Method and device for recognition of paravasal bleeding
A perivascular and equipment technology, applied in application, medical equipment, blood circulation treatment, etc., can solve problems such as slow pressure, identification of perivascular hemorrhage, and injury to patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
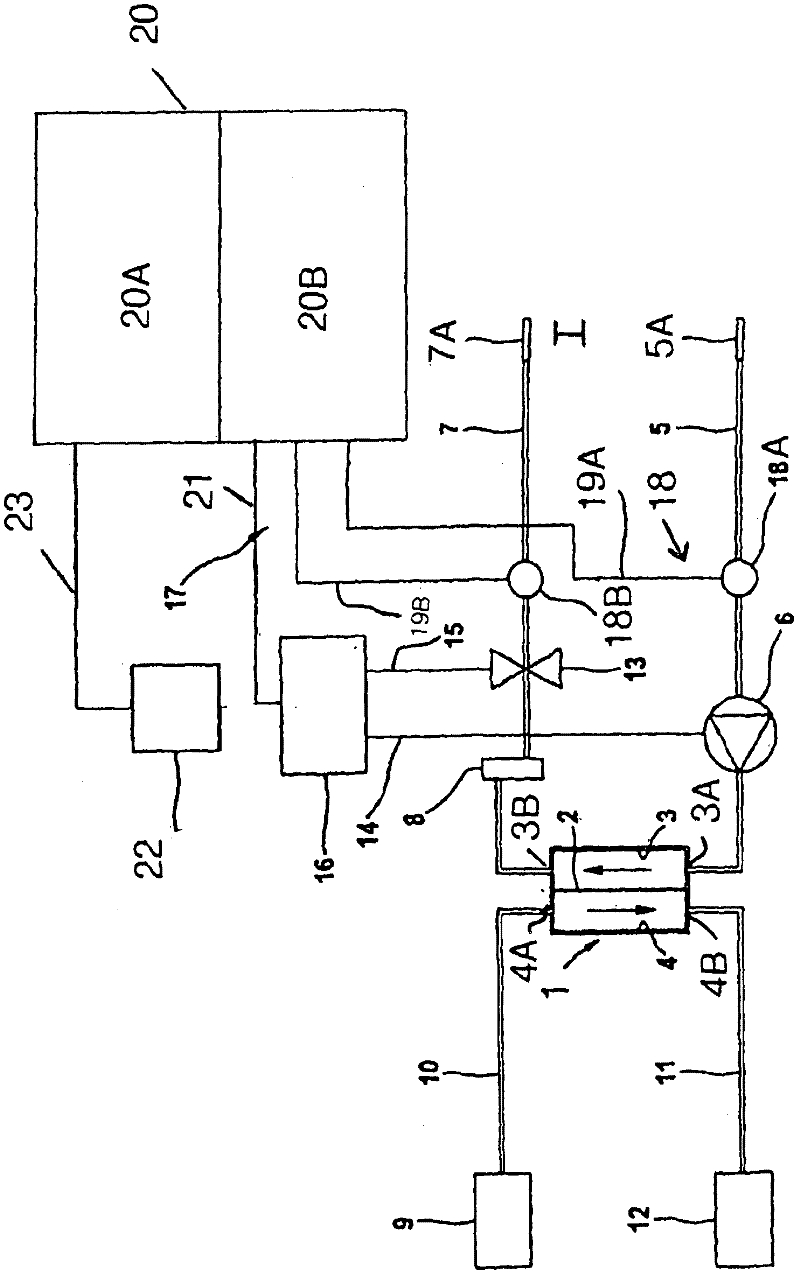
[0028] figure 1 A dialysis system is shown in an extremely simplified schematic diagram as an example of an extracorporeal blood treatment system.
[0029] As a blood treatment device, the dialysis device has a dialyzer 1 which is divided by a semipermeable membrane 2 into a blood chamber 3 and a dialysate chamber 4 . An arterial blood line 5 , into which a peristaltic blood pump 6 is connected, is connected to the inlet 3A of the blood chamber 3 . A venous blood line 7 leads from the outlet 3B of said blood chamber 3 to the patient. The drip chamber 8 is connected to the venous blood conduit 7 . Connected to the ends of the arterial and venous blood conduits 5, 7 are needle tubes 5A and 7A that are inserted into corresponding arterial or venous vessels (shunts) of the patient, respectively. The arterial and venous blood conduits 5, 7 form arterial or venous branches of the extracorporeal blood circulation I. The blood line is part of a disposable hose line system that is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com