Patents
Literature
237 results about "Biopsy sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
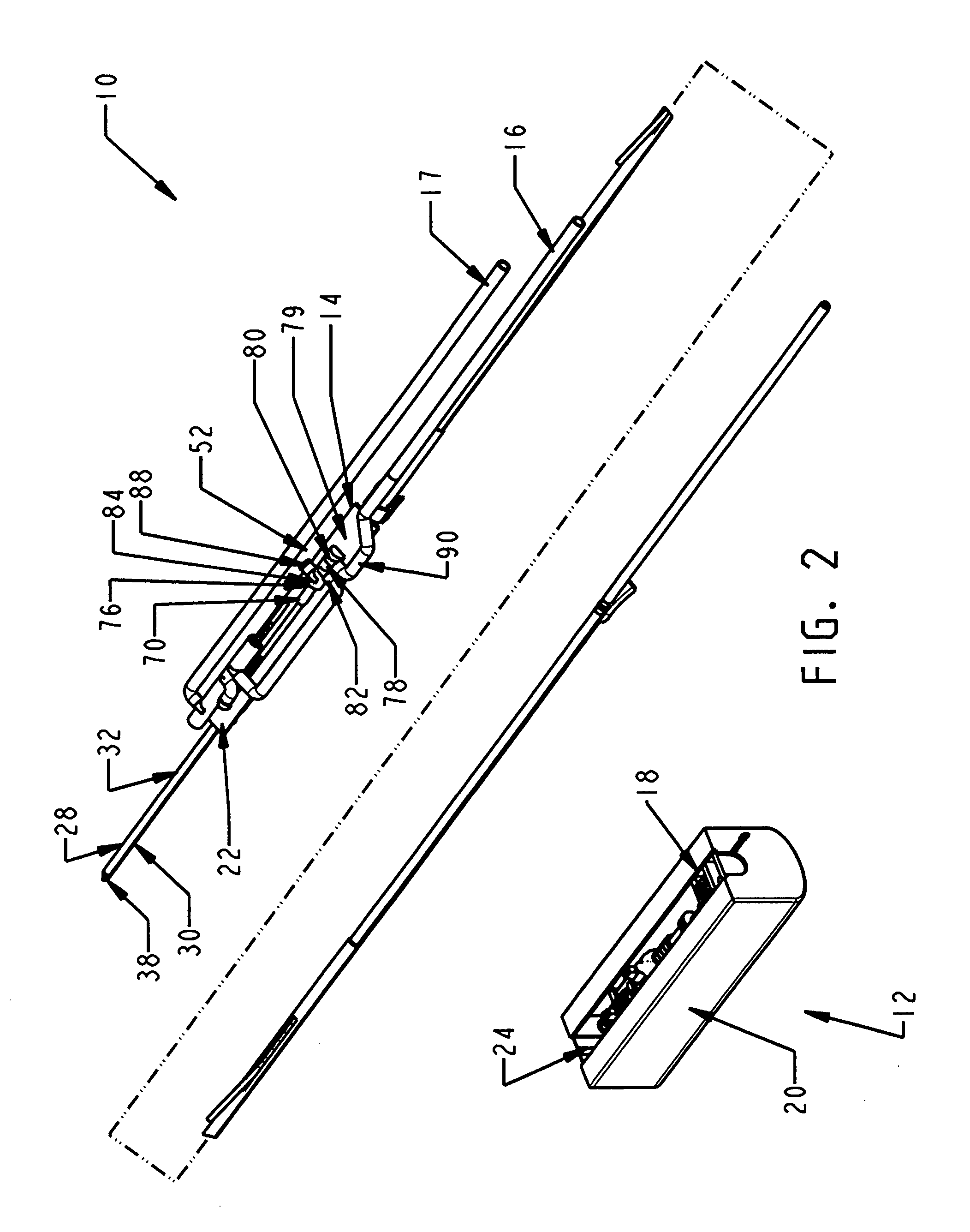
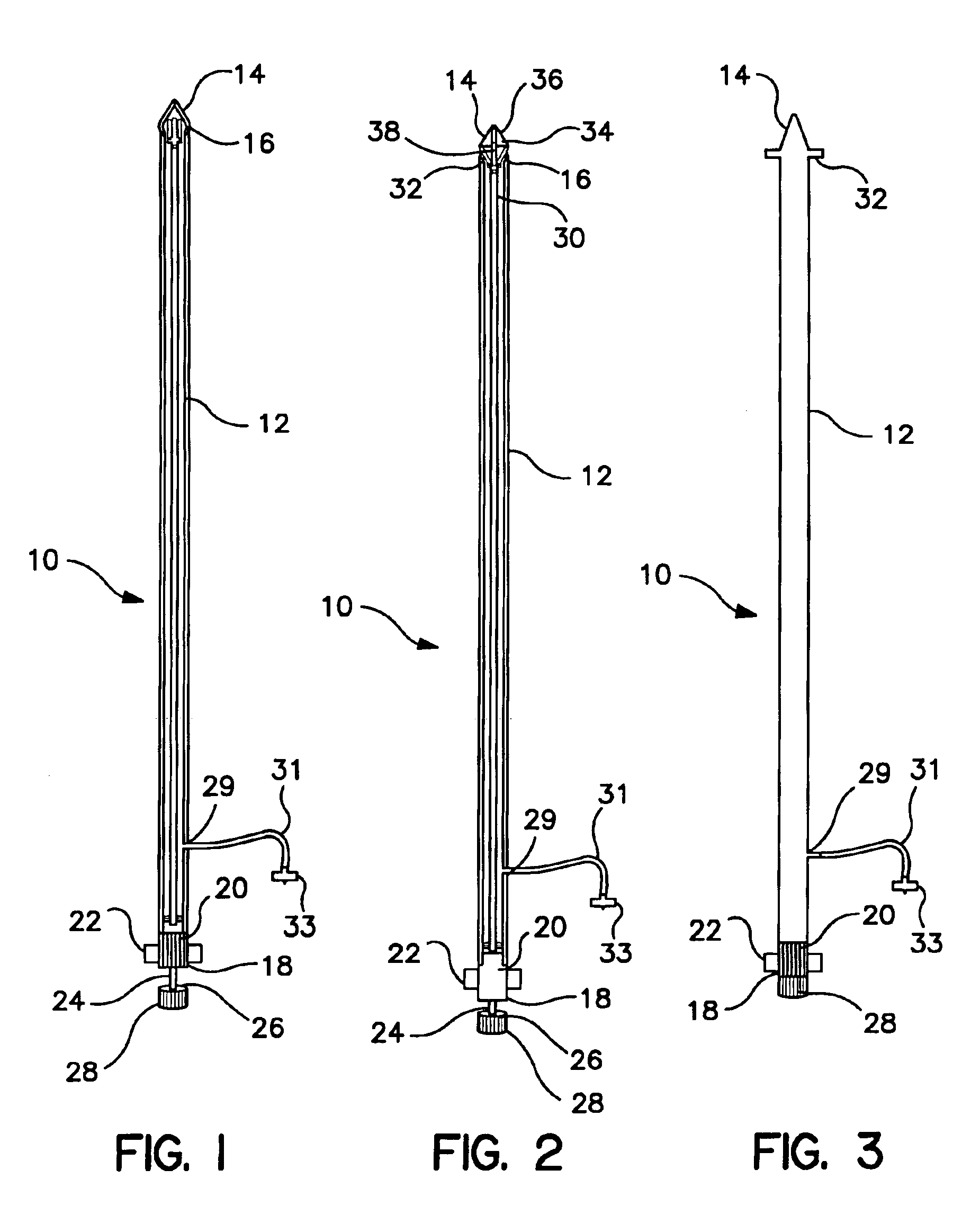
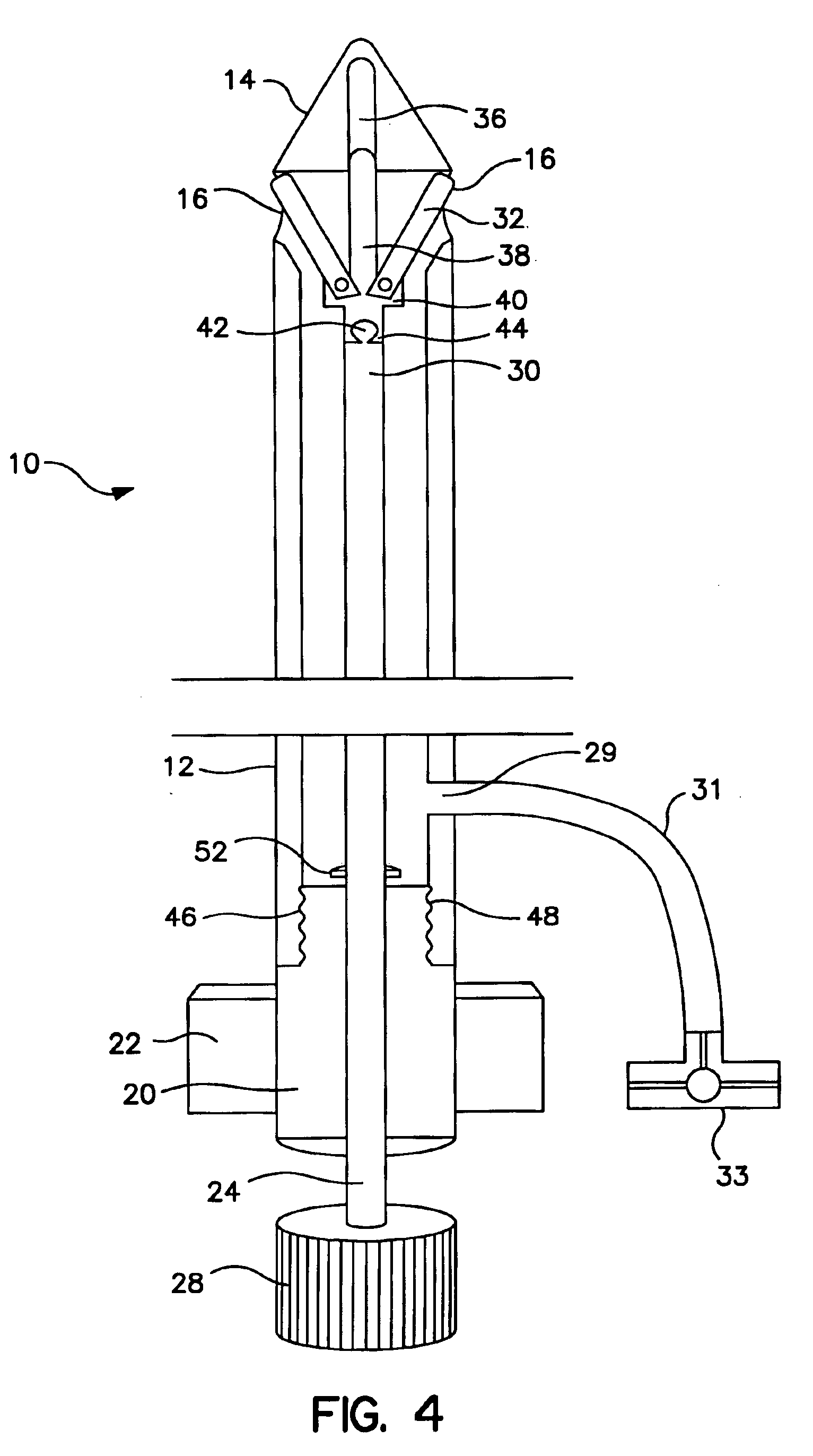
Core sampling biopsy device with short coupled MRI-compatible driver
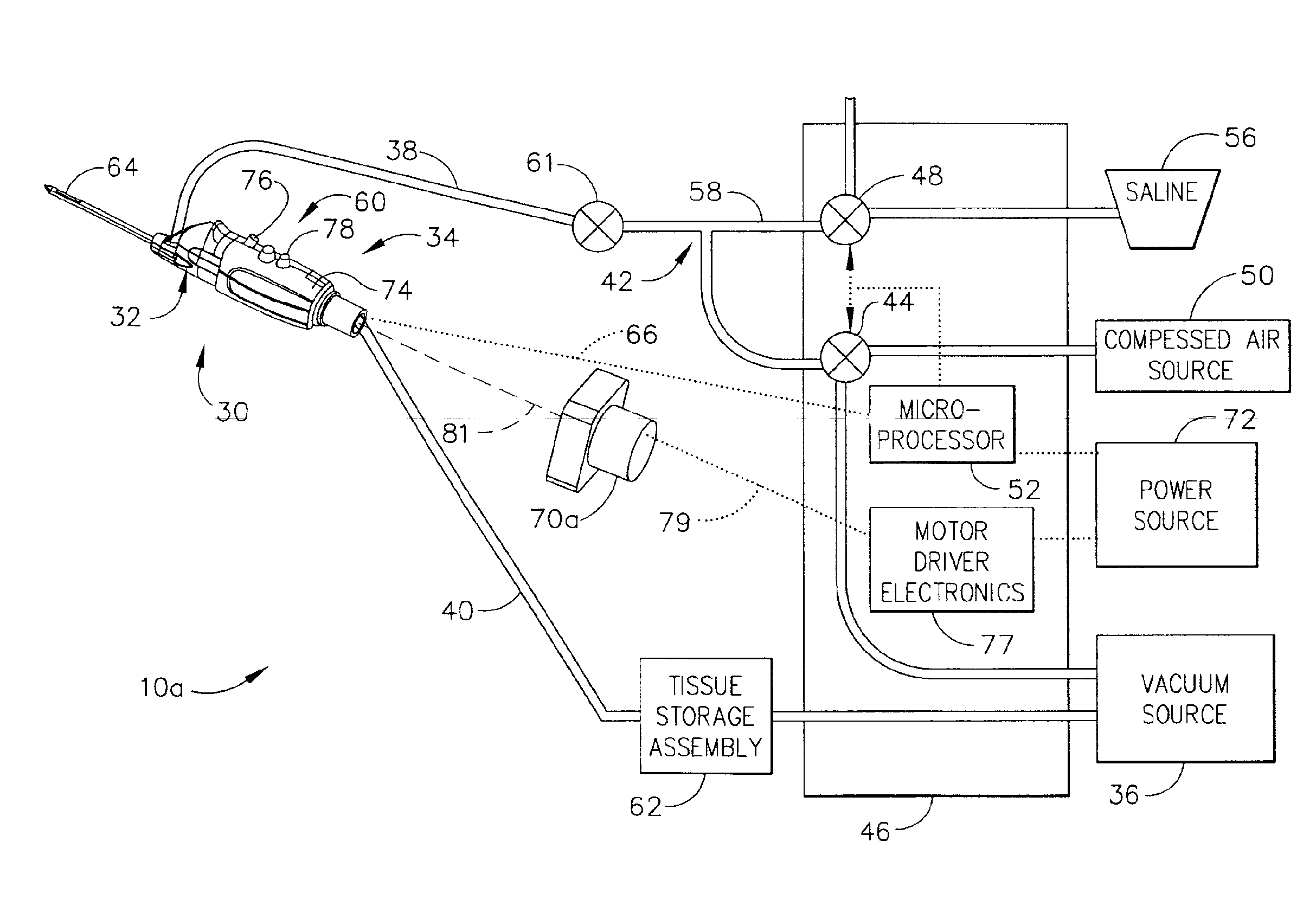
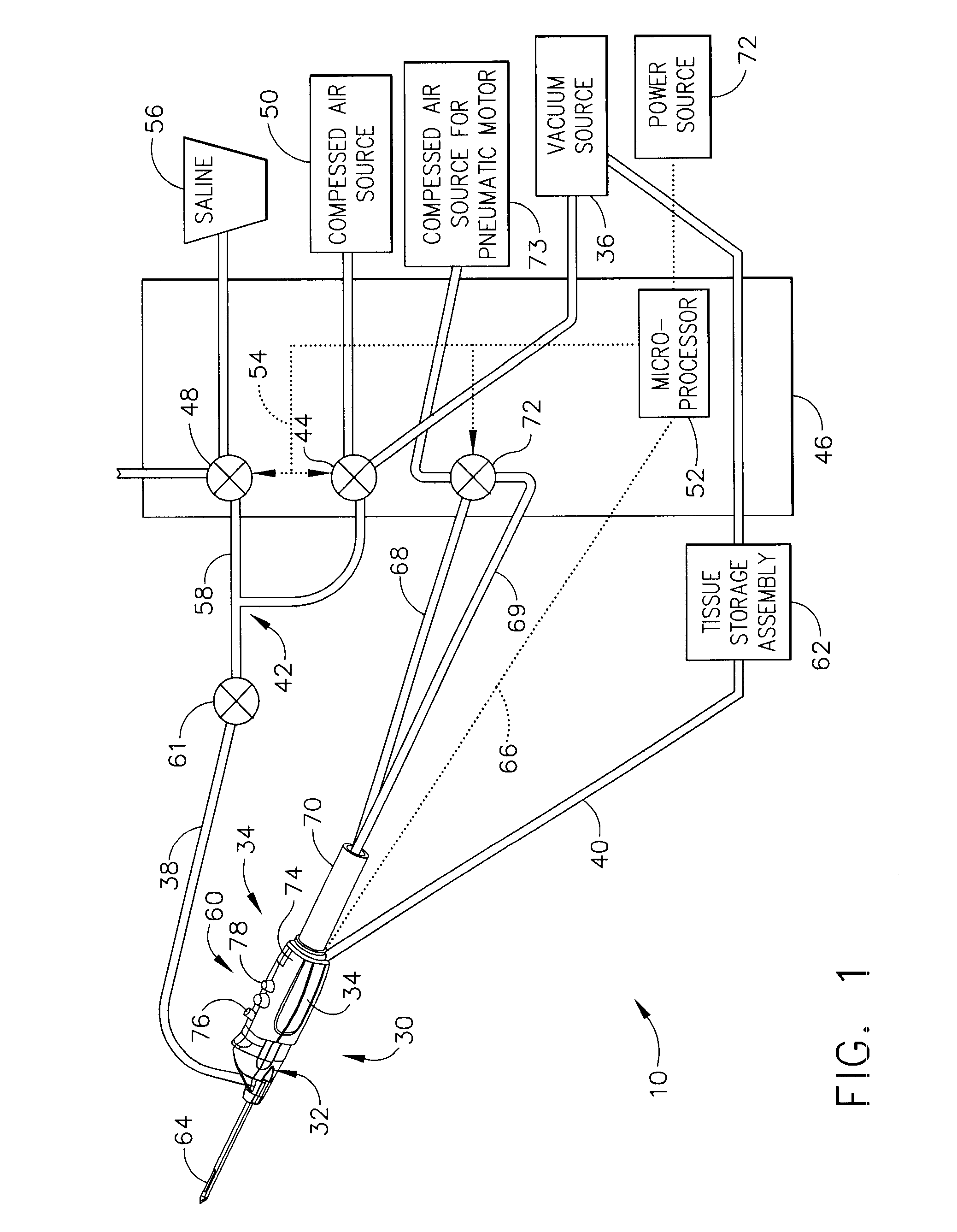
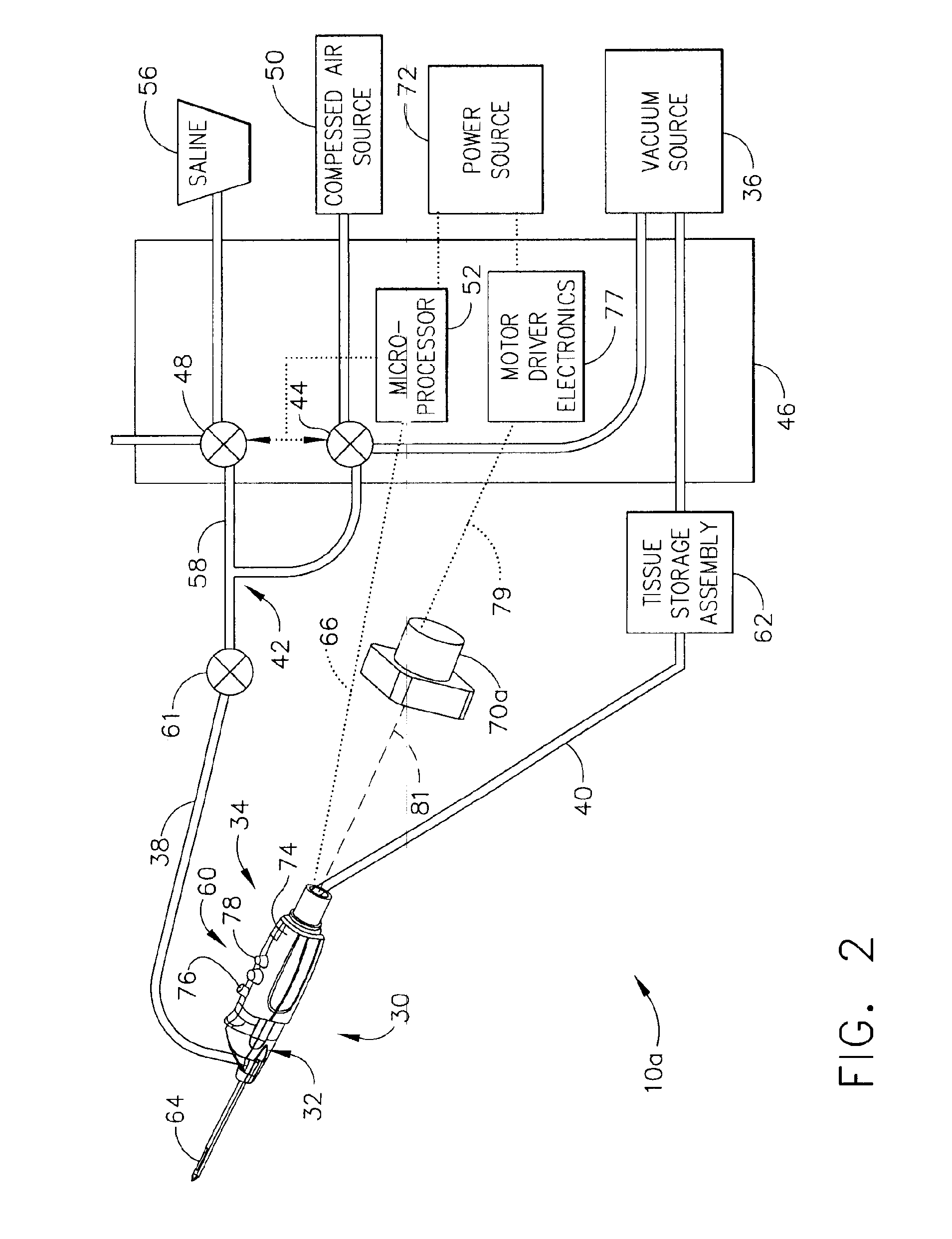
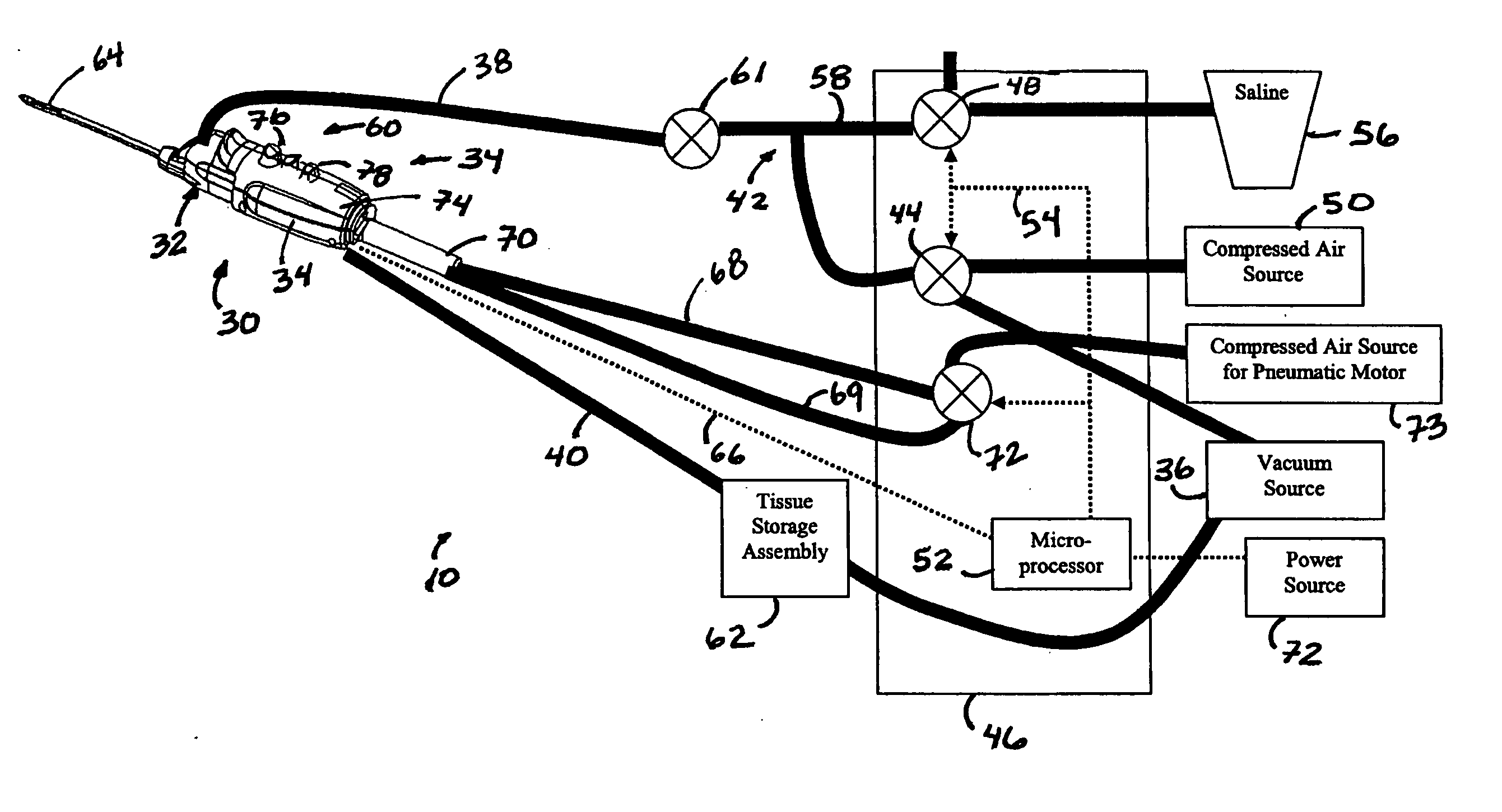
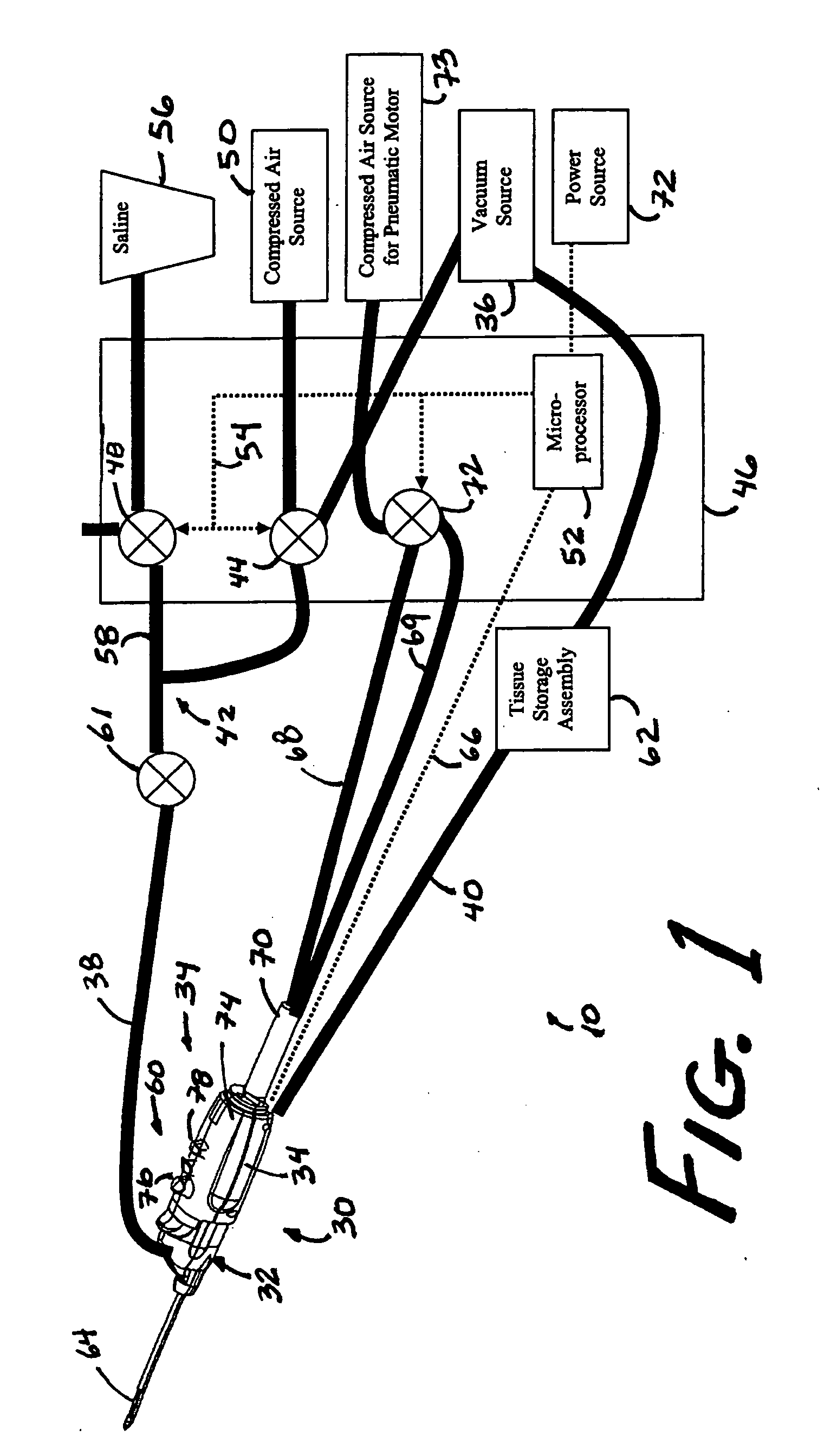
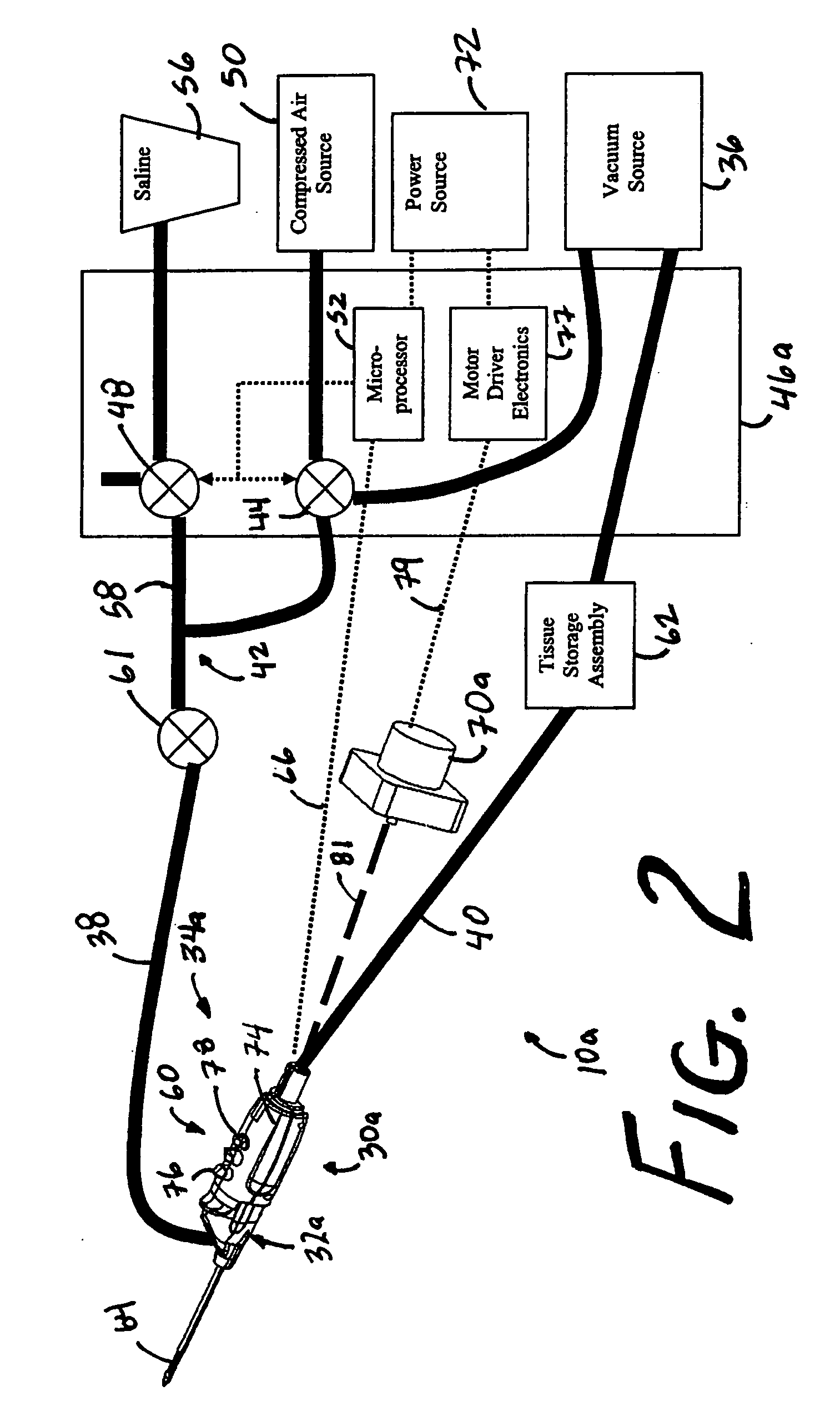
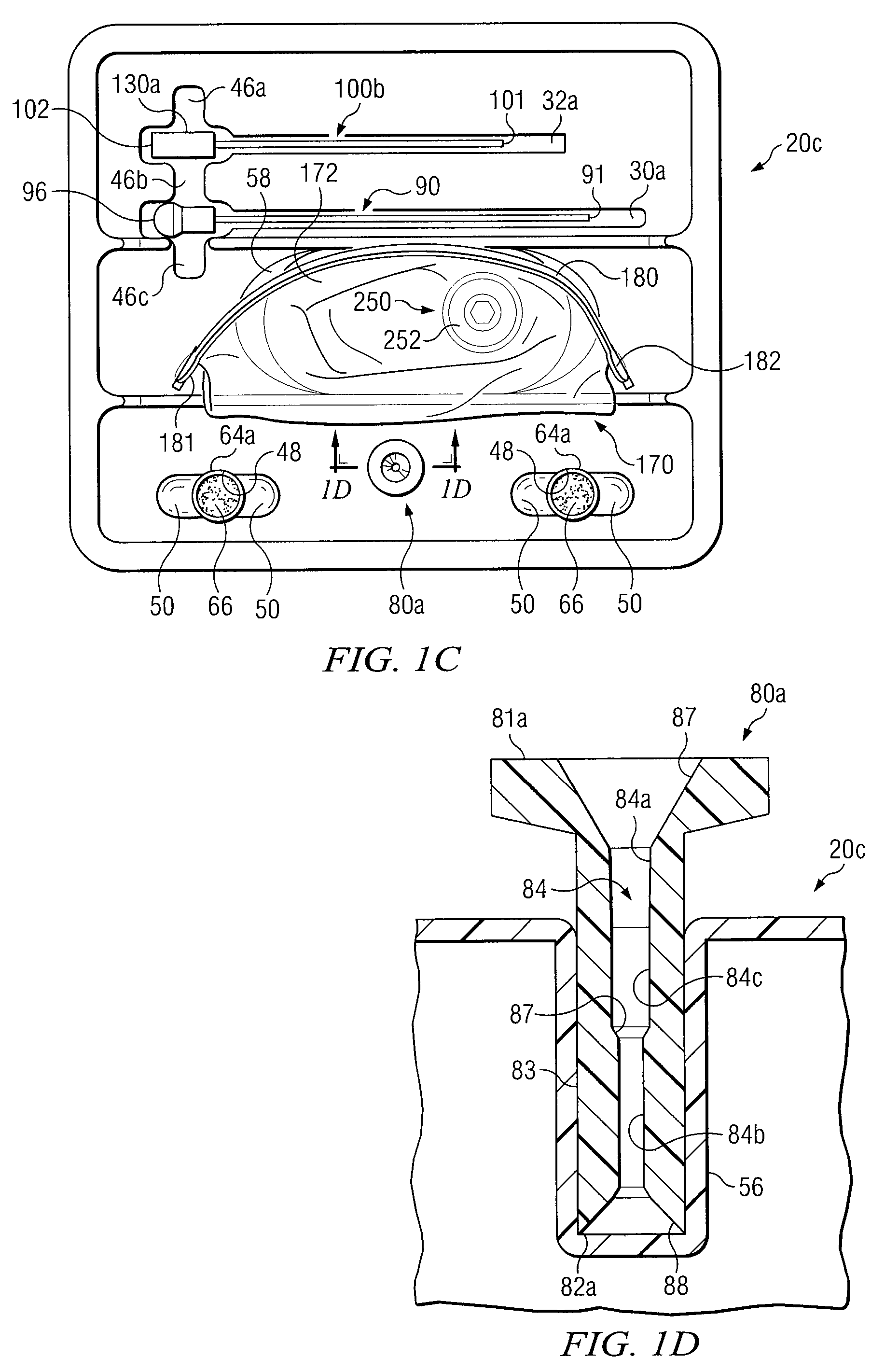
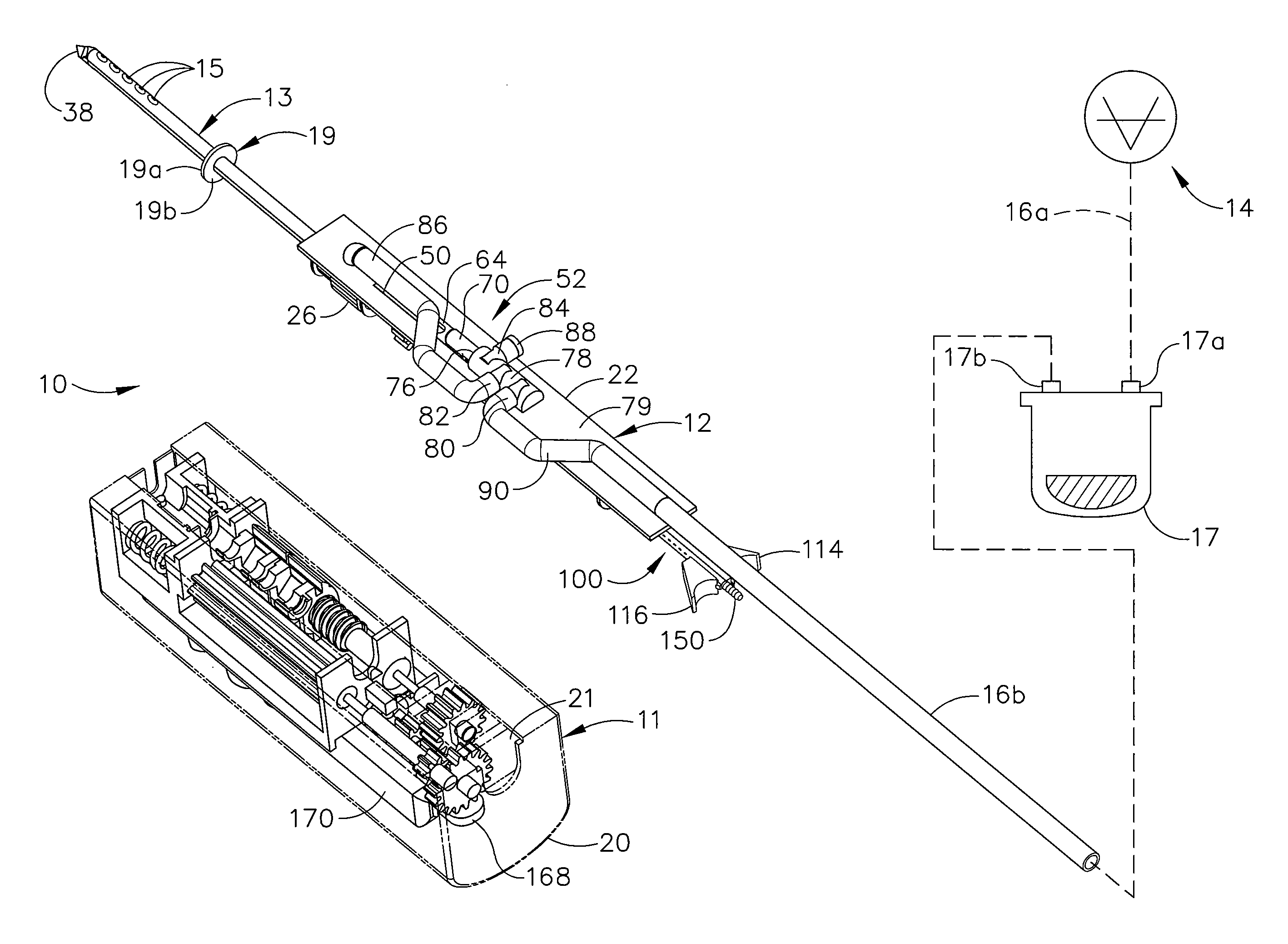
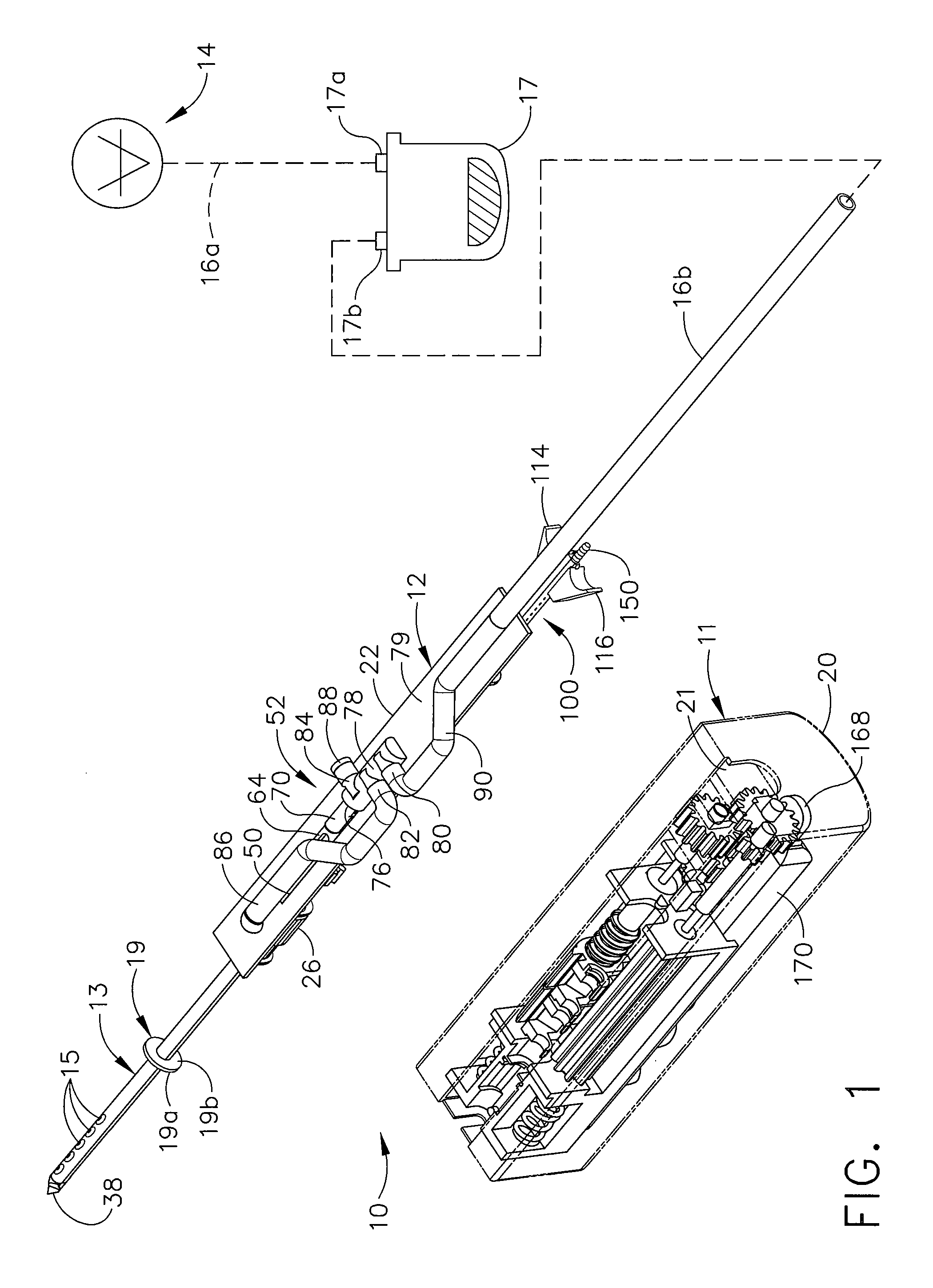
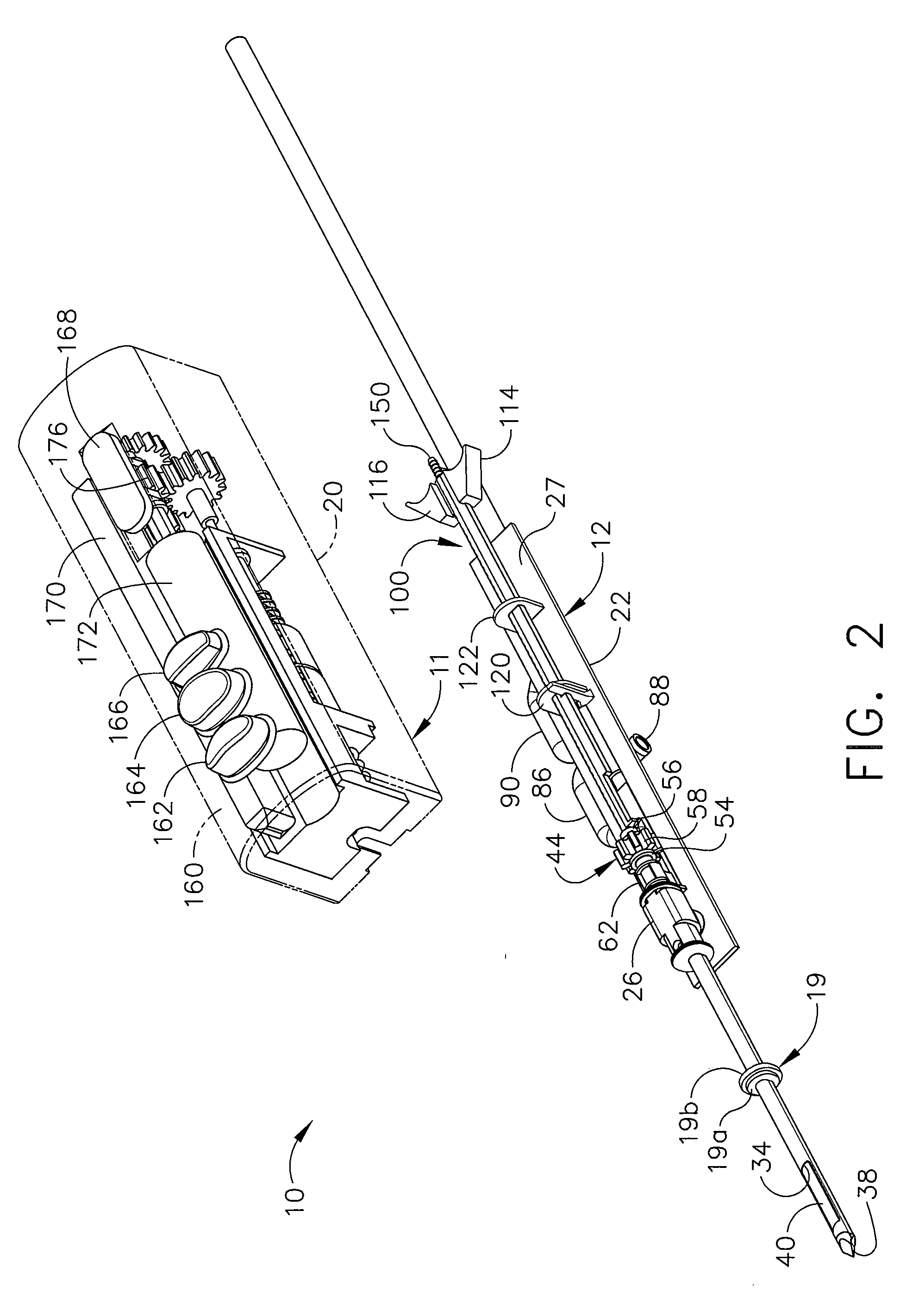
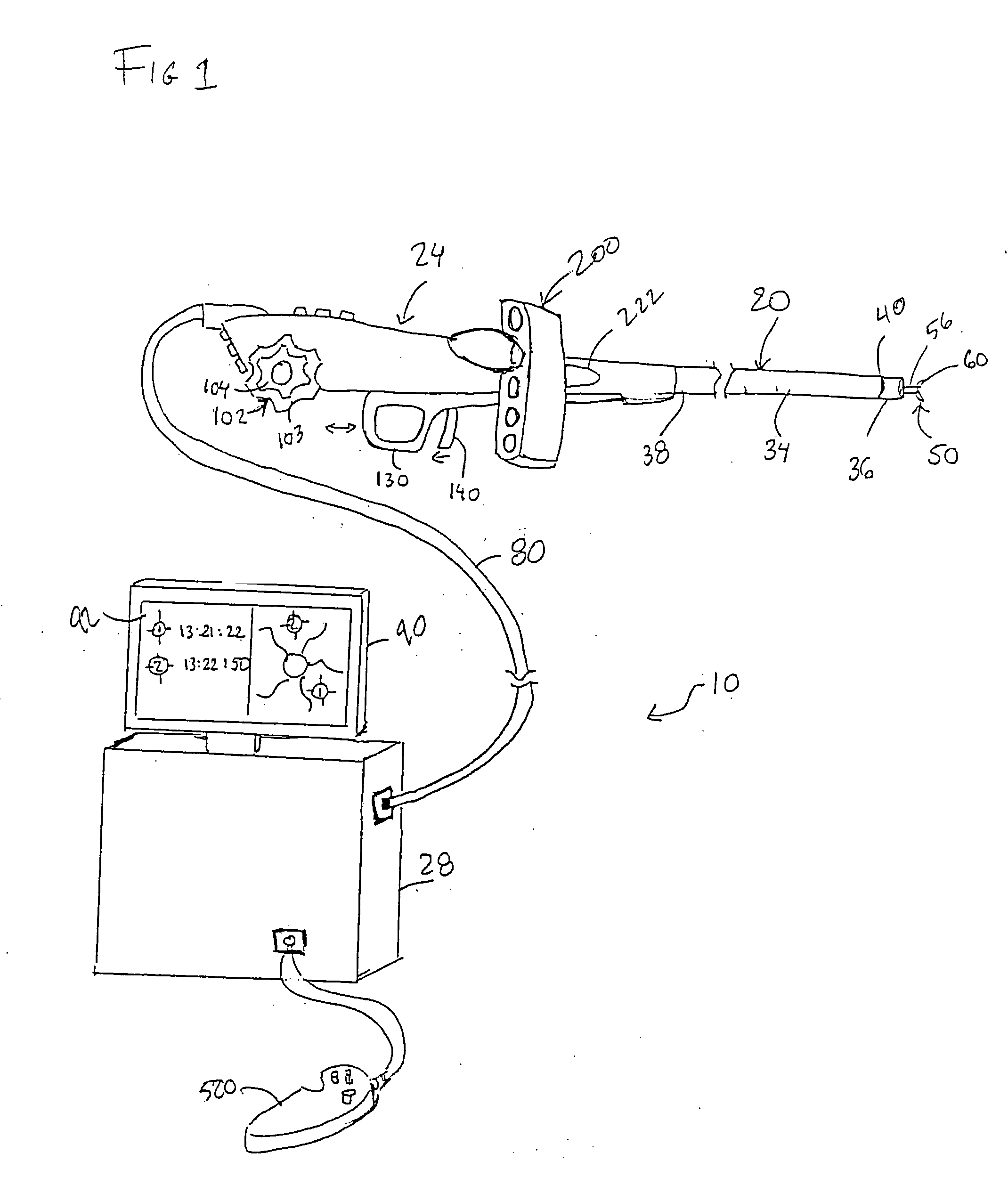
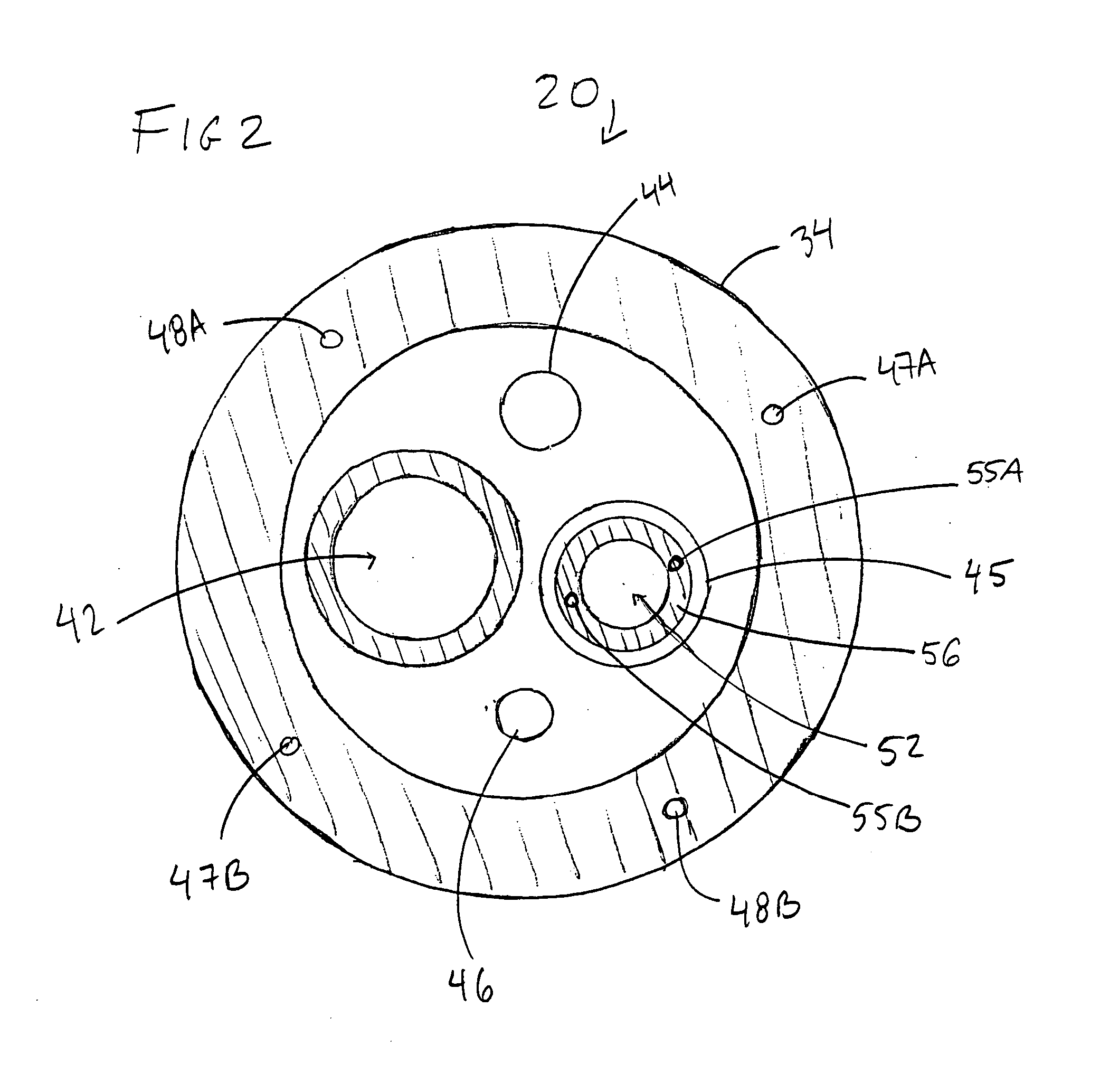
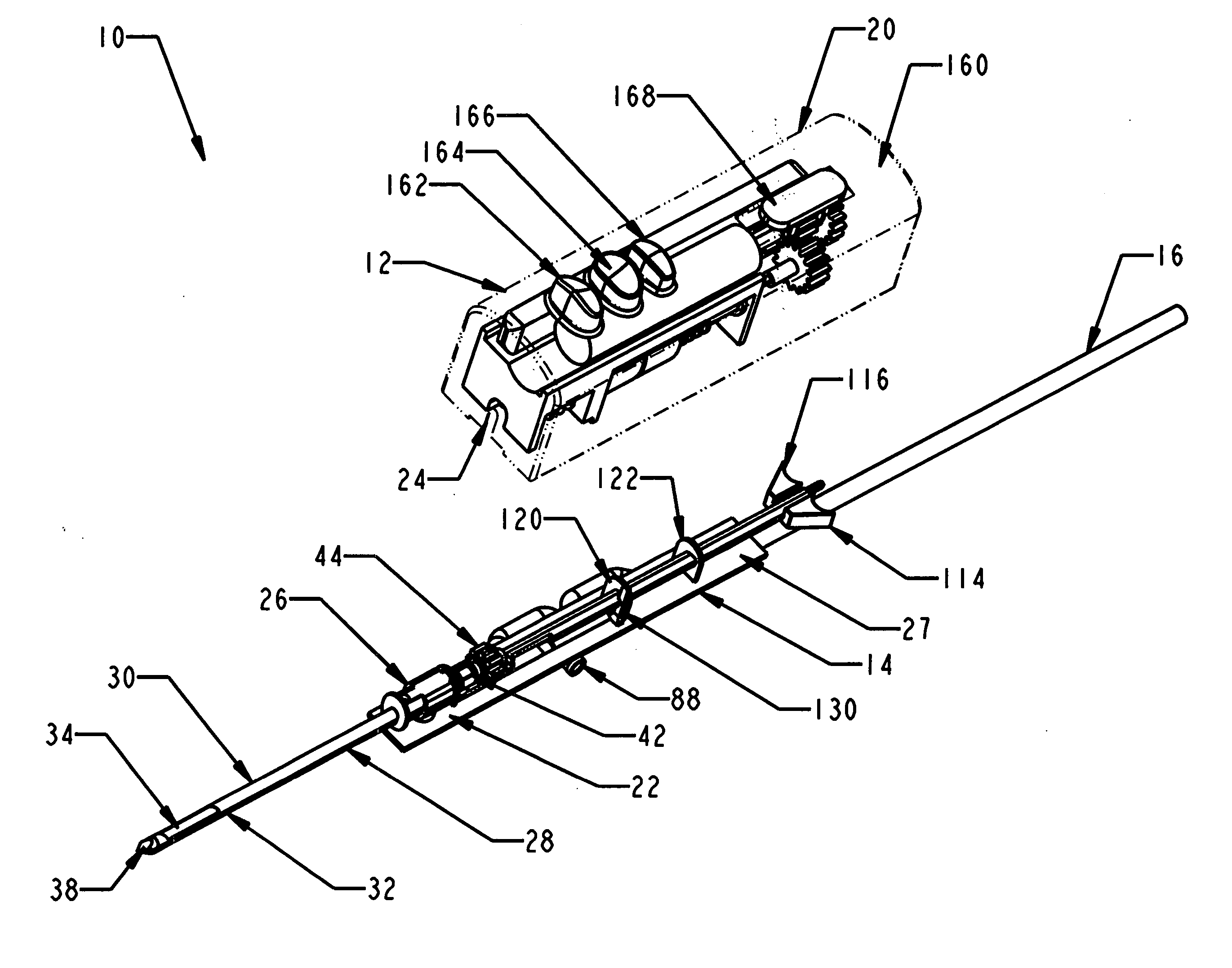
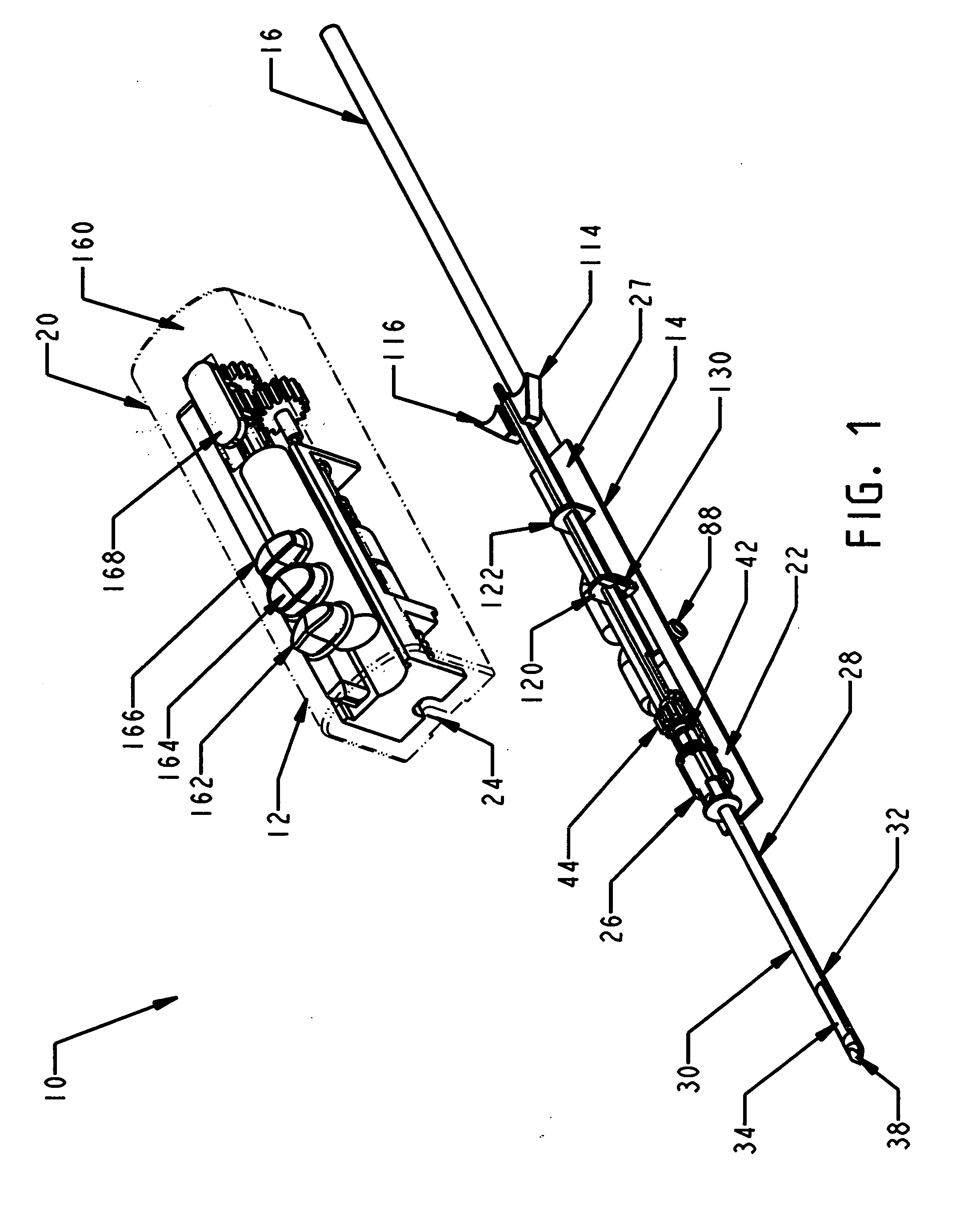
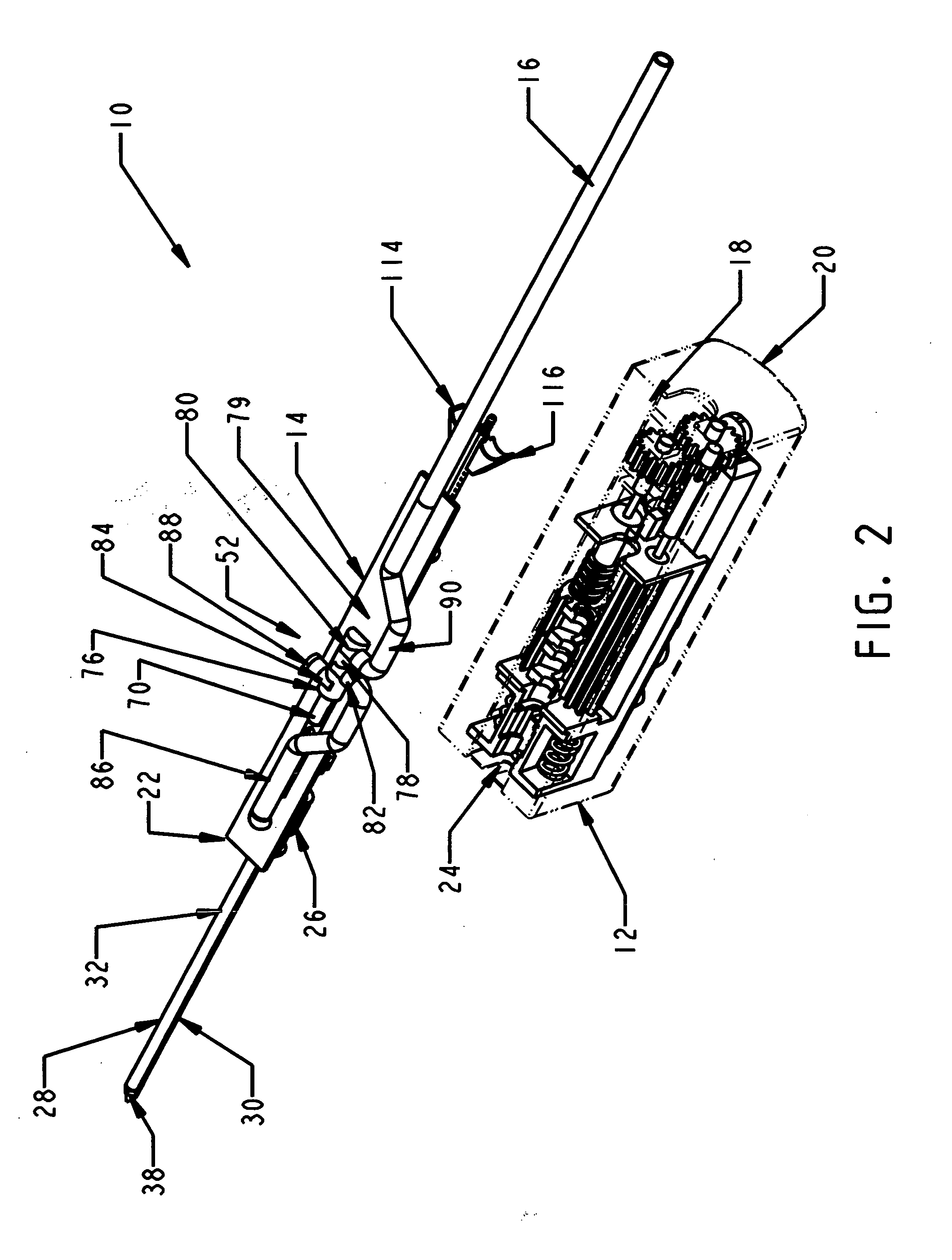
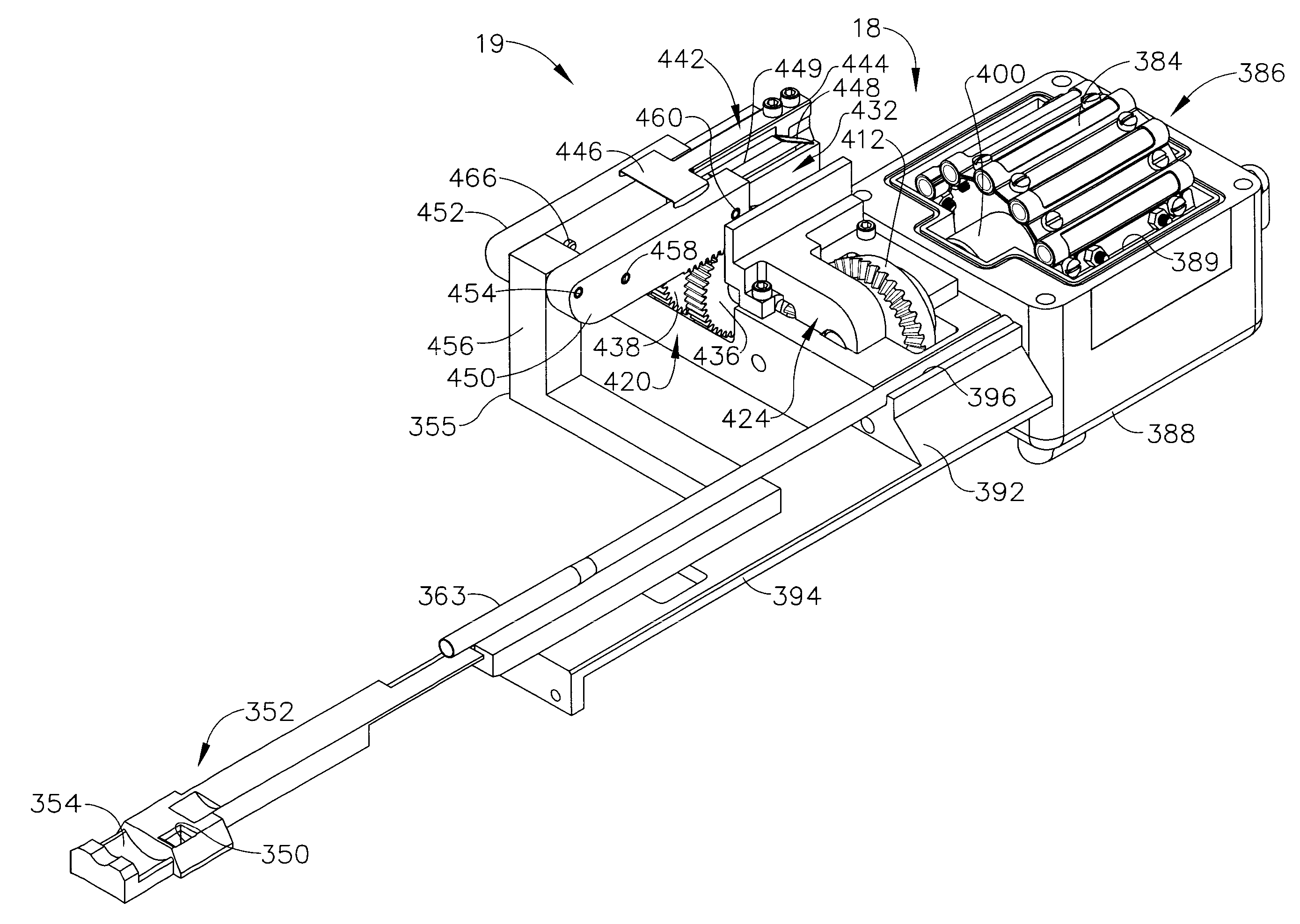
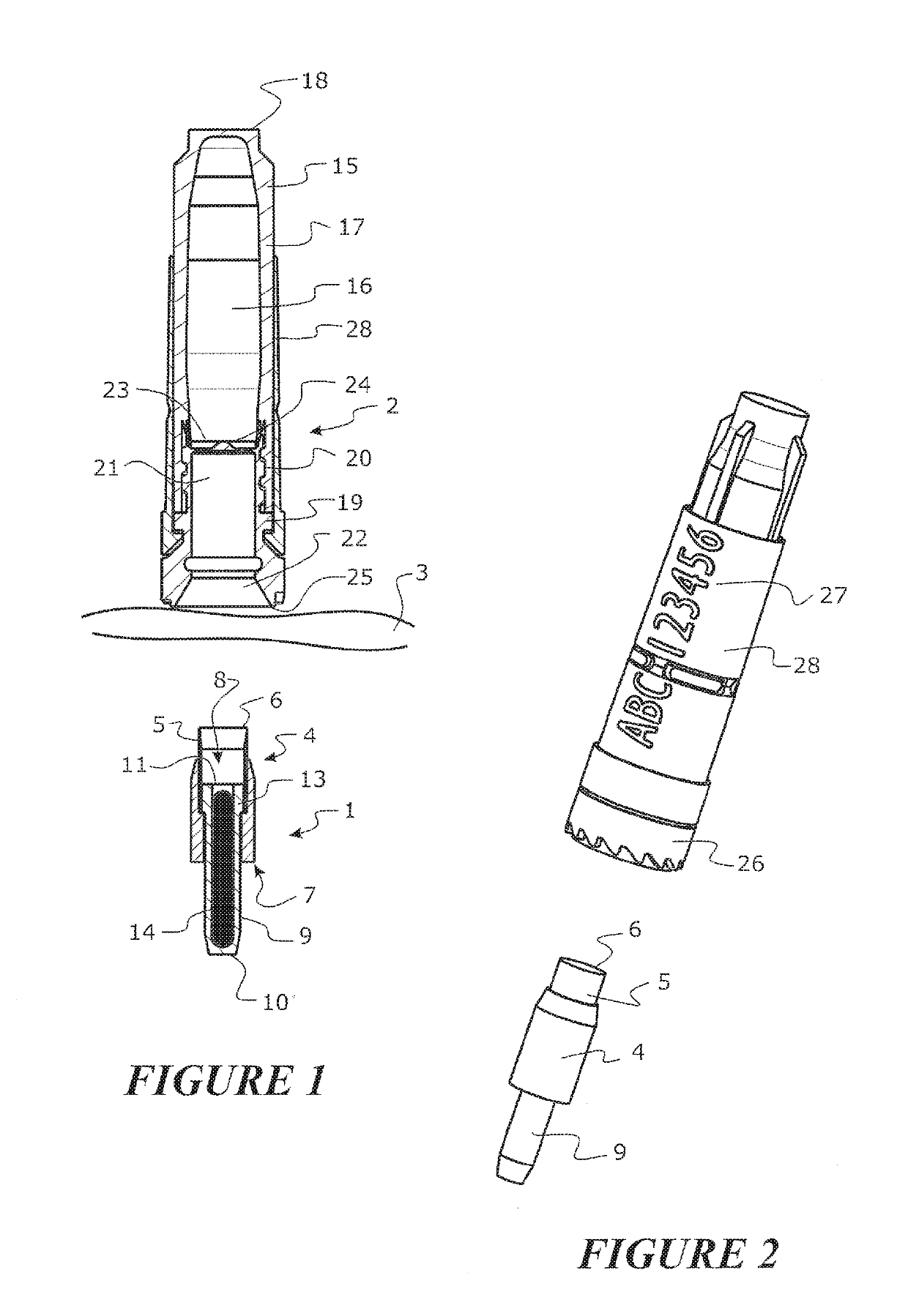
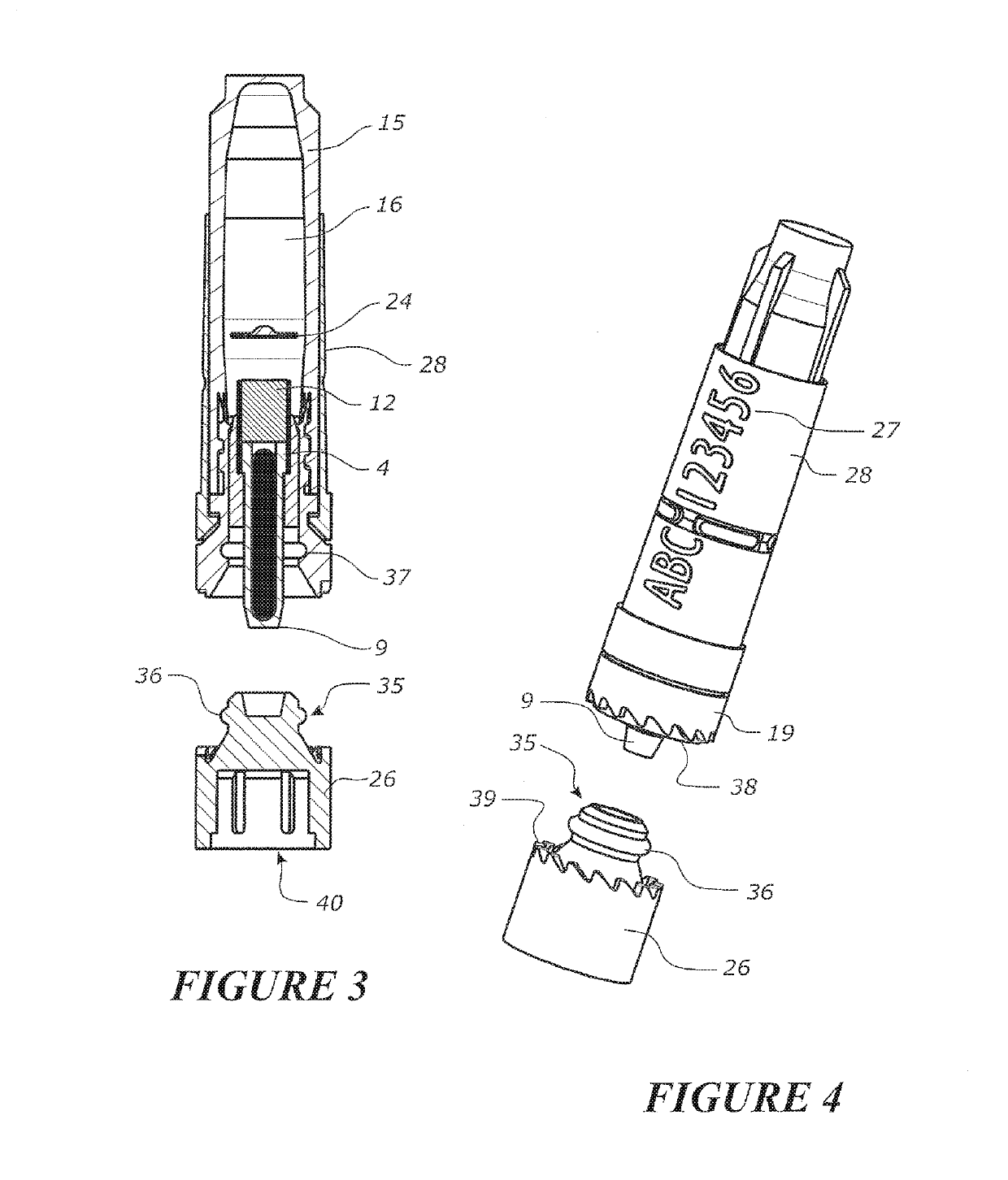
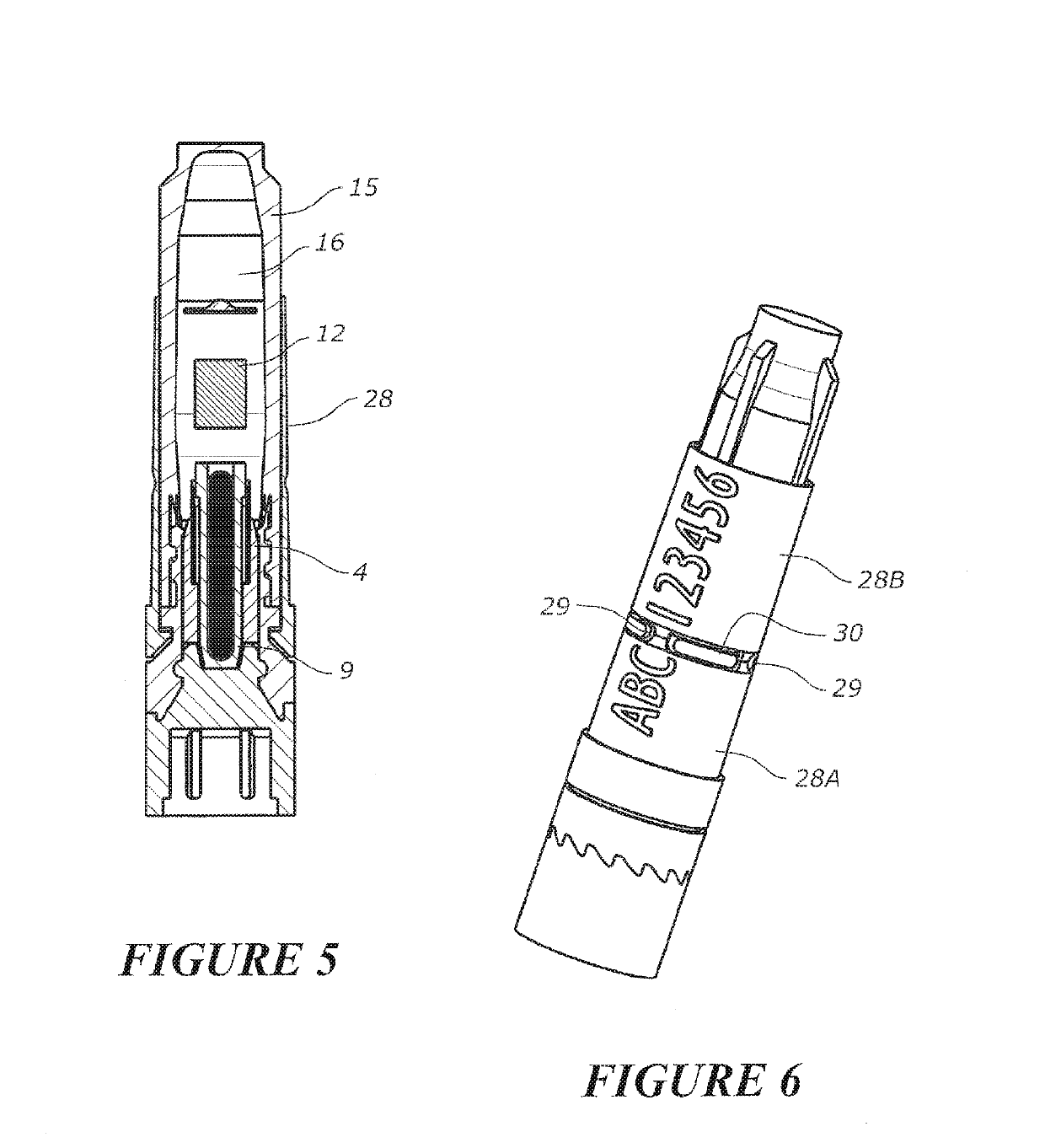
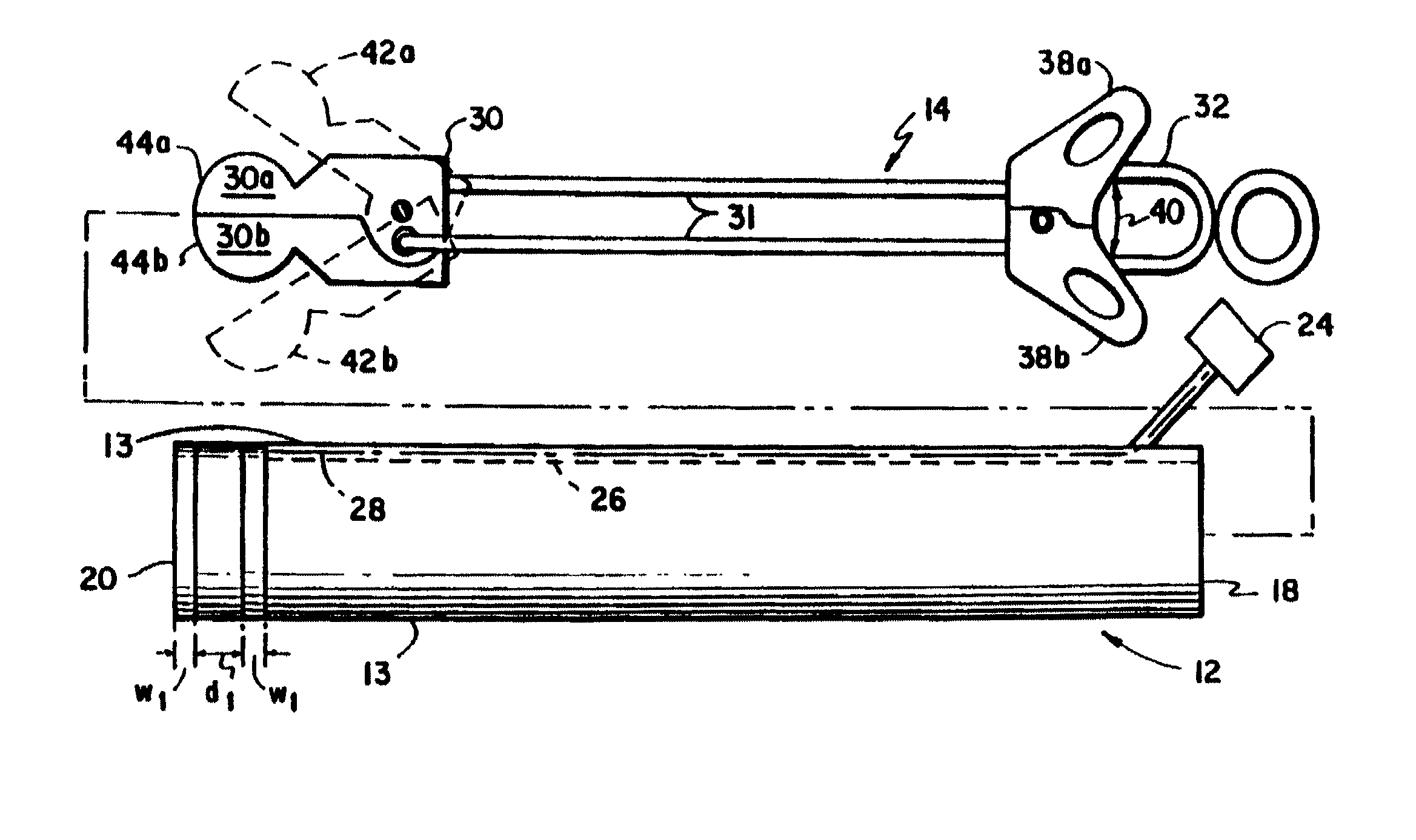
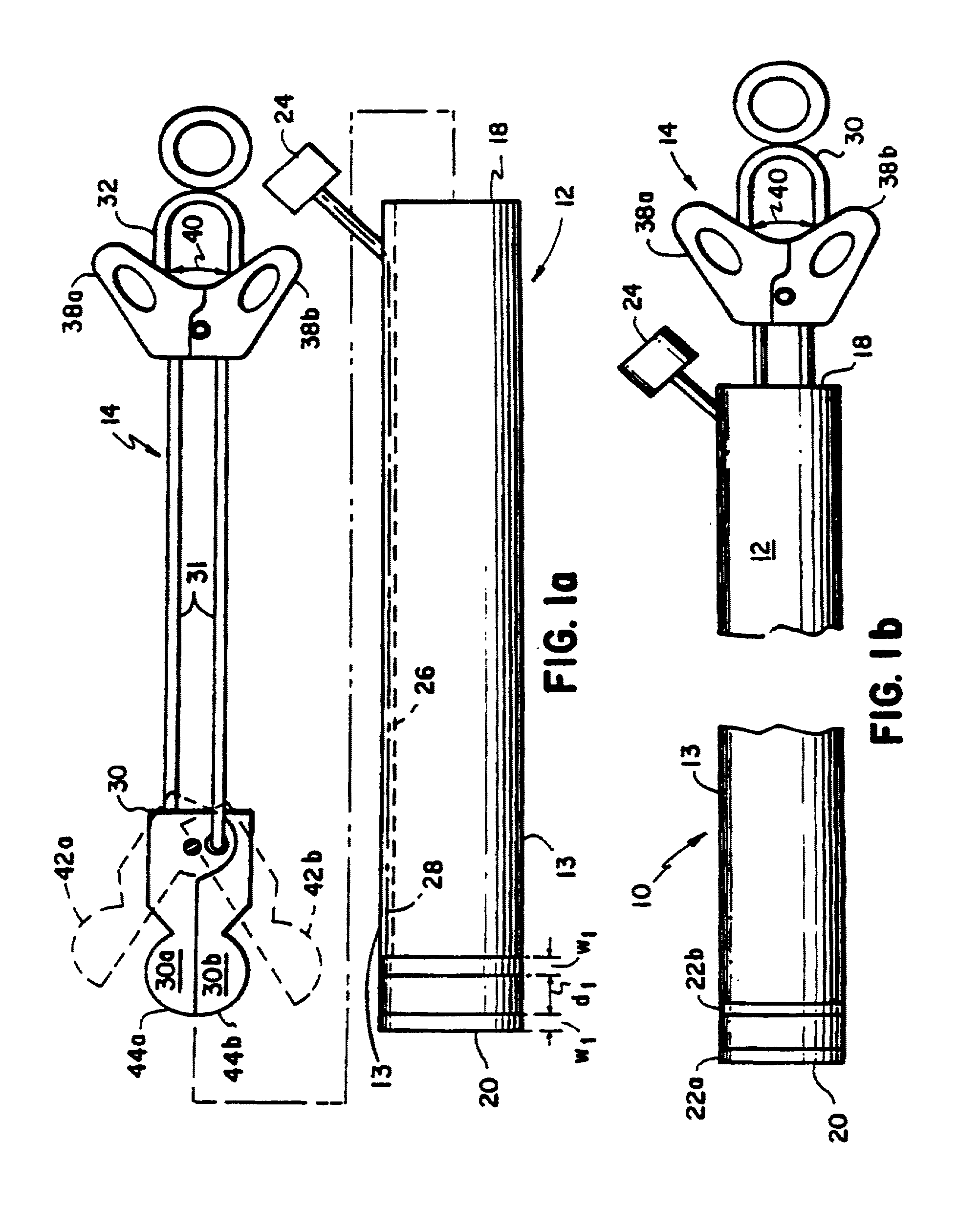
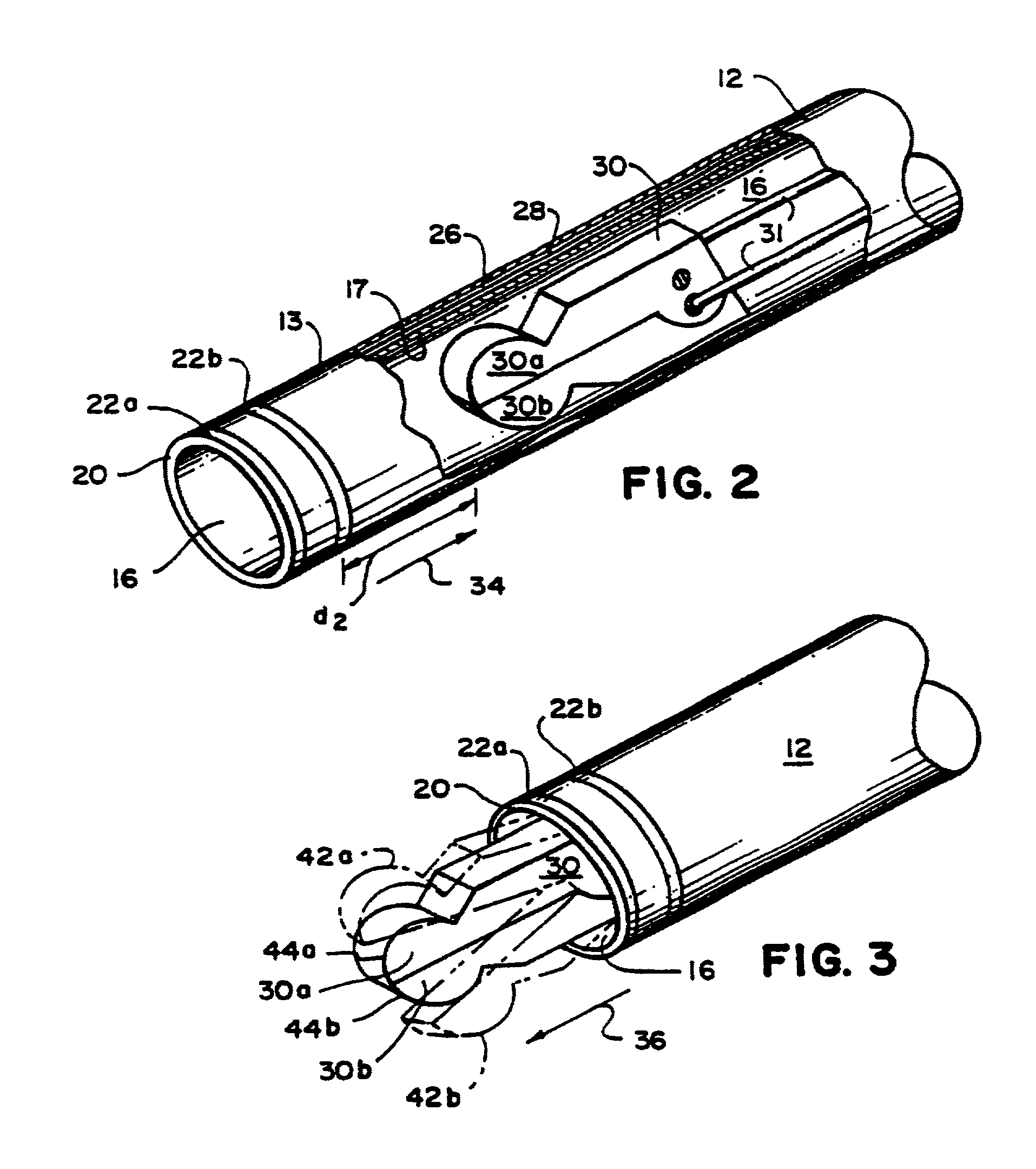
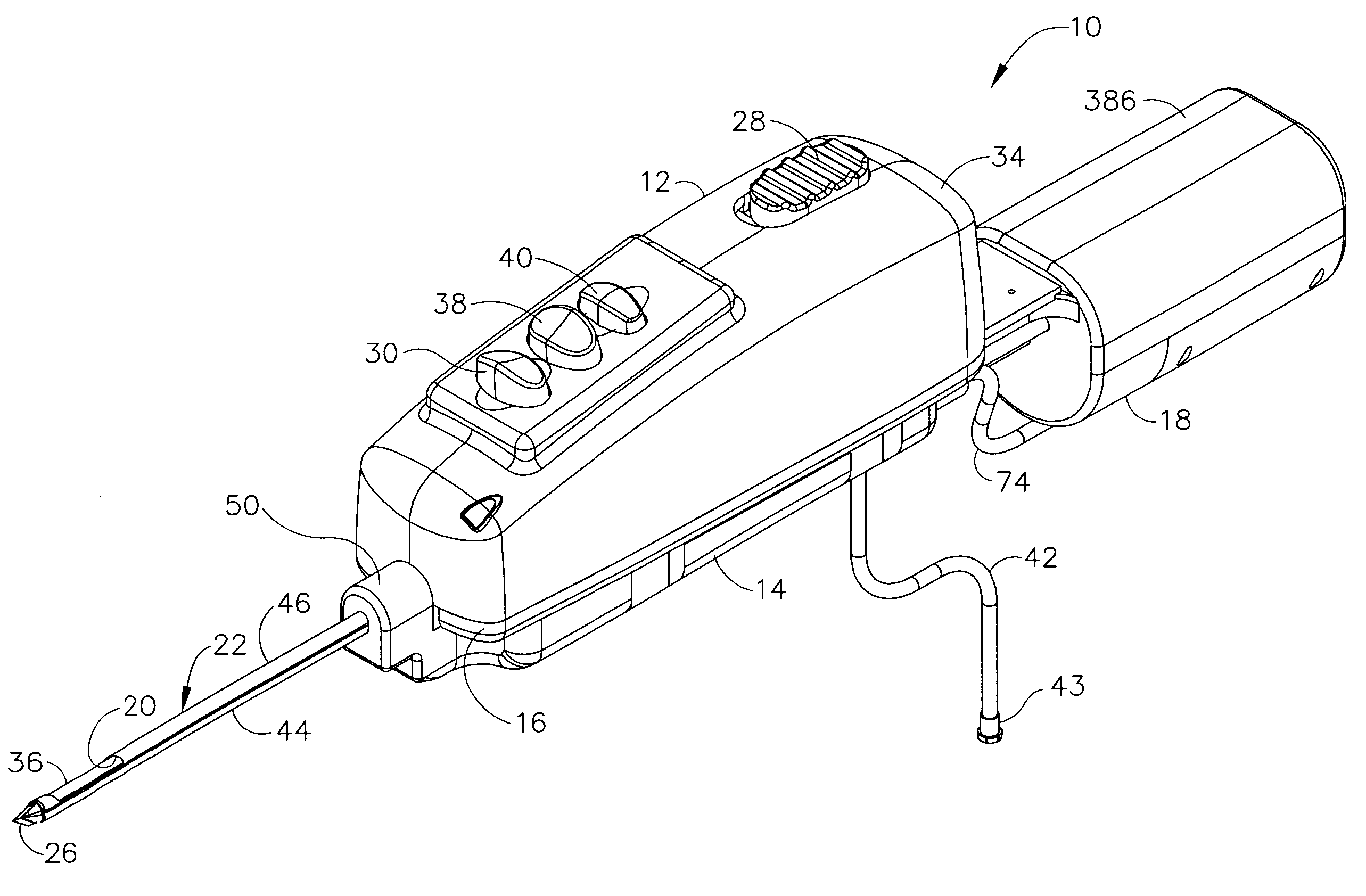
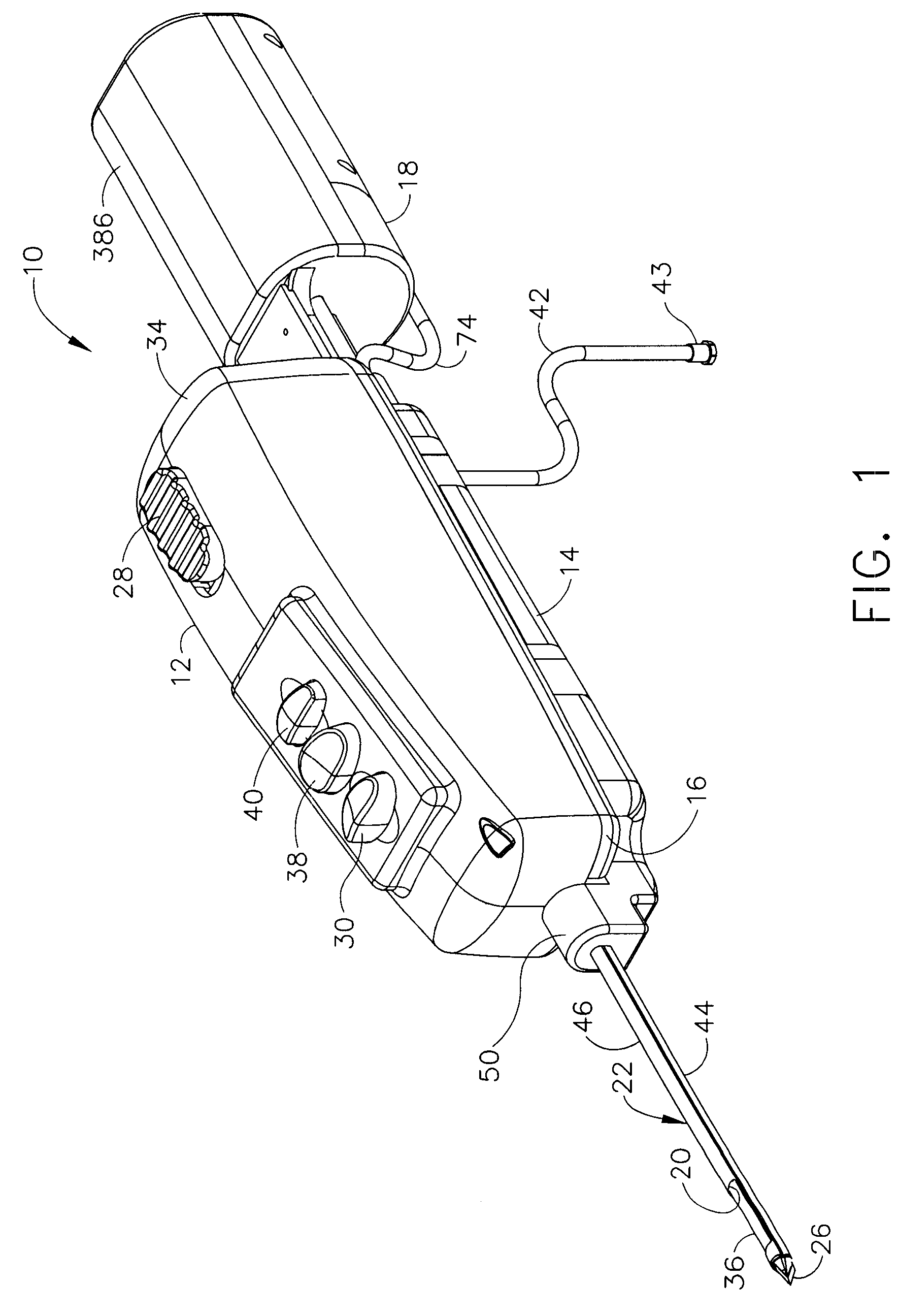
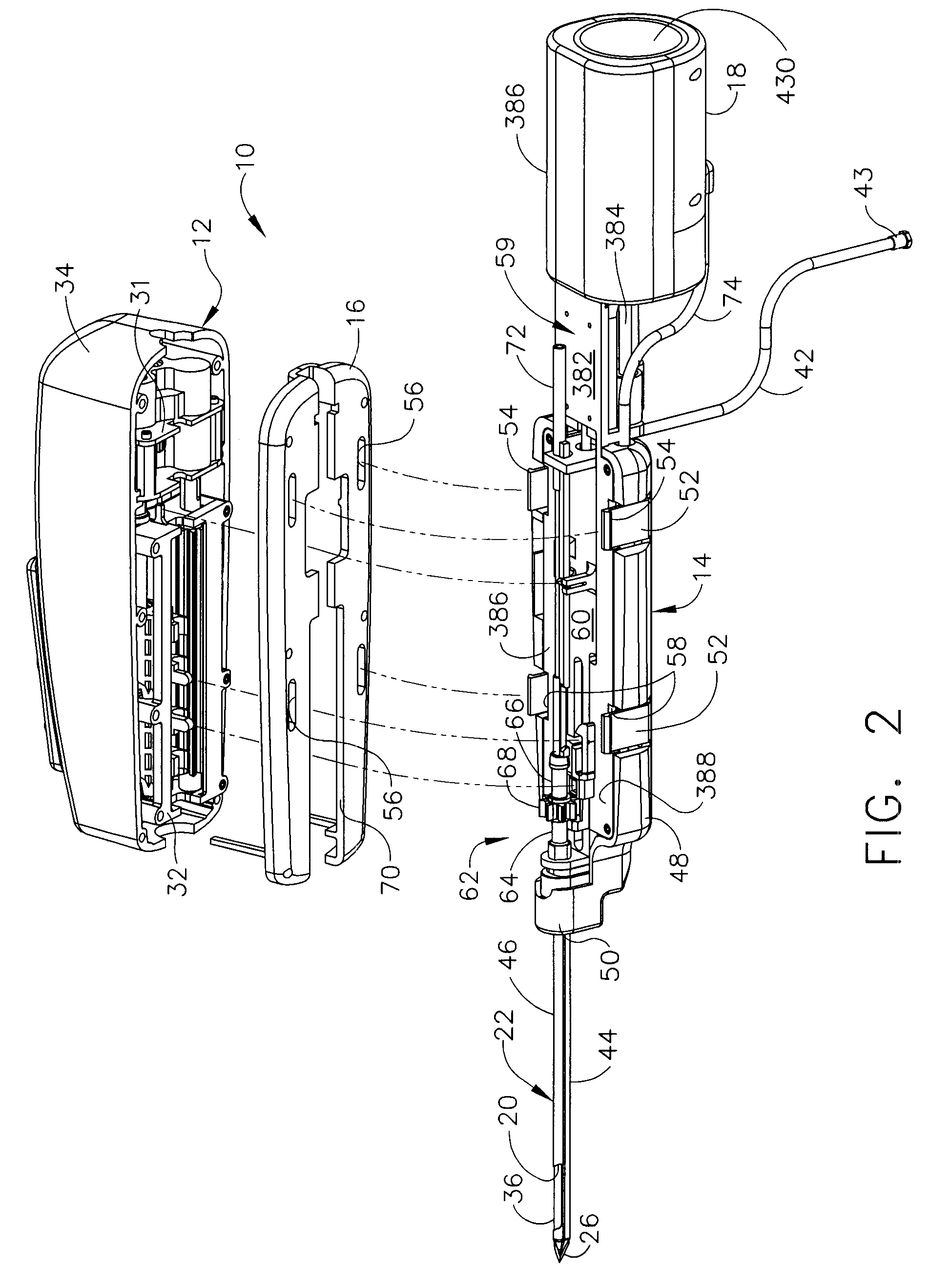
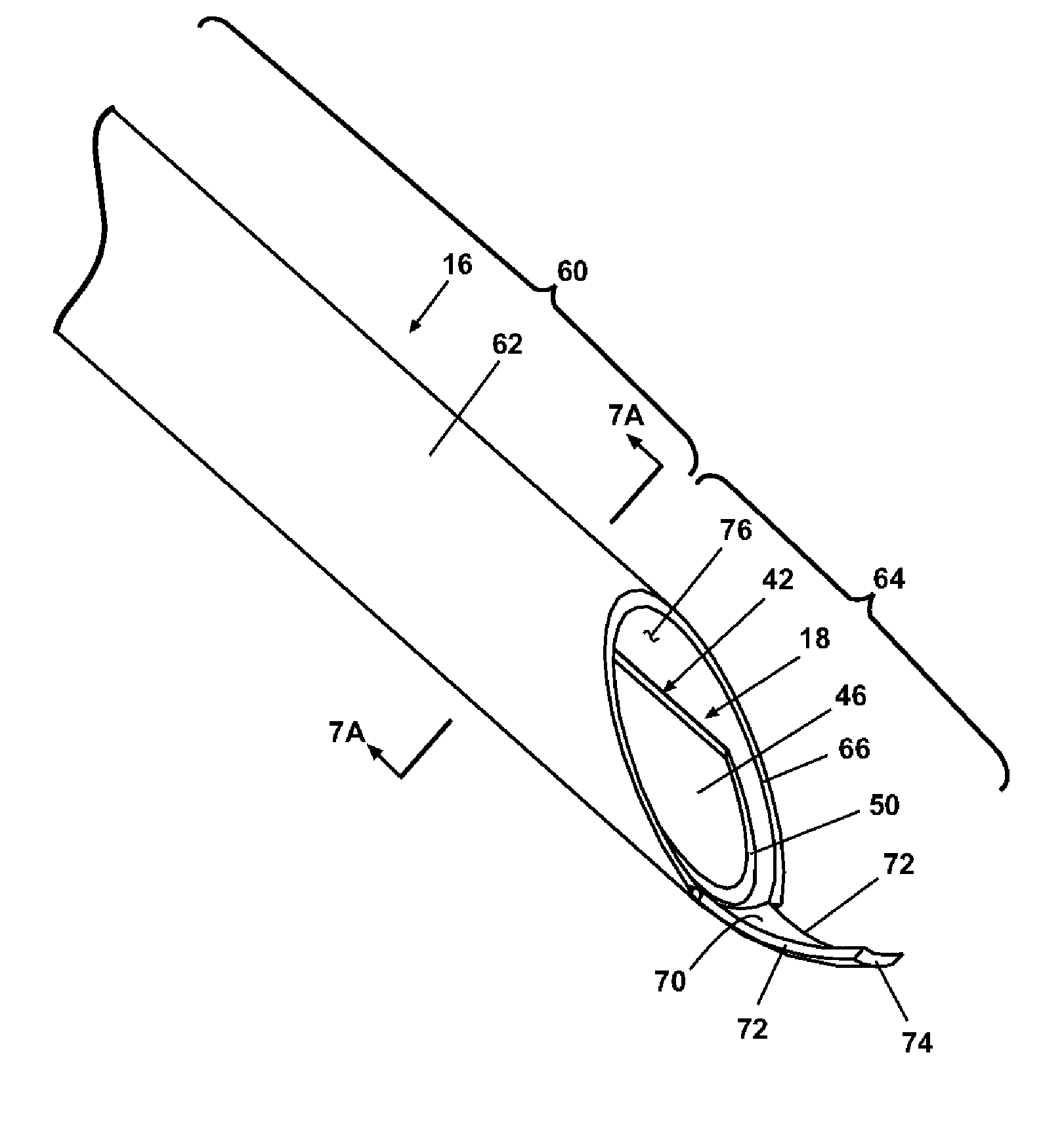
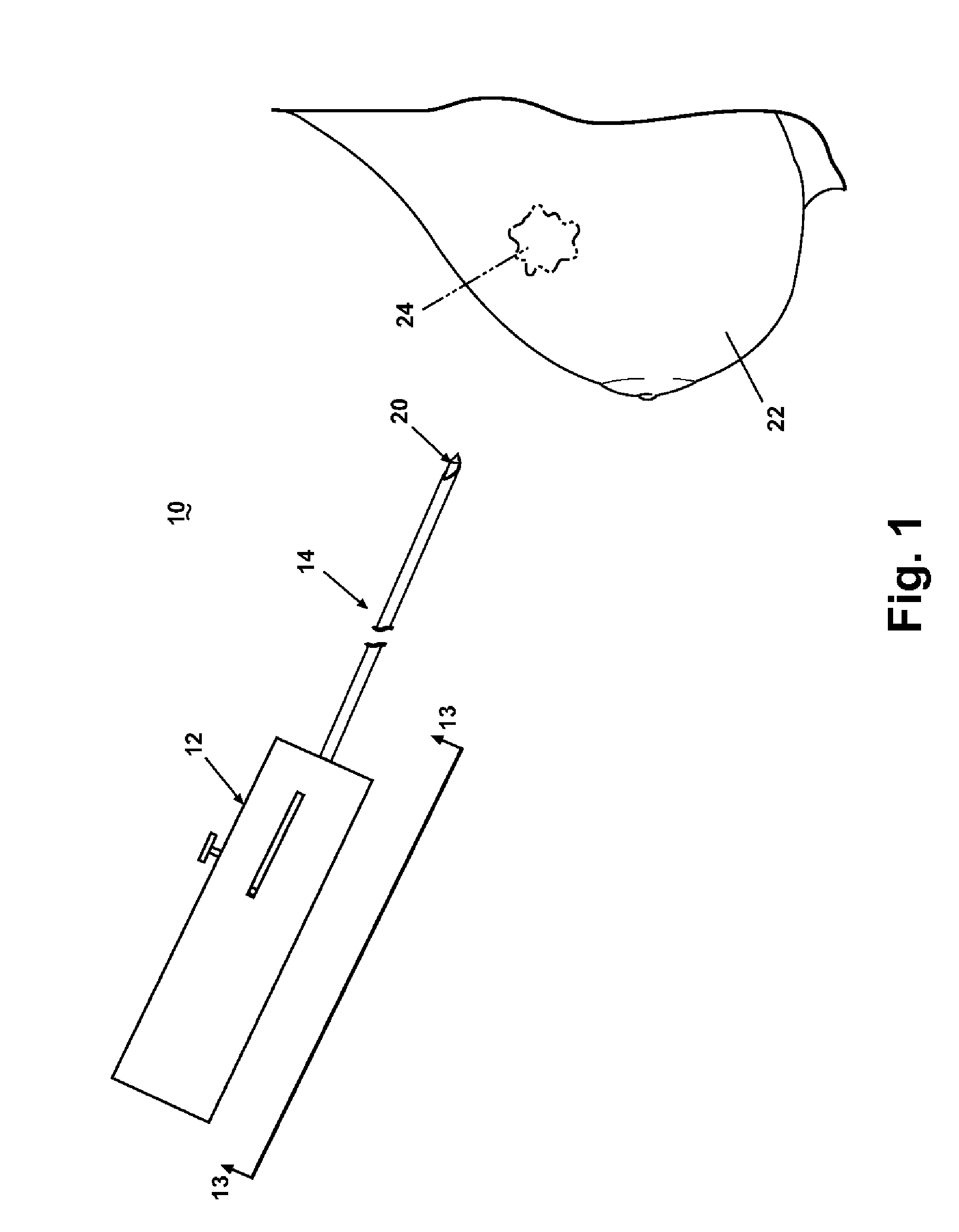
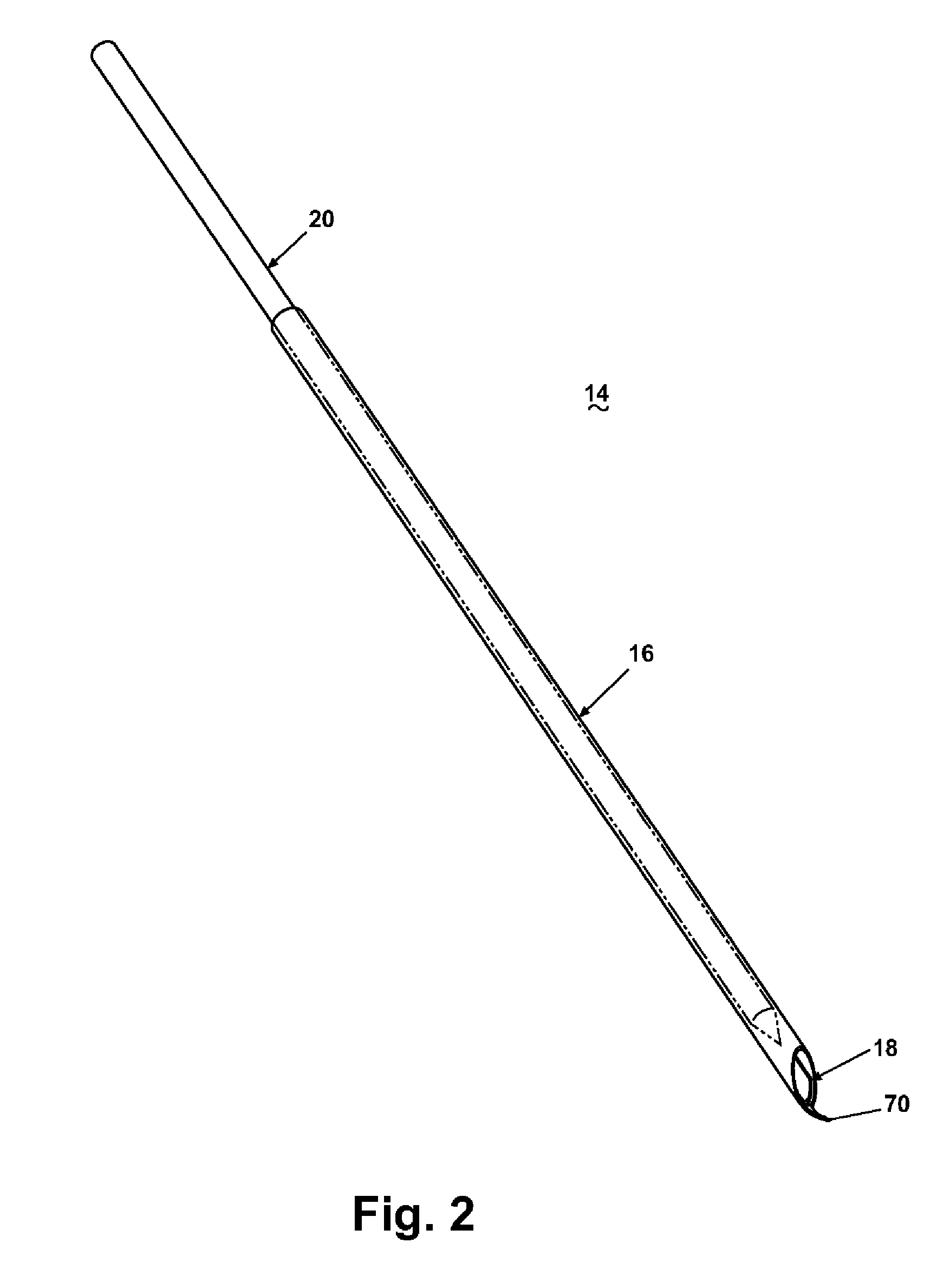
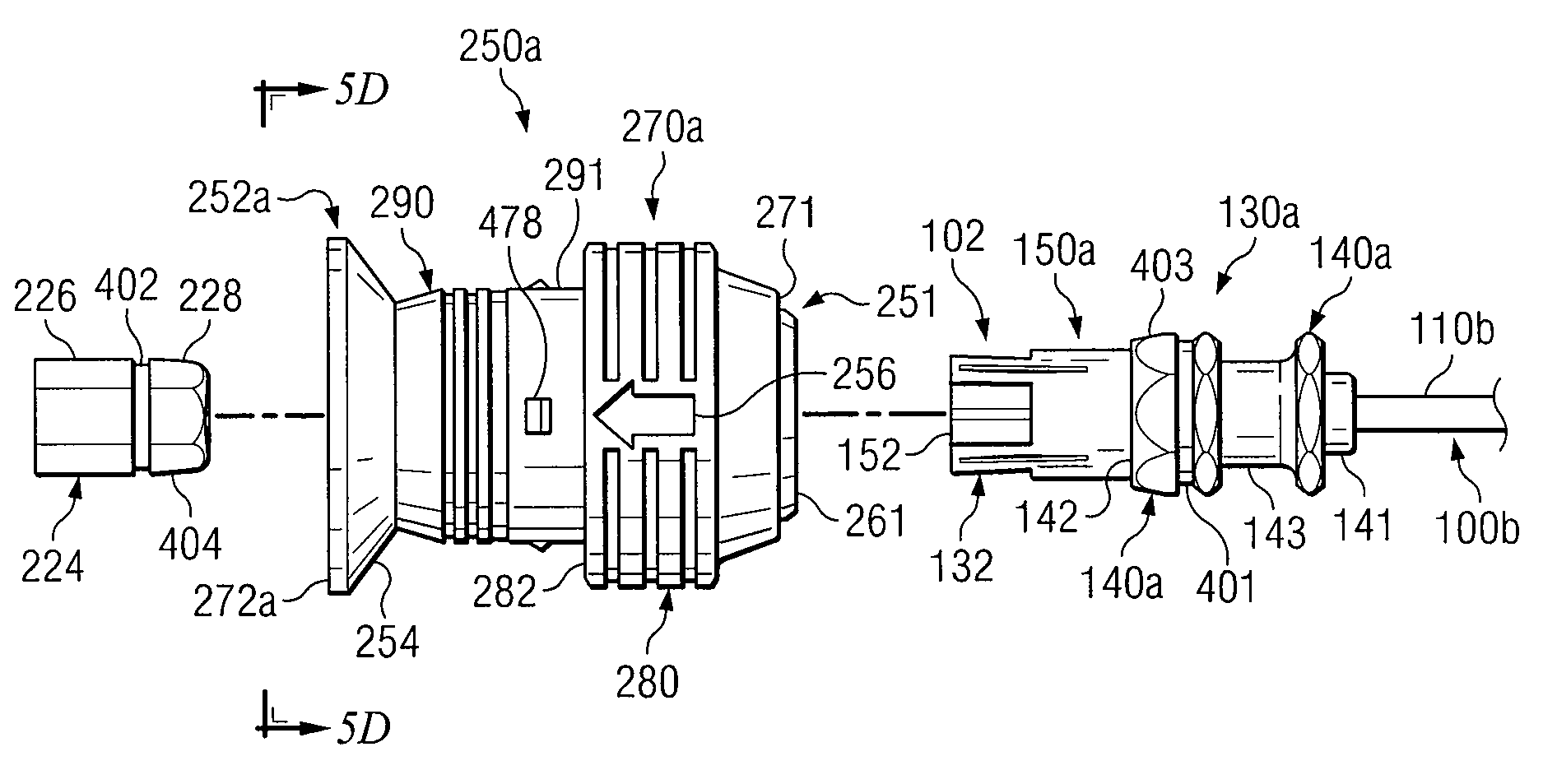
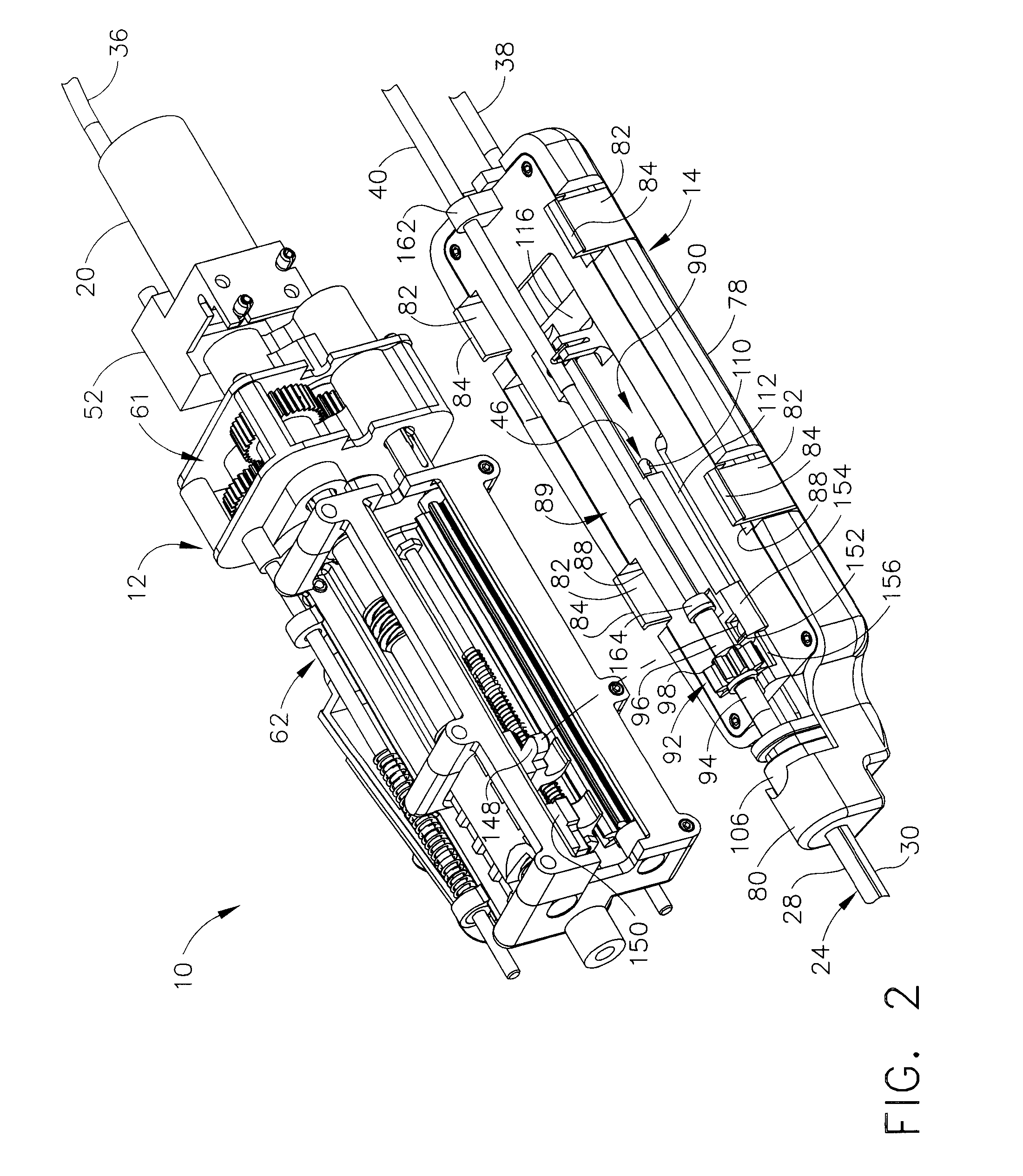
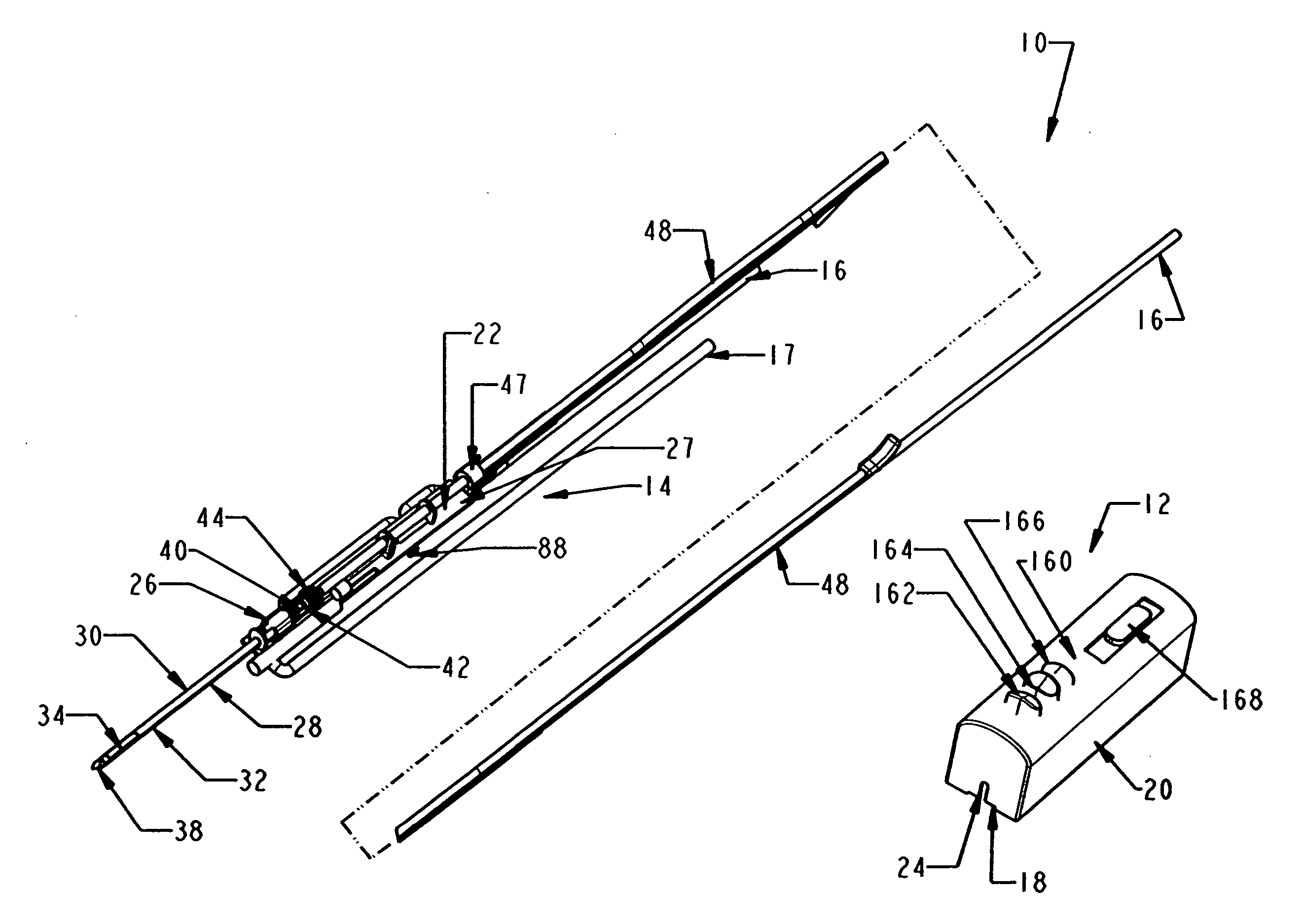
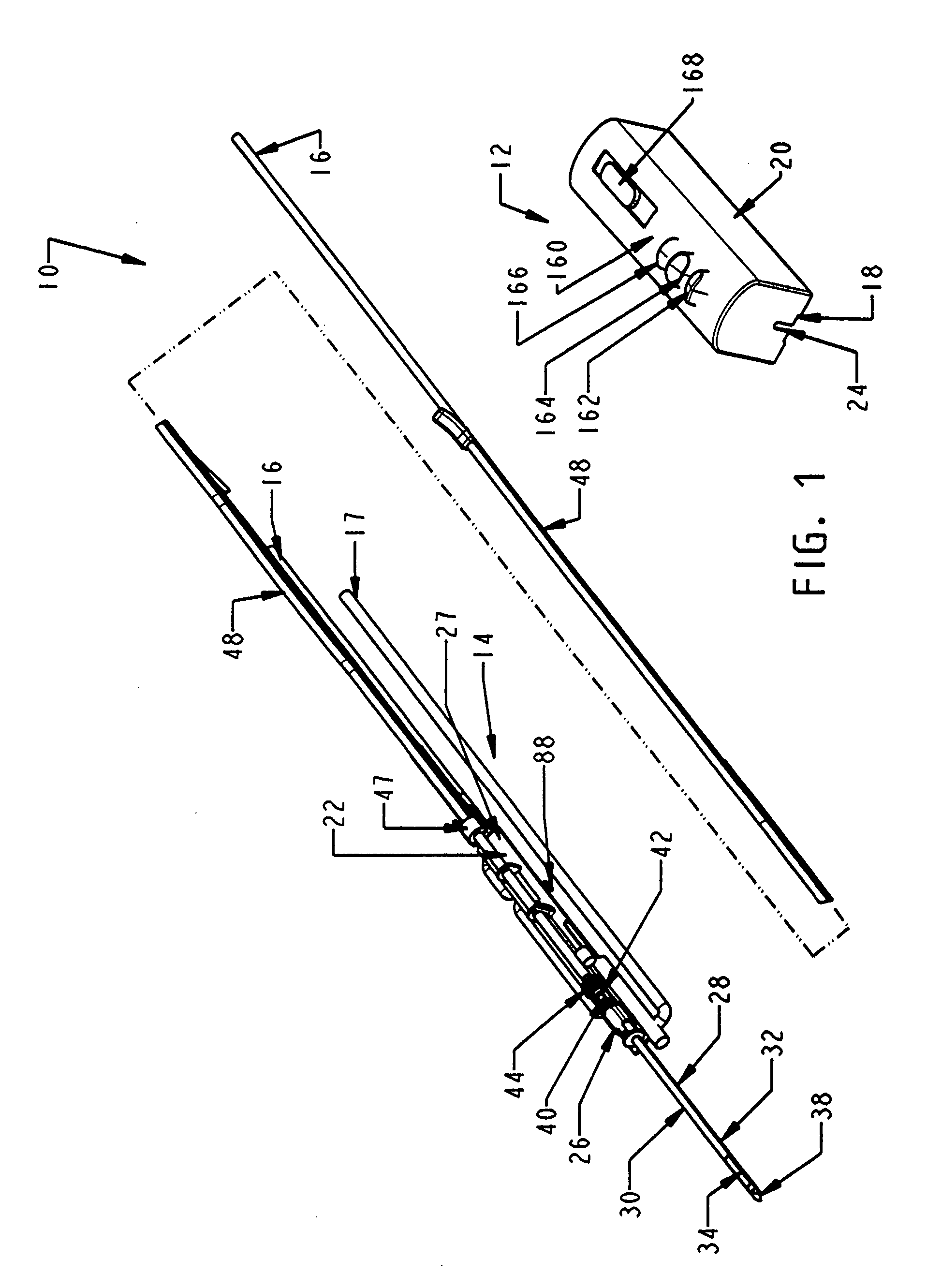
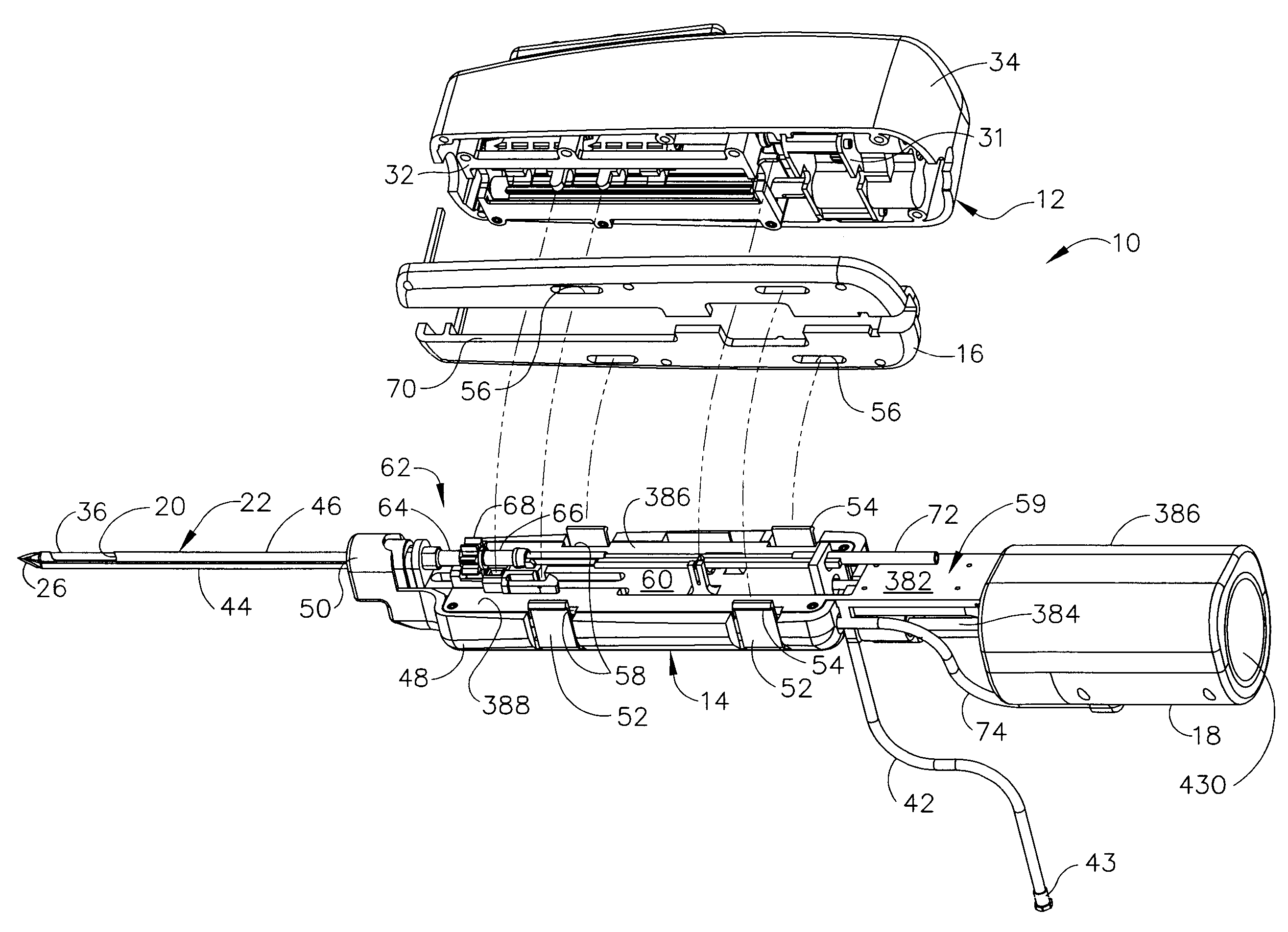
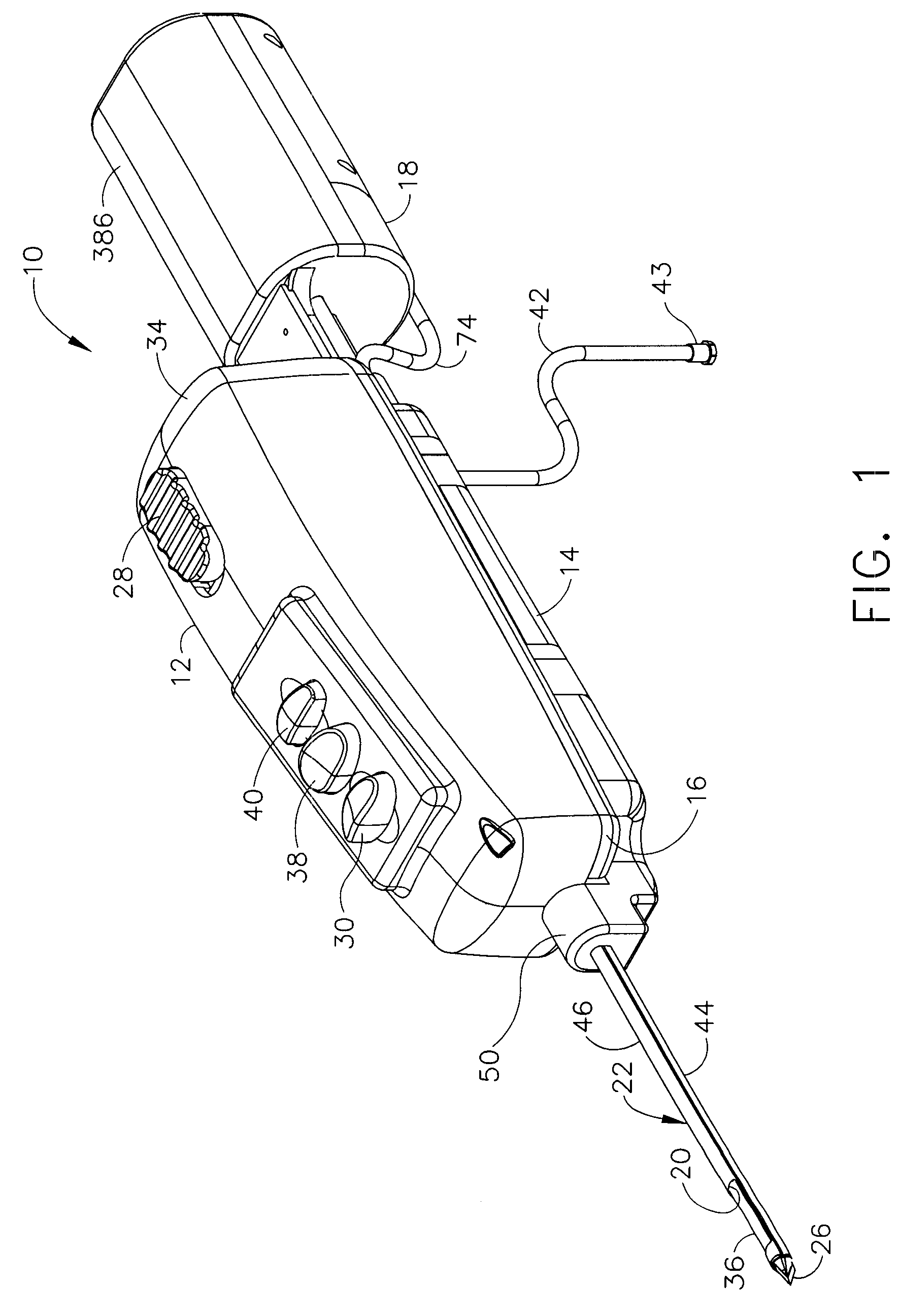
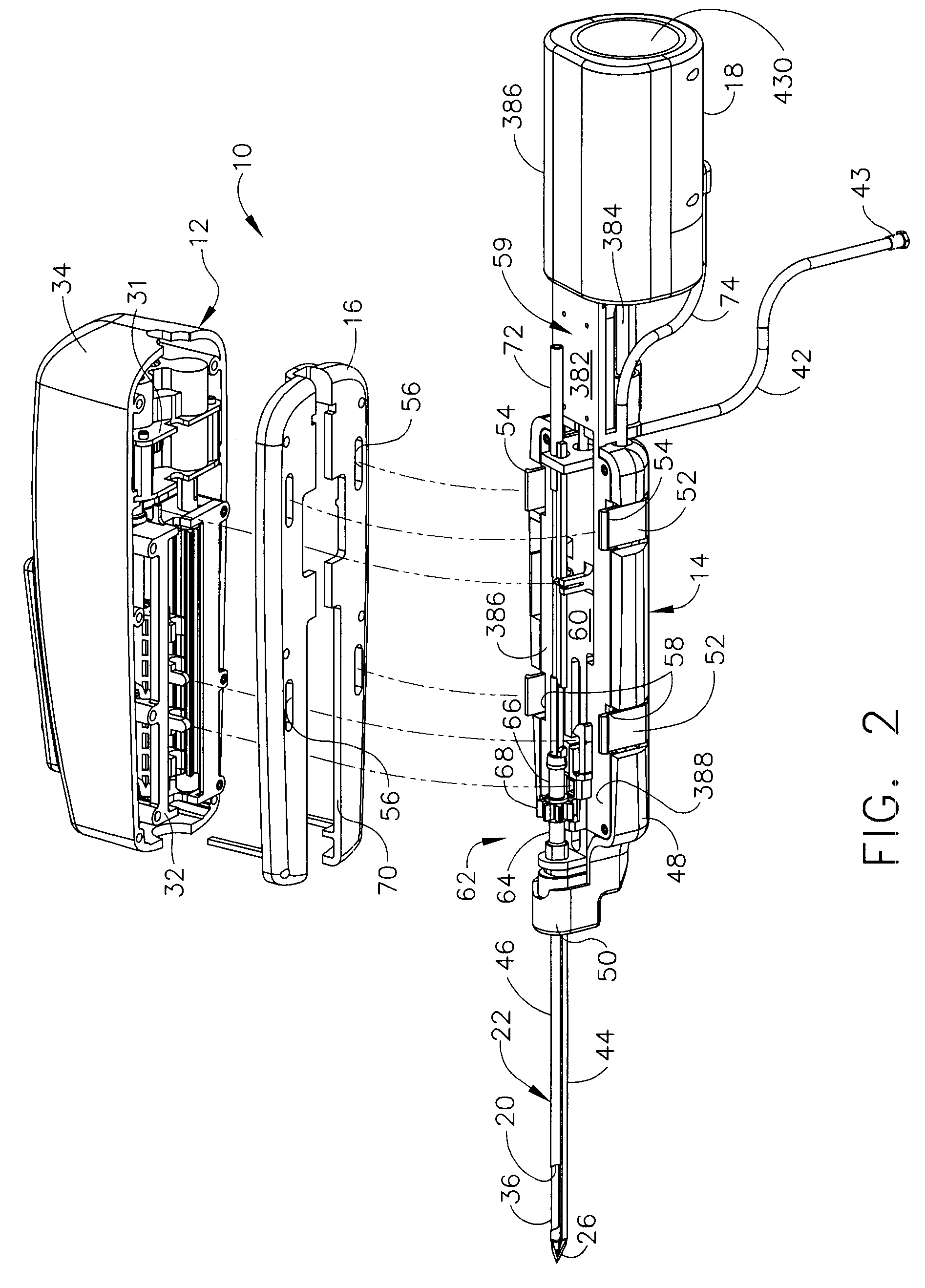
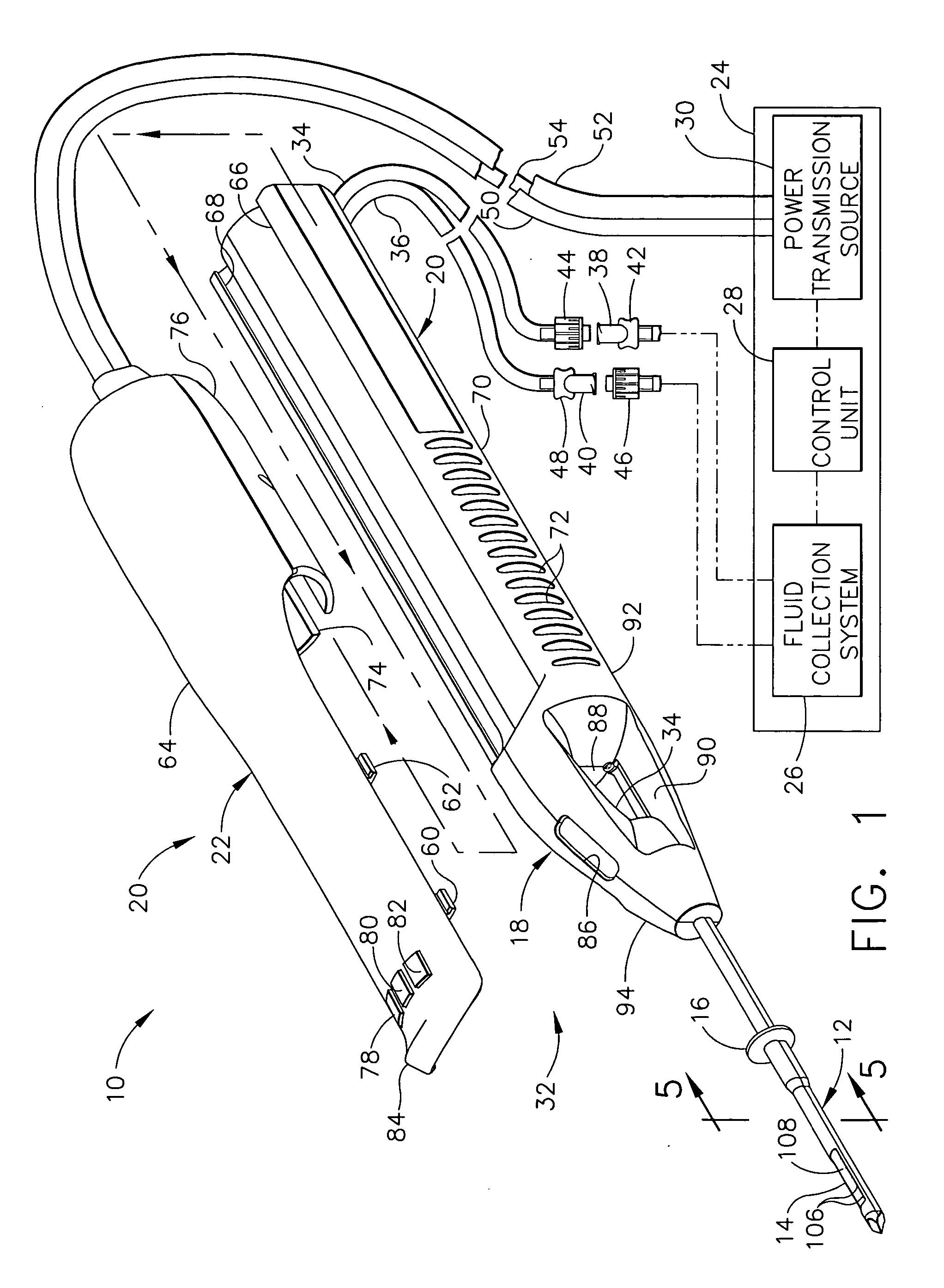
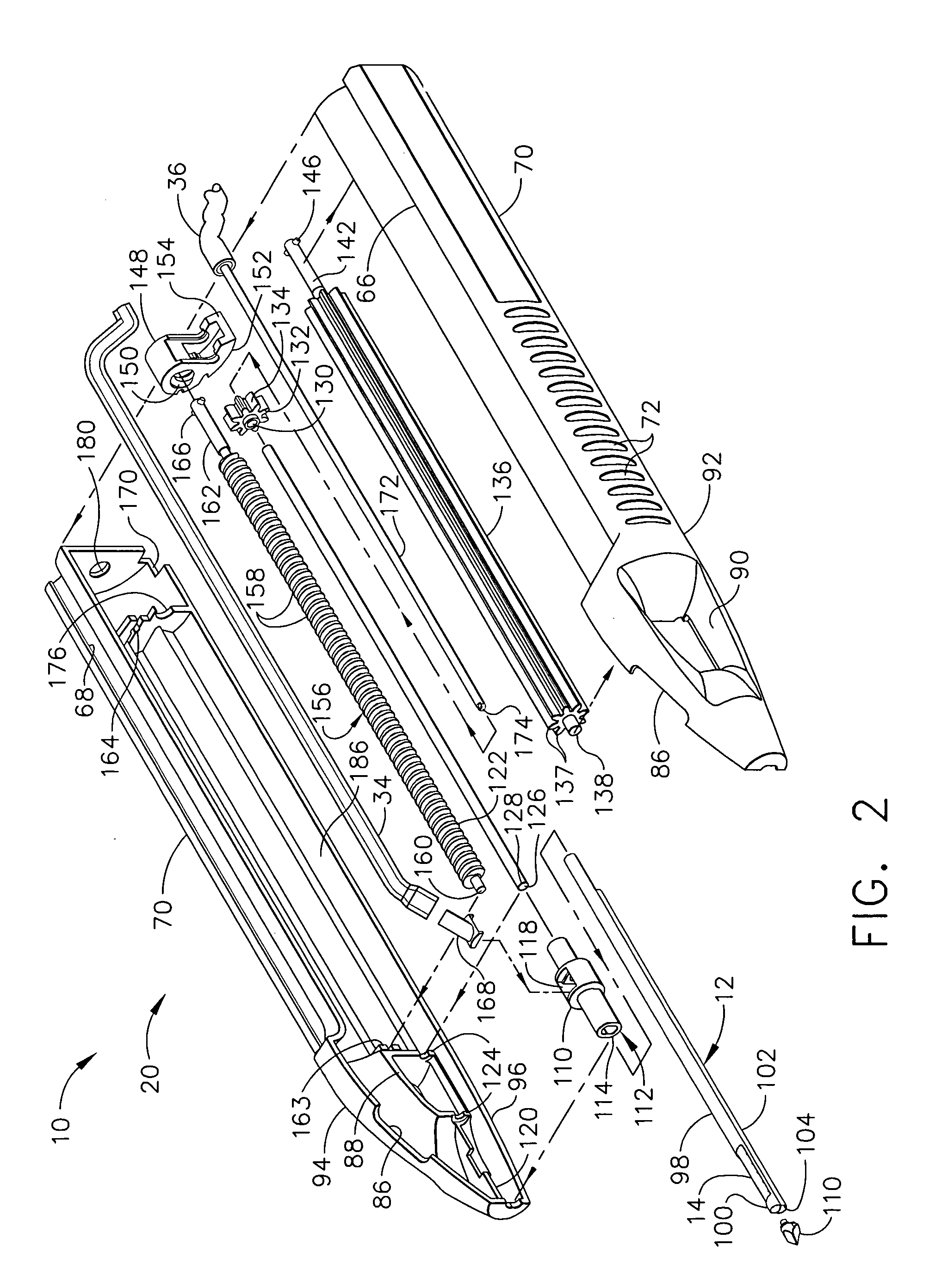
A core sampling biopsy device is compatible with use in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) environment by being driven by either a pneumatic rotary motor or a piezoelectric drive motor. The core sampling biopsy device obtains a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample, for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample. A cutter drive assembly maintains a fixed gear ratio relationship between a cutter rotation speed and translation speed of the inner cutter regardless of the density of the tissue encountered to yield consistent sample size.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Core sampling biopsy device with short coupled MRI-compatible driver
InactiveUS20060149163A1Reduce speedTranslation speed is decreasedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue sampleOuter Cannula
A core sampling biopsy device is compatible with use in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) environment by being driven by either a pneumatic rotary motor or a piezoelectric drive motor. The core sampling biopsy device obtains a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample, for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
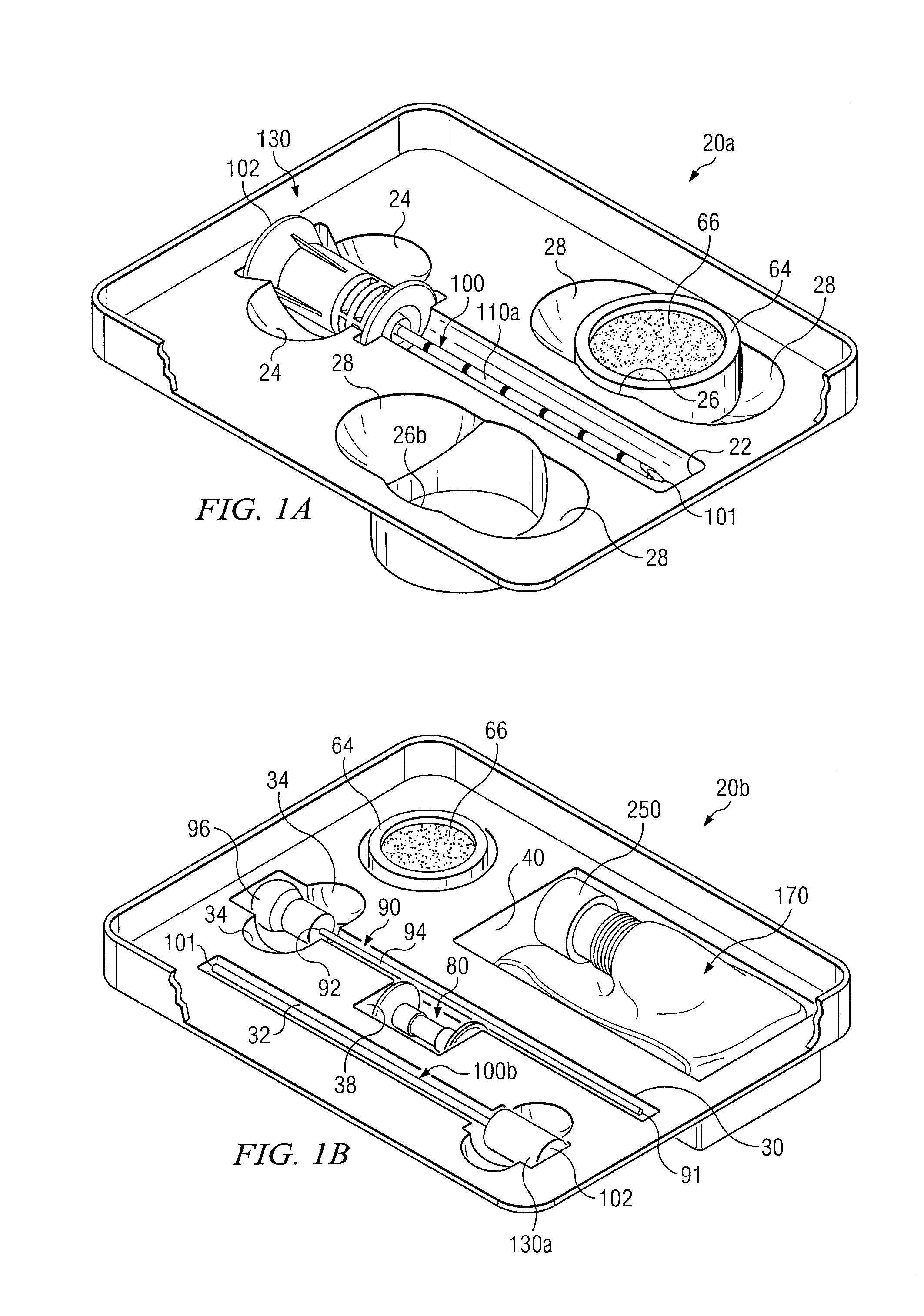
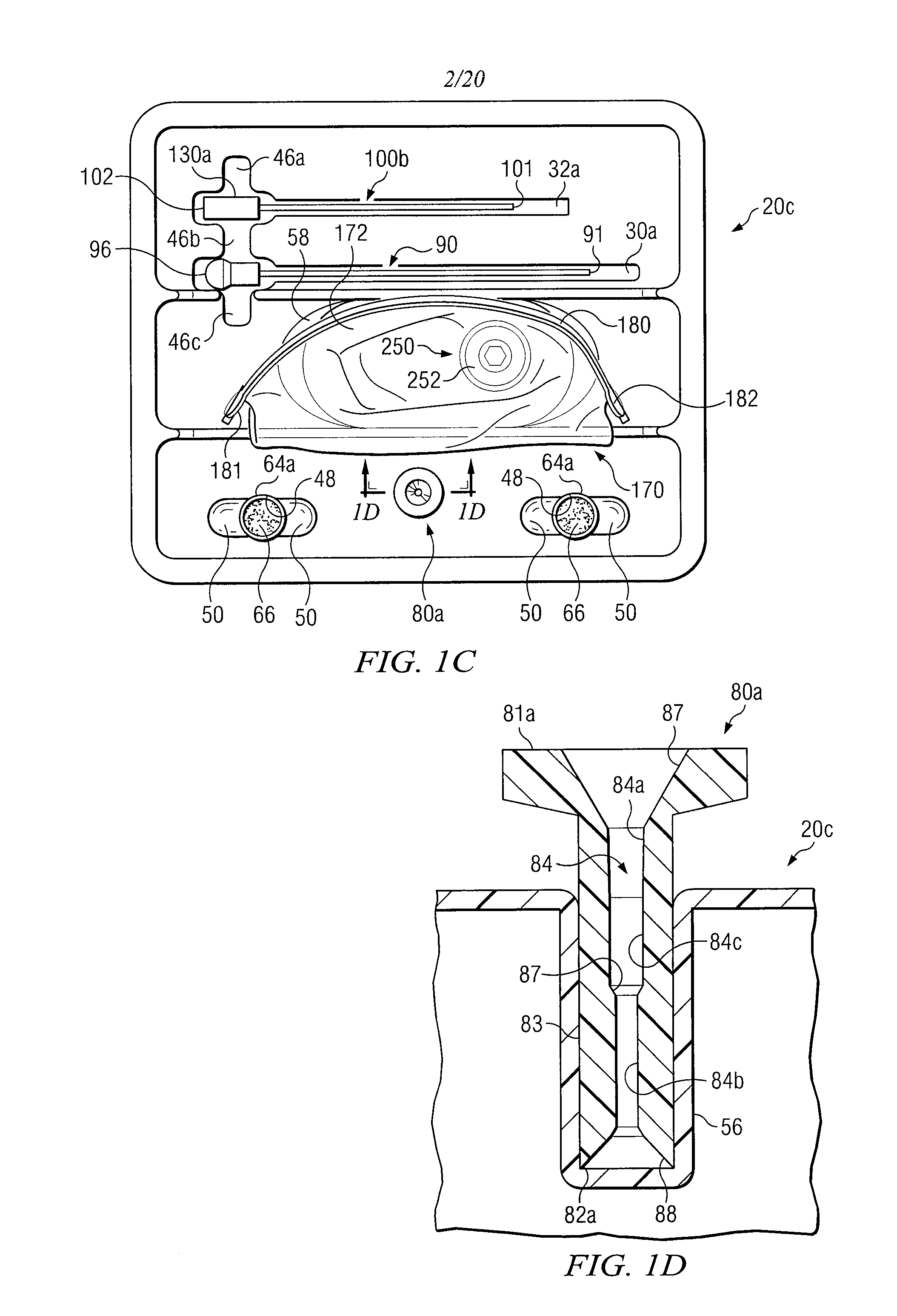
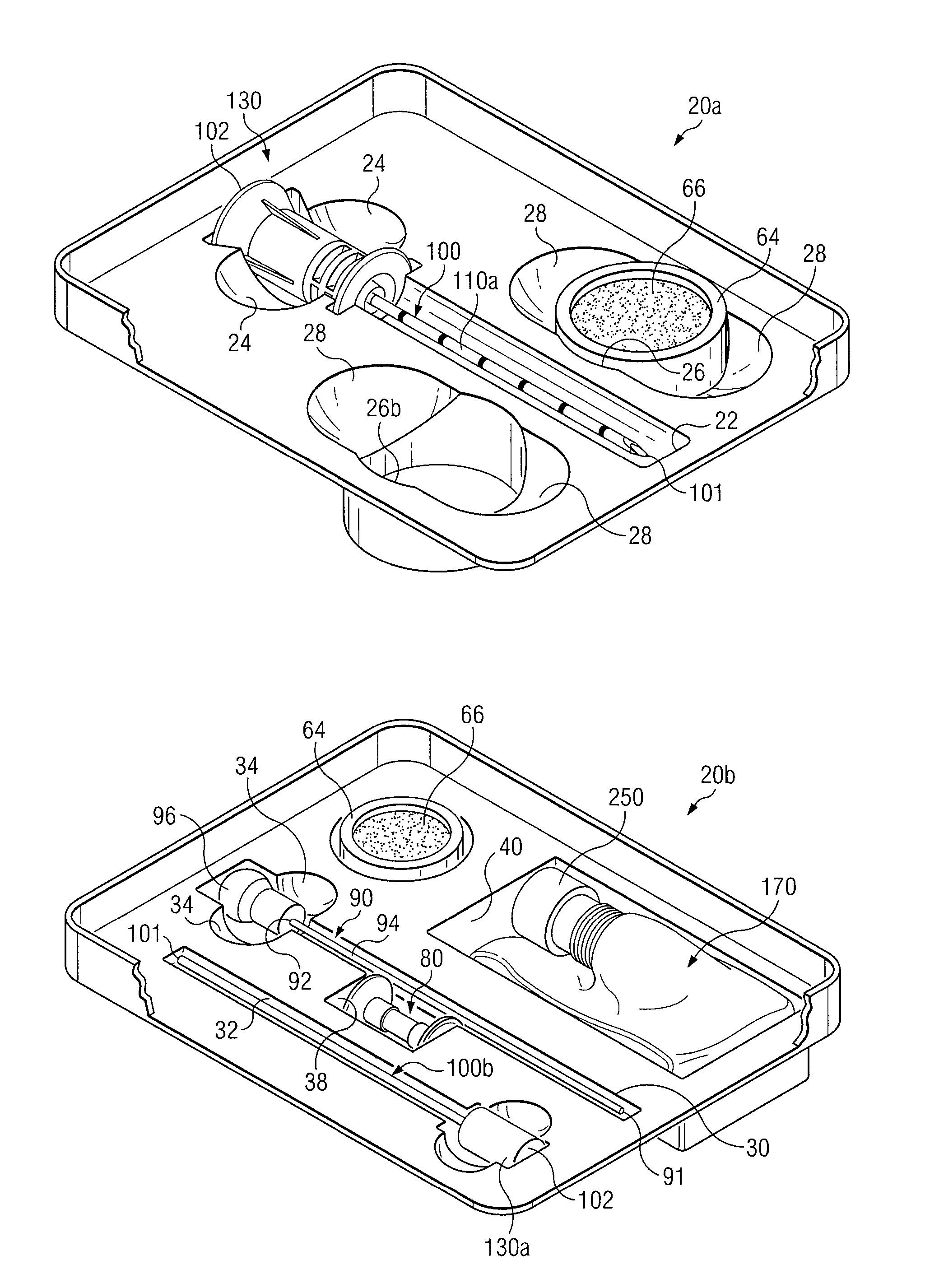
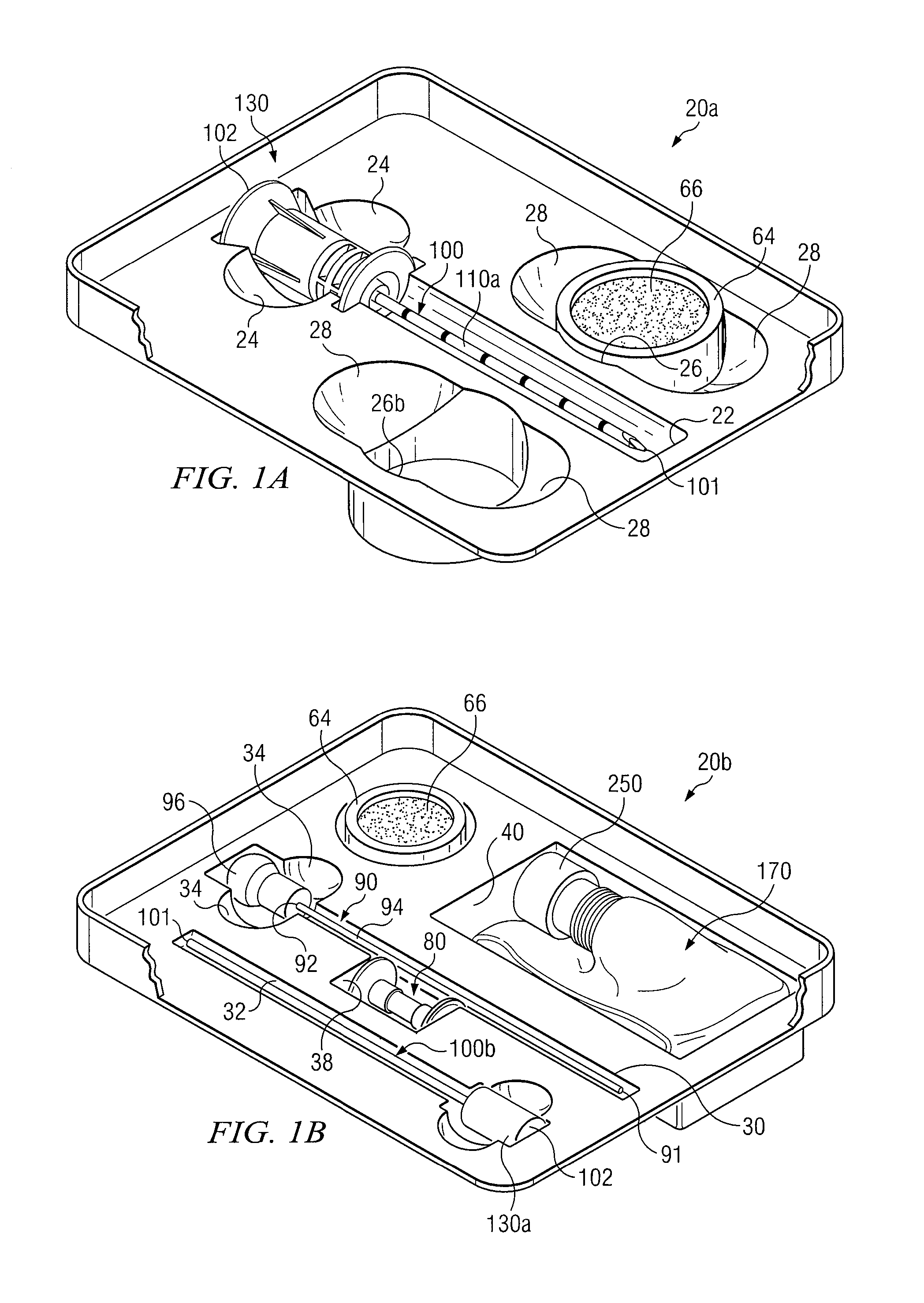
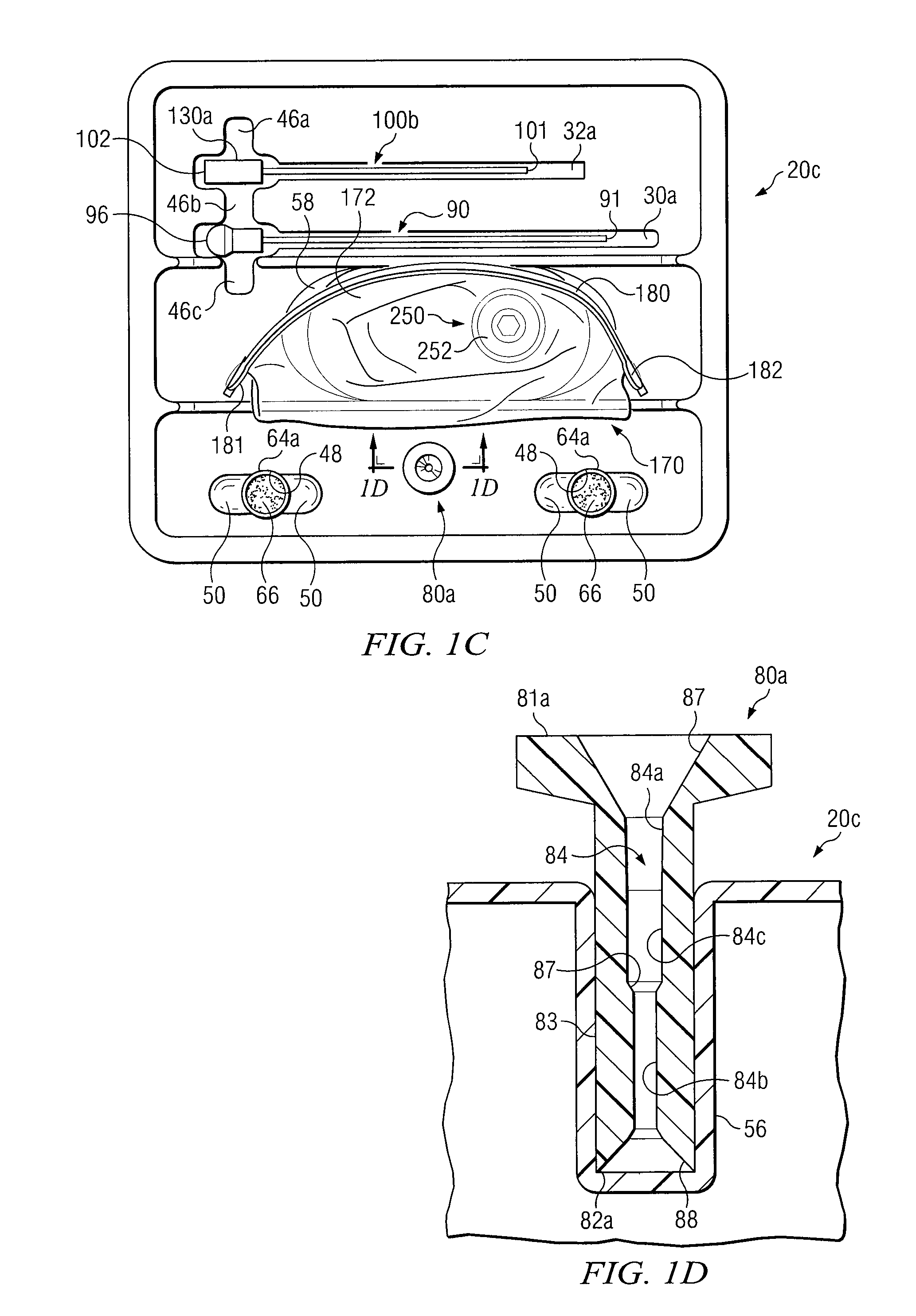
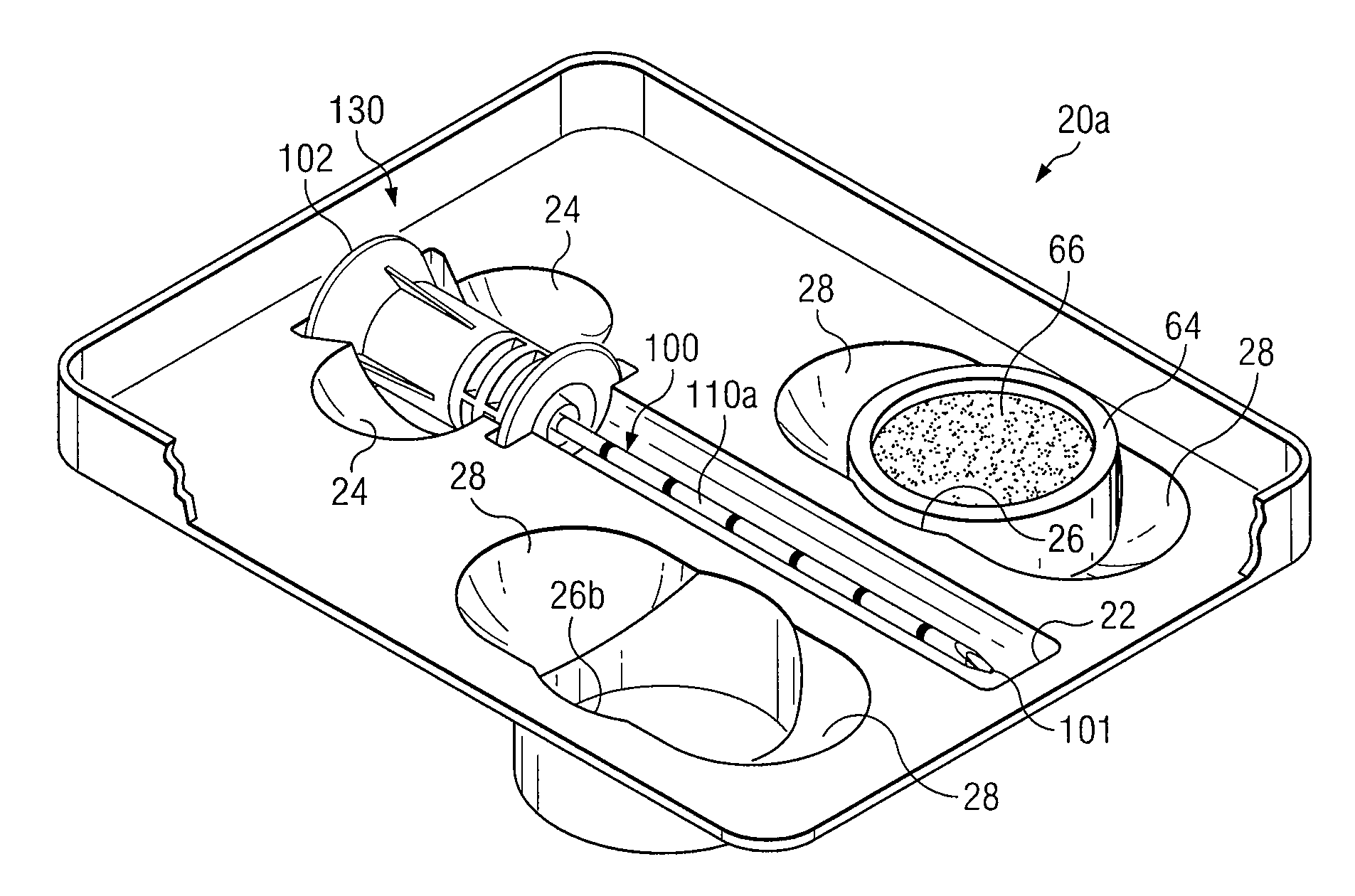
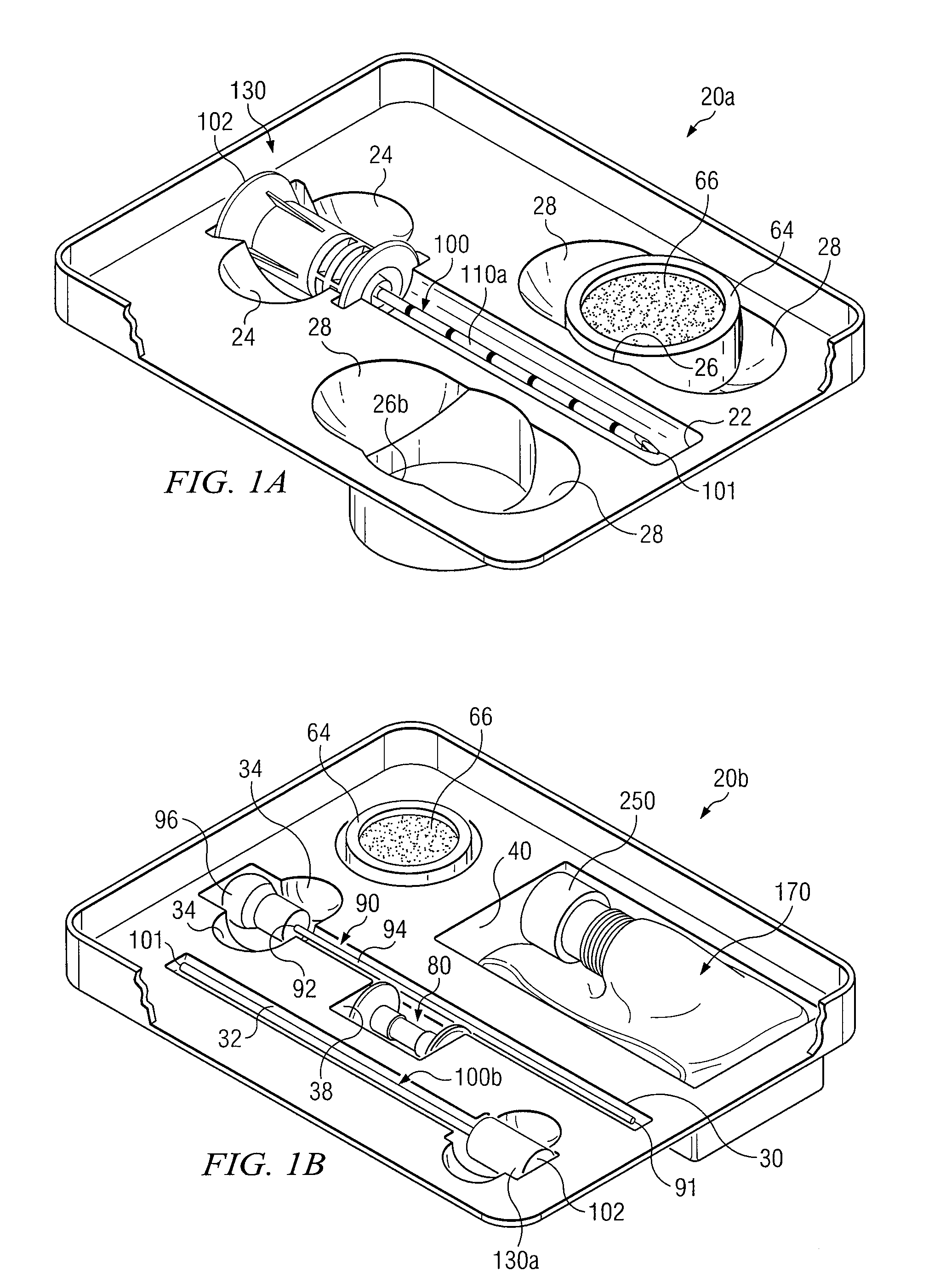
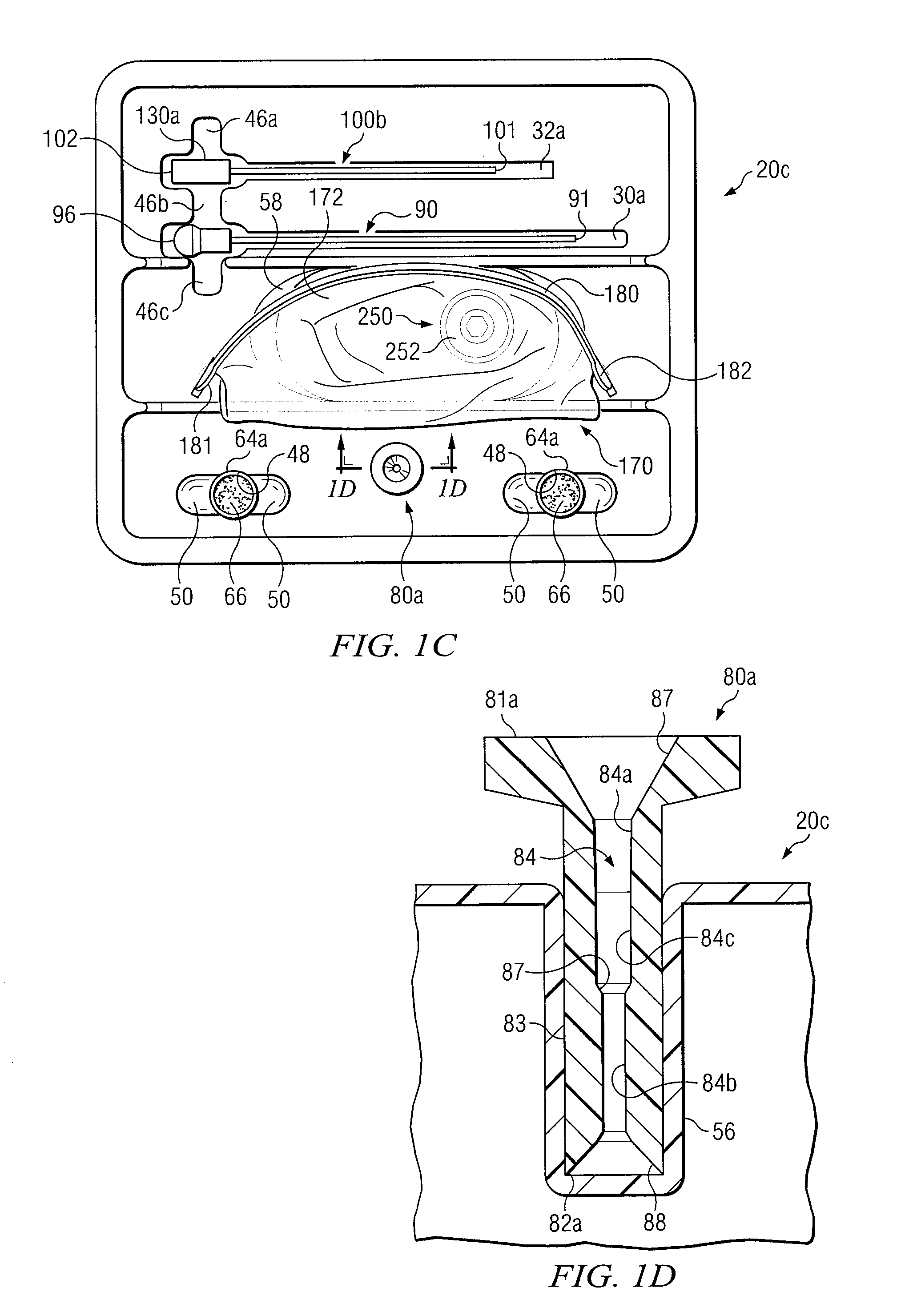
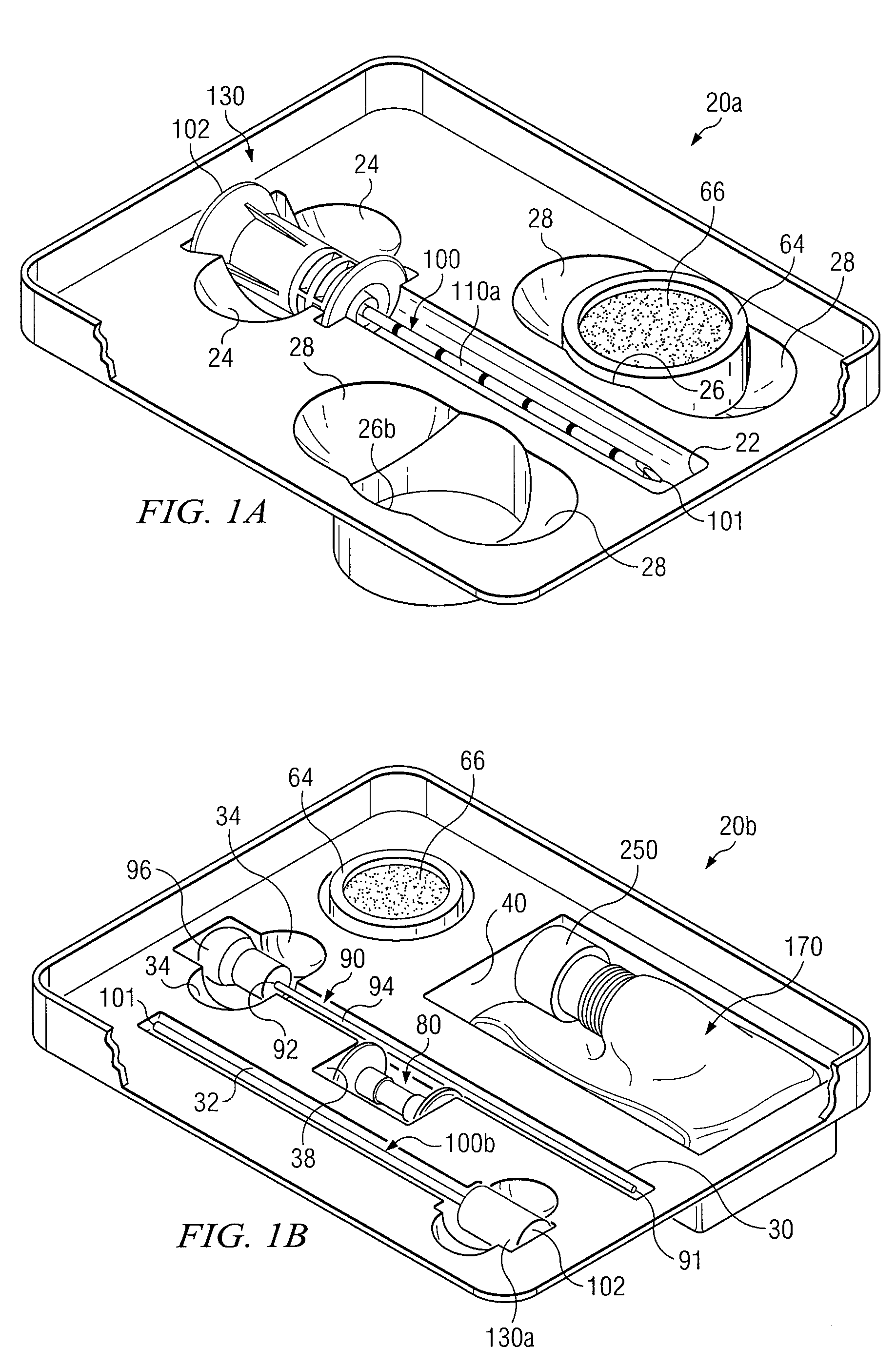
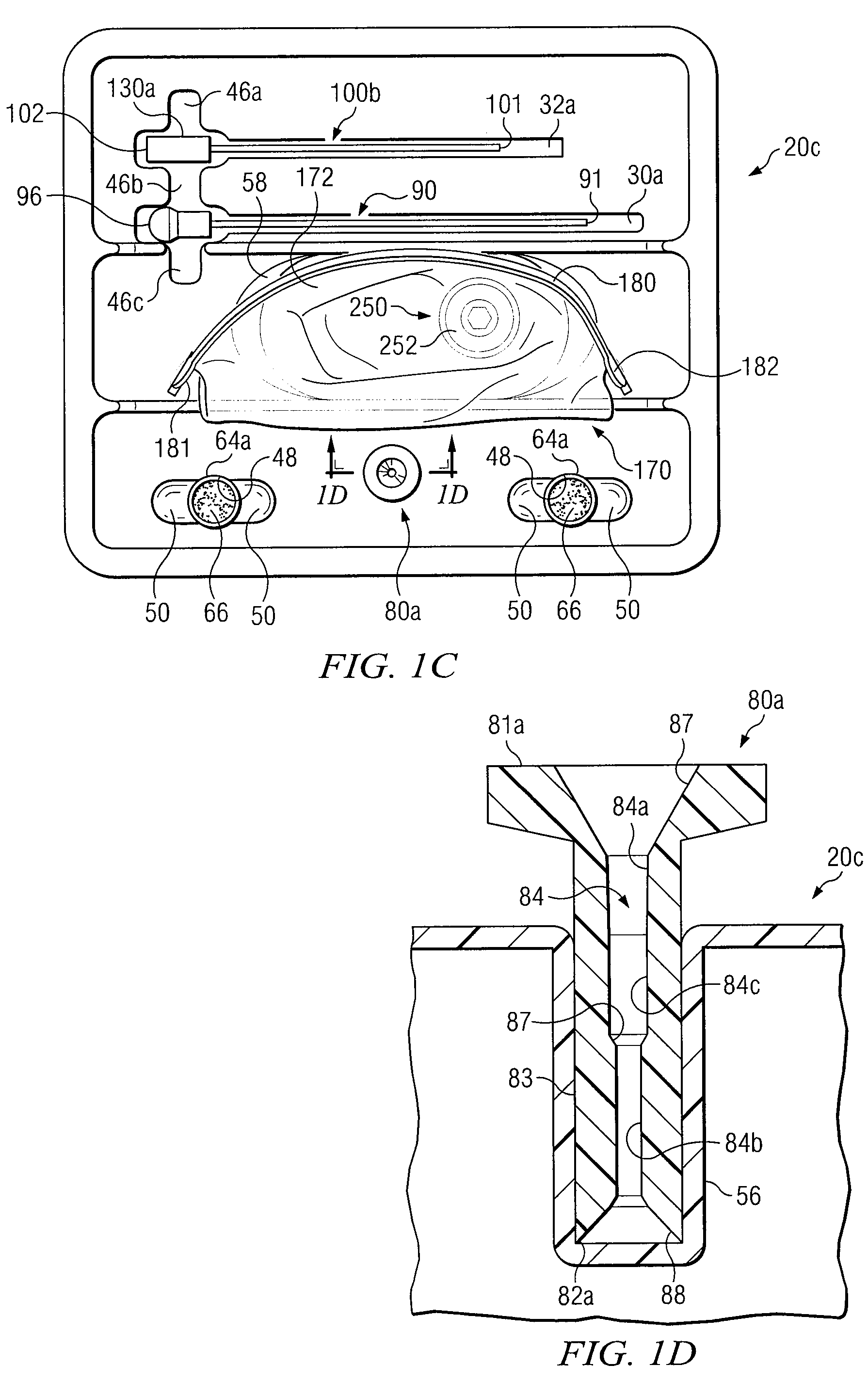
Medical procedures trays and related methods
ActiveUS8656929B2Easy to captureIncrease speedSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusTransplant ProcedureSurgery
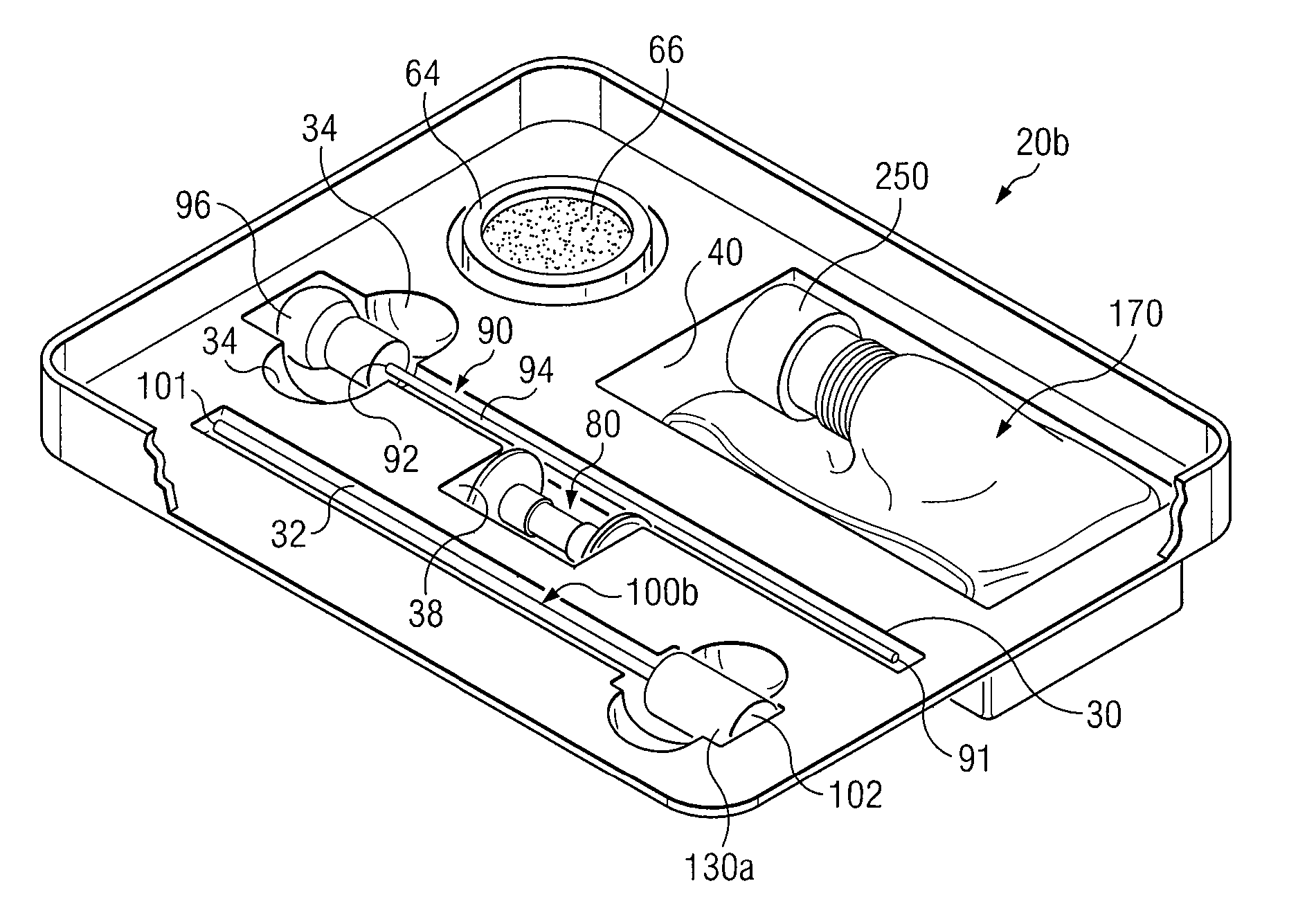
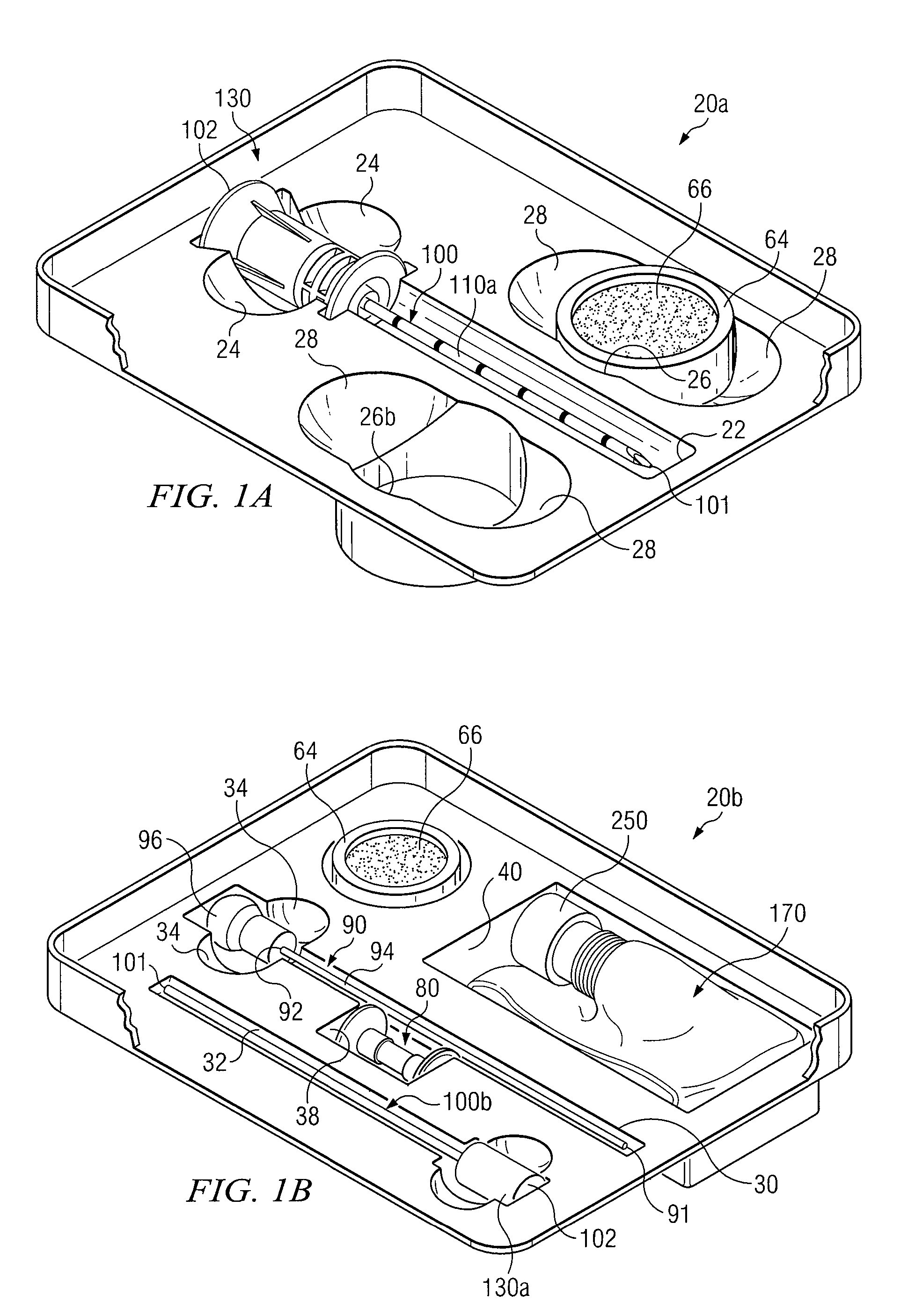
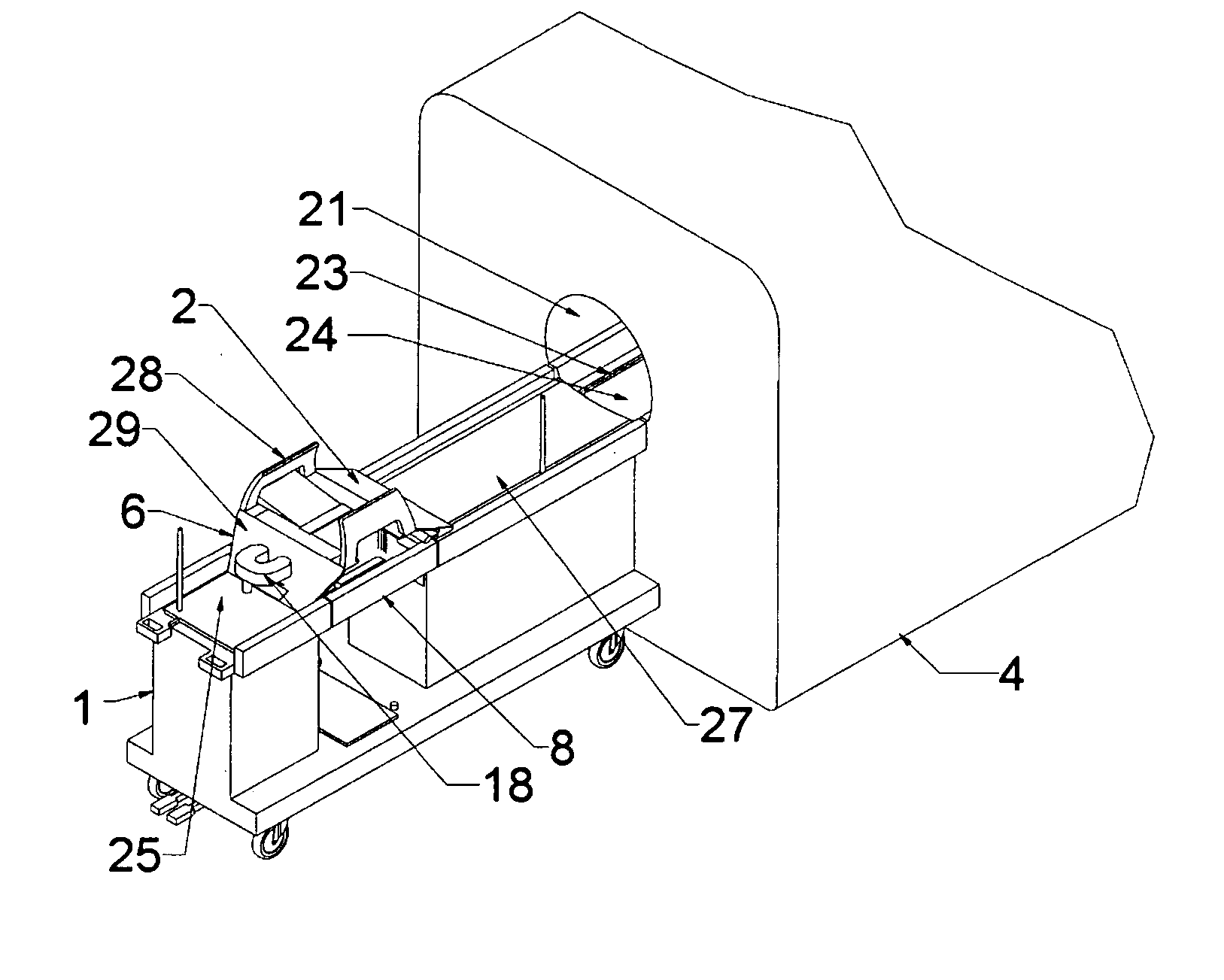
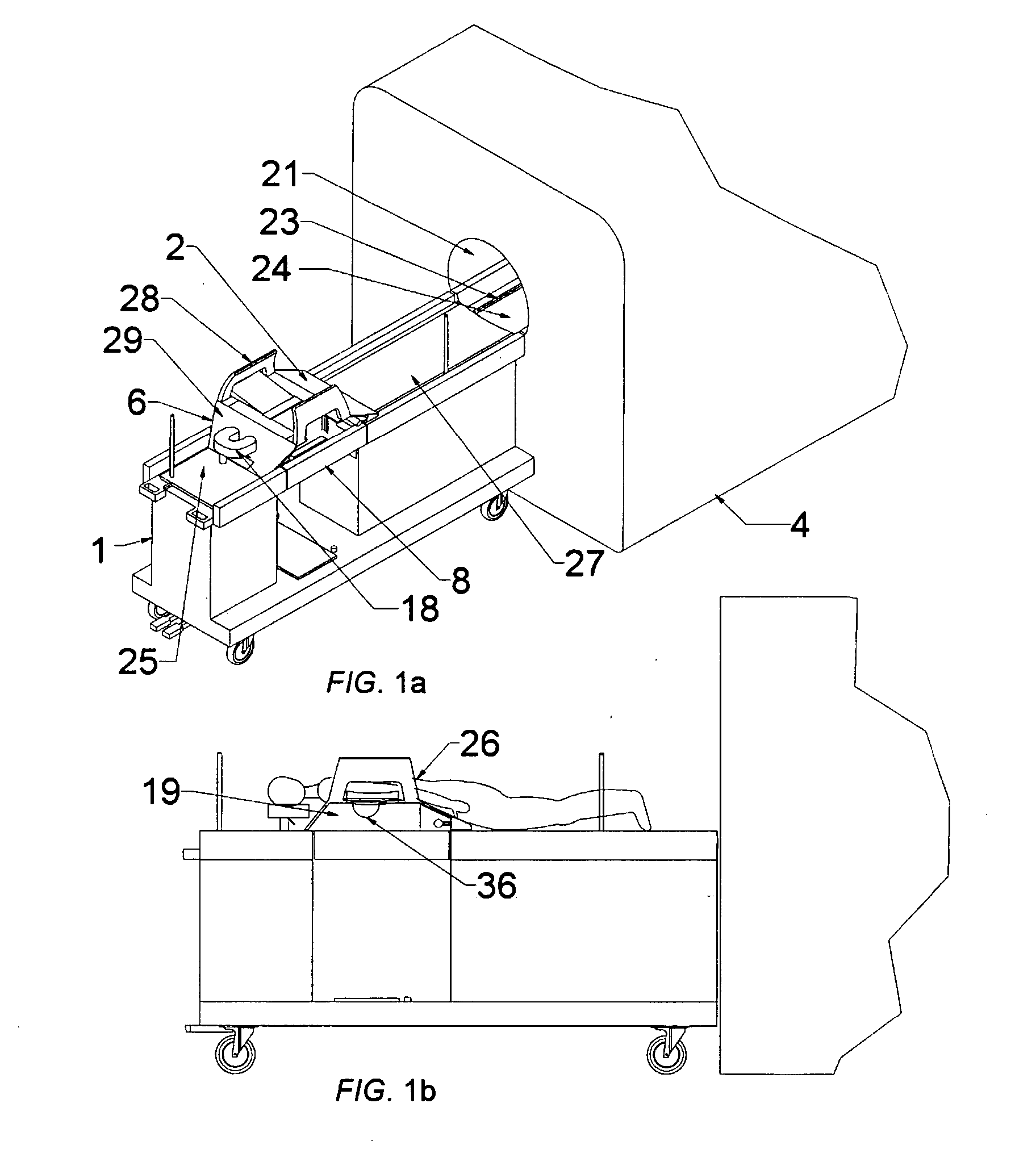
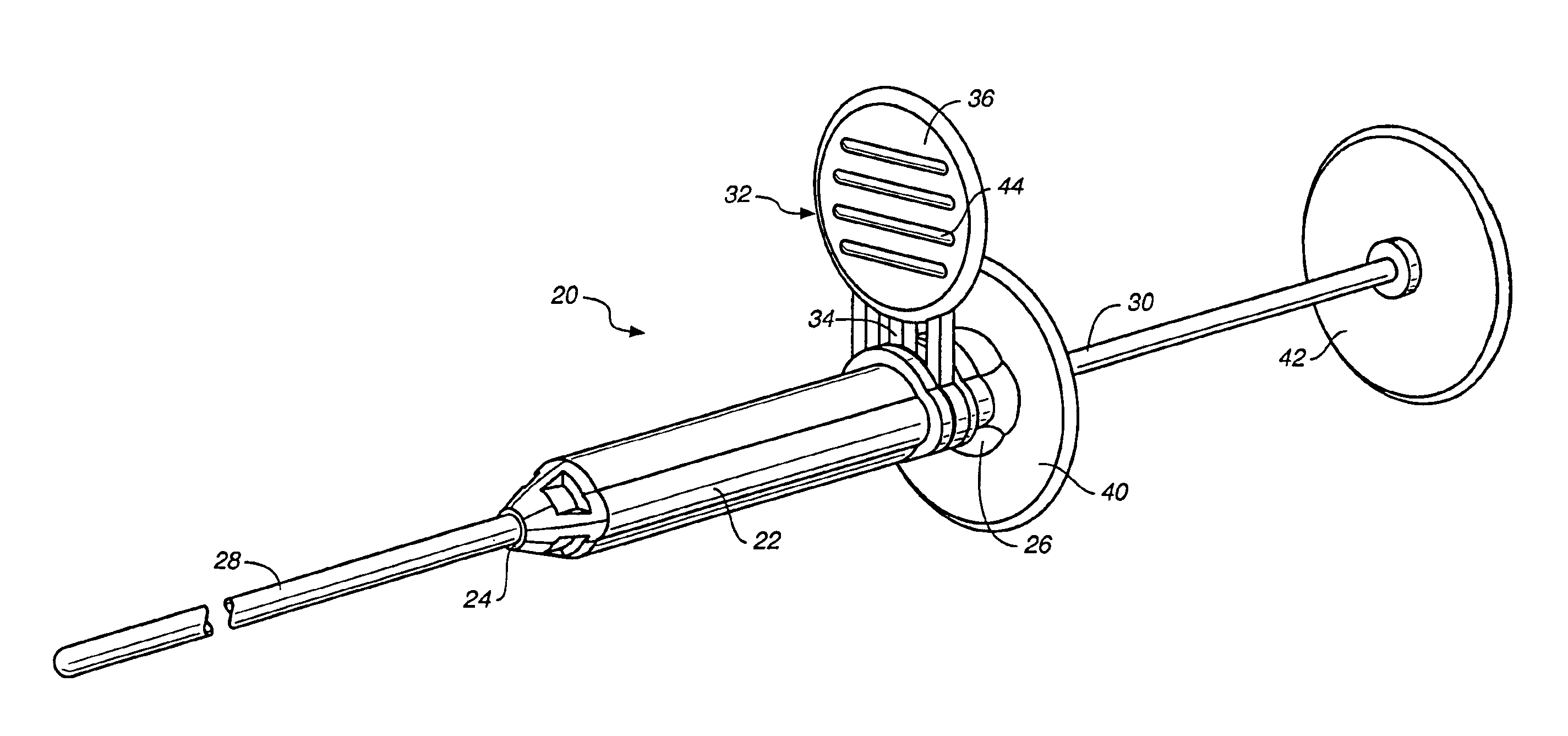
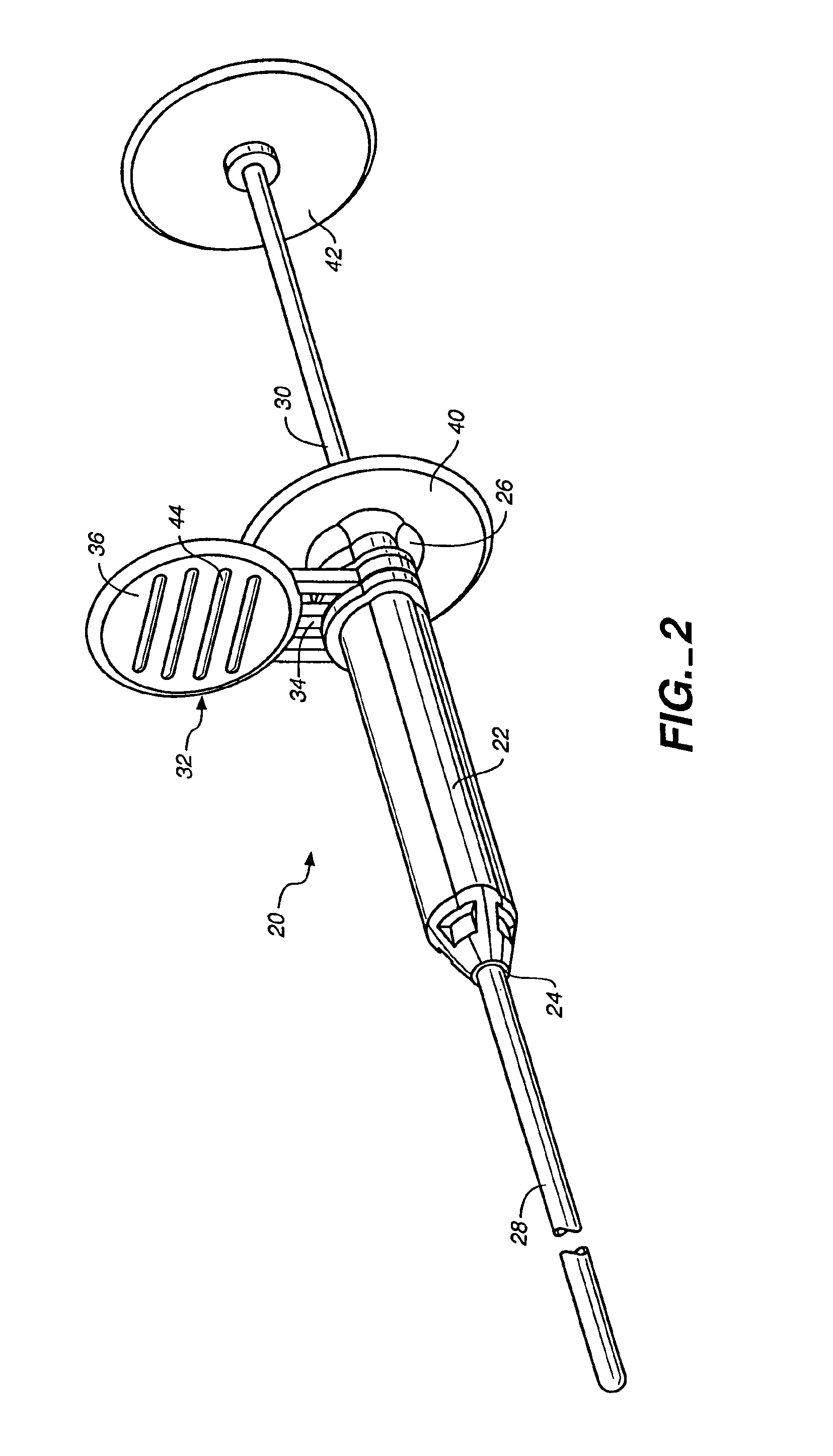
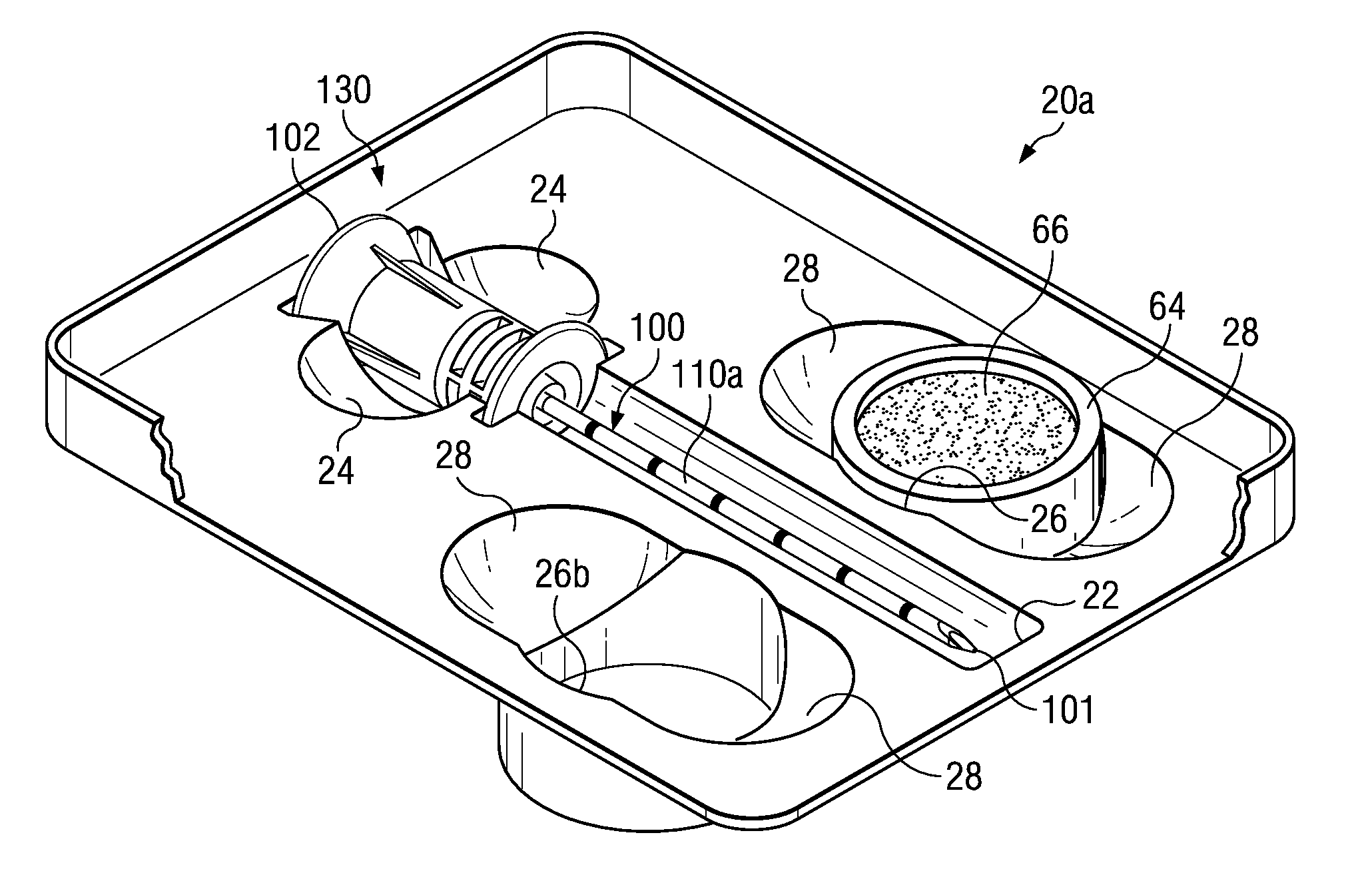
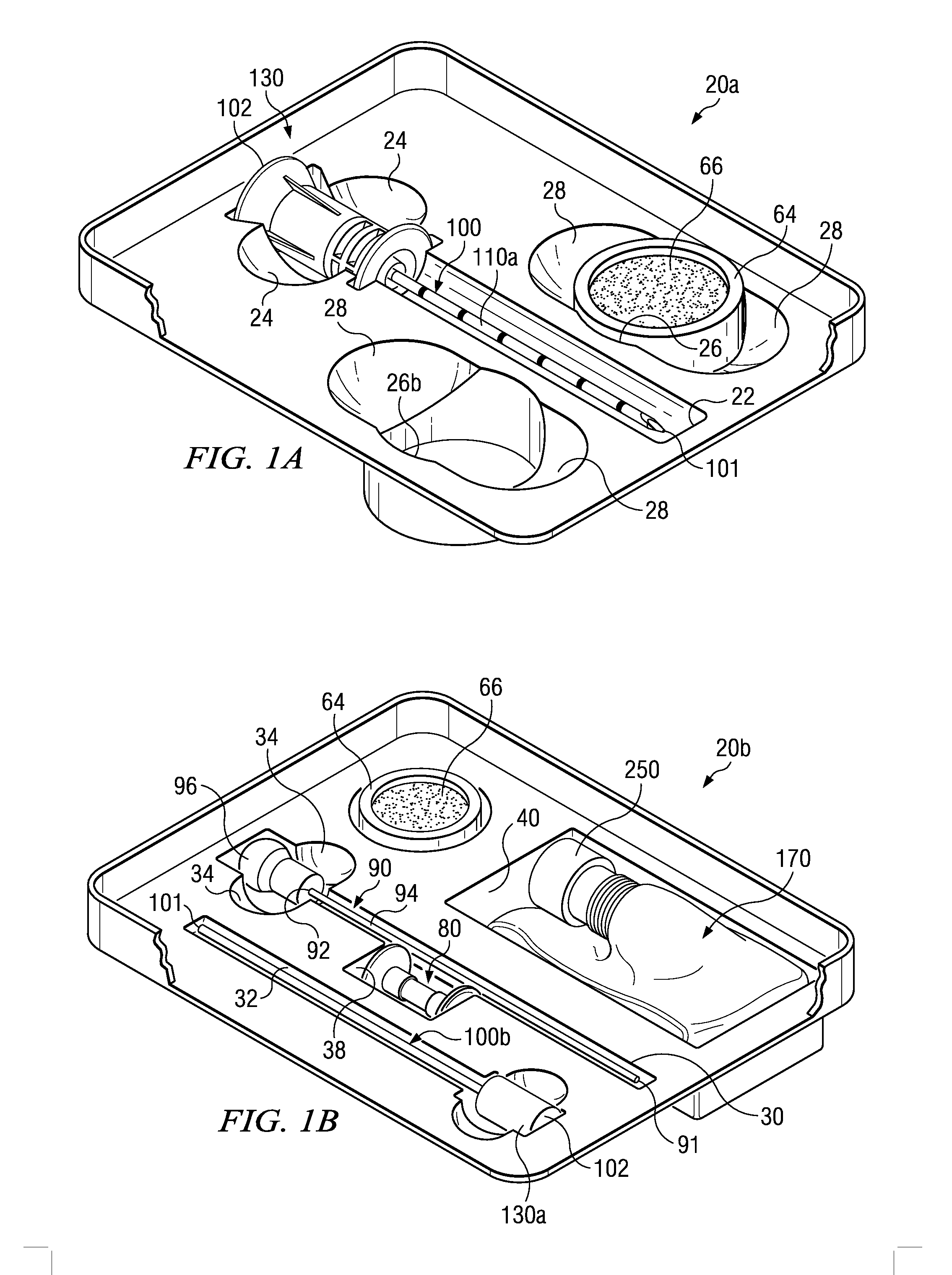
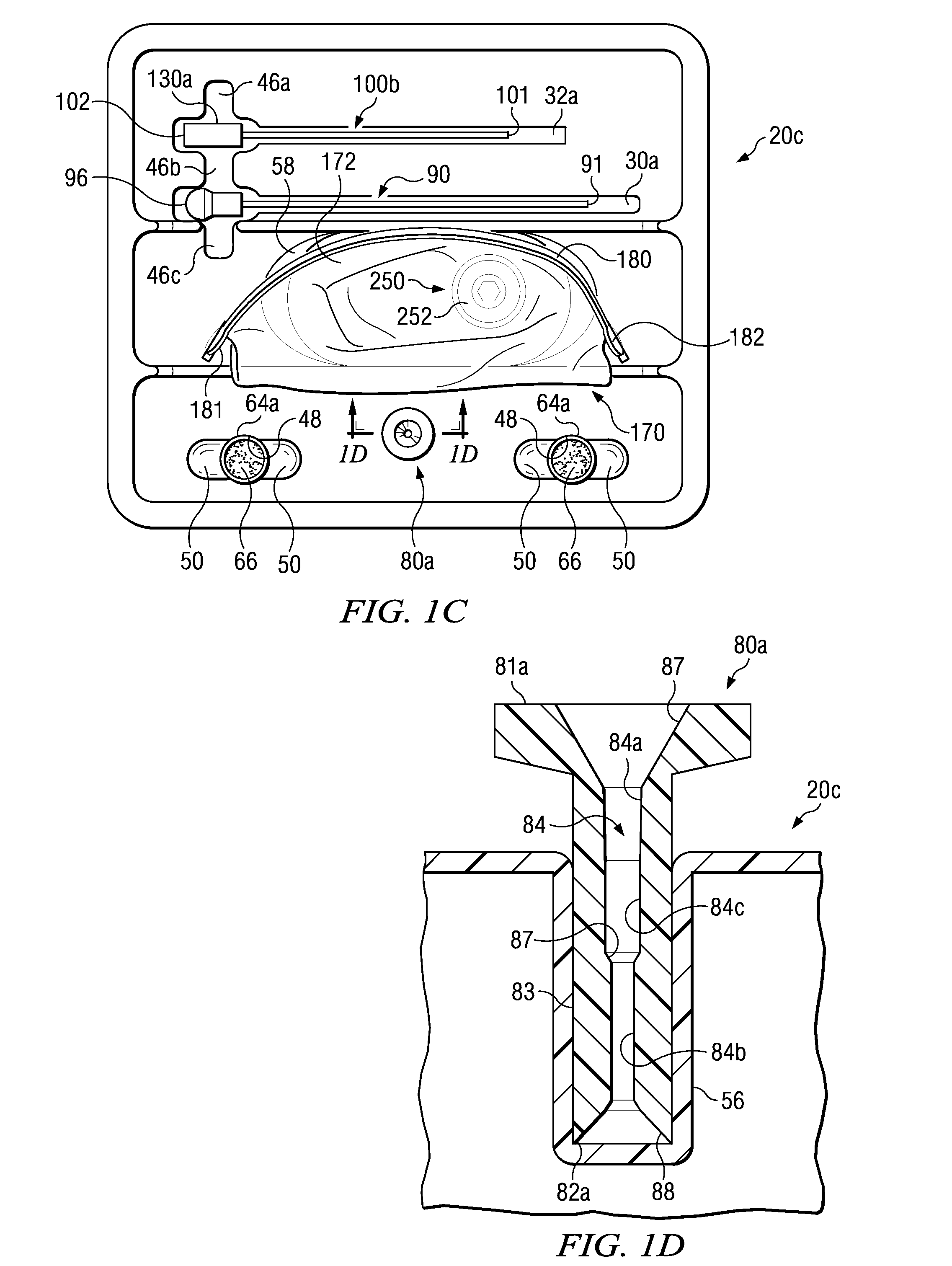
Medical procedure trays and related methods are provided to accommodate joining a first non-sterile medical device with a second sterile medical device and maintaining required sterilization of the second sterile medical device to perform an associated medical procedure. One example of such medical procedures includes biopsy of a bone and / or associated bone marrow using a non-sterile powered drive and a sterile biopsy needle or biopsy needle set. Medical procedure trays and related methods may also be provided for use during aspiration of bone marrow and / or stem cell transplant procedures. Each medical procedure tray may include a containment bag or sterile sleeve. A coupler assembly, one or more sharps protectors, a biopsy sample ejector and / or associated ejector funnel may also be included. Some medical procedure trays may allow engaging a non-sterile powered driver with one end of a coupler assembly and sealing the non-sterile powered driver in a sterile sleeve or containment bag without compromising sterility of other components in the medical procedure tray.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Biopsy sampler
The invention features an assembly for taking a biopsy sample from a site within the body of a patient. The assembly includes a resecting device having a cutter near its distal end for resecting and containing a tissue sample and a sheath exterior to the resecting device and sized to be present within the body with the resecting device. The sheath includes an electrode element electrically isolated from the resecting device and disposed on the sheath's outer surface for cauterizing tissue. The electrode element may reside on the outer sheath, the distal end or both the outer sheath and the distal end of the assembly. The resecting device and the sheath cooperate to permit sequential resecting of a tissue sample from a resecting site and cauterizing of the site with the cutter sufficiently spaced from the electrode element to avoid heat damage to the tissue sample.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
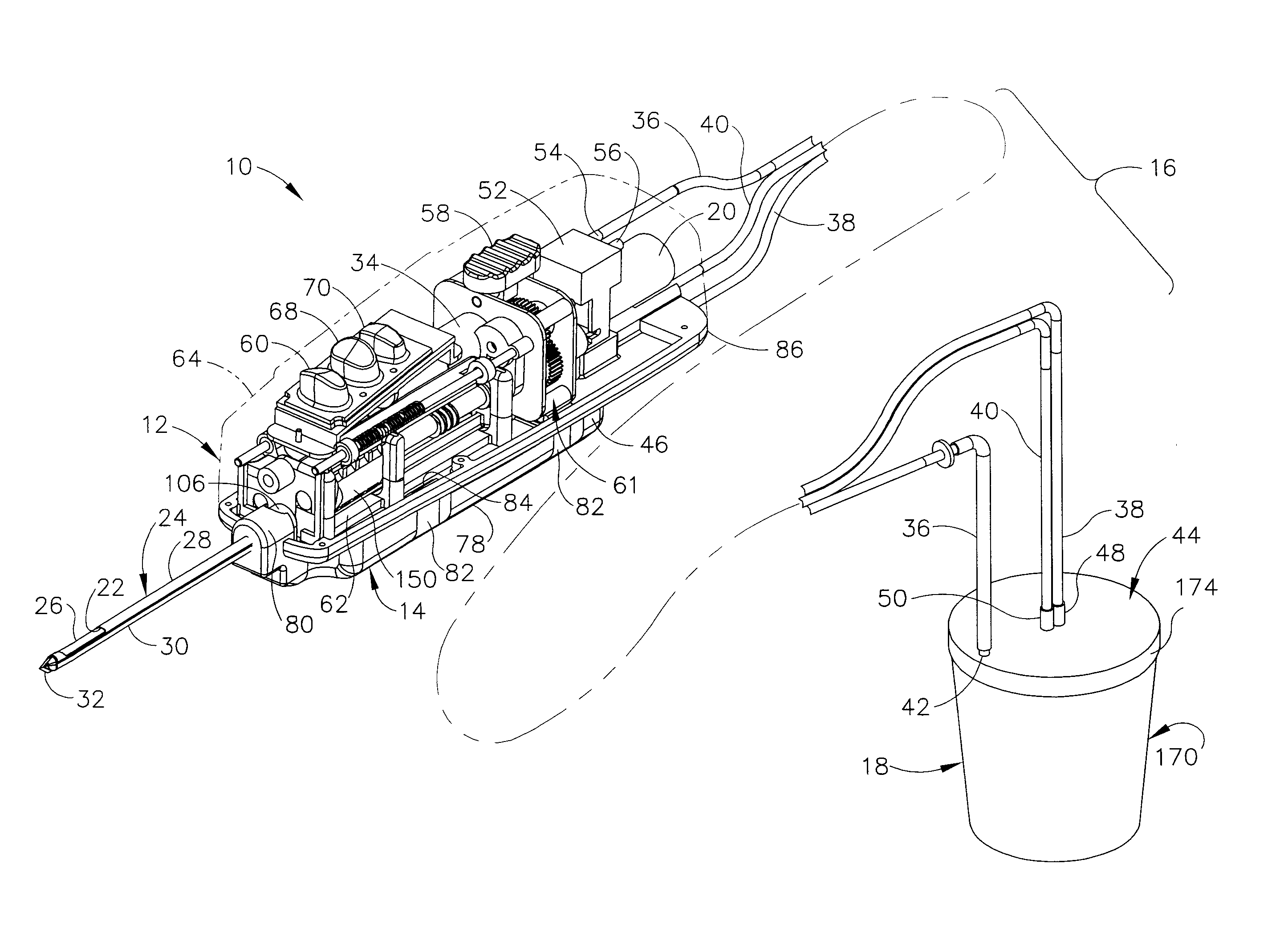
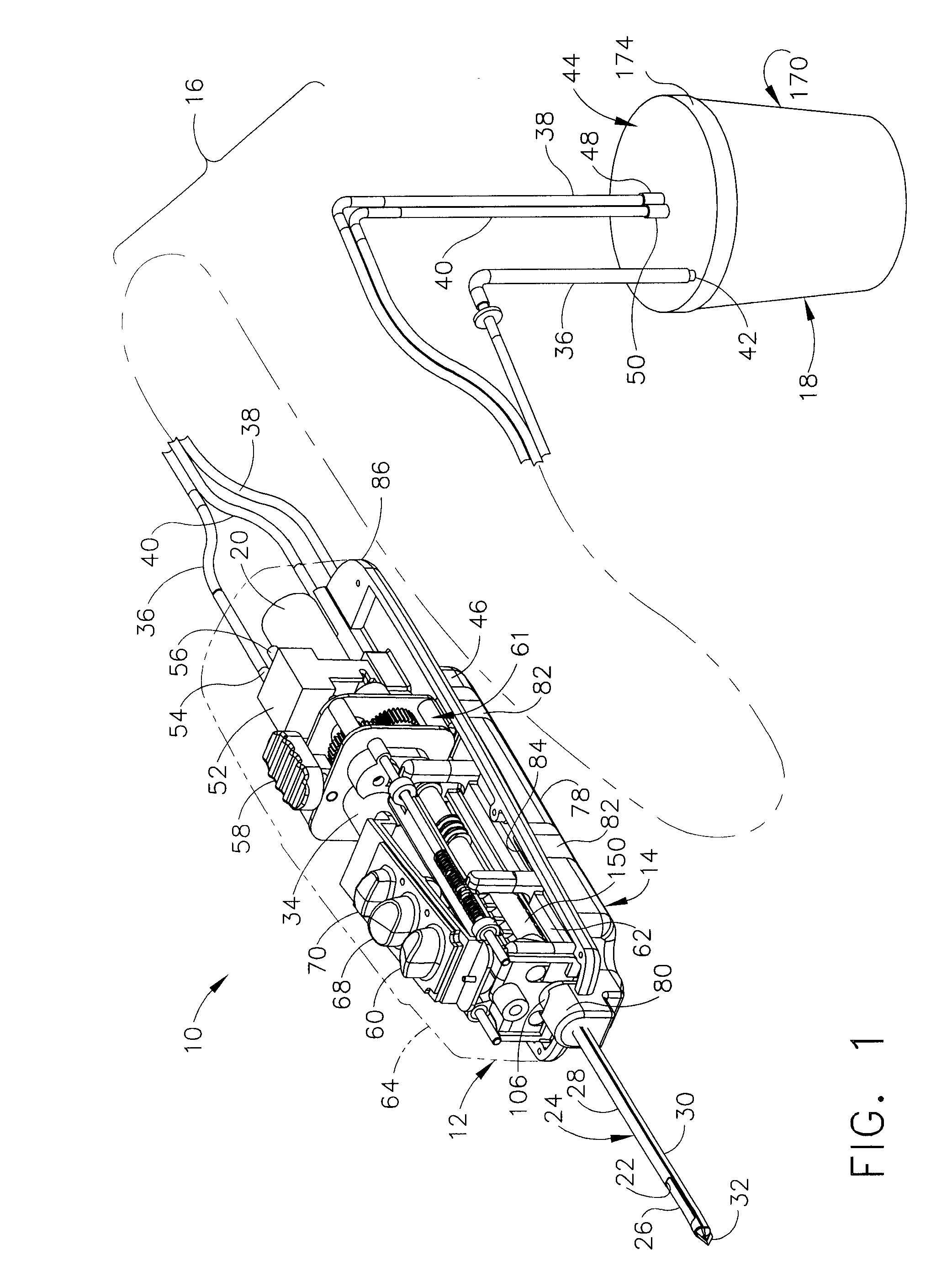
Biopsy Device with Vacuum Assisted Bleeding Control
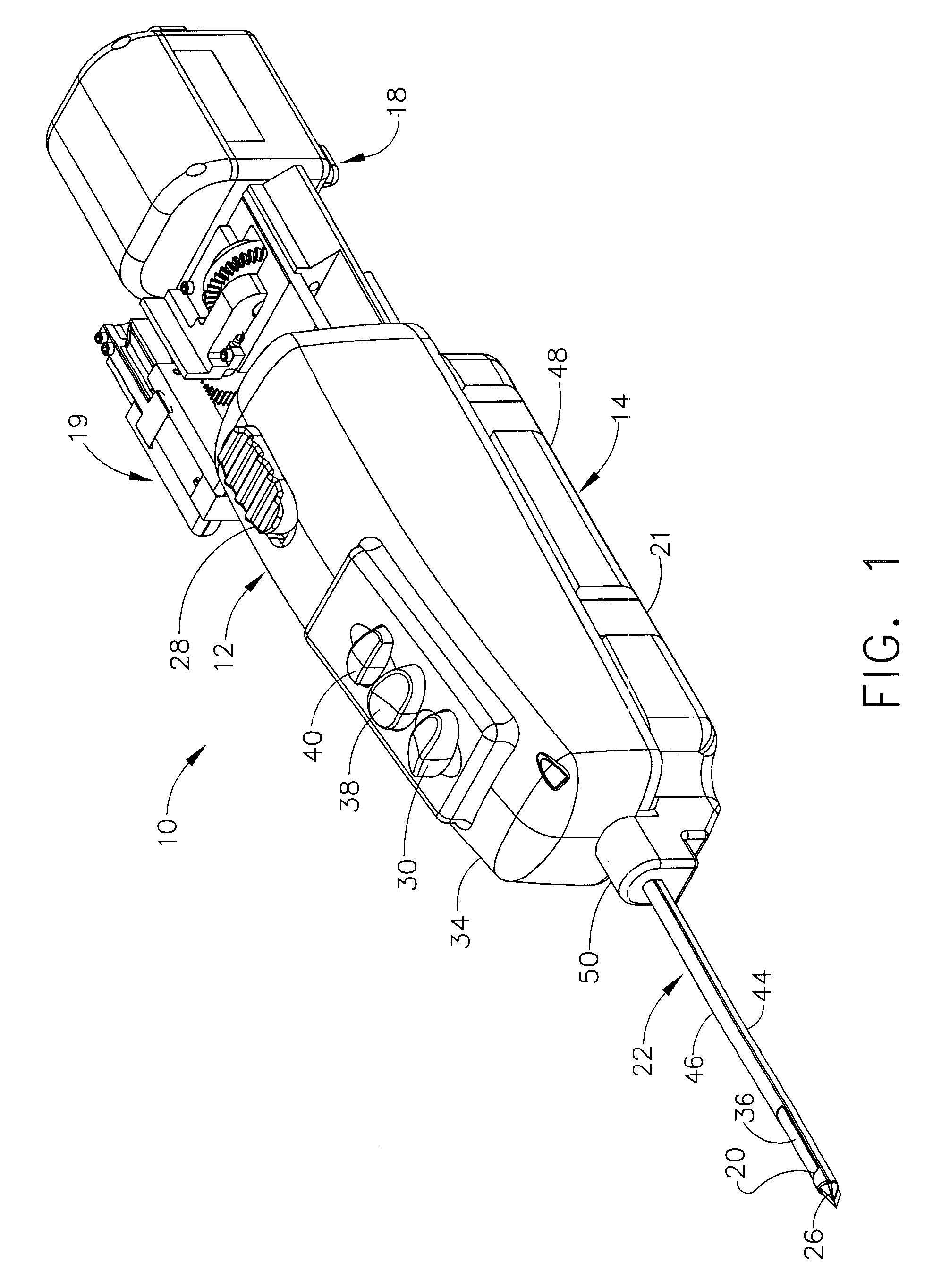
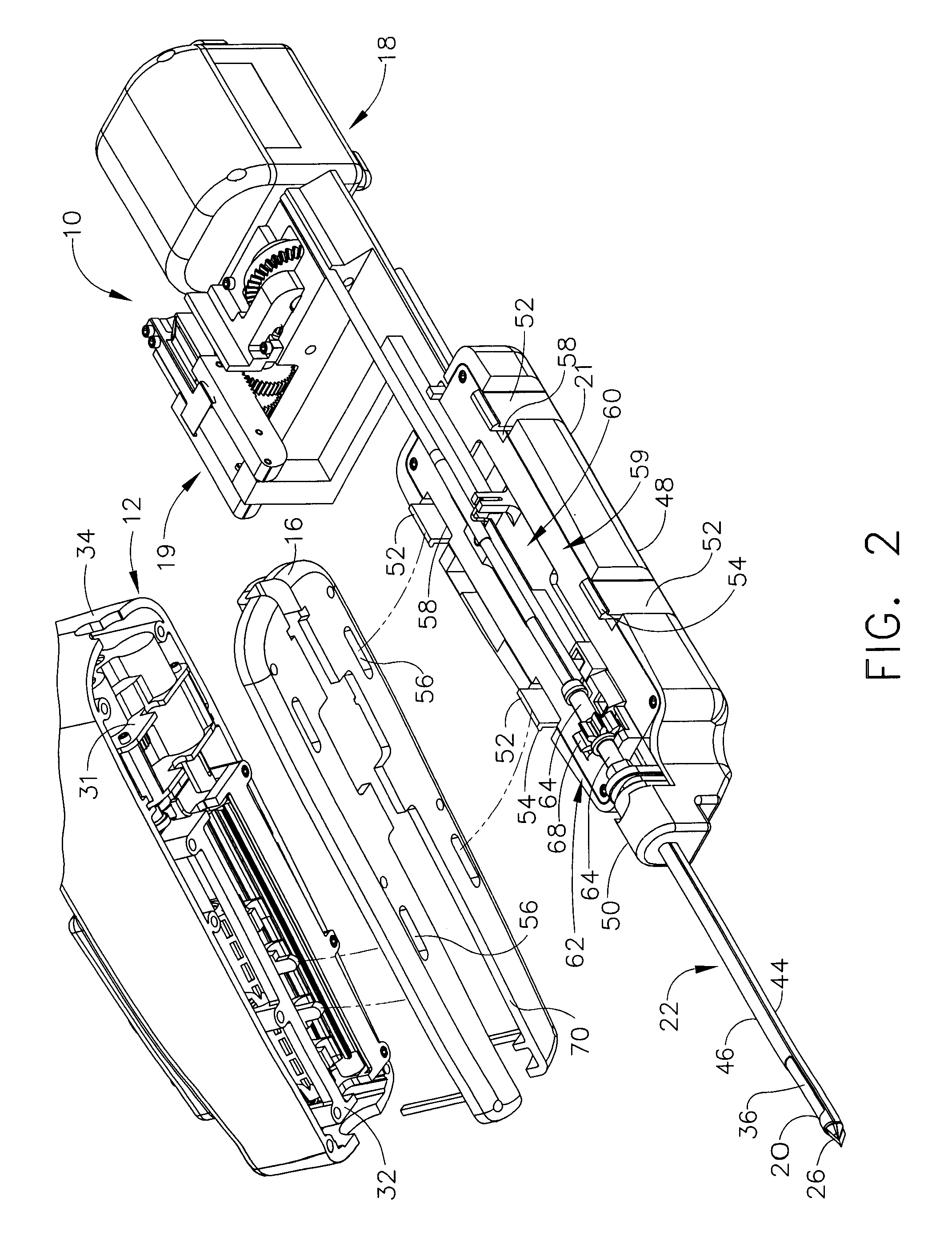
ActiveUS20070032742A1Fluid management is facilitatedEasy to manageSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsVacuum assistedOuter Cannula
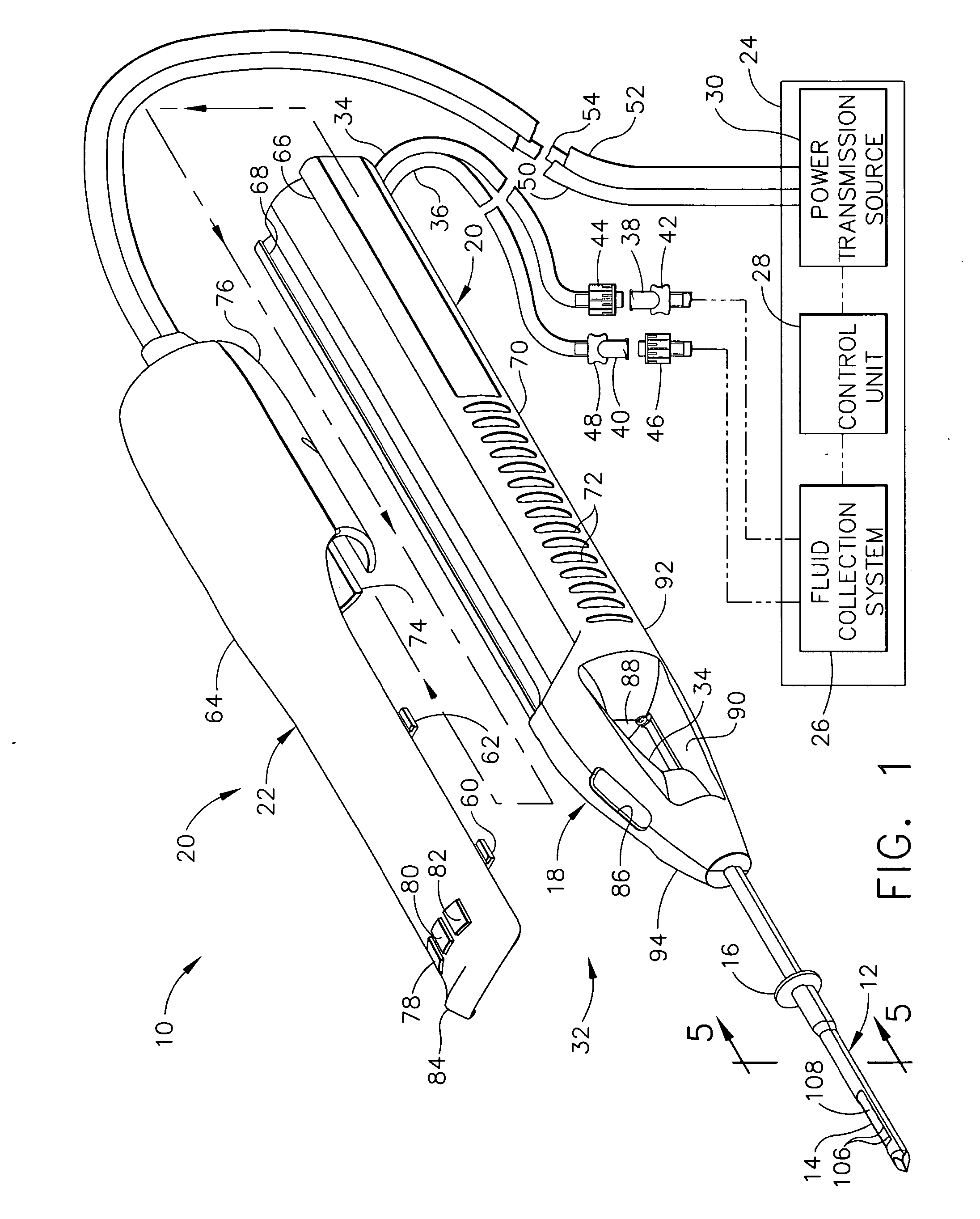
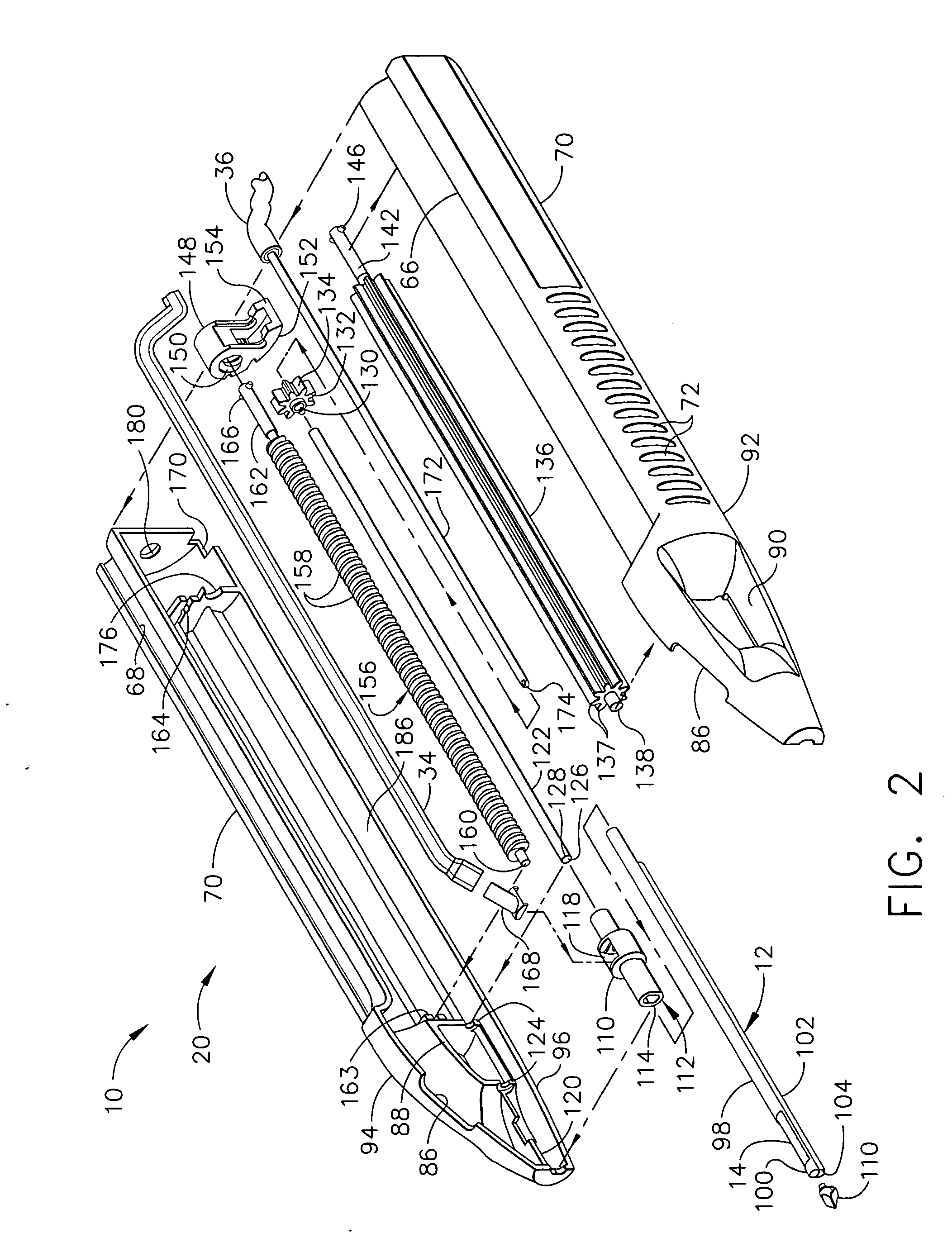
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable hand piece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable hand piece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. External vacuum holes along the outer cannula (probe) that communicate with a vacuum and cutter lumen withdraw bodily fluids while a hemostatic disk-shaped ring pad around the probe applies compression to an external hole in the skin and absorbs fluids.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Endoscopic apparatus with integrated multiple biopsy device
An imaging endoscope comprising a shaft having a proximal end adapted to be secured to a handle, and a distal end having a biopsy forceps disposed therein. The biopsy forceps includes one or more end-effector elements that are actuated with a control cable that may be connected to the handle. The endoscope shaft includes a biopsy sample lumen that is configured to receive a biopsy sample obtained from the forceps assembly. A sample collection apparatus is attached to the handle to capture multiple biopsy samples. In some embodiments, the endoscope is a single-use endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biopsy device with replaceable probe and incorporating vibration insertion assist and static vacuum source sample stacking retrieval
InactiveUS20070032741A1Inexpensively incorporatedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingTissue sample
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable hand piece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable hand piece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. A straw stacking assembly is automatically positioned by the reusable hand piece to retract multiple samples with a single probe insertion as well as giving a visual indication to the surgeon of the number of samples that have been taken.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Tissue Sample Revolver Drum Biopsy Device
InactiveUS20070239067A1Surgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingTissue sample
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable handpiece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable handpiece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. The motor also actuates an attached sample revolver drum assembly in coordination with movement of the cutter tube to provide sequentially stored tissue samples in a sample storage bandolier that is rotated about a revolver cylindrical drum.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biological sampler, collector and storage container
The invention relates to a storage container to receive and store a biopsy sample of an organism, held by a biopsy sample collector. The storage container comprises a container body defining a containment region with an open or openable end. The storage container further comprises a container cap located at the open end. The container cap is able to be removed from the container body by displacement in a direction (herein after “removal direction”) away from said containment region. The cap includes a passage leading to the containment region the passage able to receive a sample retaining sample collector. The storage container additionally comprises a tamper evident sleeve about at least part of the cap and the container body. The sleeve comprises of two parts that are frangibly connected. The frangible connection is in a manner such that upon displacement of the cap in the removal direction, a first part of the sleeve travels with said cap and a second part of the sleeve is prevented from movement with the first part by said container body to thereby separate the first and second parts. The first and second parts may each include information matched to each other.
Owner:SNPSHOT TRUSTEE
Biopsy sampler
The invention features an assembly for taking a biopsy sample from a site within the body of a patient. The assembly includes a resecting device having a cutter near its distal end for resecting and containing a tissue sample and a sheath exterior to the resecting device and sized to be present within the body with the resecting device. The sheath includes an electrode element electrically isolated from the resecting device and disposed on the sheath's outer surface for cauterizing tissue. The electrode element may reside on the outer sheath, the distal end or both the outer sheath and the distal end of the assembly. The resecting device and the sheath cooperate to permit sequential resecting of a tissue sample from a resecting site and cauterizing of the site with the cutter sufficiently spaced from the electrode element to avoid heat damage to the tissue sample.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
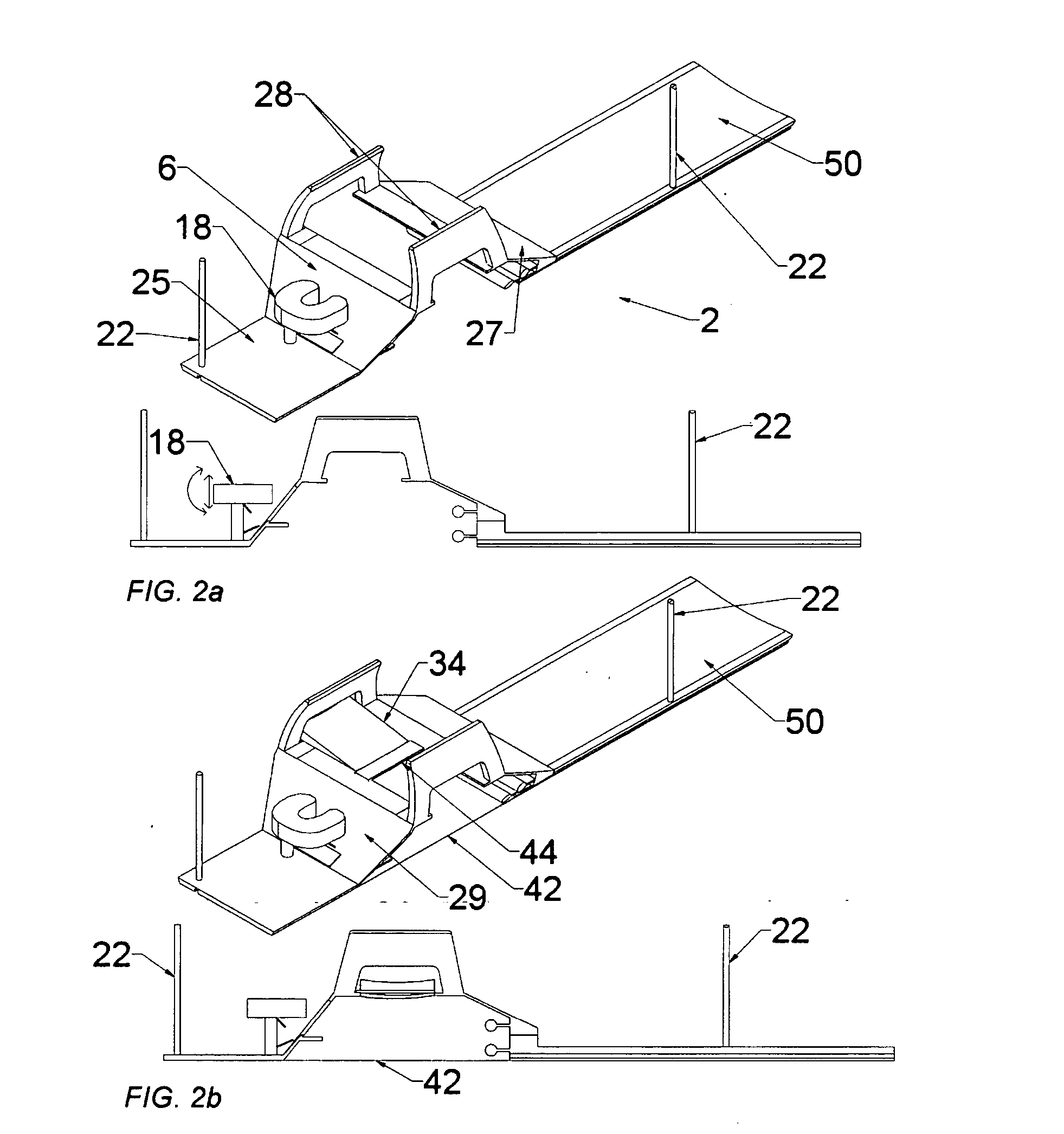
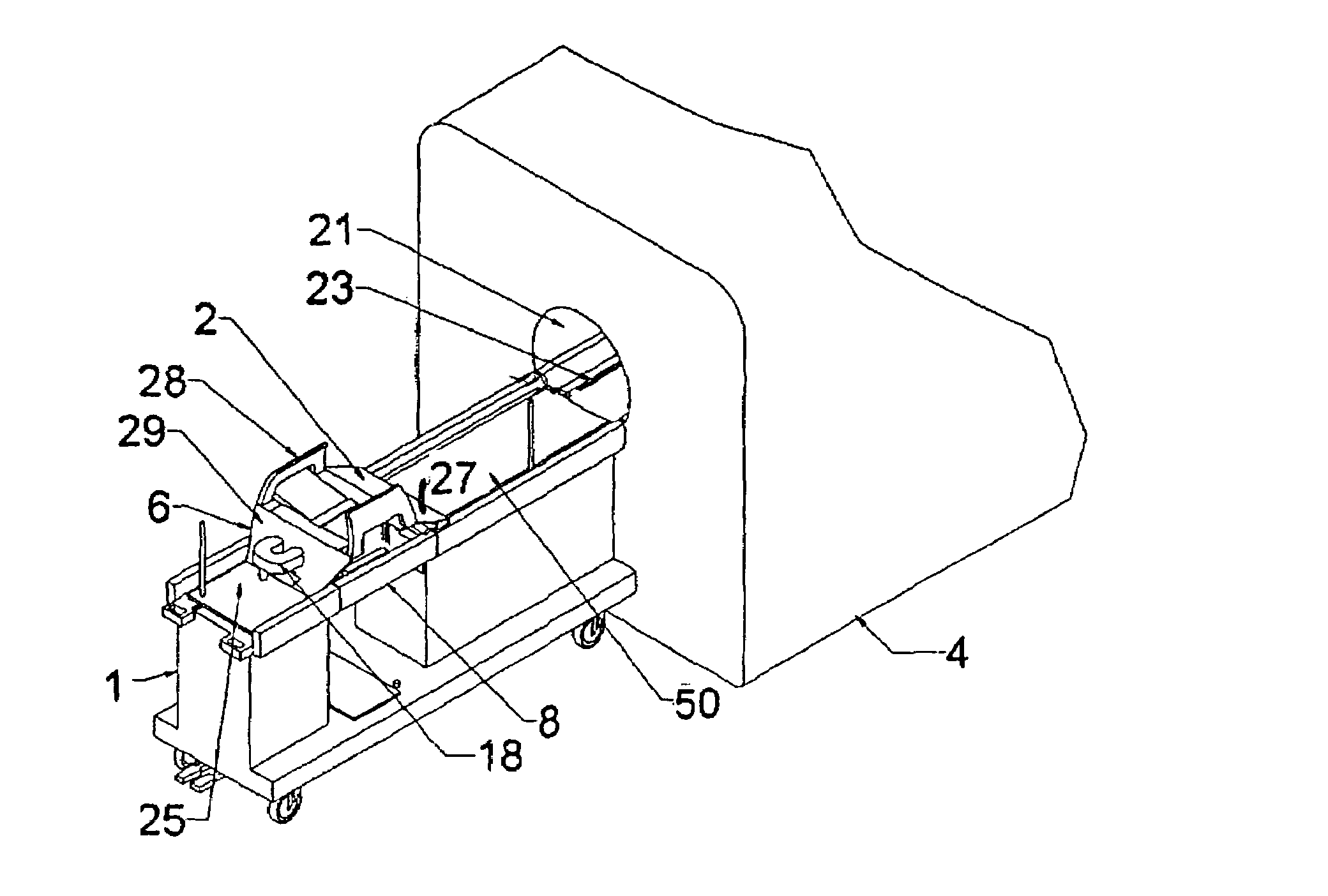
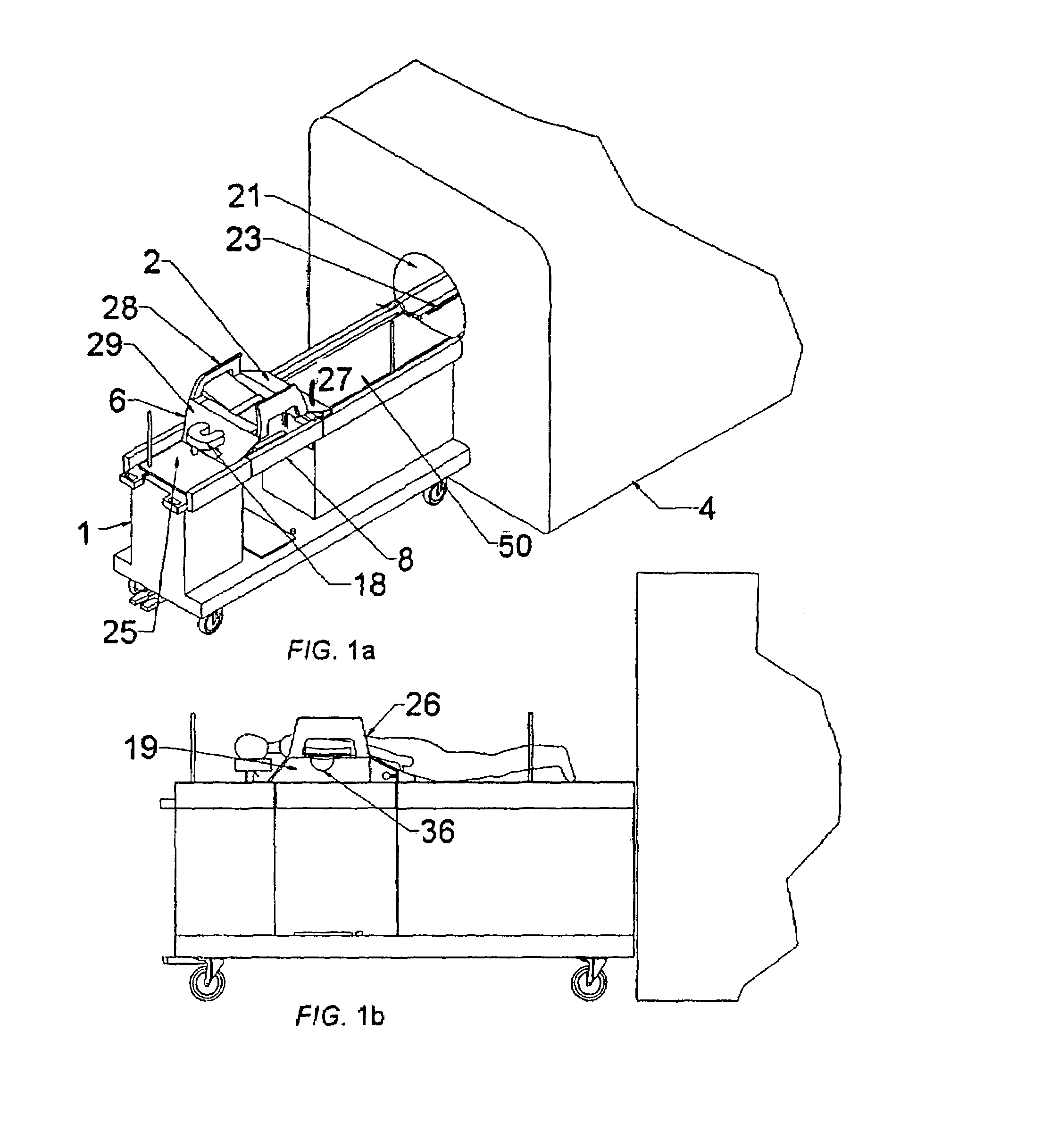
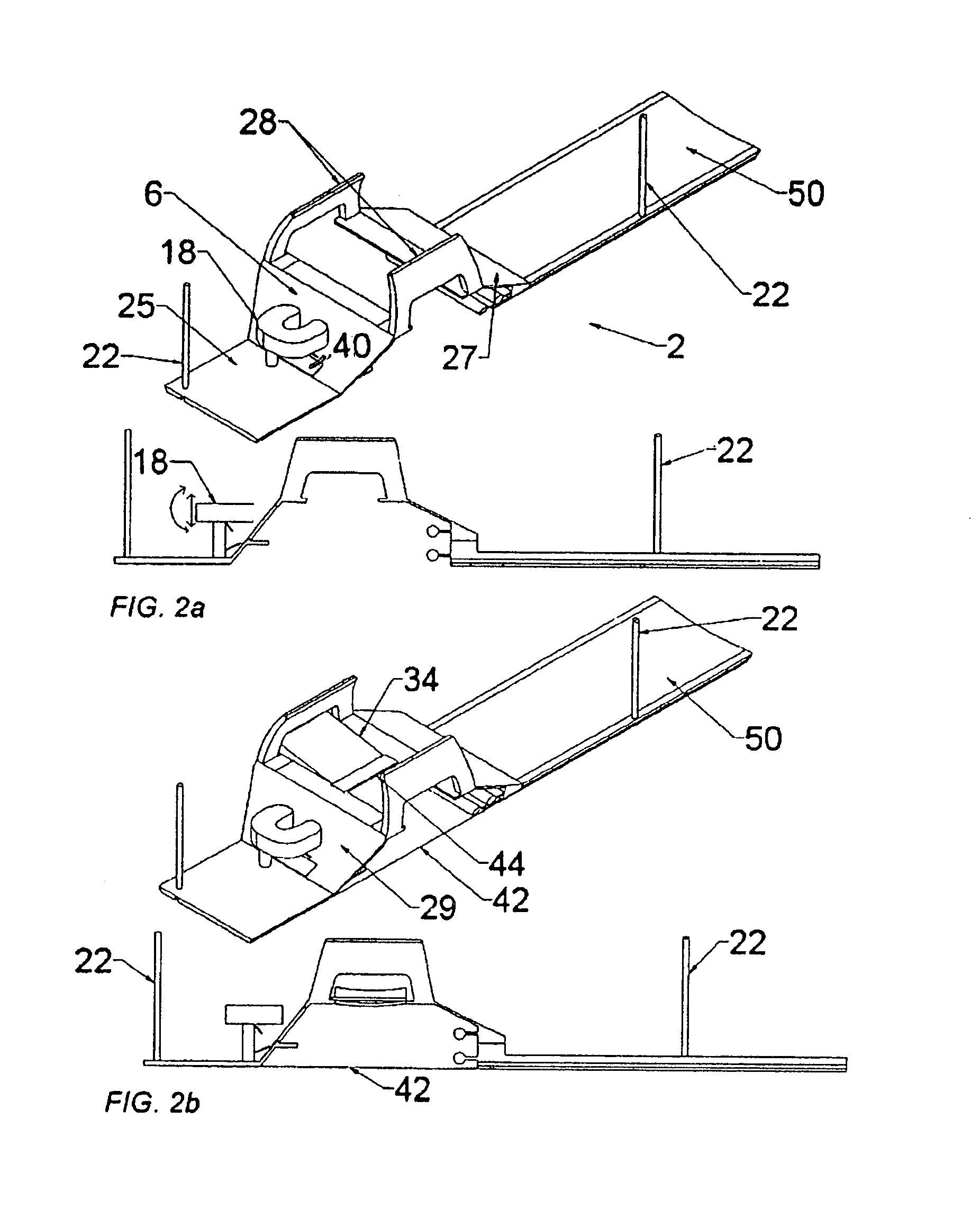
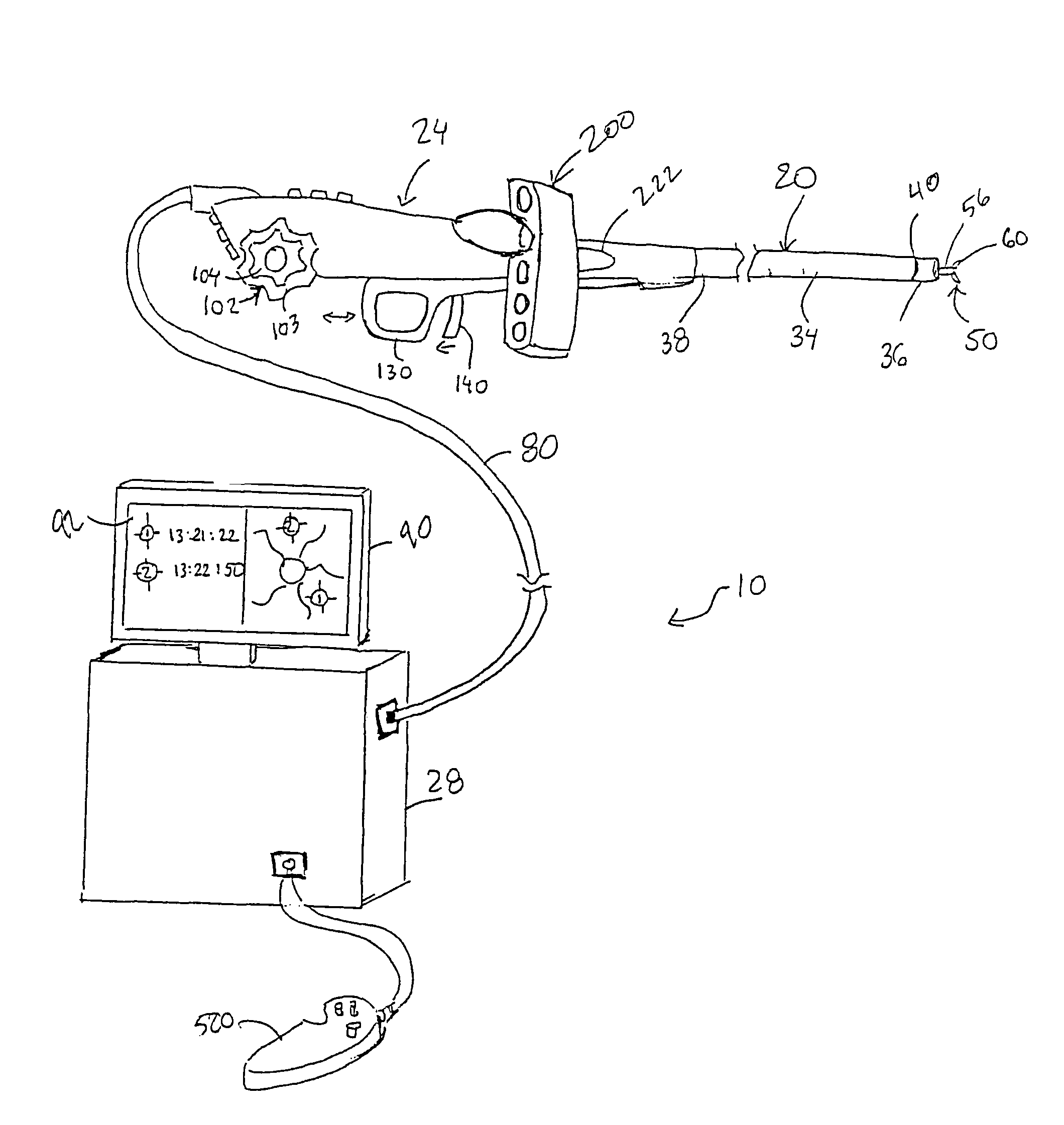
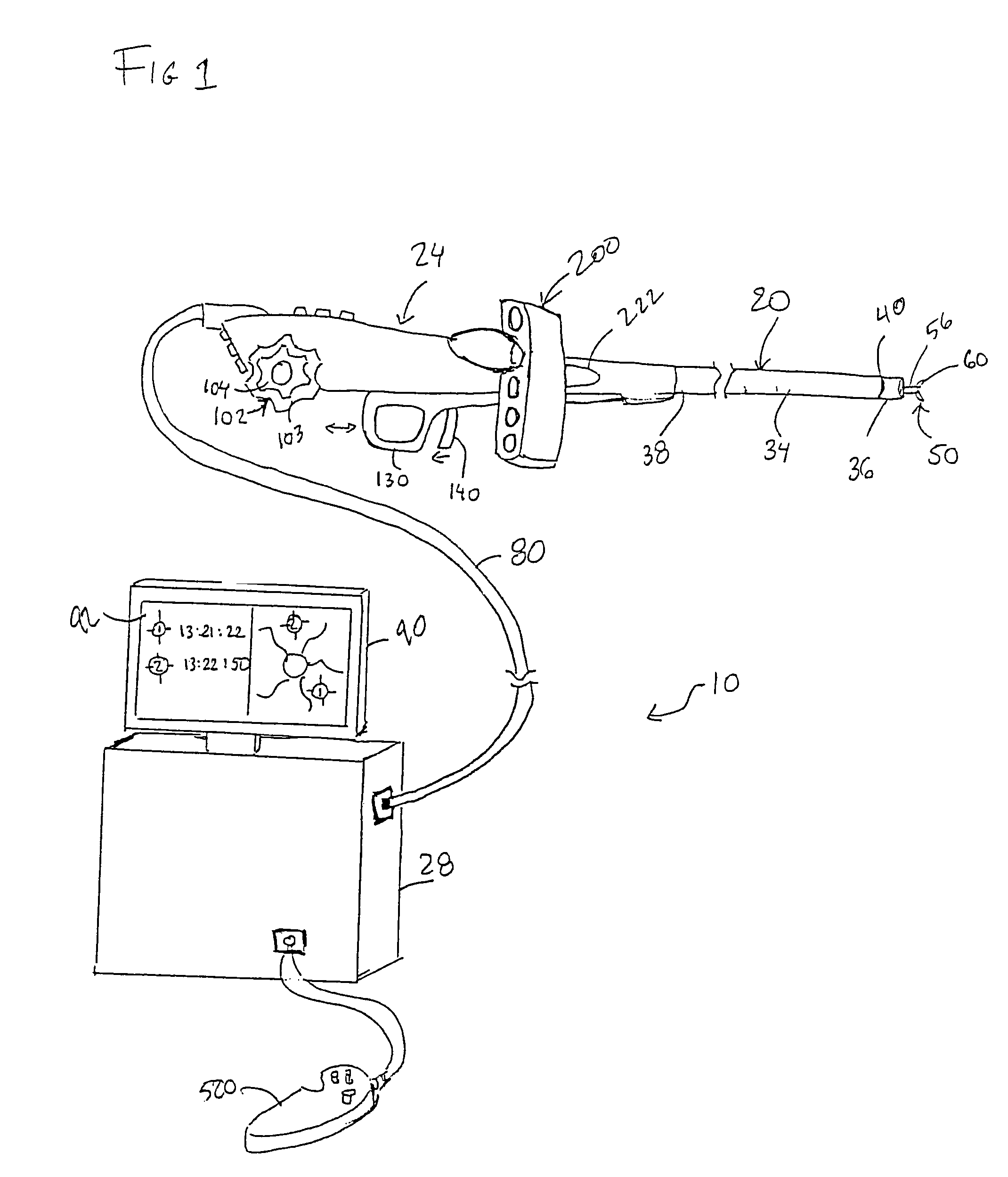
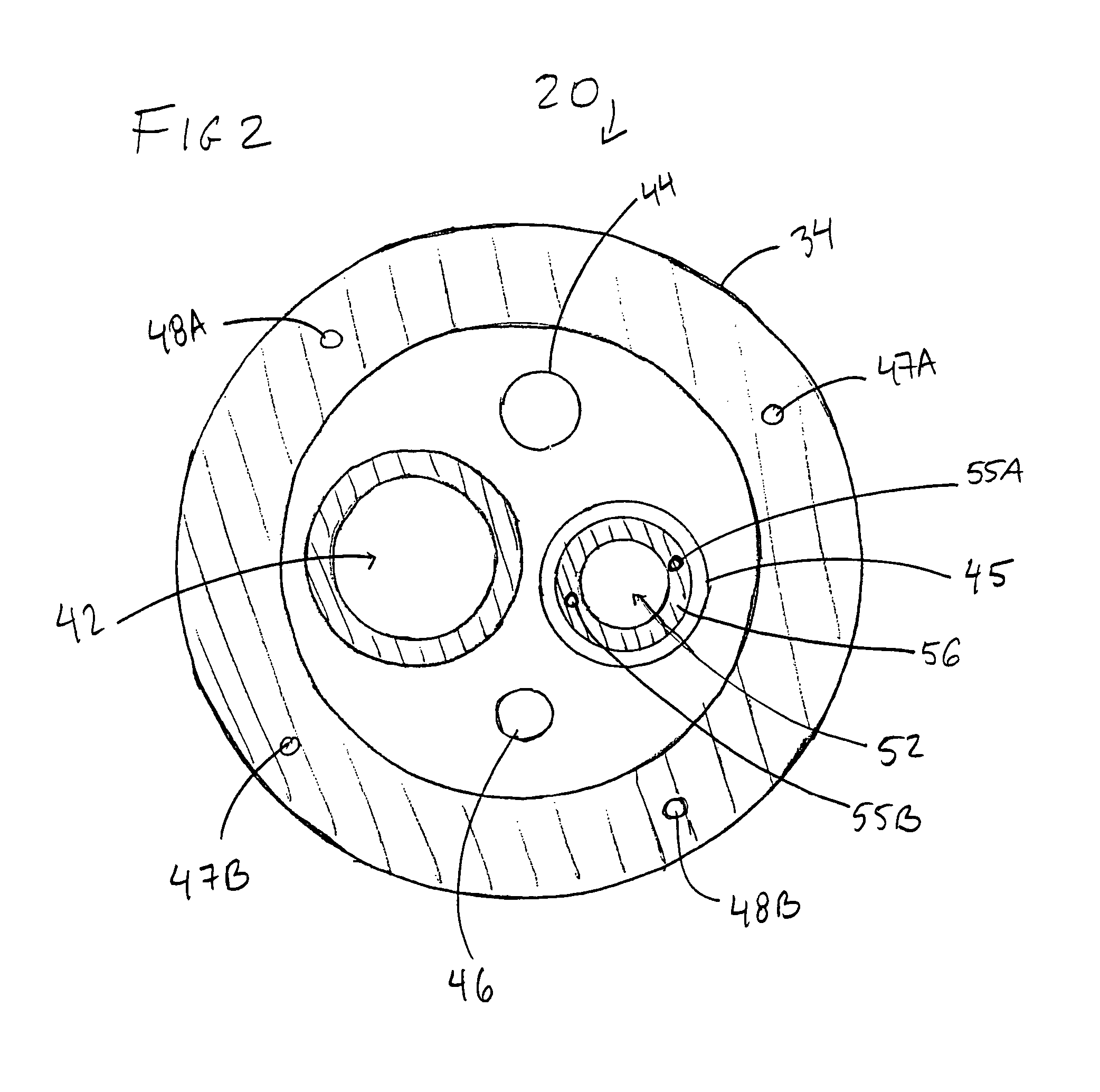
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS20050080333A1Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
This invention discloses a method and apparatus to deliver medical devices to targeted locations within human tissues using imaging data. The method enables the target location to be obtained from one imaging system, followed by the use of a second imaging system to verify the final position of the device. In particular, the invention discloses a method based on the initial identification of tissue targets using MR imaging, followed by the use of ultrasound imaging to verify and monitor accurate needle positioning. The invention can be used for acquiring biopsy samples to determine the grade and stage of cancer in various tissues including the brain, breast, abdomen, spine, liver, and kidney. The method is also useful for delivery of markers to a specific site to facilitate surgical removal of diseased tissue, or for the targeted delivery of applicators that destroy diseased tissues in-situ.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS7379769B2Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Vacuum Syringe Assisted Biopsy Device
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable handpiece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable handpiece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. The motor also actuates a vacuum syringe in coordination with movement of the cutter tube to provide vacuum assistance in prolapsing tissue and retracting tissue samples.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Apparatus and Methods for Biopsy and Aspiration of Bone Marrow
ActiveUS20080045965A1Reduced inside diameterEasy to captureSurgical furnitureVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTransplant ProcedureAbdominal trocar
Apparatus and methods are provided to remove biopsy specimens from a bone and / or associated bone marrow using a powered drive and an intraosseous (IO) needle set. The powered driver may rotate the IO needle set at an optimum speed to obtain a biopsy sample of bone and / or bone marrow. Apparatus and methods may also be provided for aspiration of bone marrow and / or stem cell transplant procedures. The apparatus may include a powered driver, a coupler assembly, a containment bag or sterile sleeve and various IO needles and IO needle sets with associated hubs and / or hub assemblies. Each IO needle set may include a cannula or catheter and an associated trocar stylet with respective tips operable to penetrate a bone and / or bone marrow with minimum trauma to a patient. Each hub assembly may be used to releasably dispose a respective stylet within an associated generally hollow cannula. Some coupler assemblies and / or hub assemblies may also be used with manual drivers.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Medical Procedures Trays And Related Methods
ActiveUS20080045861A1Reduced inside diameterEasy to captureSurgical furnitureDispensing apparatusTransplant ProcedureSurgery
Medical procedure trays and related methods are provided to accommodate joining a first non-sterile medical device with a second sterile medical device and maintaining required sterilization of the second sterile medical device to perform an associated medical procedure. One example of such medical procedures includes biopsy of a bone and / or associated bone marrow using a non-sterile powered drive and a sterile biopsy needle or biopsy needle set. Medical procedure trays and related methods may also be provided for use during aspiration of bone marrow and / or stem cell transplant procedures. Each medical procedure tray may include a containment bag or sterile sleeve. A coupler assembly, one or more sharps protectors, a biopsy sample ejector and / or associated ejector funnel may also be included. Some medical procedure trays may allow engaging a non-sterile powered driver with one end of a coupler assembly and sealing the non-sterile powered driver in a sterile sleeve or containment bag without compromising sterility of other components in the medical procedure tray.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Biopsy Devices and Related Methods
InactiveUS20080045860A1Reduced inside diameterEasy to captureSurgical furnitureSurgical needlesBiopsy deviceCancellous bone
Apparatus and methods provided to remove biopsy specimens from bone and / or associated bone marrow. A powered driver may rotate a biopsy needle at an optimum speed to obtain the biopsy specimen. A thread or a groove may be disposed on interior portions of the biopsy needle. The thread or groove may engage a biopsy specimen and enhance removal of a bone marrow core from cancellous bone. Manufacturing procedures are provided for bonding a single helical thread with interior portions of the biopsy needle. The apparatus may also include a biopsy sample ejector and / or ejector funnel. A biopsy needle set may include a cannula and a trocar with respective tips having optimum configurations, dimensions and / or orientations relative to each other to optimize penetration of a bone and / or bone marrow with minimum patient trauma and enhanced reliability of obtaining a biopsy specimen.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
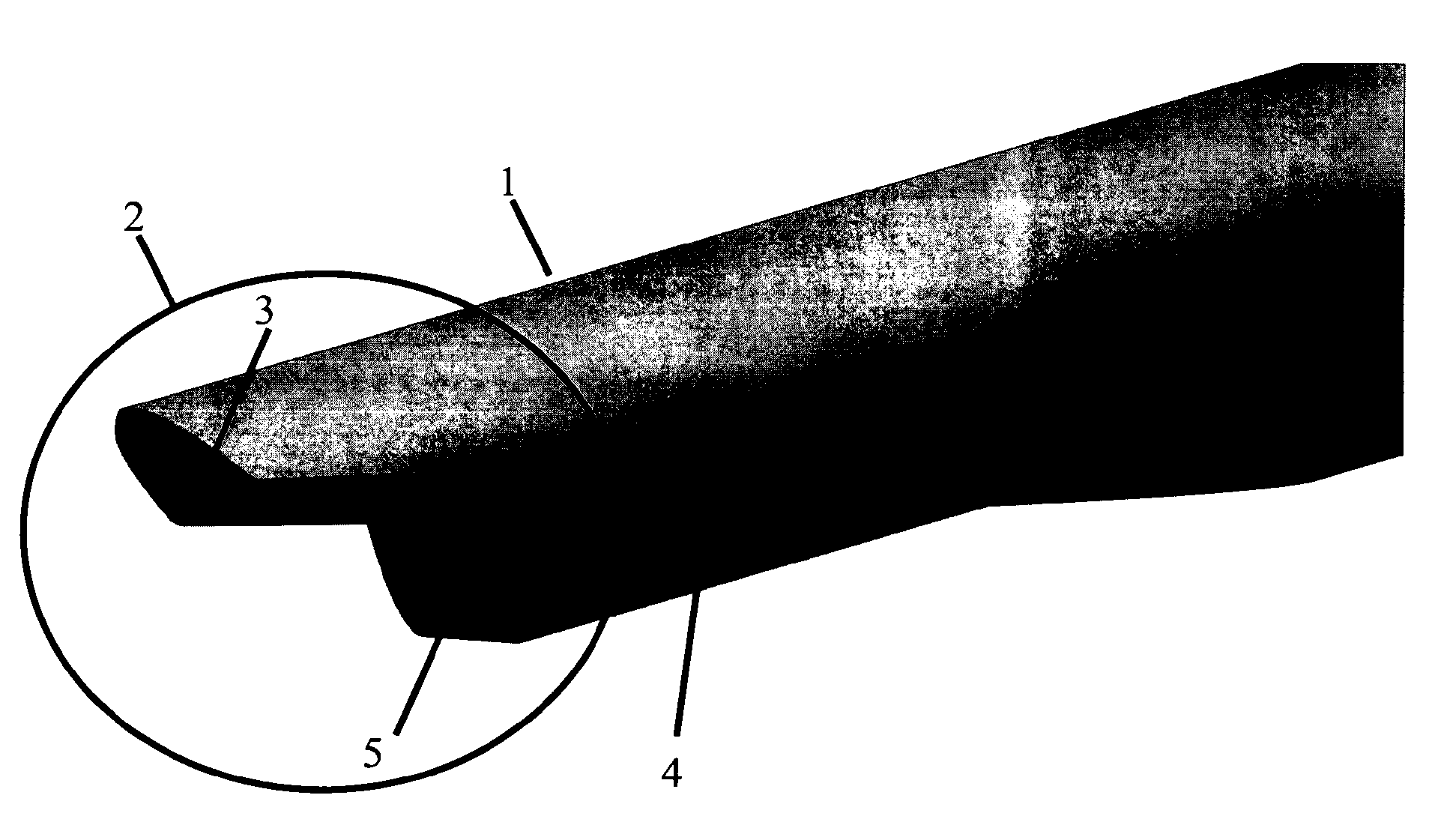
Core biopsy device
InactiveUS20060030785A1Easy to disassembleEasy to operateSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy deviceGeneral surgery
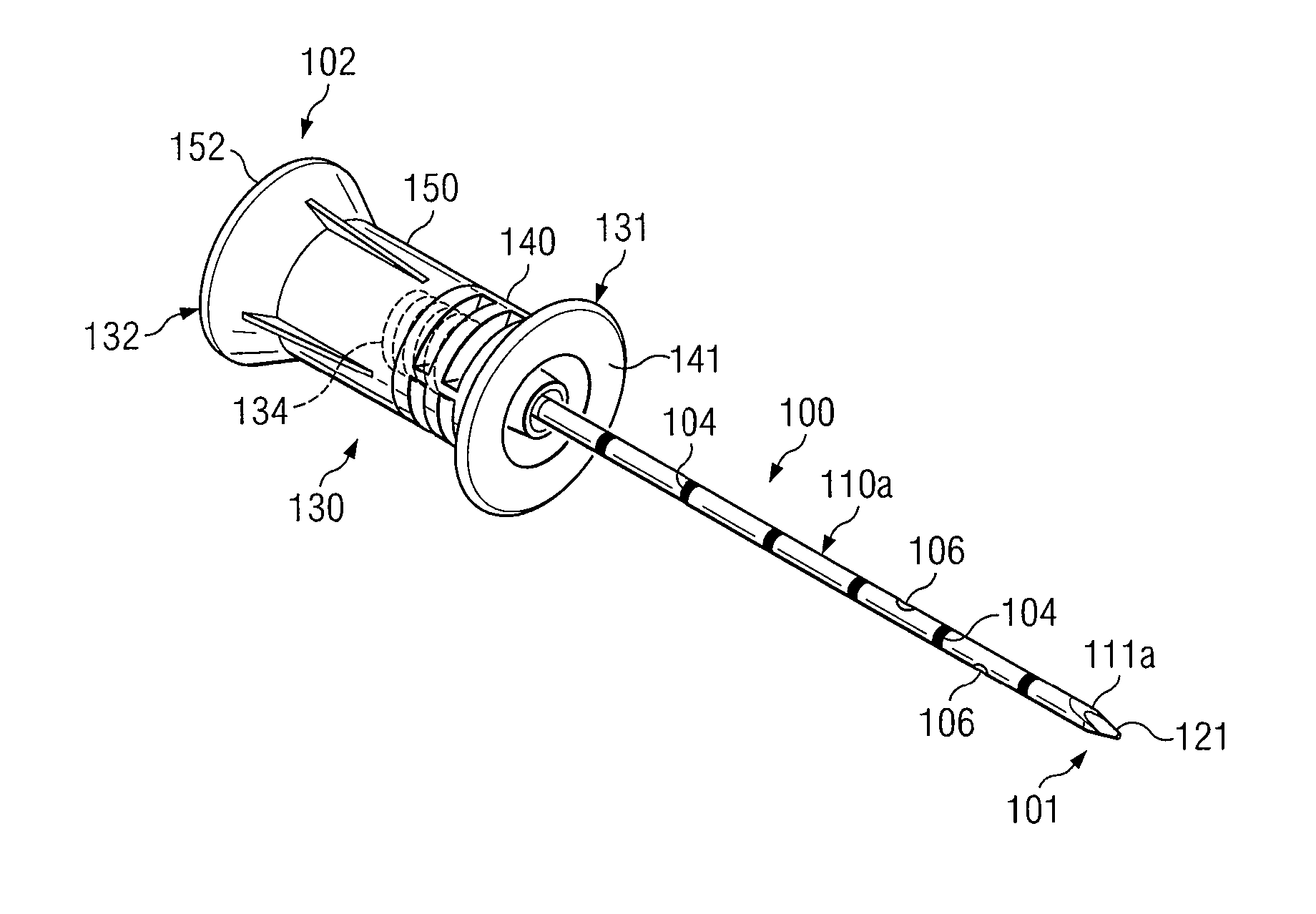
A core biopsy device comprises an outer cutting cannula in telescoping register with an inner spoon cannula. The outer cutting cannula is provided at a distal end with an arcuate excising blade that is biased radially inwardly to extend beyond the longitudinal axis of the cannula. The inner spoon cannula terminates at a distal end in an arcuate wall to form a biopsy sample spoon for supporting a biopsy sample thereon. The outer cutting cannula can be rotated relative to the inner spoon cannula so that the excising blade can excise the biopsy sample from the surrounding tissue. After removal of the core biopsy device from the tissue, the outer cutting cannula can be retracted away from the inner spoon cannula to reveal the biopsy sample and enable the sample to be removed from the biopsy device in a relatively undisturbed condition.
Owner:INRAD
Biopsy devices and related methods
InactiveUS7850620B2Easy to captureIncrease speedSurgical furnitureSurgical needlesBiopsy deviceCancellous bone
Apparatus and methods provided to remove biopsy specimens from bone and / or associated bone marrow. A powered driver may rotate a biopsy needle at an optimum speed to obtain the biopsy specimen. A thread or a groove may be disposed on interior portions of the biopsy needle. The thread or groove may engage a biopsy specimen and enhance removal of a bone marrow core from cancellous bone. Manufacturing procedures are provided for bonding a single helical thread with interior portions of the biopsy needle. The apparatus may also include a biopsy sample ejector and / or ejector funnel. A biopsy needle set may include a cannula and a trocar with respective tips having optimum configurations, dimensions and / or orientations relative to each other to optimize penetration of a bone and / or bone marrow with minimum patient trauma and enhanced reliability of obtaining a biopsy specimen.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Biopsy Device with Integral Vacuum Assist and Tissue Sample and Fluid Capturing Canister
InactiveUS20070255173A1Lower the volumeSimple methodSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsVacuum assistedClinical settings
A biopsy device is provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable handpiece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable handpiece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. An integral vacuum motor assists prolapsing tissue for effective severing as well as facilitating withdrawal of the tissue samples and bodily fluids from the biopsy site into a detachable, self-contained canister for transporting the separated biopsy samples and fluid for pathology assessment, avoiding biohazards in a clinical setting.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy device with variable side aperture
InactiveUS20060200040A1Discomfort and disfiguring scarring is avoidedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyTissue sample
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample. After the tissue sample is severed, and before the inner cutter is retracted proximally of the side tissue port, the cutter may be used to alternately cover and uncover the fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy marker delivery system
InactiveUS7083576B2Prevent distal movementPreventing further distal movementSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDelivery systemGeneral surgery
An apparatus for delivering subcutaneous cavity marking devices. More particularly, the delivery devices may be used with biopsy systems permitting efficient placement of a biopsy marker within a cavity. The device may include an intermediate member which assists in deployment of the marking device. The devices may also include a deployment lock to prevent premature deployment of a biopsy marker. The invention may further include the capability to match an orientation of a biopsy probe which has been rotated upon procurement of a biopsy sample.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy Devices and Related Methods
InactiveUS20110082387A1Easy to captureIncrease speedSurgical furnitureSurgical needlesBiopsy deviceCancellous bone
Apparatus and methods provided to remove biopsy specimens from bone and / or associated bone marrow. A powered driver may rotate a biopsy needle at an optimum speed to obtain the biopsy specimen. A thread or a groove may be disposed on interior portions of the biopsy needle. The thread or groove may engage a biopsy specimen and enhance removal of a bone marrow core from cancellous bone. Manufacturing procedures are provided for bonding a single helical thread with interior portions of the biopsy needle. The apparatus may also include a biopsy sample ejector and / or ejector funnel. A biopsy needle set may include a cannula and a trocar with respective tips having optimum configurations, dimensions and / or orientations relative to each other to optimize penetration of a bone and / or bone marrow with minimum patient trauma and enhanced reliability of obtaining a biopsy specimen.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Biopsy device with replaceable probe incorporating static vacuum source dual valve sample stacking retrieval and saline flush
InactiveUS20070179401A1Small sizeInexpensively incorporatedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSaline flushUltrasonic imaging
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable hand piece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable hand piece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. A saline valve positioned by the reusable hand piece communicates a saline supply through the probe assembly to perform saline flush of the cutter tube and outer cannula.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Endoscopic apparatus with integrated multiple biopsy device
An imaging endoscope comprising a shaft having a proximal end adapted to be secured to a handle, and a distal end having a biopsy forceps disposed therein. The biopsy forceps includes one or more end-effector elements that are actuated with a control cable that may be connected to the handle. The endoscope shaft includes a biopsy sample lumen that is configured to receive a biopsy sample obtained from the forceps assembly. A sample collection apparatus is attached to the handle to capture multiple biopsy samples. In some embodiments, the endoscope is a single-use endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Vacuum syringe assisted biopsy device
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable handpiece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable handpiece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. The motor also actuates a vacuum syringe in coordination with movement of the cutter tube to provide vacuum assistance in prolapsing tissue and retracting tissue samples.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Pleural biopsy and brushing needle
InactiveUS6846292B2Accurate and effectiveEasily withdrawnSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPleural cavityPleural biopsy
A biopsy needle and method of using the same. The biopsy needle includes a pair of articulating members that can be moved between a retracted position where the articulating members are contained within the biopsy needle and an extended position where the articulating members extend outwardly from the distal end of the biopsy needle into the pleural cavity of a patient. Once extended, the articulating members have operative surfaces that contact the parietal pleura of the patient such that a biopsy sample can be obtained as the operative surfaces are moved in contact with the parietal pleura. The operative surfaces may be a brush blade or a knife blade. A passageway within the interior of the biopsy needle allows removal of fluids from the patient.
Owner:BAKRY MOHAMED
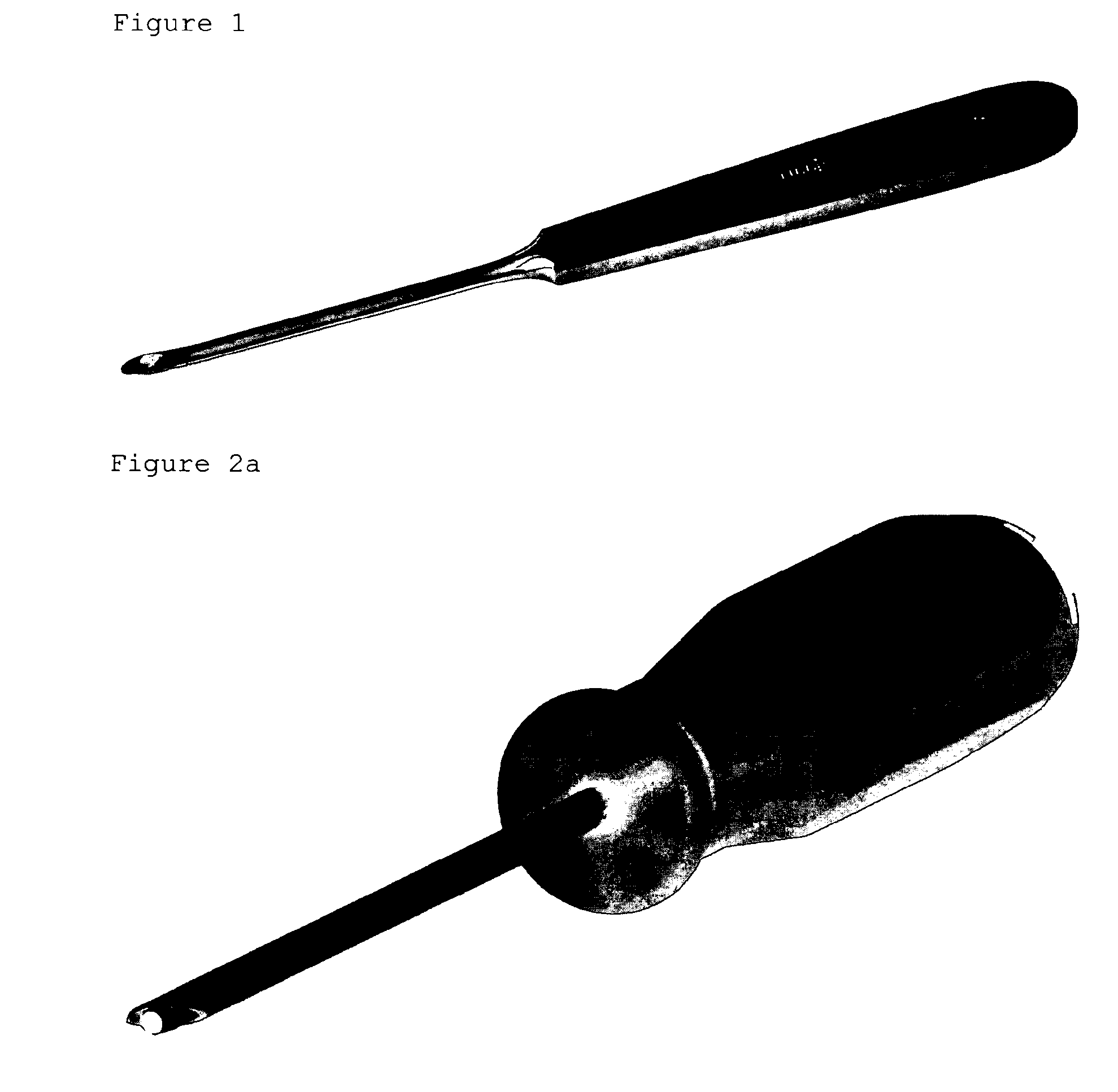
Biopsy device
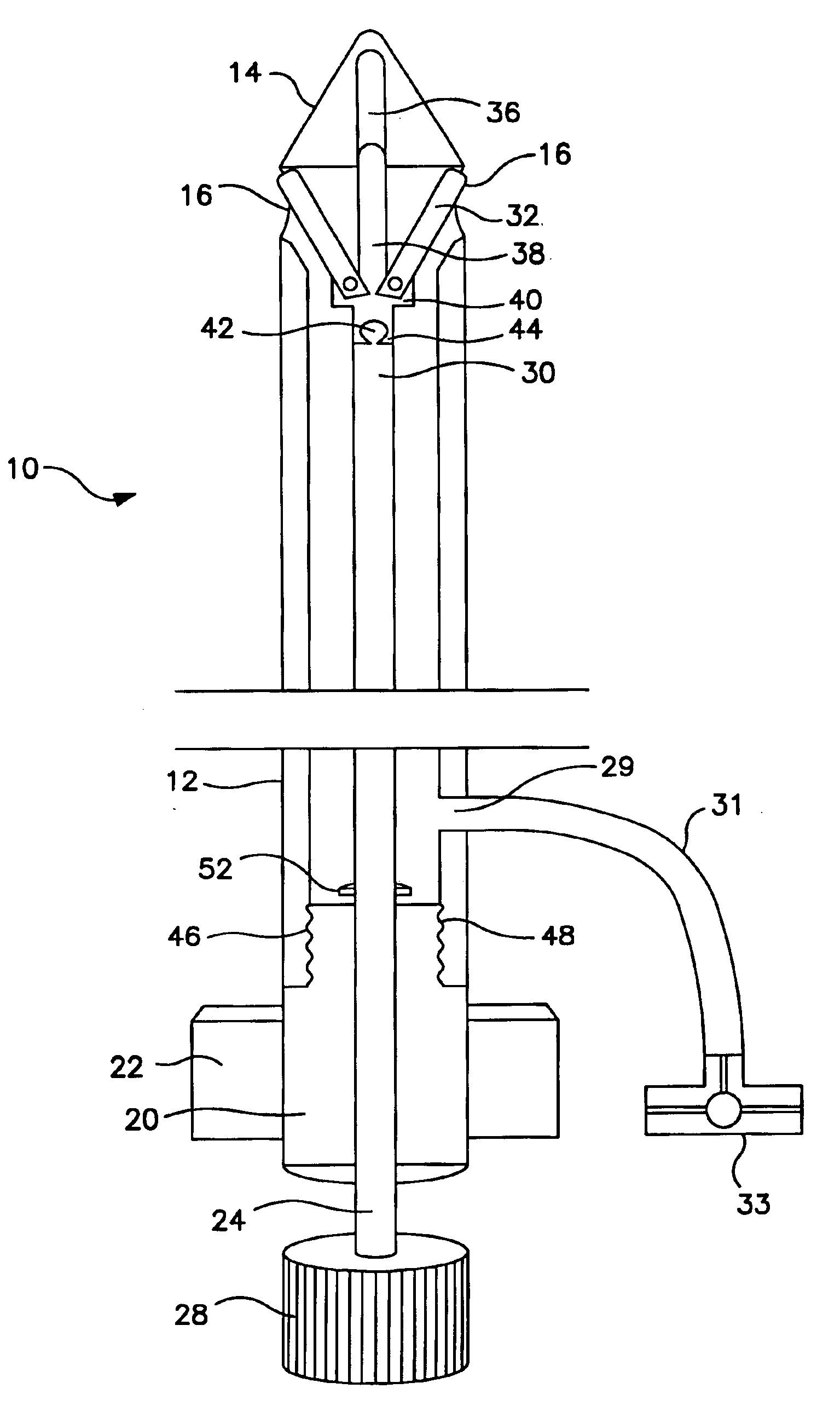
This invention relates to a biopsy device consisting of an inner cannula (4) and an outer hollow tube (1), a handle (7) which may be removably attached to the outer hollow tube, a locking system to secure the inner cannula and / or the attenuator in the outer hollow tube, and characterized in that the tip of the outer hollow tube is ellipse shaped and extends beyond the inner cannula, the latter ending in a blunt edge. The blunted tip of the outer hollow tube together with the sharpened ending of the inner cannula determines the cutting edge of the device. In combination the distal ends of inner cannula and outer hollow tube determine the biopsy depth size and shape of the biopsy sample in a reproducible way. In one embodiment of the present invention, the length of the inner cannula can be controlled, allowing varying the aforementioned sample parameters as desired.
Owner:DOKTER YVES FORTEMS
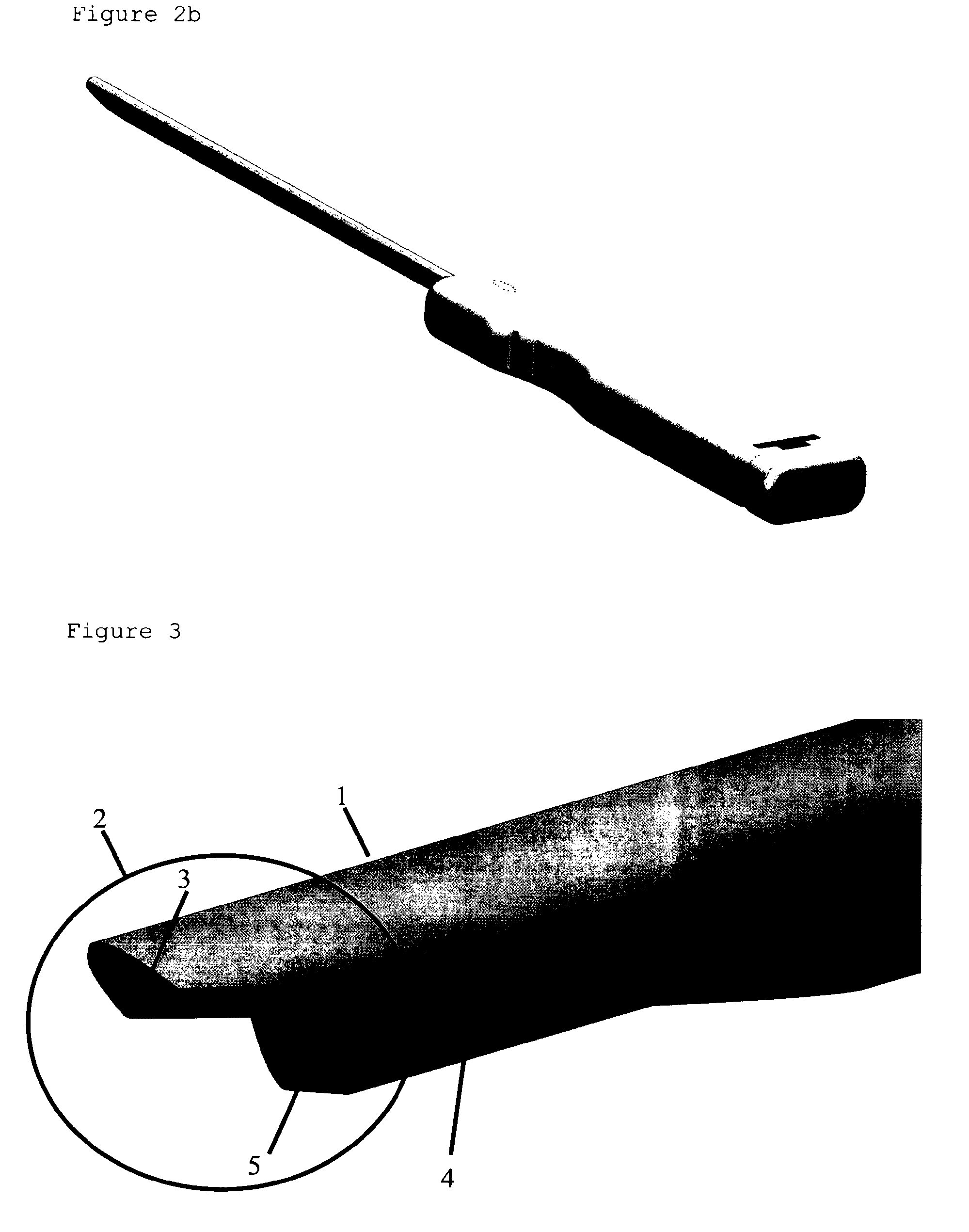
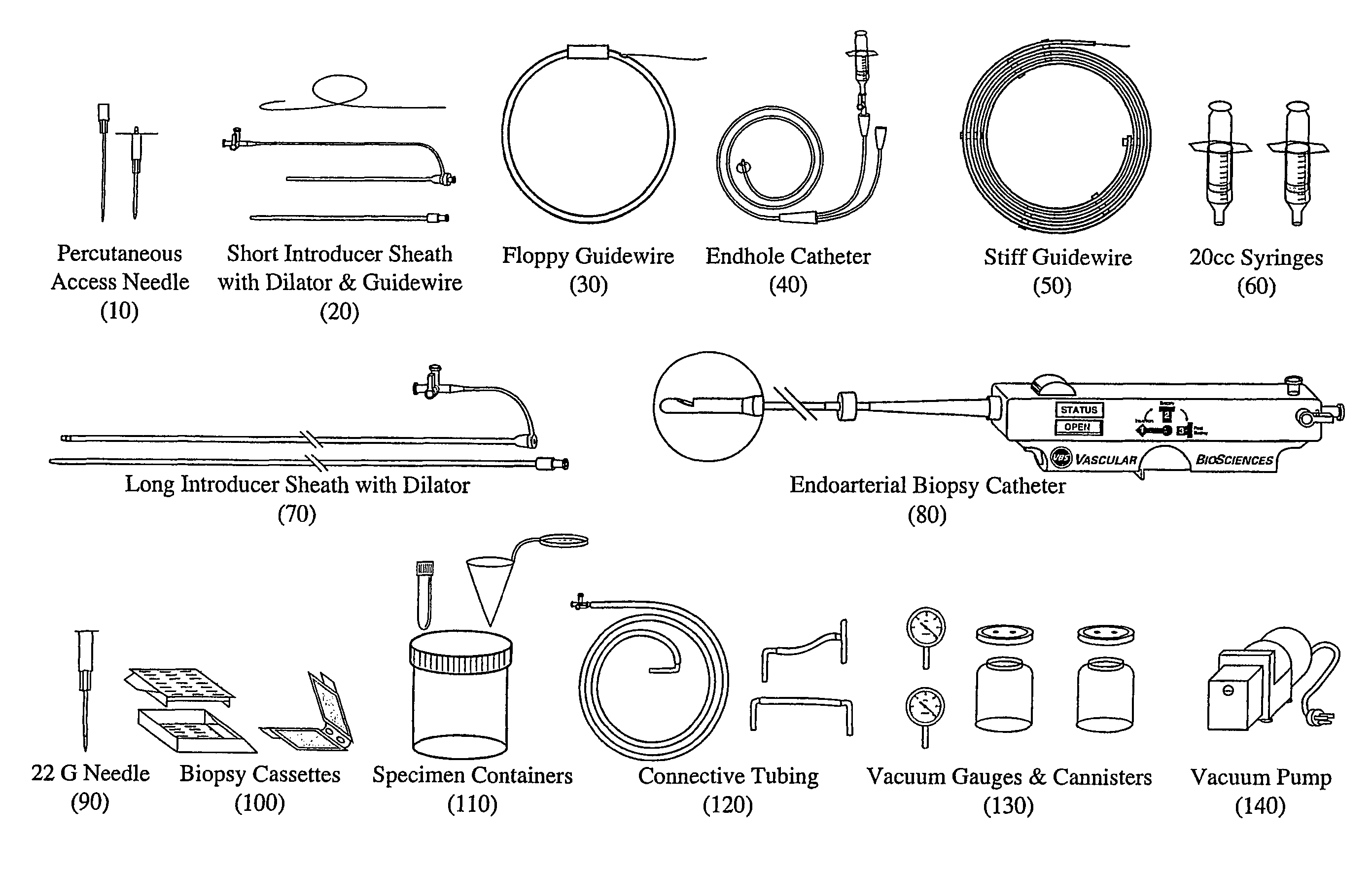
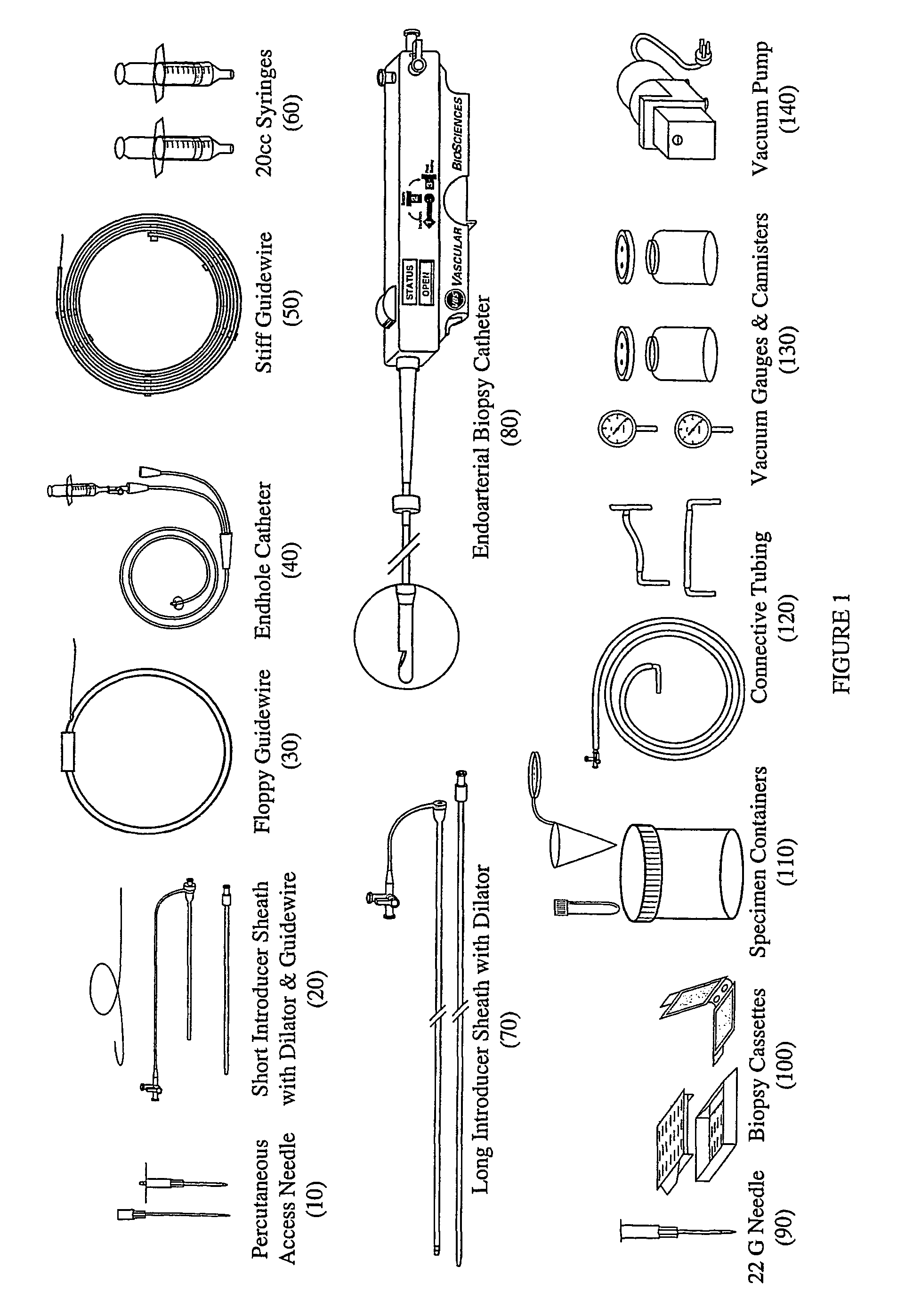
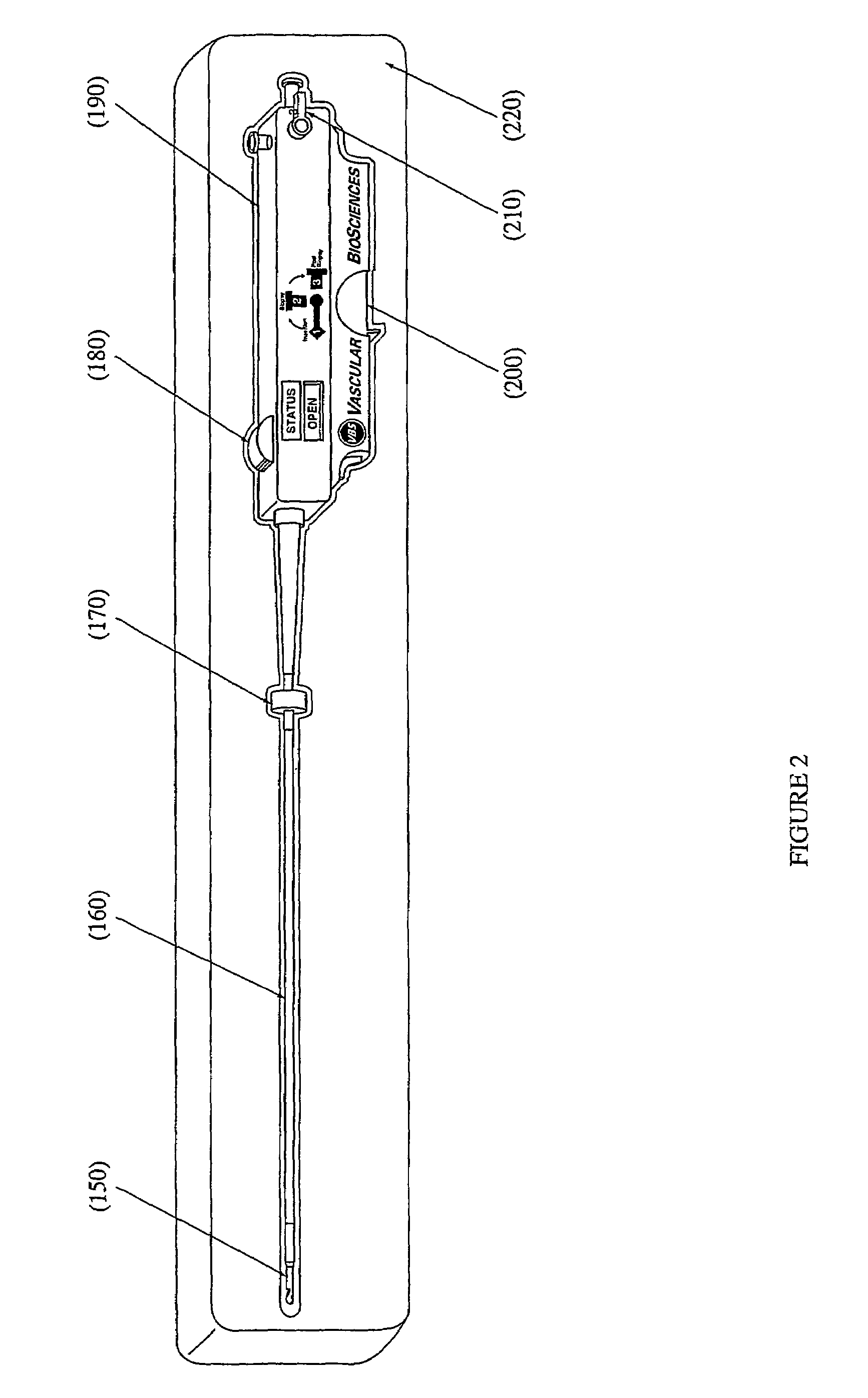
Kit for obtaining an endoarterial biopsy sample
A kit for obtaining an endoarterial biopsy sample from a patient including packaging material enclosing one or more kit components; the kit components include instruments use to perform a surgical procedure; and the kit includes separate phase specific packaging parts.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOSCI
Methods and compositions for evaluating graft survival in a solid organ transplant recipient
ActiveUS20060246485A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingOrgan transplantationProtein level
Methods are provided for evaluating a subject for graft survival, e.g., in terms of predicting graft survival, identifying the presence of a deleterious graft condition, such as CAN and DT, identifying the severity and class of acute rejection, etc, in a subject are provided. In practicing the subject methods, the expression of at least one gene in a sample from the subject, e.g., a blood or biopsy sample, is assayed, e.g., at the nucleic acid and / or protein level, to evaluate the subject. Also provided are compositions, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biopsy device incorporating an adjustable probe sleeve
InactiveUS20060200042A1Discomfort and disfiguring scarring is avoidedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue sampleRadiology
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample. After the tissue sample is severed, and before the inner cutter is retracted proximally of the side tissue port, the cutter may be used to alternately cover and uncover the fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com