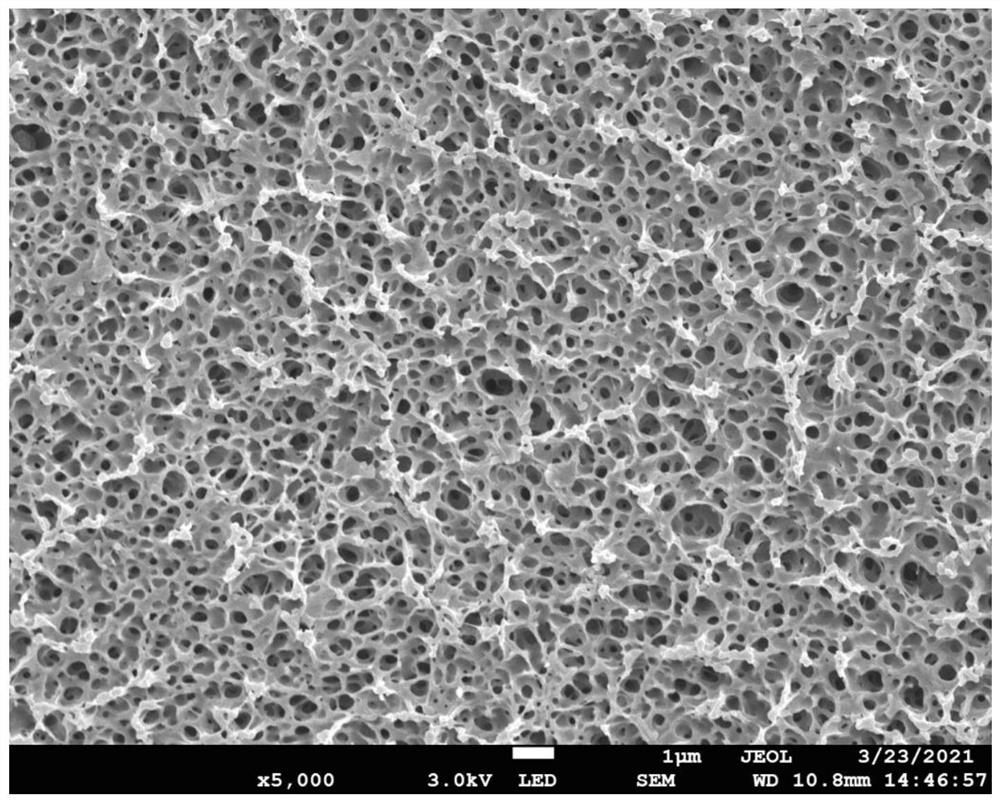
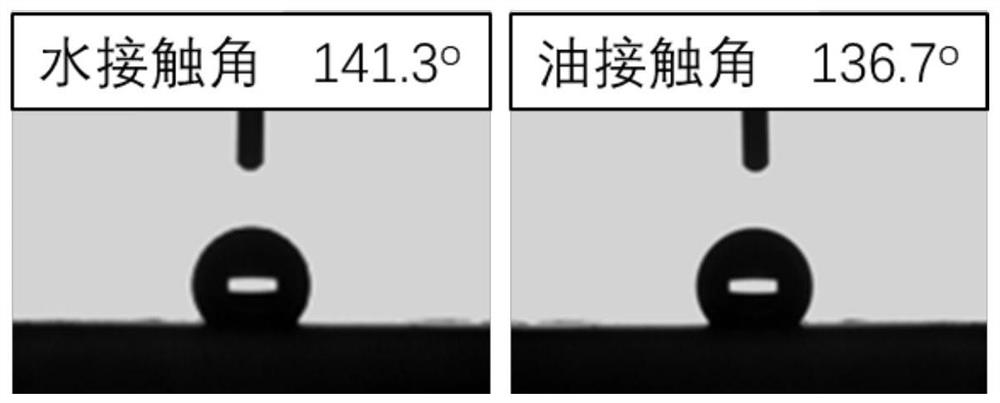
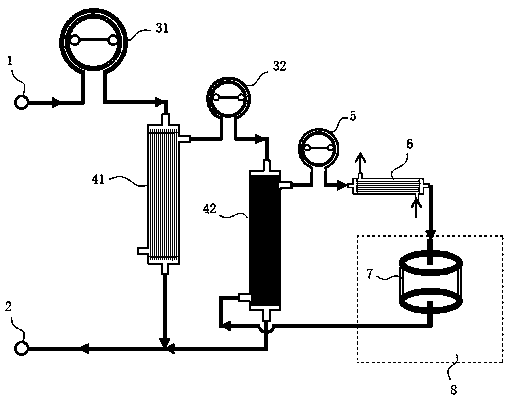
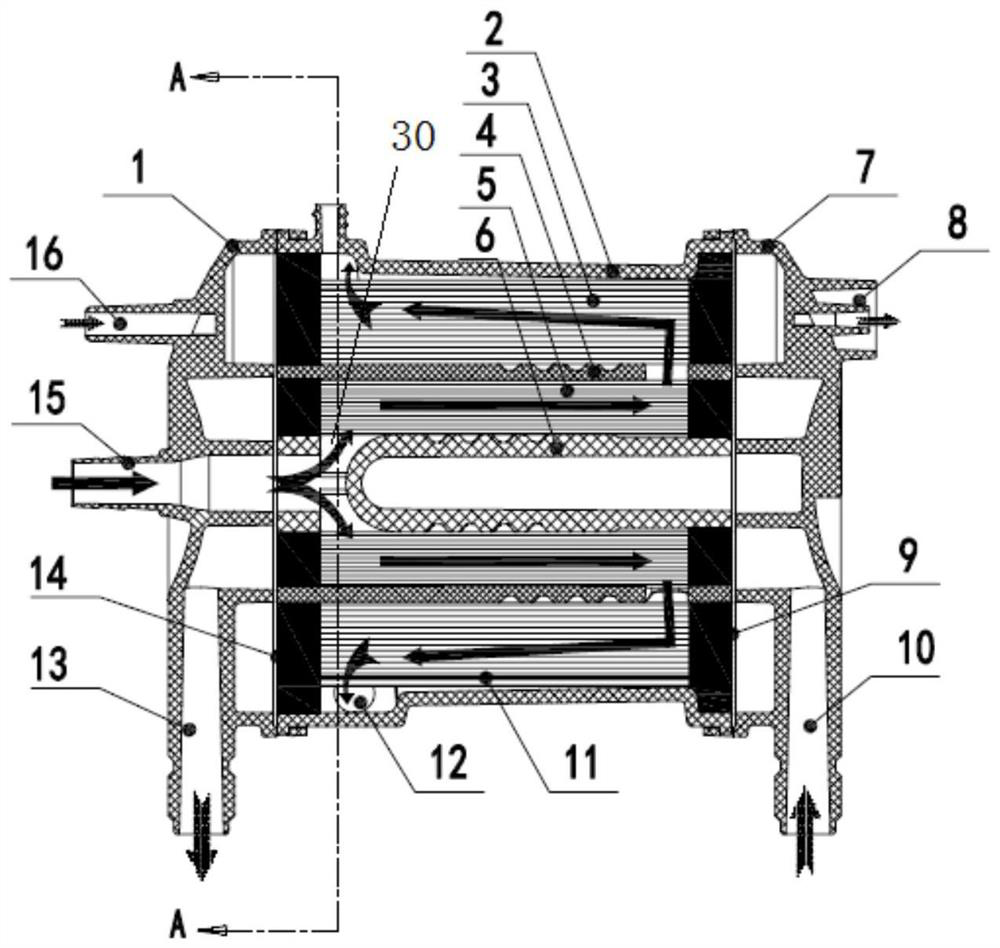
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Membrane oxygenator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
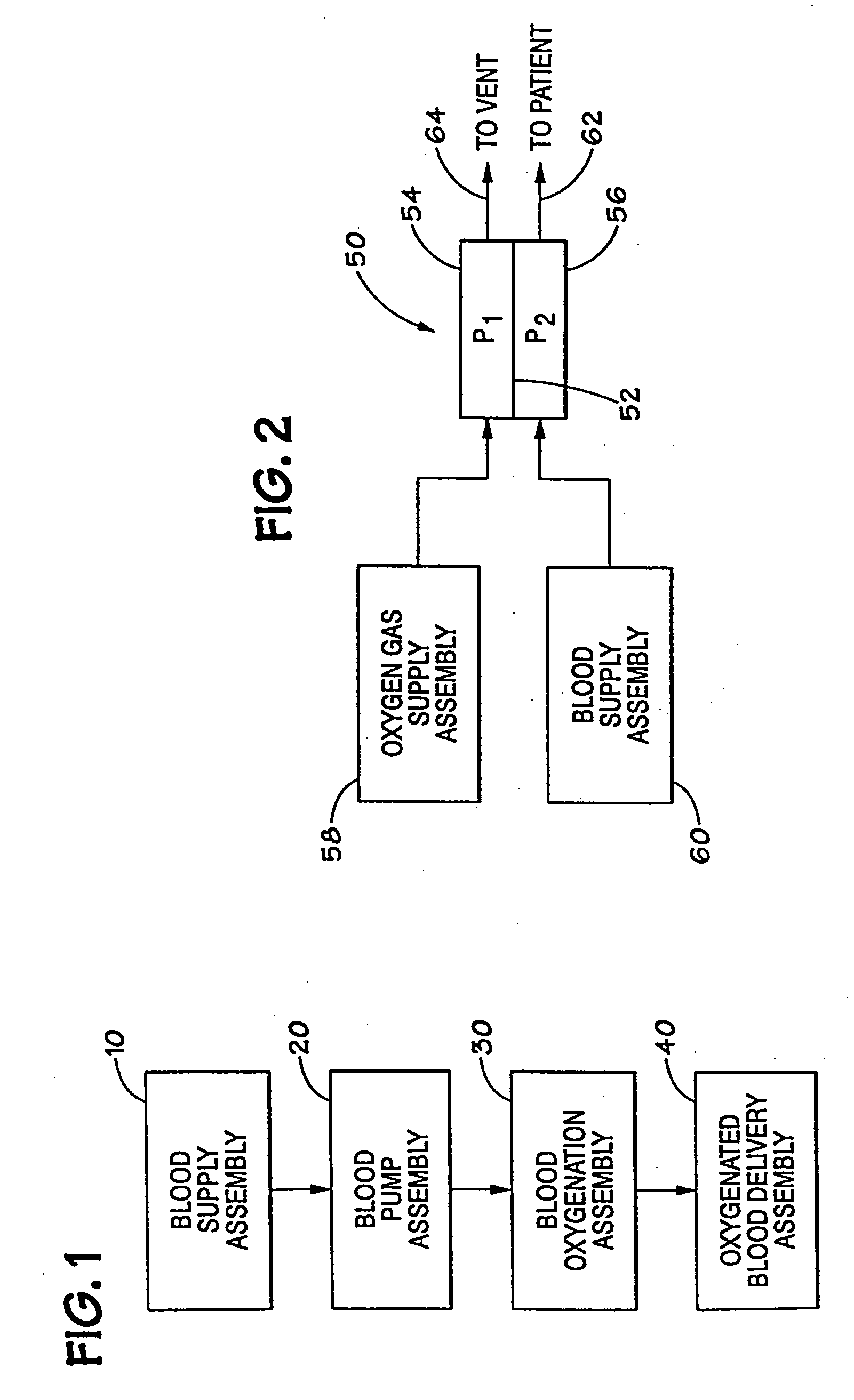
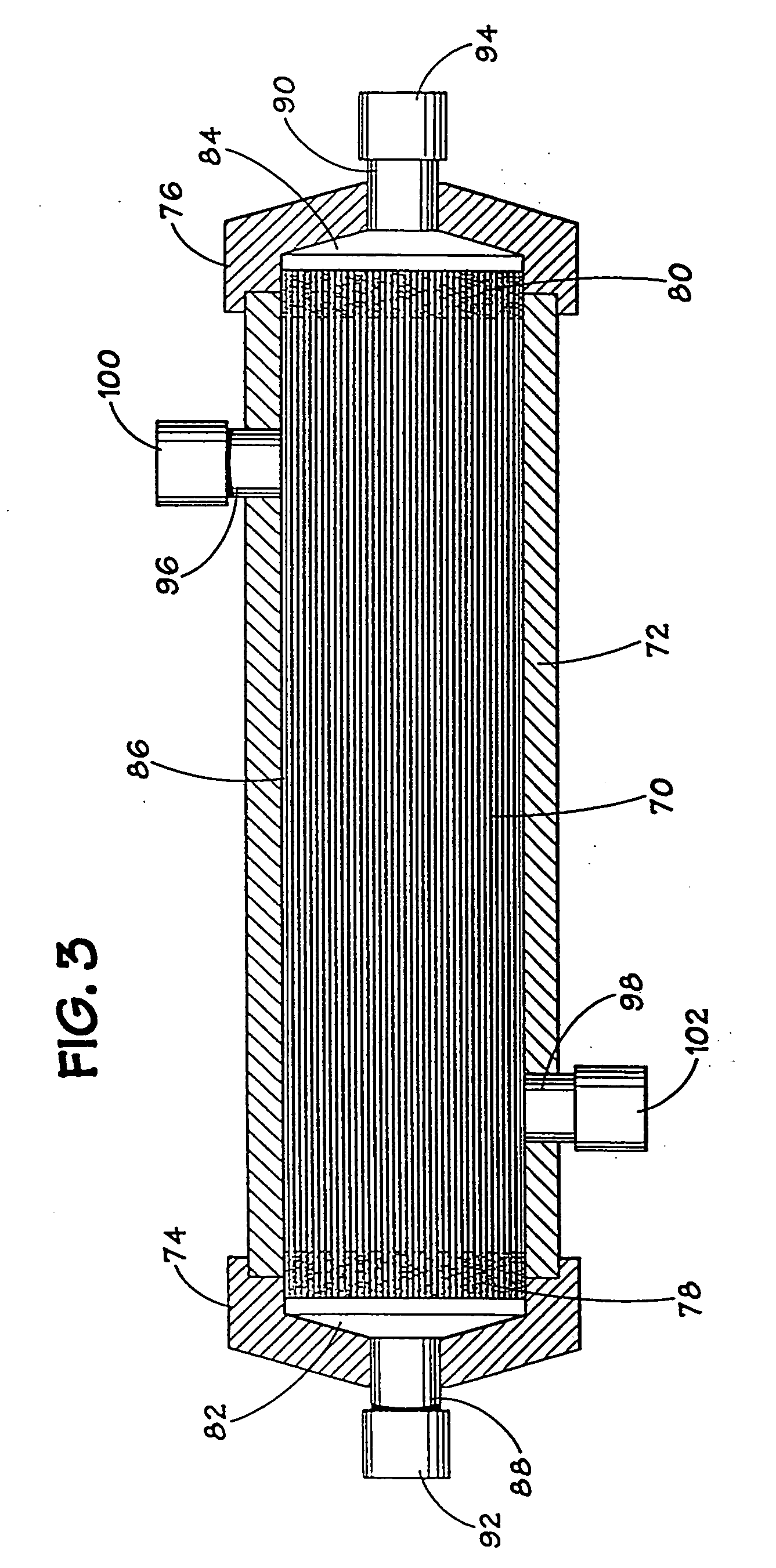
A membrane oxygenator is a device used to add oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. It can be used in two principal modes: to imitate the function of the lungs in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), and to oxygenate blood in longer term life support, termed extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, ECMO. A membrane oxygenator consists of a thin gas permeable membrane separating the blood and gas flows in the CPB circuit; oxygen diffuses from the gas side into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the gas for disposal.
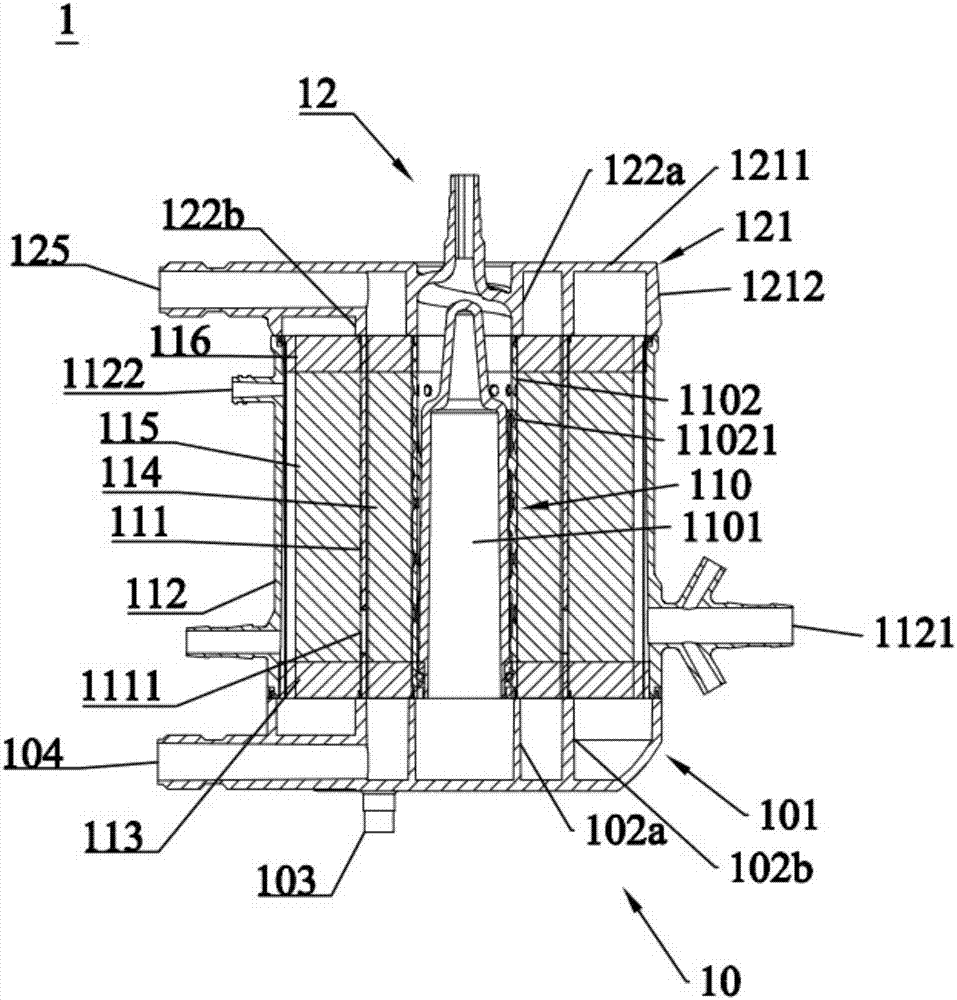
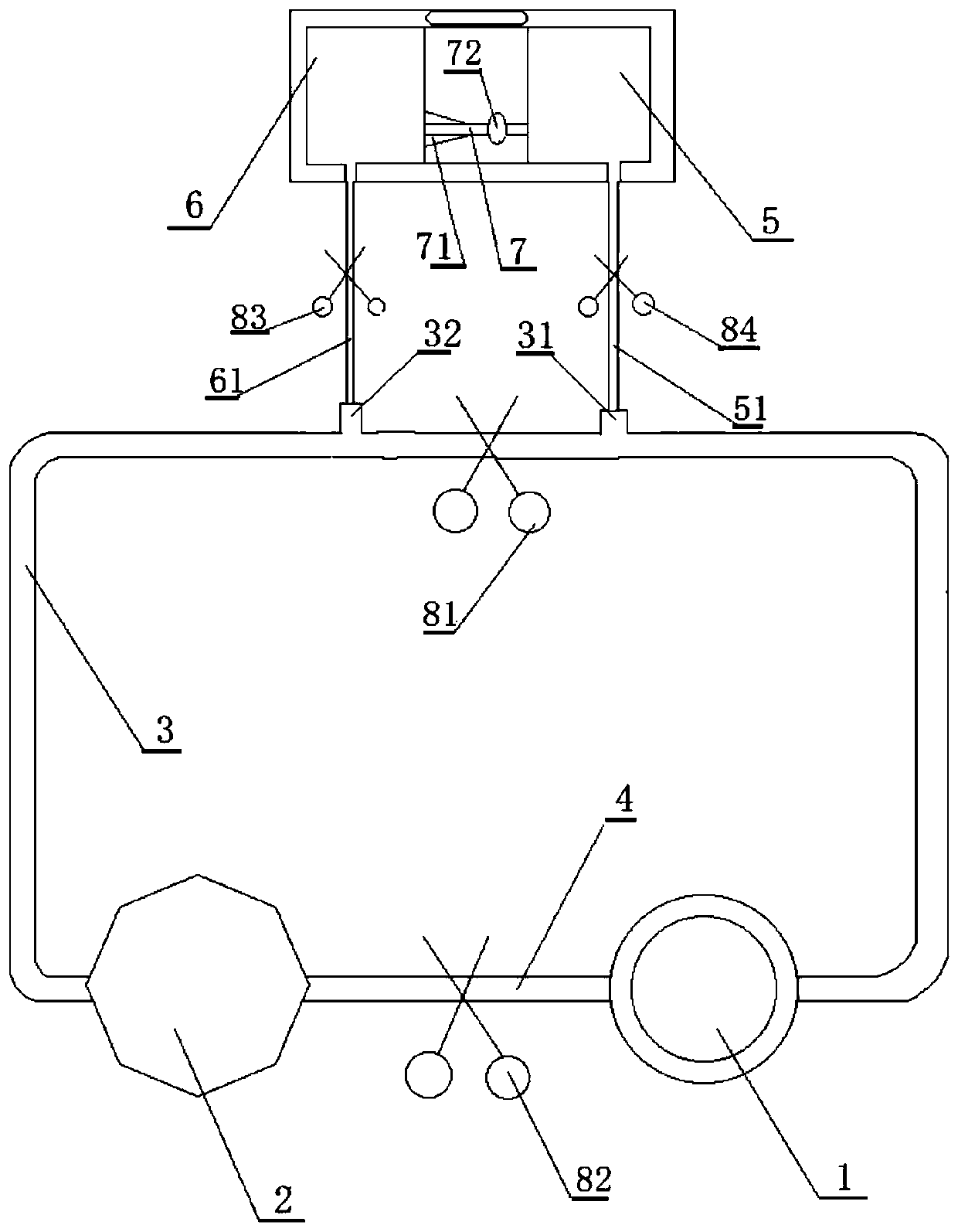
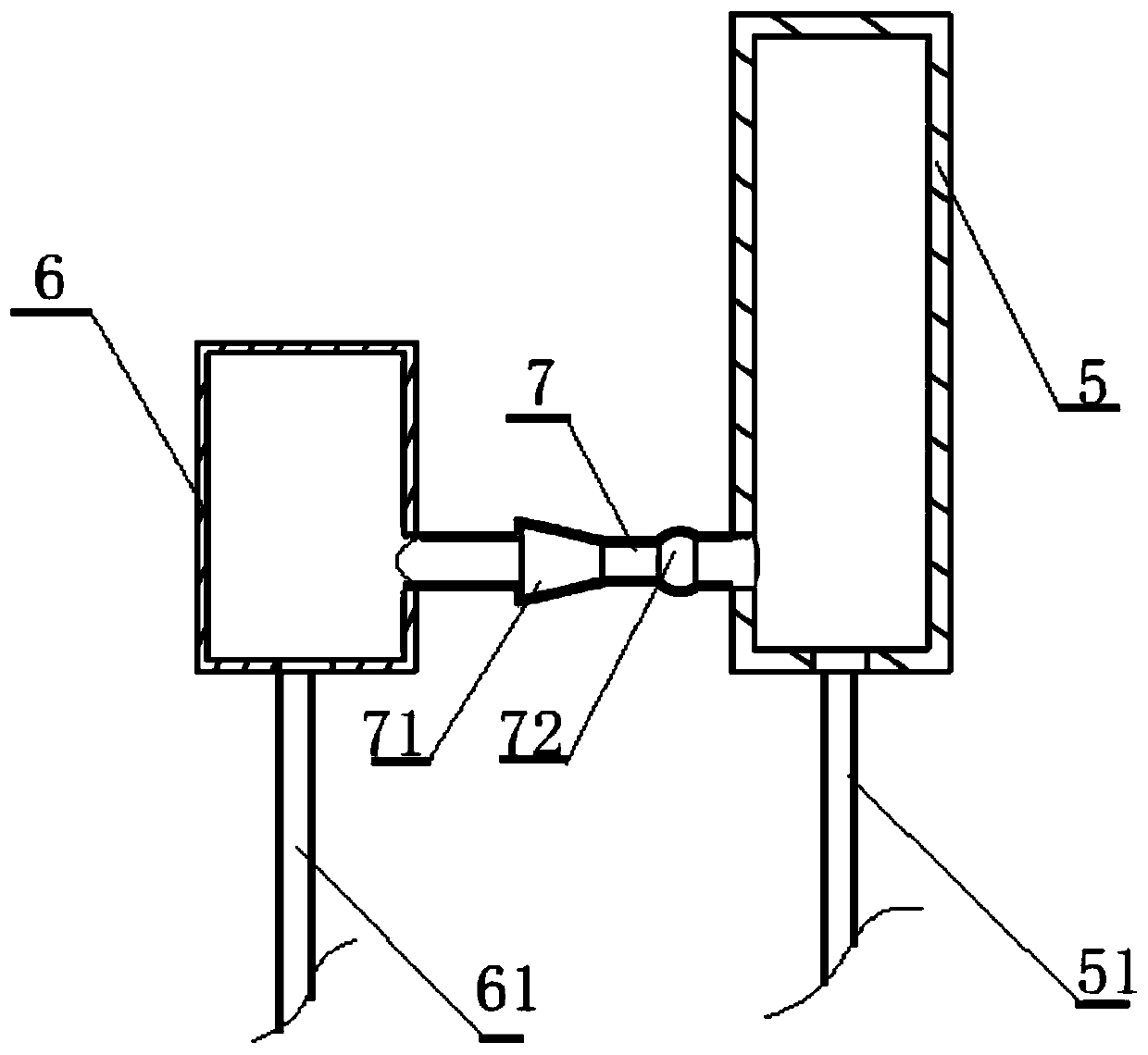
Microcapsule suspension type fluidized bed type bioreactor for artificial liver
ActiveCN101129276ASmall bottom diameterLarge top diameterSurgeryDialysis systemsArtificial liverMembrane oxygenators
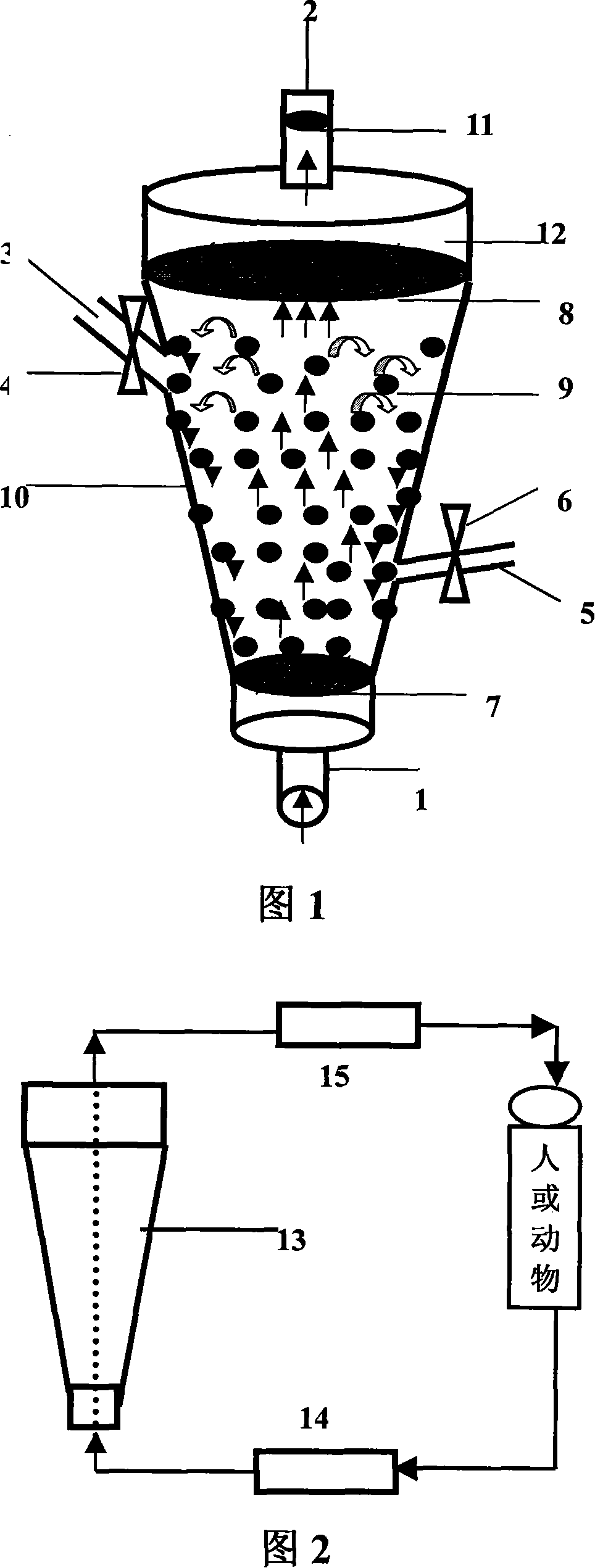
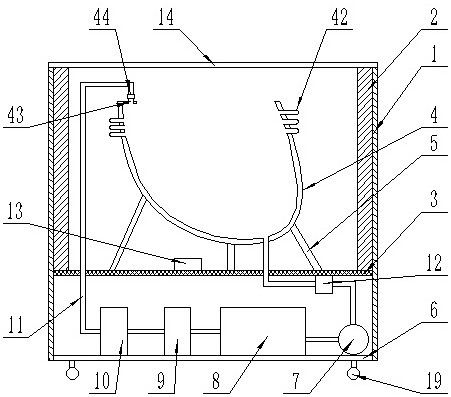
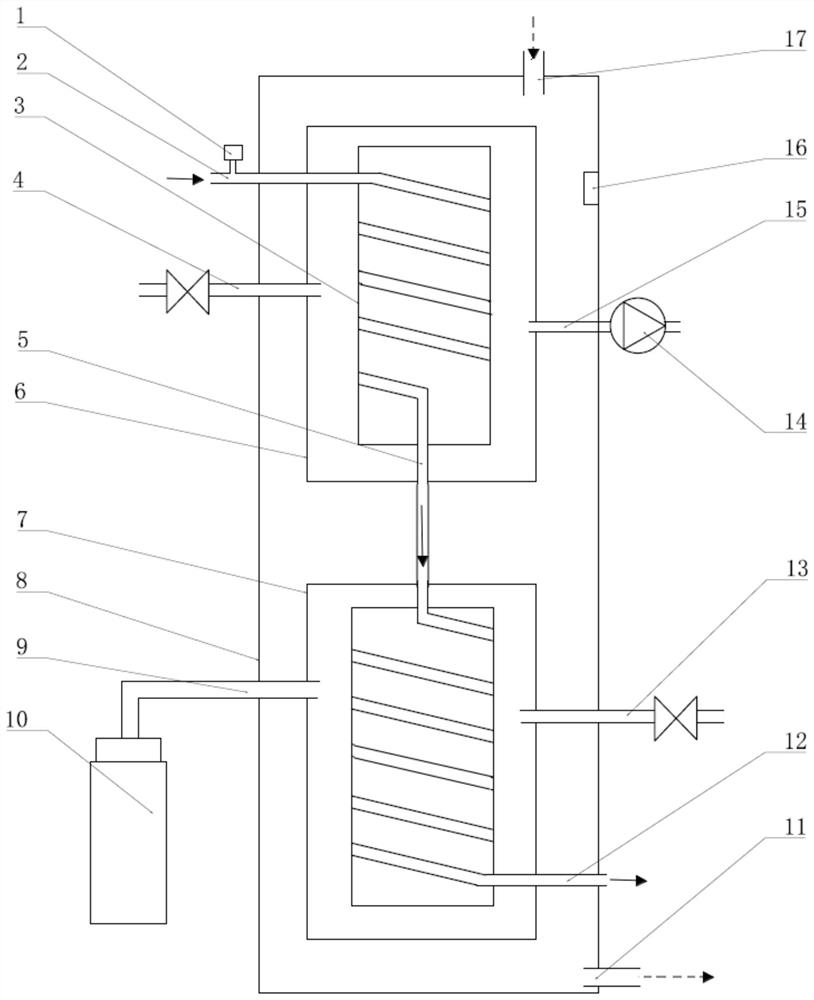
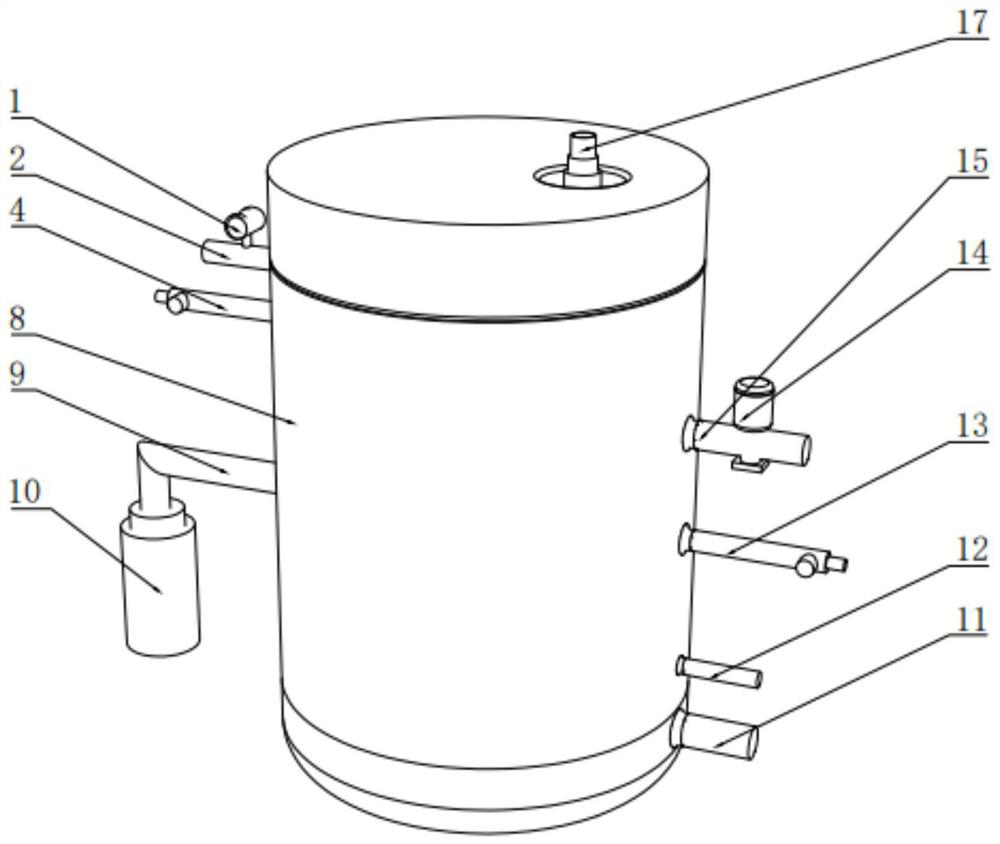
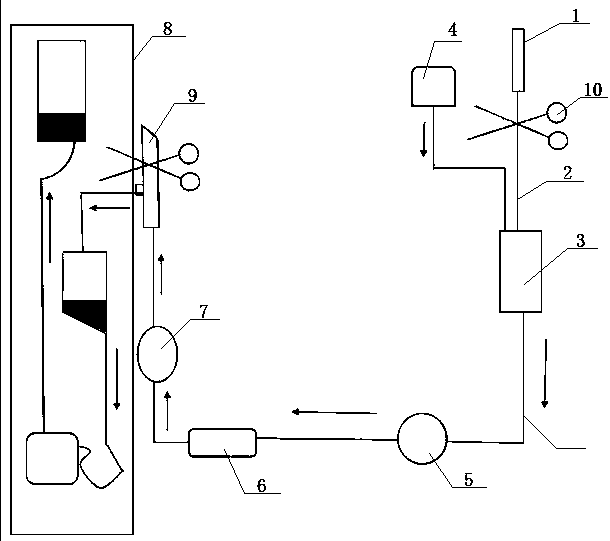
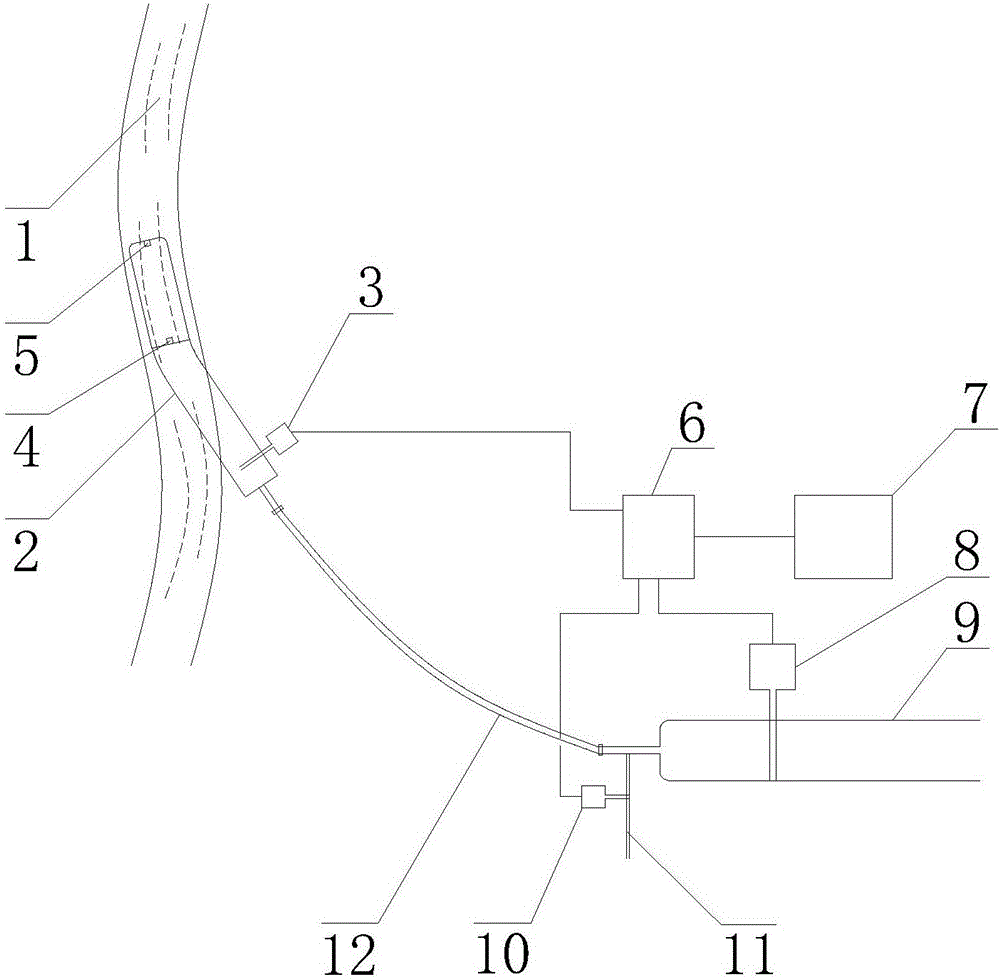
The invention discloses a microcapsule floating fluid-bed biological reactor of artificial liver in the medically biological technical domain, which is characterized by the following: displaying hopper shape with small bottom radius and large top radius; setting cell screen 8 at upper neck and cell screen 7 at lower bottom; depositing cell filter 8 at liquid outlet 2; setting buffer cavity 12 between liquid inlet 1 and cell screen 7, and between cell filter 11 and cell screen 8 respectively; containing the microcapsule liver cell 9 between cell screen 8 and cell screen 7; making the liquid inlet connect the membrane oxygenator 14 to connect immune adsorber 15 to adsorb immune macromolecule. The invention makes the moving trail of flow impaction as adjustment parabola to satisfy the character of fluid mechanics, which avoids dead perfusion cavity and ineffective perfusion to develop treating effect of biologically artificial liver obviously.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
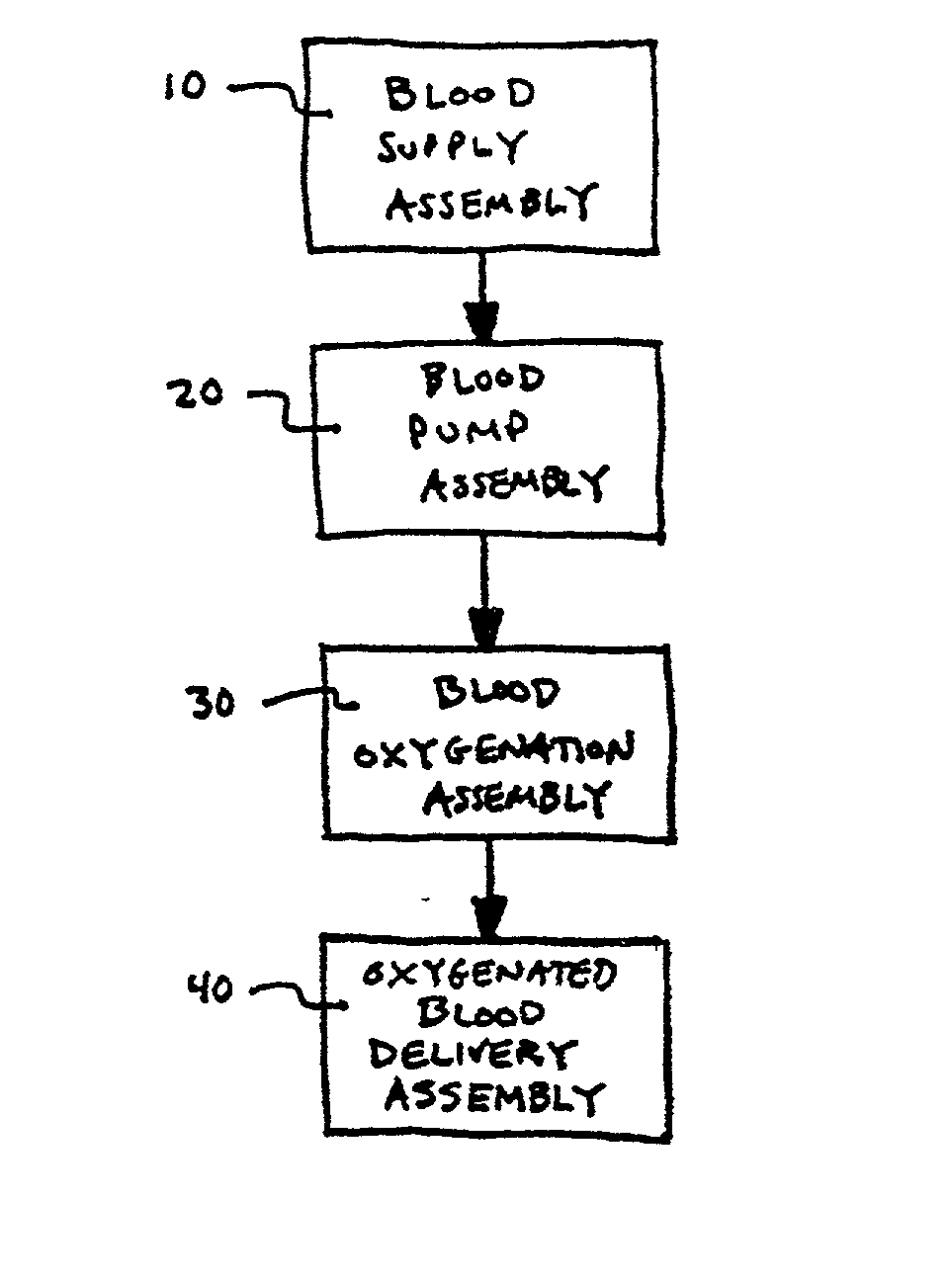
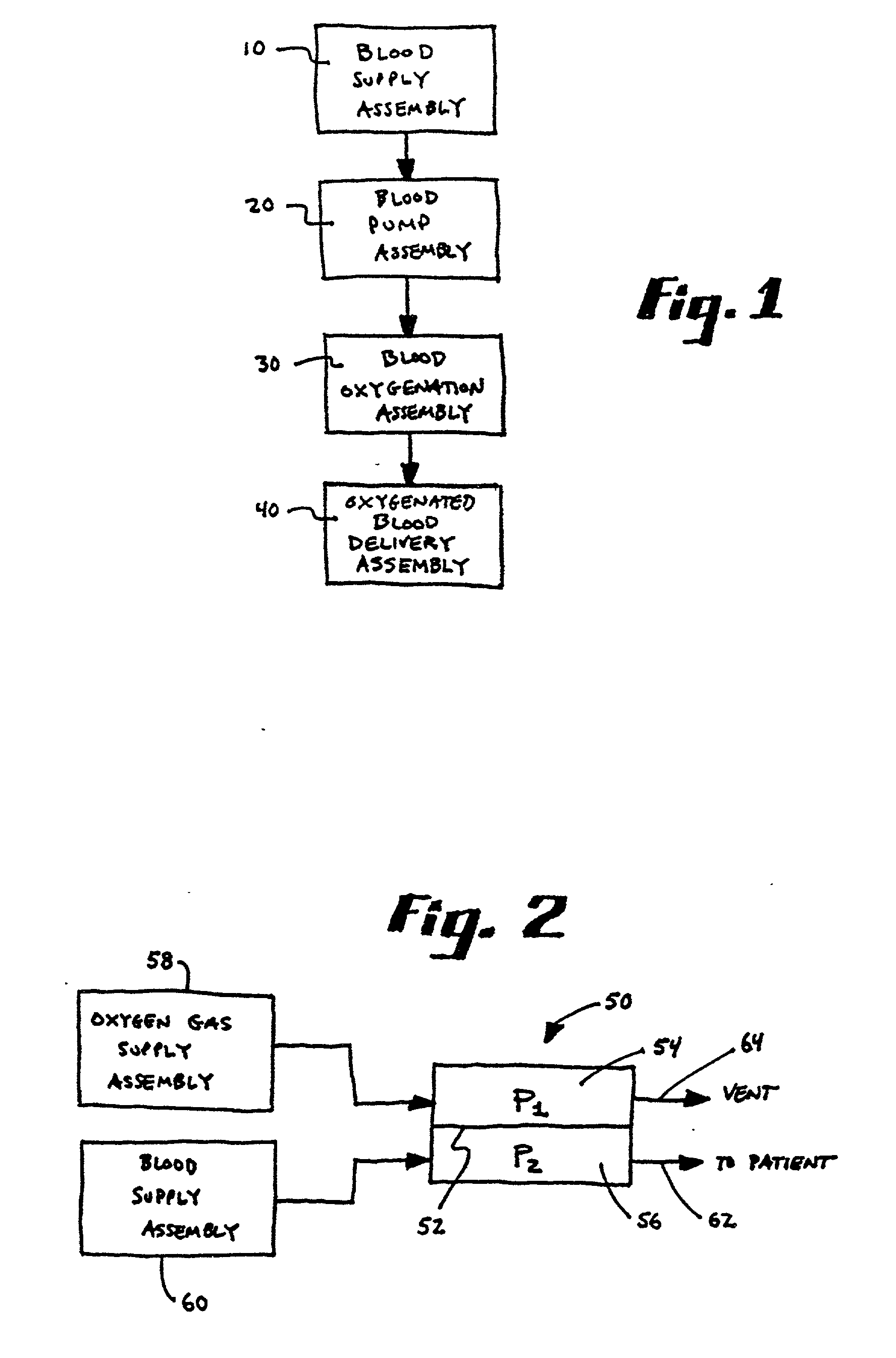
Method of blood oxygenation
InactiveUS20030091470A1Inhibition formationPrevent escapeOther blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
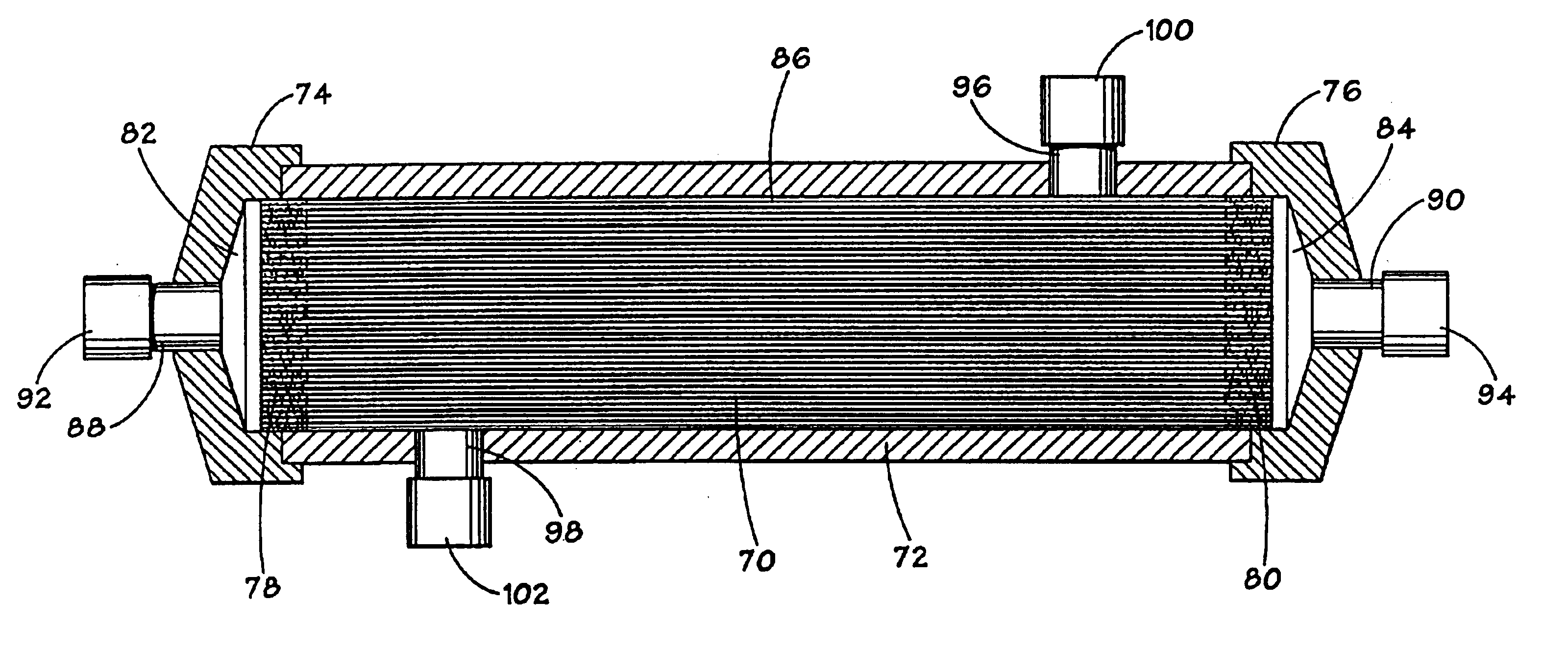
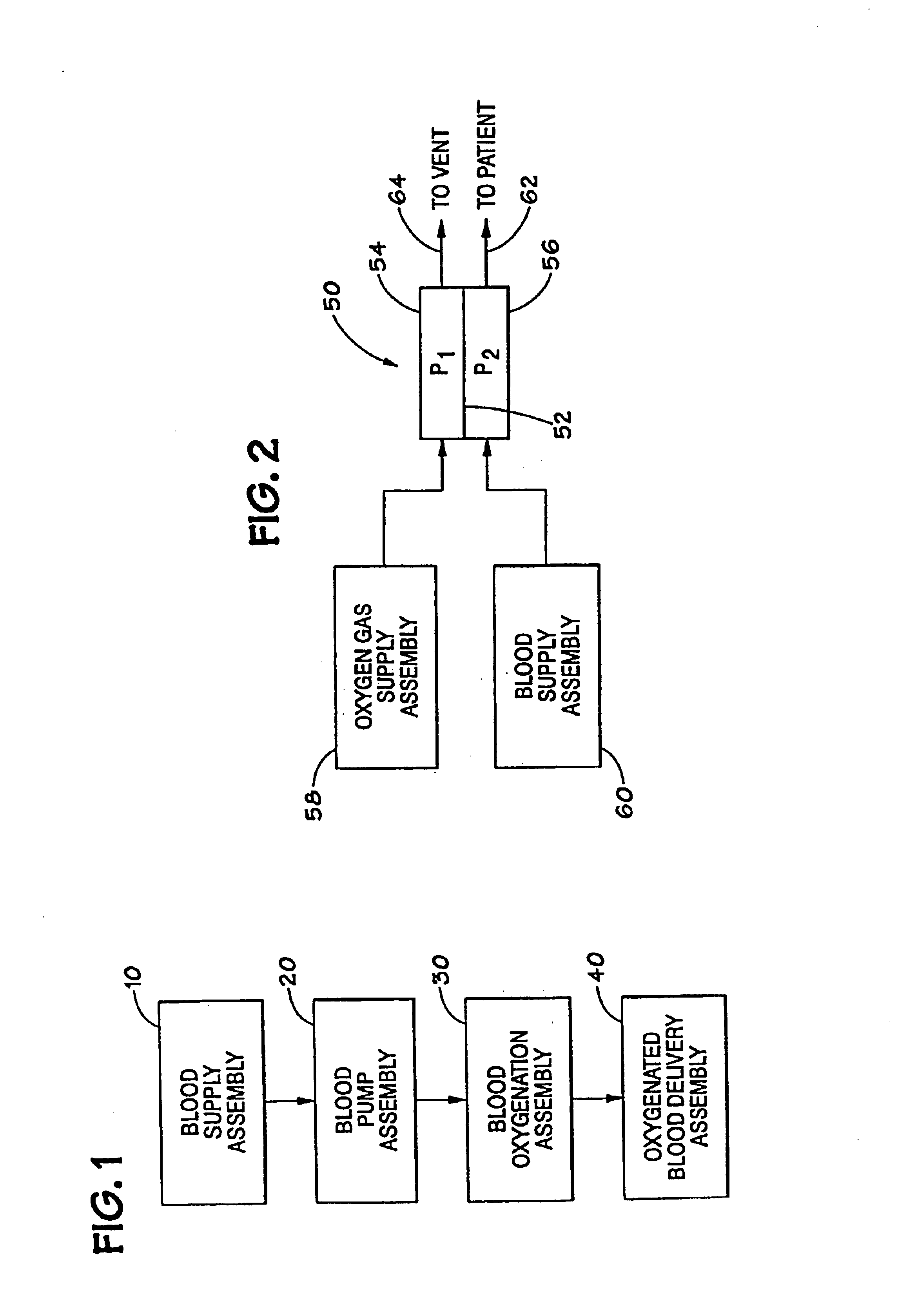
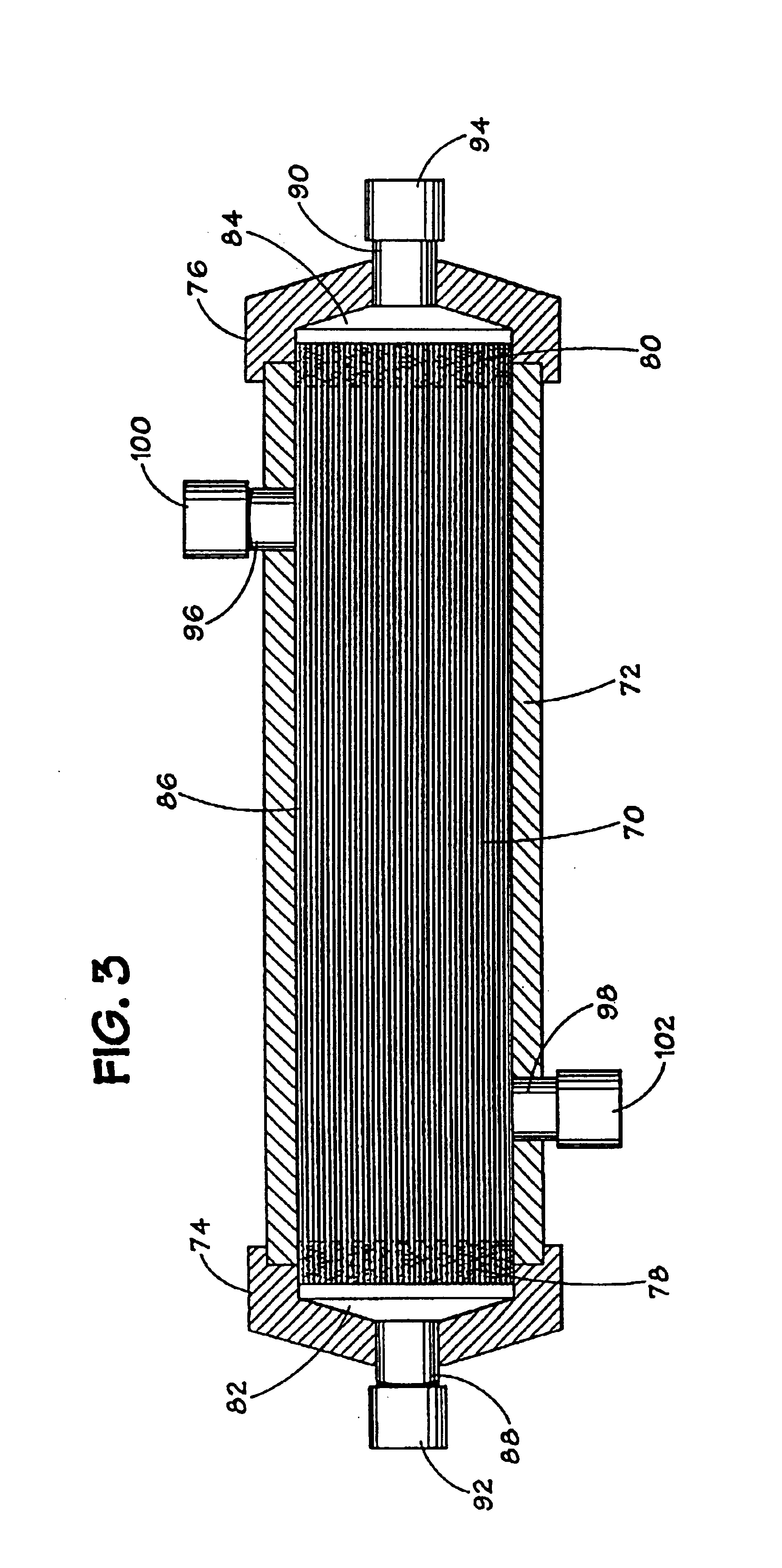
An apparatus and method for blood oxygenation is provided, advantageously comprising an extracorporeal circuit for the preparation and delivery of hyperoxic or hyperbaric blood. In one embodiment, an apparatus for gas-supersaturating fluids, e.g., physiologic saline, includes a chamber having a first inlet to receive the fluid; a second inlet to receive a gas, e.g., oxygen, from a gas supply that maintains pressure within the chamber at a predetermined level, advantageously about 600 p.s.i.; and an outlet advantageously coupled to a capillary assembly. An atomizer nozzle coupled to the first inlet advantageously creates within the chamber fine droplets of fluid into which gas diffuses to create the gas-supersaturated fluid, which collects within the chamber below the atomizer nozzle for removal via the outlet. The removed gas-supersaturated fluid mixes with blood provided by a blood pump, the mixing occurring within a liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly including a pressurizable chamber having inlets for the gas-supersaturated fluid and blood, the inlets advantageously arranged to create a vortical or cyclonic fluid flow within the chamber to promote mixing. The mixed fluid exits the chamber via an outlet for delivery to a patient (e.g., sub-selective delivery) or other site via a catheter, infusion guidewire, or other interventional fluid delivery device, the mixed fluid advantageously comprising blood having increased oxygen levels, i.e., oxygenated blood. Alternately, the blood may be provided by the pump to a high pressure hollow fiber or other type membrane oxygenator within which oxygen, advantageously provided at a pressure greater than atmospheric, diffuses across the membrane(s) and into the blood to form oxygenated blood, again for delivery to a patient or other site. Advantageously, the oxygenated blood is delivered at a target pO2 greater than about 760 mm Hg and is delivered from the liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly or membrane oxygenator via a fluid conduit having an approximate pressure drop greater than the target pO2.
Owner:THEROX
Method of blood oxygenation
InactiveUS6855291B2Increased oxygen levelsReduce deliveryOther blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingFiberMembrane oxygenators
An apparatus and method for blood oxygenation are provided. The apparatus includes a chamber having a first inlet to receive a gas-supersaturating fluid, e.g., physiologic saline; a second inlet to receive a gas, e.g., oxygen, from a gas supply; and an outlet coupled to a capillary assembly. An atomizer nozzle coupled to the first inlet creates within the chamber fine droplets of fluid into which the gas diffuses to create the gas-supersaturated fluid, which is removed via the outlet. The removed gas-supersaturated fluid mixes with blood within a liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly to form oxygenated blood for delivery to a patient. Alternately, the blood may be provided by the pump to a high pressure hollow fiber or other type membrane oxygenator within which oxygen diffuses across the membranes(s) and into the blood to form oxygenated blood, again for delivery to a patient or other site.
Owner:THEROX
Liver perfusion device
ActiveCN109362710AAvoid damageAdjust in timeDead animal preservationMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses a liver perfusion device, which comprises a main machine, an air-oxygen mixer assembly and a monitoring assembly. A consumable assembly is clamped on a worktable of the main machine, and when different livers need to be perfused, only the consumable assembly needs to be replaced, so that convenience is achieved; the main machine is internally provided with a temperature adjusting assembly in pipeline connection with the consumable assembly, thus the temperature of circulating water entering a first lung membrane oxygenator and a second lung membrane oxygenator for heatexchange can be adjusted through the temperature adjusting assembly, and then liver perfusion can be conducted under different temperature conditions according to the actual needs; and in addition, the main machine has different liver perfusion modes, a user can set hepatic artery and portal vein perfusion methods according to the actual needs, the perfusate oxygenation degree is adjusted according to an air-oxygen mixer, different drugs are injected by a micro-injection pump, and the effects of liver long-term preservation, improvement, repair and the like are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG DEVOCEAN MEDICAL INSTR CO LTD
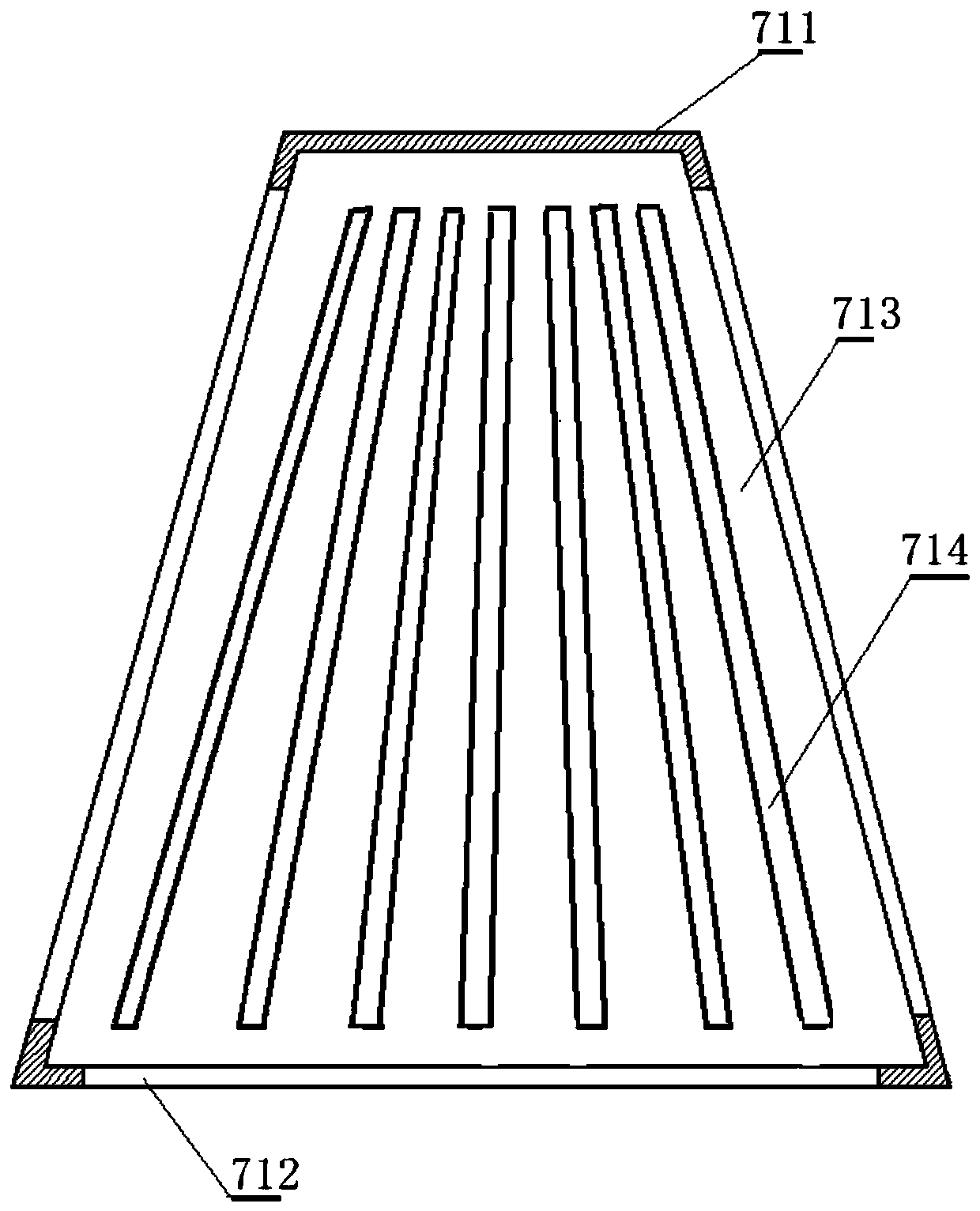
Spiral flow-guide integrated membrane oxygenator
ActiveCN107362399AIncreased diffusion areaIncrease contact areaDialysis systemsMedical devicesMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention relates to a spiral flow-guide integrated membrane oxygenator comprising a lower cover, an oxygenation portion and an upper cover. The lower cover is provided with an air outlet pipe. The oxygenation portion is arranged to the lower cover and comprises a spindle structure, an oxygenation shell and an oxygenation cortina structure, and the oxygenation shell is provided with a blood outlet pipe close to the lower cover. The upper cover is arranged to the oxygenation portion and is provided with a blood inlet pipe and an oxygen inlet pipe. The spindle structure comprises a spindle body and an annular flow guide plate, the spindle body is provided with a first end and a second end, a blood channel is formed between the first end and the upper cover, the annular flow guide plate sleeves the spindle body and is provided with at least one flow guide through hole, and the flow guide through holes of the annular flow guide plate are distributed in the annular flow guide plate. The spindle structure of the spiral flow-guide integrated membrane oxygenator is provided with the annular flow guide plate, the annular flow guide plate guides blood to diffuse through the flow guide structure with the flow guide through holes, contact area and diffusion area of blood and the cortina structure are increased, and utilization rate of the cortina structure is increased.
Owner:DONGGUAN KEWEI MEDICAL INSTR
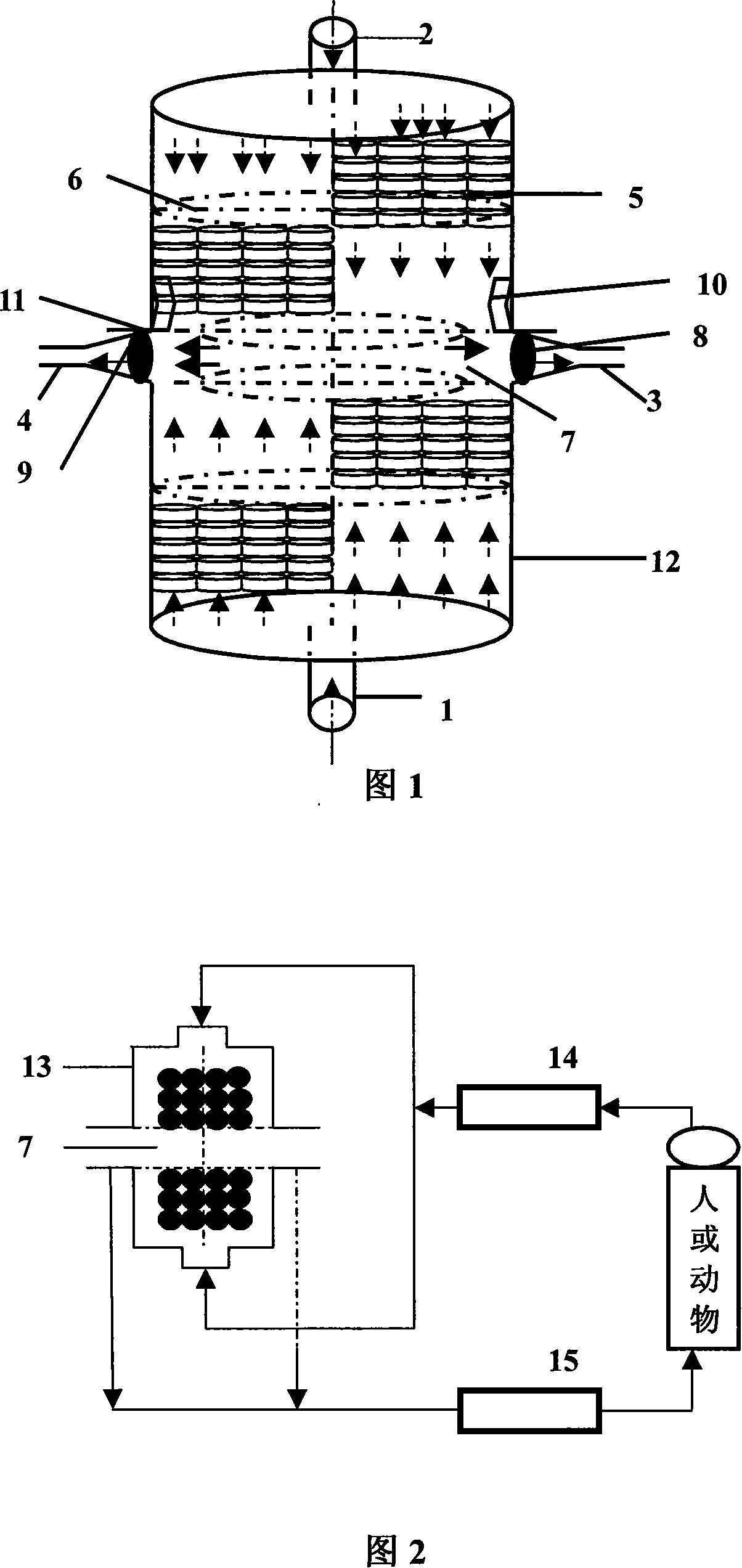
Filling bracket perfusion type bioreactor for artificial liver
ActiveCN101129277AGet the most out of the active ingredientsGood biocompatibilitySurgeryDialysis systemsArtificial liverMembrane oxygenators
The invention discloses a filling rack perfusion biological reactor of artificial liver in the medically biological technical domain, which is characterized by the following: the appearance is cylinder shaped container; the liquid outlets 1 and 2 are upper and lower ends of the cylinder container; the outlet 3 and 4 are distributed in the center of lateral wall symmetrically; the physical rack 6 has 14-16 biological racks as crossing arrangement to deposit separation area and support liver cell; the liquid buffer area 7 is set in the middle of the inner rack of the reactor; setting cell screen and cell screen brush at outlet; connecting the upstream of two outlets of biological reactor with membrane oxygenator 14; connecting the downstream of two outlets with immune adsorber 15; the biological rack of the liver cell is chitose rack or alginic acid / chitose and modified alginic acid / galactose chitose / heparin rack; possessing good biological compatibility; fitting for growing liver cell and developing the function; avoiding collapse of the biological rack of the liver cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
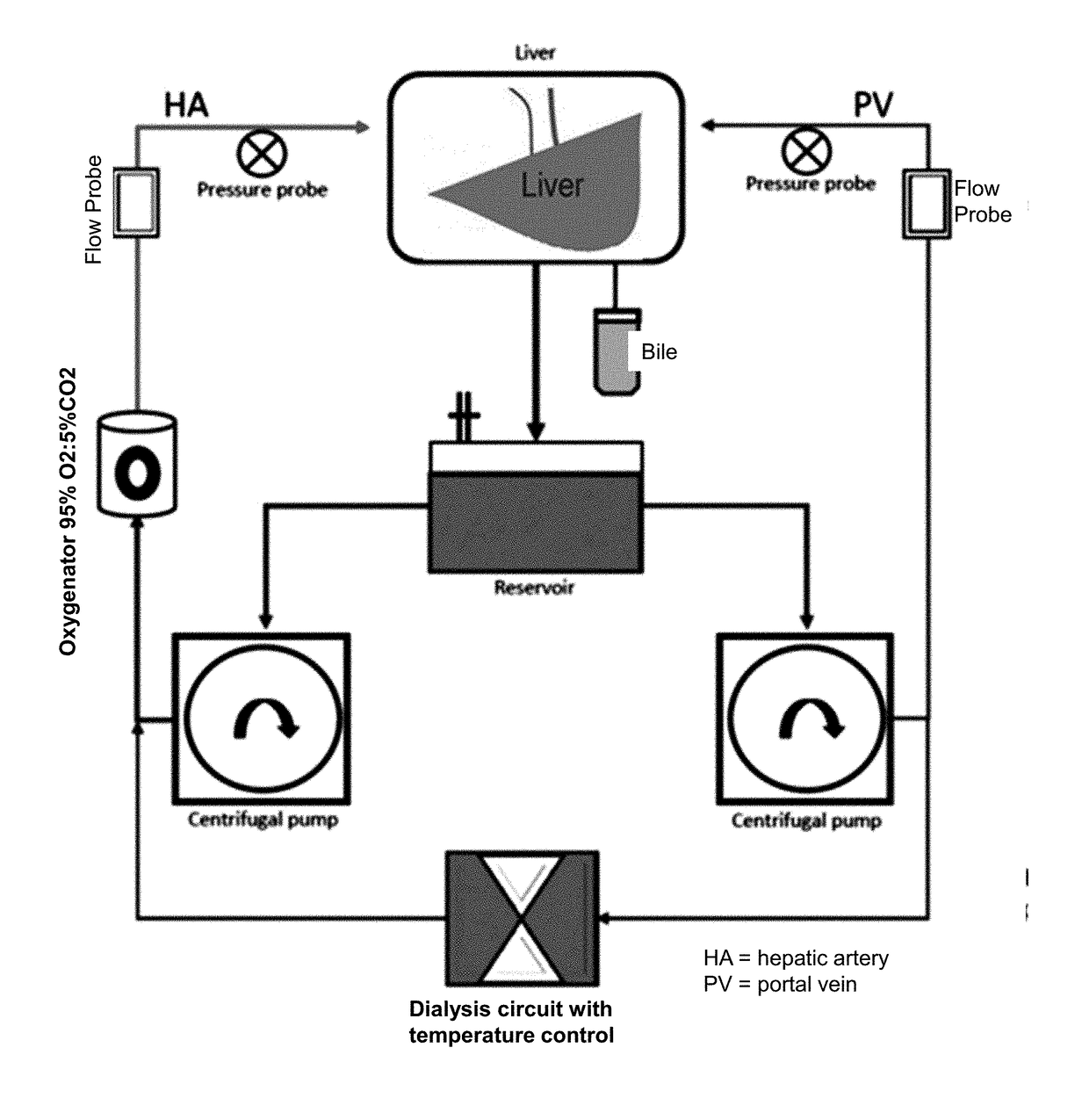
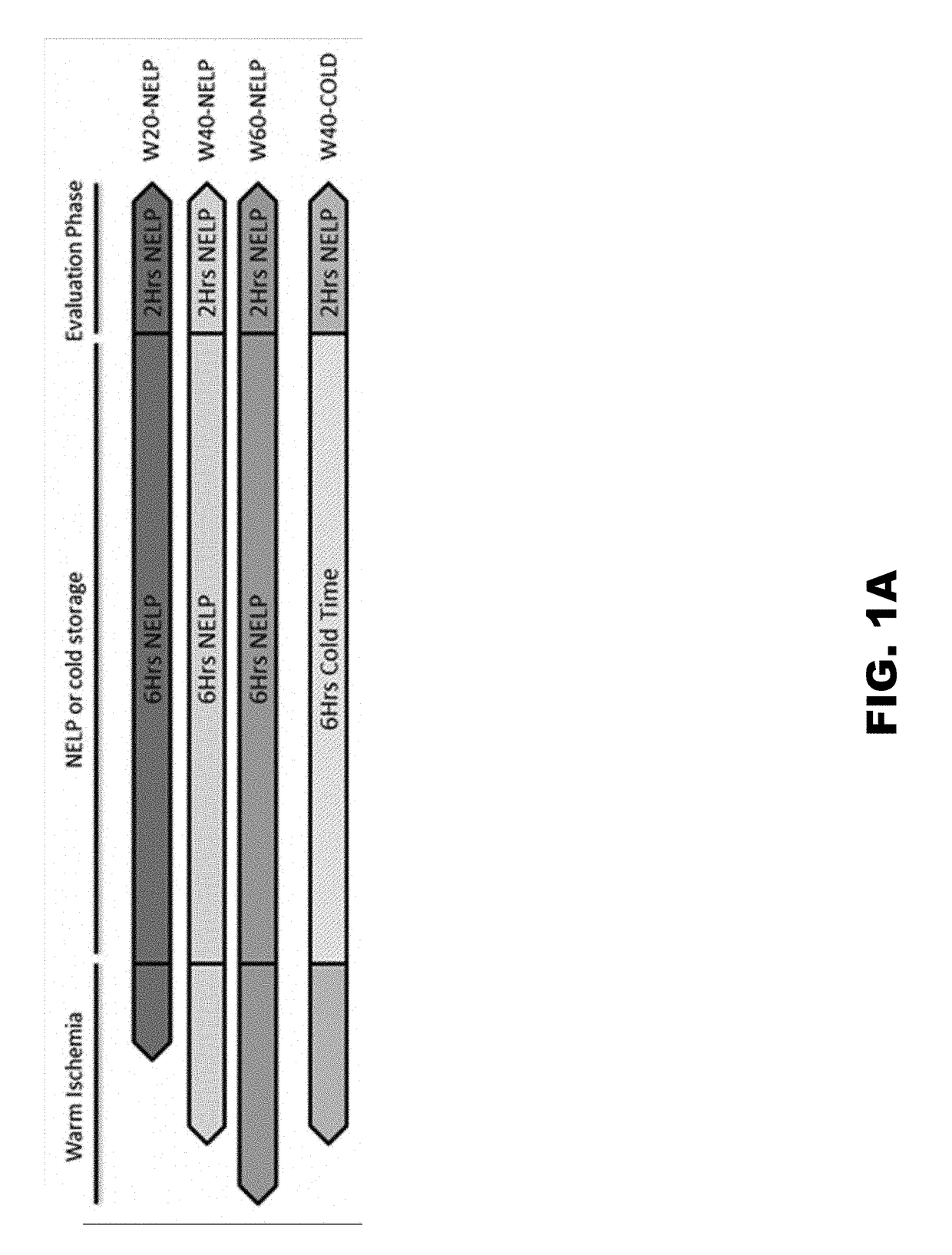
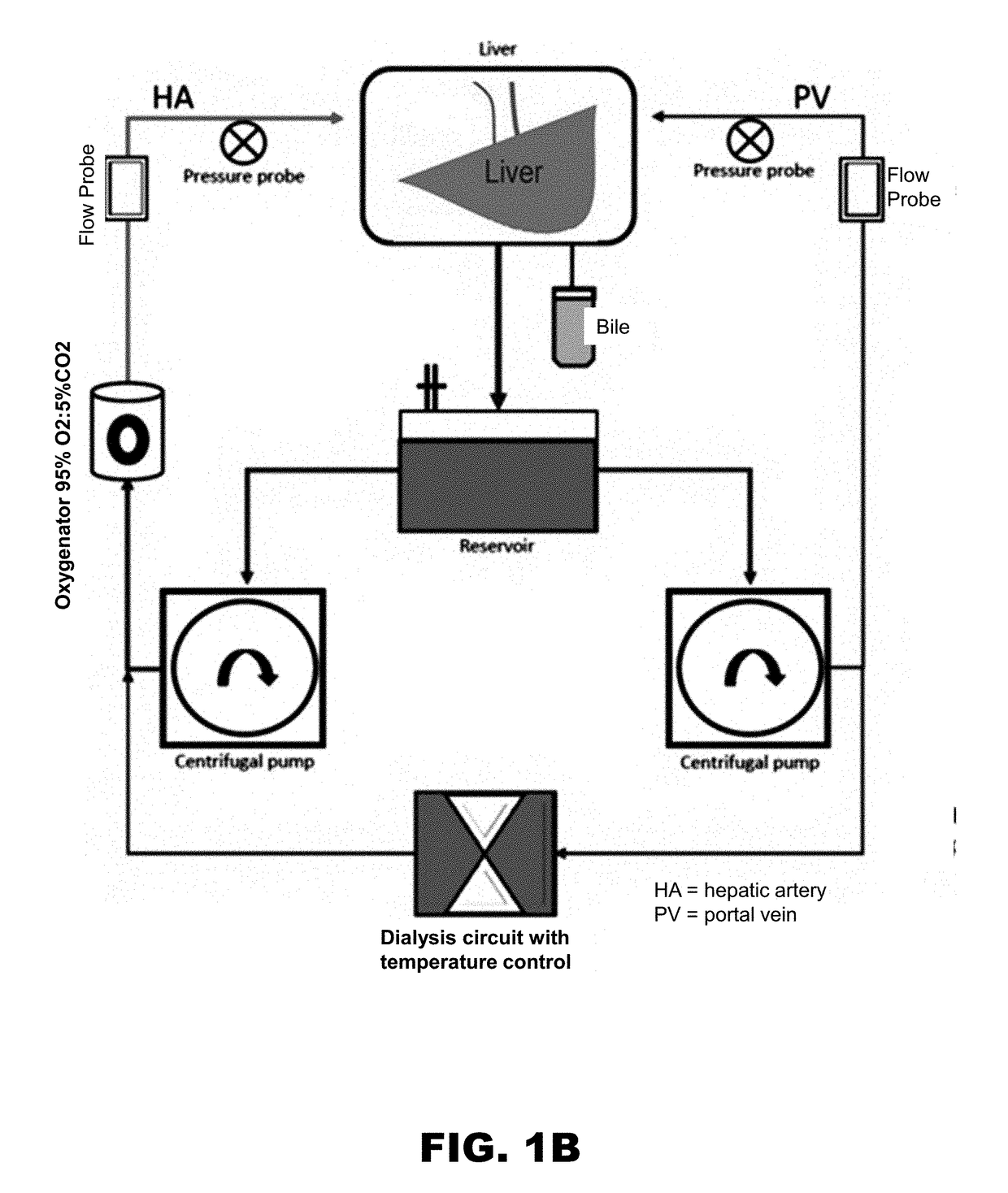
Systems and methods for normothermic extracorporeal organ perfusion
ActiveUS20170188571A1Keep for a long timeDead animal preservationMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
A system and method for perfusing an organ with a normothermic extracorporeal perfusion system is disclosed. The perfusion system is an active flow system using a centrifugal pump to aid in circulation. The system includes a dialyzer that removes excess fluid and impurities, while maintaining the pH, which allows the perfusion system to be used for an extended period that may exceed 24 hours. The system includes a parallel circuit, which includes at least one centrifugal pump, a membrane oxygenator comprising a heat exchanger; a dialyzer; a measurement cell for real-time monitoring of oxygen saturation and hematocrit in the liver; more than one flow probe; and an organ chamber.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
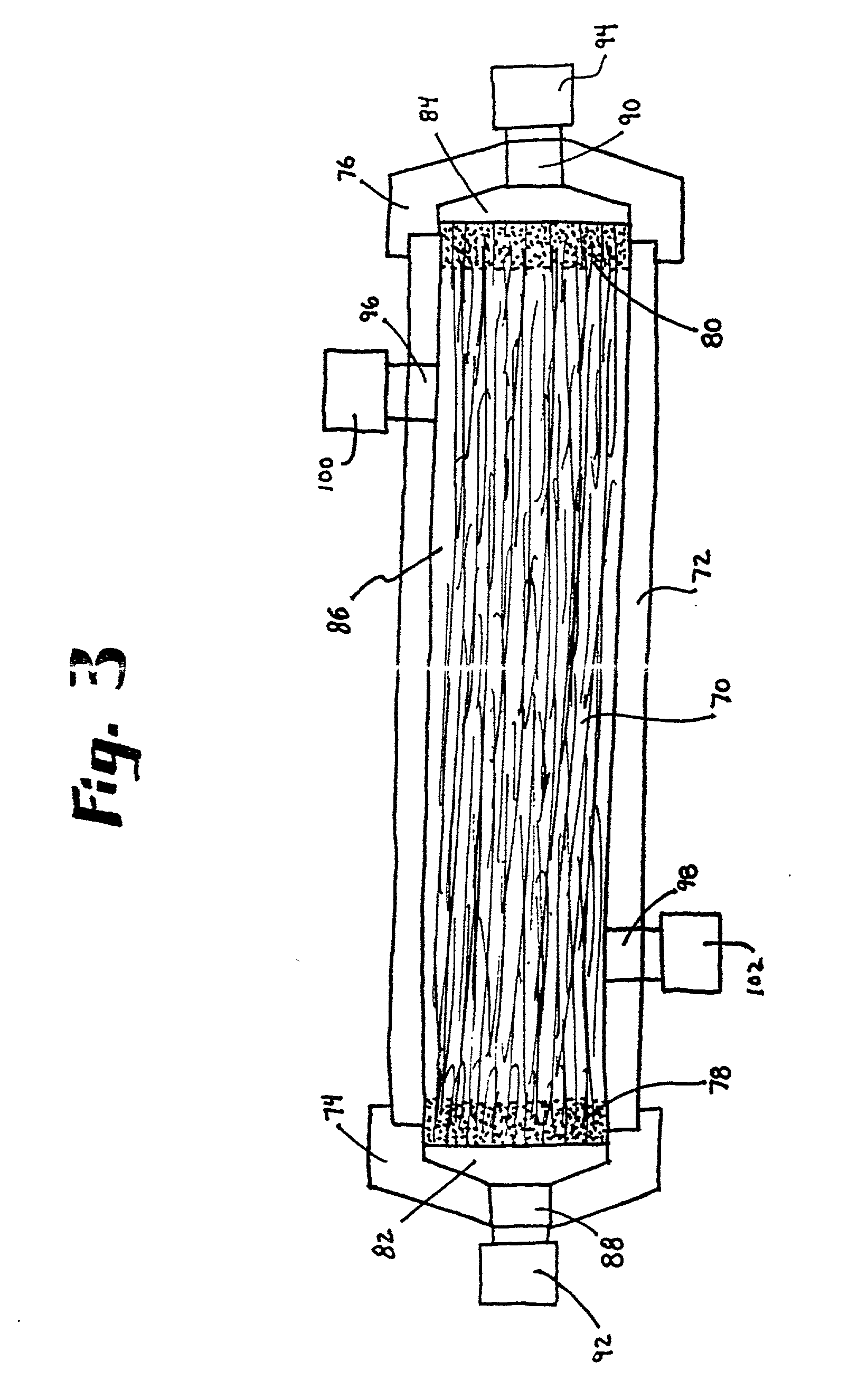
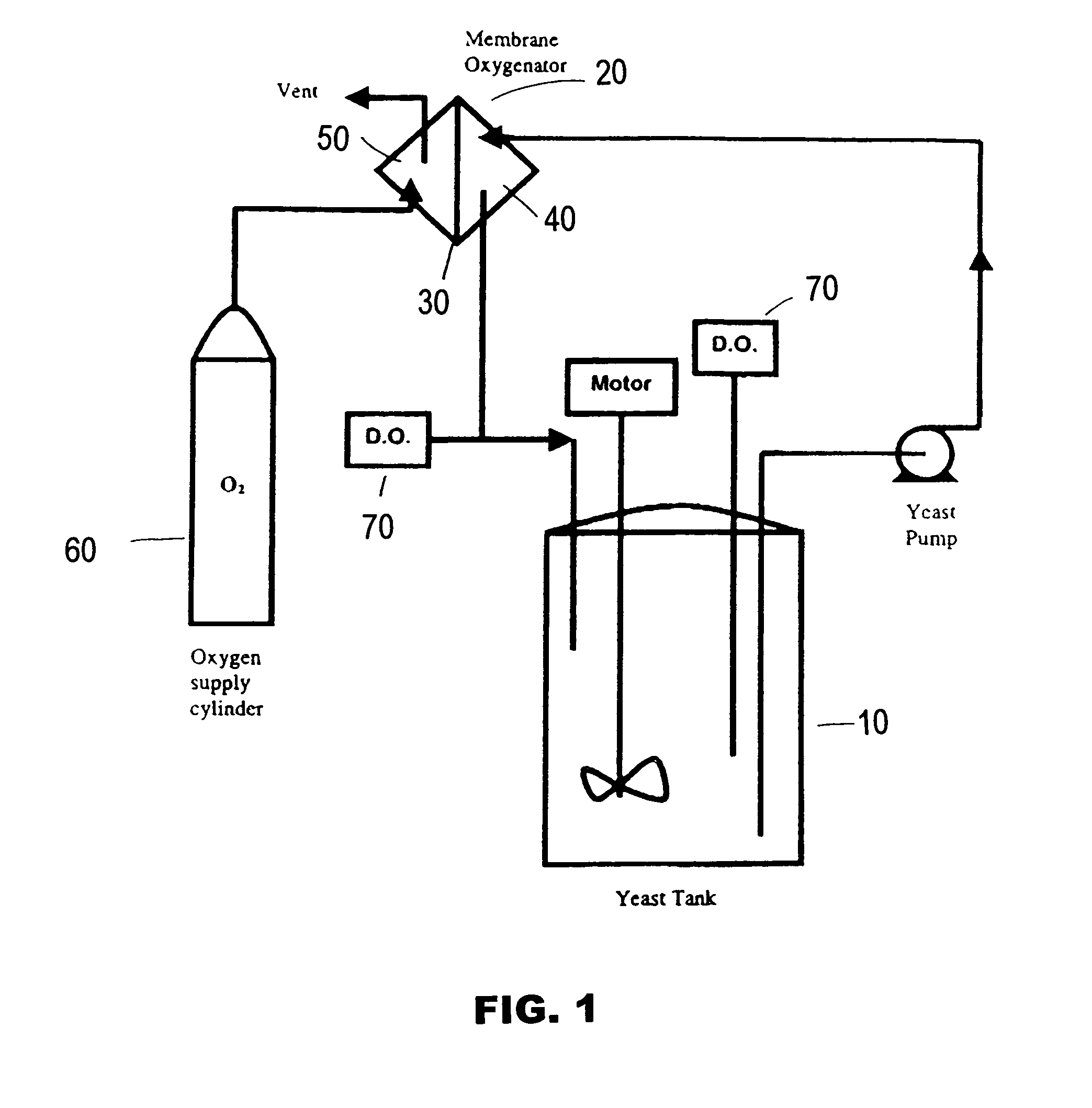
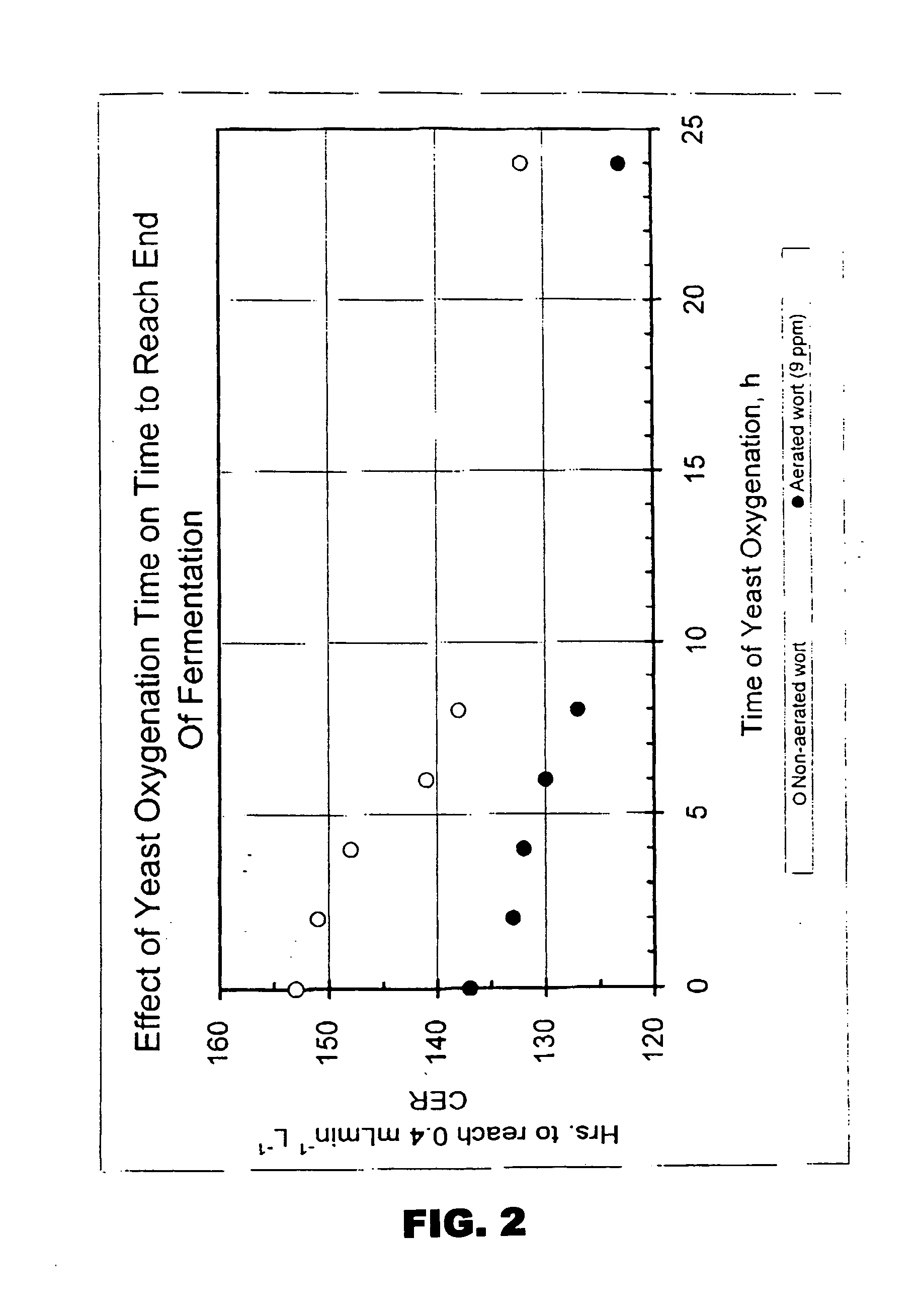
Method of oxygenating yeast slurry using hydrophobic polymer membranes
Disclosed is a an economical method of efficiently oxygenating yeast slurry without bubble formation. The method employs a membrane oxygenator comprising at least one hydrophobic, microporous membrane having a gas side and a liquid side. The yeast slurry flows over the liquid side of the membrane; oxygen is delivered to the gas side of the membrane and passes through the pores to the yeast slurry.
Owner:MILLERCOORS
Double-spiral stream guidance integrated membrane oxygenator
PendingCN107432960AIncreased diffusion areaIncrease contact areaOther blood circulation devicesMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention relates to a double-spiral stream guidance integrated membrane oxygenator, which comprises a lower cover, an oxygenation part and an upper cover, wherein a venting tube is arranged on the lower cover; the oxygenation part is arranged on the lower cover and comprises a mandrel structure, an oxygenation shell and an oxygenation silk film structure; a blood discharge tube is arranged on the oxygenation shell, and the blood discharge tube is close to the lower cover; the upper cover is arranged on the oxygenation part and is provided with a blood feeding tube and an oxygen feeding tube, wherein the mandrel structure comprises a mandrel body and an annular stream guidance plate; the mandrel body is provided with a first end and a second end; a blood passage is kept between the first end and the upper cover; the annular stream guidance plate sleeves the mandrel body; and the annular stream guidance plate is provided with at least one blood passing port and at least one spiral stream guidance groove which are distributed in an annular form. According to the double-spiral stream guidance integrated membrane oxygenator provided by the invention, by virtue of the mandrel structure, blood spread is guided by virtue of the annular stream guidance plate which is of a stream guidance structure provided with the spiral stream guidance groove, so that a contact area and a spread area of blood and a silk film structure are increased, and the utilization rate of the silk film structure is improved.
Owner:DONGGUAN KEWEI MEDICAL INSTR
Normal-temperature in-vitro heart transfer device
PendingCN112471135AAvoid damageGuaranteed fixed effectDead animal preservationPeristaltic pumpMembrane oxygenators
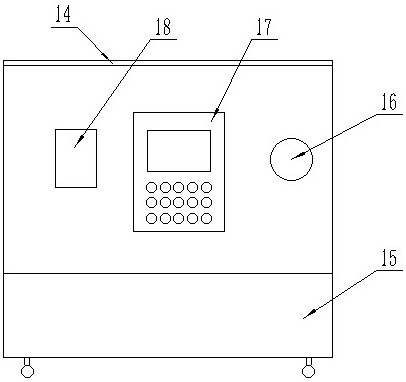
The invention relates to a normal-temperature in-vitro heart transfer device which comprises a protective shell, a first cover and a base, universal wheels are arranged at the bottom of the base, a temperature adjusting pipeline is arranged on the inner wall of the protective shell, a partition plate is arranged in the protective shell, and a heart storage device is arranged above the partition plate. The heart storage device is fixedly connected with the partition plate through a fixing rod. A peristaltic pump, a heart perfusate storage device, a temperature changer, a membrane oxygenator anda heart perfusate filter are arranged on the upper part of the base, and the heart storage device, the heart perfusate filter, the peristaltic pump, the heart perfusate storage device, the temperature changer and the membrane oxygenator are sequentially communicated through a perfusate conveying pipe. The cardiac perfusate filter is positioned on the bottom end surface of the partition plate; a buzzer, an operation panel and a control box are arranged on the front end face of the protective shell, and a second cover is arranged on the lower portion of the front end face of the protective shell.
Owner:李建朝
Apparatus for blood oxygenation
InactiveUS20050042132A1Increased oxygen levelsReduce deliveryOther blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
An apparatus and method for blood oxygenation are provided. The apparatus includes a chamber having a first inlet to receive a fluid, e.g., physiologic saline; a second inlet to receive a gas, e.g., oxygen, from a gas supply; and an outlet coupled to a capillary assembly. An atomizer nozzle coupled to the first inlet creates within the chamber fine droplets of fluid into which the gas diffuses to create a gas-supersaturated fluid, which is removed via the outlet. The removed gas-supersaturated fluid mixes with blood within a liquid-to-liquid oxygenation assembly to form oxygenated blood for delivery to a patient. Alternately, the blood may be provided by a pump to a high pressure hollow fiber or other type membrane oxygenator within which oxygen diffuses across the membrane(s) and into the blood to form oxygenated blood, again for delivery to a patient or other site.
Owner:THEROX
Membrane oxygenator with high-efficiency gas-fluid exchange
PendingCN111760107AImprove replacement efficiencyImprove hydrophilicityOther blood circulation devicesMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention provides a membrane oxygenator with high-efficiency gas-fluid exchange. The membrane oxygenator mainly comprises parts including a carbon discharge chamber, an oxygenation chamber, a temperature control chamber, a vacuum pump, a pure oxygen cylinder, a flow meter and the like. When flowing through a hollow silicone hydrogel tube placed in the carbon discharge chamber, venous blood drained from a human body permeates a tube wall to release carbon dioxide into a chamber body; a vacuum pump is utilized to apply micro-negative pressure to the carbon discharge chamber, so that the carbon dioxide is efficiently discharged; then the blood flows into a hollow silicone hydrogel spiral tube placed in the oxygenation chamber, and the pump is utilized to apply micro-positive pressure tothe oxygenation chamber, so that oxygen enters the blood efficiently and is combined with red blood cells; and the carbon discharge chamber and the oxygenation chamber are both placed in the temperature control chamber. The membrane oxygenator of the invention performs discharge of the carbon dioxide and absorption of oxygen in the blood step by step, and supplemented by a moderate negative pressure environment and positive pressure environment, the gas-fluid exchange efficiency can be effectively improved, the situation that acral necrosis of a patient is caused by using an existing oxygenator for long term to threaten life is avoided, the treatment rate is increased and sequelae are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
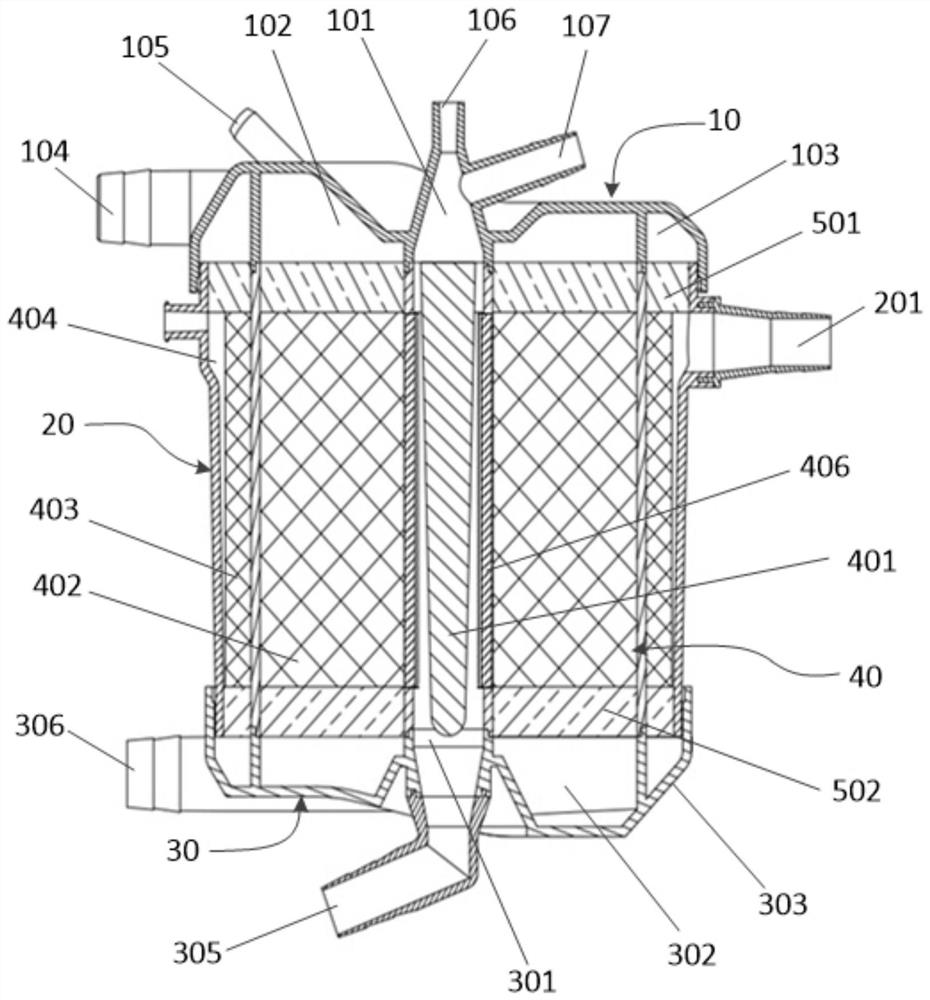
Membrane oxygenator
PendingCN113599605AImprove oxygenation efficiencyEvenly distributedOther blood circulation devicesSustainable biological treatmentMembrane oxygenatorsMedicine
The embodiment of the invention provides a membrane oxygenator. The membrane oxygenator comprises a shell, an oxygenation structure, a heat exchange structure and a first flow guide structure, wherein the oxygenation structure, the heat exchange structure and the first flow guide structure are arranged in the shell; a blood inlet channel, a blood outlet channel, an air inlet channel and an air outlet channel are formed in the shell; a through hole communicated with the blood inlet channel is formed in the first flow guide structure, and a blood outlet groove communicated with the through hole is formed in the side face of the first flow guide structure; the heat exchange structure and the oxygenation structure are sequentially arranged on the periphery of the first flow guide structure from inside to outside, and the oxygenation structure is communicated with the air inlet channel and the air outlet channel in the shell; and blood sequentially passes through the blood inlet channel, the first flow guide structure and the heat exchange structure on the shell, flows to the oxygenation structure to be oxygenated and flows out of the blood outlet channel. According to the membrane oxygenator, the first flow guide structure is arranged in the middle of the interior of the shell, the effect that the blood is evenly distributed in the oxygenator is effectively achieved, and the oxygenation efficiency of the oxygenator is high.
Owner:CHINABRIDGE (SHENZHEN) MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Life rescue box for first aid of sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients
InactiveCN101999966AEasy to operateShorten the timeFirst-aid kitsProsthesisMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses a life rescue box for first aid of sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients, which is characterized in that main components such as a blood pump, a membrane oxygenator and the like required by extracorporeal life support are assembled in the life rescue box, and the blood pump and the membrane oxygenator are fastened on an upright post in a magnetic force manner; the blood pump is provided with a first interface and a second interface, wherein the first interface is connected with a venous cannula, and the second interface is connected with the membrane oxygenator through a connecting pipe; and the membrane oxygenator is provided with a first interface and a second interface, wherein the first interface is connected with an arterial cannula, and the second interface is connected with the blood pump through a connecting pipe to form a blood circulation loop with the blood vessel of human bodies for alternatively completing the cardio-pulmonary function of the sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients. Due to small size, the life rescue box can be carried with an ambulance and an on-vehicle stretcher, is convenient to move and simple to operate, can reach the primary disease outbreak scene with medical personnel in the shortest time during first aid and can be generally used for the first aid of the sudden cardiac arrest and acute respiratory failure patients.
Owner:BEIJING KELIN BO CHONG TECH
Poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) hollow fiber alloy membrane as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113398773AStable mechanical propertiesDoes not affect gas permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesHollow fibreFiber
The invention provides a poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) hollow fiber alloy membrane as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) hollow fiber alloy membrane comprises 100 parts by weight of poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) and 0.1-50 parts by weight of a fluorine-containing polymer. The poly (4-methyl-1-pentene) hollow fiber alloy membrane provided by the invention not only has excellent mechanical strength and gas permeability, but also has excellent oleophobicity and blood compatibility, and can be used in a membrane oxygenator and an in-vitro membrane lung oxygenation system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cell circulation biological artificial liver device with oxygen supply
PendingCN110448749AImprove anaerobic stateHigh activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsArtificial liverMedical equipment
The invention discloses a cell circulation biological artificial liver device with oxygen supply, relates to the technical field of medical equipment, and solves the technical problems of improving working efficiency and liver cell activity. The artificial liver device comprises a blood introducing pipe, a blood returning pipe, a hepatocyte pump, a membrane oxygenator, a cell culture device, two-stage plasma separators and two-stage blood pumps; after the blood in the body of a patient is led out by the blood introducing pipe, the blood sequentially passes through a primary blood pump, the primary side of a primary plasma separator and the blood returning pipe, and then returns to the body of the patient; the plasma separated from the secondary side of the primary plasma separator sequentially passes through a secondary blood pump, the primary side of a secondary plasma separator and the blood returning pipe, and then returns to the body of the patient; and after matrix carrying hepatocytes in the cell culture device flows out from a liquid outlet, the matrix sequentially passes through the secondary side of the secondary plasma separator, the hepatocyte pump and the membrane oxygenator, and then returns to the cell culture device. The artificial liver device provided by the invention can realize the functions of detoxification, metabolism and synthesis of the liver.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Novel integrated membrane oxygenator
The invention relates to a novel integrated membrane oxygenator which is characterized in that a shell is provided with a horizontally-placed hollow cylindrical main body, the two ends of the main body are buckled with a front cover body and a rear cover body respectively, a blood inlet is formed in the center of the front cover body, a variable temperature cavity mandrel coaxial with the shell main body is arranged in the center of the main body, and a variable temperature membrane is arranged on the outer side of the variable temperature cavity mandrel in a surrounding mode; the outer side of the variable temperature film is sleeved with a sleeve-shaped variable temperature cavity shell, a blood circulation window is formed in the variable temperature cavity shell, and the fiber tube type oxygenation film is arranged around the outer portion of the sleeve-shaped variable temperature cavity shell; the front end of the variable temperature cavity mandrel is provided with a blood inlet which is coaxial with the blood inlet and communicated with the blood inlet, and the variable temperature cavity mandrel is sequentially provided with a two-way shunting part, a spiral pressure reduction part, a blood storage part and a mandrel rear end backwards along the blood inlet at the front end. The oxygenation and temperature changing efficiency is improved.
Owner:山东威高拓威医疗器械有限公司
Introduced in adsorption filter for inhaled halogenated anesthetics for cardiopulmonary circulation bypass
ActiveUS9861927B2Avoid pollutionReduce pollutantsGas treatmentDispersed particle separationActivated carbonMembrane oxygenators
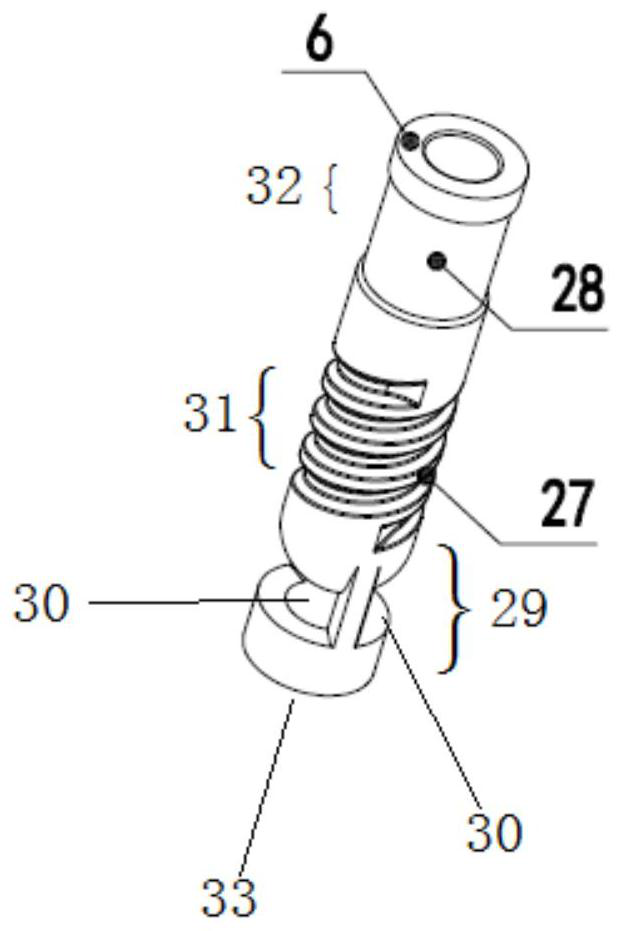
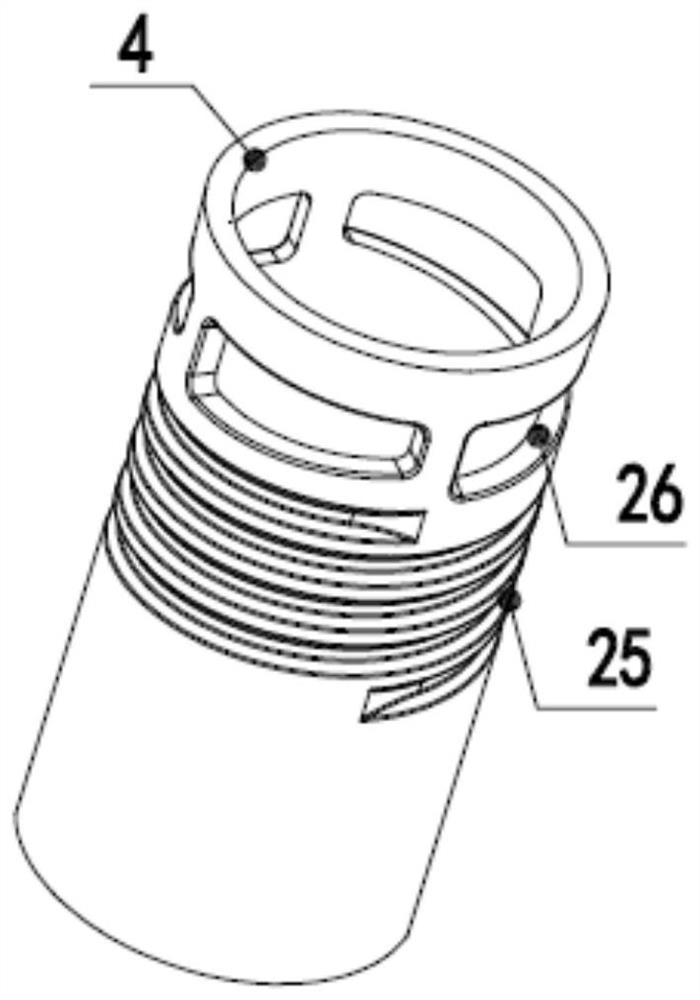
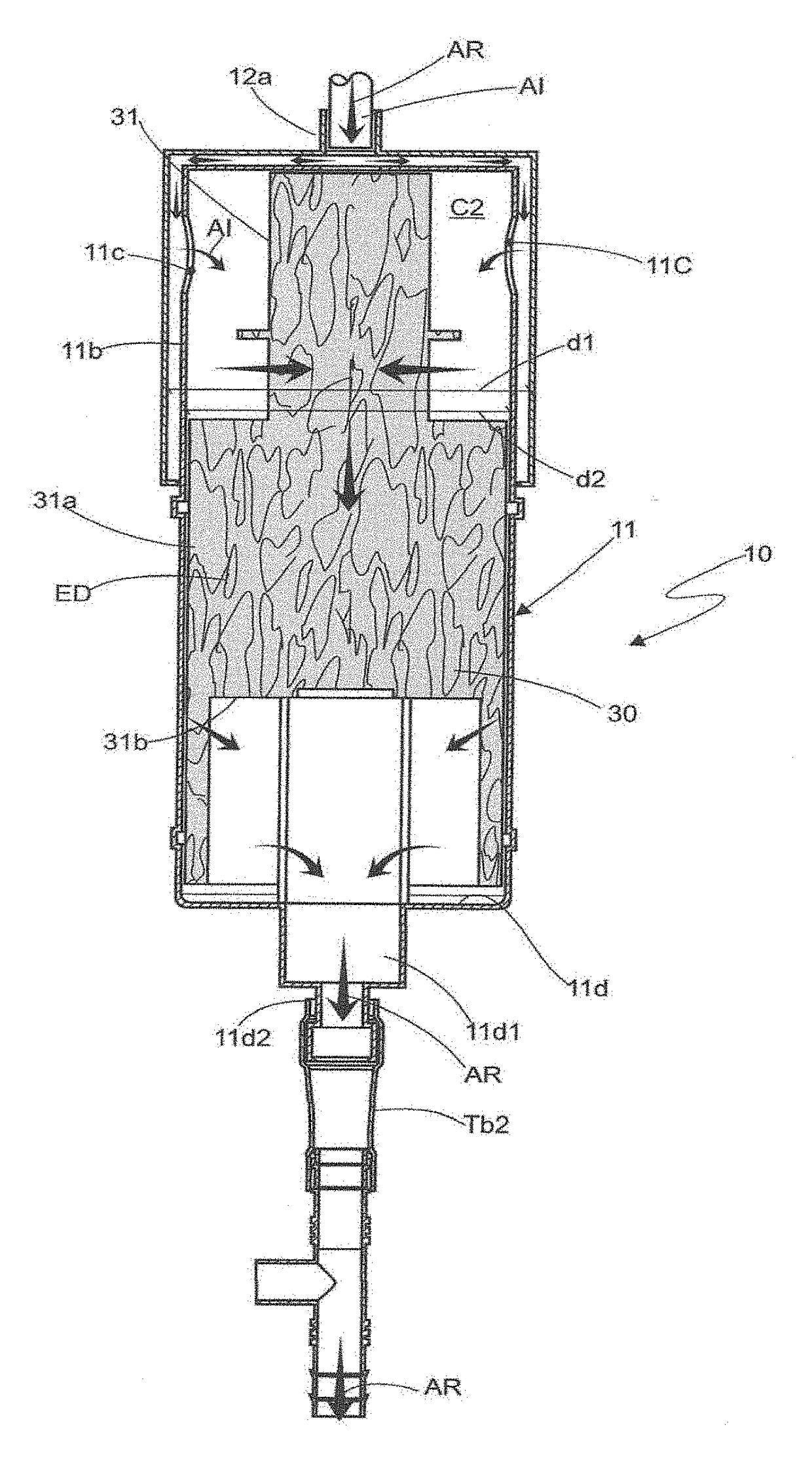
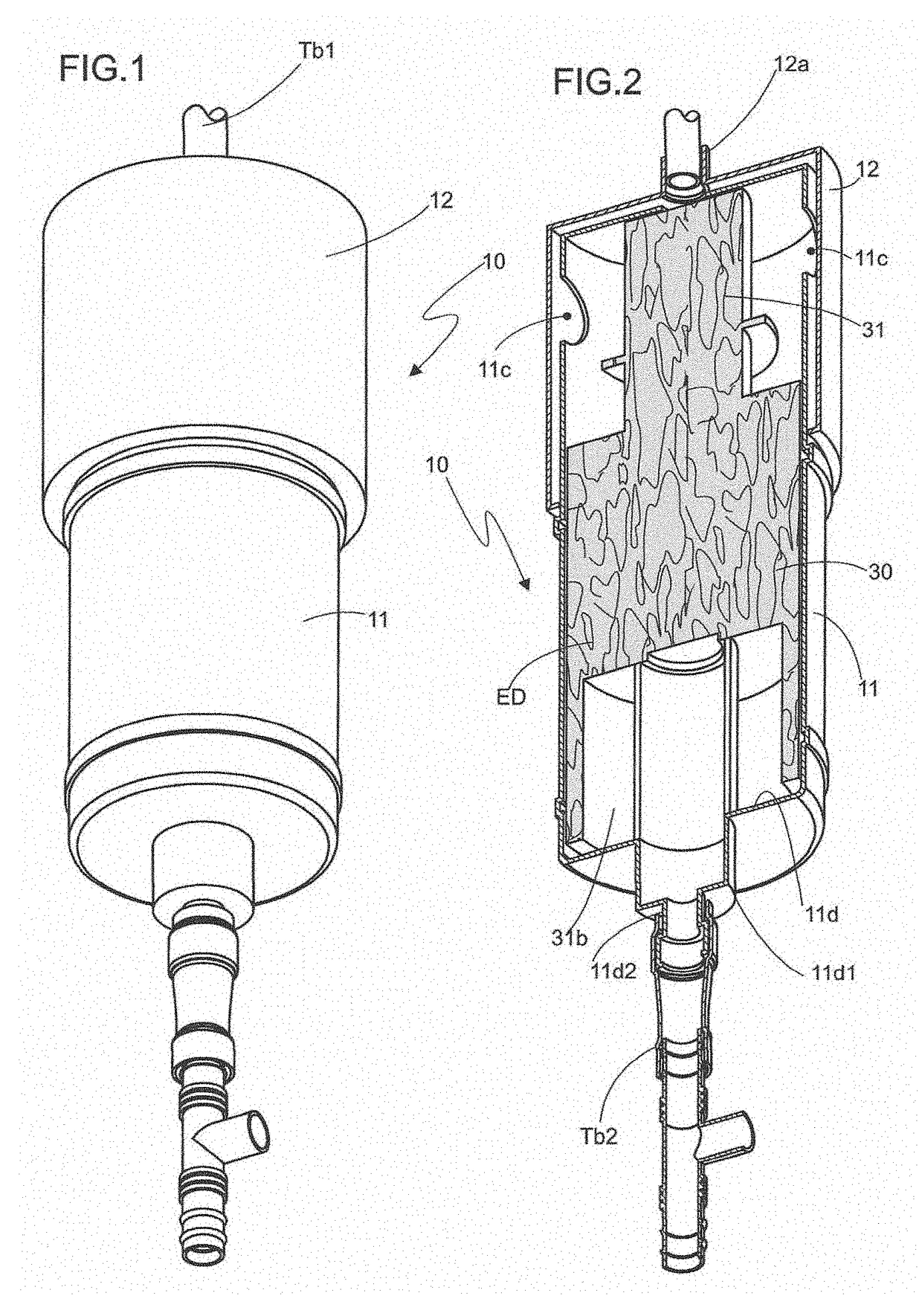
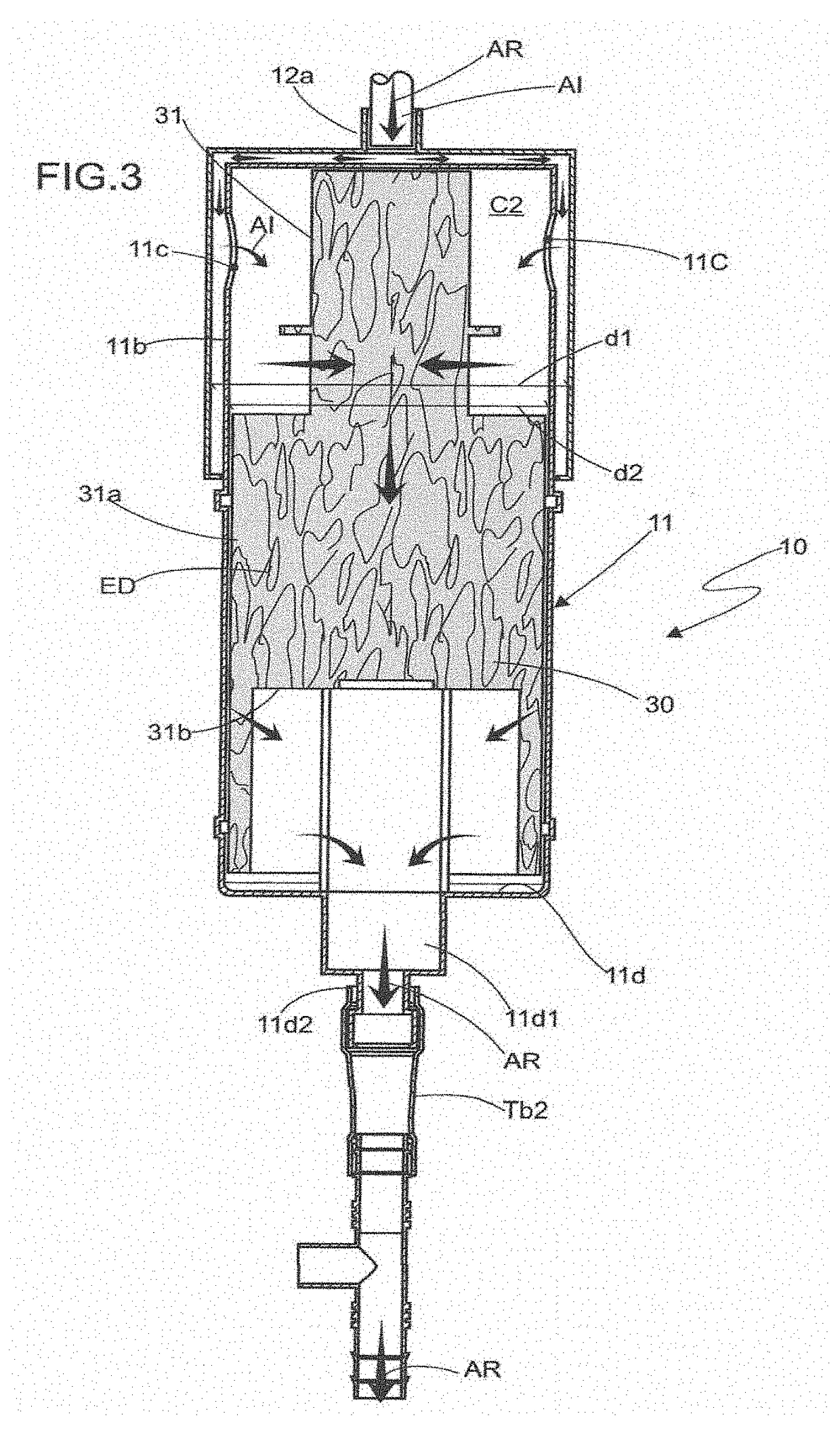
Improvements introduced in adsorption filter for inhaled halogenated anesthetics for cardiopulmonary bypass. It relates to an adsorption filter (10) of the type pertaining to the field of medical devices, more specifically, used to adsorb inhaled halogenated anesthetics that are eliminated through the output of the membrane oxygenators (20) of the cardiopulmonary bypass circuit (CPB); said filter (10) contains a hollow reservoir (11) for preservation of adsorber elements (ED) of the activated charcoal type (30), said reservoir (11) being of tubular cylindrical form, and it receives on one of the free extremities (11a) a cover (12) whose internal diameter (d1) is greater than the external diameter (d2) of the cylindrical reservoir (11), so as to produce an access chamber (C1) for the input of the inhaled anesthetic (AI) that, in turn, penetrates through a tubular member (12a) in the central portion of the cover (12), where a tube (Tb1) for connection with the oxygenator device (20) is installed.
Owner:COPEEN TREINAMENTO E CONSULTORIA EM ANESTESIA EIRELI
Extracorporeal circulation machine remaining blood reinfusion device and reinfusion method
InactiveCN108245727ARaise hemoglobin levelsLess blood transfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationVein
An extracorporeal circulation machine remaining blood reinfusion device comprises a venous cannula, a venous blood return chamber, a power pump, a membrane oxygenator, a fine thrombus filter, a main artery cannula and a blood recovering machine, wherein the venous cannula, the venous blood return chamber, the power pump, the membrane oxygenator and the fine thrombus filter are sequentially connected through extracorporeal circulation pipelines, and the blood recovering machine is connected with the main artery cannula. The main artery cannula is connected with the blood recovering machine through a pressure lengthening pipe, and normal saline is connected with an inputting opening of venous blood return chamber. The device has the advantages that the device can ensure that the extracorporeal circulation pipelines are always in state capable of transferring at any time after extracorporeal circulation is completed, blood in the pipelines is timely recovered and reinfused into the body of a patient, and the machine blood reinfusion method is safe, effect and economical and saves blood resources.
Owner:柴琳
Method for adjusting dissolved gases in boiler feed water
InactiveCN105417609AAvoid easy cloggingReduce pollutionLiquid degasificationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiberSolubility
The invention discloses a method for adjusting dissolved gases in boiler feed water. The steam of a boiler forms condensed water after the work of a steam turbine; the condensed water flows out of a condenser and enters a polishing apparatus through a condensed water pump; the condensed water is subjected to degassing or oxygenation treatment by a membrane degasser or membrane oxygenator, wherein the membrane degasser is connected with a vacuum pump, and the membrane oxygenator is connected with an oxygen bottle; the treated water enters the boiler through a low-pressure heater, a water feed pump and a high-pressure heater; and the membrane degasser and the membrane oxygenator are fiber membrane contactors. According to the adjusting method, a fiber membrane is adopted as a gas-liquid exchange interface; according to different water qualities, membrane degassing treatment is carried out in AVT (all-volatile treatment) working condition, and membrane oxygenation treatment is carried out in OT (oxygenated treatment) working condition; and the gas content of the boiler feed water can be quickly and accurately adjusted, the flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) is avoided, and the operation safety of the unit is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
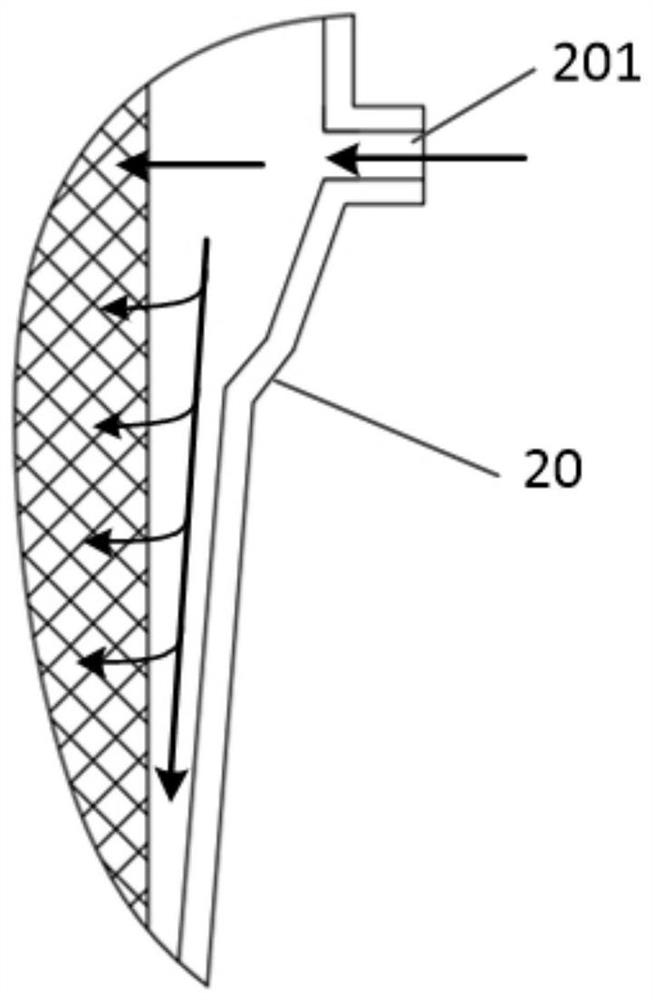
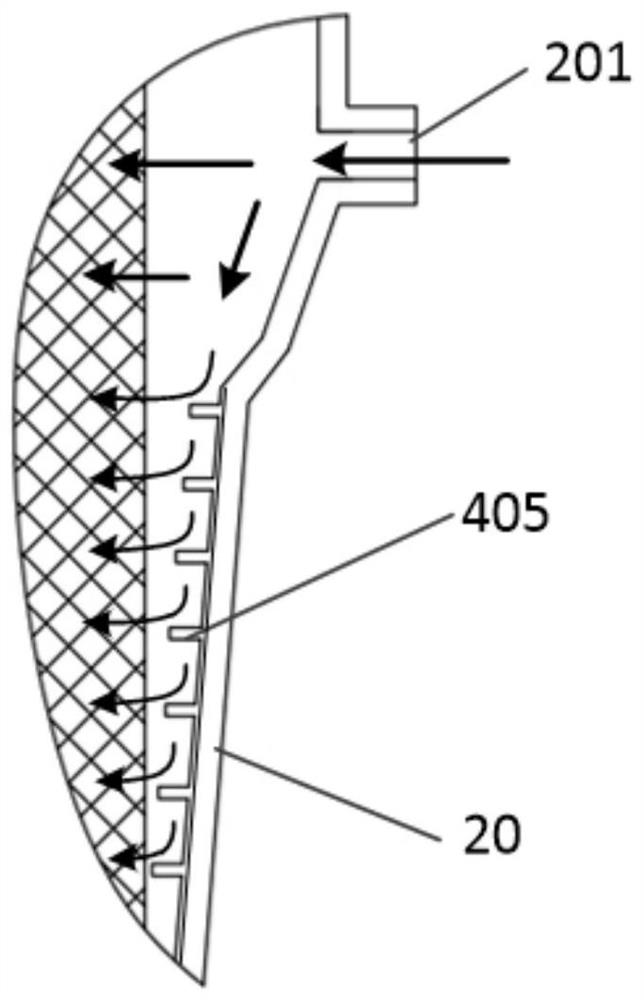
Membrane oxygenator
ActiveCN112546321AUniform distribution of flow fieldThe flow rate is kept constantOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
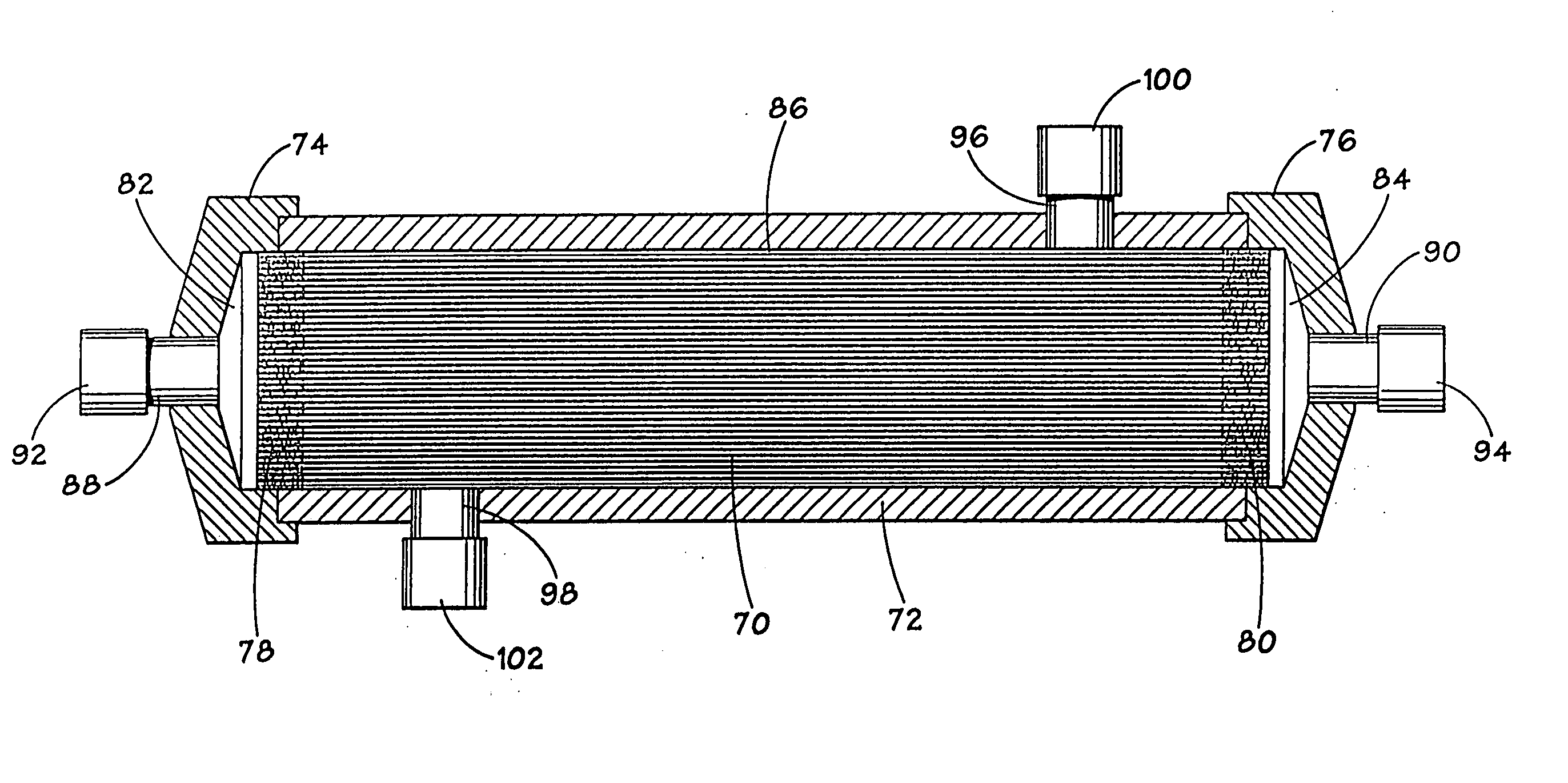
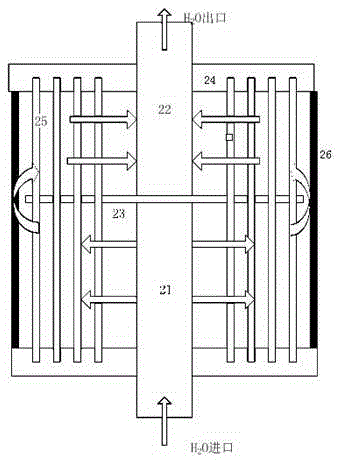
The invention relates to a membrane oxygenator. The membrane oxygenator comprises a cavity, a blood inlet and a blood outlet, wherein the blood inlet and the blood outlet are formed in two ends of thecavity; the cavity comprises a diffusion section, an oxygenation section, a gathering section and an observation section which sequentially communicate; the front end of the diffusion section is connected with the blood inlet; an oxygen inlet is formed in the upper part of the oxygenation section, a gas outlet is formed in the lower part of the oxygenation section, the oxygenation section is divided into a plurality of flow guide channels by a plurality of flow guide partition pieces in the cavity, and hollow oxygenation wires arranged in an array mode are arranged in the flow guide channels;and a flexible single-end free piece is connected to the tail part of each flow guide partition piece, and is located in the observation section, and the tail end of the observation section is connected with the blood outlet. In the process that blood passes through the oxygenator cavity in the radial direction, due to the fact that the first-order derivative of a flowing space sectional area iscontinuous and the second-order derivative of the flowing space sectional area is zero, a blood flow field is evenly distributed, and vortexes and dead zones are not generated.
Owner:成都市赛恒尔医疗科技有限公司
Membrane oxygenator with built-in filter
ActiveCN113499496AIncrease oxygenationImprove filtering effectOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses an membrane oxygenator with a built-in filter. The membrane oxygenator comprises an upper cover, a lower cover, a shell and an oxygenation structure, the two ends of the shell are connected with the upper cover and the lower cover respectively, the oxygenation structure is arranged in the shell, and the oxygenation structure sequentially comprises a mandrel, a filter screen, an oxygen pressure membrane and a temperature changing membrane from the center to the outside. Blood flows in from a blood inlet in the upper side of the membrane type oxygenator, sequentially transversely penetrates through a variable-temperature membrane, the oxygen pressure membrane and the filter screen and then flows out from the blood outlet in the lower portion of the mandrel, in the process that the blood transversely passes through the variable-temperature membrane, the oxygen pressure membrane and the filter screen, the flow speed of the blood is gradually decreased, the blood makes full contact with the oxygen pressure membrane and the filter screen, and the oxygenation effect and the filtering effect of the membrane type oxygenator can be improved.
Owner:JIANGSU STMED TECH CO LTD
Membrane oxygenator homing state recognition platform
InactiveCN111839958AEffective monitoringCompact structureImage enhancementImage analysisPatient roomMembrane oxygenators
The invention relates to a membrane oxygenator homing state recognition platform, and the platform comprises a treatment vehicle body which is located in a treatment ward of a gas exchanger, is disposed at one side of a sickbed of a patient needing the treatment of the gas exchanger, and is used for placing all parts of the gas exchanger; a manual brake arranged on a base of the treatment vehiclebody and used for locking the treatment vehicle body under manual operation so as to prevent the treatment vehicle body from sliding; a signal capturing mechanism located on the roof of the treatmentward of the gas exchanger and used for capturing image signals of the environment where the treatment vehicle body is located so as to obtain corresponding images around the vehicle body. The membraneoxygenator homing state recognition platform is effective in monitoring and compact in structure. Due to the fact that whether the membrane oxygenator is normally located on the treatment vehicle body where all components of the gas exchanger are placed or not can be monitored in real time in the process that the gas exchanger is used for treating a patient, on-site alarming is executed when themembrane oxygenator does not normally return to the original position.
Owner:方勤
ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) closed pre-flushing equipment
PendingCN110141704AEfficient implementationDifficult to enterOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, and discloses ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) closed pre-flushing equipment. The equipment comprises an ECMO device and a preciseinfusion kit communicating with the ECMO device, wherein the ECMO device comprises an ECMO machine, a centrifugal pump, a membrane oxygenator, a drainage tube from the membrane oxygenator outlet end to the centrifugal pump inlet end, a drainage tube from the centrifugal pump outlet end to the membrane oxygenator inlet end, and two interfaces on the drainage tube from the membrane oxygenator outletend to the centrifugal pump inlet end, the precise infusion kit comprises a backflow bag and a pre-flushing bag, the pre-flushing bag communicates with the backflow bag through a channel, the channelis provided with a filter head and a one-way check valve, and ECMO pre-flushing tubes connected with the two interfaces are respectively arranged at the lower parts of the pre-flushing bag and the backflow bag. According to the invention, pre-flushing liquid bubbles in the tubes are destroyed through the filter head, and the pre-flushing liquid passes through the one-way check valve and then performs circulating pre-flushing so as to realize the pipeline pre-flushing of the ECMO device. The equipment replaces air and bubbles in the pipeline, saves time, reduces the pollution, achieves thorough pre-flushing, ensures the effective implementation of ECMO, and fights for the time for rescuing patients.
Owner:赣南医学院第一附属医院
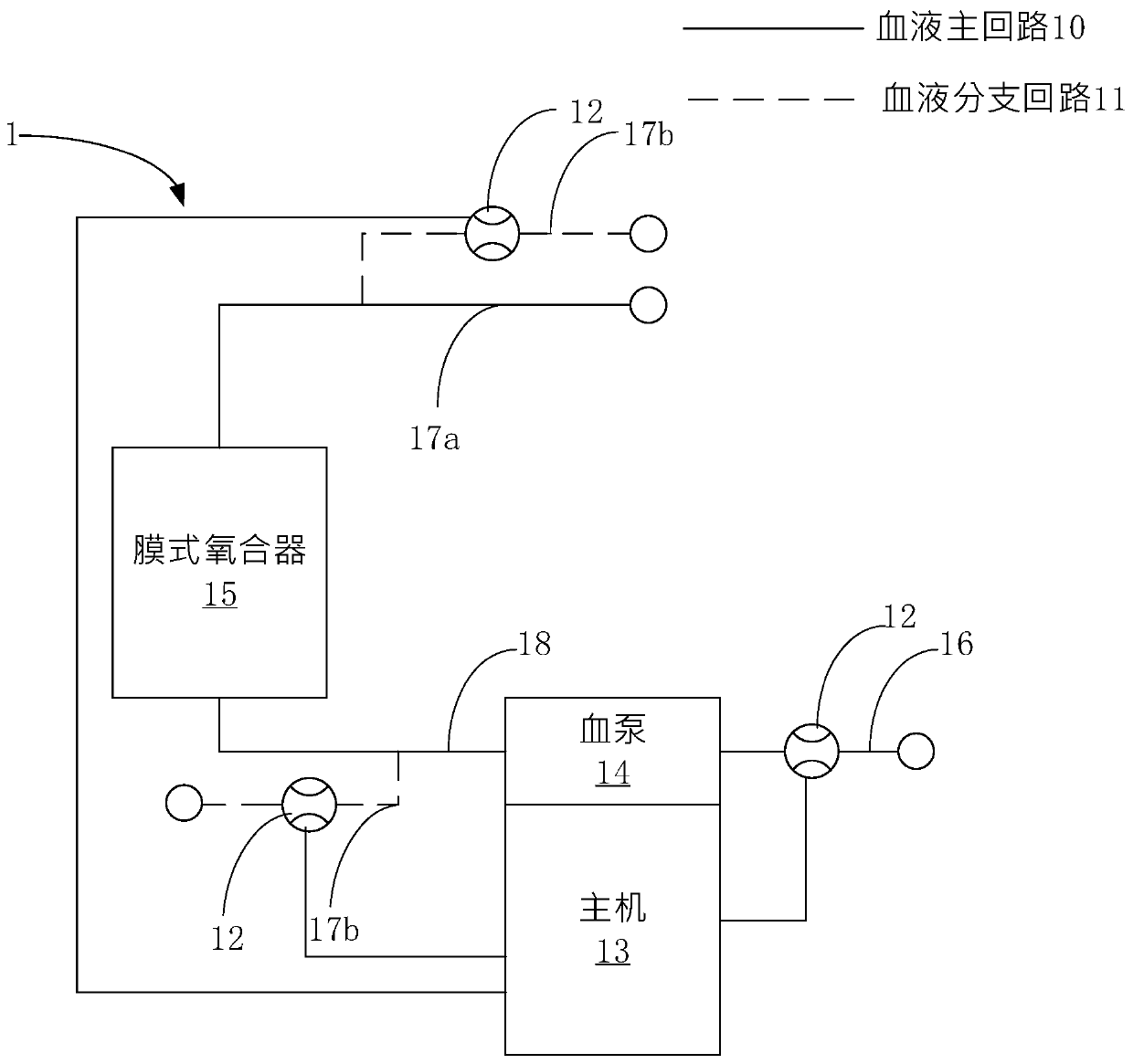
ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) system
PendingCN110538353AAccurate control of blood statusImprove securityOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses an ECMO (extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) system. The system comprises a host, a blood pump, a membrane oxygenator, a blood input pipeline, a blood transport pipeline, a main blood output pipeline, a blood output pipeline and multiple flowmeters, wherein the blood pump is connected with the host, the blood input pipeline is connected with a blood pump input end of the blood pump, the blood transport pipeline is connected with a blood pump output end of the blood pump and an oxygenator input end of the membrane oxygenator, the main blood output pipeline is connectedwith an oxygenator output end of the membrane oxygenator, the blood output pipeline is connected with the main blood output pipeline or / and blood transport pipeline, and the multiple flowmeters are arranged on the blood input pipeline and the blood output pipeline respectively. The flowmeters are arranged on the blood input pipeline and the blood output pipeline of the ECMO system, the host timelymonitors the blood state in the blood input pipeline and the blood output pipeline through the multiple flowmeters, and the safety of the medical process is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU STMED TECH CO LTD
Endovenous oxygen transporting device and oxygen transporting method
InactiveCN106237428AEffective control of oxygen flowImprove oxygenation efficiencyInfusion devicesMedical devicesVeinMembrane oxygenators
The invention discloses an endovenous oxygen transporting device and an oxygen transporting method. The oxygen transporting device comprises a vein oxygen catheter which is inserted in a vein, and a control device which is connected to the end, extending out the vein, of the vein oxygen catheter, wherein by virtue of the control device, an oxygen concentration supplied into the vein oxygen catheter can be precisely controlled. Oxygen is transported to the vein by virtue of the vein oxygen catheter which is inserted in the vein, and the oxygen, bypassing alveolus pulmonis having diffusion dysfunction, directly enters blood and oxygenates with hemoglobin, so as to better replace a lung in the case that lung failure occurs or an oxygenating effect cannot be developed temporarily; in comparison with a membrane oxygenator, an oxygen-carrying substitute or a liquid oxygen filling method, the device is simple in structure, convenient to use and capable of preventing in vitro drainage of the blood, so that various possible infections are avoided; and the device is high in blood-carrying-oxygen content and relatively good in stability.
Owner:ANHUI TONGLING BIONIC TECH CO LTD
Long-acting membrane oxygenator hollow fiber anticoagulation coating for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and preparation method
ActiveCN111760077AWill not cause blockageAchieve full coverage coatingPharmaceutical containersDialysis systemsHollow fibreFiber
The invention discloses a long-acting membrane oxygenator hollow fiber anticoagulation coating for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and a preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing PMP, a diluent and a macromolecular additive for coating preparation, heating to 200-300 DEG C in a protective gas atmosphere, stirring for 4-8 hours to form a homogeneous solution, and carrying out vacuum degassing; and (2) extruding the product obtained in the step (1) by an extruder, preparing hollow fibers while passing through a coagulating bath, extracting, and curing at30-60 DEG C. The coating macromolecular additive used in the invention is a triblock polymer obtained by free radical polymerization; then the triblock polymer is blended with a PMP polymer and a diluents, and the mixture is melted to obtain a high-temperature melt, then a thermally induced phase separation method is adopted to prepare hollow fiber evenly covered with a layer of coating with highstability on the surface, and the coating has long-acting anticoagulation performance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Oxygenation device and oxygenation method for intravenous cavity
ActiveCN106215262BNo drainageImprove stabilityDialysis systemsMedical devicesMembrane oxygenatorsMembrane oxygenator
The invention discloses a venous lumen oxygenation device and an oxygenation method. The venous lumen oxygenation device comprises a venous oxygenation tube inserting in a vein vascular and a control device connected with one end, extending out of the vein vascular, of the venous oxygenation tube, the control device is used for accurately controlling oxygen flow rate fed into the venous oxygenation tube, the longitudinal section of the venous oxygenation tube is divided into a venous oxygen catheter, an oxygenation channel and an output tube through a side wall with a nanoscale hole and a semipermeable membrane, oxygen is transferred to the venous vascular through the venous oxygen catheter and bypasses pulmonary alveoli with diffusion impairment to directly enter blood to be oxygenated with hemoglobin, and the lung can be best replaced under the condition of lung failure or an oxygenation function cannot temporarily displayed. Compared with a membrane oxygenator, oxygen carrying substitutes or liquid oxygen filling methods, the venous lumen oxygenation device has the advantages of simpleness in structure, convenience in use and no need to drain the blood in vitro, various possible infection is avoided, oxygen carrying content is high in the blood, and good stability is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI TONGLING BIONIC TECH CO LTD
Closed and pre-charge feedback type extracorporeal circulation pipeline for rats
PendingCN109771721AShorten the lengthLarge venous drainageOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsExtracorporeal circulationVein
The invention discloses a closed and pre-charge feedback type extracorporeal circulation pipeline for rats, which belongs to the technical field of experimental auxiliary equipment. The technical scheme is that the closed and pre-charge feedback type extracorporeal circulation pipeline for the rats is characterized by comprising a venous drainage tube, a blood storage chamber, a rolling pump connecting tube, a heat exchanger, a membrane oxygenator and an arterial draft tube. One end of the venous drainage tube is used for connecting veins of the rats, the other end is connected with the bloodstorage chamber; the blood storage chamber is connected with a blood inlet of the heat exchanger through the rolling pump connecting tube; the rolling pump connecting tube is externally connected witha rolling pump; a blood outlet of the heat exchanger is connected with a blood inlet of the membrane oxygenator through a butt tube, and a blood outlet of the membrane oxygenator is connected with the artery puncture needle of the rats through the artery draft tube, and therefore the closed and pre-charge feedback type extracorporeal circulation pipeline for the rats has the advantages that the external circulation tube is closed, and the situations are avoided that venous drainage is insufficient, and the blood storage chamber and other pipelines are easy to intake air, the overall pre-charge of the pipeline, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Long-acting membrane oxygenator hollow fiber anticoagulant coating for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ecmo) and preparation method
ActiveCN111760077BWill not cause blockageAchieve full coverage coatingPharmaceutical containersDialysis systemsHollow fibreFiber
The invention discloses a long-acting membrane oxygenator hollow fiber anticoagulation coating for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) and a preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing PMP, a diluent and a macromolecular additive for coating preparation, heating to 200-300 DEG C in a protective gas atmosphere, stirring for 4-8 hours to form a homogeneous solution, and carrying out vacuum degassing; and (2) extruding the product obtained in the step (1) by an extruder, preparing hollow fibers while passing through a coagulating bath, extracting, and curing at30-60 DEG C. The coating macromolecular additive used in the invention is a triblock polymer obtained by free radical polymerization; then the triblock polymer is blended with a PMP polymer and a diluents, and the mixture is melted to obtain a high-temperature melt, then a thermally induced phase separation method is adopted to prepare hollow fiber evenly covered with a layer of coating with highstability on the surface, and the coating has long-acting anticoagulation performance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com