Patents
Literature
61 results about "Intravascular filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
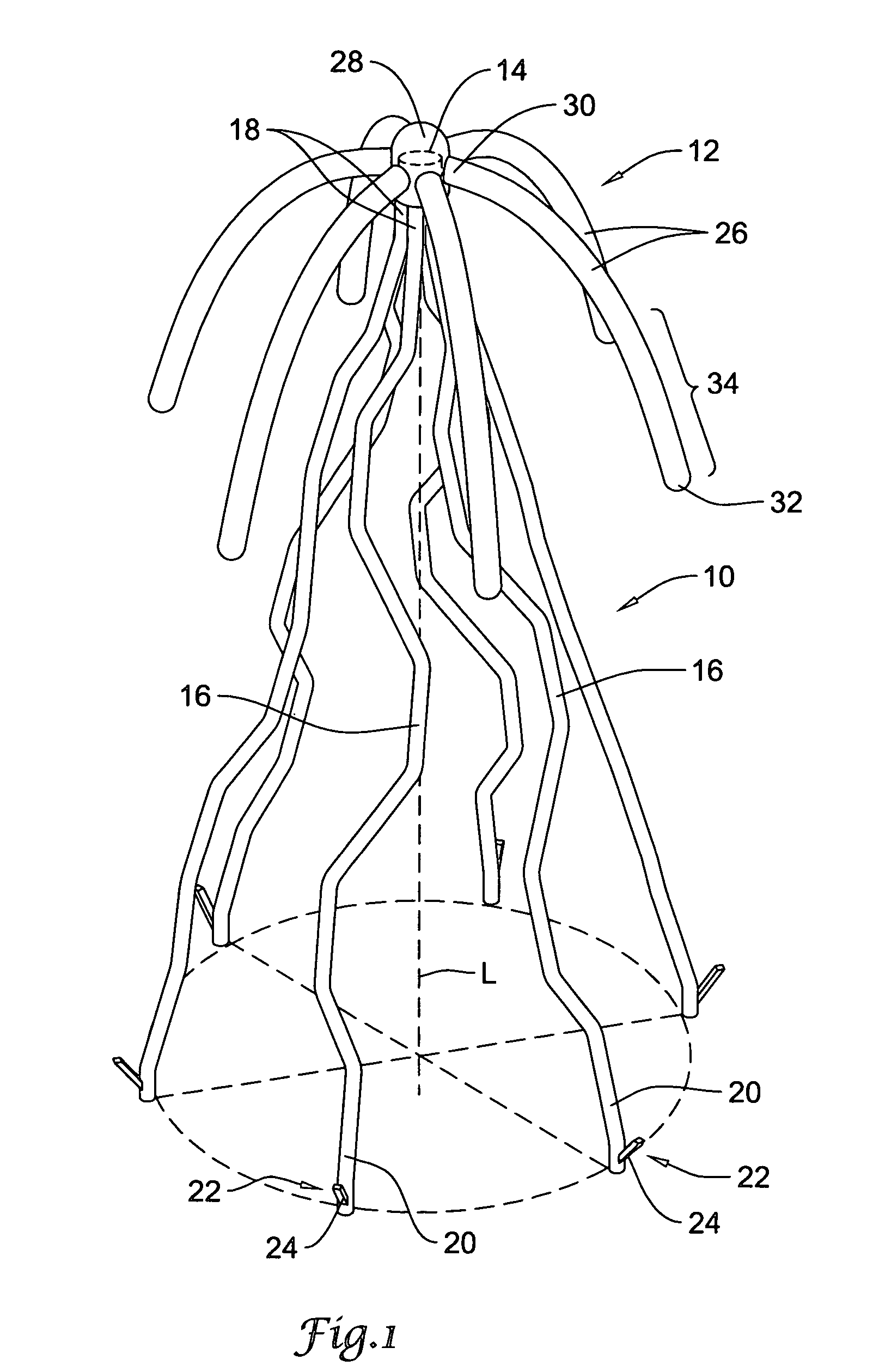
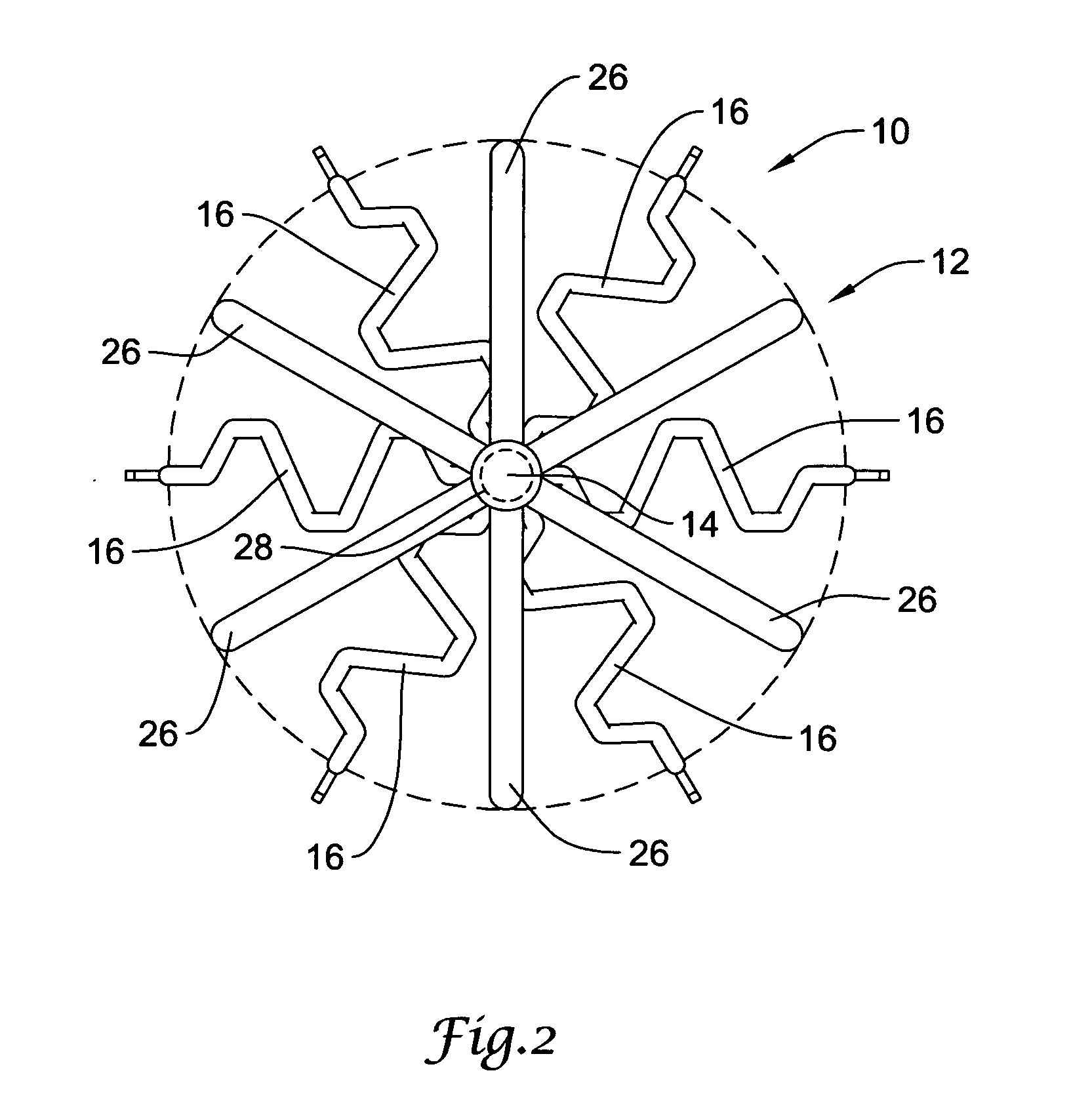
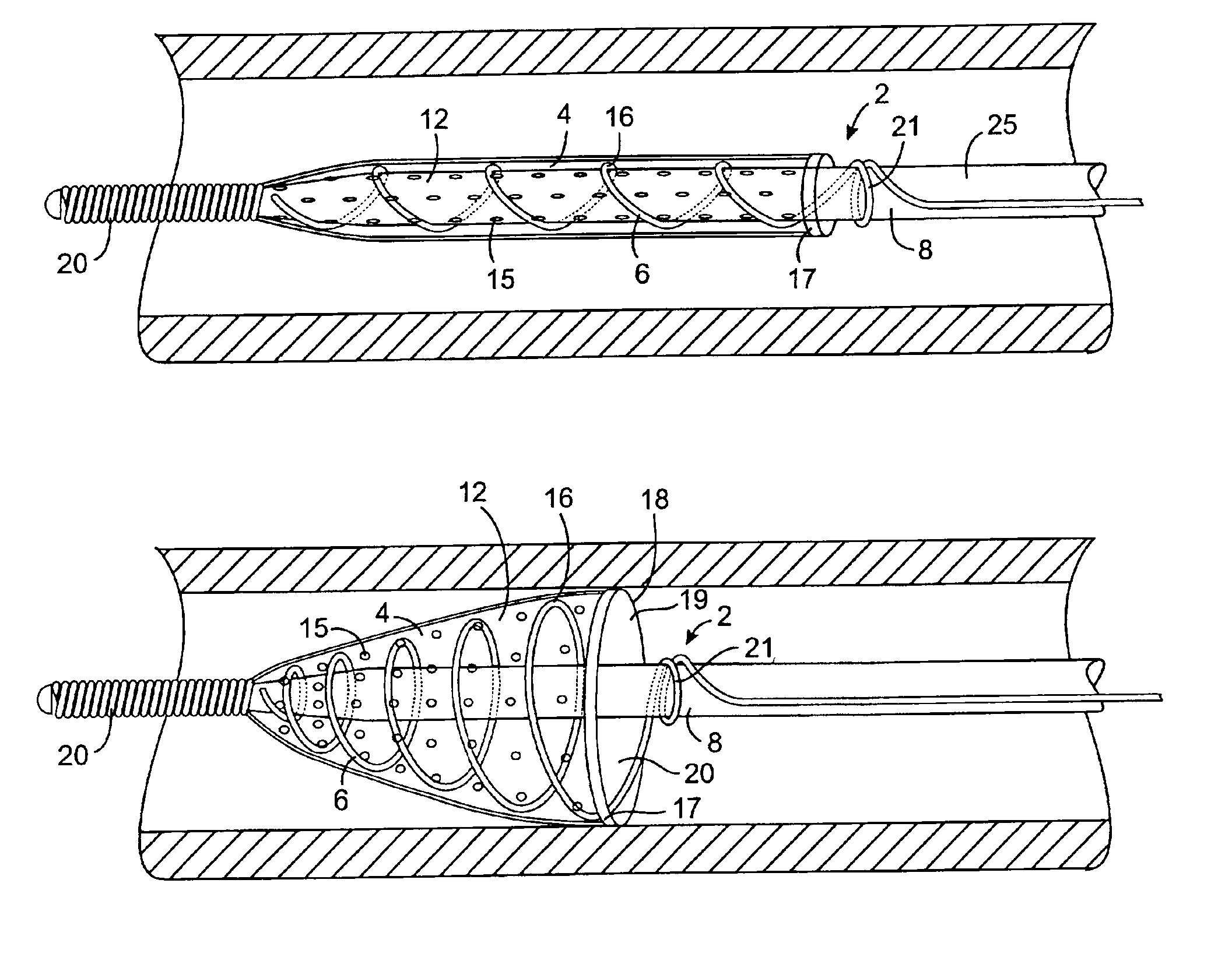
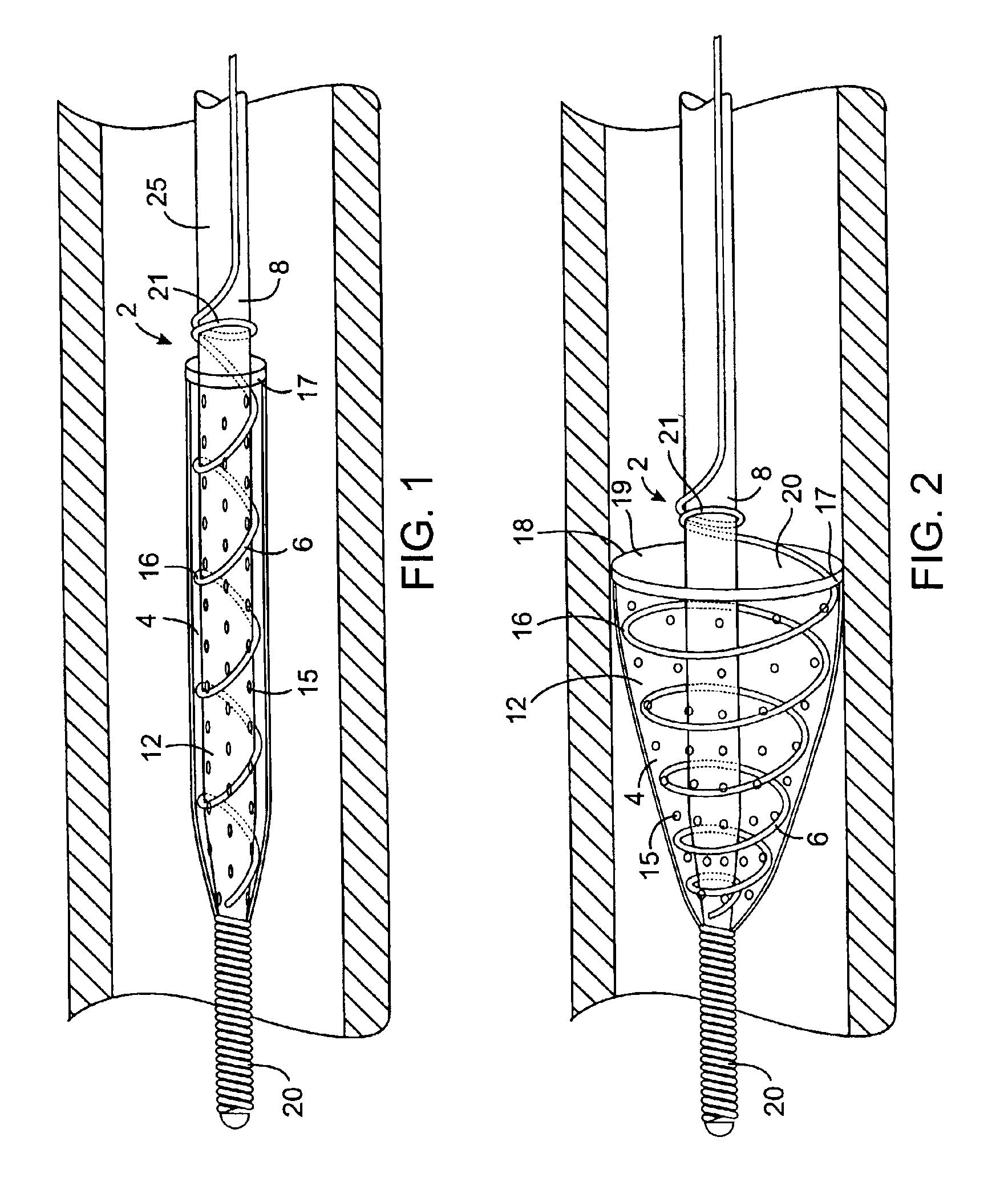
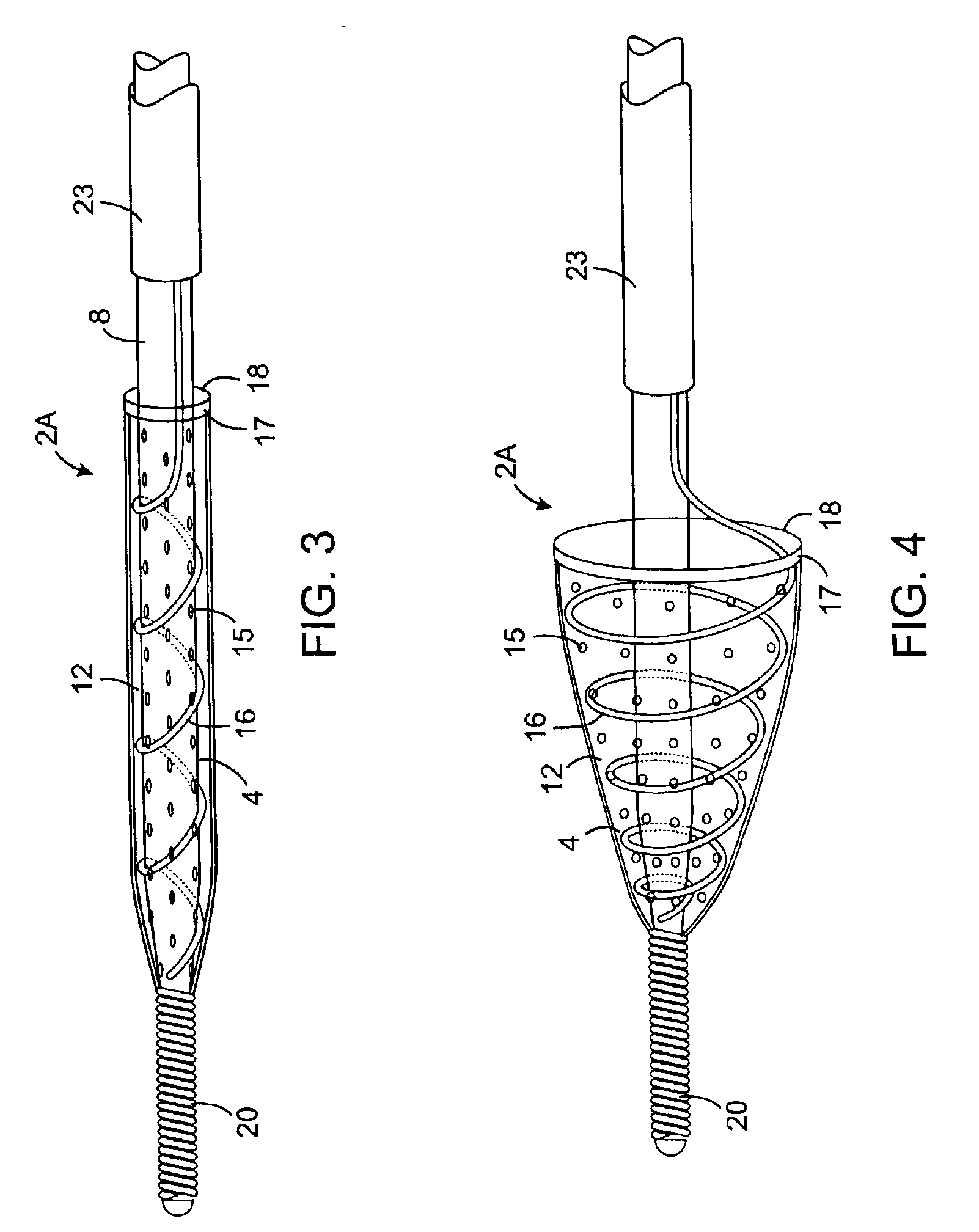
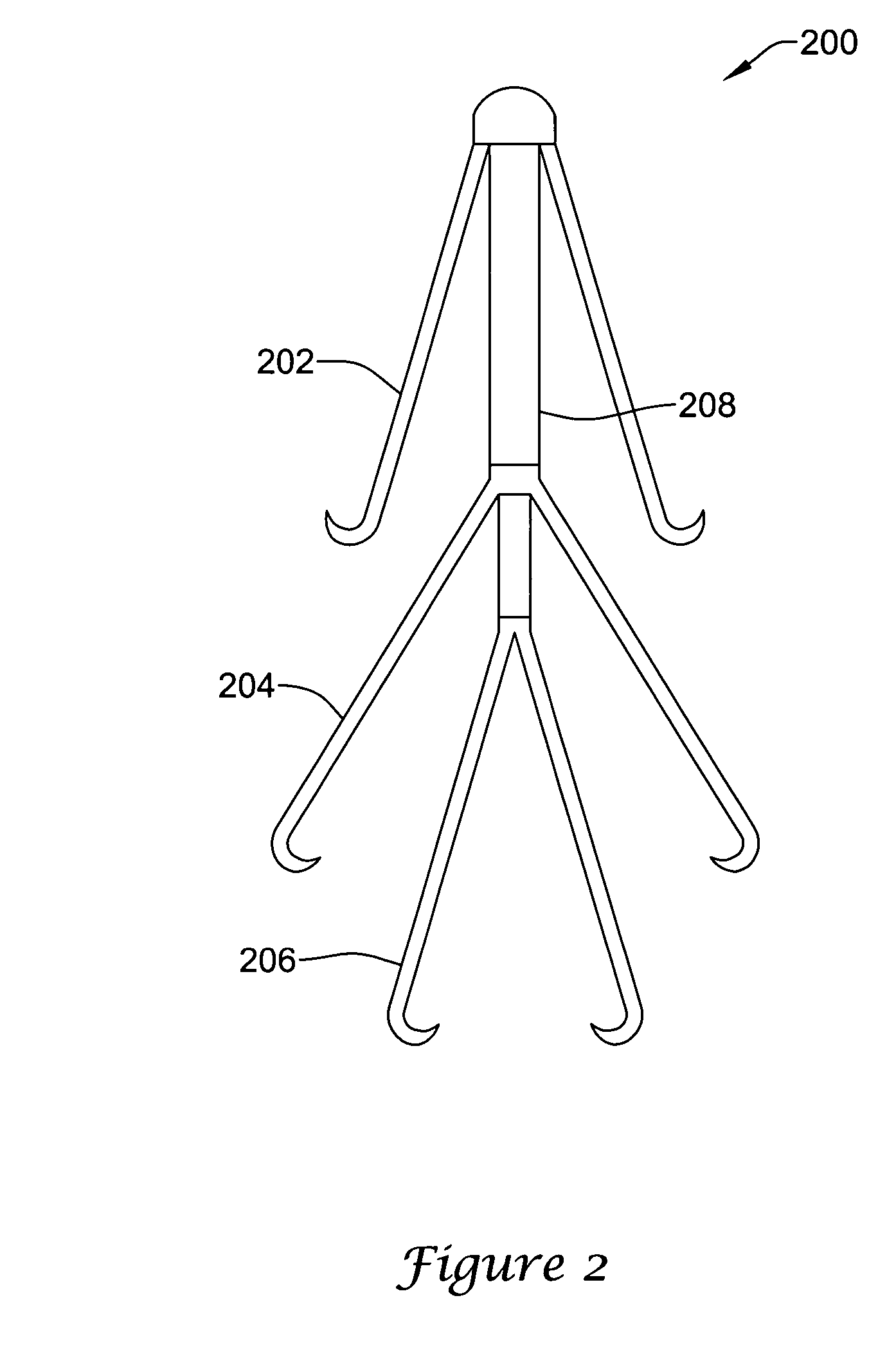
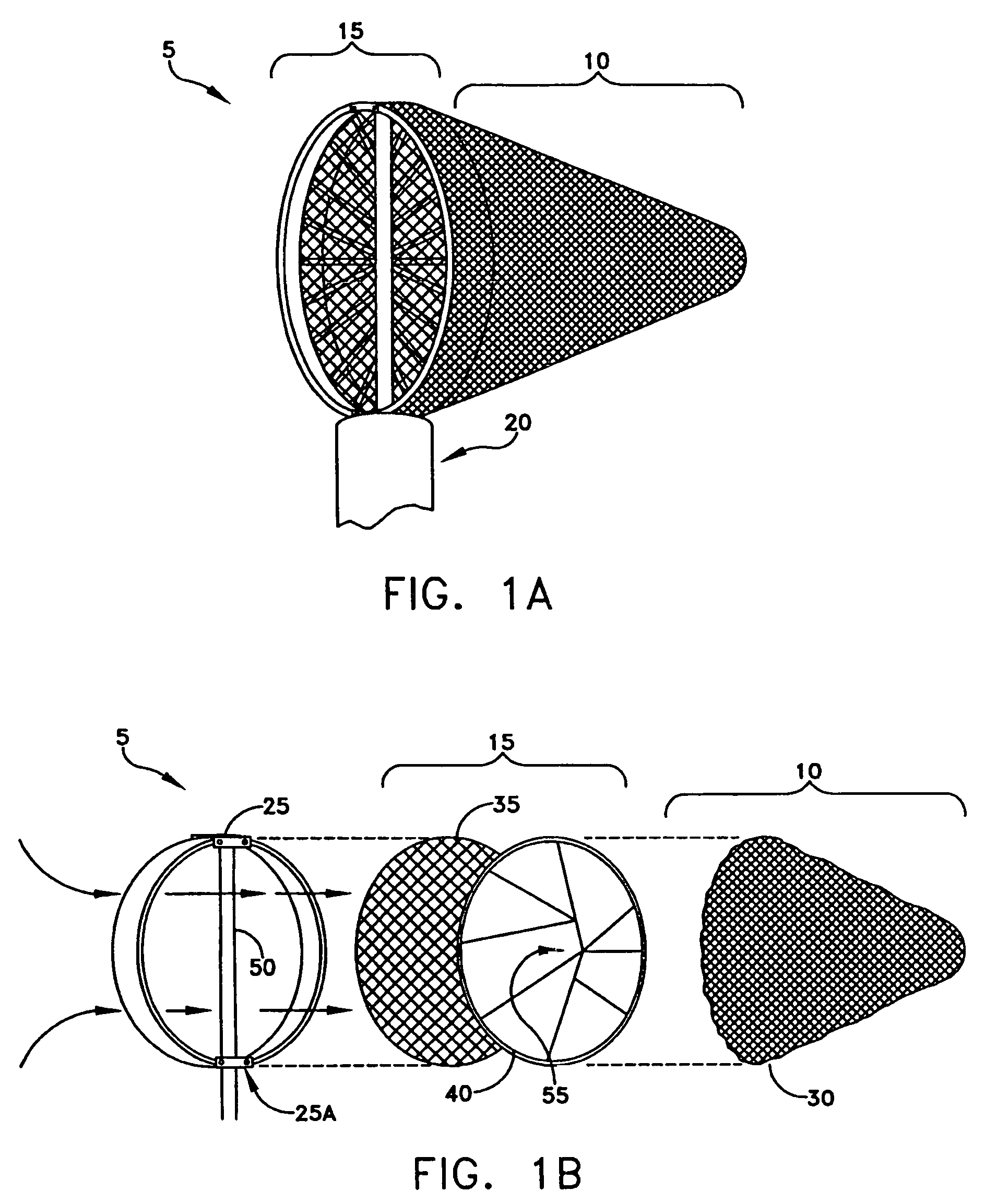
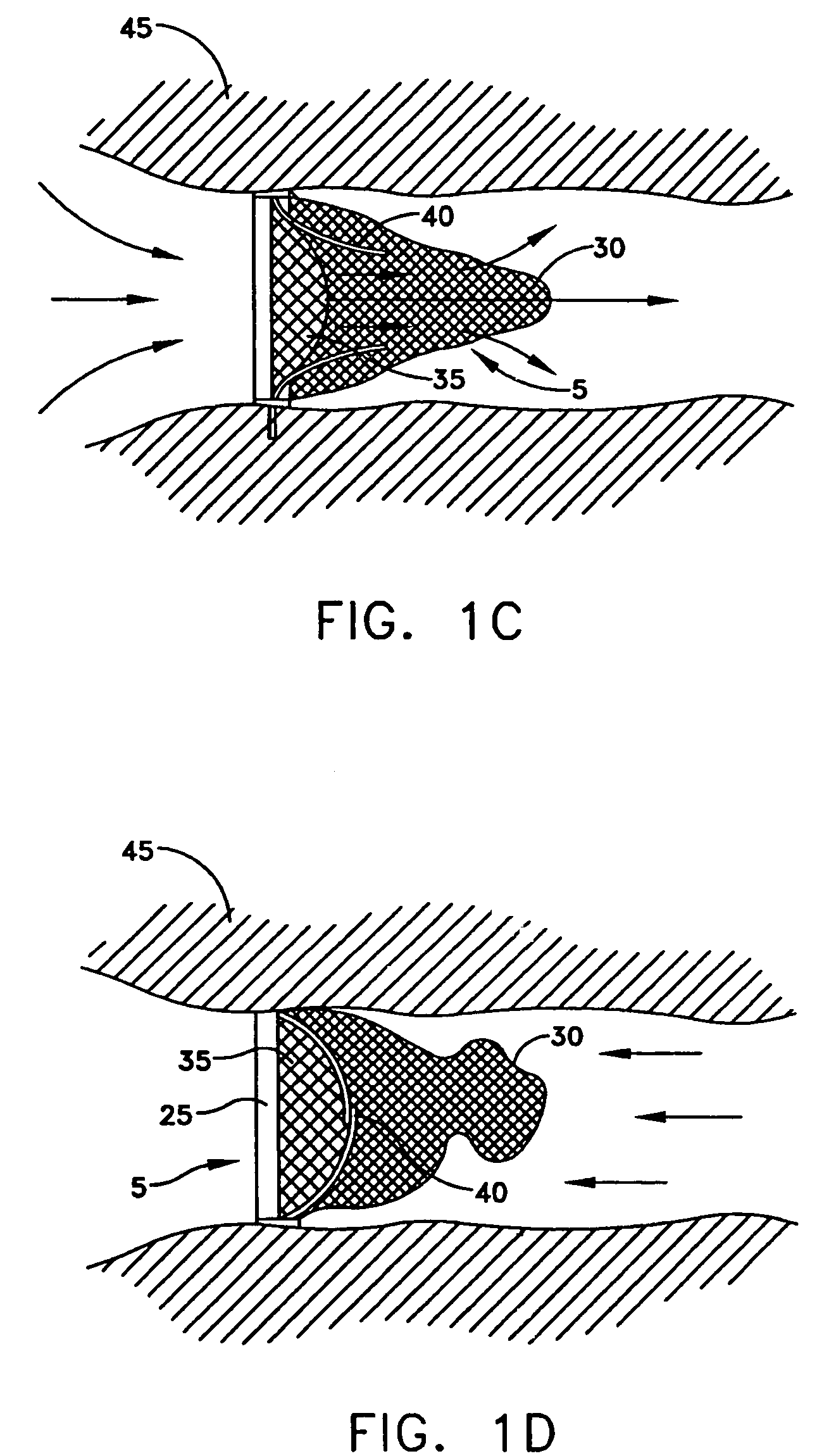
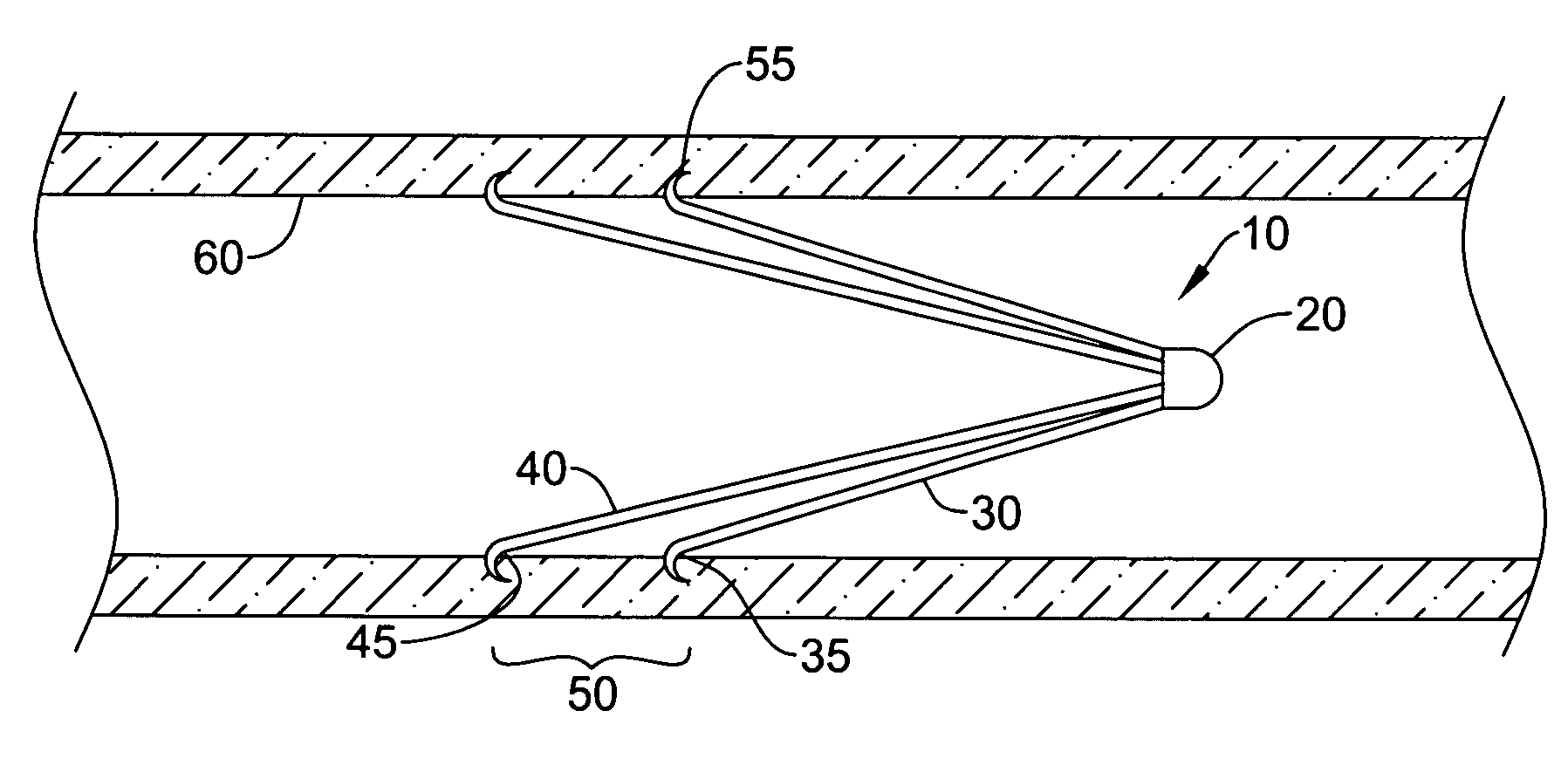
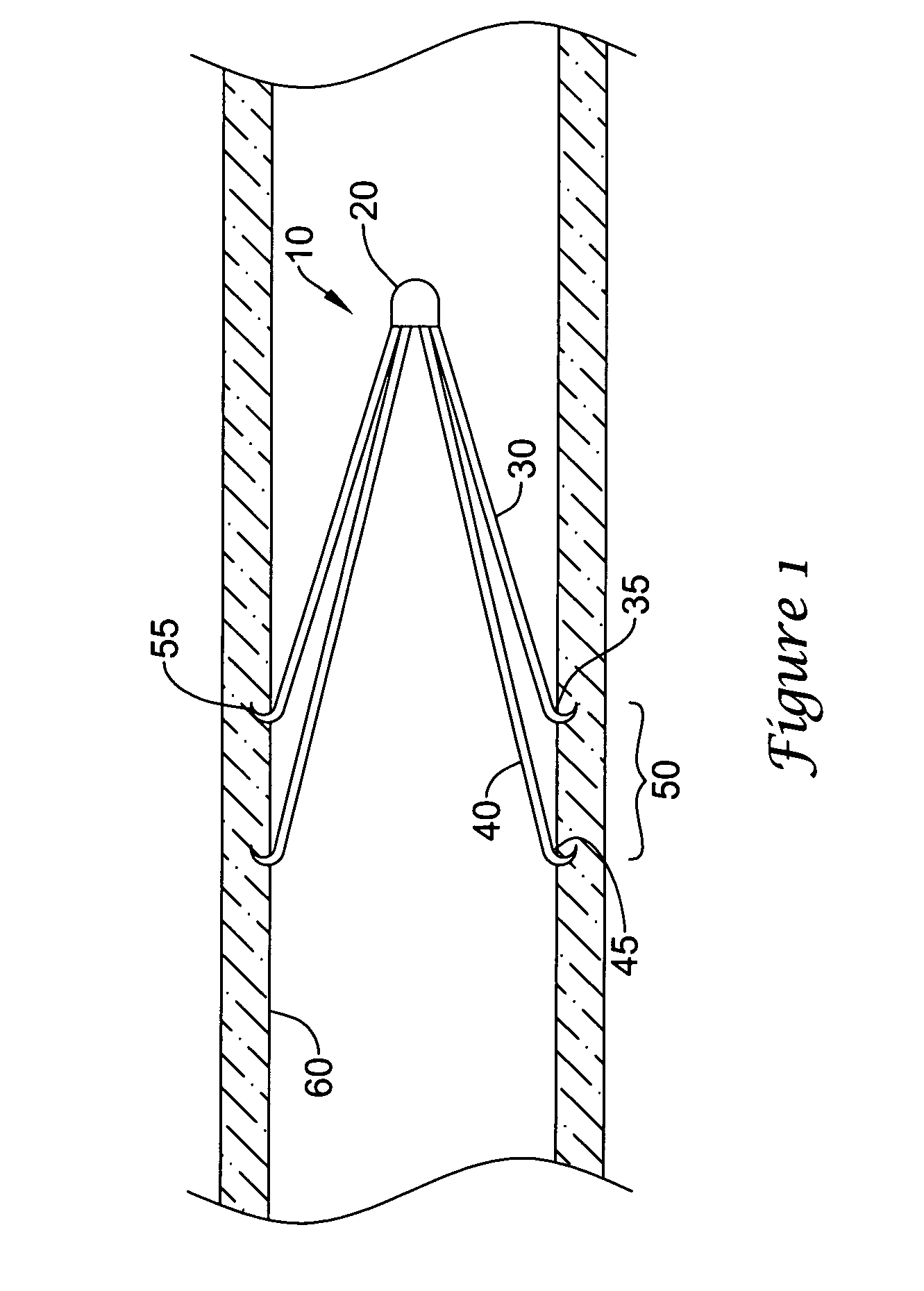
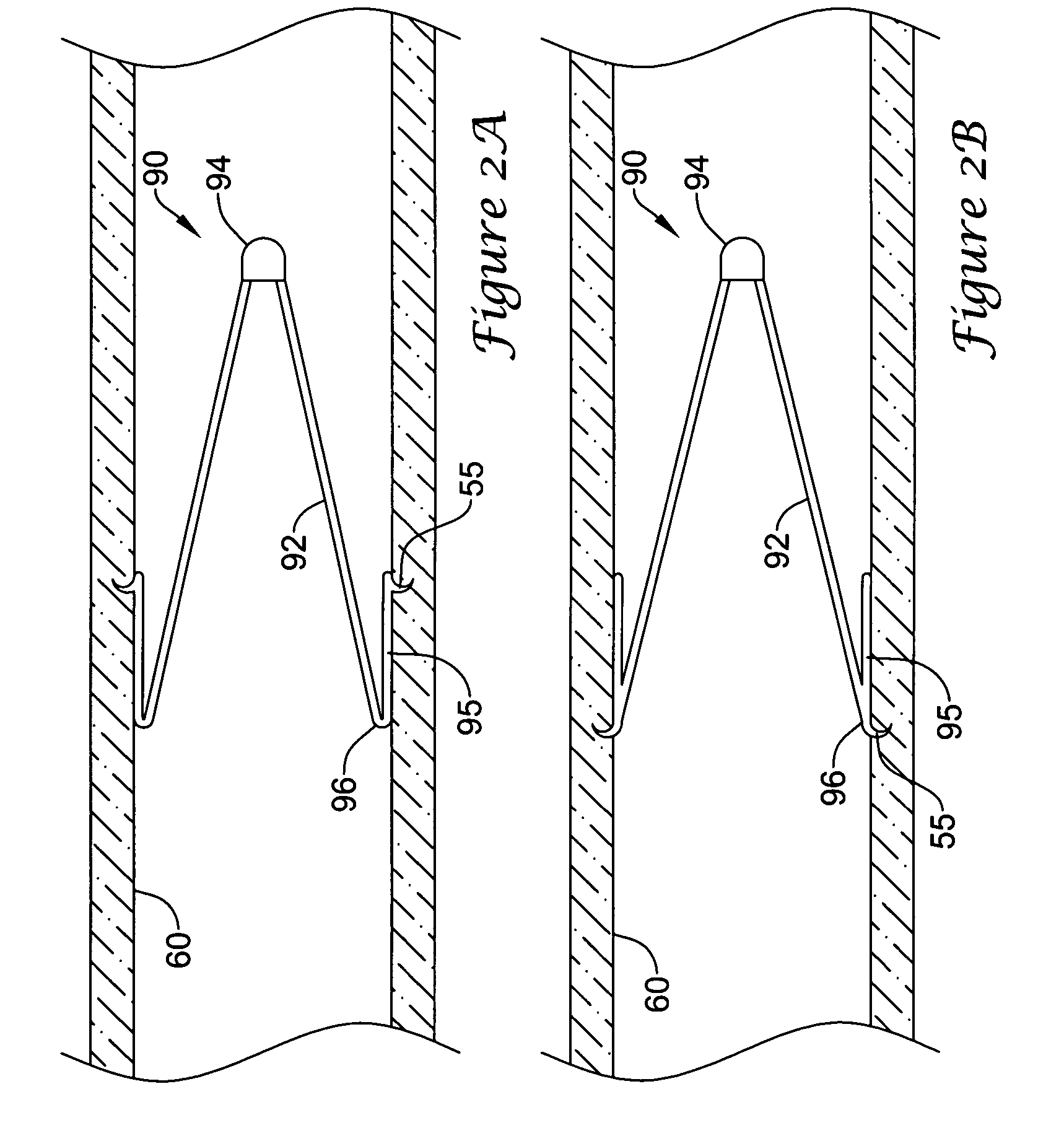
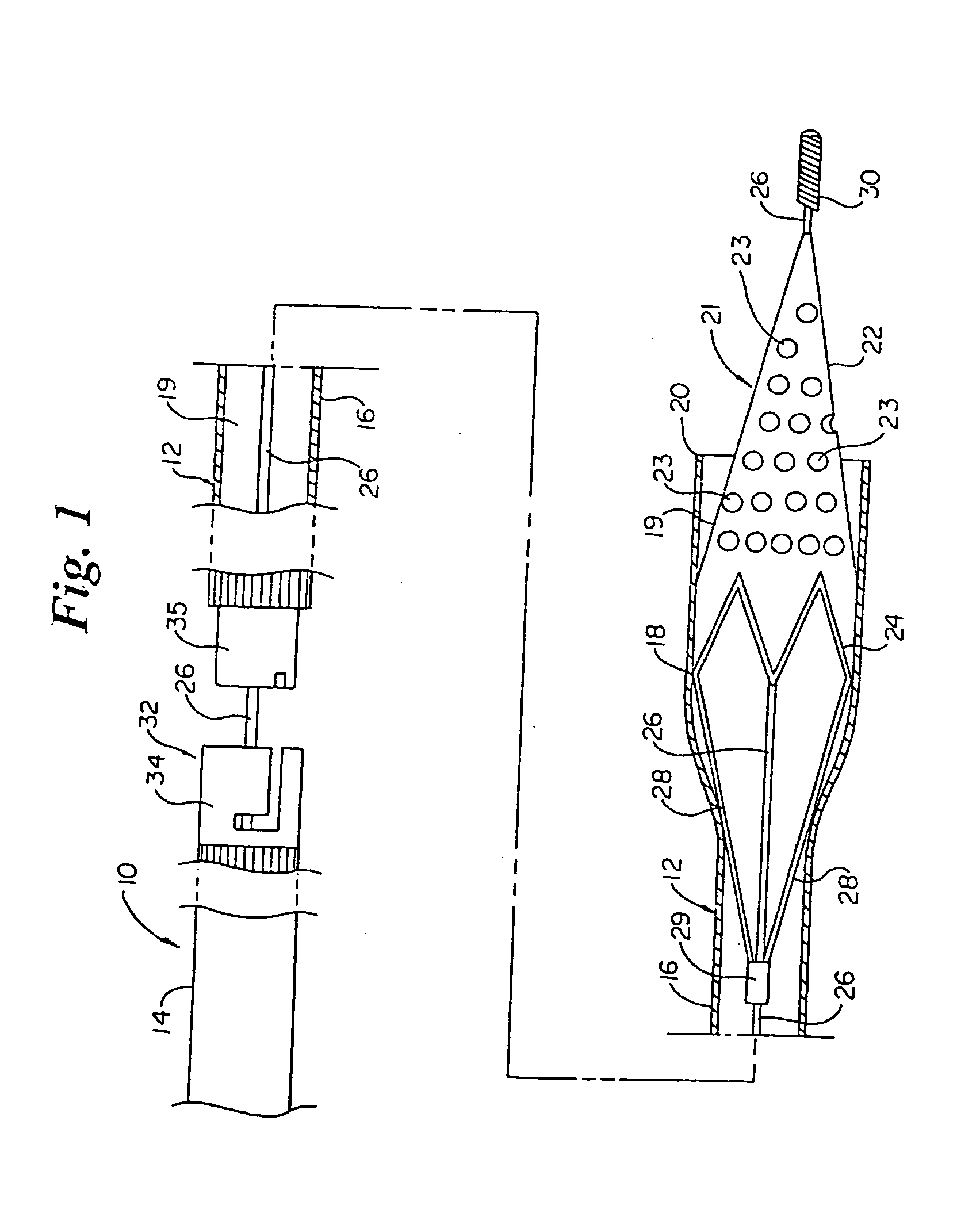
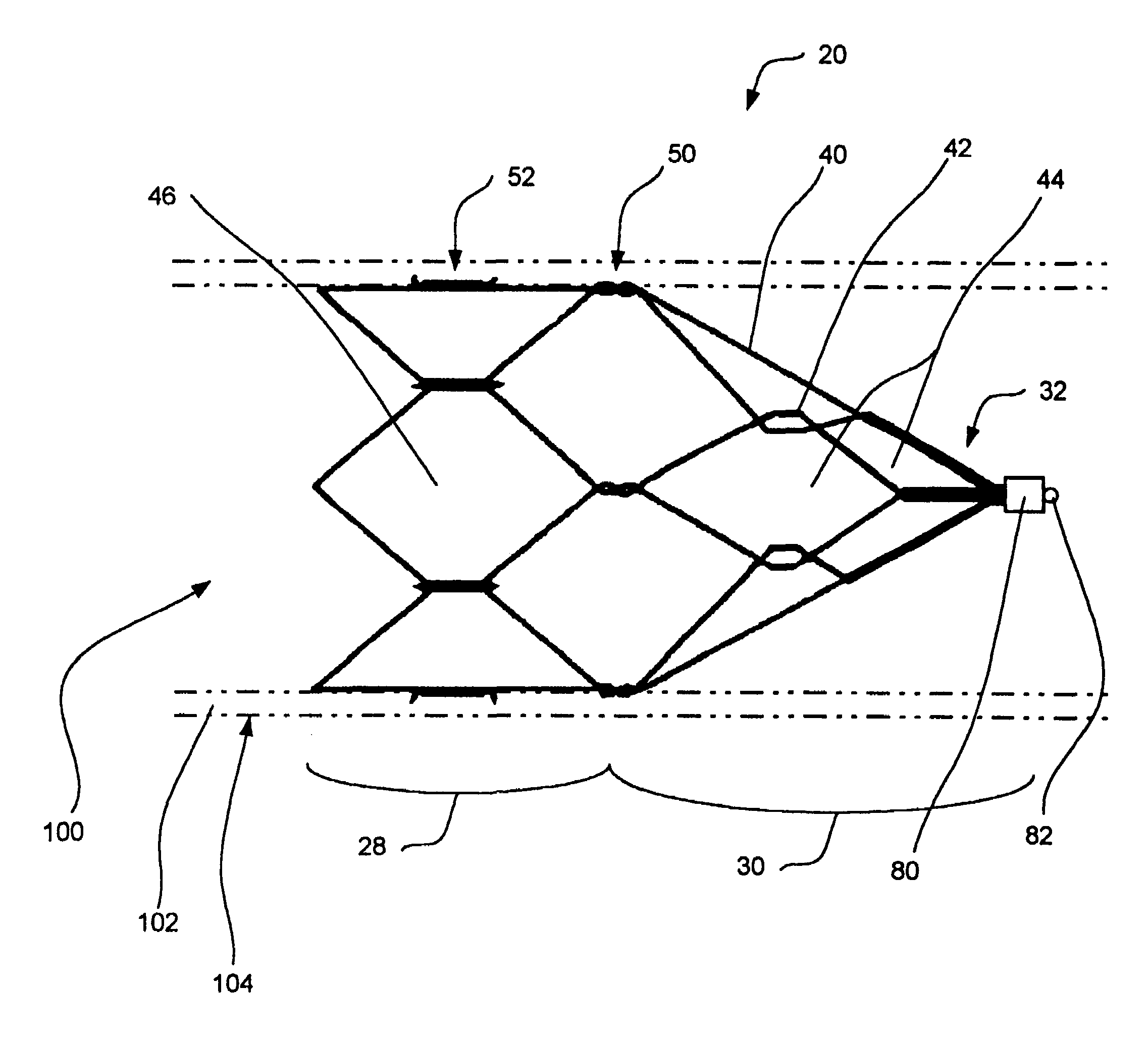
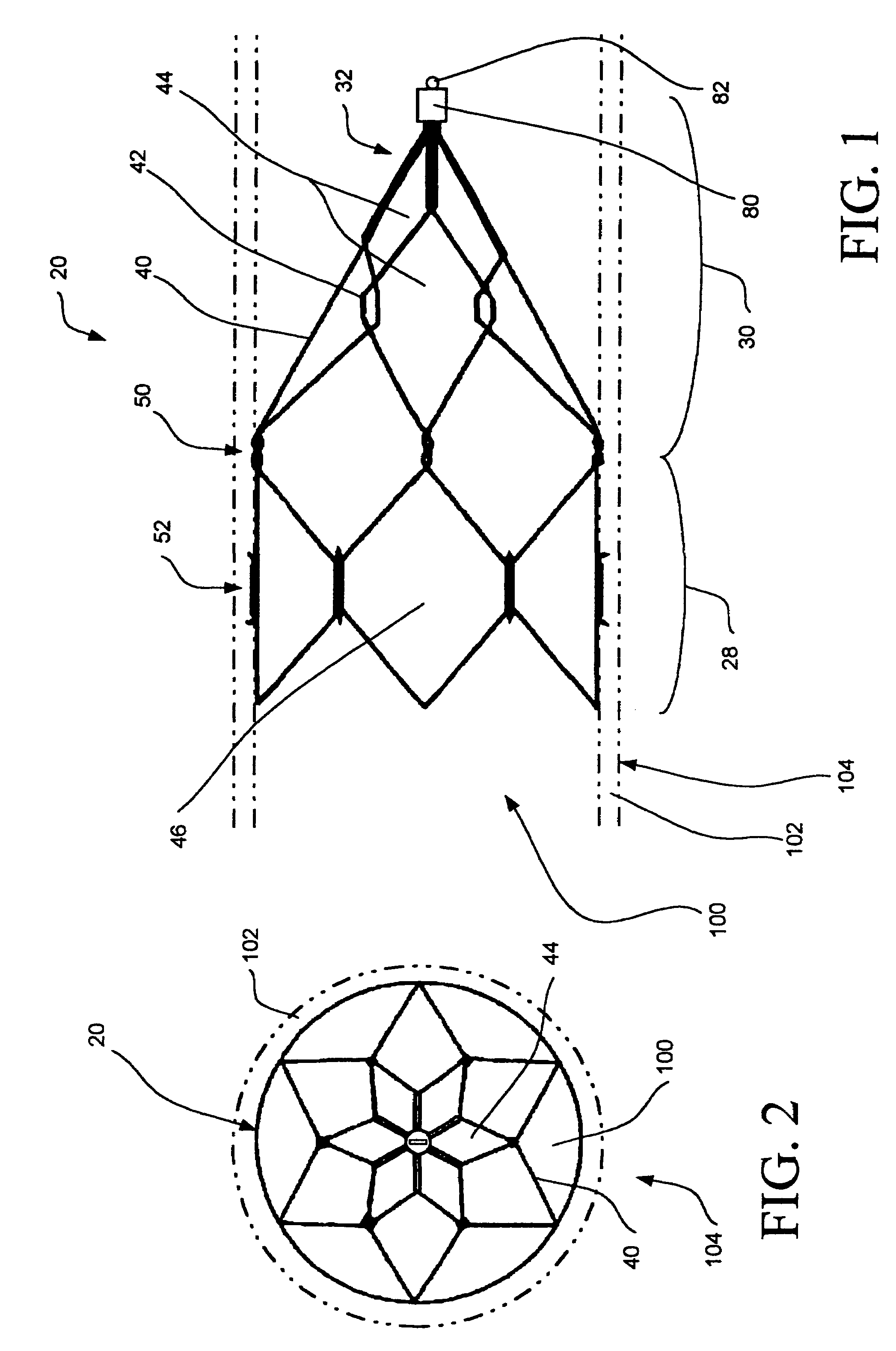
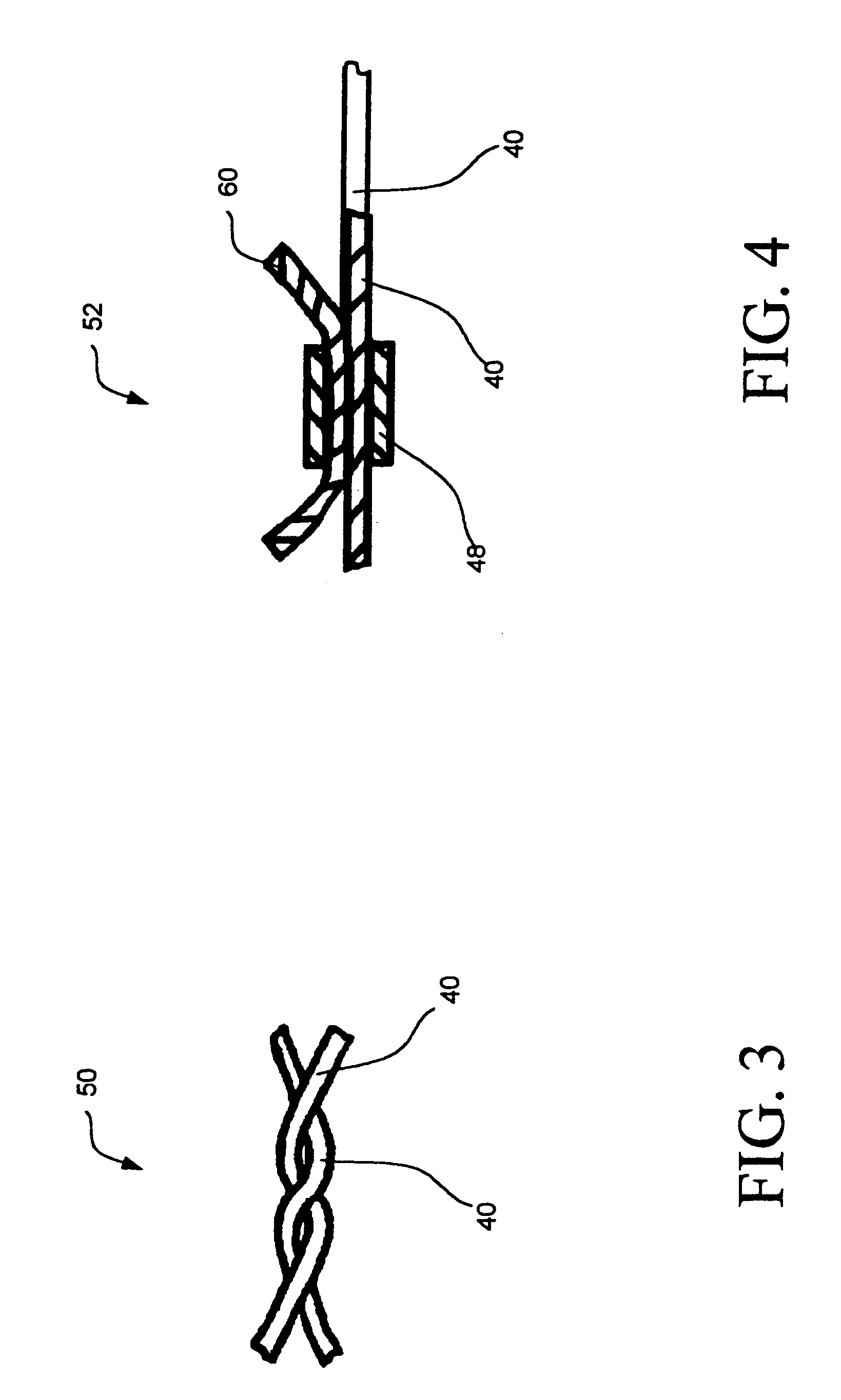
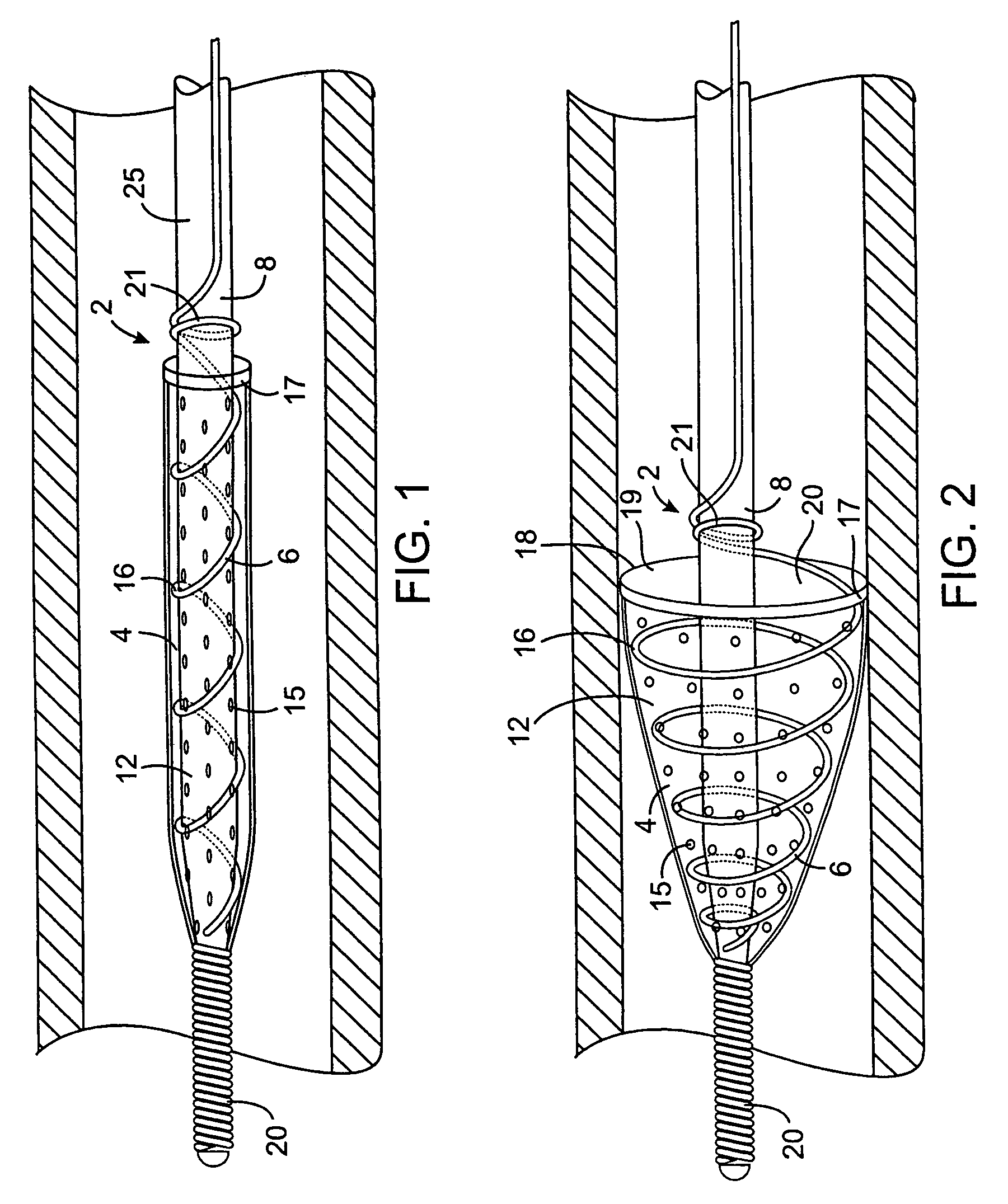
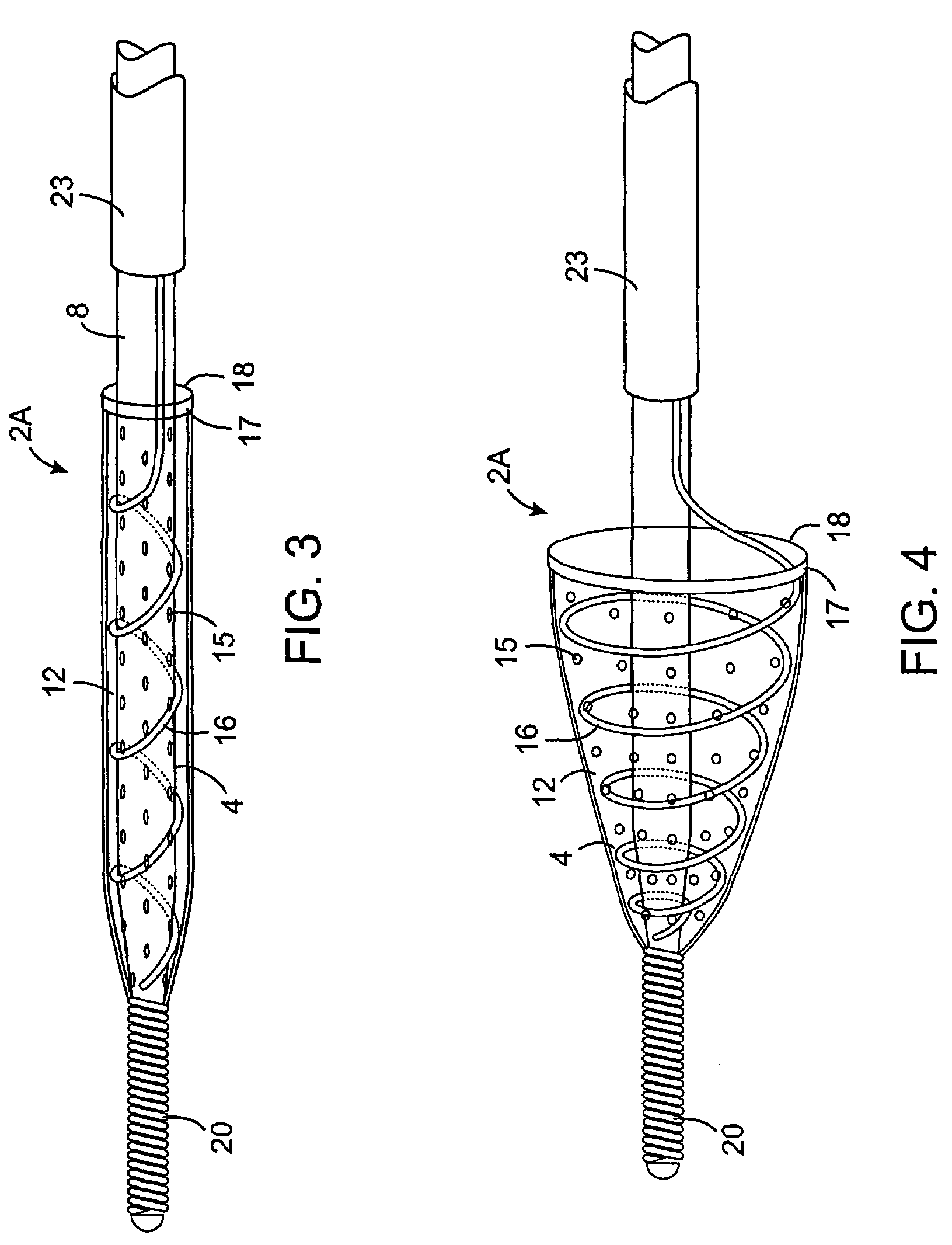
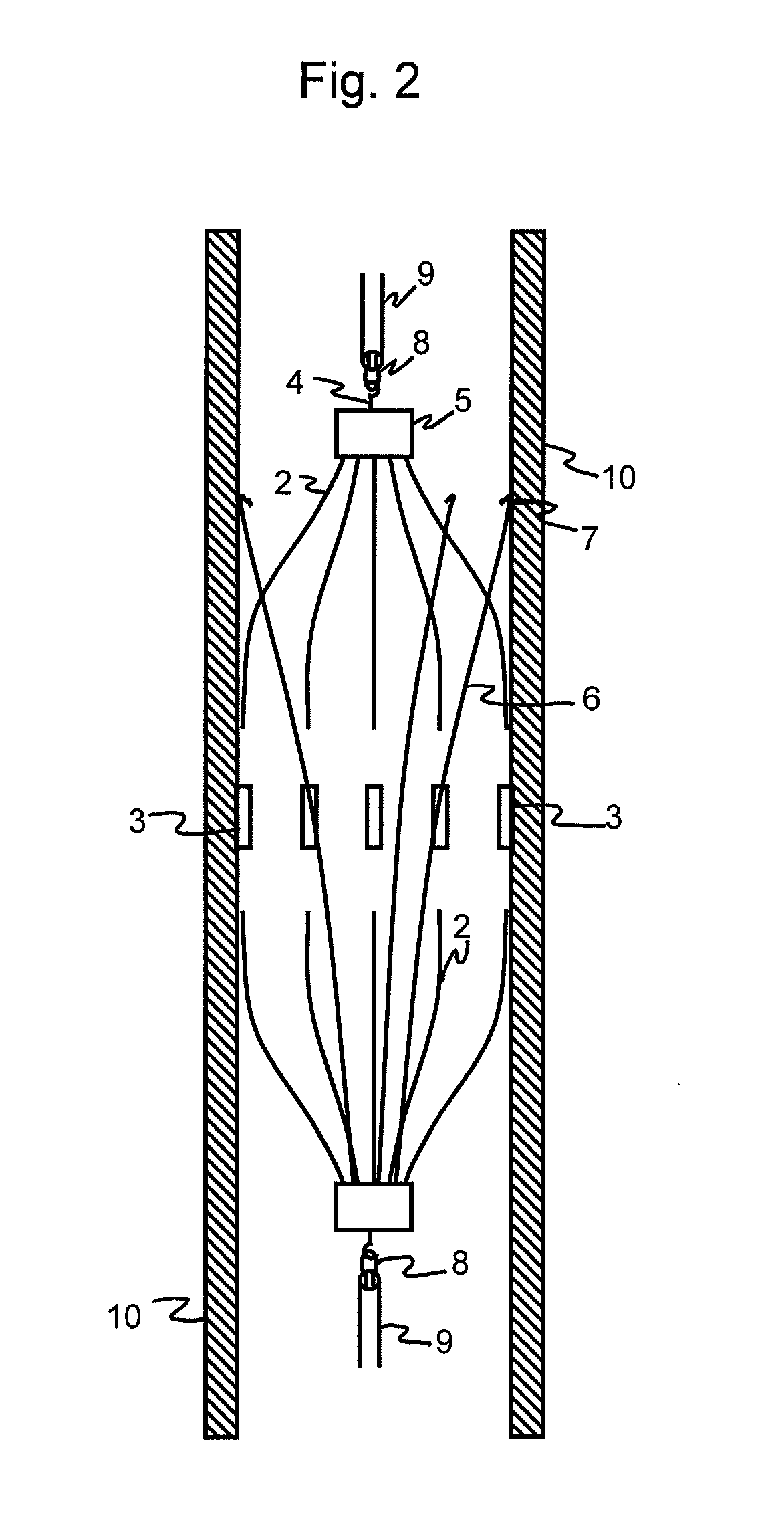
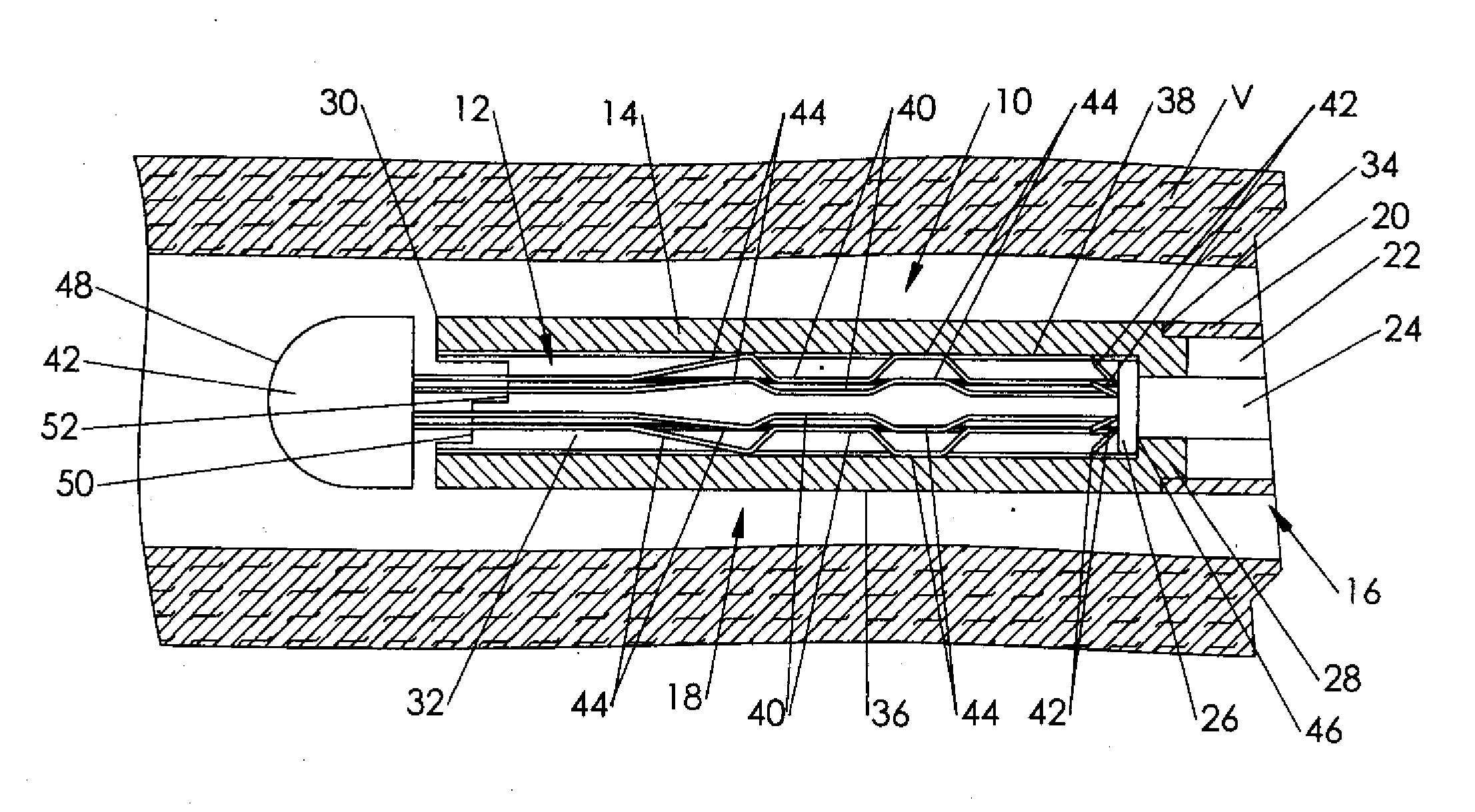
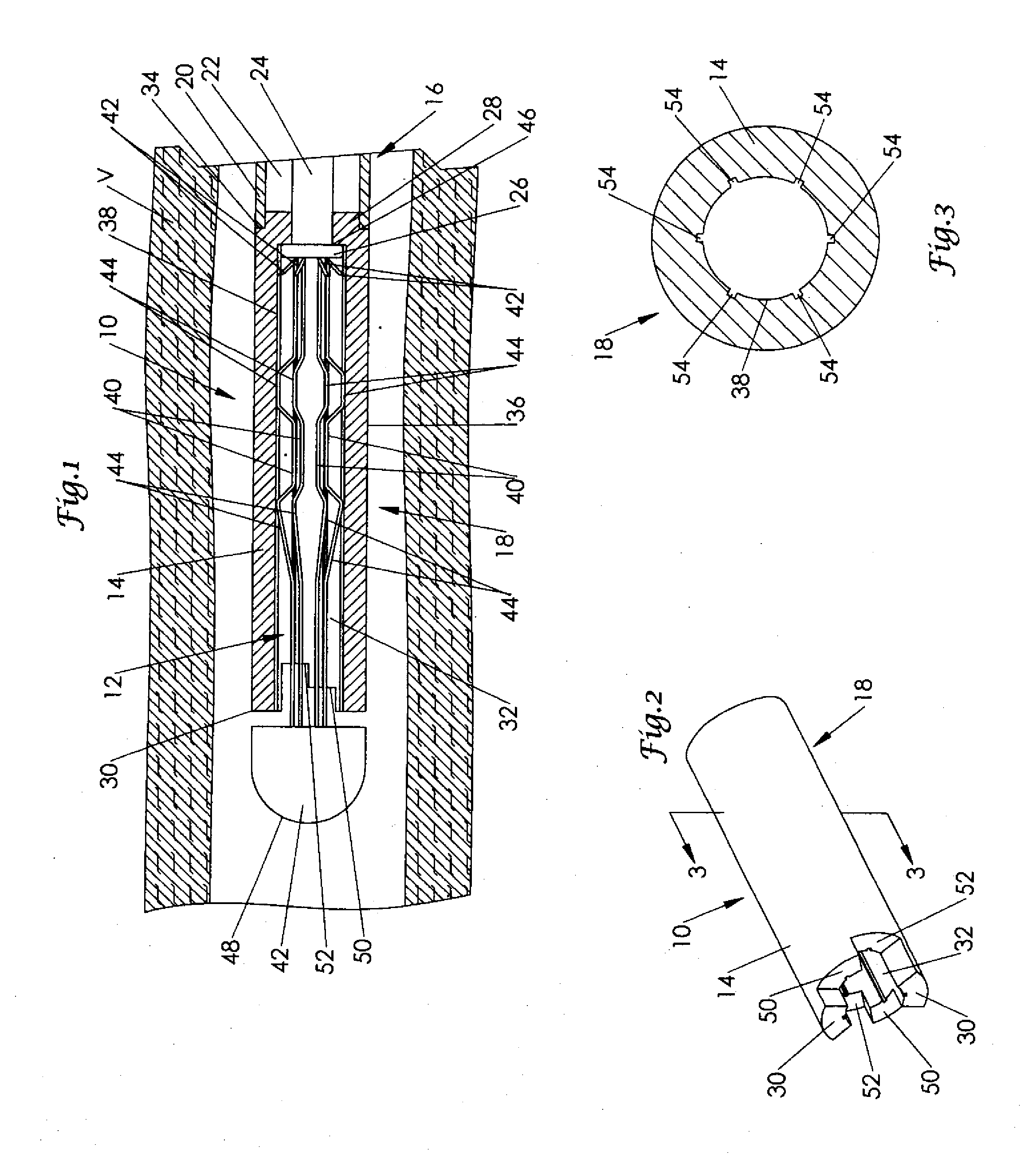
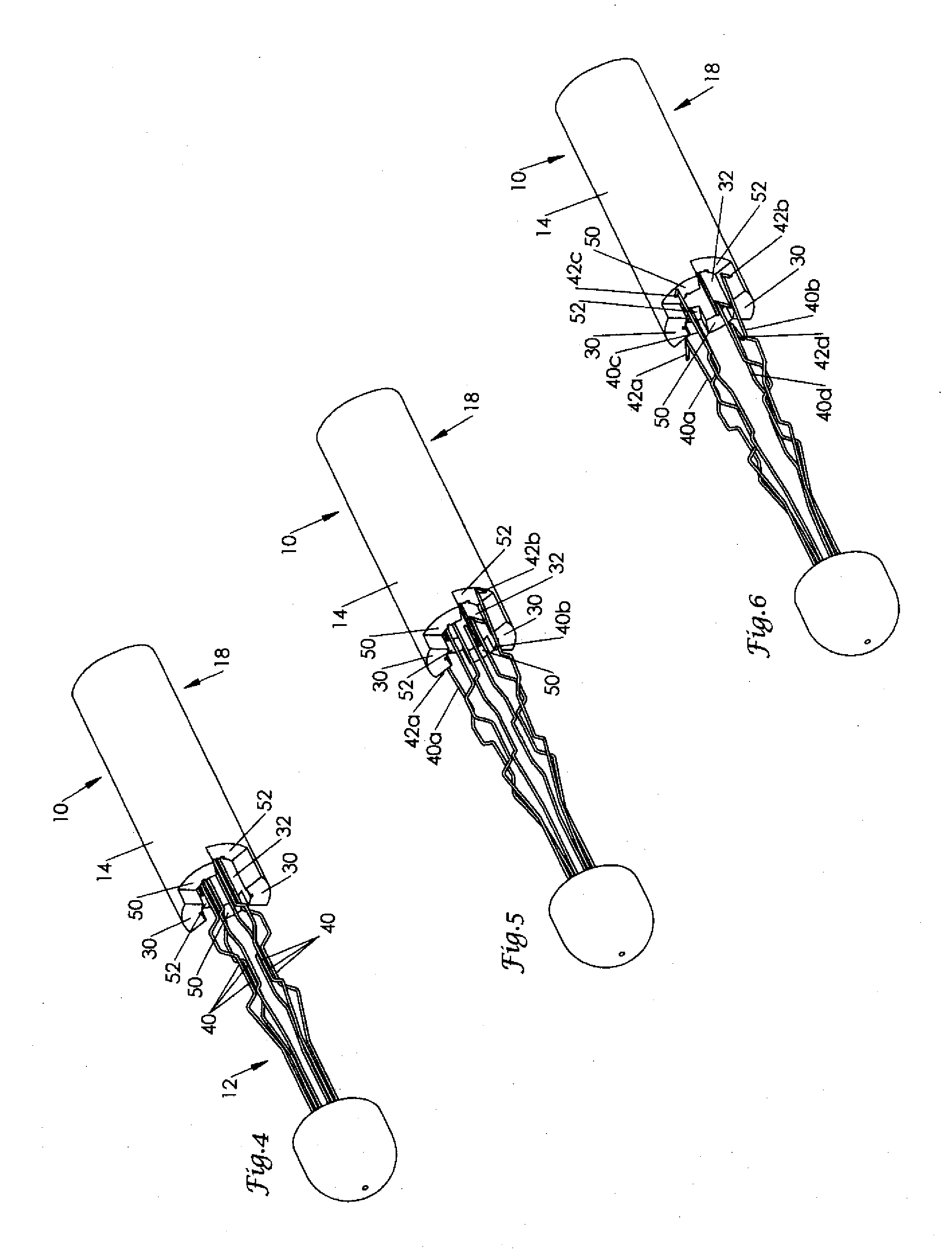
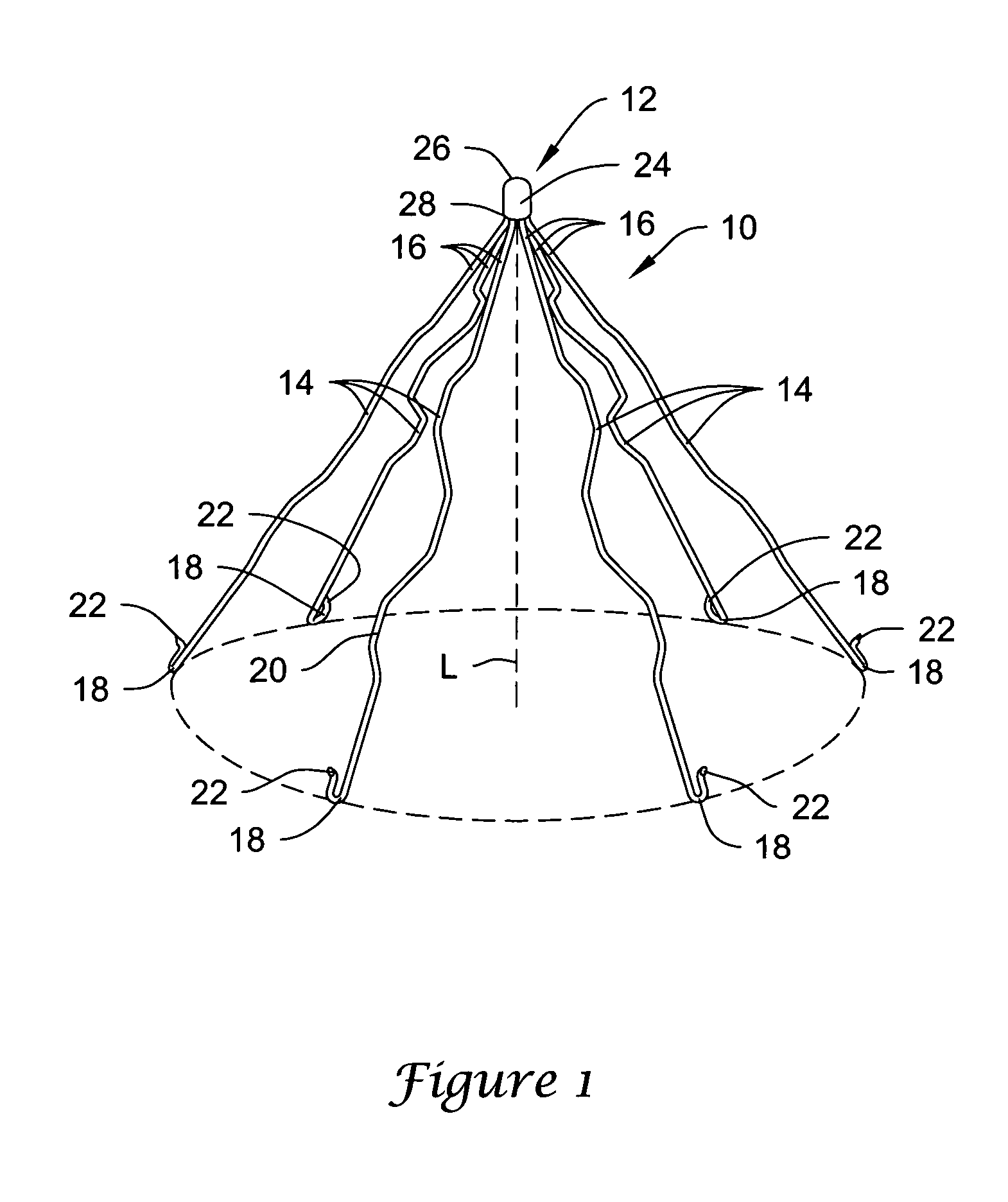
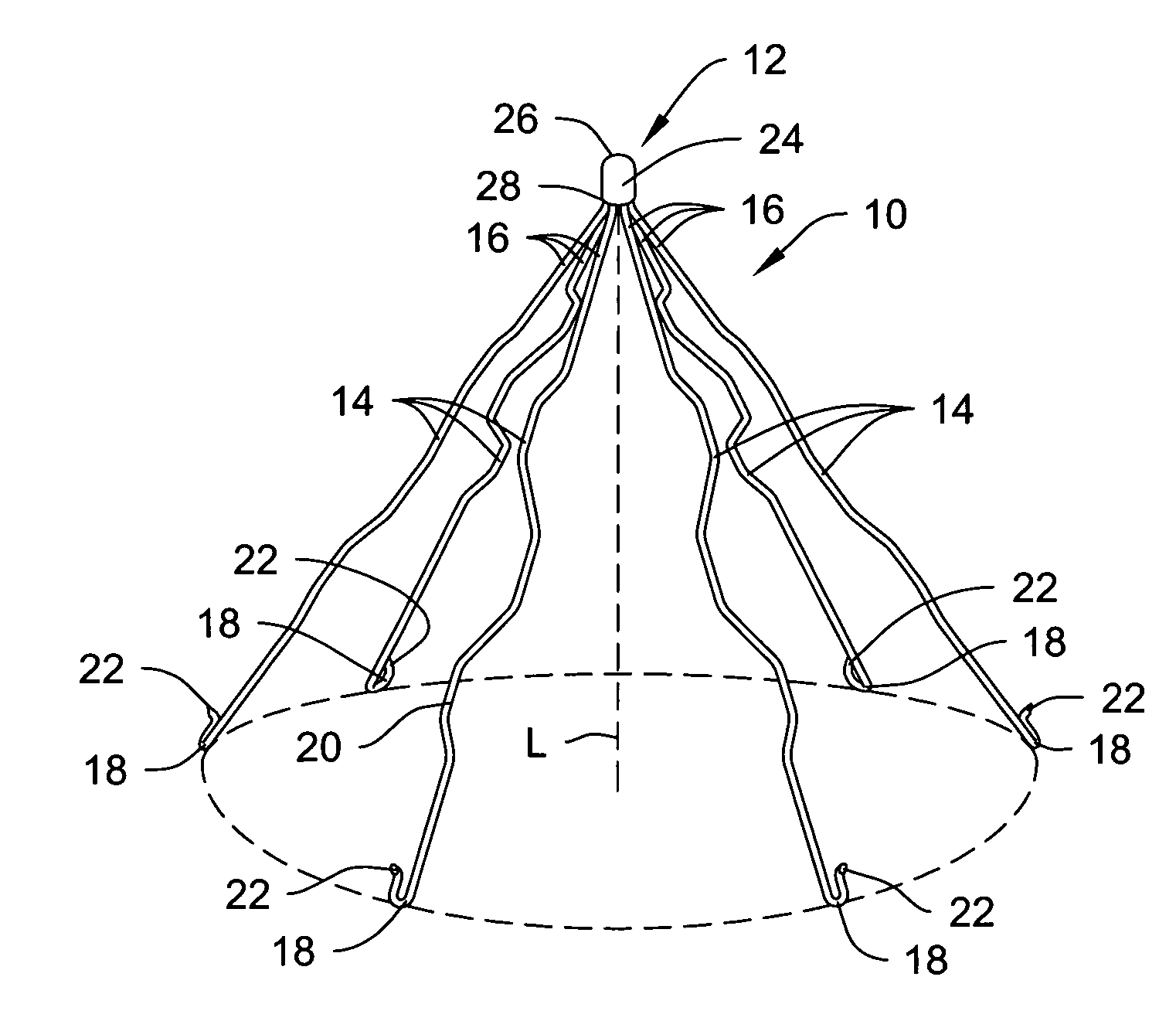
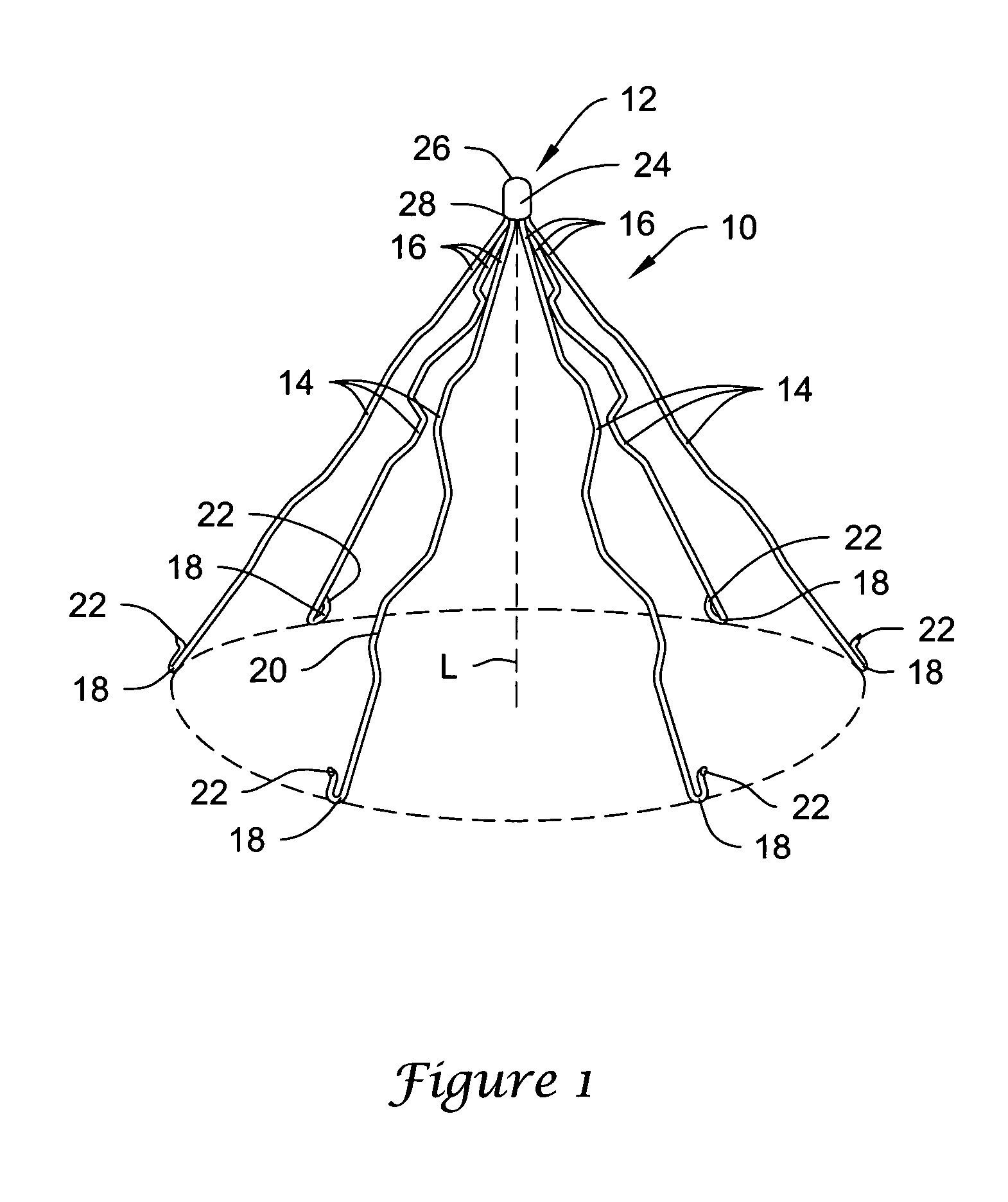
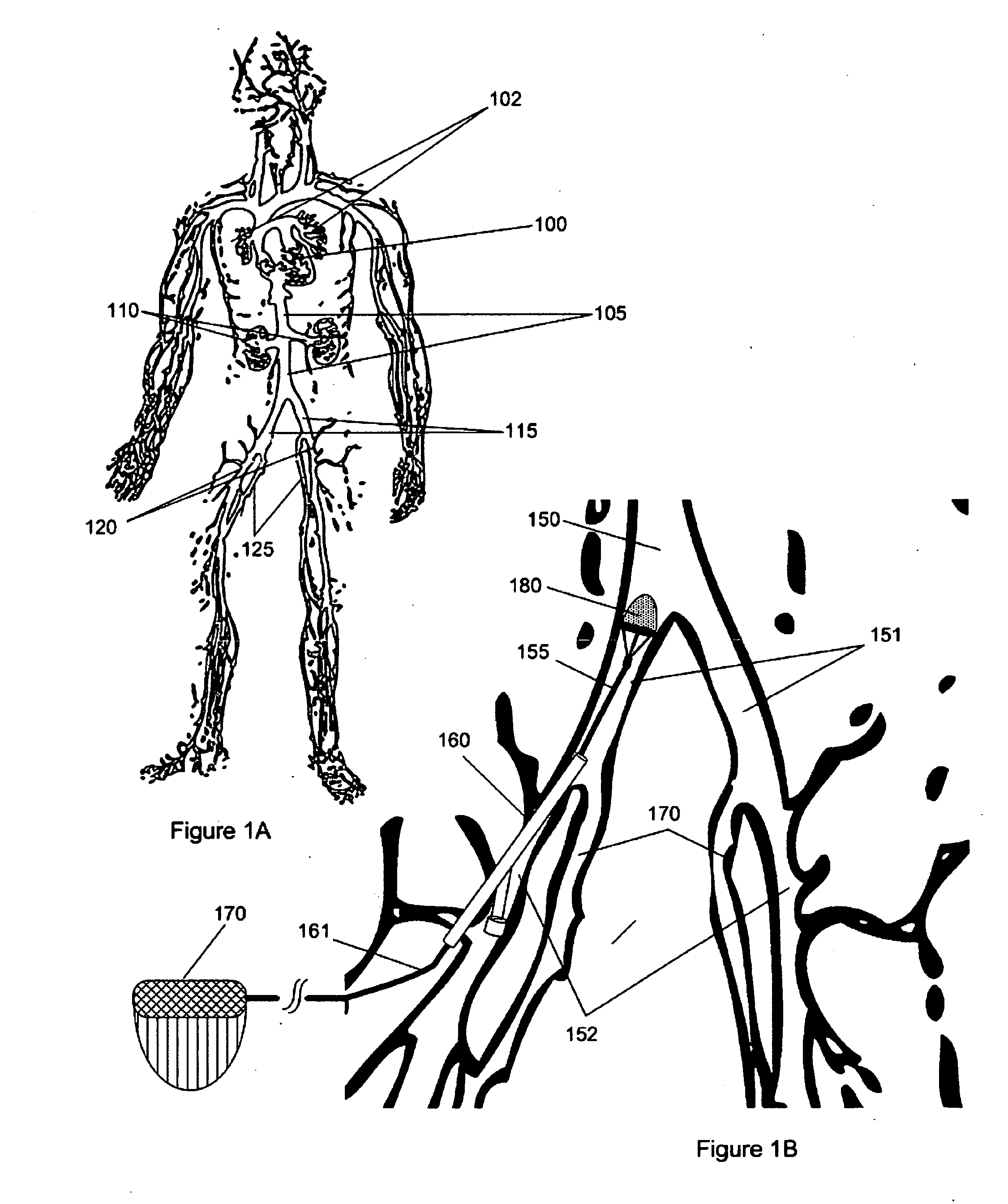
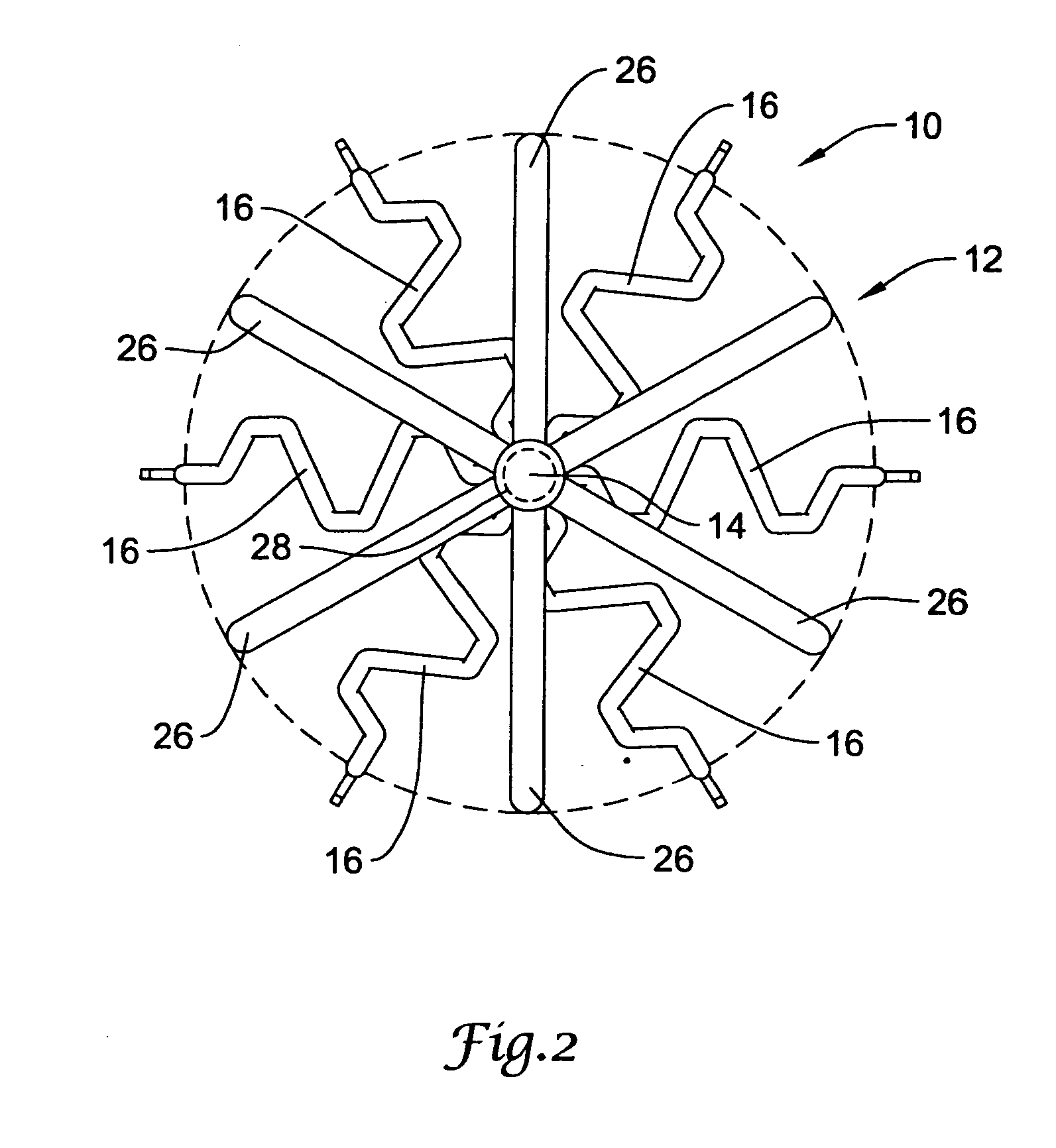
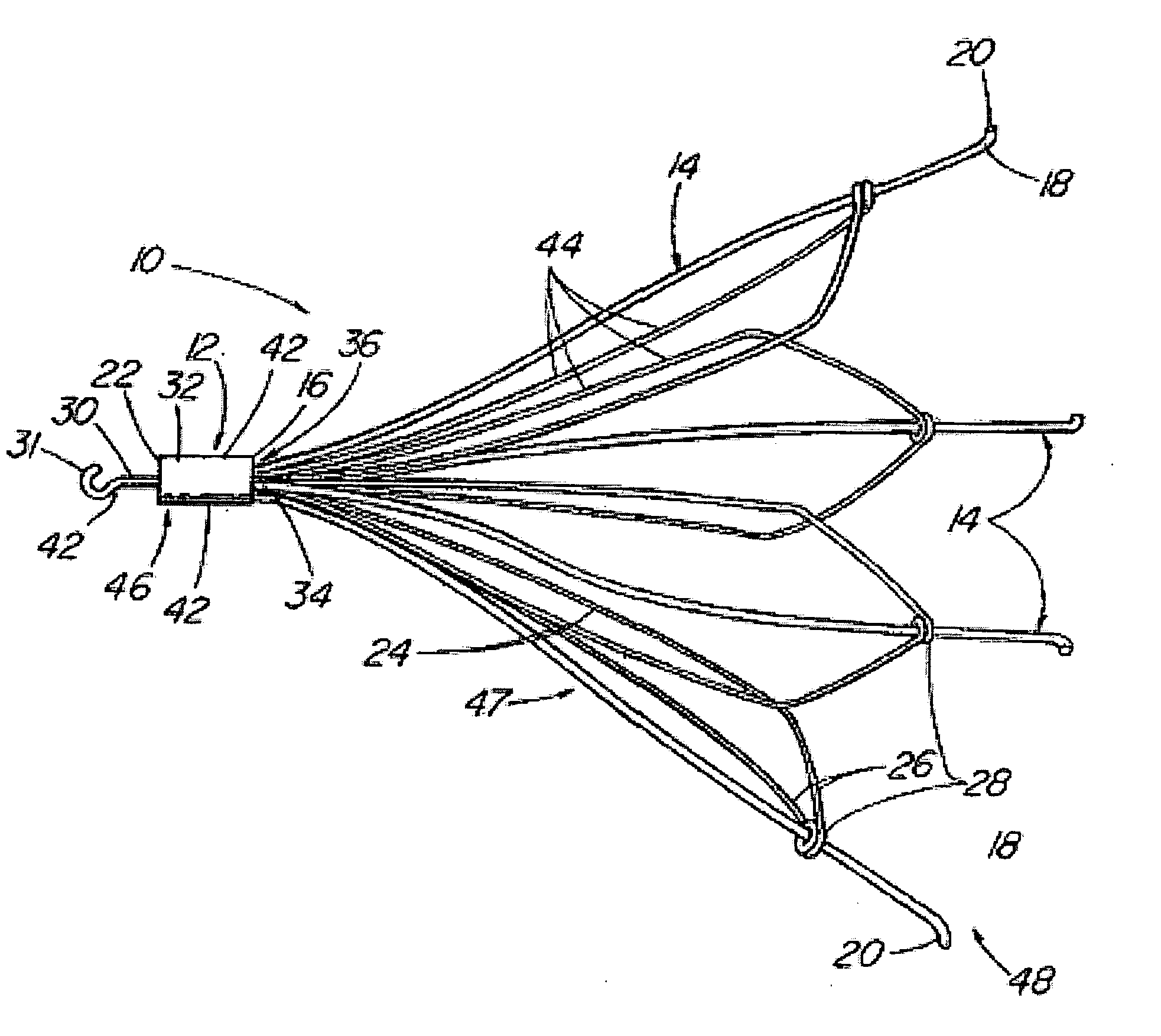
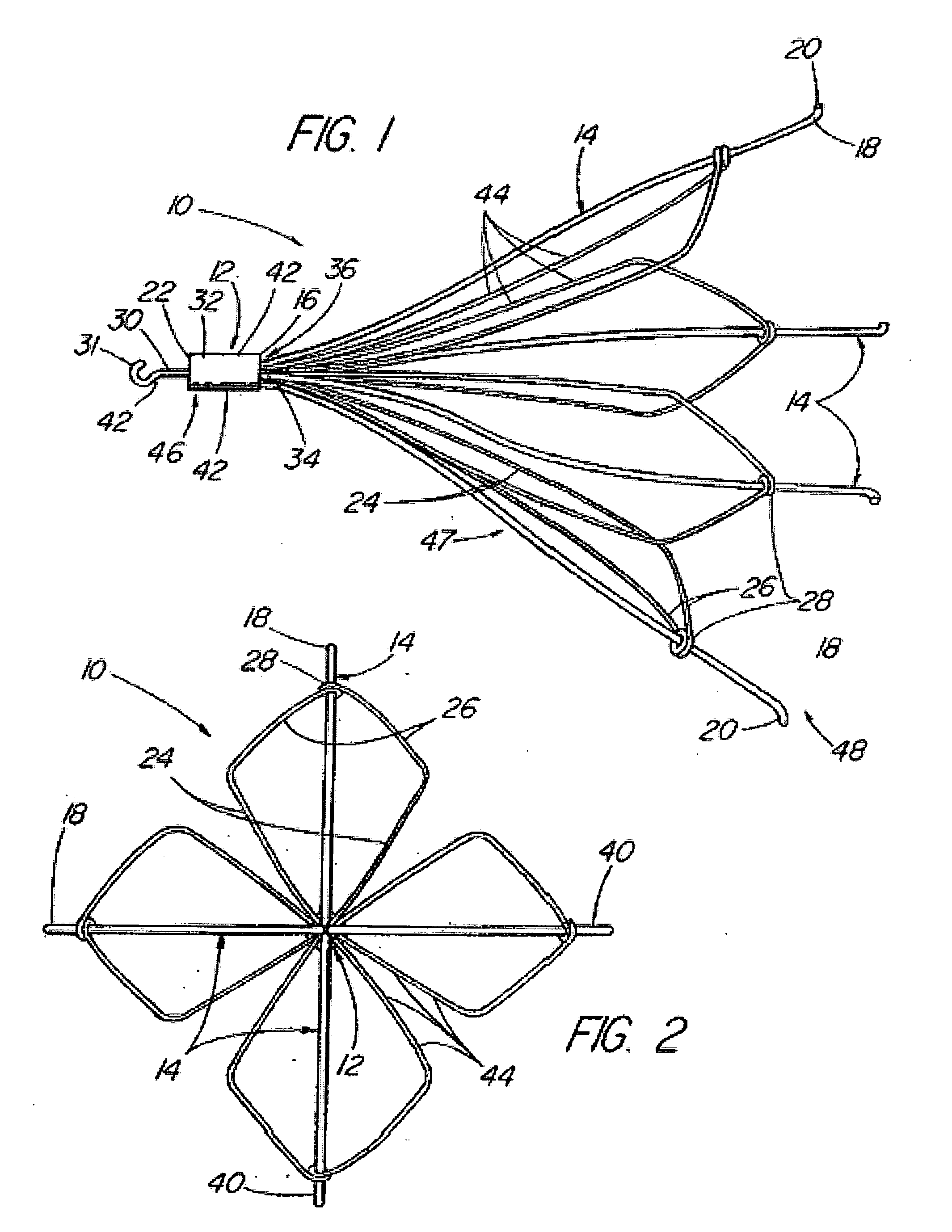
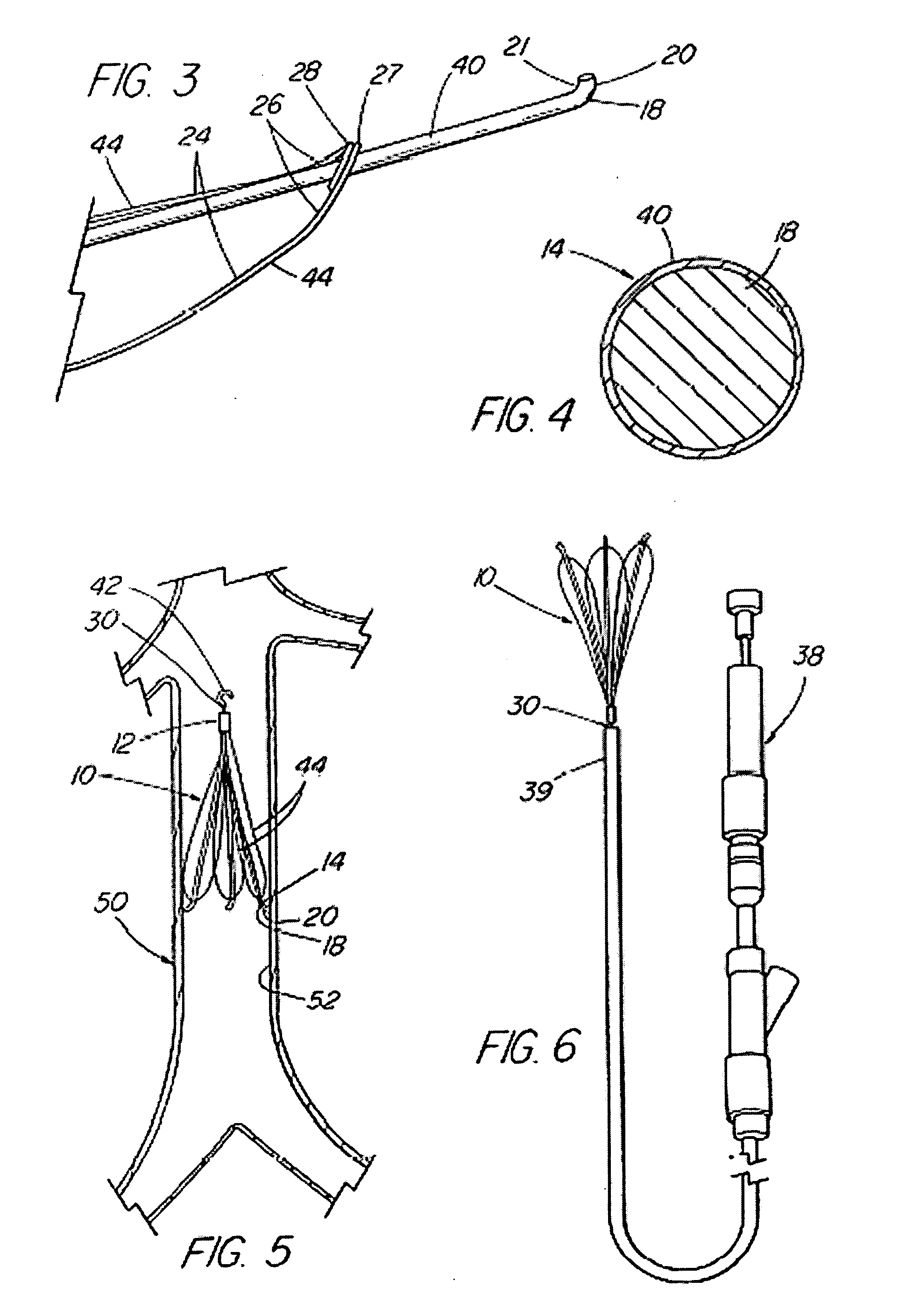
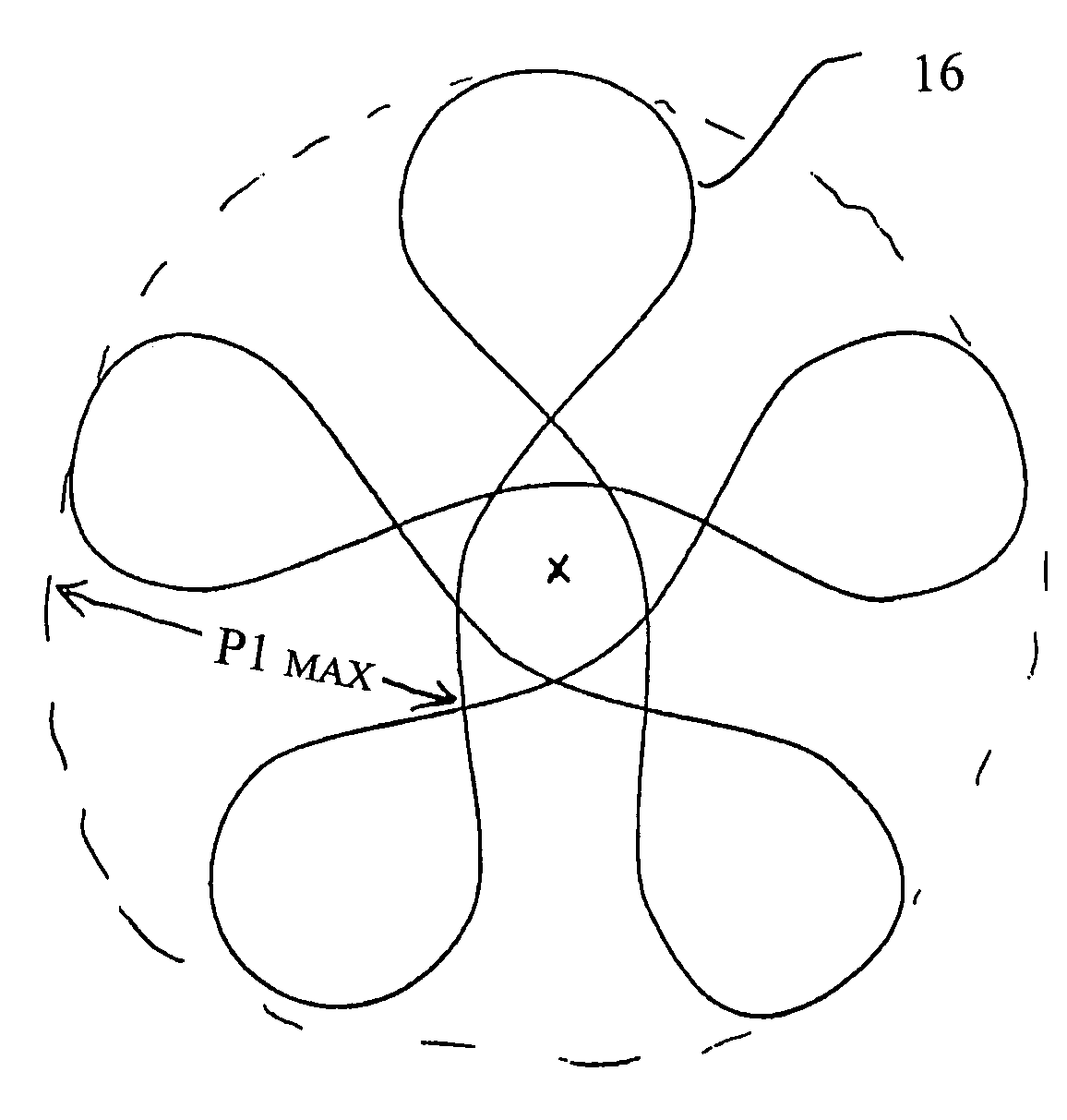
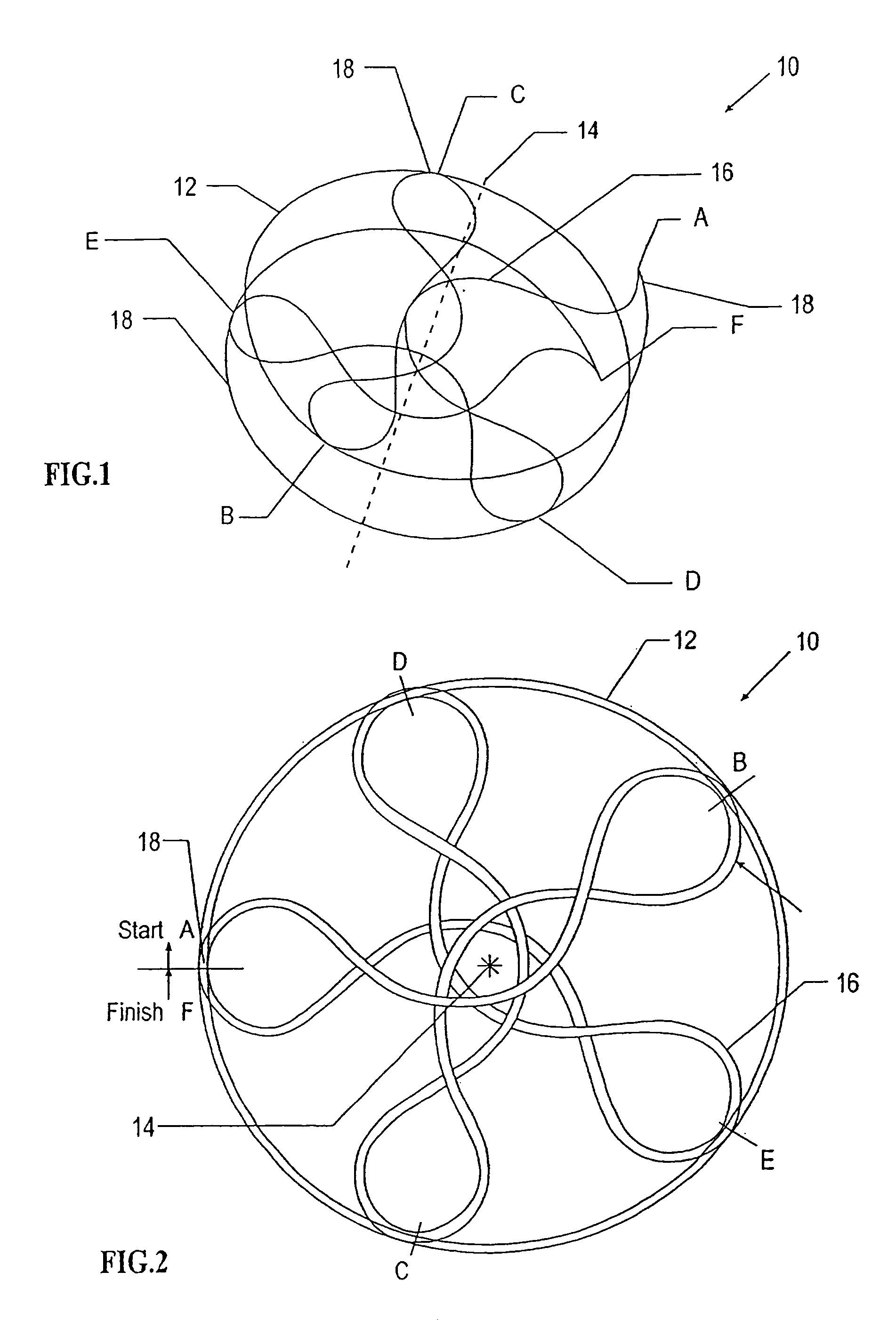
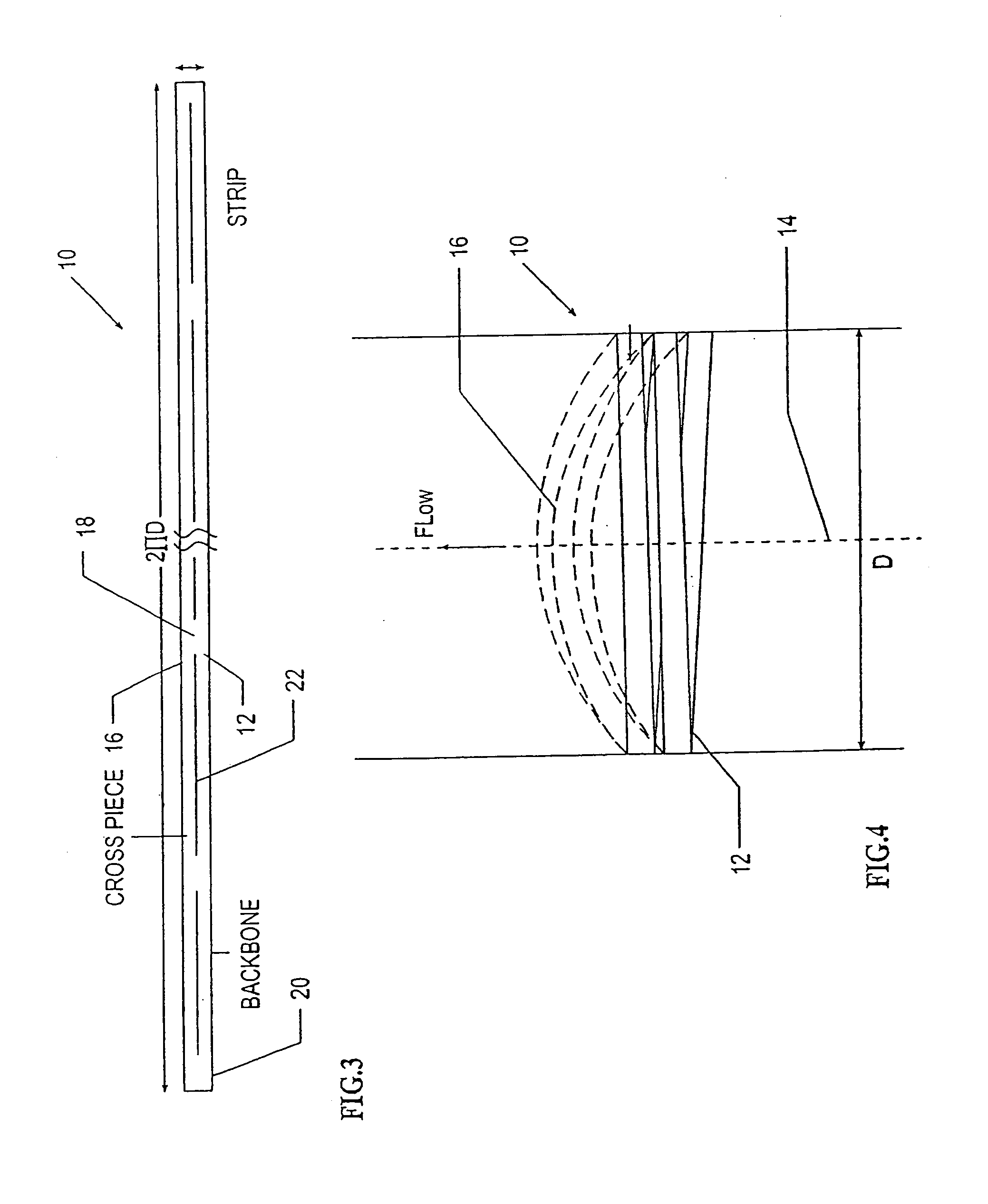
Intravascular filter with debris entrapment mechanism
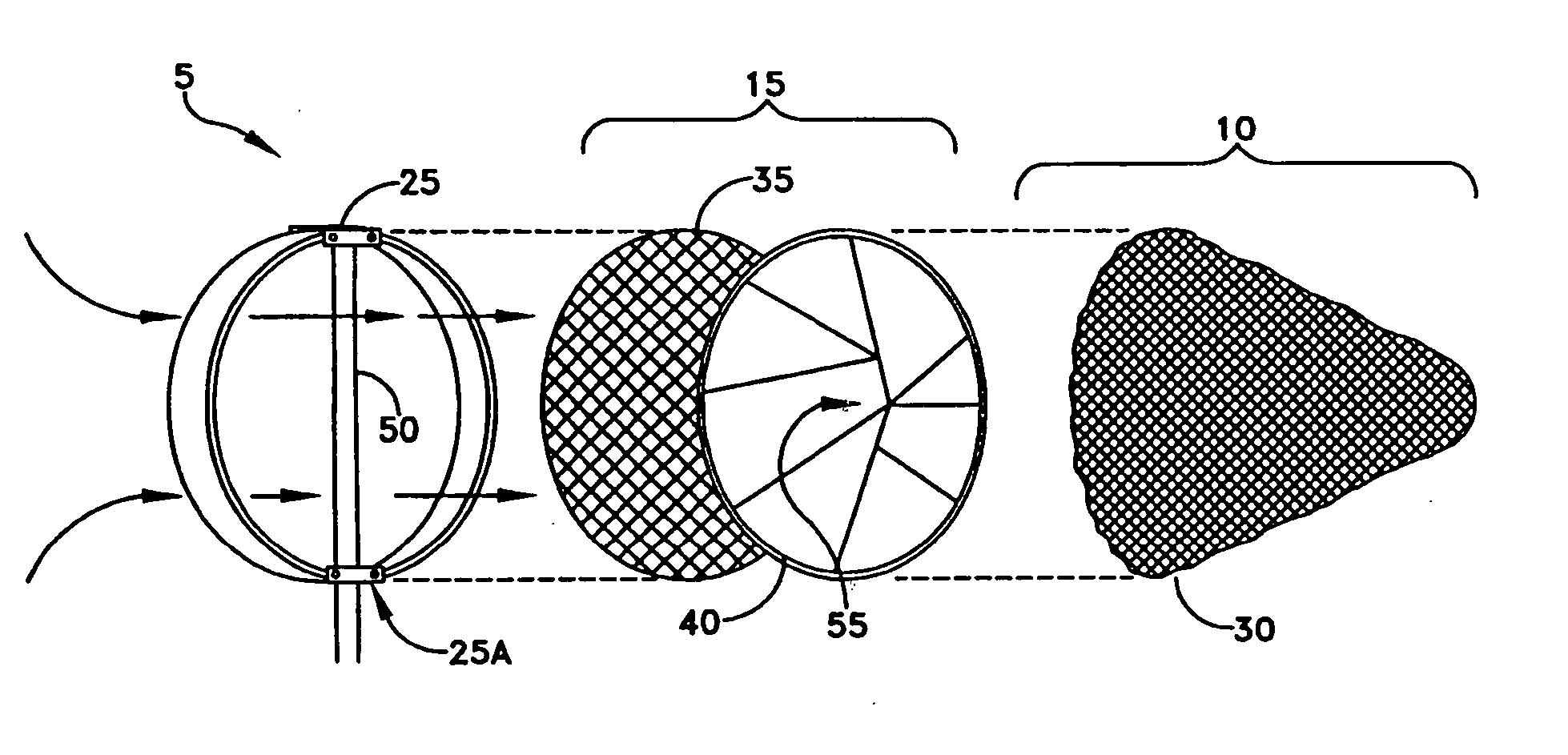
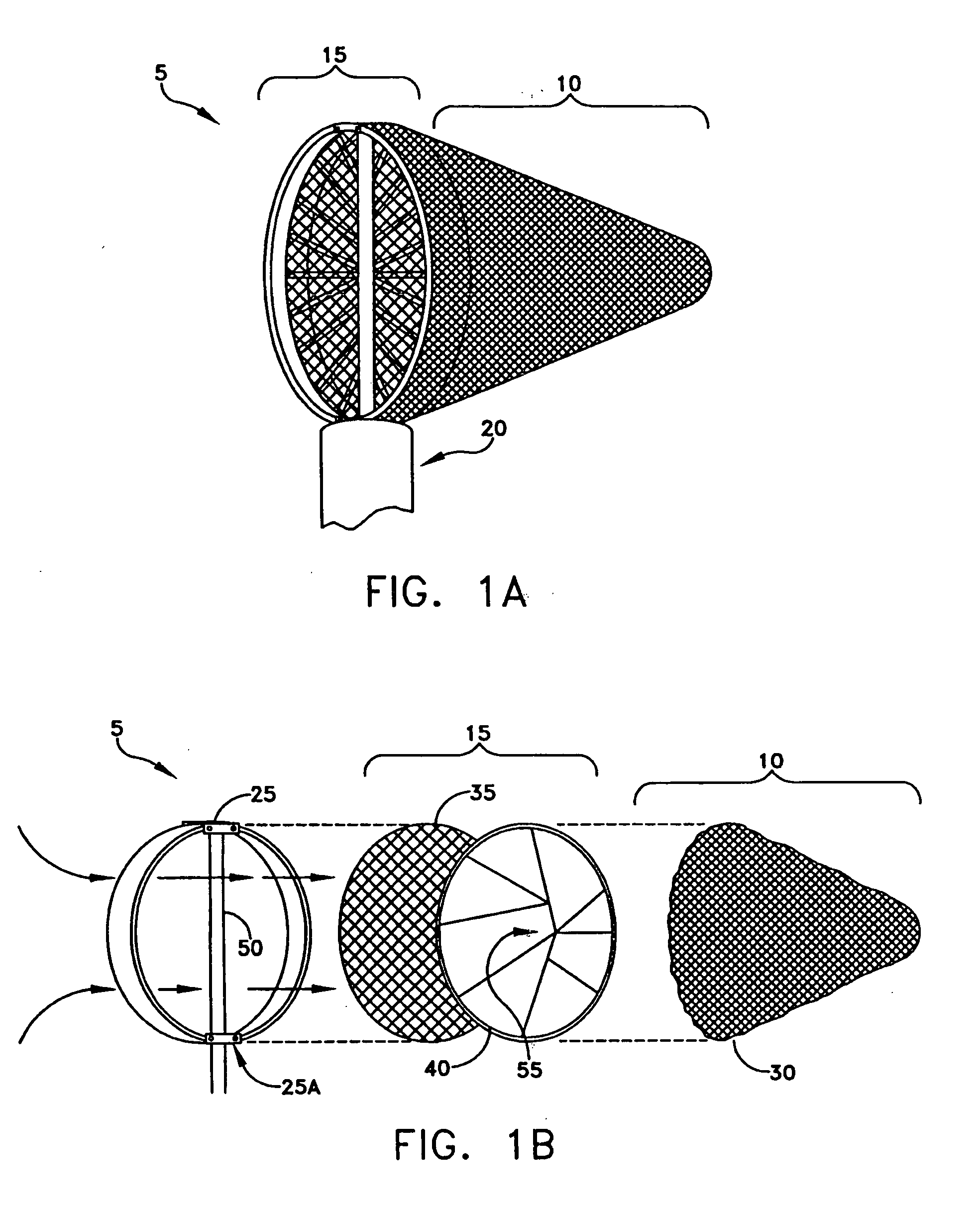
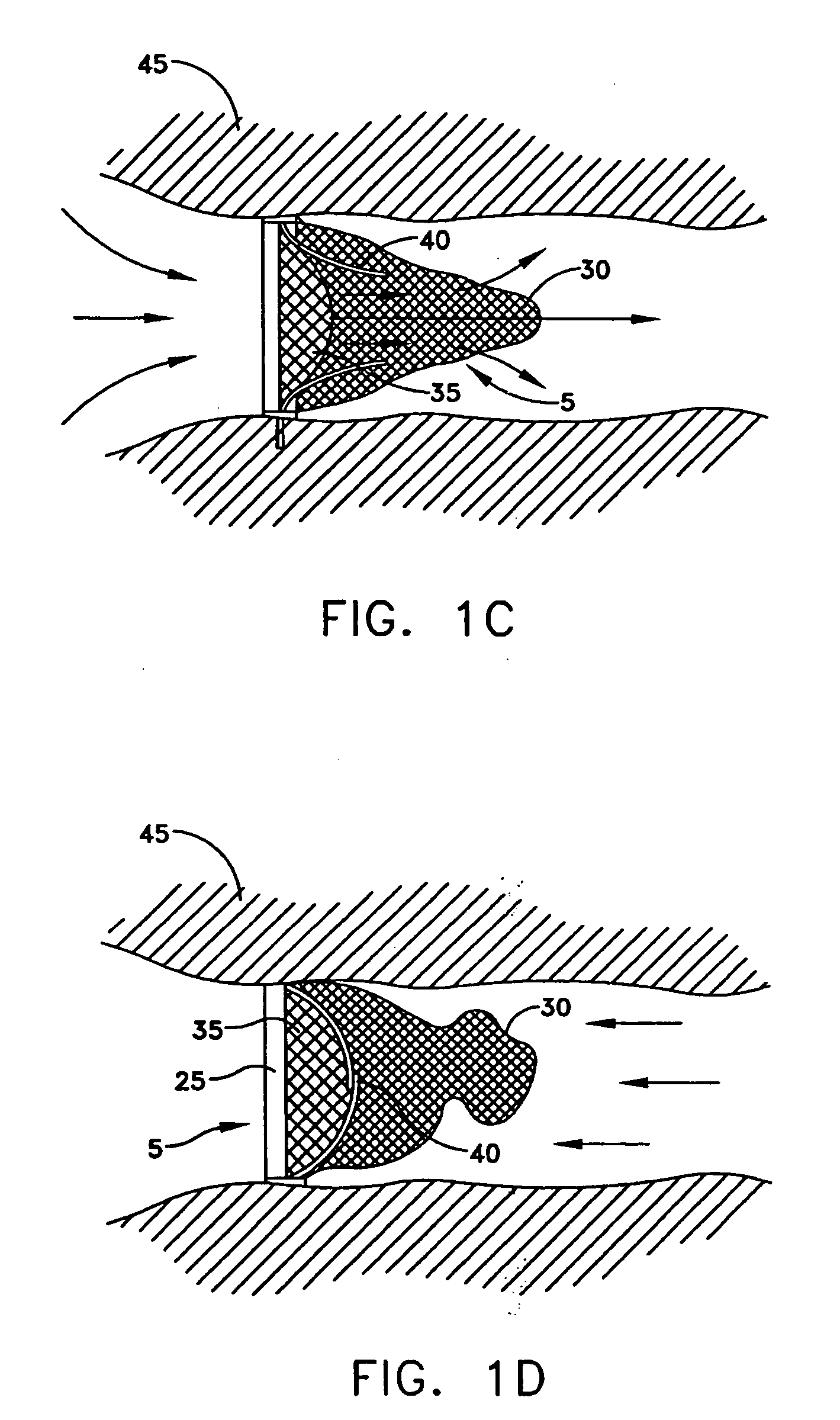
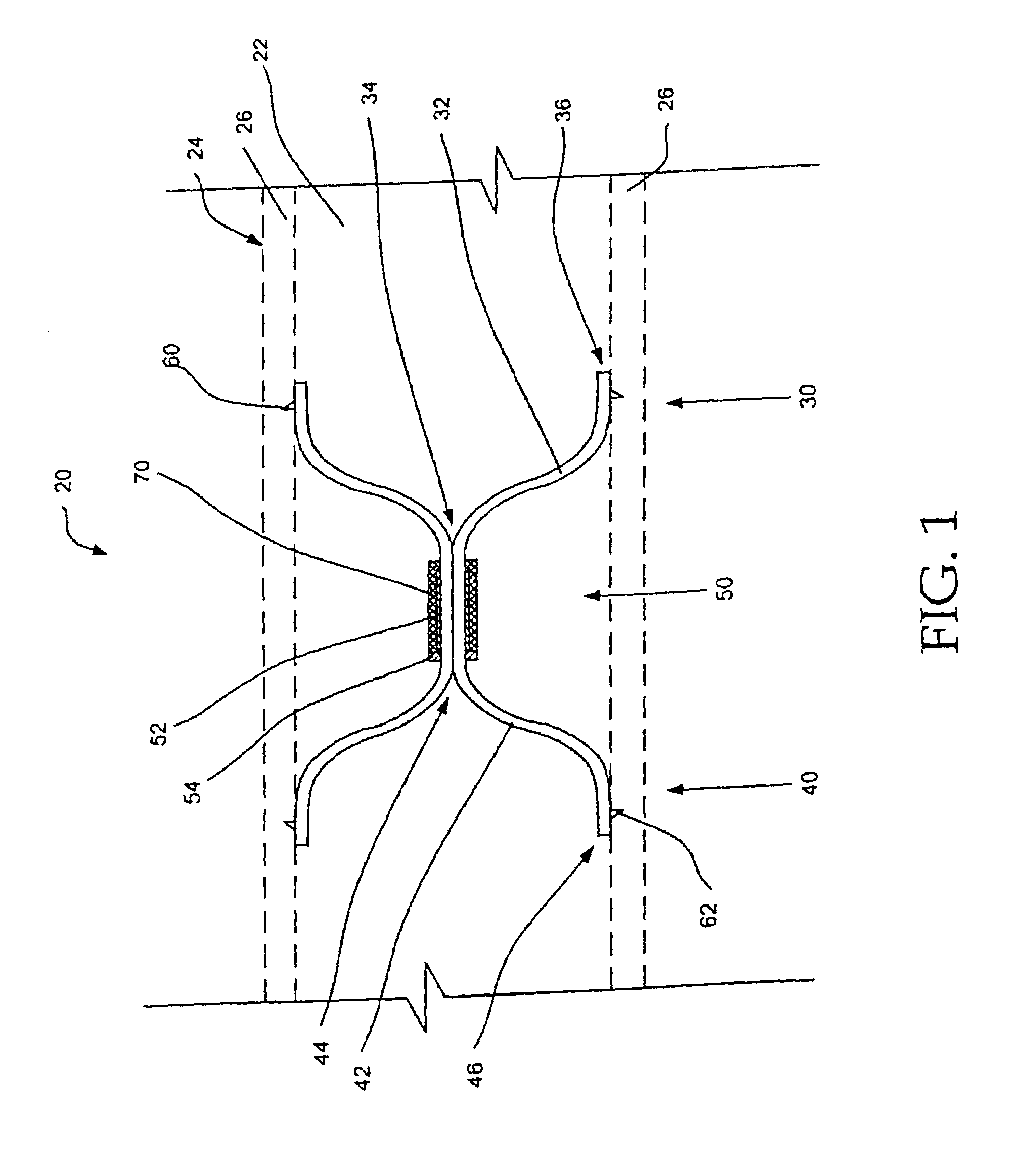
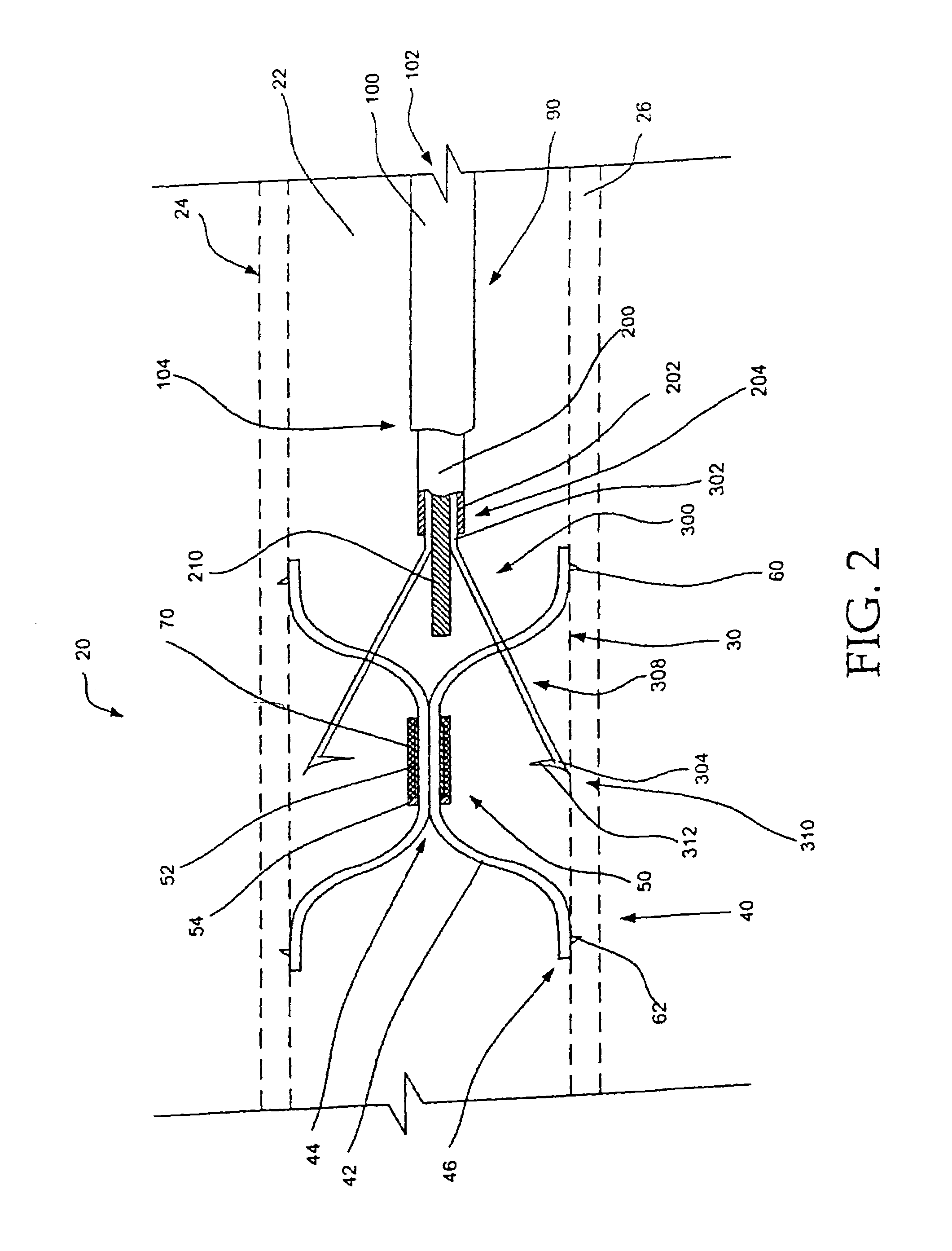
Apparatus for filtering and entrapping debris in the vascular system of a patient, the apparatus including a filter to allow blood to flow therethrough and to restrict passage of debris, wherein the filter captures debris carried in a first direction of blood flow. The apparatus further includes an entrapment mechanism which allows passage of debris and blood therethrough, in the first direction of blood flow and prevents debris passage in a second direction. The entrapment mechanism and filter allow blood and debris therethrough in the first direction of blood flow. The entrapment mechanism prevents debris flow in the second direction of blood flow. A method for filtering and entrapping debris in the vascular system includes inserting the apparatus into the vascular system, allowing blood and debris carried therein to flow through the entrapment mechanism, and removing the apparatus and accumulated debris from the vascular system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intravascular filter with bioabsorbable centering element
Bioabsorbable centering elements for use in centering an implantable intravascular device within a body vessel are disclosed. The bioabsorbable centering element may include a number of support members configured to self-expand and engage the wall of the vessel when deployed. The support members may be formed from a biodegradable material adapted to degrade in vivo within a pre-determined period of time.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
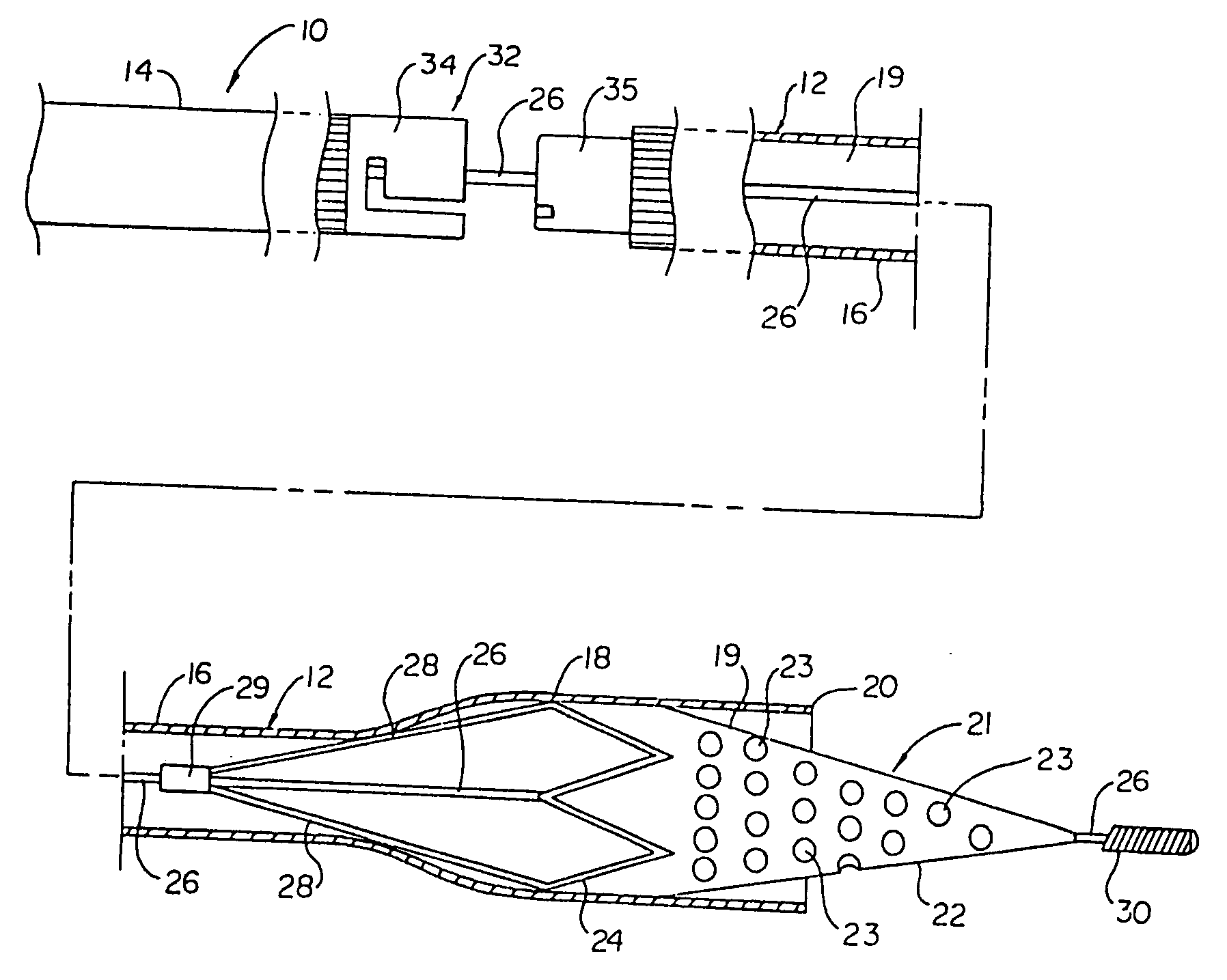
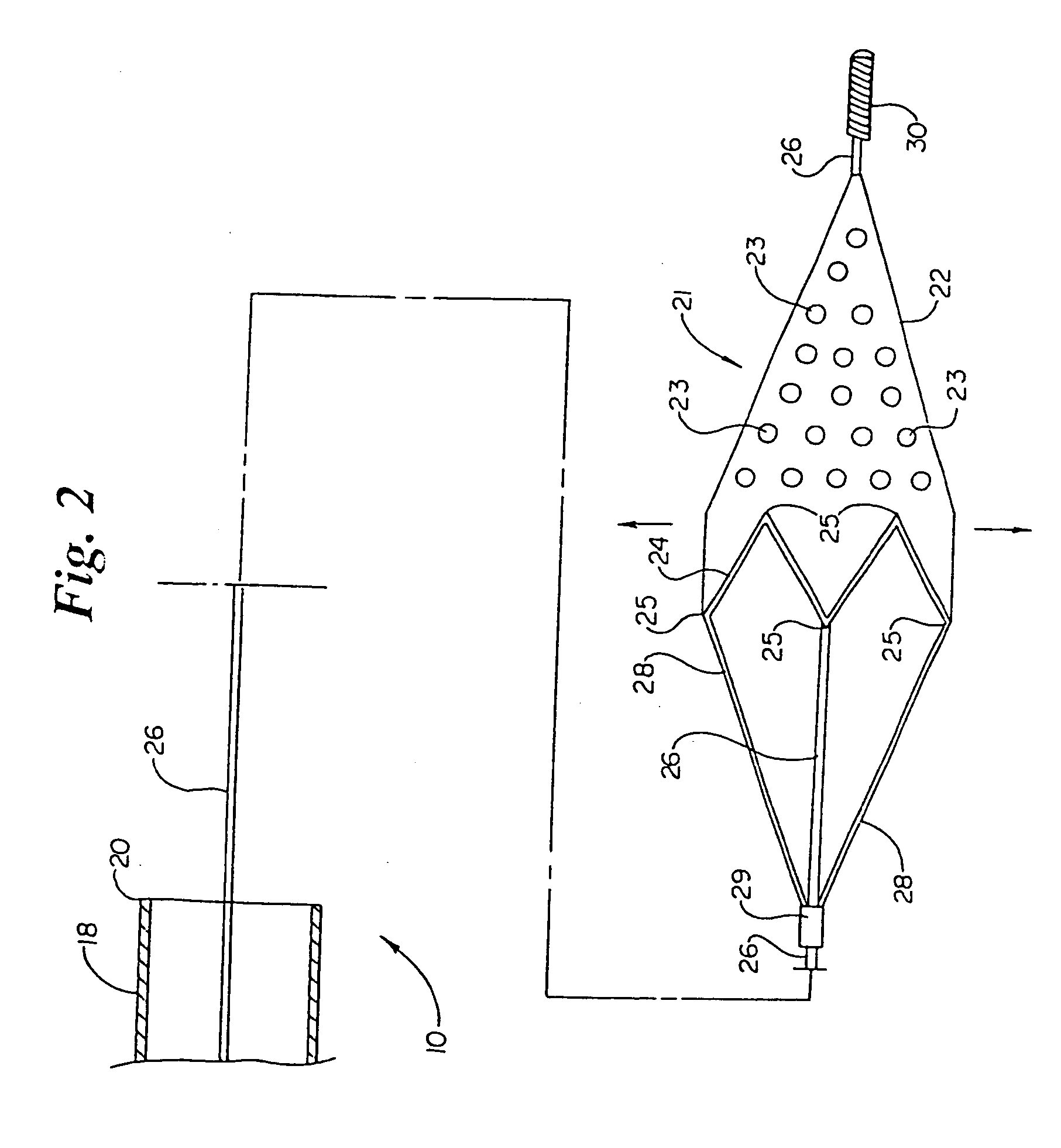
Everted filter device
ActiveUS20050283186A1Effective coverageProvide protectionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesVascular filterThrombus
Everting filter devices and methods for using the devices, including using the devices as intra-vascular filters to filter thrombus, emboli, and plaque fragments from blood vessels. The filter devices include a filter body nominally tubular in shape and having a large proximal opening. The filter body can extend from a proximal first end region distally over the non-everted exterior surface of the filter, further extending distally to a distal-most region, then converging inwardly and extending proximally toward the filter second end region, forming a distal everted cavity. The degree of eversion of the filter can be controlled by varying the distance between the filter first end region near the proximal opening and the closed second end region. Bringing the filter first and second end regions closer together can bring filter material previously on the non-everted filter exterior to occupy the distal-most region. The everting process can also bring filter material previously in the distal-most position further into the distal everted cavity. The filter devices can be used to remove filtrate from body vessels, with the filtrate eventually occluding the distal-most region. The filter can then be further everted, bringing fresh, unoccluded filter material into place to provide additional filter capacity. Some everting filters have the capability of switching between occluding and filtering modes of operation, thereby allowing a treating physician to postpone the decision to use filtering or occluding devices until well after insertion of the device into the patient's body.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Embolic filter
InactiveUS7004955B2Maintaining and restoring patencyImprove the immunitySurgeryDilatorsEndovascular surgeryBiomedical engineering
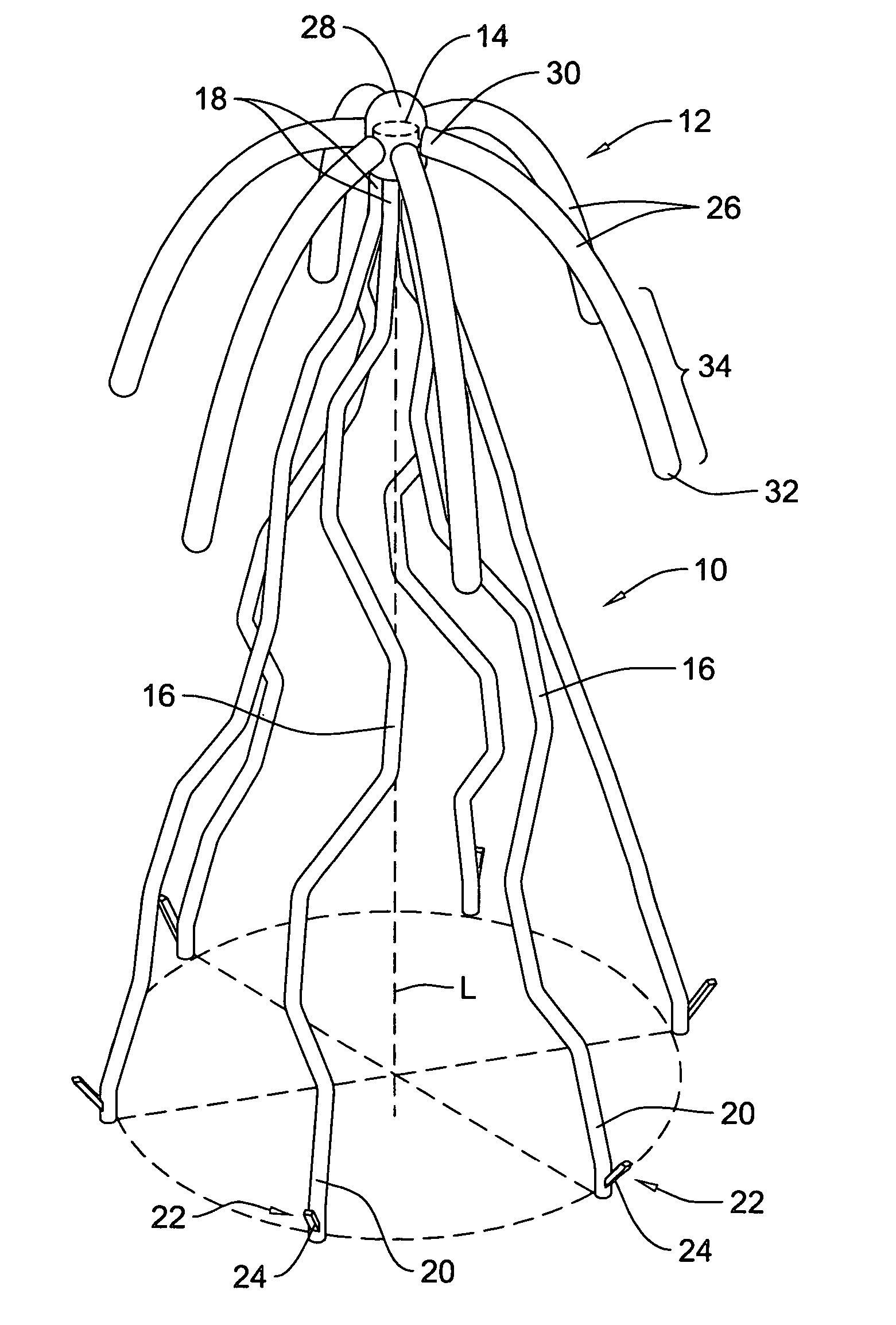
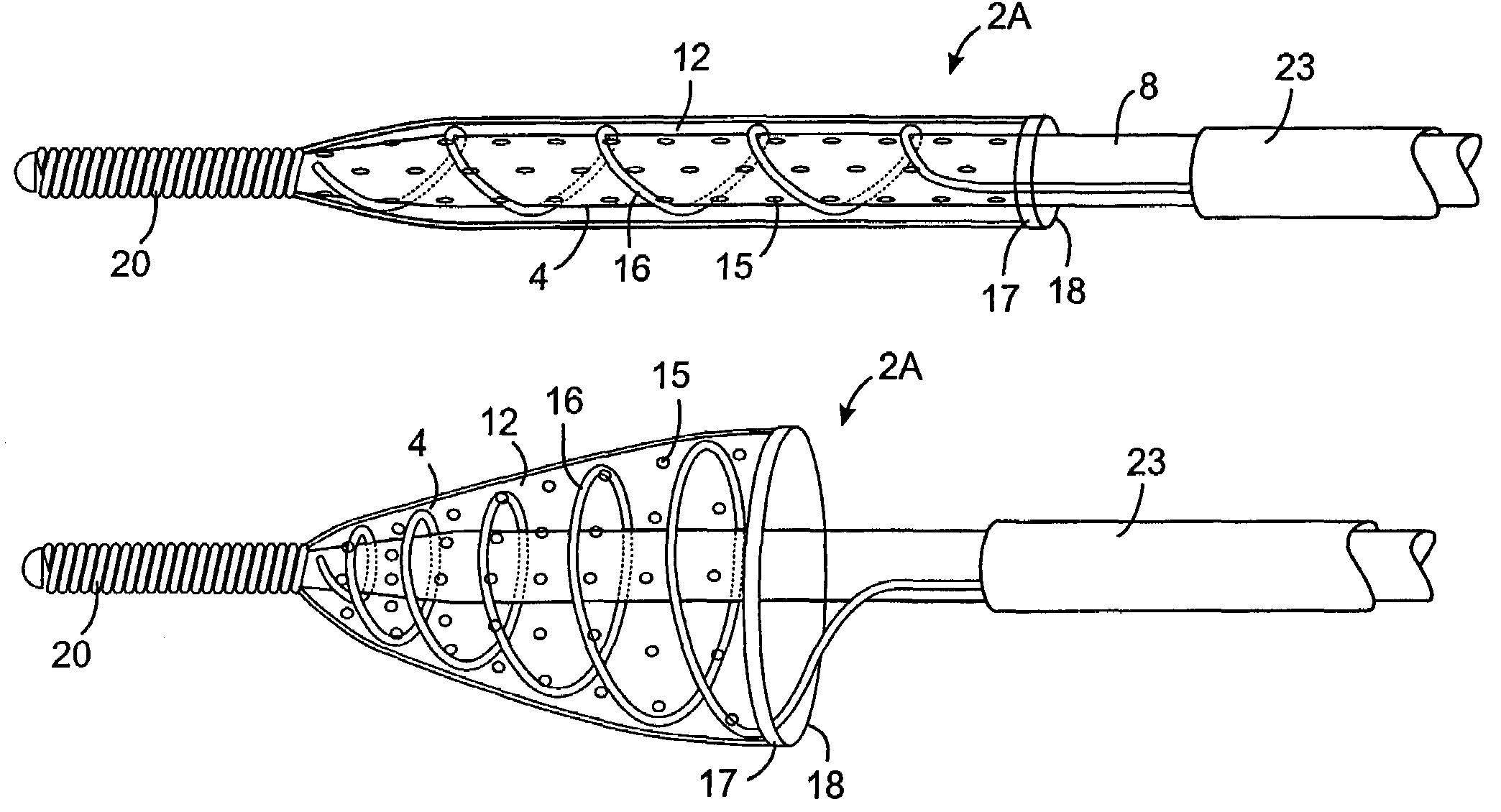
An intravascular filter device for use in capturing debris which may occur as a result of an intravascular procedure. The filter device includes a proximal section, a distal section and a mid-section. The mid-section includes three rings configured in a sixteen apices alternating V-pattern. The filter device specifically embodies structure that provides enhanced radial opening and angular resistance to collapse in its expanded state. While, in its compressed state the filter device provides an extremely small compressed profile giving it the desired ability to be delivered into very small vessels of the human vasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
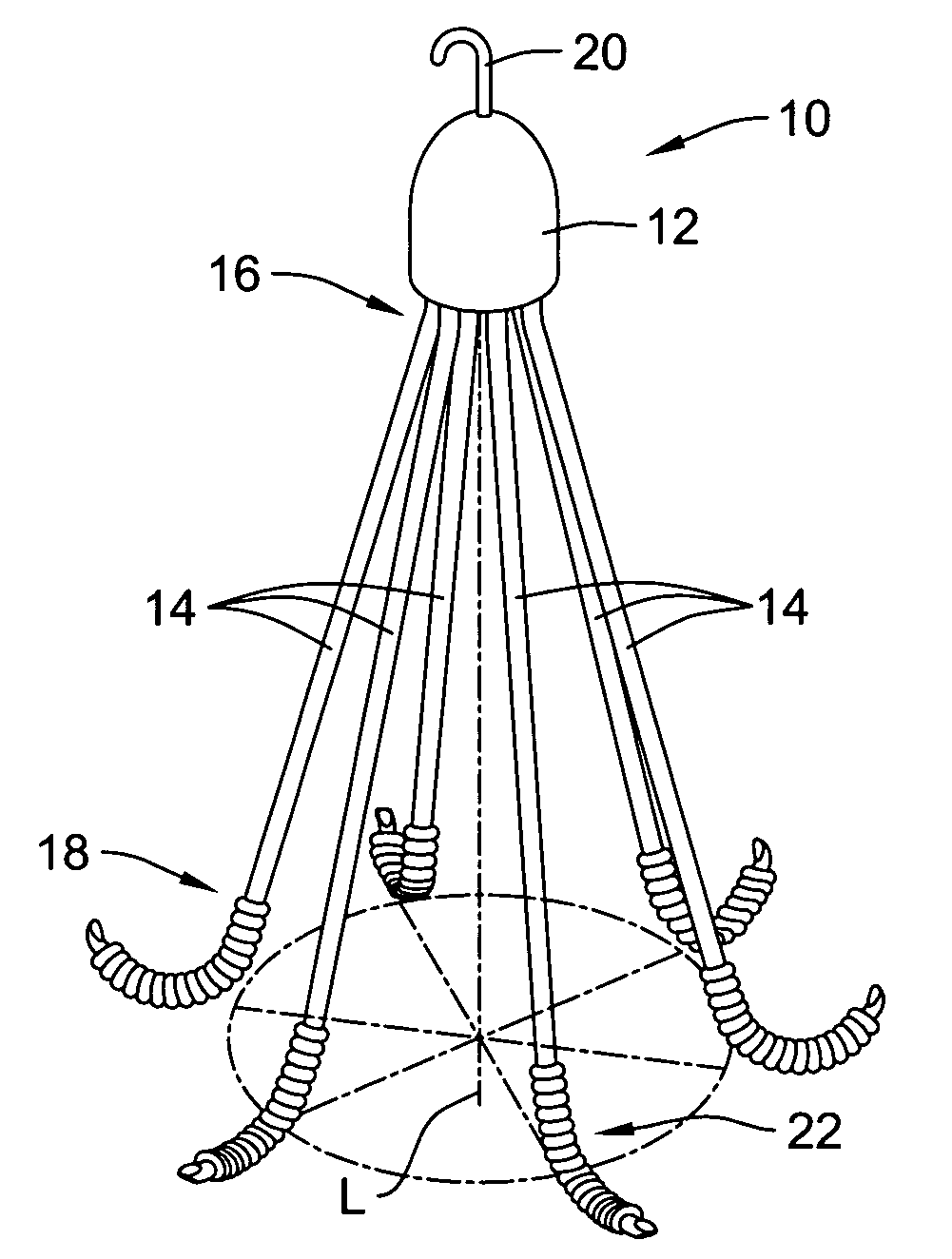
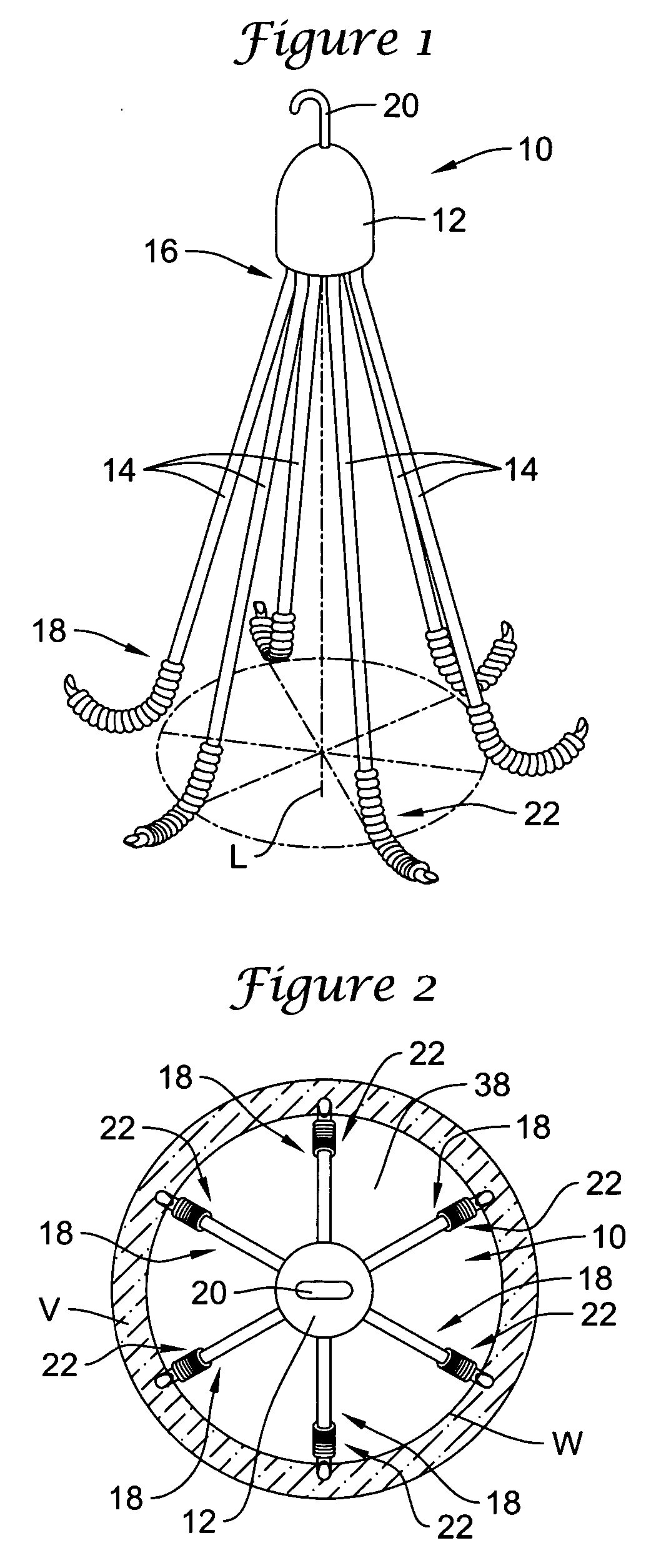
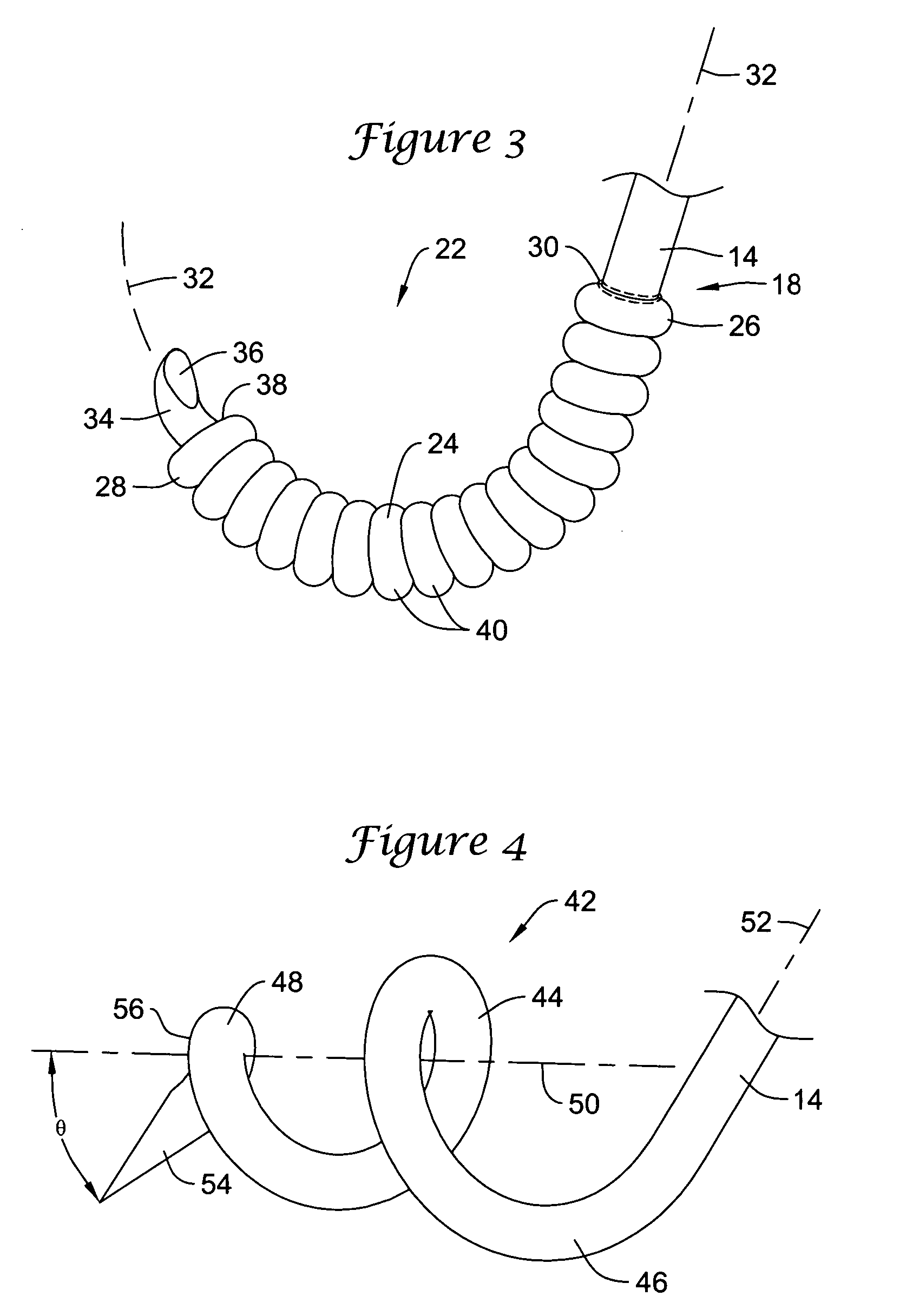
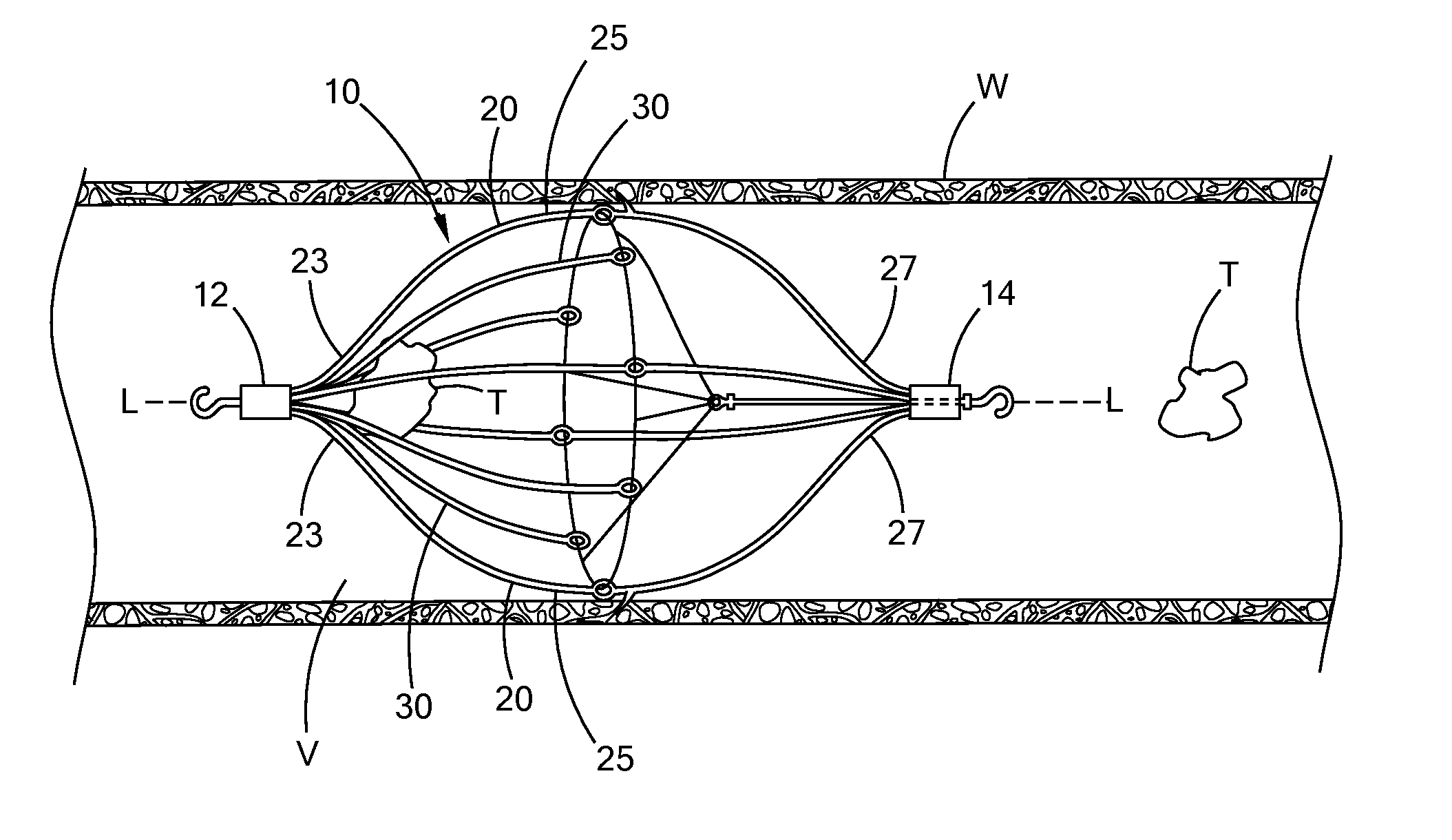
Methods and devices for filtering fluid flow through a body structure
An intravascular filter having a filament which expands a filter element. The filament is a coil which is stretched to reduce the diameter of the coil for introduction. The filter element is preferably biased toward the closed position and is opened by the coil when tension is released on the coil. The filament slides along the internal surface of the filter element so that the filter element may assume intermediate positions.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Intravascular filter retrieval device and method
InactiveUS7033376B2Inhibit migrationSurgerySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMedicineThrombus
A thrombus filter configured for placement in within a blood vessel lumen defined by a blood vessel wall. Methods and devices for selectively removing the thrombus filter when the presence of a filter in the vascular system is no longer desired. The thrombus filter includes a first strand formation, a second strand formation, and a joined portion.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
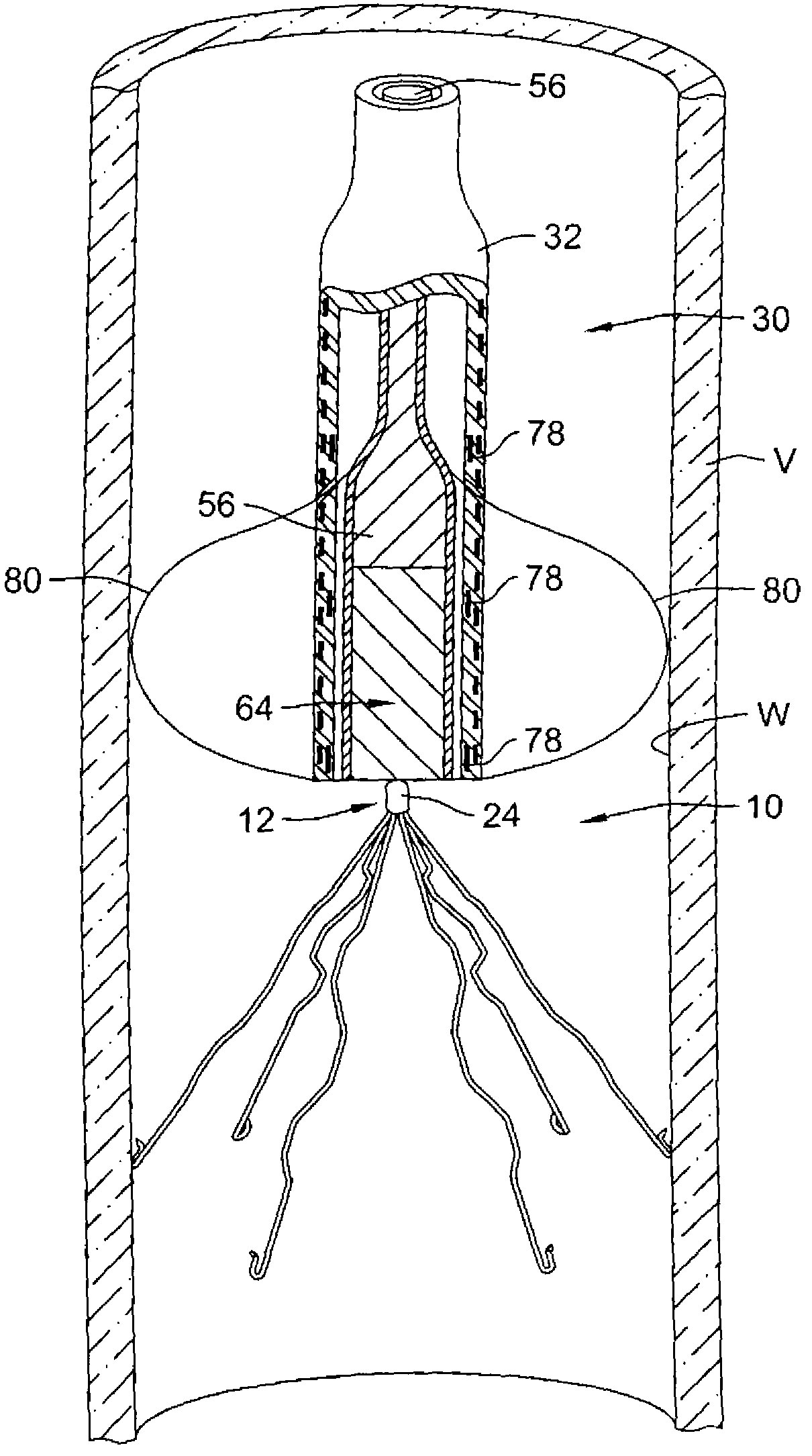
Intravascular filter assembly
An intravascular filter assembly for use in a body vessel lumen having a wall, which may include a first filter having a mouth facing in a first direction at a first location for receiving emboli and an end in a second direction opposite the first direction, and a second filter having a mouth facing in the first direction at a first location for receiving emboli and an end in the second direction, wherein the second filter is removably attached to the first filter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Retrievable intravascular filter with bendable anchoring members
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
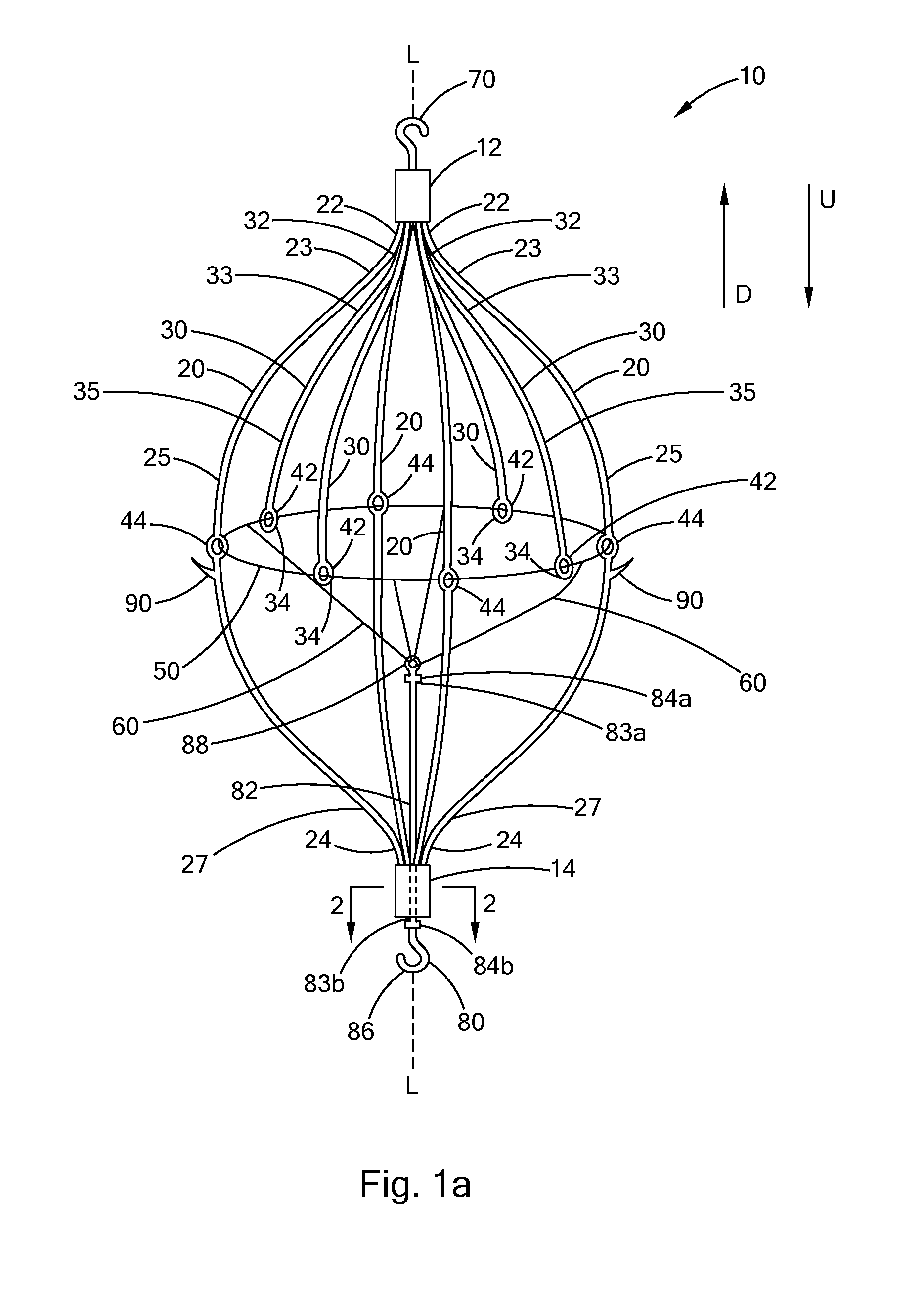
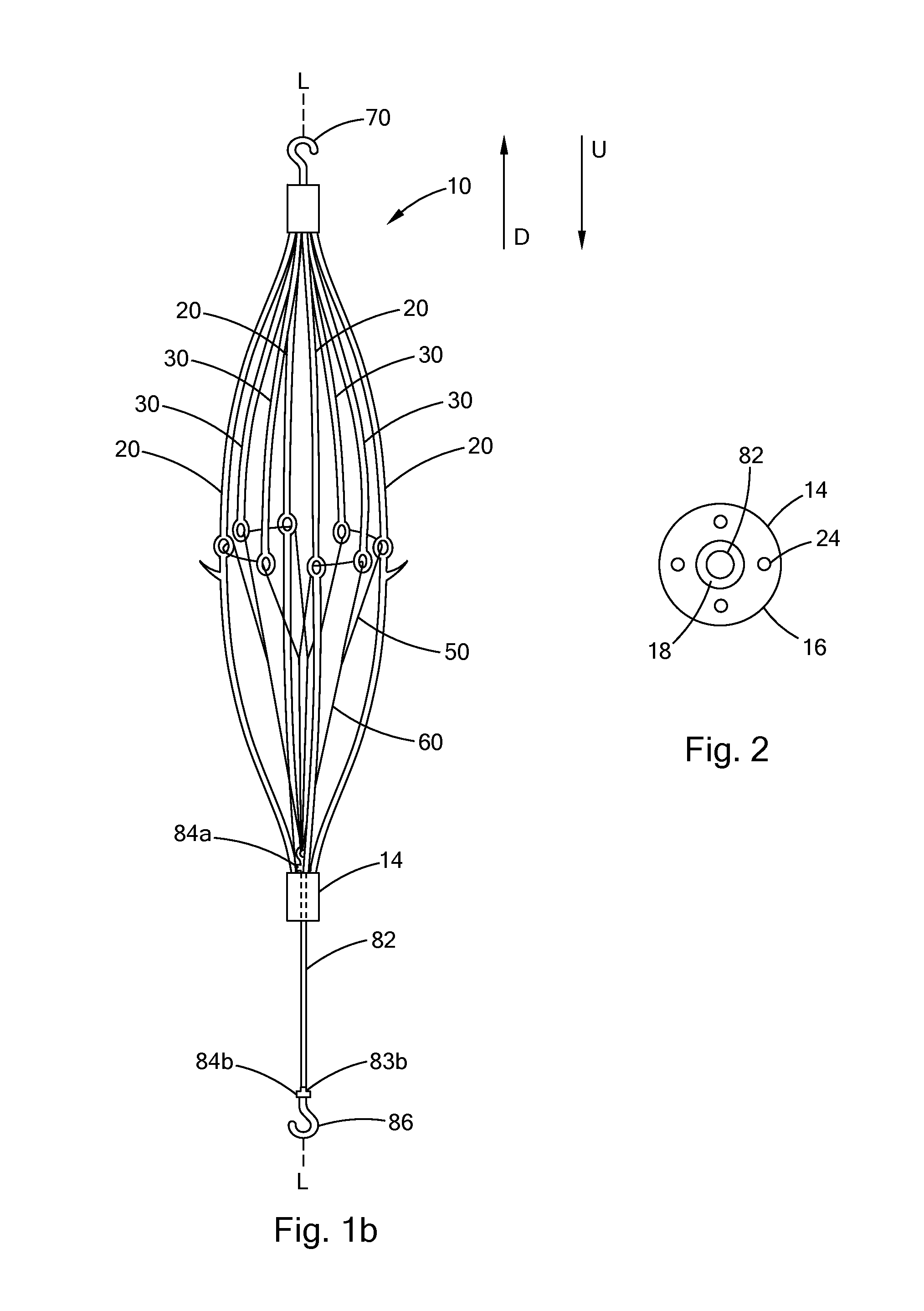
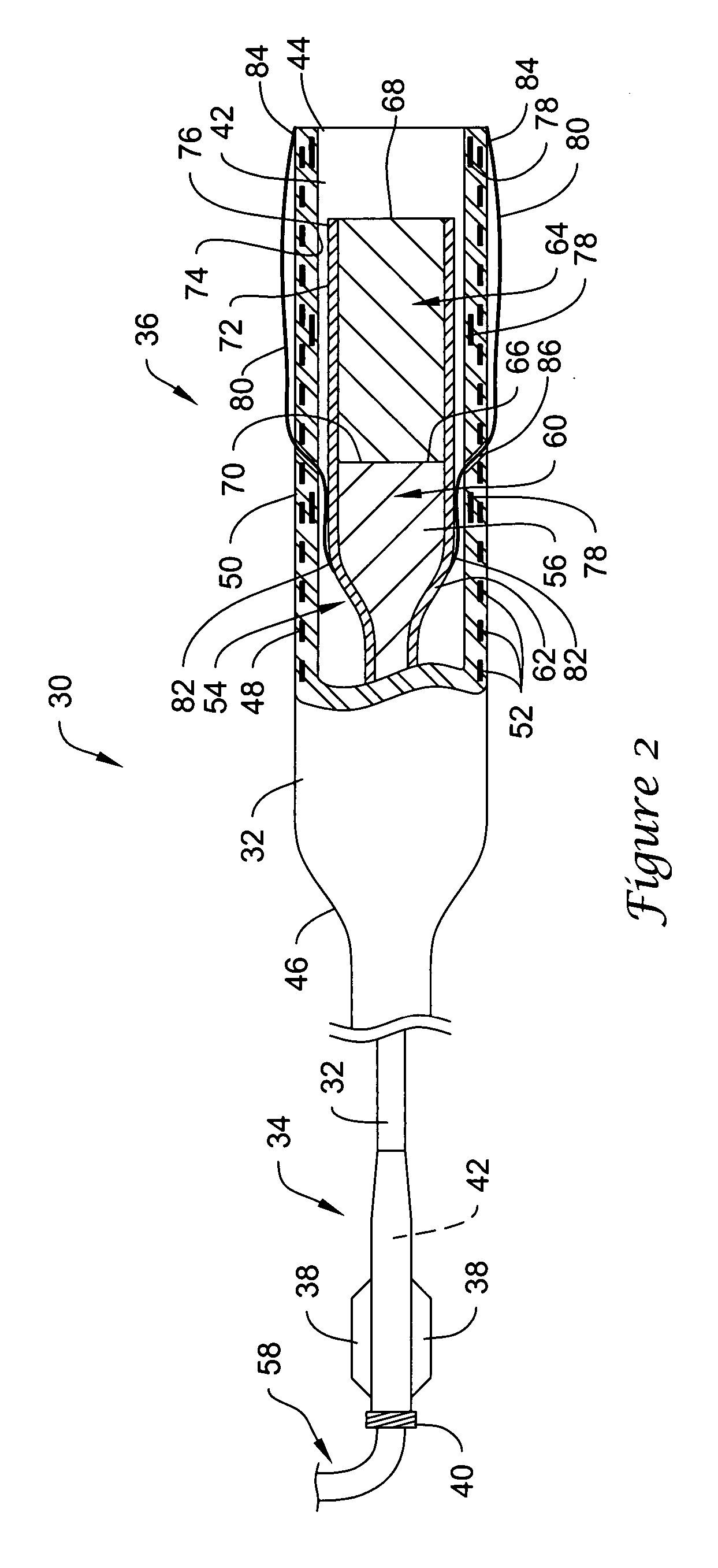
Filter with positioning and retrieval devices and methods
InactiveUS7993362B2More accurately centering the filter within a vesselAccurately center and stabilizeStentsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringIntravascular filter
An intravascular filter having centering capabilities and a device for manipulation of the filter within a vessel. The manipulation device includes a grasping member disposed at the distal end of an elongate shaft, wherein the grasping member may be used to engage a portion of the filter.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
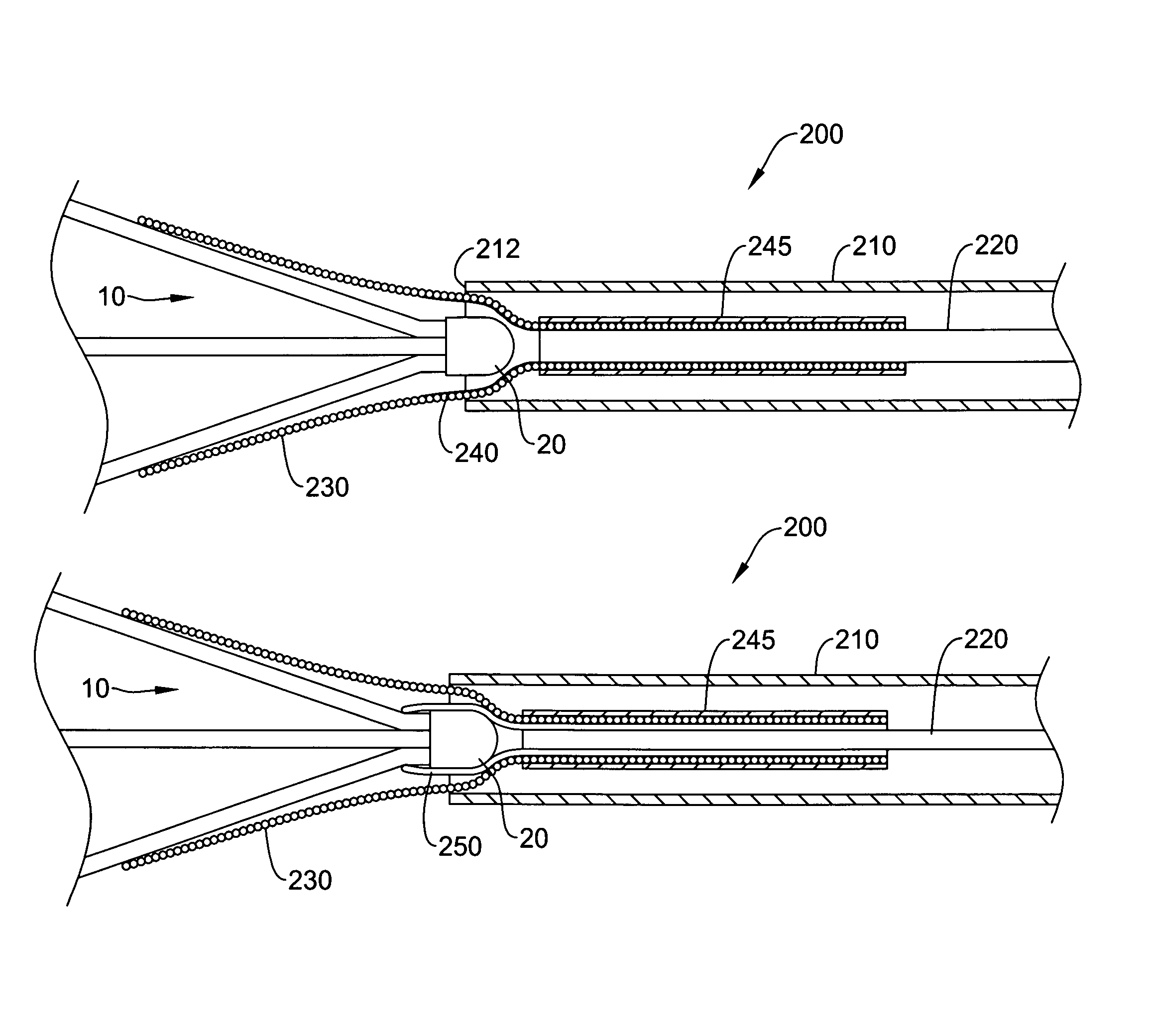
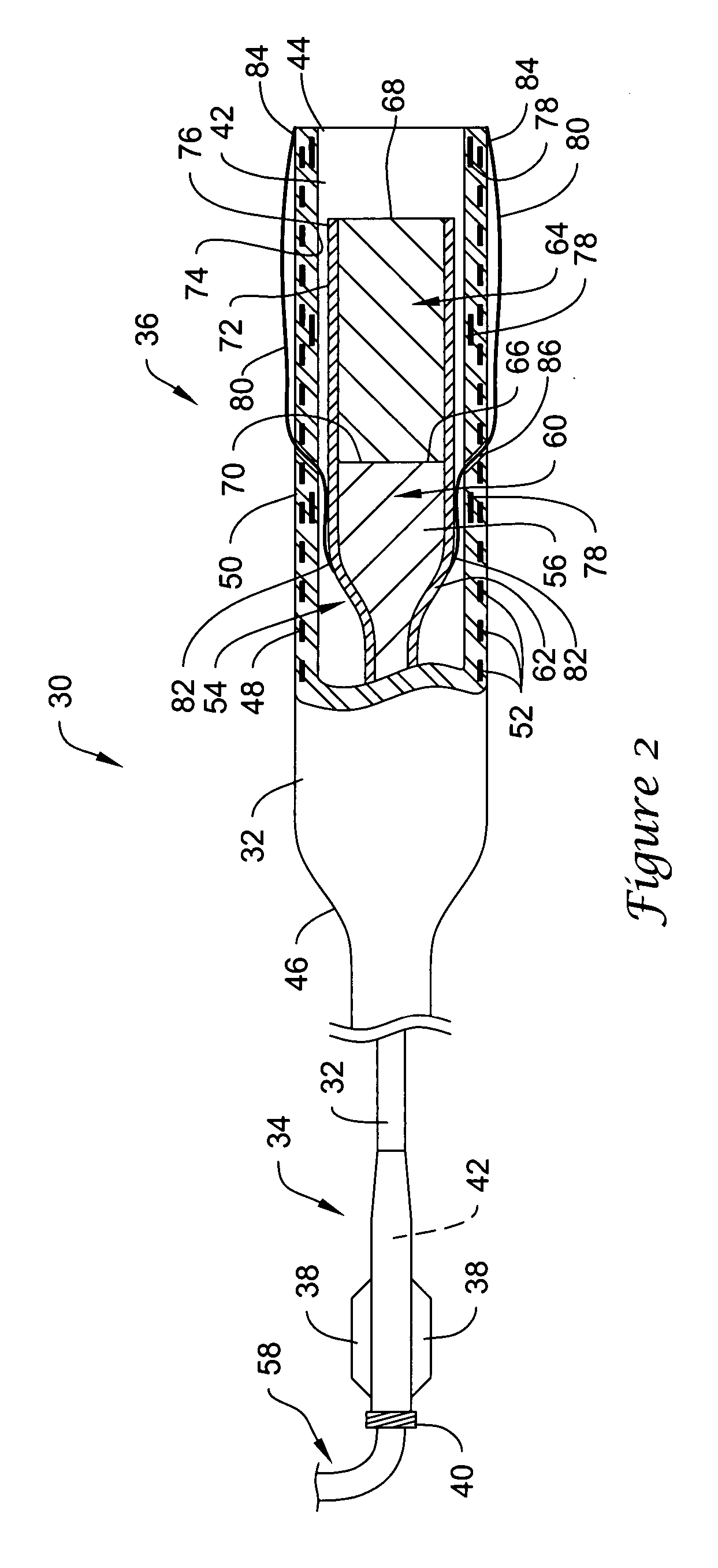
Intravascular filter with debris entrapment mechanism
InactiveUS7758606B2Great ability to collect debrisReduce in quantityHeart valvesSurgeryEntrapmentDebris flow
Apparatus for filtering and entrapping debris in the vascular system of a patient, the apparatus including a filter to allow blood to flow therethrough and to restrict passage of debris, wherein the filter captures debris carried in a first direction of blood flow. The apparatus further includes an entrapment mechanism which allows passage of debris and blood therethrough, in the first direction of blood flow and prevents debris passage in a second direction. The entrapment mechanism and filter allow blood and debris therethrough in the first direction of blood flow. The entrapment mechanism prevents debris flow in the second direction of blood flow. A method for filtering and entrapping debris in the vascular system includes inserting the apparatus into the vascular system, allowing blood and debris carried therein to flow through the entrapment mechanism, and removing the apparatus and accumulated debris from the vascular system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Dual Endovascular Filter and Methods of Use
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and devices for filtering fluid flow through a body structure
An intravascular filter having a filament which expands a filter element. The filament is a coil which is stretched to reduce the diameter of the coil for introduction. The filter element is preferably biased toward the closed position and is opened by the coil when tension is released on the coil. The filament slides along the internal surface of the filter element so that the filter element may assume intermediate positions.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Filter with positioning and retrieval devices and methods
InactiveUS20060184193A1More accurately centering the filter within a vesselAccurately center and stabilizeStentsSurgeryEngineeringBiomedical engineering
An intravascular filter having centering capabilities and a device for manipulation of the filter within a vessel. The manipulation device includes a grasping member disposed at the distal end of an elongate shaft, wherein the grasping member may be used to engage a portion of the filter.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Intravascular filter and method
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
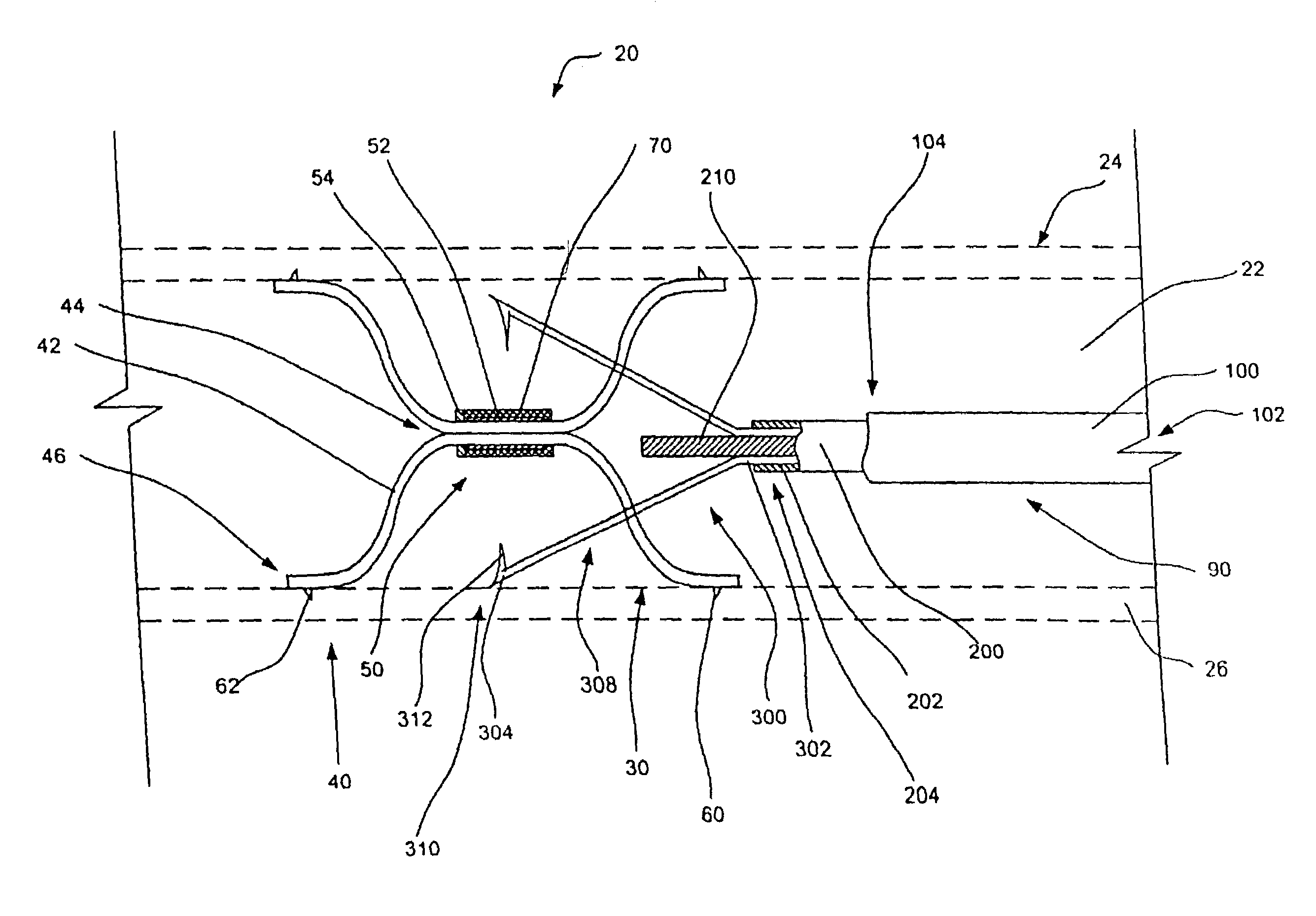
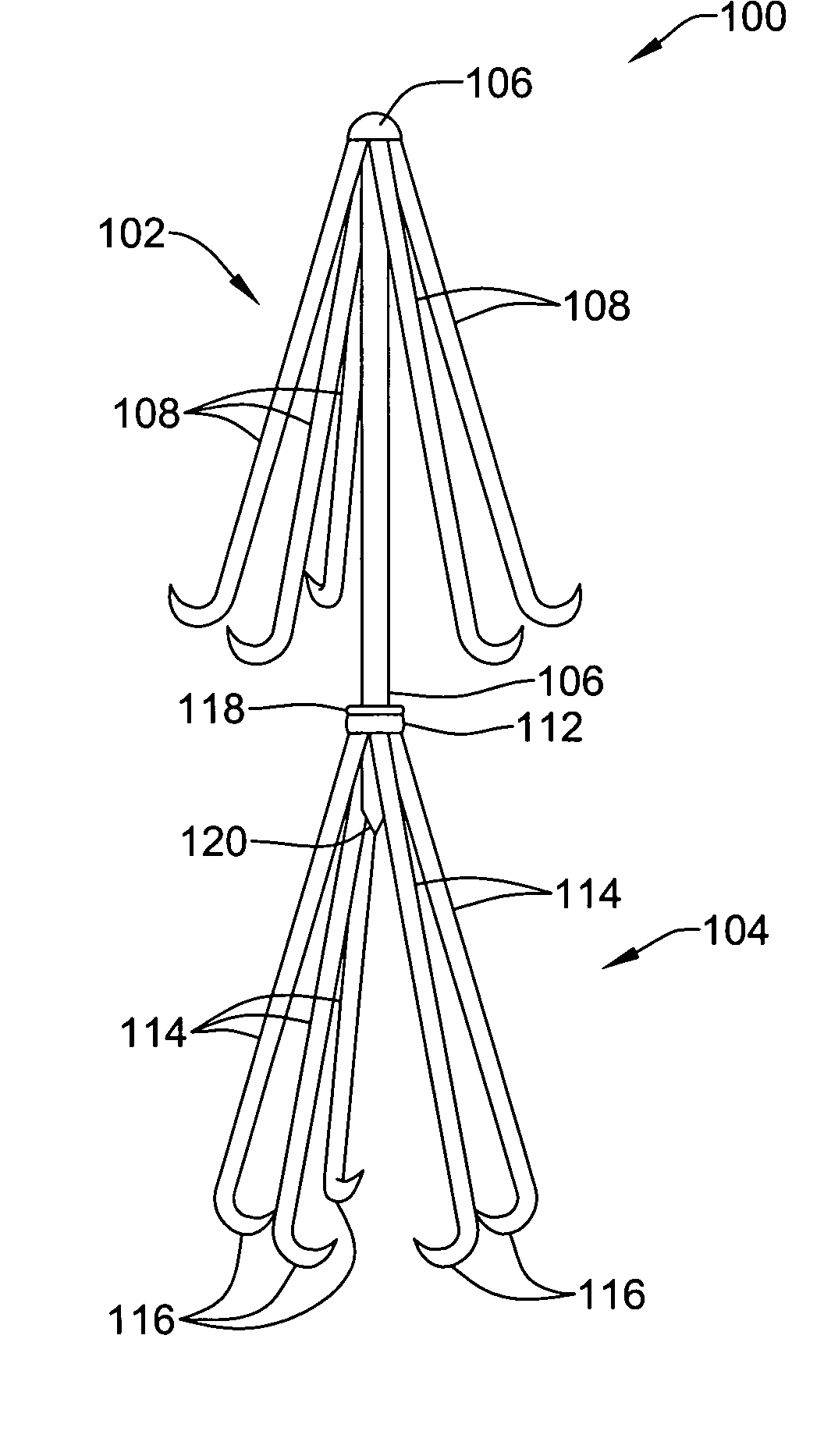
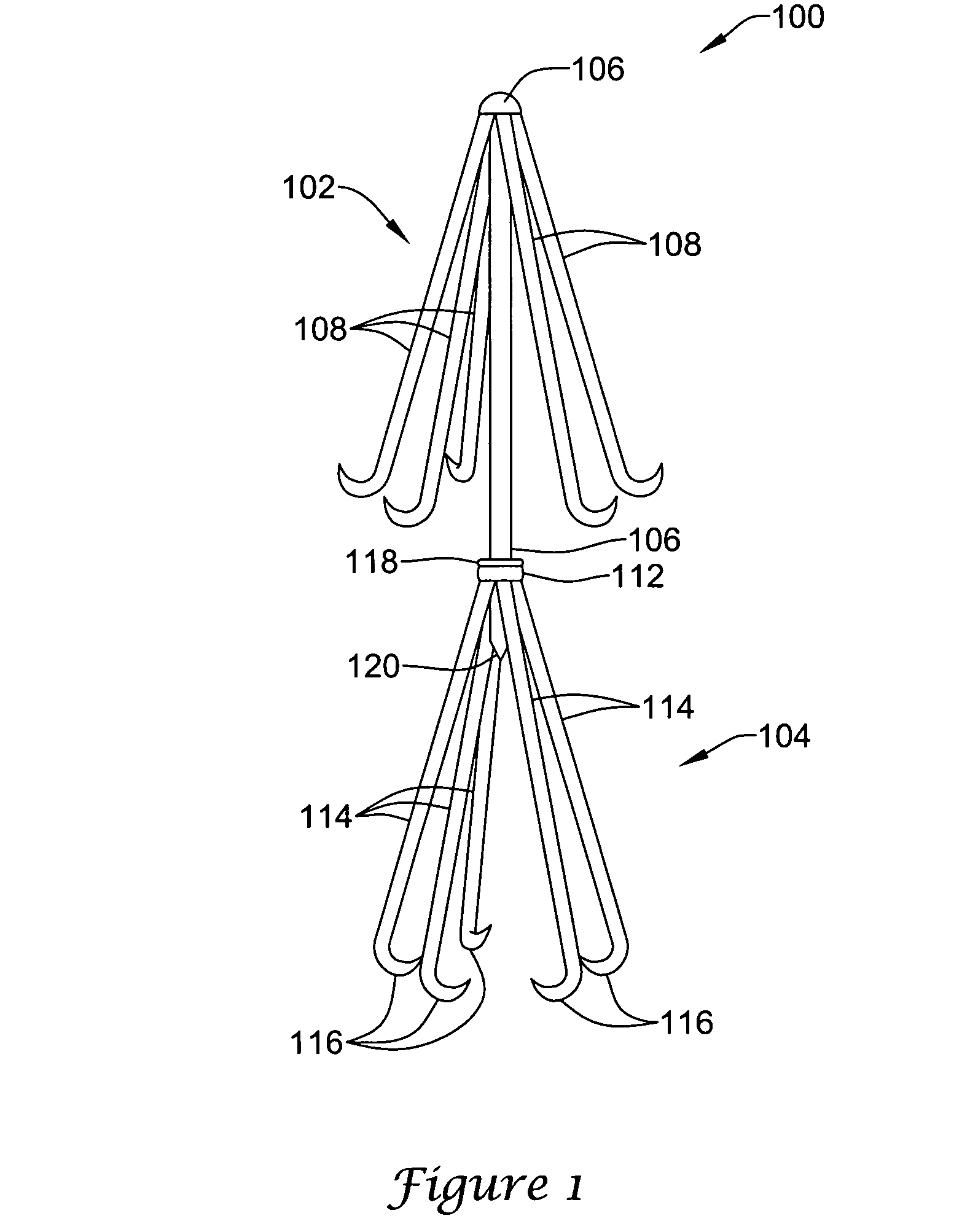
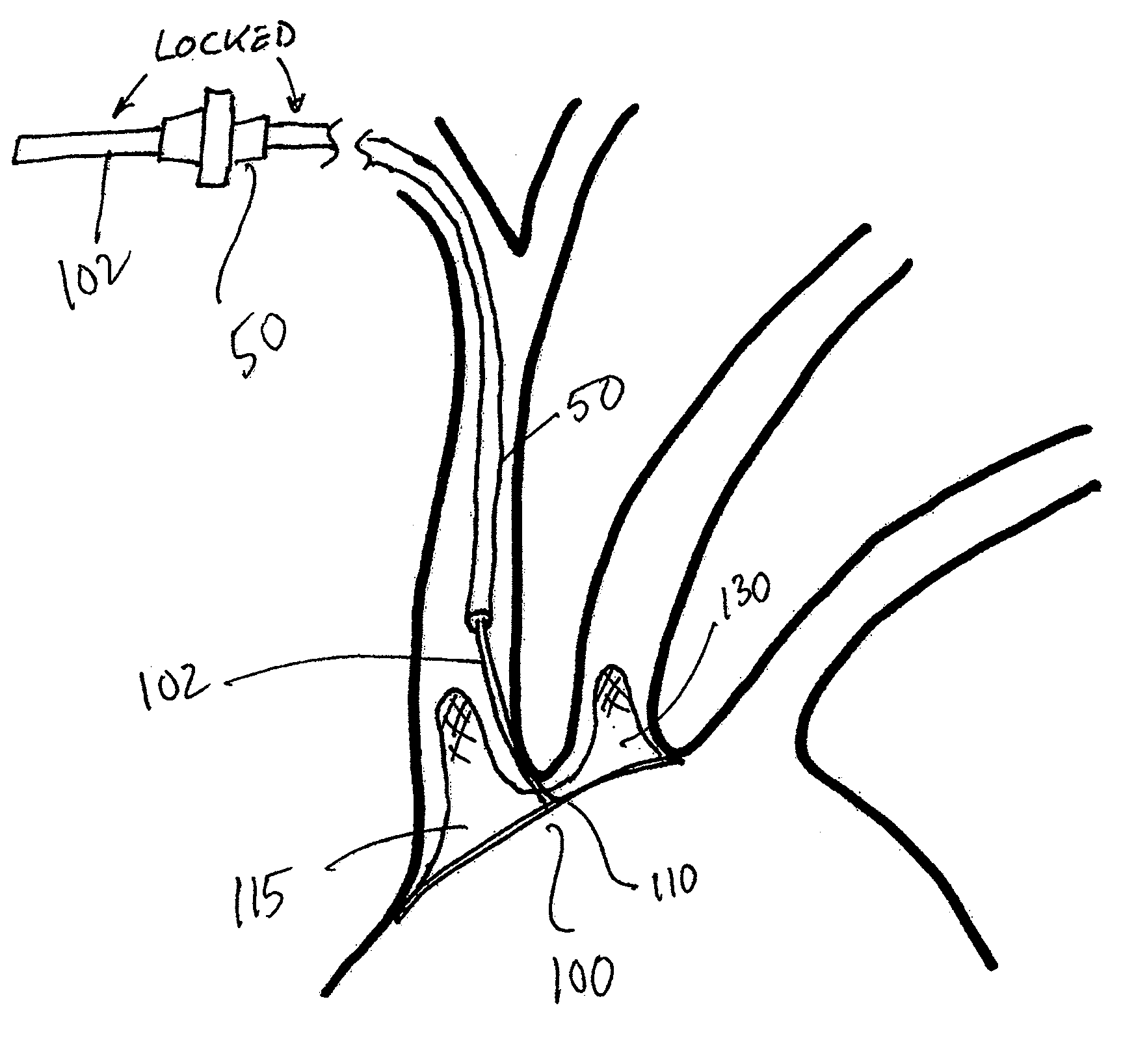
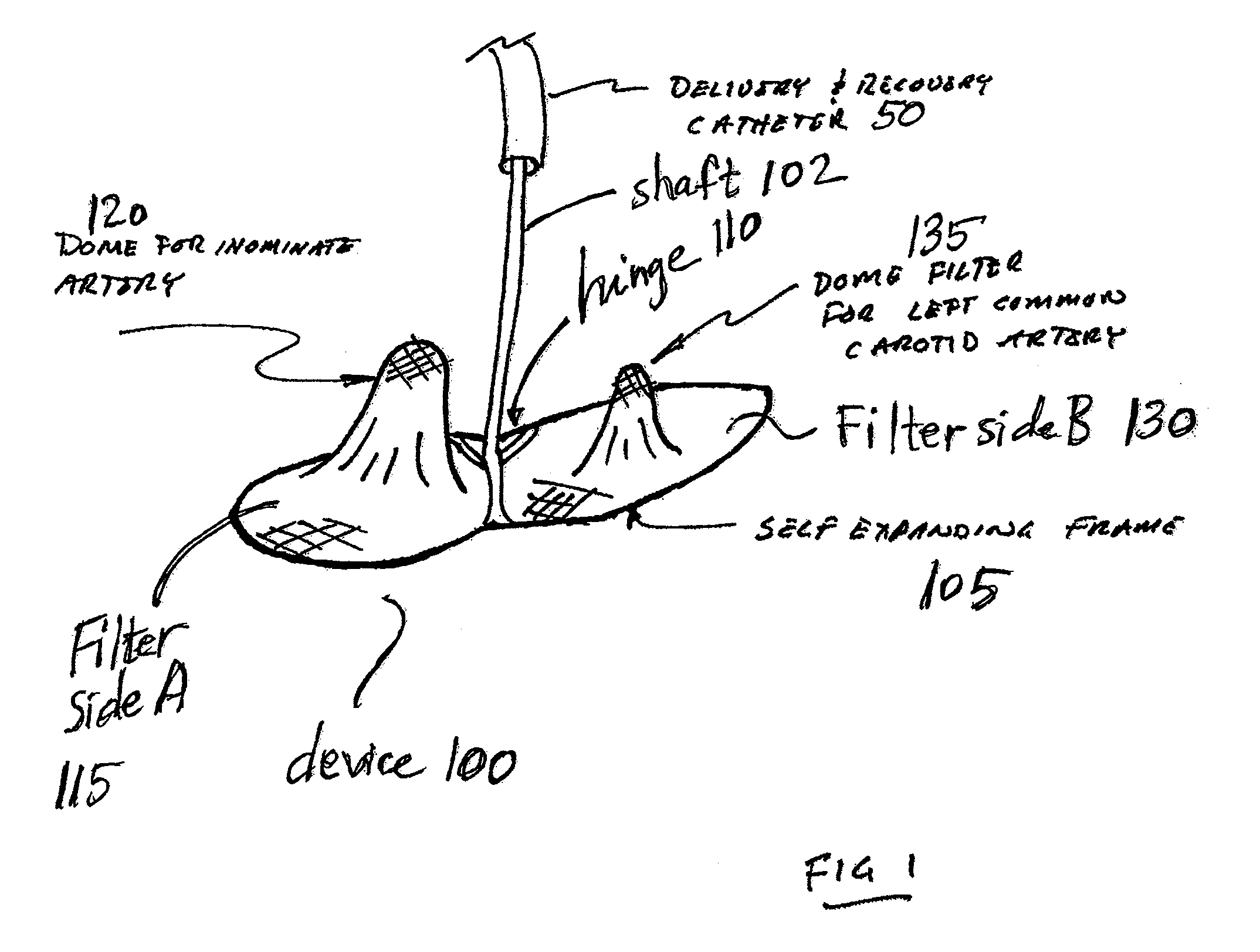
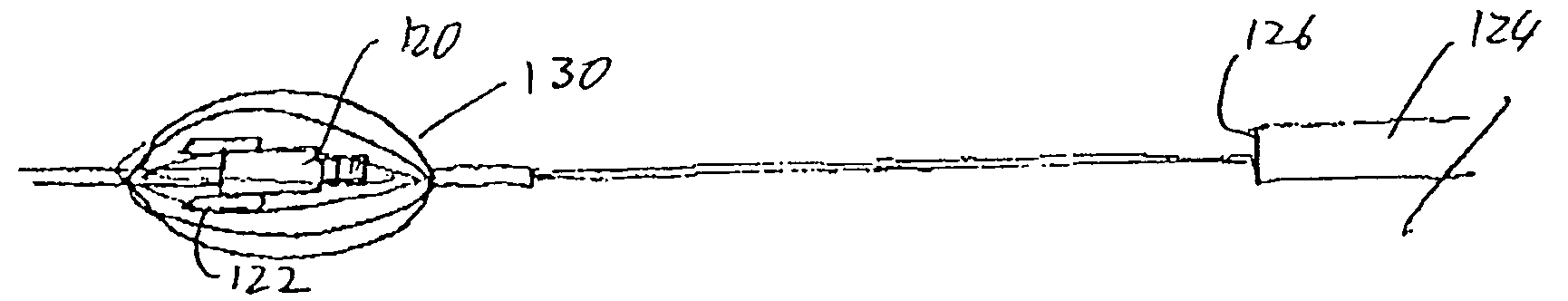
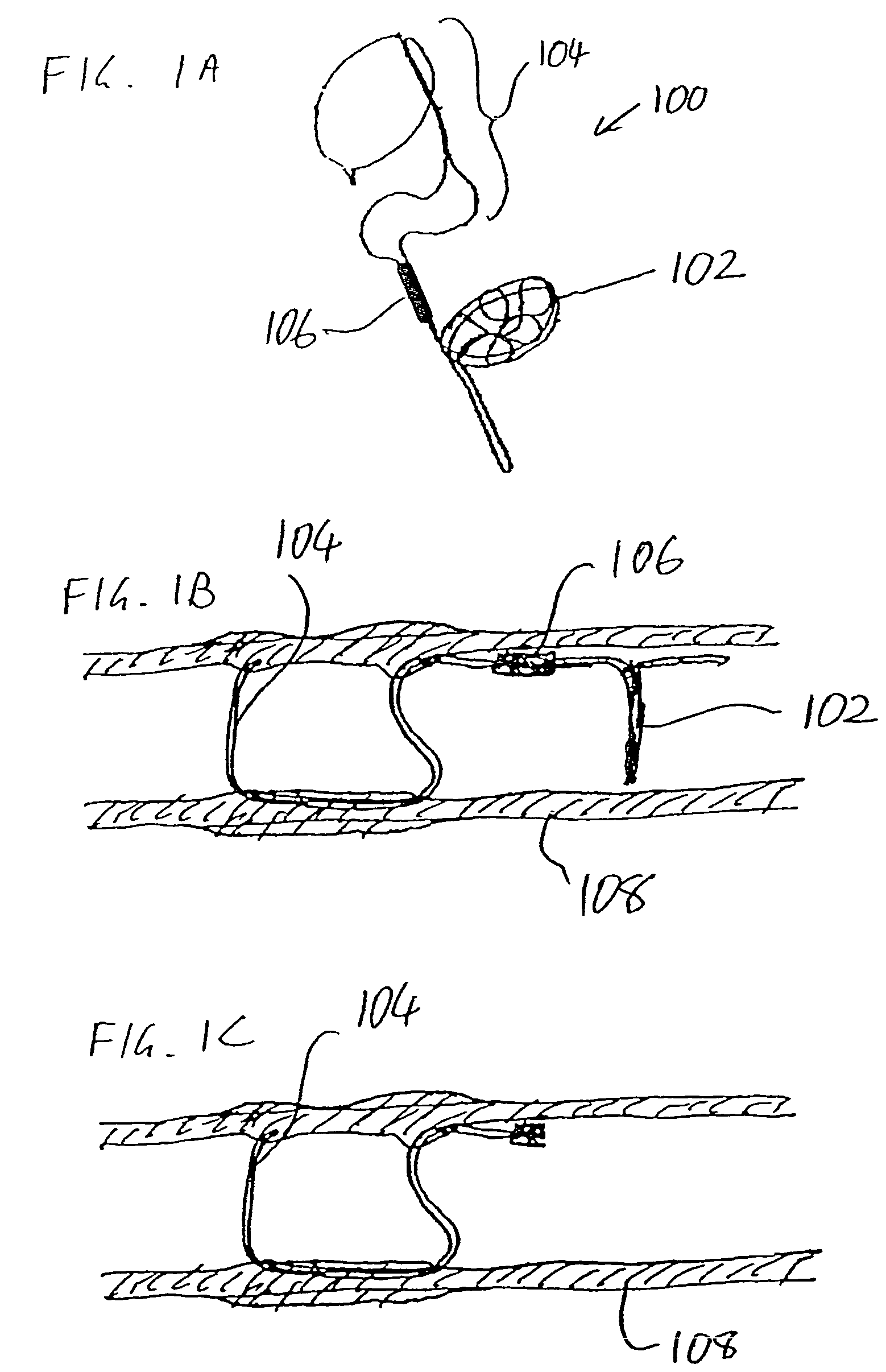
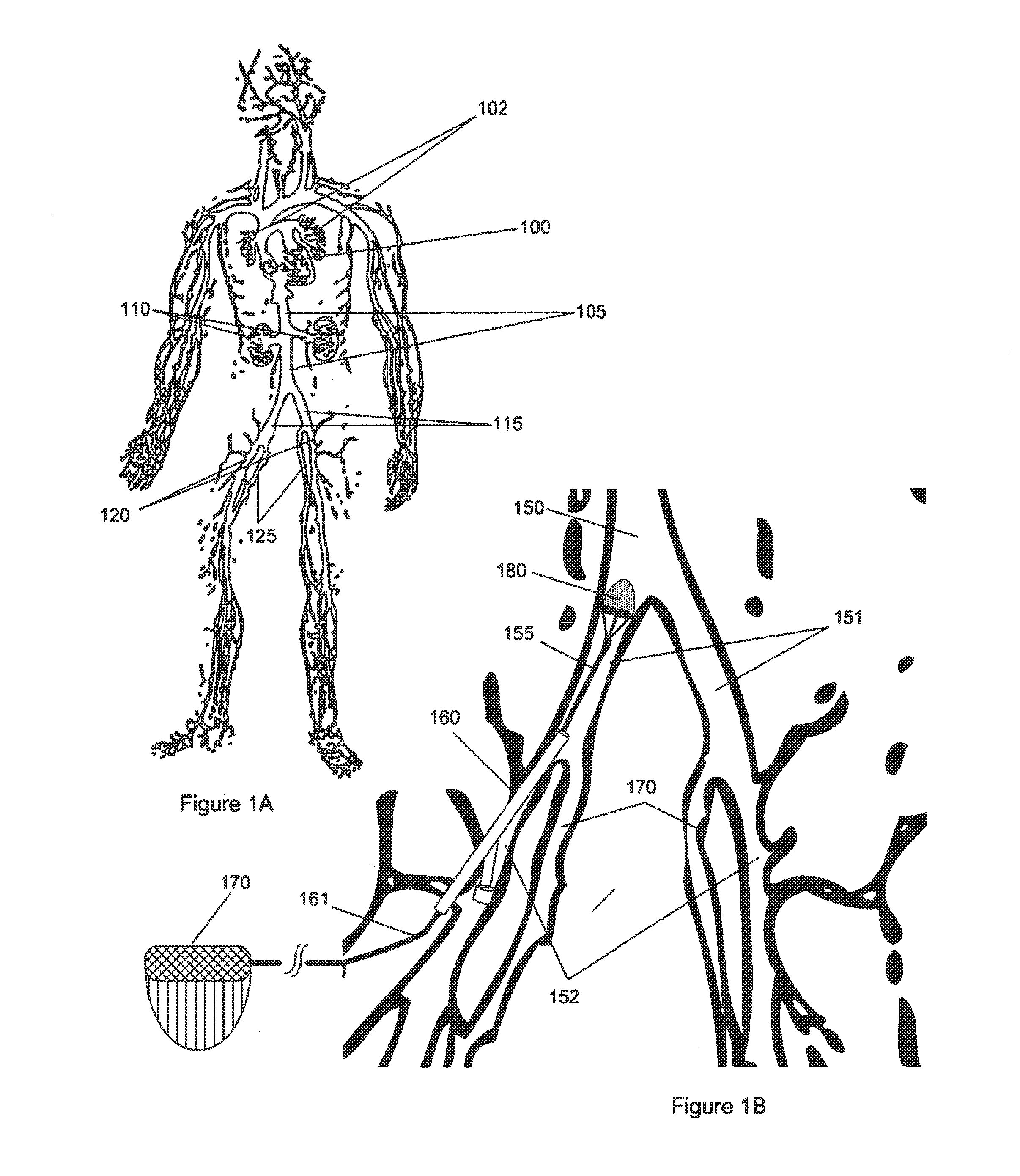
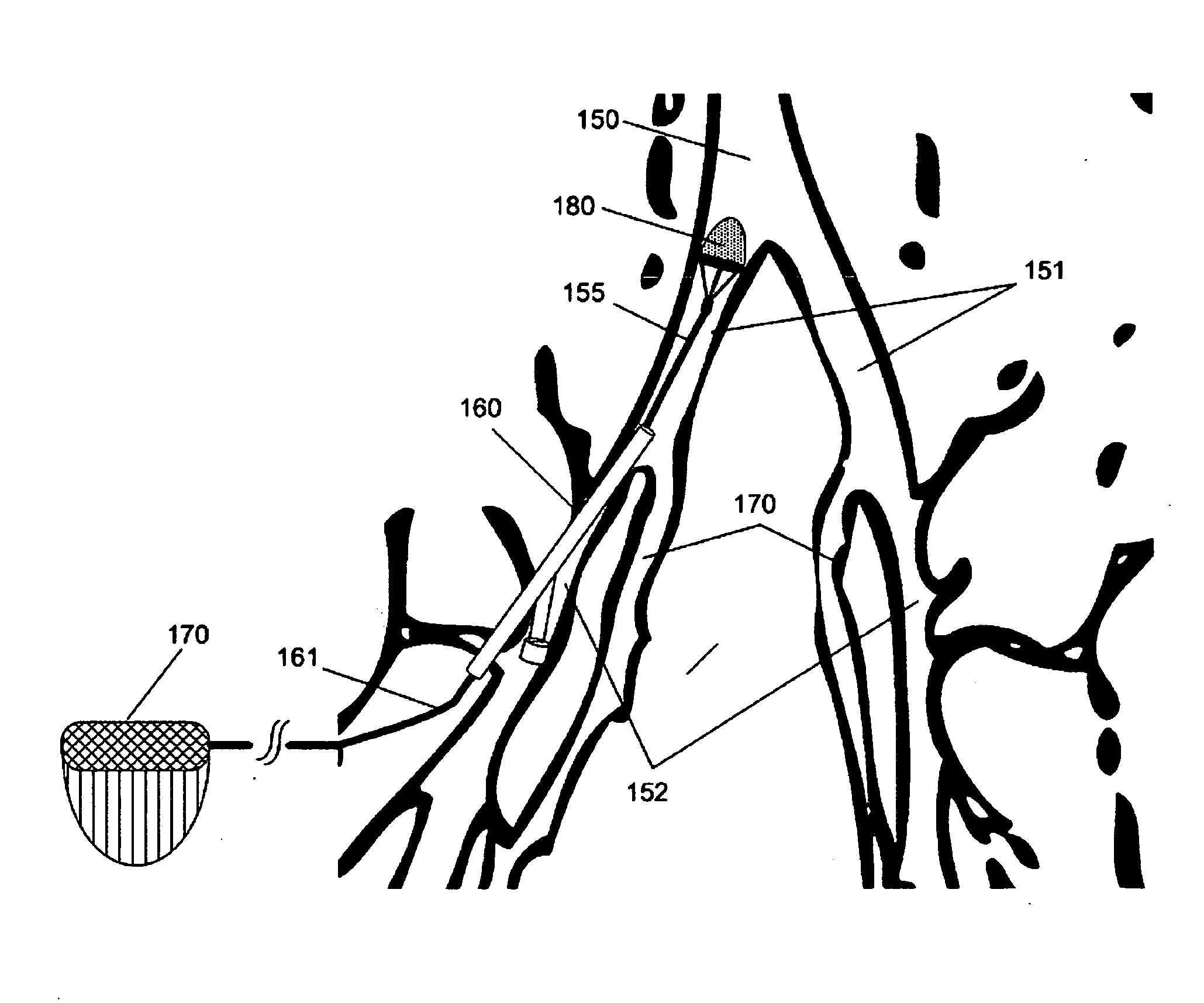
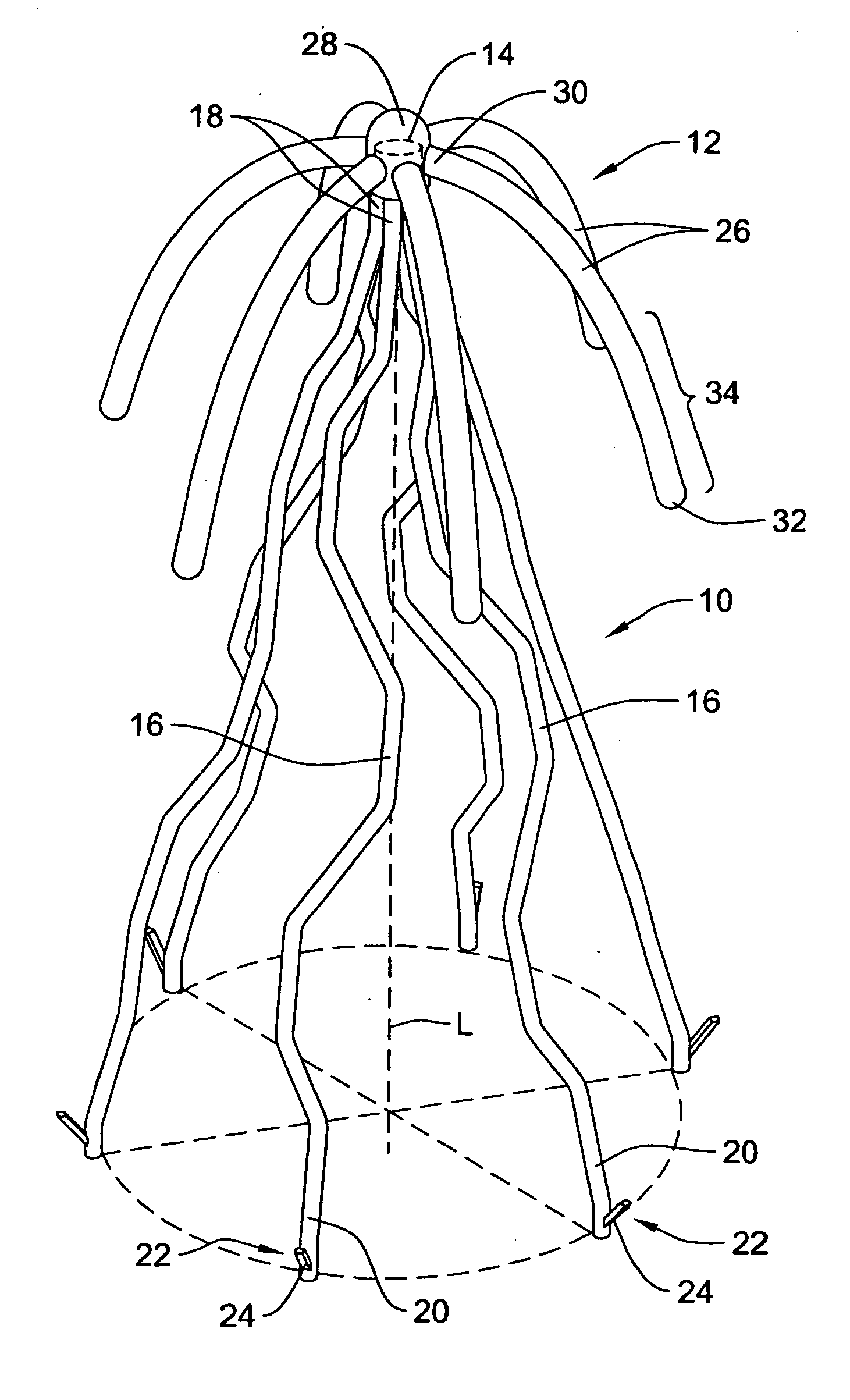
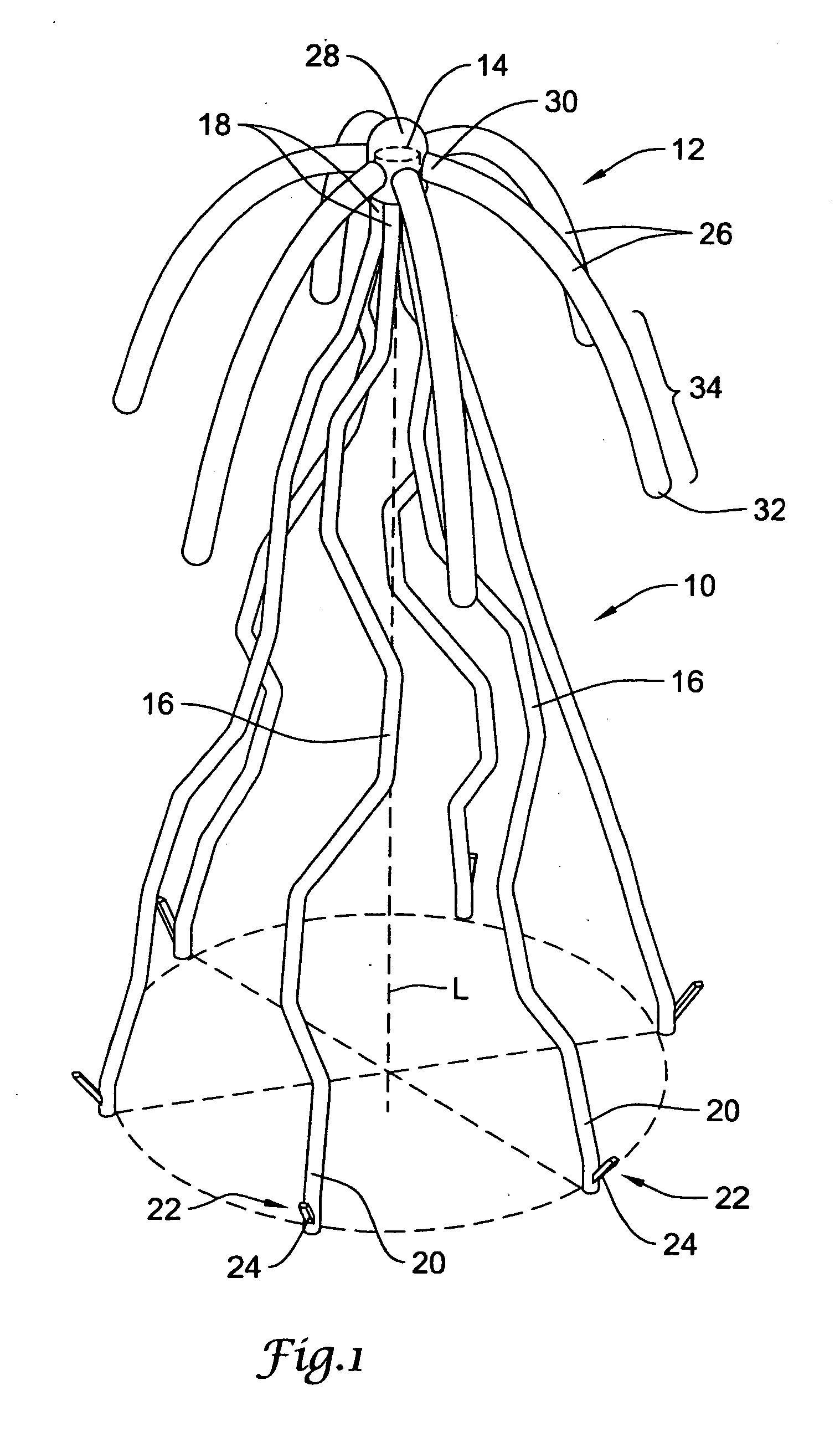
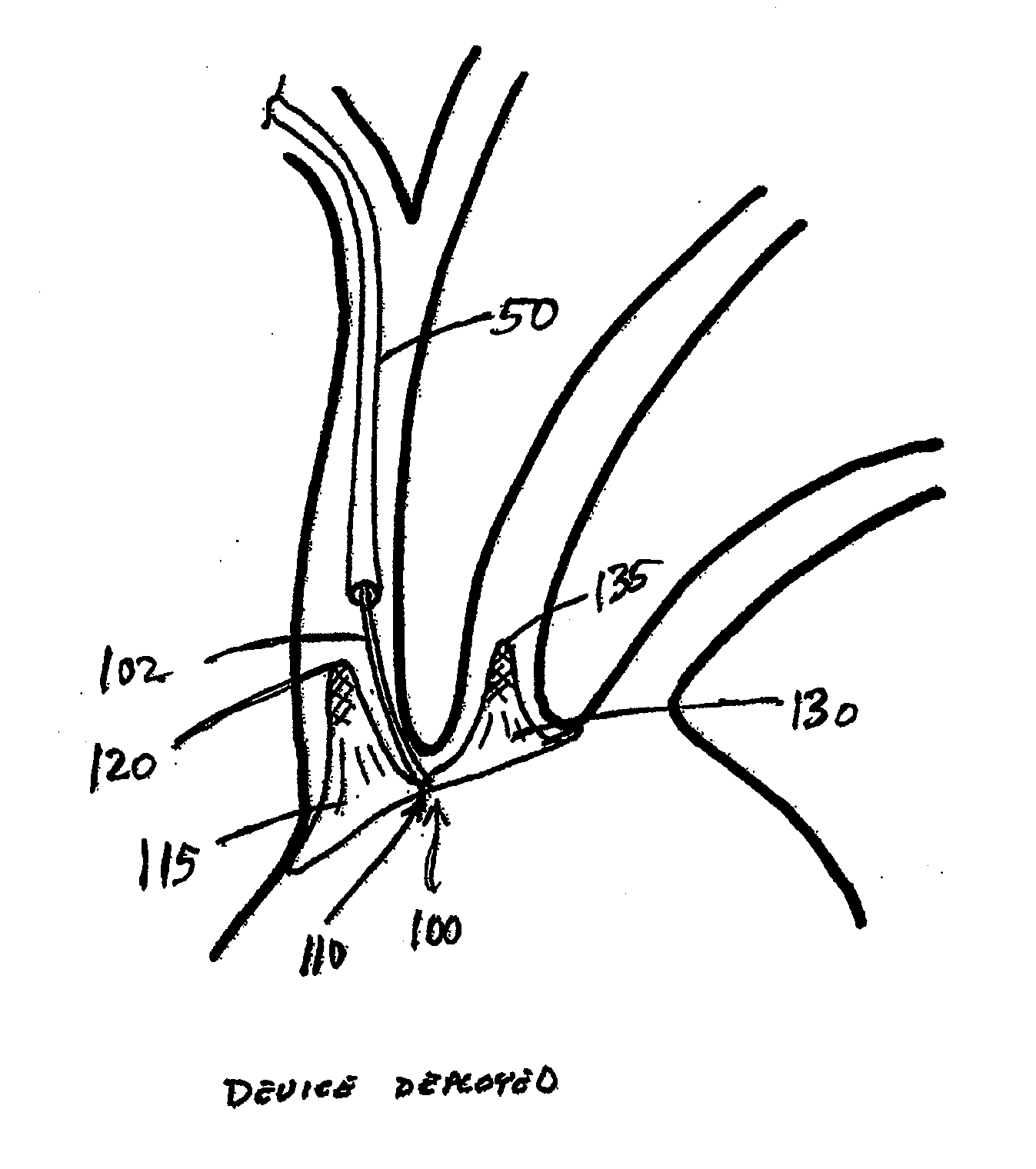
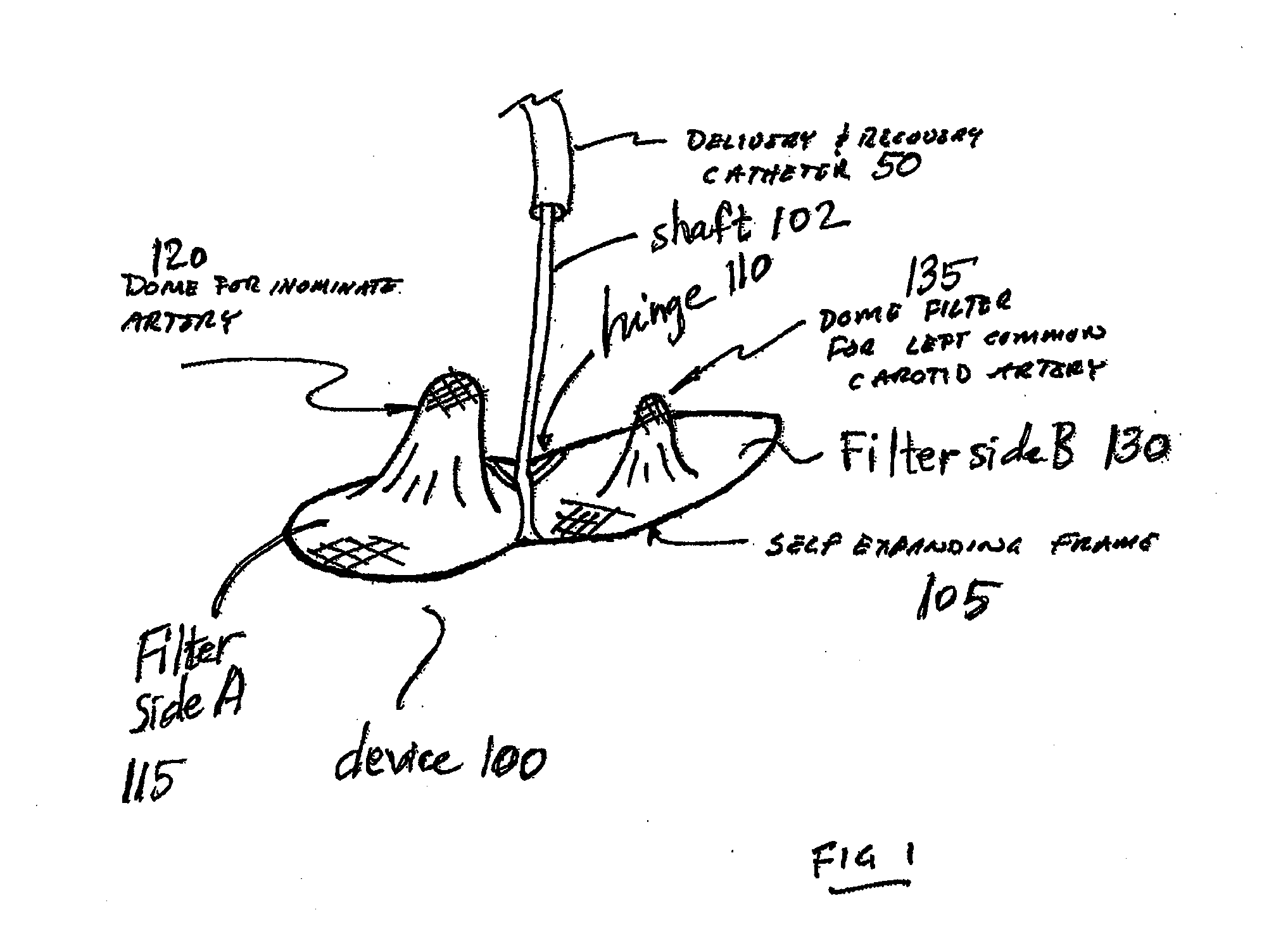
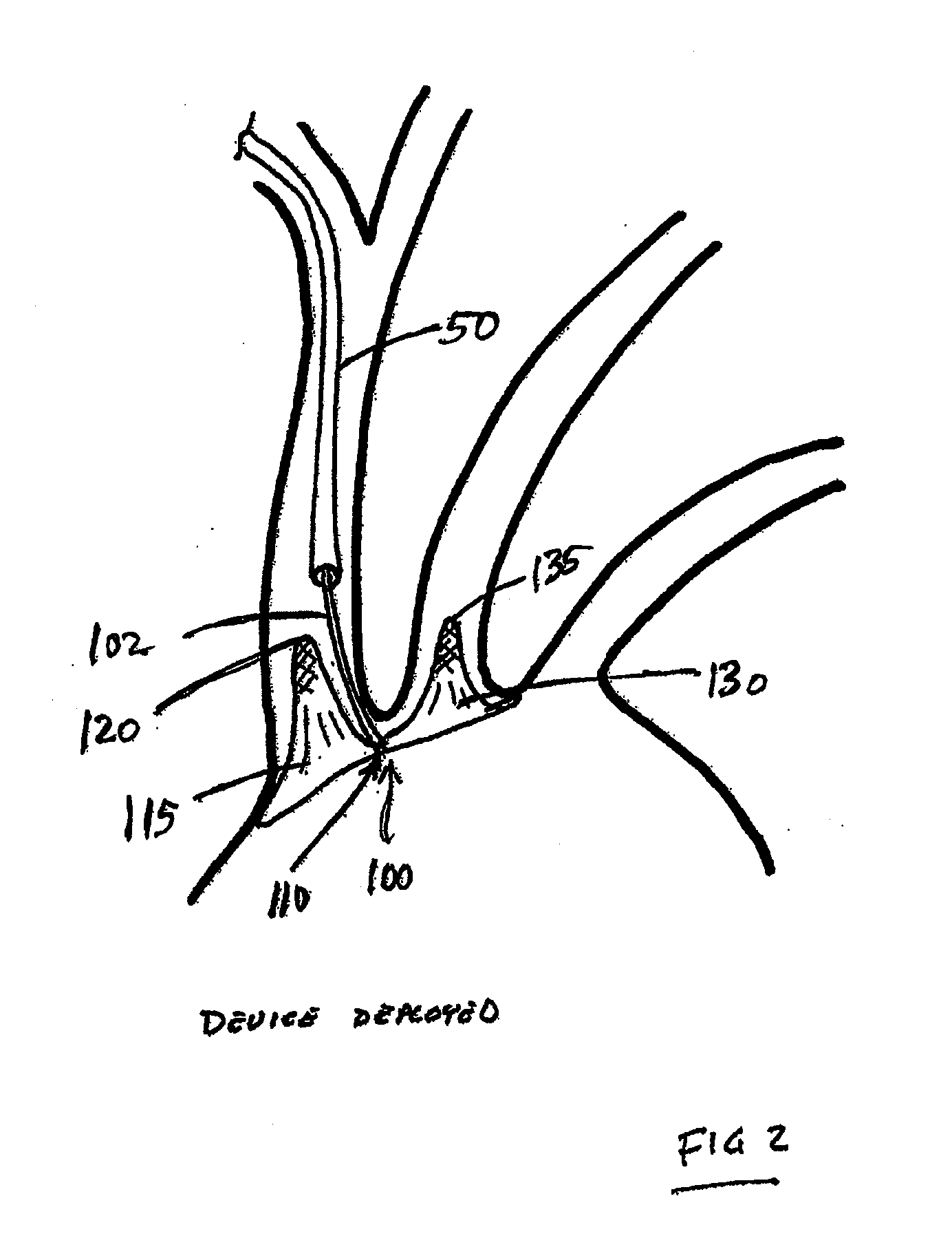
Intravascular devices, retrieval systems, and corresponding methods
A semi-retrievable intravascular filter (100) for deployment within a vessel (108) includes a support structure (104) for deployment around an internal surface of the vessel (108) and a filter structure (102) supported by interconnection with the support structure (104). The filter structure (102) is connected to the support structure (104) so as to be selectively detachable so as to facilitate removal of the filter structure (102) without the support structure (104). Also described are various retrieval systems for retrievable or semi-retrievable intravascular devices, and intravascular filter structures.
Owner:VASCULAR PLATFORMS +1
Deflectable Intravascular Filter
ActiveUS20120172920A1Improve the level ofAvoiding and minimizingHeart valvesSurgeryParticulatesFilter system
Single filter and multi-filter endolumenal methods and systems for filtering fluids within the body. In some embodiments a blood filtering system captures and removes particulates dislodged or generated during a surgical procedure and circulating in a patient's vasculature. In some embodiments a filter system protects the cerebral vasculature during a cardiac valve repair or replacement procedure.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Intravascular filtering devices and methods
A thrombus filter configured for placement within a blood vessel lumen defined by a blood vessel wall. Methods and devices for selectively reshaping the thrombus filter so that the lumen of the blood vessel is substantially unobstructed. The thrombus filter includes a generally cylindrical anchoring portion, and a generally conical filtering portion terminating at an apex.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Methods and devices for filtering fluid flow through a body structure
An intravascular filter having a filament which expands a filter element. The filament is a coil which is stretched to reduce the diameter of the coil for introduction. The filter element is preferably biased toward the closed position and is opened by the coil when tension is released on the coil. The filament slides along the internal surface of the filter element so that the filter element may assume intermediate positions.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
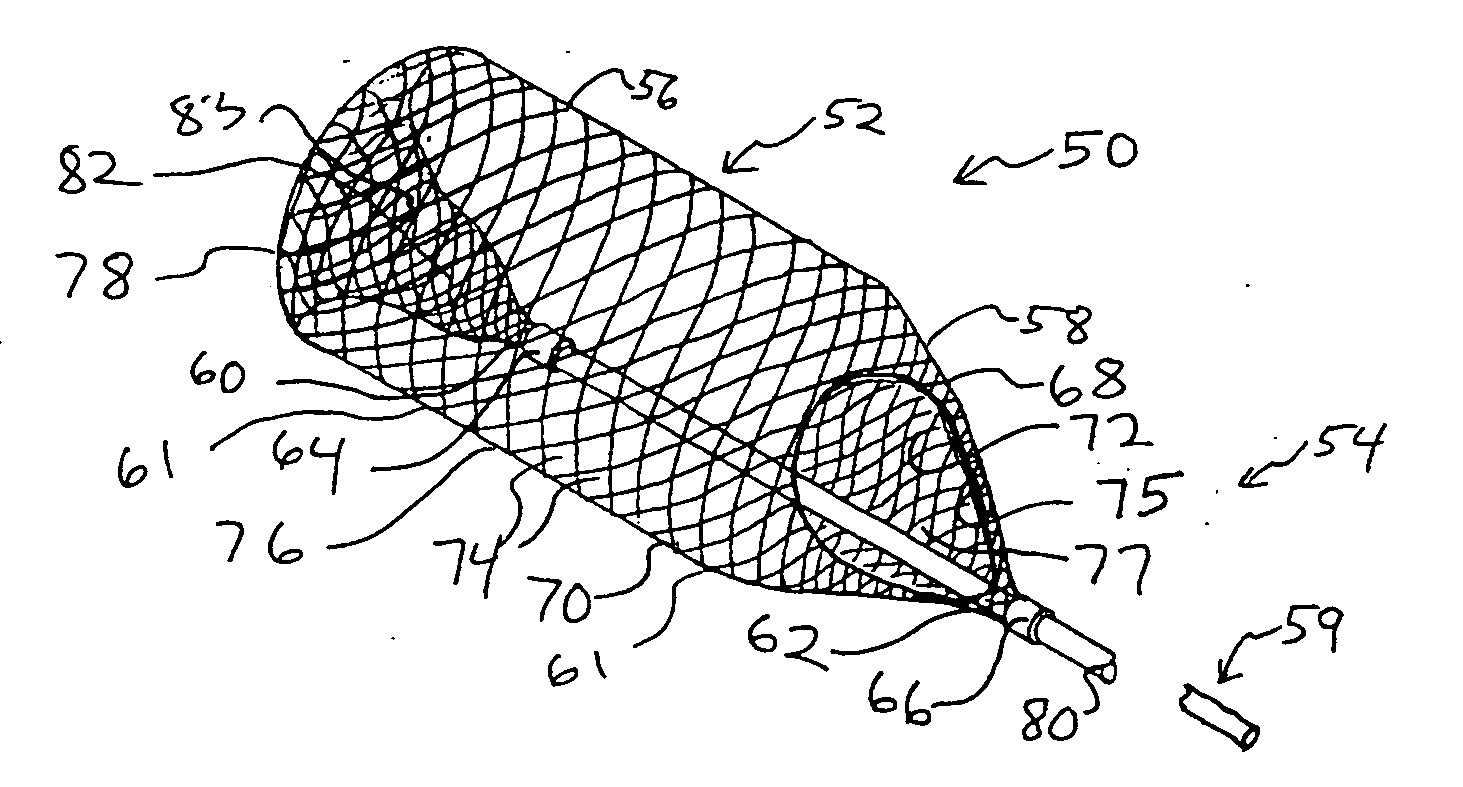
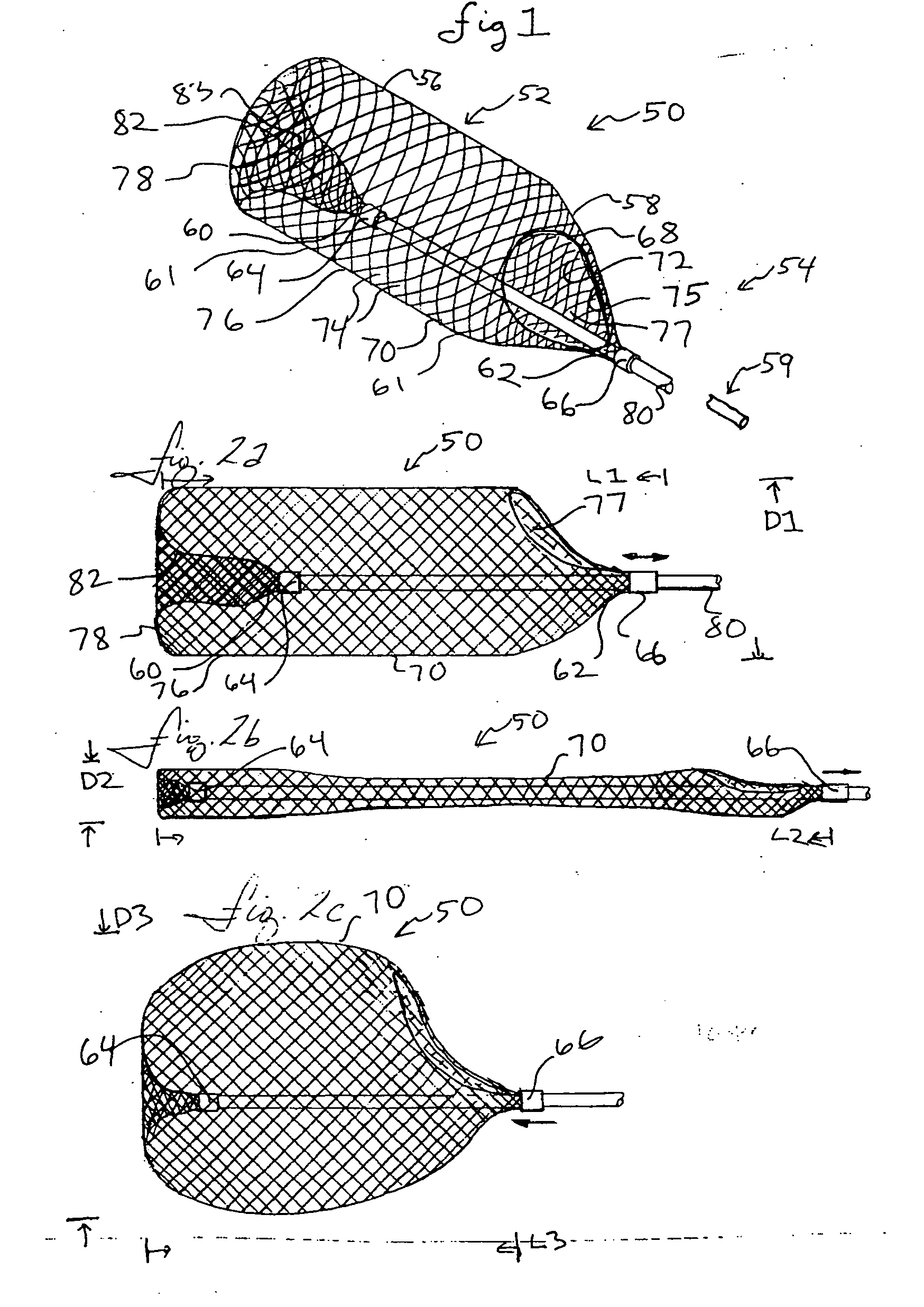
Retrievable inferior vena cava filter
InactiveUS7803171B1Invasive deploymentInhibit migrationSurgeryDilatorsInferior vena cava filterPulmonary artery
The present invention provides an intravascular filter for minimally invasive deployment into, and extraction from, a blood vessel. The invention comprises an inferior vena cava filter used to prevent migration of clots into the pulmonary artery wherein the filter has a novel architecture such that the filter can be extracted from the vessel without substantially damaging the vessel, even after prolonged periods of deployment.
Owner:UFLACKER RENAN P
Conical vena cava filter with jugular or femoral retrieval
An intravascular filter configured for upstream or downstream retrieval and a method for retrieving an intravascular filter from a patient's vena cava through the patient's femoral vein. The filter includes a downstream hub, an upstream hub, a plurality of primary struts extending from the downstream hub to the upstream hub, a plurality of secondary struts extending upstream from fixed ends housed in the downstream hub to free ends, secondary strut eyelets disposed at the free ends of the secondary struts, a loop member disposed through the secondary strut eyelets, an upstream coupling element disposed with the upstream hub, and a tether extending from the loop member to the upstream coupling element.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
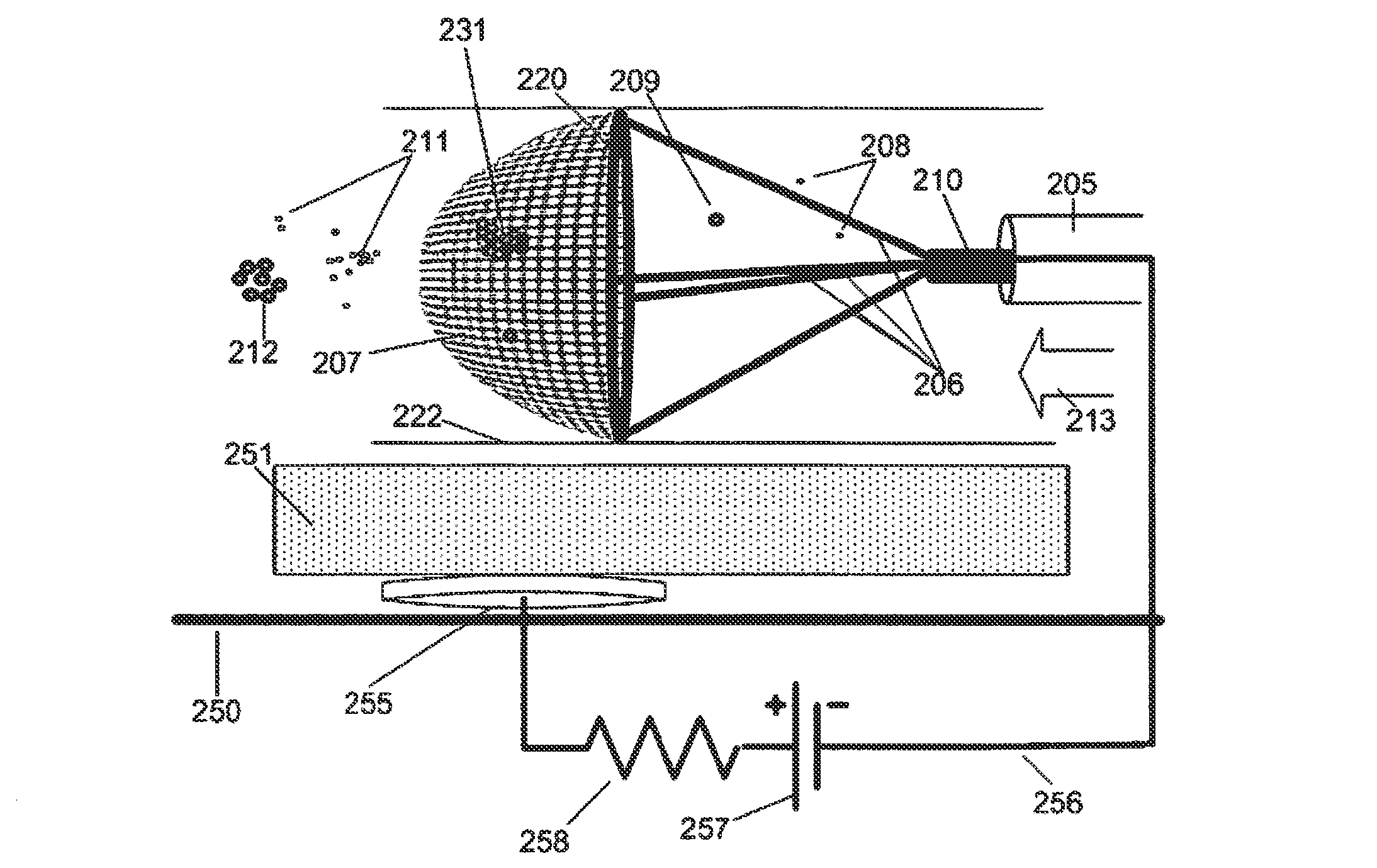
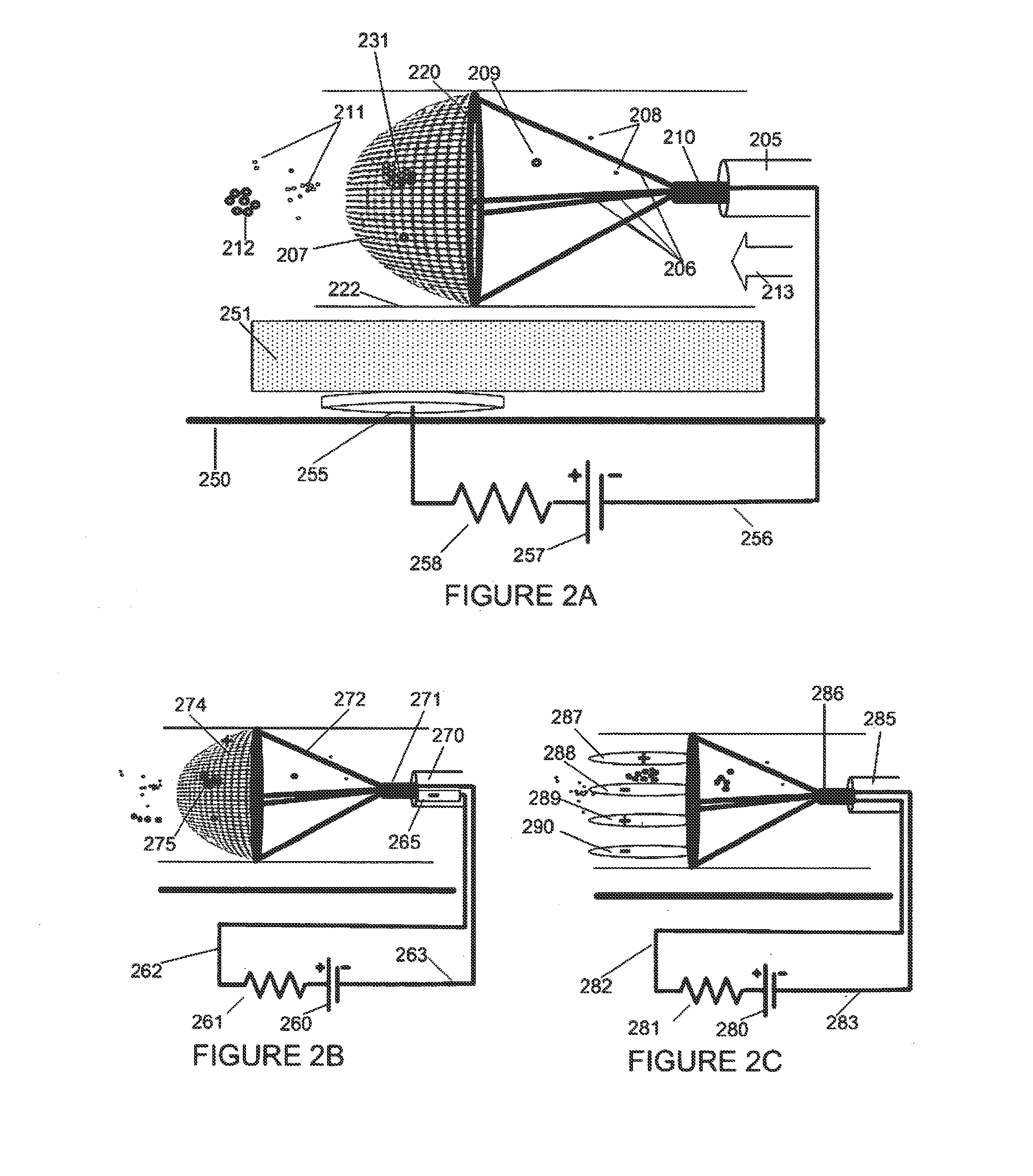
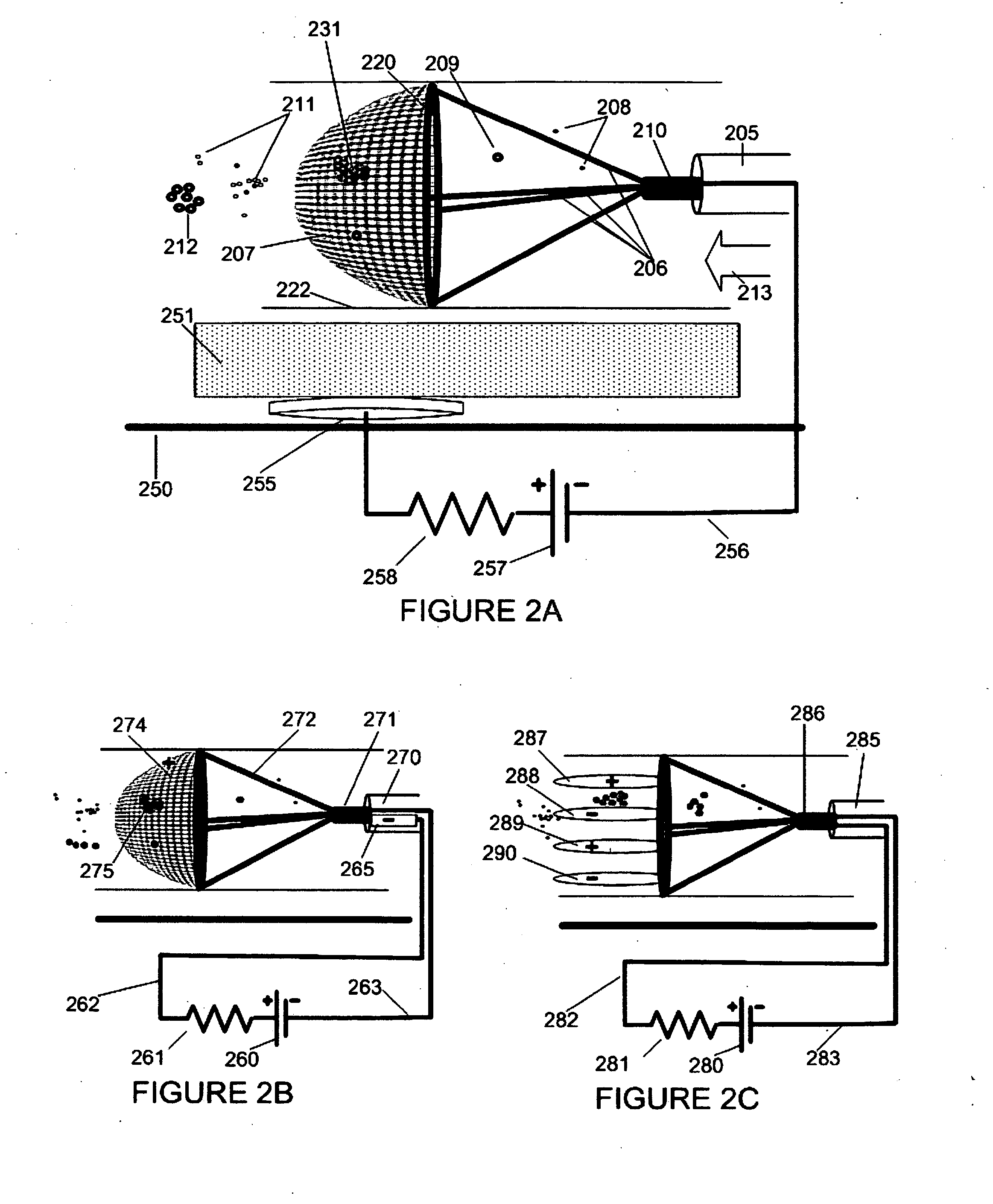
Electrostatic Vascular Filters
An intravascular filter is constructed to electrostatically capture and retain particles of a targeted type (for example fat or methacrylate emboli), even if those particles are physically small enough to slip through the filter in the absence of electrostatic attraction. Specific types of targeted particles are thereby captured and retained with improved efficiency, while permitting free flow of non-targeted particles. This improvement permits intravascular filters to be constructed with low-resistance, widely spaced filter elements. Accordingly, more targeted particles are captured, less thrombosis occurs, less pressure drop occurs across the filter, and perfusion or blood collection in downstream areas is maintained.
Owner:SCHNEIDER M BRET +1
Staged release of ivc filter legs
A catheter for stage-delivering a vena cava filter within a body lumen is disclosed. The catheter may comprise an elongated tubular member having a proximal section, a distal section, and an inner lumen configured to receive an intravascular filter. One or more notches or slits radially disposed about the distal end of the catheter may be utilized to stage-deploy the filter within the body. Several grooves or indentations disposed along an inner surface of the catheter may also be employed.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
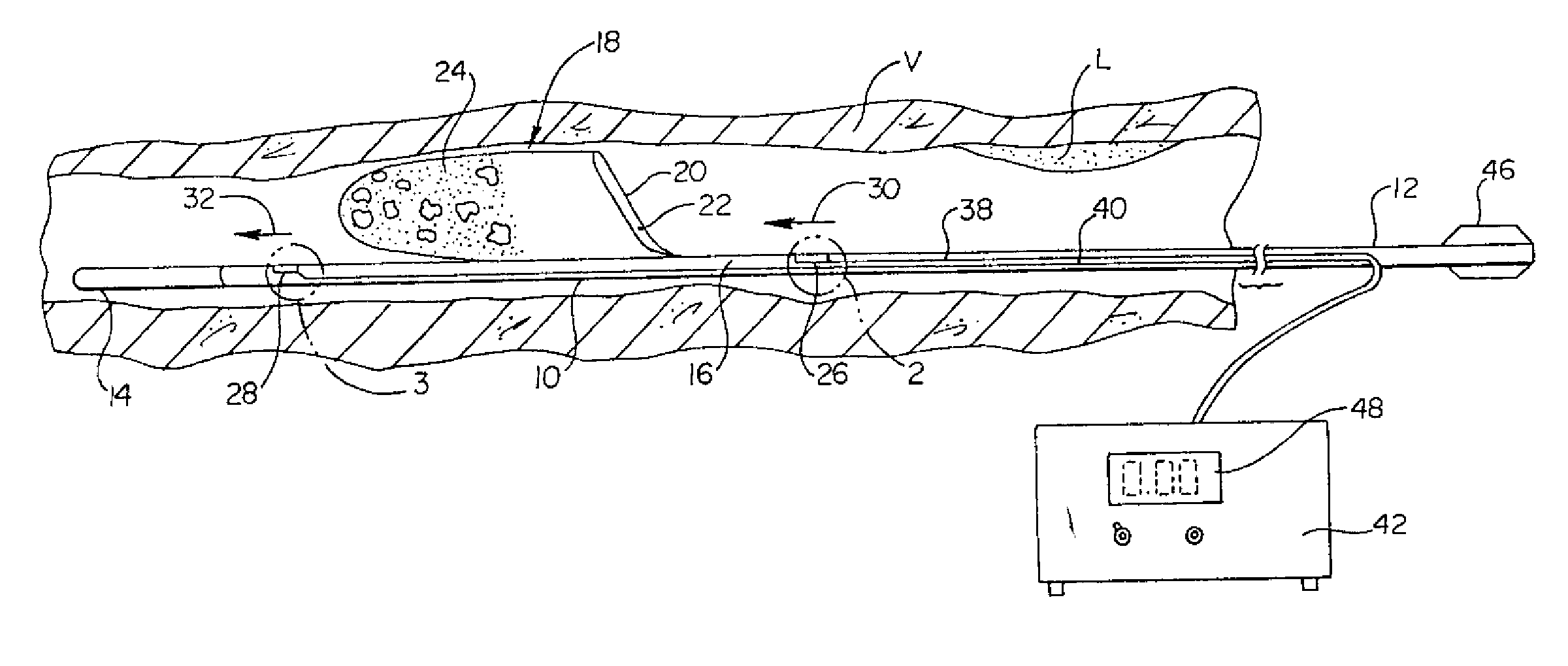
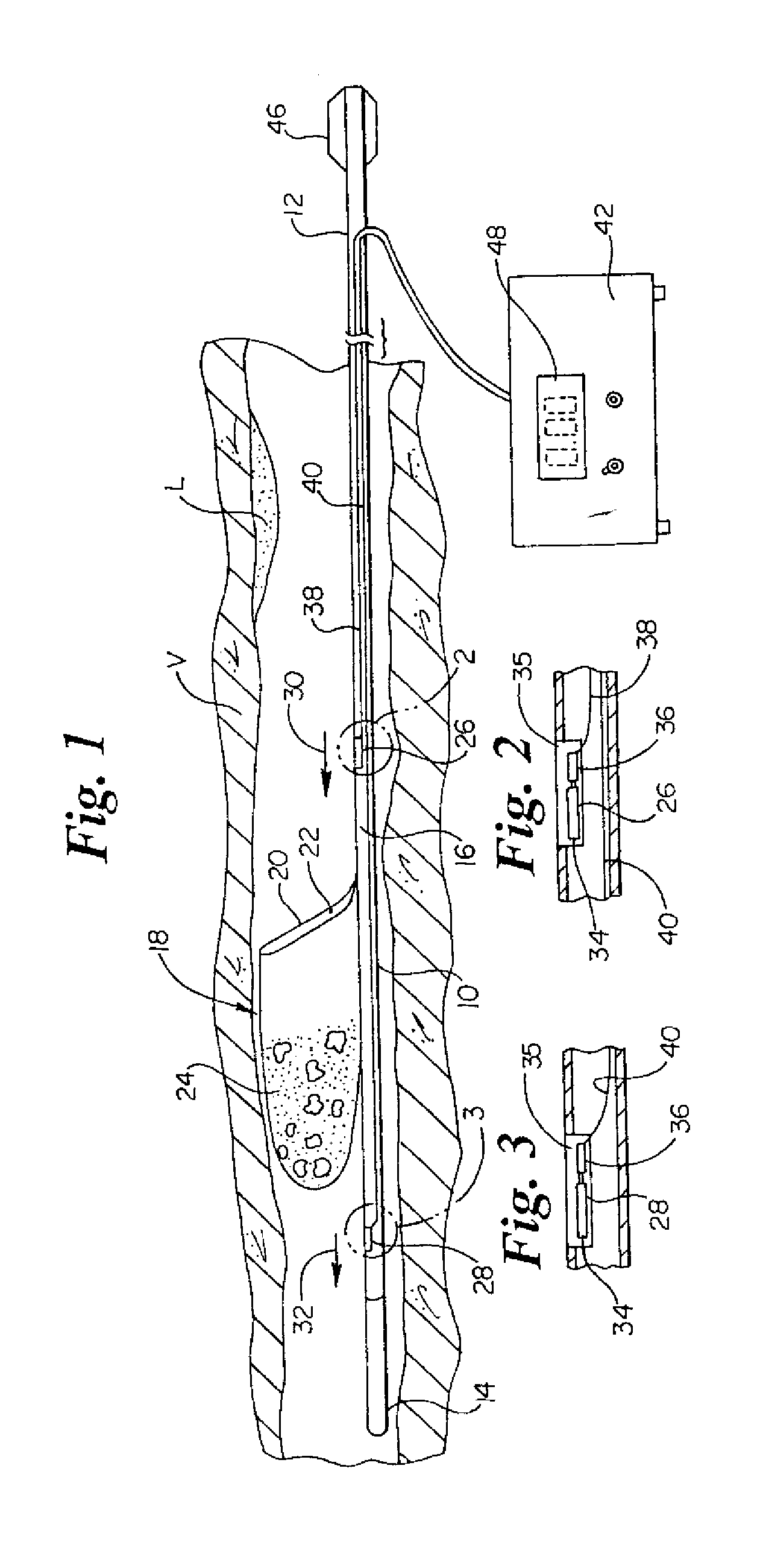
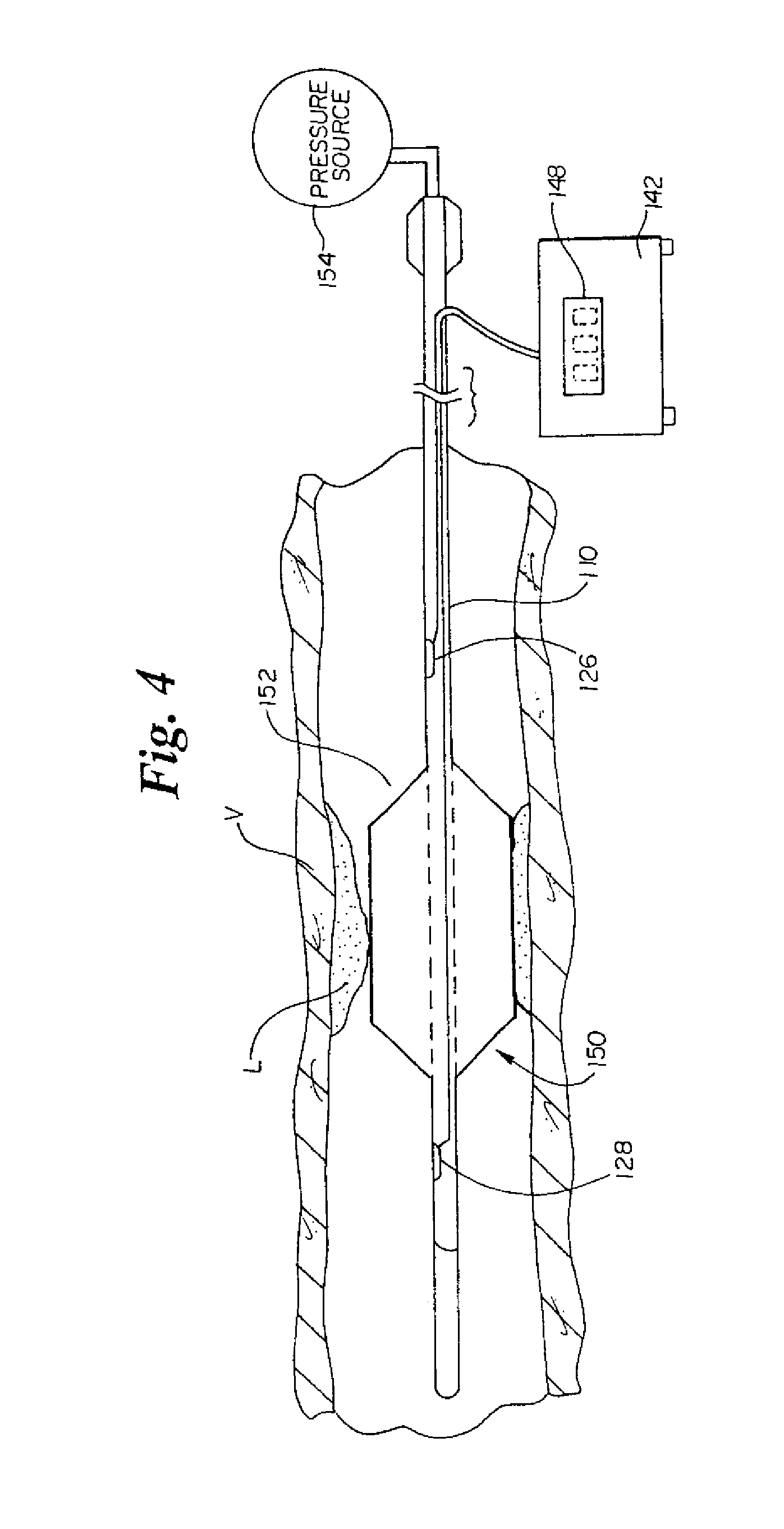
Intravascular filter monitoring
Devices and methods for monitoring the flow of blood through an intravascular device are disclosed. An apparatus for monitoring blood flow in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes an intravascular device coupled to an elongated member, a first sensor adapted to measure fluidic pressure proximal the intravascular device, a second sensor adapted to measure fluidic pressure distal the intravascular device, and a control unit for comparing the signals received from the first and second sensors to determine the pressure drop across the intravascular device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and methods for magnetically manipulating intravascular devices
Devices and methods for magnetically centering and retrieving intravascular devices within a body lumen are disclosed. An intravascular filter in accordance with an illustrative embodiment may comprise an expandable filter structure having at least one magnetic element formed therein. The intravascular filter can be retrieved using a magnetic retrieval device that includes a magnetic retrieval mechanism for centering and retrieving the intravascular filter.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Devices and methods for magnetically manipulating intravascular devices
InactiveUS20050251197A1Improve remanenceHigh curie temperatureSurgeryDilatorsMedicineIntravascular device
Devices and methods for magnetically centering and retrieving intravascular devices within a body lumen are disclosed. An intravascular filter in accordance with an illustrative embodiment may comprise an expandable filter structure having at least one magnetic element formed therein. The intravascular filter can be retrieved using a magnetic retrieval device that includes a magnetic retrieval mechanism for centering and retrieving the intravascular filter.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Electrostatic vascular filters
An intravascular filter is constructed to electrostatically capture and retain particles of a targeted type (for example fat or methacrylate emboli), even if those particles are physically small enough to slip through the filter in the absence of electrostatic attraction. Specific types of targeted particles are thereby captured and retained with improved efficiency, while permitting free flow of non-targeted particles. This improvement permits intravascular filters to be constructed with low-resistance, widely spaced filter elements. Accordingly, more targeted particles are captured, less thrombosis occurs, less pressure drop occurs across the filter, and perfusion or blood collection in downstream areas is maintained.
Owner:SCHNEIDER M BRET +1
Intravascular filter with bioabsorbable centering element
Bioabsorbable centering elements for use in centering an implantable intravascular device within a body vessel are disclosed. The bioabsorbable centering element may include a number of support members configured to self-expand and engage the wall of the vessel when deployed. The support members may be formed from a biodegradable material adapted to degrade in vivo within a pre-determined period of time.
Owner:LIFESCREEN SCI
Dual endovascular filter and methods of use
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endovascular filter
InactiveUS20070203520A1Prevents and minimizes tissue growthInhibit vascular smooth cell migrationSurgeryDilatorsSurgeryBlood vessel
Owner:COOK INC +2
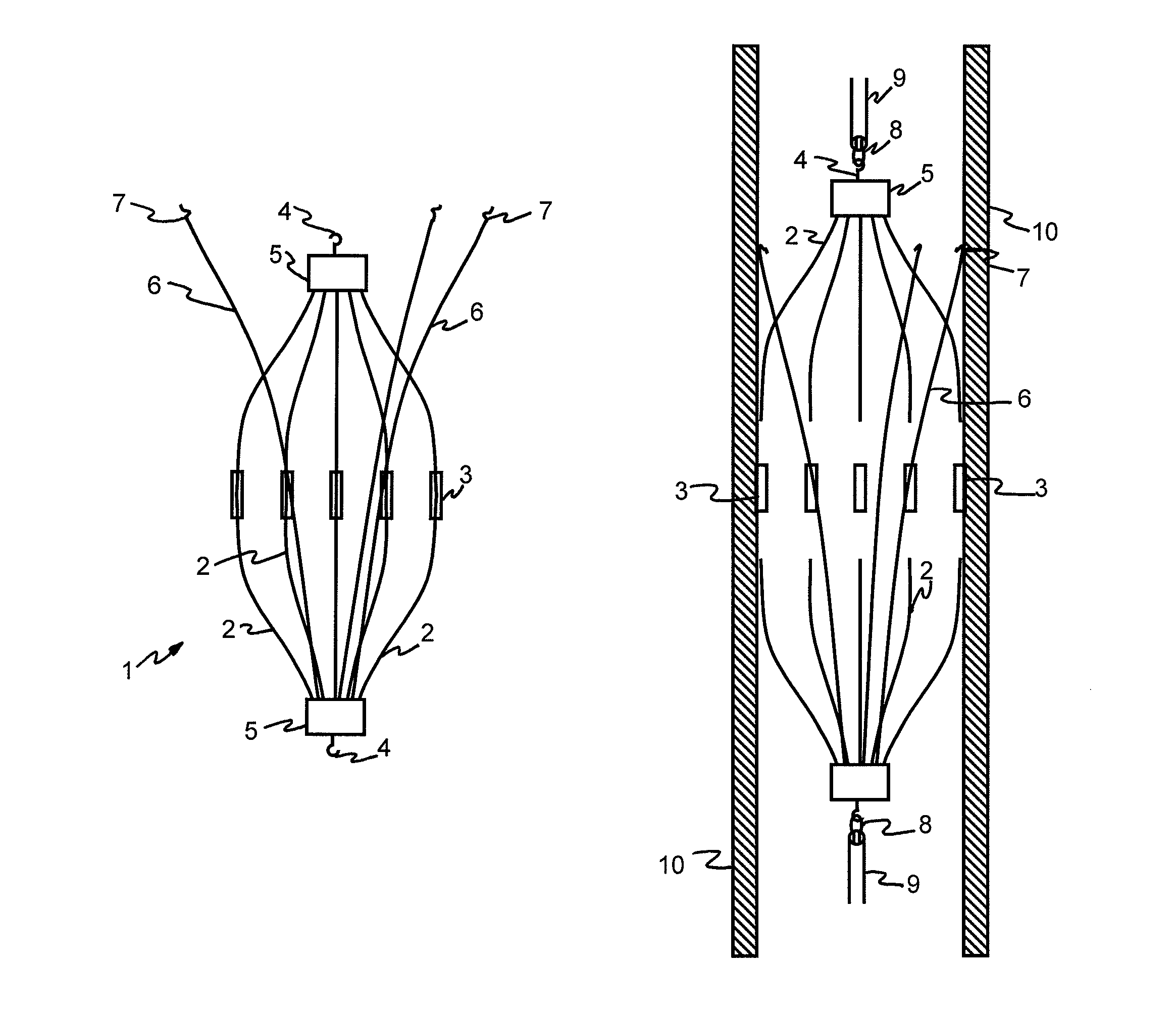
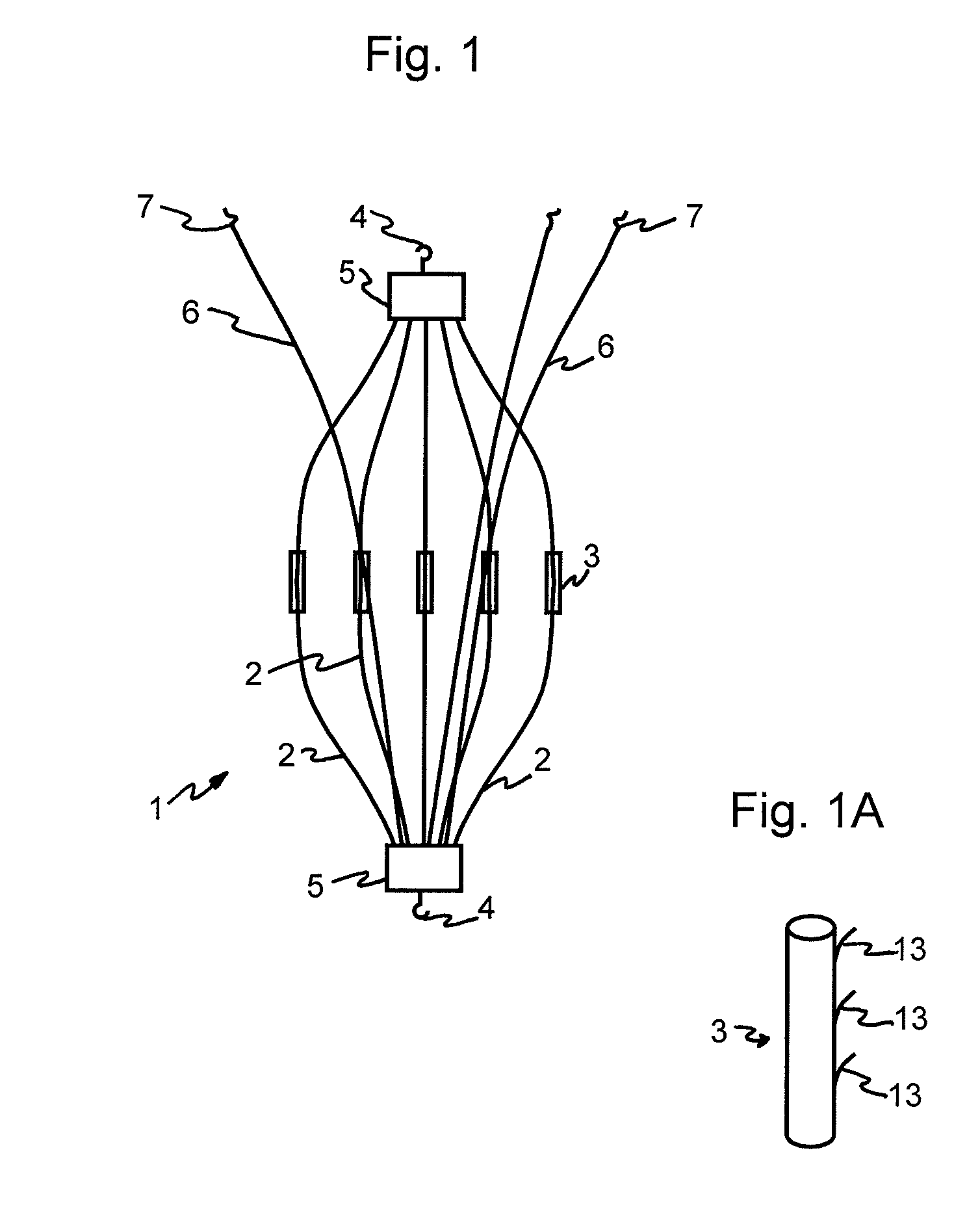
Intravascular filter
InactiveUS7179274B2Facilitate minimally invasive deploymentFacilitate minimally invasive retrievalSurgeryDilatorsEngineeringBlood vessel
An intravascular filter includes at least one elongated support member configured to assume a retention configuration, such as a generally helical form about a central axis, and at least one flexible elongated filter member supported by the support member. The filter member is configured to assume a predefined filter form in such a manner as to form an obstacle to passage through the vessel, in a direction parallel to central axis, of particles having dimensions greater than the predefined value. The support member and the filter member are preferably prepared in a generally straight configuration to facilitate minimally invasive deployment.
Owner:VASCULAR PLATFORMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com