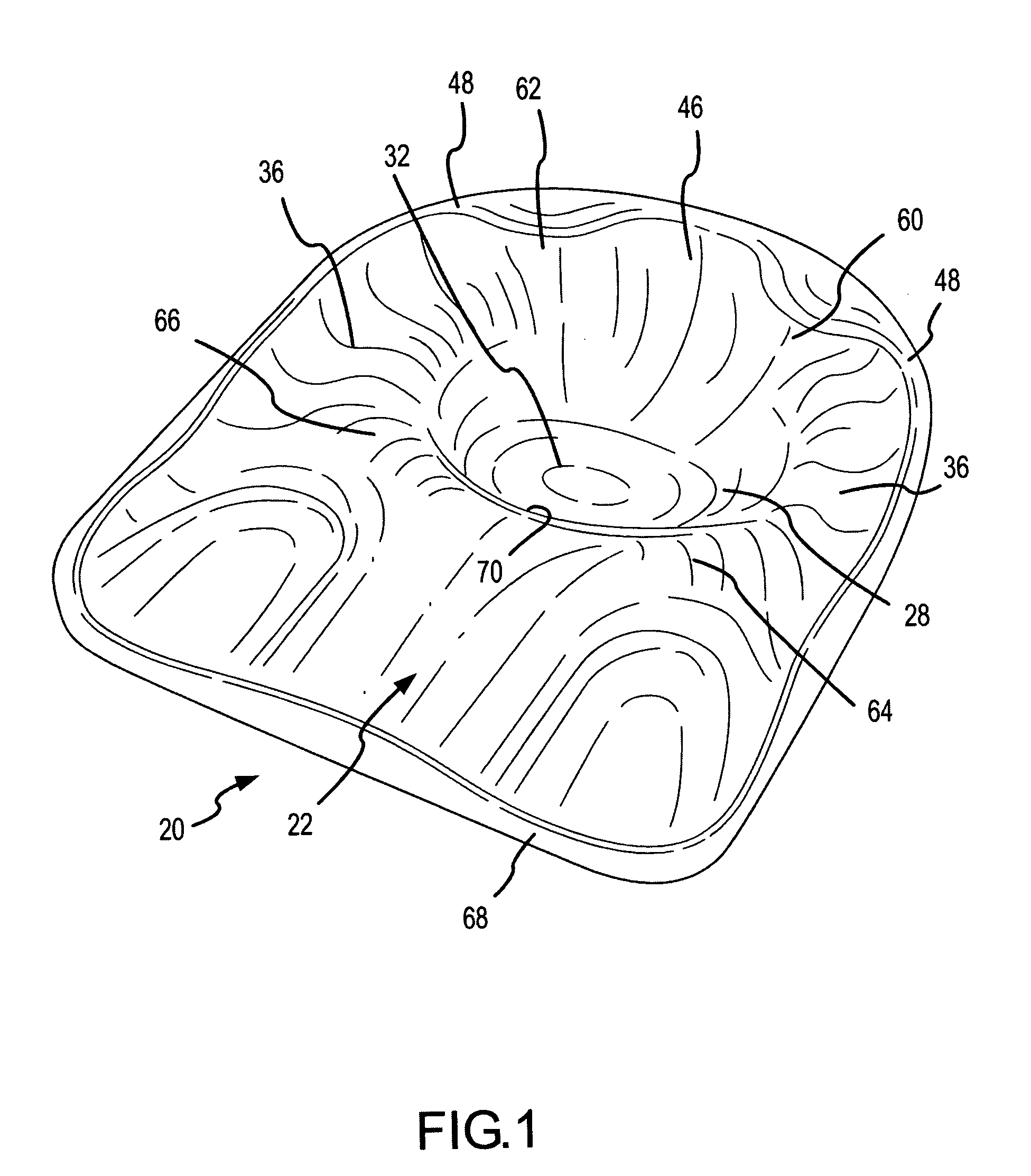
A support contour of a cushion, such as a wheelchair cushion, defines relief areas at locations adjacent to skin covering the ischial tuberosities, the greater trochanters and the coccyx and sacrum of a person sitting on the support contour. Support areas of the support contour transfer force into the pelvic area adjacent to skin covering tissue masses on opposite lateral sides of the posterior buttocks and beneath the proximal thighs of the person. Greater clearance is also provided in the perineal area. Risks of pressure ulcers from pressure and shear forces on bony prominences is reduced while providing support at the broader areas without bony prominences in such a manner to encourage postural alignment. The risks of skin breakdown perineal are diminished.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
Method, system and device for treating disorders of the pelvic floor by delivering drugs to various nerves or tissues
InactiveUS7427280B2EfficaciousMore delivery of drugElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseLigament structure
Described are implantable devices and methods for treating various disorders of the pelvic floor by delivering one or more drugs to a patient's hypogastric nerve or branches or portions thereof, prostatic plexus nerve or branches or portions thereof, sacral splanchnic nerve or branches or portions thereof, pelvic splanchnic nerve or branches or portions thereof, prostate or branches or portions thereof, pelvic floor, colon or branches or portions thereof, bladder or portions thereof, vagina or portions thereof, anus or portions thereof, external anal sphincter or portions thereof, urethra or portions thereof, penile dorsal nerve or portions thereof, inferior rectal nerves or branches or portions thereof, perineal nerves or branches or portions thereof, scrotal nerves or branches or portions thereof, scrotum or portions thereof, Alcock's Canal or branches or portions thereof, sacro-tuberous ligament or branches or portions thereof, ischial tuberosity or branches or portions thereof, greater sciatic foramen or branches or portions thereof, or lesser sciatic foramen or branches or portions thereof. One, two or more drug delivery regimes are provided on a continuous, alternating, intermittent or other basis to one or more selected nerves, nerve portions or tissues in an amount and manner effective to treat a number of disorders, including, but not limited to, urinary and / or fecal voiding dysfunctions such as constipation, incontinence disorders such as urge frequency and urinary retention disorders, sexual dysfunctions such as orgasmic and erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, prostatitis, prostatalgia and prostatodynia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
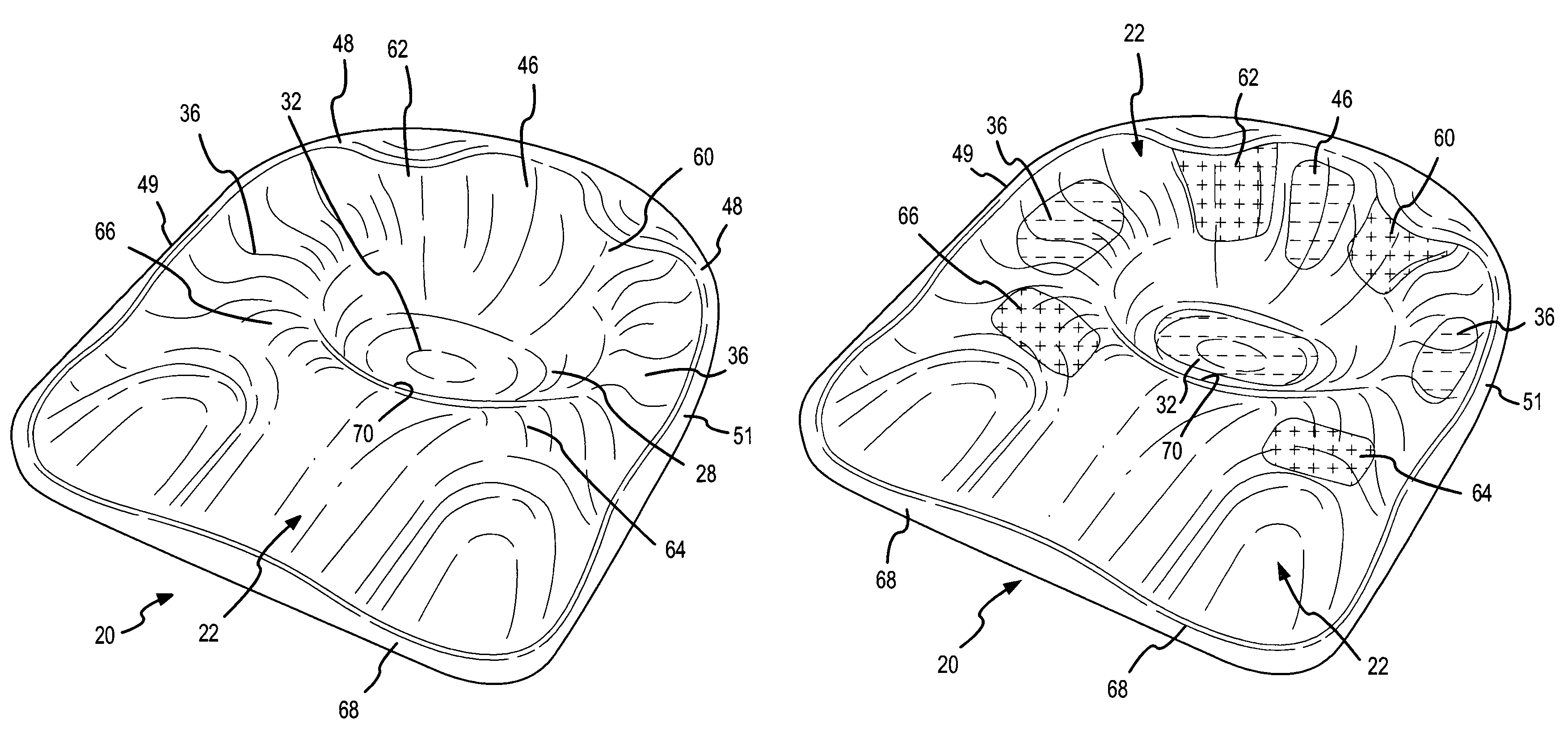
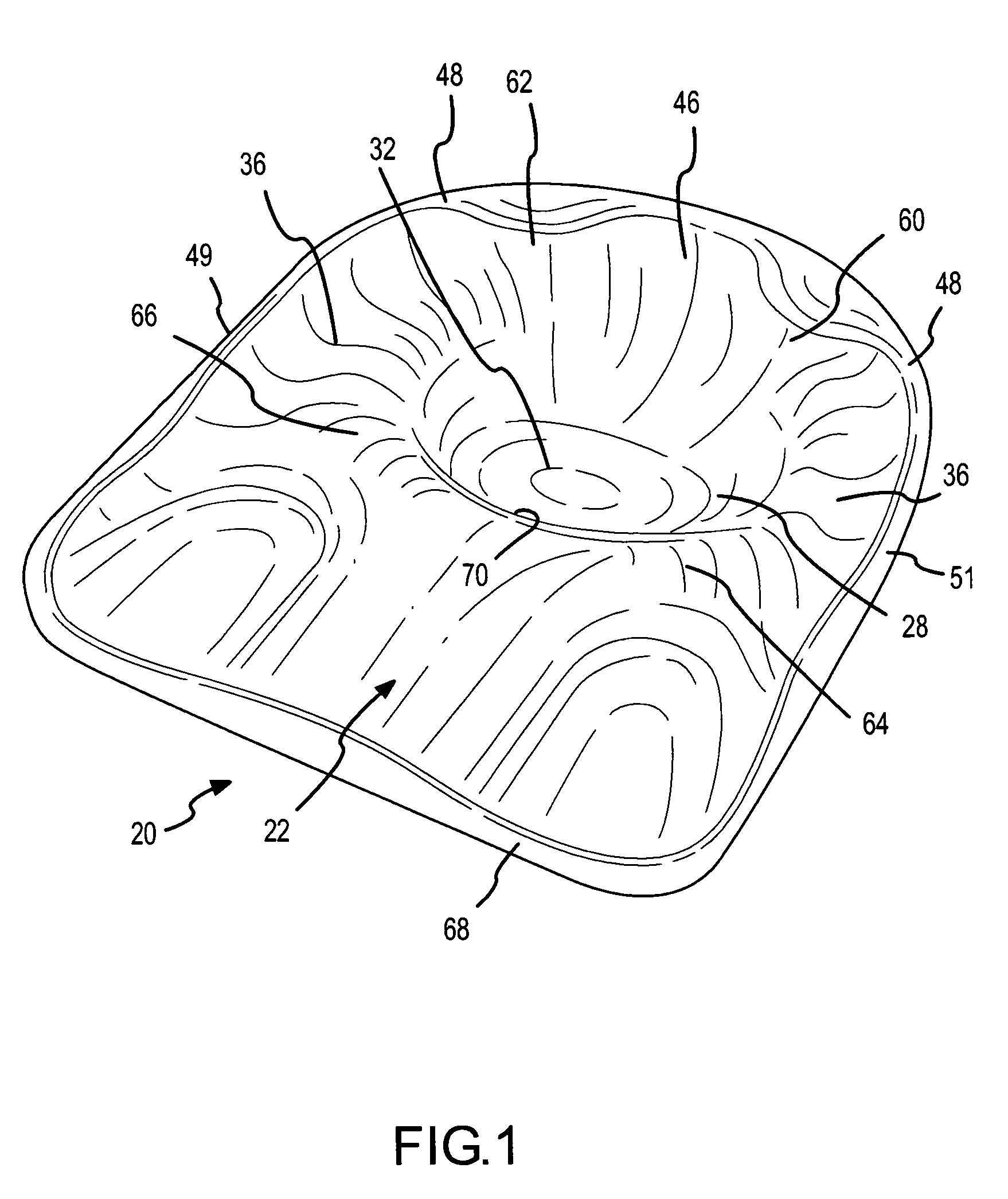
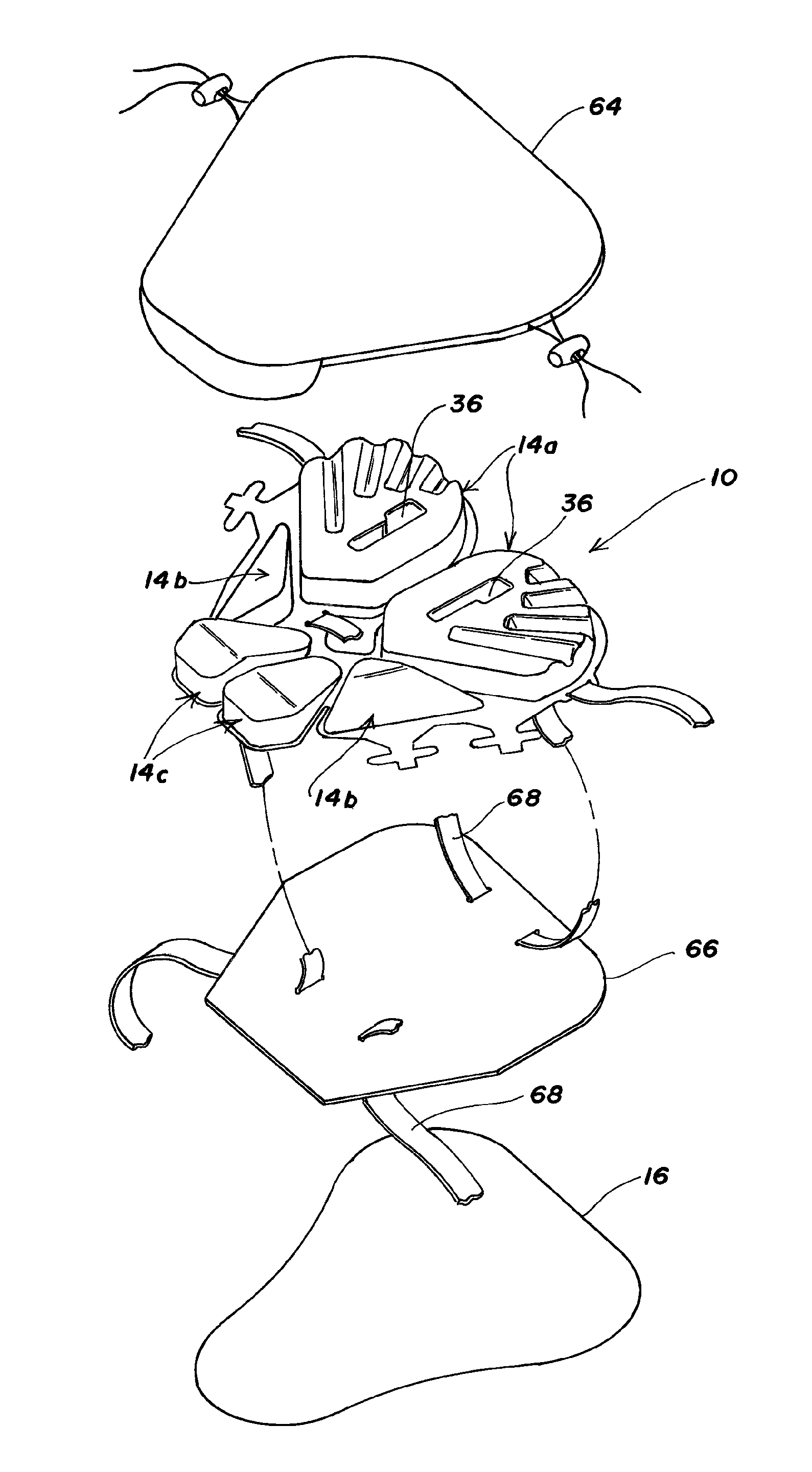
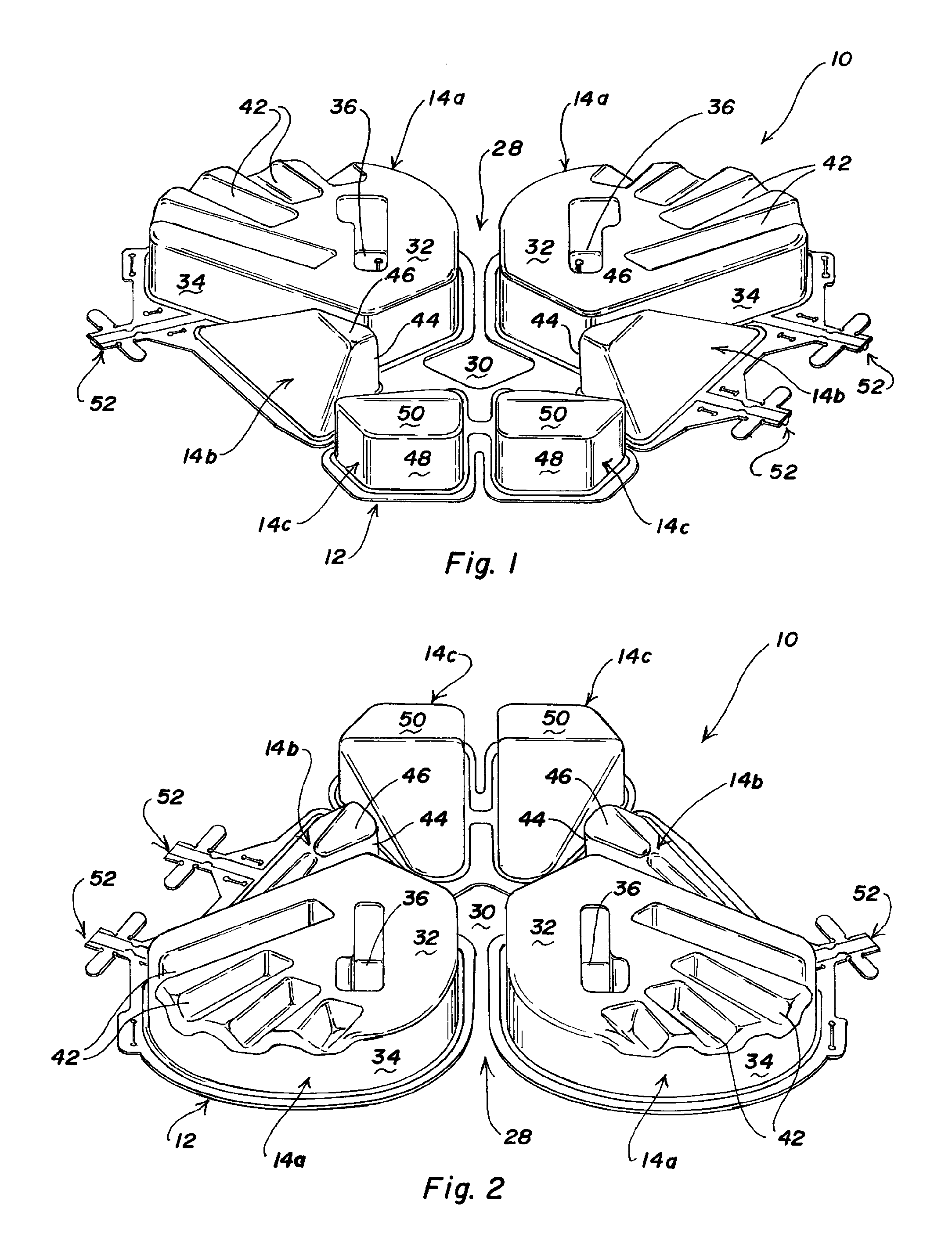
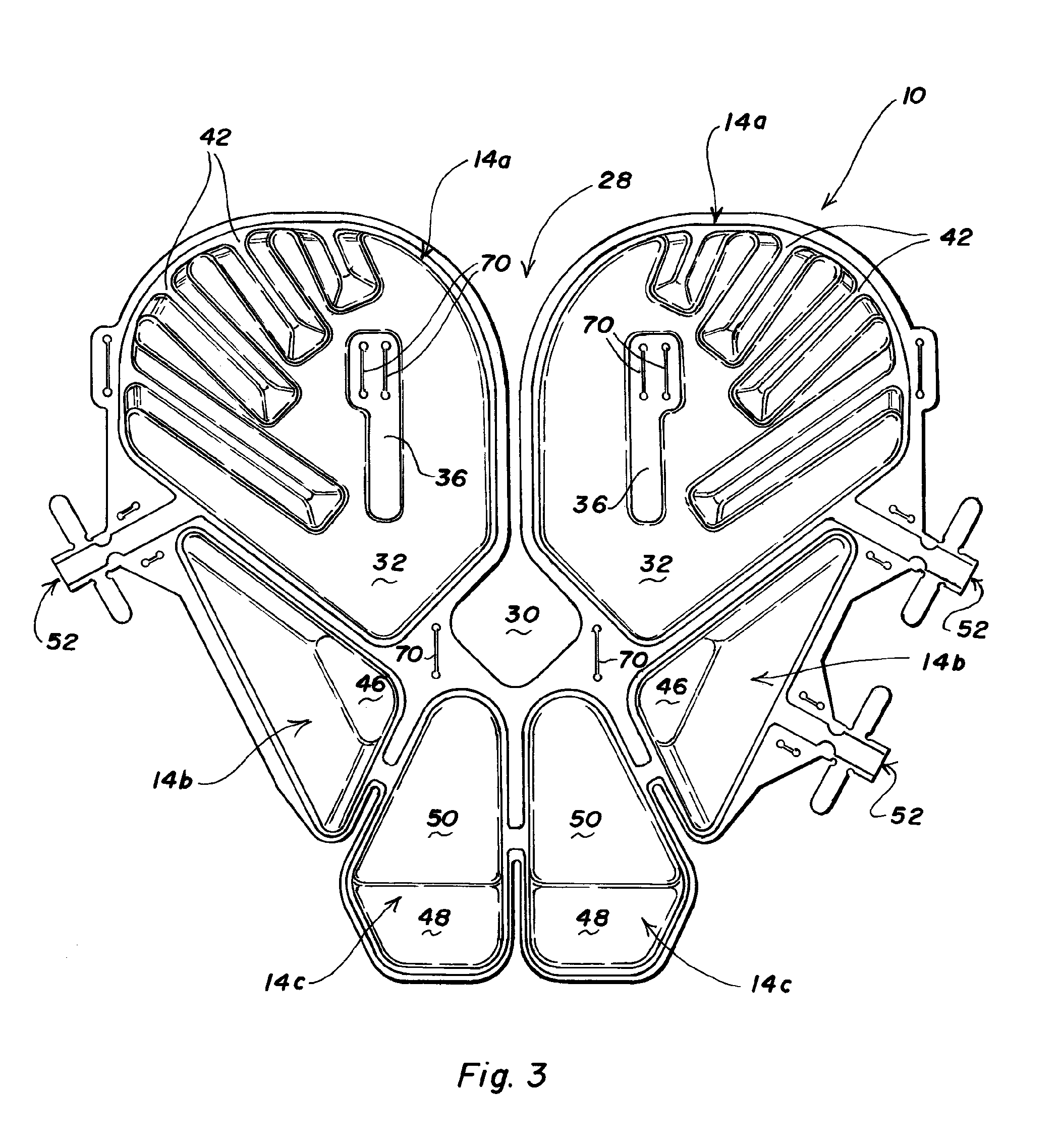
Wheelchair seat cushion
A wheelchair seat cushion has multi-density regions. The cushion assembly may have a region having a stiffer, higher density proximate the front of the seat cushion assembly beneath the user's thighs to assist the user in exiting the wheelchair. Alternatively, or additionally, an insert member having multi-density regions may be received in a recess in a base member. The insert members may be oriented in different orientations to position a softer, less dense region at different locations, to situate the softer, less dense region of the insert beneath a particular user's ischial tuberosities and / or coccyx.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL (US) LLC
Seat element
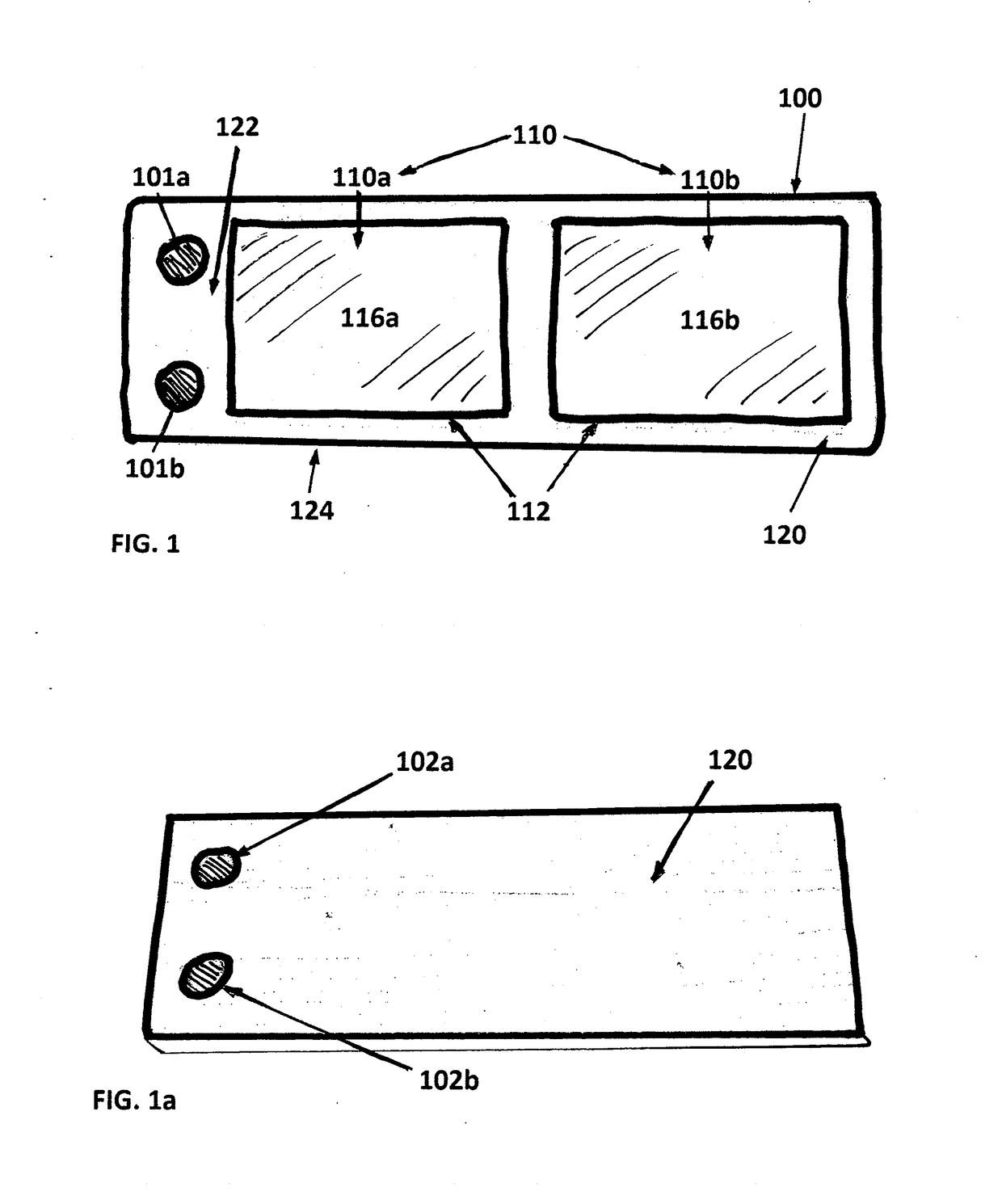
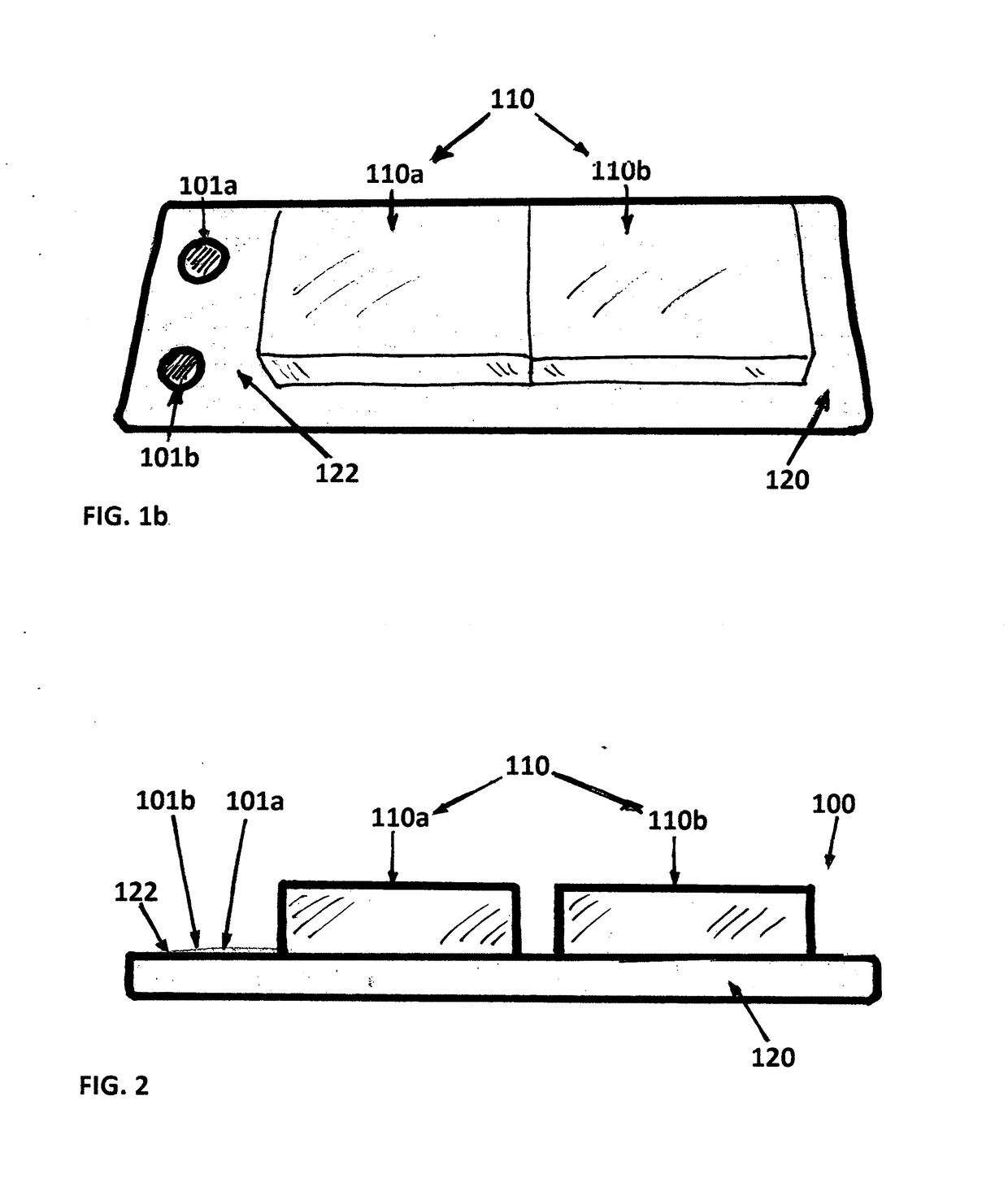
InactiveUS6213553B1Sufficient nutrientsReduce the static workforce of the paraspinal musclesOperating chairsDental chairsIschial tuberosityEngineering
Owner:FITZ WOLFGANG
Contoured seat cushion and method for offloading pressure from skeletal bone prominences and encouraging proper postural alignment
InactiveUS20050022305A1Firm supportReduce riskSofasWheelchairs/patient conveyanceSkin breakdownButtocks
A support contour of a cushion, such as a wheelchair cushion, defines relief areas at locations adjacent to skin covering the ischial tuberosities, the greater trochanters and the coccyx and sacrum of a person sitting on the support contour. Support areas of the support contour transfer force into the pelvic area adjacent to skin covering tissue masses on opposite lateral sides of the posterior buttocks and beneath the proximal thighs of the person. Greater clearance is also provided in the perineal area. Risks of pressure ulcers from pressure and shear forces on bony prominences is reduced while providing support at the broader areas without bony prominences in such a manner to encourage postural alignment. The risks of skin breakdown perineal are diminished.
Owner:ASPEN SEATING
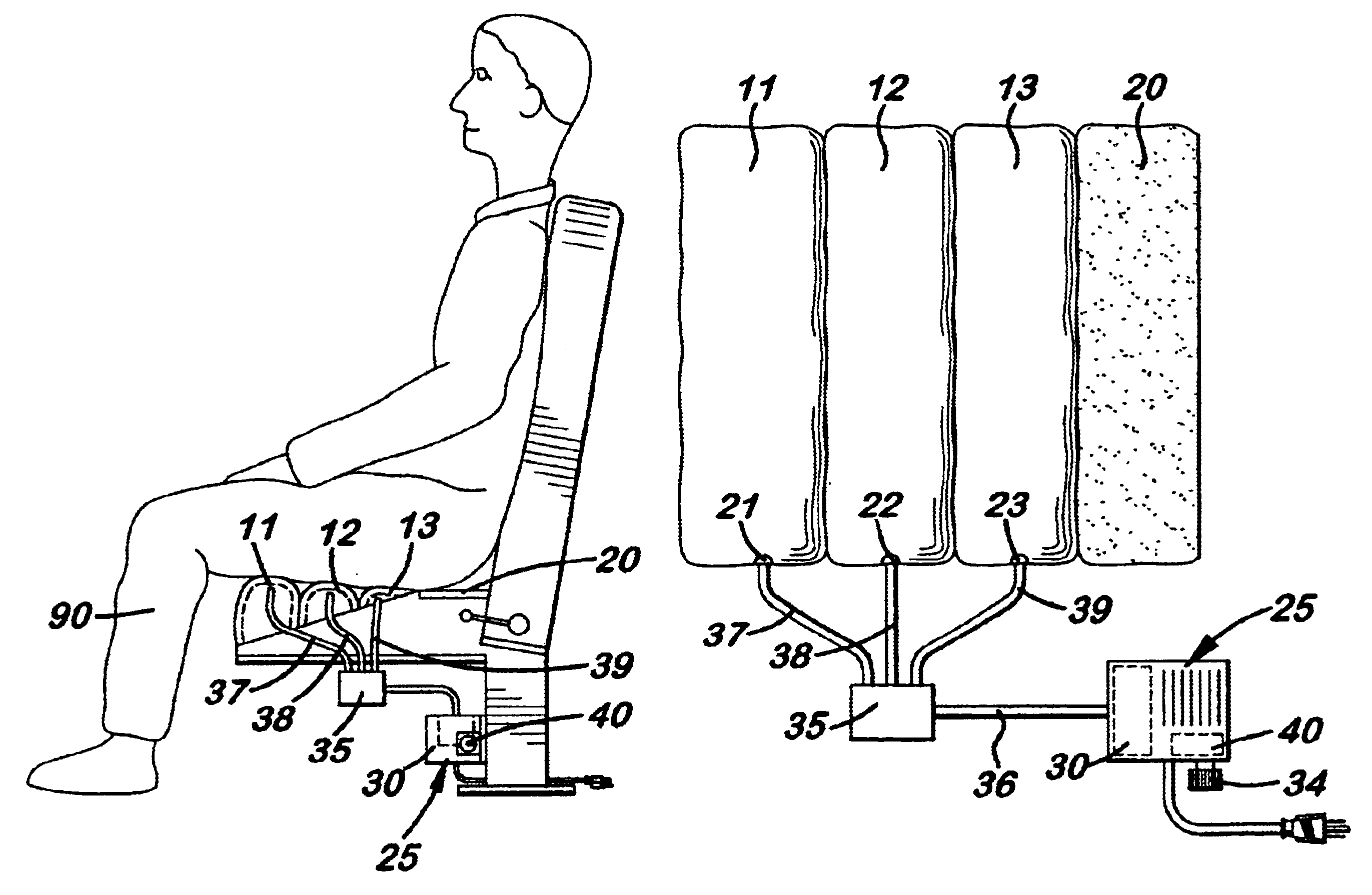
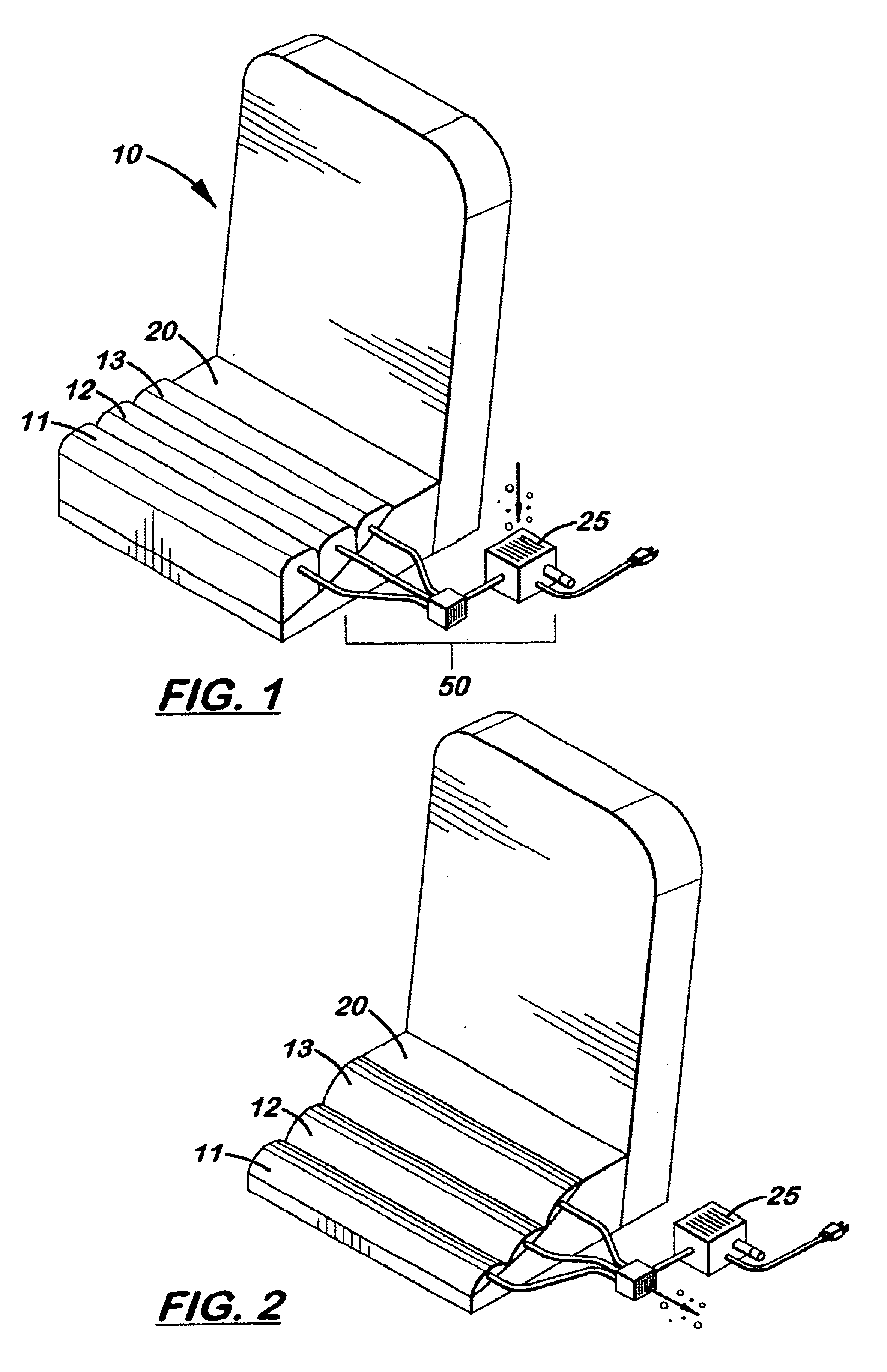
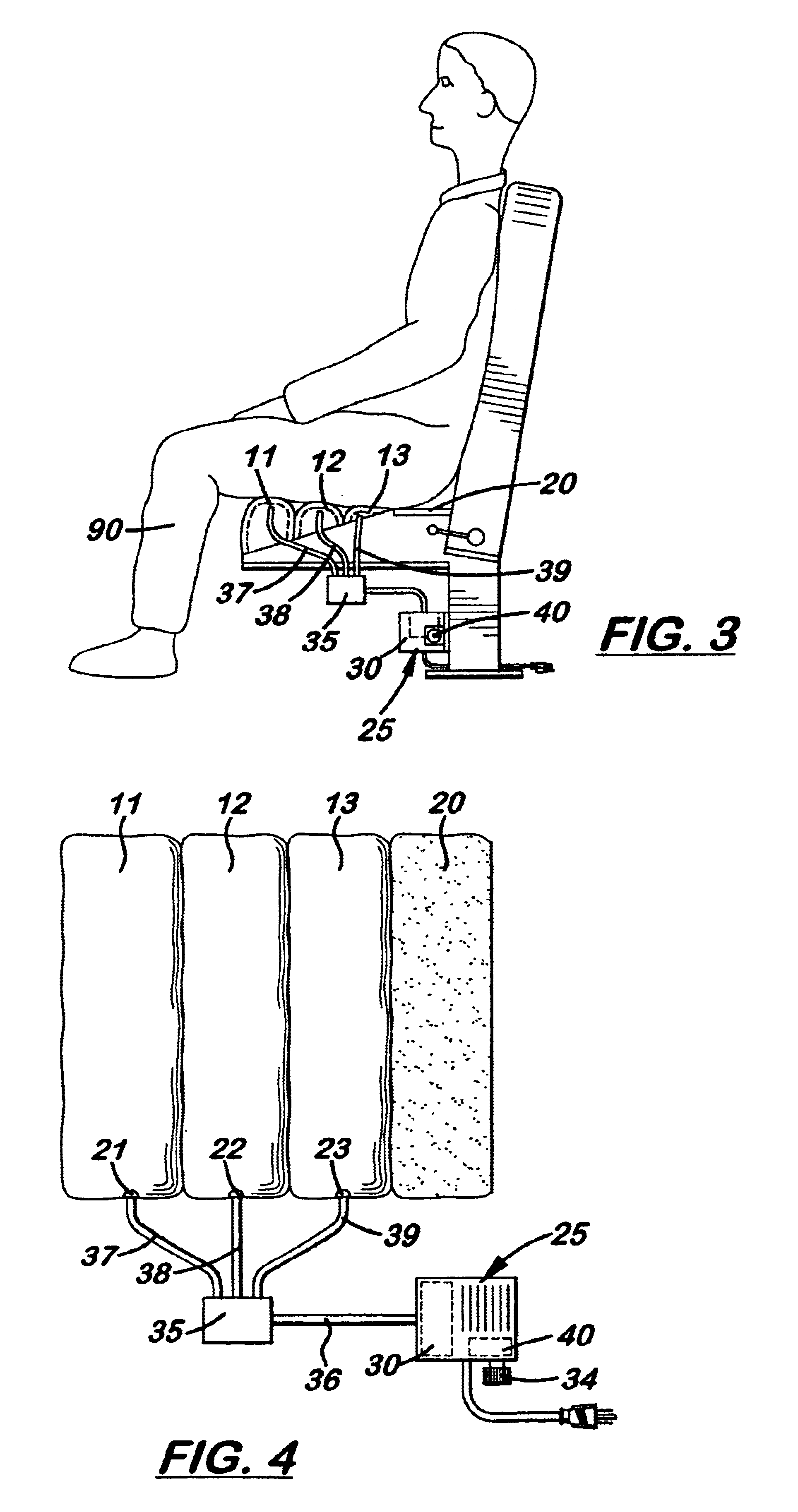
Body supporting, serial inflating seat
InactiveUS6782573B2Reducing blood poolingPrevent forward movementPhysical therapyThigh restsIschial tuberosityEngineering
A sequentially or serial inflating seat cushion comprising at least three transversely aligned inflatable air bladders connected to a pump and timer. The air bladders are inflated sequentially, from front to back, over a period of approximately eleven seconds and simultaneously deflated to slowly pump blood upward in the legs thereby reducing blood pooling. Connected to the pump is a valve that keeps the air bladders inflated a selective amount of time. The cycle is then repeated continuously. Located adjacent to the back air bladder is a transversely aligned, non-inflating seat section which continuously supports the user's ischial tuberocities to prevent slippage over the seat. An alternate embodiment offers a split seat option with six inflatable bladders.
Owner:ODDERSON IB R
Wheelchair seat cushion
InactiveUS20080079306A1Sufficiently denseSufficiently stiffVehicle seatsStuffed mattressesWheelchairHigh density
A wheelchair seat cushion has multi-density regions. The cushion assembly may have a region having a stiffer, higher density proximate the front of the seat cushion assembly beneath the user's thighs to assist the user in exiting the wheelchair. Alternatively, or additionally, an insert member having multi-density regions may be received in a recess in a base member. The insert members may be oriented in different orientations to position a softer, less dense region at different locations, to situate the softer, less dense region of the insert beneath a particular user's ischial tuberosities and / or coccyx.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL (US) LLC
Seat
ActiveUS7731294B2Mitigating pain and numbnessSit securelySeat coveringsStoolsSurface layerCoil spring
Owner:DELTA TOOLING CO LTD
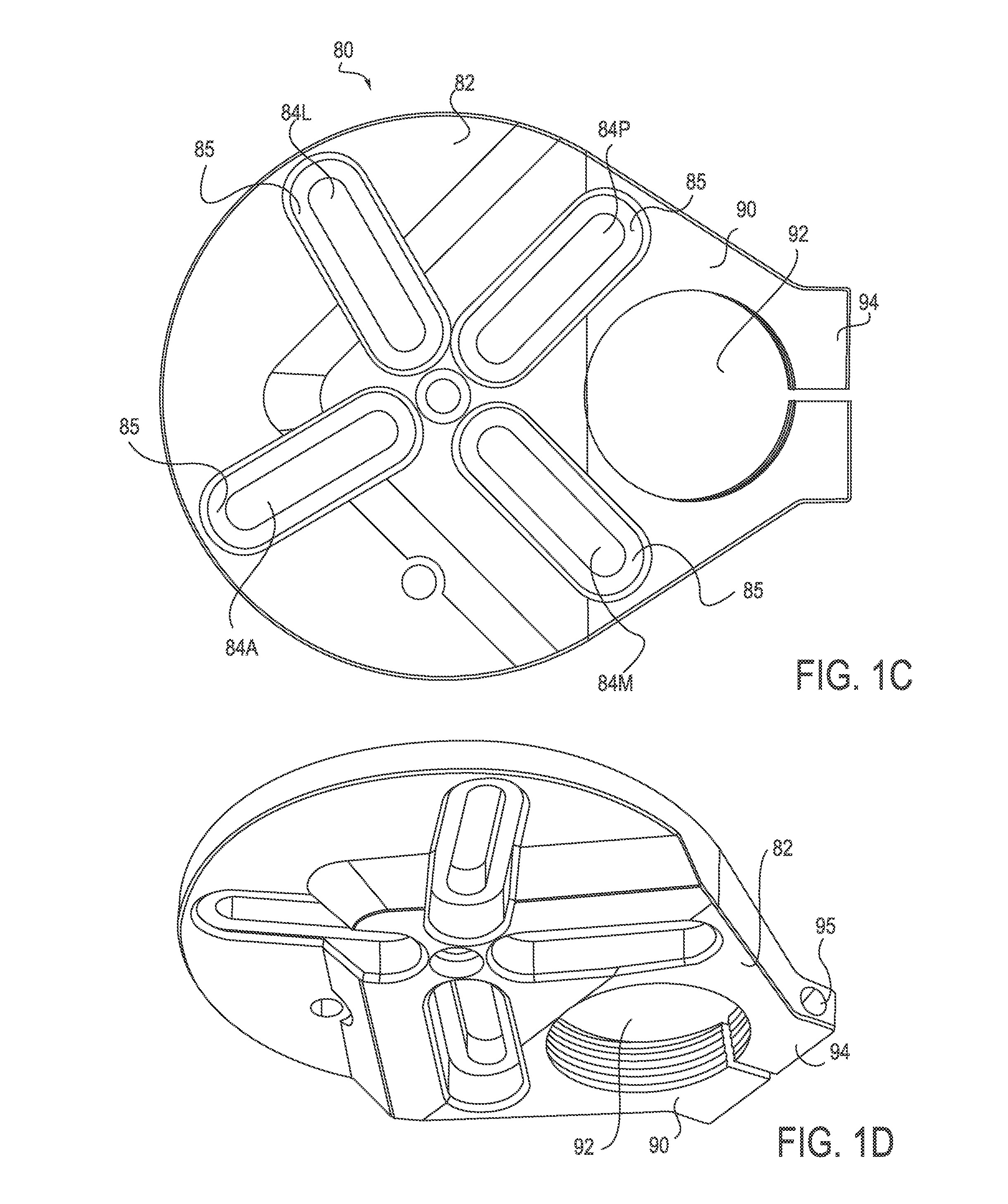
Prosthetic socket with an adjustable height ischial seat
InactiveUS20160058584A1Programme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusPhysical medicine and rehabilitationIschial tuberosity
A modular prosthetic socket for a residual limb of a lower extremity of a patient may include an adjustable height ischial seat for facilitating the distribution of body weight away from the distal end of the residual limb and channeling the weight preferentially through the ischial tuberosity. In one aspect, the modular prosthetic socket may include a base plate, multiple longitudinal struts, and an ischial seat pad adjustably coupled with the proximal end of a medial strut, such that the ischial seat pad is vertically adjustable relative to the medial strut to adjust a total length of the medial strut measured from a proximal end of the ischial seat pad to the distal end of the medial strut. The ischial seat pad is configured to engage an ischium of the patient when the prosthetic socket is worn by the patient.
Owner:LIM INNOVATIONS
Pelvic floor training device
A training device for training the pelvic floor muscles of a human, which can be externally placed on the human body and can be connected to feedback units that produce feedback signals, such as vibrations. The training device is, at least on one side, aligned with the pelvic floor, can be compressed and can be axially deformed on its sensor side. A pressure force sensor unit of the training device can be positioned during the operation in such a manner that the ischial tuberosities of the pelvic floor can be situated on both sides on the pressure sensor unit, and a gravitational force component passing through the pelvic floor acts upon the pelvic floor training device, making a precise measurement of the exertion on the pelvic floor possible.
Owner:MSYS
Adjustable seat cushion
InactiveUS7648198B1Improve stabilityAdjustable spacingVehicle seatsSeating furnitureIschial tuberosityBiomedical engineering
An adjustable seat cushion for use on a support surface such as the seat of a motorcycle. The seat cushion is cellular and laterally spreadable inwardly or outwardly depending on the space between the ischial tuberosities of a user seated on the cushion for improved comfort. In an embodiment, the cellular cushion cups the buttocks and also tilts the pelvis of a user seated on the cushion forward for enhanced seated stability.
Owner:MATSLER WINFIELD R
Pelvic floor training device
A training device for training the pelvic floor muscles of a human, which can be externally placed on the human body and can be connected to feedback units that produce feedback signals, such as vibrations. The training device is, at least on one side, aligned with the pelvic floor, can be compressed and can be axially deformed on its sensor side. A pressure force sensor unit of the training device can be positioned during the operation in such a manner that the ischial tuberosities of the pelvic floor can be situated on both sides on the pressure sensor unit, and a gravitational force component passing through the pelvic floor acts upon the pelvic floor training device, making a precise measurement of the exertion on the pelvic floor possible.
Owner:MSYS
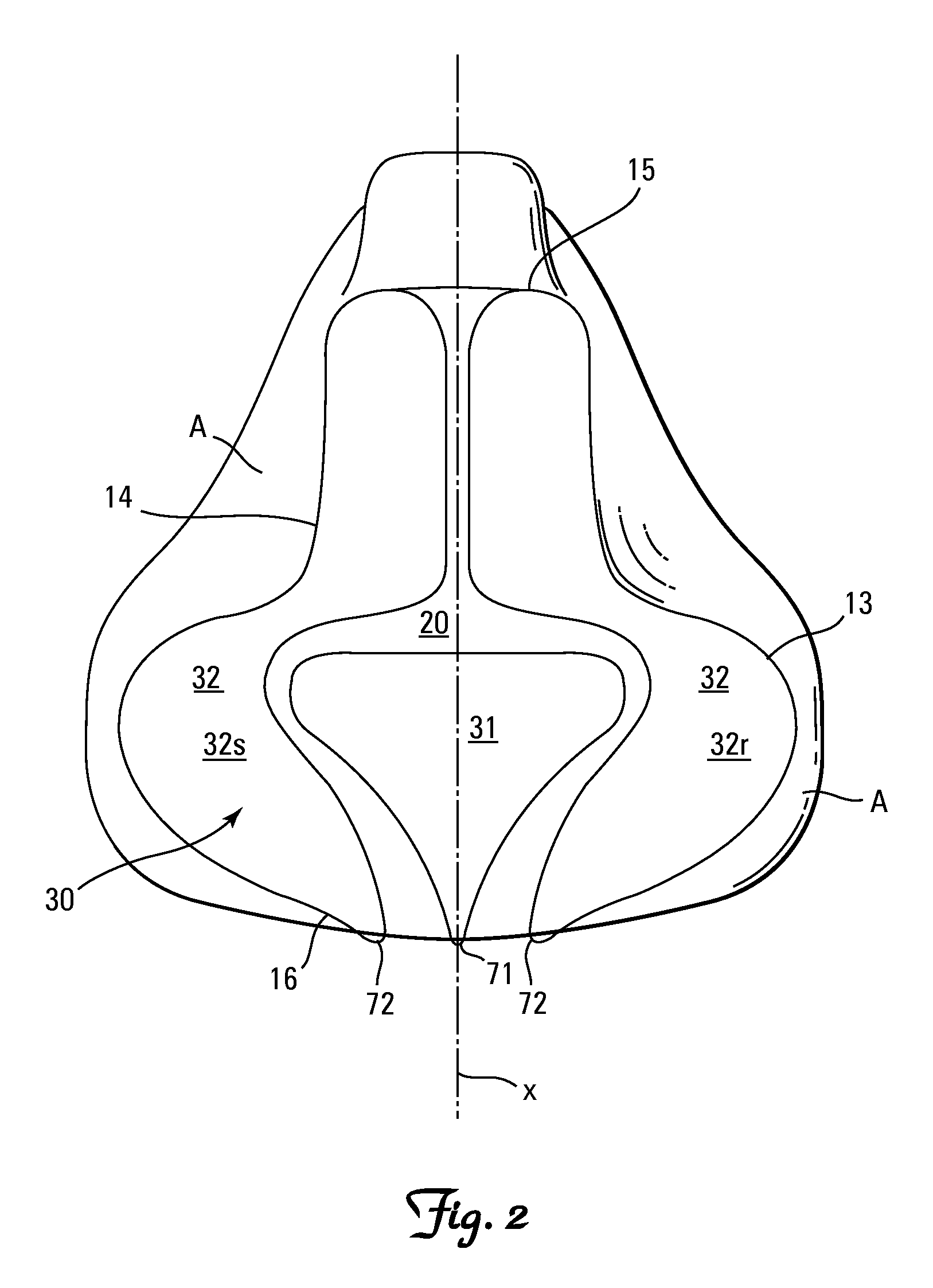
Ergonomically designed portable seat cushion
InactiveUS20060103225A1Reduce pressureMaximize contact areaStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesIschial tuberosityEngineering
A portable cushion that minimizes the blocking of blood circulation, stress, and pain in the femoral region caused by sitting on a chair for long hours or an extended time is provided. The overall shape of the cushion resembles human lungs connected to each other at the upper part with an upper surface that is flat, except for two wing portions. The wings are in a convex shape. The cushion is made of EP (Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer) rubber foam. A straight shallow center groove is concavely developed on the upper surface of the cushion along the direction of the wings. Two concave grooves, resembling hemi-oval shapes being cut along the long center axis thereof are developed on the flat upper surface of the seat cushion to receive ischial tuberosities of a user. A shell-shaped concave groove for receiving the coccyx of the user is developed on the rear part of the flat upper surface of the cushion between the two hemi-oval shape grooves. The front side of the cushion, between the two wings, is caved in for receiving and positioning of genitals of the user. The unique geometry of the cushion reduces the pressure to the ischial tuberosities and the coccyx of a user by maximizing the contact area and distribute the user's weight throughout the surface, while minimizing the blocking of blood circulation by minimizing the contact area of the wings of the cushion and the rear part of the thighs of the user.
Owner:KIM JUNGIN
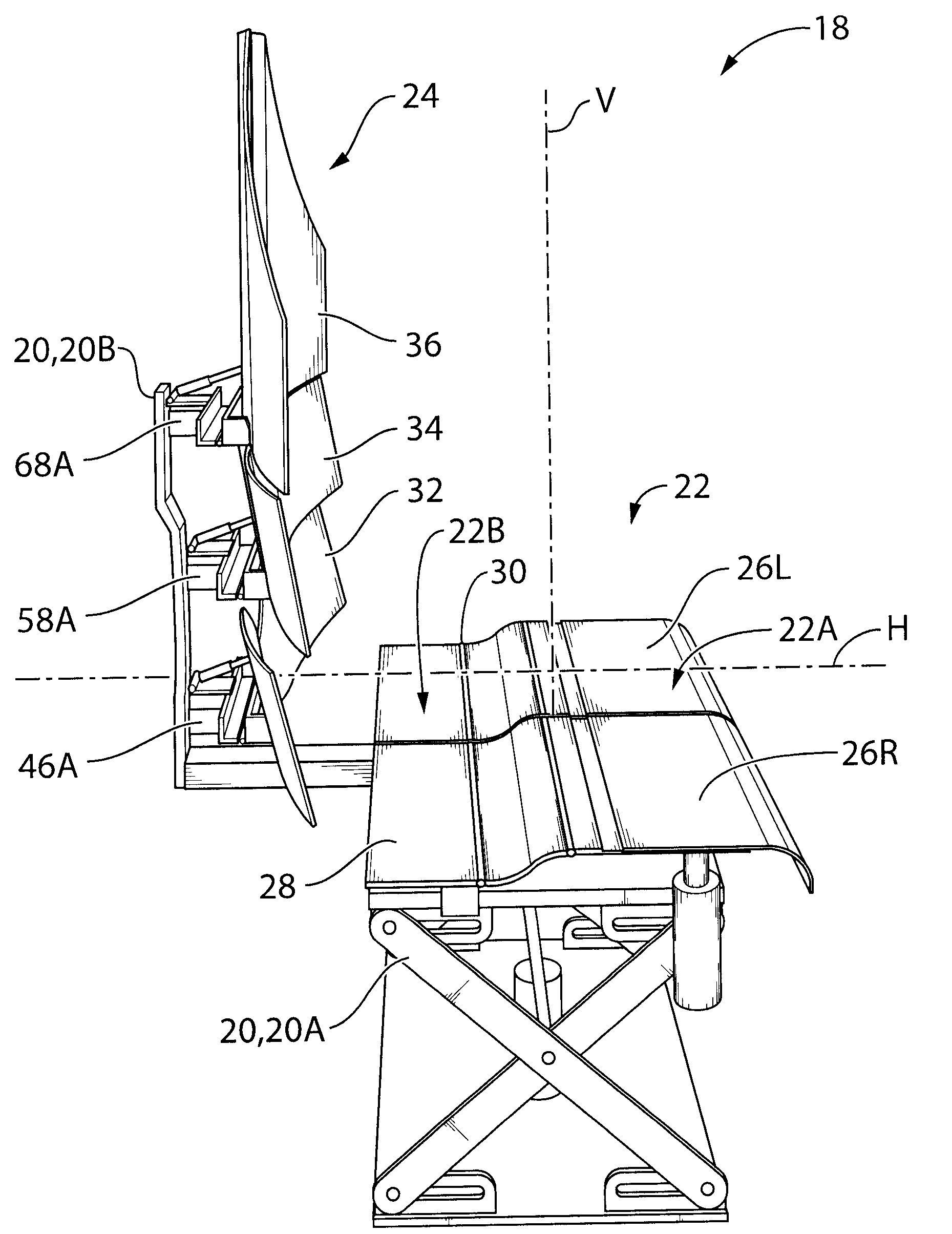
Vehicle seat and vehicle seat evaluation method
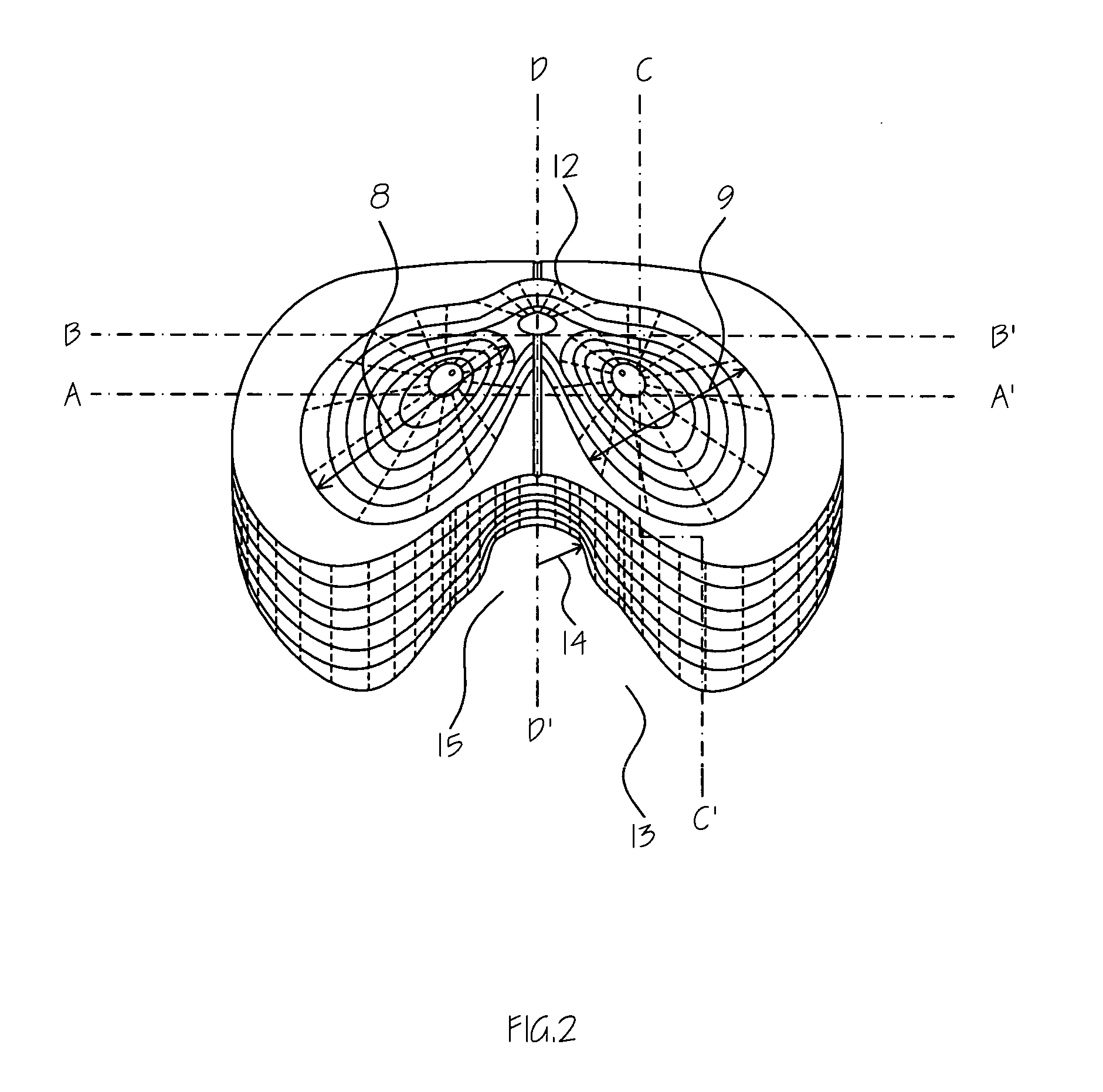
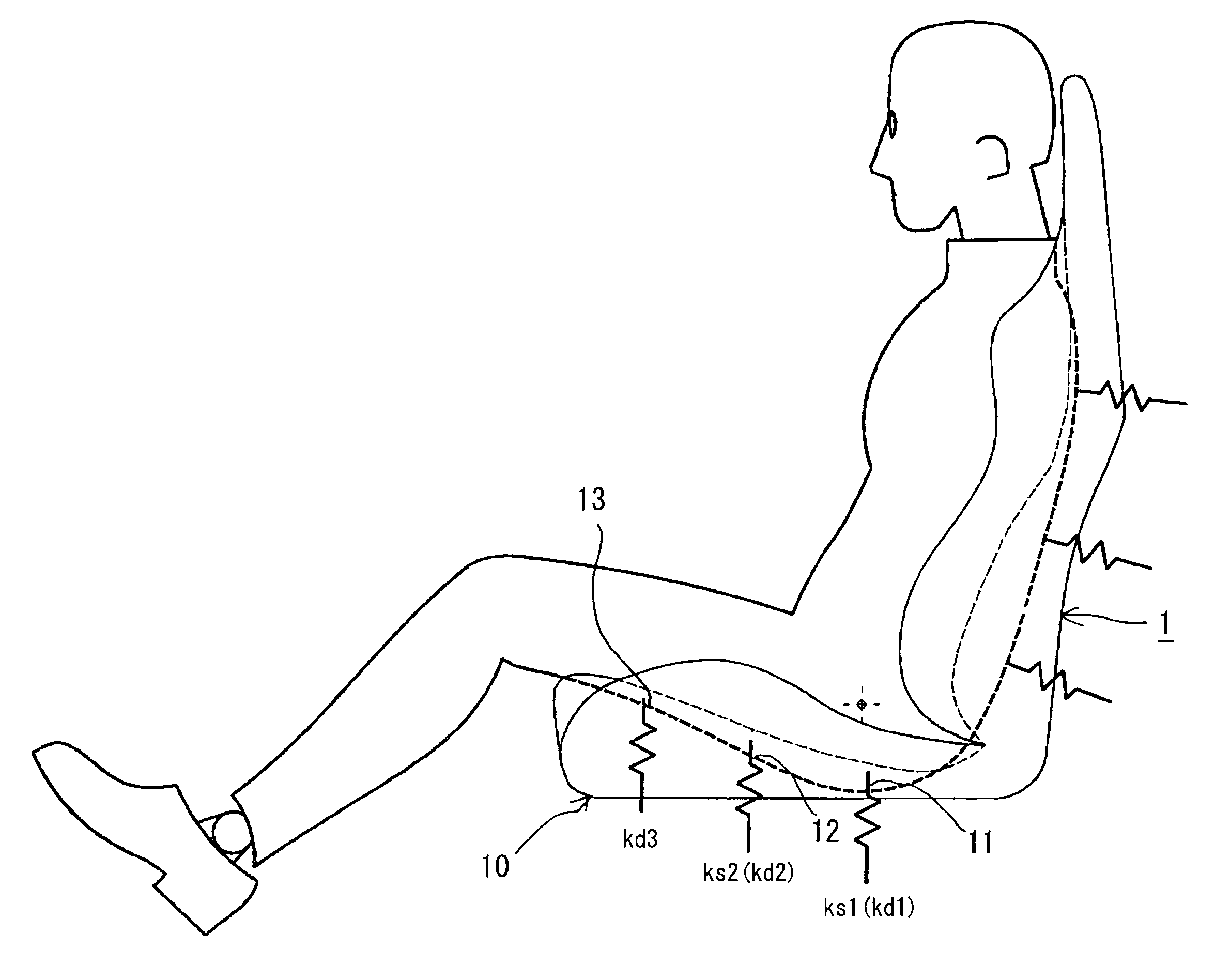
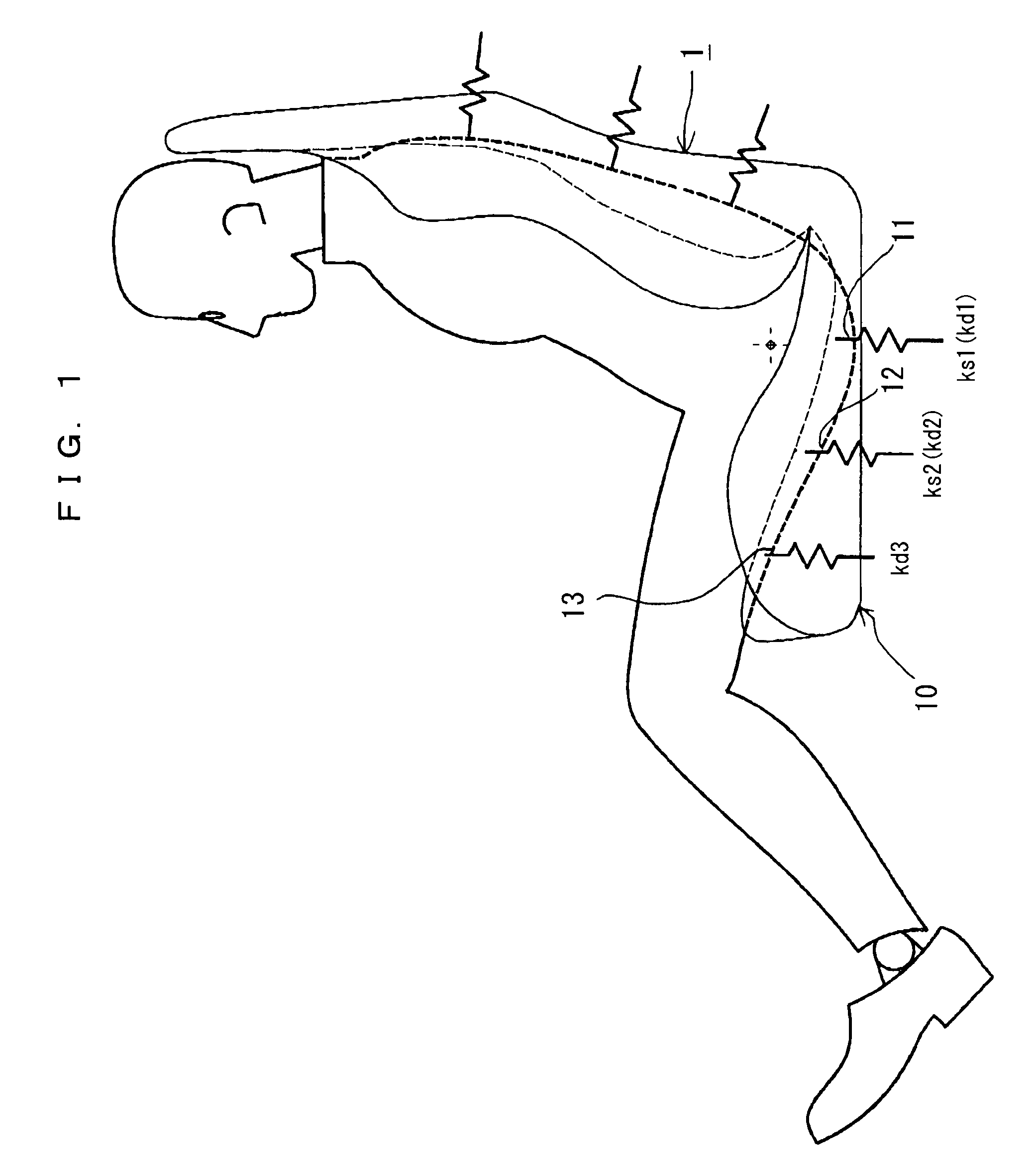
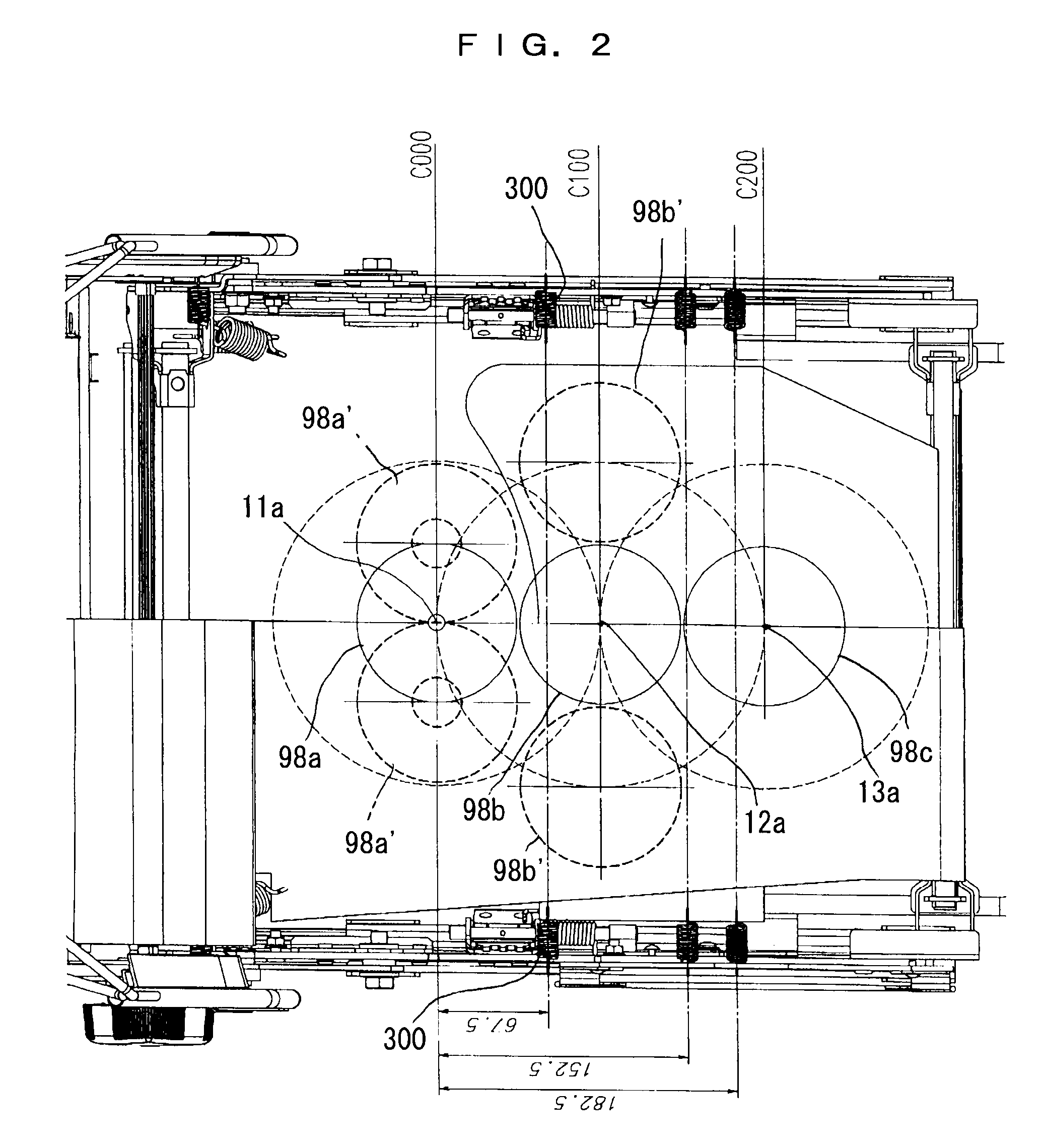
ActiveUS20090051206A1Improve linearityDifference in easiness of transmitting vibrationStoolsFurniture partsHuman bodyIschial tuberosity
A vehicle seat allowing to improve a vibration absorption characteristic, securing a stable seating posture, having high vehicle operability, and allowing to alleviate fatigue due to long time seating. In a seat cushion of a vehicle seat, a first human body support portion having a center at a position corresponding to a substantially center between the pair of ischial tuberosities of a human body, and a second human body support portion corresponding to the vicinities of femoral bases of a human body and having a center at a position located forward at a horizontal distance of 100 mm along a longitudinally center line of the seat cushion from the first human body support portion are regarded respectively as spring elements, and static spring constants and dynamic spring constants thereof are set to a predetermined relationship. Thus, stability and vibration absorbency during static seating are improved.
Owner:DELTA TOOLING CO LTD
Posterior fixing steel plate for fracture of acetabular anterior and posterior columns
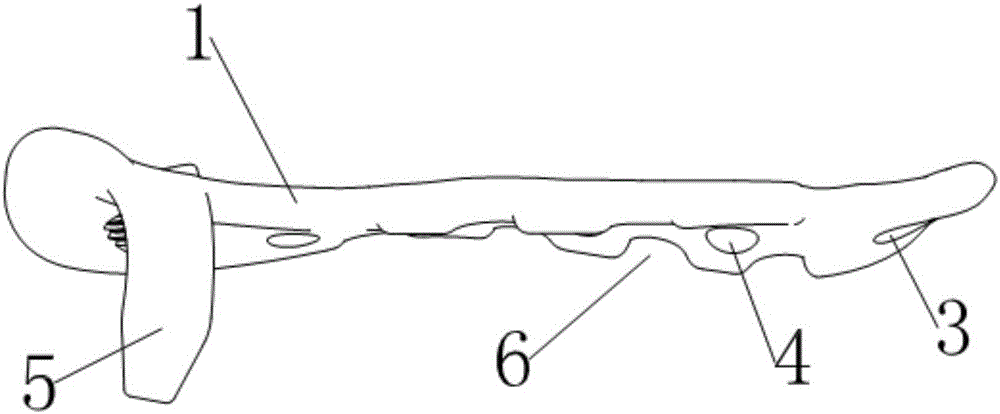
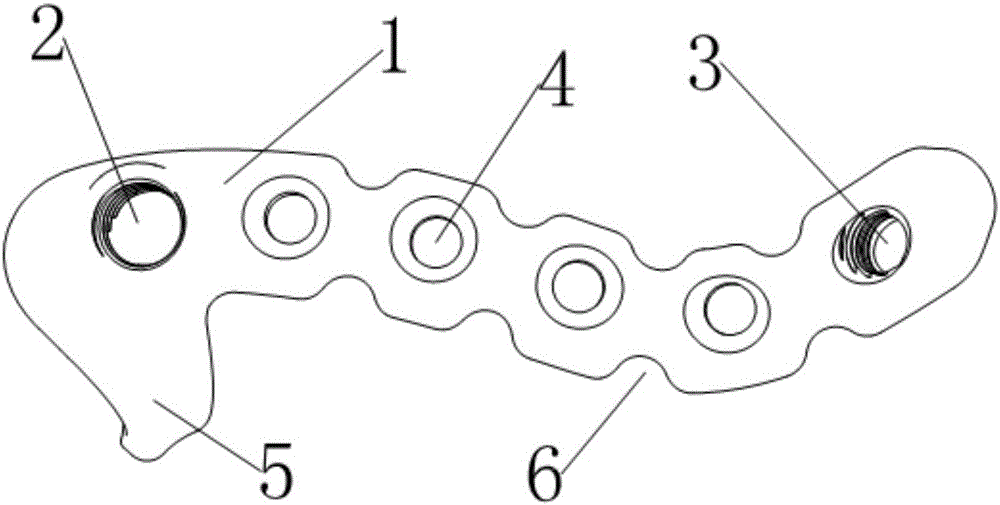
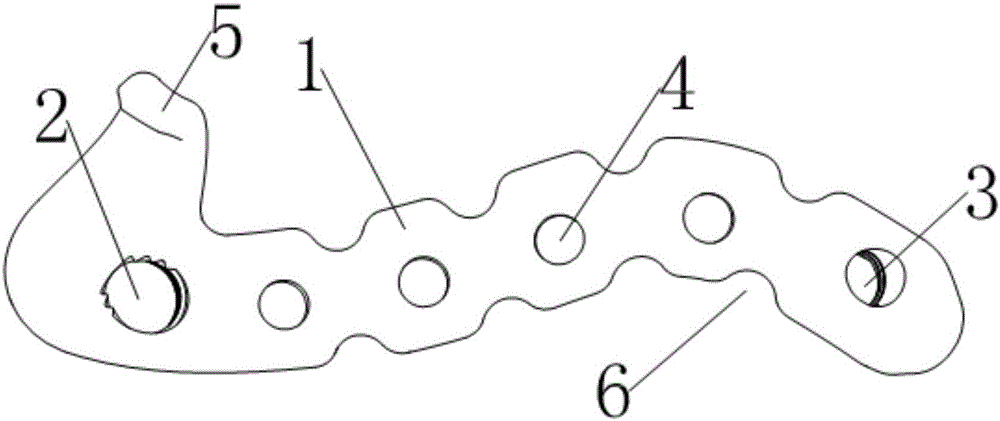
InactiveCN105769319ASimple anatomyReduce the difficulty of surgeryBone platesIschial spineIschial tuberosity
The invention relates to a posterior fixing steel plate for fracture of acetabular anterior and posterior columns. The posterior fixing steel plate comprises a plate body covering the back wall of the acetabular posterior column; the plate body extends downwards to the root of an ischial spine from the upper part close to the top end of a greater sciatic notch along the inner side edge of the acetabular posterior column and then is bent and extends to the lower part of the top end of an ischial tuberosity; an anterior column threaded hole for being connected with a guide sleeve is formed in the end, at the top end of the greater sciatic notch, of the plate body, and the axis of the anterior column threaded hole points to the acetabular anterior column through sclerotin between an acetabular fossa and a square area; a posterior column threaded hole used for being connected with the guide sleeve is formed in the other end of the ischial tuberosity and the axis of the posterior column threaded hole points to the tail end of the ischial tuberosity through sclerotin in the ischial tuberosity; a plurality of fixing screw holes arranged along the plate body are formed between the anterior column threaded hole and the posterior column threaded hole; a limiting hook hooked to the upper part of the greater sciatic notch is arranged on the side edge, which is close to the greater sciatic notch, of the end and corresponding to the anterior column threaded hole, of the plate body.
Owner:王钢
User adjustable motorcycle seat cushion with independently inflatable and deflatable ischial support cell and gluteous support cell
The invention is an inflatable seat cushion. The cushion includes inflatable cells, a pump, a flow control valve and tubing. The cells include at least one inflatable and deflatable first cell configured and arranged to support the ischial tuberosity bones of a human seated on the cushion, and at least one inflatable and deflatable second cell configured and arranged to support at least a portion of the gluteus maximus muscles of a human seated on the cushion. The flow control valve and accompanying tubing is operable to mutually exclusively place the pump in fluid communication with the at least one first cell or the at least one second cell.
Owner:AQUILA OF WISCONSIN
Adjustable seating systems and associated structures
Structures of seating systems for human users are disclosed. In one embodiment, the structure comprises: a frame; a seat structure supported by the frame; and a back rest structure supported by the frame. The seat structure comprises a thigh support region and a pelvic support region where the pelvic support region defines a pelvic well for receiving an ischial tuberosity of the user and also provides a fulcrum to assist in rotating the pelvis of the user. The back rest structure comprises a gluteal panel for supporting a gluteal mass of the user and a posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) panel disposed above the gluteal panel. The PSIS panel is adjustable to cause movement of a PSIS of the user and cooperate with the pelvic well to cause rotation of the pelvis of the user about the fulcrum provided by the pelvic well.
Owner:FORCE 3 INNOVATIONS
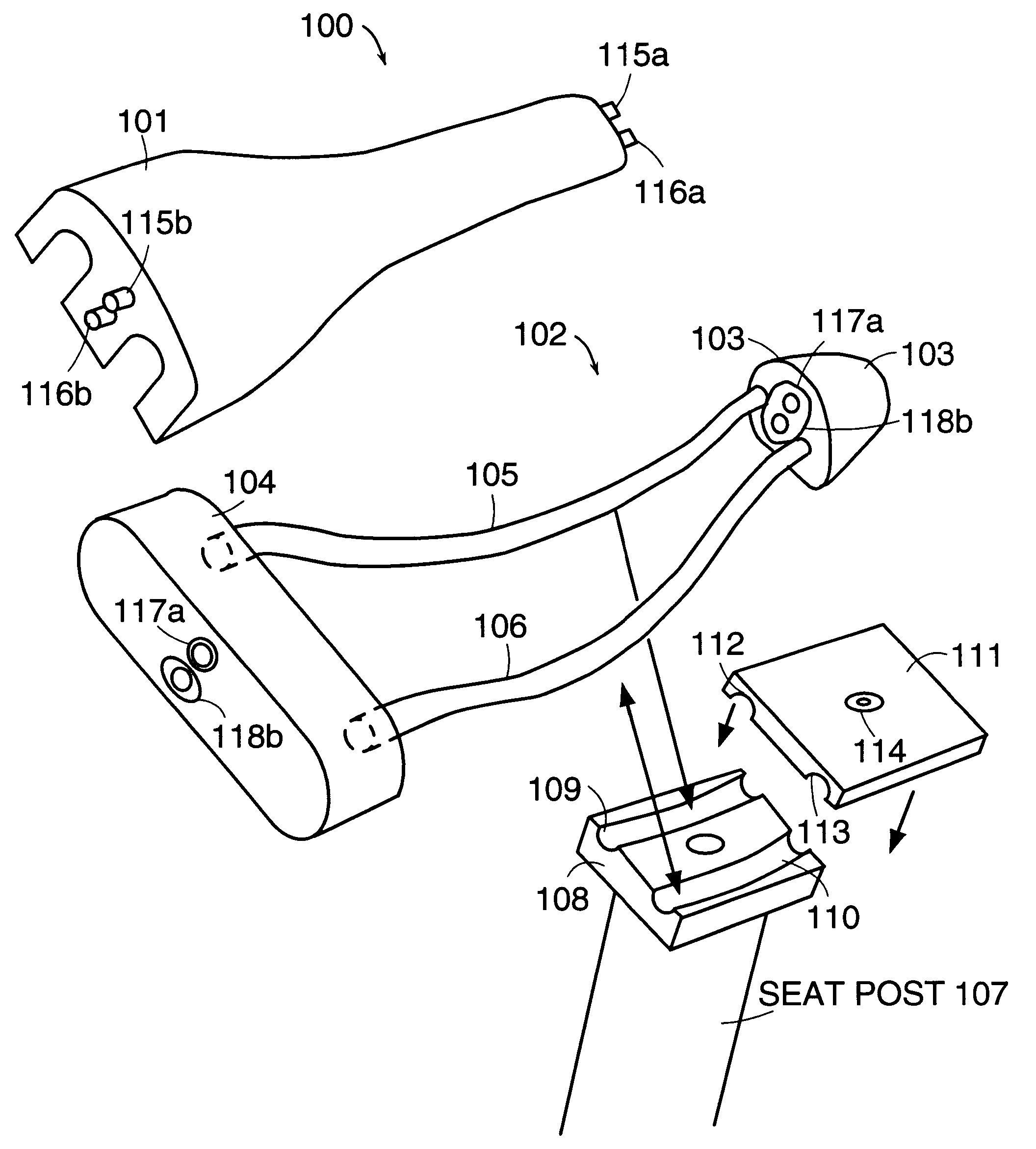
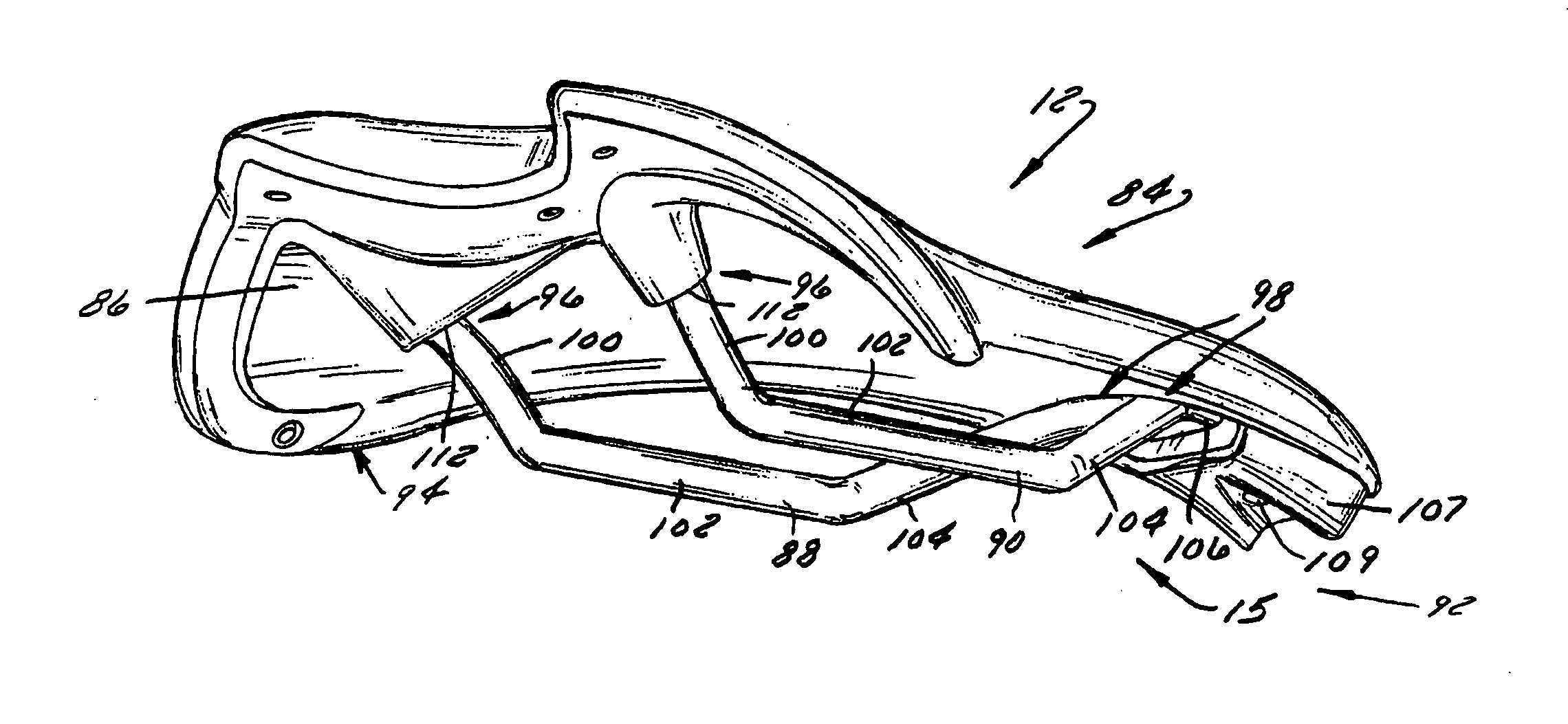
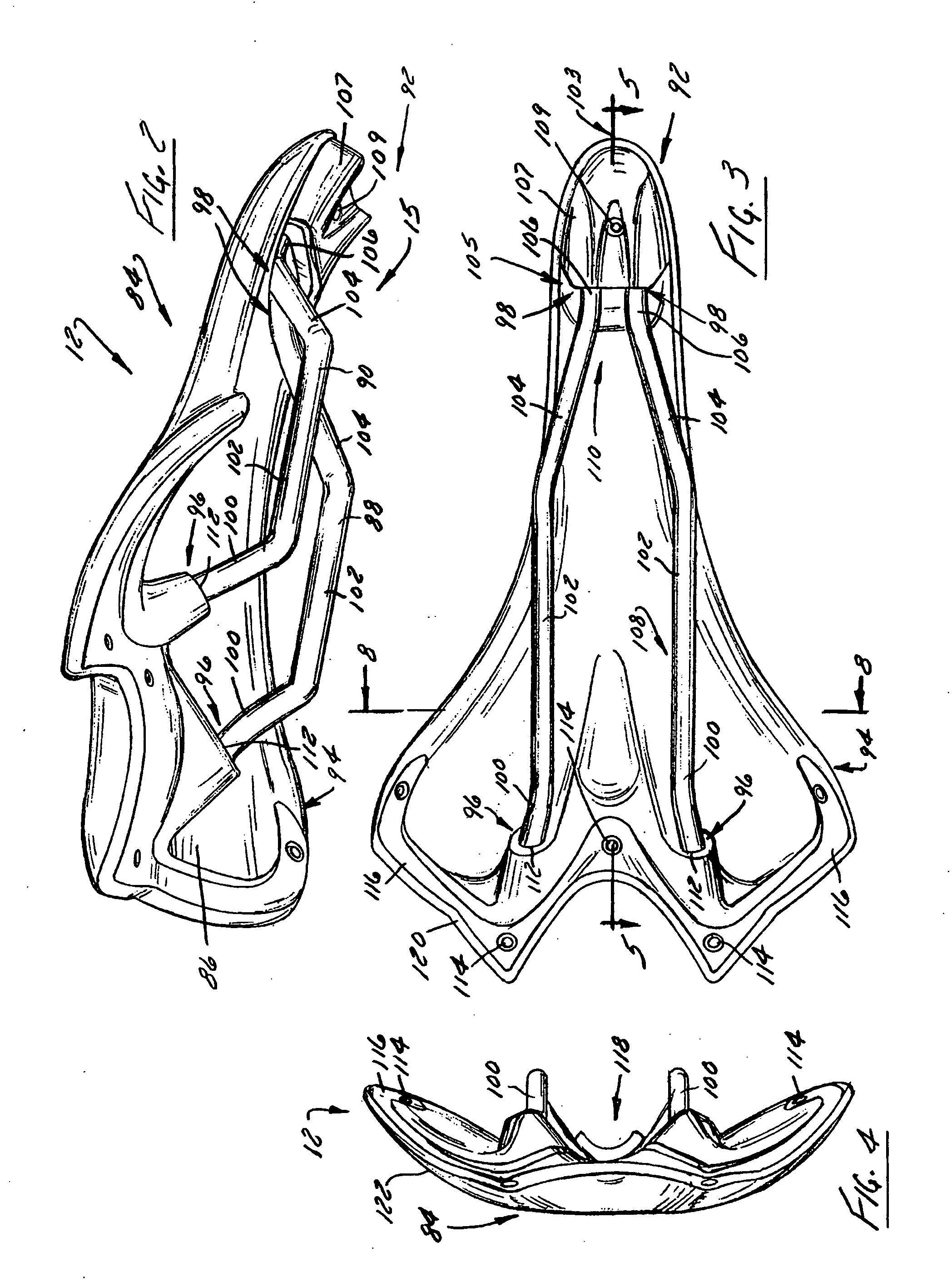
Bicycle Seat for Protecting Ischial Tuberosities
A bicycle seat has a bicycle saddle with a forward end and a rearward end, the saddle having an ischial region. One or more cushioning pads are placed on the saddle in the ischial region. The cushioning pads have an upper surface, with the cushioning pads being connected to the saddle in a manner that enables the upper surface of the cushioning pads to move either from side to side with respect to the saddle during pedaling, or forward and rearward with respect to the saddle during pedaling, or both from side to side and forward and rearward during pedaling.
Owner:JARIK MEDICAL LLC
Bicycle seat system
InactiveUS20090212608A1Limiting tangential force interactionReduce frictionCycle saddlesIschial tuberosityMechanical engineering
A seat system for providing a substantially normal contact angle between the seat and the ischial tuberosities of a rider seated thereupon. The seat system includes variable padding that is configured to generally cooperate with the physiology of the rider. The padding is secured to a base that includes a pair of rails extending from an underside of the base. The rails are attached to permit controlled motion of the seat during pedaling operation in response to the change in orientation of the rider's physiology relative to the seat. The deflection of the seat cooperates with the motion of the rider's physiology through a substantial portion of a rider's pedaling motion.
Owner:TREK BICYCLE CORPORATION
Cushion
InactiveUS20180020837A1Avoid compressionGood covering shape materialStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesIschial tuberosityEngineering
The present invention discloses a cushion for providing a user to sit on. The cushion includes a base layer, a seat layer and a supporting portion. The seat layer is configured on the base layer for providing the user to sit on. The supporting portion is configured between the base layer and the seat layer for supporting the user's ischial tuberosity. The seat layer is made with the material of the good covering shape, thus it can release user's upper body, hips and legs. Furthermore, by using the hard supporting portion for supporting the user's ischial tuberosities, the cushion makes the weight of the user's upper body be transmitted uniformly to the seat layer. Therefore, the cushion can prevent the user's hips and legs from some physical pains such as sore, ache, and pain due to long period of partial stress.
Owner:CHENG HSING I
Adjustable seating systems and associated structures
Structures of seating systems for human users are disclosed. In one embodiment, the structure comprises: a frame; a seat structure supported by the frame; and a back rest structure supported by the frame. The seat structure comprises a thigh support region and a pelvic support region where the pelvic support region defines a pelvic well for receiving an ischial tuberosity of the user and also provides a fulcrum to assist in rotating the pelvis of the user. The back rest structure comprises a gluteal panel for supporting a gluteal mass of the user and a posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) panel disposed above the gluteal panel. The PSIS panel is adjustable to cause movement of a PSIS of the user and cooperate with the pelvic well to cause rotation of the pelvis of the user about the fulcrum provided by the pelvic well.
Owner:FORCE 3 INNOVATIONS
Enhanced process for making seating elements and products thereby including those specially designed for children
InactiveUS7270376B2Increases relative lordosis in the lumbar spineReduce obstructionBack restsSofasVeinIschial tuberosity
Owner:NUBAX LTD
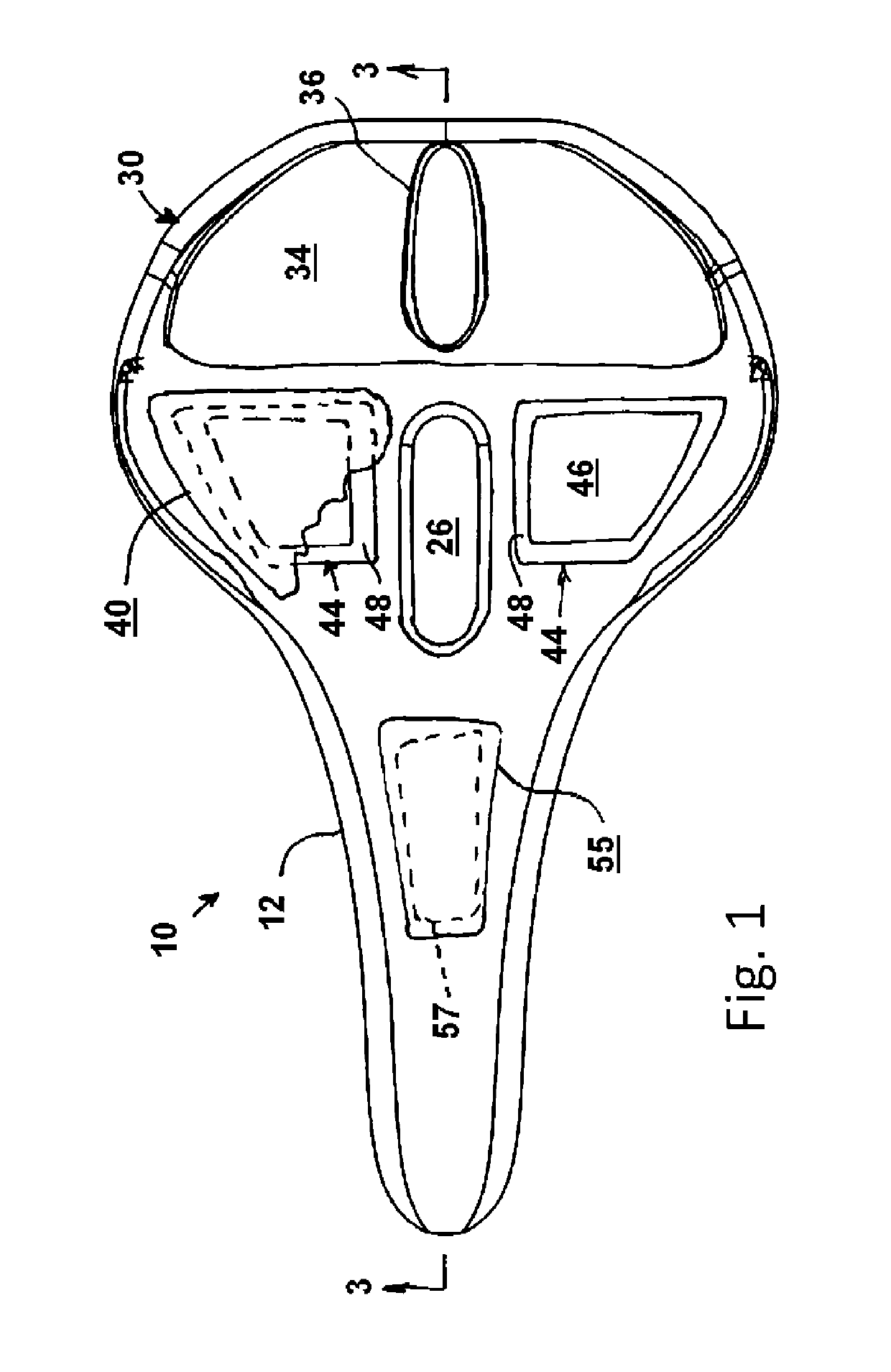
Injection Moulded Unupholstered Plastic Chair
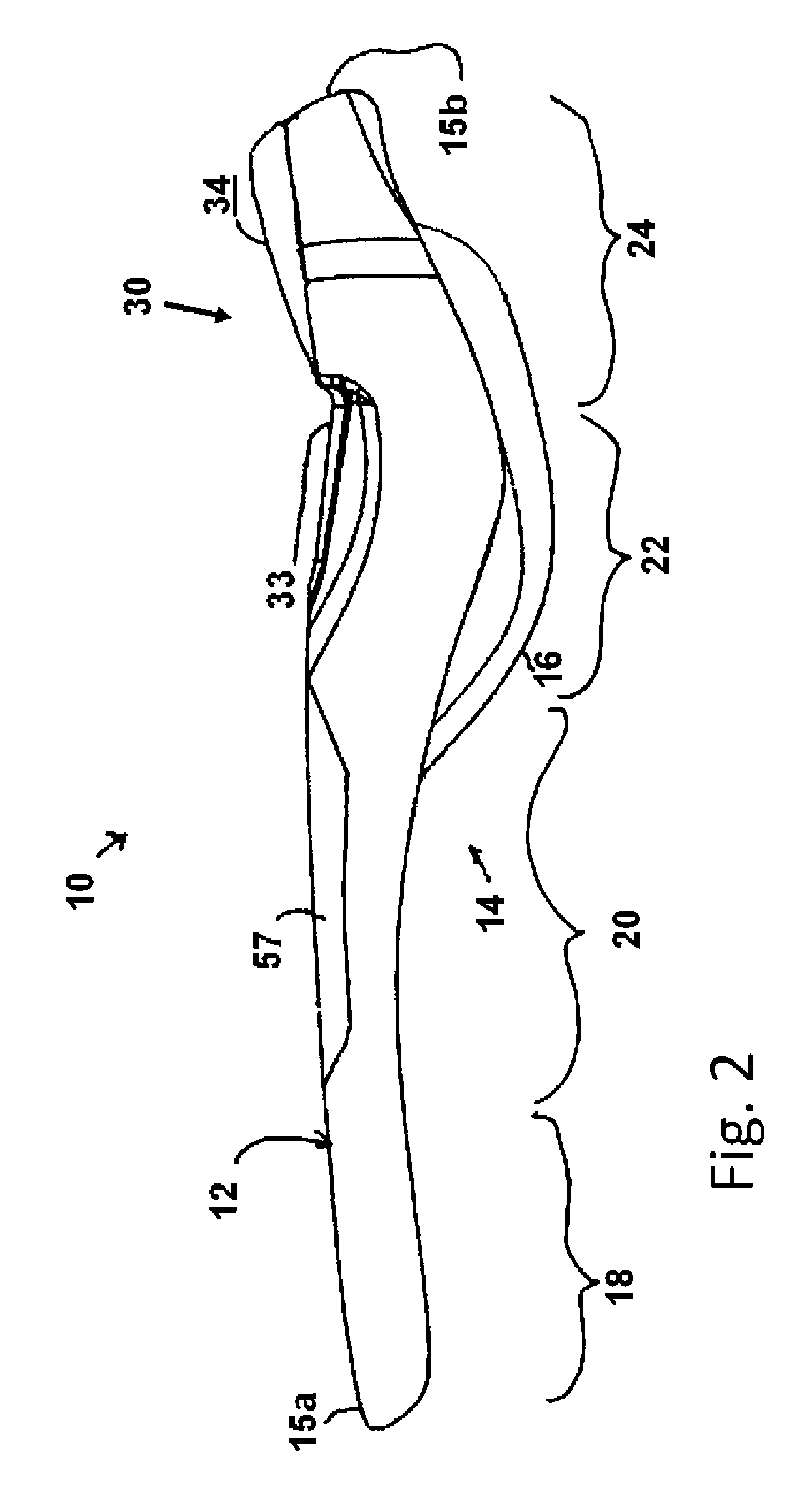
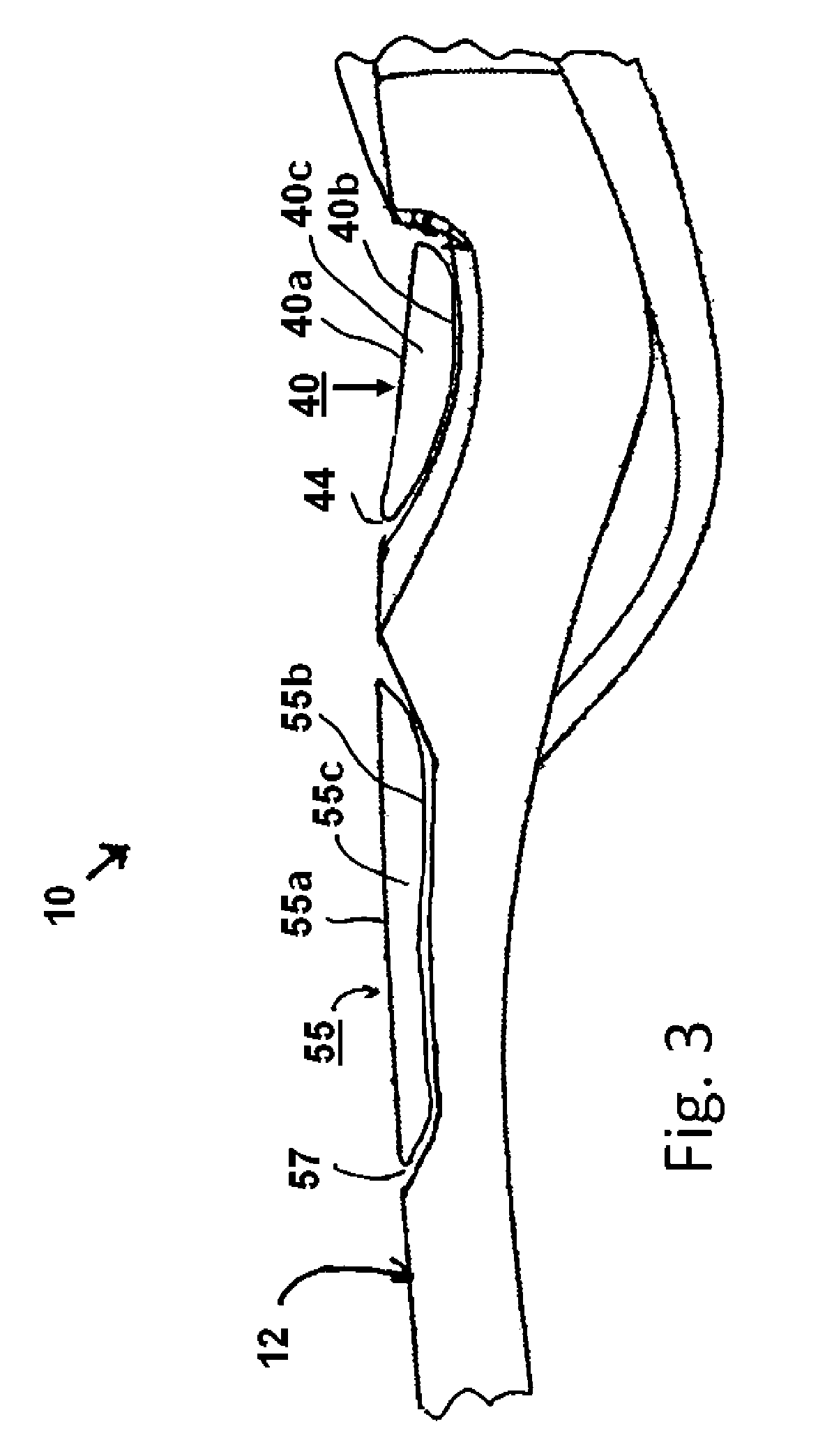
A moulded plastic seat (31, 61, 131, 161) for a chair (30, 60, 130, 160) is disclosed. The seat is provided with a pair of recesses (37, 38, 57, 58, 67, 68) or a coalesced pair of recesses (137, 138, 157, 158, 167, 168) which are spaced apart and sized to reduce, but not eliminate, pressure on the ischial tuberosities of a sitter. A range of spacing and sizing corresponding to the height range of the sitter is disclosed. The seat is relatively thin and has some 'give' in use.
Owner:SEBEL FURNITURE LTD
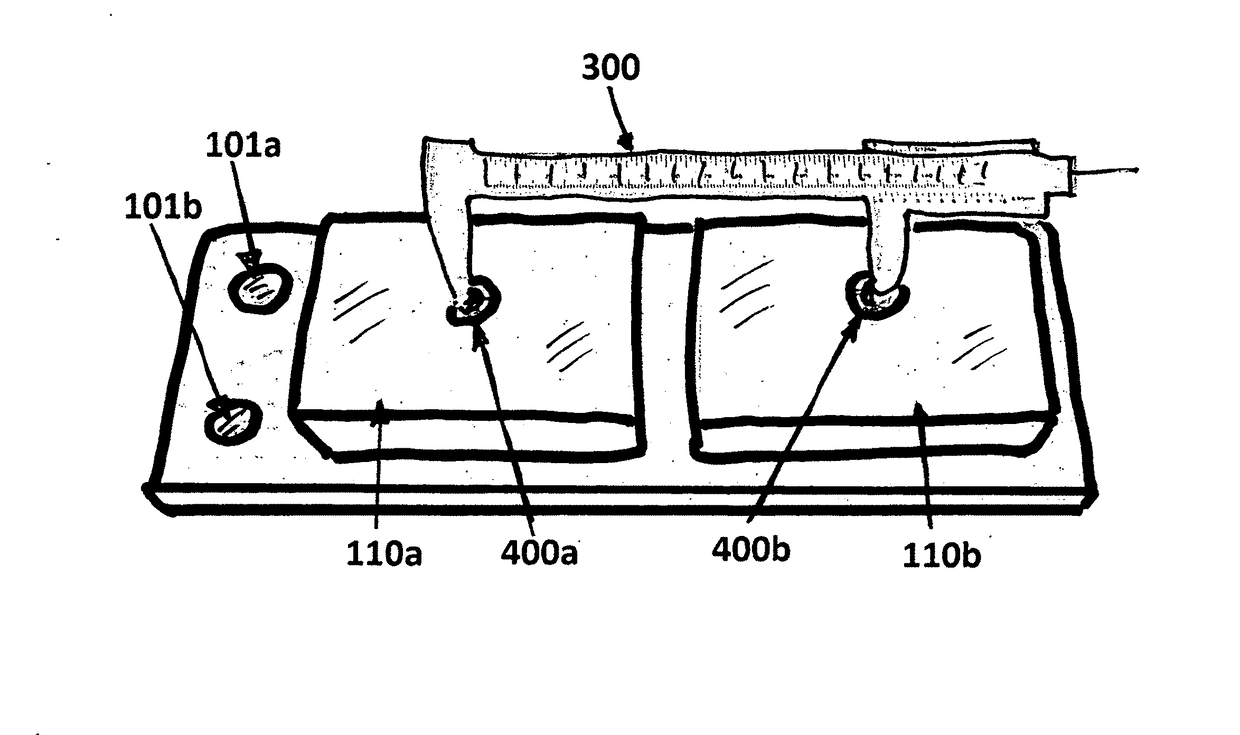
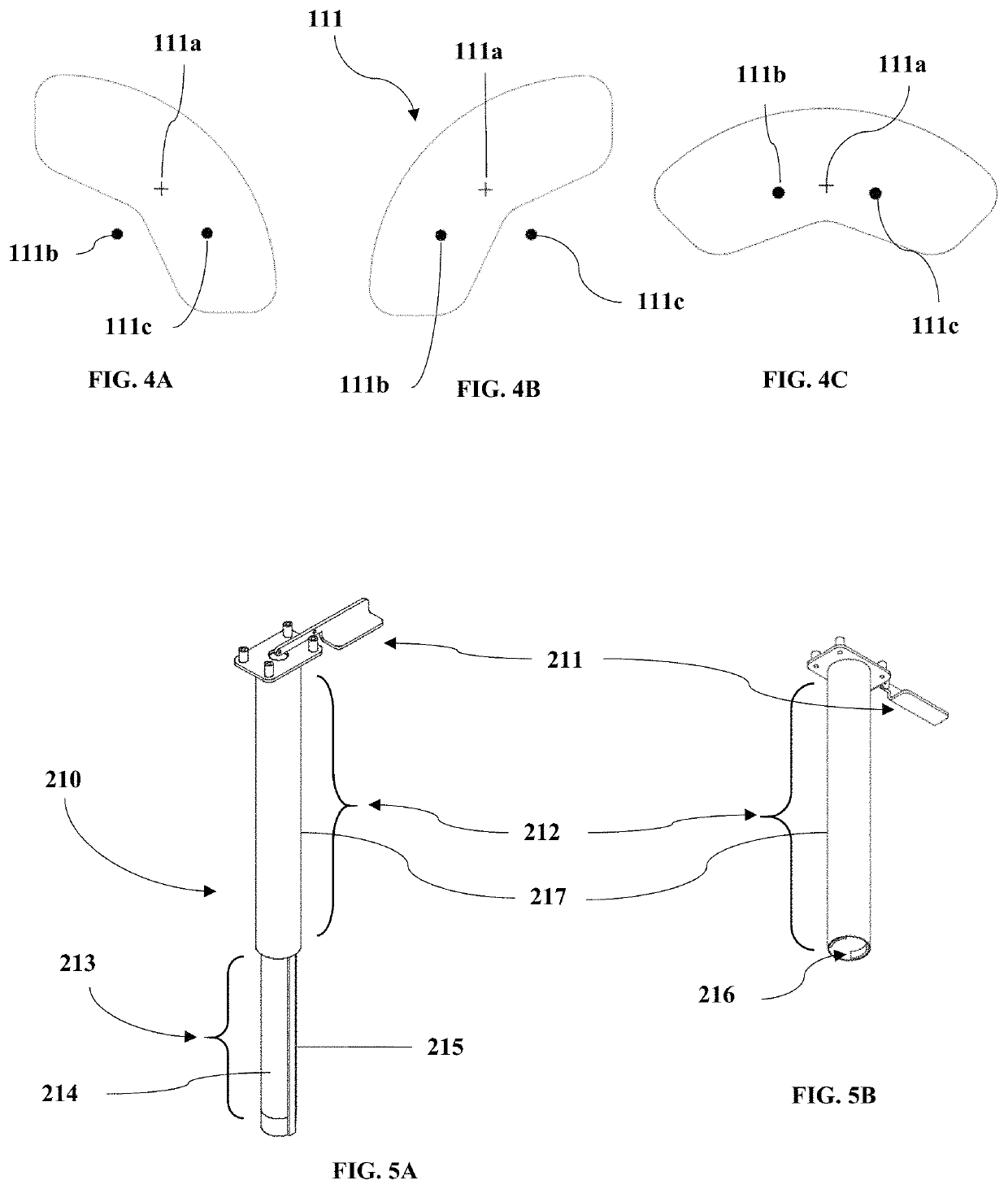
Ischial tuberosity measurement tool
Bicycle saddles come in many different shapes and sizes. Some are long, some are short, some are curved some are flat. The ultimate goal is to find the perfect saddle for the cyclist.CLARIFICATION: those that ride bicycles are commonly referred to as cyclists, bikers, cyclists, bicycle cyclists, bicyclists, cycle cyclists, cycling, etc., but for this discussion, they will be referred to as ‘cyclist(s)’As with the height of humans, the widths of Ischial Tuberosities (Sit Bones) are also numerous. The Ischial Tuberosities are the protruding bones of the hip / pelvis that sit underneath the muscles of the glute and is the part of the body that first contacts the saddle. Everyone has a different width and the importance for a cyclist in finding the exact width is critical for long-term health and cycling enjoyment.Excessive weight / pressure on the soft tissue can lead to health issues such as tumors, genital numbness and even erectile dysfunction due to Pudendal nerve compression and or crushing and or blocking of the Pudendal artery.SADDLE DESIGN—The rear area of a saddle is where the Ischial Tuberosities should rest. This area of the saddle comes in one of two shapes, either (a) flat, or (b) curved. This is where the cyclist should apply most of their weight. The most important item is for the cyclist to minimize the amount of pressure to their soft tissue, in other words, the correct saddle width and saddle shape is paramount in preventing as much of the cyclists' soft tissue from coming into contact with the saddle. Ideally, the majority of contact with the saddle will come from contact of the cyclists' Ischial Tuberosity, the Ischial Ramus and Inferior Ramus of Pubis.This Ischial Tuberosity measuring tool can measure any / all types of cyclists and can be used to measure any / all saddles where a saddle(s) that the bicycle shop carries can be recommended to the cyclist. It is important to note that the recommended saddle(s) will be the correct fitting saddle(s) for the cyclist.This saddle fit system is comprised of impression foam pad(s) that are attached to an organic or inorganic substrate that supports the cyclists weight. Also included are 2 ferrous, non-ferrous or non-metallic balls as well as a detached Vernier caliper measuring device.The cyclist sits and centers themselves on the saddle fit system. The bike fitter then has the cyclist stand thereby leaving 2 indentation impressions on the impression foam. The bike fitter then takes the 2 balls and drops one onto each side of the impression foam pad. Due to the natural force of gravity, these balls will self-center into the exact center-point of each Ischial Tuberosity impression left by the cyclist.The bike fitter will then take the supplied detached calipers and measure the distance from center-point of each ball. This dimension will be noted, shown and discussed with the customer who will then decide on a preferred saddle(s) shape and material.The bike fitter will then show the cyclist preferred saddles by laying the calipers over the top of each saddle and centering the tips of the caliper where the cyclists' Ischial Tuberosities will be contacting the saddle. A follow-on conversation regarding best-fit / best-usage of a recommended saddle based on (a) cyclists' flexibility, (b) cyclists' body shape and conditioning, (c) saddle width and (d) saddle shape can then be held with the cyclist.SIZING THE SADDLE—When the caliper is layed on top of the rear of the saddle, the drop from the Ischial Tuberosity to the top of the saddle can be easily seen and shown to the cyclist. In most cases, the difference between a flat saddle vs a curved saddle is one size difference where the curved saddle usually requires one size wider than the flat top saddle. This is important for a healthy perineum and the correct saddle sizing is easily shown with this tool. Too much of a drop between the ideal placement of the Ischial Tuberosity and contact with the saddle can cause an excessive amount of pressure to be applied to the cyclists' soft tissue.Cited Workshttp: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 20102446 http: / / www.webmd.com / men / features / biking-and-erectile-dysfunction-a-real-riskhttps: / / www.researchgate.net / publication / 265514647_Cycling-Related_Sexual_Dysfunction_in_Men_and_Women_A_Reviewhttp: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 16422816 http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 18042330 http: / / www.nchi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 17227499 http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 16230994 http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / pubmed / 3809048 http: / / www.sellesmp.com / smp4bike / images / stories / pro2016-en / index.html
Owner:SCHULTZ RICHARD
Half-sitting stool with supported sit bone
ActiveUS11213136B2Improve posturePreventing pelvic rotationOffice stoolsAdjustable chairsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationIschial tuberosity
A seating apparatus for supporting a portion of a user, the seating apparatus comprising a reorientable seat portion including a seat platform and a cutout, wherein the seat selectively underlies a first ischial tuberosity of the user but not the second ischial tuberosity, the selection of which is determined by the orientation of the reorientable seat portion.
Owner:CHANG STEVEN
Joint suspension decompression exerciser and control method thereof
InactiveCN111759559AAdjustable suspension strengthLarge decompression forceNon-surgical orthopedic devicesHuman bodyArthritis
The invention belongs to the field of medical auxiliary devices, and discloses a joint suspension decompression exerciser and a control method thereof. Left and right upper moving arms at the upper end of a joint motion supporting frame are separately inserted into two pairs of suspension sliding slots on both sides of a suspension supporting frame, and the suspension supporting frame is suspendedupwards along the long axis of the upper moving arm through the repulsion force of the magnetic suspension or the elastic repulsion force of a spring device; the suspension supporting frame upwards drives the thigh and the shank of lower limbs of a human body to be separated, so that the gap of the knee joint is increased, and the knee joint is continuously decompressed; if the action fulcrum ofthe suspension supporting frame is changed to support the ischial tuberosity, the pressure on the hip joint can be relieved. The invention can carry out full decompression on the affected knee or hipjoint and maintain the motion function of the knee or hip joint not to be influenced at the same time for patients with osteoarthritis, and provides a brand-new solution for alleviating the wear of the knee joint or the hip joint of a patient, relieving the pain of the affected limb, promoting the recovery of the motion capability of the affected knee joint, realizing virtuous cycle and finally promoting the cartilage regeneration and the perfect reconstruction of motor function.
Owner:戴江华
Bicycle seat for protecting ischial tuberosities
Owner:JARIK MEDICAL LLC
Chin-protective traction chair
The invention discloses a chin-protective traction chair which comprises a connecting rod and a chair. A cushion is arranged on the chair and provided with a projection and a concave surface, memory foam is arranged in the cushion, a traction hanging belt is arranged on the lower portion of the connecting rod, a clamping sleeve wraps the lower end of the traction hanging belt, and sweating absorbing cotton is arranged on the clamping sleeve. The traction chair is provided with the cushion and the concave surface, the pressure of ischial tuberosity is dispersed towards the periphery when a patient sits on the concave surface, sitting comfort is improved, the pressure of ischial tuberosity of a user is reduced, the memory foam is arranged in the cushion, the cushion cannot generate strong bounciness when being recessed by the pressure, the cushion slowly reset an original state when the pressure is removed, the pressure of a contact point between a human body and the cushion can be effectively and uniformly dispersed, the most comfortable state is achieved, and the traction chair solves the problem that the ischial tuberosity of the user is easily injured when the traction chair is used by the user for a long time.
Owner:王回芳
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com