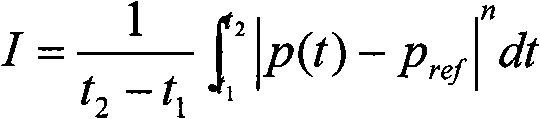Patents
Literature
52 results about "Venous cannula" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
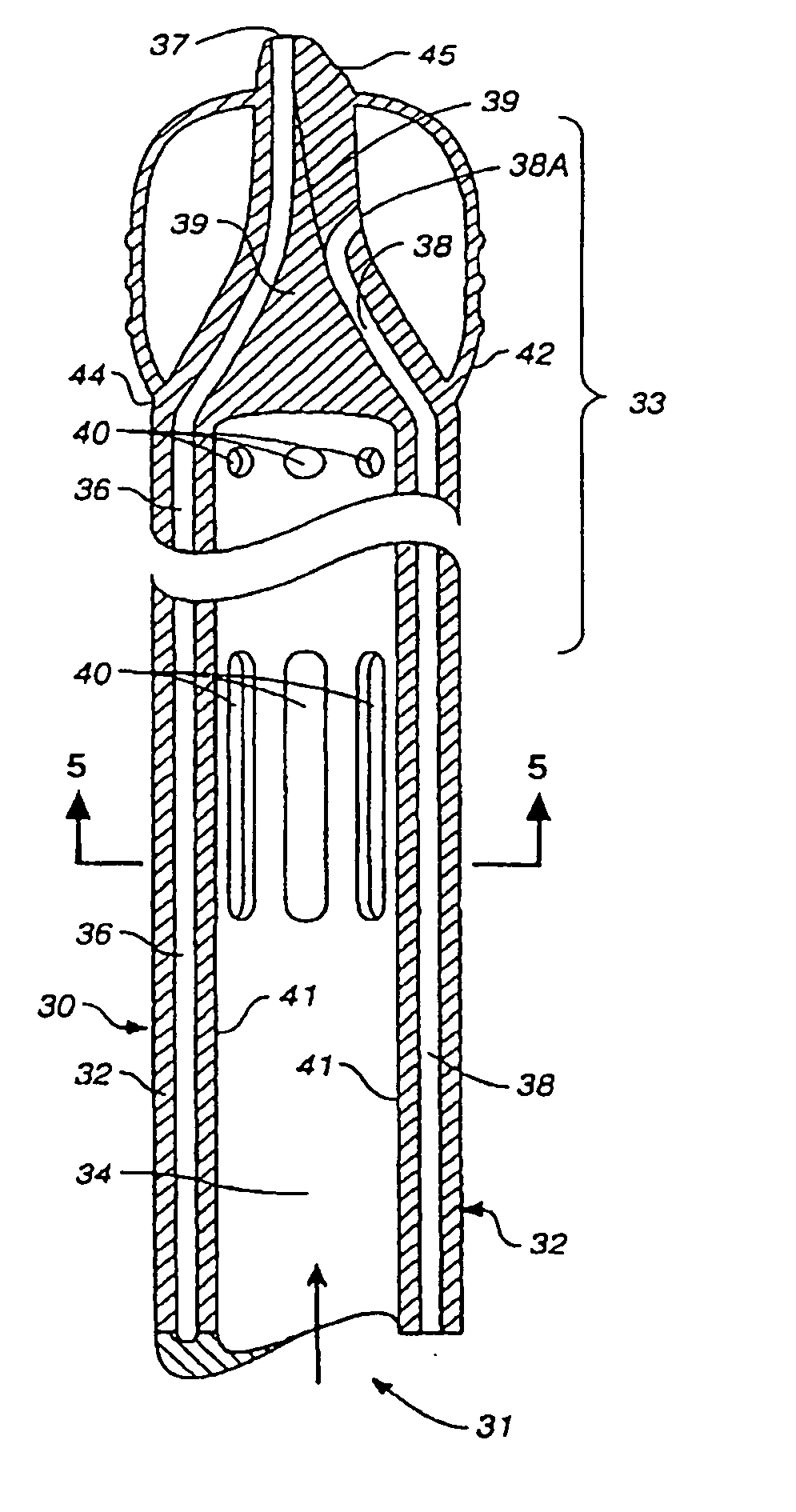
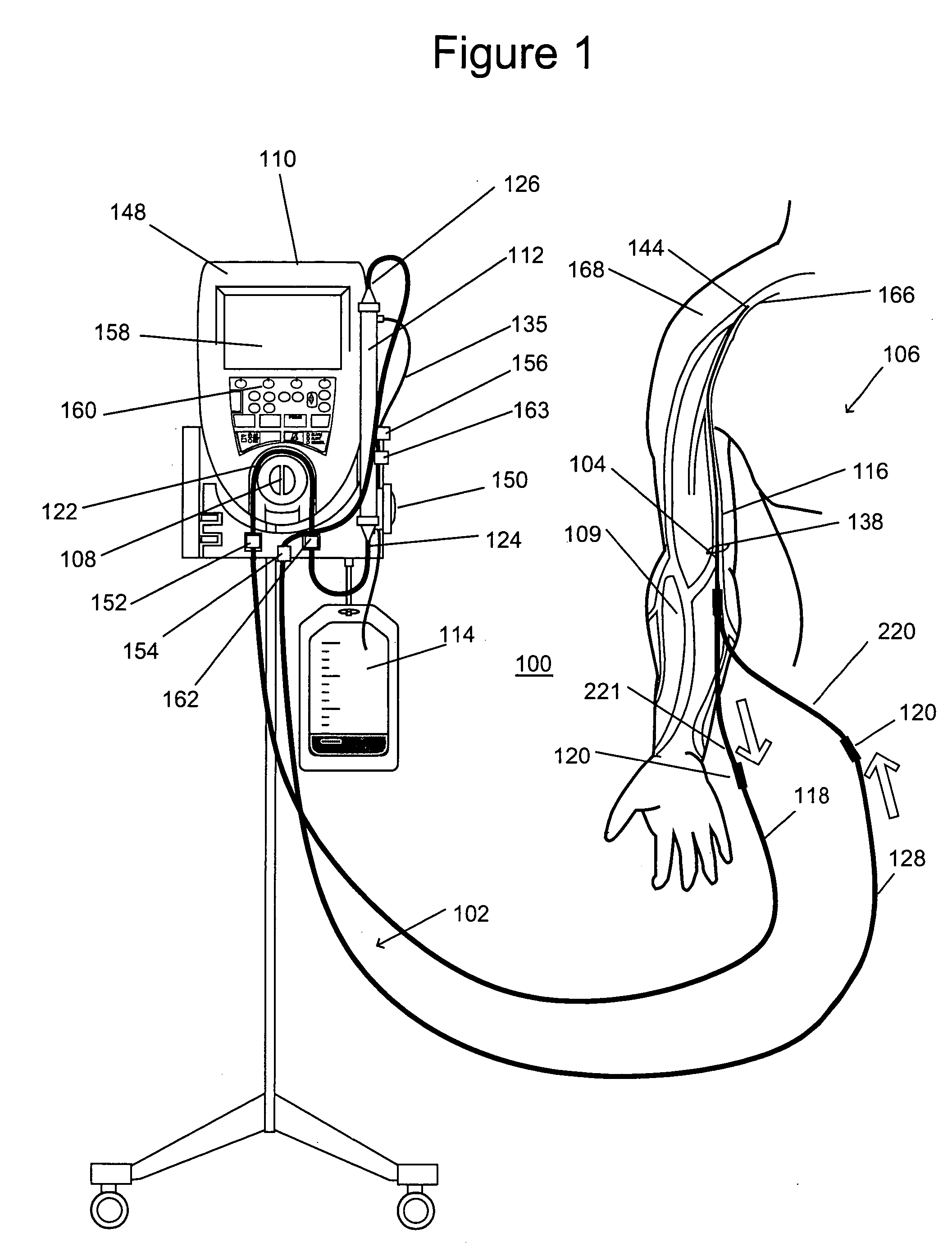
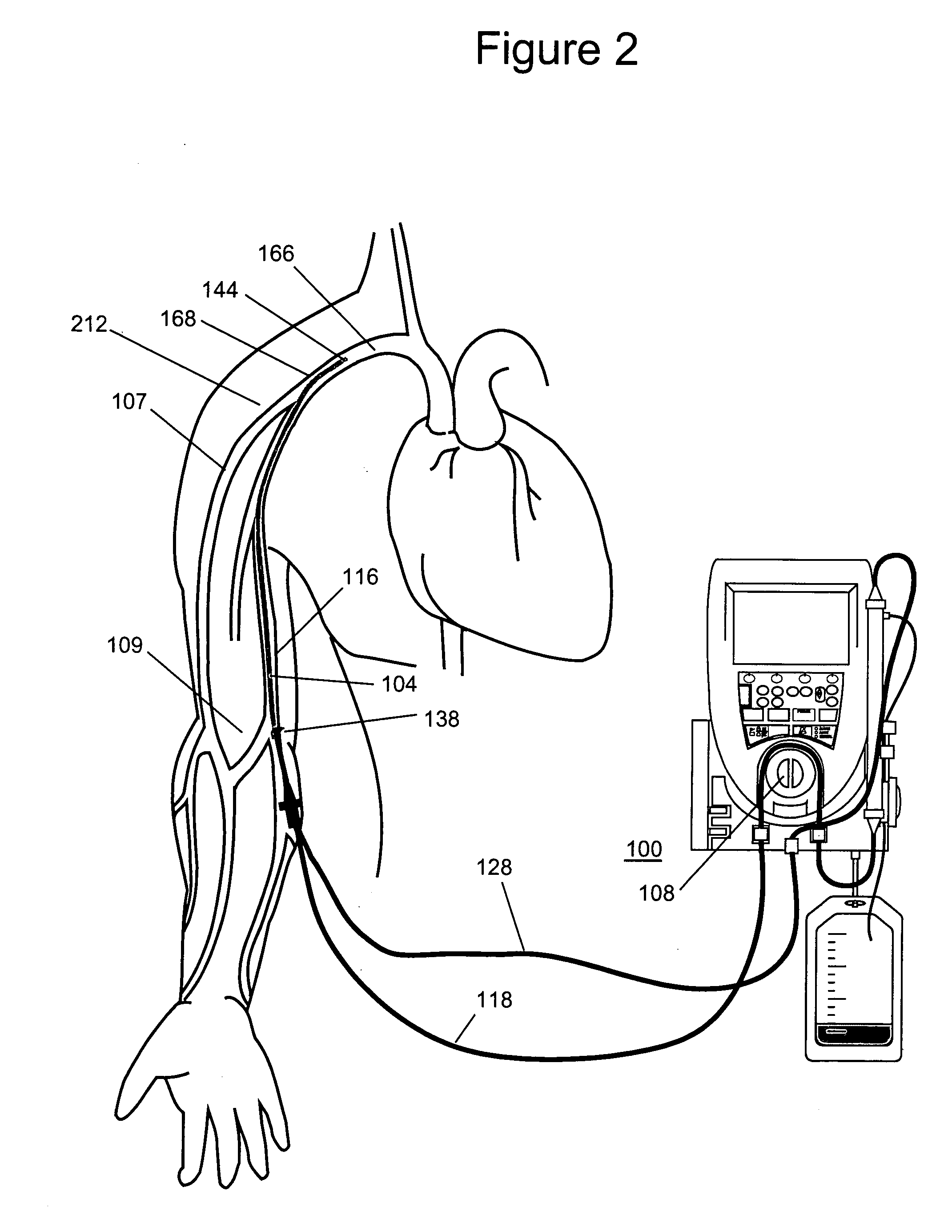
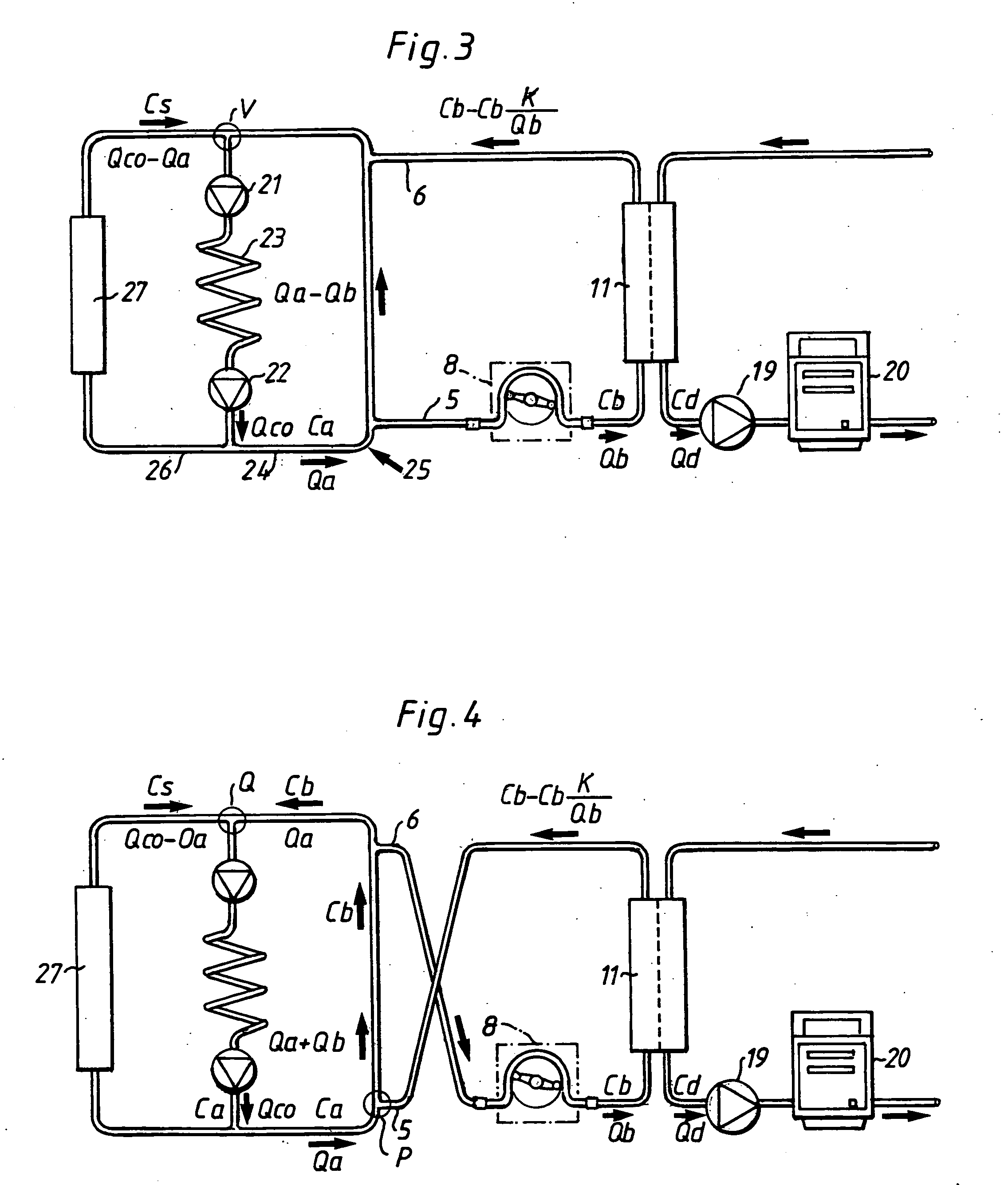
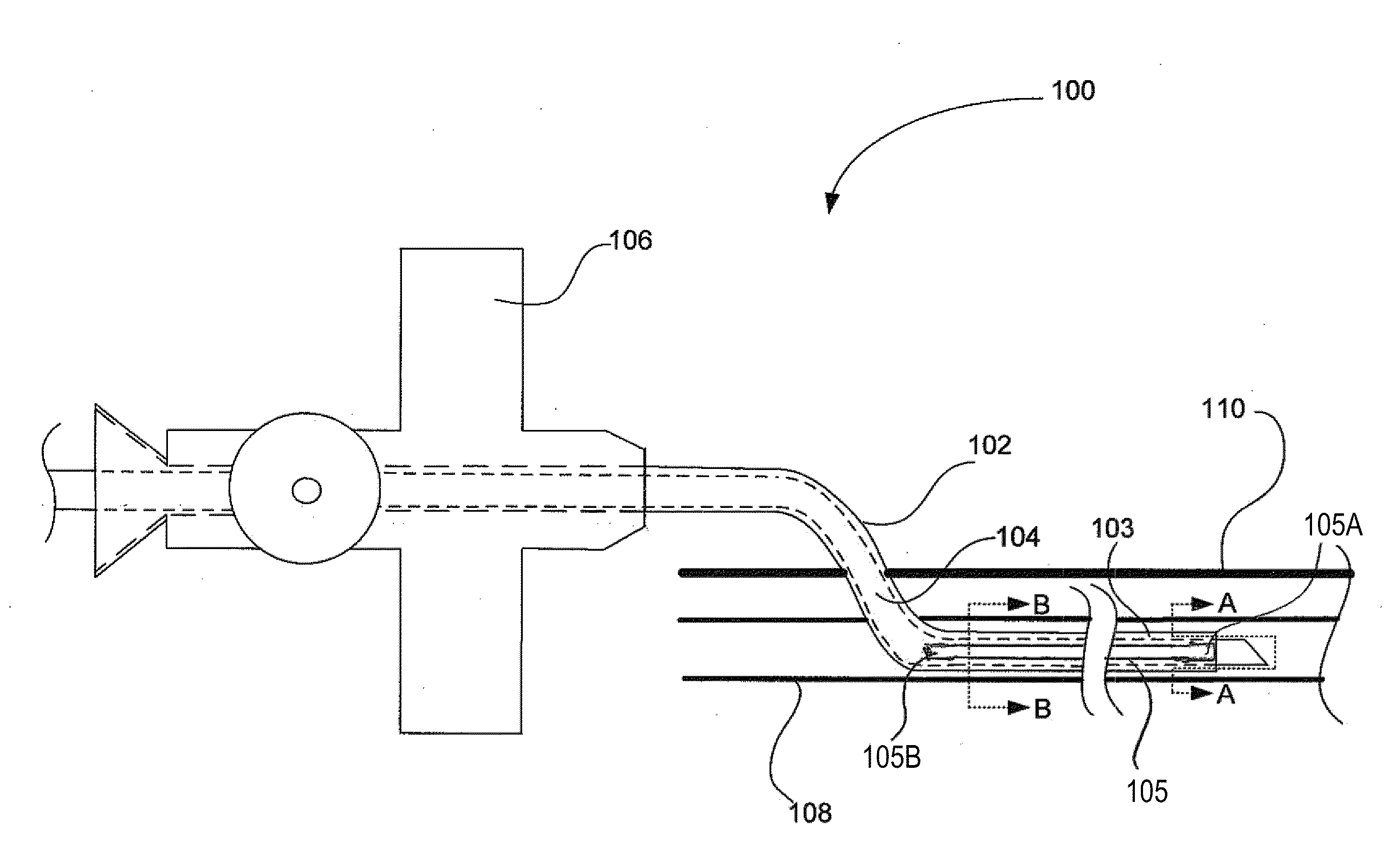
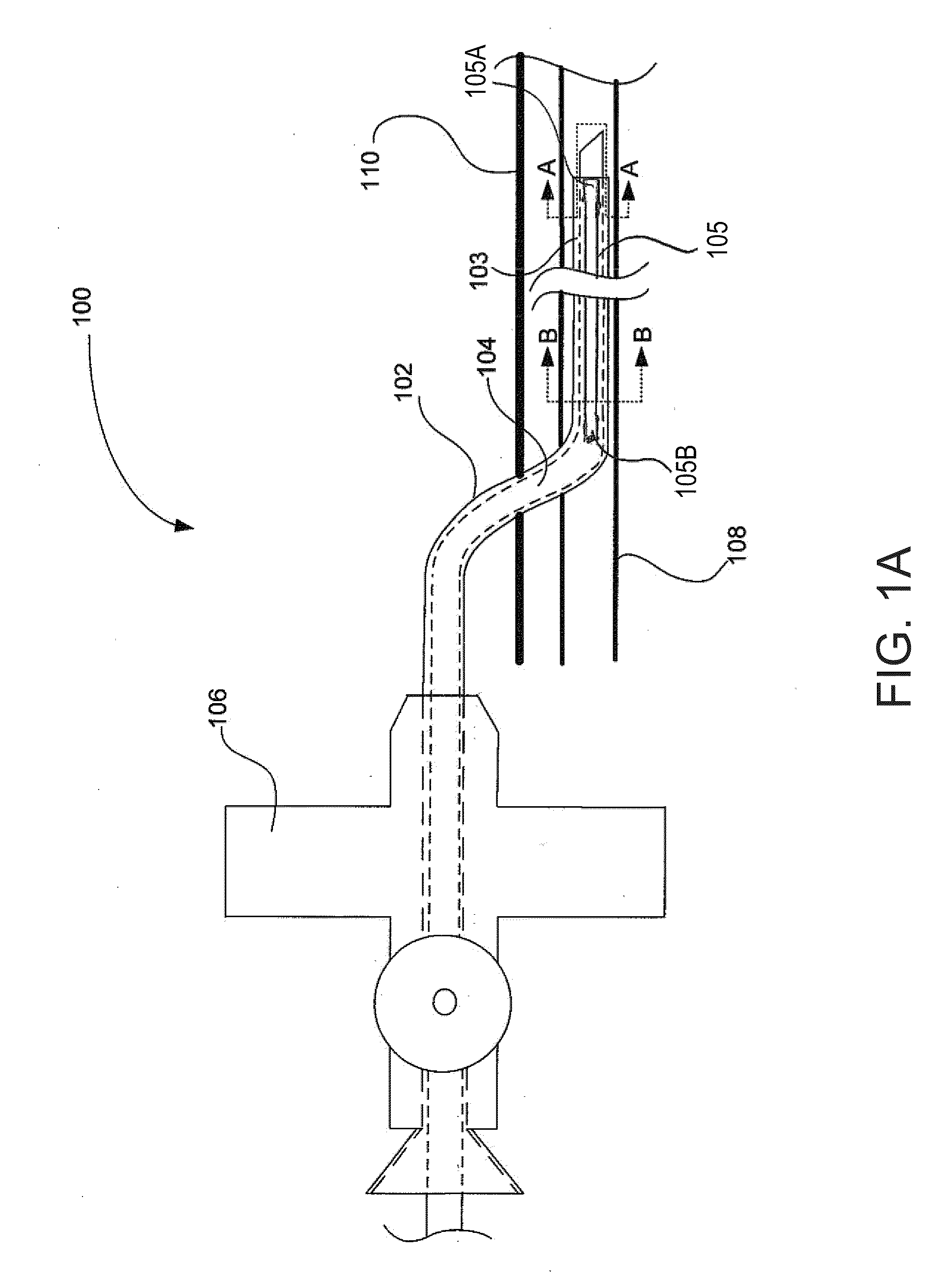
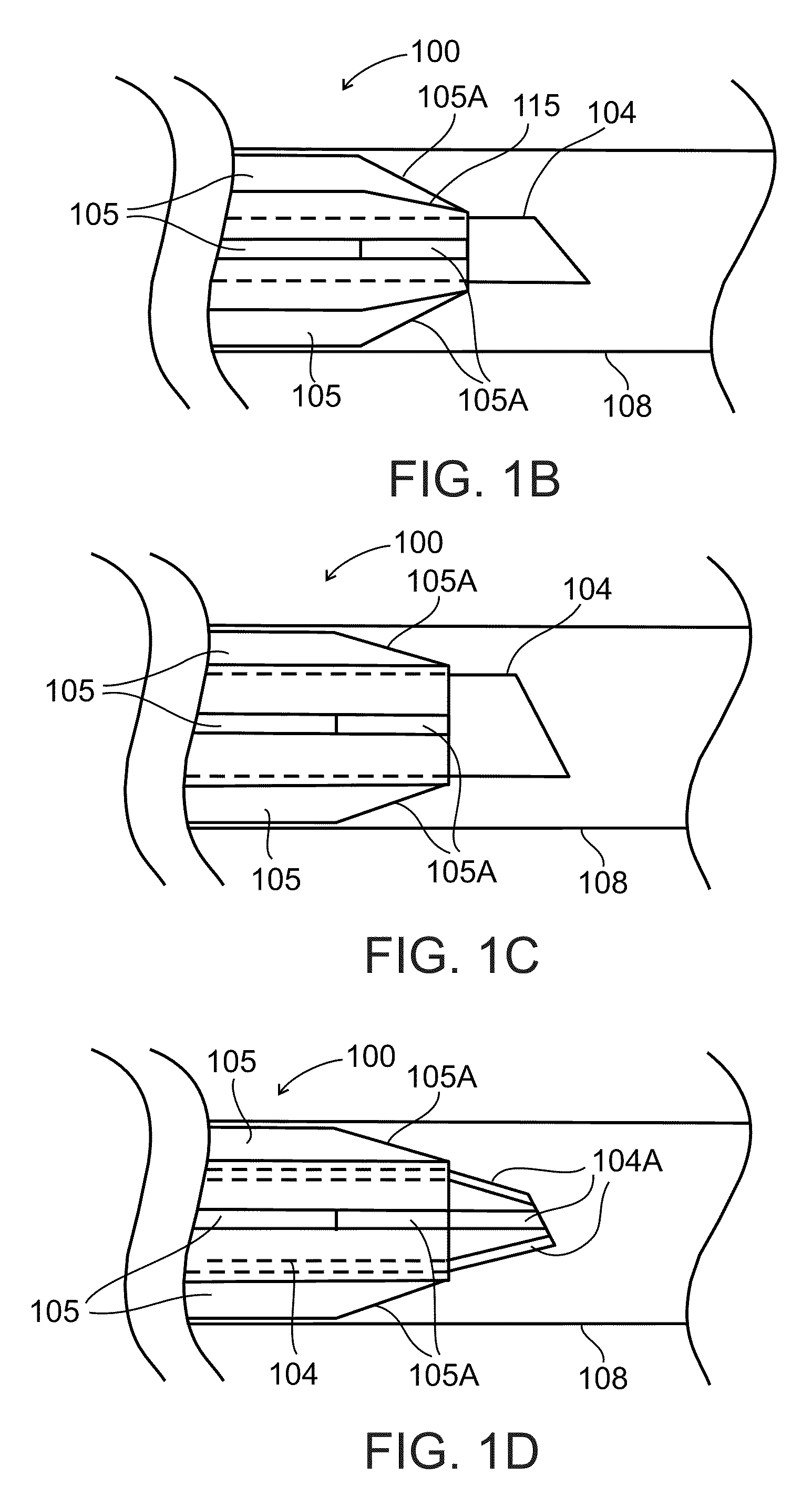
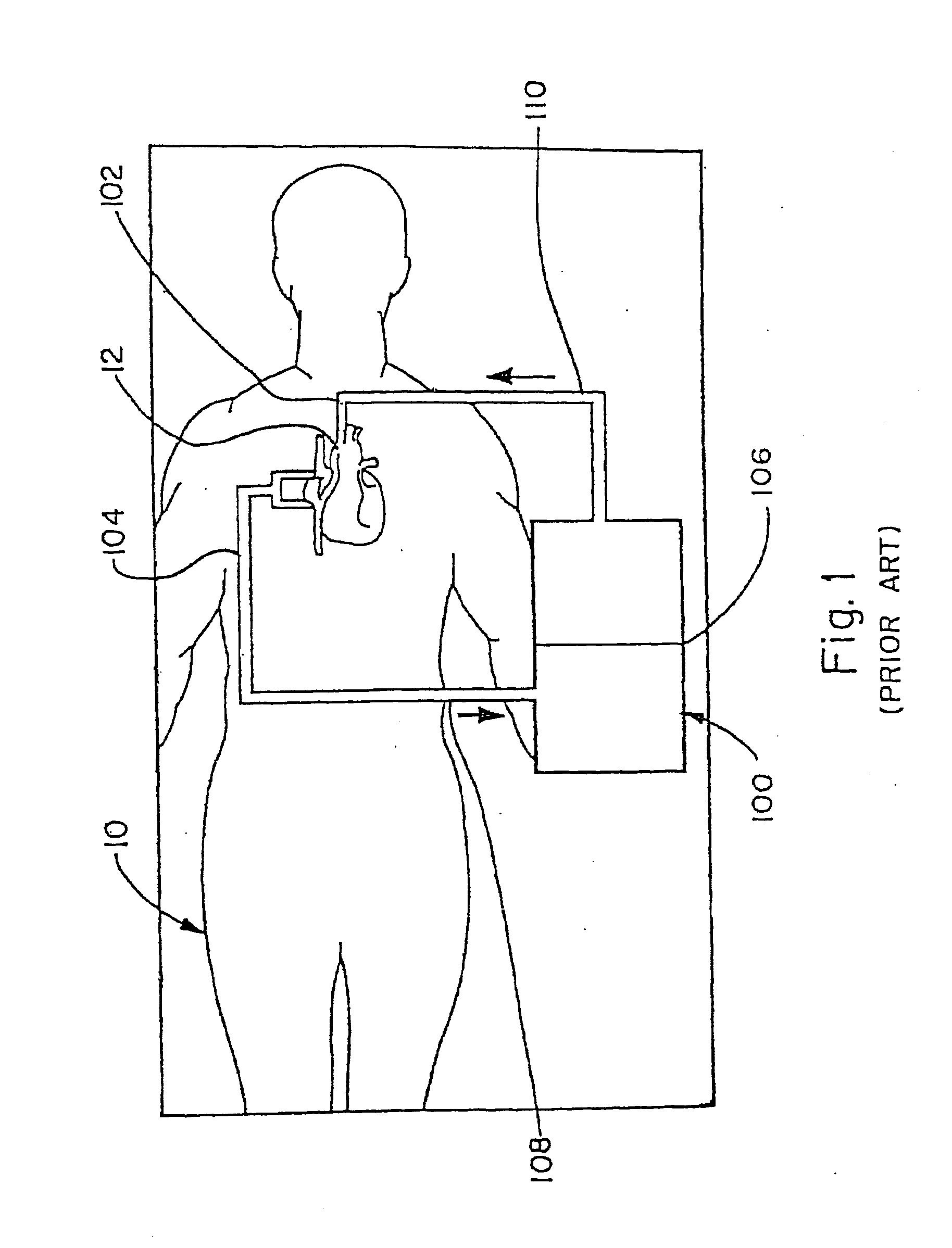
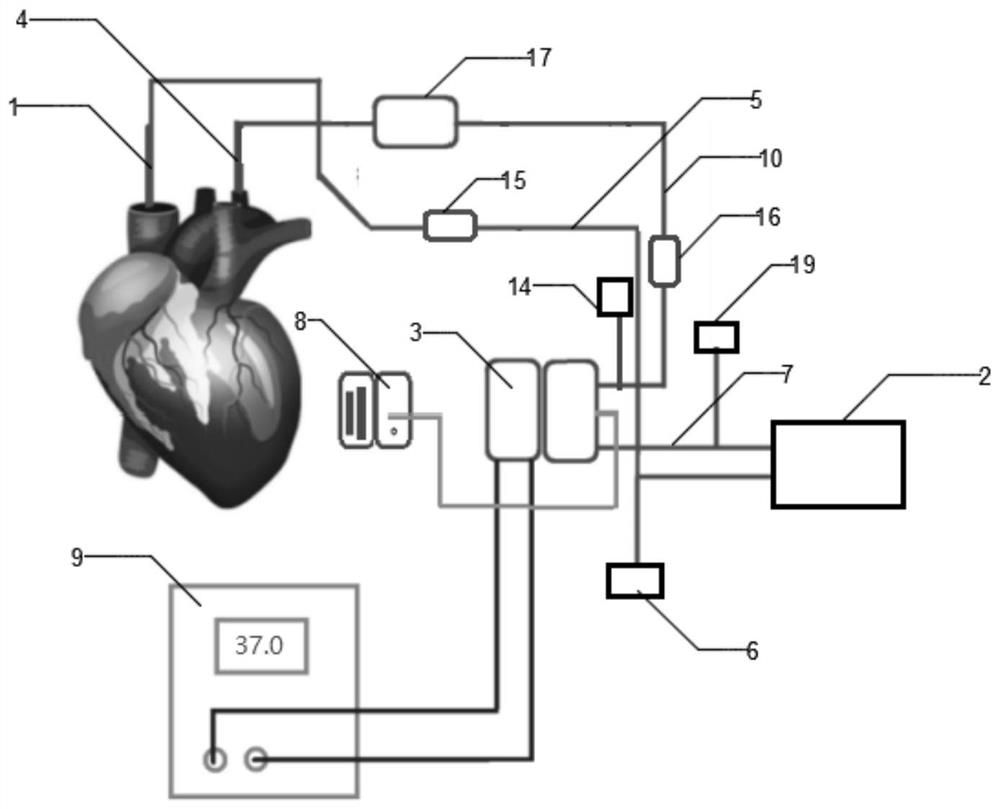
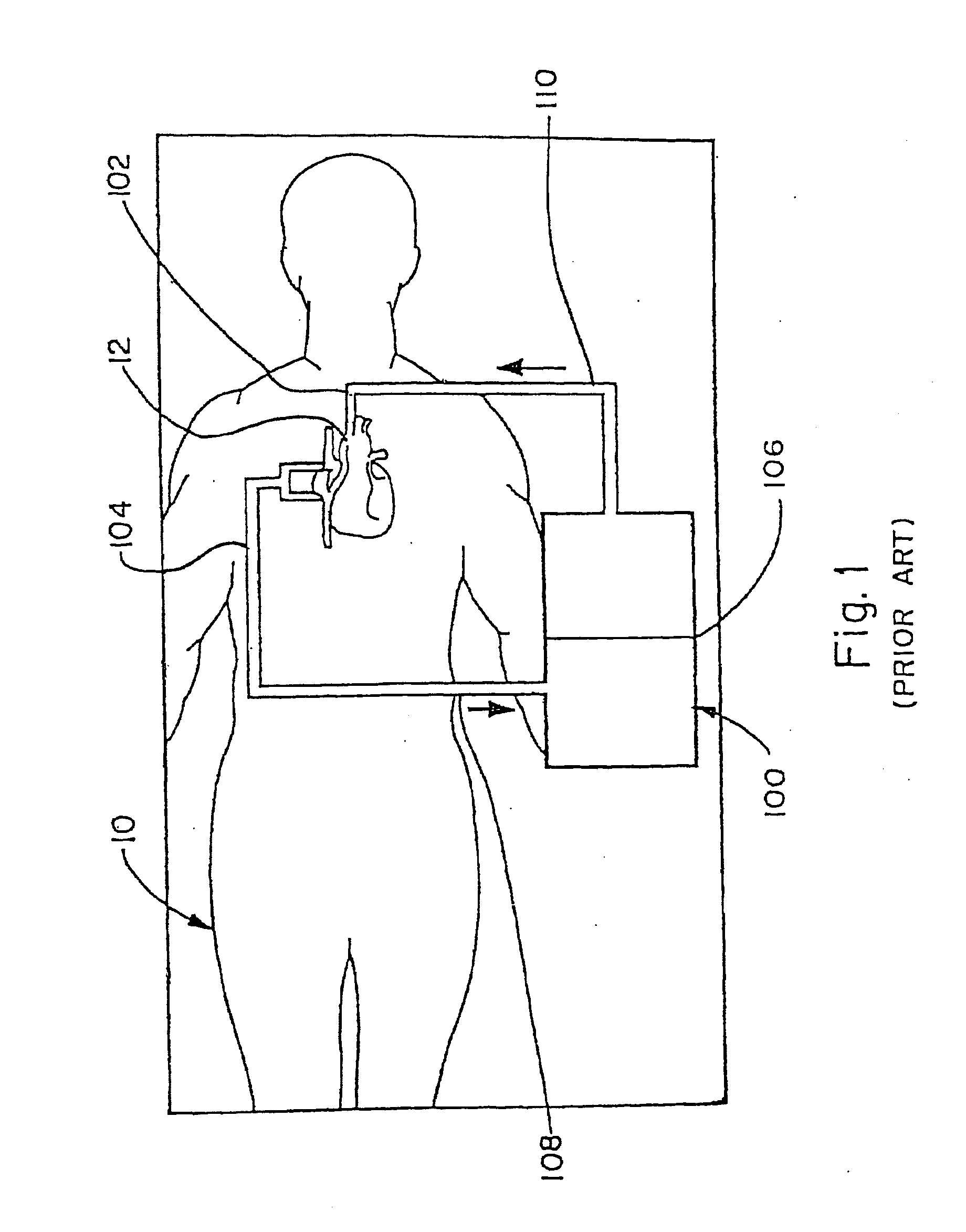
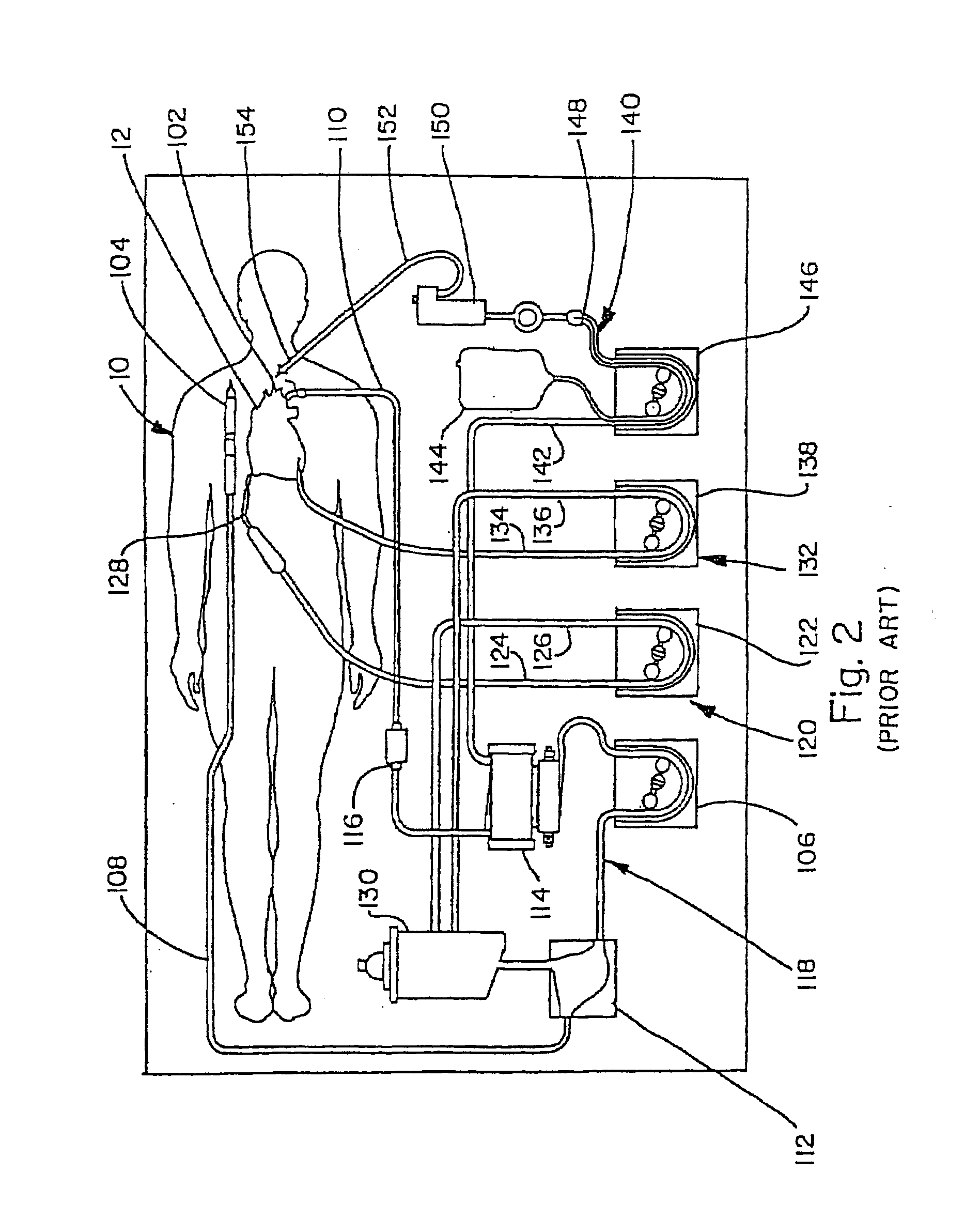
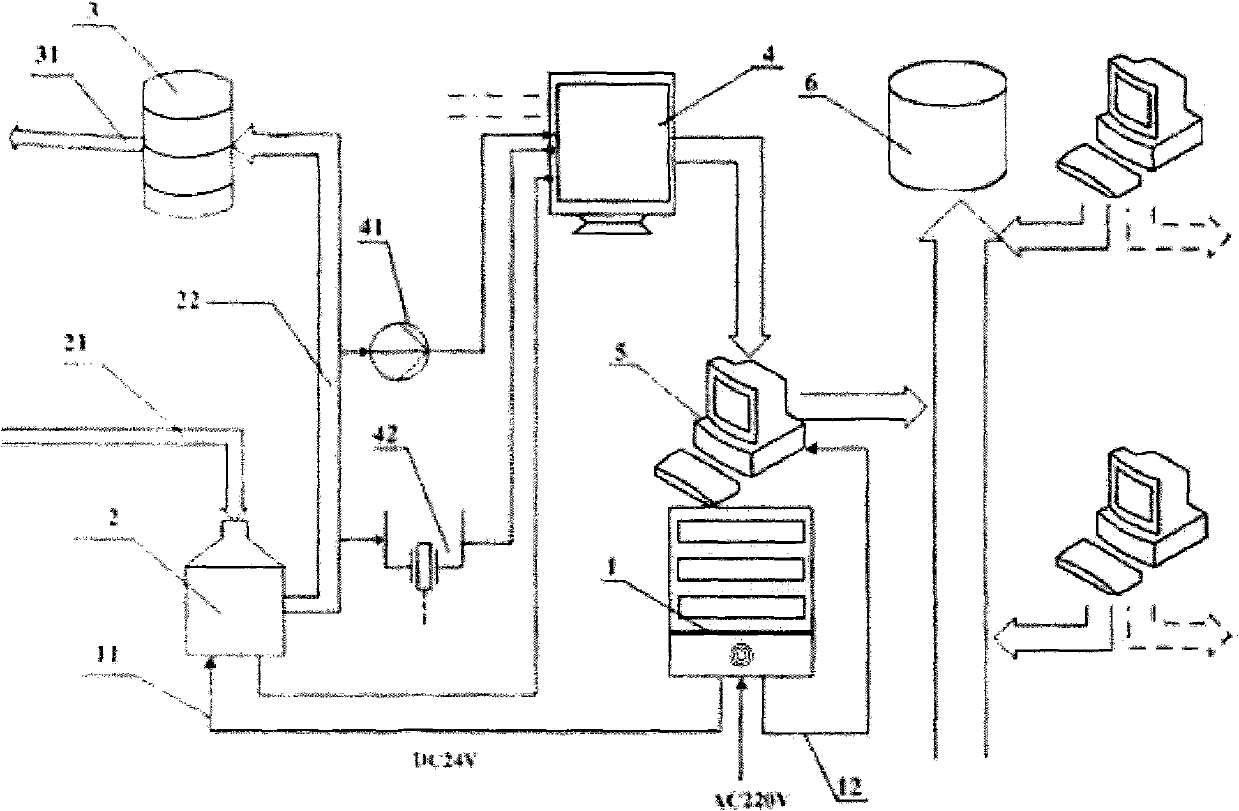
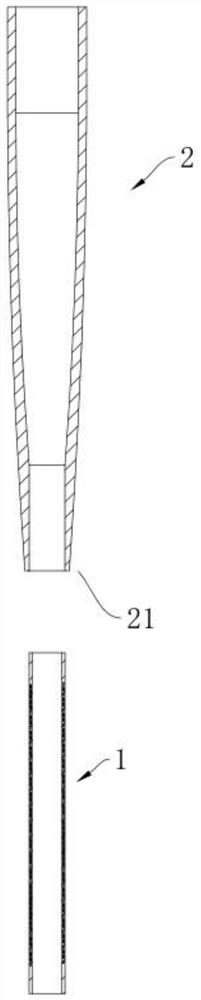
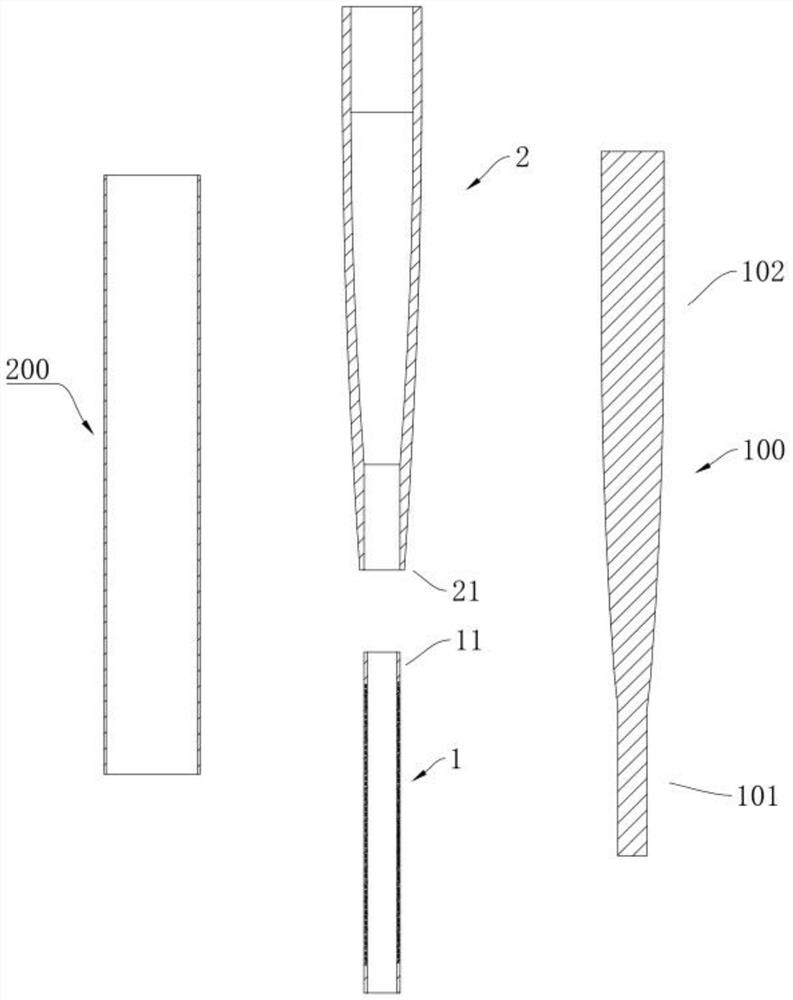
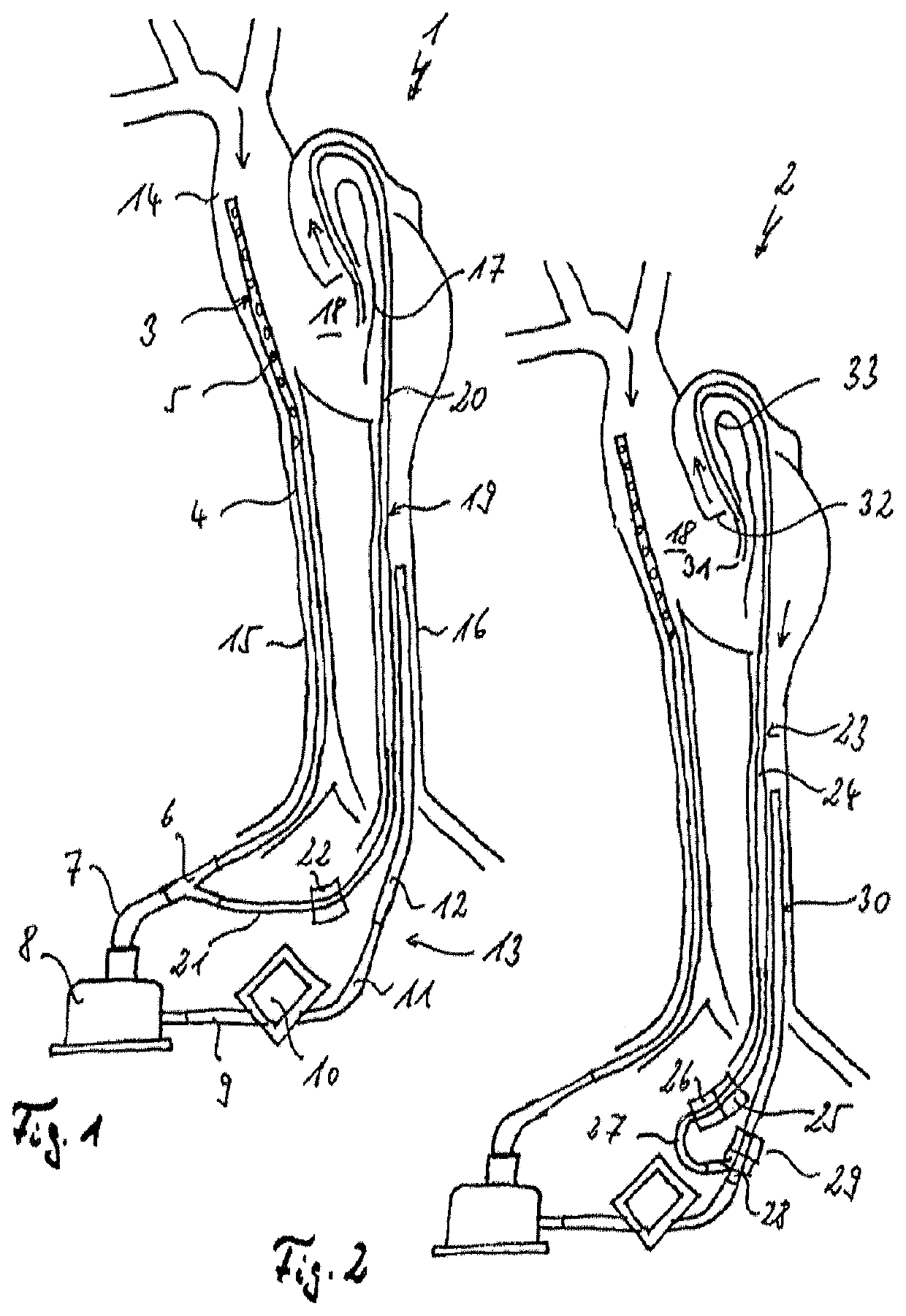
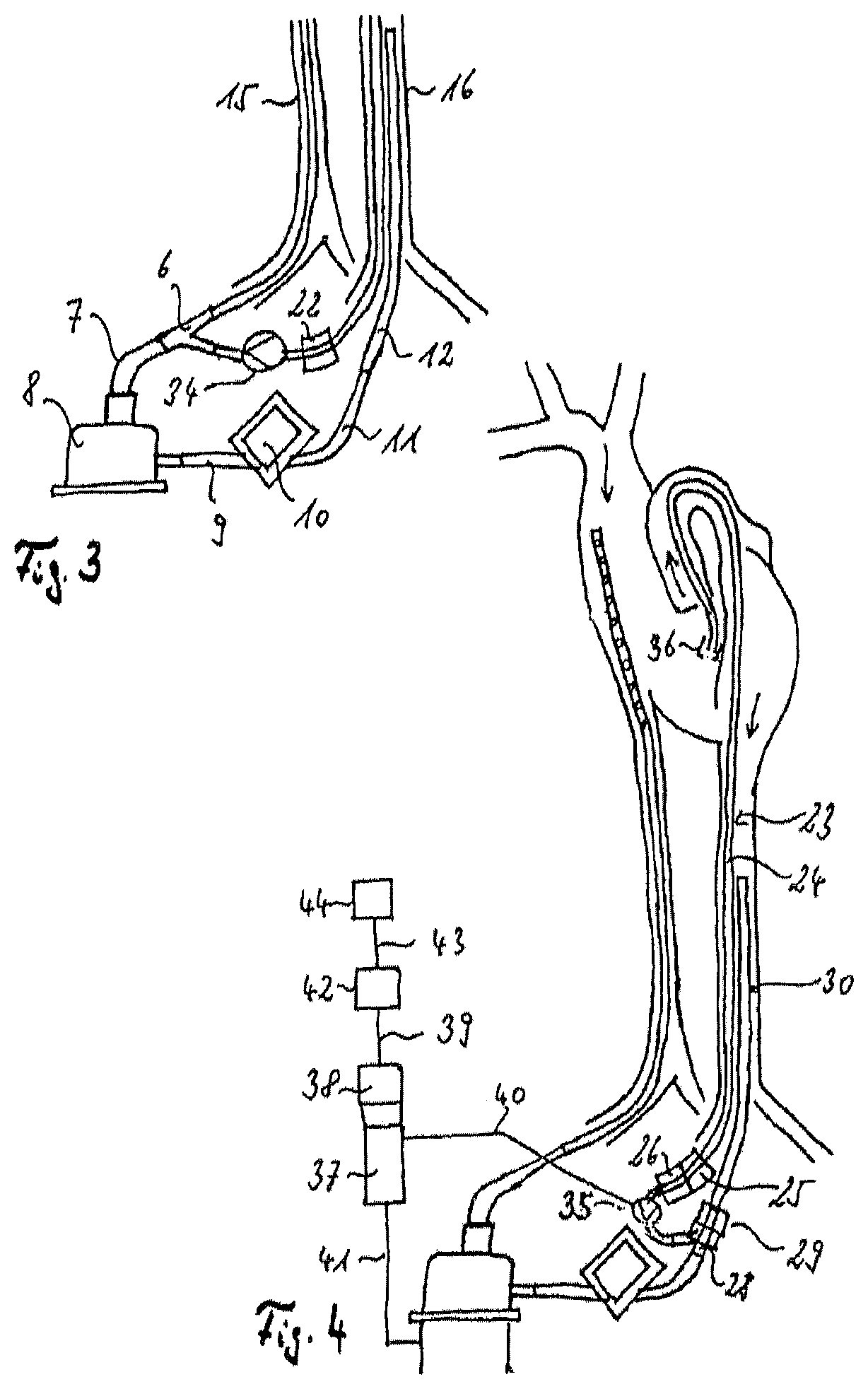
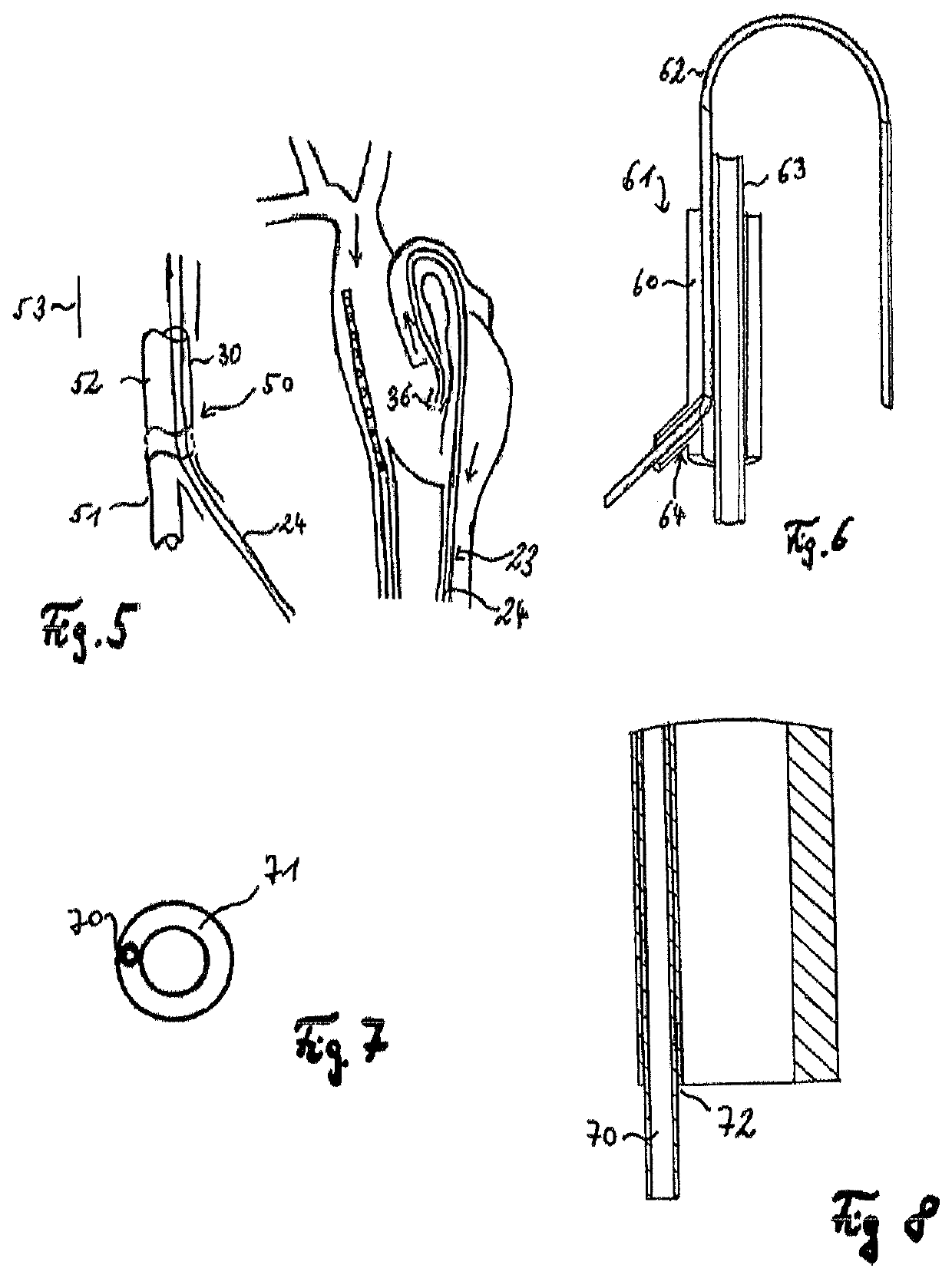
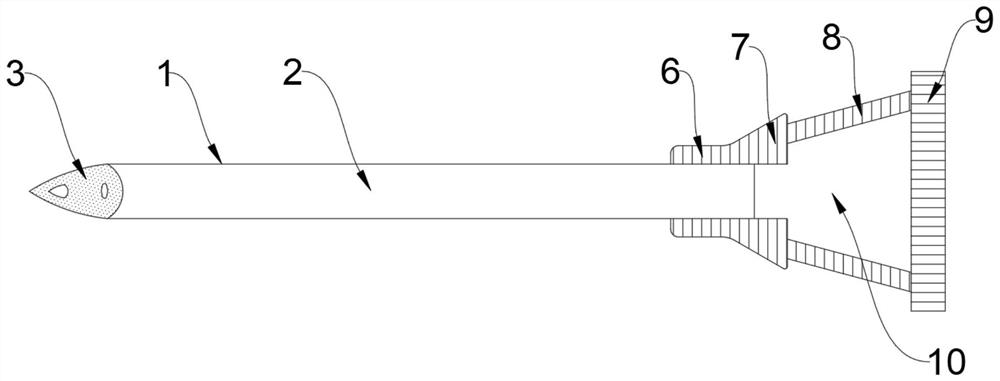
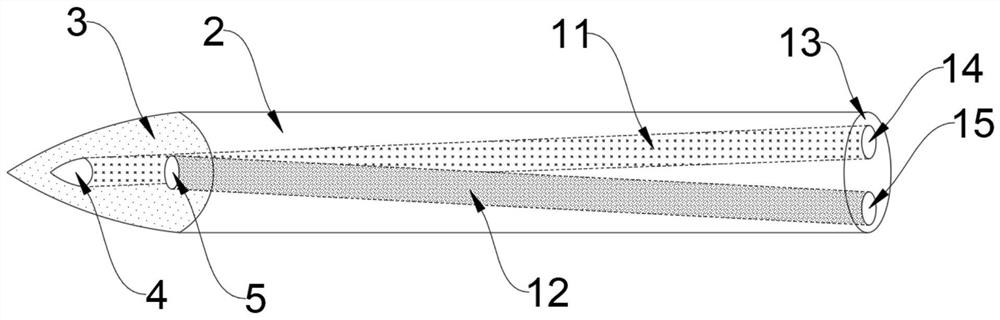
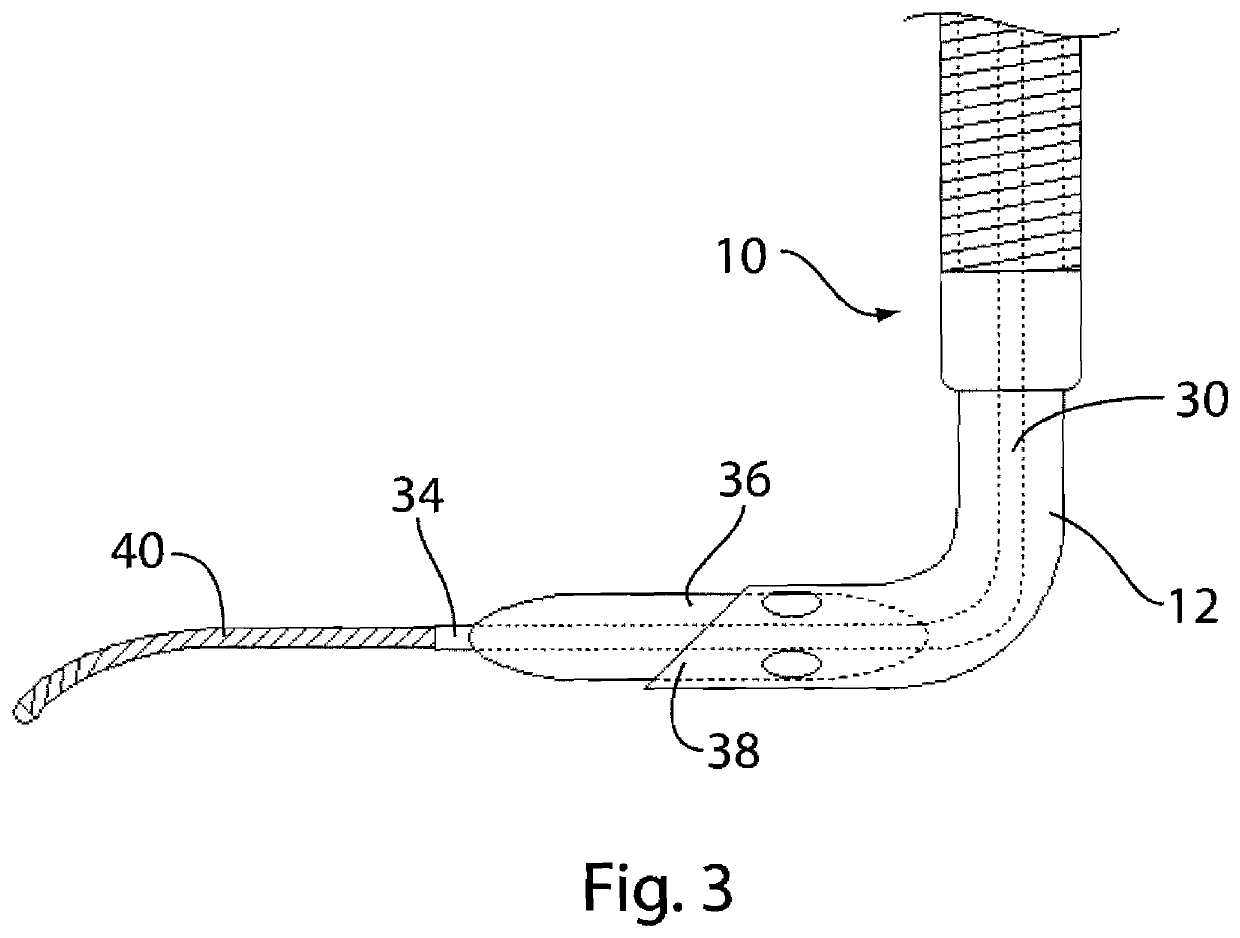
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
InactiveUS20050222532A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationVenous blood
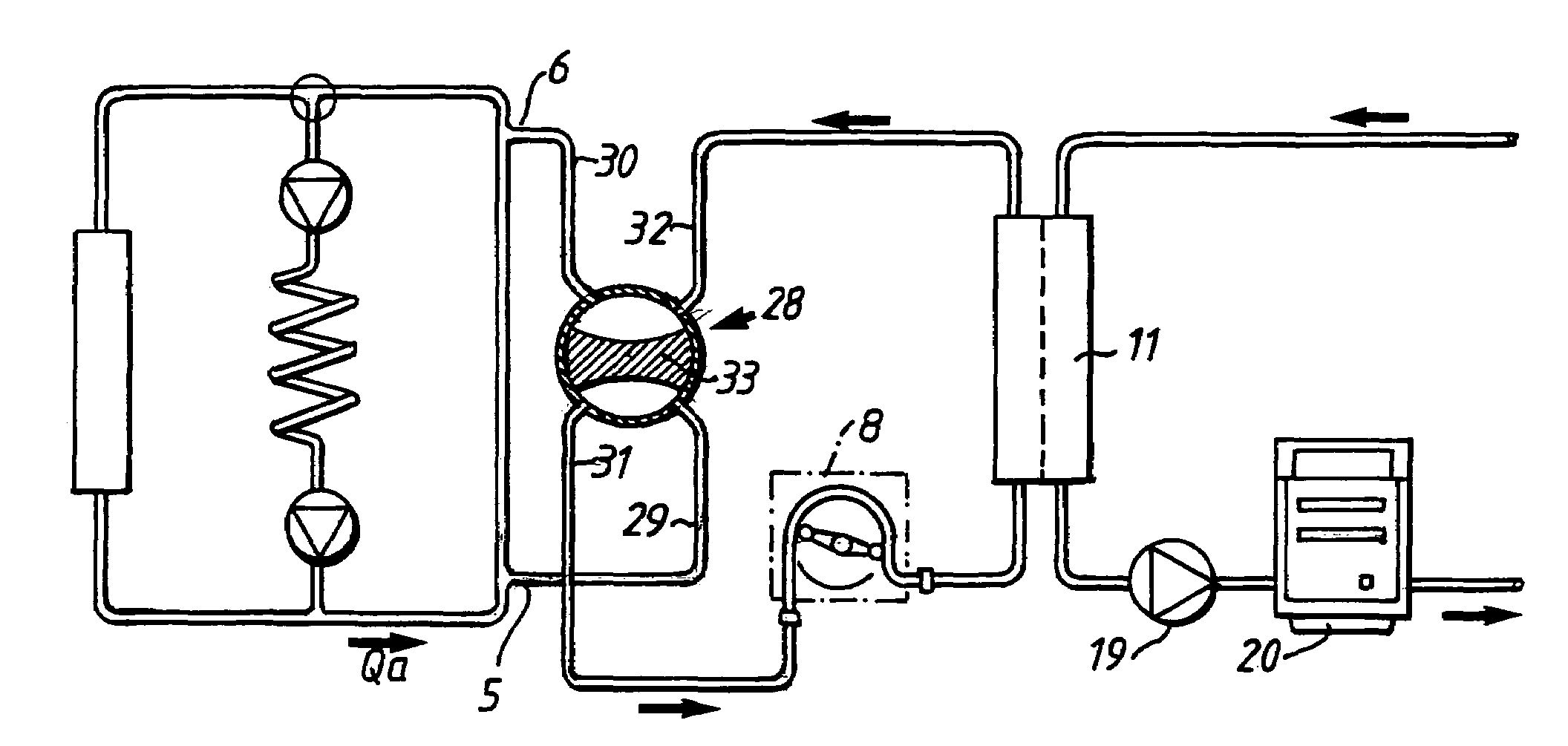
This invention relates to a venous cannula for use in conjunction with cardiovascular examinations, treatments and surgery. The venous cannula is configured for two-stage drainage of oxygen-depleted venous blood from a central venous location via a peripheral venous insertion site, such as a femoral vein. The venous cannula is optimized for use in a cardiopulmonary bypass system that includes a multichannel arterial perfusion catheter. The cardiopulmonary bypass system is advantageous for use in performing standard open chest or least invasive cardiac surgical procedures.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
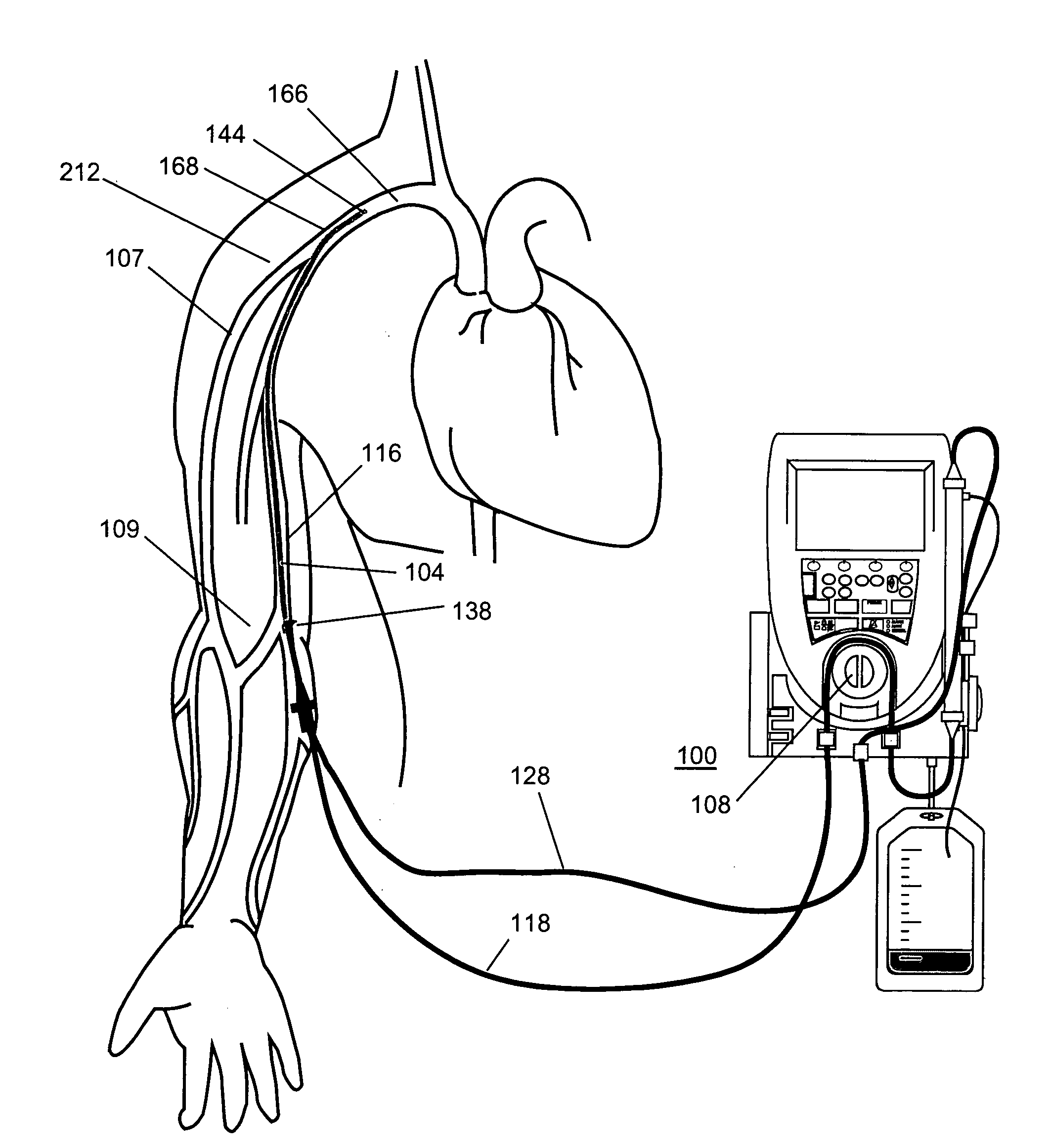
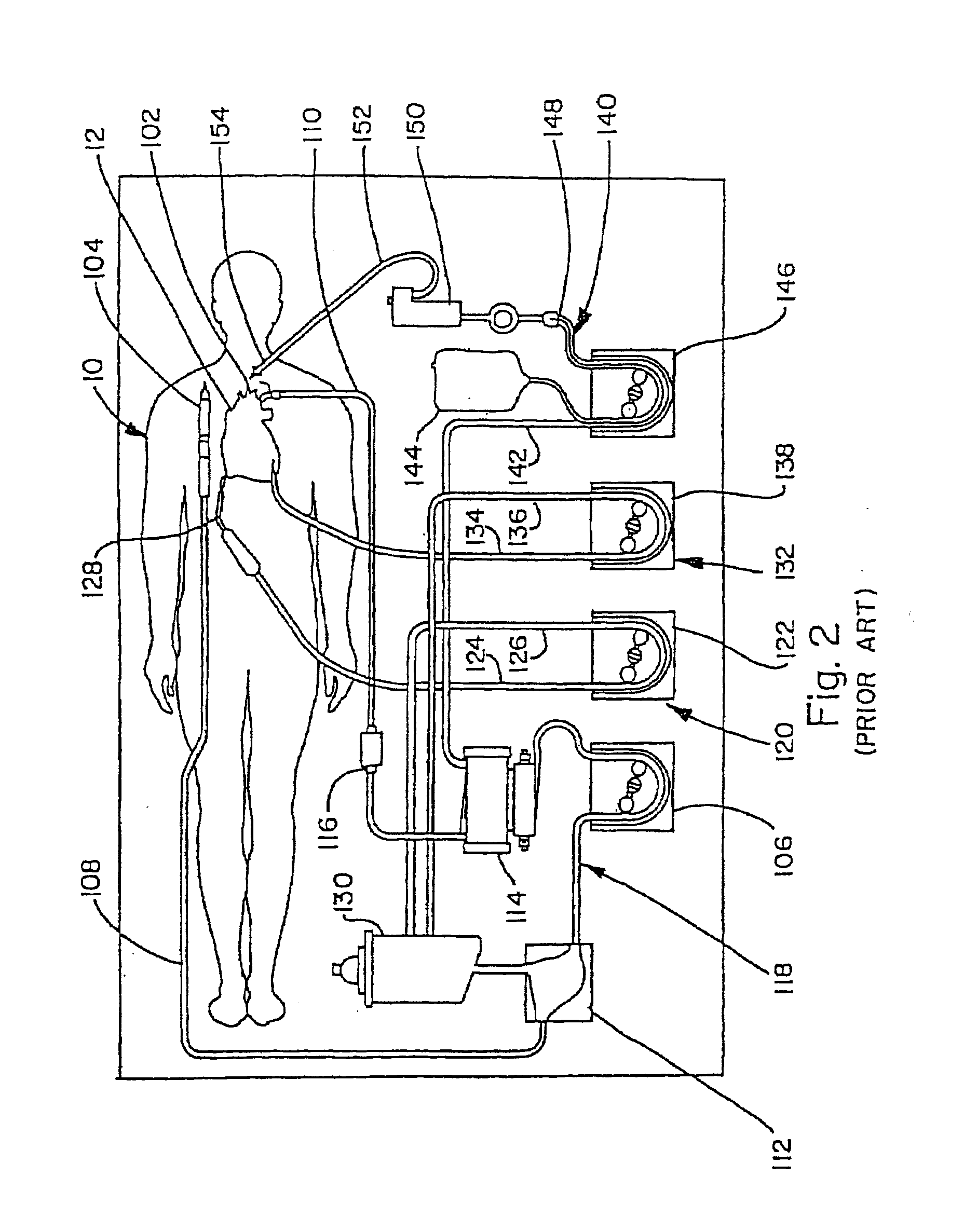
Method and apparatus for ultrafiltration utilizing a peripheral access dual lumen venous cannula
InactiveUS20050119597A1Ease and safetyInadequate blood flowSemi-permeable membranesMulti-lumen catheterUltrafiltrationCongestive heart failure chf
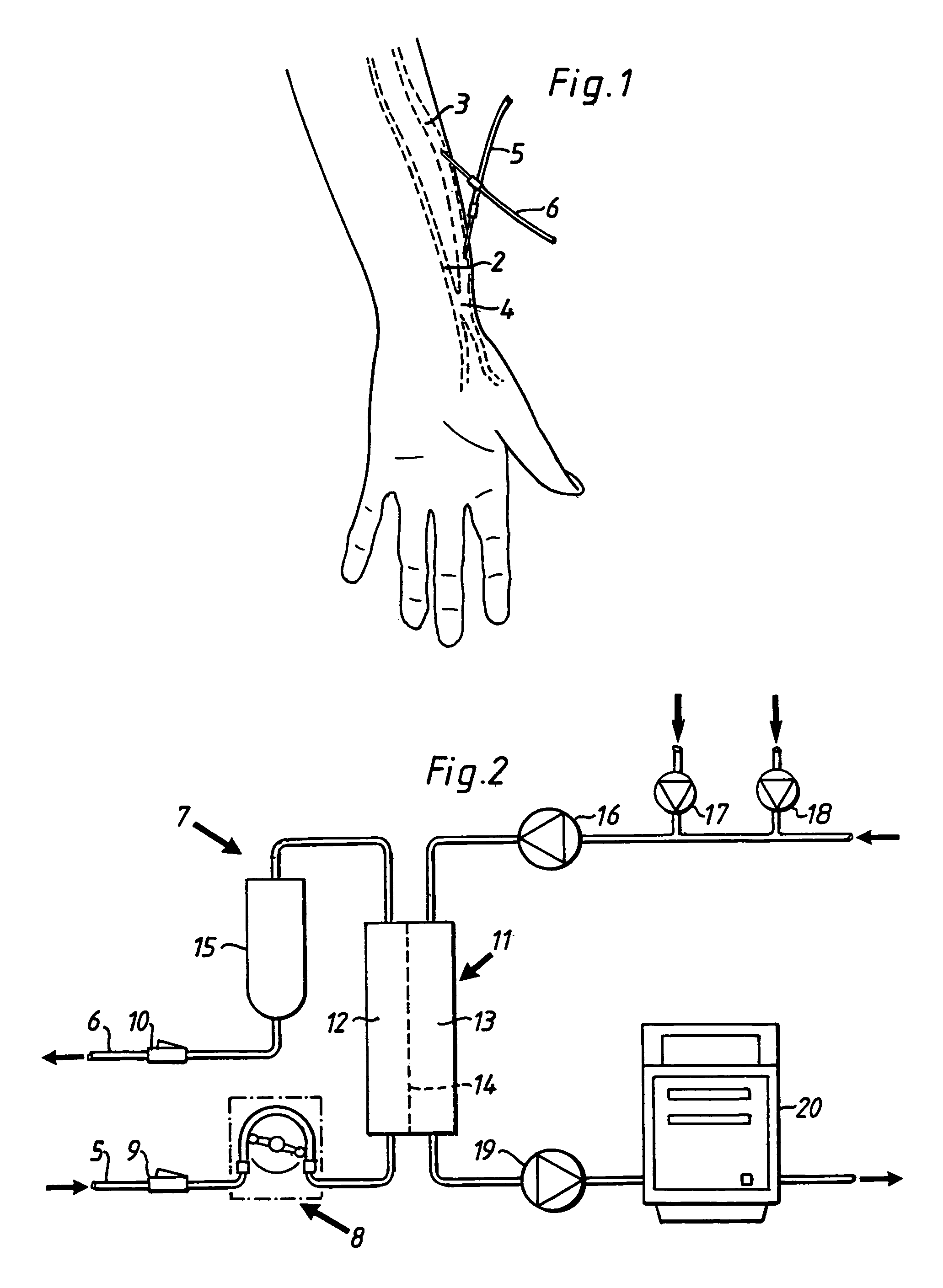
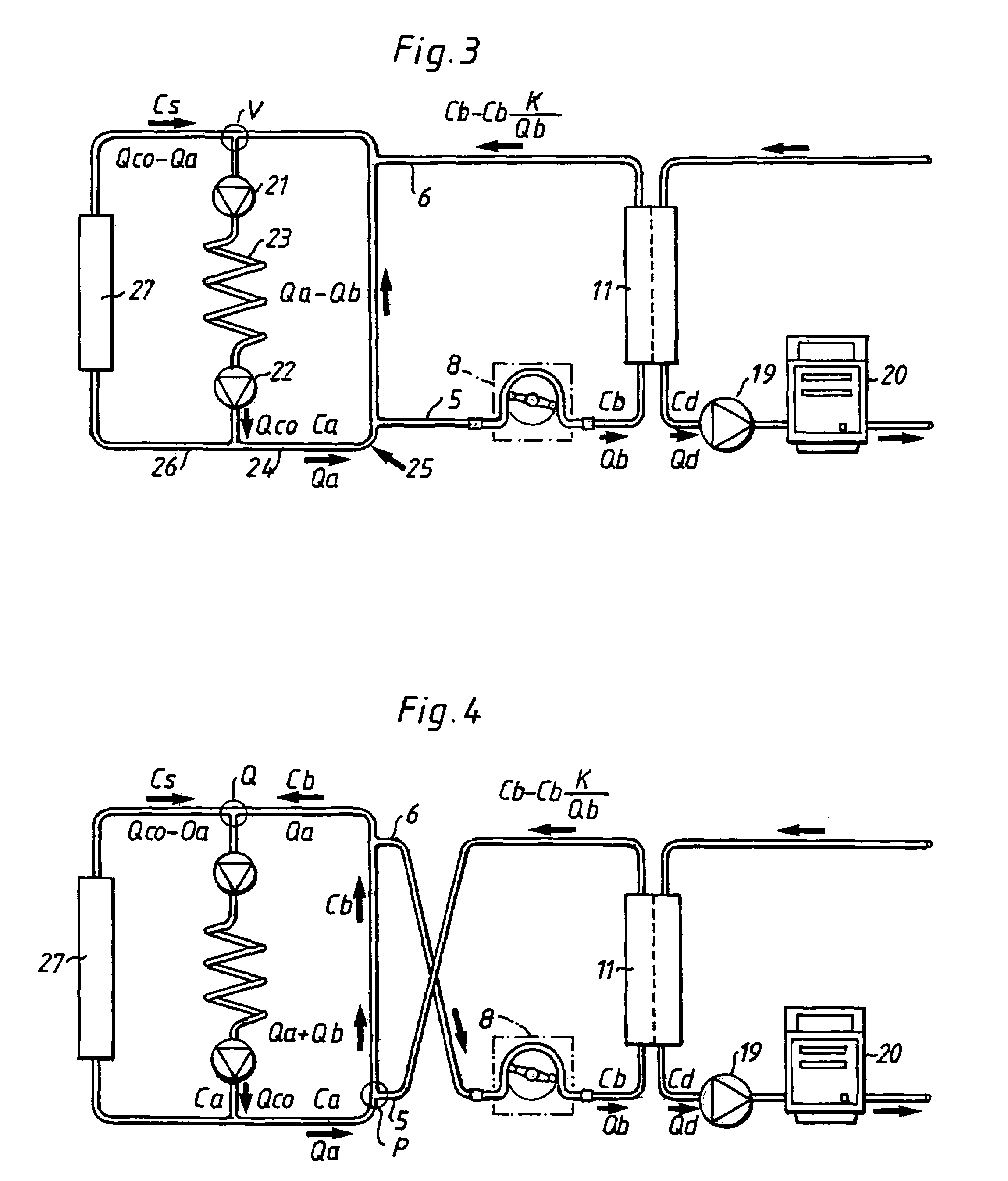
Method and apparatus for the extracorporeal treatment of blood by utilizing a peripherally inserted dual lumen catheter assembly for the continuous removal and return of blood for renal replacement treatment, in particularly, treatment of congestive heart failure and fluid overload by ultrafiltration. A catheter is inserted in a peripheral vein and maneuvered upward through the vascular system to access the reservoir of blood in the large or great veins for continuous blood withdrawal and treatment. Air-tight connectors are incorporated in the catheter assembly to overcome the untoward effects of negative pressure in blood withdrawal.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Switch valve for an extracorporeal blood circuit and circuit including such a switch valve
InactiveUS20040168969A1Semi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesArterial cannulaBiomedical engineering
A switch valve for use in an extracorporeal blood flow circuit comprises a valve housing having a chamber, four openings communicating with the chamber, and a valve member located in the valve chamber. A first opening is to be connected to a patient via an arterial cannula, a second opening is to be connected to a patient via an venous cannula, a third opening is to be connected to a first inlet / oulet of a blood treatment device, and a fourth opening is to be connected to a second inlet / outlet of a blood treatment device. The valve member is movable within the valve housing to fluidly connect the first opening to either the third or the fourth opening and to fluidly connect the second opening to either the third or the fourth opening. The width of the valve member is smaller than a peripheral dimension of the openings.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and apparatus for ultrafiltration utilizing a peripheral access dual lumen venous cannula
InactiveUS7135008B2Minimize timeConserve veinSemi-permeable membranesMulti-lumen catheterUltrafiltrationCongestive heart failure chf
Method and apparatus for the extracorporeal treatment of blood by utilizing a peripherally inserted dual lumen catheter assembly for the continuous removal and return of blood for renal replacement treatment, in particularly, treatment of congestive heart failure and fluid overload by ultrafiltration. A catheter is inserted in a peripheral vein and maneuvered upward through the vascular system to access the reservoir of blood in the large or great veins for continuous blood withdrawal and treatment. Air-tight connectors are incorporated in the catheter assembly to overcome the untoward effects of negative pressure in blood withdrawal.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Switch valve for an extracorporeal blood circuit and circuit including such a switch valve
A switch valve for use in an extracorporeal blood flow circuit comprises a valve housing having a chamber, four openings communicating with the chamber, and a valve member located in the valve chamber. A first opening is to be connected to a patient via an arterial cannula, a second opening is to be connected to a patient via an venous cannula, a third opening is to be connected to a first inlet / oulet of a blood treatment device, and a fourth opening is to be connected to a second inlet / outlet of a blood treatment device. The valve member is movable within the valve housing to fluidly connect the first opening to either the third or the fourth opening and to fluidly connect the second opening to either the third or the fourth opening. The width of the valve member is smaller than a peripheral dimension of the openings.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
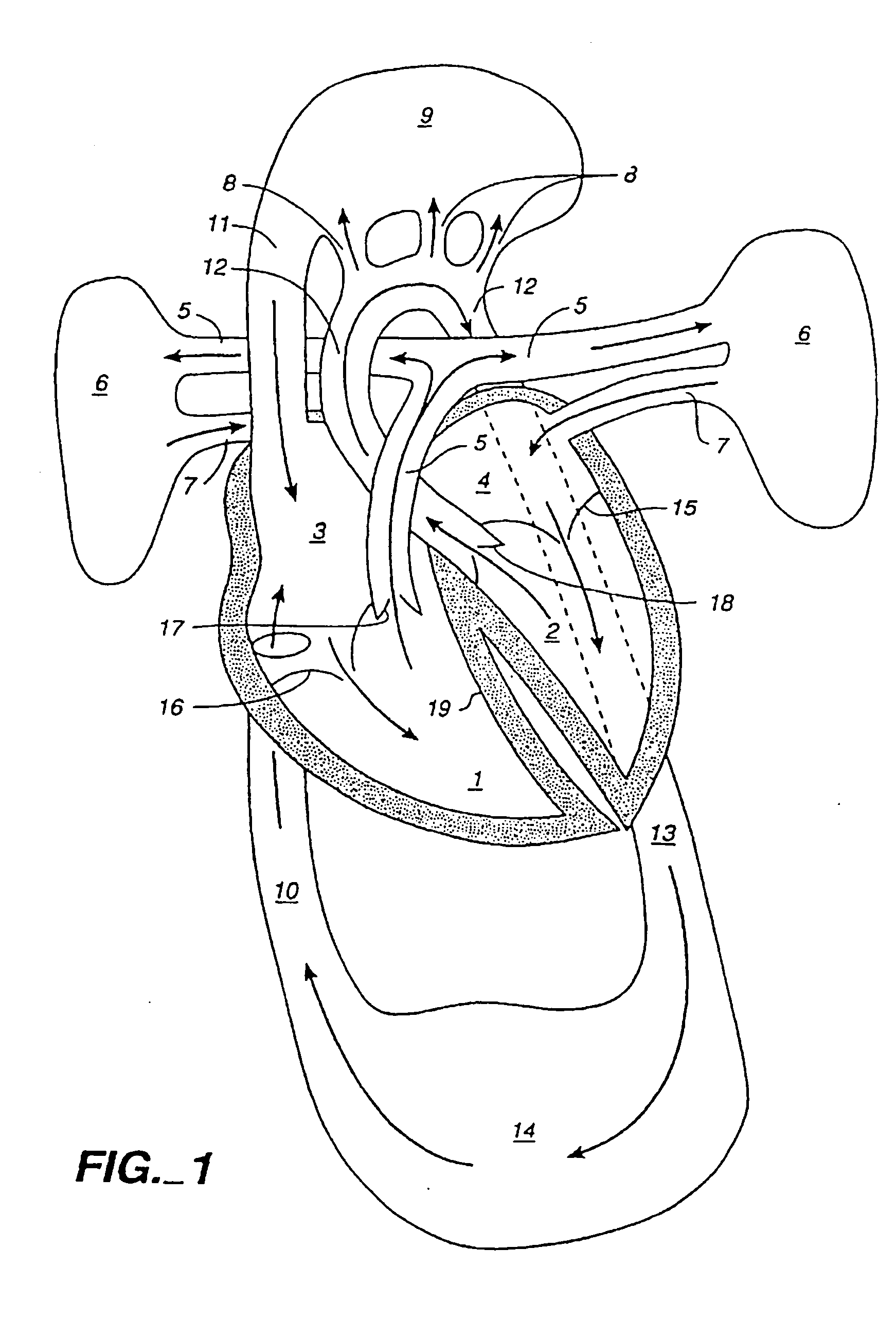
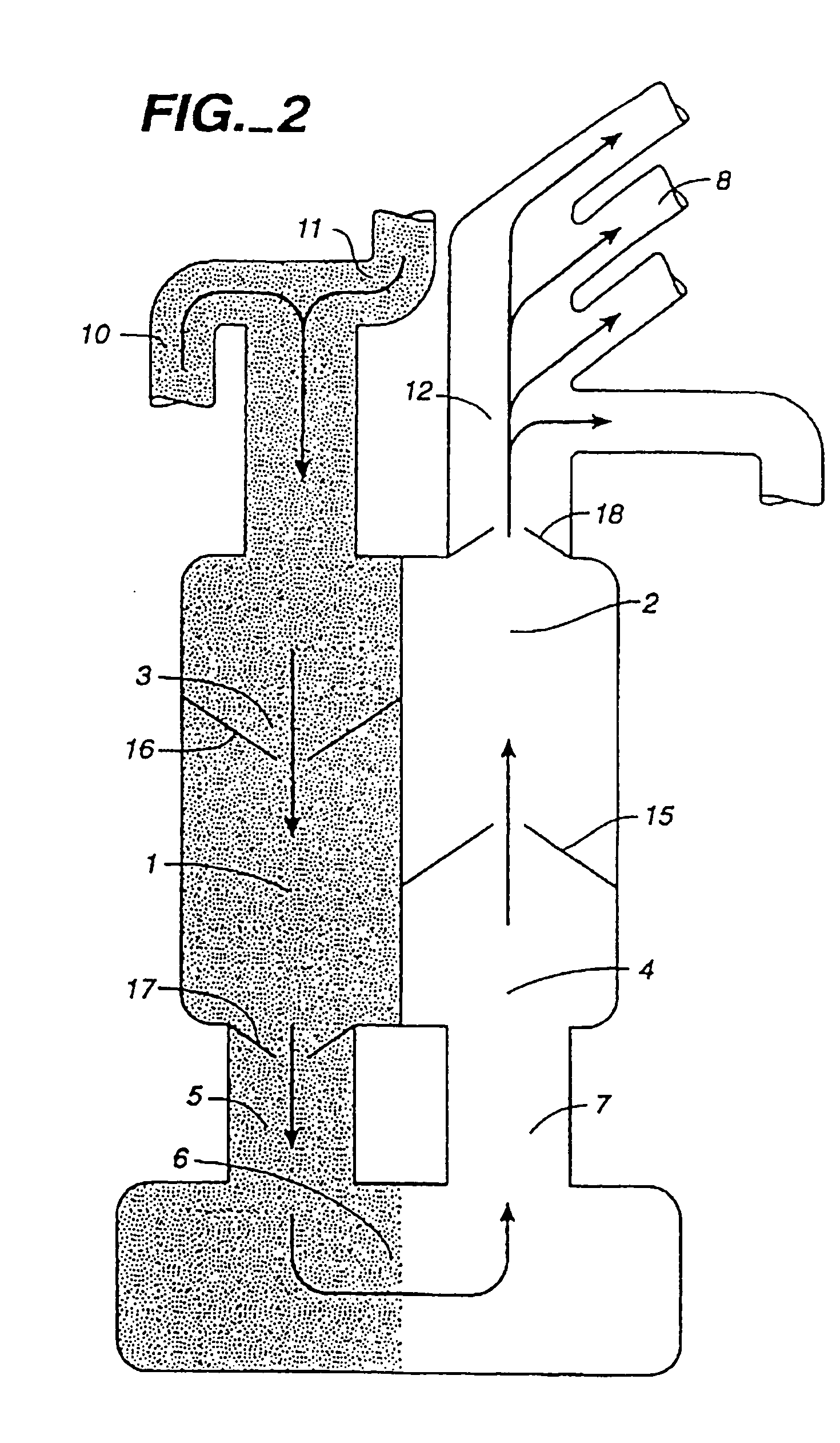
System and method for determining cardiac output
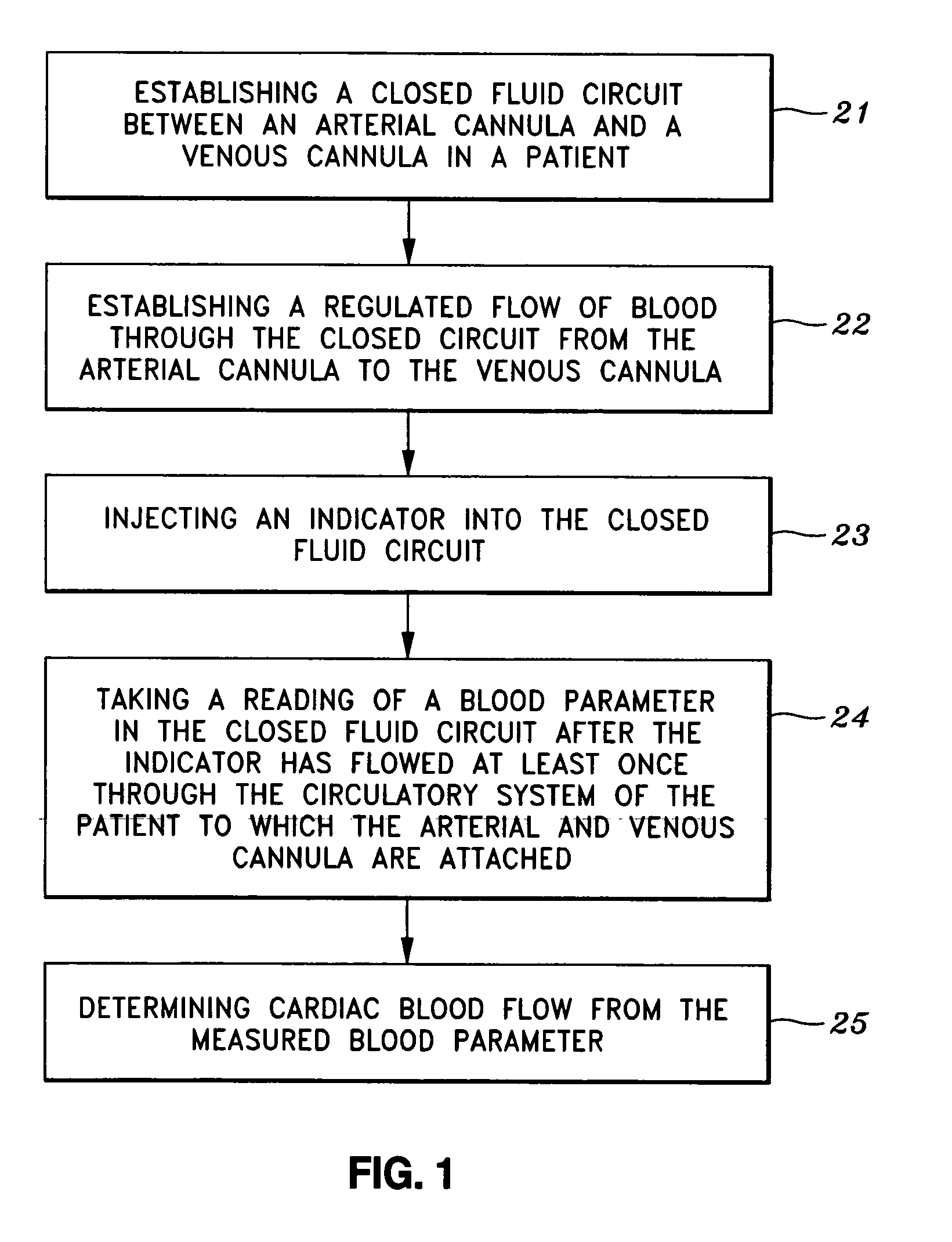
InactiveUS20060211947A1Easy to mergeEasy to implementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterArterial cannulaVenous cannula
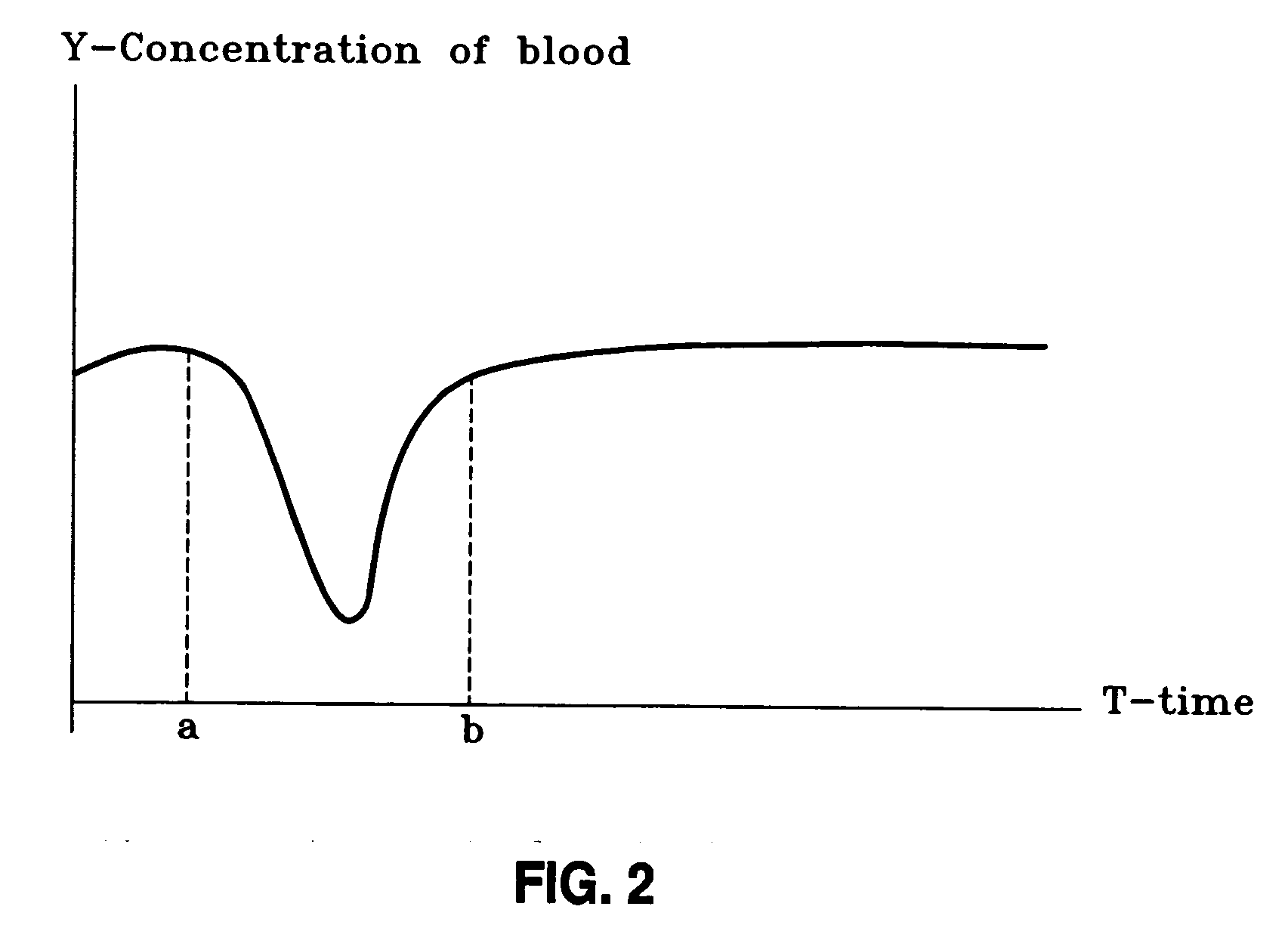
A system and method is disclosed for measuring cardiac output. A closed fluid circuit is created between a patient's arterial cannula and venous cannula. A pump regulates flow through the closed fluid circuit. The closed fluid circuit includes at least one port for injection of an indicator. At least one sensor is attached to the closed fluid circuit for taking readings of a blood parameter after the indicator has flowed through the patients system at least once.
Owner:TRANSONIC SYST
System and method for determining the hematocrit and/or blood volume
InactiveUS20080015486A1High precisionEasy to useSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesBlood treatmentsVein
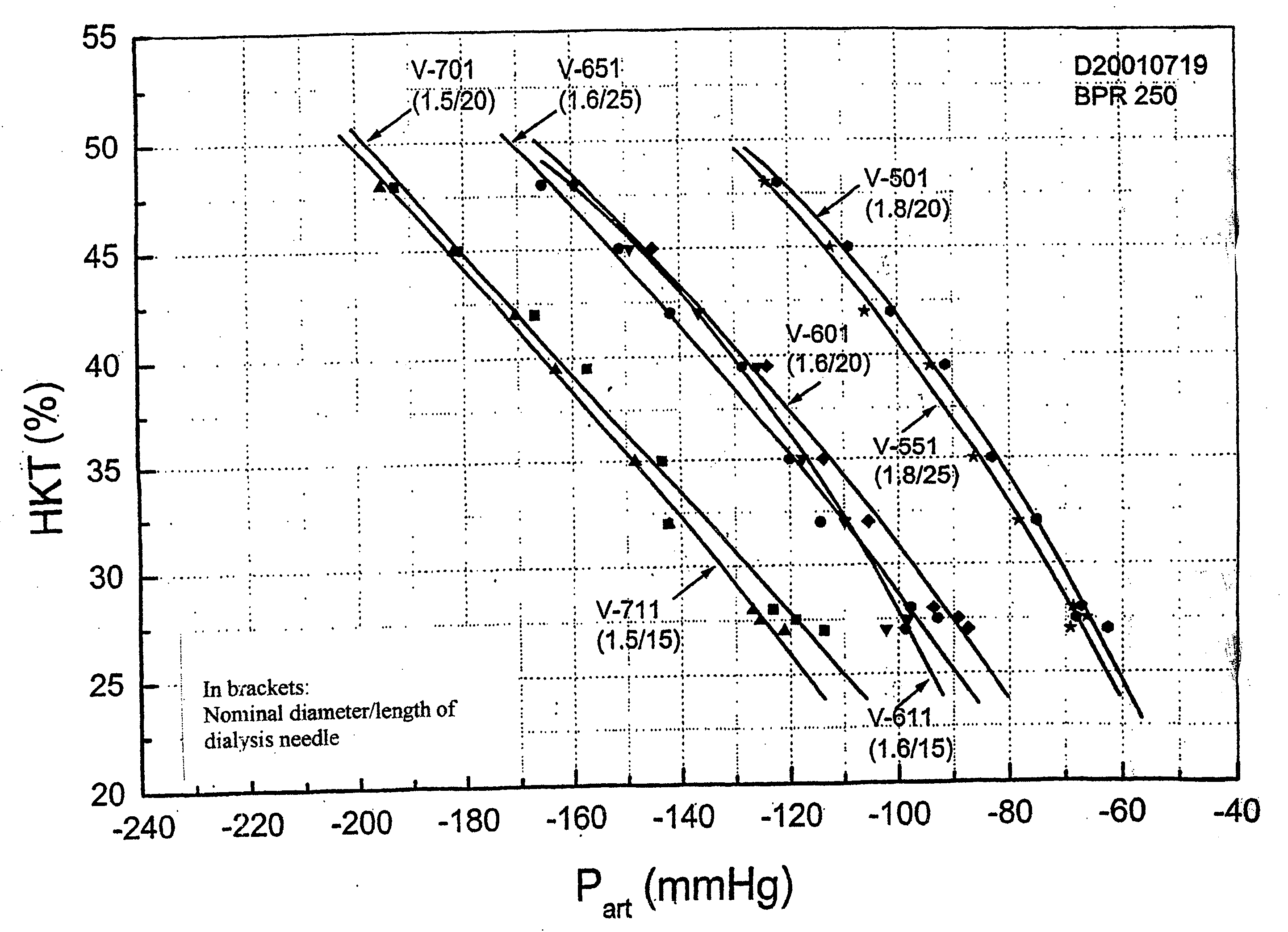
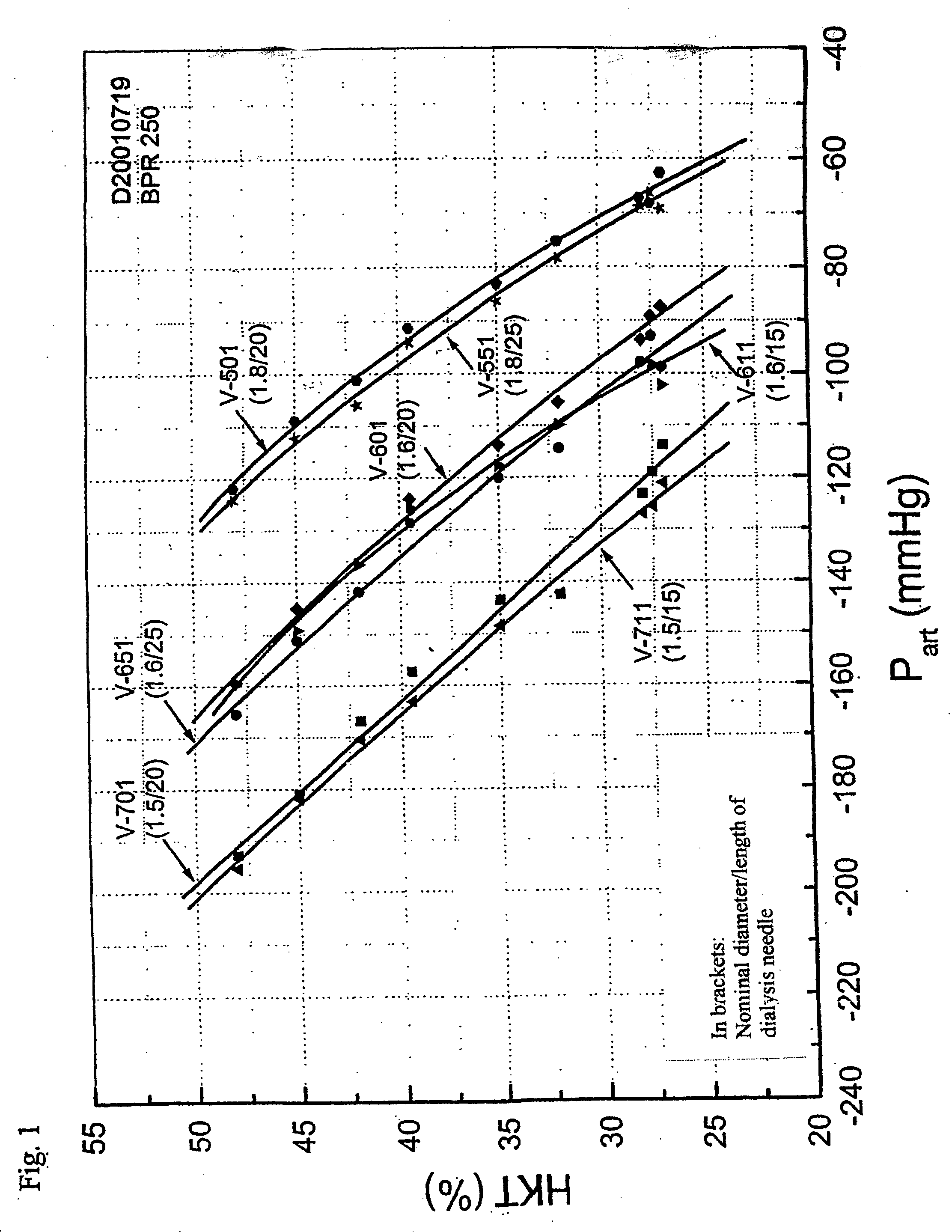
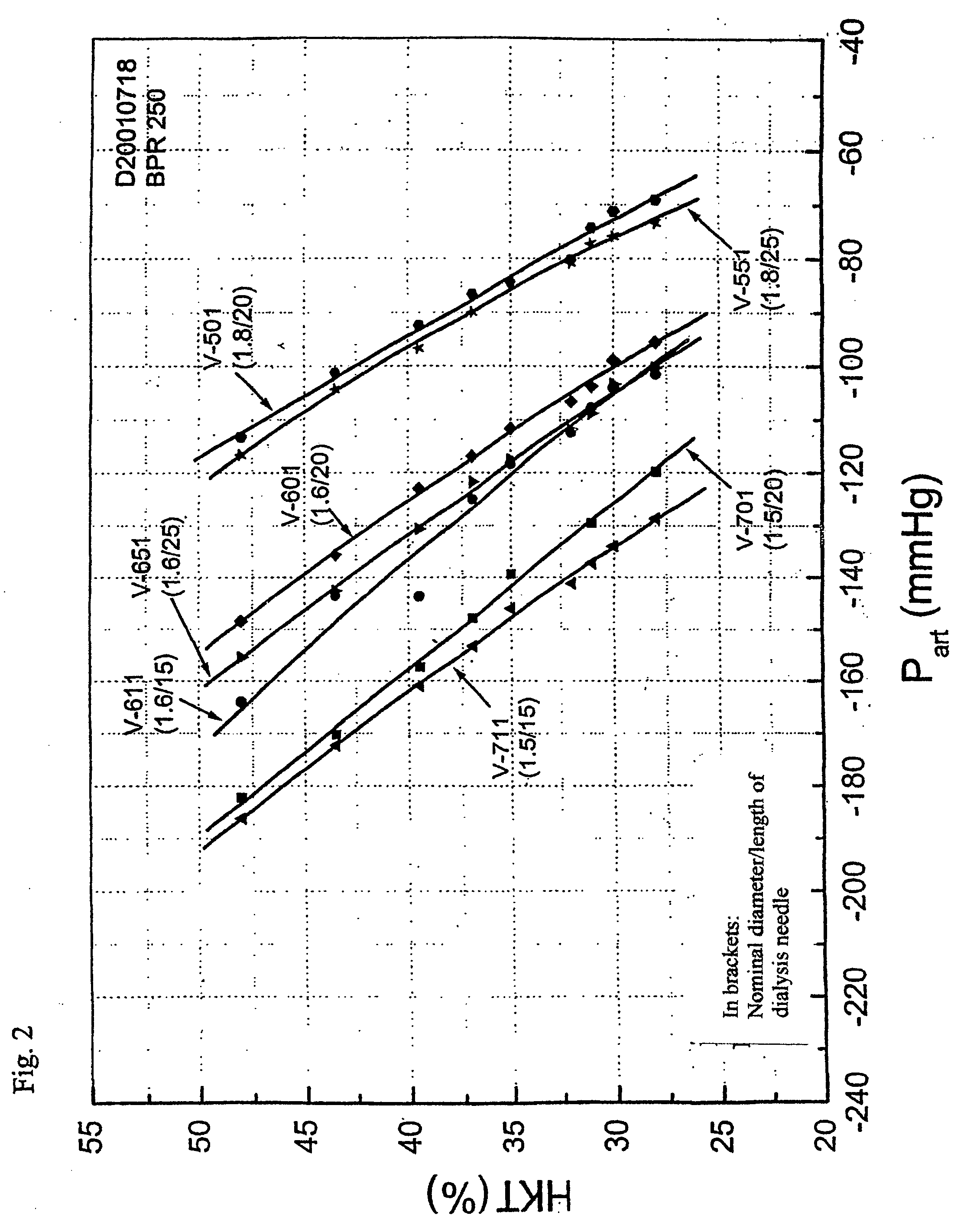
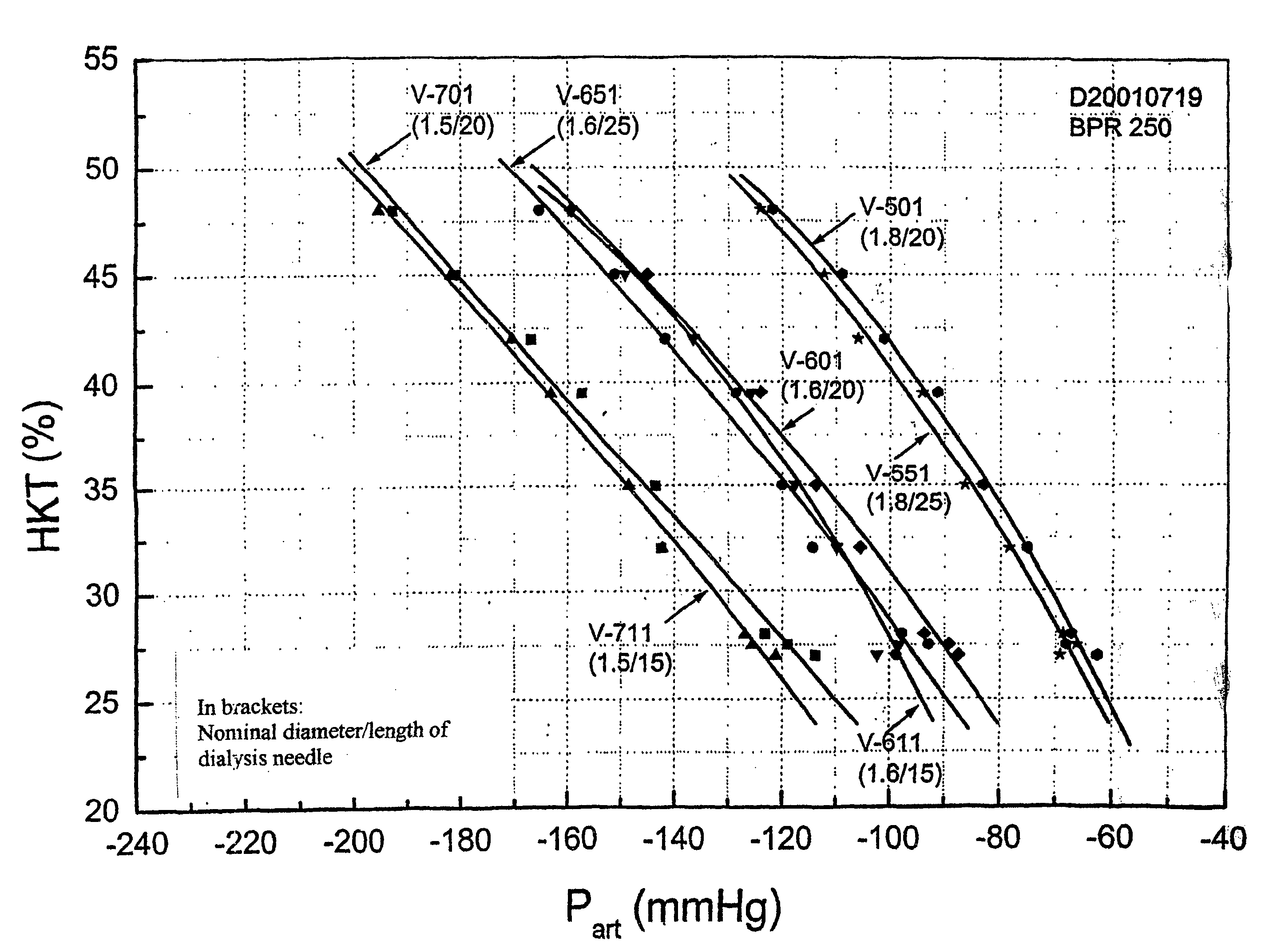
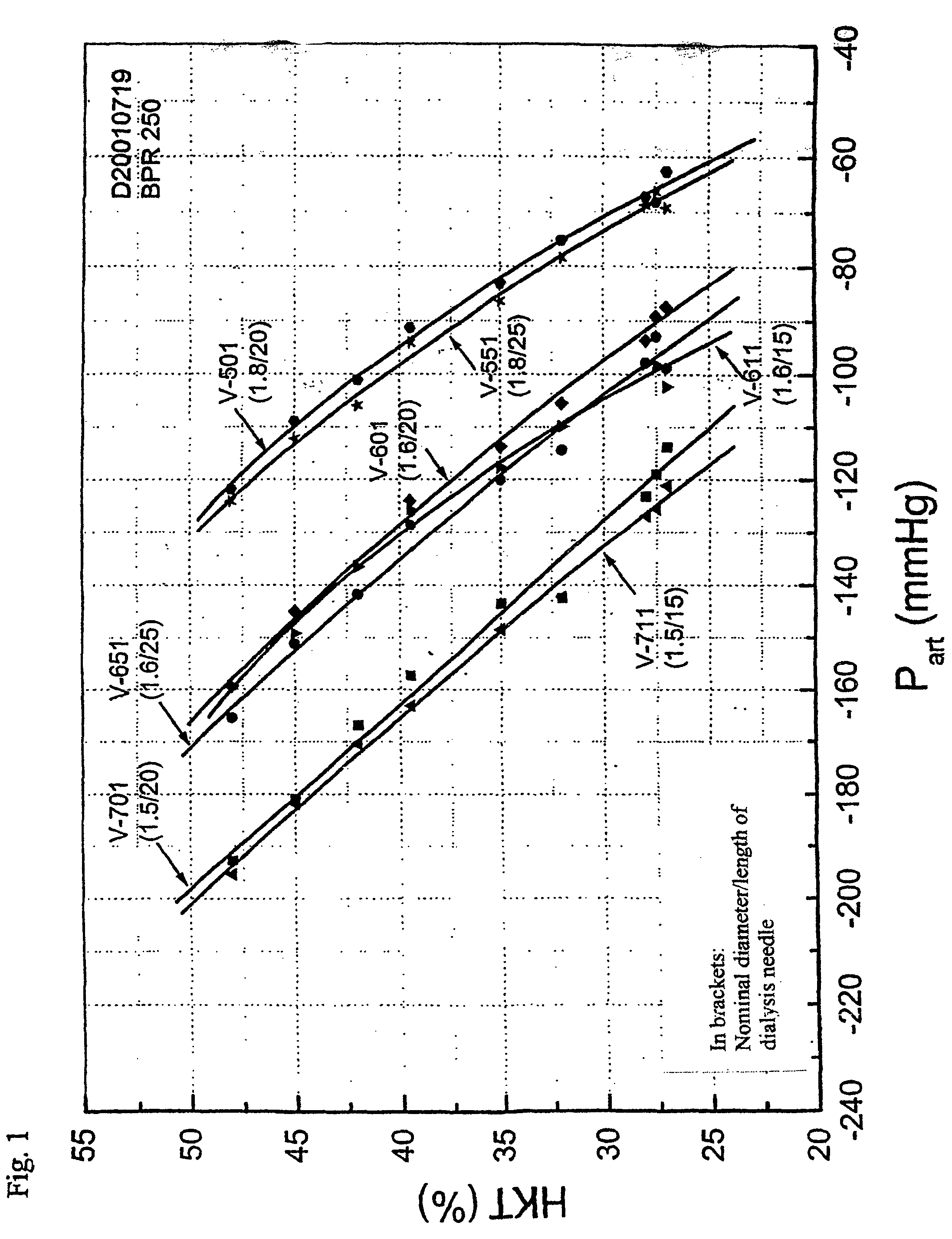
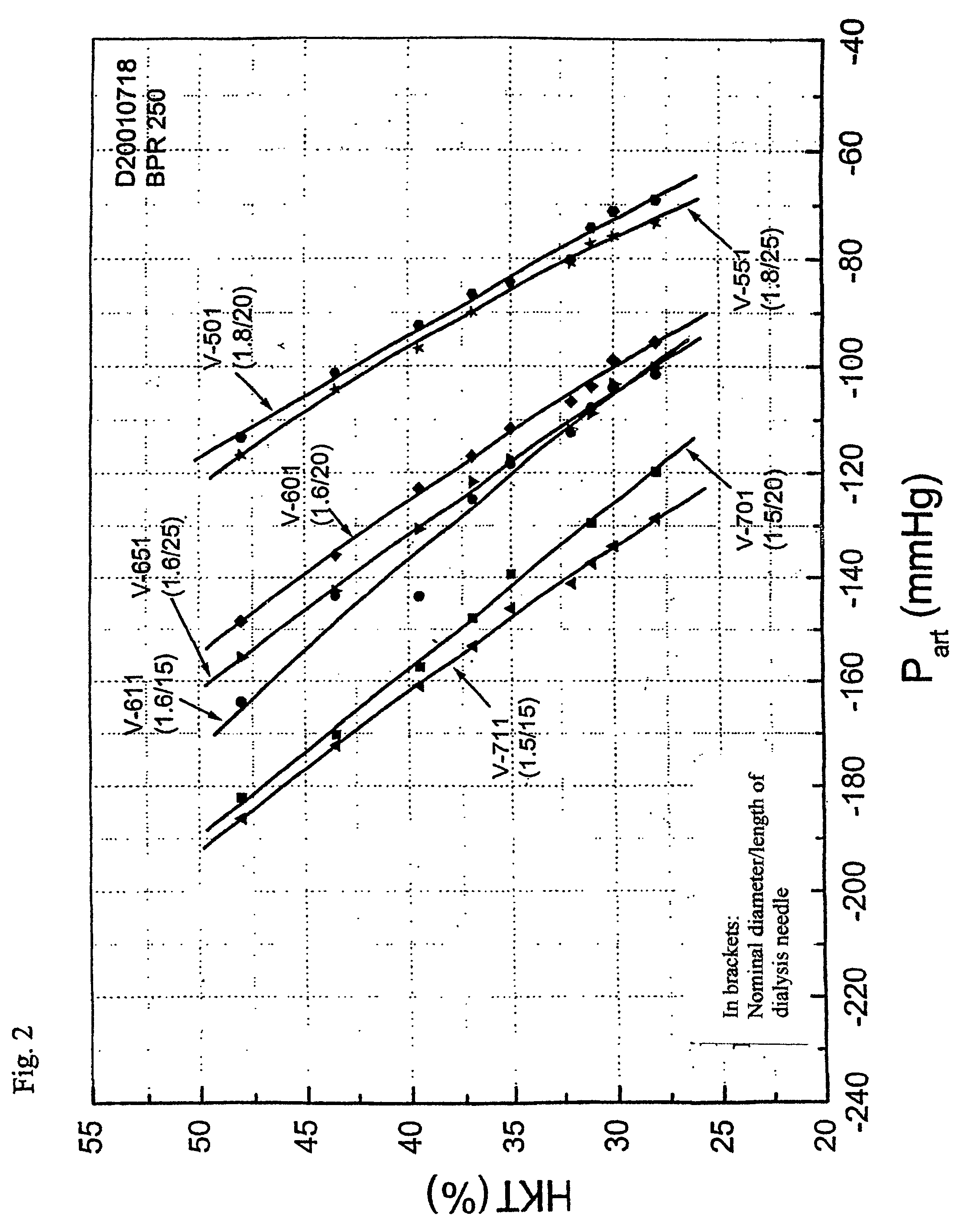
A method for determining the hematocrit and / or blood volume during an extracorporeal blood treatment with an extracorporeal blood circuit, in which blood is taken with a blood pump via an arterial cannula and an arterial flexible-tube line and blood is fed back via a venous flexible-tube line and a venous cannula. Pressure is measured in the extracorporeal blood circuit and a change in the hematocrit is determined from a change in the pressure. The respective relationship between hematocrit HKT or blood volume RBV and pressure P in the extracorporeal circuit is stored for various cannula diameters and various blood-flow values. The respective relationship for a given cannula diameter and blood flow is selected. The hematocrit and / or blood volume is determined taking account of the selected relationship.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Venous cannula and cardiopulmonary bypass system
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
In-vivo implanted composite material with X-ray developing performance and preparation method of in-vivo implanted composite material
ActiveCN103948968AWith X-ray imaging performanceGood mechanical propertiesSurgeryCatheterHuman bodyTissue repair
The invention provides an in-vivo implanted composite material with X-ray developing performance. The composite material is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5-60 percent of barium sulfate particles, 0-1 percent of an antioxidant, and the balance of a matrix material. The composite material has the advantages of clear X-ray development, excellent mechanical performance, good biocompatibility, simple preparation process and the like, and can be used for preparing a human body bone tissue repairing material, an artificial joint cartilage tissue repairing material, an intrauterine device, venous cannula, a urea catheter, a blood transfusion tube, a catheter and the like.
Owner:天津和杰医疗器械有限公司
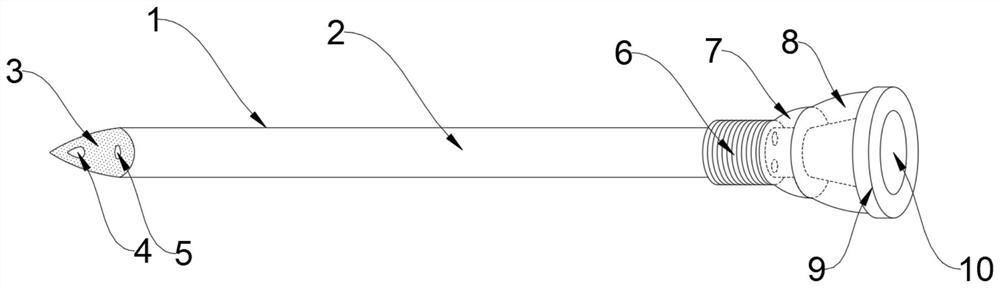
Intravenous cannula
An intravenous (IV) cannula comprising an elongated body including a distal section for insertion into a blood vessel; at least one channel extending along at least a portion of a longitudinal axis of said cannula section, the at least one channel configured to maintain an amount of at least 10% of a blood flow in the blood vessel; and a central lumen configured to allow an IV fluid flow into the blood vessel.
Owner:VEINFLOW
Amphibian isolated heart perfusion device
InactiveCN108196042AEasy to replaceAvoid phenomena that affect the stability of detection dataEducational modelsMaterial analysisLiquid storage tankArterial cannulation
The invention relates to an amphibian isolated heart perfusion device. The device comprises an arterial cannula, a venous cannula, a drip recording electrode and an electrocardio lead electrode, wherein the arterial cannula is formed by combining an arterial cannula trunk, an aorta inserting end and a liquid discharging pipe through a three-way valve; the venous cannula is formed by combining a liquid storage tank, a postcaval vein inserting end and a liquid adding pipe through a three-way valve, and parts of the arterial cannula and the venous cannula are inserted and combined into one. The drip recording electrode comprises a drip recording electrode head, a drip recording electrode rod and a signal input end; the electrocardio lead electrode comprises an electrocardio lead electrode head, an electrocardio lead electrode rod, a signal input end, a heart outer wall liquid adding pipe and a three-way valve. The multifunctional amphibian isolated heart perfusion device is suitable for one person to operate, facilitates perfusion liquid replacement, and is suitable for synchronously and dynamically detecting dynamical changes of the cardiac output, myocardial contraction tension, electrocardiogram and various cardiac function indexes.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
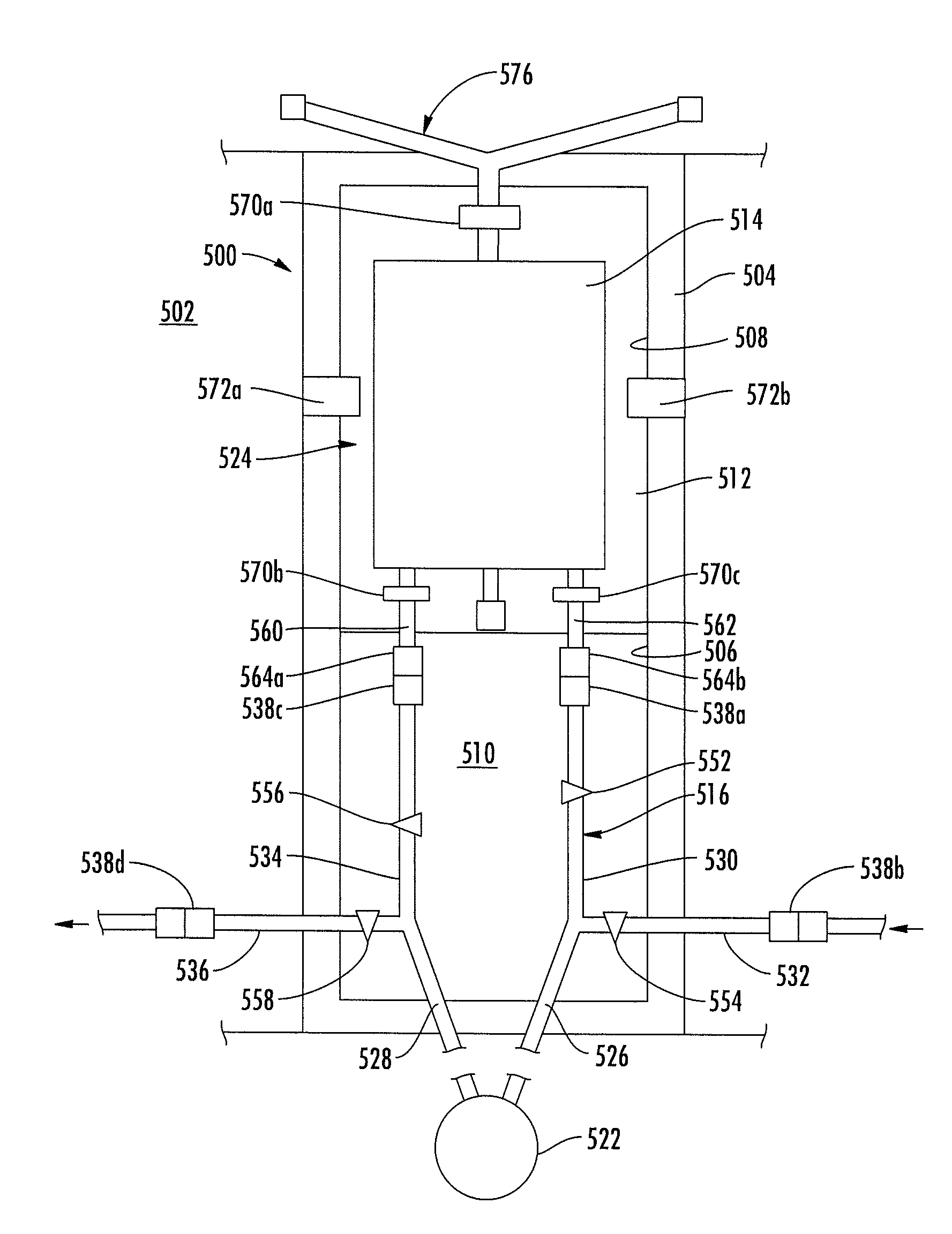
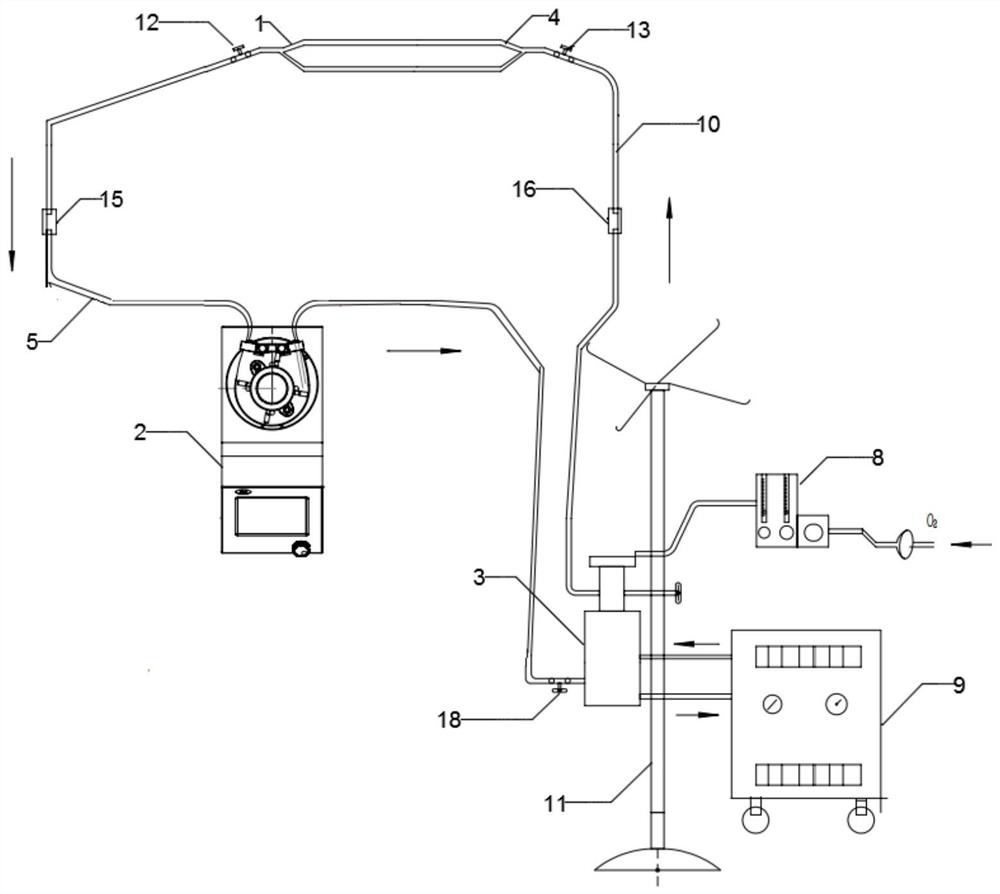
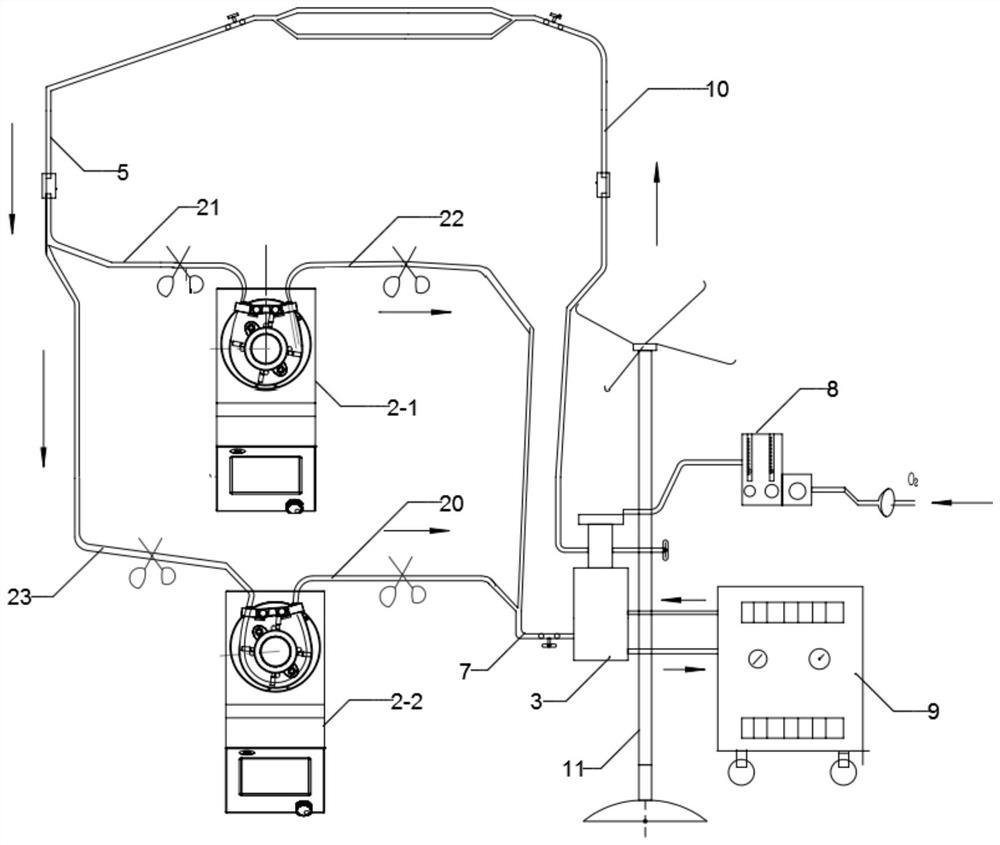
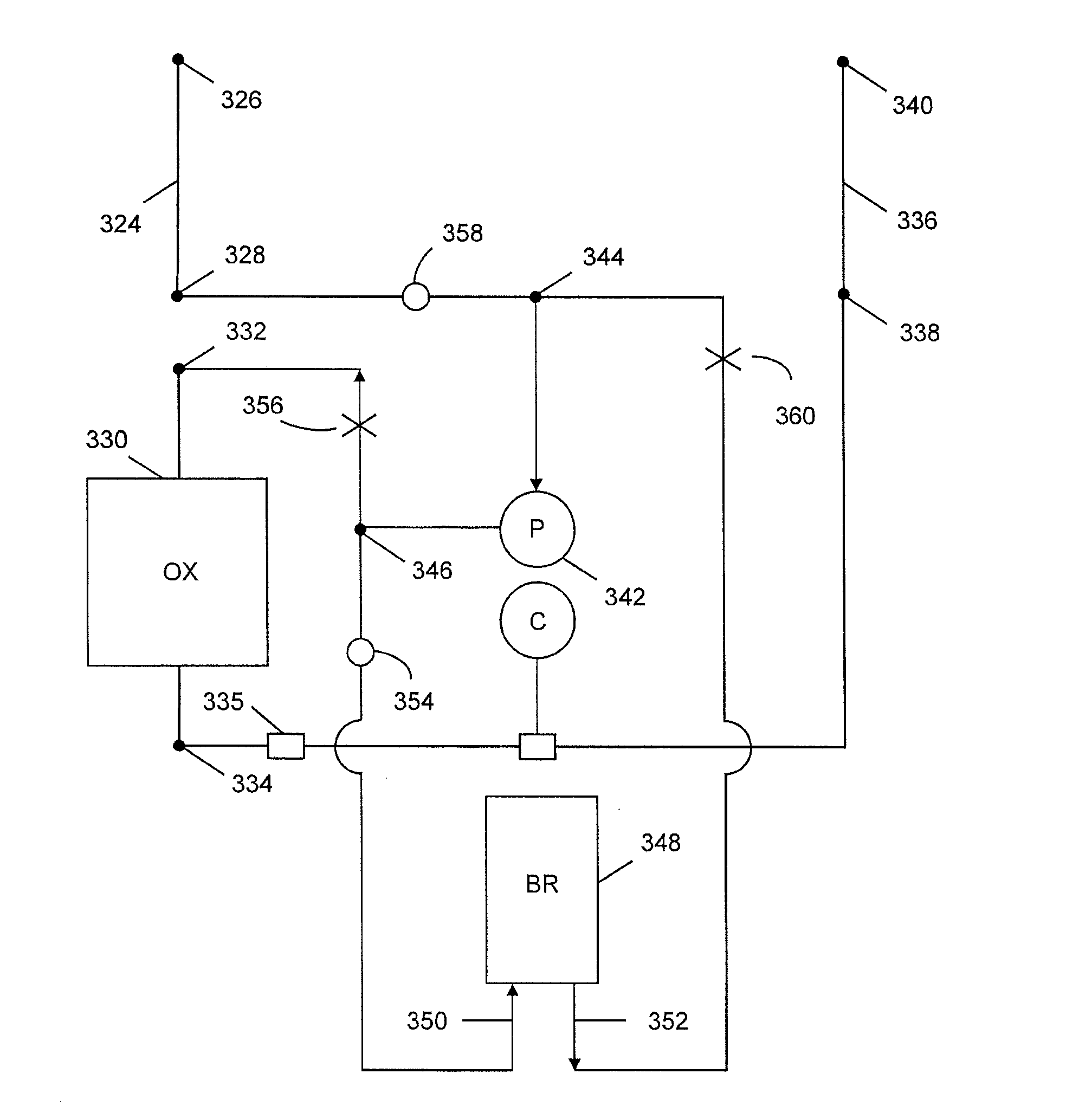
CPB System With Dual Function Blood Reservoir
ActiveUS20140271356A1Simplify and improve efficiencyOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesVenous vesselBlood vessel
The venous reservoir is omitted from an extracorporeal blood circuit system by substituting a blood reservoir in parallel with the arterial pump. The reservoir has an inlet connected to the outlet of the pump and an outlet connected to the inlet of the pump. At least three blood flow paths can be configured. A main path has the inlet and outlet of the reservoir blocked while pumped blood flows through the venous cannula, the oxygenator, and the arterial cannula. An accumulator path has the inlet to the oxygenator and the outlet of the reservoir blocked while blood flows through the venous cannula and the inlet to the reservoir. A discharge path has the inlet of the reservoir blocked while the outlet is open whereby blood from the reservoir flows into the oxygenator. In a fourth configuration, the ECC fluid can be recovered in the reservoir and hemoconcentrated for autologous transfusion.
Owner:SAMOLYK KEITH
Intelligent ECMO treatment device based on rolling type blood pump and control method of system
PendingCN114470377AAdded pressure monitoring structurePrecise control of perfusion pressureDialysis systemsBlood pumpsVeinArterial catheter
The invention provides an intelligent ECMO treatment device based on a rolling type blood pump and a control method of a system.The intelligent ECMO treatment device comprises a vein cannula, the rolling type blood pump, a membrane lung and an arterial cannula, the vein cannula is connected to an inlet of the rolling type blood pump through a first connecting pipe, and the rolling type blood pump is connected to an outlet of the artery cannula through a second connecting pipe; a venous pressure sensor is arranged on the first connecting pipe; an outlet of the rolling type blood pump is connected to an inlet of the membrane lung through an arteriovenous bridge tube, an artery overpressure sensor is arranged on the arteriovenous bridge tube, the membrane lung is further connected with an air and oxygen mixer and a temperature changing device, an outlet of the membrane lung is connected to the arterial cannula through a second connecting tube, and the arterial cannula is connected with the air and oxygen mixer through a second connecting tube. The venous pressure sensor and the artery overpressure sensor are respectively connected with the rolling type blood pump through the central processing unit. According to the invention, the perfusion pressure can be intelligently and accurately controlled, and finally constant-flow perfusion is achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN WELCOME MEDICAL EQUIP
Portable organ donation donor mechanical perfusion system
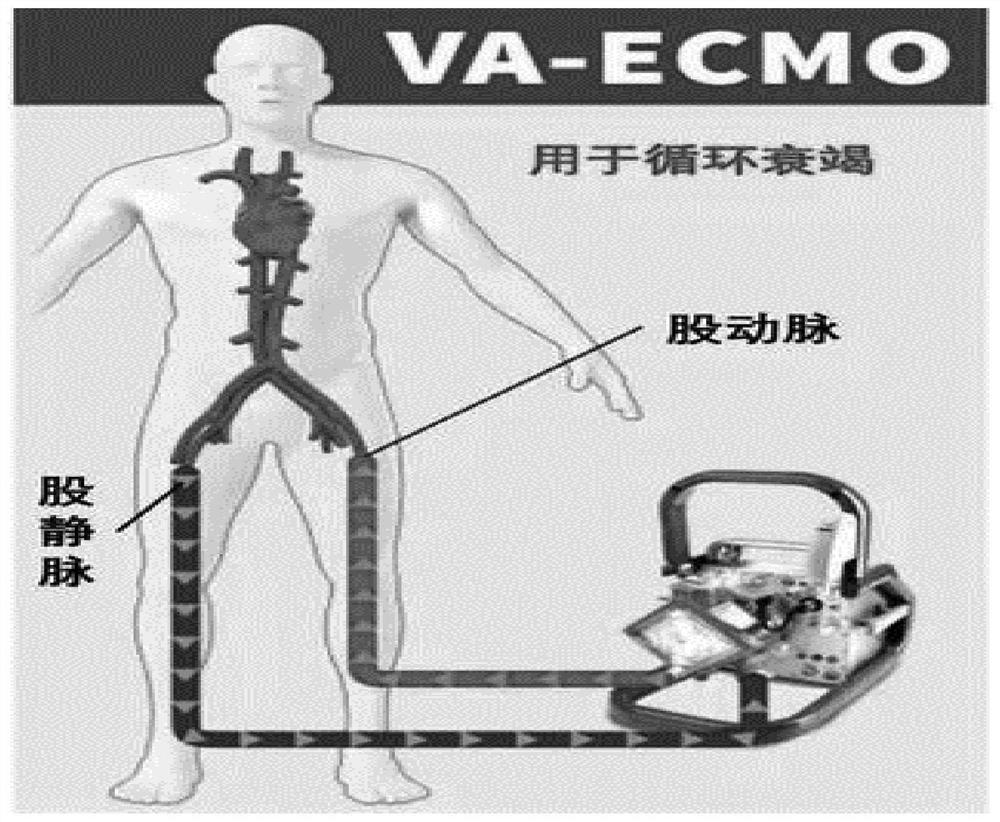
The invention discloses a portable organ donation donor mechanical perfusion system. The portable organ donation donor mechanical perfusion system comprises a blood circulation oxygenation closure device and a control device electrically connected with the blood circulation oxygenation closure device; the blood circulation oxygenation closure device comprises an oxygenator, a centrifugal pump, a blood exchanger, an arterial cannula, and a venous cannula; the blood exchanger is internally provided with a piston capable of moving vertically, the upper part of the piston is a first storage end for storing donor blood, the lower part of the piston is a second storage end for storing perfusion liquid, a blood input end and the output end of the centrifugal pump are communicated with the first storage end through a first three-way valve, and the blood input end and the output end of the centrifugal pump are communicated with the second storage end through a second three-way valve, so that low-temperature perfusion can be completed without cannulation in the abdominal aorta after laparotomy. Moreover, since a balloon is arranged at the tip end of the arterial cannula, only the balloon isneeded to be inflated or injected with water when only an abdominal organ is perfused, and convenience is realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG DEVOCEAN MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
Hot air type perforating machine
InactiveCN102909746AImprove the safety of useWon't hurtMetal working apparatusPipe fittingInsertion stent
The invention relates to a hot air type perforating machine, which is characterized by comprising a base; a core rod support frame and an electric cabinet are arranged at one end of the base, and a gripping component for clamping and fixing pipe fittings is arranged at the other end of the base through a gripping bracket; a perforating mechanism is arranged above the base corresponding to the gripping component; and a heating device is further arranged on the base positioned on one side of the perforating mechanism. The hot air type perforating machine has the advantages that air is heated on a perforating part firstly and then perforating is carried out before a venous cannula is perforated so that a concave annular ring is formed on a perforated surface after heating; the aperture is round and smooth so that a very sharp aperture is prevented from being formed on the outer wall of the body of the venous cannula on the traditional perforating machine; and moreover, when the venous cannula is inserted in the body of a patient by medical staff, other visceral organs of the patient cannot be injured, and the safety performance of the venous cannula when in use is further improved.
Owner:TIANJIN PLASTICS RES INST CO LTD
Method Of Controlling Blood Reservoir Volume And Flow In An Extracorporeal Blood Circulation System
InactiveUS20140263065A1Simplify and improve efficiencySemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesVeinReservoir volume
A method comprising recirculating a patient's blood as a fluid through an extracorporeal circuit having a venous cannula line for fluid flow from the patient to an oxygenator and an arterial cannula line for fluid flow from the oxygenator to the patient; and adjusting the volume of fluid flow from the venous cannula line to the arterial cannula line by selectively redirecting fluid flow between the venous cannula line and the arterial cannula line into or out of a closed accumulator blood bag of substantially transparent, bio-compatible material, having a selectively open and closable accumulator inlet line from the venous cannula, and a selectively open and closable accumulator outlet line to the oxygenator.
Owner:SAMOLYK KEITH
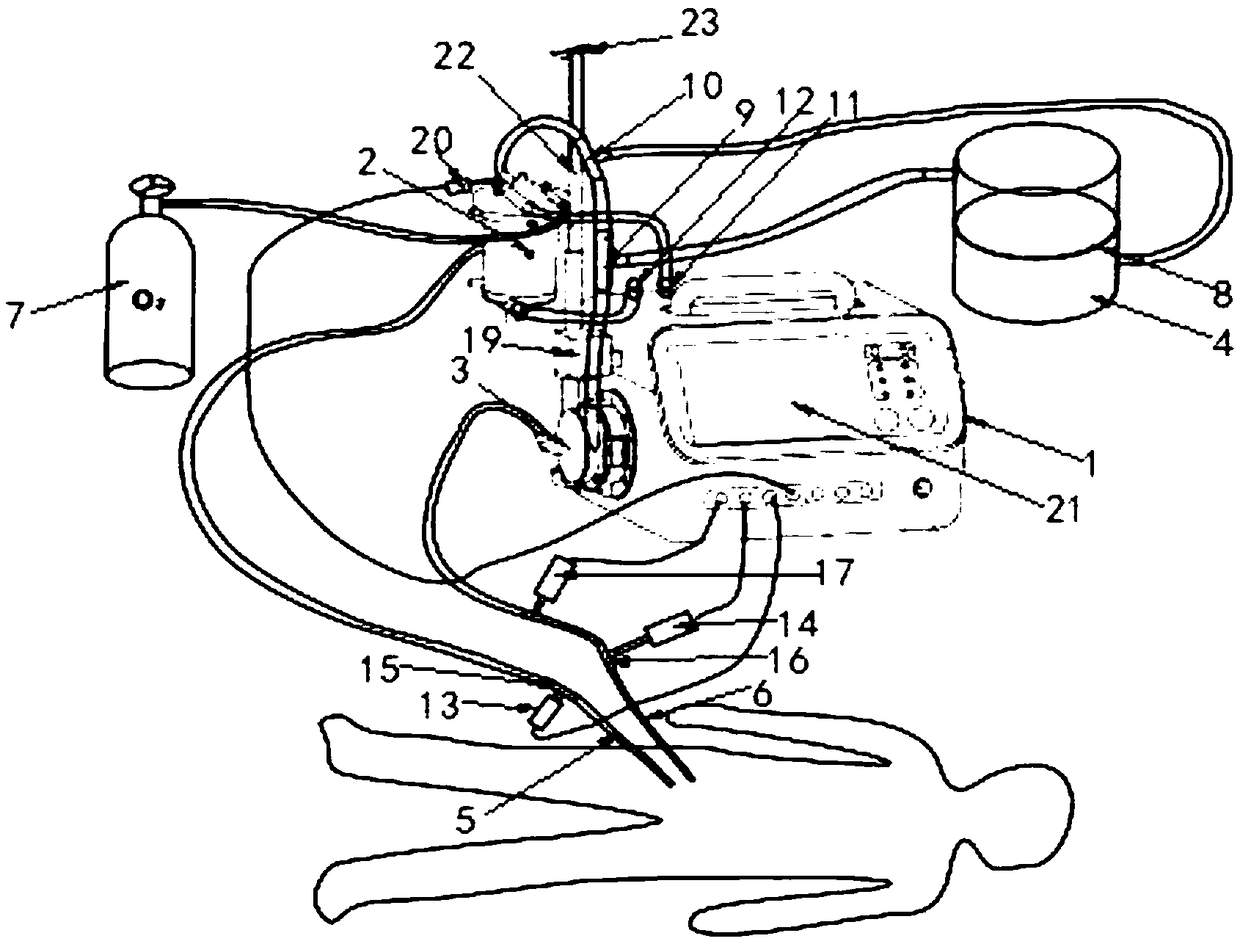
Life rescue box for first aid of sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients
InactiveCN101999966AEasy to operateShorten the timeFirst-aid kitsProsthesisMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses a life rescue box for first aid of sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients, which is characterized in that main components such as a blood pump, a membrane oxygenator and the like required by extracorporeal life support are assembled in the life rescue box, and the blood pump and the membrane oxygenator are fastened on an upright post in a magnetic force manner; the blood pump is provided with a first interface and a second interface, wherein the first interface is connected with a venous cannula, and the second interface is connected with the membrane oxygenator through a connecting pipe; and the membrane oxygenator is provided with a first interface and a second interface, wherein the first interface is connected with an arterial cannula, and the second interface is connected with the blood pump through a connecting pipe to form a blood circulation loop with the blood vessel of human bodies for alternatively completing the cardio-pulmonary function of the sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients. Due to small size, the life rescue box can be carried with an ambulance and an on-vehicle stretcher, is convenient to move and simple to operate, can reach the primary disease outbreak scene with medical personnel in the shortest time during first aid and can be generally used for the first aid of the sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients.
Owner:BEIJING KELIN BO CHONG TECH
Shaping process of medical diameter-changed cannula and cannula
The invention discloses a shaping process of a medical diameter-changed cannula. The shaping process comprises the steps of performing diameter expansion treatment on the end of a cannula body, enabling the diameter-changed end of a diameter-changed joint and the end after diameter expansion treatment, of the cannula body to be in interference fit to form an interference connecting part, sleevingthe interference connecting part with a heat shrink sleeve pipe, and heating the heat shrink sleeve outside the interference connecting part, so that the heat shrink sleeve is subjected to thermal shrinkage and cladding to the interference connecting part, and the diameter-changed joint of the interference connecting part and the cannula body are welded. The invention further provides the cannula.The diameter-changed joint and the cannula body which are in interference fit are welded, so that the diameter-changed joint and the cannula body are integrally connected, gaps are not generated, glue is avoided, arterial and venous cannulas cannot break blood after being used for a long time, and the pressure reduction level of the cannula can be guaranteed.
Owner:DONGGUAN KEWEI MEDICAL INSTR
Balloon vena cava cannula
PendingCN111408020AAvoid the risk of secondary injuryShorten operation timeBalloon catheterOcculdersExtracorporeal circulationSurgical operation
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments and discloses a balloon vena cava cannula. According to the invention, a balloon is arranged at a front end position, communicates with an injector through a thin catheter passage and is arranged in a vena cava; a vein cannula is integrally arranged between the balloon and a vein cavity; and a front end side hole of the vena cavacannula is arranged at the tail end of the vein cannula. By application of the balloon vena cava cannula provided by the invention in the extracorporeal circulation surgery process of the cardiac surgery department, the step that vena cava passes through a blocking band during construction of extracorporeal circulation in a conventional cardiac surgery can be omitted, so the operation time of thesurgery can be greatly shortened, and the risk of side damage to the local part of the heart due to the fact that upper vena cava and lower vena cava pass through the blocking band can be avoided at the same time; for situations like adhesion at the positions where the upper vena cava and the lower vena cava pass through the blocking band and inconvenience in passing through the blocking band dueto small surgery field of a minimally invasive cardiac surgery, the balloon vena cava cannula provided by the invention can omit the trouble and the risk caused by construction of extracorporeal circulation through stripping decomposition or application of unconventional intubation means like femoral vein intubation for an operator.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Extracorporeal circulation machine remaining blood reinfusion device and reinfusion method
InactiveCN108245727ARaise hemoglobin levelsLess blood transfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationVein
An extracorporeal circulation machine remaining blood reinfusion device comprises a venous cannula, a venous blood return chamber, a power pump, a membrane oxygenator, a fine thrombus filter, a main artery cannula and a blood recovering machine, wherein the venous cannula, the venous blood return chamber, the power pump, the membrane oxygenator and the fine thrombus filter are sequentially connected through extracorporeal circulation pipelines, and the blood recovering machine is connected with the main artery cannula. The main artery cannula is connected with the blood recovering machine through a pressure lengthening pipe, and normal saline is connected with an inputting opening of venous blood return chamber. The device has the advantages that the device can ensure that the extracorporeal circulation pipelines are always in state capable of transferring at any time after extracorporeal circulation is completed, blood in the pipelines is timely recovered and reinfused into the body of a patient, and the machine blood reinfusion method is safe, effect and economical and saves blood resources.
Owner:柴琳
System and method for determining the hematocrit and/or blood volume
InactiveUS7780620B2Low equipment costLow costSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationVein
A method for determining the hematocrit and / or blood volume during an extracorporeal blood treatment with an extracorporeal blood circuit, in which blood is taken with a blood pump via an arterial cannula and an arterial flexible-tube line and blood is fed back via a venous flexible-tube line and a venous cannula. Pressure is measured in the extracorporeal blood circuit and a change in the hematocrit is determined from a change in the pressure. The respective relationship between hematocrit HKT or blood volume RBV and pressure P in the extracorporeal circuit is stored for various cannula diameters and various blood-flow values. The respective relationship for a given cannula diameter and blood flow is selected. The hematocrit and / or blood volume is determined taking account of the selected relationship.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Method and device for recognition of paravasal bleeding
ActiveCN102215889AMonitor pressureImprove reliabilityOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesPressure riseHaemodialysis machine
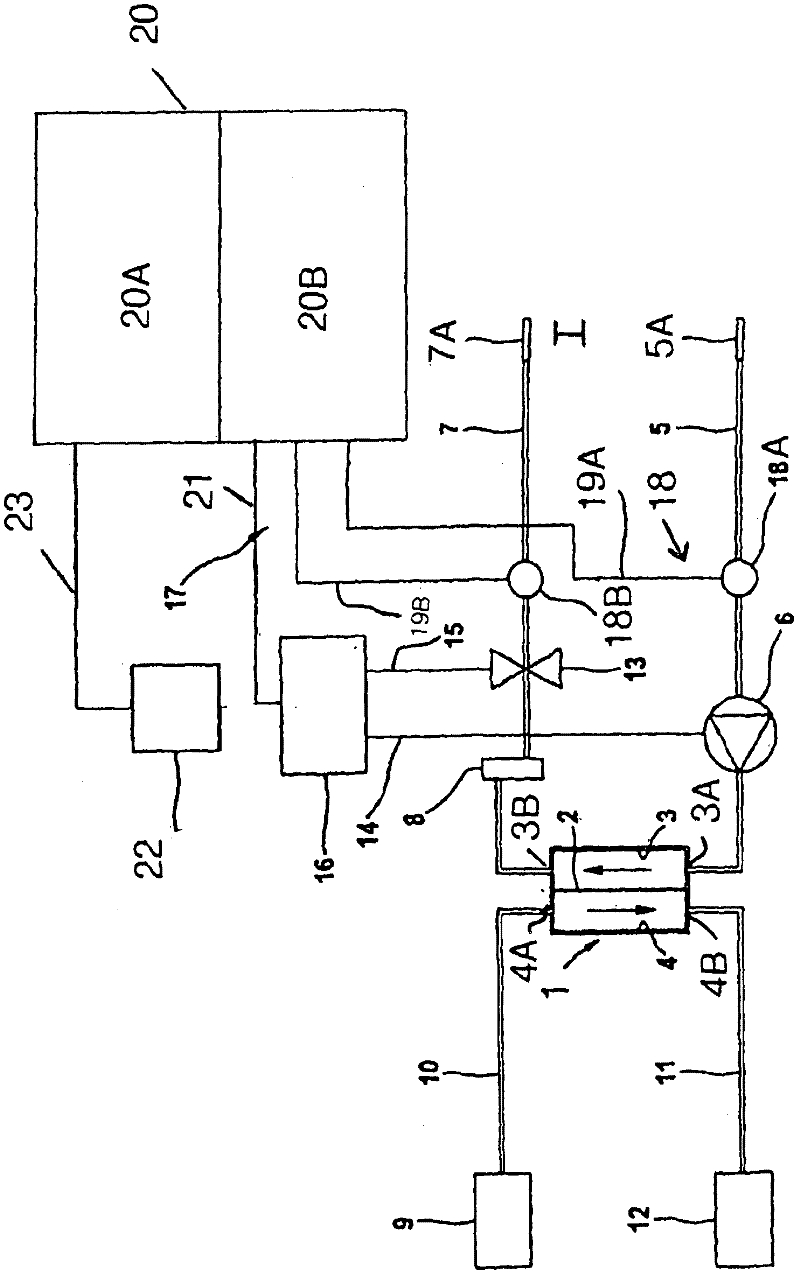
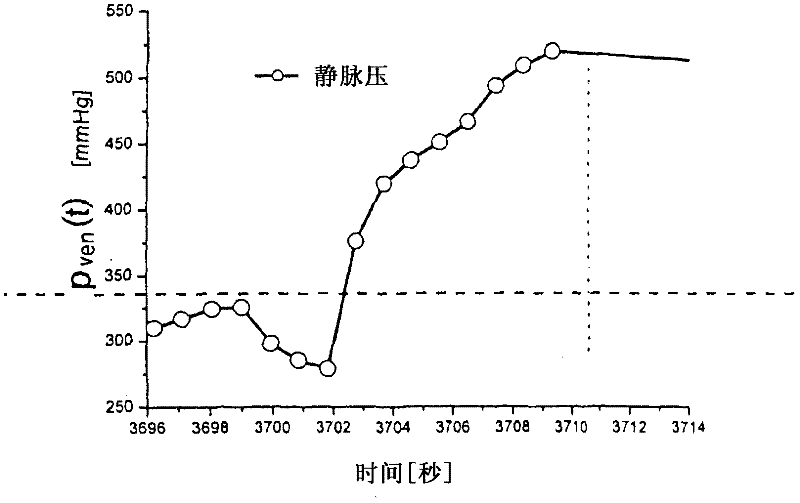
The invention relates to a method and to a device for recognition of paravasal bleeding upon a supplying of blood to a vascular access via a line and / or upon the removal of blood from a vascular access via a line, particularly paravasal bleeding during extra-corporeal blood treatment, such as for hemodialysis, hemofiltration or hemodiafiltration. The invention furthermore relates to a device for extra-corporeal blood treatment, particularly for hemodialysis, hemofiltration or hemodiafiltration, comprising a device for recognition of paravasal bleeding. The method according to the invention and the device according to the invention are based on the change of arterial pressure in the arterial branch (5) or the venous pressure in the venous branch (7) of the extra-corporeal circuit (I) being registered during the extra-corporeal blood treatment. If paravasal bleeding occurs during the blood treatment, it is shown that the positive dynamic pressure on the line leading to the vascular access rises on the venous cannula during the extra-corporeal blood treatment, or the suction pressure on the line leaving the vascular access, such as the arterial cannula during extra-corporeal blood treatment, rises; that is, the suction pressure becomes more negative. The pressure rise begins moderately at first and then becomes increasingly greater. Decisive for the method according to the invention and the device according to the invention, therefore, is that pressure changes that come from a pressure level exhibiting a large difference from the reference value find stronger consideration than those that come from a pressure level that exhibits only a minor difference from the reference value.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Separating and culturing method of primary duck liver cells
InactiveCN108728398AHigh purityA large amountVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCell separationCulture mediums
The invention provides a separating and culturing method of primary duck liver cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting male Chongqing sheldrake at the age of 1-2 months, and injecting pentobarbital sodium and heparin into enterocoelia; (2) fixing the narcotized sheldrake to a board with venter upward, and excising the enterocoelia in a sterile condition; (3) performing venous cannula, and pouring reheated HBSS buffering liquid through a constant-flow pump; (4) pouring preheated GBSS buffering liquid through the constant-flow pump; (5) pouring the preheated GBSS mixed enzyme solution through the constant-flow pump; (6) shearing the GBSS mixed enzyme solution for tissue; oscillating and digesting; filtering through a sieving net; centrifuging; and removing the supernatant; (7) detecting the cell activity of the cell filtrate through trypan blue staining; (8) counting the cells, and suspending and inoculating to a cladded culture flask through a complete culture medium; and culturing in an environment that the temperature of 37 DEG C, and 5% of CO2 is added; (9) identifying the cell forms; (10) performing through ELISA; and (11) performing RT-PCR detection. Theseparating and culturing method of the duck liver cells is simple to operate; a large amount of cells can be obtained; the survival rate is high; the method is an ideal separating and culturing methodof the primary duck liver cells; and reliable cell resources are provided to test.
Owner:JIANGYIN CHI SCI
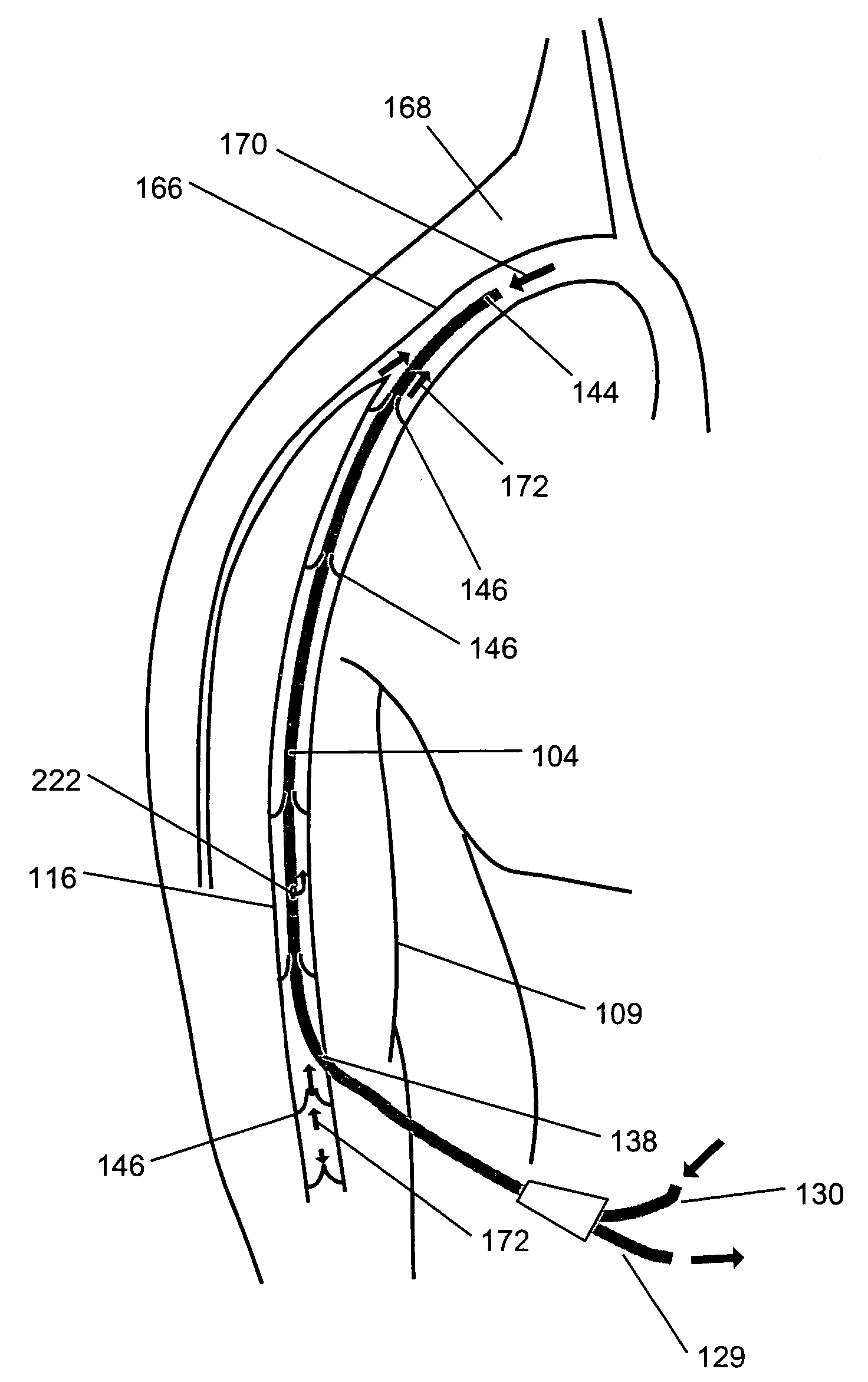
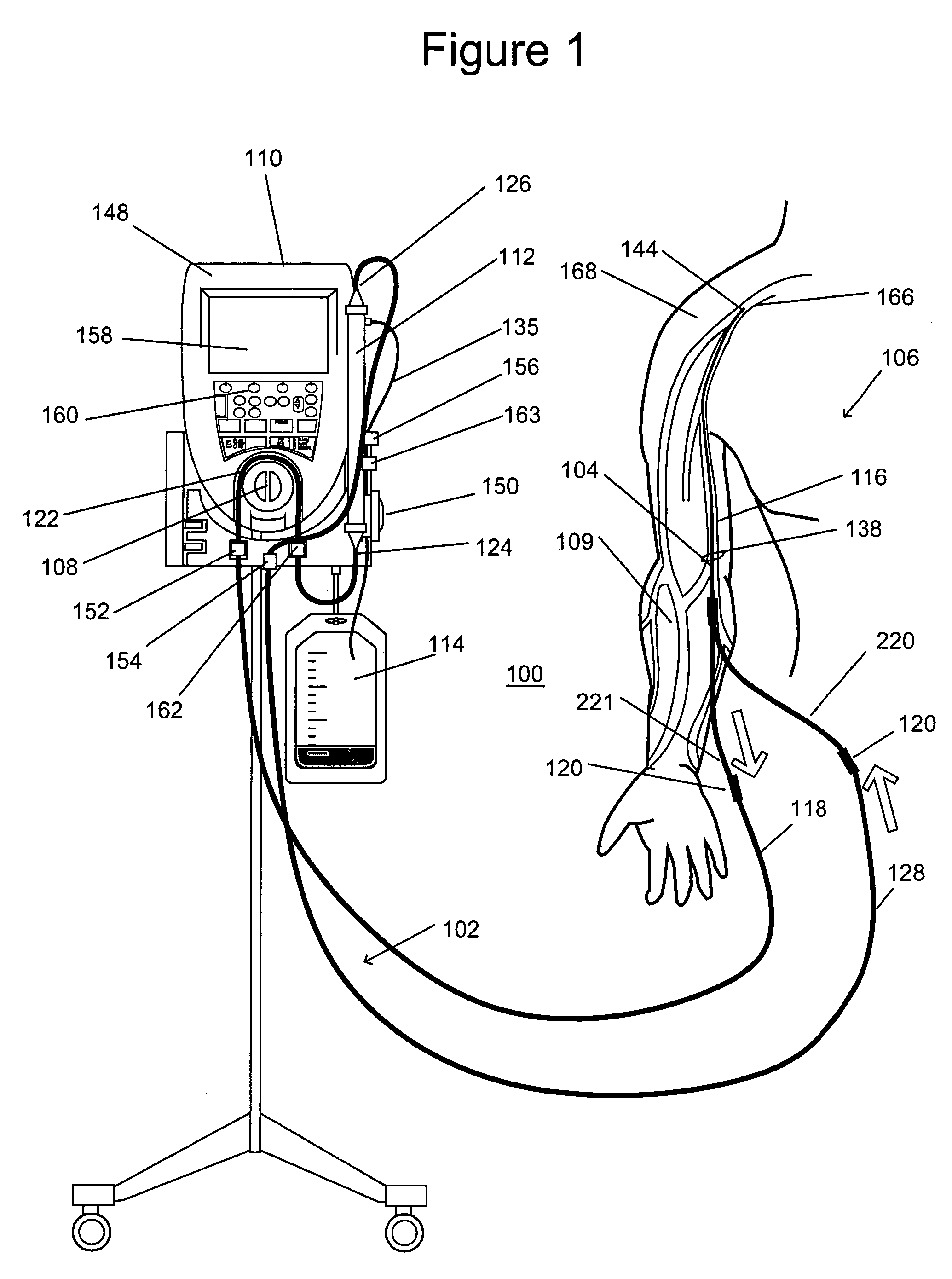
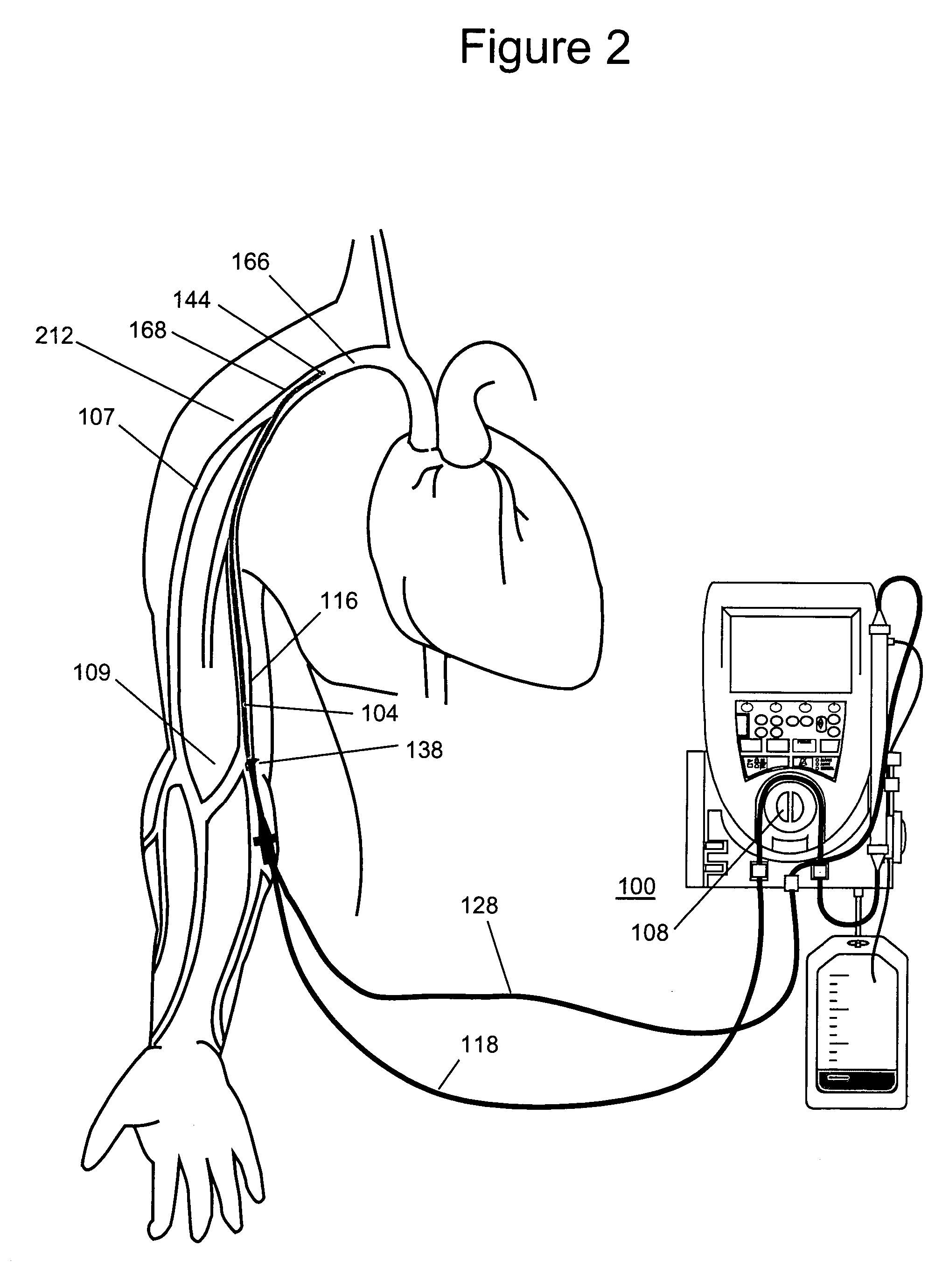
Device for measuring central venous pressure and method of use thereof
The invention discloses a medical care tool and an application method thereof and particularly discloses a device for measuring central venous pressure and the application method thereof. The device for measuring the central venous pressure comprises a horizontal pipe and a vertical pipe which are communicated with each other. The end of the vertical pipe is provided with a filter screen. The end of the horizontal pipe is provided with a protective cover. The vertical pipe is provided with a scale from the bottom to the top. The application method of the device comprises the steps that: 1) the junction of two pipes and the middle axillary line of a patient are on the same line; 2) the device is connected with a port of a three-way pipe and then is connected with a central venous cannula of the patient; 3) the three-way pipe is rotated to close the end of the central venous cannula to ensure that isotonic solution enters into a measuring device; 4) the three-way pipe is rotated to close a liquid path, a liquid pole in the vertical pipe descends, and the scale when the liquid pole stops descending is the measured value of the central venous pressure. The device and the application method have the beneficial effects of simple structure, convenient use and measuring exactly.
Owner:孙凤英
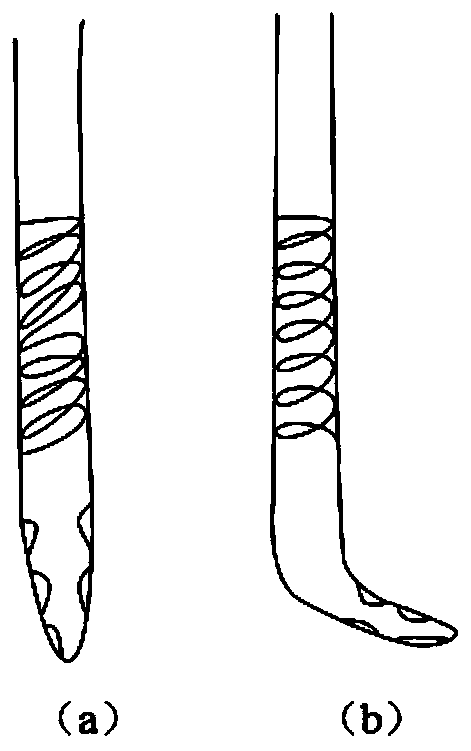
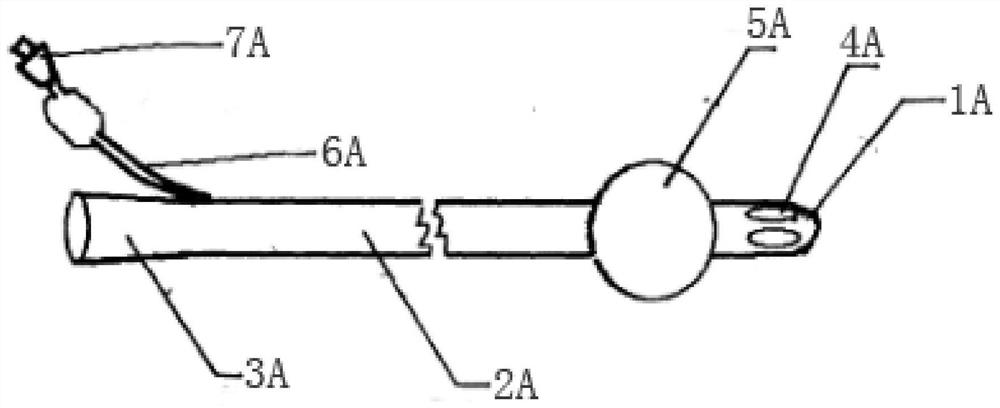
Venous cannula with balloon
PendingCN112915288ASmall tip apertureReduce back flowBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesVeinMedicine
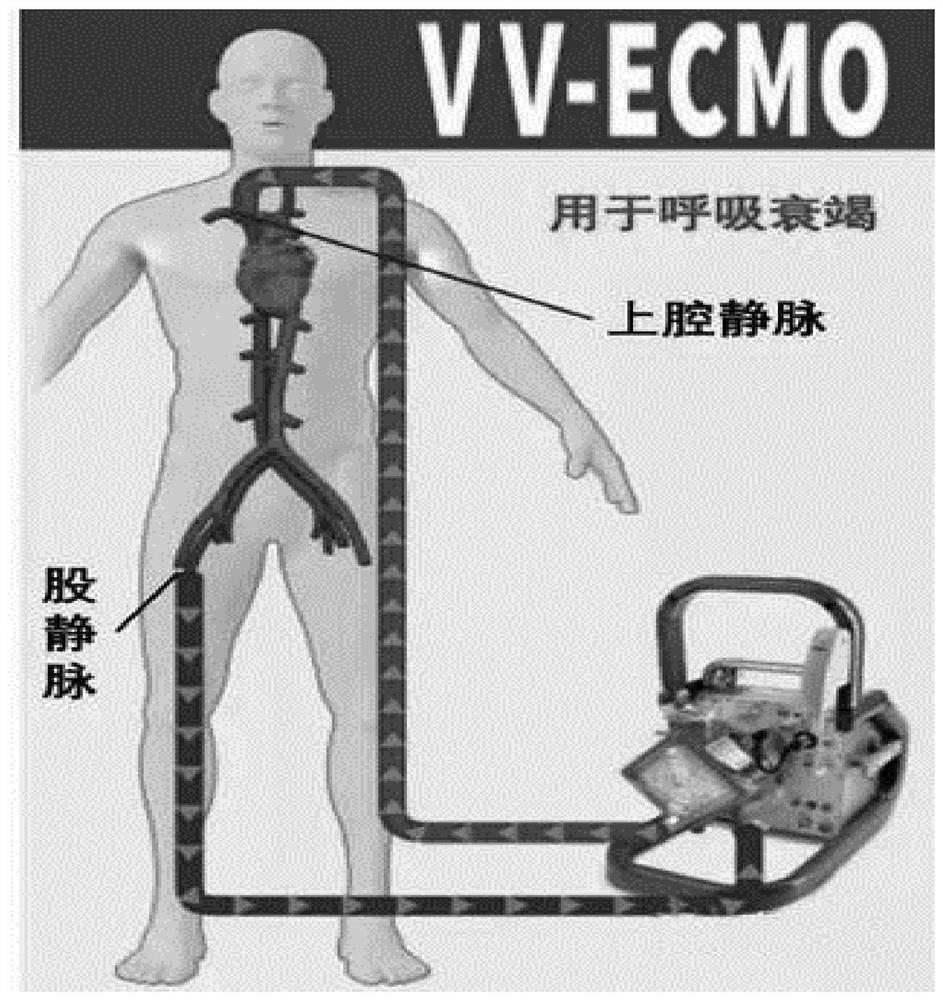
The invention discloses a venous cannula with a balloon, which comprises a cannula (1), a balloon (2), a catheter (3) and a one-way valve (4), a cavity (11) is arranged in the cannula (1), the balloon (2) is arranged outside the rear part of a front end plug (12) of the cannula (1), the balloon (2) is connected with the one-way valve (4) through the catheter (3), the venous cannula is characterized in that a plurality of side holes (13) are arranged on the wall of the cannula (1) behind the balloon (2), and the side holes (13) are communicated with the cavity (11). After the balloon blocks the inferior vena cava, blood flow in the inferior vena cava can be fully recovered; meanwhile, due to the existence of the balloon, the venous cannula is in a suspended state in the inferior vena cava, and the telecentric section of the inferior vena cava is expanded, so that the venous cannula is prevented from adhering to the wall, blocking the side holes and affecting blood flow recovery; and the balloon blocks the inferior vena cava, so that the recirculation problem of VV-ECMO is effectively avoided, and the oxygenation efficiency is improved.
Owner:胡锡祥 +1
Emergency self-expanding peripheral arteriovenous cannula and using method thereof
InactiveCN112472952APrevent side leakagePrevent leakageStentsCatheterExtracorporeal circulationGuide wires
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to an emergency self-expanding peripheral arteriovenous cannula and a using method thereof. The problem that in the prior art, under the emergency condition, when a patient has the conditions of low blood pressure and low blood volume, a peripheral vascular access cannot be quickly established for extracorporeal circulation life treatment is solved. According to the technical scheme, the product comprises a puncture assembly and an intubation assembly; wherein the front end of the cannula body is connected witha blood vessel covered stent, the outer wall of the blood vessel covered stent is sleeved with a release sleeve, the release sleeve can slide along the outer wall of the blood vessel covered stent, and the diameter of the release sleeve is larger than that of the cannula body; a guide sheath is of a hollow cylindrical structure with one conical end formed by integrally buckling a first assembly and a second assembly which are symmetrical in structure; The intubation tube assembly is arranged in the guide sheath, a puncture needle is arranged in a blood vessel covered stent and the intubation tube body in a penetrating mode, the two ends of the puncture needle extend out of the guide sheath, and the guide wire is arranged in the puncture needle in a penetrating mode.
Owner:北京嘉维科技开发有限公司
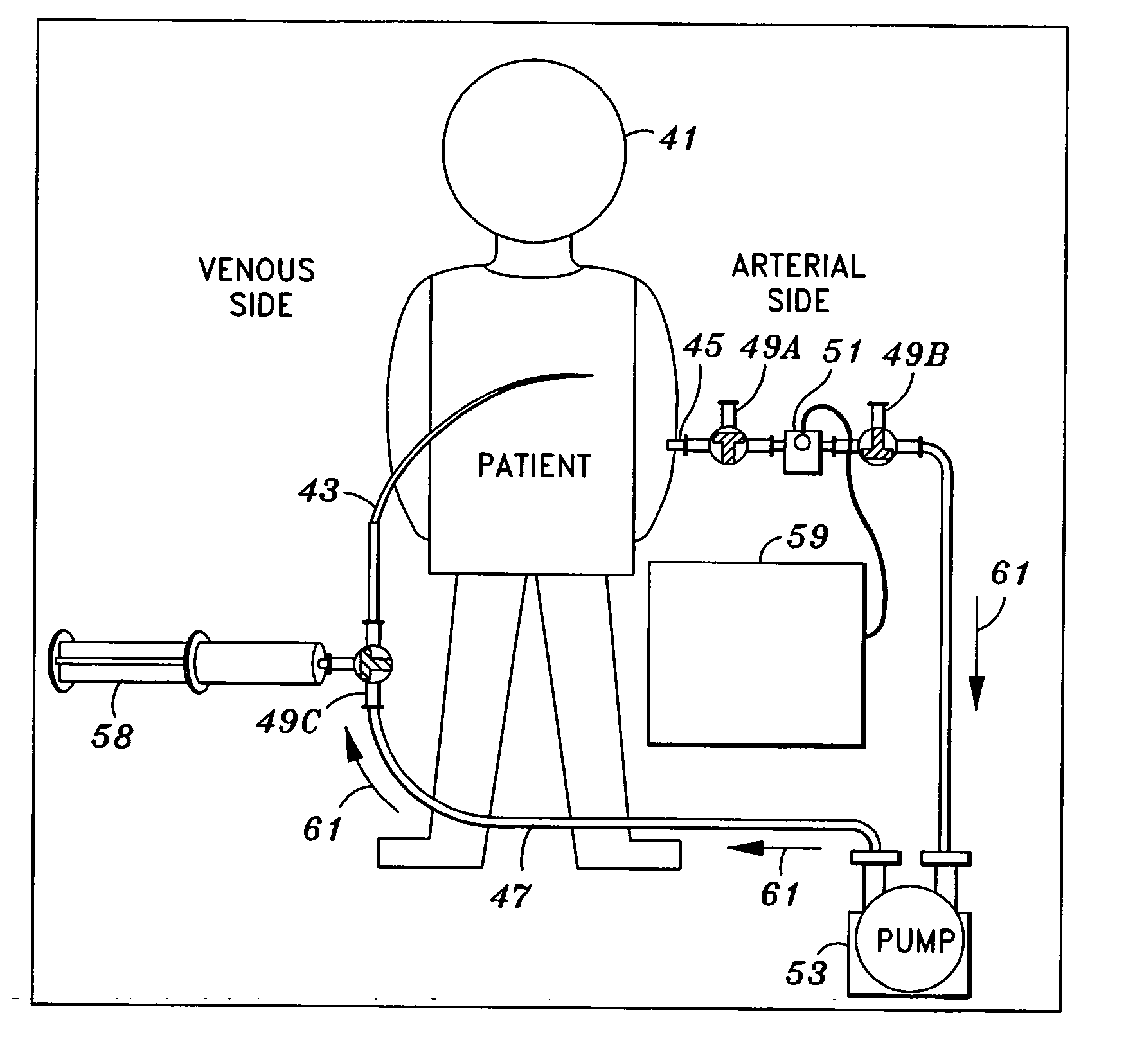
Assembly comprising a suction line, a pressure line and a pump
ActiveUS10729840B2Reduced volume flowAvoid dischargeElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesVeinArterial catheter
An assembly for an extracorporeal life support system with a suction line that features a venous cannula and a pressure line that features an arterial cannula furthermore includes a pump that is arranged between the suction line and the pressure line. This assembly has a discharge line with a discharge cannula, wherein the discharge cannula is longer than the arterial cannula, and wherein the discharge line is connected to the suction line or the pressure line.
Owner:XENIOS AG
A central venous trocar with holes
ActiveCN109771005BWithdraw smoothlyImprove the success rate of punctureSurgical needlesTrocarVeinEngineering
The invention discloses a central venous cannula with multiple holes, and relates to the related fields of venous cannulas. The frequently occurred problem that in the prior art, blood can be drawn, but the cannula cannot be inserted, and then the depth of a puncture needle cannot be judged is solved. The puncture needle comprises a puncture needle main body, a puncture needle head is arranged onone side of the puncture needle main body, a puncture needle tail is arranged on the other side of the puncture needle main body, the puncture needle head is provided with a first needle head hole anda second needle head hole, the first needle head hole is formed in one side of the second needle head hole, a fixed tube is arranged outside one side of the puncture needle main body, and a connecting variable diameter tube is arranged on one side of the fixed tube, and a syringe fixing tube is arranged on the one side of the connecting variable diameter tube, and the syringe fixing tube and a syringe locating ring are internally provided with fixed cavities respectively; a first blood drawing channel and a second blood drawing channel are arranged in the puncture needle main body.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Balloon dilator
ActiveUS11160956B1Easy to removeEasy to disassembleBalloon catheterOther blood circulation devicesDilatorCannula insertion
A dilator system for arterial and venous cannulas, where there is a smooth transition between the dilator and the outer wall of the cannula. One aspect of the subject technology provides a blunt-tip cannula that is used as a dilator for insertion of an arterial or venous cannula. The balloon might either be a single diameter or may have a larger diameter at the distal portion such that the diameter of the distal portion of the balloon dilator matches the diameter of the cannula at the tip. Another aspect of the subject technology is a balloon dilator for cannulae that may be positioned over a guidewire, for guidewire-directed placement of a cannula within a vessel, duct, lumen or heart structure of the body. Another aspect of the subject technology is an inflation system for the balloon dilator, such that the balloon dilator may be deflated and quickly removed from the cannula after the cannula has been positioned and secured within the vessel, duct, lumen or heart structure. Another aspect of the subject technology includes a stiffening element in the balloon dilator along its shaft to increase the rigidity of the combined balloon dilator and cannula to provide improved ease of insertion. Another aspect of the subject technology is an improved curvature of the shape of the right angle dilator that achieves more uniform flow within the dilator and ease of insertion and more even flow within the cannula, and ease of insertion of and retraction of the balloon dilator. Another aspect of the subject technology is a gel-filled balloon dilator that improves ease of insertion of the cannula within the vessel, duct, lumen or heart structure, and can be removed without deflation.
Owner:HOGANSON DAVID M
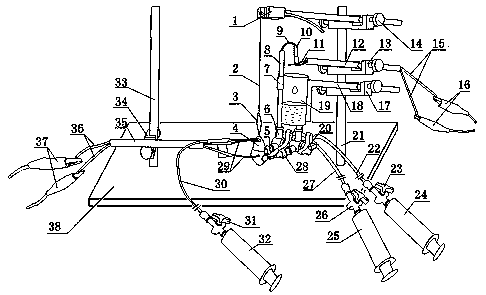
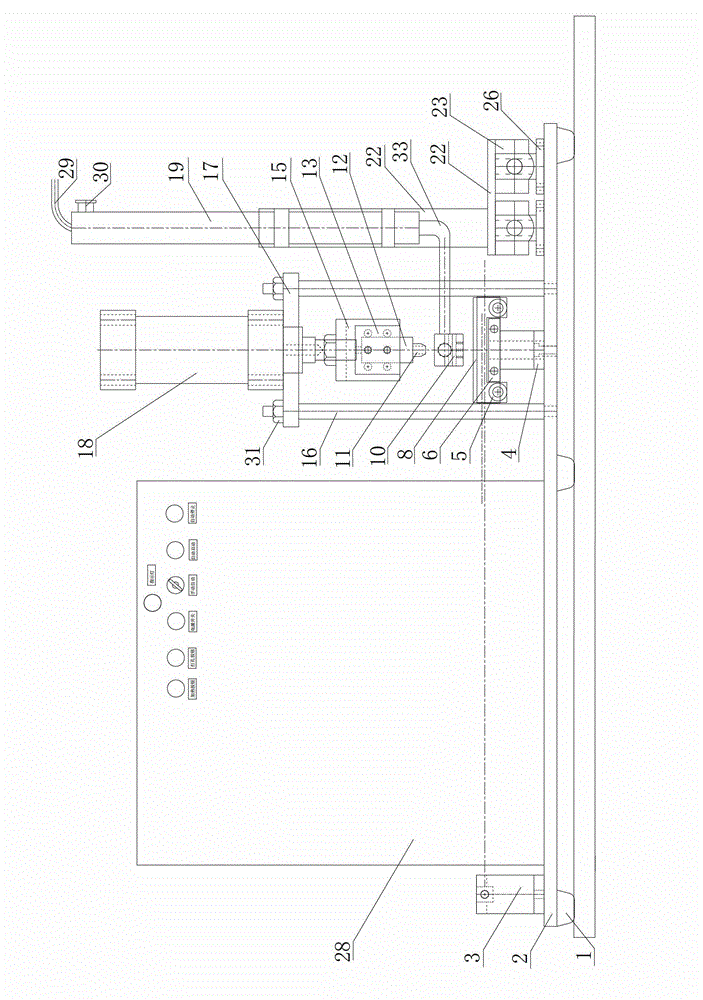
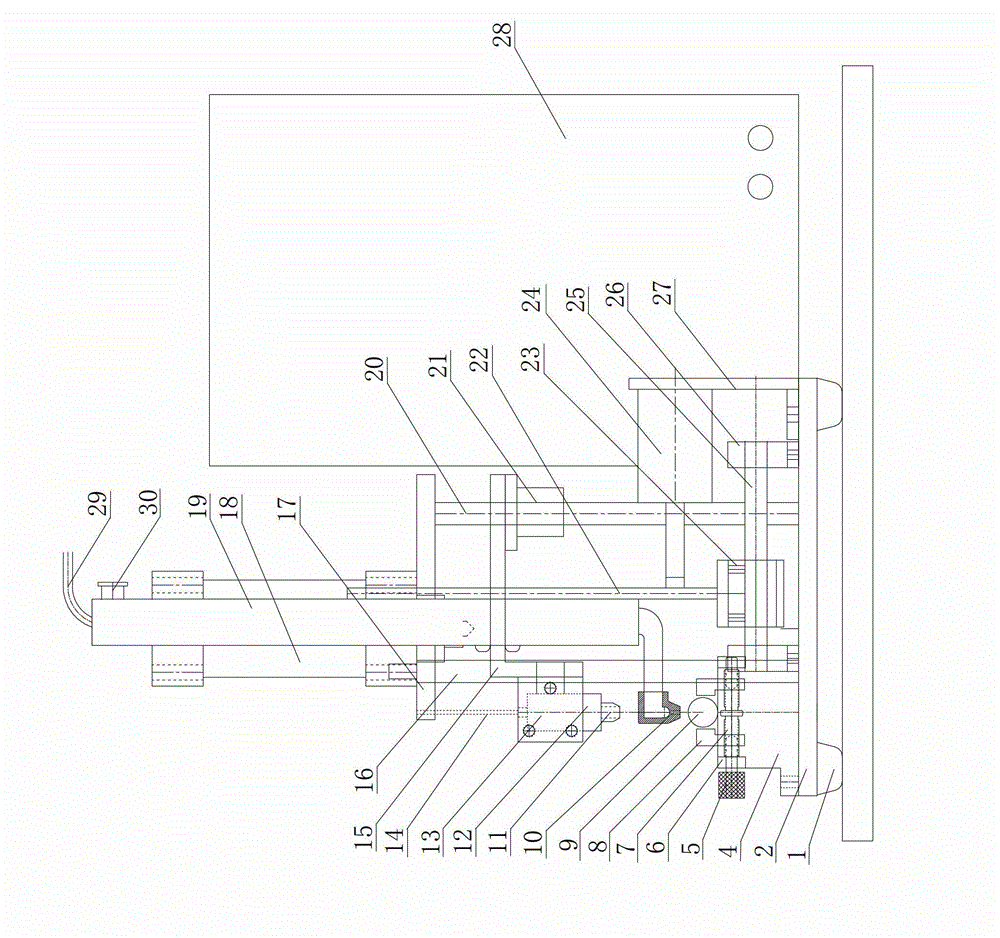
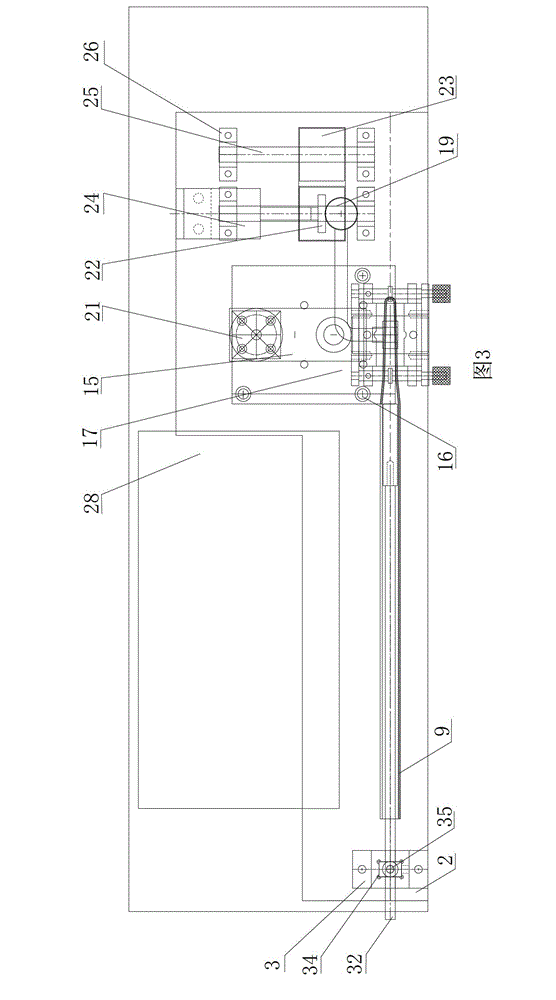
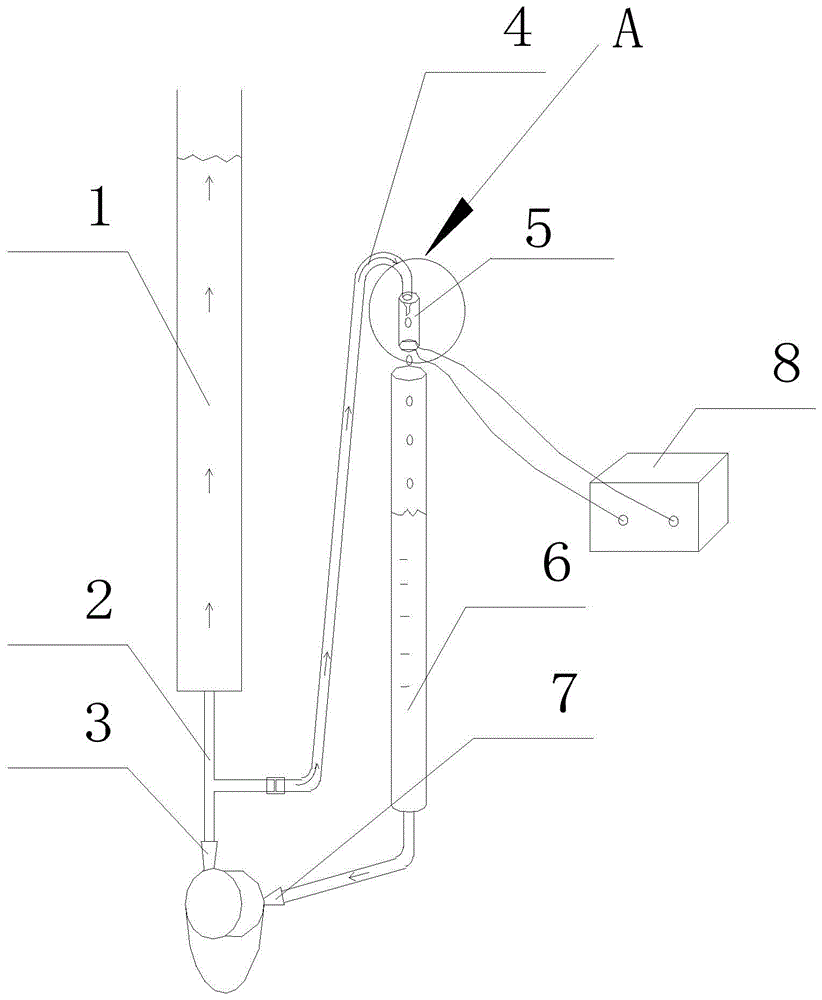
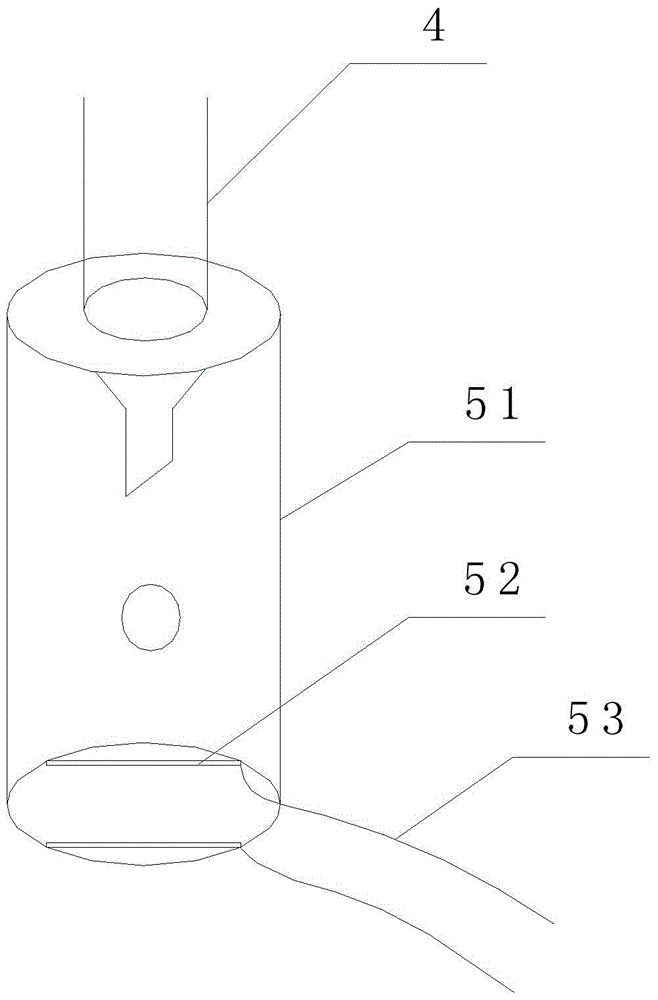
A frog heart perfusion experimental device
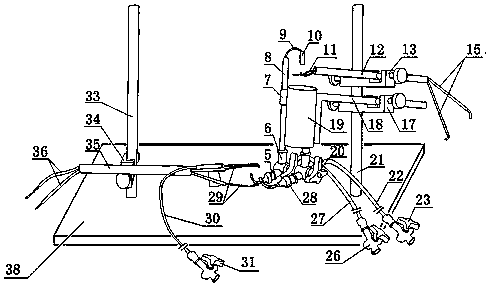
The invention relates to an experimental device for medical function and physiology, in particular to an improved experimental device for frog heart perfusion. The improved experimental device comprises a buffer tube, a three-way buffer artery tube, an artery plug, an artery cannula, a quantitative drop device, a venous cannula and a venous plug, wherein an opening is formed in the top of the buffer tube; the three-way buffer artery tube is connected with the buffer tube; the artery plug is connected with one branch tube of the three-way buffer artery tube; the artery cannula is connected with the other branch tube of the three-way buffer artery tube; the quantitative drop device is connected with the artery cannula; the venous cannula is arranged below the quantitative drop device; the venous plug is connected with the venous cannula; the artery plug is inserted into an aorta of a frog heart; the venous plug is inserted into a postcaval vein of the frog heart. According to the improved experimental device for the frog heart perfusion, disclosed by the invention, the buffer action for perfused liquid ejected in the blood ejection process of the frog heart is realized, uninterrupted dropwise outflow of the perfused liquid can be kept, the perfused liquid can flow at the systole and diastole of the heart, and quantitative record of liquid can be realized by the quantitative drop device.
Owner:NANYANG MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com