Patents
Literature
54 results about "Blood withdrawal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Withdrawing Blood. Blood samples for laboratory testing may be obtained in several ways. The most common procedure is venipuncture, withdrawl of blood from a vein using a needle and collecting tube, which contains various additives, A tourniquet is wrapped around the arm above the venipuncture site, which causes blood to accumulate in the vein.
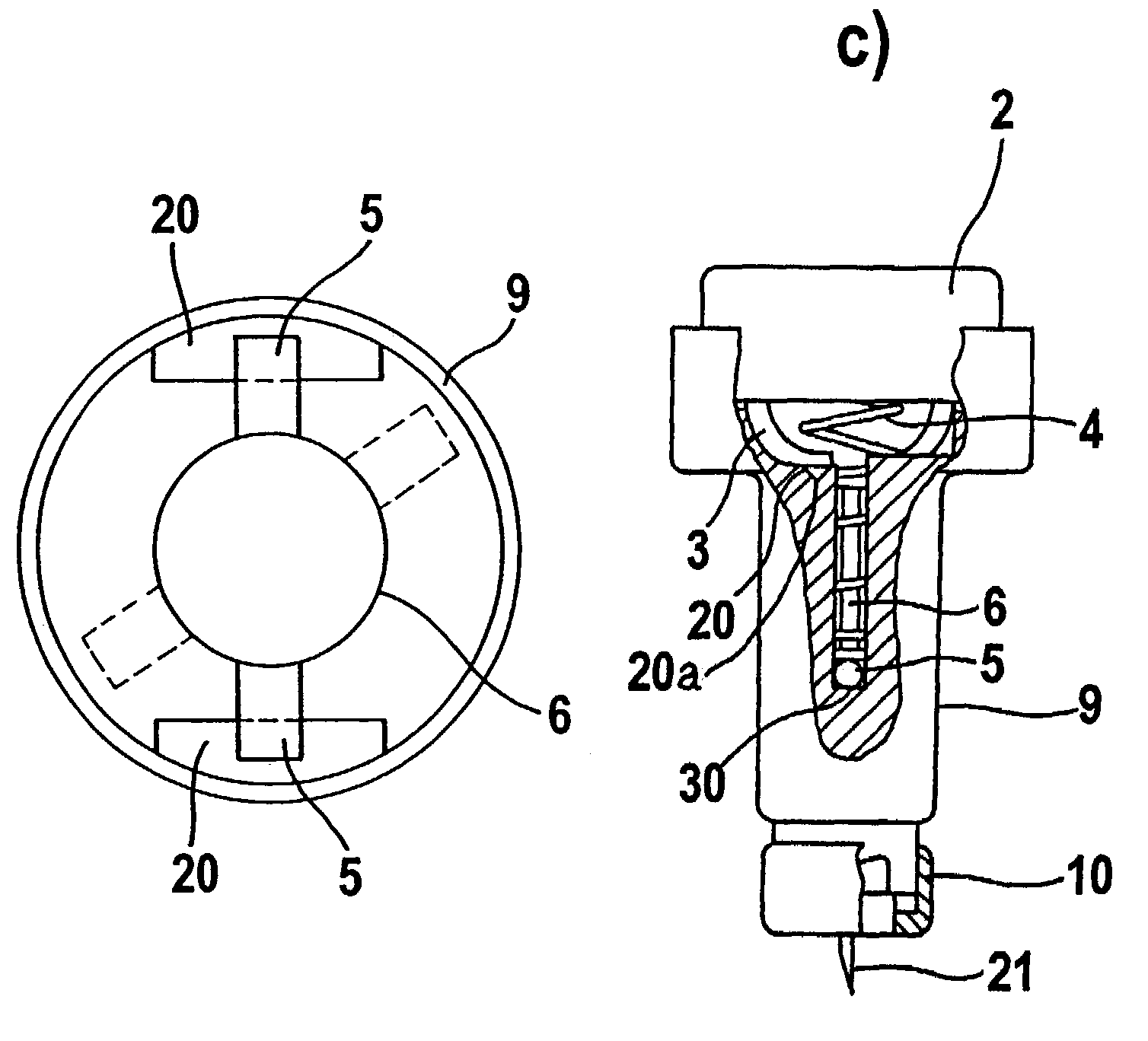
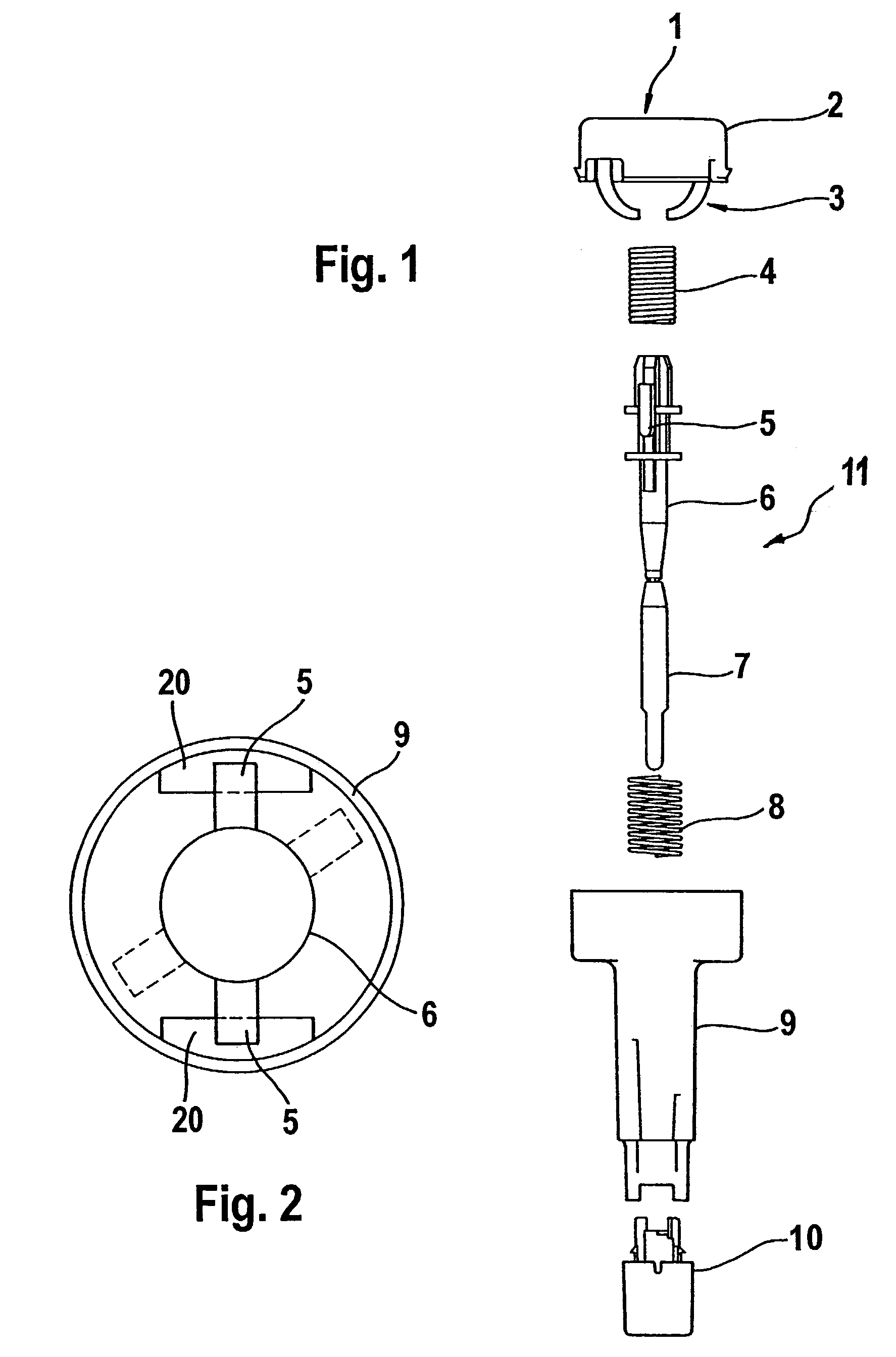
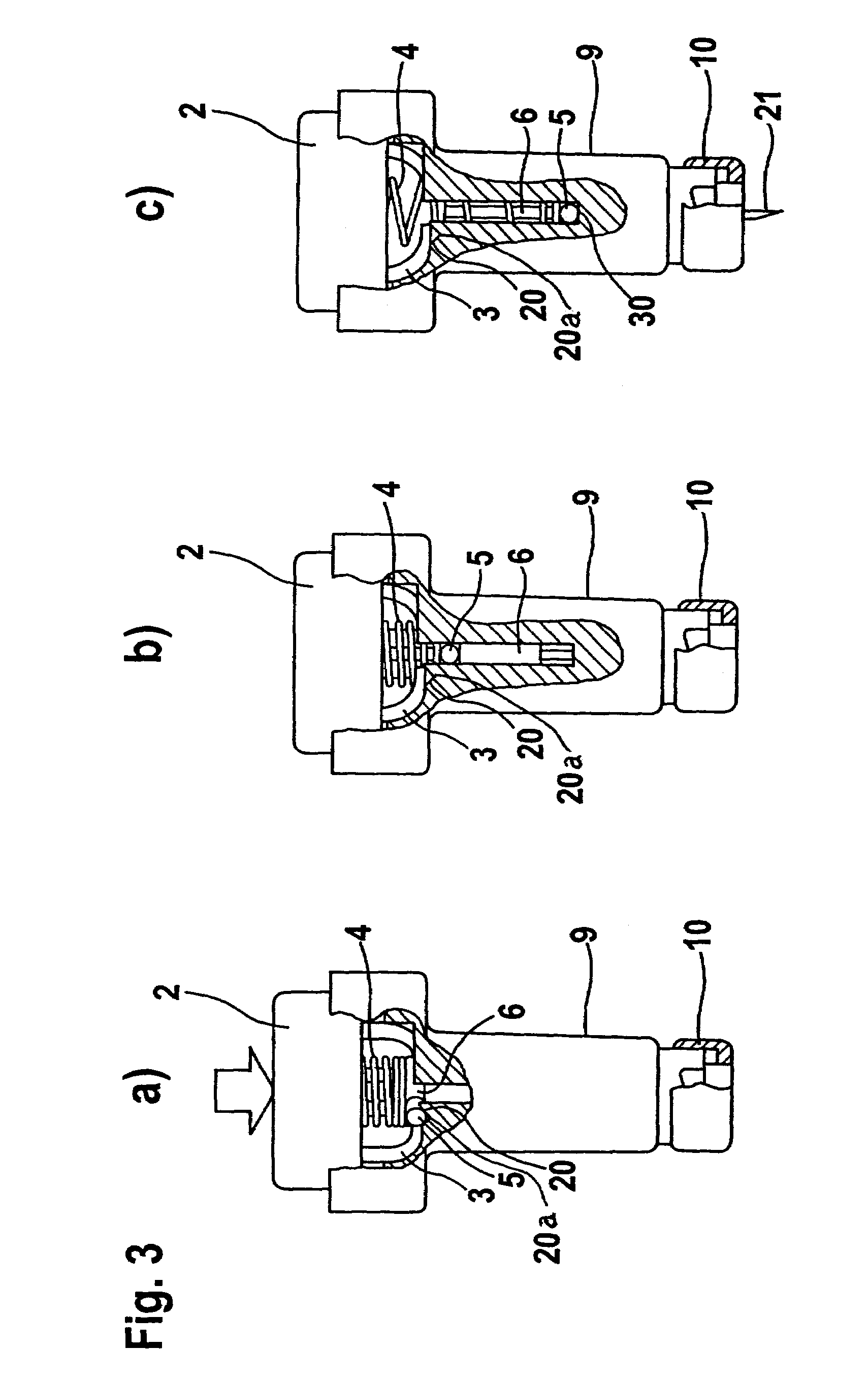
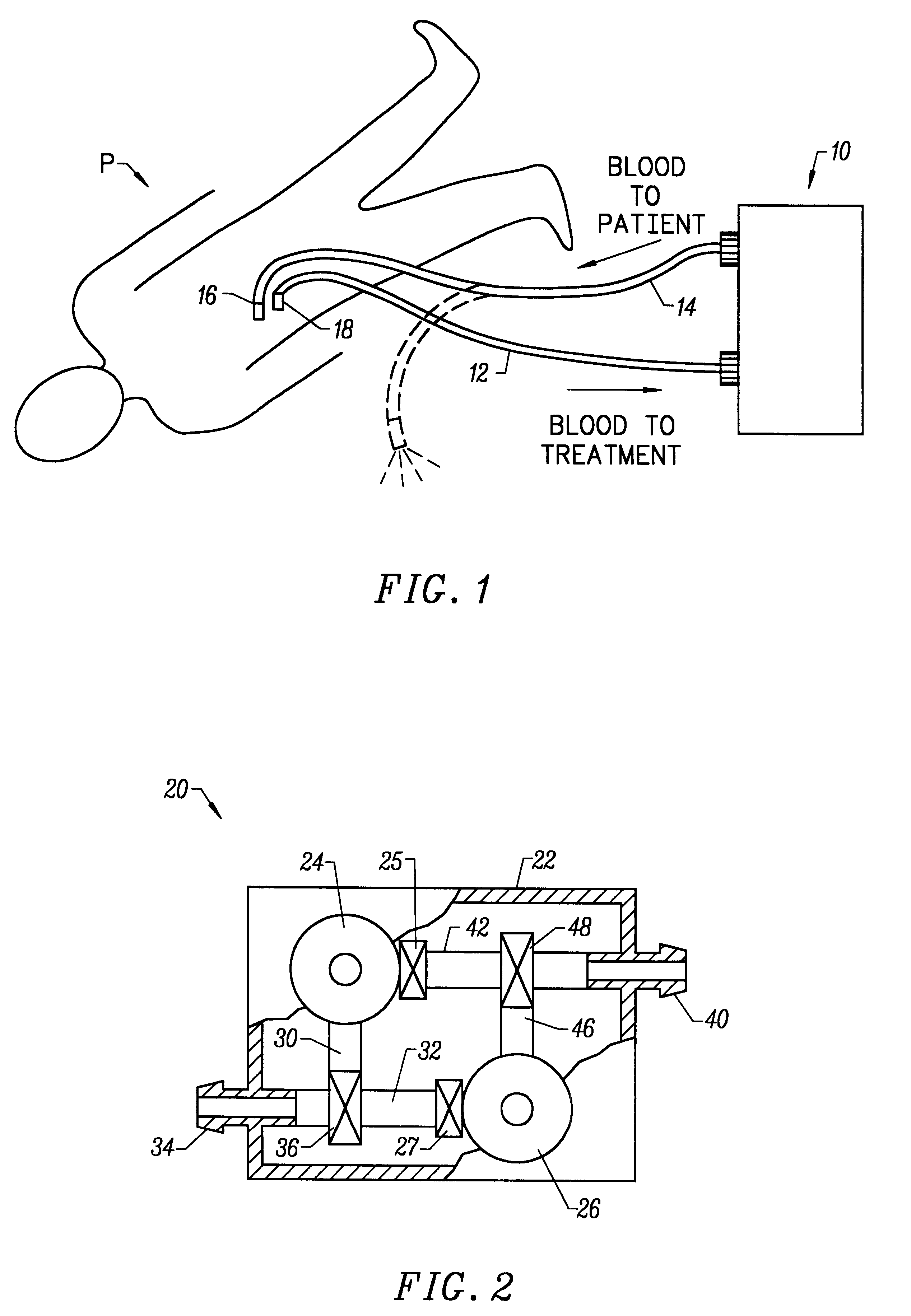
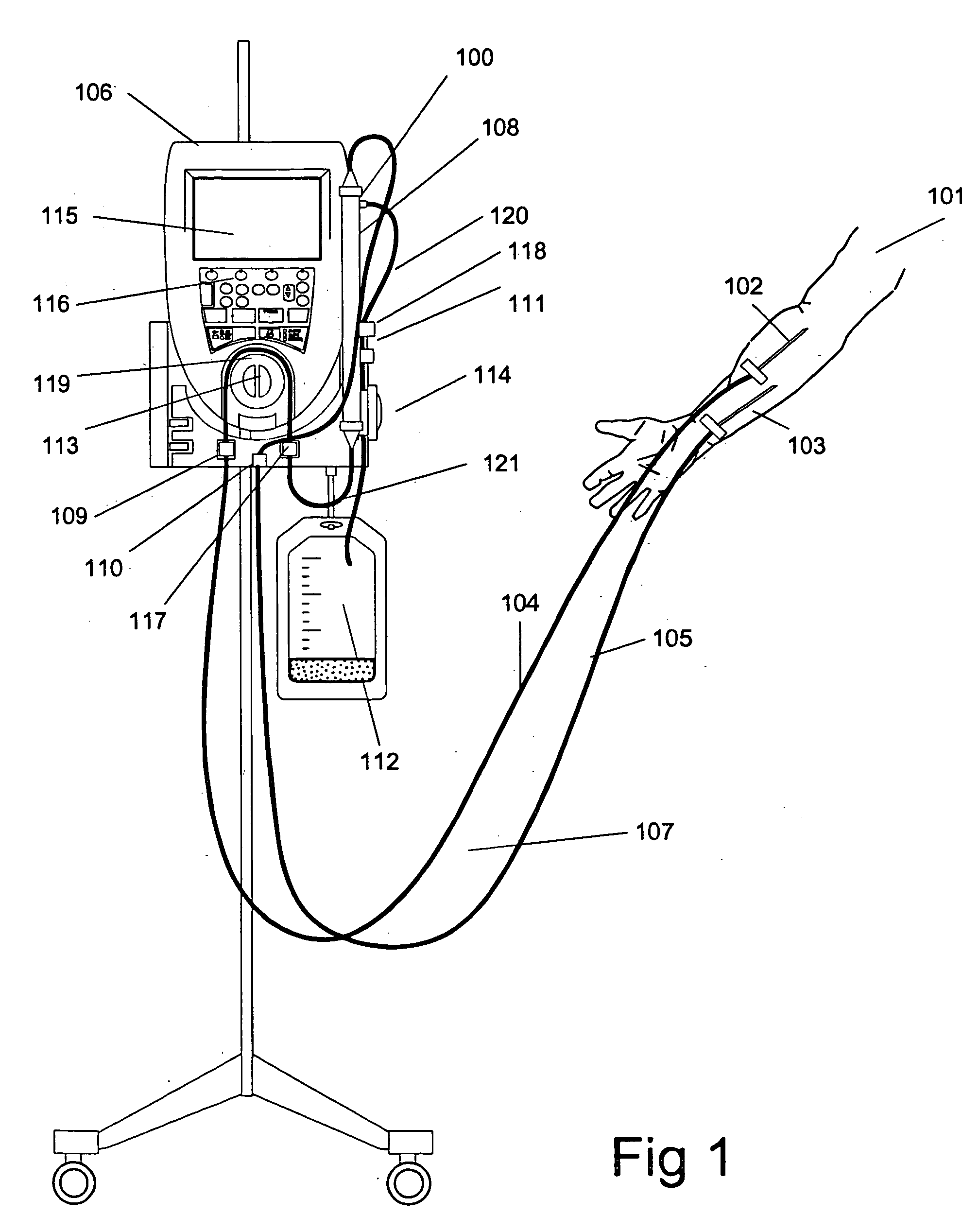
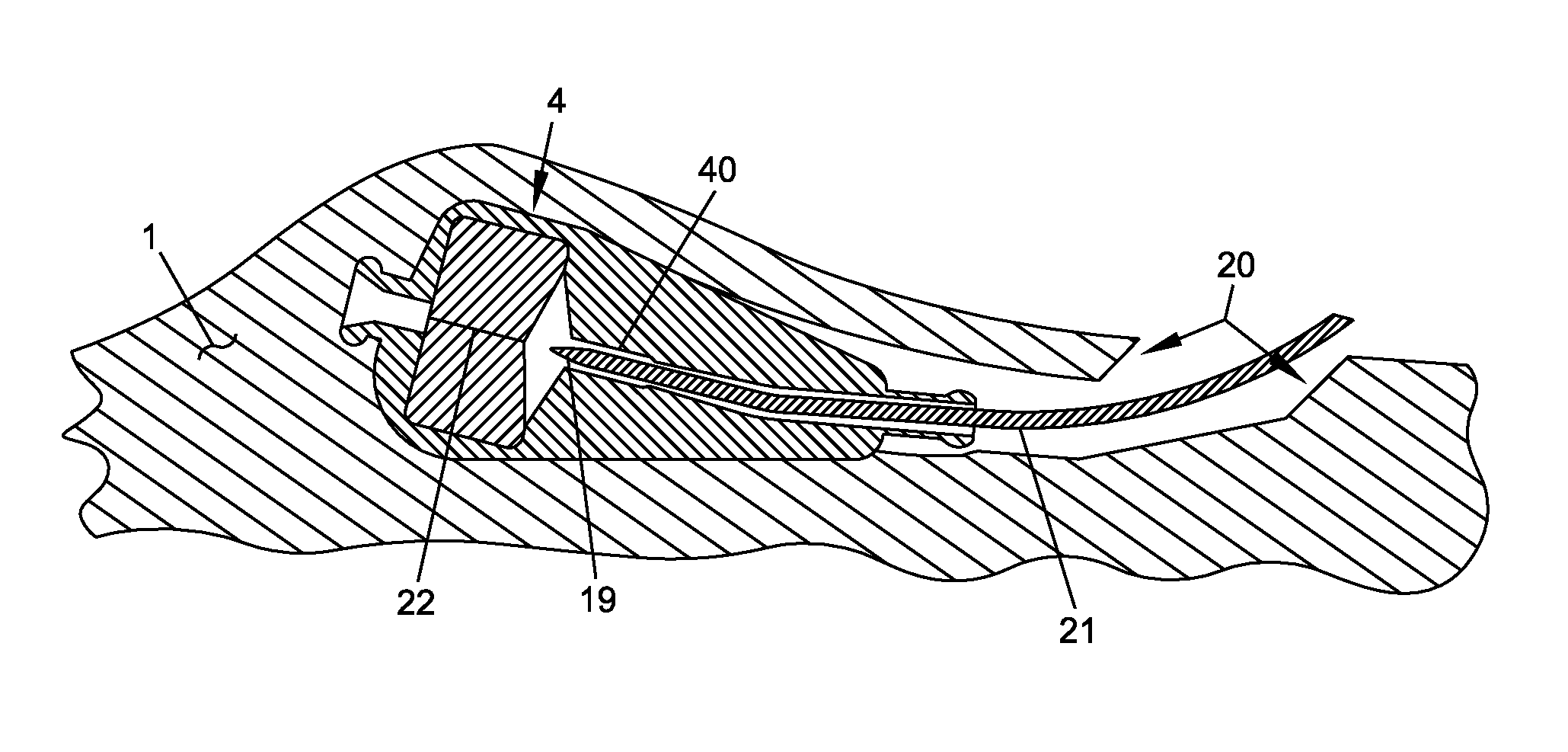
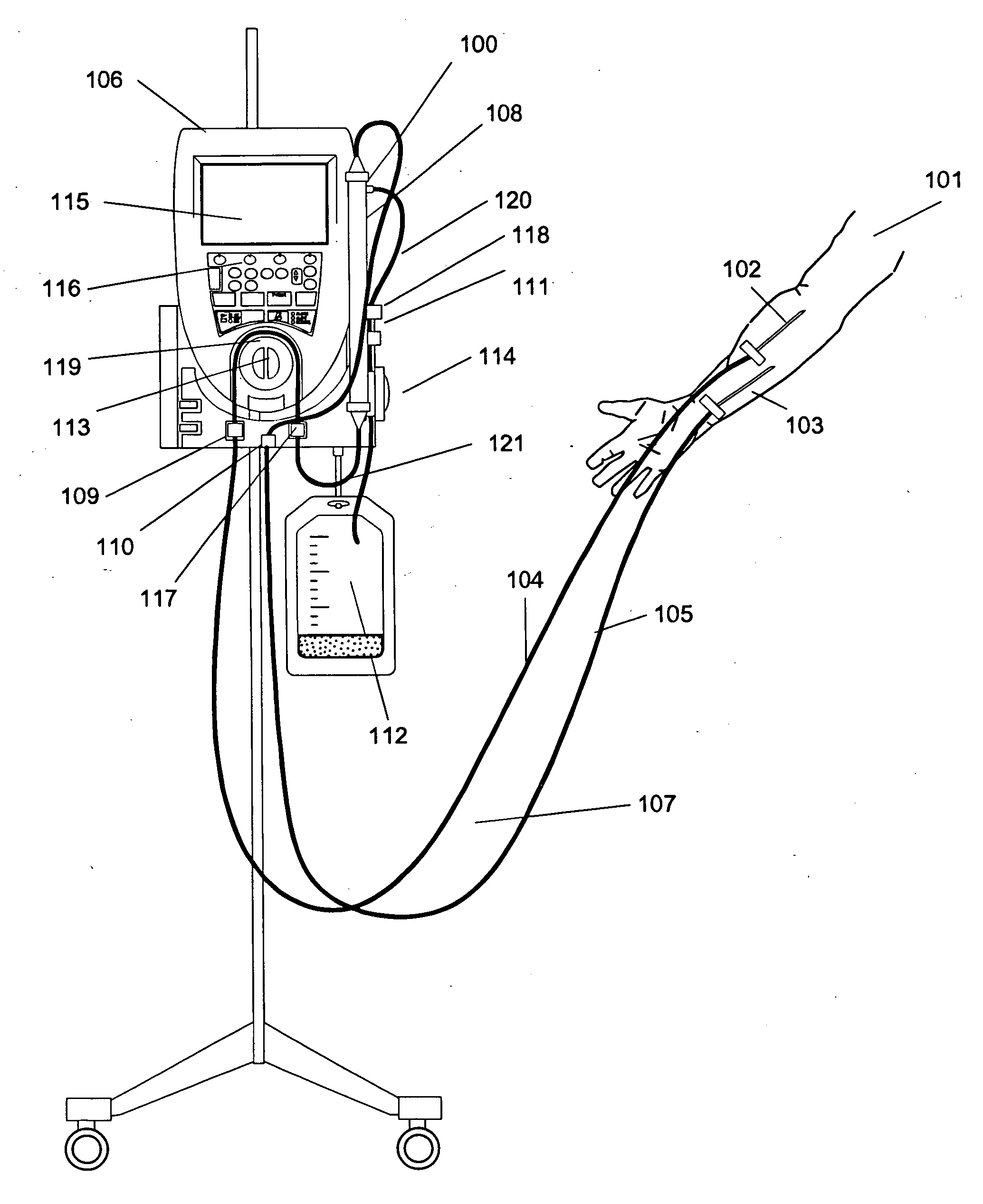
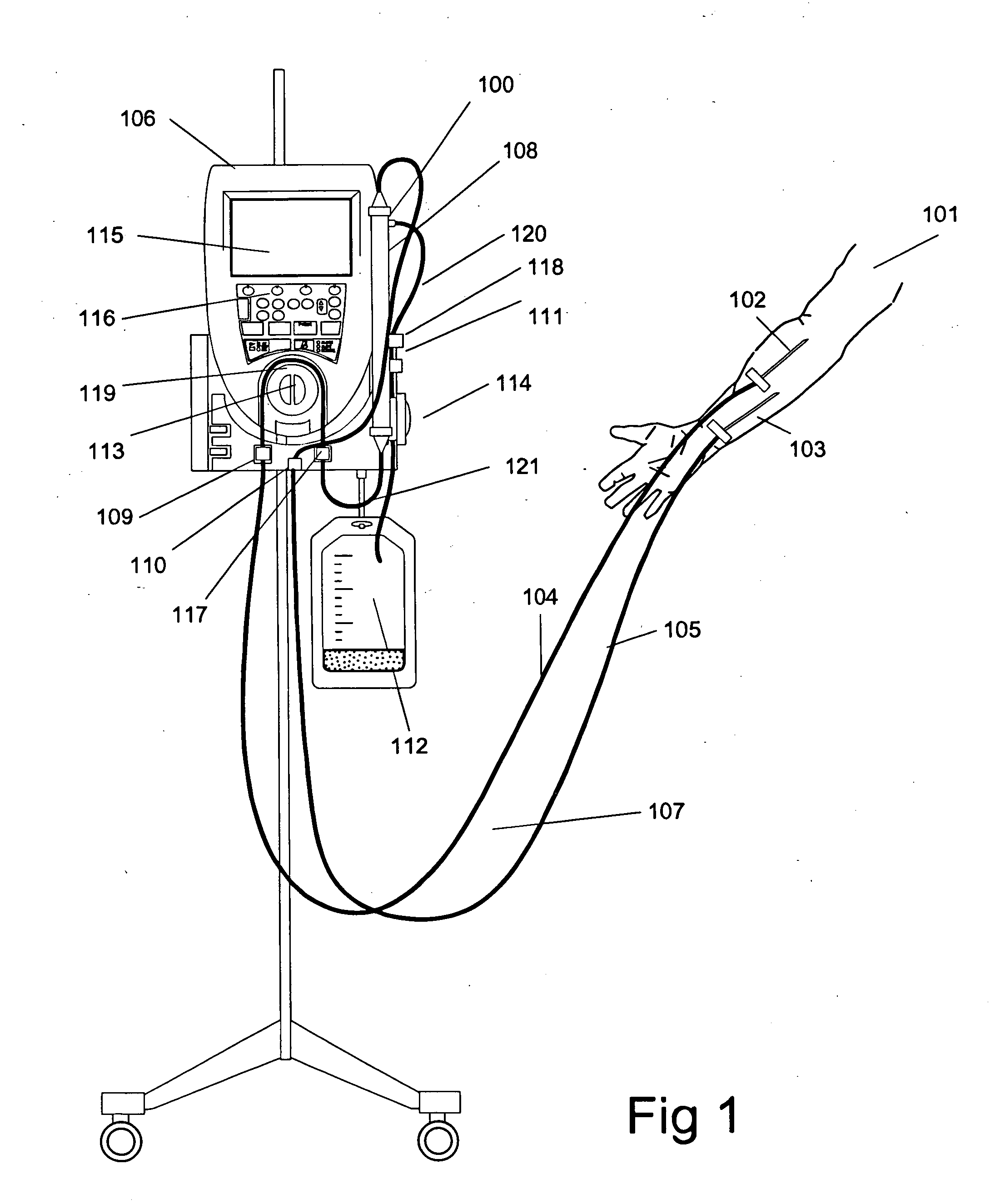
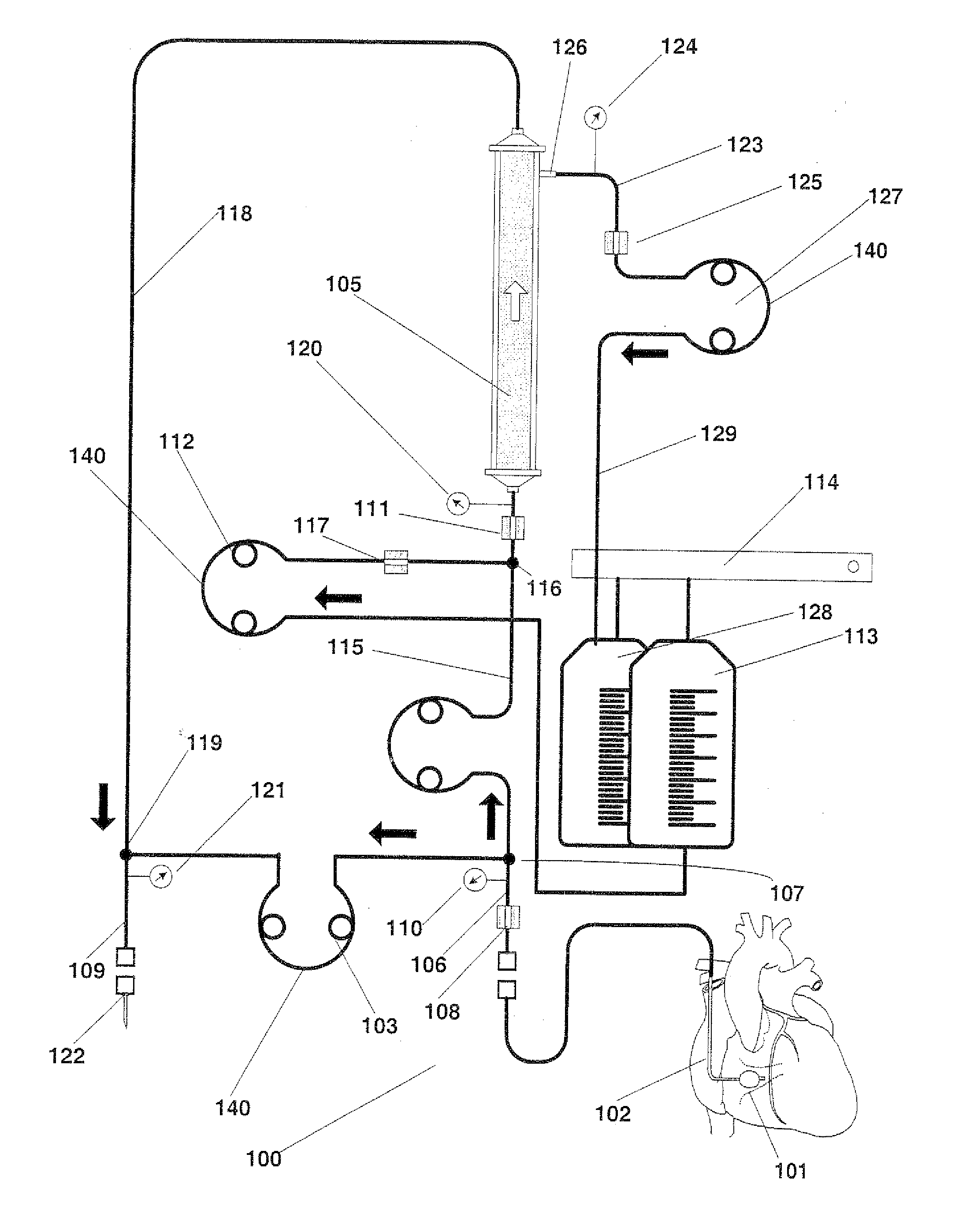
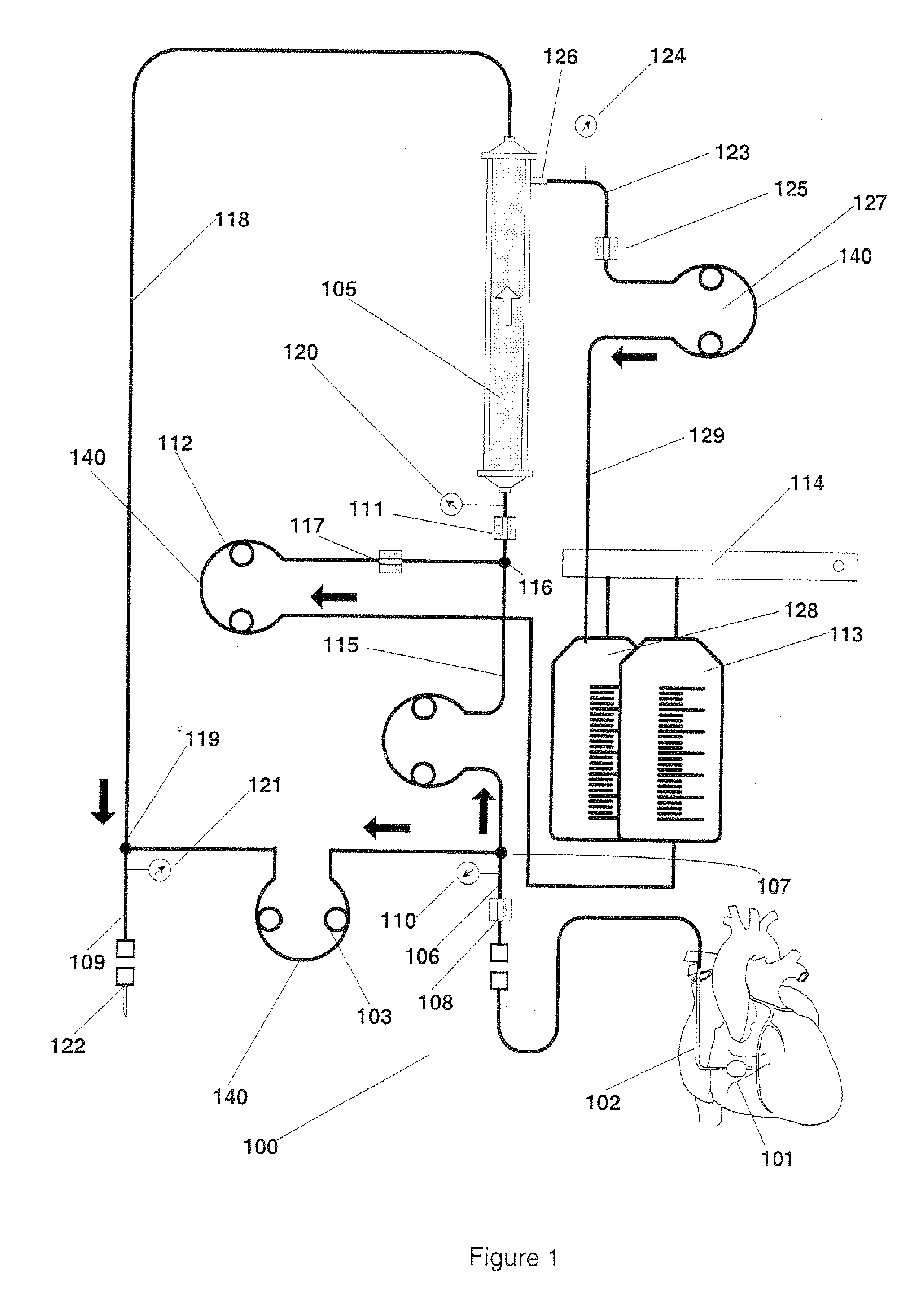
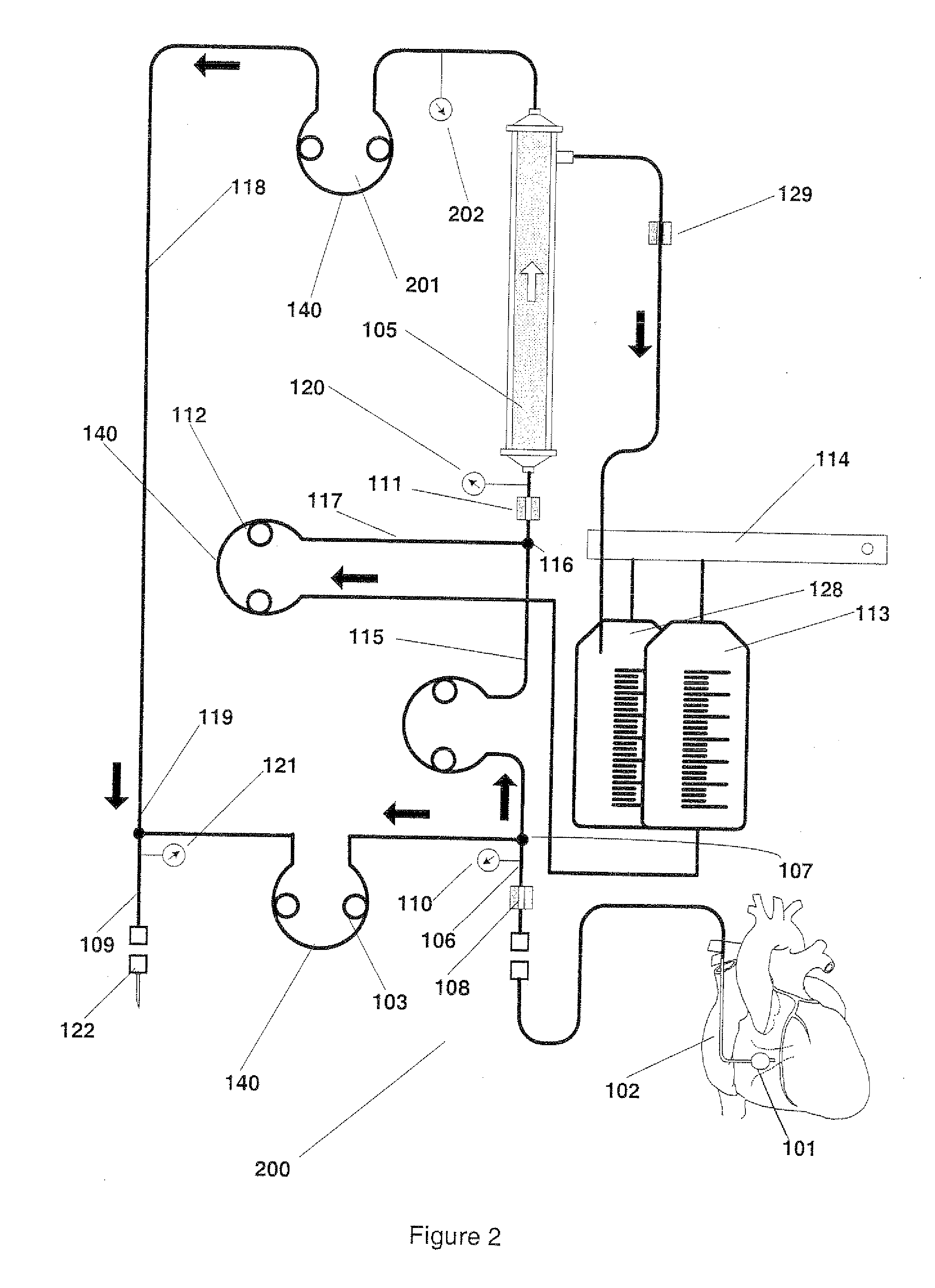
Blood withdrawal system
ActiveUS7238192B2Relieve painCost-effectiveSensorsBlood sampling devicesBiomedical engineeringBlood withdrawal
A blood withdrawal system for withdrawing blood for diagnostic purposes including a lancing device having a housing with an opening and a support surface, and a lancet holder movably mounted in the opening including a lancet and a bearing member that rests on the support surface. The device further includes a trigger unit which, when moved linearly, causes a rotational movement to initiate a lancing process.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Valve port assembly with interlock
InactiveUS6565525B1Semi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesBiomedical engineeringBlood vessel
A dual port vascular access assembly comprises a first access port and a second access port. The linkage is coupled between the first access port to close the second access port in the absence of an access tube in the first access port. Such port assemblies are particularly useful for implantation in patients receiving hemodialysis. By connecting the first access port to the blood withdrawal side of the system, blood withdrawal will be automatically terminated upon cessation of blood returned to due loss of the return access tube in the port assembly.
Owner:VASCA
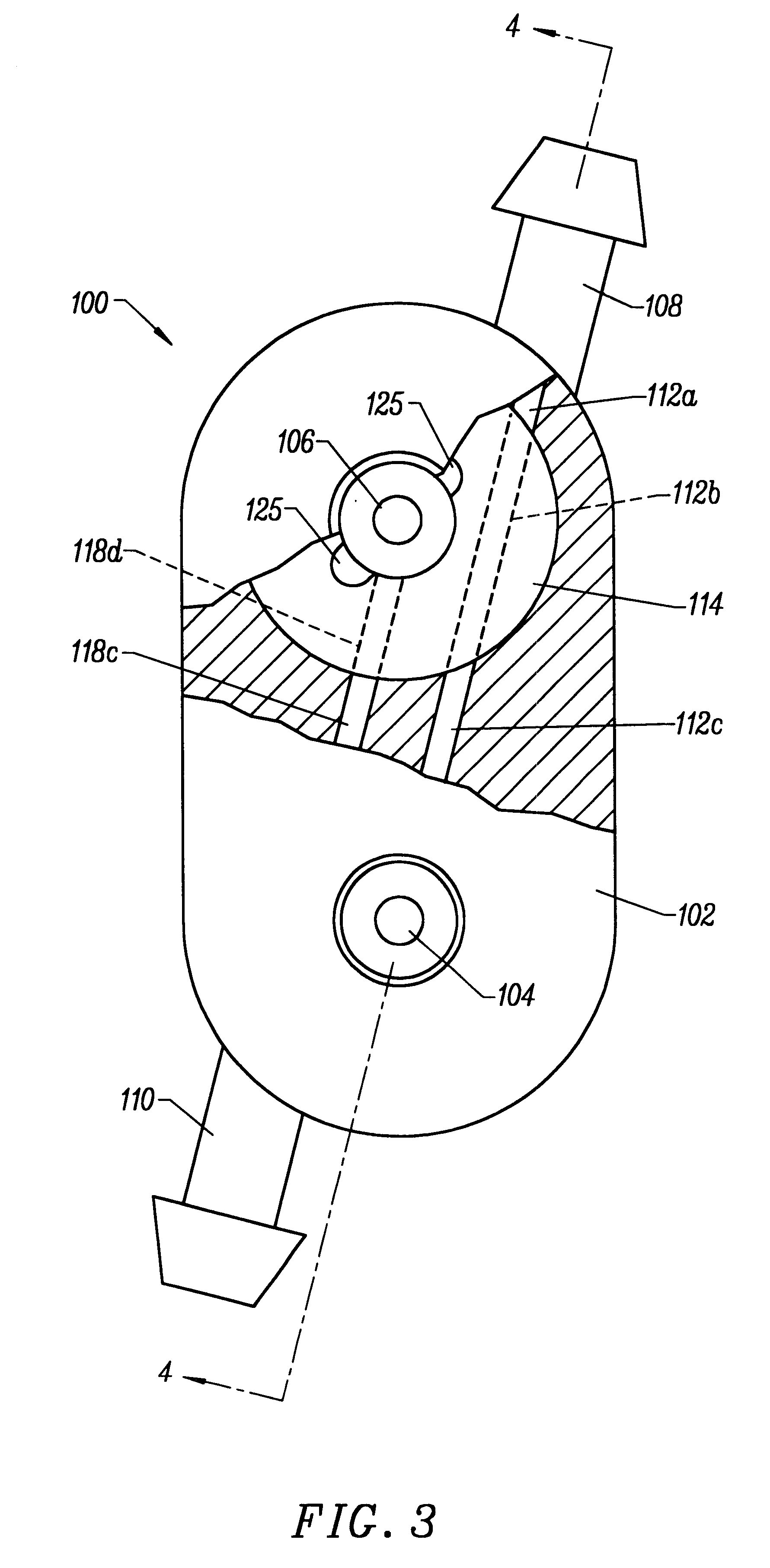
Blood withdrawal system
InactiveUS20080033469A1Reduce frictionHandling device is simpleCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringBody region
A blood withdrawal system for producing blood from a body part for diagnostic purposes, comprising a housing with a lancet guide capable of guiding a lancet on a predetermined puncturing path and a lancet drive for driving a puncturing movement of a lancet on the predetermined path. The lancet drive comprises a drive rotor driven by a drive spring and rotates about an axis during the puncturing movement, and a coupling mechanism which converts the rotational movement of the drive rotor into a puncturing movement, wherein the lancet is moved during a forward phase of the puncturing movement in the puncturing direction until its tip penetrates into the body part to create a wound and is retracted from the skin during a retraction phase of the puncturing movement. The coupling mechanism includes a translation element coupled to the lancet and guided by a guide on a movement path.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Dialysis catheter
Owner:ARGON MEDICAL DEVICES
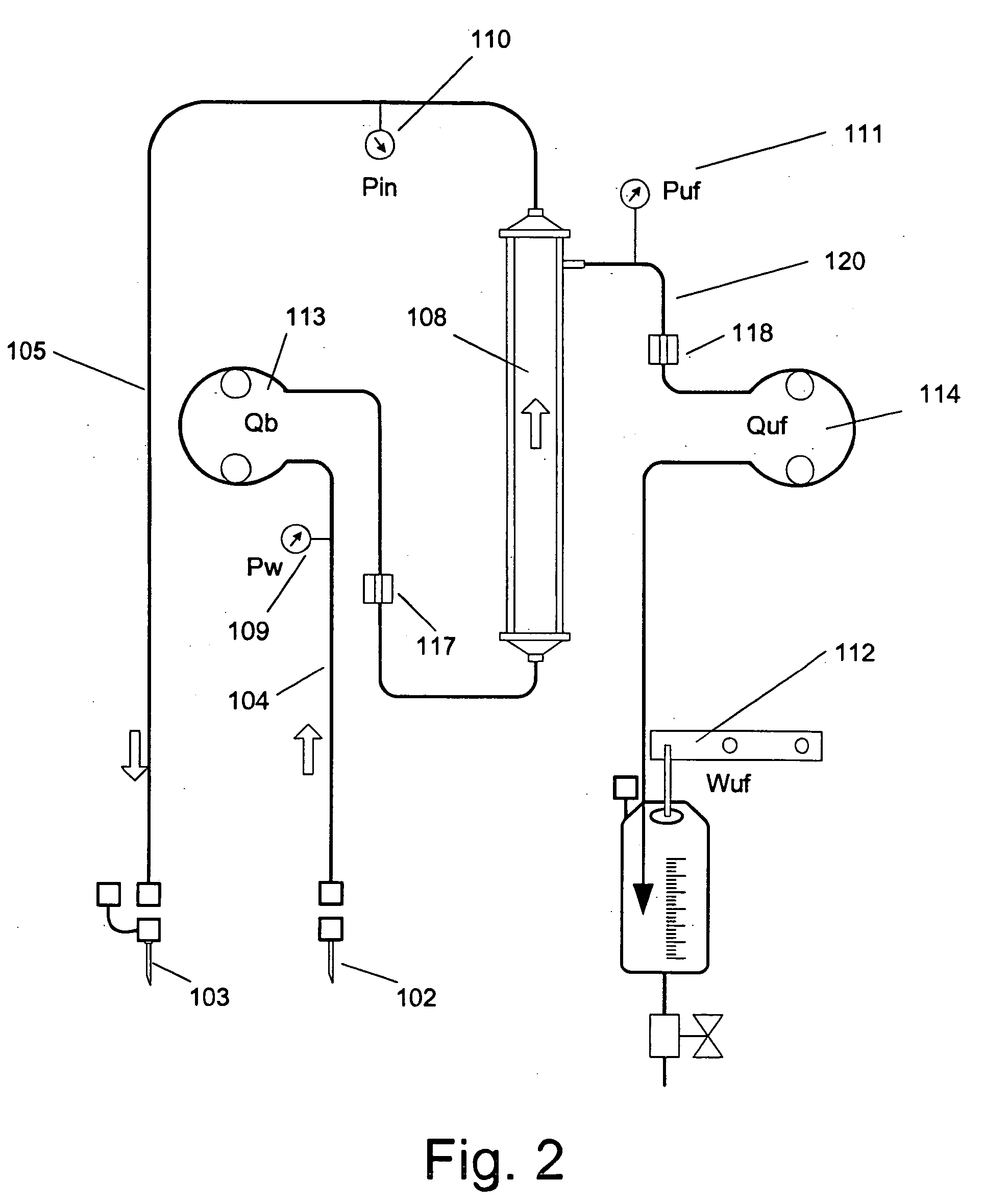
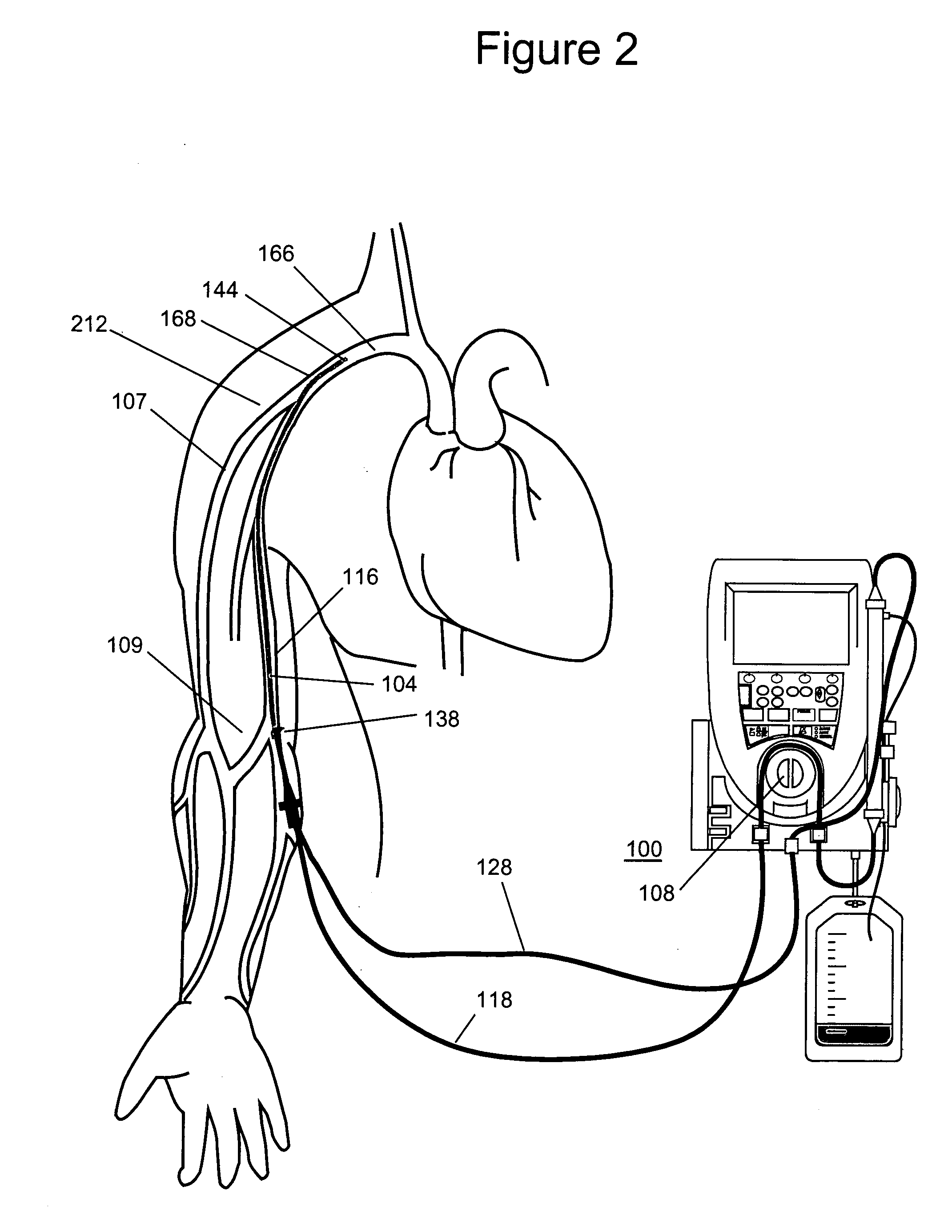
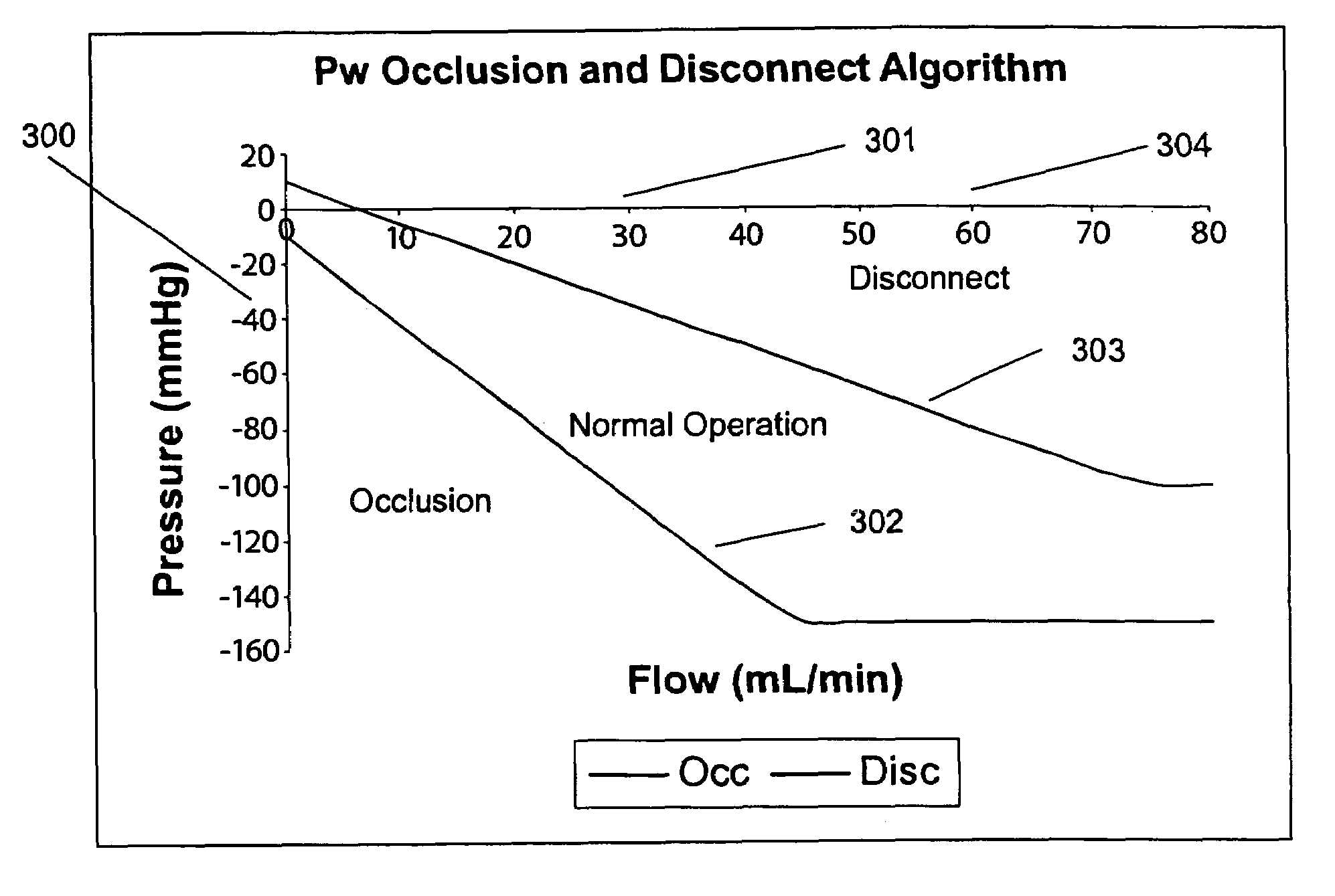
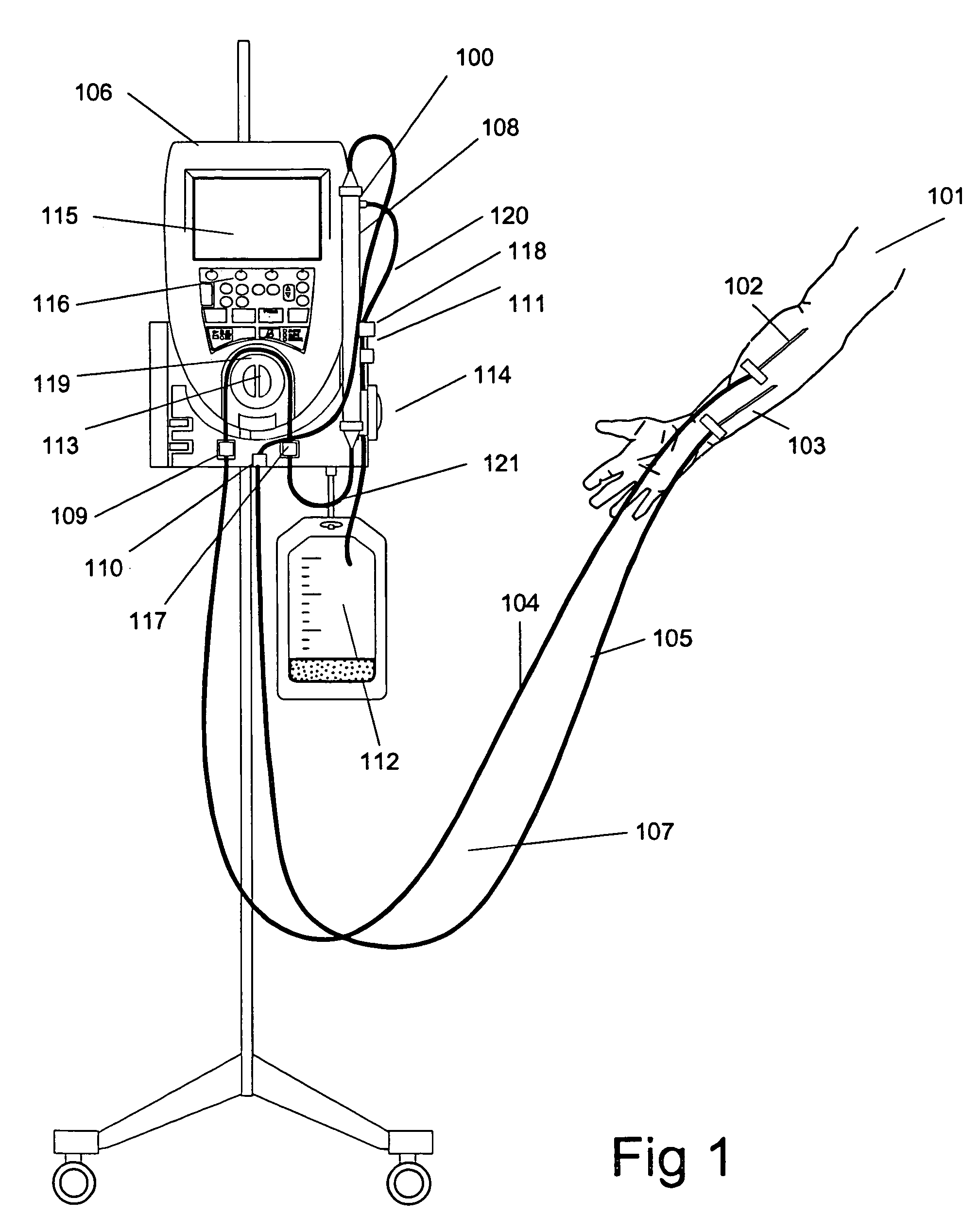
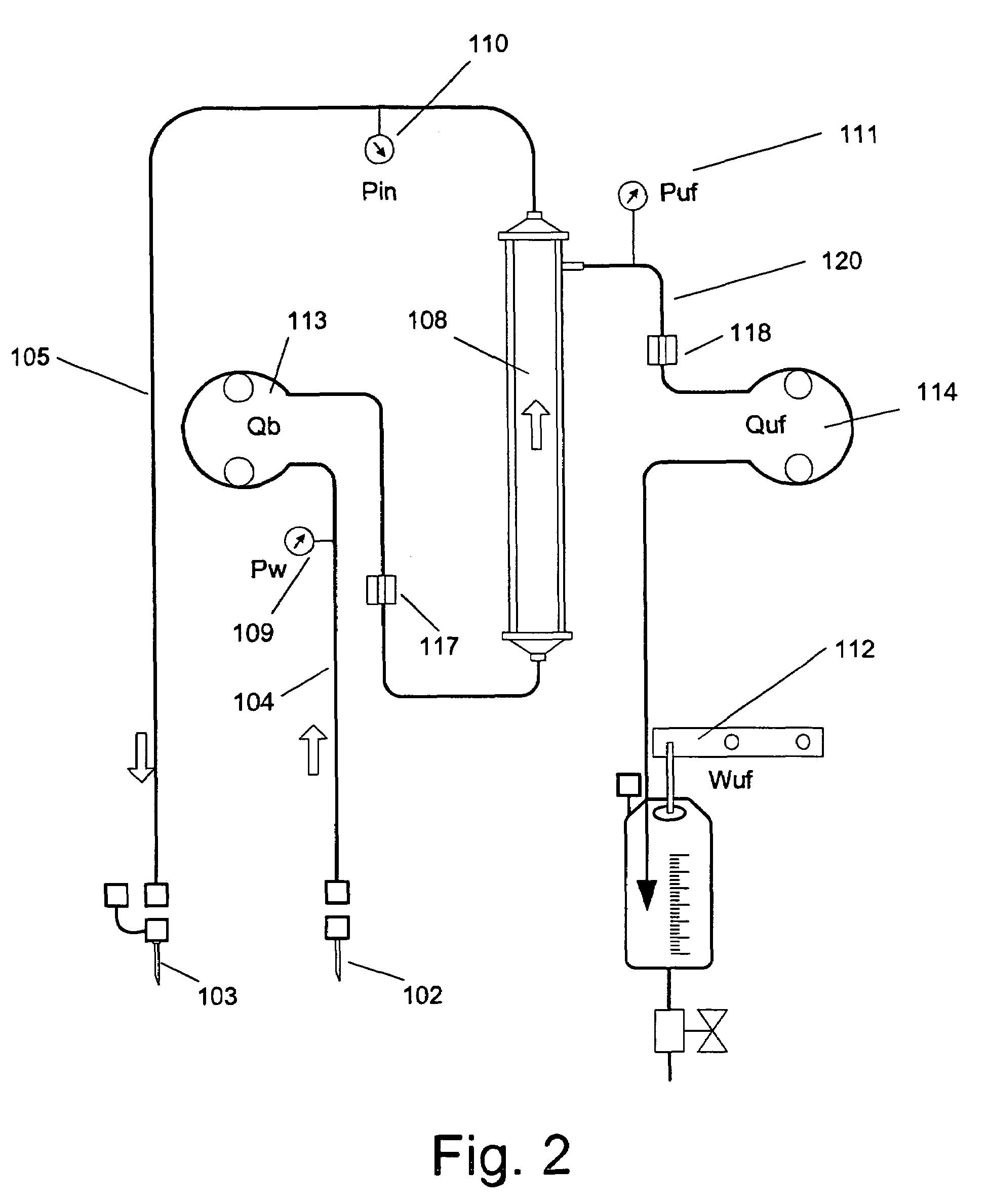
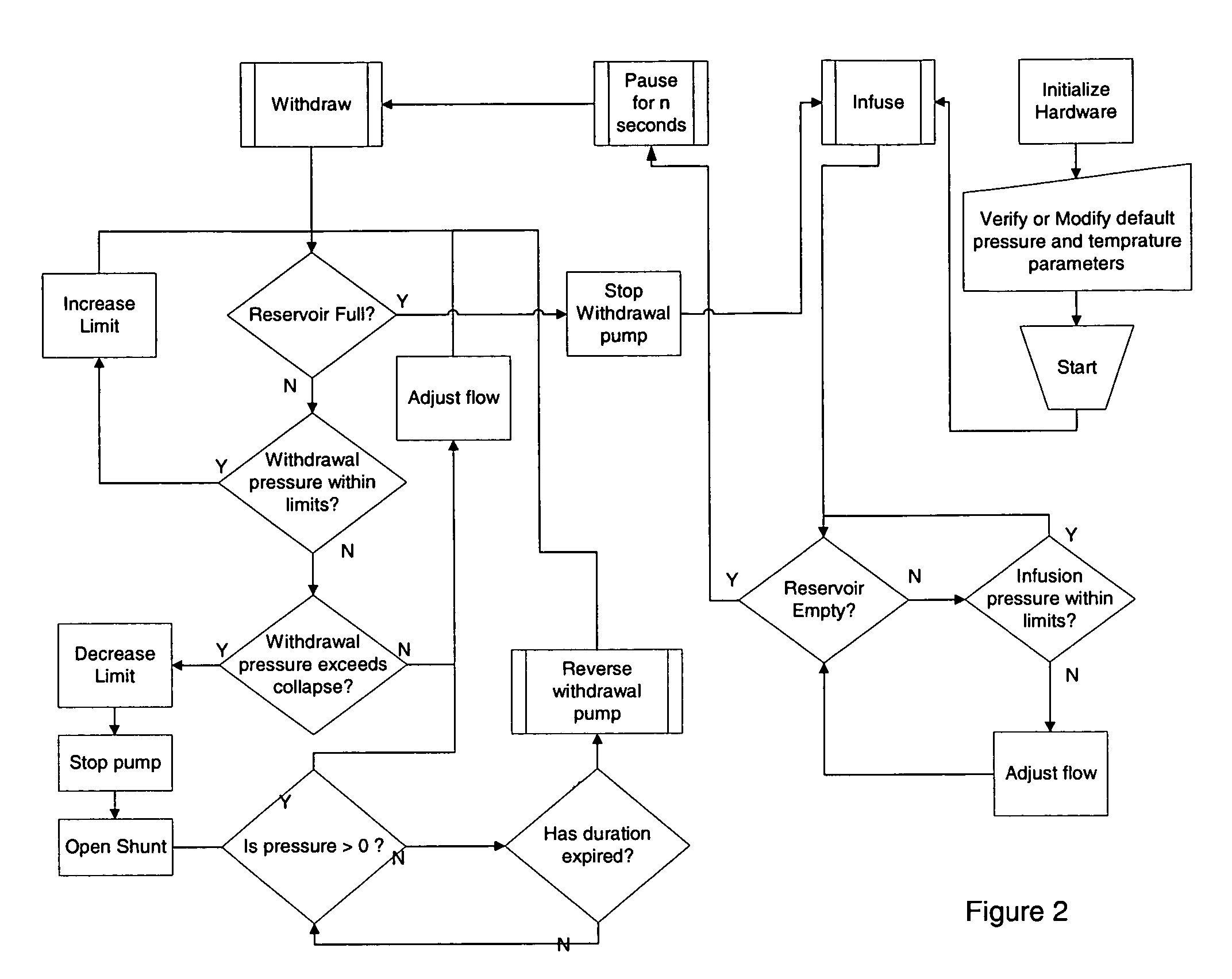
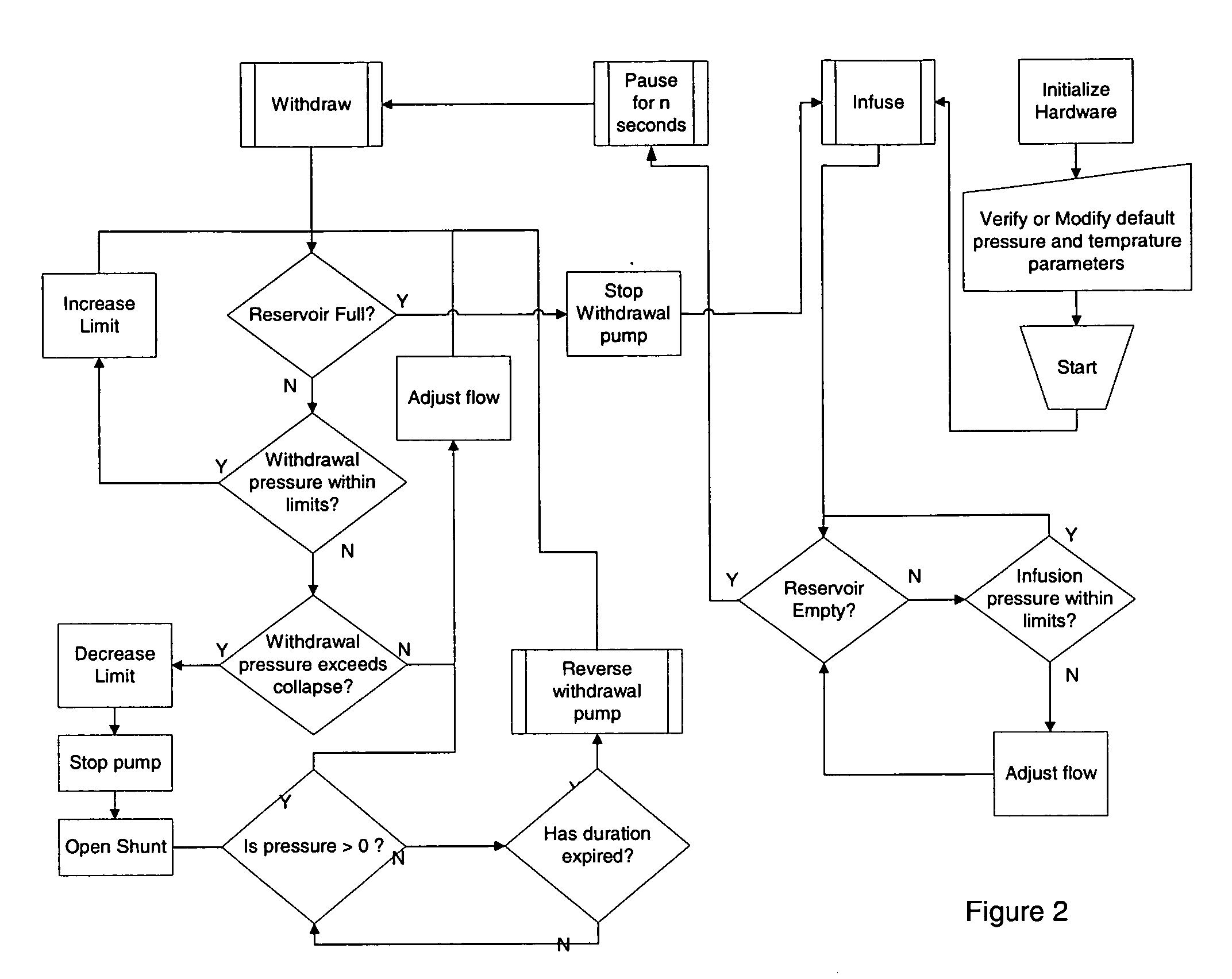
Method and apparatus for blood withdrawal and infusion using a pressure controller
InactiveUS20050230313A1Decreased blood flowIncrease heightSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesVeinTotal occlusion
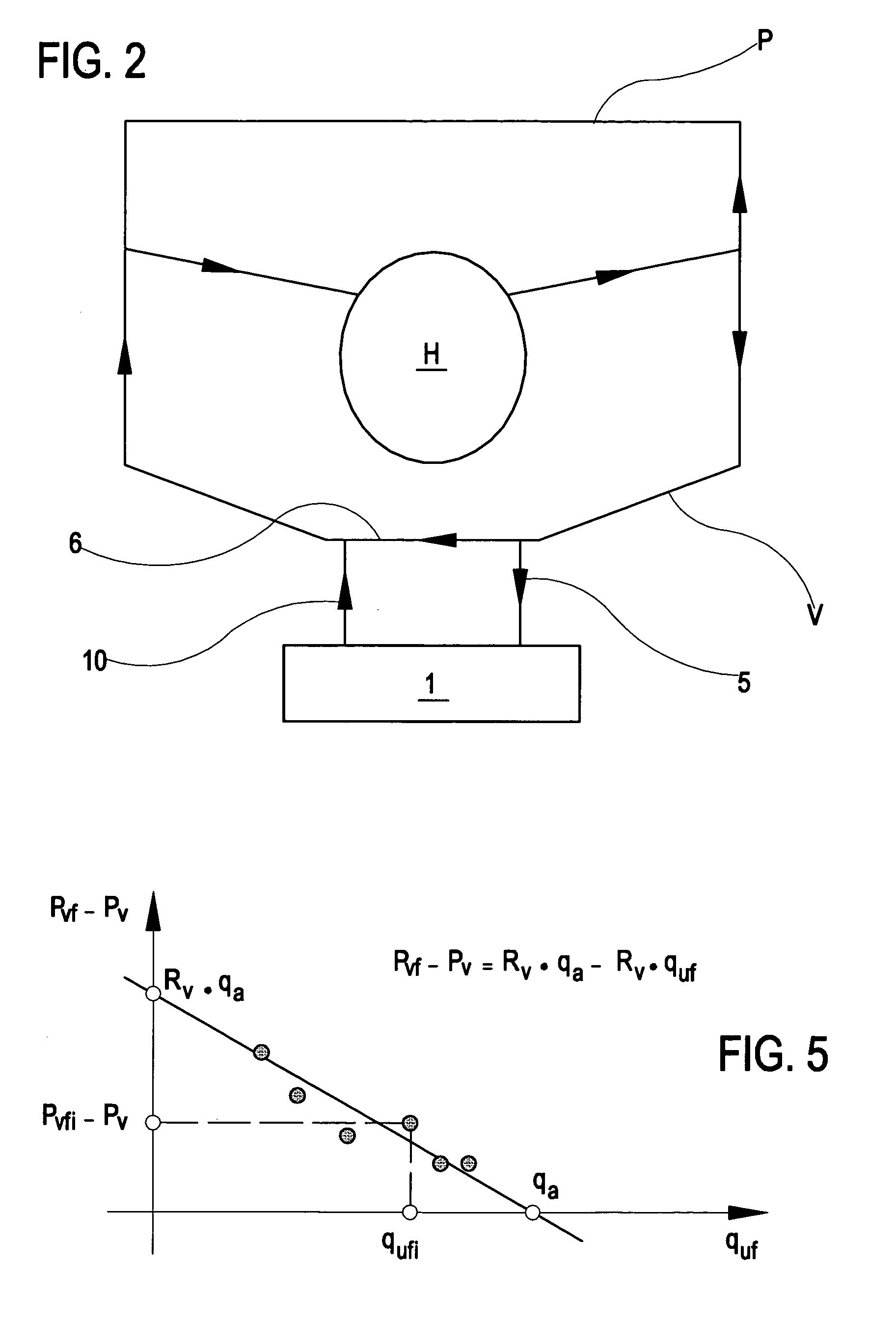
A method and apparatus for controlling blood withdrawal and infusion flow rate with the use of a pressure controller. The pressure controller uses pressure targets based upon occlusion limits that are calculated as a function of flow. The controller has the ability to switch from controlling withdrawal pressure to controlling infusion pressure based upon the detection of an occlusion. The controller distinguishes between partial and total occlusions of the withdrawal vein providing blood access. Depending on the nature of occlusion, the controller limits or temporarily reverses blood flow and, thus, prevents withdrawal vessel collapse or reverses blood flow to quickly infuse blood into the vessel without participation from operator.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and apparatus for ultrafiltration utilizing a peripheral access dual lumen venous cannula
InactiveUS20050119597A1Ease and safetyInadequate blood flowSemi-permeable membranesMulti-lumen catheterUltrafiltrationCongestive heart failure chf
Method and apparatus for the extracorporeal treatment of blood by utilizing a peripherally inserted dual lumen catheter assembly for the continuous removal and return of blood for renal replacement treatment, in particularly, treatment of congestive heart failure and fluid overload by ultrafiltration. A catheter is inserted in a peripheral vein and maneuvered upward through the vascular system to access the reservoir of blood in the large or great veins for continuous blood withdrawal and treatment. Air-tight connectors are incorporated in the catheter assembly to overcome the untoward effects of negative pressure in blood withdrawal.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and apparatus for blood withdrawal and infusion using a pressure controller
InactiveUS7462161B2Decreased blood flowIncrease heightSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesVeinTotal occlusion
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
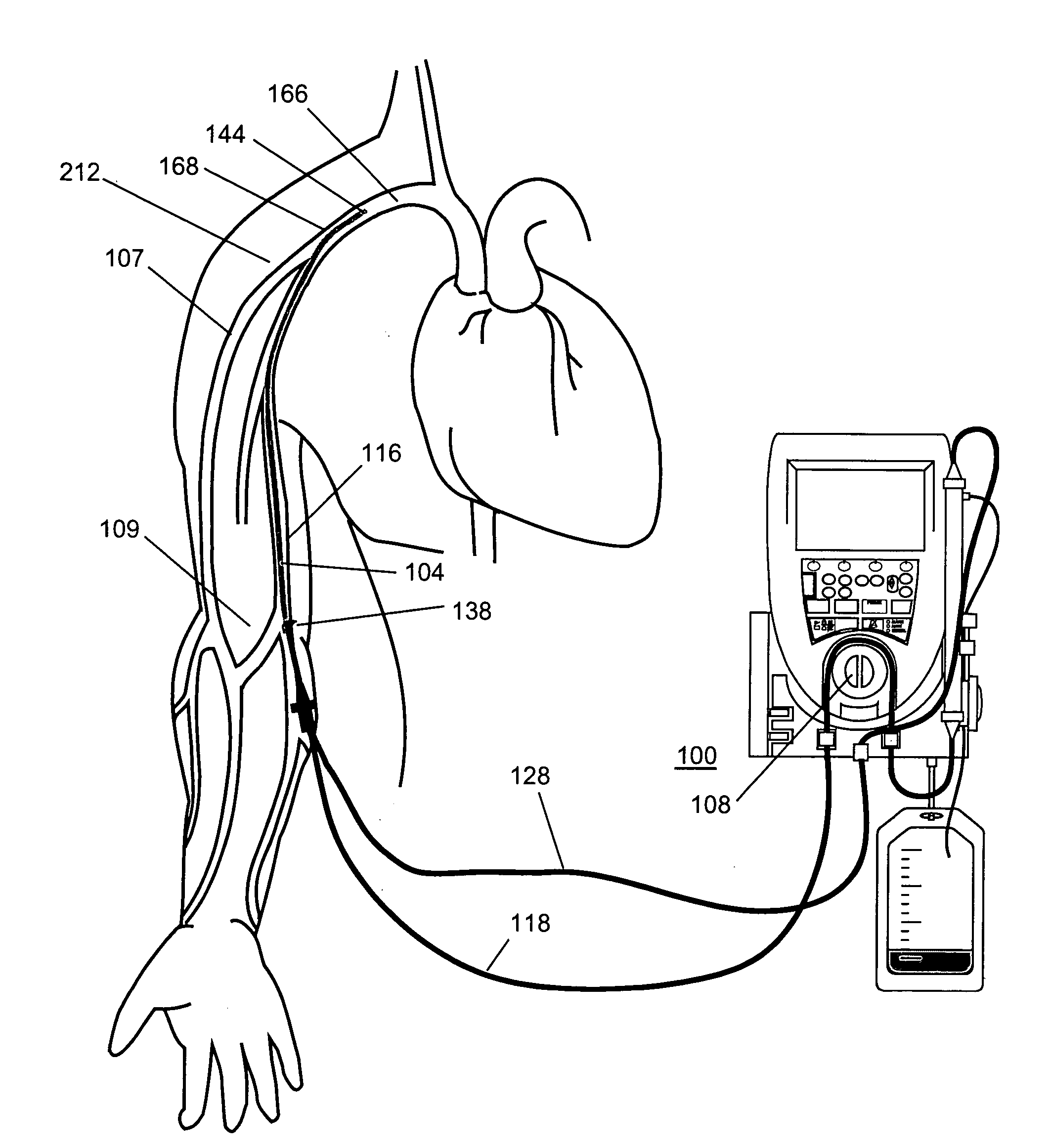
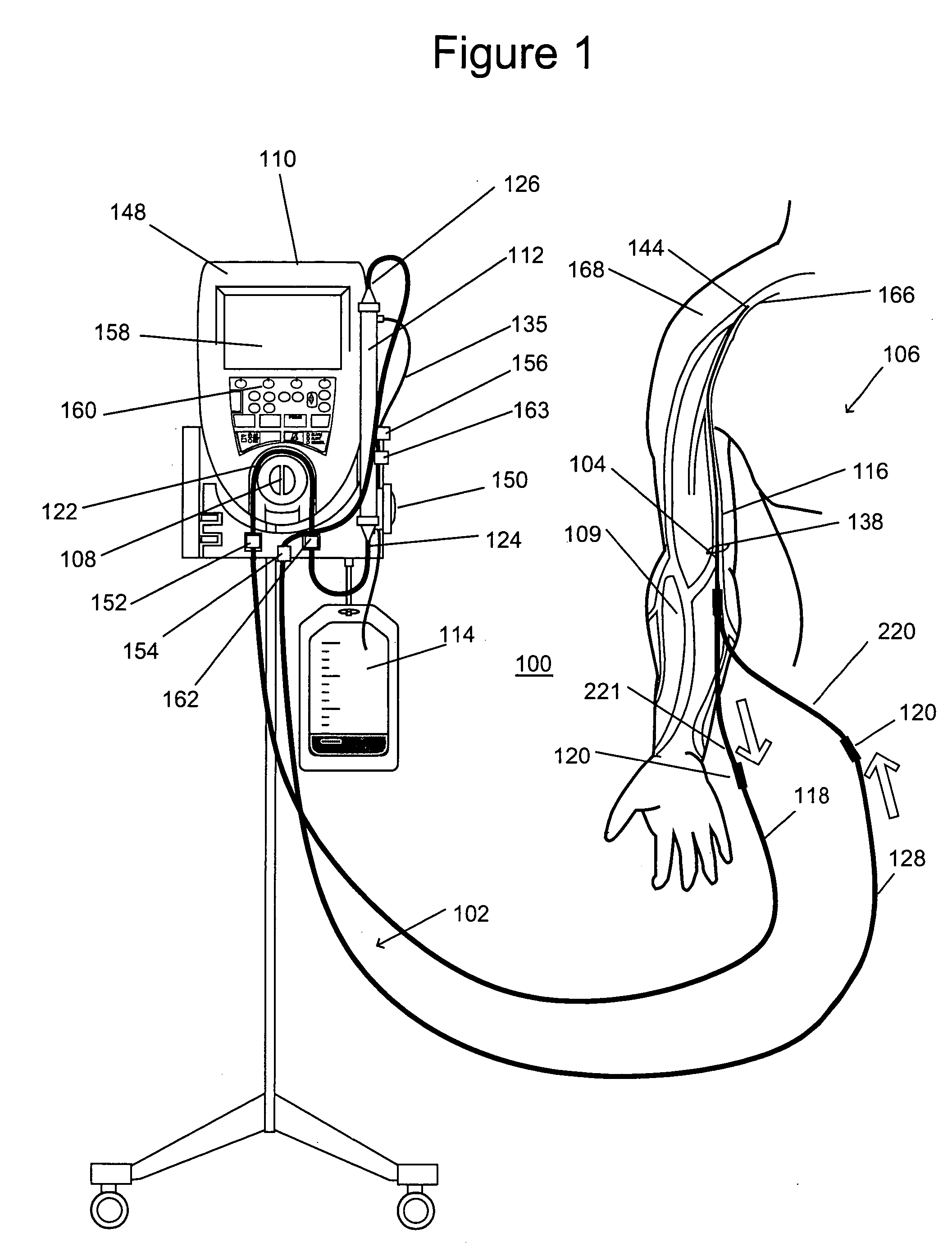
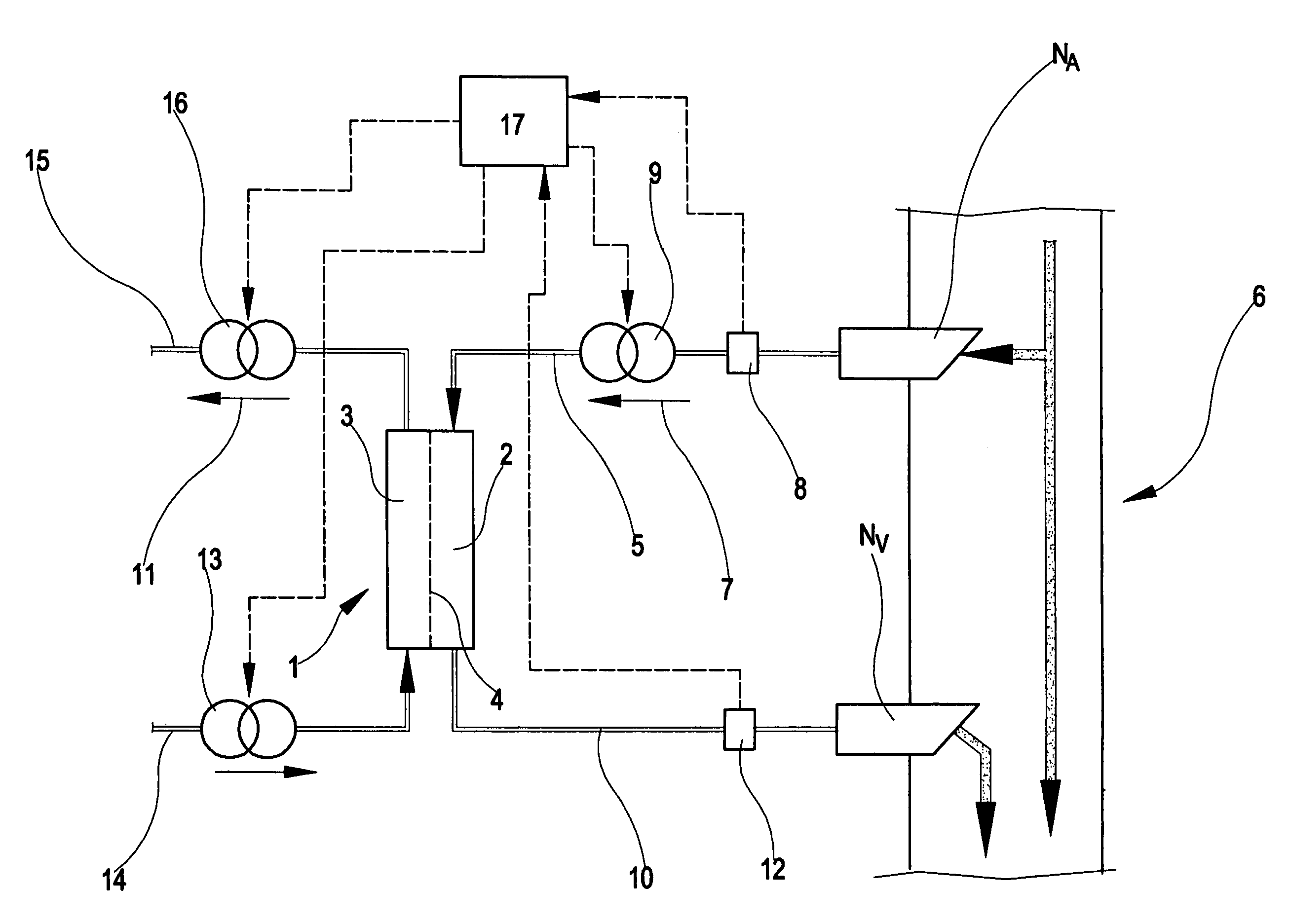
Apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access of a patient subjected to an extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS7172570B2Possible to selectSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationHaemodialysis machine
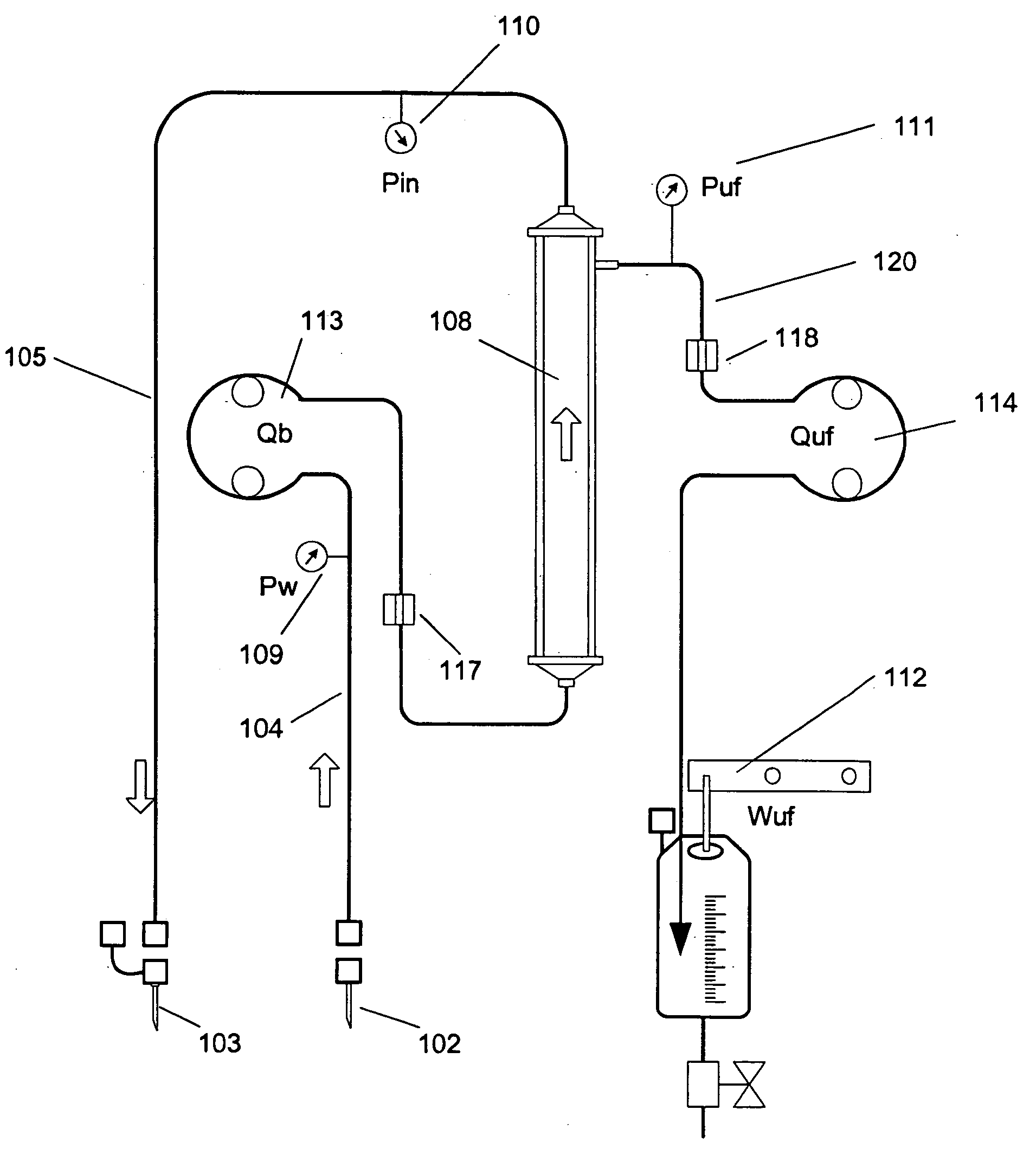
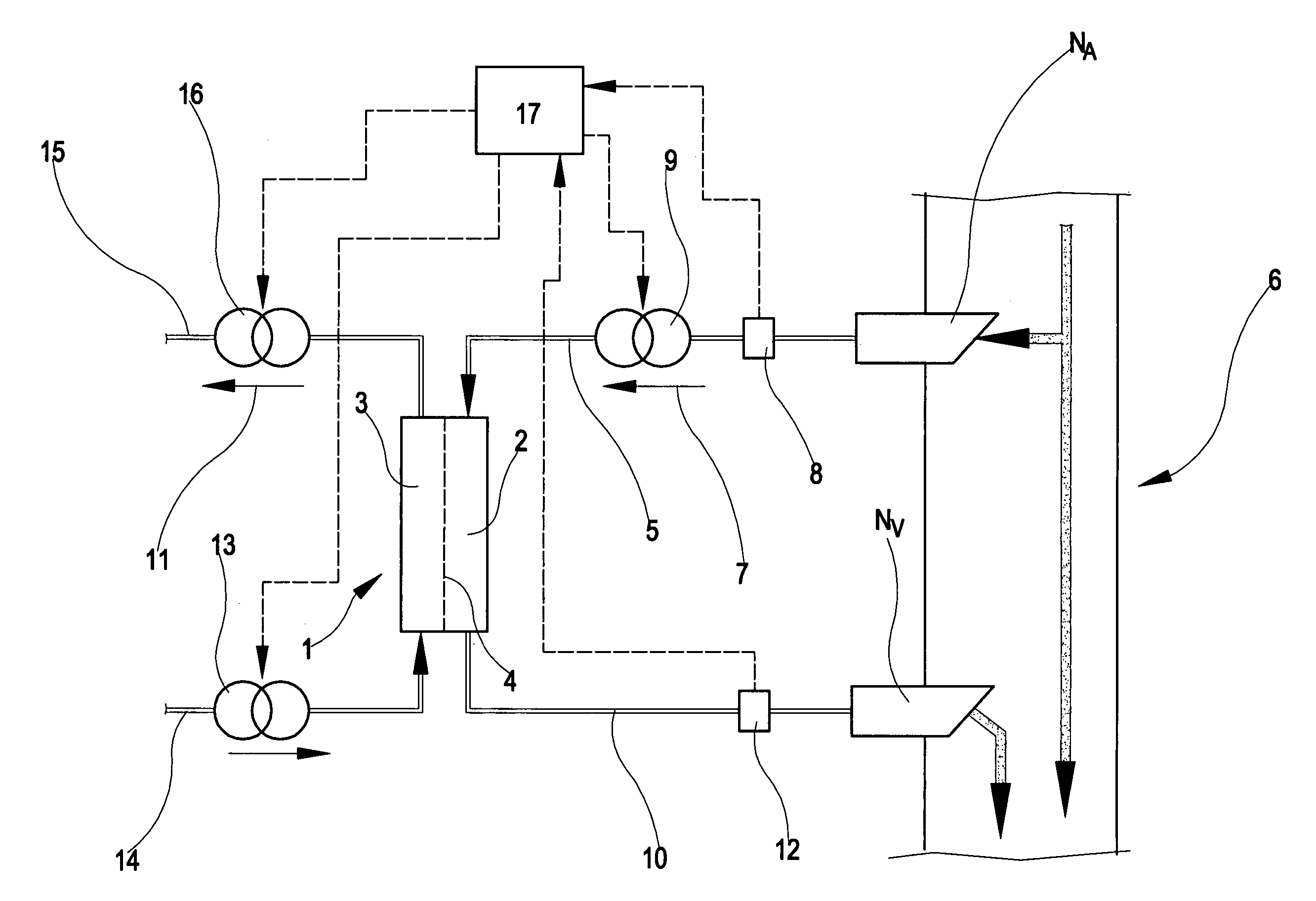
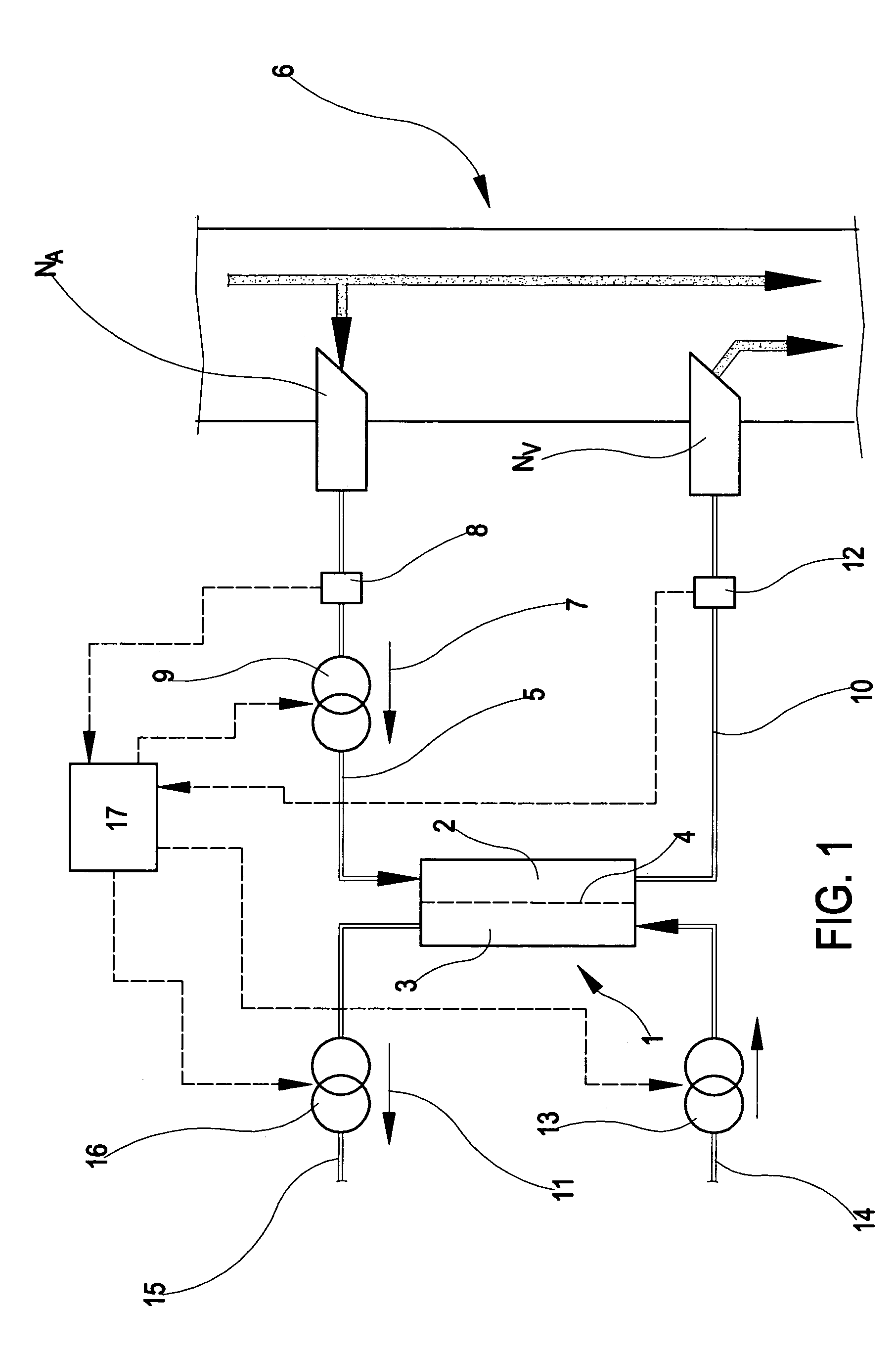
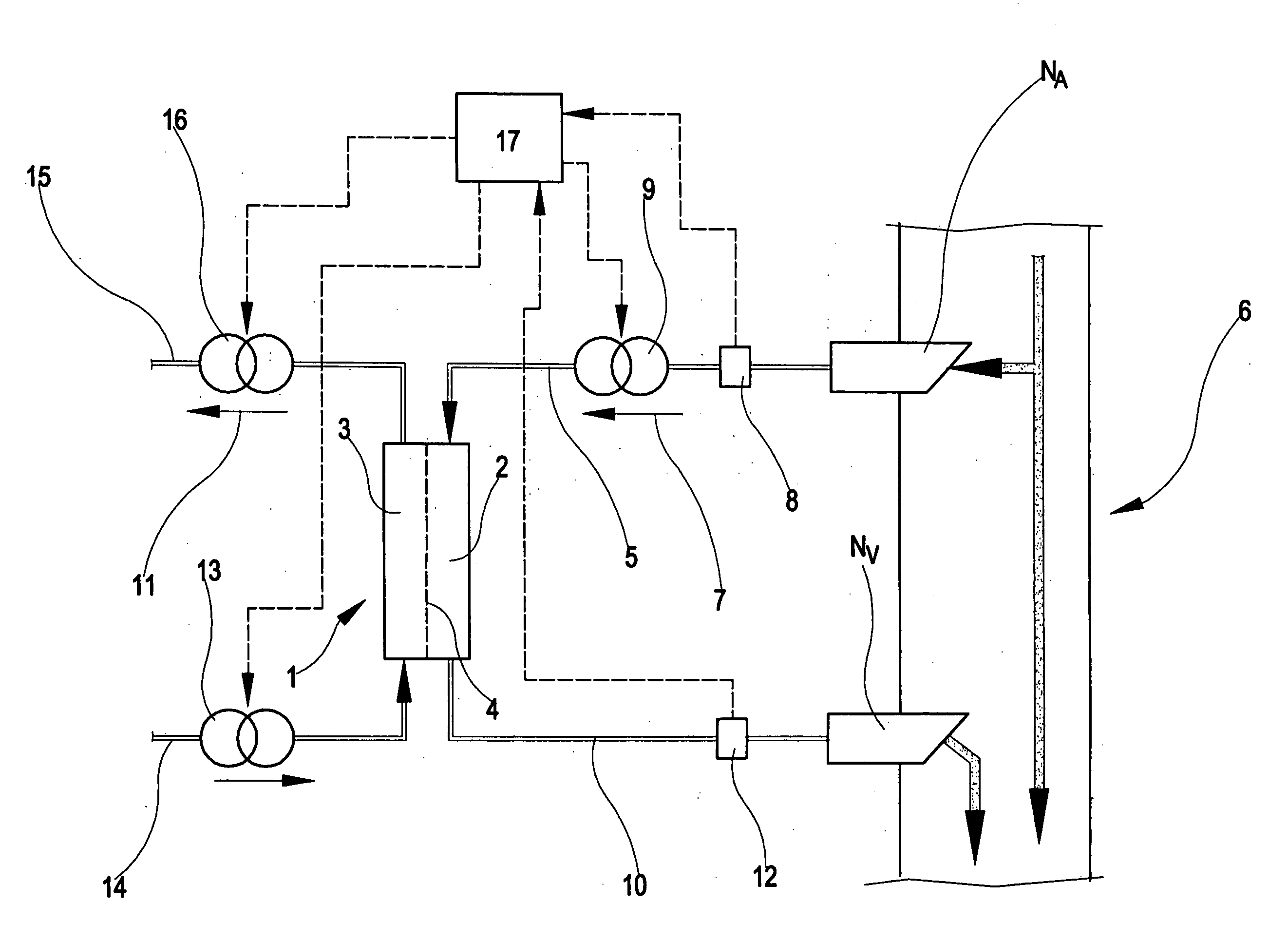
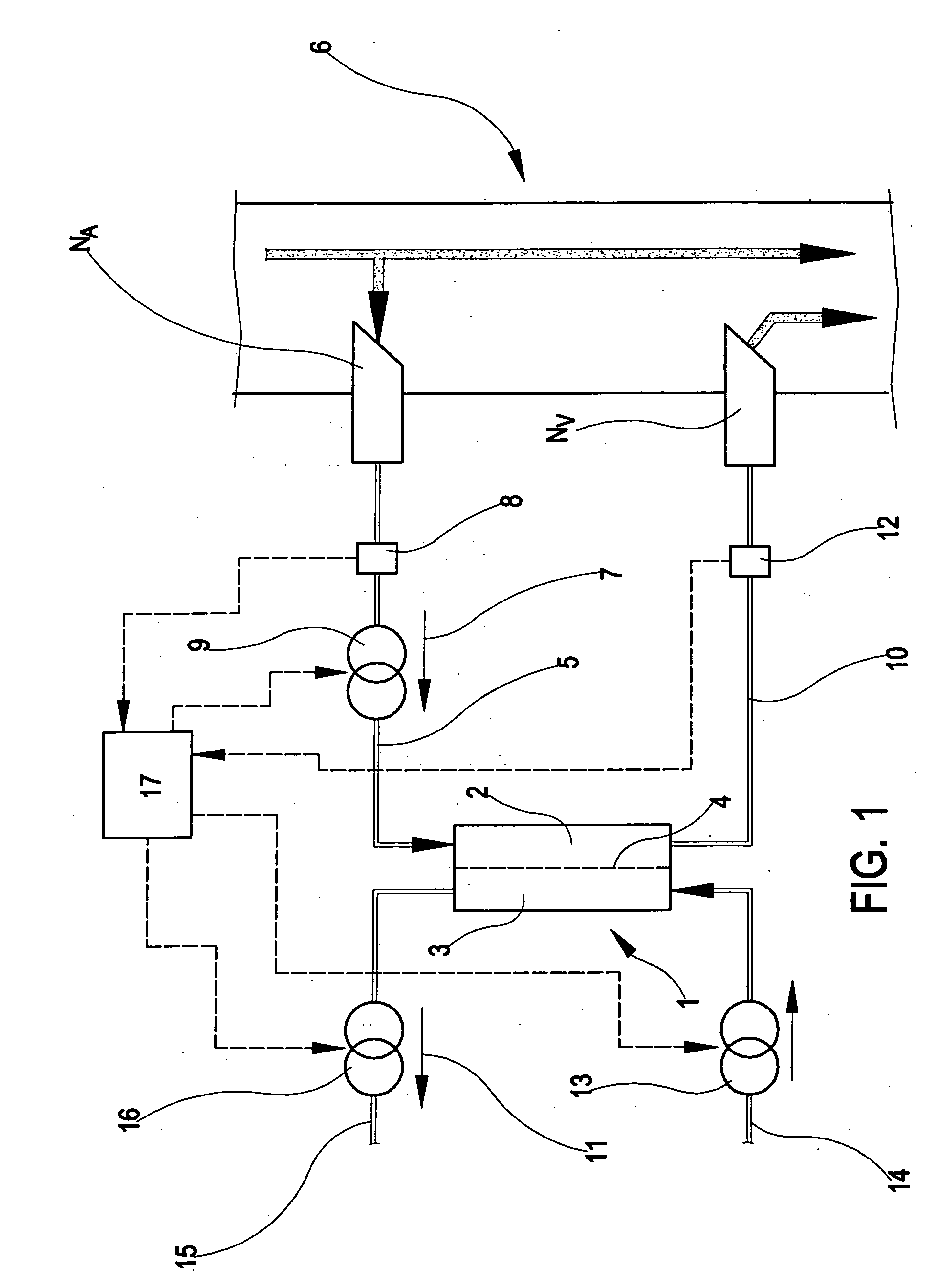
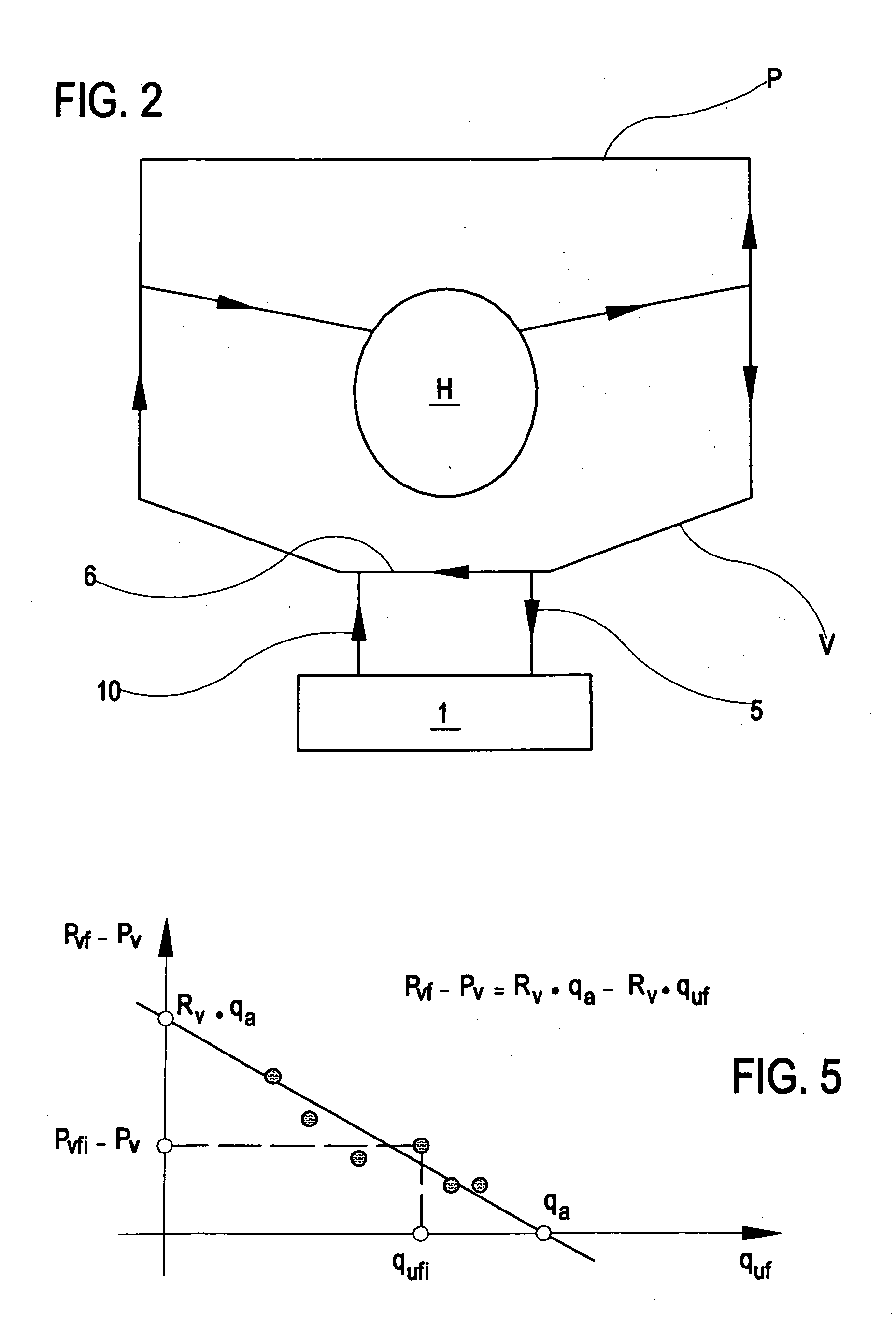
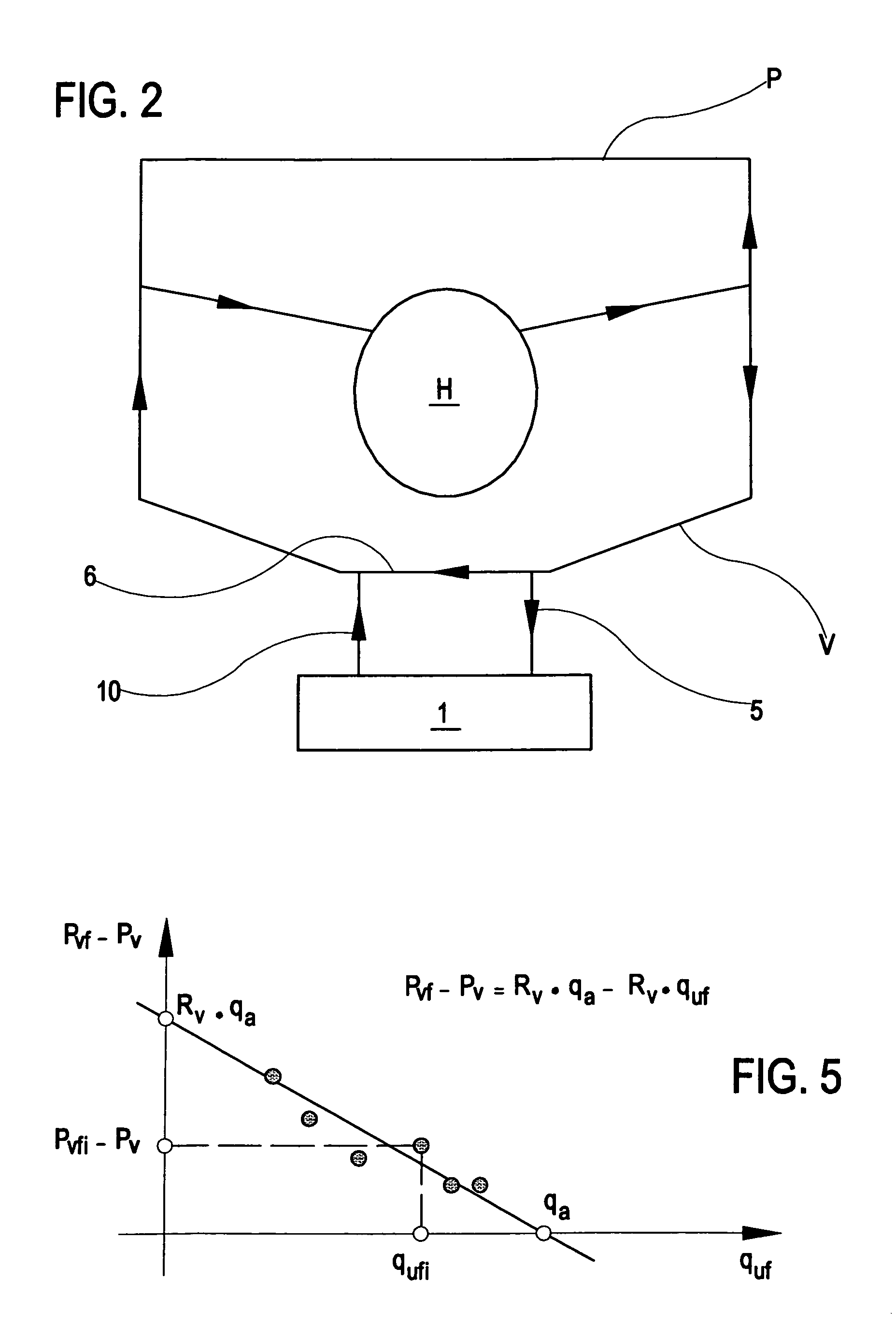
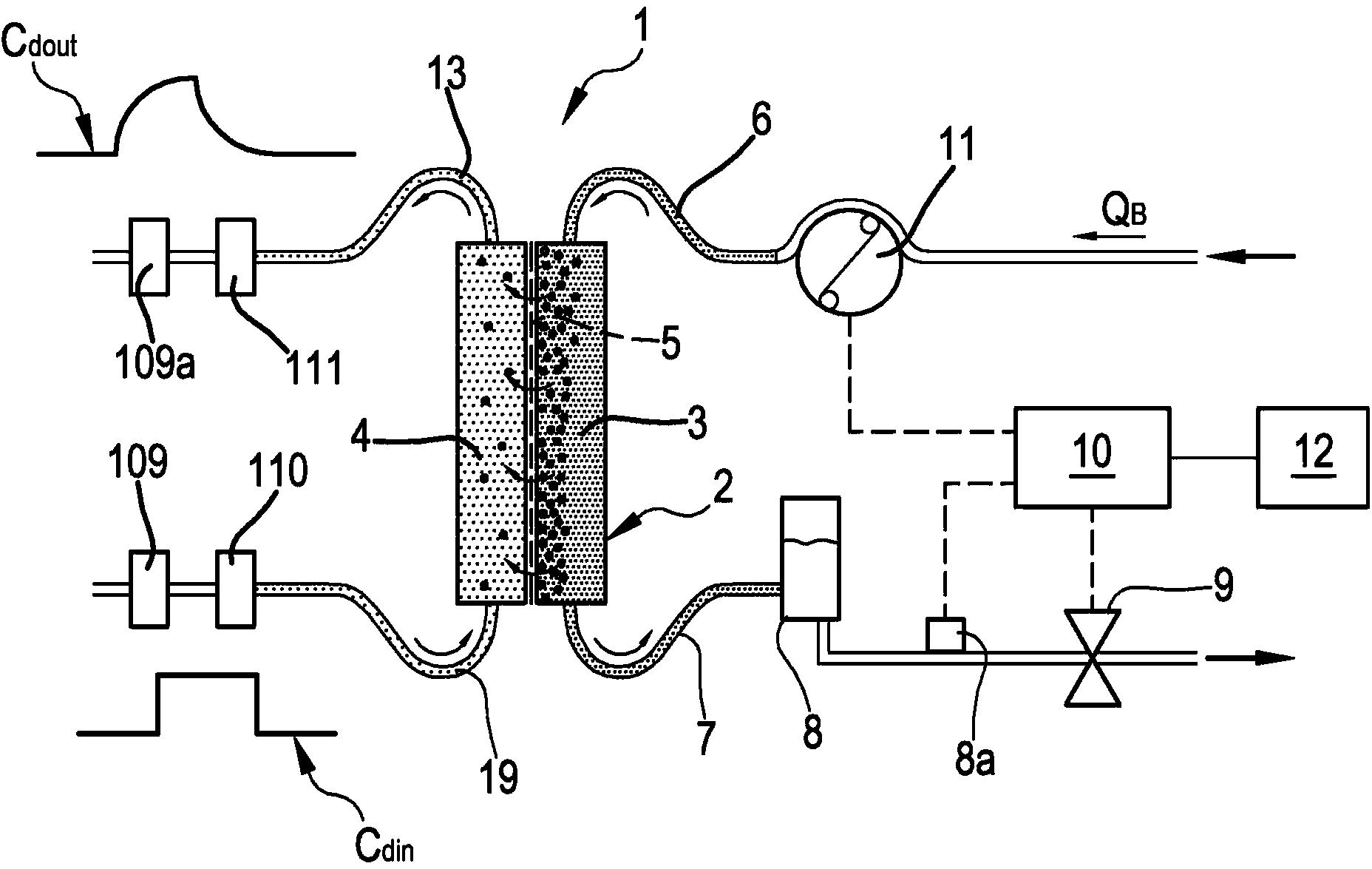
In the apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access (6) of an extracorporeal circuit (5; 10) of a patient, a control and calculation unit (17) varies a flow rate of a blood pump (9) predisposed to cause blood to circulate in the extracorporeal circuit. The control and calculation unit receives the pressure values in the blood withdrawal line (5) and the blood return line (10) from two pressure sensors (8, 12); the pressure values are a series of different values of the blood flow rate. The control and calculation unit processes the data gathered by means of a mathematical model which describes the variation of pressure in the vascular access as a function of the flow rate, in order to determine the blood flow rate in the vascular access. The invention detects the presence and location of a stenosis at the vascular access of a patient subjected to a hemodialysis treatment.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Method and apparatus for ultrafiltration utilizing a peripheral access dual lumen venous cannula
InactiveUS7135008B2Minimize timeConserve veinSemi-permeable membranesMulti-lumen catheterUltrafiltrationCongestive heart failure chf
Method and apparatus for the extracorporeal treatment of blood by utilizing a peripherally inserted dual lumen catheter assembly for the continuous removal and return of blood for renal replacement treatment, in particularly, treatment of congestive heart failure and fluid overload by ultrafiltration. A catheter is inserted in a peripheral vein and maneuvered upward through the vascular system to access the reservoir of blood in the large or great veins for continuous blood withdrawal and treatment. Air-tight connectors are incorporated in the catheter assembly to overcome the untoward effects of negative pressure in blood withdrawal.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
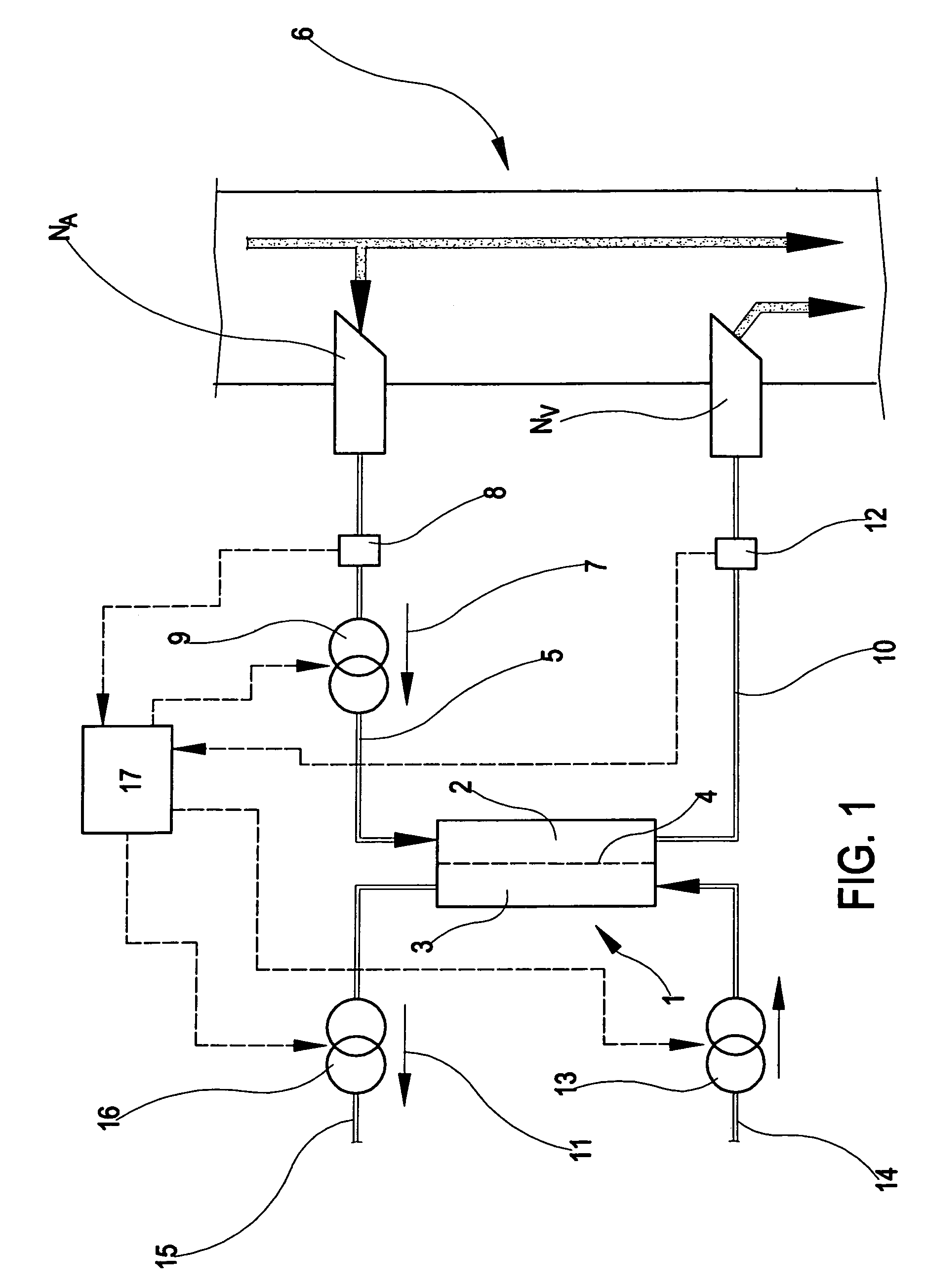
Apparatus and method of monitoring a vascular access of a patient subjected to an extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS20070112289A1Other blood circulation devicesMedical devicesHaemodialysis machineMathematical model
In the apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access (6) of an extracorporeal circuit (5; 10) of a patient, a control and calculation unit (17) varies a flow rate of a blood pump (9) predisposed to cause blood to circulate in the extracorporeal circuit. The control and calculation unit receives-the pressure values in the blood withdrawal line (5) and the blood return line (10) from two pressure sensors (8, 12); the pressure values are a series of different values of the blood flow rate. The control and calculation unit processes the data gathered by means of a mathematical model which describes the variation of pressure in the vascular access as a function of the flow rate, in order to determine the blood flow rate in the vascular access. The invention detects the presence and location of a stenosis at the vascular access of a patient subjected to a hemodialysis treatment.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Peripheral access venous cannula with infusion side holes and embedded reinforcement
A peripherally inserted catheter assembly having multiple side holes to be inserted in a peripheral vein and maneuvered upward through the vascular system to access the reservoir of blood beyond and between the venous flappers for continuous blood withdrawal and treatment.
Owner:CHF SOLUTION
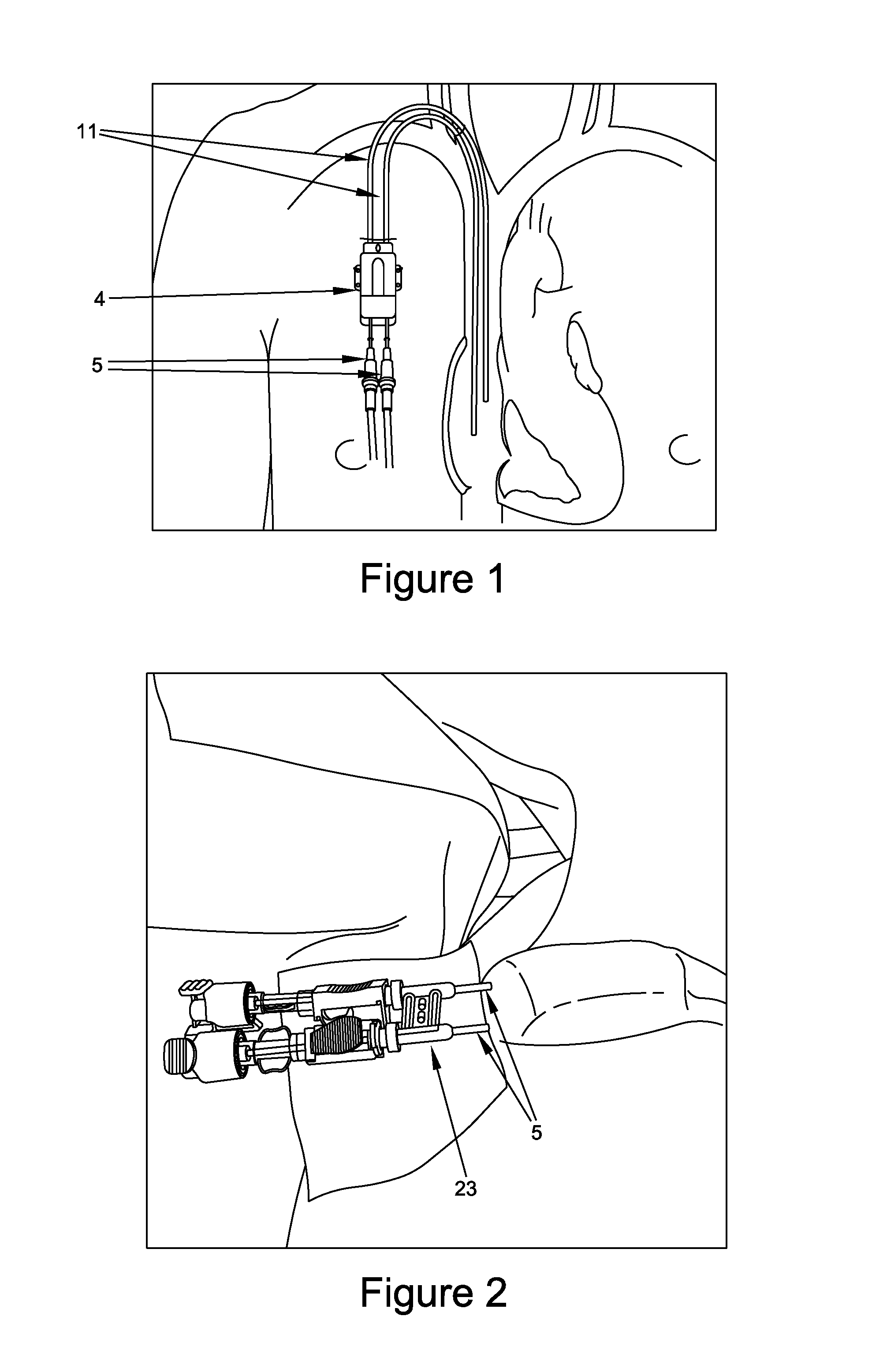
Hemodialysis access system
ActiveUS9295773B2Good man-machine interfaceEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesHaemodialysis machineDisfigurement
A medical blood access system used for hemodialysis treatment to enable blood withdrawal for processing of blood by an external apparatus and return the same blood to a patient, comprising an interfacial fluid conduit between the machine and patient's blood supply which is repeatedly connectable along a guided pathway passing through epidermis and subcutaneous tissue via a naturally formed tissue tract to enter blood space, providing improved patient safely, convenience, effective prophylaxis, without bleeding or tissue trauma or pain, and is executable by the patient to precisely connect and disconnect with minimal disfigurement or life restrictions, and is useable on virtually all patients soon after placement and is robust and safe to high blood flow.
Owner:PROSL FRANK +2
Expandable dialysis apparatus and method
A venovenous expandable dialysis apparatus includes a blood feeding needle component configured to introduce blood at a position of a first peripheral vein and a blood withdrawal needle component configured to withdraw blood at another position from a second peripheral vein located, where the first position is located away from the second position. The expandable dialysis apparatus further includes a guide wire having a central axis, an expanding sheath configured circumferentially around the guide wire to form an annular lumen between a distal blood withdrawal position and a proximal extracorporeal position; and a needle disposed around the expandable sheath.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Method and apparatus for blood withdrawal and infusion using a pressure controller
InactiveUS20090149795A1Decreased blood flowIncrease head heightOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationVeinTotal occlusion
A method and apparatus for controlling blood withdrawal and infusion flow rate with the use of a pressure controller. The pressure controller uses pressure targets based upon occlusion limits that are calculated as a function of flow. The controller has the ability to switch from controlling withdrawal pressure to controlling infusion pressure based upon the detection of an occlusion. The controller distinguishes between partial and total occlusions of the withdrawal vein providing blood access. Depending on the nature of occlusion, the controller limits or temporarily reverses blood flow and, thus, prevents withdrawal vessel collapse or reverses blood flow to quickly infuse blood into the vessel without participation from operator.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
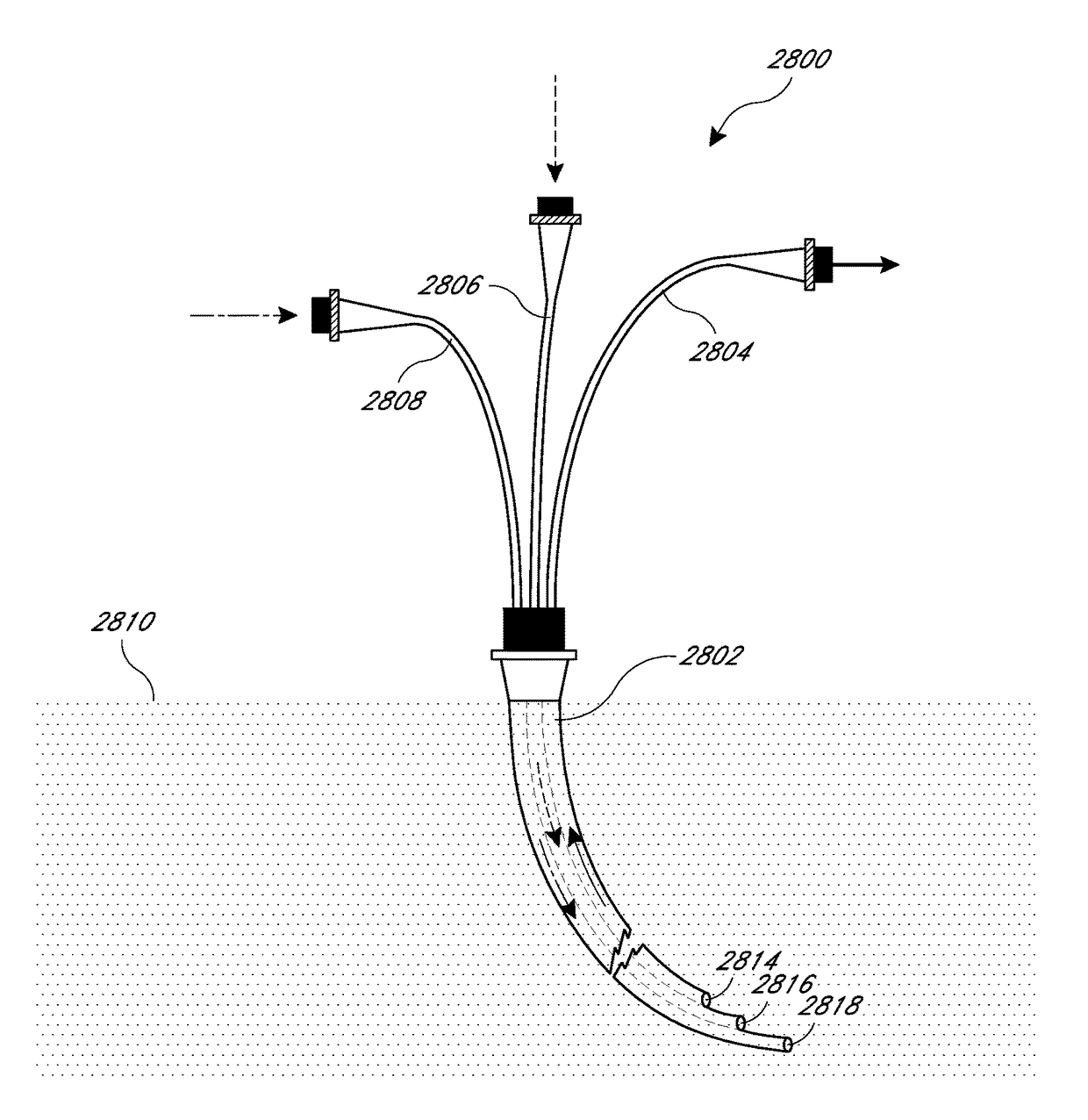
Method and device for removal of radiocontrast media from blood
ActiveUS20070123838A1Control flowIncrease probabilityOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationBlood replacementCoronary arteries
An extracorporeal blood circuit including: a withdrawal conduit connectable to a coronary withdrawal catheter; a withdrawal pump connectable to the withdrawal conduit, wherein a pumping rate of the withdrawal pump determines a blood withdrawal rate from the coronary withdrawal catheter; a filter having an input connected to the withdrawal conduit and a blood output connected to an infusion conduit and a filtrate output connected to a filtrate conduit; a filtrate measurement device to determine an amount of filtrate removed from the blood in the filter; a fluid supplementation conduit providing a blood replacement fluid to at least one of the withdrawal conduit, filter and infusion conduit; a supplementation pump connectable to the fluid supplementation conduit, wherein a pumping rate of the supplementation pump determines a rate at which the blood replacement fluid flows into the blood flowing through the blood circuit, and a controller regulating the pumping rate of the supplementation pump such that the rate of the blood replacement fluid provides an amount of blood replacement fluid to the at least one of the withdrawal conduit, filter and infusion conduit so as to substantially match the amount of filtrate removed.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Blood sampling system for improving draw success and reducing hemolysis
InactiveUS20160073937A1Improve blood draw successReduce hemolysisCatheterSensorsHemolysisBlood sampling
An intravenous system can be optimized to improve blood draw success and reduce hemolysis within the blood sample. Multiple optimizations can be made to an intravenous system, such as a peripheral intravenous catheter, to enhance the system's ability to provide blood samples having sufficient quality for many different tests. These optimizations can include features which enable an intravenous system, such as a peripheral intravenous catheter, to continue to perform efficiently when used to obtain blood samples even after the system has been placed within the patient's vasculature for a substantial duration of time. Also, these optimizations can include features for optimizing the fluid path and flow characteristics during blood withdrawal to minimize the amount of hemolysis that may be caused during withdrawal. Further, these optimizations can include features for integrating blood acquisition and dispense capabilities within the system.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Apparatus and method of monitoring a vascular access of a patient subjected to an extracorporeal blood treatment
InactiveUS7749184B2Semi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationHaemodialysis machine
In the apparatus and method for monitoring a vascular access (6) of an extracorporeal circuit (5; 10) of a patient, a control and calculation unit (17) varies a flow rate of a blood pump (9) predisposed to cause blood to circulate in the extracorporeal circuit. The control and calculation unit receives the pressure values in the blood withdrawal line (5) and the blood return line (10) from two pressure sensors (8, 12); the pressure values are a series of different values of the blood flow rate. The control and calculation unit processes the data gathered by means of a mathematical model which describes the variation of pressure in the vascular access as a function of the flow rate, in order to determine the blood flow rate in the vascular access. The invention detects the presence and location of a stenosis at the vascular access of a patient subjected to a hemodialysis treatment.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Hemodialysis access system
ActiveUS20140024998A1Good man-machine interfaceEasy to useOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesEngineeringCatheter
A medical blood access system used for hemodialysis treatment to enable blood withdrawal for processing of blood by an external apparatus and return the same blood to a patient, comprising an interfacial fluid conduit between the machine and patient's blood supply which is repeatedly connectable along a guided pathway passing through epidermis and subcutaneous tissue via a naturally formed tissue tract to enter blood space, providing improved patient safely, convenience, effective prophylaxis, without bleeding or tissue trauma or pain, and is executable by the patient to precisely connect and disconnect with minimal disfigurement or life restrictions, and is useable on virtually all patients soon after placement and is robust and safe to high blood flow.
Owner:PROSL FRANK +2
Cannula inserting system.
InactiveCN101171046APrevent insertionMinimizes the risk of damaging vessel wallsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesVeinSkin surface
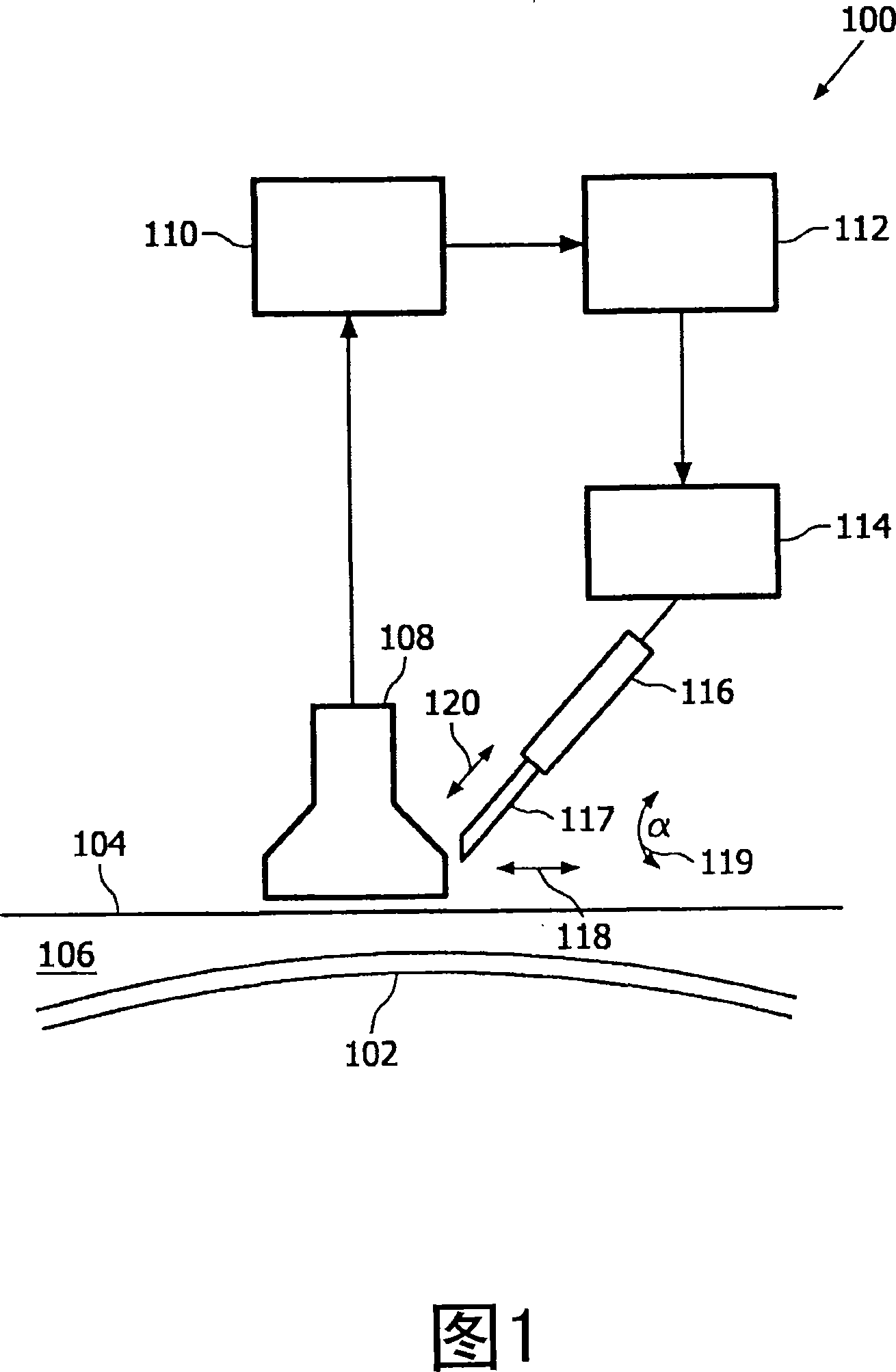
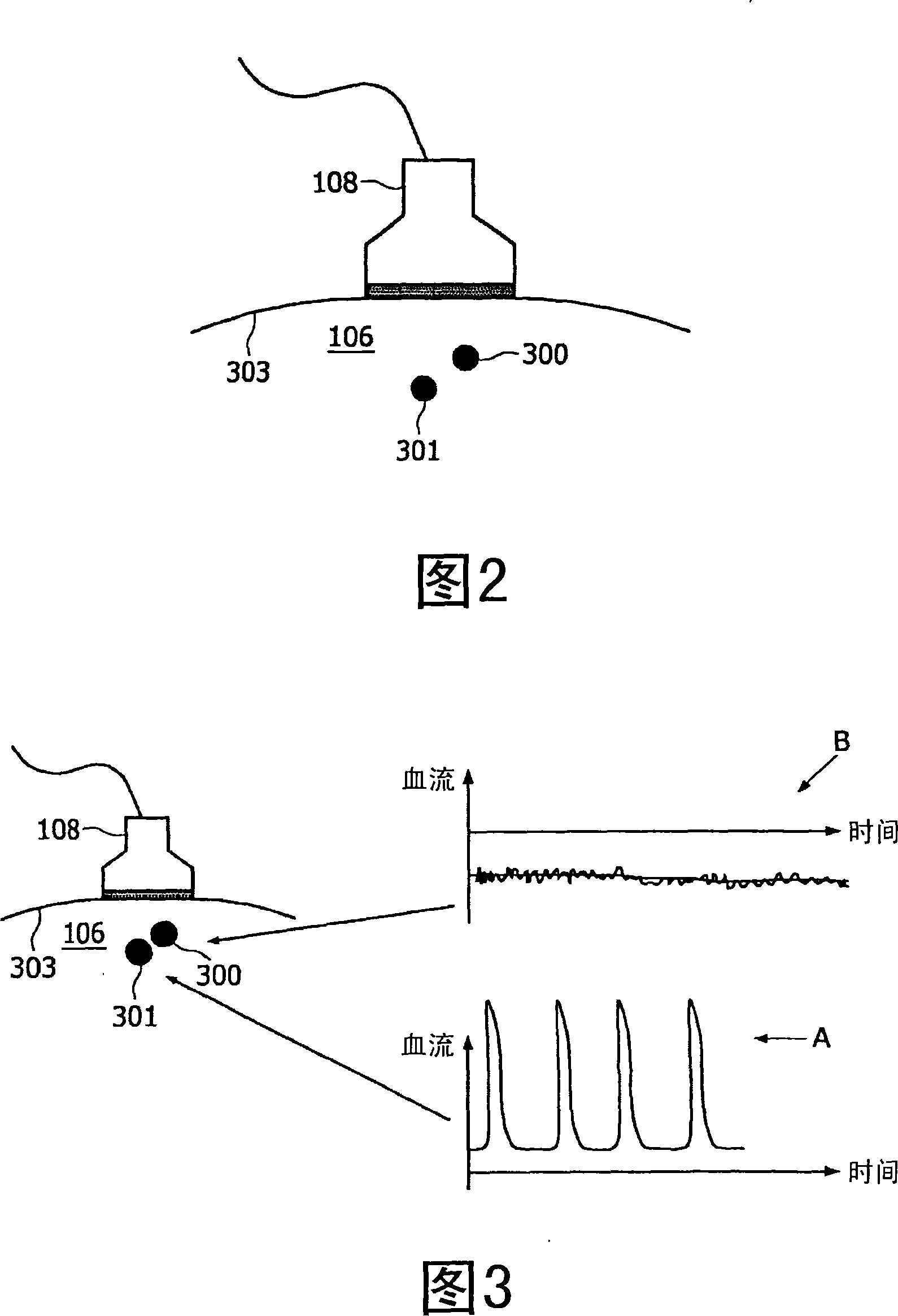
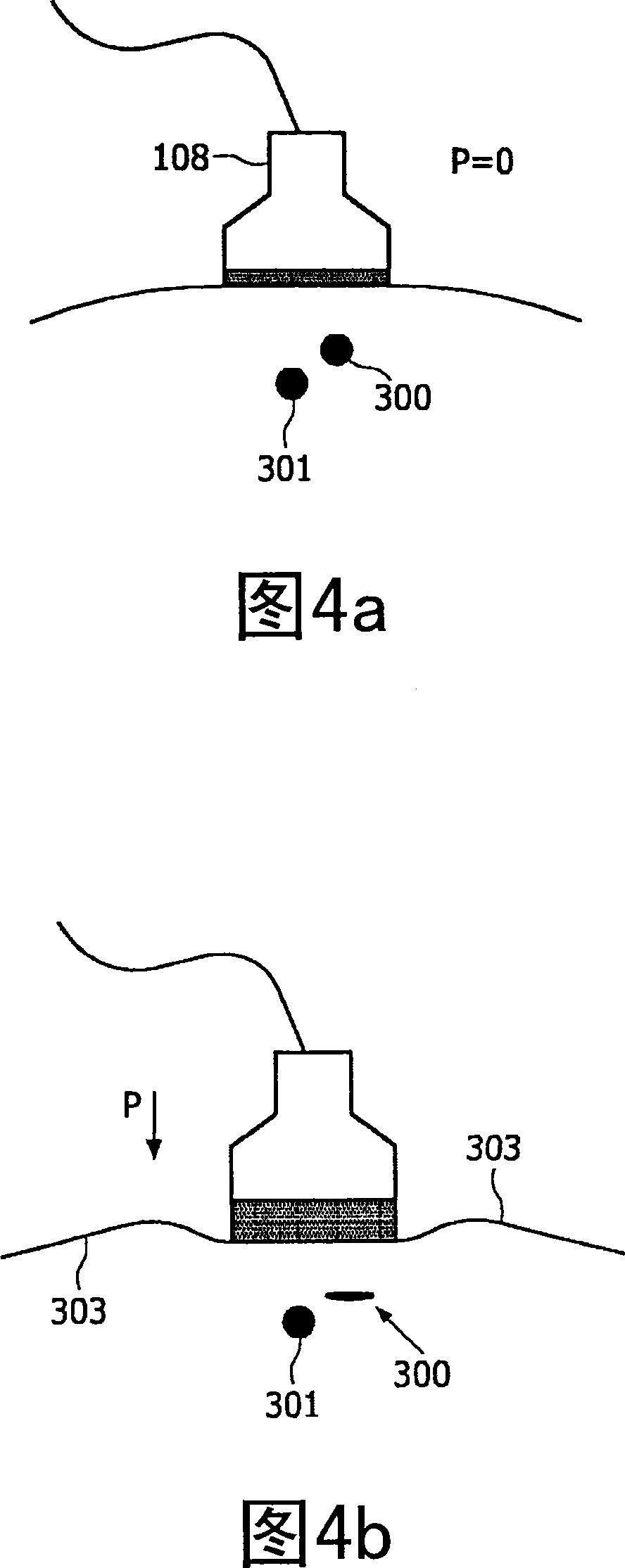
The present invention provides a highly automated puncture system for inserting a cannula or a needle into a blood vessel of a person or an animal. The puncture system has an acquisition module that allows for determining at least a location of a blood vessel underneath of the surface of a skin and is further enabled to determine an optimal puncture location that is well suitable for inserting a cannula into the blood vessel. Further, the puncture system has an actuator for moving and aligning the cannula to a determined position. The system is further adapted to autonomously insert the cannula into the blood vessel for multiple purposes, such as blood withdrawal, venous medication and infusions.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
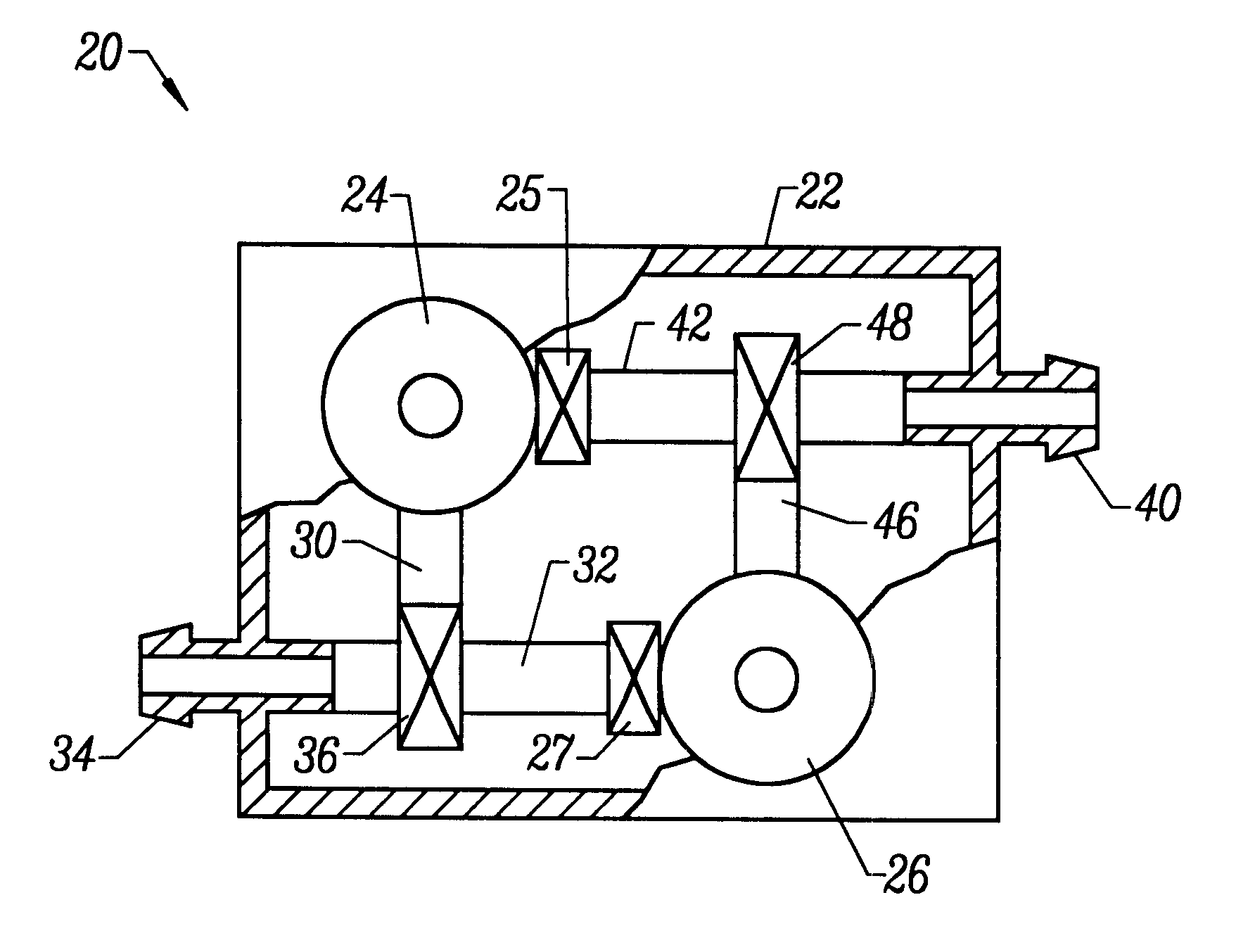
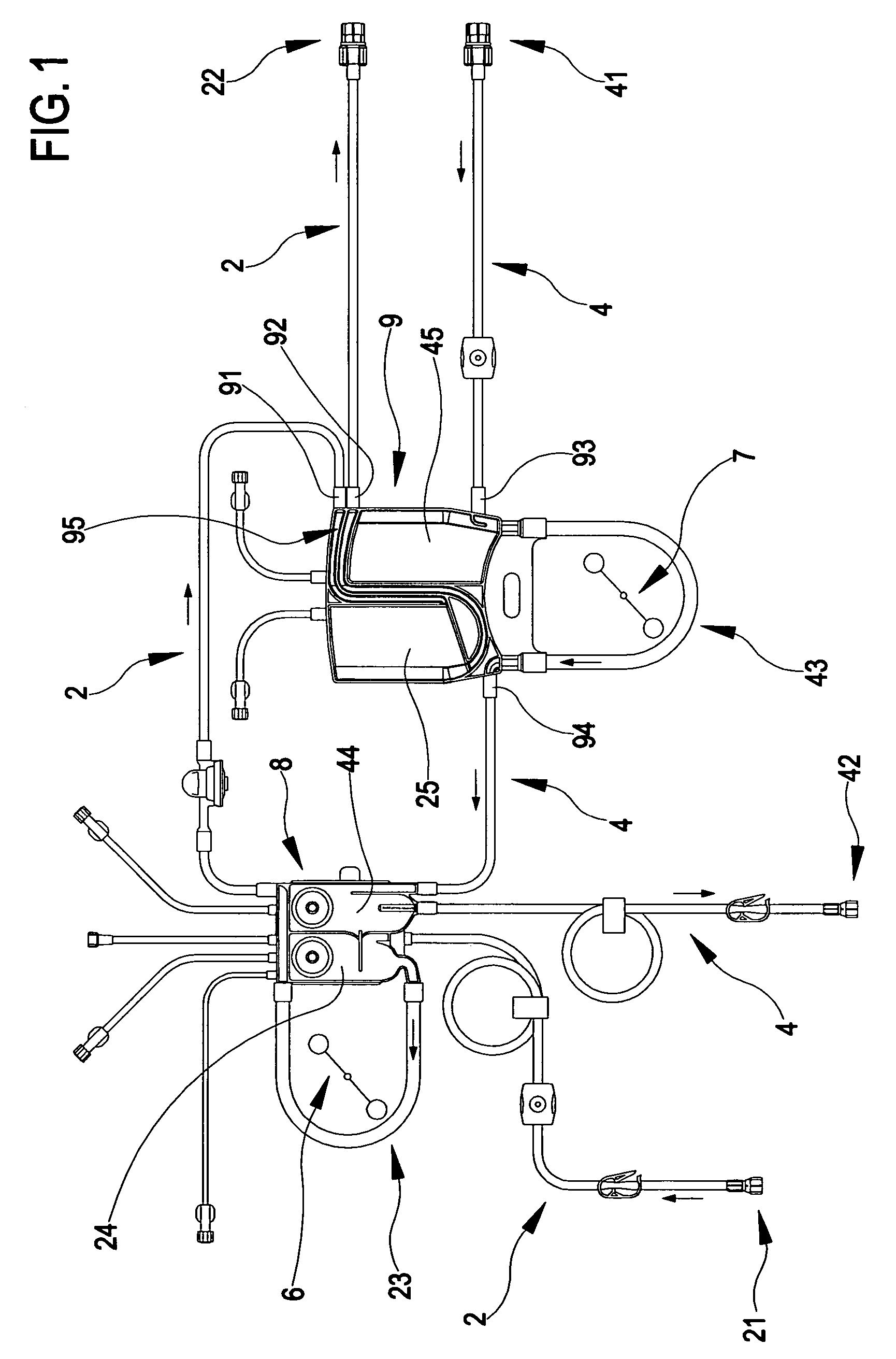
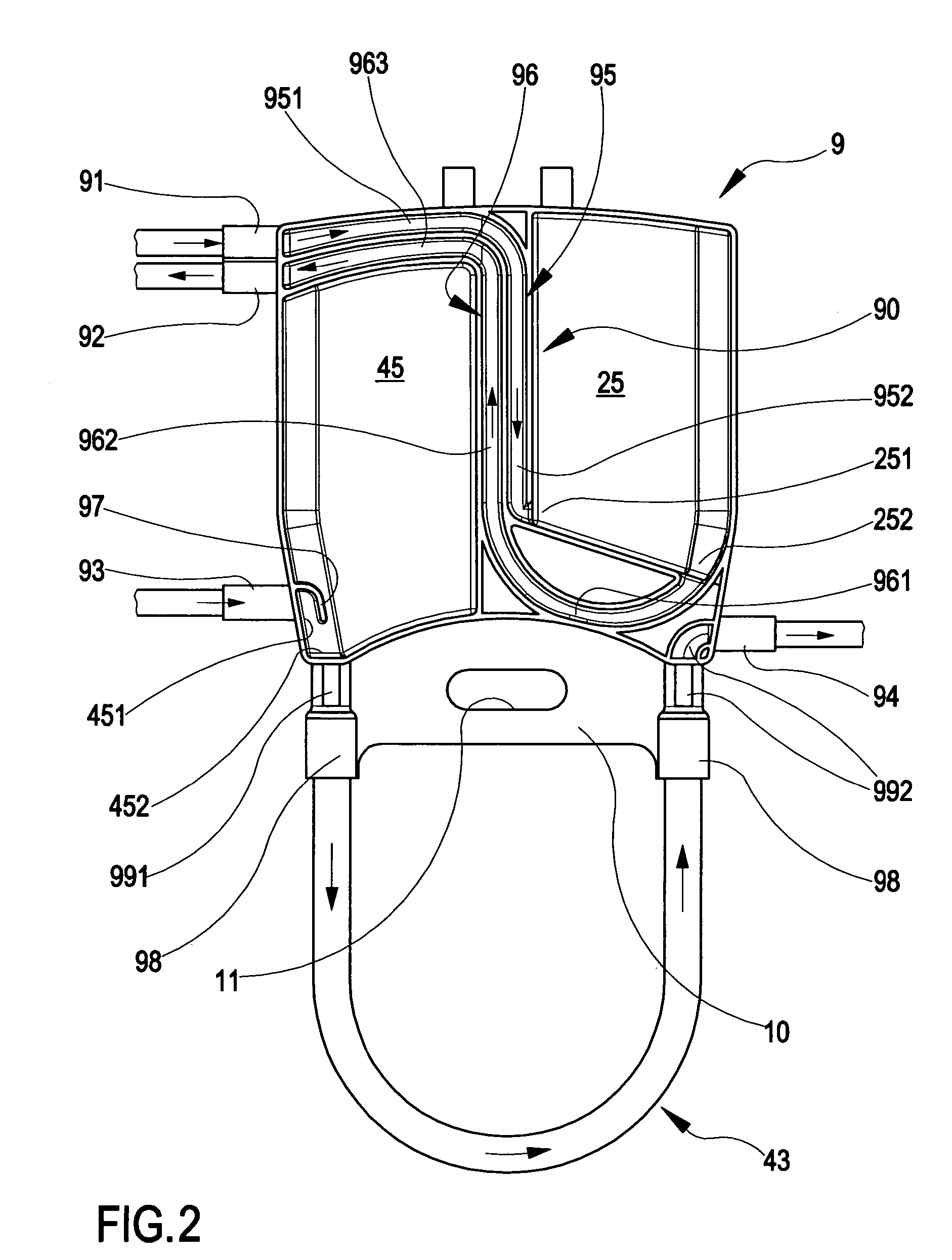
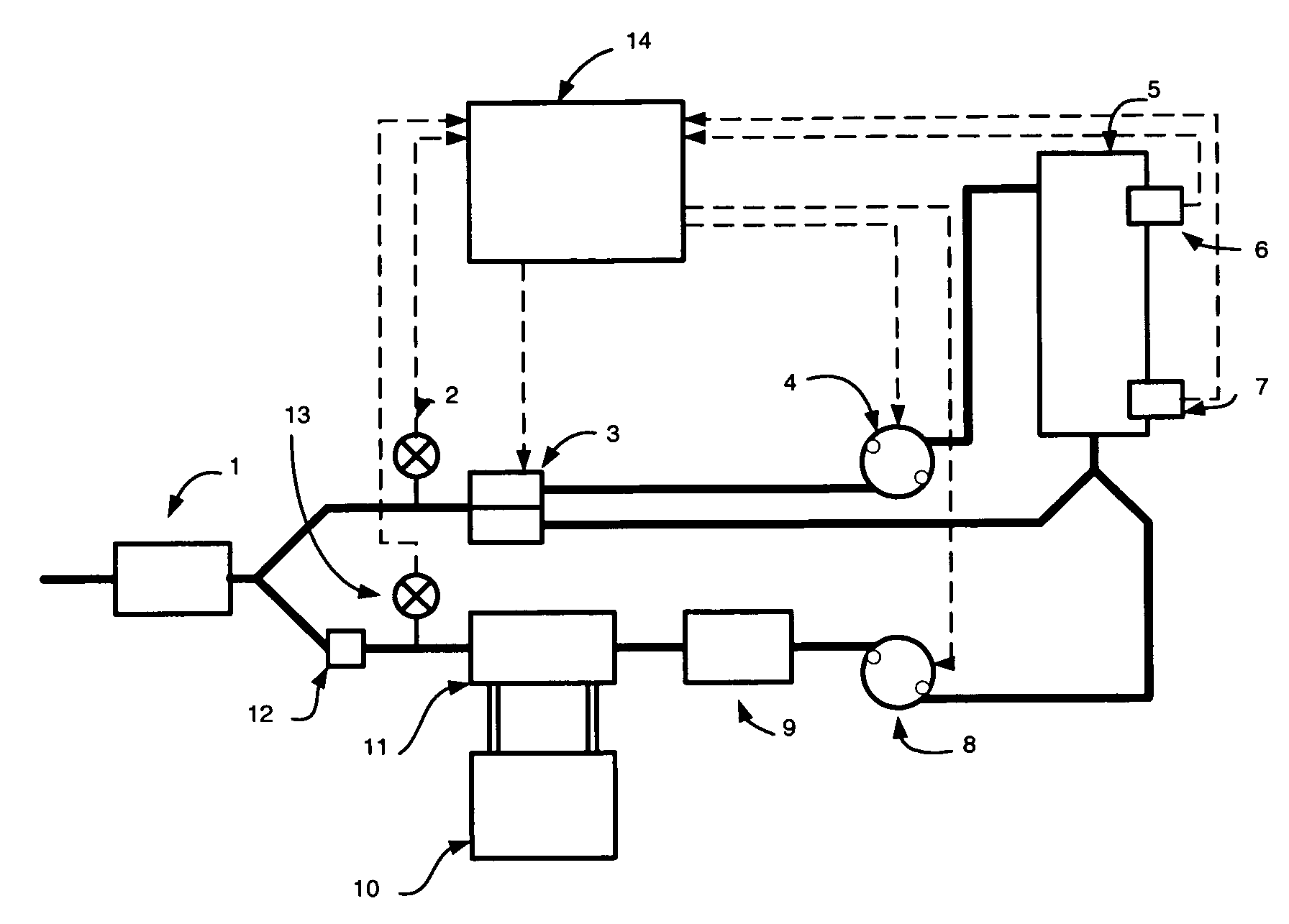
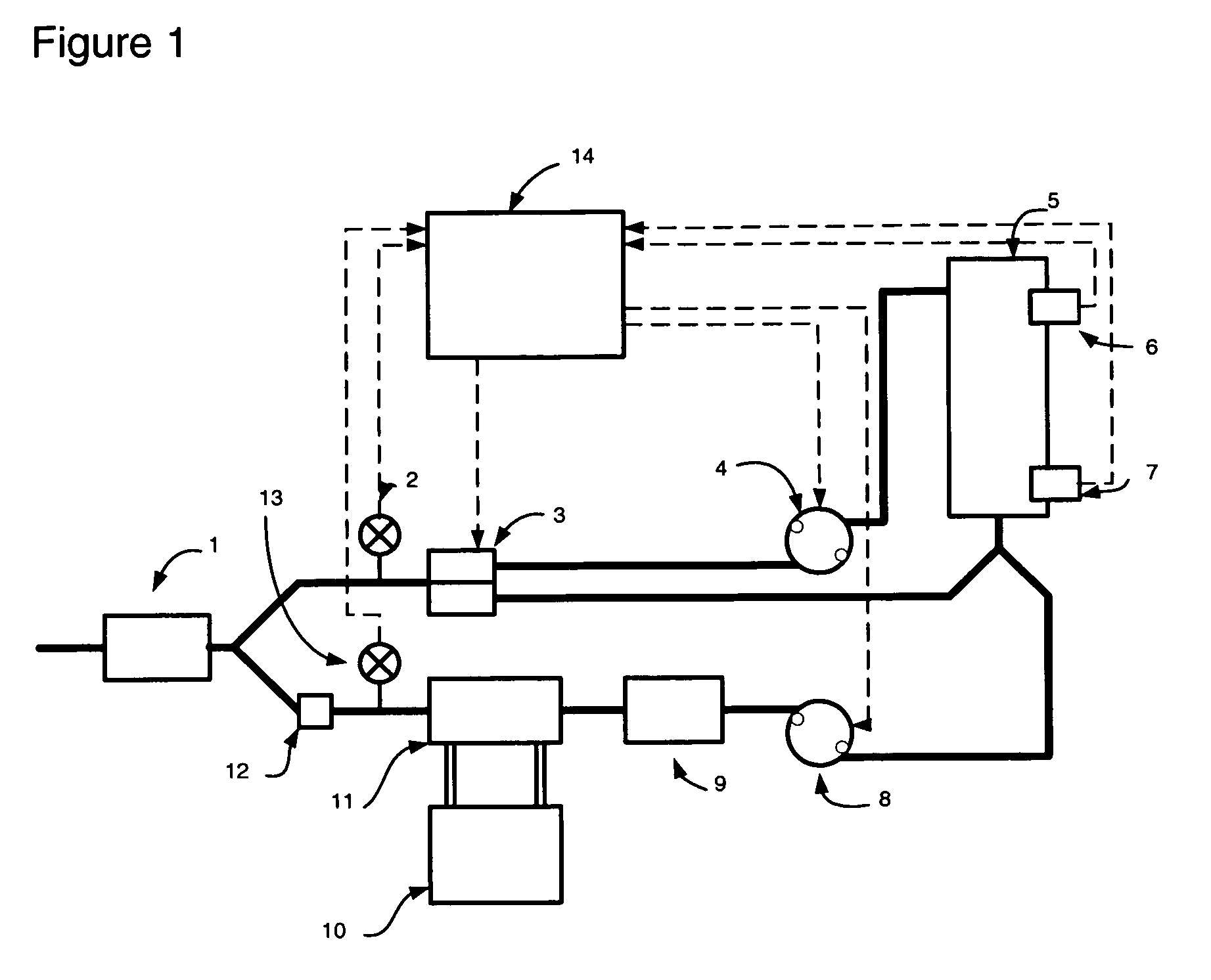
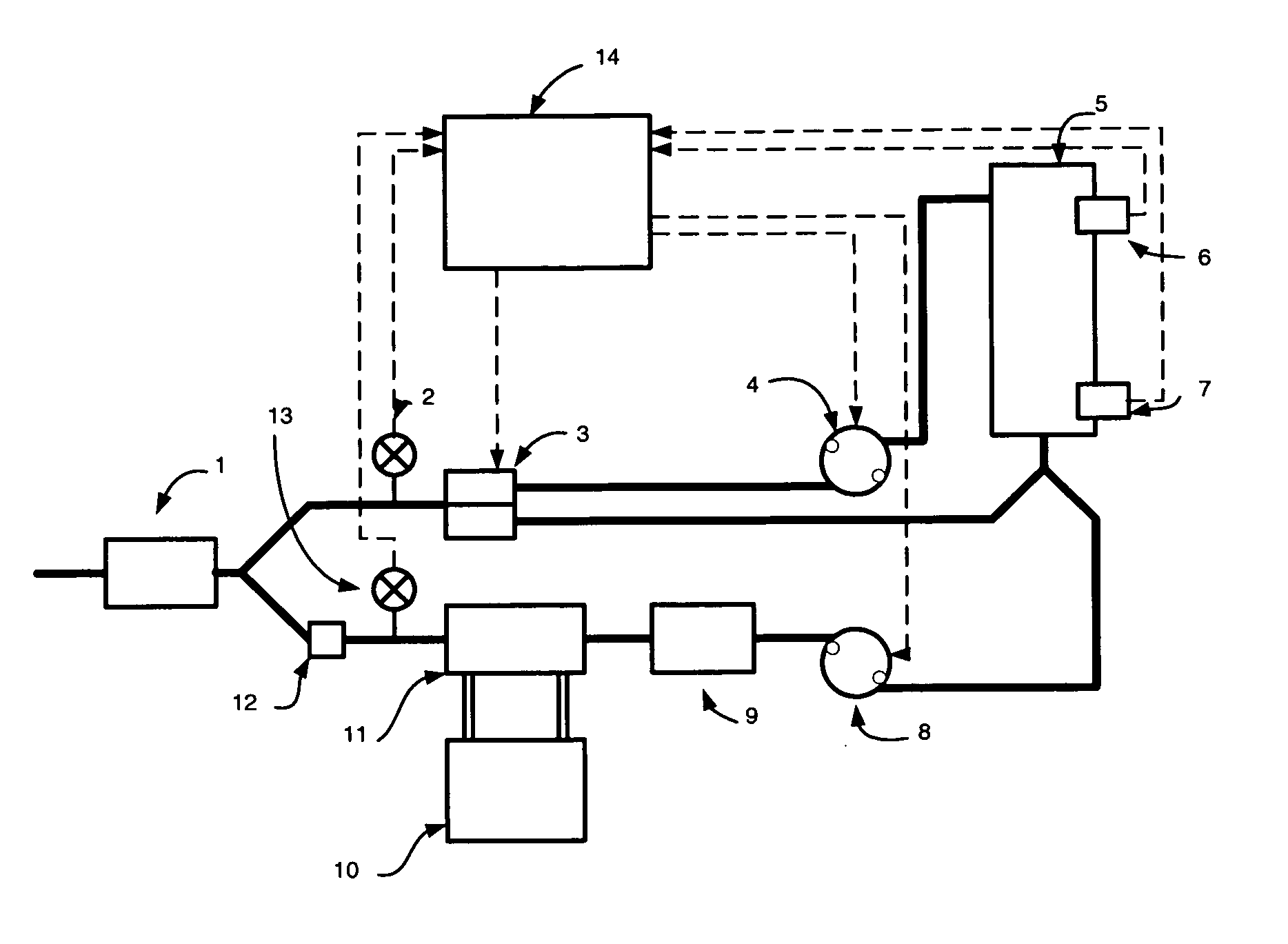
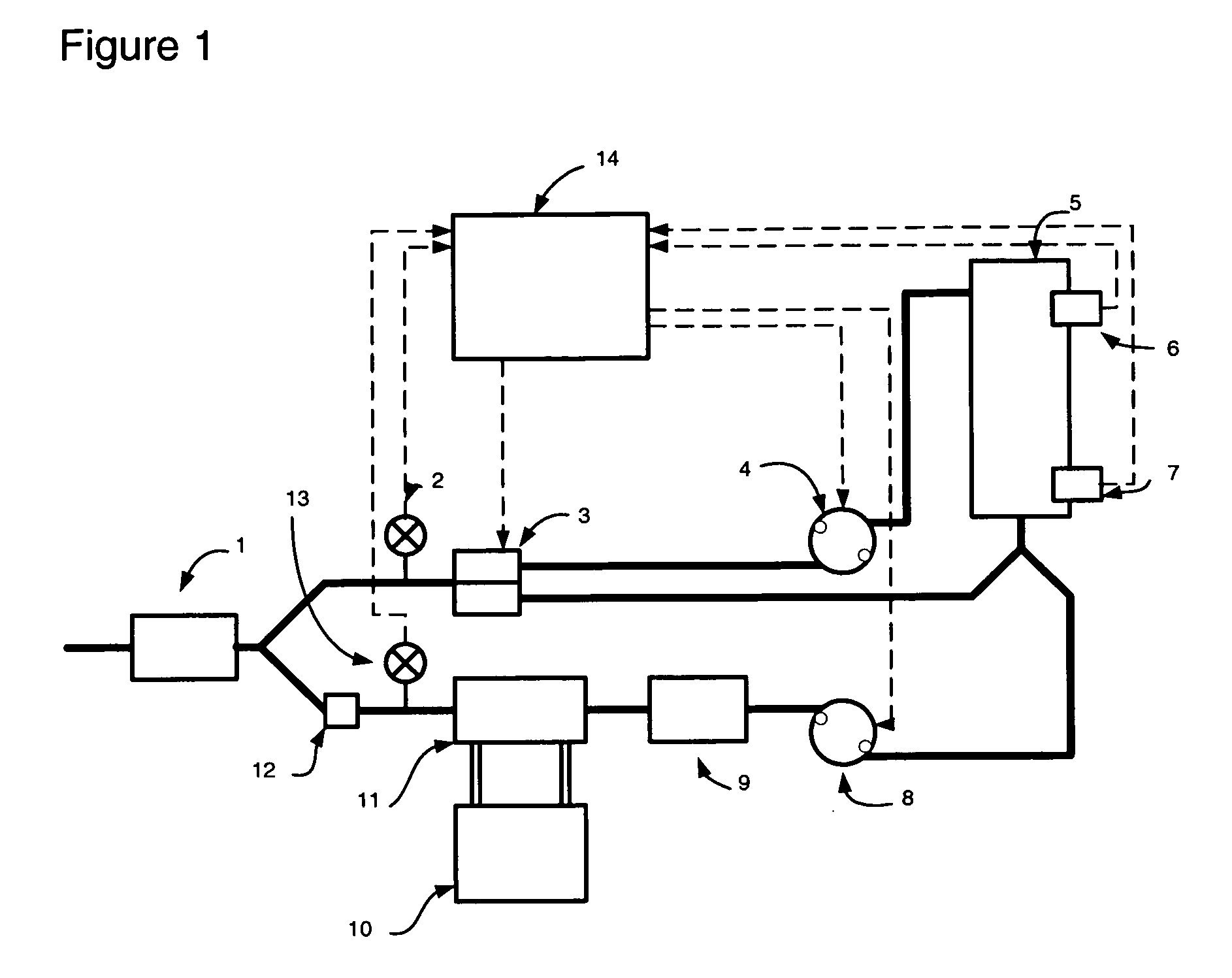
Circuit for extracorporeal blood circulation
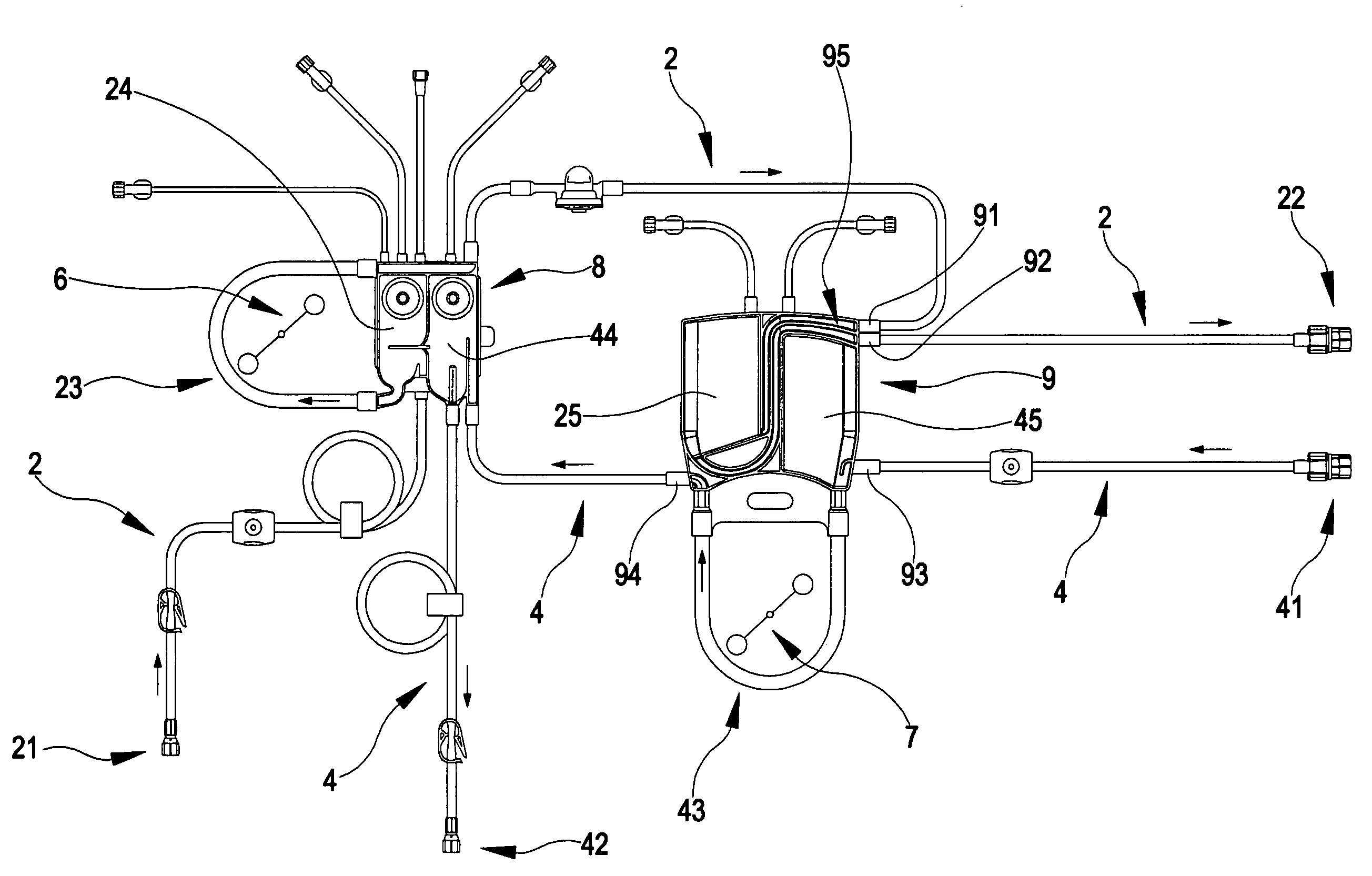
ActiveUS7264607B2Improve scalabilityEasy to operateOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationPeristaltic pump
A circuit for extracorporeal blood circulation, which is used for a single-needle dialysis, comprises a blood withdrawal line (2) having an arterial pump portion (23), and a blood return line (4) having a venous pump portion (43). Pump portions are designed to be coupled with corresponding peristaltic pumps (6), (7). An arterial expansion chamber (25) is arranged on the withdrawal line downstream from said arterial pump portion. A venous expansion chamber (45) is arranged on the return line upstream from said venous pump portion. The two expansion chambers are firmly joined one to the other into an integrated structure (9), which is equipped inside with two ducts connecting the arterial expansion chamber with two fluid connections attached outside to the integrated structure. The circuit can be assembled and disassembled from a dialysis machine easily and rapidly.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Vacuum assistant type hemostix
InactiveCN107212892AReduce and eliminate painAvoid painSensorsBlood sampling devicesBlood Collection TubeFinger structure
The invention discloses a painless blood collection device based on acupuncture in a negative pressure environment. The principle is to pre-set a vacuum environment before triggering the puncture needle. When preparing to take blood, the skin and the ejection shell form a closed space. When the puncture needle is triggered, the vacuum chamber and the closed space are connected to form a negative pressure environment. The blood collection needle only needs to puncture a very shallow area The skin, with the assistance of negative pressure, can achieve the required blood collection volume. After the finger releases the locking structure, the connected air hole can eliminate the negative pressure state and complete the blood collection process. This article provides two embodiments, one is a reusable negative pressure painless blood collection device, and the other is a disposable negative pressure painless blood collection device.
Owner:雷鸣 +1
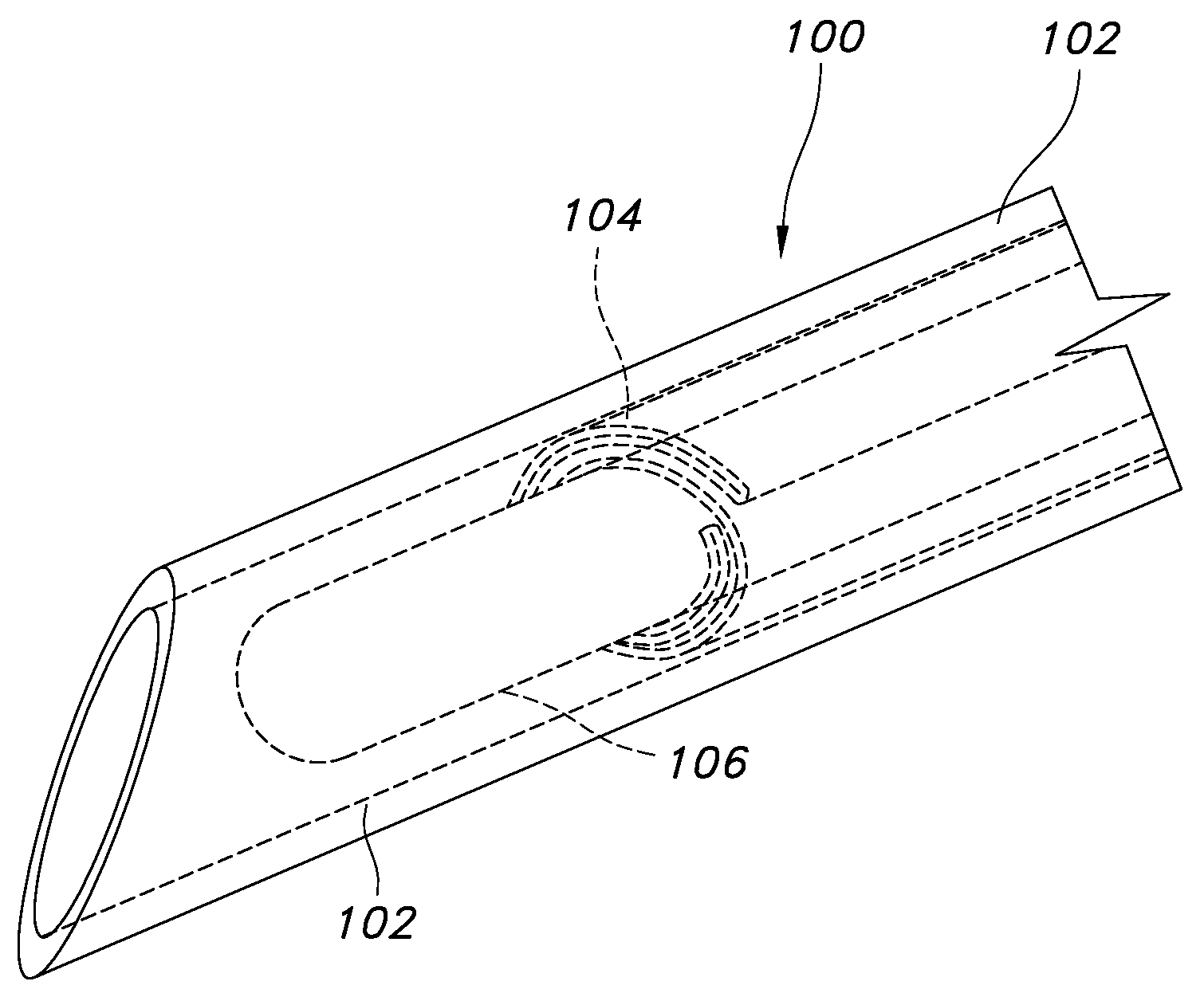
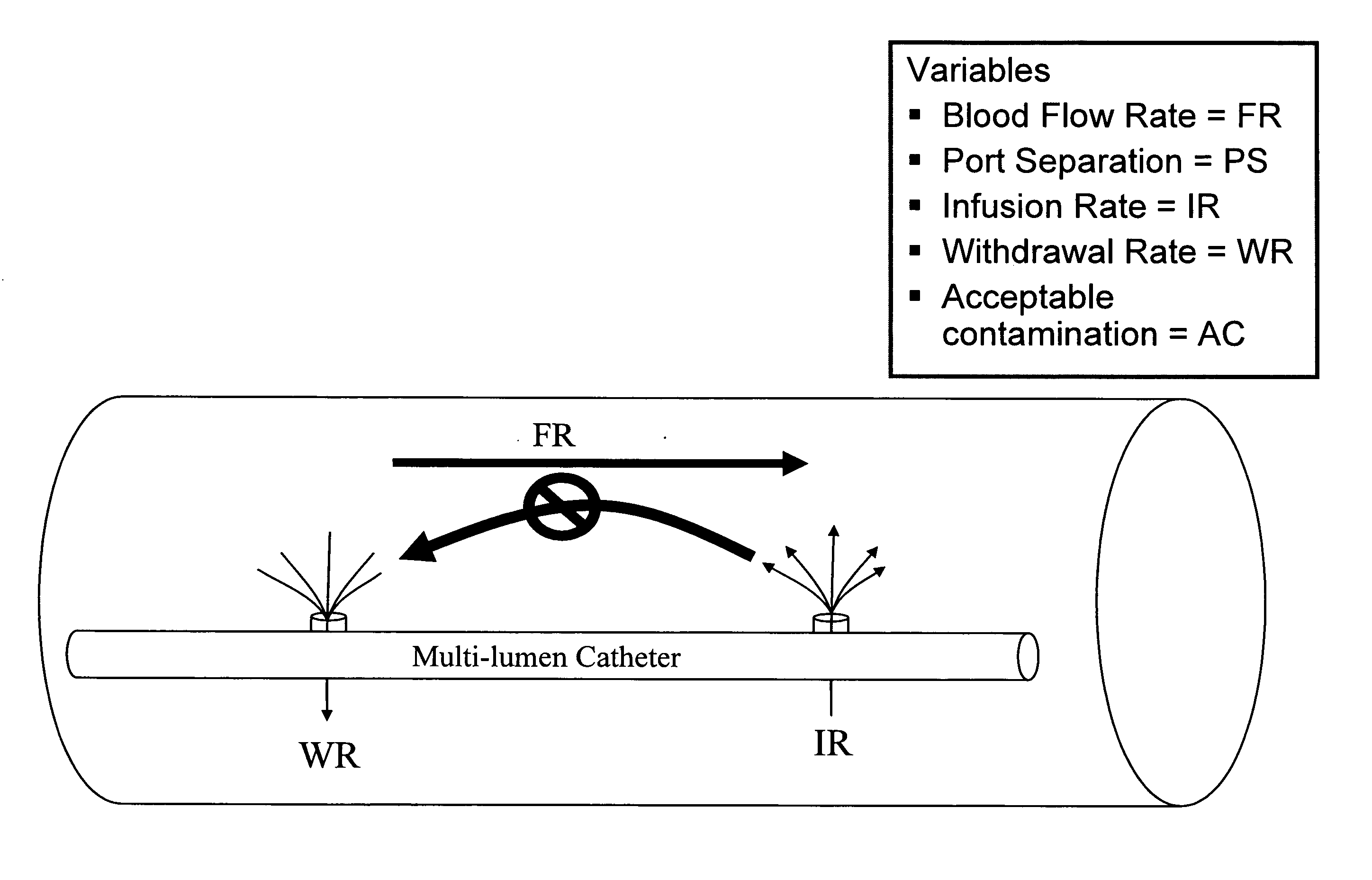
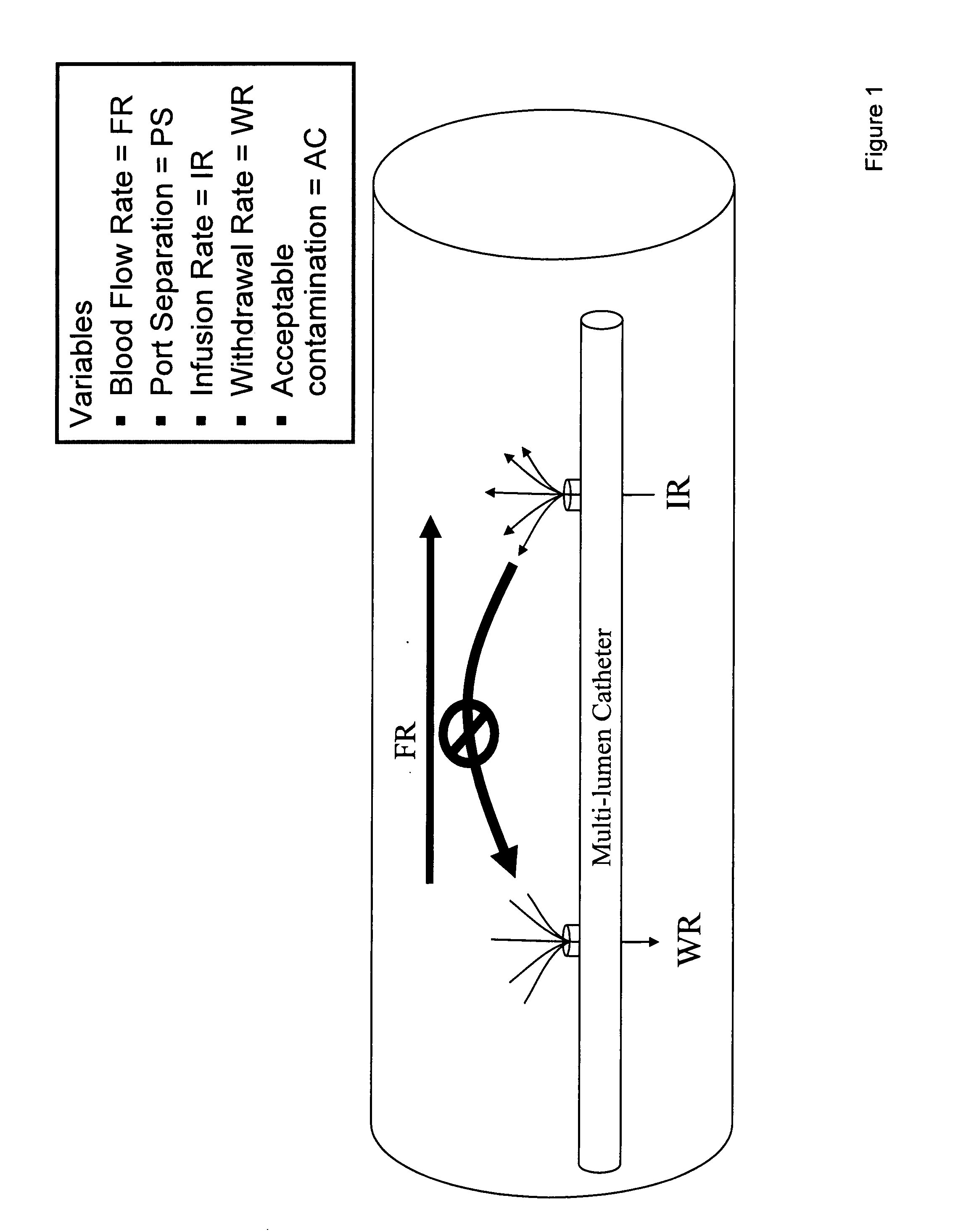
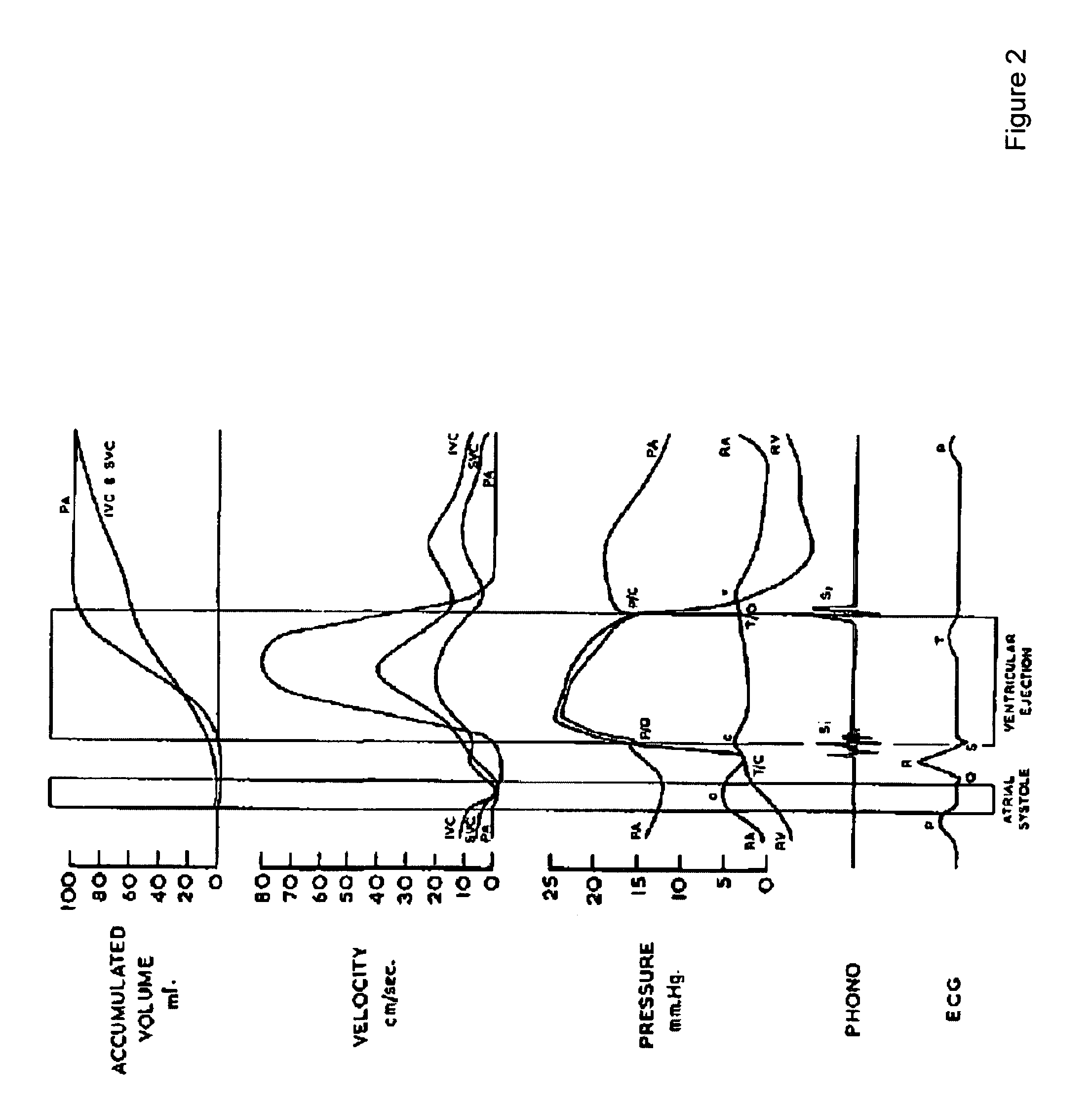
Managing Cross-contamination in Blood Samples Withdrawn from a Multilumen Catheter
InactiveUS20090048576A1Accurate measurementIncrease opportunitiesMedical devicesCatheterBlood withdrawalBlood stream
The present invention comprises methods and apparatuses that can provide accurate measurement of glucose or other analytes from a multilumen catheter in the presence of infusion of substances, including glucose. Examples of “multilumen catheters” include central venous catheters having multiple lumens, midline catheters having multiple lumens, multiple catheters configured or emplaced such that their lumens are in proximity to each other, and, in the case of indwelling analyte sensors, a catheter with a lumen for infusion and an indwelling sensor spaced apart from the infusion lumen. For blood withdrawal, anti-cross contamination controls can prevent the entrainment of blood which might be contaminated with feeding fluids or medications that are administered through other lumens within the catheter and in proximity of the blood sampling port. Cross contamination can occur under various situations, and is known to occur when the patient is connected to a ventilator. The ventilator cyclically raises the intra-thoracic pressure and diminishes blood flow rate in the central veins returning to the heart. The diminished flow can increase the chances for cross-contamination when additional lumens are introducing fluids during a draw sample.
Owner:LUMINOUS MEDICAL
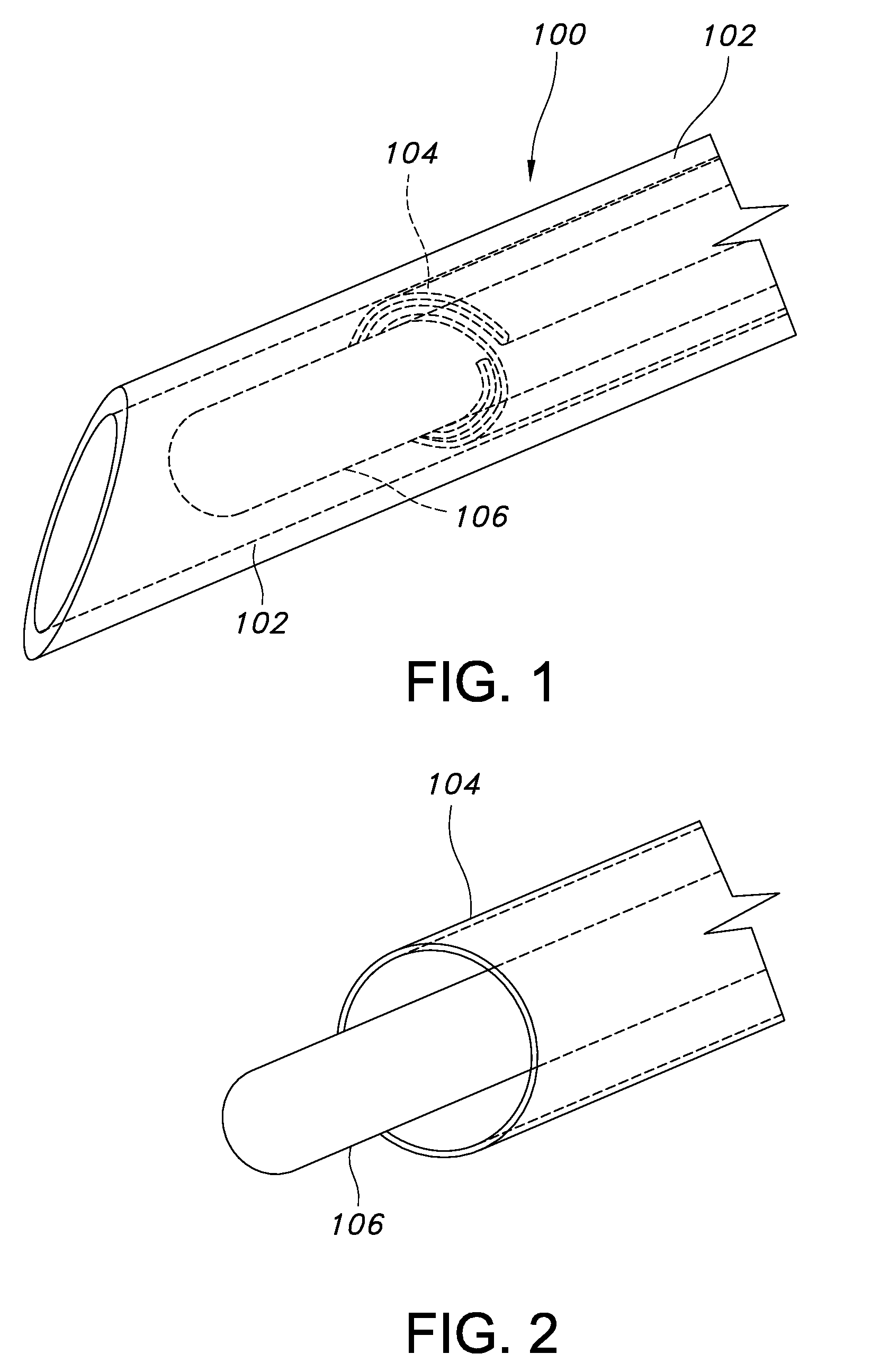
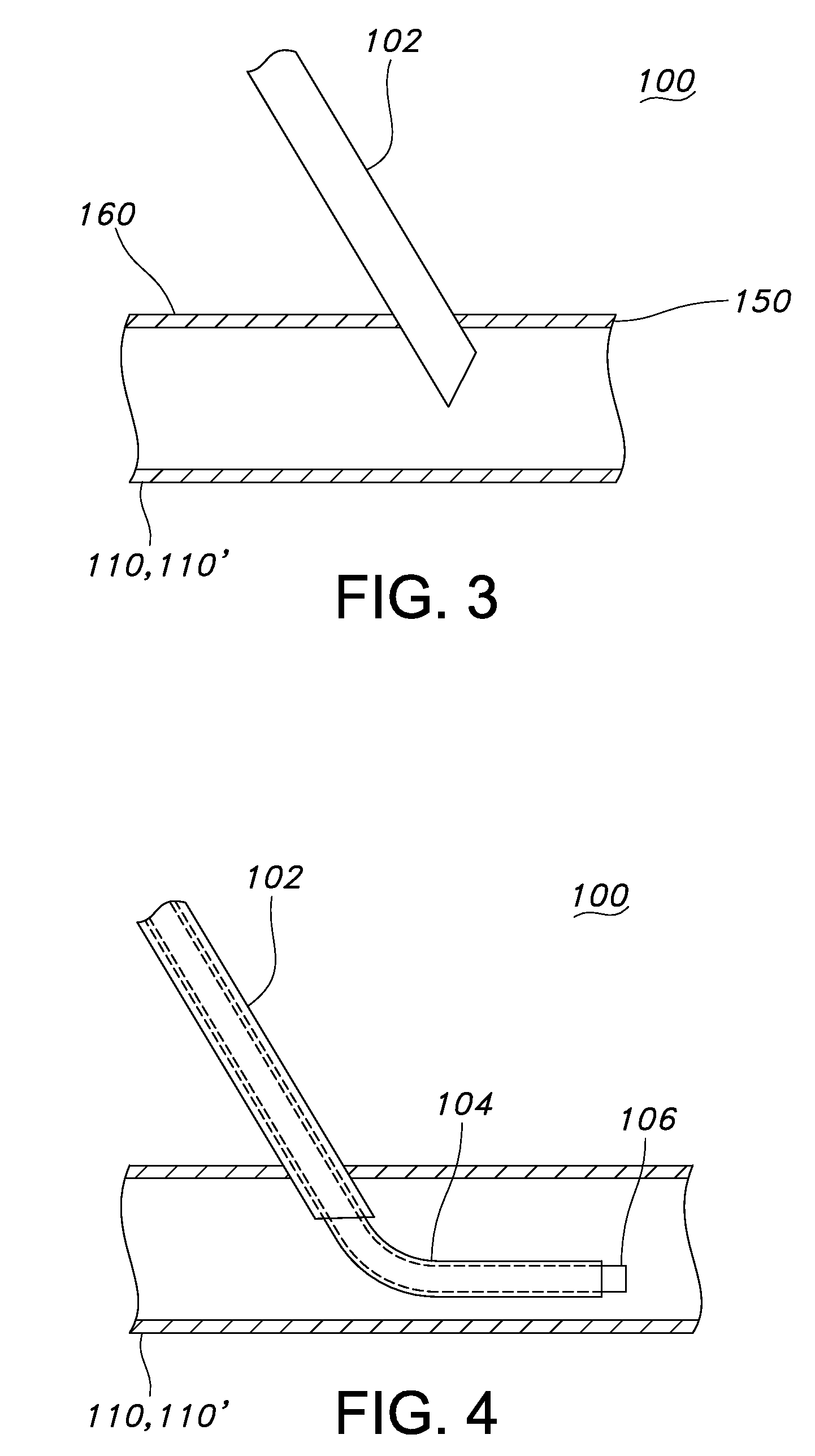
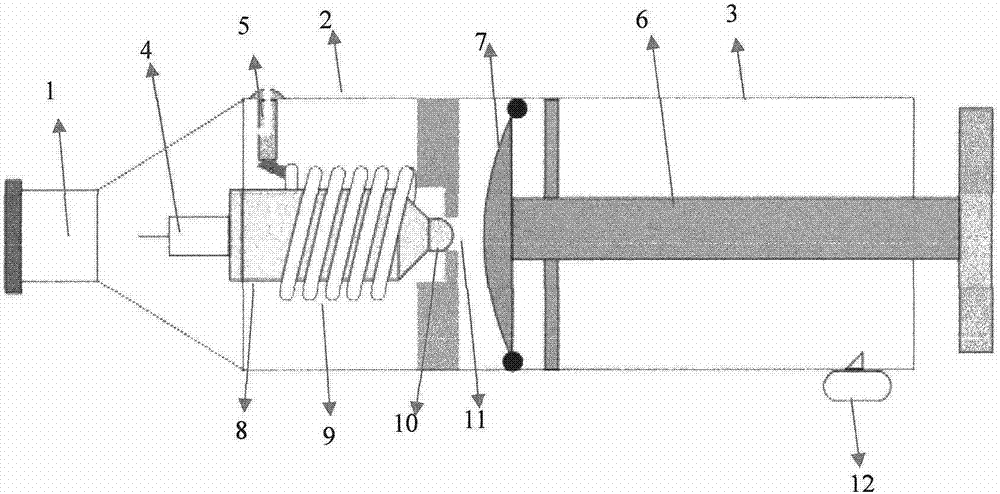
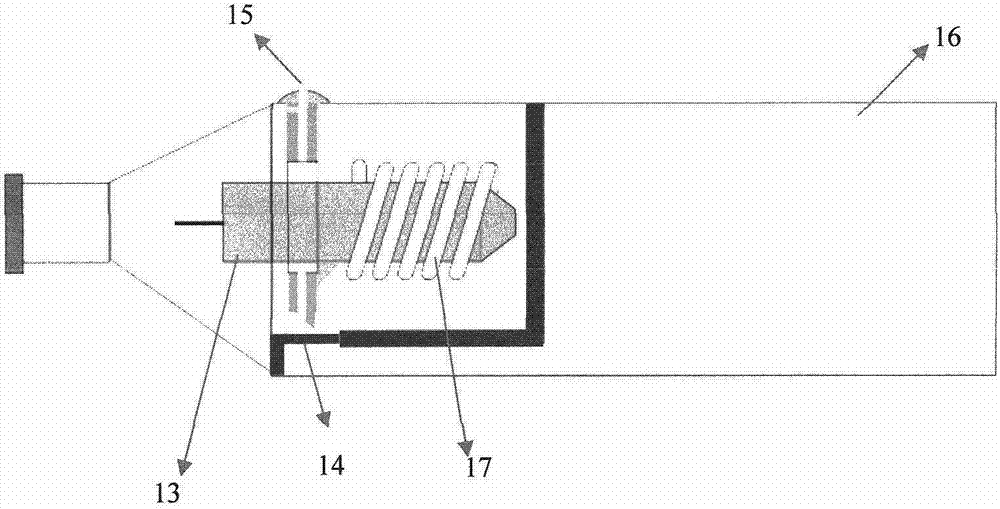
Blood withdrawal device
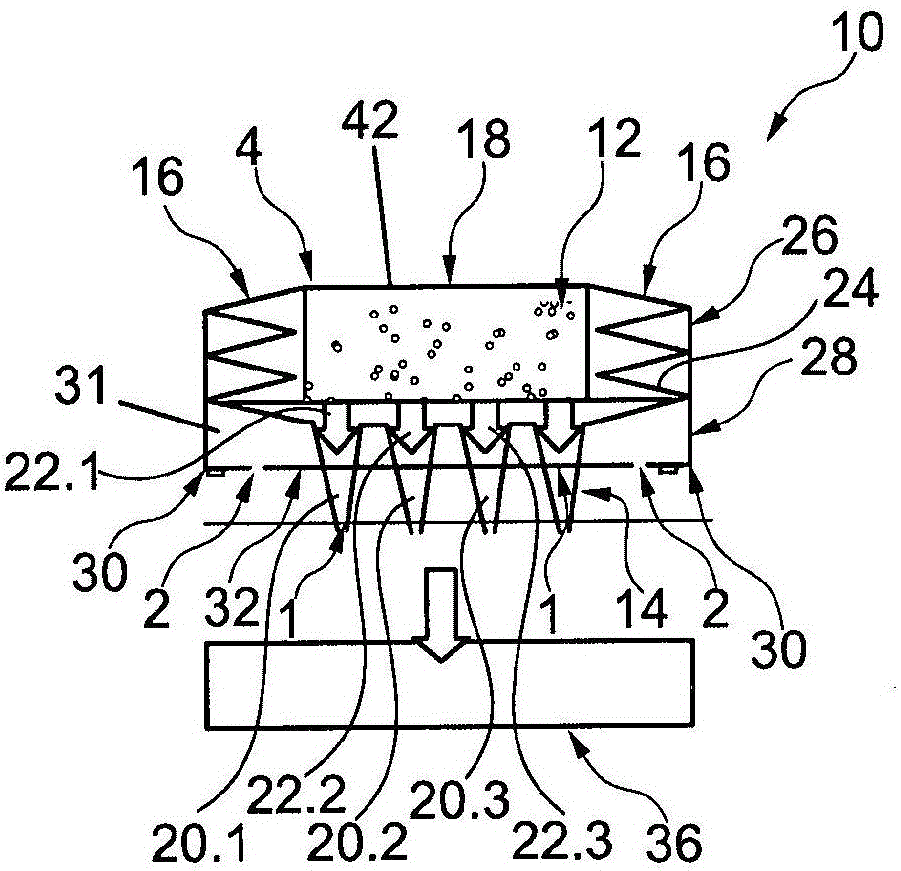
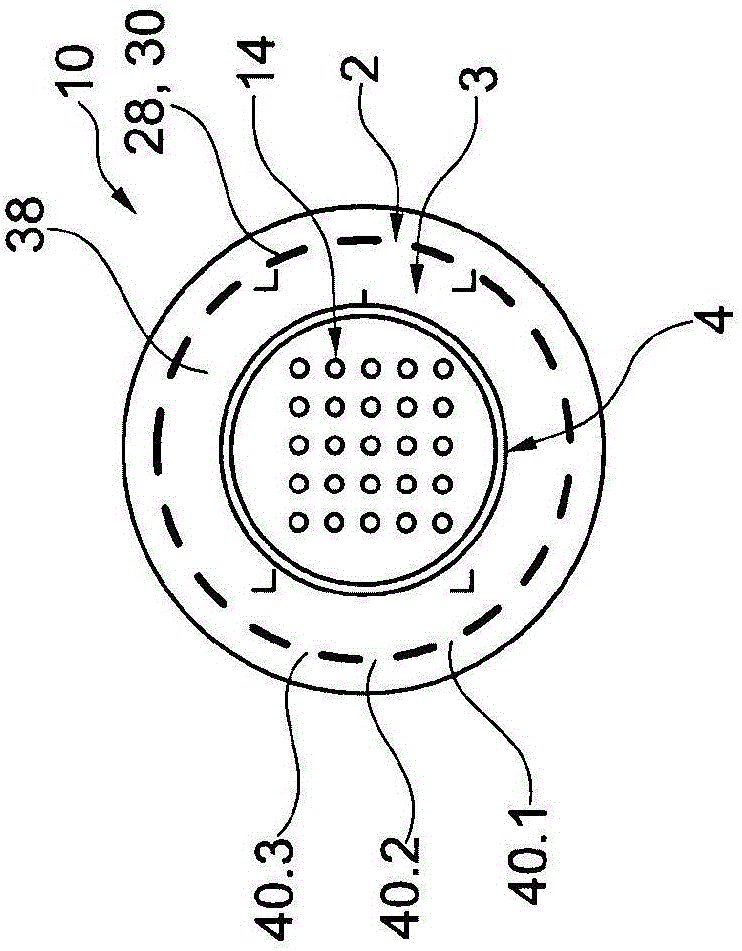
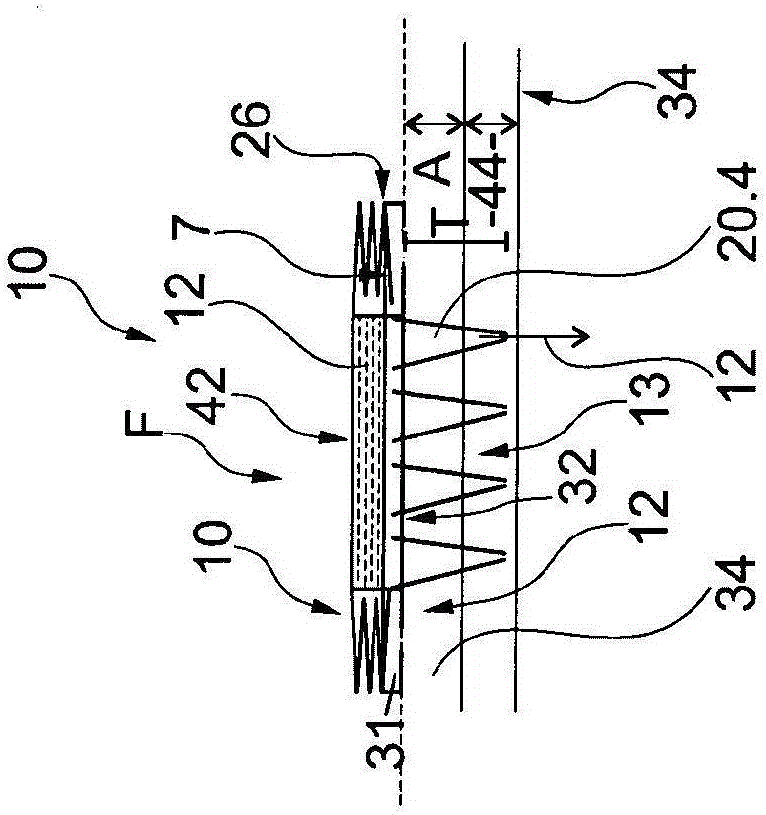
The invention relates to a blood withdrawal device (10) having an active liquid (12) containing a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a microneedle patch (14) having a plurality of microneedles (20), wherein a plurality of microneedles (20) is configured for dispensing the active liquid (12) into the skin (34) of a patient, and comprising a negative pressure generating device (16) connected to a plurality of microneedles (20) such that blood (46) can be drawn from the skin (34) by means of the microneedles (20). According to the invention the active liquid (12) contains a pain killer, the active liquid (12) is arranged in the blood reservoir (18), and the negative pressure generating device (16) is connected to the blood reservoir (18) such that by generating an excess pressure in the blood reservoir (18), the active liquid (12) can be dispensed by way of microneedles (20), and by generating a negative pressure, blood (46) can be drawn into the blood reservoir (18).
Owner:P·勒尔 +2
Apparatus for determining a parameter indicative of the progress of an extracorporeal blood treatment
An apparatus for extracorporeal treatment of blood (1) comprising a treatment unit, a blood withdrawal line, a blood return line, a preparation line and a spent dialysate line. A control unit (10) is configured to calculate values of a parameter relating to treatment effectiveness based on measures of the conductivity in the spent dialysate line. The value of the effectiveness parameter is calculated using one or more values representative of the conductivity in the spent dialysate line obtained relying on a mathematical model.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Hypothermia induction device
ActiveUS7473395B2Rapid coolingRaise the possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesVenous accessBlood vessel
A system for rapid induction of indication of hypothermia especially of the heart and brain during cardiac arrest and normal circulation. The device recirculates blood through an extracorporeal circuit using a single venous access. The blood can be cooled and / or treated before reentry to the vascular system. The device maximizes the cooling rate by optimizing the blood withdrawal rate. Cooling of the brain is achieved by flow of cooled blood from the thorax to the head. During cardiac arrest, the blood flow is generated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Owner:ZVIMAN MENEKHEM M +1
Hypothermia induction device
ActiveUS20060041217A1Rapid coolingRaise the possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesVenous accessThoracic cavity
A system for rapid induction of indication of hypothermia especially of the heart and brain during cardiac arrest and normal circulation. The device recirculates blood through an extracorporeal circuit using a single venous access. The blood can be cooled and / or treated before reentry to the vascular system. The device maximizes the cooling rate by optimizing the blood withdrawal rate. Cooling of the brain is achieved by flow of cooled blood from the thorax to the head. During cardiac arrest, the blood flow is generated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Owner:ZVIMAN MENEKHEM M +1
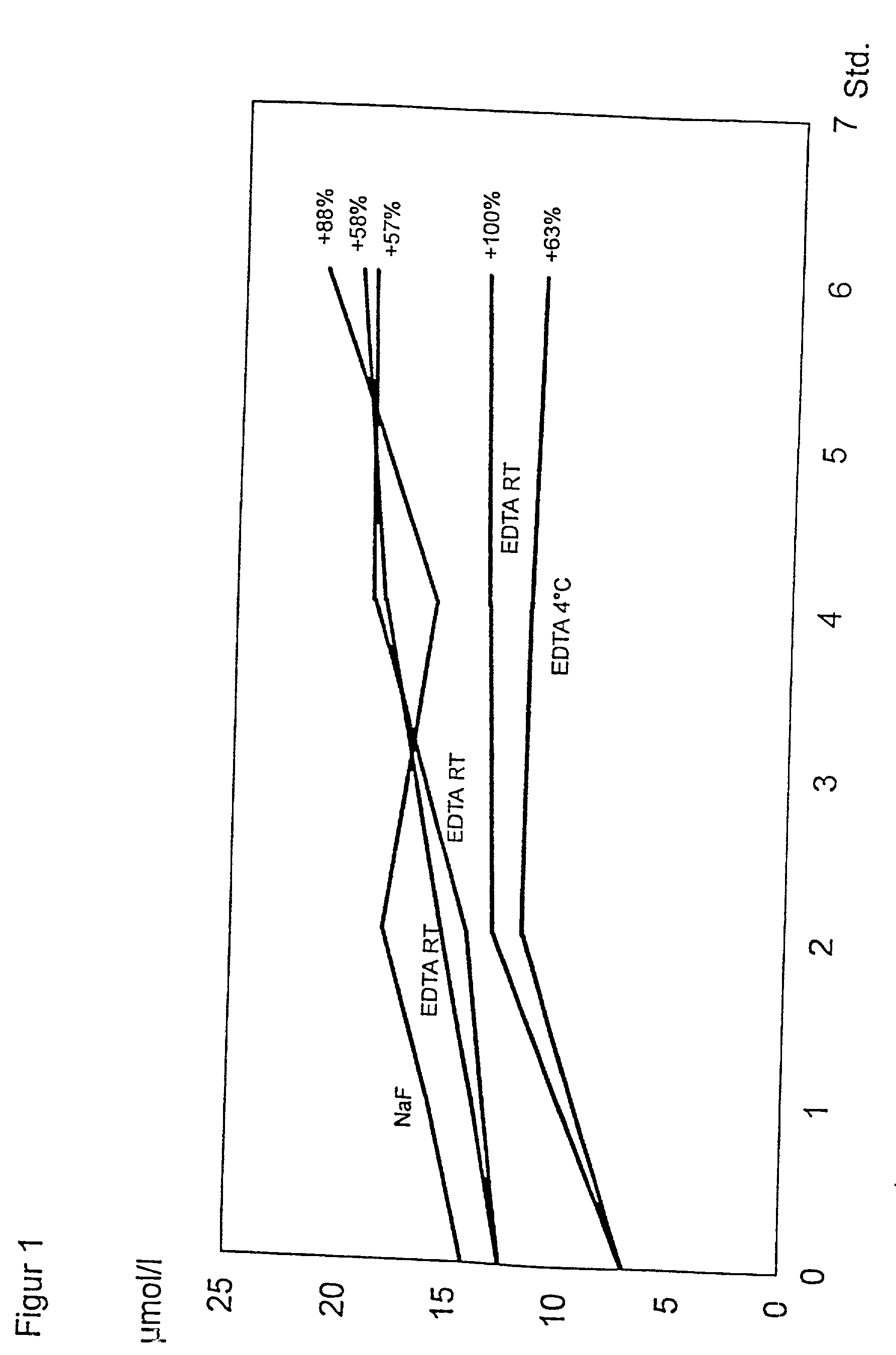
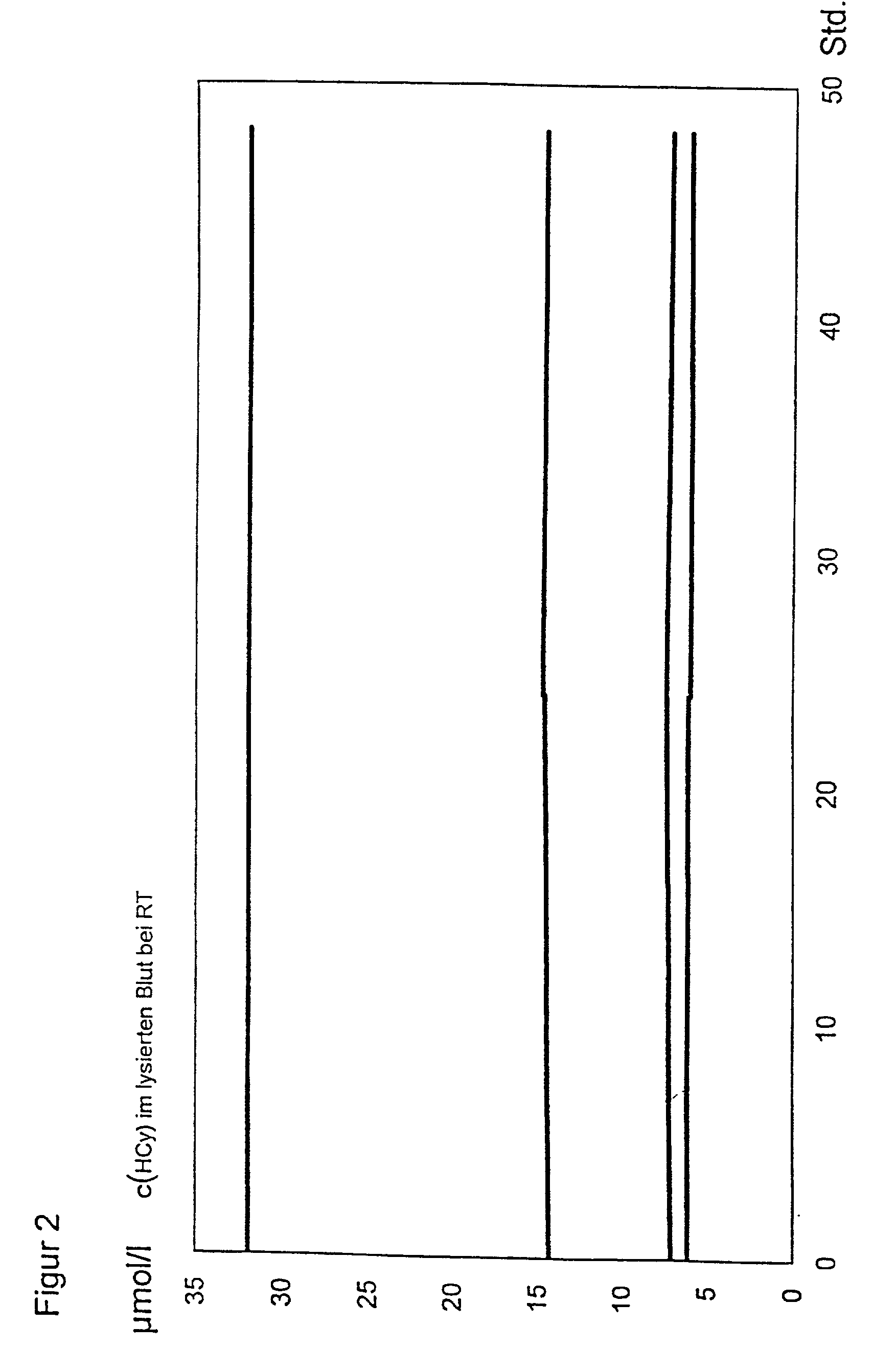
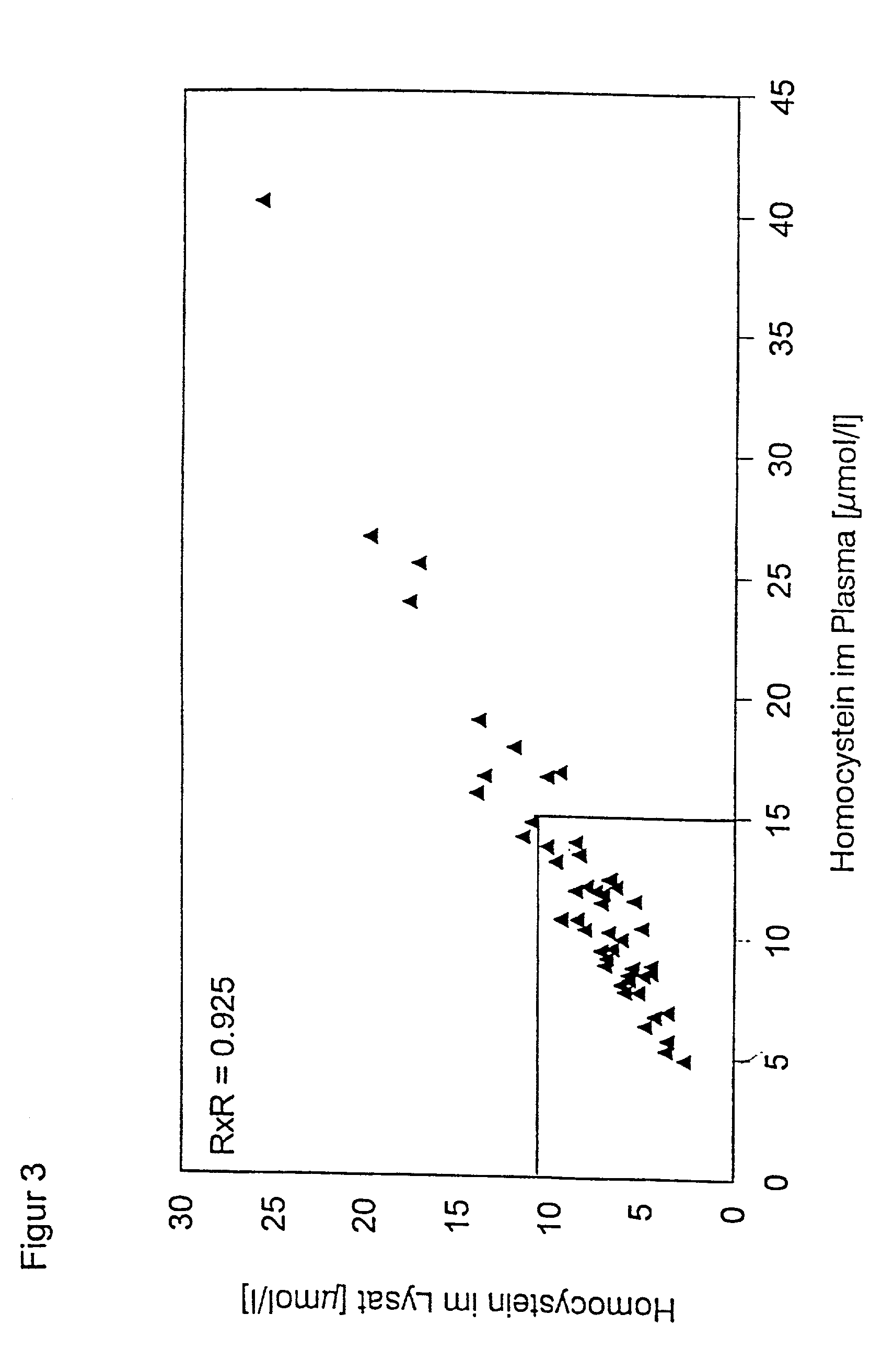
Preparation of blood samples for detecting homocysteine and/or folate
InactiveUS20020001846A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionLysisHomocysteine
Owner:PROBST REINER +1
Systems and methods to reduce fluid contamination
InactiveUS9848821B2Reduce the risk of contaminationHigh measurement accuracyWound drainsBagsAnalyteMedicine
Methods and systems for determining the concentration of one or more analytes from a sample such as blood or plasma are described. The systems described herein can be configured to withdraw a certain volume of sample from a source of bodily fluid, direct a first portion of the withdrawn sample to an analyte monitoring system and return a second portion of the sample to the patient. The analyte monitoring system can include an automated blood withdrawal system that is configured to withdraw blood from the patient's vasculature at low pressure and / or withdrawal rates so as to reduce or prevent contamination of the withdrawn fluid from the infusion fluids.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Blood withdrawal cannula of a pump replacing or assisting activity of the heart
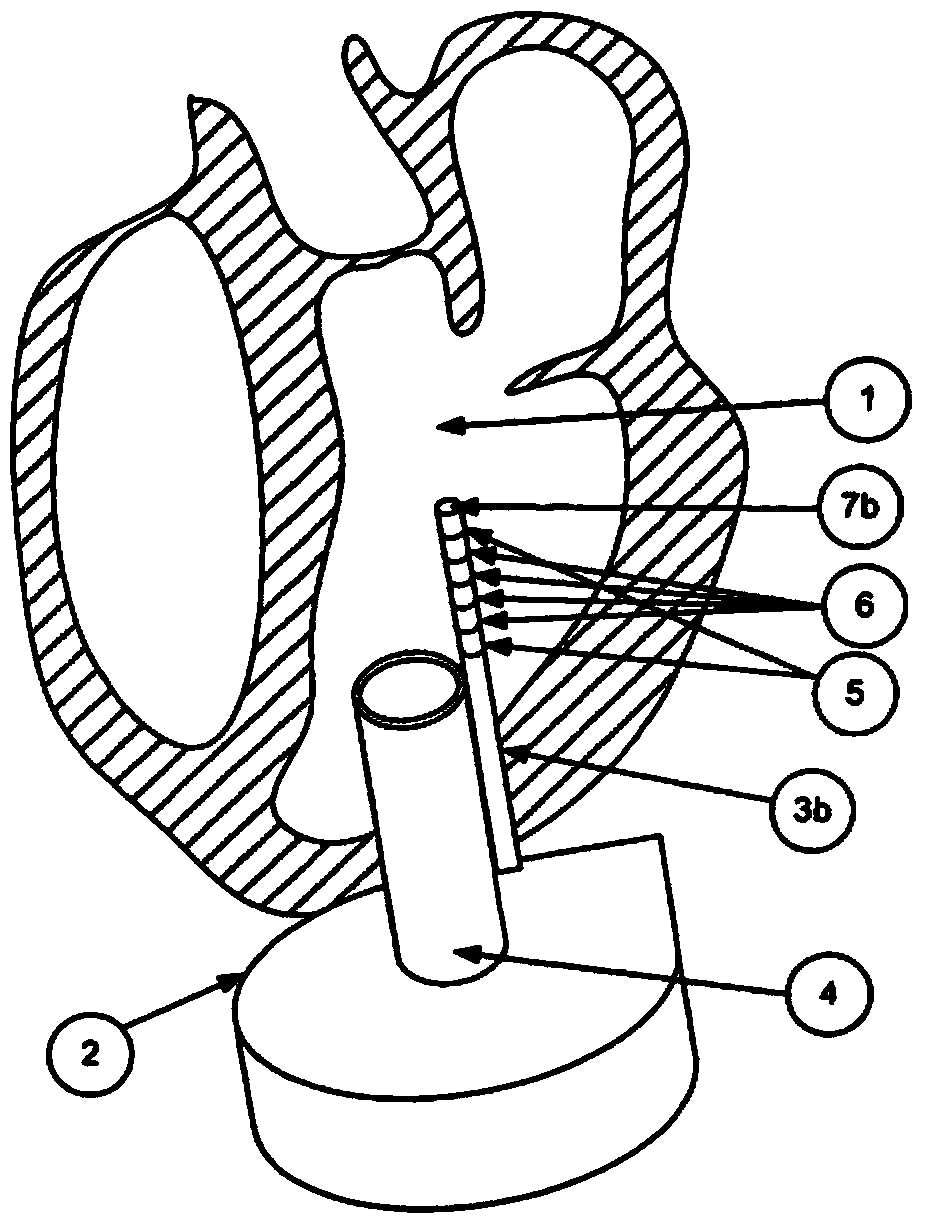
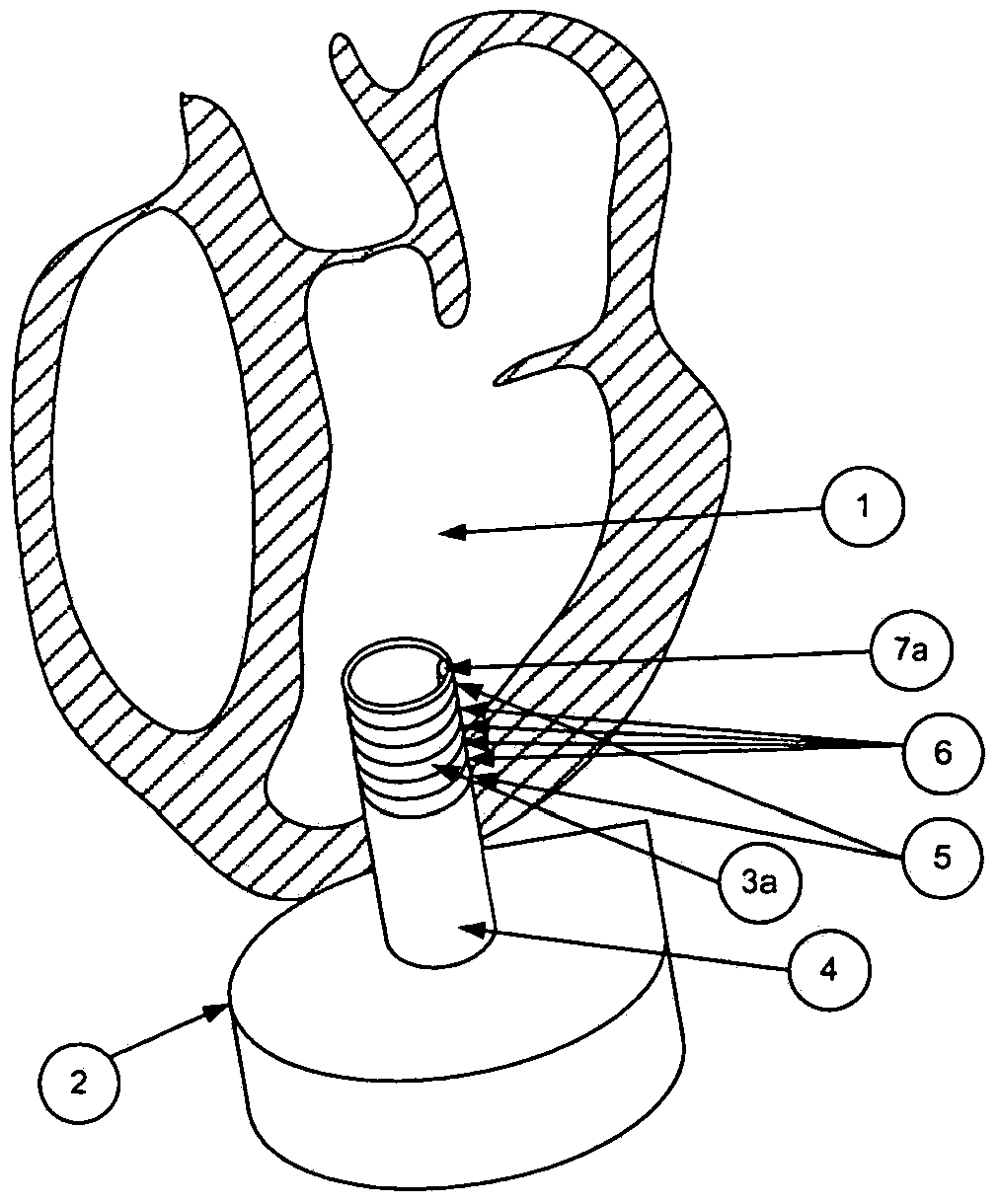
ActiveCN103857326ANo burdenSuitable for long-term surveillanceControl devicesMedical devicesCardiac functioningPressure difference
The invention relates to a blood withdrawal cannula (4) for connecting a pump (2) assisting or replacing activity of the heart to the inner volume of a heart ventricle (1), in particular the left ventricle. At the end thereof that is located in the ventricle the cannula has a pressure sensor (7a, 7b) for measuring the ventricle pressure and / or ventricle pressure differences and at the same end of the cannula has a volume sensor (3a, 3b, 5, 6) for measuring the volume and / or volume changes of the ventricle (1) in at least a partial region of the ventricle. The invention further relates to a measuring device for monitoring the ventricle contractions and / or the function of a pump replacing or assisting activity of the heart. The measuring device can be / is connected to the pressure sensor (7a, 7b) and to the volume sensor of a blood withdrawal cannula according to any one of the preceding claims and is designed to detect pressure changes and volume changes of a ventricle (1) as the heart is beating.
Owner:REINHEART
Apparatus for extracorporeal treatment of blood
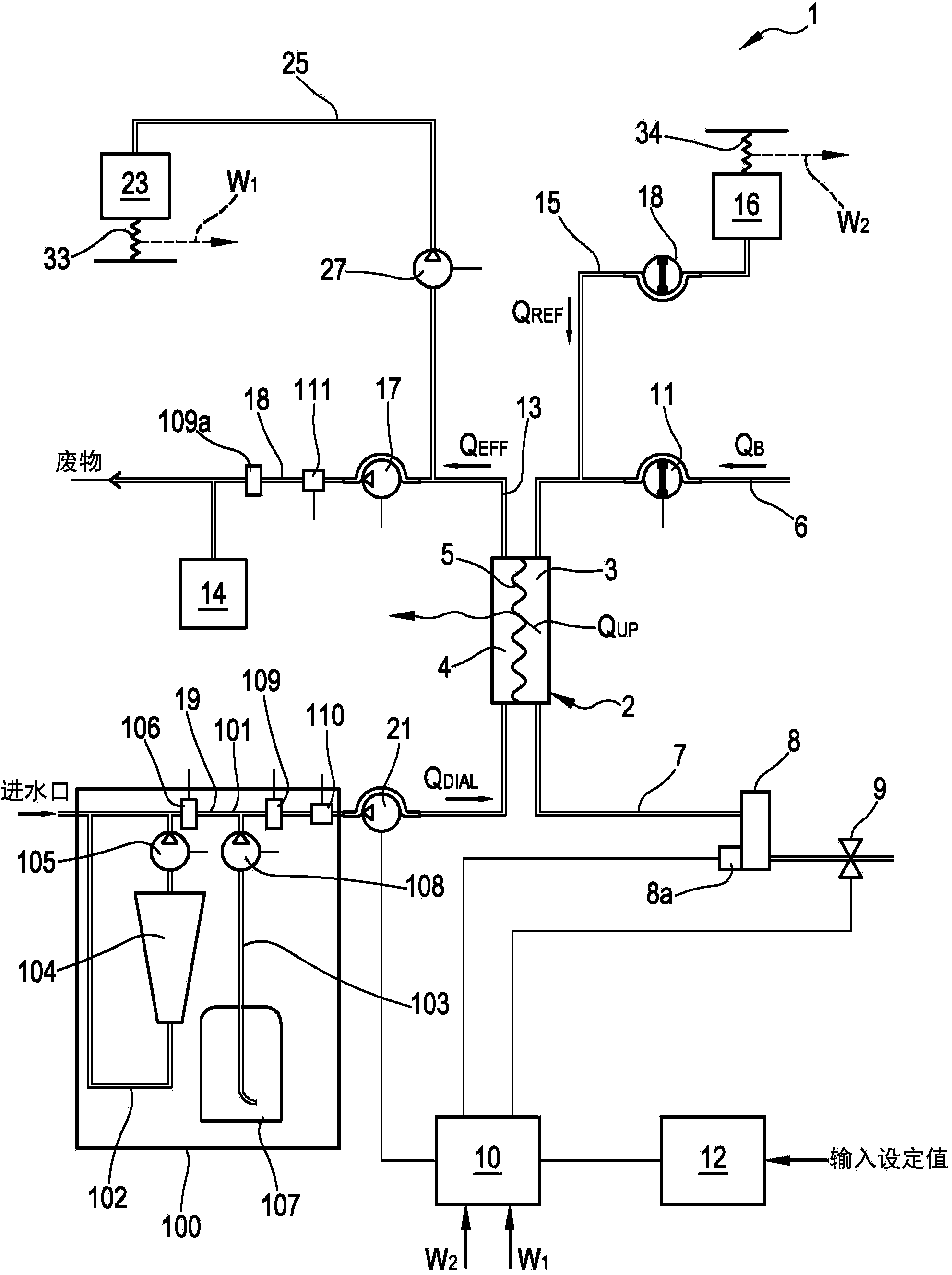
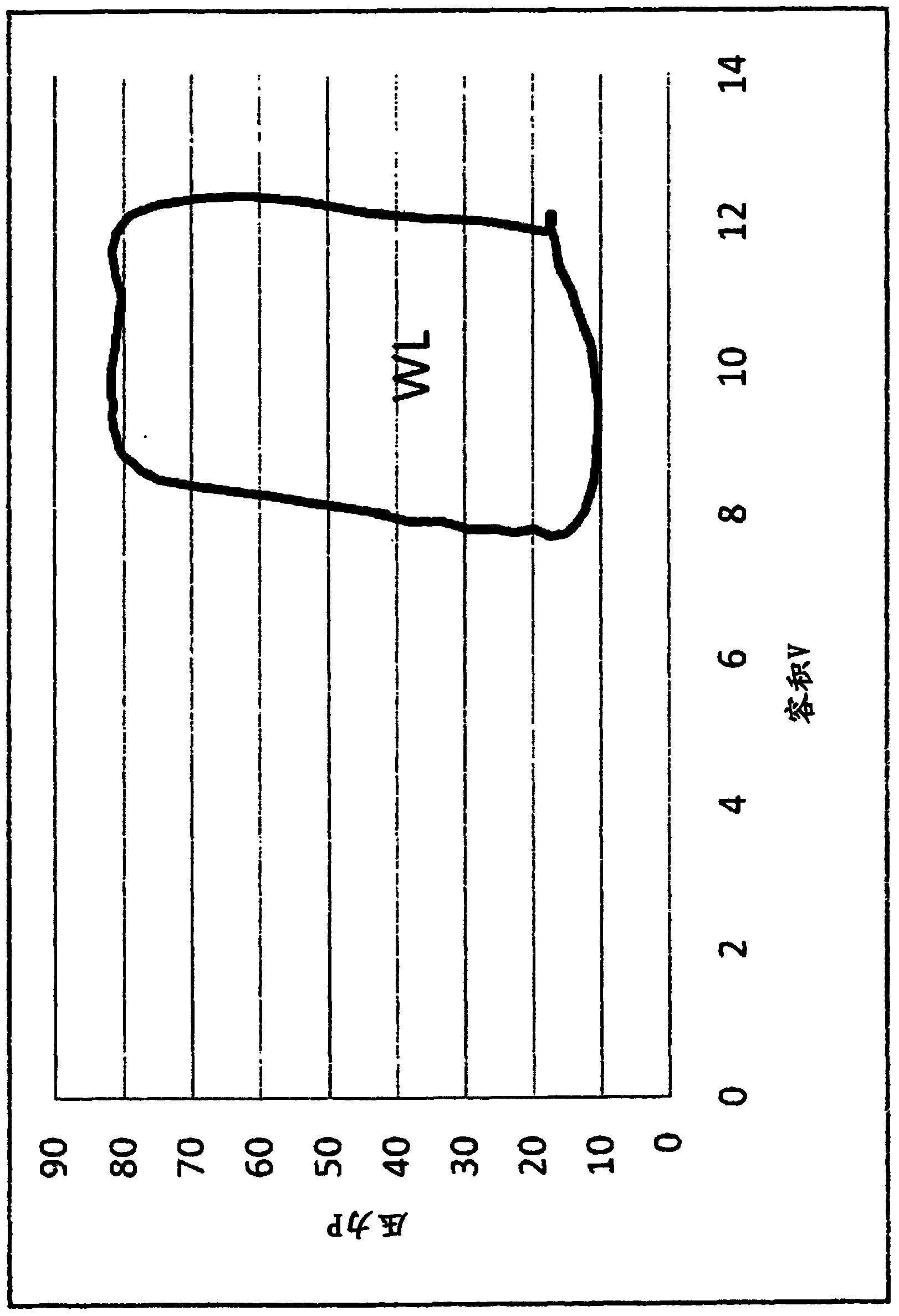
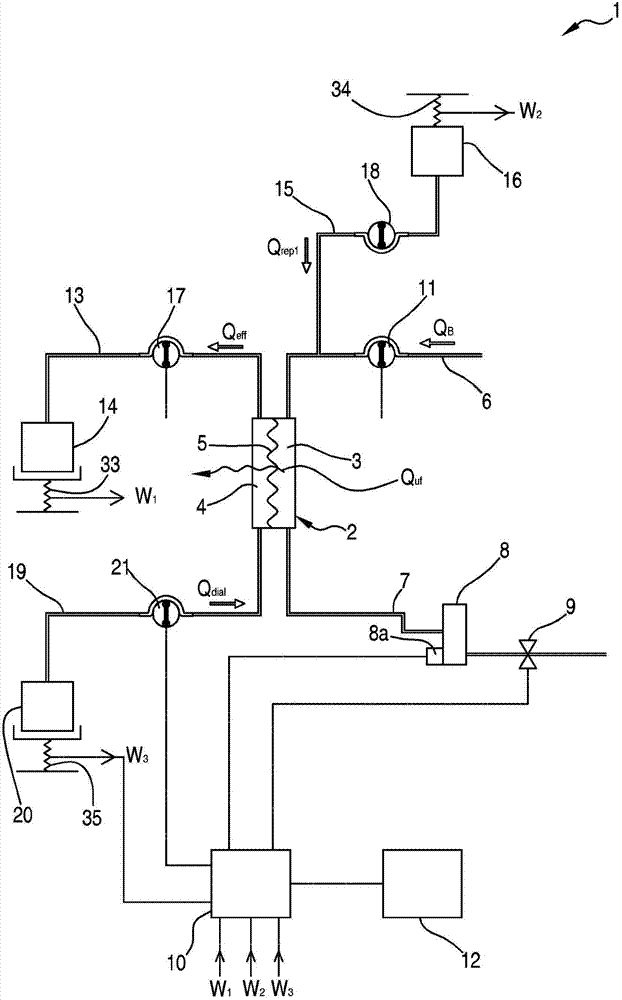
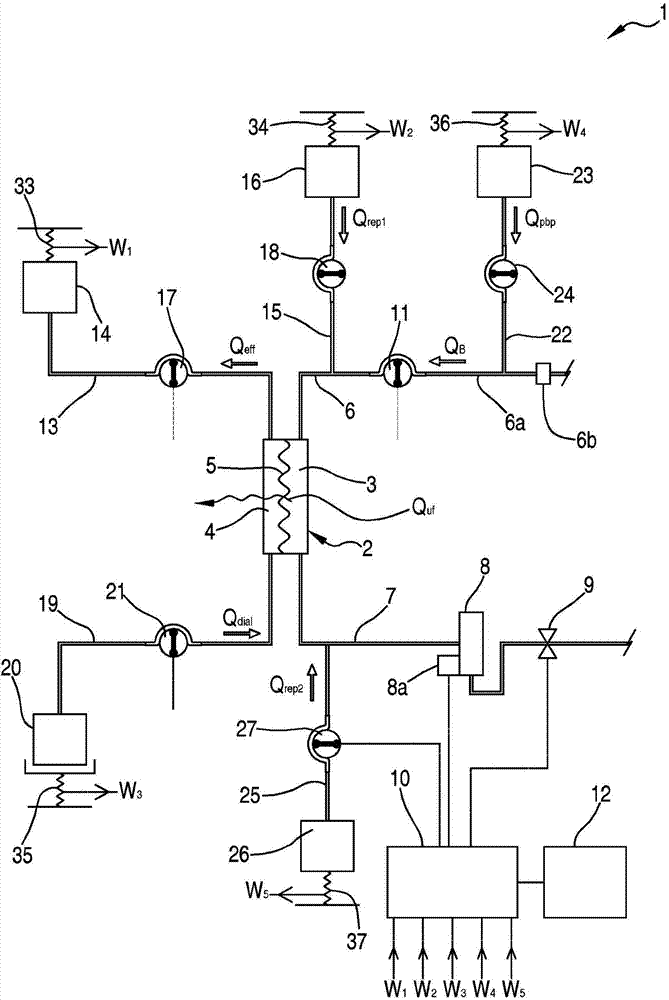
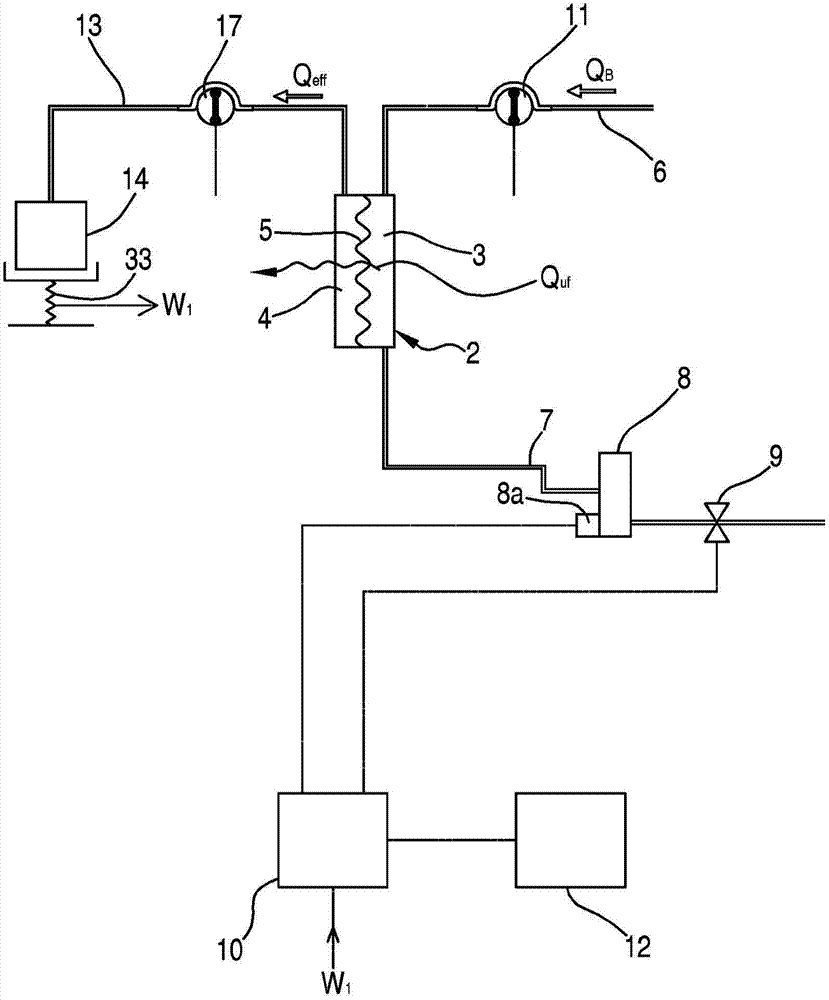
An apparatus for extracorporeal treatment of blood (1) comprising a filtration unit (2), a blood withdrawal line (6), a blood return line (7), an effluent fluid line (13), a pre and / or post-dilution fluid line (15, 25) connected to the blood withdrawal line, and a dialysis fluid line. Pumps (17, 18, 21, 22, 27) act on the fluid lines for regulating the flow of fluid. A control unit (10) is configured to periodically calculate a new value for the patient fluid removal rate to be imposed on an ultrafiltration actuator in order to keep a predefined patient fluid removal rate across a reference time interval irrespective of machine down times.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com